
site categories
Stormy daniels takes a swipe at donald trump’s complaints about her testimony: “real men” would take the stand — update, disney reorganizes into three segments, entertainment, espn & parks.
By Jill Goldsmith
Jill Goldsmith
Co-Business Editor
More Stories By Jill
- Nexstar CEO On CBS Stations – Can’t Buy Them Under Current Regulatory Regime “But If That Were To Change, Maybe Our Opinion Would Change”
- Andy Serkis To Direct, Star In New ‘Lord Of The Rings: The Hunt For Gollum’ Set For 2026 Release – Update
- WBD Q1 A Miss Vs ‘Hogwarts Legacy’ Bump A Year Ago; Advertising Dips But Streaming Is Profitable

Disney is reorganizing its sprawling businesses under three core segments, Entertainment, ESPN and Parks , Experiences & Products, as CEO Bob Iger moves to restructure the company.
Related Stories

Disney Cuts Thousands Of Jobs Amidst Latest Restructuring & Costs Trimming

Nexstar CEO On CBS Stations - Can't Buy Them Under Current Regulatory Regime "But If That Were To Change, Maybe Our Opinion Would Change"
RELATED: Disney Earnings Report & Reorganization – Full Coverage
The reorganization is a key element of a transformation that he said will also help rationalize the streaming business for sustained growth and profitability and reducing expenses in a world of increased competition and global economic challenges.
The DTC business, except for ESPN+ , will be under Entertainment.
Dana Walden and Alan Bergman will co-chair Disney Entertainment; Jimmy Pitaro will continue as head of ESPN and Josh D’Amaro as parks chief.
Iger said the moves announced today cumulatively reflect a new era in the company’s transformation over the past two decades. The first was a period of rapid growth in its core IP that saw Disney acquire Pixar, Marvel and LucasFilm. The second, from 2016, was the lead-up to Disney’s acquisition of 20 th Century Fox, and subsequent foray into streaming with the launch of ESPN+ and Disney+.
The booming parks and resorts division, which includes cruise ships and consumer products, remains as is.
With linear networks in decline and the cost of sports rights on the rise, ESPN has been a target of Disney investors like Third Point’s Daniel Loeb, who said it should be spun off, but then retracted that opinion, given its “potential as a stand-alone business and another vertical for Disney to reach a global audience to generate ad and subscriber revenues.” Iger said today that making ESPN a standalone business unit is in no way a presaged a sale of the business.
ESPN+ had 24.9 paid subscribers at the end of last year, up 2% (from 24.3 million) the year before. It is offered alone or in a bundle with Disney+ and Hulu.
Must Read Stories
‘kingdom of the planet of the apes’ thursday previews around $6 million.

Tom Hiddleston To Play Edmund Hillary In ‘Tenzing’, About First Everest Climbers
Willy wonka reality series heats up at netflix amid rise of unscripted bakeoff shows, bravo host cleared of allegations, but doubters say probe was sham.
Subscribe to Deadline Breaking News Alerts and keep your inbox happy.
Read More About:
Deadline is a part of Penske Media Corporation. © 2024 Deadline Hollywood, LLC. All Rights Reserved.
Disney's $60 billion expansion plan to make way for new lands, beloved franchises in Florida and beyond
Disney to expand parks, cruises.
The Walt Disney Company is looking to nearly double its capital expenditures over 10 years to about $60 billion, the company said in a press release. That includes expanding parks, experiences and cruises.
ORLANDO, Fla. - The Walt Disney Company plans to invest $60 billion over the next 10 years to expand its parks in Florida and around the world, cruise lines and other experiences.
Senior Disney executives, including CEO Bob Iger, met with financial analysts and investors at a summit in Orlando on Monday to reimagine the way they "continue to grow the bottom line," according to a press release .
"Throughout our history, we’ve created enormous growth by investing the right amount of capital into the right projects at the right moment," Iger said. "We are planning to turbocharge our growth yet again with a robust amount of strategic investment in this business."
Iger plans to not only expand Disney Parks around the world, but right here at Walt Disney World in Florida, too. Destination D23 wrapped up about two weeks ago, revealing a a slew of new experiences making their way to Walt Disney World , like new shows, new ride vehicles and new expansions.
News of Disney's new expansion plans come amid an ongoing legal feud with Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis , the failure of the Star Wars -inspired resort and the recent unveiling of new details about Universal Orlando Resort's Epic Universe set to open in 2025.
Here's a look at what Disney has planned for the next decade:
1,000 acres of land ready to use
Disney said there is "significant room for further expansion."
Disney Parks has over a thousand acres of land ready to use for future projects, which is the equivalent of seven new Disneyland Parks, the company said in a press release.
They said this land could be used to expand theme park space at its already existing parks.
"We stand alone when it comes to scale," said Experiences and Products Chairman of Disney Parks Josh D’Amaro. "And while our scale is impressive, we have no shortage of space or regions of the world in which to tell new stories."
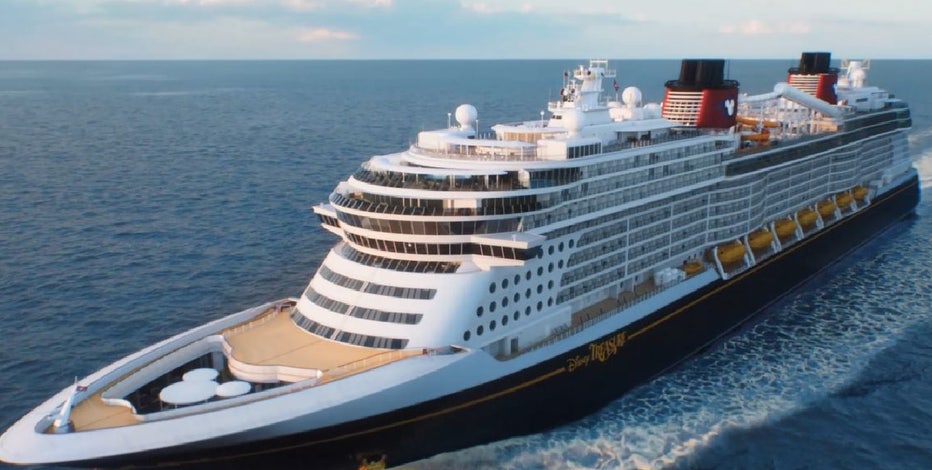

Disney Treasure reservations now open: See pricing, deck plans & amenities ahead of first voyage in 2024
Reservations for the all-new Disney Treasure are now open!
MORE DISNEY NEWS :
- Walt Disney World welcomed more than 300 fur babies this year
- Black bear spotted at Disney World's Magic Kingdom released into Florida national forest
- Walt Disney World unwraps exclusive offer for Florida residents ahead of busy holiday season
- Walt Disney World fires up all-new eats to celebrate Hispanic Heritage Month: Lechón asado, mojito taco & more
Never-before-explored characters, franchises could come to life
The Walt Disney Company said there is a whole new world of characters and franchises they have yet to tap into – and they'll plan to do so amid a "new period of significant growth domestically and internationally in its parks and resorts," according to a press release.
D'Amaro said Frozen – which is coming soon to Hong Kong Disneyland, Walt Disney Studios Park in Paris and Tokyo Disney Resort – could make its way to the Disneyland Resort in California.
Wakanda is another franchise on the table, as and so is Coco .
"There's a lot of storytelling opportunity," D'Amaro said.
Take a look inside new Disney Treasure ship
The new Disney Treasure ship is ready to set sail in 2024, but tickets are available starting September 20. Take a look inside Disney's newest cruise ship!
Disney Cruise Line to nearly double worldwide capacity
Disney Cruise Line will add two ships in 2025 and another in 2026.
Recently, Disney lovers got a sneak peek of inside the new Disney Treasure , which getting ready to set sail in 2024.
There's also a new homeport in Australia and New Zealand slated to open later this year, followed by Singapore in 2025.
Check out photos from inside the new Disney Treasure below:
Photo: Disney Cruise Line
Walt Disney World to get a few major upgrades
At Destination D23, the Walt Disney Company unveiled several new projects coming to Walt Disney World.
Here's a rundown:
- New Zootopia show replacing A Bug's Life at Tree of Life Theater at Disney's Animal Kingdom
- New Pirates of the Caribbean -themed lounge at Adventureland at Disney's Magic Kingdom
- New act at Country Bear Jamboree at Disney's Magic Kingdom in 2024
- Test Track at EPCOT to be reimagined
- Dinoland U.S.A. to become Tropical Americas
- Encanto and Indiana Jones are being considered for reimagined land at Disney's Animal Kingdom
Dinoland U.S.A. will be turned into a Tropical Americas land. (Photo: The Walt Disney Company)
"There's a long way to go and a lot more to discover but Imagineering teams in Florida are up for the challenge," said Bruce Vaugn, chief creative officer at Walt Disney Imagineering.
The thread on X, formerly known as Twitter, below shows all the new projects coming to Disney Parks around the world:
Disney still looking to reach more consumers
The Walt Disney Company said there is "enormous untapped potential" for reaching more consumers. There are over 700 million people who love Disney that have yet to visit a Disney Park, according to Disney's internal research. They added that for every one guest who visits a park, there are more than 10 people who don't.
"Ultimately what is most important to us is the relationship that we have with every guest," D'Amaro said. "Guests can spend a day with us at our Parks, a week with us on a Cruise, or the rest of their lives with us through Disney Vacation Club membership."
All in all, Disney said if it expands its offerings and experiences, they'll be able to reach not only its loyal fans, but tap into a whole new world of more consumers.
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Company Profiles
- Consumer Discretionary
How Disney Makes Money
Disney’s Parks, Experiences and Products business generates most of its profits
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/david-kindness-cpa-headshot1-beab5f883dec4a11af658fd86cb9009c.jpg)
The Walt Disney Co. ( DIS ) is a diversified global entertainment company that operates theme parks, resorts, cruise lines, broadcast television networks, and related products. It's a favorite blue-chip dividend-paying stock for many investors. The company also produces live entertainment events and produces and streams a broad array of film and TV entertainment content through its new digital content streaming services.
Disney faces an unusually large number of competitors, including Paramount Global ( PARA ), Comcast Corp. ( CMCSA ), Sony Group Corp. ( SONY ), AT&T Inc. ( T ) , Netflix Inc. ( NFLX ), Apple Inc. ( AAPL ), and Amazon.com Inc. ( AMZN ); and smaller niche rivals, including theme park and resort companies Six Flags Entertainment Corp. ( SIX ), SeaWorld Entertainment Inc. ( SEAS ), and Hilton Worldwide Holdings Inc. ( HLT ).
Key Takeaways
- Disney is a diversified global entertainment company that operates theme parks, resorts, broadcast networks, and streams TV shows and movies.
- Disney’s Linear Networks currently generates the most revenue, but its Parks, Experiences and Products business is recovering from the COVID-19 pandemic and currently generates the most profits.
- Disney’s domestic theme parks and resorts have been reopened gradually and no longer face mandatory capacity restrictions.
- Disney recently appointed executive Mike White to oversee the implementation of the company’s metaverse strategy.
- Disney+ finished the first quarter (Q1) of fiscal year (FY) 2022 with nearly 130 million subscribers, up 36.8% year over year (YOY).
Disney’s Financials
In early February 2024, Disney announced February financial results for the first quarter (Q1) of the fiscal year (FY) , the three-month period ended Dec. 30, 2023. The company posted net income of $2.15 billion, almost up 58% to Q1 2022. Revenue rose less than 1% year over year (YOY) to $23.55 billion. Disney uses operating income as the profit metric for its individual business segments. Segment operating income rose 27% to $3.88 billion in fiscal Q1.
In its earnings report, Disney highlighted the adverse impacts of the COVID-19 pandemic since early 2020. Its Parks, Experiences and Products segment has been affected the most by those impacts. Disney was forced to close theme parks and resorts and suspend cruise ship sailings and guided tours. However, beginning in May 2020, the company has gradually reopened its theme parks, albeit at reduced capacity. Disney’s domestic parks and experiences are now generally operating without significant mandatory capacity restrictions. Its cruises and guided tours also have begun to return to service. Disruptions to film and TV production also have contributed to less content for its media and entertainment business.
Disney’s Business Segments
Starting in fiscal 2023, Disney reorganized its reportable business segments. The company now operates through three main business segments: Entertainment, Sports and Experiences (renamed from Disney Parks, Experiences and Products). The first of these segments, which is composed of Disney’s media and entertainment businesses, is further separated into three components: Linear Networks; Direct-to-Consumer; and Content Sales/Licensing and Other. Disney provides a breakdown of revenue and operating income for each of these segments. Prior to this change, the company operated through two primary business segments: Disney Media and Entertainment Distribution (DMED) and Disney Parks, Experiences and Products (DPEP).
Entertainment: Linear Networks
Disney’s Linear Networks segment operates a long list of properties, including domestic and international cable networks such as Disney, ESPN, and National Geographic; ABC broadcast television network and eight domestic television stations; and a 50% equity investment in A+E Television Networks.
The Linear Networks segment posted revenue of $2.8 billion in Q1 FY 2024, only slightly lower than revenue in the YOY quarter. Operating income fell 7% YOY to $1.2 billion. The segment accounts for about 28% of total revenue and carries total operating income.
Entertainment: Direct-to-Consumer
Disney’s Direct-to-Consumer (DTC) segment is composed of its various streaming services, including Disney+; Disney+ Hotstar; ESPN+; Hulu; and Star+.
The DTC segment posted revenue of $5.55 billion in Q1 FY 2024, up 15% from the same three-month period a year ago. The segment reported an operating loss of $138 million, widening from the operating loss of $984 million reported in the year-ago quarter. The DTC segment accounts for 55.57% of total revenue.
Entertainment: Content Sales/Licensing and Other
Disney’s Content Sales/Licensing and Other segment sells film and television content to third-party TV and subscription video-on-demand (VOD) services. The segment also includes the following operations: theatrical distribution; home entertainment distribution, such as DVD and Blu-ray; music distribution; staging and licensing of live entertainment events on Broadway and around the world; post-production services through Industrial Light & Magic and Skywalker Sound; and a 30% ownership interest in Tata Sky Ltd., an India-based operator of a direct-to-home satellite distribution platform.
The Content Sales/Licensing and Other segment posted revenue of $1.63 billion in Q1 FY 2024, down 38% from the year-ago quarter. The segment reported an operating loss of $224 million, a significant deterioration from operating loss of $1 million posted in the year-ago quarter. The Content Sales/Licensing and Other segment accounts for 16% of total revenue.
Experiences
Disney’s Experiences segment is composed of theme parks and resorts in Florida, California, Hawaii, Paris, Hong Kong, and Shanghai. It also includes a cruise line and vacation club. Revenue comes mainly from selling theme park admissions, food, beverages, various merchandise, resort and vacation stays, and royalties from licensing intellectual properties.
The Experiences segment reported revenue of $9.13 billion in Q1 FY 2024, rising 6.87% from the year-ago quarter. The segment posted operating income of $3.1 billion, an 8% increase YOY. The segment accounts for about 39% of Disney’s total revenue and about 80% of total operating income.
A note to readers: The segment revenue and operating income figures in the breakdowns above and in the pie charts do include intersegment transactions.
Disney’s Recent Developments
On Feb. 15, 2022, Reuters reported that Disney has appointed one of the company’s executives to lead its metaverse strategy. Chief Executive Officer (CEO) Bob Chapek appointed Mike White, an executive in the company’s Media and Entertainment Distribution group, to take up the new role of senior vice president of Next Generation Storytelling and Consumer Experiences. In his new role, White will be in charge of designing the consumer experience of Disney’s forthcoming metaverse.
In Disney’s fiscal Q1 earnings report released on Feb. 7, 2024, the company discussed the performance of its DTC business. Total subscriptions across Disney+ and Hulu rose less than 1% YOY to 199.3 million subscribers. Disney+ finished the quarter with 149.6 million subscribers, up less than 1% YOY.
On Jan. 19, 2022, Disney announced that it was creating a new hub for international content creation to support the expansion of its streaming services business. The company appointed Rebecca Campbell as chairperson of International Content and Operations to lead the new content creation hub. Under her newly expanded role, Campbell will focus on local and regional content production for the company’s streaming services and continue to oversee its global international media teams.
How Disney Reports Diversity and Inclusiveness
As part of our effort to improve the awareness of the importance of diversity in companies , we offer investors a glimpse into the transparency of Disney and its commitment to diversity, inclusiveness, and social responsibility. We examined the data that Disney releases to show you how it reports the diversity of its board and workforce, to help readers make educated purchasing and investing decisions.
Below is a table of potential diversity measurements. It shows whether Disney discloses its data about the diversity of its board of directors , C-Suite , general management, and employees overall, as is marked with a ✔. It also shows whether Disney breaks down those reports to reveal the diversity of itself by race, gender, ability, veteran status, and LGBTQ+ identity.
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " The Walt Disney Company, Form 10-K, For The Fiscal Year Ended September 30, 2023 ." Pages 3-16.
The Walt Disney Company. " The Walt Disney Company Reports First Quarter Earnings for Fiscal 2024 ." Pages 3, 14.
The Walt Disney Co. “ The Walt Disney Company Reports First Quarter Earnings for Fiscal 2022 ,” Pages 2 and 7.
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " The Walt Disney Company, Form 10-K, For The Fiscal Year Ended September 30, 2023 ." Page 86.
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " The Walt Disney Co., Form 10-Q for the Quarterly Period Ended January 2, 2021 ." Pages 8–10.
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " The Walt Disney Company, Form 10-K, For The Fiscal Year Ended September 30, 2023 ." Pages 86-87.
The Walt Disney Company. " The Walt Disney Company Reports First Quarter Earnings for Fiscal 2024 ." Pages 3-4.
The Walt Disney Company. " The Walt Disney Company Reports First Quarter Earnings for Fiscal 2024 ." Pages 3, 5.
The Walt Disney Company. " The Walt Disney Company Reports First Quarter Earnings for Fiscal 2024 ." Pages 3, 7
U.S. Securities and Exchange Commission. " The Walt Disney Company, Form 10-K, For The Fiscal Year Ended September 30, 2023 ." Page 88.
The Walt Disney Company. " The Walt Disney Company Reports First Quarter Earnings for Fiscal 2024 ." Page 3.
Reuters. “ EXCLUSIVE Disney Names Executive to Oversee Metaverse Strategy —Memo .”
The Walt Disney Company. " The Walt Disney Company Reports First Quarter Earnings for Fiscal 2024 ." Page 5.
The Walt Disney Co. “ The Walt Disney Company Creates International Content Group to Expand Pipeline of Local Content and Continue to Grow Its Global Direct-to-Consumer Business .”
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-10326508581-5c3144ea46e0fb00016afd8a.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Disney+ pricing
Prices for a Disney+ subscription can vary depending on which plan you sign up for:
Are you ready to sign up? Learn more about getting started , signing up , and managing your subscription with Disney+. Please note that at this time, Disney+ does not offer a free trial.
TIP: If you have an existing ESPN+ subscription and wish to add Disney+ and Hulu, you can choose to bundle all three services instead.
*Pricing through third-party billing partners may vary, depending on platform limitations from country-specific pricing and/or currencies in the region.
**Video and audio quality vary depending on your supported device, internet download speed, and the content you are watching at the time.
***May include promos for Disney+ programs. Limited live programs may include ads. For more details, read about ads on Disney+ .
****U.S. residents, 18+ only. Access content from each service separately. Location data required to watch certain content. Select Hulu content available via Disney+ with valid Hulu and Disney+ subscriptions; additional content only available via Hulu app. Hulu content can be streamed via Disney+ on up to 2 devices simultaneously. Additional app feature and device restrictions apply. Offer valid for eligible subscribers only. Subject to Disney+ and ESPN+ Subscriber Agreement.
- Updated Terms of Use
- New Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
- Closed Captioning Policy
Quotes displayed in real-time or delayed by at least 15 minutes. Market data provided by Factset . Powered and implemented by FactSet Digital Solutions . Legal Statement .
This material may not be published, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed. ©2024 FOX News Network, LLC. All rights reserved. FAQ - New Privacy Policy
Disneyland's $1.9B expansion plan approved by Anaheim City Council
Disneylandforward received unanimous approval from all 7 members.

Are Disney CEO Bob Iger's troubles now behind him?
'The Claman Countdown' panelists Robbie Whelan and Kenneth Leon break down Disney's battle against Trian Partners.
Disney on Tuesday received final approval to move forward with its nearly $2 billion expansion plan for its Disneyland theme park in California.
The Anaheim City Council said the company’s proposal — "DisneylandForward" — received its second unanimous approval from all seven members.
DISNEY SHARES SINK AS STREAMING BUSINESS FALLS SHY OF PROFITABILITY
The plan "shifts development amounts already approved by the city to other land Disney now operates on," the city council said.
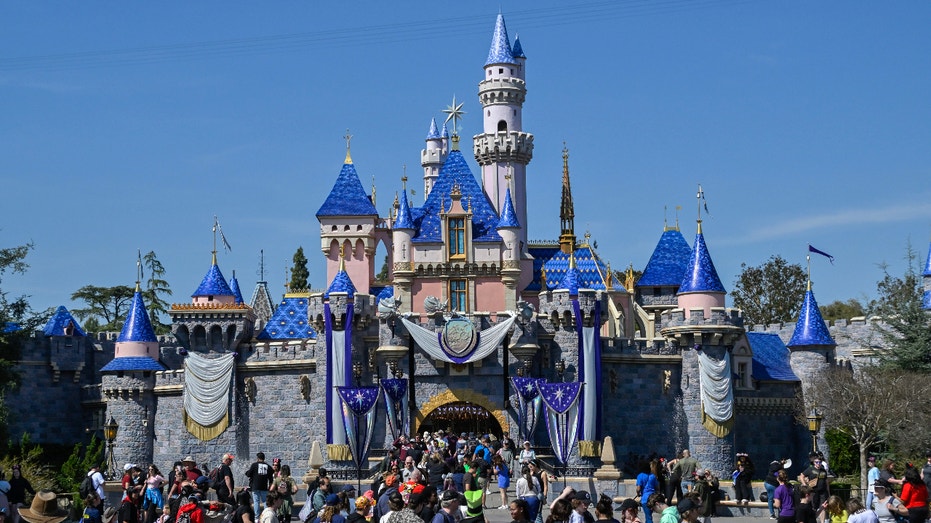

Sleeping Beauty Castle at Disneyland in Anaheim, California. (Jeff Gritchen, Orange County Register/SCNG via Getty Images / Getty Images)
Disney has about 490 acres of land in Anaheim across Disneyland and California Adventure Park, FOX Business previously reported .
The zoning changes Disney sought for the project "would allow for the building of additional theme park and other visitor attractions in Anaheim " without giving Disney any new land, according to the council.
CLICK HERE TO READ MORE ON FOX BUSINESS
"I’m grateful the city council agrees and voted to work with us on this legacy project that will set up Disneyland Resort and the City of Anaheim for an incredibly bright future," Disneyland Resort President Ken Potrock said in a Disney Parks blog post.

Disney received the second approval from Anaheim's city council on Tuesday. (Disney)
Disney asked the city council to give it the permissions needed to build "theme park attractions alongside hotels on the west side of Disneyland Drive and theme park attractions alongside new shopping, dining and entertainment to the southeast on what is today the Toy Story Parking Area at Katella Avenue and Harbor Boulevard," the city council said.

Disney has said its Disneyland expansion work could potentially draw inspiration from popular movies like "Tangled" or "Frozen." (Disney)
The entertainment giant is "incredibly excited for the many potential new stories our guests could experience at Walt’s original theme park, including the much-anticipated opportunity to bring Avatar to Disneyland," CEO Bob Iger said of DisneylandForward on Tuesday morning, prior to the city council giving approval.
Some other possible inspiration Disney has identified for future additions to its California theme park complex are "Tangled," "Frozen," "Zootopia" and "Toy Story Land," according to the company’s website dedicated to the project.
The Walt Disney Co.
With the expansion plan, Disney will put $1.9 billion toward the California resort in a 10-year span.
DISNEYLAND CAST MEMBERS FILE FOR UNION ELECTION
"DisneylandForward" has been described as a "multiyear" initiative that will play out over decades.
Disney created a rendering of a possible "Avatar"-themed area. (Disney)
The company also agreed to give $48 million for affordable housing, sewer improvements and city parks, the city council said.
Theme parks are an important revenue driver for Disney.
Its domestic parks and experiences, which includes Disneyland, Disney World and certain other offerings, generated $5.96 billion in revenue and $1.61 billion in operating income in the second quarter.

- About / Contact
- Privacy Policy
- Alphabetical List of Companies
- Business Analysis Topics
Disney’s Generic Competitive Strategy & Growth Strategies

The Walt Disney Company has a generic competitive strategy that capitalizes on the uniqueness of products offered in the entertainment, mass media, and amusement park industries. Michael E. Porter’s model indicates that a generic competitive strategy enables the business to develop and maintain its competitiveness in the target market. Disney’s generic competitive strategy is based on making its products different from those of competitors. On the other hand, the corporation’s intensive strategies for growth are focused on developing new products that suit global market trends. The company grows through innovation and creativity that enable the business to compete against large firms. Disney competes with the entertainment businesses of Sony and Comcast (owner of Universal Studios), and the movie streaming businesses of Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, Google ’s YouTube, Facebook (Meta) , and Apple TV Plus. The Walt Disney Company’s generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies address such a competitive landscape. Through corresponding strategic objectives and competitive advantages, the entertainment conglomerate manages challenges in its industry environment.
This business analysis reflects Disney’s strategic management efforts. The company’s generic strategy focuses on developing competitive advantages based on innovation in product development. Disney’s intensive growth strategies are implemented with strategic objectives for maximizing the growth benefits of such innovation. For example, the company grows by introducing technologically enhanced products, such as movies for customers in the international market. The Walt Disney Company’s generic competitive strategy and intensive growth strategies are aligned for product-focused development.
Walt Disney’s Generic Competitive Strategy (Porter’s Model)
Disney uses product differentiation as its generic strategy for competitive advantage. Michael Porter’s model states that this strategy involves unique products offered to many market segments. For example, the corporation offers its entertainment products to practically every person in the world, especially with the core emphasis on family-oriented programming. In this generic competitive strategy, Walt Disney’s operations management prioritizes quality and uniqueness through innovation that differentiates the company’s products from competitors. The subsidiary, Walt Disney Imagineering Research & Development, has dedicated teams to ensure the uniqueness of entertainment experiences at the company’s theme parks and resorts. Disney’s intensive growth strategies and associated strategic objectives are applied alongside this generic competitive strategy, with emphasis on differentiated competitive advantage to support and manage business growth.
The Walt Disney Company’s generic competitive strategy pushes for product-focused strategic objectives. Such a business focus is necessary for supporting product development efforts to differentiate the company from competitors. For example, the strategic objective of developing new augmented reality products adds to the uniqueness of the Disney experience. Based on this generic strategy, another relevant strategic objective is to strengthen competitive advantages through marketing strategies that reinforce the uniqueness of the company’s brand. These marketing strategies relate to Disney’s marketing mix or 4Ps . Also, this generic competitive strategy involves managerial efforts that contribute to the achievement of the goals of Disney’s mission statement and vision statement in the global market for entertainment, mass media, theme/amusement parks, and related products. Brand uniqueness helps in achieving industry leadership. Considering differentiation as a generic competitive strategy, Disney’s intensive growth strategies must involve differentiation to grow the business.
Walt Disney’s Intensive Growth Strategies
Product Development (Primary) . Product development is The Walt Disney Company’s primary intensive growth strategy. This strategy involves offering new products in the company’s current or existing markets. For example, the company releases new movies with corresponding merchandise to generate more profits from its target customers worldwide. This company analysis also sheds light on the importance of Disney’s organizational structure (company structure) , which provides the organizational design to effectively manage product development. This intensive growth strategy links to the generic competitive strategy of differentiation in emphasizing uniqueness in product development. A related strategic objective is to achieve business growth by effectively persuading customers to purchase Disney’s products based on their unique attributes.
Market Penetration (Secondary) . The Walt Disney Company achieves growth partly through market penetration. As a secondary intensive strategy, market penetration enables growth by increasing sales of existing products in the company’s current markets. For example, one of the corporation’s strategic objectives is to use aggressive advertising to increase its revenues from products released in the global entertainment industry. The business strengths shown in the SWOT analysis of Disney contribute to success in implementing this intensive growth strategy. A strong brand based on the generic competitive strategy of differentiation creates competitive advantages to attract customers to the company’s media and entertainment products, and to manage customers’ expectations.
Market Development . Market development is an intensive growth strategy that is less frequently used in The Walt Disney Company’s business. In growing the business, this intensive strategy requires the company to introduce its existing products to new markets or market segments. For example, growth is achieved by establishing operations in new markets, such as through a new Disneyland amusement park to capture a regional market. Even with competitive challenges, entry into new markets can increase the company’s strengths to manage the industry’s competitive forces shown in the Five Forces analysis of Disney . A key strategic objective in market development is to use differentiation as a generic competitive strategy to successfully introduce the company’s products into new tourism and entertainment markets.
Diversification . The Walt Disney Company uses diversification as a minor intensive strategy for business growth. Ansoff’s matrix states that developing or acquiring new businesses is the typical approach in this intensive growth strategy. For example, through the establishment of Disney Cruise Line, the company grew by entering the cruise line market of the tourism and hospitality industries. The generic competitive strategy of differentiation develops the competitive advantage of new business operations that use the company’s brand. Under diversification, a strategic objective is to manage competitive challenges by developing new businesses that grow Disney’s presence and brand popularity in the international market.
- Disney’s Unrivaled Commitment to Creativity and Innovation Brought to Life at 2023 Upfront Presentation .
- Kunze, P. C. (2023). Staging a Comeback: Broadway, Hollywood, and the Disney Renaissance . Rutgers University Press.
- Liang, X., Luo, Y., Shao, X., & Shi, X. (2022). Managing complementors in innovation ecosystems: A typology for generic strategies. Industrial Management & Data Systems, 122 (9), 2072-2090.
- The Walt Disney Company – Form 10-K .
- The Walt Disney Company – Investor Relations .
- Copyright by Panmore Institute - All rights reserved.
- This article may not be reproduced, distributed, or mirrored without written permission from Panmore Institute and its author/s.
- Educators, Researchers, and Students: You are permitted to quote or paraphrase parts of this article (not the entire article) for educational or research purposes, as long as the article is properly cited and referenced together with its URL/link.
Bob Iger reveals Disney's new plan for Marvel: quality over quantity
- Disney CEO Bob Iger plans to cut back on the number of Marvel films and TV shows released each year.
- The decision comes after a number of Marvel films underperformed at the box office.
- The only MCU film that will be released this year is " Deadpool & Wolverine."

Disney CEO Bob Iger's turn-around tour continues, and he let us in on the plan for what is arguably the House of Mouse's most successful IP: Marvel.
In Disney's first earnings call since successfully fending off a proxy battle from Nelson Peltz and its former Marvel Entertainment chairman Ike Perlmutter, Iger spoke about the future of the Marvel Cinematic Universe. The studio is now looking to release about two or three Marvel films and two Marvel television series a year rather than around four of each.
"I've been working hard with the studio to reduce output and focus more on quality," Iger said on the call.
Related stories
As it undergoes a sort of reset, the only MCU movie that's slated for release this year is "Deadpool & Wolverine" in July. "Echo," "X-Men '97," and "Agatha" will be this year's television releases. The next Avengers film, "Avengers 5," is scheduled for 2026.
The CEO has not been shy about his thoughts on the diminishing quality of Marvel films and television shows — something he has blamed mostly on his short-lived successor, Bob Chapek, even though Iger was in charge when several recent projects were developed.
"Some of what is coming up is a vestige of basically a desire in the past to increase volume," he said on the call.
Between 2021 and 2023, Marvel released 10 feature films and 13 TV series, including two specials, which appears to have left superhero fans fatigued .
MCU movies , which were once fail-safe productions, have struggled recently. Last year's "Ant-Man and the Wasp: Quantumania" grossed less than $500 million globally on a combined production and marketing budget of over $300 million — meaning it failed to break even at the box office. ( Typically, a movie must make back double its budget for the studio to reap a profit.) "The Marvels" fared even worse, grossing only $206 million worldwide on a budget exceeding $270 million. Both films received poor reviews .
"I'm mindful of the fact that our performance, from a quality perspective, wasn't up to the standards we set for ourselves," Iger said on an earnings call last year.
Disney's stock is down about 10% today.
Watch: What 12 movies from 2022 looked like behind the scenes
- Main content
Disney’s streaming business gets closer to becoming profitable
D isney Plus and Hulu posted a profit for the first time today. In Disney’s earnings report released on Tuesday, the company revealed that both streaming services made $47 million combined this past quarter — a huge turnaround from the $587 million loss reported at the same time last year.
But Disney’s streaming business wasn’t entirely profitable. ESPN Plus still lost $65 million, dragging its combined streaming earnings $18 million in the red. Despite this, the narrowing losses mark a huge milestone for Disney as it continues to invest more in streaming. The entertainment company says it expects its streaming business to become profitable in the fourth quarter of this year.
“Our results were driven in large part by our experiences, segments and our streaming business, which achieved an important milestone with the entertainment portion of the streaming business,” Disney CEO Bob Iger said during the call. “We fully expect streaming to be a growth driver for the company in the future.”
Over the past few months, Disney Plus added 7.9 million subscribers in the US and Canada, bringing total subscribers to 54 million. The company launched its combined Disney Plus and Hulu app in March, and now it plans on integrating ESPN Plus into the app, too. During the company’s earnings call, Iger said it’s going to add an ESPN Plus tile to Disney Plus this fall, “giving all subscribers access to select live games and studio programming” within the app.
Disney didn’t specify what prompted the turnaround of its streaming business, but it could have to do with the growth of its ad-supported tier. The company launched the $7.99 per month option in December 2022 and began nudging subscribers toward the tier ever since. Hugh Johnston, Disney’s chief financial officer, said during today’s earnings call that the company’s deal with the cable provider Charter helped drive the growth of its ad-supported tier this quarter, which it ended with 22.5 million subscribers.
Disney also plans on launching a standalone ESPN streaming service in the fall of 2025, along with a dedicated sports streaming service with Warner Bros. Discovery and Fox that’s launching later this year.

The Definitive Voice of Entertainment News
Subscribe for full access to The Hollywood Reporter
site categories
Bob iger details “reduced” marvel output: “at most” three films per year, two series.
The Disney CEO explained his plans to reduce Marvel Studios' output on the company's earnings call.
By Alex Weprin
Alex Weprin
Media & Business Writer
- Share this article on Facebook
- Share this article on Twitter
- Share this article on Flipboard
- Share this article on Email
- Show additional share options
- Share this article on Linkedin
- Share this article on Pinit
- Share this article on Reddit
- Share this article on Tumblr
- Share this article on Whatsapp
- Share this article on Print
- Share this article on Comment

Disney is planning to reevaluate its slate of films and TV shows from Marvel Studios, with the company set to reduce its output from the comic book franchise studio.
On Disney’s fiscal second-quarter earnings call, Disney CEO Bob Iger told analysts that the company is finally moving away from “a vestige, basically a desire in the past to increase volume.
Related Stories
Disney+, max and hulu bundle planned in major streaming team-up, jeremy strong in talks to join jeremy allen white in bruce springsteen movie for 20th century.
“We’re slowly going to decrease volume and go to probably about two TV series a year instead of what had become four, and reduce our film output from maybe four a year to two or at the maximum three,” Iger added. “And we’re working hard on what that path is, we’ve got a couple of good films in ’25 and then we’re heading to more Avengers , which we’re extremely excited about.” Avengers: The Kang Dynasty is listed for 2026.
“Overall I feel great about the slate,” he continued. “It’s something that I’ve committed to spending more and more time on, the team is one that I have tremendous confidence in and the IP that we’re mining, including all the sequels that we’re doing, is second to none.”
The future of Marvel has been a hot-button topic for Disney, with the past few films underperforming. By reducing both film and TV output, Iger is suggesting that the company plans to make the films more of an event, rather than a quarterly obligation.
THR Newsletters
Sign up for THR news straight to your inbox every day
More from The Hollywood Reporter
Supreme court opens doors to massive copyright infringement damages in case against warner music, apple apologizes for ipad pro ad after criticism: “we missed the mark”, art directors guild pauses training program amid industry challenges, harry j. pappas, owner of lots of tv and radio stations, dies at 78, cineplex ceo credits ‘dune: part two’ for keeping box office afloat, did ‘lord of the rings’ give warner bros. discovery a stock boost.

- Search 54563
- Search 61085
- Search 44857

Disney’s Business Model | How does Disney make money?
Disney is a world-renowned brand and requires no introduction. This company is an indispensable part of an individual’s life through its TV programs, theme parks, movies, games, and music. However, it is interesting to know how Disney went from a passion project to a multinational giant in a century!
Table of Contents
What is Disney?
Founded by Walt Disney and Roy O. Disney on October 16, 1923, Walt Disney is a multinational family entertainment company with headquarters in Burbank, California. This enterprise’s core business segments include Disney Entertainment, Disney Parks, Experiences and Products, and ESPN.
Disney began its journey as a humble cartoon studio and became a household name by introducing the iconic Mickey Mouse in Steamboat Willie in 1928 . After the resounding success of the mouse, the company began producing feature-length animated films, television shows, and full-length feature movies.
The year 1955 marked another milestone for the entertainment conglomerate when it welcomed the first Disneyland into the family. Then came live-action feature films, Walt Disney World, The Disney Channel, global expansion , the acquisition of studios like Pixar, and the launch of sports and entertainment channels, like ESPN+ and Disney+.
Disney’s Customer Segmentation
Disney primarily caters to three types of customer segments :
- Children and youngsters : After over nine decades of its introduction, Mickey Mouse and his friends remain a favorite among children and youngsters. Moreover, the brand’s timeless productions and characters make it the ideal stop for children and youngsters to get their entertainment fix.
- Families : Disney promotes family entertainment, and its theme parks, resorts, cruises, vacation experiences, and consumer products are extremely popular among families. In fact, the Magic Kingdom (Walt Disney World), USA, is a leading amusement park and welcomed 17.13 million visitors in 2022 alone.
- Entertainment lovers : Disney isn’t just limited to children and families. It’s incredibly popular among entertainment lovers who love movies, TV shows, and sports.
Disney’s Value Propositions
Disney’s unique value propositions for its customers include the following:
1. Disney entertainment
Disney has an enviable repertoire of entertainment channels. Its global entertainment media and content companies, along with streaming, include The Walt Disney Studios, Walt Disney Animation Studios, Pixar Animation Studios, Marvel Studios, ABC Entertainment, Hulu, National Geographic, Hotstar, and more.
Disney owns ESPN networks, including the brand’s international sports channels, and launched ESPN+ in April 2018.
3. Disney Parks, Experiences and Products
Disney’s lovable characters, imaginative stories, and franchises have allowed it to offer its avid consumers one-of-a-kind theme parks, resorts and spas, adventures, vacation clubs, and cruises. Its range of consumer products includes toys, clothes, books, music, and video games.
Who are the Key Partners of Disney?
Disney’s goal is to entertain, educate, and encourage individuals to let their imaginations run wild. Its key partners include:
- Artists: The company partners with varied artists globally to present out-of-the-box shows and products and keep the magic alive.
- Suppliers: A dependable network of suppliers helps make company-related merchandise and other products available to the general public.
- Investors: Walt Disney Productions went public in 1940 and, since then, has enjoyed unequivocal support from its numerous investors.
- Marketing partners : They help ensure Disney’s magic never dims .
- Affiliates: Disney collaborates with affiliates through its shop Disney.com’s affiliate program. The affiliates help drive traffic to the website for a commission and increase its merchandise sales. The company has partnered with Commission Junction to make the commission part easier while it handles the ordering, billing, and logistics.
- Movie companies and advertisers: They distribute the company’s movies and shows digitally.
- Developers and IT partners: Technology partners ensure Disney’s many entertainment channels function without glitches.
Similarly, Disney pa
rtnered with the Make-A-Wish ® charity to celebrate its 100th anniversary. It commemorated this partnership by donating $1 million and continues to work closely with the initiative to raise funds and awareness.
What are Disney’s Key Resources?
Disney’s key resources include:
- Disney’s physical presence through its theme parks and resorts around the globe.
- User-friendly websites and entertainment resources.
- Patents, copyrights, and trademarks to protect all intellectual property.
- A dependable brand name that allows it to break into new markets with ease.
- Profitable partnerships with media networks.
- An enviable brand portfolio and affiliate relationships.
- Disney’s ecosystem of employees and other human resources.
What are Disney’s Channels?
Disney uses multiple channels to reach customers globally, including its website, TV channels, affiliate programs, subsidiaries, parks, resorts, online shops, cruise lines, and on-demand streaming services like Disney+ and ESPN+.
Additionally, the international brand is active on multiple social channels— Facebook , X (formerly Twitter ), Instagram , and YouTube —and leverages them to connect with its existing customers and acquire new ones globally.
How Does Disney Maintain Customer Relationships?
Disney customers can go through the Guest Support page to resolve most of their queries related to shopDisney. The offerings including return policy, product inquiry, gift cards, accessibility, shipping and delivery, gifting options, sales price adjustment, how to apply online for Disney Visa card, payment-related concerns, discounts and promotions, questions about rewards card, careers, and order cancellation.
They can also reach out to customer support executives by choosing their request type and submitting their concerns with the relevant details, such as email address and inquiry details.
Alternatively, US customers can call (800) 328-0368, whereas outside US consumers can call 001 (407) 827-7044 from Monday to Friday between 7 AM and 11 PM CST, Saturday from 8 AM to 4:30 PM CST, and Sunday between 12 PM and 8:30 PM CST.
Moreover, team members are available throughout Disney’s physical locations to assist all visitors.
What is Disney’s Cost Structure?
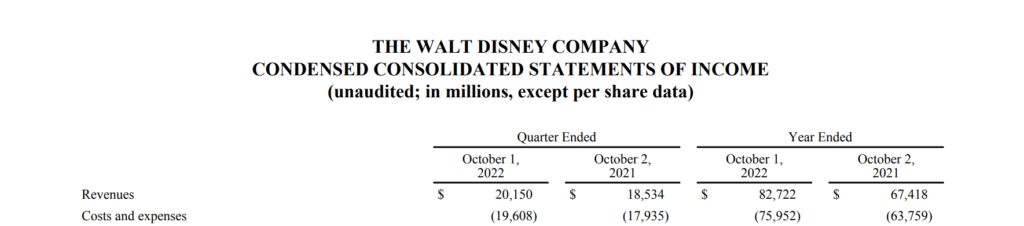
Disney incurred a total expenditure of over $78 billion for the year ended October 1, 2022. It spent nearly $76 billion on costs and expenses, $237 million on restructuring and impairment, $1.4 billion on interest expense, and $667 million on other expenses.
How Does Disney Make Money?
Disney reported a revenue of $82.7 billion for the year ended October 1, 2022. Its net income for the 2021-2022 fiscal year was $3.2 billion. However, how does The Walt Disney Company make money? Which streams does it earn revenue from? Let’s find out.
Disney’s revenue streams can be categorized into five sections:
1. Theme parks, resorts, cruises, and adventures
Millions visit Disney’s various theme parks annually to meet Mickey, his friends, and other Disney characters in real life. The company earns a significant portion of its revenue from the sale of admission tickets to its parks and adventures. Income from the sale of rooms in its various resorts, cruises, and other vacations is an added bonus.
Further, the sale of merchandise, toys, and other consumer products at parks and related experiences supplement Disney’s income. The food stalls, restaurants, candy stores, and Disney-themed food and beverage sources generate a pretty penny for this conglomerate. It also earns royalties from the licensing of intellectual properties.
2. Cable networks
Disney’s repertoire of cable networks—national and international—account for a significant portion of its revenue. Its list includes the homegrown Disney channel and network along with acquired networks like National Geographic, ESPN, ABC broadcast television network, and eight other domestic TV channels. It also owns a 50% stake in A+E Television Networks.
3. Subscription and advertising
Disney owns and operates multiple streaming services on a global scale, including Disney+, Disney+Hotstar, Hulu, Star+, and ESPN+. The company earns money through the subscription fees of these streaming services.
It also earns advertising income by showing advertisements on its streaming channels.
4. Merchandise sales
Disney earns income by selling company-specific clothes, toys, homeware, and collectibles through its website. It also partners with affiliates to increase sales and drive revenue. Moreover, it generates revenue through merchandise licensing and retail.

5. Content sales and licensing
Disney sells its film and television content to other TV stations and streaming and video-on-demand networks. Theatrical distribution of Disney’s movies—animated and real-life, home entertainment distribution, and music distribution account for a good chunk of its fee revenue.
It also earns licensing fees from live entertainment productions like those on Broadway and other stages around the world.
The Bottom Line: Disney is the ideal Family Entertainment Conglomerate
Disney is growing and expanding YoY (year-on-year). Its commitment and drive to produce family entertainment content and products, offer one-of-a-kind experiences, and iconic mouse mascot have made it a beloved household name worldwide.
References & more information
- Daniel Pereira (Jun 6, 2023). Disney Business Model . The Business Model Analyst
- Disney – Leadership, History, Corporate Social Responsibility
- Statista Research Department (Sep 18, 2023). Most visited theme parks in the world 2022 . Statista
- Nikita Sheth (Aug 17, 2023). How Disney Makes Money: The Business Model Explained . Finty
- Disney Parks, Experiences and Products
- Adventures by Disney
- Affiliates Page | shopDisney
- THE WALT DISNEY COMPANY REPORTS FOURTH QUARTER and FULL YEAR EARNINGS FOR FISCAL 2022
- Matthew Johnston (Nov 28, 2022). How Disney Makes Money: Media, Entertainment, Parks, and Experiences . Investopedia
- Iulia Cristina Uta (May 26, 2023). Disney: The Story Behind The Brand . Brandminds
- Featured Image by Younho Choo
Tell us what you think? Did you find this article interesting? Share your thoughts and experiences in the comments section below.
She is a data scientist and serial marketer, she brings a unique analytical perspective and extensive knowledge in marketing from her years of experience working for tech giants and starts ups.
Add comment
Cancel reply, you may also like.

20 Most Unique Business Models
Every company follows a certain business model. The growth and success of a company are based on the business model it follows. Therefore, it is essential for a business model to be diverse and adaptable. However, there...
How does Bumble work & make money?
Company: Bumble Founders: Whitney Wolfe Herd Year founded: 2014 Headquarter: Austin, TX Registered Users (2019): 75 million Valuation (2019): $3 Billion Annual Revenue (2018): $162 million Products &...

Airbnb Business Model | How does Airbnb make money?
Company: Airbnb Founder(s): Brian Chesky, Nathan Blecharczyk, Joe Gebbia Year founded: 2008 CEO(s): Brian Chesky Headquarter: San Francisco, California Number of Employees (2020): 6,000 Type: Public Market Cap...

How Does Turnitin Work & Make Money
Last updated: May 30, 2020 Company: Turnitin CEO: Chris Caren Founders: John Barrie Year founded: 1998 Headquarter: Oakland, California, USA Employees: Est. 417 Type: Private Annual...

Diving Deep into Peloton’s Business Model
The US home fitness equipment industry is expected to reach a valuation of $5.09 billion by 2023, from its valuation of $4.81 billion in 2022. While increasing health awareness is fueling this industry’s growth, body...
Walmart Business Model | How does Walmart Make Money ?
Company: Walmart Inc. (NYSE: WMT) Founders: Sam Walton Year founded: 1962 CEO: Doug McMillan Headquarter: Bentonville, Arkansas Number of Employees (2023): 2.1 million Type: Public Market Capitalization (July...

How Does Popmoney Work ?
Last updated: May 18, 2020 Company: Popmoney (Division of Fiserv) CEO: Jeffery W. Yabuki Founders: Sanjeev Dheer Year founded: 2010 Headquarter: New York, NY Products & Services: Peer...

How does DealDash work & make money?
Company: DealDash Founders: William Wolfram CEO: Pasi Lohi Year founded: 2009 Headquarter: Minneapolis, MN Number of Employees (Dec 2018): 50 Type: Private Annual Revenue (Dec 2018): Estimated $9.7M Products...
Flipkart Business Model | How does Flipkart make money?
Company: Flipkart.com (a subsidiary of Walmart) Founder: Sachin Bansal, Binny Bansal Year founded: 2007 Headquarter: Bengaluru, India CEO (Jan 2017 – Present):Kalyan Krishnamurthy Number of Employees...

How Does eBay Make Money? (2022)
Last updated: May 23, 2020 Company: eBay Founder: Pierre Omidyar CEO: Devin Wenig Year founded: 1995 Headquarter: San Jose, California, USA Number of Employees (Dec 2019): 13,300 Type: Public Ticker Symbol: EBAY Market...
Recent Posts
- Who Owns Truist Bank?
- Who Owns Alfa Romeo?
- Who Owns Burt’s Bees?
- Top 15 Ruggable Competitors and Alternatives
- Top 15 Ticketmaster Competitors and Alternatives
- Who owns Kidz Bop?
- Top 20 Zapier Competitors and Alternatives
- Top 15 Boxabl Competitors and Alternatives
- Who Owns High Noon?
- Top 20 Canva’s Competitors and Alternatives
Business Strategy Hub
- A – Z Companies
- Privacy Policy
Subscribe to receive updates from the hub!
- Red Queen Effect
- Blue Ocean Strategy
- Only the paranoid survives
- Co-opetition Strategy
- Mintzberg’s 5 Ps
- Ansoff Matrix
- Target Right Customers
- Product Life Cycle
- Diffusion of Innovation Theory
- Bowman’s Strategic Clock
- Pricing Strategies
- 7S Framework
- Porter’s Five Forces
- Strategy Diamond
- Value Innovation
- PESTLE Analysis
- Gap Analysis
- SWOT Analysis
- Strategy Canvas
- Business Model
- Mission & Vision
- Competitors
Disney’s Entertainment Streaming Business Ekes Out Surprise Profit as Disney+ Core Subscribers Top 117 Million
Disney+ will add 'modest amount' of ESPN live sports to flagship streamer by end of 2024, Iger says
By Todd Spangler
Todd Spangler
NY Digital Editor
- Apple Apologizes for iPad Ad Amid Controversy: ‘We Missed the Mark’ 12 hours ago
- Vice Digital Properties Will Live on Under New Joint Venture; Vice News Not Part of Deal 15 hours ago
- ‘Cheers’ Stars Ted Danson, Woody Harrelson Reunite for Weekly Podcast With Celebrity Friends 17 hours ago

Disney ‘s entertainment streaming segment, anchored by Disney+, scored its first profitable quarter, helping to partially offset continued weakness in the media conglomerate’s linear TV business for the first three months of 2024.
To be sure, Disney’s overall streaming business was still in the red for the quarter when factoring in ESPN+, which had an operating loss of $65 million. The company reiterated its expectation that its combined streaming operations will achieve profitability in the September 2024 quarter.
Popular on Variety
Disney’s entertainment direct-to-consumer business, encompassing Disney+, Hulu and Disney+ Hotstar, turned a profit in the quarter: Operating income was $47 million (compared with a loss of $587 million a year ago) on revenue of $5.64 billion (up 13%) for the period, which was the company’s Q2 of fiscal 2024.
Disney+ Core (which excludes Disney+ Hotstar in India and other Southeast Asian countries) gained 6.3 million subscribers in the period to hit 117.6 million — above forecasts — up 6% sequentially. The company previously projected Disney+ Core subscriber net adds of 5.5 million-6 million.
SEE ALSO: Marvel Will Release No More Than Three Movies and Two Shows Per Year, Bob Iger Says
“While we are expecting softer Entertainment DTC results in Q3 to be driven by Disney+ Hotstar, we continue to expect our combined streaming businesses to be profitable in the fourth quarter, and to be a meaningful future growth driver for the company, with further improvements in profitability in fiscal 2025,” the company said.
CEO Bob Iger said in prepared remarks, “Our strong performance in Q2, with adjusted EPS up 30% compared to the prior year, demonstrates we are delivering on our strategic priorities and building for the future. Our results were driven in large part by our Experiences segment as well as our streaming business. Importantly, entertainment streaming was profitable for the quarter, and we remain on track to achieve profitability in our combined streaming businesses in Q4.”
By the end of 2024, the company will add an ESPN tile to Disney+ to provide a “modest amount” of live games and other sports programming to all Disney+ U.S. subscribers, Iger said on the call, saying that’s “the first step to bringing ESPN to Disney+ viewers” ahead of the launch of a standalone ESPN streaming service in 2025 . In addition, the plan is to give ESPN+ subscribers access to that content through Disney+, he said. Iger framed the move in the context of the “encouraging” results of the integration of Hulu with Disney+ .
Iger also noted that Disney will begin cracking down on streaming users who are “improperly” sharing passwords starting in some markets in June, followed by a wide rollout in September.
Alluding to Disney’s lack of big movie premieres in the March quarter, Iger said, “We have a number of highly anticipated theatrical releases arriving over the next few months.” On the call, he cited upcoming films including “Kingdom of the Planet of the Apes” (premiering May 10) followed by “Inside Out 2” and “Deadpool & Wolverine.”
The results come after Iger and the 11 other incumbent Disney-backed board members last month won reelection by a wide margin at the annual shareholders meeting. That followed a contentious, months-long proxy fight brought by activist investor Nelson Peltz , whose Trian Partners had unsuccessfully lobbied to get a pair of board seats. Peltz had argued that Disney’s stock underperformance required new directors to provide fresh thinking.
For the March quarter, Disney’s domestic linear TV revenue (excluding ESPN) dropped 7%, to $2.27 billion, and operating income slumped 22%, to $520 million. Disney attributed the decrease in operating income to “the impact of the nonrenewal of carriage of certain networks by an affiliate” (a reference to Charter dropping eight cable networks last fall) and a decline in ad revenue reflecting lower average viewership.
ESPN revenue was up 3%, to $4.21 billion, and operating income declined 9%, to $799 million. ESPN+ dropped 400,000 subscribers in the quarter, declining 2% sequentially to 24.8 million.
Overall, Disney posted revenue of $22.08 billion (up 1.2%) and a net loss of $20 million (versus net income of $1.27 billion in the year-earlier period), or a loss of 1 cent per share.
Disney shares were down more than 5% in premarket trading Tuesday. As of Monday, May 6, the stock was up 29% year to date.
Excluding the $2 billion goodwill impairment charge (as well as amortization of 21st Century Fox and Hulu intangible assets and fair value step-up on film and TV costs), Disney’s adjusted earnings per share for the quarter came in at $1.21 — up 30% year over year. Wall Street analysts on average expected revenue of $22.12 billion and adjusted earnings per share of $1.10 for the quarter, according to data provider LSEG.
As a result of the “outperformance” in the second fiscal quarter, Disney raised its full-year adjusted EPS growth target to 25% (from “at least 20%” previously). The company said it repurchased $1 billion worth of shares in the quarter and that it “look[s] forward to continuing to return capital to shareholders.”
More From Our Brands
Watch paramore perform ‘burning down the house’ live in paris, drew barrymore’s bucolic hamptons retreat can be yours for $8.4 million, wnba taps delta airlines as charter flights this season, the best loofahs and body scrubbers, according to dermatologists, is law & order: organized crime preparing to lose a stabler read episode 12 recap, verify it's you, please log in.

Presentations made painless
- Get Premium
Walt Disney: Business Model, SWOT Analysis, and Competitors 2023
Inside This Article
In this blog article, we will delve into the fascinating world of Walt Disney, exploring its business model, conducting a SWOT analysis, and examining its competitors as we look ahead to the year 2023. Walt Disney, renowned for its timeless entertainment and magical experiences, has captivated audiences worldwide. By understanding its business model, we can gain insights into the company's success. Additionally, conducting a SWOT analysis will shed light on its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Lastly, exploring its competitors will provide a comprehensive view of the industry landscape in the near future.
What You Will Learn:
- Who owns Walt Disney and the significance of their ownership structure.
- The mission statement of Walt Disney and how it guides the company's operations and decision-making.
- How Walt Disney makes money through its diversified revenue streams and strategic business model.
- An in-depth explanation of Walt Disney's Business Model Canvas and how it helps the company thrive in the entertainment industry.
- The key competitors of Walt Disney and their impact on the company's market position.
- A comprehensive SWOT analysis of Walt Disney, highlighting its strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats in the current market landscape.
Who owns Walt Disney?
The walt disney company: a brief overview.
The Walt Disney Company, often referred to as Disney, is one of the world's largest and most influential entertainment conglomerates. Founded in 1923 by Walt Disney and Roy O. Disney, the company has grown exponentially over the years, encompassing various sectors such as film production, theme parks, television networks, and merchandise.
The Founders and Their Legacy
Walt Disney, the creative genius behind Disney's animated characters, brought to life iconic creations like Mickey Mouse, Donald Duck, and Snow White. His brother, Roy O. Disney, played a crucial role in managing the business side of the company. Together, they established the foundation for what would become a global entertainment powerhouse.
A Publicly Traded Company
As of today, The Walt Disney Company is a publicly traded company, listed on the New York Stock Exchange under the ticker symbol "DIS." This means that ownership of Disney is distributed among numerous shareholders who hold shares of the company's stock.
Major Shareholders
While Disney has a vast number of individual and institutional shareholders, some major stakeholders hold significant portions of the company's stock. One such example is The Vanguard Group, an investment management firm, which holds a substantial stake in Disney. Other major shareholders include BlackRock, State Street Corporation, and Berkshire Hathaway, among others.
The Disney Family Trust
Although the Disney family does not hold a majority stake in the company, they still maintain a presence in Disney's ownership structure. The Disney Family Trust, established by Walt Disney's descendants, holds a notable number of shares, ensuring the family's ongoing association with the company and its legacy.
The Influence of Bob Iger
Bob Iger, the former CEO of The Walt Disney Company, played a pivotal role in shaping the company's recent success. During his tenure, Iger led several strategic acquisitions, including Pixar Animation Studios, Marvel Entertainment, and Lucasfilm (the company behind Star Wars). These acquisitions added immensely to Disney's intellectual property portfolio and expanded its global reach.
The Future of Disney's Ownership
As with any publicly traded company, ownership of Disney can fluctuate due to stock market activity and changes in shareholder positions. However, the enduring legacy of the Disney family, coupled with the company's strategic acquisitions and continued success, ensure that Walt Disney's vision and influence remain an integral part of the company's identity.
What is the mission statement of Walt Disney?
The mission statement of walt disney: creating happiness and magic for all.
Walt Disney, the legendary entertainment company, has a well-defined mission statement that has guided its operations and growth over the years. The mission statement of Walt Disney is to "create happiness and magic for all." This simple yet powerful statement encapsulates the primary goal and purpose of the company.
At its core, the mission statement reflects Walt Disney's commitment to delivering exceptional and enchanting experiences to people of all ages. The company aims to bring joy, inspiration, and entertainment to its audience through various forms of storytelling, including movies, theme parks, television shows, and merchandise.
By emphasizing the concept of happiness, Walt Disney's mission statement highlights its dedication to creating positive and uplifting experiences for individuals worldwide. The company focuses on delivering content and experiences that evoke emotions such as joy, wonder, and nostalgia, allowing people to escape from their everyday lives and immerse themselves in magical worlds.
Furthermore, the mission statement's inclusion of the term "magic" underscores Disney's commitment to enchantment and imagination. Walt Disney believes in the power of storytelling and the ability to transport people to extraordinary realms where dreams come true. Whether it's through beloved animated characters like Mickey Mouse or immersive theme park attractions, the company aims to create magical moments that leave a lasting impact on its audience.
Importantly, the mission statement's use of the phrase "for all" highlights Disney's commitment to inclusivity and accessibility. The company strives to make its content and experiences available to a wide range of people, irrespective of age, background, or location. Whether it's through its diverse cast of characters or its efforts to expand into international markets, Walt Disney aims to touch the lives of individuals from all walks of life.
In conclusion, Walt Disney's mission statement of "creating happiness and magic for all" serves as a guiding principle for the company's operations and aspirations. By focusing on delivering exceptional experiences, fostering imagination, and promoting inclusivity, Disney continues to fulfill its mission and bring joy to millions of people around the world.
How does Walt Disney make money?
Box office revenue.
One of the primary ways Walt Disney makes money is through box office revenue. Disney owns several film studios, including Walt Disney Pictures, Pixar Animation Studios, Marvel Studios, and Lucasfilm. These studios produce and distribute movies that generate billions of dollars at the box office worldwide. From beloved animated classics to blockbuster superhero films, Disney's movies consistently attract large audiences and generate substantial ticket sales.
Theme Parks and Resorts
Disney's theme parks and resorts are another major source of revenue. With iconic locations such as Disneyland in California, Walt Disney World in Florida, and Disneyland Paris, Disney's parks attract millions of visitors each year. Ticket sales, accommodation bookings, merchandise sales, and food and beverage sales all contribute to the revenue generated by the theme parks and resorts. Additionally, Disney operates Disney Cruise Line, providing another avenue for revenue through vacation packages and onboard spending.
Merchandise and Licensing
Disney characters and franchises are extremely popular and have a significant presence in the consumer goods market. Through merchandise sales, Disney earns substantial revenue from toys, clothing, accessories, and other products featuring its beloved characters. Additionally, Disney licenses its intellectual property to other companies, allowing them to produce and sell products based on Disney's characters and franchises. This includes everything from clothing lines to video games, generating significant licensing revenue for the company.
Media Networks
Disney's media networks, including ABC, ESPN, and various Disney-owned television channels, play a crucial role in the company's revenue stream. Advertising revenue, affiliate fees, and content licensing contribute to the financial success of Disney's media networks. These networks broadcast a wide range of content, including sports events, news programs, and popular television shows, attracting large audiences and generating substantial revenue through advertisements and partnerships.
Streaming Services
In recent years, Disney has launched its own streaming services, namely Disney+ and Hulu (in which Disney has a controlling stake). These platforms offer subscribers access to a vast library of Disney-owned content, including movies, TV shows, and original productions. The subscription fees from these streaming services contribute to Disney's revenue, with the increasing popularity and growth of streaming further enhancing the company's financial success.
Consumer Products and Interactive Media
Disney's consumer products and interactive media division focuses on digital content, video games, e-books, and interactive experiences. By creating and distributing digital content and engaging interactive experiences, Disney generates revenue from consumers who are increasingly embracing digital forms of entertainment. Additionally, the division oversees Disney's online platforms, apps, and websites, which serve as additional revenue streams through advertising and subscription services.
Overall, Walt Disney generates revenue through a diverse range of sources, leveraging its iconic brands, characters, and franchises to capture the attention and wallets of millions of consumers worldwide.
Walt Disney Business Model Canvas Explained
Introduction to the business model canvas.
The Business Model Canvas is a strategic management tool that allows organizations to define, analyze, and design their business models. Developed by Alexander Osterwalder and Yves Pigneur, this visual framework provides a holistic view of a company's key components, helping to identify strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement.
In this blog post, we will explore the Walt Disney Company's business model using the Business Model Canvas. By examining the different elements of Disney's business model, we can gain insights into how the company has achieved its success and sustained its position as a global entertainment powerhouse.
Key Partnerships
One of the key strengths of Disney's business model lies in its strategic partnerships. Disney has established strong partnerships with various entities that have contributed significantly to its success. These partnerships include collaborations with other entertainment companies, such as Pixar, Marvel Studios, and Lucasfilm, which have expanded Disney's portfolio of intellectual properties and enhanced its ability to create captivating content.
Moreover, Disney has formed partnerships with distribution networks, both traditional and digital, to ensure wide reach and accessibility for its content. This includes agreements with cable and satellite providers, streaming platforms like Netflix and Hulu, and even theme park operators worldwide. These partnerships enable Disney to distribute its content through multiple channels, maximizing its revenue streams and ensuring a strong market presence.
Key Activities
Disney's key activities revolve around content creation, theme park operations, and merchandising. Content creation lies at the heart of Disney's business model, as the company continuously develops and produces high-quality movies, TV shows, and other media content. Through its various subsidiaries and partnerships, Disney is able to leverage its intellectual properties and iconic characters to create captivating stories that resonate with audiences of all ages.
Disney's theme park operations are another critical aspect of its business model. The company owns and operates multiple theme parks globally, including Disneyland Resort in California, Walt Disney World Resort in Florida, and Disneyland Paris. These theme parks offer immersive experiences for visitors, combining entertainment, storytelling, and customer service excellence. The revenue generated from theme park admissions, merchandise sales, and food and beverage offerings contributes significantly to Disney's overall financial performance.
Merchandising is yet another important activity for Disney. The company has built a strong presence in the consumer products industry, capitalizing on its extensive portfolio of characters and franchises. Through licensing agreements and retail partnerships, Disney merchandise can be found in stores worldwide, allowing fans to bring a piece of the Disney magic into their homes. This diversification of revenue streams helps Disney mitigate risks and maintain a stable financial position.
Key Resources
Disney's key resources can be categorized into intellectual property, human capital, and physical assets. Intellectual property is at the core of Disney's business model, with its vast collection of iconic characters, stories, and franchises serving as valuable intangible assets. These intellectual properties not only drive content creation but also form the basis for merchandise, theme park attractions, and other revenue-generating activities.
Disney's human capital is another crucial resource. The company employs a diverse and talented workforce across various disciplines, including animation, film production, theme park operations, marketing, and more. The expertise and creativity of its employees contribute to the continued success of Disney's content creation and operational activities.
In terms of physical assets, Disney owns and operates theme parks, production studios, and distribution facilities worldwide. These physical assets provide the necessary infrastructure for Disney to deliver its products and services effectively. The theme parks, in particular, are iconic symbols of the Disney brand, attracting millions of visitors each year and generating significant revenue for the company.
By examining the Walt Disney Company's business model using the Business Model Canvas, we can appreciate the strategic partnerships, key activities, and essential resources that have contributed to Disney's success. Disney's ability to create compelling content, operate immersive theme parks, and leverage its intellectual properties has allowed the company to establish a strong brand presence and generate substantial revenue streams. The Business Model Canvas provides a comprehensive framework for understanding the intricacies of Disney's business model and serves as a valuable tool for analyzing and improving any organization's strategic approach.
Which companies are the competitors of Walt Disney?
Introduction.
Walt Disney, a global entertainment and media conglomerate, has established itself as a powerhouse in the industry. However, it is not without competitors. Several companies strive to challenge Disney's dominance in various segments of the entertainment market. Let's explore some of the key competitors of Walt Disney.
1. Comcast Corporation (NBCUniversal)
Comcast Corporation, one of the largest media and entertainment companies, poses a significant competition to Walt Disney. Through its subsidiary, NBCUniversal, Comcast operates a diverse range of businesses, including broadcast networks (NBC), cable channels (USA Network, Bravo, E!, and more), theme parks (Universal Parks & Resorts), and film production (Universal Pictures). With its extensive media portfolio and successful franchises such as "Jurassic Park" and "Fast & Furious," NBCUniversal competes directly with Disney in areas like film production, theme parks, and television networks.
2. WarnerMedia (AT&T)
WarnerMedia, a subsidiary of telecommunications giant AT&T, presents formidable competition to Walt Disney. With properties like Warner Bros. Entertainment, HBO, and Turner Broadcasting System, WarnerMedia boasts an impressive array of assets. Warner Bros. Entertainment, in particular, competes head-on with Disney in the film production industry, as it owns iconic franchises like "Harry Potter," "DC Comics," and "The Lord of the Rings." Additionally, HBO's popular shows and streaming platform, HBO Max, challenge Disney's dominance in the streaming space.
Netflix, the world's leading streaming service, has emerged as a significant competitor to Walt Disney, particularly in the realm of digital entertainment. With millions of subscribers across the globe, Netflix offers a vast library of original and licensed content, ranging from TV shows to movies. As Disney has entered the streaming market with Disney+, it directly competes with Netflix for subscribers and viewership. Both companies invest heavily in creating exclusive content and expanding their user bases, making this rivalry intense and ever-evolving.
4. ViacomCBS
ViacomCBS, a conglomerate resulting from the merger of Viacom and CBS Corporation, represents another rival of Walt Disney. With a diverse portfolio of television networks (MTV, Nickelodeon, Comedy Central, and more), film production (Paramount Pictures), and streaming services (Paramount+), ViacomCBS competes with Disney in various aspects of the entertainment industry. Paramount Pictures, in particular, vies with Disney's film production arm, releasing popular franchises like "Transformers" and "Mission: Impossible."
5. Sony Corporation
Sony Corporation, a Japanese multinational conglomerate, also competes with Walt Disney in specific entertainment sectors. Sony Pictures Entertainment, the film production and distribution arm of Sony, produces major blockbuster franchises such as "Spider-Man," "Jumanji," and "James Bond." While not as extensive as Disney's overall media empire, Sony's film division remains a formidable competitor in terms of box office success and attracting audiences worldwide.
Walt Disney faces fierce competition from several prominent companies across various segments of the entertainment industry. Comcast Corporation (NBCUniversal), WarnerMedia (AT&T), Netflix, ViacomCBS, and Sony Corporation are just a few of the key competitors that challenge Disney's dominance. As the entertainment landscape continues to evolve, the rivalry between these companies intensifies, leading to innovative content offerings and an exciting race for consumers' attention.
Walt Disney SWOT Analysis
- Strong brand reputation: Walt Disney has built a strong brand image and reputation over the years. It is widely recognized and associated with quality entertainment and family-friendly content.
- Diversified business portfolio: The company operates in various segments, including media networks, theme parks, studio entertainment, and consumer products. This diversification helps Walt Disney mitigate risks and capitalize on different revenue streams.
- Iconic characters and franchises: Walt Disney owns a vast library of beloved characters and franchises, such as Mickey Mouse, Marvel, Star Wars, and Pixar. These properties have a large fan base and provide the company with a steady flow of revenue through merchandise sales, movies, and theme park attractions.
- Strong distribution network: Walt Disney has an extensive distribution network that spans across multiple platforms, including movies, television, streaming services, and merchandise. This allows the company to reach a wide audience and maximize its market reach.
- Innovation and technological advancements: Walt Disney has consistently embraced innovation and adopted new technologies to enhance its offerings. For example, the company has invested in virtual reality experiences and developed its streaming platform, Disney+. These initiatives help Walt Disney stay relevant in an ever-changing media landscape.
- Dependence on specific franchises: While Walt Disney's iconic franchises are a strength, the company also faces the risk of overreliance on them. If a particular franchise underperforms, it could have a significant impact on the company's revenue and profitability.
- High operating costs: Operating theme parks, producing movies, and maintaining a vast distribution network require substantial financial resources. This exposes Walt Disney to cost pressures and limits its flexibility in allocating funds to other areas of the business.
- Vulnerability to economic downturns: The entertainment industry is sensitive to economic cycles, and Walt Disney is not immune to this. During economic downturns, consumers may cut back on discretionary spending, impacting theme park attendance and merchandise sales.
Opportunities
- Expanding into emerging markets: Walt Disney has the opportunity to tap into growing markets, particularly in Asia, such as China and India. The rising middle class and increasing disposable income in these regions present opportunities for the company to expand its theme parks, movies, and consumer products.
- Streaming services growth: The launch of Disney+ has opened up new possibilities for the company to compete in the streaming industry. As more consumers shift towards digital content consumption, Walt Disney can leverage its vast library of content to attract subscribers and generate additional revenue.
- Cross-promotion and synergies: With its diverse portfolio, Walt Disney can capitalize on cross-promotion and synergies between its various segments. For example, successful movies can drive merchandise sales, and popular characters can be incorporated into theme park attractions, creating a seamless and immersive experience for consumers.
- Increasing competition: The entertainment industry is highly competitive, with numerous players vying for consumers' attention. Streaming services, in particular, have become crowded, with competitors like Netflix, Amazon Prime Video, and Hulu. This intense competition could impact Walt Disney's market share and profitability.
- Changing consumer preferences: Consumer preferences and trends are constantly evolving, and Walt Disney needs to adapt to these changes to remain relevant. Failure to keep up with shifting preferences could lead to a decline in audience engagement and reduced demand for its products and services.
- Regulatory and legal challenges: As a large multinational corporation, Walt Disney is subject to various regulatory and legal challenges. These include copyright and intellectual property disputes, antitrust regulations, labor laws, and content censorship. Compliance with these regulations can be costly and time-consuming.
Key Takeaways
- The Walt Disney Company is owned by shareholders, with the largest shareholders being institutional investors like Vanguard Group and BlackRock.
- The mission statement of Walt Disney is to "entertain, inform, and inspire people around the globe through the power of unparalleled storytelling, reflecting the iconic brands, creative minds, and innovative technologies that make ours the world's premier entertainment company."
- Walt Disney makes money through various sources, including its theme parks and resorts, media networks (such as ABC and ESPN), studio entertainment (producing and distributing films), consumer products, and direct-to-consumer streaming services.
- The Walt Disney Business Model Canvas encompasses key elements such as customer segments (families, children, and entertainment enthusiasts), value proposition (high-quality entertainment experiences and merchandise), channels (theme parks, TV networks, and online platforms), customer relationships (loyalty programs and personalized experiences), and revenue streams (ticket sales, advertising, licensing, and subscriptions).
- Some of the main competitors of Walt Disney include Comcast Corporation (NBCUniversal), WarnerMedia (owned by AT&T), and ViacomCBS Inc., as well as streaming services like Netflix and Amazon Prime Video.
- In terms of a SWOT analysis, Walt Disney's strengths include its strong brand recognition, diversified business portfolio, and extensive intellectual property. However, it faces weaknesses such as dependence on specific franchises and potential risks related to piracy and content distribution. Opportunities for the company include expanding into emerging markets and the growing demand for streaming services, while threats include competition, changing consumer preferences, and economic downturns.
In conclusion, Walt Disney is a conglomerate entertainment company that has become a household name. While it was founded by Walt Disney and Roy O. Disney, it is now owned by shareholders who hold its publicly traded stock. The mission statement of Walt Disney is to entertain, inform, and inspire people around the globe through the power of storytelling and imagination.
Walt Disney's primary revenue streams come from various sources, including its theme parks and resorts, media networks, studio entertainment, and consumer products. The company's ability to diversify its operations has allowed it to maintain a strong financial position and continue expanding its reach.
By utilizing the Business Model Canvas, we can understand the key elements that contribute to Walt Disney's success. These include its value proposition of providing high-quality entertainment experiences, its key activities of creating and distributing content, its customer segments that range from families to individuals of all ages, and its strong relationships with partners and suppliers.
However, Walt Disney does face competition in the entertainment industry. Some of its notable competitors include Universal Studios, Warner Bros., and Comcast NBCUniversal. These companies also strive to capture the attention and loyalty of consumers, leading to a constant battle for market share and innovative offerings.
To assess the company's strengths and weaknesses, we conducted a SWOT analysis. Walt Disney's strengths lie in its strong brand recognition, extensive intellectual property portfolio, and global presence. However, it also faces weaknesses such as high operating costs and dependence on certain franchises. Opportunities for growth include expanding into new markets and leveraging technological advancements, while threats include changing consumer preferences and increasing competition.
Overall, Walt Disney's success can be attributed to its ability to create magical experiences and connect with audiences worldwide. By staying true to its mission and continuously adapting to evolving consumer demands, it remains a dominant force in the entertainment industry.
What is the SWOT analysis of Disney?
- Strong brand recognition and reputation: Disney is one of the most recognizable and beloved brands globally.
- Diversified business portfolio: Disney operates in various segments, including media networks, theme parks, film production, and merchandise, allowing for revenue stability.
- Extensive intellectual property: The company owns a vast library of iconic characters, stories, and franchises, such as Mickey Mouse, Marvel, Star Wars, and Pixar, providing a competitive advantage.
- Global presence: Disney has a strong international presence with theme parks, resorts, and media networks in multiple countries, allowing for global reach and revenue generation.
- Innovation and technology: The company has embraced technological advancements, such as interactive experiences, digital streaming platforms, and virtual reality, to enhance customer engagement and satisfaction.
Weaknesses:
- Dependence on specific markets: Disney's theme parks and resorts heavily rely on tourism, making it vulnerable to economic downturns, natural disasters, and geopolitical tensions.
- High operational costs: Maintaining and expanding theme parks and resorts requires significant investments and ongoing expenses, impacting profitability.
- Reliance on third-party distribution: Disney relies on third-party distributors for its media content, which might limit its control over pricing and distribution strategies.
- Limited control over content consumption: The shift towards digital streaming platforms challenges Disney's traditional distribution channels, potentially impacting revenue streams.
Opportunities:
- Expansion in emerging markets: Disney can further expand its presence in emerging markets, such as China and India, by opening theme parks, launching localized content, and partnerships.
- Growth in digital streaming: The increasing popularity of streaming services presents an opportunity for Disney's Disney+ platform to capture a larger market share and compete with established players like Netflix.
- Synergy among franchises: Cross-promotion and integration among Disney's various franchises can drive increased consumer engagement and revenue, as seen with the Marvel Cinematic Universe.
- Expansion into new business segments: Disney can explore new industries, such as virtual reality, esports, or augmented reality, to diversify its revenue streams.
- Intense competition: Disney faces competition from major media conglomerates, streaming platforms, and theme park operators, which may impact market share and profitability.
- Changing consumer preferences: Evolving consumer preferences, such as a shift towards digital content consumption or experiences beyond traditional theme parks, may pose a threat to Disney's existing business models.
- Piracy and illegal distribution: The unauthorized distribution of Disney's content through piracy or illegal streaming platforms can result in revenue loss and impact the company's intellectual property.
- Economic downturns and travel restrictions: Economic recessions, political instability, or travel restrictions, as seen during the COVID-19 pandemic, can significantly impact Disney's theme park attendance and revenue.
What are the weaknesses of Disney in SWOT analysis?
Some potential weaknesses of Disney in a SWOT analysis include:
Dependence on franchises and intellectual property: Disney relies heavily on its successful franchises like Marvel, Star Wars, and Pixar. If these franchises fail to resonate with audiences or face declining popularity, it could adversely affect Disney's financial performance.
High operating costs: Disney operates numerous theme parks, resorts, and entertainment properties worldwide, which require significant investments and ongoing operational expenses. This high cost structure can pose a challenge, especially during periods of economic downturn or reduced consumer spending.
Vulnerability to external factors: Disney's business is susceptible to various external factors such as natural disasters, political instability, disease outbreaks, and changes in government regulations. These factors can disrupt operations, impact revenue, and lead to reputational damage.
Limited international footprint in some markets: Although Disney has a strong global presence, it may face limitations in certain markets where cultural differences, language barriers, or local competition pose challenges. Expanding into new international markets can be expensive and subject to regulatory hurdles.
Decline in traditional media consumption: With the rise of digital streaming platforms and changing consumer preferences, traditional media channels like cable television have experienced declining viewership. As a result, Disney's cable networks, such as ESPN, may face challenges in retaining subscribers and generating advertising revenue.
Employee relations and labor costs: Disney has faced criticism and legal controversies related to labor practices, particularly concerning low wages and poor working conditions for some of its employees. These issues can impact the company's reputation and employee morale.
It is important to note that weaknesses can vary over time, and Disney's management continuously works to address and mitigate these challenges.
What are the strengths and weaknesses of the Walt Disney Company?
Strong brand image and recognition: The Walt Disney Company is one of the most recognizable and beloved brands in the world. Its characters, parks, and movies have a large and loyal fan base.
Diversified business portfolio: Disney operates in various sectors including movies, theme parks, television, and merchandise. This diversification helps the company mitigate risks and generate revenue from multiple sources.
Innovative storytelling and creativity: Disney has a long history of creating compelling and innovative stories that resonate with audiences of all ages. This creativity has allowed the company to produce successful movies and TV shows.
Global reach and market presence: Disney has a strong global presence and operates in many countries. It has successfully expanded its brand and operations internationally, including opening theme parks in different parts of the world.
Strong financial performance: The company has consistently delivered strong financial results, driven by its diverse revenue streams and successful franchises.
Dependence on specific franchises: While Disney has a diversified business portfolio, it heavily relies on a few specific franchises for its success. This creates a risk if any of these franchises face decline or fail to resonate with audiences.
High production and marketing costs: Producing high-quality movies and running theme parks require significant investments. Disney's success relies on its ability to continue investing in these areas, which can be challenging.
Vulnerability to economic downturns: The entertainment industry is sensitive to economic cycles, and Disney is not immune to economic downturns. Consumer spending on movies, theme parks, and merchandise may decline during tough economic times.
Limited control over external factors: Disney's success can be influenced by factors beyond its control, such as changes in government regulations, piracy, and disruptions in the supply chain.
Criticism and controversies: As a large and influential company, Disney has faced criticism and controversies, including allegations of cultural appropriation and lack of diversity in its storytelling. These issues can negatively impact the company's reputation and brand image.
What are some of the strengths of Walt Disney?
Some of the strengths of Walt Disney include:
Creativity: Walt Disney was known for his unparalleled creativity and imagination. He was able to create captivating stories, memorable characters, and innovative theme park experiences that continue to resonate with audiences today.
Visionary Leadership: Disney had a clear vision for his company and was able to inspire and lead his team to achieve his goals. He was not afraid to take risks and push boundaries, which resulted in groundbreaking achievements and successes.
Strong Branding: Disney has built an iconic brand that is recognized and loved globally. The Disney brand represents family-friendly entertainment, magical experiences, and a commitment to storytelling.
Innovation: Disney was an innovator in the entertainment industry, constantly pushing the boundaries of technology and storytelling. From the creation of the first synchronized sound and full-color cartoons to the development of advanced animatronics and immersive theme park experiences, Disney's focus on innovation has set the company apart.
Strong Intellectual Property: Disney has a vast library of intellectual property, including beloved characters like Mickey Mouse, Cinderella, and Buzz Lightyear. These characters and stories have become timeless and continue to generate revenue through various mediums such as movies, merchandise, and theme park attractions.
Strong Financial Performance: Disney has consistently performed well financially, with a strong track record of revenue growth and profitability. The company's diverse revenue streams, including film, television, theme parks, and merchandise, contribute to its financial stability.
Customer Loyalty: Disney has a loyal fan base that spans generations. The company has built a strong emotional connection with its audience through its storytelling and immersive experiences, resulting in repeat visits and a dedicated following.
Global Reach: Disney has a global presence, with theme parks, entertainment channels, and merchandise available in multiple countries. This global reach allows the company to tap into various markets and expand its audience base.
Strong Talent Pool: Disney has attracted and nurtured a talented pool of artists, animators, and storytellers over the years. The company's commitment to fostering creativity and innovation has resulted in a team of skilled professionals who bring Disney's vision to life.
Commitment to Corporate Social Responsibility: Disney has a strong commitment to corporate social responsibility, with initiatives focused on environmental sustainability, diverse and inclusive storytelling, and community engagement. This commitment contributes to Disney's positive reputation and enhances its brand image.
Want to create a presentation now?
Instantly Create A Deck
Let PitchGrade do this for me
Hassle Free
We will create your text and designs for you. Sit back and relax while we do the work.
Explore More Content
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service
© 2023 Pitchgrade
The Walt Disney Company
Recent news.

‘Kingdom of the Planet of the Apes’ Director/Producer on Creating a ‘P…
‘kingdom of the planet of the apes’ director/producer on creating a ‘prequel and a sequel’ to the iconic franchise.

Rita Ferro, Disney’s President of Global Advertising, on the Company’s U…
Rita ferro, disney’s president of global advertising, on the company’s upfront and the differentiator of storytelling.

Disney Entertainment and Warner Bros. Discovery Announce Disney+, Hulu, Max …
Disney entertainment and warner bros. discovery announce disney+, hulu, max bundle.

Our Future Starts Now with DisneylandForward

Marvel Studios and ILM Immersive Announce ‘What If…? – An Immersiv…
Marvel studios and ilm immersive announce ‘what if… – an immersive story,’ coming exclusively to apple vision pro.

The mission of The Walt Disney Company is to entertain, inform and inspire people around the globe through the power of unparalleled storytelling, reflecting the iconic brands, creative minds and innovative technologies that make ours the world’s premier entertainment company.

Investor Relations
Our commitment to creativity, technology and innovation generates unparalleled experiences that drive long-term value for our shareholders.

Explore a variety of opportunities to start a new chapter in your career at Disney.

SOCIAL RESPONSIBILITY
Our approach to corporate social responsibility is built upon the Company’s long and enduring legacy of engagement in our workplaces and communities and our actions to protect the environment.

IMAGES
COMMENTS
BURBANK, Calif., February 9, 2023 - The Walt Disney Company announced details of its strategic restructuring that will refocus the organization on creativity, empower creative leaders and ensure they are accountable for all aspects of their businesses globally, and put the company's streaming business on a path to sustained growth and profitability.
In a dramatic expansion of its theme parks, products and cruise line business, The Walt Disney Co. says that it will spend $60 billion over the next 10 years to turbocharge growth in the lucrative ...
February 8, 2023 1:39pm. Getty. Disney is reorganizing its sprawling businesses under three core segments, Entertainment, ESPN and Parks, Experiences & Products, as CEO Bob Iger moves to ...
In a memo recently released to company employees, Bob Chapek, CEO of The Walt Disney Company, outlined three strategic pillars that will guide the company in 2022 and beyond.
Disney World celebrated its 50th anniversary in April 2022. Disney said in a securities filing Tuesday it will nearly double its planned investment in its parks division to roughly $60 billion ...
News of Disney's new expansion plans come amid an ongoing legal feud with Florida Gov. Ron DeSantis, the failure of the Star Wars-inspired resort and the recent unveiling of new details about ...
On Wednesday, during its quarterly earnings call with investors, Disney also announced it would be cutting $5.5 billion in costs, which will be made up of $3 billion from content, excluding sports ...
New Constructs, LLC. If Disney earns a 12% ROIC (in-line with its 2018 ROIC) on the $71 billion Fox acquisition, the company will earn an additional $8.5 billion in after-tax operating profit ...
The Walt Disney Company is a diversified family entertainment and media enterprise. It has five business segments: Media Networks, Parks and Resorts, Studio Entertainment, Consumer Products, and Interactive. All of these individual segments are money spinners for the company.
The Disney Plus Basic plan with ads includes: Ad-supported streaming for thousands of Disney movies and TV shows Up to 4K playback with HDR and Dolby Vision support on select titles
In Disney's fiscal Q1 earnings report released on Feb. 7, 2024, the company discussed the performance of its DTC business. Total subscriptions across Disney+ and Hulu rose less than 1% YOY to ...
Disney+ is the ultimate streaming service for fans of Disney, Pixar, Marvel, Star Wars, National Geographic and more. Find out how much it costs to subscribe, what plans are available, and how to get the best value for your money. Visit Disney+ pricing and start your free trial today.
Disney on Tuesday received final approval to move forward with its nearly $2 billion expansion plan for its Disneyland theme park in California. The Anaheim City Council said the company's ...
The Walt Disney Company has a generic competitive strategy that capitalizes on the uniqueness of products offered in the entertainment, mass media, and amusement park industries. Michael E. Porter's model indicates that a generic competitive strategy enables the business to develop and maintain its competitiveness in the target market.
The success of the original park, which opened July 17, 1955, sparked the 1971 opening of Walt Disney World in Orlando, Florida, and eventually led to the construction of nine other parks and ...
Disney CEO Bob Iger plans to cut back on the number of Marvel films and TV shows released each year. The decision comes after a number of Marvel films underperformed at the box office.
Disney also plans on launching a standalone ESPN streaming service in the fall of 2025, along with a dedicated sports streaming service with Warner Bros. Discovery and Fox that's launching later ...
The Disney CEO explained his plans to reduce Marvel Studios' output on the company's earnings call. By Alex Weprin Media & Business Writer Disney is planning to reevaluate its slate of films and ...
Disney incurred a total expenditure of over $78 billion for the year ended October 1, 2022. It spent nearly $76 billion on costs and expenses, $237 million on restructuring and impairment, $1.4 billion on interest expense, and $667 million on other expenses.
Disney's entertainment direct-to-consumer business, encompassing Disney+, Hulu and Disney+ Hotstar, turned a profit in the quarter: Operating income was $47 million (compared with a loss of $587 ...
The Walt Disney Company today announced details of its strategic restructuring that will refocus the organization on creativity, empower creative leaders and ensure they are accountable for all aspects of their businesses globally, and put the company's streaming business on a path to sustained growth and profitability.
The Walt Disney Business Model Canvas encompasses key elements such as customer segments (families, children, and entertainment enthusiasts), value proposition (high-quality entertainment experiences and merchandise), channels (theme parks, TV networks, and online platforms), customer relationships (loyalty programs and personalized experiences ...
"2022 was a strong year for Disney, with some of our best storytelling yet, record results at our Parks, Experiences and Products segment, and outstanding subscriber growth at our direct-to-consumer services, which added nearly 57 million subscriptions this year for a total of more than 235 million," said Bob Chapek, Chief Executive Officer ...
Disney and Warner will bundle their services. The plan is designed to attract more subscribers for both companies, which are competing with the likes of Netflix, Apple, Paramount, and Amazon Prime
The mission of The Walt Disney Company is to entertain, inform and inspire people around the globe through the power of unparalleled storytelling, reflecting the iconic brands, creative minds and innovative technologies that make ours the world's premier entertainment company. View More.
Plan Selection Page