Graphical Representation of Data
Graphical representation of data is an attractive method of showcasing numerical data that help in analyzing and representing quantitative data visually. A graph is a kind of a chart where data are plotted as variables across the coordinate. It became easy to analyze the extent of change of one variable based on the change of other variables. Graphical representation of data is done through different mediums such as lines, plots, diagrams, etc. Let us learn more about this interesting concept of graphical representation of data, the different types, and solve a few examples.
| 1. | |
| 2. | |
| 3. | |
| 4. | |
| 5. | |
| 6. | |
| 7. |

Definition of Graphical Representation of Data
A graphical representation is a visual representation of data statistics-based results using graphs, plots, and charts. This kind of representation is more effective in understanding and comparing data than seen in a tabular form. Graphical representation helps to qualify, sort, and present data in a method that is simple to understand for a larger audience. Graphs enable in studying the cause and effect relationship between two variables through both time series and frequency distribution. The data that is obtained from different surveying is infused into a graphical representation by the use of some symbols, such as lines on a line graph, bars on a bar chart, or slices of a pie chart. This visual representation helps in clarity, comparison, and understanding of numerical data.
Representation of Data
The word data is from the Latin word Datum, which means something given. The numerical figures collected through a survey are called data and can be represented in two forms - tabular form and visual form through graphs. Once the data is collected through constant observations, it is arranged, summarized, and classified to finally represented in the form of a graph. There are two kinds of data - quantitative and qualitative. Quantitative data is more structured, continuous, and discrete with statistical data whereas qualitative is unstructured where the data cannot be analyzed.
Principles of Graphical Representation of Data
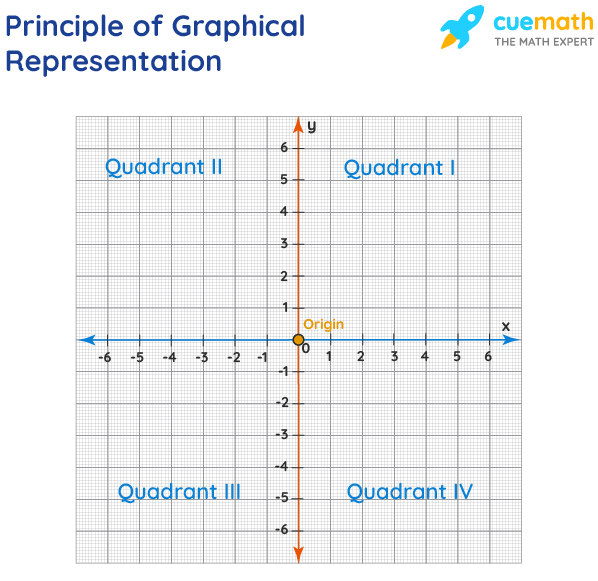
The principles of graphical representation are algebraic. In a graph, there are two lines known as Axis or Coordinate axis. These are the X-axis and Y-axis. The horizontal axis is the X-axis and the vertical axis is the Y-axis. They are perpendicular to each other and intersect at O or point of Origin. On the right side of the Origin, the Xaxis has a positive value and on the left side, it has a negative value. In the same way, the upper side of the Origin Y-axis has a positive value where the down one is with a negative value. When -axis and y-axis intersect each other at the origin it divides the plane into four parts which are called Quadrant I, Quadrant II, Quadrant III, Quadrant IV. This form of representation is seen in a frequency distribution that is represented in four methods, namely Histogram, Smoothed frequency graph, Pie diagram or Pie chart, Cumulative or ogive frequency graph, and Frequency Polygon.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Graphical Representation of Data
Listed below are some advantages and disadvantages of using a graphical representation of data:
- It improves the way of analyzing and learning as the graphical representation makes the data easy to understand.
- It can be used in almost all fields from mathematics to physics to psychology and so on.
- It is easy to understand for its visual impacts.
- It shows the whole and huge data in an instance.
- It is mainly used in statistics to determine the mean, median, and mode for different data
The main disadvantage of graphical representation of data is that it takes a lot of effort as well as resources to find the most appropriate data and then represent it graphically.
Rules of Graphical Representation of Data
While presenting data graphically, there are certain rules that need to be followed. They are listed below:
- Suitable Title: The title of the graph should be appropriate that indicate the subject of the presentation.
- Measurement Unit: The measurement unit in the graph should be mentioned.
- Proper Scale: A proper scale needs to be chosen to represent the data accurately.
- Index: For better understanding, index the appropriate colors, shades, lines, designs in the graphs.
- Data Sources: Data should be included wherever it is necessary at the bottom of the graph.
- Simple: The construction of a graph should be easily understood.
- Neat: The graph should be visually neat in terms of size and font to read the data accurately.
Uses of Graphical Representation of Data
The main use of a graphical representation of data is understanding and identifying the trends and patterns of the data. It helps in analyzing large quantities, comparing two or more data, making predictions, and building a firm decision. The visual display of data also helps in avoiding confusion and overlapping of any information. Graphs like line graphs and bar graphs, display two or more data clearly for easy comparison. This is important in communicating our findings to others and our understanding and analysis of the data.
Types of Graphical Representation of Data
Data is represented in different types of graphs such as plots, pies, diagrams, etc. They are as follows,
| Data Representation | Description |
|---|---|
|
A group of data represented with rectangular bars with lengths proportional to the values is a . The bars can either be vertically or horizontally plotted. | |
|
The is a type of graph in which a circle is divided into Sectors where each sector represents a proportion of the whole. Two main formulas used in pie charts are: | |
|
The represents the data in a form of series that is connected with a straight line. These series are called markers. | |
|
Data shown in the form of pictures is a . Pictorial symbols for words, objects, or phrases can be represented with different numbers. | |
|
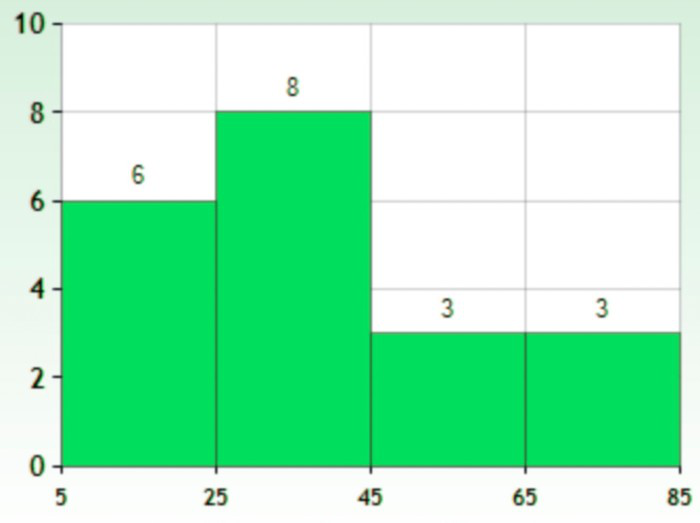
The is a type of graph where the diagram consists of rectangles, the area is proportional to the frequency of a variable and the width is equal to the class interval. Here is an example of a histogram. | |
|
The table in statistics showcases the data in ascending order along with their corresponding frequencies. The frequency of the data is often represented by f. | |
|
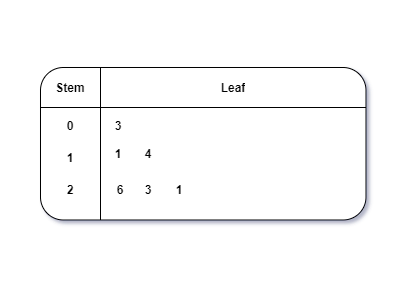
The is a way to represent quantitative data according to frequency ranges or frequency distribution. It is a graph that shows numerical data arranged in order. Each data value is broken into a stem and a leaf. | |
|
Scatter diagram or is a way of graphical representation by using Cartesian coordinates of two variables. The plot shows the relationship between two variables. |
Related Topics
Listed below are a few interesting topics that are related to the graphical representation of data, take a look.
- x and y graph
- Frequency Polygon
- Cumulative Frequency
Examples on Graphical Representation of Data
Example 1 : A pie chart is divided into 3 parts with the angles measuring as 2x, 8x, and 10x respectively. Find the value of x in degrees.
We know, the sum of all angles in a pie chart would give 360º as result. ⇒ 2x + 8x + 10x = 360º ⇒ 20 x = 360º ⇒ x = 360º/20 ⇒ x = 18º Therefore, the value of x is 18º.
Example 2: Ben is trying to read the plot given below. His teacher has given him stem and leaf plot worksheets. Can you help him answer the questions? i) What is the mode of the plot? ii) What is the mean of the plot? iii) Find the range.
| Stem | Leaf |
| 1 | 2 4 |
| 2 | 1 5 8 |
| 3 | 2 4 6 |
| 5 | 0 3 4 4 |
| 6 | 2 5 7 |
| 8 | 3 8 9 |
| 9 | 1 |
Solution: i) Mode is the number that appears often in the data. Leaf 4 occurs twice on the plot against stem 5.
Hence, mode = 54
ii) The sum of all data values is 12 + 14 + 21 + 25 + 28 + 32 + 34 + 36 + 50 + 53 + 54 + 54 + 62 + 65 + 67 + 83 + 88 + 89 + 91 = 958
To find the mean, we have to divide the sum by the total number of values.
Mean = Sum of all data values ÷ 19 = 958 ÷ 19 = 50.42
iii) Range = the highest value - the lowest value = 91 - 12 = 79
go to slide go to slide

Book a Free Trial Class
Practice Questions on Graphical Representation of Data
Faqs on graphical representation of data, what is graphical representation.
Graphical representation is a form of visually displaying data through various methods like graphs, diagrams, charts, and plots. It helps in sorting, visualizing, and presenting data in a clear manner through different types of graphs. Statistics mainly use graphical representation to show data.
What are the Different Types of Graphical Representation?
The different types of graphical representation of data are:
- Stem and leaf plot
- Scatter diagrams
- Frequency Distribution
Is the Graphical Representation of Numerical Data?
Yes, these graphical representations are numerical data that has been accumulated through various surveys and observations. The method of presenting these numerical data is called a chart. There are different kinds of charts such as a pie chart, bar graph, line graph, etc, that help in clearly showcasing the data.
What is the Use of Graphical Representation of Data?
Graphical representation of data is useful in clarifying, interpreting, and analyzing data plotting points and drawing line segments , surfaces, and other geometric forms or symbols.
What are the Ways to Represent Data?
Tables, charts, and graphs are all ways of representing data, and they can be used for two broad purposes. The first is to support the collection, organization, and analysis of data as part of the process of a scientific study.
What is the Objective of Graphical Representation of Data?
The main objective of representing data graphically is to display information visually that helps in understanding the information efficiently, clearly, and accurately. This is important to communicate the findings as well as analyze the data.
- School Guide
- Mathematics
- Number System and Arithmetic
- Trigonometry
- Probability
- Mensuration
- Maths Formulas
- Class 8 Maths Notes
- Class 9 Maths Notes
- Class 10 Maths Notes
- Class 11 Maths Notes
- Class 12 Maths Notes
- CBSE Class 9 Maths Revision Notes
Chapter 1: Number System
- Number System in Maths
- Natural Numbers | Definition, Examples & Properties
- Whole Numbers - Definition, Properties and Examples
- Rational Numbers: Definition, Examples, Worksheet
- Irrational Numbers: Definition, Examples, Symbol, Properties
- Real Numbers
- Decimal Expansion of Real Numbers
- Decimal Expansions of Rational Numbers
- Representation of Rational Numbers on the Number Line | Class 8 Maths
- Represent √3 on the number line
- Operations on Real Numbers
- Rationalization of Denominators
- Laws of Exponents for Real Numbers
Chapter 2: Polynomials
- Polynomials in One Variable | Polynomials Class 9 Maths
- Polynomial Formula
- Types of Polynomials (Based on Terms and Degrees)
- Zeros of Polynomial
- Factorization of Polynomial
- Remainder Theorem
- Factor Theorem
- Algebraic Identities
Chapter 3: Coordinate Geometry
- Coordinate Geometry
- Cartesian Coordinate System
- Cartesian Plane
Chapter 4: Linear equations in two variables
- Linear Equations in One Variable
- Linear Equation in Two Variables
- Graph of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Graphical Methods of Solving Pair of Linear Equations in Two Variables
- Equations of Lines Parallel to the x-axis and y-axis
Chapter 5: Introduction to Euclid's Geometry
- Euclidean Geometry
- Equivalent Version of Euclid’s Fifth Postulate
Chapter 6: Lines and Angles
- Lines and Angles
- Types of Angles
- Pairs of Angles - Lines & Angles
- Transversal Lines
- Angle Sum Property of a Triangle
Chapter 7: Triangles
- Triangles in Geometry
- Congruence of Triangles |SSS, SAS, ASA, and RHS Rules
- Theorem - Angle opposite to equal sides of an isosceles triangle are equal | Class 9 Maths
- Triangle Inequality Theorem, Proof & Applications
Chapter 8: Quadrilateral
- Angle Sum Property of a Quadrilateral
- Quadrilateral - Definition, Properties, Types, Formulas, Examples
- Introduction to Parallelogram: Properties, Types, and Theorem
- Rhombus: Definition, Properties, Formula and Examples
- Trapezium in Maths | Formulas, Properties & Examples
- Square in Maths - Area, Perimeter, Examples & Applications
- Kite - Quadrilaterals
- Properties of Parallelograms
- Mid Point Theorem
Chapter 9: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- Area of Triangle | Formula and Examples
- Area of Parallelogram | Definition, Formulas & Examples
- Figures on the Same Base and between the Same Parallels
Chapter 10: Circles
- Circles in Maths
- Radius of Circle
- Tangent to a Circle
- What is the longest chord of a Circle?
- Circumference of Circle - Definition, Perimeter Formula, and Examples
- Angle subtended by an arc at the centre of a circle
- What is Cyclic Quadrilateral
- The sum of opposite angles of a cyclic quadrilateral is 180° | Class 9 Maths Theorem
Chapter 11: Construction
- Basic Constructions - Angle Bisector, Perpendicular Bisector, Angle of 60°
- Construction of Triangles
Chapter 12: Heron's Formula
- Area of Equilateral Triangle
- Area of Isosceles Triangle
- Heron's Formula
- Applications of Heron's Formula
- Area of Quadrilateral
- Area of Polygons
Chapter 13: Surface Areas and Volumes
- Surface Area of Cuboid
- Volume of Cuboid | Formula and Examples
- Surface Area of Cube
- Volume of a Cube
- Surface Area of Cylinder | Curved and Total Surface Area of Cylinder
- Volume of a Cylinder: Formula, Definition and Examples
- Surface Area of Cone
- Volume of Cone: Formula, Derivation and Examples
- Surface Area of Sphere: Formula, Derivation and Solved Examples
- Volume of a Sphere
- Surface Area of a Hemisphere
- Volume of Hemisphere
Chapter 14: Statistics
- Collection and Presentation of Data
Graphical Representation of Data
- Bar Graphs and Histograms
- Central Tendency in Statistics- Mean, Median, Mode
- Mean, Median and Mode
Chapter 15: Probability
- Experimental Probability
- Empirical Probability
- CBSE Class 9 Maths Formulas
- NCERT Solutions for Class 9 Maths: Chapter Wise PDF 2024
- RD Sharma Class 9 Solutions
Graphical Representation of Data: Graphical Representation of Data,” where numbers and facts become lively pictures and colorful diagrams . Instead of staring at boring lists of numbers, we use fun charts, cool graphs, and interesting visuals to understand information better. In this exciting concept of data visualization, we’ll learn about different kinds of graphs, charts, and pictures that help us see patterns and stories hidden in data.
There is an entire branch in mathematics dedicated to dealing with collecting, analyzing, interpreting, and presenting numerical data in visual form in such a way that it becomes easy to understand and the data becomes easy to compare as well, the branch is known as Statistics .
The branch is widely spread and has a plethora of real-life applications such as Business Analytics, demography, Astro statistics, and so on . In this article, we have provided everything about the graphical representation of data, including its types, rules, advantages, etc.
Table of Content
What is Graphical Representation
Types of graphical representations, line graphs, histograms , stem and leaf plot , box and whisker plot .
- Graphical Representations used in Maths
Value-Based or Time Series Graphs
Frequency based, principles of graphical representations, advantages and disadvantages of using graphical system, general rules for graphical representation of data, frequency polygon, solved examples on graphical representation of data.
Graphics Representation is a way of representing any data in picturized form . It helps a reader to understand the large set of data very easily as it gives us various data patterns in visualized form.
There are two ways of representing data,
- Pictorial Representation through graphs.
They say, “A picture is worth a thousand words”. It’s always better to represent data in a graphical format. Even in Practical Evidence and Surveys, scientists have found that the restoration and understanding of any information is better when it is available in the form of visuals as Human beings process data better in visual form than any other form.
Does it increase the ability 2 times or 3 times? The answer is it increases the Power of understanding 60,000 times for a normal Human being, the fact is amusing and true at the same time.
Check: Graph and its representations
Comparison between different items is best shown with graphs, it becomes easier to compare the crux of the data about different items. Let’s look at all the different types of graphical representations briefly:
A line graph is used to show how the value of a particular variable changes with time. We plot this graph by connecting the points at different values of the variable. It can be useful for analyzing the trends in the data and predicting further trends.
A bar graph is a type of graphical representation of the data in which bars of uniform width are drawn with equal spacing between them on one axis (x-axis usually), depicting the variable. The values of the variables are represented by the height of the bars.
This is similar to bar graphs, but it is based frequency of numerical values rather than their actual values. The data is organized into intervals and the bars represent the frequency of the values in that range. That is, it counts how many values of the data lie in a particular range.
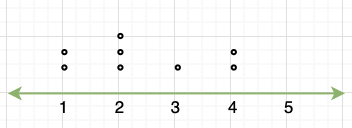
It is a plot that displays data as points and checkmarks above a number line, showing the frequency of the point.
This is a type of plot in which each value is split into a “leaf”(in most cases, it is the last digit) and “stem”(the other remaining digits). For example: the number 42 is split into leaf (2) and stem (4).
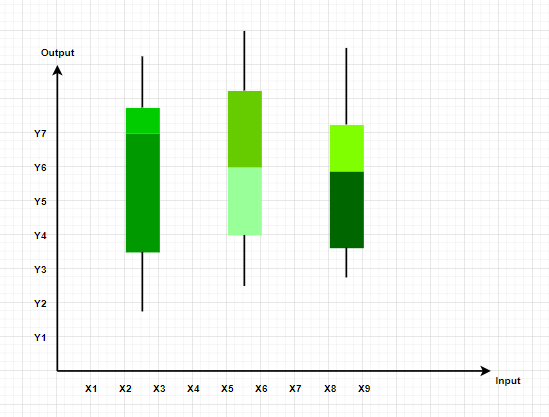
These plots divide the data into four parts to show their summary. They are more concerned about the spread, average, and median of the data.
It is a type of graph which represents the data in form of a circular graph. The circle is divided such that each portion represents a proportion of the whole.

Graphical Representations used in Math’s
Graphs in Math are used to study the relationships between two or more variables that are changing. Statistical data can be summarized in a better way using graphs. There are basically two lines of thoughts of making graphs in maths:
- Value-Based or Time Series Graphs
These graphs allow us to study the change of a variable with respect to another variable within a given interval of time. The variables can be anything. Time Series graphs study the change of variable with time. They study the trends, periodic behavior, and patterns in the series. We are more concerned with the values of the variables here rather than the frequency of those values.
Example: Line Graph
These kinds of graphs are more concerned with the distribution of data. How many values lie between a particular range of the variables, and which range has the maximum frequency of the values. They are used to judge a spread and average and sometimes median of a variable under study.
Also read: Types of Statistical Data
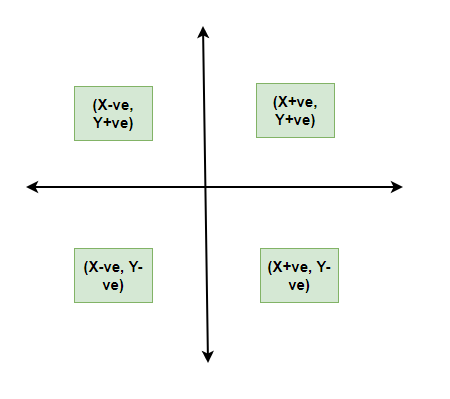
- All types of graphical representations follow algebraic principles.
- When plotting a graph, there’s an origin and two axes.
- The x-axis is horizontal, and the y-axis is vertical.
- The axes divide the plane into four quadrants.
- The origin is where the axes intersect.
- Positive x-values are to the right of the origin; negative x-values are to the left.
- Positive y-values are above the x-axis; negative y-values are below.
- It gives us a summary of the data which is easier to look at and analyze.
- It saves time.
- We can compare and study more than one variable at a time.
Disadvantages
- It usually takes only one aspect of the data and ignores the other. For example, A bar graph does not represent the mean, median, and other statistics of the data.
- Interpretation of graphs can vary based on individual perspectives, leading to subjective conclusions.
- Poorly constructed or misleading visuals can distort data interpretation and lead to incorrect conclusions.
Check : Diagrammatic and Graphic Presentation of Data
We should keep in mind some things while plotting and designing these graphs. The goal should be a better and clear picture of the data. Following things should be kept in mind while plotting the above graphs:
- Whenever possible, the data source must be mentioned for the viewer.
- Always choose the proper colors and font sizes. They should be chosen to keep in mind that the graphs should look neat.
- The measurement Unit should be mentioned in the top right corner of the graph.
- The proper scale should be chosen while making the graph, it should be chosen such that the graph looks accurate.
- Last but not the least, a suitable title should be chosen.
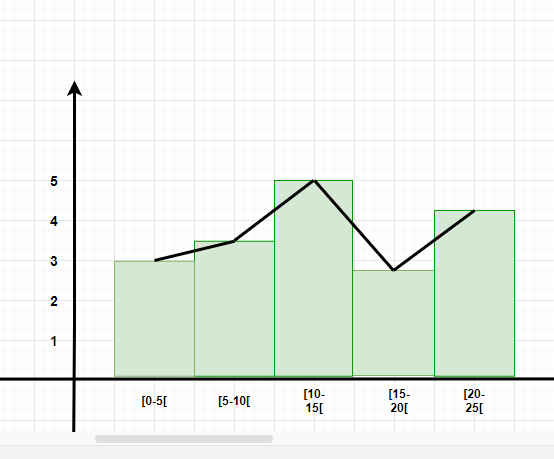
A frequency polygon is a graph that is constructed by joining the midpoint of the intervals. The height of the interval or the bin represents the frequency of the values that lie in that interval.
Question 1: What are different types of frequency-based plots?
Types of frequency-based plots: Histogram Frequency Polygon Box Plots
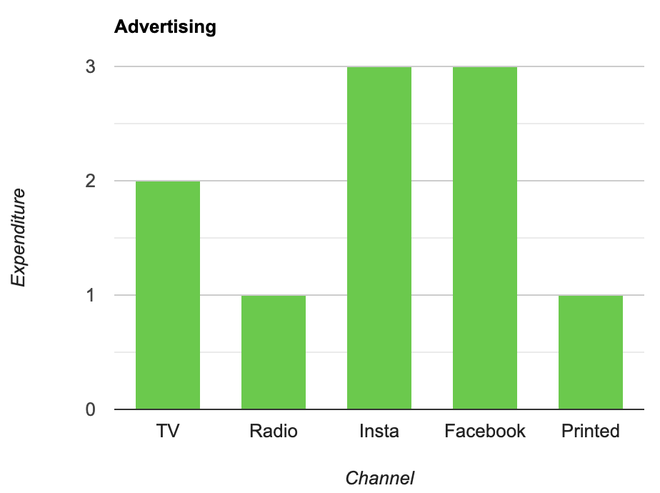
Question 2: A company with an advertising budget of Rs 10,00,00,000 has planned the following expenditure in the different advertising channels such as TV Advertisement, Radio, Facebook, Instagram, and Printed media. The table represents the money spent on different channels.
Draw a bar graph for the following data.
- Put each of the channels on the x-axis
- The height of the bars is decided by the value of each channel.
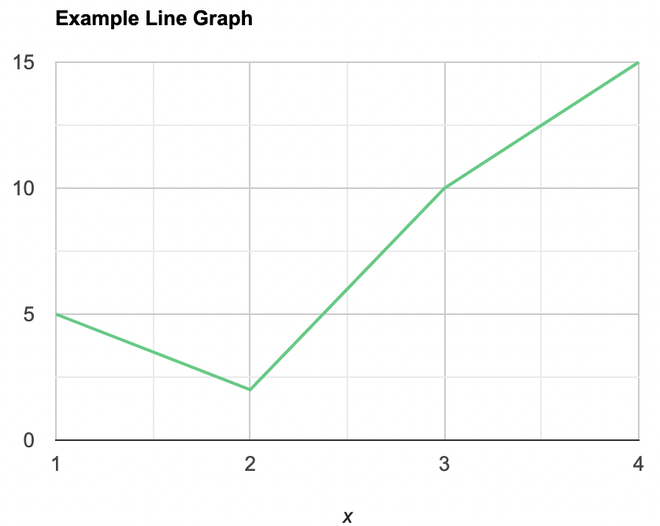
Question 3: Draw a line plot for the following data
- Put each of the x-axis row value on the x-axis
- joint the value corresponding to the each value of the x-axis.
Question 4: Make a frequency plot of the following data:
- Draw the class intervals on the x-axis and frequencies on the y-axis.
- Calculate the midpoint of each class interval.
| Class Interval | Mid Point | Frequency |
| 0-3 | 1.5 | 3 |
| 3-6 | 4.5 | 4 |
| 6-9 | 7.5 | 2 |
| 9-12 | 10.5 | 6 |
Now join the mid points of the intervals and their corresponding frequencies on the graph.
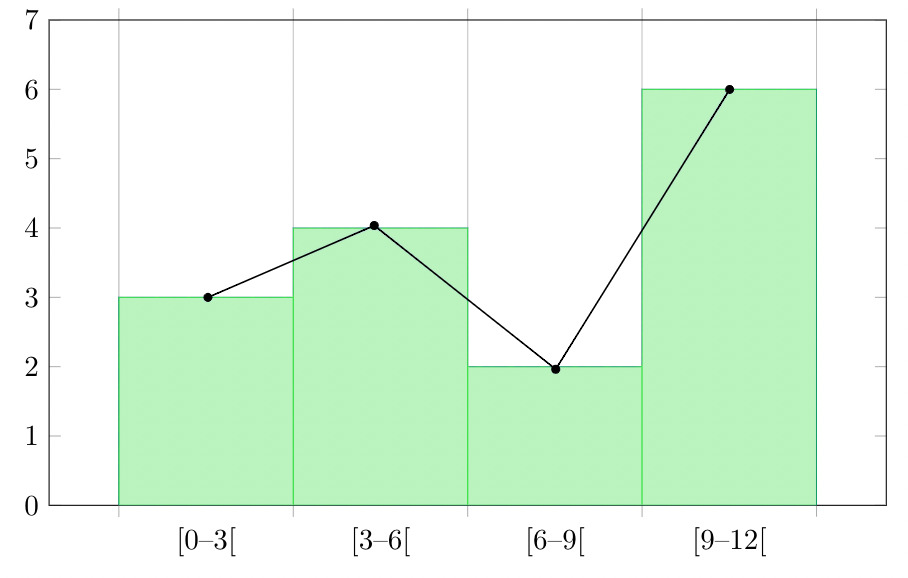
This graph shows both the histogram and frequency polygon for the given distribution.
Related Article:
Graphical Representation of Data| Practical Work in Geography Class 12 What are the different ways of Data Representation What are the different ways of Data Representation? Charts and Graphs for Data Visualization
Conclusion of Graphical Representation
Graphical representation is a powerful tool for understanding data, but it’s essential to be aware of its limitations. While graphs and charts can make information easier to grasp, they can also be subjective, complex, and potentially misleading . By using graphical representations wisely and critically, we can extract valuable insights from data, empowering us to make informed decisions with confidence.
Graphical Representation of Data – FAQs
What are the advantages of using graphs to represent data.
Graphs offer visualization, clarity, and easy comparison of data, aiding in outlier identification and predictive analysis.
What are the common types of graphs used for data representation?
Common graph types include bar, line, pie, histogram, and scatter plots , each suited for different data representations and analysis purposes.
How do you choose the most appropriate type of graph for your data?
Select a graph type based on data type, analysis objective, and audience familiarity to effectively convey information and insights.
How do you create effective labels and titles for graphs?
Use descriptive titles, clear axis labels with units, and legends to ensure the graph communicates information clearly and concisely.
How do you interpret graphs to extract meaningful insights from data?
Interpret graphs by examining trends, identifying outliers, comparing data across categories, and considering the broader context to draw meaningful insights and conclusions.
Please Login to comment...
Similar reads.
- Maths-Class-9
- School Learning
Improve your Coding Skills with Practice
What kind of Experience do you want to share?
- Math Article
Graphical Representation

Graphical Representation is a way of analysing numerical data. It exhibits the relation between data, ideas, information and concepts in a diagram. It is easy to understand and it is one of the most important learning strategies. It always depends on the type of information in a particular domain. There are different types of graphical representation. Some of them are as follows:
- Line Graphs – Line graph or the linear graph is used to display the continuous data and it is useful for predicting future events over time.
- Bar Graphs – Bar Graph is used to display the category of data and it compares the data using solid bars to represent the quantities.
- Histograms – The graph that uses bars to represent the frequency of numerical data that are organised into intervals. Since all the intervals are equal and continuous, all the bars have the same width.
- Line Plot – It shows the frequency of data on a given number line. ‘ x ‘ is placed above a number line each time when that data occurs again.
- Frequency Table – The table shows the number of pieces of data that falls within the given interval.
- Circle Graph – Also known as the pie chart that shows the relationships of the parts of the whole. The circle is considered with 100% and the categories occupied is represented with that specific percentage like 15%, 56%, etc.
- Stem and Leaf Plot – In the stem and leaf plot, the data are organised from least value to the greatest value. The digits of the least place values from the leaves and the next place value digit forms the stems.
- Box and Whisker Plot – The plot diagram summarises the data by dividing into four parts. Box and whisker show the range (spread) and the middle ( median) of the data.
General Rules for Graphical Representation of Data
There are certain rules to effectively present the information in the graphical representation. They are:
- Suitable Title: Make sure that the appropriate title is given to the graph which indicates the subject of the presentation.
- Measurement Unit: Mention the measurement unit in the graph.
- Proper Scale: To represent the data in an accurate manner, choose a proper scale.
- Index: Index the appropriate colours, shades, lines, design in the graphs for better understanding.
- Data Sources: Include the source of information wherever it is necessary at the bottom of the graph.
- Keep it Simple: Construct a graph in an easy way that everyone can understand.
- Neat: Choose the correct size, fonts, colours etc in such a way that the graph should be a visual aid for the presentation of information.
Graphical Representation in Maths
In Mathematics, a graph is defined as a chart with statistical data, which are represented in the form of curves or lines drawn across the coordinate point plotted on its surface. It helps to study the relationship between two variables where it helps to measure the change in the variable amount with respect to another variable within a given interval of time. It helps to study the series distribution and frequency distribution for a given problem. There are two types of graphs to visually depict the information. They are:
- Time Series Graphs – Example: Line Graph
- Frequency Distribution Graphs – Example: Frequency Polygon Graph
Principles of Graphical Representation
Algebraic principles are applied to all types of graphical representation of data. In graphs, it is represented using two lines called coordinate axes. The horizontal axis is denoted as the x-axis and the vertical axis is denoted as the y-axis. The point at which two lines intersect is called an origin ‘O’. Consider x-axis, the distance from the origin to the right side will take a positive value and the distance from the origin to the left side will take a negative value. Similarly, for the y-axis, the points above the origin will take a positive value, and the points below the origin will a negative value.
Generally, the frequency distribution is represented in four methods, namely
- Smoothed frequency graph
- Pie diagram
- Cumulative or ogive frequency graph
- Frequency Polygon
Merits of Using Graphs
Some of the merits of using graphs are as follows:
- The graph is easily understood by everyone without any prior knowledge.
- It saves time
- It allows us to relate and compare the data for different time periods
- It is used in statistics to determine the mean, median and mode for different data, as well as in the interpolation and the extrapolation of data.
Example for Frequency polygonGraph
Here are the steps to follow to find the frequency distribution of a frequency polygon and it is represented in a graphical way.
- Obtain the frequency distribution and find the midpoints of each class interval.
- Represent the midpoints along x-axis and frequencies along the y-axis.
- Plot the points corresponding to the frequency at each midpoint.
- Join these points, using lines in order.
- To complete the polygon, join the point at each end immediately to the lower or higher class marks on the x-axis.
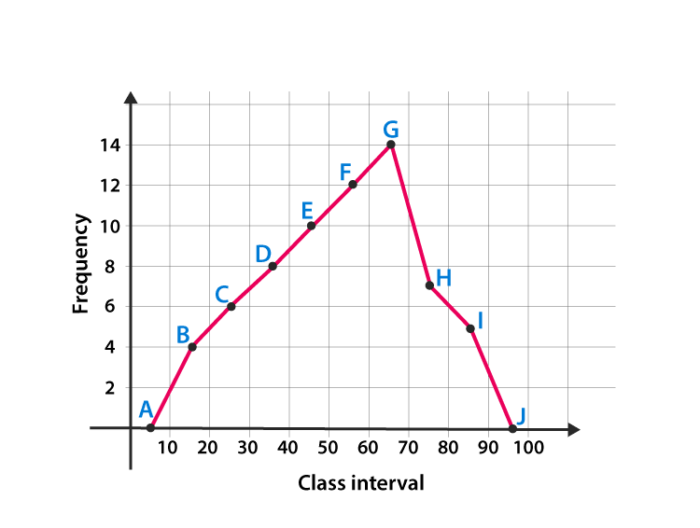
Draw the frequency polygon for the following data
| 10-20 | 20-30 | 30-40 | 40-50 | 50-60 | 60-70 | 70-80 | 80-90 | |
| 4 | 6 | 8 | 10 | 12 | 14 | 7 | 5 |
Mark the class interval along x-axis and frequencies along the y-axis.
Let assume that class interval 0-10 with frequency zero and 90-100 with frequency zero.
Now calculate the midpoint of the class interval.
| 0-10 | 5 | 0 |
| 10-20 | 15 | 4 |
| 20-30 | 25 | 6 |
| 30-40 | 35 | 8 |
| 40-50 | 45 | 10 |
| 50-60 | 55 | 12 |
| 60-70 | 65 | 14 |
| 70-80 | 75 | 7 |
| 80-90 | 85 | 5 |
| 90-100 | 95 | 0 |
Using the midpoint and the frequency value from the above table, plot the points A (5, 0), B (15, 4), C (25, 6), D (35, 8), E (45, 10), F (55, 12), G (65, 14), H (75, 7), I (85, 5) and J (95, 0).
To obtain the frequency polygon ABCDEFGHIJ, draw the line segments AB, BC, CD, DE, EF, FG, GH, HI, IJ, and connect all the points.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of graphical representation.
Some of the various types of graphical representation include:
- Line Graphs
- Frequency Table
- Circle Graph, etc.
Read More: Types of Graphs
What are the Advantages of Graphical Method?
Some of the advantages of graphical representation are:
- It makes data more easily understandable.
- It saves time.
- It makes the comparison of data more efficient.
| MATHS Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Very useful for understand the basic concepts in simple and easy way. Its very useful to all students whether they are school students or college sudents
Thanks very much for the information
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

Guide On Graphical Representation of Data – Types, Importance, Rules, Principles And Advantages
What are Graphs and Graphical Representation?
Graphs, in the context of data visualization, are visual representations of data using various graphical elements such as charts, graphs, and diagrams. Graphical representation of data , often referred to as graphical presentation or simply graphs which plays a crucial role in conveying information effectively.
Principles of Graphical Representation
Effective graphical representation follows certain fundamental principles that ensure clarity, accuracy, and usability:Clarity : The primary goal of any graph is to convey information clearly and concisely. Graphs should be designed in a way that allows the audience to quickly grasp the key points without confusion.
- Simplicity: Simplicity is key to effective data visualization. Extraneous details and unnecessary complexity should be avoided to prevent confusion and distraction.
- Relevance: Include only relevant information that contributes to the understanding of the data. Irrelevant or redundant elements can clutter the graph.
- Visualization: Select a graph type that is appropriate for the supplied data. Different graph formats, like bar charts, line graphs, and scatter plots, are appropriate for various sorts of data and relationships.
Rules for Graphical Representation of Data
Creating effective graphical representations of data requires adherence to certain rules:
- Select the Right Graph: Choosing the appropriate type of graph is essential. For example, bar charts are suitable for comparing categories, while line charts are better for showing trends over time.
- Label Axes Clearly: Axis labels should be descriptive and include units of measurement where applicable. Clear labeling ensures the audience understands the data’s context.
- Use Appropriate Colors: Colors can enhance understanding but should be used judiciously. Avoid overly complex color schemes and ensure that color choices are accessible to all viewers.
- Avoid Misleading Scaling: Scale axes appropriately to prevent exaggeration or distortion of data. Misleading scaling can lead to incorrect interpretations.
- Include Data Sources: Always provide the source of your data. This enhances transparency and credibility.
Importance of Graphical Representation of Data
Graphical representation of data in statistics is of paramount importance for several reasons:
- Enhances Understanding: Graphs simplify complex data, making it more accessible and understandable to a broad audience, regardless of their statistical expertise.
- Helps Decision-Making: Visual representations of data enable informed decision-making. Decision-makers can easily grasp trends and insights, leading to better choices.
- Engages the Audience: Graphs capture the audience’s attention more effectively than raw data. This engagement is particularly valuable when presenting findings or reports.
- Universal Language: Graphs serve as a universal language that transcends linguistic barriers. They can convey information to a global audience without the need for translation.
Advantages of Graphical Representation
The advantages of graphical representation of data extend to various aspects of communication and analysis:
- Clarity: Data is presented visually, improving clarity and reducing the likelihood of misinterpretation.
- Efficiency: Graphs enable the quick absorption of information. Key insights can be found in seconds, saving time and effort.
- Memorability: Visuals are more memorable than raw data. Audiences are more likely to retain information presented graphically.
- Problem-Solving: Graphs help in identifying and solving problems by revealing trends, correlations, and outliers that may require further investigation.
Use of Graphical Representations
Graphical representations find applications in a multitude of fields:
- Business: In the business world, graphs are used to illustrate financial data, track performance metrics, and present market trends. They are invaluable tools for strategic decision-making.
- Science: Scientists employ graphs to visualize experimental results, depict scientific phenomena, and communicate research findings to both colleagues and the general public.
- Education: Educators utilize graphs to teach students about data analysis, statistics, and scientific concepts. Graphs make learning more engaging and memorable.
- Journalism: Journalists rely on graphs to support their stories with data-driven evidence. Graphs make news articles more informative and impactful.
Types of Graphical Representation
There exists a diverse array of graphical representations, each suited to different data types and purposes. Common types include:
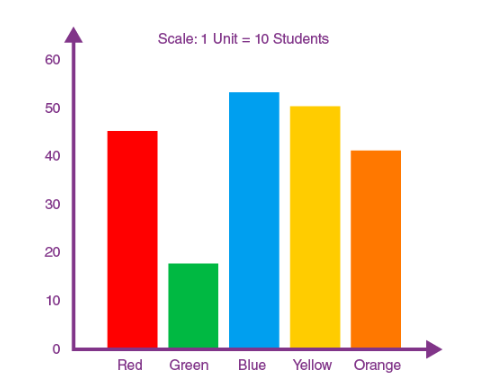
1.Bar Charts:
Used to compare categories or discrete data points, often side by side.
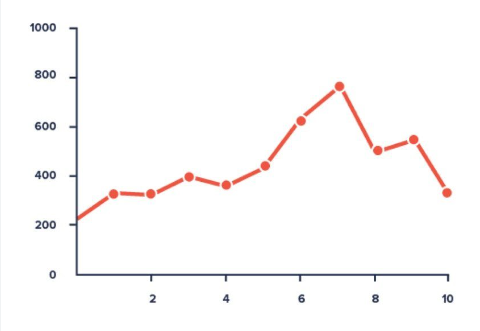
2. Line Charts:
Ideal for showing trends and changes over time, such as stock market performance or temperature fluctuations.
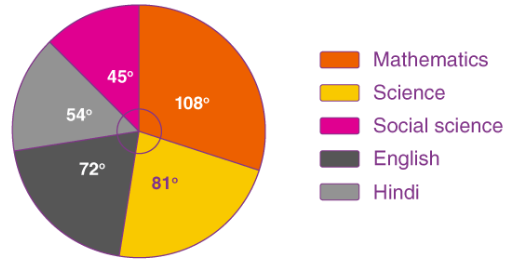
3. Pie Charts:
Display parts of a whole, useful for illustrating proportions or percentages.
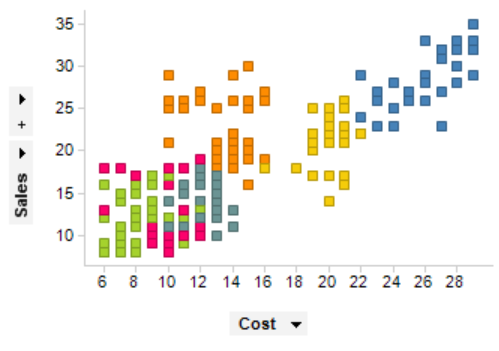
4. Scatter Plots:
Reveal relationships between two variables and help identify correlations.
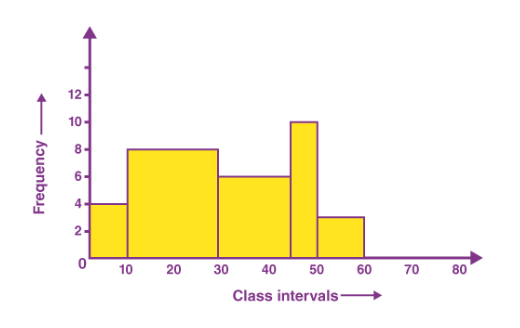
5. Histograms:
Depict the distribution of data, especially in the context of continuous variables.
In conclusion, the graphical representation of data is an indispensable tool for simplifying complex information, aiding in decision-making, and enhancing communication across diverse fields. By following the principles and rules of effective data visualization, individuals and organizations can harness the power of graphs to convey their messages, support their arguments, and drive informed actions.
Download PPT of Graphical Representation
Video On Graphical Representation
FAQs on Graphical Representation of Data
What is the purpose of graphical representation.
Graphical representation serves the purpose of simplifying complex data, making it more accessible and understandable through visual means.
Why are graphs and diagrams important?
Graphs and diagrams are crucial because they provide visual clarity, aiding in the comprehension and retention of information.
How do graphs help learning?
Graphs engage learners by presenting information visually, which enhances understanding and retention, particularly in educational settings.
Who uses graphs?
Professionals in various fields, including scientists, analysts, educators, and business leaders, use graphs to convey data effectively and support decision-making.
Where are graphs used in real life?
Graphs are used in real-life scenarios such as business reports, scientific research, news articles, and educational materials to make data more accessible and meaningful.
Why are graphs important in business?
In business, graphs are vital for analyzing financial data, tracking performance metrics, and making informed decisions, contributing to success.
Leave a comment
Cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Related Posts

Best Google AdWords Consultants in India...
What is a Google Ads Consultant? A Google Ads Consultant is an expert who specializes in delivering expertise and advice on Google Ads, which is Google’s online advertising medium. Google Ads permits companies to develop and run ads that are visible on Google’s search engine and other Google platforms. The function of a Google Ads […]

Best PPC Consultants in India –...
What Is a PPC Consultant? A PPC consultant or a pay per click consultant is an expert who specializes in handling and optimizing PPC advertisement drives for companies. PPC is a digital marketing model where advertisers pay a price each time their ad is clicked. Standard PPC mediums include Bing Ads, Google Ads, and social media advertisement platforms like […]

Top 20 Generic Digital Marketing Interview...
1. What is Digital Marketing? Digital marketing is also known as online marketing which means promoting and selling products or services to potential customers using the internet and online platforms. It includes email, social media, and web-based advertising, but also text and multimedia messages as a marketing channel. 2. What are the types of Digital […]

Best Social Media Consultants in India...
What Is a Social Media Consultant? A social media advisor is a specialist who delivers direction, recommendation, and assistance linked to the usage of social media for people, companies, or associations. Their prime objective is to support customers effectively by employing social media platforms to gain specific objectives, such as improving brand awareness, entertaining target […]

Gaurav Mittal
Had a great time spent with some awesome learning at The Digital Education Institute. It really helped me to build my career and i am thankful to the institute for making me what i am today.
Company where our students are working

Enroll Now for 2 Hour Free Digital Marketing Class
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry
Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry . Lorem Ipsum is simply dummy text of the printing and typesetting industry
- Graphic Presentation of Data
Apart from diagrams, Graphic presentation is another way of the presentation of data and information. Usually, graphs are used to present time series and frequency distributions. In this article, we will look at the graphic presentation of data and information along with its merits, limitations , and types.
Suggested Videos
Construction of a graph.
The graphic presentation of data and information offers a quick and simple way of understanding the features and drawing comparisons. Further, it is an effective analytical tool and a graph can help us in finding the mode, median, etc.
We can locate a point in a plane using two mutually perpendicular lines – the X-axis (the horizontal line) and the Y-axis (the vertical line). Their point of intersection is the Origin .
We can locate the position of a point in terms of its distance from both these axes. For example, if a point P is 3 units away from the Y-axis and 5 units away from the X-axis, then its location is as follows:

Browse more Topics under Descriptive Statistics
- Definition and Characteristics of Statistics
- Stages of Statistical Enquiry
- Importance and Functions of Statistics
- Nature of Statistics – Science or Art?
- Application of Statistics
- Law of Statistics and Distrust of Statistics
- Meaning and Types of Data
- Methods of Collecting Data
- Sample Investigation
- Classification of Data
- Tabulation of Data
- Frequency Distribution of Data
- Diagrammatic Presentation of Data
- Measures of Central Tendency
- Mean Median Mode
- Measures of Dispersion
- Standard Deviation
- Variance Analysis
Some points to remember:
- We measure the distance of the point from the Y-axis along the X-axis. Similarly, we measure the distance of the point from the X-axis along the Y-axis. Therefore, to measure 3 units from the Y-axis, we move 3 units along the X-axis and likewise for the other coordinate .
- We then draw perpendicular lines from these two points.
- The point where the perpendiculars intersect is the position of the point P.
- We denote it as follows (3,5) or (abscissa, ordinate). Together, they are the coordinates of the point P.
- The four parts of the plane are Quadrants.
- Also, we can plot different points for a different pair of values.
General Rules for Graphic Presentation of Data and Information
There are certain guidelines for an attractive and effective graphic presentation of data and information. These are as follows:
- Suitable Title – Ensure that you give a suitable title to the graph which clearly indicates the subject for which you are presenting it.
- Unit of Measurement – Clearly state the unit of measurement below the title.
- Suitable Scale – Choose a suitable scale so that you can represent the entire data in an accurate manner.
- Index – Include a brief index which explains the different colors and shades, lines and designs that you have used in the graph. Also, include a scale of interpretation for better understanding.
- Data Sources – Wherever possible, include the sources of information at the bottom of the graph.
- Keep it Simple – You should construct a graph which even a layman (without any exposure in the areas of statistics or mathematics) can understand.
- Neat – A graph is a visual aid for the presentation of data and information. Therefore, you must keep it neat and attractive. Choose the right size, right lettering, and appropriate lines, colors, dashes, etc.
Merits of a Graph
- The graph presents data in a manner which is easier to understand.
- It allows us to present statistical data in an attractive manner as compared to tables. Users can understand the main features, trends, and fluctuations of the data at a glance.
- A graph saves time.
- It allows the viewer to compare data relating to two different time-periods or regions.
- The viewer does not require prior knowledge of mathematics or statistics to understand a graph.
- We can use a graph to locate the mode, median, and mean values of the data.
- It is useful in forecasting, interpolation, and extrapolation of data.
Limitations of a Graph
- A graph lacks complete accuracy of facts.
- It depicts only a few selected characteristics of the data.
- We cannot use a graph in support of a statement.
- A graph is not a substitute for tables.
- Usually, laymen find it difficult to understand and interpret a graph.
- Typically, a graph shows the unreasonable tendency of the data and the actual values are not clear.
Types of Graphs
Graphs are of two types:
- Time Series graphs
- Frequency Distribution graphs
Time Series Graphs
A time series graph or a “ histogram ” is a graph which depicts the value of a variable over a different point of time. In a time series graph, time is the most important factor and the variable is related to time. It helps in the understanding and analysis of the changes in the variable at a different point of time. Many statisticians and businessmen use these graphs because they are easy to understand and also because they offer complex information in a simple manner.
Further, constructing a time series graph does not require a user with technical skills. Here are some major steps in the construction of a time series graph:
- Represent time on the X-axis and the value of the variable on the Y-axis.
- Start the Y-value with zero and devise a suitable scale which helps you present the whole data in the given space.
- Plot the values of the variable and join different point with a straight line.
- You can plot multiple variables through different lines.
You can use a line graph to summarize how two pieces of information are related and how they vary with each other.
- You can compare multiple continuous data-sets easily
- You can infer the interim data from the graph line
Disadvantages
- It is only used with continuous data.
Use of a false Base Line
Usually, in a graph, the vertical line starts from the Origin. However, in some cases, a false Base Line is used for a better representation of the data. There are two scenarios where you should use a false Base Line:
- To magnify the minor fluctuation in the time series data
- To economize the space
Net Balance Graph
If you have to show the net balance of income and expenditure or revenue and costs or imports and exports, etc., then you must use a net balance graph. You can use different colors or shades for positive and negative differences.
Frequency Distribution Graphs
Let’s look at the different types of frequency distribution graphs.
A histogram is a graph of a grouped frequency distribution. In a histogram, we plot the class intervals on the X-axis and their respective frequencies on the Y-axis. Further, we create a rectangle on each class interval with its height proportional to the frequency density of the class.

Frequency Polygon or Histograph
A frequency polygon or a Histograph is another way of representing a frequency distribution on a graph. You draw a frequency polygon by joining the midpoints of the upper widths of the adjacent rectangles of the histogram with straight lines.

Frequency Curve
When you join the verticals of a polygon using a smooth curve, then the resulting figure is a Frequency Curve. As the number of observations increase, we need to accommodate more classes. Therefore, the width of each class reduces. In such a scenario, the variable tends to become continuous and the frequency polygon starts taking the shape of a frequency curve.
Cumulative Frequency Curve or Ogive
A cumulative frequency curve or Ogive is the graphical representation of a cumulative frequency distribution. Since a cumulative frequency is either of a ‘less than’ or a ‘more than’ type, Ogives are of two types too – ‘less than ogive’ and ‘more than ogive’.

Scatter Diagram
A scatter diagram or a dot chart enables us to find the nature of the relationship between the variables. If the plotted points are scattered a lot, then the relationship between the two variables is lesser.

Solved Question
Q1. What are the general rules for the graphic presentation of data and information?
Answer: The general rules for the graphic presentation of data are:
- Use a suitable title
- Clearly specify the unit of measurement
- Ensure that you choose a suitable scale
- Provide an index specifying the colors, lines, and designs used in the graph
- If possible, provide the sources of information at the bottom of the graph
- Keep the graph simple and neat.
Customize your course in 30 seconds
Which class are you in.

Descriptive Statistics
- Nature of Statistics – Science or Art?
2 responses to “Stages of Statistical Enquiry”
Im trying to find out if my mother ALICE Desjarlais is registered with the Red Pheasant Reserve, I applied with Metie Urban Housing and I need my Metie card. Is there anyway you can help me.
Quite useful details about statistics. I’d also like to add one point. If you need professional help with a statistics project? Find a professional in minutes!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Download the App


Graphical Representation
Graphical representation definition.
Graphical representation refers to the use of charts and graphs to visually display, analyze, clarify, and interpret numerical data, functions, and other qualitative structures.

What is Graphical Representation?
Graphical representation refers to the use of intuitive charts to clearly visualize and simplify data sets. Data is ingested into graphical representation of data software and then represented by a variety of symbols, such as lines on a line chart, bars on a bar chart, or slices on a pie chart, from which users can gain greater insight than by numerical analysis alone.
Representational graphics can quickly illustrate general behavior and highlight phenomenons, anomalies, and relationships between data points that may otherwise be overlooked, and may contribute to predictions and better, data-driven decisions. The types of representational graphics used will depend on the type of data being explored.
Types of Graphical Representation
Data charts are available in a wide variety of maps, diagrams, and graphs that typically include textual titles and legends to denote the purpose, measurement units, and variables of the chart. Choosing the most appropriate chart depends on a variety of different factors -- the nature of the data, the purpose of the chart, and whether a graphical representation of qualitative data or a graphical representation of quantitative data is being depicted. There are dozens of different formats for graphical representation of data. Some of the most popular charts include:
- Bar Graph -- contains a vertical axis and horizontal axis and displays data as rectangular bars with lengths proportional to the values that they represent; a useful visual aid for marketing purposes
- Choropleth -- thematic map in which an aggregate summary of a geographic characteristic within an area is represented by patterns of shading proportionate to a statistical variable
- Flow Chart -- diagram that depicts a workflow graphical representation with the use of arrows and geometric shapes; a useful visual aid for business and finance purposes
- Heatmap -- a colored, two-dimensional matrix of cells in which each cell represents a grouping of data and each cell’s color indicates its relative value
- Histogram – frequency distribution and graphical representation uses adjacent vertical bars erected over discrete intervals to represent the data frequency within a given interval; a useful visual aid for meteorology and environment purposes
- Line Graph – displays continuous data; ideal for predicting future events over time; a useful visual aid for marketing purposes
- Pie Chart -- shows percentage values as a slice of pie; a useful visual aid for marketing purposes
- Pointmap -- CAD & GIS contract mapping and drafting solution that visualizes the location of data on a map by plotting geographic latitude and longitude data
- Scatter plot -- a diagram that shows the relationship between two sets of data, where each dot represents individual pieces of data and each axis represents a quantitative measure
- Stacked Bar Graph -- a graph in which each bar is segmented into parts, with the entire bar representing the whole, and each segment representing different categories of that whole; a useful visual aid for political science and sociology purposes
- Timeline Chart -- a long bar labelled with dates paralleling it that display a list of events in chronological order, a useful visual aid for history charting purposes
- Tree Diagram -- a hierarchical genealogical tree that illustrates a family structure; a useful visual aid for history charting purposes
- Venn Diagram -- consists of multiple overlapping usually circles, each representing a set; the default inner join graphical representation
Proprietary and open source software for graphical representation of data is available in a wide variety of programming languages. Software packages often provide spreadsheets equipped with built-in charting functions.
Advantages and Disadvantages of Graphical Representation of Data
Tabular and graphical representation of data are a vital component in analyzing and understanding large quantities of numerical data and the relationship between data points. Data visualization is one of the most fundamental approaches to data analysis, providing an intuitive and universal means to visualize, abstract, and share complex data patterns. The primary advantages of graphical representation of data are:
- Facilitates and improves learning: graphics make data easy to understand and eliminate language and literacy barriers
- Understanding content: visuals are more effective than text in human understanding
- Flexibility of use: graphical representation can be leveraged in nearly every field involving data
- Increases structured thinking: users can make quick, data-driven decisions at a glance with visual aids
- Supports creative, personalized reports for more engaging and stimulating visual presentations
- Improves communication: analyzing graphs that highlight relevant themes is significantly faster than reading through a descriptive report line by line
- Shows the whole picture: an instantaneous, full view of all variables, time frames, data behavior and relationships
Disadvantages of graphical representation of data typically concern the cost of human effort and resources, the process of selecting the most appropriate graphical and tabular representation of data, greater design complexity of visualizing data, and the potential for human bias.
Why Graphical Representation of Data is Important
Graphic visual representation of information is a crucial component in understanding and identifying patterns and trends in the ever increasing flow of data. Graphical representation enables the quick analysis of large amounts of data at one time and can aid in making predictions and informed decisions. Data visualizations also make collaboration significantly more efficient by using familiar visual metaphors to illustrate relationships and highlight meaning, eliminating complex, long-winded explanations of an otherwise chaotic-looking array of figures.
Data only has value once its significance has been revealed and consumed, and its consumption is best facilitated with graphical representation tools that are designed with human cognition and perception in mind. Human visual processing is very efficient at detecting relationships and changes between sizes, shapes, colors, and quantities. Attempting to gain insight from numerical data alone, especially in big data instances in which there may be billions of rows of data, is exceedingly cumbersome and inefficient.
Does HEAVY.AI Offer a Graphical Representation Solution?
HEAVY.AI's visual analytics platform is an interactive data visualization client that works seamlessly with server-side technologies HEAVY.AIDB and Render to enable data science analysts to easily visualize and instantly interact with massive datasets. Analysts can interact with conventional charts and data tables, as well as big data graphical representations such as massive-scale scatterplots and geo charts. Data visualization contributes to a broad range of use cases, including performance analysis in business and guiding research in academia.
Data Presentation
Josée Dupuis, PhD, Professor of Biostatistics, Boston University School of Public Health
Wayne LaMorte, MD, PhD, MPH, Professor of Epidemiology, Boston University School of Public Health
Introduction
| "Modern data graphics can do much more than simply substitute for small statistical tables. At their best, graphics are instruments for reasoning about quantitative information. Often the most effective was to describe, explore, and summarize a set of numbers - even a very large set - is to look at pictures of those numbers. Furthermore, of all methods for analyzing and communicating statistical information, well-designed data graphics are usually the simplest and at the same time the most powerful." Edward R. Tufte in the introduction to "The Visual Display of Quantitative Information" |
While graphical summaries of data can certainly be powerful ways of communicating results clearly and unambiguously in a way that facilitates our ability to think about the information, poorly designed graphical displays can be ambiguous, confusing, and downright misleading. The keys to excellence in graphical design and communication are much like the keys to good writing. Adhere to fundamental principles of style and communicate as logically, accurately, and clearly as possible. Excellence in writing is generally achieved by avoiding unnecessary words and paragraphs; it is efficient. In a similar fashion, excellence in graphical presentation is generally achieved by efficient designs that avoid unnecessary ink.
Excellence in graphical presentation depends on:
- Choosing the best medium for presenting the information
- Designing the components of the graph in a way that communicates the information as clearly and accurately as possible.
Table or Graph?
- Tables are generally best if you want to be able to look up specific information or if the values must be reported precisely.
- Graphics are best for illustrating trends and making comparisons
The side by side illustrations below show the same information, first in table form and then in graphical form. While the information in the table is precise, the real goal is to compare a series of clinical outcomes in subjects taking either a drug or a placebo. The graphical presentation on the right makes it possible to quickly see that for each of the outcomes evaluated, the drug produced relief in a great proportion of subjects. Moreover, the viewer gets a clear sense of the magnitude of improvement, and the error bars provided a sense of the uncertainty in the data.
|
Source: Connor JT. Statistical Graphics in AJG: Save the Ink for the Information. Am J of Gastroenterology. 2009; 104:1624-1630. |
|
Principles for Table Display
- Sort table rows in a meaningful way
- Avoid alphabetical listing!
- Use rates, proportions or ratios in addition (or instead of) totals
- Show more than two time points if available
- Multiple time points may be better presented in a Figure
- Similar data should go down columns
- Highlight important comparisons
- Show the source of the data
Consider the data in the table below from http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/types/commoncancers
|
| Incidence | Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| Bladder | 72,570 | 5.7% |
| Breast | 232,340 | 18.2% |
| Colon | 142,820 | 11.2% |
| Kidney | 59,938 | 4.7% |
| Leukemia | 48,610 | 3.8% |
| Lung | 228,190 | 17.9% |
| Melanoma | 76,690 | 6.0% |
| Lymphoma | 69,740 | 5.5% |
| Pancreas | 45,220 | 3.5% |
| Prostate | 238,590 | 18.7% |
| Thyroid | 60,220 | 4.7% |
Our ability to quickly understand the relative frequency of these cancers is hampered by presenting them in alphabetical order. It is much easier for the reader to grasp the relative frequency by listing them from most frequent to least frequent as in the next table.
| Type | Incidence | Proportion |
|---|---|---|
| Prostate | 238,590 | 18.7% |
| Breast | 232,340 | 18.2% |
| Lung | 228,340 | 17.9% |
| Colon | 142,820 | 11.2% |
| Melanoma | 76,690 | 6.0% |
| Bladder | 72,570 | 5.7% |
| Lymphoma | 69,740 | 5.5% |
| Thyroid | 60,220 | 4.7% |
| Kidney | 59,938 | 4.7% |
| Leukemia | 48,610 | 3.8% |
| Pancreas | 45,220 | 3.5% |
However, the same information might be presented more effectively with a dot plot, as shown below.

Data from http://www.cancer.gov/cancertopics/types/commoncancers
Principles of Graphical Excellence from E.R. Tufte
|
From E. R. Tufte. The Visual Display of Quantitative Information, 2nd Edition. Graphics Press, Cheshire, Connecticut, 2001.
|
Pattern Perception
Pattern perception is done by
- Detection: recognition of geometry encoding physical values
- Assembly: grouping of detected symbol elements; discerning overall patterns in data
- Estimation: assessment of relative magnitudes of two physical values
Geographic Variation in Cancer
As an example, Tufte offers a series of maps that summarize the age-adjusted mortality rates for various types of cancer in the 3,056 counties in the United States. The maps showing the geographic variation in stomach cancer are shown below.
|
|
Adapted from Atlas of Cancer Mortality for U.S. Counties: 1950-1969, TJ Mason et al, PHS, NIH, 1975
|
These maps summarize an enormous amount of information and present it efficiently, coherently, and effectively.in a way that invites the viewer to make comparisons and to think about the substance of the findings. Consider, for example, that the region to the west of the Great Lakes was settled largely by immigrants from Germany and Scand anavia, where traditional methods of preserving food included pickling and curing of fish by smoking. Could these methods be associated with an increased risk of stomach cancer?
John Snow's Spot Map of Cholera Cases
Consider also the spot map that John Snow presented after the cholera outbreak in the Broad Street section of London in September 1854. Snow ascertained the place of residence or work of the victims and represented them on a map of the area using a small black disk to represent each victim and stacking them when more than one occurred at a particular location. Snow reasoned that cholera was probably caused by something that was ingested, because of the intense diarrhea and vomiting of the victims, and he noted that the vast majority of cholera deaths occurred in people who lived or worked in the immediate vicinity of the broad street pump (shown with a red dot that we added for clarity). He further ascertained that most of the victims drank water from the Broad Street pump, and it was this evidence that persuaded the authorities to remove the handle from the pump in order to prevent more deaths.

Humans can readily perceive differences like this when presented effectively as in the two previous examples. However, humans are not good at estimating differences without directly seeing them (especially for steep curves), and we are particularly bad at perceiving relative angles (the principal perception task used in a pie chart).
The use of pie charts is generally discouraged. Consider the pie chart on the left below. It is difficult to accurately assess the relative size of the components in the pie chart, because the human eye has difficulty judging angles. The dot plot on the right shows the same data, but it is much easier to quickly assess the relative size of the components and how they changed from Fiscal Year 2000 to Fiscal Year 2007.
|
|
Adapted from Wainer H.:Improving data displays: Ours and the media's. Chance, 2007;20:8-15. Data from http://www.taxpolicycenter.org/taxfacts/displayafact.cfm?Docid=203 |
Consider the information in the two pie charts below (showing the same information).The 3-dimensional pie chart on the left distorts the relative proportions. In contrast the 2-dimensional pie chart on the right makes it much easier to compare the relative size of the varies components..
|
Adapted from Cawley S, et al. (2004) Unbiased mapping of transcription factor binding sites along human chromosomes 21 and 22 points to widespread regulation of noncoding RNAs. Cell 116:499-509, Figure 1 |
|
|
More Principles of Graphical Excellence
|
Adapted from Frank E. Harrell Jr. on graphics: http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/twiki/pub/Main/StatGraphCourse/graphscourse.pdf ] |
Exclude Unneeded Dimensions
|
Source: Cotter DJ, et al. (2004) Hematocrit was not validated as a surrogate endpoint for survival among epoetin-treated hemodialysis patients. Journal of Clinical Epidemiology 57:1086-1095, Figure 2. |
Source: Roeder K (1994) DNA fingerprinting: A review of the controversy (with discussion). Statistical Science 9:222-278, Figure 4. |
These 3-dimensional techniques distort the data and actually interfere with our ability to make accurate comparisons. The distortion caused by 3-dimensional elements can be particularly severe when the graphic is slanted at an angle or when the viewer tends to compare ends up unwittingly comparing the areas of the ink rather than the heights of the bars.
It is much easier to make comparisons with a chart like the one below.

Source: Huang, C, Guo C, Nichols C, Chen S, Martorell R. Elevated levels of protein in urine in adulthood after exposure to
the Chinese famine of 1959–61 during gestation and the early postnatal period. Int. J. Epidemiol. (2014) 43 (6): 1806-1814 .
Omit "Chart Junk"
Consider these two examples.
| Hash lines are what E.R. Tufte refers to as "chart junk."
This graphic uses unnecessary bar graphs, pointless and annoying cross-hatching, and labels with incomplete abbreviations. The cluttered legend expands the inadequate bar labels, but it is difficult to go back and forth from the legend to the bar graph, and the use of all uppercase letters is visually unappealing. This presentation would have been greatly enhanced by simply using a horizontal dot plot that rank ordered the categories in a logical way. This approach could have been cleared and would have completely avoided the need for a legend. | This grey background is a waste of ink, and it actually detracts from the readability of the graph by reducing contrast between the data points and other elements of the graph. Also, the axis labels are too small to be read easily. |
|
Source: Miller AH, Goldenberg EN, Erbring L. (1979) Type-Set Politics: Impact of Newspapers on Public Confidence. American Political Science Review, 73:67-84. |
Source: Jorgenson E, et al. (2005) Ethnicity and human genetic linkage maps. 76:276-290, Figure 2 |
Here is a simple enumeration of the number of pets in a neighborhood. There is absolutely no reason to connect these counts with lines. This is, in fact, confusing and inappropriate and nothing more than "chart junk."

Source: http://www.go-education.com/free-graph-maker.html
Moiré Vibration
Moiré effects are sometimes used in modern art to produce the appearance of vibration and movement. However, when these effects are applied to statistical presentations, they are distracting and add clutter because the visual noise interferes with the interpretation of the data.
Tufte presents the example shown below from Instituto de Expansao Commercial, Brasil, Graphicos Estatisticas (Rio de Janeiro, 1929, p. 15).
While the intention is to present quantitative information about the textile industry, the moiré effects do not add anything, and they are distracting, if not visually annoying.
Present Data to Facilitate Comparisons
| Tips
|
Here is an attempt to compare catches of cod fish and crab across regions and to relate the variation to changes in water temperature. The problem here is that the Y-axes are vastly different, making it hard to sort out what's really going on. Even the Y-axes for temperature are vastly different.

http://seananderson.ca/courses/11-multipanel/multipanel.pdf1
The ability to make comparisons is greatly facilitated by using the same scales for axes, as illustrated below.

Data source: Dawber TR, Meadors GF, Moore FE Jr. Epidemiological approaches to heart disease:
the Framingham Study. Am J Public Health Nations Health. 1951;41(3):279-81. PMID: 14819398
It is also important to avoid distorting the X-axis. Note in the example below that the space between 0.05 to 0.1 is the same as space between 0.1 and 0.2.

Source: Park JH, Gail MH, Weinberg CR, et al. Distribution of allele frequencies and effect sizes and
their interrelationships for common genetic susceptibility variants. Proc Natl Acad Sci U S A. 2011; 108:18026-31.
Consider the range of the Y-axis. In the examples below there is no relevant information below $40,000, so it is not necessary to begin the Y-axis at 0. The graph on the right makes more sense.
|
|
|
| Data from http://www.myplan.com/careers/registered-nurses/salary-29-1111.00.html | |
Also, consider using a log scale. this can be particularly useful when presenting ratios as in the example below.

Source: Broman KW, Murray JC, Sheffield VC, White RL, Weber JL (1998) Comprehensive human genetic maps:
Individual and sex-specific variation in recombination. American Journal of Human Genetics 63:861-869, Figure 1
We noted earlier that pie charts make it difficult to see differences within a single pie chart, but this is particularly difficult when data is presented with multiple pie charts, as in the example below.

Source: Bell ML, et al. (2007) Spatial and temporal variation in PM2.5 chemical composition in the United States
for health effects studies. Environmental Health Perspectives 115:989-995, Figure 3
When multiple comparisons are being made, it is essential to use colors and symbols in a consistent way, as in this example.

Source: Manning AK, LaValley M, Liu CT, et al. Meta-Analysis of Gene-Environment Interaction:
Joint Estimation of SNP and SNP x Environment Regression Coefficients. Genet Epidemiol 2011, 35(1):11-8.
Avoid putting too many lines on the same chart. In the example below, the only thing that is readily apparent is that 1980 was a very hot summer.

Data from National Weather Service Weather Forecast Office at
http://www.srh.noaa.gov/tsa/?n=climo_tulyeartemp
Make Efficient Use of Space
|
More Tips: |
Reduce the Ratio of Ink to Information
This isn't efficient, because this graphic is totally uninformative.

Source: Mykland P, Tierney L, Yu B (1995) Regeneration in Markov chain samplers. Journal of the American Statistical Association 90:233-241, Figure 1
| Bar charts are not appropriate for indicating means ± SEs. The only important information is the mean and the variation about the mean. Consider the figure to the right. By representing a mean with a number and a bar that has width, the information is representing one number over and over with:
|
|
Bar graphs add ink without conveying any additional information, and they are distracting. The graph below on the left inappropriately uses bars which clutter the graph without adding anything. The graph on the right displays the same data, by does so more clearly and with less clutter.
|
Source: Conford EM, Huot ME. Glucose transfer from male to female schistosomes. Science. 1981 213:1269-71 |
|
| "Just as a good editor of prose ruthlessly prunes unnecessary words, so a designer of statistical graphics should prune out ink that fails to present fresh data-information. Although nothing can replace a good graphical idea applied to an interesting set of numbers, editing and revision are as essential to sound graphical design work as they are to writing." Edward R. Tufte, "The Visual Display of Quantitative Information" |
Multiple Types of Information on the Same Figure
|
|
|
Choosing the Best Graph Type
| Adapted from Frank E Harrell, Jr: on Graphics: http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/twiki/pub/Main/StatGraphCourse/graphscourse.pdf
|
Bar Charts, Error Bars and Dot Plots
As noted previously, bar charts can be problematic. Here is another one presenting means and error bars, but the error bars are misleading because they only extend in one direction. A better alternative would have been to to use full error bars with a scatter plot, as illustrated previously (right).
|
Source: Hummer BT, Li XL, Hassel BA (2001) Role for p53 in gene induction by double-stranded RNA. J Virol 75:7774-7777, Figure 4 |
|
Consider the four graphs below presenting the incidence of cancer by type. The upper left graph unnecessary uses bars, which take up a lot of ink. This layout also ends up making the fonts for the types of cancer too small. Small font is also a problem for the dot plot at the upper right, and this one also has unnecessary grid lines across the entire width.
The graph at the lower left has more readable labels and uses a simple dot plot, but the rank order is difficult to figure out.
The graph at the lower right is clearly the best, since the labels are readable, the magnitude of incidence is shown clearly by the dot plots, and the cancers are sorted by frequency.
| ************************* + |
|
|
|
|
Single Continuous Numeric Variable
In this situation a cumulative distribution function conveys the most information and requires no grouping of the variable. A box plot will show selected quantiles effectively, and box plots are especially useful when stratifying by multiple categories of another variable.
Histograms are also possible. Consider the examples below.
| Density Plot | Histogram | Box Plot |
|
|
|
|
Two Variables
| Adapted from Frank E. Harrell Jr. on graphics: http://biostat.mc.vanderbiltedu/twiki/pub/Main/StatGraphCourse/graphscourse.pdf |
The two graphs below summarize BMI (Body Mass Index) measurements in four categories, i.e., younger and older men and women. The graph on the left shows the means and 95% confidence interval for the mean in each of the four groups. This is easy to interpret, but the viewer cannot see that the data is actually quite skewed. The graph on the right shows the same information presented as a box plot. With this presentation method one gets a better understanding of the skewed distribution and how the groups compare.
The next example is a scatter plot with a superimposed smoothed line of prediction. The shaded region embracing the blue line is a representation of the 95% confidence limits for the estimated prediction. This was created using "ggplot" in the R programming language.

Source: Frank E. Harrell Jr. on graphics: http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/twiki/pub/Main/StatGraphCourse/graphscourse.pdf (page 121)
Multivariate Data
The example below shows the use of multiple panels.

Source: Cleveland S. The Elements of Graphing Data. Hobart Press, Summit, NJ, 1994.
Displaying Uncertainty
- Error bars showing confidence limits
- Confidence bands drawn using two lines
- Shaded confidence bands
- Bayesian credible intervals
- Bayesian posterior densities
Confidence Limits
Shaded Confidence Bands

Source: Frank E. Harrell Jr. on graphics: http://biostat.mc.vanderbilt.edu/twiki/pub/Main/StatGraphCourse/graphscourse.pdf

Source: Tweedie RL and Mengersen KL. (1992) Br. J. Cancer 66: 700-705
Forest Plot
This is a Forest plot summarizing 26 studies of cigarette smoke exposure on risk of lung cancer. The sizes of the black boxes indicating the estimated odds ratio are proportional to the sample size in each study.

Data from Tweedie RL and Mengersen KL. (1992) Br. J. Cancer 66: 700-705
Summary Recommendations
- In general, avoid bar plots
- Avoid chart junk and the use of too much ink relative to the information you are displaying. Keep it simple and clear.
- Avoid pie charts, because humans have difficulty perceiving relative angles.
- Pay attention to scale, and make scales consistent.
- Explore several ways to display the data!
12 Tips on How to Display Data Badly
Adapted from Wainer H. How to Display Data Badly. The American Statistician 1984; 38: 137-147.
- Show as few data as possible
- Hide what data you do show; minimize the data-ink ratio
- Ignore the visual metaphor altogether
- Only order matters
- Graph data out of context
- Change scales in mid-axis
- Emphasize the trivial; ignore the important
- Jiggle the baseline
- Alphabetize everything.
- Make your labels illegible, incomplete, incorrect, and ambiguous.
- More is murkier: use a lot of decimal places and make your graphs three dimensional whenever possible.
- If it has been done well in the past, think of another way to do it
Additional Resources
- Stephen Few: Designing Effective Tables and Graphs. http://www.perceptualedge.com/images/Effective_Chart_Design.pdf
- Gary Klaas: Presenting Data: Tabular and graphic display of social indicators. Illinois State University, 2002. http://lilt.ilstu.edu/gmklass/pos138/datadisplay/sections/goodcharts.htm (Note: The web site will be discontinued to be replaced by the Just Plain Data Analysis site).
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Graphical Representation

What is a Graph
In mathematics, a graph is a diagrammatic illustration that is used to represent data values in a systematic, organized and understandable manner. It is indeed a very tedious task to analyze lots of data. However, when the same numerical data is represented in a pictorial form, it becomes easy to understand the relationship between the provided data objects and the concepts represented. It is often said that a picture is worth a thousand words. Therefore, graphs are particularly useful when it comes to displaying and analyzing data.
The data have shown on the graph usually represents a relationship between various things for comparison among them. It could also help us to understand the changing trends over some time. With the help of graphs, it becomes easier to comprehend information.
Types of Graphical Representation
To represent various kinds of data, different kinds of graphs are used. Some of the commonly used graphs are as follows:
In a line graph, a line shows trends in data. It can also be used to predict the changing trends of the displayed data objects in the future.
A bar graph is used when data has been categorized or sorted. It is the best kind of graph for comparing data. In this, solid bars are used to represent different categories or data values.
A histogram is similar to a bar graph. However, instead of making comparisons, it groups the numerical data into ranges. It is most commonly used to show frequency distributions.
Pie or Circle Graph
In a pie chart, a circle represents statistical graphics. It is divided into many slices or pies to represent the proportion of numbers. The length of the arc of each pipe corresponds to the quantity represented by it.
Stem and Leaf Graph
A stem and leaf plot is a special type of table in which the data values are divided into a stem, which represents the initial digit or digits, and a leaf, which usually represents the last digit.
How to plot the Data Accurately on Graphs?
It is of utmost importance that the information which is being represented graphically should be accurate and easy to understand. The various points that should be kept in mind are:
The scale chosen to plot the graph should be according to the data values that have to be represented.
The index makes it easier for the reader to read and interpret the data represented by various colours, patterns, designs, etc.
The Source of Data
As and when necessary, the source of data can be mentioned at the bottom of the graph.
The purpose of making the graph is defeated if the representation does not look tidy. Hence, it must be ensured that the data so represented is neat and visually appealing.
There is no need to unnecessarily complicate the graph. The simpler, the better.
Basics of Graphical Representation
A graph usually consists of two lines called the coordinate axes. The horizontal line is called the x-axis, and the vertical line is called the y axis. The intersection of the two axes is the point of origin. The values on the x-axis towards the right of the origin are considered positive, and towards the left are negative. Similarly, on the y-axis, the values above the origin will be positive and the values below the origin will be negative.
Benefits of using Graphs
Graphs save time. If the same information is written down, it becomes a period process to spot the trends and be able to analyze the data properly.
A graph can be used to represent information neatly and also takes less space.
It is easy to understand.
Analysing a graphical representation of data does not take much and helps in making quick decisions.
Graphs give you a summarized version of a long report that contains a large amount of data.
Graphs and tables are less likely to have any errors and mistakes.
Graphical representation of two or more data sets will allow you to compare the information and take preventive measures to avoid mistakes in the future.
By making the data easy to understand, graphs eliminate the literacy barriers so that anyone can analyse and interpret the presented data.
With just a glance at the graphical representation, a person can make quick and informed decisions.
Some Rules for Graphical Representation of Data
Like any other mathematical concept, graphical representation also has some rules you must follow. These rules will help you present the information on a graph effectively. Below are the rules for graphical representation of data:
When you are making a graph, you should give it an appropriate title that highlights the subject of the given data.
While making a graph, do not forget to mention the measurement unit.
Make an index using colours, designs, shades, lines, etc. to make the graphical representation easier to understand.
You have to choose an appropriate scale to represent the given set of data.
Construct the graph as simple as possible so that everyone can easily understand the presented data.
Whether you are making a pie chart or a bar graph, it should look neat and clean so that the teacher can easily read the figures.
Importance of Graphical Representation
Graphical representation gives you a visual presentation of the given data to make it easier to understand. Graphs help you identify different patterns over a short and long period. It assists you in the interpretation of data and comparison of two or more data sets. Here are reasons why graphical representation is important:
Graphs are widely accepted in the corporate world as it summarises the data into an understandable format and avoids wastage of time.
When you want to compare two or more different data sets, graphs are your best choice. A graphical representation of all the data sets will allow you to quickly analyze the information and help you in making quick decisions.
Through descriptive reports and information, it becomes difficult to make decisions. However, with graphs, the management can analyse the situation more clearly and make the right decisions.
With tables and graphs, the information can be presented in an organised and logical manner, making it easier to understand for anyone.
Graphical representation of data does not demand much of your time, improving the overall efficiency. You can quickly make the graphs within minutes and focus on other important work.
Qualitative representation might include many grammatical errors and other mistakes that can mislead the person reading it. Since graphs involve numerical representation of data, there are fewer chances of errors and mistakes.
Graphs give you the entire summary of a large amount of data.

FAQs on Graphical Representation
1. What is a frequency polygon graph?
A frequency polygon graph can be used to represent the same set of data which is represented by a histogram. In this type of graph, lines are used to connect the midpoints of each interval. The frequencies of the data interval are represented by the height at which the midpoints are plotted in the graph. A frequency polygon can be created using the already drawn histogram, or by calculating the midpoint from the intervals of the frequency distribution table. To calculate the midpoint, we need to find the average of the upper and the lower values of the interval/range.
Frequency polygon gives us an idea regarding the shape of the data and the trends that it follows during a particular duration of time.
Steps to draw a frequency polygon:
Calculate the classmark for each interval, which is equal to (upper limit + lower limit)/2.
Represent the class marks on the x-axis and their corresponding frequencies on the y-axis.
For every class mark on the x-axis, plot the frequencies of the y-axis.
Join all the obtained points to get a curve.
The figure obtained is called a frequency polygon.
2. What is the difference between a Bar Graph and a Histogram?
The most commonly visible difference between a bar graph and a histogram is that, in a bar graph, the bars have spaces between them, whereas, in a histogram, the bars are drawn adjacent to each other, without leaving any spaces.
As they both make use of bars to represent the data, it becomes slightly difficult to understand the fundamental difference between the two. A histogram is a graphical representation that uses bars to demonstrate the frequency of numerical data. In a histogram, elements are grouped, so they can be considered as ranges.
A bar graph is a diagrammatic representation that uses bars for the comparison of different categories of data. The plotted elements are treated as individual entities, and not as a range. The bars can be drawn horizontally or vertically. The height of the bar corresponds to the size of the data object.
3. From which platform can I learn Graphical Representation?
Vedantu is the best e-learning platform from where you can learn Graphical Representation. To start studying the concept of graphical representations, you can visit our official website or download our mobile app from the app store or play store. Our learning platform is available to all students across the globe for absolutely free. Apart from the Graphical Representation, you will find plenty of study material for different topics of Maths. From the website, you can learn concepts, such as Number System, Area of Triangle, Factorisation, and much more.
4. What are the advantages of a Bar Graph?
A bar graph is the most widely used method of graphical representation. Below are some of the advantages of a bar graph:
A bar graph shows every category from the given frequency distribution.
Bar graphs summarize a large chunk of data into a simple, understandable, and interpretable form.
With a bar graph, you can easily compare two or more different data sets.
You can study the varying patterns in a bar graph over a long period.
A bar graph makes the trends easier to highlight than other types of graphical representation.
5. How to decide which graph is suitable for a situation?
Sometimes, the question does not specify which type of graph you have to use. In these cases, you will have to analyze the given data and decide which graph will be more suitable. When you have to compare two different categories of data sets, you should use a bar graph as it makes the data easy to interpret. If you have to find the trends and progress over a short period, you can use line graphs. Moreover, when you have to represent a whole graphically, a pie chart is the best option.
Home Blog Design How to Make a Presentation Graph
How to Make a Presentation Graph

Visuals are a core element of effective communication, and regardless of the niche, graphs facilitate understanding data and trends. Data visualization techniques aim to make data engaging, easy to recall and contextualize while posing as a medium to simplify complex concepts .
In this article, we’ll guide you through the process of creating a presentation graph, briefly covering the types of graphs you can use in presentations, and how to customize them for maximum effectiveness. Additionally, you can find references on how to narrate your graphs while delivering a presentation.
Table of Contents
What is a Presentation Graph?
Types of graphs commonly used in presentations, how to select a presentation graph type, design principles for effective presentation graphs, working with presentation graph templates, integrating the graph into your presentation, common mistakes to avoid when making a presentation graph, final words.
A presentation graph is a visual representation of data, crafted in either 2D or 3D format, designed to illustrate relationships among two or more variables. Its primary purpose is to facilitate understanding of complex information, trends, and patterns, making it easier for an audience to grasp insights during a presentation.
By visually encoding data, presentation graphs help highlight correlations, distributions, and anomalies within the dataset, thereby supporting more informed decision-making and discussion.
Various types of graphs are commonly used in presentations. Each type serves specific purposes, allowing presenters to choose the most suitable format for conveying their data accurately. Here, we’ll discuss some common examples of presentation graphs.
Check our guide for more information about the differences between charts vs. graphs .
A bar chart is a visual tool that represents data using horizontal bars, where the length of each bar correlates with the data value it represents. This type of chart is used to compare discrete categories or groups, highlighting differences in quantities or frequencies across these categories.
For more information check our collection of bar chart PowerPoint templates .

Column Graphs
Column graphs are a variation of bar charts. They display data through vertical columns, allowing for comparing values across different categories or over time. Each column’s height indicates the data value, making it straightforward to observe differences and trends.

Line Graphs
Line graphs depict information as a series of data points connected by straight lines. They are primarily used to show trends over time or continuous data, with the x-axis typically representing time intervals and the y-axis representing the measured values. Line graphs highlight the rate of change between the data points, indicating trends and fluctuations.
For more information check our collection of line chart PowerPoint templates .

Circle Graphs
Circle graphs, commonly known as pie charts or donut charts, present the data distribution as fractions of an entity. They provide a quick understanding of the relative sizes of each component within a dataset. Pie charts are particularly effective when the goal is to highlight the contribution of each part to the whole data.
For more information check our collection of circle diagram templates .

Area Graphs
Area graphs are similar to line graphs, but the space below the line is filled in, emphasizing the volume beneath the curve. They represent cumulative totals over time through the use of sequential data points, making it easier to see total values and the relative significance of different parts of the data.
For more information check our collection of area chart PowerPoint templates .

Cone, Cylinder, and Pyramid Graphs
Three-dimensional graphs, such as cones, cylinders, and pyramids, create a dynamic visual impact on presentations. While not as common as the other types, they are used for their ability to add depth and dimension to data representation. These graphs create a visually engaging experience for the audience, although sometimes they sacrifice accuracy for the sake of visuals.
For more information check our collection of pyramid diagram PowerPoint templates .
As a presenter, you must be aware of both the topic’s requirements to discuss and your audience’s needs. Different graphs fulfill distinct purposes, and selecting the right one is critical for effective communication.
Line Graphs for Trends Over Time
A line graph is effective when you want to present trends or changes over a continuous period, like sales performance over months. Each point on the line represents a specific time, offering a clear visual representation of the data’s progression.
Bar Graphs for Comparing Quantities
If your goal is to compare quantities or values across different categories, such as sales figures for various products, a bar graph is suitable. The varying lengths of bars make it easy to compare the magnitudes of different categories.
Pie Charts for Showing Proportions
Use pie charts when you want to illustrate parts of a whole. For example, to represent the percentage distribution of expenses in a budget, a pie chart divides the total into segments, each corresponding to a category.
Follow these guidelines to create your presentation graph for the data you intend to represent.
How to Make a Presentation Graph in PowerPoint
Start by opening your presentation slide deck. For this tutorial’s purpose, we’ll work with a blank slide.

Switch to the Insert tab and click on Chart .

A new dialogue window will open, where you have to select the chart type and the specific representation type—i.e., for area charts, you can choose from 2D or 3D area charts and their distribution method.

If you hover over the selected chart, it will zoom in to check the details. Double-click to insert the chosen graph into the slide.

As we can see, a spreadsheet to edit the data is now available. If you accidentally close it, go to Chart Design > Edit Data.

Replace the data in the numbers to reflect the data you need to showcase. The columns’ titles indicate the text the legend shows for each series. Then, we can close the spreadsheet and continue customizing it.

By clicking on the paintbrush, we access the Style options for the graph. We can change the background color, layout style, and more.

If we switch to the Color tab inside of Style , we can modify the color scheme for the presentation graph. And as simple as that is how to make a graph in PowerPoint.

How to Make a Presentation Graph in Google Slides
Now, let’s see how to create a graph in Google Slides. We start once again from a blank slide.

Go to Insert > Chart . Select your desired presentation graph option. In our case, we will work with a Pie Chart.

To change the placeholder data, click on Edit Data .

If you missed the emergent tab, you can go to the three points in the graph, click on them, and select Open Source .

The graph will most likely cover the data spreadsheet, so move it to one side to see the entire data range. In this case, the auto-generated graph is wrong as the sum gives 110%. We’ll correct that now.

And this is how it looks with the corrected data.

Next, we click on the three dots on the chart and select Edit the Chart . This shall open all customization options.

At the Setup tab, we can change the chart style and select from various options.

The data will refresh in that case and adapt its representation to the new style.

If we switch to the Customize tab (it says Customise, as the selected language is UK English), we can fine-tune our presentation graph starting from the background color.

Activate the 3D checkbox to change to a 3D pie chart (applicable to any graph).

We can find tailored settings for the Pie Chart to convert it to a donut chart, with settings like the donut hole size.

The Pie Slice section helps us change the color scheme for each one of the slices.

We can change the title and axis titles in the Chart and axis titles section.

Finally, the Legend section offers many customization options to alter the legend’s format.

Once the customization process is completed, close the Google Spreadsheets tab, go to your presentation chart, and click Update .

Google Slides will refresh the data for your created presentation graph with the last synced data.

Adhering to certain design principles is imperative for creating graphs and communicating information effectively.
Simplicity and Clarity
A graph should be clean and free from unnecessary details. Clear graphs have visible data points and helpful short texts for better understanding. Even if it looks simple, it can still show important information. To make it easy to understand, avoid adding distortions, shading, weird perspectives, too many colors, unnecessary decorations, or 3D effects [2]. It is also essential to ensure the plotted data points are clear, not hidden or covered.
Use of Color and Contrast
Thoughtful use of color and contrast enhances visual appeal and distinguishes different elements within the graph. Colors can effectively improve the chart presentation in three ways: highlighting specific data, grouping items, and encoding quantitative values. However, do not use fancy or varying colors in the background. We suggest resisting decorating graphs excessively, as it can hinder clear data presentation [4]. Only use different colors when they highlight important differences in the data.
Labeling and Legends
Accurate labeling is crucial to provide context and understanding. While designing graphs, we don’t expect the viewer to guess. Instead, we clearly label titles and axes. Clear labeling means displaying both axes on your graph, including measurement units if needed. Identify symbols and patterns in a legend or caption [3]. Legends explain symbols and patterns in a graph.
Scale and Proportion
For more clarity, we keep the measurement scales consistent and avoid distortions for accuracy. This ensures the exact difference between all the values. It will present data relationships and prevent misinterpretation due to skewed visual perceptions.
Tips for Customizing Graphs
PowerPoint provides various customization options—Right-click on elements like axes, data points, or legends to format them. You can also change colors, fonts, and styles to match your presentation’s look.
Coloring Your Data
When you want to make different parts of your chart stand out, click on a bar or line. Then, right-click and choose “Format Data Series.” Here, you can pick a color that helps each set of data pop. Do this for each part of your chart to make it visually appealing.

Changing the Chart Background
If you want to change the background color around your chart, right-click on the white space. Choose “Format Chart Area” and change the background color to something that complements your data.
Customizing Line Styles
Change the appearance of your lines for a unique look. Click on a line in your chart, right-click, and select “Format Data Series.” Experiment with different line styles, such as solid, dashed, or dotted.
Fine-tuning Axis Appearance
To make your chart axes look polished, right-click on the X or Y axis and choose “Format Axis.” Adjust properties like line color, tick marks, and label font to suit your design.
Perfecting Legends
Legends can be tweaked for a more integrated look. Right-click on the legend, select “Format Legend,” and adjust options like placement, font size, and background color to enhance the overall appearance.
Creating graphs in PowerPoint or Google Slides from scratch can be time-consuming, and ultimately, it won’t yield the same results as professional-made designs. We invite you to discover some cool designs for presentation graphs PPT templates made by SlideModel.
1. Dashboard Presentation Graph for PowerPoint & Google Slides

Don’t worry about how to make a graph in PowerPoint – let’s us bring the resources in the shape of a cool dashboard layout. Ideal for any kind of e-commerce business, you can track expenses or income, evaluate metrics, and much more.
Use This Template
2. Infographic Donut Chart Presentation Template

Explain concepts in different hierarchy levels, or processes that require a set of sequential steps by implementing this donut chart PPT template. Each segment has a bubble callout to expand further information for the areas required.
3. Presentation Graph Slide Deck PPT Template

All that’s required to create a data-driven presentation is here. Customize donut charts, funnels, histograms, point & figure charts, and more to create professionally-designed presentation slides.
4. PowerPoint Charts Slide Deck

If you’re looking for clean layouts for column graphs, area charts, line graphs and donut charts, this is the template you need in your toolbox. Perfect for marketing, financial and academic reports.
Consider its relevance to the content when incorporating your graph into the presentation. Insert the graph in a slide where it logically fits within the flow of information.
Positioning the Graph Appropriately in the Presentation
Deciding where to put your graph in the presentation is essential. You want it to be where everyone can see it easily and where it makes sense. Usually, you place the graph on a slide that talks about the data or topic related to the graph. This way, people can look at the graph simultaneously when you talk about it. Make sure it is not too small. If needed, you can make it bigger or smaller to fit nicely on the slide. The goal is to position the graph so that it helps your audience understand your information better.
Ensuring Consistency with the Overall Design of the Presentation
Align the graph with the overall design of your presentation to maintain a cohesive visual appeal. You can use consistent colors, fonts, and styles to integrate the graph seamlessly. The graph must complement the theme and tone of your slides. Therefore, you should avoid flashy or distracting elements that may deviate from the established design. The goal is to create a harmonious and professional presentation where the graph blends naturally without causing visual disruptions. However, we recommend you use bar chart templates already available for presentation.
Narrating Your Graph
When explaining your graph during the presentation, start by providing context. Clearly state what the graph illustrates and its significance to the audience. Use simple and direct language, avoiding unnecessary jargon. It is important to walk through the axes, data points, and any trends you want to highlight. Speaking moderately allows the audience to absorb the information without feeling rushed. You can take pause when needed to emphasize crucial points or transitions.
You can learn more about creative techniques to narrate your graph in our data storytelling guide.
Overloading with Information
One common mistake is presenting too much information on a single graph. Avoid filling the graph with excessive data points or unnecessary details.
Misleading Scales or Axes
Scale mistakes, such as uneven intervals or a bar chart with zero baselines, are common graphical mistakes [5]. Misleading scales can distort the interpretation of the graph and lead to incorrect conclusions. Scales should accurately present the data without exaggerating certain aspects.
Inappropriate Graph Types for the Data
Selecting an inappropriate graph type for your data is a mistake to avoid. Choose a graph type that effectively communicates the nature of your data. For instance, a pie chart for time-based trends might not be the most suitable choice. Match the graph type to the data characteristics to convey information accurately.
Working with presentation graphs may feel challenging for a beginner in presentation design software. Still, practice makes the master. Start by clearly stating your objectives in terms of data representation—this will make the presentation graph-type selection process much easier. Customize the graph by working with appropriate color combinations (you can learn more about this in our color theory guide), as this can also help highlight relevant data sections that may influence an informed decision.
Everything depends on your creative skills and how you want to showcase information. As a final piece of advice, we highly recommend working with one graph per slide, unless you opted for a dashboard layout. Ideally, graphs should be seen from a distance, and working with reduced sizes may hinder accurate data representation.
[1] https://uogqueensmcf.com/wp-content/uploads/2020/BA Modules/Medical Laboratory/Medical Laboratory Courses PPT/Year III Sem II/Biostatistics/lecture 1.pdf (Accessed: 06 March 2024).
[2] Five Principles of Good Graphs. https://scc.ms.unimelb.edu.au/resources/data-visualisation-and-exploration/data-visualisation
[3} Guide to fairly good graphs. Statistics LibreTexts. https://stats.libretexts.org/Bookshelves/Applied_Statistics/Biological_Statistics_(McDonald)/07%3A_Miscellany/7.02%3A_Guide_to_Fairly_Good_Graphs
[4] Practical rules for using color in charts. https://nbisweden.github.io/Rcourse/files/rules_for_using_color.pdf
[5] https://iase-web.org/islp/documents/Media/How%20To%20Avoid.pdf [6] Duquia, R.P. et al. (2014) Presenting data in tables and charts , Anais brasileiros de dermatologia . 10.1590/abd1806-4841.20143388

Like this article? Please share
Data Analysis, Data Science, Data Visualization, Presentation Approaches Filed under Design
Related Articles

Filed under PowerPoint Tutorials • June 28th, 2024
How to Represent Branching Scenarios in PowerPoint
Do you have a situation to expose with multiple possible outcomes? If so, check our guide on branching scenarios in PowerPoint.

Filed under Design • June 27th, 2024
How to Repurpose Your Content on Presentations
Adapt your content from presentation slides into other mediums and viceversa by learning how to repurpose your presentations. Detailed guide here.
![type of graphical presentation How to Make a Financial Presentation [Templates + Examples]](https://cdn.slidemodel.com/wp-content/uploads/00-financial-presentation-cover-640x360.png)
Filed under Business • June 13th, 2024
How to Make a Financial Presentation [Templates + Examples]
Learn how to make a stellar financial presentation by discovering which slides should be included, the best templates to make your job easier, and more.
Leave a Reply
.css-1qrtm5m{display:block;margin-bottom:8px;text-transform:uppercase;font-size:14px;line-height:1.5714285714285714;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.35px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.35px;letter-spacing:-0.35px;font-weight:300;color:#606F7B;}@media (min-width:600px){.css-1qrtm5m{font-size:16px;line-height:1.625;-webkit-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-moz-letter-spacing:-0.5px;-ms-letter-spacing:-0.5px;letter-spacing:-0.5px;}} Best Practices The #1 rule for improving your presentation slides
by Tom Rielly • May 12, 2020

When giving presentations, either on a video conference call or in person, your slides, videos and graphics (or lack of them) can be an important element in helping you tell your story or express your idea. This is the first of a series of blog posts that will give you tips and tricks on how to perfect your visual presentations.
Your job as a presenter is to build your idea -- step-by-step -- in the minds of your audience members. One tool to do that is presentation graphics, such as slides and videos.
Why graphics for your presentation?
A common mistake is using slides or videos as a crutch, even if they don’t actually add anything to your presentation. Not all presentations need graphics. Lots of presentations work wonderfully with just one person standing on a stage telling a story, as demonstrated by many TED Talks.
You should only use slides if they serve a purpose: conveying scientific information, art, and things that are hard to explain without pictures. Once you have decided on using slides, you will have a number of decisions to make. We’ll help you with the basics of making a presentation that is, above all, clear and easy to understand. The most important thing to remember here is: less is more.
Less is so much more
You want to aim for the fewest number of slides, the fewest number of photos, the fewest words per slide, the least cluttered slides and the most white space on your slides. This is the most violated slide rule, but it is the secret to success. Take a look at these examples.

As you can see in the above example, you don’t need fancy backgrounds or extra words to convey a simple concept. If you take “Everything you need to know about Turtles”, and delete “everything you need to know about” leaving just “turtles”, the slide has become much easier for your audience to read, and tells the story with economy.

The above example demonstrates that a single image that fills the entire screen is far more powerful than a slide cluttered with images. A slide with too many images may be detrimental to your presentation. The audience will spend more mental energy trying to sort through the clutter than listening to your presentation. If you need multiple images, then put each one on its own slide. Make each image high-resolution and have it fill the entire screen. If the photos are not the same dimensions as the screen, put them on a black background. Don’t use other colors, especially white.
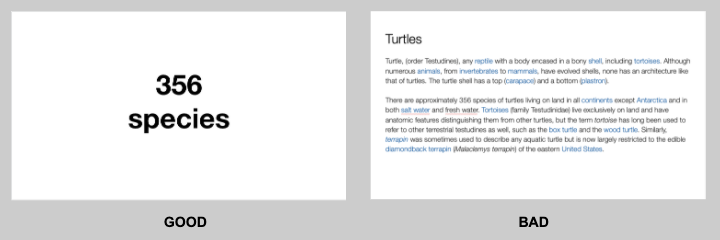
Your slides will be much more effective if you use the fewest words, characters, and pictures needed to tell your story. Long paragraphs make the audience strain to read them, which means they are not paying attention to you. Your audience may even get stressed if you move on to your next slide before they’ve finished reading your paragraph. The best way to make sure the attention stays on you is to limit word count to no more than 10 words per slide. As presentation expert Nancy Duarte says “any slide with more than 10 words is a document.” If you really do need a longer explanation of something, handouts or follow-up emails are the way to go.
Following a “less is more” approach is one of the simplest things you can do to improve your presentation visuals and the impact of your presentation overall. Make sure your visuals add to your presentation rather than distract from it and get your message across.
Ready to learn more about how to make your presentation even better? Get TED Masterclass and develop your ideas into TED-style talks.
© 2024 TED Conferences, LLC. All rights reserved. Please note that the TED Talks Usage policy does not apply to this content and is not subject to our creative commons license.
We use essential cookies to make Venngage work. By clicking “Accept All Cookies”, you agree to the storing of cookies on your device to enhance site navigation, analyze site usage, and assist in our marketing efforts.
Manage Cookies
Cookies and similar technologies collect certain information about how you’re using our website. Some of them are essential, and without them you wouldn’t be able to use Venngage. But others are optional, and you get to choose whether we use them or not.
Strictly Necessary Cookies
These cookies are always on, as they’re essential for making Venngage work, and making it safe. Without these cookies, services you’ve asked for can’t be provided.
Show cookie providers
- Google Login
Functionality Cookies
These cookies help us provide enhanced functionality and personalisation, and remember your settings. They may be set by us or by third party providers.
Performance Cookies
These cookies help us analyze how many people are using Venngage, where they come from and how they're using it. If you opt out of these cookies, we can’t get feedback to make Venngage better for you and all our users.
- Google Analytics
Targeting Cookies
These cookies are set by our advertising partners to track your activity and show you relevant Venngage ads on other sites as you browse the internet.
- Google Tag Manager
- Infographics
- Daily Infographics
- Popular Templates
- Accessibility
- Graphic Design
- Graphs and Charts
- Data Visualization
- Human Resources
- Beginner Guides
Blog Data Visualization 10 Data Presentation Examples For Strategic Communication
10 Data Presentation Examples For Strategic Communication
Written by: Krystle Wong Sep 28, 2023

Knowing how to present data is like having a superpower.
Data presentation today is no longer just about numbers on a screen; it’s storytelling with a purpose. It’s about captivating your audience, making complex stuff look simple and inspiring action.
To help turn your data into stories that stick, influence decisions and make an impact, check out Venngage’s free chart maker or follow me on a tour into the world of data storytelling along with data presentation templates that work across different fields, from business boardrooms to the classroom and beyond. Keep scrolling to learn more!
Click to jump ahead:
10 Essential data presentation examples + methods you should know
What should be included in a data presentation, what are some common mistakes to avoid when presenting data, faqs on data presentation examples, transform your message with impactful data storytelling.
Data presentation is a vital skill in today’s information-driven world. Whether you’re in business, academia, or simply want to convey information effectively, knowing the different ways of presenting data is crucial. For impactful data storytelling, consider these essential data presentation methods:
1. Bar graph
Ideal for comparing data across categories or showing trends over time.
Bar graphs, also known as bar charts are workhorses of data presentation. They’re like the Swiss Army knives of visualization methods because they can be used to compare data in different categories or display data changes over time.
In a bar chart, categories are displayed on the x-axis and the corresponding values are represented by the height of the bars on the y-axis.
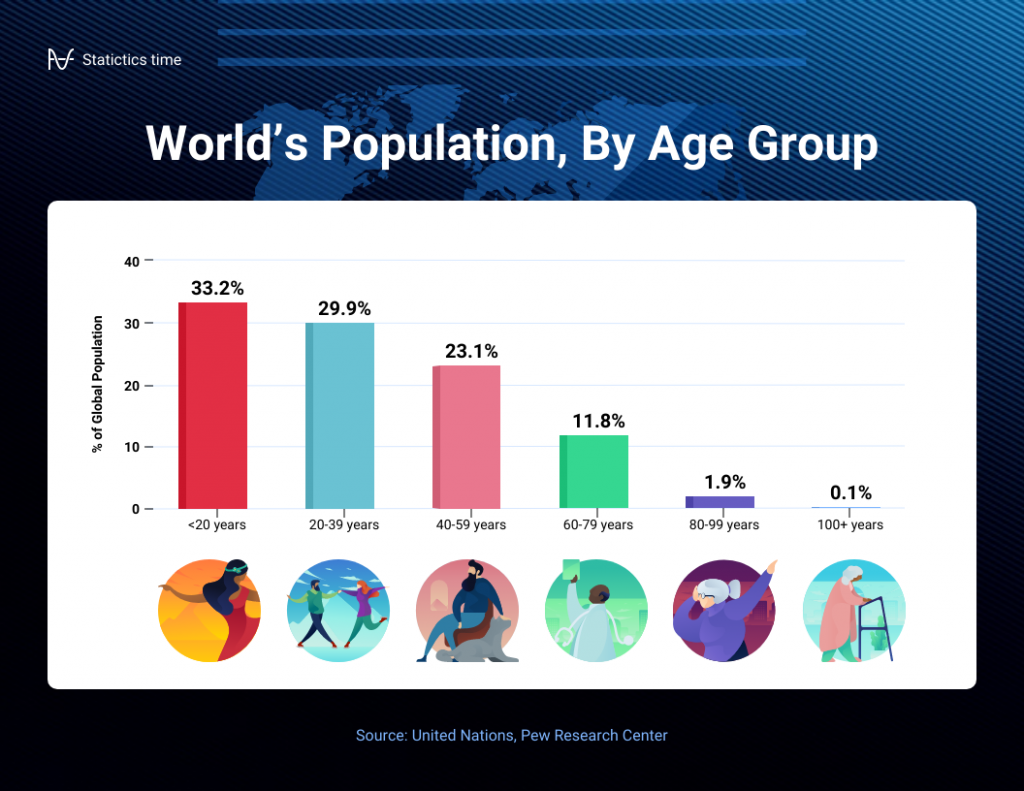
It’s a straightforward and effective way to showcase raw data, making it a staple in business reports, academic presentations and beyond.
Make sure your bar charts are concise with easy-to-read labels. Whether your bars go up or sideways, keep it simple by not overloading with too many categories.
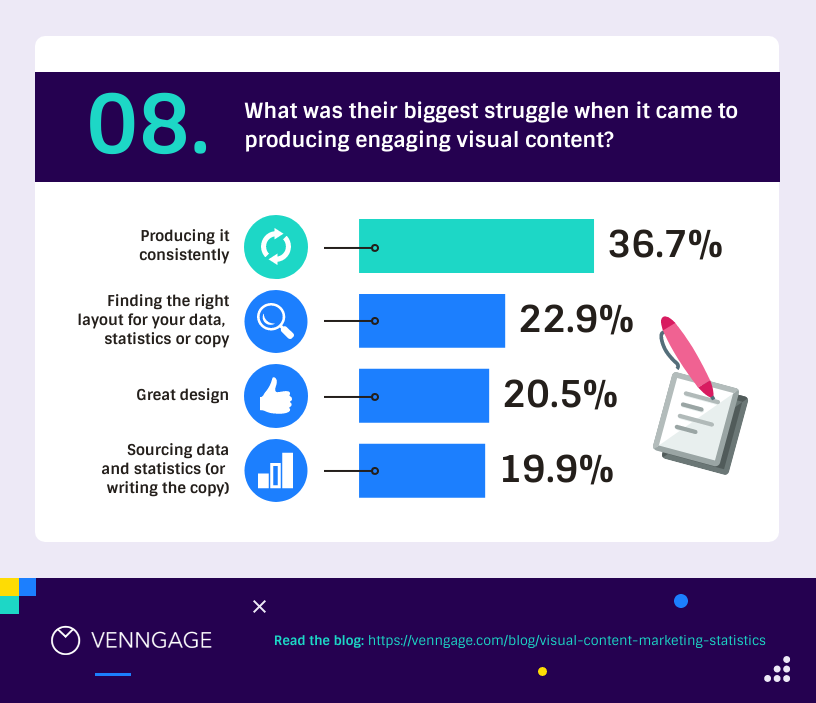
2. Line graph
Great for displaying trends and variations in data points over time or continuous variables.
Line charts or line graphs are your go-to when you want to visualize trends and variations in data sets over time.
One of the best quantitative data presentation examples, they work exceptionally well for showing continuous data, such as sales projections over the last couple of years or supply and demand fluctuations.
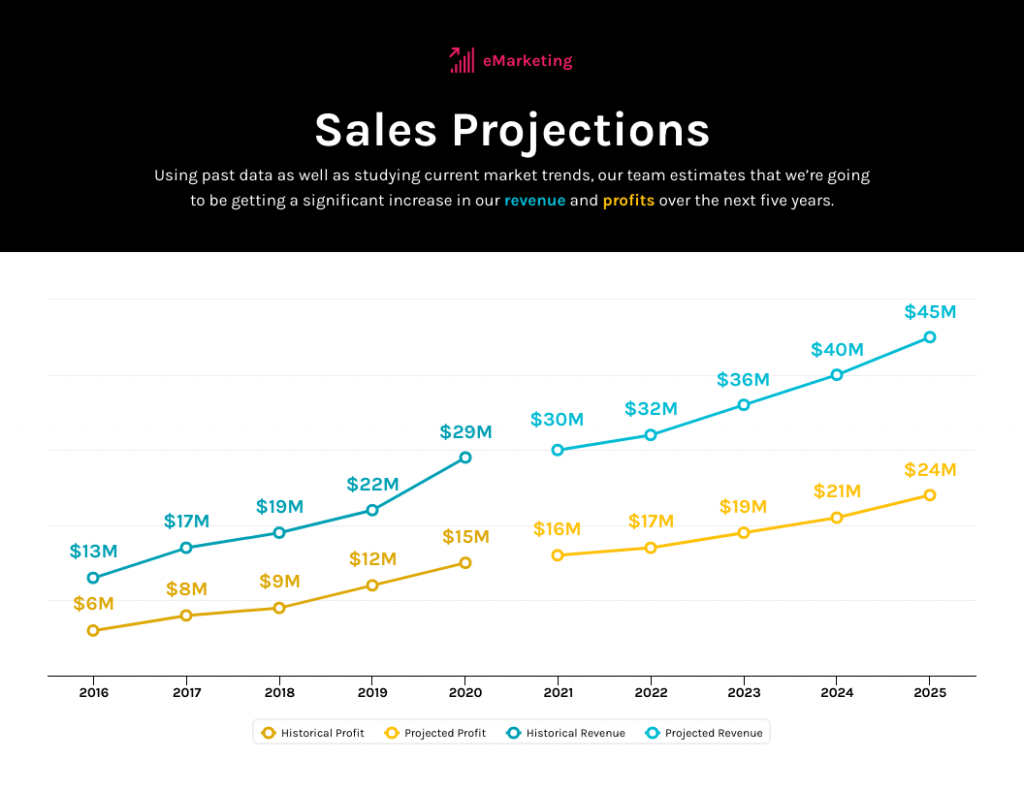
The x-axis represents time or a continuous variable and the y-axis represents the data values. By connecting the data points with lines, you can easily spot trends and fluctuations.
A tip when presenting data with line charts is to minimize the lines and not make it too crowded. Highlight the big changes, put on some labels and give it a catchy title.
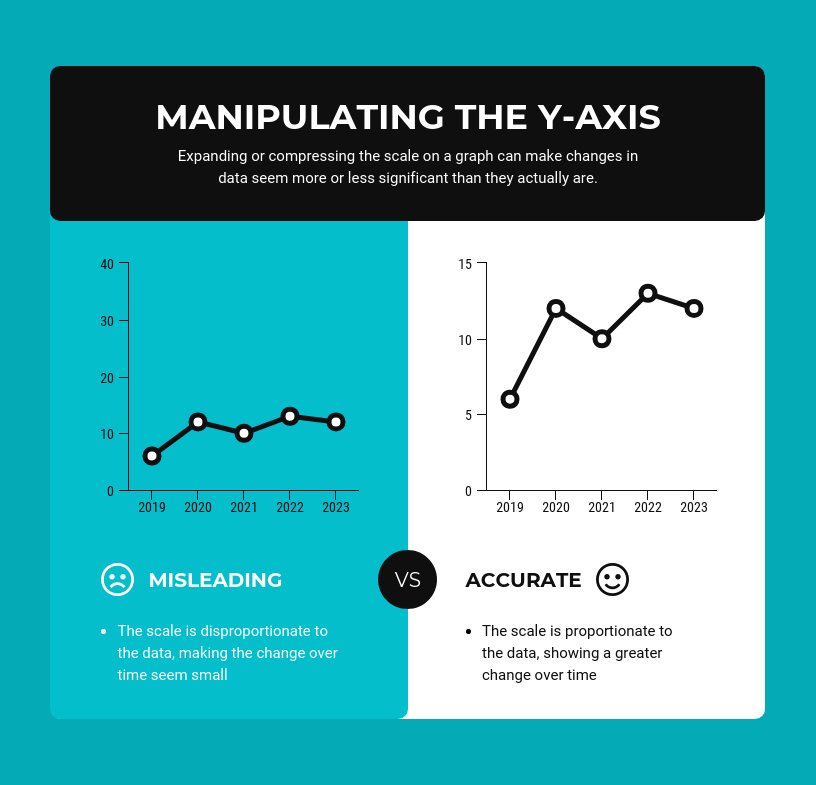
3. Pie chart
Useful for illustrating parts of a whole, such as percentages or proportions.
Pie charts are perfect for showing how a whole is divided into parts. They’re commonly used to represent percentages or proportions and are great for presenting survey results that involve demographic data.
Each “slice” of the pie represents a portion of the whole and the size of each slice corresponds to its share of the total.
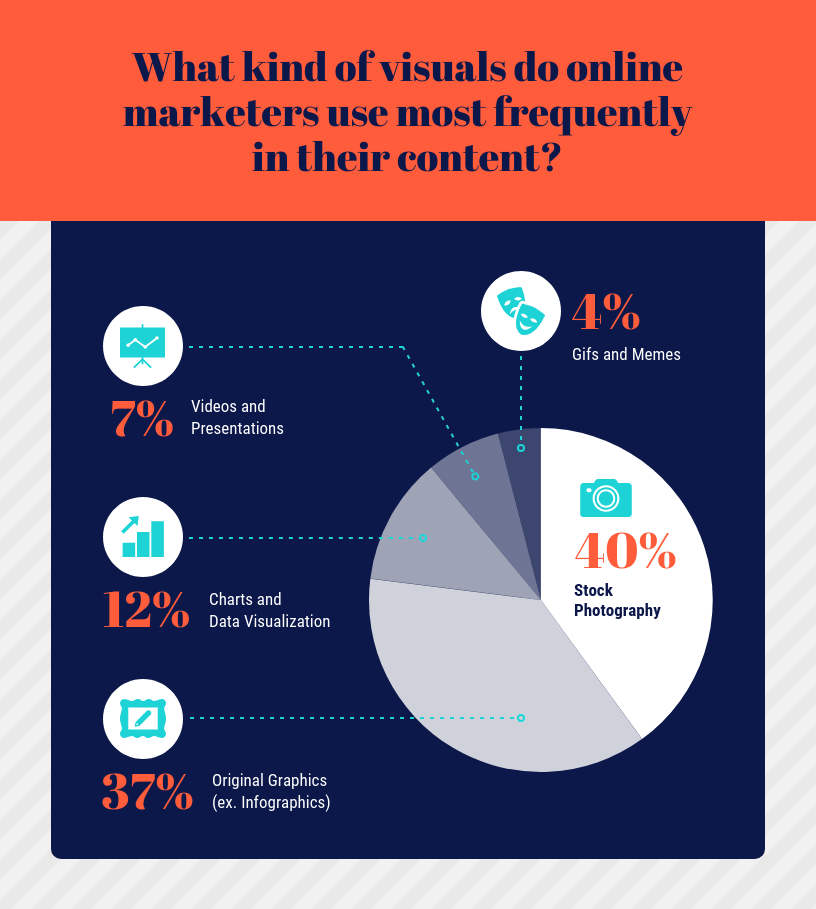
While pie charts are handy for illustrating simple distributions, they can become confusing when dealing with too many categories or when the differences in proportions are subtle.
Don’t get too carried away with slices — label those slices with percentages or values so people know what’s what and consider using a legend for more categories.
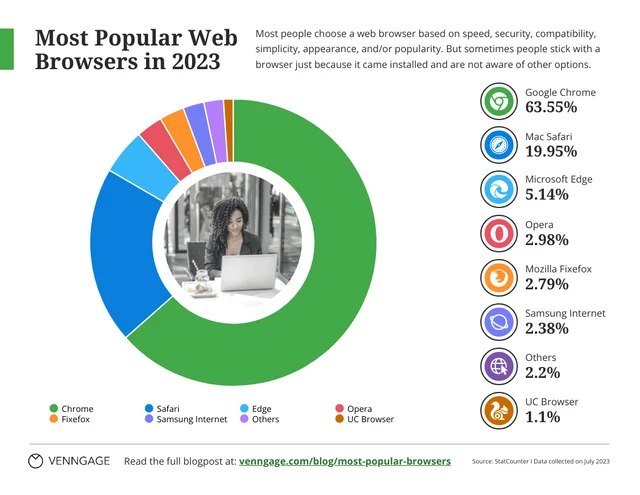
4. Scatter plot
Effective for showing the relationship between two variables and identifying correlations.
Scatter plots are all about exploring relationships between two variables. They’re great for uncovering correlations, trends or patterns in data.
In a scatter plot, every data point appears as a dot on the chart, with one variable marked on the horizontal x-axis and the other on the vertical y-axis.
By examining the scatter of points, you can discern the nature of the relationship between the variables, whether it’s positive, negative or no correlation at all.
If you’re using scatter plots to reveal relationships between two variables, be sure to add trendlines or regression analysis when appropriate to clarify patterns. Label data points selectively or provide tooltips for detailed information.
5. Histogram
Best for visualizing the distribution and frequency of a single variable.
Histograms are your choice when you want to understand the distribution and frequency of a single variable.
They divide the data into “bins” or intervals and the height of each bar represents the frequency or count of data points falling into that interval.
Histograms are excellent for helping to identify trends in data distributions, such as peaks, gaps or skewness.
Here’s something to take note of — ensure that your histogram bins are appropriately sized to capture meaningful data patterns. Using clear axis labels and titles can also help explain the distribution of the data effectively.
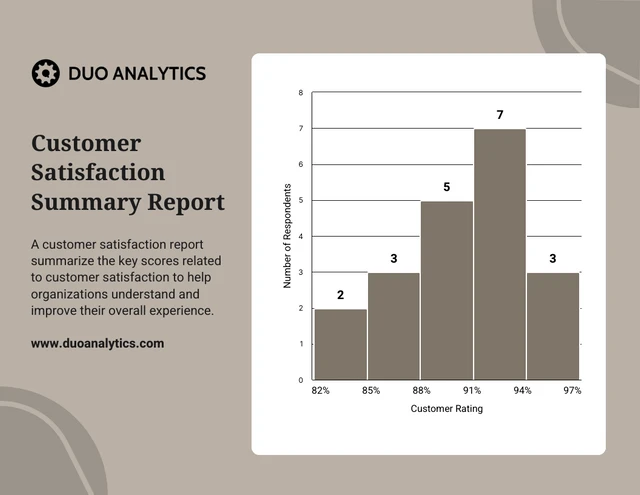
6. Stacked bar chart
Useful for showing how different components contribute to a whole over multiple categories.
Stacked bar charts are a handy choice when you want to illustrate how different components contribute to a whole across multiple categories.
Each bar represents a category and the bars are divided into segments to show the contribution of various components within each category.
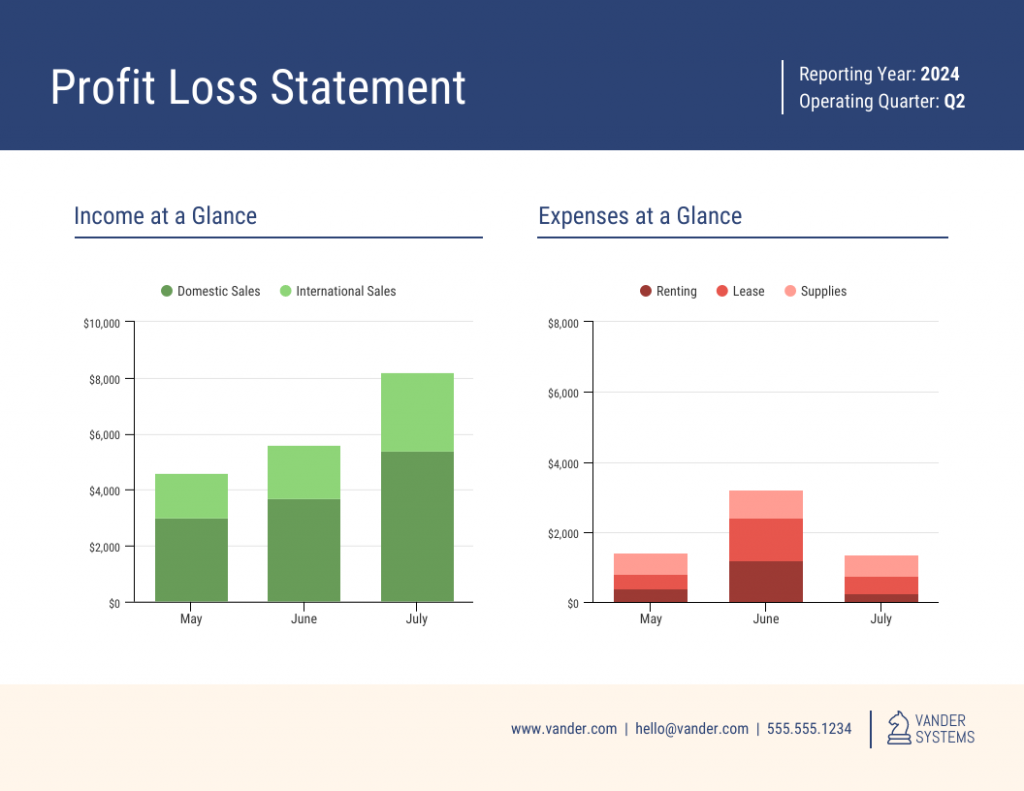
This method is ideal for highlighting both the individual and collective significance of each component, making it a valuable tool for comparative analysis.
Stacked bar charts are like data sandwiches—label each layer so people know what’s what. Keep the order logical and don’t forget the paintbrush for snazzy colors. Here’s a data analysis presentation example on writers’ productivity using stacked bar charts:
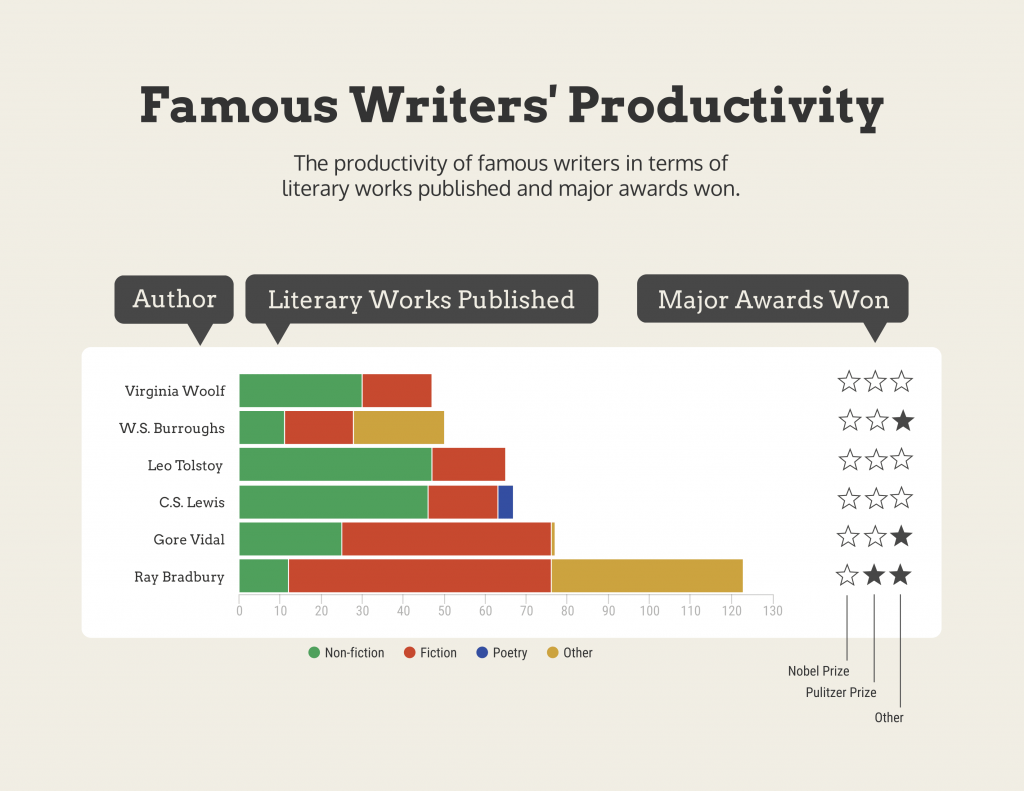
7. Area chart
Similar to line charts but with the area below the lines filled, making them suitable for showing cumulative data.
Area charts are close cousins of line charts but come with a twist.
Imagine plotting the sales of a product over several months. In an area chart, the space between the line and the x-axis is filled, providing a visual representation of the cumulative total.
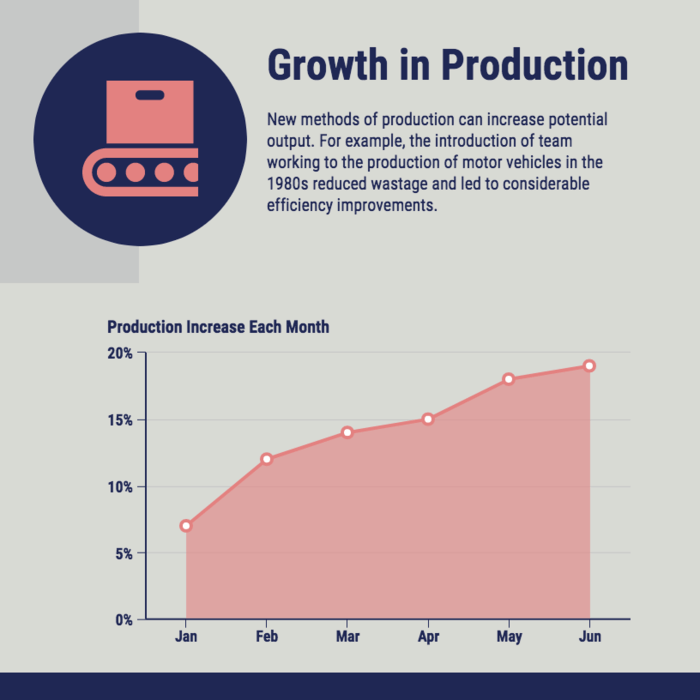
This makes it easy to see how values stack up over time, making area charts a valuable tool for tracking trends in data.
For area charts, use them to visualize cumulative data and trends, but avoid overcrowding the chart. Add labels, especially at significant points and make sure the area under the lines is filled with a visually appealing color gradient.
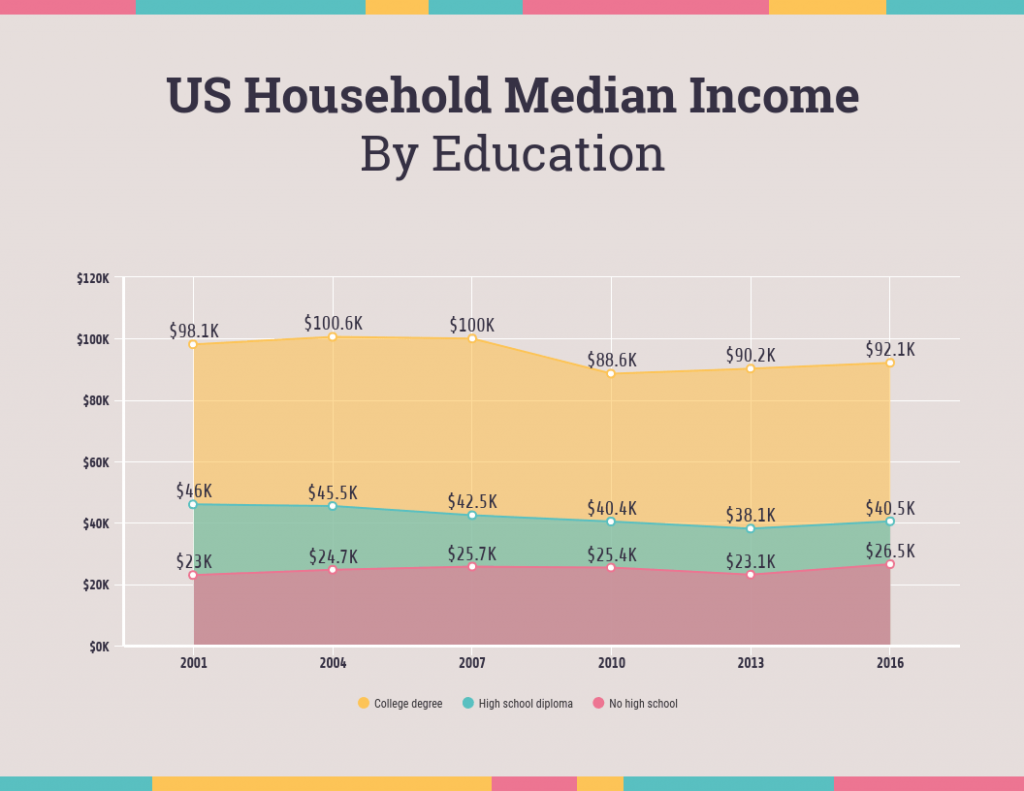
8. Tabular presentation
Presenting data in rows and columns, often used for precise data values and comparisons.
Tabular data presentation is all about clarity and precision. Think of it as presenting numerical data in a structured grid, with rows and columns clearly displaying individual data points.
A table is invaluable for showcasing detailed data, facilitating comparisons and presenting numerical information that needs to be exact. They’re commonly used in reports, spreadsheets and academic papers.
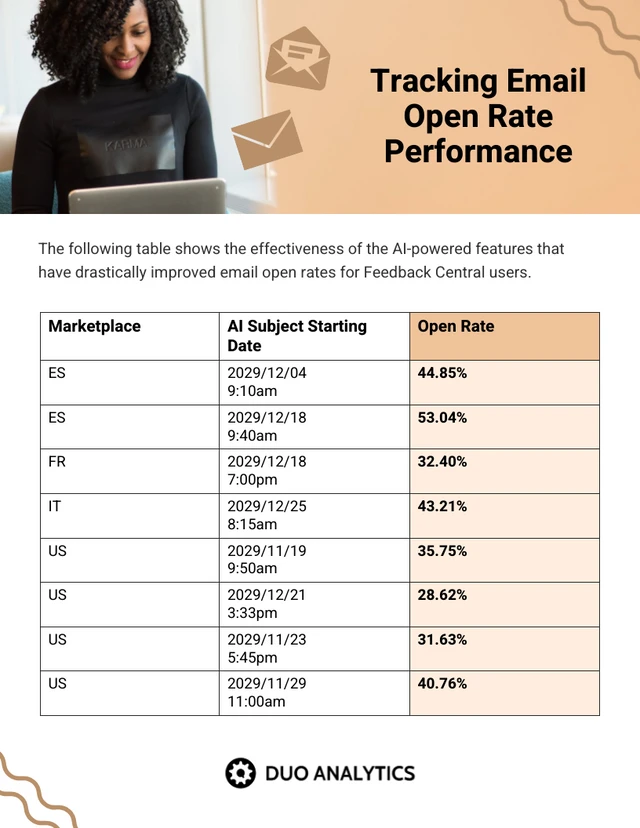
When presenting tabular data, organize it neatly with clear headers and appropriate column widths. Highlight important data points or patterns using shading or font formatting for better readability.
9. Textual data
Utilizing written or descriptive content to explain or complement data, such as annotations or explanatory text.
Textual data presentation may not involve charts or graphs, but it’s one of the most used qualitative data presentation examples.
It involves using written content to provide context, explanations or annotations alongside data visuals. Think of it as the narrative that guides your audience through the data.
Well-crafted textual data can make complex information more accessible and help your audience understand the significance of the numbers and visuals.
Textual data is your chance to tell a story. Break down complex information into bullet points or short paragraphs and use headings to guide the reader’s attention.
10. Pictogram
Using simple icons or images to represent data is especially useful for conveying information in a visually intuitive manner.
Pictograms are all about harnessing the power of images to convey data in an easy-to-understand way.
Instead of using numbers or complex graphs, you use simple icons or images to represent data points.
For instance, you could use a thumbs up emoji to illustrate customer satisfaction levels, where each face represents a different level of satisfaction.

Pictograms are great for conveying data visually, so choose symbols that are easy to interpret and relevant to the data. Use consistent scaling and a legend to explain the symbols’ meanings, ensuring clarity in your presentation.
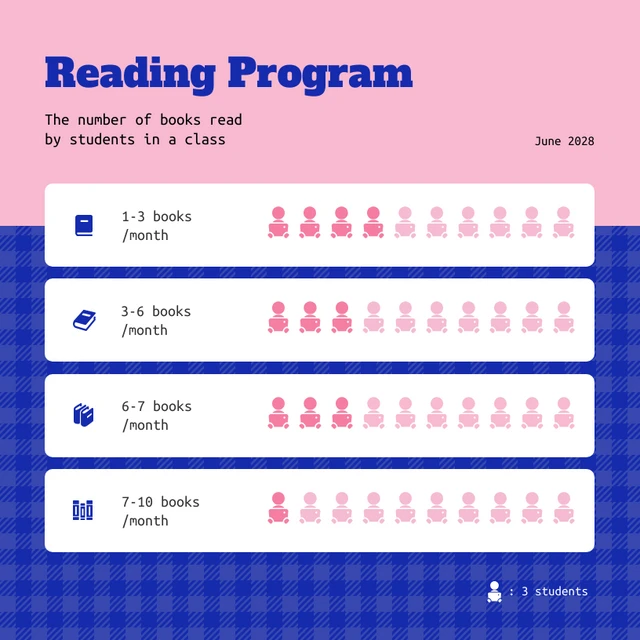
Looking for more data presentation ideas? Use the Venngage graph maker or browse through our gallery of chart templates to pick a template and get started!
A comprehensive data presentation should include several key elements to effectively convey information and insights to your audience. Here’s a list of what should be included in a data presentation:
1. Title and objective
- Begin with a clear and informative title that sets the context for your presentation.
- State the primary objective or purpose of the presentation to provide a clear focus.

2. Key data points
- Present the most essential data points or findings that align with your objective.
- Use charts, graphical presentations or visuals to illustrate these key points for better comprehension.
3. Context and significance
- Provide a brief overview of the context in which the data was collected and why it’s significant.
- Explain how the data relates to the larger picture or the problem you’re addressing.
4. Key takeaways
- Summarize the main insights or conclusions that can be drawn from the data.
- Highlight the key takeaways that the audience should remember.
5. Visuals and charts
- Use clear and appropriate visual aids to complement the data.
- Ensure that visuals are easy to understand and support your narrative.
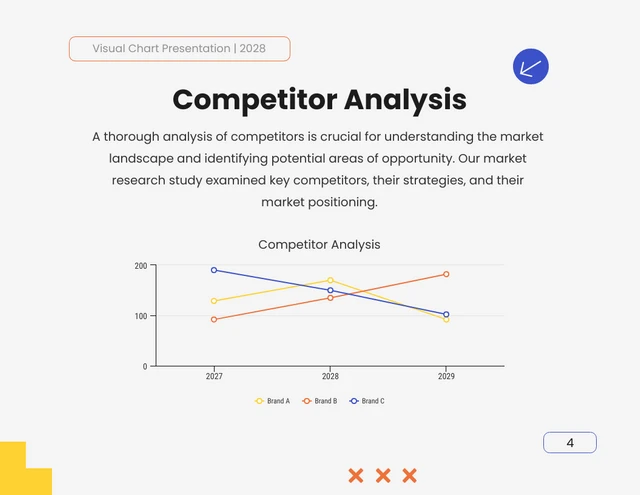
6. Implications or actions
- Discuss the practical implications of the data or any recommended actions.
- If applicable, outline next steps or decisions that should be taken based on the data.
7. Q&A and discussion
- Allocate time for questions and open discussion to engage the audience.
- Address queries and provide additional insights or context as needed.
Presenting data is a crucial skill in various professional fields, from business to academia and beyond. To ensure your data presentations hit the mark, here are some common mistakes that you should steer clear of:
Overloading with data
Presenting too much data at once can overwhelm your audience. Focus on the key points and relevant information to keep the presentation concise and focused. Here are some free data visualization tools you can use to convey data in an engaging and impactful way.
Assuming everyone’s on the same page
It’s easy to assume that your audience understands as much about the topic as you do. But this can lead to either dumbing things down too much or diving into a bunch of jargon that leaves folks scratching their heads. Take a beat to figure out where your audience is coming from and tailor your presentation accordingly.
Misleading visuals
Using misleading visuals, such as distorted scales or inappropriate chart types can distort the data’s meaning. Pick the right data infographics and understandable charts to ensure that your visual representations accurately reflect the data.
Not providing context
Data without context is like a puzzle piece with no picture on it. Without proper context, data may be meaningless or misinterpreted. Explain the background, methodology and significance of the data.
Not citing sources properly
Neglecting to cite sources and provide citations for your data can erode its credibility. Always attribute data to its source and utilize reliable sources for your presentation.
Not telling a story
Avoid simply presenting numbers. If your presentation lacks a clear, engaging story that takes your audience on a journey from the beginning (setting the scene) through the middle (data analysis) to the end (the big insights and recommendations), you’re likely to lose their interest.
Infographics are great for storytelling because they mix cool visuals with short and sweet text to explain complicated stuff in a fun and easy way. Create one with Venngage’s free infographic maker to create a memorable story that your audience will remember.
Ignoring data quality
Presenting data without first checking its quality and accuracy can lead to misinformation. Validate and clean your data before presenting it.
Simplify your visuals
Fancy charts might look cool, but if they confuse people, what’s the point? Go for the simplest visual that gets your message across. Having a dilemma between presenting data with infographics v.s data design? This article on the difference between data design and infographics might help you out.
Missing the emotional connection
Data isn’t just about numbers; it’s about people and real-life situations. Don’t forget to sprinkle in some human touch, whether it’s through relatable stories, examples or showing how the data impacts real lives.
Skipping the actionable insights
At the end of the day, your audience wants to know what they should do with all the data. If you don’t wrap up with clear, actionable insights or recommendations, you’re leaving them hanging. Always finish up with practical takeaways and the next steps.
Can you provide some data presentation examples for business reports?
Business reports often benefit from data presentation through bar charts showing sales trends over time, pie charts displaying market share,or tables presenting financial performance metrics like revenue and profit margins.
What are some creative data presentation examples for academic presentations?
Creative data presentation ideas for academic presentations include using statistical infographics to illustrate research findings and statistical data, incorporating storytelling techniques to engage the audience or utilizing heat maps to visualize data patterns.
What are the key considerations when choosing the right data presentation format?
When choosing a chart format , consider factors like data complexity, audience expertise and the message you want to convey. Options include charts (e.g., bar, line, pie), tables, heat maps, data visualization infographics and interactive dashboards.
Knowing the type of data visualization that best serves your data is just half the battle. Here are some best practices for data visualization to make sure that the final output is optimized.
How can I choose the right data presentation method for my data?
To select the right data presentation method, start by defining your presentation’s purpose and audience. Then, match your data type (e.g., quantitative, qualitative) with suitable visualization techniques (e.g., histograms, word clouds) and choose an appropriate presentation format (e.g., slide deck, report, live demo).
For more presentation ideas , check out this guide on how to make a good presentation or use a presentation software to simplify the process.
How can I make my data presentations more engaging and informative?
To enhance data presentations, use compelling narratives, relatable examples and fun data infographics that simplify complex data. Encourage audience interaction, offer actionable insights and incorporate storytelling elements to engage and inform effectively.
The opening of your presentation holds immense power in setting the stage for your audience. To design a presentation and convey your data in an engaging and informative, try out Venngage’s free presentation maker to pick the right presentation design for your audience and topic.
What is the difference between data visualization and data presentation?
Data presentation typically involves conveying data reports and insights to an audience, often using visuals like charts and graphs. Data visualization , on the other hand, focuses on creating those visual representations of data to facilitate understanding and analysis.
Now that you’ve learned a thing or two about how to use these methods of data presentation to tell a compelling data story , it’s time to take these strategies and make them your own.
But here’s the deal: these aren’t just one-size-fits-all solutions. Remember that each example we’ve uncovered here is not a rigid template but a source of inspiration. It’s all about making your audience go, “Wow, I get it now!”
Think of your data presentations as your canvas – it’s where you paint your story, convey meaningful insights and make real change happen.
So, go forth, present your data with confidence and purpose and watch as your strategic influence grows, one compelling presentation at a time.
Discover popular designs

Infographic maker

Brochure maker

White paper online

Newsletter creator

Flyer maker

Timeline maker

Letterhead maker

Mind map maker

Ebook maker

- Graphical Presentation of Data
Table of Contents
Graphical presentation of data is an essential tool for researchers and decision-makers to convey complex information in a clear and concise manner. It involves using different types of charts, graphs, and diagrams to represent numerical data visually. In this blog, we will explore the different types of graphical representation and their applications in research.
Types of Graphs and Charts
- Bar Graphs: Used to compare discrete values, such as sales figures for different products.
- Line Graphs: Used to show trends over time, such as stock prices over a period.
- Pie Charts: Used to represent parts of a whole, such as the percentage of revenue by product category.
- Scatter Plots: Used to show the relationship between two variables, such as the correlation between temperature and ice cream sales.
- Heat Maps: Used to show the density of data, such as the concentration of customer complaints by region.
Choosing the Right Graphical Representation
The choice of graphical representation depends on the nature of the data and the purpose of the analysis. Some factors to consider include:
- Data type (discrete or continuous)
- Data distribution (normal or skewed)
- Number of variables
- Audience preferences
Best Practices for Graphical Presentation of Data
- Keep it simple and uncluttered
- Use appropriate scales and axes labels
- Use colors and patterns judiciously
- Avoid 3D effects and unnecessary embellishments
- Provide clear titles and captions
- Use appropriate fonts and font sizes
- Ensure readability for colorblind individuals
Graphical presentation of data is a powerful tool for visualizing complex information and communicating insights effectively. By selecting the appropriate chart or graph for the data and following best practices for presentation, researchers and decision-makers can make informed decisions and gain a deeper understanding of their data.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
Average rating 0 / 5. Vote count: 0
No votes so far! Be the first to rate this post.
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you! 😔
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
Research Methodology for Management Decisions
1 Research Methodology: An Overview
- Meaning of Research
- Research Methodology
- Research Method
- Business Research Method
- Types of Research
- Importance of business research
- Role of research in important areas
2 Steps for Research Process
- Research process
- Define research problems
- Research Problem as Hypothesis Testing
- Extensive literature review in research
- Development of working hypothesis
- Preparing the research design
- Collecting the data
- Analysis of data
- Preparation of the report or the thesis
3 Research Designs
- Functions and Goals of Research Design
- Characteristics of a Good Design
- Different Types of Research Designs
- Exploratory Research Design
- Descriptive Research Design
- Experimental Research Design
- Types of Experimental Designs
4 Methods and Techniques of Data Collection
- Primary and Secondary Data
- Methods of Collecting Primary Data
- Merits and Demerits of Different Methods of Collecting Primary Data
- Designing a Questionnaire
- Pretesting a Questionnaire
- Editing of Primary Data
- Technique of Interview
- Collection of Secondary Data
- Scrutiny of Secondary Data
5 Attitude Measurement and Scales
- Attitudes, Attributes and Beliefs
- Issues in Attitude Measurement
- Scaling of Attitudes
- Deterministic Attitude Measurement Models: The Guttman Scale
- Thurstone’s Equal-Appearing Interval Scale
- The Semantic Differential Scale
- Summative Models: The Likert Scale
- The Q-Sort Technique
- Multidimensional Scaling
- Selection of an Appropriate Attitude Measurement Scale
- Limitations of Attitude Measurement Scales
6 Questionnaire Designing
- Introductory decisions
- Contents of the questionnaire
- Format of the questionnaire
- Steps involved in the questionnaire
- Structure and Design of Questionnaire
- Management of Fieldwork
- Ambiguities in the Questionnaire Methods
7 Sampling and Sampling Design
- Advantage of Sampling Over Census
- Simple Random Sampling
- Sampling Frame
- Probabilistic As pects of Sampling
- Stratified Random Sampling
- Other Methods of Sampling
- Sampling Design
- Non-Probability Sampling Methods
8 Data Processing
- Editing of Data
- Coding of Data
- Classification of Data
- Statistical Series
- Tables as Data Presentation Devices
9 Statistical Analysis and Interpretation of Data: Nonparametric Tests
- One Sample Tests
- Two Sample Tests
- K Sample Tests
10 Multivariate Analysis of Data
- Regression Analysis
- Discriminant Analysis
- Factor Analysis
11 Ethics in Research
- Principles of research ethics
- Advantages of research ethics
- Limitations of the research ethics
- Steps involved in ethics
- What are research misconducts?
12 Substance of Reports
- Research Proposal
- Categories of Report
- Reviewing the Draft
13 Formats of Reports
- Parts of a Report
- Cover and Title Page
- Introductory Pages
- Reference Section
- Typing Instructions
- Copy Reading
- Proof Reading
14 Presentation of a Report
- Communication Dimensions
- Presentation Package
- Audio-Visual Aids
- Presenter’s Poise
PowerPoint Charts, Graphs, & Tables Made Easy | Tips & Tricks

In today's digital world, effective communication is key, especially in presentations. After all, in a world saturated with information, the power to express your message clearly and impactfully can make all the difference.
We know that conveying complex information can be challenging, but guess what? It doesn't have to be! After discussing this with our 200+ expert presentation designers , I've gathered their best practices and strategies to create this comprehensive guide.
Below, you will find expert tips and tricks for making, customizing, and presenting PowerPoint charts, graphs, and tables. Stay with us!

Today, we'll explore the following topics:
- PowerPoint Charts and Graphs
Tables in PowerPoint
Free powerpoint charts, graphs, and tables templates, ready to enhance your presentations our team at 24slides is here to help, powerpoint charts and graphs.
If you are thinking of adding tables to your PowerPoint presentation, let me first show you two other great options: charts and graphs.
Charts and graphs stand out for making complex information easy to read at a glance. They’re ideal for identifying trends, representing patterns, and making decisions easier. In addition, charts and graphs capture the audience's attention.
You have many types to choose from, and we'll go over the most important ones later. In the meantime, here are some examples:
Undoubtedly, one of the best ways to take your presentations to the next level.
But you may have a question in mind: What is the difference between a chart and a graph in PowerPoint? Charts refer to any visual representation of data, whether graphical or non-graphical (such as tables). Graphs, on the other hand, refer specifically to the graphical representation of data (such as bar charts).
In other words, all graphs are charts, but not all charts are graphs.
People often confuse these terms in PowerPoint, but they actually refer to different visual elements.
How to Make a Chart in PowerPoint?
First, go to the Insert tab. Then, click on Chart and select your favorite chart type. Finally, enter your data or copy it from somewhere else. Simple!
Here you have the detailed step-by-step instructions:
- Select the slide where you want to add the chart. Choose the Insert tab, then select the Illustrations group's Chart option.
- A dialog box for inserting charts will appear. Choose a category on the left, then double-click the chart you want on the right.
- When inserted, the chart appears alongside a spreadsheet. Here, you have to replace the placeholder data with your own details.
To edit your chart's content, use the selection handles in the spreadsheet to add or remove data.
- When inserting a chart, you will see small buttons on the upper right side of the chart.
Format using the Chart Elements button. Click on “+” to tweak the chart title, data labels, and more. Use the Chart Styles button (brush) to change the chart's color or style. Finally, the Chart Filters button (funnel) will show or hide data from your chart.
Customizing Charts in PowerPoint
We already know about the power of PowerPoint charts, but we still have one more step to take: customizing them.
- Edit data: You can modify data directly in PowerPoint. Just double-click on the chart to open the associated Excel spreadsheet. Here, you can add, delete, or edit data. If you want to do it like a pro, check out how to Link or Embed an Excel File in PowerPoint.
- Change the design: Go to the design tab. Here, you can add or remove elements such as titles, captions, labels, etc.
- Change color and style: Select the format tab. In this section, you will find options to change the chart's color and style. You can even make individual changes.
- Add shape effects: Go to the format tab and unleash your creativity. You can add shadows, reflections, and 3D effects.
And there you have it; now you know how to customize your PowerPoint Chart. If you are looking for more inspiration, take a look at our detailed Flowchart and Gantt Chart articles.
Chart vs table
Is a chart better than a table?
We already know the importance of using tables in PowerPoint presentations. However, you may have a question in mind: are charts better than tables? The short answer is: it depends.
First off, think about what type of data you are dealing with and, most importantly, what message you are trying to get across.
Charts are great for showing trends, making comparisons, and connecting data points. They’re also visually appealing. Conversely, tables could be your perfect selection for numerical data and comprehensive details.
The most important types of charts in PPT and which one is best for you
We have checked out why adding visuals is a game-changer for your presentations. However, which one is best for your needs?
Based on our more than 10 years of expertise and creating around 17,500 slides per month, these are the charts most requested by our customers. Let's explore each one!
“Columns, bars, lines, and pie charts are top picks for clients because they're more descriptive and easier to get for the audience.” Briana/ Design Manager
Column Chart
Ideal for making comparisons. You can represent data in an attractive and clear way. It’s also a great option for showing changes over time. Here, you can emphasize the difference in quantities.
Imagine you're tracking sales for a store. If you have many categories of sales data and need to compare them, a column chart could be just what you need.
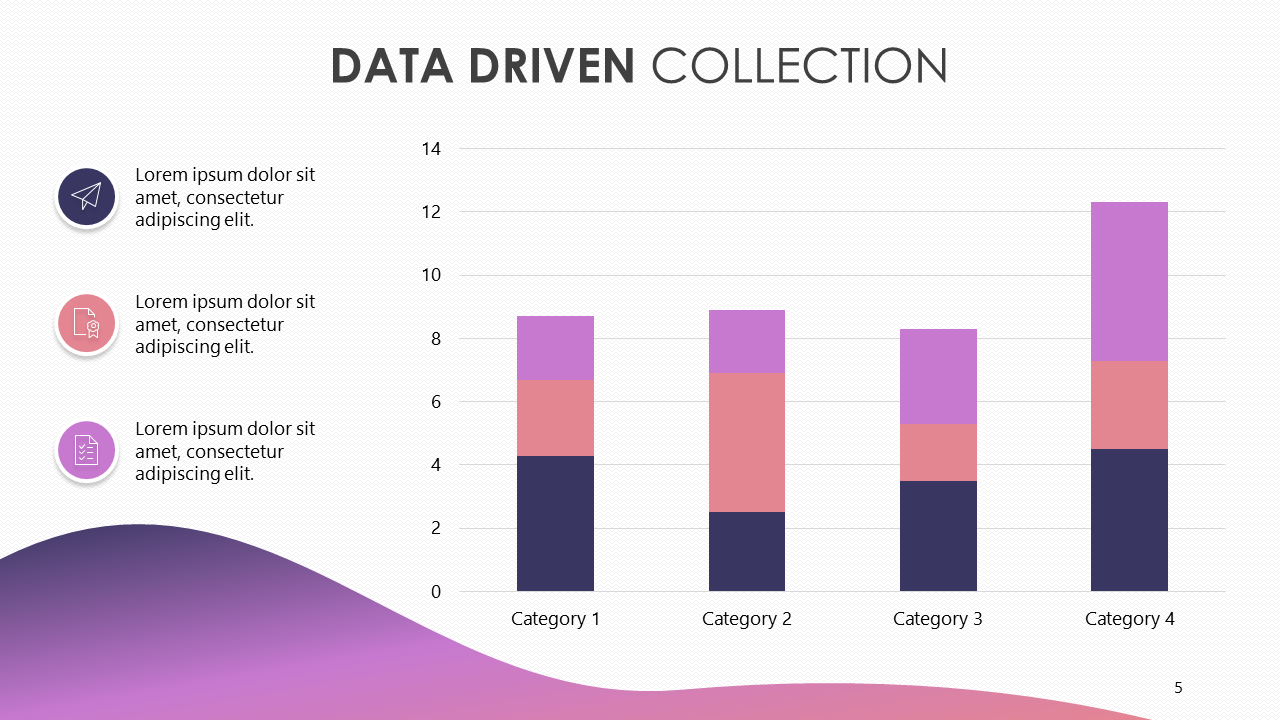
Download our Free Column Chart Template here.
Like the column chart, the bar chart can simplify complex information quickly , especially when comparing data. But, the horizontal layout might influence how people see things, potentially altering how they understand your data. Keep this in mind!
When you have long category labels or many categories, choose a bar chart instead of a column chart. Horizontal bars are easier to read and take up less space in the presentation.
Download our Free Bar Chart Template here.
The top choice for showing trends over time. You can even combine it with other charts. For example, you can add them to a column chart to display different data at a glance. This makes it easier for viewers to understand complex information.
But how to make a line graph in PowerPoint? First, click on the Insert tab. Then, click on Graph and select Line Graph. That's it—it's as simple as that.
Download our Free Line Chart Template here .
The best for showing proportions. Not only is it easy to understand, but you will also be able to illustrate percentages or parts of a whole.
Pie charts are easy to create, you need to figure out the percentages or proportions of each data category. But remember, keep the chart to six or fewer sections. This maintains data impact, avoiding confusion.
Download our Free Pie Chart Template here .
How to Use Charts and Graphs Effectively?
We already know how to use PowerPoint charts, graphs, and tables, but we want to go one step further. Here are the best tips for making effective PowerPoint presentations.
- Choose the right type of chart. Choose graphics that best suit your data. For example, use column or bar charts to compare categories, line charts to show trends over time, and pie charts to display parts of a whole.
- Be selective. Avoid using too much information, eliminate irrelevant details, and keep it simple. By focusing on the most important data points, you enhance the clarity of the information for your audience.
- Pay attention to color. When presenting data , keep in mind the consistency of the colors and make sure essential information stands out. Avoid using too many colors here, as this can be distracting.
- Add context. Make your titles clear and descriptive. Labels should also serve as a guide for viewers to understand everything easily. This could mean explaining trends, defining terms, or just describing where the data comes from.
- Consistency. Use the same style and format for your graphics and data. Ensure brand consistency in a presentation is key. This creates a professional and polished visual presentation.
- Be creative. Try unique ways to showcase your data, like infographics or custom graphics. For example, you can use a bar chart to compare categories and a line chart to show the trend over time.
Pro Tip: Creating a PowerPoint infographic is one of the most creative ways to present data. They provide a visually engaging and easy-to-follow format for presenting complex information. Briana/ Design Manager
PowerPoint tables help organize and display data in a structured way for presentations. They’re made up of rows and columns containing text, numerical data, or other information.
Tables are awesome for showing comparisons, summarizing information, sharing research findings, and planning. Because of all that, they are a top choice for visualizing financial or statistical data. They’re incredibly versatile and practical!
All you need to do is put the right labels on, and reading should be a breeze. Believe us, your audience will appreciate it. Do you want to present data in detail and make comparisons? Then, this is your best option.
People have been using PowerPoint tables for a long time. Why? That's simple: they’re easy to read.
Here's an example:

Download our Free Table Template here .
How to Make a Table in PowerPoint?
Inserting tables in PowerPoint is quite simple. Just click on Insert and then on Table . Next, just drag the mouse down to choose the number of rows and columns you need.
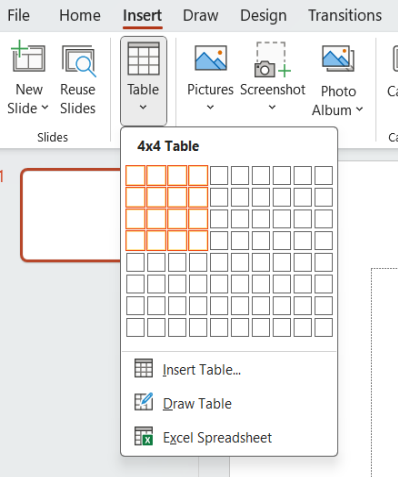
Should you require a bigger table? You can manually select the values for the columns and rows.
Customizing tables in PowerPoint
Now that we know how to create a table in PowerPoint, let's customize it. But first, let's learn how to add rows and columns in PowerPoint.
- How to add a row to a table in PowerPoint?
Click on a cell in the existing table. Go to the Layout tab in the ribbon and select Insert . Select Insert Rows Above or Insert Rows Below , depending on where you want to add the new row.
- How to add a column to a table in PowerPoint?
Click on an adjacent cell in the table. Go to the Layout tab in the ribbon and then select Insert . Choose either Insert Columns Left or Insert Columns Right , depending on where you want to add the new column.
Now that you have the structure of your table ready, let's give it some styling:
- Applying style in your table presentation
To edit your tables, first select a cell. Then, click on the Design tab to pick the style you like best. Finally, click on the drop-down arrow to see the complete Table Styles gallery .
That's it. Now you know how to use tables in PowerPoint.
How to Use Tables Effectively?
Tables are powerful tools for presenting data in a structured format. They can enhance clarity, facilitate comparisons, and convey complex information.
However, when you don't use them correctly, they can have the opposite effect, making the information flat and boring. So here are golden rules to help you:
Keep it simple
Don't overload your table with too much information. Focus on the most important information to keep it clear and easy to read. Remember, the powerful presentation of data is in simplicity.
Consider whether gridlines are necessary for your table. Removing them can make your board look cleaner and more professional.
Although many don't mention it, choosing the right words is vital. The more you can say of the same idea in fewer words, the better. Avoid using words or connectors that add nothing to the message.
Highlight key data points
Make your table pop using bold, italics, or fun colors to highlight important data or headings. This will make the table easier to read.
Consider adding shades for alternate rows to make your table easier to read. Make the shadow subtle, to avoid distraction from the data itself.
You can use color to emphasize backgrounds or text. No matter which method you opt for to add contrast, remember that “less is more” when creating an effective table.
Consistency
Consistency is crucial in tables, as it is in graphics. Ensure that the font style, size, and color are the same across the entire table. This helps maintain visual harmony.
Align your text and numbers properly so they're easier to read and give your table a polished look. If you will use decimals, think about aligning them to facilitate comparisons.
In this article, we have explored the benefits of incorporating visuals like charts, graphs, and presentation tables in PowerPoint. We also know how to add them and ensure they look good.
Just remember to pick the right chart and keep your presentations consistent.
And as I said at the beginning, conveying complex information doesn't have to be challenging! Our Templates by 24Slides platform has hundreds of free PowerPoint charts, graphs, and table templates.
You can download and combine different templates to create a shiny PowerPoint Presentation. All the examples in this article are fully customizable, allowing you to insert your data without worrying about design. Enjoy them!
Knowing how to use PowerPoint charts, graphs, and tables can make the difference between a successful presentation and a failed one. However, mastering the art of presenting data takes more time and effort.
The good news? You can always trust professionals to do the heavy work, allowing you to focus on improving your product or service — what really matters to your business.
With an average satisfaction score of 4.8 out of 5 from over 1.3 million redesigned slides, it's safe to say we're incredibly proud of the product we deliver.
We're the world's largest presentation design company.
Not only will you receive an attractive presentation, but we will create one that fits your brand's visual guidelines. Most importantly, it will help emphasize your message and engage your audience.

Ready to elevate your PowerPoint presentations? Explore this content!
- PowerPoint 101: The Ultimate Guide for Beginners
- Mastering the Art of Presenting Data in PowerPoint
- The Ultimate Brand Identity Presentation Guide [FREE PPT Template]
- 7 Essential Storytelling Techniques for your Business Presentation
- The Cost of PowerPoint Presentations: Discover the hidden expenses you might overlook!
Create professional presentations online
Other people also read
How To Write Effective Emails That Will Improve Your Communi...

How to Make a Marketing Plan Presentation in PowerPoint

Alternative presentation styles: Takahashi

Find the images you need to make standout work. If it’s in your head, it’s on our site.
- Images home
- Curated collections
- AI image generator
- Offset images
- Backgrounds/Textures
- Business/Finance
- Sports/Recreation
- Animals/Wildlife
- Beauty/Fashion
- Celebrities
- Food and Drink
- Illustrations/Clip-Art
- Miscellaneous
- Parks/Outdoor
- Buildings/Landmarks
- Healthcare/Medical
- Signs/Symbols
- Transportation
- All categories
- Editorial video
- Shutterstock Select
- Shutterstock Elements
- Health Care
- PremiumBeat
- Templates Home
- Instagram all
- Highlight covers
- Facebook all
- Carousel ads
- Cover photos
- Event covers
- Youtube all
- Channel Art
- Etsy big banner
- Etsy mini banner
- Etsy shop icon
- Pinterest all
- Pinterest pins
- Twitter all
- Twitter Banner
- Infographics
- Zoom backgrounds
- Announcements
- Certificates
- Gift Certificates
- Real Estate Flyer
- Travel Brochures
- Anniversary
- Baby Shower
- Mother’s Day
- Thanksgiving
- All Invitations
- Party invitations
- Wedding invitations
- Book Covers
- Editorial home
- Entertainment
- About Creative Flow
- Create editor
- Content calendar
- Photo editor
- Background remover
- Collage maker
- Resize image
- Color palettes
- Color palette generator
- Image converter
- Contributors
- PremiumBeat blog
- Invitations
- Design Inspiration
- Design Resources
- Design Elements & Principles
- Contributor Support
- Marketing Assets
- Cards and Invitations
- Social Media Designs
- Print Projects
- Organizational Tools
- Case Studies
- Platform Solutions
- Generative AI
- Computer Vision
- Free Downloads
- Create Fund

8 Types of Presentations and Examples of When You Can Use Them
Presentations help you communicate ideas in a simple way that sticks with your target audience. here’s what you need to know to have success with all types of presentations..
For your presentation to be effective, you need to choose the right format and recognize the nuances of each one. Here’s a look at eight types of presentations you can use to share your knowledge.
8 Types of Presentations

1. Providing Information
The primary purpose of any type of presentation is to provide information to an audience. The difference between this method and others is that there are many elements you have to consider in order to be effective. That includes slide design , talking points, and usually, a time limit.
2. Teaching
When you’re educating, use several examples to illustrate your points. If your audience doesn’t understand something you’re talking about, give them specific examples so they can see for themselves what you mean.
Repetition is key when you teach a new concept. It’s important to include a variety examples throughout your slide deck to reinforce your information. This helps combat your audience getting bored or tired from hearing the same thing over and over again.
3. Reporting
You can use presentations when reporting by showing research findings and conclusions. The most important thing to remember is that you need to design your slides to highlight your most critical data. That way, your audience will walk away understanding its high points.
It’s important to know your audience before you jump into your presentation and start selling. Research must be the first step of the process, so you can design a presentation that speaks to your people.
Also, be sure to not overwhelm yourself or others by packing too much information into one slide.
5. Problem-Solving
While it’s a less common use case, you can also use presentations to sort out problems. This is especially useful when you’re working with a team. It acts as a simple way to get everyone on the same page before making a decision.
6. Decision Making
Once you come to an agreement that something is an issue and discover some ways to solve it, there are still choices you need to make. You can use presentations to explore and explain different options before you finalize your next step forward.
7. Entertaining
Creating a presentation with entertainment in mind is a nice way to break up any potential monotony and deliver important information, at the same time.
The entertainment factor doesn’t necessarily have to be goofy or fun, but it should be compelling for the audience and capture their attention. Visuals are particularly important here.
8. Motivational
Stories are good tools for bringing any message home. Use personal anecdotes and examples that illustrate points. This will help people remember your message when they need it most, and it also makes it easier for the audience to connect with you.
3 Presentation Use Cases

Want to take your information and put it in presentation format for your audience? Before you start, use these examples to gain inspiration.
1. Business Presentation Examples
Business presentations don’t have to be boring. Take these tips to wow your colleagues and your audience.
Conferences
There are many different companies and ideas competing for attention at conferences. Use storytelling and bold design choices to stand out.
Raising Awareness
Getting a new initiative going in an organization is no easy feat. Use a presentation to fill in stakeholders on what you want to do and get their approval.
Sales Decks
Selling has a direct impact on revenue goals, so it’s critical for your presentation to support that. Include questions, pain points, and supporting data to let your potential customers know you “get” them.
2. Presentation Ideas for Kids and Students
Education requires a lot of listening and absorbing information. Help kids and students show what they know with these presentation formats.
All About Them
For younger or new students, this is an easy presentation idea. They can create slides that explain details about themselves to learn the art of public speaking. It also helps their peers get to know them better.
Charts and Graphics
Facts and data play a key role in understanding a concept. However, keeping track of them all can be intimidating. Take them through the process of communicating complex ideas visually, with this presentation idea for students.
Storytelling
Stories are an important part of early learning but, eventually, we all learn there’s a place for stories outside of a book. Students and kids can create presentations that focus on this skill.
3. Virtual Presentation Ideas
Virtual presentations are more prevalent than ever, but engaging an audience when you aren’t in the same room isn’t easy.
If you’re sharing ideas with a group, make it interactive by giving a workshop-style presentation. Be sure to leave room to ask and answer questions, as well as save space for group discussions.
Ask Me Anything
The question and answer format is a popular presentation type, but you can add even more interest with slides. Use images, fonts , and colors that are on brand and increase engagement.
Information and Gamification
Gamification results in 14% higher scores on skill-based assessments. To amplify people’s understanding of the concepts you present, use gamification throughout your slide deck.
How to Put Together Presentation Ideas without PowerPoint

If you’re looking for creative presentation ideas without PowerPoint , Shutterstock Create’s slideshow presentation maker is easy to use. Our designer-crafted templates are super-simple to customize and make your own in just a few clicks.
We have thousands of graphics in a multitude of styles, shapes, and sizes you can use to create designs that others will notice. We also offer gorgeous stock photos to help you communicate exactly what you need to with each visual. Everyone has something to teach, now it’s your turn. Use these ideas to create all types of presentations and communicate effectively.
Need some more presentation inspo? We’ve got you covered:
- How to Make a Professional Video Presentation
- 10 Fun “Presentation Night” Ideas
- Google Slides vs. PowerPoint: Which Is Best to Make a Slideshow?
License this cover image via AlexandrWell .
Recently viewed
Related Posts

11 Profile Picture Ideas to Stand Out on Any Platform
While social media is designed to be fun and casual,…

Shutterstock’s Vast Library of Data Now Available on Google Cloud Marketplace
You need data you can trust. Whether you’re building models for…

10 Genius Print Advertising Ideas (with Examples and Tips)
If you thought print was dead, think again! Print advertising…

Creative Poster Design Ideas and Templates to Inspire You
Learn how to come up with your own poster design ideas and see the process of bringing your idea to life in an online image editing tool.
© 2023 Shutterstock Inc. All rights reserved.
- Terms of use
- License agreement
- Privacy policy
- Social media guidelines
Diagramming Build diagrams of all kinds from flowcharts to floor plans with intuitive tools and templates.
Whiteboarding collaborate with your team on a seamless workspace no matter where they are., data generate diagrams from data and add data to shapes to enhance your existing visuals., enterprise friendly easy to administer and license your entire organization., security see how we keep your data safe., apps & integrations connect to all the tools you use from microsoft, google workspace, atlassian, and more..
- What's New Read about new features and updates.
Product Management Roadmap features, brainstorm, and report on development, so your team can ship features that users love.
Software engineering design and maintain complex systems collaboratively., information technology visualize system architecture, document processes, and communicate internal policies., sales close bigger deals with reproducible processes that lead to successful onboarding and training..
- Getting Started Learn how to make any type of visual with SmartDraw. Familiarize yourself with the UI, choosing templates, managing documents, and more.
- Templates get inspired by browsing examples and templates available in SmartDraw.
Diagrams Learn about all the types of diagrams you can create with SmartDraw.
Whiteboard learn how to combine free-form brainstorming with diagram blueprints all while collaborating with your team., data visualizers learn how to generate visuals like org charts and class diagrams from data., development platform browse built-in data visualizers and see how you can build your own custom visualization., open api the smartdraw api allows you to skip the drawing process and generate diagrams from data automatically., shape data add data to shapes, import data, export manifests, and create data rules to change dashboards that update..
- Explore SmartDraw Check out useful features that will make your life easier.
- Blog Read articles about best practices, find tips on collaborating, learn to give better presentations and more.
Support Search through SmartDraw's knowledge base, view frequently asked questions, or contact our support team.
- Site License Site licenses start as low as $2,995 for your entire organization.
- Team License The SmartDraw team License puts you in control with powerful administrative features.
Apps & Integrations Connect to all the tools you use.
- Contact Sales
What's New?

Solutions By Team
License everyone for as low as $1 per user per month.
Save money, and replace Visio, Lucidchart, Lucidspark, and Miro with a SmartDraw site license.
Getting Started Learn to make visuals, familiarize yourself with the UI, choosing templates, managing documents, and more.
Templates get inspired by browsing examples and templates available in smartdraw., developer resources, additional resources.
Site License As low as $1 per user per month for your entire organization.
Team license get powerful administrative features for your team., solutions for your team.
Choosing the Right Graphic for your Report

Whether you're writing a business report, technical paper, or making a presentation, using diagrams or graphics can help clarify your message.
But which graphic is best for the information at hand?
Here is a list of some diagram types you may want to use in various situations to enhance your presentation or report.
Use a bar graph to compare sets of data against one another, or show changes in data over time. Bar graphs can be vertical (as shown here), horizontal, or stacked. Problems can arise if proportions and spacing are inconsistent, although SmartDraw eliminates this problem by doing the formatting for you.
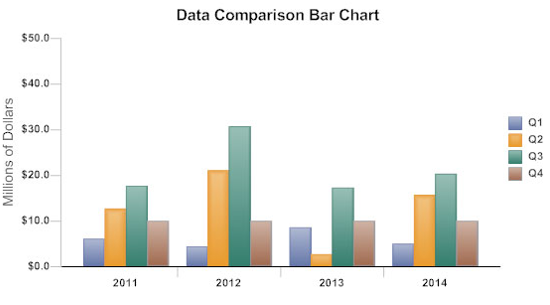
A line graph is useful for showing trends over time. It's best for illustrating dramatic changes. Make sure the scale is appropriate and don't clutter the chart with too much information.
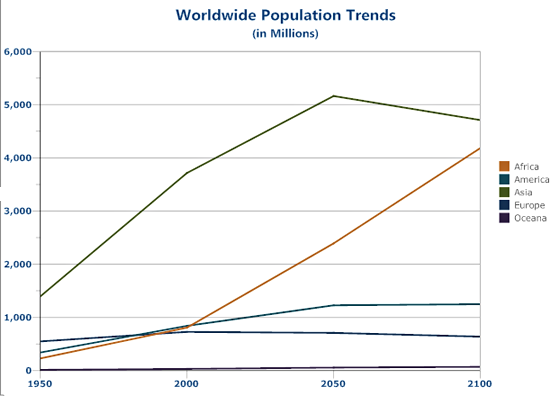
A pie chart displays the distribution of several items in one data category. The main thing to remember when using a pie chart is that the sum of the data must equal 100 percent. Pie charts work best when there are no more than five "slices," or data points, and the amounts vary enough to make the diagram visually compelling. In this example, the five data points range from 1 to 48 percent, so the differences are illustrated quite effectively.
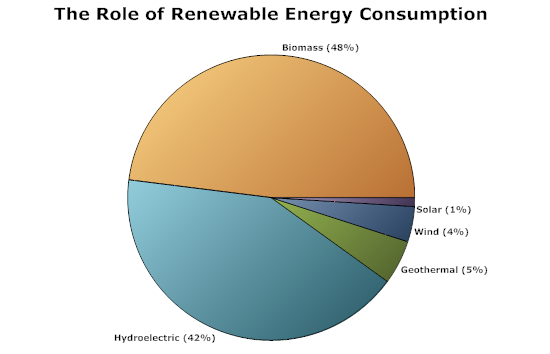
To show the sequence of steps in a process or the effects of decisions, use a flowchart. Flow the information from left to right or top down, and keep the diagram clean and simple. It should be easy for anyone to follow and understand with no explanation.
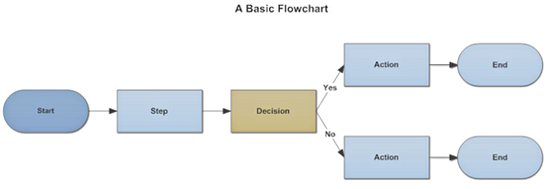
Instead of categorized lists of bullet-point information, a mind map provides a visual structure that makes the information easier to find and comprehend.
Mind maps created in SmartDraw are also a very useful tool for a presentation, because hyperlinks to web pages or documents can be inserted in any box, making the linked information easy to access with just a click.
Gantt Chart
For projects, a Gantt chart is a good way to show a quick summary of tasks, assignments, timelines, and to report progress. For larger projects, a Gantt chart may have too much detail for a report or presentation. In that event, it may be preferable to just show a timeline.
A timeline is a straightforward graphic that shows events as they occur, or or scheduled to occur. Major milestones or deadlines serve as markers on a scaled timeline, which typically runs horizontally along the bottom of the graphic.
A map is an excellent way to show geographically based information. They might include sales territories, airline routes, or numerical data defined by geography, as shown in the map below. It's important to make sure colors are easy to differentiate and labels or legends are clear. Don't try and pack too much detail into a map, as it may confuse the reader or audience.
More Articles
- SmartDraw Blog
- Productivity
Collaboration
The cure for the powerpoint ® blues, write better reports faster, how to give a ted talk (or make any presentation memorable), smartdraw makes diagramming easy.

- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
How to Make a “Good” Presentation “Great”
- Guy Kawasaki

Remember: Less is more.
A strong presentation is so much more than information pasted onto a series of slides with fancy backgrounds. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others. Here are some unique elements that make a presentation stand out.
- Fonts: Sans Serif fonts such as Helvetica or Arial are preferred for their clean lines, which make them easy to digest at various sizes and distances. Limit the number of font styles to two: one for headings and another for body text, to avoid visual confusion or distractions.
- Colors: Colors can evoke emotions and highlight critical points, but their overuse can lead to a cluttered and confusing presentation. A limited palette of two to three main colors, complemented by a simple background, can help you draw attention to key elements without overwhelming the audience.
- Pictures: Pictures can communicate complex ideas quickly and memorably but choosing the right images is key. Images or pictures should be big (perhaps 20-25% of the page), bold, and have a clear purpose that complements the slide’s text.
- Layout: Don’t overcrowd your slides with too much information. When in doubt, adhere to the principle of simplicity, and aim for a clean and uncluttered layout with plenty of white space around text and images. Think phrases and bullets, not sentences.
As an intern or early career professional, chances are that you’ll be tasked with making or giving a presentation in the near future. Whether you’re pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something else, a great presentation can give you a competitive advantage, and be a powerful tool when aiming to persuade, educate, or inspire others.
- Guy Kawasaki is the chief evangelist at Canva and was the former chief evangelist at Apple. Guy is the author of 16 books including Think Remarkable : 9 Paths to Transform Your Life and Make a Difference.
Partner Center
- For Tech Brands
- For Startups
- Get an estimate
- Success stories
- Video For Growth Blog
- About Vidico
- Get in touch
15 Best Types of Motion Graphics for Your Projects (2024)
Imagine your brand launching a new campaign where vibrant motion graphics capture viewers’ attention in the bustling digital landscape.
But what exactly are motion graphics, and how can they elevate your brand’s storytelling?
Continue reading to explore various styles and discover which ones best align with your brand’s goals and audience expectations.
By the end of this article, you’ll know how to choose motion graphics that boost your storytelling and engage your audience effectively.
15 Different Types of Motion Graphics
1. animated typography.

Description: Animated typography, or kinetic typography, is one of the most popular types of motion graphics that brings text to life by adding movement and animation. This style is incredibly effective for grabbing attention and emphasizing key points.
Imagine your most important messages appearing with a dynamic flair, captivating your target audience from the first moment. Animated typography is perfect for highlighting quotes, a call to action, or any critical information you want to stand out.
Kinetic typography transforms static images into liquid motion with an engaging visual experience, making your content more memorable and impactful.
- Lyric videos
- Opening credits of TV Shows or Movies
- Kinetic typography with text as a major visual element
Ready to enhance your brand’s visual storytelling? Try our VidiFit Quiz for an instant pricing estimate in just 2 minutes. Collaborate with Vidico [ 1 ] to maximize the impact of motion graphics animation.
2. Advanced Animated Titles
Description: Advanced animated titles are designed to captivate your audience from the beginning. These titles go beyond simple animated text, incorporating intricate graphics, stunning effects, and smooth transitions that instantly engage your video.
Advanced animated titles set the tone for your content and add a professional touch that elevates your brand. They combine creativity with precision, making your content visually appealing and highly effective in communicating your brand’s story.
- Logo animations to reveal your brand identity in a dynamic and engaging way.
- Lower thirds display additional information or context during an interview, such as the speaker’s name and title.
- End screens to wrap up your video and encourage further action, like subscribing to a channel or visiting a website.
3. Animated Graphic Loops
Description: Animated graphic loops are continuous motion graphics that repeat seamlessly, creating an endless animation cycle. These loops are highly effective for adding a dynamic visual element to your projects without the distraction of a start or end point.
They are perfect for maintaining viewer engagement and adding visual interest to backgrounds, web design, presentations, or as part of a marketing strategy.
- Seamless Loops provides a smooth and continuous visual experience.
- Cinemagraphs that combine still images with a subtle motion to create a mesmerizing effect where only part of the image moves
- Lottie Animations that use vector graphics and JSON data for web and mobile applications
4. Animated Ads

Description: Animated ads [ 2 ] are dynamic and visually engaging, using motion graphics animation to capture attention and convey messages effectively. These video ads are ideal for promoting products, services, or brand messages in a compelling and memorable way.
By combining movement, graphics, music, and sound effects, animated ads or promotional videos can tell a story, demonstrate a product, or highlight key features in a way that static ads cannot.
- Product demos that shows how a product works through engaging animations and highlight its features and benefits.
- Explainer videos are short, animated videos that explain a service or concept and understandably.
- Social media ads and instructional videos that designed to grab attention as users scroll through their feeds.
5. Product Animations
Description: Product animations are motion graphics that showcase a product’s features, benefits, and functionality in an engaging and visually appealing way. These animations are perfect for bringing a product to life, demonstrating how it works, and highlighting what makes it unique.
Using different types of motion graphics, product animations can effectively communicate complex ideas and capture the viewer’s attention.
- 360-degree rotations that show every angle of a product.
- Exploded views that break down a product into its components, like instructional videos
- Feature highlight videos that focus on key aspects of a product.
6. UI/UX Animations
Description: UX/UI animations are motion graphics designed to enhance digital product user experience and interface. These animations make interactions more intuitive, engaging, and enjoyable by providing visual feedback and guiding users through an application or website.
User interface animations can simplify complex processes, indicate actions, and improve a digital product’s overall aesthetic appeal.
- Loading animations that keep users engaged while content is being fetched.
- Button animations that provide feedback when clicked or hovered over.
- Micro-interactions that offer subtle visual cues to improve usability.
7. Explainer Videos

Description: Explainer videos are concise, engaging motion graphics that simplify complex ideas, products, or services into easy-to-understand visual stories. These motion graphic videos capture your audience’s attention and convey your message quickly and effectively.
An explainer video can help demystify your offerings and highlight their value by combining clear narration with compelling visuals, making it an excellent tool for education and promotion.
- Animated overviews that break down how a product or service works.
- Instructional video that walks viewers through a process.
- Company story videos that introduce your brand and its mission.
8. Transparent Animated Assets
Description: Transparent animated assets are motion graphics with transparent backgrounds, allowing them to seamlessly integrate into various projects without obstructing the underlying content.
These versatile animations can add dynamic elements to videos, websites, presentations, or other digital media. They enhance visual appeal and can be layered over different backgrounds to create a cohesive and engaging experience.
- Animated icons that add flair to your website or app interface.
- Moving logos that can be overlaid on videos without blocking important content.
- Animated call-to-action buttons that draw attention to web pages.
9. Infographics

Description: Infographics are visual representations of information, data, or knowledge intended to present complex information quickly and clearly.
Animated infographics take this a step further by adding motion, which can help highlight key data points, illustrate processes, and make the information more engaging and memorable.
Unlike live-action footage, infographics are perfect for breaking down statistics, explaining complex concepts, and telling a story with data.
- Data visualizations that dynamically display statistics and trends.
- Process animations that illustrate steps in a workflow or procedure.
- Comparison charts that animate to show differences between options or periods.
10. Template Editing
Description: Template editing involves customizing pre-designed motion graphic templates to fit your needs.
These templates provide a foundation tailored to your brand’s colors, text, images, and other elements, saving time and ensuring consistency. Template editing is perfect for creating videos that are polished, professional-looking.
- Customizing explainer video intros and outros with your brand’s animated logo and colors.
- Editing presentation templates to include your data and key points.
- Adapting social media templates for posts, stories, and ads.
11. Transitions
Description: Transitions, even those lasting just a split second, are crucial in visual storytelling. They help establish the mood and tone from scene to scene, ensuring a smooth narrative flow.
Effective transitions, such as hard cuts, dissolves, and glitch effects, guide the viewer naturally through your story. Conversely, poorly chosen transitions can be jarring and disrupt the viewer’s experience.
- Hard cuts that provide a sharp and direct change between scenes.
- Glitch effects that add a dynamic, modern twist to scene changes.
- Fade-out/fade-in transitions that signal the end of one scene and the beginning of another.
Description: Animated icons are small, dynamic visual elements that add a touch of interactivity and engagement to your digital content. These icons can enhance user experience, draw attention to specific features, or add a bit of personality to your projects.
By incorporating motion graphics, animated icons can effectively communicate ideas, actions, or statuses in a way that static icons cannot.
- Loading icons that show progress and keep users informed.
- Interactive icons that respond to user actions, such as clicks or hovers.
- Notification icons that draw attention to alerts or messages.
13. Animated Logos
Description: Animated logos bring your brand identity to life by adding movement and energy to your static logo design. These animations can create a lasting impression, capturing the viewer’s attention and enhancing brand recognition.
Animated logos are perfect for intros and outros in videos, websites, presentations, and other digital media, providing a dynamic and professional touch.
- Logos that transform or reveal themselves through creative animations.
- Subtle animations that add a sparkle or glow effect to your logo.
- Logos that interact with other visual elements on the screen, such as text or background graphics.
Description: GIFs, or Graphics Interchange Format animations, are short, looping animations that can be easily shared across different social media platforms. They are perfect for conveying emotions, reactions, or simple messages in a fun and engaging way.
GIFs are widely used on social media, emails, and websites to capture attention and enhance communication with a touch of humor or creativity.
- Reaction GIFs that convey emotions like joy, surprise, or frustration.
- Promotional GIFs that highlight a product feature or announcement.
- Decorative GIFs that add a dynamic element to web pages or emails.
15. Presentations

Description: Animated presentations use motion graphics to create dynamic, engaging slideshows that communicate information effectively. By incorporating animations, transitions, and visual effects, these presentations can capture the audience’s attention and make complex ideas easier to understand.
Animated presentations are perfect for business pitches, educational lectures, and conference talks. They add a professional and polished touch to your video content.
- Animated charts and graphs that engagingly visualize data.
- Text animations that highlight key points or quotes.
- Interactive elements that encourage audience participation or feedback.
What are Motion Graphics?
Motion graphics are a captivating form of animation that blends visual elements such as text, graphics, and images to create the illusion of movement. They are designed to convey information, tell stories, and add visual interest to digital content.
By integrating motion, motion graphics enhance the viewer’s engagement and understanding, making them a powerful tool for communication.
Widely used in various media, including videos, presentations, websites, and advertisements, motion graphics can bring data to life in animated infographics, set the tone with dynamic title sequences in movies or TV shows, simplify complex ideas in explainer videos, and boost engagement with animated social media posts.
Different types of motion graphics are versatile and can transform static visuals into dynamic experiences, making them an essential component of modern digital content.
How Does It Work?
Motion graphics combine visual elements such as text, graphics, and images with animation techniques to create the illusion of movement. The process typically begins with conceptualization, where the idea or message is developed into a storyboard or visual plan.
Using graphic design software, designers then create the visual assets, including illustrations, icons, and typography. These assets are imported into animation software, where animators add motion, timing, and effects to bring the visuals to life.
The final step involves rendering the animated sequence into motion graphics video that can be used on any social media platform.
Using motion and whiteboard animation, these graphics capture attention, convey complex information more effectively, and add a dynamic element to digital content, which can be helpful for video marketing.
Benefits of Motion Graphics
- Capture attention quickly with dynamic and engaging visuals.
- Motion graphics can simplify complex information through eye-catching animations [ 3 ].
- Motion design can enhance brand recognition by incorporating consistent design elements.
- Motion graphic design improves user experience with smooth transitions and animations.
- Different types of motion graphics can increase conversion rates and boost sales and engagement on social media and digital platforms.
- Add a professional and polished touch to presentations and motion graphics videos.
- Motion design can make content more memorable and impactful.
- Different types of motion graphics can be used across various media, including websites, advertisements, and educational materials.
What is the difference between motion graphics and animation?
Motion graphics and animation involve moving visual elements but serve different purposes and styles.
Motion graphics styles primarily focus on animating graphic design elements like text, simple shapes, and icons to convey information or create visual interest. They are often used in explainer videos, title sequences, and presentations.
Conversely, animation encompasses a broader range of styles and techniques, including character animation and storytelling in films, TV shows, and animated video games.
While different types of motion graphics are typically more abstract and design-oriented, animation, like whiteboard animation, often involves creating lifelike animated characters, animated objects, and narratives.
What are motion graphics most useful for?
Motion graphics are most useful for presenting information in an engaging and easily digestible manner. They simplify concepts through storytelling, making them ideal for explainer videos, educational content, and data visualizations.
Additionally, by adding dynamic movement, motion graphic styles enhance the aesthetic appeal of digital content, such as social media posts, advertisements, and website elements. They are also effective in branding, helping to reinforce brand identity through logos, intros, and outros in videos.
Key Takeaways
Motion graphics encompass various styles and applications, each uniquely enhancing how we communicate and engage with audiences.
From animated typography and advanced animated titles to UI/UX animations, explainer videos [ 4 ], and logo animation, motion graphics animation brings ideas to life with dynamic visuals and compelling storytelling.
They simplify complex information, capture attention, and polish your digital content professionally. By integrating these various types of motion graphics, you can create engaging, memorable experiences that leave a lasting impact on your audience.
Ready to elevate your brand’s visual storytelling using motion graphics techniques? Use our VidiFit Quiz to get clear pricing in less than 2 minutes. Partner with Vidico to leverage the power of motion graphics on every video piece.
References :
- https://www.globenewswire.com/en/news-release/2022/08/12/2497652/0/en/Video-Production-Company-Vidico-Launch-Rebrand-To-Offer-Their-Customers-Clarity-Precision-And-An-Even-Higher-Level-Of-Communication.html
- https://medium.com/@digitalpanorama/using-animation-in-advertising-why-is-it-important-how-to-do-it-5de1713027dc
- https://www.adobe.com/uk/creativecloud/animation/discover/motion-graphics.html
- https://www.forbes.com/sites/forbescommunicationscouncil/2020/03/04/how-to-create-explainer-videos-that-drive-marketing-success/

Video For Growth Newsletter
Join 9,169+ product marketers, brand managers and startup founders learning to create effective and impactful video content.
- 10 Best 2D Explainer Video Examples: Must-Watch (2024)
- 2D Animation Styles & Examples: Comprehensive Guide (2024)
Stand out with advanced video marketing insights.
Start with a free strategy session.

Microsoft 365 Life Hacks > Presentations > How many slides does your presentation need?
How many slides does your presentation need?
When you’re creating a presentation, it’s important to consider the amount of information you’re sharing with your audience. You don’t want to overwhelm them, but you also want to be comprehensive and ensure that you’re covering all your bases. Whether you’re giving a 10, 15, or 30-minute presentation, see how many slides your presentation needs to get your point across.

Rules and guidance for PowerPoint presentations
PowerPoint is a powerful visual aid for introducing data, statistics, and new concepts to any audience. In PowerPoint, you can create as many slides as you want—which might sound tempting at first. But length doesn’t always guarantee a successful presentation . Most presentations last around 10-15 minutes, and anything longer than that (such as a 30-minute presentation) may have additional visual aids or speakers to enhance your message.
A handy rule to keep in mind is to spend about 1-2 minutes on each slide. This will give you ample time to convey your message, let data sink in, and allow you to memorize your presentation . When you limit each slide to this length of time, you also need to be selective about how much information you put on each slide and avoid overloading your audience.
For 10-minute presentations
Ten minutes is usually considered the shortest amount of time you need for a successful presentation. For a shorter 10-minute presentation, you’ll need to be selective with your content. Limit your slide count to approximately 7 to 10 slides.
For 15-minute presentations
When preparing for a 15-minute presentation, concise and focused content is key. Aim for around 10 to 15 slides to maintain a good pace, which will fit with the 1-2 minute per slide rule.
For 30-minute presentations
A longer presentation gives you more room to delve deeper into your topic. But to maintain audience engagement, you’ll need to add interactivity , audience participation, and elements like animations . Aim for around 20 to 30 slides, allowing for a balanced distribution of content without overwhelming your audience.

Tell your story with captivating presentations
Powerpoint empowers you to develop well-designed content across all your devices
Using the 10-20-30 rule
The 10-20-30 rule is an effective way to structure your presentation. It calls for no more than 10 slides and no longer than 20 minutes (as well as a 30-point font).
Tips for crafting an effective presentation
No matter how long a presentation is, there are guidelines for crafting one to enhance understanding and retention. Keep these tips in mind when creating your PowerPoint masterpiece:
- Avoid overload: Ensure that each slide communicates a single idea clearly, avoiding cluttered layouts or excessive text.
- Pay attention to structure: Think of slides as bullet points with introductions, endings, and deep dives within each subject.
- Add visual appeal: Incorporate images, charts, and graphics to convey information without using too many words to make your audience read.
- Engage with your audience: Encourage interaction through questions, polls, or storytelling techniques to keep your audience actively involved.
- Put in the practice: Familiarize yourself with your slides and practice your delivery to refine your timing and confidence.
Ultimately, the ideal number of slides for your presentation depends on the allocated time frame and how detailed your content is. By striking a balance between informative content and engaging delivery, you can create a compelling presentation that can teach your audience something new.
Get started with Microsoft 365
It’s the Office you know, plus the tools to help you work better together, so you can get more done—anytime, anywhere.
Topics in this article
More articles like this one.

How to introduce yourself in a presentation
Gain your audience’s attention at the onset of a presentation. Craft an impressionable introduction to establish tone, presentation topic, and more.

How to add citations to your presentation
Conduct research and appropriately credit work for your presentation. Understand the importance of citing sources and how to add them to your presentation.

How to work on a group presentation
Group presentations can go smoothly with these essential tips on how to deliver a compelling one.

How to create a sales presentation
Engage your audience and get them interested in your product with this guide to creating a sales presentation.

Everything you need to achieve more in less time
Get powerful productivity and security apps with Microsoft 365

Explore Other Categories

Fokker-Planck diffusion maps of multiple single cell microglial transcriptomes reveals radial differentiation into substates associated with Alzheimer's pathology
- Find this author on Google Scholar
- Find this author on PubMed
- Search for this author on this site
- ORCID record for Andrew Baumgartner
- For correspondence: [email protected]
- ORCID record for Cory C. Funk
- ORCID record for Jennifer Hadlock
- ORCID record for Todd Golde
- Info/History
- Preview PDF
The identification of microglia subtypes is important for understanding the role of innate immunity in neurodegenerative diseases. Current methods of unsupervised cell type identification assume a small noise-to-signal ratio of transcriptome measurements that would produce well-separated cell clusters. However, identification of subtypes is obscured by gene expression noise, diminishing the distances in transcriptome space between distinct cell types and blurring boundaries. Here we use Fokker-Planck (FP) diffusion maps to model cellular differentiation as a stochastic process whereby cells settle into local minima, corresponding to cell subtypes, in a potential landscape constructed from transcriptome data using a nearest neighbor graph approach. By applying critical transition fields, we identify individual cells on the verge of transitioning between subtypes, revealing microglial cells in inactivated, homeostatic state before radially transitioning into various specialized subtypes. Specifically, we show that cells from Alzheimer's disease patients are enriched in a microglia subtype associated to antigen presentation and T-cell recruitment.
Competing Interest Statement
T.G. is a co-founder of Andante Therapeutics and Inventor on multiple patents related to Alzheimer's Disease.
View the discussion thread.
Thank you for your interest in spreading the word about bioRxiv.
NOTE: Your email address is requested solely to identify you as the sender of this article.

Citation Manager Formats
- EndNote (tagged)
- EndNote 8 (xml)
- RefWorks Tagged
- Ref Manager
- Tweet Widget
- Facebook Like
- Google Plus One
Subject Area
- Systems Biology
- Animal Behavior and Cognition (5415)
- Biochemistry (12217)
- Bioengineering (9147)
- Bioinformatics (30171)
- Biophysics (15487)
- Cancer Biology (12596)
- Cell Biology (18082)
- Clinical Trials (138)
- Developmental Biology (9755)
- Ecology (14628)
- Epidemiology (2067)
- Evolutionary Biology (18785)
- Genetics (12555)
- Genomics (17233)
- Immunology (12323)
- Microbiology (29051)
- Molecular Biology (12056)
- Neuroscience (63266)
- Paleontology (464)
- Pathology (1938)
- Pharmacology and Toxicology (3373)
- Physiology (5192)
- Plant Biology (10815)
- Scientific Communication and Education (1710)
- Synthetic Biology (3006)
- Systems Biology (7544)
- Zoology (1692)

COMMENTS
Graphical representation is a form of visually displaying data through various methods like graphs, diagrams, charts, and plots. It helps in sorting, visualizing, and presenting data in a clear manner through different types of graphs. Statistics mainly use graphical representation to show data.
A bar graph is a type of graphical representation of the data in which bars of uniform width are drawn with equal spacing between them on one axis (x-axis usually), depicting the variable. The values of the variables are represented by the height of the bars. Histograms.
A visual presentation is a communication method that utilizes visual elements such as images, graphics, charts, slides and other visual aids to convey information, ideas or messages to an audience. Visual presentations aim to enhance comprehension engagement and the overall impact of the message through the strategic use of visuals.
There are certain rules to effectively present the information in the graphical representation. They are: Suitable Title: Make sure that the appropriate title is given to the graph which indicates the subject of the presentation. Measurement Unit: Mention the measurement unit in the graph. Proper Scale: To represent the data in an accurate ...
Graphical representation of data, often referred to as graphical presentation or simply graphs which plays a crucial role in conveying information effectively. ... Choosing the appropriate type of graph is essential. For example, bar charts are suitable for comparing categories, while line charts are better for showing trends over time. ...
Understanding Data Presentations (Guide + Examples) Design • March 20th, 2024. In this age of overwhelming information, the skill to effectively convey data has become extremely valuable. Initiating a discussion on data presentation types involves thoughtful consideration of the nature of your data and the message you aim to convey.
Data Sources - Wherever possible, include the sources of information at the bottom of the graph. Keep it Simple - You should construct a graph which even a layman (without any exposure in the areas of statistics or mathematics) can understand. Neat - A graph is a visual aid for the presentation of data and information.
CREATE THIS PRESENTATION. 2. Persuasive presentation. If you've ever been swayed by a passionate speaker armed with compelling arguments, you've experienced a persuasive presentation . This type of presentation is like a verbal tug-of-war, aiming to convince the audience to see things from a specific perspective.
Types of Graphical Methods. Here are some of the most common types of graphical methods for data analysis and visual presentation: Line Graphs. These are commonly used to show trends over time, such as the stock prices of a particular company or the temperature over a certain period. They consist of a series of data points connected by a line ...
The types of representational graphics used will depend on the type of data being explored. Types of Graphical Representation. Data charts are available in a wide variety of maps, diagrams, and graphs that typically include textual titles and legends to denote the purpose, measurement units, and variables of the chart.
Title - The title of the graph should focus on the interpretation of the data, not the data itself. Remember that we are using a graph to help make a point, and the title will be a key factor in the audience interpreting the graph properly. For example, instead of a title like "Sales 1996-2001", you could say "Sales Up 42% '96-'01".
Excellence in graphical presentation depends on: ... Consider the four graphs below presenting the incidence of cancer by type. The upper left graph unnecessary uses bars, which take up a lot of ink. This layout also ends up making the fonts for the types of cancer too small. Small font is also a problem for the dot plot at the upper right, and ...
Importance of Graphical Representation. Graphical representation gives you a visual presentation of the given data to make it easier to understand. Graphs help you identify different patterns over a short and long period. It assists you in the interpretation of data and comparison of two or more data sets.
Switch to the Insert tab and click on Chart . Insert > Chart to add a presentation graph in PowerPoint. A new dialogue window will open, where you have to select the chart type and the specific representation type—i.e., for area charts, you can choose from 2D or 3D area charts and their distribution method.
Solved Examples of Graphical Representation. Example 1: Determine the following pair of equations has no solution, unique solution or infinitely many solutions using graphical method: 5x + 8y = -1, 3x - 24 5 24 5 y + 3 5 3 5 = 0. Solution: From equation 5x + 8y = -1, we have. y = 5x+1 8 5 x + 1 8. x. 3.
Graphical displays are useful tools for organizing and summarizing data in statistics. This webpage introduces different types of graphs, such as histograms, bar charts, pie charts, and scatterplots, and explains how to choose the appropriate one for your data. You will also learn how to create and interpret graphs using LibreTexts, a free online platform for learning science and math.
The best way to make sure the attention stays on you is to limit word count to no more than 10 words per slide. As presentation expert Nancy Duarte says "any slide with more than 10 words is a document.". If you really do need a longer explanation of something, handouts or follow-up emails are the way to go.
8. Tabular presentation. Presenting data in rows and columns, often used for precise data values and comparisons. Tabular data presentation is all about clarity and precision. Think of it as presenting numerical data in a structured grid, with rows and columns clearly displaying individual data points.
•The graph, not its title, occupies the most space. •Colors can be distin‐ guished, even by a color‐ blind reader Graph 3 Graph 3 • Same data as in #1 & 2 • WRONG TYPE of graph! • Discrete points connected in a line graph. • The connecting segments suggest that there are values between age
Graphical presentation of data is an essential tool for researchers and decision-makers to convey complex information in a clear and concise manner. It involves using different types of charts, graphs, and diagrams to represent numerical data visually. In this blog, we will explore the different types of graphical representation and their ...
Choose the right type of chart. Choose graphics that best suit your data. For example, use column or bar charts to compare categories, line charts to show trends over time, and pie charts to display parts of a whole. ... Remember, the powerful presentation of data is in simplicity. Consider whether gridlines are necessary for your table ...
3. Reporting. You can use presentations when reporting by showing research findings and conclusions. The most important thing to remember is that you need to design your slides to highlight your most critical data. That way, your audience will walk away understanding its high points. 4. Selling.
But which graphic is best for the information at hand? Here is a list of some diagram types you may want to use in various situations to enhance your presentation or report. Bar Graph . Use a bar graph to compare sets of data against one another, or show changes in data over time. Bar graphs can be vertical (as shown here), horizontal, or stacked.
A strong presentation is so much more than information pasted onto a series of slides with fancy backgrounds. Whether you're pitching an idea, reporting market research, or sharing something ...
With the right trial graphics presentation, you can help guide jurors from confusion to understanding. ... This is a pattern type cookie set by Google Analytics, where the pattern element on the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. It appears to be a variation of the _gat cookie which is used to ...
Motion graphic design improves user experience with smooth transitions and animations. Different types of motion graphics can increase conversion rates and boost sales and engagement on social media and digital platforms. Add a professional and polished touch to presentations and motion graphics videos.
For 15-minute presentations. When preparing for a 15-minute presentation, concise and focused content is key. Aim for around 10 to 15 slides to maintain a good pace, which will fit with the 1-2 minute per slide rule. For 30-minute presentations. A longer presentation gives you more room to delve deeper into your topic.
The identification of microglia subtypes is important for understanding the role of innate immunity in neurodegenerative diseases. Current methods of unsupervised cell type identification assume a small noise-to-signal ratio of transcriptome measurements that would produce well-separated cell clusters. However, identification of subtypes is obscured by gene expression noise, diminishing the ...