We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Graphic Design 15 Effective Visual Presentation Tips To Wow Your Audience

15 Effective Visual Presentation Tips To Wow Your Audience
Written by: Krystle Wong Sep 28, 2023

So, you’re gearing up for that big presentation and you want it to be more than just another snooze-fest with slides. You want it to be engaging, memorable and downright impressive.
Well, you’ve come to the right place — I’ve got some slick tips on how to create a visual presentation that’ll take your presentation game up a notch.
Packed with presentation templates that are easily customizable, keep reading this blog post to learn the secret sauce behind crafting presentations that captivate, inform and remain etched in the memory of your audience.
Click to jump ahead:
What is a visual presentation & why is it important?
15 effective tips to make your visual presentations more engaging, 6 major types of visual presentation you should know , what are some common mistakes to avoid in visual presentations, visual presentation faqs, 5 steps to create a visual presentation with venngage.
A visual presentation is a communication method that utilizes visual elements such as images, graphics, charts, slides and other visual aids to convey information, ideas or messages to an audience.
Visual presentations aim to enhance comprehension engagement and the overall impact of the message through the strategic use of visuals. People remember what they see, making your point last longer in their heads.
Without further ado, let’s jump right into some great visual presentation examples that would do a great job in keeping your audience interested and getting your point across.
In today’s fast-paced world, where information is constantly bombarding our senses, creating engaging visual presentations has never been more crucial. To help you design a presentation that’ll leave a lasting impression, I’ve compiled these examples of visual presentations that will elevate your game.
1. Use the rule of thirds for layout
Ever heard of the rule of thirds? It’s a presentation layout trick that can instantly up your slide game. Imagine dividing your slide into a 3×3 grid and then placing your text and visuals at the intersection points or along the lines. This simple tweak creates a balanced and seriously pleasing layout that’ll draw everyone’s eyes.
2. Get creative with visual metaphors
Got a complex idea to explain? Skip the jargon and use visual metaphors. Throw in images that symbolize your point – for example, using a road map to show your journey towards a goal or using metaphors to represent answer choices or progress indicators in an interactive quiz or poll.
3. Visualize your data with charts and graphs
The right data visualization tools not only make content more appealing but also aid comprehension and retention. Choosing the right visual presentation for your data is all about finding a good match.
For ordinal data, where things have a clear order, consider using ordered bar charts or dot plots. When it comes to nominal data, where categories are on an equal footing, stick with the classics like bar charts, pie charts or simple frequency tables. And for interval-ratio data, where there’s a meaningful order, go for histograms, line graphs, scatterplots or box plots to help your data shine.
In an increasingly visual world, effective visual communication is a valuable skill for conveying messages. Here’s a guide on how to use visual communication to engage your audience while avoiding information overload.

4. Employ the power of contrast
Want your important stuff to pop? That’s where contrast comes in. Mix things up with contrasting colors, fonts or shapes. It’s like highlighting your key points with a neon marker – an instant attention grabber.
5. Tell a visual story
Structure your slides like a storybook and create a visual narrative by arranging your slides in a way that tells a story. Each slide should flow into the next, creating a visual narrative that keeps your audience hooked till the very end.
Icons and images are essential for adding visual appeal and clarity to your presentation. Venngage provides a vast library of icons and images, allowing you to choose visuals that resonate with your audience and complement your message.
6. Show the “before and after” magic
Want to drive home the impact of your message or solution? Whip out the “before and after” technique. Show the current state (before) and the desired state (after) in a visual way. It’s like showing a makeover transformation, but for your ideas.
7. Add fun with visual quizzes and polls
To break the monotony and see if your audience is still with you, throw in some quick quizzes or polls. It’s like a mini-game break in your presentation — your audience gets involved and it makes your presentation way more dynamic and memorable.
8. End with a powerful visual punch
Your presentation closing should be a showstopper. Think a stunning clip art that wraps up your message with a visual bow, a killer quote that lingers in minds or a call to action that gets hearts racing.

9. Engage with storytelling through data
Use storytelling magic to bring your data to life. Don’t just throw numbers at your audience—explain what they mean, why they matter and add a bit of human touch. Turn those stats into relatable tales and watch your audience’s eyes light up with understanding.

10. Use visuals wisely
Your visuals are the secret sauce of a great presentation. Cherry-pick high-quality images, graphics, charts and videos that not only look good but also align with your message’s vibe. Each visual should have a purpose – they’re not just there for decoration.
11. Utilize visual hierarchy
Employ design principles like contrast, alignment and proximity to make your key info stand out. Play around with fonts, colors and placement to make sure your audience can’t miss the important stuff.
12. Engage with multimedia
Static slides are so last year. Give your presentation some sizzle by tossing in multimedia elements. Think short video clips, animations, or a touch of sound when it makes sense, including an animated logo . But remember, these are sidekicks, not the main act, so use them smartly.
13. Interact with your audience
Turn your presentation into a two-way street. Start your presentation by encouraging your audience to join in with thought-provoking questions, quick polls or using interactive tools. Get them chatting and watch your presentation come alive.

When it comes to delivering a group presentation, it’s important to have everyone on the team on the same page. Venngage’s real-time collaboration tools enable you and your team to work together seamlessly, regardless of geographical locations. Collaborators can provide input, make edits and offer suggestions in real time.
14. Incorporate stories and examples
Weave in relatable stories, personal anecdotes or real-life examples to illustrate your points. It’s like adding a dash of spice to your content – it becomes more memorable and relatable.
15. Nail that delivery
Don’t just stand there and recite facts like a robot — be a confident and engaging presenter. Lock eyes with your audience, mix up your tone and pace and use some gestures to drive your points home. Practice and brush up your presentation skills until you’ve got it down pat for a persuasive presentation that flows like a pro.
Venngage offers a wide selection of professionally designed presentation templates, each tailored for different purposes and styles. By choosing a template that aligns with your content and goals, you can create a visually cohesive and polished presentation that captivates your audience.
Looking for more presentation ideas ? Why not try using a presentation software that will take your presentations to the next level with a combination of user-friendly interfaces, stunning visuals, collaboration features and innovative functionalities that will take your presentations to the next level.
Visual presentations come in various formats, each uniquely suited to convey information and engage audiences effectively. Here are six major types of visual presentations that you should be familiar with:
1. Slideshows or PowerPoint presentations
Slideshows are one of the most common forms of visual presentations. They typically consist of a series of slides containing text, images, charts, graphs and other visual elements. Slideshows are used for various purposes, including business presentations, educational lectures and conference talks.

2. Infographics
Infographics are visual representations of information, data or knowledge. They combine text, images and graphics to convey complex concepts or data in a concise and visually appealing manner. Infographics are often used in marketing, reporting and educational materials.
Don’t worry, they are also super easy to create thanks to Venngage’s fully customizable infographics templates that are professionally designed to bring your information to life. Be sure to try it out for your next visual presentation!
3. Video presentation
Videos are your dynamic storytellers. Whether it’s pre-recorded or happening in real-time, videos are the showstoppers. You can have interviews, demos, animations or even your own mini-documentary. Video presentations are highly engaging and can be shared in both in-person and virtual presentations .
4. Charts and graphs
Charts and graphs are visual representations of data that make it easier to understand and analyze numerical information. Common types include bar charts, line graphs, pie charts and scatterplots. They are commonly used in scientific research, business reports and academic presentations.
Effective data visualizations are crucial for simplifying complex information and Venngage has got you covered. Venngage’s tools enable you to create engaging charts, graphs,and infographics that enhance audience understanding and retention, leaving a lasting impression in your presentation.

5. Interactive presentations
Interactive presentations involve audience participation and engagement. These can include interactive polls, quizzes, games and multimedia elements that allow the audience to actively participate in the presentation. Interactive presentations are often used in workshops, training sessions and webinars.
Venngage’s interactive presentation tools enable you to create immersive experiences that leave a lasting impact and enhance audience retention. By incorporating features like clickable elements, quizzes and embedded multimedia, you can captivate your audience’s attention and encourage active participation.
6. Poster presentations
Poster presentations are the stars of the academic and research scene. They consist of a large poster that includes text, images and graphics to communicate research findings or project details and are usually used at conferences and exhibitions. For more poster ideas, browse through Venngage’s gallery of poster templates to inspire your next presentation.

Different visual presentations aside, different presentation methods also serve a unique purpose, tailored to specific objectives and audiences. Find out which type of presentation works best for the message you are sending across to better capture attention, maintain interest and leave a lasting impression.
To make a good presentation , it’s crucial to be aware of common mistakes and how to avoid them. Without further ado, let’s explore some of these pitfalls along with valuable insights on how to sidestep them.
Overloading slides with text
Text heavy slides can be like trying to swallow a whole sandwich in one bite – overwhelming and unappetizing. Instead, opt for concise sentences and bullet points to keep your slides simple. Visuals can help convey your message in a more engaging way.
Using low-quality visuals
Grainy images and pixelated charts are the equivalent of a scratchy vinyl record at a DJ party. High-resolution visuals are your ticket to professionalism. Ensure that the images, charts and graphics you use are clear, relevant and sharp.
Choosing the right visuals for presentations is important. To find great visuals for your visual presentation, Browse Venngage’s extensive library of high-quality stock photos. These images can help you convey your message effectively, evoke emotions and create a visually pleasing narrative.
Ignoring design consistency
Imagine a book with every chapter in a different font and color – it’s a visual mess. Consistency in fonts, colors and formatting throughout your presentation is key to a polished and professional look.
Reading directly from slides
Reading your slides word-for-word is like inviting your audience to a one-person audiobook session. Slides should complement your speech, not replace it. Use them as visual aids, offering key points and visuals to support your narrative.
Lack of visual hierarchy
Neglecting visual hierarchy is like trying to find Waldo in a crowd of clones. Use size, color and positioning to emphasize what’s most important. Guide your audience’s attention to key points so they don’t miss the forest for the trees.
Ignoring accessibility
Accessibility isn’t an option these days; it’s a must. Forgetting alt text for images, color contrast and closed captions for videos can exclude individuals with disabilities from understanding your presentation.
Relying too heavily on animation
While animations can add pizzazz and draw attention, overdoing it can overshadow your message. Use animations sparingly and with purpose to enhance, not detract from your content.
Using jargon and complex language
Keep it simple. Use plain language and explain terms when needed. You want your message to resonate, not leave people scratching their heads.
Not testing interactive elements
Interactive elements can be the life of your whole presentation, but not testing them beforehand is like jumping into a pool without checking if there’s water. Ensure that all interactive features, from live polls to multimedia content, work seamlessly. A smooth experience keeps your audience engaged and avoids those awkward technical hiccups.
Presenting complex data and information in a clear and visually appealing way has never been easier with Venngage. Build professional-looking designs with our free visual chart slide templates for your next presentation.
What software or tools can I use to create visual presentations?
You can use various software and tools to create visual presentations, including Microsoft PowerPoint, Google Slides, Adobe Illustrator, Canva, Prezi and Venngage, among others.
What is the difference between a visual presentation and a written report?
The main difference between a visual presentation and a written report is the medium of communication. Visual presentations rely on visuals, such as slides, charts and images to convey information quickly, while written reports use text to provide detailed information in a linear format.
How do I effectively communicate data through visual presentations?
To effectively communicate data through visual presentations, simplify complex data into easily digestible charts and graphs, use clear labels and titles and ensure that your visuals support the key messages you want to convey.
Are there any accessibility considerations for visual presentations?
Accessibility considerations for visual presentations include providing alt text for images, ensuring good color contrast, using readable fonts and providing transcripts or captions for multimedia content to make the presentation inclusive.
Most design tools today make accessibility hard but Venngage’s Accessibility Design Tool comes with accessibility features baked in, including accessible-friendly and inclusive icons.
How do I choose the right visuals for my presentation?
Choose visuals that align with your content and message. Use charts for data, images for illustrating concepts, icons for emphasis and color to evoke emotions or convey themes.
What is the role of storytelling in visual presentations?
Storytelling plays a crucial role in visual presentations by providing a narrative structure that engages the audience, helps them relate to the content and makes the information more memorable.
How can I adapt my visual presentations for online or virtual audiences?
To adapt visual presentations for online or virtual audiences, focus on concise content, use engaging visuals, ensure clear audio, encourage audience interaction through chat or polls and rehearse for a smooth online delivery.
What is the role of data visualization in visual presentations?
Data visualization in visual presentations simplifies complex data by using charts, graphs and diagrams, making it easier for the audience to understand and interpret information.
How do I choose the right color scheme and fonts for my visual presentation?
Choose a color scheme that aligns with your content and brand and select fonts that are readable and appropriate for the message you want to convey.
How can I measure the effectiveness of my visual presentation?
Measure the effectiveness of your visual presentation by collecting feedback from the audience, tracking engagement metrics (e.g., click-through rates for online presentations) and evaluating whether the presentation achieved its intended objectives.
Ultimately, creating a memorable visual presentation isn’t just about throwing together pretty slides. It’s about mastering the art of making your message stick, captivating your audience and leaving a mark.
Lucky for you, Venngage simplifies the process of creating great presentations, empowering you to concentrate on delivering a compelling message. Follow the 5 simple steps below to make your entire presentation visually appealing and impactful:
1. Sign up and log In: Log in to your Venngage account or sign up for free and gain access to Venngage’s templates and design tools.
2. Choose a template: Browse through Venngage’s presentation template library and select one that best suits your presentation’s purpose and style. Venngage offers a variety of pre-designed templates for different types of visual presentations, including infographics, reports, posters and more.
3. Edit and customize your template: Replace the placeholder text, image and graphics with your own content and customize the colors, fonts and visual elements to align with your presentation’s theme or your organization’s branding.
4. Add visual elements: Venngage offers a wide range of visual elements, such as icons, illustrations, charts, graphs and images, that you can easily add to your presentation with the user-friendly drag-and-drop editor.
5. Save and export your presentation: Export your presentation in a format that suits your needs and then share it with your audience via email, social media or by embedding it on your website or blog .
So, as you gear up for your next presentation, whether it’s for business, education or pure creative expression, don’t forget to keep these visual presentation ideas in your back pocket.
Feel free to experiment and fine-tune your approach and let your passion and expertise shine through in your presentation. With practice, you’ll not only build presentations but also leave a lasting impact on your audience – one slide at a time.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

7 Types of Visual Presentations

When it comes to delivering a presentation, visuals can be extremely helpful in getting your point across. There are many types of visual presentations that can be used to communicate your message.
This blog post will discuss seven different types of visual presentations and when they might be appropriate to use. We will also provide examples of each kind of presentation. Let’s get started!
What are Visual Presentations?
3. whiteboards, 5. infographics, 7. paper handouts, which one is right for you.
Visual presentations are a visual aid that can be used in both business and academia to help explain concepts or topics that might otherwise be difficult for an audience member to understand without seeing them firsthand.
In addition, visuals allow the presenter to provide more information than just words alone would do on their own because they provide context and give the audience something concrete to look at while listening.
There are many types of visual presentations, but we will focus on seven of the most common ones here. Each type has its own strengths and weaknesses, so it’s important to understand when each would be appropriate to use.
Slides are the most common type of visual aid. You can use slides to demonstrate your point and make it easier for the audience to follow along with what you’re saying. They are also pretty easy to prepare.
For example, a slide that shows how much money was spent on advertising last year might be useful in an annual meeting where everyone’s attention span is short or they don’t want to take the time to read a long report.
Graphs and charts are other types of visual presentation that can be used to show trends or compare data.
For example, you might use a graph to illustrate how your company’s revenue has increased or decreased over the past five years. Or, you could use a chart to compare the number of sales your company has made this year compared to last year.
Whiteboards are a great way to explain something in detail, as they allow you to draw pictures and write on them. For example, if your company is thinking about designing a new website but needs some ideas first, then using whiteboards would help everyone get their thoughts out.
One issue about using whiteboards is that they cannot be easily saved and shared with others. Moreover, as you need to write manually, it can be time-consuming and prone to errors.
Videos are another type of visual aid that can be used to demonstrate a concept or show how something works. It’s beneficial when you want to show live instances of your products or services through movements.
For example, if you’re selling cars, then showing them driving around would help people get an idea of what they look like in action (and not just sitting still on a lot).
The downside to using videos is that creating one from scratch can be time-consuming and expensive, so this isn’t always feasible. In addition, videos can be challenging to follow if they are not properly edited.
Infographics are visual presentations that use images and text to convey information. They can be used in many ways, from illustrating trends or comparing data points graphically; to explaining complex concepts in an easy-to-understand manner.
Infographics are especially handy when trying to illustrate a point based on a massive number of data. For example, if you wanted to show how much data your company has collected over the past year, you could use an infographic.
Posters are used primarily in academic settings because they allow students to display their research findings at conferences or other events where the audiences are present.
For example, if someone were presenting on the use of social media in politics, they might create a poster with an image of the political landscape and then use text to explain how social media is being used.
Posters can be created using software or hand-drawing, but they should always be designed with legibility.
Paper handouts are visual aids that can be used to supplement slides or other visuals.
They can be especially useful if you want to provide the audience with additional information that isn’t easily conveyed in a slide or chart.
For example, you might use paper handouts to give the audience more details about the data shown in a graph or provide them with a list of your company’s products and services.
Now that you know about the different types of visuals, how do you decide which one is right for your presentation?
Well, it depends on what you’re trying to accomplish. If you want to make your presentation more interesting and engaging, then using slides or videos might be a good option.
However, if you need to show complex data or explain a concept in detail, charts, whiteboards, or infographics might be better.
In the end, it’s crucial to pick the right type of visual that will help you communicate your message most effectively.
While there are many different types of visual presentations, the seven we’ve outlined in this blog post should give you a good place to start when creating your own visual presentation.
Keep in mind the tone and purpose of your presentation as you select which type will work best for you. And always be sure to test out your visuals on a small audience before presenting them to a larger group. Happy presenting!
Related Posts:

The 8 Types of Presentation Styles: Which Category Do You Fall Into?
Updated: December 16, 2020
Published: September 24, 2018
Types of Presentations
- Visual Style
- Freeform Style
- Instructor Style
- Coach Style
- Storytelling Style
- Connector Style
- Lessig Style
- Takahashi Style
Everyone on the internet has an opinion on how to give the “perfect” presentation.

One group champions visual aids, another thinks visual aids are a threat to society as we know it. One expert preaches the benefits of speaking loudly, while another believes the softer you speak the more your audience pays attention. And don’t even try to find coordinating opinions on whether you should start your presentation with a story, quote, statistic, or question.
But what if there wasn’t just one “right” way to give a presentation? What if there were several? Below, I’ve outlined eight types of presentation styles. They’re used by famous speakers like Steve Jobs and Al Gore -- and none of them are wrong.
Check out each one and decide which will be most effective for you.
![visual presentation types → Free Download: 10 PowerPoint Presentation Templates [Access Now]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/2d0b5298-2daa-4812-b2d4-fa65cd354a8e.png)
Types of Presentation Styles
1. visual style.
What it is: If you’re a firm believer slides simply exist to complement your talking points, this style is for you. With this speaking style, you might need to work a little harder to get your audience engaged, but the dividends can be huge for strong public speakers, visionaries, and storytellers.
When to use it: This style is helpful when speaking to a large audience with broad interests. It’s also great for when you need to throw together slides quickly.
Visual style presenter: Steve Jobs
2. Freeform Style
What it is: This impromptu style of presenting doesn’t require slides. Instead, the speaker relies on strong stories to illustrate each point. This style works best for those who have a short presentation time and are extremely familiar with their talking points.
When to use it: Elevator pitches, networking events, and impromptu meetings are all scenarios in which to use a freeform style of speaking. You’ll appear less rehearsed and more conversational than if you were to pause in the middle of a happy hour to pull up your presentation on a tablet.
Freeform style presenter: Sir Ken Robinson
3. Instructor Style
What it is: This presentation style allows you to deliver complex messages using figures of speech, metaphors, and lots of content -- just like your teachers and professors of old. Your decks should be built in logical order to aid your presentation, and you should use high-impact visuals to support your ideas and keep the audience engaged.
When to use it: If you’re not a comfortable presenter or are unfamiliar with your subject matter (i.e., your product was recently updated and you’re not familiar with the finer points), try instructor-style presenting.
Instructor style presenter: Al Gore
4. Coach Style
What it is: Energetic and charismatic speakers gravitate towards this style of presenting. It allows them to connect and engage with their audience using role play and listener interaction.
When to use it: Use this presentation style when you’re speaking at a conference or presenting to an audience who needs to be put at ease. For example, this style would work well if you were speaking to a group of executives who need to be sold on the idea of what your company does rather than the details of how you do it.
Coach style presenter: Linda Edgecombe
5. Storytelling Style
What it is: In this style, the speaker relies on anecdotes and examples to connect with their audience. Stories bring your learning points to life, and the TED’s Commandments never let you down: Let your emotions out and tell your story in an honest way.
When to use it: Avoid this style if you’re in the discovery phase of the sales process. You want to keep the conversation about your prospect instead of circling every point or question back to you or a similar client. This style is great for conference speaking, networking events, and sales presentations where you have adequate time to tell your stories without taking minutes away from questions.
Storytelling style presenter: Jill Bolte Taylor
6. Connector Style
What it is: In this style, presenters connect with their audience by showing how they’re similar to their listeners. Connectors usually enjoy freeform Q&A and use gestures when they speak. They also highly encourage audience reaction and feedback to what they’re saying.
When to use it: Use this style of presenting early in the sales process as you’re learning about your prospect’s pain points, challenges, and goals. This type of speaking sets your listener at ease, elicits feedback on how you’re doing in real time, and is more of a dialogue than a one-sided presentation
Connector style presenter: Connie Dieken
7. Lessig Style
What it is: The Lessig Style was created by Lawrence Lessig , a professor of law and leadership at Harvard Law School. This presentation style requires the presenter to pass through each slide within 15 seconds. When text is used in a slide, it’s typically synchronized with the presenter’s spoken words.
When to use it: This method of presentation is great for large crowds -- and it allows the speaker to use a balance of text and image to convey their message. The rapid pace and rhythm of the slide progression keeps audiences focused, engaged, and less likely to snooze.
Lessig style presenter: Lawrence Lessig
8. Takahashi Style
What it is: This method features large, bold text on minimal slides. It was devised by Masayoshi Takahashi , who found himself creating slides without access to a presentation design tool or PowerPoint. The main word is the focal point of the slide, and phrases, used sparingly, are short and concise.
When to use it: If you find yourself in Takahashi’s shoes -- without presentation design software -- this method is for you. This style works well for short presentations that pack a memorable punch.
Takahashi style presenter: Masayoshi Takahashi
Slides from one of Takahashi’s presentations:
Whether you’re speaking on a conference stage or giving a sales presentation , you can find a method that works best for you and your audience. With the right style, you’ll capture attention, engage listeners, and effectively share your message. You can even ask an AI presentation maker tool to create presentations for you in your preferred style
![visual presentation types Blog - Beautiful PowerPoint Presentation Template [List-Based]](https://no-cache.hubspot.com/cta/default/53/013286c0-2cc2-45f8-a6db-c71dad0835b8.png)
Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.
![visual presentation types 10 Best Sales Presentations To Inspire Your Sales Deck [+ 5 Tips]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/sales-deck.jpg)
10 Best Sales Presentations To Inspire Your Sales Deck [+ 5 Tips]

15 Sales Presentation Techniques That Will Help You Close More Deals Today

9 Ways to End Your Sales Presentation With a Bang

7 Apps That Help Salespeople Become Even Better Speakers

7 Secrets of a Winning Capabilities Presentation

Insight Selling: The 8-Slide Framework for a Better Pitch

The Best Work-Appropriate GIFs to Use in Your Next Sales Slide Deck
![visual presentation types How to Make a Business Presentation in 7 Easy Steps [Free Business Presentation Templates]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/how-to-make-a-business-presentation.jpg)
How to Make a Business Presentation in 7 Easy Steps [Free Business Presentation Templates]

How to Handle Difficult Sales Calls Like a Pro

Technology Give You the Middle Finger in a Demo? 7 Reactions to Avoid
Download ten free PowerPoint templates for a better presentation.
Powerful and easy-to-use sales software that drives productivity, enables customer connection, and supports growing sales orgs
Presentation Types and Styles Explained
Table of Contents
From high school, then all through college, and now in the workplace — presentations have been a pillar of passing down knowledge to various audiences.
But, what are presentations?
They are a tool used to inform and educate audiences in a fun and informative way.
Well, that is the simple way of explaining their purpose and meaning.
We want to dig in deeper, and that is what this article will bring to you — a deeper understanding of different types and styles of presentation, so you never get overwhelmed or confused when you need to make a presentation.
We will discuss:
- Different types and styles of presentations,
- The purpose of using presentations in the workplace, and
- How to utilize and recognize types and styles of presentations.
We will also show you:
- Famous presenters for each style,
- How you can use each presentation style, and
- A quote for each style to work as a useful reminder if you ever get confused.
Let’s dive in, shall we?
What are the purposes of presentations?
Sometimes, when a term is widely used, to the point where we subconsciously know the meaning and its purpose, it’s hard to pinpoint the true definition from memory.
So, let’s start with the basics — what is the definition of presentations?
Presentation is a manner of passing down knowledge from the speaker to the audience. A presentation can be a:
- Demonstration,
- Lecture, or
- Speech.
The purpose of a presentation is whatever goal you set up to achieve. Those goals can be:
- To educate,
- To persuade, and/or
- To entertain.
According to LinkedIn’s article 4 goals for any speech, pitch or presentation , when you combine the goals we mentioned, your presentation will become powerful, meaningful, and impactful. The goals mentioned above are general and can be applied to any situation. Different types and styles of presentation can lead to different results. With the right type and style, you can:
- Better your work and image with clients,
- Be more effective when presenting new ideas or solutions, and
- Ensure more progressive career growth.
These are only some of the business goals you can achieve with the right presentation type and presenting style. The more types and styles you try out, the more skillful you become, which helps you achieve your goals more efficiently.
Free team communication software
Try Pumble, a secure, reliable, and easy-to-use communication tool.
FREE FOREVER • UNLIMITED COMMUNICATION
What are the different presentation types?
Presentation types illustrate the way you structure your presentation .
We’ve mentioned the 4 purposes of presentations — every goal or purpose corresponds to a certain type. Before you can choose a structure, you need to answer the question “ What is the purpose of this presentation? ”
And methods and techniques, which we’ll talk about later, help you maintain that structure.
Once you know what you want to achieve with your presentation, you can choose its type.
Here’s what you need to know about each presentation type:
Type #1: Informative presentations
Informative presentations are analytical and, as the name states, informative. With this type of presentation, your end goal is to inform and educate .
Your audience only has to listen and soak up all the knowledge that is given by you.
With this type of presentation, you can report on new findings and new data or deliver a lecture.
Since the goal is to educate, your presentation must be precise and correct. Make sure that the information you are communicating has real value. When presenting, try to engage your audience with visuals of your data to help them understand.
Type #2: Persuasive presentations
To use persuasive presentations, you must answer the question “ What do I want my audience to do after listening to me ?”
The point of this type of presentation is to persuade your audience, change their minds, or offer a new point of view, so that they take action .
Persuasive presentation comes in handy if you are presenting a new product or a service and you want your audience to feel the urge to buy said product.
When you use this presentation type you must exude confidence, since you are your audience’s only source of information for your product.
Type #3: Motivational presentations
You’ve probably heard of motivational speakers, and if you haven’t, here’s a quick crash course. Motivational presentations have a purpose to inspire and change people’s minds .
Most people who use this type of presentation have a story to tell. These people use their own experiences as key points in their presentations to help the audience to relate to them.
Since the goal is to inspire and change people’s minds, you have to have a powerful topic to discuss.
Remember to cater to your audience and adjust your presentation to them and their level.
Type #4: Instructive presentations
Instructive presentation is technical, precise, and often longer than other types we mentioned. This type is here to offer instructions to an audience.
So, if your goal is to explain step by step how to achieve a goal or do a task— an instructive presentation should be your choice.
When you are delivering this type of presentation you need to make sure that every instruction is clear, understandable, and easy to follow.
How to determine which presentation type you should use?
To choose the correct type for your presentation, you must determine your goal. Once you have your goals clear, it will be easy to see which type works best with your presentation.
Here are some helpful questions that will help you to narrow it down to one type:
- What do I want the audience to take away from my presentation?’
- What am I trying to give the audience? Is it information, a lecture, or a look into a new product/feature?
- What obstacles are keeping me from delivering my presentation effectively?
Determining the correct type for your presentation is a trial-and-error process. You will find that some types are more your speed, while others might give you trouble. But, keep in mind that the end goal should always be to give your audience what they came for.
No matter which type you prefer, they all exist for a reason. Give them all a chance, and remember that practice makes perfect.
Presentation methods and techniques
When you define the type of your presentation, it’s time to get into methods and techniques for delivering a presentation.
There are a lot of ways you can deliver your presentation, and here is our take on it.
Presentation methods
A method is how you approach your problem .
When it comes to presentation methods, we linked them with public speaking. Methods cover:
- How you choose to deliver your presentation and
- How you structure your speech.
Here are the 4 main methods:
Method #1: Impromptu or unscripted
The impromptu method applies to speeches that are:
- Not prepared ,
- Emotionally charged, and
- ‘Given on the spot’.
This method of speaking is purely done by improvising, so there are no written rules on how it should be done.
Improvising and making up your speech as you go is not a wrong way to deliver your presentation. Still, instead of basing your entire speech on your ability to ramble on, incorporate this method in segments where you see fit or feel inspired to do so.
Method #2: Memorizing
The memorizing method implies that the speaker needs to know their speech word for word.
It is mostly used in oratory contests for high school and college students. This method is difficult, and you would need to spend a lot of time reading and memorizing your text.
But, this method is the easiest when it comes to performance anxiety. Since the text is perfectly constructed and your only job is to memorize and relay it to the audience, it’s less nerve-racking.
💡 Pumble Pro-Tip
If you struggle with anxiety before a presentation, we have an article to help you with that:
- How not to be nervous for a presentation
The memorizing method, while being challenging at its core, can be freeing once the speaker is on stage. With this method, you can practice your body language to go with the text. And since the text is scripted and perfected, the speaker can move around the stage as they see fit.
Method #3: Extemporaneous
Extemporaneous is a synonym for impromptu and unscripted — so why is a synonym to a method we’ve already covered, now a completely new method?
Well, that is because when it comes to the extemporaneous method, we think of a speaker that allows help during their performance .
The extemporaneous method is a combination of the first two methods we mentioned. This method allows the speaker to prepare their speech and use notes and key points as an aid to keep on course. However, they will not learn their presentation by heart, but use their own words and speak in a conversational manner.
Method #4: Scripting
The scripting method used to require a written speech from which the orator reads to the audience. Nowadays, we can see this method used by news outlets, with a teleprompter.
So, to make use of this method, you need to write down your speech and read it proficiently to your audience.
When it comes to in-person presentations and public speaking, this method is not the go-to.
You shouldn’t spend the whole presentation just reading off of papers. When we present, we need to maintain eye contact and overall connection with the audience — and holding a piece of paper in front of the audience will get in the way of that connection.
Presentation techniques
Presentation techniques are what you use before and during the presentation to make it compelling, informative, and easier to understand .
Here are some of the techniques that we find quite useful:
Technique #1: Practice
As a presenter, you want to make sure that everything goes smoothly — and for that to happen, you need to practice. The key to giving the best presentation is to practice relentlessly.
Some useful tips to help you make the most of your practice are to:
- Practice in front of a friend. — Practicing in front of a friend will not only help you with performance anxiety, but a friend might also have some useful tips on how to perform better.
- Film yourself practicing. — When you film yourself giving your presentation aloud, it will help you to get used to cameras and the spotlight. Also, the camera will capture every mistake you make, and from there you can see what needs to be worked on.
- Practice in the auditorium. — It will do you good if you can practice giving your presentation in a meeting room or the auditorium. If you practice in the place you will be presenting, you will get used to the space, and it will be familiar to you on the day of your presentation.
Technique #2: Use visuals
There is no need to overwhelm your audience with endless blocks of text. Think about how you can transform the data or information into a simple visual .
The important thing to remember is that your audience might not be on the same level of knowledge as you. So, use visuals to help them follow your point.
Technique #3: Incorporate stories
No matter how informative and to the point your presentation is, including a story that is illustrating your point can be very helpful to your audience.
Not only is storytelling a great way to engage and entertain your audience, but it is also a great way to show how your information is relevant to real-world events.
If you are curious to see what more you can do to prepare for your presentation, check out our article:
- How to prepare for a presentation: Your 9-step guide to a successful presentation
Technique #4: Incorporate appropriate style
Your presentation style is how you choose to deliver your presentation as a speaker. Style builds on the methods we have mentioned earlier, and it comes down to how you choose to speak to your audience. You can be a storyteller or a coach to your audience, and with each style comes a different influence.
Methods and techniques are a great starting point when you are approaching your presentation structure and topic.
But, there are different styles of presentation that you also should consider before walking up to that stage. Let’s learn more about them.
What is a presentation style?
A style is your preferred way of doing things, and when it comes to presentations, a style is how you choose to deliver your speech . Everything from your vocabulary to your tone defines your presenting style.
If you are not sure what your personal presentation style is, you can always pick and choose from the already-established styles. Those include:
- Storyteller,
- Instructor,
- Closer,
- Connector,
- Coach,
- Lessig style, and
- Visual style.
Let’s get into more detail about each one of them.
Style #1: The Storyteller
The storytelling style consists of a (usually personal) story or anecdote.
This style is used when the presentation doesn’t have any data or numbers that need to be explained.
You can use this style to emphasize your point and to easily relay your goal to the audience.
The storytelling style is great for the beginning of the presentation, as it is there to capture the audience’s attention.
Formality level for the Storyteller style: Low
Since this style uses the speaker’s personal experiences and anecdotes to help the audience relate to the topic easily, the language used is conversational. There is no need for any excessive formality , and the speaker can address the audience in a friendly and familiar tone.
The Storyteller style characteristics
What characteristics should you be aware of when you want to utilize this style?
The vocabulary that storytellers use is simple and conversational. Think about how you tell a story to your friends, colleagues, or family. Once you have that in mind, becoming a storyteller on stage won’t be a problem.
Since the formality level is low, there is no need to overcomplicate things or to use synonyms for words that already have simpler and more known versions.
Your story should have an introduction, where you will introduce the problem. Then, you can move into the main plot point that explains your topic. And finally, you should have a conclusion where you can circle back to the beginning and where you will untangle the web you cast and leave your audience with a final thought.
The pros of the Storyteller style
Now let’s look at some of the pros of this style:
- It’s easy to follow.
- It illustrates your problem and solution in a creative way.
- It’s relatable and, therefore, more influential to the audience.
The cons of the Storyteller style
Here are the cons of being the storyteller type:
- A story that’s too long or not interesting enough can leave your audience bored.
- Getting too caught up in the story can make your presentation longer than it should be.
Who is the Storyteller style best suitable for?
This style is great if you want to truly connect with your audience and have them feel as if you speak to them, rather than at them. Many people don’t like to be lectured, and if you are trying to make a point or a message stick out, try out the storytelling style.
Famous presenter with the Storyteller style
The storytelling style is preferred among TED talk speakers.
But, when we think of storytelling, one particular speaker comes to mind — Nick Vujicic. He overcame great obstacles and has learned how to take what’s best from life. So now, when he tries to spread his message of endurance, he puts his trust into the storytelling style and lets his emotions and experiences speak to his audience.
Quote by Nik Vujicic that embodies the Storyteller style
“ What really matters are the lives you touch along the way and how you finish your journey .” ― Nick Vujicic
Secure, real-time communication for professionals.
Style #2: The Instructor
The instructing style of presenting shares some traits of the storytelling style. It still uses the power of metaphors to get the message across to the audience.
But, the difference is that the instructing style has more of a commanding voice . The instructor can carefully align the story and the data in a logical and compelling manner, leaving the audience convinced and educated.
Formality level for the Instructor style: Medium
A lot of politicians use the Instructor style when they are trying to influence a larger crowd. Since this style has a higher formality level than the storytelling one, it allows the speaker to use more serious vocabulary and address the audience as superior.
The Instructor style characteristics:
The Instructor’s style is characterized by logic and command. As we mentioned, the speaker who is fond of the Instructor’s style needs to be able to handle the facts and connect with the audience.
So, the main characteristics of this style would be:
- More formal use of language,
- Commanding voice, and
- Persuasive nature.
The pros of the Instructor style
Let’s take a look at some of the pros of this style:
- It helps get a complicated message across.
- It’s persuasive.
- It’s fairly easy to use.
The cons of the Instructor style
Here are some of the cons to be aware of:
- The speaker could be deemed distant or cold.
- The audience can lose interest if the presentation is too focused on pure data.
Who is the Instructor style best suitable for?
This style is great if the speaker has a complicated topic to discuss with a less knowledgeable audience. This style is used mainly for lectures and political speeches.
Famous presenter with the Instructor style
A famous presenter with the Instructor style is none other than the former Vice President of the United States, Al Gore. He uses metaphors, data, his own personal experience, and even visuals to bring complex issues closer to a wide audience.
Quote by Al Gore that embodies the Instructor style
“ When you have the facts on your side, argue the facts. When you have the law on your side, argue the law. When you have neither, holler. ” — Al Gore
Style #3: The Closer style
The Closer style of presenting is a style that demands action from the audience . Presenters who opt for this style want their audience to not only learn something new but to get up from their seats with a newfound urge to make a change.
This style is a personification of a call to action. The presentations made in this style are short, since the speaker has a goal in mind. They then use this style to convincingly reach said goal.
Formality level for the Closer style: Medium
This style is a great tool to connect with the audience. So, to make a connection between the speaker and the audience, the formality level drops. But instead of treating the audience as friends, the speaker simply talks to them.
The Closer style characteristics
The Closer style is persuasive and somewhat commanding. People who are fond of the Closer style cut right to the chase and make their audience get to a decision. With this presentation style, there are no boring statistics or data. The key points are clear and delivered with a short and clear explanation.
The pros of the Closer style
Here are some of the pros of the Closer style:
- The presentation is short.
- The Closer is confident and knows how to deliver a point.
- The audience rarely gets bored with this style.
The cons of the Closer style
Take a look at some of the cons of this style:
- Some audiences aren’t ready to make a quick decision.
- Some audiences might feel that this style is too harsh or rash.
Who is the Closer style best suitable for?
The Closer style is best to use when you need your audience to make a decision or to give them the urge to make things happen.
This style is mainly used by CEOs and salesmen.
Famous presenter with the Closer style
Many presenters use this style, but the one that stands out the most is the philosopher Ruth Chang. She has delivered great presentations on how to make hard decisions. She keeps her presentations short, sweet, and straight to the point.
Quote by Ruth Chang that embodies the Closer style
“A world full of only easy choices would enslave us to reasons.” — Ruth Chang
Style #4: The Connector style
The Connector style speaker is most comfortable engaging with the audience . Some could say that the storytelling style is very similar to the Connector in that sense. Both styles base their presentations on the connection with the audience. The difference here is that the Connector is both a presenter and a member of the audience — and they are comfortable in both roles.
This style of presentation (as the name suggests) allows the speaker to connect to the audience, and therefore deliver the materials easier. One way that this style connects the speaker and the audience is through Q&A.
Formality level for the Connector: Low
Since this style’s main purpose is to connect the speaker to the audience, the formality level is low. The speaker appears as one of the audience, even though they are on stage. To keep the audience engaged and get them to ask questions, the Connector treats the audience as friends and acquaintances.
The Connector style characteristics
The user of this style needs to appear as if they are one of the members of the audience, but they just happen to be on the stage instead in a seat. One of the main characteristics that stand out for this style is the eagerness of the speaker to engage with the audience. When a speaker is a Connector, they will constantly ask questions and listen to the audience’s opinions.
The pros of the Connector style
Let’s take a look at the pros of this style:
- The audience is engaged and encouraged to participate.
- The presentation flows at a relaxed pace.
- The audience feels connected to the subject.
The cons of the Connector style
- Audience might not be comfortable with asking questions.
- The presentation might be longer than planned.
- Too many opinions will derail the presentation.
Who is the Connector style best suitable for?
The great thing about the Connector style is that it can be used in any presentation and any setting. Since the main goal of this style is to connect the speaker and the topic with the audience, there are no rules or limits as to where it can and where cannot be used.
Famous presenter with the Connector style
Padraig Hyland is a TED Talk speaker and a specialist in audience engagement, so it is only natural that he uses the Connector style. He has delivered countless speeches on how to be a great presenter and how to connect with any audience.
Quote by Padraig Hyland that embodies the Connector style
“ To successfully navigate the current disruption, organizations need to nourish their authentic leadership voice and create a new story that engages their people on the journey .” — Padraig Hyland
Style #5: The Coach style
What is a coach? In every sense of the word, a coach is a person who guides you, teaches you, and helps you achieve your goals.
It is the same with the coaching style. The person who uses this style guides their audience with their own enthusiasm for the subject. The Coach style is mainly used in motivational speeches, as it allows the coaches to interact with the audience and share knowledge on a topic they feel passionate about.
Formality level for the Coach style: Medium
The Coach style serves as a guide . It gives the speaker freedom to use their knowledge and personal experience to drive the audience to feel the same passion about the subject as the speaker does. To achieve that level of familiarity with the audience, the formality level drops, and the speaker talks to the audience as a teacher and, well, as a coach would.
The Coach style characteristics
The Coach style allows the speaker to guide their audience from point A to point Z, through knowledge and passion, which makes the presentation interactive and informative.
This style of presentation can be seen in motivational speeches, lectures, and speeches delivered by sports coaches. The main characteristic that follows this style is that it is delivered by enthusiastic speakers.
The pros of the Coach style
Here are some of the pros of this style to look into:
- It allows the speaker to connect to the audience through enthusiasm.
- Presentations in this style are interactive and engaging.
- It gives the audience step-by-step instructions on the topic.
The cons of the Coach style
Let’s examine some of the cons:
- The speaker’s passion can be overwhelming to the audience.
- The speaker can forget to ask for feedback .
Who is the Coach style best suitable for?
The Coach style, since it serves as a guide, is commonly used by motivational speakers and in self-help presentations.
They tend to choose this presentation style because it allows them to connect with the audience while still delivering a detailed step-by-step on the topic they are discussing.
Famous presenter with this style
There are a lot of motivational speakers today that are a fan of the Coach style, but the one that caught our attention is Mel Robbins. She is a lawyer and a motivational speaker that helps her audience to form healthy habits and attain discipline to achieve their goals.
Quote by Mel Robbins that embodies the Coach style
“ You have been assigned this mountain so you can show others that it can be moved .” — Mel Robbins
Style #6: The Lessig style
If you are in a time crunch, but you have a lot of material to cover, then the Lessig style is the perfect style for you.
The Lessig style was invented by Lawrence Lessig, and it states that a speaker should spend only 15 seconds on each slide or point during a presentation . This style usually agrees very well with the visual style.
Since not all presentations have slides, this style cannot be used with any type of presentation. However, if you have too many slides and too many points to make, then the Lessig style can help you use your time slot well.
Formality level for the Lessig style: Depends
The Lessig style is not a style of speaking per se, but a style for presentation time management . So, the formality of the language you use will be up to you and your topic. You can decrease or increase the formality level and the Lessig style would still be the same.
The Lessig style characteristics
The main characteristic of this style is that it includes slides or at least some visual aid.
This style is also the one that is not concerned with your verbal cues and style of speaking. If you choose to try out this style you can combine it with any of the styles we previously mentioned.
The pros of the Lessig style
Here are the pros of this style:
- It’s easy to use.
- It helps you keep track.
- It saves time.
The cons of the Lessig style
Here are some of the cons of this style:
- It is not applicable to presentations without slides.
- Sometimes the suggested 15-second rule isn’t enough.
- The presentation may feel rushed or unfinished.
Who is the Lessig style best suitable for?
The Lessig style bases its rules on slides and visual aids, so it’s best suitable for presentations that consist of slides. The topics for this style are endless, and it is up to the speaker to see where this style works best in their presentation.
The most logical choice is, of course, the founder of this style — Lawrence Lessig, a lawyer and a political activist.
Quote by Lawrence Lessig that embodies the Lessig style
“ Technology means you can now do amazing things easily .” — Lawrence Lessig
Style #7: The Visual style
Presentations can be all about the slides, data, or videos, and there are also powerful presentations that are delivered with only the speaker on the stage. But, technology is not something to shy away from . There are great advantages to using technology and feeding your audience with visuals that will support your claims. As they say, a picture is worth a thousand words.
Formality level for the Visual style: Depends
The formality of this style doesn’t depend on the visuals used, but on the speaker and the topic. The great thing about the visual style is that it can be used with almost any topic and type of data. So, when using this style of presentation, you can choose the level of formality you feel comfortable with.
The Visual style characteristics
The Visual presentation style’s main characteristics are the visuals, as the name suggests. The visuals can be anything from a picture, video, or creatively shown data and statistics.
This style can be used together with any other style that we mentioned, as long as you add some pictures or other visual elements.
The pros of the Visual style
Here are the pros of the Visual style:
- Visuals help the audience understand the presentation better — sometimes, they can illustrate your point better than your own words.
- Visuals can help you move your presentation forward.
The cons of the Visual style
Here are some of the cons of the Visual style:
- Overusing visuals in your presentation can take focus away from you.
- Visuals can be redundant.
Who is the Visual style best suitable for?
If you are creative enough or confident enough to not let the glamor of visuals take over your spotlight, you can incorporate visuals into any workplace presentation. Visuals can be helpful almost everywhere, and they can aid your audience if the topic is too complicated for them to follow.
Famous presenter with the Visual style
One of the best visual presenters is Steve Jobs. He was one of the founders of Apple, and every year he used to give a great visual presentation or a rundown of Apple’s new product releases.
Quote by Steve Jobs that embodies the Visual style
“ For you to sleep well at night, the aesthetic, the quality, has to be carried all the way through .” — Steve Jobs
How to determine which presentation style to use?
If you are wondering which style to use, first you need to ask yourself what kind of audience will be attending your presentation . Once you have an idea of who you will be talking to, you can start to think about your presentation style.
Also, you need to know what is the purpose of your presentation and what you wish to achieve.
Beyond that, try out different styles until you find the one you are comfortable with.
Collaborate easily with Pumble — Even when creating presentations
If you’re working on a presentation with your colleagues — no matter what type of a presentation it might be — you’ll probably find yourself in need of an efficient communication tool.
Luckily, Pumble, a team communication app , makes your collaboration more simple and efficient, while keeping communication lines open at all times.
Here are all the ways Pumble can help you create various types of presentations:
- Thanks to the voice call feature, you can stay connected to your colleagues while you work together on the presentation.
- If there is a problem you have to address , you can always give them a quick video call and share your screen with them so you can brainstorm or problem-solve together.
- If you need a second (or third, fourth, etc.) opinion , you can always ask for it on some of the Pumble channels .
- If you have to provide further explanations or continue the discussion without cramming the channel space, you can continue your conversation in threads or reach out to particular colleagues via direct messages .
Finally, one of the best things about Pumble is that you can never lose important information or shared files because it has unlimited history .

Jana Pavlovic is a communication author and researcher. She enjoys educating herself and others on various team collaboration and technology topics. She found that working from home in a hybrid-type company is her perfect combination for work-life balance, and she’s eager to share her new-found knowledge with you.
What's on your to-do?
START COLLABORATING
with Pumble

Related posts
Harness the power of hr hilarity: 60+ funny hr memes for 2024.
Like any other job, HR has its ups and downs, with plenty of humor to be found on either end of the spectrum. These funny HR memes should prove our po…
60+ Absurdly Funny Meeting Memes to Share With Your Work Buddies
The next time you’re stuck in a meeting that has no end, feel free to peruse our compilation of funny meeting memes. …
10+ Tips for Conducting an Effective Job Interview
Learn how to conduct an effective job interview and improve a candidate’s experience with expert tips. …
60+ Hilarious Quips to Use As Your Joke of the Day for Work
Looking for the perfect joke of the day for work? Here are 60+ hilarious jokes for work. …
Who Gets a Write-Up at Work and Why? Everything You Need to Know
Our guide to dealing with a write-up at work will help you understand the disciplinary process better….
What Is a Skip-Level Meeting & How Do You Prepare for One?
How should you prepare for your next skip-level meeting? Read this article to find out. …
Need better team communication??
Pumble is an all-in-one team collaboration app. Send messages and files, and start video conferencing with one click, and reduce emails. Free forever.
Free team chat app
Improve collaboration and cut down on emails by moving your team communication to Pumble.
Unlimited users • Unlimited chat history • Free forever
.css-1qrtm5m{display:block;margin-bottom:8px;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:14px;line-height:1.5714285714285714;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.35px;letter-spacing:-0.35px;font-weight:300;color:#606F7B;}@media (min-width:600px){.css-1qrtm5m{font-size:16px;line-height:1.625;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.5px;letter-spacing:-0.5px;}} Best Practices The #1 rule for improving your presentation slides
by Tom Rielly • May 12, 2020

When giving presentations, either on a video conference call or in person, your slides, videos and graphics (or lack of them) can be an important element in helping you tell your story or express your idea. This is the first of a series of blog posts that will give you tips and tricks on how to perfect your visual presentations.
Your job as a presenter is to build your idea -- step-by-step -- in the minds of your audience members. One tool to do that is presentation graphics, such as slides and videos.
Why graphics for your presentation?
A common mistake is using slides or videos as a crutch, even if they don’t actually add anything to your presentation. Not all presentations need graphics. Lots of presentations work wonderfully with just one person standing on a stage telling a story, as demonstrated by many TED Talks.
You should only use slides if they serve a purpose: conveying scientific information, art, and things that are hard to explain without pictures. Once you have decided on using slides, you will have a number of decisions to make. We’ll help you with the basics of making a presentation that is, above all, clear and easy to understand. The most important thing to remember here is: less is more.
Less is so much more
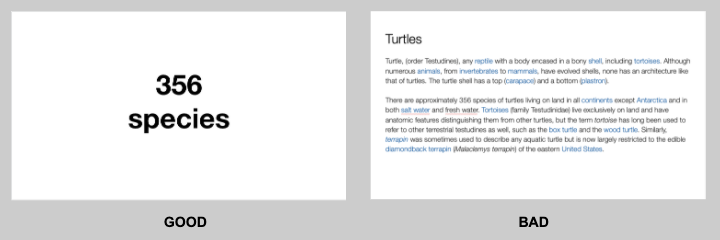
You want to aim for the fewest number of slides, the fewest number of photos, the fewest words per slide, the least cluttered slides and the most white space on your slides. This is the most violated slide rule, but it is the secret to success. Take a look at these examples.

As you can see in the above example, you don’t need fancy backgrounds or extra words to convey a simple concept. If you take “Everything you need to know about Turtles”, and delete “everything you need to know about” leaving just “turtles”, the slide has become much easier for your audience to read, and tells the story with economy.

The above example demonstrates that a single image that fills the entire screen is far more powerful than a slide cluttered with images. A slide with too many images may be detrimental to your presentation. The audience will spend more mental energy trying to sort through the clutter than listening to your presentation. If you need multiple images, then put each one on its own slide. Make each image high-resolution and have it fill the entire screen. If the photos are not the same dimensions as the screen, put them on a black background. Don’t use other colors, especially white.
Your slides will be much more effective if you use the fewest words, characters, and pictures needed to tell your story. Long paragraphs make the audience strain to read them, which means they are not paying attention to you. Your audience may even get stressed if you move on to your next slide before they’ve finished reading your paragraph. The best way to make sure the attention stays on you is to limit word count to no more than 10 words per slide. As presentation expert Nancy Duarte says “any slide with more than 10 words is a document.” If you really do need a longer explanation of something, handouts or follow-up emails are the way to go.
Following a “less is more” approach is one of the simplest things you can do to improve your presentation visuals and the impact of your presentation overall. Make sure your visuals add to your presentation rather than distract from it and get your message across.
Ready to learn more about how to make your presentation even better? Get TED Masterclass and develop your ideas into TED-style talks.
© 2024 TED Conferences, LLC. All rights reserved. Please note that the TED Talks Usage policy does not apply to this content and is not subject to our creative commons license.
11 Types Of Presentations To Engage Your Audience
Key Takeaways
- Presentations serve diverse purposes, from educating and persuading to motivating and problem-solving, and various styles are offered to engage audiences effectively.
- Educational presentations foster understanding through structured learning objectives and interactive elements like quizzes, while persuasive style of PowerPoint presentations sway opinions with compelling narratives and strategic visuals.
- Motivational style of presentations inspire action through personal stories and powerful messages, while progress report presentations track advancements transparently, aiding informed decision-making.
- Demonstrations and instructional presentations guide audiences step-by-step, fostering interaction and skill acquisition, while sales presentations blend charm and persuasion to showcase solutions effectively. Storytelling presentations captivate with relatable narratives, fostering genuine connections, and problem-solution presentations tackle challenges strategically, proposing viable solutions.
- Informative style of presentations empower audiences with valuable insights, simplifying complex topics with clear visuals and relatable examples, while visual presentations enhance understanding concisely, leveraging the power of images to engage effectively.
- Mastering these engaging presentation styles unlocks the potential to inform and inspire, ensuring audience engagement and success in dynamic environments.
Presentations serve various purposes in the business world, catering to different needs and goals. They inform by sharing strategies and educating about organizational goals, instruct employees with directions and new skills, induce with emotion and logic to drive action, and aid decision-making by presenting crucial information.
The essential purposes of presentations lie in their ability to transfer knowledge from speaker to audience. They encompass demonstrations, lectures, or speeches aiming to inform, educate, or entertain. Combining these goals enhances a presentation’s power and impact, improving outcomes in various situations.
Informing involves updating on projects, sharing research, or presenting data. Persuading seeks to sway opinions or prompt specific actions, such as proposing ideas or making sales pitches. Educating aims to teach new skills, demonstrate product usage, or share insights. Entertaining captivates audiences through humor, storytelling, or engaging performances.
Different presentation types and styles lead to diverse results, improving work relationships with clients, effectiveness in proposing ideas, and career growth. Experimenting with various approaches enhances skills, enabling more efficient goal achievement. When wielded adeptly, different presentation styles become potent tools for success in the dynamic business landscape.
The following are 11 types of presentation styles that can be used to engage your audience.
Educational Presentations
Educational presentations introduce unfamiliar audiences to specific topics, making them invaluable for explaining complex processes and sharing crucial information. They are instrumental in teaching audiences about various subjects and fostering understanding and engagement.
Educational presentations are structured around clear learning objectives. They aim to facilitate comprehension and retention of the material being presented. They often incorporate detailed visuals and instructions, which is beneficial for teaching new employees company procedures and policies.
Aids like charts, graphs, images, and videos are commonly used to illustrate and reinforce key concepts, enhancing audience understanding. Additionally, interactive elements like quizzes, activities, or group discussions deepen learning and engagement.
Lectures, workshops, training sessions, webinars, and e-learning modules exemplify educational presentations. These versatile formats cater to diverse learning needs and preferences, providing interactive learning experiences and knowledge acquisition opportunities.
Persuasive Presentations

Persuasive presentations wield the power of conviction to sway audiences towards a particular viewpoint or action. These presentations function as verbal negotiations, employing compelling arguments, logical reasoning, and emotional appeals to win over listeners.
Understanding your audience’s motivations is vital to tailoring your message to their interests and concerns. Crafting a narrative with a strong opening, solid arguments, and a memorable close enhances persuasion. Strategic use of visuals reinforces key points, aiding in audience engagement .
Examples of this style of presentations abound, from pitches for environmental conservation to advocacy for policy change or addressing social issues. They aim to influence beliefs, attitudes, or behaviors, urging audiences towards specific actions or adopting new perspectives.
In business, these kinds of presentations are ubiquitous, whether pitching for funding, advocating for technology adoption, or pushing educational reform. They articulate problems and propose solutions backed by data to compel stakeholders towards desired outcomes.
These presentations demand confidence as they seek to prompt action, such as purchasing a product or embracing a new idea. Unlike informative type of presentations, persuasive ones inform and seek to change minds and inspire action. They utilize research findings, storytelling, and emotional connections to bolster their case.
Persuasive presentations are effective tools for sales pitches, marketing initiatives, or political speeches. They utilize rhetorical devices, metaphors, and aids to engage audiences, offering new perspectives while appealing to emotions and logic. Ultimately, they aim to influence decisions and drive desired outcomes, making them indispensable in various contexts.
Motivational Presentations
Motivational presentations inspire and uplift audiences, urging them to overcome challenges and embrace positive change. They employ personal stories and powerful messages to resonate with listeners and spark enthusiasm.
These inspirational presentations are effective tools for organizational leaders to motivate employees and boost morale. Recruiters also leverage motivational kind of presentations, sharing success stories to attract new candidates.
Utilizing personal experiences as focal points, motivational speakers captivate audiences and drive them to action. Adapting to the audience’s level of engagement is crucial for maximum impact.
These types of presentations foster excitement and empowerment through storytelling, encouraging individuals to pursue personal or professional growth. Aids like slides and videos enhance key points and emotional connections.
Keynote speeches, team-building events, and personal development workshops exemplify motivational style of presentations. While not as dramatic as TED Talks, company overview presentations serve to connect with audiences, boost morale, and inspire action.
In various fields, like sports and entertainment, these presentations stir emotions and inspire audiences to achieve excellence. Athletes share stories of resilience, while industry professionals discuss creative journeys and societal impacts.
Motivational style of presentations typically inspire confidence, encourage change, and uplift spirits by forming emotional connections and delivering clear calls to action, making them invaluable tools for personal and professional development.
Progress Report Presentations

Progress report presentations update stakeholders on the advancement of projects, campaigns, or initiatives, akin to progress reports. These presentations encompass vital metrics, status updates, potential hurdles, and pending tasks. They offer a platform for project teams to share their progress, inviting questions and contributions.
Consider a company implementing a marketing strategy. In such cases, progress presentations become essential. They offer insights into the campaign’s journey, including status updates, data collection, and task adjustments. Take, for instance, the team stand-up presentation, characterized by its structured agenda, updates, discussions, and Q&A sessions, ensuring alignment and focus.
Projects and businesses evolve continuously, like living organisms. Status presentations act as navigational aids, providing updates on achievements, challenges, and future plans, like a team GPS. Transparency reigns supreme, utilizing visuals like infographics and charts to simplify complex data, facilitating trend identification and informed decision-making. Visual representation enhances comprehension, aiding prediction and strategy formulation grounded in evidence.
Demonstration Presentations
Demonstration presentations, also known as How-To presentations, guide audiences through step-by-step processes or techniques, offering clear instructions for replication. They excel in teaching practical skills and hands-on procedures, commonly found in workshops, training sessions, and cooking classes. Creative slides enhance engagement and aid information retention.
Incorporating visuals, props, and live demonstrations, speakers break down complex tasks into manageable steps, fostering audience interaction and effectively addressing queries.
Demonstration presentations elucidate complex concepts using visuals and demonstrations. They cater to diverse audiences, from internal employees seeking software insights to potential investors exploring technological innovations.
Preparation is vital, involving extensive research to distill intricate topics into digestible sections. Aids like graphs and charts simplify complex information, ensuring accessibility for all audience members. This meticulous approach ensures comprehension and engagement across varied knowledge levels.
Instructional Presentations
Instructional presentations guide audiences through specific tasks or processes to enhance understanding and facilitate action. Similar to educational presentations but more focused on providing instructions, they offer step-by-step guidance on achieving goals or performing activities.
Webinars, workshops, and training sessions exemplify instructive presentations, which deliver new information and teach new skills. For instance, a human resources instructional presentation might detail how employees can enroll in a new insurance plan.
Technical and detailed, instructional presentations explain tasks systematically, ensuring clarity and ease of comprehension. Each instruction must be clear, understandable, and actionable, fostering successful implementation.
Presenters may use aids like diagrams and videos to elucidate each step, making complex processes accessible. Tutorials, product demonstrations, and how-to guides exemplify instructional presentations, empowering audiences to learn and apply new knowledge effectively.
In corporate settings, instructional presentations train employees on software usage or policy changes, fostering practical skills acquisition. Similarly, they break down complex concepts into manageable parts in educational contexts, encouraging engagement through interactive elements and practical demonstrations.
Whether guiding new employees through software usage or instructing chefs on culinary techniques, instructional presentations aim to transform novices into experts. By breaking down concepts, using real-life examples, and incorporating interactive elements, they maximize learning and practical application, ensuring audiences leave equipped with valuable skills and knowledge.
Sales Presentations
Sales presentations are the cornerstone for businesses seeking to win over potential clients or customers, blending charm and charisma to showcase products, services, or ideas. They prioritize a clear value proposition, engaging storytelling, confidence, and a compelling call to action. Emphasizing benefits over features, adept presenters preempt objections and employ storytelling to demonstrate solutions to audience-specific problems. Visual aids enhance memorability and impact.
In the sports industry, sales presentations often involve sponsorship proposals, leveraging demographic data, engagement statistics, and past successes to illustrate potential returns. Similarly, presentations pitch new projects or content distribution deals in the media and entertainment sector. For instance, production companies pitch series concepts to streaming platforms, highlighting creative aspects and market analysis to align with the platform’s brand and audience demographics.
Sales presentations infuse enthusiasm with persuasion, aiming to translate it into tangible business outcomes. They are versatile tools for promoting service offerings, product launches, or consultancy proposals, leveraging industry expertise and experience to captivate stakeholders and secure deals.
Storytelling Presentations

Storytelling presentations captivate audiences by weaving narratives to convey information effectively. This approach finds utility across academic and business domains, fostering engagement and resonance with specific audiences. Incorporating personal anecdotes or relevant examples enhances relevance and understanding.
This style revolves around personal stories or anecdotes, eschewing data-heavy content. Its conversational tone facilitates easy comprehension and audience connection. Storytellers employ simple, familiar language akin to casual conversation, ensuring accessibility and relatability.
Presenters structure their stories with an introduction that presents the problem, followed by the main plot point elucidating the topic, and concluding with a reflection that resonates with the audience. This approach fosters genuine connection and audience engagement, steering clear of a lecturing tone.
While effective for conference speaking and networking events, storytelling may not suit sales discovery phases, where the focus should remain on the prospect. However, it shines in settings, allowing ample time for storytelling without detracting from audience interaction.
Ultimately, storytelling presentations breathe life into learning points, adhering to principles like TED’s Commandments to evoke genuine emotions and honesty. This style fosters a profound connection with the audience, transcending mere dissemination of information.
Problem-Solution Presentations

Problem-solution presentations offer a strategic approach to tackling organizational or client-centric challenges. They begin by identifying and analyzing a problem before proposing one or more solutions, a format prevalent in the consulting and tech industries.
In consulting scenarios, presentations delve into operational inefficiencies backed by data analysis or market research, offering tailored solutions like new technologies or process enhancements. Similarly, tech companies pitch software solutions to address data management or security challenges.
Problem-solution presentations expedite internal decision processes by outlining problems, solution options, and potential outcomes. For instance, a company aiming to boost social media engagement explores strategies like giveaways or enhanced content creation, using marketing presentation templates to organize discussions and guide decisions.
These presentations follow a logical approach, identifying root causes, proposing solutions, and detailing implementation plans and timelines. They serve diverse purposes, from business proposals to project plans and research reports, aiding decision-making efforts by presenting problems and offering viable solutions for consideration.
Informative Presentations
Informative presentations serve as foundational tools in public speaking , aiming to educate and enlighten audiences on specific topics. Unlike presentations designed to entertain or inspire, the primary objective here is to share valuable information clearly and concisely.
These presentations rely on factual accuracy and clarity, often incorporating data and research to support the information presented. They follow a logical structure, starting with an introduction, explaining the primary information in the body, and concluding with a summary or conclusion.
Language in informative kind of presentations should be clear and straightforward, avoiding confusing jargon. Visual aids like charts and graphs enhance audience understanding.
Examples of informative type of presentations span various contexts, from academic lectures on scientific findings to business workshops explaining software features. In educational settings, professors impart knowledge on historical events or scientific discoveries. In business, financial analysts present market trends to inform strategic decisions.
The audience’s enhanced understanding and knowledge retention measure informative style of presentations’ success. They empower audiences with valuable insights, making complex topics accessible and relevant. Effective delivery involves simplifying content, providing relatable examples, and encouraging audience engagement through questions for clarity.
Visual Presentations
Visual presentations include infographics, images, charts, and other visual elements and offer concise and engaging ways to convey information. They are ideal for time-constrained topics or those needing minimal explanation. They aim to enhance audience understanding and attention and are often used by businesses to showcase product benefits, such as before-and-after images in a hair product presentation.
Technology complements visual presentations, offering advantages in supporting claims with compelling visuals. This style recognizes the adage that “a picture is worth a thousand words.” Formality in this style hinges more on the speaker and topic than the visuals, providing flexibility in adapting to different contexts.
Key characteristics include the emphasis on visuals, ranging from images to creatively presented data, and the ability to adapt to various presentation styles. Visuals can supplement any presentation, aiding comprehension of complex topics.
Various forms, including slideshows, videos, infographics, or posters, serve as vehicles for visual presentations, facilitating quick comprehension and creating memorable experiences. Techniques like color schemes and layout design enhance visual appeal and are suitable for marketing campaigns, educational materials, and scientific presentations.
Mastering Different Types of Presentations: A Guide for Engaging Audiences
Presentations are versatile tools, offering a spectrum of styles to captivate audiences. Each approach serves a unique purpose, from educating and persuading to motivating and solving problems.
Educational presentations foster understanding through structured learning objectives and interactive elements like quizzes. Persuasive presentations sway opinions with compelling narratives and strategic visuals.
Motivational presentations inspire action through personal anecdotes and powerful messages. Progress report presentations track advancements transparently, aiding informed decision-making.
Demonstration presentations guide audiences step-by-step, fostering interaction and comprehension. Instructional presentations offer practical guidance, empowering skill acquisition.
Sales presentations blend charm and persuasion to showcase solutions effectively. Storytelling presentations captivate with relatable narratives, fostering genuine connections. Problem-solution presentations tackle challenges strategically, proposing viable solutions.
Informative type of presentations empower audiences with valuable insights, simplifying complex topics with clear visuals and relatable examples. Visual presentations concisely enhance understanding, leveraging images’ power to engage effectively.
Mastering these successful presentation styles unlocks the potential to inform and inspire, ensuring audience engagement and success in dynamic environments.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What are educational presentations, and why are they important?
Educational presentations introduce unfamiliar audiences to specific topics, aiming to explain complex processes and share crucial information. They are instrumental in teaching audiences various subjects, fostering understanding and engagement. Examples include lectures, workshops, training sessions, webinars, and e-learning modules. These presentations use structured learning objectives and interactive elements like quizzes to facilitate comprehension and retention.
2. How do informative style of presentations differ from other types of presentations?
Informative type of presentations focus on sharing valuable information clearly and concisely. Unlike presentations designed to entertain or inspire, their primary objective is to educate and enlighten audiences on specific topics. They rely on factual accuracy and clarity, often incorporating data and research. Language should be clear and straightforward, avoiding confusing jargon. Visual aids like charts and graphs enhance audience understanding.
3. What are some examples of informative presentations, and where are they commonly used?
Examples of informative presentations span various contexts, from academic lectures on scientific findings to business workshops explaining software features. In academic settings, professors impart knowledge on historical events or scientific discoveries. In business, financial analysts present market trends to inform strategic decisions. The success of informative presentations is measured by the audience’s enhanced understanding and knowledge retention.
4. How can visual presentations enhance audience engagement?
Visual presentations rely primarily on infographics, images, charts, and other visual elements to offer concise and engaging ways to convey information. They aim to enhance audience understanding and attention, suitable for time-constrained topics or those needing minimal explanation. Visuals can supplement any presentation, aiding comprehension of complex issues. Techniques like color schemes and layout design enhance visual appeal and are suitable for marketing campaigns, educational materials, and scientific presentations.
Unlock the Power of Effective Presentations with Prezentium
Are you ready to captivate your audience and achieve your goals? Let Prezentium be your partner in mastering the best presentation styles tailored to your needs.
Overnight Presentations : Need to make a presentation ASAP? Email us your requirements by 5:30 pm PST, and we’ll deliver a top-notch presentation to your inbox by 9:30 am PST the next business day.
Prezentation Specialist : Let our team of experts transform your ideas into exquisite presentations. From refining meeting notes to creating new designs, we’ve got you covered.
Zenith Learning : Elevate your communication skills with our interactive workshops and training programs. Discover the best of structured problem-solving and visual storytelling to engage and enlighten your audience.
Whether you’re educating, persuading, motivating, or solving problems, Prezentium has the expertise and tools to help you succeed. Don’t miss out on the opportunity to unlock the full potential of your presentations. Contact us today!

Engage your audience with powerful visual presentations.
Visual tools are critical to have in any presentation as they’re one of the key presentation aids that will help enhance your overall presentation .
We’ll give you tips on how to develop a sense of good presentation design whether you’re using PowerPoint, Prezi, Google Slides or any presentation software under the sun. The secret to creating a great presentation does not lie in a superior software, but understanding a few universal design concepts that can applied for all types of visual presentations.
Don’t be afraid to use a few presentation templates – there are ways to make the presentation ideas in those templates your own ideas and advance it in several different ways. Let’s make your next presentation on point and designed beautifully.
Presentations Are The Visual Communication Tool To Your Story

In the age of information, people remember facts faster through stories. Keep your bullet points and information short. You can use a rule of thumb to not put more than a paragraph and 3 points per slide to start.
Make your presentation the visual component of your story, but not something your audience has to read. Something that is short and succinct on screen will capture your audience’s attention and make sure they retain the main points of your message.
This does not mean incomplete slides. A common mistake presenters make is putting too little information on a slide in the name of simplicity when in fact they’re leaving out the main context.
A well designed visual presentation has a great story behind it and a well rehearsed voice telling it as well. Engaging the audience is also a great way to associate meaning or connection to the content of your slide decks. Ask questions and tell stories while showing off a great visual presentation! Think of writing the copy like writing for social media – you only have a certain amount of characters to use and a short audience attention span.
General Tips For Visual Presentations
Before you begin creating your presentation, you first need to know what makes effective presentations – storytelling. Such presentations target the audience’s emotions leading to a stronger connection to the audience member and the main point of the presentation.
Below are some storytelling tips for your slides, but remember to keep the presentation itself simple and practice makes perfect. And again, these are more for your spoken component that accompanies the visual component. These tips can be useful because they can be applied to all your presentations in general.
Step 1 is to ask yourself who your audience is and how to convey the key message you have in mind to them. Once you settle on your message, you can start designing your slides with that direction in mind.
You may wonder how to connect with an audience with your slides. Look to your own experiences, your own speaking style and tailor your message to what you know. Not many people want to hear others recite facts with no real meaning driving the story. Ask yourself, “Why does this matter to the audience and why should they care?”.
There is a lot of trust that can be built when the audience has a genuine connection to the presenter. Overall, if you have something that can solve a problem or teach someone complex things, that is enough to form a connection with your audience.
Think of the last app you used, the last email you read or perhaps the last business you purchased from. What was the content or visual elements that pulled you in?
Are you making a PowerPoint, Prezi or other form of visual presentation but it’s taking too much of your time? Enlist the help of Presentation Geeks and consider outsourcing your presentation design . Outsourcing your presentation slides allows you to free more of your time while still getting the results of an interesting presentation. You’ll have the support of expert slide designers who know what presentation visuals work and don’t work thanks to years of presentation feedback and background knowledge.
Color Design Tips For Presentation Slides
When designing your presentation, make sure you take into consideration the colors you’re using. We’ve listed a few background color combinations you might want to consider when developing the overall slide deck and the font to use.
Color Wheel Alignments:

Primary Colors: Red, yellow, blue
Secondary Colors: Green, orange, purple
Tertiary Colors: Yellow-orange, red-orange, red-purple, blue-purple, blue-green & yellow-green
Analogous Colors: These are any three colors which are side by side on a color wheel. (Think green, lime green, yellow)
Complementary Colors: These are colors that are directly opposite of a color wheel. (Think green vs. purple, red vs. blue)
Monochromatic Colors: This is when you use one color and various shades or hues of it. It works well for minimal looks.
Color moods:
Red/Orange/Yellow: Generally these convey a sense of energy, are warm colors and catch your attention. Yellow is a happy warm color on one end and red is very striking and can warn of danger, and symbolizes importance, passion and sometimes violence.
Blue/Purple/Green: These colors are calming, reserved, elegant and often used for corporate slides. Think of how indigo blue is used for many large corporate entities. Green often is branded with earth or medical brands. Purple often conveys a sense of royalty, money and creativity.
Use The Power Of Photography Or Video

Pictures and videos are great visuals to incorporate into any presentation. Remember the saying, “A picture is worth a thousand words”? Well, it’s true! Photos help visualize complex information. You’ll often come across a lot of photos in research presentations as they help the audience understand examples better.
They can also save you from having to put a thousand thoughts into the PowerPoint presentation slide!
The first tip we can give to make a great visual presentation is to choose all your photos before you start. This way you can keep the consistency of the images across your slide deck and make sure they’re somewhat alike in terms of composition, mood and brand.
Use free stock photos
You don’t have to take the photos or videos yourself.
There are plenty of free resources and web pages for stock photos online – Unsplash , Pexels , Pixabay , Free Range , Creative Commons and some photos from Freepik are free to use with some accreditation.
Effective photo use
Make sure you pick an image that will focus on the main theme of the slide. One image is usually enough if the image choice is very relevant to the slide. If you have multiple photos, avoid poor or loose placement of photos all over the slide. Try to use a grid or gallery placement and it will immediately enhance the layout of the slide.
If you pick great images, making presentations can be faster. Instead of having to create an elaborate template with multiple elements, a photo with a couple of bullet points can go a long way in terms of capturing attention and making your presentation slides look professional. This is true on any presentation design platform – whether its PowerPoint, Google Slides, etc.

You can also embed videos whether they’re located on your computer, YouTube, Vimeo or other major video streaming sites. If you’re feeling nervous about your presentation or have a complex message that would be hard to condense in one slide, a video is a dynamic way of conveying your message in any type of presentation.
The Typography You Use Matters

Typography is how you will arrange and present the words in your presentation. An audience can engage when text is readable, functional and works well with the other elements in the presentation. Fonts and sizing are a good place to start establishing the tone of your presentation.
Overview of Font Choices
Elegant fonts often denote a sense of luxury or lifestyle tone. Use script fonts sparingly, but as titles they immediately give this polished and high-end look. This should not be used as body text or something lengthy to read. Think about if you sent an email in that text – it would be tedious to read. However, maybe if it were a title or a way to name email, the choice may be more correct.
Corporate fonts often are traditional, serif fonts or clean sans serif fonts that evoke a sense of trust and a clear message. Think of the fonts Lato, Helvetica or Arial – they’re go-to fonts that are easy to read, and work across many systems. This is especially helpful if you are working across teams when creating content or having to approve the content, idea or visuals.
Of course, you can incorporate more stylistic or playful fonts if you want to give your presentation a personal feel. Much like the scripted font, when used sparingly but in large titles, this choice of font can be very effective at conveying a certain personality.
Adding Symbols & Icons To Your Presentation

You can consolidate information by using symbols or icons to direct your eye to information such as an arrow symbol. What if you used a symbol instead of a bullet point? Think of symbols as anchors for the eye to quickly find information. You can collect symbols off free stock sites or use the built-in ones in PowerPoint that are free to use!
Depending on if your presentation is formal or informal , you may also want to consider adding emojis! Emojis are fun ways to express different emotions and can help connect with a younger demographic.
Overall Branding, Tone of Voice & Consistency

Another tool you may have at your disposal is if your brand, business or company has brand guidelines. It will be the guide and compass to your presentation’s information that goes within it. By keeping consistent you can achieve a polished look even if it looks very simple.
Use your business voice to communicate ideas and set the tone for your presentation. Are you in an investment banking business and want people to rely on the information given to you? That would inform perhaps using blues and purples, which are calmer colors and a cleaner look. Are you an influencer who’s buying power and spending choices matter to your audience? Maybe choosing bright colors with personal touches will make the connection. Are you designing an innovative app? Maybe more interactive slides would do the trick.
Use these questions to make sure your text and tone is consistent as this is a foundation of a well articulated brand or personal identity.
Consistent Hierarchy
Visual hierarchy is how you will arrange objects and text in relation to one another to guide your user and not confuse the objects and how they should read them in your slides. Setting rules helps differentiate and prioritize what’s important in order.
Look at the difference between these two.
Snoop Dogg just launched a wine and it’s coming to Canada
Daily hive branded content | aug 11 2020, 6:30 am.
Australian winery 19 Crimes recently announced that its new Cali Red wine, created in collaboration with Entertainment Icon, entrepreneur, and hip-hop artist Snoop Dogg, will be hitting shelves across Canada later this summer.
The collaboration offers a refreshing take on celebrity partnerships as the apparent shared values and history between the brand and famous rapper make for a perfectly organic pairing.
Comment Name:
By browsing the site, you agree to the use of cookies on this website. see our user agreement for the use of cookies..
You can see a clear distinction in the example below:
Think of hierarchy of a form of narration or story structure. Your eye goes to the title, then to the subtitle, then to the body copy in a logical manner. Where the eye travels is one of those things we don’t think about often. But you can also utilize eye lines in photos. Is your subject in the photo looking left or right? Consider placing text to where your subject is looking and see how effectively your eye travels to that text.
We’ll look at hierarchy strictly as sizing of words for now, but note you can establish hierarchy with type, white space, alignment, etc. As a general rule of thumb, you should have consistent sizing for your Header (or title slide / slide title), your subtitles and your body text. That’s it! If the sizing in your PowerPoint is consistent, your words will look uniform and clean. Everything will be much easier to read and the eye will be trained to move each slide.
Don’t Forget Your Own Style
Also don’t forget to incorporate your own style and what kind of visuals you like. Even if your early visuals may seem simple, build up that design muscle with the basics and design techniques that look clean and consistent.
You’ll find as you design these basics, you’ll probably start noticing other visuals and things you like in other mediums and presentations. Keep a note or screenshot the presentation that inspired you. Create a mood-board that you can refer to in the future for quick idea inspiration. Copying gets a bad rap, but learning how to design something you like even if it’s a clone copy will teach you many things about design. Build a collection of images that informs everything you do: for your color scheme, your designs, the cadence of images, etc.
That being said, you can also use free stock websites like Freepik for some design layouts inspiration. Creative Market is a paid website but the site offers a ton of design inspiration. This site has design templates for what’s currently in and trending. You can subscribe to an email newsletter on either site to get bite sized design influence each day that goes straight to your inbox.
However, don’t be afraid to try something new!
Once you get to a level of comfortable designing, these new ideas will be much easier to execute with the technical knowledge you amassed when you started. You could even try using a new app to design your ideas to keep your knowledge fresh! (Keep in mind that most online apps like SlideShare use cookies to improve functionality and performance.)
Ask your friends or people at your organization to give you feedback and critique, as that’s also crucial to honing your design skills. The people around you also represent different audiences!

The above image looks boring, right?
That’s because there are no visual elements!
Powerful visual presentations can engage audiences psychologically with both the presentation itself and the energy of the presenter. By understanding a few universal design concepts, you can begin your journey creating wonderful visual presentations and becoming a better presenter ! Thanks for reading this blog post, tell us your tips in the comments below.
Author: Content Team
Related posts.

FREE PROFESSIONAL RESOURCES DELIVERED TO YOUR INBOX.
Subscribe for free tips, resources, templates, ideas and more from our professional team of presentation designers.

How it works
For Business
Join Mind Tools
Article • 12 min read
Creating Effective Presentation Visuals
Connecting people with your message.
By the Mind Tools Content Team

Apple® founder Steve Jobs was known widely for his great presentations. His unveiling of the iPhone® in 2007 is considered to have been one of his best presentations ever, and, if you were one of the millions who watched it online, you'll know why. The presentation was engaging, and passionate.
Jobs was particularly well known for building his presentations around powerful visual aids. He knew that slides are most effective when they tell a story rather than convey information, so his visuals were simple, elegant, and image-based. They complemented and reinforced his message, and they never competed with him for his audience's attention.
You don't have to be Steve Jobs to give a great presentation, but you do need great visuals. They convey a powerful message about your ideas and your brand, so it's essential to get them right. In this article, we'll look at how you can create effective presentation visuals – slides that connect your audience with your message.
Why Simplicity Speaks Volumes
The saying "A picture is worth a thousand words" is popular for a good reason: the human brain processes information more effectively when it is accompanied by images, or by short, memorable statements. This means that when you use simple, image-based slides to support your message, your audience can better grasp the information you're communicating.
However, many people use too many slides, or they build presentations around visual aids that are word-heavy or excessively complex.
These kinds of visual aids can negatively affect your presentation. Let's look at some examples:
- You're trying to convince the board to support a new product idea. Your slides are made up of graphs, numbers, and blocks of text from top to bottom, and board members spend most of their time reading the slides instead of listening to you. The result? You don't make a real connection, and your passion for the project is lost on them. They vote unanimously not to take the idea forward.
- You're pitching to a promising potential client. You spent a lot of time creating your slides, using many colors, animations, and fonts. However, the slides are so complex that your client has trouble understanding them. She leaves the presentation feeling overwhelmed and tired, and avoids using your firm because she fears, subconsciously, that dealing with your firm in the future could be similarly draining.
- You're giving a presentation to your department to highlight its good work. You want to feature everyone, so you make a slide detailing each person's accomplishments. Your department has dozens of people, so by the end, your team cares more about leaving than their results.
Now think about what happens when you use simple and engaging visuals. Instead of generating confusion or exhaustion, your slides create a positive connection with your audience. People might not remember exactly what you said, but they will remember a powerful image. They'll recall the positive emotions that they experienced during your presentation, and they'll start to associate your brand with clear, intelligent communication.
The results will be profound. You'll win new clients, convince colleagues to act on your ideas, and earn recognition for your team members' hard work. In short, you'll make positive impressions that will remain in people's minds long after the details of your presentation have faded.
Creating Great Visuals
Your visual aids have one job: to support your presentation . However, it takes considerable time, creativity, and effort to develop slides that do this well. Use the tips below to make the most of your preparation time.
1. Be Consistent
A common mistake is choosing different colors and fonts for each slide. This can confuse your audience and divert attention away from your message. Stay consistent with your slides, so that they form part of a seamless whole.
First, choose colors carefully, as color will affect your presentation's mood and tone. Also, think about the space that you'll be presenting in. If the room will be dark (with lights off), choose a darker background color, such as dark blue, black, or gray, with white or light-colored text. If the room will be light (with lights on or plenty of ambient light), choose a white or light-colored background, with black or dark-colored text.
You also need to match color with the tone and message of your presentation. Bright colors convey energy and excitement, while darker colors may seem more conservative and serious. Align the color palette you choose with your subject matter.
Microsoft® PowerPoint and Apple's Keynote are the most widely used presentation packages. They feature useful templates and tools, and most people are familiar with the layout of their presentations.
However, cloud-based presentation tools have features and templates that might be new to your audience, increasing the potential impact of your presentations.
2. Consider Culture
Before you create your visuals, make sure that you understand your audience. This is especially true if you're presenting to a culturally diverse group.
For example, not everyone reads from left to right, and people from some cultures may consider a particular color offensive or bad luck in business settings (look out for examples of this in our Managing Around the World articles). Additionally, jargon or slang may cause confusion with your audience.
When designing your visuals, use images and photographs that reflect the culture to which you're speaking. If you're presenting to a culturally diverse group, use pictures and images that reflect this diversity.
And keep graphics and phrases simple; remember, not everyone in the room will be a native English speaker. Whenever possible, use images to replace bullet points and sentences.
Our article on Cross-Cultural Communication has more tips for communicating with an ethnically diverse group.
3. Use Images Intelligently
When Steve Jobs unveiled the MacBook Air® , he needed to show just how small this new laptop was. The audience wasn't going to remember that it was 0.68 x 11.8 x 7.56 inches; those numbers don't create an emotional response. Instead, he showed them that the MacBook Air would fit easily into a standard manila envelope. This was a powerful way to show its size.
This kind of creativity is essential when choosing images. Your audience has probably seen plenty of bad clip-art and too many pictures of cross-cultural handshakes. Brainstorm creative, clever approaches with your imagery, and look for photographs or illustrations that tell a story in a less obvious way.
Thoughtful images will keep your audience engaged, reinforce your professionalism, and make a lasting impression.
4. Break Complex Data Down
When you have to communicate complex data or large chunks of information, avoid putting it all on one slide, as your audience may struggle to take in all of the details. Instead, either summarize the information, or split it up over several slides.
You can also use handouts to communicate complex information. Handouts allow your audience to look at data closely. This is especially important when you're presenting to analytical people, such as engineers, scientists, or finance professionals. They are trained to be skeptical about data, and a handout will give them a closer look. Once again, this kind of attention to the needs of your audience will highlight your professionalism and support your message.
5. Keep It Simple
Each slide should focus on one idea or concept. This allows your audience to grasp quickly what you want to communicate. Keep your text to a bare minimum (10 words or fewer if possible), and, where you can, use an image to convey a message rather than words: for example, consider using a graph instead of a list to show changing trends. Each slide should take three seconds or fewer to process. If it takes longer, the slide is probably too complex.
It can sometimes be helpful to follow a clear structure when creating your presentation; for example, if it is focused on a document or process with which audience members are familiar. This will help them make connections between your content and their existing knowledge.
Avoid bulleted lists whenever possible; they make it too easy to put several ideas on one slide, which can be overwhelming for your audience. If you do need to use bullets, don't use sentences; instead, simply list the fact, statistic, or idea you want to communicate. Then use your narrative to educate the audience about what these mean.
To simplify the wording on your slides further, highlight the key word in every sentence.
Next, look at the layout of your slides. Aim to use a plain background and plenty of blank space: this will help to focus audience members' eyes on your message. Avoid decorating slides with background pictures, logos or patterns that could distract attention.
Last, consider using blank slides when you need the audience's complete focus; a blank slide is equivalent to a pause, and it will add drama, tension, and focus to your words.
Many people underestimate how much time they need to set aside to prepare for a presentation. They'll spend days creating content and visuals but only a few hours practicing. Allow extra preparation time to hone your message and feel fully confident in your presentation.
First, take our interactive quiz, How Good Are Your Presentation Skills? to get an idea of how well you speak. Our articles on Delivering Great Presentations and Better Public Speaking contain tips and strategies that will help you communicate with clarity and intention.
When you practice your presentation, use your visuals. You should be able to glance at each slide and know exactly what you want to say.
If you're not confident in creating your own slides, think about outsourcing the task to a professional. This can be a smart option when a lot is at stake, or when you don't have the technical skills to create the type of presentation you want.
Consider using an outsourcing service such as Elance , Guru , or PeoplePerHour to find a suitable professional.
If you do, keep in mind that managing a freelancer requires a different approach from managing a regular staff member. Be clear about the project details, communicate your goals for the presentation, and set deadlines that give you plenty of time to revise and add as necessary.
Presentations that are too complex or lengthy can undermine your message. To create better visuals, do the following:
- Stay consistent.
- Consider culture.
- Use images intelligently.
- Break down complex data.
- Keep it simple.
If the stakes are high with your presentation and you don't feel confident with your technical skills, consider outsourcing slide preparation.
"iPhone," "Apple," "MacBook Air," and "Keynote" are trademarks of Apple Inc. (see www.apple.com ). "Microsoft" and "PowerPoint" are trademarks of Microsoft Corporation (see www.microsoft.com ). We have no association or connection with these organizations.
You've accessed 1 of your 2 free resources.
Get unlimited access
Discover more content
Expert Interviews
The Art of Public Speaking
With Professor Steve Lucas
Self-Assessment
How Good Are Your Presentation Skills?
Understanding Your Impact
Add comment
Comments (0)
Be the first to comment!

Get 30% off your first year of Mind Tools
Great teams begin with empowered leaders. Our tools and resources offer the support to let you flourish into leadership. Join today!
Sign-up to our newsletter
Subscribing to the Mind Tools newsletter will keep you up-to-date with our latest updates and newest resources.
Subscribe now
Business Skills
Personal Development
Leadership and Management
Member Extras
Most Popular
Latest Updates

Starting a New Job

The Role of a Facilitator
Mind Tools Store
About Mind Tools Content
Discover something new today
Decision-making mistakes and how to avoid them.
Explore some common decision-making mistakes and how to avoid them with this Skillbook
Using Decision Trees
What decision trees are, and how to use them to weigh up your options
How Emotionally Intelligent Are You?
Boosting Your People Skills
What's Your Leadership Style?
Learn About the Strengths and Weaknesses of the Way You Like to Lead
Recommended for you
Top tips for handling office politics.
Protect and Empower Yourself at Work
Business Operations and Process Management
Strategy Tools
Customer Service
Business Ethics and Values
Handling Information and Data
Project Management
Knowledge Management
Self-Development and Goal Setting
Time Management
Presentation Skills
Learning Skills
Career Skills
Communication Skills
Negotiation, Persuasion and Influence
Working With Others
Difficult Conversations
Creativity Tools
Self-Management
Work-Life Balance
Stress Management and Wellbeing
Coaching and Mentoring
Change Management
Team Management
Managing Conflict
Delegation and Empowerment
Performance Management
Leadership Skills
Developing Your Team
Talent Management
Problem Solving
Decision Making
Member Podcast
Visual Aids In Presentations: The Complete Guide
@danishd This is a sample bio. You can change it from WordPress Dashboard, Users → Biographical Info. Biographical Info
Published Date : August 21, 2020
Reading Time :
A picture, they say, is worth a thousand words. Using visual aids in presentations helps you pass a lot of information in a relatively shorter time. With the right visual aids, you can create the desired impact that you want your presentation to make on your audience. Learning how to use visual aids effectively will boost the quality of your presentations. We discuss some of the top visual aids in our recent YouTube video :
Visual Aid Definition
What are visual aids? Simply put, visual aids are things that your listening can look at while you give your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation. Visual aid appeals to the audience’s vision more than any other sensory organ.
Why use visuals for presentations?
There is no such thing as a perfect Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech . However, there are ways to make a presentation closer to perfection. What are they? Simple: Visual aids. Visual aids can bring life back into a tedious Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , and they take less time to come up with than long notes. This article discusses how you can use visual aids effectively and conquer an audience. Before that, we discuss how visuals can help you achieve a better presentation.
They help you structure your work.
Using the right types of visual aids can help you create a perfect picture of what you want your audience to see in your presentations. Instead of struggling to condense a lot of information into a long text, you can present your information in one straightforward image or video and save yourself the stress.
It is easier to engage the audience.
An excellent visual setup can help elicit audience interest and sometimes their input in the presentation. When the audience is engaged, they tend to be more interested in the presenter’s work. Also, an interactive audience can boost your morale and encourage you.
You save time on your presentation.
When presenting, time is of the essence. So, you can effectively reduce your presentation time if you have useful visual aids and use them properly. Would you prefer to go on and on for minutes about a topic when you can cut your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech down by inserting a few images or videos?
What are visual aids?
A visual aid is any material that gives shape and form to words or thoughts. Types of visual aids include physical samples, models, handouts, pictures, videos, infographics, etc. Visual aids have come a long way, including digital tools such as overhead projectors, PowerPoint presentations, and interactive boards.
Different Types Of Creative Visual Aid Ideas To Awe Your Audience
Have you ever been tasked with making a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or a presentation but don’t know how to make it truly remarkable? Well, visual aid is your answer.
Giving a presentation or Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech is hard. You have to strike a balance between persuading or informing your audience while also maintaining their attention. The fear of your audience slipping away is very real. And a visual aid can help.
We surveyed the Orai community to vote for their preferred visual aid. Here are the top ten creative visual aid ideas that you could use in your next presentation:
Videos emerged as the clear winner in all our surveys. We ran these surveys on all our social handles and contacted successful speakers. 27.14% of all respondents prefer visual aids because they are easy to understand, can be paused during a presentation, and can trigger all sorts of emotions. That being said, it is also very tough to create good videos. However, more and more tools are available to help you create amazing videos without professional help.
Hans Rosling’s TED talk, titled ‘the best stats you have ever seen,’ is one of the best speeches. He uses video for the Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech ’s entirety while not diverting the audience’s attention away from him. He does all this while also bringing out some optimism for the world’s future. We highly recommend this TED talk to learn how to use videos effectively as a visual aid and inject some positivity into your lives during these trying times.
2. Demonstrations
Demonstrations, also known as demos, are undoubtedly among the most effective visual aids for communication. You can use demonstrations in two ways. One as a hook to captivate your audience. Prof. Walter Lewin was famous for using demonstrations as a hook during lectures. In his most famous lecture, he puts his life in danger by releasing a heavy pendulum to show that a pendulum’s period remains constant despite the mass.
Demonstrations can also be used to show how some things are done or work. We use demonstrations to showcase how Orai works and how you can use them to improve your speaking skills.
18.57% voted for demonstrations because they are unique, interactive, up close, and have a personal touch.
3. Roleplays
Jokes aside, why do you think comedy shows are memorable? You guessed it right. Roleplays! Role – play is any speaking activity when you put yourself into somebody else’s shoes or stay in your shoes but put yourself into an imaginary situation!
Nothing is more boring than a comedian delivering lines straight from a joke book. Legendary comedians like George Carlin, Kevin Hart, Chris Rock, and Bill Burr use roleplays effectively and make a mundane joke genuinely memorable.
Jokes aside, you can use roleplays in business presentations and speeches. Use real-life stories or examples in your role plays to make them authentic.
15.71% of the survey respondents voted for roleplays because they are very close to real life and do not take the audience’s attention away from the speaker.
With 12.86% of the votes, Props is number 4. A prop is any concrete object used to deliver a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation. Props add another dimension to our Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech and help the listeners visualize abstract concepts like vision, milestones, targets, and expectations. It ties verbal to visual. Introducing a prop into your Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech or presentation should not seem forced. Use them sparingly to highlight your address’s most critical points or stories.
People voted for props because they feel 3D visualization is more useful than 2D visualization. Props will make your presentations stand out because few people use them today.
When we sent out the survey to the Orai community and some highly successful speakers, we were sure that slides/presentations would come out on top. However, we were surprised by the results. With 12.86% votes, slides are number five on our list.
Presentations are effortless to create and, therefore, the most commonly used visual aid in business communications. Today, dozens of software programs are available to help you make beautiful presentations. Microsoft PowerPoint is the pioneer in the space and holds a significant market share.
Whatever is your preferred software, you need to keep your audience at the center while making presentations.
People described the ease of creation and the ability to incorporate other visual aids when asked why they chose presentations as their top visual aid.
The inclusion of Audio in this list can appear controversial. But it got a significant vote share in our survey and cannot be ignored. Audio can add a new dimension to your presentations where the audience is hearing your voice and other sound cues that can trigger various emotional responses. Especially when coupled with other visual aids, audio can be a powerful tool for making impactful presentations.
Vote share:
Audio aid is number six, with 4.29% of the votes.
7. Handouts
What is a handout.
A handout is a structured view of your presentation or Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech that you can distribute to the audience.
What are the benefits of a handout?
Like how this blog gives more information than our YouTube video on the different visual aids, handouts can be used to furnish more information than your discourse itself. They give your audience something to take away after your presentation, making you and your presentation more memorable.
Are you going to be speaking about something overly technical? Then handouts are your friends. Handouts are also an opportunity to facilitate follow-ups if you specify your contact details.
Handouts are tied with whiteboards and got 2.86% of the votes in our survey.
8. Physical & Online Whiteboards
What is a whiteboard.
Traditionally, whiteboards are white, shiny, and smooth boards on which texts and diagrams are made using non-permanent markers. It is widely used in professional presentations, Brainstorming <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:132">A collaborative process to generate ideas freely and spontaneously, fostering creative thinking and problem-solving.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:12"><strong>Purpose:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73">Develop a wide range of innovative ideas without judgment or criticism.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:60">Overcome creative blocks and stimulate fresh perspectives.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:67">Encourage participation and engagement from diverse team members.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0">Build upon and combine individual ideas to reach breakthrough solutions.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:17"><strong>Key elements:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:96"><strong>Openness:</strong> All ideas are welcomed, regardless of their initial feasibility or practicality.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:109"><strong>Quantity over quality:</strong> Focus on generating as many ideas as possible, even if they seem unconventional.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:93"><strong>Spontaneity:</strong> Encourage quick thinking and rapid-fire suggestions without overanalyzing.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:114"><strong>Building upon ideas:</strong> Combine, adapt, and improve upon existing ideas to generate even more unique solutions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Positive environment:</strong> Maintain a supportive atmosphere where participants feel comfortable sharing their thoughts freely.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:13"><strong>Benefits:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:68">Sparks creativity and innovation, leading to unexpected solutions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:95">Encourages participation and team building, fostering collaboration and a sense of ownership.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:78">It breaks down communication barriers and allows diverse perspectives to shine.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0">It helps identify potential flaws and roadblocks early in the ideation process.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:16"><strong>Application:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-32:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:69">Idea generation for new products, projects, or marketing campaigns.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:78">Problem-solving for existing challenges or obstacles within an organization.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-32:0">Developing communication strategies or messaging frameworks.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="33:1-33:38"><strong>Brainstorming for Public Speaking:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="35:1-38:0"> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-35:86">Use brainstorming with your team to research and develop <strong>public speaking topics</strong>.</li> <li data-sourcepos="36:1-36:122">Generate creative ideas for introductions, transitions, and conclusions in your <strong>professional speaking</strong> presentations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="37:1-38:0">Brainstorm innovative ways to incorporate storytelling, humor, or visuals into your speeches.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="39:1-39:190"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="39:1-39:190">While brainstorming offers numerous advantages, it's crucial to have a strong facilitator, clear objectives, and a follow-up process to evaluate and refine the generated ideas.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/brainstorming/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">brainstorming sessions, and group discussions. Post-COVID, more and more companies are moving to online whiteboards. Online whiteboards are software that provides a space where individuals across the globe can collaborate online. Many companies have moved beyond the whiteboard and started using online whiteboards for meetings and discussions.
What are the benefits of a whiteboard?
A whiteboard helps listeners better visualize thoughts, concepts, and ideas. It is also a better alternative to the blackboard for a smaller audience as it is tidier and easier to use. Online whiteboards can be used instead of traditional whiteboards without being limited by space constraints. Online whiteboards will transform virtual meetings into a collaborative experience.
With 2.86% of the votes, whiteboards stand at eight on our list.
9. Blackboard
What is a blackboard.
A blackboard (aka chalkboard) is a surface on which texts or diagrams are made using chalk made from calcium sulfate or calcium carbonate. Blackboards are typically used in classrooms for large groups of students.
What are the benefits of blackboards?
Blackboard is one of the foremost and most popular teaching aids. Blackboard is useful for teaching as it helps instructors move from easy to complex topics in an organized manner. Diagrams, symbols, charts, and drawings can be introduced in discourse to bring life to rather dull topics. Blackboards are highly interactive, where the teacher and students can participate during a Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech .
With 1.43% of the vote share, the blackboard stands at the bottom, along with flipcharts.
10. Flipchart
What is a flipchart.
Flipcharts consist of a pad of large sheets of paper bound together. It is typically fixed to the upper edge of a whiteboard or canvas. Flipcharts are easy to create and inexpensive fit for small groups of people.
What are the benefits of presenting using a flipchart?
Nowadays, everybody seems only interested in making presentations powered by computer-generated slide decks. However, the flip chart has its charm. Since most presentations consist of less than ten people, flip charts can be a refreshing change to the standard slide deck. Moreover, flipchart does not require electricity. No electricity and no software means fewer of those last-minute hick-ups.
Flipchart got 1.43% of the vote and shared the bottom position with its counterpart, which we will discuss in the next section.
Master the art of Speech <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:271">A form of communication involving spoken language, it is used to express ideas, share information, tell stories, persuade, or entertain. Public speaking is a powerful tool used in diverse contexts, ranging from casual conversations to formal presentations.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:27"><strong>Components of a Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-10:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:73"><strong>Content:</strong> The information, message, or story conveyed through words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:106"><strong>Delivery:</strong> The vocal and physical presentation, including clarity, volume, gestures, and eye contact.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-10:0"><strong>Structure:</strong> The organization of the content, typically following an introduction, body, and conclusion.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="11:1-11:21"><strong>Speech in Action:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="13:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="13:1-13:88"><strong>Informing:</strong> Sharing knowledge and facts, educating an audience on a specific topic.</li> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:119"><strong>Persuading:</strong> Advocating for a particular viewpoint, using arguments and evidence to influence thoughts or actions.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:93"><strong>Motivating:</strong> Inspiring and energizing an audience, fostering action and positive change.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Entertaining:</strong> Engaging and delighting an audience through humor, storytelling, or creative language.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:32"><strong>Public Speaking and Anxiety:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="20:1-20:227">Many people experience <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong>, a fear of speaking in front of an audience. While it's common, effective preparation, practice, and breathing techniques can significantly reduce anxiety and improve delivery.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="22:1-22:32"><strong>Different Types of Speeches:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="24:1-28:0"> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:81"><strong>Informative speech:</strong> Focuses on conveying information clearly and concisely.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:102"><strong>Persuasive speech:</strong> Aims to convince the audience to adopt a particular viewpoint or take action.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-26:99"><strong>Motivational speech:</strong> Inspires and energizes the audience, building enthusiasm and commitment.</li> <li data-sourcepos="27:1-28:0"><strong>Entertaining speech:</strong> Aim to amuse and delight the audience, often using humor, storytelling, or anecdotes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="29:1-29:33"><strong>Crafting a Compelling Speech:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="31:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:106"><strong>Know your audience:</strong> Tailor your content and delivery to their interests, needs, and prior knowledge.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:107"><strong>Have a clear message:</strong> Identify the main point you want to convey and structure your speech around it.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:111"><strong>Engage your audience:</strong> Use varied vocal techniques, storytelling, and visual aids to keep them interested.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Practice, practice, practice:</strong> Rehearse your speech out loud to refine your delivery and build confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:13"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="38:1-38:281">Speech is a powerful tool for communication, connection, and influence. By understanding its elements, addressing potential anxieties, and tailoring your delivery to different contexts, you can harness the power of speech to achieve your intended goals and captivate your audience.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/speech/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">speech , practice with Orai
How to make an informative speech with visual aids in presentations
If you have a presentation coming up soon, you can follow the instructions below to learn how you can take advantage of visual aids:
Determine your overall objective
The aim of your presentations depends on you, what information is being presented, and your audience. The motivational speaker and the classroom teacher may approach the same types of visual aids differently due to differences in overall objectives. For instance, if you aim to inspire and remind your audience of salient points, a poster template should serve well; infographics work well when trying to show relationships between complex information. A chart will be quite effective if you seek to explain a given data set.
Choose appropriate visual aids in presentations.
After identifying the overall aim of your presentation, you have to match it with the right visual aids example. Will a graph, picture, or video suffice?
If you use the PowerPoint Presenter, focus mainly on the media that best conveys your message. Make sure that the notes you add are bold and brief. Try to keep your sentence in one line of text.
Prepare thoroughly
You will spend some time preparing your visual aids before the day of your presentation. It is good to allow yourself enough time to prepare so you can perfect your work accordingly. Take note of when, where, and how you will use your visual aids. If you discover some inconsistencies, you can compensate for them by adjusting your choice or using visual aids in presentations.
After you have a final draft of your visual aids, run a series of sessions with them. Let your friends or colleagues be your audience and ask for their honest feedback. Make appropriate adjustments where necessary.
During presentation
First, you need to be comfortable and confident. A neat and appropriate dress should boost your Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence . Follow the tips below during presentations.
- Keep your face on your audience. It may help to look a little above their heads while presenting.
- Only point to or take the visual aid when needed. When you do, explain what you mean immediately.
- Do not read texts on your visual aids verbatim.
- Once a visual aid has served its purpose, you should keep it away from your audience’s view.
If you need more help boosting your Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence , we have written a detailed piece on how to conquer your fear of speaking in front of people.

What is the importance of using visuals in giving a presentation?
Visual aids in presentations are invaluable to you and the audience you hope to enlighten. They make the job easier for you, and the audience leaves feeling like they learned something. Apart from their time-saving abilities, here are some reasons why you need to incorporate visual aids in your presentations:
- Visual aids can help your audience retain the information long-term.
- The human brain processes images faster than text, so visuals make us understand things faster.
- Using visual aids makes your presentations more enjoyable, interactive, and memorable.
- Visual aids help your audience connect and relate with you better
- Presentations with visual aids are less likely to be misunderstood or misrepresented. They are usually easier to understand and leave little room for confusion
- Visual designs help stimulate cognition and they are great for people with learning disabilities.
- Visual aids act as key cards and pointers for the presenter and help you keep track of what you’re saying
What are the ideas for speech topics using visual aids?
- Use a picture or image that closely represents the topic. A one-hundred-dollar note can suggest topics revolving around money and finances.
- Use a chart showing trends or statistics that your audience finds appealing. You can use popular sayings or quotes to generate topics your audience can relate to.
- Newspaper headlines on related issues can be good starters for opinion-based topics.
Why is the use of color important in presentations, according to research?
Color plays a crucial role in presentations, boosting audience engagement with its ability to enhance motivation and create visually appealing visuals. By understanding color theory and using shades thoughtfully, presenters can ensure their work is professional and organized and accessible to a diverse audience, considering color blindness and cultural associations.
What are the key points to consider when using visual aids in a presentation?
Ensure effective and engaging visuals in your presentation by considering the space, practicing beforehand, utilizing and limiting color strategically (considering color blindness), and maintaining consistency throughout your presentation.
What are some tips for using objects or artifacts as visual aids in presentations?
Objects in presentations can captivate your audience! Choose relevant objects for demonstrations or explanations. In small groups, pass the object around but manage time. For larger audiences, move it around for clear visibility. Reveal the object at the right moment with context and explanation. If demonstrating, use deliberate movements and explain each step clearly to keep them engaged.
What are some tips for using visual aids to engage the audience and maintain their interest?
Capture and keep your audience’s attention with impactful visuals! Ensure clear visibility, maintain eye contact, and use visuals to complement your spoken words, not replace them. Explain each visual promptly and remove it seamlessly when finished to refocus attention on your message.
How can visual aids be tailored to suit the audience and make the presentation more effective?
Craft impactful presentations by tailoring visuals to your audience and goals. Choose relevant and resonant visuals, be it a graph, picture, or video, accompanied by clear, concise notes. Prepare thoroughly, refining visuals and considering timing, context, and integration. Seek feedback to fine-tune for optimal audience connection.
How should one prepare and use visual aids effectively during a presentation?
Prepare polished visuals beforehand, considering timing, context, and integration. Seek feedback. During your presentation, prioritize Clarity <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:269">In <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>clarity</strong> refers to the quality of your message being readily understood and interpreted by your audience. It encompasses both the content and delivery of your speech, ensuring your message resonates and leaves a lasting impact.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-13:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:133"><strong>Conciseness:</strong> Avoid unnecessary details, digressions, or excessive complexity. Focus on delivering the core message efficiently.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:149"><strong>Simple language:</strong> Choose words and phrases your audience understands readily, avoiding jargon or technical terms unless you define them clearly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:145"><strong>Logical structure:</strong> Organize your thoughts and ideas logically, using transitions and signposts to guide your audience through your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:136"><strong>Effective visuals:</strong> If using visuals, ensure they are clear, contribute to your message, and don't distract from your spoken words.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-11:144"><strong>Confident delivery:</strong> Speak clearly and articulately, avoiding mumbling or rushing your words. Maintain good eye contact with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="12:1-13:0"><strong>Active voice:</strong> Emphasize active voice for better flow and avoid passive constructions that can be less engaging.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="14:1-14:24"><strong>Benefits of Clarity:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="16:1-20:0"> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:123"><strong>Enhanced audience engagement:</strong> A clear message keeps your audience interested and helps them grasp your points easily.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:123"><strong>Increased credibility:</strong> Clear communication projects professionalism and expertise, building trust with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-18:111"><strong>Improved persuasiveness:</strong> A well-understood message is more likely to resonate and win over your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="19:1-20:0"><strong>Reduced confusion:</strong> Eliminating ambiguity minimizes misinterpretations and ensures your message arrives as intended.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="21:1-21:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="23:1-27:0"> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:129"><strong>Condensing complex information:</strong> Simplifying complex topics without sacrificing crucial details requires skill and practice.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:128"><strong>Understanding your audience:</strong> Tailoring your language and structure to resonate with a diverse audience can be challenging.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-25:85"><strong>Managing nerves:</strong> Nerves can impact your delivery, making it unclear or rushed.</li> <li data-sourcepos="26:1-27:0"><strong>Avoiding jargon:</strong> Breaking technical habits and simplifying language requires constant awareness.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="28:1-28:22"><strong>Improving Clarity:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="30:1-35:0"> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:117"><strong>Practice and rehearse:</strong> The more you rehearse your speech, the more natural and clear your delivery will become.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:107"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Share your draft speech with others and ask for feedback on clarity and comprehension.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:161"><strong>Consider a public speaking coach:</strong> A coach can provide personalized guidance on structuring your message, simplifying language, and improving your delivery.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:128"><strong>Join a public speaking group:</strong> Practicing in a supportive environment can help you gain confidence and refine your clarity.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-35:0"><strong>Listen to effective speakers:</strong> Analyze how clear and impactful others achieve communication.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="36:1-36:250"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="36:1-36:250"><strong>Clarity</strong> is a cornerstone of impactful <strong>public speaking</strong>. By honing your message, focusing on delivery, and actively seeking feedback, you can ensure your audience receives your message clearly and leaves a lasting impression.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/clarity/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">clarity , avoid overwhelming the audience, and use visuals purposefully to enhance, not replace, your message. Practice beforehand and maintain audience engagement through confident delivery.
The visual aid definition is very clear on how much impact using visual aids in Public Speaking <!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking refers to any live presentation or speech. It can cover a variety of topics on various fields and careers (you can find out more about public speaking careers here: https://orai.com/blog/public-speaking-careers/. Public speaking can inform, entertain, or educate an audience and sometimes has visual aids.</p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:paragraph --> <p>Public speaking is done live, so the speakers need to consider certain factors to deliver a successful speech. No matter how good the speech is, if the audience doesn't connect with the speaker, then it may fall flat. Therefore, speakers have to use a lot more nonverbal communication techniques to deliver their message. </p> <!-- /wp:paragraph --><br /><!-- wp:heading --> <h2>Tips for public speaking</h2> <!-- /wp:heading --><br /><!-- wp:list --> <ul> <li>Have a sense of humor.</li> <li>Tell personal stories that relate to the speech you're giving.</li> <li>Dress appropriately for the event. Formal and business casual outfits work best.</li> <li>Project a confident and expressive voice.</li> <li>Always try to use simple language that everyone can understand.</li> <li>Stick to the time given to you.</li> <li>Maintain eye contact with members of your audience and try to connect with them.</li> </ul> <!-- /wp:list --> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/public-speaking/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">public speaking has on an audience. With a great selection of visual aids, you can transform your presentations into a pleasant experience that you and your audience will always look forward to.
Become a confident speaker. Practice with Orai and get feedback on your tone, tempo, Conciseness <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:326">In the realm of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>conciseness</strong> refers to the ability to express your message clearly and effectively using the fewest possible words. It's about conveying your ideas precisely, avoiding unnecessary details and rambling while maintaining your message's essence and impact.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:33"><strong>Benefits for Public Speakers:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-11:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:137"><strong>Engaged audience:</strong> A concise speech keeps your audience focused and prevents them from losing interest due to excessive information.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:117"><strong>Increased clarity:</strong> By removing unnecessary clutter, your core message becomes clearer and easier to understand.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:137"><strong>Enhanced credibility:</strong> Concise communication projects professionalism and efficiency, making you appear more confident and prepared.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-11:0"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Knowing you have a clear and concise message can help manage <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong> by minimizing the pressure to fill time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="12:1-12:35"><strong>Challenges for Public Speakers:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="14:1-17:0"> <li data-sourcepos="14:1-14:126"><strong>Striking a balance:</strong> Knowing where to draw the line between conciseness and omitting important information can be tricky.</li> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:115"><strong>Avoiding oversimplification:</strong> Complex topics may require elaboration to ensure clarity and understanding.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-17:0"><strong>Overcoming natural tendencies:</strong> Some speakers naturally use more words than others, requiring a conscious effort to be concise.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="18:1-18:41"><strong>Strategies for Achieving Conciseness:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="20:1-25:0"> <li data-sourcepos="20:1-20:92"><strong>Identify your core message:</strong> What is your audience's main point to remember?</li> <li data-sourcepos="21:1-21:128"><strong>Prioritize and eliminate:</strong> Analyze your content and remove any information not directly supporting your core message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:133"><strong>Use strong verbs and active voice:</strong> This makes your sentences more impactful and avoids passive constructions that can be wordy.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:109"><strong>Simplify your language:</strong> Avoid jargon and technical terms unless they are essential and clearly defined.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-25:0"><strong>Practice and refine:</strong> Rehearse your speech aloud and identify areas where you can tighten your wording or eliminate redundancies.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="26:1-26:20"><strong>Additional Tips:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="28:1-31:0"> <li data-sourcepos="28:1-28:93"><strong>Use storytelling:</strong> Engaging narratives can convey complex ideas concisely and memorably.</li> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:110"><strong>Focus on the visuals:</strong> Powerful visuals can support your message without extensive explanation.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-31:0"><strong>Embrace silence:</strong> Pausing deliberately can emphasize key points and give your audience time to absorb your message.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="32:1-32:404"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="32:1-32:404"><strong>Conciseness</strong> is a powerful tool for <strong>public speakers</strong>. By eliminating unnecessary words and focusing on your core message, you can create a more engaging, impactful, and memorable presentation for your audience. This can also help manage <strong>public speaking anxiety</strong> by reducing the pressure to fill time and enabling you to focus on delivering your message with clarity and confidence.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/conciseness/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">conciseness , and Confidence <p data-sourcepos="3:1-3:305">In the context of <strong>public speaking</strong>, <strong>confidence</strong> refers to the belief in one's ability to communicate effectively and deliver one's message with clarity and impact. It encompasses various elements, including self-belief, composure, and the ability to manage one's <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>.</p><br /><h2 data-sourcepos="5:1-5:16"><strong>Key Aspects:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="7:1-12:0"> <li data-sourcepos="7:1-7:108"><strong>Self-belief:</strong> A strong conviction in your knowledge, skills, and ability to connect with your audience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="8:1-8:95"><strong>Composure:</strong> Maintaining calmness and poise under pressure, even in challenging situations.</li> <li data-sourcepos="9:1-9:100"><strong>Assertiveness:</strong> Expressing your ideas clearly and concisely, avoiding hesitation or self-doubt.</li> <li data-sourcepos="10:1-10:104"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Countering negative thoughts with affirmations and focusing on your strengths.</li> <li data-sourcepos="11:1-12:0"><strong>Strong body language:</strong> Using gestures, posture, and eye contact that project confidence and professionalism.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="13:1-13:27"><strong>Benefits of Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="15:1-19:0"> <li data-sourcepos="15:1-15:99"><strong>Reduced anxiety:</strong> Feeling confident helps manage <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and stage fright.</li> <li data-sourcepos="16:1-16:133"><strong>Engaging delivery:</strong> Confident speakers project their voices, hold eye contact, and connect with their audience more effectively.</li> <li data-sourcepos="17:1-17:137"><strong>Increased persuasiveness:</strong> A confident presentation inspires belief and motivates your audience to listen and remember your message.</li> <li data-sourcepos="18:1-19:0"><strong>Greater impact:</strong> Confidently delivered speeches leave a lasting impression and achieve desired outcomes.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="20:1-20:15"><strong>Challenges:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="22:1-26:0"> <li data-sourcepos="22:1-22:112">Overcoming <strong>fear of public speaking</strong>: Many people experience some level of anxiety when speaking publicly.</li> <li data-sourcepos="23:1-23:101"><strong>Imposter syndrome:</strong> Doubting your abilities and qualifications, even when objectively qualified.</li> <li data-sourcepos="24:1-24:92"><strong>Negative self-talk:</strong> Internalized criticism and limiting beliefs can hamper confidence.</li> <li data-sourcepos="25:1-26:0"><strong>Past negative experiences:</strong> Unsuccessful presentations or negative feedback can erode confidence.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="27:1-27:24"><strong>Building Confidence:</strong></h2> <ul data-sourcepos="29:1-36:0"> <li data-sourcepos="29:1-29:102"><strong>Practice and preparation:</strong> Thoroughly rehearse your speech to feel comfortable with the material.</li> <li data-sourcepos="30:1-30:101"><strong>Visualization:</strong> Imagine yourself delivering a successful presentation with confidence and poise.</li> <li data-sourcepos="31:1-31:100"><strong>Positive self-talk:</strong> Actively replace negative thoughts with affirmations about your abilities.</li> <li data-sourcepos="32:1-32:106"><strong>Seek feedback:</strong> Ask trusted individuals for constructive criticism and use it to improve your skills.</li> <li data-sourcepos="33:1-33:157">Consider a <strong>speaking coach</strong>: Working with a coach can provide personalized guidance and support to address specific challenges and confidence barriers.</li> <li data-sourcepos="34:1-34:114"><strong>Start small:</strong> Gradually increase the size and complexity of your speaking engagements as you gain experience.</li> <li data-sourcepos="35:1-36:0"><strong>Focus on progress:</strong> Celebrate small successes and acknowledge your improvement over time.</li> </ul> <h2 data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Remember:</strong></h2> <p data-sourcepos="37:1-37:282"><strong>Confidence</strong> in public speaking is a journey, not a destination. By actively practicing, embracing feedback, and focusing on your strengths, you can overcome <strong>fear of public speaking</strong> and develop the <strong>confidence</strong> to deliver impactful and memorable presentations.</p> " href="https://orai.com/glossary/confidence/" data-gt-translate-attributes="[{"attribute":"data-cmtooltip", "format":"html"}]" tabindex="0" role="link">confidence .
You might also like
2023 complete guide to presentation templates 📊, how to improve your speaking skills: 50 experts reveal their secrets [in..., quick links.
- Presentation Topics
Useful Links
- Start free trial
- The art of public speaking
- improve public speaking
- mastering public speaking
- public speaking coach
- professional speaking
- public speaking classes - Courses
- public speaking anxiety
- © Orai 2023
Automated page speed optimizations for fast site performance

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
14.2 Incorporating Effective Visuals into a Presentation
Learning objectives.
- Recognize the characteristics of effective visual aids.
- Analyze different types of visual aids and appropriate ways to use them.
- Determine how to create original visual aids and how to locate visual aids created by others.
Good communication is a multisensory experience. Children first learning how to read often gravitate toward books with engaging pictures. As adults, we graduate to denser books without pictures, yet we still visualize ideas to help us understand the text. Advertisers favor visual media—television, magazines, and billboards—because they are the best way to hook an audience. Websites rely on color, graphics, icons, and a clear system of visual organization to engage Internet surfers.
Bringing visuals into a presentation adds color, literally and figuratively. There is an art to doing it well. This section covers how to use different kinds of visual aids effectively.
Using Visual Aids: The Basics
Good writers make conscious choices. They understand their purpose and audience. Every decision they make on the page, from organizing an essay to choosing a word with just the right connotations, is made with their purpose and audience in mind.
The same principle applies to visual communication. As a presenter, you choose the following:
- When to show images or video for maximum impact
- Which images will best produce the effect you want
- When to present information using a table, chart, or other graphic
- How much text to include in slides or informational graphics
- How to organize graphics so they present information clearly
Your goal is to use visual media to support and enhance your presentation. At the same time, you must make sure these media do not distract your audience or interfere with getting your point across. Your ideas, not your visuals, should be the focus.
As you develop the visual side of your presentation, you will follow a process much like the process you follow when you write. You will brainstorm ideas, form an organizational plan, develop drafts, and then refine and edit your work. The following sections provide guidelines to help you make good decisions throughout the process.
What Makes Visual Aids Effective?
To help you get a sense of what makes visual media work, think about what does not work. Try to recall occasions when you have witnessed the following visual media failures:
- Websites crammed with so many images, flashing phrases, and clashing colors that they are almost unreadable
- Assembly instructions with illustrations or diagrams that are impossible to follow
- Photographs that are obviously (and badly) altered with photo-editing software
- Distracting typos or other errors in signs, advertisements, or headlines
- Tables, charts, or graphs with tiny, dense text or missing labels
In each case, the problem is that the media creator did not think carefully enough about the purpose and audience. The purpose of images, color, or flashing text on a website is to attract attention. Overusing these elements defeats the purpose because the viewer may become overwhelmed or distracted. Tables, charts, and graphs are intended to simplify complex information, but without clear labels and legible text, they will confuse the audience.
In contrast, effective visual elements are chosen or created with the purpose and audience in mind. Although a photo shoot for a magazine article might result in dozens of images, editors choose those few that work best with the article. Web designers and video game creators have an audience test their products before they are released, to ensure that people will understand how to use them. Understanding the function of different visual aids will help you use them with purpose.
Types of Visual Aids
Visual aids fall into two main categories—images and informational graphics. Images include photographs, illustrations and clip art, and video footage. Informational graphics include tables, charts, bar graphs, and line graphs.
These visual aids serve two purposes: to add emotional impact to your presentation and to organize information more clearly. With that in mind, read to find out how specific types of visual aids achieve those purposes.
Photographs
A striking photograph can capture your audience’s attention far more successfully than words can. Consider including photographs at the beginning or end of your presentation to emphasize your main ideas or to accompany a particularly important point in the body of your presentation. Remember that, as with other types of graphics, less is often more. Two or three well-chosen photographs are more effective than a dozen mediocre ones.
When you choose photographs, ask yourself these questions:
- What purpose does this image serve? Will it surprise the audience? Will it provoke a strong emotional response? Does it support an important point?
- Will this photograph be more effective if shown with only a caption, or does it need additional text?
- Will the audience understand what is happening in the photograph? Is the meaning immediately evident, or does the photo need some context?
- Would editing the image make it more effective? Consider using image-editing software to crop the photo, change the brightness, or make other cosmetic changes. (Do not go overboard, though. A slightly imperfect but authentic image is preferable to one that has been obviously altered.)
To illustrate the sense of helplessness people felt in the midst of tragedy, a student could use a photograph that shows fear, weariness, or defeat on the face of the photograph’s subject.
Figure 14.3

Neil Moralee – On The Scrap Heap . – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Illustrations
Illustrations, such as editorial or political cartoons, serve much the same purpose as photographs. Because an illustration does not capture a moment in time the way a photo does, it may have less impact. However, depending on your topic and the effect you want to achieve, illustrations can still be very useful. Use the same criteria for choosing photographs to help you choose illustrations.
Figure 14.4

Humor Blog – Political Cartoon about Budget Cuts – CC BY 2.0.
The style of an illustration or photograph affects viewers just as the content does. Keep this in mind if you are working with the stock images available in office software programs. Many of these images have a comical tone. This may be fine for some topics—for instance, a presentation on television shows for children. However, if you need to project a more serious tone, make sure you choose images to suit that purpose. Many free (or reasonably priced) image banks are available online.
Video Footage
Even more than photographs, video footage can create a sense of immediacy, especially if your video includes sound. Showing a brief video clip can help your audience feel as if they are present at an important event, connect with a person being interviewed, or better understand a process. Again, ask yourself the following questions to ensure you are using the footage well:
- What purpose does this video serve? (Never rely on video clips just to fill time.)
- How much footage should be shown to achieve your purpose?
- What will need to be explained, before or after showing the video, to ensure that your audience understands its significance?
- Will it be necessary to edit the video to stay within time requirements or to focus on the most important parts?
Informational graphics, such as tables, charts, and graphs, do not provoke the same response that images do. Nevertheless, these graphics can have a powerful impact. Their primary purpose is to organize and simplify information.
Tables are effective when you must classify information and organize it in categories. Tables are an especially good choice when you are presenting qualitative data that are not strictly numerical. Table 14.1 “Example of Qualitative Data Table” was created for a presentation discussing the subprime mortgage crisis. It presents information about people who have held powerful positions both in the government and at one of the investment banking firms involved in the subprime mortgage market.
Table 14.1 Example of Qualitative Data Table
Sources: http://www.rollingstone.com/politics/news/%3Bkw=%5B3351,11459%5D ; http://www.nytimes.com/2008/10/19/business/19gold.html ; http://topics.nytimes.com/top/reference/timestopics/people/p/henry_m_jr_paulson/index.html?inline=nyt-per ; http://topics.nytimes.com/top/reference/timestopics/people/r/robert_e_rubin/index.html?inline=nyt-per , http://www.nytimes.com/2002/12/13/us/man-in-the-news-economic-adviser-from-other-side-of-the-deficit-stephen-friedman.html ; http://news.bbc.co.uk/2/hi/business/342086.stm .
If you are working with numerical information, consider whether a pie chart, bar graph, or line graph might be an effective way to present the content. A table can help you organize numerical information, but it is not the most effective way to emphasize contrasting data or to show changes over time.
Pie charts are useful for showing numerical information in percentages. For example, you can use a pie chart to represent presidential election results by showing what percentage of voters voted for the Democratic presidential candidate, the Republican candidate, and candidates from other political parties.
Figure 14.5
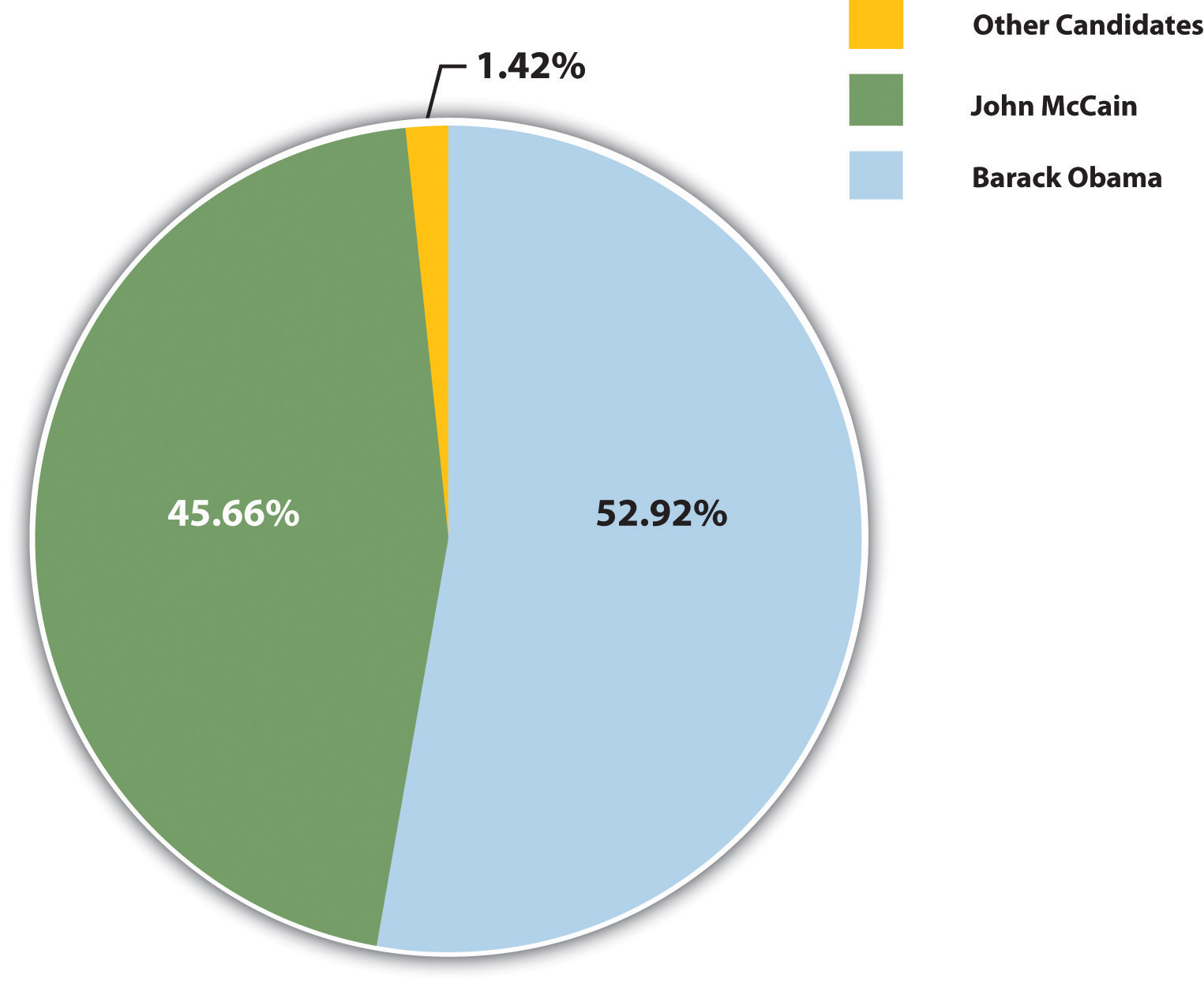
Source: http://www.fec.gov/pubrec/fe2008/2008presgeresults.pdf
Bar graphs work well when you want to show similarities and differences in numerical data. Horizontal or vertical bars help viewers compare data from different groups, different time periods, and so forth. For instance, the bar graph in Figure 14.6 allows the viewer to compare data on the five countries that have won the most Olympic medals since the modern games began in 1924: Norway, the United States, the former Soviet Union, Germany, and Austria. Bar graphs can effectively show trends or patterns in data as well.
Figure 14.6
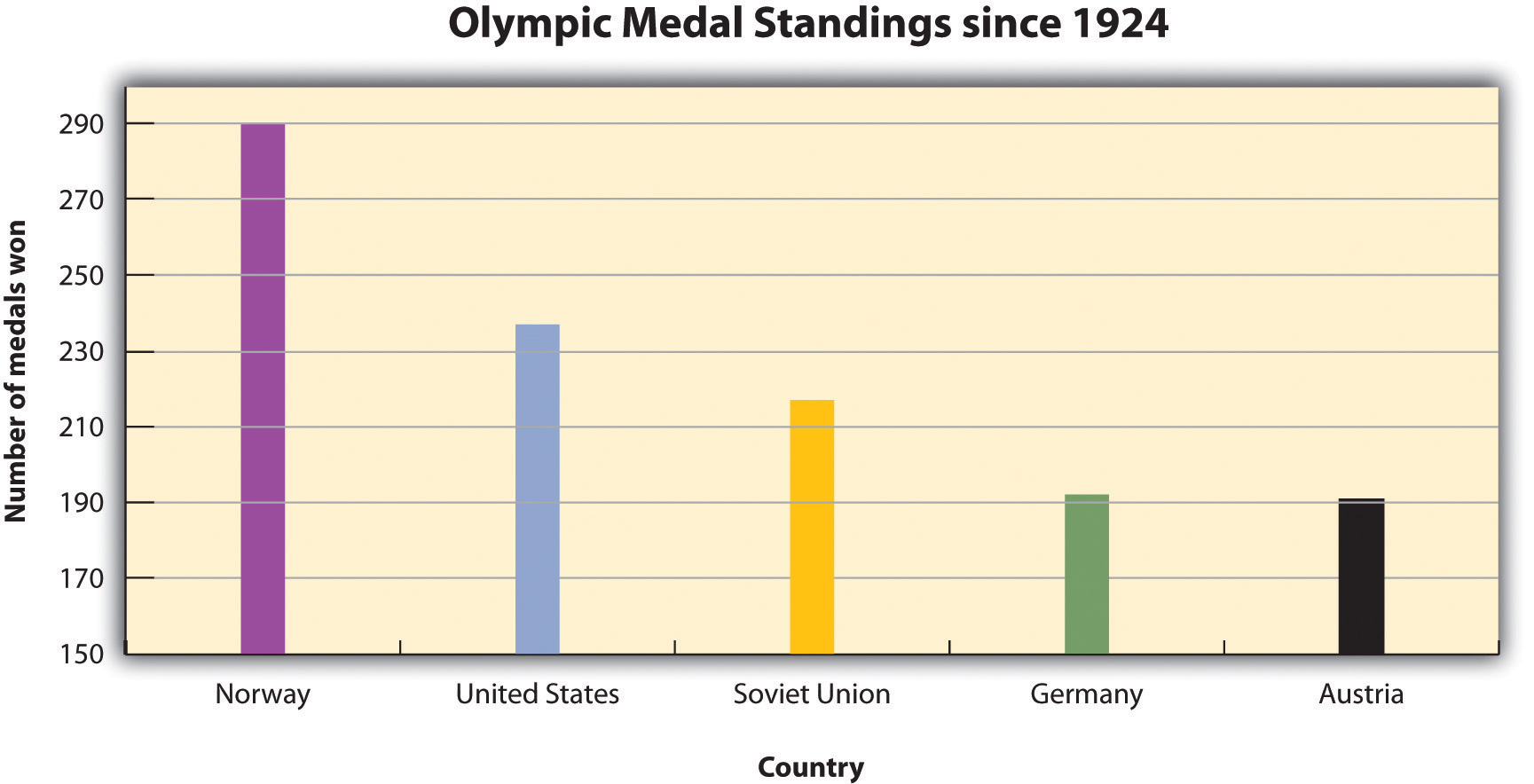
Source: http://www.nbcolympics.com/medals/all-time-standings/index.html
Line Graphs
Like bar graphs, line graphs show trends in data. Line graphs are usually used to show trends in data over time. For example, the line graph in Figure 14.7 shows changes in the Dow Jones Industrial Average—an economic index based on trading information about thirty large, US-based public companies. This graph shows where the Dow closed at the end of each business day over a period of five days.
Figure 14.7
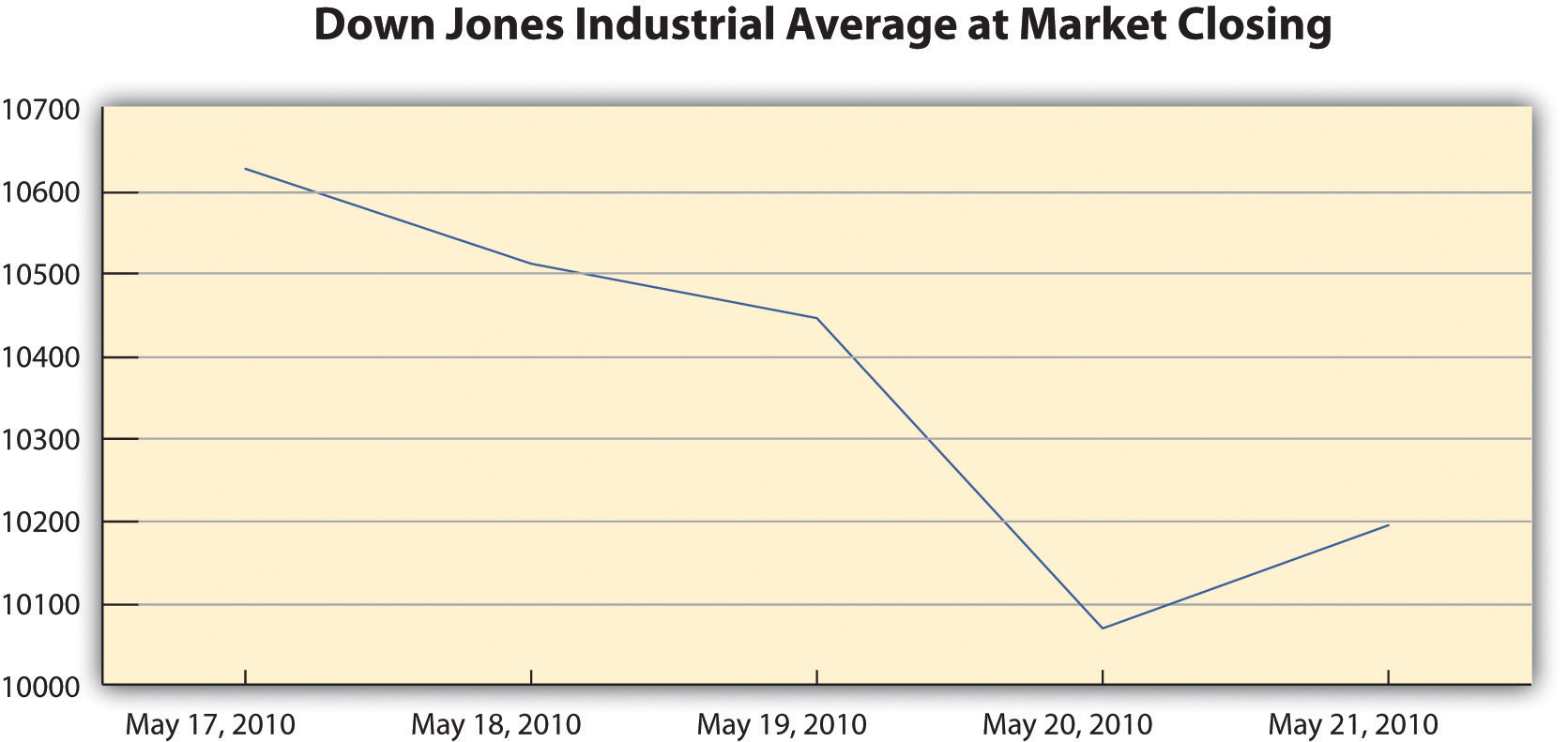
Source: http://www.google.com/finance/historical?cid=983582&startdate=May+17%2C+2010&enddate=May+21%2C+2010
In this exercise, you will begin to refine your ideas for incorporating media into your presentation. Complete the following steps on your own sheet of paper.
- Revisit the list you brainstormed for Note 14.12 “Exercise 3” in Chapter 14 “Creating Presentations: Sharing Your Ideas” , Section 14.1 “Organizing a Visual Presentation” and the annotated outline you developed for Note 14.17 “Exercise 4” .
- Analyze the two different types of visual aids: images and informational graphics. Identify at least two places in your presentation where you might incorporate visual aids.
- Evaluate the purpose of the visual aid. Does it create emotional impact, or does it organize information? Is the visual effective?
- Determine whether you will be able to create the visual aid yourself or will need to find it.
Creating Original Visual Aids
You will include original visual aids in your presentation to add interest, present complex information or data more clearly, or appeal to your audience’s emotions. You may wish to create some visual aids by hand—for instance, by mounting photographs on poster board for display. More likely, however, you will use computer-generated graphics.
Computer-generated visual aids are easy to create once you learn how to use certain office software. They also offer greater versatility. You can print hard copies and display them large or include them in a handout for your audience. Or, if you are working with presentation software, you can simply insert the graphics in your slides.
Regardless of how you proceed, keep the following guidelines in mind:
- Create visual aids with purpose. Think carefully about how they will enhance your message, and choose a form that is appropriate for your content.
- Strive for quality. You do not need the skills of a professional photographer or designer, but do take time to make sure your visual aids are neat, attractive, and legible. Proofread for errors, too.
Using Software to Create Visual Aids
You can use standard office software to create simple graphics easily. The following guidelines describe how to work with word-processing software and presentation software.
Working with Photographs
Most personal computers come equipped with some basic image-editing software, and many people choose to purchase more advanced programs as well. You can upload photographs from a digital camera (or in some cases, a cell phone) or scan and upload printed photographs. The images can then be edited and incorporated into your presentation. Be sure to save all of your images in one folder for easy access.
Creating Tables
To create a table within a word-processing document consult your software program’s help feature or an online tutorial. Once you have created the table, you can edit and make any additional changes. Be sure that the table has no more than six to seven rows or columns because you do not want to compromise the size of the text or the readability. Aligning with precision will help your table look less crowded. Also, the row and column titles should spell out their contents.
Creating Graphs
Figure 14.8
Pie charts and bar and line graphs can also be created using standard office software. Although you can create these graphics within a document, you will need to work with both your word-processing application and your spreadsheet application to do so. The graph should visually explain the data using colors, titles, and labels. The use of color will help the audience distinguish information; however, avoid colors that are hard on the eyes, such as lime green or hot pink. The title should clearly state what the graph explains. Lastly, avoid using acronyms in the titles and other labels.
Creating Graphics in an Electronic Presentation
If you plan to work only with hard copy graphics during your presentation, you may choose to create them as word-processing documents. However, if you are using presentation software, you will need to choose one of the following options:
- Create your graphics using the presentation software program.
- Create your graphics within another program and import them.
Standard office presentation software allows you to create informational graphics in much the same way you would create them within a word-processing application. Keep the formatting palette, a menu option that allows you to customize the graphic, open while you use the software. The formatting menu provides options for inserting other types of graphics, such as pictures and video. You may insert pictures from an image bank available within the program, or insert images or video from your own desktop files. Shape your use of multimedia in accordance with the message your presentation is trying to convey, the purpose, and your audience.
Creating Visual Aids by Hand
Most of the time, using computer-generated graphics is more efficient than creating them by hand. Using office software programs helps give your graphics a polished appearance while also teaching you skills that are useful in a variety of jobs. However, it may make sense to use hand-created visual aids in some cases—for instance, when showing a 3-D model would be effective. If you follow this route, be sure to devote extra time to making sure your visual aids are neat, legible, and professional.
Flip charts are inexpensive and quick visual aids used during face-to-face presentations. The flip chart can be prepared before, as well as during, the presentation. Each sheet of paper should contain one theme, idea, or sketch and must be penned in large letters to be seen by audience members farthest away from the speaker.
Writing Captions
Any media you incorporate should include a caption or other explanatory text. A caption is a brief, one- to two-sentence description or explanation of a visual image. Make sure your captions are clear, accurate, and to the point. Use full sentences when you write them.
Captions should always be used with photographs, and in some cases, they can be useful for clarifying informational graphics, which represent qualitative data visually. However, informational graphics may not require a caption if the title and labels are sufficiently clear. For other visual media, such as video footage, providing explanatory text before or after the footage will suffice. The important thing is to make sure you always include some explanation of the media.
In this exercise, you will begin to develop visual aids for your presentation. Complete the steps in this exercise—and enjoy the chance to be creative. Working with visuals can be a pleasant way to take a break from the demands of writing.
- Revisit the ideas you developed in Note 14.24 “Exercise 1” . Choose at least two ideas that you can create. ( Note: If you are using software to develop a slideshow presentation, count this as one of your self-created visual aids. Include at least one other self-created visual aid, such as an original photograph, within your slideshow.)
- Get creative! Take your photographs, construct a 3-D model, create informational graphics, or work on your presentation slides. Develop good working drafts.
- After you have completed drafts of your visual aids, set them aside for a while. Then revisit them with a critical eye. First, check any text included with the graphic. Make sure your facts are correct, your words are clear and concise, and your language is free of errors.
- Next, evaluate how well your aids work visually. Are they large enough to be seen and read from a distance? Are captions and labels easy to find? Are photographs of reasonably high quality? Ask someone else for feedback, too.
- Begin making any needed changes. As you proceed through the rest of this section, continue to revisit your work to improve it as needed.
Collaboration
Please share the first version of your visual aids with a classmate. Examine what they have produced. On a separate piece of paper, note both the elements that catch your attention and those that would benefit from clarification. Return and compare notes.
Testing and Evaluating Visual Aids
Regardless of how you create your visual aids, be sure to test-drive them before you deliver your presentation. Edit and proofread them, and if possible, show them to someone who can give you objective feedback. Use the following checklist.
Checklist 14.1
Visual Aid Evaluation Checklist
- Visual aids are clearly integrated with the content of the presentation
- Photographs and illustrations suit the overall tone of the presentation
- Images and text are large and clear enough for the viewer to see or read
- Images are shown with explanatory text or a caption
- Informational graphics include clear, easy-to-read labels and headings
- Text within informational graphics is easy to read (Watch out for wordiness and crowded text or a font that is too small and hard to read.)
- Formatting choices (color, different fonts, etc.) organize information effectively
- Any text within graphics is free of errors
- Hyperlinks within slides function properly
- Display text for hyperlinks is concise and informative (Never paste a link into a slide without modifying the display text.)
Writing at Work
Office software includes many options for personalizing a presentation. For instance, you can choose or create a theme and color scheme, modify how one slide transitions to the next, or even include sound effects. With so many options, students and employees sometimes get carried away. The result can seem amateurish and detract from, rather than enhance, your presentation.
Remember, you are delivering a presentation, not producing a movie. Use the customization options to help give your presentations a consistent, polished, appearance. However, do not let these special effects detract from the substance of your slides.
Using Existing Visual Media
Depending on your topic, you may be able to find images and other graphics you can use instead of creating your own. For instance, you might use photographs from a reputable news source or informational graphics created by a government agency. If you plan to use visual aids created by others, keep the following guidelines in mind:
- Set a purpose before you begin your search. You will search more efficiently if you start with a general idea of what you are looking for—a line graph of unemployment rates for the past twelve months, for example, or a video clip of the most recent State of the Union address.
- Filter out visual aids that are not relevant. You may come across eye-catching graphics and be tempted to use them even if they are only loosely related to your topic, simply because they are attention getting. Resist the temptation. If the graphic is not clearly connected to your point, it does not belong in your presentation.
- Read carefully. In addition to reading labels, headings, and captions, read any text that accompanies the visual. Make sure you understand the visual in its original context. For informational graphics, make sure you understand exactly what information is being represented. (This may seem obvious, but it is easy to misread graphic information. Take the time to examine it carefully.)
- Evaluate sources carefully and record source information. When you look for visual media to complement your presentation, you are conducting research. Apply the same standards you used for your research paper. Choose reliable sources, such as reputable news organizations, government and nonprofit organizations, and educational institutions. Verify data in additional sources. Finally, be sure to document all source information as you proceed.
Searching Efficiently for Visual Media
You will probably find it most efficient to use the Internet to search for visual aids. Many students begin by typing keywords into a search engine to locate related images. However, this search technique is not necessarily efficient, for several reasons:
- It often pulls up hundreds or even thousands of images, which may be only loosely related to your search terms.
- It can sometimes be difficult to understand the image in its original context.
- It can be hard to find copyright information about how you may use the image.
A more efficient strategy is to identify a few sources that are likely to have what you are looking for, and then search within those sites. For instance, if you need a table showing average life expectancy in different countries, you might begin with the website of the World Health Organization. If you hope to find images related to current events, news publications are an obvious choice. The Library of Congress website includes many media related to American history, culture, and politics.
Searching this way has the following advantages:
- You will often find what you are looking for faster because you are not wasting time scrolling through many irrelevant results.
- If you have chosen your sources well, you can be reasonably certain that you are getting accurate, up-to-date information.
- Images and informational graphics produced by reputable sources are likely to be high quality—easy to read and well designed.
If you do choose to use a search engine to help you locate visual media, make sure you use it wisely. Begin with a clear idea of what you are looking for. Use the advanced search settings to narrow your search. When you locate a relevant image, do not download it immediately. Read the page or site to make sure you understand the image in context. Finally, read the site’s copyright or terms of use policy—usually found at the bottom of the home page—to make sure you may use the material.
If you are unable to find what you are looking for on the Internet consider using print sources of visual media. You may choose to mount these for display or scan them and incorporate the files into an electronic presentation. (Scanning printed pages may lower the quality of the image. However, if you are skilled at using photo-editing software, you may be able to improve the quality of the scanned image.)
Inserting Hyperlinks in an Electronic Presentation
If you are working with images, audio, or video footage available online, you may wish to insert a link within your presentation. Then, during your presentation, you can simply click the link to open the website in a separate window and toggle between windows to return to your presentation slides.
To insert a hyperlink within your presentation, click on insert in the toolbar and then select hyperlink from the menu. Doing so will open a dialogue box where you can paste your link and modify the accompanying display text shown on your slide.
Copyright and Fair Use
Before you download (or scan) any visual media, make sure you have the right to use it. Most websites state their copyright and terms of use policy on their home page. In general, you may not use other people’s visual media for any commercial purpose without contacting the copyright holder to obtain permission and pay any specified fees.
Copyright restrictions are somewhat more ambiguous when you wish to download visual media for educational uses. Some educational uses of copyrighted materials are generally considered fair use —meaning that it is legally and ethically acceptable to use the material in your work. However, do not assume that because you are using the media for an educational purpose, you are automatically in the clear. Make sure your work meets the guidelines in the following checklist. If it does, you can be reasonably confident that it would be considered fair use in a court of law and always give credit to the source.
Checklist 14.2
Media Fair Use Checklist
- You are using the media for educational purposes only.
- You will make the work available only for a short period and to a limited audience. For instance, showing a copyrighted image in a classroom presentation is acceptable. Posting a presentation with copyrighted images online is problematic. In addition, avoid any uses that would allow other people to easily access and reproduce the work.
- You have used only as much of the work as needed for your purposes. For video and audio footage, limit your use to no more than 10 percent of the media—five minutes of an hour-long television show, for example. Image use is harder to quantify, but you should avoid using many images from the same source.
- You are using the media to support your own ideas, not replace them. Your use should include some commentary or place the media in context. It should be a supporting player in your presentation—not the star of the show.
- You have obtained the material legally. Purchase the media if necessary rather than using illegally pirated material.
- Your use of the media will not affect the copyright holder or benefit you financially.
By following these guidelines, you are respecting the copyright holder’s right to control the distribution of the work and to profit from it.
In some fields, such as teaching, job applicants often submit a professional portfolio to a prospective employer. Recent college graduates may include relevant course work in their portfolios or in applications to graduate school. What should you do if your course work uses copyrighted visual media?
This use of media is acceptable according to fair use guidelines. Even though you are using the work for your personal professional advancement, it is not considered an infringement on copyright as long as you follow the additional guidelines listed in the previous checklist.
Crediting Sources
As you conduct your research, make sure you document sources as you proceed. Follow the guidelines when you download images, video, or other media from the Internet or capture media from other sources. Keep track of where you accessed the media and where you can find additional information about it. You may also provide a references page at the end of the presentation to cite not only media and images but also the information in the text of your presentation. See Chapter 13 “APA and MLA Documentation and Formatting” for more information on creating a reference page.
Write captions or other explanatory text for visual media created by others, just as you would for media you created. Doing so helps keep your audience informed. It also helps ensure that you are following fair use guidelines by presenting the media with your commentary, interpretation, or analysis. In your caption or elsewhere in your presentation, note the source of any media you did not create yourself. You do not need to provide a full bibliographical citation, but do give credit where it is due.
In this exercise, you will locate visual aids created by others and continue developing the work you began earlier. Complete these steps.
1. Revisit the ideas you developed in Note 14.24 “Exercise 1” . Choose at least two ideas for which it would make more sense to find the visual aid than to create it yourself. 2. Use the search tips provided in this section to locate at least two visual aids from reputable sources that you can use. Prepare them for your presentation by adding clarifying text as needed. Be sure to credit your source. 3. Incorporate the visual aids you created in Note 14.26 “Exercise 2” and Note 14.32 “Exercise 3” into your presentation. This may involve preparing physical copies for display or inserting graphic files into an electronic presentation.
4. Take some time now to review how you will integrate the visual and verbal components of your presentation.
- If you are working with presentation software, refine your slides. Make sure the visual approach is consistent and suits your topic. Give your text a final proofread.
- If you are not using presentation software, review the annotated outline you created in Note 14.24 “Exercise 1” . Update it as needed to reflect your current plan. Also, determine how you will physically set up your visual aids.
Key Takeaways
- Visual aids are most effective when they are chosen with the purpose and audience in mind. They serve to add emotional impact to a presentation and to organize information more clearly.
- Visual aids should always be clearly related to the presenter’s ideas. Captions, labels, and other explanatory text help make the connection clear for the audience.
- Like writing, developing the visual components of a presentation is a process. It involves generating ideas, working with them in a draft format, and then revising and editing one’s work.
- Visual aids can be divided into two broad categories—image-based media and informational graphics.
- Widely available software programs make it relatively easy to create visual aids electronically, such as photo images, charts, and graphs.
- When using visual aids created by others, it is important to apply good research skills, follow guidelines for fair use, and credit sources appropriately.
Writing for Success Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
- Sign In Sign Up
Home / Design / 6 Different Types of Presentation Styles
6 Different Types of Presentation Styles
Presentations have several use cases. Designing an effective presentation is a skill and a task. Since different situations call for different types of presentations, it can be confusing to choose a specific presentation style.
In this blog, we’ll explore six different types of presentations and where to use them. From informative to persuasive, motivational to instructional, we’ll cover each type in detail, providing tips and strategies to help you deliver powerful and engaging presentations that leave a lasting impact on your audience.
So, let’s dive in and discover the secrets to mastering the art of presentation!
Purpose of a Presentation
- Informing: The primary purpose of a presentation can be to provide information to the audience. This can include updates on the progress of a project, sharing research findings, or presenting data and statistics.
- Persuading: Another purpose of a presentation can be to persuade the audience to take a specific action or to change their thinking about a topic. This can include presenting a proposal, making a sales pitch, or advocating for a particular cause.
- Educating: Presentations can also be used to educate the audience on a particular topic, such as teaching a new skill, demonstrating how to use a product, or sharing insights on a subject.
- Entertaining: In some cases, the purpose of a presentation can be to entertain the audience. This can include delivering a keynote speech at a conference or event, performing a stand-up comedy routine, or using humor and storytelling to engage and captivate the audience.
Bonus: 10 Insanely Creative Presentation Ideas You Can Steal
6 Different Presentation Styles
To ensure that the presentation resonates with your audience, it’s important to first understand each type of presentation. Let’s take a closer look at different presentation styles:
1. Educational
An educational presentation aims to teach or inform the audience about a specific subject or topic. It is usually structured around a clear learning objective or outcomes and is designed to facilitate understanding, retention, and engagement with the material being presented.
You can include a range of visual aids like charts, graphs, images, or videos to illustrate and reinforce key concepts. This presentation style can include interactive elements like quizzes, activities, or group discussions to enable deeper learning.
Examples of educational presentations are lectures, workshops, training sessions, webinars, and e-learning modules.
2. Instructional
An instructional presentation is designed to provide step-by-step guidance on how to perform a particular task or activity. The goal is to help the audience understand and follow a set of instructions or procedures that will enable them to accomplish a goal or objective.
Instructional presentations typically involve clear and concise explanations of each step in the process, along with visual aids such as diagrams, illustrations, or videos to help demonstrate the steps visually. The presenter may also use props or other tools to help illustrate key concepts.
Instructional presentations include tutorials, how-to guides, product demonstrations, and training sessions for specific skills or processes.
3. Motivational
A motivational presentation inspires and energizes the audience, encouraging them to take action or adopt a particular mindset. The goal is to create excitement, enthusiasm, and empowerment in the audience, motivating them to strive for personal or professional success.
It features powerful storytelling, personal anecdotes, or quotes that convey a positive message or reinforce key themes. Visual aids such as slides, videos, or props can illustrate key points or create an emotional connection with the audience.
Examples of motivational presentations are keynote speeches, team-building events, and personal development workshops.
4. Persuasive
A persuasive presentation convinces the audience to adopt a specific viewpoint. The goal is to persuade them with a particular idea, product, or service. To create a persuasive presentation, identify and understand the needs and desires of the audience and tailor the content accordingly.
The presentation will often include a clear call to action along with statistical data, case studies, testimonials, or other forms of evidence to support the argument. Storytelling or personal anecdotes create an emotional connection with the audience and reinforce the key message.
A persuasive presentation can be for sales pitches, marketing presentations, and political speeches.
5. Problem-solving
A problem-solving presentation identifies, analyzes, and solves a specific problem. It presents a clear and logical approach to solving a problem and gaining the audience’s buy-in and support for the proposed solution.
The content involves identifying and analyzing the root causes of a problem and proposing a viable solution. The presenter can use diagrams or flowcharts to illustrate the problem and proposed solution. It can also include a plan for implementing the solution and a timeline for achieving results.
Problem-solving presentations can be related to business proposals, project plans, and research reports.
Bonus: 5 Online Presentation Tools That Will Make Your Deck Stand Out
A visual presentation emphasizes the use of visual aids to convey information. It uses graphics, images, videos, or other visual elements to enhance the audience’s understanding and retention of the presented material.
Visual presentations can be in different forms – slideshows, videos, infographics, or posters. These are used to communicate complex information quickly and clearly, or when you want to create a memorable and engaging experience.
The presenter may use a variety of techniques to create a visually appealing presentation, such as color schemes, typography, and layout design. It can be used for marketing campaigns, educational materials, and scientific presentations.
The AI presentation maker from Simplified offers an effortless way to design stunning presentations that will impress any audience. It offers a library of thousands of photos and videos and lets you add gifs directly to your artboard. You don’t have to spend hours generating professional and on-brand decks.
The AI presentation maker enables you to create outstanding presentations in a few steps. Start by going to the Design Dashboard and clicking “Generate with AI.” Then, choose “AI Presentation,” input your presentation topic, and click “Generate.” The AI Presentation Maker will automatically create a visually appealing and customizable presentation in seconds.
Simplified indeed simplifies making presentations and is all you need to create a powerful and engaging presentation.
Make your presentations with Simplified’s AI tool!

5 AI Customer Support Solutions for Businesses
Choosing the best ai copywriting app: simplified (free forever) vs. jasper ai ($984 paid annually), you may also like.

How to Remove the Background of an Emoji in Minutes
![7 Best AI Image Restoration Tools to Try in 2024 [Free & Paid] 7 Best AI Image Restoration Tools to Try in 2024 [Free & Paid]](https://siteimages.simplified.com/blog/Best-Free-Paid-AI-Image-Restoration-Tools-01.png?auto=compress&fit=crop&fm=png&h=400&w=400)
7 Best AI Image Restoration Tools to Try in 2024 [Free & Paid]
![How to Use Photoshop AI Generative Fill Feature [2024] How to Use Photoshop AI Generative Fill Feature [2024]](https://siteimages.simplified.com/blog/How-to-Use-Photoshop-AI-Generative-Fill-01-1.png?auto=compress&fit=crop&fm=png&h=400&w=400)
How to Use Photoshop AI Generative Fill Feature [2024]
![20 Podcast Thumbnail Ideas to Boost Your Show’s Visual Appeal + Best Practices [2024] 20 Podcast Thumbnail Ideas to Boost Your Show’s Visual Appeal + Best Practices [2024]](https://siteimages.simplified.com/blog/Podcast-Thumbnail-Ideas-to-Boost-Your-Show-02-1.png?auto=compress&fit=crop&fm=png&h=400&w=400)
20 Podcast Thumbnail Ideas to Boost Your Show’s Visual Appeal + Best Practices [2024]

7 Best Background Changer Apps To Try in 2024

Best AI Carousel Makers in 2024 | Simplified
A comprehensive guide to effective presentation skills, how to create a youtube banner in minutes: the simplified guide, 10 powerful ways to bounce back from creative burnout, types, examples & tips: all about grids in graphic design, the 10-step blueprint to craft memorable posters (2024), 12 basic principles of layout and composition in design (2024), how to write the best sales resume for your dream job (with examples), 10 best mesh gradient generators of 2024, 3 simple steps to blend two images in photoshop like a pro.
Comments are closed.
More in: Design
How to remove green screen in photoshop: a step-by-step guide, tiktok ratio explained: what you need to know, how to add a gif to your instagram comments: step-by-step guide.

3 Quick Ways to Remove Backgrounds from Signatures
How to make an invoice: a step-by-step guide for new entrepreneurs, 6 ai icon generator tools to make your branding pop, the ultimate guide to email banner size: best practices in 2024, the ultimate guide to crafting a perfect graphic design resume in 2024 + examples, a comprehensive guide on creating a sample resume for an assistant controller (tips & examples), start with simplified it's free forever.
Design, Write, Edit videos, and Publish Content from one app
Sign up now

- Graphic Design
- Video & Animations
- Social Media Planner
- Background Remover
- Magic Resizer
- Animation Maker
- Content Rewriter
- Long Form Writer
- Instagram Reels
- Customer Testimonial
- Convert mov to mp4
- Convert jpg to png
- Instagram Stories
- Facebook Posts
- Linkedin Posts
- Pinterest Pins
- Half Page Ads
- Instagram Ads
- Facebook Feed Ads
- Billboard Ads
- Newsletter Popup
- Shopify Mobile Banner
- Shopify Home Page
- Business Cards
- Explore Static Templates
- YouTube Shorts
- Pinterest Video Pins
- TikTok Videos
- Explore Videos
- Hashtag Generator
- Youtube Video Titles
- Photo Captions
- Amazon Product Features
- Review Responder
- Blog Ideas + Title
- Sentence Expander
- Before After Bridge
- Social Media Quotes
- Meme Generator
- Explore AI Templates
- Google My Business
- Social Media Planning
- Social Media Analytics
- Video Academy
- Help center
- Affiliate Program
Latest Posts
Ai agents are not just llm prompts, 9 best ai text-to-video tools for 2024 [free & paid], 8 best messenger chatbot tools in 2024 [free & paid], 9 best whatsapp chatbot tools in 2024 [free & paid], 7 best ai task manager tools for 2024 [free & paid].
Round up of presentations by type

Presentations are a common way of sharing information between people. Used for a variety of purposes in different settings, it’s important to hone in on what your goals are in presenting information and in what context it will be shared. From there, you can better create a presentation that suits your needs. Let’s look through the nuts and bolts of presentations and consider common types you could utilize regardless of your content themes.
Summary/Overview:
The why, who, and what of presentations
We make presentations to easily share information from a presenter to an audience. In thinking about the why, we are also able to focus more intently on the type of presentation we could create. Are we attempting to educate or inform, persuade, or even tell a story? By considering the goal or problem to be solved, we can more readily form our presentation in line with common frameworks.
The two primary parties involved in presentations are the presenter(s) and the audience. When planning a presentation, it is important to consider who is presenting and who is receiving the information. This relationship alone may easily identify the type of presentation.
Most presentations use a narrow widescreen size (16:9), which is 1920px by 1080px. Standard slides (4:3) measure at 1024px x 768px. In Adobe Express, you can choose whichever format you prefer and use the Resize tool to change the slide size at any time.
The power and the point of presentations
Presentations are a useful medium because they pair textual information with visual images. Whether using diagrams, charts, or pictures to illustrate the information, the visual aspect supports a concise body of text so that they are easily read. The presenter will typically have more to say than what is provided within the presentation, but the presentation serves as an outline or summary of the main points.
Presentations should be easily understood in an immediate way. As mentioned before, the physical presentation serves as a summary for the more thorough information provided by the speaker. When done well, presentations can be referenced down the line and call to mind a more complete picture of the presenter’s work.
When to use presentations and for whom
Anytime you have a specific time window and audience, presentations can be a useful tool. Whether this is in a professional or educational context, or even just between friends, there are many times when presentations can be used to share information.
Some examples might be:
- A work meeting in which you are reporting on a project’s status
- Teaching a webinar
- Pitching an idea
- Making a speech
- Presenting a project in school
The essential elements of any type of presentation
Making compelling presentations that complement and strengthen your objective is not the easiest task. What makes a presentation successful, and what should you include?
To start with, you'll want to make sure the message you're sharing with your audience is conveyed in a verbal and visual way. There should also be a balance of visual elements like graphs, charts, images, and text that help you back up insights you have to share. Animation is a common tool that captures an audience’s attention. It can help you emphasize key points and add interest and a sense of fun to your presentation. By bringing a dynamic aspect to your visuals, you make your work more memorable and often get your points across more effectively.
Common types of presentations
Here we will look at common types of presentations focusing on their goals. Does your presentation aim to inform, persuade, instruct, or educate? With a defined intention in mind, the type can be applied to a variety of different settings.
This kind of presentation aims to convince the audience of something. Whether you are pitching an idea for a book to an editor or providing a marketing plan to a potential client, presentations can be a useful vehicle in which to make an argument. This type of presentation is often used in competitive circumstances, such as during an election cycle. Whether it be an idea for a product or project, you can lay out for your audience what you're offering and how you will go about accomplishing it.
Informative or educational
Presentations can be used for sharing knowledge and insight on a particular topic. Whether the topic is design history or the chemical properties of an element, these aim to increase understanding. This kind of presentation is given in a class or webinar setting and can benefit from space to discuss or clarify. Provided that information defines this kind of presentation, it’s important to be mindful about keeping it as essential and easily digestible as possible. You don’t want your audience to be overloaded. By finding the right balance of strong text-based points and visual support, your work will better serve its purpose of informing your audience.
Instructional
Whereas an informative presentation is often the who, what, when, and where, the instructional presentation deals with the how. If there’s a process or practice that your audience could benefit from learning, this is the presentation for you. These provide practical instructions for accomplishing a given task, often moving step-by-step to guide the audience. Clarity and concision are key here; too much information or jargon has the potential to overload the audience and take away from your efforts. Live demonstration can be a useful supplement alongside instructional presentations.
Progress or status reporting
If you are in the process of accomplishing something and you are asked for an update, a presentation can be a useful way of showing what you’ve done thus far. Demonstrating your progress communicates effort to your team and commitment to your mission, instilling more confidence in your audience. It also offers a chance to communicate about potential changes if needed towards the goal's completion. This kind of presentation suits an educational or professional setting, whether tracking a student’s work through the academic year or following the status of a professional project for a client or supervisor.
Motivational or inspirational
Sometimes you just need a little boost. A motivational or inspirational presentation is aimed at an audience that could benefit from a positive perspective. This form is typically more personal and emotional than the others, working to build confidence and meaningfully shift the energy of an audience. Whether focusing on a historical figure’s overcoming of an obstacle or using the presenter’s own story to catalyze and inspire, the goal here is to engage in a way that encourages your audience. Energy is everything, so keep it light.
Design any type of presentation with Adobe Express
Build amazing presentations that are engaging, educational, and impactful. From clearly conveying complex information and highlighting your brand to boosting your marketing efforts and fostering collaboration, you can quickly and easily make captivating presentations that will win your audience over with the help of our extensive template collections.
Get inspired with our gigantic collection of professionally designed presentation templates , then choose one to customize. Drop in your information, add your own images, or even organize information with icons. Send your presentation to team members to collaborate via the share link and download whenever you’re finished. It’s as easy as choosing a template, customizing, and sharing.

- Storytelling Learning Journey
- Crafting Strategic Visual Stories
- Influencing with Visuals
- Presenting Data Visually
- Everyday Business Storytelling
- In-Person Training
- Virtual Training
- Resource Center
Easy Guide to Choosing the Right Presentation Visuals
Home / TPC Blog / Easy Guide to Choosing the Right Presentation Visuals

We live in a visual world. Billboards on the highway, TV commercials, and social media newsfeeds are constantly trying to sell us messages. But these visuals aren’t built merely to be colorful or pretty. Clever visuals are designed for a more strategic purpose – to get us to notice and respond to ideas.
This same logic directly applies to business communications: relevant visuals help our insights and recommendations be more easily understood, remembered, and acted on. Here’s a quick and easy guide to understanding how to make clear, powerful visuals in your presentation:
Why do visuals help us remember things?

In one word: neuroscience. Neuroscientists have discovered that an idea expressed in visual form is processed 60,000 times faster than the same information either printed or spoken.
But visuals do more than just help us remember something – they spur action . Visuals trigger our right brain where we process emotion and feelings. And it’s emotion (even more than pure logic) that motivates us into action.
Why are visuals important in presentations?

To understand why getting visuals right is so important, ask yourself this one question: what is the purpose of any presentation? Or email ? Or proposal? Isn’t it to help decisions get made? Or move business conversations forward? Clear, simple visuals help our ideas be quickly interpreted and decisions get made faster because they humanize your ideas and infuse emotion (rather than relying on pure logic.) Conversely, distracting visuals slow decision-making down. Slower decisions mean slower business.
What are common mistakes for presentation visuals?

Visuals often go wrong when we lack either time or an overarching visual slide strategy (or both!). Business presenters are—understandably—always looking to save time, reuse, and repurpose existing slides. As a quick fix, we throw together slides from past decks, or borrow slides from a co-worker without giving thought to the intent of the message we are trying to communicate for the specific purpose (we call these “ Frankendecks .”)
Let’s face it: it’s easy to fall prey to bad visuals. Business presentations are essentially known for including too much text and data, while often using off-brand colors, fonts, and imagery (and let’s not forget about cheesy stock photography .)
On the other hand, even slides that are “pretty” aren’t always designed with a clear, easy-to-digest message, ultimately causing confusion rather than advancing the story we need to tell.
What are the visual elements that make a strong presentation?
There are five main ways to display information in presentations: photos, diagrams, data, text, and video.
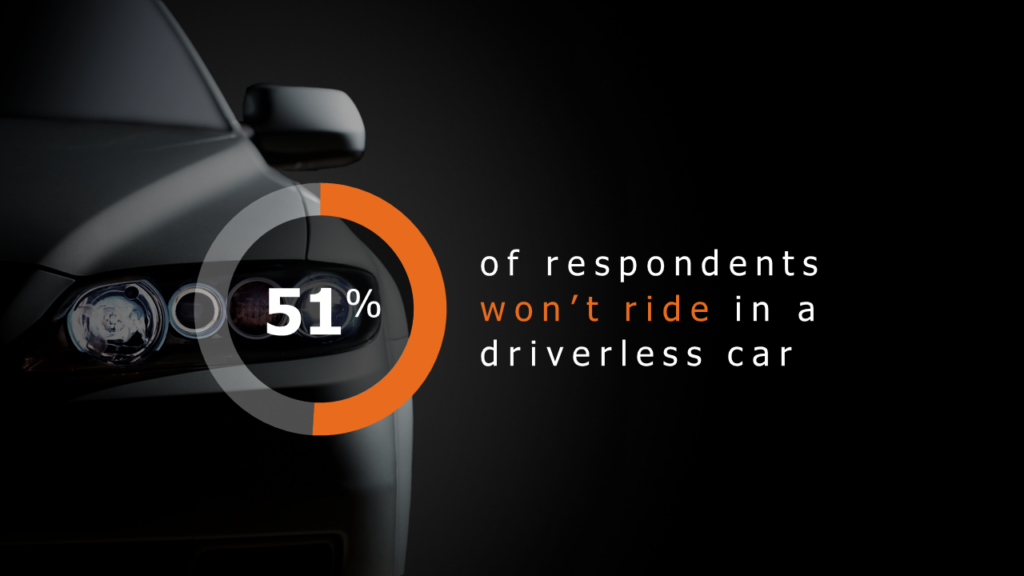
Photos are powerful. They’ll humanize your message help you connect your ideas to your audience on an emotional level. Photos can also build a mood or theme for your presentation.

Diagrams help breakdown and ‘cluster’ information into digestible concepts. We often suggesting using shapes or icons to call-out key messages. An example of a diagram would be a timeline or an organizational chart.

Data is most often presented in charts and tables. But sometimes, like in the case of the image below, only key data – that advances the story – is displayed. Also notice how the use of contrasting colors is used to draw the eye to the data point, and gray is used to subdue data that is simply there for context.
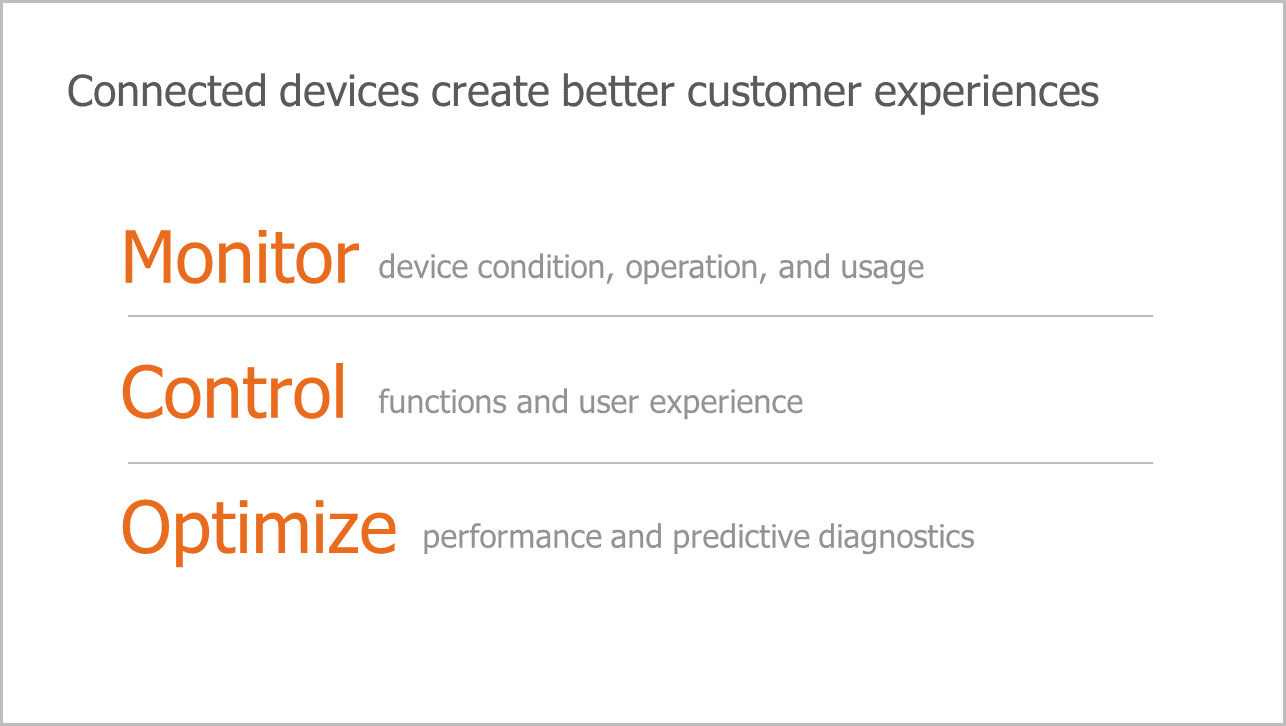
Text is the most common – and overused – visual we see in business presentations (hello bullets!). Text used sparingly with contrasting color and size, however, creates an easy-to-digest message.
Video is an excellent to way to change the pace, the voice, and the medium of a presentation. It’s usually a good idea to keep it brief and embedded straight into the slide deck. To ensure good flow to your visuals, it’s important that any change of medium – such as video – is seamlessly integrated.
Now that we’ve established how critical strong visuals are to business presentations…
Let’s get into some simple tips that will help jumpstart visual thinking the next time you open PowerPoint:
TIP 1: Callouts are Visual Eye-Candy
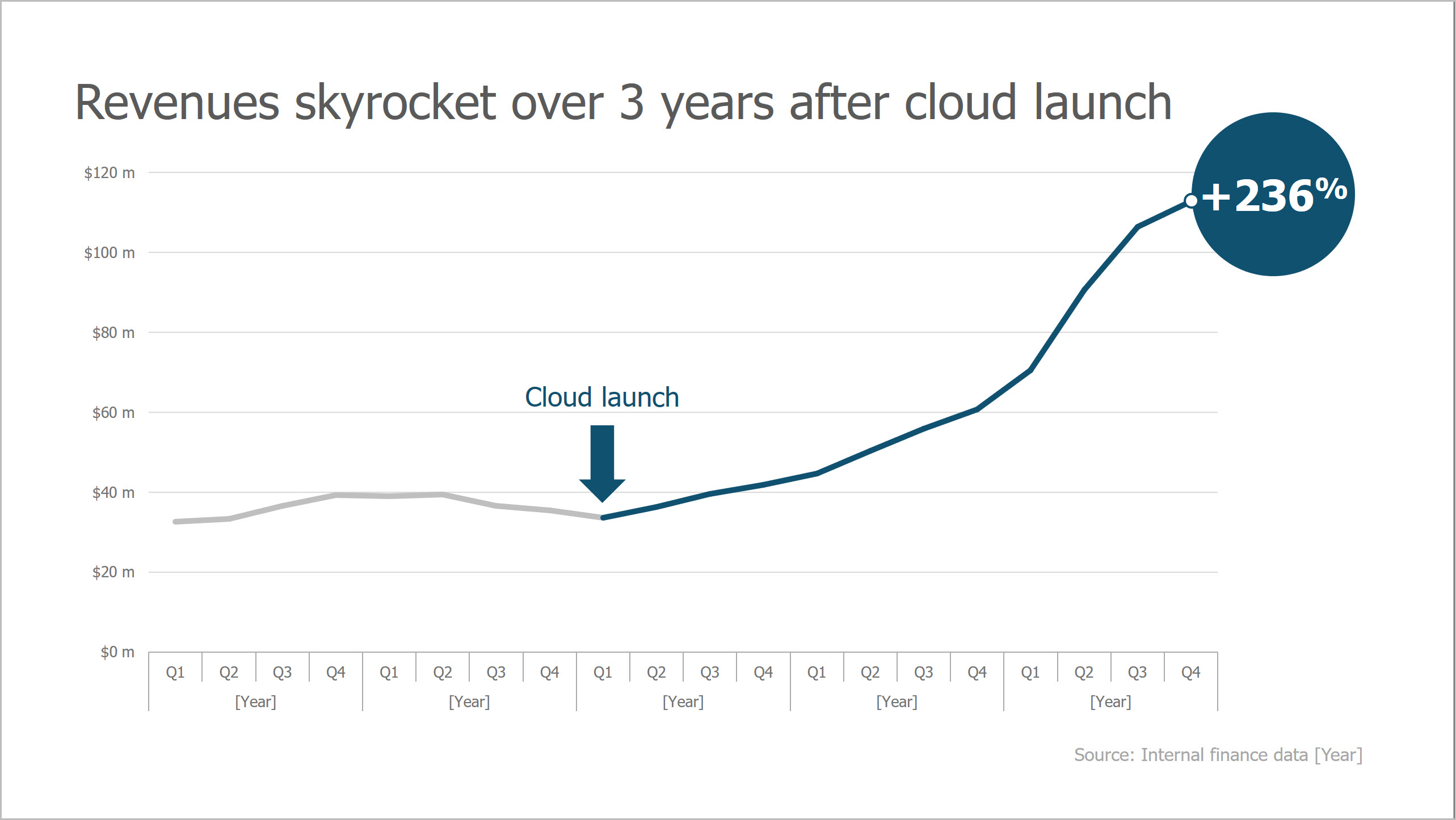
Callouts are one of the easiest and most potent data visualization techniques. By calling out key information with a contrasting color, size, or shape, you can easily highlight key points. This is a gift to your audience because with a simple visual ‘gesture’ you are helping them digest your message in one glance. This is one of the fastest ways to move your ideas forward.
TIP 2: Slide headlines refer to key visuals and help tell a story
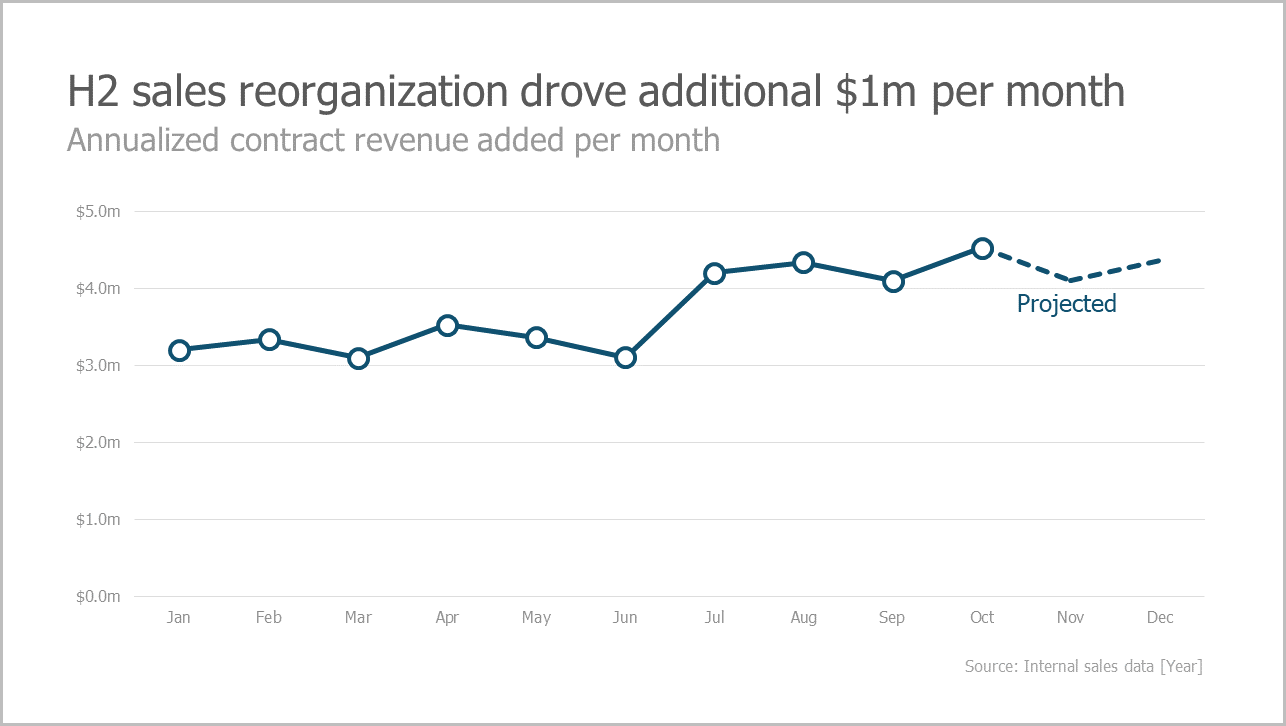
Hands down , the best place to summarize the key message of your slide is in the headline (particularly if you are offering a lot of facts or data). Summing up your “big idea” in the slide title offers your audience the gift of clarity.
What’s more, slide headlines – like chapter headings – offer a logical outline to the overall story you are telling in your presentation. No data or facts are thrown in just because you have them. Everything should fit together logically.
TIP 3: Create a Landing Page for Easy Navigation
Not every presentation needs to be delivered in a linear format. As you can see from this slide, grouping your presentation into sections on a landing page gives an instant visual picture of everywhere you can go in this presentation.
Even better, each of the tabs on this landing page are portals to dive deeper into those sections, offering not only a visual orientation of your deck from start to finish but a way to jump around depending on your audience’s needs. This non-linear approach is particularly helpful for decks that are presented by someone else or being emailed.
Here are some additional questions we often get about creating memorable, authentic visuals for presentations…
Does Color Matter in Presentations?
So much has been written on the psychology of color and using it in presentations to incite emotion and convey ideas . So yes, red incites passion. And yellow conveys happiness. White is calm and neutral. Always consider color when planning your presentation. However, first and foremost, always select colors from your corporate palette to keep your visuals coordinated and brand-consistent.
How Do I Create Great Visuals Without Being a Graphic Designer?
Our best advice? Keep it simple. Clean, easy-to-interpret visuals are not only efficient to create, but keep the spotlight on your key message, rather than distract from it. Even a common list can be improved with basic icons or shapes. There are many easy, visual tactics that let you prioritize your ideas and offer an easy way to connect with and motivate your audience.
Looking for meaningful, authentic ways to visually express your ideas? We have loads of tips and resources for you. Stock photos don’t have to be cheesy – try adding search terms like “authentic,” “candid,” “context,” or “interactive” after the main search term to find real looking photos that aren’t posed or cliché. And while there’s no harm in trying free stock photo sites first, we’ve found that you often get what you pay for. Our favorite paid stock photos sites are iStock , Getty Images , Adobe Stock , and Shutterstock .
Alternatively, ditch photography altogether and try using icons to represent ideas. The Noun Project has millions of curated, editable icons created by people around the globe. And the best part? They’re all royalty free with attribution, or less than $40 per year for a subscription. Interested in learning best practices for transforming text- and data-heavy presentation slides into visuals that are easy to scan and highlight your key points? Our Influencing with Visuals workshop teaches teams how to organize ideas into visual messages that are clear, memorable, and (you guessed it) authentic.
The 6 types of presentation (and why you need them)
Hrideep barot.
- Presentation , Public Speaking

We all have been exposed to different types of presentations right from school years.
Group presentations, lectures by teachers and professors, seminars, webinars or online presentations, e-learning, e-conferences, etc., are all different types of presentations that we come across in our daily lives.
But each of them work for different settings.
In this article, we will take a look at 6 such types of presentations and when and why you need them.
1. Informative Presentations
This is the most common type of presentation, be it in an educational setting or business or corporate setting.
The aim of an informative presentation is to give detailed information about a product, concept, or idea to a specific kind of audience.
They are often analytical or require a rational analysis of the data presented.
Training sessions or one-day workshops are good examples where this kind of presentation is used.
Here is an example of an informative presentation on public speaking and presentations.
Now, there are different situations where you can use informative presentations.
a) Reporting

Although a report is a written explanation of an event, it can also be verbal.
A perfect place to use informative presentations is news reporting , as it requires the presenter to present information systematically.
b) Briefing

This involves explaining both positive and negative aspects of a particular topic in a few words.
It is providing information quickly and effectively about an issue to influence decisions or to come to solutions.
Hence, the decision-making bodies of an organization can make use of this kind of presentation to save time and effectively come to conclusions.
c) Research
Informative presentations are often used to present research findings to a specific audience , as it involves reporting the findings and briefing it to the audience.
Hence, almost everywhere where research takes place, be it in an educational context or occupational , can make use of this kind of presentation.
Tips for giving informative presentations
- As there would be a lot of technical information and statistics, focus on the main points or agenda first and if you have more time, you can add them at the end
- Keep your presentation simple and clear . Avoid complex sentence structures and graphics
- Tell the outline of your presentation briefly in the introduction for a better flow
- Make sure that your presentation does not stretch for too long. 10-15 minutes is what your audience can concentrate on
- Restate your keyphrase at the end and briefly summarize all the important points of your presentation
Speech topics for an informative presentation
- Cropping techniques
- Organic Farming
- Corporate Farming
- Hydroponics
- Sustainable Agriculture, etc
- Climate change
- Environmental issues
- Eco-friendly ways of management
- Eco-politics
- Eco-feminism, etc
- Gender studies
- Gender and education
- Religious studies
- History of education
- Philosophy of education, etc
- Ethnic cultures
- Indigenous cultures
- Multiculturalism
- Popular culture
- Cultural trends, etc
- Business administration
- Business ethics
- Business models
- Promotion and marketing communications
- Finance, etc
2. Persuasive presentations
Persuasion is the art of motivating or convincing someone to act or make a change in their actions or thoughts.
If you are planning to give a persuasive presentation, and are looking for how to give a persuasive speech, check out our article on A Comprehensive Guide to Writing a Persuasive Speech to gain in-depth knowledge about the art of giving persuasive presentations.
Persuasive presentations are also widely used form after informative presentations.
There are various circumstances where persuasive presentations can be used.
a) Policy-making

Government bodies make use of persuasion almost every time, be it the legislative or decision-making bodies, executive bodies, or even courts.
Even election campaigns involve using persuasive presentations as an instrument of their pre-determined goals of swaying the citizens.
For that matter, any executive or management body of an organization can make use of these kinds of presentations.
b) Value judgment

This kind involves answering the question “why” and supplementing it with possible benefits.
Most Ted talks and YouTube videos try to persuade the audience and fall into the persuasive presentation category.
Even religious heads use this as a means of persuading their believers to follow their belief system.
Deciding on a procedure or telling an audience the correct procedure of doing something is another situation.
An example of a persuasive presentation
Bailey parnell: is social media hurting your mental health.
This TED talk by Bailey Parnell is a good example of a persuasive presentation.
She starts strong by asking rhetorical questions that set the mood for her further points.
We can also see how the speaker is genuinely concerned regarding the issue, engaging the audience till the end.
Tips for giving a persuasive presentation
- Start your presentation with a relevant quote or statistics about your topic to establish credibility
- Tell personal anecdotes and examples wherever necessary to develop an emotional connection with your audience
- Deliver your presentation with passion and genuine interest to motivate your audience to think
- Answer the question “why” for better understanding and clarity in your presentation
- State your viewpoint clearly and clarify doubts if your audience seems to have any
Speech topics for persuasive presentations
- Is animal testing ethical?
- Should cosmetic surgery be banned?
- Can the death penalty be the only solution to the rising crime rates?
- Should the legal age be 18?
- Should immigration laws be revised?
- Why you should never add your parents on Facebook
- Guys are more interested in gossip than girls
- It is your major duty to annoy your parents
- You are not enjoying student life if you are not procrastinating
- Endless memes can be made on my life, etc
- Is taming wild and exotic animals ethical?
- The importance of emotional support animals
- Why are bunnies the perfect pet?
- Why do animals make the best companions?
- Why there is a need for patients to have emotional support animals, etc
- How and why there is a need to do business analysis before opening your business?
- Why small businesses are successful and more profitable?
- Why do sales and customer service departments need to be paid more?
- Why does the HR department need to be polite and understanding?
- Why should you not do business with a family member?
- How charity is a means of converting black money to white?
- Why is detaining people on the suspicion of terrorism justified?
- Should euthanasia be made legal?
- Should violent crime offenders be sentenced to death?
- Should foreigners be allowed to buy a property?
3. Demonstrative presentations
This involves demonstrating a process or the functioning of a product in a step-by-step fashion.
So, a master class on communication skills or making a product model is an example of a demonstrative presentation.
Usually, the audience is an active part of such presentations and these can work in any context where you want the audience to learn a new skill.
a) Instructions

This involves giving guidelines or steps of a process or work .
Teaching how to make a car model step-by-step is a good example where you can use this kind of informative presentation to guide your audience.
Another instance can be at the workplace , to train the employees or introduce them to a new product at work.
This type also works with demonstrating recipes and cooking workshops.
An example of demonstrative presentation
The easy guide on making just about any smoothie.
In this recipe demonstration, he tells his audience how many ingredients are involved and briefs them about the outline of his presentation at the start of his speech.
He also shows all steps in real-time so that the audience have a better understanding of the process and keeps them engaged.
Tips to give a demonstrative presentation
- Introduce your product and its function to your audience before telling them how to go about with the steps
- Explain the steps with diagrams or show them in real-time along with the audience
- Give equal time to every person in the audience for clearing doubts, if any
- Keep your introduction short. Not more than 5 minutes
- Discuss options or variations that the audience can try at the end of the presentation
Speech topics for demonstrative presentations
- How to administer CPR
- How to wrap a gift professionally
- How to budget your monthly income
- How to choose a car insurance
- How to restore a piece of antique furniture
4. Inspirational presentations
As the name suggests, this type of presentation involves inspiring others!
The main aim of an inspirational presentation is to motivate or move your audience and is also known as a motivational presentation.
Using techniques like storytelling, narrating personal anecdotes , or even humor work wonders as your audience develops an emotional connection to the message.
This TED talk by Luvvie Ajayi Jones is humorous but a lot more inspirational. Check it out!
Tips for giving an inspirational presentation
- Start with a question that will leave the audience thinking. Pause for some time and then begin with your presentation
- Develop a sense of connection by narrating personal incidents and experiences to grow empathy
- Have some main points that you want to emphasize on
- Make use of humor ! It instantly builds a connection with the listener
- Non-verbal elements like paralanguage, body language, speech modulations, tone, etc., makes a huge difference
Speech topics for an inspirational presentation
- Importance of diversity and inclusion
- Building mental resilience
- Need for change management
- Valuing small victories in life
- How procrastinating is your enemy
5. Business presentations
In the corporate world, presentations are the go-to solution to do anything: planning or strategizing, articulating company goals, screening candidates, status reports , and many more.
Let us take a dive into the different types of business presentations.
a) Sales presentation

Also known as sales pitches , sales presentations involve providing information about a product or a service to sell it.
It has a pre-defined strategy of initiating and closing the sales deal.
This can be done in person or nowadays, on the phone, or via e-communication .
b) Training sessions

Often employees have on-the-job training sessions that are aimed to increase the knowledge and skills of the employees.
This kind can also involve the audience to participate , like in demonstrative presentations.
c) Meetings

Meetings can be called for for different reasons and can be of different forms as well.
Conferences ( both video and in-person), board meetings, informal team meetings, daily reporting, etc., are all various contexts of meeting in a business setting.
d) E- presentations
E- presentations existed before the COVID pandemic as well but were used seldom.
But, with the ongoing pandemic, e-presentations or remote presentations have replaced all other types of presentations and will be with us for a while longer.
However, on the brighter side, it is an eco-friendly alternative to normal face-to-face kind of a set-up, and it also saves transportation and other costs !
e) Seminars

Seminars are widely used in the health sector , usually involving a panel of speakers on a topic. The audience is anywhere between 10 to 100.
It ends with a question and answers session , and the audience gets to take handouts with them.
f) One-on-one or 1:1

Interviews are usually one-on-one and involve presenting your achievements and capabilities to your prospective employer.
Apart from interviews, 1:1 meetings are also used in sales and marketing to crack a business deal.
Tips for giving business presentations
- Include key phrases and other important details on your slides and make them bold
- Avoid casual slangs and informal tone of speech
- If you are giving a sales presentation, explain your product or service in simple and clear words , and list the reasons why it is beneficial for your potential clients
- Make sure to be on time ! Delaying your audience will work against you and leave a bad impression on you and your company
- Know your material or content thoroughly to answer the questions asked by your audience
Speech topics for business presentations
- Implementing an Agile Project
- Introduction to data modeling
- Introduction to UML(Unified Modeling Language)
- Social Media strategies for a successful business
- Business writing for managers
6. Powerpoint presentations
PowerPoint presentations or PPTs are the most effective ones among all types of presentations simply because they are convenient and easy to understand .
They are available in different formats and are suitable to use in practically any type of presentation and context, be it business, educational, or for informal purposes.
There are various types of PowerPoint presentations that you can use depending on the context.
a) PPTs for general audience

- For general audiences, avoid using jargon terms
If you feel that you need to use them, provide the audience some background information about the field or topic being covered
- Avoid using more than 8 words per line, as anything more than that becomes difficult to remember
- Use bullets or a numbered list for better retention
- Try not to read from your PPT
- Give handouts or record your presentation in case anyone wants it
b) PPTs for teaching

- In this case, the PowerPoint is content-based
- Make sure that the words on the slides are visible
- Use bigger font and avoid fancy fonts
- Add relevant pictures and graphics to keep your audience engaged
- You can also add documentaries or relevant videos to aid in understanding
c) Repurpose PPTs
- This involves reinventing an earlier ppt or combining 1 or more than 1 PowerPoints
- Giving new touches to an earlier PPT or changing the format
- You can take any slide of your PPT and upload it on social media for growing your brand or business
- You can even convert your PPT into mp4 , i.e, video format
- You can even add voice and save the mp4 format, and you have a good marketing plan!
d) PechaKucha

- This type of PowerPoint presentation comes from the Japanese word PechaKucha meaning sound of a conversation or chit-chat
- This involves changing slides every 20 seconds
- There can be a maximum of 20 slides , which means your presentation lasts for only 6 minutes and 40 seconds
- The PPT mostly has graphics and fewer words
- This type of presentation is best suited for telling a story or a personal anecdote
e) Multimedia presentations

- This is the best kind of PPT to engage your audience
- It contains texts along with pictures, videos, infographics, music, illustrations, GIFs , and many more
- Add higher resolution images and videos , or even a 360-degree snapshot if you are in the sales and marketing industry
- Adding infographics such as charts and graphs makes the process of understanding easier and saves time
- Music in a PPT helps your audience to be relaxed, at the same time making them alert and engaged
Types of slides in a presentation
PowerPoint presentation slides are broadly classified into 3 categories: Text, Visual, and Mixed slides.
1. Text slides
As the name suggests, this category of slides involve words or texts.
You can format the text as plain sentences or pointers.
You may even arrange them all in a single slide or one line per slide.
The slide seen below is an example where every point is mentioned in a single slide.
2. Visual slides
This type of slide has visual elements such as images or videos , and are better known as conceptual slides since they are a better option than text slide to explain a particular concept.
You can use them at the start of the presentation to better visualize and grasp the meaning of the presentation.
The slide right below is a good example of a visual slide.

3. Mixed slides
Mixed slides combine the texts and visuals to give a comprehensive understanding of any concept or a speech.
Graphs and charts are the best examples of mixed slides.
Mixed slides have an advantage over the other slides; they keep your audience engaged, listening and participating more actively!
![visual presentation types Presentation Design: A Visual Guide to Creating Beautiful Slides [Free E-Book]](https://visme.co/blog/wp-content/uploads/2017/10/Say-It-Visually.jpg)
Types of Oral presentations
So far we came across 6 types of presentations, and they all share one common feature. They are all one of the types of oral presentations.
Oral presentations involve the use of verbal and non-verbal elements to deliver a speech to a particular or general audience.
All the types we discussed fall into these 4 broad categories:
1. Extemporaneous presentations
This type of presentation involves making short pointers or key phrases to aid while speaking.
You do not memorize, but organize the points and structure the speech way in advance.
Hence, on the day of your presentation, by just looking at the key points , you expand on them and move to the next point.
2. Impromptu presentations
Impromptu presentations are spoken without any preparation . It can be nerve-wracking for many, and hence not many are in favor of it.
There is a valid reason for their fear, as you have to make your speech as you say it!
However, those who are experts in their fields and are called upon to share a few words can easily give this type of presentation.
3. Manuscript presentations
The other extreme of the spectrum is manuscript presentations.
Here you have a script and you speak from it, word by word.
News anchors and show announcers usually engage in this type, since there are a lot of specific details that cannot be said wrong, and also, time constraints.
Usually, a prompter is used, from which the speaker speaks to their audience.
Nowadays, there are teleprompters , that are heavily used in the entertainment and media industry.
It is a digital screen that displays the contents, and the speaker speaks from it.
4. Memorized presentations
This type does not have any notes or cues , but you memorize or rote learn the whole speech.
School and some presentations at the workplace involve using this kind of presentation.
In most cases, we recommend not to memorise your speech in most cases. We’ve made a video on the same and how it could lead to you potentially blanking out on stage. Highly recommend you view this quick vid before choosing memorisation as a presentation path:
But, if you do choose it for whatever reason, since you are free from notes, you are free to focus on other aspects, such as body language and gestures.
Types of presentation styles
There are various presenting styles, but they do not work for all types of presentations.
Let us get familiar with them, and know which style works with which type.
a) The storyteller

This style of presentation involves the speaker narrating stories and engaging the audience emotionally .
This technique works best with persuasive and inspirational types of presentation.
So, how to tell a story in a presentation?
- Understand and know your audience : Knowing your audience will help you with how you will frame your story, at the same time gauging the relevance of your narrative
- Know your message : Be clear with what you want to convey through your story or how you are connecting the story with your actual presentation
- Try narrative a real-life story : Inspiring presenters often take their own stories or the stories of people whom they know as a supplement to their presentation. When the audience listens to your real-life examples, they become genuinely interested in your story
- Add visual aids : Using visual aids such as pictures, videos, multimedia, etc., increases the memory retention and engagement of your audience
- Use the “you” attitude : Tell the story keeping your audience in mind because ultimately they are going to be the receivers and hence, the story should be relevant and should include their point of view as well
Want more storytelling tactics? Mystery, characterisation and the final takeaway are some more key elements of a good story for your next presentation. We’ve gone deeper into this topic in this video if you would like to know more:
b) The Visual style

Most of us are visual learners, making visual information easy to understand and retain.
Visual aids like graphics, images, diagrams, key pointers or phrases , etc., are very useful when giving any type of presentation.
Some tips of presenting with visual style:
- Include only important pointers in your PowerPoint presentation and highlight or bold them
- Try including visuals that complement what you are saying and use them as a supplementary tool to aid in understanding your audience
- If you are giving a business presentation and want to include visuals, instead of plain texts, include graphics and charts to make information simpler to present and understand
- Avoid overly complex visuals as it will confuse the audience more
- Avoid using more than 6 lines per slide
c) Analytic style

If you have data records or statistical information to be presented, an analytic style will be more helpful.
It works best for Informative and Business types of presentations.
Tips to deliver in analytic style:
- Give handouts so that the audience is on track with your presentation and the information will be easier to comprehend
- Focus and speak on selected data as too much data statistics can be overwhelming for the audience
- You can make use of humor and personal anecdotes to keep the presentation interesting and engaging
- If you have too much data and are worried that you will not be able to explain it in the time frame given, avoid writing content of more than 2000 words
Quick tip: In case you have a PDF to present and want to edit the data points, there are multiple software programs that you can use to allow you to easily do this. Check out this list of the Best Free Recording Software Programs to know more.
d) The Connector

The connector style of presentation involves the speaker establishing a connection with the audience by pointing out similarities between them and the listeners.
This style works well with Sales and marketing presentations.
How to give a presentation using connector style?
- Have a Q & A round with the audience at the end of your presentation for clarifying any doubts and avoiding miscommunication
- Use audience polls at the start of your presentation to know your audience and tailor your speech accordingly
- Make use of body language and gestures for delivering your presentation effectively. If you are confused or want to know more about the aspects of how to use body and gestures, check out our article on To walk or stand still: How should you present when on stage?
- Ask questions to your audience at regular intervals for a better audience engagement
- Make use of multimedia sources to keep your audience engaged and entertained
Which type of presentation is best?
Although all the presentation types have their own bonuses and are suitable for certain circumstances, some are universal and can be used with a little bit of modification almost everywhere!
These are persuasive presentations!
You can use them in various settings; from political, business to educational.
Just remember to choose the right topic for the right audience, and a style that you think is the most suitable and you are good to go!
Level up your public speaking in 15 minutes!
Get the exclusive Masterclass video delivered to your inbox to see immediate speaking results.
You have successfully joined our subscriber list.
To conclude
We saw 6 types of presentation and understood it in detail.
We also gained some tips on how to make our presentation more engaging and also came across things to avoid as well.
We then explored the types of slides that you can use, and also the types of presenting orally.
We also gave you some tips and a few topic ideas that you can incorporate in your next speech!
Enroll in our transformative 1:1 Coaching Program
Schedule a call with our expert communication coach to know if this program would be the right fit for you

7 Keys to Emcee Like a Pro: Unlock Your Hosting Potential

8 Ways to Rise Above the Noise to Communicate Better

How to Negotiate: The Art of Getting What You Want

- [email protected]
- +91 98203 57888
Get our latest tips and tricks in your inbox always
Copyright © 2023 Frantically Speaking All rights reserved
Kindly drop your contact details so that we can arrange call back
Select Country Afghanistan Albania Algeria AmericanSamoa Andorra Angola Anguilla Antigua and Barbuda Argentina Armenia Aruba Australia Austria Azerbaijan Bahamas Bahrain Bangladesh Barbados Belarus Belgium Belize Benin Bermuda Bhutan Bosnia and Herzegovina Botswana Brazil British Indian Ocean Territory Bulgaria Burkina Faso Burundi Cambodia Cameroon Canada Cape Verde Cayman Islands Central African Republic Chad Chile China Christmas Island Colombia Comoros Congo Cook Islands Costa Rica Croatia Cuba Cyprus Czech Republic Denmark Djibouti Dominica Dominican Republic Ecuador Egypt El Salvador Equatorial Guinea Eritrea Estonia Ethiopia Faroe Islands Fiji Finland France French Guiana French Polynesia Gabon Gambia Georgia Germany Ghana Gibraltar Greece Greenland Grenada Guadeloupe Guam Guatemala Guinea Guinea-Bissau Guyana Haiti Honduras Hungary Iceland India Indonesia Iraq Ireland Israel Italy Jamaica Japan Jordan Kazakhstan Kenya Kiribati Kuwait Kyrgyzstan Latvia Lebanon Lesotho Liberia Liechtenstein Lithuania Luxembourg Madagascar Malawi Malaysia Maldives Mali Malta Marshall Islands Martinique Mauritania Mauritius Mayotte Mexico Monaco Mongolia Montenegro Montserrat Morocco Myanmar Namibia Nauru Nepal Netherlands Netherlands Antilles New Caledonia New Zealand Nicaragua Niger Nigeria Niue Norfolk Island Northern Mariana Islands Norway Oman Pakistan Palau Panama Papua New Guinea Paraguay Peru Philippines Poland Portugal Puerto Rico Qatar Romania Rwanda Samoa San Marino Saudi Arabia Senegal Serbia Seychelles Sierra Leone Singapore Slovakia Slovenia Solomon Islands South Africa South Georgia and the South Sandwich Islands Spain Sri Lanka Sudan Suriname Swaziland Sweden Switzerland Tajikistan Thailand Togo Tokelau Tonga Trinidad and Tobago Tunisia Turkey Turkmenistan Turks and Caicos Islands Tuvalu Uganda Ukraine United Arab Emirates United Kingdom United States Uruguay Uzbekistan Vanuatu Wallis and Futuna Yemen Zambia Zimbabwe land Islands Antarctica Bolivia, Plurinational State of Brunei Darussalam Cocos (Keeling) Islands Congo, The Democratic Republic of the Cote d'Ivoire Falkland Islands (Malvinas) Guernsey Holy See (Vatican City State) Hong Kong Iran, Islamic Republic of Isle of Man Jersey Korea, Democratic People's Republic of Korea, Republic of Lao People's Democratic Republic Libyan Arab Jamahiriya Macao Macedonia, The Former Yugoslav Republic of Micronesia, Federated States of Moldova, Republic of Mozambique Palestinian Territory, Occupied Pitcairn Réunion Russia Saint Barthélemy Saint Helena, Ascension and Tristan Da Cunha Saint Kitts and Nevis Saint Lucia Saint Martin Saint Pierre and Miquelon Saint Vincent and the Grenadines Sao Tome and Principe Somalia Svalbard and Jan Mayen Syrian Arab Republic Taiwan, Province of China Tanzania, United Republic of Timor-Leste Venezuela, Bolivarian Republic of Viet Nam Virgin Islands, British Virgin Islands, U.S.

2024’s Must-See Visual Presentation Examples to Power Up Your Deck
Anh Vu • 05 April, 2024 • 9 min read
Keep on reading because these visual presentation examples will blow your boring decks away! For many people, delivering a presentation is a daunting project, even before it turns to hybrid and virtual displays due to the pandemic. To avoid the Death By PowerPoint phenomenon, it is time to adopt new techniques to make your presentations more visual and impressive.
This article tries to encourage you to think outside of the slide by providing essential elements of a successful visual presentation, especially for the new presenter and those who want to save time, money, and effort for the upcoming presentation deadline.
Table of Contents
What is a visual presentation.
- Types of Visual Presentation Examples
How to Create a Visual Presentation
- What Makes a Good Presentation Visual?
Frequently Asked Questions
How ahaslides supports a good visual presentation.
As mentioned before, you need a presentation tool to make your presentation more visual and engaging. The art of leveraging visual elements is all intended visual aids make sense and kick off audiences’ imagination, curiosity, and interest from the entire presentation.
The easiest way to create interaction between the presenter and the audience is by asking for rhetorical and thought-provoking quizzes and quick surveys during the presentation. AhaSlides , with a range of live polls , live Q&A , word clouds , interactive questions, image questions, creative fonts, and integration with streaming platforms can help you to make a good visual presentation in just a second.
- Types of Presentation
- College Presentation
- Creative Presentation Ideas
- AhaSlides Free Public Templates

Start in seconds.
Get free templates for your next interactive presentation. Sign up for free and take what you want from the template library!
So, what are the visual presentation examples? When providing as much information as possible, many presenters think that text-heavy slides may help, but by contrast, they may lead to distraction. As we explore the characteristics of good presentations, illustrations and graphics play an important role in delivering compelling content and turning complex concepts more clearly, precisely, and instantly to understand. A visual presentation is the adoption of a range of visual aids on presentation to ensure information is easier to understand and memorize.
In addition, visual aids can also help to keep presenters on track, which can be used as a cue for reviving a train of thought. They build better interaction and communication between presenters and the audience, making them notice more deeply what you are saying.
Types of Visual Presentation Examples
Some possible visual presentations include infographics , charts, diagrams, posters, flipcharts, idea board , whiteboards, and video presentation examples.
An infographic is a collection of different graphic visual presentations to represent information, data, or knowledge intended more visually quickly and clearly to grab the audience’s attention.
To illustrate quantitative data effectively, it is important to make use of graphs and charts. For both business use and research use, graphs and charts can show multiple and complex data in a way that is easy to understand and memory.
When it comes to presenting information systematically and logically, you can use diagrams. A diagram is a powerful tool for effective communication and brainstorming processes. It also is time-saving for people to read and collect information.
A poster, especially a research project poster, provides brief and concrete information about a research paper straightforwardly. The audiences can grab all important data knowledge and findings through posters.
A flipchart and whiteboard are the most basic presentation aids and work best to supplement lecture slides. Excellent whiteboard and flipchart composite of well-chosen words, and clear diagram will help to explain complex concepts.
A video presentation is not a new concept, it is a great way to spread ideas lively and quickly attract the audience’s attention. The advantages of a video presentation lie in its animation and illustration concepts, fascinating sound effects, and user-friendliness.
In addition, we can add many types of visual aids in the presentations as long as they can give shapes and form words or thoughts into visual content. Most popular visual aids include graphs, statistics, charts, and diagrams that should be noted in your mind. These elements combined with verbal are a great way to engage the listeners’ imagination and also emphasize vital points more memorable.

It is simply to create more visual presentations than you think. With the development of technology and the internet, you can find visual presentation examples and templates for a second. PowerPoint is a good start, but there are a variety of quality alternatives, such as AhaSlides , Keynote, and Prezi.
When it comes to designing an effective visual presentation, you may identify some key steps beforehand:
Visual Presentation Examples – Focus on Your Topic
Firstly, you need to determine your purpose and understand your audience’s needs. If you are going to present in a seminar with your audience of scientists, engineers, business owners… They are likely to care about data under simple charts and graphs, which explain the results or trends. Or if you are going to give a lecture for secondary students, your slides should be something fun and interesting, with more colourful pictures and interactive questions.
Visual Presentation Examples – Animation and Transition
When you want to add a bit of excitement to a slideshow and help to keep the listener more engaged, you use animation and transition. These functions help to shift the focus of audiences between elements on slides. When the transition style and setting are set right, it can help to give fluidity and professionalism to a slideshow.
Visual Presentation Examples – Devices for Interactivity
One of the approaches that improve communication between audiences and the use of visual aids is using technology assistance. You don’t want to take too much time to create well-designed visual aids while ensuring your presentation is impressive, so why not leverage a presentation app like AhaSlides ? It properly encourages participant engagement with interactive visual features and templates and is time-saving. With its help, you can design your presentation either formally or informally depending on your interest.
Visual Presentation Examples – Give an Eye-catching Title
Believe it or not, the title is essential to attracting audiences at first sight. Though don’t “read the book by its cover”, you still can put your thoughts into a unique title that conveys the topic while piquing the viewer’s interest.
Visual Presentation Examples – Play a Short Video
Creative video presentation ideas are always important. “Videos evoke emotional responses”, it will be a mistake if you don’t leverage short videos with sound to reel in and captivate the audience’s attention. You can put the video at the beginning of the presentation as a brief introduction to your topic, or you can play it as a supplement to explain difficult concepts.
Visual Presentation Examples – Use a Prop or Creative Visual Aid to Inject Humour
It is challenging to keep your audience interested and engaged with your audience from the whole presentation. It is why to add a prop or creative visual aid to pull your audience’s focus on what you say. Here are some ideas to cover it:
- Use neon colour and duotones
- Tell a personal story
- Show a shocking heading
- Use isometric illustrations
- Go vertical
Visual Presentation Examples – Rehearsal and Get Feedback
It is an important step to make your visual presentation really work out. You won’t know any unexpected mirrors may come out on D-day if you don’t make the rehearsal and get feedback from a reliable source. If they say that your visual image is in bad-quality, the data is overwhelming, or the pictures are misunderstood, you can have an alternative plan in advance.

What Makes a Good Visual Presentation?
Incorporate visual or audio media appropriately. Ensure you arrange and integrate suitable data presentation in your slides or videos. You can read the guidelines for visual aids applications in the following:
- Choose a readable text size about the slide room and text spacing in about 5-7 doubted-spaced.
- Use consistent colour for overall presentation, visual aids work better in white yellow and blue backgrounds.
- Take care of data presentation, and avoid oversimplification or too much detail.
- Keep the data shown minimum and highlight really important data points only.
- Choose font carefully, keep in mind that lowercase is easier to read than uppercase
- Don’t mix fonts.
- Printed text is easier to read than handwritten text.
- Use the visual to emphasize punctuation in your verbal presentation.
- Say no to poor-quality images or videos.
- Visual elements need to be strategic and relevant.
What well-designed visual aids should have?
To make an effective visual aid, you must follow principles of design, including contrast, alignment, repetition, and proximity.
Why is it important to keep visual aids simple?
Simple ads help to keep things clear and understandable, so the message can be communicated effectively.
What is the purpose of visual aids in the classroom?
To encourage the learning process and make it easier and more interesting so students would want to engage in lessons more.

Tips to Engage with Polls & Trivia
More from AhaSlides

6 Major Types of Visual Presentation
Visual presentation refers to the expression of ideas about some matters while using visual aids such as visual multimedia. From electronic media such as television screens and web pages to environmental contexts such as retail displays and road signs, visual communication is virtually everywhere. Visual presentations such as graphs, tables, charts, and diagrams bring together the verbal and visual to add another dimension to the information and create a totally new path towards understanding its meaning.
A presenter can, therefore, use visual interpretation of information to maximize the effectiveness by making sure that the elements are presented as clearly as possible. The more complex and detailed the information is, the more important the information will be. If used well, visual presentation will support the presentation by strengthening audience involvement and impact. However, if badly managed, they can interfere with the presentation. Most visual presentations require prior preparation and should be operated with a lot of efficiencies. If you wish to use such presentations in an unfamiliar room, you need to check the facilities that are there in advance so as to plan your presentation well. Overall, the visual presentation must focus on the relevant information.
There are many different types of visual presentations. Here are main ones.
1. ezTalks Meetings
ezTalks is one of the best cloud video conferencing providers that will allow you to host a number of videos in HD quality with over 100 participants. It also provides free audio conferencing, instant messaging, file sharing, whiteboard collaboration, and remote control apps for presentations. Once you have ezTalks you can choose a plan that's suitable for you. It also gives you 24/7 customer support where you can contact their managers and get solutions to your queries or problems. As compared to other video conferencing providers, they have the best features and an excellent customer support.
2. Whiteboards and Interactive Whiteboard
When it comes to explaining the sequence of routines and ideas, whiteboards can be very useful. Whiteboards are good for developing diagrams and simple headings and for recording the interaction with the audience during the sessions. Writing on whiteboards not only take time but you will also have to turn your back to the audience in order to do so. While using a whiteboard, ensure that your handwriting is aligned horizontally and is legible and large enough for the audience to see. You should also ensure that you use nonpermanent instead of permanent markers. You also need to know that the background of whiteboard can lead to contrast issues for people with vision problems.
3. Flip Charts
A flip chart refers to a low cost, popular and low tech solution to record online meetings . A flip chart is a very flexible and useful way to recording information during a presentation. To help recap your main points, you can flip back through the pad. To show the progression from one point to another, use the turning of the page. A flip chart is not only portable but can also be prepared in advance. It requires no technical expertise or power source. They are suitable for collecting responses and ideas from the audience. However, if you have a large audience, a flip chart may be too small for everyone to see.
4. Paper Handouts
Handouts summarizing the main points are not only useful but also a good addition hence must be relevant. If you are presenting packages such as power slides you can easily generate handouts from your slides. Since giving out handouts at the start of the talk might consume time you need to know the best time to give handouts. However, if your handouts have complex figures and graphs, it's advisable to give the audience handouts before the presentation starts. The audience may also be able to make their own notes during the presentation. Overall, you need to consider the best method and time to distribute handouts including either giving them at the end of the presentation or placing them on the seats prior the start. If your presentation includes discussions and questions, this will give them enough time to summarize them well.
Video is a type of presentation that gives you an opportunity to show visual information. You can use videos to bring pictures, movement, and sound into your presentation. When using videos, it's important to ensure that the clip is relevant to your content. Avoid showing more film than you need and ensure that your audience knows what to look for. If there is a computer connected to the projector then videos can be shown as files through you tube or from a DVD and other online sources. Videos can also be used to build presentations in various video presentation software .
High-quality slides, crucial for impactful presentations, require effective blackout for clear images and eye contact. Numbering ensures easy reordering if dropped. However, the prevalence of digital photography has diminished the reliance on slides. When opting for a visual presentation, consider your preferences, audience needs, and enlist the expertise of a presentation writer .
7. Digital flipbooks
Captivating your audience's attention is essential, especially when it comes to visual presentations. One powerful tool gaining popularity is the digital flipbook maker, offering a dynamic and engaging way to present your ideas through digital flipbooks. A flipbook maker allows you to create interactive presentations with a page-flipping effect and animations. You have many features you can use like adding interactive elements, previewing, and sharing your presentation. By using a digital flipbook for your presentation, you can easily capture the attention of your audience.

14 Practical Tips to Improve Your Presentation Skills
- The Speaker Lab
- May 11, 2024
Table of Contents
Ever felt complete dread and fear at the thought of stepping up to deliver a presentation? If so, you’re not alone. The fear of public speaking is more common than you might think, but with the right presentation skills , it’s a hurdle that can be overcome.
In this article, we’ll help you master basic confidence-building techniques and conquer advanced communication strategies for engaging presentations. We’ll explore how body language and eye contact can make or break your connection with your audience; delve into preparation techniques like dealing with filler words and nervous habits; discuss tailoring content for different audiences; and much more.
Whether you’re prepping for job interviews or gearing up for big presentations, being prepared is key. With adequate practice and the proper attitude, you can crush your speech or presentation!
Mastering the Basics of Presentation Skills
Presentation skills are not just about speaking in front of a crowd. It’s also about effective communication, audience engagement, and clarity. Mastering these skills can be transformative for everyone, from students to corporate trainers.
Building Confidence in Presentations
Becoming confident when presenting is no small feat. But fear not. Even those who feel jittery at the mere thought of public speaking can become masters with practice and patience. Just remember: stage fright is common and overcoming it is part of the process towards becoming an effective presenter.
Taking deep breaths before you start helps calm nerves while visualizing success aids in building confidence. Also, know that nobody minds if you take a moment to gather your thoughts during your presentation—everybody minds more if they cannot understand what you’re saying because you’re rushing.
The Role of Practice in Enhancing Presentation Skills
In line with old wisdom, practice indeed makes perfect, especially when improving presentation skills. Consistent rehearsals allow us to fine-tune our delivery methods like maintaining eye contact or controlling body language effectively.
You’ll learn better control over filler words through repeated drills. Plus, the extra practice can help you troubleshoot any technical glitches beforehand, saving you the sudden panic during your actual presentations.
Remember that great presenters were once beginners too. Continuous effort will get you there sooner rather than later.
Find Out Exactly How Much You Could Make As a Paid Speaker
Use The Official Speaker Fee Calculator to tell you what you should charge for your first (or next) speaking gig — virtual or in-person!
Body Language and Eye Contact in Presentations
The effectiveness of your presentation can hinge on more than just the words you say. Just as important is your body language .
Impact of Posture on Presentations
Your posture speaks volumes before you utter a word. Standing tall exudes confidence while slouching could signal nervousness or lack of preparation.
If there’s one lesson to take away from our YouTube channel , it’s this: good presenters know their message but great ones feel it through every fiber (or muscle) of their being. The audience can sense that energy when they see open body language rather than crossed arms.
Maintaining Eye Contact During Your Presentation
Eyes are often called windows to the soul for a reason. They’re communication powerhouses. Making eye contact helps build trust with your audience members and keeps them engaged throughout your speech.
Avoid staring at note cards or visual aids too much as this might give an impression that you’re unprepared or uncertain about your chosen topic. Instead, aim to maintain eye contact between 50% of the time during presentations. This commonly accepted “50/70 rule” will help you exhibit adequate confidence to your audience.
If stage fright has gotten a hold on you, take deep breaths before you start speaking in order to stay calm. Make sure that fear doesn’t disrupt your ability to maintain eye-contact during presentations.
If body language and eye contact still feel like a lot to manage during your big presentation, remember our golden rule: nobody minds small mistakes. It’s how you handle questions or mishaps that truly makes a difference—so stay positive and enthusiastic.
Preparation Techniques for Successful Presentations
Presentation skills are like a craft that requires meticulous preparation and practice. Aspects like visual aids and time management contribute to the overall effectiveness of your delivery.
The first step towards delivering an impactful presentation is research and organization. The content should be well-researched, structured logically, and presented in simple language. This will make sure you deliver clear messages without any room for misinterpretation.
Dealing with Filler Words and Nervous Habits
Nervous habits such as excessive use of filler words can distract from your message. Luckily, there are plenty of strategies that can address these issues. For instance, try taking deep breaths before speaking or using note cards until fluency is achieved. In addition, practice regularly to work on eliminating these verbal stumbling blocks.
Avoiding Distractions During Presentations
In a digital age where distractions abound, maintaining focus during presentations has become an even more crucial part of the preparation process. This video by motivational speaker Brain Tracy provides insights on how one could achieve this level of focus required for effective presentations.
Maintaining Confidence Throughout Your Presentation
Confidence comes from thorough understanding of the chosen topic combined with regular practice sessions before the big day arrives. Make use of note cards or cue cards as needed but avoid reading from them verbatim.
Taking control over stage fright starts by arriving early at the venue so that you familiarize yourself with the surroundings, which generally calms nerves down considerably. So next time you feel nervous before a big presentation, remember—thorough preparation can make all the difference.
Engaging Your Audience During Presentations
Connecting with your audience during presentations is an art, and mastering it can take your presentation skills to the next level. Making the message conveyed reach an emotional level is essential, not just conveying facts.
Understanding Your Target Audience
The first step towards engaging your audience is understanding them. Tailor the content of your presentation to their needs and interests. Speak in their language—whether that be professional jargon or everyday slang—to establish rapport and ensure comprehension.
An effective presenter understands who they’re speaking to, what those individuals care about, and how best to communicate complex ideas understandably.
Making Complex Information Understandable
Dense data or complicated concepts can lose even the most interested listener if presented ineffectively. Breaking your key points down into manageable chunks helps maintain attention while promoting retention. Analogies are especially useful for this purpose as they make unfamiliar topics more relatable.
Audience Participation & Questions: A Two-Way Street
Incorporating opportunities for audience participation encourages engagement at another level. It allows listeners to become active participants rather than passive receivers of knowledge.
Consider techniques like live polls or interactive Q&A sessions where you invite questions from attendees mid-presentation instead of saving all queries until the end.
This gives you a chance not only engage but also address any misunderstandings right on spot.
- Treat each question asked as an opportunity—it’s evidence someone has been paying attention. Even challenging questions should be welcomed as they demonstrate an engaged, thoughtful audience.
- Encourage participation. It can be as simple as a show of hands or the use of interactive technologies for live polling during your presentation. This keeps your audience active and invested in the content.
Remember, your presentation isn’t just about putting on a show—it’s about meaningful interaction.
Free Download: 6 Proven Steps to Book More Paid Speaking Gigs in 2024
Download our 18-page guide and start booking more paid speaking gigs today!
Presentation Skills in Specific Contexts
Whether you’re nailing your next job interview, presenting an exciting marketing campaign, or delivering insightful educational content, the context matters. Let’s take a look.
The Art of Job Interviews
A successful job interview often hinges on effective communication and confidence. Here, the target audience is usually small but holds significant influence over your future prospects. Body language plays a crucial role; maintain eye contact to show sincerity and interest while open body language communicates approachability.
Bullet points summarizing key experiences are also helpful for quick recall under pressure. This allows you to present your chosen topic with clarity and positive enthusiasm without relying heavily on note or cue cards.
Pitching in Public Relations & Marketing
In public relations (PR) and marketing contexts, presentations need to capture attention quickly yet hold it long enough to deliver key messages effectively. Visual aids are valuable tools here—they help emphasize points while keeping the audience engaged.
Your aim should be highlighting presentation benefits that resonate with potential clients or partners, making them feel as though ignoring such opportunities would mean missing out big time.
Educational Presentations
An educational setting demands its own unique set of presentation skills where deep understanding trumps flashy visuals. You must make complex information understandable without oversimplifying essential details—the use of analogies can be beneficial here.
Keeping the audience’s attention is critical. Encourage questions and participation to foster a more interactive environment, enhancing learning outcomes for all audience members.
Tips for Becoming a Great Presenter
No single method is suitable for everyone when it comes to speaking in public. However, incorporating continuous improvement and practice into your routine can make you an exceptional presenter.
Tailor Your Presentation to Your Audience
Becoming an excellent speaker isn’t just about delivering information; it’s also about making a connection with the audience. So make sure that you’re taking setting, audience, and topic into consideration when crafting your presentation. What works for one audience may not work for another, so be sure to adapt your presentation styles according to the occasion in order to be truly effective.
The Power of Practice
The art of mastering public speaking skills requires practice —and lots of it . To become a great presenter, focus on improving communication skills through practice and feedback from peers or mentors. Try to seek feedback on every speech delivered and incorporate those pointers in your future presentations. Over time, this cycle of delivery-feedback-improvement significantly enhances your ability to connect with audiences and convey ideas effectively.
If you’re looking for examples of good speakers, our speech breakdowns on YouTube provide excellent examples of experienced presenters who masterfully utilize speaking techniques. Analyzing their strategies could give you great ideas for enhancing your own style.
Finding Your Style
A crucial part of captivating any audience lies in how you deliver the message rather than the message itself. Developing a unique presentation style lets you stand out as an engaging speaker who commands attention throughout their talk. Through — you guessed it — practice, you can develop a personal presentation style that resonates with listeners while showcasing your expertise on the chosen topic.
Your body language plays a pivotal role here: open gestures communicate confidence and enthusiasm towards your subject matter, two qualities essential for keeping audiences hooked. Similarly, using vocal variety adds dynamism to speeches by emphasizing points when needed or creating suspense during storytelling parts of your talk.
Cultivating Passion & Enthusiasm
Showcasing genuine passion for the subject helps keep listeners engaged throughout even lengthy presentations. Sharing stories related to the topic or expressing excitement about sharing knowledge tends to draw people in more than mere data recitation ever could.
Recognize that everybody is distinctive; don’t expect identical results from every speaker. The path to becoming a great presenter involves recognizing your strengths and working tirelessly on areas that need improvement.
FAQs on Presentation Skills
What are good presentation skills.
Good presentation skills include a clear message, confident delivery, engaging body language, audience understanding, and interaction. They also involve effective preparation and practice.
What are the 5 steps of presentation skills?
The five steps of presenting include: planning your content, preparing visual aids if needed, practicing the delivery aloud, performing it with confidence, and finally post-presentation reflection for improvements.
What are the 5 P’s of presentation skills?
The five P’s stand for Preparation (researching your topic), Practice (rehearsing your talk), Performance (delivering with confidence), Posture (standing tall), and Projection (using a strong voice).
What are your presentation skills?
Your personal set of abilities to deliver information effectively is what we call your presentation skill. It can encompass public speaking ability, clarity in speech or writing as well as visual communication talent.
Mastering presentation skills isn’t an overnight process, but practice and perseverance will put you well on your way to becoming an effective speaker.
You’ve learned that confidence plays a crucial role in effective presentations, so take deep breaths, make eye contact, and keep your body language open. As always, preparation is key. Tackle filler words head-on and get comfortable with visual aids for impactful storytelling.
Remember the importance of audience engagement — it’s all about understanding their needs and tailoring your content accordingly. This way, complex information turns into digestible insights.
Above all else: practice! After all, nothing beats experience when it comes to improving public speaking abilities.
- Last Updated: May 9, 2024

Explore Related Resources
Learn How You Could Get Your First (Or Next) Paid Speaking Gig In 90 Days or Less
We receive thousands of applications every day, but we only work with the top 5% of speakers .
Book a call with our team to get started — you’ll learn why the vast majority of our students get a paid speaking gig within 90 days of finishing our program .
If you’re ready to control your schedule, grow your income, and make an impact in the world – it’s time to take the first step. Book a FREE consulting call and let’s get you Booked and Paid to Speak ® .
About The Speaker Lab
We teach speakers how to consistently get booked and paid to speak. Since 2015, we’ve helped thousands of speakers find clarity, confidence, and a clear path to make an impact.
Get Started
Let's connect.
Copyright ©2023 The Speaker Lab. All rights reserved.
Data Topics
- Data Architecture
- Data Literacy
- Data Science
- Data Strategy
- Data Modeling
- Governance & Quality
- Education Resources For Use & Management of Data
Types of Data Visualization and Their Uses
In today’s data-first business environment, the ability to convey complex information in an understandable and visually appealing manner is paramount. Different types of data visualization help transform analyzed data into comprehensible visuals for all types of audiences, from novices to experts. In fact, research has shown that the human brain can process images in as little as […]

In today’s data-first business environment, the ability to convey complex information in an understandable and visually appealing manner is paramount. Different types of data visualization help transform analyzed data into comprehensible visuals for all types of audiences, from novices to experts. In fact, research has shown that the human brain can process images in as little as 13 milliseconds.

In essence, data visualization is indispensable for distilling complex information into digestible formats that support both quick comprehension and informed decision-making. Its role in analysis and reporting underscores its value as a critical tool in any data-centric activity.
Types of Data Visualization: Charts, Graphs, Infographics, and Dashboards
The diverse landscape of data visualization begins with simple charts and graphs but moves beyond infographics and animated dashboards. Charts , in their various forms – be it bar charts for comparing quantities across categories or line charts depicting trends over time – serve as efficient tools for data representation. Graphs extend this utility further: Scatter plots reveal correlations between variables, while pie graphs offer a visual slice of proportional relationships within a dataset.
Venturing beyond these traditional forms, infographics emerge as powerful storytelling tools, combining graphical elements with narrative to enlighten audiences on complex subjects. Unlike standard charts or graphs that focus on numerical data representation, infographics can incorporate timelines, flowcharts, and comparative images to weave a more comprehensive story around the data.
A dashboard, when effectively designed , serves as an instrument for synthesizing complex data into accessible and actionable insights. Dashboards very often encapsulate a wide array of information, from real-time data streams to historical trends, and present it through an amalgamation of charts, graphs, and indicators.
A dashboard’s efficacy lies in its ability to tailor the visual narrative to the specific needs and objectives of its audience. By selectively filtering and highlighting critical data points, dashboards facilitate a focused analysis that aligns with organizational goals or individual projects.
The best type of data visualization to use depends on the data at hand and the purpose of its presentation. Whether aiming to highlight trends, compare values, or elucidate complex relationships, selecting the appropriate visual form is crucial for effectively communicating insights buried within datasets. Through thoughtful design and strategic selection among these varied types of visualizations, one can illuminate patterns and narratives hidden within numbers – transforming raw data into meaningful knowledge.
Other Types of Data Visualization: Maps and Geospatial Visualization
Utilizing maps and geospatial visualization serves as a powerful method for uncovering and displaying insightful patterns hidden within complex datasets. At the intersection of geography and data analysis, this technique transforms numerical and categorical data into visual formats that are easily interpretable, such as heat maps, choropleths, or symbolic representations on geographical layouts. This approach enables viewers to quickly grasp spatial relationships, distributions, trends, and anomalies that might be overlooked in traditional tabular data presentations.
For instance, in public health, geospatial visualizations can highlight regions with high incidences of certain diseases, guiding targeted interventions. In environmental studies, they can illustrate changes in land use or the impact of climate change across different areas over time. By embedding data within its geographical context, these visualizations foster a deeper understanding of how location influences the phenomena being studied.
Furthermore, the advent of interactive web-based mapping tools has enhanced the accessibility and utility of geospatial visualizations. Users can now engage with the data more directly – zooming in on areas of interest, filtering layers to refine their focus, or even contributing their own data points – making these visualizations an indispensable tool for researchers and decision-makers alike who are looking to extract meaningful patterns from spatially oriented datasets.
Additionally, scatter plots excel in revealing correlations between two variables. By plotting data points on a two-dimensional graph, they allow analysts to discern potential relationships or trends that might not be evident from raw data alone. This makes scatter plots a staple in statistical analysis and scientific research where establishing cause-and-effect relationships is crucial.
Bubble charts take the concept of scatter plots further by introducing a third dimension – typically represented by the size of the bubbles – thereby enabling an even more layered understanding of data relationships. Whether it’s comparing economic indicators across countries or visualizing population demographics, bubble charts provide a dynamic means to encapsulate complex interrelations within datasets, making them an indispensable tool for advanced data visualization.
Innovative Data Visualization Techniques: Word Clouds and Network Diagrams
Some innovative techniques have emerged in the realm of data visualization that not only simplify complex datasets but also enhance engagement and understanding. Among these, word clouds and network diagrams stand out for their unique approaches to presenting information.
Word clouds represent textual data with size variations to emphasize the frequency or importance of words within a dataset. This technique transforms qualitative data into a visually appealing format, making it easier to identify dominant themes or sentiments in large text segments.
Network diagrams introduce an entirely different dimension by illustrating relationships between entities. Through nodes and connecting lines, they depict how individual components interact within a system – be it social networks, organizational structures, or technological infrastructures. This visualization method excels in uncovering patterns of connectivity and influence that might remain hidden in traditional charts or tables.
Purpose and Uses of Each Type of Data Visualization
The various types of data visualization – from bar graphs and line charts to heat maps and scatter plots – cater to different analytical needs and objectives. Each type is meticulously designed to highlight specific aspects of the data, making it imperative to understand their unique applications and strengths. This foundational knowledge empowers users to select the most effective visualization technique for their specific dataset and analysis goals.
Line Charts: Tracking Changes Over Time Line charts are quintessential in the realm of data visualization for their simplicity and effectiveness in showcasing trends and changes over time. By connecting individual data points with straight lines, they offer a clear depiction of how values rise and fall across a chronological axis. This makes line charts particularly useful for tracking the evolution of quantities – be it the fluctuating stock prices in financial markets, the ebb and flow of temperatures across seasons, or the gradual growth of a company’s revenue over successive quarters. The visual narrative that line charts provide helps analysts, researchers, and casual observers alike to discern patterns within the data, such as cycles or anomalies.
Bar Charts and Histograms: Comparing Categories and Distributions Bar charts are highly suitable for representing comparative data. By plotting each category of comparison with a bar whose height or length reflects its value, bar charts make it easy to visualize relative values at a glance.
Histograms show the distribution of groups of data in a dataset. This is particularly useful for understanding the shape of data distributions – whether they are skewed, normal, or have any outliers. Histograms provide insight into the underlying structure of data, revealing patterns that might not be apparent.
Pie Charts: Visualizing Proportional Data Pie charts serve as a compelling visualization tool for representing proportional data, offering a clear snapshot of how different parts contribute to a whole. By dividing a circle into slices whose sizes are proportional to their quantity, pie charts provide an immediate visual comparison among various categories. This makes them especially useful in illustrating market shares, budget allocations, or the distribution of population segments.
The simplicity of pie charts allows for quick interpretation, making it easier for viewers to grasp complex data at a glance. However, when dealing with numerous categories or when precise comparisons are necessary, the effectiveness of pie charts may diminish. Despite this limitation, their ability to succinctly convey the relative significance of parts within a whole ensures their enduring popularity in data visualization across diverse fields.
Scatter Plots: Identifying Relationship and Correlations Between Variables Scatter plots are primarily used for spotting relationships and correlations between variables. These plots show data points related to one variable on one axis and a different variable on another axis. This visual arrangement allows viewers to determine patterns or trends that might indicate a correlation or relationship between the variables in question.
For instance, if an increase in one variable consistently causes an increase (or decrease) in the other, this suggests a potential correlation. Scatter plots are particularly valuable for preliminary analyses where researchers seek to identify variables that warrant further investigation. Their straightforward yet powerful nature makes them indispensable for exploring complex datasets, providing clear insights into the dynamics between different factors at play.
Heat Maps: Representing Complex Data Matrices through Color Gradients Heat maps serve as a powerful tool in representing complex data matrices, using color gradients to convey information that might otherwise be challenging to digest. At their core, heat maps transform numerical values into a visual spectrum of colors, enabling viewers to quickly grasp patterns, outliers, and trends within the data. This method becomes more effective when the complex relationships between multiple variables need to be reviewed.
For instance, in fields like genomics or meteorology, heat maps can illustrate gene expression levels or temperature fluctuations across different regions and times. By assigning warmer colors to higher values and cooler colors to lower ones, heat maps facilitate an intuitive understanding of data distribution and concentration areas, making them indispensable for exploratory data analysis and decision-making processes.
Dashboards and Infographics: Integrating Multiple Data Visualizations Dashboards and infographics represent a synergistic approach in data visualization, blending various graphical elements to offer a holistic view of complex datasets. Dashboards, with their capacity to integrate multiple data visualizations such as charts, graphs, and maps onto a single interface, are instrumental in monitoring real-time data and tracking performance metrics across different parameters. They serve as an essential tool for decision-makers who require a comprehensive overview to identify trends and anomalies swiftly.
Infographics, on the other hand, transform intricate data sets into engaging, easily digestible visual stories. By illustrating strong narratives with striking visuals and solid statistics, infographics make complex information easily digestible to any type of audience.
Together, dashboards and infographics convey multifaceted data insights in an integrated manner – facilitating informed decisions through comprehensive yet clear snapshots of data landscapes.
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Welcome to the Purdue Online Writing Lab

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
The Online Writing Lab at Purdue University houses writing resources and instructional material, and we provide these as a free service of the Writing Lab at Purdue. Students, members of the community, and users worldwide will find information to assist with many writing projects. Teachers and trainers may use this material for in-class and out-of-class instruction.
The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives. The Purdue OWL offers global support through online reference materials and services.
A Message From the Assistant Director of Content Development
The Purdue OWL® is committed to supporting students, instructors, and writers by offering a wide range of resources that are developed and revised with them in mind. To do this, the OWL team is always exploring possibilties for a better design, allowing accessibility and user experience to guide our process. As the OWL undergoes some changes, we welcome your feedback and suggestions by email at any time.
Please don't hesitate to contact us via our contact page if you have any questions or comments.
All the best,
Social Media
Facebook twitter.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

9.2: Types of Visual Aids
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 54957
\( \newcommand{\vecs}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vecd}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash {#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\) \( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\) \( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\) \( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\) \( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\inner}[2]{\langle #1, #2 \rangle}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\)
\( \newcommand{\id}{\mathrm{id}}\)
\( \newcommand{\kernel}{\mathrm{null}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\range}{\mathrm{range}\,}\)
\( \newcommand{\RealPart}{\mathrm{Re}}\)
\( \newcommand{\ImaginaryPart}{\mathrm{Im}}\)
\( \newcommand{\Argument}{\mathrm{Arg}}\)
\( \newcommand{\norm}[1]{\| #1 \|}\)
\( \newcommand{\Span}{\mathrm{span}}\) \( \newcommand{\AA}{\unicode[.8,0]{x212B}}\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorA}[1]{\vec{#1}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorAt}[1]{\vec{\text{#1}}} % arrow\)
\( \newcommand{\vectorB}[1]{\overset { \scriptstyle \rightharpoonup} {\mathbf{#1}} } \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorC}[1]{\textbf{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorD}[1]{\overrightarrow{#1}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectorDt}[1]{\overrightarrow{\text{#1}}} \)
\( \newcommand{\vectE}[1]{\overset{-\!-\!\rightharpoonup}{\vphantom{a}\smash{\mathbf {#1}}}} \)
For many people, the term “visual aids” for presentations or speeches is synonymous with PowerPoint, but this is just one type of visual aid. You should consider all the available options to determine what will be most effective and appropriate for your presentation.
If you wear clothes that don’t suit you, you’re a fashion victim. You have to wear clothes that make you look better.
~ Vivienne Westwood
Personal Appearance
Some people chose to dress up as part of their presentation, and this can help set the tone of the speech or reinforce a specific point. A speaker may choose to wear a handmade sweater in a talk about knitting in order to inspire others to begin the hobby. Another speaker may opt for a firefighter’s uniform in a speech about joining the local volunteer fire department in an effort to appeal to the respect most people have for people in uniform.
If you aren’t dressing in relation to your topic, you should dress appropriately for your audience and venue. A presentation to a professional audience or at a professional conference would lend itself to appropriate business attire. If you are giving a presentation to your local Girl Scout troop, more casual clothing may be the best choice. Any time you are doing a demonstration, make sure you are dressed appropriately to give the demonstration. It is difficult for a speaker to show how to correctly put on a rock climbing harness if she is wearing a skirt the day of the presentation.
Your dress, mannerisms, the way you greet the audience when they are arriving, how you are introduced, and the first words out of your mouth all impact your credibility and ability to connect with your audience. Make sure you are calm and welcoming to your audience when they arrive and greet them in a professional manner.
Objects and Props
Objects and props, such as a bicycle helmet for a speech on bike safety or an actual sample of the product you are trying to sell, can greatly enhance your presentation. Seeing the actual item will often make it easier for your audience to understand your meaning and will help you connect with your audience on an emotional level. Props can be used as part of demonstrations (discussed below) or as a stand-alone item that you refer to in your speech.
There are several important considerations for using props in your presentation. If you have a large audience, showing the prop at the front of the venue may mean that audience members can’t see the item. The alternative to this is to pass the item around, though Young and Travis (2008) advise caution in passing objects around during your speech, as most people will be seeing the object after you have moved on with your talk.
Having your prop out of sync with your presentation, either as it is passed around disrupting your audience’s attention or by having your prop visible when you aren’t talking about it, is distracting to your audience and message. To make the most effective use of props in your presentation, carefully consider how the object will be visible to your entire audience when you are speaking about it, and make sure it is out of sight when you are not.
Demonstration
A demonstration can serve two different purposes in a speech. First, it can be used to “wow” the audience. Showing off the features of your new product, illustrating the catastrophic failure of a poorly tied climbing knot, or launching a cork across the room during a chemistry experiment are all ways of capturing the audience’s attention. Demonstration should not be gimmicky, but should add value to your presentation. When done well, it can be a memorable moment from your speech, so make sure it reinforces the central message of your talk.
Demonstration can also be used to show how something is done. People have different learning styles, and a process demonstration can help visual learners better understand the concept being taught. Consider for a moment the difference between reading the instructions on how to perform CPR, watching someone perform CPR, and trying CPR on the training dummy. As evidenced by the huge number of online videos illustrating how to do something, there is great value in watching while you learn a new task.
Posters and Flip Charts
If you are presenting to a small audience, around a dozen people, you may choose to use a poster rather than PowerPoint. The focus of your poster should be to support your core message and can be left behind to remind those in attendance of your presentation after you have left. Posters should look professional (e.g., not handwritten) and be visible to everyone in the room.
Other text-based visual aids include white boards and flip charts. Both can be used to write or draw on during the presentation and should be used with several caveats. Writing during your presentation actually takes away from your speaking time, so make sure to factor this into your speaking time.
Speaking and writing at the same time can be tricky because the audience will have a difficult time processing what they are hearing when they are also trying to read what you write. Additionally, if you are writing, you need to be careful not to turn your back on your audience, which makes it harder for them to hear you and for you to connect with your audience.
The soul never thinks without a picture.
~ Aristotle
Audio and Video
A large amount of digitized audio and video is now available to be included and embedded in your presentation. Select short clips; Young and Travis (2008) recommend only 10–20 seconds, but this will depend in part on the length of the presentation, the purpose of the presentation, and clip content and relevance. You should not have a presentation primarily composed of audio/video clips. Select only clips that reinforce the message or serve as an appropriate segue into your next topic.
When including audio or video in your speech, there are several technical considerations. It is important that the clip be properly cued to start at exactly where you want it to begin playing. It distracts from both your audience’s attention and your credibility when you are fumbling with technology during a speech. It is also important that your file format can be played on the computer you are using. Since not all computers will play all file formats, be sure to test playability and audio volume before your presentation. Again, going back to providing a professional appearance from your first interaction with your audience, you should iron out the technical details before they enter the room. As with a demonstration, if your clip isn’t playing properly, move on rather than attempt to correct the issue. Fumbling with technology is a waste of your audience’s valuable time.
There are many schools of thought on the use of handouts during a presentation. The most common current practice is that the presenters provide a copy of their PowerPoint slides to the participants before or after the presentation. Despite this prevailing trend, you should avoid using your slides as handouts because they serve different purposes. Using your presentation slides as the handout both shortchanges your slides and fails as a handout.
Handouts are best used to supplement the content of your talk. If you are providing statistical data, your slide may only show the relevant statistic focusing on the conclusion you want your audience to draw. Your handout, on the other hand, can contain the full table of data. If you need to show a complex diagram or chart, a handout will be more legible than trying to cram all that information on a slide. Since you need to simplify the data to make it understandable on a slide, the handout can contain the evidence for your message in a way that is legible, detailed, complex, and shows respect for the audience’s time and intelligence (Reynolds, 2008).
You don’t need to include everything in your talk, and you don’t need to pack all your information into your slides. Write a handout document with as much detail as you want and keep the slides simple. Presenters often feel the need to display all the data and information they have so they will appear knowledgeable, informed, and thoroughly prepared. You can help ease this feeling by creating a handout with all of the detailed data you wish, which leaves your slides open to focus on your key message (Mayer, 2001).
There are many true statements about complex topics that are too long to fit on a PowerPoint slide. ~ Edward
When to distribute handouts is also heavily debated. So common is the practice of providing handouts at the beginning of a presentation that it may seem wrong to break the convention. It is important to understand, however, that if people have paper in front of them while you are speaking, their attention will be split between the handout, your other visual aids, and your words. To counter this, you might consider distributing handouts as they are needed during the presentation and allowing time for people to review them before continuing on (Reynolds, 2008). This may not be a viable option for shorter presentations, and the interruption in the flow of the presentation may be hard to recover from. Unless having the documents in front of your audience is absolutely critical to the success of the presentation, handouts should be distributed at the end of the presentation .
Slideware is a generic term for the software used to create and display slide shows such as Microsoft PowerPoint, Apple iWorks Keynote, Google Drive Presentation, Zoho Show, and others. Composed of individual slides, collectively known as the slide deck , slideware is a de facto standard for presentation visual aids despite criticisms and complaints about the format. In truth, the problem is not with the software but in the use of the program. The focus of much of the remainder of this chapter will be suggestions and best practices for creating effective slide decks that will be high impact and avoid many of the complaints of slideware detractors. Before this discussion, there is one distinct slideware presentation styles that should be mentioned.
A picture is a poem without words.
While not quite slideware, Prezi is digital presentation software that breaks away from the standard slide deck presentation. It requires users to plot out their themes before adding primarily image-focused content (Williams, 2004). Instead of flipping through the slide deck, the presenter zooms in and out of the presentation to visually demonstrate connections not available in other slideware. The design of the software lends itself toward more rapidly changing visuals. This helps to keep the viewer engaged but also lends itself to over-populating the blank canvas with images (Kadavy, 2011).
Prezi’s fast moving images and, at times, unusual movement can make users dizzy or disoriented. Careful work is needed during planning and practice so that the point of the talk isn’t the wow factor of the Prezi software, but that your visuals enhance your presentation. The best way to learn more about this emerging tool is to visit the Prezi website to view examples. If opting to use Prezi in a corporate environment, you should strongly consider one of the paid options for the sole purpose of removing the Prezi logo from the presentation.
Contributors and Attributions
- Template:ContribCCComm105
- Open access
- Published: 17 August 2023
Data visualisation in scoping reviews and evidence maps on health topics: a cross-sectional analysis
- Emily South ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-2187-4762 1 &
- Mark Rodgers 1
Systematic Reviews volume 12 , Article number: 142 ( 2023 ) Cite this article
3614 Accesses
13 Altmetric
Metrics details
Scoping reviews and evidence maps are forms of evidence synthesis that aim to map the available literature on a topic and are well-suited to visual presentation of results. A range of data visualisation methods and interactive data visualisation tools exist that may make scoping reviews more useful to knowledge users. The aim of this study was to explore the use of data visualisation in a sample of recent scoping reviews and evidence maps on health topics, with a particular focus on interactive data visualisation.
Ovid MEDLINE ALL was searched for recent scoping reviews and evidence maps (June 2020-May 2021), and a sample of 300 papers that met basic selection criteria was taken. Data were extracted on the aim of each review and the use of data visualisation, including types of data visualisation used, variables presented and the use of interactivity. Descriptive data analysis was undertaken of the 238 reviews that aimed to map evidence.
Of the 238 scoping reviews or evidence maps in our analysis, around one-third (37.8%) included some form of data visualisation. Thirty-five different types of data visualisation were used across this sample, although most data visualisations identified were simple bar charts (standard, stacked or multi-set), pie charts or cross-tabulations (60.8%). Most data visualisations presented a single variable (64.4%) or two variables (26.1%). Almost a third of the reviews that used data visualisation did not use any colour (28.9%). Only two reviews presented interactive data visualisation, and few reported the software used to create visualisations.
Conclusions
Data visualisation is currently underused by scoping review authors. In particular, there is potential for much greater use of more innovative forms of data visualisation and interactive data visualisation. Where more innovative data visualisation is used, scoping reviews have made use of a wide range of different methods. Increased use of these more engaging visualisations may make scoping reviews more useful for a range of stakeholders.
Peer Review reports
Scoping reviews are “a type of evidence synthesis that aims to systematically identify and map the breadth of evidence available on a particular topic, field, concept, or issue” ([ 1 ], p. 950). While they include some of the same steps as a systematic review, such as systematic searches and the use of predetermined eligibility criteria, scoping reviews often address broader research questions and do not typically involve the quality appraisal of studies or synthesis of data [ 2 ]. Reasons for conducting a scoping review include the following: to map types of evidence available, to explore research design and conduct, to clarify concepts or definitions and to map characteristics or factors related to a concept [ 3 ]. Scoping reviews can also be undertaken to inform a future systematic review (e.g. to assure authors there will be adequate studies) or to identify knowledge gaps [ 3 ]. Other evidence synthesis approaches with similar aims have been described as evidence maps, mapping reviews or systematic maps [ 4 ]. While this terminology is used inconsistently, evidence maps can be used to identify evidence gaps and present them in a user-friendly (and often visual) way [ 5 ].
Scoping reviews are often targeted to an audience of healthcare professionals or policy-makers [ 6 ], suggesting that it is important to present results in a user-friendly and informative way. Until recently, there was little guidance on how to present the findings of scoping reviews. In recent literature, there has been some discussion of the importance of clearly presenting data for the intended audience of a scoping review, with creative and innovative use of visual methods if appropriate [ 7 , 8 , 9 ]. Lockwood et al. suggest that innovative visual presentation should be considered over dense sections of text or long tables in many cases [ 8 ]. Khalil et al. suggest that inspiration could be drawn from the field of data visualisation [ 7 ]. JBI guidance on scoping reviews recommends that reviewers carefully consider the best format for presenting data at the protocol development stage and provides a number of examples of possible methods [ 10 ].
Interactive resources are another option for presentation in scoping reviews [ 9 ]. Researchers without the relevant programming skills can now use several online platforms (such as Tableau [ 11 ] and Flourish [ 12 ]) to create interactive data visualisations. The benefits of using interactive visualisation in research include the ability to easily present more than two variables [ 13 ] and increased engagement of users [ 14 ]. Unlike static graphs, interactive visualisations can allow users to view hierarchical data at different levels, exploring both the “big picture” and looking in more detail ([ 15 ], p. 291). Interactive visualizations are often targeted at practitioners and decision-makers [ 13 ], and there is some evidence from qualitative research that they are valued by policy-makers [ 16 , 17 , 18 ].
Given their focus on mapping evidence, we believe that scoping reviews are particularly well-suited to visually presenting data and the use of interactive data visualisation tools. However, it is unknown how many recent scoping reviews visually map data or which types of data visualisation are used. The aim of this study was to explore the use of data visualisation methods in a large sample of recent scoping reviews and evidence maps on health topics. In particular, we were interested in the extent to which these forms of synthesis use any form of interactive data visualisation.
This study was a cross-sectional analysis of studies labelled as scoping reviews or evidence maps (or synonyms of these terms) in the title or abstract.
The search strategy was developed with help from an information specialist. Ovid MEDLINE® ALL was searched in June 2021 for studies added to the database in the previous 12 months. The search was limited to English language studies only.
The search strategy was as follows:
Ovid MEDLINE(R) ALL
(scoping review or evidence map or systematic map or mapping review or scoping study or scoping project or scoping exercise or literature mapping or evidence mapping or systematic mapping or literature scoping or evidence gap map).ab,ti.
limit 1 to english language
(202006* or 202007* or 202008* or 202009* or 202010* or 202011* or 202012* or 202101* or 202102* or 202103* or 202104* or 202105*).dt.
The search returned 3686 records. Records were de-duplicated in EndNote 20 software, leaving 3627 unique records.
A sample of these reviews was taken by screening the search results against basic selection criteria (Table 1 ). These criteria were piloted and refined after discussion between the two researchers. A single researcher (E.S.) screened the records in EPPI-Reviewer Web software using the machine-learning priority screening function. Where a second opinion was needed, decisions were checked by a second researcher (M.R.).
Our initial plan for sampling, informed by pilot searching, was to screen and data extract records in batches of 50 included reviews at a time. We planned to stop screening when a batch of 50 reviews had been extracted that included no new types of data visualisation or after screening time had reached 2 days. However, once data extraction was underway, we found the sample to be richer in terms of data visualisation than anticipated. After the inclusion of 300 reviews, we took the decision to end screening in order to ensure the study was manageable.
Data extraction
A data extraction form was developed in EPPI-Reviewer Web, piloted on 50 reviews and refined. Data were extracted by one researcher (E. S. or M. R.), with a second researcher (M. R. or E. S.) providing a second opinion when needed. The data items extracted were as follows: type of review (term used by authors), aim of review (mapping evidence vs. answering specific question vs. borderline), number of visualisations (if any), types of data visualisation used, variables/domains presented by each visualisation type, interactivity, use of colour and any software requirements.
When categorising review aims, we considered “mapping evidence” to incorporate all of the six purposes for conducting a scoping review proposed by Munn et al. [ 3 ]. Reviews were categorised as “answering a specific question” if they aimed to synthesise study findings to answer a particular question, for example on effectiveness of an intervention. We were inclusive with our definition of “mapping evidence” and included reviews with mixed aims in this category. However, some reviews were difficult to categorise (for example where aims were unclear or the stated aims did not match the actual focus of the paper) and were considered to be “borderline”. It became clear that a proportion of identified records that described themselves as “scoping” or “mapping” reviews were in fact pseudo-systematic reviews that failed to undertake key systematic review processes. Such reviews attempted to integrate the findings of included studies rather than map the evidence, and so reviews categorised as “answering a specific question” were excluded from the main analysis. Data visualisation methods for meta-analyses have been explored previously [ 19 ]. Figure 1 shows the flow of records from search results to final analysis sample.
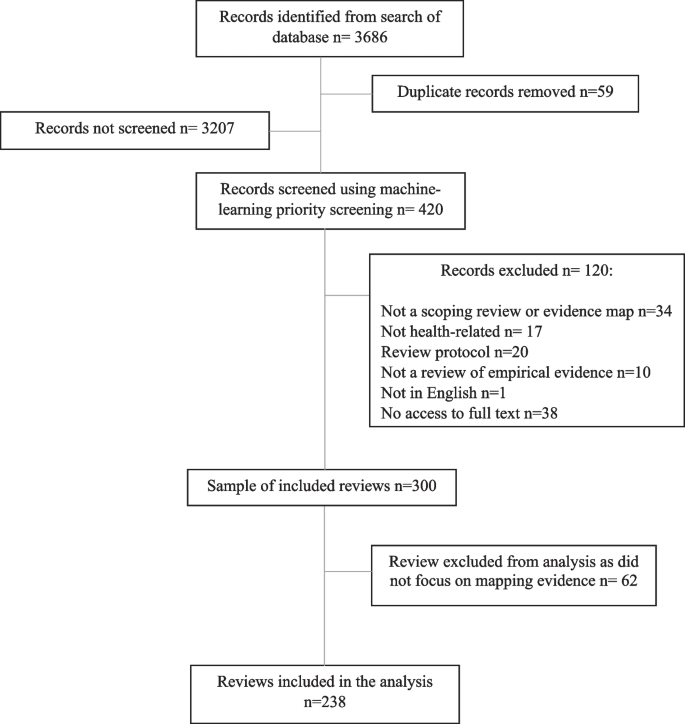
Flow diagram of the sampling process
Data visualisation was defined as any graph or diagram that presented results data, including tables with a visual mapping element, such as cross-tabulations and heat maps. However, tables which displayed data at a study level (e.g. tables summarising key characteristics of each included study) were not included, even if they used symbols, shading or colour. Flow diagrams showing the study selection process were also excluded. Data visualisations in appendices or supplementary information were included, as well as any in publicly available dissemination products (e.g. visualisations hosted online) if mentioned in papers.
The typology used to categorise data visualisation methods was based on an existing online catalogue [ 20 ]. Specific types of data visualisation were categorised in five broad categories: graphs, diagrams, tables, maps/geographical and other. If a data visualisation appeared in our sample that did not feature in the original catalogue, we checked a second online catalogue [ 21 ] for an appropriate term, followed by wider Internet searches. These additional visualisation methods were added to the appropriate section of the typology. The final typology can be found in Additional file 1 .
We conducted descriptive data analysis in Microsoft Excel 2019 and present frequencies and percentages. Where appropriate, data are presented using graphs or other data visualisations created using Flourish. We also link to interactive versions of some of these visualisations.
Almost all of the 300 reviews in the total sample were labelled by review authors as “scoping reviews” ( n = 293, 97.7%). There were also four “mapping reviews”, one “scoping study”, one “evidence mapping” and one that was described as a “scoping review and evidence map”. Included reviews were all published in 2020 or 2021, with the exception of one review published in 2018. Just over one-third of these reviews ( n = 105, 35.0%) included some form of data visualisation. However, we excluded 62 reviews that did not focus on mapping evidence from the following analysis (see “ Methods ” section). Of the 238 remaining reviews (that either clearly aimed to map evidence or were judged to be “borderline”), 90 reviews (37.8%) included at least one data visualisation. The references for these reviews can be found in Additional file 2 .
Number of visualisations
Thirty-six (40.0%) of these 90 reviews included just one example of data visualisation (Fig. 2 ). Less than a third ( n = 28, 31.1%) included three or more visualisations. The greatest number of data visualisations in one review was 17 (all bar or pie charts). In total, 222 individual data visualisations were identified across the sample of 238 reviews.
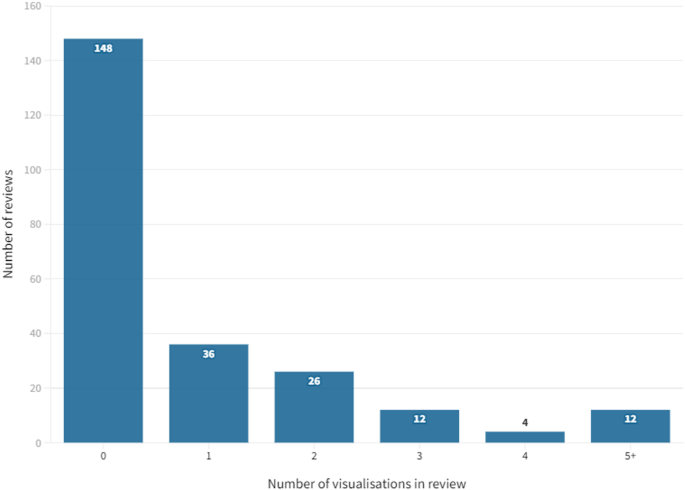
Number of data visualisations per review
Categories of data visualisation
Graphs were the most frequently used category of data visualisation in the sample. Over half of the reviews with data visualisation included at least one graph ( n = 59, 65.6%). The least frequently used category was maps, with 15.6% ( n = 14) of these reviews including a map.
Of the total number of 222 individual data visualisations, 102 were graphs (45.9%), 34 were tables (15.3%), 23 were diagrams (10.4%), 15 were maps (6.8%) and 48 were classified as “other” in the typology (21.6%).
Types of data visualisation
All of the types of data visualisation identified in our sample are reported in Table 2 . In total, 35 different types were used across the sample of reviews.
The most frequently used data visualisation type was a bar chart. Of 222 total data visualisations, 78 (35.1%) were a variation on a bar chart (either standard bar chart, stacked bar chart or multi-set bar chart). There were also 33 pie charts (14.9% of data visualisations) and 24 cross-tabulations (10.8% of data visualisations). In total, these five types of data visualisation accounted for 60.8% ( n = 135) of all data visualisations. Figure 3 shows the frequency of each data visualisation category and type; an interactive online version of this treemap is also available ( https://public.flourish.studio/visualisation/9396133/ ). Figure 4 shows how users can further explore the data using the interactive treemap.
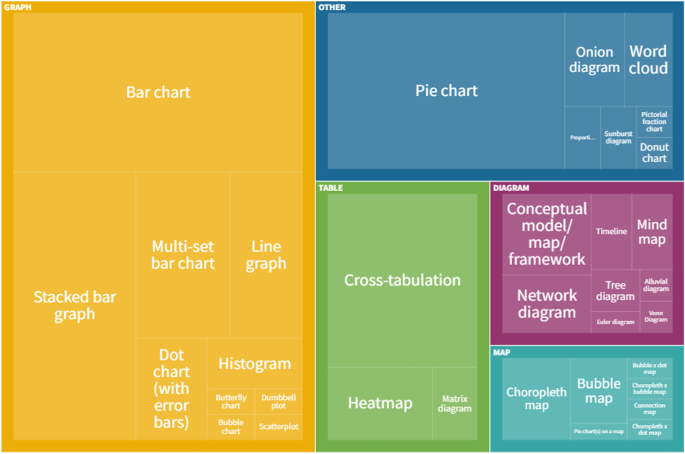
Data visualisation categories and types. An interactive version of this treemap is available online: https://public.flourish.studio/visualisation/9396133/ . Through the interactive version, users can further explore the data (see Fig. 4 ). The unit of this treemap is the individual data visualisation, so multiple data visualisations within the same scoping review are represented in this map. Created with flourish.studio ( https://flourish.studio )
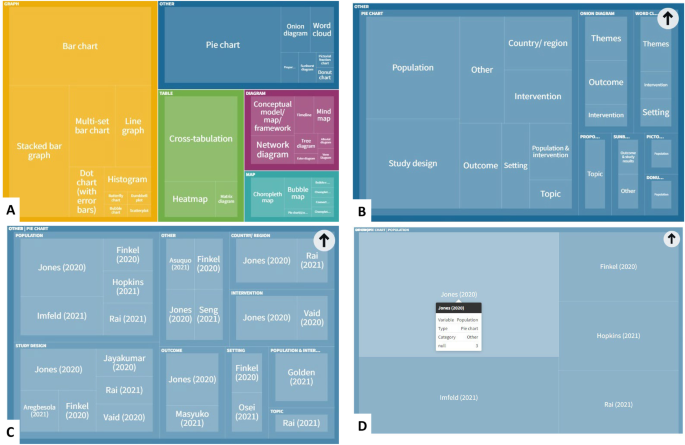
Screenshots showing how users of the interactive treemap can explore the data further. Users can explore each level of the hierarchical treemap ( A Visualisation category > B Visualisation subcategory > C Variables presented in visualisation > D Individual references reporting this category/subcategory/variable permutation). Created with flourish.studio ( https://flourish.studio )
Data presented
Around two-thirds of data visualisations in the sample presented a single variable ( n = 143, 64.4%). The most frequently presented single variables were themes ( n = 22, 9.9% of data visualisations), population ( n = 21, 9.5%), country or region ( n = 21, 9.5%) and year ( n = 20, 9.0%). There were 58 visualisations (26.1%) that presented two different variables. The remaining 21 data visualisations (9.5%) presented three or more variables. Figure 5 shows the variables presented by each different type of data visualisation (an interactive version of this figure is available online).
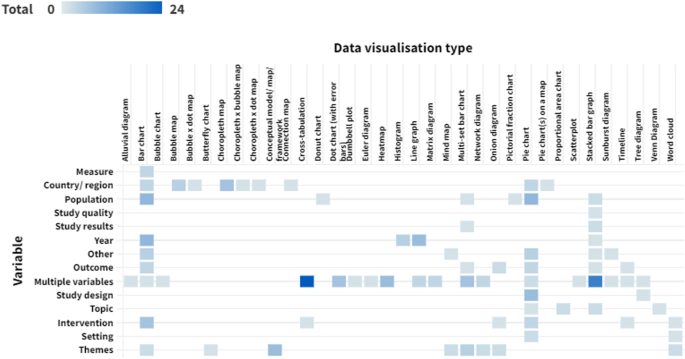
Variables presented by each data visualisation type. Darker cells indicate a larger number of reviews. An interactive version of this heat map is available online: https://public.flourish.studio/visualisation/10632665/ . Users can hover over each cell to see the number of data visualisations for that combination of data visualisation type and variable. The unit of this heat map is the individual data visualisation, so multiple data visualisations within a single scoping review are represented in this map. Created with flourish.studio ( https://flourish.studio )
Most reviews presented at least one data visualisation in colour ( n = 64, 71.1%). However, almost a third ( n = 26, 28.9%) used only black and white or greyscale.
Interactivity
Only two of the reviews included data visualisations with any level of interactivity. One scoping review on music and serious mental illness [ 22 ] linked to an interactive bubble chart hosted online on Tableau. Functionality included the ability to filter the studies displayed by various attributes.
The other review was an example of evidence mapping from the environmental health field [ 23 ]. All four of the data visualisations included in the paper were available in an interactive format hosted either by the review management software or on Tableau. The interactive versions linked to the relevant references so users could directly explore the evidence base. This was the only review that provided this feature.
Software requirements
Nine reviews clearly reported the software used to create data visualisations. Three reviews used Tableau (one of them also used review management software as discussed above) [ 22 , 23 , 24 ]. Two reviews generated maps using ArcGIS [ 25 ] or ArcMap [ 26 ]. One review used Leximancer for a lexical analysis [ 27 ]. One review undertook a bibliometric analysis using VOSviewer [ 28 ], and another explored citation patterns using CitNetExplorer [ 29 ]. Other reviews used Excel [ 30 ] or R [ 26 ].
To our knowledge, this is the first systematic and in-depth exploration of the use of data visualisation techniques in scoping reviews. Our findings suggest that the majority of scoping reviews do not use any data visualisation at all, and, in particular, more innovative examples of data visualisation are rare. Around 60% of data visualisations in our sample were simple bar charts, pie charts or cross-tabulations. There appears to be very limited use of interactive online visualisation, despite the potential this has for communicating results to a range of stakeholders. While it is not always appropriate to use data visualisation (or a simple bar chart may be the most user-friendly way of presenting the data), these findings suggest that data visualisation is being underused in scoping reviews. In a large minority of reviews, visualisations were not published in colour, potentially limiting how user-friendly and attractive papers are to decision-makers and other stakeholders. Also, very few reviews clearly reported the software used to create data visualisations. However, 35 different types of data visualisation were used across the sample, highlighting the wide range of methods that are potentially available to scoping review authors.
Our results build on the limited research that has previously been undertaken in this area. Two previous publications also found limited use of graphs in scoping reviews. Results were “mapped graphically” in 29% of scoping reviews in any field in one 2014 publication [ 31 ] and 17% of healthcare scoping reviews in a 2016 article [ 6 ]. Our results suggest that the use of data visualisation has increased somewhat since these reviews were conducted. Scoping review methods have also evolved in the last 10 years; formal guidance on scoping review conduct was published in 2014 [ 32 ], and an extension of the PRISMA checklist for scoping reviews was published in 2018 [ 33 ]. It is possible that an overall increase in use of data visualisation reflects increased quality of published scoping reviews. There is also some literature supporting our findings on the wide range of data visualisation methods that are used in evidence synthesis. An investigation of methods to identify, prioritise or display health research gaps (25/139 included studies were scoping reviews; 6/139 were evidence maps) identified 14 different methods used to display gaps or priorities, with half being “more advanced” (e.g. treemaps, radial bar plots) ([ 34 ], p. 107). A review of data visualisation methods used in papers reporting meta-analyses found over 200 different ways of displaying data [ 19 ].
Only two reviews in our sample used interactive data visualisation, and one of these was an example of systematic evidence mapping from the environmental health field rather than a scoping review (in environmental health, systematic evidence mapping explicitly involves producing a searchable database [ 35 ]). A scoping review of papers on the use of interactive data visualisation in population health or health services research found a range of examples but still limited use overall [ 13 ]. For example, the authors noted the currently underdeveloped potential for using interactive visualisation in research on health inequalities. It is possible that the use of interactive data visualisation in academic papers is restricted by academic publishing requirements; for example, it is currently difficult to incorporate an interactive figure into a journal article without linking to an external host or platform. However, we believe that there is a lot of potential to add value to future scoping reviews by using interactive data visualisation software. Few reviews in our sample presented three or more variables in a single visualisation, something which can easily be achieved using interactive data visualisation tools. We have previously used EPPI-Mapper [ 36 ] to present results of a scoping review of systematic reviews on behaviour change in disadvantaged groups, with links to the maps provided in the paper [ 37 ]. These interactive maps allowed policy-makers to explore the evidence on different behaviours and disadvantaged groups and access full publications of the included studies directly from the map.
We acknowledge there are barriers to use for some of the data visualisation software available. EPPI-Mapper and some of the software used by reviews in our sample incur a cost. Some software requires a certain level of knowledge and skill in its use. However numerous online free data visualisation tools and resources exist. We have used Flourish to present data for this review, a basic version of which is currently freely available and easy to use. Previous health research has been found to have used a range of different interactive data visualisation software, much of which does not required advanced knowledge or skills to use [ 13 ].
There are likely to be other barriers to the use of data visualisation in scoping reviews. Journal guidelines and policies may present barriers for using innovative data visualisation. For example, some journals charge a fee for publication of figures in colour. As previously mentioned, there are limited options for incorporating interactive data visualisation into journal articles. Authors may also be unaware of the data visualisation methods and tools that are available. Producing data visualisations can be time-consuming, particularly if authors lack experience and skills in this. It is possible that many authors prioritise speed of publication over spending time producing innovative data visualisations, particularly in a context where there is pressure to achieve publications.
Limitations
A limitation of this study was that we did not assess how appropriate the use of data visualisation was in our sample as this would have been highly subjective. Simple descriptive or tabular presentation of results may be the most appropriate approach for some scoping review objectives [ 7 , 8 , 10 ], and the scoping review literature cautions against “over-using” different visual presentation methods [ 7 , 8 ]. It cannot be assumed that all of the reviews that did not include data visualisation should have done so. Likewise, we do not know how many reviews used methods of data visualisation that were not well suited to their data.
We initially relied on authors’ own use of the term “scoping review” (or equivalent) to sample reviews but identified a relatively large number of papers labelled as scoping reviews that did not meet the basic definition, despite the availability of guidance and reporting guidelines [ 10 , 33 ]. It has previously been noted that scoping reviews may be undertaken inappropriately because they are seen as “easier” to conduct than a systematic review ([ 3 ], p.6), and that reviews are often labelled as “scoping reviews” while not appearing to follow any established framework or guidance [ 2 ]. We therefore took the decision to remove these reviews from our main analysis. However, decisions on how to classify review aims were subjective, and we did include some reviews that were of borderline relevance.
A further limitation is that this was a sample of published reviews, rather than a comprehensive systematic scoping review as have previously been undertaken [ 6 , 31 ]. The number of scoping reviews that are published has increased rapidly, and this would now be difficult to undertake. As this was a sample, not all relevant scoping reviews or evidence maps that would have met our criteria were included. We used machine learning to screen our search results for pragmatic reasons (to reduce screening time), but we do not see any reason that our sample would not be broadly reflective of the wider literature.
Data visualisation, and in particular more innovative examples of it, is currently underused in published scoping reviews on health topics. The examples that we have found highlight the wide range of methods that scoping review authors could draw upon to present their data in an engaging way. In particular, we believe that interactive data visualisation has significant potential for mapping the available literature on a topic. Appropriate use of data visualisation may increase the usefulness, and thus uptake, of scoping reviews as a way of identifying existing evidence or research gaps by decision-makers, researchers and commissioners of research. We recommend that scoping review authors explore the extensive free resources and online tools available for data visualisation. However, we also think that it would be useful for publishers to explore allowing easier integration of interactive tools into academic publishing, given the fact that papers are now predominantly accessed online. Future research may be helpful to explore which methods are particularly useful to scoping review users.
Availability of data and materials
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Organisation formerly known as Joanna Briggs Institute
Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses
Munn Z, Pollock D, Khalil H, Alexander L, McLnerney P, Godfrey CM, Peters M, Tricco AC. What are scoping reviews? Providing a formal definition of scoping reviews as a type of evidence synthesis. JBI Evid Synth. 2022;20:950–952.
Peters MDJ, Marnie C, Colquhoun H, Garritty CM, Hempel S, Horsley T, Langlois EV, Lillie E, O’Brien KK, Tunçalp Ӧ, et al. Scoping reviews: reinforcing and advancing the methodology and application. Syst Rev. 2021;10:263.
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Munn Z, Peters MDJ, Stern C, Tufanaru C, McArthur A, Aromataris E. Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2018;18:143.
Sutton A, Clowes M, Preston L, Booth A. Meeting the review family: exploring review types and associated information retrieval requirements. Health Info Libr J. 2019;36:202–22.
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Miake-Lye IM, Hempel S, Shanman R, Shekelle PG. What is an evidence map? A systematic review of published evidence maps and their definitions, methods, and products. Syst Rev. 2016;5:28.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien K, Colquhoun H, Kastner M, Levac D, Ng C, Sharpe JP, Wilson K, et al. A scoping review on the conduct and reporting of scoping reviews. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2016;16:15.
Khalil H, Peters MDJ, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Alexander L, McInerney P, Godfrey CM, Munn Z. Conducting high quality scoping reviews-challenges and solutions. J Clin Epidemiol. 2021;130:156–60.
Lockwood C, dos Santos KB, Pap R. Practical guidance for knowledge synthesis: scoping review methods. Asian Nurs Res. 2019;13:287–94.
Article Google Scholar
Pollock D, Peters MDJ, Khalil H, McInerney P, Alexander L, Tricco AC, Evans C, de Moraes ÉB, Godfrey CM, Pieper D, et al. Recommendations for the extraction, analysis, and presentation of results in scoping reviews. JBI Evidence Synthesis. 2022;10:11124.
Google Scholar
Peters MDJ GC, McInerney P, Munn Z, Tricco AC, Khalil, H. Chapter 11: Scoping reviews (2020 version). In: Aromataris E MZ, editor. JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis. JBI; 2020. Available from https://synthesismanual.jbi.global . Accessed 1 Feb 2023.
Tableau Public. https://www.tableau.com/en-gb/products/public . Accessed 24 January 2023.
flourish.studio. https://flourish.studio/ . Accessed 24 January 2023.
Chishtie J, Bielska IA, Barrera A, Marchand J-S, Imran M, Tirmizi SFA, Turcotte LA, Munce S, Shepherd J, Senthinathan A, et al. Interactive visualization applications in population health and health services research: systematic scoping review. J Med Internet Res. 2022;24: e27534.
Isett KR, Hicks DM. Providing public servants what they need: revealing the “unseen” through data visualization. Public Adm Rev. 2018;78:479–85.
Carroll LN, Au AP, Detwiler LT, Fu T-c, Painter IS, Abernethy NF. Visualization and analytics tools for infectious disease epidemiology: a systematic review. J Biomed Inform. 2014;51:287–298.
Lundkvist A, El-Khatib Z, Kalra N, Pantoja T, Leach-Kemon K, Gapp C, Kuchenmüller T. Policy-makers’ views on translating burden of disease estimates in health policies: bridging the gap through data visualization. Arch Public Health. 2021;79:17.
Zakkar M, Sedig K. Interactive visualization of public health indicators to support policymaking: an exploratory study. Online J Public Health Inform. 2017;9:e190–e190.
Park S, Bekemeier B, Flaxman AD. Understanding data use and preference of data visualization for public health professionals: a qualitative study. Public Health Nurs. 2021;38:531–41.
Kossmeier M, Tran US, Voracek M. Charting the landscape of graphical displays for meta-analysis and systematic reviews: a comprehensive review, taxonomy, and feature analysis. BMC Med Res Methodol. 2020;20:26.
Ribecca, S. The Data Visualisation Catalogue. https://datavizcatalogue.com/index.html . Accessed 23 November 2021.
Ferdio. Data Viz Project. https://datavizproject.com/ . Accessed 23 November 2021.
Golden TL, Springs S, Kimmel HJ, Gupta S, Tiedemann A, Sandu CC, Magsamen S. The use of music in the treatment and management of serious mental illness: a global scoping review of the literature. Front Psychol. 2021;12: 649840.
Keshava C, Davis JA, Stanek J, Thayer KA, Galizia A, Keshava N, Gift J, Vulimiri SV, Woodall G, Gigot C, et al. Application of systematic evidence mapping to assess the impact of new research when updating health reference values: a case example using acrolein. Environ Int. 2020;143: 105956.
Article CAS PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Jayakumar P, Lin E, Galea V, Mathew AJ, Panda N, Vetter I, Haynes AB. Digital phenotyping and patient-generated health data for outcome measurement in surgical care: a scoping review. J Pers Med. 2020;10:282.
Qu LG, Perera M, Lawrentschuk N, Umbas R, Klotz L. Scoping review: hotspots for COVID-19 urological research: what is being published and from where? World J Urol. 2021;39:3151–60.
Article CAS PubMed Google Scholar
Rossa-Roccor V, Acheson ES, Andrade-Rivas F, Coombe M, Ogura S, Super L, Hong A. Scoping review and bibliometric analysis of the term “planetary health” in the peer-reviewed literature. Front Public Health. 2020;8:343.
Hewitt L, Dahlen HG, Hartz DL, Dadich A. Leadership and management in midwifery-led continuity of care models: a thematic and lexical analysis of a scoping review. Midwifery. 2021;98: 102986.
Xia H, Tan S, Huang S, Gan P, Zhong C, Lu M, Peng Y, Zhou X, Tang X. Scoping review and bibliometric analysis of the most influential publications in achalasia research from 1995 to 2020. Biomed Res Int. 2021;2021:8836395.
Vigliotti V, Taggart T, Walker M, Kusmastuti S, Ransome Y. Religion, faith, and spirituality influences on HIV prevention activities: a scoping review. PLoS ONE. 2020;15: e0234720.
van Heemskerken P, Broekhuizen H, Gajewski J, Brugha R, Bijlmakers L. Barriers to surgery performed by non-physician clinicians in sub-Saharan Africa-a scoping review. Hum Resour Health. 2020;18:51.
Pham MT, Rajić A, Greig JD, Sargeant JM, Papadopoulos A, McEwen SA. A scoping review of scoping reviews: advancing the approach and enhancing the consistency. Res Synth Methods. 2014;5:371–85.
Peters MDJ, Marnie C, Tricco AC, Pollock D, Munn Z, Alexander L, McInerney P, Godfrey CM, Khalil H. Updated methodological guidance for the conduct of scoping reviews. JBI Evid Synth. 2020;18:2119–26.
Tricco AC, Lillie E, Zarin W, O’Brien KK, Colquhoun H, Levac D, Moher D, Peters MDJ, Horsley T, Weeks L, et al. PRISMA Extension for Scoping Reviews (PRISMA-ScR): checklist and explanation. Ann Intern Med. 2018;169:467–73.
Nyanchoka L, Tudur-Smith C, Thu VN, Iversen V, Tricco AC, Porcher R. A scoping review describes methods used to identify, prioritize and display gaps in health research. J Clin Epidemiol. 2019;109:99–110.
Wolffe TAM, Whaley P, Halsall C, Rooney AA, Walker VR. Systematic evidence maps as a novel tool to support evidence-based decision-making in chemicals policy and risk management. Environ Int. 2019;130:104871.
Digital Solution Foundry and EPPI-Centre. EPPI-Mapper, Version 2.0.1. EPPI-Centre, UCL Social Research Institute, University College London. 2020. https://eppi.ioe.ac.uk/cms/Default.aspx?tabid=3790 .
South E, Rodgers M, Wright K, Whitehead M, Sowden A. Reducing lifestyle risk behaviours in disadvantaged groups in high-income countries: a scoping review of systematic reviews. Prev Med. 2022;154: 106916.
Download references
Acknowledgements
We would like to thank Melissa Harden, Senior Information Specialist, Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, for advice on developing the search strategy.
This work received no external funding.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Centre for Reviews and Dissemination, University of York, York, YO10 5DD, UK
Emily South & Mark Rodgers
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
Both authors conceptualised and designed the study and contributed to screening, data extraction and the interpretation of results. ES undertook the literature searches, analysed data, produced the data visualisations and drafted the manuscript. MR contributed to revising the manuscript, and both authors read and approved the final version.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Emily South .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
Not applicable.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Supplementary Information
Additional file 1..
Typology of data visualisation methods.
Additional file 2.
References of scoping reviews included in main dataset.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ . The Creative Commons Public Domain Dedication waiver ( http://creativecommons.org/publicdomain/zero/1.0/ ) applies to the data made available in this article, unless otherwise stated in a credit line to the data.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
South, E., Rodgers, M. Data visualisation in scoping reviews and evidence maps on health topics: a cross-sectional analysis. Syst Rev 12 , 142 (2023). https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02309-y
Download citation
Received : 21 February 2023
Accepted : 07 August 2023
Published : 17 August 2023
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s13643-023-02309-y
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Scoping review
- Evidence map
- Data visualisation
Systematic Reviews
ISSN: 2046-4053
- Submission enquiries: Access here and click Contact Us
- General enquiries: [email protected]

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here are six major types of visual presentations that you should be familiar with: 1. Slideshows or PowerPoint presentations. Slideshows are one of the most common forms of visual presentations. They typically consist of a series of slides containing text, images, charts, graphs and other visual elements. Slideshows are used for various ...
For example, a slide that shows how much money was spent on advertising last year might be useful in an annual meeting where everyone's attention span is short or they don't want to take the time to read a long report. 2. Charts. Graphs and charts are other types of visual presentation that can be used to show trends or compare data.
Now that you have an idea of good vs. bad visuals, let's talk about 7 types of visuals you can use in your presentation. 1. Use stock photos for your presentation slides. When I'm giving a presentation training workshop, I ask people what types of visuals they should avoid, and a lot of them say "stock photos!".
Now, let's dive into our look at effective presentation styles. 10+ Different Types of Effective Presentation Styles. Here are more than ten common different effective presentation styles: 1. Visual Presentation Style. The visual style is great for anyone who wants to use your presentation to complement the main points of your speech.
Instructor Style. Coach Style. Storytelling Style. Connector Style. Lessig Style. Takahashi Style. Everyone on the internet has an opinion on how to give the "perfect" presentation. One group champions visual aids, another thinks visual aids are a threat to society as we know it. One expert preaches the benefits of speaking loudly, while ...
Style #6: The Lessig style. If you are in a time crunch, but you have a lot of material to cover, then the Lessig style is the perfect style for you. The Lessig style was invented by Lawrence Lessig, and it states that a speaker should spend only 15 seconds on each slide or point during a presentation.
The best way to make sure the attention stays on you is to limit word count to no more than 10 words per slide. As presentation expert Nancy Duarte says "any slide with more than 10 words is a document.". If you really do need a longer explanation of something, handouts or follow-up emails are the way to go.
Techniques like color schemes and layout design enhance visual appeal and are suitable for marketing campaigns, educational materials, and scientific presentations. Mastering Different Types of Presentations: A Guide for Engaging Audiences. Presentations are versatile tools, offering a spectrum of styles to captivate audiences.
The secret to creating a great presentation does not lie in a superior software, but understanding a few universal design concepts that can applied for all types of visual presentations. Don't be afraid to use a few presentation templates - there are ways to make the presentation ideas in those templates your own ideas and advance it in ...
Apple® founder Steve Jobs was known widely for his great presentations. His unveiling of the iPhone® in 2007 is considered to have been one of his best presentations ever, and, if you were one of the millions who watched it online, you'll know why. The presentation was engaging, and passionate. Jobs was particularly well known for building his presentations around powerful visual aids.
A visual aid is any material that gives shape and form to words or thoughts. Types of visual aids include physical samples, models, handouts, pictures, videos, infographics, etc. Visual aids have come a long way, including digital tools such as overhead projectors, PowerPoint presentations, and interactive boards.
Exercise 2. In this exercise, you will begin to develop visual aids for your presentation. Complete the steps in this exercise—and enjoy the chance to be creative. Working with visuals can be a pleasant way to take a break from the demands of writing. Revisit the ideas you developed in Note 14.24 "Exercise 1".
13.3: Types of Visual Aids. In the past, transparencies displayed with overhead projectors, posters, and flip charts were common visual aids, but these have mostly been replaced with computer technology. For many people, the term "visual aids" for presentations or speeches is synonymous with PowerPoint (often long, dry, painful PowerPoint ...
Visual aids help clarify and contextualize your points for your audience. Whether you deliver your presentation in person or over the web, the goal is to clearly communicate with your audience. Presentation aids help achieve this goal. Visual aids also help a presenter stay on a predefined train of thought while presenting.
6. Visual. A visual presentation emphasizes the use of visual aids to convey information. It uses graphics, images, videos, or other visual elements to enhance the audience's understanding and retention of the presented material. Visual presentations can be in different forms - slideshows, videos, infographics, or posters.
Whether this is in a professional or educational context, or even just between friends, there are many times when presentations can be used to share information. Some examples might be: A work meeting in which you are reporting on a project's status. Teaching a webinar. Pitching an idea. Making a speech.
Now that we've established how critical strong visuals are to business presentations…. Let's get into some simple tips that will help jumpstart visual thinking the next time you open PowerPoint: TIP 1: Callouts are Visual Eye-Candy. Callouts are one of the easiest and most potent data visualization techniques.
Visual aids like graphics, images, diagrams, key pointers or phrases, etc., are very useful when giving any type of presentation. Some tips of presenting with visual style: Include only important pointers in your PowerPoint presentation and highlight or bold them
Types of Visual Presentation Examples. Some possible visual presentations include infographics, charts, diagrams, posters, flipcharts, idea board, whiteboards, and video presentation examples. An infographic is a collection of different graphic visual presentations to represent information, data, or knowledge intended more visually quickly and ...
Effective visual presentations can be accomplished if you use the right visual aids. To help you ace your next presentation, in this post we will be going through the top 5 types of visuals for a presentation. In addition to the visual presentation examples, we will provide some helpful visual presentation tips to make your presentation a ...
There are different types of visual aids you can use in your presentation be more successful. Visual aids is a term used in public speaking to refer to all of the various tangible objects a speaker may use in a presentation with the goal of facilitating understanding. Visual aids are typically projected or placed on easels for all presenters ...
6 Major Types of Visual Presentation. Visual presentation refers to the expression of ideas about some matters while using visual aids such as visual multimedia. From electronic media such as television screens and web pages to environmental contexts such as retail displays and road signs, visual communication is virtually everywhere.
Instead, aim to maintain eye contact between 50% of the time during presentations. This commonly accepted "50/70 rule" will help you exhibit adequate confidence to your audience. If stage fright has gotten a hold on you, take deep breaths before you start speaking in order to stay calm.
The best type of data visualization to use depends on the data at hand and the purpose of its presentation. Whether aiming to highlight trends, compare values, or elucidate complex relationships, selecting the appropriate visual form is crucial for effectively communicating insights buried within datasets.
Mission. The Purdue On-Campus Writing Lab and Purdue Online Writing Lab assist clients in their development as writers—no matter what their skill level—with on-campus consultations, online participation, and community engagement. The Purdue Writing Lab serves the Purdue, West Lafayette, campus and coordinates with local literacy initiatives.
For many people, the term "visual aids" for presentations or speeches is synonymous with PowerPoint, but this is just one type of visual aid. You should consider all the available options to determine what will be most effective and appropriate for your presentation. If you wear clothes that don't suit you, you're a fashion victim.
Scoping reviews and evidence maps are forms of evidence synthesis that aim to map the available literature on a topic and are well-suited to visual presentation of results. A range of data visualisation methods and interactive data visualisation tools exist that may make scoping reviews more useful to knowledge users. The aim of this study was to explore the use of data visualisation in a ...