Advisory boards aren’t only for executives. Join the LogRocket Content Advisory Board today →

- Product Management
- Solve User-Reported Issues
- Find Issues Faster
- Optimize Conversion and Adoption

A guide to problem-solving techniques, steps, and skills

You might associate problem-solving with the math exercises that a seven-year-old would do at school. But problem-solving isn’t just about math — it’s a crucial skill that helps everyone make better decisions in everyday life or work.

Problem-solving involves finding effective solutions to address complex challenges, in any context they may arise.
Unfortunately, structured and systematic problem-solving methods aren’t commonly taught. Instead, when solving a problem, PMs tend to rely heavily on intuition. While for simple issues this might work well, solving a complex problem with a straightforward solution is often ineffective and can even create more problems.
In this article, you’ll learn a framework for approaching problem-solving, alongside how you can improve your problem-solving skills.
The 7 steps to problem-solving
When it comes to problem-solving there are seven key steps that you should follow: define the problem, disaggregate, prioritize problem branches, create an analysis plan, conduct analysis, synthesis, and communication.
1. Define the problem
Problem-solving begins with a clear understanding of the issue at hand. Without a well-defined problem statement, confusion and misunderstandings can hinder progress. It’s crucial to ensure that the problem statement is outcome-focused, specific, measurable whenever possible, and time-bound.
Additionally, aligning the problem definition with relevant stakeholders and decision-makers is essential to ensure efforts are directed towards addressing the actual problem rather than side issues.
2. Disaggregate
Complex issues often require deeper analysis. Instead of tackling the entire problem at once, the next step is to break it down into smaller, more manageable components.
Various types of logic trees (also known as issue trees or decision trees) can be used to break down the problem. At each stage where new branches are created, it’s important for them to be “MECE” – mutually exclusive and collectively exhaustive. This process of breaking down continues until manageable components are identified, allowing for individual examination.
The decomposition of the problem demands looking at the problem from various perspectives. That is why collaboration within a team often yields more valuable results, as diverse viewpoints lead to a richer pool of ideas and solutions.
3. Prioritize problem branches
The next step involves prioritization. Not all branches of the problem tree have the same impact, so it’s important to understand the significance of each and focus attention on the most impactful areas. Prioritizing helps streamline efforts and minimize the time required to solve the problem.

Over 200k developers and product managers use LogRocket to create better digital experiences
4. Create an analysis plan
For prioritized components, you may need to conduct in-depth analysis. Before proceeding, a work plan is created for data gathering and analysis. If work is conducted within a team, having a plan provides guidance on what needs to be achieved, who is responsible for which tasks, and the timelines involved.
5. Conduct analysis
Data gathering and analysis are central to the problem-solving process. It’s a good practice to set time limits for this phase to prevent excessive time spent on perfecting details. You can employ heuristics and rule-of-thumb reasoning to improve efficiency and direct efforts towards the most impactful work.
6. Synthesis
After each individual branch component has been researched, the problem isn’t solved yet. The next step is synthesizing the data logically to address the initial question. The synthesis process and the logical relationship between the individual branch results depend on the logic tree used.
7. Communication
The last step is communicating the story and the solution of the problem to the stakeholders and decision-makers. Clear effective communication is necessary to build trust in the solution and facilitates understanding among all parties involved. It ensures that stakeholders grasp the intricacies of the problem and the proposed solution, leading to informed decision-making.
Exploring problem-solving in various contexts
While problem-solving has traditionally been associated with fields like engineering and science, today it has become a fundamental skill for individuals across all professions. In fact, problem-solving consistently ranks as one of the top skills required by employers.
Problem-solving techniques can be applied in diverse contexts:
- Individuals — What career path should I choose? Where should I live? These are examples of simple and common personal challenges that require effective problem-solving skills
- Organizations — Businesses also face many decisions that are not trivial to answer. Should we expand into new markets this year? How can we enhance the quality of our product development? Will our office accommodate the upcoming year’s growth in terms of capacity?
- Societal issues — The biggest world challenges are also complex problems that can be addressed with the same technique. How can we minimize the impact of climate change? How do we fight cancer?
Despite the variation in domains and contexts, the fundamental approach to solving these questions remains the same. It starts with gaining a clear understanding of the problem, followed by decomposition, conducting analysis of the decomposed branches, and synthesizing it into a result that answers the initial problem.
Real-world examples of problem-solving
Let’s now explore some examples where we can apply the problem solving framework.
Problem: In the production of electronic devices, you observe an increasing number of defects. How can you reduce the error rate and improve the quality?
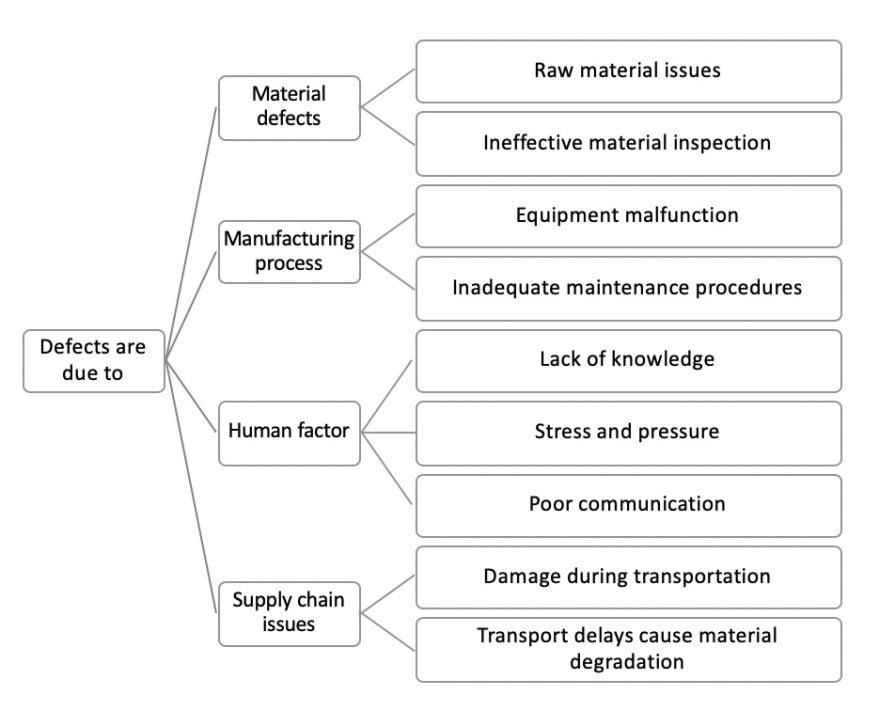
Before delving into analysis, you can deprioritize branches that you already have information for or ones you deem less important. For instance, while transportation delays may occur, the resulting material degradation is likely negligible. For other branches, additional research and data gathering may be necessary.
Once results are obtained, synthesis is crucial to address the core question: How can you decrease the defect rate?
While all factors listed may play a role, their significance varies. Your task is to prioritize effectively. Through data analysis, you may discover that altering the equipment would bring the most substantial positive outcome. However, executing a solution isn’t always straightforward. In prioritizing, you should consider both the potential impact and the level of effort needed for implementation.
By evaluating impact and effort, you can systematically prioritize areas for improvement, focusing on those with high impact and requiring minimal effort to address. This approach ensures efficient allocation of resources towards improvements that offer the greatest return on investment.
Problem : What should be my next job role?
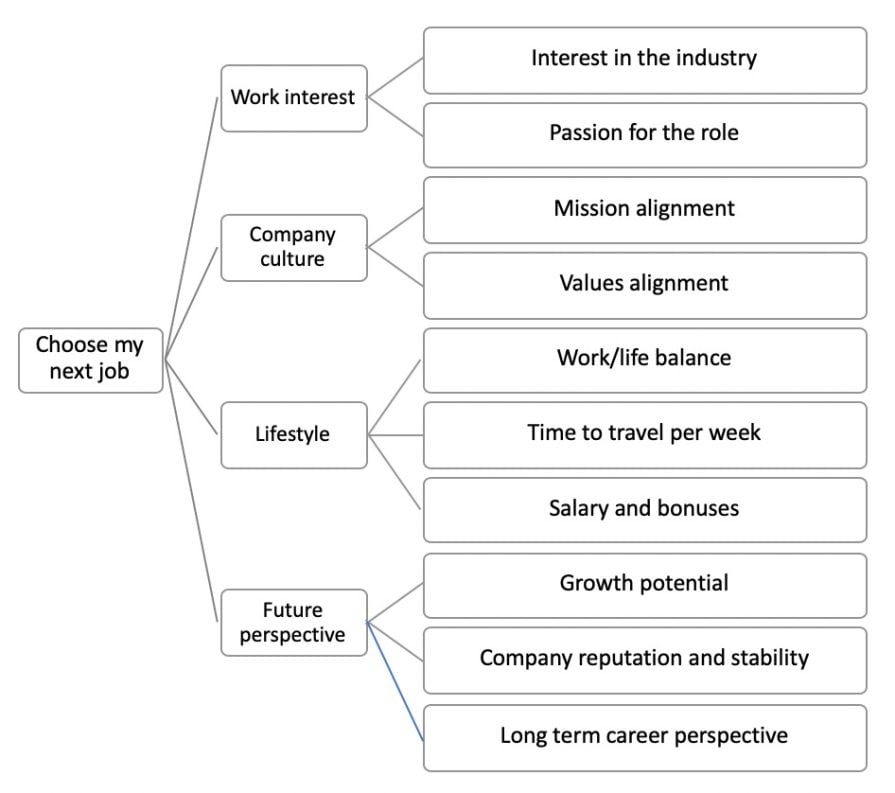
When breaking down this problem, you need to consider various factors that are important for your future happiness in the role. This includes aspects like the company culture, our interest in the work itself, and the lifestyle that you can afford with the role.
However, not all factors carry the same weight for us. To make sense of the results, we can assign a weight factor to each branch. For instance, passion for the job role may have a weight factor of 1, while interest in the industry may have a weight factor of 0.5, because that is less important for you.
By applying these weights to a specific role and summing the values, you can have an estimate of how suitable that role is for you. Moreover, you can compare two roles and make an informed decision based on these weighted indicators.
Key problem-solving skills
This framework provides the foundation and guidance needed to effectively solve problems. However, successfully applying this framework requires the following:
- Creativity — During the decomposition phase, it’s essential to approach the problem from various perspectives and think outside the box to generate innovative ideas for breaking down the problem tree
- Decision-making — Throughout the process, decisions must be made, even when full confidence is lacking. Employing rules of thumb to simplify analysis or selecting one tree cut over another requires decisiveness and comfort with choices made
- Analytical skills — Analytical and research skills are necessary for the phase following decomposition, involving data gathering and analysis on selected tree branches
- Teamwork — Collaboration and teamwork are crucial when working within a team setting. Solving problems effectively often requires collective effort and shared responsibility
- Communication — Clear and structured communication is essential to convey the problem solution to stakeholders and decision-makers and build trust
How to enhance your problem-solving skills
Problem-solving requires practice and a certain mindset. The more you practice, the easier it becomes. Here are some strategies to enhance your skills:
- Practice structured thinking in your daily life — Break down problems or questions into manageable parts. You don’t need to go through the entire problem-solving process and conduct detailed analysis. When conveying a message, simplify the conversation by breaking the message into smaller, more understandable segments
- Regularly challenging yourself with games and puzzles — Solving puzzles, riddles, or strategy games can boost your problem-solving skills and cognitive agility.
- Engage with individuals from diverse backgrounds and viewpoints — Conversing with people who offer different perspectives provides fresh insights and alternative solutions to problems. This boosts creativity and helps in approaching challenges from new angles
Final thoughts
Problem-solving extends far beyond mathematics or scientific fields; it’s a critical skill for making informed decisions in every area of life and work. The seven-step framework presented here provides a systematic approach to problem-solving, relevant across various domains.
Now, consider this: What’s one question currently on your mind? Grab a piece of paper and try to apply the problem-solving framework. You might uncover fresh insights you hadn’t considered before.
Featured image source: IconScout
LogRocket generates product insights that lead to meaningful action
Get your teams on the same page — try LogRocket today.
Share this:
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- #career development
- #tools and resources

Stop guessing about your digital experience with LogRocket
Recent posts:.
Creating a successful product launch plan: A step-by-step guide
Follow this 7-step checklist to maximize your chances at running a successful product launch.

What is DMAIC in Six Sigma?
Bring Six Sigma’s approach and its DMAIC process to your next product analysis to solve project problems and implement lasting solutions.

Leader Spotlight: The importance of understanding the customer, with Adam Cardarelli
Adam Cardarelli highlights the importance of deeply understanding the customer and creating awe-inspiring products that truly delight them.
What is a product designer? Skills, duties, and career path
Product designers bridge the gap between user needs, business goals, and technological possibilities. Let’s take a deeper look at the role.

Leave a Reply Cancel reply

What is Problem Solving? (Steps, Techniques, Examples)
By Status.net Editorial Team on May 7, 2023 — 5 minutes to read
What Is Problem Solving?
Definition and importance.
Problem solving is the process of finding solutions to obstacles or challenges you encounter in your life or work. It is a crucial skill that allows you to tackle complex situations, adapt to changes, and overcome difficulties with ease. Mastering this ability will contribute to both your personal and professional growth, leading to more successful outcomes and better decision-making.
Problem-Solving Steps
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps:
- Identify the issue : Recognize the problem that needs to be solved.
- Analyze the situation : Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present.
- Generate potential solutions : Brainstorm a list of possible solutions to the issue, without immediately judging or evaluating them.
- Evaluate options : Weigh the pros and cons of each potential solution, considering factors such as feasibility, effectiveness, and potential risks.
- Select the best solution : Choose the option that best addresses the problem and aligns with your objectives.
- Implement the solution : Put the selected solution into action and monitor the results to ensure it resolves the issue.
- Review and learn : Reflect on the problem-solving process, identify any improvements or adjustments that can be made, and apply these learnings to future situations.
Defining the Problem
To start tackling a problem, first, identify and understand it. Analyzing the issue thoroughly helps to clarify its scope and nature. Ask questions to gather information and consider the problem from various angles. Some strategies to define the problem include:
- Brainstorming with others
- Asking the 5 Ws and 1 H (Who, What, When, Where, Why, and How)
- Analyzing cause and effect
- Creating a problem statement
Generating Solutions
Once the problem is clearly understood, brainstorm possible solutions. Think creatively and keep an open mind, as well as considering lessons from past experiences. Consider:
- Creating a list of potential ideas to solve the problem
- Grouping and categorizing similar solutions
- Prioritizing potential solutions based on feasibility, cost, and resources required
- Involving others to share diverse opinions and inputs
Evaluating and Selecting Solutions
Evaluate each potential solution, weighing its pros and cons. To facilitate decision-making, use techniques such as:
- SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats)
- Decision-making matrices
- Pros and cons lists
- Risk assessments
After evaluating, choose the most suitable solution based on effectiveness, cost, and time constraints.
Implementing and Monitoring the Solution
Implement the chosen solution and monitor its progress. Key actions include:
- Communicating the solution to relevant parties
- Setting timelines and milestones
- Assigning tasks and responsibilities
- Monitoring the solution and making adjustments as necessary
- Evaluating the effectiveness of the solution after implementation
Utilize feedback from stakeholders and consider potential improvements. Remember that problem-solving is an ongoing process that can always be refined and enhanced.
Problem-Solving Techniques
During each step, you may find it helpful to utilize various problem-solving techniques, such as:
- Brainstorming : A free-flowing, open-minded session where ideas are generated and listed without judgment, to encourage creativity and innovative thinking.
- Root cause analysis : A method that explores the underlying causes of a problem to find the most effective solution rather than addressing superficial symptoms.
- SWOT analysis : A tool used to evaluate the strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats related to a problem or decision, providing a comprehensive view of the situation.
- Mind mapping : A visual technique that uses diagrams to organize and connect ideas, helping to identify patterns, relationships, and possible solutions.
Brainstorming
When facing a problem, start by conducting a brainstorming session. Gather your team and encourage an open discussion where everyone contributes ideas, no matter how outlandish they may seem. This helps you:
- Generate a diverse range of solutions
- Encourage all team members to participate
- Foster creative thinking
When brainstorming, remember to:
- Reserve judgment until the session is over
- Encourage wild ideas
- Combine and improve upon ideas
Root Cause Analysis
For effective problem-solving, identifying the root cause of the issue at hand is crucial. Try these methods:
- 5 Whys : Ask “why” five times to get to the underlying cause.
- Fishbone Diagram : Create a diagram representing the problem and break it down into categories of potential causes.
- Pareto Analysis : Determine the few most significant causes underlying the majority of problems.
SWOT Analysis
SWOT analysis helps you examine the Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats related to your problem. To perform a SWOT analysis:
- List your problem’s strengths, such as relevant resources or strong partnerships.
- Identify its weaknesses, such as knowledge gaps or limited resources.
- Explore opportunities, like trends or new technologies, that could help solve the problem.
- Recognize potential threats, like competition or regulatory barriers.
SWOT analysis aids in understanding the internal and external factors affecting the problem, which can help guide your solution.
Mind Mapping
A mind map is a visual representation of your problem and potential solutions. It enables you to organize information in a structured and intuitive manner. To create a mind map:
- Write the problem in the center of a blank page.
- Draw branches from the central problem to related sub-problems or contributing factors.
- Add more branches to represent potential solutions or further ideas.
Mind mapping allows you to visually see connections between ideas and promotes creativity in problem-solving.
Examples of Problem Solving in Various Contexts
In the business world, you might encounter problems related to finances, operations, or communication. Applying problem-solving skills in these situations could look like:
- Identifying areas of improvement in your company’s financial performance and implementing cost-saving measures
- Resolving internal conflicts among team members by listening and understanding different perspectives, then proposing and negotiating solutions
- Streamlining a process for better productivity by removing redundancies, automating tasks, or re-allocating resources
In educational contexts, problem-solving can be seen in various aspects, such as:
- Addressing a gap in students’ understanding by employing diverse teaching methods to cater to different learning styles
- Developing a strategy for successful time management to balance academic responsibilities and extracurricular activities
- Seeking resources and support to provide equal opportunities for learners with special needs or disabilities
Everyday life is full of challenges that require problem-solving skills. Some examples include:
- Overcoming a personal obstacle, such as improving your fitness level, by establishing achievable goals, measuring progress, and adjusting your approach accordingly
- Navigating a new environment or city by researching your surroundings, asking for directions, or using technology like GPS to guide you
- Dealing with a sudden change, like a change in your work schedule, by assessing the situation, identifying potential impacts, and adapting your plans to accommodate the change.
- How to Resolve Employee Conflict at Work [Steps, Tips, Examples]
- How to Write Inspiring Core Values? 5 Steps with Examples
- 30 Employee Feedback Examples (Positive & Negative)
What Are Problem-Solving Skills? Definition and Examples
- Share on Twitter Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn Share on LinkedIn

Forage puts students first. Our blog articles are written independently by our editorial team. They have not been paid for or sponsored by our partners. See our full editorial guidelines .
Why do employers hire employees? To help them solve problems. Whether you’re a financial analyst deciding where to invest your firm’s money, or a marketer trying to figure out which channel to direct your efforts, companies hire people to help them find solutions. Problem-solving is an essential and marketable soft skill in the workplace.
So, how can you improve your problem-solving and show employers you have this valuable skill? In this guide, we’ll cover:
Problem-Solving Skills Definition
Why are problem-solving skills important, problem-solving skills examples, how to include problem-solving skills in a job application, how to improve problem-solving skills, problem-solving: the bottom line.
Problem-solving skills are the ability to identify problems, brainstorm and analyze answers, and implement the best solutions. An employee with good problem-solving skills is both a self-starter and a collaborative teammate; they are proactive in understanding the root of a problem and work with others to consider a wide range of solutions before deciding how to move forward.
Examples of using problem-solving skills in the workplace include:
- Researching patterns to understand why revenue decreased last quarter
- Experimenting with a new marketing channel to increase website sign-ups
- Brainstorming content types to share with potential customers
- Testing calls to action to see which ones drive the most product sales
- Implementing a new workflow to automate a team process and increase productivity
Problem-solving skills are the most sought-after soft skill of 2022. In fact, 86% of employers look for problem-solving skills on student resumes, according to the National Association of Colleges and Employers Job Outlook 2022 survey .
It’s unsurprising why employers are looking for this skill: companies will always need people to help them find solutions to their problems. Someone proactive and successful at problem-solving is valuable to any team.
“Employers are looking for employees who can make decisions independently, especially with the prevalence of remote/hybrid work and the need to communicate asynchronously,” Eric Mochnacz, senior HR consultant at Red Clover, says. “Employers want to see individuals who can make well-informed decisions that mitigate risk, and they can do so without suffering from analysis paralysis.”
Showcase new skills
Build the confidence and practical skills that employers are looking for with Forage’s free job simulations.
Problem-solving includes three main parts: identifying the problem, analyzing possible solutions, and deciding on the best course of action.
>>MORE: Discover the right career for you based on your skills with a career aptitude test .
Research is the first step of problem-solving because it helps you understand the context of a problem. Researching a problem enables you to learn why the problem is happening. For example, is revenue down because of a new sales tactic? Or because of seasonality? Is there a problem with who the sales team is reaching out to?
Research broadens your scope to all possible reasons why the problem could be happening. Then once you figure it out, it helps you narrow your scope to start solving it.
Analysis is the next step of problem-solving. Now that you’ve identified the problem, analytical skills help you look at what potential solutions there might be.
“The goal of analysis isn’t to solve a problem, actually — it’s to better understand it because that’s where the real solution will be found,” Gretchen Skalka, owner of Career Insights Consulting, says. “Looking at a problem through the lens of impartiality is the only way to get a true understanding of it from all angles.”
Decision-Making
Once you’ve figured out where the problem is coming from and what solutions are, it’s time to decide on the best way to go forth. Decision-making skills help you determine what resources are available, what a feasible action plan entails, and what solution is likely to lead to success.
On a Resume
Employers looking for problem-solving skills might include the word “problem-solving” or other synonyms like “ critical thinking ” or “analytical skills” in the job description.
“I would add ‘buzzwords’ you can find from the job descriptions or LinkedIn endorsements section to filter into your resume to comply with the ATS,” Matthew Warzel, CPRW resume writer, advises. Warzel recommends including these skills on your resume but warns to “leave the soft skills as adjectives in the summary section. That is the only place soft skills should be mentioned.”
On the other hand, you can list hard skills separately in a skills section on your resume .

Forage Resume Writing Masterclass
Learn how to showcase your skills and craft an award-winning resume with this free masterclass from Forage.
Avg. Time: 5 to 6 hours
Skills you’ll build: Resume writing, professional brand, professional summary, narrative, transferable skills, industry keywords, illustrating your impact, standing out
In a Cover Letter or an Interview
Explaining your problem-solving skills in an interview can seem daunting. You’re required to expand on your process — how you identified a problem, analyzed potential solutions, and made a choice. As long as you can explain your approach, it’s okay if that solution didn’t come from a professional work experience.
“Young professionals shortchange themselves by thinking only paid-for solutions matter to employers,” Skalka says. “People at the genesis of their careers don’t have a wealth of professional experience to pull from, but they do have relevant experience to share.”
Aaron Case, career counselor and CPRW at Resume Genius, agrees and encourages early professionals to share this skill. “If you don’t have any relevant work experience yet, you can still highlight your problem-solving skills in your cover letter,” he says. “Just showcase examples of problems you solved while completing your degree, working at internships, or volunteering. You can even pull examples from completely unrelated part-time jobs, as long as you make it clear how your problem-solving ability transfers to your new line of work.”
Learn How to Identify Problems
Problem-solving doesn’t just require finding solutions to problems that are already there. It’s also about being proactive when something isn’t working as you hoped it would. Practice questioning and getting curious about processes and activities in your everyday life. What could you improve? What would you do if you had more resources for this process? If you had fewer? Challenge yourself to challenge the world around you.
Think Digitally
“Employers in the modern workplace value digital problem-solving skills, like being able to find a technology solution to a traditional issue,” Case says. “For example, when I first started working as a marketing writer, my department didn’t have the budget to hire a professional voice actor for marketing video voiceovers. But I found a perfect solution to the problem with an AI voiceover service that cost a fraction of the price of an actor.”
Being comfortable with new technology — even ones you haven’t used before — is a valuable skill in an increasingly hybrid and remote world. Don’t be afraid to research new and innovative technologies to help automate processes or find a more efficient technological solution.
Collaborate
Problem-solving isn’t done in a silo, and it shouldn’t be. Use your collaboration skills to gather multiple perspectives, help eliminate bias, and listen to alternative solutions. Ask others where they think the problem is coming from and what solutions would help them with your workflow. From there, try to compromise on a solution that can benefit everyone.
If we’ve learned anything from the past few years, it’s that the world of work is constantly changing — which means it’s crucial to know how to adapt . Be comfortable narrowing down a solution, then changing your direction when a colleague provides a new piece of information. Challenge yourself to get out of your comfort zone, whether with your personal routine or trying a new system at work.
Put Yourself in the Middle of Tough Moments
Just like adapting requires you to challenge your routine and tradition, good problem-solving requires you to put yourself in challenging situations — especially ones where you don’t have relevant experience or expertise to find a solution. Because you won’t know how to tackle the problem, you’ll learn new problem-solving skills and how to navigate new challenges. Ask your manager or a peer if you can help them work on a complicated problem, and be proactive about asking them questions along the way.
Career Aptitude Test
What careers are right for you based on your skills? Take this quiz to find out. It’s completely free — you’ll just need to sign up to get your results!
Step 1 of 3
Companies always need people to help them find solutions — especially proactive employees who have practical analytical skills and can collaborate to decide the best way to move forward. Whether or not you have experience solving problems in a professional workplace, illustrate your problem-solving skills by describing your research, analysis, and decision-making process — and make it clear that you’re the solution to the employer’s current problems.
Image Credit: Christina Morillo / Pexels

Related Posts
6 negotiation skills to level up your work life, how to build conflict resolution skills: case studies and examples, what is github uses and getting started, upskill with forage.

Build career skills recruiters are looking for.
Explore Jobs
- Jobs Near Me
- Remote Jobs
- Full Time Jobs
- Part Time Jobs
- Entry Level Jobs
- Work From Home Jobs
Find Specific Jobs
- $15 Per Hour Jobs
- $20 Per Hour Jobs
- Hiring Immediately Jobs
- High School Jobs
- H1b Visa Jobs
Explore Careers
- Business And Financial
- Architecture And Engineering
- Computer And Mathematical
Explore Professions
- What They Do
- Certifications
- Demographics
Best Companies
- Health Care
- Fortune 500
Explore Companies
- CEO And Executies
- Resume Builder
- Career Advice
- Explore Majors
- Questions And Answers
- Interview Questions
What Are Problem-Solving Skills? (Definition, Examples, And How To List On A Resume)
- What Are Skills Employers Look For?
- What Are Inductive Reasoning?
- What Are Problem Solving Skills?
- What Are Active Listening Skills?
- What Are Management Skills?
- What Are Attention To Detail?
- What Are Detail Oriented Skills?
- What Are Domain Knowledge?
- What Is Professionalism?
- What Are Rhetorical Skills?
- What Is Integrity?
- What Are Persuasion Skills?
- How To Start A Conversation
- How To Write A Conclusion For A Research Paper
- Team Player
- Visual Learner
- High Income Skills
- The Most Important Professional Skills
Find a Job You Really Want In
Summary. Problem-solving skills include analysis, creativity, prioritization, organization, and troubleshooting. To solve a problem, you need to use a variety of skills based on the needs of the situation. Most jobs essentially boil down to identifying and solving problems consistently and effectively. That’s why employers value problem-solving skills in job candidates for just about every role. We’ll cover problem-solving methods, ways to improve your problem-solving skills, and examples of showcasing your problem-solving skills during your job search . Key Takeaways: If you can show off your problem-solving skills on your resume , in your cover letter , and during a job interview, you’ll be one step closer to landing a job. Companies rely on employees who can handle unexpected challenges, identify persistent issues, and offer workable solutions in a positive way. It is important to improve problem solving skill because this is a skill that can be cultivated and nurtured so you can become better at dealing with problems over time. In This Article Skip to section What Are Problem Solving Skills? Types of Problem-Solving Skills How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills Example Answers to Problem-Solving Interview Questions How to Show Off Problem-Solving Skills on a Resume Example Resume and Cover Letter With Problem-Solving Skills More About Problem-Solving Skills Problem Solving Skills FAQs References Sign Up For More Advice and Jobs Show More What Are Problem Solving Skills?
Problem-solving skills are skills that help you identify and solve problems effectively and efficiently . Your ability to solve problems is one of the main ways that hiring managers and recruiters assess candidates, as those with excellent problem-solving skills are more likely to autonomously carry out their responsibilities.
A true problem solver can look at a situation, find the cause of the problem (or causes, because there are often many issues at play), and then come up with a reasonable solution that effectively fixes the problem or at least remedies most of it.
The ability to solve problems is considered a soft skill , meaning that it’s more of a personality trait than a skill you’ve learned at school, on the job, or through technical training.
That being said, your proficiency with various hard skills will have a direct bearing on your ability to solve problems. For example, it doesn’t matter if you’re a great problem-solver; if you have no experience with astrophysics, you probably won’t be hired as a space station technician .
Types of Problem-Solving Skills
Problem-solving is considered a skill on its own, but it’s supported by many other skills that can help you be a better problem solver. These skills fall into a few different categories of problem-solving skills.
Problem recognition and analysis. The first step is to recognize that there is a problem and discover what it is or what the root cause of it is.
You can’t begin to solve a problem unless you’re aware of it. Sometimes you’ll see the problem yourself and other times you’ll be told about the problem. Both methods of discovery are very important, but they can require some different skills. The following can be an important part of the process:
Active listening
Data analysis
Historical analysis
Communication
Create possible solutions. You know what the problem is, and you might even know the why of it, but then what? Your next step is the come up with some solutions.
Most of the time, the first solution you come up with won’t be the right one. Don’t fall victim to knee-jerk reactions; try some of the following methods to give you solution options.
Brainstorming
Forecasting
Decision-making
Topic knowledge/understanding
Process flow
Evaluation of solution options. Now that you have a lot of solution options, it’s time to weed through them and start casting some aside. There might be some ridiculous ones, bad ones, and ones you know could never be implemented. Throw them away and focus on the potentially winning ideas.
This step is probably the one where a true, natural problem solver will shine. They intuitively can put together mental scenarios and try out solutions to see their plusses and minuses. If you’re still working on your skill set — try listing the pros and cons on a sheet of paper.
Prioritizing
Evaluating and weighing
Solution implementation. This is your “take action” step. Once you’ve decided which way to go, it’s time to head down that path and see if you were right. This step takes a lot of people and management skills to make it work for you.
Dependability
Teambuilding
Troubleshooting
Follow-Through
Believability
Trustworthiness
Project management
Evaluation of the solution. Was it a good solution? Did your plan work or did it fail miserably? Sometimes the evaluation step takes a lot of work and review to accurately determine effectiveness. The following skills might be essential for a thorough evaluation.
Customer service
Feedback responses
Flexibility
How to Improve Your Problem-Solving Skills
You now have a ton of skills in front of you. Some of them you have naturally and some — not so much. If you want to solve a problem, and you want to be known for doing that well and consistently, then it’s time to sharpen those skills.
Develop industry knowledge. Whether it’s broad-based industry knowledge, on-the-job training , or very specific knowledge about a small sector — knowing all that you can and feeling very confident in your knowledge goes a long way to learning how to solve problems.
Be a part of a solution. Step up and become involved in the problem-solving process. Don’t lead — but follow. Watch an expert solve the problem and, if you pay attention, you’ll learn how to solve a problem, too. Pay attention to the steps and the skills that a person uses.
Practice solving problems. Do some role-playing with a mentor , a professor , co-workers, other students — just start throwing problems out there and coming up with solutions and then detail how those solutions may play out.
Go a step further, find some real-world problems and create your solutions, then find out what they did to solve the problem in actuality.
Identify your weaknesses. If you could easily point out a few of your weaknesses in the list of skills above, then those are the areas you need to focus on improving. How you do it is incredibly varied, so find a method that works for you.
Solve some problems — for real. If the opportunity arises, step in and use your problem-solving skills. You’ll never really know how good (or bad) you are at it until you fail.
That’s right, failing will teach you so much more than succeeding will. You’ll learn how to go back and readdress the problem, find out where you went wrong, learn more from listening even better. Failure will be your best teacher ; it might not make you feel good, but it’ll make you a better problem-solver in the long run.
Example Answers to Problem-Solving Interview Questions
Once you’ve impressed a hiring manager with top-notch problem-solving skills on your resume and cover letter , you’ll need to continue selling yourself as a problem-solver in the job interview.
There are three main ways that employers can assess your problem-solving skills during an interview:
By asking questions that relate to your past experiences solving problems
Posing hypothetical problems for you to solve
By administering problem-solving tests and exercises
The third method varies wildly depending on what job you’re applying for, so we won’t attempt to cover all the possible problem-solving tests and exercises that may be a part of your application process.
Luckily, interview questions focused on problem-solving are pretty well-known, and most can be answered using the STAR method . STAR stands for situation, task, action, result, and it’s a great way to organize your answers to behavioral interview questions .
Let’s take a look at how to answer some common interview questions built to assess your problem-solving capabilities:
At my current job as an operations analyst at XYZ Inc., my boss set a quarterly goal to cut contractor spending by 25% while maintaining the same level of production and moving more processes in-house. It turned out that achieving this goal required hiring an additional 6 full-time employees, which got stalled due to the pandemic. I suggested that we widen our net and hire remote employees after our initial applicant pool had no solid candidates. I ran the analysis on overhead costs and found that if even 4 of the 6 employees were remote, we’d save 16% annually compared to the contractors’ rates. In the end, all 6 employees we hired were fully remote, and we cut costs by 26% while production rose by a modest amount.
I try to step back and gather research as my first step. For instance, I had a client who needed a graphic designer to work with Crello, which I had never seen before, let alone used. After getting the project details straight, I began meticulously studying the program the YouTube tutorials, and the quick course Crello provides. I also reached out to coworkers who had worked on projects for this same client in the past. Once I felt comfortable with the software, I started work immediately. It was a slower process because I had to be more methodical in my approach, but by putting in some extra hours, I turned in the project ahead of schedule. The client was thrilled with my work and was shocked to hear me joke afterward that it was my first time using Crello.
As a digital marketer , website traffic and conversion rates are my ultimate metrics. However, I also track less visible metrics that can illuminate the story behind the results. For instance, using Google Analytics, I found that 78% of our referral traffic was coming from one affiliate, but that these referrals were only accounting for 5% of our conversions. Another affiliate, who only accounted for about 10% of our referral traffic, was responsible for upwards of 30% of our conversions. I investigated further and found that the second, more effective affiliate was essentially qualifying our leads for us before sending them our way, which made it easier for us to close. I figured out exactly how they were sending us better customers, and reached out to the first, more prolific but less effective affiliate with my understanding of the results. They were able to change their pages that were referring us traffic, and our conversions from that source tripled in just a month. It showed me the importance of digging below the “big picture” metrics to see the mechanics of how revenue was really being generated through digital marketing.
How to Show Off Problem-Solving Skills on a Resume
You can bring up your problem-solving skills in your resume summary statement , in your work experience , and under your education section , if you’re a recent graduate. The key is to include items on your resume that speak direclty to your ability to solve problems and generate results.
If you can, quantify your problem-solving accomplishments on your your resume . Hiring managers and recruiters are always more impressed with results that include numbers because they provide much-needed context.
This sample resume for a Customer Service Representative will give you an idea of how you can work problem solving into your resume.
Example Resume and Cover Letter With Problem-Solving Skills
Michelle Beattle 111 Millennial Parkway Chicago, IL 60007 (555) 987-6543 [email protected] Professional Summary Qualified Customer Services Representative with 3 years in a high-pressure customer service environment. Professional, personable, and a true problem solver. Work History ABC Store — Customer Service Representative 01/2015 — 12/2017 Managed in-person and phone relations with customers coming in to pick up purchases, return purchased products, helped find and order items not on store shelves, and explained details and care of merchandise. Became a key player in the customer service department and was promoted to team lead. XYZ Store — Customer Service Representative/Night Manager 01/2018 — 03/2020, released due to Covid-19 layoffs Worked as the night manager of the customer service department and filled in daytime hours when needed. Streamlined a process of moving customers to the right department through an app to ease the burden on the phone lines and reduce customer wait time by 50%. Was working on additional wait time problems when the Covid-19 pandemic caused our stores to close permanently. Education Chicago Tech 2014-2016 Earned an Associate’s Degree in Principles of Customer Care Skills Strong customer service skills Excellent customer complaint resolution Stock record management Order fulfillment New product information Cash register skills and proficiency Leader in problem solving initiatives
You can see how the resume gives you a chance to point out your problem-solving skills and to show where you used them a few times. Your cover letter is your chance to introduce yourself and list a few things that make you stand out from the crowd.
Michelle Beattle 111 Millennial Parkway Chicago, IL 60007 (555) 987-6543 [email protected] Dear Mary McDonald, I am writing in response to your ad on Zippia for a Customer Service Representative . Thank you for taking the time to consider me for this position. Many people believe that a job in customer service is simply listening to people complain all day. I see the job as much more than that. It’s an opportunity to help people solve problems, make their experience with your company more enjoyable, and turn them into life-long advocates of your brand. Through my years of experience and my educational background at Chicago Tech, where I earned an Associate’s Degree in the Principles of Customer Care, I have learned that the customers are the lifeline of the business and without good customer service representatives, a business will falter. I see it as my mission to make each and every customer I come in contact with a fan. I have more than five years of experience in the Customer Services industry and had advanced my role at my last job to Night Manager. I am eager to again prove myself as a hard worker, a dedicated people person, and a problem solver that can be relied upon. I have built a professional reputation as an employee that respects all other employees and customers, as a manager who gets the job done and finds solutions when necessary, and a worker who dives in to learn all she can about the business. Most of my customers have been very satisfied with my resolution ideas and have returned to do business with us again. I believe my expertise would make me a great match for LMNO Store. I have enclosed my resume for your review, and I would appreciate having the opportunity to meet with you to further discuss my qualifications. Thank you again for your time and consideration. Sincerely, Michelle Beattle
More About Problem-Solving Skills
You’ve no doubt noticed that many of the skills listed in the problem-solving process are repeated. This is because having these abilities or talents is so important to the entire course of getting a problem solved.
In fact, they’re worthy of a little more attention. Many of them are similar, so we’ll pull them together and discuss how they’re important and how they work together.
Communication, active listening, and customer service skills. No matter where you are in the process of problem-solving, you need to be able to show that you’re listening and engaged and really hearing what the problem is or what a solution may be.
Obviously, the other part of this is being able to communicate effectively so people understand what you’re saying without confusion. Rolled into this are customer service skills , which really are all about listening and responding appropriately — it’s the ultimate in interpersonal communications.
Analysis (data and historical), research, and topic knowledge/understanding. This is how you intellectually grasp the issue and approach it. This can come from studying the topic and the process or it can come from knowledge you’ve gained after years in the business. But the best solutions come from people who thoroughly understand the problem.
Creativity, brainstorming, troubleshooting, and flexibility. All of you creative thinkers will like this area because it’s when your brain is at its best.
Coming up with ideas, collaborating with others, leaping over hurdles, and then being able to change courses immediately, if need be, are all essential. If you’re not creative by nature, then having a team of diverse thinkers can help you in this area.
Dependability, believability, trustworthiness, and follow-through. Think about it, these are all traits a person needs to have to make change happen and to make you comfortable taking that next step with them. Someone who is shifty and shady and never follows through, well, you’re simply not going to do what they ask, are you?
Leadership, teambuilding, decision-making, and project management. These are the skills that someone who is in charge is brimming with. These are the leaders you enjoy working for because you know they’re doing what they can to keep everything in working order. These skills can be learned but they’re often innate.
Prioritizing, prediction, forecasting, evaluating and weighing, and process flow. If you love flow charts, data analysis, prediction modeling, and all of that part of the equation, then you might have some great problem-solving abilities.
These are all great skills because they can help you weed out bad ideas, see flaws, and save massive amounts of time in trial and error.
Problem Solving Skills FAQs
What is a good example of problem-solving skills?
Good examples of porblem-solving skills include research, analysis, creativity, communciation, and decision-making. Each of these skills build off one another to contribute to the problem solving process. Research and analysis allow you to identify a problem.
Creativity and analysis help you consider different solutions. Meanwhile, communication and decision-making are key to working with others to solve a problem on a large scale.
What are 3 key attributes of a good problem solver?
3 key attributes of a good problem solver are persistence, intellegince, and empathy. Persistence is crucial to remain motivated to work through challenges. Inellegince is needed to make smart, informed choices. Empathy is crucial to maintain positive relationships with others as well as yourself.
What can I say instead of problem-solving skills?
Instead of saying problem-solving skills, you can say the following:
Critical thinker
Solutions-oriented
Engineering
Using different words is helpful, especially when writing your resume and cover letter.
What is problem-solving in the workplace?
Problem-solving in the workplace is the ability to work through any sort of challenge, conflict, or unexpected situation and still achieve business goals. Though it varies by profession, roblem-solving in the workplace is very important for almost any job, because probelms are inevitable. You need to have the appropriate level of problem-solving skills if you want to succeed in your career, whatever it may be.
Department of Labor – Problem Solving and Critical Thinking
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating / 5. Vote count:
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.

Kristin Kizer is an award-winning writer, television and documentary producer, and content specialist who has worked on a wide variety of written, broadcast, and electronic publications. A former writer/producer for The Discovery Channel, she is now a freelance writer and delighted to be sharing her talents and time with the wonderful Zippia audience.

Related posts

How To List Microsoft Office Skills On A Resume (With Examples)

Most Common Resume Items of Business Founders and CEOs

What Is Organizational Behavior Management (OBM)? (With Examples)

What Is Aptitude And Why Do You Need To Know About It?
- Career Advice >
- Desired Traits >
- Problem Solving Skills

Ask Another Question
Follow class ace :.
Search form
Critical thinking and problem solving with technology.
Brief Summary: Critical thinking and problem solving is a crucial skill in a technical world that can immediately be applied to academics and careers. A highly skilled individual in this competency can choose the appropriate tool to accomplish a task, easily switch between tools, has a basic understanding of different file types, and can troubleshoot technology when it’s not working properly. They can also differentiate between true information and falsified information online and has basic proficiency in data gathering, processing and interpretation.
Learners with proficient skills in critical thinking and problem solving should be able to:
- Troubleshoot computers and mobile devices when issues arise, like restarting the device and checking if it requires a software or operating system update
- Move across tools to complete a task (for example, adding PowerPoint slides into a note taking app for annotation)
- Differentiate between legitimate and falsified information online
- Understand basic file types and know when to use them (for example, the difference between .doc and .pdf files)
Market/Employer Trends: Employers indicate value in employee ability to problem solve using technology, particularly related to drawing information from data to identify and solve challenges. Further, knowing how to leverage technology tools to see a problem, break it down into manageable pieces, and work toward solving is of important value. Employers expect new employees to be able to navigate across common toolsets, making decisions to use the right tool for the right task.
Self-Evaluation:
Key questions for reflection:
- How comfortable are you when technology doesn’t work the way you expect?
- Do you know basic troubleshooting skills to solve tech issues?
- Do you know the key indicators of whether information you read online is reliable?
Strong digital skills in this area could appear as:
- Updating your computer after encountering a problem and resolving the issue
- Discerning legitimate news sources from illegitimate ones to successfully meet goals
- Converting a PowerPoint presentation into a PDF for easy access for peers who can’t use PowerPoint
- Taking notes on a phone and seamlessly completing them on a computer
Ways to Upskill:
Ready to grow your strength in this competency? Try:
- Reviewing University Libraries’ resources on research and information literacy
- Read about troubleshooting in college in the Learner Technology Handbook
- Registering for ESEPSY 1359: Critical Thinking and Collaboration in Online Learning
Educator Tips to Support Digital Skills:
- Create an assignment in Carmen prompting students to find legitimate peer-reviewed research
- Provide links to information literacy resources on research-related assignments or projects for student review
- Develop assignments that require using more than one tech tool to accomplish a single task
- Resume Writing
- Resume Examples
- Cover Letter
- Remote Work
- Famous Resumes
- Try Kickresume
7 Problem Solving Skills That Aren’t Just Buzzwords (+ Resume Example)
- Julia Mlcuchova ,
- Updated April 8, 2024 9 min read
Problem-solving skills are something everybody should include on their resume, yet only a few seem to understand what these skills actually are. If you've always felt that the term "problem-solving skills" is rather vague and wanted to know more, you've come to the right place.
In this article, we're going to explain what problem-solving skills really mean. We'll talk about what makes up good problem-solving skills and give you tips on how to get better at them. You'll also find out how to make your problem-solving abilities look more impressive to those who might want to hire you.
Sounds good, right? Curious to learn more?
In this article we’ll show you:
- What are problem solving skills;
- Why are they important;
- Specific problem solving skills examples;
- How to develop your problem solving skills;
- And, how to showcase them on your resume.
Table of Contents
Click on a section to skip
What are problem solving skills?
Why are problem solving skills important, the best 7 problem solving skills examples, how to develop problem solving skills, problem solving skills resume example, key takeaways: problem solving skills.
First of all, they're more than just a buzzword!
Problem-solving skills are a set of specific abilities that allow you to deal with unexpected situations in the workplace, whether it be job related or team related.
It's a complex process that involves several “sub skills” or “sub steps,” namely:
- Recognizing and identifying the issue at hand.
- Breaking the problem down into smaller parts and analyzing how they relate to one another.
- Creating potential solutions to the problem, evaluating them and picking the best one.
- Applying the chosen solution and assessing its outcome.
- Learning from the whole process to deal with future problems more effectively.
As you can see, it's not just about solving problems that are right in front of us, but also about predicting potential issues and being prepared to deal with them before they arise.
Despite what you may believe, problem-solving skills aren't just for managers .
Think about it this way: Why do employers hire employees in the first place? To solve problems for them!
And, as we all know, problems don't discriminate. In other words, it doesn't matter whether you're just an intern, an entry-level professional, or a seasoned veteran, you'll constantly face some kind of challenges. And the only difference is in how complex they will get.
This is also reflected in the way employers assess suitability of potential job candidates.
In fact, research shows that the ability to deal with unexpected complications is prioritized by an overwhelming 60% of employers across all industries, making it one of the most compelling skills on your resume.
So, regardless of your job description or your career level, you're always expected to find solutions for problems, either independently or as a part of a team.
And that's precisely what makes problem-solving skills so invaluable and universal !
Wondering how good is your resume?
Find out with our AI Resume Checker! Just upload your resume and see what can be improved.
As we've said before, problem-solving isn't really just one single skill.
Instead, your ability to handle workplace issues with composure depends on several different “sub-skills”.
So, which specific skills make an employee desirable even for the most demanding of recruiters?
In no particular order, you should focus on these 7 skills :
- Analytical skills
- Research skills
- Critical thinking
- Decision-making
- Collaboration
- Having a growth mindset
Let's have a look at each of them in greater detail!
#1 Analytical skills
Firstly, to truly understand complex problems, you need to break them down into more manageable parts . Then, you observe them closely and ask yourself: “ Which parts work and which don't,” How do these parts contribute to the problem as a whole,” and "What exactly needs to be fixed?” In other words, you gather data , you study it, and compare it - all to pinpoint the cause of the issue as closely as possible.
#2 Research skills
Another priceless tool is your research skills (sometimes relying on just one source of information isn't enough). Besides, to make a truly informed decision , you'll have to dig a little deeper. Being a good researcher means looking for potential solutions to a problem in a wider context. For example: going through team reports, customer feedback, quarterly sales or current market trends.
#3 Critical thinking
Every employer wants to hire people who can think critically. Yet, the ability to evaluate situations objectively and from different perspectives , is actually pretty hard to come by. But as long as you stay open-minded, inquisitive, and with a healthy dose of skepticism, you'll be able to assess situations based on facts and evidence more successfully. Plus, critical thinking comes in especially handy when you need to examine your own actions and processes.
#4 Creativity
Instead of following the old established processes that don't work anymore, you should feel comfortable thinking outside the box. The thing is, problems have a nasty habit of popping up unexpectedly and rapidly. And sometimes, you have to get creative in order to solve them fast. Especially those that have no precedence. But this requires a blend of intuition, industry knowledge, and quick thinking - a truly rare combination.
#5 Decision-making
The analysis, research, and brainstorming are done. Now, you need to look at the possible solutions, and make the final decision (informed, of course). And not only that, you also have to stand by it ! Because once the train gets moving, there's no room for second guessing. Also, keep in mind that you need to be prepared to take responsibility for all decisions you make. That's no small feat!
#6 Collaboration
Not every problem you encounter can be solved by yourself alone. And this is especially true when it comes to complex projects. So, being able to actively listen to your colleagues, take their ideas into account, and being respectful of their opinions enables you to solve problems together. Because every individual can offer a unique perspective and skill set. Yes, democracy is hard, but at the end of the day, it's teamwork that makes the corporate world go round.
#7 Having a growth mindset
Let's be honest, no one wants their work to be riddled with problems. But facing constant challenges and changes is inevitable. And that can be scary! However, when you're able to see these situations as opportunities to grow instead of issues that hold you back, your problem solving skills reach new heights. And the employers know that too!
Now that we've shown you the value problem-solving skills can add to your resume, let's ask the all-important question: “How can I learn them?”
Well…you can't. At least not in the traditional sense of the word.
Let us explain: Since problem-solving skills fall under the umbrella of soft skills , they can't be taught through formal education, unlike computer skills for example. There's no university course that you can take and graduate as a professional problem solver.
But, just like other interpersonal skills, they can be nurtured and refined over time through practice and experience.
Unfortunately, there's no one-size-fits-all approach, but the following tips can offer you inspiration on how to improve your problem solving skills:
- Cultivate a growth mindset. Remember what we've said before? Your attitude towards obstacles is the first step to unlocking your problem-solving potential.
- Gain further knowledge in your specialized field. Secondly, it's a good idea to delve a little deeper into your chosen profession. Because the more you read on a subject, the easier it becomes to spot certain patterns and relations.
- Start with small steps. Don't attack the big questions straight away — you'll only set yourself up for failure. Instead, start with more straightforward tasks and work your way up to more complex problems.
- Break problems down into more digestible pieces. Complex issues are made up of smaller problems. And those can be further divided into even smaller problems, and so on. Until you're left with only the basics.
- Don't settle for a single solution. Instead, keep on exploring other possible answers.
- Accept failure as a part of the learning process. Finally, don't let your failures discourage you. After all, you're bound to misstep a couple of times before you find your footing. Just keep on practicing.
How to improve problem solving skills with online courses
While it’s true that formal education won’t turn you into a master problem solver, you can still hone your skills with courses and certifications offered by online learning platforms :
- Analytical skills. You can sharpen your analytical skills with Data Analytics Basics for Everyone from IBM provided by edX (Free); or Decision Making and Analytical Thinking: Fortune 500 provided by Udemy ($21,74).
- Creativity. And, to unlock your inner creative mind, you can try Creative Thinking: Techniques and Tools for Success from the Imperial College London provided by Coursera (Free).
- Critical thinking. Try Introduction to Logic and Critical Thinking Specialization from Duke University provided by Coursera (Free); or Logical and Critical Thinking offered by The University of Auckland via FutureLearn.
- Decision-making. Or, you can learn how to become more confident when it's time to make a decision with Decision-Making Strategies and Executive Decision-Making both offered by LinkedIn Learning (1 month free trial).
- Communication skills . Lastly, to improve your collaborative skills, check out Communicating for Influence and Impact online at University of Cambridge.
The fact that everybody and their grandmothers put “ problem-solving skills ” on their CVs has turned the phrase into a cliche.
But there's a way to incorporate these skills into your resume without sounding pretentious and empty. Below, we've prepared a mock-up resume that manages to do just that.
FYI, if you like this design, you can use the template to create your very own resume. Just click the red button and fill in your information (or let the AI do it for you).
Problem solving skills on resume example
This resume was written by our experienced resume writers specifically for this profession.
Why this example works?
- Firstly, the job description itself is neatly organized into bullet points .
- Instead of simply listing soft skills in a skills section , you can incorporate them into the description of your work experience entry.
- Also, the language here isn't vague . This resume puts each problem-solving skill into a real-life context by detailing specific situations and obstacles.
- And, to highlight the impact of each skill on your previous job position, we recommend quantifying your results whenever possible.
- Finally, starting each bullet point with an action verb (in bold) makes you look more dynamic and proactive.
To sum it all up, problem-solving skills continue gaining popularity among employers and employees alike. And for a good reason!
Because of them, you can overcome any obstacles that stand in the way of your professional life more efficiently and systematically.
In essence, problem-solving skills refer to the ability to recognize a challenge, identify its root cause, think of possible solutions , and then implement the most effective one.
Believing that these skills are all the same would be a serious misconception. In reality, this term encompasses a variety of different abilities , including:
In short, understanding, developing, and showcasing these skills, can greatly boost your chances at getting noticed by the hiring managers. So, don't hesitate and start working on your problem-solving skills right now!
Julia has recently joined Kickresume as a career writer. From helping people with their English to get admitted to the uni of their dreams to advising them on how to succeed in the job market. It would seem that her career is on a steadfast trajectory. Julia holds a degree in Anglophone studies from Metropolitan University in Prague, where she also resides. Apart from creative writing and languages, she takes a keen interest in literature and theatre.
Related Posts
How many skills to list on resume this is the magic number.
- 11 min read
Should You Include GPA on Your Resume? (Tips & Examples)
Share this article, join our newsletter.
Every month, we’ll send you resume advice, job search tips, career hacks and more in pithy, bite-sized chunks. Sounds good?
What Is Problem Solving? How Software Engineers Approach Complex Challenges

From debugging an existing system to designing an entirely new software application, a day in the life of a software engineer is filled with various challenges and complexities. The one skill that glues these disparate tasks together and makes them manageable? Problem solving .
Throughout this blog post, we’ll explore why problem-solving skills are so critical for software engineers, delve into the techniques they use to address complex challenges, and discuss how hiring managers can identify these skills during the hiring process.
What Is Problem Solving?
But what exactly is problem solving in the context of software engineering? How does it work, and why is it so important?
Problem solving, in the simplest terms, is the process of identifying a problem, analyzing it, and finding the most effective solution to overcome it. For software engineers, this process is deeply embedded in their daily workflow. It could be something as simple as figuring out why a piece of code isn’t working as expected, or something as complex as designing the architecture for a new software system.
In a world where technology is evolving at a blistering pace, the complexity and volume of problems that software engineers face are also growing. As such, the ability to tackle these issues head-on and find innovative solutions is not only a handy skill — it’s a necessity.
The Importance of Problem-Solving Skills for Software Engineers
Problem-solving isn’t just another ability that software engineers pull out of their toolkits when they encounter a bug or a system failure. It’s a constant, ongoing process that’s intrinsic to every aspect of their work. Let’s break down why this skill is so critical.
Driving Development Forward
Without problem solving, software development would hit a standstill. Every new feature, every optimization, and every bug fix is a problem that needs solving. Whether it’s a performance issue that needs diagnosing or a user interface that needs improving, the capacity to tackle and solve these problems is what keeps the wheels of development turning.
It’s estimated that 60% of software development lifecycle costs are related to maintenance tasks, including debugging and problem solving. This highlights how pivotal this skill is to the everyday functioning and advancement of software systems.
Innovation and Optimization
The importance of problem solving isn’t confined to reactive scenarios; it also plays a major role in proactive, innovative initiatives . Software engineers often need to think outside the box to come up with creative solutions, whether it’s optimizing an algorithm to run faster or designing a new feature to meet customer needs. These are all forms of problem solving.
Consider the development of the modern smartphone. It wasn’t born out of a pre-existing issue but was a solution to a problem people didn’t realize they had — a device that combined communication, entertainment, and productivity into one handheld tool.
Increasing Efficiency and Productivity
Good problem-solving skills can save a lot of time and resources. Effective problem-solvers are adept at dissecting an issue to understand its root cause, thus reducing the time spent on trial and error. This efficiency means projects move faster, releases happen sooner, and businesses stay ahead of their competition.
Improving Software Quality
Problem solving also plays a significant role in enhancing the quality of the end product. By tackling the root causes of bugs and system failures, software engineers can deliver reliable, high-performing software. This is critical because, according to the Consortium for Information and Software Quality, poor quality software in the U.S. in 2022 cost at least $2.41 trillion in operational issues, wasted developer time, and other related problems.
Problem-Solving Techniques in Software Engineering
So how do software engineers go about tackling these complex challenges? Let’s explore some of the key problem-solving techniques, theories, and processes they commonly use.
Decomposition
Breaking down a problem into smaller, manageable parts is one of the first steps in the problem-solving process. It’s like dealing with a complicated puzzle. You don’t try to solve it all at once. Instead, you separate the pieces, group them based on similarities, and then start working on the smaller sets. This method allows software engineers to handle complex issues without being overwhelmed and makes it easier to identify where things might be going wrong.
Abstraction
In the realm of software engineering, abstraction means focusing on the necessary information only and ignoring irrelevant details. It is a way of simplifying complex systems to make them easier to understand and manage. For instance, a software engineer might ignore the details of how a database works to focus on the information it holds and how to retrieve or modify that information.
Algorithmic Thinking
At its core, software engineering is about creating algorithms — step-by-step procedures to solve a problem or accomplish a goal. Algorithmic thinking involves conceiving and expressing these procedures clearly and accurately and viewing every problem through an algorithmic lens. A well-designed algorithm not only solves the problem at hand but also does so efficiently, saving computational resources.
Parallel Thinking
Parallel thinking is a structured process where team members think in the same direction at the same time, allowing for more organized discussion and collaboration. It’s an approach popularized by Edward de Bono with the “ Six Thinking Hats ” technique, where each “hat” represents a different style of thinking.
In the context of software engineering, parallel thinking can be highly effective for problem solving. For instance, when dealing with a complex issue, the team can use the “White Hat” to focus solely on the data and facts about the problem, then the “Black Hat” to consider potential problems with a proposed solution, and so on. This structured approach can lead to more comprehensive analysis and more effective solutions, and it ensures that everyone’s perspectives are considered.
This is the process of identifying and fixing errors in code . Debugging involves carefully reviewing the code, reproducing and analyzing the error, and then making necessary modifications to rectify the problem. It’s a key part of maintaining and improving software quality.
Testing and Validation
Testing is an essential part of problem solving in software engineering. Engineers use a variety of tests to verify that their code works as expected and to uncover any potential issues. These range from unit tests that check individual components of the code to integration tests that ensure the pieces work well together. Validation, on the other hand, ensures that the solution not only works but also fulfills the intended requirements and objectives.
Explore verified tech roles & skills.
The definitive directory of tech roles, backed by machine learning and skills intelligence.
Explore all roles
Evaluating Problem-Solving Skills
We’ve examined the importance of problem-solving in the work of a software engineer and explored various techniques software engineers employ to approach complex challenges. Now, let’s delve into how hiring teams can identify and evaluate problem-solving skills during the hiring process.
Recognizing Problem-Solving Skills in Candidates
How can you tell if a candidate is a good problem solver? Look for these indicators:
- Previous Experience: A history of dealing with complex, challenging projects is often a good sign. Ask the candidate to discuss a difficult problem they faced in a previous role and how they solved it.
- Problem-Solving Questions: During interviews, pose hypothetical scenarios or present real problems your company has faced. Ask candidates to explain how they would tackle these issues. You’re not just looking for a correct solution but the thought process that led them there.
- Technical Tests: Coding challenges and other technical tests can provide insight into a candidate’s problem-solving abilities. Consider leveraging a platform for assessing these skills in a realistic, job-related context.

Assessing Problem-Solving Skills
Once you’ve identified potential problem solvers, here are a few ways you can assess their skills:
- Solution Effectiveness: Did the candidate solve the problem? How efficient and effective is their solution?
- Approach and Process: Go beyond whether or not they solved the problem and examine how they arrived at their solution. Did they break the problem down into manageable parts? Did they consider different perspectives and possibilities?
- Communication: A good problem solver can explain their thought process clearly. Can the candidate effectively communicate how they arrived at their solution and why they chose it?
- Adaptability: Problem-solving often involves a degree of trial and error. How does the candidate handle roadblocks? Do they adapt their approach based on new information or feedback?
Hiring managers play a crucial role in identifying and fostering problem-solving skills within their teams. By focusing on these abilities during the hiring process, companies can build teams that are more capable, innovative, and resilient.
Key Takeaways
As you can see, problem solving plays a pivotal role in software engineering. Far from being an occasional requirement, it is the lifeblood that drives development forward, catalyzes innovation, and delivers of quality software.
By leveraging problem-solving techniques, software engineers employ a powerful suite of strategies to overcome complex challenges. But mastering these techniques isn’t simple feat. It requires a learning mindset, regular practice, collaboration, reflective thinking, resilience, and a commitment to staying updated with industry trends.
For hiring managers and team leads, recognizing these skills and fostering a culture that values and nurtures problem solving is key. It’s this emphasis on problem solving that can differentiate an average team from a high-performing one and an ordinary product from an industry-leading one.
At the end of the day, software engineering is fundamentally about solving problems — problems that matter to businesses, to users, and to the wider society. And it’s the proficient problem solvers who stand at the forefront of this dynamic field, turning challenges into opportunities, and ideas into reality.
This article was written with the help of AI. Can you tell which parts?
Get started with HackerRank
Over 2,500 companies and 40% of developers worldwide use HackerRank to hire tech talent and sharpen their skills.
Problem solving skills and how to improve them (with examples)
What’s life without its challenges? All of us will at some point encounter professional and personal hurdles. That might mean resolving a conflict with coworkers or making a big life decision. With effective problem solving skills, you’ll find tricky situations easier to navigate, and welcome challenges as opportunities to learn, grow and thrive.
In this guide, we dive into the importance of problem solving skills and look at examples that show how relevant they are to different areas of your life. We cover how to find creative solutions and implement them, as well as ways to refine your skills in communication and critical thinking. Ready to start solving problems? Read on.
What is problem solving?
Before we cover strategies for improving problem solving skills, it's important to first have a clear understanding of the problem solving process. Here are the steps in solving a problem:
- Recognise the issue you are facing
- Take a look at all the information to gain insights
- Come up with solutions
- Look at the pros and cons of each solution and how it might play out
- Plan, organise and implement your solution
- Continuously assess the effectiveness of the solution and make adjustments as needed
Problem solving skills
There’s more to problem solving than coming up with a quick fix. Effective problem solving requires wide range of skills and abilities, such as:
- Critical thinking: the ability to think logically, analyse information and look at situations from different perspectives.
- Creativity: being able to come up with innovative, out-of-the-box solutions.
- Decision-making: making informed choices by considering all the available information.
- Communication: being able to express ideas clearly and effectively.
- Analytical skills: breaking down complex problems into smaller parts and examining each one.
- Time management: allocating time and resources effectively to address problems.
- Adaptability: being open to change and willing to adjust strategies.
- Conflict resolution: skillfully managing conflicts and finding solutions that work for all.
Examples of problem solving skills
Problem solving skills in the workplace are invaluable, whether you need them for managing a team, dealing with clients or juggling deadlines. To get a better understanding of how you might use these skills in real-life scenarios, here are some problem solving examples that are common in the workplace.
- Analytical thinking
Analytical thinking is something that comes naturally to some, while others have to work a little harder. It involves being able to look at problem solving from a logical perspective, breaking down the issues into manageable parts.
Example scenarios of analytical thinking
Quality control: in a manufacturing facility, analytical thinking helps identify the causes of product defects in order to pinpoint solutions.
Market research: marketing teams rely on analytical thinking to examine consumer data, identify market trends and make informed decisions on ad campaigns.
- Critical thinking
Critical thinkers are able to approach problems objectively, looking at different viewpoints without rushing to a decision. Critical thinking is an important aspect of problem solving, helping to uncover biases and assumptions and weigh up the quality of the information before making any decisions.
Example scenarios of critical thinking
- Strategic planning: in the boardroom, critical thinking is important for assessing economic trends, competitor threats and more. It guides leaders in making informed decisions about long-term company goals and growth strategies.
- Conflict resolution: HR professionals often use critical thinking when dealing with workplace conflicts. They objectively analyse the issues at hand and find an appropriate solution.
Decision-making
Making decisions is often the hardest part of problem solving. How do you know which solution is the right one? It involves evaluating information, considering potential outcomes and choosing the most suitable option. Effective problem solving relies on making well-informed decisions.
Example scenarios of decision-making
- Budget allocation: financial managers must decide how to allocate resources to various projects or departments.
- Negotiation: salespeople and procurement professionals negotiate terms, pricing and agreements with clients, suppliers and partners.
Research skills
Research skills are pivotal when it comes to problem solving, to ensure you have all the information you need to make an informed decision. These skills involve searching for relevant data, critically evaluating information sources, and drawing meaningful conclusions.
Example scenarios of research skills
- Product development: a tech startup uses research skills to conduct market research to identify gaps and opportunities in the market.
- Employee engagement: an HR manager uses research skills to conduct employee surveys and focus groups.
A little creative flair goes a long way. By thinking outside the box, you can approach problems from different angles. Creative thinking involves combining existing knowledge, experiences and perspectives in new and innovative ways to come up with inventive solutions.
Example scenarios of creativity
- Cost reduction: creative problem solvers within a manufacturing company might look at new ways to reduce production costs by using waste materials.
- Customer experience: a retail chain might look at implementing interactive displays and engaging store layouts to increase customer satisfaction and sales.
Collaboration
It’s not always easy to work with other people, but collaboration is a key element in problem solving, allowing you to make use of different perspectives and areas of expertise to find solutions.
Example scenarios
- Healthcare diagnosis: in a hospital setting, medical professionals collaborate to diagnose complex medical cases.
- Project management: project managers coordinate efforts, allocate resources and address issues that may arise during a project's lifecycle.
Conflict Resolution
Being able to mediate conflicts is a great skill to have. It involves facilitating open communication, understanding different perspectives and finding solutions that work for everyone. Conflict resolution is essential for managing any differences in opinion that arise.
Example scenarios of conflict resolution
- Client dispute: a customer might be dissatisfied with a product or service and demand a refund. The customer service representative addresses the issue through active listening and negotiation to reach a solution.
- Project delay: a project manager might face resistance from team members about a change in project scope and will need to find a middle ground before the project can continue.
Risk management
Risk management is essential across many workplaces. It involves analysing potential threats and opportunities, evaluating their impact and implementing strategies to minimise negative consequences. Risk management is closely tied to problem solving, as it addresses potential obstacles and challenges that may arise during the problem solving process.
Example scenarios of risk management
- Project risk management: in a construction project, risk management involves identifying potential delays, cost overruns and safety hazards. Risk mitigation strategies are developed, such as scheduling buffers and establishing safety protocols.
- Financial risk management: in financial institutions, risk management assesses and manages risks associated with investments and lending.
Communication
Effective communication is a skill that will get you far in all areas of life. When it comes to problem solving, communication plays an important role in facilitating collaboration, sharing insights and ensuring that all stakeholders have the same expectations.
Example scenarios of communication
- Customer service improvement: in a retail environment, open communication channels result in higher customer satisfaction scores.
- Safety enhancement: in a manufacturing facility, a robust communication strategy that includes safety briefings, incident reporting and employee training helps minimise accidents and injuries.
How to improve problem solving skills
Ready to improve your problem solving skills? In this section we explore strategies and techniques that will give you a head start in developing better problem solving skills.
Adopt the problem solving mindset
Developing a problem solving mindset will help you tackle challenges effectively . Start by accepting problems as opportunities for growth and learning, rather than as obstacles or setbacks. This will allow you to approach every challenge with a can-do attitude.
Patience is also essential, because it will allow you to work through the problem and its various solutions mindfully. Persistence is also important, so you can keep adapting your approach until you find the right solution.
Finally, don’t forget to ask questions. What do you need to know? What assumptions are you making? What can you learn from previous attempts? Approach problem solving as an opportunity to acquire new skills . Stay curious, seek out solutions, explore new possibilities and remain open to different problem solving approaches.
Understand the problem
There’s no point trying to solve a problem you don’t understand. To analyse a problem effectively, you need to be able to define it. This allows you to break it down into smaller parts, making it easier to find causes and potential solutions. Start with a well-defined problem statement that is precise and specific. This will help you focus your efforts on the core issue, so you don’t waste time and resources on the wrong concerns.
Strategies for problem analysis
- Start with the problem statement and ask ‘Why?’ multiple times to dig deeper.
- Gather relevant data and information related to the problem.
- Include those affected by the problem in the analysis process.
- Compare the current problem with similar situations or cases to gain valuable insights.
- Use simulations to explore potential outcomes of different solutions.
- Continuously gather feedback during the problem solving process.
Develop critical thinking and creativity skills
Critical thinking and creativity are both important when it comes to looking at the problem objectively and thinking outside the box. Critical thinking encourages you to question assumptions, recognise biases and seek evidence to support your conclusions. Creative thinking allows you to look at the problem from different angles to reveal new insights and opportunities.
Enhance research and decision-making skills
Research and decision-making skills are pivotal in problem solving as they enable you to gather relevant information, analyse options and choose the best course of action. Research provides the information and data needed, and ensures that you have a comprehensive understanding of the problem and its context. Effective decision-making is about selecting the solution that best addresses the problem.
Strategies to improve research and decision-making skills
- Clearly define what you want to achieve through research.
- Use a variety of sources, including books, articles, research papers, interviews, surveys and online databases.
- Evaluate the credibility and reliability of your information sources.
- Incorporate risk assessment into your decision-making process.
- Seek input from experts, colleagues and mentors when making important decisions.
- After making decisions, reflect on the outcomes and lessons learned. Use this to improve your decision-making skills over time.
Strengthen collaboration skills
Being able to work with others is one of the most important skills to have at work. Collaboration skills enable everyone to work effectively as a team, share their perspectives and collectively find solutions.
Tips for improving teamwork and collaboration
- Define people’s roles and responsibilities within the team.
- Encourage an environment of open communication where team members feel comfortable sharing ideas.
- Practise active listening by giving full attention to others when they speak.
- Hold regular check-in sessions to monitor progress, discuss challenges and make adjustments as needed.
- Use collaboration tools and platforms to facilitate communication and document progress.
- Acknowledge and celebrate team achievements and milestones.
Learn from past experiences
Once you’ve overcome a challenge, take the time to look back with a critical eye. How effective was the outcome? Could you have tweaked anything in your process? Learning from past experiences is important when it comes to problem solving. It involves reflecting on both successes and failures to gain insights, refine strategies and make more informed decisions in the future.
Strategies for learning from past mistakes
- After completing a problem solving effort, gather your team for a debriefing session. Discuss what went well and what could have been better.
- Conduct a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) of resolved problems.
- Evaluate the outcomes of past solutions. Did they achieve the desired results?
- Commit to continuous learning and improvement.
Leverage problem solving tools and resources
Problem-solving tools and resources are a great help when it comes to navigating complex challenges. These tools offer structured approaches, methodologies and resources that can streamline the process.
Tools and resources for problem solving
- Mind mapping: mind maps visually organise ideas, concepts and their relationships.
- SWOT (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) Analysis: helps in strategic planning and decision-making.
- Fishbone diagram (Ishikawa Diagram): this tool visually represents the potential root causes of a problem, helping you identify underlying factors contributing to an issue.
- Decision matrices: these assist in evaluating options by assigning weights and scores to criteria and alternatives.
- Process flowcharts: these allow you to see the steps of a process in sequence, helping identify where the problem is occuring.
- Decision support software: software applications and tools, such as data analytics platforms, can help in data-driven decision-making and problem solving.
- Online courses and training: allow you to acquire new skills and knowledge.
Regular practice
Practice makes perfect! Using your skills in real life allows you to refine them, adapt to new challenges and build confidence in your problem solving capabilities. Make sure to try out these skills whenever you can.
Practical problem solving exercises
- Do puzzles, riddles and brainteasers regularly.
- Identify real-life challenges or dilemmas you encounter and practice applying problem solving techniques to these situations.
- Analyse case studies or scenarios relevant to your field or industry.
- Regularly review past problem solving experiences and consider what you learned from them.
- Attend workshops, webinars or training sessions focused on problem solving.
How to highlight problem solving skills on a resumé
Effectively showcasing your problem solving skills on your resumé is a great way to demonstrate your ability to address challenges and add value to a workplace. We'll explore how to demonstrate problem solving skills on your resumé, so you stand out from the crowd.
Incorporating problem solving skills in the resumé summary
A resumé summary is your introduction to potential employers and provides an opportunity to succinctly showcase your skills. The resumé summary is often the first section employers read. It offers a snapshot of your qualifications and sets the tone for the rest of your resumé.
Your resumé summary should be customised for different job applications, ensuring that you highlight the specific problem solving skills relevant to the position you’re applying for.
Example 1: Project manager with a proven track record of solving complex operational challenges. Skilled in identifying root causes, developing innovative solutions and leading teams to successful project completion.
Example 2: Detail-oriented data analyst with strong problem solving skills. Proficient in data-driven decision-making, quantitative analysis and using statistical tools to solve business problems.
Highlighting problem solving skills in the experience section
The experience section of your resumé presents the perfect opportunity to demonstrate your problem solving skills in action.
- Start with action verbs: begin each bullet point in your job descriptions with strong action verbs such as, analysed, implemented, resolved and optimised.
- Quantify achievements: use numbers and percentages to illustrate the impact of your solutions. For example: Increased efficiency by 25% by implementing a new workflow process.
- Emphasise challenges: describe the specific challenges or problems you faced in your roles.
- Solution-oriented language: mention the steps you took to find solutions and the outcomes achieved.
Including problem solving skills in the skills section
The skills section of your resumé should showcase your top abilities, including problem solving skills. Here are some tips for including these skills.
- Use a subsection: within your skills section, you could create a subsection specifically dedicated to problem solving skills – especially if the role calls for these skills.
- Be specific: when listing problem solving skills, be specific about the types of role-related problems you can address.
- Prioritise relevant skills: tailor the list of problem solving skills to match the requirements of the job you're applying for.
Examples of problem solving skills to include:
- Creative problem solving
- Decision making
- Root cause analysis
- Strategic problem solving
- Data-driven problem solving
- Interpersonal conflict resolution
- Adaptability
- Communication skills
- Problem solving tools
- Negotiation skills
Demonstrating problem solving skills in project sections or case studies
Including a dedicated section for projects or case studies in your resumé allows you to provide specific examples of your problem solving skills in action. It goes beyond simply listing skills, to demonstrate how you are able to apply those skills to real-world challenges.
Example – Data Analysis
Case Study: Market Expansion Strategy
- Challenge: the company was looking to expand into new markets but lacked data on consumer preferences and market dynamics.
- Solution: conducted comprehensive market research, including surveys and competitor analysis. Applied this research to identify target customer segments and developed a data-driven market-entry strategy.
- Result: successfully launched in two new markets, reaching our target of 30% market share within the first year.
Using problem solving skills in cover letters
A well-crafted cover letter is your first impression on any potential employer. Integrating problem solving skills can support your job application by showcasing your ability to address challenges and contribute effectively to their team. Here’s a quick run-down on what to include:
- Begin your cover letter by briefly mentioning the position you're applying for and your enthusiasm for it.
- Identify a specific challenge or issue that the company may be facing, to demonstrate your research and understanding of their needs.
- Include a brief story or scenario from your past experiences where you successfully applied problem solving skills to address a similar challenge.
- Highlight the positive outcomes or results achieved through your problem solving efforts.
- Explain how your skills make you the ideal person to address their specific challenges.
Problem solving skills are essential in all areas of life, enabling you to overcome challenges, make informed decisions, settle conflicts and drive innovation. We've explored the significance of problem solving skills and how to improve, demonstrate and leverage them effectively. It’s an ever-evolving skill set that can be refined over time.
By actively incorporating problem solving skills into your day-to-day, you can become a more effective problem solver at work and in your personal life as well.
What are some common problem solving techniques?
Common problem solving techniques include brainstorming, root cause analysis, SWOT analysis, decision matrices, the scientific method and the PDCA (Plan-Do-Check-Act) cycle. These techniques offer structured approaches to identify, analyse and address problems effectively.
How can I improve my critical thinking skills?
Improving critical thinking involves practising skills such as analysis, evaluation and problem solving. It helps to engage in activities like reading, solving puzzles, debating and self-reflection.
What are some common obstacles to problem solving?
Common obstacles to problem solving include biases, lack of information or resources, and resistance to change. Recognising and addressing these obstacles is essential for effective problem solving.
How can I overcome resistance to change when implementing a solution?
To overcome resistance to change, it's essential to communicate the benefits of the proposed solution clearly, involve stakeholders in the decision-making process, address concerns and monitor the implementation's progress to demonstrate its effectiveness.
How can problem solving skills benefit my career?
Problem solving skills are highly valuable in a career as they enable you to navigate challenges, make informed decisions, adapt to change and contribute to innovation and efficiency. These skills enhance your professional effectiveness and can lead to career advancement and increased job satisfaction.
Top search terms
Explore related topics, subscribe to career advice.
Learn Creative Problem Solving Techniques to Stimulate Innovation in Your Organization
By Kate Eby | October 20, 2017 (updated August 27, 2021)
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In today’s competitive business landscape, organizations need processes in place to make strong, well-informed, and innovative decisions. Problem solving - in particular creative problem solving (CPS) - is a key skill in learning how to accurately identify problems and their causes, generate potential solutions, and evaluate all the possibilities to arrive at a strong corrective course of action. Every team in any organization, regardless of department or industry, needs to be effective, creative, and quick when solving problems.
In this article, we’ll discuss traditional and creative problem solving, and define the steps, best practices, and common barriers associated. After that, we’ll provide helpful methods and tools to identify the cause(s) of problematic situations, so you can get to the root of the issue and start to generate solutions. Then, we offer nearly 20 creative problem solving techniques to implement at your organization, or even in your personal life. Along the way, experts weigh in on the importance of problem solving, and offer tips and tricks.
What Is Problem Solving and Decision Making?
Problem solving is the process of working through every aspect of an issue or challenge to reach a solution. Decision making is choosing one of multiple proposed solutions — therefore, this process also includes defining and evaluating all potential options. Decision making is often one step of the problem solving process, but the two concepts are distinct.
Collective problem solving is problem solving that includes many different parties and bridges the knowledge of different groups. Collective problem solving is common in business problem solving because workplace decisions typically affect more than one person.
Problem solving, especially in business, is a complicated science. Not only are business conflicts multifaceted, but they often involve different personalities, levels of authority, and group dynamics. In recent years, however, there has been a rise in psychology-driven problem solving techniques, especially for the workplace. In fact, the psychology of how people solve problems is now studied formally in academic disciplines such as psychology and cognitive science.

Joe Carella is the Assistant Dean for Executive Education at the University of Arizona . Joe has over 20 years of experience in helping executives and corporations in managing change and developing successful business strategies. His doctoral research and executive education engagements have seen him focus on corporate strategy, decision making and business performance with a variety of corporate clients including Hershey’s, Chevron, Fender Musical Instruments Corporation, Intel, DP World, Essilor, BBVA Compass Bank.
He explains some of the basic psychology behind problem solving: “When our brain is engaged in the process of solving problems, it is engaged in a series of steps where it processes and organizes the information it receives while developing new knowledge it uses in future steps. Creativity is embedded in this process by incorporating diverse inputs and/or new ways of organizing the information received.”

Laura MacLeod is a Professor of Social Group Work at City University of New York, and the creator of From The Inside Out Project® , a program that coaches managers in team leadership for a variety of workplaces. She has a background in social work and over two decades of experience as a union worker, and currently leads talks on conflict resolution, problem solving, and listening skills at conferences across the country.
MacLeod thinks of problem solving as an integral practice of successful organizations. “Problem solving is a collaborative process — all voices are heard and connected, and resolution is reached by the group,” she says. “Problems and conflicts occur in all groups and teams in the workplace, but if leaders involve everyone in working through, they will foster cohesion, engagement, and buy in. Everybody wins.”
10 tips that will make you more productive.

Uncover the top three factors that are killing your productivity and 10 tips to help you overcome them.
Download the free e-book to overcome my productivity killers
Project Management Guide
Your one-stop shop for everything project management

Ready to get more out of your project management efforts? Visit our comprehensive project management guide for tips, best practices, and free resources to manage your work more effectively.
View the guide
What Is the First Step in Solving a Problem?
Although problem solving techniques vary procedurally, experts agree that the first step in solving a problem is defining the problem. Without a clear articulation of the problem at stake, it is impossible to analyze all the key factors and actors, generate possible solutions, and then evaluate them to pick the best option.

Dr. Elliott Jaffa is a behavioral and management psychologist with over 25 years of problem solving training and management experience. “Start with defining the problem you want to solve,” he says, “And then define where you want to be, what you want to come away with.” He emphasizes these are the first steps in creating an actionable, clear solution.

Bryan Mattimore is Co-Founder of Growth Engine, an 18-year old innovation agency based in Norwalk, CT. Bryan has facilitated over 1,000 ideation sessions and managed over 200 successful innovation projects leading to over $3 billion in new sales. His newest book is 21 Days to a Big Idea . When asked about the first critical component to successful problem solving, Mattimore says, “Defining the challenge correctly, or ‘solving the right problem’ … The three creative techniques we use to help our clients ‘identify the right problem to be solved’ are questioning assumptions, 20 questions, and problem redefinition. A good example of this was a new product challenge from a client to help them ‘invent a new iron. We got them to redefine the challenge as first: a) inventing new anti-wrinkle devices, and then b) inventing new garment care devices.”
What Are Problem Solving Skills?
To understand the necessary skills in problem solving, you should first understand the types of thinking often associated with strong decision making. Most problem solving techniques look for a balance between the following binaries:
- Convergent vs. Divergent Thinking: Convergent thinking is bringing together disparate information or ideas to determine a single best answer or solution. This thinking style values logic, speed, and accuracy, and leaves no chance for ambiguity. Divergent thinking is focused on generating new ideas to identify and evaluate multiple possible solutions, often uniting ideas in unexpected combinations. Divergent thinking is characterized by creativity, complexity, curiosity, flexibility, originality, and risk-taking.
- Pragmatics vs. Semantics: Pragmatics refer to the logic of the problem at hand, and semantics is how you interpret the problem to solve it. Both are important to yield the best possible solution.
- Mathematical vs. Personal Problem Solving: Mathematical problem solving involves logic (usually leading to a single correct answer), and is useful for problems that involve numbers or require an objective, clear-cut solution. However, many workplace problems also require personal problem solving, which includes interpersonal, collaborative, and emotional intuition and skills.
The following basic methods are fundamental problem solving concepts. Implement them to help balance the above thinking models.
- Reproductive Thinking: Reproductive thinking uses past experience to solve a problem. However, be careful not to rely too heavily on past solutions, and to evaluate current problems individually, with their own factors and parameters.
- Idea Generation: The process of generating many possible courses of action to identify a solution. This is most commonly a team exercise because putting everyone’s ideas on the table will yield the greatest number of potential solutions.
However, many of the most critical problem solving skills are “soft” skills: personal and interpersonal understanding, intuitiveness, and strong listening.
Mattimore expands on this idea: “The seven key skills to be an effective creative problem solver that I detail in my book Idea Stormers: How to Lead and Inspire Creative Breakthroughs are: 1) curiosity 2) openness 3) a willingness to embrace ambiguity 4) the ability to identify and transfer principles across categories and disciplines 5) the desire to search for integrity in ideas, 6) the ability to trust and exercise “knowingness” and 7) the ability to envision new worlds (think Dr. Seuss, Star Wars, Hunger Games, Harry Potter, etc.).”
“As an individual contributor to problem solving it is important to exercise our curiosity, questioning, and visioning abilities,” advises Carella. “As a facilitator it is essential to allow for diverse ideas to emerge, be able to synthesize and ‘translate’ other people’s thinking, and build an extensive network of available resources.”
MacLeod says the following interpersonal skills are necessary to effectively facilitate group problem solving: “The abilities to invite participation (hear all voices, encourage silent members), not take sides, manage dynamics between the monopolizer, the scapegoat, and the bully, and deal with conflict (not avoiding it or shutting down).”
Furthermore, Jaffa explains that the skills of a strong problem solver aren’t measurable. The best way to become a creative problem solver, he says, is to do regular creative exercises that keep you sharp and force you to think outside the box. Carella echoes this sentiment: “Neuroscience tells us that creativity comes from creating novel neural paths. Allow a few minutes each day to exercise your brain with novel techniques and brain ‘tricks’ – read something new, drive to work via a different route, count backwards, smell a new fragrance, etc.”
What Is Creative Problem Solving? History, Evolution, and Core Principles
Creative problem solving (CPS) is a method of problem solving in which you approach a problem or challenge in an imaginative, innovative way. The goal of CPS is to come up with innovative solutions, make a decision, and take action quickly. Sidney Parnes and Alex Osborn are credited with developing the creative problem solving process in the 1950s. The concept was further studied and developed at SUNY Buffalo State and the Creative Education Foundation.
The core principles of CPS include the following:
- Balance divergent and convergent thinking
- Ask problems as questions
- Defer or suspend judgement
- Focus on “Yes, and…” rather than “No, but…”
According to Carella, “Creative problem solving is the mental process used for generating innovative and imaginative ideas as a solution to a problem or a challenge. Creative problem solving techniques can be pursued by individuals or groups.”
When asked to define CPS, Jaffa explains that it is, by nature, difficult to create boundaries for. “Creative problem solving is not cut and dry,” he says, “If you ask 100 different people the definition of creative problem solving, you’ll get 100 different responses - it’s a non-entity.”
Business presents a unique need for creative problem solving. Especially in today’s competitive landscape, organizations need to iterate quickly, innovate with intention, and constantly be at the cutting-edge of creativity and new ideas to succeed. Developing CPS skills among your workforce not only enables you to make faster, stronger in-the-moment decisions, but also inspires a culture of collaborative work and knowledge sharing. When people work together to generate multiple novel ideas and evaluate solutions, they are also more likely to arrive at an effective decision, which will improve business processes and reduce waste over time. In fact, CPS is so important that some companies now list creative problem solving skills as a job criteria.
MacLeod reiterates the vitality of creative problem solving in the workplace. “Problem solving is crucial for all groups and teams,” she says. “Leaders need to know how to guide the process, hear all voices and involve all members - it’s not easy.”
“This mental process [of CPS] is especially helpful in work environments where individuals and teams continuously struggle with new problems and challenges posed by their continuously changing environment,” adds Carella.
Problem Solving Best Practices
By nature, creative problem solving does not have a clear-cut set of do’s and don’ts. Rather, creating a culture of strong creative problem solvers requires flexibility, adaptation, and interpersonal skills. However, there are a several best practices that you should incorporate:
- Use a Systematic Approach: Regardless of the technique you use, choose a systematic method that satisfies your workplace conditions and constraints (time, resources, budget, etc.). Although you want to preserve creativity and openness to new ideas, maintaining a structured approach to the process will help you stay organized and focused.
- View Problems as Opportunities: Rather than focusing on the negatives or giving up when you encounter barriers, treat problems as opportunities to enact positive change on the situation. In fact, some experts even recommend defining problems as opportunities, to remain proactive and positive.
- Change Perspective: Remember that there are multiple ways to solve any problem. If you feel stuck, changing perspective can help generate fresh ideas. A perspective change might entail seeking advice of a mentor or expert, understanding the context of a situation, or taking a break and returning to the problem later. “A sterile or familiar environment can stifle new thinking and new perspectives,” says Carella. “Make sure you get out to draw inspiration from spaces and people out of your usual reach.”
- Break Down Silos: To invite the greatest possible number of perspectives to any problem, encourage teams to work cross-departmentally. This not only combines diverse expertise, but also creates a more trusting and collaborative environment, which is essential to effective CPS. According to Carella, “Big challenges are always best tackled by a group of people rather than left to a single individual. Make sure you create a space where the team can concentrate and convene.”
- Employ Strong Leadership or a Facilitator: Some companies choose to hire an external facilitator that teaches problem solving techniques, best practices, and practicums to stimulate creative problem solving. But, internal managers and staff can also oversee these activities. Regardless of whether the facilitator is internal or external, choose a strong leader who will value others’ ideas and make space for creative solutions. Mattimore has specific advice regarding the role of a facilitator: “When facilitating, get the group to name a promising idea (it will crystalize the idea and make it more memorable), and facilitate deeper rather than broader. Push for not only ideas, but how an idea might specifically work, some of its possible benefits, who and when would be interested in an idea, etc. This fleshing-out process with a group will generate fewer ideas, but at the end of the day will yield more useful concepts that might be profitably pursued.” Additionally, Carella says that “Executives and managers don’t necessarily have to be creative problem solvers, but need to make sure that their teams are equipped with the right tools and resources to make this happen. Also they need to be able to foster an environment where failing fast is accepted and celebrated.”
- Evaluate Your Current Processes: This practice can help you unlock bottlenecks, and also identify gaps in your data and information management, both of which are common roots of business problems.
MacLeod offers the following additional advice, “Always get the facts. Don’t jump too quickly to a solution – working through [problems] takes time and patience.”
Mattimore also stresses that how you introduce creative problem solving is important. “Do not start by introducing a new company-wide innovation process,” he says. “Instead, encourage smaller teams to pursue specific creative projects, and then build a process from the ground up by emulating these smaller teams’ successful approaches. We say: ‘You don’t innovate by changing the culture, you change the culture by innovating.’”
Barriers to Effective Problem Solving
Learning how to effectively solve problems is difficult and takes time and continual adaptation. There are several common barriers to successful CPS, including:
- Confirmation Bias: The tendency to only search for or interpret information that confirms a person’s existing ideas. People misinterpret or disregard data that doesn’t align with their beliefs.
- Mental Set: People’s inclination to solve problems using the same tactics they have used to solve problems in the past. While this can sometimes be a useful strategy (see Analogical Thinking in a later section), it often limits inventiveness and creativity.
- Functional Fixedness: This is another form of narrow thinking, where people become “stuck” thinking in a certain way and are unable to be flexible or change perspective.
- Unnecessary Constraints: When people are overwhelmed with a problem, they can invent and impose additional limits on solution avenues. To avoid doing this, maintain a structured, level-headed approach to evaluating causes, effects, and potential solutions.
- Groupthink: Be wary of the tendency for group members to agree with each other — this might be out of conflict avoidance, path of least resistance, or fear of speaking up. While this agreeableness might make meetings run smoothly, it can actually stunt creativity and idea generation, therefore limiting the success of your chosen solution.
- Irrelevant Information: The tendency to pile on multiple problems and factors that may not even be related to the challenge at hand. This can cloud the team’s ability to find direct, targeted solutions.
- Paradigm Blindness: This is found in people who are unwilling to adapt or change their worldview, outlook on a particular problem, or typical way of processing information. This can erode the effectiveness of problem solving techniques because they are not aware of the narrowness of their thinking, and therefore cannot think or act outside of their comfort zone.
According to Jaffa, the primary barrier of effective problem solving is rigidity. “The most common things people say are, ‘We’ve never done it before,’ or ‘We’ve always done it this way.’” While these feelings are natural, Jaffa explains that this rigid thinking actually precludes teams from identifying creative, inventive solutions that result in the greatest benefit.
“The biggest barrier to creative problem solving is a lack of awareness – and commitment to – training employees in state-of-the-art creative problem-solving techniques,” Mattimore explains. “We teach our clients how to use ideation techniques (as many as two-dozen different creative thinking techniques) to help them generate more and better ideas. Ideation techniques use specific and customized stimuli, or ‘thought triggers’ to inspire new thinking and new ideas.”
MacLeod adds that ineffective or rushed leadership is another common culprit. “We're always in a rush to fix quickly,” she says. “Sometimes leaders just solve problems themselves, making unilateral decisions to save time. But the investment is well worth it — leaders will have less on their plates if they can teach and eventually trust the team to resolve. Teams feel empowered and engagement and investment increases.”
Strategies for Problem Cause Identification
As discussed, most experts agree that the first and most crucial step in problem solving is defining the problem. Once you’ve done this, however, it may not be appropriate to move straight to the solution phase. Rather, it is often helpful to identify the cause(s) of the problem: This will better inform your solution planning and execution, and help ensure that you don’t fall victim to the same challenges in the future.
Below are some of the most common strategies for identifying the cause of a problem:
- Root Cause Analysis: This method helps identify the most critical cause of a problem. A factor is considered a root cause if removing it prevents the problem from recurring. Performing a root cause analysis is a 12 step process that includes: define the problem, gather data on the factors contributing to the problem, group the factors based on shared characteristics, and create a cause-and-effect timeline to determine the root cause. After that, you identify and evaluate corrective actions to eliminate the root cause.
Download Fishbone Diagram Template - Excel
Download 5 Whys Template Excel | Word | PDF
Problem Solving Techniques and Strategies
In this section, we’ll explain several traditional and creative problem solving methods that you can use to identify challenges, create actionable goals, and resolve problems as they arise. Although there is often procedural and objective crossover among techniques, they are grouped by theme so you can identify which method works best for your organization.
Divergent Creative Problem Solving Techniques
Brainstorming: One of the most common methods of divergent thinking, brainstorming works best in an open group setting where everyone is encouraged to share their creative ideas. The goal is to generate as many ideas as possible – you analyze, critique, and evaluate the ideas only after the brainstorming session is complete. To learn more specific brainstorming techniques, read this article .
Mind Mapping: This is a visual thinking tool where you graphically depict concepts and their relation to one another. You can use mind mapping to structure the information you have, analyze and synthesize it, and generate solutions and new ideas from there. The goal of a mind map is to simplify complicated problems so you can more clearly identify solutions.
Appreciative Inquiry (AI): The basic assumption of AI is that “an organization is a mystery to be embraced.” Using this principle, AI takes a positive, inquisitive approach to identifying the problem, analyzing the causes, and presenting possible solutions. The five principles of AI emphasize dialogue, deliberate language and outlook, and social bonding.
Lateral Thinking: This is an indirect problem solving approach centered on the momentum of idea generation. As opposed to critical thinking, where people value ideas based on their truth and the absence of errors, lateral thinking values the “movement value” of new ideas: This means that you reward team members for producing a large volume of new ideas rapidly. With this approach, you’ll generate many new ideas before approving or rejecting any.
Problem Solving Techniques to Change Perspective
Constructive Controversy: This is a structured approach to group decision making to preserve critical thinking and disagreement while maintaining order. After defining the problem and presenting multiple courses of action, the group divides into small advocacy teams who research, analyze, and refute a particular option. Once each advocacy team has presented its best-case scenario, the group has a discussion (advocacy teams still defend their presented idea). Arguing and playing devil’s advocate is encouraged to reach an understanding of the pros and cons of each option. Next, advocacy teams abandon their cause and evaluate the options openly until they reach a consensus. All team members formally commit to the decision, regardless of whether they advocated for it at the beginning. You can learn more about the goals and steps in constructive controversy here .
Carella is a fan of this approach. “Create constructive controversy by having two teams argue the pros and cons of a certain idea,” he says. “It forces unconscious biases to surface and gives space for new ideas to formulate.”
Abstraction: In this method, you apply the problem to a fictional model of the current situation. Mapping an issue to an abstract situation can shed extraneous or irrelevant factors, and reveal places where you are overlooking obvious solutions or becoming bogged down by circumstances.
Analogical Thinking: Also called analogical reasoning , this method relies on an analogy: using information from one problem to solve another problem (these separate problems are called domains). It can be difficult for teams to create analogies among unrelated problems, but it is a strong technique to help you identify repeated issues, zoom out and change perspective, and prevent the problems from occurring in the future. .
CATWOE: This framework ensures that you evaluate the perspectives of those whom your decision will impact. The factors and questions to consider include (which combine to make the acronym CATWOE):
- Customers: Who is on the receiving end of your decisions? What problem do they currently have, and how will they react to your proposed solution?
- Actors: Who is acting to bring your solution to fruition? How will they respond and be affected by your decision?
- Transformation Process: What processes will you employ to transform your current situation and meet your goals? What are the inputs and outputs?
- World View: What is the larger context of your proposed solution? What is the larger, big-picture problem you are addressing?
- Owner: Who actually owns the process? How might they influence your proposed solution (positively or negatively), and how can you influence them to help you?
- Environmental Constraints: What are the limits (environmental, resource- and budget-wise, ethical, legal, etc.) on your ideas? How will you revise or work around these constraints?
Complex Problem Solving
Soft Systems Methodology (SSM): For extremely complex problems, SSM can help you identify how factors interact, and determine the best course of action. SSM was borne out of organizational process modeling and general systems theory, which hold that everything is part of a greater, interconnected system: This idea works well for “hard” problems (where logic and a single correct answer are prioritized), and less so for “soft” problems (i.e., human problems where factors such as personality, emotions, and hierarchy come into play). Therefore, SSM defines a seven step process for problem solving:
- Begin with the problem or problematic situation
- Express the problem or situation and build a rich picture of the themes of the problem
- Identify the root causes of the problem (most commonly with CATWOE)
- Build conceptual models of human activity surrounding the problem or situation
- Compare models with real-world happenings
- Identify changes to the situation that are both feasible and desirable
- Take action to implement changes and improve the problematic situation
SSM can be used for any complex soft problem, and is also a useful tool in change management .
Failure Mode and Effects Analysis (FMEA): This method helps teams anticipate potential problems and take steps to mitigate them. Use FMEA when you are designing (redesigning) a complex function, process, product, or service. First, identify the failure modes, which are the possible ways that a project could fail. Then, perform an effects analysis to understand the consequences of each of the potential downfalls. This exercise is useful for internalizing the severity of each potential failure and its effects so you can make adjustments or safeties in your plan.
Download FMEA Template
Problem Solving Based on Data or Logic (Heuristic Methods)
TRIZ: A Russian-developed problem solving technique that values logic, analysis, and forecasting over intuition or soft reasoning. TRIZ (translated to “theory of inventive problem solving” or TIPS in English) is a systematic approach to defining and identifying an inventive solution to difficult problems. The method offers several strategies for arriving at an inventive solution, including a contradictions matrix to assess trade-offs among solutions, a Su-Field analysis which uses formulas to describe a system by its structure, and ARIZ (algorithm of inventive problem solving) which uses algorithms to find inventive solutions.
Inductive Reasoning: A logical method that uses evidence to conclude that a certain answer is probable (this is opposed to deductive reasoning, where the answer is assumed to be true). Inductive reasoning uses a limited number of observations to make useful, logical conclusions (for example, the Scientific Method is an extreme example of inductive reasoning). However, this method doesn’t always map well to human problems in the workplace — in these instances, managers should employ intuitive inductive reasoning , which allows for more automatic, implicit conclusions so that work can progress. This, of course, retains the principle that these intuitive conclusions are not necessarily the one and only correct answer.
Process-Oriented Problem Solving Methods
Plan Do Check Act (PDCA): This is an iterative management technique used to ensure continual improvement of products or processes. First, teams plan (establish objectives to meet desired end results), then do (implement the plan, new processes, or produce the output), then check (compare expected with actual results), and finally act (define how the organization will act in the future, based on the performance and knowledge gained in the previous three steps).
Means-End Analysis (MEA): The MEA strategy is to reduce the difference between the current (problematic) state and the goal state. To do so, teams compile information on the multiple factors that contribute to the disparity between the current and goal states. Then they try to change or eliminate the factors one by one, beginning with the factor responsible for the greatest difference in current and goal state. By systematically tackling the multiple factors that cause disparity between the problem and desired outcome, teams can better focus energy and control each step of the process.
Hurson’s Productive Thinking Model: This technique was developed by Tim Hurson, and is detailed in his 2007 book Think Better: An Innovator’s Guide to Productive Thinking . The model outlines six steps that are meant to give structure while maintaining creativity and critical thinking: 1) Ask “What is going on?” 2) Ask “What is success?” 3) Ask “What is the question?” 4) Generate answers 5) Forge the solution 6) Align resources.
Control Influence Accept (CIA): The basic premise of CIA is that how you respond to problems determines how successful you will be in overcoming them. Therefore, this model is both a problem solving technique and stress-management tool that ensures you aren’t responding to problems in a reactive and unproductive way. The steps in CIA include:
- Control: Identify the aspects of the problem that are within your control.
- Influence: Identify the aspects of the problem that you cannot control, but that you can influence.
- Accept: Identify the aspects of the problem that you can neither control nor influence, and react based on this composite information.
GROW Model: This is a straightforward problem solving method for goal setting that clearly defines your goals and current situation, and then asks you to define the potential solutions and be realistic about your chosen course of action. The steps break down as follows:
- Goal: What do you want?
- Reality: Where are you now?
- Options: What could you do?
- Will: What will you do?
OODA Loop: This acronym stands for observe, orient, decide, and act. This approach is a decision-making cycle that values agility and flexibility over raw human force. It is framed as a loop because of the understanding that any team will continually encounter problems or opponents to success and have to overcome them.
There are also many un-named creative problem solving techniques that follow a sequenced series of steps. While the exact steps vary slightly, they all follow a similar trajectory and aim to accomplish similar goals of problem, cause, and goal identification, idea generation, and active solution implementation.
| Identify Goal | Define Problem | Define Problem |
| Gather Data | Define Causes | Identify Options |
| Clarify Problem | Generate Ideas | Evaluate Options |
| Generate Ideas | Choose the Best Solution | Implement Solution |
| Select Solution | Take Action | - |
MacLeod offers her own problem solving procedure, which echoes the above steps:
“1. Recognize the Problem: State what you see. Sometimes the problem is covert. 2. Identify: Get the facts — What exactly happened? What is the issue? 3. and 4. Explore and Connect: Dig deeper and encourage group members to relate their similar experiences. Now you're getting more into the feelings and background [of the situation], not just the facts. 5. Possible Solutions: Consider and brainstorm ideas for resolution. 6. Implement: Choose a solution and try it out — this could be role play and/or a discussion of how the solution would be put in place. 7. Evaluate: Revisit to see if the solution was successful or not.”
Many of these problem solving techniques can be used in concert with one another, or multiple can be appropriate for any given problem. It’s less about facilitating a perfect CPS session, and more about encouraging team members to continually think outside the box and push beyond personal boundaries that inhibit their innovative thinking. So, try out several methods, find those that resonate best with your team, and continue adopting new techniques and adapting your processes along the way.
Improve Problem Solving with Work Management in Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Additional menu

The 5 steps of the solving problem process
August 17, 2023 by MindManager Blog
Whether you run a business, manage a team, or work in an industry where change is the norm, it may feel like something is always going wrong. Thankfully, becoming proficient in the problem solving process can alleviate a great deal of the stress that business issues can create.
Understanding the right way to solve problems not only takes the guesswork out of how to deal with difficult, unexpected, or complex situations, it can lead to more effective long-term solutions.
In this article, we’ll walk you through the 5 steps of problem solving, and help you explore a few examples of problem solving scenarios where you can see the problem solving process in action before putting it to work.
Understanding the problem solving process
When something isn’t working, it’s important to understand what’s at the root of the problem so you can fix it and prevent it from happening again. That’s why resolving difficult or complex issues works best when you apply proven business problem solving tools and techniques – from soft skills, to software.
The problem solving process typically includes:
- Pinpointing what’s broken by gathering data and consulting with team members.
- Figuring out why it’s not working by mapping out and troubleshooting the problem.
- Deciding on the most effective way to fix it by brainstorming and then implementing a solution.
While skills like active listening, collaboration, and leadership play an important role in problem solving, tools like visual mapping software make it easier to define and share problem solving objectives, play out various solutions, and even put the best fit to work.
Before you can take your first step toward solving a problem, you need to have a clear idea of what the issue is and the outcome you want to achieve by resolving it.
For example, if your company currently manufactures 50 widgets a day, but you’ve started processing orders for 75 widgets a day, you could simply say you have a production deficit.
However, the problem solving process will prove far more valuable if you define the start and end point by clarifying that production is running short by 25 widgets a day, and you need to increase daily production by 50%.
Once you know where you’re at and where you need to end up, these five steps will take you from Point A to Point B:
- Figure out what’s causing the problem . You may need to gather knowledge and evaluate input from different documents, departments, and personnel to isolate the factors that are contributing to your problem. Knowledge visualization software like MindManager can help.
- Come up with a few viable solutions . Since hitting on exactly the right solution – right away – can be tough, brainstorming with your team and mapping out various scenarios is the best way to move forward. If your first strategy doesn’t pan out, you’ll have others on tap you can turn to.
- Choose the best option . Decision-making skills, and software that lets you lay out process relationships, priorities, and criteria, are invaluable for selecting the most promising solution. Whether it’s you or someone higher up making that choice, it should include weighing costs, time commitments, and any implementation hurdles.
- Put your chosen solution to work . Before implementing your fix of choice, you should make key personnel aware of changes that might affect their daily workflow, and set up benchmarks that will make it easy to see if your solution is working.
- Evaluate your outcome . Now comes the moment of truth: did the solution you implemented solve your problem? Do your benchmarks show you achieved the outcome you wanted? If so, congratulations! If not, you’ll need to tweak your solution to meet your problem solving goal.
In practice, you might not hit a home-run with every solution you execute. But the beauty of a repeatable process like problem solving is that you can carry out steps 4 and 5 again by drawing from the brainstorm options you documented during step 2.
Examples of problem solving scenarios
The best way to get a sense of how the problem solving process works before you try it for yourself is to work through some simple scenarios.
Here are three examples of how you can apply business problem solving techniques to common workplace challenges.
Scenario #1: Manufacturing
Building on our original manufacturing example, you determine that your company is consistently short producing 25 widgets a day and needs to increase daily production by 50%.
Since you’d like to gather data and input from both your manufacturing and sales order departments, you schedule a brainstorming session to discover the root cause of the shortage.
After examining four key production areas – machines, materials, methods, and management – you determine the cause of the problem: the material used to manufacture your widgets can only be fed into your equipment once the machinery warms up to a specific temperature for the day.
Your team comes up with three possible solutions.
- Leave your machinery running 24 hours so it’s always at temperature.
- Invest in equipment that heats up faster.
- Find an alternate material for your widgets.
After weighing the expense of the first two solutions, and conducting some online research, you decide that switching to a comparable but less expensive material that can be worked at a lower temperature is your best option.
You implement your plan, monitor your widget quality and output over the following week, and declare your solution a success when daily production increases by 100%.
Scenario #2: Service Delivery
Business training is booming and you’ve had to onboard new staff over the past month. Now you learn that several clients have expressed concern about the quality of your recent training sessions.
After speaking with both clients and staff, you discover there are actually two distinct factors contributing to your quality problem:
- The additional conference room you’ve leased to accommodate your expanding training sessions has terrible acoustics
- The AV equipment you’ve purchased to accommodate your expanding workforce is on back-order – and your new hires have been making do without
You could look for a new conference room or re-schedule upcoming training sessions until after your new equipment arrives. But your team collaboratively determines that the best way to mitigate both issues at once is by temporarily renting the high-quality sound and visual system they need.
Using benchmarks that include several weeks of feedback from session attendees, and random session spot-checks you conduct personally, you conclude the solution has worked.
Scenario #3: Marketing
You’ve invested heavily in product marketing, but still can’t meet your sales goals. Specifically, you missed your revenue target by 30% last year and would like to meet that same target this year.
After collecting and examining reams of information from your sales and accounting departments, you sit down with your marketing team to figure out what’s hindering your success in the marketplace.
Determining that your product isn’t competitively priced, you map out two viable solutions.
- Hire a third-party specialist to conduct a detailed market analysis.
- Drop the price of your product to undercut competitors.
Since you’re in a hurry for results, you decide to immediately reduce the price of your product and market it accordingly.
When revenue figures for the following quarter show sales have declined even further – and marketing surveys show potential customers are doubting the quality of your product – you revert back to your original pricing, revisit your problem solving process, and implement the market analysis solution instead.
With the valuable information you gain, you finally arrive at just the right product price for your target market and sales begin to pick up. Although you miss your revenue target again this year, you meet it by the second quarter of the following year.
Kickstart your collaborative brainstorming sessions and try MindManager for free today !
Ready to take the next step?
MindManager helps boost collaboration and productivity among remote and hybrid teams to achieve better results, faster.
Why choose MindManager?
MindManager® helps individuals, teams, and enterprises bring greater clarity and structure to plans, projects, and processes. It provides visual productivity tools and mind mapping software to help take you and your organization to where you want to be.
Explore MindManager
14 Major Tech Issues — and the Innovations That Will Resolve Them
Members of the Young Entrepreneur Council discuss some of the past year’s most pressing technology concerns and how we should address them.
The past year has seen unprecedented challenges to public-health systems and the global economy. Many facets of daily life and work have moved into the digital realm, and the shift has highlighted some underlying business technology issues that are getting in the way of productivity, communication and security.
As successful business leaders, the members of the Young Entrepreneur Council understand how important it is to have functional, up-to-date technology. That ’ s why we asked a panel of them to share what they view as the biggest business tech problem of the past year. Here are the issues they ’ re concerned about and the innovations they believe will help solve them.
Current Major Technology Issues
- Need For Strong Digital Conference Platforms
- Remote Internet Speed and Connections
- Phishing and Data Privacy Issues
- Deepfake Content
- Too Much Focus on Automation
- Data Mixups Due to AI Implementation
- Poor User Experience
1. Employee Productivity Measurement
As most companies switched to 100 percent remote almost overnight, many realized that they lacked an efficient way to measure employee productivity. Technology with “ user productivity reports ” has become invaluable. Without being able to “ see ” an employee in the workplace, companies must find technology that helps them to track and report how productive employees are at home. — Bill Mulholland , ARC Relocation
2. Digital Industry Conference Platforms
Nothing beats in-person communication when it comes to business development. In the past, industry conferences were king. Today, though, the move to remote conferences really leaves a lot to be desired and transforms the largely intangible value derived from attending into something that is purely informational. A new form or platform for industry conferences is sorely needed. — Nick Reese , Elder Guide
3. Remote Internet Speed and Equipment
With a sudden shift to most employees working remotely, corporations need to boost at-home internet speed and capacity for employees that didn ’ t previously have the requirements to produce work adequately. Companies need to invest in new technologies like 5G and ensure they are supported at home. — Matthew Podolsky , Florida Law Advisers, P.A.
4. Too Much Focus on Automation
Yes, automation and multi-platform management might be ideal for big-name brands and companies, but for small site owners and businesses, it ’ s just overkill. Way too many people are overcomplicating things. Stick to your business model and what works without trying to overload the process. — Zac Johnson , Blogger
5. Phishing Sites
There are many examples of phishing site victims. Last year, I realized the importance of good pop-up blockers for your laptop and mobile devices. It is so scary to be directed to a website that you don ’ t know or to even pay to get to sites that actually don ’t exist. Come up with better pop-up blockers if possible. — Daisy Jing , Banish
6. Data Privacy
I think data privacy is still one of the biggest business tech issues around. Blockchain technology can solve this problem. We need more and more businesses to understand that blockchains don’t just serve digital currencies, they also protect people’s privacy. We also need Amazon, Facebook, Google, etc. to understand that personal data belongs in the hands of the individual. — Amine Rahal , IronMonk Solutions
7. Mobile Security
Mobile security is a big issue because we rely so much on mobile internet access today. We need to be more aware of how these networks can be compromised and how to protect them. Whether it ’ s the IoT devices helping deliver data wirelessly to companies or people using apps on their smartphones, we need to become more aware of our mobile cybersecurity and how to protect our data. — Josh Kohlbach , Wholesale Suite
8. Deepfake Content
More and more people are embracing deepfake content, which is content created to look real but isn ’ t. Using AI, people can edit videos to look like someone did something they didn ’ t do and vice versa, which hurts authenticity and makes people question what ’ s real. Lawmakers need to take this issue seriously and create ways to stop people from doing this. — Jared Atchison , WPForms
9. Poor User Experience
I ’ ve noticed some brands struggling with building a seamless user experience. There are so many themes, plugins and changes people can make to their site that it can be overwhelming. As a result, the business owner eventually builds something they like, but sacrifices UX in the process. I suspect that we will see more businesses using customer feedback to make design changes. — John Brackett , Smash Balloon LLC
10. Cybersecurity Threats
Cybersecurity threats are more prevalent than ever before with increased digital activities. This has drawn many hackers, who are becoming more sophisticated and are targeting many more businesses. Vital Information, such as trade secrets, price-sensitive information, HR records, and many others are more vulnerable. Strengthening cybersecurity laws can maintain equilibrium. — Vikas Agrawal , Infobrandz
11. Data Backup and Recovery
As a company, you ’ ll store and keep lots of data crucial to keeping business moving forward. A huge tech issue that businesses face is their backup recovery process when their system goes down. If anything happens, you need access to your information. Backing up your data is crucial to ensure your brand isn ’ t at a standstill. Your IT department should have a backup plan in case anything happens. — Stephanie Wells , Formidable Forms
12. Multiple Ad and Marketing Platforms
A major issue that marketers are dealing with is having to use multiple advertising and marketing platforms, with each one handling a different activity. It can overload a website and is quite expensive. We ’ re already seeing AdTech and MarTech coming together as MAdTech. Businesses need to keep an eye on this convergence of technologies and adopt new platforms that support it. — Syed Balkhi , WPBeginner
13. Location-Based Innovation
The concentration of tech companies in places like Seattle and San Francisco has led to a quick rise in living costs in these cities. Income isn ’ t catching up, and there ’ s stress on public infrastructure. Poor internet services in rural areas also exacerbate this issue. Innovation should be decentralized. — Samuel Thimothy , OneIMS
14. Artificial Intelligence Implementation
Businesses, especially those in the tech industry, are having trouble implementing AI. If you ’ ve used and improved upon your AI over the years, you ’ re likely having an easier time adjusting. But new online businesses test multiple AI programs at once and it ’ s causing communication and data mix-ups. As businesses settle with specific programs and learn what works for them, we will see improvements. — Chris Christoff , MonsterInsights
Recent Corporate Innovation Articles


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Although problem-solving is a skill in its own right, a subset of seven skills can help make the process of problem-solving easier. These include analysis, communication, emotional intelligence, resilience, creativity, adaptability, and teamwork. 1. Analysis. As a manager, you'll solve each problem by assessing the situation first.
Examples of technology skills. Here are 12 vital technology skills that individuals can use in their professional lives: 1. Word processing. Word processors are software programs that allow individuals to type, organize, edit and share writing on a computer system. Many companies require their employees to use these programs so they can compose ...
The 7 steps to problem-solving. When it comes to problem-solving there are seven key steps that you should follow: define the problem, disaggregate, prioritize problem branches, create an analysis plan, conduct analysis, synthesis, and communication. 1. Define the problem. Problem-solving begins with a clear understanding of the issue at hand.
Creativity. Communication. Decision-making. Team-building. Problem-solving skills are important in every career at every level. As a result, effective problem-solving may also require industry or job-specific technical skills. For example, a registered nurse will need active listening and communication skills when interacting with patients but ...
The problem-solving process typically includes the following steps: Identify the issue: Recognize the problem that needs to be solved. Analyze the situation: Examine the issue in depth, gather all relevant information, and consider any limitations or constraints that may be present. Generate potential solutions: Brainstorm a list of possible ...
Social media management. Coding. Network configuration. Hardware deployment. Operating system knowledge. Database management. Related: Technical Skills: List, Definitions and Examples. Technical writing. The ability to communicate intricate instructions and ideas more simply can help you stand out.
Problem-solving skills are the ability to identify problems, brainstorm and analyze answers, and implement the best solutions. An employee with good problem-solving skills is both a self-starter and a collaborative teammate; they are proactive in understanding the root of a problem and work with others to consider a wide range of solutions ...
Summary. Problem-solving skills include analysis, creativity, prioritization, organization, and troubleshooting. To solve a problem, you need to use a variety of skills based on the needs of the situation. Most jobs essentially boil down to identifying and solving problems consistently and effectively. That's why employers value problem ...
Problem-solving skills are skills that allow individuals to efficiently and effectively find solutions to issues. This attribute is a primary skill that employers look for in job candidates and is essential in a variety of careers. This skill is considered to be a soft skill, or an individual strength, as opposed to a learned hard skill.
1) Analytical skills: Being able to break down complex problems into smaller, more manageable components and analyze the relationships between them. 2) Critical thinking: Developing a logical and systematic approach to problem solving, evaluating options, and making informed decisions. 3) Troubleshooting: Identifying and diagnosing problems ...
Brief Summary: Critical thinking and problem solving is a crucial skill in a technical world that can immediately be applied to academics and careers.A highly skilled individual in this competency can choose the appropriate tool to accomplish a task, easily switch between tools, has a basic understanding of different file types, and can troubleshoot technology when it's not working properly.
Decision-making. Collaboration. Having a growth mindset. In short, understanding, developing, and showcasing these skills, can greatly boost your chances at getting noticed by the hiring managers. So, don't hesitate and start working on your problem-solving skills right now! 1.
Problem solving, in the simplest terms, is the process of identifying a problem, analyzing it, and finding the most effective solution to overcome it. For software engineers, this process is deeply embedded in their daily workflow. It could be something as simple as figuring out why a piece of code isn't working as expected, or something as ...
Example 1: Project manager with a proven track record of solving complex operational challenges. Skilled in identifying root causes, developing innovative solutions and leading teams to successful project completion. Example 2: Detail-oriented data analyst with strong problem solving skills.
Troubleshooting skills, or problem-solving skills, can help you correctly assess an issue and use your knowledge to find realistic solutions. These skills are particularly helpful in the IT industry, as many roles require the ability to either solve issues directly or instruct others on how to solve them. This skill is complementary to other IT ...
Defer or suspend judgement. Focus on "Yes, and…" rather than "No, but…". According to Carella, "Creative problem solving is the mental process used for generating innovative and imaginative ideas as a solution to a problem or a challenge. Creative problem solving techniques can be pursued by individuals or groups.".
The problem solving process typically includes: Pinpointing what's broken by gathering data and consulting with team members. Figuring out why it's not working by mapping out and troubleshooting the problem. Deciding on the most effective way to fix it by brainstorming and then implementing a solution. While skills like active listening ...
Improve your problem-solving skills. Problem-solving is an important skill for managers, and it involves analysing the situation, communicating effectively, and coming up with creative solutions. As a current or future manager looking to build your problem-solving skills, it is often helpful to take a professional course.
Some of the most valued hard and soft skills employers seek are: 1. Communication. IT professionals communicate with others in many ways, including verbal communication, documentation, presentations and emails. IT professionals have excellent communication skills to convey technical information to others effectively.
Too Much Focus on Automation. Data Mixups Due to AI Implementation. Poor User Experience. 1. Employee Productivity Measurement. As most companies switched to 100 percent remote almost overnight, many realized that they lacked an efficient way to measure employee productivity. Technology with " user productivity reports " has become ...
Establish the Performance Objective. For nearly all technology skill problems, the goal is performance: the target learners becoming sufficiently competent to perform at the required level. Understanding what the performance standard or measure of success is or will be helps focus all stakeholders on the same goal.