How to Write a Bibliography for a Research Paper

Do not try to “wow” your instructor with a long bibliography when your instructor requests only a works cited page. It is tempting, after doing a lot of work to research a paper, to try to include summaries on each source as you write your paper so that your instructor appreciates how much work you did. That is a trap you want to avoid. MLA style, the one that is most commonly followed in high schools and university writing courses, dictates that you include only the works you actually cited in your paper—not all those that you used.

Academic Writing, Editing, Proofreading, And Problem Solving Services
Get 10% off with 24start discount code, assembling bibliographies and works cited.
- If your assignment calls for a bibliography, list all the sources you consulted in your research.
- If your assignment calls for a works cited or references page, include only the sources you quote, summarize, paraphrase, or mention in your paper.
- If your works cited page includes a source that you did not cite in your paper, delete it.
- All in-text citations that you used at the end of quotations, summaries, and paraphrases to credit others for their ideas,words, and work must be accompanied by a cited reference in the bibliography or works cited. These references must include specific information about the source so that your readers can identify precisely where the information came from.The citation entries on a works cited page typically include the author’s name, the name of the article, the name of the publication, the name of the publisher (for books), where it was published (for books), and when it was published.
The good news is that you do not have to memorize all the many ways the works cited entries should be written. Numerous helpful style guides are available to show you the information that should be included, in what order it should appear, and how to format it. The format often differs according to the style guide you are using. The Modern Language Association (MLA) follows a particular style that is a bit different from APA (American Psychological Association) style, and both are somewhat different from the Chicago Manual of Style (CMS). Always ask your teacher which style you should use.
A bibliography usually appears at the end of a paper on its own separate page. All bibliography entries—books, periodicals, Web sites, and nontext sources such radio broadcasts—are listed together in alphabetical order. Books and articles are alphabetized by the author’s last name.
Most teachers suggest that you follow a standard style for listing different types of sources. If your teacher asks you to use a different form, however, follow his or her instructions. Take pride in your bibliography. It represents some of the most important work you’ve done for your research paper—and using proper form shows that you are a serious and careful researcher.
Bibliography Entry for a Book
A bibliography entry for a book begins with the author’s name, which is written in this order: last name, comma, first name, period. After the author’s name comes the title of the book. If you are handwriting your bibliography, underline each title. If you are working on a computer, put the book title in italicized type. Be sure to capitalize the words in the title correctly, exactly as they are written in the book itself. Following the title is the city where the book was published, followed by a colon, the name of the publisher, a comma, the date published, and a period. Here is an example:
Format : Author’s last name, first name. Book Title. Place of publication: publisher, date of publication.
- A book with one author : Hartz, Paula. Abortion: A Doctor’s Perspective, a Woman’s Dilemma . New York: Donald I. Fine, Inc., 1992.
- A book with two or more authors : Landis, Jean M. and Rita J. Simon. Intelligence: Nature or Nurture? New York: HarperCollins, 1998.
Bibliography Entry for a Periodical
A bibliography entry for a periodical differs slightly in form from a bibliography entry for a book. For a magazine article, start with the author’s last name first, followed by a comma, then the first name and a period. Next, write the title of the article in quotation marks, and include a period (or other closing punctuation) inside the closing quotation mark. The title of the magazine is next, underlined or in italic type, depending on whether you are handwriting or using a computer, followed by a period. The date and year, followed by a colon and the pages on which the article appeared, come last. Here is an example:
Format: Author’s last name, first name. “Title of the Article.” Magazine. Month and year of publication: page numbers.
- Article in a monthly magazine : Crowley, J.E.,T.E. Levitan and R.P. Quinn.“Seven Deadly Half-Truths About Women.” Psychology Today March 1978: 94–106.
- Article in a weekly magazine : Schwartz, Felice N.“Management,Women, and the New Facts of Life.” Newsweek 20 July 2006: 21–22.
- Signed newspaper article : Ferraro, Susan. “In-law and Order: Finding Relative Calm.” The Daily News 30 June 1998: 73.
- Unsigned newspaper article : “Beanie Babies May Be a Rotten Nest Egg.” Chicago Tribune 21 June 2004: 12.
Bibliography Entry for a Web Site
For sources such as Web sites include the information a reader needs to find the source or to know where and when you found it. Always begin with the last name of the author, broadcaster, person you interviewed, and so on. Here is an example of a bibliography for a Web site:
Format : Author.“Document Title.” Publication or Web site title. Date of publication. Date of access.
Example : Dodman, Dr. Nicholas. “Dog-Human Communication.” Pet Place . 10 November 2006. 23 January 2014 < http://www.petplace.com/dogs/dog-human-communication-2/page1.aspx >
After completing the bibliography you can breathe a huge sigh of relief and pat yourself on the back. You probably plan to turn in your work in printed or handwritten form, but you also may be making an oral presentation. However you plan to present your paper, do your best to show it in its best light. You’ve put a great deal of work and thought into this assignment, so you want your paper to look and sound its best. You’ve completed your research paper!
Back to How To Write A Research Paper .
ORDER HIGH QUALITY CUSTOM PAPER

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Referencing
- Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples
Published on 1 May 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on 7 November 2022.
In Harvard style , the bibliography or reference list provides full references for the sources you used in your writing.
- A reference list consists of entries corresponding to your in-text citations .
- A bibliography sometimes also lists sources that you consulted for background research, but did not cite in your text.
The two terms are sometimes used interchangeably. If in doubt about which to include, check with your instructor or department.
The information you include in a reference varies depending on the type of source, but it usually includes the author, date, and title of the work, followed by details of where it was published. You can automatically generate accurate references using our free reference generator:
Harvard Reference Generator
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Formatting a harvard style bibliography, harvard reference examples, referencing sources with multiple authors, referencing sources with missing information, frequently asked questions about harvard bibliographies.
Sources are alphabetised by author last name. The heading ‘Reference list’ or ‘Bibliography’ appears at the top.
Each new source appears on a new line, and when an entry for a single source extends onto a second line, a hanging indent is used:

Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Reference list or bibliography entries always start with the author’s last name and initial, the publication date and the title of the source. The other information required varies depending on the source type. Formats and examples for the most common source types are given below.
- Entire book
- Book chapter
- Translated book
- Edition of a book
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . City: Publisher. |
| Example | Coetzee, J. M. (2000) . London: Vintage. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Chapter title’, in Editor name (ed(s).) . City: Publisher, pp. page range. |
| Example | Greenblatt, S. (2010) ‘The traces of Shakespeare’s life’, in De Grazia, M. and Wells, S. (eds.) . Cambridge: Cambridge University Press, pp. 1–14. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Translated from the [language] by ranslator name. City: Publisher. |
| Example | Saramago, J. (1997) . Translated from the Portuguese by G. Gontiero. London: Vintage. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Edition. City: Publisher. |
| Example | Danielson, D. (ed.) (1999) . 2nd edn. Cambridge: Cambridge University Press. |
| Notes |
Journal articles
- Print journal
- Online-only journal with DOI
- Online-only journal without DOI
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue), pp. page range. |
| Example | Maceachen, D. B. (1950) ‘Wilkie Collins and British law’, , 5(2), pp. 121–139. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue), page range. DOI. |
| Example | Adamson, P. (2019) ‘American history at the foreign office: Exporting the silent epic Western’, , 31(2), pp. 32–59. doi:10.2979/filmhistory.31.2.02. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue), pagerange. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Theroux, A. (1990) ‘Henry James’s Boston’, , 20(2), pp. 158–165. Available at: https://www.jstor.org/stable/20153016 (Accessed: 13 February 2020). |
| Notes |
- General web page
- Online article or blog
- Social media post
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Google (2019) . Available at: https://policies.google.com/terms?hl=en-US (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Date. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Rakich, N. (2020) ‘How does Biden stack up to past Democratic nominees?’, , 28 April. Available at: https://fivethirtyeight.com/features/how-does-biden-stack-up-to-past-democratic-nominees/ (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. [username] (Year) or text [Website name] Date. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Dorsey, J. [@jack] (2018) We’re committing Twitter to help increase the collective health, openness, and civility of public conversation … [Twitter] 1 March. Available at: https://twitter.com/jack/status/969234275420655616 (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) [Medium]. Institution, City or Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Bosch, H. (1482) [Triptych]. Groeningemuseum, Bruges. |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) . Date. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Vox (2020) . 10 April. Available at: https://youtu.be/BE-cA4UK07c (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
Newspapers and magazines
- Newspaper article
- Magazine article
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , date, p. page number. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Butler, S. (2020) ‘Women’s fashion manufacturer to make reusable gowns for NHS’, , 28 April. Available at: https://www.theguardian.com/society/2020/apr/28/womens-fashion-manufacturer-to-make-reusable-gowns-for-nhs (Accessed: 29 April 2020). |
| Notes |
| Format | Author surname, initial. (Year) ‘Article title’, , Volume(Issue) or (Month) or (Season), pp. page range. Available at: URL (Accessed: Day Month Year). |
| Example | Newman, J. (2020) ‘For autistic youths entering adulthood, a new world of challenges awaits’, , (May), pp. 20–24. |
| Notes |
When a source has up to three authors, list all of them in the order their names appear on the source. If there are four or more, give only the first name followed by ‘ et al. ’:
| Number of authors | Reference example |
|---|---|
| 1 author | Davis, V. (2019) … |
| 2 authors | Davis, V. and Barrett, M. (2019) … |
| 3 authors | Davis, V., Barrett, M. and McLachlan, F. (2019) … |
| 4+ authors | Davis, V. (2019) … |
Sometimes a source won’t list all the information you need for your reference. Here’s what to do when you don’t know the publication date or author of a source.
Some online sources, as well as historical documents, may lack a clear publication date. In these cases, you can replace the date in the reference list entry with the words ‘no date’. With online sources, you still include an access date at the end:
When a source doesn’t list an author, you can often list a corporate source as an author instead, as with ‘Scribbr’ in the above example. When that’s not possible, begin the entry with the title instead of the author:
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Though the terms are sometimes used interchangeably, there is a difference in meaning:
- A reference list only includes sources cited in the text – every entry corresponds to an in-text citation .
- A bibliography also includes other sources which were consulted during the research but not cited.
In Harvard referencing, up to three author names are included in an in-text citation or reference list entry. When there are four or more authors, include only the first, followed by ‘ et al. ’
| In-text citation | Reference list | |
|---|---|---|
| 1 author | (Smith, 2014) | Smith, T. (2014) … |
| 2 authors | (Smith and Jones, 2014) | Smith, T. and Jones, F. (2014) … |
| 3 authors | (Smith, Jones and Davies, 2014) | Smith, T., Jones, F. and Davies, S. (2014) … |
| 4+ authors | (Smith , 2014) | Smith, T. (2014) … |
In Harvard style referencing , to distinguish between two sources by the same author that were published in the same year, you add a different letter after the year for each source:
- (Smith, 2019a)
- (Smith, 2019b)
Add ‘a’ to the first one you cite, ‘b’ to the second, and so on. Do the same in your bibliography or reference list .
To create a hanging indent for your bibliography or reference list :
- Highlight all the entries
- Click on the arrow in the bottom-right corner of the ‘Paragraph’ tab in the top menu.
- In the pop-up window, under ‘Special’ in the ‘Indentation’ section, use the drop-down menu to select ‘Hanging’.
- Then close the window with ‘OK’.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 07). Harvard Style Bibliography | Format & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 27 July 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/referencing/harvard-bibliography/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, a quick guide to harvard referencing | citation examples, harvard in-text citation | a complete guide & examples, referencing books in harvard style | templates & examples, scribbr apa citation checker.
An innovative new tool that checks your APA citations with AI software. Say goodbye to inaccurate citations!


In order to continue enjoying our site, we ask that you confirm your identity as a human. Thank you very much for your cooperation.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Citing sources
Citation Styles Guide | Examples for All Major Styles
Published on June 24, 2022 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on November 7, 2022.
A citation style is a set of guidelines on how to cite sources in your academic writing . You always need a citation whenever you quote , paraphrase , or summarize a source to avoid plagiarism . How you present these citations depends on the style you follow. Scribbr’s citation generator can help!
Different styles are set by different universities, academic associations, and publishers, often published in an official handbook with in-depth instructions and examples.
There are many different citation styles, but they typically use one of three basic approaches: parenthetical citations , numerical citations, or note citations.
Parenthetical citations
- Chicago (Turabian) author-date
CSE name-year
Numerical citations
CSE citation-name or citation-sequence
Note citations
- Chicago (Turabian) notes and bibliography
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Types of citation: parenthetical, note, numerical, which citation style should i use, parenthetical citation styles, numerical citation styles, note citation styles, frequently asked questions about citation styles.
The clearest identifying characteristic of any citation style is how the citations in the text are presented. There are three main approaches:
- Parenthetical citations: You include identifying details of the source in parentheses in the text—usually the author’s last name and the publication date, plus a page number if relevant ( author-date ). Sometimes the publication date is omitted ( author-page ).
- Numerical citations: You include a number in brackets or in superscript, which corresponds to an entry in your numbered reference list.
- Note citations: You include a full citation in a footnote or endnote, which is indicated in the text with a superscript number or symbol.
Citation styles also differ in terms of how you format the reference list or bibliography entries themselves (e.g., capitalization, order of information, use of italics). And many style guides also provide guidance on more general issues like text formatting, punctuation, and numbers.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
In most cases, your university, department, or instructor will tell you which citation style you need to follow in your writing. If you’re not sure, it’s best to consult your institution’s guidelines or ask someone. If you’re submitting to a journal, they will usually require a specific style.
Sometimes, the choice of citation style may be left up to you. In those cases, you can base your decision on which citation styles are commonly used in your field. Try reading other articles from your discipline to see how they cite their sources, or consult the table below.
| Discipline | Typical citation style(s) |
|---|---|
| Economics | |
| Engineering & IT | |
| Humanities | ; ; |
| Law | ; |
| Medicine | ; ; |
| Political science | |
| Psychology | |
| Sciences | ; ; ; ; |
| Social sciences | ; ; ; |
The American Anthropological Association (AAA) recommends citing your sources using Chicago author-date style . AAA style doesn’t have its own separate rules. This style is used in the field of anthropology.
| AAA reference entry | Clarke, Kamari M. 2013. “Notes on Cultural Citizenship in the Black Atlantic World.” 28, no. 3 (August): 464–474. https://www.jstor.org/stable/43898483. |
| AAA in-text citation | (Clarke 2013) |
APA Style is defined by the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . It was designed for use in psychology, but today it’s widely used across various disciplines, especially in the social sciences.
| Wagemann, J. & Weger, U. (2021). Perceiving the other self: An experimental first-person account of nonverbal social interaction. , (4), 441–461. https://doi.org/10.5406/amerjpsyc.134.4.0441 | |
| (Wagemann & Weger, 2021) |
Generate accurate APA citations with Scribbr
The citation style of the American Political Science Association (APSA) is used mainly in the field of political science.
| APSA reference entry | Ward, Lee. 2020. “Equity and Political Economy in Thomas Hobbes.” , 64 (4): 823–35. doi: 10.1111/ajps.12507. |
| APSA in-text citation | (Ward 2020) |
The citation style of the American Sociological Association (ASA) is used primarily in the discipline of sociology.
| ASA reference entry | Kootstra, Anouk. 2016. “Deserving and Undeserving Welfare Claimants in Britain and the Netherlands: Examining the Role of Ethnicity and Migration Status Using a Vignette Experiment.” 32(3): 325–338. doi:10.1093/esr/jcw010. |
| ASA in-text citation | (Kootstra 2016) |
Chicago author-date
Chicago author-date style is one of the two citation styles presented in the Chicago Manual of Style (17th edition). It’s used mainly in the sciences and social sciences.
| Encarnação, João, and Gonçalo Calado. 2018. “Effects of Recreational Diving on Early Colonization Stages of an Artificial Reef in North-East Atlantic.” 22, no. 6 (December): 1209–1216. https://www.jstor.org/stable/45380397. | |
| (Encarnação and Calado 2018) |
The citation style of the Council of Science Editors (CSE) is used in various scientific disciplines. It includes multiple options for citing your sources, including the name-year system.
| CSE name-year reference entry | Graham JR. 2019. The structure and stratigraphical relations of the Lough Nafooey Group, South Mayo. Irish Journal of Earth Sciences. 37: 1–18. |
| CSE name-year citation | (Graham 2019) |
Harvard style is often used in the field of economics. It is also very widely used across disciplines in UK universities. There are various versions of Harvard style defined by different universities—it’s not a style with one definitive style guide.
| Hoffmann, M. (2016) ‘How is information valued? Evidence from framed field experiments’, , 126(595), pp. 1884–1911. doi:10.1111/ecoj.12401. | |
| (Hoffmann, 2016) |
Check out Scribbr’s Harvard Reference Generator
MLA style is the official style of the Modern Language Association, defined in the MLA Handbook (9th edition). It’s widely used across various humanities disciplines. Unlike most parenthetical citation styles, it’s author-page rather than author-date.
| Davidson, Clare. “Reading in Bed with .” , vol. 55, no. 2, Apr. 2020, pp. 147–170. https://doi.org/10.5325/chaucerrev.55.2.0147. | |
| (Davidson 155) |
Generate accurate MLA citations with Scribbr
The American Chemical Society (ACS) provides guidelines for a citation style using numbers in superscript or italics in the text, corresponding to entries in a numbered reference list at the end. It is used in chemistry.
| ACS reference entry | 1. Hutchinson, G.; Alamillo-Ferrer, C.; Fernández-Pascual, M.; Burés, J. Organocatalytic Enantioselective α-Bromination of Aldehydes with -Bromosuccinimide. , 87, 7968–7974. |
The American Medical Association ( AMA ) provides guidelines for a numerical citation style using superscript numbers in the text, which correspond to entries in a numbered reference list. It is used in the field of medicine.
| 1. Jabro JD. Predicting saturated hydraulic conductivity from percolation test results in layered silt loam soils. . 2009;72(5):22–27. |
CSE style includes multiple options for citing your sources, including the citation-name and citation-sequence systems. Your references are listed alphabetically in the citation-name system; in the citation-sequence system, they appear in the order in which you cited them.
| CSE citation-sequence or citation-name reference entry | 1. Nell CS, Mooney KA. Plant structural complexity mediates trade-off in direct and indirect plant defense by birds. Ecology. 2019;100(10):1–7. |
The Institute of Electrical and Electronics Engineers ( IEEE ) provides guidelines for citing your sources with IEEE in-text citations that consist of numbers enclosed in brackets, corresponding to entries in a numbered reference list. This style is used in various engineering and IT disciplines.
| IEEE reference entry | 1. J. Ive, A. Max, and F. Yvon, “Reassessing the proper place of man and machine in translation: A pre-translation scenario,” , vol. 32, no. 4, pp. 279–308, Dec. 2018, doi: 10.1007/s10590-018-9223-9. |
The National Library of Medicine (NLM) citation style is defined in Citing Medicine: The NLM Style Guide for Authors, Editors, and Publishers (2nd edition).
| NLM reference entry | 1. Hage J, Valadez JJ. Institutionalizing and sustaining social change in health systems: the case of Uganda. Health Policy Plan. 2017 Nov;32(9):1248–55. doi:10.1093/heapol/czx066. |
Vancouver style is also used in various medical disciplines. As with Harvard style, a lot of institutions and publications have their own versions of Vancouver—it doesn’t have one fixed style guide.
| Vancouver reference entry | 1. Bute M. A backstage sociologist: Autoethnography and a populist vision. Am Soc. 2016 Mar 23; 47(4):499–515. Available from: https://link.springer.com/article/10.1007/s12108-016-9307-z doi:10.1007/s12108-016-9307-z |
Don't submit your assignments before you do this
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students. Free citation check included.

Try for free
The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation is the main style guide for legal citations in the US. It’s widely used in law, and also when legal materials need to be cited in other disciplines.
| Bluebook footnote citation | David E. Pozen, , 165, U. P🇦. L. R🇪🇻. 1097, 1115 (2017). |
Chicago notes and bibliography
Chicago notes and bibliography is one of the two citation styles presented in the Chicago Manual of Style (17th edition). It’s used mainly in the humanities.
| Best, Jeremy. “Godly, International, and Independent: German Protestant Missionary Loyalties before World War I.” 47, no. 3 (September 2014): 585–611. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0008938914001654. | |
| 1. Jeremy Best, “Godly, International, and Independent: German Protestant Missionary Loyalties before World War I,” 47, no. 3 (September 2014): 599. https://doi.org/10.1017/S0008938914001654. |
The Oxford University Standard for the Citation of Legal Authorities ( OSCOLA ) is the main legal citation style in the UK (similar to Bluebook for the US).
| OSCOLA footnote citation | 1. Chris Thornhill, ‘The Mutation of International Law in Contemporary Constitutions: Thinking Sociologically about Political Constitutionalism’ [2016] MLR 207. |
There are many different citation styles used across different academic disciplines, but they fall into three basic approaches to citation:
- Parenthetical citations : Including identifying details of the source in parentheses —usually the author’s last name and the publication date, plus a page number if available ( author-date ). The publication date is occasionally omitted ( author-page ).
- Numerical citations: Including a number in brackets or superscript, corresponding to an entry in your numbered reference list.
- Note citations: Including a full citation in a footnote or endnote , which is indicated in the text with a superscript number or symbol.
Check if your university or course guidelines specify which citation style to use. If the choice is left up to you, consider which style is most commonly used in your field.
- APA Style is the most popular citation style, widely used in the social and behavioral sciences.
- MLA style is the second most popular, used mainly in the humanities.
- Chicago notes and bibliography style is also popular in the humanities, especially history.
- Chicago author-date style tends to be used in the sciences.
Other more specialized styles exist for certain fields, such as Bluebook and OSCOLA for law.
The most important thing is to choose one style and use it consistently throughout your text.
A scientific citation style is a system of source citation that is used in scientific disciplines. Some commonly used scientific citation styles are:
- Chicago author-date , CSE , and Harvard , used across various sciences
- ACS , used in chemistry
- AMA , NLM , and Vancouver , used in medicine and related disciplines
- AAA , APA , and ASA , commonly used in the social sciences
APA format is widely used by professionals, researchers, and students in the social and behavioral sciences, including fields like education, psychology, and business.
Be sure to check the guidelines of your university or the journal you want to be published in to double-check which style you should be using.
MLA Style is the second most used citation style (after APA ). It is mainly used by students and researchers in humanities fields such as literature, languages, and philosophy.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2022, November 07). Citation Styles Guide | Examples for All Major Styles. Scribbr. Retrieved July 27, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/citing-sources/citation-styles/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, apa vs. mla | the key differences in format & citation, the basics of in-text citation | apa & mla examples, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources, what is your plagiarism score.

What is Bibliography?: Meaning, Types, and Importance
A bibliography is a fundamental component of academic research and writing that serves as a comprehensive list of sources consulted and referenced in a particular work. It plays a crucial role in validating the credibility and reliability of the information presented by providing readers with the necessary information to locate and explore the cited sources. A well-constructed bibliography not only demonstrates the depth and breadth of research undertaken but also acknowledges the intellectual contributions of others, ensuring transparency and promoting the integrity of scholarly work. By including a bibliography, writers enable readers to delve further into the subject matter, engage in critical analysis, and build upon existing knowledge.
1.1 What is a Bibliography?
A bibliography is a compilation of sources that have been utilized in the process of researching and writing a piece of work. It serves as a comprehensive list of references, providing information about the various sources consulted, such as books, articles, websites, and other materials. The purpose of a bibliography is twofold: to give credit to the original authors or creators of the sources used and to allow readers to locate and access those sources for further study or verification. A well-crafted bibliography includes essential details about each source, including the author’s name, the title of the work, publication date, and publication information. By having a bibliography, writers demonstrate the extent of their research, provide a foundation for their arguments, and enhance the credibility and reliability of their work.
1.2 Types of Bibliography.
The bibliography is a multifaceted discipline encompassing different types, each designed to serve specific research purposes and requirements. These various types of bibliographies provide valuable tools for researchers, scholars, and readers to navigate the vast realm of literature and sources available. From comprehensive overviews to specialized focuses, the types of bibliographies offer distinct approaches to organizing, categorizing, and presenting information. Whether compiling an exhaustive list of sources, providing critical evaluations, or focusing on specific subjects or industries, these types of bibliographies play a vital role in facilitating the exploration, understanding, and dissemination of knowledge in diverse academic and intellectual domains.
As a discipline, a bibliography encompasses various types that cater to different research needs and contexts. The two main categories of bibliographies are
1. General bibliography, and 2. Special bibliography.
1.2.1. General Bibliography:
A general bibliography is a comprehensive compilation of sources covering a wide range of subjects, disciplines, and formats. It aims to provide a broad overview of published materials, encompassing books, articles, journals, websites, and other relevant resources. A general bibliography typically includes works from various authors, covering diverse topics and spanning different periods. It is a valuable tool for researchers, students, and readers seeking a comprehensive collection of literature within a specific field or across multiple disciplines. General bibliographies play a crucial role in guiding individuals in exploring a subject, facilitating the discovery of relevant sources, and establishing a foundation for further research and academic pursuits.
The general bibliography encompasses various subcategories that comprehensively cover global, linguistic, national, and regional sources. These subcategories are as follows:
- Universal Bibliography: Universal bibliography aims to compile a comprehensive list of all published works worldwide, regardless of subject or language. It seeks to encompass human knowledge and includes sources from diverse fields, cultures, and periods. Universal bibliography is a monumental effort to create a comprehensive record of the world’s published works, making it a valuable resource for scholars, librarians, and researchers interested in exploring the breadth of human intellectual output.
- Language Bibliography: Language bibliography focuses on compiling sources specific to a particular language or group of languages. It encompasses publications written in a specific language, regardless of the subject matter. Language bibliographies are essential for language scholars, linguists, and researchers interested in exploring the literature and resources available in a particular language or linguistic group.
- National Bibliography: The national bibliography documents and catalogs all published materials within a specific country. It serves as a comprehensive record of books, journals, periodicals, government publications, and other sources published within a nation’s borders. National bibliographies are essential for preserving a country’s cultural heritage, facilitating research within specific national contexts, and providing a comprehensive overview of a nation’s intellectual output.
- Regional Bibliography: A regional bibliography compiles sources specific to a particular geographic region or area. It aims to capture the literature, publications, and resources related to a specific region, such as a state, province, or local area. Regional bibliographies are valuable for researchers interested in exploring a specific geographic region’s literature, history, culture, and unique aspects.
1.2.2. Special Bibliography:
Special bibliography refers to a type of bibliography that focuses on specific subjects, themes, or niche areas within a broader field of study. It aims to provide a comprehensive and in-depth compilation of sources specifically relevant to the chosen topic. Special bibliographies are tailored to meet the research needs of scholars, researchers, and enthusiasts seeking specialized information and resources.
Special bibliographies can cover a wide range of subjects, including but not limited to specific disciplines, subfields, historical periods, geographical regions, industries, or even specific authors or works. They are designed to gather and present a curated selection of sources considered important, authoritative, or influential within the chosen subject area.
Special bibliography encompasses several subcategories that focus on specific subjects, authors, forms of literature, periods, categories of literature, and types of materials. These subcategories include:
- Subject Bibliography: Subject bibliography compiles sources related to a specific subject or topic. It aims to provide a comprehensive list of resources within a particular field. Subject bibliographies are valuable for researchers seeking in-depth information on a specific subject area, as they gather relevant sources and materials to facilitate focused research.
- Author and Bio-bibliographies: Author and bio-bibliographies focus on compiling sources specific to individual authors. They provide comprehensive lists of an author’s works, including their books, articles, essays, and other publications. Bio-bibliographies include biographical information about the author, such as their background, career, and contributions to their respective fields.
- Bibliography of Forms of Literature: This bibliography focuses on specific forms or genres of literature, such as poetry, drama, fiction, or non-fiction. It provides a compilation of works within a particular literary form, enabling researchers to explore the literature specific to their interests or to gain a comprehensive understanding of a particular genre.
- Bibliography of Materials of Particular Periods: Bibliographies of materials of particular periods compile sources specific to a particular historical period or time frame. They include works published or created during that period, offering valuable insights into the era’s literature, art, culture, and historical context.
- Bibliographies of Special Categories of Literature: This category compiles sources related to special categories or themes. Examples include bibliographies of children’s literature, feminist literature, postcolonial literature, or science fiction literature. These bibliographies cater to specific interests or perspectives within the broader field of literature.
- Bibliographies of Specific Types of Materials: Bibliographies of specific materials focus on compiling sources within a particular format or medium. Examples include bibliographies of manuscripts, rare books, visual art, films, or musical compositions. These bibliographies provide valuable resources for researchers interested in exploring a specific medium or format.
1.3 Functions of Bibliography
A bibliography serves several important functions in academic research, writing, and knowledge dissemination. Here are some key functions:
- Documentation: One of the primary functions of a bibliography is to document and record the sources consulted during the research process. By providing accurate and detailed citations for each source, it can ensure transparency, traceability, and accountability in scholarly work. It allows readers and other researchers to verify the information, trace the origins of ideas, and locate the original sources for further study.
- Attribution and Credit: The bibliography plays a crucial role in giving credit to the original authors and creators of the ideas, information, and materials used in research work. By citing the sources, the authors acknowledge the intellectual contributions of others and demonstrate academic integrity. This enables proper attribution and prevents plagiarism, ensuring ethical research practices and upholding the principles of academic honesty.
- Verification and Quality Control: It acts as a means of verification and quality control in academic research. Readers and reviewers can assess the information’s reliability, credibility, and accuracy by including a list of sources. This allows others to evaluate the strength of the evidence, assess the validity of the arguments, and determine the scholarly rigor of a work.
- Further Reading and Exploration: The bibliography is valuable for readers who wish to delve deeper into a particular subject or topic. By providing a list of cited sources, the bibliography offers a starting point for further reading and exploration. It guides readers to related works, seminal texts, and authoritative materials, facilitating their intellectual growth and expanding their knowledge base.
- Preservation of Knowledge: The bibliography contributes to the preservation of knowledge by cataloguing and documenting published works. It records the intellectual output within various fields, ensuring that valuable information is not lost over time. A bibliography facilitates the organization and accessibility of literature, making it possible to locate and retrieve sources for future reference and research.
- Intellectual Dialogue and Scholarship: The bibliography fosters intellectual dialogue and scholarship by facilitating the exchange of ideas and enabling researchers to build upon existing knowledge. By citing relevant sources, researchers enter into conversations with other scholars, engaging in a scholarly discourse that advances knowledge within their field of study.
A bibliography serves the important functions of documenting sources, crediting original authors, verifying information, guiding further reading, preserving knowledge, and fostering intellectual dialogue. It plays a crucial role in maintaining academic research’s integrity, transparency, and quality and ensures that scholarly work is built upon a solid foundation of evidence and ideas.
1.4 Importance of Bibliographic Services
Bibliographic services are crucial in academia, research, and information management. They are a fundamental tool for organizing, accessing, and preserving knowledge . From facilitating efficient research to ensuring the integrity and credibility of scholarly work, bibliographic services hold immense importance in various domains.
Bibliographic services are vital for researchers and scholars. These services provide comprehensive and reliable access to various resources, such as books, journals, articles, and other scholarly materials. By organizing these resources in a structured manner, bibliographic services make it easier for researchers to locate relevant information for their studies. Researchers can explore bibliographic databases, catalogues, and indexes to identify appropriate sources, saving them valuable time and effort. This accessibility enhances the efficiency and effectiveness of research, enabling scholars to stay up-to-date with the latest developments in their fields.
Bibliographic services also aid in the process of citation and referencing. Proper citation is an essential aspect of academic integrity and intellectual honesty. Bibliographic services assist researchers in accurately citing the sources they have used in their work, ensuring that credit is given where it is due. This not only acknowledges the original authors and their contributions but also strengthens the credibility and authenticity of the research. By providing citation guidelines, formatting styles, and citation management tools, bibliographic services simplify the citation process, making it more manageable for researchers.
Another crucial aspect of bibliographic services is their role in preserving and archiving knowledge. Libraries and institutions that provide bibliographic services serve as custodians of valuable information. They collect, organize, and preserve various physical and digital resources for future generations. This preservation ensures that knowledge is not lost or forgotten over time. Bibliographic services enable researchers, students, and the general public to access historical and scholarly materials, fostering continuous learning and intellectual growth.
Bibliographic services contribute to the dissemination of research and scholarly works. They provide platforms and databases for publishing and sharing academic outputs. By cataloguing and indexing research articles, journals, and conference proceedings, bibliographic services enhance the discoverability and visibility of scholarly work. This facilitates knowledge exchange, collaboration, and innovation within academic communities. Researchers can rely on bibliographic services to share their findings with a broader audience, fostering intellectual dialogue and advancing their respective fields.
In Summary, bibliographic services are immensely important in academia, research, and information management. They facilitate efficient analysis, aid in proper citation and referencing, preserve knowledge for future generations, and contribute to the dissemination of research. These services form the backbone of scholarly pursuits, enabling researchers, students, and professionals to access, utilize, and contribute to the vast wealth of knowledge available. As we continue to rely on information and research to drive progress and innovation, the significance of bibliographic services will only grow, making them indispensable resources in pursuing knowledge.
References:
- Reddy, P. V. G. (1999). Bio bibliography of the faculty in social sciences departments of Sri Krishnadevaraya university Anantapur A P India.
- Sharma, J.S. Fundamentals of Bibliography, New Delhi : S. Chand & Co.. Ltd.. 1977. p.5.
- Quoted in George Schneider, Theory of History of Bibliography. Ralph Robert Shaw, trans., New York : Scare Crow Press, 1934, p.13.
- Funk Wagnalls Standard Dictionary of the English language – International ed – Vol. I – New York : Funku Wagnalls Co., C 1965, p. 135.
- Shores, Louis. Basic reference sources. Chicago : American Library Association, 1954. p. 11-12.
- Ranganathan, S.R., Documentation and its facts. Bombay : Asia Publishing House. 1963. p.49.
- Katz, William A. Introduction to reference work. 4th ed. New York : McGraw Hill, 1982. V. 1, p.42.
- Robinson, A.M.L. Systematic Bibliography. Bombay : Asia Publishing House, 1966. p.12.
- Chakraborthi, M.L. Bibliography : In Theory and practice, Calcutta : The World press (P) Ltd.. 1975. p.343.
How To Write a Bibliography (Plus Printable Guide With Examples)
Give credit where credit is due.

Writing a research paper involves a lot of work. Students need to consult a variety of sources to gather reliable information and ensure their points are well supported. Research papers include a bibliography, which can be a little tricky for students. Learn how to write a bibliography in multiple styles and find basic examples below.
Plus grab our printable Bibliography Guide for Students with examples from all three major style guides: APA (American Psychological Association), MLA (Modern Language Association), or The Chicago Manual of Style . Just fill out the form on this page to get the free guide.
IMPORTANT: Each style guide has its own very specific rules, and they often conflict with one another. Additionally, each type of reference material has many possible formats, depending on a variety of factors. The overviews shown here are meant to guide students in writing basic bibliographies, but this information is by no means complete. Students should always refer directly to the preferred style guide to ensure they’re using the most up-to-date formats and styles.
What is a bibliography?
When you’re researching a paper, you’ll likely consult a wide variety of sources. You may quote some of these directly in your work, summarize some of the points they make, or simply use them to further the knowledge you need to write your paper. Since these ideas are not your own, it’s vital to give credit to the authors who originally wrote them. This list of sources, organized alphabetically, is called a bibliography.
A bibliography should include all the materials you consulted in your research, even if you don’t quote directly from them in your paper. These resources could include (but aren’t limited to):
- Books and e-books
- Periodicals like magazines or newspapers
- Online articles or websites
- Primary source documents like letters or official records
Bibliography vs. References
These two terms are sometimes used interchangeably, but they actually have different meanings. As noted above, a bibliography includes all the materials you used while researching your paper, whether or not you quote from them or refer to them directly in your writing.
A list of references only includes the materials you cite throughout your work. You might use direct quotes or summarize the information for the reader. Either way, you must ensure you give credit to the original author or document. This section can be titled “List of Works Cited” or simply “References.”
Your teacher may specify whether you should include a bibliography or a reference list. If they don’t, consider choosing a bibliography to show all the works you used in researching your paper. This can help the reader see that your points are well supported and allow them to do further reading on their own if they’re interested.
Bibliography vs. Citations
Citations refer to direct quotations from a text that are woven into your own writing. There are a variety of ways to write citations, including footnotes and endnotes. These are generally shorter than the entries in a reference list or bibliography. Learn more about writing citations here.
What does a bibliography entry include?
Depending on the reference material, bibliography entries include a variety of information intended to help a reader locate the material if they want to refer to it themselves. These entries are listed in alphabetical order and may include:
- Author/s or creator/s
- Publication date
- Volume and issue numbers
- Publisher and publication city
- Website URL
These entries don’t generally need to include specific page numbers or locations within the work (except for print magazine or journal articles). That type of information is usually only needed in a footnote or endnote citation.
What are the different bibliography styles?
In most cases, writers use one of three major style guides: APA (American Psychological Association), MLA (Modern Language Association), or The Chicago Manual of Style . There are many others as well, but these three are the most common choices for K–12 students.
Many teachers will state their preference for one style guide over another. If they don’t, you can choose your own preferred style. However, you should also use that guide for your entire paper, following their recommendations for punctuation, grammar, and more. This will ensure you are consistent throughout.
Below, you’ll learn how to write a simple bibliography using each of the three major style guides. We’ve included details for books and e-books, periodicals, and electronic sources like websites and videos. If the reference material type you need to include isn’t shown here, refer directly to the style guide you’re using.
APA Style Bibliography and Examples

Technically, APA style calls for a list of references instead of a bibliography. If your teacher requires you to use the APA style guide , you can limit your reference list to only items you cite throughout your work.
How To Write a Bibliography (References) Using APA Style
Here are some general notes on writing an APA reference list:
- Title your bibliography section “References” and center the title on the top line of the page.
- Do not center your references; they should be left-aligned. For longer items, subsequent lines should use a hanging indent of 1/2 inch.
- Include all types of resources in the same list.
- Alphabetize your list by author or creator, last name first.
- Do not spell out the author/creator’s first or middle name—only use their initials.
- If there are multiple authors/creators, use an ampersand (&) before the final author/creator.
- Place the date in parentheses.
- Capitalize only the first word of the title and subtitle, unless the word would otherwise be capitalized (proper names, etc.).
- Italicize the titles of books, periodicals, and videos.
- For websites, include the full site information, including the http:// or https:// at the beginning.
Books and E-Books APA Bibliography Examples
For books, APA reference list entries use this format (only include the publisher’s website for e-books):
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Publication date). Title with only first word capitalized (unless there’s a proper name/noun) . Publisher. Publisher’s website
- Wynn, S. (2020). City of London at war 1939–45 . Pen & Sword Military. https://www.pen-and-sword.co.uk/City-of-London-at-War-193945-Paperback/p/17299
Periodical APA Bibliography Examples
For journal or magazine articles, use the following format. If you viewed the article online, include the URL at the end of the citation.
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Publication date). Title of article. Magazine or Journal Title (Volume number) Issue number, page numbers. URL
- Bell, A. (2009). Landscapes of fear: Wartime London, 1939–1945. Journal of British Studies (48) 1, 153–175. https://www.jstor.org/stable/25482966
Here’s the format for newspapers. For print editions, include the page number/s. For online articles, include the full URL:
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Year, Month Date) Title of article. Newspaper title. Page number/s. URL
- Blakemore, E. (2022, November 12) Researchers track down two copies of fossil destroyed by the Nazis. The Washington Post. https://www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/11/12/ichthyosaur-fossil-images-discovered/
Electronic APA Bibliography Examples
For articles with a specific author on a website, use this format:
Last Name, First Initial. Middle Initial. (Year, Month Date). Title . Site name. URL
- Wukovits, J. (2023, January 30). A World War II survivor recalls the London Blitz . British Heritage . https://britishheritage.com/history/world-war-ii-survivor-london-blitz
When an online article doesn’t include a specific author or date, list it like this:
Title . (Year, Month Date). Site name. Retrieved Month Date, Year, from URL
- Growing up in the Second World War . (n.d.). Imperial War Museums. Retrieved May 12, 2023, from https://www.iwm.org.uk/history/growing-up-in-the-second-world-war
When you need to list a YouTube video, use the name of the account that uploaded the video, and format it like this:
Name of Account. (Upload year, month day). Title [Video]. YouTube. URL
- War Stories. (2023, January 15). How did London survive the Blitz during WW2? Cities at war: London [Video]. YouTube. https://youtu.be/uwY6JlCvbxc
For more information on writing APA bibliographies, see the APA Style Guide website.
APA Bibliography (Reference List) Example Pages

MLA Style Bibliography Examples

MLA style calls for a Works Cited section, which includes all materials quoted or referred to in your paper. You may also include a Works Consulted section, including other reference sources you reviewed but didn’t directly cite. Together, these constitute a bibliography. If your teacher requests an MLA Style Guide bibliography, ask if you should include Works Consulted as well as Works Cited.
How To Write a Bibliography (Works Cited and Works Consulted) in MLA Style
For both MLA Works Cited and Works Consulted sections, use these general guidelines:
- Start your Works Cited list on a new page. If you include a Works Consulted list, start that on its own new page after the Works Cited section.
- Center the title (Works Cited or Works Consulted) in the middle of the line at the top of the page.
- Align the start of each source to the left margin, and use a hanging indent (1/2 inch) for the following lines of each source.
- Alphabetize your sources using the first word of the citation, usually the author’s last name.
- Include the author’s full name as listed, last name first.
- Capitalize titles using the standard MLA format.
- Leave off the http:// or https:// at the beginning of a URL.
Books and E-Books MLA Bibliography Examples
For books, MLA reference list entries use the following format. Add the URL at the end for e-books.
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. Title . Publisher, Date. URL
- Wynn, Stephen. City of London at War 1939–45 . Pen & Sword Military, 2020. www.pen-and-sword.co.uk/City-of-London-at-War-193945-Paperback/p/17299
Periodical MLA Bibliography Examples
Here’s the MLA-style format for magazines, journals, and newspapers. For online articles, add the URL at the end of the listing:
For magazines and journals:
Last Name, First Name. “Title: Subtitle.” Name of Journal , volume number, issue number, Date of Publication, First Page Number–Last Page Number.
- Bell, Amy. “Landscapes of Fear: Wartime London, 1939–1945.” Journal of British Studies , vol. 48, no. 1, January 2009, pp. 153–175. www.jstor.org/stable/25482966
When citing newspapers, include the page number/s for print editions or the URL for online articles:
Last Name, First Name. “Title of article.” Newspaper title. Page number/s. Year, month day. Page number or URL
- Blakemore, Erin. “Researchers Track Down Two Copies of Fossil Destroyed by the Nazis.” The Washington Post. 2022, Nov. 12. www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/11/12/ichthyosaur-fossil-images-discovered/
Electronic MLA Bibliography Examples
Last Name, First Name. Year. “Title.” Month Day, Year published. URL
- Wukovits, John. 2023. “A World War II Survivor Recalls the London Blitz.” January 30, 2023. https://britishheritage.com/history/world-war-ii-survivor-london-blitz
Website. n.d. “Title.” Accessed Day Month Year. URL.
- Imperial War Museum. n.d. “Growing Up in the Second World War.” Accessed May 9, 2023. www.iwm.org.uk/history/growing-up-in-the-second-world-war.
Here’s how to list YouTube and other online videos:
Creator, if available. “Title of Video.” Website. Uploaded by Username, Day Month Year. URL.
- “How did London survive the Blitz during WW2?” Cities at war: London | War stories.” YouTube . Uploaded by War Stories, 15 Jan. 2023. youtu.be/uwY6JlCvbxc.
For more information on writing MLA-style bibliographies, see the MLA Style website.
MLA Bibliography (Works Cited) Example Pages

Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
The Chicago Manual of Style (sometimes called “Turabian”) actually has two options for citing reference material: Notes and Bibliography and Author-Date. Regardless of which you use, you’ll need a complete detailed list of reference items at the end of your paper. The examples below demonstrate how to write that list.
How To Write a Bibliography Using The Chicago Manual of Style

Here are some general notes on writing a Chicago -style bibliography:
- You may title it “Bibliography” or “References.” Center this title at the top of the page and add two blank lines before the first entry.
- Left-align each entry, with a hanging half-inch indent for subsequent lines of each entry.
- Single-space each entry, with a blank line between entries.
- Include the “http://” or “https://” at the beginning of URLs.
Books and E-Books Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
For books, Chicago -style reference list entries use the following format. (For print books, leave off the information about how the book was accessed.)
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. Title . City of Publication: Publisher, Date. How e-book was accessed.
- Wynn, Stephen. City of London at War 1939–45 . Yorkshire: Pen & Sword Military, 2020. Kindle edition.
Periodical Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
Here’s the style format for magazines, journals, and newspapers. For online articles, add the URL at the end of the listing.
For journal and magazine articles, use this format:
Last Name, First Name. Year of Publication. “Title: Subtitle.” Name of Journal , Volume Number, issue number, First Page Number–Last Page Number. URL.
- Bell, Amy. 2009. “Landscapes of Fear: Wartime London, 1939–1945.” Journal of British Studies, 48 no. 1, 153–175. https://www.jstor.org/stable/25482966.
When citing newspapers, include the URL for online articles:
Last Name, First Name. Year of Publication. “Title: Subtitle.” Name of Newspaper , Month day, year. URL.
- Blakemore, Erin. 2022. “Researchers Track Down Two Copies of Fossil Destroyed by the Nazis.” The Washington Post , November 12, 2022. https://www.washingtonpost.com/science/2022/11/12/ichthyosaur-fossil-images-discovered/.
Electronic Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Examples
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. “Title.” Site Name . Year, Month Day. URL.
- Wukovits, John. “A World War II Survivor Recalls the London Blitz.” British Heritage. 2023, Jan. 30. britishheritage.com/history/world-war-ii-survivor-london-blitz.
“Title.” Site Name . URL. Accessed Month Day, Year.
- “Growing Up in the Second World War.” Imperial War Museums . www.iwm.org.uk/history/growing-up-in-the-second-world-war. Accessed May 9, 2023.
Creator or Username. “Title of Video.” Website video, length. Month Day, Year. URL.
- War Stories. “How Did London Survive the Blitz During WW2? | Cities at War: London | War Stories.” YouTube video, 51:25. January 15, 2023. https://youtu.be/uwY6JlCvbxc.
For more information on writing Chicago -style bibliographies, see the Chicago Manual of Style website.
Chicago Manual of Style Bibliography Example Pages

Get Your Free Printable Bibliography Style Guide

Just fill out the form on this page to grab our printable Bibliography Guide for Students with examples from all three major style guides: APA (American Psychological Association), MLA (Modern Language Association), or The Chicago Manual of Style .
Now that you know how to write a bibliography, take a look at the Best Websites for Teaching & Learning Writing .
Plus, get all the latest teaching tips and ideas when you sign up for our free newsletters , you might also like.
70 Higher-Order Thinking Questions To Challenge Your Students (Free Printable)
Plus 45 lower-order thinking questions too. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2024. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

The Plagiarism Checker Online For Your Academic Work
Start Plagiarism Check
Editing & Proofreading for Your Research Paper
Get it proofread now
Online Printing & Binding with Free Express Delivery
Configure binding now
- Academic essay overview
- The writing process
- Structuring academic essays
- Types of academic essays
- Academic writing overview
- Sentence structure
- Academic writing process
- Improving your academic writing
- Titles and headings
- APA style overview
- APA citation & referencing
- APA structure & sections
- Citation & referencing
- Structure and sections
- APA examples overview
- Commonly used citations
- Other examples
- British English vs. American English
- Chicago style overview
- Chicago citation & referencing
- Chicago structure & sections
- Chicago style examples
- Citing sources overview
- Citation format
- Citation examples
- College essay overview
- Application
- How to write a college essay
- Types of college essays
- Commonly confused words
- Definitions
- Dissertation overview
- Dissertation structure & sections
- Dissertation writing process
- Graduate school overview
- Application & admission
- Study abroad
- Master degree
- Harvard referencing overview
- Language rules overview
- Grammatical rules & structures
- Parts of speech
- Punctuation
- Methodology overview
- Analyzing data
- Experiments
- Observations
- Inductive vs. Deductive
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative
- Types of validity
- Types of reliability
- Sampling methods
- Theories & Concepts
- Types of research studies
- Types of variables
- MLA style overview
- MLA examples
- MLA citation & referencing
- MLA structure & sections
- Plagiarism overview
- Plagiarism checker
- Types of plagiarism
- Printing production overview
- Research bias overview
- Types of research bias
- Example sections
- Types of research papers
- Research process overview
- Problem statement
- Research proposal
- Research topic
- Statistics overview
- Levels of measurment
- Frequency distribution
- Measures of central tendency
- Measures of variability
- Hypothesis testing
- Parameters & test statistics
- Types of distributions
- Correlation
- Effect size
- Hypothesis testing assumptions
- Types of ANOVAs
- Types of chi-square
- Statistical data
- Statistical models
- Spelling mistakes
- Tips overview
- Academic writing tips
- Dissertation tips
- Sources tips
- Working with sources overview
- Evaluating sources
- Finding sources
- Including sources
- Types of sources
Your Step to Success
Plagiarism Check within 10min
Printing & Binding with 3D Live Preview
Bibliography – Types, Formats & Examples
How do you like this article cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Bibliographies are the backbone of academic research, providing a roadmap to the citing sources that shape scholarly discourse. Assembled with precision, and care, they not only acknowledge intellectual debts, but also offer pathways for further exploration. In this article, we delve into the significance of bibliography, exploring its role in guiding researchers through the labyrinth of knowledge.
Inhaltsverzeichnis
- 1 Bibliography in a nutshell
- 2 Definition: Bibliography
- 3 Basic Bibliographic Entries
- 4 Types of Bibliographies
- 5 Analytical Bibliography
- 6 Annotated Bibliography
- 7 Enumerative Bibliography
- 8 Bibliographic Formats
Bibliography in a nutshell
A bibliography is an alphabetically organized list of sources, that you need to reference when writing scholarly articles, books, or research papers to avoid plagiarism.
Definition: Bibliography
A bibliography is a comprehensive list of sources , such as books and websites, that have been consulted or cited in a particular work. It serves as a reference list , providing readers with information about the sources used by the author, and allowing them to locate and verify those sources. Typically, they include detailed information for each source, such as the author’s name, title, publication date, publisher, and page numbers.
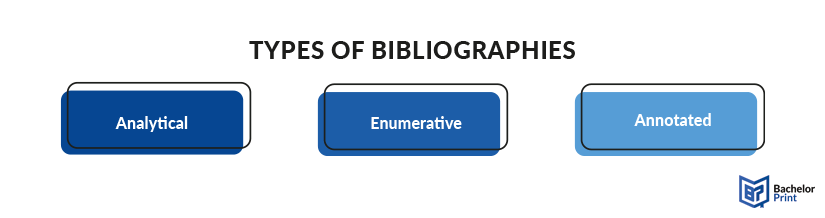
There are three major style guides, when it comes to citation: the APA citation style (American Psychological Association), MLA citation style (Modern Language Association), and Chicago style of citation. These include analytical bibliographies, enumerative bibliographies, and lastly, annotated bibliographies.
The term “bibliography” is generally used for any list of sources cited at the of an academic work. Some style guides refer to them using particular terminology . MLA format refers to it as a Works Cited page. Whereas, the American Psychological Association refers to it as an APA Reference page .
Basic Bibliographic Entries
Entries for each source cited or consulted, are listed in alphabetical order. Each entry includes essential bibliographic details such as:
- Authors or editors
- Title of the work
- Publishing date
- Relevant page numbers
Types of Bibliographies
There are three common kinds of bibliography, each serving different purposes and focusing on various aspects of research and scholarship:
Enumerative
Analytical bibliographies go beyond simple description to analyze the content and structure of works. They include variations between different editions , each work’s number of pages , information concerning the booksellers and printers, paper and binding descriptions, and any insights that unfold as a book evolved from a manuscript to a published book. They are used by researchers interested in the history of books and printing.
- Details about each source, including the author’s name, publication title, etc.
- Analysis focusing on textual evidence, editorial decisions, etc.
- Explanation of the purpose and goal of the bibliography.
- Historical context on the source’s production, including printing technology etc.
- Comparison with other editions or versions, highlighting textual variations etc.
Annotated bibliographies include brief summaries or annotations of each source listed alphabetically, in addition to bibliographic information. This type provides an outline of the content and quality of the source, helping researchers evaluate its relevance for their own work.
- Details about each source, including the author’s name, title, etc.
- Brief summary (2-4 sentences) of the main points and arguments of each source.
- Assessment of quality, reliability, relevance, and credibility.
- Explanation of why the source was chosen and who it is intended for.
- Explanation of how the source relates to the research topic or question.
Students writing research papers commonly use enumerative bibliography. It is the most basic type, where the writer lists all sources used, providing bibliographic details for each work. Those sources share common characteristics such as language, topic, or period of time. Information concerning the source is then given by the writer to provide directions to the readers towards the source.
- A list of sources including details of the author’s name, title, etc.
- Method of organizing the bibliographic entries, such as alphabetical by author, etc.
- Description of the scope, including and specific criteria used to select or exclude sources.
- May include annotations providing further information, such as evaluations or summaries.
Analytical Bibliography
There are several distinctions for the analytical type. Three of them will be explained below.
Critical Analytical
Descriptive analytical, historical analytical.
Critical analytical bibliographies analyze the significance and meaning of textual variations . They may examine the implications of editorial decisions or printing errors on the interpretation and reception of a work. They often engage with literary theory, textual criticism, and scholarly debates. By critically examining the production history of a work, critical analytical bibliographies aim to shed light on the intentions of authors and editors, as well as the cultural and social contexts in which works were produced.
This analysis includes the following features:
- Providing textual analysis on variations, changes, and decisions
- Offering contextual information about the cultural, social, or political milieu
- Identifying differences, similarities, and unique contributions with other works
- Assessing the scholarly significance and impact of the work
Focus on providing detailed descriptions of the physical characteristics of books and printed materials. They aim to analyze aspects such as typography, binding, paper quality, illustrations, and textual variations. By documenting these features, descriptive analytical bibliographies facilitate the identification of different versions of a work, helping others trace the history of printing and publishing processes.
This analysis includes elements such as:
- Detailed description of physical characteristics
- Documentation of textual variations and discrepancies
- Analysis of editorial decisions or interventions
- Examination of printing history
- Comparison with other editions or versions
Historical analysis examines the production history and reception of relevant materials within their context. This involves studying factors such as printing technology, publishing practices, censorship, and readership. It aims to uncover the cultural, political, and intellectual significance of printed materials, shedding light on their roles in shaping historical developments and cultural movements.
This analysis generally outlines:
- Contextualization within historical, cultural, and social frameworks
- Documentation of publication history and evolution over time
- Analysis of reception and impact within historical context
- Examination of editorial practices and textual transmission
- Assessment of cultural, political, and intellectual significance
Annotated Bibliography
There are a few distinctions for the annotated bibliography type. Three of them will be explained in the following paragraph.
Critical Annotated
Descriptive annotated, informative annotated.
Critical annotations evaluate the strengths , weaknesses , and overall significance of the source, considering factors such as methodology , empirical evidence, authority, and bias. Critical annotations may include both positive and negative comments , and provide readers with insights into the credibility and usefulness of each source, helping them make informed decisions about its inclusion in their research.
This annotation may include the following elements:
- Examining the author’s bias or tone
- Evaluating the author’s qualifications
- Verifying the accuracy of the information
- Comparing the work with other publications on the topic
- Assessing the significance of the work’s contribution
These annotations provide a concise summary of the source’s content, focusing on key points and findings. Descriptive annotations aim to give readers a clear understanding of what the source covers without offering evaluation or critique. They are commonly used to provide basic information about each source listed in the annotated bibliography.
This annotation typically outlines:
- The primary objective of the work
- The contents covered in the work
- The conclusion drawn by the author
- The target audience
- The research methods employed by the author
- Distintice elements within the work, such as illustrations and tables.
Informative annotations serve as a hybrid between descriptive and critical ones, providing both a summary and evaluation of the source’s content. This type aims to inform readers about the key aspects, while also offering insights into its strengths and weaknesses. Overall, informative annotations aim to strike a balance between providing descriptive information and offering critical insights.
An informative annotation comprises the following aspects:
- Summary of the source’s content and message
- Includes the hypothesis, methodology, main points, and conclusion
- Does not offer editorial evaluative comment on the content.
Enumerative Bibliography
There are different types of the enumerative bibliography. Three of them will be explained down below.
Comprehensive Enumerative
Selective numerative, subject enumerative.
This type of bibliography aims to provide an exhaustive list of works on a particular subject without imposing strict selection criteria, offering researches a comprehensive overview of the literature available.
This specific type may include the following elements:
- Comprehensive coverage of relevant literature
- Emphasis on inclusivity, striving to list all known and available sources
- May include annotations or descriptive notes for further information about each source
- Regularly updating and maintaining the bibliography to ensure currency and relevance
The selective enumerative type includes only a subset of the available literature on a topic. It focuses on key works, seminal text, or authoritative sources based on specific criteria, Unlike comprehensive ones, selective bibliographies prioritize quality over quantity , offering users a curated selection of the most important and influential works within the subject area.
It typically outlines these elements:
- Clearly defining the criteria used to select sources
- Carefully curating a selection of sources
- Excluding sources that do not meet the specified criteria
- May include evaluative annotations or commentary to justify the selection
- Providing guidance to users on how to effectively use it
The subject-specific enumerative type focuses on compiling sources related to a specific subject , catering to the research needs of practitioners, students, and scholars within that domain. They are tailored to the needs and interests of users within a particular specialization .
A subject enumerative comprises the following aspects:
- Organized according to the subject area, facilitating easy access of resources
- Coverage of a broad range of topics within the chosen subject area
- May include thematic categorization or subheadings to further organize it
- Tailored annotations, offering insights into the relevance of each source

Bibliographic Formats
Bibliographies can be formatted in various styles, each with its own set of guidelines for organizing and presenting bibliographic information. In this format, we will provide you with the three most common formats, as well as examples for each.
When writing bibliographies (references) using the APA format, the following steps should be observed:
- At the end of the paper on a new page, “ References ” entitled with center-alignment .
- The references themselves should be left-aligned .
- Subsequent lines need a hanging indent of 1/2 inch.
- Only use the author’s full last name and the initial of the first (and middle) name.
- If there are multiple authors, the names are separated with an ampersand (&).
- Place the date in parentheses .
- Italicize the title of the source material & use sentence case .
- For websites, use the full URL .
Smith, J. (2020). The Impact of Social Media on Adolescent Mental Health: A Comprehensive Analysis. Academic Press.
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. (Publication Date). Title . Publisher. URL.
The image below contains an example of an annotated bibliography in APA format.

When writing a bibliography (Works Cited) using MLA, it appears in this format:
- Start “ Works Cited ” list on a new page with center-alignment .
- If you add a Works Consulted list , start it on a new page after Works Cited.
- Each source is left-aligned .
- Alphabetize your sources, usually the author’s last name.
- Full name of the author, last name is mentioned first .
- Remove the https:// of the URL.
Litfin, Karen. “Introduction to Political Economy.” Political Science 203. The University of Washington. Seattle, 2000.
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. Title . Publisher, Date. URL
The image below illustrates an example of an annotated bibliography in MLA format.

Chicago Style Format
Here are some general notes on writing a Chicago Style bibliography:
- “Bibliography” or “References” in center-alignment .
- Before the first entry, add t wo blank lines .
- Left-align each entry, 1/2 hanging indent for each subsequent line.
- Single-space entry, with a blank line between each.
- Include the full URL .
Wynn, Stephen. 2020. City of London at War 1939–45 . Yorkshire: Pen & Sword Military.
Last Name, First Name Middle Name. Date. Title . City of Publication: Publisher. URL
The image below serves as an example of an annotated bibliography in Chicago format.

What is a bibliography?
A bibliography generally entails the listing of books, articles, websites, and other study materials used to compose a piece of academic writing or literary work. It typically appears at the end of the document and provides readers with detailed information about each source, allowing them to locate and verify the information used by the author.
What is in a bibliography?
A bibliography should include
- The authors’ names
- Date of publication
- Name of publishers and publisher city
- If there are multiple volumes or editions, add page number
- URL if required
What is the difference between bibliographies and a works cited page?
“Works Cited” is a specific term used in MLA citation to refer to a list of sources cited directly in the text, whereas a bibliography includes sources that were consulted, but not directly cited.
What are examples of bibliography?
The exact method and formatting required, will depend on the referencing style that your institution uses.
APA: Last Name, First Name Middle Name. (Publication Date). Title . Publisher. URL.
MLA: Last Name, First Name Middle Name. Title . Publisher, Date. URL
Chicago: Last Name, First Name Middle Name. Date. Title . City of Publication: Publisher. URL
What are the different types of bibliographies?
There are three main types of bibliographies. Check with your institution which method you’re required to use. This may depend on the referencing and citation style you’re using, as well as your field of research.
Analytical: Includes information and new insights that come to light as the book or research paper progresses.
Annotated: Outlines the research that was conducted and provides feedback on specific sources.
Enumerative: A list of sources in a particular order.
Amazing experience having my dissertation bound with them would highly...
We use cookies on our website. Some of them are essential, while others help us to improve this website and your experience.
- External Media
Individual Privacy Preferences
Cookie Details Privacy Policy Imprint
Here you will find an overview of all cookies used. You can give your consent to whole categories or display further information and select certain cookies.
Accept all Save
Essential cookies enable basic functions and are necessary for the proper function of the website.
Show Cookie Information Hide Cookie Information
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Eigentümer dieser Website, |
| Zweck | Speichert die Einstellungen der Besucher, die in der Cookie Box von Borlabs Cookie ausgewählt wurden. |
| Cookie Name | borlabs-cookie |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
| Name | |
|---|---|
| Anbieter | Bachelorprint |
| Zweck | Erkennt das Herkunftsland und leitet zur entsprechenden Sprachversion um. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | ip-api.com |
| Cookie Name | georedirect |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1 Jahr |
Statistics cookies collect information anonymously. This information helps us to understand how our visitors use our website.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Cookie von Google zur Steuerung der erweiterten Script- und Ereignisbehandlung. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Cookie Name | _ga,_gat,_gid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
Content from video platforms and social media platforms is blocked by default. If External Media cookies are accepted, access to those contents no longer requires manual consent.
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Facebook-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .facebook.com |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird zum Entsperren von Google Maps-Inhalten verwendet. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Meta Platforms Ireland Limited, 4 Grand Canal Square, Dublin 2, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Instagram-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .instagram.com |
| Cookie Name | pigeon_state |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Sitzung |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Openstreetmap Foundation, St John’s Innovation Centre, Cowley Road, Cambridge CB4 0WS, United Kingdom |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um OpenStreetMap-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .openstreetmap.org |
| Cookie Name | _osm_location, _osm_session, _osm_totp_token, _osm_welcome, _pk_id., _pk_ref., _pk_ses., qos_token |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 1-10 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Twitter International Company, One Cumberland Place, Fenian Street, Dublin 2, D02 AX07, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Twitter-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | .twimg.com, .twitter.com |
| Cookie Name | __widgetsettings, local_storage_support_test |
| Cookie Laufzeit | Unbegrenzt |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Vimeo Inc., 555 West 18th Street, New York, New York 10011, USA |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um Vimeo-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | player.vimeo.com |
| Cookie Name | vuid |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 2 Jahre |
| Akzeptieren | |
|---|---|
| Name | |
| Anbieter | Google Ireland Limited, Gordon House, Barrow Street, Dublin 4, Ireland |
| Zweck | Wird verwendet, um YouTube-Inhalte zu entsperren. |
| Datenschutzerklärung | |
| Host(s) | google.com |
| Cookie Name | NID |
| Cookie Laufzeit | 6 Monate |
Privacy Policy Imprint

- Citation Generator
- Style Guides
- Chicago/Turabian Format
Category Style Guides
When you are talking about styles for a bibliography page, there are a lot of them out there. Each different style has its own look and feel. They are also designed for a different type of work, whether it be a business thesis or a humanities essay.
What is a Bibliography Page?
Citing your work can come in all different forms. You can cite only the works that you specifically reference in a essay or you can cite everything that you used to create a thesis. What you are citing is what makes one a bibliography and one a works cited.
Bibliography Definition and Examples
Simply put, a bibliography is all the works that you used to created your thesis or essay. This can be a professional paper used in a scholarly journal or an essay for your high school humanities class. Either way, the bibliography offers insight into where your sources and statistics came from. This isn’t just what you cited either; it is every single piece of scholarly information that you used to create your work. To really understand the creation of a bibliography and the style, it’s important to discuss some examples.
Style Examples
When creating a bibliography, there are several different styles that you can use. Each style has different formatting for citations and set up. Each style also has different citation formats for different sources, including but not limited too, books, magazines, websites and blogs. The core styles that you can use are:
American Psychological Association Modern Language Association Harvard Referencing Chicago Manual of Style
When it comes to writing styles, there are a lot of them. Whether you’re writing a biology, communications, theology or philosophy research paper or essay, there is a writing style for you. Learn about the different styles for formatting your paper, as well as how the reference and bibliography styles differ between them. What’s in a Name? In the world of writing, there are bibliographies...
Research papers take a lot of different steps to format your outline and discuss where your sources came from. Every paper ends with a citation page or bibliography. The type of bibliography that you use will depend on your research and subject matter. Bibliography Uncovered Before you can even get into the steps of creating your bibliography, you need to understand specifically what a...
You’ve been looking over the different writing styles and noticed that MLA and APA are similar. Staring at the citation page, you really can’t see a difference between the two. While MLA and APA do have a lot of similarities in the citation pages, there are a few distinct differences that you’ll notice if you really look at them. MLA vs. APA If you are comparing MLA and APA citation styles...
Your professor required that you create endnotes for your in-text citation. You’ve composed your endnote page beautifully. Now, you’re looking at creating the bibliography. But why? Didn’t you already cover everything in your endnotes? Learn about the differences and similarities between a bibliography and endnotes. Find out when you’ll use each and why. Endnotes, Bibliography or Both...
Your eyes are crossed. You haven’t showered in three days, but your paper is done. Pushing away from your computer, you breathe a much needed sigh of relief. That is until you realize that you haven’t created your bibliography. What’s your style again? How do you create it? Don’t worry, your guide to bibliography rules is right here, ready to help. Not All Bibliographies Are Equal In the...
Your professor has told you to write your paper in Turabian style, but you’re clueless. You keep seeing this style and Chicago combined. Now you are really confused. Find your answers to what Turabian is and how it’s created. What Is Turabian Style? Turabian is a style covered under the Chicago Manual of Style (CMOS). The difference in these styles is who they are created for...
Is your head spinning over the difference? Don’t let the terminology get to you. In their most basic form, references, works cited and a bibliography are all essentially the same thing. They’re a page (or pages) at the end of your paper where you cite the sources you used to form your essay. Learn when to use a list of references, a bibliography or a works cited list, along with how they’re...
References and citations are the apples and oranges of the writing world. While it might seem like these two words are interchangeable. They are distinctly different within a scholarly writing piece. Learn what they are and how to use each one. Citations or References No matter what writing style that you use, you’ll come across the reference or citation dilemma, especially if you’re a...
Is your professor asking you to write an annotated bibliography? Are you clueless? You’ve come to the right place. The world of bibliographies can be a difficult web to weave, especially when you are talking about annotated bibliographies. Take a deep breath and get ready. You’re going to learn everything you need to know to make an annotated bibliography in MLA style. What Is an Annotated...
Figuring out how to format your work with just one author was hard enough. Now, you have a book that has three different authors and one with eleven different authors. You know all those names are just going to clutter up your APA essay. Learn the right way to source multiple authors in the APA style. Creating a Parenthetical Citation Whether you have a book or magazine with multiple sources, the...
Images add diversity and visual information that sometimes just isn’t possible with words alone. But, how do you cite a picture and add it to your MLA works cited list? Learn the ins and outs of citing a picture in your work and a little about the legalities. Adding a Reproduced Image in Text Sometimes, it makes sense to reference images visually to prove a point. This is especially true if you...
You think citing quotes in your APA paper is going to be simple. But, suddenly you have one book with multiple authors and another book with no date. You’re trying to add a citation for a website quote with no author or date. Plus, you have an interview. Simple citations have become a mess. Break down citations for books, websites and even interviews in even the most difficult of situations...
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
Bibliography.
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Choosing a Title
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
In addition to the sources cited in the individual text boxes of this writing guide, listed below are books about how to effectively write and organize a college-level research paper or dissertation [which frequently have good advice on writing, regardless of their purpose]. Enter the title of the book in the USC Libraries' search engine to check the availability of these or any other books on college-level writing and research. If the library does not own a particular title, you can request to borrow the book free of charge from the USC Libraries' interlibrary loan department .
- Abbott, Andrew. Digital Paper: A Manual for Research and Writing with Library and Internet Materials . Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2014.
- Anders, Marian. The Practical Grammar Handbook for College Writers . 2nd edition. Durham, NC: Carolina Academic Press, 2015.
- Aveyard, Helen. Doing a Literature Review in Health and Social Care: A Practical Guide . 3rd edition. New York: McGraw-Hill Education, 2014.
- Axelrod, Rise B. and Charles Raymond Cooper. The St. Martin's Guide to Writing . 10th edition. Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martins, 2013.
- Badke, William. Research Strategies: Finding Your Way through the Information Fog . 5th edition. Bloomington, IN: iUniverse, LLC, 2014.
- Ballenger, Bruce P. The Curious Researcher: A Guide to Writing Research Papers . 8th edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2015.
- Barnet, Sylvan, Pat Bellanca, and Marcia Stubbs. A Short Guide to College Writing . 5th edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2013.
- Becker, Lucinda. Writing Successful Reports and Dissertations . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2014.
- Birkenstein, Cathy and Gerald Graff. “They Say/I Say”: The Moves That Matter in Academic Writing . 4th edition. New York: W.W. Norton and Company, 2018.
- Cahn, Steven M. and Victor Cahn. Polishing Your Prose: How to Turn First Drafts Into Finished Work . New York: Columbia University Press, 2013.
Carter, Caron, editor. Successful Dissertations: The Complete Guide for Education, Childhood and Early Childhood Studies Students . New York: Bloomsbury Academic, 2018.
- Channell, Carolyn. Engaging Questions: A Guide to Writing . 2nd edition. New York: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2016.
- Cioffi, Frank L. The Imaginative Argument: A Practical Manifesto for Writers . Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press, 2017.
- Clark, Roy Peter. Help! for Writers: 210 Solutions to the Problems Every Writer Faces . New York: Little, Brown, 2011.
- Clouse, Barbara Fine. A Troubleshooting Guide for Writers: Strategies and Process . 7th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill, 2013.
- Cottrell, Stella. Dissertations and Project Reports: A Step by Step Guide . Basingstoke, UK: Palgrave Macmillan, 2014.
- Cutts, Martin. Oxford Guide to Plain English . 4th edition. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press, 2013.
- Eby, Erika. The College Student's Guide to Writing a Great Research Paper: 101 Easy Tips and Tricks to Make Your Work Stand Out . Ocala, FL: Atlantic Pub. Group, 2012.
- Edwards, Mark. Writing in Sociology . Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2014.
- Evans, David, Paul Gruba, and Justin Zobel. How to Write a Better Thesis . 3rd edition. Melbourne, Australia: Melbourne University. Publishing, 2011.
- Faigley, Lester. Writing: A Guide for College and Beyond . 4th edition. Boston, MA: Pearson Higher Ed, 2016.
- Fiske, Robert Hartwell. To the Point: A Dictionary of Concise Writing . New York: W.W. Norton and Company, 2014.
Floyd, Randy G., editor. Publishing in School Psychology and Related Fields: An Insider's Guide . New York: Routledge, Taylor and Francis Group, 2018.
- Gelman, Howard. Everyone Can Write: A Guide to Get You Started . Wollombi, NSW, Australia: Exisle Publishing, 2014.
- Gill, Charlene. Essential Writing Skills for College and Beyond . Cincinnati, OH: Writer's Digest Books, 2014.
- Giltrow, Janet, Richard Gooding, Daniel Burgoyne, and Marlene Sawatsky. Academic Writing: An Introduction . 3rd edition. Tonawanda, NY: Broadview Press, 2014.
- Gibson, Twyla, and Mark Lipton. Research, Write, Create: Connecting Scholarship and Digital Media . Ontario, Canada: Oxford University Press, 2014.
- Glaser, Joe. Understanding Style: Practical Ways to Improve Your Writing . 3rd edition. New York: Oxford University Press, 2016.
- Goodson, Patricia. Becoming an Academic Writer: 50 Exercises for Paced, Productive, and Powerful Writing . 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2016.
Graff, Gerald and Cathy Birkenstein. "They Say / I Say": The Moves that Matter in Academic Writing . New York: W.W. Norton and Company, 2017.
- Hacker, Diana and Nancy Sommers. Rules for Writers . 9th edition. Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martin's, 2018.
- Hart, Chris. Doing a Literature Review: Releasing the Research Imagination . 2nd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage, 2018.
- Harvey, Michael. The Nuts and Bolts of College Writing . Indianapolis, IN: Hackett Publishing, 2013.
- Hjortshoj, Keith. The Transition to College Writing . Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martins, 2009.
- Howard, Rebecca Moore. Writing Matters: A Handbook for Writing and Research . 2nd edition. New York: McGraw-Hill Higher Education, 2013.
- Johnson, William A. A Criminal Justice Student's Writer's Manual . 6th edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2015.
- Johnson Jr, William A., Gregory M. Scott, and Stephen M. Garrison. The Sociology Student Writer's Manual and Reader's Guide . 7th edition. Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield, 2017.
- Joyner, Randy L., William A. Rouse, and Allan A. Glatthorn. Writing the Winning Thesis or Dissertation: A Step-by-step Guide . 3rd edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin Press, 2013.
- Kirszner, Laurie G. and Stephen R. Mandell. Patterns for College Writing: A Rhetorical Reader and Guide . 12th edition. Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martins, 2012.
- Koerber, Duncan and Guy Allen. Clear, Precise, Direct: Strategies for Writing . Ontario, Canada: Oxford University Press, 2015.
- Langan, John. Exploring Writing: Paragraphs and Essays . 3rd edition. Dubuque, IA: McGraw-Hill, 2013.
- Lee, Kooi Cheng. Effective College Writing: A Process-Genre Approach . 2nd edition. Singapore: McGraw-Hill, 2009.
- Lerych, Lynne and Allison DeBoer Criswell. Everything You Need to Know about College Writing . Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martin's, 2016.
- Lester, James D. and James D. Lester. Writing Research Papers: A Complete Guide . 14th edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2012.
- Lindemann, Kurt. Composing Research, Communicating Results: Writing the Communication Research Paper . Hoboken, NJ: John Wiley and Sons, 2017.
- Marsen, Sky. Professional Writing . 3rd edition. New York: Palgrave Macmillan, 2013.
- McMillan, Kathleen and Jonathan Weyers. How to Improve Your Critical Thinking and Reflective Skills . Harlow, UK: Pearson Education Limited, 2013.
- McNiff, Jean. Writing Up Your Action Research Project . New York: Routledge, 2015.
- Miller, Scott A. Writing in Psychology . New York: Routledge, 2014.
- Muller, Jake. Writing in the Social Sciences: A Guide for Term Papers and Book Reviews . 2nd edition. Ontario, Canada: Oxford University Press Canada, 2015.
- Northey, Margot, Dianne Draper, and David B. Knight. Making Sense: A Student's Guide to Research and Writing: Geography and Environmental Sciences . 6th edition. Oxford: Oxford University Press, 2015.
- Oliver, Paul. Writing Your Thesis . 3rd edition. London: Sage, 2013.
- Parsons, Tony, and Peter G. Knight. How to Do Your Dissertation in Geography and Related Disciplines . New York: Routledge, 2015.
- Pyrczak, Fred. Writing Empirical Research Reports: A Basic Guide for Students of the Social and Behavioral Sciences . 8th edition. Glendale, CA: Pyrczak Publishing, 2014.
- Raimes, Ann and Susan K. Miller-Cochran. Keys for Writers . 7th edition. Boston, MA: Wadsworth Publishing, 2014.
- Reinking, James A. Strategies for Successful Writing: A Rhetoric, Research Guide, Reader, and Handbook . 1oth edition. Boston, MA: Pearson, 2014.
- Reynolds, Nedra and Elizabeth Davis. Portfolio Keeping: A Guide for Students. 3rd edition. Boston, MA: Bedford/St. Martins, 2013.
- Ridley, Diana. The Literature Review: A Step-by-step Guide for Students . 2nd edition. Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2012.
- Roen, Duane, Gregory Glau, and Barry Maid. The McGraw-Hill Guide: Writing for College, Writing for Life . 4th edition. New York: McGraw-Hill Education, 2018.
- Rudestam, Kjell Erik and Rae R. Newton. Surviving Your Dissertation: A Comprehensive Guide to Content and Process . 4th edition. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications, 2014.
- Scott, Gregory M. and Stephen M. Garrison. The Political Science Student Writer's Manual and Reader's Guide . 8th edition. Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield, 2017.
- Spencer, Linda. Writing Well in the 21st Century: The Five Essentials . Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield, 2014.
- Starr, Douglas Perret and Deborah Williams Dunsford. Working the Story: A Guide to Reporting and News Writing for Journalists and Public Relations Professionals . Lanham, MD: Rowman and Littlefield, 2014.
- Szuchman, Lenore T. Writing with Style: APA Style Made Easy . 6th edition. Belmont, CA: Wadsworth Cengage Learning, 2014.
- Thurman, Susan and Larry Shea. The Only Grammar Book You'll Ever Need: A One-Stop Source for Every Writing Assignment . Avon, MA: Adams Media, 2015.
- Turabian, Kate L. A Manual for Writers of Research Papers, Theses, and Dissertations: Chicago Style for Students and Researchers . 9th edition. Chicago, IL: University of Chicago Press, 2018.
- Wallwork, Adrian. English for Research: Usage, Style, and Grammar . New York: Springer Science and Business Media, 2012.
- Wang, Gabe T. and Keumjae Park. Student Research and Report Writing: From Topic Selection to the Complete Paper . Malden, MA: Wiley Blackwell, 2016.
- Warner, John. The Writer's Practice: Building Confidence in Your Non-Fiction Writing . New York: Penguin/Random House, 2019.
- Watt, Jane. Report Writing for Social Workers . Los Angeles, CA: Sage, 2012.
- Wyrick, Jean. Steps to Writing Well . 12th edition. Boston, MA: Cengage Learning, 2014.
- Wyse, Dominic and Kate Cowan. The Good Writing Guide for Education Students . 4th edition. London: Sage, 2017.
- Yagoda, Ben. How to Not Write Bad: The Most Common Writing Problems and the Best Ways to Avoid Them . New York: Riverhead Books, 2013.
- << Previous: USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Next: Last Word >>
- Last Updated: Jul 3, 2024 10:07 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide

Bibliography: Definition, Types, Format & How-To Guide
Writing Guides
What is Bibliography?
A bibliography is a comprehensive list of sources that were consulted or referenced in the process of researching and writing a scholarly work. These sources can include books, articles, websites, and other materials. The bibliography provides readers with the information needed to locate the original sources and gives credit to the authors whose works have contributed to the research.
Table of Contents
Bibliography Types:
Below are some common types of bibliography:
1. Annotated Bibliography
An annotated bibliography includes a brief summary or evaluation of each source. The annotation can provide a summary of the content, an evaluation of the source’s reliability, and its relevance to the research topic. It typically follows one of the standard citation styles (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago).
2. Working Bibliography
A working bibliography is a preliminary list of sources that you might use in your research. It is not as formal or complete as a final bibliography and can be modified as the research progresses. It helps in keeping track of potential references.
3. Enumerative Bibliography
An enumerative bibliography lists sources according to a specific criterion, such as author, subject, or date of publication. It provides a systematic overview of a body of literature and is often used in academic research.
4. Descriptive Bibliography
Descriptive bibliography provides detailed information about the physical characteristics of books and other printed materials, such as the format, paper, binding, and typographical details. It is commonly used in the field of rare books and manuscripts.
5. Analytical Bibliography
Analytical bibliography examines the history and methods of book production, including the printing process, textual variations, and publishing practices. It focuses on the physical creation of the book and the text’s transmission over time.
6. Subject Bibliography
A subject bibliography lists sources related to a specific subject or field. It helps researchers find relevant literature in a particular area of study. Subject bibliographies can be found in libraries and databases.
7. Period Bibliography
Period bibliography covers works published during a specific time period. It is useful for historical research and understanding the literature of a particular era.
8. National Bibliography
A national bibliography lists all the publications produced in a particular country. It is usually compiled by a national library or bibliographic agency and helps preserve the country’s literary heritage.
9. Personal Bibliography
A personal bibliography is a compilation of works by a specific author. It includes all the known publications of the author, providing a comprehensive view of their contributions.
10. Universal Bibliography
A universal bibliography aims to list all the books and publications available worldwide. While achieving this is practically impossible, attempts are made through international cooperation and cataloging efforts.
Bibliography Format:
The format for a bibliography can vary depending on the citation style you are using. Here are examples of bibliography formats for some of the most common citation styles: APA, MLA, and Chicago.
APA (7th Edition)
The American Psychological Association (APA) style is commonly used in the social sciences.
Books: Author, A. A. (Year of publication). Title of work: Capital letter also for subtitle. Publisher.
Example: Smith, J. A. (2020). Understanding psychology: Basics and applications. Psychology Press.
Journal Articles: Author, A. A. (Year). Title of article. Title of Periodical, volume number(issue number), page range. https://doi.org/xx.xxx/yyyy
Example: Doe, J. (2019). Cognitive development in children. Journal of Child Psychology, 45(3), 234-245. https://doi.org/10.1234/jcp.2019.4567
MLA (9th Edition)
The Modern Language Association (MLA) style is often used in the humanities.
Books: Author’s Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Publisher, Year of Publication.
Example: Smith, John. Understanding Psychology: Basics and Applications. Psychology Press, 2020.
Journal Articles: Author’s Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal, vol. number, no. number, Year, pages. DOI or URL (if applicable).
Example: Doe, Jane. “Cognitive Development in Children.” Journal of Child Psychology, vol. 45, no. 3, 2019, pp. 234-245. https://doi.org/10.1234/jcp.2019.4567

Chicago (17th Edition)
The Chicago Manual of Style offers two systems: Notes and Bibliography, and Author-Date. Below is the Bibliography style.
Books: Author Last Name, First Name. Title of Book. Place of Publication: Publisher, Year.
Example: Smith, John. Understanding Psychology: Basics and Applications. New York: Psychology Press, 2020.
Journal Articles: Author Last Name, First Name. “Title of Article.” Title of Journal volume number, no. issue number (Year): page range. DOI or URL (if applicable).
Example: Doe, Jane. “Cognitive Development in Children.” Journal of Child Psychology 45, no. 3 (2019): 234-245. https://doi.org/10.1234/jcp.2019.4567
How to Write a Bibliography?
Writing a bibliography involves compiling a list of sources you have referenced in your work. The format and style of a bibliography can vary depending on the citation style you are required to use. Here are the general steps to create a bibliography.
Steps to Write a Bibliography
- Collect Information: Gather all the necessary information about your sources, such as the author(s), title, publication date, publisher, and any other relevant details.
- Choose a Citation Style: Determine which citation style is required or preferred (APA, MLA, Chicago, etc.).
- Format Each Entry: Follow the specific rules for formatting each entry according to the chosen citation style.
- Organize Entries: List the entries in alphabetical order by the author’s last name or by the title if there is no author.
Bibliography vs Footnotes
A bibliography and footnotes are both methods of citing sources in academic writing, but they serve different purposes and are formatted differently. Below are some major differences between bibliography and footnotes.
- Placement: Footnotes appear at the bottom of the same page where the reference or comment is made, while a bibliography is placed at the end of the document.
- Purpose: Footnotes provide immediate access to source information or additional context related to specific points in the text, while a bibliography offers a comprehensive list of all sources consulted or cited throughout the entire document.
- Content: Footnotes typically include specific source information or additional comments relevant to the page content, while a bibliography includes full bibliographic details for each source, such as author names, titles, publication dates, publishers, and page numbers.
- Numbering: Footnotes are numbered consecutively throughout the document, while a bibliography is generally not numbered but may be alphabetically organized.
- Format: Footnotes can vary in format depending on the citation style and often require page-specific details, while a bibliography entry follows a consistent format and does not include page numbers unless referring to a specific part of a source.
Related Posts

How to Write a Friendship Letter

How to Write Proposal Letter to Offer Services

How to Write a Thank You Letter
- U.S. Locations
- UMGC Europe
- Learn Online
- Find Answers
- 855-655-8682
- Current Students
Online Guide to Writing and Research
Academic integrity and documentation, explore more of umgc.
- Online Guide to Writing
Types of Documentation
Bibliographies and Source Lists
What is a bibliography.
A bibliography is a list of books and other source material that you have used in preparing a research paper. Sometimes these lists will include works that you consulted but did not cite specifically in your assignment. Consult the style guide required for your assignment to determine the specific title of your bibliography page as well as how to cite each source type. Bibliographies are usually placed at the end of your research paper.
What is an annotated bibliography?
A special kind of bibliography, the annotated bibliography, is often used to direct your readers to other books and resources on your topic. An instructor may ask you to prepare an annotated bibliography to help you narrow down a topic for your research assignment. Such bibliographies offer a few lines of information, typically 150-300 words, summarizing the content of the resource after the bibliographic entry.
Example of Annotated Bibliographic Entry in MLA Style
Waddell, Marie L., Robert M. Esch, and Roberta R. Walker. The Art of Styling Sentences: 20 Patterns for Success. 3rd ed. New York: Barron’s, 1993. A comprehensive look at 20 sentence patterns and their variations to teach students how to write effective sentences by imitating good style.
Mailing Address: 3501 University Blvd. East, Adelphi, MD 20783 This work is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License . © 2022 UMGC. All links to external sites were verified at the time of publication. UMGC is not responsible for the validity or integrity of information located at external sites.
Table of Contents: Online Guide to Writing
Chapter 1: College Writing
How Does College Writing Differ from Workplace Writing?
What Is College Writing?
Why So Much Emphasis on Writing?
Chapter 2: The Writing Process
Doing Exploratory Research
Getting from Notes to Your Draft
Introduction
Prewriting - Techniques to Get Started - Mining Your Intuition
Prewriting: Targeting Your Audience
Prewriting: Techniques to Get Started
Prewriting: Understanding Your Assignment
Rewriting: Being Your Own Critic
Rewriting: Creating a Revision Strategy
Rewriting: Getting Feedback
Rewriting: The Final Draft
Techniques to Get Started - Outlining
Techniques to Get Started - Using Systematic Techniques
Thesis Statement and Controlling Idea
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Freewriting
Writing: Getting from Notes to Your Draft - Summarizing Your Ideas
Writing: Outlining What You Will Write
Chapter 3: Thinking Strategies
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone
A Word About Style, Voice, and Tone: Style Through Vocabulary and Diction
Critical Strategies and Writing
Critical Strategies and Writing: Analysis
Critical Strategies and Writing: Evaluation
Critical Strategies and Writing: Persuasion
Critical Strategies and Writing: Synthesis
Developing a Paper Using Strategies
Kinds of Assignments You Will Write
Patterns for Presenting Information
Patterns for Presenting Information: Critiques
Patterns for Presenting Information: Discussing Raw Data
Patterns for Presenting Information: General-to-Specific Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Problem-Cause-Solution Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Specific-to-General Pattern
Patterns for Presenting Information: Summaries and Abstracts
Supporting with Research and Examples
Writing Essay Examinations
Writing Essay Examinations: Make Your Answer Relevant and Complete
Writing Essay Examinations: Organize Thinking Before Writing
Writing Essay Examinations: Read and Understand the Question
Chapter 4: The Research Process
Planning and Writing a Research Paper
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Ask a Research Question
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Cite Sources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Collect Evidence
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Decide Your Point of View, or Role, for Your Research
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Draw Conclusions
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Find a Topic and Get an Overview
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Manage Your Resources
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Outline
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Survey the Literature
Planning and Writing a Research Paper: Work Your Sources into Your Research Writing
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Human Resources
Research Resources: What Are Research Resources?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found?
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Electronic Resources
Research Resources: Where Are Research Resources Found? - Print Resources
Structuring the Research Paper: Formal Research Structure
Structuring the Research Paper: Informal Research Structure
The Nature of Research
The Research Assignment: How Should Research Sources Be Evaluated?
The Research Assignment: When Is Research Needed?
The Research Assignment: Why Perform Research?
Chapter 5: Academic Integrity
Academic Integrity
Giving Credit to Sources
Giving Credit to Sources: Copyright Laws
Giving Credit to Sources: Documentation
Giving Credit to Sources: Style Guides
Integrating Sources
Practicing Academic Integrity
Practicing Academic Integrity: Keeping Accurate Records
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Paraphrasing Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Quoting Your Source
Practicing Academic Integrity: Managing Source Material - Summarizing Your Sources
Types of Documentation: Bibliographies and Source Lists
Types of Documentation: Citing World Wide Web Sources
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - APA Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - CSE/CBE Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - Chicago Style
Types of Documentation: In-Text or Parenthetical Citations - MLA Style
Types of Documentation: Note Citations
Chapter 6: Using Library Resources
Finding Library Resources
Chapter 7: Assessing Your Writing
How Is Writing Graded?
How Is Writing Graded?: A General Assessment Tool
The Draft Stage
The Draft Stage: The First Draft
The Draft Stage: The Revision Process and the Final Draft
The Draft Stage: Using Feedback
The Research Stage
Using Assessment to Improve Your Writing
Chapter 8: Other Frequently Assigned Papers
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Article and Book Reviews
Reviews and Reaction Papers: Reaction Papers
Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Adapting the Argument Structure
Writing Arguments: Purposes of Argument
Writing Arguments: References to Consult for Writing Arguments
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Anticipate Active Opposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Determine Your Organization
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Develop Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Introduce Your Argument
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - State Your Thesis or Proposition
Writing Arguments: Steps to Writing an Argument - Write Your Conclusion
Writing Arguments: Types of Argument
Appendix A: Books to Help Improve Your Writing
Dictionaries
General Style Manuals
Researching on the Internet
Special Style Manuals
Writing Handbooks
Appendix B: Collaborative Writing and Peer Reviewing
Collaborative Writing: Assignments to Accompany the Group Project
Collaborative Writing: Informal Progress Report
Collaborative Writing: Issues to Resolve
Collaborative Writing: Methodology
Collaborative Writing: Peer Evaluation
Collaborative Writing: Tasks of Collaborative Writing Group Members
Collaborative Writing: Writing Plan
General Introduction
Peer Reviewing
Appendix C: Developing an Improvement Plan
Working with Your Instructor’s Comments and Grades
Appendix D: Writing Plan and Project Schedule
Devising a Writing Project Plan and Schedule
Reviewing Your Plan with Others
By using our website you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about how we use cookies by reading our Privacy Policy .
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Annotated Bibliographies

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Definitions
A bibliography is a list of sources (books, journals, Web sites, periodicals, etc.) one has used for researching a topic. Bibliographies are sometimes called "References" or "Works Cited" depending on the style format you are using. A bibliography usually just includes the bibliographic information (i.e., the author, title, publisher, etc.).
An annotation is a summary and/or evaluation. Therefore, an annotated bibliography includes a summary and/or evaluation of each of the sources. Depending on your project or the assignment, your annotations may do one or more of the following.
For more help, see our handout on paraphrasing sources.
For more help, see our handouts on evaluating resources .
- Reflect : Once you've summarized and assessed a source, you need to ask how it fits into your research. Was this source helpful to you? How does it help you shape your argument? How can you use this source in your research project? Has it changed how you think about your topic?
Your annotated bibliography may include some of these, all of these, or even others. If you're doing this for a class, you should get specific guidelines from your instructor.
Why should I write an annotated bibliography?
To learn about your topic : Writing an annotated bibliography is excellent preparation for a research project. Just collecting sources for a bibliography is useful, but when you have to write annotations for each source, you're forced to read each source more carefully. You begin to read more critically instead of just collecting information. At the professional level, annotated bibliographies allow you to see what has been done in the literature and where your own research or scholarship can fit. To help you formulate a thesis: Every good research paper is an argument. The purpose of research is to state and support a thesis. So, a very important part of research is developing a thesis that is debatable, interesting, and current. Writing an annotated bibliography can help you gain a good perspective on what is being said about your topic. By reading and responding to a variety of sources on a topic, you'll start to see what the issues are, what people are arguing about, and you'll then be able to develop your own point of view.
To help other researchers : Extensive and scholarly annotated bibliographies are sometimes published. They provide a comprehensive overview of everything important that has been and is being said about that topic. You may not ever get your annotated bibliography published, but as a researcher, you might want to look for one that has been published about your topic.
The format of an annotated bibliography can vary, so if you're doing one for a class, it's important to ask for specific guidelines.
The bibliographic information : Generally, though, the bibliographic information of the source (the title, author, publisher, date, etc.) is written in either MLA or APA format. For more help with formatting, see our MLA handout . For APA, go here: APA handout .
The annotations: The annotations for each source are written in paragraph form. The lengths of the annotations can vary significantly from a couple of sentences to a couple of pages. The length will depend on the purpose. If you're just writing summaries of your sources, the annotations may not be very long. However, if you are writing an extensive analysis of each source, you'll need more space.
You can focus your annotations for your own needs. A few sentences of general summary followed by several sentences of how you can fit the work into your larger paper or project can serve you well when you go to draft.

How to Write a Bibliography

In this post
A bibliography is nothing more than a written list of your sources, outlining everything you used in the creation of the work, even if you didn’t cite it directly. This is something that almost all students will be asked to compile and add to their works at some point. Bibliographies are generally used in academic documents and from a student’s point of view they are most commonly used within your undergraduate or master’s dissertation. But what does a bibliography actually look like? When is a bibliography used? And how do you create a bibliography for your essay or research paper? Here’s everything you need to know about how to write a bibliography:
What is a Bibliography?
For many students creating a bibliography can be a daunting prospect, and part of the reason for this is that many students aren’t sure what a bibliography is. The good news is that a bibliography is much simpler than it sounds. A bibliography is nothing more than a list of all of the sources that you have used to help you write an essay or other extensive document. This includes not only the sources that you have directly quoted or referred to in your essay but also any works that you have read throughout your research for the piece. Even if a work is not cited directly, if you have read it as part of your essay preparation, or if your essay has otherwise been influenced by the work then it should be included and cited in your bibliography.
Bibliographies are commonly used in academic documents , such as at the end of an undergraduate or master’s level dissertation. But brief and less formal versions of bibliographies can also be used at the end of a journalistic piece, presentation, or video to lend them legitimacy and to visibly demonstrate that they have been well-researched. But academia is the main focus of the bibliography. So, if you’re thinking of pursuing further education and studying at degree level then it’s important that you understand what a bibliography is and how to create one. If an undergraduate essay or dissertation doesn’t include a properly cited and formatted bibliography, then it isn’t completed. As the way students access information has changed, so too has the information that you can include in your bibliography. Traditionally these were lists of books, essays and articles, but now websites, videos, and other multimedia sources should be cited in your bibliography too if they are accessed as part of your research.
There are many benefits of using a bibliography. These include:
- Demonstrating to your tutor, instructor, or anyone else assessing your essay that you have conducted the necessary research for your assignment and that you know how to put together a robust and comprehensive bibliography.
- Crediting the authors of any source materials that you have based your piece on for the research that they have conducted, ensuring that your piece does not appear plagiarised because all source materials used in your piece have been fully cited.
- Finally, as well as benefitting the authors you have cited and your tutor, the primary reason a bibliography should be included in your work is to benefit your readers. It will make it much easier for them to find the sources you have cited, read those works themselves, and conduct their own research on the same topic too. Bibliographies play an essential role in sharing knowledge and advancing understanding of a subject.
When is a Bibliography Used?
We have established that bibliographic information is descriptive information about a piece of work. Now we need to assess when we will need this bibliographic information: when is a bibliography used? Bibliographies are generally used in a wide range of academic research projects and disciplines. Secondary school students, college students and distance learning students, university students and postgraduate students may all be required to create bibliographies in their academic works. The bibliography in a research paper or project is typically one of the last pages of the paper adding to the piece after your own content but before any appendices.
The terms bibliography, references and cited works are often used interchangeably, but these three are actually unique ways of referencing your work and your sources. A “Works Cited” list is an alphabetical list of works cited or sources you specifically called out while composing your paper. This differs from a bibliography because you don’t need to include any additional sources that you have read or that may have otherwise influenced your piece in a works cited list. As a general rule, this means that works cited lists are much shorter than bibliographies. Reference lists are very similar to works cited lists, but they are written in APA (American Psychological Association) format, whilst bibliographies often use the Harvard referencing system . Reference lists are arranged alphabetically by the author’s last name. Whilst cited works and reference lists are similar, bibliographies are very different. A bibliography should list all the material you have consulted in preparing your essay, whether you have actually referred to and cited the work or not. So even if you only read a page or two or a text, and don’t directly reference it in your work, it should still be included in your bibliography. For this reason, bibliographies include longer references and are significant blocks of text.

Primary and Secondary Sources
The sources that you will cite within your academic works fall into two main categories: primary sources and secondary sources. But students often have difficulty differentiating between the two. However, the differences between primary sources and secondary sources are easy to work out. If you are quoting a first-hand account of something, or an original work, then this is a primary source.
Some examples of primary sources include: news articles, photographs, autobiographies, novels and short stories, letters and diary entries, and original works of art. From a multimedia point of view, documentaries, radio broadcasts and podcasts, and recordings of music or speeches are also considered to be primary sources. Working with a primary source means that you examine the source material, analyse it, and then reach your own conclusions. If you read a novel and then write an essay about its themes, for example, then you are using the novel as your primary source and you draw your own conclusions from it. In science-based subjects, any research or data you gather for yourself, by conducting your own studies or research, is considered to be a primary source. But if you are analysing data that has been gathered by someone else then this is then considered to be a secondary source. This example is important because it demonstrates that primary sources don’t always have to be documents you have created yourself: if you’re taking raw data that has been produced by someone else then this is still considered a primary source.
Secondary sources differ from primary sources because they are further removed from them. If a piece of art is the primary source, for example, then an essay analysing that piece of art would be considered to be a secondary source. Other examples of secondary sources include: textbooks that discuss other concepts, theories, or source material, biographies written about other famous figures, works written by critics or other academics and key political commentary. In short, a primary source provides direct access to material which you can then discuss and analyse, whilst a secondary source requires you to look at the material through the lens of another person or another point of view. If you are reading another critic’s analysis of a work, then their perspective is likely to have some influence on your critical approach or opinion. For this reason, many academics believe primary sources to be more reliable than secondary sources. But that is a one-dimensional approach: working with secondary sources can be beneficial because it allows you to understand how others perceive the work you are discussing. It also provides a clear insight into the cultural perspective that surrounds the work.
Types of Bibliography
There is no singular type of bibliography: different kinds of academic work require different kinds of bibliography, and they are each laid out and formatted slightly differently. Some of the main types of bibliography that you need to be aware of include:
- Analytical bibliography. This is a bibliography that analyses the route that a work makes from its initial manuscript stage to publication. When creating an analytical bibliography you should not only detail the high-level information about a cited source, such as the title and the name of the author, but also more specific details about the work, such as its number of pages, any illustrations it includes, and even the type of binding it is held together with.
- Annotated bibliography. As the name suggests, this type of bibliography includes annotations. An annotation is a short note that concisely and clearly explains why you chose each of your sources. Each annotation included within an annotated bibliography is usually just a few sentences long but will provide your readers with valuable insight into your view of the source. Although they are similar to literature review bibliographies, annotated bibliographies do not discuss how the research is conducted in the same level of depth.
- National bibliography. Source material is categorised into groups depending on where they were published, or the time period in which they were published. Often texts in a national bibliography are organised by region or nation.
- Personal bibliography. If you have included a range of pieces in your essay that are unpublished works, or hard-to-find works, then a personal bibliography is the best way to list these. This type of bibliography is best used for academic pieces that focus on multiple works by the same author: biographically focused pieces, for example.
- Corporate bibliography. As the name implies, a corporate bibliography will group sources in relation to specific organisations or corporations.
- Subject bibliography. Finally, sources within subject bibliographies are grouped depending on which subjects they cover. Generally, these bibliographies list primary and secondary sources, which makes them more in-depth. Other bibliographies on this list may not always outline both primary and secondary sources in this way.
Information Required from Print Sources
All of the bibliographic material that you will need from print sources can be found on their title page. The information that you will need to include in your citation will depend on the type of bibliography that you are compiling, but regardless of what citation style is being used, there are key pieces of information that you will always need to collect in order to create the citation in a bibliography. This information is:
- The name of the author you are citing.
- The title of the publication you are citing.
- Article title (if using a journal or magazine article).
- The volume number of the journal, magazine or encyclopaedia you are citing, or the edition you are citing in the case of a printed publication.
- Date of publication.
- Place of publication.
- Page number(s) relevant to your research, and that you are citing within your work.
Information Required from Web Sources
The way in which you will cite a website or other web sources differs from the way in which you would cite a traditional printed text. The way in which you will cite a web source will depend on whether you are citing an online article or a web page. In the case of a web article, you will need to share:
- The author and/or editor name of the web piece that you are citing.
- The title of the website that you are citing.
- Company or organisation that owns or posts to the website.
- URL (website address).
- The date that you accessed the information you are citing and, where possible, the date that the information you are citing was originally published.
Read another one of our posts
Essential skills every babysitter should master.

Community Health Initiatives – Promoting Wellness Locally

Enhancing Language Development in Early Years

GCSE Maths in Everyday Life: Practical Applications You Never Knew
Acing A-Level Exams- Revision and Exam Preparation Tips

Balancing Work and Personal Life in Home-based Childcare

Managing Stress and Anxiety in Parenthood

The Impact of Social Media on Youth Mental Health

Save your cart?

Annotated Bibliographies
What this handout is about.
This handout will explain why annotated bibliographies are useful for researchers, provide an explanation of what constitutes an annotation, describe various types of annotations and styles for writing them, and offer multiple examples of annotated bibliographies in the MLA, APA, and CBE/CSE styles of citation.
Introduction
Welcome to the wonderful world of annotated bibliographies! You’re probably already familiar with the need to provide bibliographies, reference pages, and works cited lists to credit your sources when you do a research paper. An annotated bibliography includes descriptions and explanations of your listed sources beyond the basic citation information you usually provide.
Why do an annotated bibliography?
One of the reasons behind citing sources and compiling a general bibliography is so that you can prove you have done some valid research to back up your argument and claims. Readers can refer to a citation in your bibliography and then go look up the material themselves. When inspired by your text or your argument, interested researchers can access your resources. They may wish to double check a claim or interpretation you’ve made, or they may simply wish to continue researching according to their interests. But think about it: even though a bibliography provides a list of research sources of all types that includes publishing information, how much does that really tell a researcher or reader about the sources themselves?
An annotated bibliography provides specific information about each source you have used. As a researcher, you have become an expert on your topic: you have the ability to explain the content of your sources, assess their usefulness, and share this information with others who may be less familiar with them. Think of your paper as part of a conversation with people interested in the same things you are; the annotated bibliography allows you to tell readers what to check out, what might be worth checking out in some situations, and what might not be worth spending the time on. It’s kind of like providing a list of good movies for your classmates to watch and then going over the list with them, telling them why this movie is better than that one or why one student in your class might like a particular movie better than another student would. You want to give your audience enough information to understand basically what the movies are about and to make an informed decision about where to spend their money based on their interests.
What does an annotated bibliography do?
A good annotated bibliography:
- encourages you to think critically about the content of the works you are using, their place within a field of study, and their relation to your own research and ideas.
- proves you have read and understand your sources.
- establishes your work as a valid source and you as a competent researcher.
- situates your study and topic in a continuing professional conversation.
- provides a way for others to decide whether a source will be helpful to their research if they read it.
- could help interested researchers determine whether they are interested in a topic by providing background information and an idea of the kind of work going on in a field.
What elements might an annotation include?
- Bibliography according to the appropriate citation style (MLA, APA, CBE/CSE, etc.).
- Explanation of main points and/or purpose of the work—basically, its thesis—which shows among other things that you have read and thoroughly understand the source.
- Verification or critique of the authority or qualifications of the author.
- Comments on the worth, effectiveness, and usefulness of the work in terms of both the topic being researched and/or your own research project.
- The point of view or perspective from which the work was written. For instance, you may note whether the author seemed to have particular biases or was trying to reach a particular audience.
- Relevant links to other work done in the area, like related sources, possibly including a comparison with some of those already on your list. You may want to establish connections to other aspects of the same argument or opposing views.
The first four elements above are usually a necessary part of the annotated bibliography. Points 5 and 6 may involve a little more analysis of the source, but you may include them in other kinds of annotations besides evaluative ones. Depending on the type of annotation you use, which this handout will address in the next section, there may be additional kinds of information that you will need to include.
For more extensive research papers (probably ten pages or more), you often see resource materials grouped into sub-headed sections based on content, but this probably will not be necessary for the kinds of assignments you’ll be working on. For longer papers, ask your instructor about their preferences concerning annotated bibliographies.
Did you know that annotations have categories and styles?
Decisions, decisions.
As you go through this handout, you’ll see that, before you start, you’ll need to make several decisions about your annotations: citation format, type of annotation, and writing style for the annotation.
First of all, you’ll need to decide which kind of citation format is appropriate to the paper and its sources, for instance, MLA or APA. This may influence the format of the annotations and bibliography. Typically, bibliographies should be double-spaced and use normal margins (you may want to check with your instructor, since they may have a different style they want you to follow).
MLA (Modern Language Association)
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic MLA bibliography formatting and rules.
- MLA documentation is generally used for disciplines in the humanities, such as English, languages, film, and cultural studies or other theoretical studies. These annotations are often summary or analytical annotations.
- Title your annotated bibliography “Annotated Bibliography” or “Annotated List of Works Cited.”
- Following MLA format, use a hanging indent for your bibliographic information. This means the first line is not indented and all the other lines are indented four spaces (you may ask your instructor if it’s okay to tab over instead of using four spaces).
- Begin your annotation immediately after the bibliographic information of the source ends; don’t skip a line down unless you have been told to do so by your instructor.
APA (American Psychological Association)
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic APA bibliography formatting and rules.
- Natural and social sciences, such as psychology, nursing, sociology, and social work, use APA documentation. It is also used in economics, business, and criminology. These annotations are often succinct summaries.
- Annotated bibliographies for APA format do not require a special title. Use the usual “References” designation.
- Like MLA, APA uses a hanging indent: the first line is set flush with the left margin, and all other lines are indented four spaces (you may ask your instructor if it’s okay to tab over instead of using four spaces).
- After the bibliographic citation, drop down to the next line to begin the annotation, but don’t skip an extra line.
- The entire annotation is indented an additional two spaces, so that means each of its lines will be six spaces from the margin (if your instructor has said that it’s okay to tab over instead of using the four spaces rule, indent the annotation two more spaces in from that point).
CBE (Council of Biology Editors)/CSE (Council of Science Editors)
See the UNC Libraries citation tutorial for basic CBE/CSE bibliography formatting and rules.
- CBE/CSE documentation is used by the plant sciences, zoology, microbiology, and many of the medical sciences.
- Annotated bibliographies for CBE/CSE format do not require a special title. Use the usual “References,” “Cited References,” or “Literature Cited,” and set it flush with the left margin.
- Bibliographies for CSE in general are in a slightly smaller font than the rest of the paper.
- When using the name-year system, as in MLA and APA, the first line of each entry is set flush with the left margin, and all subsequent lines, including the annotation, are indented three or four spaces.
- When using the citation-sequence method, each entry begins two spaces after the number, and every line, including the annotation, will be indented to match the beginning of the entry, or may be slightly further indented, as in the case of journals.
- After the bibliographic citation, drop down to the next line to begin the annotation, but don’t skip an extra line. The entire annotation follows the indentation of the bibliographic entry, whether it’s N-Y or C-S format.
- Annotations in CBE/CSE are generally a smaller font size than the rest of the bibliographic information.
After choosing a documentation format, you’ll choose from a variety of annotation categories presented in the following section. Each type of annotation highlights a particular approach to presenting a source to a reader. For instance, an annotation could provide a summary of the source only, or it could also provide some additional evaluation of that material.
In addition to making choices related to the content of the annotation, you’ll also need to choose a style of writing—for instance, telescopic versus paragraph form. Your writing style isn’t dictated by the content of your annotation. Writing style simply refers to the way you’ve chosen to convey written information. A discussion of writing style follows the section on annotation types.
Types of annotations
As you now know, one annotation does not fit all purposes! There are different kinds of annotations, depending on what might be most important for your reader to learn about a source. Your assignments will usually make it clear which citation format you need to use, but they may not always specify which type of annotation to employ. In that case, you’ll either need to pick your instructor’s brain a little to see what they want or use clue words from the assignment itself to make a decision. For instance, the assignment may tell you that your annotative bibliography should give evidence proving an analytical understanding of the sources you’ve used. The word analytical clues you in to the idea that you must evaluate the sources you’re working with and provide some kind of critique.
Summary annotations
There are two kinds of summarizing annotations, informative and indicative.
Summarizing annotations in general have a couple of defining features:
- They sum up the content of the source, as a book report might.
- They give an overview of the arguments and proofs/evidence addressed in the work and note the resulting conclusion.
- They do not judge the work they are discussing. Leave that to the critical/evaluative annotations.
- When appropriate, they describe the author’s methodology or approach to material. For instance, you might mention if the source is an ethnography or if the author employs a particular kind of theory.
Informative annotation
Informative annotations sometimes read like straight summaries of the source material, but they often spend a little more time summarizing relevant information about the author or the work itself.
Indicative annotation
Indicative annotation is the second type of summary annotation, but it does not attempt to include actual information from the argument itself. Instead, it gives general information about what kinds of questions or issues are addressed by the work. This sometimes includes the use of chapter titles.
Critical/evaluative
Evaluative annotations don’t just summarize. In addition to tackling the points addressed in summary annotations, evaluative annotations:
- evaluate the source or author critically (biases, lack of evidence, objective, etc.).
- show how the work may or may not be useful for a particular field of study or audience.
- explain how researching this material assisted your own project.
Combination
An annotated bibliography may combine elements of all the types. In fact, most of them fall into this category: a little summarizing and describing, a little evaluation.
Writing style
Ok, next! So what does it mean to use different writing styles as opposed to different kinds of content? Content is what belongs in the annotation, and style is the way you write it up. First, choose which content type you need to compose, and then choose the style you’re going to use to write it
This kind of annotated bibliography is a study in succinctness. It uses a minimalist treatment of both information and sentence structure, without sacrificing clarity. Warning: this kind of writing can be harder than you might think.
Don’t skimp on this kind of annotated bibliography. If your instructor has asked for paragraph form, it likely means that you’ll need to include several elements in the annotation, or that they expect a more in-depth description or evaluation, for instance. Make sure to provide a full paragraph of discussion for each work.
As you can see now, bibliographies and annotations are really a series of organized steps. They require meticulous attention, but in the end, you’ve got an entire testimony to all the research and work you’ve done. At the end of this handout you’ll find examples of informative, indicative, evaluative, combination, telescopic, and paragraph annotated bibliography entries in MLA, APA, and CBE formats. Use these examples as your guide to creating an annotated bibliography that makes you look like the expert you are!
MLA Example
APA Example
CBE Example
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
American Psychological Association. 2010. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . 6th ed. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Bell, I. F., and J. Gallup. 1971. A Reference Guide to English, American, and Canadian Literature . Vancouver: University of British Columbia Press.
Bizzell, Patricia, and Bruce Herzburg. 1991. Bedford Bibliography for Teachers of Writing , 3rd ed. Boston: Bedford Books.
Center for Information on Language Teaching, and The English Teaching Information Center of the British Council. 1968. Language-Teaching Bibliography . Cambridge: Cambridge University.
Engle, Michael, Amy Blumenthal, and Tony Cosgrave. 2012. “How to Prepare an Annotated Bibliography.” Olin & Uris Libraries. Cornell University. Last updated September 25, 2012. https://olinuris.library.cornell.edu/content/how-prepare-annotated-bibliography.
Gibaldi, Joseph. 2009. MLA Handbook for Writers of Research Papers , 7th ed. New York: The Modern Language Association of America.
Huth, Edward. 1994. Scientific Style and Format: The CBE Manual for Authors, Editors, and Publishers . New York: University of Cambridge.
Kilborn, Judith. 2004. “MLA Documentation.” LEO: Literacy Education Online. Last updated March 16, 2004. https://leo.stcloudstate.edu/research/mla.html.
Spatt, Brenda. 1991. Writing from Sources , 3rd ed. New York: St. Martin’s.
University of Kansas. 2018. “Bibliographies.” KU Writing Center. Last updated April 2018. http://writing.ku.edu/bibliographies .
University of Wisconsin-Madison. 2019. “Annotated Bibliography.” The Writing Center. Accessed June 14, 2019. https://writing.wisc.edu/handbook/assignments/annotatedbibliography/ .
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
All Formats
Table of Contents
Bibliography definition & meaning, what is a bibliography, 10 types of bibliography, bibliography uses, purpose, importance, what’s in a bibliography parts, how to design a bibliography, bibliography vs. references, what’s the difference between bibliography, literature, and biography, bibliography sizes, bibliography ideas & examples, bibliography.
A bibliography gives credit to all the author’s hard work that was consulted in someone’s research. This list is usually found on the last portion or on the last page of books and/or magazines, most of which can be academic.

Download the Bibliography Article in PDF
Sustainable development bibliography.

School Project Bibliography

Preliminary Bibliography

Elementary Bibliography

Books Bibliography

Project Bibliography

Disaster Management Bibliography

High School Bibliography

Annotated Bibliography

Students Bibliography

It serves as an optimal resource
Plagiarism prevention, maintaining accuracy, enhances the value of a paper, it acts as a source tracker, author names, publication information, publication date, access date.

- Bibliography Ideas and Examples
- College Bibliography Ideas and Examples
- Kids Bibliography Ideas and Examples
- Middle School Bibliography Ideas and Examples
- Consumer Awareness Bibliography Ideas and Examples
- Internet Bibliography Ideas and Examples
- Writing Bibliography Ideas and Examples
- MLA Bibliography Ideas and Examples
- Bibliography Outline Ideas and Examples
- Annotated Bibliography Research Ideas and Examples
- School Bibliography Ideas and Examples
What is a bibliography in research?
How do you add a bibliography to a table of contents, which is a correct bibliography entry, what are four resources of bibliography, what are the methods of preparing a bibliography, when was the bibliography invented, what are the branches of a bibliography, what is the bibliography in a college project, how should each reference be formatted in a bibliography, what is bibliographic documentation, what is a bibliography citation, more in documents.
Preliminary Bibliography Template
Research & annotated bibliography template, child care project annotated bibliography template, scientific bibliography template, literature review bibliography template, academic bibliography template, reference bibliography template, asa format bibliography template, annotated bibliography worksheet template, faculty bibliography template.
- How To Create a Schedule in Microsoft Word [Template + Example]
- How To Create a Schedule in Google Docs [Template + Example]
- How To Create a Quotation in Google Docs [Template + Example]
- How To Create a Quotation in Microsoft Word [Template + Example]
- How To Make a Plan in Google Docs [Template + Example]
- How To Make a Plan in Microsoft Word [Template + Example]
- How To Make/Create an Inventory in Google Docs [Templates + Examples]
- How To Create Meeting Minutes in Microsoft Word [Template + Example]
- How To Create Meeting Minutes in Google Docs [Template + Example]
- How To Make/Create an Estimate in Microsoft Word [Templates + Examples] 2023
- How To Make/Create an Estimate in Google Docs [Templates + Examples] 2023
- How To Make/Create a Manual in Google Docs [Templates + Examples] 2023
- How To Make/Create a Manual in Microsoft Word [Templates + Examples] 2023
- How To Make/Create a Statement in Google Docs [Templates + Examples] 2023
- How To Make/Create a Statement in Microsoft Word [Templates + Examples] 2023
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.
- Turnitin Guides
- Administrator hub
- Release notes and known issues
- Welcome to Turnitin Guides
Welcome to Turnitin’s new website for guidance!
In 2024, we migrated our comprehensive library of guidance from https://help.turnitin.com to this site, guides.turnitin.com. During this process we have taken the opportunity to take a holistic look at our content and how we structure our guides.
This page is here to help you orientate yourself with these changes and update your resources
What's new?
We have restructured the content to help you navigate it more efficiently.
We are consolidating numerous pages to make our individual guides more valuable as well as removing duplicated content.
For example, our Similarity Report guidance on help.turnitin is repeated in numerous places to cater for each individual integration and license type. On guides.turnitin this content will exist in a single place to allow for users of all integrations and licenses to find it easily. We have made slight modifications to these guides to help you understand which guides are pertinent to you and your institution.
Our guidance search has greatly improved
As a result of our content restructure, the search functionality for guides.turnitin has improved. Use the search bar at the top of any page to locate the guidance you’re searching for.
Dedicated student and administrator guidance hubs
Visit the Student hub area to locate student guidance. For students who access Turnitin via an LMS or VLE, check out the subsection Submitting to Turnitin .
Visiting the Administrator hub area to locate administrator guidance and release notes.
iThenticate and Crossref Similarity Check guidance is now located on a separate site
To improve the experience for our iThenticate and Crossref Similiarity Check customers we have move their help content onto a separate help site, guides.ithenticate.com . This will improve the search for all users.
We have also created an orientation page for this site to help users become acclimatised.
Some guidance is no longer grouped within the LMS umbrella
Some guidance which was previously provided under each LMS has been moved to sections that reflect those workflows’ outcomes. Use the table below as a cheatsheet to quickly locate guidance.
| Student guidance | |
| LMS guidance for administrators and instructors | |
| Similarity Report and AI Writing guidance | |
| Creating PeerMark assignments guidance | |
| Creating and managing QuickMarks, rubrics and grading PeerMark assignments guidance | |
| User profile guidance for administrators and instructors |
|
| Administrator account settings and migration help | |
| Release notes and known issues |
Articles in this section
- Turnitin release notes
- Integrations release notes
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

Beginning of end of HIV epidemic?

Between bright light and a good mood, plenty of sleep

You won’t even know you’re exercising, but your body will

Can good sleep help prevent diabetes?
Study links irregular sleep patterns with higher disease risk
BWH Communications
Getting consistent sleep could help stave off Type 2 diabetes, new research suggests.
A team led by investigators at Brigham and Women’s Hospital analyzed the sleep patterns of study participants over seven nights and then followed them for more than seven years. The researchers found those with the most irregular sleep patterns had a 34 percent higher chance of developing diabetes. The findings were published in Diabetes Care .
“Our study identified a modifiable lifestyle factor that can help lower the risk of developing Type 2 diabetes,” said lead author Sina Kianersi , a research fellow in the Channing Division of Network Medicine at Brigham and Women’s Hospital.
Type 2 diabetes affects close to half a billion people worldwide and is one of the top 10 leading causes of death and disability. The number of people with the disease is expected to more than double to 1.3 billion by 2050.
1.3 billion People worldwide are expected to have Type 2 diabetes by 2050
The new study analyzed accelerometry data from more than 84,000 participants in the U.K. Biobank Study. Participants were an average age of 62 years (57 percent female, 97 percent white) and were initially free of diabetes. They wore accelerometers — devices like watches that monitor 7½ years, tracking diabetes development mostly through medical records.
The study set out to investigate two key questions: first, to discover whether irregular sleep durations may promote diabetes development through circadian disruption and sleep disturbances; second, to explore whether this association varies across genetic predispositions to the condition.
The investigators found that more irregular sleep duration was associated with higher diabetes risk after adjusting for a wide range of risk factors. This association was more pronounced in individuals with longer sleep duration and lower polygenic risk score for the disease.
The data revealed that compared with participants with regular sleep patterns, those with irregular sleep (where day-to-day sleep duration varied by more than 60 minutes on average) had a 34 percent higher risk of developing diabetes. The risk decreased, yet persisted, even after accounting for lifestyle, co-morbidities, family history of diabetes, and obesity indicators.
There were some study limitations. Certain lifestyle information used in the research was collected up to five years before the accelerometer study began. This might have affected the accuracy of the results. Also, the assessment of sleep duration based on seven days may not capture long-term sleep patterns. Lastly, study participants were mainly healthy, older, and white, and may not represent outcomes for more diverse populations.
The researchers plan to study participants from younger age groups and with diverse racial backgrounds. They are also interested in exploring the biological reasons why sleep irregularity increases the risk of diabetes.
“Our findings have the potential to improve diabetes prevention on multiple levels,” said Kianersi. “Clinically, they might inform better patient care and treatment plans. Public health guidelines could promote regular sleep patterns. However, more research is needed to fully understand the mechanism and confirm the results in other populations.”
Authorship: In addition to Kianersi, Brigham authors include Heming Wang, Tamar Sofer, and Susan Redline. Additional authors include Raymond Noordam, Andrew Phillips, Martin K. Rutter, and Tianyi Huang (formerly at Brigham and Women’s).
Disclosures: Phillips has received research funding from Versalux and Delos, and he is a director and founder of Circadian Health Innovations PTY LTD.
Funding: This study was supported by the National Institutes of Health (grant number R01HL155395) and the UKB project 85501. Kianersi was supported by the American Heart Association Postdoctoral Fellowship (grant number: 24POST1188091).
Share this article
You might like.
Scientists cautiously optimistic about trial results of new preventative treatment, prospects for new phase in battle with deadly virus

Researchers outline path to lower risk of depression

Real surfing is better than channel surfing, says research focused on healthy aging. But housework is better than nothing.
What the judge was thinking and what’s next in Trump documents case
Obama-era White House counsel says key point in Nixon decision should have ended inquiry
The way forward for Democrats — and the country
Danielle Allen is more worried about identity politics and gaps in civic education than the power of delegates
Finding right mix on campus speech policies
Legal, political scholars discuss balancing personal safety, constitutional rights, academic freedom amid roiling protests, cultural shifts
Suggestions or feedback?
MIT News | Massachusetts Institute of Technology
- Machine learning
- Sustainability
- Black holes
- Classes and programs
Departments
- Aeronautics and Astronautics
- Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Architecture
- Political Science
- Mechanical Engineering
Centers, Labs, & Programs
- Abdul Latif Jameel Poverty Action Lab (J-PAL)
- Picower Institute for Learning and Memory
- Lincoln Laboratory
- School of Architecture + Planning
- School of Engineering
- School of Humanities, Arts, and Social Sciences
- Sloan School of Management
- School of Science
- MIT Schwarzman College of Computing
Study reveals how an anesthesia drug induces unconsciousness
Press contact :, media download.

*Terms of Use:
Images for download on the MIT News office website are made available to non-commercial entities, press and the general public under a Creative Commons Attribution Non-Commercial No Derivatives license . You may not alter the images provided, other than to crop them to size. A credit line must be used when reproducing images; if one is not provided below, credit the images to "MIT."

Previous image Next image
There are many drugs that anesthesiologists can use to induce unconsciousness in patients. Exactly how these drugs cause the brain to lose consciousness has been a longstanding question, but MIT neuroscientists have now answered that question for one commonly used anesthesia drug.
Using a novel technique for analyzing neuron activity, the researchers discovered that the drug propofol induces unconsciousness by disrupting the brain’s normal balance between stability and excitability. The drug causes brain activity to become increasingly unstable, until the brain loses consciousness.
“The brain has to operate on this knife’s edge between excitability and chaos. It’s got to be excitable enough for its neurons to influence one another, but if it gets too excitable, it spins off into chaos. Propofol seems to disrupt the mechanisms that keep the brain in that narrow operating range,” says Earl K. Miller, the Picower Professor of Neuroscience and a member of MIT’s Picower Institute for Learning and Memory.
The new findings, reported today in Neuron , could help researchers develop better tools for monitoring patients as they undergo general anesthesia.
Miller and Ila Fiete, a professor of brain and cognitive sciences, the director of the K. Lisa Yang Integrative Computational Neuroscience Center (ICoN), and a member of MIT’s McGovern Institute for Brain Research, are the senior authors of the new study. MIT graduate student Adam Eisen and MIT postdoc Leo Kozachkov are the lead authors of the paper.
Losing consciousness
Propofol is a drug that binds to GABA receptors in the brain, inhibiting neurons that have those receptors. Other anesthesia drugs act on different types of receptors, and the mechanism for how all of these drugs produce unconsciousness is not fully understood.
Miller, Fiete, and their students hypothesized that propofol, and possibly other anesthesia drugs, interfere with a brain state known as “dynamic stability.” In this state, neurons have enough excitability to respond to new input, but the brain is able to quickly regain control and prevent them from becoming overly excited.
Previous studies of how anesthesia drugs affect this balance have found conflicting results: Some suggested that during anesthesia, the brain shifts toward becoming too stable and unresponsive, which leads to loss of consciousness. Others found that the brain becomes too excitable, leading to a chaotic state that results in unconsciousness.
Part of the reason for these conflicting results is that it has been difficult to accurately measure dynamic stability in the brain. Measuring dynamic stability as consciousness is lost would help researchers determine if unconsciousness results from too much stability or too little stability.
In this study, the researchers analyzed electrical recordings made in the brains of animals that received propofol over an hour-long period, during which they gradually lost consciousness. The recordings were made in four areas of the brain that are involved in vision, sound processing, spatial awareness, and executive function.
These recordings covered only a tiny fraction of the brain’s overall activity, so to overcome that, the researchers used a technique called delay embedding. This technique allows researchers to characterize dynamical systems from limited measurements by augmenting each measurement with measurements that were recorded previously.
Using this method, the researchers were able to quantify how the brain responds to sensory inputs, such as sounds, or to spontaneous perturbations of neural activity.
In the normal, awake state, neural activity spikes after any input, then returns to its baseline activity level. However, once propofol dosing began, the brain started taking longer to return to its baseline after these inputs, remaining in an overly excited state. This effect became more and more pronounced until the animals lost consciousness.
This suggests that propofol’s inhibition of neuron activity leads to escalating instability, which causes the brain to lose consciousness, the researchers say.
Better anesthesia control
To see if they could replicate this effect in a computational model, the researchers created a simple neural network. When they increased the inhibition of certain nodes in the network, as propofol does in the brain, network activity became destabilized, similar to the unstable activity the researchers saw in the brains of animals that received propofol.
“We looked at a simple circuit model of interconnected neurons, and when we turned up inhibition in that, we saw a destabilization. So, one of the things we’re suggesting is that an increase in inhibition can generate instability, and that is subsequently tied to loss of consciousness,” Eisen says.
As Fiete explains, “This paradoxical effect, in which boosting inhibition destabilizes the network rather than silencing or stabilizing it, occurs because of disinhibition. When propofol boosts the inhibitory drive, this drive inhibits other inhibitory neurons, and the result is an overall increase in brain activity.”
The researchers suspect that other anesthetic drugs, which act on different types of neurons and receptors, may converge on the same effect through different mechanisms — a possibility that they are now exploring.
If this turns out to be true, it could be helpful to the researchers’ ongoing efforts to develop ways to more precisely control the level of anesthesia that a patient is experiencing. These systems, which Miller is working on with Emery Brown, the Edward Hood Taplin Professor of Medical Engineering at MIT, work by measuring the brain’s dynamics and then adjusting drug dosages accordingly, in real-time.
“If you find common mechanisms at work across different anesthetics, you can make them all safer by tweaking a few knobs, instead of having to develop safety protocols for all the different anesthetics one at a time,” Miller says. “You don’t want a different system for every anesthetic they’re going to use in the operating room. You want one that’ll do it all.”
The researchers also plan to apply their technique for measuring dynamic stability to other brain states, including neuropsychiatric disorders.
“This method is pretty powerful, and I think it’s going to be very exciting to apply it to different brain states, different types of anesthetics, and also other neuropsychiatric conditions like depression and schizophrenia,” Fiete says.
The research was funded by the Office of Naval Research, the National Institute of Mental Health, the National Institute of Neurological Disorders and Stroke, the National Science Foundation Directorate for Computer and Information Science and Engineering, the Simons Center for the Social Brain, the Simons Collaboration on the Global Brain, the JPB Foundation, the McGovern Institute, and the Picower Institute.
Share this news article on:
Press mentions.
MIT scientists have discovered how propofol, a commonly used anesthetic, induces unconsciousness, reports Adam Kovac for Gizmodo . “The new research indicates that [propofol] works by interfering with a brain’s ‘dynamic stability’ – a state where neurons can respond to input, but the brain is able to keep them from getting too excited,” explains Kovac.
IFL Science
MIT researchers have discovered how propofol, a commonly used anesthetic, works on the brain, reports Francesca Benson for IFL Science . The research studied “the differences between an awake brain and one under anesthesia by looking at the stability of the brain’s activity,” writes Bensen.
Previous item Next item
Related Links
- Earl Miller
- Department of Brain and Cognitive Sciences
- Picower Institute
- McGovern Institute
Related Topics
- Brain and cognitive sciences
- National Institutes of Health (NIH)
- National Science Foundation (NSF)
Related Articles
Anesthesia technology precisely controls unconsciousness in animal tests

The brain may learn about the world the same way some computational models do
Anesthesia doesn't simply turn off the brain — it changes its rhythms
More mit news.

Edgerton Center hosts workshop for deaf high school students in STEM
Read full story →

MIT Global SCALE Network expands by adding center at Loughborough University
New transistor’s superlative properties could have broad electronics applications

When learning at MIT means studying thousands of miles away

Flying high to enable sustainable delivery, remote care

Professor Emeritus Ralph Gakenheimer, mobility planner and champion of international development, dies at 89
- More news on MIT News homepage →
Massachusetts Institute of Technology 77 Massachusetts Avenue, Cambridge, MA, USA
- Map (opens in new window)
- Events (opens in new window)
- People (opens in new window)
- Careers (opens in new window)
- Accessibility
- Social Media Hub
- MIT on Facebook
- MIT on YouTube
- MIT on Instagram

Study across multiple brain regions discerns Alzheimer’s vulnerability and resilience factors
Genomics and lab studies reveal numerous findings, including a key role for Reelin amid neuronal vulnerability, and for choline and antioxidants in sustaining cognition
An MIT study published today in Nature provides new evidence for how specific cells and circuits become vulnerable in Alzheimer’s disease, and hones in on other factors that may help some people show resilience to cognitive decline, even amid clear signs of disease pathology. To highlight potential targets for interventions to sustain cognition and memory, the authors engaged in a novel comparison of gene expression across multiple brain regions in people with or without Alzheimer’s disease, and conducted lab experiments to test and validate their major findings.
Brain cells all have the same DNA but what makes them differ, both in their identity and their activity, are their patterns of how they express those genes. The new analysis measured gene expression differences in more than 1.3 million cells of more than 70 cell types in six brain regions from 48 tissue donors, 26 of whom died with an Alzheimer’s diagnosis and 22 of whom without. As such, the study provides a uniquely large, far-ranging and yet detailed accounting of how brain cell activity differs amid Alzheimer’s disease by cell type, by brain region, by disease pathology, and by each person’s cognitive assessment while still alive.
“Specific brain regions are vulnerable in Alzheimer’s and there is an important need to understand how these regions or particular cell types are vulnerable,” said co-senior author Li-Huei Tsai , Picower Professor of Neuroscience and director of The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory and the Aging Brain Initiative at MIT. “And the brain is not just neurons. It’s many other cell types. How these cell types may respond differently, depending on where they are, is something fascinating we are only at the beginning of looking at.”
Co-senior author Manolis Kellis , professor of computer science and head of MIT’s Computational Biology Group, likened the technique used to measure gene expression comparisons, single cell RNA profiling, to being a much more advanced “microscope” than the ones that first allowed Alois Alzheimer to characterize the disease’s pathology more than a century ago.
“Where Alzheimer saw amyloid protein plaques and phosphorylated tau tangles in his microscope, our single-cell ‘microscope’ tells us, cell by cell and gene by gene, about thousands of subtle yet important biological changes in response to pathology,” said Kellis. “Connecting this information with the cognitive state of patients reveals how cellular responses relate with cognitive loss or resilience, and can help propose new ways to treat cognitive loss. Pathology can precede cognitive symptoms by a decade or two before cognitive decline becomes diagnosed. If there’s not much we can do about the pathology at that stage, we can at least try to safeguard the cellular pathways that maintain cognitive function.”
Hansruedi Mathys, a former MIT postdoc in the Tsai Lab, who is now an assistant professor at the University of Pittsburgh, Carles Boix, a former graduate student in Kellis’s lab who is now a postdoc at Harvard Medical School, and Leyla Akay, a graduate student in Tsai’s lab, led the study analyzing the prefrontal cortex, entorhinal cortex, hippocampus, anterior thalamus, angular gyrus, and the midtemporal cortex. The brain samples came from the Religious Order Study and the Rush Memory and Aging Project at Rush University.
Neural vulnerability and Reelin
Some of the earliest signs of amyloid pathology and neuron loss in Alzheimer’s occurs in memory-focused regions called the hippocampus and the entorhinal cortex. In those regions, and in other parts of the cerebral cortex, the researchers were able to pinpoint a potential reason why. One type of excitatory neuron in the hippocampus and four in the entorhinal cortex were significantly less abundant in people with Alzheimer’s than in people without. Individuals with depletion of those cells performed significantly worse on cognitive assessments. Moreover, many vulnerable neurons were interconnected in a common neuronal circuit. And just as importantly, several either directly expressed a protein called Reelin, or were directly affected by Reelin signaling. In all, therefore, the findings distinctly highlight especially vulnerable neurons, whose loss is associated with reduced cognition, that share a neuronal circuit and a molecular pathway.

Tsai noted that Reelin has become prominent in Alzheimer’s research because of a recent study of a man in Colombia. He had a rare mutation in the Reelin gene that caused the protein to be more active, and was able to stay cognitively healthy at an advanced age despite having a strong family predisposition to early-onset Alzheimer’s. The new study shows that loss of Reelin-producing neurons is associated with cognitive decline. Taken together it may mean that the brain benefits from Reelin, but that neurons that produce it may be lost in at least some Alzheimer’s patients.
“We can think of Reelin as having maybe some kind of protective or beneficial effect,” Akay said. “But we don’t yet know what it does or how it could confer resilience.”
In further analysis the researchers also found that specifically vulnerable inhibitory neuron subtypes identified in a previously study from this group in the prefrontal cortex also were involved in reelin signaling, further reinforcing the significance of the molecule and its signaling pathway.
To further check their results, the team directly examined the human brain tissue samples and the brains of two kinds of Alzheimer’s model mice. Sure enough, those experiments also showed a reduction in Reelin-positive neurons in the human and mouse entorhinal cortex.
Resilience associated with choline metabolism in astrocytes
To find factors that might preserve cognition, even amid pathology, the team examined which genes, in which cells, and in which regions, were most closely associated with cognitive resilience, which they defined as residual cognitive function, above the typical cognitive loss expected given the observed pathology.
Their analysis yielded a surprising and specific answer: across several brain regions astrocytes that expressed genes associated with antioxidant activity and with choline metabolism and polyamine biosynthesis were significantly associated with sustained cognition, even amid high levels of tau and amyloid. The results reinforced previous research findings led by Tsai and Susan Lundqvist in which they showed that dietary supplement of choline helped astrocytes cope with the dysregulation of lipids caused by the most significant Alzheimer’s risk gene, the APOE4 variant. The antioxidant findings also pointed to a molecule that can be found as a dietary supplement, spermidine, which may have anti-inflammatory properties, although such an association would need further work to be established causally.
As before, the team went beyond the predictions from the single-cell RNA expression analysis to make direct observations in the brain tissue of samples. Those that came from cognitively resilient individuals indeed showed increased expression of several of the astrocyte-expressed genes predicted to be associated with cognitive resilience.

New analysis method, open dataset
To analyze the mountains of single-cell data, the researchers developed a new robust methodology based on groups of coordinately-expressed genes (known as “gene modules”), thus exploiting the expression correlation patterns between functionally-related genes in the same module.
“In principle, the 1.3 million cells we surveyed could use their 20,000 genes in an astronomical number of different combinations,” explain Kellis. “In practice, however, we observe a much smaller subset of coordinated changes. Recognizing these coordinated patterns allow us to infer much more robust changes, because they are based on multiple genes in the same functionally-connected module.”
He offered this analogy: With many joints in their bodies, people could move in all kinds of crazy ways, but in practice they engage in many fewer coordinated movements like walking, running, or dancing. The new method enables scientists to identify such coordinated gene expression programs as a group.
While Kellis and Tsai’s labs already reported several noteworthy findings from the dataset, the researchers expect that many more possibly significant discoveries still wait to be found in the trove of data. To facilitate such discovery the team posted handy analytical and visualization tools along with the data on Kellis’s website at: https://compbio.mit.edu/ad_multiregion .
“The dataset is so immensely rich. We focused on only a few aspects that are salient that we believe are very, very interesting, but by no means have we exhausted what can be learned with this dataset,” Kellis said. “We expect many more discoveries ahead, and we hope that young researchers (of all ages) will dive right in and surprise us with many more insights.”
Going forward, Kellis said, the researchers are studying the control circuitry associated with the differentially expressed genes, to understand the genetic variants, the regulators, and other driver factors that can be modulated to reverse disease circuitry across brain regions, cell types, and different stages of the disease.
Additional authors of the study include Ziting Xia, Jose Davila Velderrain, Ayesha P. Ng, Xueqiao Jiang, Ghada Abdelhady, Kyriaki Galani, Julio Mantero, Neil Band, Benjamin T. James, Sudhagar Babu, Fabiola Galiana-Melendez, Kate Louderback, Dmitry Prokopenko, Rudolph E. Tanzi, and David A. Bennett.
Support for the research came from the National Institutes of Health, The Picower Institute for Learning and Memory, The JPB Foundation, the Cure Alzheimer’s Fund, The Robert A. and Renee E. Belfer Family Foundation, Eduardo Eurnekian, and Joseph DiSabato.
In the media
Related articles, fellowship supports student’s work to advance alzheimer’s research and equity.
Tsai presents non-invasive stimulation study at Massachusetts Down Syndrome Congress

A noninvasive treatment for “chemo brain”

How sensory gamma rhythm stimulation clears amyloid in Alzheimer’s mice


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A bibliography entry for a book begins with the author's name, which is written in this order: last name, comma, first name, period. After the author's name comes the title of the book. If you are handwriting your bibliography, underline each title. If you are working on a computer, put the book title in italicized type.
Formatting a Harvard style bibliography. Sources are alphabetised by author last name. The heading 'Reference list' or 'Bibliography' appears at the top. Each new source appears on a new line, and when an entry for a single source extends onto a second line, a hanging indent is used: Harvard bibliography example.
An annotated bibliography is a type of bibliography usually used early on in research projects. Annotated bibliographies have a list of sources to support a research project and brief "annotations ...
Now among citation pages, there are three different types: reference list, bibliography and works cited. A reference list and a works cited list only the ideas or quotes used in the body of the paper. A bibliography, on the other hand, will list all the sources used in the creation of the body of the paper, even if they weren't cited in the ...
The Bluebook: A Uniform System of Citation is the main style guide for legal citations in the US. It's widely used in law, and also when legal materials need to be cited in other disciplines. Bluebook footnote citation. 1 David E. Pozen, Freedom of Information Beyond the Freedom of Information Act, 165, U. P🇦 . L.
The bibliography is a multifaceted discipline encompassing different types, each designed to serve specific research purposes and requirements. These various types of bibliographies provide valuable tools for researchers, scholars, and readers to navigate the vast realm of literature and sources available.
Different types of sources have different formatting in the bibliography. In American schools, the two most commonly used guidelines for this formatting are published by the MLA (Modern Language Association) and the APA (American Psychological Association). The MLA guidelines call for the bibliography to be called Works Cited.
The choice of the bibliography type depends on the nature of the research and the objectives of the bibliography; however, the basics are universal, and the bibliography is always arranged by the author's last name for each source. Some of the bibliography types commonly used in academic and research contexts are: Annotated Bibliography:
Title your bibliography section "References" and center the title on the top line of the page. Do not center your references; they should be left-aligned. For longer items, subsequent lines should use a hanging indent of 1/2 inch. Include all types of resources in the same list.
The type of bibliography formats you use depends on your research and subject matter. Bibliography Uncovered. Before you can even get into the steps of creating your bibliography, you need to understand specifically what a bibliography is and the best style bibliography formats to use for your paper. Simply put, a bibliography is a list of ...
Step 1. Develop an initial reference page. While accumulating data for research papers, establishing an initial bibliography can be advantageous. It simplifies the final stages of your work and aids in the organization of your ideas. When composing an initial draft, ensure to compile details: Author (s) and editor (s);
Students writing research papers commonly use enumerative bibliography. It is the most basic type, where the writer lists all sources used, providing bibliographic details for each work. Those sources share common characteristics such as language, topic, or period of time. Information concerning the source is then given by the writer to provide ...
Research papers take a lot of different steps to format your outline and discuss where your sources came from. Every paper ends with a citation page or bibliography. The type of bibliography that you use will depend on your research and subject matter.
English for Research: Usage, Style, and Grammar. New York: Springer Science and Business Media, 2012. Wang, Gabe T. and Keumjae Park. Student Research and Report Writing: From Topic Selection to the Complete Paper. Malden, MA: Wiley Blackwell, 2016. Warner, John. The Writer's Practice: Building Confidence in Your Non-Fiction Writing. New York ...
Bibliography Types: Below are some common types of bibliography: 1. Annotated Bibliography. An annotated bibliography includes a brief summary or evaluation of each source. The annotation can provide a summary of the content, an evaluation of the source's reliability, and its relevance to the research topic.
A special kind of bibliography, the annotated bibliography, is often used to direct your readers to other books and resources on your topic. An instructor may ask you to prepare an annotated bibliography to help you narrow down a topic for your research assignment. Such bibliographies offer a few lines of information, typically 150-300 words ...
Research papers take a lot of different steps to format your outline and discuss where your sources came from. Every paper ends with a citation page or bibliography. The type of bibliography formats you use depends on your research and subject matter.
A bibliography is a list of sources (books, journals, Web sites, periodicals, etc.) one has used for researching a topic. Bibliographies are sometimes called "References" or "Works Cited" depending on the style format you are using. A bibliography usually just includes the bibliographic information (i.e., the author, title, publisher, etc.).
The bibliography in a research paper or project is typically one of the last pages of the paper adding to the piece after your own content but before any appendices. ... or hard-to-find works, then a personal bibliography is the best way to list these. This type of bibliography is best used for academic pieces that focus on multiple works by ...
What this handout is about. This handout will explain why annotated bibliographies are useful for researchers, provide an explanation of what constitutes an annotation, describe various types of annotations and styles for writing them, and offer multiple examples of annotated bibliographies in the MLA, APA, and CBE/CSE styles of citation.
A bibliography for students is a type of bibliography that's most commonly used by students for various academic projects such as research projects. When this type of bibliography is used for school projects, regardless of the style of citation, the sources need to be in alphabetical order, as is the case with all types of bibliographies.
For example, our Similarity Report guidance on help.turnitin is repeated in numerous places to cater for each individual integration and license type. On guides.turnitin this content will exist in a single place to allow for users of all integrations and licenses to find it easily.
"What makes our research unique is our use of computer utilization as a possible indicator of, and proxy for, work productivity in all three workstation types," Aguilar said. Participants were placed in three study groups according to the type of workstation they used (stand-biased, sit-stand or traditional), with those using traditional ...
Getting consistent sleep could help stave off Type 2 diabetes, new research suggests. A team led by investigators at Brigham and Women's Hospital analyzed the sleep patterns of study participants over seven nights and then followed them for more than seven years. The researchers found those with the most irregular sleep patterns had a 34 ...
Other anesthesia drugs act on different types of receptors, and the mechanism for how all of these drugs produce unconsciousness is not fully understood. Miller, Fiete, and their students hypothesized that propofol, and possibly other anesthesia drugs, interfere with a brain state known as "dynamic stability." ... The research was funded by ...
Classification Title: OPS HOURLY NON-SECRETARY/CLERICAL. Job Description: The Department of Applied Physiology and Kinesiology at the University of Florida is seeking a part-time OPS Research Coordinator n the laboratory of Dr. Rachael Seidler to assist with human subjects research on the neural control of movement through ~December 31, 2024.
The new analysis measured gene expression differences in more than 1.3 million cells of more than 70 cell types in six brain regions from 48 tissue donors, 26 of whom died with an Alzheimer's diagnosis and 22 of whom without. As such, the study provides a uniquely large, far-ranging and yet detailed accounting of how brain cell activity ...
Undergraduate research experience, experience in managing large events, skilled in excel, experience interacting with students. Special Instructions to Applicants: In order to be considered, applicants must upload a resume, cover letter and a list of professional references. Application must be submitted by 11:55 p.m. (ET) of the posting end date.
Among this year's cohort of roughly 11,000 athletes from around the world, 23 Aggies will compete in six sports, while Texas A&M women's basketball head coach Joni Taylor will serve as an assistant coach for the USA Basketball Women's National Team. Palomo said it's always great to see fellow Aggies representing the U.S. and other nations during the games, knowing that all of them are ...
New research finds that alternate workstation options, such as standing and sit-stand desks, can be a win-win solution for both employees and employers. Health & Environment AgriLife Extension Disaster Response Teams Respond To Landowners' Requests Following Hurricane Beryl