Globalization and Economic Growth
- Living reference work entry
- First Online: 14 April 2021
- Cite this living reference work entry

- Ishak Demir 7 , 10 ,
- Mehmet Canakci 8 &
- Taha Egri 9
Part of the book series: Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals ((ENUNSDG))
483 Accesses
1 Citations
Economic Growth , Integration and growth , Economic development.

Definitions
Globalization, or the increased interconnectedness and interdependence of peoples, companies, institutions and countries. It is generally understood to include two inter-related elements: the opening of international borders to increasingly fast flows of goods, services, finance, investment, people, information, ideas and technology; and the changes in institutions and policies at national and international levels that facilitate or promote such flows (WHO 2020 ). Globalization process has impacts on economies, prosperity, development of societies, political systems, environment, and cultures around the world.
Economic globalization can be defined as the increasing interdependence of world economies as a result of the growing scale of cross-border trade of commodities and services, flow of international capital and wide and rapid spread of technologies. It reflects the continuing expansion and mutual...
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
Institutional subscriptions
Alesina A et al (1994) The political economy of capital controls. In: Leiderman L, Razin A (eds) Capital mobility: the impact on consumption, investment and growth. Cambridge University Press, Cambridge, pp 289–321
Google Scholar
Bauman Z (1998) Globalization the human consequences. Columbia University Press, New York
Berger PL (1997) Four faces of global culture. Nat Int 49:23–29
Brenner N (1999) Beyond state-centrism? Space, territoriality, and geographical scale in globalization studies. Theory Soc 28(1):39–78
Article Google Scholar
Castells M (2000) Materials for an exploratory theory of the network society. Br J Soc 51(1):5–24
Demirguc-Kunt A, Levine R (2008) Finance, financial sector policies, and long-run growth. The World Bank
Dollar D (1992) Outward-oriented developing economies really do grow more rapidly: evidence from 95 LDCs. Econ Dev Cult Chang 40(3):523–544
Dowrick S, DeLong JB (2003) Globalization and convergence. In: Bordo MD et al (eds) Globalization in historical perspective. University of Chicago Press, pp 191–226
Dreher A (2006) Does globalization affects growth? Empirical evidence from a new index. Appl Econ 38(10):1091–1110
Easterly W (2004) Channels from globalization to inequality: productivity world vs factor world. Paper presented at the Brookings Trade Forum on Globalization, Poverty and Inequality, 13–14 May, Washington, DC
Edwards S (1998) Openness, productivity and growth: what do we really know? Econ J 108:383–398
Edwards S (2005) Capital controls, sudden stops, and current account reversals. NBER Working Paper No. 11170. https://www.nber.org/papers/w11170.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2020
Falk R (1999) Predatory globalization: a critique. Polity Press, Cambridge
Fouquin M, Hugot J (2016) Two centuries of bilateral trade and gravity data: 1827–2014. CEPII Working Paper, 2016–14. http://www.cepii.fr/pdf_pub/wp/2016/wp2016-14.pdf . Accessed 15 May 2020
Frankel JA, Romer DH (1999) Does trade cause growth? Am Econ Rev 89(3):379–399
Gao S (2000) Economic globalization: trends, risks and risk prevention. CDP Background Papers 001, United Nations, Department of Economics and Social Affairs
Georgantzas N, Katsamakas E, Solowiej D (2010) Giddens’ globalization: exploring dynamic implications. Syst Res Behav Sci 27(6):622–638
Giddens A (1990) Consequences of modernity. Standford University Press, Standford
Gilpin R (2000) The challenge of global capitalism: the world economy in the 21 st century. Princeton University Press, Princeton
Book Google Scholar
Gu XH, Dong BM (2011) A theory of financial liberalisation: why are developing countries so reluctant? World Econ 34:1106–1123
Held D et al (1999) Global transformations: politics, economics and cultures. Polity Press, Cambridge
Hernández RA (2003) Neoclassical and endogenous growth models: theory and practice. Warwick University. https://doi.org/10.13140/RG.2.1.5069.1600
Hirst P, Thompson G (2001) Globalization in question: the international economy and the possibilities of governance
Intriligator MD (2004) Globalization of the world economy: potential benefits and costs and a net assessment. J Policy Model 26(4):485–498
Lane DC, Husemann E (2008) Steering without Circe: attending to reinforcing loops in social systems. Syst Dyn Rev 24(1):27–61
Levine R (2001) International financial liberalization and economic growth. Rev Int Econ 9:688–702
Luhmann N (1982) The world society as a social system. Int J Gen Syst 8(3):131–138
Nissanke M, Thorbecke E (2007) The impact of globalization on the world’s poor: transmission mechanisms. Palgrave Macmillan
Nye J (2002) The paradox of American power: why the world’s only superpower can’t go it alone. Oxford University Press, New York
OECD (2002) Foreign direct investment for development: maximising benefits, minimising costs. OECD Publications
Rodriguez F, Rodrik D (2000) Trade policy and economic growth: a sceptic’s guide to the cross-national evidence. NBER Mac Ann 15:261–325
Stiglitz J (2003) Globalization and growth in emerging markets and the new economy. J Policy Model
Stiglitz J (2007) Making globalization work. Penguin Books, New York
Wallerstein I (2016) The scholarly mainstream and reality: we at a turning point. In: Wallerstein I (ed) Modern world-system in the longue Duree. Routledge, London\New York
World Health Organizations (2020) www.who.int/topics/globalization/en (visited on 25.05.2020)
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
University of Lincoln, Lincoln, UK
Ishak Demir
Inonu University, Battalgazi/Malatya, Turkey
Mehmet Canakci
Kirklareli University, Merkez/Kırklareli, Turkey
Ekonomi Arastirmalari Platformu, Istanbul, Turkey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Ishak Demir .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
European School of Sustainability, Hamburg University of Applied Sciences, Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
Walter Leal Filho
Center for Neuroscience & Cell Biology, University of Coimbra, Coimbra, Portugal
Anabela Marisa Azul
Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Passo Fundo University Faculty of Engineering and Architecture, Passo Fundo, Brazil
Luciana Brandli
HAW Hamburg, Hamburg, Hamburg, Germany
Amanda Lange Salvia
International Centre for Thriving, University of Chester, Chester, UK
Section Editor information
Polimoda Fashion Institute, Florence, Italy
Marco Tortora
Fair Association, Florence, Italy
School of Economics and Management, University of Florence, Florence, Italy
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 Springer Nature Switzerland AG
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Demir, I., Canakci, M., Egri, T. (2021). Globalization and Economic Growth. In: Leal Filho, W., Azul, A.M., Brandli, L., Lange Salvia, A., Wall, T. (eds) Decent Work and Economic Growth. Encyclopedia of the UN Sustainable Development Goals. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-71058-7_90-1
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-319-71058-7_90-1
Received : 29 May 2020
Accepted : 29 May 2020
Published : 14 April 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-319-71058-7
Online ISBN : 978-3-319-71058-7
eBook Packages : Springer Reference Earth and Environm. Science Reference Module Physical and Materials Science Reference Module Earth and Environmental Sciences
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
Term Paper: Globalization – Definition & Types | Processes | Economics
After reading this term paper you will learn about:- 1. Definition of Globalization 2. Phases of Globalization 3. Types 4. Measurement 5. Factors 6. Effects 7. Advantages 8. Disadvantages.
Term Paper on Globalization
Term Paper Contents:
- Term Paper on the Disadvantages of Globalization
ADVERTISEMENTS:
1. Term Paper on Globalization (Definition):
Globalization is the process of organizing the whole world into a single integrated marketing unit. It is also defined as the process of trans border free flow of products, services, people, culture, technology, and finance.
It leads to the integration of economic, cultural, political, and social systems across national borders Globalization is also referred to as internationalization by some persons. Both these terms are used as synonyms. However, some people use these terms separately.
With various globalization such as phases of globalization, types (kinds) of globalization, global connectivity, measurement of globalization, factors affecting globalization, advantages of globalization and disadvantages of globalization.
ADVERTISEMENTS: (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); 2. Term Paper on Globalization (Phases):
Globalization is not a new phenomenon. It started with human civilization.
In the past 130 years, modern historians have identified three stages or phases of globalization, viz.:
(i) First phase,
(ii) Second phase, and
(iii) Third phase.
i. First Phase of Globalization:
This phase of globalization started from 1870 and ended in 1913 with outbreak of the First World War.
The main features of first phase are given below:
(i) There was marked mobility of capital.
(ii) The labour mobility was high.
(iii) The magnitude of free trade was limited.
(iv) The global institutions were non-existent.
(v) The National Institutions were heterogeneous and were not well organized.
The First World War had adverse effects on the process of globalization i.e. flow of products, services, labour, and technology across the countries. It started resuming since 1930 gain and got setback from 1940 to 1944 due to Second World War.
ii. Second Phase of Globalization:
The second phase of globalization started from 1945 and culminated in 1973.
The main features of this phase are given below:
(i) The mobility of capital was low than first phase.
(ii) The labour mobility was low.
(iii) The magnitude of free trade was low.
(iv) The global Institutions were getting created during this period.
(v) The National Institutions were heterogeneous and were not standardizes.
iii. Third Phase of Globalization:
The third phase of globalization started from 1974 and is still in progress. It is also known as the current phase of globalization.
Main features of this phase are given below:
(i) The mobility of the capital is high.
(ii) The labour mobility is low.
(iii) The magnitude of free trade is extreme.
(iv) The International Institutes started functioning.
(v) The National Institutions have been standardized.
(vi) The on line global transactions are possible.
(vii) Information technology is being used extensively.
ADVERTISEMENTS: (adsbygoogle = window.adsbygoogle || []).push({}); 3. Term Paper on Globalization (Types):
There are five main types of globalization, viz.:
i. Economic Globalization:
It refers to trans-country flow of capital/finance or money.
Main effects of economic globalization are:
(a) Enhancement in world-wide economic relationships.
(b) Increase in international trade at a faster rate than the growth in the world economy..
(c) Increase in international flow of capital including foreign direct investment.
(d) Creation, of international agreements leading to organizations like the WTO and OPEC.
(e) Development of global financial systems.
(f) Increased role of international organizations such as WTO, WIPO, and IMF that deal with international transactions.
(g) Increase of economic practices like outsourcing, by multinational corporations.
ii. Production Globalization:
It refers to trans-country flow of goods or products. It leads to transnational production of various goods or products. In such system, a product can be manufactured in several countries of the world with same quality.
iii. Cultural Globalization:
It refers to trans-country flow of culture.
The main effects of cultural globalization are:
(a) Greater international cultural exchange,
(b) Spreading of multiculturalism, and better individual access to cultural diversity,
(c) Greater international travel and tourism,
(d) Greater immigration, including illegal immigration
(e) Spread of local foods such as pizza and Indian food to other countries
(f) Development of a global telecommunications infrastructure and greater trans-border data flow, using such technologies as the Internet, communication satellites and telephones.
(g) Increase in the number of standards applied globally; e.g. copyright laws and patents.
(h) Formation or development of a set of universal values.
(i) Spread of local goods, dresses and language to other countries.
iv. Information Globalization:
It refers to trans-border flow of knowledge, ideas and information. It is also known as communication globalization or technological globalization. It makes use of information technology and permits on line global transactions.
v. Ecological Globalization:
It refers to global protection of ecosystem from degradation and pollution.
Main features of ecological globalization are given below:
(a) It prevents ecosystem from various types of risks.
(b) It requires global collective action.
(c) It is also known as ecosystem globalization or environmental globalization.
(d) It leads to protection of environment globalization.
4. Term Paper on Globalization (Measurement):
The rate or extent of globalization is measured on yearly basis.
Different types of globalizations are measured separately as follows:
The data transfer border flow of capital or finance or money and direct foreign investment.
The data of trans country mobility of goods and products.
The mobility of tourist, travellers, and traders across the countries.
The data of information flow across the borders.
The work done for the protection of global ecosystem.
5. Term Paper on Globalization (Factors):
The rate of globalization is affected by several factors such as:
(i) Global Atmosphere:
The peaceful global atmosphere promotes globalization, whereas the war situation restricts globalization. The globalization was adversely affected during First and Second World war period.
(ii) Natural Calamities:
Natural calamities such as earth quake, tornadoes, floods and disease epidemic have adverse effects on the rate of globalization.
(iii) International Relationships:
Harmonious relationships among countries enhance the rate of globalization, whereas disharmonious relationships restrict the process of globalization.
(iv) Means of Transportation:
Better means of transportation among countries promotes globalization, whereas poor transportation system restricts the globalization.
(v) Means of Communication:
Better means of communication promotes globalization, whereas poor means of communication restricts the globalization.
(vi) Tourist Places:
Good and large number of tourist places in a country will attract tourists and travelers and vice versa.
(vii) Demand:
The demand of goods, services and information in other countries will enhance the international trade and the globalization.
6. Term Paper on Globalization (Effects):
The globalization has effects on movement of goods, services, information, finance, people, spread of cultures and ideas, markets, export and intellectual properties etc.
These are briefly discussed below:
i. Flow of Goods, Services Information etc.:
There is enhancement in the information flow between geographically remote locations and more trans-border data flow using communication satellites, the Internet, wireless telephones etc.
ii. Markets:
The global common market has a freedom of exchange of goods and capital. The worldwide production and financial markets emerge. The free trade zones are formed having less or no tariffs.
iii. Access to Goods and Finance:
There is a broad access to a range of goods for consumers and companies. Corporate, national and sub-national borrowers have a better access to external finance.
iv. Solution of Global Problems:
Global environmental problems like cross- boundary pollution, over fishing on oceans, climate changes are solved by discussions International criminal courts and international justice movements are launched.
v. Uniform Standards:
The standards applied globally like patents, copyright laws and world trade agreements increase.
vi. Spread of Culture:
Globalization leads to spread of cultures as there is individual access to cultural diversity. This diversity decreases due to hybridization or assimilation. There is enhancement in worldwide fads and pop culture. The cross-cultural contacts grow and cultural diffusion takes place.
vii. Movement of People:
The international travel and tourism increases and immigration between countries increases. The worldwide sporting events like the Olympic Games and the FIFA World Cup are held. The free circulation of people of different nations leads to social benefits.
viii. Export:
The local consumer products are exported to other countries. There is an increase in the desire to use foreign ideas and products, adopt new practices and technologies and be a part of world culture.
ix. Reduction in Transport Cost and Subsidies:
Due to development of containerization for ocean shipping, the transportation costs are reduced. The subsidies for local businesses decrease and there is reduction in capital controls.
x. Recognition of Intellectual Property:
There is supranational recognition of intellectual property restrictions i.e. patents authorized by one country are recognized in another.
7. Term Paper on Globalization (Advantages):
Some important advantages of globalization are listed below:
i. Connectivity:
People around the world are more connected to each other than ever before. Global mass media connects all the people in the world.
ii. Relationships:
The relationships between counties improve and the possibility of war between the developed countries decreases. The interdependence among Nations increases.
iii. Freedom of Trade:
It increases free trade between countries and reduces the international barriers.
iv. Investment Opportunity:
As the liquidity of capital increases, developed countries can invest in developing ones. The flexibility of corporations to operate across borders increases.
v. Integration:
It leads to integration or consolidation of global markets. In other words the markets are interlinked. It is much easier for people to travel, communicate and do business internationally.
vi. Quality and Price:
There is improvement in quality and reduction in price due to competition among different companies.
vii. Flow of Goods and Services:
Information, money, technology and products flow across the border quicker than ever before. Products produced in one part of a country are available to the rest of the world. There is increase flow of communication between the individuals and corporations in the world. The movement of goods and people across the border is faster than ever before.
viii. Standard of Living:
Globalization offers a higher standard of living for people in rich countries and is the only realistic route out of poverty for the world’s poor. It is claimed that globalization increases the economic prosperity and opportunity in the developing world. All the countries involved in the free trade are at a profit. As a result, there are lower prices, more employment and a better standard of life in these developing nations.
ix. Efficient use of Resources:
The civil liberties are enhanced and there is a more efficient use of resources. The environmental protection in developed countries increases.
x. Spread of Culture:
Globalization leads to better cultural understanding and tolerance. Due to improved transport facilities, more and more people are traveling to different countries, thereby spreading their culture to other parts of the world. Reduction of cultural barriers increases the global village effect. There is spread of democratic ideals.
8. Term Paper on Globalization (Disadvantages):
There are some disadvantages of globalization which are listed below:
i. Increase in Population:
Trans country flow of people will lead to increase in the population of certain countries especially in developed countries due to better facilities.
ii. Small Industries:
It will have adverse effects on small scale industries which cannot compete in global market in terms of quality and price, Thus there will be hold of big industries.
iii. Employment:
There will be adverse effect on employment due to close down of small industries.
iv. Monetary Gain:
This will lead to tough competition among companies leading to loss in monetary gain.
v. Terrorism:
Trans border flow of people may lead to increase in criminal activities and terrorism.
vi. Spread of Diseases:
There is greater risk of unintentional transmission of diseases between nations,
vii. This may lead to widening of gap between rich and poor countries.
viii. This may lead to exploitation of workers specially labours.
Related Articles:
- Globalization: Definition, Brighter and Darker Sides
- Forces Behind Globalization (With Diagram)
- International Gold Standard | Term Paper | Economics
- Term Paper on the Supply of Money | Economics
Globalization: What Globalization Is and Its Impact Essay
Primary source data, secondary source data, comparative analysis.
Bibliography
Globalization is a complex phenomenon that has a big influence on various fields of human life, including economics, society, and culture. Even though trade between countries has existed since time immemorial, in the 21st-century, globalization has become an integral part of the world’s development. While businesses try to expand on a global scale, and countries’ economies are intertwined in the international network, several outcomes occur out of this process. The purpose of this paper is to analyze and evaluate the impact of globalization on the world economy, whether it is good or bad. To achieve this goal, a comprehensive review of the relevant literature will be conducted. The information will be extracted from both primary and secondary sources. The primary sources will include an interview and a chart, while the secondary sources will consist of scholarly articles and books published from the year 2015 forward. The main argument of this research is that even though globalization offers endless business opportunities, it has a number of effects that negatively influence the resources and the economy.
First of all, in order to understand this phenomenon, it is important to define the term “globalization.” Several researchers have conducted a thorough study of this subject. For example, Martell describes globalization as “the intensification of worldwide social relations which link distant localities in such a way that local happenings are shaped by events occurring many miles away” 1 . It is a complex and multidimensional mechanism that allows a local business subdivision to integrate into the global economic system. The biggest companies of the 21st century are no longer limited to one country; they have become more multinational: businesses from several countries exchange resources, money, data, and employees. Nowadays, international relations are becoming more intense not only in politics but in the economy as well. Moreover, globalization has a significant influence on the distribution of not only skilled and unskilled labor but of capital and labor as well, both locally and globally. The tendencies of this process were analyzed by experts, for example, in the research by Chandy and Seidel, where they presented globalization trends in the form of a chart (Figure 1).
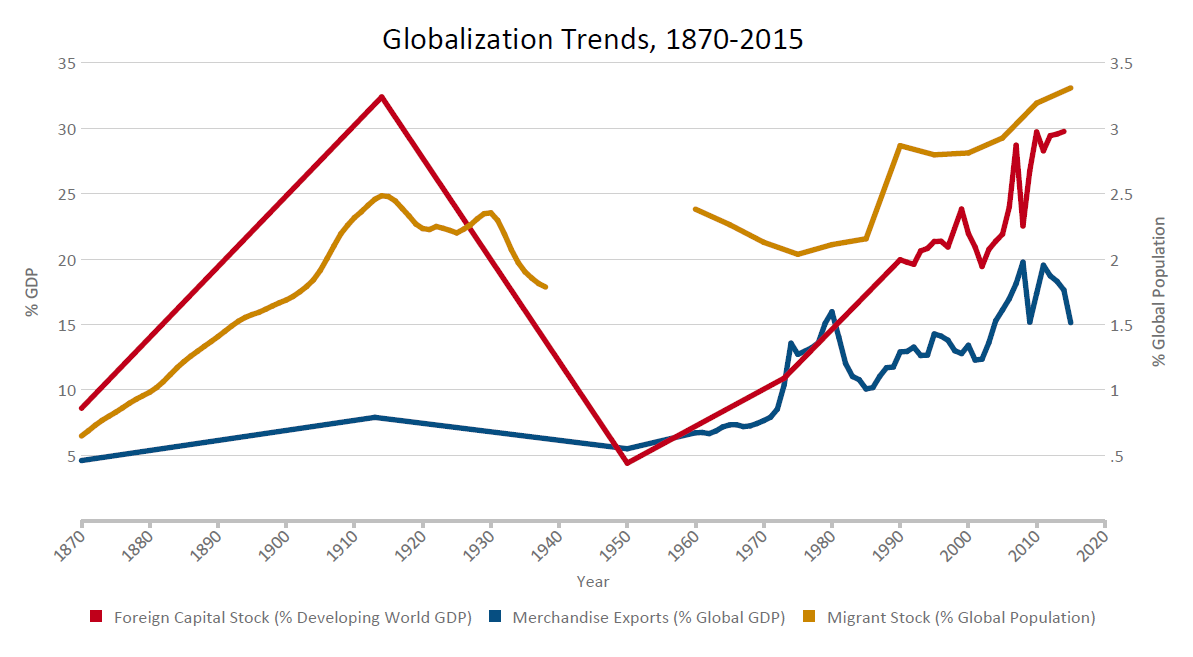
The chart above demonstrates how the GDP of the U.S. was changing while the global population was also growing. The diagram includes the analysis of foreign capital stock, merchandise exports, and migrant stock. According to it, it becomes evident that even though the world GDP was high during the 1910s, the global economy is more integrated in the 21st century. However, the researchers also point out that the economy of the U.S. is a relatively closed economy, which is surprising. Nevertheless, the study states that “it accounts for only 11 percent of global trade volumes, which is far below its 24 percent share of global GDP” 2 . In addition, despite the attempts to find evidence of the recession of globalization, Chandy and Seidel did not manage to present any. It means that the trend keeps developing as money, goods, and people continue to move around the world.
It is evident that one cannot talk about globalization without mentioning international companies. Global corporations are defined by the fact that they execute business in at least two countries 3 . They conduct various types of economic activities, for example, foreign investment, managing plants in different countries to avoid transaction costs. An example of an international firm that obtains cost advantages through foreign investments in international plants is Apple Inc.
To understand how companies conduct business internationally, several types of multinational corporations must be indicated: economists usually divide them into four categories. The first type of firm is determined by the fact that it has a strong presence in its home country. Another category is characterized by acquiring cost advantage through the means of buying cheaper resources in other countries, despite being controlled by one central office. The third type is a company that is based on the Research and Development of the parent corporation. The fourth and final category is a transnational business, which includes all features that are peculiar to the corporations that were mentioned above 3 . Since global companies generally combine different approaches to business, sometimes it can be hard to distinguish between these four categories. Nestle S.A. may serve as an example of a big transnational corporation that conducts its financial operations in many countries outside of the headquarters.
Since globalization is a complicated phenomenon, many analysts and businessmen have different views on its impact. For instance, the former Director-General of the World Trade Organization, Pascal Lamy, expressed his point of view in the interview, “Can Europe Civilize Globalization?”. Despite the fact that the concerns about European civilization may recede due to this process, he states that he does not see globalization as a threat. Instead, he sees it as a reality that has to be dealt with in a professional way. Lamy explains his opinion by pointing out the fact that some European countries have managed to gain more benefits than others by means of global trade 4 . As examples, he presents Sweden and Germany, which, during the last decades of the 20th century, conducted structural reforms that allowed them to get profit from international trade.
Moreover, Lamy notes that globalization presents new challenges for businesses. They include promoting “more actively global norms in the environmental and job protection, health protection, than the reduction of trade barriers that have been now largely operated worldwide”4. In other words, the ex-director of WTO believes that this process can have a positive impact on Europe’s economy as it provides opportunities for countries to develop and grow their benefits.
As for other researchers, Burlacu, Gutu, and Matei overview both sides of globalization, pointing out positive and negative impacts. For example, the advantages include reducing the economic isolation of poor countries as they are given the opportunity to sell their goods on the global market and participate in the trade 5 . Moreover, as the economy expands, the information does it as well. It means that access to education becomes more easy and available, which increases the number of professionals who are capable of expanding and developing the business even further. In addition, according to the study, globalization “enhances the speed of commercial, financial, and technological operations”5. It can be seen even nowadays as new products and devices continue to appear on the market every year. Furthermore, globalization ensures the efficiency of the entire economic activity on a global scale.
Other researchers have also pointed out several positive aspects of this process. For example, Parente et al. talk about the sharing economy, which is a new phenomenon. Their study indicated that due to internet globalization, some companies managed to perform business online, which helped them to expand around the world and raise funds 6 . Therefore, globalization allowed firms to achieve worldwide success at an unprecedented pace. Furthermore, Martell et al. elaborated on reasons for how exactly the internalization changed economic activities. The reasons included “the speeding up of global interactions and processes as a result of the development of transport and communications”1. In other words, the spread of resources, ideas, capital, and products accelerated, which allowed businesses to develop quicker.
However, aside from positive results that can come from globalization, researchers also indicate some negative aspects to it. For instance, Burlacu et al. Note that harmful effects include an international security deficit and an increased amount of illegal migrations5. Globalization opened borders for a large number of people to move to other countries illegally. Moreover, it allowed corrupt businessmen to employ these migrants and make them work for a lesser wage, which is a violation of human rights. Moreover, economists believe that nowadays, the export of human resources has risen, which means that some countries have lost intellectual potential5. The other downsides include the deterioration of the environment, which is caused by the rapid growth of the economy.
While rethinking the effects of globalization, Broner and Ventura elaborated on the negative consequences that it can bring to domestic markets. The researchers gathered data from other scholars and concluded that “financial globalization, in addition to providing a new, cheaper source of funding for emerging markets, can have indirect effects by affecting the workings of domestic financial markets” 7 . For example, according to them, with the rise of globalization, the incidence of domestic financial crises also grows. In addition, Mamedov et al. discusses the impact on traditional economies, which, according to the study, will reach a new level of their development 8 . It is difficult to say whether such changes are positive or not since some people may be reluctant to abandon the old economic structures.
As it can be observed, primary sources and secondary sources seem to express various opinions about globalization. First and foremost, most of them seem to agree that this phenomenon is relatively new and only recently began to spread. However, then the standpoints start to differ among experts. While the interview with Lamy demonstrates that the former leader of the World Trade Organization seems optimistic about it, such secondary sources as scholarly articles and books differentiate in positions.
Some researchers identify the internalization of the economy as a beneficial process that can create new opportunities for countries to develop and expand their businesses. However, other studies make a link between globalization and several other problems, such as environmental deterioration, security issues, and the increasing number of domestic crises. The last factor is especially interesting since it contradicts the general assumption that increased international trade opportunities can improve the country’s welfare.
Moreover, the recent events that were caused by the outbreak of coronavirus exposed vulnerabilities in the current globalized economy. Since traveling is restricted, the transportation of resources has become difficult. While big international corporations managed to stay afloat, some local firms were forced to shut down, and the suspension of one company factory can lead to a closing of another. Experts argue that such an intertwined international economic relationship is what caused changes in a global supply chain, and overall, stock declines 9 . The current situation provided proof that globalization may not be that good for the world economy.
While the system offers opportunities for businesses to grow, it also has some loopholes and weak points that seriously damage the economy of not only one country but of the whole world. Moreover, the situation with the pandemic supports the argument made by Broner and Ventura. The outbreak caused domestic market crises in Asian countries, and then in Europe and America, which significantly affected the global economy. Even the help of Widespread Disease Emergency Financing Facility 10 would not be enough to restore all financial damage. As the recession of the international market became apparent, businesses in other countries have also suffered.
In addition, the environmental aspect of globalization is also important since it affects the increasing deficiency of natural resources. While companies are trying to expand their business everywhere, new factories and new plants are built around the world. While new products and new technology continue to appear on the market and the demand grows, more damage is inflicted upon the environment by the constant production.
Moreover, the higher need for transportation means that more fossil fuels are used, causing harm to the climate. There is no doubt that such issues can be resolved with the creation of new technology. However, the process of development is complicated and expensive, which can lead to additional expenditures. It can cause more federal budget deficits and increased government debt; therefore, the economy is also negatively affected by environmental issues of globalization.
For this reason, it can be said that despite all the positive aspects of globalization, it definitely has several downsides. Internationalization brought not only different cultures but the economies of various countries together, allowing businesses to grow and reach financial benefits. Furthermore, it opened opportunities for people to find jobs and expand their profit. Nevertheless, the current system is vulnerable during difficult situations, and if there is a crisis in one country, it tends to spread to others like dominoes, because the economies are deeply connected. Moreover, globalization also causes harm to other fields of human life, which are can also negatively influence not only the financial state of a particular country but the economy of the world as well.
It is evident that more research needs to be conducted as the process of globalization is complex and ongoing. There are several topics that can be further explored while studying the impact of globalization on the world’s economy. For example, one can investigate the methods that can be implemented to minimize the negative consequences of globalization that were described earlier in this paper. In order to obtain the information, one can look through the suggestions of other researchers, analyze them, and select the ones that seem the most effective.
Moreover, as the current situation with the outbreak has a major impact on the international economy, it would be interesting to study the experts’ opinions on how it will affect globalization. A huge amount of relevant information can be gathered from recent interviews, news, and scholarly articles. In conclusion, it would appear that the topic of globalization and its influence is broad and can provide a good starting point for further discussion and analysis.
Chandy, Laurence, and Brina Seidel. “Donald Trump and the future of globalization.” The Brookings Institution , 2016. Web.
Broner, Fernando, and Jaume Ventura. “Rethinking the Effects of Financial Globalization.” The Quarterly Journal of Economics 131, no. 3 (2016): 1497-1542.
Burlacu, Sorin, Corneliu Gutu, and Florin Octavian Matei. “Globalization – Pros and Cons.” Calitatea 19, no. S1 (2018): 122-125.
Lamy, Pascal. “Interview. Can Europe Civilize Globalization?”, The Federalist Debate 28, no. 1 (2015): 60-63.
Mamedov, Oktay, Irina Movchan, Oksana Ishchenko-Padukova, and Monika Grabowska. “Traditional Economy: Innovations, Efficiency and Globalization.” Economics & Sociology 9, no. 2 (2016): 61.
Martell, Luke. The Sociology of Globalization . John Wiley & Sons, 2016.
Parente, Ronaldo C., José-Mauricio G. Geleilate, and Ke Rong. “The Sharing Economy Globalization Phenomenon: A Research Agenda.” Journal of International Management 24, no. 1 (2018): 52-64.
- Sułkowski, Łukasz. “Covid-19 Pandemic; Recession, Virtual Revolution Leading to De-globalization?”, Journal of Intercultural Management 12, no. 1 (2020): 1-11.
- Luke Martell. The Sociology of Globalization (John Wiley & Sons, 2016), 10.
- Laurence Chandy and Brina Seidel. “Donald Trump and the future of globalization.” The Brookings Institution , 2016.
- Lecture on Multinational Corporation (MNC)
- Pascal Lamy. “Interview. Can Europe Civilize Globalization?”, The Federalist Debate 28, no. 1 (2015): 60.
- Burlacu, Sorin, Corneliu Gutu, and Florin Octavian Matei. “Globalization – Pros and Cons.” Calitatea 19, no. S1 (2018): 124.
- Parente, Ronaldo C., José-Mauricio G. Geleilate, and Ke Rong. “The Sharing Economy Globalization Phenomenon: A Research Agenda.” Journal of International Management 24, no. 1 (2018): 53.
- Broner, Fernando, and Jaume Ventura. “Rethinking the Effects of Financial Globalization.” The Quarterly Journal of Economics 131, no. 3 (2016): 1533.
- Mamedov, Oktay, Irina Movchan, Oksana Ishchenko-Padukova, and Monika Grabowska. “Traditional Economy: Innovations, Efficiency, and Globalization.” Economics & Sociology 9, no. 2 (2016): 61.
- Lecture on the World Bank
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2022, February 16). Globalization: What Globalization Is and Its Impact. https://ivypanda.com/essays/globalization-what-globalization-is-and-its-impact/
"Globalization: What Globalization Is and Its Impact." IvyPanda , 16 Feb. 2022, ivypanda.com/essays/globalization-what-globalization-is-and-its-impact/.
IvyPanda . (2022) 'Globalization: What Globalization Is and Its Impact'. 16 February.
IvyPanda . 2022. "Globalization: What Globalization Is and Its Impact." February 16, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/globalization-what-globalization-is-and-its-impact/.
1. IvyPanda . "Globalization: What Globalization Is and Its Impact." February 16, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/globalization-what-globalization-is-and-its-impact/.
IvyPanda . "Globalization: What Globalization Is and Its Impact." February 16, 2022. https://ivypanda.com/essays/globalization-what-globalization-is-and-its-impact/.
- Humanizing Globalization’ Professional Analysis of Speech
- Protectionism as a Way to Protect Home Industries From Overseas Competition
- The $ 787 Billion Economic Stimulus Bill
- Globalization and its influences
- Globalization: An Economic Perspective
- Globalization Positive and Negative Impacts
- Globalization is not a Peaceful Process
- Positive and Negative Impacts of Globalization in Britain
- The Effects of Globalization on the World
- Is Globalization the Main Culprit for the 2008 Global Financial Crisis?
- Guanxi in Chinese Business and Global Economy
- Cross-Cultural Negotiation Analysis
- Intercultural Competencies: Environmental Scan and Analysis
- Uncertainty and Risks Regarding Multinational Corporations’ Functioning
- Multicultural Problems in Organizations
Globalisation
Globalization is a process of interaction and integration among the people, companies, and governments of different nations, a process driven by international trade and investment and aided by information technology. This process has effects on the environment, on culture, on political systems, on economic development and prosperity, and on human physical well-being in societies around the world.
There are countless indicators that illustrate how goods, capital, and people, have become more globalized.
The value of trade (goods and services) as a percentage of world GDP increased from 42.1 percent in 1980 to 62.1 percent in 2007. Foreign direct investment increased from 6.5 percent of world GDP in 1980 to 31.8 percent in 2006. The stock of international claims (primarily bank loans), as a percentage -of world GDP, increased from roughly 10 percent in 1980 to 48 percent in 2006. The number of minutes spent on cross-border telephone calls, on a per-capita basis, increased from 7.3 in 1991 to 28.8 in 2006. The number of foreign workers has increased from 78 million people (2.4 percent of the world population) in 1965 to 191 million people (3.0 percent of the world population) in 2005.
The growth in global markets has helped to promote efficiency through competition and the division of labor—the specialization that allows people and economies to focus on what they do best. Global markets also offer greater opportunity for people to tap into more diversified and larger markets around the world. It means that they can have access to more capital, technology, cheaper imports, and larger export markets. But markets do not necessarily ensure that the benefits of increased efficiency are shared by all. Countries must be prepared to embrace the policies needed, and, in the case of the poorest countries, may need the support of the international community as they do so. The broad reach of globalization easily extends to daily choices of personal, economic, and political life. For example, greater access to modern technologies, in the world of health care, could make the difference between life and death. In the world of communications, it would facilitate commerce and education, and allow access to independent media. Globalization can also create a framework for cooperation among nations on a range of non-economic issues that have cross-border implications, such as immigration, the environment, and legal issues. At the same time, the influx of foreign goods, services, and capital into a country can create incentives and demands for strengthening the education system, as a country's citizens recognize the competitive challenge before them. Perhaps more importantly, globalization implies that information and knowledge get dispersed and shared. Innovators—be they in business or government—can draw on ideas that have been successfully implemented in one jurisdiction and tailor them to suit their own jurisdiction. Just as important, they can avoid the ideas that have a clear track record of failure. Joseph Stiglitz, a Nobel laureate and frequent critic of globalization, has nonetheless observed that globalization "has reduced the sense of isolation felt in much of the developing world and has given many people in the developing world access to knowledge well beyond the reach of even the wealthiest in any country a century ago."
FORCES OF GLOBALIZATION
Why go global.
The playing field is wide open for small business. Here's why both men and women should consider going global: — Increase sales. — Generate economies of scale in production. — Raise profitability. — Insulate seasonal domestic sales by finding new foreign markets. — Create jobs, productivity growth and wealth. — Encourage the exchange of views, ideas and information. Small business in particular can take a mentoring role in educating other men and women in going global. They can establish educational programs, conferences and other activities to advance their colleagues, and in doing so, promote professional growth and leadership among all small business owners. The best is truly yet to come.
What Does It Take To Go Global?
Any small business owner must be adaptable, strategic and willing to take calculated risks. But becoming a successful global small business requires the following commitments: — Be comfortable with change. — Welcome new experiences; and learn as much as possible about the culture in which you are interested in doing business. — Be willing to take risks, even though it may create short term challenges. — Push yourself to continuously innovate.
Controversy
The negative impact of globalization in european job market, effect of globalization on different aspects.
Globalization is an interesting phenomenon since it is obvious that the world has been going through this process of change towards increasing economic, financial, social, cultural, political, market, and environmental interdependence among nations. Virtually, everyone is affected by this process. Given these changes, globalization brings about a borderless world. Globalization drives people to change their ways of living, prompts firms to change their ways of conducting business, and, spurs nations to establish new national policies. Events transpiring in different parts of the world now have dramatic consequences to other parts of the world at a faster pace than anyone could imagine in the past. For example, the Asian financial crisis in 1997 has severely affected businesses around the world and the outbreak of SARS (Severe Acute Respiratory Syndrome) in 2003 has shown how globalization permits the rapid spread of the disease, which affects many airlines, the hospitality industry, and other businesses around the globe. On the positive side, globalization enables firms to outsource and find customers around the world, e.g., the auto and electronics industries. The globalization of production and operations benefits firms through the realization of economies of scales and scope. Hence, no one can deny that globalization has changed the way we conduct business. Although globalization is a worldwide phenomenon, the extent to which each country is globalized is not identical. To measure the degree of globalization of each nation, a globalization index was recently developed by a cooperation between Foreign Policy Magazine, AT Kearney and EDS Company. The index indicates that some small developing countries in emerging economies such as Singapore and Malaysia were among the top twenty most globalized nations from 2001 to 2004 with Singapore being ranked as the most globalized nation. Thus, it is clear that globalization is an important phenomenon, one that cannot be simply ignored, because every nation — regardless of size or level of development — is globalized and affected by globalization. With the prevalence of this worldwide phenomenon, it is not surprising that businesses are inevitably affected.
Throughout this dissertation, the effects of globalization are classified into two broad Categories: 1) Global market opportunities and 2) Global market threats.
Present scenario of the topic
International trade.
A core element of globalization is the expansion of world trade through the elimination or reduction of trade barriers, such as import tariffs. Greater imports offer consumers a wider variety of goods at lower prices, while providing strong incentives for domestic industries to remain competitive. Exports, often a source of economic growth for developing nations, stimulate job creation as industries sell beyond their borders. More generally, trade enhances national competitiveness by driving workers to focus on those vocations where they, and their country, have a competitive advantage. Trade promotes economic resilience and Flexibility, as higher imports help to offset adverse domestic supply shocks. Greater openness can also stimulate foreign investment, which would be a source of employment for the local workforce and could bring along new technologies—thus promoting higher productivity.
Restricting international trade—that is, engaging in protectionism—generates adverse consequences for a country that undertakes such a policy. For example, tariffs raise the prices of imported goods, harming consumers, many of which may be poor. Protectionism also tends to reward concentrated, well-organized and politically-connected groups, at the expense of those whose interests may be more diffuse (such as consumers). It also reduces the variety of goods available and generates inefficiency by reducing competition and encouraging resources to flow into protected sectors. Developing countries can benefit from an expansion in international trade. Ernesto Zedillo, the former president of Mexico, has observed that, "In every case where a poor nation has significantly overcome its poverty, this has been achieved while engaging in production for export markets and opening itself to the influx of foreign goods, investment, and technology."4And the trend is clear. In the late 1980s, many developing countries began to dismantle their barriers to international trade, as a result of poor economic performance under protectionist policies and various economic crises. In the 1990s, many former Eastern bloc countries integrated into the global trading system and developing Asia—one of the most closed regions to trade in 1980—progressively dismantled barriers to trade. Overall, while the average tariff rate applied by developing countries is higher than that applied by advanced countries, it has declined significantly over the last several decades.
The implications of globalized financial markets
The world's financial markets have experienced a dramatic increase in globalization in recent years. Global capital flows fluctuated between 2 and 6 percent of world GDP during the period 1980-95, but since then they have risen to 14.8 percent of GDP, and in 2006 they totaled $7.2 trillion, more than tripling since 1995. The most rapid increase has been experienced by advanced economies, but emerging markets and developing countries have also become more financially integrated. As countries have strengthened their capital markets they have attracted more investment capital, which can enable a broader entrepreneurial class to develop, facilitate a more efficient allocation of capital, encourage international risk sharing, and foster economic growth. Data series begin in 1995 for central and eastern Europe and the Commonwealth of Independent States. Yet there is an energetic debate underway, among leading academics and policy experts, on the precise impact of financial globalization. Some see it as a catalyst for economic growth and stability. Others see it as injecting dangerous—and often costly—volatility into the economies of growing middle-income countries. A recent paper by the IMF's Research Department takes stock of what is known about the effects of financial globalization. The analysis of the past 30 years of data reveals two main lessons for countries to consider. First, these pictures support the view that countries must carefully weigh the risks and benefits of unfettered capital flows. The evidence points to largely unambiguous gains from financial integration for advanced economies. In emerging and developing countries, certain factors are likely to influence the effect of financial globalization on economic volatility and growth: countries with well-developed financial sectors, strong institutions, sounds macroeconomic policies, and substantial trade openness are more likely to gain from financial liberalization and less likely to risk increased macroeconomic volatility and to experience financial crises. For example, well-developed financial markets help moderate boom-bust cycles that can be triggered by surges and sudden stops in international capital flows, while strong domestic institutions and sound macroeconomic policies help attract "good" capital, such as portfolio equity flows and FDI.
The second lesson to be drawn from them is that there are also costs associated with being overly cautious about opening to capital flows. These costs include lower international trade, higher investment costs for firms, poorer economic incentives, and additional administrative/monitoring costs. Opening up to foreign investment may encourage changes in the domestic economy that eliminate these distortions and help foster growth.
Looking forward, the main policy lesson that can be drawn from these results is that capital account liberalization should be pursued as part of a broader reform package encompassing a country's macroeconomic policy framework, domestic financial system, and prudential regulation. Moreover, long-term, non-debt-creating flows, such as FDI, should be liberalized before short-term, debt-creating inflows. Countries should still weigh the possible risks involved in opening up to capital flows against the efficiency costs associated with controls, but under certain conditions (such as good institutions, sound domestic and foreign policies, and developed financial markets) the benefits from financial globalization are likely to outweigh the risks.
Globalization, income inequality, and poverty
As some countries have embraced globalization, and experienced significant income increases, other countries that have rejected globalization, or embraced it only tepidly, have fallen behind. A similar phenomenon is at work within countries—some people have, inevitably, been bigger beneficiaries of globalization than others.
Over the past two decades, income inequality has risen in most regions and countries. At the same time, per capita incomes have risen across virtually all regions for even the poorest segments of population, indicating that the poor are better off in an absolute sense during this phase of globalization, although incomes for the relatively well off have increased at a faster pace. Consumption data from groups of developing countries reveal the striking inequality that exists between the richest and the poorest in populations across different regions.
The future of globalization
Like a snowball rolling down a steep mountain, globalization seems to be gathering more and more momentum. And the question frequently asked about globalization is not whether it will continue, but at what pace.
A disparate set of factors will dictate the future direction of globalization, but one important entity—sovereign governments—should not be overlooked. They still have the power to erect significant obstacles to globalization, ranging from tariffs to immigration restrictions to military hostilities. Nearly a century ago, the global economy operated in a very open environment, with goods, services, and people able to move across borders with little if any difficulty. That openness began to wither away with the onset of World War I in 1914, and recovering what was lost is a process that is still underway. Along the process, governments recognized the importance of international cooperation and coordination, which led to the emergence of numerous international organizations and financial institutions (among which the IMF and the World Bank, in 1944).
Indeed, the lessons included avoiding fragmentation and the breakdown of cooperation among nations. The world is still made up of nation states and a global marketplace. We need to get the right rules in place so the global system is more resilient, more beneficial, and more legitimate. International institutions have a difficult but indispensable role in helping to bring more of globalization's benefits to more people throughout the world. By helping to break down barriers—ranging from the regulatory to the cultural—more countries can be integrated into the global economy, and more people can seize more of the benefits of globalization.
STEPS FOR GOING GLOBAL
As with any sound business plan, the first step is doing your homework. Here are ten action steps for taking on the world: 1. Conduct market research to identify your prime target markets. 2. Search out the data you need to predict how your product will sell in a specific geographic location. 3. Update your database rigorously with a view to focusing more closely on those products or services which are in demand and dropping those which are not. 4. Articulate your business plan for accessing global markets. 5. Get companywide commitment. 6. Build a web site and implement your international plan sensibly. 7. Factor in a two year lead time for world market penetration. 8. Make personal contact with your new targets armed with culture specific information and courtesies, professionalism and consistency. 9. Value the relationship more than the deal; the individual is more important than closing the deal under discussion. 10. Welcome the unknown.
Advantages of Globalization:
Globalization has several advantages on the —Economic, —Cultural, —Technological, and - Social and some other fronts.
Globalization means increasing the - Interdependence, - Connectivity and - Integration on a
Global level with respect to the - Social, - Cultural, - Political, - Technological, - Economic and - Ecological levels Advantages of Globalization — Goods and people are transported with more easiness and speed — The possibility of war between the developed countries decreases — Free trade between countries increases — Global mass media connects all the people in the world — As the cultural barriers reduce, the global village dream becomes more realistic — There is a propagation of democratic ideals — The interdependence of the nation-states increases — As the liquidity of capital increases, developed countries can invest in developing ones — The flexibility of corporations to operate across borders increases — The communication between the individuals and corporations in the world increases — Environmental protection in developed countries increases — Increased free trade between nations — Increased liquidity of capital allowing investors in developed nations to invest in developing nations — Corporations have greater flexibility to operate across borders — Global mass media ties the world together — Increased flow of communications allows vital information to be shared between individuals and corporations around the world — Greater ease and speed of transportation for goods and people — Reduction of cultural barriers increases the global village effect — Spread of democratic ideals to developed nations — Greater interdependence of nation-states — Reduction of likelihood of war between developed nations — Increases in environmental protection in developed nation However, such doubts are futile as globalization is a positive-sum chance in which the skills and technologies enable to increase the living standards throughout the world. Liberals look at globalization as an efficient tool to eliminate penury and allow the poor people a firm foothold in the global economy. In two decades from 1981 to 2001, the number of people surviving on $1 or less per day decreased from 1.5 billion to 1.1 billion. Simultaneously, the world population also increased. Thus, the percentage of s uch people decreased from 40% to 20% in such developing countries.
Disadvantages of Globalization — Increased flow of skilled and non-skilled jobs from developed to developing nations as corporations seek out the cheapest labor — Increased likelihood of economic disruptions in one nation effecting all nations — Corporate influence of nation-states far exceeds that of civil society organizations and average individuals — Threat that control of world media by a handful of corporations will limit cultural expression — Greater chance of reactions for globalization being violent in an attempt to preserve cultural heritage — Greater risk of diseases being transported unintentionally between nations
— Spread of a materialistic lifestyle and attitude that sees consumption as the path to prosperity — International bodies like the World Trade Organization infringe on national and individual sovereignty — Increase in the chances of civil war within developing countries and open war between developing countries as they vie for resources — Decreases in environmental integrity as polluting corporations take advantage of weak regulatory rules in developing countries

Recommendations
Globalization is not better for developing countries because the developing counties have less capital, insufficient, infrastructure, low technology and unskilled manpower. Due to all these reasons developing countries can not adopt the globalization structure. In a globally environment there is tough competition tough competition of local producers to struggle. Because the larger producers is in market and capture the whole market. Many persons have a good structure but they have not enough finance to compete the multinational organizations. There is trade deficit faced by the developing countries. This is the major problem. And due to that problem many countries is not in favorable condition to compete with developed countries. Globalization open the new horizons for investment in any other country either the country developed or not. Availability of waste market is a big advantage for multinational companies to explore the new markets. Transfer of technology is a big advantage of globalization for the developing countries so it is essential for these countries adopt and enjoy the benefit. Globalization is the threat for small and medium entrepreneurs so it is necessary to protect that industry. Threat of decrease in government revenues in shape of taxes is another problem so it is necessary to avoid and draw new policies. Protest against globalization is another issue so it is necessary to protect the consumers, small industries and developing and poor countries from the risks and develop new policies to avoid above mentioned factors. Globalization also helpful for the different economies to agree on a specific single currency so the balance is maintained. Loan also provided by the companies to finance at international level and there is no more restriction for small and medium entrepreneur's to obtain loans from the financial institutions.
This Term Paper is comprised of the effects of globalization on firms. The first thing advances prior knowledge on globalization and business by empirically investigating how this phenomenon affects firm performance. They explore the role of firms' cooperation in alliances in enhancing their performance amid globalization by specifically focusing on co-marketing alliances and international marketing performance of firms. A particular emphasis is paid to this type of alliance since superior marketing is crucial for firms to build a sustainable source of unique competitive advantage. Such advantage eventually enables firms to achieve long-run success in a hypercompetitive terrain under globalization. While this project also proposes a conceptual framework relating globalization effects to alliance cooperation and firm performance. Given that globalization is a complex phenomenon, there is a scarcity of empirical research investigating its effects on businesses. Hence, there are several significant contributions of this term paper. First, the effects of globalization on firms are classified into two key dimensions—global market opportunities and global market threats— based on an extensive review of scattered literature on the topic. Second, these major effects are operational zed and empirically tested in two conceptual models to examine the relationships among these effects, cooperation in alliances, and firm performance. Third, literature on international business, strategic management, and marketing are integrated to address the effects of globalization on firms' marketing conduct and outcomes. The first thing discussed in this term paper is how globalization affects firms. It draws from environment-organization literature. Building on this stream of research, macro environment such as globalization represents a context in which organizational characteristics and outputs are strongly shaped. For this reason, this term paper attempts to demonstrate and address how globalization influences firm performance.
The term paper proposes a conceptual framework to investigate relationships among globalization effects, degree of cooperation in co-marketing alliances, and international marketing performance. This term paper focuses on relationships between globalization effects and alliances because past research often mentions that globalization drives more collaboration and alliance participation.
Thus, this term paper explores how firms with international marketing activities can enhance their performance in the global marketplace through increased cooperation in co-marketing alliances. Building on market power perspective and transaction cost economics; this term paper proposes that increased global market threats, including competitive threats and market uncertainty, will encourage more cooperation in alliances while global market opportunities will not. While transaction costs economics considers alliances as a strategy enabling firms to expand their strategic capabilities, market power perspective regards alliances as a means to reduce competition and minimize uncertainty evoked by globalization. Such cooperation eventually increases international marketing effectiveness of firms engaging in co-marketing alliances. Whereas an increase in cooperation is influenced by higher global market threats (i.e., both competitive threats and uncertainty), it is not affected by global market opportunities. The absence of any effect of global market opportunities on alliance cooperation can be attributed to the fact that ample opportunities in the markets may result in the lack of collaboration among firms. Moreover, it is found that increased cooperation in co-marketing alliances helps firms enhance international marketing effectiveness but not efficiency. Since higher expenses may arise from such cooperative attempts, efficiency becomes difficult to realize. In sum, these results validate globalization-alliance literature by showing that globalization actually drives more cooperation among firms.
Managers should be prepared to cope with these diverse effects by capitalizing on global market opportunities while carefully managing the inherent threats. Alliance participation and cooperation presents a viable option for firms to navigate successfully in this new competitive landscape. From both theoretical and practical perspectives, globalization is a complex phenomenon. The three manuscripts included in this dissertation are among a few empirical studies emphasizing the effects of globalization on firms. Given that globalization is multifaceted and only a few key dimensions of its effects were explored here, many issues remain to be addressed. Bibliography and References
I've taken all the information from official sites of govt. Of India and Indian companies and few data from books, online journals and news paper which are given below: Websites www.globalization101 .org www.globalpolicy.org/globalization.html www.economywatch.com > Economy Articles www.tradechakra.com > Indian Economy - eac.gov.in/.../55GLOBAUZATION%o20AND%o20CHALLENGES°/o20BEFORE°/o... www.eurojournals.com/IRJFE%206%20goyal.pd economics.about.com/.../globalization trade/l/aaglobalization.html -www.fibre2fashion.com/.../8/.../impact-of-globalization1.asp -www.indiastudychannel.com > ... > Education -www.eurojournals.com/IRJFE%206%20goyal.pdf -www.busiessstandard.com www.thehindhu.com www.onlinejournal.com Newspaper - The Hindu, published by B.C.Acherakar ('Nov '09) Business standard (21 october 09) Books 1- International business environment by 'Robert' Published by Pearson publication 2- International business by 'Stephen' Publishes by Tata Mc'graw Publication
Besplatni Seminarski Radovi
FREE TERM PAPERS
266 Globalization Essay Topics & Globalization Research Topics
Welcome to our list of globalization topics and essay ideas! Here, you will find plenty of current topics about globalization trends, benefits, and challenges. But that’s not all of it! In addition to topic ideas, you will also find examples of research papers and globalization essays. Check them out below!
🔝 Top 7 Globalization Topics for Research
🏆 best essay topics on globalization, ❓ globalization research questions, 👍 good globalization research topics & essay examples, 🌶️ hot globalization ideas to write about, 🎓 most interesting globalization research titles, 💡 simple globalization essay ideas, ✍️ globalization essay topics for college.
- The Effects of Globalization to Employment and International Trade
- Apple Inc. Affected by Globalization and Technology
- Globalization’ Positive and Negative Effects
- Evaluating Cultural Dimensions of Globalization
- Globalization Impact on Sustainable Agriculture
- Communication Technology and Globalization
- Globalization and Its Impact on Society
- Impacts of Globalization on the Developing Countries The paper evaluates how globalization impacts developing countries. It is the most debated issue in the modern world, with some people supporting and others opposing it.
- Is Globalization a Threat or an Opportunity to Developing Countries? The topic on the effects of globalization has generated a lot of debate in trying to analyze its contribution to either the success or failure of some aspects of economies.
- Contemporary Globalization and Its Impact As Shakespeare predicted a long time ago, the world is shrinking into a small global scene where everyone has a role to play.
- Globalization Impacts on Trade and Employment Globalization refers to the integration of the world markets. It facilitates smooth movement of goods and people from one country to another.
- Globalization in Media: Pros and Cons Globalization in the media sphere is influenced by changes in political and cultural spheres bringing new economic opportunities and financial capitals to media giants.
- The Effects of Globalization on Sports For many people in the world, globalization is the revolution of the future. Conversely, this is not true as globalization exists in the present day.
- Apple Inc.’s Globalization Strategy and International Trade This paper will discuss Apple’s globalization strategy, global actions advocated for by this company, and how it facilitates international trade.
- Globalization and Diversity in TEDx Talk Shows This paper examines TEDx talk shows that discuss diversity and globalization issues and how globalization can reduce poverty levels in developing economies.
- Globalization and Corporate Social Responsibility The topic chosen for this research is globalization and corporate social responsibility because it is a unique and novel concept for transnational businesses.
- Effects of Globalization: The Case of LuLu Group Int To summarize this paper, globalization is an unstoppable interstate integration process, leading to the erasure of national boundaries and the formation of a single cultural layer
- Globalization Advantages and Negative Cultural Impact This paper focuses on globalization. Drivers of the globalization agenda are multinationals corporations, international financial markets, and transnational agencies.
- Impact of Globalization on Norms and Experiences around Gender Inequality is one of the most prolonged global debates that have refused to go away despite the great strides made through globalization
- The Advantages of Globalization Globalization is the process of growth and interconnection of world economies and cultures, which are aided by transport and trade.
- Americanization Is Not a Synonym for Globalization Globalization is the process of international integration, whereas Americanization means the influence of American culture on other countries’ cultural development.
- Coca-Cola Company’s Strategy & Globalization Issues Multinational corporations are increasing day by day and they are usually criticized because of issues like environmental stability, sustainability etc.
- The Impact of Technology on Globalization The paper states that advances in technology have contributed to the main forces behind globalization. Organizations are compelled to become global.
- The Impact of Globalization on World Politics Globalization as the process that creates preconditions for the eventual emergence of World Government, which will exercise an authority over planet’s natural and human resources.
- Impact of Globalization on Netflix Company Netflix made two significant strategic moves that led to its success. The company did not explore all the available markets at once but in phases.
- Ford Motor Company’s Globalization Strategy This paper assesses Bangladesh and Rwanda as the two potential countries for Ford to globalize its operations. They are among the best fast-growing economies.
- Dell Business Model: Globalization & Corporate Strategy The Dell Computer company research and development department is mandated with the task of advising the company on the nature of products it should manufacture.
- Globalization as a Phenomenon and Its Impacts Globalization is a phenomenon, which has been made possible due to the development of communication technologies and multifaceted relationships among countries.
- Pros and Cons of Globalization The advantages of globalization outweigh the disadvantages. The concept has enhanced the rapid developments of impoverished nations.
- Regional Integration Inconsistency with Globalization With the term of Globalization being in vogue and regional integration agreements being signed across the globe, the coalition of the concepts has been questioned.
- Globalization and Cultural Hybridization Globalization affects all spheres of human activity starting from education, policy, management, and ending with art, culture, etc.
- Importance of Globalization on International Business Globalization is very important in that it promotes worldwide growth as well as promotes peaceful coexistence globally through understanding.
- Ways of Eating Around the World: Impact of Globalization Globalization is essentially to blame for the rapid rise in obesity and foodborne illness resulting from improved access to a diverse range of healthy foods.
- Impact of Globalization on Australia Globalization has enhanced the quality of life in Australia due to the fact that foreign investors are allowed to open up ventures in the country.
- Globalization’s Role for Developing Countries: Zambia In this paper, the results of globalization and its positive and negative consequences are discussed through the case of Zambia and the condition of its economy.
- Globalization and Human Resource Policies and Practices The current paper aims to discuss the concept of globalizing HR policies and the potential positive and negative outcomes of this process.
- How Globalization Affects Governance? The process of globalization inevitably affects governance all over the world. In this paper, the peculiarities of the process of affecting governance by globalization will be addressed in detail.
- Coca – Cola: Business Strategy and Globalization The presence of the globalization phenomenon in the Company’s strategy can be proven by its effective presence in more then two hundred countries around the world.
- Peru – Globalization, Environment, Crime and Disease The paper synthesizes a number of legitimate sources to focus on globalization and its effects on Peru with special relation to environmental issues, crime, and diseases.
- Globalization Affecting the Role of Leaders in Organizations Globalization is influencing leadership because of the way it affects society through its processes. It has caused changes in the political, social, and economical aspects.
- Why Youth and Community Workers Should Understand Globalization?
- What Has Been the Effect of Globalization on Terrorism?
- Who Are the Main Losers in the Process of Globalization?
- Why Is Customer Service Needed in the Globalization of Logistics?
- Why Resisting Globalization Can Be Reasonable?
- Why Are the Critics So Convinced That Globalization Is Bad for the Poor?
- What Would Our Nation Do Without Globalization and International Trade?
- What Are the Costs and Benefits of Globalization?
- Why Globalization Manufacturing Since the 1980s Has Changed Labor Relations?
- Why Did General Motors fail to Compete With Globalization?
- What Are the Challenges of International Development in the Age of Globalization?
- What Impact Does Globalization Have On E-commerce?
- Does Globalization Benefit Both Developed and Developing Countries?
- What the Public Should Know About Globalization and the World Trade Organization?
- What Are the Positive and Negative Effects of Globalization?
- Why Did Germany’s Hidden Champions Succeed in Globalization?
- Who Benefits From Globalization of Labor?
- Does Economic Globalization Affect Interstate Military?
- What Does the Globalization of Drug Trade Benefit?
- Why Does Globalization Generate Winners and Losers?
- The Impact of Racism on Globalization Racism is a great impediment to globalization, the bad blood between the said people of color and those of no color has dealt a big blow to development.
- Globalization: More Positive Effects Than Negative Ones Globalization refers to the “increasing interconnectedness of people and places through the converging process of economic, political and cultural change.”
- Social Media Impact on Globalization Among the many drivers of globalization, the advancement of digital social media platforms has been one of the most influential.
- Globalization of Video Games and Its Influence in the Society The research paper describes the positive impact of gaming, such as reducing flashbacks from posttraumatic stress defects and chronic pain reduction.
- Globalization Influence on Product Development This essay presents a critical analysis of the marketing strategies as they apply to the international marketing efforts of firms in the context of globalization.
- Ethics and Globalization in Business A business will only manage to keep up its reputation if it recognizes the established business ethics in its environment. Every firm must follow to the letter the code of conduct.
- Globalization of the SK-II Brand SK-II Brand has been said to concentrate on its core business through innovation, expanding penetration in developing countries and restructuring its existing business.
- Globalization and Health A planned urban society has access to safe and clean drinking water with appropriate sanitation and waste removal mechanisms.
- “The Globalization of Markets” by Theodore Levitt In his article “The Globalization of Markets,” Theodore Levitt anticipated the effects of globalization and advancement in technology to international business.
- Economic Globalization and Daily Life The stated factors belong to the concept of economic globalization, which implies the process through which states and corporations expand to the global scale.
- Relationship Between Urbanization, Globalization, and People The relationship between urbanization, globalization, and people is one of the most interesting and provocative topics in many discussions.
- Globalization and Its Ethical Implications The paper states that the negative implications of globalization result in ethical dilemmas as people with diverse backgrounds participate in world development.
- Globalization in Modern Business Along with the development of technology, communication, and transportation, it becomes easier for companies to expand the scope of their operations and enter new markets.
- Total Quality Management: Impact of Globalization on Quality There are several ways to ensure that information technology (IT) has been implemented into a business process with respects to Total Quality Management (TQM).
- Outsourcing and Globalization as Driving Force The major driving forces behind outsourcing include the force of globalization, cost of production, labor issues, and the problem of unionization.
- Bauman’s Concept of Globalization in Understanding the Rise in Human Displacement This paper discusses the concept of globalization as viewed by Bauman, assesses the concept of increasing numbers of refugees, asylum seekers, and economic migrants in the world.
- International Marketing – Impact of Globalization This paper seeks to identify the impact of globalization in international business and how companies can fully utilize the concept in order to attain their objectives
- Globalization and Cultural Diversity in the Workplace Cultural diversity should be incorporated into the company’s policies combined with teaching workers this fundamental issue in the business environment.
- Globalization and National Security Issues International security researchers have taken side of the big debate, with some arguing that globalization has indeed contributed to national and international security.
- Globalization and the Social Interest of Workers The paper sets out to demonstrate that globalization is not in the social interest of low-wage workers in developing nations and factory workers in the developed countries.
- John Deere Company in View of Globalization John Deere is one of the most successful agricultural machinery companies in the world today. In 1963, the company became the world’s largest manufacturer.
- The Impact of Globalization Discussing globalization objectively in its entirety is a challenging endeavor, since it touches upon almost every aspect of the modern world, and its influences differ from one region to the other.
- Netflix’s Globalization in Brazil The modern world has become more connected due to globalization and multinational dependence on areas that support socioeconomic development.
- Reflection of “Globalization of Missions” Article The “Globalization of Missions: An Exegesis on the Great Commission” article is the author’s call for making proselytizing more aware of non-Western cultures.
- Globalization in a Global Economy World economies and societies have come together to work as a global economy by having common means of transportation, communication, and marketing.
- The Globalization of Walmart Back in the 1990s, Walmart planned to conquer nations with large populations and growing purchasing power: Mexico, Argentina, and Brazil, and China.
- Globalization Theories in the Business Environment The paper elaborates on the neo-classical, Marxist and structuralist perspectives on globalization before closing with the most concurrent theorem out of the three perspectives.
- The Impact of Globalization on Immigration Control Globalization is one of the key factors that influence immigration. The effects are extensive to the extent of complicating the efforts of controlling immigration.
- Globalization Essence by M. Steger and N. Bisley Globalization: A very short introduction by Manfred Steger and Rethinking globalization by Nick Bisley define the necessity to treat the globalization and consider its complexity.
- “The Globalization of Eating Disorders” by Susan Bordo This paper analyzes the text of an article written in 2002 by Susan Bordo, an American professor, and philosopher, whose works are marked by several prestigious awards.
- Air Transport and Its Benefits for Globalization With excellent transportation systems, the world is exposed to better trading in terms of exports and imports of goods and services.
- Globalization and Democratization Relationship This paper explores the existing relationship between democracy and globalization. It focuses on democratization, globalization and their imperativeness.
- Globalization Impact on Trade and Employment One of the notable effects of globalization is heightened trade liberalization and opening up of global labor markets.
- Globalization: Managing Across Cultures Managing across culture is a product of globalization, that expatriate from a foreign culture moves to a totally new culture and is required to manage people from diverse cultures and backgrounds.
- Evaluation of the Meaning and Impact of Globalization in Relation to Criminal Justice The globalization process has a significant impact on criminal justice. Globalization has led to increased interdependence among various economies.
- Globalization and Education – Economic, Political and Cultural Dimensions The surge in Information technology usage, increasing interest in the Internet, and global communication have melted the country’s borders in terms of education availability.
- Motivation and Globalization in Multinational Companies Motivation in the case of globalization becomes a burning issue of multinational companies as they should establish the most appropriate way to motivate their employees.
- Leadership in the Context of Globalization This paper aims to outline the issue of leadership in the context of globalization, conduct a GAP analysis, offer recommendations for developing necessary leadership competencies.
- Qualitative Threshold: Globalization and Communication Technologies Globalization is a long-term phenomenon involving a gradual change of events. This process has occurred in distinct phases with each having unique characteristics.
- Globalization’s Role in Improving Women’s Rights On the one hand, globalization unites people and makes them follow the same standards or use similar opportunities.
- Modern Imperialism and Economic Globalization This paper discusses how does the study of modern imperialism help us to understand why some former colonies fear economic globalization today.
- Globalization’s Impact on International Marketing Strategies International marketing strategies are influenced by globalization. The operations of multinational firms are shaped by the confrontation between standardization and adaptation.
- Globalization and Technology Impacts on Ethics The evaluation will center on analyzing how technology and globalization have contributed to the spread of poverty in third-world nations, violated individuals’ rights to privacy.
- Globalization, Its Defenders and Critics Globalization is an ambiguous process with its advantages and disadvantages. It is impossible without significant changes in the ordinary life of people.
- Human Resources Management and How It Is Affected by Globalization and Technology? HRM functions have been widely affected by the changing trends around the world: various parts of the world are integrating, newer technologies and better concepts are evolving.
- International Organizations Role in Globalization Process The representatives of international organizations have a common agenda: turning the world into a “global village” and prompting the world’s population to think of neoLiberalism.
- Issues in the International Politics: Globalization Globalization in the international political system is considered to be centralized due to its impact on external links and close connection with political structures and mechanisms
- China’s Aviation Industry: Impact of Globalization This paper investigates the impact of globalization on China’s aviation industry. The report covers a wide range of topics, including history, global treaties, and critical forces.
- The Social Media Impact on Globalization This paper explains the impact of media on globalization and how it has affected businesses. Many people are currently using social media to run business organizations.
- Geographical Conditions’ Affect of Globalization The scholars of the 20th century conceptualized this idea, by creating the North-South divide – a geographic line between the countries that signifies the division on wealthy and emerging nations
- Globalization Effect on Small and Medium Size Business This section will introduce the paper based on the concept that globalization and development of SMEs may not be separated from each other.
- Globalization and Christian Mission Globalization has changed the landscape of industrial and business environments, and religion was inevitably affected by it, as well.
- Globalization Negative Effects on Canadian Labour Union Globalization is directly and indirectly affected labor unions in Canada. Positive effect was in form of developing the country’s economy and creating job opportunities to Canadian citizens.
- Impact of New Technologies and Globalization on Literature The issue of globalization’s effect on the development of different countries has always been rather controversial.
- Globalization and Knowledge Management This paper outlines the knowledge management in the context of globalization and using personal experience with virtual learning.
- Globalization’s Impact on Education Globalization will likely diversify educational opportunities while diminishing the competitive advantages of weaker educational systems.
- Interconnection of Globalization and Culture Despite serious issues, globalization has encouraged the funding of various initiatives in contemporary acts, contributing to the development of the market.
- Globalization: Impact on Modern Society Globalization contributes to establishing relationships between individuals, independent social objects, and phenomena, embracing all spheres of people’s lives.
- History of Globalization and World Integration The process of globalization is often viewed as an exclusively modern phenomenon that has arisen due to the development of multinational corporations.
- Process of Globalization and Nationalist Movements The transition between globalism and nationalism is frequently perceived as a threat to the government and its people.
- International Finance and Globalization The monetary authorities of a country can use monetary tools to keep the value of their currencies lower than the value which would have been set by the market forces.
- The Dark Side of Globalization Buoyancy on the Bayou: Shrimpers Face the Rising Tide of Globalization by Jill Ann Harrison explores the effect of globalization on local worlds.
- Leadership and Globalization in the US and Japan Leadership is a social influence in which a person can motivate or influence others and acquire their support in order to work together and accomplish a certain task.
- Globalization and Indigenous Communities in Canada In Canada, indigenous people feel both the austerities of environmental and cultural destruction and the potential for development.
- The Fourth Industrial Revolution and Globalization The fourth industrial revolution has made it possible for countries and manufacturing companies to produce and stabilize their economies.
- Globalization and Geographic Information System Globalization is the process by which the globe becomes increasingly interconnected due to the exchange of commodities and services, information, knowledge, and cultural values.
- Food and Water Security as Globalization Issues Globalization has several implications for the business environment, among which are the expanded access to resources, and the interdependence of international companies.
- Globalization: Arguments For and Against The process of globalization continues today, and arguments both in support and against this phenomenon are expressed regularly.
- Geographical Diversification and Globalization With current terms of business operations between countries, it has been possible for businesses to diversify their market by venturing into other local and international markets.
- Globalization in Anthropological Perspective The anthropological perspective is a powerful model that guides scholars to analyze human diversity and empower individuals from different backgrounds.
- How Residents of Georgia Understand and React to Globalization In the case of the state of Georgia, the understanding and reaction to globalization focus on economic integration and social well-being.
- Capitalism, Climate Change, and Globalization Globalization allowed significant corporations to put a substantial strain on the environment in developing countries.
- The Positive and Negative Aspects of Globalization Globalization is the result of many socio-economic processes associated with the widespread use of information technology and new means of communication.
- Chinese Companies and Globalization Issues People are the driving force of a company; to unleash that force, the patrimonial approach should be changed to more liberal and liberating methods.
- “Globalization, Lifelong Learning and the Learning Society: Sociological Perspectives: 2” by Peter Jarvis The book by Peter Jarvis “Globalization, Lifelong Learning and the Learning Society: Sociological Perspectives: 2” is a research book with an overall perspective on the value of education.
- The Impact of Globalization on Labor Market and Trade Globalization is the process that refers to the coming together of the international markets. This report examines the impacts of globalization on trade and employment.
- Hard Rock Café: E-Commerce and Globalization Hard Rock Café can utilize ICT and e-commerce models by hiring customer care executives working from home and submitting their work loads to the café’s head quarters.
- Spiritual Perspectives on Globalization by Ira Rifkin Cultural element of globalization describes regional side and national cultural peculiarities which are seen by the world society.
- The Globalization Index and Singapore as the Leading State This paper discusses the Globalization Index and what challenges the United States or any other developed country would face if it attempted to replace Singapore in the top spot.
- Netflix: Globalization and Information Research In a three-stage expansion process, Netflix could make strategic decisions and establish effective policies in those markets
- Effects of Colonialism and Globalization During the era of colonialism, colonies were perceived to be a major source of raw materials for the industries of the developed nations.
- Project Management Analysis and Globalization Technological supply chain management strategies and the development of dependable distribution systems in globalization are crucial components.
- Globalization and Health Systems in India This research paper examines the effects of globalization on India’s healthcare system. It explores various areas such as healthcare delivery, acquisition, financing, and ethics.
- Cultural Globalization as the Americanization of the World’s Cultures Americanization as a significant part of globalization may still be possible major industries vow it as a source of financial rewards.
- Tangible & Inevitable: Globalization as a Worldwide Phenomenon Globalization may be defined as the process of integration and interaction among countries worldwide and the growing interdependence of their economies, populations, and cultures.
- Globalization and Immigration: Globalization Policies Leaders and citizens in such nations feel threatened by the influx of both legal and illegal immigrants into their nations.
- Market Globalization and Global Marketing Pitfalls Customization is fraught with several outcomes that may inhibit the further advancement of a company in the global economy.
- Supply Chain Management in Globalization Era In the accelerating process of globalization, supply chain management is an integral part of most organizations which is essential to a company’s success.
- Globalization Concept and Its Impact on the State Globalization does not make the state redundant. On the contrary, it makes it important for the full exploitation of the opportunities that come as a result of international integration.
- Ethics in Reporting: Globalization and Media Ethics in reporting tends to distance itself from the manipulation of the media, which advocates for a well-organized and political dichotomization in media reportage.
- Identity Politics as a Response to Globalization Despite numerous positive outcomes that it promises, the concept of globalization as the basis for multicultural communication and learning is not fully devoid of certain issues.
- Religion, Globalization, and Language in China This research paper examines the problems of religion, globalization, and language from the Chinese perspective.
- Globalization and Use of Fossil Fuel as Environmental Threats Both the process of globalization and the burning of fossil fuels have been significant contributors to the deterioration of the environment’s health on a worldwide scale.
- Reshaping Globalization and Digital Media Over the decades, distinctive events and activities have contributed to the construction of the current global spectrum.
- Education Under Impact of Globalization The negative impact of globalization was the widening gap in access to education. Globalization has made English the main language of education, which can lead to discrimination.
- Globalization and Technological Development Technological development continues to facilitate globalization, with individuals from third-world countries coming to the forefront of the modern workforce.
- The Globalization Impact on Cultural Production Human culture is evolving in the context of globalization, as many states are no longer in colonial relationships. It leads to global hegemony and diminishing diversity.
- Addressing Global Inequality in the Era of Globalization While globalization has led to social, political, and economic increase, it has also given rise to global inequality, particularly through the exploitation of developing countries.
- Globalization: Impact on International Business With higher levels of globalization, the overall international business will be safer as there will be more suppliers and manufacturers on the market.
- Response to Globalization Pressure This paper aims to introduce a plan of action to ensure my continued employability as a professional in the sphere of international affairs.
- Globalization and its Impact on the World A phenomenon that gathered speed after World War II, globalization has tremendously impacted the international economy, society, and culture by enabling greater interconnectedness and cross-border exchange of people and ideas. Globalization is a complex phenomenon that has benefited developed countries economically while unfairly distributing wealth to underdeveloped nations and disenfranchising…
- The Globalization Impact on the US Foreign Policy The ability of the US to use its influence to alter international events is limited by globalization. America cannot deal with the issues brought on by globalization on its own.
- Globalization Challenges in Developing Countries and Japan The participation of nations in global trade has several benefits, even though various problems impede countries from accessing global markets.
- Globalization and Democratic Peace Theory In the context of globalization, it is necessary to consider the theory of democratic peace, which recognizes democracy as the best form of government for society.
- Globalization: Climate Crisis and Capitalist Ideology One of the main features of the development of the world community in recent decades has been globalization as part of integration processes that are changing the world structure.
- Globalization and Its Pros and Cons It is hard to disagree that there is probably nothing universally positive or negative in this world. Everything has a price.
- The Phenomenon of Terrorism and Its Relation to Globalization This paper states that the phenomenon of terrorism is tightly connected to the concept of inequality of globalization.
- Globalization and Its Scale in the World Regardless of all opportunities provided by technological progress, the world remains less globalized than the majority of people expect.
- Globalization and Poverty: Trade Openness and Poverty Reduction in Nigeria Globalization can be defined as the process of interdependence on the global culture, economy, and population. It is brought about by cross-border trade.
- The Impact of Globalization on Business in India and the USA Since globalization started to affect the economy of the USA and India, it has had various positive and negative impacts on business.
- Impact of Progressive Globalization One of the key processes in the development of the world economy on the verge of the XX-XXI centuries is the progressive globalization.
- Globalization After World War I The emergence of the global economy corresponds to the aftermath of World War I, and the battle of governments and markets for control over the field brought unexpected results.
- Researching the Concept of Globalization The paper aims to analyze the global playing field and support it with arguments why it is considered to be level.
- Globalization: Beauty Sculpt for You Today society is filled with the obsession with promoting a self-image of beauty and perfection. Individuals take extreme measures to reach the goal of a flawless body.
- Ethnic Violence in the Era of Economic Globalization Economic globalization refers to the interdependence of the world’s financial giants due to increased technology and trade across the borders.
- Globalization Impact on Socioeconomic Inequality This paper analyzes the link between globalization and socioeconomic inequality, and how the inequality problem can be mitigated.
- Solving Problems Through Globalization The paper discusses the importance of uniting to create a global world. Globalization makes it easier to solve universal challenges that affect populations.
- Globalization and Personal Identity Intersection The conditions dictated by globalization actualize the problem of cultural uniqueness and cultural self-determination, including identity.
- Negative Sentiments Against Trade and Globalization Although the authors’ views are robust and applicable to developed economies, rising negative sentiments against trade and globalization remain relevant in developing countries.
- Anthropocene and Its Role in Globalization The role of the Anthropocene in globalization can hardly be overestimated since, due to human activities, the world is becoming more and more interconnected.
- Globalization Opportunities and Challenges for Companies
- Globalization Strategies for Multinational Enterprises
- Human Sense of Place in the Context of Globalization
- American Dominant Minority Relations and Impact of Globalization
- Hip Hop’s Globalization and Influence of Hip-Hop Music in Japan
- The Effects of Globalization on the Environment
- The Food and Drug Administration (FDA) and Globalization
- Wireless Industry and Globalization for US Economy
- Global Poverty and Economic Globalization Relations
- “Globalization” by Peter Temin: Article Analysis
- Globalization Effect on Social Movements
- Globalization and Technology in Health Care
- Economics: The Impact of Globalization
- Globalization of Nursing: Infant Mortality Rate in the US and Other States
- Foreign Direct Investment: Globalization of Production
- Globalization: On the Importance of ICT & Transnational Corporations
- Economic Globalization and Labour Rights
- The Facets of Globalization in Internet Security
- Globalization and American Productivity
- Globalization and Economic Inequality
- Globalization and Competition: The USA, Western Europe, Japan
- Pop Culture as a Potent Globalization Tool
- The Financial Crisis and Its Connection With Globalization
- The Effects of Globalization on Trade
- Why Globalization Causes Turbulence and Disruption
- Globalization of Healthcare in the US and Haiti
- Globalization and Related Environmental Issues
- Globalization and the Formation of New Claims
- Overcoming CSR Challenges in the Age of Globalization
- Present Day Resistance Historical Roots to the Trade Globalization
- Energy Crisis: The Processes of Globalization and the Unification
- Long-Term Impacts of the Chinese-American Trade War and Globalization of the World Economy
- Free Trade as a Fundamental Principle of Modern Globalization
- Global Governance Institutions in Context of Globalization
- Leadership and Organizational Change: Diversity and Globalization
- Globalization and Career of University of East London’s Students
- Globalization: Impact and Consequences
- Role of Globalization in Asian Market
- Globalization and Its Effects on World Economies
- Economic Globalization: The Role of Geography
- Globalization and Transformative Process Drivers
- “The Globalization of American Law” by R. D. Kelemen and E. C. Sibbitt
- Education With Regard to Globalization Issues
- Whether Globalization Makes Consumer Powerless?
- World Is Flat: Globalization Effect
- Globalization and Its Impact on Firms
- Environment: Rapid Increasing in Industrialization and Globalization
- Ethics In The Business Globalization
- Contemporary Globalization Since 1914
- Asian Film Industry Globalization
- Survival of Minority Ethnic Groups in Globalization
- “Globalization, Poverty and Inequality” by Kaplinsky
- Globalization’s Impact on Banks in Canada
- Global Politics: Women’s Rights, Economy, Globalization
- TNCs Contribution to Globalization of Retail Industry
- Globalization and Cultural Difference of Societies
- Globalization, the Sex Trade and HIV-AIDS
- Media Production and Connections in Globalization
- International Economy. Oakley’s Globalization Theory
- China’s Impact on Globalization and International Security
- Three Areas of Concern for Committee on Globalization
- Moving Away From Globalization: Consequences
- Globalization and Russian Influence
- “The Globalization of Markets” Book by Levitt
- American Popular Culture and Globalization Effects
- Chapters 2 and 9 of “Sociology of Globalization” by Smith
- Human Rights, Globalization and Economic Development
- Globalization Influences Discussed in TED Talks
- Education History and Globalization
- Globalization and Its Consequences: Economic Crossroads
- Germany’ Sovereignty in the Age of Globalization
- Globalization vs. Traditions in Eastern Culture
- Globalization Effect on Developing Countries’ Business
- Impact of Globalization on Gender Norms and Experiences
- Globalization and Cultural Knowledge of China
- Millenium Development Goals and Globalization
- The Pitfalls of Globalization
- Aspects of Globalization: Positive and Negative Effects
- Globalization and Its Benefits for the United States
- Globalization and Businesses in New Economies
- The Effect of Globalization in Economic Development
- Evaluating the Effects: Advantages of Globalization
- Child Labor Role in Westernization and Globalization
- Singapore Globalization: Criterias and Ranks
- Globalization Impacts on the United Nations Institution
- Globalization and Citizenship in EU
Cite this post
- Chicago (N-B)
- Chicago (A-D)
StudyCorgi. (2021, September 9). 266 Globalization Essay Topics & Globalization Research Topics. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/globalization-essay-topics/
"266 Globalization Essay Topics & Globalization Research Topics." StudyCorgi , 9 Sept. 2021, studycorgi.com/ideas/globalization-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . (2021) '266 Globalization Essay Topics & Globalization Research Topics'. 9 September.
1. StudyCorgi . "266 Globalization Essay Topics & Globalization Research Topics." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/globalization-essay-topics/.
Bibliography
StudyCorgi . "266 Globalization Essay Topics & Globalization Research Topics." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/globalization-essay-topics/.
StudyCorgi . 2021. "266 Globalization Essay Topics & Globalization Research Topics." September 9, 2021. https://studycorgi.com/ideas/globalization-essay-topics/.
These essay examples and topics on Globalization were carefully selected by the StudyCorgi editorial team. They meet our highest standards in terms of grammar, punctuation, style, and fact accuracy. Please ensure you properly reference the materials if you’re using them to write your assignment.
This essay topic collection was updated on January 21, 2024 .

- Guide on Writing a Stellar Essay
- Tips on Writing an Effective Term Paper
Term Paper on Globalization
Globalization term paper:.
The concept of globalization is essential to understand the patterns of economic, political and cultural change in the contemporary world. Introduction Globalization is known as the name of the social, economic and political processes taking place in our world. During the last years, globalization has become an important subject for various popular and academic debates. Today the concept of globalization is implemented to describe different aspects of contemporary life. It includes such aspects as complexity of contemporary capitalism, the difficulties of the nation-state system and the increasing quantity of transnational corporations and organizations as well as essential competitiveness between global culture to local cultures, the rise of the communications revolution due to introducing of new technologies in the world (Szeman 2001). In other words, globalization is a concept that has both positive and negative sides of the contemporary existence. This paper discusses the concept of globalization and its perspective on the changing patterns of the economic, political and cultural life in the contemporary world. Additionally, it focuses special attention on the discourse of fordism, post fordism, post modernity and postcolonial theory as well as the development of the networked society in the time of globalization.
The concept of globalization and its development The concept of globalization appeared at the end of the 19th century and the beginning of the 20th century (1850 –1914) (Rourke and Williamson 1999, p. 5).
We can write a Custom Term Paper on Globalization for you!
At that time, the concept of globalization paid its main attention to the money aspect mainly characterized by the rise of international trade and the increasing flow of migrants. People have been migrating and travelling having different aims. For example, European migrants went the New World – America – in the hope to become rich, while Asian migrants showed their negative relation to America negatively as a colonial country. In addition, the intensive development of industry and the global industrial division of labour in America resulted in large female migration. (Sassen 1998, pp. 41-45)
Today many social theorists are stating that modern world characterized by rising globalization with the dominant economic system of world capitalism. It gives priority for transnational corporations and organizations in contrast to the nations, and destroys local traditions and cultures developing a global culture.
There is a great diversity of theorists’ views on the concept of globalization. Some of them believe that globalization may cause the Westernization of the world (Latouche 1996), but others (Ferguson 1992) consider that it entails the ascendancy of capitalism (Kellner). Some theorists state that globalization increases homogeneity, while others believe that it produces heterogeneity and diversity because of increased hybridization. For many theorists globalization and modernity are similar (e.g. Giddens 1990; Beck 1992), but others state that the “global age” and “modern age” are different (Albrow 1996) (Kellner).
In contrast, postmodernists support diversity, the local, difference, and heterogeneity, and sometimes they note that globalization itself produces multiplicity and hybridity. They argue that with the help of global culture special appropriations and developments are possible in the entire world. Globalization will create new types of hybrid syntheses of the global and the local, helping to widespread heterogeneity and difference. Postmodernists also argue that, “every local context involves its own appropriation and reworking of global products and signifiers, thus producing more variety and diversity” (Kellner).
In turn, Axtmann suggests that global citizenship and accordingly the impact of globalization could lead to a real acceptance of heterogeneity, diversity, and otherness contrasting with globalization that just promotes sameness and homogeneity (Kellner).
Globalization is able to produce new forms of imperialist domination in accordance with globality and universality. There is a danger that globalization just disguises a indefatigable Westernization, or Americanization, of the world. However, restoration of ethno-nationalism, tradition, religious fundamentalisms, and other types of resistance to globalization are active to certain degree by a deviation of the homogenization and probably Westernization connected with some globalization forms.
Coming back to Westernization, it is worth to note that globalization is frequently characterized by the rising dominance of western or American forms of economic, political, and cultural life (“westernization” or “Americanization”) (Westernisation). Westernization had a great and a pervasive influence on the world during the past decades. The collapse of imperialism and colonialism over the decades was noticed by the two World Wars of the 20th century, after which many smaller countries, which were created by former colonial authorities (primarily European), obtained independence and involved different aspects and features of Western culture and tradition. After a downfall of the former Soviet Union at the end of the 20th century, many of its component states became the subject for Westernization. It also included privatization of hitherto state-controlled industry.
Special attention must paid to the fordism and post fordism movement. Fordism is known as the system of mass production and consumption characteristic of highly developed economies and it existed in the 1940s-1960s. According to Fordism theory, the combination of mass consumption with mass production is necessary to achieve material advancement and economic growth. The period of 1970s-1990s is characterized by slower growth and rising inequality of income. At that time, the system of production and consumption organization has transformed. That was a second transformation – post fordism – which led to the second rise of economic growth. This new system is called the “flexible system of production” (FSP) or the “Japanese management system.” On the production side, the main features of FSP are high reductions in information expenditures and overheads, Total Quality Management (TQM), leaderless work groups and just-in-time inventory control (Fordism, Post-Fordism and the flexible system of production). On the consumption side, the main features of FSP are the globalization of consumer goods markets, quicker product life cycles, and far bigger product/market differentiation and segmentation (Fordism, Post-Fordism and the flexible system of production).
Along with process engineering, the second transformation is making transformations not only how we produce things, but also how we live and what we consume accordingly. It illustrates the decreasing essentiality of scale and scope and is made with the help of costs reductions in logistics, communications, and information processing – these reductions occur in result of the computers’ introduction and rising ability of people to use them. (Reschenthaler and Thompson 1996, pp. 125-144).
So, globalization must be illustrated as a difficult and multidimensional phenomenon that includes various levels, flows, and conflicts as well as its possible future.
A critical theory of globalization deals with the reality of globalization, its authority and influence. However, it also studies different forces of resistance and fight that try to resist to the most destructive sides of globalization or global forces.
For example, the constant issue of local and political fight with complex causes is race, ethnicity, class and nationalist problem. It is well-known that the period from the end of 1980s to the present time is characterized by a rise of traditionalism, nationalism, and religious fundamentalism along with increasing globalization.
It is also worth to admit that the resurgence of regional, cultural, and religious differences in the former USSR and Yugoslavia along with intensive tribal conflicts in Africa and in other places allows us to make a suggestion that globalization and homogenization were not so much connected and deep as it was considered by its supporters and critics. In result, culture has become a new source of conflict and an essential indicator of fight between the local and the global. National cultures caused many conflicts between Muslims, Serbs, and Croats, Azarbaijanis and Armenians, Mohawk First Nation peoples and Quebecois. In South Africa, these are the fight between the Umkatha tribe and the African National Congress.
The other important reason of resistance and struggle is the gender inequality and difference. At the level of policy, the influence of globalization on women and gender relations is still ignored on the national and international levels.
Due to gender inequalities and discrimination in many countries worldwide, globalization processes may render their negative influence on women in greater degree than on men.
Nevertheless, many advocates of women admit that globalization influences various groups of women differently. It even creates new treatment standards for women, and assists some groups of women to mobilize. Thus, the role of globalization for many women is still in debate and it is evidently different.
Consequently, globalization is very complex concept and it stimulates to occurrence of different theories, economical, political and cultural studies. There are a lot of reasons due to which globalization has been perceived as mainly an economic phenomenon that additionally has had an evident impact on political, social, and cultural life. Economic globalization means, that it is a long-run upward tendency. Thus, it will be useful to measure globalization. There is a lot of various indicators of economic globalization and they may or may not illustrate familiar patterns in regards to change over time. Trade globalization can be distinguished as the certain share of the production all over the world. Investment globalization would be the share of all world capital invested that belongs to non-nationals capital in the world that belongs to non-nationals (i.e. “foreigners”) (Chase-Dunn, Kawano and Nikitin). Also it is possible to investigate the degree of economic integration of countries by defining the extent to which national economic growth rates correspond to each other in the world countries.
From the economic point of view, globalization is connected with the transnationalization and deterritorialization of industry and capital, which has permitted companies to cross national borders and to travel over the world to succeed from cheaper labor and to open, develop and promote new markets for different services and goods. In addition, economic globalization has been connected with the occurrence of international free trade agreements as the General Agreement on Tariffs and Trades (GATT), and the foundation of an around-the-clock global financial market (Szeman 2001, p. 212).
Contemporary patterns of economic globalization have been much connected with a new development of the relationship between markets and states.
Together with financial integration, the operations of multinational corporations also played the important role. They integrated national and local economies into global and regional production networks. Due to such conditions, national economies are no longer autonomous systems of wealth creation since national boundaries no longer function as essential barriers to the organization of economic activity and its conduct (Held and McGrew).
As it was above-mentioned, the multinational corporation (further – MNCs) was significant to the establishment of a new global capitalist order. In 1999 their number accounted for more than 60,000 MNCs worldwide with 500,000 foreign subsidiaries, selling $9.5 trillion of services and goods globally (Held and McGrew). Modern transnational production essentially exceeds the level of global exports and has become the main means for exporting services and goods. According to some estimates, multinational corporations now make for at least 20 per cent of world production and 70 per cent of world trade (Held and McGrew).
Economic globalization has also been characterized by an evident internationalization of political power connected with a relevant globalization of political activity. Thus, it is worth to deal with the political meaning of globalization.
A special attention has been paid to the threats caused by globalization in regards of the sovereignty and power of nation-states and accordingly, on the occurrence of new sites of transnational politics placed in global cities, international organizations (such as NGOs and the United Nations) and transnational corporations (Szeman 2001, pp. 209-217).
At that time global cities were the spaces where labor, capital, infrastructure, and information are concentrated (Irvine 1999). From this point of view, globalization is considered to be a networked urbanization, a reconcentration of production, capital, and labor in cities as “the nodes of the networked economy” (Irvine 1999). It means that global cities are the nodes of cyberspace, the space of flows including the simultaneous concentration and decentralization of people, economic activity, communications, technical infrastructure, and information (Irvine 1999). From the point of the diffusion of cultural productions on the Net, cultural globalization follows the logic of urban concentration in the global information economy. In turn, cyberpace is a segmented and segregated space that is similar to global cities where IT infrastructure, firms, capital, labor, and services are concentrated, as it was already above mentioned.
Research of the politics of globalization consists of estimation of the growing militarization of global relations, the occurrence of new nationalisms and ethnic confrontations, and the intensive migrations of peoples across regions or even across the world. This process concerns essential problems on notions of cultural belonging and citizenship in almost all countries in the West (Szeman 2001).
The concept of globalization has also been researched in regards of the development of new communication technologies that are significant in destroying our world spatially. With the help of these global communication technologies, it has become possible to perceive our globe as a single space shared by all human beings. It does not only mean that with the help of computer and communication technologies we can instantaneously transmit and transfer information each other all over the world. It mainly means that by circulating of information, images and ideas, people (and especially global elites) around the globe can find similar cultural referents. The emergence of a “global culture,” has been possible only due to the invention of new technologies. Today people in different countries can see the same news events or TV-show programs. Now it is evidently clear for all interesting hybrid cultural forms of global culture that the global distribution of cultural forms and ideas hardly equal. Many cultural critics in globalization has focused their special interest on the influence of the global distribution of a capitalist culture “anchored in the United States” and on its evident threat to the continued existence of local traditions and cultures (Szeman 2001). Probably, it is just here the study of globalization and postcolonial studies is most clearly imposed. The relationship between globalization and the specific issues of postcolonial studies is too difficult and complex. This can be partially explained by distinctions in emphasis and that these two concepts have the disciplinary origins. In usual, globalization is still a term used mainly in the social sciences, where it is employed to depict contemporary Western experience, but postcolonial studies are introduced in the humanities and pay their main attention on the practices and experiences of non-Western countries, especially in the case if they are related to Western economic, cultural and political priority.
The primary issues of postcolonial studies have been determined in accordance with the complex consequences of 19th and 20th-centuries – imperialism and colonialism. Along with the fact that globalization is originated from the European ideas of colonialism and imperialism, it defines some contemporary transformations that have directly changed some of the strong concepts of postcolonial studies, such as identity, place, the nation, and ways of the resistance connected to these concepts.
In the 20th-century, the current implementation of the term globalization is used according to Marshall McLuhan’s vision of a “global village” made by the world-wide spread of communication technologies, and in “world-systems theory” of Immanuel Wallerstein (Szeman 2001). The central point of Wallerstein’s theory, as first developed in The Modern World System (1974) is that the world economic system has been only capitalist one from its first occurrence in the 16th century. The postcolonial studies revealed a big insistence on the cultural changes of colonialism and imperialism. Postcolonial criticism has asserted that must be noticed as a basis to creation, production and maintenance of colonial relationship.
From this vision, and particularly due to the diffusion of a global mass culture, globalization may be perceived as “the continuation and strengthening of Western imperialist relations in the period after decolonization and postcolonial nationalist movements” (Szeman 2001).
Conclusion A critical theory of globalization determines the interdependencies and interconnections between various levels such as the political, economic, psychological and cultural as well as between various flows of people, products, ideas, information and technology. The speed of globalization development with its space-time compression, its instant financial transactions, its simultaneous forms of mass communication, and a highly incorporated world market is certainly a novelty in our world. New technologies make significant changes in the nature of work and create new leisure forms. The hyperreality of cyberspace, new virtual realities, and new information and entertainment modes are the other main characteristic features of globalization.
Present-day globalization explains the matrix of global and local forces as well as of forces of resistance and domination, of a condition of quick change and a “great transformation” caused by the global restructuring of capital and multivariate effects of new technologies. Therefore, globalization is evidently a force of homogenization. The influence of globalization much depends from a position of country in global political, economic and military hierarchies as well as from its domestic political and economic structures, the institutional pattern of inner politics of the state, certain government and societal strategies for contesting, ameliorating and managing imperatives of globalization (Held and McGrew). The future will show what visions, perspectives and concepts best characterize globalization in present.

Related Posts:
- Political Concept of State Essay
- Postmodernism Term Paper
- Domestic Migration Essay
- Liberal Democracy Term Paper
- Health Care Delivery System Term Paper
Leave a Reply Cancel Reply
Current ye@r *
Leave this field empty
Below you have a great opportunity to hire a professional term paper writer for getting custom writing help now:

- Term papers
- Uncategorized
As globalization unwinds, the world is still growing more unequal

You’re reading an excerpt from the Today’s WorldView newsletter. Sign up to get the rest free , including news from around the globe and interesting ideas and opinions to know, sent to your inbox every weekday.
A year ago, White House national security adviser Jake Sullivan announced the advent of a new “Washington consensus.” The speech he delivered at a think tank then was something of a bombshell in the foreign policy community — a declaration by a senior U.S. official that the world’s leading superpower wanted to move on from decades of economic orthodoxy and unfettered globalization to a different arrangement between nations and their societies.
The old “Washington consensus” was shorthand for a set of neoliberal policies and prescriptions put forward in the last decades of the 20th century by the International Monetary Fund and the World Bank, its sister organization. The diktats of these Washington-based institutions — mandating austerity, deregulation and privatization — prefigured a wave of globalization that crested into the 21st century. They undergirded a sense of the world bound together by commerce and trade, and lifted up by a shared prosperity, that became a kind of dogma for political elites in the West and elsewhere.
Such convictions are no longer commonly held. In the West, political leaders now speak of globalization in pejorative terms — a legacy of economic policy that made some rich while weakening the middle classes of their own societies, where manufacturing jobs dried up, wages stagnated and life grew more precarious. Sullivan pointed to the Biden administration’s embrace of industrial policy and major stimulus spending as a major paradigm shift — and a key cog in the United States' plans to compete with China in the decades to come.
The world was not “flat,” Sullivan seemed to argue, but bumpy. And it was up to governments and alliances of like-minded states to smooth out the disturbances and disruptions caused by shocks such as the pandemic, the ambitions of rising great powers like China and wars that snarl global supply chains. Move over, laissez faire capitalism — welcome back, mercantilism and protectionism.
Even as the contours of the new orthodoxy are still taking shape, some underlying global realities remain the same — perhaps, even more pronounced. As the IMF and World Bank staged their annual meetings this week in Washington, officials and economists put forward somewhat gloomy prognostications. The IMF projected annual global growth at levels still below what took place before the pandemic, and warned of longer-term troubles ahead.
“Rising geopolitical risks, including signs of a global trading system dividing into separate blocs oriented around the United States and China, are also troubling fund officials,” my colleague David Lynch reported . “If that split widens, nations could suffer ‘large output losses’ as goods and capital move around the world less efficiently, the fund warned in its flagship World Economic Outlook.”
This sluggishness has major ramifications for the West’s graying societies, but it’s all the more concerning for poorer nations in the developing world. The ambitious programs of stimulus and subsidies put forward by the United States and the European Union may cut against investment and opportunities elsewhere. “Poorer and less-developed countries could be deprived of the benefits of globalization as the major economies turn inward and as trade and financial flows fragment and fall in line with deepening geopolitical fissures,” Eswar Prasad, an international trade expert at Cornell University, told Bloomberg News .
Many countries, especially in sub-Saharan Africa and Latin America, are also buckling under crippling public debt burdens and struggling to chart a way out. “With growth being slow, the chances to catch up are actually worsened,” IMF managing director Kristalina Georgieva said earlier this year. “You have countries that are truly facing life or death, economic, social difficulties.”
To some in the Global South, institutions like the IMF and World Bank remain part of the problem . A new analysis by Oxfam found that “income inequality is high or increasing” in 60 percent of low- and middle-income countries that receive grants or loans from the IMF and World Bank. That’s in part due to enforced cuts in public spending that impact the lives of ordinary citizens in these countries.
Grieve Chelwa , a Zambian economist based in the United Arab Emirates, pointed to his country’s recent experience, where IMF mandates have hobbled social spending, contributed to a rise in food prices and exacerbated a cost of living crisis. “IMF-enforced austerity,” he told me, may “lead to another lost generation for Zambia and Zambians.”
“More than ever, the U.S. and other rich nations must wake up the reality that that these institutions, as they function, have not only outlived their usefulness, but fallen into a destructive obsolescence,” said Ndongo Samba Sylla, a Senegalese development economist, speaking at an event hosted by Oxfam in Washington this week.
While Americans and citizens of other wealthy nations face their own economic headwinds, people in poorer countries find themselves trapped in situations where their governments sometimes have their hands tied. The strength of the U.S. dollar and the whims of foreign credit ratings agencies have as much impact on their lives as the policies of their own states.
In the more competitive era hailed by Sullivan, Western governments appear to be reducing their development assistance to poorer nations , at ruinous cost. Mohamed Nasheed, former president of the Maldives and the head of a bloc of nations known as Climate Vulnerable Forum, which represents some of the nations most threatened by the effects of global warming, said that the 68 economies in this bloc lost more than half a trillion dollars in wealth over the past two decades thanks to climate change, though they contributed only about 4 percent of global greenhouse gas emissions.
But many of these countries find themselves grappling with high levels of external sovereign debt, and the obligation to service these debts to lenders like the IMF “are crowding out the ability of governments to make the investments required to achieve their climate change and development goals,” Nasheed told me.
The leaders of the IMF and World Bank are keen that their institutions — which emerged at a time when much of the world was still the province of fading European empires — evolve for the needs of the 21st century. Western officials are also trying to address widening inequalities both within countries and between them. In Washington, the finance ministers of France and Brazil jointly revealed plans to crack down on tax avoidance by the wealthy. These proposals may pick up steam in the coming months as Brazil takes charge of this year’s meetings involving the Group of 20 major economies.
But to many in the Global South, the “new” Washington consensus still registers as the old one. “That advanced economies are now openly pursuing industrial strategy is a shift — yet the same international financial institutions that rich countries dominate are still prescribing a heavy dose of the Washington Consensus to developing countries,” Adriana Abdenur, a policy adviser at the office of Brazilian President Luiz Inácio Lula da Silva, said at the Oxfam event, while speaking in a personal capacity. “The system is fueling inequality rather than fighting it.”

- Undergraduate
- High School
- Architecture
- American History
- Asian History
- Antique Literature
- American Literature
- Asian Literature
- Classic English Literature
- World Literature
- Creative Writing
- Linguistics
- Criminal Justice
- Legal Issues
- Anthropology
- Archaeology
- Political Science
- World Affairs
- African-American Studies
- East European Studies
- Latin-American Studies
- Native-American Studies
- West European Studies
- Family and Consumer Science
- Social Issues
- Women and Gender Studies
- Social Work
- Natural Sciences
- Pharmacology
- Earth science
- Agriculture
- Agricultural Studies
- Computer Science
- IT Management
- Mathematics
- Investments
- Engineering and Technology
- Engineering
- Aeronautics
- Medicine and Health
- Alternative Medicine
- Communications and Media
- Advertising
- Communication Strategies
- Public Relations
- Educational Theories
- Teacher's Career
- Chicago/Turabian
- Company Analysis
- Education Theories
- Shakespeare
- Canadian Studies
- Food Safety
- Relation of Global Warming and Extreme Weather Condition
- Movie Review
Admission Essay
- Annotated Bibliography
- Application Essay
- Article Critique
- Article Review
- Article Writing
- Book Review
- Business Plan
- Business Proposal
- Capstone Project
- Cover Letter
- Creative Essay
- Dissertation
- Dissertation - Abstract
- Dissertation - Conclusion
- Dissertation - Discussion
- Dissertation - Hypothesis
- Dissertation - Introduction
- Dissertation - Literature
- Dissertation - Methodology
- Dissertation - Results
- GCSE Coursework
- Grant Proposal
- Marketing Plan
- Multiple Choice Quiz
- Personal Statement
- Power Point Presentation
- Power Point Presentation With Speaker Notes
- Questionnaire
- Reaction Paper
- Research Paper
- Research Proposal
- SWOT analysis
- Thesis Paper
- Online Quiz
- Literature Review
- Movie Analysis
- Statistics problem
- Math Problem
- All papers examples
- How It Works
- Money Back Policy
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- We Are Hiring
Globalization, Term Paper Example
Pages: 4
Words: 1109
Hire a Writer for Custom Term Paper
Use 10% Off Discount: "custom10" in 1 Click 👇
You are free to use it as an inspiration or a source for your own work.
“Social change is now proceeding so rapidly that if a social scientist had proposed as recent as 15 years ago to write a book about globalization they would have had to overcome a wall of stony and bemused comprehension.”(Globalization, 2001) Although the word ‘global’ is over 400 years old,the common usage of such words as ‘globalization’, ‘globalize’ and ‘globalizing’ didn`t begin until the early 1960 th . The definition of globalization has changed with the years including more and more specific features, starting from the general dictionaries and ending up with the WWW, where more than two or three hundred definitions from more than 101 thousand websites can be found. “Globalization is a process of interacting and integration among the people, companies, and governments of different nations, a process driven by international trade and investment and aided by information technology.”(Globalization, 2008)
The discussion of economic aspectalong with multidimensional set of social processes is one of the significant parts of any integral account of globalization. In fact, the transformative powers of globalization affect deeply the economic, political, cultural, technological, and ecological dimensions of contemporary social life.
The economic sense of globalization can be studied on the example of multinational companies and brands which influence all aspects of our lives. It is a common knowledge that the process itself refers to all of the competitors, who are involved, and today the global trade seems to widen greatly as the pragmatic calculations broaden the national economies.
As far as I`m concerned, Wal-Mart is one the most competitive and intense partakersall over the world. Launched on July 2, 1962 as the Discount city store, Wal-Mart sky rocked up to over two million employees, more than 6200 stores and the record $408.21 revenue. Figures are phenomenal, so is the influence Wal-Mart has on the whole economy of the United States. The “Save Money Live Better” slogan is of extreme benefit to the customer, but when it comes to the vendors, they always face extreme challenge when operating with the giant. Over the years Wal-Mart has become so powerful that there is hardly any supplier, who didn`t think of mutually beneficial cooperation. There are lots of examples when it had become a desperate need and the only redemption for the companies to sign up a contract even if it was far from what they were expecting. Companies just have to obey the rules set up by Wal-Mart, if not the shelves of the supermarket will be used in another way. In my opinion the passage is a bright example of how the ‘globalization’ influences the development modern business. Wal-Mart has reached a point when it makes own rules, outsources the manufacturers, implements environmental measures, makes companies change their policies and for sure the vast boost of the ‘global’ business development.
Having the economic backbone ‘globalization’ meets no borders and eventually moves to the most economically profitable places. I was taken aback by the article about the Galesbourg Maytag plant closure and the fact that from the economic point of view it was an unavoidable measure. Companies like Maytag outsource the production out of country and from the first view the case of the Galesbourg Maytag plant is local in its size,however over 2.7 manufacturing jobs are lost for last decade. Shifts out of the country benefit Mexico and China and as a result the record $600 billion trade deficit and as a consequence the fallen value of dollar is definitely to be considered as a drawback. Despite the fact that the union made an effort to increase productivity and the Maytag was still profitable, the position has dropped. The laid-off workers have to make both ends meet by working as a welder or compete with their kids for Wal-Mart jobs for example. Overall, the article depicts us the severe truth of today`s business realities.
Medical tourism is nothing new and it is likely for the most sophisticated folks to visit specific professionals from another country or their choice depends on the unique specialties the place offers. But when talking about the medical tourism to Bangkok or New Dehli, personally I find it absolutely amusing. The medical system of the United States is doubtless cutting edge and for sure if it was the question of service most of the Americans wouldn`t even try to find alternatives, but when it comes to the actual price, the situation changes a lot. It turns out that some people would rather fly thousands of miles away to spend less money for the surgeries that couldn`t afford here in the United States. For most of the Americans the benefits of the medical tourism cannot be denied as they have an opportunity to save money, get acquainted with new culture and for most of them it is a chance of a lifetime. Becoming more and more popular, the hospitals pay attention to their reputation as they apply for the accreditation, contribute a lot in the overall impression of the visitors and there is no wonder why the trend accelerates a lot. What is more, medical outsourcing is becoming one of the popular forms of business as the executives report the increasing figures as the time frame reduced significantly and there is no longer a probability to wait for a year or more. It seems to me if pointing out the definite advantages of globalization, medical tourism is one of the blessings the modern world offers us. Personally I think that health is the most important god given gifts and the fact that we have an opportunity to choose makes me feel proud.
All in all the prime goal of my term paper is to decide whether globalization is a force for good or bad and that’s a tricky question, for sure “the globalization has transformed the nature of economic activity.” (Globalization: a critical introduction,2000) Working on the paper I realized that it is rather hard to figure out all pros and cons of globalization just by learning the theory, as the real life examples show us how rich the meaning of globalization is. From my point of view, if taking into consideration the challenge that is forcing the global development and increases our life standards, I`d say that pluses overweigh minuses. Unfortunately, it is next to impossible to avoid drawbacks as some of the cases seem not to be that positive and show us the reverse side of the medal. Still we have to admit the fact that globalization is taking over and having own opinion about this process is an indispensible part of building a successful future.
Donald J. Boudreaux (2008). Globalization (1 st Ed.). Westport, CT.
Jan Aart Scholte (2000). Globalization (1 st Ed.). London
Malcolm Waters (2001). Globalization (2 nd Ed.). New York, NY
Stuck with your Term Paper?
Get in touch with one of our experts for instant help!
Creative Thinking, Admission Essay Example
Day After Tomorrow, Essay Example
Time is precious
don’t waste it!
Plagiarism-free guarantee
Privacy guarantee
Secure checkout
Money back guarantee

Related Term Paper Samples & Examples
5 ways intersectionality affects diversity and inclusion at work, term paper example.
Pages: 5
Words: 1355
Combating Climate Change Successfully Through COP26 Glasgow 2021, Term Paper Example
Pages: 9
Words: 2580
Telehealth, Term Paper Example
Pages: 3
Words: 848
Impact of Spanish, Mexican, and Anglo Social Ordering on Mexican-American Culture in California, Term Paper Example
Pages: 7
Words: 1809
Empowerment and Social Change, Term Paper Example
Pages: 2
Words: 642
Directed Energy Ethics, Term Paper Example
Pages: 18
Words: 4973
We use cookies to enhance our website for you. Proceed if you agree to this policy or learn more about it.
- Essay Database >
- Essays Samples >
- Essay Types >
- Term Paper Example
Globalization Term Papers Samples For Students
66 samples of this type
WowEssays.com paper writer service proudly presents to you a free collection of Globalization Term Papers meant to help struggling students deal with their writing challenges. In a practical sense, each Globalization Term Paper sample presented here may be a pilot that walks you through the important phases of the writing procedure and showcases how to develop an academic work that hits the mark. Besides, if you need more visionary help, these examples could give you a nudge toward an original Globalization Term Paper topic or encourage a novice approach to a banal issue.
In case this is not enough to slake the thirst for effective writing help, you can request customized assistance in the form of a model Term Paper on Globalization crafted by a pro writer from scratch and tailored to your particular instructions. Be it a simple 2-page paper or an in-depth, lengthy piece, our writers specialized in Globalization and related topics will submit it within the pre-set timeframe. Buy cheap essays or research papers now!
Does Globalization Increase Inequality Term Papers Examples
Term paper of introduction to international relations theory, free qi: globalization term paper example, correlating culture and personality term paper sample.
Culture and personality are two ideologies that compliment and supplement each other. So several times, society has never failed to use culture in the process of convincing and influencing people to believe in the same beliefs as it have. This paper sought to justify the effect of each towards one another and to establish that several of these effects can be geared towards the positive or the negative side. Keywords:Culture, personality, globalization
Consumer: Culprit to the Disintegration of Culture
Don't waste your time searching for a sample.
Get your term paper done by professional writers!
Just from $10/page
Mass Media And An Enlightened Public In The Dawn Of Globalization Term Papers Examples
[University] [Submission Date]
The Role Of Economic Globalization On China Term Paper
Term paper on cultural anthropology, gender and globalization term paper, example of importance of globalization term paper.
Globalization refers to the increased integration and global interconnectedness of markets, trade, culture and products. Globalization is enhanced by technological advancements and transnational investments. People around the world are getting more closely connected than before. Goods and services produced are becoming available in all parts of the world irrespective of where they were manufactured. Money and information is also flowing rapidly while international communication and travel are commonplace. This paper discusses the pros and cons of globalization.
Pros of Globalization
Term paper on china case study, can consumer goods from china be trusted the answer is no due to the following reasons;, free term paper on 3 exam questions.
What is meant by the term "Competitive Elitism?" Using the suggestions of Max Weber and Joseph Schumpeter, identify the ways in which the modern state has deviated from the classical notions of democracy.
Term Paper On Trans-Boundary Policy Problem
Trans-boundary policy problem is a crisis resulting from set of rules that defines the clear cut in a boundary between two separate entities. The fight between two countries on the exact boundary line is the best example of this policy problem. Some water resources lie at the border of two countries and it becomes difficult in making the correct boundary line. Learning this helps us enhance our knowledge on how such cases arise and how they are addressed (Blatter 14).
Free Term Paper On Term Research Paper; Final Project
The purpose of the term paper is to determine the effect of globalization on the organization development and change..
Assumptions and delimitations It was assumed that government will give the right information on the effect of globalization on their relations with other countries and the effect on the economy. It is also assumed that the impact of globalization on the organizational development is apparent and evident. The delimitations include the effect of globalization on the third world countries after the countries passed the free trade policies. Another one is that the research was conducted in ten African countries and eight other countries spread between Europe, Asia, and America.
Hypothesis: Globalization improves the relationships between countries and also improves the economies of countries
Globalization and global drug traffic term paper example, economic and political structure term paper, term paper on political science, economic development and the imf and the world bank in the caribbean, the us subprime problems, the 2008 international financial crisis and a possible repetition term paper, egypt term papers examples, part.1 country background:.
- Neighbouring Countries: Gaza, Israel, Libya, Sudan, - Territorial Size of the Country: 1,002, 450 square kilometres - Size of the Population: 86,000,000 (2014 estimate) - Type of Political System: Democratic System, multi-party system - Who is the Prime Minister, President?
Acting Prime Minister: Ibrahim Mahlab
Good example of term paper on marriott corporation: a multinational corporation, global competitive strategy of friend-z’s coffee house term papers example, introduction, good example of kohls in singapore term paper, kohl’s international expansion, free term paper on international marketing topics, sociology take home exam term paper examples, definition of the topic and significance term papers example, communication, coaching, and conflict skills, term paper on project communication management planning for a global project, term paper on international financial markets, the effect of outsourcing and international migration on the global economy term paper example, neo-liberalism and china term papers examples, good talent management & institutional voids in emerging market term paper example, cross cultural management: a sample term paper for inspiration & mimicking, cross-cultural management, free problem statement term paper example.
U.S. Position in the Post-cold War ERA U.S. Position in the Post-cold War ERA
Sample Term Paper On Sales Management: Analysis Of Articles
An assignment submitted by, why low income and food insecure people are vulnerable to overweight and obesity term papers example, example of world literature final term paper, good term paper on the final assignment, embracing diversity.
Organization Top Inc is a global company involved in the production of beverages. It manufactures, markets, and sells soft drinks in the global market. It is headquartered in California. The Company was established in 1992, and it is operating in different counties.
Problem Identification
Term paper on southwest airlines, a critical issue in loss prevention in security term paper.
<Name> <Subject> <Professor>
Term Paper On Foreign Direct Investments In Asian Economies
More information about affiliation, research grants, conflict of interest and how to contact..
Foreign Direct Investments in Asian Economies Introduction
Direct investments can be defined as physical investments that are made into building a factory in the domestic company (Graham and Spaulding, 2005). It is different from indirect investment that involves making a bundle investment in a broader category of assets. Foreign direct investment or FDI can be defined as foreign investing directly into the productive assets of a domestic company. It includes the acquisition of a lasting management interest in a company or enterprise outside the investing firm’s home country (Graham and Spaulding, 2005).
Term Paper On Comparative Local Government Between Canada And China
How hp has integrated global it issues to embrace sustainability and enhance decision-making term paper to use for practical writing help, executive summary, example of term paper on globalization, individual case analysis of apple inc, chikungunya term paper sample, analysis of diseases.
Overview Chikungunya (CHIK) refers to a re-emerging arboviral disease transmitted by the mosquitos Aedes aegypty and Aedes albopictus (Pialoux 318). The virus belongs to the genus Alphavirus and family Togaviridae. The word chikungunya derives from Makonde language (spoken in Tanzania and northern Mozambique), where it means “to walk bent over” (Halstead 557). This name refers to the main feature of both chronic and acute phase of the disease a change in posture causes by the arthritis and arthralgia (Charrel, Lamballerie and Raoult 769).
Good Example Of US Position In The Post-Cold War Era. Term Paper
Example of e-commerce and www term paper, the lego group term paper samples.
The Lego Group is a firm that manufacturers toys that are well known for their innovation, quality and safety. The objective of this paper is to conduct an external environment and internal competitive analysis for the firm. The paper is divided into four sections. The first section conducts a five force analysis of the firm. The second section identifies if any other environmental force (other than five forces) impact the organisation. The third section identifies the firm’s resources, capabilities and competitive advantage. The fourth section discusses if the business is sustainable given the external and internal environment.
Five Forces Analysis for the Lego Group
Good term paper on the global influence of transnational corporations: a critical exploration of their role and relationships, term paper on mcdonald’s promotion and pricing strategies, example of global business term paper, free effective communication strategies for culturally diverse people term paper sample, free term paper about marketing analysis, ipad marketing analysis, good term paper on diversity in the workplace, reasons of social inequality term paper sample.
Did the Rich World Become Rich Using Colonization and Exploitation of the Poor: A Critical Assessment of Theory and Empirical Evidence
Good FedEx Business Strategy Term Paper Example
Logistics industry overview, the understanding of business communication issues plays a major role in the term paper samples, business communication issues in an international business situation, example of comparison and contrast of two ethnic minorities in the united states term paper, is the objective of pure profit maximisation is still relevant to the modern business term paper examples, introduction 3, name term paper examples, hum 112 week 5 discussion 1, term paper on training and development in small businesses, example of term paper on origin and history and revolution of the internet, neoinstitutionalism as a theory term paper examples, immigrant discrimination in the work place term paper.
Password recovery email has been sent to [email protected]
Use your new password to log in
You are not register!
By clicking Register, you agree to our Terms of Service and that you have read our Privacy Policy .
Now you can download documents directly to your device!
Check your email! An email with your password has already been sent to you! Now you can download documents directly to your device.
or Use the QR code to Save this Paper to Your Phone
The sample is NOT original!
Short on a deadline?
Don't waste time. Get help with 11% off using code - GETWOWED
No, thanks! I'm fine with missing my deadline

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Concept. It is the world economy which we think of as being globalized. We mean that the whole of the world is increasingly behaving as though it were a part of a single market, with interdependent production, consuming similar goods, and responding to the same impulses. Globalization is manifested in the growth of world trade as a ...
globalization, integration of the world's economies, politics, and cultures.German-born American economist Theodore Levitt has been credited with having coined the term globalization in a 1983 article titled "The Globalization of Markets." The phenomenon is widely considered to have begun in the 19th century following the advent of the Industrial Revolution, but some scholars date it ...
According to Held et al. , the globalization is a long-term historical process. This important process incorporates opposites and is shaped by the factors created by the current status. ... Reaping the Benefits of Financial Globalization, IMF Discussion Paper. Notes: Based on de facto globalization and de jure capital controls, using the IMF ...
First, globalization refers to a state of being more conscious of the world as whole (Robertson, 1992). Second, it refers to new self other relations in light of global connectivity (Delanty, 2012b). Both ideas suggest a. -. more central role for psychology in research on globalization.
To understand the effects of globalization, this paper defines globalization, surveys its range and dimensions, and analyzes its pros and cons in the contemporary world. Definition of Globalization. Keohane and Nye (2000) define globalization as "the expansive networks that span intercontinental distances (p. 105).
This resource guide is created to help users understand globalization, its history, the elements it comprises, and the current trends. It also provides resources for keeping current with the latest research on the subject for further exploration. Global integration, driven by technology, transportation, and international cooperation, has ...
This paper concludes that globalization has inflicted pains and promoted gains to those individual and countries that indulge in it. Discover the world's research 25+ million members
Term Paper on Globalization (Definition): Globalization is the process of organizing the whole world into a single integrated marketing unit. It is also defined as the process of trans border free flow of products, services, people, culture, technology, and finance. It leads to the integration of economic, cultural, political, and social ...
Rapid globalization has brought new, large-scale influences to bear on patterns of human health. Various global-scale changes — economic, social, demographic, and environmental (particularly ...
A general term, globalization refers to how the world has become more connected economically, politically, socially, and culturally over time. In this general sense, its roots go back to the era of agrarian societies as empires expanded and trade networks grew. These connections really accelerated and encompassed the whole world after the ...
Globalization and Environment Theodore Panayotou Abstract Economic globalization impacts the environment and sustainable development in a wide variety of ways and through a multitude of channels. The purpose of this paper is (a) to identify the key links between globalization and environment; (b) to identify the major issues addressed in
Globalization is an important asset of the world, effects incre asing by day by on economic, social, political, cultural, environmental and technological dimensions so on. The scope of ...
Globalization and the Environment Term Paper … Globalization and the Environment This work in writing will examine and thoroughly analyze the impact that globalization has had on the environment of the world. "Global environmental problems are increasingly… Pages: 9 (2597 words) · Type: Term Paper · Bibliography Sources: ≈ 8
done, given the reality of globalization, if development is to bring about an improvement in the living conditions of people, ordinary people. The structure of the paper is as follows. Section 1 outlines the rationale of globalization as a mantra for development, to juxtapose it with conflicting perceptions and complex realities.
Globalization is a complex phenomenon that has a big influence on various fields of human life, including economics, society, and culture. Even though trade between countries has existed since time immemorial, in the 21st-century, globalization has become an integral part of the world's development. While businesses try to expand on a global ...
The term paper proposes a conceptual framework to investigate relationships among globalization effects, degree of cooperation in co-marketing alliances, and international marketing performance. This term paper focuses on relationships between globalization effects and alliances because past research often mentions that globalization drives ...
To summarize this paper, globalization is an unstoppable interstate integration process, leading to the erasure of national boundaries and the formation of a single cultural layer. ... With the term of Globalization being in vogue and regional integration agreements being signed across the globe, the coalition of the concepts has been ...
Abstract. Although globalization is a term usually restricted to economics and the social sciences, there are aspects of the phenomenon that are intimately linked to the practice and purpose of the physical and environmental sciences and exemplified through Physical Geography. At a fundamental level, Physical Geography has always sought to ...
TOPIC: Term Paper on Globalization and Its Impact on the World. Assignment At its most basic, there is nothing mysterious about globalization. The term has come into common usage since the 1980s, reflecting technological advances that have made it easier and quicker to complete international transactions -- both trade and financial flows.
Thus, globalization has led to great good, for it is about people around the world becoming so anchored that local life is molded by what is happening in other parts of society. Globalization in the Philippines. After the declaration of Philippine independence in 1945, the country may be described as a 8premature9 and 8weak state.
Term Paper: The concept of globalization is essential to understand the patterns of economic, political and cultural change in the contemporary world. Introduction Globalization is known as the name of the social, economic and political processes taking place in our world. During the last years, globalization has become an important subject for ...
A new analysis by Oxfam found that "income inequality is high or increasing" in 60 percent of low- and middle-income countries that receive grants or loans from the IMF and World Bank. That ...
All in all the prime goal of my term paper is to decide whether globalization is a force for good or bad and that's a tricky question, for sure "the globalization has transformed the nature of economic activity." (Globalization: a critical introduction,2000) Working on the paper I realized that it is rather hard to figure out all pros and ...
Term Paper of Introduction to International Relations Theory. This term paper is going to deal with the concept of globalization and inequality. The terms 'globalization' and 'inequality' are going to be well defined and their minor relation identified. After that, the relation of the two terms with capitalism in the liberation theory ...