

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of exploration. In an era marked by rapid technological advancements and an ever-expanding knowledge base, refining the process of generating research recommendations becomes imperative.
But, what is a research recommendation?
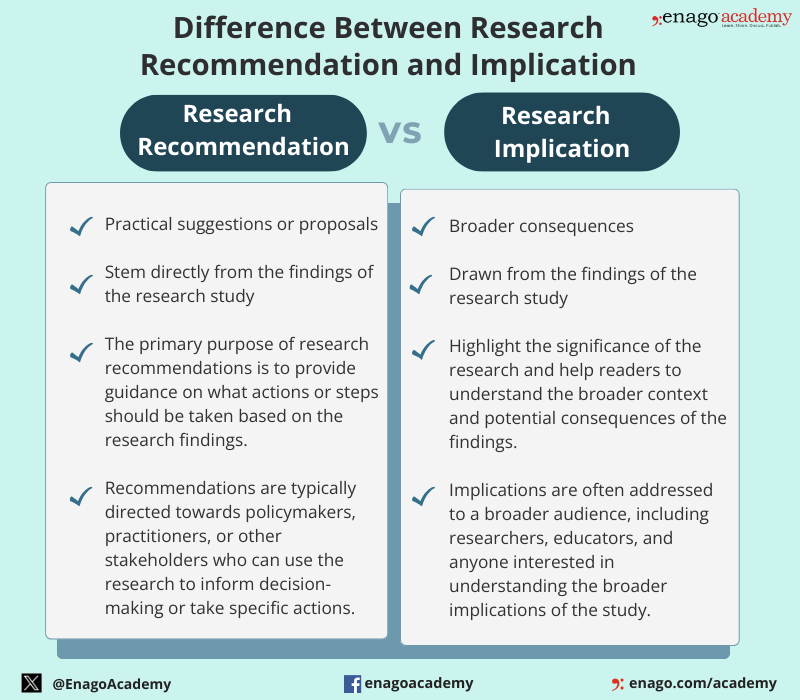
Research recommendations are suggestions or advice provided to researchers to guide their study on a specific topic . They are typically given by experts in the field. Research recommendations are more action-oriented and provide specific guidance for decision-makers, unlike implications that are broader and focus on the broader significance and consequences of the research findings. However, both are crucial components of a research study.
Difference Between Research Recommendations and Implication
Although research recommendations and implications are distinct components of a research study, they are closely related. The differences between them are as follows:
Types of Research Recommendations
Recommendations in research can take various forms, which are as follows:
These recommendations aim to assist researchers in navigating the vast landscape of academic knowledge.
Let us dive deeper to know about its key components and the steps to write an impactful research recommendation.
Key Components of Research Recommendations
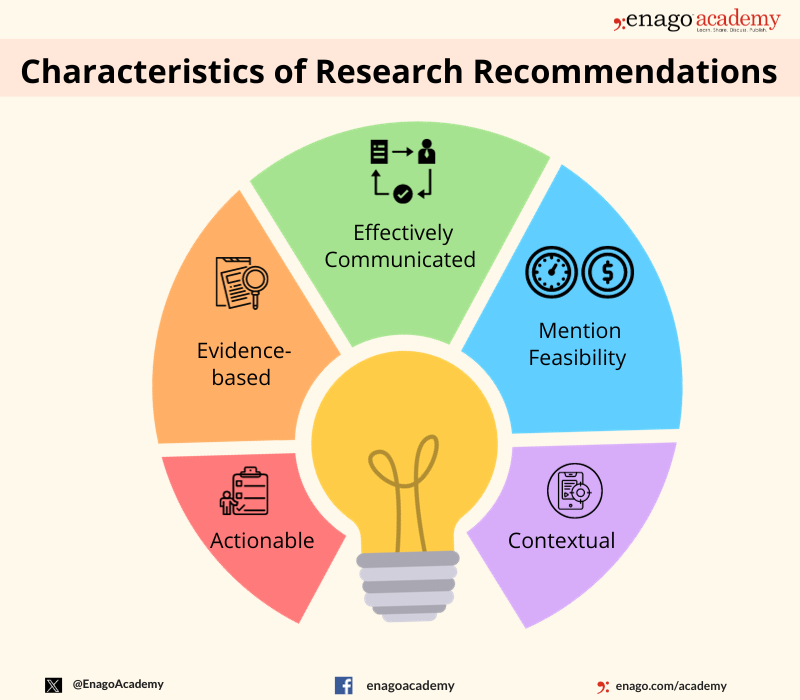
The key components of research recommendations include defining the research question or objective, specifying research methods, outlining data collection and analysis processes, presenting results and conclusions, addressing limitations, and suggesting areas for future research. Here are some characteristics of research recommendations:
Research recommendations offer various advantages and play a crucial role in ensuring that research findings contribute to positive outcomes in various fields. However, they also have few limitations which highlights the significance of a well-crafted research recommendation in offering the promised advantages.
The importance of research recommendations ranges in various fields, influencing policy-making, program development, product development, marketing strategies, medical practice, and scientific research. Their purpose is to transfer knowledge from researchers to practitioners, policymakers, or stakeholders, facilitating informed decision-making and improving outcomes in different domains.
How to Write Research Recommendations?
Research recommendations can be generated through various means, including algorithmic approaches, expert opinions, or collaborative filtering techniques. Here is a step-wise guide to build your understanding on the development of research recommendations.
1. Understand the Research Question:
Understand the research question and objectives before writing recommendations. Also, ensure that your recommendations are relevant and directly address the goals of the study.
2. Review Existing Literature:
Familiarize yourself with relevant existing literature to help you identify gaps , and offer informed recommendations that contribute to the existing body of research.
3. Consider Research Methods:
Evaluate the appropriateness of different research methods in addressing the research question. Also, consider the nature of the data, the study design, and the specific objectives.
4. Identify Data Collection Techniques:
Gather dataset from diverse authentic sources. Include information such as keywords, abstracts, authors, publication dates, and citation metrics to provide a rich foundation for analysis.
5. Propose Data Analysis Methods:
Suggest appropriate data analysis methods based on the type of data collected. Consider whether statistical analysis, qualitative analysis, or a mixed-methods approach is most suitable.
6. Consider Limitations and Ethical Considerations:
Acknowledge any limitations and potential ethical considerations of the study. Furthermore, address these limitations or mitigate ethical concerns to ensure responsible research.
7. Justify Recommendations:
Explain how your recommendation contributes to addressing the research question or objective. Provide a strong rationale to help researchers understand the importance of following your suggestions.
8. Summarize Recommendations:
Provide a concise summary at the end of the report to emphasize how following these recommendations will contribute to the overall success of the research project.
By following these steps, you can create research recommendations that are actionable and contribute meaningfully to the success of the research project.
Download now to unlock some tips to improve your journey of writing research recommendations.
Example of a Research Recommendation
Here is an example of a research recommendation based on a hypothetical research to improve your understanding.
Research Recommendation: Enhancing Student Learning through Integrated Learning Platforms
Background:
The research study investigated the impact of an integrated learning platform on student learning outcomes in high school mathematics classes. The findings revealed a statistically significant improvement in student performance and engagement when compared to traditional teaching methods.
Recommendation:
In light of the research findings, it is recommended that educational institutions consider adopting and integrating the identified learning platform into their mathematics curriculum. The following specific recommendations are provided:
- Implementation of the Integrated Learning Platform:
Schools are encouraged to adopt the integrated learning platform in mathematics classrooms, ensuring proper training for teachers on its effective utilization.
- Professional Development for Educators:
Develop and implement professional programs to train educators in the effective use of the integrated learning platform to address any challenges teachers may face during the transition.
- Monitoring and Evaluation:
Establish a monitoring and evaluation system to track the impact of the integrated learning platform on student performance over time.
- Resource Allocation:
Allocate sufficient resources, both financial and technical, to support the widespread implementation of the integrated learning platform.
By implementing these recommendations, educational institutions can harness the potential of the integrated learning platform and enhance student learning experiences and academic achievements in mathematics.
This example covers the components of a research recommendation, providing specific actions based on the research findings, identifying the target audience, and outlining practical steps for implementation.
Using AI in Research Recommendation Writing
Enhancing research recommendations is an ongoing endeavor that requires the integration of cutting-edge technologies, collaborative efforts, and ethical considerations. By embracing data-driven approaches and leveraging advanced technologies, the research community can create more effective and personalized recommendation systems. However, it is accompanied by several limitations. Therefore, it is essential to approach the use of AI in research with a critical mindset, and complement its capabilities with human expertise and judgment.
Here are some limitations of integrating AI in writing research recommendation and some ways on how to counter them.
1. Data Bias
AI systems rely heavily on data for training. If the training data is biased or incomplete, the AI model may produce biased results or recommendations.
How to tackle: Audit regularly the model’s performance to identify any discrepancies and adjust the training data and algorithms accordingly.
2. Lack of Understanding of Context:
AI models may struggle to understand the nuanced context of a particular research problem. They may misinterpret information, leading to inaccurate recommendations.
How to tackle: Use AI to characterize research articles and topics. Employ them to extract features like keywords, authorship patterns and content-based details.
3. Ethical Considerations:
AI models might stereotype certain concepts or generate recommendations that could have negative consequences for certain individuals or groups.
How to tackle: Incorporate user feedback mechanisms to reduce redundancies. Establish an ethics review process for AI models in research recommendation writing.
4. Lack of Creativity and Intuition:
AI may struggle with tasks that require a deep understanding of the underlying principles or the ability to think outside the box.
How to tackle: Hybrid approaches can be employed by integrating AI in data analysis and identifying patterns for accelerating the data interpretation process.
5. Interpretability:
Many AI models, especially complex deep learning models, lack transparency on how the model arrived at a particular recommendation.
How to tackle: Implement models like decision trees or linear models. Provide clear explanation of the model architecture, training process, and decision-making criteria.
6. Dynamic Nature of Research:
Research fields are dynamic, and new information is constantly emerging. AI models may struggle to keep up with the rapidly changing landscape and may not be able to adapt to new developments.
How to tackle: Establish a feedback loop for continuous improvement. Regularly update the recommendation system based on user feedback and emerging research trends.
The integration of AI in research recommendation writing holds great promise for advancing knowledge and streamlining the research process. However, navigating these concerns is pivotal in ensuring the responsible deployment of these technologies. Researchers need to understand the use of responsible use of AI in research and must be aware of the ethical considerations.
Exploring research recommendations plays a critical role in shaping the trajectory of scientific inquiry. It serves as a compass, guiding researchers toward more robust methodologies, collaborative endeavors, and innovative approaches. Embracing these suggestions not only enhances the quality of individual studies but also contributes to the collective advancement of human understanding.
Frequently Asked Questions
The purpose of recommendations in research is to provide practical and actionable suggestions based on the study's findings, guiding future actions, policies, or interventions in a specific field or context. Recommendations bridges the gap between research outcomes and their real-world application.
To make a research recommendation, analyze your findings, identify key insights, and propose specific, evidence-based actions. Include the relevance of the recommendations to the study's objectives and provide practical steps for implementation.
Begin a recommendation by succinctly summarizing the key findings of the research. Clearly state the purpose of the recommendation and its intended impact. Use a direct and actionable language to convey the suggested course of action.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident…
![recommendation in research template What is Academic Integrity and How to Uphold it [FREE CHECKLIST]](https://www.enago.com/academy/wp-content/uploads/2024/05/FeatureImages-59-210x136.png)
Ensuring Academic Integrity and Transparency in Academic Research: A comprehensive checklist for researchers
Academic integrity is the foundation upon which the credibility and value of scientific findings are…

- Industry News
- Publishing News
Unified AI Guidelines Crucial as Academic Writing Embraces Generative Tools
As generative artificial intelligence (AI) tools like ChatGPT are advancing at an accelerating pace, their…

How to Effectively Cite a PDF (APA, MLA, AMA, and Chicago Style)
The pressure to “publish or perish” is a well-known reality for academics, striking fear into…

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Using AI for Journal Selection — Simplifying your academic publishing journey in the smart way
Strategic journal selection plays a pivotal role in maximizing the impact of one’s scholarly work.…
How to Optimize Your Research Process: A step-by-step guide
Digital Citations: A comprehensive guide to citing of websites in APA, MLA, and CMOS…

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

As a researcher, what do you consider most when choosing an image manipulation detector?
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Recommendations – Examples and Writing Guide
Research Recommendations – Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Recommendations
Definition:
Research recommendations refer to suggestions or advice given to someone who is looking to conduct research on a specific topic or area. These recommendations may include suggestions for research methods, data collection techniques, sources of information, and other factors that can help to ensure that the research is conducted in a rigorous and effective manner. Research recommendations may be provided by experts in the field, such as professors, researchers, or consultants, and are intended to help guide the researcher towards the most appropriate and effective approach to their research project.
Parts of Research Recommendations
Research recommendations can vary depending on the specific project or area of research, but typically they will include some or all of the following parts:
- Research question or objective : This is the overarching goal or purpose of the research project.
- Research methods : This includes the specific techniques and strategies that will be used to collect and analyze data. The methods will depend on the research question and the type of data being collected.
- Data collection: This refers to the process of gathering information or data that will be used to answer the research question. This can involve a range of different methods, including surveys, interviews, observations, or experiments.
- Data analysis : This involves the process of examining and interpreting the data that has been collected. This can involve statistical analysis, qualitative analysis, or a combination of both.
- Results and conclusions: This section summarizes the findings of the research and presents any conclusions or recommendations based on those findings.
- Limitations and future research: This section discusses any limitations of the study and suggests areas for future research that could build on the findings of the current project.
How to Write Research Recommendations
Writing research recommendations involves providing specific suggestions or advice to a researcher on how to conduct their study. Here are some steps to consider when writing research recommendations:
- Understand the research question: Before writing research recommendations, it is important to have a clear understanding of the research question and the objectives of the study. This will help to ensure that the recommendations are relevant and appropriate.
- Consider the research methods: Consider the most appropriate research methods that could be used to collect and analyze data that will address the research question. Identify the strengths and weaknesses of the different methods and how they might apply to the specific research question.
- Provide specific recommendations: Provide specific and actionable recommendations that the researcher can implement in their study. This can include recommendations related to sample size, data collection techniques, research instruments, data analysis methods, or other relevant factors.
- Justify recommendations : Justify why each recommendation is being made and how it will help to address the research question or objective. It is important to provide a clear rationale for each recommendation to help the researcher understand why it is important.
- Consider limitations and ethical considerations : Consider any limitations or potential ethical considerations that may arise in conducting the research. Provide recommendations for addressing these issues or mitigating their impact.
- Summarize recommendations: Provide a summary of the recommendations at the end of the report or document, highlighting the most important points and emphasizing how the recommendations will contribute to the overall success of the research project.
Example of Research Recommendations
Example of Research Recommendations sample for students:
- Further investigate the effects of X on Y by conducting a larger-scale randomized controlled trial with a diverse population.
- Explore the relationship between A and B by conducting qualitative interviews with individuals who have experience with both.
- Investigate the long-term effects of intervention C by conducting a follow-up study with participants one year after completion.
- Examine the effectiveness of intervention D in a real-world setting by conducting a field study in a naturalistic environment.
- Compare and contrast the results of this study with those of previous research on the same topic to identify any discrepancies or inconsistencies in the findings.
- Expand upon the limitations of this study by addressing potential confounding variables and conducting further analyses to control for them.
- Investigate the relationship between E and F by conducting a meta-analysis of existing literature on the topic.
- Explore the potential moderating effects of variable G on the relationship between H and I by conducting subgroup analyses.
- Identify potential areas for future research based on the gaps in current literature and the findings of this study.
- Conduct a replication study to validate the results of this study and further establish the generalizability of the findings.
Applications of Research Recommendations
Research recommendations are important as they provide guidance on how to improve or solve a problem. The applications of research recommendations are numerous and can be used in various fields. Some of the applications of research recommendations include:
- Policy-making: Research recommendations can be used to develop policies that address specific issues. For example, recommendations from research on climate change can be used to develop policies that reduce carbon emissions and promote sustainability.
- Program development: Research recommendations can guide the development of programs that address specific issues. For example, recommendations from research on education can be used to develop programs that improve student achievement.
- Product development : Research recommendations can guide the development of products that meet specific needs. For example, recommendations from research on consumer behavior can be used to develop products that appeal to consumers.
- Marketing strategies: Research recommendations can be used to develop effective marketing strategies. For example, recommendations from research on target audiences can be used to develop marketing strategies that effectively reach specific demographic groups.
- Medical practice : Research recommendations can guide medical practitioners in providing the best possible care to patients. For example, recommendations from research on treatments for specific conditions can be used to improve patient outcomes.
- Scientific research: Research recommendations can guide future research in a specific field. For example, recommendations from research on a specific disease can be used to guide future research on treatments and cures for that disease.
Purpose of Research Recommendations
The purpose of research recommendations is to provide guidance on how to improve or solve a problem based on the findings of research. Research recommendations are typically made at the end of a research study and are based on the conclusions drawn from the research data. The purpose of research recommendations is to provide actionable advice to individuals or organizations that can help them make informed decisions, develop effective strategies, or implement changes that address the issues identified in the research.
The main purpose of research recommendations is to facilitate the transfer of knowledge from researchers to practitioners, policymakers, or other stakeholders who can benefit from the research findings. Recommendations can help bridge the gap between research and practice by providing specific actions that can be taken based on the research results. By providing clear and actionable recommendations, researchers can help ensure that their findings are put into practice, leading to improvements in various fields, such as healthcare, education, business, and public policy.
Characteristics of Research Recommendations
Research recommendations are a key component of research studies and are intended to provide practical guidance on how to apply research findings to real-world problems. The following are some of the key characteristics of research recommendations:
- Actionable : Research recommendations should be specific and actionable, providing clear guidance on what actions should be taken to address the problem identified in the research.
- Evidence-based: Research recommendations should be based on the findings of the research study, supported by the data collected and analyzed.
- Contextual: Research recommendations should be tailored to the specific context in which they will be implemented, taking into account the unique circumstances and constraints of the situation.
- Feasible : Research recommendations should be realistic and feasible, taking into account the available resources, time constraints, and other factors that may impact their implementation.
- Prioritized: Research recommendations should be prioritized based on their potential impact and feasibility, with the most important recommendations given the highest priority.
- Communicated effectively: Research recommendations should be communicated clearly and effectively, using language that is understandable to the target audience.
- Evaluated : Research recommendations should be evaluated to determine their effectiveness in addressing the problem identified in the research, and to identify opportunities for improvement.
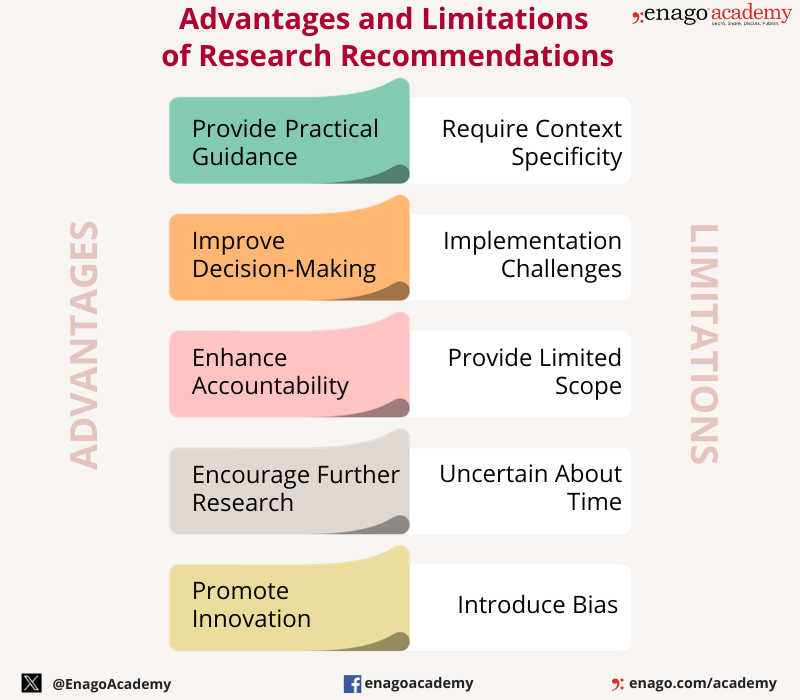
Advantages of Research Recommendations
Research recommendations have several advantages, including:
- Providing practical guidance: Research recommendations provide practical guidance on how to apply research findings to real-world problems, helping to bridge the gap between research and practice.
- Improving decision-making: Research recommendations help decision-makers make informed decisions based on the findings of research, leading to better outcomes and improved performance.
- Enhancing accountability : Research recommendations can help enhance accountability by providing clear guidance on what actions should be taken, and by providing a basis for evaluating progress and outcomes.
- Informing policy development : Research recommendations can inform the development of policies that are evidence-based and tailored to the specific needs of a given situation.
- Enhancing knowledge transfer: Research recommendations help facilitate the transfer of knowledge from researchers to practitioners, policymakers, or other stakeholders who can benefit from the research findings.
- Encouraging further research : Research recommendations can help identify gaps in knowledge and areas for further research, encouraging continued exploration and discovery.
- Promoting innovation: Research recommendations can help identify innovative solutions to complex problems, leading to new ideas and approaches.
Limitations of Research Recommendations
While research recommendations have several advantages, there are also some limitations to consider. These limitations include:
- Context-specific: Research recommendations may be context-specific and may not be applicable in all situations. Recommendations developed in one context may not be suitable for another context, requiring adaptation or modification.
- I mplementation challenges: Implementation of research recommendations may face challenges, such as lack of resources, resistance to change, or lack of buy-in from stakeholders.
- Limited scope: Research recommendations may be limited in scope, focusing only on a specific issue or aspect of a problem, while other important factors may be overlooked.
- Uncertainty : Research recommendations may be uncertain, particularly when the research findings are inconclusive or when the recommendations are based on limited data.
- Bias : Research recommendations may be influenced by researcher bias or conflicts of interest, leading to recommendations that are not in the best interests of stakeholders.
- Timing : Research recommendations may be time-sensitive, requiring timely action to be effective. Delayed action may result in missed opportunities or reduced effectiveness.
- Lack of evaluation: Research recommendations may not be evaluated to determine their effectiveness or impact, making it difficult to assess whether they are successful or not.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Data Collection – Methods Types and Examples

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Process – Steps, Examples and Tips

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

Institutional Review Board – Application Sample...

Evaluating Research – Process, Examples and...
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips
Published on 15 September 2022 by Tegan George .
Recommendations in research are a crucial component of your discussion section and the conclusion of your thesis , dissertation , or research paper .
As you conduct your research and analyse the data you collected , perhaps there are ideas or results that don’t quite fit the scope of your research topic . Or, maybe your results suggest that there are further implications of your results or the causal relationships between previously-studied variables than covered in extant research.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
What should recommendations look like, building your research recommendation, how should your recommendations be written, recommendation in research example, frequently asked questions about recommendations.
Recommendations for future research should be:
- Concrete and specific
- Supported with a clear rationale
- Directly connected to your research
Overall, strive to highlight ways other researchers can reproduce or replicate your results to draw further conclusions, and suggest different directions that future research can take, if applicable.
Relatedly, when making these recommendations, avoid:
- Undermining your own work, but rather offer suggestions on how future studies can build upon it
- Suggesting recommendations actually needed to complete your argument, but rather ensure that your research stands alone on its own merits
- Using recommendations as a place for self-criticism, but rather as a natural extension point for your work
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
There are many different ways to frame recommendations, but the easiest is perhaps to follow the formula of research question conclusion recommendation. Here’s an example.
Conclusion An important condition for controlling many social skills is mastering language. If children have a better command of language, they can express themselves better and are better able to understand their peers. Opportunities to practice social skills are thus dependent on the development of language skills.
As a rule of thumb, try to limit yourself to only the most relevant future recommendations: ones that stem directly from your work. While you can have multiple recommendations for each research conclusion, it is also acceptable to have one recommendation that is connected to more than one conclusion.
These recommendations should be targeted at your audience, specifically toward peers or colleagues in your field that work on similar topics to yours. They can flow directly from any limitations you found while conducting your work, offering concrete and actionable possibilities for how future research can build on anything that your own work was unable to address at the time of your writing.
See below for a full research recommendation example that you can use as a template to write your own.
The current study can be interpreted as a first step in the research on COPD speech characteristics. However, the results of this study should be treated with caution due to the small sample size and the lack of details regarding the participants’ characteristics.
Future research could further examine the differences in speech characteristics between exacerbated COPD patients, stable COPD patients, and healthy controls. It could also contribute to a deeper understanding of the acoustic measurements suitable for e-health measurements.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
While it may be tempting to present new arguments or evidence in your thesis or disseration conclusion , especially if you have a particularly striking argument you’d like to finish your analysis with, you shouldn’t. Theses and dissertations follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the discussion section and results section .) The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
The conclusion of your thesis or dissertation should include the following:
- A restatement of your research question
- A summary of your key arguments and/or results
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
For a stronger dissertation conclusion , avoid including:
- Generic concluding phrases (e.g. “In conclusion…”)
- Weak statements that undermine your argument (e.g. “There are good points on both sides of this issue.”)
Your conclusion should leave the reader with a strong, decisive impression of your work.
In a thesis or dissertation, the discussion is an in-depth exploration of the results, going into detail about the meaning of your findings and citing relevant sources to put them in context.
The conclusion is more shorter and more general: it concisely answers your main research question and makes recommendations based on your overall findings.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
George, T. (2022, September 15). How to Write Recommendations in Research | Examples & Tips. Scribbr. Retrieved 21 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/research-recommendations/
Is this article helpful?
Tegan George
Other students also liked, how to write a discussion section | tips & examples, how to write a thesis or dissertation conclusion, how to write a results section | tips & examples.
Research Implications & Recommendations
A Plain-Language Explainer With Examples + FREE Template
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) | Reviewers: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | May 2024

The research implications and recommendations are closely related but distinctly different concepts that often trip students up. Here, we’ll unpack them using plain language and loads of examples , so that you can approach your project with confidence.
Overview: Implications & Recommendations
- What are research implications ?
- What are research recommendations ?
- Examples of implications and recommendations
- The “ Big 3 ” categories
- How to write the implications and recommendations
- Template sentences for both sections
- Key takeaways
Implications & Recommendations 101
Let’s start with the basics and define our terms.
At the simplest level, research implications refer to the possible effects or outcomes of a study’s findings. More specifically, they answer the question, “ What do these findings mean?” . In other words, the implications section is where you discuss the broader impact of your study’s findings on theory, practice and future research.
This discussion leads us to the recommendations section , which is where you’ll propose specific actions based on your study’s findings and answer the question, “ What should be done next?” . In other words, the recommendations are practical steps that stakeholders can take to address the key issues identified by your study.
In a nutshell, then, the research implications discuss the broader impact and significance of a study’s findings, while recommendations provide specific actions to take, based on those findings. So, while both of these components are deeply rooted in the findings of the study, they serve different functions within the write up.
Need a helping hand?
Examples: Implications & Recommendations
The distinction between research implications and research recommendations might still feel a bit conceptual, so let’s look at one or two practical examples:
Let’s assume that your study finds that interactive learning methods significantly improve student engagement compared to traditional lectures. In this case, one of your recommendations could be that schools incorporate more interactive learning techniques into their curriculums to enhance student engagement.
Let’s imagine that your study finds that patients who receive personalised care plans have better health outcomes than those with standard care plans. One of your recommendations might be that healthcare providers develop and implement personalised care plans for their patients.
Now, these are admittedly quite simplistic examples, but they demonstrate the difference (and connection ) between the research implications and the recommendations. Simply put, the implications are about the impact of the findings, while the recommendations are about proposed actions, based on the findings.

The “Big 3” Categories
Now that we’ve defined our terms, let’s dig a little deeper into the implications – specifically, the different types or categories of research implications that exist.
Broadly speaking, implications can be divided into three categories – theoretical implications, practical implications and implications for future research .
Theoretical implications relate to how your study’s findings contribute to or challenge existing theories. For example, if a study on social behaviour uncovers new patterns, it might suggest that modifications to current psychological theories are necessary.
Practical implications , on the other hand, focus on how your study’s findings can be applied in real-world settings. For example, if your study demonstrated the effectiveness of a new teaching method, this would imply that educators should consider adopting this method to improve learning outcomes.
Practical implications can also involve policy reconsiderations . For example, if a study reveals significant health benefits from a particular diet, an implication might be that public health guidelines be re-evaluated.
Last but not least, there are the implications for future research . As the name suggests, this category of implications highlights the research gaps or new questions raised by your study. For example, if your study finds mixed results regarding a relationship between two variables, it might imply the need for further investigation to clarify these findings.
To recap then, the three types of implications are the theoretical, the practical and the implications on future research. Regardless of the category, these implications feed into and shape the recommendations , laying the foundation for the actions you’ll propose.

How To Write The Sections
Now that we’ve laid the foundations, it’s time to explore how to write up the implications and recommendations sections respectively.
Let’s start with the “ where ” before digging into the “ how ”. Typically, the implications will feature in the discussion section of your document, while the recommendations will be located in the conclusion . That said, layouts can vary between disciplines and institutions, so be sure to check with your university what their preferences are.
For the implications section, a common approach is to structure the write-up based on the three categories we looked at earlier – theoretical, practical and future research implications. In practical terms, this discussion will usually follow a fairly formulaic sentence structure – for example:
This research provides new insights into [theoretical aspect], indicating that…
The study’s outcomes highlight the potential benefits of adopting [specific practice] in..
This study raises several questions that warrant further investigation, such as…
Moving onto the recommendations section, you could again structure your recommendations using the three categories. Alternatively, you could structure the discussion per stakeholder group – for example, policymakers, organisations, researchers, etc.
Again, you’ll likely use a fairly formulaic sentence structure for this section. Here are some examples for your inspiration:
Based on the findings, [specific group] should consider adopting [new method] to improve…
To address the issues identified, it is recommended that legislation should be introduced to…
Researchers should consider examining [specific variable] to build on the current study’s findings.
Remember, you can grab a copy of our tried and tested templates for both the discussion and conclusion sections over on the Grad Coach blog. You can find the links to those, as well as loads of other free resources, in the description 🙂
FAQs: Implications & Recommendations
How do i determine the implications of my study.
To do this, you’ll need to consider how your findings address gaps in the existing literature, how they could influence theory, practice, or policy, and the potential societal or economic impacts.
When thinking about your findings, it’s also a good idea to revisit your introduction chapter, where you would have discussed the potential significance of your study more broadly. This section can help spark some additional ideas about what your findings mean in relation to your original research aims.
Should I discuss both positive and negative implications?
Absolutely. You’ll need to discuss both the positive and negative implications to provide a balanced view of how your findings affect the field and any limitations or potential downsides.
Can my research implications be speculative?
Yes and no. While implications are somewhat more speculative than recommendations and can suggest potential future outcomes, they should be grounded in your data and analysis. So, be careful to avoid overly speculative claims.
How do I formulate recommendations?
Ideally, you should base your recommendations on the limitations and implications of your study’s findings. So, consider what further research is needed, how policies could be adapted, or how practices could be improved – and make proposals in this respect.
How specific should my recommendations be?
Your recommendations should be as specific as possible, providing clear guidance on what actions or research should be taken next. As mentioned earlier, the implications can be relatively broad, but the recommendations should be very specific and actionable. Ideally, you should apply the SMART framework to your recommendations.
Can I recommend future research in my recommendations?
Absolutely. Highlighting areas where further research is needed is a key aspect of the recommendations section. Naturally, these recommendations should link to the respective section of your implications (i.e., implications for future research).
Wrapping Up: Key Takeaways
We’ve covered quite a bit of ground here, so let’s quickly recap.
- Research implications refer to the possible effects or outcomes of a study’s findings.
- The recommendations section, on the other hand, is where you’ll propose specific actions based on those findings.
- You can structure your implications section based on the three overarching categories – theoretical, practical and future research implications.
- You can carry this structure through to the recommendations as well, or you can group your recommendations by stakeholder.
Remember to grab a copy of our tried and tested free dissertation template, which covers both the implications and recommendations sections. If you’d like 1:1 help with your research project, be sure to check out our private coaching service, where we hold your hand throughout the research journey, step by step.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
The Ultimate Guide to Crafting Impactful Recommendations in Research

Are you ready to take your research to the next level? Crafting impactful recommendations is the key to unlocking the full potential of your study. By providing clear, actionable suggestions based on your findings, you can bridge the gap between research and real-world application.
In this ultimate guide, we'll show you how to write recommendations that make a difference in your research report or paper.
You'll learn how to craft specific, actionable recommendations that connect seamlessly with your research findings. Whether you're a student, writer, teacher, or journalist, this guide will help you master the art of writing recommendations in research. Let's get started and make your research count!
Understanding the Purpose of Recommendations
Recommendations in research serve as a vital bridge between your findings and their real-world applications. They provide specific, action-oriented suggestions to guide future studies and decision-making processes. Let's dive into the key purposes of crafting effective recommendations:
Guiding Future Research
Research recommendations play a crucial role in steering scholars and researchers towards promising avenues of exploration. By highlighting gaps in current knowledge and proposing new research questions, recommendations help advance the field and drive innovation.
Influencing Decision-Making
Well-crafted recommendations have the power to shape policies, programs, and strategies across various domains, such as:
- Policy-making
- Product development
- Marketing strategies
- Medical practice
By providing clear, evidence-based suggestions, recommendations facilitate informed decision-making and improve outcomes.
Connecting Research to Practice
Recommendations act as a conduit for transferring knowledge from researchers to practitioners, policymakers, and stakeholders. They bridge the gap between academic findings and their practical applications, ensuring that research insights are effectively translated into real-world solutions.
Enhancing Research Impact
By crafting impactful recommendations, you can amplify the reach and influence of your research, attracting attention from peers, funding agencies, and decision-makers.
Addressing Limitations
Recommendations provide an opportunity to acknowledge and address the limitations of your study. By suggesting concrete and actionable possibilities for future research, you demonstrate a thorough understanding of your work's scope and potential areas for improvement.
Identifying Areas for Future Research
Discovering research gaps is a crucial step in crafting impactful recommendations. It involves reviewing existing studies and identifying unanswered questions or problems that warrant further investigation. Here are some strategies to help you identify areas for future research:
Explore Research Limitations
Take a close look at the limitations section of relevant studies. These limitations often provide valuable insights into potential areas for future research. Consider how addressing these limitations could enhance our understanding of the topic at hand.
Critically Analyze Discussion and Future Research Sections
When reading articles, pay special attention to the discussion and future research sections. These sections often highlight gaps in the current knowledge base and propose avenues for further exploration. Take note of any recurring themes or unanswered questions that emerge across multiple studies.
Utilize Targeted Search Terms
To streamline your search for research gaps, use targeted search terms such as "literature gap" or "future research" in combination with your subject keywords. This approach can help you quickly identify articles that explicitly discuss areas for future investigation.
Seek Guidance from Experts
Don't hesitate to reach out to your research advisor or other experts in your field. Their wealth of knowledge and experience can provide valuable insights into potential research gaps and emerging trends.
By employing these strategies, you'll be well-equipped to identify research gaps and craft recommendations that push the boundaries of current knowledge. Remember, the goal is to refine your research questions and focus your efforts on areas where more understanding is needed.
Structuring Your Recommendations
When it comes to structuring your recommendations, it's essential to keep them concise, organized, and tailored to your audience. Here are some key tips to help you craft impactful recommendations:
Prioritize and Organize
- Limit your recommendations to the most relevant and targeted suggestions for your peers or colleagues in the field.
- Place your recommendations at the end of the report, as they are often top of mind for readers.
- Write your recommendations in order of priority, with the most important ones for decision-makers coming first.
Use a Clear and Actionable Format
- Write recommendations in a clear, concise manner using actionable words derived from the data analyzed in your research.
- Use bullet points instead of long paragraphs for clarity and readability.
- Ensure that your recommendations are specific, measurable, attainable, relevant, and timely (SMART).
Connect Recommendations to Research
By following this simple formula, you can ensure that your recommendations are directly connected to your research and supported by a clear rationale.
Tailor to Your Audience
- Consider the needs and interests of your target audience when crafting your recommendations.
- Explain how your recommendations can solve the issues explored in your research.
- Acknowledge any limitations or constraints of your study that may impact the implementation of your recommendations.
Avoid Common Pitfalls
- Don't undermine your own work by suggesting incomplete or unnecessary recommendations.
- Avoid using recommendations as a place for self-criticism or introducing new information not covered in your research.
- Ensure that your recommendations are achievable and comprehensive, offering practical solutions for the issues considered in your paper.
By structuring your recommendations effectively, you can enhance the reliability and validity of your research findings, provide valuable strategies and suggestions for future research, and deliver impactful solutions to real-world problems.
Crafting Actionable and Specific Recommendations
Crafting actionable and specific recommendations is the key to ensuring your research findings have a real-world impact. Here are some essential tips to keep in mind:
Embrace Flexibility and Feasibility
Your recommendations should be open to discussion and new information, rather than being set in stone. Consider the following:
- Be realistic and considerate of your team's capabilities when making recommendations.
- Prioritize recommendations based on impact and reach, but be prepared to adjust based on team effort levels.
- Focus on solutions that require the fewest changes first, adopting an MVP (Minimum Viable Product) approach.
Provide Detailed and Justified Recommendations
To avoid vagueness and misinterpretation, ensure your recommendations are:
- Detailed, including photos, videos, or screenshots whenever possible.
- Justified based on research findings, providing alternatives when findings don't align with expectations or business goals.
Use this formula when writing recommendations:
Observed problem/pain point/unmet need + consequence + potential solution
Adopt a Solution-Oriented Approach
Foster collaboration and participation.
- Promote staff education on current research and create strategies to encourage adoption of promising clinical protocols.
- Include representatives from the treatment community in the development of the research initiative and the review of proposals.
- Require active, early, and permanent participation of treatment staff in the development, implementation, and interpretation of the study.
Tailor Recommendations to the Opportunity
When writing recommendations for a specific opportunity or program:
- Highlight the strengths and qualifications of the researcher.
- Provide specific examples of their work and accomplishments.
- Explain how their research has contributed to the field.
- Emphasize the researcher's potential for future success and their unique contributions.
By following these guidelines, you'll craft actionable and specific recommendations that drive meaningful change and showcase the value of your research.
Connecting Recommendations with Research Findings
Connecting your recommendations with research findings is crucial for ensuring the credibility and impact of your suggestions. Here's how you can seamlessly link your recommendations to the evidence uncovered in your study:
Grounding Recommendations in Research
Your recommendations should be firmly rooted in the data and insights gathered during your research process. Avoid including measures or suggestions that were not discussed or supported by your study findings. This approach ensures that your recommendations are evidence-based and directly relevant to the research at hand.
Highlighting the Significance of Collaboration
Research collaborations offer a wealth of benefits that can enhance an agency's competitive position. Consider the following factors when discussing the importance of collaboration in your recommendations:
- Organizational Development: Participation in research collaborations depends on an agency's stage of development, compatibility with its mission and culture, and financial stability.
- Trust-Building: Long-term collaboration success often hinges on a history of increasing involvement and trust between partners.
- Infrastructure: A permanent infrastructure that facilitates long-term development is key to successful collaborative programs.
Emphasizing Commitment and Participation
Fostering quality improvement and organizational learning.
In your recommendations, highlight the importance of enhancing quality improvement strategies and fostering organizational learning. Show sensitivity to the needs and constraints of community-based programs, as this understanding is crucial for effective collaboration and implementation.
Addressing Limitations and Implications
If not already addressed in the discussion section, your recommendations should mention the limitations of the study and their implications. Examples of limitations include:
- Sample size or composition
- Participant attrition
- Study duration
By acknowledging these limitations, you demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of your research and its potential impact.
By connecting your recommendations with research findings, you provide a solid foundation for your suggestions, emphasize the significance of collaboration, and showcase the potential for future research and practical applications.
Crafting impactful recommendations is a vital skill for any researcher looking to bridge the gap between their findings and real-world applications. By understanding the purpose of recommendations, identifying areas for future research, structuring your suggestions effectively, and connecting them to your research findings, you can unlock the full potential of your study. Remember to prioritize actionable, specific, and evidence-based recommendations that foster collaboration and drive meaningful change.
As you embark on your research journey, embrace the power of well-crafted recommendations to amplify the impact of your work. By following the guidelines outlined in this ultimate guide, you'll be well-equipped to write recommendations that resonate with your audience, inspire further investigation, and contribute to the advancement of your field. So go forth, make your research count, and let your recommendations be the catalyst for positive change.
Q: What are the steps to formulating recommendations in research? A: To formulate recommendations in research, you should first gain a thorough understanding of the research question. Review the existing literature to inform your recommendations and consider the research methods that were used. Identify which data collection techniques were employed and propose suitable data analysis methods. It's also essential to consider any limitations and ethical considerations of your research. Justify your recommendations clearly and finally, provide a summary of your recommendations.
Q: Why are recommendations significant in research studies? A: Recommendations play a crucial role in research as they form a key part of the analysis phase. They provide specific suggestions for interventions or strategies that address the problems and limitations discovered during the study. Recommendations are a direct response to the main findings derived from data collection and analysis, and they can guide future actions or research.
Q: Can you outline the seven steps involved in writing a research paper? A: Certainly. The seven steps to writing an excellent research paper include:
- Allowing yourself sufficient time to complete the paper.
- Defining the scope of your essay and crafting a clear thesis statement.
- Conducting a thorough yet focused search for relevant research materials.
- Reading the research materials carefully and taking detailed notes.
- Writing your paper based on the information you've gathered and analyzed.
- Editing your paper to ensure clarity, coherence, and correctness.
- Submitting your paper following the guidelines provided.
Q: What tips can help make a research paper more effective? A: To enhance the effectiveness of a research paper, plan for the extensive process ahead and understand your audience. Decide on the structure your research writing will take and describe your methodology clearly. Write in a straightforward and clear manner, avoiding the use of clichés or overly complex language.
Sign up for more like this.
- - Google Chrome
Intended for healthcare professionals
- Access provided by Google Indexer
- My email alerts
- BMA member login
- Username * Password * Forgot your log in details? Need to activate BMA Member Log In Log in via OpenAthens Log in via your institution

Search form
- Advanced search
- Search responses
- Search blogs
- How to formulate...
How to formulate research recommendations
- Related content
- Peer review
- Polly Brown ( pbrown{at}bmjgroup.com ) , publishing manager 1 ,
- Klara Brunnhuber , clinical editor 1 ,
- Kalipso Chalkidou , associate director, research and development 2 ,
- Iain Chalmers , director 3 ,
- Mike Clarke , director 4 ,
- Mark Fenton , editor 3 ,
- Carol Forbes , reviews manager 5 ,
- Julie Glanville , associate director/information service manager 5 ,
- Nicholas J Hicks , consultant in public health medicine 6 ,
- Janet Moody , identification and prioritisation manager 6 ,
- Sara Twaddle , director 7 ,
- Hazim Timimi , systems developer 8 ,
- Pamela Young , senior programme manager 6
- 1 BMJ Publishing Group, London WC1H 9JR,
- 2 National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, London WC1V 6NA,
- 3 Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments, James Lind Alliance Secretariat, James Lind Initiative, Oxford OX2 7LG,
- 4 UK Cochrane Centre, Oxford OX2 7LG,
- 5 Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York, York YO10 5DD,
- 6 National Coordinating Centre for Health Technology Assessment, University of Southampton, Southampton SO16 7PX,
- 7 Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, Edinburgh EH2 1EN,
- 8 Update Software, Oxford OX2 7LG
- Correspondence to: PBrown
- Accepted 22 September 2006
“More research is needed” is a conclusion that fits most systematic reviews. But authors need to be more specific about what exactly is required
Long awaited reports of new research, systematic reviews, and clinical guidelines are too often a disappointing anticlimax for those wishing to use them to direct future research. After many months or years of effort and intellectual energy put into these projects, authors miss the opportunity to identify unanswered questions and outstanding gaps in the evidence. Most reports contain only a less than helpful, general research recommendation. This means that the potential value of these recommendations is lost.
Current recommendations
In 2005, representatives of organisations commissioning and summarising research, including the BMJ Publishing Group, the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, the National Coordinating Centre for Health Technology Assessment, the National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence, the Scottish Intercollegiate Guidelines Network, and the UK Cochrane Centre, met as members of the development group for the Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments (see bmj.com for details on all participating organisations). Our aim was to discuss the state of research recommendations within our organisations and to develop guidelines for improving the presentation of proposals for further research. All organisations had found weaknesses in the way researchers and authors of systematic reviews and clinical guidelines stated the need for further research. As part of the project, a member of the Centre for Reviews and Dissemination under-took a rapid literature search to identify information on research recommendation models, which found some individual methods but no group initiatives to attempt to standardise recommendations.
Suggested format for research recommendations on the effects of treatments
Core elements.
E Evidence (What is the current state of the evidence?)
P Population (What is the population of interest?)
I Intervention (What are the interventions of interest?)
C Comparison (What are the comparisons of interest?)
O Outcome (What are the outcomes of interest?)
T Time stamp (Date of recommendation)
Optional elements
d Disease burden or relevance
t Time aspect of core elements of EPICOT
s Appropriate study type according to local need
In January 2006, the National Coordinating Centre for Health Technology Assessment presented the findings of an initial comparative analysis of how different organisations currently structure their research recommendations. The National Institute for Health and Clinical Excellence and the National Coordinating Centre for Health Technology Assessment request authors to present recommendations in a four component format for formulating well built clinical questions around treatments: population, intervention, comparison, and outcomes (PICO). 1 In addition, the research recommendation is dated and authors are asked to provide the current state of the evidence to support the proposal.
Clinical Evidence , although not directly standardising its sections for research recommendations, presents gaps in the evidence using a slightly extended version of the PICO format: evidence, population, intervention, comparison, outcomes, and time (EPICOT). Clinical Evidence has used this inherent structure to feed research recommendations on interventions categorised as “unknown effectiveness” back to the National Coordinating Centre for Health Technology Assessment and for inclusion in the Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments ( http://www.duets.nhs.uk/ ).
We decided to propose the EPICOT format as the basis for its statement on formulating research recommendations and tested this proposal through discussion and example. We agreed that this set of components provided enough context for formulating research recommendations without limiting researchers. In order for the proposed framework to be flexible and more widely applicable, the group discussed using several optional components when they seemed relevant or were proposed by one or more of the group members. The final outcome of discussions resulted in the proposed EPICOT+ format (box).
A recent BMJ article highlighted how lack of research hinders the applicability of existing guidelines to patients in primary care who have had a stroke or transient ischaemic attack. 2 Most research in the area had been conducted in younger patients with a recent episode and in a hospital setting. The authors concluded that “further evidence should be collected on the efficacy and adverse effects of intensive blood pressure lowering in representative populations before we implement this guidance [from national and international guidelines] in primary care.” Table 1 outlines how their recommendations could be formulated using the EPICOT+ format. The decision on whether additional research is indeed clinically and ethically warranted will still lie with the organisation considering commissioning the research.
Research recommendation based on gap in the evidence identified by a cross sectional study of clinical guidelines for management of patients who have had a stroke
- View inline
Table 2 shows the use of EPICOT+ for an unanswered question on the effectiveness of compliance therapy in people with schizophrenia, identified by the Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments.
Research recommendation based on a gap in the evidence on treatment of schizophrenia identified by the Database of Uncertainties about the Effects of Treatments
Discussions around optional elements
Although the group agreed that the PICO elements should be core requirements for a research recommendation, intense discussion centred on the inclusion of factors defining a more detailed context, such as current state of evidence (E), appropriate study type (s), disease burden and relevance (d), and timeliness (t).
Initially, group members interpreted E differently. Some viewed it as the supporting evidence for a research recommendation and others as the suggested study type for a research recommendation. After discussion, we agreed that E should be used to refer to the amount and quality of research supporting the recommendation. However, the issue remained contentious as some of us thought that if a systematic review was available, its reference would sufficiently identify the strength of the existing evidence. Others thought that adding evidence to the set of core elements was important as it provided a summary of the supporting evidence, particularly as the recommendation was likely to be abstracted and used separately from the review or research that led to its formulation. In contrast, the suggested study type (s) was left as an optional element.
A research recommendation will rarely have an absolute value in itself. Its relative priority will be influenced by the burden of ill health (d), which is itself dependent on factors such as local prevalence, disease severity, relevant risk factors, and the priorities of the organisation considering commissioning the research.
Similarly, the issue of time (t) could be seen to be relevant to each of the core elements in varying ways—for example, duration of treatment, length of follow-up. The group therefore agreed that time had a subsidiary role within each core item; however, T as the date of the recommendation served to define its shelf life and therefore retained individual importance.
Applicability and usability
The proposed statement on research recommendations applies to uncertainties of the effects of any form of health intervention or treatment and is intended for research in humans rather than basic scientific research. Further investigation is required to assess the applicability of the format for questions around diagnosis, signs and symptoms, prognosis, investigations, and patient preference.
When the proposed format is applied to a specific research recommendation, the emphasis placed on the relevant part(s) of the EPICOT+ format may vary by author, audience, and intended purpose. For example, a recommendation for research into treatments for transient ischaemic attack may or may not define valid outcome measures to assess quality of life or gather data on adverse effects. Among many other factors, its implementation will also depend on the strength of current findings—that is, strong evidence may support a tightly focused recommendation whereas a lack of evidence would result in a more general recommendation.
The controversy within the group, especially around the optional components, reflects the different perspectives of the participating organisations—whether they were involved in commissioning, undertaking, or summarising research. Further issues will arise during the implementation of the proposed format, and we welcome feedback and discussion.
Summary points
No common guidelines exist for the formulation of recommendations for research on the effects of treatments
Major organisations involved in commissioning or summarising research compared their approaches and agreed on core questions
The essential items can be summarised as EPICOT+ (evidence, population, intervention, comparison, outcome, and time)
Further details, such as disease burden and appropriate study type, should be considered as required
We thank Patricia Atkinson and Jeremy Wyatt.
Contributors and sources All authors contributed to manuscript preparation and approved the final draft. NJH is the guarantor.
Competing interests None declared.
- Richardson WS ,
- Wilson MC ,
- Nishikawa J ,
- Hayward RSA
- McManus RJ ,
- Leonardi-Bee J ,
- PROGRESS Collaborative Group
- Warburton E
- Rothwell P ,
- McIntosh AM ,
- Lawrie SM ,
- Stanfield AC
- O'Donnell C ,
- Donohoe G ,
- Sharkey L ,
- Jablensky A ,
- Sartorius N ,
- Ernberg G ,
Implications or Recommendations in Research: What's the Difference?
- Peer Review
High-quality research articles that get many citations contain both implications and recommendations. Implications are the impact your research makes, whereas recommendations are specific actions that can then be taken based on your findings, such as for more research or for policymaking.
Updated on August 23, 2022

That seems clear enough, but the two are commonly confused.
This confusion is especially true if you come from a so-called high-context culture in which information is often implied based on the situation, as in many Asian cultures. High-context cultures are different from low-context cultures where information is more direct and explicit (as in North America and many European cultures).
Let's set these two straight in a low-context way; i.e., we'll be specific and direct! This is the best way to be in English academic writing because you're writing for the world.
Implications and recommendations in a research article
The standard format of STEM research articles is what's called IMRaD:
- Introduction
- Discussion/conclusions
Some journals call for a separate conclusions section, while others have the conclusions as the last part of the discussion. You'll write these four (or five) sections in the same sequence, though, no matter the journal.
The discussion section is typically where you restate your results and how well they confirmed your hypotheses. Give readers the answer to the questions for which they're looking to you for an answer.
At this point, many researchers assume their paper is finished. After all, aren't the results the most important part? As you might have guessed, no, you're not quite done yet.
The discussion/conclusions section is where to say what happened and what should now happen
The discussion/conclusions section of every good scientific article should contain the implications and recommendations.
The implications, first of all, are the impact your results have on your specific field. A high-impact, highly cited article will also broaden the scope here and provide implications to other fields. This is what makes research cross-disciplinary.
Recommendations, however, are suggestions to improve your field based on your results.
These two aspects help the reader understand your broader content: How and why your work is important to the world. They also tell the reader what can be changed in the future based on your results.
These aspects are what editors are looking for when selecting papers for peer review.

Implications and recommendations are, thus, written at the end of the discussion section, and before the concluding paragraph. They help to “wrap up” your paper. Once your reader understands what you found, the next logical step is what those results mean and what should come next.
Then they can take the baton, in the form of your work, and run with it. That gets you cited and extends your impact!
The order of implications and recommendations also matters. Both are written after you've summarized your main findings in the discussion section. Then, those results are interpreted based on ongoing work in the field. After this, the implications are stated, followed by the recommendations.
Writing an academic research paper is a bit like running a race. Finish strong, with your most important conclusion (recommendation) at the end. Leave readers with an understanding of your work's importance. Avoid generic, obvious phrases like "more research is needed to fully address this issue." Be specific.
The main differences between implications and recommendations (table)

Now let's dig a bit deeper into actually how to write these parts.
What are implications?
Research implications tell us how and why your results are important for the field at large. They help answer the question of “what does it mean?” Implications tell us how your work contributes to your field and what it adds to it. They're used when you want to tell your peers why your research is important for ongoing theory, practice, policymaking, and for future research.
Crucially, your implications must be evidence-based. This means they must be derived from the results in the paper.
Implications are written after you've summarized your main findings in the discussion section. They come before the recommendations and before the concluding paragraph. There is no specific section dedicated to implications. They must be integrated into your discussion so that the reader understands why the results are meaningful and what they add to the field.
A good strategy is to separate your implications into types. Implications can be social, political, technological, related to policies, or others, depending on your topic. The most frequently used types are theoretical and practical. Theoretical implications relate to how your findings connect to other theories or ideas in your field, while practical implications are related to what we can do with the results.
Key features of implications
- State the impact your research makes
- Helps us understand why your results are important
- Must be evidence-based
- Written in the discussion, before recommendations
- Can be theoretical, practical, or other (social, political, etc.)
Examples of implications
Let's take a look at some examples of research results below with their implications.
The result : one study found that learning items over time improves memory more than cramming material in a bunch of information at once .
The implications : This result suggests memory is better when studying is spread out over time, which could be due to memory consolidation processes.
The result : an intervention study found that mindfulness helps improve mental health if you have anxiety.
The implications : This result has implications for the role of executive functions on anxiety.
The result : a study found that musical learning helps language learning in children .
The implications : these findings suggest that language and music may work together to aid development.
What are recommendations?
As noted above, explaining how your results contribute to the real world is an important part of a successful article.
Likewise, stating how your findings can be used to improve something in future research is equally important. This brings us to the recommendations.
Research recommendations are suggestions and solutions you give for certain situations based on your results. Once the reader understands what your results mean with the implications, the next question they need to know is "what's next?"
Recommendations are calls to action on ways certain things in the field can be improved in the future based on your results. Recommendations are used when you want to convey that something different should be done based on what your analyses revealed.
Similar to implications, recommendations are also evidence-based. This means that your recommendations to the field must be drawn directly from your results.
The goal of the recommendations is to make clear, specific, and realistic suggestions to future researchers before they conduct a similar experiment. No matter what area your research is in, there will always be further research to do. Try to think about what would be helpful for other researchers to know before starting their work.
Recommendations are also written in the discussion section. They come after the implications and before the concluding paragraphs. Similar to the implications, there is usually no specific section dedicated to the recommendations. However, depending on how many solutions you want to suggest to the field, they may be written as a subsection.
Key features of recommendations
- Statements about what can be done differently in the field based on your findings
- Must be realistic and specific
- Written in the discussion, after implications and before conclusions
- Related to both your field and, preferably, a wider context to the research
Examples of recommendations
Here are some research results and their recommendations.
A meta-analysis found that actively recalling material from your memory is better than simply re-reading it .
- The recommendation: Based on these findings, teachers and other educators should encourage students to practice active recall strategies.
A medical intervention found that daily exercise helps prevent cardiovascular disease .
- The recommendation: Based on these results, physicians are recommended to encourage patients to exercise and walk regularly. Also recommended is to encourage more walking through public health offices in communities.
A study found that many research articles do not contain the sample sizes needed to statistically confirm their findings .
The recommendation: To improve the current state of the field, researchers should consider doing power analysis based on their experiment's design.
What else is important about implications and recommendations?
When writing recommendations and implications, be careful not to overstate the impact of your results. It can be tempting for researchers to inflate the importance of their findings and make grandiose statements about what their work means.
Remember that implications and recommendations must be coming directly from your results. Therefore, they must be straightforward, realistic, and plausible.
Another good thing to remember is to make sure the implications and recommendations are stated clearly and separately. Do not attach them to the endings of other paragraphs just to add them in. Use similar example phrases as those listed in the table when starting your sentences to clearly indicate when it's an implication and when it's a recommendation.
When your peers, or brand-new readers, read your paper, they shouldn't have to hunt through your discussion to find the implications and recommendations. They should be clear, visible, and understandable on their own.
That'll get you cited more, and you'll make a greater contribution to your area of science while extending the life and impact of your work.

The AJE Team
See our "Privacy Policy"
- Table of Contents
AI, Ethics & Human Agency
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process.
- Recommendation Reports
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - University of South Florida , Julie Staggers - Washington State University
Recommendation reports are texts that advise audiences about the best ways to solve a problem. Recommendation reports are a type of formal report that is widely used across disciplines and professions. Subject Matter Experts aim to make recommendations based on the best available theory, research and practice.
Different disciplines and professions have different research methods for assessing knowledge claims and defining knowledge . Thus, there is no one perfect way to write a recommendation report.
As always, when composing—especially when you’re planning your report—it’s strategic to focus on your audience, rhetorical analysis, and rhetorical reasoning. At center, keep the focus on what you want your audience to feel, think, and do.
While writers, speakers, and knowledge workers . . . may choose a variety of ways to organize their reports, below are some fairly traditional sections to formal recommendations reports:
- Letter of transmittal
- Problem Definition
- Potential solutions to the problem
- Empirical Research Methods used to investigate the problem
- Recommendations
- List of Illustrations
Report Body
Note: your specific rhetorical context will determine what headings you use in your Recommendation Report. That said, the following sections are fairly typical for this genre, and they are required, as appropriate, for this assignment.

Report back matter
Collect material for the appendices as you go. The report back matter will include:
- Bibliography, which is sometimes referred to as Works Cited or References (Use a citation format appropriate for your field (APA, MLA, Chicago, IEEE, etc.)
- Appendices, if necessary (e.g., letters of support, financial projections)
Formatting and design
Employ a professional writing style throughout, including:
- Page layout: Appropriate to audience, purpose, and context. 8.5 x 11 with 1-inch margins is a fail-safe default.
- Typography: Choose business-friendly fonts appropriate to your audience, purpose, and context; Arial for headers and Times New Roman for body text is a safe, neutral default.
- Headings and subheadings: Use a numbered heading and subheading system, formatted using the Styles function on your word processor.
- Bulleted and numbered lists: Use lists that are formatted correctly using the list buttons on your word processor with a blank line before the first bullet and after the last bullet
- Graphics and figures: Support data findings and arguments with appropriate visuals – charts, tables, graphics; Include numbered titles and captions
- Page numbering: use lower-case Roman numerals for pages before the table of contents, Arabic numerals; no page number on the TOC.
Additional Resources
- Final Reports by Angela Eward-Mangione and Katherine McGee
- Professional Writing Style

Brevity - Say More with Less

Clarity (in Speech and Writing)

Coherence - How to Achieve Coherence in Writing

Flow - How to Create Flow in Writing

Inclusivity - Inclusive Language

The Elements of Style - The DNA of Powerful Writing

Suggested Edits
- Please select the purpose of your message. * - Corrections, Typos, or Edits Technical Support/Problems using the site Advertising with Writing Commons Copyright Issues I am contacting you about something else
- Your full name
- Your email address *
- Page URL needing edits *
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Other Topics:

Citation - Definition - Introduction to Citation in Academic & Professional Writing
- Joseph M. Moxley
Explore the different ways to cite sources in academic and professional writing, including in-text (Parenthetical), numerical, and note citations.

Collaboration - What is the Role of Collaboration in Academic & Professional Writing?
Collaboration refers to the act of working with others or AI to solve problems, coauthor texts, and develop products and services. Collaboration is a highly prized workplace competency in academic...

Genre may reference a type of writing, art, or musical composition; socially-agreed upon expectations about how writers and speakers should respond to particular rhetorical situations; the cultural values; the epistemological assumptions...

Grammar refers to the rules that inform how people and discourse communities use language (e.g., written or spoken English, body language, or visual language) to communicate. Learn about the rhetorical...

Information Literacy - Discerning Quality Information from Noise
Information Literacy refers to the competencies associated with locating, evaluating, using, and archiving information. In order to thrive, much less survive in a global information economy — an economy where information functions as a...

Mindset refers to a person or community’s way of feeling, thinking, and acting about a topic. The mindsets you hold, consciously or subconsciously, shape how you feel, think, and act–and...

Rhetoric: Exploring Its Definition and Impact on Modern Communication
Learn about rhetoric and rhetorical practices (e.g., rhetorical analysis, rhetorical reasoning, rhetorical situation, and rhetorical stance) so that you can strategically manage how you compose and subsequently produce a text...

Style, most simply, refers to how you say something as opposed to what you say. The style of your writing matters because audiences are unlikely to read your work or...

The Writing Process - Research on Composing
The writing process refers to everything you do in order to complete a writing project. Over the last six decades, researchers have studied and theorized about how writers go about...

Writing Studies
Writing studies refers to an interdisciplinary community of scholars and researchers who study writing. Writing studies also refers to an academic, interdisciplinary discipline – a subject of study. Students in...
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Speech & Writing

- Walden University
- Faculty Portal
Reference List: Common Reference List Examples
Article (with doi).
Alvarez, E., & Tippins, S. (2019). Socialization agents that Puerto Rican college students use to make financial decisions. Journal of Social Change , 11 (1), 75–85. https://doi.org/10.5590/JOSC.2019.11.1.07
Laplante, J. P., & Nolin, C. (2014). Consultas and socially responsible investing in Guatemala: A case study examining Maya perspectives on the Indigenous right to free, prior, and informed consent. Society & Natural Resources , 27 , 231–248. https://doi.org/10.1080/08941920.2013.861554
Use the DOI number for the source whenever one is available. DOI stands for "digital object identifier," a number specific to the article that can help others locate the source. In APA 7, format the DOI as a web address. Active hyperlinks for DOIs and URLs should be used for documents meant for screen reading. Present these hyperlinks in blue and underlined text (the default formatting in Microsoft Word), although plain black text is also acceptable. Be consistent in your formatting choice for DOIs and URLs throughout your reference list. Also see our Quick Answer FAQ, "Can I use the DOI format provided by library databases?"
Jerrentrup, A., Mueller, T., Glowalla, U., Herder, M., Henrichs, N., Neubauer, A., & Schaefer, J. R. (2018). Teaching medicine with the help of “Dr. House.” PLoS ONE , 13 (3), Article e0193972. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0193972
For journal articles that are assigned article numbers rather than page ranges, include the article number in place of the page range.
For more on citing electronic resources, see Electronic Sources References .
Article (Without DOI)
Found in a common academic research database or in print.
Casler , T. (2020). Improving the graduate nursing experience through support on a social media platform. MEDSURG Nursing , 29 (2), 83–87.
If an article does not have a DOI and you retrieved it from a common academic research database through the university library, there is no need to include any additional electronic retrieval information. The reference list entry looks like the entry for a print copy of the article. (This format differs from APA 6 guidelines that recommended including the URL of a journal's homepage when the DOI was not available.) Note that APA 7 has additional guidance on reference list entries for articles found only in specific databases or archives such as Cochrane Database of Systematic Reviews, UpToDate, ProQuest Dissertations and Theses Global, and university archives. See APA 7, Section 9.30 for more information.
Found on an Open Access Website
Eaton, T. V., & Akers, M. D. (2007). Whistleblowing and good governance. CPA Journal , 77 (6), 66–71. http://archives.cpajournal.com/2007/607/essentials/p58.htm
Provide the direct web address/URL to a journal article found on the open web, often on an open access journal's website. In APA 7, active hyperlinks for DOIs and URLs should be used for documents meant for screen reading. Present these hyperlinks in blue and underlined text (the default formatting in Microsoft Word), although plain black text is also acceptable. Be consistent in your formatting choice for DOIs and URLs throughout your reference list.
Weinstein, J. A. (2010). Social change (3rd ed.). Rowman & Littlefield.
If the book has an edition number, include it in parentheses after the title of the book. If the book does not list any edition information, do not include an edition number. The edition number is not italicized.
American Nurses Association. (2015). Nursing: Scope and standards of practice (3rd ed.).
If the author and publisher are the same, only include the author in its regular place and omit the publisher.
Lencioni, P. (2012). The advantage: Why organizational health trumps everything else in business . Jossey-Bass. https://amzn.to/343XPSJ
As a change from APA 6 to APA 7, it is no longer necessary to include the ebook format in the title. However, if you listened to an audiobook and the content differs from the text version (e.g., abridged content) or your discussion highlights elements of the audiobook (e.g., narrator's performance), then note that it is an audiobook in the title element in brackets. For ebooks and online audiobooks, also include the DOI number (if available) or nondatabase URL but leave out the electronic retrieval element if the ebook was found in a common academic research database, as with journal articles. APA 7 allows for the shortening of long DOIs and URLs, as shown in this example. See APA 7, Section 9.36 for more information.
Chapter in an Edited Book
Poe, M. (2017). Reframing race in teaching writing across the curriculum. In F. Condon & V. A. Young (Eds.), Performing antiracist pedagogy in rhetoric, writing, and communication (pp. 87–105). University Press of Colorado.
Include the page numbers of the chapter in parentheses after the book title.
Christensen, L. (2001). For my people: Celebrating community through poetry. In B. Bigelow, B. Harvey, S. Karp, & L. Miller (Eds.), Rethinking our classrooms: Teaching for equity and justice (Vol. 2, pp. 16–17). Rethinking Schools.
Also include the volume number or edition number in the parenthetical information after the book title when relevant.
Freud, S. (1961). The ego and the id. In J. Strachey (Ed.), The standard edition of the complete psychological works of Sigmund Freud (Vol. 19, pp. 3-66). Hogarth Press. (Original work published 1923)
When a text has been republished as part of an anthology collection, after the author’s name include the date of the version that was read. At the end of the entry, place the date of the original publication inside parenthesis along with the note “original work published.” For in-text citations of republished work, use both dates in the parenthetical citation, original date first with a slash separating the years, as in this example: Freud (1923/1961). For more information on reprinted or republished works, see APA 7, Sections 9.40-9.41.
Classroom Resources
Citing classroom resources.
If you need to cite content found in your online classroom, use the author (if there is one listed), the year of publication (if available), the title of the document, and the main URL of Walden classrooms. For example, you are citing study notes titled "Health Effects of Exposure to Forest Fires," but you do not know the author's name, your reference entry will look like this:
Health effects of exposure to forest fires [Lecture notes]. (2005). Walden University Canvas. https://waldenu.instructure.com
If you do know the author of the document, your reference will look like this:
Smith, A. (2005). Health effects of exposure to forest fires [PowerPoint slides]. Walden University Canvas. https://waldenu.instructure.com
A few notes on citing course materials:
- [Lecture notes]
- [Course handout]
- [Study notes]
- It can be difficult to determine authorship of classroom documents. If an author is listed on the document, use that. If the resource is clearly a product of Walden (such as the course-based videos), use Walden University as the author. If you are unsure or if no author is indicated, place the title in the author spot, as above.
- If you cannot determine a date of publication, you can use n.d. (for "no date") in place of the year.
Note: The web location for Walden course materials is not directly retrievable without a password, and therefore, following APA guidelines, use the main URL for the class sites: https://class.waldenu.edu.
Citing Tempo Classroom Resources
Clear author:
Smith, A. (2005). Health effects of exposure to forest fires [PowerPoint slides]. Walden University Brightspace. https://mytempo.waldenu.edu
Unclear author:
Health effects of exposure to forest fires [Lecture notes]. (2005). Walden University Brightspace. https://mytempo.waldenu.edu
Conference Sessions and Presentations
Feinman, Y. (2018, July 27). Alternative to proctoring in introductory statistics community college courses [Poster presentation]. Walden University Research Symposium, Minneapolis, MN, United States. https://scholarworks.waldenu.edu/symposium2018/23/
Torgerson, K., Parrill, J., & Haas, A. (2019, April 5-9). Tutoring strategies for online students [Conference session]. The Higher Learning Commission Annual Conference, Chicago, IL, United States. http://onlinewritingcenters.org/scholarship/torgerson-parrill-haas-2019/
Dictionary Entry
Merriam-Webster. (n.d.). Leadership. In Merriam-Webster.com dictionary . Retrieved May 28, 2020, from https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/leadership
When constructing a reference for an entry in a dictionary or other reference work that has no byline (i.e., no named individual authors), use the name of the group—the institution, company, or organization—as author (e.g., Merriam Webster, American Psychological Association, etc.). The name of the entry goes in the title position, followed by "In" and the italicized name of the reference work (e.g., Merriam-Webster.com dictionary , APA dictionary of psychology ). In this instance, APA 7 recommends including a retrieval date as well for this online source since the contents of the page change over time. End the reference entry with the specific URL for the defined word.
Discussion Board Post
Osborne, C. S. (2010, June 29). Re: Environmental responsibility [Discussion post]. Walden University Canvas. https://waldenu.instructure.com
Dissertations or Theses
Retrieved From a Database
Nalumango, K. (2019). Perceptions about the asylum-seeking process in the United States after 9/11 (Publication No. 13879844) [Doctoral dissertation, Walden University]. ProQuest Dissertations and Theses.
Retrieved From an Institutional or Personal Website
Evener. J. (2018). Organizational learning in libraries at for-profit colleges and universities [Doctoral dissertation, Walden University]. ScholarWorks. https://scholarworks.waldenu.edu/cgi/viewcontent.cgi?article=6606&context=dissertations
Unpublished Dissertation or Thesis
Kirwan, J. G. (2005). An experimental study of the effects of small-group, face-to-face facilitated dialogues on the development of self-actualization levels: A movement towards fully functional persons [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Saybrook Graduate School and Research Center.
For further examples and information, see APA 7, Section 10.6.
Legal Material
For legal references, APA follows the recommendations of The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation , so if you have any questions beyond the examples provided in APA, seek out that resource as well.
Court Decisions
Reference format:
Name v. Name, Volume Reporter Page (Court Date). URL
Sample reference entry:
Brown v. Board of Education, 347 U.S. 483 (1954). https://www.oyez.org/cases/1940-1955/347us483
Sample citation:
In Brown v. Board of Education (1954), the Supreme Court ruled racial segregation in schools unconstitutional.
Note: Italicize the case name when it appears in the text of your paper.
Name of Act, Title Source § Section Number (Year). URL
Sample reference entry for a federal statute:
Individuals With Disabilities Education Act, 20 U.S.C. § 1400 et seq. (2004). https://www.congress.gov/108/plaws/publ446/PLAW-108publ446.pdf
Sample reference entry for a state statute:
Minnesota Nurse Practice Act, Minn. Stat. §§ 148.171 et seq. (2019). https://www.revisor.mn.gov/statutes/cite/148.171
Sample citation: Minnesota nurses must maintain current registration in order to practice (Minnesota Nurse Practice Act, 2010).
Note: The § symbol stands for "section." Use §§ for sections (plural). To find this symbol in Microsoft Word, go to "Insert" and click on Symbol." Look in the Latin 1-Supplement subset. Note: U.S.C. stands for "United States Code." Note: The Latin abbreviation " et seq. " means "and what follows" and is used when the act includes the cited section and ones that follow. Note: List the chapter first followed by the section or range of sections.
Unenacted Bills and Resolutions
(Those that did not pass and become law)
Title [if there is one], bill or resolution number, xxx Cong. (year). URL
Sample reference entry for Senate bill:
Anti-Phishing Act, S. 472, 109th Cong. (2005). https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/senate-bill/472
Sample reference entry for House of Representatives resolution:
Anti-Phishing Act, H.R. 1099, 109th Cong. (2005). https://www.congress.gov/bill/109th-congress/house-bill/1099
The Anti-Phishing Act (2005) proposed up to 5 years prison time for people running Internet scams.
These are the three legal areas you may be most apt to cite in your scholarly work. For more examples and explanation, see APA 7, Chapter 11.
Magazine Article
Clay, R. (2008, June). Science vs. ideology: Psychologists fight back about the misuse of research. Monitor on Psychology , 39 (6). https://www.apa.org/monitor/2008/06/ideology
Note that for citations, include only the year: Clay (2008). For magazine articles retrieved from a common academic research database, leave out the URL. For magazine articles from an online news website that is not an online version of a print magazine, follow the format for a webpage reference list entry.
Newspaper Article (Retrieved Online)
Baker, A. (2014, May 7). Connecticut students show gains in national tests. New York Times . http://www.nytimes.com/2014/05/08/nyregion/national-assessment-of-educational-progress-results-in-Connecticut-and-New-Jersey.html
Include the full date in the format Year, Month Day. Do not include a retrieval date for periodical sources found on websites. Note that for citations, include only the year: Baker (2014). For newspaper articles retrieved from a common academic research database, leave out the URL. For newspaper articles from an online news website that is not an online version of a print newspaper, follow the format for a webpage reference list entry.
OASIS Resources
Oasis webpage.
OASIS. (n.d.). Common reference list examples . Walden University. https://academicguides.waldenu.edu/writingcenter/apa/references/examples
For all OASIS content, list OASIS as the author. Because OASIS webpages do not include publication dates, use “n.d.” for the year.
Interactive Guide
OASIS. (n.d.). Embrace iterative research and writing [Interactive guide]. Walden University. https://academics.waldenu.edu/oasis/iterative-research-writing-web
For OASIS multimedia resources, such as interactive guides, include a description of the resource in brackets after the title.
Online Video/Webcast
Walden University. (2013). An overview of learning [Video]. Walden University Canvas. https://waldenu.instructure.com
Use this format for online videos such as Walden videos in classrooms. Most of our classroom videos are produced by Walden University, which will be listed as the author in your reference and citation. Note: Some examples of audiovisual materials in the APA manual show the word “Producer” in parentheses after the producer/author area. In consultation with the editors of the APA manual, we have determined that parenthetical is not necessary for the videos in our courses. The manual itself is unclear on the matter, however, so either approach should be accepted. Note that the speaker in the video does not appear in the reference list entry, but you may want to mention that person in your text. For instance, if you are viewing a video where Tobias Ball is the speaker, you might write the following: Tobias Ball stated that APA guidelines ensure a consistent presentation of information in student papers (Walden University, 2013). For more information on citing the speaker in a video, see our page on Common Citation Errors .
Taylor, R. [taylorphd07]. (2014, February 27). Scales of measurement [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PDsMUlexaMY
OASIS. (2020, April 15). One-way ANCOVA: Introduction [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/_XnNDQ5CNW8
For videos from streaming sites, use the person or organization who uploaded the video in the author space to ensure retrievability, whether or not that person is the speaker in the video. A username can be provided in square brackets. As a change from APA 6 to APA 7, include the publisher after the title, and do not use "Retrieved from" before the URL. See APA 7, Section 10.12 for more information and examples.
See also reference list entry formats for TED Talks .
Technical and Research Reports
Edwards, C. (2015). Lighting levels for isolated intersections: Leading to safety improvements (Report No. MnDOT 2015-05). Center for Transportation Studies. http://www.cts.umn.edu/Publications/ResearchReports/reportdetail.html?id=2402
Technical and research reports by governmental agencies and other research institutions usually follow a different publication process than scholarly, peer-reviewed journals. However, they present original research and are often useful for research papers. Sometimes, researchers refer to these types of reports as gray literature , and white papers are a type of this literature. See APA 7, Section 10.4 for more information.
Reference list entires for TED Talks follow the usual guidelines for multimedia content found online. There are two common places to find TED talks online, with slightly different reference list entry formats for each.
TED Talk on the TED website
If you find the TED Talk on the TED website, follow the format for an online video on an organizational website:
Owusu-Kesse, K. (2020, June). 5 needs that any COVID-19 response should meet [Video]. TED Conferences. https://www.ted.com/talks/kwame_owusu_kesse_5_needs_that_any_covid_19_response_should_meet
The speaker is the author in the reference list entry if the video is posted on the TED website. For citations, use the speaker's surname.
TED Talk on YouTube
If you find the TED Talk on YouTube or another streaming video website, follow the usual format for streaming video sites:
TED. (2021, February 5). The shadow pandemic of domestic violence during COVID-19 | Kemi DaSilvalbru [Video]. YouTube. https://www.youtube.com/watch?v=PGdID_ICFII
TED is the author in the reference list entry if the video is posted on YouTube since it is the channel on which the video is posted. For citations, use TED as the author.
Walden University Course Catalog
To include the Walden course catalog in your reference list, use this format:
Walden University. (2020). 2019-2020 Walden University catalog . https://catalog.waldenu.edu/index.php
If you cite from a specific portion of the catalog in your paper, indicate the appropriate section and paragraph number in your text:
...which reflects the commitment to social change expressed in Walden University's mission statement (Walden University, 2020, Vision, Mission, and Goals section, para. 2).
And in the reference list:
Walden University. (2020). Vision, mission, and goals. In 2019-2020 Walden University catalog. https://catalog.waldenu.edu/content.php?catoid=172&navoid=59420&hl=vision&returnto=search
Vartan, S. (2018, January 30). Why vacations matter for your health . CNN. https://www.cnn.com/travel/article/why-vacations-matter/index.html
For webpages on the open web, include the author, date, webpage title, organization/site name, and URL. (There is a slight variation for online versions of print newspapers or magazines. For those sources, follow the models in the previous sections of this page.)
American Federation of Teachers. (n.d.). Community schools . http://www.aft.org/issues/schoolreform/commschools/index.cfm
If there is no specified author, then use the organization’s name as the author. In such a case, there is no need to repeat the organization's name after the title.
In APA 7, active hyperlinks for DOIs and URLs should be used for documents meant for screen reading. Present these hyperlinks in blue and underlined text (the default formatting in Microsoft Word), although plain black text is also acceptable. Be consistent in your formatting choice for DOIs and URLs throughout your reference list.
Related Resources
Knowledge Check: Common Reference List Examples
Didn't find what you need? Email us at [email protected] .
- Previous Page: Reference List: Overview
- Next Page: Common Military Reference List Examples
- Office of Student Disability Services
Walden Resources
Departments.
- Academic Residencies
- Academic Skills
- Career Planning and Development
- Customer Care Team
- Field Experience
- Military Services
- Student Success Advising
- Writing Skills
Centers and Offices
- Center for Social Change
- Office of Academic Support and Instructional Services
- Office of Degree Acceleration
- Office of Research and Doctoral Services
- Office of Student Affairs
Student Resources
- Doctoral Writing Assessment
- Form & Style Review
- Quick Answers
- ScholarWorks
- SKIL Courses and Workshops
- Walden Bookstore
- Walden Catalog & Student Handbook
- Student Safety/Title IX
- Legal & Consumer Information
- Website Terms and Conditions
- Cookie Policy
- Accessibility
- Accreditation
- State Authorization
- Net Price Calculator
- Contact Walden
Walden University is a member of Adtalem Global Education, Inc. www.adtalem.com Walden University is certified to operate by SCHEV © 2024 Walden University LLC. All rights reserved.
Thank you for visiting nature.com. You are using a browser version with limited support for CSS. To obtain the best experience, we recommend you use a more up to date browser (or turn off compatibility mode in Internet Explorer). In the meantime, to ensure continued support, we are displaying the site without styles and JavaScript.
- View all journals
- Explore content
- About the journal
- Publish with us
- Sign up for alerts
- CAREER COLUMN
- 20 July 2020
Writing the perfect recommendation letter
Andy Tay is a freelance writer based in Singapore.
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Undergraduates need them for graduate-school applications; PhD students and postdocs use them to apply for fellowships and jobs; senior scientists often have to have them to apply for awards and promotions. But writing an effective and personal recommendation letter can be time-consuming, especially for academics who must juggle grant applications, manuscripts, teaching and student supervision. And some might struggle to say the right things to support a former employee or student in their career move, while sounding original and unique.
Access options
Access Nature and 54 other Nature Portfolio journals
Get Nature+, our best-value online-access subscription
24,99 € / 30 days
cancel any time
Subscribe to this journal
Receive 51 print issues and online access
185,98 € per year
only 3,65 € per issue
Rent or buy this article
Prices vary by article type
Prices may be subject to local taxes which are calculated during checkout
Nature 584 , 158 (2020)
doi: https://doi.org/10.1038/d41586-020-02186-8
These interviews have been edited for length and clarity.
Related Articles

- Research management

How researchers in remote regions handle the isolation
Career Feature 24 MAY 24

What steps to take when funding starts to run out

Brazil’s plummeting graduate enrolments hint at declining interest in academic science careers
Career News 21 MAY 24

Reading between the lines: application essays predict university success
Research Highlight 17 MAY 24
How to stop students cramming for exams? Send them to sea
News & Views 30 APR 24

Guidelines for academics aim to lessen ethical pitfalls in generative-AI use
Nature Index 22 MAY 24

Pay researchers to spot errors in published papers
World View 21 MAY 24
Data Analyst for Gene Regulation as an Academic Functional Specialist
The Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität Bonn is an international research university with a broad spectrum of subjects. With 200 years of his...
53113, Bonn (DE)
Rheinische Friedrich-Wilhelms-Universität
Recruitment of Global Talent at the Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOZ, CAS)
The Institute of Zoology (IOZ), Chinese Academy of Sciences (CAS), is seeking global talents around the world.
Beijing, China
Institute of Zoology, Chinese Academy of Sciences (IOZ, CAS)
Full Professorship (W3) in “Organic Environmental Geochemistry (f/m/d)
The Institute of Earth Sciences within the Faculty of Chemistry and Earth Sciences at Heidelberg University invites applications for a FULL PROFE...
Heidelberg, Brandenburg (DE)
Universität Heidelberg
Postdoc: deep learning for super-resolution microscopy
The Ries lab is looking for a PostDoc with background in machine learning.
Vienna, Austria
University of Vienna
Postdoc: development of a novel MINFLUX microscope
The Ries lab is developing super-resolution microscopy methods for structural cell biology. In this project we will develop a fast, simple, and robust
Sign up for the Nature Briefing newsletter — what matters in science, free to your inbox daily.
Quick links
- Explore articles by subject
- Guide to authors
- Editorial policies

Improved Surface Drainage of Pavements: Final Report (1998)
Chapter: chapter 5 summary, findings, and recommendations.
Below is the uncorrected machine-read text of this chapter, intended to provide our own search engines and external engines with highly rich, chapter-representative searchable text of each book. Because it is UNCORRECTED material, please consider the following text as a useful but insufficient proxy for the authoritative book pages.
CHAPIER 5 SI~MARY, FINDINGS, AND RECOMMENDATIONS SUGARY The primary objective of this research was to identify unproved methods for draining rainwater from the surface of multi-lane pavements and to develop guidelines for their use. The guidelines, along with details on the rationale for their development, are presented in a separate document' "Proposed Design Guidelines for Improving Pavement Surface Drainage" (2J. The guidelines support an interactive computer program, PAVDRN, that can be used by practicing engineers In the process of designing new pavements or rehabilitating old pavements' is outlined In figure 39. The intended audience for the guidelines is practicing highway design engineers that work for transportation agencies or consulting firms. Improved pavement surface drainage is needed for two reasons: (~) to minimize splash and spray and (2) to control the tendency for hydroplaning. Both issues are primary safety concerns. At the request of the advisory panel for the project, the main focus of this study was on ~mprov~g surface drainage to mammae the tendency for hydroplaning. In terms of reducing the tendency for hydroplaTuT g, the needed level of drainage is defined in terms of the thickness of the film of water on the pavement. Therefore, the guidelines were developed within the context of reducing the thickness of the water film on pavement surfaces to the extent that hydroplaning is unlikely at highway design speeds. Since hydroplaning is ~7
DESIGN CRITERIA Pavement Geometry Number of lanes Section type - Tangent - Horizontal curve - Transition - Vertical crest curve - Vertical sag curve Enviromnental oramaters Rainfall intensity ~ Temperature Pavement Tvpe Dense-graded asphalt Porous asphalt Portland cement concrete ~ Grooved Portland cement concrete Desion Soeed Allowable speed for onset of hydroplaning Recommend Desion Changes Alter geometry Alter pavement surface Add appurtenances Groove (Portland cement concrete) CALCULATIONS Lenoth of flow path Calculate on basis of pavement geometry IT Hydraulic Analvses . No? Water film thickness Equation No. 10 Equation No.'s. 16-19 1 Hvdroolanino Analvsis Hydroplaning speed Equation No.'s 21-24 Rainfall Intensity Equation No. 25 -A I / Meet Design ~ \ Cntena? / \<es? Accent Desinn | Figure 39. Flow diagram representing PAVI)RN design process In "Proposed Guidelines for Improving Pavement Surface DrmT~age" (2). 118
controlled primarily by the thickness of the water film on the pavement surface, the design guidelines focus on the prediction and control of ache depth of water flowing across the pavement surface as a result of rainfall, often referred to as sheet flow. Water film thickness on highway pavements can be controlled In three fundamental ways, by: I. Minimizing the length of the longest flow path of the water over We pavement and thereby the distance over which the flow can develop; 2. Increasing the texture of the pavement surface; and 3. Removing water from the pavement's surface. In the process of using PAVDRN to implement the design guidelines, the designer is guided to (~) minimize the longest drainage path length of the section under design by altering the pavement geometry and (2) reduce the resultant water film thickness that will develop along that drainage path length by increasing the mean texture depth, choosing a surface that maximizes texture, or using permeable pavements, grooving, and appurtenances to remove water from the surface. Through the course of a typical design project, four key areas need to be considered in order to analyze and eventually reduce the potential for hydroplaning. These areas are: ~9
I. Environmental conditions: 2. Geometry of the roadway surface; 3. Pavement surface (texture) properties; and 4. Appurtenances. Each of these areas and their influence on the resulting hydroplaning speed of the designed section are discussed In detail In the guidelines (21. The environmental conditions considered are rainfall ~ntensibr and water temperature, which determines the kinematic viscosity of the water. The designer has no real control over these environmental factors but needs to select appropriate values when analyzing the effect of flow over the pavement surface and hydroplaning potential. Five section types, one for each of the basic geometric configurations used In highway design, are examined. These section are: 1. TaIlgent; 2. Superelevated curve; 3. Transition; 4. Vertical crest curve; and 5. Vertical sag curve. 120
Pavement properties that affect the water fihn thickness mclude surface characteristics, such as mean texture depth and grooving of Portland cement concrete surfaces, are considered In the process of applying PAVDRN. Porous asphalt pavement surfaces can also reduce He water film thickness and thereby contribute to the reduction of hydroplaning tendency and their presence can also be accounted for when using PAVDRN. Finally, PAVDRN also allows the design engineer to consider the effect of drainage appurtenances, such as slotted drain inlets. A complete description of the various elements that are considered In the PAVDRN program is illustrated In figure 40. A more complete description of the design process, the parameters used in the design process, and typical values for the parameters is presented In the "Proposed Design Guidelines for Improving Pavement Surface Drainage" (2) alla in Appendix A. fIN1)INGS The following findings are based on the research accomplished during the project, a survey of the literature, and a state-of-the-art survey of current practice. I. Model. The one~unensional mode} is adequate as a design tool. The simplicity and stability of the one~imensional mode} offsets any increased accuracy afforded by a two-d~mensional model. The one~mensional model as a predictor of water fiDn thickness and How path length was verified by using data from a previous study (11). 121
No. of Planes Length of Plane Grade Step Increment Wdth of Plane Cross Slope Section T,rne 1) Tangent 2) Honzontal Curare 3) Transition 4) Vertical Crest 5) Vertical Sag U=tS 1)U.S. 2) S. I. Rainfall Intenstity ~ , \ |Kinematic Viscosity |Design Speed Note: PC = Point of Curvature PI. = Point of Tangency PCC = Portland cement concrete WAC = Dense graded asphalt concrete 0GAC = 0pcn~raded asphalt concrete where OGAC includes all types of intentally draining asphalt surfaces GPCC = Grooved Ponland cement concrete Taneent Pavement Type Mean Texture Depth 1) PCC 2) DGAC 3) OGAC 4) GPCC Horizontal Cun~c Grade Cross Slope Radius of Cunran~re Wdth Pavement Type _ 2) DGAC 3) OGAC 4) GPCC Mean Texture Depth Step Increment _ Transition Length of Plane Super Elevation Tangent Cross Slope Tangent Grade width of Curve Transition Width Pavement Type_ 1) PCC 3) OGAC 4) GPCC Mean Texture Depth Step Increment Horizontal Length Cross slope width PC Grade PI' Grade Elevation: Pr-PC Vertical Crest Flow Direction Step Increment Pavement Type 1) PC Side I 2) PI. Side | 1)PCC 2) DGAC 3) OGAC 4) GPCC Mean Tex~rc Depth _ _ ~ Figure 40. Factors considered in PAVDRN program. 122 ~1 r - . , Vertical Sad | Horizontal Length | Cross slope Wldth PC Grade PI Grade Elevation: PIE Flow Direction Step Increment / Stored :_ ~ cats ~ 1) PC Side | 2) PI Side | . Pavement Typed 1) PCC 3) OGAC 14) GPCC Mean Texture Depth I I
~ Stored data V ~ 3 L IN1T For use with a second nut using data from the first run.) , 1 EPRINT (Echos input to output ) 1 CONVERT (Converts units to and from SI and English.) ~ , ADVP (Advances Page of output.) KINW (Calculates Minning's n, Water Film Thickness (WEIR), and Hydroplaning Speed UPS).) , EDGE (Determines if flow has reached the edge of the pavement.) out roar Figure 40. Factors considered in PAVDRN program (continued). 123
2. Occurrence of Hydropl~r g. In general, based on the PAVDRN mode! and the assumptions inherent in its development, hydroplaning can be expected at speeds below roadway design speeds if the length of the flow path exceeds two lane widths. 3. Water Film Thickness. Hydroplaning is initiated primarily by the depth of the water film thickness. Therefore, the primary design objective when controlling hydroplaning must be to limit the depth of the water film. 4. Reducing Water Film Thickness. There are no simple means for controlling water John thickness, but a number of methods can effectively reduce water film thickness and consequently hydroplaning potential. These include: Optimizing pavement geometry, especially cross-slope. Providing some means of additional drainage, such as use of grooved surfaces (PCC) or porous mixtures (HMA). Including slotted drains within the roadway. 5. Tests Needed for Design. The design guidelines require an estimate of the surface texture (MTD) and the coefficient of permeability Porous asphalt only). The sand patch is an acceptable test method for measuring surface texture, except for the more open (20-percent air voids) porous asphalt mixes. In these cases, an estimate of the surface texture, based on tabulated data, is sufficient. As an alternative, 124
sand patch measurements can be made on cast replicas of the surface. For the open mixes, the glass beads flow into the voids within the mixture, giving an inaccurate measure of surface texture. Based on the measurements obtained In the laboratory, the coefficient of permeability for the open-graded asphalt concrete does not exhibit a wide range of values, and values of k may be selected for design purposes from tabulated design data (k versus air voids). Given the uncertainty of this property resulting from compaction under traffic and clogging from contaminants and anti-skid material, a direct measurement (e.g., drainage lag permeameter) of k is not warranted. Based on the previous discussion, no new test procedures are needed to adopt the design guidelines developed during this project. 6. Grooving. Grooving of PCC pavements provides a reservoir for surface water and can facilitate the removal of water if the grooves are placed parallel to the flow oath. Parallel orientation is generally not practical because the flow on highway pavements is typically not transverse to the pavement. Thus, the primary contribution offered by grooving is to provide a surface reservoir unless the grooves comlect with drainage at the edge of the pavement. Once the grooves are filled with water, the tops of the grooves are the datum for the Why and do not contribute to the reduction in the hydroplaning potential. 125
7. Porous Pavements. These mixtures can enhance the water removal and Hereby reduce water film tHch~ess. They merit more consideration by highway agencies In the United States, but they are not a panacea for eliminating hydroplaning. As with grooved PCC pavements, the internal voids do not contribute to the reduction of hydroplaning; based on the field tests done In this study. hv~ronImiina can be if, , , ~ expected on these mixtures given sufficient water fiLn thickness. Other than their ability to conduct water through internal flow, the large MTD offered by porous asphalt is the main contribution offered by the mixtures to the reduction of hydroplaning potential. The high-void ~ > 20 percent), modified binder mixes used In Europe merit further evaluation in the United States. They should be used In areas where damage from freezing water and the problems of black ice are not likely. 8. Slotted Drains. These fixtures, when installed between travel lanes, offer perhaps the most effective means of controlling water film thickness from a hydraulics standpoint. They have not been used extensively In the traveled lanes and questions remain unanswered with respect to their installation (especially in rehabilitation situations) and maintenance. The ability to support traffic loads and still maintain surface smoothness has not been demonstrated and they may be susceptible to clogging from roadway debris, ice, or snow. 126
RECOMMENDATIONS AND CONCLUSIONS The following recommendations are offered based on the work accomplished during this project and on the conclusions given previously: I. Implementation. The PAVDRN program and associated guidelines need to be field tested and revised as needed. The program and the guidelines are sufficiently complete so that they can be used in a design office. Some of the parameters and algorithms will I~ely need to be modified as experience is gained with the program. 2. Database of Material Properties. A database of material properties should be gathered to supplement the information contained in PAVDRN. This information should Include typical values for the permeability of porous asphalt and topical values for the surface texture (MTD) for different pavement surfaces to include toned Portland cement concrete surfaces. A series of photographs of typical pavement sections and their associated texture depths should be considered as an addition to the design guide (21. 3. Pavement Geometry. The AASHTO design guidelines (~) should be re-evaluated In terms of current design criteria to determine if they can be modified to enhance drainage without adversely affecting vehicle handling or safety. ~27
4. Use of appurtenances. Slotted drams should be evaluated In the field to determine if they are practical when Installed In the traveled way. Manufacturers should reconsider the design of slotted drains and their Installation recommendations currently In force to maximize them for use In multi-lane pavements and to determine if slotted drains are suitable for installations In the traveled right of way. 5. Porous Asphalt Mixtures. More use should be made of these mixtures, especially the modified high a~r-void mixtures as used In France. Field trials should be conducted to monitor HPS and the long-term effectiveness of these mixtures and to validate the MPS and WDT predicted by PAVDRN. 6. Two-D~mensional Model. Further work should be done with two~mensional models to determine if they improve accuracy of PAVDRN and to determine if they are practical from a computational standpoint. ADDITIONAL STUDIES On the basis of the work done during this study, a number of additional items warrant furler study. These Include: 1. Full-scale skid resistance studies to validate PAVDRN in general and the relationship between water film thickness and hydroplaning potential in particular are needed in light of the unexpectedly low hvdronlanin~ speeds predicted during 128 , . ~. , ~
this study. The effect of water infiltration into pavement cracks and loss of water by splash and spray need to be accounted for In the prediction of water fihn Sickness. Surface Irregularities, especially rutting, need to be considered in the prediction models. 2. Field trials are needed to confirm the effectiveness of alternative asphalt and Portland cement concrete surfaces. These include porous Portland cement concrete surfaces, porous asphalt concrete, and various asphalt m~cro-surfaces. 3. The permeability of porous surface mixtures needs to be confirmed with samples removed from the field, and the practicality of a simplified method for measuring in-situ permeability must be investigated and compared to alternative measurements, such as the outflow meter. 4. For measuring pavement texture, alternatives to the sand patch method should be investigated, especially for use with porous asphalt mixtures. 129
THIS PAGE INTENTIONALLY LEFT BLANK
READ FREE ONLINE
Welcome to OpenBook!
You're looking at OpenBook, NAP.edu's online reading room since 1999. Based on feedback from you, our users, we've made some improvements that make it easier than ever to read thousands of publications on our website.
Do you want to take a quick tour of the OpenBook's features?
Show this book's table of contents , where you can jump to any chapter by name.
...or use these buttons to go back to the previous chapter or skip to the next one.
Jump up to the previous page or down to the next one. Also, you can type in a page number and press Enter to go directly to that page in the book.
To search the entire text of this book, type in your search term here and press Enter .
Share a link to this book page on your preferred social network or via email.
View our suggested citation for this chapter.
Ready to take your reading offline? Click here to buy this book in print or download it as a free PDF, if available.
Get Email Updates
Do you enjoy reading reports from the Academies online for free ? Sign up for email notifications and we'll let you know about new publications in your areas of interest when they're released.
University letters of recommendation: an essential guide
Letters of recommendation can make or break a student’s university application, so it’s important that we get them right

Phillip Wenturine

You may also like

There are a plethora of documents that go into compiling the perfect college application. From transcripts to predicted grades, activity lists, resumés or CVs, essays, recommendation letters, certificates and more – each element of the application holds a different purpose and separate weight of importance, often varying from country to country and university to university.
By the senior year (Year 13), academics are nearly finalised, so there’s little wiggle room when it comes to improving that element of the application: senior GPA is set and calculated; IB predictions are nearly issued.
But beyond academics, some universities require recommendation letters, and this is where a student can stand out more, highlighting and emphasising their skills, qualities and abilities.
These recommendation letters can sometimes illuminate the true heart and soul of the student, beyond their transcripts or personal-statement essay. The words in these letters can make or break a student’s application, so it’s important we get them right and tell their story with the thought and effort it deserves.
Teacher letters of recommendation
In a teacher’s recommendation letter, students are brought to life beyond their grades, showcasing their holistic potential.
Teachers seize the chance to praise consistent academic excellence, to spotlight specific projects or skills, and to contextualise grade fluctuations resulting from personal circumstances.
These letters illustrate growth, revealing students’ readiness for university life. The emphasis is on articulating acquired skills and potential – a narrative far more impactful than grades alone. While an A-grade student may excel in tests, a B-grade student might exhibit invaluable traits, such as grit and resilience, best articulated through personalised advocacy.
Recommendation letter timelines
To support students and teachers, it’s important to highlight the importance of the teacher recommendation letter early on to teachers and students alike. Let students know as early as grades 10 and 11 (Years 11 and 12) that it’s important to build relationships with teachers well in advance of senior year. The best letters come from those teachers who have an excellent rapport with the student in question.
Ask students in the spring of junior year (Year 12) to select those teachers they would like recommendation letters from. The recommendation should ideally come from a core-subject teacher (maths, science, social studies, English) rather than an elective teacher, unless the elective is a field in which they intend to pursue a career.
To support the teachers, we work with students to compile what we call a brag sheet. Students answer a series of questions about themselves, in order to give the teacher the best context for writing the letter.
We tell teachers that if the student does not provide this brag sheet, or if they feel that the student has not performed well enough in their class to deserve a letter, they are allowed to respectfully decline the request to write the letter.
We also remind teachers that they do not need to agree to write any more than 20 letters. It is unfair if students all ask one teacher – who may then end up writing 60 letters – for a recommendation letter, while other teachers only have to write a few.. With that in mind, we also remind students of the importance of being organised and requesting the letter from their preferred teacher early on.
Writing the letters
Here are some examples of the questions we ask students on their brag sheets, which then give teachers a starting point for their letters:
- What do you hope this letter will show about you that your GPA doesn’t?
- What was a challenge that you faced in this class, and what actions did you take to overcome it?
- Describe how this class influenced you, either through academic content or teacher interaction.
- Give between one and three examples of times when you have exceeded expectations with your communication skills, and also some areas where you can reflect that you may need growth.
- What majors or careers interest you?
To support the teachers further, we host a writing workshop in the spring of each year to give them examples of strong and weak letters (all confidential). We coach them in "show, don't tell" when it comes to writing about students’ strengths, as well as giving them concrete examples of how best to advocate for students and highlight their strengths.
We review what each different country’s universities desire from these letters, as some universities – such as the US – appreciate a holistic view of the student (for example, highlighting student athletes or detailing extracurriculars). By contrast, the UK is very academic-focused and prefers to read about the student’s abilities when working on class projects, research and outside endeavours in the field of study.
Counsellor recommendation letters
Some universities – mostly in the US – also allow a counsellor letter of recommendation. This letter goes beyond academic ability in the classroom and speaks more to students’ characteristics, personality, outside involvement and external factors helpful for an admission committee to review in the context of other application documents.
The counsellor’s role is to fill in the missing pieces of an application: we help identify and tell a student’s story, covering any hardships, exceptional leadership abilities, impressive commitment to community and so on.
Now more than ever, admission committees are telling us that they trust the counsellor and teacher letters to help give them the full picture of a student, and to help them judge whether or not they will be the best fit for their incoming class and able to thrive on their campus.
We send our students what we call a junior questionnaire, in order to collect the information necessary to write these letters successfully.
Some examples of the questions on the junior questionnaire:
- What languages do you speak, and to what level of fluency?
- Please provide some details about your family and highlight any diversity and/or adversity that you have experienced.
- Have there been any major circumstances that have impacted on your personal or academic life?
- What are three adjectives you would use to describe yourself? Think deeply about this one.
- How have you used your time outside of school, and can you elaborate on any particular projects, clubs, work experience, internships, or volunteer work that speaks to consistency in an activity, leadership experience or a particular commitment to have an impact on your community?
External letters
Sometimes students may wish to have an outside recommendation letter from a coach – for example, if they are a student athlete.
Overall, references should be academic-focused, but some universities that accept more than one letter are willing to receive one from an outside observer, too. In these cases, the person should be someone who oversees the student as the coach of a sport or the supervisor of an internship or work-experience programme.
The external referee should give this letter to the counsellor to send off on their behalf, as all recommendation letters must confidential and never shared with the student.
How to Get the Best Recommendation Letters for Law School
Think through the references you will ask for letters and when and how you will approach them.
Good Law School Recommendation Letters

Getty Images
Make sure the person who writes your letter of recommendation is someone you have a good relationship with.
Although they are rarely decisive, recommendations letters are a meaningful factor in law school admissions.
Most other law school application materials, such as personal and diversity statements , present your case in your own voice. Recommendation letters are one of the few ways for admissions officers to hear others’ impressions of you.
While your transcript and test scores may say a lot about your academic skills, they don’t communicate what kind of person you are, or how you think or relate to other people. One student might get straight A's while acting like a pompous jerk, while another helped others, steadily improved through hard work or had the courage to take on challenging research.
Hearing stories about you from a professor or work supervisor helps law admissions officers build a three-dimensional picture of who you are and how you might contribute to the law school community.
This is why it is important to approach recommendation letters strategically, even though they’re just one part of your application process.
Whom to Ask for a Recommendation Letter
Unless you are an older applicant who has been in the workforce for many years, you should get at least one law school recommendation letter from a professor. Others might come from other professors, mentors or supervisors from an internship, job or activity .
One mistake that applicants make is to request a recommendation letter from someone they think is a big shot – a well-known professor, a high-level executive or a family friend who is a venerable lawyer or local politician.
This is only a good idea if such a person teaches or works with you directly and can speak knowledgeably about your work and your goals. If your relationship is more indirect or distant, it can come across as superficial and uninformative, like a vague book blurb by a celebrity who seems unlikely to have read the book.
Above all, ensure the recommendation letter will be positive! If you detect signs that you have chosen the wrong reference to write a letter, move on to someone who can speak about your strengths more knowledgeably and enthusiastically.
What a Recommendation Letter Should Include
If a recommendation letter is simply a series of compliments strung together, it will sound generic, no matter how effusive or truthful it is. An effective letter should back up its claims with specific details and examples of times when you stood out because of your dedication, helpfulness, initiative or insight.
A recommendation letter does not have to be unwaveringly positive. In fact, a letter that shows how you have grown, overcome adversity, responded constructively to feedback or taken responsibility for yourself can show the kinds of “ soft factors ” that law school admissions officers seek.
How to Request a Recommendation Letter
Once you have identified a reference who is likely to write you a strong recommendation letter, ask him or her politely. Explain why you are applying to law school, why you think he or she would be a good reference and when you will need the letter.
Be prepared for the recommender to ask for your resume or other materials. For example, a professor might ask to see copies of your papers for the class, or any feedback received.
You might offer to provide more information or details as needed or to discuss the letter in a meeting or phone call. However, do not crowd your initial request with ideas and advice. That could come across as presumptuous.
If a recommender has a personal connection to a school you are applying to, consider requesting a school-specific letter , in addition to a more general recommendation letter.
Finally, avoid writing a recommendation letter yourself . If a recommender asks you to do so, gently explain why this is a bad idea and instead offer to provide ideas and notes that he or she could incorporate into his or her own letter.
How Many Recommendation Letters to Request
Very few law schools require more than one recommendation letter. Many limit you to two, although some allow up to five.
It is important that all your recommendation letters are strong and substantive, because they may take time away from other aspects of your application. Quality matters more than quantity.
If you are worried that one of your letters is not as strong as the others, don’t submit it. A mediocre letter could very well overshadow better letters read alongside it. Just think about how often you read a mixed review that turns you off of a business, even if the other reviews seem positive.
When to Request a Recommendation Letter
Recommendation letters are submitted and processed through the Credential Assembly Service of the Law School Admission Council. Since they can take a couple of weeks to process, it’s a good idea to get them in before you plan to apply.
Anticipate that your recommender may need at least a few weeks to write the letter, particularly at busy times of the year. That means that you should request recommendation letters more than a month before you plan to apply.
For applicants planning to apply in the fall, it is best to request letters over the summer or early fall. It’s OK to request letters earlier, as well. For example, if you just finished a summer internship where you worked together well with your boss, you might request the letter before leaving, even if you don’t plan to apply anytime soon.
What if Your Recommendation Letter Is Delayed?
While law school admissions are rolling , a week or so of delay will not be of consequence. So, consider waiting until your application is complete before you submit it.
That said, if it is late in the cycle, or if you are aiming to meet an early decision deadline , waiting may not be an option. As long as you have the minimum number of recommendation letters required, your application can be submitted. You can always add further letters to your file later.
Remember that a law school is unlikely to review your application as soon as it is received. So, if a recommendation letter is delayed for a few days, it is unlikely to matter. If the letter is important and it may be delayed for some time, notify the admissions office by phone or email that another recommendation letter is forthcoming and ask if your application could be put on hold until it is received.
Of course, the best way to ensure that a recommendation letter does not hold up your application is to request it several weeks in advance. The law school admissions process is stressful enough without having to wait on other people!
Tips to Boost a Law School Application

Tags: law school , graduate schools , education , students
About Law Admissions Lowdown
Law Admissions Lowdown provides advice to prospective students about the law school application process, LSAT prep and potential career paths. Previously authored by contributors from Stratus Admissions Counseling, the blog is currently authored by Gabriel Kuris, founder of Top Law Coach , an admissions consultancy. Kuris is a graduate of Harvard Law School and has helped hundreds of applicants navigate the law school application process since 2003. Got a question? Email [email protected] .
Popular Stories

Paying for College

Applying to Graduate School

Best Colleges

Medical School Admissions Doctor

You May Also Like
How to choose a civil rights law school.
Anayat Durrani May 22, 2024
Avoid Procrastinating in Medical School
Kathleen Franco, M.D., M.S. May 21, 2024
Get Accepted to Multiple Top B-schools
Anayat Durrani May 16, 2024

Premeds and Emerging Medical Research
Zach Grimmett May 14, 2024

How to Get a Perfect Score on the LSAT
Gabriel Kuris May 13, 2024

Premeds Take 5 Public Health Courses
Rachel Rizal May 7, 2024

Fortune 500 CEOs With a Law Degree
Cole Claybourn May 7, 2024

Why It's Hard to Get Into Med School
A.R. Cabral May 6, 2024

Pros, Cons of Unaccredited Law Schools
Gabriel Kuris May 6, 2024

An MBA and Management Consulting
Sammy Allen May 2, 2024

An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it's official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- Browse Titles
NCBI Bookshelf. A service of the National Library of Medicine, National Institutes of Health.
National Research Council (US) and Institute of Medicine (US) Panel to Review the National Children's Study Research Plan. The National Children's Study Research Plan: A Review. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2008.

The National Children's Study Research Plan: A Review.
- Hardcopy Version at National Academies Press
6 Conclusions and Recommendations
D uring the past several months the panel has met and reviewed the research plan for the National Children’s Study (NCS), various working papers of the study, and additional documents provided by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The panel believes that this landmark study offers an unparalleled opportunity to examine the effects of environmental influences on child health and development, as well as to explore the complex interactions between genes and environments. The database derived from the study will be valuable for investigating the hypotheses described in the research plan as well as additional hypotheses that will evolve.
The critique, suggestions, and recommendations offered in the preceding chapters, therefore, are intended to improve the capabilities of the study to carry out the important mandate of the Children’s Health Act of 2000. This chapter highlights the panel’s key conclusions and recommendations resulting from its review organized by chapter and subject area.
CHAPTER 2: NCS GOALS, CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK, AND CORE HYPOTHESES
Conclusion 2-1: The stated overall and specific goals for the NCS—and the design of the NCS to achieve those goals—largely reflect the stipulations of the Children’s Health Act of 2000. In the broadest terms, the NCS goals and design are responsive to the call in the act for a “national longitudinal study of environmental influences (including physical, chemical, biological, and psychosocial) on children’s health and development.” Conclusion 2-2: The large, nationally representative, equal probability sample design, together with the inclusion of a large number of outcome and exposure measures over a long time span, are major strengths of the NCS. In particular, the sample design is an appropriate platform for the study, considering resource constraints, the need to represent all population groups and geographic areas, and the difficulty of devising an alternative disproportionate sampling scheme that would not unduly disadvantage some groups and areas that turn out to be of analytical interest. Conclusion 2-3: In four overarching areas, the NCS design, as represented in the research plan, is not, or may not be, optimal for achieving the goals of the Children’s Health Act. These areas are: insufficient attention to understanding disparities in child health and development among population groups of children defined by race, ethnicity, language, socioeconomic status, and geographic area, which the act explicitly mandates; inadequate conceptualization of important constructs, including health and development, and an overemphasis on disease and impairment relative to health and functionality and on risk factors relative to protective health-promoting factors; impaired data collection schedules and types of measures to support evaluation of some of the effects of chronic and intermittent exposures on child health and development; and underappreciation of the challenges to obtaining the highest possible quality of data from an observational design, which include the decentralized data collection structure of the study and limitations on the frequency of home and clinic visits and on the collection of medical and other administrative records for study participants.
Recommendation 2-1: The NCS should give priority attention to seeking ways to bolster the ability of the study to contribute to understanding of health disparities among children in different racial, ethnic, and other population groups, including the reestablishment of a working group to oversee this area and the encouragement of appropriate adjunct studies. Recommendation 2-2: The NCS should seek resources and develop methods to obtain more frequent in-person measures and medical and other administrative records data on study participants.
Conceptual Framework
Recommendation 2-3: The NCS should clearly define the key constructs of child health and development and more fully develop a conceptual framework for understanding child health and development over the course of infancy, childhood, and adolescence.
Using the Vanguard Centers as Pilots
Recommendation 2-4: We strongly urge the NCS to delay enrollment at new sites to make effective use of initial findings from participant enrollment and data collection in the Vanguard Center sites to improve study procedures, as appropriate, and to refine key concepts, hypotheses, and measures of outcomes and exposures. Throughout the life of the study, the NCS should use the Vanguard Centers to pilot test and experiment with data collection methods and instrumentation.
CHAPTER 3: PRIORITY OUTCOME AND EXPOSURE MEASURES
Pregnancy outcomes.
Recommendation 3-1: The NCS should consider replacing research on subclinical maternal hypothyroidism as a factor in adverse pregnancy outcomes with research on the effects of a broader set of maternal physical and mental health conditions, such as maternal depression, maternal perceived stress, and maternal periodontal disease. Recommendation 3-2: The NCS should develop refined, detailed protocols for investigating all pregnancy outcomes, specifically a detailed protocol for obtaining information on various types of pregnancy loss, before beginning data collection at the Vanguard Centers, given that pregnancy outcomes are among the first outcomes to be examined; many outcomes lack clarity in measurement; and there are important questions regarding the adequacy of statistical power and the planned data collection (for example, the need for prepregnancy measurements of some exposures).
Neurodevelopment and Behavior and Child Health and Development
Recommendation 3-3: The NCS should develop a clearer rationale for the selection of specific neurodevelopment and behavior disorders to be considered in the study and a clearer conceptual basis for the assessment of normal child health and development trajectories and outcomes. Clarity is needed to guide the choice of outcome measures and exposure measures and the frequency and types of contacts (at the home, in clinics) with study participants in order to obtain the best information possible within resource and burden constraints.
Recommendation 3-4: The NCS should develop a clearer rationale for its hypotheses about factors that may increase the incidence of asthma. These should focus on prenatal and early life risk factors.
Obesity and Growth
Recommendation 3-5: The NCS should reevaluate its main hypotheses to be addressed in the study of childhood obesity and consider adopting a broader approach that incorporates social and psychological factors as well as biogenetic ones. Such an approach would help the study identify the constellations of key factors and their interrelationships that are important to understand in order to develop the most effective public health measures to reduce childhood obesity.
Recommendation 3-6: The NCS should consider replacing research on repeated mild traumatic brain injury (rMTBI) with more nuanced research on other injury-related topics, such as environmental factors in childhood injuries and the effects of clinical response to injury (treatment or nontreatment).
Hormonally Active Agents and Reproductive Development
Recommendation 3-7: The NCS should develop refined and detailed protocols for studying reproductive development outcomes, which, as presented in the research plan, often lack clarity in measurement and research design. Outcomes that are measured at birth for which there is little time to refine research protocols require immediate attention. The NCS should use results from the Vanguard Centers, such as estimates of the prevalence of specific reproductive development outcomes, to assist in protocol development, and it should consider the usefulness of substudies of high-exposure population groups.
Demographic and Socioeconomic Measures
Recommendation 3-8: The NCS should add to its well-planned battery of demographic and socioeconomic measures questions on immigrant generation, languages spoken, and, if possible, the legal status of the parents and child.
Chemical Exposure Measures
Recommendation 3-9: The NCS should consider the use of personal air sampling methods for a subsample of participating women and their children for measuring exposure to air pollutants. Recommendation 3-10: The NCS should incorporate methodology to measure paternal exposure to environmental chemicals (both persistent and nonpersistent). More generally, the NCS should consider collecting for fathers, not only chemical exposures, but also biological samples and interview data on paternal characteristics that may affect children’s health and development to the same degree as it collects such information for mothers.
Physical Exposure Measures
Recommendation 3-11: The NCS should provide a clearer rationale for some of the housing and neighborhood conditions it proposes to measure and revisit its data collection plans to ensure that needed measures are obtained at developmental stages when children may be more vulnerable to risk factors. The goal should be a set of measures and data collection plans that are optimal with regard to analytic utility and response burden.
Psychosocial Exposure Measures
Recommendation 3-12: The NCS should reconsider its psychosocial measures to ensure that they will provide high-quality data for outcomes of interest for child health and development. In the face of resource and respondent burden constraints, the NCS should emphasize the quality and analytic utility of information, even if some measures must be dropped in order to substitute other assessments more desirable on various grounds. Recommendation 3-13: The NCS should dedicate a portion of funds to support research and development of reliable and valid instruments of key psychosocial measures that are practical and economical to administer.
Biological Exposure Measures
Recommendation 3-14: The NCS should review some of the proposed measures of biological exposures, such as maternal glucose metabolism and child cortisol levels, to ensure that the proposed times for data collection are appropriate for capturing the underlying exposure.
Genetic Measures
Recommendation 3-15: The NCS should adopt a clear mechanism by which genetic association studies are internally and, optimally, externally validated before any results are published or released to the media. The NCS should also revise its proposed “established” candidate gene approach to take advantage of the new information emanating from the current wave of genome-wide association studies, with appropriate replication. Recommendation 3-16: The NCS should consider consolidating its genetics studies in order to reduce costs and to coordinate the best science at the least cost to the project. One approach would be to simply collect the biological samples and properly store them for later genetic analysis when a better selection of polymorphisms and cost-effective genotyping across studies are possible.
Missing Exposures
Recommendation 3-17: The NCS should add measures of access to and quality of services, including medical care, education, child care, and services, as potential mediators of health and development outcomes and to improve the assessment of information obtained through maternal reports.
Data Linkage
Recommendation 3-18: To facilitate linkages of NCS data with environmental exposures from other databases, such as measures of demographics, crime, government programs, and pollution, the NCS should develop a plan for geocoding the residential addresses from prebirth through adulthood of all participating children to standard census geographic units. In addition, the study should develop arrangements by which researchers, both inside and outside the NCS study centers, can access geocodes for respondent addresses and are encouraged to perform linkages and make their environmental information available to the NCS analysis community. Such arrangements must safeguard the confidentiality of NCS respondents.
CHAPTER 4: STUDY DESIGN, DATA COLLECTION, AND ANALYSIS
Sampling design.
Conclusion 4-1: We strongly endorse the use of probability sampling to select the NCS national sample of births. Conclusion 4-2: While we endorse the decision to select an equal probability national sample of births as a reasonable strategy given the many key scientific objectives of the NCS, we recognize that a proportionate representation of the study’s target population will result in estimates for some subgroups that are not as precise as they would be had those groups been oversampled. Conclusion 4-3: The process of identifying births from a national sample of households is complex and subject to numerous sources of attrition of uncertain magnitude. Because of this, it will be difficult to predict how many households must be initially selected to produce a probability sample of 1,000 births in each of the NCS sites. Recommendation 4-1: The NCS should consider modifying the sampling design to allow for flexibility in increasing the number of study participants in the event that the estimated number of screened households needed to reach 1,000 births per primary sampling unit (PSU) is incorrect. Recommendation 4-2: The NCS should consider the proposed household enumeration approach to be experimental and should conduct carefully designed field studies to clearly establish the statistical and practical implications of the proposed adjudicated listing approach. Recommendation 4-3: To ensure a diverse exposure profile in the sample, the NCS should consider a careful assessment of variation in ambient exposure to chemical agents within each PSU. If the set of segments in a PSU can be classified by combined exposure to a group of important chemical agents, this information could then be used to form varying exposure-level strata for segment sampling in each PSU and thus ensure a range of ambient exposure to relevant environmental agents.
Data Collection
Conclusion 4-4: The data collection model adopted by the NCS is complex, will challenge the abilities of the staff and coordinating center to achieve a uniform and consistent national data collection, and may compromise key study objectives. Conclusion 4-5: The NCS research plan does not provide sufficient information on the use of data collection guidelines and quality-control procedures to enable evaluation of the planned implementation of a uniform national data collection system. Conclusion 4-6: The NCS research plan does not address directly the issue of respondent burden, except to say that “some” effort is being made to reduce it, nor does the plan make clear the total number of hours the respondent must commit to the study. In particular, in light of the estimate of the interview length (4 hours) for the baseline interview, a critical collection for the study, the research plan pays little attention to respondent burden and its impact on the quality of the data. Conclusion 4-7: The NCS research plan provides little information concerning best methods for sample recruitment to achieve initial and follow-up target response rates, sample maintenance and sample retention procedures for implementation at the study sites, community involvement plans consistent with the uniform implementation of data collection procedures, or contingency plans to support study sites that do not achieve target response rates. Conclusion 4-8: The NCS research plan does not address the ongoing methodological needs of the study—to study data collection procedures and instruments, conduct experiments, and evaluate the quality of the survey operations and the quality of the data—nor does the plan make the best use of the Vanguard Centers. Recommendation 4-4: The NCS should consider ways in which the survey data collection could be consolidated into a smaller number of highly qualified survey organizations. Recommendation 4-5: Because of the complexity of the proposed organizational model for data collection and the difficulty of maintaining the quality and uniformity of data collection procedures across a large number of study sites, the NCS program office should establish and monitor strict standards for enrollment, retention, and data collection at each of the study sites and be prepared to take immediate corrective action if sites do not meet high-quality standards in data collection. Recommendation 4-6: The NCS should prepare a plan for monitoring progress of the study in reaching its sample size goals. As part of the plan, the NCS should take advantage of the experience of the Vanguard Centers to evaluate initial enrollment rates, the effectiveness and potential respondent burden of the interview instrument, and the ability of the Vanguard Centers to obtain the required household environmental measures reliably. Recommendation 4-7: To resolve issues that arise during data collection, the NCS should set aside sufficient resources to maintain an ongoing program of methods research and field experimentation. Among the issues that might be addressed in this research are the reliability and validity of previously untested survey questions and measurement strategies, the effectiveness of sample retention procedures, predictors of response outcomes associated with sample initial recruitment and subsequent annual retention, error implications of unit nonresponse, adjustment strategies for unit nonresponse, and methods for dealing with item nonresponse.
Data Analysis and Dissemination
Recommendation 4-8: The NCS should begin planning for the rapid dissemination of the core study data, subject to respondent protection, to the general research community and for supporting the use of the data after dissemination. The costs of implementing this plan should be estimated and set aside in future NCS budgets. Dissemination includes not only the publication of findings through reports and scientific papers and the production of documented data files for researchers, but also active support in the use of NCS data by the broadest possible range of qualified investigators.
CHAPTER 5: ETHICAL PROCEDURES AND COMMUNITY ENGAGEMENT
Criteria for giving information to participants.
Recommendation 5-1: The NCS should define the criteria and the process for deciding what individual clinical and research information, such as environmental assessments, test results, and survey scales, will be given to children and their families.
Protection and Release of Information
Recommendation 5-2: NCS and non-NCS investigators should be given equal access to the full NCS data as soon as they are cleaned and documented. To protect respondent confidentiality, all analyses should be performed with the kind of strict safeguards employed by the Census Bureau research data centers.
Community Engagement
Recommendation 5-3: The NCS should engage communities in selected study implementation, data analysis, and data interpretation activities that go beyond recruitment. The NCS should consider requiring every study center to formulate a more detailed plan to engage and collaborate with local communities.
In summary, it is clear from our review that the NCS offers not only enormous potential, but also a large number of conceptual, methodological, and administrative challenges. In addition, funding uncertainties make it difficult to plan beyond the relatively short period for which funds have been appropriated. Like the scientists associated with the study itself, we are eager for it to succeed. We present our conclusions and recommendations in the hope that, as it goes forward, the NCS will achieve its intended objectives and serve as a model of methodological and substantive contributions to important scientific and policy discussions on children’s health and development.
- Cite this Page National Research Council (US) and Institute of Medicine (US) Panel to Review the National Children's Study Research Plan. The National Children's Study Research Plan: A Review. Washington (DC): National Academies Press (US); 2008. 6, Conclusions and Recommendations.
- PDF version of this title (784K)
In this Page
- NCS GOALS, CONCEPTUAL FRAMEWORK, AND CORE HYPOTHESES
- PRIORITY OUTCOME AND EXPOSURE MEASURES
- STUDY DESIGN, DATA COLLECTION, AND ANALYSIS
- ETHICAL PROCEDURES AND COMMUNITY ENGAGEMENT
Other titles in this collection
- The National Academies Collection: Reports funded by National Institutes of Health
Recent Activity
- Conclusions and Recommendations - The National Children's Study Research Plan Conclusions and Recommendations - The National Children's Study Research Plan
Your browsing activity is empty.
Activity recording is turned off.
Turn recording back on
Connect with NLM
National Library of Medicine 8600 Rockville Pike Bethesda, MD 20894
Web Policies FOIA HHS Vulnerability Disclosure
Help Accessibility Careers
NTRS - NASA Technical Reports Server
Available downloads, related records.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to FDA Search
- Skip to in this section menu
- Skip to footer links

The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you're on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
U.S. Food and Drug Administration
- Search
- Menu
- Recalls, Outbreaks & Emergencies
- Outbreaks of Foodborne Illness
Investigations of Foodborne Illness Outbreaks

Note: Not all recalls and alerts result in an outbreak of foodborne illness . Check recent Food Recalls and Safety Alerts .
The following is a list of outbreak and adverse event investigations primarily being managed by FDA’s CORE Response Teams . The investigations are in a variety of stages, meaning that some have limited information, while others may be near completion. If you think you have symptoms of foodborne illness, talk to your healthcare provider and public health officials to provide them with details of what you ate before becoming sick. This often aids in helping solve emerging or ongoing outbreaks.
A public health advisory will be issued for investigations that have resulted in specific, actionable steps for consumers to take to protect themselves. Please direct your attention to those pages for the most up to date information on the investigation and for consumer protection information.
Outbreak and adverse event investigations that do not result in specific, actionable steps for consumers may or may not conclusively identify a source or reveal any contributing factors. Adverse event investigations rely on self-reported data. Although these reports may name a particular product, FDA will only indicate a product category in the table and will not publicly name a specific product until there is sufficient evidence to implicate that product as a cause of illnesses or adverse events. If a cause and/or contributing factors are identified that could inform future prevention, FDA commits to providing a summary of those findings.
- An outbreak of Salmonella Africana illnesses (ref # 1227) linked to a not yet identified product has been added to the table. FDA has initiated traceback.
- For the outbreak of E. coli O157:H7 (ref # 1221) linked to bulk organic walnuts, FDA has initiated an onsite inspection and sample collection and analysis.
Active Investigations
Closed investigations, 2024 investigations, 2023 investigations, 2022 investigations, 2021 investigations.
1 This cluster represents a subset of the total number of domestically-acquired cases of cyclosporiasis cases in the U.S.
2 Based on CDC’s epidemiological investigation of two large multistate outbreaks of cyclosporiasis , ill people reported eating a variety of leafy greens before becoming sick. For both investigations, CDC, FDA, and state and local partners conducted epidemiologic and traceback investigations and collected and analyzed product and environmental samples. All samples collected were reported as negative for Cyclospora . Due to the lack of additional detail in the epidemiological data and the absence of supporting evidence collected from traceback and sample collection, FDA could not identify a specific product as the source of either outbreak.
2020 Investigations
Related links.
CDC Investigations
FSIS Investigations
Table Definitions
Date Posted : Date the investigation is posted to the table. This happens once CORE begins to actively coordinate an investigation. In collaboration with federal and state partners, CORE initiates response activities to control the outbreak or adverse events.
Reference Number : This number is assigned to incidents that CORE is working on. Each foodborne illness investigation on the table will have a unique reference number and this is provided to help users of this table differentiate between investigations. Those reference numbers beginning with an “E” have carried over from an older numbering system that will not be used by CORE in the future.
Pathogen or Cause of Illness : A bacterium, virus, other microorganism, toxin, or other contaminant that can cause disease.
Product(s) Linked to Illnesses (if any) : During an outbreak or adverse event investigation, the FDA and CDC, along with state and local authorities collect and analyze three types of information: epidemiological information, laboratory analyses of food and/or samples taken from food production environments, and traceback investigation findings. Each outbreak or adverse event is unique and the information available to investigators varies from outbreak to outbreak – however, through rigorous analysis of the information collected, investigators are often able to identify a likely or confirmed food source of an outbreak or adverse events. Additionally, adverse event investigations rely on self-reported data, which may not include all necessary information to fully investigate the product or event. It is important to note that before a specific food is linked to an outbreak or adverse events, the investigation of a commodity or a specific food by the FDA, CDC and state and local partners does not mean that the food is the cause of an outbreak or adverse events. In many cases the investigation is also looking to rule out specific foods even as it identifies the particular suspect. If there is evidence that a specific food is linked to illnesses, it will be reflected here and health authorities will warn the public about that food.
Total Case Count : Updated weekly. For outbreak investigations, the case count is provided to the FDA by the CDC. Case counts are dynamic and the exact number of illnesses constantly changes during an investigation. This number is provided in order to provide an estimate of the size of an outbreak each week. In the case of adverse event investigations, FDA will provide the number of adverse events that have been self-reported by consumers to FDA consumer complaint coordinators and the CFSAN Adverse Event Reporting System (CAERS), which could include duplicate reports. More formalized data will be published in CDC Investigation Notices or in FDA and CDC advisories, should they be posted.
Investigation Status : Communicates whether this outbreak is still under investigation by CORE or the investigational activities have ended. Options for this column would be either “Active” or “Closed”. At times an FDA investigation may be active after an outbreak has ended.
Outbreak/Event Status : Communicates whether this outbreak or series of adverse event reports is ongoing or has ended.
Recall Initiated : A recall occurs when a firm takes a product off the market because there is reason to believe that it may cause consumers to become ill. In some situations, FDA may request the company recall a potentially contaminated food. In other situations, FDA may issue a mandatory recall if there is a reasonable probability that the food is adulterated under certain FDA authorities, and that the food could cause serious illnesses or death.
FDA Traceback Initiated : Used to identify the source and distribution of the implicated food and remove the contaminated product from the marketplace, to distinguish between two or more implicated food products, and to determine potential routes and/or sources of contamination in order to help prevent future illnesses. For additional information, see How the FDA Uses Traceback to Respond to Foodborne Illness Outbreaks .
FDA Inspection Initiated : An official examination by FDA of the operational processes of a facility to determine its compliance with federal law, which may include, among other things, record and sample collection. Activities reported on the table are limited to those conducted by FDA; however, state and local partners work in coordination with FDA and may also conduct inspectional activities. Additional information on the different types of inspections conducted by FDA can be found on the FDA website .
FDA Sampling Initiated : Collection of samples for the presence or absence of a pathogen in a food or in the environment surrounding the food. Samples reported on the table include those collected by the FDA or state collected samples that are analyzed by the FDA. Significant sample findings are reviewed by FDA and are reported in Public Health Advisories .
Who to Contact if you Have Symptoms of Foodborne Illness
Consumers who have symptoms of foodborne illness should contact their health care provider to report their symptoms and receive care.
To report a complaint or adverse event (illness or serious allergic reaction), you have three choices:
- Call an FDA Consumer Complaint Coordinator if you wish to speak directly to a person about your problem.
- Complete an electronic Voluntary MedWatch form online.
- Complete a paper Voluntary MedWatch form that can be mailed to FDA.
Visit www.fda.gov/fcic for additional consumer and industry assistance.
Get email updates delivered to your inbox.
Get regular FDA email updates delivered on this topic to your inbox.
A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
A lock ( ) or https:// means you've safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
- Test for Fentanyl
- if You Think Someone is Overdosing
- Stop Overdose
- Naloxone FAQs
- Stigma Reduction
About Stop Overdose
- Through preliminary research and strategic workshops, CDC identified four areas of focus to address the evolving drug overdose crisis.
- Stop Overdose resources speak to the reality of drug use, provide practical ways to prevent overdoses, educate about the risks of illegal drug use, and show ways to get help.

Drugs take nearly 300 lives every day. 1 To address the increasing number of overdose deaths related to both prescription opioids and illegal drugs, we created a website to educate people who use drugs about the dangers of illegally manufactured fentanyl, the risks and consequences of mixing drugs, the lifesaving power of naloxone, and the importance of reducing stigma around recovery and treatment options. Together, we can stop drug overdoses and save lives.
What you can do
- Get the facts on fentanyl
- Learn about lifesaving naloxone
- Understand the risks of polysubstance use
- Reduce stigma around recovery and treatment
Explore and download Stop Overdose and other educational materials on CDC's Overdose Resource Exchange .
- Centers for Disease Control and Prevention, National Center for Health Statistics. National Vital Statistics System, Mortality 2018-2021 on CDC WONDER Online Database, released in 2023. Data are from the Multiple Cause of Death Files, 2018-2021, as compiled from data provided by the 57 vital statistics jurisdictions through the Vital Statistics Cooperative Program. Accessed at http://wonder.cdc.gov/mcd-icd10-expanded.html on Mar 5, 2024
Every day, drugs claim hundreds of lives. The Stop Overdose website educates drug users on fentanyl, naloxone, polysubstance use, and dealing with stigma.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Recommendations for future research should be: Concrete and specific. Supported with a clear rationale. Directly connected to your research. Overall, strive to highlight ways other researchers can reproduce or replicate your results to draw further conclusions, and suggest different directions that future research can take, if applicable.
Here is a step-wise guide to build your understanding on the development of research recommendations. 1. Understand the Research Question: Understand the research question and objectives before writing recommendations. Also, ensure that your recommendations are relevant and directly address the goals of the study. 2.
Research recommendations may be provided by experts in the field, such as professors, researchers, or consultants, and are intended to help guide the researcher towards the most appropriate and effective approach to their research project. ... Example of Research Recommendations sample for students: Further investigate the effects of X on Y by ...
Recommendation in research example. See below for a full research recommendation example that you can use as a template to write your own. Recommendation section. The current study can be interpreted as a first step in the research on COPD speech characteristics. However, the results of this study should be treated with caution due to the small ...
Remember to grab a copy of our tried and tested free dissertation template, which covers both the implications and recommendations sections. If you'd like 1:1 help with your research project, be sure to check out our private coaching service, where we hold your hand throughout the research journey, step by step.
Crafting impactful recommendations is a vital skill for any researcher looking to bridge the gap between their findings and real-world applications. By understanding the purpose of recommendations, identifying areas for future research, structuring your suggestions effectively, and connecting them to your research findings, you can unlock the ...
Make sure your solutions cover all relevant areas within your research scope. Consider different contexts, stakeholders, and perspectives affected by the recommendations. Be thorough in identifying potential improvement areas and offering appropriate actions. Don't add new information to this part of your paper.
Your research: Research recommendations can be based on your topic, research objectives, literature review, and analysis, or evidence collected. For example, if your data points to the role of faculty involvement in developing effective programs, recommendations in research can include developing policies to increase faculty participation.
How to formulate research recommendations. "More research is needed" is a conclusion that fits most systematic reviews. But authors need to be more specific about what exactly is required. Long awaited reports of new research, systematic reviews, and clinical guidelines are too often a disappointing anticlimax for those wishing to use them ...
Suggested sample size >300 (powered to find 10% difference between groups for the primary outcome) ... The proposed statement on research recommendations applies to uncertainties of the effects of any form of health intervention or treatment and is intended for research in humans rather than basic scientific research. Further investigation is ...
The conclusions are as stated below: i. Students' use of language in the oral sessions depicted their beliefs and values. based on their intentions. The oral sessions prompted the students to be ...
Implications are the impact your research makes, whereas recommendations are specific actions that can then be taken based on your findings, such as for more research or for policymaking. Updated on August 23, 2022. High-quality research articles that get many citations contain both implications and recommendations.
The initially stated overarching aim of this research was to identify the contextual factors and mechanisms that are regularly associated with effective and cost-effective public involvement in research. While recognising the limitations of our analysis, we believe we have largely achieved this in our revised theory of public involvement in research set out in Chapter 8. We have developed and ...
The following recommendations for research are based on the study findings: Limited and variable access to services in the wider health and social care system is a significant barrier to reducing inappropriate conveyance to A&E. More research is needed to identify effective ways of improving the delivery of care across service boundaries ...
Recommendation reports are texts that advise audiences about the best ways to solve a problem. Recommendation reports are a type of formal report that is widely used across disciplines and professions. Subject Matter Experts aim to make recommendations based on the best available theory, research and practice. Different disciplines and professions have different research methods
Table of contents. Step 1: Restate the problem. Step 2: Sum up the paper. Step 3: Discuss the implications. Research paper conclusion examples. Frequently asked questions about research paper conclusions.
For legal references, APA follows the recommendations of The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation, so if you have any questions beyond the examples provided in APA, seek out that resource as well. Court Decisions. Reference format: Name v. Name, Volume Reporter Page (Court Date). URL . Sample reference entry: Brown v.
Writing recommendation letters is great fun — it allows me to reflect on my interactions with pupils, remember the creative times together and promote them in their future careers. It is like ...
In general, a letter or recommendation can be broken down into the following sections: Date. Recipient Name. Recipient Title. Recipient Address. Greeting: Address the recipient by name if possible (Dear Ms/Mr). Personal introduction: Begin the body of your letter by introducing who you are and your relationship to the applicant.
5.1 INTRODUCTION. In this chapter the conclusions derived from the findings of this study on the experiences of registered nurses involved in the termination of pregnancy at Soshanguve Community Health Centre are described. The conclusions were based on the purpose, research questions and results of the study. The implications of these findings ...
CHAPIER 5 SI~MARY, FINDINGS, AND RECOMMENDATIONS SUGARY The primary objective of this research was to identify unproved methods for draining rainwater from the surface of multi-lane pavements and to develop guidelines for their use.
2. Follow the Right Report Writing Format: Adhere to a structured format, including a clear title, table of contents, summary, introduction, body, conclusion, recommendations, and appendices. This ensures clarity and coherence. Follow the format suggestions in this article to start off on the right foot. 3.
The recommendation should ideally come from a core-subject teacher (maths, science, social studies, English) rather than an elective teacher, unless the elective is a field in which they intend to pursue a career. ... research and outside endeavours in the field of study. Counsellor recommendation letters. Some universities - mostly in the US ...
Very few law schools require more than one recommendation letter. Many limit you to two, although some allow up to five. It is important that all your recommendation letters are strong and ...
During the past several months the panel has met and reviewed the research plan for the National Children's Study (NCS), various working papers of the study, and additional documents provided by the National Institute of Child Health and Human Development. The panel believes that this landmark study offers an unparalleled opportunity to examine the effects of environmental influences on ...
Through KSC IRTD funding in 2022, this project brought a list of 18, 3D printed filaments into formal characterization testing to provide a reference for their behaviors under relevant applications. The project format set up a series of tests to expose 3D printed specimens. A total of 1,989 individual 3D printed test specimens were sent across KSC to be scrutinized by three laboratories to ...
Reference Number: This number is assigned to incidents that CORE is working on. Each foodborne illness investigation on the table will have a unique reference number and this is provided to help ...
Key points. Through preliminary research and strategic workshops, CDC identified four areas of focus to address the evolving drug overdose crisis. Stop Overdose resources speak to the reality of drug use, provide practical ways to prevent overdoses, educate about the risks of illegal drug use, and show ways to get help.