- Search Menu
- Sign in through your institution
- Browse content in Arts and Humanities
- Browse content in Archaeology
- Prehistoric Archaeology
- Browse content in Art
- History of Art
- Browse content in Classical Studies
- Classical History
- Classical Literature
- Classical Reception
- Greek and Roman Archaeology
- Digital Humanities
- Browse content in History
- Diplomatic History
- Environmental History
- Genocide and Ethnic Cleansing
- History by Period
- Legal and Constitutional History
- Regional and National History
- Social and Cultural History
- Theory, Methods, and Historiography
- World History
- Browse content in Language Teaching and Learning
- Language Teaching Theory and Methods
- Browse content in Linguistics
- Applied Linguistics
- Language Evolution
- Language Families
- Lexicography
- Browse content in Literature
- Bibliography
- Literary Studies (American)
- Literary Studies (20th Century onwards)
- Literary Studies (British and Irish)
- Literary Studies (Women's Writing)
- Literary Theory and Cultural Studies
- Shakespeare Studies and Criticism
- Browse content in Media Studies
- Browse content in Music
- Applied Music
- Medicine and Music
- Music Theory and Analysis
- Musical Structures, Styles, and Techniques
- Musicology and Music History
- Browse content in Philosophy
- Aesthetics and Philosophy of Art
- Epistemology
- History of Western Philosophy
- Metaphysics
- Moral Philosophy
- Philosophy of Science
- Philosophy of Mind
- Philosophy of Mathematics and Logic
- Practical Ethics
- Browse content in Religion
- Christianity
- Judaism and Jewish Studies
- Religion and Science
- Religion and Law
- Religion and Art, Literature, and Music
- Religious Studies
- Browse content in Society and Culture
- Ethical Issues and Debates
- Browse content in Law
- Arbitration
- Company and Commercial Law
- Comparative Law
- Competition Law
- Browse content in Constitutional and Administrative Law
- Parliamentary and Legislative Practice
- Employment and Labour Law
- Environment and Energy Law
- Financial Law
- History of Law
- Human Rights and Immigration
- Intellectual Property Law
- Browse content in International Law
- Private International Law and Conflict of Laws
- Public International Law
- IT and Communications Law
- Jurisprudence and Philosophy of Law
- Law and Society
- Legal System and Practice
- Medical and Healthcare Law
- Browse content in Medicine and Health
- Browse content in Allied Health Professions
- Dietetics and Nutrition
- Physiotherapy
- Radiography
- Anaesthetics
- Browse content in Clinical Medicine
- Acute Medicine
- Cardiovascular Medicine
- Clinical Pharmacology and Therapeutics
- Dermatology
- Endocrinology and Diabetes
- Gastroenterology
- Geriatric Medicine
- Infectious Diseases
- Medical Toxicology
- Medical Oncology
- Rheumatology
- Sleep Medicine
- Clinical Neuroscience
- Community Medical Services
- Critical Care
- Forensic Medicine
- History of Medicine
- Browse content in Medical Dentistry
- Restorative Dentistry and Orthodontics
- Medical Skills
- Medical Ethics
- Medical Statistics and Methodology
- Browse content in Neurology
- Neuropathology
- Nursing Studies
- Browse content in Obstetrics and Gynaecology
- Gynaecology
- Occupational Medicine
- Paediatrics
- Browse content in Pathology
- Clinical Cytogenetics and Molecular Genetics
- Medical Microbiology and Virology
- Patient Education and Information
- Browse content in Pharmacology
- Psychopharmacology
- Browse content in Preclinical Medicine
- Molecular Biology and Genetics
- Reproduction, Growth and Development
- Primary Care
- Professional Development in Medicine
- Browse content in Psychiatry
- Child and Adolescent Psychiatry
- Forensic Psychiatry
- Browse content in Public Health and Epidemiology
- Epidemiology
- Public Health
- Browse content in Radiology
- Clinical Radiology
- Interventional Radiology
- Radiation Oncology
- Reproductive Medicine
- Browse content in Surgery
- Cardiothoracic Surgery
- Gastro-intestinal and Colorectal Surgery
- Neurosurgery
- Plastic and Reconstructive Surgery
- Trauma and Orthopaedic Surgery
- Browse content in Science and Mathematics
- Browse content in Biological Sciences
- Aquatic Biology
- Biochemistry
- Bioinformatics and Computational Biology
- Developmental Biology
- Ecology and Conservation
- Evolutionary Biology
- Genetics and Genomics
- Microbiology
- Molecular and Cell Biology
- Plant Sciences and Forestry
- Research Methods in Life Sciences
- Structural Biology
- Systems Biology
- Zoology and Animal Sciences
- Browse content in Chemistry
- Medicinal Chemistry
- Mineralogy and Gems
- Physical Chemistry
- Browse content in Computer Science
- Artificial Intelligence
- Computer Architecture and Logic Design
- Human-Computer Interaction
- Mathematical Theory of Computation
- Browse content in Computing
- Computer Security
- Computer Networking and Communications
- Browse content in Earth Sciences and Geography
- Atmospheric Sciences
- Environmental Geography
- Geology and the Lithosphere
- Meteorology and Climatology
- Browse content in Engineering and Technology
- Agriculture and Farming
- Biological Engineering
- Civil Engineering, Surveying, and Building
- Energy Technology
- Engineering (General)
- Environmental Science, Engineering, and Technology
- Transport Technology and Trades
- Browse content in Environmental Science
- Environmental Sustainability
- Management of Land and Natural Resources (Environmental Science)
- Browse content in Materials Science
- Ceramics and Glasses
- Composite Materials
- Nanotechnology
- Browse content in Mathematics
- Applied Mathematics
- Biomathematics and Statistics
- Mathematical Education
- Mathematical Analysis
- Probability and Statistics
- Pure Mathematics
- Browse content in Neuroscience
- Cognition and Behavioural Neuroscience
- Neuroscientific Techniques
- Browse content in Physics
- Astronomy and Astrophysics
- Classical Mechanics
- Relativity and Gravitation
- Browse content in Psychology
- Clinical Psychology
- Cognitive Psychology
- Cognitive Neuroscience
- Health Psychology
- Music Psychology
- Neuropsychology
- Organizational Psychology
- Browse content in Social Sciences
- Browse content in Anthropology
- Human Evolution
- Browse content in Business and Management
- Human Resource Management
- Industrial and Employment Relations
- Industry Studies
- Information and Communication Technologies
- Organizational Theory and Behaviour
- Public and Nonprofit Management
- Browse content in Criminology and Criminal Justice
- Criminology
- Browse content in Economics
- Agricultural, Environmental, and Natural Resource Economics
- Behavioural Economics and Neuroeconomics
- Econometrics and Mathematical Economics
- Economic History
- Economic Development and Growth
- Financial Markets
- Financial Institutions and Services
- Health, Education, and Welfare
- Labour and Demographic Economics
- Law and Economics
- Public Economics
- Urban, Rural, and Regional Economics
- Browse content in Education
- Schools Studies
- Teaching of Specific Groups and Special Educational Needs
- Environment
- Browse content in Human Geography
- Economic Geography
- Browse content in Interdisciplinary Studies
- Communication Studies
- Museums, Libraries, and Information Sciences
- Browse content in Politics
- Foreign Policy
- Gender and Politics
- International Relations
- International Organization (Politics)
- Political Sociology
- Political Behaviour
- Political Economy
- Political Institutions
- Political Theory
- Public Administration
- Public Policy
- Quantitative Political Methodology
- Regional Political Studies
- Security Studies
- Browse content in Regional and Area Studies
- African Studies
- Japanese Studies
- Research and Information
- Browse content in Social Work
- Addictions and Substance Misuse
- Browse content in Sociology
- Economic Sociology
- Gender and Sexuality
- Gerontology and Ageing
- Health, Illness, and Medicine
- Migration Studies
- Race and Ethnicity
- Social Movements and Social Change
- Social Research and Statistics
- Social Stratification, Inequality, and Mobility
- Sociology of Religion
- Urban and Rural Studies
- Journals A to Z
- Books on Oxford Academic


High Impact Sociology Research
Oxford University Press publishes a portfolio of leading Sociology journals. To keep up to date with the latest research your peers are reading and citing, browse our selection of high impact articles on a diverse breadth of topics below.
All articles are freely available to read, download, and enjoy until May 2023.
- Community Development Journal
- European Sociological Review
- International Political Sociology
- Journal of Human Rights Practice
- Journal of Refugee Studies
- Refugee Survey Quarterly
- Social Forces
- Social Politics
- Social Problems
- Social Science Japan Journal
- Sociology of Religion
- The British Journal of Criminology
Community Development Journal
Covid-19 and community development Sue Kenny Community Development Journal , Volume 55, Issue 4, October 2020, Pages 699–703, https://doi.org/10.1093/cdj/bsaa020
Financialization, real estate and COVID-19 in the UK Grace Blakeley Community Development Journal , Volume 56, Issue 1, January 2021, Pages 79–99, https://doi.org/10.1093/cdj/bsaa056
Financial subordination and uneven financialization in 21st century Africa Ingrid Harvold Kvangraven, Kai Koddenbrock, Ndongo Samba Sylla Community Development Journal , Volume 56, Issue 1, January 2021, Pages 119–140, https://doi.org/10.1093/cdj/bsaa047
CDJ Editorial—What is this Covid-19 crisis? Rosie R. Meade Community Development Journal , Volume 55, Issue 3, July 2020, Pages 379–381, https://doi.org/10.1093/cdj/bsaa013
There’s a time and a place: temporal aspects of place-based stigma Alice Butler-Warke Community Development Journal , Volume 56, Issue 2, April 2021, Pages 203–219, https://doi.org/10.1093/cdj/bsaa040
European Sociological Review
Cohort Changes in the Level and Dispersion of Gender Ideology after German Reunification: Results from a Natural Experiment Christian Ebner, Michael Kühhirt, Philipp Lersch European Sociological Review , Volume 36, Issue 5, October 2020, Pages 814–828, https://doi.org/10.1093/esr/jcaa015
‘Cologne Changed Everything’—The Effect of Threatening Events on the Frequency and Distribution of Intergroup Conflict in Germany Arun Frey European Sociological Review , Volume 36, Issue 5, October 2020, Pages 684–699, https://doi.org/10.1093/esr/jcaa007
The Accumulation of Wealth in Marriage: Over-Time Change and Within-Couple Inequalities Nicole Kapelle, Philipp M. Lersch European Sociological Review , Volume 36, Issue 4, August 2020, Pages 580–593, https://doi.org/10.1093/esr/jcaa006
Three Worlds of Vocational Education: Specialized and General Craftsmanship in France, Germany, and The Netherlands Jesper Rözer, Herman G. van de Werfhorst European Sociological Review , Volume 36, Issue 5, October 2020, Pages 780–797, https://doi.org/10.1093/esr/jcaa025
Intergenerational Class Mobility among Men and Women in Europe: Gender Differences or Gender Similarities? Erzsébet Bukodi, Marii Paskov European Sociological Review , Volume 36, Issue 4, August 2020, Pages 495–512, https://doi.org/10.1093/esr/jcaa001
International Political Sociology
Confronting the International Political Sociology of the New Right Rita Abrahamsen, Jean-François Drolet, Alexandra Gheciu, Karin Narita, Srdjan Vucetic, Michael Williams International Political Sociology , Volume 14, Issue 1, March 2020, Pages 94–107, https://doi.org/10.1093/ips/olaa001
Collective Discussion: Toward Critical Approaches to Intelligence as a Social Phenomenon Hager Ben Jaffel, Alvina Hoffmann, Oliver Kearns, Sebastian Larsson International Political Sociology , Volume 14, Issue 3, September 2020, Pages 323–344, https://doi.org/10.1093/ips/olaa015
The Cruel Optimism of Militarism: Feminist Curiosity, Affect, and Global Security Amanda Chisholm, Hanna Ketola International Political Sociology, Volume 14 , Issue 3, September 2020, Pages 270–285, https://doi.org/10.1093/ips/olaa005
Feminist Commodity Activism: The New Political Economy of Feminist Protest Jemima Repo International Political Sociology , Volume 14, Issue 2, June 2020, Pages 215–232, https://doi.org/10.1093/ips/olz033
Affect and the Response to Terror: Commemoration and Communities of Sense Angharad Closs Stephens, Martin Coward, Samuel Merrill, Shanti Sumartojo International Political Sociology , Volume 15, Issue 1, March 2021, Pages 22–40, https://doi.org/10.1093/ips/olaa020
Journal of Human Rights Practice
Africa, Prisons and COVID-19 Lukas M. Muntingh Journal of Human Rights Practice , Volume 12, Issue 2, July 2020, Pages 284–292, https://doi.org/10.1093/jhuman/huaa031
Pandemic Powers: Why Human Rights Organizations Should Not Lose Focus on Civil and Political Rights Eda Seyhan Journal of Human Rights Practice , Volume 12, Issue 2, July 2020, Pages 268–275, https://doi.org/10.1093/jhuman/huaa035
Affirming Radical Equality in the Context of COVID-19: Human Rights of Older People and People with Disabilities Supriya Akerkar Journal of Human Rights Practice , Volume 12, Issue 2, July 2020, Pages 276–283, https://doi.org/10.1093/jhuman/huaa032
Digital Dead Body Management (DDBM): Time to Think it Through Kristin Bergtora Sandvik Journal of Human Rights Practice, Volume 12 , Issue 2, July 2020, Pages 428–443, https://doi.org/10.1093/jhuman/huaa002
Legal Reasoning for Legitimation of Child Marriage in West Java: Accommodation of Local Norms at Islamic Courts and the Paradox of Child Protection Hoko Horii Journal of Human Rights Practice , Volume 12, Issue 3, November 2020, Pages 501–523, https://doi.org/10.1093/jhuman/huaa041
Journal of Refugee Studies
Refugee-Integration-Opportunity Structures: Shifting the Focus From Refugees to Context Jenny Phillimore Journal of Refugee Studies , Volume 34, Issue 2, June 2021, Pages 1946–1966, https://doi.org/10.1093/jrs/feaa012
What Difference do Mayors Make? The Role of Municipal Authorities in Turkey and Lebanon's Response to Syrian Refugees Alexander Betts, Fulya MemiŞoĞlu, Ali Ali Journal of Refugee Studies , Volume 34, Issue 1, March 2021, Pages 491–519, https://doi.org/10.1093/jrs/feaa011
Old Concepts Making New History: Refugee Self-reliance, Livelihoods and the ‘Refugee Entrepreneur’ Claudena Skran, Evan Easton-Calabria Journal of Refugee Studies , Volume 33, Issue 1, March 2020, Pages 1–21, https://doi.org/10.1093/jrs/fez061
Research with Refugees in Fragile Political Contexts: How Ethical Reflections Impact Methodological Choices Lea Müller-Funk Journal of Refugee Studies , Volume 34, Issue 2, June 2021, Pages 2308–2332, https://doi.org/10.1093/jrs/feaa013
The Kalobeyei Settlement: A Self-reliance Model for Refugees? Alexander Betts, Naohiko Omata, Olivier Sterck Journal of Refugee Studies , Volume 33, Issue 1, March 2020, Pages 189–223, https://doi.org/10.1093/jrs/fez063
Migration Studies
International migration management in the age of artificial intelligence Ana Beduschi Migration Studies , Volume 9, Issue 3, September 2021, Pages 576–596, https://doi.org/10.1093/migration/mnaa003
Migration as Adaptation? Kira Vinke, Jonas Bergmann, Julia Blocher, Himani Upadhyay, Roman Hoffmann Migration Studies , Volume 8, Issue 4, December 2020, Pages 626–634, https://doi.org/10.1093/migration/mnaa029
Research on climate change and migration where are we and where are we going? Elizabeth Ferris Migration Studies , Volume 8, Issue 4, December 2020, Pages 612–625, https://doi.org/10.1093/migration/mnaa028
The emotional journey of motherhood in migration. The case of Southern European mothers in Norway Raquel Herrero-Arias, Ragnhild Hollekim, Haldis Haukanes, Åse Vagli Migration Studies , Volume 9, Issue 3, September 2021, Pages 1230–1249, https://doi.org/10.1093/migration/mnaa006
'I felt like the mountains were coming for me.'-The role of place attachment and local lifestyle opportunities for labour migrants' staying aspirations in two Norwegian rural municipalities Brit Lynnebakke Migration Studies , Volume 9, Issue 3, September 2021, Pages 759–782, https://doi.org/10.1093/migration/mnaa002
Refugee Survey Quarterly
Refugee Rights Across Regions: A Comparative Overview of Legislative Good Practices in Latin America and the EU Luisa Feline Freier, Jean-Pierre Gauci Refugee Survey Quarterly , Volume 39, Issue 3, September 2020, Pages 321–362, https://doi.org/10.1093/rsq/hdaa011
Syrian Refugee Migration, Transitions in Migrant Statuses and Future Scenarios of Syrian Mobility Marko Valenta, Jo Jakobsen, Drago Župarić-Iljić, Hariz Halilovich Refugee Survey Quarterly , Volume 39, Issue 2, June 2020, Pages 153–176, https://doi.org/10.1093/rsq/hdaa002
Ambiguous Encounters: Revisiting Foucault and Goffman at an Activation Programme for Asylum-seekers Katrine Syppli Kohl Refugee Survey Quarterly , Volume 39, Issue 2, June 2020, Pages 177–206, https://doi.org/10.1093/rsq/hdaa004
Behind the Scenes of South Africa’s Asylum Procedure: A Qualitative Study on Long-term Asylum-Seekers from the Democratic Republic of Congo Liesbeth Schockaert, Emilie Venables, Maria-Teresa Gil-Bazo, Garret Barnwell, Rodd Gerstenhaber, Katherine Whitehouse Refugee Survey Quarterly , Volume 39, Issue 1, March 2020, Pages 26–55, https://doi.org/10.1093/rsq/hdz018
Improving SOGI Asylum Adjudication: Putting Persecution Ahead of Identity Moira Dustin, Nuno Ferreira Refugee Survey Quarterly , Volume 40, Issue 3, September 2021, Pages 315–347, https://doi.org/10.1093/rsq/hdab005
Social Forces
Paths toward the Same Form of Collective Action: Direct Social Action in Times of Crisis in Italy Lorenzo Bosi, Lorenzo Zamponi Social Forces , Volume 99, Issue 2, December 2020, Pages 847–869, https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/soz160
Attitudes toward Refugees in Contemporary Europe: A Longitudinal Perspective on Cross-National Differences Christian S. Czymara Social Forces , Volume 99, Issue 3, March 2021, Pages 1306–1333, https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/soaa055
Opiate of the Masses? Inequality, Religion, and Political Ideology in the United States Landon Schnabel Social Forces , Volume 99, Issue 3, March 2021, Pages 979–1012, https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/soaa027
Re-examining Restructuring: Racialization, Religious Conservatism, and Political Leanings in Contemporary American Life John O’Brien, Eman Abdelhadi Social Forces , Volume 99, Issue 2, December 2020, Pages 474–503, https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/soaa029
Evidence from Field Experiments in Hiring Shows Substantial Additional Racial Discrimination after the Callback Lincoln Quillian, John J Lee, Mariana Oliver Social Forces , Volume 99, Issue 2, December 2020, Pages 732–759, https://doi.org/10.1093/sf/soaa026
Social Politics
Varieties of Gender Regimes Sylvia Walby Social Politics: International Studies in Gender, State & Society , Volume 27, Issue 3, Fall 2020, Pages 414–431, https://doi.org/10.1093/sp/jxaa018
The Origins and Transformations of Conservative Gender Regimes in Germany and Japan Karen A. Shire, Kumiko Nemoto Social Politics: International Studies in Gender, State & Society , Volume 27, Issue 3, Fall 2020, Pages 432–448, https://doi.org/10.1093/sp/jxaa017
Counteracting Challenges to Gender Equality in the Era of Anti-Gender Campaigns: Competing Gender Knowledges and Affective Solidarity Elżbieta Korolczuk Social Politics: International Studies in Gender, State & Society , Volume 27, Issue 4, Winter 2020, Pages 694–717, https://doi.org/10.1093/sp/jxaa021
Gender, Violence, and Political Institutions: Struggles over Sexual Harassment in the European Parliament Valentine Berthet, Johanna Kantola Social Politics: International Studies in Gender, State & Society , Volume 28, Issue 1, Spring 2021, Pages 143–167, https://doi.org/10.1093/sp/jxaa015
Gender Regime Change in Decentralized States: The Case of Spain Emanuela Lombardo, Alba Alonso Social Politics: International Studies in Gender, State & Society , Volume 27, Issue 3, Fall 2020, Pages 449–466, https://doi.org/10.1093/sp/jxaa016
Social Problems
Technologies of Crime Prediction: The Reception of Algorithms in Policing and Criminal Courts Sarah Brayne, Angèle Christin Social Problems , Volume 68, Issue 3, August 2021, Pages 608–624, https://doi.org/10.1093/socpro/spaa004
White Christian Nationalism and Relative Political Tolerance for Racists Joshua T. Davis, Samuel L. Perry Social Problems , Volume 68, Issue 3, August 2021, Pages 513–534, https://doi.org/10.1093/socpro/spaa002
The Increasing Effect of Neighborhood Racial Composition on Housing Values, 1980-2015 Junia Howell, Elizabeth Korver-Glenn Social Problems , Volume 68, Issue 4, November 2021, Pages 1051–1071, https://doi.org/10.1093/socpro/spaa033
Transition into Liminal Legality: DACA' Mixed Impacts on Education and Employment among Young Adult Immigrants in California Erin R. Hamilton, Caitlin Patler, Robin Savinar Social Problems , Volume 68, Issue 3, August 2021, Pages 675–695, https://doi.org/10.1093/socpro/spaa016
Constructing Allyship and the Persistence of Inequality J. E. Sumerau, TehQuin D. Forbes, Eric Anthony Grollman, Lain A. B. Mathers Social Problems , Volume 68, Issue 2, May 2021, Pages 358–373, https://doi.org/10.1093/socpro/spaa003
Social Science Japan Journal
Nuclear Restart Politics: How the ‘Nuclear Village’ Lost Policy Implementation Power Florentine Koppenborg Social Science Japan Journal , Volume 24, Issue 1, Winter 2021, Pages 115–135, https://doi.org/10.1093/ssjj/jyaa046
Factors Affecting Household Disaster Preparedness Among Foreign Residents in Japan David Green, Matthew Linley, Justin Whitney, Yae Sano Social Science Japan Journal , Volume 24, Issue 1, Winter 2021, Pages 185–208, https://doi.org/10.1093/ssjj/jyaa026
Climate Change Policy: Can New Actors Affect Japan's Policy-Making in the Paris Agreement Era? Yasuko Kameyama Social Science Japan Journal , Volume 24, Issue 1, Winter 2021, Pages 67–84, https://doi.org/10.1093/ssjj/jyaa051
Japan Meets the Sharing Economy: Contending Frames Thomas G. Altura, Yuki Hashimoto, Sanford M. Jacoby, Kaoru Kanai, Kazuro Saguchi Social Science Japan Journal , Volume 24, Issue 1, Winter 2021, Pages 137–161, https://doi.org/10.1093/ssjj/jyaa041
Administrative Measures Against Far-Right Protesters: An Example of Japan’s Social Control Ayaka Löschke Social Science Japan Journal , Volume 24, Issue 2, Summer 2021, Pages 289–309, https://doi.org/10.1093/ssjj/jyab005
Sociology of Religion
Religion in the Age of Social Distancing: How COVID-19 Presents New Directions for Research Joseph O. Baker, Gerardo Martí, Ruth Braunstein, Andrew L Whitehead, Grace Yukich Sociology of Religion , Volume 81, Issue 4, Winter 2020, Pages 357–370, https://doi.org/10.1093/socrel/sraa039
Keep America Christian (and White): Christian Nationalism, Fear of Ethnoracial Outsiders, and Intention to Vote for Donald Trump in the 2020 Presidential Election Joseph O. Baker, Samuel L. Perry, Andrew L. Whitehead Sociology of Religion , Volume 81, Issue 3, Autumn 2020, Pages 272–293, https://doi.org/10.1093/socrel/sraa015
Formal or Functional? Traditional or Inclusive? Bible Translations as Markers of Religious Subcultures Samuel L. Perry, Joshua B. Grubbs Sociology of Religion , Volume 81, Issue 3, Autumn 2020, Pages 319–342, https://doi.org/10.1093/socrel/sraa003
Political Identity and Confidence in Science and Religion in the United States Timothy L. O’Brien, Shiri Noy Sociology of Religion , Volume 81, Issue 4, Winter 2020, Pages 439–461, https://doi.org/10.1093/socrel/sraa024
Religious Freedom and Local Conflict: Religious Buildings and Zoning Issues in the New York City Region, 1992–2017 Brian J. Miller Sociology of Religion , Volume 81, Issue 4, Winter 2020, Pages 462–484, https://doi.org/10.1093/socrel/sraa006
The British Journal of Criminology
Reporting Racist Hate Crime Victimization to the Police in the United States and the United Kingdom: A Cross-National Comparison Wesley Myers, Brendan Lantz The British Journal of Criminology , Volume 60, Issue 4, July 2020, Pages 1034–1055, https://doi.org/10.1093/bjc/azaa008
Does Collective Efficacy Matter at the Micro Geographic Level?: Findings from a Study Of Street Segments David Weisburd, Clair White, Alese Wooditch The British Journal of Criminology , Volume 60, Issue 4, July 2020, Pages 873–891, https://doi.org/10.1093/bjc/azaa007
Responses to Wildlife Crime in Post-Colonial Times. Who Fares Best? Ragnhild Aslaug Sollund, Siv Rebekka Runhovde The British Journal of Criminology , Volume 60, Issue 4, July 2020, Pages 1014–1033, https://doi.org/10.1093/bjc/azaa005
‘Playing the Game’: Power, Authority and Procedural Justice in Interactions Between Police and Homeless People in London Arabella Kyprianides, Clifford Stott, Ben Bradford The British Journal of Criminology , Volume 61, Issue 3, May 2021, Pages 670–689, https://doi.org/10.1093/bjc/azaa086
Live Facial Recognition: Trust and Legitimacy as Predictors of Public Support For Police Use of New Technology Ben Bradford, Julia A Yesberg, Jonathan Jackson, Paul Dawson The British Journal of Criminology , Volume 60, Issue 6, November 2020, Pages 1502–1522, https://doi.org/10.1093/bjc/azaa032
Affiliations
- Copyright © 2024
- About Oxford Academic
- Publish journals with us
- University press partners
- What we publish
- New features
- Open access
- Institutional account management
- Rights and permissions
- Get help with access
- Accessibility
- Advertising
- Media enquiries
- Oxford University Press
- Oxford Languages
- University of Oxford
Oxford University Press is a department of the University of Oxford. It furthers the University's objective of excellence in research, scholarship, and education by publishing worldwide
- Copyright © 2024 Oxford University Press
- Cookie settings
- Cookie policy
- Privacy policy
- Legal notice
This Feature Is Available To Subscribers Only
Sign In or Create an Account
This PDF is available to Subscribers Only
For full access to this pdf, sign in to an existing account, or purchase an annual subscription.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
Sociology articles from across Nature Portfolio

Rising food and water insecurity among US children
Concurrent food and water insecurity doubled among children from 2005 to 2020, with minoritized children facing far more insecurity than their white counterparts.
- J. Tom Mueller
Latest Research and Reviews
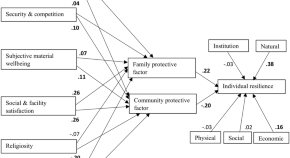
A dual pathway for understanding the relation between wellbeing and resilience
- Missiliana Riasnugrahani
- Tery Setiawan
- Bagus Takwin
Advancing criminal justice through mediation: analyzing the integration of mediation in Emirati criminal legislation
- Ahmed Ali Alnuaimi
- Mohammad Amin Alkrisheh
From “transitions” to “trajectories”: towards a holistic interactionistic analysis of educational inequality in contemporary China
- Xiangyang Bi
- Xueling Liu
Relation between attitudes towards pornography consumption, peer sexual behaviors and attitudes towards premarital sex among the college students in Guangdong province, China
- Yangzhi Peng
- Yongru Zheng
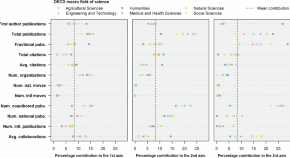
A global perspective on social stratification in science
- Aliakbar Akbaritabar
- Andrés Felipe Castro Torres
- Vincent Larivière
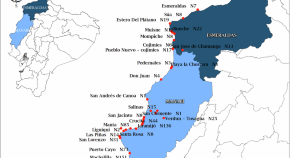
Sustainability and climate change: gender perspective in the traditional fishing sector in Ecuador
- Ana Gabriela Vélez Santana
- Barlin Orlando Olivares
- Rocío Serrano Rodríguez
News and Comment
Political obstacles to carbon capture and storage for carbon removal.
Using carbon dioxide capture and storage (CCS) for carbon removal is crucial to climate policy, but implementation at scale is at risk owing to political obstacles. Climate policies must avoid relying on empty promises of CCS for carbon removal without necessary financial resourcing and support emissions reductions separately from carbon removal.
- Nils Markusson
Safeguarding Saint Petersburg’s Skyline
Historical preservation of buildings can entail a preservation of the whole skyline. Anna Zhelnina tells the story of Saint Petersburg’s ‘city defenders’ and their mobilization.
- Anna Zhelnina

The science of protests: how to shape public opinion and swing votes
Demonstrations are on the rise, and scientists are revealing which types work best.
- Helen Pearson

‘It can feel like there’s no way out’ — political scientists face pushback on their work
In a year in which numerous countries are going to the polls, many election-watching scientists are under pressure.
- Dyani Lewis
- Alison Abbott
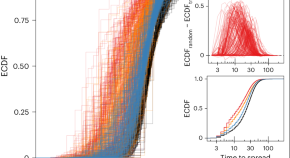
Long ties across networks accelerate the spread of social contagions
Long ties that bridge socially separate regions of networks are critical for the spread of contagions, such as innovations or adoptions of new norms. Contrary to previous thinking, long ties have now been found to accelerate social contagions, even for behaviours that involve the social reinforcement of adoption by network neighbours.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies
Sociology Research Network

Welcome to SociologyRN
The Sociology Research Network
- Conference Proceedings
- Job Openings
- Partners in Publishing
- Professional Announcements
- Research Paper Series
Sociology Preprints
Sociology is the systematic study of the society in which we live and the social causes and consequences of human behavior. The Sociology Research Network on SSRN is an open access preprint server that provides a venue for authors to showcase their research papers in our digital library, speeding up the dissemination and providing the scholarly community access to groundbreaking working papers and early stage research. SSRN provides the opportunity to share different outputs of research such as preprints, preliminary or exploratory investigations, book chapters, PhD dissertations, course and teaching materials, presentations, and posters among others. SSRN provides a platform for the early sharing of work, making it available for subsequent work to be built upon more quickly.
Sociologists investigate social inequalities related to race and ethnicity, socioeconomic status, and gender to enrich our understanding of the connections between individual lives and larger social structures. As a multidisciplinary field, sociology draws from a variety of other subjects within the social sciences. SSRN helps sociology scholars discover the latest research in their own and other areas of research including anthropology, political science, psychology, education, law, and economics while providing a unique opportunity for researchers to submit early and novel work for review, feedback, and use by researchers within and beyond sociology.

Sociology Papers
| . |
The American Sociological Association publishes 13 scholarly journals, including general interest journals and those focused on specialized areas of knowledge .

- Advertising
- American Sociological Review
- Annual Reports
- ASA Style Guide
- Be an Editor
- Mailing and Receipt Dates
- Online Posting Policy
- Reprint Permissions
- Submit Your Manuscript
1717 K Street NW, Suite 900 Washington, D.C. 20006 202.247.9840 [email protected]
- Join/Renew ASA Connect Find/Post a Job Donate
- Online Program
- Plenary Sessions
- Special Sessions
- Thematic Sessions
- Regional Spotlight
- Preconferences and Courses
- Access for All
- Exhibit Hall
- Regular Sessions
- Section Sessions
- Student Forum
- Practice Settings Symposium
- Teaching and Learning Symposium
- Preconferences
- Call for Submissions
- Registration
- Program Committee
- Call for Proposals
- Future Annual Meetings
- Annual Meeting Video Archive
- Previous Annual Meetings
- Teaching Ethics Throughout the Curriculum
- Professional Development Videos and Webinars
- ASA Department Affiliates
- ASA Program Reviewers and Consultants
- Major in Sociology
- Careers with a Sociology PhD
- Career Center
- ASA Doctoral Dissertation Research Improvement Grants
- Annual Meeting Travel Fund Awards
- CARI Award Recipients
- Howery Teaching Enhancement Fund Grants
- Sorokin Lecture Grants
- Student Forum Travel Awards
- Data Dashboard
- ASA Membership
- ASA Reports
- Bachelor’s and Beyond FAQ
- 2012 Participating Departments
- URM Scholars in Sociology and Economics
- Project Advisory Committee
- Current Sections
- Membership Data
- Award Nomination Calls
- Filipino Sociologists
- First-Generation and Working-Class Sociologists
- Korean Sociologists in America
- Sociologists Working Everywhere
- South Asian Sociologists
- For Students
- For Community College Faculty
- For Contingent Faculty
- For High School Faculty
- For Sociologists in Practice Settings
- Annual Invited Lecture
- Access Journals
- Rose Series
- Member News & Notes
- Status Committees
- Communities
- Organizational Diversity Data
- Disciplinary DEI
- Current Fellows
- Former Fellows
- Case Statement
- Testimonials
- Difference Makers Recognition Wall
- Donate/Pledge Now
- Value of Sociology
- Tools for Sociologists
- Podcast Library
- Advisory Board
- SAN Resources
- What is ASA?
- What is Sociology?
- Diversity Statement
- Standing Committees
- Audited Financial Statements
- Solicitation and Gift Acceptance Policy
- 2024 ASA Award Winners
- Advertising and Mailing Lists
- Find an Expert
- Press Releases
- Join or Renew Your Membership
- Membership Benefits
- Countries Eligible for International Associate Membership
- My ASA Member Portal
- Frequently Asked Questions
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Most Cited Papers
- Most Downloaded Papers
- Newest Papers
- Last »
- Social Theory Follow Following
- Political Sociology Follow Following
- Cultural Sociology Follow Following
- Sociological Theory Follow Following
- Sociology of Culture Follow Following
- Social Movements Follow Following
- Historical Sociology Follow Following
- Sociology of Knowledge Follow Following
- Critical Theory Follow Following
- Neoliberalism Follow Following
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- Academia.edu Journals
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
2.1 Approaches to Sociological Research
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you should be able to:
- Define and describe the scientific method.
- Explain how the scientific method is used in sociological research.
- Describe the function and importance of an interpretive framework.
- Describe the differences in accuracy, reliability and validity in a research study.
When sociologists apply the sociological perspective and begin to ask questions, no topic is off limits. Every aspect of human behavior is a source of possible investigation. Sociologists question the world that humans have created and live in. They notice patterns of behavior as people move through that world. Using sociological methods and systematic research within the framework of the scientific method and a scholarly interpretive perspective, sociologists have discovered social patterns in the workplace that have transformed industries, in families that have enlightened family members, and in education that have aided structural changes in classrooms.
Sociologists often begin the research process by asking a question about how or why things happen in this world. It might be a unique question about a new trend or an old question about a common aspect of life. Once the question is formed, the sociologist proceeds through an in-depth process to answer it. In deciding how to design that process, the researcher may adopt a scientific approach or an interpretive framework. The following sections describe these approaches to knowledge.
The Scientific Method
Sociologists make use of tried and true methods of research, such as experiments, surveys, and field research. But humans and their social interactions are so diverse that these interactions can seem impossible to chart or explain. It might seem that science is about discoveries and chemical reactions or about proving ideas right or wrong rather than about exploring the nuances of human behavior.
However, this is exactly why scientific models work for studying human behavior. A scientific process of research establishes parameters that help make sure results are objective and accurate. Scientific methods provide limitations and boundaries that focus a study and organize its results.
The scientific method involves developing and testing theories about the social world based on empirical evidence. It is defined by its commitment to systematic observation of the empirical world and strives to be objective, critical, skeptical, and logical. It involves a series of six prescribed steps that have been established over centuries of scientific scholarship.
Sociological research does not reduce knowledge to right or wrong facts. Results of studies tend to provide people with insights they did not have before—explanations of human behaviors and social practices and access to knowledge of other cultures, rituals and beliefs, or trends and attitudes.
In general, sociologists tackle questions about the role of social characteristics in outcomes or results. For example, how do different communities fare in terms of psychological well-being, community cohesiveness, range of vocation, wealth, crime rates, and so on? Are communities functioning smoothly? Sociologists often look between the cracks to discover obstacles to meeting basic human needs. They might also study environmental influences and patterns of behavior that lead to crime, substance abuse, divorce, poverty, unplanned pregnancies, or illness. And, because sociological studies are not all focused on negative behaviors or challenging situations, social researchers might study vacation trends, healthy eating habits, neighborhood organizations, higher education patterns, games, parks, and exercise habits.
Sociologists can use the scientific method not only to collect but also to interpret and analyze data. They deliberately apply scientific logic and objectivity. They are interested in—but not attached to—the results. They work outside of their own political or social agendas. This does not mean researchers do not have their own personalities, complete with preferences and opinions. But sociologists deliberately use the scientific method to maintain as much objectivity, focus, and consistency as possible in collecting and analyzing data in research studies.
With its systematic approach, the scientific method has proven useful in shaping sociological studies. The scientific method provides a systematic, organized series of steps that help ensure objectivity and consistency in exploring a social problem. They provide the means for accuracy, reliability, and validity. In the end, the scientific method provides a shared basis for discussion and analysis (Merton 1963). Typically, the scientific method has 6 steps which are described below.
Step 1: Ask a Question or Find a Research Topic
The first step of the scientific method is to ask a question, select a problem, and identify the specific area of interest. The topic should be narrow enough to study within a geographic location and time frame. “Are societies capable of sustained happiness?” would be too vague. The question should also be broad enough to have universal merit. “What do personal hygiene habits reveal about the values of students at XYZ High School?” would be too narrow. Sociologists strive to frame questions that examine well-defined patterns and relationships.
In a hygiene study, for instance, hygiene could be defined as “personal habits to maintain physical appearance (as opposed to health),” and a researcher might ask, “How do differing personal hygiene habits reflect the cultural value placed on appearance?”
Step 2: Review the Literature/Research Existing Sources
The next step researchers undertake is to conduct background research through a literature review , which is a review of any existing similar or related studies. A visit to the library, a thorough online search, and a survey of academic journals will uncover existing research about the topic of study. This step helps researchers gain a broad understanding of work previously conducted, identify gaps in understanding of the topic, and position their own research to build on prior knowledge. Researchers—including student researchers—are responsible for correctly citing existing sources they use in a study or that inform their work. While it is fine to borrow previously published material (as long as it enhances a unique viewpoint), it must be referenced properly and never plagiarized.
To study crime, a researcher might also sort through existing data from the court system, police database, prison information, interviews with criminals, guards, wardens, etc. It’s important to examine this information in addition to existing research to determine how these resources might be used to fill holes in existing knowledge. Reviewing existing sources educates researchers and helps refine and improve a research study design.
Step 3: Formulate a Hypothesis
A hypothesis is an explanation for a phenomenon based on a conjecture about the relationship between the phenomenon and one or more causal factors. In sociology, the hypothesis will often predict how one form of human behavior influences another. For example, a hypothesis might be in the form of an “if, then statement.” Let’s relate this to our topic of crime: If unemployment increases, then the crime rate will increase.
In scientific research, we formulate hypotheses to include an independent variables (IV) , which are the cause of the change, and a dependent variable (DV) , which is the effect , or thing that is changed. In the example above, unemployment is the independent variable and the crime rate is the dependent variable.
In a sociological study, the researcher would establish one form of human behavior as the independent variable and observe the influence it has on a dependent variable. How does gender (the independent variable) affect rate of income (the dependent variable)? How does one’s religion (the independent variable) affect family size (the dependent variable)? How is social class (the dependent variable) affected by level of education (the independent variable)?
| Hypothesis | Independent Variable | Dependent Variable |
|---|---|---|
| The greater the availability of affordable housing, the lower the homeless rate. | Affordable Housing | Homeless Rate |
| The greater the availability of math tutoring, the higher the math grades. | Math Tutoring | Math Grades |
| The greater the police patrol presence, the safer the neighborhood. | Police Patrol Presence | Safer Neighborhood |
| The greater the factory lighting, the higher the productivity. | Factory Lighting | Productivity |
| The greater the amount of media coverage, the higher the public awareness. | Observation | Public Awareness |
Taking an example from Table 12.1, a researcher might hypothesize that teaching children proper hygiene (the independent variable) will boost their sense of self-esteem (the dependent variable). Note, however, this hypothesis can also work the other way around. A sociologist might predict that increasing a child’s sense of self-esteem (the independent variable) will increase or improve habits of hygiene (now the dependent variable). Identifying the independent and dependent variables is very important. As the hygiene example shows, simply identifying related two topics or variables is not enough. Their prospective relationship must be part of the hypothesis.
Step 4: Design and Conduct a Study
Researchers design studies to maximize reliability , which refers to how likely research results are to be replicated if the study is reproduced. Reliability increases the likelihood that what happens to one person will happen to all people in a group or what will happen in one situation will happen in another. Cooking is a science. When you follow a recipe and measure ingredients with a cooking tool, such as a measuring cup, the same results is obtained as long as the cook follows the same recipe and uses the same type of tool. The measuring cup introduces accuracy into the process. If a person uses a less accurate tool, such as their hand, to measure ingredients rather than a cup, the same result may not be replicated. Accurate tools and methods increase reliability.
Researchers also strive for validity , which refers to how well the study measures what it was designed to measure. To produce reliable and valid results, sociologists develop an operational definition , that is, they define each concept, or variable, in terms of the physical or concrete steps it takes to objectively measure it. The operational definition identifies an observable condition of the concept. By operationalizing the concept, all researchers can collect data in a systematic or replicable manner. Moreover, researchers can determine whether the experiment or method validly represent the phenomenon they intended to study.
A study asking how tutoring improves grades, for instance, might define “tutoring” as “one-on-one assistance by an expert in the field, hired by an educational institution.” However, one researcher might define a “good” grade as a C or better, while another uses a B+ as a starting point for “good.” For the results to be replicated and gain acceptance within the broader scientific community, researchers would have to use a standard operational definition. These definitions set limits and establish cut-off points that ensure consistency and replicability in a study.
We will explore research methods in greater detail in the next section of this chapter.
Step 5: Draw Conclusions
After constructing the research design, sociologists collect, tabulate or categorize, and analyze data to formulate conclusions. If the analysis supports the hypothesis, researchers can discuss the implications of the results for the theory or policy solution that they were addressing. If the analysis does not support the hypothesis, researchers may consider repeating the experiment or think of ways to improve their procedure.
However, even when results contradict a sociologist’s prediction of a study’s outcome, these results still contribute to sociological understanding. Sociologists analyze general patterns in response to a study, but they are equally interested in exceptions to patterns. In a study of education, a researcher might predict that high school dropouts have a hard time finding rewarding careers. While many assume that the higher the education, the higher the salary and degree of career happiness, there are certainly exceptions. People with little education have had stunning careers, and people with advanced degrees have had trouble finding work. A sociologist prepares a hypothesis knowing that results may substantiate or contradict it.
Sociologists carefully keep in mind how operational definitions and research designs impact the results as they draw conclusions. Consider the concept of “increase of crime,” which might be defined as the percent increase in crime from last week to this week, as in the study of Swedish crime discussed above. Yet the data used to evaluate “increase of crime” might be limited by many factors: who commits the crime, where the crimes are committed, or what type of crime is committed. If the data is gathered for “crimes committed in Houston, Texas in zip code 77021,” then it may not be generalizable to crimes committed in rural areas outside of major cities like Houston. If data is collected about vandalism, it may not be generalizable to assault.
Step 6: Report Results
Researchers report their results at conferences and in academic journals. These results are then subjected to the scrutiny of other sociologists in the field. Before the conclusions of a study become widely accepted, the studies are often repeated in the same or different environments. In this way, sociological theories and knowledge develops as the relationships between social phenomenon are established in broader contexts and different circumstances.
Interpretive Framework
While many sociologists rely on empirical data and the scientific method as a research approach, others operate from an interpretive framework . While systematic, this approach doesn’t follow the hypothesis-testing model that seeks to find generalizable results. Instead, an interpretive framework, sometimes referred to as an interpretive perspective , seeks to understand social worlds from the point of view of participants, which leads to in-depth knowledge or understanding about the human experience.
Interpretive research is generally more descriptive or narrative in its findings. Rather than formulating a hypothesis and method for testing it, an interpretive researcher will develop approaches to explore the topic at hand that may involve a significant amount of direct observation or interaction with subjects including storytelling. This type of researcher learns through the process and sometimes adjusts the research methods or processes midway to optimize findings as they evolve.
Critical Sociology
Critical sociology focuses on deconstruction of existing sociological research and theory. Informed by the work of Karl Marx, scholars known collectively as the Frankfurt School proposed that social science, as much as any academic pursuit, is embedded in the system of power constituted by the set of class, caste, race, gender, and other relationships that exist in the society. Consequently, it cannot be treated as purely objective. Critical sociologists view theories, methods, and the conclusions as serving one of two purposes: they can either legitimate and rationalize systems of social power and oppression or liberate humans from inequality and restriction on human freedom. Deconstruction can involve data collection, but the analysis of this data is not empirical or positivist.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Tonja R. Conerly, Kathleen Holmes, Asha Lal Tamang
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Introduction to Sociology 3e
- Publication date: Jun 3, 2021
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/introduction-sociology-3e/pages/2-1-approaches-to-sociological-research
© Jan 18, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List

The Social Consequences of Poverty: An Empirical Test on Longitudinal Data
Carina mood.
Institute for Futures Studies, Box 591, 101 31 Stockholm, Sweden
Swedish Institute for Social Research (SOFI), Stockholm University, Stockholm, Sweden
Jan O. Jonsson
Nuffield College, OX1 1NF Oxford, England, UK
Poverty is commonly defined as a lack of economic resources that has negative social consequences, but surprisingly little is known about the importance of economic hardship for social outcomes. This article offers an empirical investigation into this issue. We apply panel data methods on longitudinal data from the Swedish Level-of-Living Survey 2000 and 2010 (n = 3089) to study whether poverty affects four social outcomes—close social relations (social support), other social relations (friends and relatives), political participation, and activity in organizations. We also compare these effects across five different poverty indicators. Our main conclusion is that poverty in general has negative effects on social life. It has more harmful effects for relations with friends and relatives than for social support; and more for political participation than organizational activity. The poverty indicator that shows the greatest impact is material deprivation (lack of cash margin), while the most prevalent poverty indicators—absolute income poverty, and especially relative income poverty—appear to have the least effect on social outcomes.

Introduction
According to the most influential definitions, poverty is seen as a lack of economic resources that have negative social consequences—this is in fact a view that dominates current theories of poverty (Townsend 1979 ; Sen 1983 ; UN 1995 ), and also has a long heritage (Smith 1776 /1976). The idea is that even when people have food, clothes, and shelter, economic problems lead to a deterioration of social relations and participation. Being poor is about not being able to partake in society on equal terms with others, and therefore in the long run being excluded by fellow citizens or withdrawing from social and civic life because of a lack of economic resources, typically in combination with the concomitant shame of not being able to live a life like them (e.g., Sen 1983 ). Economic hardship affects the standard of life, consumption patterns, and leisure time activities, and this is directly or indirectly related to the possibility of making or maintaining friends or acquaintances: poverty is revealed by not having appropriate clothes, or a car; by not being able to afford vacation trips, visits to the restaurant, or hosting dinner parties (e.g., Mack and Lansley 1985 ; Callan et al. 1993 )—in short, low incomes prevent the poor from living a life in “decency” (Galbraith 1958 ).
The relational nature of poverty is also central to the social exclusion literature, which puts poverty in a larger perspective of multiple disadvantages and their interrelationships (Hills et al. 2002 , Rodgers et al. 1995 ; Room 1995 ). While there are different definitions of the social exclusion concept, the literature is characterized by a move from distributional to relational concerns (Gore 1995 ) and by an emphasis on the importance of social integration and active participation in public life. The inability of living a decent or “ordinary” social life may in this perspective erode social networks, social relations, and social participation, potentially setting off a downward spiral of misfortune (Paugam 1995 ) reinforcing disadvantages in several domains of life. This perspective on poverty and social exclusion is essentially sociological: the playing field of the private economy is social. It is ultimately about individuals’ relations with other people—not only primary social relations, with kin and friends, but extending to secondary relations reflected by participation in the wider community, such as in organizations and in political life (UN 1995 ).
Despite the fact that the social consequences of limited economic resources are central to modern perspectives on poverty and marginalization, this relation is surprisingly seldom studied empirically. Qualitative research on the poor give interesting examples on how the negative effects of poverty works, and portray the way that economic problems are transformed into social ones (Ridge and Millar 2011 ; Attree 2006 ). Such studies, however, have too small sample sizes to generalize to the population, and they cannot tell us much about the range of the problem. The (relatively few) studies that have addressed the association between poverty and social outcomes on larger scale tend to verify that the poor have worse social relations (Böhnke 2008 ; Jonsson and Östberg 2004 ; Levitas 2006 ), but Barnes et al. ( 2002 ) did not find any noteworthy association between poverty (measured as relative income poverty, using the 60 %-limit) and social relations or social isolation. Dahl et al. ( 2008 ) found no relation between poverty and friendships, but report less participation in civic organizations among the poor. All these studies have however been limited to cross-sectional data or hampered by methodological shortcomings, and therefore have not been able to address the separation of selection effects from potentially causal ones.
Our aim in this study is to make good these omissions. We use longitudinal data from the Swedish Level of Living Surveys (LNU) 2000 and 2010 to study how falling into poverty, or rising from it, is associated with outcomes in terms of primary and secondary social relations, including participation in civil society. These panel data make it possible to generalize the results to the Swedish adult population (19–65 in 2000; 29–75 in 2010), to address the issue of causality, and to estimate how strong the relation between economic vulnerability and social outcomes is. Because the data provide us with the possibility of measuring poverty in several ways, we are also able to address the question using different—alternative or complementary—indicators. Poverty is measured as economic deprivation (lack of cash margin, self-reported economic problems), income poverty (absolute and relative), and long-term poverty, respectively. The primary, or core, social outcomes are indicated by having social support if needed, and by social relations with friends and relatives. We expand our analysis to secondary, or fringe, social outcomes in terms of participation in social life at large, such as in civil society: our indicators here include the participation in organizations and in political life.
Different Dimensions/Definitions of Poverty
In modern welfare states, the normal take on the issue of poverty is to regard it as the relative lack of economic resources, that is, to define the poor in relation to their fellow citizens in the same country at the same time. Three approaches dominate the scholarly literature today. The first takes as a point of departure the income deemed necessary for living a life on par with others, or that makes possible an “acceptable” living standard—defined as the goods and services judged necessary, often on the basis of consumer or household budget studies. This usage of a poverty threshold is often (somewhat confusingly) called absolute income poverty , and is most common in North America (cf. Corak 2006 for a review), although most countries have poverty lines defined for different kinds of social benefits. In Europe and in the OECD, the convention is instead to use versions of relative income poverty , defining as poor those whose incomes fall well behind the median income in the country in question (European Union using 60 % and OECD 50 % of the median as the threshold). As an alternative to using purchasing power (as in the “absolute” measure), this relative measure defines poverty by income inequality in the bottom half of the income distribution (Atkinson et al. 2002 ; OECD 2008 ).
The third approach argues that income measures are too indirect; poverty should instead be indicated directly by the lack of consumer products and services that are necessary for an acceptable living standard (Mack and Lansley 1985 ; Ringen 1988 ; Townsend 1979 ). This approach often involves listing a number of possessions and conditions, such as having a car, washing machine, modern kitchen; and being able to dine out sometimes, to have the home adequately heated and mended, to have sufficient insurances, and so on. An elaborate version includes information on what people in general see as necessities, what is often termed “consensual” poverty (e.g., Mack and Lansley 1985 ; Gordon et al. 2000 ; Halleröd 1995 ; van den Bosch 2001 ). Other direct indicators include the ability to cover unforeseen costs (cash margin) and subjective definitions of poverty (e.g., van den Bosch 2001 ). The direct approach to poverty has gained in popularity and measures of economic/material deprivation and consensual poverty are used in several recent and contemporary comparative surveys such as ECHP (Whelan et al. 2003 ) and EU-SILC (e.g., UNICEF 2012 ; Nolan and Whelan 2011 ).
It is often pointed out that, due to the often quite volatile income careers of households, the majority of poverty episodes are short term and the group that is identified as poor in the cross-section therefore tends to be rather diluted (Bane and Ellwood 1986 ; Duncan et al. 1993 ). Those who suffer most from the downsides of poverty are, it could be argued, instead the long-term, persistent, or chronically poor, and there is empirical evidence that those who experience more years in poverty also are more deprived of a “common lifestyle” (Whelan et al. 2003 ). Poverty persistence has been defined in several ways, such as having spent a given number of years below a poverty threshold, or having an average income over a number of years that falls under the poverty line (e.g., Duncan and Rodgers 1991 ; Rodgers and Rodgers 1993 ). The persistently poor can only be detected with any precision in longitudinal studies, and typically on the basis of low incomes, as data covering repeated measures of material deprivation are uncommon.
For the purposes of this study, it is not essential to nominate the best or most appropriate poverty measure. The measures outlined above, while each having some disadvantage, all provide plausible theoretical grounds for predicting negative social outcomes. Low incomes, either in “absolute” or relative terms, may inhibit social activities and participation because these are costly (e.g., having decent housing, needing a car, paying membership fees, entrance tickets, or new clothes). Economic deprivation, often indicated by items or habits that are directly relevant to social life, is also a valid representation of a lack of resources. Lastly, to be in long-term poverty is no doubt a worse condition than being in shorter-term poverty.
It is worth underlining that we see different measures of poverty as relevant indicators despite the fact that the overlap between them often is surprisingly small (Bradshaw and Finch 2003 ). The lack of overlap is not necessarily a problem, as different people may have different configurations of economic problems but share in common many of the experiences of poverty—experiences, we argue, that are (in theory at least) all likely to lead to adverse social outcomes. Whether this is the case or not is one of the questions that we address, but if previous studies on child poverty are of any guidance, different definitions of poverty may show surprisingly similar associations with a number of outcomes (Jonsson and Östberg 2004 ).
What are the Likely Social Consequences of Poverty?
We have concluded that poverty is, according to most influential poverty definitions, manifested in the social sphere. This connects with the idea of Veblen ( 1899 ) of the relation between consumption and social status. What you buy and consume—clothes, furniture, vacation trips—in part define who you are, which group you aspire to belong to, and what view others will have of you. Inclusion into and exclusion from status groups and social circles are, in this view, dependent on economic resources as reflected in consumption patterns. While Veblen was mostly concerned about the rich and their conspicuous consumption, it is not difficult to transfer these ideas to the less fortunate: the poor are under risk of exclusion, of losing their social status and identity, and perhaps also, therefore, their friends. It is however likely that this is a process that differs according to outcome, with an unknown time-lag.
If, as outlined above, we can speak of primary and secondary social consequences, the former should include socializing with friends, but also more intimate relations. Our conjecture is that the closer the relation, the less affected is it by poverty, simply because intimate social bonds are characterized by more unconditional personal relations, typically not requiring costs to uphold.
When it comes to the secondary social consequences, we move outside the realm of closer interpersonal relations to acquaintances and the wider social network, and to the (sometimes relatively anonymous) participation in civil or political life. This dimension of poverty lies at the heart of the social exclusion perspective, which strongly emphasizes the broader issues of societal participation and civic engagement, vital to democratic societies. It is also reflected in the United Nation’s definition, following the Copenhagen summit in 1995, where “overall poverty” in addition to lack of economic resources is said to be “…characterized by lack of participation in decision-making and in civil, social, and cultural life” (UN 1995 , p. 57). Poverty may bring about secondary social consequences because such participation is costly—as in the examples of travel, need for special equipment, or membership fees—but also because of psychological mechanisms, such as lowered self-esteem triggering disbelief in civic and political activities, and a general passivity leading to decreased organizational and social activities overall. If processes like these exist there is a risk of a “downward spiral of social exclusion” where unemployment leads to poverty and social isolation, which in turn reduce the chances of re-gaining a footing in the labour market (Paugam 1995 ).
What theories of poverty and social exclusion postulate is, in conclusion, that both what we have called primary and secondary social relations will be negatively affected by economic hardship—the latter supposedly more than the former. Our strategy in the following is to test this basic hypothesis by applying multivariate panel-data analyses on longitudinal data. In this way, we believe that we can come further than previous studies towards estimating causal effects, although, as is the case in social sciences, the causal relation must remain preliminary due to the nature of observational data.
Data and Definitions
We use the two most recent waves of the Swedish Level-of-living Survey, conducted in 2000 and 2010 on random (1/1000) samples of adult Swedes, aged 18–75. 1 The attrition rate is low, with 84 % of panel respondents remaining from 2000 to 2010. This is one of the few data sets from which we can get over-time measures of both poverty and social outcomes for a panel that is representative of the adult population (at the first time point, t 0 )—in addition, there is annual income information from register data between the waves. The panel feature obviously restricts the age-groups slightly (ages 19–65 in 2000; 29–75 in 2010), the final number of analyzed cases being between 2995 and 3144, depending on the number of missing cases on the respective poverty measure and social outcome variable. For ease of interpretation and comparison of effect sizes, we have constructed all social outcome variables and poverty variables to be dichotomous (0/1). 2
In constructing poverty variables, we must balance theoretical validity with the need to have group sizes large enough for statistical analysis. For example, we expand the absolute poverty measure to include those who received social assistance any time during the year. As social assistance recipients receive this benefit based on having an income below a poverty line that is similar to the one we use, this seems justifiable. In other cases, however, group sizes are small but we find no theoretically reasonable way of making the variables more inclusive, meaning that some analyses cannot be carried out in full detail.
Our income poverty measures are based on register data and are thus free from recall error or misreporting, but—as the proponents of deprivation measures point out—income poverty measures are indirect measures of hardship. The deprivation measure is more direct, but self-reporting always carries a risk of subjectivity in the assessment. To the extent that changes in one’s judgment of the economic situation depend on changes in non-economic factors that are also related to social relations, the deprivation measure will give upwardly biased estimates. 3 As there is no general agreement about whether income or deprivation definitions are superior, our use of several definitions is a strength because the results will give an overall picture that is not sensitive to potential limitations in any one measure. In addition, we are able to see whether results vary systematically across commonly used definitions.
Poverty Measures
- Cash margin whether the respondent can raise a given sum of money in a week, if necessary (in 2000, the sum was 12,000 SEK; in 2010, 14,000 SEK, the latter sum corresponding to approximately 1600 Euro, 2200 USD, or 1400 GBP in 2013 currency rates). For those who answer in the affirmative, there is a follow-up question of how this can be done: by (a) own/household resources, (b) borrowing.
- Economic crisis Those who claim that they have had problems meeting costs for rent, food, bills, etc. during the last 12 months (responded “yes” to a yes/no alternative).
- Absolute poverty is defined as either (a) having a disposable family income below a poverty threshold or (b) receiving social assistance, both assessed in 1999 (for the survey 2000) or 2009 (for the survey 2010). The poverty line varies by family type/composition according to a commonly used calculation of household necessities (Jansson 2000 ). This “basket” of goods and services is intended to define an acceptable living standard, and was originally constructed for calculating an income threshold for social assistance, with addition of estimated costs for housing and transport. The threshold is adjusted for changes in the Consumer Price Index, using 2010 as the base year. In order to get analyzable group sizes, we classify anyone with an income below 1.25 times this threshold as poor. Self-employed are excluded because their nominal incomes are often a poor indicator of their economic standard.
- Deprived and income poor A combination of the indicator of economic deprivation and the indicator of absolute poverty. The poor are defined as those who are economically deprived and in addition are either absolute income-poor or have had social assistance some time during the last calendar year.
- Long - term poor are defined as those interviewed in 2010 (2000) who had an equivalized disposable income that fell below the 1.25 absolute poverty threshold (excluding self-employed) or who received social assistance in 2009 (1999), and who were in this situation for at least two of the years 2000–2008 (1990–1998). The long-term poor (coded 1) are contrasted to the non-poor (coded 0), excluding the short-term poor (coded missing) in order to distinguish whether long-term poverty is particularly detrimental (as compared to absolute poverty in general).
- Relative poverty is defined, according to the EU standard, as having a disposable equivalized income that is lower than 60 % of the median income in Sweden the year in question (EU 2005). 4 As for absolute poverty, this variable is based on incomes the year prior to the survey year. Self-employed are excluded.
Social and Participation Outcomes
Primary (core) social relations.
- Social support The value 1 (has support) is given to those who have answered in the positive to three questions about whether one has a close friend who can help if one (a) gets sick, (b) needs someone to talk to about troubles, or (c) needs company. Those who lack support in at least one of these respects are coded 0 (lack of support).
- Frequent social relations This variable is based on four questions about how often one meets (a) relatives and (b) friends, either (i) at ones’ home or (ii) at the home of those one meets, with the response set being “yes, often”, “sometimes”, and “no, never”. Respondents are defined as having frequent relations (1) if they have at least one “often” of the four possible and no “never”, 5 and 0 otherwise.
Secondary (fringe) Social Relations/Participation
- Political participation : Coded 1 (yes) if one during the last 12 months actively participated (held an elected position or was at a meeting) in a trade union or a political party, and 0 (no) otherwise. 6
- Organizational activity : Coded 1 (yes) if one is a member of an organization and actively participate in its activities at least once in a year, and 0 (no) otherwise.
Control Variables
- Age (in years)
- Educational qualifications in 2010 (five levels according to a standard schema used by Statistics Sweden (1985), entered as dummy variables)
- Civil status distinguishes between single and cohabiting/married persons, and is used as a time-varying covariate (TVC) where we register any changes from couple to single and vice versa.
- Immigrant origin is coded 1 if both parents were born in any country outside Sweden, 0 otherwise.
- Labour market status is also used as a TVC, with four values indicating labour market participation (yes/no) in 2000 and 2010, respectively.
- Global self - rated health in 2000, with three response alternatives: Good, bad, or in between. 7
Table 1 shows descriptive statistics for the 2 years we study, 2000 and 2010 (percentages in the upper panel; averages, standard deviations, max and min values in the lower panel). Recall that the sample is longitudinal with the same respondents appearing in both years. This means, naturally, that the sample ages 10 years between the waves, the upper age limit being pushed up from 65 to 75. Both the change over years and the ageing of the sample have repercussions for their conditions: somewhat more have poor health, for example, fewer lack social support but more lack frequent social relations, and more are single in 2010 (where widows are a growing category). The group has however improved their economic conditions, with a sizeable reduction in poverty rates. Most of the changes are in fact period effects, and it is particularly obvious for the change in poverty—in 2000 people still suffered from the deep recession in Sweden that begun in 1991 and started to turn in 1996/97 (Jonsson et al. 2010 ), while the most recent international recession (starting in 2008/09) did not affect Sweden that much.
Table 1
Descriptive statistics of dependent and independent variables in the LNU panel
| Categorical variables | % in 2000 | % in 2010 | N |
|---|---|---|---|
| Social support | 93 | 95 | 3150 |
| Frequent social relations | 89 | 84 | 3157 |
| Civic participation (organizations) | 52 | 44 | 3139 |
| Political participation | 27 | 24 | 3157 |
| Economically deprived | 15 | 10 | 3083 |
| Poor (“absolute”) | 15 | 6 | 3156 |
| Poor (relative) | 19 | 10 | 3139 |
| Long-term poor/social assistance | 12 | 5 | 3156 |
| Deprived + income-poor/social assistance | 7 | 3 | 3082 |
| Unemployed | 5 | 3 | 3153 |
| Woman | 49 | 3157 | |
| Single | 25 | 29 | 3157 |
| Immigrant origin | 11 | 3157 | |
| 3149 | |||
| Comprehensive school | 15 | ||
| Vocational secondary | 28 | ||
| Academic upper secondary | 17 | ||
| Short-cycle tertiary | 16 | ||
| University degree | 24 | ||
| 3157 | |||
| Good | 78 | 75 | |
| In between | 18 | 20 | |
| Poor | 4 | 5 |
| Metric variable | Mean | Stddev | Min | Max | N |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Age 2010 | 52 | 13 | 29 | 75 | 3157 |
N for variables used as change variables pertains to non-missing observations in both 2000 and 2010
The overall decrease in poverty masks changes that our respondents experienced between 2000 and 2010: Table 2 reveals these for the measure of economic deprivation, showing the outflow (row) percentages and the total percentages (and the number of respondents in parentheses). It is evident that there was quite a lot of mobility out of poverty between the years (61 % left), but also a very strong relative risk of being found in poverty in 2010 among those who were poor in 2000 (39 vs. 5 % of those who were non-poor in 2000). Of all our respondents, the most common situation was to be non-poor both years (81 %), while few were poor on both occasions (6 %). Table 2 also demonstrates some small cell numbers: 13.3 % of the panel (9.4 % + 3.9 %), or a good 400 cases, changed poverty status, and these cases are crucial for identifying our models. As in many panel studies based on survey data, this will inevitably lead to some problems with large standard errors and difficulties in arriving at statistically significant and precise estimates; but to preview the findings, our results are surprisingly consistent all the same.
Table 2
Mobility in poverty (measured as economic deprivation) in Sweden between 2000 and 2010
| Poor in 2010 | Not poor in 2010 | Total | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Row % | 39.1 | 60.9 | 100.0 |
| Total % | 6.0 | 9.4 | 15.4 |
| (n) | (186) | (290) | (476) |
| Row % | 4.6 | 95.4 | 100.0 |
| Total % | 3.9 | 80.7 | 84.6 |
| (n) | (119) | (2488) | (2607) |
| 9.9 | 90.1 | 100.0 | |
| (n) | (305) | (2778) | (3083) |
Outflow percentage (row %), total percentage, and number of cases (in parentheses). LNU panel 2000–2010
We begin with showing descriptive results of how poverty is associated with our outcome variables, using the economic deprivation measure of poverty. 8 Figure 1 confirms that those who are poor have worse social relationships and participate less in political life and in organizations. Poverty is thus connected with both primary and secondary social relations.

The relation between poverty (measured as economic deprivation) and social relations/participation in Sweden, LNU 2010. N = 5271
The descriptive picture in Fig. 1 does not tell us anything about the causal nature of the relation between poverty and social outcomes, only that such a relation exists, and that it is in the predicted direction: poor people have weaker social relations, less support, and lower levels of political and civic participation. Our task now is to apply more stringent statistical models to test whether the relation we have uncovered is likely to be of a causal nature. This means that we must try to rid the association of both the risk for reverse causality—that, for example, a weaker social network leads to poverty—and the risk that there is a common underlying cause of both poverty and social outcomes, such as poor health or singlehood.
The Change Model
First, as we have panel data, we can study the difference in change across two time-points T (called t 0 and t 1 , respectively) in an outcome variable (e.g., social relations), between groups (i.e. those who changed poverty status versus those who did not). The respondents are assigned to either of these groups on the grounds of entering or leaving poverty; in the first case, one group is non-poor at t 0 but experiences poverty at t 1 , and the change in this group is compared to the group consisting of those who are non-poor both at t 0 and t 1 . The question in focus then is: Do social relations in the group entering poverty worsen in relation to the corresponding change in social relations in the group who remains non-poor? Because we have symmetric hypotheses of the effect of poverty on social outcomes—assuming leaving poverty has positive consequences similar to the negative consequences of entering poverty—we also study whether those who exit poverty improve their social outcomes as compared to those remaining poor. We ask, that is, not only what damage falling into poverty might have for social outcomes, but also what “social gains” could be expected for someone who climbs out of poverty.
Thus, in our analyses we use two different “change groups”, poverty leavers and poverty entrants , and two “comparison groups”, constantly poor and never poor , respectively. 9 The setup comparing the change in social outcomes for those who change poverty status and those who do not is analogous to a so-called difference-in-difference design, but as the allocation of respondents to comparison groups and change groups in our data cannot be assumed to be random (as with control groups and treatment groups in experimental designs), we take further measures to approach causal interpretations.
Accounting for the Starting Value of the Dependent Variable
An important indication of the non-randomness of the allocation to the change and comparison groups is that their average values of the social outcomes (i.e. the dependent variable) at t 0 differ systematically: Those who become poor between 2000 and 2010 have on average worse social outcomes already in 2000 than those who stay out of poverty. Similarly, those who stay in poverty both years have on average worse social outcomes than those who have exited poverty in 2010. In order to further reduce the impact of unobserved variables, we therefore make all comparisons of changes in social outcomes between t 0 and t 1 for fixed t 0 values of both social outcome and poverty status.
As we use dichotomous outcome variables, we get eight combinations of poverty and outcome states (2 × 2 × 2 = 8), and four direct strategic comparisons:
- Poverty leavers versus constantly poor, positive social outcome in 2000 , showing if those who exit poverty have a higher chance of maintaining the positive social outcome than those who stay in poverty
- Poverty leavers versus constantly poor, negative social outcome in 2000 , showing if those who exit poverty have a higher chance of improvement in the social outcome than those who stay in poverty
- Poverty entrants versus never poor, positive social outcome in 2000 , showing if those who enter poverty have a higher risk of deterioration in the social outcome than those who stay out of poverty, and
- Poverty entrants versus never poor, negative social outcome in 2000 , showing if those who enter poverty have a lower chance of improvement in the social outcome.
Thus, we hold the initial social situation and poverty status fixed, letting only the poverty in 2010 vary. 10 The analytical strategy is set out in Table 3 , showing estimates of the probability to have frequent social relations in 2010, for poverty defined (as in Table 2 and Fig. 1 above) as economic deprivation.
Table 3
Per cent with frequent social relations in “comparison” and “change” groups in 2000 and 2010, according to initial value on social relations in 2000 and poverty (measured as economic deprivation) in 2000 and 2010
| Non-frequent social relations 2000 | Frequent social relations 2000 | |
|---|---|---|
| 0–0 (never poor) | 0.59 | 0.90 |
| 0–1 (became poor) | 0.52 | 0.72 |
| −0.07 | −0.17 | |
| 1–1 (constantly poor) | 0.39 | 0.72 |
| 1–0 (escaped poverty) | 0.72 | 0.86 |
| 0.33 | 0.14 | |
LNU panel 2000–2010. N = 3083
The figures in Table 3 should be read like this: 0.59 in the upper left cell means that among those who were poor neither in 2000 nor in 2010 (“never poor”, or 0–0), and who had non-frequent social relations to begin with, 59 % had frequent social relations in 2010. Among those never poor who instead started out with more frequent social relations, 90 per cent had frequent social relations in 2010. This difference (59 vs. 90) tells us either that the initial conditions were important (weak social relations can be inherently difficult to improve) or that there is heterogeneity within the group of never poor people, such as some having (to us perhaps unobserved) characteristics that support relation building while others have not.
Because our strategy is to condition on the initial situation in order to minimize the impact of initial conditions and unobserved heterogeneity, we focus on the comparisons across columns. If we follow each column downwards, that is, for a given initial social outcome (weak or not weak social relations, respectively) it is apparent that the outcome is worse for the “poverty entrants” in comparison with the “never poor” (upper three lines). Comparing the change group [those who became poor (0–1)] with the comparison group [never poor (0–0)] for those who started out with weak social relations (left column), the estimated probability of frequent social relations in 2010 is 7 % points lower for those who became poor. Among those who started out with frequent relations, those who became poor have a 17 % points lower probability of frequent relations in 2010 than those who stayed out of poverty.
If we move down Table 3 , to the three bottom lines, the change and comparison groups are now different. The comparison group is the “constantly poor” (1–1), and the change group are “poverty leavers” (1–0). Again following the columns downwards, we can see that the change group improved their social relations in comparison with the constantly poor; and this is true whether they started out with weak social relations or not. In fact, the chance of improvement for those who started off with non-frequent social relations is the most noteworthy, being 33 % units higher for those who escaped poverty than for those who did not. In sum, Table 3 suggests that becoming poor appears to be bad for social relations whereas escaping poverty is beneficial.
Expanding the Model
The model exemplified in Table 3 is a panel model that studies change across time within the same individuals, conditioning on their initial state. It does away with time-constant effects of observed and unobserved respondent characteristics, and although this is far superior to a cross-sectional model (such as the one underlying Fig. 1 ) there are still threats to causal interpretations. It is possible (if probably unusual) that permanent characteristics may trigger a change over time in both the dependent and independent variables; or, put in another way, whether a person stays in or exits poverty may be partly caused by a variable that also predicts change in the outcome (what is sometimes referred to as a violation of the “common trend assumption”). In our case, we can for example imagine that health problems in 2000 can affect who becomes poor in 2010, at t 1 , and that the same health problems can lead to a deterioration of social relations between 2000 and 2010, so even conditioning on the social relations at t 0 will not be enough. This we handle by adding control variables, attempting to condition the comparison of poor and non-poor also on sex, age, highest level of education (in 2010), immigrant status, and health (in 2000). 11
Given the set-up of our data—with 10 years between the two data-points and with no information on the precise time ordering of poverty and social outcomes at t 1 , the model can be further improved by including change in some of the control variables. It is possible, for example, that a non-poor and married respondent in 2000 divorced before 2010, triggering both poverty and reduced social relations at the time of the interview in 2010. 12 There are two major events that in this way may bias our results, divorce/separation and unemployment (because each can lead to poverty, and possibly also affect social outcomes). We handle this by controlling for variables combining civil status and unemployment in 2000 as well as in 2010. To the extent that these factors are a consequence of becoming poor, there is a risk of biasing our estimates downwards (e.g., if becoming poor increases the risk of divorce). However, as there is no way to distinguish empirically whether control variables (divorce, unemployment) or poverty changed first we prefer to report conservative estimates. 13
Throughout, we use logistic regression to estimate our models (one model for each social outcome and poverty definition). We create a dummy variable for each of the combinations of poverty in 2000, poverty in 2010 and the social outcome in 2000, and alternate the reference category in order to get the four strategic comparisons described above. Coefficients do thus express the distance between the relevant change and comparison groups. The coefficients reported are average marginal effects (AME) for a one-unit change in the respective poverty variable (i.e. going from non-poor to poor and vice versa), which are straightforwardly interpretable as percentage unit differences and (unlike odds ratios or log odds ratios) comparable across models and outcomes (Mood 2010 ).
Regression Results
As detailed above, we use changes over time in poverty and social outcomes to estimate the effects of interest. The effect of poverty is allowed to be heterogeneous, and is assessed through four comparisons of the social outcome in 2010 (Y 1 ):
- Those entering poverty relative to those in constant non-poverty (P 01 = 0,1 vs. P 01 = 0,0) when both have favourable social outcomes at t 0 (Y 0 = 1)
- Those exiting poverty relative to those in constant poverty (P 01 = 1,0 vs. P 01 = 1,1) when both have favourable social outcomes at t 0 (Y 0 = 1)
- Those entering poverty relative to those in constant non-poverty (P 01 = 0,1 vs. P 01 = 0,0) when both have non-favourable social outcomes at t 0 (Y 0 = 0)
- Those exiting poverty relative to those in constant poverty (P 01 = 1,0 vs. P 01 = 1,1) when both have non-favourable social outcomes at t 0 (Y 0 = 0)
Poverty is a rare outcome, and as noted above it is particularly uncommon to enter poverty between 2000 and 2010 because of the improving macro-economic situation. Some of the social outcomes were also rare in 2000. This unfortunately means that in some comparisons we have cell frequencies that are prohibitively small, and we have chosen to exclude all comparisons involving cells where N < 20.
The regression results are displayed in Table 4 . To understand how the estimates come to be, consider the four in the upper left part of the Table (0.330, 0.138, −0.175 and −0.065), reflecting the effect of poverty, measured as economic deprivation, on the probability of having frequent social relations. Because these estimates are all derived from a regression without any controls, they are identical (apart from using three decimal places) to the percentage comparisons in Table 3 (0.33, 0.14, −0.17, −0.07), and can be straightforwardly interpreted as average differences in the probability of the outcome in question. From Table 4 it is clear that the three first differences are all statistically significant, whereas the estimate −0.07 is not (primarily because those who entered poverty in 2010 and had infrequent social relations in 2000 is a small group, N = 25).
Table 4
Average marginal effects (from logistic regression) of five types of poverty (1–5) on four social outcomes (A-D) comparing those with different poverty statuses in 2000 and 2010 and conditioning on the starting value of the social outcome (in 2000)
| Economically deprived (1) | Absolute poor (2) | Deprived and abs. poor (3) | Long-term poor (4) | Relative poor (5) | ||||||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| No controls | Controls | No controls | Controls | No controls | Controls | No controls | Controls | No controls | Controls | |
| P11 versus P10, Y0 = negative | 0.172 | 0.291 | 0.134 | 0.082 | 0.130 | |||||
| (0.000) | (0.029) | (0.000) | (0.114) | (0.000) | (0.052) | (0.008) | (0.251) | (0.479) | (0.240) | |
| P11 versus P10, Y0 = positive | 0.050 | 0.035 | −0.048 | 0.065 | 0.026 | 0.034 | ||||
| (0.002) | −0.048 | −0.005 | (0.260) | (0.676) | (0.374) | (0.003) | (0.225) | (0.546) | (0.455) | |
| P00 versus P01, Y0 = positive | − | − | − | −0.070 | − | − | − | −0.091 | 0.013 | −0.013 |
| (0.000) | (0.002) | (0.009) | (0.084) | (0.001) | (0.012) | (0.012) | (0.082) | (0.583) | (0.645) | |
| P00 versus P01, Y0 = negative | −0.065 | −0.048 | – | – | – | – | – | – | 0.116 | 0.042 |
| (0.536) | (0.635) | (0.241) | (0.668) | |||||||
| P11 versus P10, Y0 = negative | 0.102 | 0.200 | 0.102 | – | – | 0.200 | 0.108 | – | – | |
| (0.030) | (0.190) | (0.079) | (0.177) | (0.133) | (0.235) | |||||
| P11 versus P10, Y0 = positive | 0.030 | 0.002 | 0.018 | 0.056 | −0.006 | 0.021 | 0.042 | 0.052 | ||
| (0.248) | (0.928) | −0.039 | (0.532) | (0.356) | (0.882) | (0.039) | (0.524) | (0.147) | (0.105) | |
| P00 versus P01, Y0 = positive | − | − | − | −0.045 | − | − | −0.063 | −0.045 | ||
| (0.023) | (0.050) | (0.050) | (0.089) | (0.025) | (0.037) | (0.112) | (0.176) | (0.002) | (0.022) | |
| P00 versus P01, Y0 = negative | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| P11 versus P10, Y0 = negative | 0.047 | 0.032 | ||||||||
| (0.001) | (0.006) | (0.003) | (0.038) | (0.391) | (0.616) | (0.005) | (0.041) | (0.015) | −0.034 | |
| P11 versus P10, Y0 = positive | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – | – |
| P00 versus P01, Y0 = negative | − | − | − | −0.066 | −0.077 | −0.058 | −0.044 | −0.034 | −0.044 | −0.036 |
| (0.008) | (0.023) | (0.029) | (0.090) | (0.140) | (0.343) | (0.374) | (0.516) | (0.113) | (0.222) | |
| P00 versus P01, Y0 = positive | −0.0508 | −0.023 | 0.111 | 0.104 | – | – | – | – | −0.121 | −0.121 |
| (0.589) | (0.815) | (0.301) | (0.334) | (0.113) | (0.115) | |||||
| P11 versus P10, Y0 = negative | 0.091 | 0.048 | 0.029 | 0.093 | 0.108 | 0.089 | 0.083 | 0.026 | 0.012 | |
| (0.032) | (0.091) | (0.408) | (0.680) | (0.155) | (0.188) | (0.164) | (0.295) | (0.636) | (0.845) | |
| P11 versus P10, Y0 = positive | 0.068 | 0.047 | 0.188 | – | – | 0.149 | 0.151 | −0.017 | −0.067 | |
| (0.372) | (0.543) | (0.041) | (0.055) | (0.157) | (0.167) | (0.843) | (0.396) | |||
| P00 versus P01, Y0 = negative | −0.078 | −0.039 | − | − | − | − | − | − | 0.009 | 0.029 |
| (0.126) | (0.493) | (0.000) | (0.001) | (0.008) | (0.042) | (0.003) | (0.017) | (0.853) | (0.570) | |
| P00 versus P01, Y0 = positive | − | −0.125 | −0.008 | 0.032 | −0.080 | −0.056 | −0.008 | 0.054 | −0.039 | 0.002 |
| (0.035) | (0.107) | (0.920) | (0.682) | (0.478) | (0.625) | (0.943) | (0.611) | (0.453) | (0.973) | |
Right columns control for sex, education, age, immigrant status, health in 2000, civil status change between 2000 and 2010, and unemployment change between 2000 and 2010. P values in parentheses. Excluded estimates involve variable categories with N < 20. Shaded cells are in hypothesized direction, bold estimates are statistically significant ( P < 0.05). N in regressions: 1A: 3075; 1B: 3073; 1C: 3075; 1D: 3069; 2A: 3144; 2B: 3137; 2C: 3144; 2D: 3130; 3A: 3074, 3B: 3072; 3C: 3074; 3D: 3068; 4A: 2995; 4B: 2988; 4C: 2995; 4D: 2981; 5A: 3128; 5B: 3121; 5C: 3128; 5D: 3114
In the column to the right, we can see what difference the controls make: the estimates are reduced, but not substantially so, and the three first differences are still statistically significant.
The estimates for each social outcome, reflecting the four comparisons described above, support the hypothesis of poverty affecting social relations negatively (note that the signs of the estimates should differ in order to do so, the upper two being positive as they reflect an effect of the exit from poverty, and the lower two being negative as they reflect an effect of entering poverty). We have indicated support for the hypothesis in Table 4 by shading the estimates and standard errors for estimates that go in the predicted direction.
Following the first two columns down, we can see that there is mostly support for the hypothesis of a negative effect of poverty, but when controlling for other variables, the effects on social support are not impressive. In fact, if we concentrate on each social outcome (i.e., row-wise), one conclusion is that, when controlling for confounders, there are rather small effects of poverty on the probability of having access to social support. The opposite is true for political participation, where the consistency in the estimated effects of poverty is striking.
If we instead follow the columns, we ask whether any of the definitions of poverty is a better predictor of social outcomes than the others. The measure of economic deprivation appears to be the most stable one, followed by absolute poverty and the combined deprivation/absolute poverty variable. 14 The relative poverty measure is less able to predict social outcomes: in many instances it even has the non-expected sign. Interestingly, long-term poverty (as measured here) does not appear to have more severe negative consequences than absolute poverty in general.
Because some of our comparison groups are small, it is difficult to get high precision in the estimates, efficiency being a concern particularly in view of the set of control variables in Table 4 . Only 14 out of 62 estimates in models with controls are significant and in the right direction. Nonetheless, with 52 out of 62 estimates in these models having the expected sign, we believe that the hypothesis of a negative effect of poverty on social outcomes receives quite strong support.
Although control variables are not shown in the table, one thing should be noted about them: The reduction of coefficients when including control variables is almost exclusively driven by changes in civil status. 15 The time constant characteristics that are included are cross-sectionally related to both poverty and social outcomes, but they have only minor impacts on the estimated effects of poverty. This suggests that the conditioning on prior values of the dependent and independent variables eliminates much time invariant heterogeneity, which increases the credibility of estimates.
Conclusions
We set out to test a fundamental, but rarely questioned assumption in dominating definitions of poverty: whether shortage of economic resources has negative consequences for social relations and participation. By using longitudinal data from the Swedish Level-of-living Surveys 2000 and 2010, including repeated measures of poverty (according to several commonly used definitions) and four social outcome variables, we are able to come further than previous studies in estimating the relation between poverty and social outcomes: Our main conclusion is that there appears to be a causal relation between them.
Panel models suggest that falling into poverty increases the risk of weakening social relations and decreasing (civic and political) participation. Climbing out of poverty tends to have the opposite effects, a result that strengthens the interpretation of causality. The sample is too small to estimate the effect sizes with any precision, yet they appear to be substantial, with statistically significant estimates ranging between 5 and 21 % units.
While these findings are disquieting insofar as poverty goes, our results also suggest two more positive results. First, the negative effects of poverty appear to be reversible: once the private economy recovers, social outcomes improve. Secondly, the negative consequences are less for the closest social relations, whether there is someone there in cases of need (sickness, personal problems, etc.). This is in line with an interpretation of such close relations being unconditional: our nearest and dearest tend to hang on to us also in times of financial troubles, which may bolster risks for social isolation and psychological ill-being,
Our finding of negative effects of poverty on civic and political participation relates to the fears of a “downward spiral of social exclusion”, as there is a risk that the loss of less intimate social relations shrinks social networks and decreases the available social capital in terms of contacts that can be important for outcomes such as finding a job (e.g., Lin 2001 ; Granovetter 1974 ). However, Gallie et al. ( 2003 ) found no evidence for any strong impact of social isolation on unemployment, suggesting that the negative effects on social outcomes that we observe are unlikely to lead to self-reinforcement of poverty. Nevertheless, social relations are of course important outcomes in their own right, so if they are negatively affected by poverty it matters regardless of whether social relations in turn are important for other outcomes. Effects on political and civic participation are also relevant in themselves beyond individuals’ wellbeing, as they suggest a potentially democratic problem where poor have less of a voice and less influence on society than others.
Our results show the merits of our approach, to study the relation between poverty and social outcomes longitudinally. The fact that the poor have worse social relations and lower participation is partly because of selection. This may be because the socially isolated, or those with a weaker social network, more easily fall into poverty; or it can be because of a common denominator, such as poor health or social problems. But once we have stripped the analysis of such selection effects, we also find what is likely to be a causal relation between poverty and social relations. However, this effect of poverty on social outcomes, in turn, varies between different definitions of poverty. Here it appears that economic deprivation, primarily indicated by the ability of raising money with short notice, is the strongest predictor of social outcomes. Income poverty, whether in absolute or (particularly) relative terms, are weaker predictors of social outcomes, which is interesting as they are the two most common indicators of poverty in existing research.
Even if we are fortunate to have panel data at our disposal, there are limitations in our analyses that render our conclusions tentative. One is that we do not have a random allocation to the comparison groups at t 0 ; another that there is a 10-year span between the waves that we analyze, and both poverty and social outcomes may vary across this time-span. We have been able to address these problems by conditioning on the outcome at t 0 and by controlling for confounders, but in order to perform more rigorous tests future research would benefit from data with a more detailed temporal structure, and preferably with an experimental or at least quasi-experimental design.
Finally, our analyses concern Sweden, and given the position as an active welfare state with a low degree of inequality and low poverty rates, one can ask whether the results are valid also for other comparable countries. While both the level of poverty and the pattern of social relations differ between countries (for policy or cultural reasons), we believe that the mechanisms linking poverty and social outcomes are of a quite general kind, especially as the “costs for social participation” can be expected to be relative to the general wealth of a country—however, until comparative longitudinal data become available, this must remain a hypothesis for future research.
1 http://www.sofi.su.se/english/2.17851/research/three-research-departments/lnu-level-of-living .
2 We have tested various alternative codings and the overall pattern of results in terms of e.g., direction of effects and differences across poverty definitions are similar, but more difficult to present in an accessible way.
3 Our deprivation questions are however designed to reduce the impact of subjectivity by asking, e.g., about getting a specified sum within a specified time (see below).
4 In the equivalence scale, the first adult gets a weight of one, the second of 0.6, and each child gets a weight of 0.5.
5 We have also tried using single indicators (either a/b or i/ii) without detecting any meaningful difference between them. One would perhaps have assumed that poverty would be more consequential for having others over to one’s own place, but the absence of support for this can perhaps be understood in light of the strong social norm of reciprocity in social relations.
6 We have refrained from using information on voting and membership in trade unions and political parties, because these indicators do not capture the active, social nature of civic engagement to the same extent as participation in meetings and the holding of positions.
7 We have also estimated models with a more extensive health variable, a s ymptom index , which sums responses to 47 questions about self-reported health symptoms. However, this variable has virtually zero effects once global self-rated health is controlled, and does not lead to any substantive differences in other estimates. Adding the global health measure and the symptom index as TVC had no effect either.
8 Using the other indicators of poverty yields very similar results, although for some of those the difference between poor and non-poor is smaller.
9 We call these comparison groups ”never poor” and ”constantly poor” for expository purposes, although their poverty status pertains only to the years 2000 and 2010, i.e., without information on the years in between.
10 With this design we allow different effects of poverty on improvement versus deterioration of the social outcome. We have also estimated models with a lagged dependent variable, which constrains the effects of poverty changes to be of the same size for deterioration as for improvement of the social outcome. Conclusions from that analysis are roughly a weighted average of the estimates for deterioration and improvement that we report. As our analyses suggest that effects of poverty differ in size depending on the value of the lagged dependent variable (the social outcome) our current specification gives a more adequate representation of the process.
11 We have also tested models with a wider range of controls for, e.g., economic and social background (i.e. characteristics of the respondent’s parents), geography, detailed family type and a more detailed health variable, but none of these had any impact on the estimated poverty effects.
12 It is also possible that we register reverse causality, namely if worsening social outcomes that occur after t 0 lead to poverty at t 1 . This situation is almost inevitable when using panel data with no clear temporal ordering of events occurring between waves. However, reverse causality strikes us, in this case, as theoretically implausible.
13 We have also estimated models controlling for changes in health, which did not change the results.
14 If respondents’ judgments of the deprivation questions (access to cash margin and ability to pay rent, food, bills etc.) change due to non-economic factors that are related to changes in social relations, the better predictive capacity of the deprivation measure may be caused by a larger bias in this measure than in the (register-based) income measures.
15 As mentioned above, this variable may to some extent be endogenous (i.e., a mediator of the poverty effect rather than a confounder), in which case we get a downward bias of estimates.
Contributor Information
Carina Mood, Phone: +44-8-402 12 22, Email: [email protected] .
Jan O. Jonsson, Phone: +44 1865 278513, Email: [email protected] .
- Atkinson AB, Cantillon B, Marlier E, Nolan B. Social indicators: The EU and social inclusion. Oxford: Oxford University Press; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Attree P. The social costs of child poverty: A systematic review of the qualitative evidence. Children and Society. 2006; 20 :54–66. [ Google Scholar ]
- Bane MJ, Ellwood DT. Slipping into and out of Poverty: The Dynamics of Spells. Journal of Human Resources. 1986; 21 :1–23. doi: 10.2307/145955. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Barnes M, Heady C, Middleton S, Millar J, Papadopoulos F, Room G, Tsakloglou P. Poverty and social exclusion in Europe. Cheltenham: Edward Elgar; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Böhnke P. Are the poor socially integrated? The link between poverty and social support in different welfare regimes. Journal of European Social Policy. 2008; 18 :133–150. doi: 10.1177/0958928707087590. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bradshaw J, Finch N. Overlaps in dimensions of poverty. Journal of Social Policy. 2003; 32 :513–525. doi: 10.1017/S004727940300713X. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Callan T, Nolan B, Whelan CT. Resources, deprivation, and the measurement of poverty. Journal of Social Policy. 1993; 22 :141–172. doi: 10.1017/S0047279400019280. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Corak M. Principles and practicalities for measuring child poverty in the rich countries. International Social Security Review. 2006; 59 :3–36. doi: 10.1111/j.1468-246X.2006.00237.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Dahl E, Flotten T, Lorentzen T. Poverty dynamics and social exclusion: An analysis of Norwegian panel data. Journal of Social Policy. 2008; 37 :231–249. doi: 10.1017/S0047279407001729. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Duncan GJ, Gustafsson B, Hauser R, Schmauss G, Messinger H, Muffels R, Nolan B, Ray J-C. Poverty dynamics in eight countries. Journal of Population Economics. 1993; 6 :215–234. doi: 10.1007/BF00163068. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Duncan GJ, Rodgers W. Has children’s poverty become more persistent? American Sociological Review. 1991; 56 :538–550. doi: 10.2307/2096273. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Galbraith J. The affluent society. Boston: Houghton-Mifflin; 1958. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gallie D, Paugam S, Jacobs S. Unemployment, poverty and social isolation: Is there a vicious cycle of social exclusion? European Societies. 2003; 5 :1–32. doi: 10.1080/1461669032000057668. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Gordon D, Adelman L, Ashworth K, Bradshaw J, Levitas R, Middleton S, Pantazis C, Patsios D, Payne S, Townsend P, Williams J. Poverty and social exclusion in Britain. York: Joseph Rowntree Foundation; 2000. [ Google Scholar ]
- Gore C. Introduction: Markets, citizenship and social exclusion. In: Rodgers G, Gore C, Figueiredo JB, editors. Social exclusion: Rhetoric, reality, responses. Geneva: International Labour Organization; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Granovetter, M. S. (1974). Getting a job. A study of contacts and careers . Cambridge: Harvard University Press.
- Halleröd B. The truly poor: Direct and indirect measurement of consensual poverty in Sweden. Journal of European Social Policy. 1995; 5 :111–129. doi: 10.1177/095892879500500203. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Hills J, Le Grand J, Piachaud D. Understanding social exclusion. Oxford: OUP; 2002. [ Google Scholar ]
- Jansson, K. (2000). Inkomstfördelningen under 1990-talet. In Välfärd och försörjning 2000, pp. 15–60. SOU 2000:40.
- Jonsson, J. O., Mood, C., & Bihagen, E. (2010). Fattigdomens förändring, utbredning och dynamik, Chapter 3. In Social Rapport 2010 . Stockholm: Socialstyrelsen.
- Jonsson, J. O., & Östberg, V. (2004). Resurser och levnadsförhållanden bland ekonomiskt utsatta 10-18-åringar: Analys av Barn-LNU och Barn-ULF. pp. 203–55 in Ekonomiskt utsatta barn, Socialdepartementet, Ds. 2004:41. Stockholm: Fritzes.
- Levitas R. The concept and measurement of social exclusion. In: Pantazis C, Gordon D, Levitas R, editors. Poverty and social exclusion in Britain. Bristol: Policy Press; 2006. pp. 123–162. [ Google Scholar ]
- Lin, N. (2001). Social capital. A theory of social structure and action . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press.
- Mack J, Lansley S. Poor Britain. London: Allen & Unwin Ltd; 1985. [ Google Scholar ]
- Mood C. Logistic regression: Why we cannot do what we think we can do and what we can do about it. European Sociological Review. 2010; 26 :67–82. doi: 10.1093/esr/jcp006. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Nolan B, Whelan CT. Poverty and deprivation in Europe. New York: Oxford University Press; 2011. [ Google Scholar ]
- OECD . Growing unequal? Income distribution and poverty in OECD countries. Paris: OECD Publishing; 2008. [ Google Scholar ]
- Paugam S. The spiral of precariousness: A multidimensional approach to the process of social disqualification in France. In: Room G, editor. Beyond the threshold: The measurement and analysis of social exclusion. Bristol: Policy Press; 1995. pp. 47–79. [ Google Scholar ]
- Ridge T, Millar J. Following families: Working lone-mother families and their children. Social Policy & Administration. 2011; 45 :85–97. doi: 10.1111/j.1467-9515.2010.00755.x. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ringen S. Direct and indirect measures of poverty. Journal of Social Policy. 1988; 17 :351–365. doi: 10.1017/S0047279400016858. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rodgers G, Gore C, Figueiredo JB, editors. Social exclusion: Rhetoric, reality, responses. Geneva: International Labour Organization; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Rodgers JR, Rodgers JL. Chronic poverty in the United States. Journal of Human Resources. 1993; 28 :25–54. doi: 10.2307/146087. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Room G, editor. Beyond the threshold: The measurement and analysis of social exclusion. Bristol: Policy Press; 1995. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sen A. Poor, relatively speaking. Oxford Economic Papers. 1983; 35 :153–169. [ Google Scholar ]
- Smith, A. (1776). An inquiry into the nature and causes of the wealth of nations (republished by R. H. Campbell and A. S. Skinner (Eds.). Oxford: Clarendon Press, 1976).
- Townsend P. Poverty in the United Kingdom. Harmondsworth: Penguin; 1979. [ Google Scholar ]
- van den Bosch K. Identifying the poor: Using subjective and consensual measures. Aldershot: Ashgate; 2001. [ Google Scholar ]
- United Nations. (1995). United nations world summit (Copenhagen) for social development. programme of action , Chapter 2. New York: United Nations.
- UNICEF. (2012). Measuring child poverty. New league tables of child poverty in the world’s rich countries. In Innocenti Report Card 10 . Florence: UNICEF Innocenti Research Centre.
- Veblen T. The theory of the leisure class. New York: McMillan; 1899. [ Google Scholar ]
- Whelan CT, Layte R, Maitre B. Persistent income poverty and deprivation in the European Union: An analysis of the first three waves of the European community household panel. Journal of Social Policy. 2003; 32 :1–18. doi: 10.1017/S0047279402006864. [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

Sociology Class Supplement: Writing Your Sociology Research Paper
- Formatting Your Paper
- In-Text Citations
- Direct Quotations
- Reference Page
- MARRIAGE & FAMILY - SOCI 2010
- Social Problems Research
- Music Research Paper
- Critical Thinking Cheatsheet
- Writing Your Sociology Research Paper
- Cultural Anthropology
Writing Guides
- Writing in Sociology Created by The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, this handout discusses scholarly research and writing in sociology, with helpful hints.
- APA Guide for Walters State Students This guide shows you how to format your paper in Word 2013, create in-text references, and complete your reference list.
- Organizing Your Social Sciences Paper (by University of Southern California) Created by USC Library, this guide can offer insight in how to organize a research paper in the social sciences.
- Official APA Style Guide This resource includes several tutorials, frequently asked questions, and blogs -- all addressing APA style.
Organizing Your Research Paper
- UNC Handout on Introductions Learn how to craft an effective introduction with this information!
- UNC Handout on Creating a Thesis Statement Want to produce a clear thesis statement? Read this!
- UNC Handout on Transitions Help from University of North Carolina Writing Center on how to make your essay flow smoothly.
- UNC Handout on Conclusions Make sure your conclusion wraps your thoughts up perfectly with these guidelines!
Sample APA Paper- Anthropology
- Sample APA Anthropology Paper
- SOCI1010 Music Paper Template
Research Coach

- << Previous: Critical Thinking Cheatsheet
- Next: Cultural Anthropology >>
- Last Updated: May 8, 2024 12:15 PM
- URL: https://library.ws.edu/sociology
Physical Address
304 North Cardinal St. Dorchester Center, MA 02124

Major Sociological Theories
- July 16, 2024
A Comprehensive List of Sociological Theories, Concepts, and Frameworks
Our understanding of societies, relationships, and social behavior has been profoundly shaped by a variety of sociological theories. Students of sociology invest significant time delving into these diverse social theories. Although some theories are no longer prevalent, others continue to be widely endorsed, each playing a crucial role in enriching our comprehension of societal dynamics. Engaging with these theories offers deeper insights into the historical, current, and future contexts of sociology.
Symbolic Interaction Theory
Symbolic Interaction Theory, also known as symbolic interactionism, stands as a principal sociological theory framework. It centers on the symbolic meanings that individuals create and depend upon during social interactions. This theory explores how people define and interpret their social roles through communication. It emphasizes the importance of language and gestures in forming identities and social bonds . By understanding these interactions, sociologists can gain insights into the complexities of human behavior and societal functioning.
Conflict Theory
Conflict theory highlights the influence of coercion and power in establishing social order. This perspective originates from Karl Marx’s view of society as a structure split into groups competing for economic and social resources, with social order maintained by those wielding the most power.
Functionalist Theory
Functionalist theory, often referred to as functionalism, is a major theoretical perspective in sociology. Originating from Emile Durkheim, it explores how social order is achievable and how societies maintain stability.
Feminist Theory
Feminist theory represents a contemporary sociological perspective that examines the roles and statuses of women and men in society to improve women’s lives. It focuses on empowering women and illuminating their societal contributions.
Critical Theory
Critical theory is a type of social theory aimed at critiquing and transforming societal structures and power systems to promote egalitarian changes. It challenges the status quo by examining the ways in which society perpetuates inequalities. This theory draws on various disciplines, including philosophy, sociology, and cultural studies, to understand and dissect power dynamics and ideologies that sustain social injustices and cultural hierarchies. It seeks to empower marginalized communities by advocating for social reform and systemic change.
Labeling Theory
Labeling theory offers a pivotal approach to understanding deviant and criminal behavior, positing that no act is inherently criminal but is defined as such by those in power. It emphasizes the significant role of societal reaction to behavior, suggesting that once labeled, individuals may embrace this identity, leading to further deviant acts. This perspective focuses on the consequences of labeling, exploring how stigma and societal reactions reinforce criminal identities and behaviors, potentially trapping individuals in a cycle of deviance.
Social Learning Theory
Social learning theory explains how socialization influences self-development. It considers the individual learning process and the societal impact on this process, often used to analyze deviance and crime. This theory asserts that behaviors are learned through observing and mimicking others within a social context, highlighting the role of role models, peers, and media. It argues that individuals acquire behaviors, norms, and values primarily through social interaction and observation, rather than through genetic or innate factors, emphasizing the importance of nurture in shaping human behavior.
Structural Strain Theory
Developed by Robert K. Merton, structural strain theory extends the functionalist view on deviance, attributing deviant behaviors to the discrepancies between cultural objectives and the available means to achieve them.
Rational Choice Theory
Rational choice theory suggests that human behavior is largely influenced by economic calculations, with individuals assessing potential costs and benefits before taking actions. This theory posits that people make decisions that maximize their personal advantage, assuming rationality in their choices. It applies not only to economic transactions but also to social interactions, where individuals weigh the potential gains and losses of their actions in various contexts, from business to personal relationships.
Game Theory
Game theory models human interactions as strategic games, providing insights into the dynamics of social interactions. It examines how individuals make decisions in situations where the outcome depends not only on their own actions but also on the actions of others. This theory highlights the strategic nature of decision-making, illustrating how people often act based on anticipated responses from others, leading to a variety of outcomes in competitive and cooperative scenarios.
Sociobiology
Sociobiology applies evolutionary principles to social behaviors, suggesting that many behaviors are partially innate and shaped by evolutionary forces. It explores how biological and genetic factors influence social structures and individual behaviors, arguing that evolutionary history plays a significant role in shaping patterns of behavior that enhance survival and reproduction. This perspective emphasizes the genetic underpinnings of social behavior, linking biology with social interaction in the context of evolutionary adaptation.
Social Exchange Theory
Social exchange theory views society as a network of interactions driven by the evaluation of rewards and punishments, where all human relationships derive from a subjective cost-benefit analysis.
Chaos Theory
Although primarily a mathematical study, chaos theory also applies to sociology and other social sciences , exploring complex, nonlinear systems and their intricate orders. This theory delves into how small changes can lead to significant consequences, known as the butterfly effect, within social systems. It examines unpredictable behaviors in systems that are sensitive to initial conditions, offering insights into the dynamics of societal change and the emergence of order from apparent randomness.
Social Phenomenology
Social phenomenology is a sociological approach that investigates how human awareness influences the creation of social actions, situations, and environments, positing that society is a human construct.
Disengagement Theory
Disengagement theory argues that as individuals age, they gradually withdraw from social engagements, a theory that has faced significant criticism for its perspective on aging and social interaction.
The application of sociological theories is crucial for comprehending the intricate layers of social interactions and institutions. By employing these social theories, sociologists can dissect various societal issues, such as inequality, deviance, and the dynamics of power. These sociological perspectives enable a deeper analysis of how individual behaviors are influenced by broader social forces, providing insights that can inform policy decisions, improve social practices, and foster more equitable communities.
In educational settings, introducing students to a range of sociological theories encourages critical thinking and a broader understanding of societal structures. By exploring different social theories, learners can appreciate the diversity of thought within the field and the various methodologies used to study social phenomena. These sociological perspectives not only enhance academic knowledge but also prepare students to engage thoughtfully and effectively with the social world around them.
Last Articles

Sociology Research Paper

This sample sociology research paper features: 10800 words (approx. 36 pages), an outline, and a bibliography with 59 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers for help. This is how your paper can get an A! Feel free to contact our writing service for professional assistance. We offer high-quality assignments for reasonable rates.
More Sociology Research Paper Examples:
- Disaster Research Paper
- Gambling Research Paper
- Group Dynamics Research Paper
- Human Ecology Research Paper
- Knowledge Research Paper
- Love Research Paper
- Quality of Life Research Paper
- Social Change Research Paper
- Social Movements Research Paper
- Social Networks Research Paper
- Social Stratification Research Paper
- Socialization Research Paper
- Sociology of Religion Research Paper
Introduction
The early sociology, the foundation of social science: statistical studies, the rise of american sociology, the substance of the sociological perspective, the passion for sociology, conclusion: the future of sociology.
- Bibliography
A commonly accepted definition of sociology as a special science is that it is the study of social aggregates and groups in their institutional organization, of institutions and their organization, and of the causes and consequences of changes in institutions and social organization. (Albert J. Reiss, Jr. 1968:1)
Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code.
Within the contemporary context, sociologists are interested in human social interaction as people take one another into account as each behaves toward the other. Sociologists also take into analytical consideration the systemic units of interaction within social groups, social relations, and social organizations. As stated by Reiss (1968), the purview of sociology extends to
Governments, corporations, and school systems to such territorial organizations as communities or to the schools, factories, and churches . . . that are components of communities. . . . are also concerned with social aggregates, or populations, in their institutional organization. (P. 1) (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({});
Sociology is, as Touraine (1990) suggests, an interpretation of social experience and is thus a part of the reality that the practitioners of the discipline attempt to observe and explain. To these areas we can add that sociology is a discipline that demystifies its subject matter, and it is, as Dennis H. Wrong (1990:21–22) notes, a debunker of popular beliefs, holds skeptical and critical views of the institutions that are studied (Smelser 1990), and challenges myth making (Best 2001).
The early history of sociology is a history of ideas developed in the European tradition, whereas the sociological approach of the last 150 years involved the development of concepts, methodology, and theories, especially in the United States (Goudsblom and Heilbron 2001). As American sociologists trained in the traditional theory and methods developed during the first eight decades of the twentieth century, we acknowledge our intellectual debt to the European founders. But beyond an earnest recognition of the classic work of the early founders, including Auguste Comte, Émile Durkheim, Alexis de Tocqueville, Frederic LePlay, Marcell Mauss, Max Weber, Karl Marx, and Harriet Martineau, most of whom were attracted to the European environment that included the liberalism, radicalism, and conservatism of the early to mid-nineteenth century (Nisbet 1966; Friedrichs 1970) and to what C. Wright Mills (1959) refers to as the sociological imagination that “enables us to grasp history and biography and the relations between the two within society” (p. 6), our approach to sociology is deeply embedded with and indebted to those individuals who established the Chicago, Harvard, Iowa, and Berkeley schools of thought. Similarly, as practitioners, our approach to the discipline of sociology is reflected in these distinctive American scholarly perspectives.
The American tradition of sociology has focused on social policy issues relating to social problems, the recognition of which grew out of the dynamic periods of social transformation wrought by the Industrial Revolution, the Progressive Era, world crises engendered by war, worldwide population shifts, increasing mechanization, and the effort of sociologists to create a specific niche for the discipline within a growing scientific community. This effort occurred first in North America and Western Europe and then, similar to cultural transitions of the past, within a global context. In every instance, the motives embedded within a science of society lie in the attempt to understand and offer proposals for solutions to whatever problems gain significant attention at a particular point in time.
In a most interesting work, Goudsblom and Heilbron (2001) pose that sociology represents a great diversity, or what some analysts may refer to as fragmentation, because the discipline grew as a part of the processes affecting societies and cultures worldwide throughout the nineteenth and twentieth centuries. Thus, as we move well into a new era and a new stage of academic development, it remains important that we recognize the sociological heritage as identified and discussed by these analysts. The five stages that sociology has experienced to date are (1) the predisciplinary stage prior to 1830, further identified as “protosociologies”; (2) the formation of the intellectual discipline, 1830–1890; (3) the formation of an academic discipline with diverging national traditions, 1890–1930; (4) the establishment of an international academic discipline, 1930–1970; and (5) a period of crisis, fragmentation, and attempts to develop a new synthesis, 1970–2000 (Goudsblom and Heilbron 2001:14574–80).
Consistent with the fifth stage, for almost four decades we have been witness to major changes in the substantive topics that undergo sociological inquiry both in the United States and, given the influence on the discipline by Canadian, European, and Scandinavian scholars, internationally. Among the areas more fully developed that might be identified as fragmentation are many of the most interesting sociological topics, including deviant behavior, the family, religion, gender, aging, health, the environment, science and technology, among so many seemingly unrelated topics. The unique conceptual paradigms of sociology serve as a template or pattern for seeing the social world in a special way. Every discipline and, indeed, every occupation employs templates or patterns to see and accomplish things in a unique fashion. Disciplines such as sociology rely on intellectual templates based on certain conceptual schemes or paradigms that have evolved through the development of a body of knowledge in those disciplines.
In its early era of the mid- to late nineteenth century, sociology was understood to represent anything relating to the study of social problems. Indeed, it was thought that the methods of the social sciences could be applied to social problems and used to develop solutions (Bernard and Bernard 1943). In focusing on such substance, O’Neill (1967:168–69) notes that periodicals of this early period had a sociological section in which news items relating to family matters, poverty, and labor often appeared. These early social scientists did not hold any special talents other than their training in theology. This situation was similar in the United States as well. It is not difficult, then, to imagine that, as Bramson (1961) notes, “For many American sociologists these problems evoked a moral response” (p. 75). Thus, the process of solving the problems of society was attempted by application of the conventional morality and the validation of Christian principles of piety rather than reform or progress.
Sociology was born as a result of a process, a process that directed a method of inquiry away from philosophy and toward positivism (MacIver 1934). Sociology was the result of a process caused by two major forces—namely, the Industrial Revolution and the French Revolution. The events, changes, and ideas that emerged from these two revolutions are found in the nineteenth-century thought pertaining to social order (Eisenstadt 1968). Following in the wake of the Age of Reason and the Renaissance, according to Nisbet (1966), this was a period of word formation:
Perhaps the richest period of word formation in history . . . which were either invented during this period or were modified to their present meanings: industry, industrialist, democracy, class, middle class, ideology, intellectual, rationalism, humanitarian, atomistic, masses, commercialism, proletariat, collectivism, equalitarian, liberal, conservative, scientist, crisis . . . [among others]. (P. 23)
These were words that held great moral and partisan interest in the European economy and culture; such passions were identified with politics as well.
Identified with European conservatism, which became infused by and with science, the visionary perspective promoted by Auguste Comte during the 1830s in his six-volume Positive Philosophy, later translated from the French and condensed into two volumes by Harriet Martineau, was based on the medieval model of European society.
This model of family, community, authority, tradition, and the sacred became the core of scientific sociology that was to serve notice that a science of society was essential to provide for more than commonsense analysis and to reestablish social order (MacIver 1934). Although unsuccessful in his quest to secure a professorship, Auguste Comte was a positivist, mathematician, and promoter of the scientific identity of the engineering profession (Noble 1999). Comte argued that positivism and the still-to-beidentified area of “sociology” would serve as a means of supporting his intention to create a unique perspective of human relations and a system to reestablish the social order and organization of society. Reestablishment of this new social order was to proceed in accordance with the positivist stage of evolution with its ineluctable natural laws that could and would be established through engaging the scientific perspective. Along with the arts, the science of sociology, according to Comte, was to emerge as the queen of the sciences, the scientia scientorum, and would ultimately supplant biology and cosmology.
If the restoration of order in French society was a preoccupation for many early-nineteenth-century scholars, including Auguste Comte, it was also the case, as Bramson (1961) notes, that
many of the key concepts of sociology illustrate this concern with the maintenance and conservation of order; ideas such as status, hierarchy ritual, integration, social function and social control are themselves a part of the history of the reaction to the ideals of the French Revolution. What conservative critics saw as resulting from these movements was not the progressive liberation of individuals, but increasing insecurity and alienation, the breakdown of traditional associations and group ties. (Pp. 13–14)
For social scientists of the early nineteenth century, many of the problems of the time were much more well defined than is the case in the contemporary experience.
Comte was fervently religious, and he believed those interested in science would constitute a “priesthood of positivism” that would ultimately lead to a new social order. According to Noble (1999),
A theist in spite of himself, Comte declared that the existence of the Great Being “is deeply stamped on all its creations, in moral, in the arts and sciences, in industry,” and he insisted, as had previous like-minded prophets since Erigena, that all such manifestations of divinity were equally vital means of mankind’s regeneration . . . Comte was convinced that people like himself, science-minded engineering savants occupied with the study of the sciences of observation are the only men whose capacity and intellectual culture fulfill the necessary conditions. (P. 85)
The legacy of this enthusiastic perspective is that sociology has been at the heart of the positivists’ contribution to the understanding of the human condition. It was also to serve in part as a basis for the reactions of conflict theorist Karl Marx, especially as these writings referred to the religious opiate of the masses deemed by Comte as critical to the reorganization of society (Noble 1999:87). The discipline continues to present an array of perspectives that have served to stimulate much controversy within both society and the discipline (see Turner 2001).
Although the sociological legacy of Harriet Martineau is substantial, as outlined by Lengermann and NiebruggeBrantley (1998), it was Martineau’s effort to translate and condense Auguste Comte’s six-volume magnum opus into a two-volume set of writings published in 1853 that allowed this important work to be available to the Englishspeaking world. Interestingly, Comte’s English translation came after Martineau’s sociological contributions, the richness of which was finally recognized by feminist researchers during the 1980s and 1990s. Martineau engaged in “participant observation” of the United States during the mid-1830s and subsequently published the two-volume Society in America (1836/1837), which is based on this excursion to the North American continent. Because of this experience, Martineau was able to lay the foundation for her treatise on research methodology in How to Observe Morals and Manners (1838).
Perhaps it is ironic that the distinctive difference between the European theoretical sociology and the empirical sociology practiced in the United States was advanced by events in Europe. Indeed, the origin of empirical sociology is rooted in Europe. Statistical studies began in the 1660s, thereby preceding the birth of all of the social sciences by a couple of centuries. The early statistical gatherers and analysts were involved in “political arithmetic” or the gathering of data considered relevant to public policy matters of the state, and as noted by Reiss (1968), the gathering of such data may have been accelerated to meet the needs of the newly emerging insurance industry and other commercial activities of the time. But it was the early work of the moral statisticians interested in reestablishing social order in the emerging industrial societies that was to lay the quantitative foundation for the discipline, especially the early scientific work of the French sociologist Émile Durkheim (Whitt 2001:229–35).
The second stage in the early history of quantification may have been related to the development of probability theory, the rise of the insurance industry, other commercial activities, and political necessity (Lecuyer and Oberschall 1968; Reiss 1968). English political arithmeticians, including John Graunt and William Petty, were destined to be followed by the efforts of the moral statisticians who engaged in data gathering in Belgium and France. Indeed, as early as 1831, the Belgian Adolphe Quetelet and the Frenchman Andre Michel de Guerry de Champneuf, in building on the early efforts of the practitioners of the “political arithmetic” that first began in the 1660s, were engaging in the government-sponsored data-gathering activity pertaining to data on moral topics, including suicide, prostitution, and illegitimacy. Such activities would prove quite instrumental in the establishment of the empirical social sciences. Even many of the methodologies developed during this same era of the early nineteenth century, as well as awareness of important ecological methodological issues such as statistical interactions, the ecological fallacy, and spuriousness, were developed by early moral statisticians such as Andre-Michel de Guerry and Adolphe Quetelet. Later, the work of Henry Morselli, Enrico Ferri, and Alfred Maury during this same century were to serve well the needs of aspiring European sociologists and even later members of the Chicago School of Sociology (Whitt 2001:229–31).
American sociology is one of the intellectual creations that has most deeply influenced our century. No other society ( the American ) has been more actively involved in understanding its own organizational change for the sake of knowledge itself. (Touraine 1990:252)
The birth of the social sciences in general and of sociology in particular is traced to the liberal democratic ideas generated by the British social philosophies of the seventeenth century—ideas that later were to be enhanced by the French Enlightenment of the eighteenth century and then transformed in the United States where these ideas served as the foundation for practical democratic society. The rise of American sociology can be traced to the early-nineteenthcentury social science movement, a movement that by the mid-1800s became a new discipline that was widely introduced into college and university curricula. The movement also led to the establishment of a national social science association that was to later spawn various distinctive social sciences, including sociology, as well as social reform associations (Bernard and Bernard 1943:1–8).
Although the promotion of the social sciences in the United States began as early as 1865 with the establishment of the American Association for the Promotion of Social Sciences and then, in 1869, creation of the American Social Science Association with its associationsponsored publication the Journal of Social Science, prior to the 1880s there had been no organized and systematic scientific research in the United States. This was the case simply because, as Howard W. Odum ([1927] 1965:3–20) noted, there was no university per se in which research as a scientific pursuit could be conducted. It is within the context of the movement to organize such a university that sociology and many other social sciences were embraced as viable academic disciplines, thereby allowing systematic research to be conducted in a rigorous manner. This also was a period of great emphasis on pursuing answers to new research questions through the evaluation of knowledge and the employment of methodological and statistical tools within an interdisciplinary context. Indeed, L. L. Bernard and Jessie Bernard (1943) posit that the vision of the founders of the American Social Science Association was “to establish a unified science of society which could and would see all human problems in their relationships and make an effort to solve these problems as unified wholes” (p. 601).
Thus, the social sciences in general and sociology in particular owe a great intellectual debt to the American intellects who studied at length with the masters of Europe. Included among these are notables such as William Graham Sumner, Lester Frank Ward, Albion Woodbury Small, Franklin Henry Giddings, John William Burgess, Herbert B. Adams, Thorstein Veblen, Frederick Jackson
Turner, James Harvey Robinson, George Vincent, Charles Horton Cooley, Edward Alsworth Ross, George Howard, Frank W. Blackmar, Ulysses G. Weatherly, John R. Commons, and Richard T. Ely (see Odum 1951, [1927] 1965); each of whom were well versed in scholarly areas other than sociology, including history, theology, economics, political science, and statistics. With the decline of the social science movement and its national association, the general discipline that emerged from the remains of social science was in fact sociology (Bernard and Bernard 1943:835).
The development of an intellectual and academic American sociology, like sociology in any part of the world, was and continues to be dependent on the social and political conditions of the country. In the United States, a liberal political climate and, in the aftermath of the Civil War, the advent of a system of a mass public education system, American sociology flourished. Thus, in countries in which the structure of the system of higher education was open to free inquiry, research was supported by private foundations and government contributions (Wright 1895), and the university was organized albeit loosely, sociology, subject to the polemics of its status as an academic science, gained entry if not acceptance among university faculty. Where education was available to the elite rather than the masses, sociology was less apt to flourish (Reiss 1968).
Another important factor is that American sociology arose basically without roots other than the growing influence of the social science movement in the United States and the emphasis on the virtues of science that permeated the intellectual and social environs of this same period. As noted by Neil J. Smelser (1990:49–60), American sociology did not experience the yoke of either European feudalism or any peculiar intellectual history. Rather, sociology came into being within American higher education during the 1880s and only after several other disciplines, including psychology and economics, had been accepted within the academy. Attempts among adherents of these other disciplines led to the establishment of the scientific theme within the social sciences. Early sociologists embraced this same scientific theme.
A second factor that had a profound effect on the early adherents of the sociological perspective is the social reform theme of the 1890s. The legacy of these two themes—namely, scientific respectability and social reform—became the dual platforms on which the unique American sociological perspective was to be based.
Although there was a great, direct influence of European thought, research, and the philosophy of the British Social Science Association on sociology to focus on attempting to solve America’s problems (Odum 1951:36–50), the rise of American sociology, at least during the first half of the twentieth century, was concomitant with the most dynamic period of technological, economic, and social reform changes ever recorded. In this context, Howard W. Odum (1951:52) views sociology as a product of the American social and cultural experience and places sociology’s heritage to be as “American as American literature,American culture, and the freedoms of the new world democracy” (p. 3). American sociology is thus part European and part American. Indeed, American sociology was envisioned early on as a social science that could and would assist policymakers and concerned citizens in creating the “American Dream.”
Consistent with this ideology, Odum (1951:59–60) identified three unique American developments, each of which influenced the direction of American sociology throughout the entire twentieth century. The first of these developments is the symbiotic relationship between the discipline and the American society and culture. The ideology that focused on the American Dream and its realization had a great influence.
The second development, according to Odum, is the emphasis on moral development and the motivation to establish ethics as a component of the educational curricula,American literature, and the social sciences, especially as these relate to ethical conduct, social justice, and public morality. Within sociology, this orientation is found in the application of sociological principles into economic and organizational behavior and the founding of the American Institute of Christian Sociology.
Finally, Odum (1951) notes, the American experience led to a research emphasis on social problems of a moral and economic nature. In an effort to better understand these social problems, sociologists organized the systematic study of issues such as waves of immigration, the working class, public disorder, neglect of children, violence toward women, intergroup conflict, urbanism, alcoholism, suicide, crime, mental illness, delinquency, and poverty (see also Fine 2006). This was the application side of sociology that held important social policy implication. However, there was also an early emphasis on a “general sociology” as opposed to a “special sociology” as was found at the more elite institutions of higher learning. Clearly, this difference foreshadowed the pure versus applied dichotomy that has generated so much discussion within the discipline (see Odum 1951:51–74).
Because of the important influence of the social science movement in the United States, there is some disagreement pertaining to who the founders and members of the first generation of American sociologists are (see Odum 1951, [1927] 1965). But publication of Lester Ward’s book Dynamic Sociology in 1883 does appear to mark the beginning of American sociology (Bramson 1961:84–85). On the other hand, there does not seem to be any disagreement as to the purpose of the American founders, and that was to establish a scientific theoretical base. Later, at the University of Chicago the goals were to establish a relationship between sociology and the classical problems of philosophy by focusing on process issues relating to elements of social control, such as conflict, competition, and accommodation (Kurtz 1986:95).
American sociology emerged concomitant with the challenges to legal philosophy and the discussion of questions relating to myriad questions that arose as the effects of industrialization were observed Calhoun (1919). Such questions have their focus on marriage, divorce, immigration, poverty, and health and how to employ the emerging scientific model to topical data that had been gathered by the nineteenth-century moral statisticians.
Leon Bramson (1961:47–48) observed that the most interesting aspect of American sociology in the first half of the twentieth century is that when affected by European theories of mass behavior and collective behavior, American sociologists, in their haste to establish a role for sociology in America, either transformed the meaning of the concepts to meet their needs or created new concepts to apply to the more liberal American social and political context. American sociologists, according to Bramson, also applied European theoretical concepts such as social pathology, social disorganization, and social control to the data referring to the American experience without regard for whatever special conditions should have been accounted for or even possible theoretical distortions; this issue is also discussed by Lester R. Kurtz (1986:60–83) in his evaluation of the Chicago School of Sociology.
Albert J. Reiss, Jr. (1968) notes that the first formal instruction of a sociology course in the United States was offered by William Graham Sumner, a professor of political and social science at Yale University, during 1876. The first, second, and third American Departments of Sociology were established at Brown University, the University of Chicago, and Columbia University, respectively (Kurtz 1986:93–97). Between 1889 and 1892, 18 American colleges and universities offered instruction in sociology, but in 1893, the University of Chicago was the first to develop a program that led to the granting of a Ph.D.
Despite the recognition of the emerging field of sociology as a distinctive area of inquiry, the focal point of a religious orientation and perhaps fervor expressed by social commentators in their discussions and analyses of the social issues that were to constitute the purview of sociology also engaged the attention of other early practitioners of the discipline. The social problems identified in the wake of expansion of the American West and the building of the railroads included issues relating to “the influx of immigrants, the rise of the factory system and the concentration of people in big cities. These comprised the now familiar catalogue of crime, delinquency, divorce, poverty, suicide, alcoholism, minority problems and slums” (Bramson 1961:75).
Alfred McClung Lee (1978:69) notes that ever since that time, sociologists have been attempting to divorce themselves from an ancestry that is historically rooted in the clergy, the police, utopian ideologues, social reformers, conservative apologists, journalistic muckrakers, radical thinkers, agitators, and civil libertarians.
Given the moral tone of much of the writing of many early American sociologists, it is noteworthy that in articulating the six “aims” of the American Journal of Sociology established at the University of Chicago in 1895, the scientific view of sociological concern so clearly defined several decades later by E. A. Ross (1936) was not so clear to many if not all of the moral philosophers of this earlier period. Witness the following comments offered by the founding editor of the American Journal of Sociology, Albion W. Small (1895):
Sociology has a foremost place in the thought of modern men. Approve or deplore the fact at pleasure, we cannot escape it. . . . To many possible readers the most important question abut the conduct of the Journal will be with reference to its attitude toward “Christian Sociology.” The answer is, in a word, towards Christian sociology sincerely deferential, toward “Christian sociologists” severely suspicious. (Pp. 1, 15)
These comments were of particular significance given that the American Journal of Sociology was not only the first journal of sociology created anywhere, but it was also, until 1936, the official journal of the American Sociological Society. Thus, the influence of both the Chicago School and the large number of contributions by its faculty and students to the American Journal of Sociology placed the work of the Chicago School at the forefront in shaping the early direction and substance of American, Canadian, and Polish sociology (Kurtz 1986:93–97). This was especially true in the subareas of urban and community studies, race and ethnic relations, crime and juvenile delinquency, deviance, communications and public opinion, and political sociology.
Leon Bramson (1961:73–95) identified three important phases in the rise of American sociology. The first period began in 1883 with the publication of Lester Ward’s Dynamic Sociology to about 1915 or 1918 with the publication of Robert E. Park’s essay on the city and/or the end of World War I, respectively. During this period, the founders began their earnest quest to establish the theoretical foundation as it related to the American experience focusing on “a liberal sociology of change and process, rather than one of conservation and equilibrium” (Bramson 1961:85).
This focus on change and process became even more evident during the second stage of American sociology, identified as the period between the two world wars. This was a period of academic expansion, with major increases in faculty and students, but even more important, led by sociologists at the University of Chicago, this was a period of specialization and the beginning of differentiation within sociology as the quest to develop a viable methodology began in earnest. This also was a meaningful period during which sociologists worked to establish the scientific status of the discipline and to earn respectability and academic legitimization. It was also a period during which many of the conceptual problems of sociology first began to emerge as its practitioners developed an increasingly complex technical vocabulary, a vast array of classification schema, and other abstract systems categories of thought. Perhaps assuming the need to compensate for a past that included so many nonscientifically moral reformistoriented representatives of the discipline, sociologists responded during this phase of development by creating complex theories that, for an extended period of time, were not only unintelligible to the layperson, but also the abstract nature of these grand theories exceeded the ability of social scientists to create methodologies appropriate to empirically test these theoretical models (Lee 1978). But despite this theoretical/methodological problem, this second stage of sociological development was also one in which much substance was created.
The history of sociology in America from prior to World War I to approximately the mid-1930s is, according to Kurtz (1986), a history of the school of thought promoted by the University of Chicago. If the second phase of American sociology is to be distinguished as a period dominated by the Chicago sociologists, it is also one that led Pitirim Sorokin to observe that American sociology was emerging as a distinctive brand:
The bulk of the sociological works in America are marked by their quantitative and empirical character while the bulk of the sociological literature of Europe is still marked by an analytical elaboration of concepts and definitions; by a philosophical and epistemological polishing of words. (Cited in Bramson 1961:89)
The period is characterized by a marked increase in the development of new and expanding methodologies and measurement. These new techniques included a plethora of scales intended to measure the theoretical concepts developed previously.
As noted, Goudsblom and Heilbron (2001) identify five phases of development of the discipline that cover the period prior to 1830 to the very end of the twentieth century. But the third phase of the development of American sociology, identified by Bramson (1961) as covering the period from 1940 to 1960, is noteworthy because this was a period during which the development and adoption of theories of the “middle-range” advocated by Robert K. Merton led to even greater specialization and differentiation of the discipline. In turn, sociologists began to develop ever-expanding areas of inquiry. Robert K. Merton ([1957] 1968), who wrote in reaction to the abstractness of the previous dominant position of the functionalist school of sociology, stated that theories of the middle range are
theories that lie between the minor but necessary working hypotheses that evolve in abundance during day-to-day research and the all-inclusive systematic efforts to develop a unified theory that will explain all the observed uniformities of social behavior, social organization and social change. (P. 39)
The all-inclusive efforts refer, of course, to the contributions of Talcott Parsons in The Structure of Social Action, originally published in 1937, and in 1951 with the appearance of The Social System.
The third phase of development can be characterized as the most enthusiastic period during which greater emphasis was placed on the application of sociological knowledge. As the field expanded, new outlets for sociological studies and knowledge were created, sociologists found employment in nonacademic settings such as government and business, and the new specialty areas of interest reflected the changes in American society, including a growing rise in membership in the middle class, the expansion of the suburbs, more leisure time, and the growth of bureaucracy. In lieu of the previous sociological interest in the reform of society and the more traditional social problems orientation of the discipline, the new sociology opted to leave such concerns to the social work profession and to special studies programs such as criminology. Thus, specialty areas emerged—areas such as the sociology of marriage and the family, and aging (later to be defined as gerontology), industrial sociology, public opinion, organizations, communications, and social psychiatry (later called mental health). From this point forward, the continued rise to respectability of sociology is attributed by analysts such as Robert Nisbet (1966) to the public recognition that societal problems are more integrative in nature than previously thought. This may also serve as a partial explanation for why the discipline is viewed by some as fragmented.
The logic and ethos of science is the search for the truth, the objective truth. Thus, the most fundamental problem the social scientist confronts, according to Gunnar Myrdal (1969), is this:
What is objectivity, and how can the student attain objectivity in trying to find out the facts and the causal relationships between facts? [That is,] How can a biased view be avoided? The challenge is to maintain an objectivity of that which the sociologist is a part. (P. 3)
Although the sociologies of the United States and Europe differ in perspective, both attempt to answer similar albeit distinguishable questions. In his discussion of “the two faces of sociology,” Touraine (1990:240) states that these differences lie in the scholarly research response to two problems: (1) How does society exist? (2) How are culture and society historically created and transformed by work, by the specific way nature and its resources are put to use, and through systems of political, economic, and social organization? Because the intellectual legacy of American sociological thought has been shaped to a large extent by the historical experience of creating a nation in which the rights and the will of the American people have been dominant, American sociologists have long focused on “institution” as a central concept and the significance of efforts of reform movements within the American society to affect its social organization. Thus, the substance of American sociology has been on topics such as the family, social organization, community, the criminal justice system, and law and society among the numerous institutionallevel areas of inquiry that are evaluated within the context of yet another American theoretical focus—namely, the emphasis on theories of the middle range. European sociologists, on the other hand, tend to focus on the second question while emphasizing the concept “revolution” in their analyses. Thus, even when similar topics such as social movements serve as the focus of inquiry, the American and European sociology responds from a different perspective (Touraine 1990). To understand the importance of this difference in perspective between the two sociologies, Alain Touraine (1990) poses the view that American sociology has a symbiotic relationship between culture and society, whereas European sociology integrates society and its history. Americans sociologists focus on society; the European sociology is focused on the rich history that serves as the backdrop for any attempt to understand social change.
Because the American experience is predicated on building a nation through the rule of law; the concepts of individualism, capitalism, and territorial conquest; and the attempt at integration of successive waves of immigrants to the North American continent,American sociology began its rise in prominence through an elitist intellectual process that dominated the academy during the early formative years of the discipline. Thus, it is perhaps ironic that an American sociology housed within the university setting would assume a critical teaching and research posture toward an elitist system of institutions that the early sociology assisted in creating. Within the context of certain kinds of social problems areas, such as ethnic studies, discrimination, and segregation, sociology and sociologists have been able to exert some influence. But in other important areas within which issues relating to elitist society may be involved, such as social class relations and economic and political power, the official and public perceptions of the efforts of American sociologists may not be as well received.
Many analysts of the past can be called on to render testimony in support of or apologize for the past efforts of sociologists to provide useful information, but none is perhaps more relevant than the following statement offered by George A. Lundberg (1947): “Good intentions are not a substitute for good techniques in either achieving physical or social goals” (p. 135). During the 1960s and 1970s, sociology, psychology, and other social science undergraduate job candidates customarily responded to interviewer queries with “I want to help people.” Similar to those who attended graduate school after World War II, these individuals were influenced by the potential of sociology to make a difference. But good intentions aside, the real issue is, How do we go about assisting/helping people? Perhaps the more educated and sophisticated we become, the more difficult are the answers to social problems and social arrangements that are deemed inappropriate or at least in need of some form of rearrangement. That is, the more we believe we already know the answers, the less apt we are to recognize the importance of the sociological perspective. Within this context, sociology necessarily must adhere to and advocate the use of the methods of science in approaching any social problem, whether this is local or international in scope.
Sociology has utility beyond addressing social problems and contributing to the development of new social policy. Indeed, the sociological perspective is empowering. Those who use it are in a position to bring about certain behavior in others. It has been said that “behavior that can be understood can be predicted, and behavior that can be predicted can likely be controlled.” It is not surprising that sociologists are often used to help select juries, develop effective advertising campaigns, plan political strategies for elections, and solve human relations problems in the workplace. As Peter Berger (1963) phrases it, “Sociological understanding can be recommended to social workers, but also to salesmen, nurses, evangelists and politicians—in fact to anyone whose goals involve the manipulation of men, for whatever purpose and with whatever moral justification” (p. 5). In some ways, it might be said that the sociological perspective puts one “in control.”
The manipulation of others, even for commendable purposes, however, is not without critical reaction or detractors. Some years back, industrial sociologists who worked for, or consulted with, industrial corporations to aid them to better address problems in the workplace were sometimes cynically labeled as “cow sociologists” because “they helped management milk the workers.” Knowledge is power that can be used for good or evil. The sociological perspective is utilitarian and empowering in that it can accomplish things for whatever purposes. Berger (1963) goes on to reflect the following:
If the sociologist can be considered a Machiavellian figure, then his talents can be employed in both humanly nefarious and humanly liberating enterprises. If a somewhat colorful metaphor may be allowed here, one can think of the sociologist as a condottiere of social perception. Some condottieri fight for the oppressors of men, others for their liberators. Especially if one looks around beyond the frontiers of America as well as within them, one can find enough grounds to believe that there is a place in today’s world for the latter type of condottiere. (P. 170)
Responding to the question, “Can science save us?” George A. Lundberg (1947) states “yes,” but he also equates the use of brain (the mind) as tantamount to employing science. Lundberg also posed the following: “Shall we place our faith in science or in something else?” (p. 142). Physical science is not capable of responding to human social issues. If sociologists have in a vain effort failed to fulfill the promise of the past, this does not indicate that they will not do so at some future time. Again, as Lundberg (1947) heeded long ago, “Science is at best a growth, not a sudden revelation. We also can use it imperfectly and in part while it is developing” (pp. 143–144).
And a few years later but prior to the turmoil that was to embroil the decades of the 1960s and 1970s, John Madge (1962) urged that a century after the death of the positivist Auguste Comte (now 150 years later) the structure of sociology remains incomplete. However, Madge recognized and demonstrates in The Origins of Scientific Sociology that sociology was slowly gaining in maturity and with this growth was on the verge of or within reach of achieving the status of a science. But it is also important to keep in focus the goals of science as articulated by Gunnar Myrdal (1969)—more specifically, “The goals of objectivity and effectiveness in research are honesty, clarity, and effectiveness” (p. 72). If the results of sociological research have been less than to the liking of policymakers and government and corporate leaders, then yet another of Myrdal’s insights is especially germane. That is,
Research is always and by logical necessity based on moral and political valuations, and the researcher should be obligated to account for them explicitly. When these valuations are brought out into the open any one who finds a particular piece of research to have been founded on what is considered wrong valuation can challenge it on that ground. (P. 74)
There are other reasons as well, reasons that complicate the delivery of the important message promoted by the discipline’s practitioners, for as noted by Joel Best (2003:11), sociology “is a perspective built on relativism, built on the recognition that people understand the world differently.” Indeed, many years earlier George C. Homans (1967) observed,
If some of the social sciences seem to have made little progress, at least in the direction of generalizing and explanatory science, the reason lies neither in lack of intelligence on the part of the scientists nor in the newness of the subject as an academic discipline. It lies rather in what is out there in the world of nature. (P. 89)
Such statements lie at the heart of the epistemological debate that began in the 1920s (see Reiss 1968:10–11) and continues into the modern era. Despite the vastness of sociological inquiry, it is obvious that a strong orientation toward the scientific study of human behavior, social interaction, and organizations continues and that this scientific focus is predicated on the assumption that such study is possible because it is based on the examination of phenomena that are subject to the operation of universal laws, a point not lost in the minds of the discipline’s founders. The counterpoint that the social sciences are cultural sciences and thereby fundamentally different from the physical sciences and also subject to different methodology and other evaluative criteria is representative of a longstanding European influence that also began in the 1920s.
Given the diversity and fluidity of the topics addressed and the levels of theories employed by sociologists, it is not surprising that many others do not agree. The counterargument is based on the premise that given the circumstances behind the evolution of science and the support it received in the past and the more repressive attention it receives in the contemporary experience from powerful interest groups, objective social science and the establishment of universal laws that are based on such inquiry may not be possible (see Turner 2001).
Whether or not one argues that the study of human society is unique, it is still extraordinary given the vast array of extant theories used to express the human experience and capacity. Witness the statement of one contemporary analyst who, in an intriguing assessment of the contemporary American “wilding” experience, wrote,
Sociology arose as an inquiry into the dangers of modern individualism, which could potentially kill society itself. The prospect of the death of society gave birth to the question . . . what makes society possible and prevents it from disintegrating into a mass of sociopathic and self-interested isolates? This core question of sociology has become the vital issue of our times. (Charles Derber 2003:18)
Only in part is Derber referring to the American experience. His assessment also speaks to the experience of Western Europe. Much social change has taken place, and the efforts of sociologists to describe and explain this change and to draw upon these insights to develop predictive models has led to a diversity of theories. Indeed, over time, the scientific paradigm shifts more generally described by Thomas Kuhn ([1962] 1970) are obvious in our discipline (see Friedrichs 1970). There have been, there are at present, and there undoubtedly will be future paradigm shifts within this evolving and apparently expanding discipline of sociology, many of which will focus, as has been the case in the past, on the social change process. And for all the so-called objectivity of a scientific sociology advocated by analysts such as George A. Lundberg (1947), the development of which is so eloquently described by Leon Bramson (1961)), sociologists have been involved in social activism and social engineering, that first occurred during the embryonic years of the discipline’s development (Volkart 1968). Such activism occurred again during the 1960s and 1970s, in many social justice areas, and in occupational settings such as those of the criminal justice system.
At present, sociological inquiry represents a vast array of topics and offers many competing theoretical models while its practitioners attempt to make sense of a rapidly changing world. For all its middle-range theories and studies that reflect the efforts of those dedicated to cumulative knowledge, it is also important that we recognize that the building of a paradigm as well as challenges to an extant paradigm are not relegated to the gathering of information alone. Indeed, if sociology is to advantage itself in the twenty-first century, it may be imperative that a dominant paradigm begins to identify the kinds of community needs that it can usually serve, for as Joseph R. Gusfield (1990) so clearly notes, sociology has been at odds with and a critic of the classical economic and individualistic interpretations of American life. Thus, whatever issues sociology may need to address at this juncture, perhaps we are hampered only by the limits of the sociological imagination. Again, the following comment by Homans (1967) is noteworthy:
The difficulties of social science lie in explanation rather than discovery. . . . Our trouble has not been with making discoveries but with organizing them theoretically—showing how they follow under a variety of given conditions from a few general principles. (Pp. 79, 105)
The present diversity of the discipline welcomed by so many social critics also serves as a barrier to the creation of a dominant theoretical paradigm. Without this focus, sociology remains in the minds of many of the discipline’s representatives a less-than-coherent discipline. Perhaps this is not different from the struggle of the 1960s as described by Gouldner (1970), a period that also was far less than organized and coherent and certainly far less civil in disagreement. It is important that sociologists take stock of their trade and question in earnest the utility of the work we do. As noted by Herbert L. Gans (1990),
By and large, we sociologists have been too distant from the society in which we operate and in which we are embedded, which funds us even if too poorly and which influences us surely more than we influence it. We are too busy trying to understand how that society functions . . . that we rarely think about our own functions—and dysfunctions. To some extent our failure to do so stems from a typical professional blindness, which results in our inability to distance ourselves sufficiently from ourselves and our routines to look systematically at what we are for and to whom. (Pp. 12–13)
Not all may agree, of course. Indeed, sociology in the United States and in Europe has been a critique of modern urban life with its emphasis on the individual, capitalism, and bureaucracy. In some instances, this critique of American society has been radical and reformist in its thrust (Gusfield 1990:31–46). And although American sociology had been shaped in part by psychology in establishing its methodology during the first two-thirds of the twentieth century, especially through a common socialpsychological area (see, e.g., Reiss 1968), it can be safely stated that American sociology has been transformed during the latter decades of the twentieth century.
Sociologists may be accused of engaging in an affair with their work. Witness the stirring comments of one colleague:
I fell in love with sociology when I was twelve. . . . Sociology was my savior. It saved me from the vexing confusion caused by my once despising the mundaneness of everyday life and deeply loving and admiring my people. It stabilized me by articulating the dedication that I felt for social justice. (Shahidian 1999:303–04)
We share this passionate approach to social science based on the insightful development of theory and empirical research, an approach that has, in turn, led to a vast array of subject matter. In light of these impressive contributions, the only aspect of this endeavor that may seem perplexing to some is that as we move further into the twenty-first century, there are those who continue to believe in and practice the scientific method; there also are those who argue that if the logic of science and the methods of scientific objectivity are to be carried to an extreme, sociology will lose or has already lost its humanistic perspective and, with this loss, the inclination toward active community involvement through social policy advocacy and practical intervention. As Peter L. Berger (1963) phrases it,
At the same time it is quite true that some sociologists, especially in America, have become so preoccupied with methodological questions that they have ceased to be interested in society at all. As a result, they have found out nothing of significance about any aspect of social life, since in science as in love a concentration on technique is quite likely to lead to impotence. (P. 13)
This dichotomy certainly is a matter of considerable debate, but perhaps most advocates and active practitioners of the discipline would fall somewhere in between these two orientations (see, e.g., Reiss 1968:10–11). In this regard, we are also optimistic that the sociological imagination will continue to be an important part of the work of sociologists as they take into consideration “a quality of mind that will help them to use information and to develop reason in order to achieve lucid summations of what is going on in the world and of what may be happening within themselves” (Mills 1959:5).
More than 170 years ago, sociology began to emerge from its philosophical and biological roots to it current status as an important social science. Early sociologists achieved renown based on their interest in providing information useful to appraise social policy issues. However, in the contemporary instance, there are strong indicators that sociology has not achieved the eminent position envisioned by the founders. Note the less-than-enthusiastic assessment offered by Black (1999):
The problems endemic to the discipline of sociology include the lack of a paradigm, disciplinary fragmentation, and the irreconcilability of science, ideology, and politics . . . and the lack of an occupational niche—[all these] place sociologists in the position of having constantly to defend the profession. (Pp. 261, 263)
Thus, as we move well into the twenty-first century, it is clear that sociology is engaged in yet another struggle to (re)identify itself. Perhaps such a struggle is to be expected of any science of human behavior. And nowhere is this situation more contentious than in the responses of representatives of the discipline to the question as to whether sociology is or is not yet considered an activity worthy of the label “scientific activity.”
At the center of this struggle lies the heart of any discipline—namely, sociological theory. Among the eminent theorists reporting on the status of sociology in this Handbook are individuals who represent the very best of what the discipline has to offer. That the message is suggestive of a continuing debate within the discipline is both disheartening and encouraging. It is disheartening in that after a period of more than 175 years, representatives of the discipline should be able to exclaim with great pride the accomplishments of so much activity instead of debating their scientific worth. It is encouraging because the current debate over the theory and the substance of the work sociologists engage in can only lead to the exploration of new and challenging frontiers. But the substance of sociological inquiry also represents a matter of contention for many research- and practitioner-oriented representatives of the discipline. Some contemporary analysts who have observed the developments within the academy during the past several decades call for a critical reevaluation of that which sociologists identify as the substance of research and understanding. Sociology has given birth to and generated intense interest in many areas of study that are no longer identified with the discipline. Because the specific subareas developed by sociologists became well accepted as legitimate applied disciplines within the academy, independent, overlapping units within the academy have been created.
If the 1960s represent the golden era of sociology, it is also a period, as described by Turner and Sica (2006), that is “remembered as a time of violence, massive social change, and personal transformation” (p. 4). The period had a profound effect on an entire generation of students, many of whom were instrumental in creating the new sociological emphasis that today is criticized for its diversity, the lack of continuity, and a failure to develop a unified paradigm. Whatever reservations that may continue to exist as we progress well into the twenty-first century, these can be hailed as a challenge. Thus, at the same time that community involvement and applied research are increasingly being devalued in the academic world, there is a distinct pressure, according to Harris and Wise (1998), for sociologists to become increasingly involved in the community and society.
This call to establish a public sociology may well combine with the three types of knowledge identified by Burawoy (2005)—the professional, critical, and policyspecific databases. In each of these areas, the initiative would be consistent with enthusiastic proclamations of the past. George A. Lundberg’s (1947) Can Science Save Us? serves as but one important example of those who promoted the application of social science insights to solve social problems. Of course, one major difference between the time when Lundberg wrote and now is that we are not rebounding from the tragedy of a world war. Indeed, it was during the post-World War II period and during the subsequent several decades that American sociology assumed its theoretical and empirical dominance (Odum 1951), especially in the area of deviant behavior (see Touraine 1990). Yet another important difference between then and now, as Harris and Wise (1998) suggest, is that sociologists need to be perceived as problem solvers rather than as social critics, and similar to the pleas of Marion Talbot (1896) at the end of the nineteenth century, much of the sociological may necessarily become interdisciplinary in nature. This perspective is supported as a portion of a more scholarly editorial philosophy articulated by Wharton (2006:1–2). Most noteworthy for our purpose are points three and four:
(3) Be aware and reflective about the . . . broader contributions to scholarship, policy, and/or activism . . . ; (4) produce useful knowledge—not merely in the applied sense of solving problems, but knowledge that is useful as basic research that can help people better understand and transform the social world. (P. 1)
These same kinds of issues—social activism and public policy research—were recognized at the end of the nineteenth century as strengths of the new discipline.
Thus, there appears to be hopeful as well as worrisome aspects of sociology at the end of the twentieth century (Lewis 1999). But this kind of enthusiasm and concern appears to be periodic throughout the history of the discipline as sociologists attempt to both define and then redefine the parameters of what some argue is too extensive a range of topics to allow practitioners of the discipline to be definitively identified (Best 2003). Witness the statement attributed to one of the coeditors of this Handbook who, in the early 1980s, wrote the following:
Future prospects for sociology(ists) no doubt will depend upon our ability to identify and respond to community needs, to compete for funds available from nontraditional sources, to work in applied areas, and to establish creative problemsolving strategies. The challenge before us should generate a healthy response. (Peck 1982:319–20)
Since that time and in the wake of a declining influence of the social sciences, there has been a response as evidenced by the many new areas of inquiry, many interdisciplinary in nature, that currently curry attention from sociologists. Indeed, there does appear to be a fragmentation, but this so-called fragmentation is consistent with an assessment offered by Beck (1999), “Sociology today, as throughout its history, is not unified. . . . we have never been able to sustain . . . unanimity and consistency for very long. Thank goodness” (p. 121).
Perhaps we do not engage in “normal science,” at least not in the sense that Thomas Kuhn ([1962] 1970) refers to it. That is, academic sociologists continue to function quite well even though they are outside the single frame of reference that usually serves as the paradigmatic foundation for the physical sciences. Normal science is rigid, but it is also burdened by uncertainty and inconsistency, as Friedrichs (1970) observes. In the case of sociology, this is found in the diversity of theoretical models and topical areas. Although some analysts lament the current state of the discipline, Jacobs (2004) recently observed that “some might view this diversity [of topics] as evidence of excessive fragmentation, (but) there are important theoretical connections” (p. v). Of course, the substance of manuscripts submitted for possible publication, the rubrics under which the research can be categorized, is quite different from the search for a common sociological paradigm. To wit, classic studies do exist, but none serve to forge a single paradigm. Thus, the future of the discipline will depend, as usual, on the contributions of those who may be relatively silent in the wake of less-than-acceptable “scholarship,” as suggested by Lewis (1999), but who nonetheless commit themselves to excellence by producing significant contributions to theory and application (see, e.g., Rossi 1999) that should, in the long run, counter the myriad productions that are less significant. Concomitant with this effort will be an increased awareness of and involvement in the applied and an earnest effort to again be a viable force in the policy-related aspects of sociology and society. In other words, we believe there will be a reawakening of and involvement in those aspects of sociology that served the discipline well during its early years of development in the United States (see Ross 1936) even as the applied social work-oriented practitioners broke away to form their own professional association (Odum 1951; Rossi 1999). Indeed, there exists a need for answers to myriad policy-oriented questions as well as applied concerns at all governmental levels.
But in the end, sociologists may, as Beck (1999:123) suggests, go where they go, where they want to go. This may again mean that sociologists will abandon important areas of inquiry that they helped to establish, leaving the sociological legacy to others. Sociologists will also move to create other areas of inquiry while questioning past and present assumptions and knowledge claims in an ongoing quest to better understand social arrangements and to engage in, as Beck (1999) observes, “life, liberty, the pursuit of happiness, and the sociological imagination” (p. 124). To this we can add the quest to establish the meaning of social justice in a rapidly changing democratic society.
Thus, contrary to dubious predictions of an ominous obscure future, the content of this Handbook attests to a much more positive and grand future orientation within the discipline that will include much more than the rigorous efforts to clean up conceptual problems that sociologists are supposedly noted for. Moreover, the epistemological debates of the past will undoubtedly continue as Turner (2001) and Best (2003) suggest, but in so doing, the future of academic sociology will again be broadened. This expansion will again, we think, involve the applied aspects of the discipline and engagement of the public through active involvement of sociologists in the four traditional areas—namely, through a public sociology with an emphasis on further development of the profession and a critical civic activism with the intent to broadly influence social policy. Moreover, the increasing influence of European sociology in the global community will undoubtedly continue; this influence is not only important, it is most welcome. Given the above, it may well be that another call to arms will result. There has been a movement, albeit a small movement, among highly regarded intellectuals (the National Association of Scholars) to enhance the substance and quality of academic teaching and scholarly activity. This, too, is welcome in sociology.
The world that engages a scientist, as noted by Friedrichs (1970), is one that emerges from a scientific tradition, along with its special vocabulary and grammar and environment. Sociology’s laboratory is the social world and on occasion its practitioners are criticized by those who argue the arcane nature of all that is considered scientific. If the normal science, as described by Thomas Kuhn ([1962] 1970) and Robert W. Friedrichs (1970), is to be realized within the discipline of sociology, then it may depend on efforts of young sociologists (see, e.g., Frickel and Gross 2005) who may capture the essence of such a paradigm in a general theory of scientific/intellectual movements. Such work may also serve to stimulate more thought as to the requisite initiatives essential for subsequently developing the kind of intellectual movement that will define once again, and actively promote, the substance of the sociological perspective.
If the emphasis of American sociology at the beginning of the twentieth century was unsophisticated, armchair science that “featured the study of general society and the ‘system’ of social theory, it reflected not only the almost universal philosophical approach but also the consistency of the best minds in interaction with European philosophy and American higher education” (Odum 1951:421–22). In the mid-twentieth century, sociology, similar to other social and physical sciences, struggled to determine whether the future of the discipline would continue to pursue a general systems theory of society or whether the discipline’s practitioners would develop more theory and then relate these theories to research and the scientific method (Odum 1951:422). At this critical midpoint of the century past, and in recognition of the importance of the discipline, Odum (1951) wrote that there is
the extraordinary need in the contemporary world for a social science to seek special knowledge of human society and welfare and meet the crises brought on by science and technology, so often out of perspective to human relations, and so to provide the basis for not only a social morale in an age of science but for societal survival as well. (P. 3)
At the end of the twentieth century, these comments rang clear, and as we move forward and well into the greater twenty-first-century experience, Odum’s words seem no less germane today than in the past.
Toward establishing the prospects for the future of this great academic discipline, we hasten to add how critical it is and will be to again acknowledge the important work of the founding mothers and fathers of sociology. Thus, at the end of the twentieth century, the state of sociology may have been debatable, but during the initial decades of the twenty-first century, sociologists will undoubtedly take up the challenge to pursue answers to vexing social problems that are, as Fine (2006:14–15) states, embedded with complex, dynamic, interconnected social systems. Some of the solutions to be tendered in the near future may not serve well the needs of all citizens, but these should nonetheless address policy issues relating to social freedom, social justice, and social equality while recognizing that such policies determine the behavior of those actors whom sociologists are intent to study. Herein American sociologists may now have achieved the requisite disciplinary maturity to employ the kind of sociological imagination envisioned by C. Wright Mills (1959) half a century ago. Such a sociology would, in the tradition of Europe, encompass a biography and history within society, thereby allowing sociology to represent not only a scientific enterprise but also to serve as a sensitizing discipline that allows us to continue to view the world in a new and interpretive fashion.
Finally, in some peculiar ways, the vexing problems that capture our attention during the early portion of the twenty-first century parallel those of the early twentieth century; this is true at all levels of society and perhaps even more so within those sectors that heretofore were barricaded from a critical analyses. The actors may have changed but, in general, the public concerns regarding the kinds of behavior tolerated and considered to be appropriate tend to remain the same. And as the moral entrepreneurs of the twenty-first century push their agendas, the new prohibitionist movements continue to capture the attention of policymakers, which may of necessity be cause for some sociologists at least to revisit many of the same topics that held sway in the past. Thus, we will continue to use templates in our lives to understand the world, physical and social, in which we exist. The sociological templates derived from the many conceptual constructs available provide us with a unique and perceptive perspective. As sociology further develops, new conceptual constructs will be added and will contribute to its unique perspective, thereby enhancing our ability to better analyze and understand human social behavior.
Bibliography:
- Beck, Bernard. 1999. “The Future of Sociology.” Sociological Inquiry 69:121–29.
- Berger, Peter L. 1963. Invitation to Sociology: A Humanistic Perspective. Garden City, NY: Anchor Books.
- Bernard, L. L. and Jessie Bernard. 1943. Origins of American Sociology. New York: Thomas Y. Crowell.
- Best, Joel. 2001. Damned Lies and Statistics: Untangling Numbers from the Media, Politicians, and Activists. Berkeley: University of California Press.
- Best, Joel. 2003. “Killing the Messenger: The Social Problems of Sociology.” Social Problems 50:1–13.
- Black, Timothy. 1999. “Going Public: How Sociology Might Matter Again.” Special Section: Saving Sociology (Part II) Sociological Inquiry 690:257–75.
- Bramson, Leon. 1961. The Political Context of Sociology. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
- Burawoy, Michael. 2005. “For Public Sociology.” American Sociological Review 70:4–28.
- Calhoun, Arthur W. 1919. A Social History of the American Family: From Colonial Times to the Present. 3. Cleveland, OH: Arthur H. Clark.
- Crothers, Charles. 2001. “History of Sociology.” Pp. 1550–52 in Reader’s Guide to the Social Sciences, edited by J. Michie. Chicago, IL: Fitzroy Dearborn.
- Derber, Charles. 2003. The Wilding of America: Money, Mayhem, and the New American Dream. New York: Worth.
- Eisenstadt, Shmuel N. 1968. “The Development of Sociological Thought.” Pp. 23–36 in International Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences, edited by D. L. Sills. New York: Macmillan/Free Press.
- Fine, Gary Alan. 2006. “The Chaining of Social Problems: Solution, and Unintended Consequences in the Age of Betrayal.” Social Problems 53:3–17.
- Frickel, Scott and Neil Gross. 2005. “A General Theory of Scientific/Intellectual Movements.” American Journal of Sociology 70:204–32.
- Friedrichs, Robert W. 1970. A Sociology of Sociology. New York: Free Press.
- Gans, Herbert J., ed. 1990. Sociology in America. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
- Goudsblom, J. and J. Heilbron. 2001. “History of Sociology.” Pp. 14574–80 in International Encyclopedia of the Social & Behavioral Sciences, edited by N. J. Smelser and P. B. Baltes. Amsterdam: Elsevier.
- Gouldner, Alvin W. 1970. The Coming Crisis in Western Sociology. New York: Basic Books.
- Gusfield, Joseph R. 1990. “Sociology’s Effects on Society.” Pp. 31–46 in Sociology in America, edited by H. J. Gans. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
- Harris, Catherine and Michael Wise. 1998. “Grassroots Sociology and the Future of the Discipline.” American Sociologist Winter:29–47.
- Hollander, Paul. 1999. “Saving Sociology?” Sociological Inquiry 69:130–47.
- Homans, George C. 1967. The Nature of Social Science. New York: Harcourt, Brace & World.
- Jacobs, Jerry A. 2004. “ASR: Yesterday, Today, Tomorrow.” American Sociological Review 69:v–vi.
- Kuhn, Thomas S. [1962] 1970. The Structure of Scientific Revolutions. 2d ed. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Kurtz, Lester R. 1986. Evaluating Chicago Sociology. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press.
- Lecuyer, Bernard and Anthony R. Oberschall. 1968. “The Early History of Social Research.” Pp. 36–52 in International Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences, edited by D. L. Sills. New York: Macmillan/Free Press.
- Lee, Alfred McClung. 1978. Sociology for Whom? New York: Oxford University Press.
- Lengermann, Patricia Madoo and Jill Niebrugge-Brantley. 1998. The Women Founders: Sociology and Social Theory, 1830–1930. Boston, MA: McGraw-Hill.
- Lewis, Michael. 1999. “Introduction: Saving Sociology (Part I).” Sociological Inquiry 69:106–109.
- Lundberg, George A. 1947. Can Science Save Us? New York: David McKay.
- MacIver, R. M. 1934. “Sociology.” Pp. 232–46 in Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences, edited by E. R. A. Seligman and A. Johnson. New York: Macmillan.
- Madge, John. 1962. The Origins of Scientific Sociology. New York: Free Press.
- Martineau, Harriet. 1836/1837 . Society in America. London, England: Saunders & Otley .
- Martineau, Harriet. 1838. How to Observe Morals and Manners. London, England: Charles Knight.
- Merton, Robert K. [1957] 1968. Social Theory and Social Structure. New York: Free Press.
- Mills, C. Wright. 1959. The Sociological Imagination. New York: Oxford University Press.
- Myrdal, Gunnar. 1969. Objectivity in Social Research. New York: Pantheon Books.
- Nisbet, Robert A. 1966. The Sociological Tradition. New York: Basic Books.
- Noble, David F. 1999. The Religion of Technology. New York: Penguin Putnam.
- Odum, Howard W. 1951. American Sociology: The Story of Sociology in the United States through 1950. New York: Longmans, Green.
- Odum, Howard W. [1927] 1965. American Masters of Social Science. Port Washington, NY: Kennikat Press.
- O’Neill, William L. 1967. Divorce in the Progressive Era. New Haven, CT: Yale University Press.
- Peck, Dennis L. 1982. “Future Prospects for Sociology(ists): Observations of a Non-Rural Sociologist.” The Rural Sociologist 2:315–21 .
- Reiss, Albert J. 1968. “Sociology: The Field.” Pp. 1–22 in International Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences, edited by D. L. Sills. New York: Macmillan/Free Press.
- Ross, E. A. 1936. “Some Contributions of Sociology to the Guidance of Society.” American Sociological Review 1:29–32.
- Rossi, Peter H. 1999. “Saving Academic Sociology.” Sociological Inquiry 69:110–20.
- Shahidian, Hammed. 1999. “Saving the Savior.” Sociological Inquiry 69:303–27.
- Small, A. W. 1895. “The Era of Sociology.” American Journal of Sociology 1:1–15.
- Smelser, Neil J. 1990. “External Influences on Sociology.” Pp. 49–60 in Sociology in America, edited by H. J. Gans. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
- Talbot, Marion. 1896. “Sanitation and Sociology.” American Journal of Sociology 2:74–81.
- Touraine, Alain. 1990. “American Sociology Viewed from Abroad.” Pp. 239–52 in Sociology in America, edited by H. J. Gans. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
- Turner, Jonathan H. 2001. “Sociology, Survey.” Pp. 1538–50 in Reader’s Guide to the Social Sciences, edited by J. Michie. Chicago, IL: Fitzroy Dearborn.
- Turner, Stephen and Alan Sica. 2006. “Two Scholars Examine Golden Decade’s Imprint on Today’s Sociologists.” Footnotes 34(2):4.
- Volkart, E. H. 1968. “Thomas, W. I.” Pp. 1–6 in International Encyclopedia of the Social Sciences, 16, edited by D. L. Sills. New York: Macmillan/Free Press.
- Ward, Lester A. 1896. “Contributions to Social Philosophy. IX. The Purpose of Sociology.” American Journal of Sociology 2:446–60.
- Wharton, Amy S. 2006. “Letter from the Editor.” Social Problems 59:1–2.
- Whitt, Hugh P. 2001. “The Moral Statisticians” Pp. 229–35 in Encyclopedia of Criminology and Deviant Behavior, Historical, Conceptual, and Theoretical Issues, 1, edited by P. A. Adler, P. Adler, and J. Corzine. Philadelphia, PA: Brunner-Routledge.
- Wright, Carroll D. 1895. “Contributions of the United States Government to Social Science.” American Journal of Sociology 1(3):241–75.
- Wrong, Dennis H. 1990. “Sociology’s Effects on America.” Pp. 19–30 in Sociology in America, edited by H. J. Gans. Newbury Park, CA: Sage.
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Sociological Research Online was launched as the first online-only peer-reviewed Sociology journal in 1996. This enables faster publication times and a range of formats, including giving readers direct access to audio, visual and video data, and thematic … | View full journal description. This journal is a member of the Committee on ...
Journal of Sociology features high quality sociological scholarship in all its forms. We are dedicated to showcasing theory as well as applied sociology, quantitative and qualitative research. Interdisciplinary pieces are welcome, as are submissions … | View full journal description. This journal is a member of the Committee on Publication ...
Current issues are now on the Chicago Journals website. Read the latest issue. Established in 1895 as the first US scholarly journal in its field, the American Journal of Sociology (AJS) presents pathbreaking work from all areas of sociology, with an emphasis on theory building and innovative methods.AJS strives to speak to the general sociology reader and is open to contributions from across ...
Oxford University Press publishes a portfolio of leading Sociology journals. To keep up to date with the latest research your peers are reading and citing, browse our selection of high impact articles on a diverse breadth of topics below. All articles are freely available to read, download, and enjoy until May 2023.
Sociology, flagship journal of the British Sociological Association, publishes peer-reviewed articles advancing theoretical understanding and reporting empirical research about the widest range of sociological topics.Sociology encourages submissions using quantitative and qualitative research methods; articles challenging conventional concepts and proposing new approaches; and accounts of ...
Sociological Research, Volume 60, Issue 1-3 (2022) See all volumes and issues. Volume 60, 2022 Vol 59, 2021 Vol 58, 2019 Vol 57, 2018 Vol 56, 2017 Vol 55, 2016 Vol 54, 2015 Vol 53, 2014 Vol 52, 2013 Vol 51, 2012 Vol 50, 2011 Vol 49, 2010 Vol 48, 2009 Vol 47, 2008 Vol 46, 2007 Vol 45, 2006 Vol 44, 2005 Vol 43, 2004 Vol 42, 2003 Vol 41, 2002 Vol ...
Rising food and water insecurity among US children. Concurrent food and water insecurity doubled among children from 2005 to 2020, with minoritized children facing far more insecurity than their ...
Sociology is the systematic study of the society in which we live and the social causes and consequences of human behavior. The Sociology Research Network on SSRN is an open access preprint server that provides a venue for authors to showcase their research papers in our digital library, speeding up the dissemination and providing the scholarly ...
The American Sociological Association publishes 13 scholarly journals, including general interest journals and those focused on specialized areas of knowledge . The American Sociological Review, ASA's flagship journal, includes the latest general interest scholarship in sociology that advances our understanding of fundamental social processes ...
Drawing on empirical data from two recent research studies in post-Apartheid South Africa, this paper asks what it means to be poor, young and black, and belong in a society that has suffered debilitating and dehumanising racial subjugation, actively excluding people from citizenship, and how poverty serves to perpetuate this exclusion.
Sociology, flagship journal of the British Sociological Association, publishes peer-reviewed articles advancing theoretical understanding and reporting empirical research about the widest range of sociological topics.Sociology encourages submissions using quantitative and qualitative research methods. View full journal description
Review and research papers on the development and challenges of SSR to the existing literature are historical and continuous. However, the present paper differed by offering a justification and establishing its importance for SSR enterprise stakeholders. ... (Citation 2012) work was on trends and challenges in sociological research; Aro-Gordon ...
Sociological Inquiry (SI) is the journal of Alpha Kappa Delta, the International Sociology Honor Society. SI is committed to the exploration of the human condition in all of its social and cultural complexity. See the breadth and depth of our journal coverage with this keyword cloud of research published in Sociological Inquiry:
original research worthy of fulfilling the university's independent research requirements for sociology: a junior paper for juniors, and a senior thesis for seniors. Together with the mentorship of your faculty advisor, this handbook will help you think through the various steps of your independent research, and
Critical sociology focuses on deconstruction of existing sociological research and theory. Informed by the work of Karl Marx, scholars known collectively as the Frankfurt School proposed that social science, as much as any academic pursuit, is embedded in the system of power constituted by the set of class, caste, race, gender, and other ...
What kind of sociology research topics have you looked at lately? Do they make the right impact? Check out this list that assures you'll be passionate! ... Essays; 101 Sociology Research Topics That Make an Impact By Mary Gormandy White, M.A. , Staff Writer . Updated May 19, 2021 Image Credits.
Abstract. Poverty is commonly defined as a lack of economic resources that has negative social consequences, but surprisingly little is known about the importance of economic hardship for social outcomes. This article offers an empirical investigation into this issue. We apply panel data methods on longitudinal data from the Swedish Level-of ...
An official journal of the International Sociological Association, Current Sociology is one of the oldest sociology journals in the world. It is a fully peer-reviewed, international journal that publishes original research and innovative critical commentary both on current debates within sociology as a developing discipline, and the contribution that sociologists can make to modern societies ...
Writing Your Sociology Research Paper; Cultural Anthropology; Writing Guides. Writing in Sociology. Created by The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill, this handout discusses scholarly research and writing in sociology, with helpful hints. APA Guide for Walters State Students.
Explore fifteen key sociological theories in the field of sociology, their applications, and the debates surrounding some of these ideas. ... research papers, and educational resources focused on sociology. It aims to deepen understanding of society, culture, and human behavior. Topics covered include social issues, research summaries ...
American Sociological Review (ASR), the ASA's flagship journal, was founded in 1936 with the mission to publish original works of interest to the discipline of sociology in general, new theoretical developments, results of research that advance understanding of fundamental social processes, and important methodological innovations. Peer-reviewed and published bi-monthly, all areas of sociology ...
The Sociological Review is one of the world's foremost journals for sociological inquiry in all traditions, with over 100 years of publishing high quality and innovative articles. It offers a space to question taken for granted understandings of the social world, and provides a platform for thinking about alternative possibilities for what it might be.
Sociology Research Paper. This sample sociology research paper features: 10800 words (approx. 36 pages), an outline, and a bibliography with 59 sources. Browse other research paper examples for more inspiration. If you need a thorough research paper written according to all the academic standards, you can always turn to our experienced writers ...
Preview abstract. Open Access Research article First published August 10, 2023 pp. 507-524. xml PDF / EPUB. Table of contents for Sociological Research Online, 29, 2, Jun 01, 2024.
This paper is for sociologists seeking to make the best use of this technology in their work. It presents a practice-oriented framework for using AI chatbots in sociology, building on considerations of the technical conditions of LLMs to introduce both a task categorization and the concept of a 'knowledge funnel'.