Essay Papers Writing Online
A comprehensive guide to crafting a successful comparison essay.

Comparison essays are a common assignment in academic settings, requiring students to analyze and contrast two or more subjects, concepts, or ideas. Writing a comparison essay can be challenging, but with the right approach and guidance, you can craft a compelling and informative piece of writing.
In this comprehensive guide, we will provide you with valuable tips and examples to help you master the art of comparison essay writing. Whether you’re comparing two literary works, historical events, scientific theories, or any other topics, this guide will equip you with the tools and strategies needed to create a well-structured and persuasive essay.
From choosing a suitable topic and developing a strong thesis statement to organizing your arguments and incorporating effective evidence, this guide will walk you through each step of the writing process. By following the advice and examples provided here, you’ll be able to produce a top-notch comparison essay that showcases your analytical skills and critical thinking abilities.

Understanding the Basics
Before diving into writing a comparison essay, it’s essential to understand the basics of comparison writing. A comparison essay, also known as a comparative essay, requires you to analyze two or more subjects by highlighting their similarities and differences. This type of essay aims to show how these subjects are similar or different in various aspects.
When writing a comparison essay, you should have a clear thesis statement that identifies the subjects you are comparing and the main points of comparison. It’s essential to structure your essay effectively by organizing your ideas logically. You can use different methods of organization, such as the block method or point-by-point method, to present your comparisons.
Additionally, make sure to include evidence and examples to support your comparisons. Use specific details and examples to strengthen your arguments and clarify the similarities and differences between the subjects. Lastly, remember to provide a strong conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces the significance of your comparison.
Choosing a Topic for Comparison Essay
When selecting a topic for your comparison essay, it’s essential to choose two subjects that have some similarities and differences to explore. You can compare two books, two movies, two historical figures, two theories, or any other pair of related subjects.
Consider selecting topics that interest you or that you are familiar with to make the writing process more engaging and manageable. Additionally, ensure that the subjects you choose are suitable for comparison and have enough material for analysis.
It’s also helpful to brainstorm ideas and create a list of potential topics before making a final decision. Once you have a few options in mind, evaluate them based on the relevance of the comparison, the availability of credible sources, and your own interest in the subjects.
Remember that a well-chosen topic is one of the keys to writing a successful comparison essay, so take your time to select subjects that will allow you to explore meaningful connections and differences in a compelling way.
Finding the Right Pairing
When writing a comparison essay, it’s crucial to find the right pairing of subjects to compare. Choose subjects that have enough similarities and differences to make a meaningful comparison. Consider the audience and purpose of your essay to determine what pairing will be most effective.
Look for subjects that you are passionate about or have a deep understanding of. This will make the writing process easier and more engaging. Additionally, consider choosing subjects that are relevant and timely, as this will make your essay more interesting to readers.
Don’t be afraid to think outside the box when finding the right pairing. Sometimes unexpected combinations can lead to the most compelling comparisons. Conduct thorough research on both subjects to ensure you have enough material to work with and present a balanced comparison.
Structuring Your Comparison Essay
When writing a comparison essay, it is essential to organize your ideas in a clear and logical manner. One effective way to structure your essay is to use a point-by-point comparison or a block comparison format.
| Point-by-Point Comparison | Block Comparison |
|---|---|
| In this format, you will discuss one point of comparison between the two subjects before moving on to the next point. | In this format, you will discuss all the points related to one subject before moving on to the next subject. |
| Allows for a more detailed analysis of each point of comparison. | Provides a clear and structured comparison of the two subjects. |
| Can be helpful when the subjects have multiple similarities and differences to explore. | May be easier to follow for readers who prefer a side-by-side comparison of the subjects. |
Whichever format you choose, make sure to introduce your subjects, present your points of comparison, provide evidence or examples to support your comparisons, and conclude by summarizing the main points and highlighting the significance of your comparison.
Creating a Clear Outline
Before you start writing your comparison essay, it’s essential to create a clear outline. An outline serves as a roadmap that helps you stay organized and focused throughout the writing process. Here are some steps to create an effective outline:
1. Identify the subjects of comparison: Start by determining the two subjects you will be comparing in your essay. Make sure they have enough similarities and differences to make a meaningful comparison.
2. Brainstorm key points: Once you have chosen the subjects, brainstorm the key points you want to compare and contrast. These could include characteristics, features, themes, or arguments related to each subject.
3. Organize your points: Arrange your key points in a logical order. You can choose to compare similar points side by side or alternate between the two subjects to highlight differences.
4. Develop a thesis statement: Based on your key points, develop a clear thesis statement that states the main purpose of your comparison essay. This statement should guide the rest of your writing and provide a clear direction for your argument.
5. Create a structure: Divide your essay into introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion. Each section should serve a specific purpose and contribute to the overall coherence of your essay.
By creating a clear outline, you can ensure that your comparison essay flows smoothly and effectively communicates your ideas to the reader.
Engaging the Reader
When writing a comparison essay, it is crucial to engage the reader right from the beginning. You want to hook their attention and make them want to keep reading. Here are some tips to engage your reader:
- Start with a strong opening statement or question that entices the reader to continue reading.
- Use vivid language and descriptive imagery to paint a clear picture in the reader’s mind.
- Provide interesting facts or statistics that pique the reader’s curiosity.
- Create a compelling thesis statement that outlines the purpose of your comparison essay.
By engaging the reader from the start, you set the stage for a successful and impactful comparison essay that keeps the reader engaged until the very end.
Point-by-Point vs Block Method

When writing a comparison essay, you have two main options for structuring your content: the point-by-point method and the block method. Each method has its own advantages and may be more suitable depending on the type of comparison you are making.
- Point-by-Point Method: This method involves discussing one point of comparison at a time between the two subjects. You will go back and forth between the subjects, highlighting similarities and differences for each point. This method allows for a more detailed and nuanced analysis of the subjects.
- Block Method: In contrast, the block method involves discussing all the points related to one subject first, followed by all the points related to the second subject. This method provides a more straightforward and organized comparison but may not delve as deeply into the individual points of comparison.
Ultimately, the choice between the point-by-point and block methods depends on the complexity of your comparison and the level of detail you want to explore. Experiment with both methods to see which one best suits your writing style and the specific requirements of your comparison essay.
Selecting the Best Approach
When it comes to writing a comparison essay, selecting the best approach is crucial to ensure a successful and effective comparison. There are several approaches you can take when comparing two subjects, including the block method and the point-by-point method.
The block method: This approach involves discussing all the similarities and differences of one subject first, followed by a thorough discussion of the second subject. This method is useful when the two subjects being compared are quite different or when the reader may not be familiar with one of the subjects.
The point-by-point method: This approach involves alternating between discussing the similarities and differences of the two subjects in each paragraph. This method allows for a more in-depth comparison of specific points and is often preferred when the two subjects have many similarities and differences.
Before selecting an approach, consider the nature of the subjects being compared and the purpose of your comparison essay. Choose the approach that will best serve your purpose and allow for a clear, organized, and engaging comparison.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Comparing and contrasting in an essay | Tips & examples
Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples
Published on August 6, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
Comparing and contrasting is an important skill in academic writing . It involves taking two or more subjects and analyzing the differences and similarities between them.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
When should i compare and contrast, making effective comparisons, comparing and contrasting as a brainstorming tool, structuring your comparisons, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about comparing and contrasting.
Many assignments will invite you to make comparisons quite explicitly, as in these prompts.
- Compare the treatment of the theme of beauty in the poetry of William Wordsworth and John Keats.
- Compare and contrast in-class and distance learning. What are the advantages and disadvantages of each approach?
Some other prompts may not directly ask you to compare and contrast, but present you with a topic where comparing and contrasting could be a good approach.
One way to approach this essay might be to contrast the situation before the Great Depression with the situation during it, to highlight how large a difference it made.
Comparing and contrasting is also used in all kinds of academic contexts where it’s not explicitly prompted. For example, a literature review involves comparing and contrasting different studies on your topic, and an argumentative essay may involve weighing up the pros and cons of different arguments.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
As the name suggests, comparing and contrasting is about identifying both similarities and differences. You might focus on contrasting quite different subjects or comparing subjects with a lot in common—but there must be some grounds for comparison in the first place.
For example, you might contrast French society before and after the French Revolution; you’d likely find many differences, but there would be a valid basis for comparison. However, if you contrasted pre-revolutionary France with Han-dynasty China, your reader might wonder why you chose to compare these two societies.
This is why it’s important to clarify the point of your comparisons by writing a focused thesis statement . Every element of an essay should serve your central argument in some way. Consider what you’re trying to accomplish with any comparisons you make, and be sure to make this clear to the reader.
Comparing and contrasting can be a useful tool to help organize your thoughts before you begin writing any type of academic text. You might use it to compare different theories and approaches you’ve encountered in your preliminary research, for example.
Let’s say your research involves the competing psychological approaches of behaviorism and cognitive psychology. You might make a table to summarize the key differences between them.
| Behaviorism | Cognitive psychology |
|---|---|
| Dominant from the 1920s to the 1950s | Rose to prominence in the 1960s |
| Mental processes cannot be empirically studied | Mental processes as focus of study |
| Focuses on how thinking is affected by conditioning and environment | Focuses on the cognitive processes themselves |
Or say you’re writing about the major global conflicts of the twentieth century. You might visualize the key similarities and differences in a Venn diagram.
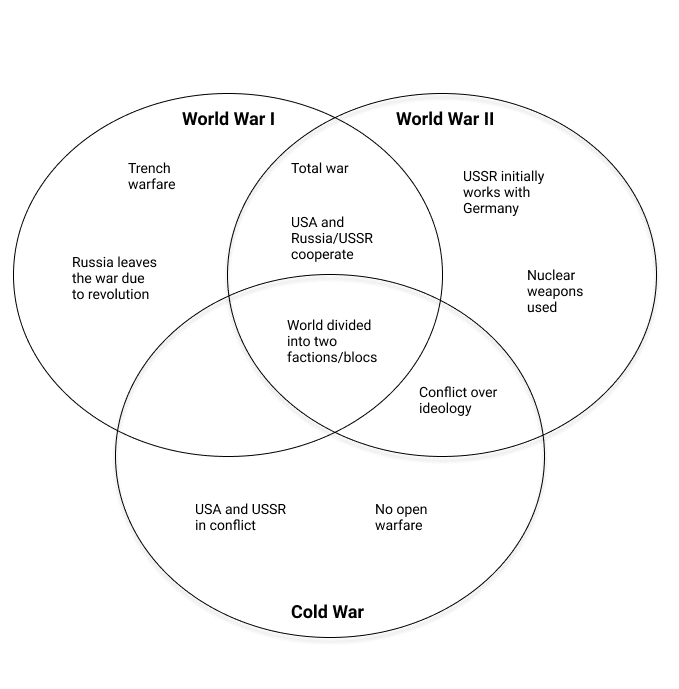
These visualizations wouldn’t make it into your actual writing, so they don’t have to be very formal in terms of phrasing or presentation. The point of comparing and contrasting at this stage is to help you organize and shape your ideas to aid you in structuring your arguments.
When comparing and contrasting in an essay, there are two main ways to structure your comparisons: the alternating method and the block method.
The alternating method
In the alternating method, you structure your text according to what aspect you’re comparing. You cover both your subjects side by side in terms of a specific point of comparison. Your text is structured like this:
Mouse over the example paragraph below to see how this approach works.
One challenge teachers face is identifying and assisting students who are struggling without disrupting the rest of the class. In a traditional classroom environment, the teacher can easily identify when a student is struggling based on their demeanor in class or simply by regularly checking on students during exercises. They can then offer assistance quietly during the exercise or discuss it further after class. Meanwhile, in a Zoom-based class, the lack of physical presence makes it more difficult to pay attention to individual students’ responses and notice frustrations, and there is less flexibility to speak with students privately to offer assistance. In this case, therefore, the traditional classroom environment holds the advantage, although it appears likely that aiding students in a virtual classroom environment will become easier as the technology, and teachers’ familiarity with it, improves.
The block method
In the block method, you cover each of the overall subjects you’re comparing in a block. You say everything you have to say about your first subject, then discuss your second subject, making comparisons and contrasts back to the things you’ve already said about the first. Your text is structured like this:
- Point of comparison A
- Point of comparison B
The most commonly cited advantage of distance learning is the flexibility and accessibility it offers. Rather than being required to travel to a specific location every week (and to live near enough to feasibly do so), students can participate from anywhere with an internet connection. This allows not only for a wider geographical spread of students but for the possibility of studying while travelling. However, distance learning presents its own accessibility challenges; not all students have a stable internet connection and a computer or other device with which to participate in online classes, and less technologically literate students and teachers may struggle with the technical aspects of class participation. Furthermore, discomfort and distractions can hinder an individual student’s ability to engage with the class from home, creating divergent learning experiences for different students. Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
Note that these two methods can be combined; these two example paragraphs could both be part of the same essay, but it’s wise to use an essay outline to plan out which approach you’re taking in each paragraph.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
Some essay prompts include the keywords “compare” and/or “contrast.” In these cases, an essay structured around comparing and contrasting is the appropriate response.
Comparing and contrasting is also a useful approach in all kinds of academic writing : You might compare different studies in a literature review , weigh up different arguments in an argumentative essay , or consider different theoretical approaches in a theoretical framework .
Your subjects might be very different or quite similar, but it’s important that there be meaningful grounds for comparison . You can probably describe many differences between a cat and a bicycle, but there isn’t really any connection between them to justify the comparison.
You’ll have to write a thesis statement explaining the central point you want to make in your essay , so be sure to know in advance what connects your subjects and makes them worth comparing.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 10, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/compare-and-contrast/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write an expository essay, how to write an argumentative essay | examples & tips, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
Comparing and Contrasting: A Guide to Improve Your Essays

Walter Akolo

Essays that require you to compare and contrast two or more subjects, ideas, places, or items are common.
They call for you to highlight the key similarities (compare) and differences (contrast) between them.
This guide contains all the information you need to become better at writing comparing and contrasting essays.
This includes: how to structure your essay, how to decide on the content, and some examples of essay questions.
Let’s dive in.

What Is Comparing and Contrasting?
Is compare and contrast the same as similarities and differences, what is the purpose of comparing and contrasting, can you compare and contrast any two items, how do you compare and contrast in writing, what are some comparing and contrasting techniques, how do you compare and contrast in college level writing, the four essentials of compare and contrast essays, what can you learn from a compare and contrast essay.
At their most basic, both comparing and contrasting base their evaluation on two or more subjects that share a connection.
The subjects could have similar characteristics, features, or foundations.
But while a comparison discusses the similarities of the two subjects, e.g. a banana and a watermelon are both fruit, contrasting highlights how the subjects or items differ from each other, e.g. a watermelon is around 10 times larger than a banana.
Any question that you are asked in education will have a variety of interesting comparisons and deductions that you can make.
Compare is the same as similarities.
Contrast is the same as differences.
This is because comparing identifies the likeness between two subjects, items, or categories, while contrasting recognizes disparities between them.
When you compare things, you represent them regarding their similarity, but when you contrast things, you define them in reference to their differences.
As a result, if you are asked to discuss the similarities and differences between two subjects, you can take an identical approach to if you are writing a compare and contrast essay.
In writing, the purpose of comparing and contrasting is to highlight subtle but important differences or similarities that might not be immediately obvious.

By illustrating the differences between elements in a similar category, you help heighten readers’ understanding of the subject or topic of discussion.
For instance, you might choose to compare and contrast red wine and white wine by pointing out the subtle differences. One of these differences is that red wine is best served at room temperature while white is best served chilled.
Also, comparing and contrasting helps to make abstract ideas more definite and minimizes the confusion that might exist between two related concepts.
Can Comparing and Contrasting Be Useful Outside of Academia?
Comparing enables you to see the pros and cons, allowing you to have a better understanding of the things under discussion. In an essay, this helps you demonstrate that you understand the nuances of your topic enough to draw meaningful conclusions from them.
Let's use a real-word example to see the benefits. Imagine you're contrasting two dresses you could buy. You might think:
- Dress A is purple, my favorite color, but it has a difficult zip and is practically impossible to match a jacket to.
- Dress B is more expensive but I already have a suitable pair of shoes and jacket and it is easier to move in.
You're linking the qualities of each dress to the context of the decision you're making. This is the same for your essay. Your comparison and contrast points will be in relation to the question you need to answer.
Comparing and contrasting is only a useful technique when applied to two related concepts.
To effectively compare two or more things, they must feature characteristics similar enough to warrant comparison.
In addition to this they must also feature a similarity that generates an interesting discussion. But what do I mean by “interesting” here?
Let’s look at two concepts, the Magna Carta and my third grade poetry competition entry.
They are both text, written on paper by a person so they fulfil the first requirement, they have a similarity. But this comparison clearly would not fulfil the second requirement, you would not be able to draw any interesting conclusions.
However, if we compare the Magna Carta to the Bill of Rights, you would be able to come to some very interesting conclusions concerning the history of world politics.
To write a good compare and contrast essay, it’s best to pick two or more topics that share a meaningful connection .
The aim of the essay would be to show the subtle differences or unforeseen similarities.
By highlighting the distinctions between elements in a similar category you can increase your readers’ understanding.
Alternatively, you could choose to focus on a comparison between two subjects that initially appear unrelated.
The more dissimilar they seem, the more interesting the comparison essay will turn out.
For instance, you could compare and contrast professional rugby players with marathon runners.
Can You Compare and Contrast in an Essay That Does Not Specifically Require It?
As a writer, you can employ comparing and contrasting techniques in your writing, particularly when looking for ideas you can later apply in your argument.
You can do this even when the comparison or contrast is not a requirement for the topic or argument you are presenting. Doing so could enable you to build your evaluation and develop a stronger argument.
Note that the similarities and differences you come up with might not even show up in the final draft.
While the use of compare and contrast can be neutral, you can also use it to highlight one option under discussion. When used this way, you can influence the perceived advantages of your preferred option.
As a writing style, comparing and contrasting can encompass an entire essay. However, it could also appear in some select paragraphs within the essay, where making some comparisons serves to better illustrate a point.
What Should You Do First?
Before you compare two things, always start by deciding on the reason for your comparison, then outline the criteria you will use to compare them.
Words and phrases commonly used for comparison include:
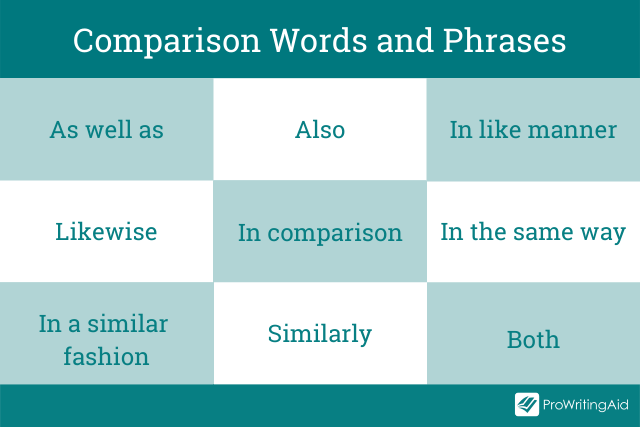
In writing, these words and phrases are called transitions . They help readers to understand or make the connection between sentences, paragraphs, and ideas.
Without transition words writing can feel clumsy and disjointed making it difficult to read. ProWritingAid’s transition report highlights all of a documents transitions and suggests that 25% of any sentences in a piece include a transition.
Sign up for a free ProWritingAid account to use the Transitions Report.
So, how do you form all of this into a coherent essay? It's a good idea to plan first, then decide what your paragraph layout will look like.
Venn diagrams are useful tool to start generating ideas. The, for your essay, you need to choose between going idea by idea and going point by point.
Using a Venn Diagram
A Venn diagram helps you to clearly see the similarities and differences between multiple objects, things, or subjects.
The writing tool comprises two, or more, simple, overlapping circles in which you list down the things that are alike (within the overlapping area) and those that differ (outside the overlapping area).
It’s great for brainstorming ideas and for creating your essay’s outline. You could even use it in an exam setting because it is quick and simple.
Going Subject by Subject
Going subject by subject is a structural choice for your essay.
Start by saying all you have to say on the first subject, then proceed to do the same about the second subject.
Depending on the length of your essay, you can fit the points about each subject into one paragraph or have several sections per each subject, ending with a conclusion.
This method is best for short essays on simple topics. Most university-level essays will go point by point instead.
Going Point by Point
Going point by point, or alternating, is the opposite essay structure from going subject by subject. This is ideal when you want to do more direct comparing and contrasting. It entails discussing one comparison point at a time. It allows you to use a paragraph to talk about how a certain comparing/contrasting point relates to the subjects or items you are discussing.
Alternatively, if you have lots of details about the subject, you might decide to use a paragraph for each point.
An academic compare and contrast essay looks at two or more subjects, ideas, people, or objects, compares their likeness, and contrasts their differences.
It’s an informative essay that provides insights on what is similar and different between the two items.
Depending on the essay’s instructions, you can focus solely on comparing or contrasting, or a combination of the two.
Examples of College Level Compare and Contrast Essay Questions
Here are eleven examples of compare and contrast essay questions that you might encounter at university:

- Archaeology: Compare and contrast the skulls of homo habilis, homo erectus, and homo sapiens.
- Art: Compare and contrast the working styles of any two Neoclassic artists.
- Astrophysics: Compare and contrast the chemical composition of Venus and Neptune.
- Biology: Compare and contrast the theories of Lamarck and Darwin.
- Business: Compare and contrast 2 or more business models within the agricultural industry.
- Creative writing: Compare and contrast free indirect discourse with epistolary styles.
- English Literature: Compare and contrast William Wordsworth with Robert Browning.
- Geography: Compare and contrast the benefit of solar panels with the benefit of wind turbines.
- History: Compare and contrast WWI to WWII with specific reference to the causes and outcomes.
- Medicine: Compare and contrast England’s health service with America’s health service.
- Psychology: Compare and contrast the behaviorist theory with the psychodynamic theory.
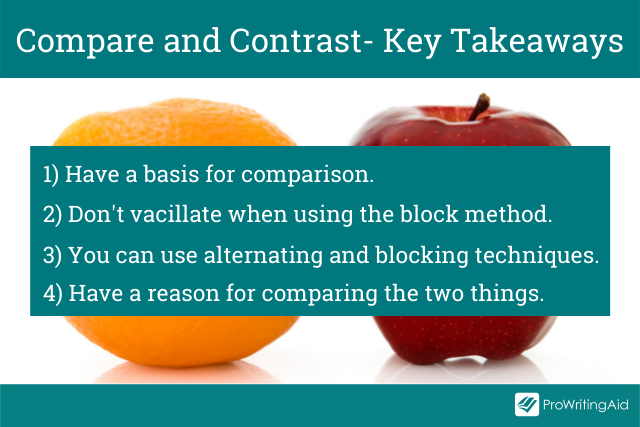
So, the key takeaways to keep in mind are:
Have a basis for comparison. The two things need to have enough in common to justify a discussion about their similarities and disparities.
Don’t go back and forth when using the block method. The best way to write your essay is to begin with a paragraph discussing all the facets of the first topic. Then, move on to another paragraph and talk through all the aspects of the second subject.
You can use both alternating and blocking techniques. Combining the two approaches is also an option. You can apply the alternating method in some paragraphs, then switch and use the block method. This method will help you offer a much deeper analysis of the subjects.
Have a reason for comparing the two things. Only select the points of comparison that resonate with your purpose.
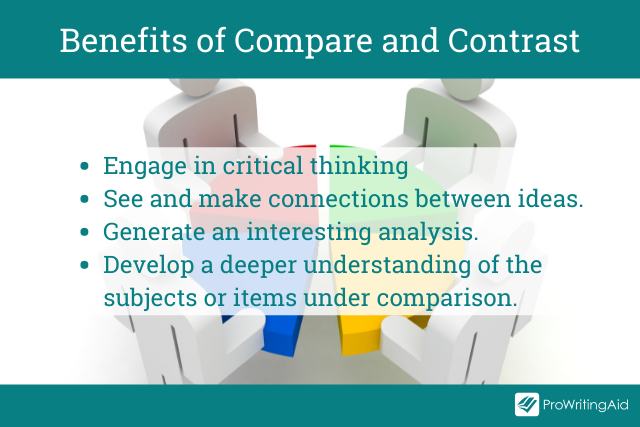
Comparing and contrasting are essential analytical skills in academic writing. When your professor issues you with such an essay, their primary goal is to teach you how to:
- Engage in critical thinking
- See and make connections between words or ideas
- Move beyond mere descriptions or summaries to developing interesting analysis
- Get a deeper understanding of the subjects or items under comparison, their key features, and their interrelationships with each other.
Ultimately, your essay should enlighten readers by providing useful information.
Want to use ProWritingAid with your classroom? Download this free book now:

ProWritingAid Teacher’s Manual
Editing technology like prowritingaid provides immediate, personalized feedback that will help students to better understand grammar and writing techniques., in this guide , we walk you through exactly how to use prowritingaid in your classroom and give you tools and templates for creating a rigorous, effective independent writing practice with your students..
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Walter Akolo is a freelance writer, internet marketer, trainer, and blogger for hire. He loves helping businesses increase their reach and conversion through excellent and engaging content. He has gotten millions of pageviews on his blog, FreelancerKenya, where he mentors writers. Check out his website walterakolo.com.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :

Comparing and Contrasting
What this handout is about.
This handout will help you first to determine whether a particular assignment is asking for comparison/contrast and then to generate a list of similarities and differences, decide which similarities and differences to focus on, and organize your paper so that it will be clear and effective. It will also explain how you can (and why you should) develop a thesis that goes beyond “Thing A and Thing B are similar in many ways but different in others.”
Introduction
In your career as a student, you’ll encounter many different kinds of writing assignments, each with its own requirements. One of the most common is the comparison/contrast essay, in which you focus on the ways in which certain things or ideas—usually two of them—are similar to (this is the comparison) and/or different from (this is the contrast) one another. By assigning such essays, your instructors are encouraging you to make connections between texts or ideas, engage in critical thinking, and go beyond mere description or summary to generate interesting analysis: when you reflect on similarities and differences, you gain a deeper understanding of the items you are comparing, their relationship to each other, and what is most important about them.
Recognizing comparison/contrast in assignments
Some assignments use words—like compare, contrast, similarities, and differences—that make it easy for you to see that they are asking you to compare and/or contrast. Here are a few hypothetical examples:
- Compare and contrast Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of oppression.
- Compare WWI to WWII, identifying similarities in the causes, development, and outcomes of the wars.
- Contrast Wordsworth and Coleridge; what are the major differences in their poetry?
Notice that some topics ask only for comparison, others only for contrast, and others for both.
But it’s not always so easy to tell whether an assignment is asking you to include comparison/contrast. And in some cases, comparison/contrast is only part of the essay—you begin by comparing and/or contrasting two or more things and then use what you’ve learned to construct an argument or evaluation. Consider these examples, noticing the language that is used to ask for the comparison/contrast and whether the comparison/contrast is only one part of a larger assignment:
- Choose a particular idea or theme, such as romantic love, death, or nature, and consider how it is treated in two Romantic poems.
- How do the different authors we have studied so far define and describe oppression?
- Compare Frye’s and Bartky’s accounts of oppression. What does each imply about women’s collusion in their own oppression? Which is more accurate?
- In the texts we’ve studied, soldiers who served in different wars offer differing accounts of their experiences and feelings both during and after the fighting. What commonalities are there in these accounts? What factors do you think are responsible for their differences?
You may want to check out our handout on understanding assignments for additional tips.
Using comparison/contrast for all kinds of writing projects
Sometimes you may want to use comparison/contrast techniques in your own pre-writing work to get ideas that you can later use for an argument, even if comparison/contrast isn’t an official requirement for the paper you’re writing. For example, if you wanted to argue that Frye’s account of oppression is better than both de Beauvoir’s and Bartky’s, comparing and contrasting the main arguments of those three authors might help you construct your evaluation—even though the topic may not have asked for comparison/contrast and the lists of similarities and differences you generate may not appear anywhere in the final draft of your paper.
Discovering similarities and differences
Making a Venn diagram or a chart can help you quickly and efficiently compare and contrast two or more things or ideas. To make a Venn diagram, simply draw some overlapping circles, one circle for each item you’re considering. In the central area where they overlap, list the traits the two items have in common. Assign each one of the areas that doesn’t overlap; in those areas, you can list the traits that make the things different. Here’s a very simple example, using two pizza places:
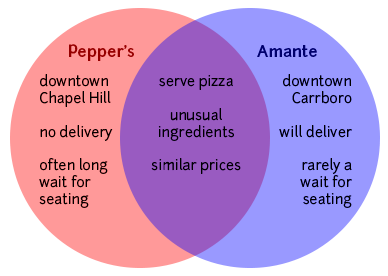
To make a chart, figure out what criteria you want to focus on in comparing the items. Along the left side of the page, list each of the criteria. Across the top, list the names of the items. You should then have a box per item for each criterion; you can fill the boxes in and then survey what you’ve discovered.
Here’s an example, this time using three pizza places:
| Pepper’s | Amante | Papa John’s | |
|---|---|---|---|
| Location | |||
| Price | |||
| Delivery | |||
| Ingredients | |||
| Service | |||
| Seating/eating in | |||
| Coupons |
As you generate points of comparison, consider the purpose and content of the assignment and the focus of the class. What do you think the professor wants you to learn by doing this comparison/contrast? How does it fit with what you have been studying so far and with the other assignments in the course? Are there any clues about what to focus on in the assignment itself?
Here are some general questions about different types of things you might have to compare. These are by no means complete or definitive lists; they’re just here to give you some ideas—you can generate your own questions for these and other types of comparison. You may want to begin by using the questions reporters traditionally ask: Who? What? Where? When? Why? How? If you’re talking about objects, you might also consider general properties like size, shape, color, sound, weight, taste, texture, smell, number, duration, and location.
Two historical periods or events
- When did they occur—do you know the date(s) and duration? What happened or changed during each? Why are they significant?
- What kinds of work did people do? What kinds of relationships did they have? What did they value?
- What kinds of governments were there? Who were important people involved?
- What caused events in these periods, and what consequences did they have later on?
Two ideas or theories
- What are they about?
- Did they originate at some particular time?
- Who created them? Who uses or defends them?
- What is the central focus, claim, or goal of each? What conclusions do they offer?
- How are they applied to situations/people/things/etc.?
- Which seems more plausible to you, and why? How broad is their scope?
- What kind of evidence is usually offered for them?
Two pieces of writing or art
- What are their titles? What do they describe or depict?
- What is their tone or mood? What is their form?
- Who created them? When were they created? Why do you think they were created as they were? What themes do they address?
- Do you think one is of higher quality or greater merit than the other(s)—and if so, why?
- For writing: what plot, characterization, setting, theme, tone, and type of narration are used?
- Where are they from? How old are they? What is the gender, race, class, etc. of each?
- What, if anything, are they known for? Do they have any relationship to each other?
- What are they like? What did/do they do? What do they believe? Why are they interesting?
- What stands out most about each of them?
Deciding what to focus on
By now you have probably generated a huge list of similarities and differences—congratulations! Next you must decide which of them are interesting, important, and relevant enough to be included in your paper. Ask yourself these questions:
- What’s relevant to the assignment?
- What’s relevant to the course?
- What’s interesting and informative?
- What matters to the argument you are going to make?
- What’s basic or central (and needs to be mentioned even if obvious)?
- Overall, what’s more important—the similarities or the differences?
Suppose that you are writing a paper comparing two novels. For most literature classes, the fact that they both use Caslon type (a kind of typeface, like the fonts you may use in your writing) is not going to be relevant, nor is the fact that one of them has a few illustrations and the other has none; literature classes are more likely to focus on subjects like characterization, plot, setting, the writer’s style and intentions, language, central themes, and so forth. However, if you were writing a paper for a class on typesetting or on how illustrations are used to enhance novels, the typeface and presence or absence of illustrations might be absolutely critical to include in your final paper.
Sometimes a particular point of comparison or contrast might be relevant but not terribly revealing or interesting. For example, if you are writing a paper about Wordsworth’s “Tintern Abbey” and Coleridge’s “Frost at Midnight,” pointing out that they both have nature as a central theme is relevant (comparisons of poetry often talk about themes) but not terribly interesting; your class has probably already had many discussions about the Romantic poets’ fondness for nature. Talking about the different ways nature is depicted or the different aspects of nature that are emphasized might be more interesting and show a more sophisticated understanding of the poems.
Your thesis
The thesis of your comparison/contrast paper is very important: it can help you create a focused argument and give your reader a road map so they don’t get lost in the sea of points you are about to make. As in any paper, you will want to replace vague reports of your general topic (for example, “This paper will compare and contrast two pizza places,” or “Pepper’s and Amante are similar in some ways and different in others,” or “Pepper’s and Amante are similar in many ways, but they have one major difference”) with something more detailed and specific. For example, you might say, “Pepper’s and Amante have similar prices and ingredients, but their atmospheres and willingness to deliver set them apart.”
Be careful, though—although this thesis is fairly specific and does propose a simple argument (that atmosphere and delivery make the two pizza places different), your instructor will often be looking for a bit more analysis. In this case, the obvious question is “So what? Why should anyone care that Pepper’s and Amante are different in this way?” One might also wonder why the writer chose those two particular pizza places to compare—why not Papa John’s, Dominos, or Pizza Hut? Again, thinking about the context the class provides may help you answer such questions and make a stronger argument. Here’s a revision of the thesis mentioned earlier:
Pepper’s and Amante both offer a greater variety of ingredients than other Chapel Hill/Carrboro pizza places (and than any of the national chains), but the funky, lively atmosphere at Pepper’s makes it a better place to give visiting friends and family a taste of local culture.
You may find our handout on constructing thesis statements useful at this stage.
Organizing your paper
There are many different ways to organize a comparison/contrast essay. Here are two:
Subject-by-subject
Begin by saying everything you have to say about the first subject you are discussing, then move on and make all the points you want to make about the second subject (and after that, the third, and so on, if you’re comparing/contrasting more than two things). If the paper is short, you might be able to fit all of your points about each item into a single paragraph, but it’s more likely that you’d have several paragraphs per item. Using our pizza place comparison/contrast as an example, after the introduction, you might have a paragraph about the ingredients available at Pepper’s, a paragraph about its location, and a paragraph about its ambience. Then you’d have three similar paragraphs about Amante, followed by your conclusion.
The danger of this subject-by-subject organization is that your paper will simply be a list of points: a certain number of points (in my example, three) about one subject, then a certain number of points about another. This is usually not what college instructors are looking for in a paper—generally they want you to compare or contrast two or more things very directly, rather than just listing the traits the things have and leaving it up to the reader to reflect on how those traits are similar or different and why those similarities or differences matter. Thus, if you use the subject-by-subject form, you will probably want to have a very strong, analytical thesis and at least one body paragraph that ties all of your different points together.
A subject-by-subject structure can be a logical choice if you are writing what is sometimes called a “lens” comparison, in which you use one subject or item (which isn’t really your main topic) to better understand another item (which is). For example, you might be asked to compare a poem you’ve already covered thoroughly in class with one you are reading on your own. It might make sense to give a brief summary of your main ideas about the first poem (this would be your first subject, the “lens”), and then spend most of your paper discussing how those points are similar to or different from your ideas about the second.
Point-by-point
Rather than addressing things one subject at a time, you may wish to talk about one point of comparison at a time. There are two main ways this might play out, depending on how much you have to say about each of the things you are comparing. If you have just a little, you might, in a single paragraph, discuss how a certain point of comparison/contrast relates to all the items you are discussing. For example, I might describe, in one paragraph, what the prices are like at both Pepper’s and Amante; in the next paragraph, I might compare the ingredients available; in a third, I might contrast the atmospheres of the two restaurants.
If I had a bit more to say about the items I was comparing/contrasting, I might devote a whole paragraph to how each point relates to each item. For example, I might have a whole paragraph about the clientele at Pepper’s, followed by a whole paragraph about the clientele at Amante; then I would move on and do two more paragraphs discussing my next point of comparison/contrast—like the ingredients available at each restaurant.
There are no hard and fast rules about organizing a comparison/contrast paper, of course. Just be sure that your reader can easily tell what’s going on! Be aware, too, of the placement of your different points. If you are writing a comparison/contrast in service of an argument, keep in mind that the last point you make is the one you are leaving your reader with. For example, if I am trying to argue that Amante is better than Pepper’s, I should end with a contrast that leaves Amante sounding good, rather than with a point of comparison that I have to admit makes Pepper’s look better. If you’ve decided that the differences between the items you’re comparing/contrasting are most important, you’ll want to end with the differences—and vice versa, if the similarities seem most important to you.
Our handout on organization can help you write good topic sentences and transitions and make sure that you have a good overall structure in place for your paper.
Cue words and other tips
To help your reader keep track of where you are in the comparison/contrast, you’ll want to be sure that your transitions and topic sentences are especially strong. Your thesis should already have given the reader an idea of the points you’ll be making and the organization you’ll be using, but you can help them out with some extra cues. The following words may be helpful to you in signaling your intentions:
- like, similar to, also, unlike, similarly, in the same way, likewise, again, compared to, in contrast, in like manner, contrasted with, on the contrary, however, although, yet, even though, still, but, nevertheless, conversely, at the same time, regardless, despite, while, on the one hand … on the other hand.
For example, you might have a topic sentence like one of these:
- Compared to Pepper’s, Amante is quiet.
- Like Amante, Pepper’s offers fresh garlic as a topping.
- Despite their different locations (downtown Chapel Hill and downtown Carrboro), Pepper’s and Amante are both fairly easy to get to.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift

In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay

- 5-minute read
- 9th March 2021
In a compare and contrast essay , you look at the similarities and differences between two subjects. How do you write one, though? Key steps include:
- Pick two things to compare based on the assignment you were given.
- Brainstorm the similarities and differences between your chosen subjects.
- Choose a structure for your essay and plan how you will write it.
- Write up your comparison and use evidence to support your argument.
- Revise and proofread your essay to make sure it is perfect.
For more advice on each stage, check out our guide below.
1. Pick Two Subjects to Compare and Contrast
A compare and contrast assignment will ask you, unsurprisingly, to compare and contrast two things. In some cases, the assignment question will make this clear. For instance, if the assignment says “Compare how Mozart and Beethoven use melody,” you will have a very clear sense of what to write about!
Other times, you will have a choice of what to compare. In this case, you will want to pick two things that are similar enough to make a useful comparison.
For example, comparing Mozart and Beethoven makes sense because both are classical composers. This means there will be lots of points of comparison between them. But comparing Mozart to a Ferrari SF90 Stradale would just be confusing: one is a renowned composer and musician, the other is a high-end sports car, so they have very little in common that we could usefully compare.

At the same time, the things you pick should be different enough that you can find points of contrast. Were you asked to compare the calorific content of two types of fast food, for example, it might not make sense to compare hamburgers and cheeseburgers as they are too similar. But you could compare hamburgers and pizzas since both are forms of fast food but they differ in other respects.
As such, if you need to pick the subjects of your essay, read your assignment question carefully and try to find two things that will produce a helpful comparison.
2. Brainstorm Their Similarities and Differences
The next step is to brainstorm similarities and differences between your chosen subjects. You can do this as a simple list, but you could also use a Venn diagram .
This is a set of overlapping circles, each of which represents one subject. You can then add characteristics to each circle, with anything your subjects have in common going in the overlapping bit in the middle.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.

Once you’ve listed characteristics, you’ll need to pick out the similarities and differences relevant to your essay. If you were assigned a question, use this to guide your choices. Otherwise, look for features that seem surprising or interesting and plan your essay around these. The key is to pick points of comparison that help us to understand each thing better, or where the similarities and differences show us something that we might not have expected or noticed otherwise.
3. Choose a Structure for Your Essay
As with any essay, you will want to start with a short introduction where you introduce your topic and what you will argue. Beyond this, most compare and contrast essays are structured in one of two ways. Decide which approach to take before you write your essay outline :
- Divide by subject – Cover each subject in turn, looking at the key features you’ve identified in the previous step. You can then include a final section where you highlight what comparing the subjects tell us.
- Divide by individual points – Break your essay down into a series of sections. Each section will then focus on one of the key features you’ve identified, explaining the similarities and differences between your chosen subjects.
For instance, if you were comparing two novels, you could write about each novel in turn and then compare them at the end. Alternatively, you could structure your essay so that each section covers an individual idea (e.g., one on structure, one on characters, one on language), looking at how each book uses these things.
In either case, you will want to end on a conclusion where you summarize what the comparison has shown us about the two subjects.
4. Use Supporting Evidence for Your Argument
It is important that you also back up your statements with supporting evidence. In some cases, this will simply involve pointing to the features of each subject that you’re discussing (e.g., citing specific parts of the novels you’re comparing).
However, you can also do extra research to back up your arguments. Were you comparing two countries’ economic performance, for example, you could use statistics from other studies or reports to show the similarities and differences.
5. Proofread Your Compare and Contrast Essay
Once you have a first draft of your compare and contrast essay, take a break. If you have time, leave it overnight. The aim is to come back to it with fresh eyes and reread it, looking for any areas you could improve. After this, you can redraft your essay to make sure your argument is clear, concise, and convincing.
It is also a good idea to have your essay proofread before submitting it. This will ensure your work is error free and help you get the marks you deserve.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...
How to Ace Slack Messaging for Contractors and Freelancers
Effective professional communication is an important skill for contractors and freelancers navigating remote work environments....
3-minute read
How to Insert a Text Box in a Google Doc
Google Docs is a powerful collaborative tool, and mastering its features can significantly enhance your...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Academic Editing and Proofreading
- Tips to Self-Edit Your Dissertation
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- Journal Article Proofreading: Process, Cost, & Checklist
- The A–Z of Dissertation Editing: Standard Rates & Involved Steps
- Research Paper Editing | Guide to a Perfect Research Paper
- Dissertation Proofreading | Definition & Standard Rates
- Thesis Proofreading | Definition, Importance & Standard Pricing
- Research Paper Proofreading | Definition, Significance & Standard Rates
- Essay Proofreading | Options, Cost & Checklist
- Top 10 Paper Editing Services of 2024 (Costs & Features)
- Top 10 Essay Checkers in 2024 (Free & Paid)
- Top 10 AI Proofreaders to Perfect Your Writing in 2024
- Top 10 English Correctors to Perfect Your Text in 2024
- Top 10 Essay Editing Services of 2024
- 10 Advanced AI Text Editors to Transform Writing in 2024
Academic Research
- Research Paper Outline: Templates & Examples
- How to Write a Research Paper: A Step-by-Step Guide
- How to Write a Lab Report: Examples from Academic Editors
- Research Methodology Guide: Writing Tips, Types, & Examples
- The 10 Best Essential Resources for Academic Research
- 100+ Useful ChatGPT Prompts for Thesis Writing in 2024
- Best ChatGPT Prompts for Academic Writing (100+ Prompts!)
- Sampling Methods Guide: Types, Strategies, and Examples
- Independent vs. Dependent Variables | Meaning & Examples
Academic Writing & Publishing
- Difference Between Paper Editing and Peer Review
- What are the different types of peer review?
- How to deal with rejection from a journal?
- Editing and Proofreading Academic Papers: A Short Guide
- How to Carry Out Secondary Research
- The Results Section of a Dissertation
- Checklist: Is my Article Ready for Submitting to Journals?
- Types of Research Articles to Boost Your Research Profile
- 8 Types of Peer Review Processes You Should Know
- The Ethics of Academic Research
- How does LaTeX based proofreading work?
- How to Improve Your Scientific Writing: A Short Guide
- Chicago Title, Cover Page & Body | Paper Format Guidelines
- How to Write a Thesis Statement: Examples & Tips
- Chicago Style Citation: Quick Guide & Examples
- The A-Z Of Publishing Your Article in A Journal
- What is Journal Article Editing? 3 Reasons You Need It
- 5 Powerful Personal Statement Examples (Template Included)
- Complete Guide to MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Book in APA Style | Format & Examples
- How to Start a Research Paper | Step-by-step Guide
- APA Citations Made Easy with Our Concise Guide for 2024
- A Step-by-Step Guide to APA Formatting Style (7th Edition)
- Top 10 Online Dissertation Editing Services of 2024
- Academic Writing in 2024: 5 Key Dos & Don’ts + Examples
- What Are the Standard Book Sizes for Publishing Your Book?
- MLA Works Cited Page: Quick Tips & Examples
- 2024’s Top 10 Thesis Statement Generators (Free Included!)
- Top 10 Title Page Generators for Students in 2024
- What Is an Open Access Journal? 10 Myths Busted!
- Primary vs. Secondary Sources: Definition, Types & Examples
- How To Write a College Admissions Essay That Stands Out
- How to Write a Dissertation & Thesis Conclusion (+ Examples)
- APA Journal Citation: 7 Types, In-Text Rules, & Examples
- What Is Predatory Publishing and How to Avoid It!
- What Is Plagiarism? Meaning, Types & Examples
- How to Write a Strong Dissertation & Thesis Introduction
- How to Cite a Book in MLA Format (9th Edition)
- How to Cite a Website in MLA Format | 9th Edition Rules
- 10 Best AI Conclusion Generators (Features & Pricing)
- Top 10 Academic Editing Services of 2024 [with Pricing]
- Additional Resources
- Plagiarism: How to avoid it in your thesis?
- Final Submission Checklist | Dissertation & Thesis
- 7 Useful MS Word Formatting Tips for Dissertation Writing
- How to Write a MEAL Paragraph: Writing Plan Explained in Detail
- Em Dash vs. En Dash vs. Hyphen: When to Use Which
- The 10 Best Citation Generators in 2024 | Free & Paid Plans!
- 2024’s Top 10 Self-Help Books for Better Living
- Citation and Referencing
- Citing References: APA, MLA, and Chicago
- How to Cite Sources in the MLA Format
- MLA Citation Examples: Cite Essays, Websites, Movies & More
- Citations and References: What Are They and Why They Matter
- APA Headings & Subheadings | Formatting Guidelines & Examples
- Formatting an APA Reference Page | Template & Examples
- Research Paper Format: APA, MLA, & Chicago Style
- How to Create an MLA Title Page | Format, Steps, & Examples
- How to Create an MLA Header | Format Guidelines & Examples
- MLA Annotated Bibliography | Guidelines and Examples
- APA Website Citation (7th Edition) Guide | Format & Examples
- APA Citation Examples: The Bible, TED Talk, PPT & More
- APA Header Format: 5 Steps & Running Head Examples
- APA Title Page Format Simplified | Examples + Free Template
- How to Write an Abstract in MLA Format: Tips & Examples
- 10 Best Free Plagiarism Checkers of 2024 [100% Free Tools]
- 5 Reasons to Cite Your Sources Properly | Avoid Plagiarism!
- Dissertation Writing Guide
- Writing a Dissertation Proposal
- The Acknowledgments Section of a Dissertation
- The Table of Contents Page of a Dissertation
- The Introduction Chapter of a Dissertation
- The Literature Review of a Dissertation
- The Only Dissertation Toolkit You’ll Ever Need!
- 5 Thesis Writing Tips for Master Procrastinators
- How to Write a Dissertation | 5 Tips from Academic Editors
- The Title Page of a Dissertation
- The 5 Things to Look for in a Dissertation Editing Service
- Top 10 Dissertation Editing & Proofreading Services
- Why is it important to add references to your thesis?
- Thesis Editing | Definition, Scope & Standard Rates
- Expert Formatting Tips on MS Word for Dissertations
- A 7-Step Guide on How to Choose a Dissertation Topic
- 350 Best Dissertation Topic Ideas for All Streams in 2024
- A Guide on How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- Dissertation Defense: What to Expect and How to Prepare
- Essay Writing Guide
- Essential Research Tips for Essay Writing
- What Is a Mind Map? Free Mind Map Templates & Examples
- How to Write an Essay Outline: 5 Examples & Free Template
- How to Write an Essay Header: MLA and APA Essay Headers
- What Is an Essay? Structure, Parts, and Types
- How to Write an Essay in 8 Simple Steps (Examples Included)
- 8 Types of Essays | Quick Summary with Examples
- Expository Essays | Step-by-Step Manual with Examples
- Narrative Essay | Step-by-Step Guide with Examples
- How to Write an Argumentative Essay (Examples Included)
- Guide to a Perfect Descriptive Essay [Examples & Outline Included]
- How to Start an Essay: 4 Introduction Paragraph Examples
- How to Write a Conclusion for an Essay (Examples Included!)
- How to Write an Impactful Personal Statement (Examples Included)
- Literary Analysis Essay: 5 Steps to a Perfect Assignment
Compare and Contrast Essay | Quick Guide with Examples
- Top 10 Essay Writing Tools in 2024 | Plan, Write, Get Feedback
- Top AI Essay Writers in 2024: 10 Must-Haves
- 100 Best College Essay Topics & How to Pick the Perfect One!
- College Essay Format: Tips, Examples, and Free Template
- Structure of an Essay: 5 Tips to Write an Outstanding Essay
Still have questions? Leave a comment
Add Comment
Checklist: Dissertation Proposal
Enter your email id to get the downloadable right in your inbox!
Examples: Edited Papers
Need editing and proofreading services.

- Tags: Academic Writing , Essay , Essay Writing
A compare and contrast essay, as the name suggests, is used to analyze the similarities and differences between two or more congruent topics. Contrary to popular belief, a compare and contrast essay doesn’t simply list out the similarities and distinctions between two subjects. Rather, it analyzes these similarities or distinctions and explains their significance.
Do you have difficulty writing a compare and contrast essay? In this article, we will walk you through the basics of this essay and how to write it. To give you a gist of how these essays are written, we will also provide plenty of compare and contrast essay formats and examples.
Eliminate all errors with our expert essay editing services! Get started
Let’s start with the basics: What is a compare and contrast essay?
What is a compare and contrast essay?
A compare and contrast essay is a type of essay in which the similarities and differences between two or more corresponding subjects are highlighted and analyzed. The main goal of this essay is to come up with an original argument based on the breakdown of two or more topics.
1. Comparing two subjects that can be better analyzed as a pair.
A compare and contrast essay can be used to highlight the similarities or differences between two subjects that cannot be explained on their own. For instance, comparing the marketing strategies of two competing fast-food chains can uncover similarities in their advertising techniques and consumer appeal. In this way, a compare and contrast essay can help you analyze two subjects that cannot be explained on their own.
2. Highlighting differences between two seemingly identical subjects.
You can use this essay to highlight the distinction between two subjects that are often confused. For instance, poisonous and venomous are two terms often used interchangeably, but they have distinct meanings and implications. Your compare and contrast essay could highlight the differences between these two kinds of organisms.
3. Highlighting similarities between two seemingly unrelated subjects.
You can also use the compare and contrast essay to point out similarities between seemingly dissimilar subjects. For instance, the 1970s and the 2020s are separated by several decades and have distinct characteristics. However, both these eras have been marked by significant sociopolitical activism.
To guide you further, we’ve included additional topics for compare and contrast essays.
Compare and contrast essay topics
While choosing an essay topic, it is important enough to pick topics that are comparable yet not too similar. The goal is to find dissimilarities to analyze the assets and drawbacks of each subject. However, the subjects should still be analogous enough to be compared.
To better understand this let’s take a look at a few good compare and contrast essay topics:
- Traditional education vs. online education
- Ancient Greek vs. Roman civilization
- Examining the similarities between the American and French Revolution
- Eastern philosophies vs. Western philosophies
- Capitalism vs. socialism
- Examining the differences between Romanticism and Realism in Literature
- Traditional medicine vs. alternative medicine
- Comprehensive analysis of dystopian societies in George Orwell’s “1984” and Aldous Huxley’s “Brave New World.”
- Examining the similarities and differences between classical and operant conditioning.
- Psychiatry vs. Psychology
Now that we’ve got the gist of standard compare and contrast essay topics, let’s move on to the tricky part of actually writing compare and contrast essays.
How to write a compare and contrast essay
Before you begin writing your compare and contrast essay, it is important to make sure that you are using the same metrics to compare both your subjects. For instance, you cannot make a comparison by stating that an apple is red or green while a papaya produces a large number of seeds!
You must use identical metrics for comparison. For instance:
- An apple is red or green in color while a papaya is yellow or orange.
- The apple is a winter fruit, whereas the papaya grows in a tropical climate.
- Both apples and papayas are seed-bearing fruits.
Let’s take a look at writing a comparative essay in a bit more detail:
1. Establish similarities and differences between the two subjects
If you’re still debating how to start a compare and contrast essay, you can follow this simple step. You can create two or more columns for your subjects and note down their major characteristics. You can then compare their characteristics and note down any similarities or differences.
Here’s an example:
Now that we’ve listed the characteristics of each bird, let’s note down the similarities and differences between the two:
- Both sparrows and hummingbirds feed on nectar.
- The sparrow is much larger in size as compared to the hummingbird. The average sparrow measures 15–18cm. whereas the average hummingbird only measures 7–13cm.
- The sparrows are much more adaptable and can be found in grasslands, woodlands as well as urban areas. However, the hummingbird is confined to the Americas, generally residing in subtropical regions.
If you are more of a visual learner, you can also make use of a Venn diagram. You can simply draw two circles with an overlapping portion. Note down the characteristics unique to each subject in the portion that does not overlap, and note down the similarities in the overlapping portion. Here’s an example:
2. Create a meaningful argument and thesis statement
A thesis statement explains the reason why two subjects need to be compared. It establishes the significance of their comparison. Although developing a meaningful thesis statement can be tricky, you can figure it out by asking yourself “So what?”.
For instance, if you’re comparing the lifestyle of the royal families in the Eastern and Western civilizations, you must have a reason to choose those particular subjects. One reason could be to study the impact of these civilizations on modern-day society. Here’s an example thesis statement based on this premise:
The contrasting lifestyles of royal families in Eastern and Western civilizations, rooted in cultural traditions and historical developments, have shaped their roles as figureheads and influencers, impacting modern-day society through ceremonial symbolism, media presence, cultural preservation, and fashion trends.
3. Create an essay outline
If you’re still contemplating how to start a compare and contrast essay, you can create a flow for all your ideas with the help of an essay structure. This structure or outline divides your essay into three basic sections:
- Introduction
- Body paragraphs
Most school and college essays consist of an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion. However, this is not a hard and fast rule. You can certainly extend the number of body paragraphs of your essay depending on the topic and complexity of your essay. However, the number of paragraphs in the introduction and conclusion remains the same.
An essay introduction consists of an opening line, relevant background information, and the thesis statement. The body paragraphs are arranged according to different topic sentences. Relevant explanations, facts, and statistics are provided to substantiate the claims made in these topic sentences. The conclusion, like the introduction, also consists of three facets. It includes an updated version of your thesis statement, a summary of the main points of your essay, and a conclusion.
The outline for your compare and contrast essay serves as a base you can build upon. You can use it as a guide while writing your essay. We will take a closer look at compare and contrast essay outlines in the next section of the article.
4. Begin writing your first draft
After constructing a well-structured outline, you can start building your essay with the help of the key points that you’ve jotted down. The comparisons that you’ve noted down earlier can provide the talking points in your essay. Each paragraph consists of three main aspects:
- Topic sentence : The aspect paragraph revolves around
- Explanation : For compare and contrast essays this may include the characteristics of both your subjects and how they relate to each other
- Transition statement : A connecting link to the subject of the next topic sentence
Since you’ve already created a rough outline, your job becomes much easier. You can elaborate on the main talking points of your essay by data collated from various reputed sources. This can include facts, statistics, experiments/studies conducted, or even expert opinions. To make your argument stronger, you can also include tables, figures, or diagrams.
Here’s an example of how you can build on your basic outline:
Topic sentence : A comparison of the Aztecs and Mayans reveals distinct differences in their social structures shedding light on the unique characteristics of these two Mesoamerican civilizations.
Explanation: The Aztecs and Mayans, two prominent Mesoamerican civilizations, displayed striking disparities in their social structures, religious beliefs, and artistic expressions. The Aztecs established a centralized empire with a powerful government headed by an emperor, wielding supreme authority. This hierarchical society comprised nobles, commoners, and slaves, offering limited social mobility. In contrast, the Mayans organized themselves into independent city-states, each with its own ruler and governing system. Their social structure encompassed rulers, nobles, priests, merchants, farmers, and artisans, allowing for some degree of social mobility.
Translation statement: Along with the social structure, the Mayans and Aztecs also had very different everyday routines.
5. Revise and edit
After completing the first draft of your essay, take a break for a day or two before getting back to it. This not only helps you look at your work from an objective point of view but also makes room for new ideas.
In case you notice an abundance of errors while revising your essay, don’t fret, it’s a part of the process. You may need two or three revisions, but make sure to tweak and revise your essay until it is up to the mark. If required, you can also get help from friends, seniors, or even family members.
Once you’re satisfied with the structure and content of your essay, you can start with the editing process. The editing process involves everything from making major structural adjustments for the sake of clarity to correcting mechanical and typesetting errors for the sake of readability.
If the deadline is drawing closer and there’s not enough time, you can also consider working with an essay editing service . These services help you avoid the convoluted and time-consuming process of editing your essay.
Compare and contrast essay outline
Although the introduction and conclusion paragraphs of a compare and contrast essay format remain the same, there are three main methods by which body paragraphs can be arranged. They are:
- Block method: Discussing one subject in its entirety before moving on to the other
- Alternating method: Discussing the stance of both the subjects on one metric, before moving on to the other.
- Similarities and differences: Discussing all the similarities between the two subjects before moving on to the differences.
Depending on the purpose and topic of your essay, you can make use of any of the three formats. Let’s take a closer look at the outlines of each of these compare and contrast essay formats:
Block outline
In the block outline, the analysis of the characteristics of one subject is completed before moving on to the next. Although this method discusses a subject in its entirety and creates a flow, it’s often difficult to draw parallels between the two subjects.
Let’s understand this outline with the help of an example. The following comparative essay block outline example analyzes the positive effects of the color green and the drawbacks of the color red on the human mind.
The Impact of Colors on Your State of Mind
I. Introduction
A. Engaging opening statement about the impact of colors on human perception
B. The significance of colors and their effects on emotions
C. Main argument stating that green is more soothing to the eye than red and should be implemented more often
A. Discussion of Green
1. Characteristics of green and its association with nature and tranquility
2. Examples, statistics, or research findings that demonstrate the soothing effects of green on the human eye
3. Positive impact of green on mental well-being and stress reduction
B. Discussion of Red
1. Characteristics of red and its association with intensity and stimulation
2. Examples, statistics, or research findings that show the potentially overwhelming or agitating effects of red on the human eye
3. Negative impact of red on mental state and a potential increase in stress levels as a result
C. Comparison of Green and Red
1. Visual contrast between the calming effect of green and the stimulating effect of red
2. Emotional responses elicited by green and red, that emphasize the soothing nature of green and the potentially disruptive nature of red
3. Surveys or studies that indicate a higher preference for green in various settings
III. Conclusion
A. Updated main argument: Green is more soothing to the eye than red and should be implemented more often
B. Summary of the key points from the body paragraphs: The benefits of green and the drawbacks of red
C. Using green in various environments, such as interior design, healthcare facilities, and urban planning, to promote a soothing visual experience for individuals
D. Impactful ending sentence: The importance of color choices for a harmonious environment
Alternating outline
If you want to establish a stronger connection between your different points of comparison, consider using the alternating outline. In this type of outline, the comparison between subjects is much more blatant as both of the subjects are evaluated against a particular metric. However, the alternating outline can result in two disjointed sections.
Each body paragraph consists of a single metric against which both subjects are measured. Let’s better understand the alternating essay outline with the help of the same example:
A. Captivating hook about the influence of colors on human perception
B. Overview of the significance of colors and their impact on emotions
C. Thesis statement stating that green is more soothing to the eye than red and should be implemented more often
II. Body Paragraph 1: Comparison of Green and Red
A. Visual Characteristics
1. Green: Associated with nature, calmness, and tranquility
2. Red: Associated with intensity, excitement, and stimulation
B. Emotional Impact
1. Green: Elicits feelings of relaxation, harmony, and rejuvenation
2. Red: Evokes emotions like passion, energy, and even agitation or stress
C. Effects on Eye Fatigue
1. Green: More restful for the eyes due to its position in the color spectrum
2. Red: Prolonged exposure to red can strain the eyes and potentially lead to eye fatigue
III. Body Paragraph 2: Benefits of Implementing Green
A. Psychological Well-being
1. Green: Promotes a sense of calmness, reduces stress, and improves overall mental well-being
2. Red: Excessive exposure to red can potentially increase stress levels and negatively impact psychological health
B. Environmental Impact
1. Green: Incorporating green elements in urban environments, interior design, and healthcare facilities can create a soothing atmosphere
2. Red: Potential disruptive effects of excessive red usage in certain settings and its contrasting impact on visual comfort
IV. Conclusion
A. Updated thesis statement: Green is more soothing to the eye than red and should be implemented more often
B. Summary of key points in body paragraphs: Difference between green and red, emphasizing the soothing qualities of green and the potential drawbacks of red
C. Implementation of green in various contexts, and its positive impact on well-being and creating visually comfortable environments
D. Impactful concluding statement: The significance of color choices and their influence on our daily lives
Similarities and differences outline
If you want the focus to be on the comparison between the two topics, it is a good idea to implement the similarities and differences outline. This format bears a resemblance to the alternating outline.
However, the metrics of comparison are the similarities and differences between the two subjects, as opposed to certain characteristics. A single paragraph lists all the similarities between the two topics, followed by a paragraph that lists all the distinctions.
Here’s an example outline for a compare and contrast essay using the similarities and differences method:
A. Intriguing statement about the impact of colors on visual perception
B. Brief overview of the significance of colors and their effects on emotions
II. Body Paragraph 1: Similarities between Green and Red
1. Green: Visual characteristics of green, such as its association with nature and tranquility
2. Red: Visual characteristics of red, such as its association with intensity and stimulation
1. Green: Both green and red can evoke emotional responses, such as calmness or excitement, albeit to different degrees
2. Red: Both green and red can elicit emotions, but red tends to evoke more intense and stimulating feelings
III. Body Paragraph 2: Differences between Green and Red
A. Soothing Qualities
1. Green: Green is inherently soothing to the eye due to its position in the color spectrum and its association with nature
2. Red: Red, on the other hand, can be visually intense and potentially overwhelming, making it less soothing
B. Psychological Effects
1. Green: Green promotes relaxation, reduces stress, and enhances mental well-being
2. Red: Prolonged exposure to red can potentially increase stress levels and negatively impact psychological health
C. Eye Fatigue
1. Green: Green is considered more restful for the eyes, as it requires less eye strain and can reduce eye fatigue
2. Red: Excessive exposure to red can strain the eyes and potentially lead to eye fatigue
IV. Body Paragraph 3: Benefits of Implementing Green
A. Environmental Impact
1. Incorporating green elements in various environments, such as interior design, urban planning, and healthcare facilities, can create a soothing atmosphere
2. Potential positive effects on mental well-being and overall quality of life
V. Conclusion
B. Summary of key points in body paragraphs: Similarities and differences between green and red, that emphasize the soothing qualities of green and the potential drawbacks of red
C. Need for the implementation of green in different settings, and its positive impact on visual comfort and well-being
D. Thought-provoking statement: Significance of color choices and their influence on our daily lives
Now that we’ve understood the three basic outlines for compare and contrast essays let’s take a look at compare and contrast essay examples for these three formats.
Compare and contrast essay examples
There are three main formats that you can use to write a compare and contrast essay. You can select one of these formats depending on what you’d like to convey to the reader. We will provide example essays for all three formats and pick a topic best suited for each essay format.
Let’s take a look:
Block method essay example
The following compare and contrast essay example is based on the comparative analysis of two of Edgar Allan Poe’s greatest works.
A Comparative Analysis of The Raven and The Tell-Tale Heart
Edgar Allan Poe, a master of Gothic literature, created two captivating and chilling tales, The Raven and The Tell-Tale Heart . While both stories delve into the realms of madness, guilt, and obsession, they differ in their narrative structures, character portrayals, and themes. Take a closer look at and uncover the unique elements that make these literary masterpieces enduring classics in the world of dark fiction.
The Raven is a narrative poem composed of eighteen stanzas, employing a rhyming scheme of ABCBBB. It follows a straightforward linear progression, recounting the narrator’s interaction with the mysterious raven, which repeatedly utters the word “nevermore.” The narrator is a grieving man consumed by sorrow and melancholy, haunted by the loss of his beloved Lenore. The raven assumes a symbolic role, representing an otherworldly and ominous presence that fuels the narrator’s descent into madness. The poem primarily explores themes of grief, loss, and the inability to escape from painful memories, while also delving into the supernatural, the macabre, and the fragility of the human mind when faced with the unknown.
On the other hand, The Tell-Tale Heart is a short story narrated in the first person by an unnamed protagonist who is determined to prove their sanity. The story follows a non-linear structure, with the narrator recounting the events leading up to and after the murder of the old man with a “vulture eye.” The protagonist is an unnamed and unreliable narrator whose intense obsession with the old man’s eye leads to murder. The old man, with his “vulture eye,” becomes a symbol of the narrator’s guilt and paranoia, fueling the story’s suspense. The Tell-Tale Heart explores themes of guilt, paranoia, and the dark recesses of the human mind. It delves into the thin line between sanity and insanity, highlighting the overwhelming power of a guilty conscience.
The Raven and The Tell-Tale Heart , both masterpieces by Edgar Allan Poe, showcase his profound understanding of the human psyche. While The Raven takes the form of a narrative poem and focuses on grief, loss, and the supernatural, The Tell-Tale Heart is a short story with an unreliable narrator, delving into guilt, paranoia, and the blurred boundaries of sanity. Despite their structural and thematic differences, both works captivate readers with their exploration of the darkest aspects of the human soul. Through their masterful storytelling, Poe leaves an indelible mark on literature, inviting readers to confront their own fears and delve into the depths of the human psyche.
Alternating method essay example
The following compare and contrast essay example highlights the stark contrast between life during the 1800s and the present day.
Contrasting Life During the 1800s and Life Today
Society during the 1800s and present-day society are characterized by stark differences in technological advancements, societal norms, and overall quality of life. There have been significant developments areas of communication, transportation, healthcare, and social dynamics between the two eras. By examining the contrasting aspects of life during the 1800s and present-day life, we can gain a deeper insight into how society has evolved.
In the 1800s people relied primarily on written letters, which often took weeks or even months to reach their destination. The introduction of the telegraph provided a faster means of long-distance communication but remained limited in accessibility. Today, communication is instant and global, thanks to the widespread use of smartphones, social media platforms, and the internet. People can connect through video calls, messaging apps, and social networking sites, bridging distances and facilitating real-time conversations.
People in the 1800s primarily relied on horse-drawn carriages, ships, and railways as modes of transportation. Long-distance travel was slow and arduous, often taking weeks or even months to complete, while local transportation was limited to walking or horseback riding. In contrast, modern transportation is characterized by the advent of automobiles, airplanes, and high-speed trains. These advancements enable swift and efficient travel across the globe. Air travel has become commonplace, allowing people to reach distant locations in a matter of hours, while cars provide individual mobility and flexibility.
Healthcare in the 1800s was marked by rudimentary medical knowledge and practices. There was often a lack of scientific understanding and proper sanitation measures, resulting in limited and ineffective medical treatments. This led to high mortality rates for common illnesses and diseases. In recent times, advances in medical science, technology, and research have revolutionized healthcare. Cutting-edge treatments, vaccines, and surgical procedures have significantly increased life expectancy and improved overall well-being.
The 1800s were characterized by strict social hierarchies, class divisions, and limited opportunities for social mobility. Gender roles were rigidly defined, with limited rights and opportunities for women. However, contemporary society has made significant strides toward equality and inclusivity. Movements advocating for gender, racial, and LGBTQ+ rights have pushed for social progress. Social mobility and opportunities for personal and professional growth have expanded, promoting a more diverse and inclusive society.
In conclusion, life during the 1800s and life today differ significantly in terms of communication, transportation, healthcare, and social dynamics. Technological advancements, scientific progress, and societal changes have transformed the way we live and interact with the world. While the 1800s were marked by limitations and hardships, the modern era offers unprecedented convenience, connectivity, and opportunities for personal growth. By examining these contrasting aspects, we gain a deeper appreciation for the advancements that have shaped our lives today and a better understanding of the progress humanity has made over time.
Similarities and differences method essay example
The following example of a compare and contrast essay studies the similarities and differences between amphibians and reptiles.
Exploring the Fascinating Worlds of Amphibians and Reptiles
Amphibians and reptiles are two distinct groups of animals that belong to the larger classification of vertebrates. While they share some similarities, they also exhibit significant differences in their physical characteristics, life cycles, habitats, and reproductive strategies. Let’s take a closer look at both these species by highlighting their unique features and adaptations to their respective environments.
Although different species, amphibians, and reptiles share several similarities. Both groups are cold-blooded, or ectothermic, which means their body temperatures are regulated by the environment. This characteristic influences their behavior and activity levels, as they rely on external heat sources to warm their bodies. Both species also lay eggs for reproduction. The eggs of both groups are covered by protective membranes, which provide a suitable environment for development outside the parent’s body. Additionally, amphibians and reptiles have a similar general body plan, characterized by a backbone, four limbs (or remnants of limbs), and a well-developed skull.
Despite these similarities, there are notable differences between the two species. Amphibians have a dual life cycle, which involves an aquatic larval stage and a terrestrial adult stage. They typically lay their eggs in water and undergo metamorphosis from aquatic larvae, into terrestrial adults with lungs. A frog is one classic example of an amphibian. In contrast, reptiles have a direct life cycle, with offspring hatching from eggs that are laid on land. They bypass the aquatic larval stage and are born as miniature versions of the adults, equipped for a terrestrial existence. Alligators and crocodiles are the most commonly known reptiles.
Another significant difference lies in their respective habitats. Amphibians are often associated with moist environments, such as swamps, rivers, and ponds, as they require
water for breeding and maintaining skin moisture. They are highly adapted to live in both aquatic and terrestrial habitats. Reptiles, on the other hand, have evolved to inhabit a wider range of environments. They can be found in various habitats, including deserts, forests, grasslands, and even oceans. Reptiles have developed strategies to conserve water, such as the ability to excrete uric acid instead of urea, allowing them to thrive in arid conditions.
Physiologically, amphibians and reptiles differ in their skin structure and respiration. Amphibians have moist and permeable skin that serves multiple functions, including gas exchange and water absorption. This unique characteristic allows them to respire through their skin, particularly during their larval stage. In contrast, reptiles have dry and scaly skin that acts as a protective barrier against water loss. They rely on lungs for respiration and have more efficient respiratory systems compared to amphibians.
In conclusion, while amphibians and reptiles share some similarities, such as being ectothermic and laying eggs, they have distinct differences in their life cycles, habitats, and physiological characteristics. Amphibians undergo metamorphosis and have a dual life cycle, adapting to both aquatic and terrestrial environments. Reptiles, on the other hand, have a direct life cycle and are adapted to a wide range of habitats. Understanding these similarities and differences helps us appreciate the diverse adaptations that have allowed these fascinating creatures to thrive in different ecosystems across the world.
We hope that these examples of compare and contrast essays guide you in acing your essay assignment! As editing and proofreading experts, we realize the importance of submitting error-free essays.
To help you minimize errors, we have created detailed resources about several important aspects of essay writing. Go through the following resources to enhance your essay-writing skills!
- Guide to Essay Editing: Methods, Tips, & Examples
- How to Format a College Essay: Format Template & Tips
Frequently Asked Questions
How to write an introduction paragraph for a compare and contrast essay, how to write a conclusion paragraph for a compare and contrast essay, how to title a compare and contrast essay, what is a good title for a compare and contrast essay, what is a good topic sentence for a compare and contrast essay.
Found this article helpful?
Leave a Comment: Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published.
Your vs. You’re: When to Use Your and You’re
Your organization needs a technical editor: here’s why, your guide to the best ebook readers in 2024, writing for the web: 7 expert tips for web content writing.
Subscribe to our Newsletter
Get carefully curated resources about writing, editing, and publishing in the comfort of your inbox.
How to Copyright Your Book?
If you’ve thought about copyrighting your book, you’re on the right path.
© 2024 All rights reserved
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- Self Publishing Guide
- Pre-Publishing Steps
- Fiction Writing Tips
- Traditional Publishing
- Academic Writing and Publishing
- Partner with us
- Annual report
- Website content
- Marketing material
- Job Applicant
- Cover letter
- Resource Center
- Case studies
5 Compare and Contrast Essay Examples (Full Text)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process
A compare and contrast essay selects two or more items that are critically analyzed to demonstrate their differences and similarities. Here is a template for you that provides the general structure:

A range of example essays is presented below.
Compare and Contrast Essay Examples
#1 jean piaget vs lev vygotsky essay.
1480 Words | 5 Pages | 10 References
(Level: University Undergraduate)

Thesis Statement: “This essay will critically examine and compare the developmental theories of Jean Piaget and Lev Vygotsky, focusing on their differing views on cognitive development in children and their influence on educational psychology, through an exploration of key concepts such as the role of culture and environment, scaffolding, equilibration, and their overall implications for educational practices..”
#2 Democracy vs Authoritarianism Essay

Thesis Statement: “The thesis of this analysis is that, despite the efficiency and control offered by authoritarian regimes, democratic systems, with their emphasis on individual freedoms, participatory governance, and social welfare, present a more balanced and ethically sound approach to governance, better aligned with the ideals of a just and progressive society.”
#3 Apples vs Oranges Essay
1190 Words | 5 Pages | 0 References
(Level: 4th Grade, 5th Grade, 6th Grade)

Thesis Statement: “While apples and oranges are both popular and nutritious fruits, they differ significantly in their taste profiles, nutritional benefits, cultural symbolism, and culinary applications.”
#4 Nature vs Nurture Essay
1525 Words | 5 Pages | 11 References
(Level: High School and College)

Thesis Statement: “The purpose of this essay is to examine and elucidate the complex and interconnected roles of genetic inheritance (nature) and environmental influences (nurture) in shaping human development across various domains such as physical traits, personality, behavior, intelligence, and abilities.”
#5 Dogs vs Cats Essay
1095 Words | 5 Pages | 7 Bibliographic Sources
(Level: 6th Grade, 7th Grade, 8th Grade)
Thesis Statement: “This essay explores the distinctive characteristics, emotional connections, and lifestyle considerations associated with owning dogs and cats, aiming to illuminate the unique joys and benefits each pet brings to their human companions.”
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
I’ve recorded a full video for you on how to write a compare and contrast essay:
Get the Compare and Contrast Templates with AI Prompts Here
In the video, I outline the steps to writing your essay. Here they are explained below:
1. Essay Planning
First, I recommend using my compare and contrast worksheet, which acts like a Venn Diagram, walking you through the steps of comparing the similarities and differences of the concepts or items you’re comparing.
I recommend selecting 3-5 features that can be compared, as shown in the worksheet:

Grab the Worksheet as Part of the Compare and Contrast Essay Writing Pack
2. Writing the Essay
Once you’ve completed the worksheet, you’re ready to start writing. Go systematically through each feature you are comparing and discuss the similarities and differences, then make an evaluative statement after showing your depth of knowledge:

Get the Rest of the Premium Compare and Contrast Essay Writing Pack (With AI Prompts) Here
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Thesis Statement
Compare and contrast thesis statements can either:
- Remain neutral in an expository tone.
- Prosecute an argument about which of the items you’re comparing is overall best.
To write an argumentative thesis statement for a compare and contrast essay, try this AI Prompts:
💡 AI Prompt to Generate Ideas I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that pass a reasonable judgement.
Ready to Write your Essay?

Take action! Choose one of the following options to start writing your compare and contrast essay now:
Read Next: Process Essay Examples

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 15 Body Language Signs He Likes You
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 25 Classroom Wall Decoration Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 31 Cute & Cozy Play Corner Ideas
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd-2/ 24 Steiner-Waldorf Classroom Design Ideas
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
10.7 Comparison and Contrast
Learning objectives.
- Determine the purpose and structure of comparison and contrast in writing.
- Explain organizational methods used when comparing and contrasting.
- Understand how to write a compare-and-contrast essay.
The Purpose of Comparison and Contrast in Writing
Comparison in writing discusses elements that are similar, while contrast in writing discusses elements that are different. A compare-and-contrast essay , then, analyzes two subjects by comparing them, contrasting them, or both.
The key to a good compare-and-contrast essay is to choose two or more subjects that connect in a meaningful way. The purpose of conducting the comparison or contrast is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities. For example, if you wanted to focus on contrasting two subjects you would not pick apples and oranges; rather, you might choose to compare and contrast two types of oranges or two types of apples to highlight subtle differences. For example, Red Delicious apples are sweet, while Granny Smiths are tart and acidic. Drawing distinctions between elements in a similar category will increase the audience’s understanding of that category, which is the purpose of the compare-and-contrast essay.
Similarly, to focus on comparison, choose two subjects that seem at first to be unrelated. For a comparison essay, you likely would not choose two apples or two oranges because they share so many of the same properties already. Rather, you might try to compare how apples and oranges are quite similar. The more divergent the two subjects initially seem, the more interesting a comparison essay will be.
Writing at Work
Comparing and contrasting is also an evaluative tool. In order to make accurate evaluations about a given topic, you must first know the critical points of similarity and difference. Comparing and contrasting is a primary tool for many workplace assessments. You have likely compared and contrasted yourself to other colleagues. Employee advancements, pay raises, hiring, and firing are typically conducted using comparison and contrast. Comparison and contrast could be used to evaluate companies, departments, or individuals.
Brainstorm an essay that leans toward contrast. Choose one of the following three categories. Pick two examples from each. Then come up with one similarity and three differences between the examples.
- Romantic comedies
- Internet search engines
- Cell phones
Brainstorm an essay that leans toward comparison. Choose one of the following three items. Then come up with one difference and three similarities.
- Department stores and discount retail stores
- Fast food chains and fine dining restaurants
- Dogs and cats
The Structure of a Comparison and Contrast Essay
The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both and the reason for doing so. The thesis could lean more toward comparing, contrasting, or both. Remember, the point of comparing and contrasting is to provide useful knowledge to the reader. Take the following thesis as an example that leans more toward contrasting.
Thesis statement: Organic vegetables may cost more than those that are conventionally grown, but when put to the test, they are definitely worth every extra penny.
Here the thesis sets up the two subjects to be compared and contrasted (organic versus conventional vegetables), and it makes a claim about the results that might prove useful to the reader.
You may organize compare-and-contrast essays in one of the following two ways:
- According to the subjects themselves, discussing one then the other
- According to individual points, discussing each subject in relation to each point
See Figure 10.1 “Comparison and Contrast Diagram” , which diagrams the ways to organize our organic versus conventional vegetables thesis.
Figure 10.1 Comparison and Contrast Diagram
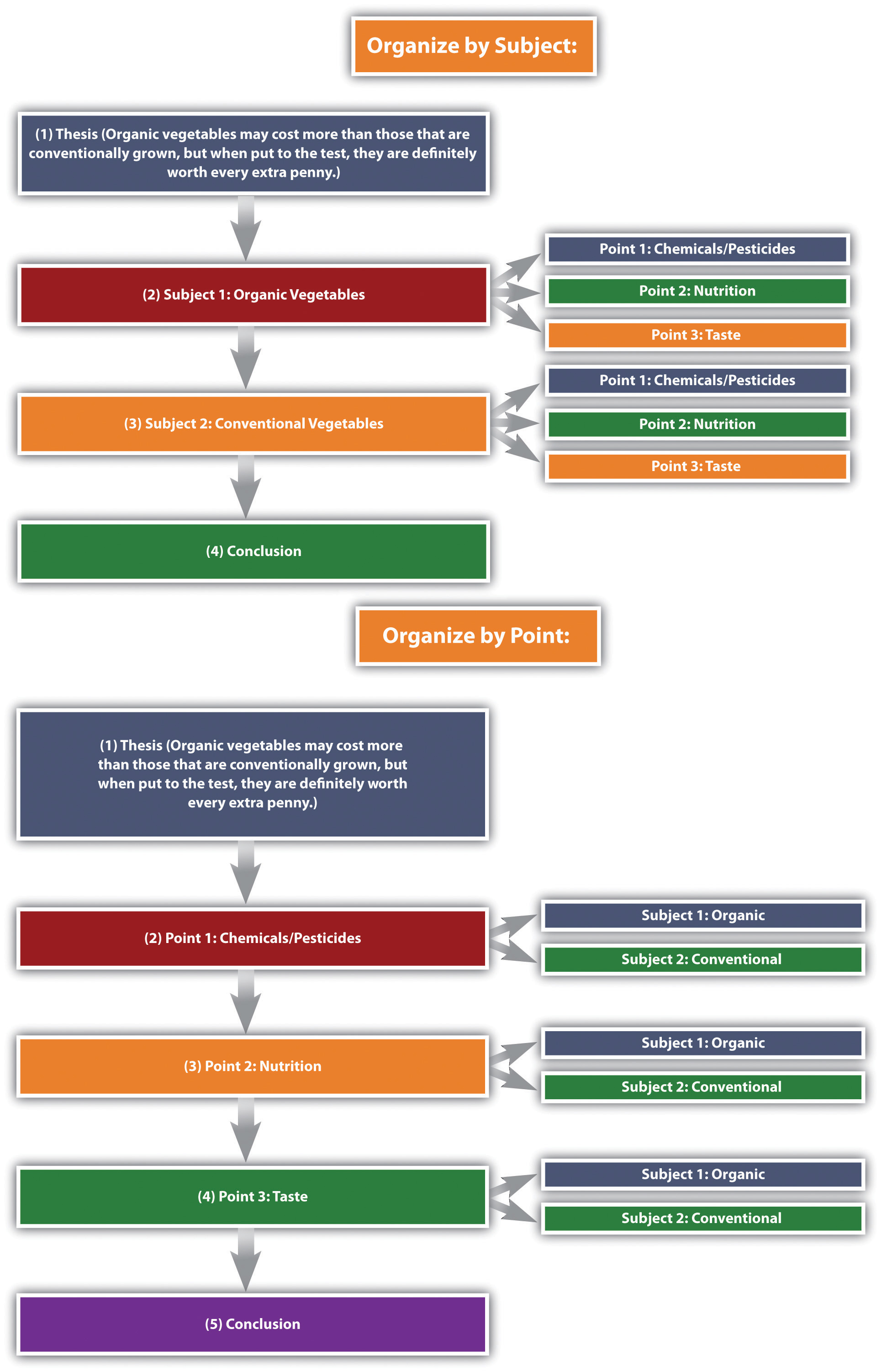
The organizational structure you choose depends on the nature of the topic, your purpose, and your audience.
Given that compare-and-contrast essays analyze the relationship between two subjects, it is helpful to have some phrases on hand that will cue the reader to such analysis. See Table 10.3 “Phrases of Comparison and Contrast” for examples.
Table 10.3 Phrases of Comparison and Contrast
| Comparison | Contrast |
|---|---|
| one similarity | one difference |
| another similarity | another difference |
| both | conversely |
| like | in contrast |
| likewise | unlike |
| similarly | while |
| in a similar fashion | whereas |
Create an outline for each of the items you chose in Note 10.72 “Exercise 1” and Note 10.73 “Exercise 2” . Use the point-by-point organizing strategy for one of them, and use the subject organizing strategy for the other.
Writing a Comparison and Contrast Essay
First choose whether you want to compare seemingly disparate subjects, contrast seemingly similar subjects, or compare and contrast subjects. Once you have decided on a topic, introduce it with an engaging opening paragraph. Your thesis should come at the end of the introduction, and it should establish the subjects you will compare, contrast, or both as well as state what can be learned from doing so.
The body of the essay can be organized in one of two ways: by subject or by individual points. The organizing strategy that you choose will depend on, as always, your audience and your purpose. You may also consider your particular approach to the subjects as well as the nature of the subjects themselves; some subjects might better lend themselves to one structure or the other. Make sure to use comparison and contrast phrases to cue the reader to the ways in which you are analyzing the relationship between the subjects.
After you finish analyzing the subjects, write a conclusion that summarizes the main points of the essay and reinforces your thesis. See Chapter 15 “Readings: Examples of Essays” to read a sample compare-and-contrast essay.
Many business presentations are conducted using comparison and contrast. The organizing strategies—by subject or individual points—could also be used for organizing a presentation. Keep this in mind as a way of organizing your content the next time you or a colleague have to present something at work.
Choose one of the outlines you created in Note 10.75 “Exercise 3” , and write a full compare-and-contrast essay. Be sure to include an engaging introduction, a clear thesis, well-defined and detailed paragraphs, and a fitting conclusion that ties everything together.
Key Takeaways
- A compare-and-contrast essay analyzes two subjects by either comparing them, contrasting them, or both.
- The purpose of writing a comparison or contrast essay is not to state the obvious but rather to illuminate subtle differences or unexpected similarities between two subjects.
- The thesis should clearly state the subjects that are to be compared, contrasted, or both, and it should state what is to be learned from doing so.
There are two main organizing strategies for compare-and-contrast essays.
- Organize by the subjects themselves, one then the other.
- Organize by individual points, in which you discuss each subject in relation to each point.
- Use phrases of comparison or phrases of contrast to signal to readers how exactly the two subjects are being analyzed.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Writing a Paper: Comparing & Contrasting
A compare and contrast paper discusses the similarities and differences between two or more topics. The paper should contain an introduction with a thesis statement, a body where the comparisons and contrasts are discussed, and a conclusion.
Address Both Similarities and Differences
Because this is a compare and contrast paper, both the similarities and differences should be discussed. This will require analysis on your part, as some topics will appear to be quite similar, and you will have to work to find the differing elements.
Make Sure You Have a Clear Thesis Statement
Just like any other essay, a compare and contrast essay needs a thesis statement. The thesis statement should not only tell your reader what you will do, but it should also address the purpose and importance of comparing and contrasting the material.
Use Clear Transitions
Transitions are important in compare and contrast essays, where you will be moving frequently between different topics or perspectives.
- Examples of transitions and phrases for comparisons: as well, similar to, consistent with, likewise, too
- Examples of transitions and phrases for contrasts: on the other hand, however, although, differs, conversely, rather than.
For more information, check out our transitions page.
Structure Your Paper
Consider how you will present the information. You could present all of the similarities first and then present all of the differences. Or you could go point by point and show the similarity and difference of one point, then the similarity and difference for another point, and so on.
Include Analysis
It is tempting to just provide summary for this type of paper, but analysis will show the importance of the comparisons and contrasts. For instance, if you are comparing two articles on the topic of the nursing shortage, help us understand what this will achieve. Did you find consensus between the articles that will support a certain action step for people in the field? Did you find discrepancies between the two that point to the need for further investigation?
Make Analogous Comparisons
When drawing comparisons or making contrasts, be sure you are dealing with similar aspects of each item. To use an old cliché, are you comparing apples to apples?
- Example of poor comparisons: Kubista studied the effects of a later start time on high school students, but Cook used a mixed methods approach. (This example does not compare similar items. It is not a clear contrast because the sentence does not discuss the same element of the articles. It is like comparing apples to oranges.)
- Example of analogous comparisons: Cook used a mixed methods approach, whereas Kubista used only quantitative methods. (Here, methods are clearly being compared, allowing the reader to understand the distinction.

Related Webinar
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Developing Arguments
- Next Page: Avoiding Logical Fallacies
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
)
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
Published September 27, 2020. Updated May 4, 2022.
Compare and Contrast Essay Definition
A compare and contrast essay discusses similarities and differences between two subjects. The discussion shows the writer’s deep understanding of both subjects.
Overview of a Compare and Contrast Essay
- Choose what two subjects to compare and contrast.
- Brainstorm similarities and differences between the two subjects.
- Develop a thesis statement and write an introduction.
- Write an analysis, using the block method or the point-by-point method.
- Write a conclusion.
This page will cover the following points:
Key Takeaways
What is a compare and contrast essay, step 1: choose what to compare and contrast, step 2: brainstorm similarities and differences, step 3: write an introduction and a thesis, step 4: use block method or point-to-point, step 5: write a conclusion.
- Why Do Teachers Assign Compare and Contrast Essays?
- A compare and contrast essay discusses the similarities and differences between two subjects to show a deep understanding of both.
- Pick subjects and points that are relevant to your class .
- Use your essay’s thesis statement to show the reader why the similarities and differences are important.
- Choose whether you’d like to focus on one subject at a time ( block method ) or move back and forth between subjects ( point-to-point method ).
- A compare and contrast essay outline includes a full thesis statement and uses appropriate structure ( block method or point-to-point ).
- A thesis statement is the foundation of an essay, listing your paper’s main comparisons and explaining why they’re important.
- With block structure , you dedicate each body paragraph to one of your two subjects.
- With point-to-point , you dedicate each body paragraph to one of your main points about both subjects.
A compare and contrast essay discusses the similarities and differences between two subjects. This shows a deep understanding of both subjects.
Sometimes, instructors ask students to weigh the positives and negatives of both subjects, choose which subject is better, and defend their position. Read the essay prompt carefully!
Worried about your writing? Submit your paper for a Chegg Writing essay check , or for an Expert Check proofreading . Both can help you find and fix potential writing issues.
In some classes, your instructor will tell you which two subjects to focus on. They’ll usually pick topics discussed in lectures.
For example, in an American literature course, your instructor may ask you to compare and contrast two writers like Allen Ginsberg and Jack Kerouac. Both were part of the same literary movement (the Beat Generation) but still had unique styles and priorities.
Your instructor may let you choose your subjects. Pick two people, things, or ideas discussed in class with clear differences but something in common, too.
Let’s say, for example, your class is talking about pizza (what a great class, right?). You’ll want to choose two subjects in that category that are comparable, such as New York-style pizza and Chicago deep-dish pizza. Both are types of pizza, and they both mean a lot to certain American cities.
You can also find ways to contrast these two pizzas. They both have a distinct shape and are eaten differently (try eating deep-dish pizza with your hands!).
Although your class probably isn’t talking about pizza, the point here is to pick two subjects that:
- Your instructor or textbook discussed.
- You feel confident about and which have several important similarities and differences.
But how will you know if any given similarity or difference is important ? In the next section, you’ll brainstorm your essay’s main points and pick the ones that are most appropriate for your class.
By now, you’ve chosen (or were told) your two subjects. Next, it’s time to think about what differences and similarities your paper should focus on.
Since this brainstorming session is just for you, feel free to use whichever method you prefer. Some people like to use Venn diagrams to organize their thoughts. Others prefer a T-chart or just jotting ideas down.
Not all compare and contrast points are made equal. Think about what your instructor has talked about in class so far. Then, decide which points would sound the most appropriate for your course.
This is also a good time to revisit the prompt. Your instructor may have already hinted at what they’d like you to discuss in the instructions.
Here’s an example of a brainstorming session about New York- and Chicago-style pizza. Let’s figure out which of these compare and contrast points would be best for the paper:
| Point #1: Because of the size, often sold by the slice, it is a quick fast-food option | Point #1: Mostly sold by the pie, making it more common for “sit-down” restaurants or at-home cooking |
| Point #2: Hand-tossed crust | Point #2: Thick, deep crust |
| Point #3: Important for NYC’s identity | Point #3: Important for Chicago’s identity |
| Point #4: Many restaurants nearby make it | Point #4: Many restaurants nearby make it |
After brainstorming, you have four very different points for your pizza paper. Each could be helpful, depending on the class.
If the class is about local history, then the last point, “many restaurants nearby make it,” will be useful. If not, then that point is likely the least relevant.
Meanwhile, a class about United States history will care deeply about how these different foods helped shape the identity of Chicago and New York City, respectively (point #3).
Points #1 and #2 talk about the size and shape of the pizza. These would be great choices for a home economics class, where the preparation and presentation of the dish are important.
Whichever points you choose for your compare and contrast essay, make sure they make sense and seem relevant to your class. Never throw in an extra point just to reach the word count for the paper. Your instructor will be able to tell!
Once you have three or four relevant points for your compare and contrast essay, it’s time to write the thesis statement. This will tell your instructor why these similarities and differences are important and worth talking about in an essay.
The introduction is where you’ll tell your audience what your two subjects are. You’ll also discuss the main ways you plan to compare and contrast them.
One of the most important parts of your introduction (and the whole paper) is your thesis statement. The thesis is the main argument of your essay.
Why should someone care about the similarities and differences between these two subjects? That’s the question your thesis statement should answer.
Let’s think, for example, about the New York- and Chicago-style pizza essay. Why should your instructor care about comparing and contrasting these two pizza types?
Here’s an example thesis statement for that paper:
Both New York-style and Chicago deep-dish pizza are important to the identities of their respective cities. However, the fast, portable nature of by-the-slice New York-style pizza makes it easier for the average New Yorker to eat frequently than does the deep-dish pizza for Chicago residents.
This thesis statement not only points out differences and similarities between the pizzas but also begins to say why those differences matter. Remember that the rest of your paper should support the points made in your thesis statement and address important questions.
For example, in the pizza-paper thesis, common questions might include:
What makes New York-style pizza more portable? In what ways are these pizzas important to each city’s identity?
Now, you have a compelling thesis statement for your paper ready to go. Next, you’ll spend some time thinking about how you want to present the similarities and differences between your two subjects.
Would you like to talk about one subject at a time? Or would you prefer to switch between the two to better highlight their differences?
In the next section, you’ll learn the pros and cons of both of these styles. Then, you’ll decide which one is right for your paper.
Here’s what a well-outlined introduction looks like:
– Begin with a lighthearted discussion about the centuries-long debate over cats and dogs.
– Thesis statement: Cats and dogs have varying activity levels, maintenance needs, and ways of showing affection, which potential owners should keep in mind before deciding between the two.
There are many ways to format your compare and contrast paper. But to keep things simple, let’s focus on the two most popular strategies.
With the block method , you make all your points about subject #1 before switching to subject #2. You may dedicate one or even two full paragraphs to the first subject before comparing it with the second one.
Here’s an example outline for a block method essay:
Paragraph 1: Introduction
P2: Subject #1
P3: Subject #1 (continued)
P4: Subject #2
P5: Subject #2 (continued)
P6: Conclusion
There are pros and cons to each method. The main benefit of the block method is that it is easy to keep your paper organized. Because you’re only discussing one subject at a time, your instructor can easily tell what you’re talking about.
There are still cons to this structure, though. For example, it will be harder for your audience to remember the points you made about subject #1 when you finally get to subject #2.
If you want to more closely compare and contrast your two subjects, you’ll want to use the point-to-point approach.
With point-to-point, you’ll dedicate each of your body paragraphs to a similarity or difference between the two subjects. You’ll compare and contrast both subjects in each body paragraph.
Let’s take a look at an outline organized for the point-to-point method:
P2: Similarity #1
P3: Similarity #2
P4: Difference #1
P5: Difference #2
The main benefit of point-to-point is that the similarities and differences between your two subjects will be more clear. After all, you’re going back and forth between the two at all times.
Because you are switching so often, though, you’ll want to write very clearly. Be sure to use plenty of transition words, which you’ll learn more about in the next section. Otherwise, your instructor may lose track of what you’re discussing.
Both of these methods will work with most compare and contrast essays. You’ll have to decide for yourself if you feel your subjects would be better discussed one at a time (block method) or back and forth (point-to-point).
Template on block structure and point-to-point examples
Transition words for a compare and contrast essay.
In a compare and contrast essay, you’ll be discussing at least two different subjects throughout the paper. That’s why it’s helpful to use transition words. These words will let your audience know when you’re moving on to a new topic or directly contrasting two ideas.
Here are some useful transition words for compare and contrast essays:
- in contrast
As you can guess, some of these words (ex: “similarly” and “likewise”) help you compare your two subjects. Here’s an example:
Pizza-by-the-slice places are an iconic image of New York City. Similarly , visitors to Chicago make it a point to find a deep-dish pizza restaurant.
Other transition words (ex: “in contrast” and “unlike”) point to an important difference. Let’s try one out:
Unlike New York-style pizza, which can be enjoyed on the go, Chicago deep-dish pizza is suited better for a traditional, sit-down restaurant.
Use these and other transition words to make your points more clear. Try using different transition words throughout your paper, such as using “similarly” once and then “likewise” the next time. That way, you can avoid monotonous sentences.
By the time you reach the conclusion of a compare and contrast paper, you’ve already done a lot of planning and writing. It’s completely understandable if you feel a bit burned out.
Like many other papers, you’ll want to use the conclusion of your compare and contrast essay to remind your instructor of your main points. But it’s also important not to copy and paste your introduction into the conclusion.
Try to find a new, eye-catching way to transition back into your main points and restate your thesis. Here’s an example for the New York- and Chicago-style pizzas:
In the season 2 episode of The Office (US), “Valentine’s Day,” Michael Scott visits downtown New York City and immediately runs into a Sbarro’s restaurant for a “New York slice.” The scene is a joke about Michael’s naïveté. But it also points to how second nature New York-style pizza is for experiencing the area. Both New York-style and Chicago deep-dish pizza hold a special place in their city’s identities…
As always, make sure whatever you write is appropriate for your class. With a topic as light-hearted as pizza, a quick The Office reference fits right in. But in other essays, a pop culture reference would be distracting.
Here’s an example of an outline for a conclusion:
– Talk about famous cats and dogs in pop culture and their personalities, like Chloe and Max from The Secret Life of Pets .
– Restate thesis: From the palaces of Ancient Egypt to the condos of modern-day New York City, both cats and dogs have long been revered for their companionship. Potential owners should consider cats and dogs’ varying activity levels, grooming needs, and ways of showing affection before deciding which pet is right for them.
Use your conclusion to reinforce the points made throughout the paper. Adding anecdotes like the one above can make your paper stand out and keep the attention of your instructor. It’s also a way to let them know that you took the assignment seriously from the beginning to the very end.
Example Compare and Contrast Essay on J azz vs. Rock
Before you turn in that paper, don’t forget to cite your sources in APA format , MLA format , or a style of your choice.
Why Do Teachers assign Compare and Contrast Essays?
In many cases, your instructor assigns compare and contrast papers to test your comprehension of two subjects, as well as to see how well you understand authors, historical periods, or other concepts discussed in class.
Planning and writing these essays can be intimidating at first. In this guide, though, you’ll find helpful tips, from the first brainstorming session all the way to wrapping up the conclusion.
Published August 19, 2020.
By James Ardis. James is a writer who earned his MFA in Poetry from the University of Mississippi. He’s also taught English as a Second Language in South Korea, Thailand, and to refugees living in America.
Common Writing Assignments, Apps & Tests
- Analytical Essay
- AP synthesis Essay
- Argumentative Essay
- Book Report
- Compare and Contrast Essay
- Cause and Effect Essay
- College Admissions Essay
- Critical Analysis Essay
- Definition Essay
- Descriptive Essay
- Dissertation
- Explanatory Essay
- Expository Essay
- Informative Essay
- Narrative Essay
- Opinion Essay
- Personal Essay
- Persuasive Essay
- Reflective Essay
- Research Paper
- Rhetorical Analysis
- Scholarship Essay
- Short Essay
- Thesis Paper

What’s included with a Chegg Writing subscription
- Unlimited number of paper scans
- Plagiarism detection: Check against billions of sources
- Expert proofreading for papers on any subject
- Grammar scans for 200+ types of common errors
- Automatically create & save citations in 7,000+ styles
- Cancel subscription anytime, no obligation
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
Last Updated: May 12, 2023 Approved
This article was co-authored by Megan Morgan, PhD . Megan Morgan is a Graduate Program Academic Advisor in the School of Public & International Affairs at the University of Georgia. She earned her PhD in English from the University of Georgia in 2015. wikiHow marks an article as reader-approved once it receives enough positive feedback. This article has 29 testimonials from our readers, earning it our reader-approved status. This article has been viewed 3,105,294 times.
The purpose of a compare and contrast essay is to analyze the differences and/or the similarities of two distinct subjects. A good compare/contrast essay doesn’t only point out how the subjects are similar or different (or even both!). It uses those points to make a meaningful argument about the subjects. While it can be a little intimidating to approach this type of essay at first, with a little work and practice, you can write a great compare-and-contrast essay!
Formulating Your Argument

- You could pick two subjects that are in the same “category” but have differences that are significant in some way. For example, you could choose “homemade pizza vs. frozen grocery store pizza.”
- You could pick two subjects that don’t appear to have anything in common but that have a surprising similarity. For example, you could choose to compare bats and whales. (One is tiny and flies, and the other is huge and swims, but they both use sonar to hunt.)
- You could pick two subjects that might appear to be the same but are actually different. For example, you could choose "The Hunger Games movie vs. the book."

- For example, ask yourself: What can we learn by thinking about “The Hunger Games” and “Battle Royale” together that we would miss out on if we thought about them separately?
- It can be helpful to consider the “So what?” question when deciding whether your subjects have meaningful comparisons and contrasts to be made. If you say “The Hunger Games and Battle Royale are both similar and different,” and your friend asked you “So what?” what would your answer be? In other words, why bother putting these two things together?

- A “Venn diagram” can often be helpful when brainstorming. This set of overlapping circles can help you visualize where your subjects are similar and where they differ. In the outer edges of the circle, you write what is different; in the overlapping middle area, you write what’s similar. [2] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
- You can also just draw out a list of all of the qualities or characteristics of each subject. Once you’ve done that, start looking through the list for traits that both subjects share. Major points of difference are also good to note.

- For example, if you are comparing and contrasting cats and dogs, you might notice that both are common household pets, fairly easy to adopt, and don’t usually have many special care needs. These are points of comparison (ways they are similar).
- You might also note that cats are usually more independent than dogs, that dogs may not provoke allergies as much as cats do, and that cats don’t get as big as many dogs do. These are points of contrast (ways they are different).
- These points of contrast can often be good places to start thinking about your thesis, or argument. Do these differences make one animal a superior type of pet? Or a better pet choice for a specific living situation (e.g., an apartment, a farm, etc.)?

- Show readers why one subject is more desirable than the other. Example: "Cats are better pets than dogs because they require less maintenance, are more independent, and are more adaptable."
- Help readers make a meaningful comparison between two subjects. Example: "New York City and San Francisco are both great cities for young professionals, but they differ in terms of their job opportunities, social environment, and living conditions."
- Show readers how two subjects are similar and different. Example: "While both The Catcher in the Rye and To Kill a Mockingbird explore the themes of loss of innocence and the deep bond between siblings, To Kill a Mockingbird is more concerned with racism while The Catcher in the Rye focuses on the prejudices of class."
- In middle school and high school, the standard format for essays is often the “5-paragraph form,” with an introduction, 3 body paragraphs, and a conclusion. If your teacher recommends this form, go for it. However, you should be aware that especially in college, teachers and professors tend to want students to break out of this limited mode. Don’t get so locked into having “three main points” that you forget to fully explore your topic.
Organizing Your Essay

- Subject by subject. This organization deals with all of the points about Topic A, then all of the points of Topic B. For example, you could discuss all your points about frozen pizza (in as many paragraphs as necessary), then all your points about homemade pizza. The strength of this form is that you don’t jump back and forth as much between topics, which can help your essay read more smoothly. It can also be helpful if you are using one subject as a “lens” through which to examine the other. The major disadvantage is that the comparisons and contrasts don’t really become evident until much further into the essay, and it can end up reading like a list of “points” rather than a cohesive essay. [4] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source
- Point by point. This type of organization switches back and forth between points. For example, you could first discuss the prices of frozen pizza vs. homemade pizza, then the quality of ingredients, then the convenience factor. The advantage of this form is that it’s very clear what you’re comparing and contrasting. The disadvantage is that you do switch back and forth between topics, so you need to make sure that you use transitions and signposts to lead your reader through your argument.
- Compare then contrast. This organization presents all the comparisons first, then all the contrasts. It’s a pretty common way of organizing an essay, and it can be helpful if you really want to emphasize how your subjects are different. Putting the contrasts last places the emphasis on them. However, it can be more difficult for your readers to immediately see why these two subjects are being contrasted if all the similarities are first.

- Introduction. This paragraph comes first and presents the basic information about the subjects to be compared and contrasted. It should present your thesis and the direction of your essay (i.e., what you will discuss and why your readers should care).
- Body Paragraphs. These are the meat of your essay, where you provide the details and evidence that support your claims. Each different section or body paragraph should tackle a different division of proof. It should provide and analyze evidence in order to connect those proofs to your thesis and support your thesis. Many middle-school and high-school essays may only require three body paragraphs, but use as many as is necessary to fully convey your argument.
- Acknowledgement of Competitive Arguments/Concession. This paragraph acknowledges that other counter-arguments exist, but discusses how those arguments are flawed or do not apply.
- Conclusion. This paragraph summarizes the evidence presented. It will restate the thesis, but usually in a way that offers more information or sophistication than the introduction could. Remember: your audience now has all the information you gave them about why your argument is solid. They don’t need you to just reword your original thesis. Take it to the next level!

- Introduction: state your intent to discuss the differences between camping in the woods or on the beach.
- Body Paragraph 1 (Woods): Climate/Weather
- Body Paragraph 2 (Woods): Types of Activities and Facilities
- Body Paragraph 3 (Beach): Climate/Weather
- Body Paragraph 4 (Beach): Types of Activities and Facilities

- Introduction

- Body Paragraph 1: Similarity between woods and beaches (both are places with a wide variety of things to do)
- Body Paragraph 2: First difference between woods and beaches (they have different climates)
- Body Paragraph 3: Second difference between woods and beaches (there are more easily accessible woods than beaches in most parts of the country)
- Body Paragraph 4: Emphasis on the superiority of the woods to the beach

- Topic sentence: This sentence introduces the main idea and subject of the paragraph. It can also provide a transition from the ideas in the previous paragraph.
- Body: These sentences provide concrete evidence that support the topic sentence and main idea.
- Conclusion: this sentence wraps up the ideas in the paragraph. It may also provide a link to the next paragraph’s ideas.
Putting It All Together

- If you are having trouble finding evidence to support your argument, go back to your original texts and try the brainstorming process again. It could be that your argument is evolving past where it started, which is good! You just need to go back and look for further evidence.

- For example, in a body paragraph about the quality of ingredients in frozen vs. homemade pizza, you could close with an assertion like this: “Because you actively control the quality of the ingredients in pizza you make at home, it can be healthier for you than frozen pizza. It can also let you express your imagination. Pineapple and peanut butter pizza? Go for it! Pickles and parmesan? Do it! Using your own ingredients lets you have fun with your food.” This type of comment helps your reader understand why the ability to choose your own ingredients makes homemade pizza better.

- Reading your essay aloud can also help you find problem spots. Often, when you’re writing you get so used to what you meant to say that you don’t read what you actually said.

- Avoid bias. Don't use overly negative or defamatory language to show why a subject is unfavorable; use solid evidence to prove your points instead.
- Avoid first-person pronouns unless told otherwise. In some cases, your teacher may encourage you to use “I” and “you” in your essay. However, if the assignment or your teacher doesn’t mention it, stick with third-person instead, like “one may see” or “people may enjoy.” This is common practice for formal academic essays.
- Proofread! Spelling and punctuation errors happen to everyone, but not catching them can make you seem lazy. Go over your essay carefully, and ask a friend to help if you’re not confident in your own proofreading skills.
Sample Body Paragraphs

- "When one is deciding whether to go to the beach or the woods, the type of activities that each location offers are an important point to consider. At the beach, one can enjoy the water by swimming, surfing, or even building a sandcastle with a moat that will fill with water. When one is in the woods, one may be able to go fishing or swimming in a nearby lake, or one may not be near water at all. At the beach, one can keep one's kids entertained by burying them in sand or kicking around a soccer ball; if one is in the woods, one can entertain one's kids by showing them different plans or animals. Both the beach and the woods offer a variety of activities for adults and kids alike."

- "The beach has a wonderful climate, many activities, and great facilities for any visitor's everyday use. If a person goes to the beach during the right day or time of year, he or she can enjoy warm, yet refreshing water, a cool breeze, and a relatively hot climate. At the beach, one can go swimming, sunbathe, or build sandcastles. There are also great facilities at the beach, such as a changing room, umbrellas, and conveniently-located restaurants and changing facilities. The climate, activities, and facilities are important points to consider when deciding between the beach and the woods."
Sample Essay Outline

Community Q&A
- Collect your sources. Mark page numbers in books, authors, titles, dates, or other applicable information. This will help you cite your sources later on in the writing process. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 2
- Don't rush through your writing. If you have a deadline, start early. If you rush, the writing won't not be as good as it could be. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- Use reputable sources. While Wikipedia may be an easy way to start off, try to go to more specific websites afterwards. Many schools refuse to accept Wikipedia as a valid source of information, and prefer sources with more expertise and credibility. Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- If you have external sources, make sure you always cite them. Otherwise, you may be guilty of plagiarism. Thanks Helpful 3 Not Helpful 0
You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://writingcenter.unc.edu/handouts/comparing-and-contrasting/
- ↑ http://www.readwritethink.org/files/resources/interactives/compcontrast/
About This Article

To write a compare and contrast essay, try organizing your essay so you're comparing and contrasting one aspect of your subjects in each paragraph. Or, if you don't want to jump back and forth between subjects, structure your essay so the first half is about one subject and the second half is about the other. You could also write your essay so the first few paragraphs introduce all of the comparisons and the last few paragraphs introduce all of the contrasts, which can help emphasize your subjects' differences and similarities. To learn how to choose subjects to compare and come up with a thesis statement, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Huma Bukhari
Feb 16, 2019
Did this article help you?

Alain Vilfort
Mar 2, 2017
Aida Mirzaie
Aug 19, 2018
Michaela Mislerov
Apr 2, 2017
Subhashini Gunasekaran
Jul 31, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter
Search form
How to write a compare and contrast essay, by luisa brenton.
As a student, you’ve got to write a lot of different essays and writing assignments, which all have different requirements and expectations. To get the best grade possible, it is important that you understand these differences and make use of them as best you can. In this way, you don’t spend time barking up the wrong tree.
Now, it would be great if we could deal with each and every essay expectations. That would make for a rather unwieldy blog post. So, instead, here we’re going to look at one of the most popular forms, which is the compare and contrast essay.
Recognizing the compare and contrast essay
Often they’re not actually that hard to spot. Some will even have the word ‘compare’ and ‘contrast’ in the title. For example, you might have ‘compare two romantic poets and explore the differences between them’ or ‘contrast the first and the Second World War and the political reasons for them’. Other words that you might see are such words as ‘differences’, ‘similarities’ or other words like that.
But it doesn’t always work out that easily. Sometimes you’re going to find questions that are far more subtle. For example, ‘take a major literary theme and explore how Virginia Wolfe and F Scott Fitzgerald dealt with them’ or ‘How does liberty evolve from the 15 th to the 16 th century?’
Yet, the idea though they might not use the words ‘compare’ and ‘contrast’ you can still find it between the lines.
Representing differences and similarities visually
When you’ve been asked to discuss the similarities or differences between two things (or three) then the best thing you can do is draw a Venn diagram. You know the one I’m talking about – where you draw as many circles as there are concepts (e.g. first world war and second world war) where they each overlap all the other circles?
Then you write the differences in the areas where the circles don’t overlap and the similarities in the areas where they do. In this way, you’ll have an easy time of knowing what the differences and similarities are.
Of course, don’t get carried away. Remember that you’re writing for a specific class, which means that you’re supposed to write about areas that fit within the structure thereof.
One trick that might work if you’re struggling to know what’s relevant is to include another circle in your diagram so that you can write those things that fall within the scope of the class inside of that circle and those that don’t outside of it.
Note that this strategy works a lot better if you’re only asked to compare two things, as when you’re asked to compare more it can get very confusing very quickly as there are just too many circles.
Decide what to write about
The next thing that you’ll need to decide on is what you’re going to include in your essay. The first things to focus on is what is absolutely essential to the argument you’re going to make. These points will need to be included no matter what.
If that alone does not fill up your essay, however, then it’s time to pull out a point system. Give things a score from one to five (or ten, if you’ve got a lot of topics and need the extra differentiation).
Things to base your score on:
- Is it relevant to the class?
- Is it interesting and informative?
- Does it fit into the argument that you’re going to make or is it a tangent?
- Is it a topic that the teacher or professor seems particularly interested in?
- How obvious is it? (The more obvious, the less the need to include it)
Time to formulate your structure
The first thing that you want to do at this point is formulated your thesis. You probably already had a central argument outline above (otherwise you would have struggled to complete the last section) but now it’s time to put it down in words.
Don’t skip this part! Often you can realize where you’re making errors in your reasoning simply by writing down what you’re trying to argue. Also, always answer the most important question of all about your thesis and that is ‘why should I care about this particular question? Why is it relevant?’ That question will need to be answered somewhere in your essay.
That done, it’s time to create a structure. Return to your Venn diagram and take the pieces that you’ve ranked highest (as well as those that you decided are central to the question and your argument) and put them in order.
Make sure you start out with a whopper of an argument – something that’s engaging and interesting so that you draw in the reader. Take your second strongest argument and put it right at the end (this is important due to the peak and end effect, which states that we remember the end of things better than what comes in the middle).
Start writing
Now you’ve got everything worked out, all you’ve got to do is fill in the gaps. Now remember to use clear paragraphs and well-defined sentences. Also, remember to focus on good transitions, so that people can spot when you’re moving on from one area to another.
Now, if this is a struggle, don’t stress out too much. There are plenty of tools available to help you online – from other websites that deal with this kind of thing in more detail, to services that can help you with the process (check out the best sites for writing help).
And remember, if you’re struggling at this point, that doesn’t mean you always will. Essay writing (actually all writing) is something that you get better at over time, particularly if you pay attention to what your professors and teachers are saying and not just the grades they give you.
So with those thoughts, you should be much better prepared to deal with the contrast and comparison essay. Let me know how it goes.
Luisa Brenton is an ex-marketer, present writer, and a future professor at the Chicago University. She has been working as an educational blogger for top websites.You can contact her on Twitter.
One comment on “How to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay”
Hi Luisa, I was searching for the tips to write an perfect essay for my college and found this. Thanks for the wonderful tips, will apply it and let you know the results.
Leave a comment
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Stanford Home
- Maps & Directions
- Search Stanford
- Emergency Info
- Terms of Use
- Non-Discrimination
- Accessibility
© Stanford University , Stanford , California 94305 .
Beef Up Critical Thinking and Writing Skills: Comparison Essays
Organizing the Compare-Contrast Essay
- Teaching Resources
- An Introduction to Teaching
- Tips & Strategies
- Policies & Discipline
- Community Involvement
- School Administration
- Technology in the Classroom
- Teaching Adult Learners
- Issues In Education
- Becoming A Teacher
- Assessments & Tests
- Elementary Education
- Secondary Education
- Special Education
- Homeschooling
- M.Ed., Curriculum and Instruction, University of Florida
- B.A., History, University of Florida
The compare/contrast essay is an excellent opportunity to help students develop their critical thinking and writing skills. A compare and contrast essay examines two or more subjects by comparing their similarities and contrasting their differences.
Compare and contrast is high on Bloom's Taxonomy of critical reasoning and is associated with a complexity level where students break down ideas into simpler parts in order to see how the parts relate. For example, in order to break down ideas for comparison or to contrast in an essay, students may need to categorize, classify, dissect, differentiate, distinguish, list, and simplify.
Preparing to Write the Essay
First, students need to select pick comparable objects, people, or ideas and list their individual characteristics. A graphic organizer, like a Venn Diagram or top hat chart, is helpful in preparing to write the essay:
- What is the most interesting topic for comparison? Is the evidence available?
- What is the most interesting topic to contrast? Is the evidence available?
- Which characteristics highlight the most significant similarities?
- Which characteristics highlight the most significant differences?
- Which characteristics will lead to a meaningful analysis and an interesting paper?
A link to 101 compare and contrast essay topics for students provides opportunities for students to practice the similarities and differences such as
- Fiction vs. Nonfiction
- Renting a home vs. Owning a home
- General Robert E. Lee vs General Ulysses S. Grant
Writing the Block Format Essay: A, B, C points vs A, B, C points
The block method for writing a compare and contrast essay can be illustrated using points A, B, and C to signify individual characteristics or critical attributes.
A. history B. personalities C. commercialization
This block format allows the students to compare and contrast subjects, for example, dogs vs. cats, using these same characteristics one at a time.
The student should write the introductory paragraph to signal a compare and contrast essay in order to identify the two subjects and explain that they are very similar, very different or have many important (or interesting) similarities and differences. The thesis statement must include the two topics that will be compared and contrasted.
The body paragraph(s) after the introduction describe characteristic(s) of the first subject. Students should provide the evidence and examples that prove the similarities and/or differences exist, and not mention the second subject. Each point could be a body paragraph. For example,
A. Dog history. B. Dog personalities C. Dog commercialization.
The body paragraphs dedicated to the second subject should be organized in the same method as the first body paragraphs, for example:
A. Cat history. B. Cat personalities. C. Cat commercialization.
The benefit of this format is that it allows the writer to concentrate on one characteristic at a time. The drawback of this format is that there may be some imbalance in treating the subjects to the same rigor of comparing or contrasting.
The conclusion is in the final paragraph, the student should provide a general summary of the most important similarities and differences. The student could end with a personal statement, a prediction, or another snappy clincher.
Point by Point Format: AA, BB, CC
Just as in the block paragraph essay format, students should begin the point by point format by catching the reader's interest. This might be a reason people find the topic interesting or important, or it might be a statement about something the two subjects have in common. The thesis statement for this format must also include the two topics that will be compared and contrasted.
In the point by point format, the students can compare and/or contrast the subjects using the same characteristics within each body paragraph. Here the characteristics labeled A, B, and C are used to compare dogs vs. cats together, paragraph by paragraph.
A. Dog history A Cat history
B. Dog personalities B. Cat personalities
C. Dog commercialization C. Cat commercialization
This format does help students to concentrate on the characteristic(s) which may be may result in a more equitable comparison or contrast of the subjects within each body paragraph(s).
Transitions to Use
Regardless of the format of the essay, block or point-by-point, the student must use transition words or phrases to compare or contrast one subject to another. This will help the essay sound connected and not sound disjointed.
Transitions in the essay for comparison can include:
- in the same way or by the same token
- in like manner or likewise
- in similar fashion
Transitions for contrasts can include:
- nevertheless or nonetheless
- however or though
- otherwise or on the contrary
- in contrast
- notwithstanding
- on the other hand
- at the same time
In the final concluding paragraph, the student should give a general summary of the most important similarities and differences. The student could also end with a personal statement, a prediction, or another snappy clincher.
Part of the ELA Common Core State Standards
The text structure of compare and contrast is so critical to literacy that it is referenced in several of the English Language Arts Common Core State Standards in both reading and writing for K-12 grade levels. For example, the reading standards ask students to participate in comparing and contrasting as a text structure in the anchor standard R.9 :
"Analyze how two or more texts address similar themes or topics in order to build knowledge or to compare the approaches the authors take."
The reading standards are then referenced in the grade level writing standards, for example, as in W7.9
"Apply grade 7 Reading standards to literature (e.g., 'Compare and contrast a fictional portrayal of a time, place, or character and a historical account of the same period as a means of understanding how authors of fiction use or alter history')."
Being able to identify and create compare and contrast text structures is one of the more important critical reasoning skills that students should develop, regardless of grade level.
- 100 Persuasive Essay Topics
- Organizing Compare-Contrast Paragraphs
- How to Teach the Compare and Contrast Essay
- How to Teach Topic Sentences Using Models
- 101 Compare and Contrast Essay Topics
- Write a Compare and Contrast Essay
- The Ultimate Guide to the 5-Paragraph Essay
- T.E.S.T. Season for Grades 7-12
- Compare-Contrast Prewriting Chart
- Topical Organization Essay
- How to Write and Format an MBA Essay
- Expository Essay Genre With Suggested Prompts
- 501 Topic Suggestions for Writing Essays and Speeches
- Writing About Literature: Ten Sample Topics for Comparison & Contrast Essays
- Comparison in Composition
- What Is Expository Writing?
- Essay Editor
How to Write About Yourself: Basic Tips & Examples

Writing about yourself isn't always easy, but it is definitely an important skill to have. You might need to do this for a school application, a job, or just to understand yourself better. When you think about how to start an essay about yourself, it's good to consider what makes you special. What has happened in your life that's important to you? What do you care about? These questions can help you find the main parts of your story to share.
Why Writing About Yourself Matters
Writing about who you are is more than just something you do for yourself. It's a skill that many people think is important. When you can explain what makes you unique, you might come up with new ideas that can help in different areas of life.
When you're looking for a job, hiring people often want to know how well you can talk about yourself. Schools also use personal essays to learn more about students than just their grades. The National Association for College Admission Counseling (NACAC) found that 56% of schools think essays are important when deciding which students to accept.
Also, writing about yourself can help you grow as a person. Some psychologists use this kind of writing to help people understand themselves better and feel less stressed. When you write down your thoughts and experiences, you can look at them more closely and learn from them.
How to Start and Structure an Essay About Yourself
When thinking about how to start an essay about yourself, it's good to have a plan for organizing your ideas. Usually, an essay about yourself should have an introduction, body paragraphs, and a suitable conclusion.
- Introduction: Start with something interesting to get the reader's attention. You could ask a question that makes people think, share a surprising fact about yourself, or tell a short story that shows what you're like.
- Body paragraphs: Talk about different things about you, what you've done, or what you want to do. Each paragraph should focus on one main idea and give examples from your life.
- Conclusion: Sum up the main points you wrote about and leave the reader with something to remember. You could talk about what you want to do in the future or explain how your experiences have made you who you are.
Remember, the most important thing when writing about yourself is to be truthful and real. Your essay should sound like you wrote it, not someone else.
Helpful Tips for Writing About Yourself
Here are some good ideas to make your writing about yourself more real and interesting.
- Be yourself: It's most important to tell your story honestly.
- Use clear examples: Instead of just saying, "I work hard," talk about a time when you did work hard.
- Show how you've changed: Talk about how things you've done have helped you grow.
- Be selective: Choose things to write about yourself that fit who will read it and why you're writing.
- Keep things even: It's good to talk about what you're good at and also mention things you're trying to improve.
- Use active voice: This makes your writing more interesting to read.
- Check your work: Mistakes can make people ignore what you're saying.
How to write a paragraph about yourself? Here's an idea: focus on one main thing in each paragraph. For example:
"I started caring about nature after a school trip to a big forest. Seeing trees being cut down made me feel sad. When I got home, I started a program at school to recycle more. We made 30% less trash in the first year. This taught me that one person can help with big problems."
This paragraph discusses something that happened, what the person did about it, and what they learned. It shows what's important to them and what they've done.
Another Way to Present Your Story: Writing a Letter About Yourself
Writing about yourself in a letter can be a nice way to do it. When you're learning how to write a paragraph about yourself like this, think about this example:
Dear Me in the Future, I'm 22 now and thinking about how I became who I am. I grew up in a small town and never thought I'd care so much about how cities are built. But that changed when I helped fix up our town park. I learned how to make things good for people and nature simultaneously. Now I'm studying this in college. I've learned that I can make things better by working hard and not giving up. I hope in the future, I'll be using what I've learned to make cities better places to live. Future me, I hope you're happy with what we've done so far.
This paragraph shows how to write about yourself in a letter. It discusses the past, what's happening now, and hopes for the future. It's clear and thoughtful and shows what kind of person the writer is.
Wrapping Up
Putting your story on paper can be hard, but learning how to do it is good. The tips we discussed can help you write about yourself in a way that really shows who you are. Remember, being real is the most important thing – your experiences and thoughts make your story interesting.
Need a hand with your writing? Aithor might be just what you're looking for. This clever AI tool can whip up essays, academic papers, and creative pieces in no time. It keeps your original ideas intact while polishing your work to shine.
Related articles
Classification essay guide.
A classification essay is a powerful tool in academic writing, enabling writers to break down broad topics into organized categories for better understanding. This guide will show you how to write a classification essay, from designing a perfect outline to selecting compelling topics. Continue reading to learn how to create a clear, insightful, and engaging classification essay. What is a Classification Essay? A Brief Overview A classification essay is a type of academic writing that involves ...
A Guide to Writing a Great Short Essay
As a student, you're no stranger to the countless writing assignments your teachers toss your way. When you see that your next assignment is a short essay, you might think, "Oh, this will be easy!" I mean, it's only a few hundred words, right? How hard could it be? But here's the thing: writing a short essay can sometimes be even harder than writing a longer paper. So, let's work together and figure out how to make your short essays really stand out! The Basics of a Short Essay Format A short ...
Full Guide to Writing an Analytical Essay
In academic writing, an analytical essay is considered one of the most difficult papers. Not only does it require an extensive understanding of the topic, but also a high level of critical thinking skills. In this article, we’ll break down what analytical essays are, their structure, and how to write an analytical essay for the first time. What is an analytical essay? Analytical writing focuses on demonstrating how exactly an author arrived at a given conclusion. It showcases the entire thoug ...
Writing a Compare and Contrast Essay: A Complete Guide
Compare and contrast essay is an academic text that encourages authors to take a look at the differences between two or more subjects. Read this article to find out how to write a comparative essay for your assignment. What is a compare and contrast essay? As the name suggests, compare and contrast papers aim to provide two main perspectives on separate subjects by finding their similarities and dissecting their differences. Oftentimes, the purpose of compare and contrast essays is to presen ...
How to Write a Good Conclusion For a Lab Report
Writing a good conclusion for your science lab report can be the difference between a good grade and a great one. It's your last chance to show you understand the experiment and why it matters. This article will help you learn how to write a lab conclusion that sums up your work and shows your teacher that you understood what you did. What Should Be in Your Lab Report Conclusion? A good lab report conclusion wraps up your lab work in a neat package. When you're thinking about how to write a c ...
Rhetorical Analysis: A Comprehensive Guide
A rhetorical analysis essay is a part of the AP English Language and Composition exam. Due to its unorthodox purpose, rhetorical analysis can be hard to master at first. This article will help you understand what a rhetorical analysis essay is, learn about main rhetorical analysis strategies, and find out how to write a rhetorical analysis. What is a rhetorical analysis? As you can probably guess, a rhetorical analysis is a type of analytical essay. Alongside a synthesis essay and argument es ...
How to Write a Business Report With Example
One of the most effective ways to convey essential information is through a business report. This article will guide you through the purpose of a business report, provide valuable writing tips, outline how to format your business report correctly and offer an example for better understanding. What is the Purpose of a Business Report? A business report serves as a critical tool for decision-making within an organization. Its primary purpose is to analyze a particular situation or issue, evalua ...
Argumentative Essay: A Comprehensive Guide to Academic Writing
An argumentative essay is one of the most common pieces of academic writing. It tests your ability to analyze a topic and use solid arguments to defend your position. In this article, you will learn how to write an argumentative essay and find argument essay examples. What is an argumentative essay? In academic writing, an argumentative essay is a paper where a writer provides arguments for and against a certain topic. The purpose of an argumentative essay is to persuade the audience to accep ...

- OUR CENTERS Bangalore Delhi Lucknow Mysuru --> Srinagar Dharwad Hyderabad
Call us @ 08069405205

Search Here

- An Introduction to the CSE Exam
- Personality Test
- Annual Calendar by UPSC-2024
- Common Myths about the Exam
- About Insights IAS
- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director's Desk
- Meet Our Team
- Our Branches
- Careers at Insights IAS
- Daily Current Affairs+PIB Summary
- Insights into Editorials
- Insta Revision Modules for Prelims
- Current Affairs Quiz
- Static Quiz
- Current Affairs RTM
- Insta-DART(CSAT)
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Prelims 2024
- Secure (Mains Answer writing)
- Secure Synopsis
- Ethics Case Studies
- Insta Ethics
- Weekly Essay Challenge
- Insta Revision Modules-Mains
- Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains
- Secure (Archive)
- Anthropology
- Law Optional
- Kannada Literature
- Public Administration
- English Literature
- Medical Science
- Mathematics
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Monthly Magazine: CURRENT AFFAIRS 30
- Content for Mains Enrichment (CME)
- InstaMaps: Important Places in News
- Weekly CA Magazine
- The PRIME Magazine
- Insta Revision Modules-Prelims
- Insta-DART(CSAT) Quiz
- Insta 75 days Revision Tests for Prelims 2022
- Insights SECURE(Mains Answer Writing)
- Interview Transcripts
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Prelims
- Answer Keys for Prelims PYQs
- Solve Prelims PYQs
- Previous Years' Question Papers-Mains
- UPSC CSE Syllabus
- Toppers from Insights IAS
- Testimonials
- Felicitation
- UPSC Results
- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Ancient Indian History
- Medieval Indian History
- Modern Indian History
- World History
- World Geography
- Indian Geography
- Indian Society
- Social Justice
- International Relations
- Agriculture
- Environment & Ecology
- Disaster Management
- Science & Technology
- Security Issues
- Ethics, Integrity and Aptitude

- Indian Heritage & Culture
- Enivornment & Ecology

Compare and contrast the major features of the constitutions of India and Britain.
Q4. Compare and contrast the major features of the constitutions of India and Britain. (150 words)

- Our Mission, Vision & Values
- Director’s Desk
- Commerce & Accountancy
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Prelims
- Previous Years’ Question Papers-Mains
- Environment & Ecology
- Science & Technology
Plagiarism in Business: Why It Matters and How to Avoid
Table of contents
- 1.1 Types of plagiarism in business
- 2.1 Major causes of plagiarism in business
- 2.2 The outcome of plagiarism in business
- 3.1 Examples of business plagiarism
- 3.2 Cases of plagiarism in business
- 4 7 Proven tips to avoid plagiarism in business
- 5 Conclusion
This guide aims to take you through some typical cases of plagiarism in business and provide tips on how to avoid them.

Generally, plagiarism in business is a critical issue, as it undermines the integrity of the work and can lead to legal and reputational consequences. In the corporate world, originality and creativity are highly valued, and using someone else’s work without permission or proper attribution can harm the company’s reputation and credibility.
Sadly, several professionals are not overly concerned about the consequences of plagiarism in business. So, they keep repeating it in their operations regardless of the outcome. Unfortunately, the act can lead to potential legal action and loss of trust from customers and stakeholders.
So, businesses must have clear policies to detect and prevent plagiarism. They also need to educate their employees on the importance of ethical practices in the workplace.
What is plagiarism in business?
There are diverse definitions of plagiarism in business. But generally, it refers to using another person’s ideas, words, or work, attributing it to them, or obtaining their permission, before presenting it as your original effort.
This can occur in various contexts in business, such as social media plagiarism, copying content from a competitor’s website, presenting someone else’s research as one’s own, or using another company’s branding or logo without permission.
Plagiarism in business is unethical and can bring legal consequences. It can damage the reputation of a firm and cause the customers and stakeholders to lose their trust. As such, businesses must create policies to guide all employees and stakeholders to pursue ethical practices in their work.
Types of plagiarism in business
At the corporate level, plagiarism comes in different forms, including:
- Copying and pasting
This is one of the most common type, which nearly every individual in the business space understands. Copying and pasting are commonly referred to as direct plagiarism. It involves taking texts from another source, such as a website or a document, without altering the information and pasting it into a present task.
- Paraphrasing without citation
Restating another person’s ideas or words in a different way constitutes paraphrasing. This can still be considered plagiarism if there is no proper credit to the main source. For example, plagiarism in politics is also found, where candidates increase their chances of winning by finding plagiarized data in the form of a speech or political education.
- Accidental plagiarism
It occurs when someone unintentionally uses another person’s ideas, words, or work without proper attribution or citation. It can happen for various reasons, including a lack of knowledge about rules, careless note-taking, or failure to paraphrase or quote sources properly.
While it may not be intentional, it still constitutes plagiarism and can have serious consequences, such as loss of credibility, academic sanctions, and legal penalties in some cases.
- Image plagiarism
As the name suggests, when you use images in your work without obtaining permission or giving proper credit to the main source, it’s called plagiarism. This can include copying and pasting pictures from the Internet or utilizing copyrighted images without permission.
- Data plagiarism
It involves using data or statistics from another source without proper attribution. This kind of plagiarism is commonly seen in research, marketing, or other types of business analysis, where data is a vital instrument that supports claims or conclusions.
Plagiarism in the business sector
As stated earlier, it is a common aspect in the corporate world, with the majority of business owners imbibing the strategy.
But businesses that value originality, innovation, and ethical conduct tend to have a very low tolerance for plagiarism. Many companies have policies and procedures to prevent and detect, and employees are often required to sign agreements acknowledging that they understand and will comply with these policies.
Although this move can help to mitigate the act, the possibility of eradicating piracy completely from the system is farfetched.
Major causes of plagiarism in business
There are several reasons behind piracy in the corporate world. Usually, businesses adopt this approach due to poor time management. Here are some more causes of plagiarism in a business setting include:
- Time constraints
Professionals may be under pressure to meet deadlines and may resort to copying and pasting from existing sources instead of taking the time to create original content.
- Lack of knowledge
Some professionals may not understand what constitutes plagiarism and the importance of giving proper credit. They may unintentionally use content without attribution.
- Easy access to information
With the Internet and other technology, finding and copying content from various sources is easy. This can make it tempting to use someone else’s work without proper attribution.
- Competitive pressure
Professionals may sometimes feel burdened to produce content similar to their competitors’ work. This can lead to plagiarism as they try to replicate the same ideas and language to impress their readers or audiences.
Some professionals may simply be lazy and not want to put in the effort to create original content. They may copy and paste from existing sources rather than doing the work themselves.
The outcome of plagiarism in business
It comes with several consequences, some of which could ultimately damage your firm’s reputation. A few common outcomes of plagiarism in business may include:
- Damage to reputation
If a company plagiarizes, it can harm its status among customers, partners, and other stakeholders. This can lead to a loss of trust and credibility, harming the business’s ability to attract and retain customers and investors.
- Legal consequences
Plagiarism can lead to lawful action, including lawsuits and fines. This can be particularly damaging for small businesses, which may not have the resources to fight legal battles.
- Loss of income
Plagiarism can result in a loss of income for the plagiarized party, including the company itself. Aside from this fact, if a business plagiarizes a competitor’s product, it may be forced to pay damages or even cease production of the offending party.
- Loss of business opportunities
Plagiarism can also lead to losing chances, as customers and partners may choose to work with companies they perceive as more ethical and trustworthy.
Examples of plagiarism in business & some famous cases
There are many instances where individuals can apply it in the corporate world, including academic fraud, copying and pasting market materials and business plans, and so on.
Examples of business plagiarism
- Copying marketing materials
It can occur when a company copies advertising materials from another corporation, such as slogans, logos, taglines, and advertisements, without permission or attribution. This can lead to legal issues and negative publicity for the company.
- Academic fraud
In the business world, qualifications and certifications are highly valued. Plagiarism can occur when individuals falsely claim to have earned degrees or certifications or submit a job that doesn’t belong to them to obtain academic qualifications.
- Copying business plans
Plagiarism can also occur when a firm copies another company’s plan or proposal without permission or attribution. Again, this can bring about legal disputes and a loss of reputation for the company.
- Copying website content
Businesses can also be guilty of plagiarism when they copy content from other sites without proper attribution. This can result in search engine penalties, loss of credibility, and legal action.
Cases of plagiarism in business
Here are some famous case studies of plagiarism in the business world.
- Volkswagen’s emissions scandal
In 2015, it was revealed that Volkswagen had installed software in their diesel engines to cheat emissions tests. The application was detected during the car test, reducing emissions to meet regulatory standards. However, during normal driving conditions, the car emitted up to 40 times the allowed limit of nitrogen oxides.
This scandal was a clear case of plagiarism, as Volkswagen copied the technology from other car manufacturers without their permission.
- Apple’s copying of Xerox’s GUI
In the late 1970s, Xerox developed the first graphical user interface (GUI) for computers. This technology revolutionized how people interacted with computers, which inspired Apple to develop its own GUI for the Macintosh computer.
However, the outcome of Apple’s GUI appeared very similar to Xerox’s. The company believed that Apple made a copyright infringement of its GUI and sued Apple for the same. To settle the lawsuit Xerox filed against Apple, Apple granted the company access to its technology and shares.
- Microsoft’s Windows OS
Microsoft was also accused of copying code from other operating systems to create its version of the Windows OS. This case saw many legal battles, with many companies claiming that Microsoft had copied their technology without prior consent or attribution.
However, in the end, Microsoft settled the lawsuit by paying millions in damages and promising to stop using certain parts of the competing operating systems.
- Oracle vs Google
In 2010, Oracle sued Google for copying its Java code to create its Android operating system. The case went all the way to the Supreme Court, and in the end, Google was found not guilty of copyright infringement due to a ruling that declared application programming interfaces (APIs) are free from copyright law.
- Apple vs Samsung
In 2012, Apple sued Samsung for copying the design of its iPhone. The case continued for several years, with both companies claiming the other had copied their technology without permission. Ultimately, Apple was awarded more than $1 billion in damages from Samsung.
- Adobe vs Apple
In 2010, Adobe sued Apple for using its Flash technology without permission on the iPhone. The case eventually settled out of court, with Adobe receiving a licensing agreement and payment from Apple.
7 Proven tips to avoid plagiarism in business
Misinterpreting the idea of information is one of the quickest ways to indulge in piracy. However, you can use a few tips to avoid the temptation, as plagiarism can have serious consequences in the business world. Check them below:
- Whenever you use someone else’s ideas, data, or words, ensure you give them credit by citing and referencing the source appropriately. This applies to any content, including reports, presentations, and social media posts. In addition, include your ideas and analysis in your work, post, article. This will show that you deeply understand the topic and are not simply regurgitating information from other sources.
- Many effective tools are available online, and the Fixgerald plagiarism checker is one of them. You might be wondering how do plagiarism checkers work and if they are accurate. This tool is useful for identifying any instances of unintentional plagiarism in your work. Moreover, the accuracy of the results is impressive, as the tool identifies not only exact matches but also paraphrased content, which is essential when checking for plagiarism.
- Instead of copying and pasting text from other sources, paraphrase and summarize the information in your words. This will help you avoid accidental plagiarism. But always remember to give credit to the source of information.
- Make sure that you and your team members understand what plagiarism is and how to avoid it. This can include providing training and resources, such as style guides and checklists.
- Ultimately, the best way to avoid plagiarism in business is to foster a culture of integrity within your organization. This includes leading by example, encouraging open communication, and emphasizing the importance of ethical behavior.
Generally, plagiarism can have severe consequences for businesses, including damage to their reputation, legal action, and financial losses. This makes it crucial for professionals to understand the causes of piracy and take steps to ensure that they’re creating original content and giving proper credit where it’s due.
Readers also enjoyed

WHY WAIT? PLACE AN ORDER RIGHT NOW!
Just fill out the form, press the button, and have no worries!
We use cookies to give you the best experience possible. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy.
- Original article
- Open access
- Published: 08 July 2024
Can you spot the bot? Identifying AI-generated writing in college essays
- Tal Waltzer ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-4464-0336 1 ,
- Celeste Pilegard 1 &
- Gail D. Heyman 1
International Journal for Educational Integrity volume 20 , Article number: 11 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
536 Accesses
14 Altmetric
Metrics details
The release of ChatGPT in 2022 has generated extensive speculation about how Artificial Intelligence (AI) will impact the capacity of institutions for higher learning to achieve their central missions of promoting learning and certifying knowledge. Our main questions were whether people could identify AI-generated text and whether factors such as expertise or confidence would predict this ability. The present research provides empirical data to inform these speculations through an assessment given to a convenience sample of 140 college instructors and 145 college students (Study 1) as well as to ChatGPT itself (Study 2). The assessment was administered in an online survey and included an AI Identification Test which presented pairs of essays: In each case, one was written by a college student during an in-class exam and the other was generated by ChatGPT. Analyses with binomial tests and linear modeling suggested that the AI Identification Test was challenging: On average, instructors were able to guess which one was written by ChatGPT only 70% of the time (compared to 60% for students and 63% for ChatGPT). Neither experience with ChatGPT nor content expertise improved performance. Even people who were confident in their abilities struggled with the test. ChatGPT responses reflected much more confidence than human participants despite performing just as poorly. ChatGPT responses on an AI Attitude Assessment measure were similar to those reported by instructors and students except that ChatGPT rated several AI uses more favorably and indicated substantially more optimism about the positive educational benefits of AI. The findings highlight challenges for scholars and practitioners to consider as they navigate the integration of AI in education.
Introduction
Artificial intelligence (AI) is becoming ubiquitous in daily life. It has the potential to help solve many of society’s most complex and important problems, such as improving the detection, diagnosis, and treatment of chronic disease (Jiang et al. 2017 ), and informing public policy regarding climate change (Biswas 2023 ). However, AI also comes with potential pitfalls, such as threatening widely-held values like fairness and the right to privacy (Borenstein and Howard 2021 ; Weidinger et al. 2021 ; Zhuo et al. 2023 ). Although the specific ways in which the promises and pitfalls of AI will play out remain to be seen, it is clear that AI will change human societies in significant ways.
In late November of 2022, the generative large-language model ChatGPT (GPT-3, Brown et al. 2020 ) was released to the public. It soon became clear that talk about the consequences of AI was much more than futuristic speculation, and that we are now watching its consequences unfold before our eyes in real time. This is not only because the technology is now easily accessible to the general public, but also because of its advanced capacities, including a sophisticated ability to use context to generate appropriate responses to a wide range of prompts (Devlin et al. 2018 ; Gilson et al. 2022 ; Susnjak 2022 ; Vaswani et al. 2017 ).
How AI-generated content poses challenges for educational assessment
Since AI technologies like ChatGPT can flexibly produce human-like content, this raises the possibility that students may use the technology to complete their academic work for them, and that instructors may not be able to tell when their students turn in such AI-assisted work. This possibility has led some people to argue that we may be seeing the end of essay assignments in education (Mitchell 2022 ; Stokel-Walker 2022 ). Even some advocates of AI in the classroom have expressed concerns about its potential for undermining academic integrity (Cotton et al. 2023 ; Eke 2023 ). For example, as Kasneci et al. ( 2023 ) noted, the technology might “amplify laziness and counteract the learners’ interest to conduct their own investigations and come to their own conclusions or solutions” (p. 5). In response to these concerns, some educational institutions have already tried to ban ChatGPT (Johnson, 2023; Rosenzweig-Ziff 2023 ; Schulten, 2023).
These discussions are founded on extensive scholarship on academic integrity, which is fundamental to ethics in higher education (Bertram Gallant 2011 ; Bretag 2016 ; Rettinger and Bertram Gallant 2022 ). Challenges to academic integrity are not new: Students have long found and used tools to circumvent the work their teachers assign to them, and research on these behaviors spans nearly a century (Cizek 1999 ; Hartshorne and May 1928 ; McCabe et al. 2012 ). One recent example is contract cheating, where students pay other people to do their schoolwork for them, such as writing an essay (Bretag et al. 2019 ; Curtis and Clare 2017 ). While very few students (less than 5% by most estimates) tend to use contract cheating, AI has the potential to make cheating more accessible and affordable and it raises many new questions about the relationship between technology, academic integrity, and ethics in education (Cotton et al. 2023 ; Eke 2023 ; Susnjak 2022 ).
To date, there is very little empirical evidence to inform debates about the likely impact of ChatGPT on education or to inform what best practices might look like regarding use of the technology (Dwivedi et al. 2023 ; Lo 2023 ). The primary goal of the present research is to provide such evidence with reference to college-essay writing. One critical question is whether college students can pass off work generated by ChatGPT as their own. If so, large numbers of students may simply paste in ChatGPT responses to essays they are asked to write without the kind of active engagement with the material that leads to deep learning (Chi and Wylie 2014 ). This problem is likely to be exacerbated when students brag about doing this and earning high scores, which can encourage other students to follow suit. Indeed, this kind of bragging motivated the present work (when the last author learned about a college student bragging about using ChatGPT to write all of her final papers in her college classes and getting A’s on all of them).
In support of the possibility that instructors may have trouble identifying ChatGPT-generated test, some previous research suggests that ChatGPT is capable of successfully generating college- or graduate-school level writing. Yeadon et al. ( 2023 ) used AI to generate responses to essays based on a set of prompts used in a physics module that was in current use and asked graders to evaluate the responses. An example prompt they used was: “How did natural philosophers’ understanding of electricity change during the 18th and 19th centuries?” The researchers found that the AI-generated responses earned scores comparable to most students taking the module and concluded that current AI large-language models pose “a significant threat to the fidelity of short-form essays as an assessment method in Physics courses.” Terwiesch ( 2023 ) found that ChatGPT scored at a B or B- level on the final exam of Operations Management in an MBA program, and Katz et al. ( 2023 ) found that ChatGPT has the necessary legal knowledge, reading comprehension, and writing ability to pass the Bar exam in nearly all jurisdictions in the United States. This evidence makes it very clear that ChatGPT can generate well-written content in response to a wide range of prompts.
Distinguishing AI-generated from human-generated work
What is still not clear is how good instructors are at distinguishing between ChatGPT-generated writing and writing generated by students at the college level given that it is at least possible that ChatGPT-generated writing could be both high quality and be distinctly different than anything people generally write (e.g., because ChatGPT-generated writing has particular features). To our knowledge, this question has not yet been addressed, but a few prior studies have examined related questions. In the first such study, Gunser et al. ( 2021 ) used writing generated by a ChatGPT predecessor, GPT-2 (see Radford et al. 2019 ). They tested nine participants with a professional background in literature. These participants both generated content (i.e., wrote continuations after receiving the first few lines of unfamiliar poems or stories), and determined how other writing was generated. Gunser et al. ( 2021 ) found that misclassifications were relatively common. For example, in 18% of cases participants judged AI-assisted writing to be human-generated. This suggests that even AI technology that is substantially less advanced than ChatGPT is capable of generating writing that is hard to distinguish from human writing.
Köbis and Mossink ( 2021 ) also examined participants’ ability to distinguish between poetry written by GPT-2 and humans. Their participants were given pairs of poems. They were told that one poem in each pair was written by a human and the other was written by GPT-2, and they were asked to determine which was which. In one of their studies, the human-written poems were written by professional poets. The researchers generated multiple poems in response to prompts, and they found that when the comparison GPT-2 poems were ones they selected as the best among the set generated by the AI, participants could not distinguish between the GPT-2 and human writing. However, when researchers randomly selected poems generated by GPT-2, participants were better than chance at detecting which ones were generated by the AI.
In a third relevant study, Waltzer et al. ( 2023a ) tested high school teachers and students. All participants were presented with pairs of English essays, such as one on why literature matters. In each case one essay was written by a high school student and the other was generated by ChatGPT, and participants were asked which essay in each pair had been generated by ChatGPT. Waltzer et al. ( 2023a ) found that teachers only got it right 70% of the time, and that students’ performance was even worse (62%). They also found that well-written essays were harder to distinguish from those generated by ChatGPT than poorly written ones. However, it is unclear the extent to which these findings are specific to the high school context. It should also be noted that there were no clear right or wrong answers in the types of essays used in Waltzer et al. ( 2023a ), so the results may not generalize to essays that ask for factual information based on specific class content.
AI detection skills, attitudes, and perceptions
If college instructors find it challenging to distinguish between writing generated by ChatGPT and college students, it raises the question of what factors might be correlated with the ability to perform this discrimination. One possible correlate is experience with ChatGPT, which may allow people to recognize patterns in the writing style it generates, such as a tendency to formally summarize previous content. Content-relevant knowledge is another possible predictor. Individuals with such knowledge will presumably be better at spotting errors in answers, and it is plausible that instructors know that AI tools are likely to get content of introductory-level college courses correct and assume that essays that contain errors are written by students.
Another possible predictor is confidence about one’s ability to discriminate on the task or on particular items of the task (Erickson and Heit 2015 ; Fischer & Budesco, 2005 ; Wixted and Wells 2017 ). In other words, are AI discriminations made with a high degree of confidence more likely to be accurate than low-confidence discriminations? In some cases, confidence judgments are a good predictor of accuracy, such as on many perceptual decision tasks (e.g., detecting contrast between light and dark bars, Fleming et al. 2010 ). However, in other cases correlations between confidence and accuracy are small or non-existent, such as on some deductive reasoning tasks (e.g., Shynkaruk and Thompson 2006 ). Links to confidence can also depend on how confidence is measured: Gigerenzer et al. ( 1991 ) found overconfidence on individual items, but good calibration when participants were asked how many items they got right after seeing many items.
In addition to the importance of gathering empirical data on the extent to which instructors can distinguish ChatGPT from college student writing, it is important to examine how college instructors and students perceive AI in education given that such attitudes may affect behavior (Al Darayseh 2023 ; Chocarro et al. 2023 ; Joo et al. 2018 ; Tlili et al. 2023 ). For example, instructors may only try to develop precautions to prevent AI cheating if they view this as a significant concern. Similarly, students’ confusion about what counts as cheating can play an important role in their cheating decisions (Waltzer and Dahl 2023 ; Waltzer et al. 2023b ).
The present research
In the present research we developed an assessment that we gave to college instructors and students (Study 1) and ChatGPT itself (Study 2). The central feature of the assessment was an AI Identification Test , which included 6 pairs of essays. In each case (as was indicated in the instructions), one essay in each pair was generated by ChatGPT and the other was written by college students. The task was to determine which essay was written by the chatbot. The essay pairs were drawn from larger pools of essays of each type.
The student essays were written by students as part of a graded exam in a psychology class, and the ChatGPT essays were generated in response to the same essay prompts. Of interest was overall performance and to assess potential correlates of performance. Performance of college instructors was of particular interest because they are the ones typically responsible for grading, but performance of students and ChatGPT were also of interest for comparison. ChatGPT was also of interest given anecdotal evidence that college instructors are asking ChatGPT to tell them whether pieces of work were AI-generated. For example, the academic integrity office at one major university sent out an announcement asking instructors not to report students for cheating if their evidence was solely based on using ChatGPT to detect AI-generated writing (UCSD Academic Integrity Office, 2023 ).
We also administered an AI Attitude Assessment (Waltzer et al. 2023a ), which included questions about overall levels of optimism and pessimism about the use of AI in education, and the appropriateness of specific uses of AI in academic settings, such as a student submitting an edited version of a ChatGPT-generated essay for a writing assignment.
Study 1: College instructors and students
Participants were given an online assessment that included an AI Identification Test , an AI Attitude Assessment , and some demographic questions. The AI Identification Test was developed for the present research, as described below (see Materials and Procedure). The test involved presenting six pairs of essays, with the instructions to try to identify which one was written by ChatGPT in each case. Participants also rated their confidence before the task and after responding to each item, and reported how many they thought they got right at the end. The AI Attitude Assessment was drawn from Waltzer et al. ( 2023a ) to assess participants’ views of the use of AI in education.
Participants
For the testing phase of the project, we recruited 140 instructors who had taught or worked as a teaching assistant for classes at the college level (69 of them taught psychology and 63 taught other subjects such as philosophy, computer science, and history). We recruited instructors through personal connections and snowball sampling. Most of the instructors were women (59%), white (60%), and native English speakers (67%), and most of them taught at colleges in the United States (91%). We also recruited 145 undergraduate students ( M age = 20.90 years, 80% women, 52% Asian, 63% native English speakers) from a subject recruitment system in the psychology department at a large research university in the United States. All data collection took place between 3/15/2023 and 4/15/2023 and followed our pre-registration plan ( https://aspredicted.org/mk3a2.pdf ).
Materials and procedure
Developing the ai identification test.
To create the stimuli for the AI Identification Test, we first generated two prompts for the essays (Table 1 ). We chose these prompts in collaboration with an instructor to reflect real student assignments for a college psychology class.
Fifty undergraduate students hand-wrote both essays as part of a proctored exam in their psychology class on 1/30/2023. Research assistants transcribed the essays and removed essays from the pool that were not written in third-person or did not include the correct number of sentences. Three additional essays were excluded for being illegible, and another one was excluded for mentioning a specific location on campus. This led to 15 exclusions for the Phonemic Awareness prompt and 25 exclusions for the Studying Advice prompt. After applying these exclusions, we randomly selected 25 essays for each prompt to generate the 6 pairs given to each participant. To prepare the texts for use as stimuli, research assistants then used a word processor to correct obvious errors that could be corrected without major rewriting (e.g., punctuation, spelling, and capitalization).
All student essays were graded according to the class rubric on a scale from 0 to 10 by two individuals on the teaching team of the class: the course’s primary instructor and a graduate student teaching assistant. Grades were averaged together to create one combined grade for each essay (mean: 7.93, SD: 2.29, range: 2–10). Two of the authors also scored the student essays for writing quality on a scale from 0 to 100, including clarity, conciseness, and coherence (combined score mean: 82.83, SD : 7.53, range: 65–98). Materials for the study, including detailed scoring rubrics, are available at https://osf.io/2c54a/ .
The ChatGPT stimuli were prepared by entering the same prompts into ChatGPT ( https://chat.openai.com/ ) between 1/23/2023 and 1/25/2023, and re-generating the responses until there were 25 different essays for each prompt.
Testing Phase
In the participant testing phase, college instructors and students took the assessment, which lasted approximately 10 min. All participants began by indicating the name of their school and whether they were an instructor or a student, how familiar they were with ChatGPT (“Please rate how much experience you have with using ChatGPT”), and how confident they were that they would be able to distinguish between writing generated by ChatGPT and by college students. Then they were told they would get to see how well they score at the end, and they began the AI Identification Test.
The AI Identification Test consisted of six pairs of essays: three Phonemic Awareness pairs, and three Studying Advice pairs, in counterbalanced order. Each pair included one text generated by ChatGPT and one text generated by a college student, both drawn randomly from their respective pools of 25 possible essays. No essays were repeated for the same participant. Figure 1 illustrates what a text pair looked like in the survey.

Example pair of essays for the Phonemic Awareness prompt. Top: student essay. Bottom: ChatGPT essay
For each pair, participants selected the essay they thought was generated by ChatGPT and indicated how confident they were about their choice (slider from 0 = “not at all confident” to 100 = “extremely confident”). After all six pairs, participants estimated how well they did (“How many of the text pairs do you think you answered correctly?”).
After completing the AI Identification task, participants completed the AI Attitude Assessment concerning their views of ChatGPT in educational contexts (see Waltzer et al. 2023a ). On this assessment, participants first estimated what percent of college students in the United States would ask ChatGPT to write an essay for them and submit it. Next, they rated their concerns (“How concerned are you about ChatGPT having negative effects on education?”) and optimism (“How optimistic are you about ChatGPT having positive benefits for education?”) about the technology on a scale from 0 (“not at all”) to 100 (“extremely”). On the final part of the AI Attitude Assessment, they evaluated five different possible uses of ChatGPT in education (such as submitting an essay after asking ChatGPT to improve the vocabulary) on a scale from − 10 (“really bad”) to + 10 (“really good”).
Participants also rated the extent to which they already knew the subject matter (i.e., cognitive psychology and the science of learning), and were given optional open-ended text boxes to share any experiences from their classes or suggestions for instructors related to the use of ChatGPT, or to comment on any of the questions in the Attitude Assessment. Instructors were also asked whether they had ever taught a psychology class and to describe their teaching experience. At the end, all participants reported demographic information (e.g., age, gender). All prompts are available in the online supplementary materials ( https://osf.io/2c54a/ ).
Data Analysis
We descriptively summarized variables of interest (e.g., overall accuracy on the Identification Test). We used inferential tests to predict Identification Test accuracy from group (instructor or student), confidence, subject expertise, and familiarity with ChatGPT. We also predicted responses to the AI Attitude Assessment as a function of group (instructor or student). All data analysis was done using R Statistical Software (v4.3.2; R Core Team 2021 ).
Key hypotheses were tested using Welch’s two-sample t-tests for group comparisons, linear regression models with F-tests for other predictors of accuracy, and Generalized Linear Mixed Models (GLMMs, Hox 2010 ) with likelihood ratio tests for within-subjects trial-by-trial analyses. GLMMs used random intercepts for participants and predicted trial performance (correct or incorrect) using trial confidence and essay quality as fixed effects.
Overall performance on AI identification test
Instructors correctly identified which essay was written by the chatbot 70% of the time, which was above chance (chance: 50%, binomial test: p < .001, 95% CI: [66%, 73%]). Students also performed above chance, with an average score of 60% (binomial test: p < .001, 95% CI: [57%, 64%]). Instructors performed significantly better than students (Welch’s two-sample t -test: t [283] = 3.30, p = .001).
Familiarity With subject matter
Participants rated how much previous knowledge they had in the essay subject matter (i.e., cognitive psychology and the science of learning). Linear regression models with F- tests indicated that familiarity with the subject did not predict instructors’ or students’ accuracy, F s(1) < 0.49, p s > .486. Psychology instructors did not perform any better than non-psychology instructors, t (130) = 0.18, p = .860.
Familiarity with ChatGPT
Nearly all participants (94%) said they had heard of ChatGPT before taking the survey, and most instructors (62%) and about half of students (50%) said they had used ChatGPT before. For both groups, participants who used ChatGPT did not perform any better than those who never used it before, F s(1) < 0.77, p s > .383. Instructors’ and students’ experience with ChatGPT (from 0 = not at all experienced to 100 = extremely experienced) also did not predict their performance, F s(1) < 0.77, p s > .383.
Confidence and estimated score
Before they began the Identification Test, both instructors and students expressed low confidence in their abilities to identify the chatbot ( M = 34.60 on a scale from 0 = not at all confident to 100 = extremely confident). Their confidence was significantly below the midpoint of the scale (midpoint: 50), one-sample t -test: t (282) = 11.46, p < .001, 95% CI: [31.95, 37.24]. Confidence ratings that were done before the AI Identification test did not predict performance for either group, Pearson’s r s < .12, p s > .171.
Right after they completed the Identification Test, participants guessed how many text pairs they got right. Both instructors and students significantly underestimated their performance by about 15%, 95% CI: [11%, 18%], t (279) = -8.42, p < .001. Instructors’ estimated scores were positively correlated with their actual scores, Pearson’s r = .20, t (135) = 2.42, p = .017. Students’ estimated scores were not related to their actual scores, r = .03, p = .731.
Trial-by-trial performance on AI identification test
Participants’ confidence ratings on individual trials were counted as high if they fell above the midpoint (> 50 on a scale from 0 = not at all confident to 100 = extremely confident). For these within-subjects trial-by-trial analyses, we used Generalized Linear Mixed Models (GLMMs, Hox 2010 ) with random intercepts for participants and likelihood ratio tests (difference score reported as D ). Both instructors and students performed better on trials in which they expressed high confidence (instructors: 73%, students: 63%) compared to low confidence (instructors: 65%, students: 56%), D s(1) > 4.59, p s < .032.
Student essay quality
We used two measures to capture the quality of each student-written essay: its assigned grade from 0 to 10 based on the class rubric, and its writing quality score from 0 to 100. Assigned grade was weakly related to instructors’ accuracy, but not to students’ accuracy. The text pairs that instructors got right tended to include student essays that earned slightly lower grades ( M = 7.89, SD = 2.22) compared to those they got wrong ( M = 8.17, SD = 2.16), D (1) = 3.86, p = .050. There was no difference for students, D (1) = 2.84, p = .092. Writing quality score did not differ significantly between correct and incorrect trials for either group, D (1) = 2.12, p = .146.
AI attitude assessment
Concerns and hopes about chatgpt.
Both instructors and students expressed intermediate levels of concern and optimism. Specifically, on a scale from 0 (“not at all”) to 100 (“extremely”), participants expressed intermediate concern about ChatGPT having negative effects on education ( M instructors = 59.82, M students = 55.97) and intermediate optimism about it having positive benefits ( M instructors = 49.86, M students = 54.08). Attitudes did not differ between instructors and students, t s < 1.43, p s > .154. Participants estimated that just over half of college students (instructors: 57%, students: 54%) would use ChatGPT to write an essay for them and submit it. These estimates also did not differ by group, t (278) = 0.90, p = .370.
Evaluations of ChatGPT uses
Participants evaluated five different uses of ChatGPT in educational settings on a scale from − 10 (“really bad”) to + 10 (“really good”). Both instructors and students rated it very bad for someone to ask ChatGPT to write an essay for them and submit the direct output, but instructors rated it significantly more negatively (instructors: -8.95, students: -7.74), t (280) = 3.59, p < .001. Attitudes did not differ between groups for any of the other scenarios (Table 2 ), t s < 1.31, p s > .130.
Exploratory analysis of demographic factors
We also conducted exploratory analyses looking at ChatGPT use and attitudes among different demographic groups (gender, race, and native English speakers). We combined instructors and students because their responses to the Attitude Assessment did not differ. In these exploratory analyses, we found that participants who were not native English speakers were more likely to report using ChatGPT and to view it more positively. Specifically, 69% of non-native English speakers had used ChatGPT before, versus 48% of native English speakers, D (1) = 12.00, p < .001. Regardless of native language, the more experience someone had with ChatGPT, the more optimism they reported, F (1) = 18.71, p < .001, r = .37). Non-native speakers rated the scenario where a student writes an essay and asks ChatGPT to improve its vocabulary slightly positively (1.19) whereas native English speakers rated it slightly negatively (-1.43), F (1) = 11.00, p = .001. Asian participants expressed higher optimism ( M = 59.14) than non-Asian participants ( M = 47.29), F (1) = 10.05, p = .002. We found no other demographic differences.
Study 2: ChatGPT
Study 1 provided data on college instructors’ and students’ ability to recognize ChatGPT-generated writing and about their views of the technology. In Study 2, of primary interest was whether ChatGPT itself might perform better at identifying ChatGPT-generated writing. Indeed, the authors have heard discussions of this as a possible solution to recognize AI-generated writing. We addressed this question by repeatedly asking ChatGPT to act as a participant in the AI Identification Task. While doing so, we administered the rest of the assessment given to participants in Study 1. This included our AI Attitude Assessment, which allowed us to examine the extent to which ChatGPT produced attitude responses that were similar to those of the participants in Study 1.
Participants, materials, and procedures
There were no human participants for Study 2. We collected 40 survey responses from ChatGPT, each run in a separate session on the platform ( https://chat.openai.com/ ) between 5/4/2023 and 5/15/2023.
Two research assistants were trained on how to run the survey in the ChatGPT online interface. All prompts from the Study 1 survey were used, with minor modifications to suit the chat format. For example, slider questions were explained in the prompt, so instead of “How confident are you about this answer?” the prompt was “How confident are you about this answer from 0 (not at all confident) to 100 (extremely confident)?”. In pilot testing, we found that ChatGPT sometimes failed to answer the question (e.g., by not providing a number), so we prepared a second prompt for every question that the researcher used whenever the first prompt was not answered (e.g., “Please answer the above question with one number between 0 to 100.”). If ChatGPT still failed on the second prompt, the researcher marked it as a non-response and moved on to the next question in the survey.
Data analysis
Like Study 1, all analyses were done in R Statistical Software (R Core Team 2021 ). Key analyses first used linear regression models and F -tests to compare all three groups (instructors, students, ChatGPT). When these omnibus tests were significant, we followed up with post-hoc pairwise comparisons using Tukey’s method.
AI identification test
Overall accuracy.
ChatGPT generated correct responses on 63% of trials in the AI Identification Test, which was significantly above chance, binomial test p < .001, 95% CI: [57%, 69%]. Pairwise comparisons found that this performance by ChatGPT was not any different from that of instructors or students, t s(322) < 1.50, p s > .292.
Confidence and estimated performance
Unlike the human participants, ChatGPT produced responses with very high confidence before the task generally ( m = 71.38, median = 70) and during individual trials specifically ( m = 89.82, median = 95). General confidence ratings before the test were significantly higher from ChatGPT than from the humans (instructors: 34.35, students: 34.83), t s(320) > 9.47, p s < .001. But, as with the human participants, this confidence did not predict performance on the subsequent Identification task, F (1) = 0.94, p = .339. And like the human participants, ChatGPT’s reported confidence on individual trials did predict performance: ChatGPT produced higher confidence ratings on correct trials ( m = 91.38) than incorrect trials ( m = 87.33), D (1) = 8.74, p = .003.
ChatGPT also produced responses indicating high confidence after the task, typically estimating that it got all six text pairs right ( M = 91%, median = 100%). It overestimated performance by about 28%, and a paired t -test confirmed that ChatGPT’s estimated performance was significantly higher than its actual performance, t (36) = 9.66, p < .001. As inflated as it was, estimated performance still had a small positive correlation with actual performance, Pearson’s r = .35, t (35) = 2.21, p = .034.
Essay quality
The quality of the student essays as indexed by their grade and writing quality score did not significantly predict performance, D s < 1.97, p s > .161.
AI attitude Assessment
Concerns and hopes.
ChatGPT usually failed to answer the question, “How concerned are you about ChatGPT having negative effects on education?” from 0 (not at all concerned) to 100 (extremely concerned). Across the 40% of cases where ChatGPT successfully produced an answer, the average concern rating was 64.38, which did not differ significantly from instructors’ or students’ responses, F (2, 294) = 1.20, p = .304. ChatGPT produced answers much more often for the question, “How optimistic are you about ChatGPT having positive benefits for education?”, answering 88% of the time. The average optimism rating produced by ChatGPT was 73.24, which was significantly higher than that of instructors (49.86) and students (54.08), t s > 4.33, p s < .001. ChatGPT only answered 55% of the time for the question about how many students would use ChatGPT to write an essay for them and submit it, typically generating explanations about its inability to predict human behavior and the fact that it does not condone cheating when it did not give an estimate. When it did provide an estimate ( m = 10%), it was vastly lower than that of instructors (57%) and students (54%), t s > 7.84, p s < .001.
Evaluation of ChatGPT uses
ChatGPT produced ratings of the ChatGPT use scenarios that on average were rank-ordered the same as the human ratings, with direct copying rated the most negatively and generating practice problems rated the most positively (see Fig. 2 ).

Average ratings of ChatGPT uses, from − 10 = really bad to + 10 = really good. Human responses included for comparison (instructors in dark gray and students in light gray bars)
Compared to humans’ ratings, ratings produced by ChatGPT were significantly more positive in most scenarios, t s > 3.09, p s < .006, with two exceptions. There was no significant difference between groups in the “format” scenario (using ChatGPT to format an essay in another style such as APA), F (2,318) = 2.46, p = .087. And for the “direct” scenario, ChatGPT tended to rate direct copying more negatively than students ( t [319] = 4.08, p < .001) but not instructors (t[319] = 1.57, p = .261), perhaps because ratings from ChatGPT and instructors were already so close to the most negative possible rating.
In 1950, Alan Turing said he hoped that one day machines would be able to compete with people in all intellectual fields (Turing 1950 ; see Köbis and Mossink 2021 ). Today, by many measures, the large-language model, ChatGPT, appears to be getting close to achieving this end. In doing so, it is raising questions about the impact this AI and its successors will have on individuals and the institutions that shape the societies in which we live. One important set of questions revolves around its use in higher education, which is the focus of the present research.
Empirical contributions
Detecting ai-generated text.
Our central research question focused on whether instructors can identify ChatGPT-generated writing, since an inability to do so could threaten the ability of institutions of higher learning to promote learning and assess competence. To address this question, we developed an AI Identification Test in which the goal was to try to distinguish between psychology essays written by college students on exams versus essays generated by ChatGPT in response to the same prompts. We found that although college instructors performed substantially better than chance, they still found the assessment to be challenging, scoring an average of only 70%. This relatively poor performance suggests that college instructors have substantial difficulty detecting ChatGPT-generated writing. Interestingly, this performance by the college instructors was the same average performance as Waltzer et al. ( 2023a ) observed among high school instructors (70%) on a similar test involving English literature essays, suggesting the results are generalizable across the student populations and essay types. We also gave the assessment to college students (Study 1) and to ChatGPT (Study 2) for comparison. On average, students (60%) and ChatGPT (63%) performed even worse than instructors, although the difference only reached statistical significance when comparing students and instructors.
We found that instructors and students who went into the study believing they would be very good at distinguishing between essays written by college students versus essays generated by ChatGPT were in fact no better at doing so than participants who lacked such confidence. However, we did find that item-level confidence did predict performance: when participants rated their confidence after each specific pair (i.e., “How confident are you about this answer?”), they did perform significantly better on items they reported higher confidence on. These same patterns were observed when analyzing the confidence ratings from ChatGPT, though ChatGPT produced much higher confidence ratings than instructors or students, reporting overconfidence while instructors and students reported underconfidence.
Attitudes toward AI in education
Instructors and students both thought it was very bad for students to turn in an assignment generated by ChatGPT as their own, and these ratings were especially negative for instructors. Overall, instructors and students looked similar to one another in their evaluations of other uses of ChatGPT in education. For example, both rated submitting an edited version of a ChatGPT-generated essay in a class as bad, but less bad than submitting an unedited version. Interestingly, the rank orderings in evaluations of ChatGPT uses were the same when the responses were generated by ChatGPT as when they were generated by instructors or students. However, ChatGPT produced more favorable ratings of several uses compared to instructors and students (e.g., using the AI tool to enhance the vocabulary in an essay). Overall, both instructors and students reported being about as optimistic as they were concerned about AI in education. Interestingly, ChatGPT produced responses indicative of much more optimism than both human groups of participants.
Many instructors commented on the challenges ChatGPT poses for educators. One noted that “… ChatGPT makes it harder for us to rely on homework assignments to help students to learn. It will also likely be much harder to rely on grading to signal how likely it is for a student to be good at a skill or how creative they are.” Some suggested possible solutions such as coupling writing with oral exams. Others suggested that they would appreciate guidance. For example, one said, “I have told students not to use it, but I feel like I should not be like that. I think some of my reluctance to allow usage comes from not having good guidelines.”
And like the instructors, some students also suggested that they want guidance, such as knowing whether using ChatGPT to convert a document to MLA format would count as a violation of academic integrity. They also highlighted many of the same problems as instructors and noted beneficial ways students are finding to use it. One student noted that, “I think ChatGPT definitely has the potential to be abused in an educational setting, but I think at its core it can be a very useful tool for students. For example, I’ve heard of one student giving ChatGPT a rubric for an assignment and asking it to grade their own essay based on the rubric in order to improve their writing on their own.”
Theoretical contributions and practical implications
Our findings underscore the fact that AI chatbots have the potential to produce confident-sounding responses that are misleading (Chen et al. 2023 ; Goodwins 2022 ; Salvi et al. 2024 ). Interestingly, the underconfidence reported by instructors and students stands in contrast to some findings that people often expressed overconfidence in their abilities to detect AI (e.g., deepfake videos, Köbis et al. 2021 ). Although general confidence before the task did not predict performance, specific confidence on each item of the task did predict performance. Taken together, our findings are consistent with other work suggesting confidence effects are context-dependent and can differ depending on whether they are assessed at the item level or more generally (Gigerenzer et al. 1991 ).
The fact that college instructors have substantial difficulty differentiating between ChatGPT-generated writing and the writing of college students provides evidence that ChatGPT poses a significant threat to academic integrity. Ignoring this threat is also likely to undermine central aspects of the mission of higher education in ways that undermine the value of assessments and disincentivize the kinds of cognitive engagement that promote deep learning (Chi and Wylie 2014 ). We are skeptical of answers that point to the use of AI detection tools to address this issue given that they will always be imperfect and false accusations have potential to cause serious harm (Dalalah and Dalalah 2023 ; Fowler 2023 ; Svrluga, 2023 ). Rather, we think that the solution will have to involve developing and disseminating best practices regarding creating assessments and incentivizing cognitive engagement in ways that help students learn to use AI as problem-solving tools.
Limitations and future directions
Why instructors perform better than students at detecting AI-generated text is unclear. Although we did not find any effect of content-relevant expertise, it still may be the case that experience with evaluating student writing matters, and instructors presumably have more such experience. For example, one non-psychology instructor who got 100% of the pairs correct said, “Experience with grading lower division undergraduate papers indicates that students do not always fully answer the prompt, if the example text did not appear to meet all of the requirements of the prompt or did not provide sufficient information, I tended to assume an actual student wrote it.” To address this possibility, it will be important to compare adults who do have teaching experience with those who do not.
It is somewhat surprising that experience with ChatGPT did not affect the performance of instructors or students on the AI Identification Test. One contributing factor may be that people pick up on some false heuristics from reading the text it generates (see Jakesch et al. 2023 ). It is possible that giving people practice at distinguishing the different forms of writing with feedback could lead to better performance.
Why confidence was predictive of accuracy at the item level is still not clear. One possibility is that there are some specific and valid cues many people were using. One likely cue is grammar. We revised grammar errors in student essays that were picked up by a standard spell checker in which the corrections were obvious. However, we left ungrammatical writing that didn’t have obvious corrections (e.g., “That is being said, to be able to understand the concepts and materials being learned, and be able to produce comprehension.“). Many instructors noted that they used grammatical errors as cues that writing was generated by students. As one instructor remarked, “Undergraduates often have slight errors in grammar and tense or plurality agreement, and I have heard the chat bot works very well as an editor.” Similarly, another noted, “I looked for more complete, grammatical sentences. In my experience, Chat-GPT doesn’t use fragment sentences and is grammatically correct. Students are more likely to use incomplete sentences or have grammatical errors.” This raises methodological questions about what is the best comparison between AI and human writing. For example, it is unclear which grammatical mistakes should be corrected in student writing. Also of interest will be to examine the detectability of writing that is generated by AI and later edited by students, since many students will undoubtedly use AI in this way to complete their course assignments.
We also found that student-written essays that earned higher grades (based on the scoring rubric for their class exam) were harder for instructors to differentiate from ChatGPT writing. This does not appear to be a simple effect of writing quality given that a separate measure of writing quality that did not account for content accuracy was not predictive. According to the class instructor, the higher-scoring essays tended to include more specific details, and this might have been what made them less distinguishable. Relatedly, it may be that the higher-scoring essays were harder to distinguish because they appeared to be generated by more competent-sounding writers, and it was clear from instructor comments that they generally viewed ChatGPT as highly competent.
The results of the present research validate concerns that have been raised about college instructors having difficulty distinguishing writing generated by ChatGPT from the writing of their students, and document that this is also true when students try to detect writing generated by ChatGPT. The results indicate that this issue is particularly pronounced when instructors evaluate high-scoring student essays. The results also indicate that ChatGPT itself performs no better than instructors at detecting ChatGPT-generated writing even though ChatGPT-reported confidence is much higher. These findings highlight the importance of examining current teaching and assessment practices and the potential challenges AI chatbots pose for academic integrity and ethics in education (Cotton et al. 2023 ; Eke 2023 ; Susnjak 2022 ). Further, the results show that both instructors and students have a mixture of apprehension and optimism about the use of AI in education, and that many are looking for guidance about how to ethically use it in ways that promote learning. Taken together, our findings underscore some of the challenges that need to be carefully navigated in order to minimize the risks and maximize the benefits of AI in education.
Data availability
Supplementary materials, including data, analysis, and survey items, are available on the Open Science Framework: https://osf.io/2c54a/ .
Abbreviations
Artificial Intelligence
Confidence Interval
Generalized Linear Mixed Model
Generative Pre-trained Transformer
Standard Deviation
Al Darayseh A (2023) Acceptance of artificial intelligence in teaching science: Science teachers’ perspective. Computers Education: Artif Intell 4:100132. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.caeai.2023.100132
Article Google Scholar
Bertram Gallant T (2011) Creating the ethical academy. Routledge, New York
Book Google Scholar
Biswas SS (2023) Potential use of Chat GPT in global warming. Ann Biomed Eng 51:1126–1127. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10439-023-03171-8
Borenstein J, Howard A (2021) Emerging challenges in AI and the need for AI ethics education. AI Ethics 1:61–65. https://doi.org/10.1007/s43681-020-00002-7
Bretag T (ed) (2016) Handbook of academic integrity. Springer
Bretag T, Harper R, Burton M, Ellis C, Newton P, Rozenberg P, van Haeringen K (2019) Contract cheating: a survey of Australian university students. Stud High Educ 44(11):1837–1856. https://doi.org/10.1080/03075079.2018.1462788
Brown TB, Mann B, Ryder N, Subbiah M, Kaplan JD, Dhariwal P, Neelakantan A, Shyam P, Sastry G, Askell A, Agarwal S, Herbert-Voss A, Krueger G, Henighan T, Child R, Ramesh A, Ziegler D, Wu J, Winter C, Amodei D (2020) Language models are few-shot learners. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 33. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2005.14165
Chen Y, Andiappan M, Jenkin T, Ovchinnikov A (2023) A manager and an AI walk into a bar: does ChatGPT make biased decisions like we do? SSRN 4380365. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4380365
Chi MTH, Wylie R (2014) The ICAP framework: linking cognitive engagement to active learning outcomes. Educational Psychol 49(4):219–243. https://doi.org/10.1080/00461520.2014.965823
Chocarro R, Cortiñas M, Marcos-Matás G (2023) Teachers’ attitudes towards chatbots in education: a technology acceptance model approach considering the effect of social language, bot proactiveness, and users’ characteristics. Educational Stud 49(2):295–313. https://doi.org/10.1080/03055698.2020.1850426
Cizek GJ (1999) Cheating on tests: how to do it, detect it, and prevent it. Routledge
R Core Team (2021) R: A language and environment for statistical computing R Foundation for Statistical Computing, Vienna, Austria. https://www.R-project.org/
Cotton DRE, Cotton PA, Shipway JR (2023) Chatting and cheating: ensuring academic integrity in the era of ChatGPT. Innovations Educ Teach Int. https://doi.org/10.1080/14703297.2023.2190148
Curtis GJ, Clare J (2017) How prevalent is contract cheating and to what extent are students repeat offenders? J Acad Ethics 15:115–124. https://doi.org/10.1007/s10805-017-9278-x
Dalalah D, Dalalah OMA (2023) The false positives and false negatives of generative AI detection tools in education and academic research: the case of ChatGPT. Int J Manage Educ 21(2):100822. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijme.2023.100822
Devlin J, Chang M-W, Lee K, Toutanova K (2018) BERT: pre-training of deep bidirectional transformers for language understanding. ArXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.1810.04805
Dwivedi YK, Kshetri N, Hughes L, Slade EL, Jeyaraj A, Kar AK, Baabdullah AM, Koohang A, Raghavan V, Ahuja M, Albanna H, Albashrawi MA, Al-Busaidi AS, Balakrishnan J, Barlette Y, Basu S, Bose I, Brooks L, Buhalis D, Wright R (2023) So what if ChatGPT wrote it? Multidisciplinary perspectives on opportunities, challenges, and implications of generative conversational AI for research, practice, and policy. Int J Inf Manag 71:102642. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijinfomgt.2023.102642
Eke DO (2023) ChatGPT and the rise of generative AI: threat to academic integrity? J Responsible Technol 13:100060. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jrt.2023.100060
Erickson S, Heit E (2015) Metacognition and confidence: comparing math to other academic subjects. Front Psychol 6:742. https://doi.org/10.3389/fpsyg.2015.00742
Fischer I, Budescu DV (2005) When do those who know more also know more about how much they know? The development of confidence and performance in categorical decision tasks. Organ Behav Hum Decis Process 98:39–53. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.obhdp.2005.04.003
Fleming SM, Weil RS, Nagy Z, Dolan RJ, Rees G (2010) Relating introspective accuracy to individual differences in brain structure. Science 329:1541–1543. https://doi.org/10.1126/science.1191883
Fowler GA (2023), April 14 We tested a new ChatGPT-detector for teachers. It flagged an innocent student. The Washington Post . https://www.washingtonpost.com/technology/2023/04/01/chatgpt-cheating-detection-turnitin/
Gigerenzer G (1991) From tools to theories: a heuristic of discovery in cognitive psychology. Psychol Rev 98:254. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.98.2.254
Gigerenzer G, Hoffrage U, Kleinbölting H (1991) Probabilistic mental models: a brunswikian theory of confidence. Psychol Rev 98(4):506–528. https://doi.org/10.1037/0033-295X.98.4.506
Gilson A, Safranek C, Huang T, Socrates V, Chi L, Taylor RA, Chartash D (2022) How well does ChatGPT do when taking the medical licensing exams? The implications of large language models for medical education and knowledge assessment. MedRxiv. https://doi.org/10.1101/2022.12.23.22283901
Goodwins T (2022), December 12 ChatGPT has mastered the confidence trick, and that’s a terrible look for AI. The Register . https://www.theregister.com/2022/12/12/chatgpt_has_mastered_the_confidence/
Gunser VE, Gottschling S, Brucker B, Richter S, Gerjets P (2021) Can users distinguish narrative texts written by an artificial intelligence writing tool from purely human text? In C. Stephanidis, M. Antona, & S. Ntoa (Eds.), HCI International 2021 , Communications in Computer and Information Science , (Vol. 1419, pp. 520–527). Springer. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-78635-9_67
Hartshorne H, May MA (1928) Studies in the nature of character: vol. I. studies in deceit. Macmillan, New York
Google Scholar
Hox J (2010) Multilevel analysis: techniques and applications, 2nd edn. Routledge, New York, NY
Jakesch M, Hancock JT, Naaman M (2023) Human heuristics for AI-generated language are flawed. Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, 120 (11), e2208839120. https://doi.org/10.1073/pnas.2208839120
Jiang F, Jiang Y, Zhi H, Dong Y, Li H, Ma S, Wang Y, Dong Q, Shen H, Wang Y (2017) Artificial intelligence in healthcare: past, present and future. Stroke Vascular Neurol 2(4):230–243. https://doi.org/10.1136/svn-2017-000101
Joo YJ, Park S, Lim E (2018) Factors influencing preservice teachers’ intention to use technology: TPACK, teacher self-efficacy, and technology acceptance model. J Educational Technol Soc 21(3):48–59. https://www.jstor.org/stable/26458506
Kasneci E, Seßler K, Küchemann S, Bannert M, Dementieva D, Fischer F, Kasneci G (2023) ChatGPT for good? On opportunities and challenges of large language models for education. Learn Individual Differences 103:102274. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.lindif.2023.102274
Katz DM, Bommarito MJ, Gao S, Arredondo P (2023) GPT-4 passes the bar exam. SSRN Electron J. https://doi.org/10.2139/ssrn.4389233
Köbis N, Mossink LD (2021) Artificial intelligence versus Maya Angelou: experimental evidence that people cannot differentiate AI-generated from human-written poetry. Comput Hum Behav 114:106553. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.chb.2020.106553
Köbis NC, Doležalová B, Soraperra I (2021) Fooled twice: people cannot detect deepfakes but think they can. iScience 24(11):103364. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.isci.2021.103364
Lo CK (2023) What is the impact of ChatGPT on education? A rapid review of the literature. Educ Sci 13(4):410. https://doi.org/10.3390/educsci13040410
McCabe DL, Butterfield KD, Treviño LK (2012) Cheating in college: why students do it and what educators can do about it. Johns Hopkins, Baltimore, MD
Mitchell A (2022) December 26). Professor catches student cheating with ChatGPT: ‘I feel abject terror’. New York Post. https://nypost.com/2022/12/26/students-using-chatgpt-to-cheat-professor-warns
Radford A, Wu J, Child R, Luan D, Amodei D, Sutskever I (2019) Language models are unsupervised multitask learners. OpenAI https://openai.com/research/better-language-models
Rettinger DA, Bertram Gallant T (eds) (2022) Cheating academic integrity: lessons from 30 years of research. Jossey Bass
Rosenzweig-Ziff D (2023) New York City blocks use of the ChatGPT bot in its schools. Wash Post https://www.washingtonpost.com/education/2023/01/05/nyc-schools-ban-chatgpt/
Salvi F, Ribeiro MH, Gallotti R, West R (2024) On the conversational persuasiveness of large language models: a randomized controlled trial. ArXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arXiv.2403.14380
Shynkaruk JM, Thompson VA (2006) Confidence and accuracy in deductive reasoning. Mem Cognit 34(3):619–632. https://doi.org/10.3758/BF03193584
Stokel-Walker C (2022) AI bot ChatGPT writes smart essays — should professors worry? Nature. https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-022-04397-7
Susnjak T (2022) ChatGPT: The end of online exam integrity? ArXiv . https://arxiv.org/abs/2212.09292
Svrluga S (2023) Princeton student builds app to detect essays written by a popular AI bot. Wash Post https://www.washingtonpost.com/education/2023/01/12/gptzero-chatgpt-detector-ai/
Terwiesch C (2023) Would Chat GPT3 get a Wharton MBA? A prediction based on its performance in the Operations Management course. Mack Institute for Innovation Management at the Wharton School , University of Pennsylvania. https://mackinstitute.wharton.upenn.edu/wp-content/uploads/2023/01/Christian-Terwiesch-Chat-GTP-1.24.pdf
Tlili A, Shehata B, Adarkwah MA, Bozkurt A, Hickey DT, Huang R, Agyemang B (2023) What if the devil is my guardian angel: ChatGPT as a case study of using chatbots in education. Smart Learn Environ 10:15. https://doi.org/10.1186/s40561-023-00237-x
Turing AM (1950) Computing machinery and intelligence. Mind - Q Rev Psychol Philos 236:433–460
UCSD Academic Integrity Office (2023) GenAI, cheating and reporting to the AI office [Announcement]. https://adminrecords.ucsd.edu/Notices/2023/2023-5-17-1.html
Vaswani A, Shazeer N, Parmar N, Uszkoreit J, Jones L, Gomez AN, Polosukhin I (2017) Attention is all you need. Adv Neural Inf Process Syst 30. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.1706.03762
Waltzer T, Dahl A (2023) Why do students cheat? Perceptions, evaluations, and motivations. Ethics Behav 33(2):130–150. https://doi.org/10.1080/10508422.2022.2026775
Waltzer T, Cox RL, Heyman GD (2023a) Testing the ability of teachers and students to differentiate between essays generated by ChatGPT and high school students. Hum Behav Emerg Technol 2023:1923981. https://doi.org/10.1155/2023/1923981
Waltzer T, DeBernardi FC, Dahl A (2023b) Student and teacher views on cheating in high school: perceptions, evaluations, and decisions. J Res Adolescence 33(1):108–126. https://doi.org/10.1111/jora.12784
Weidinger L, Mellor J, Rauh M, Griffin C, Uesato J, Huang PS, Gabriel I (2021) Ethical and social risks of harm from language models. ArXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2112.04359
Wixted JT, Wells GL (2017) The relationship between eyewitness confidence and identification accuracy: a new synthesis. Psychol Sci Public Interest 18(1):10–65. https://doi.org/10.1177/1529100616686966
Yeadon W, Inyang OO, Mizouri A, Peach A, Testrow C (2023) The death of the short-form physics essay in the coming AI revolution. Phys Educ 58:035027. https://doi.org/10.1088/1361-6552/acc5cf
Zhuo TY, Huang Y, Chen C, Xing Z (2023) Red teaming ChatGPT via jailbreaking: bias, robustness, reliability and toxicity. ArXiv. https://doi.org/10.48550/arxiv.2301.12867
Download references
Acknowledgements
We thank Daniel Chen and Riley L. Cox for assistance with study design, stimulus preparation, and pilot testing. We also thank Emma C. Miller for grading the essays and Brian J. Compton for comments on the manuscript.
This work was partly supported by a National Science Foundation Postdoctoral Fellowship for T. Waltzer (NSF SPRF-FR# 2104610).
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Psychology, University of California San Diego, 9500 Gilman Drive, La Jolla, San Diego, CA, 92093-0109, USA
Tal Waltzer, Celeste Pilegard & Gail D. Heyman
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors collaborated in the conceptualization and design of the research. C. Pilegard facilitated recruitment and coding for real class assignments used in the study. T. Waltzer led data collection and analysis. G. Heyman and T. Waltzer wrote and revised the manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Tal Waltzer .
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Waltzer, T., Pilegard, C. & Heyman, G.D. Can you spot the bot? Identifying AI-generated writing in college essays. Int J Educ Integr 20 , 11 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s40979-024-00158-3
Download citation
Received : 16 February 2024
Accepted : 11 June 2024
Published : 08 July 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s40979-024-00158-3
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Artificial intelligence
- Academic integrity
- Higher education
International Journal for Educational Integrity
ISSN: 1833-2595
- Submission enquiries: [email protected]
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
4. Provide evidence: Support your comparisons with evidence from the subjects you are analyzing. This could include quotes, statistics, or examples. 5. Use transitions: Transition words and phrases help to guide the reader through your essay and make it easier to follow your arguments. 6. Revise and edit: After you have written your essay, be ...
Make sure they have enough similarities and differences to make a meaningful comparison. 2. Brainstorm key points: Once you have chosen the subjects, brainstorm the key points you want to compare and contrast. These could include characteristics, features, themes, or arguments related to each subject. 3.
Compare and Contrast Essay Outline Template A. Introduction a. Introduction to the broad topic b. Specific topic c. Thesis statement B. Body Paragraphs a. Body paragraph #1—First aspect that's similar or different i. Subject #1 1. Detail #1 2. Detail #2 ii. Subject #2 1. Detail #1 2. Detail #2 b.
In the block method, you cover each of the overall subjects you're comparing in a block. You say everything you have to say about your first subject, then discuss your second subject, making comparisons and contrasts back to the things you've already said about the first. Your text is structured like this: Subject 1. Point of comparison A.
An academic compare and contrast essay looks at two or more subjects, ideas, people, or objects, compares their likeness, and contrasts their differences. It's an informative essay that provides insights on what is similar and different between the two items. Depending on the essay's instructions, you can focus solely on comparing or ...
Making a Venn diagram or a chart can help you quickly and efficiently compare and contrast two or more things or ideas. To make a Venn diagram, simply draw some overlapping circles, one circle for each item you're considering. In the central area where they overlap, list the traits the two items have in common.
Compare and Contrast Essay Outline. The point-by-point method uses a standard five-paragraph essay structure: Introduction (contains the attention-getter, preview of main points, and thesis) Body ...
Key steps include: Pick two things to compare based on the assignment you were given. Brainstorm the similarities and differences between your chosen subjects. Choose a structure for your essay and plan how you will write it. Write up your comparison and use evidence to support your argument.
Contact Sales Learn More. Compare and contrast essays examine topics from multiple viewpoints. This kind of essay, often assigned in middle school and high school, teaches students about the analytical writing process and prepares them for more advanced forms of academic writing. Compare and contrast essays are relatively easy to write if you ...
To better understand this let's take a look at a few good compare and contrast essay topics: Traditional education vs. online education. Ancient Greek vs. Roman civilization. Examining the similarities between the American and French Revolution. Eastern philosophies vs. Western philosophies. Capitalism vs. socialism.
4.1 Comparison Essay Outline Example. 5 Tips to Write a Compare and Contrast Essay. 5.1 Comparison Essay Format. 6 Bringing It All Together. As we navigate our lives, we can't help but notice the elements in our environment, whether it's the latest car, a fashion trend, or even some experiences. Think about your favorite Mexican restaurant ...
Here they are explained below: 1. Essay Planning. First, I recommend using my compare and contrast worksheet, which acts like a Venn Diagram, walking you through the steps of comparing the similarities and differences of the concepts or items you're comparing. I recommend selecting 3-5 features that can be compared, as shown in the worksheet:
The Purpose of Comparison and Contrast in Writing. Comparison in writing discusses elements that are similar, while contrast in writing discusses elements that are different. A compare-and-contrast essay, then, analyzes two subjects by comparing them, contrasting them, or both.. The key to a good compare-and-contrast essay is to choose two or more subjects that connect in a meaningful way.
Key Elements of the Compare and Contrast: The key to a good compare-and-contrast essay is to choose two or more subjects that connect in a meaningful way. Comparison and contrast is simply telling how two things are alike or different. The compare-and-contrast essay starts with a thesis that clearly states the two subjects that are to be ...
Use Clear Transitions. Transitions are important in compare and contrast essays, where you will be moving frequently between different topics or perspectives. Examples of transitions and phrases for comparisons: as well, similar to, consistent with, likewise, too. Examples of transitions and phrases for contrasts: on the other hand, however ...
Follow these essential steps to write an effective compare and contrast essay: Choose what two subjects to compare and contrast. Brainstorm similarities and differences between the two subjects. Develop a thesis statement and write an introduction. Write an analysis, using the block method or the point-by-point method.
The purpose of a compare and contrast essay is to analyze the differences and/or the similarities of two distinct subjects. A good compare/contrast essay doesn't only point out how the subjects are similar or different (or even both!). ... In middle school and high school, the standard format for essays is often the "5-paragraph form," with ...
A compare and contrast essay does two things: It discusses the similarities and differences of at least two different things. First, you must find a basis of comparison to be sure that the two things have enough in common. After that, you identify their differences. You may structure the compare and contrast essay using either the alternating ...
Contrast. Emphasizes the differences between two things, ideas, concepts, or points of view. ison/Contrast Essay:The two items should make sense to. compare or contrast. For example, you might compare two baseball teams, but not a football team. and a baseball team. As you select your topic, keep in mind that you won't merely be describing ...
Compare/Contrast by Topic: Your paragraph will discuss all the points for one topic first, then do the same for the other topic. For example: End with a Concluding Sentence: Conclude your paragraph by stating your decision as to which topic you prefer and why, or by explaining the purpose of the comparison. You can be persuasive in this final ...
The first things to focus on is what is absolutely essential to the argument you're going to make. These points will need to be included no matter what. If that alone does not fill up your essay, however, then it's time to pull out a point system. Give things a score from one to five (or ten, if you've got a lot of topics and need the ...
The block method for writing a compare and contrast essay can be illustrated using points A, B, and C to signify individual characteristics or critical attributes. This block format allows the students to compare and contrast subjects, for example, dogs vs. cats, using these same characteristics one at a time.
So, let's work together and figure out how to make your short essays really stand out! The Basics of a Short Essay Format A short... July 9, 2024 Writing a Compare and Contrast Essay: A Complete Guide. Compare and contrast essay is an academic text that encourages authors to take a look at the differences between two or more subjects.
Weekly Essay Challenge; Insta Revision Modules-Mains; Insta 75 Days Revision Tests for Mains; Secure (Archive) ... Compare and contrast the major features of the constitutions of India and Britain. (150 words) ... 3rd Floor, Nanda Ashirwad Building, Chandra Layout Main Rd, Maruthi Nagar, Attiguppe, Bengaluru, Karnataka 560040 ...
Table of contents1 What is plagiarism in business?1.1 Types of plagiarism in business2 Plagiarism in the business sector2.1 Major causes of plagiarism in business2.2 The outcome of plagiarism in business3 Examples of plagiarism in business & some famous cases3.1 Examples of business plagiarism3.2 Cases of plagiarism in business4 7 Proven tips to avoid plagiarism in […]
The task was to determine which essay was written by the chatbot. The essay pairs were drawn from larger pools of essays of each type. The student essays were written by students as part of a graded exam in a psychology class, and the ChatGPT essays were generated in response to the same essay prompts.