

6 Important Tips on Writing a Research Paper Title
When you are searching for a research study on a particular topic, you probably notice that articles with interesting, descriptive research titles draw you in. By contrast, research paper titles that are not descriptive are usually passed over, even though you may write a good research paper with interesting contents. This shows the importance of coming up with a good title for your research paper when drafting your own manuscript.
Importance of a Research Title
The research title plays a crucial role in the research process, and its importance can be summarized as follows:
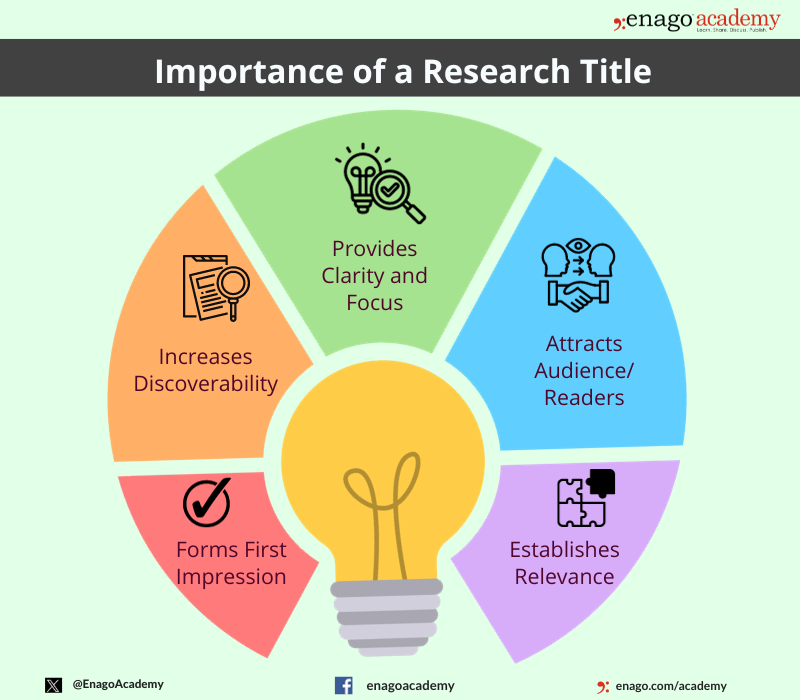
Why do Research Titles Matter?
Before we look at how to title a research paper, let’s look at a research title example that illustrates why a good research paper should have a strong title.
Imagine that you are researching meditation and nursing, and you want to find out if any studies have shown that meditation makes nurses better communicators. You conduct a keyword search using the keywords “nursing”, “communication”, and “meditation.” You come up with results that have the following titles:
- Benefits of Meditation for the Nursing Profession: A Quantitative Investigation
- Why Mindful Nurses Make the Best Communicators
- Meditation Gurus
- Nurses on the Move: A Quantitative Report on How Meditation Can Improve Nurse Performance
All four of these research paper titles may describe very similar studies—they could even be titles for the same study! As you can see, they give very different impressions.
- Title 1 describes the topic and the method of the study but is not particularly catchy.
- Title 2 partly describes the topic, but does not give any information about the method of the study—it could simply be a theoretical or opinion piece.
- Title 3 is somewhat catchier but gives almost no information at all about the article.
- Title 4 begins with a catchy main title and is followed by a subtitle that gives information about the content and method of the study.
As we will see, Title 4 has all the characteristics of a good research title.
Characteristics of a Good Research Title
According to rhetoric scholars Hairston and Keene, making a good title for a paper involves ensuring that the title of the research accomplishes four goals as mentioned below:
- It should predict the content of the research paper .
- It should be interesting to the reader .
- It should reflect the tone of the writing .
- It should contain important keywords that will make it easier to be located during a keyword search.
Let’s return to the examples in the previous section to see how to make a research title.
As you can see in the table above, only one of the four example titles fulfills all of the criteria of a suitable research paper title.
Related: You’ve chosen your study topic, but having trouble deciding where to publish it? Here’s a comprehensive course to help you identify the right journal .
Tips for Writing an Effective Research Paper Title
When writing a research title, you can use the four criteria listed above as a guide. Here are a few other tips you can use to make sure your title will be part of the recipe for an effective research paper :
- Make sure your research title describes (a) the topic, (b) the method, (c) the sample, and (d) the results of your study. You can use the following formula:
[ Result ]: A [ method ] study of [ topic ] among [ sample ] Example : Meditation makes nurses perform better: a qualitative study of mindfulness meditation among German nursing students
- Avoid unnecessary words and jargons. Keep the title statement as concise as possible. You want a title that will be comprehensible even to people who are not experts in your field. Check our article for a detailed list of things to avoid when writing an effective research title .
- Make sure your title is between 5 and 15 words in length.
- If you are writing a title for a university assignment or for a particular academic journal, verify that your title conforms to the standards and requirements for that outlet. For example, many journals require that titles fall under a character limit, including spaces. Many universities require that titles take a very specific form, limiting your creativity.
- Use a descriptive phrase to convey the purpose of your research efficiently.
- Most importantly, use critical keywords in the title to increase the discoverability of your article.

Resources for Further Reading
In addition to the tips above, there are many resources online that you can use to help write your research title. Here is a list of links that you may find useful as you work on creating an excellent research title:
- The University of Southern California has a guide specific to social science research papers: http://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/title
- The Journal of European Psychology Students has a blog article focusing on APA-compliant research paper titles: http://blog.efpsa.org/2012/09/01/how-to-write-a-good-title-for-journal-articles/
- This article by Kristen Hamlin contains a step-by-step approach to writing titles: http://classroom.synonym.com/choose-title-research-paper-4332.html
Are there any tips or tricks you find useful in crafting research titles? Which tip did you find most useful in this article? Leave a comment to let us know!
- Hairston, M., & Keene, M. 2003. Successful writing . 5th ed. New York: Norton.
- University of Southern California. 2017. Organizing your social sciences research paper: choosing a title . [Online] Available at: http://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide/title
Thank you so much:) Have a nice day!
Thank you so much, it helped me.. God bless..
Thank you for the excellent article and tips for creating a research work, because I always forget about such an essential element as the keywords when forming topics. In particular, I have found a rapid help with the formation of informative and sound titles that also conforms to the standards and requirements.
I am doing a research work on sales girls or shop girls using qualititative method. Basicly I am from Pakistan and writing on the scenario of mycountry. I am really confused about my research title can you kindly give some suggestions and give me an approperaite tilte

Hi Zubair, Thank you for your question. However, the information you have provided is insufficient for drafting an appropriate title. Information on what exactly you intend to study would be needed in order to draft a meaningful title. Meanwhile, you can try drafting your own title after going through the following articles our website: https://www.enago.com/academy/top-10-tips-on-choosing-an-attractive-research-title/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/writing-a-good-research-title-things-to-avoid/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/write-irresistible-research-paper-title/ We would be happy to give you feedback and suggest changes if required. Did you get a chance to install our free Mobile App? https://www.enago.com/academy/mobile-app/ . Make sure you subscribe to our weekly newsletter https://www.enago.com/academy/subscribe-now/ .
thanks for helping me like this!!
Thank you for this. It helped me improve my research title. I just want to verify to you the title I have just made. “Ensuring the safety: A Quantitative Study of Radio Frequency Identification system among the selected students of ( school’s name ).
(I need your reply asap coz we will be doing the chap. 1 tomorrow. Thank u in advance. 🙂 )
I am actually doing a research paper title. I want to know more further in doing research title. Can you give me some tips on doing a research paper?
Hi Joan, Thank you for your question. We are glad to know that you found our resources useful. Your feedback is very valuable to us. You can try drafting your own title after going through the following articles on our website: https://www.enago.com/academy/top-10-tips-on-choosing-an-attractive-research-title/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/writing-a-good-research-title-things-to-avoid/ , https://www.enago.com/academy/write-irresistible-research-paper-title/
We would be happy to give you feedback and suggest changes if required. Did you get a chance to install our free Mobile App? https://www.enago.com/academy/mobile-app/ . Make sure you subscribe to our weekly newsletter https://www.enago.com/academy/subscribe-now/ .
That really helpful. Thanks alot
Thank you so much. It’s really help me.
Thanks for sharing this tips. Title matters a lot for any article because it contents Keywords of article. It should be eye-catchy. Your article is helpful to select title of any article.
nice blog that you have shared
This blog is very informative for me. Thanks for sharing.
nice information that you have shared
i’m found in selecting my ma thesis title ,so i’m going to do my final research after the proposal approved. Your post help me find good title.
I need help. I need a research title for my study about early mobilization of the mechanically ventilated patients in the ICU. Any suggestions would be highly appreciated.
Thank you for posting your query on the website. When writing manuscripts, too many scholars neglect the research title. This phrase, along with the abstract, is what people will mostly see and read online. Title research of publications shows that the research paper title does matter a lot. Both bibliometrics and altmetrics tracking of citations are now, for better or worse, used to gauge a paper’s “success” for its author(s) and the journal publishing it. Interesting research topics coupled with good or clever yet accurate research titles can draw more attention to your work from peers and the public alike. You can check through the following search results for titles on similar topics: https://www.google.com/search?q=early+mobilization+of+the+mechanically+ventilated+patients+in+the+icu&rlz=1C1GCEU_enIN907IN907&oq=&aqs=chrome.0.69i59.4920093j0j7&sourceid=chrome&ie=UTF-8 .
We hope this would be helpful in drafting an attractive title for your research paper.
Please let us know in case of any other queries.
I’ve been surfing online more than 3 hours these days, but I never found any interesting article like yours. It is lovely worth enough for me. In my opinion, if all website owners and bloggers made just right content material as you did, the internet will be much more helpful than ever before.
Wonderful article! We will bee linking to this particularly great post on our site. Keep up the good writing.
Wow that was odd. I just wrote an very long comment but after I clicked submit my comment didn’t show up. Grrrr… well I’m not writing all that over again. Anyhow, just wanted to say fantastic blog!
In case the topic is new research before you’re writing. And then to stand out, you end up being different.and be inclined to highlight yourself.
There are many free directories, and more paid lists.
To be honest your article is informative. I search many site to know about writing but I didn’t get the information I needed. I saw your site and I read it. I got some new information from here. I think some of your tips can be applied to those too! Thank you so very much for such informative and useful content.
Nice and well written content you have shared with us. thanks a lot!
Thanks for sharing these tips… Rockwide
Its helpful. a person can grab knowledge through it.
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…

- Career Corner
Unlocking the Power of Networking in Academic Conferences
Embarking on your first academic conference experience? Fear not, we got you covered! Academic conferences…

Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making
Research recommendations play a crucial role in guiding scholars and researchers toward fruitful avenues of…

- AI in Academia
Disclosing the Use of Generative AI: Best practices for authors in manuscript preparation
The rapid proliferation of generative and other AI-based tools in research writing has ignited an…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
How to Design Effective Research Questionnaires for Robust Findings

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

What should universities' stance be on AI tools in research and academic writing?
- USC Libraries
- Research Guides
Organizing Your Social Sciences Research Paper
- Choosing a Title
- Purpose of Guide
- Design Flaws to Avoid
- Independent and Dependent Variables
- Glossary of Research Terms
- Reading Research Effectively
- Narrowing a Topic Idea
- Broadening a Topic Idea
- Extending the Timeliness of a Topic Idea
- Academic Writing Style
- Applying Critical Thinking
- Making an Outline
- Paragraph Development
- Research Process Video Series
- Executive Summary
- The C.A.R.S. Model
- Background Information
- The Research Problem/Question
- Theoretical Framework
- Citation Tracking
- Content Alert Services
- Evaluating Sources
- Primary Sources
- Secondary Sources
- Tiertiary Sources
- Scholarly vs. Popular Publications
- Qualitative Methods
- Quantitative Methods
- Insiderness
- Using Non-Textual Elements
- Limitations of the Study
- Common Grammar Mistakes
- Writing Concisely
- Avoiding Plagiarism
- Footnotes or Endnotes?
- Further Readings
- Generative AI and Writing
- USC Libraries Tutorials and Other Guides
- Bibliography
The title summarizes the main idea or ideas of your study. A good title contains the fewest possible words needed to adequately describe the content and/or purpose of your research paper.
Importance of Choosing a Good Title
The title is the part of a paper that is read the most, and it is usually read first . It is, therefore, the most important element that defines the research study. With this in mind, avoid the following when creating a title:
- If the title is too long, this usually indicates there are too many unnecessary words. Avoid language, such as, "A Study to Investigate the...," or "An Examination of the...." These phrases are obvious and generally superfluous unless they are necessary to covey the scope, intent, or type of a study.
- On the other hand, a title which is too short often uses words which are too broad and, thus, does not tell the reader what is being studied. For example, a paper with the title, "African Politics" is so non-specific the title could be the title of a book and so ambiguous that it could refer to anything associated with politics in Africa. A good title should provide information about the focus and/or scope of your research study.
- In academic writing, catchy phrases or non-specific language may be used, but only if it's within the context of the study [e.g., "Fair and Impartial Jury--Catch as Catch Can"]. However, in most cases, you should avoid including words or phrases that do not help the reader understand the purpose of your paper.
- Academic writing is a serious and deliberate endeavor. Avoid using humorous or clever journalistic styles of phrasing when creating the title to your paper. Journalistic headlines often use emotional adjectives [e.g., incredible, amazing, effortless] to highlight a problem experienced by the reader or use "trigger words" or interrogative words like how, what, when, or why to persuade people to read the article or click on a link. These approaches are viewed as counter-productive in academic writing. A reader does not need clever or humorous titles to catch their attention because the act of reading research is assumed to be deliberate based on a desire to learn and improve understanding of the problem. In addition, a humorous title can merely detract from the seriousness and authority of your research.
- Unlike everywhere else in a college-level social sciences research paper [except when using direct quotes in the text], titles do not have to adhere to rigid grammatical or stylistic standards. For example, it could be appropriate to begin a title with a coordinating conjunction [i.e., and, but, or, nor, for, so, yet] if it makes sense to do so and does not detract from the purpose of the study [e.g., "Yet Another Look at Mutual Fund Tournaments"] or beginning the title with an inflected form of a verb such as those ending in -ing [e.g., "Assessing the Political Landscape: Structure, Cognition, and Power in Organizations"].
Appiah, Kingsley Richard et al. “Structural Organisation of Research Article Titles: A Comparative Study of Titles of Business, Gynaecology and Law.” Advances in Language and Literary Studies 10 (2019); Hartley James. “To Attract or to Inform: What are Titles for?” Journal of Technical Writing and Communication 35 (2005): 203-213; Jaakkola, Maarit. “Journalistic Writing and Style.” In Oxford Research Encyclopedia of Communication . Jon F. Nussbaum, editor. (New York: Oxford University Press, 2018): https://oxfordre.com/communication.
Structure and Writing Style
The following parameters can be used to help you formulate a suitable research paper title:
- The purpose of the research
- The scope of the research
- The narrative tone of the paper [typically defined by the type of the research]
- The methods used to study the problem
The initial aim of a title is to capture the reader’s attention and to highlight the research problem under investigation.
Create a Working Title Typically, the final title you submit to your professor is created after the research is complete so that the title accurately captures what has been done . The working title should be developed early in the research process because it can help anchor the focus of the study in much the same way the research problem does. Referring back to the working title can help you reorient yourself back to the main purpose of the study if you find yourself drifting off on a tangent while writing. The Final Title Effective titles in research papers have several characteristics that reflect general principles of academic writing.
- Indicate accurately the subject and scope of the study,
- Rarely use abbreviations or acronyms unless they are commonly known,
- Use words that create a positive impression and stimulate reader interest,
- Use current nomenclature from the field of study,
- Identify key variables, both dependent and independent,
- Reveal how the paper will be organized,
- Suggest a relationship between variables which supports the major hypothesis,
- Is limited to 5 to 15 substantive words,
- Does not include redundant phrasing, such as, "A Study of," "An Analysis of" or similar constructions,
- Takes the form of a question or declarative statement,
- If you use a quote as part of the title, the source of the quote is cited [usually using an asterisk and footnote],
- Use correct grammar and capitalization with all first words and last words capitalized, including the first word of a subtitle. All nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs that appear between the first and last words of the title are also capitalized, and
- Rarely uses an exclamation mark at the end of the title.
The Subtitle Subtitles are frequently used in social sciences research papers because it helps the reader understand the scope of the study in relation to how it was designed to address the research problem. Think about what type of subtitle listed below reflects the overall approach to your study and whether you believe a subtitle is needed to emphasize the investigative parameters of your research.
1. Explains or provides additional context , e.g., "Linguistic Ethnography and the Study of Welfare Institutions as a Flow of Social Practices: The Case of Residential Child Care Institutions as Paradoxical Institutions." [Palomares, Manuel and David Poveda. Text & Talk: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Language, Discourse and Communication Studies 30 (January 2010): 193-212]
2. Adds substance to a literary, provocative, or imaginative title or quote , e.g., "Listen to What I Say, Not How I Vote": Congressional Support for the President in Washington and at Home." [Grose, Christian R. and Keesha M. Middlemass. Social Science Quarterly 91 (March 2010): 143-167]
3. Qualifies the geographic scope of the research , e.g., "The Geopolitics of the Eastern Border of the European Union: The Case of Romania-Moldova-Ukraine." [Marcu, Silvia. Geopolitics 14 (August 2009): 409-432]
4. Qualifies the temporal scope of the research , e.g., "A Comparison of the Progressive Era and the Depression Years: Societal Influences on Predictions of the Future of the Library, 1895-1940." [Grossman, Hal B. Libraries & the Cultural Record 46 (2011): 102-128]
5. Focuses on investigating the ideas, theories, or work of a particular individual , e.g., "A Deliberative Conception of Politics: How Francesco Saverio Merlino Related Anarchy and Democracy." [La Torre, Massimo. Sociologia del Diritto 28 (January 2001): 75 - 98]
6. Identifies the methodology used , e.g. "Student Activism of the 1960s Revisited: A Multivariate Analysis Research Note." [Aron, William S. Social Forces 52 (March 1974): 408-414]
7. Defines the overarching technique for analyzing the research problem , e.g., "Explaining Territorial Change in Federal Democracies: A Comparative Historical Institutionalist Approach." [ Tillin, Louise. Political Studies 63 (August 2015): 626-641.
With these examples in mind, think about what type of subtitle reflects the overall approach to your study. This will help the reader understand the scope of the study in relation to how it was designed to address the research problem.
Anstey, A. “Writing Style: What's in a Title?” British Journal of Dermatology 170 (May 2014): 1003-1004; Balch, Tucker. How to Compose a Title for Your Research Paper. Augmented Trader blog. School of Interactive Computing, Georgia Tech University; Bavdekar, Sandeep B. “Formulating the Right Title for a Research Article.” Journal of Association of Physicians of India 64 (February 2016); Choosing the Proper Research Paper Titles. AplusReports.com, 2007-2012; Eva, Kevin W. “Titles, Abstracts, and Authors.” In How to Write a Paper . George M. Hall, editor. 5th edition. (Oxford: John Wiley and Sons, 2013), pp. 33-41; Hartley James. “To Attract or to Inform: What are Titles for?” Journal of Technical Writing and Communication 35 (2005): 203-213; General Format. The Writing Lab and The OWL. Purdue University; Kerkut G.A. “Choosing a Title for a Paper.” Comparative Biochemistry and Physiology Part A: Physiology 74 (1983): 1; “Tempting Titles.” In Stylish Academic Writing . Helen Sword, editor. (Cambridge, MA: Harvard University Press, 2012), pp. 63-75; Nundy, Samiran, et al. “How to Choose a Title?” In How to Practice Academic Medicine and Publish from Developing Countries? A Practical Guide . Edited by Samiran Nundy, Atul Kakar, and Zulfiqar A. Bhutta. (Springer Singapore, 2022), pp. 185-192.
- << Previous: Applying Critical Thinking
- Next: Making an Outline >>
- Last Updated: Apr 22, 2024 9:12 AM
- URL: https://libguides.usc.edu/writingguide
- Affiliate Program

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
How to Make a Research Paper Title with Examples
What is a research paper title and why does it matter?
A research paper title summarizes the aim and purpose of your research study. Making a title for your research is one of the most important decisions when writing an article to publish in journals. The research title is the first thing that journal editors and reviewers see when they look at your paper and the only piece of information that fellow researchers will see in a database or search engine query. Good titles that are concise and contain all the relevant terms have been shown to increase citation counts and Altmetric scores .
Therefore, when you title research work, make sure it captures all of the relevant aspects of your study, including the specific topic and problem being investigated. It also should present these elements in a way that is accessible and will captivate readers. Follow these steps to learn how to make a good research title for your work.
How to Make a Research Paper Title in 5 Steps
You might wonder how you are supposed to pick a title from all the content that your manuscript contains—how are you supposed to choose? What will make your research paper title come up in search engines and what will make the people in your field read it?
In a nutshell, your research title should accurately capture what you have done, it should sound interesting to the people who work on the same or a similar topic, and it should contain the important title keywords that other researchers use when looking for literature in databases. To make the title writing process as simple as possible, we have broken it down into 5 simple steps.
Step 1: Answer some key questions about your research paper
What does your paper seek to answer and what does it accomplish? Try to answer these questions as briefly as possible. You can create these questions by going through each section of your paper and finding the MOST relevant information to make a research title.
Step 2: Identify research study keywords
Now that you have answers to your research questions, find the most important parts of these responses and make these your study keywords. Note that you should only choose the most important terms for your keywords–journals usually request anywhere from 3 to 8 keywords maximum.
Step 3: Research title writing: use these keywords
“We employed a case study of 60 liver transplant patients around the US aged 20-50 years to assess how waiting list volume affects the outcomes of liver transplantation in patients; results indicate a positive correlation between increased waiting list volume and negative prognosis after the transplant procedure.”
The sentence above is clearly much too long for a research paper title. This is why you will trim and polish your title in the next two steps.
Step 4: Create a working research paper title
To create a working title, remove elements that make it a complete “sentence” but keep everything that is important to what the study is about. Delete all unnecessary and redundant words that are not central to the study or that researchers would most likely not use in a database search.
“ We employed a case study of 60 liver transplant patients around the US aged 20-50 years to assess how the waiting list volume affects the outcome of liver transplantation in patients ; results indicate a positive correlation between increased waiting list volume and a negative prognosis after transplant procedure ”
Now shift some words around for proper syntax and rephrase it a bit to shorten the length and make it leaner and more natural. What you are left with is:
“A case study of 60 liver transplant patients around the US aged 20-50 years assessing the impact of waiting list volume on outcome of transplantation and showing a positive correlation between increased waiting list volume and a negative prognosis” (Word Count: 38)
This text is getting closer to what we want in a research title, which is just the most important information. But note that the word count for this working title is still 38 words, whereas the average length of published journal article titles is 16 words or fewer. Therefore, we should eliminate some words and phrases that are not essential to this title.
Step 5: Remove any nonessential words and phrases from your title
Because the number of patients studied and the exact outcome are not the most essential parts of this paper, remove these elements first:
“A case study of 60 liver transplant patients around the US aged 20-50 years assessing the impact of waiting list volume on outcomes of transplantation and showing a positive correlation between increased waiting list volume and a negative prognosis” (Word Count: 19)
In addition, the methods used in a study are not usually the most searched-for keywords in databases and represent additional details that you may want to remove to make your title leaner. So what is left is:
“Assessing the impact of waiting list volume on outcome and prognosis in liver transplantation patients” (Word Count: 15)
In this final version of the title, one can immediately recognize the subject and what objectives the study aims to achieve. Note that the most important terms appear at the beginning and end of the title: “Assessing,” which is the main action of the study, is placed at the beginning; and “liver transplantation patients,” the specific subject of the study, is placed at the end.
This will aid significantly in your research paper title being found in search engines and database queries, which means that a lot more researchers will be able to locate your article once it is published. In fact, a 2014 review of more than 150,000 papers submitted to the UK’s Research Excellence Framework (REF) database found the style of a paper’s title impacted the number of citations it would typically receive. In most disciplines, articles with shorter, more concise titles yielded more citations.
Adding a Research Paper Subtitle
If your title might require a subtitle to provide more immediate details about your methodology or sample, you can do this by adding this information after a colon:
“ : a case study of US adult patients ages 20-25”
If we abide strictly by our word count rule this may not be necessary or recommended. But every journal has its own standard formatting and style guidelines for research paper titles, so it is a good idea to be aware of the specific journal author instructions , not just when you write the manuscript but also to decide how to create a good title for it.
Research Paper Title Examples
The title examples in the following table illustrate how a title can be interesting but incomplete, complete by uninteresting, complete and interesting but too informal in tone, or some other combination of these. A good research paper title should meet all the requirements in the four columns below.
Tips on Formulating a Good Research Paper Title
In addition to the steps given above, there are a few other important things you want to keep in mind when it comes to how to write a research paper title, regarding formatting, word count, and content:
- Write the title after you’ve written your paper and abstract
- Include all of the essential terms in your paper
- Keep it short and to the point (~16 words or fewer)
- Avoid unnecessary jargon and abbreviations
- Use keywords that capture the content of your paper
- Never include a period at the end—your title is NOT a sentence
Research Paper Writing Resources
We hope this article has been helpful in teaching you how to craft your research paper title. But you might still want to dig deeper into different journal title formats and categories that might be more suitable for specific article types or need help with writing a cover letter for your manuscript submission.
In addition to getting English proofreading services , including paper editing services , before submission to journals, be sure to visit our academic resources papers. Here you can find dozens of articles on manuscript writing, from drafting an outline to finding a target journal to submit to.
View the latest institution tables
View the latest country/territory tables
How to write a good research paper title
“Unread science is lost science .”

Credit: Mykyta Dolmatov/Getty
“Unread science is lost science.”
28 July 2020

Mykyta Dolmatov/Getty
With the influx of publications brought on by the pandemic, it’s become more challenging than ever for researchers to attract attention to their work.
Understanding which elements of a title will attract readers – or turn them away – has been proven to increase a paper’s citations and Altmetric score .
“In the era of information overload, most students and researchers do not have time to browse the entire text of a paper,” says Patrick Pu , a librarian at the National University of Singapore.
“The title of a paper, together with its abstract, become very important to capture and sustain the attention of readers.”
1. A good title avoids technical language
Since the primary audience of a paper is likely to be researchers working in the same field, using technical language in the title seems to make sense.
But this alienates the wider lay audience, which can bring valuable attention to your work . It can also alienate inexperienced researchers, or those who have recently entered the field.
“A good title does not use unnecessary jargon,” says Elisa De Ranieri , editor-in-chief at the Nature Communications journal (published by Springer Nature, which also publishes Nature Index.) “It communicates the main results in the study in a way that is clear and accessible, ideally to non-specialists or researchers new to the field.”
How-to: When crafting a title, says De Ranieri, write down the main result of the manuscript in a short paragraph. Shorten the text to make it more concise, while still remaining descriptive. Repeat this process until you have a title of fewer than 15 words.
2. A good title is easily searchable
Most readers today are accessing e-journals, which are indexed in scholarly databases such as Scopus and Google Scholar.
“Although these databases usually index the full text of papers, retrieval weightage for ‘Title’ is usually higher than other fields, such as ‘Results’,” Pu explains.
At the National University of Singapore, Pu and his colleagues run information literacy programmes for editors and authors. They give advice for publishing best practice, such as how to identify the most commonly used keywords in literature searches in a given field.
“A professor once told us how he discovered that industry experts were using a different term or keyword to describe his research area,” says Pu.
“He had written a seminal paper that did not include this ‘industry keyword’. He believes his paper, which was highly cited by academics, would have a higher citation count if he had included this keyword in the title. As librarians, we try to highlight this example to our students so that they will consider all possible keywords to use in their searches and paper titles.”
How-to: Authors should speak to an academic librarian at their institution to gain an understanding of keyword and search trends in their field of research. This should inform how the paper title is written.
3. A good title is substantiated by data
Authors should be cautious to not make any claims in the title that can’t be backed up by evidence.
“For instance, if you make a discovery with potential therapeutic relevance, the title should specify whether it was tested or studied in animals or humans/human samples,” says Irene Jarchum , senior editor at the journal Nature Biotechnology (also published by Springer Nature, which publishes the Nature Index.)
Jarchum adds that titles can be contentious because different authors have different views on the use of specific words, such as acronyms, or more fundamentally, what the main message of the title should be.
Some authors may over-interpret the significance of their preliminary findings, and want to reflect this in the title.
How-to: If you know your paper will be contentious within the scientific community, have the data ready to defend your decisions .
4. A good title sparks curiosity
A one-liner that sparks a reader’s interest can be very effective.
“A title has to pique the interest of the person searching for literature in a split-second – enough that they click on the title to read the abstract. Unread science is lost science,” says Christine Mayer , editor-in-chief of the journal Advanced Therapeutics .
Paper titles such as, "White and wonderful? Microplastics prevail in snow from the Alps to the Arctic" ( 2019 Science ), and “Kids these days: Why the youth of today seem lacking” ( 2019 Science Advances ) are good examples of this principle. Both papers have high Altmetric Attention scores, indicating that they have been widely read and discussed online.
How-to: Take note of the characteristics of paper titles that spark your own interest. Keep a record of these and apply the same principles to your own paper titles.
When you choose to publish with PLOS, your research makes an impact. Make your work accessible to all, without restrictions, and accelerate scientific discovery with options like preprints and published peer review that make your work more Open.
- PLOS Biology
- PLOS Climate
- PLOS Complex Systems
- PLOS Computational Biology
- PLOS Digital Health
- PLOS Genetics
- PLOS Global Public Health
- PLOS Medicine
- PLOS Mental Health
- PLOS Neglected Tropical Diseases
- PLOS Pathogens
- PLOS Sustainability and Transformation
- PLOS Collections
- How to Write a Great Title

Maximize search-ability and engage your readers from the very beginning
Your title is the first thing anyone who reads your article is going to see, and for many it will be where they stop reading. Learn how to write a title that helps readers find your article, draws your audience in and sets the stage for your research!
How your title impacts the success of your article
Researchers are busy and there will always be more articles to read than time to read them. Good titles help readers find your research, and decide whether to keep reading. Search engines use titles to retrieve relevant articles based on users’ keyword searches. Once readers find your article, they’ll use the title as the first filter to decide whether your research is what they’re looking for. A strong and specific title is the first step toward citations, inclusion in meta-analyses, and influencing your field.
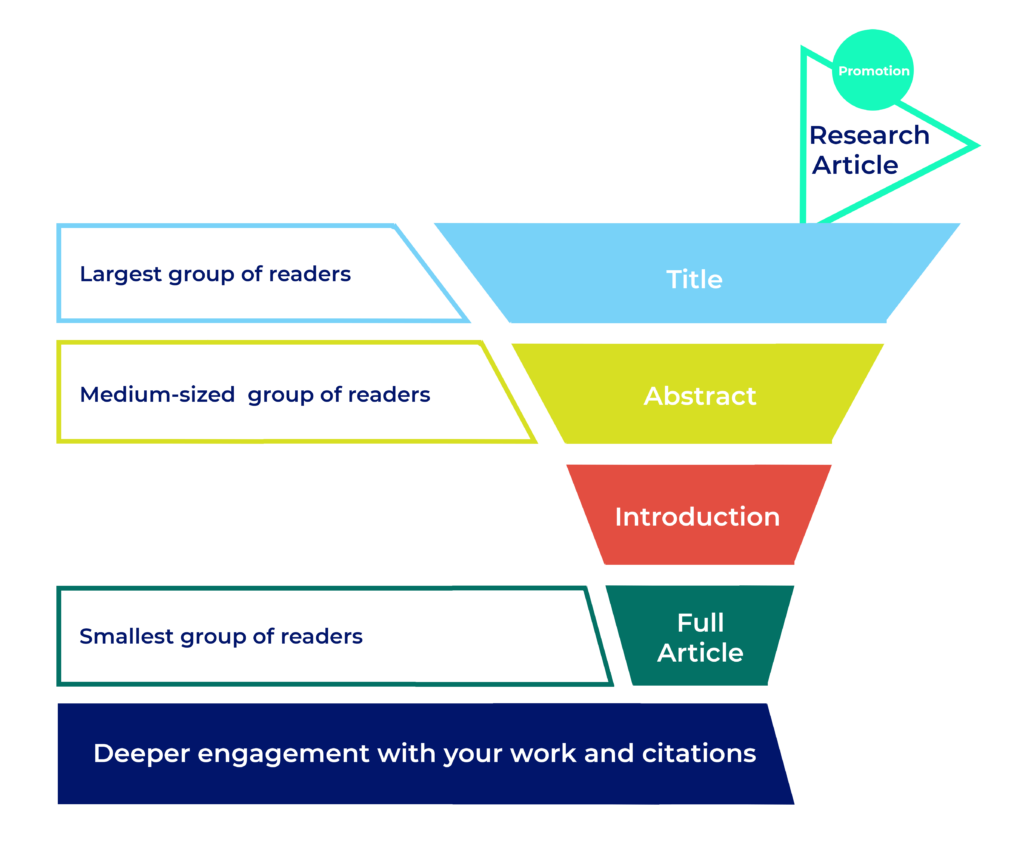
What to include in a title
Include the most important information that will signal to your target audience that they should keep reading.
Key information about the study design
Important keywords
What you discovered
Writing tips
Getting the title right can be more difficult than it seems, and researchers refine their writing skills throughout their career. Some journals even help editors to re-write their titles during the publication process!

- Keep it concise and informative What’s appropriate for titles varies greatly across disciplines. Take a look at some articles published in your field, and check the journal guidelines for character limits. Aim for fewer than 12 words, and check for journal specific word limits.
- Write for your audience Consider who your primary audience is: are they specialists in your specific field, are they cross-disciplinary, are they non-specialists?
- Entice the reader Find a way to pique your readers’ interest, give them enough information to keep them reading.
- Incorporate important keywords Consider what about your article will be most interesting to your audience: Most readers come to an article from a search engine, so take some time and include the important ones in your title!
- Write in sentence case In scientific writing, titles are given in sentence case. Capitalize only the first word of the text, proper nouns, and genus names. See our examples below.

Don’t
- Write your title as a question In most cases, you shouldn’t need to frame your title as a question. You have the answers, you know what you found. Writing your title as a question might draw your readers in, but it’s more likely to put them off.
- Sensationalize your research Be honest with yourself about what you truly discovered. A sensationalized or dramatic title might make a few extra people read a bit further into your article, but you don’t want them disappointed when they get to the results.
Examples…
Format: Prevalence of [disease] in [population] in [location]
Example: Prevalence of tuberculosis in homeless women in San Francisco
Format: Risk factors for [condition] among [population] in [location]
Example: Risk factors for preterm births among low-income women in Mexico City
Format (systematic review/meta-analysis): Effectiveness of [treatment] for [disease] in [population] for [outcome] : A systematic review and meta-analysis
Example: Effectiveness of Hepatitis B treatment in HIV-infected adolescents in the prevention of liver disease: A systematic review and meta-analysis
Format (clinical trial): [Intervention] improved [symptoms] of [disease] in [population] : A randomized controlled clinical trial
Example: Using a sleep app lessened insomnia in post-menopausal women in southwest United States: A randomized controlled clinical trial
Format (general molecular studies): Characterization/identification/evaluation of [molecule name] in/from [organism/tissue] (b y [specific biological methods] )
Example: Identification of putative Type-I sex pheromone biosynthesis-related genes expressed in the female pheromone gland of Streltzoviella insularis
Format (general molecular studies): [specific methods/analysis] of organism/tissue reveal insights into [function/role] of [molecule name] in [biological process]
Example: Transcriptome landscape of Rafflesia cantleyi floral buds reveals insights into the roles of transcription factors and phytohormones in flower development
Format (software/method papers): [tool/method/software] for [what purpose] in [what research area]
Example: CRISPR-based tools for targeted transcriptional and epigenetic regulation in plants
Tip: How to edit your work
Editing is challenging, especially if you are acting as both a writer and an editor. Read our guidelines for advice on how to refine your work, including useful tips for setting your intentions, re-review, and consultation with colleagues.
- How to Write an Abstract
- How to Write Your Methods
- How to Report Statistics
- How to Write Discussions and Conclusions
- How to Edit Your Work
The contents of the Peer Review Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
The contents of the Writing Center are also available as a live, interactive training session, complete with slides, talking points, and activities. …
There’s a lot to consider when deciding where to submit your work. Learn how to choose a journal that will help your study reach its audience, while reflecting your values as a researcher…
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- v.3(9); 2018 Sep
Creating effective titles for your scientific publications
Associated data.
You work for months, maybe years, to plan and conduct your study. You write it up carefully, reporting every piece of data accurately. You get the approval of your co-authors and double-check everyone’s conflicts of interest for the disclosure form. You are ready to submit it when you remember that your work needs a title. “No problem,” you say. “I’ll just throw something together.”
Hold on—that’s not a good idea. The title of a scholarly article really does matter, for several reasons ( Video 1 , available online at www.VideoGIE.org ). It is the first thing a reader will see, so it helps him or her decide whether to read the rest of the article ( Fig. 1 ). 1 If you are publishing in a subscription model, it helps the reader decide whether to buy the whole article. Later, when the reader is writing his own article and wants to cite yours, he can find it more easily if you have given it an effective title. If the article is cited more, it will help your H-Index and G-Index, building your reputation and credibility. Furthermore, if your article is highly cited, it helps the publishing journal’s Impact Factor. Journal editors know which authors’ articles are highly cited and will react with interest when they see another article submitted by that author in the future.

Example of a poor title. It has a problem with grammar (“Are” instead of “Is”), it attempts to be funny, it is in the form of a question, uses abbreviations, does not have clear keywords, and does not make the point of the article clear.
Several elements make up an effective title ( Table 1 ). Studies have shown that shorter titles receive more citations; most recommend 10 to 15 words or between 31 and 40 characters. 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 Punctuation is important: commas and colons have been shown to increase citations, but articles with question marks or exclamation points are cited less frequently. 7 Keywords that help researchers find your article when they use search algorithms are critical, so make sure that your title accurately reflects the key concepts of your article. 4 , 8 , 9
Table 1
Elements of a good title for a scholarly publication
Avoid abbreviations or jargon in your title. 3 , 4 , 9 People from other fields whose research intersects with yours might cite you if they can find your article, but if you use abbreviations or jargon specific to your field, their searches won’t uncover your article.
Some authors think attracting attention with humor or puns is a good idea, but that practice is actually counterproductive. 3 , 4 , 5 , 9 Your title should reflect the tone of the article and of the journal, and because we are dealing with scholarly publications, that means the title should be formal as well. If you are writing an editorial or opinion piece, you might get away with a less-formal title, but for the most part, making your readers laugh should not be a priority.
Poor grammar and incorrect spelling are jarring and irritating to many readers as well as to editors and reviewers, so check and double check that the title is grammatical and everything is spelled and punctuated correctly. If you are using an editing or translation service to assist you with the composition of your article, be sure to include the title in the content submitted for review to catch errors you may have overlooked.
Above all, remember that your title is a reader’s first impression of your article, so make sure that impression is effective. Do all you can to create a title that is professional and does justice to the article you have worked so hard to create.
All authors disclosed no financial relationships relevant to this publication.
Supplementary data
Creating effective titles for scientific articles takes planning and knowledge. In this video, we discuss the elements of a good title.
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
Writing Effective Research Paper Titles: Advice and Examples

Are you ready to submit your research paper for publication but haven't settled on a title yet? Do you have a title but aren't sure if it will be the right one for the journal editor or research database search engines? This article will help you fine tune or create an effective research paper title for your work.
Now that you have finished your research and analysis, and you're ready to take the final step before sending your work to journal editors and reviewers. The first thing journal editors and search engine results will see and show is your research paper title. Creating an effective research paper title is highly important to getting your paper in front of the right people. It is also going to be the only part of your paper that is available to everyone for free, and it will be what search engines use to index and show your work in search results. You therefore must design a clear and persuasive title that accurately represents your work.
When writing an effective research paper title, you want to ensure that the title includes all the relevant aspects of your work. Showcase those aspects in a way that entices the audience to read more. Be sure to use the nomenclature common in your field of study, because that will help your work show up in more search results and it will grab the attention of journal editors looking for articles that clearly represent the industry. If you are studying landslides, for example, you will want to include keywords relating to soil composition or grain size; if you are working on a study about organ transplants, then include the specific feature or procedure that affected successful transplants. Identify what parts of your research are going to interest your intended audience.
There are two key pieces of information that people will need to see in your paper title: the subject and the objective. Because you are already familiar with your study and its purpose, creating an effective research paper title is simply a matter of whittling down the words that describe the important aspects of your paper. The advice below will help you take steps to identify key areas of your research, organize the information, and trim it down to the right size for a title.
Develop a topic statement
To get started, consider a topic statement of your paper that includes the subject and scope of the study. The first step in building a topic statement is to ask yourself the following questions:
- What is your research paper about? "My paper is about gene therapy and how it can improve cognitive function in dementia patients."
- What was the subject of your study? "I used data from 40 dementia patients from 10 states in the US."
- What method did you use to perform your research? "I performed a randomized trial."
- What were the results? "My study showed that gene therapy improved cognitive function in those who received the treatment."
Once you have answered those questions (such as in the example answers above), make a list of the keywords you used. For this example, those keywords would include the following:
- gene therapy
- cognitive function
- 40 dementia patients
- improved cognitive function
- 10 states in the US
- randomized trial
Then, create your topic statement using those keywords. It might read something like this:
"This study is a randomized trial that investigates whether gene therapy improved cognitive function in 40 dementia patients from 10 states in the US. The results show improved cognitive function in those who received the treatment."
This statement has 36 words — too long for a title. However, it does contain the main required elements: the subject and the objective. It also includes a summary of the results, which can be used to increase the persuasive nature of the title. If you are writing this down on paper, it may be helpful to underline or circle the keywords you used in the statement, as this will help you visually see how the keywords work together in your statement.
Trim the statement
The next step is to remove all unnecessary words to create a working title. Unnecessary words include elements that make the sentences complete sentences. Also remove words that are not central to your study or that would not be used in a research database search.
" This study is a randomized trial that investigates whether gene therapy improved cognitive function in 40 dementia patients from 10 states in the US. The results show improved cognitive function in those who received the treatment ."
Next, take those words and move them around to form a new phrase. This may take a few tries to get it right, but it is worth the time.
"A randomized trial investigating whether gene therapy improved cognitive function in 40 dementia patients from 10 states in the US showed improved cognitive function."
This sample now has 24 words. We still need to get it down to the ideal 15 or fewer total words, with just the exact information journal editors will want. One way to do this is to use the keywords at the beginning and end of your title. Remove any irrelevant facts that other researchers will not be searching for. For example, the method you used is not usually the most searched-for keyword.
" A randomized trial investigating whether gene therapy improved cognitive function in 40 dementia patients from 10 states in the US showed improved cognitive function. "
The final result may be something like this:
"Investigating the impact of gene therapy on cognitive function in dementia patients"
The resulting title has 13 words, had the main action at the beginning, and the main subject of the study at the end. This is a good example of how to create an effective research paper title that will increase journal editors' and reviewers' interest, and it may even help your paper receive more citations down the road.
Main tips to remember
If you are working on your first research paper title, the process can seem intimidating. Even with the process outlined above, creating the best research paper title possible for your work can be difficult and time consuming. Be sure to set aside a good amount of time to developing your title so that you don't feel rushed. Some writers go through 20 or more iterations before they arrive at a title that achieves effectiveness, persuasiveness, and clarity of purpose all in one.
In addition to the above process, keep the following main tips in mind when writing an effective research paper title:
- Write your paper and abstract first, then work on your title. This will make the process much easier than trying to nail a title down without a full, finished paper to start from.
- Keep your title short! Do not include more than 15 words.
- Do not use a period at the end of your title.
- Be sure that the keywords you use truly represent the content of your paper.
- Do not use abbreviations in your title.
- Include all essential key terms from your paper. This ensures your paper will be indexed properly in research databases and search engines. If you are unsure of the best keywords to use, talk to an academic librarian at your institution. They can help you identify keyword and search trends in your research field.
Examples of research paper titles
The lists below illustrate what effective and ineffective research paper titles look like. Use these examples to help guide your research paper title.
Effective titles
- Nurses on the Move: A Quantitative Report on How Meditation Can Improve Nurse Performance
- Correction of the ion transport defect in cystic fibrosis transgenic mice by gene therapy
- Landslide mapping techniques and their use in the assessment of the landslide hazard
- HLA compatibility and organ transplant survival: Collaborative Transplant Study
Ineffective titles
- Meditation Gurus
- The landslide story
- Landslide hazard and risk assessment
- Pharmacodynamics of oral ganciclovir and valganciclovir in solid organ transplant recipients
No matter what kind of field you are doing research in, you have the opportunity to create an amazing and effective research paper title that will engage your readers and get your paper in front of the journal editors and reviewers you want. By taking the time to go through the title development process, you will finish your work with a title that matches the work outlined in your research paper.
Header photo by Stokkete .
Related Posts

8 Necessary Considerations When Writing Study Limitations and Alternatives

Want to Master Your Synthesis Essay Assignment? Here's How.
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Elevate your research paper with expert editing services
Elements of Research: Important, Elements, Conducting & More

Want to know everything about elements of research, then you are at the right place. Research is an essential part of any academic or scientific endeavor. Whether you are a student writing a thesis, a researcher conducting a study, or a scientist working on a new discovery, research is the foundation of your work. However, conducting research can be a daunting task, especially if you are new to the field.
In this blog, we will explore the key elements of research and provide a guide to help you understand the building blocks of a successful study.
What is Research?
Table of Contents
Research involves a systematic process of proving a relationship between variables. This can be done through statistical methods, qualitative methods or a combination of both.
A good research design must contain a clear statement, techniques for data collection, processing and analysis.
Elements of Research: Important, Elements, Conducting & More
Here in this section you get to know about elements of research: Important, Elements, Conducting & More:
Why is Research Important?
If you want to know the Elements of Research then you must first know why Research is important. Then here are some reasons why research is important which are as follows:
1. Advancing Knowledge
Research helps to advance knowledge by generating new ideas, theories, and concepts. It helps to build on existing knowledge and expand our understanding of the world.
2. Solving Problems
Research is used to solve problems and to find solutions to complex issues. It helps to identify the root causes of problems and to develop effective strategies for addressing them.
3. Informing Decision-Making
Research provides valuable information that can be used to inform decision-making. It helps to identify the potential risks and benefits of different courses of action, and to determine the most effective approach to solving problems.
4. Improving Quality Of Life
Research has the potential to improve the quality of life for individuals and communities. It can lead to the development of new technologies, medicines, and treatments, and can help to address social and environmental issues.
5. Economic Development
Research can contribute to economic development by driving innovation, creating new jobs, and generating new industries. It can help to create a more competitive and dynamic economy.
6. Personal Growth
Conducting research can also contribute to personal growth by providing opportunities for learning, developing new skills, and gaining a deeper understanding of a particular subject.
The Elements of Research – Things You Need To Know
Here in this section we will tell you some of the elements of research that you must know:
Research is a systematic process of finding evidence to support a knowledge claim. It involves a variety of methods, including observation, experimentation and logical reasoning, which are used to gather data.
Researchers work to develop new concepts and ideas that are relevant, useful and practical. They also explore gaps in current knowledge to identify needs for more research and improve how people think about a problem.
There are a few different types of research, which can be classified into basic and applied research. Fundamental research aims to understand the reasons behind something, whereas applied research seeks to find solutions to problems and create commercially viable applications.
Both methods are based on a systematic approach to capture accurate data. Researchers must practice a code of conduct and follow ethical guidelines to ensure that their research is valid and reliable. This is why it is so important to make sure that all of the data collected has been accurately analyzed and there are no anomalies in the results. This is the first elements of research.
2. Variable
A variable is an element of research that can be measured, manipulated or controlled. It can be any property or characteristic that changes over time, can be a number or can take on different values (such as height, age, temperature or test scores).
In experiments, independent and dependent variables are manipulated to test causal relationships between them. In an experiment where you give one group of people an active drug and another group a placebo, the dependent variable is the response of each person to the drug.
The independent variable is the one you manipulate in the experiment to test its effect on the dependent variable. It’s called an independent variable because it’s not affected by other factors that are being measured in your experiment.
In a study where you want to see how the amount of fertilizers affects plant growth, the independent variable is the amount of fertilizers. The dependent variable is the plant’s growth.
3. Hypothesis
A hypothesis is a statement that explains the predictions and reasoning of your research–an “educated guess” about how your scientific experiments will end. It is the foundation of your research, which should be as clear, specific and testable as possible.
A research hypothesis can be either simple or complex. A simple hypothesis looks at a relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable, while a complex hypothesis explores the effects of multiple variables on each other.
In science, researchers often use a null hypothesis to confirm if the results of an experiment are due to chance or if they support a theory. A null hypothesis states that no relationship exists between two variables, and any changes that occur when the independent variable is manipulated are not due to chance.
A researcher can also choose an alternative hypothesis to narrow down the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. This is called deductive research.
4. Operational Definition
The operational definition of research is a detailed specification of how you will go about measuring a variable. It includes what instrument you will use, how you plan to interpret the data and how you will make comparisons.
A good operational definition will eliminate ambiguity, ensure consistency and reduce measurement errors. It will also be consistent with the theoretical constructs being studied and the methodology used in the study.
For example, if a researcher wants to measure the relationship between age and substance abuse they would define their variable as age measured in years.
Similarly, if they want to measure the relationship between hot weather and violent crime they would define their variable as temperature.
It’s important to have an operational definition of a concept because it helps other researchers to understand the method you used in your study and makes it more replicable. It also helps to avoid misinterpreting your findings, which can lead to erroneous conclusions and poor outcomes. This is the last elements of research.
- Accounting Research Topics
- How To Write a Statistical Research Paper
Ways of Conducting Research?
After knowing the elements of research now you have to know the ways to conduct research. On the other hand, there is a systematic approach to be adopted while conducting research. It involves the following:
1. Defining the Research Problem
The first step in conducting research is to identify the research problem. The research problem is the question or issue that you want to investigate. It should be clearly defined and focused, so that you can design a study that will provide meaningful results. To identify the research problem, you need to start by asking questions about the topic you want to investigate. These questions should be open-ended and designed to help you explore the issue in depth.
Once you have identified the research problem, you can start to develop a research question. The research question should be specific and focused, and should outline the main objective of your study. It should also be clear and concise, so that it can be easily communicated to others.
2. Reviewing the Literature
Before you start to design your study, you need to conduct a literature review. A literature review is a comprehensive analysis of the existing research on your topic. It involves identifying and analyzing relevant literature, including books, articles, and other sources of information.
The purpose of a literature review is to identify the gaps in the existing research and to determine the most effective research methods to use in your study. It also helps you to refine your research question and to develop hypotheses that can be tested in your study.
3. Designing the Study
Once you have identified the research problem and reviewed the literature, you can start to design your study. The study design is the blueprint for your research, and it outlines the methods and procedures that you will use to collect and analyze data.
There are several different types of study designs, including experimental studies, observational studies, and surveys. The type of study design that you choose will depend on the research question, the available resources, and the nature of the data that you want to collect.
4. Collecting Data
The next step in conducting research is to collect data. There are several different methods that you can use to collect data, including surveys, interviews, observations, and experiments. The method that you choose will depend on the nature of your research question and the type of data that you want to collect.
When collecting data, it is important to ensure that the data is accurate and reliable. This involves using appropriate sampling methods, ensuring that the data is collected in a consistent manner, and taking steps to minimize bias and error.
5. Analyzing the Data
Once you have collected the data, you need to analyze it. Data analysis involves examining the data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships. There are several different methods that you can use to analyze data, including descriptive statistics, inferential statistics, and qualitative analysis .
The method that you choose will depend on the nature of your research question and the type of data that you have collected. It is important to use appropriate statistical techniques and to ensure that the results are reliable and valid.
6. Reporting the Results
The final step in conducting research is to report the results. The purpose of reporting the results is to communicate the findings of your study to others. This involves writing a research report that outlines the research question, the methods that were used, the results that were obtained, and the conclusions that were drawn.
The research report should be written in a clear and concise manner, and should be organized in a logical and coherent manner. It should also be accompanied by appropriate tables, graphs, and figures to enhance the clarity and visualization of the results. Additionally, the research report should include a discussion section that interprets the results and discusses their implications.
It is important to use appropriate language and to avoid making unsupported claims. The research report should also include a reference list that provides a complete list of the sources that were used in the study.

7. Ethical Considerations in Research
When conducting research, it is important to consider ethical issues. Ethical considerations involve ensuring that the rights and welfare of research participants are protected, and that the research is conducted in a responsible and ethical manner.
Some of the key ethical considerations in research include obtaining informed consent from participants, maintaining confidentiality, minimizing risks to participants, and ensuring that the benefits of the research outweigh any potential harms.
In addition, researchers should be aware of potential conflicts of interest and should disclose any conflicts of interest to ensure that the research is conducted in an impartial and unbiased manner.
Ways How To Find And Use Research Resources
Here are some ways to find and use research resources:
1. Start With Your Library
Your library is a great place to find research resources, including books, articles, databases, and websites. The librarians at your library can help you find the resources you need and teach you how to use them.
2. Use Online Databases
Many online databases provide access to scholarly articles, books, and other research materials. Some of these websites are free to use, but you have to pay to use the others.
3. Search The Web
You can also find research resources on the web. However, it is important to be critical of the information you find online, as not all websites are created equal.
4. Talk To Experts
If you are stuck, talk to experts in your field. They may be able to point you to helpful resources or provide you with insights that you would not have found on your own.
5. Use Social Media
Social media can be a great way to connect with experts in your field and find research resources. Many experts have their own blogs or Twitter accounts where they share their research and insights.
6. Attend Conferences
Conferences are a great way to learn about new research and meet experts in your field. You can also find research resources such as books, articles, and posters at conferences.
7. Use Government Websites
Government websites can be a great source of research resources. Many government agencies publish reports, studies, and data that can be helpful for research projects.
Tips For Writing Effective Research Paper In 2023
Here are some tips for writing effective research paper in 2023 :
1. Choose A Topic That You Are Interested In And That You Know Something About
This will make it easier and more fun to study. When choosing a topic, it is important to consider your interests, your skills, and your knowledge. You should also consider the length and scope of the paper you must write.
2. Do Your Research Thoroughly
This means reading a variety of sources and carefully evaluating their credibility. When doing your research, it is important to use a variety of sources, including books, articles, websites, and interviews. You should also be critical of your sources and evaluate their credibility.
3. Take Notes On Your Research
This will help you to keep track of your findings and to organize your thoughts. When taking notes, it is important to be selective and only to include the most important information. You should also organize your notes in a way that makes sense to you.
4. Write An Outline For Your Paper
This will help you to structure your paper and to make sure that all of your points are covered. When writing an outline, it is important to include an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. You should also include subheadings to help organize your thoughts.
5. Write A Strong Introduction
Your introduction should grab the reader’s attention and introduce the topic of your paper. A strong introduction should include a clear thesis statement, which is a sentence that states the main point of your paper.
6. Write A Clear And Concise Body Text
Your body text should present your findings and arguments logically and easily. When writing the body of your paper, it is important to use evidence to support your claims. You should also use transition words to help guide your reader through your argument.
7. Write A Strong Conclusion
Your conclusion should clarify your thesis statement and proceed over your important points. A strong conclusion should also leave the reader with something to think about.
8. Proofread Your Paper Carefully
This will help you find any mistakes in writing, grammar, or punctuation. When proofreading your paper, it is helpful to read it aloud. This will help you find errors you might not have noticed otherwise.
Conducting research can be a challenging and complex process. However, by understanding the key elements of research, you can develop a successful study that provides meaningful results. The key elements of research include defining the research problem, reviewing the literature, designing the study, collecting data, analyzing the data, and reporting the results.
Additionally, it is important to consider ethical issues when conducting research to ensure that the rights and welfare of research participants are protected. By following these guidelines, you can conduct research that makes a valuable contribution to your field of study.
Q 1. Why is defining the research problem important?
Defining the research problem is essential because it sets the direction and focus of the study. It helps researchers stay on track and investigate a specific issue effectively.
Q 2. What is the importance of a literature study in research?
The literature review is important as it provides an overview of existing knowledge on the research topic. It helps researchers identify gaps, build on previous work, and ensure their study is relevant and contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
Related Posts

Step by Step Guide on The Best Way to Finance Car

The Best Way on How to Get Fund For Business to Grow it Efficiently

Module 3: Elements of Research

By the end of this module, you will be able to:
- Explain how associations between variables are used to answer research questions.
- Explain why random assignment and random selection are used in research.
- Explain why some information about a research study cannot be told to a research participant.
An understanding of the basic elements of research is essential for good research practices. Among the most important elements to be considered are variables, associations, sampling, random selection, random assignment, and blinding. For a more detailed explanation of other research concepts, please see the list of references provided at the end of this curriculum.
Email Updates

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Elements of a Research Essay
Stephanie Ojeda Ponce
This section is an overview of the elements or parts of a research essay. Scholarly essays are long. There are several different styles of research essays and each have their own structure. For the argument-driven research essay, these are the main elements:
- Purpose or research question
- Your claim or thesis.
- One or more reasons for your thesis.
- Evidence for each reason.
- Others’ objections, counterarguments, or alternative solutions.
- Your acknowledgment of others’ objections, counterarguments, or alternative solutions.
- Your response to others’ objections, counterarguments, or alternative solutions.
The Purpose or Goal
Sometimes your professor will give you the research question, but probably more often you will need to develop your own research topic. Even though you are likely writing an essay for an assignment or as part of a class, you are also developing your own purpose for the research and writing. This part of the essay may not be written down, but it can be helpful to keep in mind a purpose or overall question. That question might even be something you answer through your research, but don’t have
Examples: Purpose and Goal for Research Essays
- How do at least some animals’ bones help control their weight?
- Did the death of his beloved daughter have any effect on the writings of Mark Twain?
Your Claim or Thesis
You write the claim or thesis–it doesn’t come directly from a source. Instead, it is the conclusion you come to in answer to your question after you’ve read/listened to/viewed some sources. So it is a statement, not a question or a hypothesis that you plan to prove or disprove with your research.
After you’ve read/listened to/viewed more sources, you may need to change your thesis. That happens all the time–not because you did anything wrong but because you learned more.
Examples: Claims (or Theses) for Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers
- Bone cells monitor whether more or less weight is pressing down on the skeleton and send biochemical signals to appetite centers in their brains to turn appetite down or up, accordingly.
- Mark Twain wrote more urgently and with less humor during the four years immediately after the death of his daughter.
One or More Reasons
You write what you believe makes your claim or thesis (the answer to your research question) true. That’s your reason or reasons. Each reason is a summary statement of evidence you found in your research. The kinds of evidence considered convincing varies by discipline, so you will be looking at different sources, depending on your discipline. How many reasons you need depends on how complex your thesis and subject matter are, what you found in your sources, and how long your essay or research paper must be. It’s always a good idea to write your reasons in a way that is easy for your audience to understand and be persuaded by.
Examples: Reasons in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers
- Animals (including humans) have a biological tendency to regain any weight that they lose and lose any weight that they gain, seemingly in an effort to maintain whatever weight they have sustained for some time. Skeletons are logical places where any gains or losses could be noted, and recent studies seem to show that osteocytes (a kind of bone cell) are involved in whether appetites go up or down after weight gain or loss.
- My content analysis and a comparison of publication rates four years before and after Mark Twain’s daughter died indicate that his writing was more urgent and less humorous for four years after. It is reasonable to conclude that her death caused that change.
Evidence for Each Reason
You write this also. This is the evidence you summarized earlier as each reason your thesis is true. You will be directly quoting, paraphrasing, and summarizing your sources to make the case that your answer to your research question is correct, or at least reasonable.
Examples: Evidence for Reasons in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers
- Report the results of studies about osteocyctes’ possible effect on weight grain or loss.
- Report the results of your comparison of writing content and publication rate before and after Twain’s daughter’s death.
Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions
Do any of your sources not agree with your thesis? You’ll have to bring those up in your research paper. In addition, put yourself in your readers’ shoes. What might they not find logical in your argument? In other words, which reason(s) and corresponding evidence might they find lacking? Did you find clues to what these could be in your sources? Or maybe you can imagine them thinking some aspect of what you think is evidence doesn’t make sense.
Examples: Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers
- Imagine that some readers might think: The hormone leptin is released by fat cells when they are added to animals’ bodies so it is leptin that tells appetite centers to turn down when weight is gained.
- Imagine that some readers might think: Computerized content analysis tools are sort of blunt instruments and shouldn’t be used to do precise work like this.
Your Acknowledgement of Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions
So what will you write to bring up each of those objections, counterarguments, and alternative solutions? Some examples:
- I can imagine skeptics wanting to point out…
- Perhaps some readers would say…
- I think those who come from XYZ would differ with me…
It all depends on what objections, counterarguments, and alternative solutions your audience or your imagination come up with.
Examples: Acknowledgement of Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers:
- Some readers may point out that the hormone leptin, which is released by fat cells, signals appetite centers to lower the appetite when weight is gained.
- Readers may think that a computerized content analysis tool cannot do justice to the subtleties of text.
Response to Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions
You must write your response to each objection, counterargument, or alternative solution brought up or that you’ve thought of. (You’re likely to have found clues for what to say in your sources.) The reason you have to include this is that you can’t very easily convince your audience until you show them how your claim stacks up against the opinions and reasoning of other people who don’t at the moment agree with you.
Examples: Response to Others’ Objections, Counterarguments, or Alternative Solutions in Hypothetical Essays or Term Papers:
- But leptin must not be the entire system, since many animals do keep on the new weight.
- Unlike other content tools, the XYZ Content Analysis Measure is able to take into account an author’s tone.
Adaptations
This page has been adapted from Where you Get the Components from Choosing & Using Sources: A Guide to Academic Research Copyright © 2015 by Teaching & Learning, Ohio State University Libraries. CC BY 4.0 DEED .
Reading and Writing Research for Undergraduates Copyright © 2023 by Stephanie Ojeda Ponce is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

- Customer Reviews
- Extended Essays
- IB Internal Assessment
- Theory of Knowledge
- Literature Review
- Dissertations
- Essay Writing
- Research Writing
- Assignment Help
- Capstone Projects
- College Application
- Online Class
What Are The Elements Of A Good Research Proposal?
by Antony W
March 10, 2023

The key to writing a great research proposal for your upcoming research project is to make sure the document has the right structure.
Your paper must include all the components that your professor expects to see. So in this guide, we’ll outline all the elements of a good research proposal and explain why they’re important.
The elements of a good research proposal are the title, the introduction, literature review, aims and objectives, methodology, scope of the research, outline and timetable, and bibliography.
It’s important to include these elements in your research proposal exactly in the order in which they appear in the list above.
Why The Key Elements Of A Research Proposal Matter
The basic elements of a research proposal are important because they communicate your thought process, present the originality of your ideas, and demonstrate that you’re passionate about the subject in question.
If you structure and write your research proposal well, your paper can convince your professor that your project is feasible and you have what it takes to take your research project to the next level.
Have no time to read this guide and would rather get quick writing help? Let us write your research proposal for you!
7 Key Elements of a Research Proposal
While developing a detailed and comprehensive research proposal requires a lot of planning, attention to details, and academic writing skills , understanding the core elements of the paper is the first step to getting your proposal accepted.
So here are the elements that you should include in your research proposal.
It sounds somewhat obvious when we say that your research proposal with a title. To say the least, you already know you should.
But perhaps the most common mistake that many students make is to write general titles that lack focus.
Instead of writing a long title that’s hard to read or a short title that fails to highlight the theme of your research, write a clear and concise headline that tells your reader what your research proposal is about at a first glance.
2. Introduction
The starting paragraph to a research project is one of the elements of a good research proposal because it introduces the subject you wish to address or a research problem you wish to analyze.
Because the introduction of a research proposal is what sets the tone for the rest of the paper, it’s important to start with a hook and then organize your thoughts in a logical and organized manner.
The introduction to your research proposal should give background information and explain why you believe a research question is worth exploring. While not mandatory, you can briefly describe your methodologies in the introduction and then expand them later on.
Your introduction should be clear and concise. Make sure you include only the most relevant information in this section so you don’t make it unnecessarily too long.
3. Literature Review
Although a research proposal doesn’t include a full literature review , it’s important to include an overview of the most significant studies in your field.
The section should feature evidence and statistical data to demonstrate the significance of your research.
Through the literature review, you can easily draw your reader’s attention to existing research, identify gaps in existing studies, and make your reader understand how your proposal will contribute to the already existing research.
4. Aims and Objectives
Aims and objectives are what you wish your research proposal to accomplish. Your aims will be your overall outcome or what you want the research to achieve.
Objectives tend to be narrower and more focused. More often than not, you need to provide an explanation for each of your objectives to show how they will help to meet the aims of your study.
Unless required, you don’t really have to include a hypothesis that your research proposal looks forward to test.
5. Research Methodology
Methodologies are simply the research methods you will use to conduct your study and they must appear in your research proposal whether or not you’re conducting an experimental research.
The methodologies include analysis and sampling techniques equipment, research approaches, and ethical concerns.
Make sure your explanation for each methodology is clear and precise. It helps to justify why you’ve chosen to use a certain methodology over an alternative. This will go a long way to show that you took your time to think about your methodologies before picking them.
It’s important to explain how you will collect data, the sample size you plan to consider for your research investigation, and the techniques you consider the most appropriate to analyze the data.
6. Scope of the Research
Because you’ll be working with limited time and resource, it’s reasonable to include a section on the scope of the research in your proposal. In other words, you have to show your reader that you can start and complete your research within the constraints of these two resources.
Remember, your research will more than likely have limits, and addressing them in this section not only shows that you have given them a thought but also makes your research proposal strong and authentic.
Don’t just focus on the challenges that you’re likely to come across during your studies. You should also propose alternative solutions that you can use and why they might help.
7. Outline and Timetable
Your professor expects to see an outline and a timetable in your research proposal so it’s important that you include them in your research proposal.
The purpose of the outline is to show how you plan to structure your dissertation . Briefly note what each section will cover and explain how it all fits into the argument of your research project.
The purpose of the timetable is to show how much time you’ll need to complete your research. In particular, you need to make sure you mention exactly how long you expect each stage of your study to take.
Don’t just mention how long the research process will take. Make sure you also indicate how long you’ll take to compile your research.
Get Help with Research Proposal Writing
Knowing the elements of a good research proposal is one thing. Writing the proposal is where there’s a lot of work. If you don’t have the time to complete the work yourself, feel free to take advantage of our research proposal writing and get the paper done on time.
About the author
Antony W is a professional writer and coach at Help for Assessment. He spends countless hours every day researching and writing great content filled with expert advice on how to write engaging essays, research papers, and assignments.

Three Elements for a Proper Thesis Title
- Five Ways to Improve Your English Language
- Five Elements to Include in Your Abstract
When doing research, it is critical that you come up with a title that is perfect. Your title needs to include details about what your research is about, what you did, and your results. All of this in about 15 words! After trial and error, you can come up with a suitable title. There is a strategy to use to make it easier for you. Think about the following three elements and add them to your title in order to get a perfect title that says it all.
The issue is basically the problem, or gap.
The objectives are the steps you will take to solve the issue.
The method is how you will solve the issue.
Include these three elements in your title and make it about 15 words . . . Now you have your perfect title 🙂
Related Articles

The Distinction Between Academic Proofreading and Academic Editing: A Comprehensive Analysis

The Human Touch: Why Human Academic Editors Outshine AI in Editing and Proofreading Scholarly Work

How to use Google Scholar to Write an Effective Literature Review

Ten Tips for Effectively Writing a Research Paper for Peer-Review
Leave a reply click here to cancel the reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
PM Proofreading Services Continuous Improofment
5.0 Rated 5.0 out of 5 5.0 out of 5 stars (based on 60 reviews) Excellent 97% Very good 3% Average 0% Poor 0% Terrible 0%
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » 500+ Quantitative Research Titles and Topics
500+ Quantitative Research Titles and Topics
Table of Contents

Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships among variables. This method is widely used in social sciences, psychology , economics , and other fields where researchers aim to understand human behavior and phenomena through statistical analysis. If you are looking for a quantitative research topic, there are numerous areas to explore, from analyzing data on a specific population to studying the effects of a particular intervention or treatment. In this post, we will provide some ideas for quantitative research topics that may inspire you and help you narrow down your interests.
Quantitative Research Titles
Quantitative Research Titles are as follows:
Business and Economics
- “Statistical Analysis of Supply Chain Disruptions on Retail Sales”
- “Quantitative Examination of Consumer Loyalty Programs in the Fast Food Industry”
- “Predicting Stock Market Trends Using Machine Learning Algorithms”
- “Influence of Workplace Environment on Employee Productivity: A Quantitative Study”
- “Impact of Economic Policies on Small Businesses: A Regression Analysis”
- “Customer Satisfaction and Profit Margins: A Quantitative Correlation Study”
- “Analyzing the Role of Marketing in Brand Recognition: A Statistical Overview”
- “Quantitative Effects of Corporate Social Responsibility on Consumer Trust”
- “Price Elasticity of Demand for Luxury Goods: A Case Study”
- “The Relationship Between Fiscal Policy and Inflation Rates: A Time-Series Analysis”
- “Factors Influencing E-commerce Conversion Rates: A Quantitative Exploration”
- “Examining the Correlation Between Interest Rates and Consumer Spending”
- “Standardized Testing and Academic Performance: A Quantitative Evaluation”
- “Teaching Strategies and Student Learning Outcomes in Secondary Schools: A Quantitative Study”
- “The Relationship Between Extracurricular Activities and Academic Success”
- “Influence of Parental Involvement on Children’s Educational Achievements”
- “Digital Literacy in Primary Schools: A Quantitative Assessment”
- “Learning Outcomes in Blended vs. Traditional Classrooms: A Comparative Analysis”
- “Correlation Between Teacher Experience and Student Success Rates”
- “Analyzing the Impact of Classroom Technology on Reading Comprehension”
- “Gender Differences in STEM Fields: A Quantitative Analysis of Enrollment Data”
- “The Relationship Between Homework Load and Academic Burnout”
- “Assessment of Special Education Programs in Public Schools”
- “Role of Peer Tutoring in Improving Academic Performance: A Quantitative Study”
Medicine and Health Sciences
- “The Impact of Sleep Duration on Cardiovascular Health: A Cross-sectional Study”
- “Analyzing the Efficacy of Various Antidepressants: A Meta-Analysis”
- “Patient Satisfaction in Telehealth Services: A Quantitative Assessment”
- “Dietary Habits and Incidence of Heart Disease: A Quantitative Review”
- “Correlations Between Stress Levels and Immune System Functioning”
- “Smoking and Lung Function: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Influence of Physical Activity on Mental Health in Older Adults”
- “Antibiotic Resistance Patterns in Community Hospitals: A Quantitative Study”
- “The Efficacy of Vaccination Programs in Controlling Disease Spread: A Time-Series Analysis”
- “Role of Social Determinants in Health Outcomes: A Quantitative Exploration”
- “Impact of Hospital Design on Patient Recovery Rates”
- “Quantitative Analysis of Dietary Choices and Obesity Rates in Children”
Social Sciences
- “Examining Social Inequality through Wage Distribution: A Quantitative Study”
- “Impact of Parental Divorce on Child Development: A Longitudinal Study”
- “Social Media and its Effect on Political Polarization: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “The Relationship Between Religion and Social Attitudes: A Statistical Overview”
- “Influence of Socioeconomic Status on Educational Achievement”
- “Quantifying the Effects of Community Programs on Crime Reduction”
- “Public Opinion and Immigration Policies: A Quantitative Exploration”
- “Analyzing the Gender Representation in Political Offices: A Quantitative Study”
- “Impact of Mass Media on Public Opinion: A Regression Analysis”
- “Influence of Urban Design on Social Interactions in Communities”
- “The Role of Social Support in Mental Health Outcomes: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Examining the Relationship Between Substance Abuse and Employment Status”
Engineering and Technology
- “Performance Evaluation of Different Machine Learning Algorithms in Autonomous Vehicles”
- “Material Science: A Quantitative Analysis of Stress-Strain Properties in Various Alloys”
- “Impacts of Data Center Cooling Solutions on Energy Consumption”
- “Analyzing the Reliability of Renewable Energy Sources in Grid Management”
- “Optimization of 5G Network Performance: A Quantitative Assessment”
- “Quantifying the Effects of Aerodynamics on Fuel Efficiency in Commercial Airplanes”
- “The Relationship Between Software Complexity and Bug Frequency”
- “Machine Learning in Predictive Maintenance: A Quantitative Analysis”
- “Wearable Technologies and their Impact on Healthcare Monitoring”
- “Quantitative Assessment of Cybersecurity Measures in Financial Institutions”
- “Analysis of Noise Pollution from Urban Transportation Systems”
- “The Influence of Architectural Design on Energy Efficiency in Buildings”
Quantitative Research Topics
Quantitative Research Topics are as follows:
- The effects of social media on self-esteem among teenagers.
- A comparative study of academic achievement among students of single-sex and co-educational schools.
- The impact of gender on leadership styles in the workplace.
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic performance of students.
- The effect of mindfulness meditation on stress levels in college students.
- The relationship between employee motivation and job satisfaction.
- The effectiveness of online learning compared to traditional classroom learning.
- The correlation between sleep duration and academic performance among college students.
- The impact of exercise on mental health among adults.
- The relationship between social support and psychological well-being among cancer patients.
- The effect of caffeine consumption on sleep quality.
- A comparative study of the effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy and pharmacotherapy in treating depression.
- The relationship between physical attractiveness and job opportunities.
- The correlation between smartphone addiction and academic performance among high school students.
- The impact of music on memory recall among adults.
- The effectiveness of parental control software in limiting children’s online activity.
- The relationship between social media use and body image dissatisfaction among young adults.
- The correlation between academic achievement and parental involvement among minority students.
- The impact of early childhood education on academic performance in later years.
- The effectiveness of employee training and development programs in improving organizational performance.
- The relationship between socioeconomic status and access to healthcare services.
- The correlation between social support and academic achievement among college students.
- The impact of technology on communication skills among children.
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction programs in reducing symptoms of anxiety and depression.
- The relationship between employee turnover and organizational culture.
- The correlation between job satisfaction and employee engagement.
- The impact of video game violence on aggressive behavior among children.
- The effectiveness of nutritional education in promoting healthy eating habits among adolescents.
- The relationship between bullying and academic performance among middle school students.
- The correlation between teacher expectations and student achievement.
- The impact of gender stereotypes on career choices among high school students.
- The effectiveness of anger management programs in reducing violent behavior.
- The relationship between social support and recovery from substance abuse.
- The correlation between parent-child communication and adolescent drug use.
- The impact of technology on family relationships.
- The effectiveness of smoking cessation programs in promoting long-term abstinence.
- The relationship between personality traits and academic achievement.
- The correlation between stress and job performance among healthcare professionals.
- The impact of online privacy concerns on social media use.
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating anxiety disorders.
- The relationship between teacher feedback and student motivation.
- The correlation between physical activity and academic performance among elementary school students.
- The impact of parental divorce on academic achievement among children.
- The effectiveness of diversity training in improving workplace relationships.
- The relationship between childhood trauma and adult mental health.
- The correlation between parental involvement and substance abuse among adolescents.
- The impact of social media use on romantic relationships among young adults.
- The effectiveness of assertiveness training in improving communication skills.
- The relationship between parental expectations and academic achievement among high school students.
- The correlation between sleep quality and mood among adults.
- The impact of video game addiction on academic performance among college students.
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating eating disorders.
- The relationship between job stress and job performance among teachers.
- The correlation between mindfulness and emotional regulation.
- The impact of social media use on self-esteem among college students.
- The effectiveness of parent-teacher communication in promoting academic achievement among elementary school students.
- The impact of renewable energy policies on carbon emissions
- The relationship between employee motivation and job performance
- The effectiveness of psychotherapy in treating eating disorders
- The correlation between physical activity and cognitive function in older adults
- The effect of childhood poverty on adult health outcomes
- The impact of urbanization on biodiversity conservation
- The relationship between work-life balance and employee job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing (EMDR) in treating trauma
- The correlation between parenting styles and child behavior
- The effect of social media on political polarization
- The impact of foreign aid on economic development
- The relationship between workplace diversity and organizational performance
- The effectiveness of dialectical behavior therapy in treating borderline personality disorder
- The correlation between childhood abuse and adult mental health outcomes
- The effect of sleep deprivation on cognitive function
- The impact of trade policies on international trade and economic growth
- The relationship between employee engagement and organizational commitment
- The effectiveness of cognitive therapy in treating postpartum depression
- The correlation between family meals and child obesity rates
- The effect of parental involvement in sports on child athletic performance
- The impact of social entrepreneurship on sustainable development
- The relationship between emotional labor and job burnout
- The effectiveness of art therapy in treating dementia
- The correlation between social media use and academic procrastination
- The effect of poverty on childhood educational attainment
- The impact of urban green spaces on mental health
- The relationship between job insecurity and employee well-being
- The effectiveness of virtual reality exposure therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between childhood trauma and substance abuse
- The effect of screen time on children’s social skills
- The impact of trade unions on employee job satisfaction
- The relationship between cultural intelligence and cross-cultural communication
- The effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy in treating chronic pain
- The correlation between childhood obesity and adult health outcomes
- The effect of gender diversity on corporate performance
- The impact of environmental regulations on industry competitiveness.
- The impact of renewable energy policies on greenhouse gas emissions
- The relationship between workplace diversity and team performance
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating substance abuse
- The correlation between parental involvement and social skills in early childhood
- The effect of technology use on sleep patterns
- The impact of government regulations on small business growth
- The relationship between job satisfaction and employee turnover
- The effectiveness of virtual reality therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic motivation in adolescents
- The effect of social media on political engagement
- The impact of urbanization on mental health
- The relationship between corporate social responsibility and consumer trust
- The correlation between early childhood education and social-emotional development
- The effect of screen time on cognitive development in young children
- The impact of trade policies on global economic growth
- The relationship between workplace diversity and innovation
- The effectiveness of family therapy in treating eating disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and college persistence
- The effect of social media on body image and self-esteem
- The impact of environmental regulations on business competitiveness
- The relationship between job autonomy and job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of virtual reality therapy in treating phobias
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic achievement in college
- The effect of social media on sleep quality
- The impact of immigration policies on social integration
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee well-being
- The effectiveness of psychodynamic therapy in treating personality disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and executive function skills
- The effect of parental involvement on STEM education outcomes
- The impact of trade policies on domestic employment rates
- The relationship between job insecurity and mental health
- The effectiveness of exposure therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and social mobility
- The effect of social media on intergroup relations
- The impact of urbanization on air pollution and respiratory health.
- The relationship between emotional intelligence and leadership effectiveness
- The effectiveness of cognitive-behavioral therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between early childhood education and language development
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in STEM fields
- The impact of trade policies on income inequality
- The relationship between workplace diversity and customer satisfaction
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and civic engagement in adolescents
- The effect of social media on mental health among teenagers
- The impact of public transportation policies on traffic congestion
- The relationship between job stress and job performance
- The effectiveness of group therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between early childhood education and cognitive development
- The effect of parental involvement on academic motivation in college
- The impact of environmental regulations on energy consumption
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee engagement
- The effectiveness of art therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in vocational education
- The effect of social media on academic achievement in college
- The impact of tax policies on economic growth
- The relationship between job flexibility and work-life balance
- The effectiveness of acceptance and commitment therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and social competence
- The effect of parental involvement on career readiness in high school
- The impact of immigration policies on crime rates
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee retention
- The effectiveness of play therapy in treating trauma
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in online learning
- The effect of social media on body dissatisfaction among women
- The impact of urbanization on public health infrastructure
- The relationship between job satisfaction and job performance
- The effectiveness of eye movement desensitization and reprocessing therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between early childhood education and social skills in adolescence
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in the arts
- The impact of trade policies on foreign investment
- The relationship between workplace diversity and decision-making
- The effectiveness of exposure and response prevention therapy in treating OCD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in special education
- The impact of zoning laws on affordable housing
- The relationship between job design and employee motivation
- The effectiveness of cognitive rehabilitation therapy in treating traumatic brain injury
- The correlation between early childhood education and social-emotional learning
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in foreign language learning
- The impact of trade policies on the environment
- The relationship between workplace diversity and creativity
- The effectiveness of emotion-focused therapy in treating relationship problems
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in music education
- The effect of social media on interpersonal communication skills
- The impact of public health campaigns on health behaviors
- The relationship between job resources and job stress
- The effectiveness of equine therapy in treating substance abuse
- The correlation between early childhood education and self-regulation
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in physical education
- The impact of immigration policies on cultural assimilation
- The relationship between workplace diversity and conflict resolution
- The effectiveness of schema therapy in treating personality disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in career and technical education
- The effect of social media on trust in government institutions
- The impact of urbanization on public transportation systems
- The relationship between job demands and job stress
- The correlation between early childhood education and executive functioning
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in computer science
- The effectiveness of cognitive processing therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in homeschooling
- The effect of social media on cyberbullying behavior
- The impact of urbanization on air quality
- The effectiveness of dance therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and math achievement
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in health education
- The impact of global warming on agriculture
- The effectiveness of narrative therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in character education
- The effect of social media on political participation
- The impact of technology on job displacement
- The relationship between job resources and job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of art therapy in treating addiction
- The correlation between early childhood education and reading comprehension
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in environmental education
- The impact of income inequality on social mobility
- The relationship between workplace diversity and organizational culture
- The effectiveness of solution-focused brief therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in physical therapy education
- The effect of social media on misinformation
- The impact of green energy policies on economic growth
- The relationship between job demands and employee well-being
- The correlation between early childhood education and science achievement
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in religious education
- The impact of gender diversity on corporate governance
- The relationship between workplace diversity and ethical decision-making
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in dental hygiene education
- The effect of social media on self-esteem among adolescents
- The impact of renewable energy policies on energy security
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in social studies
- The impact of trade policies on job growth
- The relationship between workplace diversity and leadership styles
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in online vocational training
- The effect of social media on self-esteem among men
- The impact of urbanization on air pollution levels
- The effectiveness of music therapy in treating depression
- The correlation between early childhood education and math skills
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in language arts
- The impact of immigration policies on labor market outcomes
- The effectiveness of hypnotherapy in treating phobias
- The effect of social media on political engagement among young adults
- The impact of urbanization on access to green spaces
- The relationship between job crafting and job satisfaction
- The effectiveness of exposure therapy in treating specific phobias
- The correlation between early childhood education and spatial reasoning
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in business education
- The impact of trade policies on economic inequality
- The effectiveness of narrative therapy in treating PTSD
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in nursing education
- The effect of social media on sleep quality among adolescents
- The impact of urbanization on crime rates
- The relationship between job insecurity and turnover intentions
- The effectiveness of pet therapy in treating anxiety disorders
- The correlation between early childhood education and STEM skills
- The effect of parental involvement on academic achievement in culinary education
- The impact of immigration policies on housing affordability
- The relationship between workplace diversity and employee satisfaction
- The effectiveness of mindfulness-based stress reduction in treating chronic pain
- The correlation between parental involvement and academic success in art education
- The effect of social media on academic procrastination among college students
- The impact of urbanization on public safety services.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

200+ Funny Research Topics

500+ Sports Research Topics

300+ American History Research Paper Topics

500+ Cyber Security Research Topics

500+ Environmental Research Topics

500+ Economics Research Topics

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Make sure your research title describes (a) the topic, (b) the method, (c) the sample, and (d) the results of your study. You can use the following formula: [ Result ]: A [ method] study of [ topic] among [ sample] Example: Meditation makes nurses perform better: a qualitative study of mindfulness meditation among German nursing students. Avoid ...
The title is the part of a paper that is read the most, and it is usually read first. It is, therefore, the most important element that defines the research study. With this in mind, avoid the following when creating a title: If the title is too long, this usually indicates there are too many unnecessary words.
Research Paper Title. Research Paper Title is the name or heading that summarizes the main theme or topic of a research paper.It serves as the first point of contact between the reader and the paper, providing an initial impression of the content, purpose, and scope of the research.A well-crafted research paper title should be concise, informative, and engaging, accurately reflecting the key ...
Step 4: Create a working research paper title. To create a working title, remove elements that make it a complete "sentence" but keep everything that is important to what the study is about. Delete all unnecessary and redundant words that are not central to the study or that researchers would most likely not use in a database search.
Shorten the text to make it more concise, while still remaining descriptive. Repeat this process until you have a title of fewer than 15 words. 2. A good title is easily searchable. Most readers ...
Entice the reader. Find a way to pique your readers' interest, give them enough information to keep them reading. Incorporate important keywords. Consider what about your article will be most interesting to your audience: Most readers come to an article from a search engine, so take some time and include the important ones in your title ...
Introduction. This article deals with drafting a suitable "title" and an appropriate "abstract" for an original research paper. Because the "title" and the "abstract" are the "initial impressions" or the "face" of a research article, they need to be drafted correctly, accurately, carefully, meticulously, and consume time and energy.[1,2,3,4,5,6,7,8,9,10] Often, these ...
3. Content of the Title. The main elements of a title include intervention, end-point or outcome, study population, and its specific conditions, design, and setting, which refers to a situation or a place that study was conducted at ().The main elements in a hypothesis-testing paper, are (1) the independent variable(s) (X), (2) dependent variable(s) (Y), and (3) the study subjects (i.e. animal ...
Published 2021 by American Chemical Society. Figure 1. Five key attributes of an article title. 3. Inquisitiveness. Just like a compelling ctional story, titles fi that raise curiosity can draw readers and make them want to nd the answer to an important scienti c issue. Here are a fi fi couple recent examples.
Avoid abbreviations or jargon in your title.3, 4, 9 People from other fields whose research intersects with yours might cite you if they can find your article, but if you use abbreviations or jargon specific to your field, their searches won't uncover your article. Some authors think attracting attention with humor or puns is a good idea, but that practice is actually counterproductive.3, 4 ...
Title. Effective titles in academic research papers have several characteristics. Indicate accurately the subject and scope of the study. Avoid using abbreviations. Use words that create a positive impression and stimulate reader interest. Use current nomenclature from the field of study. Identify key variables, both dependent and independent.
STEP 3. Create a sentence that includes the key words you listed. This study is a randomized trial that investigates whether X therapy improved cognitive function in 40 dementia patients from 6 cities in Japan; it reports improved cognitive function. (Current length: 28 words) STEP 4.
In addition to the above process, keep the following main tips in mind when writing an effective research paper title: Write your paper and abstract first, then work on your title. This will make the process much easier than trying to nail a title down without a full, finished paper to start from. Keep your title short!
Formulating the Right Title for a Research. Article. Sandeep B Bavdekar. Professor and Head, Department of Pediatrics, T opiwala National Medical College and BYL Nair Ch. Hospital, Mumbai ...
A good research paper title: So here are three basic tips to keep in mind while writing a title: 1] Keep it simple, brief and attractive: The primary function of a title is to provide a precise summary of the paper's content. So keep the title brief and clear. Use active verbs instead of complex noun-based phrases, and avoid unnecessary details.
The key elements of research include defining the research problem, reviewing the literature, designing the study, collecting data, analyzing the data, and reporting the results. Additionally, it is important to consider ethical issues when conducting research to ensure that the rights and welfare of research participants are protected.
This lecture video simplifies the way to formulate research titles. I discussed here the importance, characteristics, and elements of a good research title.
Among the most important elements to be considered are variables, associations, sampling, random selection, random assignment, and blinding. For a more detailed explanation of other research concepts, please see the list of references provided at the end of this curriculum. Go to Module 3. Section 1.
There are several different styles of research essays and each have their own structure. For the argument-driven research essay, these are the main elements: Purpose or research question. Your claim or thesis. One or more reasons for your thesis. Evidence for each reason. Others' objections, counterarguments, or alternative solutions.
So in this guide, we'll outline all the elements of a good research proposal and explain why they're important. The elements of a good research proposal are the title, the introduction, literature review, aims and objectives, methodology, scope of the research, outline and timetable, and bibliography. It's important to include these ...
Here are some of the elements of a good research design: Purpose statement. Data collection methods. Techniques of data analysis. Types of research methodologies. Challenges of the research. Prerequisites required for study. Duration of the research study. Measurement of analysis.
Your title needs to include details about what your research is about, what you did, and your results. All of this in about 15 words! After trial and error, you can come up with a suitable title. There is a strategy to use to make it easier for you. Think about the following three elements and add them to your title in order to get a perfect ...
Quantitative research involves collecting and analyzing numerical data to identify patterns, trends, and relationships among variables. This method is widely used in social sciences, psychology, economics, and other fields where researchers aim to understand human behavior and phenomena through statistical analysis.