Guide to Writing the Results and Discussion Sections of a Scientific Article
A quality research paper has both the qualities of in-depth research and good writing ( Bordage, 2001 ). In addition, a research paper must be clear, concise, and effective when presenting the information in an organized structure with a logical manner ( Sandercock, 2013 ).
In this article, we will take a closer look at the results and discussion section. Composing each of these carefully with sufficient data and well-constructed arguments can help improve your paper overall.

The results section of your research paper contains a description about the main findings of your research, whereas the discussion section interprets the results for readers and provides the significance of the findings. The discussion should not repeat the results.
Let’s dive in a little deeper about how to properly, and clearly organize each part.

How to Organize the Results Section
Since your results follow your methods, you’ll want to provide information about what you discovered from the methods you used, such as your research data. In other words, what were the outcomes of the methods you used?
You may also include information about the measurement of your data, variables, treatments, and statistical analyses.
To start, organize your research data based on how important those are in relation to your research questions. This section should focus on showing major results that support or reject your research hypothesis. Include your least important data as supplemental materials when submitting to the journal.
The next step is to prioritize your research data based on importance – focusing heavily on the information that directly relates to your research questions using the subheadings.
The organization of the subheadings for the results section usually mirrors the methods section. It should follow a logical and chronological order.
Subheading organization
Subheadings within your results section are primarily going to detail major findings within each important experiment. And the first paragraph of your results section should be dedicated to your main findings (findings that answer your overall research question and lead to your conclusion) (Hofmann, 2013).
In the book “Writing in the Biological Sciences,” author Angelika Hofmann recommends you structure your results subsection paragraphs as follows:
- Experimental purpose
- Interpretation
Each subheading may contain a combination of ( Bahadoran, 2019 ; Hofmann, 2013, pg. 62-63):
- Text: to explain about the research data
- Figures: to display the research data and to show trends or relationships, for examples using graphs or gel pictures.
- Tables: to represent a large data and exact value
Decide on the best way to present your data — in the form of text, figures or tables (Hofmann, 2013).
Data or Results?
Sometimes we get confused about how to differentiate between data and results . Data are information (facts or numbers) that you collected from your research ( Bahadoran, 2019 ).

Whereas, results are the texts presenting the meaning of your research data ( Bahadoran, 2019 ).

One mistake that some authors often make is to use text to direct the reader to find a specific table or figure without further explanation. This can confuse readers when they interpret data completely different from what the authors had in mind. So, you should briefly explain your data to make your information clear for the readers.
Common Elements in Figures and Tables
Figures and tables present information about your research data visually. The use of these visual elements is necessary so readers can summarize, compare, and interpret large data at a glance. You can use graphs or figures to compare groups or patterns. Whereas, tables are ideal to present large quantities of data and exact values.
Several components are needed to create your figures and tables. These elements are important to sort your data based on groups (or treatments). It will be easier for the readers to see the similarities and differences among the groups.
When presenting your research data in the form of figures and tables, organize your data based on the steps of the research leading you into a conclusion.
Common elements of the figures (Bahadoran, 2019):
- Figure number
- Figure title
- Figure legend (for example a brief title, experimental/statistical information, or definition of symbols).
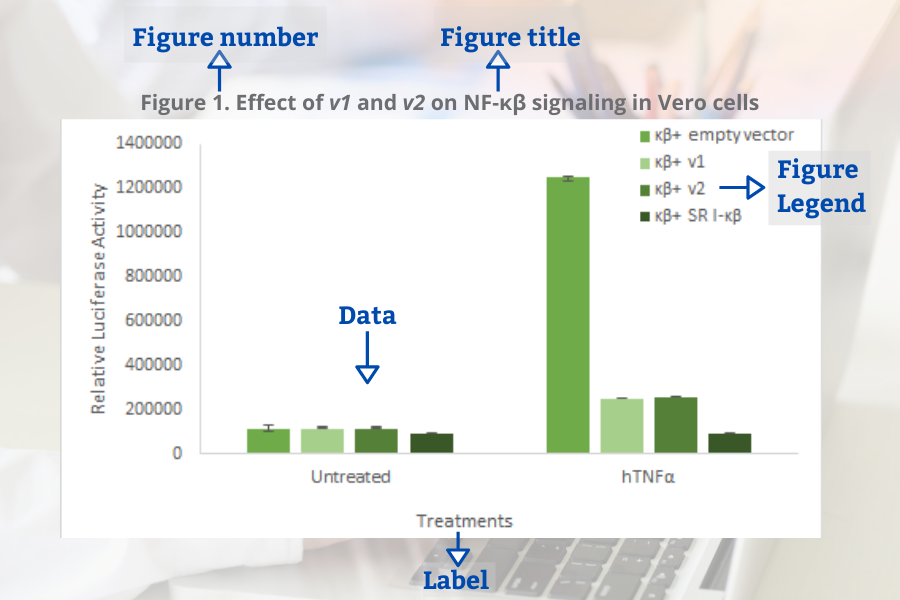
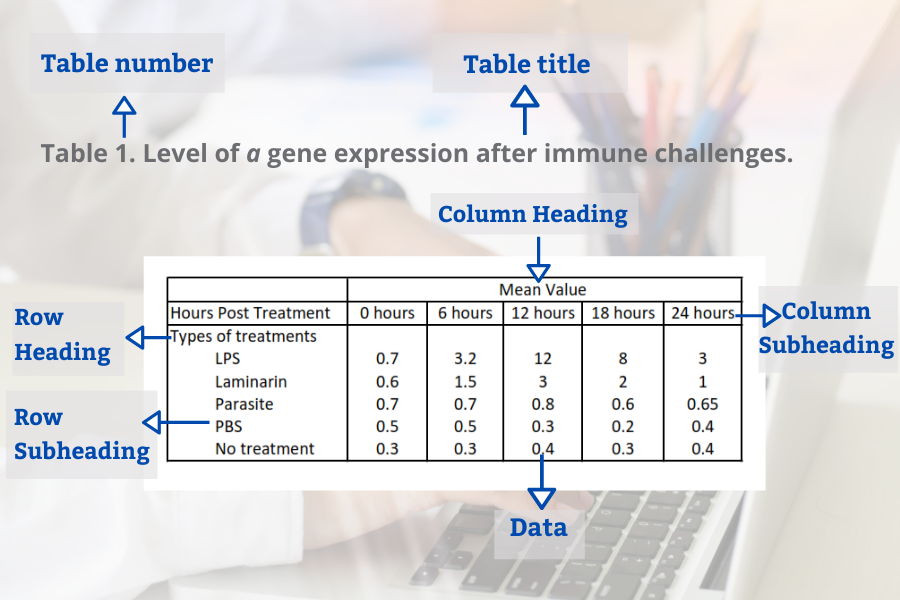
Tables in the result section may contain several elements (Bahadoran, 2019):
- Table number
- Table title
- Row headings (for example groups)
- Column headings
- Row subheadings (for example categories or groups)
- Column subheadings (for example categories or variables)
- Footnotes (for example statistical analyses)
Tips to Write the Results Section
- Direct the reader to the research data and explain the meaning of the data.
- Avoid using a repetitive sentence structure to explain a new set of data.
- Write and highlight important findings in your results.
- Use the same order as the subheadings of the methods section.
- Match the results with the research questions from the introduction. Your results should answer your research questions.
- Be sure to mention the figures and tables in the body of your text.
- Make sure there is no mismatch between the table number or the figure number in text and in figure/tables.
- Only present data that support the significance of your study. You can provide additional data in tables and figures as supplementary material.
How to Organize the Discussion Section
It’s not enough to use figures and tables in your results section to convince your readers about the importance of your findings. You need to support your results section by providing more explanation in the discussion section about what you found.
In the discussion section, based on your findings, you defend the answers to your research questions and create arguments to support your conclusions.
Below is a list of questions to guide you when organizing the structure of your discussion section ( Viera et al ., 2018 ):
- What experiments did you conduct and what were the results?
- What do the results mean?
- What were the important results from your study?
- How did the results answer your research questions?
- Did your results support your hypothesis or reject your hypothesis?
- What are the variables or factors that might affect your results?
- What were the strengths and limitations of your study?
- What other published works support your findings?
- What other published works contradict your findings?
- What possible factors might cause your findings different from other findings?
- What is the significance of your research?
- What are new research questions to explore based on your findings?
Organizing the Discussion Section
The structure of the discussion section may be different from one paper to another, but it commonly has a beginning, middle-, and end- to the section.
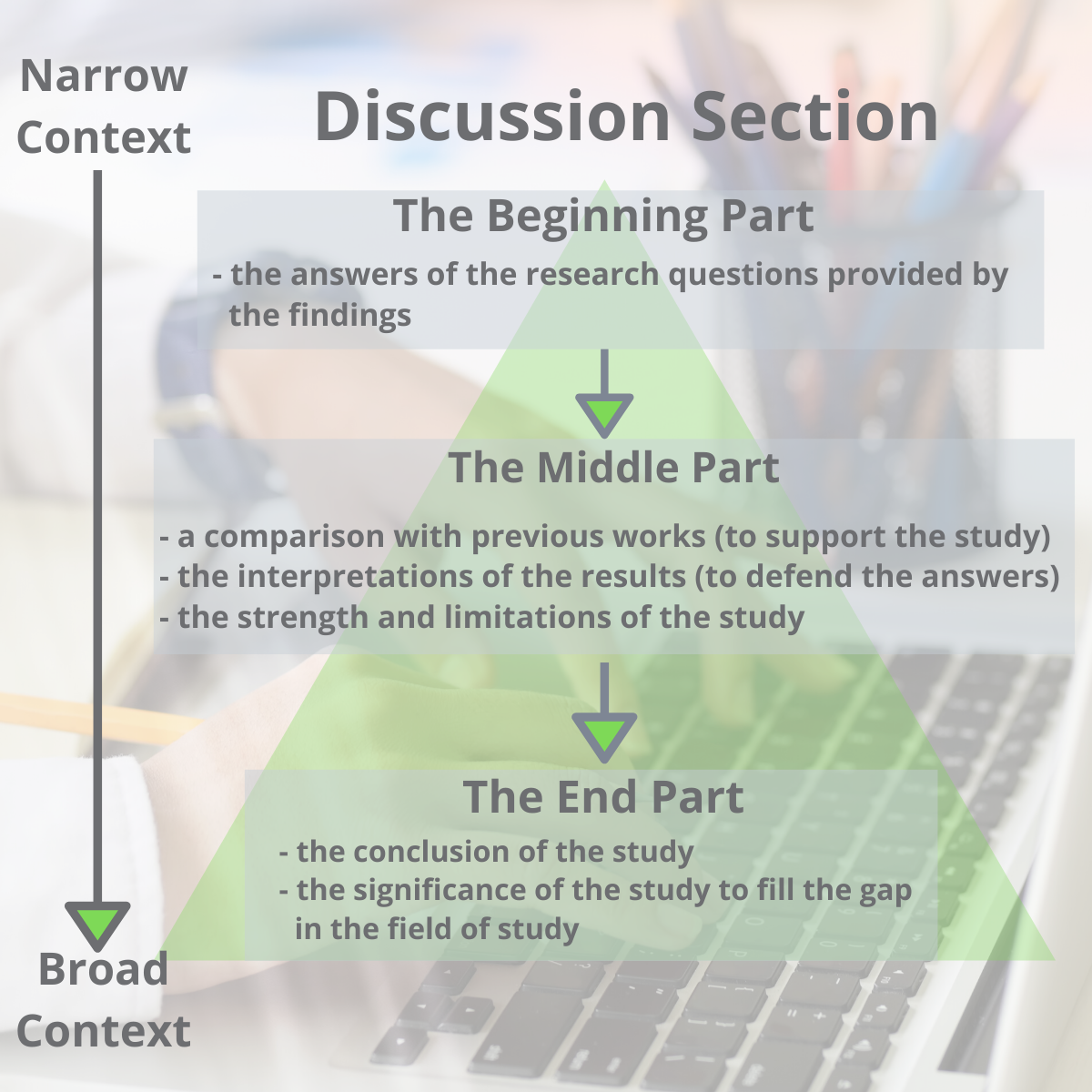
One way to organize the structure of the discussion section is by dividing it into three parts (Ghasemi, 2019):
- The beginning: The first sentence of the first paragraph should state the importance and the new findings of your research. The first paragraph may also include answers to your research questions mentioned in your introduction section.
- The middle: The middle should contain the interpretations of the results to defend your answers, the strength of the study, the limitations of the study, and an update literature review that validates your findings.
- The end: The end concludes the study and the significance of your research.
Another possible way to organize the discussion section was proposed by Michael Docherty in British Medical Journal: is by using this structure ( Docherty, 1999 ):
- Discussion of important findings
- Comparison of your results with other published works
- Include the strengths and limitations of the study
- Conclusion and possible implications of your study, including the significance of your study – address why and how is it meaningful
- Future research questions based on your findings
Finally, a last option is structuring your discussion this way (Hofmann, 2013, pg. 104):
- First Paragraph: Provide an interpretation based on your key findings. Then support your interpretation with evidence.
- Secondary results
- Limitations
- Unexpected findings
- Comparisons to previous publications
- Last Paragraph: The last paragraph should provide a summarization (conclusion) along with detailing the significance, implications and potential next steps.
Remember, at the heart of the discussion section is presenting an interpretation of your major findings.
Tips to Write the Discussion Section
- Highlight the significance of your findings
- Mention how the study will fill a gap in knowledge.
- Indicate the implication of your research.
- Avoid generalizing, misinterpreting your results, drawing a conclusion with no supportive findings from your results.
Aggarwal, R., & Sahni, P. (2018). The Results Section. In Reporting and Publishing Research in the Biomedical Sciences (pp. 21-38): Springer.
Bahadoran, Z., Mirmiran, P., Zadeh-Vakili, A., Hosseinpanah, F., & Ghasemi, A. (2019). The principles of biomedical scientific writing: Results. International journal of endocrinology and metabolism, 17(2).
Bordage, G. (2001). Reasons reviewers reject and accept manuscripts: the strengths and weaknesses in medical education reports. Academic medicine, 76(9), 889-896.
Cals, J. W., & Kotz, D. (2013). Effective writing and publishing scientific papers, part VI: discussion. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 66(10), 1064.
Docherty, M., & Smith, R. (1999). The case for structuring the discussion of scientific papers: Much the same as that for structuring abstracts. In: British Medical Journal Publishing Group.
Faber, J. (2017). Writing scientific manuscripts: most common mistakes. Dental press journal of orthodontics, 22(5), 113-117.
Fletcher, R. H., & Fletcher, S. W. (2018). The discussion section. In Reporting and Publishing Research in the Biomedical Sciences (pp. 39-48): Springer.
Ghasemi, A., Bahadoran, Z., Mirmiran, P., Hosseinpanah, F., Shiva, N., & Zadeh-Vakili, A. (2019). The Principles of Biomedical Scientific Writing: Discussion. International journal of endocrinology and metabolism, 17(3).
Hofmann, A. H. (2013). Writing in the biological sciences: a comprehensive resource for scientific communication . New York: Oxford University Press.
Kotz, D., & Cals, J. W. (2013). Effective writing and publishing scientific papers, part V: results. Journal of clinical epidemiology, 66(9), 945.
Mack, C. (2014). How to Write a Good Scientific Paper: Structure and Organization. Journal of Micro/ Nanolithography, MEMS, and MOEMS, 13. doi:10.1117/1.JMM.13.4.040101
Moore, A. (2016). What's in a Discussion section? Exploiting 2‐dimensionality in the online world…. Bioessays, 38(12), 1185-1185.
Peat, J., Elliott, E., Baur, L., & Keena, V. (2013). Scientific writing: easy when you know how: John Wiley & Sons.
Sandercock, P. M. L. (2012). How to write and publish a scientific article. Canadian Society of Forensic Science Journal, 45(1), 1-5.
Teo, E. K. (2016). Effective Medical Writing: The Write Way to Get Published. Singapore Medical Journal, 57(9), 523-523. doi:10.11622/smedj.2016156
Van Way III, C. W. (2007). Writing a scientific paper. Nutrition in Clinical Practice, 22(6), 636-640.
Vieira, R. F., Lima, R. C. d., & Mizubuti, E. S. G. (2019). How to write the discussion section of a scientific article. Acta Scientiarum. Agronomy, 41.
Related Articles

A quality research paper has both the qualities of in-depth research and good writing (Bordage, 200...

How to Survive and Complete a Thesis or a Dissertation
Writing a thesis or a dissertation can be a challenging process for many graduate students. There ar...

12 Ways to Dramatically Improve your Research Manuscript Title and Abstract
The first thing a person doing literary research will see is a research publication title. After tha...

15 Laboratory Notebook Tips to Help with your Research Manuscript
Your lab notebook is a foundation to your research manuscript. It serves almost as a rudimentary dra...
Join our list to receive promos and articles.

- Competent Cells
- Lab Startup
- Z')" data-type="collection" title="Products A->Z" target="_self" href="/collection/products-a-to-z">Products A->Z
- GoldBio Resources
- GoldBio Sales Team
- GoldBio Distributors
- Duchefa Direct
- Sign up for Promos
- Terms & Conditions
- ISO Certification
- Agarose Resins
- Antibiotics & Selection
- Biochemical Reagents
- Bioluminescence
- Buffers & Reagents
- Cell Culture
- Cloning & Induction
- Competent Cells and Transformation
- Detergents & Membrane Agents
- DNA Amplification
- Enzymes, Inhibitors & Substrates
- Growth Factors and Cytokines
- Lab Tools & Accessories
- Plant Research and Reagents
- Protein Research & Analysis
- Protein Expression & Purification
- Reducing Agents
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples
Published on August 30, 2022 by Tegan George . Revised on July 18, 2023.
A results section is where you report the main findings of the data collection and analysis you conducted for your thesis or dissertation . You should report all relevant results concisely and objectively, in a logical order. Don’t include subjective interpretations of why you found these results or what they mean—any evaluation should be saved for the discussion section .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
How to write a results section, reporting quantitative research results, reporting qualitative research results, results vs. discussion vs. conclusion, checklist: research results, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about results sections.
When conducting research, it’s important to report the results of your study prior to discussing your interpretations of it. This gives your reader a clear idea of exactly what you found and keeps the data itself separate from your subjective analysis.
Here are a few best practices:
- Your results should always be written in the past tense.
- While the length of this section depends on how much data you collected and analyzed, it should be written as concisely as possible.
- Only include results that are directly relevant to answering your research questions . Avoid speculative or interpretative words like “appears” or “implies.”
- If you have other results you’d like to include, consider adding them to an appendix or footnotes.
- Always start out with your broadest results first, and then flow into your more granular (but still relevant) ones. Think of it like a shoe store: first discuss the shoes as a whole, then the sneakers, boots, sandals, etc.
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
If you conducted quantitative research , you’ll likely be working with the results of some sort of statistical analysis .
Your results section should report the results of any statistical tests you used to compare groups or assess relationships between variables . It should also state whether or not each hypothesis was supported.
The most logical way to structure quantitative results is to frame them around your research questions or hypotheses. For each question or hypothesis, share:
- A reminder of the type of analysis you used (e.g., a two-sample t test or simple linear regression ). A more detailed description of your analysis should go in your methodology section.
- A concise summary of each relevant result, both positive and negative. This can include any relevant descriptive statistics (e.g., means and standard deviations ) as well as inferential statistics (e.g., t scores, degrees of freedom , and p values ). Remember, these numbers are often placed in parentheses.
- A brief statement of how each result relates to the question, or whether the hypothesis was supported. You can briefly mention any results that didn’t fit with your expectations and assumptions, but save any speculation on their meaning or consequences for your discussion and conclusion.
A note on tables and figures
In quantitative research, it’s often helpful to include visual elements such as graphs, charts, and tables , but only if they are directly relevant to your results. Give these elements clear, descriptive titles and labels so that your reader can easily understand what is being shown. If you want to include any other visual elements that are more tangential in nature, consider adding a figure and table list .
As a rule of thumb:
- Tables are used to communicate exact values, giving a concise overview of various results
- Graphs and charts are used to visualize trends and relationships, giving an at-a-glance illustration of key findings
Don’t forget to also mention any tables and figures you used within the text of your results section. Summarize or elaborate on specific aspects you think your reader should know about rather than merely restating the same numbers already shown.
A two-sample t test was used to test the hypothesis that higher social distance from environmental problems would reduce the intent to donate to environmental organizations, with donation intention (recorded as a score from 1 to 10) as the outcome variable and social distance (categorized as either a low or high level of social distance) as the predictor variable.Social distance was found to be positively correlated with donation intention, t (98) = 12.19, p < .001, with the donation intention of the high social distance group 0.28 points higher, on average, than the low social distance group (see figure 1). This contradicts the initial hypothesis that social distance would decrease donation intention, and in fact suggests a small effect in the opposite direction.
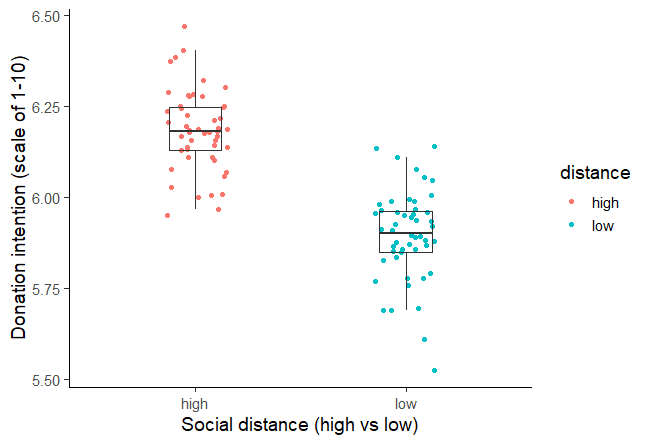
Figure 1: Intention to donate to environmental organizations based on social distance from impact of environmental damage.
In qualitative research , your results might not all be directly related to specific hypotheses. In this case, you can structure your results section around key themes or topics that emerged from your analysis of the data.
For each theme, start with general observations about what the data showed. You can mention:
- Recurring points of agreement or disagreement
- Patterns and trends
- Particularly significant snippets from individual responses
Next, clarify and support these points with direct quotations. Be sure to report any relevant demographic information about participants. Further information (such as full transcripts , if appropriate) can be included in an appendix .
When asked about video games as a form of art, the respondents tended to believe that video games themselves are not an art form, but agreed that creativity is involved in their production. The criteria used to identify artistic video games included design, story, music, and creative teams.One respondent (male, 24) noted a difference in creativity between popular video game genres:
“I think that in role-playing games, there’s more attention to character design, to world design, because the whole story is important and more attention is paid to certain game elements […] so that perhaps you do need bigger teams of creative experts than in an average shooter or something.”
Responses suggest that video game consumers consider some types of games to have more artistic potential than others.
Your results section should objectively report your findings, presenting only brief observations in relation to each question, hypothesis, or theme.
It should not speculate about the meaning of the results or attempt to answer your main research question . Detailed interpretation of your results is more suitable for your discussion section , while synthesis of your results into an overall answer to your main research question is best left for your conclusion .
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results.
I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions.
I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics .
I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported or refuted.
I have used tables and figures to illustrate my results where appropriate.
All tables and figures are correctly labelled and referred to in the text.
There is no subjective interpretation or speculation on the meaning of the results.
You've finished writing up your results! Use the other checklists to further improve your thesis.
If you want to know more about AI for academic writing, AI tools, or research bias, make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
Research bias
- Survivorship bias
- Self-serving bias
- Availability heuristic
- Halo effect
- Hindsight bias
- Deep learning
- Generative AI
- Machine learning
- Reinforcement learning
- Supervised vs. unsupervised learning
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The results chapter of a thesis or dissertation presents your research results concisely and objectively.
In quantitative research , for each question or hypothesis , state:
- The type of analysis used
- Relevant results in the form of descriptive and inferential statistics
- Whether or not the alternative hypothesis was supported
In qualitative research , for each question or theme, describe:
- Recurring patterns
- Significant or representative individual responses
- Relevant quotations from the data
Don’t interpret or speculate in the results chapter.
Results are usually written in the past tense , because they are describing the outcome of completed actions.
The results chapter or section simply and objectively reports what you found, without speculating on why you found these results. The discussion interprets the meaning of the results, puts them in context, and explains why they matter.
In qualitative research , results and discussion are sometimes combined. But in quantitative research , it’s considered important to separate the objective results from your interpretation of them.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
George, T. (2023, July 18). How to Write a Results Section | Tips & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved July 22, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/results/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Results Section – Writing Guide and Examples
Research Results Section – Writing Guide and Examples
Table of Contents

Research Results
Research results refer to the findings and conclusions derived from a systematic investigation or study conducted to answer a specific question or hypothesis. These results are typically presented in a written report or paper and can include various forms of data such as numerical data, qualitative data, statistics, charts, graphs, and visual aids.
Results Section in Research
The results section of the research paper presents the findings of the study. It is the part of the paper where the researcher reports the data collected during the study and analyzes it to draw conclusions.
In the results section, the researcher should describe the data that was collected, the statistical analysis performed, and the findings of the study. It is important to be objective and not interpret the data in this section. Instead, the researcher should report the data as accurately and objectively as possible.
Structure of Research Results Section
The structure of the research results section can vary depending on the type of research conducted, but in general, it should contain the following components:
- Introduction: The introduction should provide an overview of the study, its aims, and its research questions. It should also briefly explain the methodology used to conduct the study.
- Data presentation : This section presents the data collected during the study. It may include tables, graphs, or other visual aids to help readers better understand the data. The data presented should be organized in a logical and coherent way, with headings and subheadings used to help guide the reader.
- Data analysis: In this section, the data presented in the previous section are analyzed and interpreted. The statistical tests used to analyze the data should be clearly explained, and the results of the tests should be presented in a way that is easy to understand.
- Discussion of results : This section should provide an interpretation of the results of the study, including a discussion of any unexpected findings. The discussion should also address the study’s research questions and explain how the results contribute to the field of study.
- Limitations: This section should acknowledge any limitations of the study, such as sample size, data collection methods, or other factors that may have influenced the results.
- Conclusions: The conclusions should summarize the main findings of the study and provide a final interpretation of the results. The conclusions should also address the study’s research questions and explain how the results contribute to the field of study.
- Recommendations : This section may provide recommendations for future research based on the study’s findings. It may also suggest practical applications for the study’s results in real-world settings.
Outline of Research Results Section
The following is an outline of the key components typically included in the Results section:
I. Introduction
- A brief overview of the research objectives and hypotheses
- A statement of the research question
II. Descriptive statistics
- Summary statistics (e.g., mean, standard deviation) for each variable analyzed
- Frequencies and percentages for categorical variables
III. Inferential statistics
- Results of statistical analyses, including tests of hypotheses
- Tables or figures to display statistical results
IV. Effect sizes and confidence intervals
- Effect sizes (e.g., Cohen’s d, odds ratio) to quantify the strength of the relationship between variables
- Confidence intervals to estimate the range of plausible values for the effect size
V. Subgroup analyses
- Results of analyses that examined differences between subgroups (e.g., by gender, age, treatment group)
VI. Limitations and assumptions
- Discussion of any limitations of the study and potential sources of bias
- Assumptions made in the statistical analyses
VII. Conclusions
- A summary of the key findings and their implications
- A statement of whether the hypotheses were supported or not
- Suggestions for future research
Example of Research Results Section
An Example of a Research Results Section could be:
- This study sought to examine the relationship between sleep quality and academic performance in college students.
- Hypothesis : College students who report better sleep quality will have higher GPAs than those who report poor sleep quality.
- Methodology : Participants completed a survey about their sleep habits and academic performance.
II. Participants
- Participants were college students (N=200) from a mid-sized public university in the United States.
- The sample was evenly split by gender (50% female, 50% male) and predominantly white (85%).
- Participants were recruited through flyers and online advertisements.
III. Results
- Participants who reported better sleep quality had significantly higher GPAs (M=3.5, SD=0.5) than those who reported poor sleep quality (M=2.9, SD=0.6).
- See Table 1 for a summary of the results.
- Participants who reported consistent sleep schedules had higher GPAs than those with irregular sleep schedules.
IV. Discussion
- The results support the hypothesis that better sleep quality is associated with higher academic performance in college students.
- These findings have implications for college students, as prioritizing sleep could lead to better academic outcomes.
- Limitations of the study include self-reported data and the lack of control for other variables that could impact academic performance.
V. Conclusion
- College students who prioritize sleep may see a positive impact on their academic performance.
- These findings highlight the importance of sleep in academic success.
- Future research could explore interventions to improve sleep quality in college students.
Example of Research Results in Research Paper :
Our study aimed to compare the performance of three different machine learning algorithms (Random Forest, Support Vector Machine, and Neural Network) in predicting customer churn in a telecommunications company. We collected a dataset of 10,000 customer records, with 20 predictor variables and a binary churn outcome variable.
Our analysis revealed that all three algorithms performed well in predicting customer churn, with an overall accuracy of 85%. However, the Random Forest algorithm showed the highest accuracy (88%), followed by the Support Vector Machine (86%) and the Neural Network (84%).
Furthermore, we found that the most important predictor variables for customer churn were monthly charges, contract type, and tenure. Random Forest identified monthly charges as the most important variable, while Support Vector Machine and Neural Network identified contract type as the most important.
Overall, our results suggest that machine learning algorithms can be effective in predicting customer churn in a telecommunications company, and that Random Forest is the most accurate algorithm for this task.
Example 3 :
Title : The Impact of Social Media on Body Image and Self-Esteem
Abstract : This study aimed to investigate the relationship between social media use, body image, and self-esteem among young adults. A total of 200 participants were recruited from a university and completed self-report measures of social media use, body image satisfaction, and self-esteem.
Results: The results showed that social media use was significantly associated with body image dissatisfaction and lower self-esteem. Specifically, participants who reported spending more time on social media platforms had lower levels of body image satisfaction and self-esteem compared to those who reported less social media use. Moreover, the study found that comparing oneself to others on social media was a significant predictor of body image dissatisfaction and lower self-esteem.
Conclusion : These results suggest that social media use can have negative effects on body image satisfaction and self-esteem among young adults. It is important for individuals to be mindful of their social media use and to recognize the potential negative impact it can have on their mental health. Furthermore, interventions aimed at promoting positive body image and self-esteem should take into account the role of social media in shaping these attitudes and behaviors.
Importance of Research Results
Research results are important for several reasons, including:
- Advancing knowledge: Research results can contribute to the advancement of knowledge in a particular field, whether it be in science, technology, medicine, social sciences, or humanities.
- Developing theories: Research results can help to develop or modify existing theories and create new ones.
- Improving practices: Research results can inform and improve practices in various fields, such as education, healthcare, business, and public policy.
- Identifying problems and solutions: Research results can identify problems and provide solutions to complex issues in society, including issues related to health, environment, social justice, and economics.
- Validating claims : Research results can validate or refute claims made by individuals or groups in society, such as politicians, corporations, or activists.
- Providing evidence: Research results can provide evidence to support decision-making, policy-making, and resource allocation in various fields.
How to Write Results in A Research Paper
Here are some general guidelines on how to write results in a research paper:
- Organize the results section: Start by organizing the results section in a logical and coherent manner. Divide the section into subsections if necessary, based on the research questions or hypotheses.
- Present the findings: Present the findings in a clear and concise manner. Use tables, graphs, and figures to illustrate the data and make the presentation more engaging.
- Describe the data: Describe the data in detail, including the sample size, response rate, and any missing data. Provide relevant descriptive statistics such as means, standard deviations, and ranges.
- Interpret the findings: Interpret the findings in light of the research questions or hypotheses. Discuss the implications of the findings and the extent to which they support or contradict existing theories or previous research.
- Discuss the limitations : Discuss the limitations of the study, including any potential sources of bias or confounding factors that may have affected the results.
- Compare the results : Compare the results with those of previous studies or theoretical predictions. Discuss any similarities, differences, or inconsistencies.
- Avoid redundancy: Avoid repeating information that has already been presented in the introduction or methods sections. Instead, focus on presenting new and relevant information.
- Be objective: Be objective in presenting the results, avoiding any personal biases or interpretations.
When to Write Research Results
Here are situations When to Write Research Results”
- After conducting research on the chosen topic and obtaining relevant data, organize the findings in a structured format that accurately represents the information gathered.
- Once the data has been analyzed and interpreted, and conclusions have been drawn, begin the writing process.
- Before starting to write, ensure that the research results adhere to the guidelines and requirements of the intended audience, such as a scientific journal or academic conference.
- Begin by writing an abstract that briefly summarizes the research question, methodology, findings, and conclusions.
- Follow the abstract with an introduction that provides context for the research, explains its significance, and outlines the research question and objectives.
- The next section should be a literature review that provides an overview of existing research on the topic and highlights the gaps in knowledge that the current research seeks to address.
- The methodology section should provide a detailed explanation of the research design, including the sample size, data collection methods, and analytical techniques used.
- Present the research results in a clear and concise manner, using graphs, tables, and figures to illustrate the findings.
- Discuss the implications of the research results, including how they contribute to the existing body of knowledge on the topic and what further research is needed.
- Conclude the paper by summarizing the main findings, reiterating the significance of the research, and offering suggestions for future research.
Purpose of Research Results
The purposes of Research Results are as follows:
- Informing policy and practice: Research results can provide evidence-based information to inform policy decisions, such as in the fields of healthcare, education, and environmental regulation. They can also inform best practices in fields such as business, engineering, and social work.
- Addressing societal problems : Research results can be used to help address societal problems, such as reducing poverty, improving public health, and promoting social justice.
- Generating economic benefits : Research results can lead to the development of new products, services, and technologies that can create economic value and improve quality of life.
- Supporting academic and professional development : Research results can be used to support academic and professional development by providing opportunities for students, researchers, and practitioners to learn about new findings and methodologies in their field.
- Enhancing public understanding: Research results can help to educate the public about important issues and promote scientific literacy, leading to more informed decision-making and better public policy.
- Evaluating interventions: Research results can be used to evaluate the effectiveness of interventions, such as treatments, educational programs, and social policies. This can help to identify areas where improvements are needed and guide future interventions.
- Contributing to scientific progress: Research results can contribute to the advancement of science by providing new insights and discoveries that can lead to new theories, methods, and techniques.
- Informing decision-making : Research results can provide decision-makers with the information they need to make informed decisions. This can include decision-making at the individual, organizational, or governmental levels.
- Fostering collaboration : Research results can facilitate collaboration between researchers and practitioners, leading to new partnerships, interdisciplinary approaches, and innovative solutions to complex problems.
Advantages of Research Results
Some Advantages of Research Results are as follows:
- Improved decision-making: Research results can help inform decision-making in various fields, including medicine, business, and government. For example, research on the effectiveness of different treatments for a particular disease can help doctors make informed decisions about the best course of treatment for their patients.
- Innovation : Research results can lead to the development of new technologies, products, and services. For example, research on renewable energy sources can lead to the development of new and more efficient ways to harness renewable energy.
- Economic benefits: Research results can stimulate economic growth by providing new opportunities for businesses and entrepreneurs. For example, research on new materials or manufacturing techniques can lead to the development of new products and processes that can create new jobs and boost economic activity.
- Improved quality of life: Research results can contribute to improving the quality of life for individuals and society as a whole. For example, research on the causes of a particular disease can lead to the development of new treatments and cures, improving the health and well-being of millions of people.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...

Research Report – Example, Writing Guide and...

Conceptual Framework – Types, Methodology and...

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Assignment – Types, Examples and Writing Guide

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions

The discussion section contains the results and outcomes of a study. An effective discussion informs readers what can be learned from your experiment and provides context for the results.
What makes an effective discussion?
When you’re ready to write your discussion, you’ve already introduced the purpose of your study and provided an in-depth description of the methodology. The discussion informs readers about the larger implications of your study based on the results. Highlighting these implications while not overstating the findings can be challenging, especially when you’re submitting to a journal that selects articles based on novelty or potential impact. Regardless of what journal you are submitting to, the discussion section always serves the same purpose: concluding what your study results actually mean.
A successful discussion section puts your findings in context. It should include:
- the results of your research,
- a discussion of related research, and
- a comparison between your results and initial hypothesis.
Tip: Not all journals share the same naming conventions.
You can apply the advice in this article to the conclusion, results or discussion sections of your manuscript.
Our Early Career Researcher community tells us that the conclusion is often considered the most difficult aspect of a manuscript to write. To help, this guide provides questions to ask yourself, a basic structure to model your discussion off of and examples from published manuscripts.
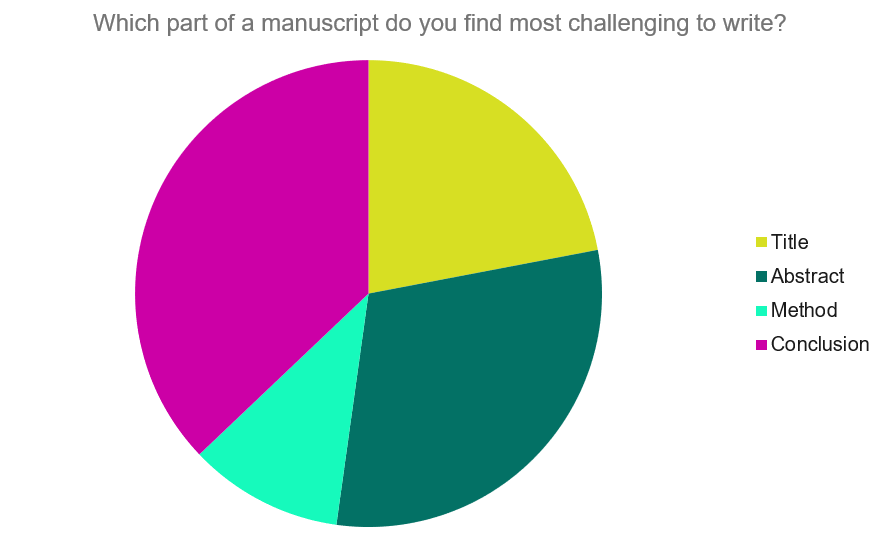
Questions to ask yourself:
- Was my hypothesis correct?
- If my hypothesis is partially correct or entirely different, what can be learned from the results?
- How do the conclusions reshape or add onto the existing knowledge in the field? What does previous research say about the topic?
- Why are the results important or relevant to your audience? Do they add further evidence to a scientific consensus or disprove prior studies?
- How can future research build on these observations? What are the key experiments that must be done?
- What is the “take-home” message you want your reader to leave with?
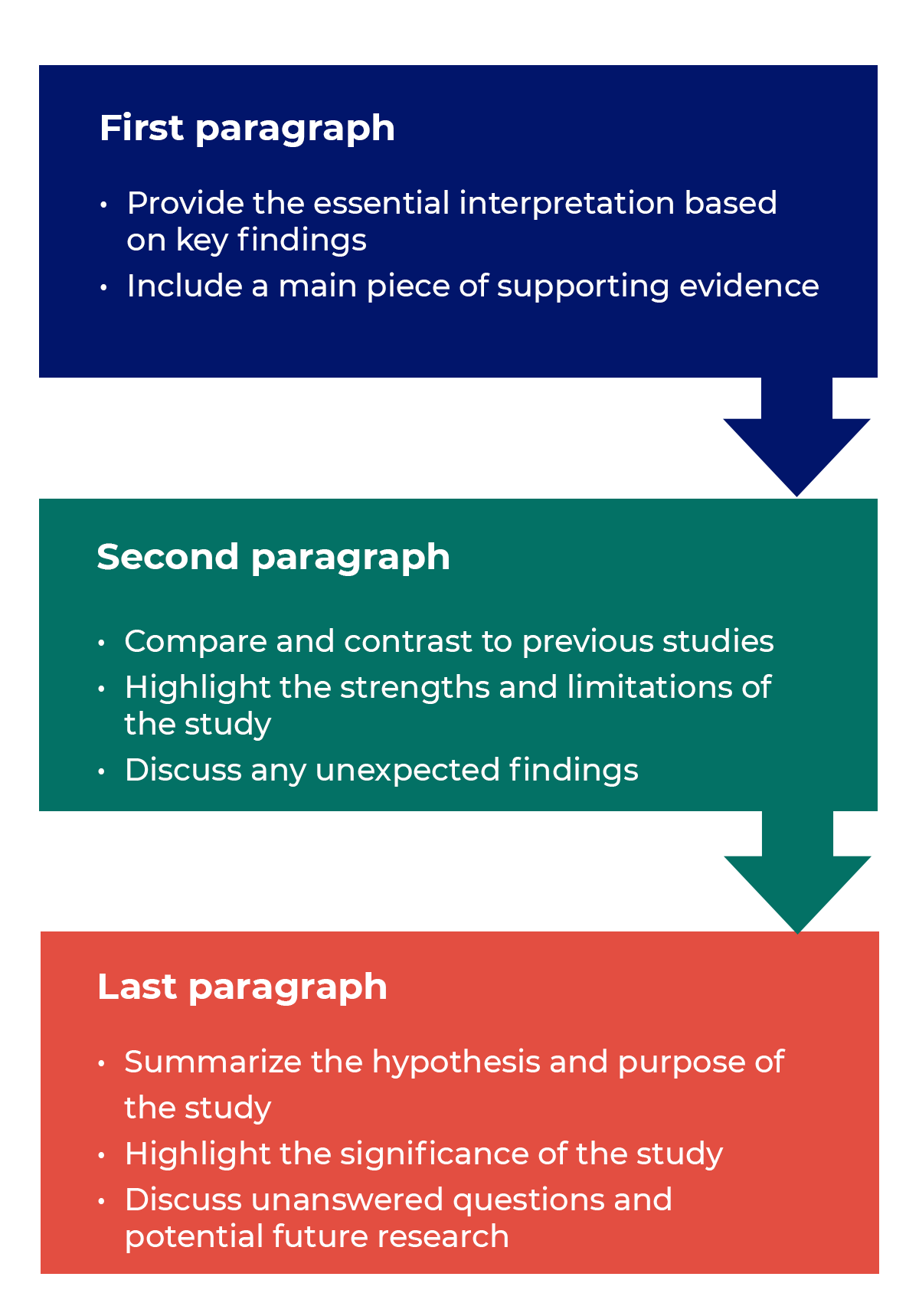
How to structure a discussion
Trying to fit a complete discussion into a single paragraph can add unnecessary stress to the writing process. If possible, you’ll want to give yourself two or three paragraphs to give the reader a comprehensive understanding of your study as a whole. Here’s one way to structure an effective discussion:
Writing Tips
While the above sections can help you brainstorm and structure your discussion, there are many common mistakes that writers revert to when having difficulties with their paper. Writing a discussion can be a delicate balance between summarizing your results, providing proper context for your research and avoiding introducing new information. Remember that your paper should be both confident and honest about the results!

- Read the journal’s guidelines on the discussion and conclusion sections. If possible, learn about the guidelines before writing the discussion to ensure you’re writing to meet their expectations.
- Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion.
- Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and limitations of the research.
- State whether the results prove or disprove your hypothesis. If your hypothesis was disproved, what might be the reasons?
- Introduce new or expanded ways to think about the research question. Indicate what next steps can be taken to further pursue any unresolved questions.
- If dealing with a contemporary or ongoing problem, such as climate change, discuss possible consequences if the problem is avoided.
- Be concise. Adding unnecessary detail can distract from the main findings.

Don’t
- Rewrite your abstract. Statements with “we investigated” or “we studied” generally do not belong in the discussion.
- Include new arguments or evidence not previously discussed. Necessary information and evidence should be introduced in the main body of the paper.
- Apologize. Even if your research contains significant limitations, don’t undermine your authority by including statements that doubt your methodology or execution.
- Shy away from speaking on limitations or negative results. Including limitations and negative results will give readers a complete understanding of the presented research. Potential limitations include sources of potential bias, threats to internal or external validity, barriers to implementing an intervention and other issues inherent to the study design.
- Overstate the importance of your findings. Making grand statements about how a study will fully resolve large questions can lead readers to doubt the success of the research.
Snippets of Effective Discussions:
Consumer-based actions to reduce plastic pollution in rivers: A multi-criteria decision analysis approach
Identifying reliable indicators of fitness in polar bears
- How to Write a Great Title
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
- Research Process
- Manuscript Preparation
- Manuscript Review
- Publication Process
- Publication Recognition
- Language Editing Services
- Translation Services

6 Steps to Write an Excellent Discussion in Your Manuscript
- 4 minute read
- 19.7K views
Table of Contents
The discussion section in scientific manuscripts might be the last few paragraphs, but its role goes far beyond wrapping up. It’s the part of an article where scientists talk about what they found and what it means, where raw data turns into meaningful insights. Therefore, discussion is a vital component of the article.
An excellent discussion is well-organized. We bring to you authors a classic 6-step method for writing discussion sections, with examples to illustrate the functions and specific writing logic of each step. Take a look at how you can impress journal reviewers with a concise and focused discussion section!
Discussion frame structure
Conventionally, a discussion section has three parts: an introductory paragraph, a few intermediate paragraphs, and a conclusion¹. Please follow the steps below:

1.Introduction—mention gaps in previous research¹⁻ ²
Here, you orient the reader to your study. In the first paragraph, it is advisable to mention the research gap your paper addresses.
Example: This study investigated the cognitive effects of a meat-only diet on adults. While earlier studies have explored the impact of a carnivorous diet on physical attributes and agility, they have not explicitly addressed its influence on cognitively intense tasks involving memory and reasoning.
2. Summarizing key findings—let your data speak ¹⁻ ²
After you have laid out the context for your study, recapitulate some of its key findings. Also, highlight key data and evidence supporting these findings.
Example: We found that risk-taking behavior among teenagers correlates with their tendency to invest in cryptocurrencies. Risk takers in this study, as measured by the Cambridge Gambling Task, tended to have an inordinately higher proportion of their savings invested as crypto coins.
3. Interpreting results—compare with other papers¹⁻²
Here, you must analyze and interpret any results concerning the research question or hypothesis. How do the key findings of your study help verify or disprove the hypothesis? What practical relevance does your discovery have?
Example: Our study suggests that higher daily caffeine intake is not associated with poor performance in major sporting events. Athletes may benefit from the cardiovascular benefits of daily caffeine intake without adversely impacting performance.
Remember, unlike the results section, the discussion ideally focuses on locating your findings in the larger body of existing research. Hence, compare your results with those of other peer-reviewed papers.
Example: Although Miller et al. (2020) found evidence of such political bias in a multicultural population, our findings suggest that the bias is weak or virtually non-existent among politically active citizens.
4. Addressing limitations—their potential impact on the results¹⁻²
Discuss the potential impact of limitations on the results. Most studies have limitations, and it is crucial to acknowledge them in the intermediary paragraphs of the discussion section. Limitations may include low sample size, suspected interference or noise in data, low effect size, etc.
Example: This study explored a comprehensive list of adverse effects associated with the novel drug ‘X’. However, long-term studies may be needed to confirm its safety, especially regarding major cardiac events.
5. Implications for future research—how to explore further¹⁻²
Locate areas of your research where more investigation is needed. Concluding paragraphs of the discussion can explain what research will likely confirm your results or identify knowledge gaps your study left unaddressed.
Example: Our study demonstrates that roads paved with the plastic-infused compound ‘Y’ are more resilient than asphalt. Future studies may explore economically feasible ways of producing compound Y in bulk.
6. Conclusion—summarize content¹⁻²
A good way to wind up the discussion section is by revisiting the research question mentioned in your introduction. Sign off by expressing the main findings of your study.
Example: Recent observations suggest that the fish ‘Z’ is moving upriver in many parts of the Amazon basin. Our findings provide conclusive evidence that this phenomenon is associated with rising sea levels and climate change, not due to elevated numbers of invasive predators.
A rigorous and concise discussion section is one of the keys to achieving an excellent paper. It serves as a critical platform for researchers to interpret and connect their findings with the broader scientific context. By detailing the results, carefully comparing them with existing research, and explaining the limitations of this study, you can effectively help reviewers and readers understand the entire research article more comprehensively and deeply¹⁻² , thereby helping your manuscript to be successfully published and gain wider dissemination.
In addition to keeping this writing guide, you can also use Elsevier Language Services to improve the quality of your paper more deeply and comprehensively. We have a professional editing team covering multiple disciplines. With our profound disciplinary background and rich polishing experience, we can significantly optimize all paper modules including the discussion, effectively improve the fluency and rigor of your articles, and make your scientific research results consistent, with its value reflected more clearly. We are always committed to ensuring the quality of papers according to the standards of top journals, improving the publishing efficiency of scientific researchers, and helping you on the road to academic success. Check us out here !
Type in wordcount for Standard Total: USD EUR JPY Follow this link if your manuscript is longer than 12,000 words. Upload
References:
- Masic, I. (2018). How to write an efficient discussion? Medical Archives , 72(3), 306. https://doi.org/10.5455/medarh.2018.72.306-307
- Şanlı, Ö., Erdem, S., & Tefik, T. (2014). How to write a discussion section? Urology Research & Practice , 39(1), 20–24. https://doi.org/10.5152/tud.2013.049

Navigating “Chinglish” Errors in Academic English Writing

A Guide to Crafting Shorter, Impactful Sentences in Academic Writing
You may also like.

Submission 101: What format should be used for academic papers?

Page-Turner Articles are More Than Just Good Arguments: Be Mindful of Tone and Structure!

A Must-see for Researchers! How to Ensure Inclusivity in Your Scientific Writing

Make Hook, Line, and Sinker: The Art of Crafting Engaging Introductions

Can Describing Study Limitations Improve the Quality of Your Paper?

How to Write Clear and Crisp Civil Engineering Papers? Here are 5 Key Tips to Consider

The Clear Path to An Impactful Paper: ②
Input your search keywords and press Enter.
How to Write the Discussion Section of a Research Paper
The discussion section of a research paper analyzes and interprets the findings, provides context, compares them with previous studies, identifies limitations, and suggests future research directions.
Updated on September 15, 2023

Structure your discussion section right, and you’ll be cited more often while doing a greater service to the scientific community. So, what actually goes into the discussion section? And how do you write it?
The discussion section of your research paper is where you let the reader know how your study is positioned in the literature, what to take away from your paper, and how your work helps them. It can also include your conclusions and suggestions for future studies.
First, we’ll define all the parts of your discussion paper, and then look into how to write a strong, effective discussion section for your paper or manuscript.
Discussion section: what is it, what it does
The discussion section comes later in your paper, following the introduction, methods, and results. The discussion sets up your study’s conclusions. Its main goals are to present, interpret, and provide a context for your results.
What is it?
The discussion section provides an analysis and interpretation of the findings, compares them with previous studies, identifies limitations, and suggests future directions for research.
This section combines information from the preceding parts of your paper into a coherent story. By this point, the reader already knows why you did your study (introduction), how you did it (methods), and what happened (results). In the discussion, you’ll help the reader connect the ideas from these sections.
Why is it necessary?
The discussion provides context and interpretations for the results. It also answers the questions posed in the introduction. While the results section describes your findings, the discussion explains what they say. This is also where you can describe the impact or implications of your research.
Adds context for your results
Most research studies aim to answer a question, replicate a finding, or address limitations in the literature. These goals are first described in the introduction. However, in the discussion section, the author can refer back to them to explain how the study's objective was achieved.
Shows what your results actually mean and real-world implications
The discussion can also describe the effect of your findings on research or practice. How are your results significant for readers, other researchers, or policymakers?
What to include in your discussion (in the correct order)
A complete and effective discussion section should at least touch on the points described below.
Summary of key findings
The discussion should begin with a brief factual summary of the results. Concisely overview the main results you obtained.
Begin with key findings with supporting evidence
Your results section described a list of findings, but what message do they send when you look at them all together?
Your findings were detailed in the results section, so there’s no need to repeat them here, but do provide at least a few highlights. This will help refresh the reader’s memory and help them focus on the big picture.
Read the first paragraph of the discussion section in this article (PDF) for an example of how to start this part of your paper. Notice how the authors break down their results and follow each description sentence with an explanation of why each finding is relevant.
State clearly and concisely
Following a clear and direct writing style is especially important in the discussion section. After all, this is where you will make some of the most impactful points in your paper. While the results section often contains technical vocabulary, such as statistical terms, the discussion section lets you describe your findings more clearly.
Interpretation of results
Once you’ve given your reader an overview of your results, you need to interpret those results. In other words, what do your results mean? Discuss the findings’ implications and significance in relation to your research question or hypothesis.
Analyze and interpret your findings
Look into your findings and explore what’s behind them or what may have caused them. If your introduction cited theories or studies that could explain your findings, use these sources as a basis to discuss your results.
For example, look at the second paragraph in the discussion section of this article on waggling honey bees. Here, the authors explore their results based on information from the literature.
Unexpected or contradictory results
Sometimes, your findings are not what you expect. Here’s where you describe this and try to find a reason for it. Could it be because of the method you used? Does it have something to do with the variables analyzed? Comparing your methods with those of other similar studies can help with this task.
Context and comparison with previous work
Refer to related studies to place your research in a larger context and the literature. Compare and contrast your findings with existing literature, highlighting similarities, differences, and/or contradictions.
How your work compares or contrasts with previous work
Studies with similar findings to yours can be cited to show the strength of your findings. Information from these studies can also be used to help explain your results. Differences between your findings and others in the literature can also be discussed here.
How to divide this section into subsections
If you have more than one objective in your study or many key findings, you can dedicate a separate section to each of these. Here’s an example of this approach. You can see that the discussion section is divided into topics and even has a separate heading for each of them.
Limitations
Many journals require you to include the limitations of your study in the discussion. Even if they don’t, there are good reasons to mention these in your paper.
Why limitations don’t have a negative connotation
A study’s limitations are points to be improved upon in future research. While some of these may be flaws in your method, many may be due to factors you couldn’t predict.
Examples include time constraints or small sample sizes. Pointing this out will help future researchers avoid or address these issues. This part of the discussion can also include any attempts you have made to reduce the impact of these limitations, as in this study .
How limitations add to a researcher's credibility
Pointing out the limitations of your study demonstrates transparency. It also shows that you know your methods well and can conduct a critical assessment of them.
Implications and significance
The final paragraph of the discussion section should contain the take-home messages for your study. It can also cite the “strong points” of your study, to contrast with the limitations section.

Restate your hypothesis
Remind the reader what your hypothesis was before you conducted the study.
How was it proven or disproven?
Identify your main findings and describe how they relate to your hypothesis.
How your results contribute to the literature
Were you able to answer your research question? Or address a gap in the literature?
Future implications of your research
Describe the impact that your results may have on the topic of study. Your results may show, for instance, that there are still limitations in the literature for future studies to address. There may be a need for studies that extend your findings in a specific way. You also may need additional research to corroborate your findings.
Sample discussion section
This fictitious example covers all the aspects discussed above. Your actual discussion section will probably be much longer, but you can read this to get an idea of everything your discussion should cover.
Our results showed that the presence of cats in a household is associated with higher levels of perceived happiness by its human occupants. These findings support our hypothesis and demonstrate the association between pet ownership and well-being.
The present findings align with those of Bao and Schreer (2016) and Hardie et al. (2023), who observed greater life satisfaction in pet owners relative to non-owners. Although the present study did not directly evaluate life satisfaction, this factor may explain the association between happiness and cat ownership observed in our sample.
Our findings must be interpreted in light of some limitations, such as the focus on cat ownership only rather than pets as a whole. This may limit the generalizability of our results.
Nevertheless, this study had several strengths. These include its strict exclusion criteria and use of a standardized assessment instrument to investigate the relationships between pets and owners. These attributes bolster the accuracy of our results and reduce the influence of confounding factors, increasing the strength of our conclusions. Future studies may examine the factors that mediate the association between pet ownership and happiness to better comprehend this phenomenon.
This brief discussion begins with a quick summary of the results and hypothesis. The next paragraph cites previous research and compares its findings to those of this study. Information from previous studies is also used to help interpret the findings. After discussing the results of the study, some limitations are pointed out. The paper also explains why these limitations may influence the interpretation of results. Then, final conclusions are drawn based on the study, and directions for future research are suggested.
How to make your discussion flow naturally
If you find writing in scientific English challenging, the discussion and conclusions are often the hardest parts of the paper to write. That’s because you’re not just listing up studies, methods, and outcomes. You’re actually expressing your thoughts and interpretations in words.
- How formal should it be?
- What words should you use, or not use?
- How do you meet strict word limits, or make it longer and more informative?
Always give it your best, but sometimes a helping hand can, well, help. Getting a professional edit can help clarify your work’s importance while improving the English used to explain it. When readers know the value of your work, they’ll cite it. We’ll assign your study to an expert editor knowledgeable in your area of research. Their work will clarify your discussion, helping it to tell your story. Find out more about AJE Editing.

Adam Goulston, PsyD, MS, MBA, MISD, ELS
Science Marketing Consultant
See our "Privacy Policy"
Ensure your structure and ideas are consistent and clearly communicated
Pair your Premium Editing with our add-on service Presubmission Review for an overall assessment of your manuscript.
- Our Mission
- Code of Conduct
- The Consultants
- Hours and Locations
- Apply to Become a Consultant
- Make an Appointment
- Face-to-Face Appointments
- Zoom Appointments
- Written Feedback Appointments
- Support for Writers with Disabilities
- Policies and Restrictions
- Upcoming Workshops
- Class Workshops
- Meet the Consultants
- Writing Guides and Tools
- Login or Register
- Graduate Writing Consultations
- Thesis and Dissertation Consultations
- Weekly Write-Ins
- ESOL Graduate Peer Feedback Groups
- Setting Up Your Own Writing Group
- Writing Resources for Graduate Students
- Support for Multilingual Students
- ESOL Opt-In Program
- About Our Consulting Services
- Promote Us to Your Students
- Recommend Consultants
IMRaD Results Discussion
Results and Discussion Sections in Scientific Research Reports (IMRaD)
After introducing the study and describing its methodology, an IMRaD* report presents and discusses the main findings of the study. In the results section, writers systematically report their findings, and in discussion , they interpret these findings. If the discussion section is not followed by a separate conclusion section, then the discussion will include elements of a conclusion as well (e.g., provide limitations, directions for future research, or other moves outlined in the handout “IMRaD Conclusions”).
* IMRaD refers to reports with the structure Introduction-Method-Results-Discussion used in empirical research in natural and social sciences. Please refer to the Writing Center quick guide “Writing an IMRaD Report” for more explanations.
Depending on the discipline, journal, and the nature of the study, the results, discussion, and even conclusion sections can be organized in varying ways:
Option 1 : Results and discussion in separate sections with conclusion moves included in the discussion section
Option 2 : Results and discussion combined; conclusion separate
Option 3 : Results , discussion , and conclusion in separate sections
Results (What did you find?): Creating a results section involves systematically presenting and describing the outcomes of the study. To summarize results, writers often use visual representations: Tables and figures are commonly included in the results sections to ensure clarity.
Discussion (What does it mean?): Discussion sections interpret the most significant results as they help shed light on the study’s research questions. While writing a discussion section, writers compare the results of their study with previous research as well as speculate on the explanations for such findings.
Common Moves in Results Sections
Below are some moves, sub-moves, and language commonly used in results and discussion sections.
| To identify the difference between A and B, ... | ||
| a) Referring to data in tables or charts b) Emphasizing significant data trends in tables or charts | a) Figure 1 compares the results obtained from the preliminary analysis of X. b) Figure 10 demonstrates a clear trend of decreasing... | |
| a) Stating a positive result b) Stating a negative result c) Highlighting interesting or surprising results | a) Strong evidence of X was found when... b) There was no evidence that X has an influence on... c) Interestingly, X was observed to... | |
| a) Reporting response rates b) Reporting proportions c) Reporting theme d) Reporting participants' views e) Introducing experts | a) Respondents were asked to indicate whether... b) 70% of those who were interviewed indicated that... c) Another reported problem was... d) One interviewee argued that... | |
| a) Seamlessly moving out of one result and into another b) Summarizing the results section | a) Comparing the two results, it can be seen that... b) Overall, the experiments show that... |
The table is based on the information from University of Manchester’s Academic Phrasebank http://www.phrasebank.manchester.ac.uk/reporting-results/
Common Moves in Discussion Sections
| a) Reference to the literature b) Reference to the question | a) Prior studies have noted the importance of... b) With respect to the first research question, it was found that... | |
| a) Summarizing results b) Supporting previous findings c) Contradicting previous findings d) Indicating an unexpected outcome e) Offering an explanation for the findings | a) The results of this study show/indicate that... b) This finding is consistent with that of Doe at al. (2000) who... c) This outcome is contrary to that of Doe et al. (2017) who found... d) One unanticipated finding was that... e) This discrepancy could be attributed to... | |
| Although exclusion of X did not..., these results should be interpreted with caution | ||
| It is therefore likely that connections exist between... |
The table is based on the information from University of Manchester’s Academic Phrasebank http://www.phrasebank.manchester.ac.uk/discussing-findings/
Activity to help you prepare for writing IMRaD results and discussion sections
Choose a journal in your discipline and read the results and discussion sections of a few IMRaD reports. Analyze these sections addressing the following questions:
- How are the sections organized? Are results and discussion presented together or in separate sections? Is the conclusion a separate section or a part of the discussion? Why do you think the authors decided to follow such organizational patterns?
- Which moves and sub-moves are present in the results and discussion sections of these reports?
- What language or contextual clues helped you identify these moves?
- How often are citations used in both sections? When or for which purposes do the authors use each citation?
- How often is passive voice used? Which tense(s) do the authors predominantly rely on? How can you explain this use?
Last updated 09/03/2019

The Writing Center
4400 University Drive, 2G8 Fairfax, VA 22030
- Johnson Center, Room 227E
- +1-703-993-1200
- [email protected]
Quick Links
- Register with us
© Copyright 2024 George Mason University . All Rights Reserved. Privacy Statement | Accessibility

- LEARNING SKILLS
- Writing a Dissertation or Thesis
- Results and Discussion
Search SkillsYouNeed:
Learning Skills:
- A - Z List of Learning Skills
- What is Learning?
- Learning Approaches
- Learning Styles
- 8 Types of Learning Styles
- Understanding Your Preferences to Aid Learning
- Lifelong Learning
- Decisions to Make Before Applying to University
- Top Tips for Surviving Student Life
- Living Online: Education and Learning
- 8 Ways to Embrace Technology-Based Learning Approaches
- Critical Thinking Skills
- Critical Thinking and Fake News
- Understanding and Addressing Conspiracy Theories
- Critical Analysis
- Study Skills
- Exam Skills
- How to Write a Research Proposal
- Ethical Issues in Research
- Dissertation: The Introduction
- Researching and Writing a Literature Review
- Writing your Methodology
- Dissertation: Results and Discussion
- Dissertation: Conclusions and Extras
Writing Your Dissertation or Thesis eBook

Part of the Skills You Need Guide for Students .
- Research Methods
- Teaching, Coaching, Mentoring and Counselling
- Employability Skills for Graduates
Subscribe to our FREE newsletter and start improving your life in just 5 minutes a day.
You'll get our 5 free 'One Minute Life Skills' and our weekly newsletter.
We'll never share your email address and you can unsubscribe at any time.
Writing your Dissertation: Results and Discussion
When writing a dissertation or thesis, the results and discussion sections can be both the most interesting as well as the most challenging sections to write.
You may choose to write these sections separately, or combine them into a single chapter, depending on your university’s guidelines and your own preferences.
There are advantages to both approaches.
Writing the results and discussion as separate sections allows you to focus first on what results you obtained and set out clearly what happened in your experiments and/or investigations without worrying about their implications.This can focus your mind on what the results actually show and help you to sort them in your head.
However, many people find it easier to combine the results with their implications as the two are closely connected.
Check your university’s requirements carefully before combining the results and discussions sections as some specify that they must be kept separate.
Results Section
The Results section should set out your key experimental results, including any statistical analysis and whether or not the results of these are significant.
You should cover any literature supporting your interpretation of significance. It does not have to include everything you did, particularly for a doctorate dissertation. However, for an undergraduate or master's thesis, you will probably find that you need to include most of your work.
You should write your results section in the past tense: you are describing what you have done in the past.
Every result included MUST have a method set out in the methods section. Check back to make sure that you have included all the relevant methods.
Conversely, every method should also have some results given so, if you choose to exclude certain experiments from the results, make sure that you remove mention of the method as well.
If you are unsure whether to include certain results, go back to your research questions and decide whether the results are relevant to them. It doesn’t matter whether they are supportive or not, it’s about relevance. If they are relevant, you should include them.
Having decided what to include, next decide what order to use. You could choose chronological, which should follow the methods, or in order from most to least important in the answering of your research questions, or by research question and/or hypothesis.
You also need to consider how best to present your results: tables, figures, graphs, or text. Try to use a variety of different methods of presentation, and consider your reader: 20 pages of dense tables are hard to understand, as are five pages of graphs, but a single table and well-chosen graph that illustrate your overall findings will make things much clearer.
Make sure that each table and figure has a number and a title. Number tables and figures in separate lists, but consecutively by the order in which you mention them in the text. If you have more than about two or three, it’s often helpful to provide lists of tables and figures alongside the table of contents at the start of your dissertation.
Summarise your results in the text, drawing on the figures and tables to illustrate your points.
The text and figures should be complementary, not repeat the same information. You should refer to every table or figure in the text. Any that you don’t feel the need to refer to can safely be moved to an appendix, or even removed.
Make sure that you including information about the size and direction of any changes, including percentage change if appropriate. Statistical tests should include details of p values or confidence intervals and limits.
While you don’t need to include all your primary evidence in this section, you should as a matter of good practice make it available in an appendix, to which you should refer at the relevant point.
For example:
Details of all the interview participants can be found in Appendix A, with transcripts of each interview in Appendix B.
You will, almost inevitably, find that you need to include some slight discussion of your results during this section. This discussion should evaluate the quality of the results and their reliability, but not stray too far into discussion of how far your results support your hypothesis and/or answer your research questions, as that is for the discussion section.
See our pages: Analysing Qualitative Data and Simple Statistical Analysis for more information on analysing your results.
Discussion Section
This section has four purposes, it should:
- Interpret and explain your results
- Answer your research question
- Justify your approach
- Critically evaluate your study
The discussion section therefore needs to review your findings in the context of the literature and the existing knowledge about the subject.
You also need to demonstrate that you understand the limitations of your research and the implications of your findings for policy and practice. This section should be written in the present tense.
The Discussion section needs to follow from your results and relate back to your literature review . Make sure that everything you discuss is covered in the results section.
Some universities require a separate section on recommendations for policy and practice and/or for future research, while others allow you to include this in your discussion, so check the guidelines carefully.
Starting the Task
Most people are likely to write this section best by preparing an outline, setting out the broad thrust of the argument, and how your results support it.
You may find techniques like mind mapping are helpful in making a first outline; check out our page: Creative Thinking for some ideas about how to think through your ideas. You should start by referring back to your research questions, discuss your results, then set them into the context of the literature, and then into broader theory.
This is likely to be one of the longest sections of your dissertation, and it’s a good idea to break it down into chunks with sub-headings to help your reader to navigate through the detail.
Fleshing Out the Detail
Once you have your outline in front of you, you can start to map out how your results fit into the outline.
This will help you to see whether your results are over-focused in one area, which is why writing up your research as you go along can be a helpful process. For each theme or area, you should discuss how the results help to answer your research question, and whether the results are consistent with your expectations and the literature.
The Importance of Understanding Differences
If your results are controversial and/or unexpected, you should set them fully in context and explain why you think that you obtained them.
Your explanations may include issues such as a non-representative sample for convenience purposes, a response rate skewed towards those with a particular experience, or your own involvement as a participant for sociological research.
You do not need to be apologetic about these, because you made a choice about them, which you should have justified in the methodology section. However, you do need to evaluate your own results against others’ findings, especially if they are different. A full understanding of the limitations of your research is part of a good discussion section.
At this stage, you may want to revisit your literature review, unless you submitted it as a separate submission earlier, and revise it to draw out those studies which have proven more relevant.
Conclude by summarising the implications of your findings in brief, and explain why they are important for researchers and in practice, and provide some suggestions for further work.
You may also wish to make some recommendations for practice. As before, this may be a separate section, or included in your discussion.
The results and discussion, including conclusion and recommendations, are probably the most substantial sections of your dissertation. Once completed, you can begin to relax slightly: you are on to the last stages of writing!
Continue to: Dissertation: Conclusion and Extras Writing your Methodology
See also: Writing a Literature Review Writing a Research Proposal Academic Referencing What Is the Importance of Using a Plagiarism Checker to Check Your Thesis?
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Write a Discussion Section for a Research Paper
We’ve talked about several useful writing tips that authors should consider while drafting or editing their research papers. In particular, we’ve focused on figures and legends , as well as the Introduction , Methods , and Results . Now that we’ve addressed the more technical portions of your journal manuscript, let’s turn to the analytical segments of your research article. In this article, we’ll provide tips on how to write a strong Discussion section that best portrays the significance of your research contributions.
What is the Discussion section of a research paper?
In a nutshell, your Discussion fulfills the promise you made to readers in your Introduction . At the beginning of your paper, you tell us why we should care about your research. You then guide us through a series of intricate images and graphs that capture all the relevant data you collected during your research. We may be dazzled and impressed at first, but none of that matters if you deliver an anti-climactic conclusion in the Discussion section!
Are you feeling pressured? Don’t worry. To be honest, you will edit the Discussion section of your manuscript numerous times. After all, in as little as one to two paragraphs ( Nature ‘s suggestion based on their 3,000-word main body text limit), you have to explain how your research moves us from point A (issues you raise in the Introduction) to point B (our new understanding of these matters). You must also recommend how we might get to point C (i.e., identify what you think is the next direction for research in this field). That’s a lot to say in two paragraphs!
So, how do you do that? Let’s take a closer look.
What should I include in the Discussion section?
As we stated above, the goal of your Discussion section is to answer the questions you raise in your Introduction by using the results you collected during your research . The content you include in the Discussions segment should include the following information:
- Remind us why we should be interested in this research project.
- Describe the nature of the knowledge gap you were trying to fill using the results of your study.
- Don’t repeat your Introduction. Instead, focus on why this particular study was needed to fill the gap you noticed and why that gap needed filling in the first place.
- Mainly, you want to remind us of how your research will increase our knowledge base and inspire others to conduct further research.
- Clearly tell us what that piece of missing knowledge was.
- Answer each of the questions you asked in your Introduction and explain how your results support those conclusions.
- Make sure to factor in all results relevant to the questions (even if those results were not statistically significant).
- Focus on the significance of the most noteworthy results.
- If conflicting inferences can be drawn from your results, evaluate the merits of all of them.
- Don’t rehash what you said earlier in the Results section. Rather, discuss your findings in the context of answering your hypothesis. Instead of making statements like “[The first result] was this…,” say, “[The first result] suggests [conclusion].”
- Do your conclusions line up with existing literature?
- Discuss whether your findings agree with current knowledge and expectations.
- Keep in mind good persuasive argument skills, such as explaining the strengths of your arguments and highlighting the weaknesses of contrary opinions.
- If you discovered something unexpected, offer reasons. If your conclusions aren’t aligned with current literature, explain.
- Address any limitations of your study and how relevant they are to interpreting your results and validating your findings.
- Make sure to acknowledge any weaknesses in your conclusions and suggest room for further research concerning that aspect of your analysis.
- Make sure your suggestions aren’t ones that should have been conducted during your research! Doing so might raise questions about your initial research design and protocols.
- Similarly, maintain a critical but unapologetic tone. You want to instill confidence in your readers that you have thoroughly examined your results and have objectively assessed them in a way that would benefit the scientific community’s desire to expand our knowledge base.
- Recommend next steps.
- Your suggestions should inspire other researchers to conduct follow-up studies to build upon the knowledge you have shared with them.
- Keep the list short (no more than two).
How to Write the Discussion Section
The above list of what to include in the Discussion section gives an overall idea of what you need to focus on throughout the section. Below are some tips and general suggestions about the technical aspects of writing and organization that you might find useful as you draft or revise the contents we’ve outlined above.
Technical writing elements
- Embrace active voice because it eliminates the awkward phrasing and wordiness that accompanies passive voice.
- Use the present tense, which should also be employed in the Introduction.
- Sprinkle with first person pronouns if needed, but generally, avoid it. We want to focus on your findings.
- Maintain an objective and analytical tone.
Discussion section organization
- Keep the same flow across the Results, Methods, and Discussion sections.
- We develop a rhythm as we read and parallel structures facilitate our comprehension. When you organize information the same way in each of these related parts of your journal manuscript, we can quickly see how a certain result was interpreted and quickly verify the particular methods used to produce that result.
- Notice how using parallel structure will eliminate extra narration in the Discussion part since we can anticipate the flow of your ideas based on what we read in the Results segment. Reducing wordiness is important when you only have a few paragraphs to devote to the Discussion section!
- Within each subpart of a Discussion, the information should flow as follows: (A) conclusion first, (B) relevant results and how they relate to that conclusion and (C) relevant literature.
- End with a concise summary explaining the big-picture impact of your study on our understanding of the subject matter. At the beginning of your Discussion section, you stated why this particular study was needed to fill the gap you noticed and why that gap needed filling in the first place. Now, it is time to end with “how your research filled that gap.”
Discussion Part 1: Summarizing Key Findings
Begin the Discussion section by restating your statement of the problem and briefly summarizing the major results. Do not simply repeat your findings. Rather, try to create a concise statement of the main results that directly answer the central research question that you stated in the Introduction section . This content should not be longer than one paragraph in length.
Many researchers struggle with understanding the precise differences between a Discussion section and a Results section . The most important thing to remember here is that your Discussion section should subjectively evaluate the findings presented in the Results section, and in relatively the same order. Keep these sections distinct by making sure that you do not repeat the findings without providing an interpretation.
Phrase examples: Summarizing the results
- The findings indicate that …
- These results suggest a correlation between A and B …
- The data present here suggest that …
- An interpretation of the findings reveals a connection between…
Discussion Part 2: Interpreting the Findings
What do the results mean? It may seem obvious to you, but simply looking at the figures in the Results section will not necessarily convey to readers the importance of the findings in answering your research questions.
The exact structure of interpretations depends on the type of research being conducted. Here are some common approaches to interpreting data:
- Identifying correlations and relationships in the findings
- Explaining whether the results confirm or undermine your research hypothesis
- Giving the findings context within the history of similar research studies
- Discussing unexpected results and analyzing their significance to your study or general research
- Offering alternative explanations and arguing for your position
Organize the Discussion section around key arguments, themes, hypotheses, or research questions or problems. Again, make sure to follow the same order as you did in the Results section.
Discussion Part 3: Discussing the Implications
In addition to providing your own interpretations, show how your results fit into the wider scholarly literature you surveyed in the literature review section. This section is called the implications of the study . Show where and how these results fit into existing knowledge, what additional insights they contribute, and any possible consequences that might arise from this knowledge, both in the specific research topic and in the wider scientific domain.
Questions to ask yourself when dealing with potential implications:
- Do your findings fall in line with existing theories, or do they challenge these theories or findings? What new information do they contribute to the literature, if any? How exactly do these findings impact or conflict with existing theories or models?
- What are the practical implications on actual subjects or demographics?
- What are the methodological implications for similar studies conducted either in the past or future?
Your purpose in giving the implications is to spell out exactly what your study has contributed and why researchers and other readers should be interested.
Phrase examples: Discussing the implications of the research
- These results confirm the existing evidence in X studies…
- The results are not in line with the foregoing theory that…
- This experiment provides new insights into the connection between…
- These findings present a more nuanced understanding of…
- While previous studies have focused on X, these results demonstrate that Y.
Step 4: Acknowledging the limitations
All research has study limitations of one sort or another. Acknowledging limitations in methodology or approach helps strengthen your credibility as a researcher. Study limitations are not simply a list of mistakes made in the study. Rather, limitations help provide a more detailed picture of what can or cannot be concluded from your findings. In essence, they help temper and qualify the study implications you listed previously.
Study limitations can relate to research design, specific methodological or material choices, or unexpected issues that emerged while you conducted the research. Mention only those limitations directly relate to your research questions, and explain what impact these limitations had on how your study was conducted and the validity of any interpretations.
Possible types of study limitations:
- Insufficient sample size for statistical measurements
- Lack of previous research studies on the topic
- Methods/instruments/techniques used to collect the data
- Limited access to data
- Time constraints in properly preparing and executing the study
After discussing the study limitations, you can also stress that your results are still valid. Give some specific reasons why the limitations do not necessarily handicap your study or narrow its scope.
Phrase examples: Limitations sentence beginners
- “There may be some possible limitations in this study.”
- “The findings of this study have to be seen in light of some limitations.”
- “The first limitation is the…The second limitation concerns the…”
- “The empirical results reported herein should be considered in the light of some limitations.”
- “This research, however, is subject to several limitations.”
- “The primary limitation to the generalization of these results is…”
- “Nonetheless, these results must be interpreted with caution and a number of limitations should be borne in mind.”
Discussion Part 5: Giving Recommendations for Further Research
Based on your interpretation and discussion of the findings, your recommendations can include practical changes to the study or specific further research to be conducted to clarify the research questions. Recommendations are often listed in a separate Conclusion section , but often this is just the final paragraph of the Discussion section.
Suggestions for further research often stem directly from the limitations outlined. Rather than simply stating that “further research should be conducted,” provide concrete specifics for how future can help answer questions that your research could not.
Phrase examples: Recommendation sentence beginners
- Further research is needed to establish …
- There is abundant space for further progress in analyzing…
- A further study with more focus on X should be done to investigate…
- Further studies of X that account for these variables must be undertaken.
Consider Receiving Professional Language Editing
As you edit or draft your research manuscript, we hope that you implement these guidelines to produce a more effective Discussion section. And after completing your draft, don’t forget to submit your work to a professional proofreading and English editing service like Wordvice, including our manuscript editing service for paper editing , cover letter editing , SOP editing , and personal statement proofreading services. Language editors not only proofread and correct errors in grammar, punctuation, mechanics, and formatting but also improve terms and revise phrases so they read more naturally. Wordvice is an industry leader in providing high-quality revision for all types of academic documents.
For additional information about how to write a strong research paper, make sure to check out our full research writing series !
Wordvice Writing Resources
- How to Write a Research Paper Introduction
- Which Verb Tenses to Use in a Research Paper
- How to Write an Abstract for a Research Paper
- How to Write a Research Paper Title
- Useful Phrases for Academic Writing
- Common Transition Terms in Academic Papers
- Active and Passive Voice in Research Papers
- 100+ Verbs That Will Make Your Research Writing Amazing
- Tips for Paraphrasing in Research Papers
Additional Academic Resources
- Guide for Authors. (Elsevier)
- How to Write the Results Section of a Research Paper. (Bates College)
- Structure of a Research Paper. (University of Minnesota Biomedical Library)
- How to Choose a Target Journal (Springer)
- How to Write Figures and Tables (UNC Writing Center)
alwaysresearching.com
never stop your research process
Guide on how to write results and discussion in a research paper.
The results and discussion section of a research paper document what you did in the entire research. You could call them the most important sections in a research paper, although other sections are also important. To write the results and discussion in research paper, you need to have the technical know-how of writing. We will give you practical tips on starting and writing results and discussions if you keep reading.
What is the difference between results and discussion in academic writing?
Before we get into how to write these two important sections in a research paper, let’s talk about their differences. The major difference between them is what aspect of the entire research they contain. The results section objectively reports your findings as they are; no speculations on why you found the results. On the other hand, the discussion section interprets the results, putting them in context, and explaining their importance.
Both sections are sometimes combined in research, particularly in qualitative research. In quantitative research, you are expected to separate the results from the discussion – that is, each section on different pages. An excellent place to get a good idea of how two write these sections is in a results and discussion example.
How to write discussion in research paper
In the discussion section of a research paper, you’re going in-depth with your findings, discussing their meaning, importance, and relevance. You’re not including any background research; you’re instead focusing on evaluating and explaining your results. Then, you’ll indicate how it relates to your research questions or thesis statement and literature review. Below is what to include in the discussion section of a research paper t:
- Results summary : In one paragraph, reiterate the research problem and briefly discuss your major results. Avoid repeating the data you already reported in the results section; clearly state the result that directly answers your research problem.
- Interpret your results : Your aim is to ensure your readers understand your results, how they answer the research questions, and their significance to them. This section typically covers identifying patterns and correlations among the data and discussing whether or not the results supported your thesis. It also contextualizes your results with previous research, explains unexpected results and their significance, considers possible explanations, and argues your position.
- Discussing the implications : While giving your interpretation of the results, don’t forget to relate them back to the articles you used in the literature review. This shows how your results fit with existing knowledge, the insights they contribute, and their consequences for practice or theory.
- State the limitations : Every research has its limitations, even the best ones; you need to acknowledge your research’s limitations to demonstrate your credibility. You’re not necessarily listing errors; you’re giving a realistic picture of what your study can and cannot do.
- Recommend : Use your findings to recommend further research or practical implementation; this part sometimes goes with the conclusion. Instead of stating that more studies be done, show what and how future work can build on the areas your paper couldn’t address.
Practical tips on how to start a results and discussion section
The results and discussion section of a research paper can be the easiest part to write or the hardest. It all depends on you knowing what to include and not include and how to start writing. Below are helpful tips for writing the results and discussion section of a research paper:
- Please don’t repeat the results in the discussion; start with repeating the research questions and explain how the results answer them.
- Start from the simple results to the complex; you can even start with the conclusion first, but ensure it is consistent with your objectives.
- Don’t explain your results in the result section; simply state your findings as directly and simply as possible.
- Emphasize what new, different, or important things your results add to knowledge in the discussion section.
- Understand the difference between statistical significance and clinical importance.
- The tables and graphs in the results section should stand alone, with texts highlighting their importance or meaning.
- Arbitrarily present your results, with sidelights results not receiving equal weight.
Now, you can write your paper’s results and discussion section with these tips, understanding what and what not to include. We recommend that you go online and check through an example of discussion in research paper – or samples. If you see how professionals write it, you’re a step closer to being good at writing it yourself.

You Might Also Like

What Is the Normal Research Paper Length?
Best way to organize research and write a perfect paper, term paper help guide for your perfect piece, leave a reply cancel.
Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Results & Discussion
Characteristics of results & discussion.
- Results section contains data collected by scientists from experiments that they conducted.
- Data can be measurements, numbers, descriptions and/or observations.
- Scientific data is typically described using graphs, tables, figures, diagrams, maps, charts, photographs and/or equations.
- Discussion section provides an interpretation of the data, especially in context to previously published research.
The Results and Discussion sections can be written as separate sections (as shown in Fig. 2 ), but are often combined in a poster into one section called Results and Discussion. This is done in order to (1) save precious space on a poster for the many pieces of information that a scientist would like to tell their audience and (2) by combining the two sections, it becomes easier for the audience to understand the significance of the research. Combining the Results section and Discussion section in a poster is different for what is typically done for a scientific journal article. In most journal articles, the Results section is separated from the Discussion section. Journal articles are different from posters in that a scientist is not standing next to their journal article explaining it to a reader. Therefore, in a journal article, an author needs to provide more detailed information so that the reader can understand the research independently. Separating the Results section and Discussion section allows an author the space necessary to write a lengthier description of the research. Journal articles typically contain more text and more content (e.g., figures, tables) than posters.
The Results and Discussion section should contain data, typically in the form of a graph, histogram, chart, image, color-coded map or table ( Figs. 1 & 4 ). Very often data means numbers that scientists collect from making measurements. These data are typically presented to an audience in the form of graphs and charts to show a reader how these numbers change over time, space or experimental conditions ( Fig. 7 ). Numbers can increase, decrease or stay the same and a graph, or another type of figure, can be effectively used to convey this information to a reader in a visual format ( Fig. 7 ).
Figure 7. Example of a Graph

An audience will be attracted to a poster because of its figures and so it is very important for the author to pay particular attention to the creation, design and placement of the figures in a poster ( Figs. 1 & 4 ). A good figure is one that is informative, easy to comprehend and allows the reader to understand the significance of the data and experiment. Very often an author will use color to draw attention to a figure.
The Discussion section should state the importance of the research that is presented in the poster. It should provide an interpretation of the results, especially in context to previously published research. It may propose future experiments that need to be conducted as a result of the research presented in the poster. It should clearly illustrate the significance of the research with regards to new knowledge, understanding and/or discoveries that were made as part of the research.
Scientific Posters: A Learner's Guide Copyright © 2020 by Ella Weaver; Kylienne A. Shaul; Henry Griffy; and Brian H. Lower is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Langson Library
- Science Library
- Grunigen Medical Library
- Law Library
- Connect From Off-Campus
- Accessibility
- Gateway Study Center

Email this link
Writing a scientific paper.
- Writing a lab report
- INTRODUCTION
Writing a "good" results section
Figures and Captions in Lab Reports
"Results Checklist" from: How to Write a Good Scientific Paper. Chris A. Mack. SPIE. 2018.
Additional tips for results sections.
- LITERATURE CITED
- Bibliography of guides to scientific writing and presenting
- Peer Review
- Presentations
- Lab Report Writing Guides on the Web
This is the core of the paper. Don't start the results sections with methods you left out of the Materials and Methods section. You need to give an overall description of the experiments and present the data you found.
- Factual statements supported by evidence. Short and sweet without excess words
- Present representative data rather than endlessly repetitive data
- Discuss variables only if they had an effect (positive or negative)
- Use meaningful statistics
- Avoid redundancy. If it is in the tables or captions you may not need to repeat it
A short article by Dr. Brett Couch and Dr. Deena Wassenberg, Biology Program, University of Minnesota
- Present the results of the paper, in logical order, using tables and graphs as necessary.
- Explain the results and show how they help to answer the research questions posed in the Introduction. Evidence does not explain itself; the results must be presented and then explained.
- Avoid: presenting results that are never discussed; presenting results in chronological order rather than logical order; ignoring results that do not support the conclusions;
- Number tables and figures separately beginning with 1 (i.e. Table 1, Table 2, Figure 1, etc.).
- Do not attempt to evaluate the results in this section. Report only what you found; hold all discussion of the significance of the results for the Discussion section.
- It is not necessary to describe every step of your statistical analyses. Scientists understand all about null hypotheses, rejection rules, and so forth and do not need to be reminded of them. Just say something like, "Honeybees did not use the flowers in proportion to their availability (X2 = 7.9, p<0.05, d.f.= 4, chi-square test)." Likewise, cite tables and figures without describing in detail how the data were manipulated. Explanations of this sort should appear in a legend or caption written on the same page as the figure or table.
- You must refer in the text to each figure or table you include in your paper.
- Tables generally should report summary-level data, such as means ± standard deviations, rather than all your raw data. A long list of all your individual observations will mean much less than a few concise, easy-to-read tables or figures that bring out the main findings of your study.
- Only use a figure (graph) when the data lend themselves to a good visual representation. Avoid using figures that show too many variables or trends at once, because they can be hard to understand.
From: https://writingcenter.gmu.edu/guides/imrad-results-discussion
- << Previous: METHODS
- Next: DISCUSSION >>
- Last Updated: Aug 4, 2023 9:33 AM
- URL: https://guides.lib.uci.edu/scientificwriting
Off-campus? Please use the Software VPN and choose the group UCIFull to access licensed content. For more information, please Click here
Software VPN is not available for guests, so they may not have access to some content when connecting from off-campus.
- Translation
Writing a compelling results and discussion section
By charlesworth author services.
- Charlesworth Author Services
- 12 March, 2021
- Academic Writing Skills
In the results section of your academic paper, you present what you found when you conducted your analyses, whereas in your discussion section you explain what your results mean and connect them to prior research studies. In other words, the results section is where you describe what you did, and the discussion sections is where you describe what this means for the field.
The results section should include the findings of your study without any interpretations or implications that you can draw from those results. Here, you present the findings using text supported by tables, charts, graphs and other figures. For example, in the following excerpt from article by Tolksdorf, Crawshaw, & Rohlfing, (2021), you can see how directly they report the results of their study.
Contrary to our hypothesis, there was no main effect of time, F(3, ∞) = 0.638, p = 0.166, and no significant interaction between experimental condition and time, F(3, ∞) = 0.427, p = 0.133, indicating that no significant changes in children's social referencing behavior were found in either group over the entire course of the sessions, including all learning and test situations. However, there was a highly significant main effect of condition F(1, 16.99) = 49.08, p < 0.001, demonstrating that children in the human condition displayed social referencing significantly more often than their peers interacting with the robotic partner. (p. 6)
Further in the results section the authors use a table to illustrate their results.
Table 1 presents an overview of the different interactional contexts in which children’s social referencing was situated during the long-term interaction. (p. 6)
As you can see, the results section is very direct and reports the outcome from the statistical analyses conducted. Tables and figures can help break up this section, as it can be very technical. In addition, using visuals in this way makes the results more accessible to readers.
The discussion section, which follows the results section, will include an explanation of the results. In this section, you should connect your results to previous research studies, make explicit connections back to your research question(s) and include an explanation about how the results might be generalized. This is where you make an argument that supports your main conclusions. Unlike the results section, the discussion section is where you interpret your results and explain what they mean, draw implications from your results and articulate why they matter, discuss any limitations of your results, and provide recommendations that can be made from these results. The following excerpts from the Tolksdorf, Crawshaw, & Rohlfing, (2021), help to further illustrate the difference between the results and discussions sections.
Contrary to our prior assumption, we could not observe a significant decrease in children’s social referencing in both groups despite the repetition of the interaction and increasing familiarity with the situation. Whereas, there appeared to be a slight decreasing tendency from the second to the third learning situation in each group, this trend may have been slowed down by the subsequent novel situation of the retention task, which again increased children’s reliance on the caregiver despite increasing familiarity with the interaction partner. (p. 8)
The large difference in children’s social referencing behavior between an interaction with the human vs. robotic partner is striking. One explanation for our findings is that a human partner naturally responds to various social cues (Kahle and Argyle, 2014) from the child in ways that social robots are not yet capable of, given their present technological limitations. (p. 8)
Notice how the authors provide a critical analysis of their results and offer explanations for what they found. In the second excerpt, observe how they tie an explanation for their result to prior research conducted in the field. Focusing on the results and discussion sections of different articles, and highlighting language that differentiates these sections from each other, can really help you to write your academic papers effectively.
Although the length and structure of the discussion section across research papers varies, there are some commonalities in the structure and content of these sections. Below is a suggested outline for a discussion section.
Paragraph 1.
In this paragraph provide a broad overview of the importance of your study. This is where you should restate your research topic. Avoid just repeating what you included in the results section. Include the main research findings that answer your primary research question(s).
Paragraph 2–3.
This section should be a critical analysis of your major findings. Here, you should articulate your interpretations of those findings. You should include whether these were the findings you expected and also whether they support any hypothesis you had. Provide explanations for the significance of the results and for any unexpected findings. Link your primary findings back to prior research studies. This section would also include any implications of your results.
Paragraph 4.
Here you would include a discussion of any secondary findings that are of note. Additionally, you would also include any limitations of your study and how future studies might mitigate these limitations. The excerpt below, from the Tolksdorf, Crawshaw, & Rohlfing, (2021) study, provides an example of this.
We would also like to point to the possibility that the study design and procedure could have impacted our results. Adapting the design of the interaction from the robot experimental setting to be suitably comparable when taking place with a human interaction partner required us to make certain decisions. (p. 9)
Paragraph 5.
This should include the conclusion of the discussion section, and future directions. In this section you could include any new research questions that arose as a result of your study. Implications from your findings for the field should also be discussed in this paragraph.
There are a number of common errors researchers make when writing the results and discussion sections. The following checklist can help you avoid these common mistakes.
Do not include interpretations or explanations of the findings in your results section. Remember that in the results section you are telling the reader what you found and in the discussion section you are telling them what it means and why it matters.
Do not exclude negative findings from your results section. Although the temptation is to report only positive findings, negative findings are important to other researchers.
You should not introduce any findings in your discussion section that were not included in the results section. These two sections should align, and you should discuss and explain only what you have already reported.
Don’t restate results in the discussion paper without an explanation or critical analysis of what they mean and why they matter.
Don’t forget to go back and check that these two sections align, and the flow from the results section to the discussion section is smooth and clear.
Tolksdorf NF, Crawshaw CE and Rohlfing KJ (2021) Comparing the Effects of a Different Social Partner (Social Robot vs. Human) on Children's Social Referencing in Interaction. Front. Educ. 5:569615. doi: 10.3389/feduc.2020.569615
Charlesworth Author Services, a trusted brand supporting the world’s leading academic publishers, institutions and authors since 1928. We only work with native English-speaking editors with advanced or postdoctoral degrees in their disciplines.
To know more about our services: Link(https://www.cwauthors.com/EditingServices)
Our academic writing and publishing training courses, online materials, and blog articles contain numerous tips and tricks to help you navigate academic writing and publishing, and maximise your potential as a researcher.
Join us on our FREE series of webinars designed to help the researchers in achieving their publication success.
Register: (https://www.cwauthors.com/article/webinar-schedule-2020)
Maximise your publication success with Charlesworth Author Services.
Scientific Editing Services
Sign up – stay updated.
We use cookies to offer you a personalized experience. By continuing to use this website, you consent to the use of cookies in accordance with our Cookie Policy.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMC Med Res Methodol

Writing a discussion section: how to integrate substantive and statistical expertise
Michael höfler.
1 Institute of Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany
5 Chair of Clinical Psychology and Behavioural Neuroscience, Institute of Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany
2 Behavioral Epidemiology, Institute of Clinical Psychology and Psychotherapy, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany
Sebastian Trautmann
Robert miller.
3 Faculty of Psychology, Technische Universität Dresden, Dresden, Germany
4 Department of Medical Epidemiology and Biostatistics, Karolinska Institute, Stockholm, Sweden
Associated Data
Not applicable.
When discussing results medical research articles often tear substantive and statistical (methodical) contributions apart, just as if both were independent. Consequently, reasoning on bias tends to be vague, unclear and superficial. This can lead to over-generalized, too narrow and misleading conclusions, especially for causal research questions.
To get the best possible conclusion, substantive and statistical expertise have to be integrated on the basis of reasonable assumptions. While statistics should raise questions on the mechanisms that have presumably created the data, substantive knowledge should answer them. Building on the related principle of Bayesian thinking, we make seven specific and four general proposals on writing a discussion section.
Misinterpretation could be reduced if authors explicitly discussed what can be concluded under which assumptions. Informed on the resulting conditional conclusions other researchers may, according to their knowledge and beliefs, follow a particular conclusion or, based on other conditions, arrive at another one. This could foster both an improved debate and a better understanding of the mechanisms behind the data and should therefore enable researchers to better address bias in future studies.
After a research article has presented the substantive background, the methods and the results, the discussion section assesses the validity of results and draws conclusions by interpreting them. The discussion puts the results into a broader context and reflects their implications for theoretical (e.g. etiological) and practical (e.g. interventional) purposes. As such, the discussion contains an article’s last words the reader is left with.
Common recommendations for the discussion section include general proposals for writing [ 1 ] and structuring (e.g. with a paragraph on a study’s strengths and weaknesses) [ 2 ], to avoid common statistical pitfalls (like misinterpreting non-significant findings as true null results) [ 3 ] and to “go beyond the data” when interpreting results [ 4 ]. Note that the latter includes much more than comparing an article’s results with the literature. If results and literature are consistent, this might be due to shared bias only. If they are not consistent, the question arises why inconsistency occurs – maybe because of bias acting differently across studies [ 5 – 7 ]. Recommendations like the CONSORT checklist do well in demanding all quantitative information on design, participation, compliance etc. to be reported in the methods and results section and “addressing sources of potential bias”, “limitations” and “considering other relevant evidence” in the discussion [ 8 , 9 ]. Similarly, the STROBE checklist for epidemiological research demands “a cautious overall interpretation of results” and "discussing the generalizability (external validity)" [ 10 , 11 ]. However, these guidelines do not clarify how to deal with the complex bias issue, and how to get to and report conclusions.
Consequently, suggestions on writing a discussion often remain vague by hardly addressing the role of the assumptions that have (often implicitly) been made when designing a study, analyzing the data and interpreting the results. Such assumptions involve mechanisms that have created the data and are related to sampling, measurement and treatment assignment (in observational studies common causes of factor and outcome) and, as a consequence, the bias this may produce [ 5 , 6 ]. They determine whether a result allows only an associational or a causal conclusion. Causal conclusions, if true, are of much higher relevance for etiology, prevention and intervention. However, they require much stronger assumptions. These have to be fully explicit and, therewith, essential part of the debate since they always involve subjectivity. Subjectivity is unavoidable because the mechanisms behind the data can never be fully estimated from the data themselves [ 12 ].
In this article, we argue that the conjunction of substantive and statistical (methodical) knowledge in the verbal integration of results and beliefs on mechanisms can be greatly improved in (medical) research papers. We illustrate this through the personal roles that a statistician (i.e. methods expert) and a substantive researcher should take. Doing so, we neither claim that usually just two people write a discussion, nor that one person lacks the knowledge of the other, nor that there were truly no researchers that have both kinds of expertise. As a metaphor, the division of these two roles into two persons describes the necessary integration of knowledge via the mode of a dialogue. Verbally, it addresses the finding of increased specialization of different study contributors in biomedical research. This has teared apart the two processes of statistical compilation of results and their verbal integration [ 13 ]. When this happens a statistician alone is limited to a study’s conditions (sampled population, experimental settings etc.), because he or she is unaware of the conditions’ generalizability. On the other hand, a A substantive expert alone is prone to over-generalize because he or she is not aware of the (mathematical) prerequisites for an interpretation.
The article addresses both (medical) researchers educated in basic statistics and research methods and statisticians who cooperate with them. Throughout the paper we exemplify our arguments with the finding of an association in a cross-tabulation between a binary X (factor) and a binary Y (outcome): those who are exposed to or treated with X have a statistically significantly elevated risk for Y as compared to the non-exposed or not (or otherwise) treated (for instance via the chi-squared independence test or logistic regression). Findings like this are frequent and raise the question which more profound conclusion is valid under what assumptions. Until some decades ago, statistics has largely avoided the related topic of causality and instead limited itself on describing observed distributions (here a two-by-two table between D = depression and LC = lung cancer) with well-fitting models.
We illustrate our arguments with the concrete example of the association found between the factor depression (D) and the outcome lung cancer (LC) [ 14 ]. Yet very different mechanisms could have produced such an association [ 7 ], and assumptions on these lead to the following fundamentally different conclusions (Fig. (Fig.1 1 ):
- D causes LC (e.g. because smoking might constitute “self-medication” of depression symptoms)
- LC causes D (e.g. because LC patients are demoralized by their diagnosis)
- D and LC cause each other (e.g. because the arguments in both a. and b. apply)
- D and LC are the causal consequence of the same factor(s) (e.g. poor health behaviors - HB)
- D and LC only share measurement error (e.g. because a fraction of individuals that has either depression or lung cancer denies both in self-report measures).

Different conclusions about an association between D and LC. a D causes LC, b LC causes B, c D and LC cause each other, d D and LC are associated because of a shared factor (HB), e D and LC are associated because they have correlated errors
Note that we use the example purely for illustrative purposes. We do not make substantive claims on what of a. through e. is true but show how one should reflect on mechanisms in order to find the right answer. Besides, we do not consider research on the D-LC relation apart from the finding of association [ 14 ].
Assessing which of a. through e. truly applies requires substantive assumptions on mechanisms: the temporal order of D and LC (a causal effect requires that the cause occurs before the effect), shared factors, selection processes and measurement error. Questions on related mechanisms have to be brought up by statistical consideration, while substantive reasoning has to address them. Together this yields provisional assumptions for inferring that are subject to readers’ substantive consideration and refinement. In general, the integration of prior beliefs (anything beyond the data a conclusion depends on) and the results from the data themselves is formalized by Bayesian statistics [ 15 , 16 ]. This is beyond the scope of this article, still we argue that Bayesian thinking should govern the process of drawing conclusions.
Building on this idea, we provide seven specific and four general recommendations for the cooperative process of writing a discussion. The recommendations are intended to be suggestions rather than rules. They should be subject to further refinement and adjustment to specific requirements in different fields of medical and other research. Note that the order of the points is not meant to structure a discussion’s writing (besides 1.).
Recommendations for writing a discussion section
Specific recommendations.
Consider the example on the association between D and LC. Rather than starting with an in-depth (causal) interpretation a finding should firstly be taken as what it allows inferring without doubt: Under the usual assumptions that a statistical model makes (e.g. random sampling, independence or certain correlation structure between observations [ 17 ]), the association indicates that D (strictly speaking: measuring D) predicts an elevated LC risk (strictly speaking: measuring LC) in the population that one has managed to sample (source population). Assume that the sample has been randomly drawn from primary care settings. In this case the association is useful to recommend medical doctors to better look at an individual’s LC risk in case of D. If the association has been adjusted for age and gender (conveniently through a regression model), the conclusion modifies to: If the doctor knows a patient’s age and gender (what should always be the case) D has additional value in predicting an elevated LC risk.
In the above example, a substantive researcher might want to conclude that D and LC are associated in a general population instead of just inferring to patients in primary care settings (a.). Another researcher might even take the finding as evidence for D being a causal factor in the etiology of LC, meaning that prevention of D could reduce the incidence rate of LC (in whatever target population) (b.). In both cases, the substantive researcher should insist on assessing the desired interpretation that goes beyond the data [ 4 ], but the statistician immediately needs to bring up the next point.
The explanation of all the assumptions that lead from a data result to a conclusion enables a reader to assess whether he or she agrees with the authors’ inference or not. These conditions, however, often remain incomplete or unclear, in which case the reader can hardly assess whether he or she follows a path of argumentation and, thus, shares the conclusion this path leads to.
Consider conclusion a. and suppose that, instead of representative sampling in a general population (e.g. all U.S. citizens aged 18 or above), the investigators were only able to sample in primary care settings. Extrapolating the results to another population than the source population requires what is called “external validity”, “transportability” or the absence of “selection bias” [ 18 , 19 ]. No such bias occurs if the parameter of interest is equal in the source and the target population. Note that this is a weaker condition than the common belief that the sample must represent the target population in everything . If the parameter of interest is the difference in risk for LC between cases and non-cases of D, the condition translates into: the risk difference must be equal in target and source population.
For the causal conclusion b., however, sufficient assumptions are very strict. In an RCT, the conclusion is valid under random sampling from the target population, random allocation of X, perfect compliance in X, complete participation and no measurement error in outcome (for details see [ 20 ]). In practice, on the other hand, the derivations from such conditions might sometimes be modest what may produce little bias only. For instance, non-compliance in a specific drug intake (treatment) might occur only in a few individuals to little extent through a random process (e.g. sickness of a nurse being responsible for drug dispense) and yield just small (downward) bias [ 5 ]. The conclusion of downward bias might also be justified if non-compliance does not cause anything that has a larger effect on a Y than the drug itself. Another researcher, however, could believe that non-compliance leads to taking a more effective, alternative treatment. He or she could infer upward bias instead if well-informed on the line of argument.
In practice, researchers frequently use causal language yet without mentioning any assumptions. This does not imply that they truly have a causal effect in mind, often causal and associational wordings are carelessly used in synonymous way. For example, concluding “depression increases the risk of lung cancer” constitutes already causal wording because it implies that a change in the depression status would change the cancer risk. Associational language like “lung cancer risk is elevated if depression occurs”, however, would allow for an elevated lung cancer risk in depression cases just because LC and D share some causes (“inducing” or “removing” depression would not change the cancer risk here).
Often, it is unclear where the path of argumentation from assumptions to a conclusion leads when alternative assumptions are made. Consider again bias due to selection. A different effect in target and source population occurs if effect-modifying variables distribute differently in both populations. Accordingly, the statistician should ask which variables influence the effect of interest, and whether these can be assumed to distribute equally in the source population and the target population. The substantive researcher might answer that the causal risk difference between D and LC likely increases with age. Given that this is true, and if elder individuals have been oversampled (e.g. because elderly are over-represented in primary care settings), both together would conclude that sampling has led to over-estimation (despite other factors, Fig. Fig.2 2 ).

If higher age is related to a larger effect (risk difference) of D on LC, a larger effect estimate is expected in an elder sample
However, the statistician might add, if effect modification is weak, or the difference in the age distributions is modest (e.g. mean 54 vs. 52 years), selection is unlikely to have produced large (here: upward) bias. In turn, another substantive researcher, who reads the resulting discussion, might instead assume a decrease of effect with increasing age and thus infer downward bias.
In practice, researchers should be extremely sensitive for bias due to selection if a sample has been drawn conditionally on a common consequence of factor and outcome or a variable associated with such a consequence [19 and references therein]. For instance, hospitalization might be influenced by both D and LC, and thus sampling from hospitals might introduce a false association or change an association’s sign; particularly D and LC may appear to be negatively associated although the association is positive in the general population (Fig. (Fig.3 3 ).

If hospitalization (H) is a common cause of D and LC, sampling conditionally on H can introduce a spurious association between D and LC ("conditioning on a collider")
Usually, only some kinds of bias are discussed, while the consequences of others are ignored [ 5 ]. Besides selection the main sources of bias are often measurement and confounding. If one is only interested in association, confounding is irrelevant. For causal conclusions, however, assumptions on all three kinds of bias are necessary.
Measurement error means that the measurement of a factor and/or outcome deviates from the true value, at least in some individuals. Bias due to measurement is known under many other terms that describe the reasons why such error occurs (e.g. “recall bias” and “reporting bias”). In contrast to conventional wisdom, measurement error does not always bias association and effect estimates downwards [ 5 , 6 ]. It does, for instance, if only the factor (e.g. depression) is measured with error and the errors occur independently from the outcome (e.g. lung cancer), or vice versa (“non-differential misclassification”) [22 and references therein]. However, many lung cancer cases might falsely report depression symptoms (e.g. to express need for care). Such false positives (non-cases of depression classified as cases) may also occur in non-cases of lung cancer but to a lesser extent (a special case of “differential misclassification”). Here, bias might be upward as well. Importantly, false positives cause larger bias than false negatives (non-cases of depression falsely classified as depression cases) as long as the relative frequency of a factor is lower than 50% [ 21 ]. Therefore, they should receive more attention in discussion. If measurement error occurs in depression and lung cancer, the direction of bias also depends on the correlation between both errors [ 21 ].
Note that what is in line with common standards of “good” measurement (e.g. a Kappa value measuring validity or reliability of 0.7) might anyway produce large bias. This applies to estimates of prevalence, association and effect. The reason is that while indices of measurement are one-dimensional, bias depends on two parameters (sensitivity and specificity) [ 21 , 22 ]. Moreover, estimates of such indices are often extrapolated to different kinds of populations (typically from a clinical to general population), what may be inadequate. Note that the different kinds of bias often interact, e.g. bias due to measurement might depend on selection (e.g. measurement error might differ between a clinical and a general population) [ 5 , 6 ].
Assessment of bias due to confounding variables (roughly speaking: common causes of factor and outcome) requires assumptions on the entire system of variables that affect both factor and outcome. For example, D and LC might share several causes such as stressful life events or socioeconomic status. If these influence D and LC with the same effect direction, this leads to overestimation, otherwise (different effect directions) the causal effect is underestimated. In the medical field, many unfavorable conditions may be positively related. If this holds true for all common factors of D and LC, upward bias can be assumed. However, not all confounders have to be taken into account. Within the framework of “causal graphs”, the “backdoor criterion” [ 7 ] provides a graphical rule for sets of confounders to be sufficient when adjusted for. Practically, such a causal graph must include all factors that directly or indirectly affect both D and LC. Then, adjustment for a set of confounders that meets the “backdoor criterion” in the graph completely removes bias due to confounding. In the example of Fig. Fig.4 4 it is sufficient to adjust for Z 1 and Z 2 because this “blocks” all paths that otherwise lead backwards from D to LC. Note that fully eliminating bias due to confounding also requires that the confounders have been collected without measurement error [ 5 , 6 , 23 ]. Therefore, the advice is always to concede at least some “residual” bias and reflect on the direction this might have (could be downward if such error is not stronger related to D and LC than a confounder itself).

Causal graph for the effect of D on LC and confounders Z 1 , Z 2 and Z 3
Whereas the statistician should pinpoint to the mathematical insight of the backdoor criterion, its application requires profound substantive input and literature review. Of course, there are numerous relevant factors in the medical field. Hence, one should practically focus on those with the highest prevalence (a very seldom factor can hardly cause large bias) and large assumed effects on both X and Y.
If knowledge on any of the three kinds of bias is poor or very uncertain, researchers should admit that this adds uncertainty in a conclusion: systematic error on top of random error. In the Bayesian framework, quantitative bias analysis formalizes this through the result of larger variance in an estimate. Technically, this additional variance is introduced via the variances of distributions assigned to “bias parameters”; for instance a misclassification probability (e.g. classifying a true depression case as non-case) or the prevalence of a binary confounder and its effects on X and Y. Of course, bias analysis also changes point estimates (hopefully reducing bias considerably). Note that conventional frequentist analysis, as regarded from the Bayesian perspective, assumes that all bias parameters were zero with a probability of one [ 5 , 6 , 23 ]. The only exceptions (bias addressed in conventional analyses) are adjustment on variables to hopefully reduce bias due to confounding and weighting the individuals (according to variables related to participation) to take into account bias due to selection.
If the substantive investigator understands the processes of selection, measurement and confounding only poorly, such strict analysis numerically reveals that little to nothing is known on the effect of X on Y, no matter how large an observed association and a sample (providing small random error) may be [ 5 , 6 , 23 ]). This insight has to be brought up by the statistician. Although such an analysis is complicated, itself very sensitive to how it is conducted [ 5 , 6 ] and rarely done, the Bayesian thinking behind it forces researchers to better understand the processes behind the data. Otherwise, he or she cannot make any assumptions and, in turn, no conclusion on causality.
Usually articles end with statements that only go little further than the always true but never informative statement “more research is needed”. Moreover, larger samples and better measurements are frequently proposed. If an association has been found, a RCT or other interventional study is usually proposed to investigate causality. In our example, this recommendation disregards that: (1) onset of D might have a different effect on LC risk than an intervention against D (the effect of onset cannot be investigated in any interventional study), (2) the effects of onset and intervention concern different populations (those without vs. those with depression), (3) an intervention effect depends on the mode of intervention [ 24 ], and (4) (applying the backdoor criterion) a well-designed observational study may approximatively yield the same result as a randomized study would [ 25 – 27 ]. If the effect of “removing” depression is actually of interest, one could propose an RCT that investigates the effect of treating depression in a strictly defined way and in a strictly defined population (desirably in all who meet the criteria of depression). Ideally, this population is sampled randomly, and non-participants and dropouts are investigated with respect to assumed effect-modifiers (differences in their distributions between participants and non-participants can then be addressed e.g. by weighting [ 27 ]). In a non-randomized study, one should collect variables supposed to meet the backdoor-criterion with the best instruments possible.
General recommendations
Yet when considering 1) through 7); i.e. carefully reflecting on the mechanisms that have created the data, discussions on statistical results can be very misleading, because the basic statistical methods are mis-interpreted or inadequately worded.
A common pitfall is to consider the lack of evidence for the alternative hypothesis (e.g. association between D and LC) as evidence for the null hypothesis (no association). In fact, such inference requires an a-priori calculated sample-size to ensure that the type-two error probability does not exceed a pre-specified limit (typically 20% or 10%, given the other necessary assumptions, e.g. on the true magnitude of association). Otherwise, the type-two error is unknown and in practice often large. This may put a “false negative result” into the scientific public that turns out to be “unreplicable” – what would be falsely interpreted as part of the “replication crisis”. Such results are neither positive nor negative but uninformative . In this case, the wording “there is no evidence for an association” is adequate because it does not claim that there is no association.
Frequently, it remains unclear which hypotheses have been a-priori specified and which have been brought up only after some data analysis. This, of course, is scientific malpractice because it does not enable the readership to assess the random error emerging from explorative data analysis. Accordingly, the variance of results across statistical methods is often misused to filter out the analysis that yields a significant result (“ p -hacking”, [ 28 ]). Pre-planned tests (via writing a grant) leave at least less room for p-hacking because they specify a-priori which analysis is to be conducted.
On the other hand, post-hoc analyses can be extremely useful for identifying unexpected phenomena and creating new hypotheses. Verbalization in the discussion section should therefore sharply separate between conclusions from hypothesis testing and new hypotheses created from data exploration. The distinction is profound, since a newly proposed hypothesis just makes a new claim. Suggesting new hypotheses cannot be wrong, this can only be inefficient if many hypotheses turn out to be wrong. Therefore, we suggest proposing only a limited number of new hypotheses that appear promising to stimulate further research and scientific progress. They are to be confirmed or falsified with future studies. A present discussion, however, should yet explicate the testable predictions a new hypothesis entails, and how a future study should be designed to keep bias in related analyses as small as possible.
Confidence intervals address the problem of reducing results to the dichotomy of significant and non-significant through providing a range of values that are compatible with the data at the given confidence level, usually 95% [ 29 ].
This is also addressed by Bayesian statistics that allows calculating what frequentist p -values are often misinterpreted to be: the probability that the alternative (or null) hypothesis is true [ 17 ]. Moreover, one can calculate how likely it is that the parameter lies within any specified range (e.g. the risk difference being greater than .05, a lower boundary for practical significance) [ 15 , 16 ]. To gain these benefits, one needs to specify how the parameter of interest (e.g. causal risk difference between D and LC) is distributed before inspecting the data. In Bayesian statistics (unlike frequentist statistics) a parameter is a random number that expresses prior beliefs via a “prior distribution”. Such a “prior” is combined with the data result to a “posterior distribution”. This integrates both sources of information.
Note that confidence intervals also can be interpreted from the Bayesian perspective (then called “credibility interval”). This assumes that all parameter values were equally likely (uniformly distributed, strictly speaking) before analyzing the data [ 5 , 6 , 20 ].
Testing just for a non-zero association can only yield evidence for an association deviating from zero. A better indicator for the true impact of an effect/association for clinical, economic, political, or research purposes is its magnitude. If an association between D and LC after adjusting for age and gender has been discovered, then the knowledge of D has additional value in predicting an elevated LC probability beyond age and gender. However, there may be many other factors that stronger predict LC and thus should receive higher priority in a doctor’s assessment. Besides, if an association is small, it may yet be explained by modest (upward) bias. Especially large samples often yield significant results with little practical value. The p -value does not measure strength of association [ 17 ]. For instance, in a large sample, a Pearson correlation between two dimensional variables could equal 0.1 only but with a p -value <.001. A further problem arises if the significance threshold of .05 is weakened post-hoc to allow for “statistical trends” ( p between .05 and .10) because a result has “failed to reach significance” (this wording claims that there is truly an association. If this was known, no research would be necessary).
It is usually the statistician’s job to insist not only on removing the attention from pure statistical significance to confidence intervals or even Bayesian interpretation, but also to point out the necessity of a meaningful cutoff for practical significance. The substantive researcher then has to provide this cutoff.
Researchers should not draw conclusions that have not been explicitly tested for. For example, one may have found a positive association between D and LC (e.g. p = .049), but this association is not significant (e.g. p = .051), when adjusting for “health behavior”. This does not imply that “health behavior” “explains” the association (yet fully). The difference in magnitude of association in both analyses compared here (without and with adjustment on HB) may be very small and the difference in p -values (“borderline significance” after adjustment) likely to emerge from random error. This often applies to larger differences in p as well.
Investigators, however, might find patterns in their results that they consider worth mentioning for creating hypotheses. In the example above, adding the words “in the sample”, would clarify that they refer just to the difference of two point estimates . By default, “association” in hypotheses testing should mean “statistically significant association” (explorative analyses should instead refer to “suggestive associations”).
Conclusions
Some issues of discussing results not mentioned yet appear to require only substantive reasoning. For instance, Bradford Hill’s consideration on “plausibility” claims that a causal effect is more likely, if it is in line with biological (substantive) knowledge, or if a dose-response relation has been found [ 30 ]. However, the application of these considerations itself depends on the trueness of assumptions. For instance, bias might act differently across the dose of exposure (e.g. larger measurement error in outcome among those with higher dosage). As a consequence, a pattern observed across dose may mask a true or pretend a wrong dose-response relation [ 30 ]. This again has to be brought up by statistical expertise.
There are, however, some practical issues that hinder the cooperation we suggest. First, substantive researchers often feel discomfort when urged to make assumptions on the mechanisms behind the data, presumably because they fear to be wrong. Here, the statistician needs to insist: “If you are unable to make any assumptions, you cannot conclude anything!” And: “As a scientist you have to understand the processes that create your data.” See [ 31 ] for practical advice on how to arrive at meaningful assumptions.
Second, statisticians have long been skeptical against causal inference. Still, most of them focus solely on describing observed data with distributional models, probably because estimating causal effects has long been regarded as unfeasible with scientific methods. Training in causality remains rather new, since strict mathematical methods have been developed only in the last decades [ 7 ].
The cooperation could be improved if education in both fields focused on the insight that one cannot succeed without the other. Academic education should demonstrate that in-depth conclusions from data unavoidably involve prior beliefs. Such education should say: Data do not “speak for themselves”, because they “speak” only ambiguously and little, since they have been filtered through various biases [ 32 ]. The subjectivity introduced by addressing bias, however, unsettles many researchers. On the other hand, conventional frequentist statistics just pretends to be objective. Instead of accepting the variety of possible assumptions, it makes the absurd assumption of “no bias with probability of one”. Or it avoids causal conclusions at all if no randomized study is possible. This limits science to investigating just associations for all factors that can never be randomized (e.g. onset of depression). However, the alternative of Bayesian statistics and thinking are themselves prone to fundamental cognitive biases which should as well be subject of interdisciplinary teaching [ 33 ].
Readers may take this article as an invitation to read further papers’ discussions differently while evaluating our claims. Rather than sharing a provided conclusion (or not) they could ask themselves whether a discussion enables them to clearly specify why they share it (or not). If the result is uncertainty, this might motivate them to write their next discussion differently. The proposals made in this article could help shifting scientific debates to where they belong. Rather than arguing on misunderstandings caused by ambiguity in a conclusion’s assumptions one should argue on the assumptions themselves.
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge support by the German Research Foundation and the Open Access Publication Funds of the TU Dresden. We wish to thank Pia Grabbe and Helen Steiner for language editing and the cited authors for their outstanding work that our proposals build on.
John Venz is funded by the German Federal Ministry of Education and Research (BMBF) project no. 01ER1303 and 01ER1703. He has contributed to this manuscript outside of time funded by these projects.
Availability of data and materials
Abbreviations.
| D | depression |
| HB | health behavior |
| LC | lung cancer |
| RCT | randomized clinical trial |
| X | factor variable |
| Y | outcome variable |
Authors’ contributions
MH and RM had the initial idea on the article. MH has taken the lead in writing. JV has contributed to the statistical parts, especially the Bayesian aspects. RM has refined the paragraphs on statistical inference. ST joined later and has added many clarifications related to the perspective of the substantive researcher. All authors have contributed to the final wording of all sections and the article’s revision. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
Consent for publication, competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Publisher’s Note
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.

- 80.8k views
- Results & Discussion
Q: How to write the Discussion section in a qualitative paper?
Asked by Shital Desai on 20 Mar, 2019
The purpose of the Discussion section is to interpret the results presented in the paper. For a quantitative study, it would involve analyzing and interpreting the data presented in the Results section. For a qualitative paper, although there is no need for statistical analysis of data, there is still a need to interpret the results for your audience in the Discussion section. Here's how you should write this section:
1. Begin by discussing the research question and talking about whether it was answered in the research paper based on the results.
2. Highlight any unexpected and/or exciting results and link them to the research question
3. Point out some previous studies and draw comparisons on how your study is different
4. State any weaknesses, loopholes, or limitations of the study
5. Recommend how the study can be used to further the knowledge in your field.
For more detailed guidance, we have an excellent handbook titled Write a convincing discussion section – The key to journal acceptance . You will definitely find it helpful.
Related reading:
- The secret to writing the results and discussion section of a manuscript
- 5 Differences between the results and discussion sections
- How to write the Discussion section for a mixed-methods research paper?
Answered by Editage Insights on 25 Mar, 2019
- Upvote this Answer

Hi Shital! We know it's been a year since your queries on writing a qualitative paper. But we were wondering how the paper proceeded, and if you were able to successfully publish it. Would be great to hear how it went. :-)
Incidentally, it would also be great if you could provide your valuable inputs (given your background in data analysis) on this recent question by another researcher on how to evaluate qualitative data: How can I evaluate qualitative data from different sources consistently and stringently without becoming too subjective and making too many assumptions?
Incidentally, I manage the Q&A Forum and keep trying to see how researchers can help one another. :-)
Answered by Irfan Syed on 08 Jun, 2020
This content belongs to the Manuscript Writing Stage
Translate your research into a publication-worthy manuscript by understanding the nuances of academic writing. Subscribe and get curated reads that will help you write an excellent manuscript.
Confirm that you would also like to sign up for free personalized email coaching for this stage.
Trending Searches
- Statement of the problem
- Background of study
- Scope of the study
- Types of qualitative research
- Rationale of the study
- Concept paper
- Literature review
- Introduction in research
- Under "Editor Evaluation"
- Ethics in research
Recent Searches
- Review paper
- Responding to reviewer comments
- Predatory publishers
- Scope and delimitations
- Open access
- Plagiarism in research
- Journal selection tips
- Editor assigned
- Types of articles
- "Reject and Resubmit" status
- Decision in process
- Conflict of interest
- Writing Center
Beginner’s Guide to Research
Click here to download a .pdf copy of our Beginner’s Guide to Research !
Last updated : July 18, 2024
Consider keeping a printed copy to have when writing and revising your resume! If you have any additional questions, make an appointment or email us at [email protected] !
Most professors will require the use of academic (AKA peer-reviewed) sources for student writing. This is because these sources, written for academic audiences of specific fields, are helpful for developing your argument on many topics of interest in the academic realm, from history to biology. While popular sources like news articles also often discuss topics of interest within academic fields, peer-reviewed sources offer a depth of research and expertise that you cannot find in popular sources. Therefore, knowing how to (1) identify popular vs. academic sources, (2) differentiate between primary and secondary sources, and (3) find academic sources is a vital step in writing research. Below are definitions of the two ways scholars categorize types of sources based on when they were created (i.e. time and place) and how (i.e. methodology):
Popular vs. academic sources:
- Popular sources are publicly accessible periodicals–newspapers, magazines, and blogs–such as The Washington Post or The New Yorker . These sources are most often written for non-academic audiences, but can be helpful for finding general information and a variety of opinions on your topic.
- Academic sources , known also as peer reviewed or scholarly articles, are those that have undergone peer review before being published. Typically, these articles are written for other scholars in the field and are published in academic journals, like Feminist Studies or The American Journal of Psychology . Literature reviews, research projects, case studies, and notes from the field are common examples.
Primary vs. secondary sources:
- Primary sources are articles written by people directly involved in what they were writing about, including: News reports and photographs, diaries and novels, films and videos, speeches and autobiographies, as well as original research and statistics.
- Secondary sources , on the other hand, are second hand accounts written about a topic based on primary sources. Whether a journal article or other academic publication is considered a secondary source depends on how you use it.
How to Find Academic Sources
Finding appropriate academic sources from the hundreds of different journal publications can be daunting. Therefore, it is important to find databases –digital collections of articles–relevant to your topic to narrow your search. Albertson’s Library has access to several different databases, which can be located by clicking the “Articles and Databases” tab on the website’s homepage, and navigating to “Databases A-Z” to refine your search. Popular databases include: Academic Search Premier and Proquest Central (non-specific databases which include a wide variety of articles), JSTOR (humanities and social sciences, from literature to history), Web of Science (formal sciences and natural sciences such as biology and chemistry), and Google Scholar (a web search engine that searches scholarly literature and academic sources). If you are unable to access articles from other databases, make sure you’re signed in to Alberton’s Library through Boise State!
Performing a Database Search
Databases include many different types of sources besides academic journals, however, including book reviews and other periodicals. Using the search bar , you can limit search results to those containing specific keywords or phrases like “writing center” or “transfer theory.” Utilizing keywords in your search–names of key concepts, authors, or ideas–rather than questions is the most effective way to find articles in databases. When searching for a specific work by title, placing the title in quotation marks will ensure your search includes only results in that specific word order. In the example below, search terms including the author (“Virginia Woolf”) and subject (“feminism”) are entered into the popular database EBSCOhost:
Refining Your Search Results
Many databases have a bar on the left of the screen where you can further refine your results. For example, if you are only interested in finding complete scholarly articles, or peer-reviewed ones, you can toggle these different options to further limit your search. These options are located under the “Refine Results” bar in EBSCOhost, divided into different sections, with a display of currently selected search filters and filter options to refine your search based on your specific needs, as seen in the figure below:
Search results can also be limited by subject : If you search “Romeo and Juliet” on Academic Search Premier to find literary analysis articles for your English class, you’ll find a lot of other sources that include this search term, such as ones about theater production or ballets based on Shakespeare’s play. However, if you’re writing a literary paper on the text of the play itself, you might limit your search results to “fiction” to see only articles that discuss the play within the field of literature. Alternatively, for a theater class discussing the play, you might limit your search results to “drama.”
The Writing Center
Unfortunately we don't fully support your browser. If you have the option to, please upgrade to a newer version or use Mozilla Firefox , Microsoft Edge , Google Chrome , or Safari 14 or newer. If you are unable to, and need support, please send us your feedback .
We'd appreciate your feedback. Tell us what you think! opens in new tab/window
Sharing research data
As a researcher, you are increasingly encouraged, or even mandated, to make your research data available, accessible, discoverable and usable.
Sharing research data is something we are passionate about too, so we’ve created this short video and written guide to help you get started.
Research Data
What is research data.
While the definition often differs per field, generally, research data refers to the results of observations or experiments that validate your research findings. These span a range of useful materials associated with your research project, including:
Raw or processed data files
Research data does not include text in manuscript or final published article form, or data or other materials submitted and published as part of a journal article.
Why should I share my research data?
There are so many good reasons. We’ve listed just a few:
How you benefit
You get credit for the work you've done
Leads to more citations! 1
Can boost your number of publications
Increases your exposure and may lead to new collaborations
What it means for the research community
It's easy to reuse and reinterpret your data
Duplication of experiments can be avoided
New insights can be gained, sparking new lines of inquiry
Empowers replication
And society at large…
Greater transparency boosts public faith in research
Can play a role in guiding government policy
Improves access to research for those outside health and academia
Benefits the public purse as funding of repeat work is reduced
How do I share my research data?
The good news is it’s easy.
Yet to submit your research article? There are a number of options available. These may vary depending on the journal you have chosen, so be sure to read the Research Data section in its Guide for Authors before you begin.
Already published your research article? No problem – it’s never too late to share the research data associated with it.
Two of the most popular data sharing routes are:
Publishing a research elements article
These brief, peer-reviewed articles complement full research papers and are an easy way to receive proper credit and recognition for the work you have done. Research elements are research outputs that have come about as a result of following the research cycle – this includes things like data, methods and protocols, software, hardware and more.

You can publish research elements articles in several different Elsevier journals, including our suite of dedicated Research Elements journals . They are easy to submit, are subject to a peer review process, receive a DOI and are fully citable. They also make your work more sharable, discoverable, comprehensible, reusable and reproducible.
The accompanying raw data can still be placed in a repository of your choice (see below).
Uploading your data to a repository like Mendeley Data
Mendeley Data is a certified, free-to-use repository that hosts open data from all disciplines, whatever its format (e.g. raw and processed data, tables, codes and software). With many Elsevier journals, it’s possible to upload and store your data to Mendeley Data during the manuscript submission process. You can also upload your data directly to the repository. In each case, your data will receive a DOI, making it independently citable and it can be linked to any associated article on ScienceDirect, making it easy for readers to find and reuse.

View an article featuring Mendeley data opens in new tab/window (just select the Research Data link in the left-hand bar or scroll down the page).
What if I can’t submit my research data?
Data statements offer transparency.
We understand that there are times when the data is simply not available to post or there are good reasons why it shouldn’t be shared. A number of Elsevier journals encourage authors to submit a data statement alongside their manuscript. This statement allows you to clearly explain the data you’ve used in the article and the reasons why it might not be available. The statement will appear with the article on ScienceDirect.

View a sample data statement opens in new tab/window (just select the Research Data link in the left-hand bar or scroll down the page).
Showcasing your research data on ScienceDirect
We have 3 top tips to help you maximize the impact of your data in your article on ScienceDirect.
Link with data repositories
You can create bidirectional links between any data repositories you’ve used to store your data and your online article. If you’ve published a data article, you can link to that too.
Enrich with interactive data visualizations
The days of being confined to static visuals are over. Our in-article interactive viewers let readers delve into the data with helpful functions such as zoom, configurable display options and full screen mode.

Cite your research data
Get credit for your work by citing your research data in your article and adding a data reference to the reference list. This ensures you are recognized for the data you shared and/or used in your research. Read the References section in your chosen journal’s Guide for Authors for more information.

Ready to get started?
If you have yet to publish your research paper, the first step is to find the right journal for your submission and read the Guide for Authors .
Find a journal by matching paper title and abstract of your manuscript in Elsevier's JournalFinder opens in new tab/window
Find journal by title opens in new tab/window
Already published? Just view the options for sharing your research data above.
1 Several studies have now shown that making data available for an article increases article citations.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Table of contents. What not to include in your discussion section. Step 1: Summarize your key findings. Step 2: Give your interpretations. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Step 4: Acknowledge the limitations. Step 5: Share your recommendations. Discussion section example. Other interesting articles.
Tips to Write the Results Section. Direct the reader to the research data and explain the meaning of the data. Avoid using a repetitive sentence structure to explain a new set of data. Write and highlight important findings in your results. Use the same order as the subheadings of the methods section.
Checklist: Research results 0 / 7. I have completed my data collection and analyzed the results. I have included all results that are relevant to my research questions. I have concisely and objectively reported each result, including relevant descriptive statistics and inferential statistics. I have stated whether each hypothesis was supported ...
Research results refer to the findings and conclusions derived from a systematic investigation or study conducted to answer a specific question or hypothesis. These results are typically presented in a written report or paper and can include various forms of data such as numerical data, qualitative data, statistics, charts, graphs, and visual aids.
Begin with a clear statement of the principal findings. This will reinforce the main take-away for the reader and set up the rest of the discussion. Explain why the outcomes of your study are important to the reader. Discuss the implications of your findings realistically based on previous literature, highlighting both the strengths and ...
1.Introduction—mention gaps in previous research¹⁻². 2. Summarizing key findings—let your data speak¹⁻². 3. Interpreting results—compare with other papers¹⁻². 4. Addressing limitations—their potential impact on the results¹⁻². 5. Implications for future research—how to explore further¹⁻².
The discussion section provides an analysis and interpretation of the findings, compares them with previous studies, identifies limitations, and suggests future directions for research. This section combines information from the preceding parts of your paper into a coherent story. By this point, the reader already knows why you did your study ...
IMRaD Results Discussion. Results and Discussion Sections in Scientific Research Reports (IMRaD) After introducing the study and describing its methodology, an IMRaD* report presents and discusses the main findings of the study. In the results section, writers systematically report their findings, and in discussion, they interpret these findings.
Papers usually end with a concluding section, often called the "Discussion.". The Discussion is your opportunity to evaluate and interpret the results of your study or paper, draw inferences and conclusions from it, and communicate its contributions to science and/or society. Use the present tense when writing the Discussion section.
DISCUSSION. Evidence does not explain itself; the results must be presented and then explained. Typical stages in the discussion: summarizing the results, discussing whether results are expected or unexpected, comparing these results to previous work, interpreting and explaining the results (often by comparison to a theory or model), and hypothesizing about their generality.
Summarise your results in the text, drawing on the figures and tables to illustrate your points. The text and figures should be complementary, not repeat the same information. You should refer to every table or figure in the text. Any that you don't feel the need to refer to can safely be moved to an appendix, or even removed.
Begin the Discussion section by restating your statement of the problem and briefly summarizing the major results. Do not simply repeat your findings. Rather, try to create a concise statement of the main results that directly answer the central research question that you stated in the Introduction section.
This handout was created to accompany the Writing in the Sciences video series. The purpose of the Results is to prepare readers for the discussion section by presenting the data in manageable chunks, in an order that corresponds with the research questions or objectives. The purpose of the Discussion section is used to contain analysis and ...
Discover exactly how to write your results and discussion section for your research paper step-by-step in only a few hours.Get the Scientific Research Paper ...
Results summary: In one paragraph, reiterate the research problem and briefly discuss your major results. Avoid repeating the data you already reported in the results section; clearly state the result that directly answers your research problem. Interpret your results: Your aim is to ensure your readers understand your results, how they answer ...
The discussion section is one of the final parts of a research paper, in which an author describes, analyzes, and interprets their findings. They explain the significance of those results and tie everything back to the research question(s). In this handout, you will find a description of what a discussion section does, explanations of how to ...
The Results and Discussion sections can be written as separate sections (as shown in Fig. 2), but are often combined in a poster into one section called Results and Discussion. This is done in order to (1) save precious space on a poster for the many pieces of information that a scientist would like to tell their audience and (2) by combining the two sections, it becomes easier for the ...
Present the results of the paper, in logical order, using tables and graphs as necessary. Explain the results and show how they help to answer the research questions posed in the Introduction. Evidence does not explain itself; the results must be presented and then explained. Avoid: presenting results that are never discussed; presenting ...
Discussion is mainly the section in a research paper that makes the readers understand the exact meaning of the results achieved in a study by exploring the significant points of the research, its ...
The discussion section, which follows the results section, will include an explanation of the results. In this section, you should connect your results to previous research studies, make explicit connections back to your research question(s) and include an explanation about how the results might be generalized.
After a research article has presented the substantive background, the methods and the results, the discussion section assesses the validity of results and draws conclusions by interpreting them. The discussion puts the results into a broader context and reflects their implications for theoretical (e.g. etiological) and practical (e.g ...
The first part of this post briefly described what to include in the introduction and materials and methods sections of a typical research paper written in the IMRaD format (Introduction, Materials and methods, Results, and Discussion). In this part, I'll discuss the results and discussion sections. Writing the results section: The results section answers the question W-H-A-T.
1. Begin by discussing the research question and talking about whether it was answered in the research paper based on the results. 2. Highlight any unexpected and/or exciting results and link them to the research question. 3. Point out some previous studies and draw comparisons on how your study is different. 4.
Literature reviews, research projects, case studies, and notes from the field are common examples. Primary vs. secondary sources: Primary sources are articles written by people directly involved in what they were writing about, including: News reports and photographs, diaries and novels, films and videos, speeches and autobiographies, as well ...
These brief, peer-reviewed articles complement full research papers and are an easy way to receive proper credit and recognition for the work you have done. Research elements are research outputs that have come about as a result of following the research cycle - this includes things like data, methods and protocols, software, hardware and more.
Results. Results: We found four red apples, one green apple, and two. yellow apples. This section provides the data the authors use to reach their conclusions. Figures are often included to make the data more compact and intuitive, and Tables organize data in one place for easier reading. Understanding Figures and Tables is . EXTREMELY
We are consolidating numerous pages to make our individual guides more valuable as well as removing duplicated content. For example, our Similarity Report guidance on help.turnitin is repeated in numerous places to cater for each individual integration and license type. On guides.turnitin this content will exist in a single place to allow for ...