
- Book Solutions
- State Boards

Case Study Questions Class 9 Science Tissues
Case study questions class 9 science chapter 6 tissues.
CBSE Class 9 Case Study Questions Science Tissues. Important Case Study Questions for Class 9 Exam. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Tissues.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks or 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science – Tissues

Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots and increases the length of the stem and the root. The girth of the stem or root increases due to lateral meristem (cambium). Intercalary meristem seen in some plants is located near the node
Cells of meristematic tissue are very active, they have dense cytoplasm, thin cellulose walls and prominent nuclei. They lack vacuoles.
(1) Which meristem helps in increasing the girth of the plant?
(a) Primary meristem
(b) Apical meristem
(c) Intercalary meristem
(d) Lateral meristem
(2) Lateral meristem is responsible for_____________
(a) Growth of apical portion
(b) Increase in the length
(c) Increasing the girth of stem and root
(d) Growth in parenchyma
(3) The meristem present at the base of the internode is_____________
(a) Lateral meristem
(b) Intercalary Meristem
(c) Apical Meristem
(d) All of the above
(4) What are the characteristic of Meristematic tissue?
(5) Enlist the type of meristematic tissue.
(4) Characteristic of Meristematic tissue
- Meristematic tissue are very active type of tissue.
- They have dense cytoplasm.
- The wall of Meristematic cells are thin cellulosic walls and prominent nuclei.
- They lack vacuoles.
(5) There are three types of meristematic tissue
- Apical Meristem
- Intercalary Meristem
- Lateral meristem
Meristematic tissue take up a specific role and lose the ability to divide. As a result, they form a permanent tissue. This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a function is called differentiation. Differentiation leads to the development of various types of permanent tissues.
Simple Permanent Tissue
Tissue made of one type of cells, which look like each other. Such tissues are called simple permanent tissue. Parenchyma is the most common simple permanent tissue. It consists of relatively unspecialised cells with thin cell walls. They are living cells. They are usually loosely arranged, thus large spaces between cells (intercellular spaces) are found in this tissue. This tissue generally stores food. In some situations, it contains chlorophyll and performs photosynthesis, and then it is called chlorenchyma . In aquatic plants, large air cavities are present in parenchyma to help them float. Such a parenchyma type is called aerenchym a.Yet another type of permanent tissue is sclerenchyma . It is the tissue which makes the plant hard and stiff. We have seen the husk of a coconut. It is made of sclerenchymatous tissue. The cells of this tissue are dead. They are long and narrow as the walls are thickened due to lignin.
Complex tissues are made of more than one type of cells. All these cells coordinate to perform a common function. Xylem and phloem are examples of such complex tissues. They are both conducting tissues and constitute a vascular bundle. Xylem fibres are mainly supportive in function. Phloem transports food from leaves to other parts of the plant. Except phloem fibres, other phloem cells are living cells.
(1) Tissue made of only one type of cell is termed as _________
(a) Simple permanent tissue
(b) Complex permanent tissue
(c) Simple Meristematic tissue
(d) Complex Meristematic tissue
(2) Xylem and phloem are examples of
(a) Meristematic tissue
(b) Simple tissue
(c) Protective tissue
(d) Complex tissue
(3) In aquatic plants, which type of parenchymatissue is found?
(a) Aerenchyma
(b) Chlorenchyma
(c) Sclerenchyma
(d) Parenchyma
(4) What is mean by Differentiation?
(5) Enlist the type of parenchyma tissue.
(4) Meristematic tissue lose the ability to divide. As a result, they form a permanent tissue. This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a function is termed as differentiation.
(5) There are three type of parenchyma tissue
- Chlorenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
The covering or protective tissues in the animal body are epithelial tissues. Epithelium covers most organs and cavities within the body. External and Internal covering of the body and organs are all made of epithelial tissue.
Epithelial tissue cells are tightly packed and form a continuous sheet. They have only a small or almost no intercellular spaces.it plays an important role in regulating the exchange of materials between the body and the external environment and also between different parts of the body.
Simple squamous epithelial cells are extremely thin and flat and form a delicate lining. The oesophagus and the lining of the mouth are also covered with squamous epithelium. The skin, which protects the body, is also made of squamous epithelium.
Where absorption and secretion occur, as in the inner lining of the intestine, tall epithelial cells are present. This columnar (meaning ‘pillar-like’) epithelium facilitates movement across the epithelial barrier. In the respiratory tract, the columnar epithelial tissue also has cilia, which are hair-like projections on the outer surfaces of epithelial cells. These cilia can move, and their movement pushes the mucus forward to clear it. This type of epithelium is thus ciliated columnar epithelium.
Cuboidal epithelium (with cube-shaped cells) forms the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands, where it provides mechanical support. Epithelial cells often acquire additional specialisation as gland cells, which can secrete substances at the epithelial surface. Sometimes a portion of the epithelial tissue folds inward, and a multicellular gland is formed. This is glandular epithelium.
(1) The ciliated columnar epithelium is present in
(a) Respiratory tract
(b) Bile duct and oesophagus
(c) Fallopian tube and urethra
(d) Eustachian tube and stomach lining
(2) The cuboidal epithelium is present in
(a) Bronchioles
(d) Kidney tubules ducts of salivary glands
(3) External and Internal covering of the body and organs are all made of ________
(a) Skin Tissue
(b) Epithelial Tissue
(c) Nerves Tissue
(d) Connective Tissue
(4) How are cells arranged in epithelial tissue?
(a) Loosely packed
(b) Closely packed
(c) Arranged in discontinuous form
(d) Both a and c
(5) Enlist the types of Epithelial Tissue?
(5) Type of epithelial tissue
- Simple squamous epithelial tissue
- Columnar epithelial tissue
- Cuboidal epithelial tissue
- Glandular epithelial tissue
Blood is a type of connective tissue. The cells of connective tissue are loosely spaced and embedded in an intercellular matrix. The matrix may be jelly like, fluid, dense or rigid. The nature of matrix differs in concordance with the function of the particular connective tissue.
Blood has a fluid (liquid) matrix called plasma, in which red blood corpuscles (RBCs), white blood corpuscles (WBCs) and platelets are suspended. The plasma contains proteins, salts and hormones. Blood flows and transports gases, digested food, hormones and waste materials to different parts of the body.
Bone is another example of a connective tissue. It forms the framework that supports the body. It also anchors the muscles and supports the main organs of the body. It is a strong and nonflexible tissue. Bone cells are embedded in a hard matrix that is composed of calcium and phosphorus compounds. Two bones can be connected to each other by another type of connective tissue called the ligament. This tissue is very elastic.
Another type of connective tissue, cartilage, has widely spaced cells. The solid matrix is composed of proteins and sugars. Cartilage smoothens bone surfaces at joints and is also present in the nose, ear, trachea and larynx.
Areolar connective tissue is found between the skin and muscles, around blood vessels and nerves and in the bone marrow. It fills the space inside the organs, supports internal organs and helps in repair of tissues.
(1) A connective tissue
(a) Has no matrix
(b) Covers the skin
(c) Has abundant matrix
(d) None of these
(2) Areolar connective tissue is found between
(a) Skin and muscles
(b) Blood vessels and nerves
(c) Both a & b
(3) Two bones are connected to each other by another type of connective tissue called__
(a) Ligament
(b) Cartilage
(c) Bone marrow
(4) What are the function of connective tissue?
(5) Give the examples of connective tissue.
(4) Functions of connective tissue
- Binding together other tissues
- Supporting various parts of the body
- Forming a packing around organs
(5) Examples of connective tissue
Muscular tissue consists of elongated cells, also called muscle fibres. This tissue is responsible for movement in our body. Muscles contain special proteins called contractile proteins, which contract and relax to cause movement
We can move some muscles by conscious will. Such muscles are called voluntary muscles. These muscles are also called skeletal muscles as they are mostly attached to bones and help in body movement. Under the microscope, these muscles show alternate light and dark bands or striations, hence they are also called striated muscles. The cells of this tissue are long, cylindrical, unbranched and multinucleate.
The movement of food in the alimentary canal or the contraction and relaxation of blood vessels are involuntary movements. We can’t control these muscle movement. The Smooth muscles or involuntary muscles control such movements. They are also found in the iris of the eye, in ureters and in the bronchi of the lungs. The cells are long with pointed ends (spindle-shaped) and uninucleate. They are also called unstriated muscles.
The muscles of the heart show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life. These involuntary muscles are called cardiac. Heart muscle cells are cylindrical, branched and uninucleate.
(1) Which of the following muscle tissue are voluntary in nature?
(a) Cardiac muscle
(b) Smooth muscle
(c) auto rhythmic muscle
(d) None of the above
(2) The muscles whose contraction is under our control are known as
(a) Voluntary muscles
(b) Involuntary movements
(c) Cardiac muscle
(d) Unstrained muscle
(3) The smooth muscle are found in the
(a) Iris of eye
(c) Bronchi of lungs
(d) All of above
(4) Give the characteristic of striated muscles.
(5) Give the characteristic of unstriated muscles.
(4) Characteristic of striated muscles,
- These muscles show alternate light and dark bands or striations, hence they are also called striated muscles.
- The cells of this tissue are long, cylindrical, unbranched and multinucleate.
(5) Characteristic of unstriated muscles
- The cells of this tissue are long with pointed ends spindle-shaped and uninucleate.
- Striations are absent, hence they are also called unstriated muscles.
There are too many ads between the content…it’s too disturbing
Very nice and easy
Not satisfied with these few questions but it is good .
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
As a health-conscious person, you noticed an advertisement in the newspaper on yoga classes in your neighbourhood. write a letter to the organizers enquiring about the duration of the course and other relevant details, madam rides the bus extra questions and answers english first flight chapter 9, ncert solutions class 10 science chapter 10 light reflection and refraction.

RS Aggarwal Class 8 Math First Chapter Rational Numbers Exercise 1A Solution
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Class 9 Science Case Study Questions Chapter 6 Tissues
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: class 9th
- Post comments: 0 Comments
Case study Questions in Class 9 Science Chapter 6 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving Class 9 Science Case Study Questions Chapter 6 Tissues
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Tissues Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: Meristematic tissue takes up a specific role and loses the ability to divide. As a result, they form permanent tissue. This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and function is called differentiation. Differentiation leads to the development of various types of permanent tissues.
Simple Permanent Tissue
Tissue is made of one type of cells, which look like each other. Such tissues are called simple permanent tissue. Parenchyma is the most common simple permanent tissue. It consists of relatively unspecialized cells with thin cell walls. They are living cells. They are usually loosely arranged, thus large spaces between cells (intercellular spaces) are found in this tissue. This tissue generally stores food. In some situations, it contains chlorophyll and performs photosynthesis, and then it is called chlorenchyma. In aquatic plants, large air cavities are present in parenchyma to help them float. Such a parenchyma type is called aerenchyma. Yet another type of permanent tissue is sclerenchyma. It is the tissue that makes the plant hard and stiff. We have seen the husk of a coconut. It is made of sclerenchymatous tissue. The cells of this tissue are dead. They are long and narrow as the walls are thickened due to lignin.
Complex tissues are made of more than one type of cell. All these cells coordinate to perform a common function. Xylem and phloem are examples of such complex tissues. They are both conducting tissues and constitute a vascular bundle. Xylem fibers are mainly supportive in function. Phloem transports food from leaves to other parts of the plant. Except for phloem fibers, other phloem cells are living cells.
(1) Tissue made of only one type of cell is termed as _________
(a) Simple permanent tissue
(b) Complex permanent tissue
(c) Simple Meristematic tissue
(d) Complex Meristematic tissue
Answer: (a) Simple permanent tissue
(2) Xylem and phloem are examples of
(a) Meristematic tissue
(b) Simple tissue
(c) Protective tissue
(d) Complex tissue
Answer: (d) Complex tissue
(3) In aquatic plants, which type of parenchyma tissue is found?
(a) Aerenchyma
(b) Chlorenchyma
(c) Sclerenchyma
(d) Parenchyma
Answer: (a) Aerenchyma
(4) What is mean by Differentiation?
Answer: Meristematic tissue lose the ability to divide. As a result, they form a permanent tissue. This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a function is termed as differentiation.
(5) Enlist the type of parenchyma tissue.
Answer: There are three type of parenchyma tissue Aerenchyma Chlorenchyma Sclerenchyma
Case Study 2: Bone is a solid, hard porous tissue. It forms the natural skeleton and gives the body its basic structure and also supports the body. Its matrix is impregnated with phosphates and carbonates of calcium and magnesium which provides hardness to it. The matrix also contains ossein protein. The matrix is arranged in concentric rings which are called lamellae. Bone cells lie between the lamellae in fluid-filled spaces called lacunae.
(i) Bone cells are also called : (a) Lacunae (b) Osteocytes (c) Neutrophils (d) Erythrocytes
Ans. (b) Osteocytes
(ii) The matrix inside the bone is arranged in concentric rings called ……… (a) Cytoplasm (b) Osteocyte (c) Lacunae (d) Lamellae
Ans. (d) Lamellae
(iii) To form natural skeleton and to give support to the body is the main function of ………. (a) Cells (b) Muscles (c) Bones (d) Ligaments
Ans. (c) Bones
(iv) The matrix of bone is impregnated with………… (a) Carbon dioxide and oxygen (b) Carbon dioxide and water (c) Sulphates of sodium (d) Phosphates and carbonates of calcium and magnesium
Ans. (d) Phosphates and carbonates of calcium and magnesium
(v) Bone cells lie between the lamellae in fluid-filled spaces called …………. (a) lamina (b) osteocytes (c) lacunae (d) ossein
Ans. (d) ossein
Case Study 3:
Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function, working together to perform specific tasks in the body. There are four main types of tissues in animals: epithelial tissue, connective tissue, muscular tissue, and nervous tissue. Epithelial tissue covers the surfaces of the body, lines the internal organs, and forms glands. It provides protection, secretion, absorption, and excretion. Connective tissue provides support and connects different body parts. It includes bone, cartilage, blood, and adipose tissue. Muscular tissue is responsible for body movements and can be categorized into three types: skeletal, smooth, and cardiac muscle. Nervous tissue consists of specialized cells called neurons that transmit and process information in the form of electrical signals. Understanding the different types and functions of tissues is essential to comprehend the organization and functioning of complex multicellular organisms.
What are tissues? a) Groups of organs in the body b) Groups of cells with similar structure and function c) Layers of skin d) Different types of body systems Answer: b) Groups of cells with similar structure and function
How many main types of tissues are there in animals? a) Two b) Three c) Four d) Five Answer: c) Four
Which type of tissue covers the surfaces of the body and forms glands? a) Epithelial tissue b) Connective tissue c) Muscular tissue d) Nervous tissue Answer: a) Epithelial tissue
What is the function of connective tissue? a) Provides support and connects different body parts b) Covers the surfaces of the body c) Responsible for body movements d) Transmits and processes information Answer: a) Provides support and connects different body parts
What is the function of nervous tissue? a) Provides protection, secretion, absorption, and excretion b) Transmits and processes information in the form of electrical signals c) Responsible for body movements d) Supports and connects different body parts Answer: b) Transmits and processes information in the form of electrical signals
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Science Tissues Case Study and passage-based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible By Team Study Rate
You Might Also Like
Best reference books for class 9th, mcq questions of class 9 social science geography chapter 5 natural vegetation and wildlife with answers.

Class 9 CBSE Science Handwritten Notes by Topper’s: Download PDF FREE
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
CBSE Expert
Case Study Questions of Chapter 6 Tissues PDF Download
Case study Questions on Class 9 Science Chapter 6 are very important to solve for your exam. Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Case Study Questions have been prepared for the latest exam pattern. You can check your knowledge by solving case study-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues

In CBSE Class 9 Science Paper, Students will have to answer some questions based on Assertion and Reason. There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Tissues Case Study Questions With answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Question 1:
Meristematic tissue takes up a specific role and loses the ability to divide. As a result, they form permanent tissue. This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and function is called differentiation. Differentiation leads to the development of various types of permanent tissues.
Simple Permanent Tissue
Tissue is made of one type of cells, which look like each other. Such tissues are called simple permanent tissue. Parenchyma is the most common simple permanent tissue. It consists of relatively unspecialized cells with thin cell walls. They are living cells. They are usually loosely arranged, thus large spaces between cells (intercellular spaces) are found in this tissue. This tissue generally stores food. In some situations, it contains chlorophyll and performs photosynthesis, and then it is called chlorenchyma. In aquatic plants, large air cavities are present in parenchyma to help them float. Such a parenchyma type is called aerenchyma. Yet another type of permanent tissue is sclerenchyma. It is the tissue that makes the plant hard and stiff. We have seen the husk of a coconut. It is made of sclerenchymatous tissue. The cells of this tissue are dead. They are long and narrow as the walls are thickened due to lignin.
Complex tissues are made of more than one type of cell. All these cells coordinate to perform a common function. Xylem and phloem are examples of such complex tissues. They are both conducting tissues and constitute a vascular bundle. Xylem fibers are mainly supportive in function. Phloem transports food from leaves to other parts of the plant. Except for phloem fibers, other phloem cells are living cells.
(1) Tissue made of only one type of cell is termed as _________
(a) Simple permanent tissue
(b) Complex permanent tissue
(c) Simple Meristematic tissue
(d) Complex Meristematic tissue
Answer: (a) Simple permanent tissue
(2) Xylem and phloem are examples of
(a) Meristematic tissue
(b) Simple tissue
(c) Protective tissue
(d) Complex tissue
Answer: (d) Complex tissue
(3) In aquatic plants, which type of parenchymatissue is found?
(a) Aerenchyma
(b) Chlorenchyma
(c) Sclerenchyma
(d) Parenchyma
Answer: (a) Aerenchyma
(4) What is mean by Differentiation?
Answer: Meristematic tissue lose the ability to divide. As a result, they form a permanent tissue. This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a function is termed as differentiation.
(5) Enlist the type of parenchyma tissue.
Answer: There are three type of parenchyma tissue Aerenchyma Chlorenchyma Sclerenchyma
Question 2:
Bone is a solid, hard porous tissue. It forms the natural skeleton and gives the body its basic structure and also supports the body. Its matrix is impregnated with phosphates and carbonates of calcium and magnesium which provides hardness to it. The matrix also contains ossein protein. The matrix is arranged in concentric rings which are called lamellae. Bone cells lie between the lamellae in fluid-filled spaces called lacunae.
(i) Bone cells are also called : (a) Lacunae (b) Osteocytes (c) Neutrophils (d) Erythrocytes
Ans. (b) Osteocytes
(ii) The matrix inside the bone is arranged in concentric rings called ……… (a) Cytoplasm (b) Osteocyte (c) Lacunae (d) Lamellae
Ans. (d) Lamellae
(iii) To form natural skeleton and to give support to the body is the main function of ………. (a) Cells (b) Muscles (c) Bones (d) Ligaments
Ans. (c) Bones
(iv) The matrix of bone is impregnated with………… (a) Carbon dioxide and oxygen (b) Carbon dioxide and water (c) Sulphates of sodium (d) Phosphates and carbonates of calcium and magnesium
Ans. (d) Phosphates and carbonates of calcium and magnesium
(v) Bone cells lie between the lamellae in fluid-filled spaces called …………. (a) lamina (b) osteocytes (c) lacunae (d) ossein
Ans. (d) ossein
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about CBSE Class 9 Science Tissues Case Study and passage-based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!
Book a Trial With Our Experts
Hey there! We receieved your request
Stay Tuned as we are going to contact you within 1 Hour
Thank you for registering.
One of our academic counsellors will contact you within 1 working day.

Click to Chat
- 1800-5470-145
- +91 7353221155
- Login | Register
- My Classroom
- My Self Study Packages
- Batch Discussion
- My Forum Activity
- Refer a Friend
- Edit Profile
- Add Question
- Add Paragraph
- Search Coupon
Use Coupon: CART20 and get 20% off on all online Study Material
Complete Your Registration (Step 2 of 2 )

Register Now and Win Upto 25% Scholorship for a Full Academic Year !
Enter your details.

Registration done!
Sit and relax as our customer representative will contact you within 1 business day
Mobile Verification
OTP to be sent to Change
- Junior Hacker
- Junior Hacker New
- Self Study Packages
- JEE Advanced Coaching
- 1 Year Study Plan
- Rank Predictor
- Paper Pattern
- Important Books
- Sample Papers
- Past Papers
- Preparation Tips
- Latest News
- JEE Main Exams
- Online Coaching
- Branch Predictor
- JEE Main Syllabus
- Past Year Papers
- Math Preparation Tips
- IIT JEE Exam Details
- JEE Syllabus
- IIT JEE Toppers Tips
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 11
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 9
- IIT JEE Preparation Tips for Class 8
- IIT JEE Preparation Time Table
- IIT JEE Online Coaching
- Correspondence Course For IIT JEE
- IIT JEE Coaching after 10th
- IIT JEE Coaching For Foundation Classes
- JEE Coaching Institutes
- IIT JEE Coaching in Kota
- IIT JEE Coaching Institutes In Kota
- BITSAT Examination
- View complete IIT JEE Section
- View All Engineering Exams
- Top Engineering Colleges
- Top Engineering Branches
- Engineering Exam Calendar
- NEET Entrance Exam
- NEET Online Coaching
- NEET Preparation Tips
- Participating States
- AIIMS Examination
- AIIMS Online Coaching
- View all Medical Exams
- Top Medical Colleges
- Medical Exam Coaching
- Best Medical Coaching In Kota
- Medical Exam Calendar
- NTSE Examination
- Notifications
- Application
- Important Dates
- Eligibility
- Study Material
- KVPY Examination
- Olympiads Examination
- Indian National Mathematics Olympiad
- Physics Olympiad
- Chemistry Olympiad
- Biology Olympiad
- Olympiads Sample Papers
- INMO Papers
- CBSE School Exams
- Solutions for Board Exam
- JEE Advanced
- Karnataka CET
- Manipal UGET
- NCERT Class 12 Solutions
- NCERT Class 11 Solutions
- NCERT Class 10 Solutions
- NCERT Class 9 Solutions
- NCERT Class 8 Solutions
- NCERT Class 7 Solutions
- NCERT Class 6 Solutions
- List of JEE Main & JEE Advanced Books
- R.D. Sharma Solutions PDFâ
- Concepts of Physics by HC Verma for JEE
- HC Verma Solutions Part 1
- HC Verma Solutions Part 2
- Most Scoring Topics in IIT JEE
- IIT JEE Entrance Exam
- Discuss with Colleagues and IITians
- Engineering Entrance Exams
- Branch Ranking of IIT
- Discuss with Askiitians Tutors
- NEET (AIPMT)
- Marks and Rank in IIT JEE
- Top Engineering Colleges in India
- AIEEE Entrance Exam
- Electric Current
- Wave Motion
- Modern Physics
- Thermal Physics
- Electromagnetic Induction
- General Physics
- Electrostatics
- Wave Optics
- Physical Chemistry
- Organic Chemistry
- Inorganic Chemistry
- Trigonometry
- Analytical Geometry
- Differential Calculus
- Integral Calculus
- Magical Mathematics
- Online Tutoring
- View complete NRI Section
- View Complete Study Material
- View Complete Revision Notes
- Ahmadi (FAIPS)
- Khaitan (Carmel School)
IIT JEE Courses

One Year IIT Programme
- Super Premium LIVE Classes
- Top IITian Faculties
- 955+ hrs of Prep
- Test Series & Analysis

Two Year IIT Programme
- 1,835+ hrs of Prep

Crash Course
- LIVE + Pre Recorded Sessions
- 300+ hrs of Prep
NEET Courses

One Year NEET Programme
- Top IITian & Medical Faculties
- 900+ hrs of Prep

Two Year NEET Programme
- 1,820+ hrs of Prep

- LIVE 1-1 Classes
- Personalized Sessions
- Design your own Courses
- Personalized Study Materials
School Board
Live online classes, class 11 & 12.
- Class 11 Engineering
- Class 11 Medical
Class 9 & 10
Class 6, 7 & 8, test series, jee test series.
- 2 Year Jee Test Series
- 1 Year Jee Test Series
NEET test series
- 2 Year NEET Test Series
- 1 Year NEET Test Series
C.B.S.E test series
- 11 Engineering
- 12 Engineering
Complete Self Study Packages
Full course.
- 2 year NEET
- Chemistry 11th & 12th
- Maths 11th & 12th
- Physics 11th & 12th
- Biology 11th & 12th
- View Complete List
For class 12th
- Chemistry class 12th
- Maths class 12th
- Physics class 12th
- Biology class 12 th
For class 11th
- Chemistry class 11th
- Maths class 11th
- Physics class 11th
- Biology class 11th
Tissues CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter 6
askIITians brings you free Science revision notes for Class 9 Chapter 6 Tissues. These notes are created by our Science teachers and are based on the latest CBSE syllabus for Class 9 Science. Once you read these detailed notes, you do not need to read the NCERT chapter again and again. These notes contain sufficient information for every topic of the chapter. They can help in exam preparation, revision and concept solidification. Our online CBSE Science revision notes for Tissues can be accessed easily from our website and referred to whenever you need them.
- Class 9 revision notes for Chapter 6 Tissues include the following topics:
- Formation of tissues
- Tissues of plants and animals
- Meristematic tissues
- Permanent tissues
- Epidermis
- Stomata
- Transpiration
- Complex permanent tissues
- Xylem and Phloem
- Epithelial tissue
- Connective tissues
- Blood
- Lymph
- Bones
- Haversian Canals
- Ligaments
- Tendons
- Areolar tissues
- Neuron anatomy
Quick Review of Chapter 6 Tissues
- Living organisms in this world comprise cells.
- There are unicellular as well as multicellular organisms present in this world.
- In unicellular organisms, the single cell is capable of performing several functions such as respiration, digestion and clearing of the cell.
- In multicellular organisms, there is a division of labour. There are different types as well as groups of cells that perform different functions in a multicellular organism.
- For Example, In animals muscle cells are responsible for causing movement, nerve cells are responsible for carrying messages and signals from one part of the body to another and blood is responsible for the transportation of food and oxygen to different parts of the body.
- In plants, there are vascular tissues that are responsible for carrying food and water to two different parts of a plant.
Free Revision Notes for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
The formation of tissues.
- The cells form groups of cells to perform a single task.
- This grouping of cells together to perform a function efficiently is called a Tissue.
- For Example, Muscles and Blood.
- The tissue cells have the same structure and they perform the same function.
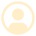
Tissues of Plants and Animals
Plant tissues.
Figure 1: Types of Plant Tissues
Meristematic Tissue
- Only certain parts of a plant tend to grow. The tissues located in such parts are called meristematic tissues.
- They can divide themselves and form new tissues.
- They have a thin cell wall made of cellulose.
- They have a dense nucleus and cytoplasm but lack vacuoles.
- Intercalary
Figure 2: Location of meristematic tissue
Why are there no vacuoles in the intercalary meristem?
- Vacuoles are responsible for the storage of food in the water. The intercalary tissues do not store them. They are rather responsible for manufacturing them.
- Moreover, vacuoles contain sap which provides rigidity to a cell. This property of vacuoles may not allow the intercalary tissues to divide and manufacture new cells. Hence vacuoles are not present in them.
Permanent Tissue
- The cells that are formed by the meristematic tissues often have to take a certain role in the plant and thus, they lose their ability to divide and form more cells. They then become the permanent tissues of the plants.
- Differentiation - The process by which cells of the meristematic tissues convert themselves into permanent tissue by taking a fixed shape, size and function is called differentiation.
- Simple Permanent Tissues
Complex Permanent Tissues
Chlorenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
Figure 3: Simple Permanent Tissue
- These tissues are similar to that of parenchyma but they also contain chlorophyll in them.
- Due to the presence of chlorophyll, they are capable of performing the process of photosynthesis in plants.
- They are found in aquatic plants.
- They are also similar in structure to that of the parenchyma but they have large air cavities in them.
- These cavities allow the aquatic plants to float in water.
What is Lignin?
The cell walls of dead cells have a substance called lignin in them which provides rigidity to the cells. Lignin acts as the cement for the cells.
- The outermost layer of the cell is known as the Epidermis.
- It covers the entire plant.
- It is a thin layer of single cells but in places with less water, the epidermis of the plants can become thick in order to avoid frequent water loss.
- The cells are flat and they have no intercellular spaces between them.
- The outer walls of the epidermal cells are thick and the inner walls are thin.
- The epidermal cells often have long hair-like structures in roots which facilitate the absorption of water.
- The main function of the epidermis is to protect the plants from fungi, water loss and any injuries by secreting a wax-like water-resistant substance called a Cuticle on the surface of the plants which protects the plants.

Figure 4: Epidermis
- Stomata are pore-like structures that are present in the epidermis of the leaves.
- These pores are enclosed by two cells that have a similar shape as a kidney. These are called Guard Cells of Stomata. Guard cells are modified epidermal cells.
- Guard cells are responsible for the exchange of gases and transpiration.
Transpiration (OLYMPIAD)
Figure 5: Transpiration
The plant cells sometimes have extra they lose it in the form of water that evaporates through stomata. This process is called Transpiration.
Role of Transpiration in Plants – (OLYMPIAD)
- Exchange of Gases - Plants absorb carbon dioxide and release oxygen through transpiration.
- Prevent the Plants from Overheating - The leaves absorb sunlight during the process of photosynthesis. Some of it is used in the photosynthesis process while the rest is radiated as Heat Energy. We know that absorption of water causes cooling of the surrounding area. Therefore transpiration keeps the leaves cool.
- Transportation of Food and Water in Plants - The roots of the plants absorb minerals and water present in the soil through transpiration and they are then distributed in the plant through the transpiration stream.
- Movement of Water in Plants – As plants lose water in the form of water vapours, the density of water in leaves becomes low. So the water from the higher density areas such as the roots move up to lower density areas through a force called Transpirational Pull.
Which gas is necessary for the process of photosynthesis?
Carbon dioxide gas is necessary for the process of photosynthesis. Plants use carbon dioxide along with water and sunlight to produce glucose in the process of photosynthesis. Plants take in carbon dioxide and release oxygen as a byproduct of the photosynthesis process.
Why do plants in desert areas have a waxy coating of cutting over them? (OLYMPIAD)
The epidermis cells of plants that are found in deserts have a waxy coating of cutting over them because it prevents water loss from the surface of plants since water is already scarce in such areas.
Why are the branches of old trees different from the stems of a new plant?
- As a plant grows older the meristematic cells start covering the upper layer of the plants instead of the epidermis.
- These are the dead cells that have no special function in the plants but to provide rigidity. They make the branches of the plants thick.
- This is often called the Bark or the thick cork of the tree.
- The bark of the trees contains a substance called Suberin which makes it waterproof and does not allow gaseous exchanges. (OLYMPIAD)
Complex Permanent Tissues comprise different kinds of cells. These different types of cells coordinate with each other and perform a common function in these tissues. Two Complex Permanent Tissues are - Xylem and Phloem.
Figure 6: Xylem and Phloem
Similarities between Xylem and Phloem
- Their main function is to carry food and water in the plant.
- Both have a vascular bundle which is a conductive tissue in plants that helps them survive in different environmental conditions.
Xylem is made up of dead cells having a thick cell lining. It consists of the following elements-
- Tracheids and Vessels – They have a broad tubular structure so that we can allow transportation of food and water in the plants vertically.
- Xylem Parenchyma – It stores food and helps in the transportation of water horizontally in the plants.
- Xylem Fibres – They support transportation
Phloem is made up of living cells and it allows the movement of food from leaves to other parts of the plant. It has the following elements –
Sieve Tubes – Broad shaped cells with porous walls
- Companion Cells – They facilitate the functions of the sieve tubes
- Phloem Fibres – Provide flexibility to the phloem
- Phloem Parenchyma – Stores starch and proteins
Animal Tissue
Figure 7: Types of Animal Tissues
1. Epithelial Tissue
- They are the protective tissues of the human body. They cover many organs and cavities that are present inside the body.
- The lining of the blood vessels
- The lining of the mouth
- Kidney tubules
- Lung alveoli
- The main function of the epithelial tissues is to act as a barrier and separate different organs and systems from each other.
- There is no space between the cells of epithelial tissues
- The cells are permeable. This makes it possible for them to exchange materials between different parts of the body and also between the body and the external environment.
- The epithelial tissues remain separated from the tissues beneath them because of a thin membrane over them.

Figure 8: Types of Epithelium
2. Connective Tissues
Structure and function of connective tissues
- They are loosely bound cells present in an intercellular Matrix.
- This matrix can be of different types – Dense, Rigid, Fluid or Jelly-like.
- Depending upon the functionality of the connective tissue, the nature of the matrix varies.
Examples of Connective Tissues
Figure 9: Connective Tissues
The main function of blood is to transport gases, food, waste materials and hormones in the body.
Therefore, blood has a fluid Matrix present in it which is called Plasma.
The plasma contains red blood cells, white blood cells and blood platelets.
The RBC has haemoglobin pigment which carries oxygen to tissues.
White blood cells fight diseases and platelets are involved in the clotting of blood when injured.
The plasma also contains proteins and hormones in it.
Lymph (OLYMPIAD)
Lymph is a colourless fluid that carries white blood cells throughout the human body in lymphatic vessels. There are lymphoid organs present in the body that produce lymph and together form the lymphatic system. Some of them are lymph nodes and tonsils.
Figure 10: Lymph Capillaries
Lymph is similar to blood except for a few differences:
- It contains only white blood cells.
- It contains less amount of blood proteins, calcium and phosphorus but more glucose.
- It flows in one direction only.
- Lymph moves in the body through its normal function, unlike blood which is pumped by the heart.
Constituents of Lymph:
Lymph Plasma – Lymph Plasma carries infection-fighting proteins along with other substances such as water, calcium and phosphorus.
Lymph Corpuscles – Lymph Corpuscles comprises white blood cells. Red blood cells and platelets are not present in lymph.
Functions of Lymph:
- It carries oxygen and minerals to the cells in the body and carries back carbon dioxide and waste materials back into the blood.
- It keeps the body cells moist.
- It maintains the volume of the blood.
- It helps in eliminating harmful bacteria and viruses from the body and hence is responsible for the immunity of human beings.
- It absorbs fats from the intestine and transports them throughout the body.
- Bones form a framework of the body over which the muscles are wrapped together.
- The bone tissue is strong and inflexible.
- Therefore, the bone cells are present in a rigid matrix that is formed from calcium and phosphorus.
Haversian Canals (OLYMPIAD)
Figure 11 Haversian Canal
- The bones comprise microscopic tubes called Haversian Canals.
- They are contained in osteons, rough cylindrical structures present along the axis of the bone.
- They allow the blood vessels, lymphatic vessels, and nerve fibres to travel through them.
- These canals have concentric channels called Lamellae around them.
- The Haversian canals communicate with bone cells through connections called Canaliculi.
- Cartilage is present over the joints of the bones and provides them with a smooth structure.
- For Example in the nose tip and ear pinna, trachea, larynx.
- They contain a solid matrix made of protein and sugar. They have a homogenous matrix.
- It provides support and flexibility to various parts of our body.
- A ligament connects two bones together.
- It has an elasticity that facilitates the connection.
- The cells of ligaments have a little matrix.
- The tendon tissues are responsible for connecting bones and muscles together.
- They have limited flexibility but very great strength.
- This tissue acts as a filter in between the spaces present inside the organs of the body.
- It helps in repairing other tissues as well.
- It is found in the skin and bone marrow.
Components of the Areolar Connective Tissue
Figure 12 Components of the areolar connective tissue
1. Cells (OLYMPIAD)
- Fat Cells (Adipocytes) – They are responsible for the secretion of lipids.
- Fibroblasts – They are present in the highest amount in areolar tissues. They are responsible for the secretion of fibres.
- Mast Cells – They release histamine that plays a role in allergic reactions
- Macrophages – They eat any germs or infectious cells in the body
- Plasma Cells – They produce antibodies
- Collagen Fibres – They provide tensile strength to the tissue
- Elastin Fibres – They provide elasticity to the tissue
- Ground Substance – It is a fluid matrix that holds cells and fibres of the tissue
- Fats are stored in our body in the adipose tissues.
- They are found below the skin and between the organs of the body.
- Provides cushioning to the organs.
3. Muscular Tissue
- It is made up of muscle fibres which are long cells.
- It allows movements in our bodies.
- How can muscles cause movement?
They contain special proteins called Contractile Proteins. These proteins cause contraction and relaxation of the muscles.
- There are two kinds of muscles found in our body - Voluntary Muscles and Involuntary Muscles.

Figure 13: Muscular Tissue
Cardiac Muscles
- These are special kinds of involuntary muscles.
- The muscles of the heart are called Cardiac Muscles. They perform rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout our life.
- They are cylindrical in shape, they have branches and there is a single nucleus.
- Cardiac muscle consists of individual heart muscle cells connected by intercalated discs to work as a single functional organ
4. The Nervous Tissue
- This is because of the nervous tissues present in our body. They are capable of transmitting information quickly from the brain to different parts of the body and vice-versa.
- Therefore nervous tissues are found in nerves, brain, and spinal cord.
- Nervous tissue is made up of cells called the Nerve Cells or Neurons.
- These neurons connect together to form the nerves of our body.
- It is an elongated cell with a Cell Body that consists of some branch-like structure called Dendrites.
- There is a Nucleus present in the centre of the cell body.
- The Nerve Endings of the cell are connected with the cell body via Axon.
- A nerve cell can be up to 1 m long.
Figure 14: Structure of Neuron
The Structure of Neuron
1. Dendrites
- They are tree-like extensions (highly-branched) at the beginning of a neuron.
- They increase the surface area of the neuron.
- They receive chemical signals from different neurons of the body.
- They then convert these chemical signals into electrical signals and pass them to the neuron cell body.
- A neuron can have a single dendrite or multiple dendrites
2. Cell Body
- Also called Soma.
- The main function of the cell body and nucleus of the neuron is to maintain the functionality of the cell.
- It does not play an active role in the transmission of the signal.
- It produces proteins that are required by different parts of the neuron to work properly.
- It contains different cell organelles such as mitochondria, Golgi apparatus etc that perform various functions of the cell.
- Neurons have one axon in general.
- It is a long structure that connects the cell body to the terminals and it also connects with other neurons, cells and organs of the body through nerve terminals.
- It allows for the fast transmission of signals. The larger the diameter of the axon the faster it will transmit signals.
- It is covered with a special insulating substance called myelin. It helps in the rapid transmission of signals.
4. Schwann Cells (OLYMPIAD)
- The Myelin sheath that covers the axon is produced by Schwann cells.
- The Myelin sheath keeps the signal intact.
Online Revision Notes for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues FAQs
1. Can you give me some study tips for preparing Chapter 6 Tissues?
- Read the NCERT chapter first and underline all the important points.
- Use our revision notes to make the notes for the chapter and solidify your conceptual understanding.
- Make sure you understand all the diagrams of the chapter.
- Solve the NCERT textbook questions given in the chapter.
- Consult your teachers in case you have any doubts and resolve them as soon as possible.
2. How can askIITians help me in preparing Chapter 6 Tissues for my exams?
- askIITians provides live online coaching sessions for CBSE Class 9 Science where you can understand all the concepts of this chapter.
- We provide many study materials for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues like NCERT Solutions, revision notes, mind maps, flashcards, mnemonics, practise papers, important questions, NCERT Exemplar solutions and more.
3. Why should I refer to CBSE Science revision notes online for Class 9 Chapter 6 Tissues?
- The revision notes created by askIITians experts are easy to understand.
- These notes include all the topics of the chapter.
- They are organised pointwise for easy understanding of the concept and important points.
- They include diagrams and tables to help you memorise the concepts better.
- They are based on the latest CBSE Class 9 Science syllabus and exam pattern.
- The notes are available for free for all the students.
4. What is Chapter 6 Tissues of Class 9 Science?
Tissue is an important chapter in CBSE Class 9 Science. This chapter deals with the definition and types of tissues found in plants and animals. This chapter helps you understand why tissues are important in plants and animals, what are their functions and structures.
TOP Your EXAMS!
Upto 50% scholarship on live classes, course features.
- Video Lectures
- Revision Notes
- Previous Year Papers
- Study Planner
- NCERT Solutions
- Discussion Forum
- Test paper with Video Solution
Book Free demo of askIITians Live class
View courses by askiitians.

Design classes One-on-One in your own way with Top IITians/Medical Professionals

Complete Self Study Package designed by Industry Leading Experts

Live 1-1 coding classes to unleash the Creator in your Child

a Complete All-in-One Study package Fully Loaded inside a Tablet!
Ask question.
Get your questions answered by the expert for free

Your Question has been posted!
You will get reply from our expert in sometime.
We will notify you when Our expert answers your question. To View your Question
POST QUESTION
Select the tag for question.

Matter in Our Surroundings CBSE Class 9 Science...
Force and Laws of Motion CBSE Class 9 Science...
Revision Notes on Structure of Atom Quick Revision...
Improvement in Food Resources CBSE Class 9 Science...
Gravitation CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes...
Natural Resources CBSE Class 9 Science Revision...
Motion CBSE Class 9 Science Notes Chapter 8 Do you...
Why Do We Fall Ill CBSE Class 9 Science Revision...
Diversity in Living Organisms CBSE Class 9 Science...
Revision Notes on Work and Energy Work The...
Atoms and Molecules CBSE Class 9 Science Revision...
Sound CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter...
The Fundamental Unit of Life CBSE Class 9 Science...
Is Matter Around Us Pure CBSE Class 9 Science...
If you're seeing this message, it means we're having trouble loading external resources on our website.
If you're behind a web filter, please make sure that the domains *.kastatic.org and *.kasandbox.org are unblocked.
To log in and use all the features of Khan Academy, please enable JavaScript in your browser.
Unit 6: Tissues
- No videos or articles available in this lesson
- Meristematic tissue Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Simple and Complex Permanent tissue Get 5 of 6 questions to level up!
- Squamous epithelium (Opens a modal)
- Ciliated epithelium (Opens a modal)
- Glandular epithelium (Opens a modal)
- Epithelial tissue Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Connective tissue Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
- Muscular tissue and neural tissue Get 3 of 4 questions to level up!
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues

CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter-6 Important Questions - Free PDF Download
There are some very important questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 that students need to know about if they want to ensure that their results for their final exams are good enough. Vedantu provides the Class 9 Science Chapter 6 important questions in PDF format, so that students can easily prepare for their examinations. Students can download the important questions PDF for free from Vedantu and practice them to get good marks in the exams. Not to mention that a few extra questions for class 9 science chapter 6 will also give them some additional knowledge for sure.
Vedantu is a platform that provides free CBSE Solutions (NCERT) and other study materials for students. Maths Students who are looking for the better solutions ,they can download Class 9 Maths NCERT Solutions to help you to revise complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.
Download CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions 2024-25 PDF
Also, check CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions for other chapters:

Study Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues
Very Short Answer Questions: (1 Marks)
1. Where is apical meristem found?
Ans: The apical meristem is found in the growing tips of stems and roots in plants.
2. Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Ans: Sclerenchyma tissue.
3. What are the constituents of phloem?
Ans: The constituents of phloem are: sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma, phloem fibres(bast).
4. Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Ans: Muscle/muscular tissue.
5. Vertical growth in plants takes place by –
(a) Lateral meristem
(b) apical meristem
(c) Intercalary meristem
(d) none of the above
Ans: (b) apical meristem
6. Which of these components of blood fight infection?
(c) Platelets
(d) serum
Ans: (b) WBC
7. In desert plants, rate of water loss gets reduced due to presence of :
(a) cuticle
(b) stomata
(d) suberin
Ans: (a) cuticle
8. Cartilage is not found in
(d) larynx
Ans: (c) kidney
9. Which of these types of cells is most likely to divide?
(a) Epidermis
(b) Parenchyma
(c) Meristem
Ans: (c) Meristem
10. Companion cells are associated with –
(a) Sieve tubes
(b) Sclerenchyma
(c) Vessels
(d) Parenchyma
Ans: (a) Sieve tubes
11. Which tissue has chloroplast in cells?
(a) Parenchyma
(b) Chlorenchyma
(c) Sclerenchyma
(d) Aerenchyma
Ans: (b) Chlorenchyma
12. Intestine absorbs due digested food materials. What type of epithelial are responsible for that?
(a) Stratified squamous epithelium
(b) columnar epithelium
(c) pseudostratified epithelium
(d) Cuboidal epithelium
Ans: (b) columnar epithelium
13. The meristematic tissue is found
(a) In flowers
(b) At the tip of the leaves
(c) Below the epidermis of stem
(d) At root tip
Ans: (d) At root tip
14. Movement of passage of food in the intestine is caused by the contraction of
(a) cardiac muscles
(b) unstriated muscles
(c) striated muscles
(d) Nerve tissue
Ans: (b) unstriated muscles
15. A long tubular outgrowth of a nerve cell which conducts impulses away from the cell body is termed as
(d) dendrite
Ans: (d) dendrite
16. You have been provided with narrow thick – walled living cells, elongated in shape and possessing thickening of cellulose and pectin these cells belong to:
(b) collenchyma
(c) sclerenchyma
Ans: (b) collenchyma
17. Which one of the following is the correct definition of the tissues?
(a) Group of dissimilar cells which perform similar function
(b) Group of similar cells which perform similar functions.
(c) group of similar cells which perform specific functions
(d) Group of dissimilar cells which perform different functions.
Ans: (a) Group of dissimilar cells which perform similar function
18. A long tree has several branches. The tissue that helps in the sideways conduction of water in the branches is:
(a) collenchyma
(b) xylem parenchyma
(c) parenchyma
(d) xylem vessels
Ans: (d) xylem vessels
19. White blood corpuscles:
(a)help in blood clotting
(b)help in transport of oxygen
(c)are enucleated
(d) protect the body from diseases
Ans: (d) protect the body from diseases
20. A person met with an accident in which two long bones of hand were dislocated. Which among the following may be possible reason?
(a) tendon break
(b) break of skeletal muscles
(c) ligament break
(d) Areolar tissue breaks
Ans: (b) ligament break
Short Answer Questions: (2 Marks)
1. What is a tissue?
Ans: It is a group of cells similar in origin and arrangement, they are specialized to perform a particular function. Tissue the cluster of cells in a manner to give the highest of possible efficiency of the required function. Examples of tissues are blood, phloem and muscle .
2. What are the constituents of phloem?
Ans: The five constituents of phloem are sieve cells, sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem parenchyma and phloem fibres
3. Name types of simple tissues.
Ans: Three types simple tissues are:
I. Parenchyma
II. Collenchyma
III. Sclerenchyma
4. What does a neuron look like?
Ans: A neuron comprises a cell body from which long thin hair-like parts(arise). Then the neuron has a single long part(axon) and many short, branched parts(dendrites).
5. How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Ans: Xylem tissue consist of four types of elements:
I. Tracheids
II. vessels
III. Xylem fibres
IV. Xylem parenchyma
6. How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Ans: Difference between simple tissues and complex tissues in plants is given below:
7. Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Ans: Difference between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall is given below:
8. What are the functions of the stomata?
Ans: The functions of stomata are:
I. Gaseous exchange with the atmosphere.
II. Transpiration (formation of water vapours for the removal of excess water)

9. What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
Ans: Cardiac muscles are the muscles of heart that pumps blood to all parts of body and it shows rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life without any fatigue. The cells of heart muscles are branched, cylindrical and uninucleate.
10. Name the following:
a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
Ans: Epithelial tissue
b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
Ans: Tendon
c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
Ans: Phloem
d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
Ans: Adipose tissue
e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
f) Tissue presents in the brain.
Ans: Nerve tissue
11. Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Ans: the type of tissues of the given is listed below:.
12. Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Ans: Parenchymatous tissue is present in the soft plant parts including leaf mesophyll , young stem, root, leaves, vascular bundles, flowers and fruits of plants.
13. What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Ans: Epidermis is a protective layer to all the plant parts. It will provide protection against water loss, Control the process of gas exchange, Epidermis secretes a waxy, water-resistant layer.
14. How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Ans: In the plant a strip of secondary meristem located in the cortex forms layers of cells that are dead and arranged in a compact manner without intercellular spaces which is cork. They have deposition of suberin in their walls which is very hard and impermeable hence protects plants from unfavorable conditions and microbial attack etc.
15. What are meristematic and permanent tissue?
Meristematic Tissue: dividing tissue is the reason for growth of plants occurs only in specific regions this is also known as meristematic tissue. Apical, lateral and intercalary are the classification of the meristematic tissues.
Permanent Tissue: The cells formed by meristematic tissue later lose the ability to divide as a result permanent tissue is formed. The process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a function is called differentiation; this also leads to the development of permanent tissues.
16. What is the function of Tendon and ligament?
Ligaments: They connect one bone to another bone and another type of connective tissue. They are strong, elastic, consisting of yellow fibers.
Tendon: They connect muscle to bone and another type of connective tissue. They are tough, non – elastic, consisting of white fibres.
17. Draw a well labeled diagram of neuron
18. Differentiate the following activities on the basis of voluntary or involuntary:
a) Jumping of frog
Ans: Voluntary
b) Pumping of the heart
Ans: Involuntary
c) writing with hand
d) Moving of chocolate in stomach
19. Name the following:
a) Tissue that stores fats in our body.
b) Tissue presents in the brain
Ans: Nervous tissue
c) Connective tissue with fluid matrix.
d) Tissue that connects muscles to bones in humans.
Ans: Tendons
20. Write the difference between cartilage and bone.
Ans: Difference between cartilage and bone is listed below:
21. Which components of xylem are living and which ones are dead?
Ans: Xylem is composed of four elements:
Tracheid: Dead
Vessels: Dead
Xylem parenchyma: Living
Xylem fibres: Dead
22. Define due process of differentiation.
Ans: Dividing tissue is the reason for growth of plants occurs only in specific regions this is also known as meristematic tissue. The cells formed by meristematic tissue later lose the ability to divide as a result permanent tissue is formed. The process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and a function is called differentiation.
23. Define tissue. What is the utility of tissue in multicellular organisms?
Ans: Group of similar cells performing similar functions are called tissue. Millions of cells will be there in multicellular organisms. Specific functions are carried out by different groups of cells.
24. Mention characteristics of permanent tissues.
Ans: Characteristics of permanent tissues are:
Cells are large, comparatively thick walls and well developed .
Cytoplasm is present as a layer along the cell wall.
Bigger nucleus , vacuole is present in the cell.
There is lack of the power for the cell division in permanent tissue
25. Mention the functions of nervous tissue.
Ans: Function of nervous tissues are:
They conduct nerve impulses from one part of the body to another part.
The nervous tissues in the body are specialised for being stimulated and then pass on the stimulus very quickly from one place to another.
26. Animals of colder regions and fishes of cold water have thick layers of subcutaneous fat. Explain, why?
Ans: Thick layer of subcutaneous fat acts as an insulator. It retains heat in animals of colder regions and fishes of cold-water and thus maintains the body temperature. The heat loss will be less when the layer of subcutaneous fat is thicker.
27. Name the two main types of plant tissues.
Ans: Plant tissues are mainly divided into two types they are:
Meristematic tissue
Permanent tissue
28. Water hyacinth floats on the water surface. Explain.
Ans: Water hyacinth floats on the surface of water due to presence of aerenchyma. It is a special form of parenchyma, which contains air cavities. It provides buoyancy because of the air trapped inside which helps water hyacinth in floating because of the air trapped inside.
29. Name the two types of vascular tissues.
Ans: Types of vascular tissues are
Xylem: It conduct water and minerals from roots to the parts of the plant
Phloem: It conduct food from leaves to all parts of plant
30. How many types of elements are present in the phloem?
Ans: There are four types of elements are present in the phloem they are:
Sieve tube: Helps in conduction of food material
Companion cells: It helps sieve tube in conduction of food material
Phloem parenchyma: storage
Phloem fibres: It provides mechanical support.
Short Answer Questions: (3 Marks)
1. What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
Ans: Millions of cells will be there in multicellular organisms. Specific functions are carried out by different groups of cells. There is a clear-cut division of labour in multicellular organisms i.e., different parts of the body of a multicellular organism perform specific functions. For example, the brain controls all other parts of the body, the heart pumps blood to all parts of the body, kidneys remove waste materials from the body, sense organs collect information from external sources and transfer to the brain etc. All these functions would never be possible without formation of tissues in multicellular organisms.
2. Give three features of cardiac muscles.
I. Cardiac muscles are involuntary i.e.; they don’t work under our will.
II. Cells of cardiac muscles are cylindrical, branched, striated and uninucleate.
III. It shows rhythmic contraction and relaxation.
3. What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Ans: Areolar tissue is a connecting tissue found between skin and muscles, around our blood vessels and nerve cells and also in the bone marrow. Its functions are,
I. To fill the space inside organs.
II. To support internal organs.
III. To help in repair tissues
4. Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
Ans: The difference is shown as below,
5. Differentiate between striated, untreated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Ans: difference between striated, untreated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body is given below :, 6. complete the table:.
7. How many types of tissues are found in animals? Name the different types.
Ans: In animal four types of tissues are found:
Epithelium or Epithelial tissue (covering tissue): It forms outer protective covering all over the body.
Connective tissue (supporting tissue): It binds cells of other tissues in the body and give them rigidity and support.
Muscular tissue (contractile tissue): It helps the movement of the body by contraction and relaxation.
Nervous tissue: Its receiver stimulates and transmit the messages
8. Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles. Give one example of each
Ans: difference between voluntary and involuntary muscles are given below:.
9. What are the major functions of blood?
Ans: Blood is a type of connective tissue, and its functions are:
Blood flow can transport oxygen, food, hormones and waste material from one part of the body to the other part of the body
Blood carries oxygen and food to all cells. It also collects wastes from all parts of the body and carries them to the liver and kidney for disposal purposes.
Regulates temperature by distributing heat within the body
WBC’S protect due body from disease and helps in wound healing
Platelets help in blood clotting
10. Write about the functions of,
a) Epidermis
Ans: Epidermis, its main function is protection. It forms a waterproof coating, which reduces loss of water.
Ans: Cork: It is protective in function. It prevents desiccation, by preventing loss of water from the plant body. It prevents infection and mechanical injury
c) Stomata.
Ans: Stomata:These are the small opening which helps in exchange of gases
11. Differentiate between parenchyma and collenchyma
Ans: difference between parenchyma and collenchyma is given below:.
12. Mention the characteristics features of connective tissue .
Ans: Characteristics of connective tissue:
The cells are loosely spaced and are embedded in a non – living intercellular matrix
The intercellular matrix may be like jelly, fluid, dense or rigid.
Depending on the connective tissues functions the nature of the matrix varies.
13. How does cardiac muscle differ from both voluntary and involuntary muscles in both structure and function?
Ans: Cardiac muscles are the muscles of the heart that pumps blood to all parts of the body and it shows rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life without any fatigue. The cells of heart muscles are branched, cylindrical and uninucleate.
Cardiac Muscles are involuntary
More akin in structure and only found in heart.
They function throughout the life
14. Write differences between blood and lymph.
Ans : difference between blood and lymph is listed below:.
15. Give reasons for:
a) Intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchyma tissues.
Ans: Sclerenchyma cells are closely packed Hence intercellular spaces are absent. Its tissues are dead simple permanent tissues.
b) Meristematic cells have a prominent muscle and dense cytoplasm but they lack muscles
Ans: Meristematic cells have continuously dividing cells. Cells of meristem are not differentiated. It continuously divides and forms new cells which increase length and girth of the plant body.
c) We get crunchy and granular feeling, when we chew pear fruit.
Ans: due to presence of stone cells or grit cells, known as sclereids
16. Why is epidermis important for the plants?
Ans: Epidermis is the Outer protective covering of plants:
Epidermis is covered with a waterproof coating or layer called cuticle which can reduce water loss.
It also helps in the exchange of gases by the small pores called stomata.
17. Describe different types of meristems.
Ans: Based on their location in the plant body, meristems are of three types.
a) Apical meristems – Occurs at the growing tips of roots and shoots and brings about an increase in length of the plant
b) Lateral meristems – It occurs on the sides almost parallel to the long axis of the root, stem and its branches. Brings about an increase in the width or girth of the stem or root.
c) Intercalary meristems – located near to the node. Cells are very active, and have dense cytoplasm and thin cellulose. lack of vacuoles in intercalary meristems.
18. If you are provided with three slides, each containing one types muscles fibres, how will you identify them?
Ans: If we are provided with three slides, each containing one types muscles fibres, we can identify them by following points:
a) Skeletal muscles or voluntary muscles show alternate light and dark bands under microscope.
b) Unstriated muscles or involuntary muscles show no light or dark bands, multinucleate.
c) Cardiac muscles fibres show light and dark bands, fibres are interconnected with one or two nuclei.
19. If a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapours appear on the wall of the glass jar. Explain why?
Ans: This is because of the process called transpiration. Plants always lose water from the surface of leaves. Water reaches leaves by xylem vessels, where evaporation takes place by stomata. Gaseous exchange and also removal of excess water are performed by the Stomata present in the leaves.
20. Identify the following tissue and mention their function.
A) Parenchyma: stores food , it sometimes contains chlorophyll so performs photosynthesis, after that it is called chlorenchyma, in aquatic plants parenchyma to help them float because of large air cavities.
B) Collenchyma: It provides mechanical strength and allows bending of various parts of a plant without breaking.
C) Sclerenchyma: Provides strength to the plant parts, makes the plant hard and stiff.
21. Differentiate between meristematic and permanent tissue.
Ans: difference between meristematic and permanent tissue is given below:.
With the help of important questions for Tissues Class 9 chapter , students can revise the chapter for their exam in a better way. They can prepare their notes by referring to these important questions and answers, hence get some time for revision as well. These important questions for class 9 science tissues can be downloaded from Vedantu mobile app and official website. Also, the CBSE Class 9 tissues important questions will help them to understand the proper answer-writing technique for this chapter.
With these questions, students will be able to learn basics such as what tissues are and what is their application in living organisms.
The students also get to know about the plant tissues and animal tissues along with some other details such as meristematic tissues and permanent tissues with the help of the Class 9 Science chapter Tissue important questions.
The students can also know about different types of muscles.
Important Questions For Class 9 Chapter 6 Science
Explain why water vapor appears on the leaves of a potted plant when it is covered with a jar of glass.
Explain the difference between voluntary and involuntary muscles. Provide examples for each.
What structure is responsible for the protection of plant bodies against parasite invasion.
Explain the importance of the epidermis for the plants.
Differentiate between meristematic and permanent tissues in plants.
These questions provide some deep insights into the chapter for the students who need to know what the topic is all about. Also, the important questions for tissues class 9 play a very important role when it comes to giving some information to the students about certain entrance examinations as biology is a very common subject in these and to download the questions would really be a great idea in such cases. All they have to do is pay attention to their classes and make sure that they practice the class 9th science chapter 6 important questions more and more to gain better knowledge and information.
Why Choose Us to Get Extra Questions of Tissues Class 9
One of the main reasons why students need to choose Vedantu’s class 9 science ch 6 important questions is that we have the best materials for studying. Students that need some help in clearing their doubts can rely on these questions to gain a better understanding of the chapter.
We also have a team of expert teachers and professors who have personally selected these important questions for class 9 science chapter 6 . So, these questions will be very authentic and reliable. Not to mention that all of these questions are created according to the CBSE syllabus as well as the NCERT guidelines. The scope of scoring marks for students becomes a lot higher due to this fact.
We certainly aspire to provide the best help available with the class 9 science chapter 6 important questions. For students that need some help in scoring some good marks in their examinations for the finals, there is no doubt that taking the help of extra questions for class 9 science chapter 6 will really be a very good idea as they might find exactly what they are looking for and much more. Download the class 9 science chapter 6 questions from us right away.
Important Related Links for CBSE Class 9

FAQs on Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues
Q1. What is the Role of the Epidermis in Plants?
The epidermis is a single layer of cells that covers the leaves, flowers, stems, roots, etc. It acts as a boundary between the plant and the external environment. The role of the epidermis in plants is to provide protection to the various parts of the plants. Moreover, it can absorb water from the soil, from the roots and allows the exchange of gases through stomata.
Q2. What is the Main Difference Between Tendons and Ligaments?
The main difference between tendons and ligaments is that tendons connect muscles to bones while ligaments connect one bone to another. Tendons are tough, non-elastic and contain white fibres. Ligaments are strong, non-elastic and consist of yellow fibres.
Q3. Which Website Caters to Important Questions for CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues?
Preparing for exams can be overwhelming for students at times. Vedantu, India’s leading online educational platform, caters to various types of study materials to make the learning process easy and effective. Among such materials, one of the most useful is chapter-wise important questions. Vedantu provides the free PDF of Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues. The questions are selected by subject matter experts. The online repository for important questions is prepared considering the exam pattern and curriculum. Students can also avail the answers to these questions. The answers are also provided by subject experts and include all the important information.
Q4. What are the Tissues? What are the Simple and Complex Tissues?
The group of cells similar in origin and structure can be defined as a tissue. These cells are specialised to perform a particular function. For instance, muscle cells in our body form muscle tissues that bring about body movement or specific functions. Tissues can be broadly classified as Simple Tissues and Complex Tissues.
Simple Tissues: It is made up of only one type of cell. All the cells of such tissues work as individual units to perform a particular function. Example: parenchyma, collenchyma, etc.
Complex Tissues: It is made up of more than one type of cells. These cells work together as a single unit to perform a particular function. Example: Xylem, Phloem, etc.
Q5. What is the importance of tissue according to Chapter 6 of Class 9 Science?
Tissues refer to a group of blood cells that work together to perform certain jobs in the body. Tissues are important to the body as they provide a level of organization in all living organisms. Apart from this, tissues help to protect the body organs for any damage or injury. It even connects body parts to other bones in the body. Tissues also provide nutrition to the body. One of the major importance of tissues is that it helps to fight many infections.
Q6. Where can I download NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 of Class 9 Science?
Vedantu provides you with an opportunity to download NCERT Solutions for Chapter 6 of Class 9 Science PDF for free. There are many important questions and answers available in NCERT Solutions that will help you ace your exams. These important questions have been taken from all the important topics and concepts of the chapter. These solutions are available at free of cost on Vedantu(vedantu.com) and mobile app. Most of these questions are a part of the NCERT Textbook, hence you will be able to understand the chapter better. There are in-text questions and exercise questions that are available in NCERT Solutions.
Q7. What is the function of stomata?
Stomata is known as the pores that are available in the cells of leaves. The outermost layer available in the cells is known as the epidermis. This epidermis is very porous in nature, and these pores are known as Stomata. Stomata are very important to keep the plants alive. One of the main functions of stomata refers to the exchange of gases in and out of plants. Apart from this, the stomata even helps in the process of transpiration.
Q8. What does a neuron look like?
Neuron helps to pass informational messages throughout the body. A neuron refers to a nerve cell. This nerve cell consists of a cell body that contains cytoplasm and a nucleus and a thin hair-like structure that emerges from it. Every neuron consists of an elongated part known as an axon. It also contains small and short branch-like structures known as dendrites. A single neuron can grow up to a meter long and not more than that.
Q9. How can I study Chapter 6 Tissues of Class 9 Science?
While you're preparing for your exams, you need to stick to the syllabus. To study for Chapter 6 Tissues of Class 9 Science, you must pay attention to all the important questions. You should solve practice papers, sample papers, and previous year's question papers. By doing this you will get an idea of all the important questions. In most sample papers there are some questions which are repeated. Looking at this, you will be able to figure out what the important questions are.
CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions
Cbse study materials.
myCBSEguide
- Class 9 Science Case...
Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
If you are wondering how to solve class 9 science case study questions, then myCBSEguide is the best platform to choose. With the help of our well-trained and experienced faculty, we provide solved examples and detailed explanations for the recently added Class 9 Science case study questions.
You can find a wide range of solved case studies on myCBSEguide, covering various topics and concepts. Class 9 Science case studies are designed to help you understand the application of various concepts in real-life situations.
The rationale behind Science
Science is crucial for Class 9 students’ cognitive, emotional, and psychomotor development. It encourages curiosity, inventiveness, objectivity, and aesthetic sense.
In the upper primary stage, students should be given a variety of opportunities to engage with scientific processes such as observing, recording observations, drawing, tabulating, plotting graphs, and so on, whereas in the secondary stage, abstraction and quantitative reasoning should take a more prominent role in science teaching and learning. As a result, the concept of atoms and molecules as matter’s building units, as well as Newton’s law of gravitation, emerges.
Science is important because it allows Class 9 Science students to understand the world around us. It helps to find out how things work and to find solutions to problems at the Class 9 Science level. Science is also a source of enjoyment for many people. It can be a hobby, a career, or a source of intellectual stimulation.
Case study questions in Class 9 Science
The inclusion of case study questions in Class 9 science CBSE is a great way to engage students in critical thinking and problem-solving. By working through real-world scenarios, Class 9 Science students will be better prepared to tackle challenges they may face in their future studies and careers. Class 9 Science Case study questions also promote higher-order thinking skills, such as analysis and synthesis. In addition, case study questions can help to foster creativity and innovation in students. As per the recent pattern of the Class 9 Science examination, a few questions based on case studies/passages will be included in the CBSE Class 9 Science Paper. There will be a paragraph presented, followed by questions based on it.
Examples of Class 9 science class case study questions
Class 9 science case study questions have been prepared by myCBSEguide’s qualified teachers. Class 9 case study questions are meant to evaluate students’ knowledge and comprehension of the material. They are not intended to be difficult, but they will require you to think critically about the material. We hope you find Class 9 science case study questions beneficial and that they assist you in your exam preparation.
The following are a few examples of Class 9 science case study questions.
Class 9 science case study question 1
- due to its high compressibility
- large volumes of a gas can be compressed into a small cylinder
- transported easily
- all of these
- shape, volume
- volume, shape
- shape, size
- size, shape
- the presence of dissolved carbon dioxide in water
- the presence of dissolved oxygen in the water
- the presence of dissolved Nitrogen in the water
- liquid particles move freely
- liquid have greater space between each other
- both (a) and (b)
- none of these
- Only gases behave like fluids
- Gases and solids behave like fluids
- Gases and liquids behave like fluids
- Only liquids are fluids
Answer Key:
- (d) all of these
- (a) shape, volume
- (b) the presence of dissolved oxygen in the water
- (c) both (a) and (b)
- (c) Gases and liquids behave like fluids
Class 9 science case study question 2
- 12/32 times
- 18 g of O 2
- 18 g of CO 2
- 18 g of CH 4
- 1 g of CO 2
- 1 g of CH 4 CH 4
- 2 moles of H2O
- 20 moles of water
- 6.022 × 1023 molecules of water
- 1.2044 × 1025 molecules of water
- (I) and (IV)
- (II) and (III)
- (II) and (IV)
- Sulphate molecule
- Ozone molecule
- Phosphorus molecule
- Methane molecule
- (c) 8/3 times
- (d) 18g of CH 4
- (c) 1g of H 2
- (d) (II) and (IV)
- (c) phosphorus molecule
Class 9 science case study question 3
- collenchyma
- chlorenchyma
- It performs photosynthesis
- It helps the aquatic plant to float
- It provides mechanical support
- Sclerenchyma
- Collenchyma
- Epithelial tissue
- Parenchyma tissues have intercellular spaces.
- Collenchymatous tissues are irregularly thickened at corners.
- Apical and intercalary meristems are permanent tissues.
- Meristematic tissues, in its early stage, lack vacuoles, muscles
- (I) and (II)
- (III) and (I)
- Transpiration
- Provides mechanical support
- Provides strength to the plant parts
- None of these
- (a) Collenchyma
- (b) help aquatic plant to float
- (b) Sclerenchyma
- (d) Only (III)
- (c) provide strength to plant parts
Cracking Class 9 Science Case Study Questions
There is no one definitive answer to Class 9 Science case study questions. Every case study is unique and will necessitate a unique strategy. There are, nevertheless, certain general guidelines to follow while answering case study questions.
- To begin, double-check that you understand the Class 9 science case study questions. Make sure you understand what is being asked by reading it carefully. If you’re unclear, seek clarification from your teacher or tutor.
- It’s critical to read the Class 9 Science case study material thoroughly once you’ve grasped the question. This will provide you with a thorough understanding of the problem as well as the various potential solutions.
- Brainstorming potential solutions with classmates or other students might also be beneficial. This might provide you with multiple viewpoints on the situation and assist you in determining the best solution.
- Finally, make sure your answer is presented simply and concisely. Make sure you clarify your rationale and back up your claim with evidence.
A look at the Class 9 Science Syllabus
The CBSE class 9 science syllabus provides a strong foundation for students who want to pursue a career in science. The topics are chosen in such a way that they build on the concepts learned in the previous classes and provide a strong foundation for further studies in science. The table below lists the topics covered in the Class 9 Science syllabus of the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE). As can be seen, the Class 9 science syllabus is divided into three sections: Physics, Chemistry and Biology. Each section contains a number of topics that Class 9 science students must study during the course.
CBSE Class 9 Science (Code No. 086)
Theme: Materials Unit I: Matter-Nature and Behaviour Definition of matter; solid, liquid and gas; characteristics – shape, volume, density; change of state-melting (absorption of heat), freezing, evaporation (cooling by evaporation), condensation, sublimation. Nature of matter: Elements, compounds and mixtures. Heterogeneous and homogenous mixtures, colloids and suspensions. Particle nature and their basic units: Atoms and molecules, Law of constant proportions, Atomic and molecular masses. Mole concept: Relationship of mole to mass of the particles and numbers. Structure of atoms: Electrons, protons and neutrons, valency, the chemical formula of common compounds. Isotopes and Isobars.
Theme: The World of the Living Unit II: Organization in the Living World Cell – Basic Unit of life: Cell as a basic unit of life; prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells, multicellular organisms; cell membrane and cell wall, cell organelles and cell inclusions; chloroplast, mitochondria, vacuoles, endoplasmic reticulum, Golgi apparatus; nucleus, chromosomes – basic structure, number. Tissues, Organs, Organ System, Organism: Structure and functions of animal and plant tissues (only four types of tissues in animals; Meristematic and Permanent tissues in plants).
Theme: Moving Things, People and Ideas Unit III: Motion, Force and Work Motion: Distance and displacement, velocity; uniform and non-uniform motion along a straight line; acceleration, distance-time and velocity-time graphs for uniform motion and uniformly accelerated motion, derivation of equations of motion by graphical method; elementary idea of uniform circular motion. Force and Newton’s laws: Force and Motion, Newton’s Laws of Motion, Action and Reaction forces, Inertia of a body, Inertia and mass, Momentum, Force and Acceleration. Elementary idea of conservation of Momentum. Gravitation: Gravitation; Universal Law of Gravitation, Force of Gravitation of the earth (gravity), Acceleration due to Gravity; Mass and Weight; Free fall. Floatation: Thrust and Pressure. Archimedes’ Principle; Buoyancy. Work, energy and power: Work done by a Force, Energy, power; Kinetic and Potential energy; Law of conservation of energy. Sound: Nature of sound and its propagation in various media, speed of sound, range of hearing in humans; ultrasound; reflection of sound; echo.
Theme: Food Unit IV: Food Production Plant and animal breeding and selection for quality improvement and management; Use of fertilizers and manures; Protection from pests and diseases; Organic farming.
PRESCRIBED BOOKS:
- Science-Textbook for class IX-NCERT Publication
- Assessment of Practical Skills in Science-Class IX – CBSE Publication
- Laboratory Manual-Science-Class IX, NCERT Publication
- Exemplar Problems Class IX – NCERT Publication
myCBSEguide: A true helper
There are numerous advantages to using myCBSEguide to achieve the highest results in Class 9 Science.
- myCBSEguide offers high-quality study materials that cover all of the topics in the Class 9 Science curriculum.
- myCBSEguide provides practice questions and mock examinations to assist students in the best possible preparation for their exams.
- On our myCBSEguide app, you’ll find a variety of solved Class 9 Science case study questions covering a variety of topics and concepts. These case studies are intended to help you understand how certain principles are applied in real-world settings
- myCBSEguide is that the study material and practice problems are developed by a team of specialists who are always accessible to assist students with any questions they may have. As a result, students may be confident that they will receive the finest possible assistance and support when studying for their exams.
So, if you’re seeking the most effective strategy to study for your Class 9 Science examinations, myCBSEguide is the place to go!
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Class 9 - NCERT Science Solutions
Intext questions 1.
What is a tissue?
A group of structurally and functionally similar cells performing a particular function is called a tissue.
What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
A group of cells that are similar in structure and/or work together to achieve a particular function forms a tissue. In multi-cellular organisms, tissues provide structural and mechanical strength and enables the division of labour. In such organisms, many tissues work together to form an organ and then an organ system.
Intext Questions 2
Name types of simple tissues.
Types of simple tissue are:
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
Where is apical meristem found?
Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots.
Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
The husk of coconut is made of sclerenchymatous tissue.
What are the constituents of phloem?
The constituents of phloem are:
- Sieve cells
- Sieve tubes
- Companion cells
- Phloem fibres
- Phloem parenchyma
Intext Questions 3
Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Muscular tissue is responsible for movement in our body.
What does a neuron look like?
A neuron cell looks like a tree. A neuron consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm, from which long thin hair-like parts arises. Usually each neuron has a single long part (process), called the axon, and many short, branched parts (processes) called dendrites.
Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Three features of cardiac muscles are:
- They are cylindrical.
- They are uninucleate.
- They are branched.
What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Following are the functions of areolar tissue:
- It fills the space inside the organs.
- It supports internal organs.
- It helps in repair of tissues.
Define the term "tissue".
How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Four types of elements together make up the xylem tissue. They are:
- Tracheids — They are thick walled and tubular dead cells. They transport water and mineral.
- Vessels — They are tubular cells and transport water and mineral.
- Xylem parenchyma — They store food.
- Xylem fibres — They are supportive in function.
How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
What are the functions of the stomata?
Following are the functions of the stomata:
- Exchange of gases with the atmosphere occur through stomata.
- Transpiration (loss of water in the form of water vapour) also takes place through stomata.
Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle?
The specific function of the cardiac muscle is to contract and expand. They show rhythmic and involuntary contraction and relaxation throughout life enabling the heart to beat and pump blood to all parts of the body.
Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
Draw a labelled diagram of a neuron.
Labelled diagram of a neuron is shown below:
Question 10
Name the following.
(a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth.
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans.
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants.
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body.
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix.
(f) Tissue present in the brain.
(a) Squamous epithelium
(b) Tendons
(d) Adipose tissue
(f) Nervous tissue
Question 11
Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
- Skin — epithelial tissues
- Bark of tree — cork (formed by secondary meristem)
- Bone — Connective tissue (Bone cells are embedded in a hard matrix that is composed of calcium and phosphorus compounds.)
- Lining of kidney tubule — Cuboidal epithelium (with cube-shaped cells)
- Vascular bundle — Xylem and phloem (Complex permanent tissue)
Question 12
Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
The parenchyma tissue can be found in the leaf, fruits, as well as flowers. It is located beneath the epidermis.
Question 13
What is the role of epidermis in plants?
The primary role of epidermis in plants is protection. The entire surface of a plant has an outer covering epidermis. It protects all the parts of the plant. Epidermal cells on the aerial parts of the plant often secrete a waxy, water resistant layer on their outer surface. This aids in protection against:
- loss of water
- mechanical injury
- invasion by parasitic fungi
Question 14
How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
A strip of secondary meristem located in the cortex forms layers of cells which constitute the cork. Cells of cork are dead and compactly arranged without intercellular spaces. They also have a substance called suberin in their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water. This is how cork act as a protective tissue protecting the plants from any physical or mechanical injuries and pathogenic infection.
Question 15
Complete the following chart:
The completed chart is shown below:

Extra Questions for Class 9th: Ch 6 Tissues Science
Extra questions for class 9th: ch 6 tissues (science) important questions answer included.
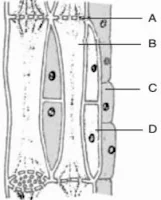
Contact Form
- CBSE Study Material
- CBSE Important Questions
- Important Questions For Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
Important Questions CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6 – Tissues
Important Questions CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter 6 – Tissues cover the key highlights of the Chapter 6 of the NCERT Science textbook. These questions are used by students to prepare well for the final exams. Students can learn the textbooks thoroughly, and then they can try solving these questions as a way to not only gauge their preparation level for the final exam but also to revise the chapter thoroughly. These CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions are considered as the best resource for the students.
Here in this article below is the clickable link to access the PDF format of the question paper. Find also the questions on the web page.
Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 tissues 1- Download Free PDF

Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
This is Very helpful
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science (biology) Chapter 6 Tissues are given below. In these solutions, we have answered all the intext and exercise questions provided in NCERT class 9 science textbook. Class 9 NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 6 provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum. Students can easily download these solutions in PDF format for free from our app.
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Textbook Questions and Answers
INTEXT QUESTIONS
PAGE NO. 69
Question 1: What is a tissue?
Answer: Tissue is a group of cells that are similar in structure and are organised together to perform a specific task.
Question 2: What is the utility of tissues in multi-cellular organisms?
Answer: In multicellular organisms, the body system is based on the division of labour (like muscle cells form muscular tissue which helps in movement). It means the cells performing a specific function are grouped together to form a particular tissue. The different tissues are organized in a way to provide the highest efficiency in the functioning of the body.
PAGE NO. 74
Question 1: Name types of simple tissues.
Answer: The types of simple tissues are as follows:
- Collenchyma
- Sclerenchyma
Question 2: Where is apical meristem found?
Answer: Apical meristem is present at the growing tips of stems and roots. Their main function is to initiate growth in new cells of seedlings, at the tip of roots, and shoots.
Question 3: Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
Answer: The husk of a coconut is made up of sclerenchyma tissue.
Question 4: What are the constituents of phloem?
Answer: Phloem is the food conducting tissue in plants. It is made up of four components:
- Sieve tubes
- Companion cells
- Phloem parenchyma
- Phloem fibres
PAGE NO. 77
Question 1: Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
Answer: The muscular tissue is responsible for movement in our body.
Question 2: What does a neuron look like?
Answer: A neuron consists of a cell body with a nucleus and cytoplasm, from which long thin hair like parts arise. Each neuron has a single long part called the axon, and many small, short branched parts called dendrite. An individual nerve cell is called neuron, it may be up to a metre long.
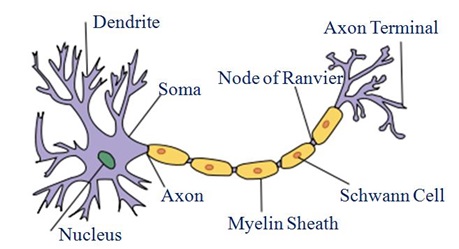
Question 3: Give three features of cardiac muscles.
Answer: Three features of cardiac muscles are:
Question 4: What are the functions of areolar tissue?
Answer: Functions of areolar tissue:
1. It fills the space inside the organs, thus acts as a packing tissue between the organs. 2. It supports many delicate organs in the body. 3. It plays role in repair of tissues.
Question 1: Define the term ‘tissue’?
Answer: A tissue is defined as a cluster of cells which are similar in structure and work together to perform a particular function.
Question 2: How many types of elements together make up the xylem tissue? Name them.
Answer: The following four types of elements make up xylem tissue:
- Xylem parenchyma.
- Xylem fibres.
Question 3: How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants?
Answer: Simple tissues are made up of one type of cells which coordinate to perform a common function.
Complex tissues are made up of more than one type of cells. All these coordinate to perform a common function.
Question 4: Differentiate between parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall.
Answer: The differences between cell walls of parenchyma, collenchyma and sclerenchyma are given in the following table:
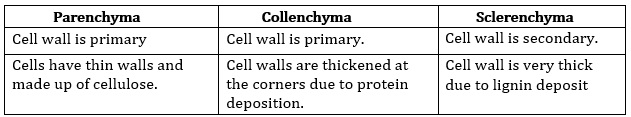
Question 5: What are the functions of Stomata?
Answer: Functions of Stomata are:
Question 6: Diagrammatically show the difference between the three types of muscle fibres.
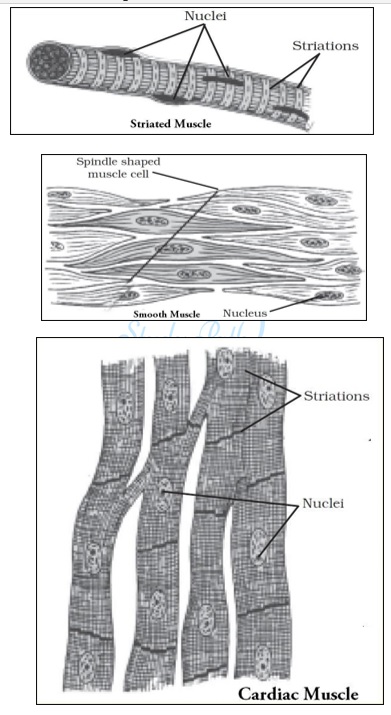
Question 7: What is the specific function of cardiac muscle?
Answer: Cardiac muscles facilitate contraction and relaxation of heart; which results in pumping action of the heart.
Question 8: Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site / location in the body.
Answer: Striated, Unstriated and Cardiac muscles are three types of muscle tissues. Their Different characteristics are as follows:
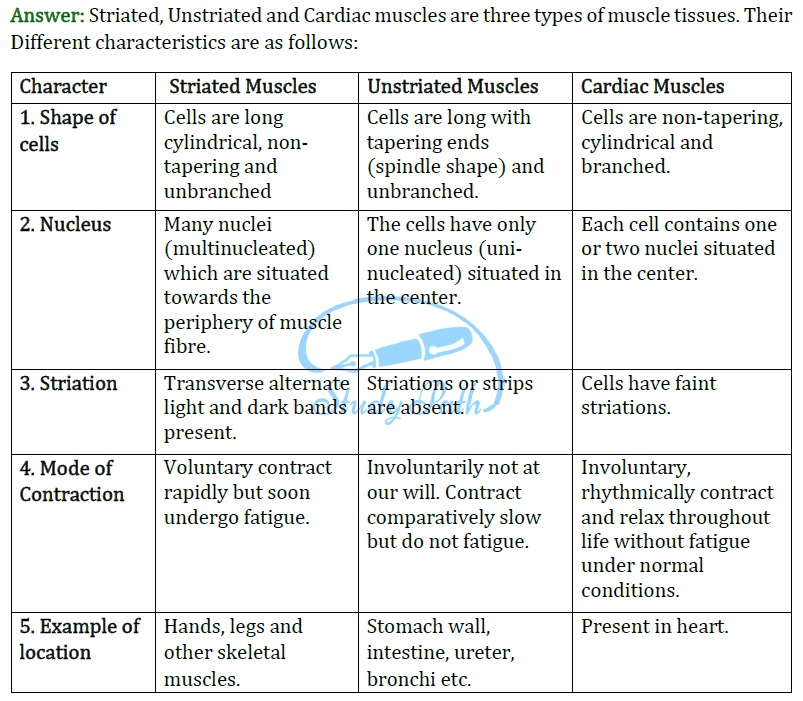
Question 9: Draw a labelled diagram of neuron.
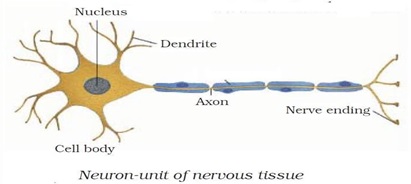
Question 10: Name the following: (a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth. (b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans. (c) Tissue that transports food in plants. (d) Tissue that stores fat in our body. (e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix. (f) Tissue present in the brain.
Answer: (a) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth → Epithelial tissue
(b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans → Dense regular connective tissue (tendons)
(c) Tissue that transports food in plants → Phloem
(d) Tissue that stores fat in our body → Adipose tissue
(e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix → Blood
(f) Tissue present in the brain → Nervous tissue
Question 11: Identify the type of tissue in the following: Skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle.
Answer: Skin: Stratified squamous epithelial tissue
Bark of tree: Simple permanent tissue
Bone: Connective tissue
Lining of kidney tubule: Cuboidal epithelial tissue
Vascular bundle: Complex permanent tissue
Question 12: Name the regions in which parenchyma tissue is present.
Answer: Parenchyma is a simple permanent tissue of angiospermic plants. It is present in cortex and pith of stem and roots. It is also present in mesophyll of leaves. When it contains chlorophyll, it is called Chlorenchyma, found in green leaves.
Question 13: What is the role of epidermis in plants?
Answer: The epidermis in plants forms an uninterrupted and continuous layer that has no intercellular spaces. It provides protection.
Epidermis is a protective tissue of angiospermic plants. It provides protections to underlying tissues. Epidermis forms outer covering of various plant organs such as roots, stem, leaves, and flowers and remains in direct contact with the environment. Any substance whether solid, liquid or gas can enter into the plant or move outside only after passing through this layer. Epidermis helps in absorption, secretion, gaseous exchange and transpiration. It helps in preventing the entry of pathogens.
Question 14: How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
Answer: The outer protective layer or bark of a tree is known as the cork. It is made up of dead cells. Therefore, it protects the plant against mechanical injury, temperature extremes, etc. It also prevents the loss of water by evaporation.
Question 15: Complete the table:
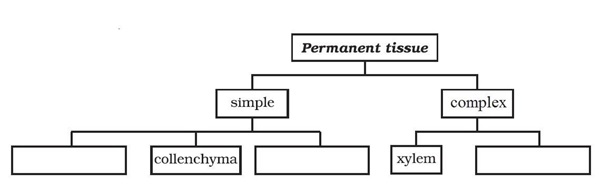
Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 6 Tissues
CBSE Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions Chapter 6 helps students to clear their doubts and to score good marks in the board exam. All the questions are solved by experts with a detailed explanation that will help students complete their assignments & homework. Having a good grasp over CBSE NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science will further help the students in their preparation for board exams and other competitive exams such as NTSE, Olympiad, etc.
NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 PDF
Below we have listed the topics discussed in NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6. The list gives you a quick look at the different topics and subtopics of this chapter.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Test: Tissues- Case Based Type Questions- 2 - Class 9 MCQ
10 questions mcq test - test: tissues- case based type questions- 2, direction: sunil while playing football with his friends got injured suddenly. his friends took him to the hospital and the doctor told that he was suffering from a sprain and advised bed rest. every afternoon, his friends visited him to enquire about his health. q. during a sprain, which type of tissue are stresses.
- B. Ligaments
- D. Connective tissues

Direction: Sunil while playing football with his friends got injured suddenly. His friends took him to the hospital and the doctor told that he was suffering from a sprain and advised bed rest. Every afternoon, his friends visited him to enquire about his health. Q. Dislocation of bones is due to ________
- A. Damage of nervous tissues
- B. Breakage of ligaments
- C. Breakage of Bones
- D. None of these
Dislocations also occur during regular activities when the muscles and tendons surrounding the joint are weak.
Direction: Study the given diagram and answer the following questions. Q. Vascular bundles are :
- A. Only Xylem
- B. Only Phloem
- C. Only Cortex
- D. Both Xylem and Phloem
Direction: Study the given diagram and answer the following questions.
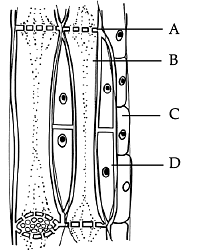
Q. What will happen if Phloem at the base of the branch is removed?
- A. Plant will die
- B. Lower parts of the plants wilted.
- C. No change occur
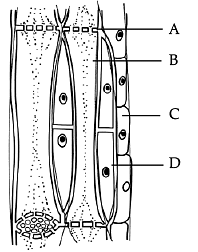
Q. Name the tissue shown in the diagram.
- C. Epidermis
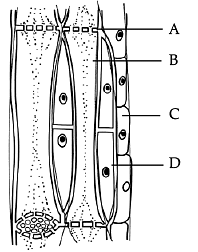
Q. Identify the parts A,B,C and D.
- A. A - Companion cell, B - Sieve tube, C - Sieve plate, D - Phloem parenchyma
- B. A - Phloem Parenchyma , B - Companion cell, C - Sieve tube, D - Sieve plate
- C. A - Sieve plate, B - Sieve tube, C - Phloem parenchyma D - Companion cell
- D. A - Sieve tube, B - Phloem parenchyma, C - Sieve plate, D - Companion cell
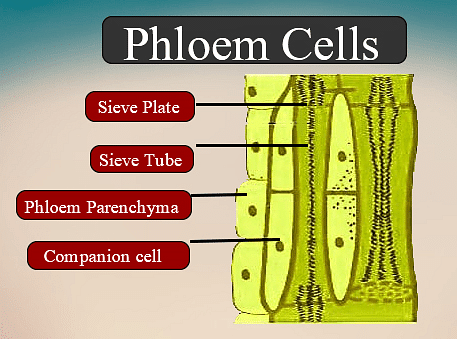
Phloem is composed of various specialized cells called sieve tubes, companion cells, phloem fibres, and phloem parenchyma cells .
Direction: Study the given descriptions and answer the following questions.
Tissue ‘A’–Repairs the injured tissues and fills spaces within organs.
Tissue ‘B’–Serves as a fat reservoir and also carries out the function of insulator.
Q. Muscular tissues that functions throughout life without fatigue :
- A. Striated muscles
- B. Smooth muscles
- C. Cardiac muscles
Q. Specialised connective tissue consist of lipid rich cells ______
- A. Adipose tissue
- B. Areolar tissue
- C. Muscular
Q. Identify the animal tissue from the given description :
- A. A - Adipose tissue , B - Areolar tissue
- B. A - Muscular tissue , B - Adipose tissue
- C. A - Areolar tissue, B - Muscular tissue
- D. A - Areolar tissue, B -Adipose tissue
(B) The adipose tissue is found beneath the skin, in the covering of the heart, around the blood vessels and kidneys and in yellow bone marrow.
Q. The fibres present in areolar tissue are :
- A. Collagen
- C. Reticular
- D. All of these
Top Courses for Class 9

Important Questions for Tissues- Case Based Type Questions- 2
Tissues- case based type questions- 2 mcqs with answers, online tests for tissues- case based type questions- 2, welcome back, create your account for free.
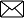
Forgot Password
- NCERT SOLUTIONS
- CHAPTER NOTES
- PRIVACY POLICY

- RD SHARMA SOLUTIONS
- IIT JEE SOLVED QUESTIONS
Class 9 Science Tissues

About STUDYGUIDE360 STUDYGUIDE360 is a student centric educational web portal which provides quality test papers and study materials for the students preparing for CBSE or targeting various entrance exams. During past few years, a number of surveys on students were made to better understand their problems regarding their studies and their basic requirement.
LIKE US ON FACEBOOK
Contact form.

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissue Study Notes
- Last modified on: 3 years ago
- Reading Time: 1 Minute

Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
2 thoughts on “ Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissue Study Notes ”
- Pingback: CBSE Class 9 Science Study Notes – Gurukul For JEE & NEET
- Pingback: Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter In Our Surrounding Study Notes – Gurukul For JEE & NEET
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
The Site is down as we are performing important server maintenance, during which time the server will be unavailable for approximately 24 hours. Please hold off on any critical actions until we are finished. As always your feedback is appreciated.

- Study Packages
- NCERT Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Online Test

- Questions Bank
- Test Series
- Ncert Solutions
- Solved Papers
- Current Affairs
- JEE Main & Advanced
- Pre-Primary
- MP State Exams
- UP State Exams
- Rajasthan State Exams
- Jharkhand State Exams
- Chhattisgarh State Exams
- Bihar State Exams
- Haryana State Exams
- Gujarat State Exams
- MH State Exams
- Himachal State Exams
- Delhi State Exams
- Uttarakhand State Exams
- Punjab State Exams
- J&K State Exams
9th Class Science Tissues Question Bank
Done 9th cbse science tissues total questions - 214.

question_answer 1) What feature helps aquatic plants to maintain buoyancy in water?
question_answer 2) What is called parenchyma containing chlorophyll?
question_answer 3) Plants are flexible due to which permanent tissue?
question_answer 4) Cells of which tissue are irregularly thickened at the corners.
question_answer 5) State one role of parenchyma in plants.
question_answer 6) Walls of sclerenchymatous cells are thickened due to which reason?
question_answer 7) Why epidermis of plants living in dry habitats is thicker?
question_answer 8) What is the function of waxy covering on epidermis of aerial parts of plants?
question_answer 9) What kind of cells enclose stomata?
question_answer 10) What is transpiration?
question_answer 11) Which complex permanent tissue conduct material in both direction?
question_answer 12) What is the function of hair-like parts on roots?
question_answer 13) What are the types of complex permanent tissues?
question_answer 14) Blood is which type of tissue?
question_answer 15) Cilia are present in which types of tissue?
question_answer 16) A selectively permeable surface is composed of what type of tissue in animals?
question_answer 17) Cells of which epithelium is cube-shaped?
question_answer 18) What kind of cells can secrete substances at the epithelial surface?
question_answer 19) Which type of conducting tissue conduct water and minerals vertically?
question_answer 20) Which conducting tissue transport food from leaves to other parts of plants?
question_answer 21) Why are cork impervious to gases and water?
question_answer 22) Which muscles can show rhythmic contraction and relaxation throughout life?
question_answer 23) Which type of muscle fibre has light and dark band on its surface?
question_answer 24) What kinds of compounds compose bone cells?
question_answer 25) What kind of blood cell is an integral part of immune system?
question_answer 26) Which biochemicals compose the solid matrix of cartilage?
question_answer 27) Which connective tissue helps in repair of tissues?
question_answer 28) Which muscle has spindle-shaped cells?
question_answer 29) State one function of bone.
question_answer 30) Which tissue is present in spinal cord?
question_answer 31) State one function of nerve impulse.
question_answer 32) Name the tissue present in soft parts of the plants like pith and cortex.
question_answer 33) What is a function of phloem?
question_answer 34) What is a the function of xylem?
question_answer 35) Name the tissue present in brain.
question_answer 36) Give two main functions of stomata.
question_answer 37) Name the dead element of phloem.
question_answer 38) Name the type of tissue which is abundantly found in animal.
question_answer 39) Write the common name of (i) xylem (ii) phloem.
question_answer 40) State when the tissue formation take place.
question_answer 41) Name the following (i) Multinucleate muscle fibre (ii) Spindle-shaped muscle fibre
question_answer 42) Which meristem is present at growing tips of stems and roots?
question_answer 43) Which process is followed by meristematic tissue to form permanent tissue?
question_answer 44) Name basic packing tissue of plant.
question_answer 45) Which pigment helps in performing photosynthesis by plants?
question_answer 46) Which tissue is present at the lining of mouth?
question_answer 47) What is the prominent function of blood?
question_answer 48) Which connective tissue is specialised for fat storage?
question_answer 49) Which body cell provides resistance against infection?
question_answer 50) Which tissue is responsible for growth of plant?
question_answer 51) What is the name of parenchyma having large air cavities?
question_answer 52) What is the role of tendon in animals.
question_answer 53) What is the living component of xylem?
question_answer 54) What is the difference between meristematic tissues and permanent tissues?
question_answer 55) Which tissue is found in an area of regular wear and tear?
question_answer 56) Name the largest blood cells.
question_answer 57) From which matter matrix of cartilage is made up of
question_answer 58) Which part of an actively growing root takes up most of water from soil?
question_answer 59) Which type of tissue contracts when it is stimulated by nerve impulse?
question_answer 63) Name the junction between the terminal part of one axon and the dendrite of adjacent neuron.
question_answer 65) Write a short note on types of meristematic tissue with their location and functions in plants.
question_answer 66) What are the functions of collenchyma in plants?
question_answer 67) Give differences between fibres and sclerids. (2)
question_answer 68) Write the functions of following chemical substances found in plant tissues. (i) Lignin (ii) Cutin

question_answer 70) Draw diagram of stomata.
question_answer 71) Write a note on vascular bundle.
question_answer 72) Why is epidermis present as a thick waxy coating of cutin in desert plants?
question_answer 73) Write difference between aerenchyma and chlorenchyma.
question_answer 74) Heart pumps blood all through the body. Can you explain the reason behind this peculiar ability of heart?
question_answer 75) Write the function of (i) Ligaments (ii) Tendons
question_answer 76) Which tissue forms the inner lining of the intestine?
question_answer 77) Under what circumstances squamous epithelium is called as stratified squamous epithelium?
question_answer 78) Cutting of rose is done timely in gardens but still it regain its length. Give reason.
question_answer 79) (i) State two important functions of areolar tissue. (ii) Why are skeletal muscles known as striated muscles?
question_answer 80) (i) Mention the location of apical meristem in plants. (ii) Name the tissue responsible for movement of body.
question_answer 81) Draw a diagrammatic labelled sketch of stem tip to show the location of meristematic tissue. Mention the function of meristematic tissue.
question_answer 82) What is the function of bones, cartilage, tendons and ligaments?
question_answer 83) What are the roles of epidermis in plants?
question_answer 84) What is epithelial tissue? State the type of epithelial tissue present in the lining of blood vessels.
question_answer 85) Name two types of process present in neuron.
question_answer 86) What type of tissue is found at shoot apex? Name one more part of the plant body where this type of tissue is found.
question_answer 88) Write the differences between simple and complex tissues. Give one examples of each.
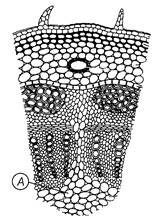
question_answer 91) Do roots of a plant continue growing after their tips are removed? Explain giving reasons.
question_answer 92) Which structure protects the plant body against the invasion of parasites?
question_answer 93) Animals of colder region and fishes of cold water have thicker layer of subcutaneous fat. Describe why?
question_answer 94) Name the different components of xylem and draw a living component.
question_answer 95) Write the features of striated muscles with diagram.
question_answer 96) Differentiate between bone ad cartilage.
question_answer 97) Name three different types of blood cells and give their functions. Draw diagram also.
question_answer 98) Write functions of the following (i) Areolar connective tissue (ii) Neuron (iii) Adipose connective tissue
question_answer 99) What will happen if cells are not organised in tissue?
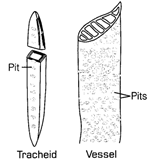
question_answer 101) Draw a well labelled diagram of cardiac muscle found in human body. Write two differences between striated and smooth muscles.
question_answer 102) Name the tissue responsible for flexibility in plants. How would you differentiate it from other permanent tissues. (2)
question_answer 103) List any six characteristic of parenchyma.
question_answer 104) Name the tissue that smoothens bones surface at joints. Describe its structure with the help of diagram.
question_answer 105) Which, type of muscles, i.e., smooth or striated are found in the iris of the eye? Why are smooth muscles called involuntary muscles? In what way they are different from striated muscles with respect to number of nuclei?
question_answer 106) List the constituents of phloem. What will happen if the phloem at the base of branch is removed?
question_answer 107) Give three differences between epithelial tissue and connective tissue.
question_answer 108) What are neurons? Where are they found in the body? What function do they perform in the body of an organism?
question_answer 109) Describe three functions of protective tissue in plants.
question_answer 110) Give one function of each of the following (i) Stomata (ii) Root nodules (iii) Cardiac muscle fibres
question_answer 111) State the functions of skeletal connective tissues.
question_answer 112) Give the name of the following. (i) Tissue concerned with the conduction of food materials. (ii) Tissue capable of cell division. (iii) Multiple pore present in epidermis of leaf.
question_answer 113) What happens when (i) formation of cork in older stem does not occur. (i) If ligament get over stretched. (iii) apical meristem is damaged in plants.
question_answer 114) Differentiate between axon and dendrite.
question_answer 115) Differentiate between blood and lymph. (3)
question_answer 116) Differentiate the following activities on the basis of voluntary or involuntary muscles
question_answer 117) Water hyacinth floats on water surface Explain.
question_answer 118) Why are xylem and phloem called complex tissue? How they different from one another? (2)
question_answer 119) Differentiate between meristematic and permanent tissues in plants.
question_answer 120) Give the differences between axon and dendron.
question_answer 121) Give the differences between tendon and ligament.
question_answer 122) Rohan's brother is an athlete, One day Rohan went to see his brother's competition. All of a sudden he saw his brother in pain and not able to run comfortably. Slowly a medical team gathered around him and he saw a doctor applying ice on his knees. (i) He is very confused as to why the doctor is applying ice on his brother's knees. Can you clear Rohan's confusion? (ii) What is ligament? (iii) What values shown by Rohan? (iii) The values shown by Rohan are inquisitive and scientific approach towards a problem.(2)
question_answer 123) Name the following. (i) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth. (ii) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans. (iii) Tissue that tr (arts fnspoood in plants. (iv) Tissue that stores fat in our body. (v) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix. (vi) Tissue present in the brain.
question_answer 124) Identify the type of tissue in the following. Skin, Bark of tree, Bone, Lining of kidney tubules, Vascular bundle
question_answer 125) Differentiate between various types of muscular tissues? Draw appropriate diagram.
question_answer 126) Explain the location of all the protective tissue in animals. Draw appropriate diagram.
question_answer 127) What are simple permanent tissues of plants? Explain in detail with diagram (also give differences in them).
question_answer 128) The transportation system of plants is composed of complex permanent tissue also have a transportation system in themselves clarify in detail with appropriate diagrams.
question_answer 129) Write difference between animal tissue and plant tissue.
question_answer 130) Our will can control some of the action of our body but some are not in our control. Comment.
question_answer 131) Ashu a student of class IX, suffered from high fever with headache. After a blood test, the doctor confirmed that he was suffering from dengue. Platelet count in his blood sample was also low and was recorded as 60,000. (i) What does a doctor advise if the platelet count is very low? (ii) What precaution one should take to get rid of dengue? (iii) What value is shown by the doctor?
question_answer 132) Write a note on the protective tissue in plants. (Give appropriate diagram also)
question_answer 133) Write two differences between muscles present in heart and the limbs of man. Also draw labelled diagram of these two kinds of muscles.
question_answer 134) Give reasons for (i) Meristematic cell have prominent nucleus and dense cytoplasm but they lackvacuole. (ii) Intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchymatous tissue. (iii) We get crunchy and granular feeling when we chew pear fruit. (iv) Branches of tree moves and bend freely in high wind velocity. (v) It is difficult to pull out husk of coconut.
question_answer 135) Differentiate between sclerenchyma and parenchyma tissue.
question_answer 136) List the characteristics of cork. How is it formed? Mention its role.
question_answer 137) Describe structure and function of different types of epithelial tissues. Draw well labelled diagram.
question_answer 138) Sunil while playing football with his friends got injured suddenly. His friends took him to the hospital and the doctor told that he was suffering from a sprain and advised bed rest. Every afternoon, his friends visited him to enquire about his health. (a)What happens during a sprain? (ii) In what other way can the friends help Sunil? (iii) What value is shown by his friends?
question_answer 139) Name a plant tissue having dead cells.
question_answer 140) What minerals is the bone matrix rich in?
question_answer 141) Name the water conducting tissue generally present in gymnosperms.
question_answer 142) Presence of which chemical in cork cells makes them impervious to water and gases?
question_answer 143) Which tissue in plants provides them flexibility?
question_answer 144) Which tissue makes up the husk of coconut?
question_answer 145) Name the muscular tissue that functions throughout life without fatigue.
question_answer 146) In desert plants, how does the rate of loss of water get reduced?
question_answer 147) Which animal tissue helps in repair of tissue and fills the space inside the organ?
question_answer 148) Name the tissue responsible for movement in our body.
question_answer 149) What does a neuron look like?
question_answer 150) What is a goblet cell?
question_answer 151) What is the name of bone cells?
question_answer 152) Which blood cells deal with immune reaction?
question_answer 153) Which cells are responsible for contraction and relaxation movements?
question_answer 154) Which cells are responsible for carrying messages?
question_answer 155) How are oxygen, food, hormone and waste material transported in the body?
question_answer 156) What is responsible for increase in girth of the stem or root?
question_answer 157) What is lignin?
question_answer 158) What is cutin?
question_answer 159) How are simple tissues different from complex tissues in plants? [NCERT]
question_answer 160) What is the specific function of the cardiac muscle? [NCERT]
question_answer 161) Which tissue forms a barrier to keep different body systems separate?
question_answer 162) What is the composition of the cartilage matrix?
question_answer 163) What are responsible for contraction and relaxation in muscles?
question_answer 164) Differentiate the following activities on the basis of voluntary (V) or involuntary (IV) muscles. Jumping of frog (b) Pumping of the heart Writing with hand (d) Movement of chocolate in your intestine [NCERT Exemplar]
question_answer 165) What stimulates the movement of muscles?
question_answer 166) Give the name of the connective tissue lacking fibres.
question_answer 167) Water hyacinth floats on water surface. Explain. [NCERT Exemplar]
question_answer 168) Which structure protects the plant body against the invasion of parasites?
question_answer 169) Why does an organism plant or animal, require different types of cells in the body?
question_answer 170) If a potted plant is covered with a glass jar, water vapour appears on the wall of the glass jar. Why? [NCERT Exemplar]
question_answer 171) Why voluntary muscles are also called skeletal muscles?
question_answer 172) What happens to the cells formed by meristematic tissue?
question_answer 173) What is the utility of tissues in multicellular organisms? [NCERT]
question_answer 174) What is the function of epidermis?
question_answer 175) Describe the structure and function of stomata.
question_answer 176) Why is the epidermis present as a thick waxy coating of cutin in desert plants?
question_answer 177) Write a short note on 'phellogen?
question_answer 178) Write the differences between xylem and phloem.
question_answer 179) Write a short note on xylem.
question_answer 180) Write a short note on phloem.
question_answer 181) Differentiate between parenchyma, Collenchyma and Sclerenchyma on the basis of their cell wall. [NCERT]
question_answer 182) Write a short note on epithelial tissue.
question_answer 183) Diagrammatically show the difference in three types of muscle fibres. [NCERT]
question_answer 184) Describe the functions of epithelium tissue.
question_answer 185) How are glandular epithelium formed?
question_answer 186) Name the following: (a)Tissue that forms inner lining of our mouth. (b) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans. (c) Tissue that transports food in plants. (d) Tissue that stores fat in our body. (e) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix. (f) Tissue present in the brain. [NCERT]
question_answer 187) Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining kidney tubule, vascular bundle. [NCERT]
question_answer 188) How does the cork act as a protective tissue?
question_answer 189) Write a short note on blood.
question_answer 190) Describe the function of bones.
question_answer 191) What are involuntary muscles? Where are they found?
question_answer 192) How are messages conveyed from one place to another within the body?
question_answer 193) Differentiate between voluntary and involuntary muscles. Give one example of each type.
question_answer 194) (a) What is the lining of blood vessels made up of? (b) What is the lining of small intestine made up of? (c) What is the lining of kidney tubules made up of? (d) Where are the epithelial cells with cilia found?
question_answer 195) Name the different components of xylem and draw a living component.
question_answer 196) Differentiate between striated, unstriated and cardiac muscles on the basis of their structure and site/location in the body.
question_answer 197) Why are plants and animals made of different types of tissue?
question_answer 198) Differentiate between parenchyma and collenchyma.
question_answer 199) Differentiate between collenchyma and sclerenchyma.
question_answer 200) What is a neuron? Write the structure and functions of a neuron.
question_answer 201) Differentiate between meristematic tissue and permanent tissue.
question_answer 202) Briefly describe striated and smooth muscles with their functions.
question_answer 203) Draw and identify different elements of phloem. [NCERT Exemplar]
question_answer 204) What is a permanent tissue? Classify permanent tissues and describe them.
question_answer 205) Describe the types of connective tissues along with their functions.
question_answer 206) Differentiate between parenchyma and sclerenchyma tissues.
question_answer 207) Describe the structure and function of different types of epithelial tissues Draw the diagram for each type of epithelial tissue.
question_answer 208) Give reasons: (a) Meristematic cells have a prominent nucleus and dense cytoplasm but they lack vacuole. (b) Intercellular spaces are absent in sclerenchymatous tissues. (c) We get a crunchy and granular feeling when we chew pear fruit. (d) Branches of a tree move and bend freely in high wind velocity. (e) It is difficult to pull out the husk of a coconut tree.
question_answer 209) List the characteristics of cork. How are they formed? [NCERT Exemplar]
question_answer 210) A person met with an accident in which two long bones of the hand were dislocated. What could be the reason?
question_answer 211) If the tip of a sugarcane plant is removed from the field, even then it keeps on growing in length. Why?
question_answer 212) A nail is inserted in the trunk of a tree at a height of 1 metre from the ground level. After 3 years, where will the nail be present?
question_answer 213) The root tips of a plant were cut and the plant was replanted. What will happen to the plant and why?
question_answer 214) Tissue A and tissue B constitute tissue C. A carries water while carries food for the plants. Identify A, B, C.
Download Complete Course
Related question.

Reset Password.
OTP has been sent to your mobile number and is valid for one hour
Mobile Number Verified
Your mobile number is verified.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 9 Science - Tissues. CASE 1. The growth of plants occurs only in certain specific regions. This is because the dividing tissue, also known as meristematic tissue, is located only at these points. Depending on the region where they are present, meristematic tissues are classified as apical, lateral and intercalary.
Case Study 1: Meristematic tissue takes up a specific role and loses the ability to divide. As a result, they form permanent tissue. This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and function is called differentiation. Differentiation leads to the development of various types of permanent tissues.
Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1: Read the following and answer any four questions below from (i) to (v): Bone is a solid, hard porous tissue. It forms the natural skeleton and gives the body its basic structure and also supports the body. Its matrix is impregnated with phosphates and carbonates of calcium and magnesium which ...
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Question 1: Meristematic tissue takes up a specific role and loses the ability to divide. As a result, they form permanent tissue. This process of taking up a permanent shape, size, and function is called differentiation. Differentiation leads to the development of various types of permanent tissues.
Tissues CBSE Class 9 Science Revision Notes Chapter 6 . ... The tissues in the case of animals are made up of living cells so that they can move and perform several functions. ... We provide many study materials for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues like NCERT Solutions, revision notes, mind maps, flashcards, mnemonics, practise papers ...
NCERT Solutions Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - CBSE Free PDF Download. The NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 - Tissues is the best study material through which students can refer and prepare their notes for their CBSE exam. These NCERT Solutions are available chapter-wise, and students can also find answers to all the questions ...
Chapter 6 Tissues Class 9 Science NCERT Solutions. These NCERT Solutions for Class 9 will improve application skills and clear your confusions. It will help the students in learning complex topics and problems in an easy way. These NCERT Solutions are prepared as per the accordance of latest CBSE guidelines so you can score maximum marks.
By Dr. Ananya Dixit Ma'am. Delve deeper into the realm of tissues in Chapter 6 of Class 9 Biology through case-based questions. These questions present real-...
This chapter 6 science class 9 along with the NCERT solutions for class 9 science chapter 6 will help us to excel in exams. We will study about two types of tissues in this class 9 science chapter 6. They are plant tissues and animal tissues. Plants. The tissues class 9 chapter has two types of tissues. Firstly, we will study plant tissues.
Class 9 Biology (India) 3 units · 12 skills. Unit 1. The fundamental unit of life. Unit 2. Tissues. Unit 3. Diversity in living organisms. ... Muscular tissue and neural tissue Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Plant tissues. Learn. Meristematic tissues (Opens a modal) Simple permanent tissues (Opens a modal) Up next for you:
Muscular tissue and neural tissue Get 3 of 4 questions to level up! Up next for you: Unit test. Level up on all the skills in this unit and collect up to 500 Mastery points! Start Unit test. UP Class 9 Science is brought to you by Kotak Mahindra Bank Logo. UP Class 9 Science is brought to you by. Our mission is to provide a free, world-class ...
Always living in nature. May be living or dead. Power of cell division is present. Power of cell division is absent. CBSE Class 9 Science Chapter-6 Important Questions - Free PDF Download. With the help of important questions for Tissues Class 9 chapter, students can revise the chapter for their exam in a better way.
Class 9 case study questions are meant to evaluate students' knowledge and comprehension of the material. They are not intended to be difficult, but they will require you to think critically about the material. ... A few layers of cells beneath the epidermis are generally simple permanent tissue. Parenchyma is the most common simple permanent ...
Question 11. Identify the type of tissue in the following: skin, bark of tree, bone, lining of kidney tubule, vascular bundle. Answer. Skin — epithelial tissues. Bark of tree — cork (formed by secondary meristem) Bone — Connective tissue (Bone cells are embedded in a hard matrix that is composed of calcium and phosphorus compounds.)
done Case Based MCQs - Tissues Total Questions - 30. question_answer 1) Read the passage given below and answer the questions from [1] to [5]. Meristematic tissue contains undifferendated cells which are the building blocks of specialised plant structures. Cells forming this tissue are very active, have dense cytoplasm, thin cellulosic walls ...
Answer: (a) The two tissues responsible for movement of the body are muscular tissue and nervous tissue. (b) The tissues present in brain and spine are nervous tissues. (c) The family members showed the value of being caring, responsible, dutiful and kind. Extra questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissues with answers is given below.
Q6. Name the following tissues: (i) The connective tissue found between the skin and muscles. (ii) The tissue which connects two bones. (iii) The epithelial tissue which forms the lining of the kidney tubules. (iv) The tissue which is present in the veins of leaves. Answer.
These CBSE Class 9 Science Important Questions are considered as the best resource for the students. Here in this article below is the clickable link to access the PDF format of the question paper. Find also the questions on the web page. Important Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 6 tissues 1- Download Free PDF
In these solutions, we have answered all the intext and exercise questions provided in NCERT class 9 science textbook. Class 9 NCERT Solutions Science Chapter 6 provided in this article are strictly based on the CBSE syllabus and curriculum. Students can easily download these solutions in PDF format for free from our app.
A - Areolar tissue, B -Adipose tissue. Detailed Solution for Test: Tissues- Case Based Type Questions- 2 - Question 9. (A) Areolar tissue helps in repair of tissue and fills up space inside the organ. (B) The adipose tissue is found beneath the skin, in the covering of the heart, around the blood vessels and kidneys and in yellow bone marrow.
Class 9 Science Tissues. 1. The cells of cork are dead and have a chemical in their walls that makes them impervious to gases and water. The chemical is. 2. The flexibility in plants is due to a tissue called, 3. The tissue present in the lining of kidney tubules and ducts of salivary glands is. 4.
April 2, 2020 June 30, 2021 Physics Gurukul 2 Comments on Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissue Study Notes. Class 9 Science Chapter 6 Tissue Study Notes. Last modified on: 3 years ago; Reading Time: 1 Minute; Download CBSE Books. ... Case Study Questions for Class 9 Science Chapter 1 Matter in Our Surroundings;
question_answer 123) Name the following. (i) Tissue that forms the inner lining of our mouth. (ii) Tissue that connects muscle to bone in humans. (iii) Tissue that tr (arts fnspoood in plants. (iv) Tissue that stores fat in our body. (v) Connective tissue with a fluid matrix. (vi) Tissue present in the brain.