Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- The four main types of essay | Quick guide with examples

The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
Published on September 4, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays.
Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and descriptive essays are about exercising creativity and writing in an interesting way. At university level, argumentative essays are the most common type.
| Essay type | Skills tested | Example prompt |
|---|---|---|
| Has the rise of the internet had a positive or negative impact on education? | ||
| Explain how the invention of the printing press changed European society in the 15th century. | ||
| Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself. | ||
| Describe an object that has sentimental value for you. |
In high school and college, you will also often have to write textual analysis essays, which test your skills in close reading and interpretation.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Argumentative essays, expository essays, narrative essays, descriptive essays, textual analysis essays, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about types of essays.
An argumentative essay presents an extended, evidence-based argument. It requires a strong thesis statement —a clearly defined stance on your topic. Your aim is to convince the reader of your thesis using evidence (such as quotations ) and analysis.
Argumentative essays test your ability to research and present your own position on a topic. This is the most common type of essay at college level—most papers you write will involve some kind of argumentation.
The essay is divided into an introduction, body, and conclusion:
- The introduction provides your topic and thesis statement
- The body presents your evidence and arguments
- The conclusion summarizes your argument and emphasizes its importance
The example below is a paragraph from the body of an argumentative essay about the effects of the internet on education. Mouse over it to learn more.
A common frustration for teachers is students’ use of Wikipedia as a source in their writing. Its prevalence among students is not exaggerated; a survey found that the vast majority of the students surveyed used Wikipedia (Head & Eisenberg, 2010). An article in The Guardian stresses a common objection to its use: “a reliance on Wikipedia can discourage students from engaging with genuine academic writing” (Coomer, 2013). Teachers are clearly not mistaken in viewing Wikipedia usage as ubiquitous among their students; but the claim that it discourages engagement with academic sources requires further investigation. This point is treated as self-evident by many teachers, but Wikipedia itself explicitly encourages students to look into other sources. Its articles often provide references to academic publications and include warning notes where citations are missing; the site’s own guidelines for research make clear that it should be used as a starting point, emphasizing that users should always “read the references and check whether they really do support what the article says” (“Wikipedia:Researching with Wikipedia,” 2020). Indeed, for many students, Wikipedia is their first encounter with the concepts of citation and referencing. The use of Wikipedia therefore has a positive side that merits deeper consideration than it often receives.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
An expository essay provides a clear, focused explanation of a topic. It doesn’t require an original argument, just a balanced and well-organized view of the topic.
Expository essays test your familiarity with a topic and your ability to organize and convey information. They are commonly assigned at high school or in exam questions at college level.
The introduction of an expository essay states your topic and provides some general background, the body presents the details, and the conclusion summarizes the information presented.
A typical body paragraph from an expository essay about the invention of the printing press is shown below. Mouse over it to learn more.
The invention of the printing press in 1440 changed this situation dramatically. Johannes Gutenberg, who had worked as a goldsmith, used his knowledge of metals in the design of the press. He made his type from an alloy of lead, tin, and antimony, whose durability allowed for the reliable production of high-quality books. This new technology allowed texts to be reproduced and disseminated on a much larger scale than was previously possible. The Gutenberg Bible appeared in the 1450s, and a large number of printing presses sprang up across the continent in the following decades. Gutenberg’s invention rapidly transformed cultural production in Europe; among other things, it would lead to the Protestant Reformation.
A narrative essay is one that tells a story. This is usually a story about a personal experience you had, but it may also be an imaginative exploration of something you have not experienced.
Narrative essays test your ability to build up a narrative in an engaging, well-structured way. They are much more personal and creative than other kinds of academic writing . Writing a personal statement for an application requires the same skills as a narrative essay.
A narrative essay isn’t strictly divided into introduction, body, and conclusion, but it should still begin by setting up the narrative and finish by expressing the point of the story—what you learned from your experience, or why it made an impression on you.
Mouse over the example below, a short narrative essay responding to the prompt “Write about an experience where you learned something about yourself,” to explore its structure.
Since elementary school, I have always favored subjects like science and math over the humanities. My instinct was always to think of these subjects as more solid and serious than classes like English. If there was no right answer, I thought, why bother? But recently I had an experience that taught me my academic interests are more flexible than I had thought: I took my first philosophy class.
Before I entered the classroom, I was skeptical. I waited outside with the other students and wondered what exactly philosophy would involve—I really had no idea. I imagined something pretty abstract: long, stilted conversations pondering the meaning of life. But what I got was something quite different.
A young man in jeans, Mr. Jones—“but you can call me Rob”—was far from the white-haired, buttoned-up old man I had half-expected. And rather than pulling us into pedantic arguments about obscure philosophical points, Rob engaged us on our level. To talk free will, we looked at our own choices. To talk ethics, we looked at dilemmas we had faced ourselves. By the end of class, I’d discovered that questions with no right answer can turn out to be the most interesting ones.
The experience has taught me to look at things a little more “philosophically”—and not just because it was a philosophy class! I learned that if I let go of my preconceptions, I can actually get a lot out of subjects I was previously dismissive of. The class taught me—in more ways than one—to look at things with an open mind.
A descriptive essay provides a detailed sensory description of something. Like narrative essays, they allow you to be more creative than most academic writing, but they are more tightly focused than narrative essays. You might describe a specific place or object, rather than telling a whole story.
Descriptive essays test your ability to use language creatively, making striking word choices to convey a memorable picture of what you’re describing.
A descriptive essay can be quite loosely structured, though it should usually begin by introducing the object of your description and end by drawing an overall picture of it. The important thing is to use careful word choices and figurative language to create an original description of your object.
Mouse over the example below, a response to the prompt “Describe a place you love to spend time in,” to learn more about descriptive essays.
On Sunday afternoons I like to spend my time in the garden behind my house. The garden is narrow but long, a corridor of green extending from the back of the house, and I sit on a lawn chair at the far end to read and relax. I am in my small peaceful paradise: the shade of the tree, the feel of the grass on my feet, the gentle activity of the fish in the pond beside me.
My cat crosses the garden nimbly and leaps onto the fence to survey it from above. From his perch he can watch over his little kingdom and keep an eye on the neighbours. He does this until the barking of next door’s dog scares him from his post and he bolts for the cat flap to govern from the safety of the kitchen.
With that, I am left alone with the fish, whose whole world is the pond by my feet. The fish explore the pond every day as if for the first time, prodding and inspecting every stone. I sometimes feel the same about sitting here in the garden; I know the place better than anyone, but whenever I return I still feel compelled to pay attention to all its details and novelties—a new bird perched in the tree, the growth of the grass, and the movement of the insects it shelters…
Sitting out in the garden, I feel serene. I feel at home. And yet I always feel there is more to discover. The bounds of my garden may be small, but there is a whole world contained within it, and it is one I will never get tired of inhabiting.
Though every essay type tests your writing skills, some essays also test your ability to read carefully and critically. In a textual analysis essay, you don’t just present information on a topic, but closely analyze a text to explain how it achieves certain effects.
Rhetorical analysis
A rhetorical analysis looks at a persuasive text (e.g. a speech, an essay, a political cartoon) in terms of the rhetorical devices it uses, and evaluates their effectiveness.
The goal is not to state whether you agree with the author’s argument but to look at how they have constructed it.
The introduction of a rhetorical analysis presents the text, some background information, and your thesis statement; the body comprises the analysis itself; and the conclusion wraps up your analysis of the text, emphasizing its relevance to broader concerns.
The example below is from a rhetorical analysis of Martin Luther King Jr.’s “I Have a Dream” speech . Mouse over it to learn more.
King’s speech is infused with prophetic language throughout. Even before the famous “dream” part of the speech, King’s language consistently strikes a prophetic tone. He refers to the Lincoln Memorial as a “hallowed spot” and speaks of rising “from the dark and desolate valley of segregation” to “make justice a reality for all of God’s children.” The assumption of this prophetic voice constitutes the text’s strongest ethical appeal; after linking himself with political figures like Lincoln and the Founding Fathers, King’s ethos adopts a distinctly religious tone, recalling Biblical prophets and preachers of change from across history. This adds significant force to his words; standing before an audience of hundreds of thousands, he states not just what the future should be, but what it will be: “The whirlwinds of revolt will continue to shake the foundations of our nation until the bright day of justice emerges.” This warning is almost apocalyptic in tone, though it concludes with the positive image of the “bright day of justice.” The power of King’s rhetoric thus stems not only from the pathos of his vision of a brighter future, but from the ethos of the prophetic voice he adopts in expressing this vision.
Literary analysis
A literary analysis essay presents a close reading of a work of literature—e.g. a poem or novel—to explore the choices made by the author and how they help to convey the text’s theme. It is not simply a book report or a review, but an in-depth interpretation of the text.
Literary analysis looks at things like setting, characters, themes, and figurative language. The goal is to closely analyze what the author conveys and how.
The introduction of a literary analysis essay presents the text and background, and provides your thesis statement; the body consists of close readings of the text with quotations and analysis in support of your argument; and the conclusion emphasizes what your approach tells us about the text.
Mouse over the example below, the introduction to a literary analysis essay on Frankenstein , to learn more.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
At high school and in composition classes at university, you’ll often be told to write a specific type of essay , but you might also just be given prompts.
Look for keywords in these prompts that suggest a certain approach: The word “explain” suggests you should write an expository essay , while the word “describe” implies a descriptive essay . An argumentative essay might be prompted with the word “assess” or “argue.”
The vast majority of essays written at university are some sort of argumentative essay . Almost all academic writing involves building up an argument, though other types of essay might be assigned in composition classes.
Essays can present arguments about all kinds of different topics. For example:
- In a literary analysis essay, you might make an argument for a specific interpretation of a text
- In a history essay, you might present an argument for the importance of a particular event
- In a politics essay, you might argue for the validity of a certain political theory
An argumentative essay tends to be a longer essay involving independent research, and aims to make an original argument about a topic. Its thesis statement makes a contentious claim that must be supported in an objective, evidence-based way.
An expository essay also aims to be objective, but it doesn’t have to make an original argument. Rather, it aims to explain something (e.g., a process or idea) in a clear, concise way. Expository essays are often shorter assignments and rely less on research.
The key difference is that a narrative essay is designed to tell a complete story, while a descriptive essay is meant to convey an intense description of a particular place, object, or concept.
Narrative and descriptive essays both allow you to write more personally and creatively than other kinds of essays , and similar writing skills can apply to both.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). The Four Main Types of Essay | Quick Guide with Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 26, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-types/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, how to write an expository essay, how to write an essay outline | guidelines & examples, what is your plagiarism score.
- How to Order
Essay Writing Guide
Types Of Essay
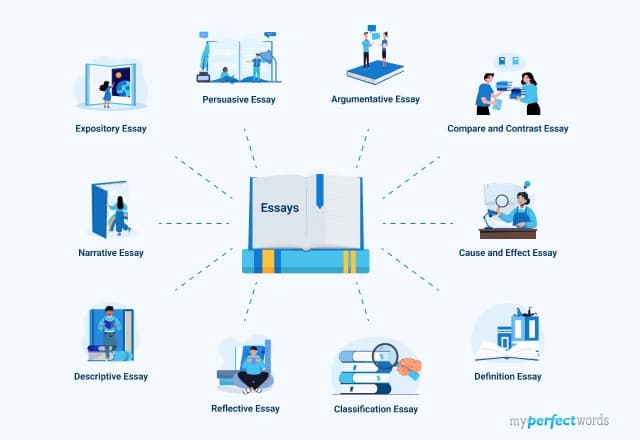
Common Types of Essays - Sub-types and Examples
11 min read
People also read
An Easy Guide to Writing an Essay
A Complete 500 Word Essay Writing Guide
A Catalog of 370+ Essay Topics for Students
Essay Format: A Basic Guide With Examples
How to Write an Essay Outline in 5 Simple Steps
How to Start an Essay? Tips for an Engaging Start
A Complete Essay Introduction Writing Guide With Examples
Learn How to Write an Essay Hook, With Examples
The Ultimate Guide to Writing Powerful Thesis Statement
20+ Thesis Statement Examples for Different Types of Essays?
How to Write a Topic Sentence: Purpose, Tips & Examples
Learn How to Write a Conclusion in Simple Steps
Transition Words For Essays - The Ultimate List
4 Types of Sentences - Definition & Examples
Writing Conventions - Definition, Tips & Examples
Essay Writing Problems - 5 Most Paralyzing Problems
Tips On How to Make an Essay Longer: 15 Easy Ways
How to Title an Essay Properly- An Easy Guide
1000 Word Essay - A Simple Guide With Examples
A Guide to Writing a Five-Paragraph Essay
How To Write A Strong Body Paragraph
Ever felt overwhelmed by the sheer number of "essays" out there? Essays are fundamental tools in education and communication, designed to inform, persuade, and narrate experiences.
Understanding the different types of essays is important in academics. There are four primary categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive and each type serves a distinct purpose.
This guide will explore each type and its subtypes with examples providing clear examples to improve your writing skills.
Let’s get started!
- 1. 4 Main Types of Essays In Academic Writing
- 2. Argumentative Essay
- 3. Descriptive Essay
- 4. Expository Essay
- 5. Narrative Essay
- 6. Other Common Essay Types
4 Main Types of Essays In Academic Writing
In academic years, essay writing develops essential skills. At the university level, argumentative essays are most common, honing critical thinking and persuasive writing.
In high school and college, textual analysis essays test close reading and interpretation, enhancing analytical thinking and clear articulation. Let's explore these essay types along with their descriptions and example prompts in the table below:
|
|
|
| Formulating arguments, critical thinking, persuasive writing. | Argue for or against the implementation of stricter gun control laws in the United States. |
| Sensory Description, Imagery, Figurative Language | Describe a place you visited recently and explain why it left a lasting impression on you. |
| Informative Writing, Research, Clarity | Explain the causes and effects of climate change, and discuss its impact on the environment and society. |
| Storytelling, Narrative Structure, Engagement | Describe a memorable childhood event that had a significant impact on your life. |
Please note that the length of these essays depends on academic level, assignment requirements, and topic complexity. University essays are usually longer due to deeper analysis, while high school essays are shorter and more focused on foundational skills. Argumentative essays often require more length than narrative or descriptive essays to support thorough argumentation.
Let’s take a look at these types of essays in detail, along with examples to further your understanding.
Argumentative Essay
An argumentative essay is an essay type that presents a well-structured argument supported by evidence and reasoning. The primary goal is to engage the reader in a discussion, provide evidence, and logically demonstrate why a particular viewpoint is more valid.
In simple terms, the writer must provide evidence and stay consistent with their viewpoint, focusing on a specific type of argument . While argumentative essays discuss both sides of an issue, they clearly advocate for one perspective.
Characteristics of Argumentative Essay
- Clear Thesis: It should have a clear thesis statement to state the writer's position.
- Balanced Presentation: An argumentative essay addresses opposing views.
- Evidence: It relies on credible and relevant evidence.
- Logical Reasoning: The essay presents arguments coherently and logically.
The argumentative essay outline follows the same basic structure as other essays but includes an additional section for the counterargument.
- Introduction: The introduction introduces the topic and thesis, engaging the reader's interest.
- Body: The body paragraphs present arguments with supporting evidence.
- Counterargument: It addresses opposing viewpoints and refutes them.
- Conclusion: The conclusion summarizes key points and reinforces the thesis, leaving a strong impression.
Argumentative Essay Example
Before beginning the writing process, it is better to go through some expertly crafted argumentative essay examples .
Here is a sample argumentative essay example for you to get an idea.
Descriptive Essay
A descriptive essay is a form of writing that aims to immerse readers in a sensory-rich experience. Unlike informational or persuasive essays, its primary goal is to vividly depict a person, place, object, event, or experience.
The descriptive essay must stimulate the senses and emotions of the reader. To put it simply, the reader should see what you saw and feel what you felt. To make it better, you can use several literary devices like;
- Alliteration
All of them help in making the experience and your essay better.
Key Characteristics
- Sensory Detail: Descriptive essays appeal to the five senses to create a multisensory experience.
- Vivid Imagery: They use figurative language and descriptive adjectives to bring the narrative to life.
- Emotional Connection: These essays often aim to establish an emotional bond between the reader and the subject.
- Structured Approach: They typically follow an introduction-body-conclusion structure.
A descriptive essay outline typically follows a 5-paragraph essay format, consisting of the following basic components:
- Introduction: Introduces the subject and purpose sometimes with a thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs: Focus on specific aspects or details using sensory language and vivid descriptions.
- Conclusion: Summarizes the central theme and leaves a lasting impression.
Descriptive Essay Example
Writing a perfect descriptive essay for an assignment is not difficult if you go through some expert descriptive essay examples first.
Here, we have provided a well-written descriptive essay for you to get inspired from and start the writing process confidently.
Expository Essay
An expository essay is a type of writing that provides clear and objective explanations of a topic without expressing personal opinions. It aims to inform and educate by presenting factual information and analysis.
There are various types of expository writing :
- Cause and effect essays
- Process essays
- Analytical essays
- Compare and contrast essays
Key Characteristics
- Objective Presentation: Expository writing maintains an impartial tone, avoiding personal biases.
- Informativeness: They focus on explaining complex ideas or processes in a straightforward manner.
- Structured: These essays follow a clear structure with an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
- Use of Evidence: They rely on credible evidence, facts, and examples to support the topic.
Like other types of essays, an expository essay outline also follows the standard essay format :
- Introduction: Introduces the topic and often includes a thesis statement.
- Body Paragraphs: Each paragraph focuses on a specific aspect and provides explanations and evidence.
- Conclusion: Restates the main idea and summarizes key points.
Expository Essay Example
Here is an expository essay example from one of our expert writers to understand the basics. For more samples visit our dedicated blog on Expository Essay Examples !
Narrative Essay
A narrative essay is a type of academic writing that tells a story or recounts a personal experience. Unlike other essays, its primary purpose is to engage and entertain the reader through storytelling.
- Narrative Structure: Follows a chronological sequence with an introduction, body, climax, and conclusion.
- First-Person Perspective: Typically written from the first-person point of view (e.g., "I" and "we") , sharing personal experiences and emotions.
- Vivid Description: Relies on descriptive language and imagery to create a clear picture of events, characters, and settings.
- Emotional Connection: Aims to establish an emotional bond with the reader by conveying the writer's thoughts and feelings.
- Introduction: Sets the stage and introduces the central theme or problem.
- Body: Presents events or experiences in chronological order with sensory details.
- Climax: Often includes a central event or turning point.
- Conclusion: Reflects on the narrative, offering insights, lessons, or resolution.
Narrative Essay Example
Wondering how to get your story into an interesting narrative? Learn the best way to write a perfect narrative essay with the help of narrative essay examples .
Other Common Essay Types
Besides the main types of essays, there are other specialized types for specific audiences. These essays offer various ways for writers to communicate their ideas.
We will go through these essay types here.
Persuasive Essay
A persuasive essay is another type of academic essay. In this essay type, the writer utilizes logic and reasoning to show one’s idea is more convincing than another idea.
In writing a persuasive essay, the main aim is to persuade the reader to accept a certain point of view. The presented argument or claim must use solid evidence and sound reasoning by stating facts, examples, and quotes. It uses persuasive techniques like ethos, pathos, and logos to persuade the audience.
Persuasive Essay Example
Since persuasive essays are the most common type of essay, it is essential to get familiar with their writing style. For that, make sure to read the persuasive essay examples for better understanding.
Here is a sample in PDF format:
Analytical Essay
An analytical essay is a type of academic essay in which the writer analyzes a topic bit by bit. Writing an analytical essay is not about convincing readers of your point of view. But wanting readers to agree with what you have written.
So, there is no need to use strong persuasive language in an analytical essay. Rather you should aim to provide enough analysis to make sure your argument is clear to the readers.
Analytical Essay Example
Let’s take a look at a sample analytical essay:
Read our analytical essay examples blog if you are looking for more sample essays!
Reflective Essay
A reflective essay requires you to examine your personal experiences through self-reflection. In the process of writing a reflective essay, you provide insight into what you have gained from those experiences.
What makes reflective essays different from other essay types is the fact that they examine the past experience from the present. Reflective essays take the reader through a journey of self-growth.
Reflective Essay Example
The following reflective essay example will help you get a clear idea of how to structure your analytical essay.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay
It is a form of a textual analysis essay in which the student examines and analyzes a persuasive text. It is like an essay, speech, or visual art and analyzes the rhetorical devices used in it. Writing a rhetorical analysis essay is different from writing other essays because it will be more than adding facts only.
Rhetorical Analysis Essay Example
Here is a rhetorical analysis essay example that will help you learn better. For more examples check out our rhetorical analysis essay examples blog for more samples!
Literary Analysis Essay
A literary analysis essay is based on close reading and analysis of a work of literature like poetry and novel. It identifies different literary factors like themes, setting, characters, setting, and the kind of language used in it. A literary analysis essay has the same 5 paragraphs as any other essay but the main subject and topic are different.
Literary Analysis Essay Example
Need help with your literary analysis essay? Below is a sample essay to help you understand better.
Summing it Up! Now you know what are the different types of essays in academic writing that you are most likely to get assigned. However, if you still find it difficult to compose your essay, leave your piece of writing to our experts.
Whether you need an argumentative essay, narrative essay, descriptive essay, or expository essay we are here to help. Our expertise extends to all types of essays, ensuring that your academic writing needs are met with precision and excellence.
Request essay help today and let our experts assist you in writing A+ grade essays within your specified timeline!
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the most important element in any essay.
The most important element in any essay is its thesis statement. The thesis statement presents the main idea or argument of the essay and sets the direction for the entire piece. It provides a clear, concise summary of what the essay will cover, helping to guide the reader and ensure that the content remains focused and coherent.
What type of essay is most common at university?
The most common type of essay at university is the argumentative essay Other common types include:
- Expository essay
- Persuasive essay
- Narrative essay
- Descriptive essay
- Cause and effect essay
- Compare and contrast essay
- Process essay
- Definition essay
- Classification essay
- Critical essay
- Analytical essay
- Argumentative essay
- Reflective essay
- Research paper
- Literature review

Write Essay Within 60 Seconds!

Nova Allison is a Digital Content Strategist with over eight years of experience. Nova has also worked as a technical and scientific writer. She is majorly involved in developing and reviewing online content plans that engage and resonate with audiences. Nova has a passion for writing that engages and informs her readers.

Paper Due? Why Suffer? That’s our Job!
Keep reading

Complete Guide to the 10 Main Types of Essays for Students
Welcome to the wonderful world of essay writing! Throughout your academic journey, knowing how to express your thoughts, ideas and opinions through the medium of essay writing will be super important. Whether you’re dealing with an assignment for your English class or any other school subject, it’s crucial to understand the different types of essays and when to use them.

The 10 Main Essay Types Explained
1. narrative essays.
Purpose : Narrative essays weave stories, allowing writers to share personal experiences, lessons learned, or memorable moments, aiming to entertain or convey a particular message.
Usage : Often employed in personal statements for college or graduate school applications, where the goal is to provide a glimpse into the writer’s character.
Structure Example :
- Introduction : Captivate the reader’s attention with an engaging opening that hints at the central theme.
- Body : Chronicle the events in chronological order, utilising literary techniques such as metaphors, alliteration, and dialogue.
- Conclusion : Summarise the main point or highlight the significance of the narrative, reinforcing the central message.
2. Descriptive Essays
Purpose : To vividly depict a subject, be it a person, place, thing, or event, invoking sensory experiences and creating a vivid picture for the reader.
Usage : Ideal for creating a detailed portrayal without necessarily constructing a complete story; often used in travel writing or to enhance the understanding of a specific concept.
- Introduction : Set the scene and establish the focus, providing a clear overview of what the reader is about to experience.
- Body : Utilise vivid imagery, actions, thoughts, and emotions to immerse the reader, using strong action verbs and descriptive adjectives.
- Conclusion : Summarise and leave a lasting impression, emphasising the overall impact of the described subject.
3. Expository Essays
Purpose : Expository essays provide a neutral explanation of a topic, demonstrating the writer’s knowledge or expertise, with the goal of informing or educating the audience.
Usage : Frequently assigned by teachers to assess understanding without incorporating personal opinions; common in academic and informational contexts.
- Introduction : Introduce the topic with a clear thesis statement that outlines the specific aspect to be explored.
- Body : Present factual information, often citing sources for credibility, using clear and concise language.
- Conclusion : Summarise the main points without introducing personal biases, leaving the reader with a comprehensive understanding.
4. Definition Essays
Purpose : Definition essays define and analyse complex or abstract terms or ideas in-depth, aiming to provide clarity and insight.
Usage : Commonly found in academic and research settings, where the goal is to delve into the nuances of a particular concept.
- Introduction : Clearly define the term or idea to be explored, providing context for the audience.
- Body : Offer a detailed analysis, examples, and explanations, breaking down the components of the term.
- Conclusion : Summarise the key points and reiterate the definition, ensuring the audience grasps the full scope of the concept.
5. Process Essays
Purpose : Process essays explain how to do something or how something works, guiding the reader through a series of steps to achieve a specific outcome.
Usage : Employed for instructional purposes, suitable for topics ranging from recipes and DIY projects to scientific procedures.
- Introduction : Introduce the process to be described, setting the stage for the step-by-step guidance.
- Body : Sequentially detail each step, using transition words for clarity and logical progression.
- Conclusion : Summarise the process for reader retention, reinforcing the significance of the final outcome.
6. Compare and Contrast Essays
Purpose : Compare and contrast essays discuss the similarities and differences between two subjects, aiming to highlight unique aspects and foster a deeper understanding.
Usage : Common in academic settings for analytical comparison, frequently used in literature, history, or scientific analysis.
- Introduction : Present the subjects to be compared, providing a brief overview of their significance.
- Body : Devote paragraphs to similarities and differences, using clear transitions for smooth readability.
- Conclusion : Summarise the key points and highlight the significance of the comparison, drawing attention to the insights gained.
7. Argumentative Essays
Purpose : Argumentative essays convince the reader to adopt a particular viewpoint based on objective information, using logical reasoning and evidence.
Usage : Rely on facts rather than emotions to sway opinions; often found in academic settings and editorials.
- Introduction : Present the argument with a clear thesis, outlining the stance to be defended.
- Body : Provide factual evidence and counterarguments, presenting a well-rounded perspective.
- Conclusion : Summarise the key points and reinforce the chosen stance, leaving a lasting impression on the reader.
8. Persuasive Essays
Purpose : Persuasive essays aim to persuade readers to adopt a specific opinion or take a particular stance using facts and emotional appeals, aiming to evoke a personal connection.
Usage : Employ moral and emotional reasoning to connect with the reader, often found in opinion pieces and marketing.
- Introduction : Clearly state the opinion or stance to be supported, capturing the reader’s attention.
- Body : Present facts and emotional appeals, crafting a compelling narrative to strengthen the argument.
- Conclusion : Reinforce the argument and call the reader to action, leaving them with a sense of urgency or agreement.
9. Cause and Effect Essays
Purpose : Cause and effect essays detail the causal relationship between events or situations, explaining why certain events or circumstances led to others.
Usage : Examine the consequences and implications of specific actions or occurrences, frequently found in scientific, historical, or sociological contexts.
- Introduction : Clearly state the cause and effect relationship, providing context for the audience.
- Body : Elaborate on the features of the initiating event and its consequences, using evidence to support claims.
- Conclusion : Summarise the key cause-and-effect connections, emphasising their broader significance.
10. Critical Essays
Purpose : Critical essays provide an in-depth analysis and critique of a topic, often found in literature and humanities courses, testing students’ ability to think critically.
Usage : Assess the ability to think critically and identify evidence from a specific work that validates observations, common in literary analysis or art criticism.
- Introduction : Introduce the subject to be critiqued, providing context for the analysis.
- Body : Analyse and support opinions with evidence, diving into specific aspects of the subject.
- Conclusion : Summarise the critical points and reiterate the analysis, leaving the reader with a comprehensive understanding of the critique.
Need Help With Essay Writing? A Team Tuition Can Help!
Mastering these essay types is a journey, and seeking guidance is a wise first step. A Team Tuition offers private tutoring and mentoring services, empowering students to excel in essay writing and beyond. Whether it’s forming study groups or personalised sessions, enhancing your child’s academic experience is just a click away.
Consider signing up for A Team’s private tutoring and mentoring services to further enhance your child’s academic experience and reach their full potential. Contact us now to schedule your child’s first session and start achieving their academic goals!
Recent Posts
- Our Partner: Olympic Gold Medallist Cam McEvoy
- 7 Effective Time Management Tips For Students
- How to Write a Comparative Essay: Structure, Tips & Examples
- How to Analyse a Text for English Class: 7 Textual Analysis Tips
- Cameron McEvoy and A Team Tuition Unite to Empower Young Minds
- Advice For Parents
- Foundations of Learning
- How to Succeed
- Neurodivergent Learning
- ATAR for University Admissions
- Career Paths
- High School Programs and Classes
- Transformation Stories
Privacy Overview
Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt
Asking analytical questions, introductions, what do introductions across the disciplines have in common, anatomy of a body paragraph, transitions, tips for organizing your essay, counterargument, conclusions.
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
- Essay Editor
How to Write a Family Essay with Examples

Writing about your family gives you a chance to think about your own experiences and what matters to you. It lets you look at how your family works together and share important stories from your life. This guide will help you write a good family essay that others will find interesting, whether you're doing it for school or just want to put your family's story on paper.
What is a Family Essay?
A family essay is a personal story that talks about your experiences with your family, your relationships, and what you value. It's a type of personal essay that teachers often ask students to write to see how well they can tell their family stories.
The main goal of a family essay is to share your own thoughts on family values, traditions, and how you're all connected. It's a chance to talk about the love in your family, share favorite memories, or describe the strong bonds between family members.
Useful Tips for Writing an Essay on Family Topics
To write a great family essay, you need to plan and write carefully. Here are some helpful tips:
- Start with something interesting: Begin your essay with a fun fact or story about your family to get the reader's attention right away.
- Make a clear main point: Write a short statement that sums up the main idea of your essay. This will guide your writing and help readers understand what you're focusing on.
- Do your research: Find out more about your family's history, traditions, and cultural background. This will make your essay more real and detailed.
- Organize your essay well: Arrange your thoughts into a clear introduction, middle sections, and conclusion. Each part should lead smoothly into the next.
- Use clear descriptions: Make your family members and experiences come to life with detailed descriptions. This will help readers feel connected to your story.
- Include your own thoughts: Share how you feel about family events or how your family works together. This makes your writing more real and personal.
- Check and fix your work: After you finish writing, take time to read over and improve your essay. Look for grammar mistakes, make sentences better, and make sure your ideas are clear.
When thinking about how to write about your family, remember that being real is important. Your own point of view and experiences will make your essay special.
Interesting Ideas on Family Essay Related Topics
Picking a good topic is important when writing about your family. Here are some ideas to get you thinking:
- How family traditions have changed over time
- How technology affects how families talk to each other
- Finding a balance between being yourself and what your family expects
- How extended family members fit into today's families
- What we learn from family arguments and how we solve them
- How cultural background affects how families work together
- What "family" means in different types of families
- Why family support is important for personal growth
- Dealing with differences between older and younger family members
- How shared experiences make family bonds stronger
When you write about these topics, think about how they relate to your own life. For example, if you're writing about how technology affects family communication, you could share a story about how video calls help you stay in touch with relatives who live far away.
Remember, the best family essays mix personal stories with concepts about how families work and how they fit into society.
Family Essay Example: Why family support is important for personal growth
“ Family support is similar to having a group of people who both encourage you and protect you. It's more than just having people nearby; it's about having individuals who truly want you to succeed. When I was afraid of speaking in front of others, my sister's encouraging words helped me get through my first presentation. And truthfully, who else but family would listen to you practice guitar poorly without complaining? This kind of support without conditions gives us the bravery to try new things outside of what we're used to. It's also a way to learn from others - I've learned many things, from cooking advice to useful life tips, from different family members. Even when we don't agree, we grow; those serious discussions at dinner taught me how to defend my opinions and express my thoughts clearly. Yes, family can be frustrating at times, but they're also the ones who will stop what they're doing to help you move or listen to you when you're worried late at night. This combination of care, challenges, and support creates a special environment where we can be our true selves and slowly become the best versions of ourselves. ”
Closing Remarks
Writing a family essay helps you learn about yourself and think deeply. It's a chance to look closely at your relationships, celebrate what makes your family special, and understand more about how your family affects your life and the world around you.
Remember, the process of writing about your family can be just as rewarding as the finished essay. Take this opportunity to think about how your family has shaped your life and let your true voice come through in your writing.
Ready to bring your family story to life? Let Aithor's intuitive AI writing tools help you write a compelling and heartfelt family essay that captures the essence of your unique experiences.
Related articles
Paraphrasing vs plagiarism: do they really differ.
Academic assignments require much knowledge and skill. One of the most important points is rendering and interpreting material one has ever studied. A person should avoid presenting word-for-word plagiarism but express his or her thoughts and ideas as much as possible. However, every fine research is certain to be based on the previous issues, data given, or concepts suggested. And here it's high time to differentiate plagiarism and paraphrasing, to realize its peculiarities and cases of usage. ...

Top 10 Use Cases for AI Writers
Writing is changing a lot because of AI. But don't worry — AI won't take human writers' jobs. It's a tool that can make our work easier and help us write better. When we use AI along with our own skills, we can create good content faster and better. AI can help with many parts of writing, from coming up with ideas to fixing the final version. Let's look at the top 10 ways how to use AI for content creation and how it can make your writing better. What Is AI Content Writing? AI content writin ...
Can Plagiarism Be Detected on PDF?
Plagiarism has been a challenge for a long time in writing. It's easy to find information online, which might make some people use it without saying where it came from. But plagiarism isn't just taking someone else's words. Sometimes, we might do it by accident or even use our own old work without mentioning it. When people plagiarize, they can get into serious trouble. They might lose others' trust or even face legal problems. Luckily, we now have tools to detect plagiarism. But what about PDF ...
Plagiarism: 7 Types in Detail
Your professor says that it is necessary to avoid plagiarism when writing a research paper, essay, or any project based on the works of other people, so to say, any reference source. But what does plagiarism mean? What types of it exist? And how to formulate the material to get rid of potential bad consequences while rendering original texts? Today we try to answer these very questions. Plagiarism: Aspect in Brief Plagiarism is considered to be a serious breach, able to spoil your successful ...
How To Write Essays Faster Using AI?
Creating various topical texts is an obligatory assignment during studies. For a majority of students, it seems like a real headache. It is quite difficult to write a smooth and complex work, meeting all the professors' requirements. However, thanks to modern technologies there appeared a good way of getting a decent project – using AI to write essays. We'd like to acquaint you with Aithor, an effective tool of this kind, able to perform fine and elaborated texts, and, of course, inspiration, i ...
What Is Self-Plagiarism & How To Avoid It
Have you ever thought about whether using your own work again could be seen as copying? It might seem strange, but self-plagiarism is a real issue in school and work writing. Let's look at what this means and learn how to avoid self-plagiarism so your work stays original and ethical. What is self-plagiarism? Self-plagiarism, also called auto-plagiarism or duplicate plagiarism, happens when a writer uses parts of their old work without saying where it came from. This isn't just about copying w ...
How to Write a Dialogue in an Essay: Useful Tips
A correct usage of dialogues in essays may seem quite difficult at first sight. Still there are special issues, for instance, narrative or descriptive papers, where this literary technique will be a good helper in depicting anyone's character. How to add dialogues to the work? How to format them correctly? Let's discuss all relevant matters to master putting conversation episodes into academic essays. Essay Dialogue: Definition & Purpose A dialogue is a literary technique for presenting a con ...
What is Citation and Why Should You Cite the Sources When Writing Content
When we write something for school, work, or just for fun, we often use ideas and facts from other places. This makes us ask: what is a citation in writing? Let's find out what this means and why it's really important when we write. What is Citation? Citation in research refers to the practice of telling your readers where you got your information, ideas, or exact words from. It's like showing them the path to the original information you used in your writing. When you cite something, you us ...
Learning Objectives
Students will be able to...
- Identify major forms of government (autocracy, monarchy, dictatorship, representative and direct democracy, oligarchy, theocracy, anarchy)
- Compare and contrast the major features of different types of government
- Analyze examples of real-world governments
- Related Resources
Students learn about the different forms of government that exist, including democracy, autocracy, oligarchy, and others. They compare and contrast these forms, and they look at real-life examples in the world today.
iCivics en español! Student and class materials for this lesson are available in Spanish.
Access engaging resources with an iCivics account!
Create your free iCivics account and discover standards aligned lessons and games that meet all of your instructional needs. Our nonpartisan classroom resources engage students with complex concepts in ways they can understand and relate to.
Pedagogy Tags

Tech Options

Integrations

View state standards alignment
More resources in the unit 'foundations of government', a dive into democracy.
The Founding Fathers had many influences. Discover how aspects of Athenian democracy shaped the structure and ideals of the U.S. government.
Familiar But Flawed
Did Americans find fault in every ounce of the British government? Maybe not. Learn how America's Founders improved upon familiar structures of British government to contain…
Foundation Basics
Meet your PALS—Power, Authority, Legitimacy, and Sovereignty! In this lesson, students are introduced to these characteristics of government and consider how…
Use the Scope & Sequence to help you plan your iCivics classroom experience!
Whether you enjoy finding opportunities within a well-structured sequence of resources or prefer looking around for pieces and bits that can be jigsawed together, our Scope & Sequence documents are a perfect reference point for planning. Scope & Sequence documents are available for elementary, middle, and high school classrooms and list all of our resources in one place.

Business Letter
Letter maker.

For businesses to grow, they seek out ways to enter into a business partnership with another company. The prospect is to look for a way to tell the person you are interested in merging businesses with them. To be able to do that, it is important to write a formal letter to the other business entity .
Business Letter Format Sample

lexpublib.org
Size: 248 KB
Different Business Letter Formats

ic.arc.losrios.edu
Size: 345 KB
Business Letter Sample
Size: 307 KB
Sample Business Letter

Size: 135 KB
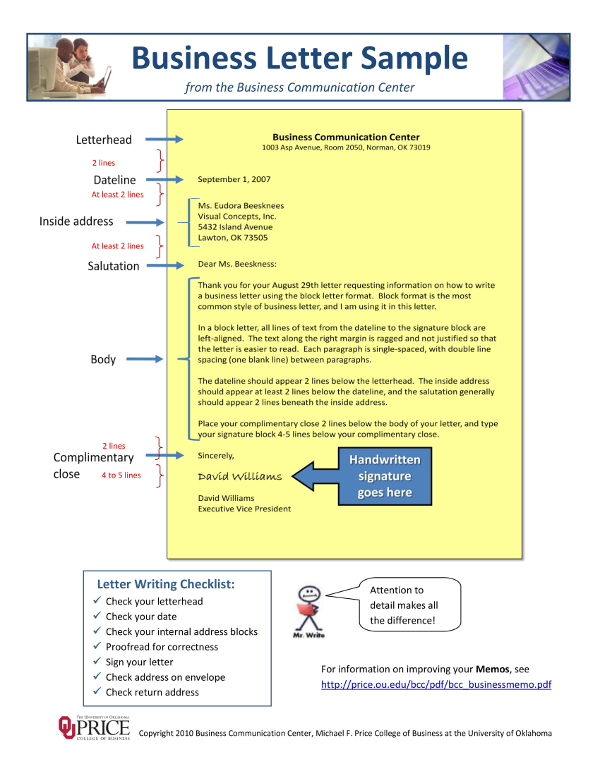
What Is a Business Letter?
An important document that holds essential information regarding a business opportunity . Businesses write these letters to explain their intentions clearly and professionally. Understanding the concept of writing a business letter will also help.
How to Write a Business Letter
The easiest way to make a business letter is to download the templates you found above. How not to write a business letter is also essential to take notice of.
Step 1: Pick Out the Correct Format to Start
Pick the right format for writing the official letter for your business . There are many types of business letters, so choosing the right one will help you when you start writing.
Step 2: Tread Carefully on the Tone and Jargon to Use
As it is a formal letter conveying important messages, it is apparent to use a formal and professional tone and language. In the printed business letter, the tone should be friendly but more professional. It must not come off as if you’re distant or a machine has written the letter.
Step 3: Make Your Handwriting Legible Enough to Be Understood
Make sure to be direct and clear. State the point of your reference letter early on. Use straightforward language to avoid miscommunication. It is important to organize and arrange thoughts and information logically. Group related information in the same paragraph to make it easier for your readers to understand.
Step 4: Proofread the Letter
The last step is to do some proofreading, editing, and polishing of the letter. Proofread, edit and polish your letter after writing. As it is a printed document, there should be no room for errors. Correct grammar mistakes, proper punctuation, and misspellings to avoid miscommunication and misunderstanding.
What is a business letter?
A business letter is a document that companies or businesses use as a means to talk about business-related information that is essential for partnerships. The letter contains details that would vary with the nature of the letter. In addition, a business letter provides companies or businesses to discuss opportunities that could benefit all partners involved. When you write a business letter, the main thing that you need to remember is to keep it professional. The tone of your letter should be about how you professionally feel and not something that may be written in a generic or computerized manner.
How to not write a business letter?
There are a lot of things you have to avoid when writing a business letter. The most common thing to avoid is making erasures of the document. Business letters are professional letters written by professionals. When there are a lot of erasures in a business letter, the chances of someone reading them are very slim. They would think your letter is only made to displease and would simply ignore it due to excessive erasures. Another thing to avoid when writing a business letter is the language you will be using. It goes without saying, the language you use should be appropriate for the
What are the types of business letters?
There are many types of business letters to choose from. Each business letter has its own set of roles to play, so choose wisely when you start writing one from scratch. The types include cover letters , thank you letters , acknowledgment letters , resignation letters , complaint letters , memos , and more.
When it comes to writing business letters, you must be careful as to the nature of your letters, how you write them and what they are for. As there are a lot of types of business letters and each serves its purpose. As you continue to scroll for the kind of business letter you plan to make, always choose the right template and follow the correct format to write your business letters. Take advantage of the examples and pick one for an easier way to start your business letter.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
Write a letter to parents informing them about the upcoming parent-teacher conference at school
Compose a letter to students congratulating them on their achievements in the recent science fair.
How do I make a PDF accessible?
What is a pdf, anyway.
PDF stands for portable document format—it’s a file type. After you create a document in an authoring tool first, such as Google Docs, Word, or InDesign, you can then export your document as a PDF.
You may have heard people say that you need Adobe Acrobat Pro to create accessible PDFs. You do need Acrobat Pro (or a comparable tool) to check the accessibility of PDFs, but it’s important to note that Acrobat Pro is not an authoring tool. Acrobat Pro is used to add accessibility and other features to PDF files.
Do you have to use a PDF?
We’ll give it to you straight: making accessible PDFs is tough. If your information can be shared as a web page instead, please do so. Web content is inherently more accessible, and with content management systems such as Open Berkeley , it’s easy to make your web content accessible.
If you must use a PDF…
If you produce PDF documents, there are some important things to be aware of:
- It’s easier to create an accessible PDF by starting with an accessible source document (if possible).
- Remediating an existing PDF that isn’t accessible is extremely difficult to learn and time-consuming.
- The accessibility of PDFs can vary widely; some PDFs are completely unusable for some users. Conversely, a PDF that was designed to be accessible can work well for most users.
- Some PDFs don’t allow text to reflow, so low vision and mobile users may have a very hard time reading them. This often happens with PDF forms, or with complex documents containing tables, multiple columns, or complex graphics. (Note: Reflow is when text adapts to screen size so it doesn’t get cut off or require horizontal scrolling.)
- Browser previews may not function correctly and users may not understand they have to download the document.
- Large PDFs may be slow to download, too large to email, or use too much data.
What does it mean for a PDF to be accessible?
- Machine readable text : If you scan in a paper document or “print to PDF”, your PDF will be an image-only file. Screen readers can not read images of text.
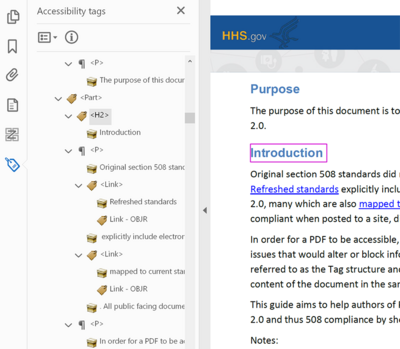
- Tags : The text in a PDF needs to have tags that describe the function and layout. This is what allows PDFs to work with assistive technologies. These tags are similar to html tags and describe paragraphs, lists, headings, and more.
- Complies with WCAG : The same accessibility features and concepts that are required for websites are required for electronic documents.
Here's an example of PDF tags shown in the Tag Pane in Adobe Acrobat Pro:
Two ways to create an accessible PDF
- Design your document to be accessible in your authoring tool . Then export it as an accessible PDF. If you have access to Acrobat Pro, use the PDF accessibility checker tool. --OR--
- Remediation : This requires you to use Acrobat Pro to add the proper tags to your document manually. This method allows you to fix a document that lacks accessibility, as is often the case with old legacy documents.
A note about authoring tools
- Word : If you use the correct styles to structure your document and design it to be accessible, you can export a tagged, accessible PDF from Word .
- Google Docs : Begin with an accessible Google Doc . Do NOT export your Google Doc as a PDF– this strips out all the tags! Instead, export as a Word document and then export it as a PDF from Word. Or, use the paid version of Grackle Docs to export accessible PDFs directly from Google Docs.
- InDesign : There are steps you can take to improve the accessibility of a PDF exported from InDesign , but in most cases, some remediation work will still need to be done.
Document types
- Important: PDF forms must be remediated to be accessible . Because of the interactivity of form fields, they require that additional tags be added in Acrobat Pro to be accessible. They can not be made accessible in authoring tools at this time. If you can use a webform instead (Qualtrics, Google Forms, etc), that’s always preferable. Another option is to make the static text portion accessible and then use Docusign to add accessible form fields.
- Simple text-based documents can be designed to be accessible in the authoring program (Google Docs or Word) and exported as accessible PDFs. (In Google Docs, use Word or the paid version of Grackle Docs as an intermediary.)
- Complex documents , such as reports with multiple columns, images, large tables, and infographics are difficult to make accessible in authoring programs. Professional remediation is recommended.
Prioritizing PDF remediation
There is no better time than now to audit the documents on your web sites. Once you’ve decided which PDFs you must keep as PDFs, focus on fixing the PDFs that create the biggest barriers:
- PDF forms: These are totally unusable for some users if they aren’t accessible. Because forms are typically a requirement for access to service, they should be a top priority.
- Critical information
- Complex documents
Professional remediation services
We are working to provide Berkeley with PDF remediation services. Please check back in Fall 2023 for updates.
- Crawford Technologies (available soon)
- Grackle (Google Add-ons and remediation services available soon)
More resources
- Adobe: Create and verify PDF accessibility (Acrobat Pro)
- University of Oregon: PDF Forms
- Accessibility Guy: PDF Accessibility video series on YouTube (2 - 7 minutes per video)
Learn to remediate PDFs on LinkedIn Learning:
- PDF remediation (5 hours)
- Advanced Accessible PDFs (6 hours)
Was this page helpful?
Tell us what you think.
Digital Document Requirements
Learn what the accessibility requirements are for PDFs and other digital documents
Steps for Site Owners
Making your digital documents accessible
Training Resources
Training resources to make your digital documents accessible
Log in using your username and password
- Search More Search for this keyword Advanced search
- Latest content
- Current issue
- BMJ Journals
You are here
- Online First
- Meta-analysis of continuous outcomes: a user’s guide for analysis and interpretation
- Article Text
- Article info
- Citation Tools
- Rapid Responses
- Article metrics
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-2845-8174 Madelin R Siedler 1 , 2 ,
- Reem A Mustafa 1 , 3 , 4 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0002-3562-9816 Lifeng Lin 5 ,
- Rebecca L Morgan 1 , 3 , 6 ,
- Yngve Falck-Ytter 1 , 6 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0003-2819-2553 Philipp Dahm 1 , 7 , 8 ,
- Shahnaz Sultan 1 , 9 ,
- http://orcid.org/0000-0001-5502-5975 Mohammad Hassan Murad 1 , 10
- 1 Evidence Foundation , Cleveland , OH , USA
- 2 Kinesiology and Sport Management , Texas Tech University , Lubbock , TX , USA
- 3 Department of Health Research Methods, Evidence and Impact , McMaster University , Hamilton , Ontario , Canada
- 4 Department of Internal Medicine , The University of Kansas Medical Center , Kansas City , Kansas , USA
- 5 Department of Epidemiology and Biostatistics , The University of Arizona Mel and Enid Zuckerman College of Public Health , Tucson , Arizona , USA
- 6 School of Medicine , Case Western Reserve University , Cleveland , Ohio , USA
- 7 Urology Section , Minneapolis VA Health Care System , Minneapolis , Minnesota , USA
- 8 Department of Urology , University of Minnesota Twin Cities , Minneapolis , Minnesota , USA
- 9 Division of Gastroenterology , University of Minnesota , Minneapolis , Minnesota , USA
- 10 Evidence-based Practice Center, Robert D. and Patricia E. Kern Center for the Science of Health Care Delivery , Mayo Clinic , Rochester , Minnesota , USA
- Correspondence to Madelin R Siedler; madelinsiedler{at}gmail.com
https://doi.org/10.1136/bmjebm-2024-113031
Statistics from Altmetric.com
Request permissions.
If you wish to reuse any or all of this article please use the link below which will take you to the Copyright Clearance Center’s RightsLink service. You will be able to get a quick price and instant permission to reuse the content in many different ways.
- Systematic Reviews as Topic
Introduction
Binary outcomes, such as mortality and myocardial infarction, are often viewed as most important to patients. However, outcomes that are expressed on a non-dichotomous scale such as quality of life, severity of depression or length of hospitalization, can also be critical to patients. For the purposes of this paper, all of the above examples will be referred to as continuous outcomes. While many binary outcomes are dichotomised from a continuous scale and in some cases can accommodate non-linear associations, such dichotomisation can also lead to loss of information. 1
Identifying continuous variables
A continuous variable is defined as a variable that assumes one of infinite values within a range. Thus, it does not assume discrete values. Continuous variables are often called ‘numerical variables’ and can be further categorised as either interval or ratio variables (box 1). Both types are usually treated similarly during statistical analysis and as outcome measures in meta-analysis. 4
Types of continuous variables
Interval variables: a continuous or numerical variable where the difference between two values is meaningful, …
X @EBMUrology
Contributors Writing—original draft: MRS and MHM. Writing—review and editing: RAM, LL, RLM, YF-Y, PD, SS and MHM.
Funding The authors have not declared a specific grant for this research from any funding agency in the public, commercial or not-for-profit sectors.
Competing interests The authors declare no financial conflicts of interest. MRS, RAM, RLM, YF-Y, PD, SS and MHM are members of the US GRADE Network. MRS is a fellow of the Evidence Foundation and receives a direct stipend. All other authors declare no conflicts of interest.
Provenance and peer review Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Read the full text or download the PDF:

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4 Make a specific point. Determine what the purpose of your essay is. State that point in your thesis statement, or controlling idea, and build upon it throughout the essay by using examples, stories, and other details that all relate back to the main idea. 4 Involve readers in the story and create a visual picture by using dialogue and ...
An essay is a focused piece of writing designed to inform or persuade. There are many different types of essay, but they are often defined in four categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive essays. Argumentative and expository essays are focused on conveying information and making clear points, while narrative and ...
1. Funding. 2. Curriculum. 3. Admissions Policy Conclusion. Sometimes organizing a comparison-and-contrast essay by subject tends to break up the analysis and make the essay seem choppy. If so, you can try organizing point-by-point. In this pattern of organization, you would discuss one assertion about both subjects, then another, and another, etc.
Answer the question; keep it relevant. Develop a logical and clearly structured argument. Support and illustrate your argument. Go beyond description to demonstrate critical thinking. Practice writing and proofreading. 3. Plan Your Essay. Every essay needs a strong and clear structure, organized around an argument.
Different Types of Essays in Composition Analysis Imagine receiving a vague text from a crush, overthinking it, wondering "What does it mean?!", interpreting it based on outside evidence and then writing an essay about it. The word "analyze" means to look deeply into a subject, ask questions about it, and reveal some
Writers learn different strategies for articulating the implications of an argument—why it matters—and putting ideas in conversation with others by finding, reading, and incorporating ... The Into the Essay examples come from papers on Shakespeare's play Hamlet. I'm a Shakespeare nut, and one key to good writing is to write about what
Some common types of expository writing assignments are the compare and contrast essay and the cause and effect essay. In a compare and contrast essay, you should investigate the similarities and differences between two things (e.g., theories, time periods, people, places, etc.), evaluate them, and then present the findings to your reader.
The four main types of writing. In many of the online resources you'll find about the types of essays, you'll find references to the four main types of writing: Persuasive. Descriptive. Narrative. Expository. These aren't four specific types of essays, but four distinct methods of communicating an essay's theme.
The most common criticisms of markers often focus on the five broad skills below: ♦ Students need to be analytical. ♦ Students need to use evidence effectively. ♦ Students need to structure their essays logically. ♦ Students need to be critical and persuasive. ♦ Students need to write in an academic style.
provide when you are writing a paper. Here are some useful guidelines: o If you're writing a research paper, do not assume that your reader has read all the sources that you are writing about. You'll need to offer context about what those sources say so that your reader can understand why you have brought them into the conversation.
Understanding the different types of essays is important in academics. There are four primary categories: argumentative, expository, narrative, and descriptive and each type serves a distinct purpose. This guide will explore each type and its subtypes with examples providing clear examples to improve your writing skills.
Introduction: Present the argument with a clear thesis, outlining the stance to be defended. Body: Provide factual evidence and counterarguments, presenting a well-rounded perspective. Conclusion: Summarise the key points and reinforce the chosen stance, leaving a lasting impression on the reader. 8. Persuasive Essays.
Strategies for Essay Writing: PDFs Strategies for Essay Writing--Complete. description. Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt. description. Asking Analytical Questions. description. Thesis. description. Introductions. description. What Do Introductions Across the Disciplines Have in Common? description. Anatomy Of a Body Paragraph.
Examples Of Different Types Of Essays Writing an essay on the topic of "Examples of Different Types of Essays" can be both challenging and rewarding. The difficulty lies in the broad scope of the subject, as it requires a comprehensive understanding of various essay types, their distinctive features, and how to effectively illustrate each category with relevant examples.
Essays Inducing Change. • Argument/Persuasion. You will be asked to write all three types of essays—papers that express feelings, explain ideas, or attempt to change a reader's mind. Sometimes essays can use more than one pattern of organization to support a larger purpose. For example, an essay that seeks to compare the presidencies of ...
Writing 101: The 8 Common Types of Essays. Whether you're a first-time high school essay writer or a professional writer about to tackle another research paper, you'll need to understand the fundamentals of essay writing before you put pen to paper and write your first sentence.
Expository essays: An expository essay is an informative piece of writing, where the writer explains a topic, using facts, statistics, and examples. An expository essay never uses personal comments, thoughts and ideas. It uses only facts. Example: The risks associated with drug experimentation depend on various factors, such as quantity ...
Situations and Purposes in Writing A Writing Situation is about taking into consideration: •The audience •The purpose The purpose in writing can be informative (such as encyclopedias, web pages, etc.), expressive (such as letters, journals, poetry).
Sentence Types and Functions, Spring 2014. 2 of 6 What Are the Different Types of Sentences? Sentences are divided into four categories: simple sentences, compound sentences, complex sentences, and compound-complex sentences. Simple Sentences Definition A simple sentence contains one independent clause. Examples Johnny rode his bike to school.
Essay Type This type of essay should be fully thought out and developed in as much detail as you have time for. ... Use specific examples from each version to argue which version is better. 2. Define what is meant by "freedom of the press." 3. Argue whether computers will or will not simulate most aspects of human intelligence in the
Free Essay. Embark on your essay writing journey with our comprehensive guide, rich in diverse essay examples. This guide is crafted to assist students, educators, and writing enthusiasts in mastering the art of essay composition. From structure to style, it covers all facets of essay writing, supplemented with illustrative essay examples for ...
Depending on the purpose for writing, a writer must develop one of the four types of paragraphs: expository (to explain or inform), persuasive (to persuade), descriptive (to describe), or narrative (to tell a story). The Persuasive Paragraph. The persuasive paragraph is an attempt by the writer to convince the audience (readers) to agree with ...
The document discusses four major types of essays: 1. Narrative essays involve telling a story from the writer's experience in an engaging way. 2. Descriptive essays paint a picture with words by describing a person, place, object, or memory in a vivid, emotive manner. 3. Expository essays present a balanced analysis and explanation of a topic using facts, examples, and statistics without ...
What "family" means in different types of families; ... Family Essay Example: Why family support is important for personal growth ... But what about PDF... August 16, 2024 How to Write a Dialogue in an Essay: Useful Tips. A correct usage of dialogues in essays may seem quite difficult at first sight. Still there are special issues, for instance ...
Students learn about the different forms of government that exist, including democracy, autocracy, oligarchy, and others. They compare and contrast these forms, and they look at real-life examples in the world today. iCivics en español! Student and class materials for this lesson are available in Spanish.
As there are a lot of types of business letters and each serves its purpose. As you continue to scroll for the kind of business letter you plan to make, always choose the right template and follow the correct format to write your business letters. Take advantage of the examples and pick one for an easier way to start your business letter.
Here's an example of PDF tags shown in the Tag Pane in Adobe Acrobat Pro: Two ways to create an accessible PDF. Design your document to be accessible in your authoring tool. Then export it as an accessible PDF. If you have access to Acrobat Pro, use the PDF accessibility checker tool. ... Document types. Important: PDF forms must be remediated ...
Binary outcomes, such as mortality and myocardial infarction, are often viewed as most important to patients. However, outcomes that are expressed on a non-dichotomous scale such as quality of life, severity of depression or length of hospitalization, can also be critical to patients. For the purposes of this paper, all of the above examples will be referred to as continuous outcomes. While ...