- Greater Jakarta
- BINUS @Greater Jakarta
- BINUS @Bekasi
- BINUS @Bandung
- BINUS @Malang
- BINUS @Semarang
- Master of Computer Science
- Master of Digital Economy
- Master of Information System Management
- Master of Digital Business Fisheries
- Master of Marine Digital Technology
- Master of Industrial Engineering
- Master of Accounting
- Master of Communication
- Master of Design
- Doctor of Computer Science
- Program Profesi Insinyur
- Admission Calendar S2
- Admission Calendar S3
- Tuition Fee
- ADMISSION PROCEDURE
- Entry Requirements BINUS GRADUATE PROGRAM
- Register Now !
- Event / News

Skripsi, Tesis, dan Disertasi, Apa Saja Perbedaannya?

Istilah skripsi, tesis, dan disertasi seharusnya terdengar familier di telinga mahasiswa. Sekilas ketiganya tampak serupa, yaitu suatu dokumen tertulis yang dibuat mahasiswa sesuai kaidah penulisan baku, sistematis, serta memakai metode ilmiah. Kemudian, tugas akhir tersebut dipertanggungjawabkan di hadapan penguji dan dosen pembimbing.
Namun, skripsi, tesis, dan disertasi adalah tiga jenis tugas akhir yang berbeda. Bukan hanya sekadar jenjang pendidikan saja, tetapi juga mencakup kualitas isi dokumen tertulis tersebut. Apa saja faktor yang membedakan ketiganya? Yuk, simak ulasan lengkap berikut ini.
Jenjang Pendidikan
Seperti diketahui, skripsi adalah tugas akhir yang dibuat untuk meraih gelar sarjana. Sementara, tesis merujuk pada karya ilmiah tertulis jenjang magister atau pascasarjana (S2). Disertasi menjadi karya tulis ilmiah mahasiswa yang hendak menyelesaikan program doktoral atau S3.
Permasalahan yang Diangkat
Kedalaman permasalahan yang diangkat juga jadi pembeda jelas antara ketiganya. Skripsi mengangkat masalah yang bersumber pada pengalaman empirik dan bersifat tidak mendalam. Tesis juga dapat berasal dari pengalaman empirik, tetapi bersifat mendalam dan teoritis. Disertasi berangkat dari kajian teoritis dengan dukungan fakta empirik sehingga permasalahan yang digali sangat mendalam dan spesifik.
Proses Penulisan
Proses penulisan berkaitan erat dengan kemandirian penulis saat pengerjaan tugas akhir. Pada skripsi, mahasiswa masih memperoleh bimbingan cukup intensif dari pembimbing dengan porsi 60% penulis dan 40% pembimbing. Persentase ini menurun saat pengerjaan tesis karena penulis berperan 80% dalam prosesnya. Ketika membuat disertasi, penulis bertanggung jawab 90% atas karya tulis ilmiah tersebut dengan sedikit pendampingan dari pembimbing.
Bobot Ilmiah Karya Tulis
Dari sudut pandang akademik, skripsi memiliki bobot ilmiah pada tingkat rendah hingga sedang. Tesis menempati bobot ilmiah sedang sampai tinggi dengan adanya pengembangan dan pendalaman teori serta penelitian yang dilakukan. Disertasi mempunyai bobot ilmiah tertinggi sehingga mahasiswa wajib menemukan teori baru atau terobosan lain untuk memperkaya bidang yang digelutinya.
Cara Pemaparan
Dari bobot ilmiah, pasti kamu bisa memperkirakan seperti apa cara pemaparan masing-masing tugas akhir. Skripsi biasanya dominan pemaparan deskriptif. Tesis dipaparkan dengan analitis dan deskriptif. Sementara itu, pemaparan disertasi biasanya bersifat analitis sehingga benar-benar mengupas tuntas permasalahan yang diusung.
Model Analisis dan Jumlah Rumusan Masalah
Dengan model analisis rendah sampai sedang, jumlah rumusan masalah yang diangkat skripsi berkisar satu sampai dua masalah saja. Untuk menyelesaikan tesis, paling tidak mahasiswa harus siap menemukan tiga rumusan masalah yang memakai model analisis tingkat sedang hingga tinggi. Artinya, disertasi mengandalkan model analisis tinggi dengan lebih dari tiga rumusan masalah.
Metode Statistik yang Digunakan
Secara umum, skripsi banyak menggunakan uji kualitatif atau uji deskriptif, uji statistik non parametrik (chi kuadrat, tes binomial, run test), uji statistik parametrik, uji hipotesis asosiatif, dan uji hipotesis komparatif. Kadang bisa juga memakai regresi, korelasi, dan uji beda.
Sementara itu, tesis kerap menggunakan uji regresi ganda atau kualitatif lanjut, multivariat dan multivariat lanjutan (persamaan simultan, data panel, regresi logistik, ekonometrika statis dan dinamis, dst), SEM, dan path analysis. Metode serupa juga digunakan pada pengerjaan disertasi, tetapi dalam cakupan lebih kompleks dan berbobot.
Jenjang Pembimbing dan Penguji
Pembimbing dan penguji minimal memiliki gelar magister untuk mahasiswa yang mengerjakan skripsi. Untuk penggarapan tesis, mahasiswa akan mendapatkan pembimbing maupun penguji dari doktor dan magister berpengalaman. Sementara, pada pembuatan disertasi, profesor dan doktor berpengalaman mengambil peran tersebut.
Keaslian Penelitian
Skripsi dapat berupa replika penelitian yang sudah ada, tetapi mengangkat tempat berbeda. Tesis mengutamakan keaslian penelitian, sedangkan disertasi harus asli alias belum pernah dilakukan sebelumnya karena diharuskan mengembangkan sesuatu yang baru.
Publikasi Penelitian
Skripsi minimal memiliki 20 daftar pustaka sehingga dapat dipublikasikan dalam lingkup internal kampus dan nasional. Tesis harus mempunyai minimal 40 daftar pustaka dan sebaiknya hasil penelitian dipublikasikan minimal skala nasional. Disertasi harus mengandung minimal 60 daftar pustaka agar dapat dipublikasikan secara nasional maupun internasional.
Demikian perbedaan skripsi, tesis, dan disertasi yang perlu kamu ketahui. Setelah mempelajari perbedaan ketiganya, jangan sampai salah lagi memakai istilah tugas akhir ini ya!
Last updated : November 06, 2021 00:00
Your browser is not fully compatible with the features of our website.
Home / Guides / Citation Guides / APA Format / How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in APA
How to Cite a Thesis or Dissertation in APA
In this citation guide, you will learn how to reference and cite an undergraduate thesis, master’s thesis, or doctoral dissertation. This guide will also review the differences between a thesis or dissertation that is published and one that has remained unpublished. The guidelines below come from the 7th edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (2020a), pages 333 and 334. Please note that the association is not affiliated with this guide.
Alternatively, you can visit EasyBib.com for helpful citation tools to cite your thesis or dissertation .
Guide Overview
Citing an unpublished thesis or dissertation, citing a published dissertation or thesis from a database, citing a thesis or dissertation published online but not from a database, citing a thesis or dissertation: reference overview, what you need.
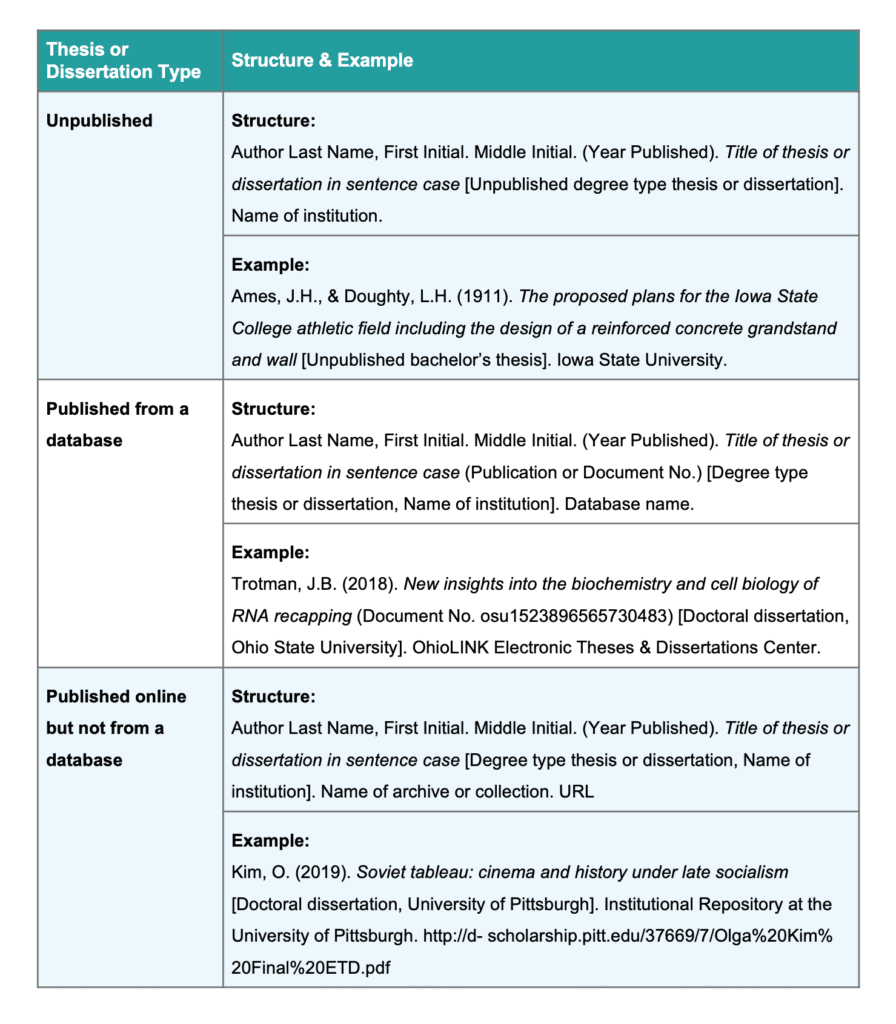
Since unpublished theses can usually only be sourced in print form from a university library, the correct citation structure includes the university name where the publisher element usually goes.
Author’s last name, F. M. (Year published). Title in sentence case [Unpublished degree type thesis or dissertation]. Name of institution.
Ames, J. H., & Doughty, L. H. (1911). The proposed plans for the Iowa State College athletic field including the design of a reinforced concrete grandstand and wall [Unpublished bachelor’s thesis]. Iowa State University.
In-text citation example:
- Parenthetical : (Ames & Doughty, 1911)
- Narrative : Ames & Doughty (1911)
If a thesis or dissertation has been published and is found on a database, then follow the structure below. It’s similar to the format for an unpublished dissertation/thesis, but with a few differences:
- The institution is presented in brackets after the title
- The archive or database name is included
Author’s last name, F. M. (Year published). Title in sentence case (Publication or Document No.) [Degree type thesis or dissertation, Name of institution]. Database name.
Examples 1:
Knight, K. A. (2011). Media epidemics: Viral structures in literature and new media (Accession No. 2013420395) [Doctoral dissertation, University of California, Santa Barbara]. ProQuest Dissertations Publishing.

Trotman, J.B. (2018). New insights into the biochemistry and cell biology of RNA recapping (Document No. osu1523896565730483) [Doctoral dissertation, Ohio State University]. OhioLINK Electronic Theses & Dissertations Center.
In the example given above, the dissertation is presented with a Document Number (Document No.). Sometimes called a database number or publication number, this is the identifier that is used by the database’s indexing system. If the database you are using provides you with such a number, then include it directly after the work’s title in parentheses.
If you are interested in learning more about how to handle works that were accessed via academic research databases, see Section 9.3 of the Publication Manual.
In-text citation examples :
- Parenthetical citation : (Trotman, 2018)
- Narrative citation : Trotman (2018)
Author’s last name, F. M. (Year Published). Title in sentence case [Degree type thesis or dissertation, Name of institution]. Name of archive or collection. URL
Kim, O. (2019). Soviet tableau: cinema and history under late socialism [Doctoral dissertation, University of Pittsburgh]. Institutional Repository at the University of Pittsburgh. https://d-scholarship.pitt.edu/37669/7/Olga%20Kim%20Final%20ETD.pdf
Stiles, T. W. (2001). Doing science: Teachers’ authentic experiences at the Lone Star Dinosaur Field Institute [Master’s thesis, Texas A&M University]. OAKTrust. https://hdl.handle.net/1969.1/ETD-TAMU-2001-THESIS-S745
It is important to note that not every thesis or dissertation published online will be associated with a specific archive or collection. If the work is published on a private website, provide only the URL as the source element.
In-text citation examples:
- Parenthetical citation : (Kim, 2019)
- Narrative citation : Kim (2019)
- Parenthetical citation : (Stiles, 2001)
- Narrative citation : Stiles (2001)
| Unpublished | Author last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year Published). [Unpublished degree type thesis or dissertation]. Name of institution | Ames, J.H., & Doughty, L.H (1911). [Unpublished bachelor’s thesis]. Iowa State University. |
| Published from a database | Author last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year Published). (Publication or Document No.) [Degree type thesis or dissertation, Name of institution]. Database name. | Trotman, J.B. (2018). (Document No. osu1523896565730483) [Doctoral dissertation, Ohio State University]. OhioLINK Electronic Thesis & Dissertations Center |
| Published online but not from a database | Author last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year Published). [Degree type thesis or dissertation, Name of institution]. Name of archive or collection. URL | Kim, O. (2019). [Doctoral dissertation, University of Pittsburgh]. Institutional Repository at the University of Pittsburgh. http://d-scholarship.pitt.edu/37669/7/Olga%20Kim%20Final%20ETD.pdf |
We hope that the information provided here will serve as an effective guide for your research. If you’re looking for even more citation info, visit EasyBib.com for a comprehensive collection of educational materials covering multiple source types.
If you’re citing a variety of different sources, consider taking the EasyBib citation generator for a spin. It can help you cite easily and offers citation forms for several different kinds of sources.
To start things off, let’s take a look at the different types of literature that are classified under Chapter 10.6 of the Publication Manual :
- Undergraduate thesis
- Master’s thesis
- Doctoral dissertation
You will need to know which type you are citing. You’ll also need to know if it is published or unpublished .
When you decide to cite a dissertation or thesis, you’ll need to look for the following information to use in your citation:
- Author’s last name, and first and middle initials
- Year published
- Title of thesis or dissertation
- If it is unpublished
- Publication or document number (if applicable; for published work)
- Degree type (bachelor’s, master’s, doctoral)
- Thesis or dissertation
- Name of institution awarding degree
- DOI (https://doi.org/xxxxx) or URL (if applicable)
Since theses and dissertations are directly linked to educational degrees, it is necessary to list the name of the associated institution; i.e., the college, university, or school that is awarding the associated degree.
To get an idea of the proper form, take a look at the examples below. There are three outlined scenarios:
- Unpublished thesis or dissertation
- Published thesis or dissertation from a database
- Thesis or dissertation published online but not from a database
American Psychological Association. (2020a). Publication manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). https://doi.org/10.1037/0000165-000
American Psychological Association. (2020b). Style-Grammar-Guidelines. https://apastyle.apa.org/style-grammar-guidelines/citations/basic-principles/parenthetical-versus-narrative
Published August 10, 2012. Updated March 24, 2020.
Written and edited by Michele Kirschenbaum and Elise Barbeau. Michele Kirschenbaum is a school library media specialist and the in-house librarian at EasyBib.com. Elise Barbeau is the Citation Specialist at Chegg. She has worked in digital marketing, libraries, and publishing.
APA Formatting Guide
APA Formatting
- Annotated Bibliography
- Block Quotes
- et al Usage
- In-text Citations
- Multiple Authors
- Paraphrasing
- Page Numbers
- Parenthetical Citations
- Reference Page
- Sample Paper
- APA 7 Updates
- View APA Guide
Citation Examples
- Book Chapter
- Journal Article
- Magazine Article
- Newspaper Article
- Website (no author)
- View all APA Examples
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
To cite a published thesis in APA style, it is important that you know some basic information such as the author, publication year, title of the thesis, institute name, archive name, and URL (uniform resource locator). The templates for an in-text citation and reference list entry of a thesis, along with examples, are given below:
In-text citation template and example:
Use the author surname and the publication year in the in-text citation.
Author Surname (Publication Year)
Cartmel (2007)
Parenthetical:
(Author Surname, Publication Year)
(Cartmel, 2007)
Reference list entry template and example:
The title of the thesis is set in sentence case and italicized. Enclose the thesis and the institute awarding the degree inside brackets following the publication year. Then add the name of the database followed by the URL.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the thesis [Master’s thesis, Institute Name]. Name of the Database. URL
Cartmel, J. (2007). Outside school hours care and schools [Master’s thesis, Queensland University of Technology]. EPrints. http://eprints.qut.edu.au/17810/1/Jennifer_Cartmel_Thesis.pdf
To cite an unpublished dissertation in APA style, it is important that you know some basic information such as the author, year, title of the dissertation, and institute name. The templates for in-text citation and reference list entry of an online thesis, along with examples, are given below:
Author Surname (Year)
Averill (2009)
(Author Surname, Year)
(Averill, 2009)
The title of the dissertation is set in sentence case and italicized. Enclose “Unpublished doctoral dissertation” inside brackets following the year. Then add the name of the institution awarding the degree.
Author Surname, F. M. (Publication Year). Title of the dissertation [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Name of the Institute.
Averill, R. (2009). Teacher–student relationships in diverse New Zealand year 10 mathematics classrooms: Teacher care [Unpublished doctoral dissertation]. Victoria University of Wellington.
APA Citation Examples
Writing Tools
Citation Generators
Other Citation Styles
Plagiarism Checker
Upload a paper to check for plagiarism against billions of sources and get advanced writing suggestions for clarity and style.
Get Started
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
APA Formatting and Style Guide (7th Edition)

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
In-Text Citations
Resources on using in-text citations in APA style
Reference List
Resources on writing an APA style reference list, including citation formats
Other APA Resources
Generate accurate APA citations for free
- Knowledge Base
- APA Style 7th edition
- APA format for academic papers and essays
APA Formatting and Citation (7th Ed.) | Generator, Template, Examples
Published on November 6, 2020 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on January 17, 2024.
The 7th edition of the APA Publication Manual provides guidelines for clear communication , citing sources , and formatting documents. This article focuses on paper formatting.
Generate accurate APA citations with Scribbr
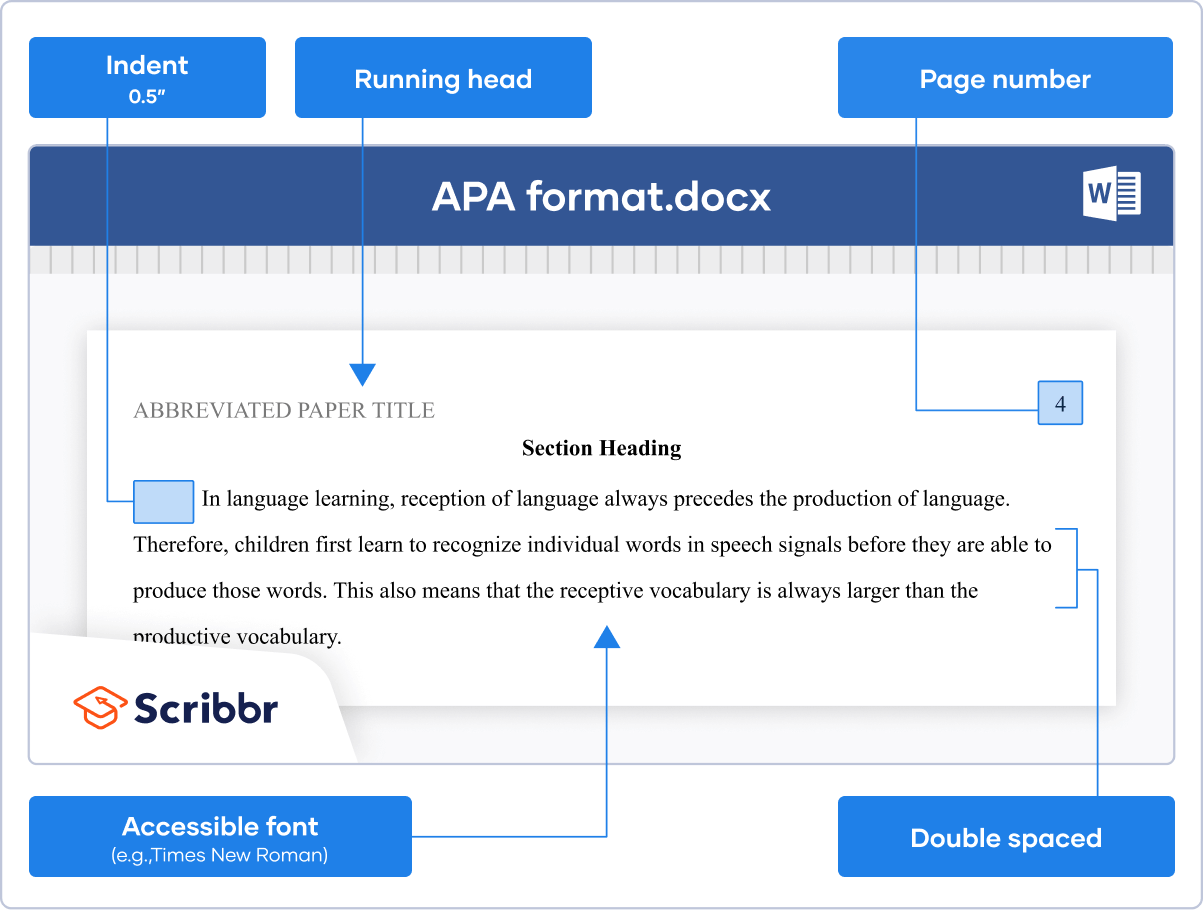
Throughout your paper, you need to apply the following APA format guidelines:
- Set page margins to 1 inch on all sides.
- Double-space all text, including headings.
- Indent the first line of every paragraph 0.5 inches.
- Use an accessible font (e.g., Times New Roman 12pt., Arial 11pt., or Georgia 11pt.).
- Include a page number on every page.
Let an expert format your paper
Our APA formatting experts can help you to format your paper according to APA guidelines. They can help you with:
- Margins, line spacing, and indentation
- Font and headings
- Running head and page numbering
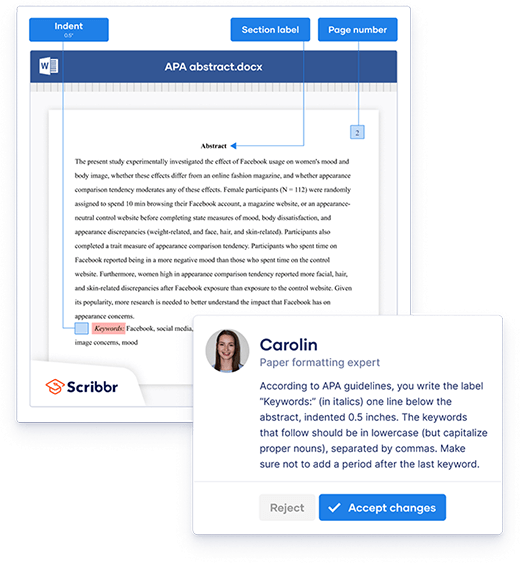
Table of contents
How to set up apa format (with template), apa alphabetization guidelines, apa format template [free download], page header, headings and subheadings, reference page, tables and figures, frequently asked questions about apa format.
Are your APA in-text citations flawless?
The AI-powered APA Citation Checker points out every error, tells you exactly what’s wrong, and explains how to fix it. Say goodbye to losing marks on your assignment!
Get started!

References are ordered alphabetically by the first author’s last name. If the author is unknown, order the reference entry by the first meaningful word of the title (ignoring articles: “the”, “a”, or “an”).
Why set up APA format from scratch if you can download Scribbr’s template for free?
Student papers and professional papers have slightly different guidelines regarding the title page, abstract, and running head. Our template is available in Word and Google Docs format for both versions.
- Student paper: Word | Google Docs
- Professional paper: Word | Google Docs
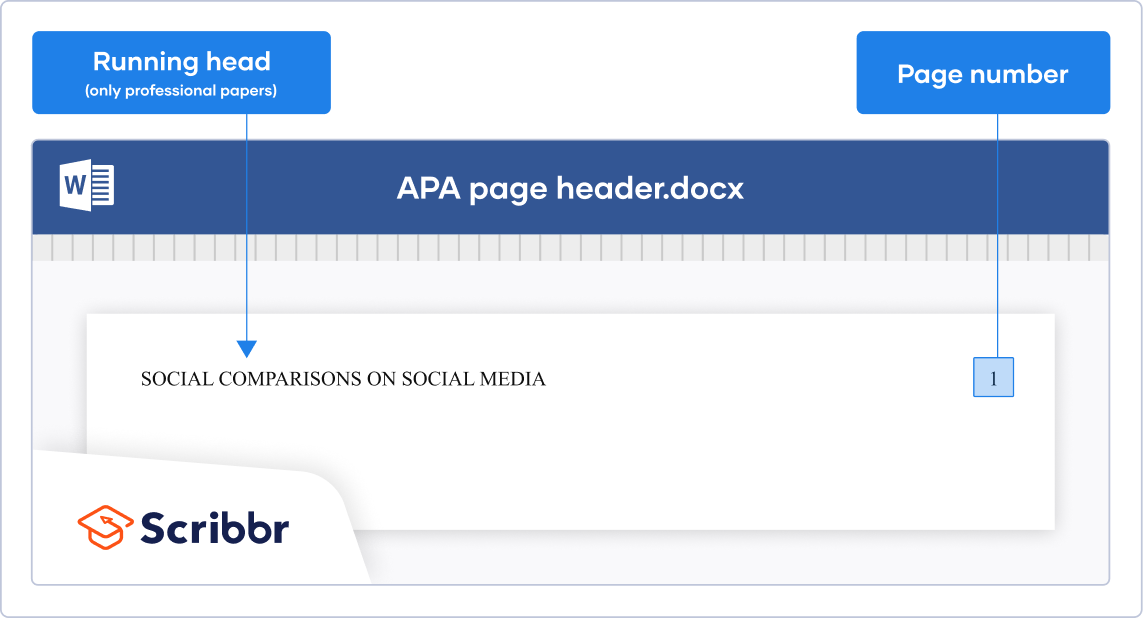
In an APA Style paper, every page has a page header. For student papers, the page header usually consists of just a page number in the page’s top-right corner. For professional papers intended for publication, it also includes a running head .
A running head is simply the paper’s title in all capital letters. It is left-aligned and can be up to 50 characters in length. Longer titles are abbreviated .
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
APA headings have five possible levels. Heading level 1 is used for main sections such as “ Methods ” or “ Results ”. Heading levels 2 to 5 are used for subheadings. Each heading level is formatted differently.
Want to know how many heading levels you should use, when to use which heading level, and how to set up heading styles in Word or Google Docs? Then check out our in-depth article on APA headings .
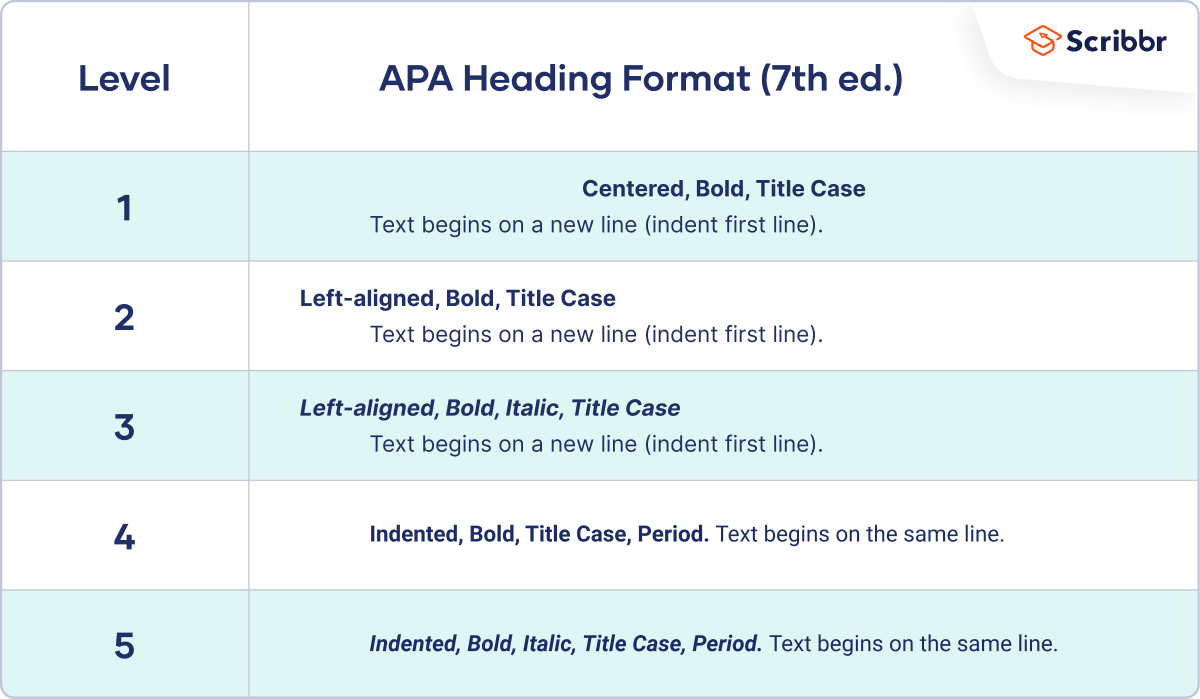
The title page is the first page of an APA Style paper. There are different guidelines for student and professional papers.
Both versions include the paper title and author’s name and affiliation. The student version includes the course number and name, instructor name, and due date of the assignment. The professional version includes an author note and running head .
For more information on writing a striking title, crediting multiple authors (with different affiliations), and writing the author note, check out our in-depth article on the APA title page .
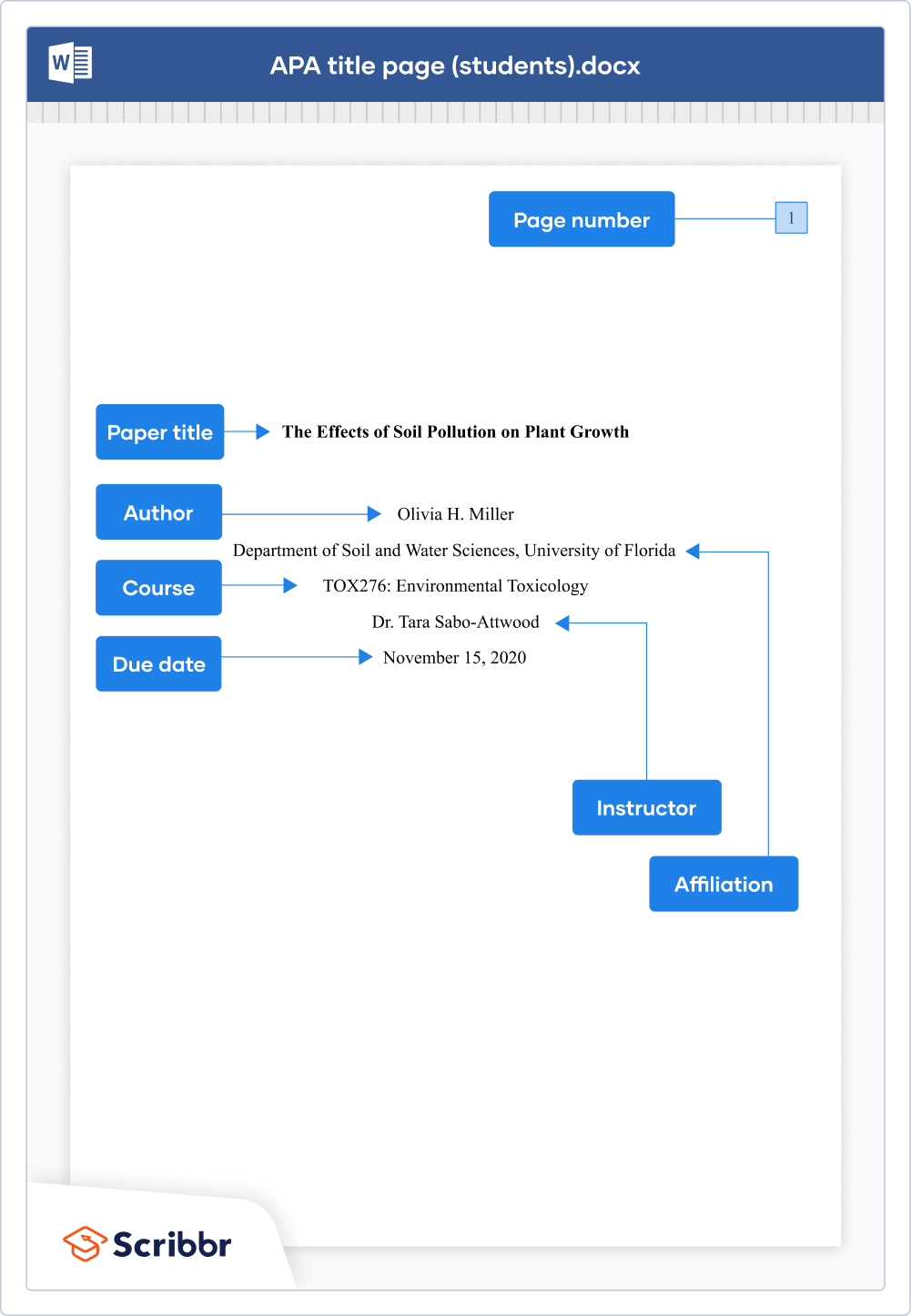
The abstract is a 150–250 word summary of your paper. An abstract is usually required in professional papers, but it’s rare to include one in student papers (except for longer texts like theses and dissertations).
The abstract is placed on a separate page after the title page . At the top of the page, write the section label “Abstract” (bold and centered). The contents of the abstract appear directly under the label. Unlike regular paragraphs, the first line is not indented. Abstracts are usually written as a single paragraph without headings or blank lines.
Directly below the abstract, you may list three to five relevant keywords . On a new line, write the label “Keywords:” (italicized and indented), followed by the keywords in lowercase letters, separated by commas.
APA Style does not provide guidelines for formatting the table of contents . It’s also not a required paper element in either professional or student papers. If your instructor wants you to include a table of contents, it’s best to follow the general guidelines.
Place the table of contents on a separate page between the abstract and introduction. Write the section label “Contents” at the top (bold and centered), press “Enter” once, and list the important headings with corresponding page numbers.
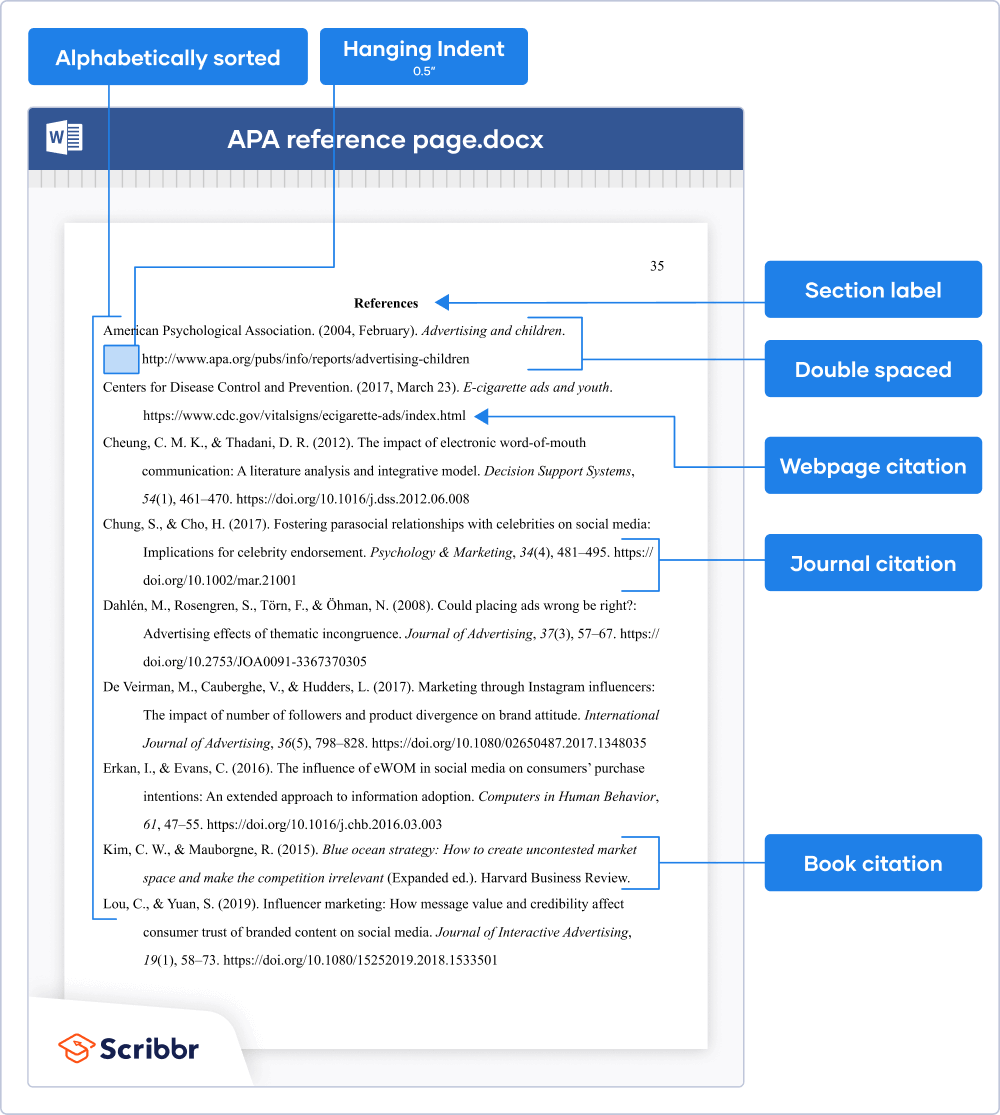
The APA reference page is placed after the main body of your paper but before any appendices . Here you list all sources that you’ve cited in your paper (through APA in-text citations ). APA provides guidelines for formatting the references as well as the page itself.
Creating APA Style references
Play around with the Scribbr Citation Example Generator below to learn about the APA reference format of the most common source types or generate APA citations for free with Scribbr’s APA Citation Generator .
Formatting the reference page
Write the section label “References” at the top of a new page (bold and centered). Place the reference entries directly under the label in alphabetical order.
Finally, apply a hanging indent , meaning the first line of each reference is left-aligned, and all subsequent lines are indented 0.5 inches.
Tables and figures are presented in a similar format. They’re preceded by a number and title and followed by explanatory notes (if necessary).
Use bold styling for the word “Table” or “Figure” and the number, and place the title on a separate line directly below it (in italics and title case). Try to keep tables clean; don’t use any vertical lines, use as few horizontal lines as possible, and keep row and column labels concise.
Keep the design of figures as simple as possible. Include labels and a legend if needed, and only use color when necessary (not to make it look more appealing).
Check out our in-depth article about table and figure notes to learn when to use notes and how to format them.
The easiest way to set up APA format in Word is to download Scribbr’s free APA format template for student papers or professional papers.
Alternatively, you can watch Scribbr’s 5-minute step-by-step tutorial or check out our APA format guide with examples.
APA Style papers should be written in a font that is legible and widely accessible. For example:
- Times New Roman (12pt.)
- Arial (11pt.)
- Calibri (11pt.)
- Georgia (11pt.)
The same font and font size is used throughout the document, including the running head , page numbers, headings , and the reference page . Text in footnotes and figure images may be smaller and use single line spacing.
You need an APA in-text citation and reference entry . Each source type has its own format; for example, a webpage citation is different from a book citation .
Use Scribbr’s free APA Citation Generator to generate flawless citations in seconds or take a look at our APA citation examples .
Yes, page numbers are included on all pages, including the title page , table of contents , and reference page . Page numbers should be right-aligned in the page header.
To insert page numbers in Microsoft Word or Google Docs, click ‘Insert’ and then ‘Page number’.
APA format is widely used by professionals, researchers, and students in the social and behavioral sciences, including fields like education, psychology, and business.
Be sure to check the guidelines of your university or the journal you want to be published in to double-check which style you should be using.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2024, January 17). APA Formatting and Citation (7th Ed.) | Generator, Template, Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 28, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/apa-style/format/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, apa title page (7th edition) | template for students & professionals, creating apa reference entries, beginner's guide to apa in-text citation, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

APA Style 7th Edition
- Single Author
- Two Authors
- Three to 20 Authors
- More Than 20 Authors
- Hyphenated Name
- Hyphenated Surname
- Two-part Surname
- Names with Suffixes such as Jr. and III
- Author - Malay Names (without family names)
- Author - Chinese Names
- Author - Chinese Names with English Names
- Author - Indian & Sikh Names (without surname / family name)
- Inherited Names
- Conferred titles
- Local Government Institution as Author
- Foreign Government Institution as Author
- Unique Corporate Body Names
- Organization as Author
- Group Authors (If more than one organization as author)
- Conference Names with Numbers
- Author Unavailable
- Page Numbers
- Narrative Citations
- Parenthetical Citations
- Combining Citations
- Articles in Periodicals
- Encyclopedia
- Secondary Source
- Government Document
- Private Organization Report
- Conference Papers
- Electronic Source
- Webpages and Websites
- Computer Software / Mobile Apps
- Other Non-Print Sources
- Social Media
|
| ||
| Academic Exercise / Thesis (Unpublished) | , W. Y. (2019).
Universiti
[Unpublished academic exercise]; [Unpublished master’s thesis]; [Unpublished doctoral dissertation] | Cheah, 2019) Cheah (2019).
|
| Master's Thesis / Doctoral Dissertation from a commercial database |
[Academic exercise]; [Master’s thesis]; [Doctoral dissertation]. |
|
| Master’s Thesis / Doctoral Dissertation from an institutional database (sometimes referred to as a Commons / Digital Archives) or Online | L. (2019). [Doctoral dissertation, Royal Institute of KTH Diva-Portal.
(2020).
[Master’s thesis, Universiti Malaya University of Malaya Student Repository.
[Master’s thesis]; [Doctoral dissertation]. |
(Aini Hayati Abdul Rahim, 2020) Aini Hayati Abdul Rahim (2020) |
- << Previous: Conference Papers
- Next: Electronic Source >>
- Last Updated: Sep 30, 2022 12:07 PM
- URL: https://umlibguides.um.edu.my/c.php?g=939660

APA Style is a set of guidelines for effective scholarly communication that helps writers present their ideas in a clear, precise, and inclusive manner. It is used by millions of people worldwide in psychology, social sciences, and many other disciplines for the preparation of manuscripts for publication as well as for writing student papers, dissertations, and theses. APA Style is described in the seventh edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association , which is a reference book that contains comprehensive guidelines on how to set up a scholarly paper; format a title page, tables, figures, and other paper elements; create references and in-text citations; and write without bias, as well as on punctuation, grammar, and writing style. For more information, please see the APA Style website .
The primary reference for APA Style is the seventh edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association . Information on the manual and its companion products, including the student-focused Concise Guide to APA Style and the digital Mastering APA Style Student Workbook , can be found on the APA Style website .
Search Support Center
Search all Support Center
Contact Support
Top Questions
- How does the APA define "psychology"?
- What are the qualifications to become licensed as a psychologist in the U.S.?
- Can psychologists prescribe medications for their patients?
- How can I join APA?
19 Mei 2022
Memahami perbedaan skripsi, tesis, dan disertasi.
Artikel - FAS,
Artikel - FET,
Artikel - FOB,
Artikel - FOE,
Skripsi, tesis, dan disertasi mungkin sudah tidak asing terdengar di telinga kalangan mahasiswa. Terutama istilah skripsi yang mungkin menjadi salah satu hal yang kerap jadi bahan pembicaraan mahasiswa bahkan anak-anak Sekolah Menengah Atas. Perbedaan skripsi dan tesis perlu dipahami agar tidak salah persepsi.
Sebenarnya, tiga istilah itu sebenarnya memiliki fungsi yang sama, yakni sebagai syarat mendapatkan gelar alias syarat kelulusan. Jadi, ketika anda mendengar ada seseorang sedang mengerjakan skripsi, tesis, atau disertasi, berarti orang itu merupakan mahasiswa tingkat akhir.
Namun, karena namanya berbeda, tentunya istilah-istilah itu pasti memiliki perbedaan. Dalam hal ini, mahasiswa wajib mengetahui perbedaan di antara ketiganya agar tidak salah ketika sedang mengerjakannya.
Lantas dimana letak perbedaan skripsi, tesis, dan disertasi? Berikut adalah penjelasan lengkapnya.
Apa itu Skripsi?
Skripsi pada dasarnya merupakan sebutan untuk tugas akhir yang digunakan sebagai syarat kelulusan bagi mahasiswa tingkat sarjana di perguruan tinggi. Skripsi ini bisa dibilang istilah yang digunakan di Indonesia.
Sedangkan secara umum, skripsi adalah suatu karya ilmiah yang dibuat sesuai dengan sistematika yang telah ditetapkan dan dapat dipertanggungjawabkan sebagai persyaratan untuk mendapatkan gelar sarjana.
Karena sifatnya wajib bisa dipertanggungjawabkan, penulisan skripsi harus melalui riset-riset yang valid dan juga mencari referensi dari sumber yang terpercaya. Skripsi juga tidak bisa ditulis secara sembarangan, tetapi ada sistematika yang harus dipatuhi untuk menyelesaikannya.
Permasalahan yang kerap dirasakan oleh mahasiswa ketika menyusun skripsi umumnya terkait dengan sumber argumen, sumber data, sampai analisis hasil penelitiannya. Hal itu terjadi karena penulisan skripsi tidak bisa asal meng copy-paste argumen dari orang lain. Mahasiswa dituntut untuk bisa menguraikan hasil buah pikirannya sendiri dengan dasar dan sumber yang terpercaya. Hal tersebutlah yang mungkin membuat skripsi dianggap menakutkan bagi sebagian mahasiswa.
Selain bertujuan untuk mendapatkan gelar S-1, skripsi juga digunakan sebagai bentuk pengembangan ilmu pengetahuan yang telah dipelajari selama meniti bangku perkuliahan. Skripsi bisa mengembangkan ilmu pengetahuan karena setiap mahasiswa nyaris pasti memiliki tema skripsi yang berbeda-beda, sehingga selalu ada pengetahuan baru yang dihasilkan dari hasil skripsi.
Berdasarkan metode pengambilan datanya, skripsi memiliki tiga metode, yaitu kualitatif, kuantitatif, dan gabungan (mix-method). Perbedaan skripsi kualitatif dan kuantitatif terletak pada data yang didapatkan. Kualitatif lebih bersifat deskriptif, sedangkan kuantitatif lebih bersifat numerik atau angka-angka.
Sementara metode campuran merupakan gabungan dari kualitatif dan kuantitatif.
Apa itu Tesis?
Jika skripsi untuk sarjana, maka tesis ini adalah tahapan selanjutnya. Jadi tesis pada dasarnya juga menjadi tugas akhir sebagai syarat kelulusan, tetapi untuk jenjang magister (S-2). Jadi tesis ini juga digunakan untuk menggambarkan kemampuan seorang mahasiswa terkait dengan disiplin ilmu tertentu yang lebih spesifik.
Tesis adalah suatu karya ilmiah yang disusun berdasarkan hasil penelitian empiris untuk nantinya dijadikan bahan kajian akademis. Sama seperti skripsi, tesis pun juga harus dapat dipertanggungjawabkan dan sesuai aturan tertentu.
Tesis disusun secara lebih mendalam ketimbang skripsi, selain itu tesis juga dikerjakan dengan minim bimbingan dari dosen. Sebisa mungkin, tesis bisa menghasilkan penemuan baru yang berguna bagi ilmu pengetahuan atau masyarakat.
Dari segi sistematika penulisan, tesis dan skripsi sebenarnya masih tetap sama. Metode penelitian tesis juga terbagi menjadi tiga, yakni kualitatif, kuantitatif, dan campuran.
Salah satu ciri-ciri dari penulisan tesis adalah sikap dari penulisnya adalah objektif, maksudnya adalah karya disampaikan dengan menggunakan gaya bahasa impersonal, pasif, serta tanpa menggunakan kata ganti orang pertama atau kedua.
Selain syarat kelulusan, tesis juga bisa dijadikan bahan rekomendasi terkait dengan isu yang diangkat pada tesis.
Apa itu Disertasi?
Disertasi merupakan karya tulis ilmiah dengan level yang lebih tinggi lagi dibanding skripsi dan tesis, jadi disertasi ini digunakan sebagai syarat untuk mendapatkan kelulusan pada jenjang doktoral atau S-3.
Disertasi adalah karya tulis ilmiah yang berkaitan dengan penemuan baru sesuai dengan program jurusan yang ditempuh oleh mahasiswa. Disertasi ini bisa dibilang juga sebagai pengembangan lebih lanjut tesis.
Karena semakin tinggi tingkatannya, maka tingkat kesulitan menulis disertasi juga lebih tinggi dibanding tesis dan skripsi.
Mahasiswa S-3 dituntut untuk bisa menghasilkan penemuan penting dan harus benar-benar melakukan penelitian secara mandiri. Penemuan penting yang dimaksudkan ini bisa dalam bentuk ide, barang, atau saran yang berpengaruh bagi masyarakat maupun ilmu pengetahuan.

Perbedaan Skripsi, Tesis, dan Disertasi
Dari penjelasan mengenai skripsi, tesis, dan disertasi di atas sebenarnya sudah terlihat dimana letak perbedaannya. Namun, secara jika diuraikan berikut ini adalah perbedaan tiga karya ilmiah di atas:
|
| ||
| Sarjana (S-1) | Magister (S-2) | Doktoral (S-3) | |
| Pengalaman empirik yang bersifat mendalam atau tidak. | Pengalaman empirik, teoritik, dan bersifat lebih mendalam. | Didapat dari kajian teoritik yang telah didukung oleh faktor empirik serta lebih mendalam jika dibandingkan skripsi dan tesis. | |
| 60% Mahasiswa Mandiri 40% Dosen Pembimbing | 80% Mahasiswa Mandiri 20% Dosen Pembimbing | 90% Mahasiswa Mandiri 10% Pembimbing | |
| Cenderung rendah ke sedang. | Cenderung sedang ke tinggi. | Cenderung tinggi karena diharuskan menghasilkan penemuan, ide, atau terobosan untuk ilmu pengetahuan. | |
| Deskriptif | Deskriptif-Analitis | Analitis | |
| Rendah-Sedang | Sedang-Tinggi | Tinggi | |
| Jumlah rumusan masalah sekitar 1-2. | Minimal rumusan masalah berjumlah 3. | Harus memiliki lebih dari 3 rumusan masalah. | |
| Menggunakan uji statistik parametrik dan nonparametrik, uji deskriptif, Chi kuadrat, serta uji hipotesis komparatif, asosiatif, korelasi, regresi, uji beda, dll. | Menggunakan uji regresi ganda atau korelasi ganda, multivariat, path analysis, SEM, dll. | Lebih kompleks lagi karena dituntut menemukan teori baru. | |
| Dosen minimal S-2. | Dosen minimal S-3. | Profesor dan Doktor. | |
| Internal kampus dan sebisa mungkin nasional. | Minimal level nasional. | Nasional dan internasional. |
Persamaan Skripsi, Tesis, dan Disertasi
Setelah melihat perbedaannya, kini kita beralih pada persamaan skripsi, tesis, dan disertasi. Persamaan itu antara lain:
- Sama-sama bentuk dari karya tulis ilmiah.
- Harus dapat dipertanggungjawabkan.
- Dilarang plagiasi.
- Sebagai syarat kelulusan.
- Dalam bentuk dokumen tertulis.
- Harus ditulis sesuai dengan kaidah penulisan karya tulis ilmiah, seperti penggunaan bahasa dan struktur penulisan.
- Meskipun targetnya berbeda, tetapi ketiga karya tulis ilmiah itu wajib dipublikasikan.
- Sumber argumentasi harus berasal dari sumber yang valid dan terpercaya.
Demikian perbedaan skripsi dan tesis serta disertasi yang perlu diketahui. Biasanya, baik skripsi maupun tesis menjadi salah satu syarat untuk mahasiswa meraih gelar akademik sesuai jenjang pendidikan yang diambil. Nantinya, kedua hal itu dapat menjadi pertimbangan dalam karir profesional mereka.
Di Sampoerna Academy , mahasiswanya akan mendapatkan layanan konseling karir yang mana akan sangat membantu perkembangan karirnya di dunia profesional. Selain itu, ada pula pengembangan mahasiswa berupa pelatihan yang dirancang untuk membantu mahasiswa meraih kesuksesan baik secara akademik maupun profesional nantinya.
Referensi Sevima – Perbedaan skripsi dan thesis
Recent Post

Mengenal SAP Consultant Dan Cara Menjadi SAP Consultant

Apa Itu Game Development? Scope Kerja Dan Jenjang Karirnya

7 Bisnis Model Yang Paling Populer
Share This Article
Recent More

Jun, 20 2024
Apa Itu SAP Consultant? Konsultan SAP adalah seorang profesional yang ahli dalam sistem perangkat...

Dunia game telah menjadi bagian tak terpisahkan dari kehidupan modern. Bagi banyak orang, game...

Jun, 15 2024
Di era yang penuh dengan persaingan dan dinamika, bisnis model menjadi pedoman penting bagi...
Apa Itu Tesis? Ini Bedanya dengan Disertasi

Tesis adalah karya tulis yang dibuat oleh mahasiswa jenjang S2 guna memperoleh gelar magister dari perguruan tinggi. Apa bedanya dengan skripsi dan disertasi?
Kamus Besar Bahasa Indonesia, mengartikan tesis sebagai pernyataan atau teori yang didukung oleh argumen yang dikemukakan dalam karangan untuk mendapatkan gelar magister.
Sedangkan dalam buku "Tesis dan Disertasi dalam Kebenaran Ilmiah" karya Muhtar, dijelaskan bahwa tesis adalah karya tulis akademik hasil studi dan/atau penelitian mendalam yang dilakukan secara mandiri.
ADVERTISEMENT
SCROLL TO CONTINUE WITH CONTENT
Apa Beda Tesis dengan Disertasi?
Jika tesis ditempuh guna mendapatkan gelar magister, maka disertasi ditulis untuk mendapatkan gelar doktor. Pada hakekatnya adalah pengembangan lebih lanjut dari suatu tesis.
Namun yang membedakan dari tesis adalah keluasan (extensive) dan kedalaman (depth) dari pembuktian tesa-nya harus lebih detail dan maju (advance).
Idealnya suatu disertasi harus lebih dari sekedar pengujian teori, tetapi harus membuka kemungkinan pengajuan suatu terobosan teoritis yang baru.
Oleh karena itu, metodologi penelitian disertasi umumnya harus lebih "advance", karena fokusnya lebih kepada membuat model teoritis baru.
Jadi bisa dikatakan, disertasi berisi sumbangan baru bagi perkembangan ilmu pengetahuan, atau menemukan jawaban baru bagi masalah ilmu pengetahuan.
Poin Perbedaan Tesis dengan Disertasi:
Melansir laman resmi Binus University dan Institut Teknologi Surabaya, berikut ini beberapa perbedaan antara tesis dengan disertasi.
Penulisan tesis bertujuan untuk mengembangkan pengetahuan/teknologi/seni menghasilkan Karya yang Inovatif dan Teruji.
Sementara penulisan disertasi memiliki tujuan untuk menemukan atau mengembangkan teori/konsepsi/ gagasan ilmiah baru (kreatif, original, dan teruji).
2. Permasalahan yang Diangkat
Tesis menggunakan pendekatan Multidisiplin atau Interdisiplin. Tesis bisa berasal dari pengalaman empirik, tetapi bersifat mendalam dan teoritis.
Sedangkan disertasi wajib dilakukan dengan pendekatan Interdisiplin dan Multidisiplin atau Transdisiplin. Disertasi bisa berangkat dari kajian teoritis dengan dukungan fakta empirik sehingga permasalahan yang digali sangat mendalam dan spesifik.
3. Proses Penulisan
Pada proses penulisan tesis, persentase pendampingan hanya 20%, sementara sisanya 80% adalah tanggung jawab penulis. Untuk disertasi, penulis bertanggung jawab 90% atas karya tulis ilmiah dan hanya sedikit pendampingan dari pembimbing.
4. Bobot Ilmiah Karya Tulis
Dari sudut pandang akademik, tesis menempati bobot ilmiah sedang sampai tinggi dengan adanya pengembangan dan pendalaman teori serta penelitian yang dilakukan.
Disertasi mempunyai bobot ilmiah tertinggi sehingga mahasiswa wajib menemukan teori baru atau terobosan lain untuk memperkaya bidang yang digelutinya.
5. Publikasi Penelitian
Tesis harus mempunyai minimal 40 daftar pustaka dan sebaiknya hasil penelitian dipublikasikan minimal skala nasional.
Sedangkan disertasi harus mengandung minimal 60 daftar pustaka agar dapat dipublikasikan secara nasional maupun internasional.
Nah, itulah penjelasan mengenai tesis dan beberapa perbedaannya dengan disertasi. Semoga menambah wawasan detikers ya!
Desy Ratnasari Angkat Tema Perempuan Politisi untuk Disertasinya
Daftar 78 formasi cpns lkpp 2024, terbuka untuk lulusan d3 hingga s2, bmkg buka 250 formasi cpns 2024, ini besaran gaji yang ditawarkan, 50 contoh motto hidup bagi mahasiswa, inspiratif dan penuh semangat, kisah rosemary fowler, fisikawan yang dapat gelar doktor di usia 98 tahun, aliansi mahasiswa-polisi gelar deklarasi damai jelang pilkada di bandung, viral mahasiswa pulang kkn, anak-anak menangis sampai tarik kakinya, gubernur kalteng minta dinas kukm bantu mahasiswa gali potensi wirausaha, terima kasih dari erina gudono untuk kaesang mau temani kuliah di as.

Universitas Indonesia

Universitas Gadjah Mada

Universitas Diponegoro

Universitas Airlangga

Institut Pertanian Bogor
5 Hari Lagi - Sebelum Event Webinar Nasional: Strategi Sukses Mempersiapkan Pendaftaran CPNS Tahun 2024 bagi Guru Dimulai.
Dunia Kampus • 05 Sep 2020
Pengertian dan Perbedaan Skripsi, Tesis, dan Disertasi?

Fadhol SEVIMA

SEVIMA.COM – Pengertian skripsi, tesis dan disertasi. Apakah anda yang saat ini sedang proses pembuatan tugas akhir untuk tugas kuliah? dan masih bingung dengan perbedaan Skripsi, Tesis, dan Disertasi. Biar bisa fokus untuk pengerjaan, yuk kita mengenal apa itu skripsi, tesis dan disertasi.
Sebelum membahas lebih jauh, Anda harus tahu juga persamaannya; secara akademik Skripsi , Tesis, dan Disertasi memiliki persamaan yaitu merupakan dokumen tertulis yang merupakan tugas akhir para mahasiswa, mengikuti kaidah penulisan yang baku dan sistematis, dan menggunakan metode ilmiah yang dapat dipertanggung jawabkan di depan dosen pembimbing dan penguji.
Baca juga: Apa Itu OBE, Penerapan dan Penilaiannya?
Apa Pengertian dan Perbedaan Skripsi, Tesis, dan Disertasi?
Apa itu skripsi? Tugas akhir atau biasa disebut skripsi adalah istilah yang di gunakan di Indonesia untuk mendapatkan gelar sarjana dari perguruan tinggi. Skripsi suatu karya untuk menghasilkan ilmu pengetahuan atau sesuatu yang dapat di pertanggung jawabkan secara ilmiah dan di kerjakan menurut aturan dan tata cara tertentu.
Tujuan skripsi secara umum bertujuan untuk mengembangkan ilmu dari berbagai pengetahuan yang telah di pelajari selama bangku perkuliahan. Mahasiswa wajib menulis skripsi selain untuk syarat kelulusan juga untuk memberi pengetahuan dan ketrampilannya dalam menganalisis, menggambarkan dan menjelaskan ilmu yang sedang di tulisnya.
Apa itu tesis? Tesis adalah tugas akhir jenjang magister (S2). Thesis salah satu karya ilmiah tertulis yang disusun secara individual berdasarkan hasil penelitian empiris untuk dijadikan bahan kajian akademis. Tesis merupakan pernyataan atau teori yang didukung oleh argumen-argumen untuk dikemukakan, merupakan hasil dari studi yang sistematis atas masalah, tesis mengandung metode pengumpulan, analisis dan pengolahan data, dan menyajikan kesimpulan serta mengajukan rekomendasi.
Disertasi adalah karya tulis ilmiah resmi akhir seorang mahasiswa dalam penyelesaian program S3. Disertasi merupakan bukti kemampuan mahasiswa dalam melakukan penelitian yang berhubungan dengan penemuan baru dalam program ilmu yang di pilih seorang mahasiswa S3. Nah, sekarang kita juga mengetahui perbedaan skripsi, tesis dan disertasi, berikut.
Perbedaan Skripsi, Tesis dan Disertasi
| 1 | S1 | S2 | S3 (tertinggi) | |
| 2 | Dapat diangkat dari pengalaman empirik, tidak mendalam | Diangkat dari pengalaman empirik, dan teoritik, bersifat mendalam | Diangkat dari kajian teoritik yang didukung fakta empirik, bersifat sangat mendalam | |
| 3 | 60% peran penulis, 40% pembimbing | 80% peran penulis, 20% pembimbing | 90% peran penulis, 10% pembimbing | |
| 4 | Rendah – sedang | Sedang – tinggi. Pendalaman / pengembangan terhadap teori dan penelitian yang ada | Tinggi, Tertinggi dibidang akademik. Diwajibkan mencari terobosan dan teori baru dalam bidang ilmu pengetahuan | |
| 5 | Dominan deskriptif | Deskriptif dan Analitis | Dominan analitis | |
| 6 | Rendah – sedang | Sedang – tinggi | Tinggi | |
| 7 | Sekitar 1-2 | Minimal 3 | Lebih dari 3 | |
| 8 | Biasanya memakai uji Kualitatif / Uji deskriptif, Uji statistik parametrik (uji 1 pihak, 2 pihak), atau Statistik non parametrik (test binomial, Chi kuadrat, run test), uji hipotesis komparatif, uji hipotesis asosiatif, Korelasi, Regresi, Uji beda, Uji Chi Square, dll | Biasanya memakai uji Kualitatif lanjut / regresi ganda, atau korelasi ganda, mulitivariate, multivariate lanjutan (regresi dummy, data panel, persamaan simultan, regresi logistic, Log linier analisis, ekonometrika static & dinamik, time series ekonometrik) Path analysis, SEM | Sama dengan tesis dengan metode lebih kompleks, berbobot yang bertujuan mencari terobosan dan teori baru dalam bidang ilmu pengetahuan | |
| 9 | Minimal Magister | Minimal Doktor dan Magister yang berpengalaman | Minimal Profesor dan Doktor yang berpengalaman | |
| 10 | Bisa replika penelitian orang lain, tempat kasus berbeda | Mengutamakan orisinalitas | Harus orisinil | |
| 11 | Tidak harus | Diutamakan | Diharuskan | |
| 12 | Kampus Internal dan disarankan nasional | Minimal Nasional | Nasional dan Internasional | |
| 13 | Minimal 20 | Minimal 40 | Minimal 60 | |
| 14 | Kualitatif / Manual, Excel, SPSS dll | Kualitatif lanjut / SPSS, Eview, Lisrel, Amos dll | Kualitatif lanjut / SPSS, Eview, Lisrel, Amos dll |
Itukah pembahasan apa pengertian dan perbedaan skripsi, tesis, dan disertasi. Bagaimana sekarang kamu tidak bingung lagi, dan kamu bisa fokus untuk mengerjakan tugas akhirmu, semoga cepat lulus ya, agar bisa nyelesaiin tugas-tugas yang lain seperti tesis S2 dan disertasi S3.

Mengenal SEVIMA
SEVIMA merupakan perusahaan Edutech (education technology) yang telah berkomitmen sejak tahun 2004 dalam menyelesaikan kendala kerumitan administrasi akademik di pendidikan tinggi (Universitas, Sekolah Tinggi, Institut, Politeknik, Akademi, dll.) dengan 99% keberhasilan implementasi melalui SEVIMA Platform, segera jadwalkan konsultasi di: Kontak Kami
Artikel Terkait

Dunia Kampus • 15 Aug 2024
[Update] Ini Cara Melaporkan Penilaian Mahasiswa pada Neo Feeder

Awas! Bukan Hanya Persentase, Ini Kunci Sukses Pelaporan PDDIKTI

Dunia Kampus • 09 Aug 2024
Ingin Meningkatkan Jumlah Responden Tracer Study? Daftar Webinar SEVIMA Ini Sekarang!

Tak Lagi Jadi Beban, Inilah Solusi Perguruan Tinggi Meningkatkan Responden Tracer Study
Sedang trending.

Dunia Kampus • 25 Jul 2024
Mengenal PEMUTU (Pemantauan, Evaluasi & Penjaminan Mutu PT/PS) Kemendikbud

Dunia Kampus • 30 Jul 2024

Mengenal Portal Penomoran Ijazah dan Sertifikasi Nasional (PISN)

Dunia Kampus • 31 May 2024
Mengenal Perkuliahan Sistem Blok pada Fakultas Kedokteran

Event | Pendaftaran • 03 Jul 2024
Webinar Nasional: Kiat Jitu Mempersiapkan dan Lulus Pendaftaran Program Profesi Guru Prajabatan serta Dalam Jabatan (2 JP)
Berita terbaru.

Berita Terbaru • 28 Aug 2024
SAMARINDA – KOPDAR SEVIMA COMMUNITY: Diskusi Meningkatkan Penerimaan Mahasiswa Baru dengan Digitalisasi & Branding Ibu Kota Nusantara

Berita Terbaru • 27 Aug 2024
KUOTA PENUH – Strategi Sukses Menyusun dan Mengimplementasikan Kurikulum MBKM

Executive Training SPMI & Auditor AMI: Sukses Menyusun & Menerapkan SPMI & AMI Perguruan Tinggi, untuk Wujudkan Kampus serta Prodi yang Unggul & Berkelas Dunia!

Webinar Nasional: Kiat Sukses Pembelajaran Daring Kolaboratif (PDK) dan Memanfaatkan Artificial Inteligence untuk Perkuliahan di Kampus

- Mode Terang
- Gabung Kompas.com+
- Konten yang disimpan
- Konten yang disukai
- Berikan Masukanmu

- Megapolitan
- Surat Pembaca
- Kilas Daerah
- Kilas Korporasi
- Kilas Kementerian
- Sorot Politik
- Kilas Badan Negara
- Kelana Indonesia
- Kalbe Health Corner
- Kilas Parlemen
- Konsultasi Hukum
- Infrastructure
- Apps & OS
- Tech Innovation
- Kilas Internet
- EV Leadership
- Elektrifikasi
- Timnas Indonesia
- Liga Indonesia
- Liga Italia
- Liga Champions
- Liga Inggris
- Liga Spanyol
- Internasional
- Relationship
- Beauty & Grooming
- Sadar Stunting
- Smartpreneur
- Kilas Badan
- Kilas Transportasi
- Kilas Fintech
- Kilas Perbankan
- Tanya Pajak
- Kilas Investasi
- Sorot Properti
- Tips Kuliner
- Tempat Makan
- Panduan Kuliner Yogyakarta
- Beranda UMKM
- Jagoan Lokal
- Perguruan Tinggi
- Pendidikan Khusus
- Kilas Pendidikan
- Jalan Jalan
- Travel Tips
- Hotel Story
- Travel Update
- Nawa Cahaya
- Ohayo Jepang
- Kehidupan sehat dan sejahtera
- Air bersih dan sanitasi layak
- Pendidikan Berkualitas
- Energi Bersih dan Terjangkau
- Penanganan Perubahan Iklim
- Ekosistem Lautan
- Ekosistem Daratan
- Tanpa Kemiskinan
- Tanpa Kelaparan
- Kesetaraan Gender
- Pekerjaan Layak dan Pertumbuhan ekonomi
- Industri, Inovasi & Infrastruktur
- Berkurangnya Kesenjangan
- Kota & Pemukiman yang Berkelanjutan
- Konsumsi & Produksi yang bertanggungjawab

Mahasiswa, Pahami Perbedaan Skripsi, Tesis dan Disertasi
Kompas.com edu.
Mahar Prastiwi,
Albertus adit.
Tim Redaksi
Mahar Prastiwi
Penulis albertus adit.
Skripsi adalah tugas akhir yang dibuat untuk meraih gelar sarjana. Sementara, tesis merujuk pada karya ilmiah tertulis jenjang magister atau pascasarjana (S2). Disertasi menjadi karya tulis ilmiah mahasiswa yang hendak menyelesaikan program doktoral atau S3.
Permasalahan yang diangkat
Kedalaman permasalahan yang diangkat juga jadi pembeda jelas antara ketiga karya ilmiah ini. Skripsi mengangkat masalah yang bersumber pada pengalaman empirik dan bersifat tidak mendalam.
Tesis juga dapat berasal dari pengalaman empirik, tetapi bersifat mendalam dan teoritis. Sedangkan disertasi berasal dari kajian teoritis dengan dukungan fakta empirik sehingga permasalahan yang digali sangat mendalam dan spesifik.
Baca juga: Siswa, Ketahui Ragam Tarian dari Jawa Barat dan Sejarah Singkatnya
Proses penulisan
Proses penulisan berkaitan erat dengan kemandirian penulis saat pengerjaan tugas akhir. Pada skripsi, mahasiswa masih memperoleh bimbingan cukup intensif dari pembimbing dengan porsi 60 persen penulis dan 40 persen pembimbing.
Persentase ini menurun saat pengerjaan tesis karena penulis berperan 80 persen dalam prosesnya. Ketika membuat disertasi, penulis bertanggung jawab 90 persen atas karya tulis ilmiah tersebut dengan sedikit pendampingan dari pembimbing.
Bobot ilmiah karya tulis
Dari sudut pandang akademik, skripsi memiliki bobot ilmiah pada tingkat rendah hingga sedang. Tesis menempati bobot ilmiah sedang sampai tinggi dengan adanya pengembangan dan pendalaman teori serta penelitian yang dilakukan.
Disertasi mempunyai bobot ilmiah tertinggi sehingga mahasiswa wajib menemukan teori baru atau terobosan lain untuk memperkaya bidang yang digelutinya.
Baca juga: Mahasiswa, Ini 6 Tingkat Kemampuan Bahasa Inggris, Kamu di Level Mana?
Cara pemaparan
Skripsi biasanya dominan pemaparan deskriptif. Tesis dipaparkan dengan analitis dan deskriptif. Sementara itu, pemaparan disertasi biasanya bersifat analitis sehingga benar-benar mengupas tuntas permasalahan yang diusung.
Model analisis dan jumlah rumusan masalah
Dengan model analisis rendah sampai sedang, jumlah rumusan masalah yang diangkat skripsi berkisar satu sampai dua masalah saja. Untuk menyelesaikan suatu tesis, paling tidak mahasiswa harus siap menemukan tiga rumusan masalah yang memakai model analisis tingkat sedang hingga tinggi.
Artinya, disertasi mengandalkan model analisis tinggi dengan lebih dari tiga rumusan masalah.
Metode statistik yang digunakan
Secara umum, skripsi banyak menggunakan uji kualitatif atau uji deskriptif, uji statistik non-parametrik (chi kuadrat, tes binomial, run test), uji statistik parametrik, uji hipotesis asosiatif, dan uji hipotesis komparatif. Kadang bisa juga memakai regresi, korelasi, dan uji beda.
Sementara itu, tesis kerap menggunakan…
Tag sarjana doktoral pascasarjana mahasiswa tingkat akhir perguruan tinggi beda skripsi, tesis dan disertasi.

Bank Mandiri Buka Lowongan Kerja bagi Lulusan S1-S2, Buruan Daftar

Dosen UB Bagikan 5 Tips Jaga Kesehatan Kulit di Musim Hujan
Pakar UGM: Virus Flu Burung Kecil Kemungkinan Jadi Wabah Baru

Mahasiswa, Ini 6 Tingkat Kemampuan Bahasa Inggris, Kamu di Level Mana?

Siswa, Ketahui Ragam Tarian dari Jawa Barat dan Sejarah Singkatnya

Begini Praktik Baik PTM Terbatas Jenjang PAUD di Aceh dan Trenggalek

Terkini Lainnya

Pemerintah Prioritaskan Guru Status P1 dalam Seleksi ASN PPPK 2024

H-3 Reklaim atau Klaim Ulang Akun KIP Kuliah 2024 Ditutup, Ini Caranya

Kemendikbud: Penerima PIP Tak Perlu Berjuang 2 Kali agar Dapat KIP Kuliah

Apakah Guru Swasta Bisa Ikut PPPK 2024? Cek Jawabannya

Bimbel Salam Cendekia Bekali Siswa dengan Strategi Hadapi Tes Kompetitif

PPPK 2024 Dibuka September, Cek Syarat dan Daftar di sscasn.bkn.go.id

OSN Tingkat SMA dan MA 2024 Dibuka, Diikuti Sekolah Luar Negeri

Siswa Indonesia Raih 3 Medali di Olimpiade Astronomi Internasional

Ikuti Festival Handai Indonesia 2024, WNA Diuji Kemahirannya Berbahasa Indonesia

KJMU Tahap II Tahun 2024 Dibuka, Daftar Klik p4op.jakarta.go.id

Seleksi PPPK 2024 Belum Dibuka, BKN Ingatkan 2 Hal Ini

Baznas-BRIN Beri Beasiswa Riset, Terbuka bagi Mahasiswa S1-S3

Kemendikbud Targetkan Penerima PIP Langsung Dapat KIP Kuliah di 2025

Link banpt.or.id "Error"? Ini Cara Cek Akreditasi di Situs Web Kampus

Data BPS: Angkatan Kerja Lulusan Diploma-Sarjana Terbanyak dari Perkotaan
4 perguruan tinggi yang bisa kuliah d3-s1 gratis, lulusannya jadi tni pangkat letda, syarat daftar kuliah di unhan, gratis dan lulus berpangkat letnan dua, cara cek akreditasi kampus lewat link banpt.or.id, buat cpns 2024, beasiswa s2-s3 ke irlandia, tanpa batas usia dan tunjangan rp 534 juta, 12 kementerian, lembaga dan pemda yang sepi pelamar di cpns 2024, beasiswa bill gates s2-s3 2025 tanpa batas usia, tunjangan rp 404 juta, lpdp buka beasiswa s2 ke australia, tanpa loa dan maksimal usia 42 tahun, kisah sariyanto, asn ugm yang jadi petani setiap sabtu dan minggu, beasiswa s2-s3 ke stanford university 2025, tanpa batas usia, 6 kementerian sepi peminat cpns 2024, ada yang tanpa toefl, now trending.

Usaha Anies Dapat Tiket Pilkada Jakarta: Pendekatan ke PDI-P Gagal, PKB Tak Minat

Transaksi Tol Non-tunai Tanpa Setop MLFF Diterapkan Tahun Ini

Opening Ceremony Paralimpiade 2024: Indonesia Tunjukkan Ragam Budaya Nusantara

Bayang-bayang Jokowi di Balik Pencalonan Pramono Anung pada Pilkada Jakarta...

Riza Patria Buka-bukaan soal Alasan Mundur dari Pilkada Tangsel 2024

Harapan Anies Kandas, Parpol Tak Bisa Ubah Dukungan usai Daftarkan Paslon

Menpan-RB Mengeluh Perjalanan Dinas ASN dan Pengadaan Aplikasi Boroskan Anggaran Negara

Resmi, Stasiun Tegalluar Summarecon Jadi Pemberhentian Akhir Whoosh
Mungkin anda melewatkan ini.

Mahasiswa, Simak 4 Manfaat Bangun Relasi dengan Dosen

Intibios Lab Buka Banyak Lowongan Kerja bagi Minimal Lulusan D3
- Entertainment
- Pesona Indonesia
- Artikel Terpopuler
- Artikel Terkini
- Topik Pilihan
- Artikel Headline
- Harian KOMPAS
- Pasangiklan.com
- GridOto.com
- BolaSport.com
- Gramedia.com
- Gramedia Digital
- Kabar Palmerah
- Ketentuan Penggunaan
- Kebijakan Data Pribadi
- Pedoman Media Siber
Copyright 2008 - 2024 PT. Kompas Cyber Media (Kompas Gramedia Digital Group). All Rights Reserved.

How To Write A Dissertation Or Thesis
8 straightforward steps to craft an a-grade dissertation.
By: Derek Jansen (MBA) Expert Reviewed By: Dr Eunice Rautenbach | June 2020
Writing a dissertation or thesis is not a simple task. It takes time, energy and a lot of will power to get you across the finish line. It’s not easy – but it doesn’t necessarily need to be a painful process. If you understand the big-picture process of how to write a dissertation or thesis, your research journey will be a lot smoother.
In this post, I’m going to outline the big-picture process of how to write a high-quality dissertation or thesis, without losing your mind along the way. If you’re just starting your research, this post is perfect for you. Alternatively, if you’ve already submitted your proposal, this article which covers how to structure a dissertation might be more helpful.
How To Write A Dissertation: 8 Steps
- Clearly understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is
- Find a unique and valuable research topic
- Craft a convincing research proposal
- Write up a strong introduction chapter
- Review the existing literature and compile a literature review
- Design a rigorous research strategy and undertake your own research
- Present the findings of your research
- Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications

Step 1: Understand exactly what a dissertation is
This probably sounds like a no-brainer, but all too often, students come to us for help with their research and the underlying issue is that they don’t fully understand what a dissertation (or thesis) actually is.
So, what is a dissertation?
At its simplest, a dissertation or thesis is a formal piece of research , reflecting the standard research process . But what is the standard research process, you ask? The research process involves 4 key steps:
- Ask a very specific, well-articulated question (s) (your research topic)
- See what other researchers have said about it (if they’ve already answered it)
- If they haven’t answered it adequately, undertake your own data collection and analysis in a scientifically rigorous fashion
- Answer your original question(s), based on your analysis findings

In short, the research process is simply about asking and answering questions in a systematic fashion . This probably sounds pretty obvious, but people often think they’ve done “research”, when in fact what they have done is:
- Started with a vague, poorly articulated question
- Not taken the time to see what research has already been done regarding the question
- Collected data and opinions that support their gut and undertaken a flimsy analysis
- Drawn a shaky conclusion, based on that analysis
If you want to see the perfect example of this in action, look out for the next Facebook post where someone claims they’ve done “research”… All too often, people consider reading a few blog posts to constitute research. Its no surprise then that what they end up with is an opinion piece, not research. Okay, okay – I’ll climb off my soapbox now.
The key takeaway here is that a dissertation (or thesis) is a formal piece of research, reflecting the research process. It’s not an opinion piece , nor a place to push your agenda or try to convince someone of your position. Writing a good dissertation involves asking a question and taking a systematic, rigorous approach to answering it.
If you understand this and are comfortable leaving your opinions or preconceived ideas at the door, you’re already off to a good start!

Step 2: Find a unique, valuable research topic
As we saw, the first step of the research process is to ask a specific, well-articulated question. In other words, you need to find a research topic that asks a specific question or set of questions (these are called research questions ). Sounds easy enough, right? All you’ve got to do is identify a question or two and you’ve got a winning research topic. Well, not quite…
A good dissertation or thesis topic has a few important attributes. Specifically, a solid research topic should be:
Let’s take a closer look at these:
Attribute #1: Clear
Your research topic needs to be crystal clear about what you’re planning to research, what you want to know, and within what context. There shouldn’t be any ambiguity or vagueness about what you’ll research.
Here’s an example of a clearly articulated research topic:
An analysis of consumer-based factors influencing organisational trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms.
As you can see in the example, its crystal clear what will be analysed (factors impacting organisational trust), amongst who (consumers) and in what context (British low-cost equity brokerage firms, based online).
Need a helping hand?
Attribute #2: Unique
Your research should be asking a question(s) that hasn’t been asked before, or that hasn’t been asked in a specific context (for example, in a specific country or industry).
For example, sticking organisational trust topic above, it’s quite likely that organisational trust factors in the UK have been investigated before, but the context (online low-cost equity brokerages) could make this research unique. Therefore, the context makes this research original.
One caveat when using context as the basis for originality – you need to have a good reason to suspect that your findings in this context might be different from the existing research – otherwise, there’s no reason to warrant researching it.
Attribute #3: Important
Simply asking a unique or original question is not enough – the question needs to create value. In other words, successfully answering your research questions should provide some value to the field of research or the industry. You can’t research something just to satisfy your curiosity. It needs to make some form of contribution either to research or industry.
For example, researching the factors influencing consumer trust would create value by enabling businesses to tailor their operations and marketing to leverage factors that promote trust. In other words, it would have a clear benefit to industry.
So, how do you go about finding a unique and valuable research topic? We explain that in detail in this video post – How To Find A Research Topic . Yeah, we’ve got you covered 😊
Step 3: Write a convincing research proposal
Once you’ve pinned down a high-quality research topic, the next step is to convince your university to let you research it. No matter how awesome you think your topic is, it still needs to get the rubber stamp before you can move forward with your research. The research proposal is the tool you’ll use for this job.
So, what’s in a research proposal?
The main “job” of a research proposal is to convince your university, advisor or committee that your research topic is worthy of approval. But convince them of what? Well, this varies from university to university, but generally, they want to see that:
- You have a clearly articulated, unique and important topic (this might sound familiar…)
- You’ve done some initial reading of the existing literature relevant to your topic (i.e. a literature review)
- You have a provisional plan in terms of how you will collect data and analyse it (i.e. a methodology)
At the proposal stage, it’s (generally) not expected that you’ve extensively reviewed the existing literature , but you will need to show that you’ve done enough reading to identify a clear gap for original (unique) research. Similarly, they generally don’t expect that you have a rock-solid research methodology mapped out, but you should have an idea of whether you’ll be undertaking qualitative or quantitative analysis , and how you’ll collect your data (we’ll discuss this in more detail later).
Long story short – don’t stress about having every detail of your research meticulously thought out at the proposal stage – this will develop as you progress through your research. However, you do need to show that you’ve “done your homework” and that your research is worthy of approval .
So, how do you go about crafting a high-quality, convincing proposal? We cover that in detail in this video post – How To Write A Top-Class Research Proposal . We’ve also got a video walkthrough of two proposal examples here .
Step 4: Craft a strong introduction chapter
Once your proposal’s been approved, its time to get writing your actual dissertation or thesis! The good news is that if you put the time into crafting a high-quality proposal, you’ve already got a head start on your first three chapters – introduction, literature review and methodology – as you can use your proposal as the basis for these.
Handy sidenote – our free dissertation & thesis template is a great way to speed up your dissertation writing journey.
What’s the introduction chapter all about?
The purpose of the introduction chapter is to set the scene for your research (dare I say, to introduce it…) so that the reader understands what you’ll be researching and why it’s important. In other words, it covers the same ground as the research proposal in that it justifies your research topic.
What goes into the introduction chapter?
This can vary slightly between universities and degrees, but generally, the introduction chapter will include the following:
- A brief background to the study, explaining the overall area of research
- A problem statement , explaining what the problem is with the current state of research (in other words, where the knowledge gap exists)
- Your research questions – in other words, the specific questions your study will seek to answer (based on the knowledge gap)
- The significance of your study – in other words, why it’s important and how its findings will be useful in the world
As you can see, this all about explaining the “what” and the “why” of your research (as opposed to the “how”). So, your introduction chapter is basically the salesman of your study, “selling” your research to the first-time reader and (hopefully) getting them interested to read more.
How do I write the introduction chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this post .

Step 5: Undertake an in-depth literature review
As I mentioned earlier, you’ll need to do some initial review of the literature in Steps 2 and 3 to find your research gap and craft a convincing research proposal – but that’s just scratching the surface. Once you reach the literature review stage of your dissertation or thesis, you need to dig a lot deeper into the existing research and write up a comprehensive literature review chapter.
What’s the literature review all about?
There are two main stages in the literature review process:
Literature Review Step 1: Reading up
The first stage is for you to deep dive into the existing literature (journal articles, textbook chapters, industry reports, etc) to gain an in-depth understanding of the current state of research regarding your topic. While you don’t need to read every single article, you do need to ensure that you cover all literature that is related to your core research questions, and create a comprehensive catalogue of that literature , which you’ll use in the next step.
Reading and digesting all the relevant literature is a time consuming and intellectually demanding process. Many students underestimate just how much work goes into this step, so make sure that you allocate a good amount of time for this when planning out your research. Thankfully, there are ways to fast track the process – be sure to check out this article covering how to read journal articles quickly .

Literature Review Step 2: Writing up
Once you’ve worked through the literature and digested it all, you’ll need to write up your literature review chapter. Many students make the mistake of thinking that the literature review chapter is simply a summary of what other researchers have said. While this is partly true, a literature review is much more than just a summary. To pull off a good literature review chapter, you’ll need to achieve at least 3 things:
- You need to synthesise the existing research , not just summarise it. In other words, you need to show how different pieces of theory fit together, what’s agreed on by researchers, what’s not.
- You need to highlight a research gap that your research is going to fill. In other words, you’ve got to outline the problem so that your research topic can provide a solution.
- You need to use the existing research to inform your methodology and approach to your own research design. For example, you might use questions or Likert scales from previous studies in your your own survey design .
As you can see, a good literature review is more than just a summary of the published research. It’s the foundation on which your own research is built, so it deserves a lot of love and attention. Take the time to craft a comprehensive literature review with a suitable structure .
But, how do I actually write the literature review chapter, you ask? We cover that in detail in this video post .
Step 6: Carry out your own research
Once you’ve completed your literature review and have a sound understanding of the existing research, its time to develop your own research (finally!). You’ll design this research specifically so that you can find the answers to your unique research question.
There are two steps here – designing your research strategy and executing on it:
1 – Design your research strategy
The first step is to design your research strategy and craft a methodology chapter . I won’t get into the technicalities of the methodology chapter here, but in simple terms, this chapter is about explaining the “how” of your research. If you recall, the introduction and literature review chapters discussed the “what” and the “why”, so it makes sense that the next point to cover is the “how” –that’s what the methodology chapter is all about.
In this section, you’ll need to make firm decisions about your research design. This includes things like:
- Your research philosophy (e.g. positivism or interpretivism )
- Your overall methodology (e.g. qualitative , quantitative or mixed methods)
- Your data collection strategy (e.g. interviews , focus groups, surveys)
- Your data analysis strategy (e.g. content analysis , correlation analysis, regression)
If these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these in plain language in other posts. It’s not essential that you understand the intricacies of research design (yet!). The key takeaway here is that you’ll need to make decisions about how you’ll design your own research, and you’ll need to describe (and justify) your decisions in your methodology chapter.
2 – Execute: Collect and analyse your data
Once you’ve worked out your research design, you’ll put it into action and start collecting your data. This might mean undertaking interviews, hosting an online survey or any other data collection method. Data collection can take quite a bit of time (especially if you host in-person interviews), so be sure to factor sufficient time into your project plan for this. Oftentimes, things don’t go 100% to plan (for example, you don’t get as many survey responses as you hoped for), so bake a little extra time into your budget here.
Once you’ve collected your data, you’ll need to do some data preparation before you can sink your teeth into the analysis. For example:
- If you carry out interviews or focus groups, you’ll need to transcribe your audio data to text (i.e. a Word document).
- If you collect quantitative survey data, you’ll need to clean up your data and get it into the right format for whichever analysis software you use (for example, SPSS, R or STATA).
Once you’ve completed your data prep, you’ll undertake your analysis, using the techniques that you described in your methodology. Depending on what you find in your analysis, you might also do some additional forms of analysis that you hadn’t planned for. For example, you might see something in the data that raises new questions or that requires clarification with further analysis.
The type(s) of analysis that you’ll use depend entirely on the nature of your research and your research questions. For example:
- If your research if exploratory in nature, you’ll often use qualitative analysis techniques .
- If your research is confirmatory in nature, you’ll often use quantitative analysis techniques
- If your research involves a mix of both, you might use a mixed methods approach
Again, if these words have got your head spinning, don’t worry! We’ll explain these concepts and techniques in other posts. The key takeaway is simply that there’s no “one size fits all” for research design and methodology – it all depends on your topic, your research questions and your data. So, don’t be surprised if your study colleagues take a completely different approach to yours.

Step 7: Present your findings
Once you’ve completed your analysis, it’s time to present your findings (finally!). In a dissertation or thesis, you’ll typically present your findings in two chapters – the results chapter and the discussion chapter .
What’s the difference between the results chapter and the discussion chapter?
While these two chapters are similar, the results chapter generally just presents the processed data neatly and clearly without interpretation, while the discussion chapter explains the story the data are telling – in other words, it provides your interpretation of the results.
For example, if you were researching the factors that influence consumer trust, you might have used a quantitative approach to identify the relationship between potential factors (e.g. perceived integrity and competence of the organisation) and consumer trust. In this case:
- Your results chapter would just present the results of the statistical tests. For example, correlation results or differences between groups. In other words, the processed numbers.
- Your discussion chapter would explain what the numbers mean in relation to your research question(s). For example, Factor 1 has a weak relationship with consumer trust, while Factor 2 has a strong relationship.
Depending on the university and degree, these two chapters (results and discussion) are sometimes merged into one , so be sure to check with your institution what their preference is. Regardless of the chapter structure, this section is about presenting the findings of your research in a clear, easy to understand fashion.
Importantly, your discussion here needs to link back to your research questions (which you outlined in the introduction or literature review chapter). In other words, it needs to answer the key questions you asked (or at least attempt to answer them).
For example, if we look at the sample research topic:
In this case, the discussion section would clearly outline which factors seem to have a noteworthy influence on organisational trust. By doing so, they are answering the overarching question and fulfilling the purpose of the research .

For more information about the results chapter , check out this post for qualitative studies and this post for quantitative studies .
Step 8: The Final Step Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications
Last but not least, you’ll need to wrap up your research with the conclusion chapter . In this chapter, you’ll bring your research full circle by highlighting the key findings of your study and explaining what the implications of these findings are.
What exactly are key findings? The key findings are those findings which directly relate to your original research questions and overall research objectives (which you discussed in your introduction chapter). The implications, on the other hand, explain what your findings mean for industry, or for research in your area.
Sticking with the consumer trust topic example, the conclusion might look something like this:
Key findings
This study set out to identify which factors influence consumer-based trust in British low-cost online equity brokerage firms. The results suggest that the following factors have a large impact on consumer trust:
While the following factors have a very limited impact on consumer trust:
Notably, within the 25-30 age groups, Factors E had a noticeably larger impact, which may be explained by…
Implications
The findings having noteworthy implications for British low-cost online equity brokers. Specifically:
The large impact of Factors X and Y implies that brokers need to consider….
The limited impact of Factor E implies that brokers need to…
As you can see, the conclusion chapter is basically explaining the “what” (what your study found) and the “so what?” (what the findings mean for the industry or research). This brings the study full circle and closes off the document.

Let’s recap – how to write a dissertation or thesis
You’re still with me? Impressive! I know that this post was a long one, but hopefully you’ve learnt a thing or two about how to write a dissertation or thesis, and are now better equipped to start your own research.
To recap, the 8 steps to writing a quality dissertation (or thesis) are as follows:
- Understand what a dissertation (or thesis) is – a research project that follows the research process.
- Find a unique (original) and important research topic
- Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal
- Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter
- Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review
- Undertake your own research
- Present and interpret your findings
Once you’ve wrapped up the core chapters, all that’s typically left is the abstract , reference list and appendices. As always, be sure to check with your university if they have any additional requirements in terms of structure or content.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
20 Comments
thankfull >>>this is very useful
Thank you, it was really helpful
unquestionably, this amazing simplified way of teaching. Really , I couldn’t find in the literature words that fully explicit my great thanks to you. However, I could only say thanks a-lot.
Great to hear that – thanks for the feedback. Good luck writing your dissertation/thesis.
This is the most comprehensive explanation of how to write a dissertation. Many thanks for sharing it free of charge.
Very rich presentation. Thank you
Thanks Derek Jansen|GRADCOACH, I find it very useful guide to arrange my activities and proceed to research!
Thank you so much for such a marvelous teaching .I am so convinced that am going to write a comprehensive and a distinct masters dissertation
It is an amazing comprehensive explanation
This was straightforward. Thank you!
I can say that your explanations are simple and enlightening – understanding what you have done here is easy for me. Could you write more about the different types of research methods specific to the three methodologies: quan, qual and MM. I look forward to interacting with this website more in the future.
Thanks for the feedback and suggestions 🙂
Hello, your write ups is quite educative. However, l have challenges in going about my research questions which is below; *Building the enablers of organisational growth through effective governance and purposeful leadership.*
Very educating.
Just listening to the name of the dissertation makes the student nervous. As writing a top-quality dissertation is a difficult task as it is a lengthy topic, requires a lot of research and understanding and is usually around 10,000 to 15000 words. Sometimes due to studies, unbalanced workload or lack of research and writing skill students look for dissertation submission from professional writers.
Thank you 💕😊 very much. I was confused but your comprehensive explanation has cleared my doubts of ever presenting a good thesis. Thank you.
thank you so much, that was so useful
Hi. Where is the excel spread sheet ark?
could you please help me look at your thesis paper to enable me to do the portion that has to do with the specification
my topic is “the impact of domestic revenue mobilization.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

Paper Format
Consistency in the order, structure, and format of a paper allows readers to focus on a paper’s content rather than its presentation.
To format a paper in APA Style, writers can typically use the default settings and automatic formatting tools of their word-processing program or make only minor adjustments.
The guidelines for paper format apply to both student assignments and manuscripts being submitted for publication to a journal. If you are using APA Style to create another kind of work (e.g., a website, conference poster, or PowerPoint presentation), you may need to format your work differently in order to optimize its presentation, for example, by using different line spacing and font sizes. Follow the guidelines of your institution or publisher to adapt APA Style formatting guidelines as needed.

Academic Writer ®
Master academic writing with APA’s essential teaching and learning resource

Course Adoption
Teaching APA Style? Become a course adopter of the 7th edition Publication Manual

Instructional Aids
Guides, checklists, webinars, tutorials, and sample papers for anyone looking to improve their knowledge of APA Style

- TECH & EDU
Apa Maksud Unggahan "Peringatan Darurat" dan Hubungannya dengan Putusan MK?
21 Aug 2024 17:08 WIB

Poster "Peringatan Darurat" yang ramai diunggah warganet usia rapat Baleg DPR RI pada Rabu (21/8/2024). (Sumber: YouTube/EAS Indonesia Concept)
Penulis: Rizal Amril
Editor: Indra Dwi Sugiyanto
Rabu (21/8/2024), warganet ramai mengunggah poster biru bertuliskan "Peringatan Darurat" dengan gambar Garuda Pancasila di bawahnya. Apa maksud poster tersebut dan bagaimana konteksnya?
Poster bertuliskan "Peringatan Darurat" tersebut merupakan penggalan dari sebuah video yang diunggah oleh akun YouTube EAS Indonesia Concept pada 22 Oktober 2022 lalu.
EAS Indonesia Concept merupakan sebuah akun YouTube yang membuat video dengan konsep The Emergency Alert System (EAS) versi Indonesia. EAS sendiri merupakan sistem peringatan kedaruratan nasional Amerika yang didesain untuk menyebarkan pesan darurat di tengah siaran televisi dan radio.
Dalam unggahan-unggahannya, akun EAS Indonesia Concept menggunakan metode EAS untuk membuat video horor fiktif yang dikenal sebagai analog horror .
Analog horror merupakan sebuah subgenre dari fiksi horor yang populer pada 2010 lalu. Melansir Videomaker , analog horror merupakan sebuah pecahan dari subgenre rekaman yang ditemukan ( found footage ), yakni pendekatan film horor yang seolah menampilkan sebuah rekaman amatir tentang kejadian supranatural. Penggunaan metode ini pada film dapat dilihat, misalnya, dalam Keramat (2012).
Ketika YouTube mulai berkembang pada 2010, analog horror digunakan sebagai metode untuk membuat sebuah video pendek yang menceritakan kisah horor. Kisah dalam video tersebut umumnya menampilkan rekaman analog suatu peristiwa-peristiwa yang janggal pada masa lalu.
Setelah itu, kemudian muncul metode yang lebih spesifik dalam membuat sebuah video analog horror , yakni dengan membuat video EAS. Video analog horror dengan metode EAS ini menampilkan sebuah siaran darurat fiktif dengan pesan berupa situasi berbahaya.
Dalam video yang penggalannya ramai diunggah di media sosial, misalnya, metode EAS digunakan oleh akun EAS Indonesia Concept untuk menampilkan kisah fiktif munculnya makhluk misterius dan berbahaya di Indonesia.
Lalu mengapa penggalan itu ramai diunggah?
Penggalan video analog horor bertuliskan "Peringatan Darurat" ramai diunggah oleh warganet sebenarnya tak berkaitan dengan analog horor . Warganet menggunakan poster dari penggalan video analog horror tersebut untuk sebagai seruan dan peringatan atas kondisi politik yang kacau jelang Pilkada Serentak 2024.
Unggahan “Peringatan Darurat” tersebut ramai diunggah setelah Badan Legislasi (Baleg) DPR RI melakukan rapat untuk membahas Rancangan Undang-Undang (RUU) Pilkada pada Rabu siang.
Rapat tersebut menjadi sorotan karena salah satu hal yang dibahas dalam rapat tersebut adalah tentang syarat dan aturan pencalonan kepala daerah dalam Pilkada serentak yang akan dilaksanakan pada November 2024 mendatang.
Banyak pihak menilai rapat tersebut dilakukan secara terburu-buru usai usai Mahkamah Konstitusi mengabulkan gugatan tentang syarat pencalonan kepada daerah dalam UU Pilkada pada Selasa (20/8).
Melalui putusan nomor 60/PUU-XII/2024, MK mengubah ambang batas ( threshold ) pencalonan kepala daerah dan wakil kepala daerah.
MK menyatakan, partai politik yang tidak mendapatkan kursi di DPRD bisa mencalonkan pasangan calon untuk maju dalam Pilkada. Penghitungan syarat pengusulan pasangan calon melalui partai politik hanya didasarkan pada perolehan suara sah dalam pemilu di daerah yang bersangkutan.
"Amar putusan, mengabulkan permohonan para pemohon untuk sebagian," kata Ketua MK Suhartoyo dalam amar putusan untuk perkara tersebut pada Selasa, dilansir dari Antara .
Putusan tersebut dianggap akan mengubah peta politik dalam Pilkada 2024 mendatang. Perubahan tersebut, misalnya, dapat terjadi dalam Pilkada Jakarta 2024.
Di Jakarta, sejumlah partai seperti PDIP dapat mencalonkan pasangan cagub-cawagub tanpa berkoalisi dengan partai lainnya.
Adanya calon yang diusung PDIP dalam Pilkada Jakarta 2024 disebut akan mengubah peta politik yang sejauh ini relatif dikuasai oleh Koalisi Indonesia Maju (KIM) Plus yang mengusung pasangan Ridwan Kamil-Suswono.
Sehari setelah putusan MK tersebut, pada Rabu siang, Baleg DPR melakukan rapat untuk membahas putusan MK nomor 60 tentang ambang batas pencalonan Pilkada.
Anggota Baleg DPR dari Fraksi Golkar, Dave Laksono, menyatakan jika rapat Revisi RUU Pilkada yang digelar Rabu siang tersebut bertujuan untuk merespons putusan MK nomor 60.
"Kan harus ada kejelasannya kan. Maka itulah dari Baleg itu mempelajari lagi untuk menegaskan supaya tidak ada multitafsir lah atas putusan tersebut," katanya pada Rabu, dikutip dari Kompascom.
Namun, dalam rapat Baleg DPR tersebut, putusan MK tentang ambang batas pencalonan ditafsirkan dengan perbedaan mekanisme antara partai peraih kursi dan bukan peraih kursi DPRD.
Dalam siaran rapat, Baleg DPRI RI menetapkan partai yang telah memiliki kursi di DPRD dapat mencalonkan diri selama memenuhi ambang batas 20 persen kursi atau 25 persen akumulasi perolehan suara sah Pemilu DPRD.
Sementara peniadaan syarat ambang batas, sebagaimana diputuskan MK, ditafsirkan DPR sebagai mekanisme untuk partai yang tidak meraih kursi di DPRD.
Tak hanya ambang batas, tetapi juga usia calon
Rapat Baleg DPR RI menjadi sorotan publik tak hanya karena membahas ambang batas pencalonan Pilkada, tetapi juga syarat usia calon kepala daerah.
Dalam RUU Pilkada yang dibahas dalam Baleg DPR pada Rabu siang tersebut, syarat batas minimum usia calon kepala daerah untuk tingkat provinsi adalah 30 tahun dan untuk tingkat kota adalah 25 tahun ketika dilantik.
Pembahasan tentang batas minimum usia calon kepala daerah ini sempat menuai perdebatan antar-fraksi dalam Baleg tentang putusan mana yang jadi rujukan aturan batas usia calon kepala daerah.
Perdebatan tersebut menyebut apakah batas usia calon kepala daerah merujuk pada putusan MA atau putusan MK Nomor 70/PUU-XXII/2024. Putusan MK menyebut jika batas usia calon kepala daerah dihitung sejak penetapan, bukan pelantikan.
Anggota Baleg DPR RI Fraksi Gerindra Habiburokhman menyatakan dalam rapat jika rujukan aturan batas usia calon kepala daerah harusnya merujuk pada putusan MA.
"Mahkota putusan itu adalah amar putusan, lagipula tidak ada kewenangan institusi Mahkamah Konstitusi menegasikan putusan Mahkamah Agung. Jadi keputusan MA tetap mengikat," ujarnya, dikutip dari Antara .
Sementara Fraksi PDIP, yang diwakili oleh Putra Nababan dan Arteria Dahlan, sempat mengutarakan pendapat bahwa seharusnya dasar aturan yang digunakan adalah putusan MK yang lebih tinggi, ketimbang MA.
Namun, Pemimpin rapat panja Baleg, Achmad Baidowi dari PPP, kemudian memutuskan untuk mengetuk palu tanda sepakat agar dasar aturan batas usia calon kepala daerah menggunakan putusan MA.
Keputusan Baleg DPR RI tentang batas usia calon kepala daerah tersebut dianggap menjadi angin segar bagi Kaesang Pangarep, anak dari Presiden Jokowi, untuk maju dalam Pilkada Jawa Tengah 2024.
Kaesang, yang lahir pada 25 Desember 1994, kini berusia 29 tahun dan digadang-gadang akan maju dalam Pilkada Jawa Tengah.
Jika batas usia calon kepala daerah merujuk pada putusan MA, maka Kaesang diperbolehkan mencalonkan diri karena akan berusia 30 tahun ketika dilantik, persis seperti putusan MA.
Apa Komentarmu?
Tulis komentar
ARTIKEL TERKAIT
Video terkait.
Latest Comment
Anda sepenuhnya bertanggung jawab atas komentar yang diberikan, hindari ujaran melanggar hukum.
Belum ada komentar
Jadilah yang pertama mengirimkan komentar untuk bertukar gagasan dengan pengguna lainnya

IMAGES
COMMENTS
To cite an unpublished dissertation (one you got directly from the author or university in print form), add "Unpublished" to the bracketed description, and list the university at the end of the reference, outside the square brackets. APA format. Author last name, Initials. ( Year ).
es. Keep all tables and figures within the margins of the page. If it is not possible to keep the table or figure within the margins, then place the table or figure on a separate page after the. and change the orientation of the page to landscape.AppendicesAppendices are always placed on separate pages at the very en.
This page contains reference examples for published dissertations or theses, ... Published dissertation or thesis references are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 10.6 and the Concise Guide Section 10.5. This guidance has been revised from the 6th edition. Date created: February 2020.
Cara Pemaparan. Dari bobot ilmiah, pasti kamu bisa memperkirakan seperti apa cara pemaparan masing-masing tugas akhir. Skripsi biasanya dominan pemaparan deskriptif. Tesis dipaparkan dengan analitis dan deskriptif. Sementara itu, pemaparan disertasi biasanya bersifat analitis sehingga benar-benar mengupas tuntas permasalahan yang diusung.
Citing a published dissertation or thesis from a database. If a thesis or dissertation has been published and is found on a database, then follow the structure below. It's similar to the format for an unpublished dissertation/thesis, but with a few differences: Structure: Author's last name, F. M. (Year published).
Tesis. Kedoktoran majlis di Biarkanlah University (7 bulan julai 1721). Yang tesis atau disertasi[ 1] adalah dokumen yang diserahkan untuk menyokong pencalonan untuk ijazah akademik atau profesional kelayakan menyampaikan penulis penyelidikan dan penemuan. [ 2] Dalam beberapa konteks, perkataan "tesis" atau sanak digunakan untuk bagian dari ...
Basic guidelines for formatting the reference list at the end of a standard APA research paper Author/Authors Rules for handling works by a single author or multiple authors that apply to all APA-style references in your reference list, regardless of the type of work (book, article, electronic resource, etc.)
Throughout your paper, you need to apply the following APA format guidelines: Set page margins to 1 inch on all sides. Double-space all text, including headings. Indent the first line of every paragraph 0.5 inches. Use an accessible font (e.g., Times New Roman 12pt., Arial 11pt., or Georgia 11pt.).
It is recommended that citation and referencing for thesis/dissertation follow either the APA, IEEE, Harvard, Chicago or House style. The chosen citation and referencing styles should be used consistently throughout the thesis/dissertation. 1.4 Process of Thesis/Dissertation Submission Binding for Submission (Viva-Voce) i. Research Programmes
dissertation, The University of Akron]. ProQuest . Dissertations and Theses Global. Note : [Academic exercise]; [Master's thesis]; [Doctoral dissertation]. (Richardson, 2019) Richardson (2019) Master's Thesis / Doctoral Dissertation from an institutional database (sometimes referred to as a Commons / Digital Archives) or Online: Ahmed, L ...
It is used by millions of people worldwide in psychology, social sciences, and many other disciplines for the preparation of manuscripts for publication as well as for writing student papers, dissertations, and theses. APA Style is described in the seventh edition of the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association, which is a ...
Edisi keempat Cetakan Pertama 2012. PANDUAN PENULISAN TESIS ISBN: 978-983-43398-2-1. Pusat Pengajian Siswazah. Hak Cipta Terpelihara, tidak dibenarkan mengeluar ulang mana-mana bahagian artikel, ilustrasi dan isi kandungan buku ini dalam apa jua bentuk dan dengan apa cara sekali pun sama ada secara elektronik, fotokopi, mekanikal, rakaman atau ...
p: skhah berjilid kera. yang telah melalui proses pembaikan.4. MAKLUMAT TAMBAHAN Penyerahan Tesis /Disertasi Calon dikehendaki menyerahkan tesis / disertasi lengkap setelah diperiksa dan diperbaiki meng. Pusat Pengajian Pascasiswazah.a) Syarat Penganugerahan IjazahPelajar dikehendaki memenuhi s.
Disertasi ini bisa dibilang juga sebagai pengembangan lebih lanjut tesis. Karena semakin tinggi tingkatannya, maka tingkat kesulitan menulis disertasi juga lebih tinggi dibanding tesis dan skripsi. Mahasiswa S-3 dituntut untuk bisa menghasilkan penemuan penting dan harus benar-benar melakukan penelitian secara mandiri.
Apa bedanya dengan skripsi dan disertasi? Kamus Besar Bahasa Indonesia, mengartikan tesis sebagai pernyataan atau teori yang didukung oleh argumen yang dikemukakan dalam karangan untuk mendapatkan gelar magister. Sedangkan dalam buku "Tesis dan Disertasi dalam Kebenaran Ilmiah" karya Muhtar, dijelaskan bahwa tesis adalah karya tulis akademik ...
Perbedaan Skripsi, Tesis dan Disertasi. Sedang - tinggi. Pendalaman / pengembangan terhadap teori dan penelitian yang ada. Tinggi, Tertinggi dibidang akademik. Diwajibkan mencari terobosan dan teori baru dalam bidang ilmu pengetahuan. Itukah pembahasan apa pengertian dan perbedaan skripsi, tesis, dan disertasi.
Skripsi mengangkat masalah yang bersumber pada pengalaman empirik dan bersifat tidak mendalam. Tesis juga dapat berasal dari pengalaman empirik, tetapi bersifat mendalam dan teoritis. Sedangkan disertasi berasal dari kajian teoritis dengan dukungan fakta empirik sehingga permasalahan yang digali sangat mendalam dan spesifik.
Craft a convincing dissertation or thesis research proposal. Write a clear, compelling introduction chapter. Undertake a thorough review of the existing research and write up a literature review. Undertake your own research. Present and interpret your findings. Draw a conclusion and discuss the implications.
utama kajian penyelidik. Tidak kira apa bidang sekalipun, pemilihan tajuk tesis yang sesuai memerlukan perhatian penyelidik dan juga penyelia. Oleh itu, bahagian ini akan memberikan fokus kepada terjemahan tajuk tesis dalam bahasa Melayu. Sambil itu, bahagian ini juga akan memfokuskan kepada jenis
To format a paper in APA Style, writers can typically use the default settings and automatic formatting tools of their word-processing program or make only minor adjustments. The guidelines for paper format apply to both student assignments and manuscripts being submitted for publication to a journal. If you are using APA Style to create ...
It is the candidate's responsibility to prepare and assemble all materials for the thesis/dissertation, and to have the pages of the thesis/dissertation in correct order. Paper. The thesis/dissertation must be written on one side only of good quality white bond paper (usually of 80g weight) of A4 size (210mm x 297mm).
Apa maksud poster tersebut dan bagaimana konteksnya? Poster bertuliskan "Peringatan Darurat" tersebut merupakan penggalan dari sebuah video yang diunggah oleh akun YouTube EAS Indonesia Concept pada 22 Oktober 2022 lalu.
Apa Maksud Dari Thesis Statement - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. The document discusses the challenges of crafting a thesis statement, particularly one that adheres to APA style guidelines. It notes that writing a thesis requires meticulous research, analysis, and strong communication skills. It also states that HelpWriting.net offers assistance to ...