Free Text Summarizer
Try our other writing services


Want to be 100% sure your summary is plagiarism-free?
Make your life easier with the free summarizer tool.
Academic research
Speed up your academic research by extracting key points.
Every day use
Reduce your reading time by summarizing long blocks of text within seconds.
Easily condense transcripts of long meetings into concise bullet points.
Difficult text
Simplify hard-to-read paragraphs, sentences or complete articles with 1 click.

Why use this summarizer?
- 100% free: Generate unlimited summaries without paying a penny
- Accurate: Get a reliable and trustworthy summary of your original text without any errors
- No signup: Use it without giving up any personal data
- Secure: No summary data is stored, guaranteeing your privacy
- Speed: Get an accurate summary within seconds, thanks to AI
- Flexible: Adjust summary length to get more (or less) detailed summaries
How to use this summarizer
1. insert, paste or download your text, 2. pick the way you want to summarize, 3. adjust your summary length, 4. get your summary in seconds.
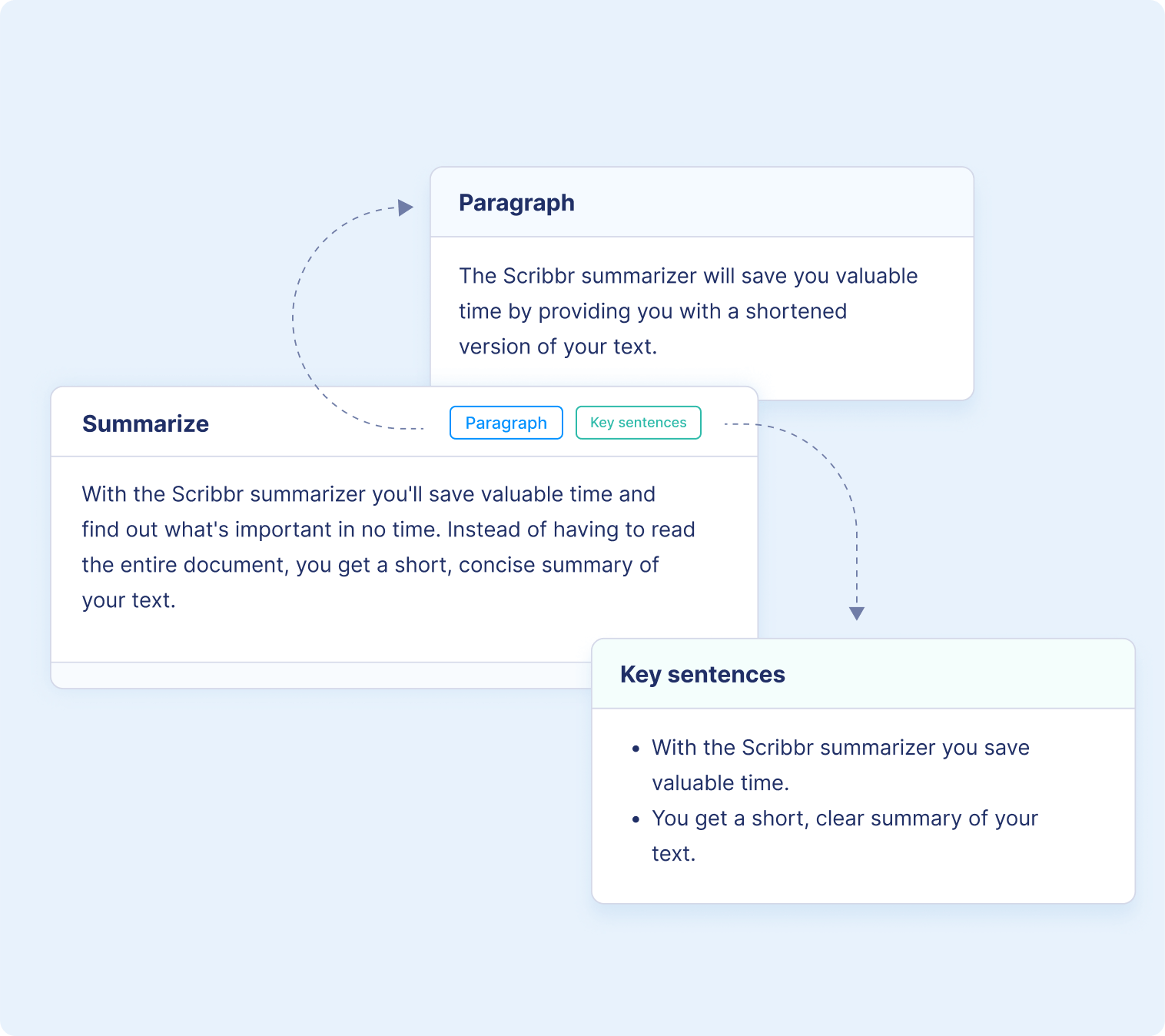
2 ways of summarizing your text
1. key sentences.
Extracts the key points of your text and turns them into digestible bullet points
2. Concise paragraphs
Summarizes your text in a concise paragraph
Summarize your text today
Want to make sure your summary doesn’t contain any plagiarism, ask our team.
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Frequently asked questions
Yes, it can. The AI has been trained on a big dataset, so technical or complex data won’t be a problem for the text summarizer .
The text summarizer is accessible on both desktop and mobile.
This text summarizer can condense long text within seconds.
At the moment, a maximum of 600 words can be summarized at once, within a few seconds. Want to summarize more? Just paste another block of text. There’s no limit on how much text you can summarize with our text summarizer .
The text summarizer can give you a longer or shorter summary, depending on your wishes. Want a more detailed summary? Just adjust the summary length at the top.

Summary: Using it Wisely
What this handout is about.
Knowing how to summarize something you have read, seen, or heard is a valuable skill, one you have probably used in many writing assignments. It is important, though, to recognize when you must go beyond describing, explaining, and restating texts and offer a more complex analysis. This handout will help you distinguish between summary and analysis and avoid inappropriate summary in your academic writing.
Is summary a bad thing?
Not necessarily. But it’s important that your keep your assignment and your audience in mind as you write. If your assignment requires an argument with a thesis statement and supporting evidence—as many academic writing assignments do—then you should limit the amount of summary in your paper. You might use summary to provide background, set the stage, or illustrate supporting evidence, but keep it very brief: a few sentences should do the trick. Most of your paper should focus on your argument. (Our handout on argument will help you construct a good one.)
Writing a summary of what you know about your topic before you start drafting your actual paper can sometimes be helpful. If you are unfamiliar with the material you’re analyzing, you may need to summarize what you’ve read in order to understand your reading and get your thoughts in order. Once you figure out what you know about a subject, it’s easier to decide what you want to argue.
You may also want to try some other pre-writing activities that can help you develop your own analysis. Outlining, freewriting, and mapping make it easier to get your thoughts on the page. (Check out our handout on brainstorming for some suggested techniques.)
Why is it so tempting to stick with summary and skip analysis?
Many writers rely too heavily on summary because it is what they can most easily write. If you’re stalled by a difficult writing prompt, summarizing the plot of The Great Gatsby may be more appealing than staring at the computer for three hours and wondering what to say about F. Scott Fitzgerald’s use of color symbolism. After all, the plot is usually the easiest part of a work to understand. Something similar can happen even when what you are writing about has no plot: if you don’t really understand an author’s argument, it might seem easiest to just repeat what he or she said.
To write a more analytical paper, you may need to review the text or film you are writing about, with a focus on the elements that are relevant to your thesis. If possible, carefully consider your writing assignment before reading, viewing, or listening to the material about which you’ll be writing so that your encounter with the material will be more purposeful. (We offer a handout on reading towards writing .)
How do I know if I’m summarizing?
As you read through your essay, ask yourself the following questions:
- Am I stating something that would be obvious to a reader or viewer?
- Does my essay move through the plot, history, or author’s argument in chronological order, or in the exact same order the author used?
- Am I simply describing what happens, where it happens, or whom it happens to?
A “yes” to any of these questions may be a sign that you are summarizing. If you answer yes to the questions below, though, it is a sign that your paper may have more analysis (which is usually a good thing):
- Am I making an original argument about the text?
- Have I arranged my evidence around my own points, rather than just following the author’s or plot’s order?
- Am I explaining why or how an aspect of the text is significant?
Certain phrases are warning signs of summary. Keep an eye out for these:
- “[This essay] is about…”
- “[This book] is the story of…”
- “[This author] writes about…”
- “[This movie] is set in…”
Here’s an example of an introductory paragraph containing unnecessary summary. Sentences that summarize are in italics:
The Great Gatsby is the story of a mysterious millionaire, Jay Gatsby, who lives alone on an island in New York. F. Scott Fitzgerald wrote the book, but the narrator is Nick Carraway. Nick is Gatsby’s neighbor, and he chronicles the story of Gatsby and his circle of friends, beginning with his introduction to the strange man and ending with Gatsby’s tragic death. In the story, Nick describes his environment through various colors, including green, white, and grey. Whereas white and grey symbolize false purity and decay respectively, the color green offers a symbol of hope.
Here’s how you might change the paragraph to make it a more effective introduction:
In The Great Gatsby, F. Scott Fitzgerald provides readers with detailed descriptions of the area surrounding East Egg, New York. In fact, Nick Carraway’s narration describes the setting with as much detail as the characters in the book. Nick’s description of the colors in his environment presents the book’s themes, symbolizing significant aspects of the post-World War I era. Whereas white and grey symbolize the false purity and decay of the 1920s, the color green offers a symbol of hope.
This version of the paragraph mentions the book’s title, author, setting, and narrator so that the reader is reminded of the text. And that sounds a lot like summary—but the paragraph quickly moves on to the writer’s own main topic: the setting and its relationship to the main themes of the book. The paragraph then closes with the writer’s specific thesis about the symbolism of white, grey, and green.
How do I write more analytically?
Analysis requires breaking something—like a story, poem, play, theory, or argument—into parts so you can understand how those parts work together to make the whole. Ideally, you should begin to analyze a work as you read or view it instead of waiting until after you’re done—it may help you to jot down some notes as you read. Your notes can be about major themes or ideas you notice, as well as anything that intrigues, puzzles, excites, or irritates you. Remember, analytic writing goes beyond the obvious to discuss questions of how and why—so ask yourself those questions as you read.
The St. Martin’s Handbook (the bulleted material below is quoted from p. 38 of the fifth edition) encourages readers to take the following steps in order to analyze a text:
- Identify evidence that supports or illustrates the main point or theme as well as anything that seems to contradict it.
- Consider the relationship between the words and the visuals in the work. Are they well integrated, or are they sometimes at odds with one another? What functions do the visuals serve? To capture attention? To provide more detailed information or illustration? To appeal to readers’ emotions?
- Decide whether the sources used are trustworthy.
- Identify the work’s underlying assumptions about the subject, as well as any biases it reveals.
Once you have written a draft, some questions you might want to ask yourself about your writing are “What’s my point?” or “What am I arguing in this paper?” If you can’t answer these questions, then you haven’t gone beyond summarizing. You may also want to think about how much of your writing comes from your own ideas or arguments. If you’re only reporting someone else’s ideas, you probably aren’t offering an analysis.
What strategies can help me avoid excessive summary?
- Read the assignment (the prompt) as soon as you get it. Make sure to reread it before you start writing. Go back to your assignment often while you write. (Check out our handout on reading assignments ).
- Formulate an argument (including a good thesis) and be sure that your final draft is structured around it, including aspects of the plot, story, history, background, etc. only as evidence for your argument. (You can refer to our handout on constructing thesis statements ).
- Read critically—imagine having a dialogue with the work you are discussing. What parts do you agree with? What parts do you disagree with? What questions do you have about the work? Does it remind you of other works you’ve seen?
- Make sure you have clear topic sentences that make arguments in support of your thesis statement. (Read our handout on paragraph development if you want to work on writing strong paragraphs).
- Use two different highlighters to mark your paper. With one color, highlight areas of summary or description. With the other, highlight areas of analysis. For many college papers, it’s a good idea to have lots of analysis and minimal summary/description.
- Ask yourself: What part of the essay would be obvious to a reader/viewer of the work being discussed? What parts (words, sentences, paragraphs) of the essay could be deleted without loss? In most cases, your paper should focus on points that are essential and that will be interesting to people who have already read or seen the work you are writing about.
But I’m writing a review! Don’t I have to summarize?
That depends. If you’re writing a critique of a piece of literature, a film, or a dramatic performance, you don’t necessarily need to give away much of the plot. The point is to let readers decide whether they want to enjoy it for themselves. If you do summarize, keep your summary brief and to the point.
Instead of telling your readers that the play, book, or film was “boring,” “interesting,” or “really good,” tell them specifically what parts of the work you’re talking about. It’s also important that you go beyond adjectives and explain how the work achieved its effect (how was it interesting?) and why you think the author/director wanted the audience to react a certain way. (We have a special handout on writing reviews that offers more tips.)
If you’re writing a review of an academic book or article, it may be important for you to summarize the main ideas and give an overview of the organization so your readers can decide whether it is relevant to their specific research interests.
If you are unsure how much (if any) summary a particular assignment requires, ask your instructor for guidance.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Barnet, Sylvan. 2015. A Short Guide to Writing about Art , 11th ed. Upper Saddle River, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Corrigan, Timothy. 2014. A Short Guide to Writing About Film , 9th ed. New York: Pearson.
Lunsford, Andrea A. 2015. The St. Martin’s Handbook , 8th ed. Boston: Bedford/St Martin’s.
Zinsser, William. 2001. On Writing Well: The Classic Guide to Writing Nonfiction , 6th ed. New York: Quill.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Have a thesis expert improve your writing
Check your thesis for plagiarism in 10 minutes, generate your apa citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Working with sources
- How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples
Published on 25 September 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 12 May 2023.
Summarising , or writing a summary, means giving a concise overview of a text’s main points in your own words. A summary is always much shorter than the original text.
There are five key steps that can help you to write a summary:
- Read the text
- Break it down into sections
- Identify the key points in each section
- Write the summary
- Check the summary against the article
Writing a summary does not involve critiquing or analysing the source. You should simply provide an accurate account of the most important information and ideas (without copying any text from the original).
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
When to write a summary, step 1: read the text, step 2: break the text down into sections, step 3: identify the key points in each section, step 4: write the summary, step 5: check the summary against the article, frequently asked questions.
There are many situations in which you might have to summarise an article or other source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to show you’ve understood the material
- To keep notes that will help you remember what you’ve read
- To give an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
When you’re writing an academic text like an essay , research paper , or dissertation , you’ll integrate sources in a variety of ways. You might use a brief quote to support your point, or paraphrase a few sentences or paragraphs.
But it’s often appropriate to summarize a whole article or chapter if it is especially relevant to your own research, or to provide an overview of a source before you analyse or critique it.
In any case, the goal of summarising is to give your reader a clear understanding of the original source. Follow the five steps outlined below to write a good summary.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
You should read the article more than once to make sure you’ve thoroughly understood it. It’s often effective to read in three stages:
- Scan the article quickly to get a sense of its topic and overall shape.
- Read the article carefully, highlighting important points and taking notes as you read.
- Skim the article again to confirm you’ve understood the key points, and reread any particularly important or difficult passages.
There are some tricks you can use to identify the key points as you read:
- Start by reading the abstract . This already contains the author’s own summary of their work, and it tells you what to expect from the article.
- Pay attention to headings and subheadings . These should give you a good sense of what each part is about.
- Read the introduction and the conclusion together and compare them: What did the author set out to do, and what was the outcome?
To make the text more manageable and understand its sub-points, break it down into smaller sections.
If the text is a scientific paper that follows a standard empirical structure, it is probably already organised into clearly marked sections, usually including an introduction, methods, results, and discussion.
Other types of articles may not be explicitly divided into sections. But most articles and essays will be structured around a series of sub-points or themes.
Now it’s time go through each section and pick out its most important points. What does your reader need to know to understand the overall argument or conclusion of the article?
Keep in mind that a summary does not involve paraphrasing every single paragraph of the article. Your goal is to extract the essential points, leaving out anything that can be considered background information or supplementary detail.
In a scientific article, there are some easy questions you can ask to identify the key points in each part.
If the article takes a different form, you might have to think more carefully about what points are most important for the reader to understand its argument.
In that case, pay particular attention to the thesis statement —the central claim that the author wants us to accept, which usually appears in the introduction—and the topic sentences that signal the main idea of each paragraph.
Now that you know the key points that the article aims to communicate, you need to put them in your own words.
To avoid plagiarism and show you’ve understood the article, it’s essential to properly paraphrase the author’s ideas. Do not copy and paste parts of the article, not even just a sentence or two.
The best way to do this is to put the article aside and write out your own understanding of the author’s key points.
Examples of article summaries
Let’s take a look at an example. Below, we summarise this article , which scientifically investigates the old saying ‘an apple a day keeps the doctor away’.
An article summary like the above would be appropriate for a stand-alone summary assignment. However, you’ll often want to give an even more concise summary of an article.
For example, in a literature review or research paper, you may want to briefly summarize this study as part of a wider discussion of various sources. In this case, we can boil our summary down even further to include only the most relevant information.
Citing the source you’re summarizing
When including a summary as part of a larger text, it’s essential to properly cite the source you’re summarizing. The exact format depends on your citation style , but it usually includes an in-text citation and a full reference at the end of your paper.
You can easily create your citations and references in APA or MLA using our free citation generators.
APA Citation Generator MLA Citation Generator
Finally, read through the article once more to ensure that:
- You’ve accurately represented the author’s work
- You haven’t missed any essential information
- The phrasing is not too similar to any sentences in the original.
If you’re summarising many articles as part of your own work, it may be a good idea to use a plagiarism checker to double-check that your text is completely original and properly cited. Just be sure to use one that’s safe and reliable.
A summary is a short overview of the main points of an article or other source, written entirely in your own words.
Save yourself some time with the free summariser.
A summary is always much shorter than the original text. The length of a summary can range from just a few sentences to several paragraphs; it depends on the length of the article you’re summarising, and on the purpose of the summary.
With the summariser tool you can easily adjust the length of your summary.
You might have to write a summary of a source:
- As a stand-alone assignment to prove you understand the material
- For your own use, to keep notes on your reading
- To provide an overview of other researchers’ work in a literature review
- In a paper , to summarise or introduce a relevant study
To avoid plagiarism when summarising an article or other source, follow these two rules:
- Write the summary entirely in your own words by paraphrasing the author’s ideas.
- Reference the source with an in-text citation and a full reference so your reader can easily find the original text.
An abstract concisely explains all the key points of an academic text such as a thesis , dissertation or journal article. It should summarise the whole text, not just introduce it.
An abstract is a type of summary , but summaries are also written elsewhere in academic writing . For example, you might summarise a source in a paper , in a literature review , or as a standalone assignment.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, May 12). How to Write a Summary | Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 1 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/working-sources/how-to-write-a-summary/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to paraphrase | step-by-step guide & examples, how to quote | citing quotes in harvard & apa, apa referencing (7th ed.) quick guide | in-text citations & references.
- Features for Creative Writers
- Features for Work
- Features for Higher Education
- Features for Teachers
- Features for Non-Native Speakers
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
How to Write a Summary (Examples Included)

Ashley Shaw

Have you ever recommended a book to someone and given them a quick overview? Then you’ve created a summary before!
Summarizing is a common part of everyday communication. It feels easy when you’re recounting what happened on your favorite show, but what do you do when the information gets a little more complex?
Written summaries come with their own set of challenges. You might ask yourself:
- What details are unnecessary?
- How do you put this in your own words without changing the meaning?
- How close can you get to the original without plagiarizing it?
- How long should it be?
The answers to these questions depend on the type of summary you are doing and why you are doing it.
A summary in an academic setting is different to a professional summary—and both of those are very different to summarizing a funny story you want to tell your friends.
One thing they all have in common is that you need to relay information in the clearest way possible to help your reader understand. We’ll look at some different forms of summary, and give you some tips on each.
Let’s get started!
What Is a Summary?
How do you write a summary, how do you write an academic summary, what are the four types of academic summaries, how do i write a professional summary, writing or telling a summary in personal situations, summarizing summaries.
A summary is a shorter version of a larger work. Summaries are used at some level in almost every writing task, from formal documents to personal messages.
When you write a summary, you have an audience that doesn’t know every single thing you know.
When you want them to understand your argument, topic, or stance, you may need to explain some things to catch them up.
Instead of having them read the article or hear every single detail of the story or event, you instead give them a brief overview of what they need to know.
Academic, professional, and personal summaries each require you to consider different things, but there are some key rules they all have in common.
Let’s go over a few general guides to writing a summary first.

1. A summary should always be shorter than the original work, usually considerably.
Even if your summary is the length of a full paper, you are likely summarizing a book or other significantly longer work.
2. A summary should tell the reader the highlights of what they need to know without giving them unnecessary details.
3. It should also include enough details to give a clear and honest picture.
For example, if you summarize an article that says “ The Office is the greatest television show of all time,” but don’t mention that they are specifically referring to sitcoms, then you changed the meaning of the article. That’s a problem! Similarly, if you write a summary of your job history and say you volunteered at a hospital for the last three years, but you don’t add that you only went twice in that time, it becomes a little dishonest.
4. Summaries shouldn’t contain personal opinion.
While in the longer work you are creating you might use opinion, within the summary itself, you should avoid all personal opinion. A summary is different than a review. In this moment, you aren’t saying what you think of the work you are summarizing, you are just giving your audience enough information to know what the work says or did.

Now that we have a good idea of what summaries are in general, let’s talk about some specific types of summary you will likely have to do at some point in your writing life.
An academic summary is one you will create for a class or in other academic writing. The exact elements you will need to include depend on the assignment itself.
However, when you’re asked for an academic summary, this usually this means one of five things, all of which are pretty similar:
- You need to do a presentation in which you talk about an article, book, or report.
- You write a summary paper in which the entire paper is a summary of a specific work.
- You summarize a class discussion, lesson, or reading in the form of personal notes or a discussion board post.
- You do something like an annotated bibliography where you write short summaries of multiple works in preparation of a longer assignment.
- You write quick summaries within the body of another assignment . For example, in an argumentative essay, you will likely need to have short summaries of the sources you use to explain their argument before getting into how the source helps you prove your point.

Regardless of what type of summary you are doing, though, there are a few steps you should always follow:
- Skim the work you are summarizing before you read it. Notice what stands out to you.
- Next, read it in depth . Do the same things stand out?
- Put the full text away and write in a few sentences what the main idea or point was.
- Go back and compare to make sure you didn’t forget anything.
- Expand on this to write and then edit your summary.
Each type of academic summary requires slightly different things. Let’s get down to details.
How Do I Write a Summary Paper?
Sometimes teachers assign something called a summary paper . In this, the entire thing is a summary of one article, book, story, or report.
To understand how to write this paper, let’s talk a little bit about the purpose of such an assignment.
A summary paper is usually given to help a teacher see how well a student understands a reading assignment, but also to help the student digest the reading. Sometimes, it can be difficult to understand things we read right away.
However, a good way to process the information is to put it in our own words. That is the point of a summary paper.

A summary paper is:
- A way to explain in our own words what happened in a paper, book, etc.
- A time to think about what was important in the paper, etc.
- A time to think about the meaning and purpose behind the paper, etc.
Here are some things that a summary paper is not:
- A review. Your thoughts and opinions on the thing you are summarizing don’t need to be here unless otherwise specified.
- A comparison. A comparison paper has a lot of summary in it, but it is different than a summary paper. In this, you are just saying what happened, but you aren’t saying places it could have been done differently.
- A paraphrase (though you might have a little paraphrasing in there). In the section on using summary in longer papers, I talk more about the difference between summaries, paraphrases, and quotes.

Because a summary paper is usually longer than other forms of summary, you will be able to chose more detail. However, it still needs to focus on the important events. Summary papers are usually shorter papers.
Let’s say you are writing a 3–4 page summary. You are likely summarizing a full book or an article or short story, which will be much longer than 3–4 pages.
Imagine that you are the author of the work, and your editor comes to you and says they love what you wrote, but they need it to be 3–4 pages instead.
How would you tell that story (argument, idea, etc.) in that length without losing the heart or intent behind it? That is what belongs in a summary paper.
How Do I Write Useful Academic Notes?
Sometimes, you need to write a summary for yourself in the form of notes or for your classmates in the form of a discussion post.
You might not think you need a specific approach for this. After all, only you are going to see it.
However, summarizing for yourself can sometimes be the most difficult type of summary. If you try to write down everything your teacher says, your hand will cramp and you’ll likely miss a lot.
Yet, transcribing doesn’t work because studies show that writing things down (not typing them) actually helps you remember them better.
So how do you find the balance between summarizing the lessons without leaving out important points?
There are some tips for this:
- If your professor writes it on the board, it is probably important.
- What points do your textbooks include when summarizing information? Use these as a guide.
- Write the highlight of every X amount of time, with X being the time you can go without missing anything or getting tired. This could be one point per minute, or three per five minutes, etc.
How Do I Create an Annotated Biography?
An annotated bibliography requires a very specific style of writing. Often, you will write these before a longer research paper . They will ask you to find a certain amount of articles and write a short annotation for each of them.
While an annotation is more than just a summary, it usually starts with a summary of the work. This will be about 2–3 sentences long. Because you don’t have a lot of room, you really have to think about what the most important thing the work says is.
This will basically ask you to explain the point of the article in these couple of sentences, so you should focus on the main point when expressing it.
Here is an example of a summary section within an annotation about this post:
“In this post, the author explains how to write a summary in different types of settings. She walks through academic, professional, and personal summaries. Ultimately, she claims that summaries should be short explanations that get the audience caught up on the topic without leaving out details that would change the meaning.”

Can I Write a Summary Within an Essay?
Perhaps the most common type of summary you will ever do is a short summary within a longer paper.
For example, if you have to write an argumentative essay, you will likely need to use sources to help support your argument.
However, there is a good chance that your readers won’t have read those same sources.
So, you need to give them enough detail to understand your topic without spending too much time explaining and not enough making your argument.
While this depends on exactly how you are using summary in your paper, often, a good amount of summary is the same amount you would put in an annotation.
Just a few sentences will allow the reader to get an idea of the work before moving on to specific parts of it that might help your argument.
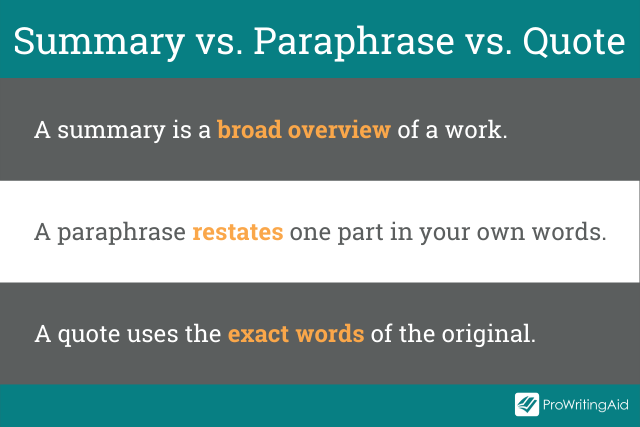
What’s the Difference Between Summarizing, Paraphrasing, and Using Quotes?
One important thing to recognize when using summaries in academic settings is that summaries are different than paraphrases or quotes.
A summary is broader and more general. A paraphrase, on the other hand, puts specific parts into your own words. A quote uses the exact words of the original. All of them, however, need to be cited.
Let’s look at an example:
Take these words by Thomas J. Watson:
”Would you like me to give you a formula for success? It’s quite simple, really. Double your rate of failure. You are thinking of failure as the enemy of success. But it isn’t as all. You can be discouraged by failure—or you can learn from it. So go ahead and make mistakes. Make all you can. Because, remember, that’s where you will find success.”
Let’s say I was told to write a summary, a paraphrase, and a quote about this statement. This is what it might look like:
Summary: Thomas J. Watson said that the key to success is actually to fail more often. (This is broad and doesn’t go into details about what he says, but it still gives him credit.)
Paraphrase: Thomas J. Watson, on asking if people would like his formula for success, said that the secret was to fail twice as much. He claimed that when you decide to learn from your mistakes instead of being disappointed by them, and when you start making a lot of them, you will actually find more success. (This includes most of the details, but it is in my own words, while still crediting the source.)
Quote: Thomas J. Watson said, ”Would you like me to give you a formula for success? It’s quite simple, really. Double your rate of failure. You are thinking of failure as the enemy of success. But it isn’t at all. You can be discouraged by failure—or you can learn from it. So go ahead and make mistakes. Make all you can. Because, remember, that’s where you will find success.” (This is the exact words of the original with quotation marks and credit given.)
Avoiding Plagiarism
One of the hardest parts about summarizing someone else’s writing is avoiding plagiarism .

That’s why I have a few rules/tips for you when summarizing anything:
1. Always cite.
If you are talking about someone else’s work in any means, cite your source. If you are summarizing the entire work, all you probably need to do (depending on style guidelines) is say the author’s name. However, if you are summarizing a specific chapter or section, you should state that specifically. Finally, you should make sure to include it in your Work Cited or Reference page.
2. Change the wording.
Sometimes when people are summarizing or paraphrasing a work, they get too close to the original, and actually use the exact words. Unless you use quotation marks, this is plagiarism. However, a good way to avoid this is to hide the article while you are summarizing it. If you don’t have it in front of you, you are less likely to accidentally use the exact words. (However, after you are done, double check that you didn’t miss anything important or give wrong details.)
3. Use a plagiarism checker.
Of course, when you are writing any summary, especially academic summaries, it can be easy to cross the line into plagiarism. If this is a place where you struggle, then ProWritingAid can help.
Just use our Plagiarism Report . It’ll highlight any unoriginal text in your document so you can make sure you are citing everything correctly and summarizing in your own words.
Find out more about ProWritingAid plagiarism bundles.
Along with academic summaries, you might sometimes need to write professional summaries. Often, this means writing a summary about yourself that shows why you are qualified for a position or organization.
In this section, let’s talk about two types of professional summaries: a LinkedIn summary and a summary section within a resume.
How Do I Write My LinkedIn Bio?
LinkedIn is all about professional networking. It offers you a chance to share a brief glimpse of your professional qualifications in a paragraph or two.
This can then be sent to professional connections, or even found by them without you having to reach out. This can help you get a job or build your network.
Your summary is one of the first things a future employer might see about you, and how you write yours can make you stand out from the competition.

Here are some tips on writing a LinkedIn summary :
- Before you write it, think about what you want it to do . If you are looking for a job, what kind of job? What have you done in your past that would stand out to someone hiring for that position? That is what you will want to focus on in your summary.
- Be professional . Unlike many social media platforms, LinkedIn has a reputation for being more formal. Your summary should reflect that to some extent.
- Use keywords . Your summary is searchable, so using keywords that a recruiter might be searching for can help them find you.
- Focus on the start . LinkedIn shows the first 300 characters automatically, and then offers the viewer a chance to read more. Make that start so good that everyone wants to keep reading.
- Focus on accomplishments . Think of your life like a series of albums, and this is your speciality “Greatest Hits” album. What “songs” are you putting on it?

How Do I Summarize My Experience on a Resume?
Writing a professional summary for a resume is different than any other type of summary that you may have to do.
Recruiters go through a lot of resumes every day. They don’t have time to spend ages reading yours, which means you have to wow them quickly.
To do that, you might include a section at the top of your resume that acts almost as an elevator pitch: That one thing you might say to a recruiter to get them to want to talk to you if you only had a 30-second elevator ride.

If you don’t have a lot of experience, though, you might want to skip this section entirely and focus on playing up the experience you do have.
Outside of academic and personal summaries, you use summary a lot in your day-to-day life.
Whether it is telling a good piece of trivia you just learned or a funny story that happened to you, or even setting the stage in creative writing, you summarize all the time.
How you use summary can be an important consideration in whether people want to read your work (or listen to you talk).
Here are some things to think about when telling a story:
- Pick interesting details . Too many and your point will be lost. Not enough, and you didn’t paint the scene or give them a complete idea about what happened.
- Play into the emotions . When telling a story, you want more information than the bare minimum. You want your reader to get the emotion of the story. That requires a little bit more work to accomplish.
- Focus. A summary of one story can lead to another can lead to another. Think about storytellers that you know that go off on a tangent. They never seem to finish one story without telling 100 others!

To wrap up (and to demonstrate everything I just talked about), let’s summarize this post into its most essential parts:
A summary is a great way to quickly give your audience the information they need to understand the topic you are discussing without having to know every detail.
How you write a summary is different depending on what type of summary you are doing:
- An academic summary usually gets to the heart of an article, book, or journal, and it should highlight the main points in your own words. How long it should be depends on the type of assignment it is.
- A professional summary highlights you and your professional, academic, and volunteer history. It shows people in your professional network who you are and why they should hire you, work with you, use your talents, etc.
Being able to tell a good story is another form of summary. You want to tell engaging anecdotes and facts without boring your listeners. This is a skill that is developed over time.
Take your writing to the next level:

20 Editing Tips from Professional Writers
Whether you are writing a novel, essay, article, or email, good writing is an essential part of communicating your ideas., this guide contains the 20 most important writing tips and techniques from a wide range of professional writers..
Be confident about grammar
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
Ashley Shaw is a former editor and marketer/current PhD student and teacher. When she isn't studying con artists for her dissertation, she's thinking of new ways to help college students better understand and love the writing process. You can follow her on Twitter, or, if you prefer animal accounts, follow her rabbits, Audrey Hopbun and Fredra StaHare, on Instagram.
Get started with ProWritingAid
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Best Summarizing Tool for Academic Texts
- Custom writing
- Summarizing
- Editing / Proofreading
Copy and paste your text
Number of sentences in results:
⚙️ 11 Best Summarizing Tools
- 🤔 How to Summarize an Article without Plagiarizing?
- 📝 How to Proofread Your Summary?
⭐ Best Summarizing Tool: the Benefits
🔗 references, ✅ 11 best summary generators to consider.
We’re here to offer the whole list of text summarizers in this article. Every tool has a strong algorithm so you won’t have to proofread a lot in order to make the summary look hand-written. The usage of such websites can be productive for your studying as long as you can focus on more important tasks and leave this routine work to online tools.
In this blog post, you’ll also find tips on successful summarizing and proofreading. These are basic skills that you will need for many assignments. To summarize text better, you’ll need to read it critically, spot the main idea, underline the essential points, and so on. As for proofreading, this skill is useful not only to students but also to professional writers.
To summarize a text, a paragraph or even an essay, you can find a lot of tools online. Here we’ll list some of these, including those that allow choose the percent of similarity and define the length of the text you’ll get.
If you’re asked to summarize some article or paragraph in your own words, one of these summary makers can become significant for getting fast results. Their user-friendly design and accurate algorithms play an important role in the summary development.
1. Summarize Bot
Summarize Bot is an easy-to-use and ad-free software for fast and accurate summary creation in our list. With its help, you can save your time for research by compressing texts. The summary maker shows the reading time, which it saves for you, and other useful statistics. To summarize any text, you should only send the message in Facebook or add the bot to Slack. The app works with various file types: including PDF, mp3, DOC, TXT, jpg, etc., and supports almost every language.
The only drawback is the absence of web version. If you don’t have a Facebook account and don’t want to install Slack, you won’t be able to enjoy this app’s features.
SMMRY has everything you need for a perfect summary—easy to use design, lots of features, and advanced settings (URL usage). If you look for a web service that changes the wording, this one would never disappoint you.
SMMRY allows you to summarize the text not only by copy-pasting but also with the file uploading or URL inserting. The last one is especially interesting. With this option, you don’t have to edit an article in any way. Just put the URL into the field and get the result. The tool is ad-free and doesn’t require registration.
Jasper is an AI-powered summary generator. It creates unique, plagiarism-free summaries, so it’s a perfect option for those who don’t want to change the wording on their own.
When using this tool, you can summarize a text of up to 12,000 characters (roughly 2,000-3,000 words) in more than 30 languages. Although Jasper doesn’t have a free plan, it offers a 7-day free trial to let you see whether this tool meets your needs.
4. Quillbot
Quillbot offers many tools for students and writers, and summarizer is one of them. With this tool, you can customize your summary length and choose between two modes: paragraph and key sentences. The former presents a summary as a coherent paragraph, while the latter gives you key ideas of the text in the form of bullet points.
What is great about Quillbot is that you can use it for free. However, there’s a limitation: you can only summarize a text of up to 1,200 words on a free plan. A premium plan extends this limit to 6,000 words. In addition, you don’t need to register to use Quillbot summarizer; just input your text and get the result.
5. TLDR This
TLDR This is a summary generator that can help you quickly summarize long text. You can paste your paper directly into the tool or provide it with a URL of the article you want to shorten.
With a free plan, you have unlimited attempts to summarize texts in the form of key sentences. TLDR This also provides advanced AI summaries, but you have only 10 of these on a free plan. To get more of them, you have to go premium, which starts at $4 per month.
HIX.AI summarizer is an AI-powered tool that can help you summarize texts of up to 10,000 characters. If you use Google Chrome or Microsoft Edge, HIX.AI has a convenient extension for you.
You can use the tool for free to check 1,000 words per week. Along with this, you get access to over 120 other AI-powered tools to help you with your writing tasks. These include essay checker, essay rewriter, essay topic generator, and many others. With a premium plan, which starts at $19.99 a month billed yearly, you also get access to GPT-4 and other advanced features.
7. Scholarcy
Scholarcy is one of the best tools for summarizing academic articles. It presents summaries in the form of flashcards, which can be downloaded as Word, PowerPoint, or Markdown files.
This tool has some outstanding features for students and researchers. For example, it creates a referenced summary, which makes it easier for you to cite the information correctly in your paper. In addition, it can find the references from the summarized article and provide you with open-access links to them. The tool can also extract tables and figures from the text and let you download them as Excel files.
Unregistered users can summarize one article per day. With a free registered account, you can make 3 summary flashcards a day. Moreover, Scholarcy offers free Chrome, Edge, and Firefox extensions that allow you to summarize short and medium-sized articles.
Frase is an AI-powered summary generator that is available for free. The tool can summarize texts of up to 600-700 words. Therefore, it’s good if you want to, say, summarize the main points of your short essay or blog post to write a conclusion. However, if you need summaries of long research articles, you should choose another option.
This summary generator allows you to adjust the level of creativity, meaning that you can generate original, plagiarism-free summaries. Frase also has lots of extra features for SEO and project management, which makes it a good option for website content creators.
9. Resoomer
Resoomer is another paraphrasing and summarizing tool that works with several languages. You’re free to use the app in English, French, German, Italian, and Spanish.
This online tool may be considered as one of the best text summarizers in IvyPanda ranking, because it allows performing many custom settings. For example, you can click to Manual and set the size of the summary (in percent or words). You can also set the number of keywords for the tool to focus on.
Among its drawbacks, we would mention that the software works only with argumentative texts and won’t reword other types correctly. Also, free version contains lots of ads and does not allow its users to import files. The premium subscription costs 4.90€ per month or 39.90€/year.
10. Summarizer
Summarizer is another good way to summarize any article you read online. This simple Chrome extension will provide you with a summary within a couple of clicks. Install the add-on, open the article or select the piece of text you want to summarize and click the button “Summarize”.
The software processes various texts in your browser, including long PDF articles. The result of summarizing has only 7% of the original article. This app is great for all who don’t want to read long publications. However, it doesn’t allow you to import file or download the result.
11. Summary Generator
The last article and essay Summary Generator in our list which can be helpful for your experience in college or university. This is free open software everyone can use.
The tool has only two buttons—one to summarize the document and the other to clear the field. With this software, you’ll get a brief summary based on your text. You don’t have to register there to get your document shortened.
Speaking about drawbacks of the website, we would mention too many ads and no options to summarize a URL or document, set up the length of the result and export it to the popular file types.
These were the best online summarizing tools to deal with the task effectively. We hope some of them became your favorite summarizers, and you’ll use them often in the future.
Not sure if a summarizer will work for your paper? Check out this short tutorial on how the text summarizing tool can come in handy for essay writing.
🤔 Techniques & Tools to Summarize without Plagiarizing
Of course, there are times when you can’t depend on online tools. For example, you may be restricted to use them in a class or maybe you have to highlight some specific paragraphs and customizing the tool’s settings would take more time and efforts than summary writing itself.
In this chapter, you’ll learn to summarize a long article, essay, research paper, report, or a book chapter with the help of helpful tips, a logical approach, and a little bit of creativity.
Here are some methods to let you create a fantastic summary.
- Know your goal. To choose the right route to your goal, you need to understand it perfectly. Why should you summarize the text? What is its style: scientific or publicistic? Who is the author? Where was the article published? There are many significant questions that can help to adapt your text better. Develop a short interview to use during the summary writing. Include all the important information on where you need to post the text and for what purpose.
- Thorough reading. To systemize your thoughts about the text, it’s significant to investigate it in detail. Read the text two or more times to grasp the basic ideas of the article and understand its goals and motives. Give yourself all the time you need to process the text. Often we need a couple of hours to extract the right results from the study or learn to paraphrase the text properly.
- Highlight the main idea. When writing a summary, you bear a responsibility for the author. Not only you have to extract the significant idea of the text but to paraphrase it correctly. It’s important not to misrepresent any of the author’s conclusions in your summary. That’s why you should find the main idea and make sure, you can paraphrase it without a loss of meaning. If possible, read a couple of professional reviews of a targeted book chapter or article. It can help you to analyze the text better.
- Mark the arguments. The process of summarizing is always easier if you have a marker to highlight important details in the text. If you don’t have a printed text, there’s always Microsoft Word to use a highlight tool on the paper. Try to mark all arguments, statistics, and facts in the text to represent them in your summary. This information will turn into key elements of the summary you’ll create, so keep attention on what you highlight exactly.
- Take care of plagiarism. Before you start writing, learn what percent of originality should you aim at. Various projects have different requirements. And they determine how many efforts you should put into writing to get a perfect summary your teacher will like. Depending on the percent of originality, build a plan for your short text. Allow yourself copy as much information as allowed to save your time.
- Build a structure. With the help of key elements, which you’ve highlighted in the text, it’s possible to create a powerful structure including all the interesting facts and arguments. Develop an outline according to a basic structure – introduction, body, and conclusion. Even if your summary is extremely short, the main idea should sound in both the first and last sentences.
- Write a draft. If you’re not a professional writer, it can be extremely difficult to develop a text with the correct word count on the first try. We advise you to develop a general text firstly – include all the information without controlling the number of sentences.
- Cut out the unnecessary parts. On this step, you should edit the draft and eliminate the unnecessary parts. Keep in mind, the number of sentences your summary must contain. Make sure the main point is fully represented in the text. You can cut out any sentence except those concluding the significant arguments.
- Wordiness – you should delete unnecessary words, which make it difficult to understand the text
- Common mistakes – mistakes made in academic papers are basically the same, so it’s helpful to have an article like this one when you’re proofreading
- Appropriate terminology – for each topic, there’s a list of the terminology you can use
- Facts and statistics – you can accidently write a wrong year or percent, make sure to avoid these mistakes
- Quotes – every quote should be written correctly and have a link to its source.
📝 How to Proofread the Summarized Text?
Now, when you know how to summarize an article, it’s time to edit your text whether it’s your own writing or a summary generator’s results.
In this chapter, you’ll see the basic ways to proofread any type of text: academic paper (essay, research paper, etc.), article, letter, book’s chapter, and so on.
- Proofread your summary. Are there times when you can’t remember an appropriate synonym? Then you should use Thesaurus and analogous services from time to time. They can expand your vocabulary a lot and help to find the right words even in the most challenging situations.
- Pay attention to easily confused words. It’s especially significant if you edit a nonfiction text – there’s a number of words people often confuse without even realizing. English Oxford Living Dictionaries have a list of these word pairs so you won’t miss any.
- Proofread one type of mistakes at a time. To edit a paper properly don’t split your attention to grammar and punctuation—this way you can miss dozens of mistakes. To get more accurate results, read the first time to edit the style, the second to eliminate grammar mistakes, and the third to proofread punctuation. Take as many times as you need to concentrate on each type.
- Take a rest from your paper. If you use an online summarizing tool, you can skip this step. But if you’ve been writing a paper for several hours and now trying to edit it without taking a break, it may be a bad idea. Why? Because without a fresh pair of eyes there’s a great possibility not to spot even obvious mistakes. Give yourself some time to slightly forget the text—go for a walk or call a friend, and then return to work as a new person.
- Hire a proofreader. If you need to get perfect results, think about hiring a professional. Skills and qualification, which they have, guarantee a perfect text without any mistakes or style issues. Once you find a proofreader, you can optimize your work perfectly. Search for specialists on freelance websites like UpWork — it’s comfortable and safe to use. Of course, there’s one flaw you should think about—hiring a pro is expensive. So, everyone should decide on their own whether they need to spend this money or not.
- Switch your paper with a friend. If you can’t afford a professional editor, there’s a less expensive option—ask a friend to look through your paper and proofread theirs in return. Make sure, you both make manual editing, not just check it with Microsoft Office or analogous software. Although there are great grammar tools, they still can’t spot many mistakes obvious to a human.
- Use grammar checking tools. We recommend you not to depend on multiple grammar tools. But the assistance it can offer is irreplaceable. Start your proofreading by scanning your text with Grammarly or an analogous tool. The service detects many types of errors including confusing words’ pairs, punctuation, misspellings, wordiness, incorrect word order, unfinished sentences, and so on. Of course, you should never correct the mistakes without thinking on every specific issue. Tools not only miss a lot of mistakes but they also can be wrong about your errors.
- Read aloud. It’s amazing how different the written text can sound when read aloud. If you practice this proofreading method, you know that many mistakes can be spotted if you actually pronounce the text. Why does it happen? People understand information better if they perceive it with the help of different senses. You can use this trick even in learning— memorize the materials with the help of reading, listening, and speaking.
These tips are developed to help students proofread their papers easily. We hope this chapter and the post itself create a helpful guide on how to summarize an article.
Here you found the best summarizing tools, which are accessible online and completely free, and learned to summarize various texts and articles on your own.
Updated: Dec 19th, 2023
- Summarizing: Academic Integrity at MIT
- 4 of the Best Online Summarizer Tools to Shorten Text: maketecheasier
- Summarizing: University of Toronto
- 5 Easy Summarizing Strategies for Students: ThoughtCo.
- Summarizing: Texas A&M University Writing Center
- Comparative Study of Text Summarization Methods: Semantic Scholar
- How to Write a Summary: UTEP
- How to Write a Summary: UW
- Free Essays
- Writing Tools
- Lit. Guides
- Donate a Paper
- Referencing Guides
- Free Textbooks
- Tongue Twisters
- Job Openings
- Expert Application
- Video Contest
- Writing Scholarship
- Discount Codes
- IvyPanda Shop
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookies Policy
- Copyright Principles
- DMCA Request
- Service Notice
This page is for anyone interested in creating a summary for an essay or any other written work. It lists the best online summarizing tools and gives advice on how to summarize an article well. Finally, you'll find tips on how to properly proofread your summary.

Introduction
Goals and Goal Setting
Goals Common to All RST Writers
Other Goals to Consider
Defining My Own Goals
Advice about Assignments
Getting Started: Listing Topics to Write about in the Tutorial
Narrative One: Personal Piece on a Significant Experience
Narrative Two: Academic Piece on a Significant Experience
Summary/Response One
Summary/Response Two
Tutorial Evaluation Postscript
On Using the Resources for Writers
Generating and Developing Ideas
Finding/Expressing Main Ideas
Showing v. Telling Sentences
Focusing Topic Sentences
Thesis Statements
Reading Strategies
Assessing Your Reading Strategies
Summarizing
Writing Effective Summary and Response Essays
Discourse Analysis Worksheet
Trade Magazines
Selecting Readings
A summary is a concise paraphrase of all the main ideas in an essay. It cites the author and the title (usually in the first sentence); it contains the essay's thesis and supporting ideas; it may use direct quotation of forceful or concise statements of the author's ideas; it will NOT usually cite the author's examples or supporting details unless they are central to the main idea. Most summaries present the major points in the order that the author made them and continually refer back to the article being summarized (i.e. "Damon argues that ..." or "Goodman also points out that ... "). The summary should take up no more than one-third the length of the work being summarized.
The Response:
A response is a critique or evaluation of the author's essay. Unlike the summary, it is composed of YOUR opinions in relation to the article being summarized. It examines ideas that you agree or disagree with and identifies the essay's strengths and weaknesses in reasoning and logic, in quality of supporting examples, and in organization and style. A good response is persuasive; therefore, it should cite facts, examples, and personal experience that either refutes or supports the article you're responding to, depending on your stance.
Two Typical Organizational Formats for Summary/Response Essays:
1. Present the summary in a block of paragraphs, followed by the response in a block:
Intro/thesis Summary (two to three paragraphs) Agreement (or disagreement) Disagreement (or agreement) Conclusion
Note: Some essays will incorporate both agreement and disagreement in a response, but this is not mandatory.
2. Introduce the essay with a short paragraph that includes your thesis. Then, each body paragraph summarizes one point and responds to it, and a conclusion wraps the essay up.
Intro/thesis Summary point one; agree/disagree Summary point two; agree/disagree Summary point three; agree/disagree Conclusion
Summarize any | in a click.
TLDR This helps you summarize any piece of text into concise, easy to digest content so you can free yourself from information overload.
Enter an Article URL or paste your Text
Browser extensions.
Use TLDR This browser extensions to summarize any webpage in a click.

Single platform, endless summaries
Transforming information overload into manageable insights — consistently striving for clarity.
100% Automatic Article Summarization with just a click
In the sheer amount of information that bombards Internet users from all sides, hardly anyone wants to devote their valuable time to reading long texts. TLDR This's clever AI analyzes any piece of text and summarizes it automatically, in a way that makes it easy for you to read, understand and act on.
Article Metadata Extraction
TLDR This, the online article summarizer tool, not only condenses lengthy articles into shorter, digestible content, but it also automatically extracts essential metadata such as author and date information, related images, and the title. Additionally, it estimates the reading time for news articles and blog posts, ensuring you have all the necessary information consolidated in one place for efficient reading.
- Automated author-date extraction
- Related images consolidation
- Instant reading time estimation

Distraction and ad-free reading
As an efficient article summarizer tool, TLDR This meticulously eliminates ads, popups, graphics, and other online distractions, providing you with a clean, uncluttered reading experience. Moreover, it enhances your focus and comprehension by presenting the essential content in a concise and straightforward manner, thus transforming the way you consume information online.

Avoid the Clickbait Trap
TLDR This smartly selects the most relevant points from a text, filtering out weak arguments and baseless speculation. It allows for quick comprehension of the essence, without needing to sift through all paragraphs. By focusing on core substance and disregarding fluff, it enhances efficiency in consuming information, freeing more time for valuable content.
- Filters weak arguments and speculation
- Highlights most relevant points
- Saves time by eliminating fluff
Who is TLDR This for?
TLDR This is a summarizing tool designed for students, writers, teachers, institutions, journalists, and any internet user who needs to quickly understand the essence of lengthy content.
Anyone with access to the Internet
TLDR This is for anyone who just needs to get the gist of a long article. You can read this summary, then go read the original article if you want to.
TLDR This is for students studying for exams, who are overwhelmed by information overload. This tool will help them summarize information into a concise, easy to digest piece of text.
TLDR This is for anyone who writes frequently, and wants to quickly summarize their articles for easier writing and easier reading.
TLDR This is for teachers who want to summarize a long document or chapter for their students.

Institutions
TLDR This is for corporations and institutions who want to condense a piece of content into a summary that is easy to digest for their employees/students.
Journalists
TLDR This is for journalists who need to summarize a long article for their newspaper or magazine.
Featured by the world's best websites
Our platform has been recognized and utilized by top-tier websites across the globe, solidifying our reputation for excellence and reliability in the digital world.
Focus on the Value, Not the Noise.

Summarizing
by jleemcga | Aug 18, 2023 | Resources for Students , Writing Resources
What is summarizing?
A summary of a text is a short overview of the main ideas written in your own words. While paraphrasing involves expressing specific ideas or details from a larger text in your own words, we generally summarize whole texts (whether it is an essay, article, chapter, book, et cetera). So, in order to ensure our summaries are not too wordy or confusing, we only cover the main ideas or argument presented within a whole text.

It’s best to summarize when you’re contextualizing a topic by letting your readers know about the current, ongoing conversation. By summarizing relevant sources, you’re providing your audience with an overview of what has already been said about this topic to help them understand how you’ll be adding to it. Summarizing material within your paper allows you to:
- Condense key ideas or arguments relevant to your paper
- Simplify the connection between a source and your own writing
How do I summarize?
To approach summarizing a source, try the following steps:
- First make sure you carefully read the original source material to understand it. Like paraphrasing, summarizing effectively requires an accurate understanding of the source material
- Identify all the main ideas from the text. It helps to look for the thesis or overall claim the author is presenting, as well as any important reasons they give to back their claim. Basically, you’re looking for why their argument is what it is
- When you begin your summary, you might use a TAG line. This stands for Title, Author, Genre and allows you to formally introduce the text before you summarize its ideas. An example of a TAG line is: In the article “Stuck on the Streets of San Francisco in a Driverless Car”, Cade Metz reports … TAG lines add a helpful framework for the summary
- Be sure not to include any specific examples, details, or evidence from the text. In summaries, we don’t describe the author’s examples (this would be like rewriting the entire text). Instead, we offer a map of the main idea and major points
- Once you finish writing your summary, check to make sure your summary concisely and accurately captures the author’s main ideas
- Remember to cite!
Examples of summarizing
Here is an example of a writer summarizing a main idea from the source Social Death: Racialized Rightlessness and the Criminalization of the Unprotected by Lisa Marie Cacho in their essay about a Salvadoran poet and her poetry’s relationship to reclaiming identity:
The ambiguity that is scored onto the bodies of Salvadoran migrants creates an impoverished sense of time and freedom by keeping these individuals indefinitely “temporary,” an ephemera that imposes a constant threat against safety and belonging for Salvadorans in the US. This weaponization of time also contributes to the condition of social death that Cacho describes as being prevalent for people of color, and particularly immigrants, in the US. According to Cacho, part of the criminalization of people of color within the US— not based on one’s behavior, but by their appearance— is heightened further by the notion of documentation. The rhetoric surrounding immigration in the US ultimately aims to invalidate those without documentation by using slurs like “illegal” (Cacho).
Note: The writer quotes some key terms, like “temporary” or “illegal” that the author emphasizes in the original source but describes the main ideas of the source in their own words. Note, too, that the summary focuses on the big-picture ideas of the source without mentioning examples that are too specific.
Things to keep in mind when summarizing
Some important things to remain mindful of while summarizing in your assignments are:
- There is no specified length for writing summaries; they may be a few sentences or a few paragraphs depending on your writing project. For most academic essays, a summary of a few sentences to a short paragraph is appropriate. Concision is key
- Do not include your opinions on the topic or the author’s ideas in your summary; your ideas are important, but summary is a genre of writing that requires objectivity
- Do not include specific details or examples from the text—just focus on the big picture ideas

Our Newest Resources!
- Transitioning to Long-form Writing
- Developing a Research Question
- Integrating Direct Quotations into Your Writing
- Nurturing a Growth Mindset to Overcome Writing Challenges and Develop Confidence in College Level Writing
- An Introduction to Paraphrasing, Summarizing, and Quoting
Additional Resources
- Graduate Writing Consultants
- Instructor Resources
- Student Resources
- Quick Guides and Handouts
- Self-Guided and Directed Learning Activities
Upload your PDF, EPUB, DOCX, ODT, or TXT file here.
PDF, EPUB, DOCX, ODT, TXT
Or import your images / photos by clicking below
(JPEG / PNG)
Please wait... or cancel
Reading speed : 0.8
Go to the main ideas in your texts, summarize them « relevantly » in 1 Click
We advice + we design + we develope.
- Text example
Text example
Initialisation...
Identify the important ideas and facts
To help you summarize and analyze your argumentative texts , your articles, your scientific texts, your history texts as well as your well-structured analyses work of art, Resoomer provides you with a "Summary text tool" : an educational tool that identifies and summarizes the important ideas and facts of your documents. Summarize in 1-Click, go to the main idea or skim through so that you can then interpret your texts quickly and develop your syntheses .
Who is Resoomer for ?
College students.
With Resoomer, summarize your Wikipedia pages in a matter of seconds for your productivity.
Identify the most important ideas and arguments of your texts so that you can prepare your lessons.
JOURNALISTS
If you prefer simplified information that summarizes the major events, then Resoomer is for you !
Identify and understand very fast the facts and the ideas of your texts that are part of the current news and events.
PRESS RELEASES
With the help of Resoomer, go to the main idea of your articles to write your arguments and critiques .
Save time, summarize your digital documents for a relevant and fast uptake of information.
Need to summarize your books' presentations ? Identify the arguments in a matter of seconds.
Too many documents ? Simplify your readings with Resoomer like a desktop tool.
Need to summarize your chapters ? With Resoomer, go to the heart of your ideas.
Identify your books' or your authors' ideas quickly. Summarize the most important main points.
From now on, create quick summaries of your artists' presentation and their artworks .
INSTITUTIONS
Identify the most important passages in texts that contains a lot of words for detailed analyses .
They Tweeted
Follow @resoomer_ Tweeter
SUMMARIZE YOUR ONLINE ARTICLES IN 1-CLICK
Download the extension for your browser
Surf online and save time when reading on internet ! Resoomer summarizes your articles in 500 words so that you can go to the main idea of your text.
HOW DOES RESOOMER WORK ?
Popular articles.
- Summary and synthesis: the difference?
- The text summarizer
- Summarize a text
- Summarize a document online
- Summarize an online article
- Read more and faster documents
- Argue and find arguments in a text
- Learn more": How to increase your knowledge?
Our partners that like Resoom(er)ing their texts :

how to write a summary
A step-by-step guide to writing a great summary.
A summary of a literary work isn't just a plain-old synopsis. It's a valuable study tool, a foundational element of all kinds of essays, a common testing mechanism, and one of the basics of literary analysis.
Whether you're in high school or college, developing a deep understanding of how and when to summarize a book or text is a valuable skill. Doing so might require a little more knowledge and effort than you'd think.
That's why we're covering all aspects of summaries, from study tools to plot summaries, below.
What Is a Summary?
A summary is a brief overview of a text (or movie, speech, podcast, etcetera) that succinctly and comprehensively covers the main ideas or plot points.
Sounds simple, right? Well, there are a lot of unique characteristics that differentiate summaries from other commentary, such as analyses, book reviews, or outlines.
Summaries are:
- In your own words. It's important that you don't just copy and paste the writer's words (in fact, that's plagiarizing). Writing the key points of a work in your own words indicates your comprehension and absorption of the material.
- Objective. While a summary should be in your own words, it shouldn't contain your opinions. Instead, you should gather the main points and intentions of the writer and present them impartially. (If you include your opinions, it instead becomes an analysis or review.)
- More than paraphrasing. Many students fall into the trap of simply paraphrasing—plainly restating the ideas or events of the work. (Is our definition starting to sound contradictory? We told you it wasn't straightforward!) Rather than recounting the events or ideas in a work chronologically or in the order they're presented, instead consider the broad scope of how they all contribute to the narrative or argument.
- Short. There are no strict rules regarding length, only that it is concise. It's largely dependent on the length of the text it summarizes: longer texts, longer summaries. It also depends on the assignment or objective. However, most are about one to two paragraphs in length.
- Comprehensive. Yes, it's another seemingly contradictory descriptor, but an important one. Summaries are comprehensive, meaning they cover all of the main plot points or ideas in a work (so they inherently contain "spoilers"). You should present those ideas in a way that condenses them into an inclusive, but not exhaustive, recounting in order to keep it short.
- Straightforward (even if the text isn't). A good summary should be easy to comprehend, presenting the reader with a simple but all-encompassing understanding of the work at hand. With complex texts, summaries can be particularly useful because they distill big, complicated ideas into a bite-sized package.
When to Write a Summary
Like so many elements of literary analysis, summaries are misunderstood. We've already explained why they aren't as simple as most people think, but neither are their uses.
Summary writing is a useful skill in a variety of circumstances, both in and outside the English and Language Arts classrooms.
Readers, writers, teachers, and students can use summaries:
- As a study tactic. The ability to summarize a book or text indicates that you've absorbed and understand the material. Plus, writing down notes (as in a summary) is a great way to retain material. Try summarizing at the end of a book chapter, after each section of an article, or periodically in textbooks. Doing so will help you digest the material you've just read, confirming you understood and retained the information therein. Stopping frequently to summarize is most effective because you're less likely to forget important plot points or ideas.
- As an assignment. Teachers and professors often ask students to summarize a text as a test to confirm they read and understood the material. Before heading into class—especially if you have a test or quiz scheduled—try practicing summarizing the text. Write it down (rather than practicing it out loud or in your head) so that you can review your ideas and ensure you're presenting them succinctly and sensibly.
- As part of an essay. If you're referencing a book or article in your own paper, you might need to summarize the source as the foundation for your argument. In this case, your summary should be particularly short so the reader doesn't lose sight of your own argument and intention. Introduce the name of the work and its author, then use one sentence (two at most) to describe their objective and how it relates to your own.
- As part of a review. Summaries are very useful in an academic setting, but they have their place outside of it too. Whether you're on a book review site or just sharing a recommendation with a friend, being able to succinctly write a book summary (with or without spoilers) will help others to make their own judgements of a book.
Your Step-by-Step Guide for How to Write a Summary
Step 1: read the work .
Summaries are often perceived as a workaround for reading the work itself. That's not a great strategy under most circumstances because you tend to lose a lot of the details and nuance of a work, but it's particularly impractical to do so when writing about the work.
Remember, a summary is supposed to present your perception of the work as a whole. So in order to develop that perception, you have to first read the original text.
Step 2: Take Notes
As you read the work, simultaneously take notes. If you own the book, it might be helpful to add your notes to the margins or highlight passages that are particularly relevant or capture a key idea. If you don't own the book, try taking notes on your computer or in a notebook. You can still notate important passages by writing down the page and paragraph number or writing an abbreviated version of the quotation. Alternatively, try marking key passages with sticky notes or tabs.
It might also be helpful to write out a short outline of the work as you go. While you won't want to use this verbatim (remember, you shouldn't just paraphrase the work), it can help you establish and remember the text's framework.
Step 3: Identify the Author's Thesis Statement, Objective, or Main Point
In some works, such as a journal article, a writer will provide a thesis statement. A thesis statement is a one-sentence synopsis of the author's argument and intention. A thesis statement can be really helpful in forming the backbone of your own summary, just as it forms the backbone of the essay.
However, even when a thesis statement isn't present—like in a novel—the writer always has an objective or main idea. You should always identify this idea and use it to form the foundation of your summary.
The main point might be apparent at the outset of the work. Other times, the author won't present it until the conclusion. Sometimes you might identify multiple objectives throughout the work. That's why it's important, as you read, to note any ideas that might be the main idea. Even those that aren't the most important will likely remain relevant.
Step 4: Note Other Important Elements
If something stands out to you about the work and seems to play an important role in the text's overall narrative or structure, make a note about it. This could be a recurring theme, an incident in the storyline, or a deviation from the overall argument.
As you identify and note important elements and moments in the work, the structure of your summary should begin to fall into place.
Step 5: Prepare to Write Your Summary
Once you've finished reading the work, review your notes and highlight the key points that came to light. Remember, your summary should be objective, so disregard any opinions you might have noted about the work. You should introduce the thesis or objective, briefly encapsulate the important ideas and moments from the work, and end with a conclusion that ties those ideas to the objective. Keep this structure in mind as you begin.
Step 6: Begin by Introducing the Work
As you begin, introduce the work, its author, and, if relevant, the context.
Depending on your situation—for example, if your teacher or professor has asked you to summarize a work as part of an assignment or quiz—this might seem redundant. However, it is standard practice to begin by introducing the work, even if the reader already knows what you're writing about.
Example: In The Great Gatsby , F. Scott Fitzgerald...
Step 7: Present the Thesis, Main Idea, or Central Argument
Once you've introduced the work, your priority is to clearly define the author's thesis, important point, or central argument. As mentioned above, sometimes the author presents this idea clearly and succinctly at the outset of their work; at other times, it's buried deep in the text.
Regardless of how the main idea is presented in the work, it should be front and center in your summary. Some teachers might refer to this as a "topic sentence" or "introductory sentence." This is the central point around which you will construct the rest of your writing. As you progress, you'll highlight other ideas or occurrences that relate or contribute to this main idea, so it's important that your representation of it is easily understood.
Example: In The Great Gatsby , F. Scott Fitzgerald uses the story of Jay Gatsby as a symbol of the social stratification, greed, and indulgence of 1920s America.
Step 8: Briefly Discuss the Important Elements of the Work
After identifying the thesis or central argument, you should provide a brief overview of the work's other elements, ideas, and plot points. For the most part, the information you present throughout this section should bolster the thesis presented previously. Each sentence should serve as a supporting point for the topic sentence. Don't simply list ideas or plot points, but show how they're connected and inform the work as a whole. Of course, there may also be important elements of the work that are not directly tied to the main idea; it's ok to include these if you feel they are vital to understanding the work.
When writing the body, you should consciously and intentionally leave out unnecessary details. They tend to bog down your writing and lose the reader.
Example: The narrator, Nick Carraway, moves to New York's "West Egg," where he reunites with his cousin, Daisy, and her husband, Tom Buchanan. Fitzgerald clearly delineates social lines between West Egg (new money) and East Egg (old money), where Tom and Daisy reside.
Nick attends a lavish party thrown by his neighbor, Jay Gatsby, and learns Jay formerly had a relationship with Daisy. The two reignite their forbidden affair. Tom reveals to Daisy that Gatsby earned his money illegally, through smuggling alcohol, and is actually a man of humble Midwestern origins. Daisy and Gatsby try to run away together, but Daisy accidentally runs over Tom's mistress. Tom, eager to exact revenge, convinces his mistress' husband that Gatsby was to blame in her death, and he murders Gatsby before committing suicide. Few of Gatsby's many friends attend his funeral.
Step 9: Write a Conclusion that Ties It All Together
Much like you introduce the author's major point at the outset of your summary, you should revisit it as you close out your writing. If you presented the author's main idea in the introduction, and then bolstered that main idea by recollecting plot points or important elements from the work, your conclusion should then reiterate how those elements relate to the main idea.
Example: Though Gatsby subscribed to the extravagance of his peers, his efforts to fit into the upper echelon of West and East Egg were negated by his humble origins; always out of place, he was rejected for his social class as much as his perceived crimes.
Step 10: Edit
Before submitting your work, read it in full, and edit out any superfluous and redundant information. It's likely that unnecessary details snuck in as you were writing, and you might find that certain plot points just feel unnecessary within the scope of your finished product.
In addition to editing for content, be sure to edit it closely for grammatical or spelling errors. Even if your summary is well thought out, its expertise is compromised if it's full of errors!
How to Write a Plot Summary
The step-by-step guide to writing an effective summary, outlined above, applies to most summaries. However, each type has its own unique elements outside of those standard requirements.
A plot or book summary, for example, should encapsulate the plot of a short story or novel. When writing one, there are unique strategies to follow.
Dos of Writing a Plot Summary
- Note plot points as the book or story unfolds. Especially in longer novels, it can be difficult to keep track of the twists and turns in the storyline. That's why we recommend taking notes as you read.
- Use online study guides for inspiration. Websites like SuperSummary provide in-depth summaries free of charge. While this is a good starting point when writing your own, it should only be for inspiration. Don't copy examples online (that's plagiarism!).
- Be sure to cover the three main arcs of every story: the exposition, climax, and conclusion. The exposition is the moment when the conflict or driving narrative is introduced. The climax is when that conflict comes to a head, and the narrative reaches its most dramatic moments. The conclusion is when the conflict is resolved or the story comes to an end. You should also include any inciting incidents (the first domino in a plot point).
- Connect the dots. Throughout, you should demonstrate an understanding of how events and characters are related, rather than introducing each element as an independent variable. Remember, you should tie each plot point back to the main idea.
Don'ts of Writing a Plot Summary
- Don't just regurgitate the storyline. Rather than drone through the story plot point by plot point, you should highlight key moments in the narrative and direct them back to the author's objective.
- Avoid repetitive phrases like "then" or "next." A key indication you're just repeating the storyline point by point is utilizing a phrase like "then" or "next." While you should recount the major incidents of the narrative, it shouldn't feel so formulaic.
- Don't let it drag on. Books are long, but summarizing a book should still be short. While it depends on the assignment and the work in question, your summary should be 200 to 600 words, max.
Example : In The Great Gatsby , F. Scott Fitzgerald uses the story of Jay Gatsby as a symbol of the social stratification, greed, and indulgence of 1920s America. The narrator, Nick Carraway, moves to New York's "West Egg," where he reunites with his cousin, Daisy, and her husband, Tom Buchanan. Fitzgerald clearly delineates social lines between West Egg (new money) and East Egg (old money), where Tom and Daisy reside.
Nick attends a lavish party thrown by his neighbor, Jay Gatsby, and learns he formerly had a relationship with Daisy. When the two reignite their forbidden affair, disaster ensues. Tom reveals to Daisy that Gatsby earned his money illegally, through smuggling alcohol, and is actually a man of humble Midwestern origins. Daisy and Gatsby try to run away together, but Daisy accidentally runs over Tom's mistress. Tom, eager to exact revenge, convinces his mistress' husband that Gatsby was to blame in her death, and he murders Gatsby before committing suicide. Few of Gatsby's many friends attend his funeral.
Though Gatsby subscribed to the extravagance of his peers, his efforts to fit into the upper echelon of West and East Egg were negated by his humble origins; always out of place, he was rejected for his social class as much as his perceived crimes.
For an in-depth analysis of The Great Gatsby , check out the our study guide (we have an audio guide, too!).
How to Summarize an Article or Essay
The nature of an article or essay is quite different from a novel or short story, and in many ways, your summary should be too. The outline above remains the same, but the details are different.
Here's what you should and shouldn't do when writing your article summary.
Dos of Writing an Article Summary
- Skim the original article first. To develop a basic understanding of the article and the writer's objectives, skim the content before reading it closely. Doing so will help you to identify some of the key points and then pay attention to the arguments around them when you read the article in full.
- Then read the article closely, marking key passages and ideas. Noting important ideas as you read will help you develop a deeper understanding of the writer's intentions.
- Note headings and subheadings, which likely identify important points. In articles and essays, the author often utilizes subheadings to introduce their most important ideas. These subheadings can help guide your own writing.
- Keep it short. The rule of brevity applies to article summaries too. In fact, because articles are usually short compared to novels or books, your text should be correlatively brief. And if you're utilizing the work as part of your own essay or argument, just a couple sentences will do.
Don'ts of Writing an Article Summary
- Don't ignore the conclusion. When reading a long article or essay, it can be tempting to overlook the conclusion and focus on the body paragraphs of the article. However, the conclusion is often where the author most clearly outlines their findings and why they matter. It can serve as a great foundation for your own writing.
- Don't copy anything from the article directly—always paraphrase. If you copy any passages word-for-word from the article, be sure to identify them as quotations and attribute them to the author. Even this should be done sparingly. Instead, you should encapsulate their ideas within your own, abbreviated words.
- Don't forget to include proper citations. If you do include a direct quotation from the article, be sure to properly cite them. You can learn how to properly cite quotations in our Academic Citation Resource Guide .
Example Summary of "Gatsby as a Drowned Sailor" : In her essay, "Gatsby as a Drowned Sailor," Margaret Lukens posits that a major, and often overlooked, motif in The Great Gatsby is that of the "drowned sailor." The novel, she points out, is immersed in nautical symbols and themes, particularly in the scenes surrounding Jay Gatsby. For example, Gatsby grew up on the shores of Lake Superior, now owns a house on the Long Island Sound, and supposedly spends much of his time on his boat.
Lukens nods to the nautical imagery throughout Gatsby's lavish party, as well as Nick's interactions with Gatsby. Many of these, she argues, foreshadow Gatsby's death in his pool. Even his funeral is a testament to the motif, with the few attendees soaked to the skin with rain. Lukens presents a thorough case for the overarching nautical motif in The Great Gatsby and her argument that though Gatsby hooked a big one, ultimately it was "the one that got away."
FAQs: How to Write a Book Summary
How do you summarize without plagiarizing .
By its very nature, a summary isn't plagiarizing because it should be written in your own words. However, there are cases where it might be difficult to identify an appropriate synonym, and the phrase remains somewhat close to the original. In this scenario, just be sure to differentiate the rest of the phrase as much as possible. And if you need to include a direct quote from the work, be sure to appropriately cite it.
How to write a summary and a reaction?
In some cases, your teacher may ask you to write a summary and a reaction. Whereas a summary is objective, a reaction is a matter of opinion. So in this case, you should present the actions or ideas of the work, then respond to those actions and ideas with your personal thoughts.
Why write a summary?
A summary is a helpful tool many educators use to test their students' comprehension of a text. However, it is also a useful study tactic because recounting what you read can help you organize and retain information.

English that goes straight to the heart
Summary Essay Examples
The summary essay is a brief account of the chief points of an essay. There’s no hard and fast rule about the length of the summary, but so much can be half of the original essay .
In this post, we have added the best 12+ Summary Essay Examples for you.
Daily Test - Attempt Now

Summary Essay Examples #1
ESSAY: When we survey our lives and efforts, we soon observe that almost the whole of our actions and desires are bound up with the existence of other human beings. We notice that the whole of nature resembles that of social animals. We eat food that others have produced, wear clothes that others have made, and live in houses that others have built. The greater part of our knowledge and beliefs has been passed on to us by other people through the medium of a language that others have created. Without language and mental capacities, we would have been poor indeed comparable to higher animals.
We have therefore to admit that we owe our principal knowledge over the least to the fact of living in human society. The individual if left alone from birth would remain primitive and beast-like in his thoughts and feelings to a degree that we can hardly imagine. The individual is what he is and has the significance that he has not much in virtue of individuality, but rather as a member of a great human community, which directs his material and spiritual existence from the cradle to the grave. (193 words)
Rough Draft
- Humans are social animals.
- They depend on each other for necessities and social needs.
- Humans use language to communicate with each other and further their mental development.
- Humans are superior to animals as they live in societies that guide their material and spiritual existence.
TITLE: Man and society
SUMMARY: Human beings have their actions and desires bound up with society as they are social animals. They depend on each other for food and clothes and share their knowledge and beliefs, and use language created by others to communicate, which helps in their mental development. They are superior to beasts because they live in human society. An individual left alone since birth would grow utterly beast-like. Human society guides man’s material and spiritual existence. (76 words)
Summary Essay Examples #2
If you will, believe me, you who are young, yours is the golden season of life. As you have heard it called, so it verily is the seed-time of life in which if you do not sow or if you sow tares instead of wheat, you will arrive at little. And in the course of years when you come to look back if you have not done what you have heard from your advisers and among many counsellors there is wisdom you will bitterly repent when it is too late.
The habit of studies acquired at universities is of the highest importance in the afterlife. At the season when you are young in years, the whole mind is, as it were, fluid, and is capable of forming itself into any shape that the owner of the mind pleases to allow it or constrain it, to form itself into. The mind is then in a plastic or fluid state but it hardens gradually to the consistency of rock or iron, and you can not alter the habits of an old man. (180 Words)
Title: The Golden Season of Life / The Importance of Sowing Good Seeds
Youth is the golden and fertile time of life. If one does not listen to and act upon the advice of his superiors, he must eventually repent. Youth is a fluid state of mind and any good habits now will stand you in good stead later in life. Then the mind becomes rigid and no good habits are formed. (58 Words)
The golden season of life is the seed-time of life in which if you do not sow or sow tares instead of wheat, you will arrive at little. The habit of studies acquired at universities is of the highest importance in the afterlife, as the mind is fluid but hardens gradually to the consistency of rock or iron. (58 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #3
Variety is the spice of life – is it not? We all practically live and strive for having better food, but food remains insipid without the addition of spices. The only difference between a good curry and a bad curry lies in the presence or absence of spices. The absence of variety makes life drab and monotonous. A man working six hours a week will have his rest on Sunday. A man wearing a coat for five days will like a shawl on the sixth day. If a man lives in Calcutta for six years, he will like to spend a month outside. We hear that Tagore could not live in the same house for a long time.
He used to change his residence pretty often, which shows a poet’s longing for novelty. Life is many stringed instruments and we must give proper attention to all the strings. Ever since creation man has gone on from progress to progress by responding to new circumstances. So, for the development of civilization, new circumstances and a new environment are necessary. (179 Words)
Title: The Need for Change and Variety / Variety: The Spice of Life
Variety is the spice of life, and without it, life is dull and monotonous. To develop civilization, new circumstances and a new environment are necessary. Tagore was a poet who changed his residence often, showing his longing for novelty. Life is many stringed instruments and we must give proper attention to all the strings. (54 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #4
Everyone has continual control during his life with the variety of experiences known as art. Their experience ranges from the craft level found in the design and execution of the practical things of life to the more imaginative because less material level is required for the enjoyment of music, painting, sculpture, and literature. In the fine arts, human creativity is no longer concerned with producing an object which will be required for use anyhow, whether it is beautiful or not, but with providing a stimulus for the satisfaction of human emotion in its various levels of manifestation.
The majority of human beings since they are culturally underprivileged, are satisfied if their emotions are roused easily and mechanically by the more simple emotional easily identified sentimentalities that easily assimilate emotional reflexes-by dance, and music, by the identified references of cinema organ sentimentalities, by the picture with a story or easily assimilated moral, and by the simple violent plots of the cheap magazine. The culturally privileged demand a more complicated satisfaction. They require because they are educated on the aesthetic aspects of the arts. (180 Words)
Title: The Power of Art / The Importance of Art Education
The most important idea is that art provides a stimulus for the satisfaction of human emotion and that the majority of people are satisfied with simple emotional sentimentalities, while the culturally privileged require a more complicated satisfaction due to their education in the aesthetic aspects of the arts. (48 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #5
The study of history depends more than any other branch of science or literature on the availability of many books. The history student nowadays is often discouraged or hampered by the lack of them, especially of those older standard works which have gone out of print. Even before the Second World War publishers were not willing to risk reprinting works often running into several big volumes for which the demand, was uncertain and the cost of production high. During the war air raids destroyed over a million books in one district of London alone, and reduced to ashes the entire stock of one firm which had specialized in historical works.
Since the war paper has been costly and scarce; the costs of printing and binding have risen sharply; and the demand, though greater, is still not large enough to make worthwhile the republication of many books which historians regard as essential. The main reason for this insufficient demand is the disappearance of the private library. Private libraries were common in Victorian Times but they no longer exist in modern small houses where there is no room for bookshelves. (190 Words)
Title: The Challenges of Historical Research in the Modern Era
The study of history is hindered by the lack of books, especially older standard works which have gone out of print due to the cost of printing and binding. The main reason is the disappearance of private libraries, which no longer exist in modern small houses. (46 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #6
Speech is a great blessing, but it can also be a great curse, for, while it helps us to make our intentions and desires known to our fellows, it can also, if we use it carelessly make our attitude completely misunderstood. A slip of the tongue. the use of an unusual or ambiguous word, and so on, may create an enemy where we had hoped to win a friend.
Again different classes of people use different vocabularies, and the ordinary speech of an educated man may strike an uneducated listener as showing pride; unwittingly we may use a word that bears a different meaning for our listener from what it does to men of our own class. Thus speech is not a gift to use lightly without thought, but one which demands careful handling. Only a fool will express himself alike to all kinds and conditions of men. (148 Words)
Title: The Blessing and Curse of Speech
Speech is a great gift, but it can also be a curse if used carelessly. Different classes of people use different vocabularies, and the ordinary speech of an educated man may strike an uneducated listener as pride. Careful handling of speech is essential, as only a fool will express himself alike to all people. (54 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #7
Man is the architect of his own fate. If he makes a proper division of his time and does his duties according he is sure to improve and prosper in life; but if he does otherwise, he is sure to repent, when it is too late and he will have dragged a miserable existence from day to day.
To kill time is as culpable as to commit suicide, but our life is nothing but the sum total of hours, days, and years. Youth is the golden season of life. In youth, the mind is pliable and soft and can be moulded in any form you like. If we lose the morning hours of life, we shall have to repent afterwards. It is called the ‘seed time of life’. If we sow good seeds, we shall reap a good harvest when we grow up. (142 Words)
Title: Youth: The Gloden Opportunity to shape your / Man is the Architect of his own Fate
Man is responsible for his own fate, and if he does not make proper use of his time, he will regret it. Youth is the golden season of life, and if we lose the morning hours of life, we will have to repent. (43 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #8
It is sometimes said that the pleasures of giving are peculiar to the rich, and no doubt the joy of giving is one of the greatest and purest that wealth can bestow. Still the poor also may be liberal and generous. The widow’s mite, so far as the widow is concerned, counts for as much as the rich man’s gold.
Moreover, as regards kindness and sympathy which are far more valuable than money, the poor can give as much as, perhaps even more than the rich. Money is not wealth. A proverb says: “A man’s true wealth is good that he does in the world”. When he dies, men will ask what property he has left behind, but Angels will inquire, “What good deeds hast thou sent before thee?” (130 Words)
Title: The Pleasure of Giving / Generosity Knows No Wealth
The poor can give as much as the rich, and kindness and sympathy are more valuable than money. A proverb states that a man’s true wealth is the good deeds he does in the world. (35 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #9
The lot of our Indian peasant is certainly a pitiable one. He labours under many disadvantages. In the first place, he is illiterate, and does not, therefore, care to know more than he has inherited from his ancestors. He laughs at his tiny piece of land from morning to evening and if the seasons favour him, earns what barely suffices to meet his daily demands. He does not grumble to pay his rent so much as he does for the loss of his plough cattle. He lives in debt over head and ears, yet he does not care to save anything for the morrow.
To ameliorate his condition, the supply of good plough cattle, the adoption of preventive measures to save the animals from diseases, and, last of all, primary education should engage the serious attention of the Indian Government. (138 Words)
Title: Illiteracy and its effect on Indian Peasant / The Pitiable Conditions of Indian Peasant
The Indian peasant is suffering from many disadvantages, such as illiteracy, poverty, and debt. To improve his situation, the supply of good plough cattle, preventive measures, and primary education should be addressed by the Indian Government. (36 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #10
The aim of culture and religion is the same. Men are all members of one great whole, and the sympathy which is in human nature will not allow one member to be different from the rest or to have perfect welfare independent of the rest. The expansion of our humanity to suit the idea of perfection that culture forms must be a general expansion. Perfection, as culture conceives it is not possible while the individual remains isolated. He must carry others along with him in his march towards perfection. Culture lays on us the same obligation as a religion which says that “to promote the kingdom of God is to increase and hasten one’s own happiness.
Culture is a harmonious expansion of all the powers which make the beauty and worth of human nature. Culture is not consistent with the over-development of any power at the expense of the rest. Here it goes beyond religion, as religion is generally conceived by us. (162 Words)
Title: Culture and Religion: The Two Sides of the Same Coin
Culture leading to perfection, like religion, complements rather than competes with the latter. Culture, like religion, demands perfection rather than the unification of everything. Culture means harmonious development of all faculties and not overdevelopment of any at the expense of others. Here it transcends religion in its emphasis on harmonious development. (50 Words)
The aim of culture and religion is the same: to expand humanity to suit the idea of perfection. Culture is a harmonious expansion of all the powers which make the beauty and worth of human nature, and is not consistent with the over-development of any power at the expense of the rest. It lays on us the same obligation as a religion to promote the kingdom of God is to increase and hasten one’s own happiness. (72 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #11
Perseverance is the very hinge of all virtues. On looking over the world, the cause of nine-tenths of the lamentable failures which occur in much of their history lies not in the want of talents, but in the manner of using them, in flying from object to object, in starting away at each little disgust, and thus applying the force which might conquer anyone difficulty to a series of difficulties so large that no human race can conquer them.
The smallest brook on earth by continuing to run has hollowed out for itself a considerable valley to flow in. Commend me, therefore, to the virtue of severance. Without it, all the rest are little better than fairy gold which glitters in your purse, but taken to the market proves to be state or cinders. (134 Words)
Title: The Importance of Perseverance / Perseverance: The Hinge of Virtues
Perseverance is the key to success, and severance is the virtue of severance. Without it, all the rest are a little better than fairy gold. (25 Words)
Perseverance is the key to all virtues and is the cause of many failures in history. It is the act of flying from object to object, starting away at each little disgust, and applying the force which might conquer anyone’s difficulty to a series of difficulties so large that no human race can conquer them. Without it, all the rest are little better than fairy gold which glitters in your purse, but when taken to the market proves to be state or cinders. (83 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #12
Films should contribute to human understanding and progress rather than hinder them antisocially. The excitement of gangsterdom is permissible so long as the antisocial quality of gangsterdom is not held up as something desirable. Frivolous gaiety may be introduced, but it should not be presented as the be-all and end-all, of living. Life can be made exciting and romantic provided it is not permanently distorted.
For there can never be much human progress if we distort things by pretending the world is much better than it actually is. Thus the attitude of a film to the grimmer side of life can not be worthwhile if it glosses it over, since that only confirms our backwardness. Nothing bad should be treated approvingly. The introduction of gangsterdom, war, idle luxury; slums unemployment, poverty, and their accompanying misery, crime, and disease, should not leave the audience complacent, but should if anything inspire them with a determination to end them. (159 Words)
Title: Films -Entertainment or Distortion of Reality / The Impact of Films on Society
Films should contribute to human understanding and progress rather than hinder them antisocially, and should not gloss over the grimmer side of life, such as gangsterdom, war, idle luxury, and poverty. (31 Words)
Films should contribute to human understanding and progress rather than hinder them antisocially. Life can be made exciting and romantic, but it should not be permanently distorted. The introduction of gangsterdom, war, idle luxury, slums unemployment, poverty, and their accompanying misery, crime, and disease should not leave the audience complacent but should inspire them with a determination to end them. (60 Words)
Summary Essay Examples #13
A poor woman once came to the Buddha and begged him to revive her dead child. The holy man was touched by the woman’s great sorrow. Then he asked him to bring a handful of mustard seeds from a house where death had never entered. The sad mother started looking for mustard seeds from door to door. One said, our little child died last year. Another said I lost my father. The evening came.
He returned to Lord Buddha with a heavy heart and told him about the results of his search. Then the Buddha gently told him not to think of his own suffering, for suffering and death are common to all.
Title: The Buddha and the Grieving Mother / The Universal Experience of Suffering and Death
Summary: A poor woman came to the Buddha and begged him to revive her dead child. He asked her to bring a handful of mustard seeds from a house where death had never entered. The mother searched for mustard seeds from door to door and returned to Lord Buddha with a heavy heart. The Buddha gently reminded her that suffering and death are common to all. (65 Words)
You Asked, We Listened – Get Free Access to All Writing Lists 😍😍

10 Famous Moral Stories

Text Summarizer for All Written Content Types
Obtain a more condensed version of any text with the Website and Text Summarizer by Smodin. All types of texts can be shortened for better comprehension, improved readability, and faster consumption. From full websites and long dissertations to single paragraphs and various texts, our text summarizer condenses it with ease.
What is a text summarizer?
A text summarizer is an online tool that uses AI and complex algorithms to condense a text from its long, detailed version to one that is short and comprehensible. A summarizer tool carries all of the key points in a text over to the condensed version. The content you receive contains a complete overview of the text. For example, pasting 2000 words worth of content into the summarizer can result in a more digestible 200-word version, eliminating nearly ¾ of the text.
What Can I Summarize?
Summarize Essays
Summarize Books
Summarize Websites
Summarize Messages
Summarize Letters
Summarize Documents
Summarize Legal Documents
Summarize Technical Documents
Summarize Blogs
Summarize Webpages
Summarize Articles
Summarize Blog Article
Summarize Research Papers
Summarize Papers
Summarize Dissertations
Summarize Assignments
Summarize Text
Summarize Paragraphs
Summarize Sentences
Summarize Manuscripts
Summarize Things
Summarize Research
Summarize Manuals
Summarize Novels
Summarize Publications
Summarize Textbooks
Summarize Writing
How does the summarizer tool work?
Our text summarizer uses AI algorithms to “read” the full content, understand its meaning, and break it down into a more condensed version. The algorithm recognizes key topics and perspectives to note the levels of importance for each word, sentence, phrase, and paragraph. In this way, the filler text can be removed without harming the value of the content. Thus, you are provided with a summary of the text you’ve pasted without compromise. Popular websites have provided summaries of textbook chapters, short stories, novels, and more for years. The Website and Text Summarizer by Smodin improve the utility of CliffsNotes by utilizing AI to summarize any text, not just popular books, with the click of a button.
What types of content does this text summarizing tool work on?
Our text summarizer works on all types of text, even full websites. You can either copy and paste the individual text into the summarizer or you can paste the link to a website at the bottom of the tool. A comprehensive list of what can be summarized is located directly underneath the tool if you are curious about exactly what pieces of content work best with the tool.
Why would you use a summarizer?
Compressing the content of any lengthy text like a research paper, essay, report, or book is beneficial to the reader in a variety of ways. Most likely, the number one reason a person would use a summarizing tool is to avoid reading the actual text. The summary that appears contains all of the main points of interest that can be read in a fraction of the time it would take someone to read the full text. Reasons for this include not having enough time, having no interest in the topic, meeting a closely approaching deadline, and more. Another reason why someone would use a text summarizer is to better understand a text they have read. Because the tool provides a condensed version of the content provided, a reader can verify their comprehension of the main topics, themes, and points of interest. In this way, a summarizing tool can be considered as a strong study guide. The purpose may be different for summarizing websites. Of course, you can paste the link to an individual blog post, article, or news piece and receive a summary as mentioned above. However, some websites are difficult to understand differently. The purpose of a product, brand, or service may not be clear when scanning the full website. Pasting the link to that website will provide a summary of the major points on that site, which means you get a better view of what that company or product does.
Who uses text summary tools?
A wide variety of people use summary tools for different reasons. Students use tools of this kind because it’s generally required that a student must read a large quantity of text. Simply put, there’s not enough time to cover all texts required in rigorous study courses. Therefore, a text summary tool can help students to complete assignments on time while ensuring they understand the content. Students also use these tools to ensure their written content covers the necessary topic. Teachers also have a lot of content to read, whether it’s for grading papers and reviewing student assignments, or creating lesson plans. A summarizer can quickly create an overview of any text, allowing teachers to avoid reviewing content that’s unrelated to the topic or focusing on assignments that need more attention than others. Journalists and editors use tools of this kind to condense information into bite-sized pieces. This improves the legibility of headlines and introductory paragraphs. Journalists also need to quote many sources or summarize an entire speech into a single paragraph. Using a summarizer tool makes it entirely possible without making an article excruciatingly long or misinterpreting what someone says. Editors, as well, can use this tool to avoid the time-consuming nature of reviewing lengthy articles. They can paste the content in the summarizer and receive a reduced text that displays the theme of the content. Copywriters (as well as students and other types of writers) can use this tool to create a closing paragraph or statement. It can be difficult to encapsulate an entire work into a single paragraph, especially after spending so much time writing the body of the story. Many writers struggle to leave out the parts they’ve become attached to or even just find the right words to finish their piece of content. With a text summarizer, writers can simply paste the reduced version of their content as the conclusion without sacrificing the intent of the article, itself.
The Difference Between Summarizing and Paraphrasing
Please note that our Text and Website Summarizer Tool is not paraphrasing. So, what is paraphrasing, and what’s the difference between summarizing and paraphrasing? Paraphrasing is changing the text at hand into your own, unique version while keeping the meaning of the original content. Usually when paraphrasing, the content becomes shorter but is not used as a summary. Rather, paraphrasing takes the information you deem most important and converts it into your own words. Summarizing is simply converting a long piece of text into a much shorter version by only keeping the major points of interest. It is not rewritten, rather it removes the unnecessary pieces of information to provide you with a short piece that explains an entire passage. Summarizers are not plagiarism-proof, meaning if you copy and paste a generated summary, you might be flagged for plagiarism. However, other tools can rewrite a summary into a unique piece of work like our Text Rewriter tool
Here, we answer the most useful and frequent questions about text summarizing tools so you can better understand what it’s used for and how to use it properly.
Summarize in Other Languages
© 2024 Smodin LLC

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
100% free: Generate unlimited summaries without paying a penny Accurate: Get a reliable and trustworthy summary of your original text without any errors No signup: Use it without giving up any personal data Secure: No summary data is stored, guaranteeing your privacy Speed: Get an accurate summary within seconds, thanks to AI Flexible: Adjust summary length to get more (or less) detailed summaries
Bullet Points & Paragraph. 💰 100% free. Unlimited summarization. QuillBot's AI Text Summarizer, trusted by millions globally, utilizes cutting-edge AI to summarize articles, papers, or documents into key summary paragraphs.
In your coursework, you may be asked to write a summary of an essay, book, film, video, or presentation. A summary is generally short, written objectively and in present tense. ... Often, a summary is a paragraph in length, but it can span several paragraphs for longer works. Always follow the guidelines of the assignment or project, including ...
Here's an example of an introductory paragraph containing unnecessary summary. Sentences that summarize are in italics: The Great Gatsby is the story of a mysterious millionaire, Jay Gatsby, who lives alone on an island in New York. F. Scott Fitzgerald wrote the book, but the narrator is Nick Carraway. Nick is Gatsby's neighbor, and he ...
Table of contents. When to write a summary. Step 1: Read the text. Step 2: Break the text down into sections. Step 3: Identify the key points in each section. Step 4: Write the summary. Step 5: Check the summary against the article. Frequently asked questions.
Even if your summary is the length of a full paper, you are likely summarizing a book or other significantly longer work. 2. A summary should tell the reader the highlights of what they need to know without giving them unnecessary details. 3. It should also include enough details to give a clear and honest picture.
3. Jasper. Jasper is an AI-powered summary generator. It creates unique, plagiarism-free summaries, so it's a perfect option for those who don't want to change the wording on their own. When using this tool, you can summarize a text of up to 12,000 characters (roughly 2,000-3,000 words) in more than 30 languages.
Summary Writing Steps. A summary is telling the main ideas of the article in your own words. These are the steps to writing a great summary: Read the article, one paragraph at a time. For each paragraph, underline the main idea sentence (topic sentence). If you can't underline the book, write that sentence on your computer or a piece of paper.
Writing Effective Summary and Response Essays. The Summary: A summary is a concise paraphrase of all the main ideas in an essay. It cites the author and the title (usually in the first sentence); it contains the essay's thesis and supporting ideas; it may use direct quotation of forceful or concise statements of the author's ideas; it will NOT usually cite the author's examples or supporting ...
TLDR This is a Free online text summarizing tool that automatically condenses long articles, documents, essays, or papers into key summary paragraphs using state-of-the-art AI.
A summary of a text is a short overview of the main ideas written in your own words. While paraphrasing involves expressing specific ideas or details from a larger text in your own words, we generally summarize whole texts (whether it is an essay, article, chapter, book, et cetera). So, in order to ensure our summaries are not too wordy or ...
Identify the important ideas and facts. To help you summarize and analyze your argumentative texts, your articles, your scientific texts, your history texts as well as your well-structured analyses work of art, Resoomer provides you with a "Summary text tool" : an educational tool that identifies and summarizes the important ideas and facts of your documents.
A summary of a literary work isn't just a plain-old synopsis. It's a valuable study tool, a foundational element of all kinds of essays, a common testing mechanism, and one of the basics of literary analysis. Whether you're in high school or college, developing a deep understanding of how and when to summarize a book or text is a valuable skill.
Summary: This is where you recap the main points you made in your body paragraphs. Final Thought: This is a concluding thought to end your essay on a strong note. ... The 5-paragraph essay is a foundational structure to help novice writers organize their thoughts. However, as you advance in your writing skills or tackle more complex topics, you ...
Summarize my text in sentences. SMMRY summarizes text to save you time. Paste an article, text or essay in this box and hit summarize; we'll return a shortened copy for you to read. You can also summarize PDF and TXT documents by uploading a file or summarize online articles and webpages by pasting the URL below...
Get your writing process off to a great start by generating fully coherent, compelling paragraphs. Paragraph Rewriter. Improve any paragraph's readability and rewrite it to make it sound more human-like with this powerful free tool. Paraphrasing Tool. Quickly rephrase and reword any text for essays, articles, emails, and more.
Summary Essay Examples #1. ESSAY: When we survey our lives and efforts, we soon observe that almost the whole of our actions and desires are bound up with the existence of other human beings. We notice that the whole of nature resembles that of social animals. We eat food that others have produced, wear clothes that others have made, and live ...
The algorithm recognizes key topics and perspectives to note the levels of importance for each word, sentence, phrase, and paragraph. In this way, the filler text can be removed without harming the value of the content. Thus, you are provided with a summary of the text you've pasted without compromise.