

What is Theme? A Look at 20 Common Themes in Literature
Sean Glatch | May 7, 2024 | 18 Comments

When someone asks you “What is this book about?” , there are a few ways you can answer. There’s “ plot ,” which refers to the literal events in the book, and there’s “character,” which refers to the people in the book and the struggles they overcome. Finally, there are themes in literature that correspond with the work’s topic and message. But what is theme in literature?
The theme of a story or poem refers to the deeper meaning of that story or poem. All works of literature contend with certain complex ideas, and theme is how a story or poem approaches these ideas.
There are countless ways to approach the theme of a story or poem, so let’s take a look at some theme examples and a list of themes in literature. We’ll discuss the differences between theme and other devices, like theme vs moral and theme vs topic. Finally, we’ll examine why theme is so essential to any work of literature, including to your own writing.
But first, what is theme? Let’s explore what theme is—and what theme isn’t.
Common Themes in Literature: Contents
- Theme Definition
20 Common Themes in Literature
- Theme Examples
Themes in Literature: A Hierarchy of Ideas
Why themes in literature matter.
- Should I Decide the Themes of a Story in Advance?
Theme Definition: What is Theme?
Theme describes the central idea(s) that a piece of writing explores. Rather than stating this theme directly, the author will look at theme using the set of literary tools at their disposal. The theme of a story or poem will be explored through elements like characters , plot, settings , conflict, and even word choice and literary devices .
Theme definition: the central idea(s) that a piece of writing explores.
That said, theme is more than just an idea. It is also the work’s specific vantage point on that idea. In other words, a theme is an idea plus an opinion: it is the author’s specific views regarding the central ideas of the work.
All works of literature have these central ideas and opinions, even if those ideas and opinions aren’t immediate to the reader.
Justice, for example, is a literary theme that shows up in a lot of classical works. To Kill a Mockingbird contends with racial justice, especially at a time when the U.S. justice system was exceedingly stacked against African Americans. How can a nation call itself just when justice is used as a weapon?
By contrast, the play Hamlet is about the son of a recently-executed king. Hamlet seeks justice for his father and vows to kill Claudius—his father’s killer—but routinely encounters the paradox of revenge. Can justice really be found through more bloodshed?
What is theme? An idea + an opinion.
Clearly, these two works contend with justice in unrelated ways. All themes in literature are broad and open-ended, allowing writers to explore their own ideas about these complex topics.
Let’s look at some common themes in literature. The ideas presented within this list of themes in literature show up in novels, memoirs, poems, and stories throughout history.
| Theme Definition | Theme Examples | |
| Circle of Life | What comes around, goes around. The Circle of Life dwells on life’s transience and impermanence: how death isn’t death, just an evolution. | by Wilson Rawls |
| Coming of Age | Also known as a bildungsroman, Coming of Age involves the intense experiences of growing up, and how these experiences shape the future of the protagonist. | by Charlotte Bronte by Charles Dickens |
| Faith vs Doubt | Whether it’s faith in God, other people, or the protagonist’s own self, believing isn’t easy—but is it worth doing anyway? | by Fyodor Dostoevsky |
| Many families are connected by blood, but to overcome certain obstacles, literary families must strengthen their ties to each other. | by Leo Tolstoy by Yaa Gyasi by Min Jin Lee by Richard Mirabella | |
| Fate vs Free Will | How much of our actions are decided by fate, and how much does free will really control? | by William Shakespeare by Paulo Coelho |
| Good vs Evil | One can argue that every story is about good vs evil, assuming the story has a protagonist and antagonist. Still, good and evil are in eternal conflict with each other, so writers must document how this conflict evolves. | by Christopher Marlowe by Robert Louis Stevenson |
| Hubris | Hubris refers to excessive self-confidence and the terrible decisions that arise from it. Many works of literature explore hubris as man’s defiance of God/the gods, or else man himself playing God. | by Mary Shelley by Homer |
| Identity | At some point in their life, the protagonist asks the question: who am I? Additionally, “Identity” refers to the qualities that make one person distinct from another. How much of a difference between you and I? | by Haruki Murakami by Elif Batuman by Carl Frode Tiller |
| Justice | What makes a society just? What are the proper consequences for people who do the wrong thing? Who is best equipped to dispense justice? Are we collectively responsible for each other’s actions? | by Harper Lee by William Shakespeare by Fyodor Dostoevsky |
| Loneliness | Loneliness affects the way people think, act, and view the world. The theme of loneliness charts how certain characters contend with their loneliness, and whether man can survive this disconnection from others. | by Haruki Murakami |
| Man vs Nature | Man’s natural inclination is to dominate the land, but nature has its own means of survival. | by William Golding by Jean Hegland by Linda Hogan |
| Man vs Self | Sometimes, the protagonist is their own adversary. In order to overcome certain challenges, the protagonist must first overcome their own internal conflicts. | by Zora Neale Hurston |
| Man vs Society | When the story’s antagonist is society-at-large, the protagonist must convince the world that it’s sick—or else die trying. Some protagonists also try to escape society altogether. | by George Orwell by Margaret Atwood by Ray Bradbury |
| Power and Corruption | Power corrupts, and absolute power corrupts absolutely. This theme is often closely related to “Man vs Society.” Additionally, “Power” can refer to a person’s political leadership, personal wealth, physical prowess, etc. | by Julia Alvarez by George Orwell |
| Pursuit of Love | Love makes the world go round, but it’s not always easy to find. Whether it’s romantic, familial, or platonic love, there’s much to be said about love’s pursuit—and the conflict that comes from pursuing it. | by Emily Bronte By Jeanette Winterson by Jane Austen |
| Revenge | When someone wrongs you or the people you love, revenge is tempting. But, is revenge worth it? Can revenge beget justice? And how far is too far? | by Alexandre Dumas |
| Sacrificial Love | When you truly love someone, you’re willing to sacrifice everything for them. Sacrifice is a component of all themes concerning love, though this is especially true for stories about motherly love. | by Toni Morrison by Lisa Ko |
| Survival | When survival is at stake, people discover the limits of their own power. The literary theme of survival applies to stories about being lost in the wilderness, but it also applies to stories about the survival of ideas, groups, and humanity-at-large. | , author unknown by Margaret Atwood by Joseph Conrad |
| The Environment | Whether it’s because of technology, climate change, or our increasingly online world, man’s relationship to the environment is ever-evolving. Themes in literature concerning the environment often coincide with “man vs nature.” | by Ruth Ozeki by Barbara Kingsolver |
| War | Mankind has been at war with itself since the dawn of civilization. The causes of war, as well as its impacts on society, are topics of frequent musing by writers—especially writers who have been at war themselves. | by Ernest Hemingway by Stephen Crane by Sun Tzu |
Theme Examples in Literature
Let’s take a closer look at how writers approach and execute theme. Themes in literature are conveyed throughout the work, so while you might not have read the books in the following theme examples, we’ve provided plot synopses and other relevant details where necessary. We analyze the following:
- Power and Corruption in the novel Animal Farm
- Loneliness in the short story “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place”
- Love in the poem “How Do I Love Thee”
Theme Examples: Power and Corruption in the Novel Animal Farm
At its simplest, the novel Animal Farm by George Orwell is an allegory that represents the rise and moral decline of Communism in Russia. Specifically, the novel uncovers how power corrupts the leaders of populist uprisings, turning philosophical ideals into authoritarian regimes.
Most of the characters in Animal Farm represent key figures during and after the Russian Revolution. On an ailing farm that’s run by the negligent farmer Mr. Jones (Tsar Nicholas II), the livestock are ready to seize control of the land. The livestock’s discontent is ripened by Old Major (Karl Marx/Lenin), who advocates for the overthrow of the ruling elite and the seizure of private land for public benefit.
After Old Major dies, the pigs Napoleon (Joseph Stalin) and Snowball (Leon Trotsky) stage a revolt. Mr. Jones is chased off the land, which parallels the Russian Revolution in 1917. The pigs then instill “Animalism”—a system of government that advocates for the rights of the common animal. At the core of this philosophy is the idea that “all animals are equal”—an ideal that, briefly, every animal upholds.
Initially, the Animalist Revolution brings peace and prosperity to the farm. Every animal is well-fed, learns how to read, and works for the betterment of the community. However, when Snowball starts implementing a plan to build a windmill, Napoleon drives Snowball off of the farm, effectively assuming leadership over the whole farm. (In real life, Stalin forced Trotsky into exile, and Trotsky spent the rest of his life critiquing the Stalin regime until he was assassinated in 1940.)
Napoleon’s leadership quickly devolves into demagoguery, demonstrating the corrupting influence of power and the ways that ideology can breed authoritarianism. Napoleon uses Snowball as a scapegoat for whenever the farm has a setback, while using Squealer (Vyacheslav Molotov) as his private informant and public orator.
Eventually, Napoleon changes the tenets of Animalism, starts walking on two legs, and acquires other traits and characteristics of humans. At the end of the novel, and after several more conflicts , purges, and rule changes, the livestock can no longer tell the difference between the pigs and humans.
Themes in Literature: Power and Corruption in Animal Farm
So, how does Animal Farm explore the theme of “Power and Corruption”? Let’s analyze a few key elements of the novel.
Plot: The novel’s major plot points each relate to power struggles among the livestock. First, the livestock wrest control of the farm from Mr. Jones; then, Napoleon ostracizes Snowball and turns him into a scapegoat. By seizing leadership of the farm for himself, Napoleon grants himself massive power over the land, abusing this power for his own benefit. His leadership brings about purges, rule changes, and the return of inequality among the livestock, while Napoleon himself starts to look more and more like a human—in other words, he resembles the demagoguery of Mr. Jones and the abuse that preceded the Animalist revolution.
Thus, each plot point revolves around power and how power is wielded by corrupt leadership. At its center, the novel warns the reader of unchecked power, and how corrupt leaders will create echo chambers and private militaries in order to preserve that power.
Characters: The novel’s characters reinforce this message of power by resembling real life events. Most of these characters represent real life figures from the Russian Revolution, including the ideologies behind that revolution. By creating an allegory around Lenin, Trotsky, Stalin, and the other leading figures of Communist Russia’s rise and fall, the novel reminds us that unchecked power foments disaster in the real world.
Literary Devices: There are a few key literary devices that support the theme of Power and Corruption. First, the novel itself is a “satirical allegory.” “ Satire ” means that the novel is ridiculing the behaviors of certain people—namely Stalin, who instilled far-more-dangerous laws and abuses that created further inequality in Russia/the U.S.S.R. While Lenin and Trotsky had admirable goals for the Russian nation, Stalin is, quite literally, a pig.
Meanwhile, “allegory” means that the story bears symbolic resemblance to real life, often to teach a moral. The characters and events in this story resemble the Russian Revolution and its aftermath, with the purpose of warning the reader about unchecked power.
Finally, an important literary device in Animal Farm is symbolism . When Napoleon (Stalin) begins to resemble a human, the novel suggests that he has become as evil and negligent as Mr. Jones (Tsar Nicholas II). Since the Russian Revolution was a rejection of the Russian monarchy, equating Stalin to the monarchy reinforces the corrupting influence of power, and the need to elect moral individuals to posts of national leadership.
Theme Examples: Loneliness in “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place”
Ernest Hemingway’s short story “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place” is concerned with the theme of loneliness. You can read this short story here . Content warning for mentions of suicide.
There are very few plot points in Hemingway’s story, so most of the story’s theme is expressed through dialogue and description. In the story, an old man stays up late drinking at a cafe. The old man has no wife—only a niece that stays with him—and he attempted suicide the previous week. Two waiters observe him: a younger waiter wants the old man to leave so they can close the cafe, while an older waiter sympathizes with the old man. None of these characters have names.
The younger waiter kicks out the old man and closes the cafe. The older waiter walks to a different cafe and ruminates on the importance of “a clean, well-lighted place” like the cafe he works at.
Themes in Literature: Loneliness in “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place”
Hemingway doesn’t tell us what to think about the old man’s loneliness, but he does provide two opposing viewpoints through the dialogue of the waiters.
The younger waiter has the hallmarks of a happy life: youth, confidence, and a wife to come home to. While he acknowledges that the old man is unhappy, he also admits “I don’t want to look at him,” complaining that the old man has “no regard for those who must work.” The younger waiter “did not wish to be unjust,” he simply wanted to return home.
The older waiter doesn’t have the privilege of turning away: like the old man, he has a house but not a home to return to, and he knows that someone may need the comfort of “a clean and pleasant cafe.”
The older waiter, like Hemingway, empathizes with the plight of the old man. When your place of rest isn’t a home, the world can feel like a prison, so having access to a space that counteracts this feeling is crucial. What kind of a place is that? The older waiter surmises that “the light of course” matters, but the place must be “clean and pleasant” too. Additionally, the place should not have music or be a bar: it must let you preserve the quiet dignity of yourself.
Lastly, the older waiter’s musings about God clue the reader into his shared loneliness with the old man. In a stream of consciousness, the older waiter recites traditional Christian prayers with “nada” in place of “God,” “Father,” “Heaven,” and other symbols of divinity. A bartender describes the waiter as “otro locos mas” (translation: another crazy), and the waiter concludes that his plight must be insomnia.
This belies the irony of loneliness: only the lonely recognize it. The older waiter lacks confidence, youth, and belief in a greater good. He recognizes these traits in the old man, as they both share a need for a clean, well-lighted place long after most people fall asleep. Yet, the younger waiter and the bartender don’t recognize these traits as loneliness, just the ramblings and shortcomings of crazy people.
Does loneliness beget craziness? Perhaps. But to call the waiter and old man crazy would dismiss their feelings and experiences, further deepening their loneliness.
Loneliness is only mentioned once in the story, when the young waiter says “He’s [the old man] lonely. I’m not lonely. I have a wife waiting in bed for me.” Nonetheless, loneliness consumes this short story and its older characters, revealing a plight that, ironically, only the lonely understand.
Theme Examples: Love in the Poem “How Do I Love Thee”
Let’s turn towards brighter themes in literature: namely, love in poetry . Elizabeth Barrett Browning’s poem “ How Do I Love Thee ” is all about the theme of love.
Themes in Literature: Love in “How Do I Love Thee”
Browning’s poem is a sonnet , which is a 14-line poem that often centers around love and relationships. Sonnets have different requirements depending on their form, but between lines 6-8, they all have a volta —a surprising line that twists and expands the poem’s meaning.
Let’s analyze three things related to the poem’s theme: its word choice, its use of simile and metaphor , and its volta.
Word Choice: Take a look at the words used to describe love. What do those words mean? What are their connotations? Here’s a brief list: “soul,” “ideal grace,” “quiet need,” “sun and candle-light,” “strive for right,” “passion,” “childhood’s faith,” “the breath, smiles, tears, of all my life,” “God,” “love thee better after death.”
These words and phrases all bear positive connotations, and many of them evoke images of warmth, safety, and the hearth. Even phrases that are morose, such as “lost saints” and “death,” are used as contrasts to further highlight the speaker’s wholehearted rejoicing of love. This word choice suggests an endless, benevolent, holistic, all-consuming love.
Simile and Metaphor: Similes and metaphors are comparison statements, and the poem routinely compares love to different objects and ideas. Here’s a list of those comparisons:
The speaker loves thee:
- To the depths of her soul.
- By sun and candle light—by day and night.
- As men strive to do the right thing (freely).
- As men turn from praise (purely).
- With the passion of both grief and faith.
- With the breath, smiles, and tears of her entire life.
- Now in life, and perhaps even more after death.
The speaker’s love seems to have infinite reach, flooding every aspect of her life. It consumes her soul, her everyday activities, her every emotion, her sense of justice and humility, and perhaps her afterlife, too. For the speaker, this love is not just an emotion, an activity, or an ideology: it’s her existence.
Volta: The volta of a sonnet occurs in the poem’s center. In this case, the volta is the lines “I love thee freely, as men strive for right. / I love thee purely, as they turn from praise.”
What surprising, unexpected comparisons! To the speaker, love is freedom and the search for a greater good; it is also as pure as humility. By comparing love to other concepts, the speaker reinforces the fact that love isn’t just an ideology, it’s an ideal that she strives for in every word, thought, and action.
“Theme” is part of a broader hierarchy of ideas. While the theme of a story encompasses its central ideas, the writer also expresses these ideas through different devices.
You may have heard of some of these devices: motif, moral, topic, etc. What is motif vs theme? What is theme vs moral? These ideas interact with each other in different ways, which we’ve mapped out below.
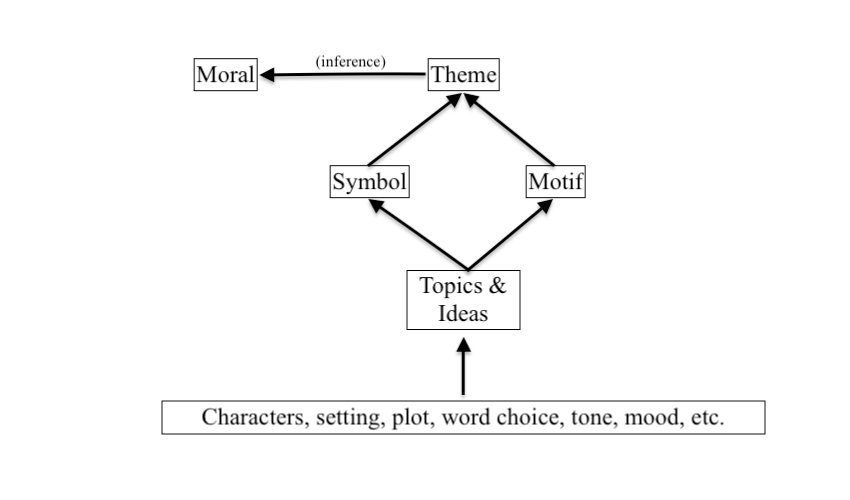
Theme vs Topic
The “topic” of a piece of literature answers the question: What is this piece about? In other words, “topic” is what actually happens in the story or poem.
You’ll find a lot of overlap between topic and theme examples. Love, for instance, is both the topic and the theme of Elizabeth Barrett Browning’s poem “How Do I Love Thee.”
The difference between theme vs topic is: topic describes the surface level content matter of the piece, whereas theme encompasses the work’s apparent argument about the topic.
Topic describes the surface level content matter of the piece, whereas theme encompasses the work’s apparent argument about the topic.
So, the topic of Browning’s poem is love, while the theme is the speaker’s belief that her love is endless, pure, and all-consuming.
Additionally, the topic of a piece of literature is definitive, whereas the theme of a story or poem is interpretive. Every reader can agree on the topic, but many readers will have different interpretations of the theme. If the theme weren’t open-ended, it would simply be a topic.
Theme vs Motif
A motif is an idea that occurs throughout a literary work. Think of the motif as a facet of the theme: it explains, expands, and contributes to themes in literature. Motif develops a central idea without being the central idea itself .
Motif develops a central idea without being the central idea itself.
In Animal Farm , for example, we encounter motif when Napoleon the pig starts walking like a human. This represents the corrupting force of power, because Napoleon has become as much of a despot as Mr. Jones, the previous owner of the farm. Napoleon’s anthropomorphization is not the only example of power and corruption, but it is a compelling motif about the dangers of unchecked power.
Theme vs Moral
The moral of a story refers to the story’s message or takeaway. What can we learn from thinking about a specific piece of literature?
The moral is interpreted from the theme of a story or poem. Like theme, there is no single correct interpretation of a story’s moral: the reader is left to decide how to interpret the story’s meaning and message.
For example, in Hemingway’s “A Clean, Well-Lighted Place,” the theme is loneliness, but the moral isn’t quite so clear—that’s for the reader to decide. My interpretation is that we should be much more sympathetic towards the lonely, since loneliness is a quiet affliction that many lonely people cannot express.
Great literature does not tell us what to think, it gives us stories to think about.
However, my interpretation could be miles away from yours, and that’s wonderful! Great literature does not tell us what to think, it gives us stories to think about, and the more we discuss our thoughts and interpretations, the more we learn from each other.
The theme of a story affects everything else: the decisions that characters make, the mood that words and images build, the moral that readers interpret, etc. Recognizing how writers utilize various themes in literature will help you craft stronger, more nuanced works of prose and poetry .
“To produce a mighty book, you must choose a mighty theme.” —Herman Melville
Whether a writer consciously or unconsciously decides the themes of their work, theme in literature acts as an organizing principle for the work as a whole. For writers, theme is especially useful to think about in the process of revision: if some element of your poem or story doesn’t point towards a central idea, it’s a sign that the work is not yet finished.
Moreover, literary themes give the work stakes . They make the work stand for something. Remember that our theme definition is an idea plus an opinion. Without that opinion element, a work of literature simply won’t stand for anything, because it is presenting ideas in the abstract without giving you something to react to. The theme of a story or poem is never just “love” or “justice,” it’s the author’s particular spin and insight on those themes. This is what makes a work of literature compelling or evocative. Without theme, literature has no center of gravity, and all the words and characters and plot points are just floating in the ether.
Should I Decide the Theme of a Story or Poem in Advance?
You can, though of course it depends on the actual story you want to tell. Some writers certainly start with a theme. You might decide you want to write a story about themes like love, family, justice, gender roles, the environment, or the pursuit of revenge.
From there, you can build everything else: plot points, characters, conflicts, etc. Examining themes in literature can help you generate some strong story ideas !
Nonetheless, theme is not the only way to approach a creative writing project. Some writers start with plot, others with character, others with conflicts, and still others with just a vague notion of what the story might be about. You might not even realize the themes in your work until after you finish writing it.
You certainly want your work to have a message, but deciding what that message is in advance might actually hinder your writing process. Many writers use their poems and stories as opportunities to explore tough questions, or to arrive at a deeper insight on a topic. In other words, you can start your work with ideas, and even opinions on those ideas, but don’t try to shoehorn a story or poem into your literary themes. Let the work explore those themes. If you can surprise yourself or learn something new from the writing process, your readers will certainly be moved as well.
So, experiment with ideas and try different ways of writing. You don’t have think about the theme of a story right away—but definitely give it some thought when you start revising your work!
Develop Great Themes at Writers.com
As writers, it’s hard to know how our work will be viewed and interpreted. Writing in a community can help. Whether you join our Facebook group or enroll in one of our upcoming courses , we have the tools and resources to sharpen your writing.
Sean Glatch
18 comments.
Sean Glatch,Thank you very much for your discussion on themes. It was enlightening and brought clarity to an abstract and sometimes difficult concept to explain and illustrate. The sample stories and poem were appreciated too as they are familiar to me. High School Language Arts Teacher
Hi Stephanie, I’m so glad this was helpful! Happy teaching 🙂
Wow!!! This is the best resource on the subject of themes that I have ever encountered and read on the internet. I just bookmarked it and plan to use it as a resource for my teaching. Thank you very much for publishing this valuable resource.
Hi Marisol,
Thank you for the kind words! I’m glad to hear this article will be a useful resource. Happy teaching!
Warmest, Sean
builders beams bristol
What is Theme? A Look at 20 Common Themes in Literature | writers.com
Hello! This is a very informative resource. Thank you for sharing.
farrow and ball pigeon
This presentation is excellent and of great educational value. I will employ it already in my thesis research studies.
John Never before communicated with you!
Brilliant! Thank you.
[…] THE MOST COMMON THEMES IN LITERATURE […]
marvellous. thumbs up
Thank you. Very useful information.
found everything in themes. thanks. so much
In college I avoided writing classes and even quit a class that would focus on ‘Huck Finn’ for the entire semester. My idea of hell. However, I’ve been reading and learning from the writers.com articles, and I want to especially thank Sean Glatch who writes in a way that is useful to aspiring writers like myself.
You are very welcome, Anne! I’m glad that these resources have been useful on your writing journey.
Thank you very much for this clear and very easy to understand teaching resources.
Hello there. I have a particular question.
Can you describe the exact difference of theme, issue and subject?
I get confused about these.
I love how helpful this is i will tell my class about it!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

- Ask LitCharts AI
- Discussion Question Generator
- Essay Prompt Generator
- Quiz Question Generator

- Literature Guides
- Poetry Guides
- Shakespeare Translations
- Literary Terms

Theme Definition
What is theme? Here’s a quick and simple definition:
A theme is a universal idea, lesson, or message explored throughout a work of literature. One key characteristic of literary themes is their universality, which is to say that themes are ideas that not only apply to the specific characters and events of a book or play, but also express broader truths about human experience that readers can apply to their own lives. For instance, John Steinbeck's The Grapes of Wrath (about a family of tenant farmers who are displaced from their land in Oklahoma) is a book whose themes might be said to include the inhumanity of capitalism, as well as the vitality and necessity of family and friendship.
Some additional key details about theme:
- All works of literature have themes. The same work can have multiple themes, and many different works explore the same or similar themes.
- Themes are sometimes divided into thematic concepts and thematic statements . A work's thematic concept is the broader topic it touches upon (love, forgiveness, pain, etc.) while its thematic statement is what the work says about that topic. For example, the thematic concept of a romance novel might be love, and, depending on what happens in the story, its thematic statement might be that "Love is blind," or that "You can't buy love . "
- Themes are almost never stated explicitly. Oftentimes you can identify a work's themes by looking for a repeating symbol , motif , or phrase that appears again and again throughout a story, since it often signals a recurring concept or idea.
Theme Pronunciation
Here's how to pronounce theme: theem
Identifying Themes
Every work of literature—whether it's an essay, a novel, a poem, or something else—has at least one theme. Therefore, when analyzing a given work, it's always possible to discuss what the work is "about" on two separate levels: the more concrete level of the plot (i.e., what literally happens in the work), as well as the more abstract level of the theme (i.e., the concepts that the work deals with). Understanding the themes of a work is vital to understanding the work's significance—which is why, for example, every LitCharts Literature Guide uses a specific set of themes to help analyze the text.
Although some writers set out to explore certain themes in their work before they've even begun writing, many writers begin to write without a preconceived idea of the themes they want to explore—they simply allow the themes to emerge naturally through the writing process. But even when writers do set out to investigate a particular theme, they usually don't identify that theme explicitly in the work itself. Instead, each reader must come to their own conclusions about what themes are at play in a given work, and each reader will likely come away with a unique thematic interpretation or understanding of the work.
Symbol, Motif, and Leitwortstil
Writers often use three literary devices in particular—known as symbol , motif , and leitwortstil —to emphasize or hint at a work's underlying themes. Spotting these elements at work in a text can help you know where to look for its main themes.
- Near the beginning of Romeo and Juliet , Benvolio promises to make Romeo feel better about Rosaline's rejection of him by introducing him to more beautiful women, saying "Compare [Rosaline's] face with some that I shall show….and I will make thee think thy swan a crow." Here, the swan is a symbol for how Rosaline appears to the adoring Romeo, while the crow is a symbol for how she will soon appear to him, after he has seen other, more beautiful women.
- Symbols might occur once or twice in a book or play to represent an emotion, and in that case aren't necessarily related to a theme. However, if you start to see clusters of similar symbols appearing in a story, this may mean that the symbols are part of an overarching motif, in which case they very likely are related to a theme.
- For example, Shakespeare uses the motif of "dark vs. light" in Romeo and Juliet to emphasize one of the play's main themes: the contradictory nature of love. To develop this theme, Shakespeare describes the experience of love by pairing contradictory, opposite symbols next to each other throughout the play: not only crows and swans, but also night and day, moon and sun. These paired symbols all fall into the overall pattern of "dark vs. light," and that overall pattern is called a motif.
- A famous example is Kurt Vonnegut's repetition of the phrase "So it goes" throughout his novel Slaughterhouse Five , a novel which centers around the events of World War II. Vonnegut's narrator repeats the phrase each time he recounts a tragic story from the war, an effective demonstration of how the horrors of war have become normalized for the narrator. The constant repetition of the phrase emphasizes the novel's primary themes: the death and destruction of war, and the futility of trying to prevent or escape such destruction, and both of those things coupled with the author's skepticism that any of the destruction is necessary and that war-time tragedies "can't be helped."
Symbol, motif and leitwortstil are simply techniques that authors use to emphasize themes, and should not be confused with the actual thematic content at which they hint. That said, spotting these tools and patterns can give you valuable clues as to what might be the underlying themes of a work.
Thematic Concepts vs. Thematic Statements
A work's thematic concept is the broader topic it touches upon—for instance:
- Forgiveness
while its thematic statement is the particular argument the writer makes about that topic through his or her work, such as:
- Human judgement is imperfect.
- Love cannot be bought.
- Getting revenge on someone else will not fix your problems.
- Learning to forgive is part of becoming an adult.
Should You Use Thematic Concepts or Thematic Statements?
Some people argue that when describing a theme in a work that simply writing a thematic concept is insufficient, and that instead the theme must be described in a full sentence as a thematic statement. Other people argue that a thematic statement, being a single sentence, usually creates an artificially simplistic description of a theme in a work and is therefore can actually be more misleading than helpful. There isn't really a right answer in this debate.
In our LitCharts literature study guides , we usually identify themes in headings as thematic concepts, and then explain the theme more fully in a few paragraphs. We find thematic statements limiting in fully exploring or explaining a the theme, and so we don't use them. Please note that this doesn't mean we only rely on thematic concepts—we spend paragraphs explaining a theme after we first identify a thematic concept. If you are asked to describe a theme in a text, you probably should usually try to at least develop a thematic statement about the text if you're not given the time or space to describe it more fully. For example, a statement that a book is about "the senselessness of violence" is a lot stronger and more compelling than just saying that the book is about "violence."
Identifying Thematic Statements
One way to try to to identify or describe the thematic statement within a particular work is to think through the following aspects of the text:
- Plot: What are the main plot elements in the work, including the arc of the story, setting, and characters. What are the most important moments in the story? How does it end? How is the central conflict resolved?
- Protagonist: Who is the main character, and what happens to him or her? How does he or she develop as a person over the course of the story?
- Prominent symbols and motifs: Are there any motifs or symbols that are featured prominently in the work—for example, in the title, or recurring at important moments in the story—that might mirror some of the main themes?
After you've thought through these different parts of the text, consider what their answers might tell you about the thematic statement the text might be trying to make about any given thematic concept. The checklist above shouldn't be thought of as a precise formula for theme-finding, but rather as a set of guidelines, which will help you ask the right questions and arrive at an interesting thematic interpretation.
Theme Examples
The following examples not only illustrate how themes develop over the course of a work of literature, but they also demonstrate how paying careful attention to detail as you read will enable you to come to more compelling conclusions about those themes.
Themes in F. Scott Fitzgerald's The Great Gatsby
Fitzgerald explores many themes in The Great Gatsby , among them the corruption of the American Dream .
- The story's narrator is Minnesota-born Nick Caraway, a New York bonds salesman. Nick befriends Jay Gatsby, the protagonist, who is a wealthy man who throws extravagant parties at his mansion.
- The central conflict of the novel is Gatsby's pursuit of Daisy, whom he met and fell in love with as a young man, but parted from during World War I.
- He makes a fortune illegally by bootlegging alcohol, to become the sort of wealthy man he believes Daisy is attracted to, then buys a house near her home, where she lives with her husband.
- While he does manage to re-enter Daisy's life, she ultimately abandons him and he dies as a result of her reckless, selfish behavior.
- Gatsby's house is on the water, and he stares longingly across the water at a green light that hangs at the edge of a dock at Daisy's house which sits across a the bay. The symbol of the light appears multiple times in the novel—during the early stages of Gatsby's longing for Daisy, during his pursuit of her, and after he dies without winning her love. It symbolizes both his longing for daisy and the distance between them (the distance of space and time) that he believes (incorrectly) that he can bridge.
- In addition to the green light, the color green appears regularly in the novel. This motif of green broadens and shapes the symbolism of the green light and also influences the novel's themes. While green always remains associated with Gatsby's yearning for Daisy and the past, and also his ambitious striving to regain Daisy, it also through the motif of repeated green becomes associated with money, hypocrisy, and destruction. Gatsby's yearning for Daisy, which is idealistic in some ways, also becomes clearly corrupt in others, which more generally impacts what the novel is saying about dreams more generally and the American Dream in particular.
Gatsby pursues the American Dream, driven by the idea that hard work can lead anyone from poverty to wealth, and he does so for a single reason: he's in love with Daisy. However, he pursues the dream dishonestly, making a fortune by illegal means, and ultimately fails to achieve his goal of winning Daisy's heart. Furthermore, when he actually gets close to winning Daisy's heart, she brings about his downfall. Through the story of Gatsby and Daisy, Fitzgerald expresses the point of view that the American Dream carries at its core an inherent corruption. You can read more about the theme of The American Dream in The Great Gatsby here .
Themes in Chinua Achebe's Things Fall Apart
In Things Fall Apart , Chinua Achebe explores the theme of the dangers of rigidly following tradition .
- Okonkwo is obsessed with embodying the masculine ideals of traditional Igbo warrior culture.
- Okonkwo's dedication to his clan's traditions is so extreme that it even alienates members of his own family, one of whom joins the Christians.
- The central conflict: Okonkwo's community adapts to colonization in order to survive, becoming less warlike and allowing the minor injustices that the colonists inflict upon them to go unchallenged. Okonkwo, however, refuses to adapt.
- At the end of the novel, Okonkwo impulsively kills a Christian out of anger. Recognizing that his community does not support his crime, Okonkwo kills himself in despair.
- Clanswomen who give birth to twins abandon the babies in the forest to die, according to traditional beliefs that twins are evil.
- Okonkwo kills his beloved adopted son, a prisoner of war, according to the clan's traditions.
- Okonkwo sacrifices a goat in repentence, after severely beating his wife during the clan's holy week.
Through the tragic story of Okonkwo, Achebe is clearly dealing with the theme of tradition, but a close examination of the text reveals that he's also making a clear thematic statement that following traditions too rigidly leads people to the greatest sacrifice of all: that of personal agency . You can read more about this theme in Things Fall Apart here .
Themes in Robert Frost's The Road Not Taken
Poem's have themes just as plot-driven narratives do. One theme that Robert Frost explores in this famous poem, The Road Not Taken , is the illusory nature of free will .
- The poem's speaker stands at a fork in the road, in a "yellow wood."
- He (or she) looks down one path as far as possible, then takes the other, which seems less worn.
- The speaker then admits that the paths are about equally worn—there's really no way to tell the difference—and that a layer of leaves covers both of the paths, indicating that neither has been traveled recently.
- After taking the second path, the speaker finds comfort in the idea of taking the first path sometime in the future, but acknowledges that he or she is unlikely to ever return to that particular fork in the woods.
- The speaker imagines how, "with a sigh" she will tell someone in the future, "I took the road less travelled—and that has made all the difference."
- By wryly predicting his or her own need to romanticize, and retroactively justify, the chosen path, the speaker injects the poem with an unmistakeable hint of irony .
- The speaker's journey is a symbol for life, and the two paths symbolize different life paths, with the road "less-travelled" representing the path of an individualist or lone-wolf. The fork where the two roads diverge represents an important life choice. The road "not taken" represents the life path that the speaker would have pursued had he or she had made different choices.
Frost's speaker has reached a fork in the road, which—according to the symbolic language of the poem—means that he or she must make an important life decision. However, the speaker doesn't really know anything about the choice at hand: the paths appear to be the same from the speaker's vantage point, and there's no way he or she can know where the path will lead in the long term. By showing that the only truly informed choice the speaker makes is how he or she explains their decision after they have already made it , Frost suggests that although we pretend to make our own choices, our lives are actually governed by chance.
What's the Function of Theme in Literature?
Themes are a huge part of what readers ultimately take away from a work of literature when they're done reading it. They're the universal lessons and ideas that we draw from our experiences of works of art: in other words, they're part of the whole reason anyone would want to pick up a book in the first place!
It would be difficult to write any sort of narrative that did not include any kind of theme. The narrative itself would have to be almost completely incoherent in order to seem theme-less, and even then readers would discern a theme about incoherence and meaninglessness. So themes are in that sense an intrinsic part of nearly all writing. At the same time, the themes that a writer is interested in exploring will significantly impact nearly all aspects of how a writer chooses to write a text. Some writers might know the themes they want to explore from the beginning of their writing process, and proceed from there. Others might have only a glimmer of an idea, or have new ideas as they write, and so the themes they address might shift and change as they write. In either case, though, the writer's ideas about his or her themes will influence how they write.
One additional key detail about themes and how they work is that the process of identifying and interpreting them is often very personal and subjective. The subjective experience that readers bring to interpreting a work's themes is part of what makes literature so powerful: reading a book isn't simply a one-directional experience, in which the writer imparts their thoughts on life to the reader, already distilled into clear thematic statements. Rather, the process of reading and interpreting a work to discover its themes is an exchange in which readers parse the text to tease out the themes they find most relevant to their personal experience and interests.
Other Helpful Theme Resources
- The Wikipedia Page on Theme: An in-depth explanation of theme that also breaks down the difference between thematic concepts and thematic statements.
- The Dictionary Definition of Theme: A basic definition and etymology of the term.
- In this instructional video , a teacher explains her process for helping students identify themes.

- End-Stopped Line
- Juxtaposition
- Figurative Language

- Quizzes, saving guides, requests, plus so much more.
The 25 Most Common Themes in Literature and Why They Matter
by Sue Weems | 0 comments
Start Your Story TODAY! We’re teaching a new LIVE workshop this week to help you start your next book. Learn more and sign up here.
If you've ever survived a high school English class, you've likely been asked to consider the most common themes in literature. What are they and why do they matter for readers and writers? Let's take a look.

Literature's first job is to entertain. But at the same time every novel has a kernel of truth in it, or perhaps several kernels, ideas about how life works or philosophies on the best way to live or some gesture to the broader meaning of life.
Taken together, these ideas may combine into a “theme.”
I say “may” because theme is more a tool of interpretation than creativity. The writer may come into the story with an idea of what their story is about. This understanding of what their story is “about ” may even help add focus and depth to their story.
Once a book is published, though, the audience owns theme, and they may depart with a totally different message than the author intended.
Which is all to say, as a writer, theme may or may not be helpful to you.
As a reader, though, you can use theme to unlock the deeper truths both in the story and in life. Let's look at what theme is, why it matters for readers and writers, how to identify them, and some common examples of theme in literature.
Why trust Sue on theme? I'm one of those annoying English teachers who helps students analyze literature. Students ask me why we do it, and I'll tell you the secrets I share with them: analyzing literature helps us understand our humanity and world– from the misuse of power to the meaning of life.
Secondly, learning to look at a part of something and understand how it functions in the whole (AKA analysis) is a skill that transcends literature. It's a low-stakes way to practice life skills.
Want to skip ahead? Click on the topic that best answers your question.
Table of Contents
What is a literary theme? Why does theme matter for a reader? How do you identify theme in a story? Types of story: a shortcut to theme Common themes in literature with examples Why theme matters for writers Practice
What is a literary theme?
A literary theme is a universal concept, idea or message explored in a story or poem. It's often a moral, lesson, or belief that the writer wants to convey to readers.
Think of theme as the underlying message that shapes the story. It’s not always obvious at first glance – sometimes it takes some close reading and analysis to identify what’s going on beneath the surface.
A universal theme is one that transcends time and place. For example, the popular theme “love conquers all” shows up in old romances such as The Epheseian Tale from 2-50 AD to Disney's Robin Hood from 1973 to Nicholas Sparks' novel The Notebook from 2004.
Why does theme matter for a reader?
You can certainly enjoy a story without knowing the theme explicitly, but most stories are about something beyond the character's actions. And we want them to be about something more.
Stories are the way we build meaning—the way we understand human life, the way we process and confront controversial ideas, the way we sometimes relate to each other on a universal level.
When someone asks you what a book you're reading is about, you likely give a sentence or two about the character, their goal, and the conflict, but you're just as likely to identify an abstract idea that the book is about. That idea is a touchpoint for our humanness.
I may not be into a book about a boy wizard who is swept into a world where he must overcome his fears and insignificance to defeat a formidable foe, but I can certainly understand what it means to belong, what it means to find your way through inadequacy, what it means to defeat your fears.
That's the power of theme. It points to deeper meaning, connecting me to a story and to other readers like me.
How do you identify theme in a story?
If you are a student or a writer trying to identify theme, it sometimes feels like trying to crack a secret English major code. But here's a trick I teach my students.
1. Find the big idea
First, ask yourself about the big ideas or concepts that seem important throughout the entire story. These may feel abstract, such as love, beauty, despair, justice, or art. Sometimes the main character has very defined beliefs (or misbeliefs!) about the idea.
2. Ask what the story suggests about the idea
Once you have one or two overarching central ideas that seem important for the story, then ask yourself this question: What does the story seem to say about this idea?
For example, if I'm reading Shirley Jackson's chilling short story “The Lottery,” I might identify that the story is about community and tradition. If I wanted to be a little more specific I'd say tradition in the vein of conformity.
Quick summary of the story (spoiler alert!): The story opens on a summer day when an entire community participates in their annual lottery. Each family in town draws a paper until a single community member has been selected. The end of the story shows the town stoning the “winner” in a barbarous act of solidarity to maintain community traditions.
Now, to identify the central theme, I'd ask myself, what does Jackson's story seem to say about community or tradition or conformity?
Some communities are willing to maintain their traditions (or conformity) at any cost.
3. Support the theme or message with examples
If I wanted to support the central theme I identified, I would pull quotes or examples from the story that support it. In this case, I could look at the children who are willing to participate, the contrast of the summer day and the dark deed, the insistence that the stoning will keep them prosperous, even though there is no evidence of such.
Are there other possible themes? Sure. There are no wrong answers, only themes that can be defended from the texts and those that don't have enough support. It takes a little practice, but try this technique and see if it doesn't help.
Types of Story: a shortcut to finding theme in a story
As a part of his book The Write Structure , Joe has identified several types of story that help writers plan and execute their books. The detailed post is here.
In short, Joe argues that all stories are built on six values frameworks, regardless of genre. The values are directly related to the human condition and identify base needs we have for moving through the world.
Knowing your story types and the value scale can be a short cut to identifying themes in books and stories, because those universal ideas are tucked inside the values.
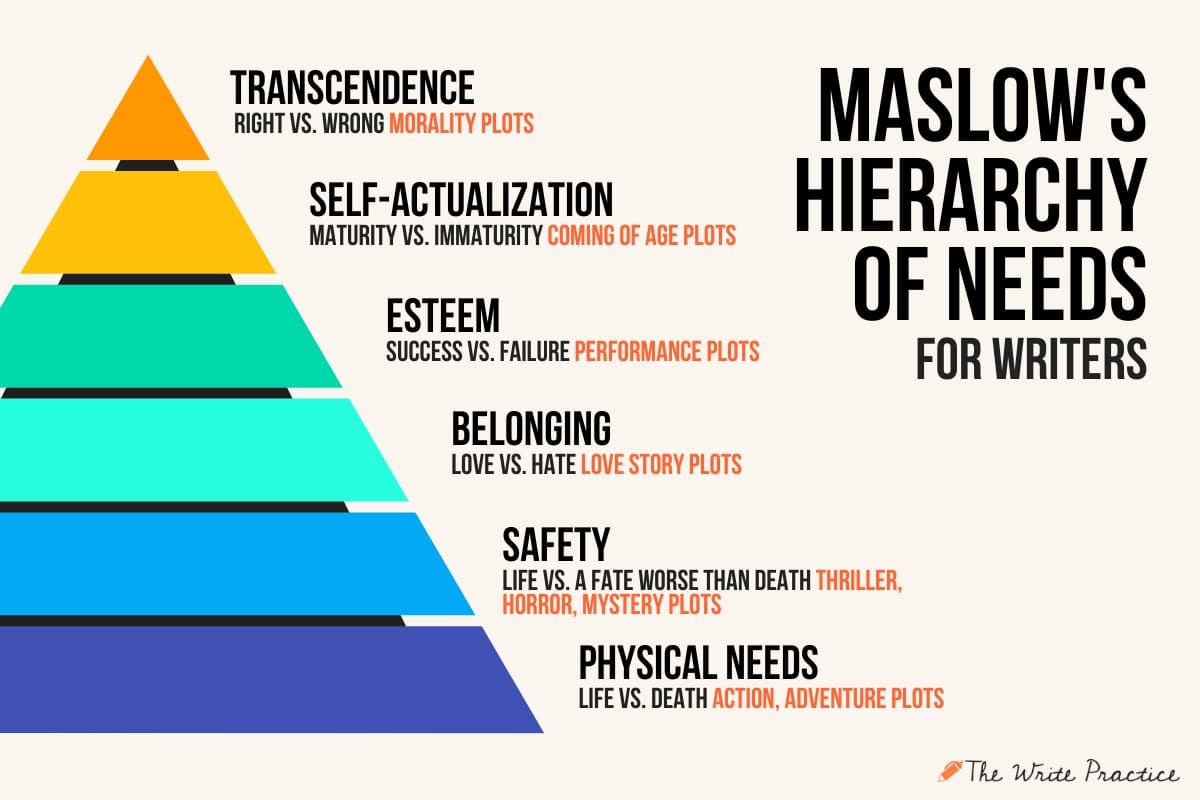
Here are the values in each type of story:
- Survival from Nature > Life vs. Death
- Survival from Others > Life vs. Fate Worse than Death
- Love/Community > Love vs. Hate
- Esteem > Accomplishment vs. Failure
- Personal Growth > Maturity vs. Immaturity
- Transcendence > Right vs. Wrong
The types can help you identify the central ideas that the story speaks into because you know that the values will be key. Your question then is what does the story seem to say about this value? Or more specifically, what does the story seem to say about the way this particular character pursues this value?
For example: If you are reading a Jack London short story or novel, you know that the protagonist is going to be facing survival from nature. The value is life versus death. So to determine the theme we ask what does the story say about life vs death or survival?
In Jack London's short story “To Build a Fire,” an arrogant man trying to survive the Yukon wilderness makes a series of novice mistakes from traveling alone to getting wet with no way to get warm and dry. Spoiler alert, he dies.
What is the theme of this story? My students usually shout out something like, “Don't be a dummy and travel alone with no way to make a fire!” And they're not wrong. The ideas here are life, death, nature, and humanity. Here are a number of ways you could frame the theme with specific support from the story:
- Nature is indifferent to human suffering.
- Human arrogance leads to death.
- There are limits to self-reliance.
As you can see, the theme is what the story suggests about the story value.
Common themes in literature with examples
James Clear collected a list of the best-selling books of all time on his website . Let's start with some of those fiction titles.
Disclaimer: I know many of these summaries and themes are vastly oversimplified and most could be fleshed out in long, complicated papers and books. But for the sake of time, let's imagine my list as limited examples of theme among many that could be argued.
Disclaimer 2: I tried to get ChatGPT to help me write the one sentence summaries for these titles even though I've read all but two of the listed books. The summaries ChatGPT wrote were weak or too general for our purposes. So if there are errors below, they are all mine—I can't blame the bots today. Let's look at the list:
1. Don Quixote by Miguel de Cervantes (1605) summary: Aging nobleman Don Quixote deludes himself into thinking he's a knight and takes on a satirical quest to prove his honor by defending the helpless and defeating the wicked.
theme: Being born a nobleman (or any class) does not automatically determine your worth.
2. Tale of Two Cities by Charles Dickens (1859) summary: In this sprawling novel of swapped (or reconstructed) identities and class warfare during the French Revolution, characters navigate the nature of love, betrayal, justice, and the possibility of transformation.
theme: Transformation is possible for enlightened individuals and societies.
3. The Lord of the Rings by J.R.R. Tolkien (1954) summary: An unlikely hobbit and his diverse team set out to find and destroy a powerful ring to save Middle-earth and defeat the dark lord Sauron.
theme: Good can defeat evil when people (or creatures) are willing to sacrifice for the common good.
4. The Little Prince by Antoine de Saint-Exupery (1943) summary: A prince visits various planets and discovers the importance of curiosity and openness to emotion.
theme: The most important things in life can't be seen with the eyes but with the heart.
5. Harry Potter and the Sorcerer's Stone by J.K. Rowling (1997) summary: An unsuspecting orphan attends a wizard school where he discovers his true identity, a dark foe, and the belonging he craves.
theme: Love and friendship transcend time and space.
6. And Then There Were None by Agatha Christie (1939) summary: Seven guests gather at a house on an island where they are killed off one-by-one as they try to discover the murderer.
theme: Death is inevitable, justice is not.
7. The Dream of the Red Chamber by Cat Xueqin (1791) summary: In this complex family drama, a nobleman's son is born with a magic jade in his mouth, and he rebels against social norms and his father resulting in an attempted arranged wedding and illness rather than reinforce oppression.
theme: Social hierarchies maintained by oppression will eventually fall.
8. The Hobbit by J.R.R. Tolkien (1937) summary: Timid hobbit Bilbo Baggins is called by a wizard to help a band of dwarves reclaim their land from a terrible dragon, Smaug.
theme: Bravery can be found in the most unlikely places.
9. She: A History of Adventure by H. Rider Haggard (1886) summary: An professor and his ward seek out a lost kingdom in Africa to find a supernatural queen.
theme: Considering the imperialism of the time as well as worry about female empowerment, the themes here are varied and problematic, but perhaps one theme might resonate: Be careful what you seek, for you may find it.
10. The Lion, the Witch, and the Wardrobe by C.S. Lewis (1950) summary: Four children venture through a wardrobe into a magical kingdom where they must work together to save Narnia, meet Aslan, and defeat the White Witch.
theme: Evil is overwhelmingly tempting and can only be defeated through sacrifice.
11. The Catcher in the Rye by J.D. Salinger (1951) summary: An expelled prep school student, Holden Caulfield, has a number of coming-of-age misadventures on his way home for the holiday break.
theme: Innocence can only be protected from the risks of growing up for so long.
12. The Alchemist by Paolo Coelho (1988) summary: A Spanish shepherd named Santiago travels to Egypt searching for treasure he saw in a dream.
theme: Anyone can make the world better if we are willing and courageous.
13. One Hundred Years of Solitude by Gabriel Garcia Marquez (1967) summary: This circle of life novel covers seven generations of the Buendia family as they build a small dysfunctional utopia in a swamp amidst a changing political and social Latin American landscape.
theme: Solitude is an inevitability for humankind.
14. Anne of Green Gables by Lucy Maud Montgomery (1908) summary: An orphan finds her place with the Cuthbert siblings, and she brings her peculiar and delightful blend of imagination and optimism to their lives and community.
theme: Every human desires and deserves belonging.
15. Charlotte's Web by E.B. White (1952) summary: Wilbur the pig and his unconventional spider friend Charlotte join forces to save Wilbur's life from the slaughterhouse.
theme: Friendship can be found in the most unlikely places.
And let's throw in a few additional well-known stories and notable examples to see how their themes stack up:
16. Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare (1597) summary: Two teens from warring families fall in love and die rather than be kept apart from their families feud.
theme: Passion is costly.
17. Frankenstein by Mary Shelley (1818) summary: An ambitious scientist creates a monster without considering the larger implications. Chaos ensues.
theme: Knowledge can be dangerous when coupled with unbridled ambition.
18. Beloved by Toni Morrison (1987) summary: Formerly enslaved mother Sethe and her daugher Denver are haunted by the ghost of Sethe's oldest daughter who died when she was two-years-old.
theme: The physical and psychological effects of slavery are damaging and long-lasting.
19. Never Let Me Go by Kazuo Ishiguro (2005) summary: In this dystopian novel, people are cloned and held in preparation to be life-long organ donors for others.
theme: Freedom is a basic human desire.
20. Raisin in the Sun by Lorraine Hansberry (1959) summary: The Younger family grapples with identity and dreams in the wake of the death of their patriarch.
theme: Dignity and family are worth more than money.
The 5 most common themes in literature
You may have been asked to define universal themes as a part of a school assignment. Universal themes are those that transcend time and cultures, meaning they are often found to be true in real life no matter who you are or where you live.
Granted, I haven't read all the books across time and space (yet), but there's a pretty good bet that one of these major themes might apply to what you're reading regardless of time period, genre, or culture:
- Love conquers all.
- Things are not always what they seem.
- Good triumphs over evil.
- Beauty is in the eye of the beholder.
- Blood (family) is thicker than water.
Which other larger themes would you list here as some of the most common in literature? Share your theme examples in the comments .
Why theme matters for writers
Why do themes matter for writers though? After all, isn't it enough to write an entertaining story? It can be, but exploring universal themes can help take your work to the next level. You don't have to identify a theme for your story and write everything to that end—in fact that might work against you. But when done well, it can enhance your story.
Here are a few reasons you may want to think about theme in your writing:
1. Coherence
Theme can bring together the various parts of a story, including plot and subplot, characters, symbols, and motifs. Readers can feel the variations on a theme laced throughout your story and done well, it's engaging and satisfying.
If your theme is love conquers all, then you likely have two people who over come incredible odds to be together. What are the other elements that subtly underscore it? Maybe there's a house that was built with love in the setting or maybe a secondary character is failing at love because they keep putting their work first. If it's subtle, those small details reinforce the main storyline.
2. Significance
As we discussed, universal themes will resonate with readers, even when they haven't experienced the same events. Many of the works we've listed above are remembered and revered due in part to their lasting themes about human experience.
3. Expression
Theme is an opportunity to weave together your world view, experiences, perspective, and beliefs with artistic and creative possibilities. Theme serves as a unifying element as you express your vision. Try playing with theme in a story or other creative work to see how it pushes boundaries or got beyond the expected.
In summary, theme can serve as the backbone of a story, giving it structure, depth, and resonance. It can help convey the writer's intended message and engage readers on multiple levels, making it a crucial element of literary and creative expression.
Which other larger themes would you list as the most common in literature? Share your theme examples in the comments .
Set your timer for 15 minutes . Choose one of the common themes above and create a character who has strong beliefs about that theme. Now, write a scene where an event or person challenges that belief. How will the character react? Will they double-down and insist on their worldview? Or will they soften and consider alternatives? Will shock at the challenge plunge them into despair? Play with their reaction.
Once you've written for 15 minutes, post your practice in the Pro Practice Workshop and leave feedback for a few other writers.
Sue Weems is a writer, teacher, and traveler with an advanced degree in (mostly fictional) revenge. When she’s not rationalizing her love for parentheses (and dramatic asides), she follows a sailor around the globe with their four children, two dogs, and an impossibly tall stack of books to read. You can read more of her writing tips on her website .

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Best Resources for Writers Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Critique Report
- Writing Reports
- Learn Blog Grammar Guide Community Events FAQ
- Grammar Guide
200 Common Themes in Literature

By Sarah Oakley

Table of Contents
What is the theme of a story, common themes in literature, universal themes in literature, full list of themes in literature, theme examples in popular novels.
The theme of a novel is the main point of the story and what it’s really about. As a writer, it’s important to identify the theme of your story before you write it.
Themes are not unique to each novel because a theme addresses a common feeling or experience your readers can relate to. If you’re aware of what the common themes are, you’ll have a good idea of what your readers are expecting from your novel .
In this article, we’ll explain what a theme is, and we’ll explore common themes in literature.
The theme of a story is the underlying message or central idea the writer is trying to show through the actions of the main characters. A theme is usually something the reader can relate to, such as love, death, and power.
Your story can have more than one theme, as it might have core themes and minor themes that become more apparent later in the story. A romance novel can have the central theme of love, but the protagonist might have to overcome some self-esteem issues, which present the theme of identity.
Themes are great for adding conflict to your story because each theme presents different issues you could use to develop your characters. For example, a novel with the theme of survival will show the main character facing tough decisions about their own will to survive, potentially at the detriment of someone else they care about.
Sometimes a secondary character will represent the theme in the way they are characterized and the actions they take. Their role is to challenge the protagonist to learn what the story is trying to say about the theme. For example, in a novel about the fear of failure, the antagonist might be a rival in a competition who challenges the protagonist to overcome their fear so they can succeed against them.
It’s important to remember that a theme is not the same as a story’s moral message. A moral is a specific lesson you can teach your readers, whereas a story’s theme is an idea or concept your readers interpret in a way that relates to them.

Write like a bestselling author
Love writing? ProWritingAid will help you improve the style, strength, and clarity of your stories.
Common literary themes are concepts and central ideas that are relatable to most readers. Therefore, it’s a good idea to use a common theme if you want your novel to appeal to a wide range of readers.
Here’s our list of common themes in literature:
Love : the theme of love appears in novels within many genres, as it can discuss the love of people, pets, objects, and life. Love is a complex concept, so there are still unique takes on this theme being published every day.
Death/Grief : the theme of death can focus on the concept of mortality or how death affects people and how everyone processes grief in their own way.
Power : there are many books in the speculative fiction genres that focus on the theme of power. For example, a fantasy story could center on a ruling family and their internal problems and external pressures, which makes it difficult for them to stay in power.
Faith : the common theme of faith appears in stories where the events test a character’s resolve or beliefs. The character could be religious or the story could be about a character’s faith in their own ability to succeed.
Beauty : the theme of beauty is good for highlighting places where beauty is mostly overlooked by society, such as inner beauty or hard work that goes unnoticed. Some novels also use the theme of beauty to show how much we take beauty for granted.
Survival : we can see the theme of survival in many genres, such as horror, thriller, and dystopian, where the book is about characters who have to survive life-threatening situations.
Identity : there are so many novels that focus on the common theme of identity because it’s something that matters to a lot of readers. Everyone wants to know who they are and where they fit in the world.
Family : the theme of family is popular because families are ripe with opportunities for conflict. The theme of family affects everyone, whether they have one or not, so it’s a relatable theme to use in your story.

Universal themes are simply concepts and ideas that almost all cultures and countries can understand and interpret. Therefore, a universal theme is great for books that are published in several languages.
If you want to write a story you can export to readers all over the world, aim to use a universal theme. The common themes mentioned previously are all universal literary themes, but there are several more you could choose for your story.
Here are some more universal literary themes:
Human nature
Self-awareness
Coming of age
Not all themes are universal or common, but that shouldn’t put you off from using them. If you believe there is something to be said about a particular theme, your book could be the one to say it.
Your book could become popular if the theme of your book addresses a current issue. For example, a theme of art is not as common as love, but in a time when AI developments are making people talk about how AI affects art, it’s a theme people will probably appreciate.
Here’s a full list of themes you can use in your writing:
Abuse of power
American dream
Celebration
Change versus tradition
Chaos and order
Circle of life
Climate change
Colonialism
Common sense
Communication
Companionship
Conservation
Convention and rebellion
Darkness and light
Disappointment
Disillusionment
Displacement
Empowerment
Everlasting love
Forbidden love
Forgiveness
Fulfillment
Gay, lesbian, bisexual, and transgender rights
Good vs evil
Imagination
Immortality
Imperialism
Impossibility
Individuality
Inspiration
Manipulation
Materialism
Nationalism
Not giving up
Opportunity
Peer pressure
Perseverance
Personal development
Relationship
Self-discipline
Self-reliance
Self-preservation
Subjectivity
Surveillance
Totalitarianism
Unconditional love
Unrequited love
Unselfishness
Winning and losing
Working class struggles
If you’ve decided on a literary theme but you’re not sure how to present it in your novel, it’s a good idea to check out how other writers have incorporated it into their novels. We’ve found some examples of themes within popular novels that could help you get started.
The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald
The Great Gatsby is famous for the theme of the American dream, but it also includes themes of gender, race, social class, and identity. We experience the themes of the novel through the eyes of the narrator, Nick Carraway, who gradually loses his optimism for the American dream as the narrative progresses.
Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare
It’s well known that Shakespeare was a connoisseur of the theme of tragedy in his plays, and Romeo and Juliet certainly features tragedy. However, forbidden love and family are the main themes.
Charlotte’s Web by E. B. White
Charlotte’s Web is a classic children’s book that features the themes of death and mortality. From the beginning of the book, the main characters have to come to terms with their own mortality. Charlotte, the spider, does what she can to prevent the slaughter of Wilbur, the pig.
Nineteen Eighty-Four by George Orwell
George Orwell’s novel, Nineteen Eighty-Four , focuses on themes of totalitarianism, repression, censorship, and surveillance. The novel is famous for introducing the concept of Big Brother, which has become synonymous with the themes of surveillance and abuse of power.

A Game of Thrones by George R. R. Martin
The fantasy novel, A Game of Thrones , is popular for its complex storylines that present themes of family, power, love, and death. The novel has multiple points of view, which give an insight into how each main character experiences the multiple themes of the story.
The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins
The Hunger Games is a popular teen novel that focuses on themes of poverty, rebellion, survival, friendship, power, and social class. The novel highlights the horrifying consequences of rebellion, as the teenage competitors have to survive the Hunger Games pageant.
Wolf Hall by Hilary Mantel
Wolf Hall features themes of power, family, faith, and a sense of duty. It’s a historical novel about the life of Oliver Cromwell and how he became the most powerful minister in King Henry VIII’s council.
As you can see, the literary theme of a novel is one of the most important parts, as it gives the reader an instant understanding of what the story is about. Your readers will connect with your novel if you have a theme that is relatable to them.
Some themes are more popular than others, but some gain popularity based on events that are happening in the world. It’s important to consider how relevant your literary theme is to your readers at the time you intend to publish your book.
We hope this list of common themes in literature will help you with your novel writing.
Sarah Oakley
Get started with prowritingaid.
Drop us a line or let's stay in touch via :
Improve your writing in one of the largest and most successful writing groups online
Join our writing group!
25 Common Themes in Literature, with Examples

by Holly Riddle
Theme is one of those elements of literature that everyone pretends to understand, but that can be a little difficult to wrap your head around.
Theme is present in all mediums of artistic expression—short stories, poems, novels, plays, even visual art. If you ask a group of people what the theme of a particular work is, they might all give you different answers. Theme is personal, open to interpretation, and is what, in many ways, makes art meaningful.
Here’s everything you need to know about common themes in literature, including theme examples.
What is theme in literature?
In creative writing, theme is the core underlying idea or message that the writer wants to communicate to the reader. For example, “the power of social status,” “the destructive nature of love,” or “the fallibility of the human condition” are all common themes. Theme can be expressed through every element of a literary work , including plot , characters , and setting .
Your story’s central idea is what makes your work matter to your readers, and why storytelling has the power to affect real change.
Because most themes are fairly straightforward, they’re often considered universal. “Universal themes” refer to common themes in literature that most people can relate to, regardless of age, gender, or cultural background. For example, most people can understand the hope that comes with new love, or the importance of a strong family.

Beyond overarching major themes, a work may additionally contain smaller, different themes that apply only to certain relationships, specific characters, or particular scenes. You can use literary devices like symbolism and metaphor to help the reader understand these themes on a deeper level.
For example, a story’s theme might be the importance of family, but one character’s arc might also explore the theme of tradition vs. independence.
Remember that literary theme can also be very personal. Even when an author approaches a story with a specific theme in mind, readers may interpret it differently depending on what they need or what they’re experiencing in that moment. Because themes are universal, they allow us to interpret them in ways that are most relevant to our own lived experience.
Common themes in literature
Let’s explore themes found in some of the most recognizable works of literature. In these well known examples, you’ll see how each writer explores popular themes that resonate with the human spirit.
1. Good versus evil
One of the most pervasive themes in literature, the good versus evil theme pits a good character against an evil character in a classic battle of moral dilemmas.
It’s not always a living character , though, that’s the evil or good one. This theme can use any clearly good or bad force , but the message is always the same—good and evil cannot coexist and there will always be a war between the two.
The Harry Potter series by J.K. Rowling
In each book of this bestselling series, the work’s theme is consistent—Harry and his friends are up against the evil forces actively launching attacks against the good and innocent. This theme is unquestionable due to the way Rowling uses the story’s key conflicts to juxtapose the “good” characters in her story against the “bad” characters in her story.
In this world, the good is very, very good and the bad is very, very bad.
2. Forbidden love
Forbidden love happens when two people are in love, but shouldn’t be.
It might be someone like a parent that verbally forbids the two individuals from being together, but it can also be society, class structure, or other forces that “forbid” the relationship.

Romeo and Juliet by William Shakespeare
The pervasive theme of forbidden love is most notably found in Shakespeare’s Romeo and Juliet . In the play, every single decision that our titular characters make is connected to their forbidden love. Without the forbidden love, there would be no story.
In Romeo and Juliet , love is both destructive and healing. The love ultimately leads to the tragic undoing of the protagonists, but it also heals the rift between their families.
3. Fated love
Fated love is very similar and this theme can be applied to Romeo and Juliet as well, as one might argue that the two were fated to be with one another regardless of the circumstances. Within works that display this theme, the couple is always drawn back together, even though the odds are seemingly impossible.
Outlander by Diana Gabaldon
Diana Gabaldon’s Outlander displays a theme of fated love, with the two main characters of the series, Jamie and Claire, always making their way back to one another and getting their happily ever after, regardless of the circumstances.
This couple is up against some serious odds. In some instances, they’re literally separated by hundreds of years of time, and only one of them can time travel (and the time travel isn’t exactly reliable). In other instances, they’re separated by oceans, and the threats against their happily ever after range from nefarious villains to illness to politics.
4. Sacrificial love
The sacrificial love theme makes the argument that true love always requires a sacrifice. In order to be happy and in order to give your true love happiness, you must make some sort of sacrificial offering, whether large or small.
“The Gift of the Magi” by O. Henry
This classic short story published in the early 1900s is a Christmas-set story that follows a young married couple. The two are relatively poor, but still want to give one another a nice Christmas, and so they each, in secret, sell the two things dearest to them in order to buy something for the other person.
However (spoiler!), they eventually discover that, in doing so, they’ve ruined the other’s present. Despite this ironic ending, there’s a happily ever after and the general idea that this is a couple that will do whatever it takes to guarantee each other’s happiness in life.
5. Unrequited love
In this theme, it’s a tragic one-sided love that drives the plot. One person loves another, but those feelings are not returned—which often leads to a series of decisions that set the broader story in motion.
A great example of the unrequited love theme can be found in Great Expectations by Charles Dickens.
Great Expectations by Charles Dickens
Great Expectations contains multiple themes, and one of those is unrequited love. There are several characters that experience this within the book, and while the protagonist Pip, does fall in love, the majority of the book’s plot hinges on the broken heart of the secondary character Miss Havisham.
6. Coming of age
As one of the most universal human experiences, the coming-of-age literary theme centers around a character who is growing up in some manner. Sometimes, they’re literally growing from a child into an adult.
Other times they may already be an adult, and are just growing into the next stage of their life and maturing in some way. This common theme explores self discovery, change, and growth, ultimately leading to a character’s inner metamorphosis.
A coming-of-age story always shows how the protagonist overcomes internal conflict, so careful attention to characters’ personal development is critical when writing about this literary theme.
Jane Eyre by Charlotte Brontë
Jane Eyre is one of those classic coming-of-age stories, following Jane’s life from childhood to her eventual marriage. However, Jane doesn’t just grow physically over the course of the story. She also grows emotionally and internally as she discovers her own self-worth, confidence, and independence.
7. Righteous justice
In stories about justice, you have a character who’s entirely driven by getting the justice they think they deserve. In the righteous justice theme, most readers can agree that the character in question is in the right and feel a sense of satisfaction when (if) the character obtains it.

To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee
To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee is a coming-of-age novel that also features a strong justice theme, as it follows the main character’s father’s quest for justice in the face of a broken, racist system and community.
8. Unrighteous justice
In stories about themes of unrighteous justice, also sometimes called the revenge theme, the character intent on getting their due is either inarguably in the wrong, or they’re going after their justice or revenge in a morally questionable manner.
The character Heathcliff in Wuthering Heights is one example of a character that’s intent on getting their justice, but his behavior as he pursues this justice is often cruel.
Wuthering Heights by Emily Brontë
Wuthering Heights certainly has its love themes, but it also can be considered a justice novel. Heathcliff demands the retribution he feels he deserves after his true love marries another person. He begins enacting a long plot to get his revenge, hurting everyone around him, including himself, in the process.
9. Corruption
The corruption theme shows how an external influence changes a character over the course of a story, and serves as a warning to the reader that they, too, could become corrupted if they’re not self aware.
Lord of the Flies by William Golding
In Lord of the Flies , a group of boys find themselves alone, self-governing on an island, where chaos and violence quickly ensue. Although it’s written as a boys’ adventure story, it has a deeper meaning: the story shows how humans, when given enough free rein and their own power, are apt to turn evil.
10. The American dream
Independence, wealth, the nuclear family. The American Dream is hyped up to an extreme degree, and often literary works that use this theme attempt to reveal the complexity behind the whitewashed exterior.
This main idea will most resonate with Americans, but the contrast of expectation and reality can exist anywhere.
The Great Gatsby by F. Scott Fitzgerald
One of the most notable examples of a literary work with this central theme is the jazz-age novel The Great Gatsby .
The titular character has seemingly everything he could want, as do all of his friends around him, living a life of extravagant wealth and freedom. However, our narrator—who is not quite so fortunate in life—reveals that these characters are, in many ways, as emotionally bankrupt as they are physically rich… which leads to their lives falling apart.
11. The circle of life
There are several types of literary themes that deal with life and death, or mortality, and for good reason. Mortality is the one thing that every single human being has in common. As such, these mortality-related themes ask (always) and answer (sometimes) big questions, like, how do humans respond to death? Why do we respond the way we do? What does trying to run from our own mortality do? What’s the purpose of death?
The circle of life theme in particular often paints the inevitability of death in a positive or neutral manner. While death is inescapable, it’s not something to be feared and part of the natural process.
Charlotte’s Web by E.B. White
In Charlotte’s Web , death is presented as a natural part of living. The story begins and ends with death, with Wilbur escaping death at the start of the book, kicking off a series of events that all ends up leading to the death of the spider Charlotte.

12. The inevitability of death
In this theme, the take on mortality is often one that strikes fear and anxiety. Death is an all-powerful, antagonistic force that the characters spend most of their time trying to avoid at all costs, often going to great lengths to escape death’s clutches.
The Picture of Dorian Gray by Oscar Wilde
In this classic example , Dorian spends all his efforts attempting to escape death and aging, going to extreme lengths. But even then, he can’t escape his ultimate fate.
13. Family dynamics
Family themes in literature often ask readers to look beyond blood ties and to analyze what the true meaning of family is. Characters may lose their biological family in some manner and then discover a new one, either with another literal blood family or with a group of friends. Or, a character’s biological family may become threatened in some way.
Whatever the case may be, a family unit is always a prominent part of the story and guides the plot points and conflict. Interpersonal relationships and character development should be at the forefront for anyone writing a story with these recurring themes.
In the family dynamics theme, the story examines how family members interact with one another, and how those dynamics are capable of driving a plot.
Anna Karenina by Leo Tolstoy
Anna Karenina deals with family complexities and looks at three different families that are all experiencing different degrees of success in their interpersonal relationships. This book shows how the family theme doesn’t always need to trend positive.
14. The power of family
In contrast to the above example, the power of family theme is always positive. These stories show how family is a powerful force that can help a character overcome challenges, both internal and external.
Little Women by Louisa May Alcott
In Little Women , the story reaches its happy ending all because the main characters rely on one another and their family unit, supporting each other through times of hardship.
Think of the hubris theme as the central character saying, “I’m great, am smarter than everyone else, and will do whatever I want because of it.” One of the most tragic themes in literature, this theme is designed to teach the reader a lesson about the limitations of human nature.
In books with this underlying focus, you’ll always have a character who plows forward into whatever they think is best, to disastrous consequences—because, of course, pride always comes before the fall.
Frankenstein by Mary Shelley
A well-known example is Frankenstein , in which Victor Frankenstein feels he can channel the power of God by creating life. When his little experiment goes awry, he digs his heels in and continues to think of himself as blameless and worthy of admiration—which ends up being his downfall.

Faith might refer to religious belief, or a belief in another spiritual entity, people around them, a political system, or a culture. A character might lose their faith, or develop a new one.
The Poisonwood Bible by Barbara Kingsolver
The Poisonwood Bible explores the great lengths we’ll go to when we have faith in something, and what happens when we lose it. A family follows their missionary father to Africa, where he intends to convert the locals and blindly digs in his heels at every challenge. However, as the challenges increase, his family begins losing their faith in both his message and him.
17. Fate vs. Free will
Are you really in control of your own actions? Or has fate determined the course of your life? Those are the questions that these stories ask, and they can be answered in limitless ways.
Oedipus Rex by Sophocles
The Greek tragedy Oedipus Rex explores what happens when you try to outwit fate. Oedipus gets into his horrible situation (marrying his mother and murdering his father) because he tried to outrun his destiny, which only brought him closer to it.
18. Self-identity
Most of us have an idea of who we are or, if we don’t, it’s a question we’re trying to figure out. Since this is such a universal experience, it should come as no surprise that this is also a theme you’ll see in a range of literature and other art mediums.
The self-identity theme follows a character who is asking: Who am I?
Jane Eyre is a coming-of-age novel that also explores the theme of self-identity. These themes often overlap because coming of age is about discovering ourselves. Jane, through the various difficulties and challenges she faces over her life, learns who she is and isn’t, who she wants to be, and how to be it.
19. Isolation
Extended isolation can do a lot to a person. Being removed from other humans can impact our mental health and cause us to think or act in ways we might not normally. In some instances, we may feel more free to act like our true selves. In others, we might behave rather poorly. The isolation theme explores these possibilities.
“The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman
In this classic short story , we see how isolation impacts our protagonist in a negative manner. The main character is isolated at home, in a single room, and eventually that isolation drives her to madness. As a result, the story brings up questions regarding mental health, gender, and domesticity, and how isolation interplays with all three.
20. The power of nature
In this theme, it’s typically the case that your hero is up against the power of nature in some way.

Nature may serve as the antagonist within the story. If not the story’s central conflict , nature may play a role in moving the plot along, forcing your character to make decisions that they might not otherwise. Nature is all-powerful and your characters are powerless in contrast.
This is not to say that a power of nature-themed book or story always has an unhappy ending. Sometimes, characters learn to live with nature, adapt to it and survive—but nature always wins.
Hatchet by Gary Paulsen
This classic childhood favorite about a boy who survives a plane crash and finds himself stranded in the wilderness is a good example of how a “power of nature” story can provide plenty of conflict without ending unhappily. Over the course of the story, the protagonist must overcome various challenges within his natural surroundings, but he eventually learns to overcome and survive.
21. The influence of the mob
Similarly to the power of nature theme, the mob mentality theme forces characters to face group dynamics that pose a large-scale problem. Maybe the social order is a threat to a character’s life. Maybe the social order is harming everyone around them, but other characters are just too blind to see it.
The message in these stories is that, under the right circumstances, a group or society’s strength can become too powerful for the group’s own good. Man becomes corrupted and that corruption is even stronger when it pervades an entire group.
“The Lottery” by Shirley Jackson
“ The Lottery ” says quite a lot about the universal human condition, and maybe that’s why so many first readers of this early horror story found it to be so disturbing. One of its main themes is how a group of people can become so blind to their own problems that there are fatal consequences.
22. Self destruction
This theme explores another relatable universal truth—sometimes, you’re just your own worst enemy. Sometimes, all of the problems around you, all of the worst things happening to you, can all be traced back to you and you alone.
Stories with these literary themes can be tragic, or they can be learning experiences.
Emma by Jane Austen
While this classic novel is a lighthearted romantic tale following our titular character’s matchmaking mishaps, Emma soon learns that all of her problems are her own fault. She has to do some soul searching before her problems can be solved and before the book can come to a satisfying conclusion.
23. Survival
The survival theme intersects with many other popular themes on our list. For example, you might have a survival theme story that’s also a power of nature story or a power of the group story. In these stories, your main characters are fighting for survival throughout the course of the book, and that continued survival is the entire focus of the plot.
The Hunger Games by Suzanne Collins
In this popular young adult novel, our main character Katniss spends nearly the entirety of the book trying to ensure her own survival, as well as the survival of those she cares about. The book also weaves in other themes, such as mob mentality and corruption, as Katniss wouldn’t need to be so focused on her own survival if her society hadn’t become so corrupt.
24. Heroism
In the heroism theme, our story’s hero is courageous, they make sacrifices, they’re saving someone or something. The heroism theme shows that sometimes life calls you to discover extraordinary strength in order to save something worth fighting for.

The Lord of the Rings series by J. R. R. Tolkien
In this book and series, as well as in many high fantasy books , a large number of characters act as heroes. They bravely walk into dangerous situations to fight for what they feel is right.
25. Redemption
The redemption theme is a hopeful one that shows how, even when our main characters behave poorly, there is often always a chance of redemption. These stories might follow a character seeking redemption throughout the entire plot, or it might follow a character’s downfall before their chance at redemption in the end.
Atonement by Ian McEwan
Atonement is often considered a coming-of-age story, but, as the title suggests, it also offer a redemptive literary theme. One of the main characters makes a tragic mistake as a child and then spends the rest of their life dealing with the fallout of that mistake, trying to find redemption in their old age.
What’s your story’s literary theme?
When it comes to theme in your fiction writing, your options are near-endless. There will always be an abundance of central ideas, experiences, and emotions that remain universal throughout time and across cultures.
The next time you pick up a novel or a book of short stories, pay special attention to the major themes and how the author weaves their message into each plot point. They can help you learn how to apply story elements like character development or conflict to create and enforce that underlying message.
What’s the theme of your current work in progress or the last thing you wrote? Can you amplify it with some attention to detail?
Once a theme emerges from your plot, taking care to weave that theme into every aspect of your work will result in a story that’s more impactful and universally appealing.
Get feedback on your writing today!
Scribophile is a community of hundreds of thousands of writers from all over the world. Meet beta readers, get feedback on your writing, and become a better writer!
Join now for free

Related articles

What is Theme? Definition & Examples of Theme in Literature

Plot-Driven vs. Character-Driven Stories: What’s the Difference?

Literary Elements: What are the 7 Elements of Literature?

What is Pacing in a Narrative? Pacing Definition

What is Mood in Literature? Mood Definition and Examples

What is Setting in a Story? With 5 Evocative Examples of Setting
How to Write a Thematic Essay

A thematic essay explores a central message or theme that runs through a piece of literature, a historical event, or even a societal trend. It analyzes evidence like characters' actions, plot development, or real-world examples to explain how this matter is revealed and unpack its significance, showing a deeper understanding of the subject at hand.
Here’s a quick breakdown of what is a thematic essay :
- Analyzes a central message (theme) in a text.
- Explains how the text explores that theme.
- Uses evidence (quotes, details) to support your analysis.
- Shows how the evidence connects to the overall theme.
If you’re having trouble with this type of assignment, feel free to use our paper writing service and streamline the process.
Dissecting a text's central message and how it unfolds can be a rewarding challenge. Here's a step-by-step breakdown to conquer your next thematic essay:
| 🔢 Step | 📝 Description |
|---|---|
| 1. Decipher the Prompt | Carefully read the prompt. Identify the specific text and theme you'll be analyzing. |
| 2. Brainstorm & Unpack the Theme | Jot down ideas related to the theme. What message does the text convey? |
| 3. Craft Your Thesis Statement | Formulate a clear, concise statement that unveils how the text explores the theme. |
| 4. Gather Evidence | Hunt for quotes, details, and examples from the text that illustrate the theme. |
| 5. Build Your Outline | Structure your essay with an introduction, body paragraphs (each focusing on a specific point related to the theme), and a conclusion. |
| 6. Write a Compelling Introduction | Grab the reader's attention with a hook, introduce the text and theme, and present your thesis statement. |
| 7. Construct Strong Body Paragraphs | Each paragraph should focus on one point related to the theme. Use evidence from the text (quotes, examples) to support your analysis. Explain how the evidence connects to your thesis statement. |
| 8. Craft a Cohesive Conclusion | Summarize your main points, restate your thesis in a new way, and leave the reader with a final thought. |
| 9. Proofread & Revise | Polish your essay by checking for grammar mistakes, clarity, and ensuring smooth transitions between paragraphs. |
If you're seeking 'someone to do my homework fast' – contact us without hesitation!
Thematic Essay Checklist
- State a focused main argument about the theme.
- Hook the reader and introduce the theme.
- Begin each with a clear topic sentence related to the theme.
- Use specific examples, quotes, or facts.
- Explain how the evidence supports the thesis.
- Link analysis back to the central theme throughout.
- Ensure paragraphs and ideas progress logically.
- Summarize key points and restate the thesis.
- Check for clarity, coherence, and grammar.
- Properly cite sources used.
How to Pick a Thematic Topic
A crucial aspect of writing a good thematic essay is choosing a theme. Follow the hints listed below to help you create a thematic topic:
| 💡Brainstorming Tips | 📝Description |
|---|---|
| 🧠Brainstorm From Your Own Experiences. | Recall what you were talking about in class, with your mates or parents. Do some of these conversations remind you of some book, novel or another piece of literature? |
| 💡Write Down Every Idea That Comes to Mind. | Sometimes, your most absurd ideas are the best way to go. |
| 📚List Your Favorite Literature Pieces. | Which literature piece was the most touching for you? Try to analyze the subject and problems the author built upon within the story; it might help you come up with your own ideas. |
| 🔍Look at the Details of Other Literature Pieces. | You might find some interesting details within other literature that can help you develop your theme. |
Thematic Essay Topics
- Star-Crossed Fate: Destiny in "Romeo and Juliet"
- Gatsby's Illusion: The Mirage of the American Dream
- Thoreau's Call to Action: Civil Disobedience and Its Echoes
- Grit and Grind: Industrial Strife in "Hard Times"
- Monster or Man? Isolation in "Frankenstein"
- Voices of Change: The Civil Rights Movement Unveiled
- Big Brother's Watch: Propaganda in "1984"
- Silent Scars: The Aftermath of War in "All Quiet on the Western Front"
- Pride, Prejudice, and Power: Women in Austen's World
- Cultural Cracks: Colonialism in "Things Fall Apart"
- Echoes of Justice: Moral Struggles in "To Kill a Mockingbird"
- Surviving Hard Times: Life During the Great Depression
- Invisible Chains: Identity in "Invisible Man"
- Worlds Apart: Control and Conformity in "Brave New World"
- Chains of Oppression: Freedom in "Uncle Tom's Cabin"
- Hester's Burden: Sin and Redemption in "The Scarlet Letter"
- Wired Society: The Tech Revolution's Impact
- Vengeance and Virtue: The Journey in "The Count of Monte Cristo"
- Island Power Struggles: Leadership in "Lord of the Flies"
- Dreams of Freedom: Martin Luther King Jr.'s Enduring Impact
How to Start a Thematic Essay
Every strong essay starts with a captivating introduction. For a thematic essay, this introduction should:
- Hook the reader: Grab their attention with a thought-provoking question, a relevant quote, or an interesting anecdote related to the theme.
- Introduce the topic: Briefly mention the literary work you'll be analyzing.
- State the theme: Clearly identify the central theme you'll be exploring.
- Preview the analysis: Briefly hint at how the theme is developed in the work.
| 🔍Part of Introduction | 📝Explanation | 📖Example |
|---|---|---|
| 🎣Hook | Grab attention with a question, quote, or anecdote | "Is revenge ever truly justified?" |
| 📚Introduce Topic | Briefly mention the literary work | "...in William Shakespeare's play Hamlet..." |
| 🎭State Theme | Identify the central theme | "...the play explores the theme of betrayal and its devastating consequences..." |
| 🔍Preview Analysis | Briefly hint at how the theme is developed | "...through the actions of Hamlet, Claudius, and other characters..." |
Here's an example of a thematic essay introduction:
“Have you ever wondered why some stories keep coming back to the idea of forgiveness? In Harper Lee's classic novel To Kill a Mockingbird , the seemingly simple town of Maycomb grapples with racial injustice. However, beneath the surface lies a powerful exploration of the theme of forgiveness, where characters must confront their own prejudices and learn to let go of resentment. This essay will analyze how Lee uses character interactions, symbolism, and the trial of Tom Robinson to demonstrate the transformative power of forgiveness.”
Feeling difficult to write a thematic essay? Leave us notice, and our persuasive essay writer we'll help.
Let our custom essay writing service do all the work for you. Check out our price calculator to estimate the cost of your assignment.
Thematic Essay Outline
A thematic essay structure has several key components. Primarily, it should be five paragraphs or more, depending on the depth of the theme. Next, it should have a concrete thesis statement, which is the thematic statement that comes from the main subject.
The introduction presents the reader with the subject and the thesis statement. The body paragraphs each discuss one literary element or more to defend the validity of your thesis, all the while providing many supporting details from the text itself.
Lastly, the thematic essay conclusion summarizes the main points presented and finishes off with a statement of significance.
Learn more: How to create a winning outline .

Introduction
The thematic essay introduction presents the main subject of discussion captivatingly. The first sentence of the intro should be a hook statement that makes some intriguing claims about the subject of discussion. If done correctly, this will grab your reader's attention.
Then, provide any necessary background information from the literature to help the audience understand your claims later. Lastly, put together a well-thought-out thesis statement that reflects the novel's central theme.
Body Paragraphs
The body paragraphs follow a thematic essay format. Since each body paragraph’s purpose should be to present a literary device as evidence, the topic sentence should introduce the claim and gateway into the evidence. Every topic sentence must mention a literary device and its relationship to the literature.
Afterward, to validate your claim, use examples from the book that strengthen the reasoning of your statement. These can be actions from the plot or quotations parallel with the central theme. Explaining how the action/quote links back to your thesis statement is imperative, as it shows that you can support your logic.
Remember : Each claim must use a literary device. It can not just be a random moment or inference. Thematic essays are all about proving thesis statements through critical literary devices.
The thematic essay conclusion has three main objectives before wrapping up the paper. It should not present any new information or facts but summarize the information already given. First of all, restate your thesis statement in a new way.
Then, summarize the central claims you made within the body of your paper and their influence on the thesis statement. To finish off the entire work, present an overall concluding statement with a global analysis of the subject. Leave your reader with another hook, making him/her interested in digging deeper into the topic.
Learn more: Poetry analysis essay .
Try also read an article on poetry analysis essay , it could be useful and can give you new insights.
Thematic Essay Example
The best way to familiarize yourself with this type of writing is to learn from thematic essay examples.
Wrap Things Up
Thematic essays are a powerful tool for students. They unlock deeper meaning in texts, sharpen critical thinking and analytical skills, and build strong writing foundations.
Before submitting your thematic essay, cross off all these items from the to-do list.
Learn more: Jem Finch character traits .
Need Help with a Thematic Essay?
Understanding the central themes of literary works is quite hard, so let our writers show you how it’s done!
If you're thinking, ' I need help with my homework fast' – contact us without hesitation!
Got Little Time Left Until Submission?
Use our service to obtain a first-class thematic essay overnight.
What Is a Thematic Essay?
How to write a thematic essay, what is the main point of a thematic essay.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

- Updated writing steps.
- Added new topics.
- Added a new example.
- Added a checklist.
- https://www.wboro.org/cms/lib/NY01914047/Centricity/Domain/1006/Thematic%20Essays%20Helpful%20Hints.pdf
- Thematic Essay - Regents Exam Rubric | New Visions - Social Studies. (n.d.). New Visions - Social Studies. https://curriculum.newvisions.org/social-studies/resources/resource/thematic-essay-regents-exam-rubric/
- How to Structure Your Essay Introduction | Essay Writing Part 2. (2023, October 31). Matrix Education. https://www.matrix.edu.au/essay-writing-guide/how-to-structure-your-essay-introduction/
.webp)
- Literary Terms
- Definition & Examples
- When & How to Use Themes
I. What is Theme?
One of the first questions to ask upon hearing someone has written a story is, “What’s it about?” or “What’s the point?” Short answers may range from love to betrayal or from the coming of age to the haziness of memory. The central idea, topic, or point of a story, essay, or narrative is its theme .
II. Examples of Theme
A man, fueled by an urge for power and control due to his own pride, builds a supercomputer. That supercomputer then takes over the world, causing chaos and struggle galore.
This sci-fi style story contains many common themes. A few of its themes include:
- Danger of excessive pride
- The risky relationship between humankind and developing technology
A boy and a girl fall in love. The boy is forced to join the army and fights to survive in a war-torn country as his beloved waits at home. When he returns from war, the two are united and married.
The love story also has many common themes in literature:
- The power of true love
- Fate, which sometimes tears lovers apart and then joins them together
As can be seen from these examples, themes can range widely from ideas, as large as love and war, to others as specific as the relationship between humankind and technology.
III. Types of Theme
Just as a life is not constantly immersed in love, the pursuit of knowledge, or the struggle of the individual versus society, themes are not always constantly present in a story or composition. Rather, they weave in and out, can disappear entirely, or appear surprisingly mid-read. This is because there are two types of themes: major and minor themes.
a. Major Themes
Major themes are, just as they sound, the more important and enduring themes of the narrative. Major themes are the most significant themes of the story, and often they are a part of the entire story. A book on war would have the major theme of war’s effect on humanity, whereas a romance novel would have the major theme of love.
b. Minor Themes
Minor themes are, on the other hand, less important and less enduring. They may appear for part of the narrative only to be replaced by another minor theme later in the narrative. They provide discussion points for a chapter or two, but do not color the entire story. A book on war may have minor themes such as the home front’s reaction to war or the political aspects of war. A romance novel may have minor themes such as flirtation, marriage, and fidelity.
IV. The Importance of Using Theme
The importance of using theme in narrative is unparalleled. The theme is the underlining idea an author is trying to convey to an audience. A story without major ideas for the character and reader to experience, think through, and learn from is not a story at all. A story, by its very nature, must have a theme, sometimes many major and minor themes, all throughout. Themes are the ideas book clubs, poets, playwrights, literature students, film enthusiasts, movie-makers, and creative writers mull over in-depth. They are the meaning behind the entire story, the deeper reasons that the story has been written and shared.
V. Examples of Theme in Literature
Theme is a prominent element in literature. Here are a few examples of theme in poetry and prose:
“i carry your heart with me(i carry it in)” by E. E. Cummings:
i carry your heart with me(i carry it in my heart)i am never without it(anywhere i go you go,my dear;and whatever is done by only me is your doing,my darling) i fear no fate(for you are my fate,my sweet)i want no world(for beautiful you are my world,my true) and it’s you are whatever a moon has always meant and whatever a sun will always sing is you here is the deepest secret nobody knows (here is the root of the root and the bud of the bud and the sky of the sky of a tree called life;which grows higher than soul can hope or mind can hide) and this is the wonder that’s keeping the stars apart i carry your heart(i carry it in my heart)
This poem’s major theme is clear: love. Minor themes include fate, togetherness, and desire.
Atonement by Ian McEwan is an example of a novel whose theme is its title. Here are a few revealing excerpts:
How can a novelist achieve atonement when, with her absolute power of deciding outcomes, she is also God? There is no one, no entity or higher form that she can appeal to, or be reconciled with, or that can forgive There is nothing outside her. In her imagination she has set the limits and the terms. No atonement for God, or novelists, even if they are atheists. It was always an impossible task, and that was precisely the point. The attempt was all.
This section reveals the main theme of atonement along with other minor themes such as the life of the writer and forgiveness.
VI. Examples of Theme in Pop Culture
Just as literary narratives require themes, songs, movies, and television shows do as well. Here are a few examples of theme in pop culture:
![theme examples in essays Godzilla - Official Main Trailer [HD]](https://i.ytimg.com/vi/vIu85WQTPRc/0.jpg)
The trailer shows that the main theme of Godzilla is nature, as a powerful and destructive force to be reckoned with. Other themes include the human effect on nature, fear of the unknown, and hubris.
Alexander and the Terrible, Horrible, No Good, Very Bad Day

The main theme of this movie is positivity in the face of a bad day, as they happen to all of us. Other themes include family, perseverance, and love.
VII. Related Terms
Because themes encompass main ideas in a narrative, they have many similar elements which do similar things for a narrative. Here are a few examples:
“And the moral of the story is…” As many fables and tales go, morals are a necessary element. They are the main message or lesson to be learned from reading a cautionary story. Although themes and morals are both major ideas in a story, they are different in that themes do not necessarily serve to teach a lesson, whereas morals always do. A theme is simply an idea to be examined, whereas a moral is a clear lesson to be learned. Here is an example of theme versus moral:
Love others the way you would like to be loved.
Whereas the theme is simply an idea, the moral is a message and instruction.
Motifs work in a story to emphasize the theme, and for this reason, is sometimes confused with the theme. Motifs are recurring images, objects, or ideas that highlight the theme. Here is one example of how motif works with theme:
A man is struggling with regret throughout a story. Motifs like dark dreams, repetitive thoughts, and dark lighting emphasize the mood and pervasiveness of the regret.
Whereas the theme is a larger idea, the motifs are smaller elements of a story which repeat in order to reflect that idea.
VIII. In Closing
Themes are the ideas that run through narratives, enlivening them with deeper meaning to be found in real life and fiction alike. They create stories that are not dull but compelling and emotional.
List of Terms
- Alliteration
- Amplification
- Anachronism
- Anthropomorphism
- Antonomasia
- APA Citation
- Aposiopesis
- Autobiography
- Bildungsroman
- Characterization
- Circumlocution
- Cliffhanger
- Comic Relief
- Connotation
- Deus ex machina
- Deuteragonist
- Doppelganger
- Double Entendre
- Dramatic irony
- Equivocation
- Extended Metaphor
- Figures of Speech
- Flash-forward
- Foreshadowing
- Intertextuality
- Juxtaposition
- Literary Device
- Malapropism
- Onomatopoeia
- Parallelism
- Pathetic Fallacy
- Personification
- Point of View
- Polysyndeton
- Protagonist
- Red Herring
- Rhetorical Device
- Rhetorical Question
- Science Fiction
- Self-Fulfilling Prophecy
- Synesthesia
- Turning Point
- Understatement
- Urban Legend
- Verisimilitude
- Essay Guide
- Cite This Website
TRY OUR FREE APP
Write your book in Reedsy Studio. Try the beloved writing app for free today.
Craft your masterpiece in Reedsy Studio
Plan, write, edit, and format your book in our free app made for authors.

Guides • Perfecting your Craft
Posted on Jun 30, 2021
12 Common Themes in Literature Everyone Must Know
About the author.
Reedsy's editorial team is a diverse group of industry experts devoted to helping authors write and publish beautiful books.
About Martin Cavannagh
Head of Content at Reedsy, Martin has spent over eight years helping writers turn their ambitions into reality. As a voice in the indie publishing space, he has written for a number of outlets and spoken at conferences, including the 2024 Writers Summit at the London Book Fair.
By nature, literary themes are broad and universal. It’s no wonder, then, that certain themes come up again and again across the spectrum of literature, from novels and short stories to poetry and different types of nonfiction . That’s not to say that works which share a common theme tackle it in the same way — indeed, the beauty of themes in literature is that they can be approached from multiple perspectives that offer different thematic statements (in other words opinions on said themes).
Here, we’ll be focusing on broader thematic concepts, with some examples of how themes are being used. Whether you’re looking to identify common themes or searching for the right kind of inspiration for your next writing project, this list is just what you need.

Like you might see anytime you turn on the news, power (or the desire for it) makes people do crazy things. This is naturally reflected in fiction. From dystopias (Suzanne Collins’s The Hunger Games trilogy, for example) to fantasy (like that other famous trilogy The Lord of the Rings , or that little-known series by George R. R. Martin called A Song of Ice and Fire ) and classics like George Orwell’s Animal Farm , the concept of power has fueled countless literary projects. Sometimes the focus is power’s corruptive abilities, sometimes it’s the exchange of power between oppressive states and individuals, sometimes it’s simply the power of dreams. Regardless, the element of power remains central.
Got your power dynamics sorted but not sure how to structure your story? Download our free template on book development.

FREE RESOURCE
Get our Book Development Template
Use this template to go from a vague idea to a solid plan for a first draft.

Family relationships and dynamics make for the most interesting and complex sources of conflict in literature. From intergenerational epics like Min Jin Lee’s Pachinko and Gabriel García Márquez’s 100 Years of Solitude to contemporary novels like Karen Joy Fowler’s We Are All Completely Beside Ourselves , books have always asked what the meaning of a family is, and will continue to highlight both the dysfunctional and wholesome relationships within them.

FREE COURSE
How to Write a Novel
Author and ghostwriter Tom Bromley will guide you from page 1 to the finish line.
3. Identity

Questions of identity and the labels that come with them are powerful animating forces in much of literature. From representing one’s ethnic or racial identity (Brit Bennet’s The Vanishing Half and Jhumpa Lahiri’s The Namesake , for example) to gender identity (e.g. George by Alex Gino) and mental health diagnoses like in Sylvia Plath’s The Bell Jar , who we are is one of the fundamental questions we must face. For some writers, literature is a place to try and answer that question for themselves or the group they identify with; for others, it’s a place to dismiss the need for labels and embrace a self that exists at the intersections of various groups. This is also a theme connected to the way society impacts the way we perceive ourselves and others.
🏳️🌈 Check out some more book recommendations about queer identity over on our list of the best LGBT books !
4. Loneliness

Is there anything more writerly (or typically associated with writerliness, anyway) than the image of a lone, isolated scribe visible inside a lit window at night, typing away into the dark? Or (let’s face it) the loner in school, symbol of misfits all over? From the famous alienated high schoolers in The Perks of Being a Wallflower and Catcher in the Rye to more recent bestsellers like Eleanor Oliphant is Completely Fine , there’s no shortage of loners, isolated misfits, or content-to-be-alone introverts in literature. Whether the theme is used to show that human nature is inherently lonely, to criticize dependence, or to argue that loneliness is a societal privilege ( A Room of One’s Own -style), these are stories that never fail to be deeply affecting.
5. Friendship

Friends, it’s often said, are the family we choose for ourselves — and the bonds we have with them are just as complex, potentially tense, or heart-warming as familial bonds. Childhood friends are often at the heart of children’s classics like The Secret Garden or Charlotte’s Web . In books for young readers, friendship is commonly praised for its selflessness and camaraderie. It remains a common theme for books that deal with young adulthood, coming-of-age narratives, and even later life, as titles like Teddy Wayne’s Apartment , Zadie Smith’s Swing Time , Hanya Yanagihara’s A Little Life and Carolina de Robertis’ Cantoras show. In such stories, friendship is also thematized for its absence, its tensions, shortfalls, and failings. No single friendship is the same, and the same is true of their literary representations.
🎉 To discover more books, head to Reedsy Discovery , our dedicated platform for readers and reviewers!
6. Free will vs. Fate

A common type of conflict as well as a literary theme, the friction between one’s ability to determine their own future and their externally determined fate can be found in many enduring classics, especially plays! From the ancient Greek play Oedipus Rex , Shakespeare’s Macbeth and Christopher Marlowe’s Doctor Faustus to beloved children’s series Harry Potter and Haruki Murakami’s Kafka on the Shore , the tension arising from the sense of external expectations and pressures and the notion of self-fulfilling prophecies is, ahem, fated to be a part of literature forever.
Fate is often what knocks at the door of the hero in the first act of a novel. Learn about the 3-act story structure in our free course.
How to Plot a Novel in Three Acts
In 10 days, learn how to plot a novel that keeps readers hooked

Hope springs in the most unlikely places — and for books, that often means stories of loss, despair, or disaster. Memoirs of suffering or hardship, like Paul Kalanithi’s When Breath Becomes Air , tend to end on a note of hope, whereas stories about social issues like racism or climate change also tend to locate reasons for optimism. Examples here include Angie Thomas’s The Hate U Give , Richard Powers’ The Overstory , and Ruth Ozeki’s A Tale for the Time Being .
📚 Our list of the best memoirs is sure to find you some more hopeful books to read.

* Sighs in lovestruck ❤️ * Ah, yes. Romance is yet another of those undying forces that has sustained works of literature since the beginning of time, and it’s not about to stop. From literary fiction and classics like Romeo and Juliet to YA heartwarmers like Rainbow Rowell’s Eleanor and Park and Casey McQuiston’s Red, White, and Royal Blue and epic historical fiction like Diana Gabaldon’s Outlander , romantic love (or the heartbreak resulting from the lack of it) lies at the center of books from more genres than just romance . Some authors use this theme to write delightfully comforting works that offer readers an escape from their routine, while others ask what it means to be dependent on another person, or observe the changing dynamics within a relationship. Whatever the overarching opinion, stories that focus on love promise to be deeply emotionally resonant.

From war poets like Siegfried Sassoon and Wilfred Owen who wrote about the toll of World War I to modern novels exploring its emotional and social consequences (e.g. Pat Barker’s Regeneration trilogy and Chimamanda Ngozi Adichie’s Half of a Yellow Sun ), violence and conflict works could constitute an entire genre of fiction in themselves.
10. Childhood

Our childhood years might not necessarily define us, but they’re still pretty integral in terms of changing who we want to be. So whether it’s to look back at our childhoods with nostalgia, to acknowledge the bitter realizations that followed it, or to simply consider the character perspective of a child, childhood keeps coming back as a prevalent theme in literature — and three examples that do just these things are Little Women by Louisa May Alcott, The Red Pony by John Steinbeck, and Room by Emma Donoghue.
11. Coming of age

Entering adulthood is another period that brings many changes, and so the time during which people come of age tends to be a common theme. In books as varied as Jane Austen’s Emma , Jeffrey Eugenides’ Middlesex , and Elena Ferrante’s My Brilliant Friend , growing up, maturing, and coming into your own are thematized to show the uncertainty and empowerment that comes with this stage of life.
💡 Head to our list of the 70 best coming-of-age books for more examples!
12. Environment and climate change

Unfortunately, the planet is warming up. And as the planet’s temperature grows, so do concerns about our future as a species — which leads to an increased prevalence of the environment or climate change appearing as core themes in literature. Now that ecofiction and “cli-fi” are becoming more popular, books like Barbara Kingsolver’s Flight Behavior , John Lanchester’s The Wall , and Dr Seuss’s The Lorax will see their themes discussed more than ever.
Test your theme-detecting skills!
See if you can identify five themes from five questions. Takes 30 seconds!
We hope this list has been handy! Remember that your own book doesn’t need to tackle a new-found, unbelievably novel theme to have merit: as long as you approach a theme in a fresh way, it’s completely natural for others to have discussed it before you.
If you're a writer who wants to start working themes into your stories, be sure to check out the final section of this guide.
Join a community of over 1 million authors
Reedsy is more than just a blog. Become a member today to discover how we can help you publish a beautiful book.
Bring your stories to life
Our free writing app lets you set writing goals and track your progress, so you can finally write that book!

1 million authors trust the professionals on Reedsy. Come meet them.
Enter your email or get started with a social account:
Literary Devices
Literary devices, terms, and elements, definition of theme, thematic concept vs. thematic statement, common examples of theme, significance of theme in literature, examples of theme in literature.
IAGO: Oh, beware, my lord, of jealousy! It is the green-eyed monster which doth mock The meat it feeds on.
( Othello by William Shakespeare)
In the end the Party would announce that two and two made five, and you would have to believe it. It was inevitable that they should make that claim sooner or later: the logic of their position demanded it. Not merely the validity of experience, but the very existence of external reality was tacitly denied by their philosophy.
( 1984 by George Orwell)
The gypsy was inclined to stay in the town. He really had been through death, but he had returned because he could not bear the solitude.
JOHN PROCTOR: Because it is my name! Because I cannot have another in my life! Because I lie and sign myself to lies! Because I am not worth the dust on the feet of them that hang! How may I live without my name? I have given you my soul; leave me my name!
( The Crucible by Arthur Miller)
Arthur Miller wrote his play The Crucible as a response to the scare tactics of the McCarthy era. As he saw his friends and peers being labeled as communists and blacklisted, Miller turned to the Salem witch-hunt as a model to artistically address the situation. One of the key themes both during the McCarthy era and in The Crucible is reputation and “having a good name.” At the end of the play, John Proctor refuses to admit to witchcraft to save his life. When asked why, he gives an impassioned speech about the importance of reputation, considering it even more important than life itself.
Do not pity the dead, Harry. Pity the living, and, above all those who live without love.
Test Your Knowledge of Theme
Why they came East I don’t know. They had spent a year in France for no particular reason, and then drifted here and there unrestfully wherever people played polo and were rich together.
“Whenever you feel like criticizing any one,” he told me, “just remember that all the people in this world haven’t had the advantages that you’ve had.”
I lived at West Egg, the – well, the least fashionable of the two, though this is a most superficial tag to express the bizarre and not a little sinister contrast between them.
A. Boredom B. Wealth and class C. Resentment [spoiler title=”Answer to Question #2″] Answer: B is the correct answer.[/spoiler]
When a child asks you something, answer him, for goodness’ sake. But don’t make a production of it. Children are children, but they can spot an evasion quicker than adults, and evasion simply muddles ’em.
After my bout with Cecil Jacobs when I committed myself to a policy of cowardice, word got around that Scout Finch wouldn’t fight any more, her daddy wouldn’t let her. This was not entirely correct: I wouldn’t fight publicly for Atticus, but the family was private ground.
First of all,” he said, “if you can learn a simple trick, Scout, you’ll get along a lot better with all kinds of folks. You never really understand a person until you consider things from his point of view […] until you climb into his skin and walk around in it.”
[spoiler title=”Answer to Question #3″] Answer: C is the correct answer.[/spoiler]
25 Themes Examples (In Literature)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

In literature, a theme is a central topic, subject, or message that the author is presenting for us to ponder.
It represents the underlying meaning or main idea that the writer explores in the book.
In my last article, I explored the six types of conflict in literature , and these represent six key literary themes as well:
- Man vs Nature
- Man vs Society
- Man vs Technology
- Man vs Self
- Man vs Destiny
But, of course, we can tease out many more themes in literature.
Themes can be as simple as love, friendship, or survival, or they can be more complex, such as the critique of societal norms, exploration of human mortality, or the struggle between individual desires and societal expectations. They often provoke thought and offer insight into the human condition.
So, in this article, I want to present 25 of them to you (which include some of those listed above, of course). For each theme, I hope to present you with an example within literature that you’ll likely be familiar with.
Themes Examples
1. love and sacrifice.
Love, as one of the most intense of human emotions, also features as a core theme in not only literature, but also music, film, and theater.
This theme can go in a variety of directions, but often examines the extent to which we will go in order to experience and maintain love (often at great personal cost), the way love makes us irrational or conduct extraordinary deeds of both good and evil, and of course, the experience of heartbreak.
Examples in Literature
Notable examples include “Romeo and Juliet” by William Shakespeare, where the two main characters sacrifice their lives for their love, and “The Gift of the Magi” by O. Henry, where a couple each sacrifice their most prized possessions to buy a gift for the other.
2. The Individual versus Society
The individual vs society theme – one of the six key types of conflict in literature – occurs when one person grapples with and stands up against established social norms, mores, and powers-that-be.
It may be just one person or a group who stands up against society. An example of the former is Katniss Everdeen in The Hunger Games who starts off as a solo fighter against a dystopian government, when no one else is willing. An example of the later is the group of children in Tomorrow When the War Began who form a band of friends standing up as a guerilla group against an occupying army.
“To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee is a strong example, with Atticus Finch standing up against societal racism. He is an outcast lawyer who is the only man willing to represent a Black man who is framed for a crime in a deeply racist town.
3. The Hero’s Journey
This theme, derived from Joseph Campbell’s monomyth theory, features characters undertaking great journeys or quests.
According to the monomyth theory, there is a common motif throughout stories – both historical and fabricated – that gain currency in the social imagination. In these theories, the journey sets out on an adventure, faces challenges that lead to a dramatic personal transformation for the better, and returns home anew.
A quintessential example of the hero’s journey can be seen in “The Lord of the Rings” by J.R.R. Tolkien, where Frodo sets out a shy hobbit having never left his shire. He goes on a journey where he develops self-belief and gains the respect of powerful people, before returning home.
4. Coming of Age
This theme, also known as the Bildungsroman, focuses on the growth and maturation of a young protagonist, usually a teenager.
Over the course of the story, they confront and overcome personal or societal hurdles, ultimately leading to self-discovery and self-acceptance.
Oftentimes, such storylines explore the unique experience of teenagers as they are developing cognitively and emotionally. Indeed, as my wife often tells me when we watch this storyline on television: “only a teenager would ever do that!”
These storylines do also have important place in society because they offer young people empathetic and supportive stories that can help young people through the important coming-of-age period of life.
“The Catcher in the Rye” by J.D. Salinger is a key example, where the main character, Holden Caulfield, goes on a journey on his own after being kicked out of school. The journey ends with him learning that he does truly value his education and family, leading him to professing he will attend school again in the Fall.
5. Power and Corruption
This theme explores how power can corrupt individuals and societies, and the destructive consequences that can result.
This theme generally tells an important story about how power operates in society, makes commentary about injustice, and the ways in which power can bring out the worst (and best) in people.
This theme is often seen in political or dystopian literature, such as “Animal Farm” and “1984” by George Orwell. Similarly, in Shakespeare’s “Macbeth”, the titular character’s quest for power leads to his tragic downfall.
6. Redemption and Forgiveness
Another common theme is the exploration of the human capacity for making mistakes and the subsequent need for redemption or forgiveness.
Characters may be haunted by their past actions, seeking atonement, or striving to make amends.
We see this, for example, in the trope of the ghost who is stuck in this life until they achieve some degree of inner peace and redeption.
It is also seen in Christian literature, where forgiveness following repentance is an important moral underpinning of the faith.
Similarly, as with in the man vs self conflict trope, the character is seeking self-forgiveness and self-atonement.
Khaled Hosseini’s “The Kite Runner” is a powerful exploration of this theme, where the protagonist, Amir, spends a significant portion of his life seeking to redeem himself for his past betrayal of his friend Hassan.
7. War and Peace
Literature that explores war and peace might depict the physical and psychological impact of war on individuals and societies, the politics of war, or the tireless pursuit of peace.
They may also explore the aftermath of war on people’s lives. It can follow people’s struggles to achieve inner peace after a conflict and the trouble of returning to civilian life.
Or, they may explore the deep brotherhood forged in battle, such as in the epic Band of Brothers storyline.
Of course, there are many directions we can take with this theme, but at the center is the extraordinariness of wartime, which opens the door for exploration of intense aspects of humanity.
“All Quiet on the Western Front” by Erich Maria Remarque provides a harrowing look at the physical and emotional trauma endured by soldiers in World War I. On the other hand, Leo Tolstoy’s “War and Peace” is an expansive work that explores war from various perspectives, including the experiences of soldiers, families, and politicians.
8. Death and Mortality
Literature is at its best when it grapples with the themes at the core of the human experience – and the inevitability of death is certainly one of these.
Some works might meditate on the grief and loss associated with death, while others might use the prospect of death as a device to reflect on the meaning of life, or to explore how people live knowing they will die.
Oftentimes, this theme overlaps with religiosity, or themes about seeking meaning in life.
“The Death of Ivan Ilyich” by Leo Tolstoy explores the protagonist’s confrontation with his own mortality, leading him to reflect on the life he has lived and the value of genuine human connection.
9. Nature and Environment
With the rising threat of climate change, this theme has seen renewed attention in recent decades.
Environmental themes often explore humanity’s relationship with the natural world (oftentimes, for example, showing how small and insignificant we are in comparison to nature).
At the same time, other themes examine the environmental consequences of human action during the age of the anthroposcene.
Themes that explore conflict between man and nature represent one of the key conflicts in literature, such as when a person is challenged by being stuck in the desert or isolated from civilization and nature becomes the main antagonist or challenge to overcome.
Some literature might emphasize the spiritual or therapeutic aspects of nature, as seen in “Walden” by Henry David Thoreau, where Thoreau embarks on a two-year retreat to a cabin in the woods to explore simple living and the natural world. Alternatively, environmental literature, like “The Lorax” by Dr. Seuss, uses storytelling to convey warnings about environmental destruction and the importance of conservation.
10. Identity and Belonging
This theme delves into the exploration of the protagonist’s place in society and their personal identity.
The earlier theme of coming of age overlaps significantly here, and so too does the hero’s journey, which commonly examines a hero’s developing sense of self.
Characters in this type of theme might struggle with societal expectations, personal self-discovery, or feelings of alienation, seeking a place or group where they feel they belong.
“Invisible Man” by Ralph Ellison, for instance, explores the protagonist’s struggle to define his identity within a society that refuses to see him as an individual rather than a racial stereotype. Similarly, “The Joy Luck Club” by Amy Tan navigates the complexities of cultural identity and generational differences among a group of Chinese-American women and their immigrant mothers.
11. Good versus Evil
One of the most fundamental themes in literature, good vs evil features a clear conflict between forces of good and forces of evil.
This theme often pits heroes against villains in a struggle that often represents larger moral, philosophical, or societal issues.
One of my complaints about many contemporary ‘pop lit’ and blockbuster films is that they fail to adequately examine the subjectivity of this false dichotomy – good vs evil themes are at their best when ‘evil’ is an elusive concept, and where we even are able to empathize with the evil character while still seeing the wrongs in their views.
J.K. Rowling’s “Harry Potter” series is a prime example, with Harry Potter and his friends constantly fighting against the dark wizard Lord Voldemort and his followers. The struggle between good and evil also underlies C.S. Lewis’s “The Chronicles of Narnia.”
12. Freedom and Confinement
This theme highlights the dichotomy between the desire for freedom and the reality of confinement.
Confinement might be physical, such as imprisonment or slavery, or it could be psychological, stemming from societal expectations or personal fears.
The ‘freedom’ element might emerge as a wistful theme, as in many coming-of-age narratives about the young character wanting to escape their hometown confines and beat culture narratives of the 1950s; or it might emerge as a struggle with physical constraint, such as themes surrounding imprisoned POWs.
“The Shawshank Redemption” by Stephen King, for example, explores both the physical confinement of prison and the ways in which characters can find freedom despite their circumstances. Similarly, “One Flew Over the Cuckoo’s Nest” by Ken Kesey features characters confined in a mental institution, highlighting their struggle for autonomy against oppressive authority.
13. Rebellion and Conformity
This theme centers on the tension between individual freedom and societal norms.
Characters might challenge authority, resist societal expectations, or fight against oppressive systems. (Here, we’re looking at strong overlap with the man vs society conflict narrative).
The theme may also explore an individual’s rebellion against a cult or religious group which they wish to escape, rebellion against parents, or search for an extraordinary life in an ordinary world. Sometimes, characters return to their roots, embracing conformity, while others escape the orbit or their cultural norms , achieving freedom through rebellion.
In Ray Bradbury’s “Fahrenheit 451,” the protagonist, Guy Montag, rebels against a dystopian society that has outlawed books and free thought. Montag’s transformation from a conformist fireman who burns books to a rebel who seeks knowledge demonstrates the struggle between conformity and rebellion.
14. Innocence and Experience
The theme of innocence vs experience often demonstrates a transition from a naive idealism to wisdom earned through experience .
For example, this theme may also explore the transition from the naivety of childhood to the disillusionment of adulthood.
Characters often face harsh realities or undergo experiences that shatter their innocence and lead them towards a more complex understanding of the world.
In “Lord of the Flies” by William Golding, a group of boys stranded on an uninhabited island gradually lose their innocence as their attempts at creating a society descend into savagery.
15. Reality versus Illusion
This theme investigates the nature of reality and the power of illusion.
Characters might grapple with distinguishing between what is real and what is not. In these situations, the story may play with the reader, not even allowing the reader an objective vision of what’s true and what not (such as in the unreliable narrator trope).
Similarly, the theme might explore how characters intentionally choose illusion over reality to escape unpleasant circumstances.
F. Scott Fitzgerald’s “The Great Gatsby” explores this theme through the character of Jay Gatsby, who constructs a grand illusion of wealth and social status to win the love of Daisy Buchanan. Similarly, in “A Streetcar Named Desire” by Tennessee Williams, Blanche DuBois often retreats into her fantasies, unable to cope with her harsh reality.
16. The Search for Self-Identity
The theme of self-identity revolves around the process of understanding oneself, and it often involves characters undergoing significant personal growth or change.
This theme often begins with characters experiencing a sense of unease or dissatisfaction with their present circumstances or sense of self.
This feeling of discomfort acts as a catalyst for the characters to embark on a quest for self-identity, an inner journey often mirrored by an outward physical journey or experience.
Example in Literature
In Franz Kafka’s “The Metamorphosis”, Gregor Samsa wakes up one day to find himself transformed into a monstrous insect. This shocking transformation forces him to reassess his identity, no longer defined by his role as a family provider, and navigate the alienation from his family and society.
17. The Injustice of Social Class
This theme explores the division of society into different social classes and the resulting inequity and conflict.
One of my favorite American authors, John Steinbeck, explores this theme in much of his literature. He takes the perspective of working-class Americans, examining how corporate interests make their life hard, how fellow Americans discriminate against them, and how they persevere through the relationships they build with other people in their social class.
In “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen, the theme of social class is prevalent, influencing characters’ attitudes, behavior, and prospects for marriage. The story continually highlights the injustices of a rigid class system , such as the Bennet sisters’ limited prospects due to their lower social status and lack of dowries.
18. Isolation and Loneliness
The theme of isolation involves characters experiencing physical or emotional separation from others.
This isolation can be self-wrought, caused by an individual’s actions or decisions, or externally imposed, such as societal exclusion, geographical displacement, or unforeseen circumstances.
This theme explores the various forms and impacts of isolation, offering a deep dive into the psychological and emotional ramifications it has on individuals.
I am often compelled by storylines that use physical isolation as a metaphor for the sense of loneliness and isolatedness within the hearts and minds of the protagonists.
In Mary Shelley’s “Frankenstein,” the creature, despite his desire for companionship, is shunned and rejected by society because of his monstrous appearance. This isolation leads to profound loneliness and ultimately, a desire for revenge against his creator, Victor Frankenstein.
19. Survival
This theme is often explored in literature through characters facing extreme conditions or challenges that test their will to survive.
There is generally a conflict here, which could be man vs nature (surviving the elements), man vs man (surviving against a foe), or even man vs technology (fighting against rogue technology, such as in Terminator ).
Survival themes can be a window into exploration of the tenacity and resilience of the human spirit against the odds.
In “Life of Pi” by Yann Martel, the protagonist Pi Patel finds himself stranded in the Pacific Ocean on a lifeboat with a Bengal tiger. Pi must use his intelligence and faith to survive in this hostile environment, with the story exploring themes of resilience, faith, and the human will to live.
20. The Human Condition
This theme delves into the shared experiences of being human, exploring a wide range of emotions, relationships, and moral dilemmas .
This theme is an examination of the joys, sorrows, conflicts, and complexities that define the human experience.
This theme has been prevalent in literature across all ages and cultures, as it captures the universality of human experiences, making it timeless and deeply relatable.
The human condition looks at the constants in human life, such as birth, growth, emotionality, aspiration, conflict, mortality, and how these shape our individual and collective experiences.
Leo Tolstoy’s “Anna Karenina” provides a complex and insightful exploration of the human condition. Through its diverse cast of characters, the novel delves into various facets of humanity, such as love, infidelity, societal pressure, and the search for meaning in life.
21. The American Dream (Illusory or Real?)
This theme critiques the idealized vision of the American Dream — the belief that anyone can achieve success and prosperity through hard work.
Some all-American storylines (Like the film Pursuit of Happyness featuring Will Smith) show how the American dream is a worthy ideal .
Similarly, in politics (and even real life, for American nationalists), the American dream is something people hold onto as an ever-present fundamental truth: if you work hard and dream big, you’ll make it in the end. It just takes hard work.
But there are many texts that challenge this idea, demonstrating how the pursuit of the American dream can sometimes be a fickle and pointless task. Below are just two examples.
In F. Scott Fitzgerald’s “The Great Gatsby,” the protagonist Jay Gatsby’s pursuit of wealth and social status, driven by his love for Daisy, ultimately leads to his downfall. Similarly, in “Death of a Salesman” by Arthur Miller, Willy Loman’s obsession with success and social acceptance blinds him to his family’s love, leading to tragedy.
22. The Absurdity of Existence
This theme underpins most texts that emerge out of existentialism and absurdism.
At the core of this theme is the exploration of the idea that life really has no meaning behind it. This can create some engaging and post-modernist texts whose storylines tend to meander, cut back in on themselves, and leave us at the end thinking “what a wild ride!”
This theme will tend to bring to the fore the chaotic, irrational, and meaningless features of a storyline.
In “The Stranger” by Albert Camus, the protagonist Meursault’s indifferent reaction to his mother’s death, his senseless murder of an Arab, and his subsequent philosophical musings in prison all point to the absurdity and meaninglessness of life.
I explore 5 more examples of existential literature here.
23. The Power of Faith
This theme looks at the role of faith or belief systems in shaping our lives and experiences.
While generally based on religion, it could also more generally represent faith in oneself, the journey of life, or family and friends.
Commonly, the theme will explore how having faith – and releasing stress, anxiety, and discontent when faith underpins our worldview – can provide strength, and hope.
For example, we’ll commonly see this theme when exploring an unbelievably tough journey – either physically (e.g. crossing a desert) or psychologically (e.g. coming to terms with death).
A darker turn, however, may demonstrate how faiths can clash and cause conflict.
In “Life of Pi” by Yann Martel, the protagonist Pi maintains his religious belief despite his extraordinary circumstances. His faith provides him comfort, hope, and strength to survive his ordeal at sea.
24. The Struggle for Women’s Rights
This theme involves the fight for gender equality, focusing on the experiences, struggles, and triumphs of women in a patriarchal society.
This theme could fit into the category of “protagonist vs society”, or rather “woman vs society!” It generally attempts to reflect real social, cultural, and political circumstances to make a social commentary about current social inequalities and the underlying patriarchy.
It may explore a woman’s attempts to assert her place in society, her struggles with discrimination, or women’s solidarity in the face of an oppressive outside world.
There has been a resurgence of so-called “bonnet dramas” in recent years that explore this theme, harking back to times when the patriarchy was far more overt.
Nevertheless, it can still be used in contemporary literature because, of course, the patriarchy does still exist in many areas of society and women often feel this intensely.
In Margaret Atwood’s “The Handmaid’s Tale,” a dystopian future is depicted where women are reduced to their reproductive functions, stripped of their rights, and segregated according to their societal roles. The protagonist Offred’s experiences and memories underscore the theme of women’s subjugation and their struggle for autonomy. In contrast, “Little Women” by Louisa May Alcott explores this theme through the everyday experiences of the March sisters as they navigate societal expectations and strive for their dreams in 19th century America.
25. Fear of the Unknown
This theme plays on the inherent human fear of the unfamiliar or unknowable and is most commonly employed in horror, drama, and murder mysteries.
The fear of unknown motif is very effective for authors who want to create suspense, dread, or anticipation. By prolonging the mystery of an unknown threat, the author can compel the reader to keep on reading until the suspense is overcome.
This fear could stem from various sources: the future, death, the supernatural, or anything beyond human comprehension. A good example in film is the ongoing narrative of the ‘monster’ in the woods in the hit television series, Lost .
H.P. Lovecraft’s body of work, often grouped as Lovecraftian horror, prominently features this theme. His stories frequently involve characters who encounter cosmic horrors or ancient, malevolent beings that defy human understanding, highlighting the insignificance and vulnerability of humankind in the face of the unknown.
Some Closing Thoughts
There are a few notes worthy of providing as we wrap up this exploration of examples of themes in literature.
First, a theme isn’t usually stated explicitly . Instead, it is revealed gradually through elements such as the actions of characters, their thoughts and dialogue, the setting, and the plot. These elements come together to express the theme or themes of the work. So, as consumers of texts, themes might be bubbling under the surface, ready to surprise us toward the end of our experience, making us finally realize the message our author is presenting us about society or humanity.
Secondly, one literary work can, and often does, contain multiple themes . For example, George Orwell’s “1984” explores themes of totalitarianism, censorship, the manipulation of information, and the loss of individuality and privacy.
So, enjoy playing with themes – whether as a consumer or producer of literary content – and always remember to reflect on how those themes can help us dig ever deeper into an empathetic understanding of the complexity of the human condition.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Green Flags in a Relationship
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Signs you're Burnt Out, Not Lazy
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Toxic Things Parents Say to their Children
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- College University and Postgraduate
- Academic Writing
How to Write a Theme Essay
Last Updated: January 4, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Jake Adams . Jake Adams is an academic tutor and the owner of Simplifi EDU, a Santa Monica, California based online tutoring business offering learning resources and online tutors for academic subjects K-College, SAT & ACT prep, and college admissions applications. With over 14 years of professional tutoring experience, Jake is dedicated to providing his clients the very best online tutoring experience and access to a network of excellent undergraduate and graduate-level tutors from top colleges all over the nation. Jake holds a BS in International Business and Marketing from Pepperdine University. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 209,911 times.
Starting the Essay

- For example, an essay prompt may ask you to reflect on the theme of good versus evil in John Steinbeck's East of Eden .

- Make a list of everything you know about the topic. This can be information you learned in class, as well as information you found on your own.
- Write down keywords or key scenes in the text that respond to the essay prompt. Think about what words or scenes from the text come to mind when you think of a specific theme.
- For example, when you brainstorm ideas on East of Eden , you may write down any moments in the text that seem to speak to the theme of good and evil.

- Your thesis statement will need to address the theme, your primary example or examples, and the stance you will take on the topic.
- For example, your thesis might be: "In East of Eden , John Steinbeck rejects the Biblical idea of good and evil and instead focuses on the contradictions and complications found in good and evil."

- Introduction: Discuss landscape as metaphor, include thesis statement.
- Body: Describe mountains in opening scene, elaborate on how they symbolize good vs. evil, state how characters live between the mountains, showing how people are caught between good and evil.
- Conclusion: Restate thesis statement, return to landscape as metaphor.
Writing Your Essay

- Questions can make fun hooks for the reader. Ask a rhetorical question that relates to the theme of the essay, such as "How does one decide what is good and what is evil?"
- You can also use a quote from the text as the hook. Find a quote in the text that explores the themes and ideas you'll be discussing in your essay.

- For example, you may introduce the role of nature plays in the text to discuss the theme of good and evil. The first sentence of your body paragraph should discuss the role of nature. This will set up the paragraph and let the reader know what the focus of the paragraph will be.

- For example, you may discuss the use of nature in the text in one paragraph. The body of the paragraph should then use quotes and scenes in the text to support this idea.
- You might write,"The descriptions of the Gabilan Mountains in the text symbolize good and evil. The characters in the story live in the Salinas Valley, trapped in a gray area between these two extremes."

- Ask yourself, "What do I want my readers to have learned through this essay?"
- Remind readers about the essay's theme. Reference some of the arguments you made in the body of your essay, reinforcing how they support your original point.
Revising Your Essay

- Check that there are transitions between paragraphs. Look at the beginning of each paragraph to make sure they all flow well together.

- Print out your paper and proofread it. Oftentimes, errors are easier to catch on paper. If you can't print out your paper, try changing the size or type of the font. Anything that alters how the work looked when you wrote it can help alert you to errors. [13] X Trustworthy Source University of North Carolina Writing Center UNC's on-campus and online instructional service that provides assistance to students, faculty, and others during the writing process Go to source

- Be open to constructive feedback from friends and peers. This will only improve the essay and ensure it is at its best when you turn it in.
Expert Q&A

You Might Also Like

- ↑ Jake Adams. Academic Tutor & Test Prep Specialist. Expert Interview. 20 May 2020.
- ↑ https://penandthepad.com/write-essay-theme-book-2200.html
- ↑ https://wts.indiana.edu/writing-guides/how-to-write-a-thesis-statement.html
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/essay-outline/
- ↑ https://www.grammarly.com/blog/how-to-write-a-hook/
- ↑ https://libguides.newcastle.edu.au/how-to-write-an-essay/conclusion
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/steps_for_revising.html
- ↑ https://owl.purdue.edu/owl/general_writing/the_writing_process/proofreading/proofreading_suggestions.html
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/editing-and-proofreading/
About This Article

When writing a theme essay, you’ll need to explore a given theme in the text you’re studying. Before you start your essay, brainstorm some notes about your theme, which you can then build your essay from. For example, if you have the theme of good and evil, think about which characters are mostly good or evil, any good or evil actions they take, description that uses light and darkness, and any religious context. In your intro, state your thesis, which should summarize your essay’s main argument. Then, choose 4 or 5 examples of your theme and write a paragraph exploring each one. Make sure you support your points with quotes from the text. In your conclusion, link your ideas back to your thesis statement. For more tips from our English co-author, including how to revise your essay to polish it up, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Mar 13, 2018
Did this article help you?
Jul 29, 2017
Dec 18, 2016
Nov 8, 2016
Ashley Ding
Nov 22, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
A Huge List of Common Themes
Related posts:, post navigation.
Home ➔ How to Write an Essay ➔ Thematic Essay
Thematic Essay Guide
Thematic writing is a staple of high school English and college writing courses. The idea behind thematic writing is to create a piece that uses a theme to tie together different ideas or topics. Thematic writing can be used for essays, short stories, novels, and even non-fiction pieces. In academic writing, thematic essays often center on a specific issue or theme and develop that theme throughout the essay.
Thematic essays are often assigned in high school English classes and college writing courses. They are also found on standardized tests such as the SAT and ACT.
If you need to refresh your memory regarding general essay writing, check our detailed guide: How to Write an Essay
There are a few different literary devices that are often used in thematic writing. These devices can help create a more cohesive essay or story and can also help emphasize the theme.
One literary device that is often used in thematic writing is symbolism. Symbolism is when an object, person, or place represents something else. For example, in the novel The Great Gatsby, the character Daisy Buchanan symbolizes wealth and shallowness. In the story “The Lottery” by Shirley Jackson, the black box that is used for the lottery represents tradition and the blind following of rules.
Definition and Purpose
A thematic essay is an essay that requires you to write about a particular question or theme. Thematic essays are often written in response to prompts that ask you to discuss a specific aspect of a larger topic.
The main point of a thematic essay is to show the development of a theme throughout a work of literature or to compare the way different authors or works deal with similar themes.
Essentials of a thematic essay:
- must be focused on a central theme
- must develop that theme with specific examples from the text(s)
- must synthesize several elements of the text(s), including plot, character, setting, style, tone, etc.
- must not be a mere plot summary
- must use evidence from the text(s) to support your argument
- must be well organized, with a clear introduction, body paragraphs, and conclusion
If you want to learn more about essays in general, we suggest you read this guide: Essay Definition
Pre-writing stage
Before you write a thematic essay, it is important first to understand the prompt and Rubric . The prompt will ask you to write about a specific theme, such as “Justice in Othello.” The Rubric will outline the specific requirements for the essay, including things like length, formatting, and the inclusion of outside sources.
So, before writing a thematic essay, you should carefully read the prompt and think about what you want to write about. Make sure that you understand what the prompt is asking you to do.
Some tips for pre-writing:
- Brainstorm possible themes or ideas that could be related to the prompt.
- Choose a central theme or idea you are interested in and think you can write about persuasively.
- Come up with specific examples from the text(s) that you can use to support your argument.
- Make a list of the different ways that the overall significance of the theme or idea can be developed.
- Decide on the main point you want to make about the theme or idea.
- Organize your thoughts and develop a thesis statement.
Analyzing the prompt and developing a thesis statement
To write a thematic essay, you need to analyze the prompt first. You will need to identify the task that the prompt is asking you to do, and you will need to identify the main idea of the passage.
For example, a prompt might ask you to write about the use of symbols in a work of literature. To answer this prompt, you would need to identify the different ways that symbols are used in the text. You also need to determine what the author is trying to communicate using symbols.
Literary theme analysis prompt example ( TKAM ):
How does Harper Lee use the symbol of the mockingbird to explore the theme of innocence in To Kill a Mockingbird?
When analyzing this prompt, consider what the mockingbird symbolizes in the novel and how this relates to the larger theme of innocence. You might discuss specific characters who embody innocence, such as Scout or Atticus, and how the events of the novel impact them. You might also discuss the impact of innocence on the town of Maycomb as a whole.
One example of how Harper Lee uses the symbol of the mockingbird to explore the theme of innocence is through the character of Scout. Scout is a young girl who is innocent and naive in many ways. She does not understand the prejudice and hatred that exists in her community. However, she can also see the good in people, even when they are not perfect. The mockingbird symbolizes this innocence.
Your thesis statement can look something like this:
The symbol of the mockingbird in To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee is used to represent the innocence of characters like Scout and Atticus, as well as the innocence of the town of Maycomb as a whole.
Other examples of thematic essay topics:
- The Catcher in the Rye: How does J.D. Salinger use the character of Holden Caulfield to explore the theme of teenage angst and rebellion?
- Heart of Darkness: How does Joseph Conrad use the character of Kurtz to explore the theme of colonialism and its effects on the human psyche?
- All Summer in a Day: How does Ray Bradbury use the character of Margot to explore the theme of bullying and its effects on victims?
- The Great Gatsby: How does F. Scott Fitzgerald use the character of Daisy Buchanan to explore the theme of the American Dream?
- Metamorphosis: How does Franz Kafka use the character of Gregor Samsa to explore the theme of alienation?
Outlining your thematic essay
After you have analyzed the prompt and developed a thesis statement, you can begin to outline your essay .
Thematic essays usually have a standard structure and consist of five paragraphs. That typically requires you to include an introduction, three body paragraphs, and a conclusion.
Each body paragraph should discuss a different aspect of your thesis. For example, if you need to write a thematic essay about the use of symbols in a work of literature, you might discuss how symbols represent different themes in the novel.
Your thematic essay outline might look something like this:
Introduction:
- Provide a brief overview of the work of literature you will be discussing
- Introduce the main idea or central theme that you will be discussing
- Thesis: The symbol of the mockingbird in To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee is used to represent the innocence of characters like Scout and Atticus, as well as the innocence of the town of Maycomb as a whole.
Body Paragraph 1: Symbols representing innocence
- The mockingbird symbolizes Scout’s innocence
- The mockingbird symbolizes Atticus’ innocence
- The mockingbird symbolizes the innocence of Maycomb
Body Paragraph 2: The loss of innocence
- Scout loses her innocence when she witnesses the trial
- Atticus loses his innocence when Mr. Ewell attacks him
- Maycomb loses its innocence when Tom Robinson is convicted
Body Paragraph 3: The importance of innocence
- Innocence is important because it allows people to see the good in others
- Innocence is important because it allows people to hope for a better future
- Innocence is important because it allows people to see the world in a more positive light
Conclusion:
- Restate your thesis statement
- Discuss the larger implications of your thesis statement
- Leave the reader with something to think about
You can also dedicate each body paragraph to one specific character or one specific event in the novel.
For example, you might discuss how Scout’s innocence is represented by the mockingbird symbol and how this innocence is lost when she witnesses the trial. In your second body paragraph, you could discuss how Atticus’ innocence is represented by the mockingbird symbol and how this innocence is lost when he is attacked by Mr. Ewell. In your third body paragraph, you might discuss how the innocence of Maycomb is represented by the mockingbird symbol and how this innocence is lost when Tom Robinson is convicted.
Writing the thematic essay
Once you have developed a clear thesis statement and created a thematic essay outline, you can begin writing. We complement each section with a thematic essay example part to better illustrate how it can look.
Introduction
The introduction of your thematic essay should briefly state what you will be discussing in your paper and provide background information. The introduction should also include your thesis statement, which is the main argument of your paper, at the end.
At the very start, you can also use a hook to grab the reader’s attention . A hook is usually a sentence or two that draws the reader in and piques their interest.
Introduction example of a thematic essay:
“Mockingbirds don’t do one thing but make music for us to enjoy. They don’t eat up people’s gardens, don’t nest in corncribs, they don’t do one thing but sing their hearts out for us. That’s why it’s a sin to kill a mockingbird.” This quote, spoken by Atticus Finch, perfectly encapsulates the symbol of the mockingbird in Harper Lee’s To Kill a Mockingbird. To Kill a Mockingbird by Harper Lee is a novel about the loss of innocence. The symbol of the mockingbird is used to represent the innocence of characters like Scout and Atticus, as well as the innocence of the town of Maycomb as a whole. The loss of innocence is an important theme in the novel, and it is represented in the characters of Scout, Atticus, and Maycomb.
Body paragraphs
Your body paragraphs should each be dedicated to one specific character or event in the novel and start with a topic sentence . After the topic sentence, you should use evidence to support it. You must analyze the evidence, not just merely state it. Lastly, end your body paragraph with a conclusion and transition to the next section.
A thematic essay body paragraph example:
One example of the loss of innocence is Scout. When the novel begins, Scout is an innocent child who does not understand the ways of the world. “‘Don’t you ever do that again,’ I said. ‘Don’t you ever do that again, it’s bad enough having Jem tell on me without you adding to it.’” (Lee 9). Scout is chastised by her father, Atticus, for fighting with her cousin, Francis. In this quote, Scout does not understand why fighting is bad and must be scolded by Atticus. However, by the end of the novel, Scout has learned the true evil that exists in the world and has lost her innocence. “It was then that I finally understood Mrs. Dubose’s courage, not because she had won, but because she had had the courage to fight and the strength to lose.” (Lee 281). Scout has come to understand that even though Mrs. Dubose lost her battle with addiction, she was still brave for fighting it. Mrs. Dubose’s courage has taught Scout that even in the face of defeat, there is still hope. Scout has lost her innocence because she has learned that the world is not a perfect place and that people are not always good.
Check our citation guide to learn more about using quotes in essay: How to Introduce a Quote
Your concluding statement should sum up the main points of your thematic essay and rephrase your thesis (restate it in different words). You can also discuss broader implications or give your opinion on the topic, but don’t add any new information.
A conclusion example of a thematic essay:
To Kill a Mockingbird is a novel about innocence—the loss of it, the destruction of it, and the fight to keep it. The characters of Scout, Atticus, and Maycomb all represent different aspects of innocence, and the novel explores how they each deal with the loss of their innocence. Scout loses innocence when she learns that the world is not perfect and people are not always good. Atticus loses his innocence when he realizes that sometimes the justice system does not work as it should. Maycomb loses its innocence when it is revealed that racism and prejudice are alive and well in the town. The loss of innocence is a sad but inevitable part of life, and To Kill a Mockingbird shows us that this loss can sometimes be for the better.
Final tips on thematic essay writing
Now that you know the main steps involved in the writing process of a decent thematic essay, here are some of the final tips and key takeaways that you should keep in mind when doing this task:
- Make sure to brainstorm first and develop a good thesis statement that will guide the rest of your essay.
- Create a thematic essay outline before starting to write the essay itself. This will help you stay on track and not miss any important points that you want to include.
- Start each body paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the paragraph’s main point.
- Use concrete and specific examples to support your points.
- Pay attention to your grammar and spelling.
- Make sure to conclude your thematic essay in a strong way that ties everything together.
- Analyze the work, not just summarize it.
- Take your time, and don’t rush the essay.
- And lastly, proofread your work before submitting it.
By following these tips, you should be able to write a thematic essay that will impress your teacher or professor.
- Solano Community College – World Literature
- Jefferson State Community College – Literary Theme Analysis
Was this article helpful?
- Kindle Unlimited Free Books
- Writing Piggy Monk Square
- Piggy Monk Square – Book Reviews
- Practical Creative Writing Exercises Book
- Authors Notes – Writing Fiction Street
- The Sunshine Girl
- Kindle Unlimited eBooks for Children
- Writing About Ballyyahoo
- Free Stories For Kids
- The Witch Of Ballyyahoo
- A Story For Cats And About Cats.
- Bonkers In Ballyyahoo
- The Little Book Of Swinging On A Gate
- Free as a Ladybird
- The Tree Hugger
- Football Mad – A Funny Children’s Story
- Football Crazy
- Creative Thinking
- Creative Writing – Flow
- Walking and Inspiration
- Dream a Little Dream
- How To Increase Your Creativity in Five Easy Steps
- On Confessing To Depression
- Giving up the Day Job to Write
- Don’t tell me nobody wants to read my stories.
- Political Satire – Funny or Not?
- Talking To Strangers
- Go Set A Watchman – Her Choice?
- Writing For The Market
- Why Women Writers Use Initials
- Ten worst things about social networks.
- How Not To Deal With Criticism
- Transparency and The Irish Film Board
- What Do I Know About Bullying?
- Valentine’s Day And My Green Heart
- Too Many Experts
- Be True To Yourself
- The Glass Castle – Jeanette Walls
- Small Great Things – Jodi Picoult
- Just Friends – Elizabeth Grey
- The Woman Who Walked Into Doors – Roddy Doyle
- Cookie Policy
Examples Of Themes
Examples of themes.
Before you look at the examples of themes below it will help you to learn more about what theme is and how it affects our writing and our stories
A story without a theme is little more than a list of events.
The events themselves may be very interesting, or exciting, but without the universal human connection, they will not engage our attention in any real way.
THEME APPEAL
Not only must the theme appeal to the reader, it must also appeal to you.
You must want to or even need to explore that particular theme for you to keep writing.
Many people tend to confuse the theme of a story with the plot.
To learn about the difference between theme and plot click here.
THE PULSE OF THE STORY
Theme is the pulse of the story and if you choose correctly you will feel compelled (in a good way) to complete your story.
If your theme is not compelling to you, it will certainly not be compelling to your readers.
So think very carefully, not just about your themes but about how you intend exploring them.
You might like to choose one of the following examples of themes – that appeals to you and try writing a story about it.
Alienation – The effects of, the loneliness of, to cure it.
Ambition – getting what you want, stunted by, thwarted.
Betrayal – the pain of, in love and friendship.
Coming of age – loss of innocence.
Courage – the courage to deal with conflict, lack of, developing, conquering with.
Deception – how to deceive, results of.
Discovery – what does it take to discover new places, inner meaning, strength, even treasure.
Escape – from life, routine, prison, family pressures.
Death – how to escape, facing, what happens after, consequences of.
Fear – driven by, dealing with, conquering.
Freedom – loss of, gaining, handling, fight for.
Good versus evil – survival of one despite the other, the triumph of one over the other.
Isolation – physical and emotional.
Jealousy – trouble caused by, denial of, driven by.
Justice – the fight for, injustice, truth versus justice.
Loss – of life, innocence, love, friends, to avoid.
Loneliness – no man is an island, or hell is other people.
Love – love fades, is blind, can overcome all obstacles, can
Lust – for power, for sex.
Power – the search for, the loss of, what we are willing to exchange for.
Prejudice – racism, bigotry, snobbery, dealing with.
Security – the loss of, the finding of the need for, how we act when security is shattered.
Spirituality and God – the struggle to find faith, live without faith etc.
Survival – man versus nature
CHOOSING YOUR STORY THEME – KEY POINTS
- Give a lot of thought to choosing your story theme. Remember you will need to be obsessed with your chosen theme to keep writing about it for long periods of time.
- Being aware of your themes can help you sell your books.
For help choosing a theme click here .
CHOOSING YOUR APPROACH TO THEME
We all approach our writing ideas differently. My own methods vary from time to time. Sometimes I decide I want to write about a particular theme and then find the story.
At other times I find the story first and the themes become apparent through the process of writing.
Whatever your approach, it is well worth putting some thought into it before you commit yourself to the hard work of writing out the story.
THE IMPORTANCE OF PREPARATION
Undertaking this initial preparation will save you from having to put too many of those unfinished stories in the bottom drawer of the filing cabinet.
I really hope these examples of themes help you.
If you have any questions or comments please use the comments box below and I will be happy to help.
Click here for Creative Writing Exercises to help kick-start your writing.
Best of luck with your writing.
P.S. All the information, exercises and tips on this site are free to you – liking, sharing or commenting all help to support this site.
I love helping writers, but there are costs involved for me. So if you find this helpful – please use the donate button below. All donations, big or small help keep this resource free for you and other writers.
Another way to show your support for the site is to buy and review Practical Creative Writing Exercises.
You won’t be sorry because this book is packed full of inspiring exercises to get your ideas flowing in minutes, get ebook from amazon.com , get ebook from amazon.co.uk, get paperback from amazon.com, get paperback from amazon.co.uk, share this:, 102 responses to examples of themes.
Hey Grace, For the longest time I’ve wanted to put my ideas to paper and write a fantasy novel and thanks to your website I think I finally have the tools and confidence to do it, thank you.
Hi Christopher, I am so glad to hear that and I hope it goes well for you – keep at it Grace
Me too! I have written many books and I have been having writers block . Thanks to this website I am able to continue!
Hi…am a young passionate writer but I don’t know how to go about it. Would you kindly help me develop it ?
HI Thomas If you are truly passionate about writing you will write at least 5 days a week. Start with short sessions of even 30 minutes, build up more time. Writing regularly is vital to your development.
Go here to start with https://www.practicalcreativewriting.com/creative-writing-exercises/
Best wishes
Did you write the novel?
Hey, I was looking for a list of themes to help give me motivation and creative guidance to make a school essay which is very important to me. I greatly appreciate this page and hope more people find it and I’m sure you yourself are a wonderful writer! Best wishes for the future! x 🙂
Hi I am so glad it helped you and I wish you all the best with your school essay and the rest of your school work. Keep in touch, Grace
hey grace, This was a very helpful page and I am so thankful for it. I have to write an essay for school soon and this website is really helping me out with my study. I hope more people will find this page in the future because it is so helpful. Thank you.
Hi Brooke I am glad it helped you with your essay and best of luck with your studies. Grace
How does your overall story goal affect your characters? What I mean to say is, if my overall goal is isolation, my character obviously wants to change this, by running away from it, etc. How does this originate? From the start of the book to the end, what makes the reader believe my character’s goal is this, and how is it shown? Is it shown subtly throughout the book? Is it spoken? (Question overload, sorry.) Lastly, what leads up to this goal being achieved? As in, what kind of inciting incidents that more or less throw the book forwards into action and new experiences. What makes this character’s thoughts consciously or no, become a reality when blah, blah, blah.. happens. (Once again, so sorry this is about a mile long. Just a question I’ve been wondering about for a long time. No one else has been able to answer this plainly enough for me to understand and/or put into action myself. )
Hi Krishna, I am not sure I am clear what your question is. Are you perhaps confusing story goal with character goal? Your goal as a writer may be to write a story about a man who wants to become President but who fails at this and instead decides to become an actor. Your characters goal might be to become president but your story goal takes him away from his goal to where you as the writer decide he should go. Sometimes writers can over think – maybe you should write your story and see where it takes you? Best of luck with your work.
Hi Krishna,
I actually have an answer for you:
The theme of your story ends up being what your character will realize in the end to conquer. It’s the backbone of your story regardless of character goals. For instance, your character goal might be to get away from being rejected (by getting a new boyfriend or sacrificing morals, etc) but the theme of the story might be that you need to accept yourself before others will accept you.
In the story, the theme is usually shown early on in the story – the first 4k if it’s a standard novel – and it’s often something mentioned by a confidante – a piece of wisdom or a question posed in a conversational way. For example, in Frozen the troll tells the royal family that “the heart is not easiliy changed, but the head can be pursuaded”. At the end, when Anna sacrifices herself, Elsa realizes that true love comes from within and it’s that love that will allow her to rule her powers. Elsa’s personal goal was to save everyone from herself.
Other examples are Man of Steel where Jonathan Kent tells young Clark that he needs to decide what kind of man he will be – in the end that allows him to save the world. In The Wizard of Oz, Dorothy’s theme comes out when she sings ‘somewhere over the rainbow’ – will she ever find a place where she belongs? A place to call home?
Once you’ve stated your theme (subtly) in conversation with another character, your main character goes through the story trying to fight it out and figure out how to reach their goal. Finally, after going through everything, they realize the theme and it helps them reach their goal.
In other words – THEME is the key to reaching CHARACTER GOAL. How do you accept love from others? Love yourself, first. How do you overcome childhood failure? Forive yourself. How do you save the world? Realize you’re worthy despite your shortcomings. You get the idea.
I hope this helps. It’s one of the most challenging parts of writing, I find, and the most important. It’s one of the first things I work on before I decide on my ending.
Hi Talea, Thanks for adding this wonderful answer and perspective on theme from the writer’s point of view. We writers have many challenges and theme is so crucial. Best of luck with your writing. Grace
Can you give me an example of a theme
choose death you can write stories about death (//death//)
An example of a theme relates to what your trying to express in a story, essay, etc. One example would be “Don’t give up on your dreams” It s an obvious theme although you can write multiple things about it.
Hi Genesis, Thanks for the comment and a great example. You’re right, there are so many great stories about people who follow their dreams and the stories can be as diverse as the imagination allows. Thanks Grace
Thank you so much for your unique post on Themes. It truly helped me understand character goals better and realize that the story goal may be different than the characters. I agree Theme really is the backbone of a story.
Grace, This website helped me with my short story theme for English. Thanks! -Jean
You are welcome. Grace
Thx this really helped with my homework
I’m so grateful to have found this page. Not many others were this helpful, this page was just what I needed. Thank you so much
So glad it helped. Best wishes Grace
Hey thanks for creating this website it helps me a alot when iam doing an essay. Thanks ☺
Hi Rosa, Thanks for commenting. Best of luck with your essays. Grace
Dear grace, Before reading this page on theme i was dumbstruck, i had no idea what any of it meant. now that i have read this i completely understand !!! thank you so much !!!!!
Glad it helped. Best wishes Grace
This page really helped my with my English essay’s . Thanks a ton! -Hunter
Glad to hear it Hunter – good luck with your work. Grace
Thank you very much grace this helped me alot.
I could not think of an idea to do my L.A. short story about and when i decided to check out this website i thought of everything i could do! Thank you Grace, you helped me think of a good story to use and great themes/story plot for my assignment. I can’t thank you enough.
Hi Caleb, I am so pleased to hear this. It’s amazing how ideas can be triggered in so many different ways. I hope you will come back and let me know how you get on with your story. Best wishes Grace
Thank you for helping me with my homework your website is the best.🙂 👍🏼
Tanks for the tips. Its a great thing people like you are out there. Keep it up. Joe
Hi Joseph – glad the tips help. Best wishes Grace
Ditto. This really helped me with my creative writing class. I can already see myself improving in writing! Grace, you are the best.
Lovely to hear from you, Maddie -keep writing.
this really help me for my critics letter essay thank you!
what is the theme of the song 50 ways to say goodbye? i need this but i can’t figure it out. i thought it was like loss of love or something because of a breakup but i dont know. can someone help me?
I believe the theme of that song is freedom…setting yourself free.
Your list of themes really helped me. All I needed was a small push. Thanks.
Great to hear – keep going now! Grace
Thank you! I have to write a speech and often find it hard to think of an overall theme on my own.
You are very welcome – best of luck with your speech. Grace
Thank you Ms.Grace,
I’m actually making a writing assignment for my teacher. This gives me a lead to my creative writing.
HI Hiromi Glad to hear this helped and the very best of luck with your creative writing assignment. Best wishes Grace
Hi I am doing an English project and for it we need to identify a thematic idea. Can you help explain it?
Hi Haydn I suggest that you read through my articles on theme https://www.practicalcreativewriting.com/what-is-a-theme/ You will find more links to other articles below this. I also suggest you look through the notes your teacher has given you. Read the text and books your teacher has suggested. Research in the library. You will find the answer to the question quite easily if you do the above. If this is an essay question then all you need to do is expand on your answer. Perhaps find some examples and explain them. Your teacher wants you to learn for yourself and prove that you can do this. I wish you all the best of luck and am sure you can do it. Best wishes Grace
Hi Grace. Thanks for posting the THEME information. I just finished my 1st novel and I’m in editing/revision making sure my themes are supported well throughout the plot. I have multiple characters and multiple subplots so I sat down and wrote out some of the themes I felt were represented. Its a science fiction genre so some themes that seemed to come into play were:
Good vs evil (the novel) Greed (antagonist) Loss (sub char) Survival (the novel) Courage (sub char) Discovery (protag) Corruption (antag) and probably Growing up (sub char) There are more but that’s a healthy batch
I kind of figure a book will always have at least a few themes that a writer would include regardless. But when I research Best Sellers – https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/List_of_best-selling_books I found a ton of information. And themes from those books. I was overwhelmed with information.
I was really trying to figure out what kind of theme would cover someone who is emotionally isolated (a scientist) that during the course of the novel grows emotionally and finds love. Is that a theme? I think I labeled it as Discovery in the list above.
hi Jeanne Glad you found the theme information useful. There is so much information out there that we writers can get overwhelmed. I think that the best themes are universal and will apply to any genre – the list you supplied above could apply to many stories not just science fiction – so that’s great! As for your character who finds love – well love is a theme. However, think about survival. I don’t know your story. But sometimes survival can apply in different ways. We can survive disease, disaster, difficult lives. She survives her isolation? It sounds like you are doing just great and I am glad to hear you are at the editing stage – that’s a great achievement. Best of luck with the project and keep in touch. I would love to hear how you get on. Grace
this was the best site that i have met for themes thank alot
Glad to have helped. Grace
Wow this website really helped me finish my homework! You look like an amazing person that obviously does amazing work… thanks for helping me!!! Best of Luck
Thanks very much. Do come back any time. Best wishes Grace
Hello Grace. What would be a good theme for bullying because of race and ethnicity?
Racism and bullying are universal themes and are good choices for story lines or even secondary story lines. Best of luck Grace
Thank you for writing this! I have many unfinished projects to revisit armed with this new knowledge. Preperation truly makes a difference.
Hi Dia So pleased this helped – good look with your projects – get them finished 🙂 Best wishes Grace
Themes don’t come easy to me so this was helpful THX
You are welcome Grace
This really helped me as well, thank you!
So glad to hear it, thanks Jack.
Excellent web site. Lots of useful info here. I am sending it to a few friends ans also sharing in delicious. And certainly, thanks in your sweat!
Glad you found it useful and thanks for sharing as well. Grace
Hey Grace, is “a story without a theme is little more than a list of events” an original quote of yours? If so, would it be okay to quote you for an essay I’m writing?
Hello, Grace, thanks for an excellent organization primer when considering a novel! Am I correct in concluding that theme is the focal point that must appear throughout the narrative of dialogue, plot, and structure? Did I say that right?
Hi Kenneth, Yes themes are important but they don’t always emerge until you the writer are immersed in the story. Being conscious of your themes comes with experience. When you are actually in the act of writing it is always best to concentrate on telling your story. If you set out to write a story about your themes you may produce a piece of non-fiction. It is a bit of a tightrope but remember to focus on your story – if you do that the themes will look after themselves. Best wishes Grace
Hey Grace, How do you get good at finding the theme of a book?
Hi Nathan I suggest reading a book carefully then when you’ve finished write down what you see as the themes. If, for example, the story was about a man who lost his wife in a murder who is determined to find her killer, then some of the themes might be revenge, love grief. Themes are different from the actual story – by reading carefully the themes will appear to you. Best of luck Grace
Thank you Grace found it very useful…
Great to hear – thanks Aswathi and take care. Grace
This is simple and very helpful thx:)
Glad to help Peter. Best wishes Grace
As many people have already said on this website, thanks for the amazing tips and themes! 😀
Hi Katie – thanks for your comment. So encouraging to get feedback like this! I will keep going then 🙂 Best of luck with your writing. Grace
Hey Grace, so I’m 14 and I really wanted to write a story, and these themes really helped me, I wanted to thank you about and appreciate it so much all the love too you.
Hi Nada So lovely to hear from you. I hope you write your story. It’s great to start young. If you have any questions – come back to me. Take care Grace
Can a story have more than one theme involved?
Hi Molly Yes you can – sometimes there are many themes involved in a story. My advice is to pick your favourite book and see if you can identify the themes involved – write them down in a list.
I think you will be surprised. Best wishes
Hi Grace1 Thanks for the post, it gave me some insights for a scholl project!
Hi Grace ! Thank you so much for these writing themes and explanations, I have a question, Does it also work when it comes to songwriting themes ?? Goodbye ! Ben
Hi Ben I’m not a musician myself but I don’t see why not – inspiration can take many forms. Best wishes
Amazing blog! Do you have any recommendations for aspiring writers? I’m hoping to start my own site soon but I’m a little lost on everything.
Would you advise starting with a free platform like WordPress or go for a paid option? There are so many choices out there that I’m totally confused .. Any recommendations? Thanks a lot!
It really depends on your budget and whether you want adverts running or not. Maybe you could start with a free option then see how you go. Good luck!
This helped me write my Essay on why picture books aren’t just for children thankyou soo much!
Hi Meghan That’s good to know and glad to have helped. Best wishes Grace
Choosing a theme could indeed be a struggle and to stay consistent with that chosen theme is another challenge. The breakdown of theme examples come in handy for writers who are in the early stages of developing their story.
This tips really helps! I m not good at writing and I don t really like it, but I have to….. I want to make short film and before I can do the fun filming Part, I have to create a Script and a Story. :/
Hi, I’m glad it helped. I suggest looking around the site – there is plenty of tips and exercises to help you with your story and script. Enjoy! Best wishes Grace
Thank you for all your tips because I had to submit a essay with theme and this helped a lot! I got a 100%!! THANK YOU!!!!!!!!
Yes, Luc, you can go ahead – please mention my website. It is my quote but that doesn’t mean other people haven’t said something similar – as always. Best of luck with your essay. Grace
Trackbacks/Pingbacks
[…] one. What do I want the story to be about? The ocean is our mother. The ocean should be respected. Practical Creative Writing.com has a list of themes. Lets go with Survival (man versus nature, nature versus man), […]
[…] Examples of Themes by Grace Jolliffe […]
[…] Practical Creative Writing […]
[…] https://www.practicalcreativewriting.com/what-is-a-theme/examples-of-themes/ […]
[…] isolation, jealousy, justice, loss, loneliness, love, power, security, and spirituality. References https://www.practicalcreativewriting.com/what-is-a-theme/examples-of-themes/ […]
[…] the now”. I specifically chose to make a book cover for this book is because it can best show the theme by foreshadowing the climax and […]
[…] meets girl.” Topic describes the general emotional environment in which the story takes place: alienation, ambition, deception, justice, security, etc. These topics can help to set the mood, the attitude, even the rationalization of the choices of […]
[…] Practical Creative Writing: Examples of Themes […]
Leave a Reply Click here to cancel reply.
Name (required)
Email (will not be published) (required)
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Glossary of Grammatical and Rhetorical Terms - Definition and Examples
- An Introduction to Punctuation
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
Definitions
(1) In literature and composition , a theme is the main idea of a text , expressed directly or indirectly. Adjective: thematic .
(2) In composition studies , a theme is a short essay or composition assigned as a writing exercise. See also:
- "Composing My First College Essay," by Sandy Klem
- Five-Paragraph Essay
- Models of Composition
- Theme Writing
- What's Wrong With the Five-Paragraph Essay?
See Examples and Observations below. Also, see:
From the Greek, "placed" or "laid down"
Examples and Observations (definition #1):
- "Simply put, a story's theme is its idea or point (formulated as a generalization). The theme of a fable is its moral; the theme of a parable is its teaching; the theme of a short story is its implied view of life and conduct. Unlike the fable and parable, however, most fiction is not designed primarily to teach or preach. Its theme, thus, is more obliquely presented. In fact, theme in fiction is rarely presented at all; readers abstract it from the details of characters and action that compose the story." (Robert DiYanni, Literature . McGraw-Hill, 2002)
- Orwell's Theme(s) in the Essay "A Hanging" - " ' A Hanging ' is [George] Orwell's first distinctive work. It gives an apparently objective account of a ritualistic execution--from fixed bayonets to a bag over the head of the condemned--in which the narrator officially and actively participates. . . . At this halfway point Orwell states his theme : 'till that moment I had never realized what it means to destroy a healthy, conscious man. When I saw the prisoner step aside to avoid the puddle, I saw the mystery, the unspeakable wrongness, of cutting a life short when it is in full tide.' Instead of invoking religion, he asserts a quasi-religious sense of life's sacredness--the first expression of the instinctive humanism that characterizes all his work." (Jeffrey Meyers, Orwell: Wintry Conscience of a Generation . Norton, 2000) - "A variation on this theme occurs in several of Orwell's most famous texts containing epiphanies , moments of illumination in which the humanity of people he has hitherto viewed in terms of dehumanizing generalizations suddenly breaks through, and Orwell's perception is jarred as he understands, with a shock, that these are people like himself. . . . In the early sketch entitled ' A Hanging' (1931), Orwell describes how his idea of what it means to kill a man is altered by the Hindu prisoner's gesture of stepping aside to avoid a puddle on the way to the gallows. What the text reveals, however, is that the prisoner at first looks to Orwell like a mere insignificant object. Into this scene, well defined in terms of the prisoner's already marginal existence, breaks the unexpected gesture, making Orwell (or the Orwellian narrative persona ) realize that the prisoner is alive, just as he is . . . . This chronicle is generally interpreted along the lines Orwell lays down, as the revelation of the barbarity of execution, but its primary meaning, I believe, is another. An inferiorized human being has for an instant become a genuine person in the eyes of one of the masters." (Daphne Patai, The Orwell Mystique: A Study in Male Ideology . University of Massachusetts Press, 1984)
- The Themes of the Novel Charlotte's Web - " Themes are subject to readers' interpretation, so different individuals may identify different themes in the same book; the dominant idea or theme, however, should be apparent to readers. " Charlotte's Web offers many layers of meaning to readers. Younger children are apt to understand this book as an animal fantasy. Older children are ready to apprehend the cycle of life and death, while adults recognize the irony in a situation that gives one character credit for the creativity of another. This is why we recommend using Charlotte's Web in the third or fourth grade, when children are ready to understand its major theme ." (Barbara Stoodt et al., Children's Literature:Discovery for a Lifetime . Macmillan, 1996) - "Identifying theme is typically a bit more difficult perhaps because theme is often confused with plot summary or motif . . . . ' Charlotte's Web (White, 1952) is a story about a pig whose life is saved by a spider' is not a theme statement! It is a plot statement. ' Charlotte's Web is a story about friendship' is also not a theme statement! Rather, it is a statement identifying one of the most important motifs in the story--friendship. 'A theme in Charlotte's Web is that true friendship involves responsibilities as well as privileges' is a theme statement!" (R. Craig Roney, The Story Performance Handbook . Lawrence Erlbaum, 2001) - "Besides mortality itself, throughout many idyllic scenes [in Charlotte's Web ] Andy [White] dabbed colorful spots of melancholy. He translated the song sparrow's aria as 'sweet, sweet, sweet interlude' and informed the reader that it referred to life's brevity. Crickets harped on the same theme . But overall Andy's theme was the joy of being alive, of reveling in the moment with visceral attention. What seemed like two themes were really one." (Michael Sims, The Story of Charlotte's Web . Walker, 2011)
- The Difference Between Plot and Theme "If you sometimes confuse plot with theme , keep the two elements separate by thinking of theme as what the story is about, and plot as the situation that brings it into focus. You might think of theme as the message of the story--the lesson to be learned, the question that is asked, or what it is the author is trying to tell us about life and the human condition. Plot is the action by which this truth will be demonstrated." (Phyllis Reynolds Naylor, quoted by Kenneth John Atchity and Chi-Li Wong in Writing Treatments That Sell , rev. ed. Henry Holt, 2003)
- Thesis and Theme "The thesis is the main point you are trying to argue [in a composition ]: for instance, that abortion is every woman's right or that housing discrimination is wrong. The theme , on the other hand, is a motif established by orchestrated connotative language that reinforces the thesis. Theme differs from thesis in that theme relies on inference and suggested meaning rather than on direct statement." (Kristin R. Woolever, About Writing: A Rhetoric for Advanced Writers . Wadsworth, 1991)
Pronunciation: THEEM
- Definition and Examples of Theme-Writing
- Definition and Examples of Progymnasmata in Rhetoric
- Definition and Examples of Formal Essays
- Unity in Composition
- Definition and Examples of Composition-Rhetoric
- Learn How to Use Extended Definitions in Essays and Speeches
- Advanced Composition
- Specificity in Writing
- Panegyric (Rhetoric)
- Monologues in Speech and Composition
- Padding and Composition
- What Is Tone In Writing?
- dramatism (rhetoric and composition)
- What Is Clarity in Composition?
- Motifs in Fiction and Nonfiction
Helping Writers Become Authors
Write your best story. Change your life. Astound the world.
- Start Here!
- Story Structure Database
- Outlining Your Novel
- Story Structure
- Character Arcs
- Archetypal Characters
- Scene Structure
- Common Writing Mistakes
- Storytelling According to Marvel
- K.M. Weiland Site

The Secret to Writing Strong Themes

Can You Write Strong Themes “On Purpose”?

Writing Your Story’s Theme (Amazon affiliate link)
In the past, a common statement that has floated around the writing community is that “writers should never consciously write the theme.” There is some truth to this (which I’ll talk about in just a second), but ultimately, I adamantly disagree with this idea.
What this is really pointing to is the truth that writers never want to preach at their readers . You don’t want to try to start with some message you’re trying to share about the world and then shoehorn that into your characters’ mouths or their perspectives of the world and try to prove it through whatever is happening in the story. You don’t want to come into a story to prove, for example, some political statement. Readers don’t want that. It doesn’t work within the story because it isn’t organic or it doesn’t flow. It feels, even if the author isn’t actually preaching at you, that they’re trying to jam some specific moral message into a story that doesn’t fit.
However, I think this unfortunate effect most often happens simply because the writer has an idea of theme but doesn’t understand how it actually works within storyform. If you do understand how theme operates, you’re much less likely to end up with fragmented themes, in which your story is saying one thing while you’re trying to say something else with the theme. Likewise, you can also avoid the problem of getting to the end and realizing what you thought was your story’s theme doesn’t seem to have anything to do with what’s actually happening.
In either case, you can end up having either stories that seem very disjointed, or even two different endings that are trying to individually address the plot and the theme. This creates a story that doesn’t feel cohesive and resonant.
However, if you understand what you’re doing and how story creates them, then you can accomplish two things.
1. You can consciously create anything you want to create within the realm of your story.
2. Perhaps most importantly, you can double-check and troubleshoot what isn’t working. If you get to the end of the story and you feel your theme is off the rails or nonexistent, you can go back and check what happened by asking, “Where do I need to work with the story in order to make the theme more powerful and pertinent?”
What Is Theme, Really?
The most important thing to understand about theme is that it doesn’t exist in a vacuum. It’s not its own thing within the story. It’s part of the greater whole. Specifically, it forms what I call “the trifecta” of plot, character, and theme. These three elements of story create each other; they do not exist by themselves in isolation. One necessarily creates the other.
We sometimes hear the idea of plot versus character , as if they were two totally separate things, when really they can’t be. The plot has to create the character, the character has to create the plot. Theme is the third part of that.
Here’s the thing: if you have a functional story that’s working, what that means is that all three of those things—plot, character, and theme—are working. Even if you’re not conscious of theme—even if you didn’t do it on purpose, so to speak—if all three are in cohesion with one another, that’s what you want. If you can bring consciousness to your administration of theme, then you can do it on purpose.
Here’s how it works. Let’s say you come up with an idea for a plot. Necessarily, there must be characters in that plot. Although it may take a little time, as you flesh out that plot in your mind, you will begin to understand what kind of people are driving this plot. What kind of people are interested in going to the places and achieving the things that you want to see happen in this plot?
This works in reverse as well. If you start with an idea for a character, obviously you don’t have anything for them to do until there’s a plot. So pretty soon you start getting ideas for what these characters will do. What are they interested in? How are they interacting with other people? What do they want? What are they moving toward? Suddenly, you have a plot. Plot and character are not separate. One necessarily creates and brings with it the other.
The same is true of theme.
How Plot and Character Arc Create Theme

Creating Character Arcs (Amazon affiliate link)
The interaction between plot and character is the engine that creates theme. We talked about in the last video about the Lie the Character Believes and how that creates this entire arc of the character’s evolution as they change their perspective, as they evolve into a new way of being and a new identity within the world. That’s character arc. And this new understanding of the world is something that has to be acted upon. It’s not just something happening in the character’s head. Otherwise, there’s no reason for the change to happen within the plot. It will be just an expression of philosophy, not a story. You have to bring this change of perspective into the action of the plot. Show what the character is going through, dramatize it through the events of the plot.
The events of the plot and the arrival of the conflict prompts the need for this change within the character. And then the change inside the character also allows them to evolve and grow what they’re doing in the external plot. If they remained the same, then either they wouldn’t be motivated to go on this story’s adventure at all or, depending on the type of story, the events of the plot will destroy them. They’ve got to evolve in order to survive. They’ve got to evolve in order to reach this next level of whatever it is the story wants them to achieve, whether that’s a relationship or a new job or saving the world or whatever the case may be. Some quiet literary stories really are just about changing that inner landscape. Whatever the case, this change must be proven in some way. It must be acted out within the plot.
Using Your Plot as a Thematic Metaphor
I like to think of the plot as a metaphor for whatever the character is changing internally , for the story’s Lie and Truth. Let’s say you start with the character’s Lie and Truth. And from there, you ask yourself what can the character do physically in the world that would dramatize and show this inner transformation from Lie to Truth.
An easy example of this would be The Hunger Games , in which the protagonist Katniss Everdeen follows a Flat Arc . This means she doesn’t change her perspective; she doesn’t grow from Lie to Truth. Instead, she uses her understanding of the Truth to change the world around her. In this case, that Truth would be her understanding that “oppression is no good,” that this Lie that has been fed to her country Panem by its oppressive government is that “their control is necessary to protect them” and the brutality of the Hunger Games is also necessary. Katniss begins her story understanding this is not true, as many people in her world do. What makes her an interesting character and protagonist is that her story gives her the opportunity to act on that Truth.
Specifically in this story, we can see how the entire premise of the Hunger Games—the entire scope of the plot in this story—is a very specific dramatization of her story’s Lie and Truth that allows her to go out and actively battle this oppression. She’s basically put in a cage and has to fight her way out. That’s a very explicit example of how your plot can operate as a thematic metaphor.

The Hunger Games (2012), Lionsgate.
When you’ve got plot and character working together beautifully, we might say one is proving the other. From this, we get a theme. Even if you try to paste on a different kind of a theme, the events of your story and how your character responds to them and interacts with them is what inevitably creates the theme. That is the point of your story; that is the message of your story. The thematic Truth that will be proved by the end of your story is whatever is shown by the events of the story. Whatever is effective in your story is your story’s Truth. This can be something very practical such as a skill, but it can also be just an effective perspective that the characters hold of themselves or the world (e.g., self-worth).
Using Plot and Characters to Identify Your Story’s Theme
When you approach a story from the idea that plot, theme, and character are all equal members of the equation and that necessarily one creates the other, it allows you to make sure you’re creating a cohesive cycle. And also, when you’re running into problems, it allows you to stop and check.
Let’s say you’re having problems with your theme. “I don’t know what my theme is.”
Look at your character’s arc and specifically at the Lie the Character Believes . Look at what they need to overcome by the time they get to the end of the story and therefore what Truth they’re moving toward. That Truth is usually a very specific and easy way to sum up your story’s theme.
You can also look at the events of the plot.
- What are the characters doing?
- What is happening?
- What is challenging them?
- Where do they fail?
- What do they have to do to succeed?
- How do they have to change in order to become someone who can succeed in gaining the plot goal within your story?
This is where you can start looking for a theme and vice versa.
Using Theme to Create Your Plot and Character Arcs
Let’s say you start out knowing you want to write a story about “love conquers all”—that’s your theme, that’s what you want to write about. There’s no reason you can’t start with just that. Now you have a map for determining what kind of characters and what kind of character arc will help exemplify this.
- How will they be challenged to grow into this?
- What Lie might oppose this idea?
- What events of the plot will be an interesting way to explore all aspects of this idea?

Story by Robert McKee (affiliate link)
Deepen Your Themes With the Thematic Square
This is where it can be really helpful to bring in a technique that Robert McKee wrote about in his book Story , which he called the Thematic Square . Start by examining your story’s thematic Truth from multiple perspectives. This prevents it from being just this simple black-and-white approach, i.e., “this is the wrong way to do it, and this is the right way to do it.” That approach is simplistic and can be on the nose and ultimately unconvincing to readers because that’s not really how it works for most of us most of the time in real life. If it was that simple, we’d always think, Ah, truth. I want to do that. I pick that one because obviously it’s better. It’s obviously going to be more effective and help me get what I want, what I need, and what’s good for me.
But it’s not that simple, right?
There are many shades and complexities to this evolution of perspective because the Lie and the Truth are actually never black and white. Rather, they represent an evolution along the spectrum, from a limited perspective to a broader perspective. Ideally, you want to be able to explore the complexities around this idea.
The Four Corners of the Thematic Square
You can do this, via McKee’s Thematic Square, by creating a square with four corners that represent four different sides or points of the thematic premise you’re exploring.

The Positive Thematic Statement
First and foremost, you have the Positive corner. Positive represents the story’s Truth. This is the good stuff you’re trying to posit in your story, i.e, “this is the way we should be”—whether the character embraces it and succeeds or fails to embrace it and fails within the story. This is the positive Truth you are suggesting is the best way for the characters to behave in this story. Examples of this would be Respect or Love. These are good qualities. These are things that we recognize as something we want to to embody in our lives, because they will help us to be more effective in whatever we’re doing.
The Contradictory Thematic Statement
Opposite that is the Contradictory corner. This represents something that is directly contradictory to the story’s positive Truth. At its simplest, this is the Lie. This is what stands opposed to the story’s Truth. In simple one-word explanations of what these might be, we have in opposition to Respect, Disrespect. In opposition to Love, we have Hate.
The Contrary Thematic Statement
Those two are obvious; they’re an obvious polarity. From there, you can start moving down to the bottom corners of your square and think about, first of all, what would be an element within this thematic exploration that would be Contrary to the Positive.
The word contrary always makes me think of somebody who’s being contrary: they’re just being annoying. They’re just being stubborn and refusing to see things. It’s not necessarily that they represent or are directly opposed to the argument, but they’re just refusing to do it. They’re opting out, saying, “talk to the hand,” as we used to say. The Contrary perspective wants to bypass the whole thematic argument. In some ways, this makes it more dangerous than the contradictory aspect, which at least is looking at the Truth—looking it in the eye and doing battle with it. In contrast, the Contrary aspect just wants to skip it. It doesn’t even want to engage with this Truth.
An example of this for a theme of Respect, could be Rudeness. Rudeness is passive-aggressive. “I don’t respect you, but I’m not actually doing you the service of coming to your face and telling you that either.” For Love, the Contrary aspect could be Indifference, which in many ways can be more painful than Hate in some relationships. We often say love is hate flipped on its head, with the idea being that if you can dig down there in the hate, you might be able to find love in the shadow and integrate it. Indifference, however, says, “I don’t care about you. You don’t exist to me. You’re dead to me. I don’t think about you at all.” And this can be more painful and certainly more difficult to move through toward that more positive Truth.
The Negated Thematic Statement
Finally, we have what McKee calls the Negation of the Negation . This is the Lie taken to its farthest extreme. It’s taken to such an extreme that it’s as if the Truth doesn’t exist. It rewrites reality. Over the course of the story, a Negation character will be given an opportunity to see the Truth and how it could potentially positively impact their life. But for whatever reason, they reject it and end up in a worse place than when they just believed the Lie or the Contradictory aspect.
In our example of Respect, the Negation of the Negation would be Self-Disrespect. Usually, even if someone disrespects someone else, there’s that place within their own ego where they are still standing within their own sense of identity and pride of self in opposition to something else. However, with Self-Disrespect, they can’t even respect themselves. If there isn’t even that ego container to hold their own identity, that is, in many ways, a worse place to be than if you’re just this egoic person disrespecting everybody else. It’s an almost plague-like effect. The seed of the Lie takes over the person’s entire being and life and perhaps beyond depending on the type of story you’re telling. The example McKee uses as the Negation of Love is Self-Hatred. Again, the Negation sees the character moving into a place where love doesn’t even exist in their universe.
How to Implement the Thematic Square in Your Story
One of the best ways to explore the Thematic Square is to have your protagonist represent any one of the thematic corners with the antagonistic force representing the polar opposite. Depending on whether you’re telling a Positive Change Arc , a Flat Arc , or a Negative Change Arc , your protagonist may or may not represent the Positive statement.
You can also use the Thematic Square to deepen this thematic complexity by looking for ways in which multiple characters—at least four characters—represent the different aspects of the square. This gives the protagonist a chance to interact with all of them, to be challenged by all of them, and to see the pros and the cons of each one so that they’re challenged. Their exploration of the theme will no longer be a simple binary choice between, “Oh, the Lie is bad and the Truth is better, so of course I’ll choose the Truth.” Rather, they have to move through all of these shadow aspects of the Lie and the Truth, to explore them, and to be challenged by them.
If your project uses characters to represent all four aspects, this also helps you develop and deepen the opportunities for your plot. Make sure every character’s actions, everything that’s happening, any opposition the protagonist faces from antagonistic forces is all thematically pertinent.
No thematic position in your story should be random. If the protagonist is trying to move toward a thematic Truth of “Love,” you don’t want another over here focusing on Freedom and Slavery. That’s a totally different theme. Of course, there can always be crossover—because ultimately everything is interconnected in real life. But applying the Thematic Square to your story can help you recognize which ideas don’t support the point of your story. If something doesn’t support the plot’s throughline and doesn’t support the protagonist’s individual arc, ask yourself how you could repurpose it so it informs the central theme.
Find Your Theme by Examining Your Story’s Ending
When thinking about how best to integrate theme into plot and character arc, look at how your story ends. The ending of your story—your Climactic Moment —will prove what your story was really about. This means it will prove what your theme is really about.
The decisions your characters make in the end, the perspectives they use to inform their choices and actions, as well as their ability to gain their plot goal—all of these things reveal your story’s theme. Examine the questions your story raises and the answers it ultimately ends up giving.
This does not mean that you need to end with some kind of moral of the story or with the mentor character coming out and giving a little speech about the lesson to be learned or something like that. Your story’s “answer” is simply whether or not the characters were effective and how they end up.
- Did they end in a better place physically, spiritually, emotionally, and mentally?
- Or is it a worse place?
If it’s a better place, then the story’s Truth (i.e., the “answer” to the questions that have been raised throughout the story), is “yes, this is an effective way of being in the world. This is a good course of action.”
If the characters fail, either ambiguously or definitively, then what the story is saying is “this is not a good way of being.” Such a story becomes, even without any need to create a moral of the story, a cautionary tale.
Find Your Theme by Examining Change and Consequence in Your Plot
Finally, think about how your story will develop change and consequence.
Change, both within your story’s character arcs and within the context of how your characters are able to enact change in the outer world of the story will prove what the story is really about. It will show you how your theme develops, what thematic questions are at play, and what answers the plot ultimately posits.
Specifically, think about consequences. Consequences aren’t always something negative. From a causal perspective, consequences can be something good. However, more often, consequences reveal a hard pill to swallow. Not only can consequences sometimes prove that “oops, the characters did not choose the best way of being. They did not choose the story’s Truth,” but consequences can also offer a resonant way to drive home that this path of change, this path of evolution that we’re all on within our lives, isn’t easy. It’s not cut and dried. It’s not black and white.
Again, if theme was simply “Lie versus truth— this is worse and this is better,” we’d always choose the right thing. There would be no need for stories because we’d always choose the right thing. Stories show us that there are, in fact, consequences even for choosing the right thing, for choosing what’s best for us, for choosing something we believe is in the best interest of ourselves and our communities and our world. Stories show us life isn’t simple, that there are always sacrifices, that letting go of a Lie or dealing with people who aren’t ready for us to let go of the Lie—it’s not easy. Embracing the Truth is often difficult.
Examining the consequences your characters face or could face if you deepen your story can be helpful in showing you not just your story’s theme, but how to deepen it and then explore all of the depth of it. Go into the shadows and explore the profundity of change. Ultimately, that’s what theme in story is about.
Admittedly, theme is an abstract concept. Zooming in and thinking of it in terms of plot and character makes it more concrete and easy to master within your story. Again, I’ve written a whole book about theme. So if you want more, you can check out Writing Your Story’s Theme .
Happy writing!
Wordplayers, tell me your opinions! What do you think is the most challenging part of writing strong themes in your stories? Tell me in the comments!
Click the “Play” button to Listen to Audio Version (or subscribe to the Helping Writers Become Authors podcast in Apple Podcast , Amazon Music , or Spotify ).
Love Helping Writers Become Authors? You can now become a patron. (Huge thanks to those of you who are already part of my Patreon family !)

Sign Up Today

Related Posts

K.M. Weiland is the award-winning and internationally-published author of the acclaimed writing guides Outlining Your Novel , Structuring Your Novel , and Creating Character Arcs . A native of western Nebraska, she writes historical and fantasy novels and mentors authors on her award-winning website Helping Writers Become Authors.
A superb post. I have struggled with theme in all my books. I don’t usually know what it is until I get to the end, but this is extremely helpful. I like the idea of the square, and I’ll definitely try it. I’m stuck in one story and I think it’ll help get me unstuck.
Theme is almost always present, even when we don’t plan it. The trick is learning how to recognize it, so we can strengthen it to best reflect the story’s events.
Thanks, Katie! I was just discussing Theme with a fellow writer, and I sent this link to her. It sure helped me!
With my Viking book, it took me forever to learn what the Theme is. For a while I thought it was faith and revenge, then I thought it was belonging, then I thought it was revenge again. Then I realized it was forgiveness, as a whole, but it also discusses God’s sovereignty and the need for us to let go of the past, both of which ties into the forgiveness aspect. The problem my book had was, the characters wanted one Theme, the plot said another, and I was forcing another on top of that. So… it was a mess. I read through your other posts concerning Theme, and learned a lot. The book’s going WAY better now. This video was a great reminder of what I’d learned, with a few new things added in.
I’ve noticed for myself that my themes rarely end up being exactly what I imagine they will be in the beginning. They develop along with the rest of the story.
Katie, you’ve given more context, flesh and meaning to my understanding of theme. I’ve used theme in other writing incorrectly. I kept looking for places to plug it in, and I never truly understood its relationship with the characters and the plot. Articles like this, I’ll read several times (printed it out) because there is more here with each reading.
All four corners of the Thematic Square is needed for the four leading characters in my story. Is that done? Is there something I should be weary of, cognizant of, should steer away from? All subplots merge into the main plot, and there’s just the one theme.
Oops! There it is.
“You can also use the Thematic Square to deepen this thematic complexity by looking for ways in which multiple characters—at least four characters—represent the different aspects of the square. This gives the protagonist a chance to interact with all of them, to be challenged by all of them, and to see the pros and the cons of each one so that they’re challenged.”
I didn’t read this until today, but I had concluded that, of course, I could utilize all 4 corners because they apply to people – the characters, and they’re not robots.
This is a long article, Katie. I’m humbled that I took the time out to reread and hi-light – we won’t even talk about my embarrassment.
So glad you enjoyed it!
That’s great! Developing all four corners of the square will help deepen your story’s complexity, which is always a good thing. Just be sure you’re aware of the difference between complexity and complication:
https://www.helpingwritersbecomeauthors.com/is-your-story-too-complicated/ https://www.helpingwritersbecomeauthors.com/7-tips-for-how-to-add-complexity-to-your-story/
I tried to write a story with a preexisting moral. I count six ways I made my story more difficult for me rather than for the characters. Primarily, I chose to tell a story about how you can help depression by helping others involving a lunatic busybody versus the moral-support-center of a dystopian group of people whose caste is called ‘Obsoletes.’ So imagine a paladin trying to convert a chaplain to the religion they already share. Specifically, my heroine wants to teach a terminal, burned out altruist to solve his trouble by thinking of other people. Assuming that people don’t hate on me for having the narrator keep narrating as a voice in his foil’s head for the last half of her final scene, I think I got through it. If you know the characters and respect them, they’ll come up with something. Specifically, she came up with The reason this dangerous life is worthwhile is because everybody we ever loved is with us. And then she realized that it was her–she had been relying on her implants to keep her sane, he had already figured it out.
“If you know the characters and respect them…”
This is so key!
Why are we programmed to write a story where the hero rides off into the sunset? Can we write outside of the box?
My opinion? It’s an overemphasis of certain archetypes at the expense of others. I’ve written about that here: https://www.helpingwritersbecomeauthors.com/how-to-write-archetypal-character-arcs/
In Hunger Games, the heroine is fighting against an oppressive government. That makes it political. I thought the books were too depressing to read. Unfortunately, that story is more truth than fiction. I am writing a trilogy of historical fiction starting in the Cold War, and ending in the Information War which began at the turn of the century. The characters react to a few events during their era, which gives me plot and character. History is caused by the choices and consequences of leaders in a country’s society or culture. Today, everything has become political. Since lies cause tyranny, the truth vs. lie theme has emerged quite strong in my stories. I think many of the literary classics have strong themes, which make them timeless.
“I think many of the literary classics have strong themes, which make them timeless.”
Great post! But I took exception to the first sentence in this statement: “You don’t want to come into a story to prove, for example, some political statement. Readers don’t want that. It doesn’t work within the story because it isn’t organic or it doesn’t flow. It feels, even if the author isn’t actually preaching at you, that they’re trying to jam some specific moral message into a story that doesn’t fit.”
I’m guessing George Orwell started “Animal Farm” and “1984” wanting to prove a political point. However, his stories are entertaining and the point “seems” to flow organically from the story.
The rest of your post shows how to avoid “jam some specific moral message into a story that doesn’t fit.”
I think the danger is that most of us will be so focused on the point that we write two-dimensional stories and characters that are trumped by the point we are trying to make. But I think we can “come into a story to prove” a statement, as long as we make sure the story is the prime focus.
For personal growth though, I think it is probably better if come into the story more open to possible challenges to the point we want to make. And I think that would probably result in a better story.
You’re right. There’s nothing wrong with coming into a story with a strong intention for the theme. The point I was trying to make was that the message can’t be shoehorned into the story, but must be strongly integrated with the premise and plot.
Yep. And you did make your point well.
Thank you for chiming in with the clarification!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Novel Outlining
- Storytelling Lessons From Marvel
As an Amazon Associate I earn from qualifying purchases.
Write Your Best Book

Check out my latest novel!

( affiliate link )

Free E-Book

Subscribe to Blog Updates
Subscribe to blog posts rss, sign up for k.m. weiland’s e-letter and get a free e-book, love helping writers become authors.
Return to top of page
Copyright © 2016 · Helping Writers Become Authors · Built by Varick Design

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Power and Corruption. Power corrupts, and absolute power corrupts absolutely. This theme is often closely related to "Man vs Society.". Additionally, "Power" can refer to a person's political leadership, personal wealth, physical prowess, etc. In the Time of the Butterflies by Julia Alvarez.
A theme is a universal idea, lesson, or message explored throughout a work of literature. One key characteristic of literary themes is their universality, which is to say that themes are ideas that not only apply to the specific characters and events of a book or play, but also express broader truths about human experience that readers can ...
Share your theme examples in the comments. Why theme matters for writers. ... Here are a few reasons you may want to think about theme in your writing: 1. Coherence. Theme can bring together the various parts of a story, including plot and subplot, characters, symbols, and motifs. Readers can feel the variations on a theme laced throughout your ...
Here's our list of common themes in literature: Love: the theme of love appears in novels within many genres, as it can discuss the love of people, pets, objects, and life. Love is a complex concept, so there are still unique takes on this theme being published every day. Death/Grief: the theme of death can focus on the concept of mortality ...
15. Hubris. Think of the hubris theme as the central character saying, "I'm great, am smarter than everyone else, and will do whatever I want because of it.". One of the most tragic themes in literature, this theme is designed to teach the reader a lesson about the limitations of human nature.
1 Map out themes and literary devices. Your story's theme should be on your mind throughout every stage of the writing process. As you brainstorm, think about the statements you want to make in your work. Jot these down, then jot down any potential symbols or concepts you can use to illustrate these statements.
Thematic Essay Checklist. State a focused main argument about the theme. Hook the reader and introduce the theme. Begin each with a clear topic sentence related to the theme. Use specific examples, quotes, or facts. Explain how the evidence supports the thesis. Link analysis back to the central theme throughout.
Why do some stories draw you back again and again? Compelling characters and authentic dialogue play a role, as do heart-stopping action scenes and heart-rending romances. And while the greatest stories ever written have a mix of these elements, there is one ingredient that stands out above the rest, catapulting works from commercial stardom to critical success and classic status: a strong ...
The theme is the underlining idea an author is trying to convey to an audience. A story without major ideas for the character and reader to experience, think through, and learn from is not a story at all. A story, by its very nature, must have a theme, sometimes many major and minor themes, all throughout.
Examples here include Angie Thomas's The Hate U Give, Richard Powers' The Overstory, and Ruth Ozeki's A Tale for the Time Being. 📚 Our list of the best memoirs is sure to find you some more hopeful books to read. 8. Love. * Sighs in lovestruck ️ * Ah, yes.
Of course, theme is an essential literary device in terms of written works. However, nearly all works of art feature theme as an underlying meaning to be understood and interpreted by the audience.Here are some famous examples of Disney movies and their related themes:. Peter Pan: out-growing the world of childhood; Mulan: girls/women can do battle as honorably as boys/men
The definition of theme can be broken into two categories: the thematic concept of a work and the thematic statement. The thematic concept refers to what a reader understands the work to be about, while the thematic statement refers to what the work says about that subject in question. The thematic concept thus is usually an abstract concept, like "love" or "solitude" as we said before ...
Cormac McCarthy's The Road is a bleak dystopian exploration of the relationship between a man and his son as they struggle to survive in a harsh and unforgiving environment. 7. Courage and heroism. Tales of heroism and courage in the face of adversity have been popular for hundreds, if not thousands of years.
Examples in Literature. "To Kill a Mockingbird" by Harper Lee is a strong example, with Atticus Finch standing up against societal racism. He is an outcast lawyer who is the only man willing to represent a Black man who is framed for a crime in a deeply racist town. 3. The Hero's Journey.
For example, you may introduce the role of nature plays in the text to discuss the theme of good and evil. The first sentence of your body paragraph should discuss the role of nature. This will set up the paragraph and let the reader know what the focus of the paragraph will be. 3. Use examples from the text.
Literature Themes in literature are often varied and hidden. Sometimes you can get through an entire book and not realize what the author meant. However, this is a good basic list that you can build from. Remember that some books… Read more →</a></p>
Thematic writing is a staple of high school English and college writing courses. The idea behind thematic writing is to create a piece that uses a theme to tie together different ideas or topics. Thematic writing can be used for essays, short stories, novels, and even non-fiction pieces. In academic writing, thematic essays often center on a ...
Use these common theme examples found in famous literary works to understand its importance. ... The mood can evoke an emotional response from your readers, helping them connect with your writing piece. In a way, the mood the author establishes creates an emotional setting. One of the ways mood can be established is through the point of view in ...
EXAMPLES OF THEMES. You might like to choose one of the following examples of themes - that appeals to you and try writing a story about it. Alienation - The effects of, the loneliness of, to cure it. Ambition - getting what you want, stunted by, thwarted. Betrayal - the pain of, in love and friendship. Coming of age - loss of innocence.
Get inspiration for writing a powerful thematic statement with these examples. Explore what these statements are and samples to help with your own. ... Take a look at different theme statement examples of love lessons in literature. Love taken to extremes can become dangerous. Loving yourself, despite your flaws, can lead to a happier life.
Examples and Observations (definition #1): "Simply put, a story's theme is its idea or point (formulated as a generalization). The theme of a fable is its moral; the theme of a parable is its teaching; the theme of a short story is its implied view of life and conduct. Unlike the fable and parable, however, most fiction is not designed ...
Explore. Featured Essays Essays on the Radio; Special Features; 1950s Essays Essays From the 1950s Series; Browse by Theme Browse Essays By Theme Use this feature to browse through the tens of thousands of essays that have been submitted to This I Believe. Select a theme to see a listing of essays that address the selected theme. The number to the right of each theme indicates how many essays ...
Themes in literature are generally universal to any type of literature and center around ideas and concepts that apply to human beings, nature, and life in general. Themes can be found in poetry ...
The interaction between plot and character is the engine that creates theme. We talked about in the last video about the Lie the Character Believes and how that creates this entire arc of the character's evolution as they change their perspective, as they evolve into a new way of being and a new identity within the world. That's character arc. And this new understanding of the world is ...