- Cookies & Privacy
- GETTING STARTED
- Introduction
- FUNDAMENTALS
- Acknowledgements
- Research questions & hypotheses
- Concepts, constructs & variables
- Research limitations
- Getting started
- Sampling Strategy
- Research Quality
- Research Ethics
- Data Analysis

Research ethics
When completing an undergraduate or master's level dissertation, there are a number of ethical requirements that must be taken into account. Some of these are formal requirements, such as the submission of an Ethics Proposal and/or the use of an Ethics Consent Form . However, at the undergraduate and master?s level, it is more likely that these ethical requirements simply have to be built into the way that you design and conduct your dissertation research. It is also important to understand what these ethical requirements are in order to write the Research Ethics section of your Research Strategy chapter (usually Chapter Three: Research Strategy ), as well as ensure that issues of research ethics are properly taken into account and do not slow you down.
When considering the research ethics in your dissertation, you need to think about: (a) the five basic ethical principles you need to take into account; and (b) how research ethics are influenced by your chosen research strategy . In addition, we set out some of the components that you will need to consider when writing an Ethics Consent Form .
- Principles of research ethics
- Research strategy and research ethics
- Ethics consent form

Ethics statement examples - ESRC
Digital wildfire: (mis)information flows, propagation and responsible governance.
Digital wildfires (spread of dubious and dangerous information, hate speech and rumours, via social media) can seriously challenge the capacity of traditional media, civil society and government to report accurately and respond to events as they unfold. But how people communicate in these digital social spaces is not well understood; users may not fully understand how these spaces ‘work’ as channels of communication and so what constitutes appropriate and responsible behaviour may be unclear. The challenge then is to develop appropriate ways of governing these spaces and how to apply and use them responsibly.
The research project, led by Dr Marina Jirotka, will attempt to address this challenge by framing the study in a programme of work known as Responsible Innovation in ICT and by developing a methodology for the study and advancement of the responsible governance of social media.
A key question is to what extent do people in these spaces ‘self-regulate’ their behaviour? If this is evident then there is a case for exploring how self-correction mechanisms may be amplified so that false rumours are identified more quickly.
The legitimacy of new governance mechanisms may be enhanced if they respect and build on such existing self-governance techniques.
Ethics statement submitted as part of the Je-S proposal
Ethical considerations are paramount in this proposed study. The team are already fully cognisant of the challenges online methods pose to social science researchers and have already composed an ESRC-funded guide to using and repurposing multi-modal data. A key objective of the current ESRC project is to expand this guide to include data harvested from social media sites.
In the proposed project we will engage with issues of harm, informed consent, privacy, civil liberties and data reuse and repurposing. The computational technology to be used in the proposed study affords users of social media complete anonymity and confidentiality. Only characteristics of the users will be recorded for analysis and all data will be stored on password protected university systems.
We will expand this guide to include data used to inform the new tool and model methodologies. We will continue to thoroughly engage with issues of harm, informed consent, privacy, civil liberties and data reuse and repurposing. The harvesting techniques used by COSMOS can collect information on the gender, location and account identifier of tweeters. This information is stored on password and firewall protected systems. All data that are presented to researchers are pre-anonymised by the system, maintaining confidentiality. Quantitative data outputs are presented at aggregate level meaning no identifying information is presented.
Qualitative data outputs can include data that renders tweeters identifiable. Twitter’s terms of service state that users of their data should not alter content in any way, and that tweets should remain as the tweeter intended. This requires tweets to be published in full and leads to important considerations regarding informed consent and the privacy of users. However a number of academic journals require tweets to be anonymised as a condition of publishing – in contradiction to Twitter’s terms of service. During the project we will engage with Twitter and other stakeholders in order to identify a best practice approach to the publication of tweets and the assessment of potential risks involved in publication. We will seek an approach that balances the rights and privacy of users with the needs of researchers.
The fieldwork will be conducted in accordance with Oxford University’s Research Governance Framework. Data collection and storage will follow the data protection policies of participating institutions, copies of which can be supplied. All data will be de-identified and raw data will be stored on a non-networked encrypted hard drive. The RA will undertake social science ethics training ahead of data collection. We will also obtain ethical approval from Oxford, Cardiff and Warwick Universities prior to the project commencement.
Read the Gateway to Research record
Last updated: 21 January 2022
This is the website for UKRI: our seven research councils, Research England and Innovate UK. Let us know if you have feedback or would like to help improve our online products and services .

Library Guides
Dissertations 4: methodology: ethics.
- Introduction & Philosophy
- Methodology
Research Ethics
In the research context, ethics can be defined as "the standards of behaviour that guide your conduct in relation to the rights of those who become the subject of your work, or are affected by it" (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill 2015, p239).
The University itself is guided by the fundamental principle that research involving humans and /or animals and/or the environment should involve no more than minimal risk of harm to physical and psychological wellbeing.
Thus, ethics relates to many aspects of your research, including the conduct towards:
The participants of your primary research (experiments, interviews etc). You will need to explain that participation is voluntary, and they have the right to withdraw at any time. You will need the participants' informed consent. You will need to avoid harming the participants, physically as well as mentally. You will need to respect the participants’ privacy and offer the right to anonymity. You will need to manage their personal data confidentially, also according to legislation such as the Data Protection Act 2018. You will need to be truthful and accurate when using the information provided by the participants.
The authors you have used as secondary sources. You will need to acknowledge their work and avoid plagiarism by doing the proper citing and referencing.
The readers of your research. You will need to exercise the utmost integrity, honesty, accuracy and objectivity in the writing of your work.
The researcher . You will need to ensure that the research will be safe for you to undertake.
Your research may entail some risk, but risk has to be analysed and minimised through risk assessment. Depending on the type of your research, your research proposal may need to be approved by an Ethics Committee, which will assess your research proposal in light of the elements mentioned above. Again, you are advised to use a research methods book for further guidance.
Research Ethics Online Course
Introduction to Research Ethics: Working with People
Find out how to conduct ethical research when working with people by studying this online course for university students. Course developed by the University of Leeds.

- << Previous: Methods
- Next: Methodology >>
- Last Updated: Sep 14, 2022 12:58 PM
- URL: https://libguides.westminster.ac.uk/methodology-for-dissertations
CONNECT WITH US
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
A Guide to Logistical/Ethical Considerations in Thesis/Dissertation Writing

4-minute read
- 14th May 2023
Why include a section on logistical/ethical considerations in your thesis/dissertation?
Ethical and logistical considerations are the guidelines that marshal your research practices and activities. With so many necessary steps to planning your dissertation , it may be tempting to dash off your logistical and ethical considerations section. However, don’t make that mistake! Including a thorough section on logistical and ethical considerations in your thesis shows that you have carefully considered your research plan, from the ethical implications of your research findings to the impact of performing the study itself.
And above all else, not providing well-thought-out ethical and logistical considerations in your research plan could derail your entire dissertation and have other grave consequences . But not to worry! Here, we offer a step-by-step guide to writing your logistical and ethical considerations section so that you can tick another essential item off your thesis checklist .
Steps for creating a logistical/ethical considerations section
- Clarify your ethical and logistical principles.
Your ethical and logistical principles will depend on many factors, such as research topic, fieldwork, and the possibility of direct interaction with vulnerable populations.
However, several overarching research principles are always helpful to remember. For example, the Belmont Report lists three often invoked principles: respect for persons, beneficence (i.e., maximize potential benefits to research subjects and minimize potential harm), and justice (i.e., people should be treated fairly). However, many other principles exist (and we offer a few other frequently cited principles below that might apply to your research).
If you haven’t done so already, discuss the ramifications of your dissertation work from an ethical standpoint with your adviser, who may bring up concerns that you’ve overlooked. You should also check with your organization’s Institutional Review Board (IRB) to confirm that there are no policies you need to be aware of.
- Evaluate each step of your research plan, as well as its potential risks and implications, and plan how you will ensure the ethical treatment of all persons involved.
Now that you have clarified your ethical and logistical principles, go through each stage of your research plan and consider the ethical impact of each step. Come up with a systematic plan to make sure that you’re protecting the ethical standards you’ve laid out for each one of the people affected by your research.
- Record your practices thoroughly and carefully during your research.
During the course of your study, keep detailed records of how you made sure the practices that address the ethical and logistical considerations were completed.
For example, if you should be obtaining verbal consent before conducting an interview, maintain a system to record that the consent was received.
Or, if it’s necessary to keep your digital data secure, be sure to make a note of the hardware and software you use. Plenty of online templates can help you keep these details organized.
- Write the ethical and logistical considerations section.
If you’ve kept detailed records, writing up your ethical and logistical considerations should be a straightforward process. It’s more common these days to see a section devoted to research ethics in dissertation structures .
Once again, check with your adviser to make sure you follow the proper protocol when you add your section on ethical and logistical considerations to your dissertation.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Potential ethical and logistical considerations
This is not a comprehensive list, but here are a few more common ethical and logistical considerations that may apply to your research work:
● Informed consent : Participants should be able to voluntarily join the study and know what the study is about and what the implications of the work are.
● Anonymity, confidentiality, and data protection : Participants should have a reasonable expectation that their confidential data will remain private.
● Nondiscrimination : You should avoid discrimination on the basis of sex, race, ethnicity, or any other factor.
● Social responsibility : Research should contribute to the common good.
Following the four steps outlined in this post will help you write an ethical and logistical considerations section in your dissertation:
1. Define your principles
2. Evaluate the risks and implications of each stage of your research
3. Record your practices carefully
4. Write up your considerations in the appropriate format for the dissertation.
Although ethical considerations vary from study to study, our guide should get you through another step in writing your thesis! Remember to include enough time for editing and proofreading your dissertation , and if you’re interested in some help from us, you can try a sample of our services for free . Good luck writing your dissertation!
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
2-minute read
How to Cite the CDC in APA
If you’re writing about health issues, you might need to reference the Centers for Disease...
5-minute read
Six Product Description Generator Tools for Your Product Copy
Introduction If you’re involved with ecommerce, you’re likely familiar with the often painstaking process of...
3-minute read
What Is a Content Editor?
Are you interested in learning more about the role of a content editor and the...
The Benefits of Using an Online Proofreading Service
Proofreading is important to ensure your writing is clear and concise for your readers. Whether...
6 Online AI Presentation Maker Tools
Creating presentations can be time-consuming and frustrating. Trying to construct a visually appealing and informative...
What Is Market Research?
No matter your industry, conducting market research helps you keep up to date with shifting...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.

Ethical Considerations in Dissertation Writing: Best Practices

Writing a dissertation is a significant milestone in an academic journey. It's a testament to your research skills, critical thinking, and ability to contribute to your field of study. However, amidst the rigorous research and writing process, it's crucial not to overlook the ethical considerations that underpin academic work. Upholding ethical principles in dissertation writing is not just a formality; it's a fundamental aspect of maintaining the integrity and credibility of your research. In this article, we'll explore some best practices for ensuring ethical conduct in your dissertation writing.
Research Ethics and Compliance:
Ethical considerations are the foundation of sound research practices. Ensuring that your dissertation adheres to ethical principles and guidelines is not just a formality; it's a fundamental aspect of maintaining the integrity and credibility of your research.
Understanding Research Ethics:
Research ethics encompass a set of principles and values that guide researchers in conducting their studies ethically and responsibly. These principles are particularly critical when your research involves human subjects, animals, or sensitive data. The following are key aspects of research ethics that every dissertation writer should be aware of:
1. Informed Consent: When your research involves human participants, obtaining informed consent is paramount. Informed consent means that participants are fully aware of the nature of the study, their involvement, potential risks, and their rights. It is essential to provide participants with clear and understandable information and allow them to voluntarily consent or decline participation.
2. Protecting Privacy: Respect for participants' privacy is another crucial ethical consideration. Ensure that you take measures to protect the confidentiality of individuals involved in your research. Anonymize data by removing any identifying information or use pseudonyms to safeguard participants' identities.
3. Honesty and Transparency: Transparency and honesty are fundamental to research ethics. Be honest about your research objectives, methodologies, and sources of data. Report your findings truthfully, even if they do not align with your initial hypotheses. Avoid any form of data manipulation or selective reporting that could compromise the integrity of your research.
4. Data Management: Implement robust data management practices from the start of your research. Keep comprehensive records of data collection, analysis, and storage. Ensure that your data is securely stored and properly backed up. Ethical data management helps ensure the accuracy and reproducibility of your findings.
5. Ethical Review Boards: Many institutions require that research involving human subjects undergo ethical review by an Institutional Review Board (IRB) or ethics committee. These boards assess research proposals to ensure that they comply with ethical standards and safeguard the well-being and rights of research participants. If your dissertation involves human subjects, it's essential to seek IRB approval.
6. Animal Research Ethics: For research involving animals, adherence to ethical guidelines is crucial. Ensure that your research complies with the "Three Rs" principles: Replacement (using alternatives to animals), Reduction (minimizing the number of animals used), and Refinement (enhancing animal welfare and minimizing harm). Institutional Animal Care and Use Committees (IACUCs) oversee ethical considerations in animal research.
7. Conflicts of Interest: Declare any potential conflicts of interest that could compromise the objectivity of your research. Conflicts of interest might include financial interests, personal relationships, or any factors that could influence your work's integrity. Transparency is vital in maintaining ethical research practices.
Receive Free Grammar and Publishing Tips via Email
Transparency and honesty.
Transparency and honesty are foundational ethical principles that must guide every aspect of your dissertation research and writing process. These principles ensure that your work is credible, reliable, and contributes to the advancement of knowledge with integrity.
Clear Research Objectives: Begin by articulating your research objectives with clarity and precision. Your dissertation's introduction should provide a transparent overview of the goals and intentions of your study. Clearly state the questions you seek to answer and the hypotheses you aim to test. By doing so, you set the stage for an honest and focused investigation.
Open Methodology: Transparency extends to your research methodology. Describe your research methods in detail, outlining how data will be collected, analyzed, and interpreted. Readers should be able to understand the steps you've taken to arrive at your conclusions. Be open about any limitations or constraints that might affect the validity of your research.
Honest Reporting of Findings: Honesty is especially critical when it comes to reporting your research findings. Regardless of whether your results align with your initial hypotheses, it's essential to present them accurately. Avoid the temptation to selectively report data or manipulate results to fit preconceived notions. Dishonest reporting erodes the trustworthiness of your work.
Ethical Consideration of Data: Ethical treatment of data is an integral aspect of transparency. Ensure that your data collection and analysis processes are free from bias or manipulation. Handle data with care, maintaining its integrity throughout the research process. If you encounter unexpected results or data that challenges your initial assumptions, address these findings honestly.
Citing Sources and Avoiding Plagiarism: Citing sources properly is a non-negotiable aspect of transparency and honesty. Whenever you use someone else's work, ideas, or words, provide appropriate citations and references. Plagiarism, whether intentional or unintentional, is a breach of academic integrity and can have serious consequences. Use citation styles recommended by your institution or field.
Acknowledging Limitations: Every research project has limitations, and it's essential to acknowledge them openly. Whether limitations relate to sample size, data availability, or methodological constraints, recognizing these factors demonstrates transparency. Discuss how these limitations may have influenced your results and interpretations.
Reproducibility and Replicability: In the spirit of transparency, aim to make your research reproducible and replicable. Clearly document your research processes, including data collection instruments and analysis procedures. Share your data and methodology whenever possible, allowing others to verify and build upon your work.
Ethical Dilemmas and Challenges: In some cases, you may encounter ethical dilemmas during your research. It's vital to address these challenges honestly and seek guidance from ethical review boards or mentors when necessary. Being transparent about how you navigated ethical complexities showcases your commitment to ethical research conduct.
Transparency and honesty are non-negotiable ethical principles in dissertation writing. They underpin the credibility of your research and demonstrate your commitment to responsible scholarship. By consistently upholding these principles, you contribute to the integrity of academic research and ensure that your dissertation is a trustworthy source of knowledge in your field.
Proper Citation and Avoiding Plagiarism
Proper citation and the avoidance of plagiarism are not just matters of academic etiquette; they are ethical imperatives that uphold the integrity of your dissertation. In the world of research and academia, giving credit where it's due is paramount.
Understanding Plagiarism: Plagiarism involves using someone else's work, ideas, or words without proper attribution. It is considered a severe breach of academic integrity and can have far-reaching consequences, including academic penalties and damage to your reputation. To avoid plagiarism, follow these essential guidelines:
1. Cite Sources Accurately:
Whenever you incorporate information, ideas, or text from a source, whether it's a book, journal article, website, or any other medium, cite it appropriately. Different academic disciplines use specific citation styles (e.g., APA, MLA, Chicago), so be sure to follow the style recommended by your institution or field.
2. Quoting and Paraphrasing: When using direct quotes from a source, enclose the text in quotation marks and provide a citation to the source. For paraphrased content (putting someone else's ideas into your own words), you must still acknowledge the original source with a citation. Paraphrasing does not make the information your own; it's essential to credit the original author.
3. Common Knowledge vs. Specific Information: Not all information requires citation. Common knowledge, which includes widely accepted facts and information that is widely known and undisputed, does not need to be cited. However, if you are in doubt about whether something qualifies as common knowledge, it's better to provide a citation.
4. Self-Plagiarism: Beware of self-plagiarism, which occurs when you reuse your previously published work without proper citation. While it's acceptable to build on your previous research, you must clearly indicate that you are referencing your earlier work and provide appropriate citations.
5. Citation Management Tools: Consider using citation management tools like EndNote, Zotero, or Mendeley to help you organize your sources, create citations, and maintain proper records of your references. These tools can significantly streamline the citation process and reduce the risk of errors.
6. Plagiarism Detection Software: Many institutions use plagiarism detection software to scan academic papers for potential plagiarism. Before submitting your dissertation, consider running it through such software to identify and rectify any unintentional instances of plagiarism.
7. Ethical Paraphrasing: When paraphrasing, ensure that you are not merely rearranging words or sentence structure but genuinely reinterpreting the content in your own words. Ethical paraphrasing respects the original author's ideas while presenting them from your perspective.
8. Academic Integrity Workshops: Some universities offer academic integrity workshops or courses that can help you better understand plagiarism and proper citation practices. Taking advantage of these resources can enhance your awareness and skills in this area.
Proper citation and avoiding plagiarism are not just technical aspects of dissertation writing but critical ethical considerations. By consistently citing sources accurately and respecting the intellectual property of others, you not only uphold academic integrity but also contribute to the trustworthiness of your research and the broader academic community.
Informed Consent and Privacy
When conducting research that involves human participants, whether through surveys, interviews, or experiments, it is essential to prioritize informed consent and safeguard the privacy of individuals. These ethical considerations are not only a moral obligation but also a legal and academic requirement in many cases.
Informed Consent:
Informed consent is the cornerstone of ethical research involving human subjects. It refers to the process of ensuring that participants fully understand the nature of the study, their role in it, potential risks, benefits, and their rights before they agree to participate. Here are key principles to keep in mind:
Clear Communication: Provide clear and comprehensive information about your research. This includes the purpose of the study, what participants will be asked to do, how their data will be used, and any potential risks or discomforts involved.
Voluntary Participation: Participation should be entirely voluntary. Participants should not feel coerced, pressured, or obligated to take part in your research. They should be free to decline or withdraw at any time without consequences.
Informed Decision-Making: Ensure that participants have the capacity to make an informed decision. This means they must have the cognitive ability to understand the information provided. If your study involves vulnerable populations, such as children or individuals with cognitive impairments, additional safeguards may be required.
Documentation: Always obtain written informed consent from participants, unless a waiver has been approved by an ethics review board. This written record should include all relevant information about the study and should be signed and dated by the participant.
Privacy Protection:
Respecting the privacy of research participants is another critical ethical consideration. Protecting their personal information and data is not just an ethical obligation but also a legal requirement in many jurisdictions. Here's how you can uphold privacy:
Anonymity and Confidentiality: When collecting data, take measures to ensure that participants' identities remain anonymous or confidential. Use participant codes or pseudonyms instead of real names, and store sensitive data securely.
Data Security: Implement robust data security practices to safeguard participant data. This includes encrypting electronic data, using secure storage methods, and restricting access to authorized personnel only.
Data Sharing: If you plan to share or publish your research data, do so in a way that protects participants' privacy. Avoid disclosing any information that could potentially identify individuals.
Ethical Review Boards: In many cases, research involving human subjects must undergo ethical review by an Institutional Review Board (IRB) or ethics committee. These bodies assess the ethical aspects of your research, including informed consent and privacy protections.
Data Retention: Develop clear data retention and disposal policies. Determine how long you will retain participant data and when it will be securely deleted or destroyed.
Participant Debriefing: After the study is completed, provide participants with a debriefing that explains the purpose and outcomes of the research. This ensures that participants leave the study with a clear understanding of their contribution.
Data Management and Retention
Effective data management and retention practices are essential for maintaining the integrity and credibility of your research. Properly handling and preserving research data not only ensures the accuracy and reliability of your findings but also aligns with ethical and legal requirements.
Data Management Principles:
Organized Data Collection: Start with organized data collection. Design clear data collection protocols, including data entry forms, surveys, or experimental procedures. Ensure that data are collected consistently and accurately.
Secure Data Storage: Store your research data securely. Whether your data is in digital or physical form, protect it from unauthorized access, loss, or damage. Use encryption for digital files and implement physical security measures for hard copies.
Data Backups: Regularly back up your data to prevent loss due to technical failures or unforeseen events. Maintain multiple copies of your data, both on-site and off-site, to safeguard against data loss.
Version Control: If you make changes to your data during the research process, use version control to track modifications. This ensures transparency and allows you to revert to previous versions if needed.
Metadata Documentation: Document metadata – information about your data – comprehensively. Metadata should include details about data sources, variables, data collection dates, and any data transformations or cleaning processes.
Data Cleaning and Validation: Perform thorough data cleaning and validation to identify and correct errors or inconsistencies in your dataset. Transparently document any data cleaning steps you take.
Data Ownership and Access: Clarify data ownership and access rights from the beginning of your research. If you are working with collaborators or collecting data from external sources, establish agreements regarding data ownership and sharing.
Data Retention Practices:
Retention Policies: Develop clear data retention policies that outline how long you will retain research data after the completion of your project. These policies should consider legal requirements, funding agency guidelines, and the value of the data.
Anonymization and De-identification: If you plan to share your research data with others, consider anonymizing or de-identifying the data to protect participants' privacy. Remove any identifying information that could link data to specific individuals.
Secure Archiving: For long-term data retention, consider using secure data archiving services or repositories that comply with data preservation standards. These repositories can ensure the long-term accessibility and integrity of your data.
Data Destruction: If you no longer require your research data or have exceeded the designated retention period, follow proper data destruction procedures. Shred physical documents, securely delete digital files, and ensure that no residual copies exist.
Documentation of Retention and Destruction: Maintain detailed records of data retention and destruction activities. This documentation serves as evidence that you have followed appropriate data management and retention practices.
Compliance with Regulations: Be aware of any legal or regulatory requirements related to data retention in your field or jurisdiction. Compliance with these regulations is crucial to avoid legal complications.
Ethical Considerations: Uphold ethical considerations when retaining or disposing of data. Ensure that data containing sensitive or personally identifiable information are treated with utmost care and respect for privacy.
Effective data management and retention practices not only protect your research but also facilitate data sharing and transparency within the academic community. By adhering to these principles, you contribute to the responsible conduct of research and enhance the credibility of your work.
In conclusion, ethical considerations are the bedrock of rigorous and credible dissertation writing. By following these best practices, you not only demonstrate your commitment to ethical research but also contribute to the advancement of knowledge with integrity and responsibility. Your dissertation should not only be a testament to your academic prowess but also a reflection of your ethical values as a scholar.
Connect With Us
Dissertation Editing and Proofreading Services Discount (New for 2018)
May 3, 2017.
For March through May 2018 ONLY, our professional dissertation editing se...
Thesis Editing and Proofreading Services Discount (New for 2018)
For March through May 2018 ONLY, our thesis editing service is discounted...
Neurology includes Falcon Scientific Editing in Professional Editing Help List
March 14, 2017.
Neurology Journal now includes Falcon Scientific Editing in its Professio...
Useful Links
Academic Editing | Thesis Editing | Editing Certificate | Resources
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.
Example Documents
Each project is different and so the documentation required for different projects is different too. Below you will find some examples of study documentation, which you may use as a guide when producing your own.
General Tips
- Use simple words and sentences.
- Ensure the information is easy to follow - consider how you format the text and whether to use flowcharts/diagrams.
- Ask rather than demand.
- Avoid using jargon.
- Use the active (not passive) voice, e.g. 'We invite you...' instead of 'You are invited to...'
- Tailor your material to the audience, e.g. consent forms for preschool children will be different to those for young adults.
- For guidance on writing a good lay summary, see VoiceNorth's short video: Bitesize Training - How to Write a Good Lay Summar y.
Ethics Application Forms
At Newcastle University, researchers must complete an ethics application form, before any research commences, either by:
- completing the University Online Ethics Form or
- by completing the HRA IRAS form (if NHS/HSC Research Ethics Committee approval required)*
*Note, if you are unsure whether your study requires NHS/HSC REC approval, you should complete the University Online Ethics Form first, which will notify you accordingly if NHS/HSC REC approval is needed.
Ethics application forms will ask the researcher for key information about the research project, including:
- Principal Investigator contact details
- Project description
- Proposed project start and end dates
- Details of the risks associated with the research
- Proposed measures to prevent/minimise the risks
- Additional details, as applicable
The information provided should be written for a lay audience, and supporting documentation should be attached with the application form (e.g. information sheets, consent forms, data management plans and other relevant research materials, including for example research questionnaires, recruitment materials).
Below are examples of ethics application forms:
1. Example Ethics Form - Cyber Bullying [PDF: 122KB]
2. Example Ethics Form - Student Project [WORD: 50KB]
3. Example Ethics Form - Food & Nutrition [PDF: 496KB]
4. Example Ethics Form - Sexual Health [PDF: 201KB]
Participant Information Sheets (PIS)
The Participant Information Sheet (PIS) provides participants with sufficient information about the research study to allow them to make an appropriate (fully informed) decision about taking part. For further information, please see the Human Participation - Informing Participants section.
Example Information Sheet
Consent Forms
On receiving the information about the research study (typically through a Participant Information Sheet), the participant should be allowed time to consider whether or not to take part. If they wish to take part, typically participants will sign a Consent Form. For further information, please refer to the section on Human Participation - Acquiring Voluntary Consent and the University's Informed Consent Guidelines .
The University has also developed an Example Consent Form that can be downloaded and adapted to the research project.
Data Management Plans
A research data management plan outlines how a researcher will collect, use and store data, during and after the research study. For further information, please see the Data - Governance considerations for research data .
DMPOnline provides access to example Data Management Plans. The online tool can also be used to develop Data Management Plans that meet different funder requirements.
Further guidance is available through the University's Research Data Service (RDS) .
Privacy Notice
A Privacy Notice sets out how personal information will be processed in accordance with the UK General Data Protection Regulation (GDPR). Participants in a research project should be provided with a Privacy Notice alongside a Participant Information Sheet (PIS), and have the opportunity to ask questions before they sign a Consent Form .
To support researchers, the University has created a template form that can be downloaded and adapted to the project:
Template Privacy Notice for research
If you wish to recommend any changes to the information above, or have any example documents that may help other researchers, please contact [email protected] .
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
Dissertation Methodology – Structure, Example and Writing Guide
- Table of Contents

Dissertation Methodology
In any research, the methodology chapter is one of the key components of your dissertation. It provides a detailed description of the methods you used to conduct your research and helps readers understand how you obtained your data and how you plan to analyze it. This section is crucial for replicating the study and validating its results.
Here are the basic elements that are typically included in a dissertation methodology:
- Introduction : This section should explain the importance and goals of your research .
- Research Design : Outline your research approach and why it’s appropriate for your study. You might be conducting an experimental research, a qualitative research, a quantitative research, or a mixed-methods research.
- Data Collection : This section should detail the methods you used to collect your data. Did you use surveys, interviews, observations, etc.? Why did you choose these methods? You should also include who your participants were, how you recruited them, and any ethical considerations.
- Data Analysis : Explain how you intend to analyze the data you collected. This could include statistical analysis, thematic analysis, content analysis, etc., depending on the nature of your study.
- Reliability and Validity : Discuss how you’ve ensured the reliability and validity of your study. For instance, you could discuss measures taken to reduce bias, how you ensured that your measures accurately capture what they were intended to, or how you will handle any limitations in your study.
- Ethical Considerations : This is where you state how you have considered ethical issues related to your research, how you have protected the participants’ rights, and how you have complied with the relevant ethical guidelines.
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations of your methodology, including any biases and constraints that might have affected your study.
- Summary : Recap the key points of your methodology chapter, highlighting the overall approach and rationalization of your research.
Types of Dissertation Methodology
The type of methodology you choose for your dissertation will depend on the nature of your research question and the field you’re working in. Here are some of the most common types of methodologies used in dissertations:
Experimental Research
This involves creating an experiment that will test your hypothesis. You’ll need to design an experiment, manipulate variables, collect data, and analyze that data to draw conclusions. This is commonly used in fields like psychology, biology, and physics.
Survey Research
This type of research involves gathering data from a large number of participants using tools like questionnaires or surveys. It can be used to collect a large amount of data and is often used in fields like sociology, marketing, and public health.
Qualitative Research
This type of research is used to explore complex phenomena that can’t be easily quantified. Methods include interviews, focus groups, and observations. This methodology is common in fields like anthropology, sociology, and education.
Quantitative Research
Quantitative research uses numerical data to answer research questions. This can include statistical, mathematical, or computational techniques. It’s common in fields like economics, psychology, and health sciences.
Case Study Research
This type of research involves in-depth investigation of a particular case, such as an individual, group, or event. This methodology is often used in psychology, social sciences, and business.
Mixed Methods Research
This combines qualitative and quantitative research methods in a single study. It’s used to answer more complex research questions and is becoming more popular in fields like social sciences, health sciences, and education.
Action Research
This type of research involves taking action and then reflecting upon the results. This cycle of action-reflection-action continues throughout the study. It’s often used in fields like education and organizational development.
Longitudinal Research
This type of research involves studying the same group of individuals over an extended period of time. This could involve surveys, observations, or experiments. It’s common in fields like psychology, sociology, and medicine.
Ethnographic Research
This type of research involves the in-depth study of people and cultures. Researchers immerse themselves in the culture they’re studying to collect data. This is often used in fields like anthropology and social sciences.
Structure of Dissertation Methodology
The structure of a dissertation methodology can vary depending on your field of study, the nature of your research, and the guidelines of your institution. However, a standard structure typically includes the following elements:
- Introduction : Briefly introduce your overall approach to the research. Explain what you plan to explore and why it’s important.
- Research Design/Approach : Describe your overall research design. This can be qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Explain the rationale behind your chosen design and why it is suitable for your research questions or hypotheses.
- Data Collection Methods : Detail the methods you used to collect your data. You should include what type of data you collected, how you collected it, and why you chose this method. If relevant, you can also include information about your sample population, such as how many people participated, how they were chosen, and any relevant demographic information.
- Data Analysis Methods : Explain how you plan to analyze your collected data. This will depend on the nature of your data. For example, if you collected quantitative data, you might discuss statistical analysis techniques. If you collected qualitative data, you might discuss coding strategies, thematic analysis, or narrative analysis.
- Reliability and Validity : Discuss how you’ve ensured the reliability and validity of your research. This might include steps you took to reduce bias or increase the accuracy of your measurements.
- Ethical Considerations : If relevant, discuss any ethical issues associated with your research. This might include how you obtained informed consent from participants, how you ensured participants’ privacy and confidentiality, or any potential conflicts of interest.
- Limitations : Acknowledge any limitations in your research methodology. This could include potential sources of bias, difficulties with data collection, or limitations in your analysis methods.
- Summary/Conclusion : Briefly summarize the key points of your methodology, emphasizing how it helps answer your research questions or hypotheses.
How to Write Dissertation Methodology
Writing a dissertation methodology requires you to be clear and precise about the way you’ve carried out your research. It’s an opportunity to convince your readers of the appropriateness and reliability of your approach to your research question. Here is a basic guideline on how to write your methodology section:
1. Introduction
Start your methodology section by restating your research question(s) or objective(s). This ensures your methodology directly ties into the aim of your research.
2. Approach
Identify your overall approach: qualitative, quantitative, or mixed methods. Explain why you have chosen this approach.
- Qualitative methods are typically used for exploratory research and involve collecting non-numerical data. This might involve interviews, observations, or analysis of texts.
- Quantitative methods are used for research that relies on numerical data. This might involve surveys, experiments, or statistical analysis.
- Mixed methods use a combination of both qualitative and quantitative research methods.
3. Research Design
Describe the overall design of your research. This could involve explaining the type of study (e.g., case study, ethnography, experimental research, etc.), how you’ve defined and measured your variables, and any control measures you’ve implemented.
4. Data Collection
Explain in detail how you collected your data.
- If you’ve used qualitative methods, you might detail how you selected participants for interviews or focus groups, how you conducted observations, or how you analyzed existing texts.
- If you’ve used quantitative methods, you might detail how you designed your survey or experiment, how you collected responses, and how you ensured your data is reliable and valid.
5. Data Analysis
Describe how you analyzed your data.
- If you’re doing qualitative research, this might involve thematic analysis, discourse analysis, or grounded theory.
- If you’re doing quantitative research, you might be conducting statistical tests, regression analysis, or factor analysis.
Discuss any ethical issues related to your research. This might involve explaining how you obtained informed consent, how you’re protecting participants’ privacy, or how you’re managing any potential harms to participants.
7. Reliability and Validity
Discuss the steps you’ve taken to ensure the reliability and validity of your data.
- Reliability refers to the consistency of your measurements, and you might discuss how you’ve piloted your instruments or used standardized measures.
- Validity refers to the accuracy of your measurements, and you might discuss how you’ve ensured your measures reflect the concepts they’re supposed to measure.
8. Limitations
Every study has its limitations. Discuss the potential weaknesses of your chosen methods and explain any obstacles you faced in your research.
9. Conclusion
Summarize the key points of your methodology, emphasizing how it helps to address your research question or objective.
Example of Dissertation Methodology
An Example of Dissertation Methodology is as follows:
Chapter 3: Methodology
- Introduction
This chapter details the methodology adopted in this research. The study aimed to explore the relationship between stress and productivity in the workplace. A mixed-methods research design was used to collect and analyze data.
Research Design
This study adopted a mixed-methods approach, combining quantitative surveys with qualitative interviews to provide a comprehensive understanding of the research problem. The rationale for this approach is that while quantitative data can provide a broad overview of the relationships between variables, qualitative data can provide deeper insights into the nuances of these relationships.
Data Collection Methods
Quantitative Data Collection : An online self-report questionnaire was used to collect data from participants. The questionnaire consisted of two standardized scales: the Perceived Stress Scale (PSS) to measure stress levels and the Individual Work Productivity Questionnaire (IWPQ) to measure productivity. The sample consisted of 200 office workers randomly selected from various companies in the city.
Qualitative Data Collection : Semi-structured interviews were conducted with 20 participants chosen from the initial sample. The interview guide included questions about participants’ experiences with stress and how they perceived its impact on their productivity.
Data Analysis Methods
Quantitative Data Analysis : Descriptive and inferential statistics were used to analyze the survey data. Pearson’s correlation was used to examine the relationship between stress and productivity.
Qualitative Data Analysis : Interviews were transcribed and subjected to thematic analysis using NVivo software. This process allowed for identifying and analyzing patterns and themes regarding the impact of stress on productivity.
Reliability and Validity
To ensure reliability and validity, standardized measures with good psychometric properties were used. In qualitative data analysis, triangulation was employed by having two researchers independently analyze the data and then compare findings.
Ethical Considerations
All participants provided informed consent prior to their involvement in the study. They were informed about the purpose of the study, their rights as participants, and the confidentiality of their responses.
Limitations
The main limitation of this study is its reliance on self-report measures, which can be subject to biases such as social desirability bias. Moreover, the sample was drawn from a single city, which may limit the generalizability of the findings.
Where to Write Dissertation Methodology
In a dissertation or thesis, the Methodology section usually follows the Literature Review. This placement allows the Methodology to build upon the theoretical framework and existing research outlined in the Literature Review, and precedes the Results or Findings section. Here’s a basic outline of how most dissertations are structured:
- Acknowledgements
- Literature Review (or it may be interspersed throughout the dissertation)
- Methodology
- Results/Findings
- References/Bibliography
In the Methodology chapter, you will discuss the research design, data collection methods, data analysis methods, and any ethical considerations pertaining to your study. This allows your readers to understand how your research was conducted and how you arrived at your results.
Advantages of Dissertation Methodology
The dissertation methodology section plays an important role in a dissertation for several reasons. Here are some of the advantages of having a well-crafted methodology section in your dissertation:
- Clarifies Your Research Approach : The methodology section explains how you plan to tackle your research question, providing a clear plan for data collection and analysis.
- Enables Replication : A detailed methodology allows other researchers to replicate your study. Replication is an important aspect of scientific research because it provides validation of the study’s results.
- Demonstrates Rigor : A well-written methodology shows that you’ve thought critically about your research methods and have chosen the most appropriate ones for your research question. This adds credibility to your study.
- Enhances Transparency : Detailing your methods allows readers to understand the steps you took in your research. This increases the transparency of your study and allows readers to evaluate potential biases or limitations.
- Helps in Addressing Research Limitations : In your methodology section, you can acknowledge and explain the limitations of your research. This is important as it shows you understand that no research method is perfect and there are always potential weaknesses.
- Facilitates Peer Review : A detailed methodology helps peer reviewers assess the soundness of your research design. This is an important part of the publication process if you aim to publish your dissertation in a peer-reviewed journal.
- Establishes the Validity and Reliability : Your methodology section should also include a discussion of the steps you took to ensure the validity and reliability of your measurements, which is crucial for establishing the overall quality of your research.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Delimitations in Research – Types, Examples and...

Research Design – Types, Methods and Examples

What is a Hypothesis – Types, Examples and...

Dissertation – Format, Example and Template

Dissertation vs Thesis – Key Differences

Ethical Considerations – Types, Examples and...
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
How to Write a Personal Ethics Statement (With Examples)
A class assignment, a scholarship requirement, or an admissions essay needs you to write the unnerving personal ethics statement. Your personal ethics statement should be drafted in a manner that is likely to impress the audience immediately.

“Integrity is doing the right thing, even if nobody is watching.” – Jim Stovall, American author
Writing a personal ethics statement may seem like a daunting task, but the reality is far different. Agreed, nobody is used to writing about themselves and the beliefs they possess. But this statement is nothing but a reflection of the writer’s personality on paper. The writer’s ability to distinguish between right and wrong, certain beliefs and opinions are all to be included in this statement that presents your morals and personal philosophies to the reader.
Personal Ethics Statement Format

The general format would be:
~ A striking introduction. ~ Body of the statement – this includes your beliefs, practices, and related justifications. ~ A decent conclusion.
Even though this statement is a reflection of you as an individual, it is still very important to keep in mind the reader who is going to be assessing it. The reader (in most cases, your professor or an admission committee) wants to know all about you in the best-possible way, and the only way to do this is keep your statement simple, emphatic, and honest.
Introduction

There are several ways of beginning your personal ethics statement. You may choose to write a little bit about yourself in order to introduce yourself to your reader. Write about profound moments that you’ve experienced till now, instances from your life that influenced you, and what you feel makes you a good person. Remember to keep it short though, you wouldn’t want to bore the reader with lengthy life stories! Pen down your little autobiography beforehand to avoid a messy start to your statement. For those who aren’t really comfortable with writing about themselves in their statement, you may choose to begin with a quote by your favorite author that is in line with what you are going to be writing. You may also begin with the importance of personal ethics.
Body of the statement

The body of the statement has to include all your core beliefs, your thoughts and opinions about what is correct individual behavior according to you, and reflect your views and philosophies. You may have to follow certain guidelines, depending on the reason why you’re writing it, but the core of the essay has to be a reflection of you and your feelings. Here are a few important points to remember when writing the body of the statement.
- Personal ethics are beliefs that you base your opinions and actions on. Hence, it is highly recommended that you mention only the ethics that you strongly believe in. In simple words, include only the practices that you unfailingly preach. Anything that is not from your core belief system will make itself apparent and establish itself to be untrue right away. For example, if you aren’t a vegetarian yourself but you write about vegetarianism being the need of the day, it will become obvious to the reader that you don’t believe what you write, and the concept of a personal ethics statement will become invalid.
- Since childhood, you have been taught how to differentiate between right and wrong. Include those morals in your statement, and don’t hesitate to provide short justifications for possessing a particular belief. Keep in mind that these beliefs belong to you, and don’t exclude any thoughts that you feel may seem unusual to the reader. For instance, if you are strongly against products made from animal hide, include your honest opinion in your statement.
- Every statement has its own requirements, and you will have to compile only those ethics that match the nature of the statement. For example, if you are writing this statement as a prerequisite for a scholarship, you will have to write about your personal ethics regarding academics and related activities. In such a case, your views about global warming probably won’t help the statement much, unless, of course, you are an environment student!
Once you have listed all your personal ethics, you can conclude your essay. It may be a good idea to conclude with the need and importance of personal ethics. You may choose to include the use of personal ethics in daily life in your conclusion. You may also want to write the ways in which following personal ethics has made you a better person.
Once you are done with writing your personal ethics statement, check it thoroughly for any factual, grammatical or spelling errors. Also, make sure that your statement is free from plagiarism and is truly a reflection of your own self.
Examples of a Personal Ethics Statement
A generic example of a personal ethics statement.
The Oxford Dictionary defines ‘ethics’ as “Moral principles that govern a person’s behavior or the conducting of an activity.” Ethics are an important part of our daily lives, and our personal moral beliefs are responsible for several of our judgments and actions. I believe that there are times in every individual’s life when (s)he has to choose the right alternative, distinguish between right and wrong and support what is appropriate for society as a whole, which is when the personal ethics system comes into the picture.
My personal ethics consist of qualities that always help me pick the legitimate option in sticky situations. I am an honest person―the truth always matters to me more than anything else at any given moment. Since childhood, this quality has always directed me away from petty distractions that many children face at some time or the other―cheating in class examinations, and stealing, for instance. I have always stood up for what is right, and this has helped me become the person I am today.
I also consider my hardworking and sincere nature to be one of my biggest strengths. I believe honesty and hard work are intricately linked, and this has always shown me the importance of dedication and sincerity for fulfilling my ambitions, which is why, I am not afraid to take up seemingly difficult tasks. I am not afraid to stand up for what I truly believe in, and being a rational person, I rarely let emotions take control of any situation, which is extremely necessary at times when justice has to prevail.
I strongly believe that in order to receive fair treatment from others, it is very important to treat others the way you want to be treated. Thus, I try my best to be polite to everyone I meet. This ensures that I don’t add to anyone’s problems, if any, and assures polite interaction for most of the time.
I also deem consistency as one of the most important personal ethics one should possess. My work is always consistent in nature, and I strive hard to deliver results that are not sporadic.
However, every coin has two sides and just like my strengths, I too possess my share of weaknesses. Sometimes, I am too frank while expressing my opinions, and that has the ability of hurting people, though unintentionally. My tendency to grab the lead also sometimes labels me as a dominating person when working in a team. I also tend to react strongly to unfair criticism, which is a strength and weakness at the same time.
I would thus like to conclude by saying that personal ethics are important not only in a professional or academic setting, but also in every individual’s personal life. My personal ethics will always influence my decisions and actions during any dilemma, and if I come across any more ethics that will help my personal and professional growth, I will not hesitate to adapt to them.
The Personal Ethics Statement Of An Aspiring Journalist

As an aspiring journalist, writing about personal ethics is provoking endless thoughts in my mind―what is right, according to me, and what is wrong? Are my beliefs in accordance to what society thinks and feels? Will my personal ethics help me go a long way in my career? As I go on thinking and penning down my thoughts, I am relieved, and proud to say that my list of ethics answers every question in my mind affirmatively.
I will always strive to be excellent at everything I do. I will not settle for anything lesser than the best, and will do everything I can to achieve the best results in all my professional endeavors. I will not procrastinate when it comes to my work and will deliver the expected results on or before time.
As a journalist and person, I will always be sincere and honest in everything I do. I will not bend any facts or rules just for personal benefit, and will always be dependable, trustworthy and reliable for the organization. I promise to build my reputation only on the basis of merit, and nothing else.
With integrity comes courage. I will never hesitate to stand up for what is right, and will do so even if I am in a difficult situation that demands me to ignore what is wrong. I will always support the truth and never let anyone influence me to do otherwise. I will not give in to peer pressure and will never let the fear of failing affect my actions.
I will always strive to remain humble and grounded. I will not let any accolades or praise affect my attitude, and will always be polite to my peers, superiors and juniors. I will make sure to never hurt or mock anyone intentionally.
I would like to conclude by saying that it is the responsibility of every journalist to abide by ethics that will benefit not only themselves, but also their working environment, and society as a whole, and my list of personal ethics will definitely help me fulfill this responsibility.
The Personal Ethics Statement Of A Student

Mr. Henry Kravis, co-founder of Kohlberg Kravis Roberts & Co, famously said, “If you don’t have integrity, you have nothing. You can’t buy it. You can have all the money in the world, but if you are not a moral or ethical person, you really have nothing.” I agree with Mr. Kravis’ views. Personal ethics are very important for every individual, be it a student, an employee, or a businessperson. I believe personal ethics are not limited to an academic setting or workplace, but extend to the family and society as well. As an individual, a daughter, and a student, I abide by some basic personal ethics which help me become a better person everyday.
I believe that to gain respect from others, you have to give it first. I strive to respect everyone I come in contact with, as I know they all might have overcome obstacles or faced tough times to get to where they are today. I don’t assign respect as per status. I have immense respect for my professors, for my peers, and for everyone else who is around me.
Integrity and Honesty
Integrity and honesty are two values which I promise to abide by in every situation. I will never engage in plagiarism, cheat, or break any rules which might result in someone else getting hurt. I promise to stand up against all that is wrong, and will always support nothing but the truth.
Intellectual Knowledge
I will always strive to expand my intellectual knowledge through thorough and comprehensive reading, and attending various seminars and lectures whenever I get the opportunity.
Conducive Behavior
I will always try my best to help those in need, be it my peers, family members, or anyone else who requires it. I will never let myself become the reason for someone else’s troubles and will always behave in a co-operative manner. I promise that I will always have a healthy competitive spirit, and I will never let competition affect my attitude towards my peers, superiors or juniors.
Effective Time Management
I promise to manage my time effectively and never let pressure affect me in a negative manner. I will try my best to balance my time between my studies and recreation, and will not let one aspect of my life affect the other.
I believe that all the qualities I have mentioned in my statement are necessary in order to be a good, sincere student. My personal ethics help me form judgments and base my actions in a certain way. I am confident that abiding by them will always lead me to the right path, in every phase of my life.
The outline examples given above are sample personal ethics statements that might be used as reference by students or working professionals alike. These statements are just a loose idea of what a personal ethics statement should be like. Add your list of personal ethics, compile your thoughts and opinions, and simply pen down what comes to your mind when you think of your beliefs and morals, and you’re good to go!
Like it? Share it!
Get Updates Right to Your Inbox
Further insights.

Privacy Overview
- Essay Guides
- Other Essays
- How to Write an Ethics Paper: Guide & Ethical Essay Examples
- Speech Topics
- Basics of Essay Writing
- Essay Topics
- Main Academic Essays
- Research Paper Topics
- Basics of Research Paper Writing
- Miscellaneous
- Chicago/ Turabian
- Data & Statistics
- Methodology
- Admission Writing Tips
- Admission Advice
- Other Guides
- Student Life
- Studying Tips
- Understanding Plagiarism
- Academic Writing Tips
- Basics of Dissertation & Thesis Writing
- Research Paper Guides
- Formatting Guides
- Basics of Research Process
- Admission Guides
- Dissertation & Thesis Guides
How to Write an Ethics Paper: Guide & Ethical Essay Examples

Table of contents
Use our free Readability checker
An ethics essay is a type of academic writing that explores ethical issues and dilemmas. Students should evaluates them in terms of moral principles and values. The purpose of an ethics essay is to examine the moral implications of a particular issue, and provide a reasoned argument in support of an ethical perspective.
Writing an essay about ethics is a tough task for most students. The process involves creating an outline to guide your arguments about a topic and planning your ideas to convince the reader of your feelings about a difficult issue. If you still need assistance putting together your thoughts in composing a good paper, you have come to the right place. We have provided a series of steps and tips to show how you can achieve success in writing. This guide will tell you how to write an ethics paper using ethical essay examples to understand every step it takes to be proficient. In case you don’t have time for writing, get in touch with our professional essay writers for hire . Our experts work hard to supply students with excellent essays.
What Is an Ethics Essay?
An ethics essay uses moral theories to build arguments on an issue. You describe a controversial problem and examine it to determine how it affects individuals or society. Ethics papers analyze arguments on both sides of a possible dilemma, focusing on right and wrong. The analysis gained can be used to solve real-life cases. Before embarking on writing an ethical essay, keep in mind that most individuals follow moral principles. From a social context perspective, these rules define how a human behaves or acts towards another. Therefore, your theme essay on ethics needs to demonstrate how a person feels about these moral principles. More specifically, your task is to show how significant that issue is and discuss if you value or discredit it.

Purpose of an Essay on Ethics
The primary purpose of an ethics essay is to initiate an argument on a moral issue using reasoning and critical evidence. Instead of providing general information about a problem, you present solid arguments about how you view the moral concern and how it affects you or society. When writing an ethical paper, you demonstrate philosophical competence, using appropriate moral perspectives and principles.
Things to Write an Essay About Ethics On
Before you start to write ethics essays, consider a topic you can easily address. In most cases, an ethical issues essay analyzes right and wrong. This includes discussing ethics and morals and how they contribute to the right behaviors. You can also talk about work ethic, code of conduct, and how employees promote or disregard the need for change. However, you can explore other areas by asking yourself what ethics mean to you. Think about how a recent game you watched with friends started a controversial argument. Or maybe a newspaper that highlighted a story you felt was misunderstood or blown out of proportion. This way, you can come up with an excellent topic that resonates with your personal ethics and beliefs.
Ethics Paper Outline
Sometimes, you will be asked to submit an outline before writing an ethics paper. Creating an outline for an ethics paper is an essential step in creating a good essay. You can use it to arrange your points and supporting evidence before writing. It also helps organize your thoughts, enabling you to fill any gaps in your ideas. The outline for an essay should contain short and numbered sentences to cover the format and outline. Each section is structured to enable you to plan your work and include all sources in writing an ethics paper. An ethics essay outline is as follows:
- Background information
- Thesis statement
- Restate thesis statement
- Summarize key points
- Final thoughts on the topic
Using this outline will improve clarity and focus throughout your writing process.
Ethical Essay Structure
Ethics essays are similar to other essays based on their format, outline, and structure. An ethical essay should have a well-defined introduction, body, and conclusion section as its structure. When planning your ideas, make sure that the introduction and conclusion are around 20 percent of the paper, leaving the rest to the body. We will take a detailed look at what each part entails and give examples that are going to help you understand them better. Refer to our essay structure examples to find a fitting way of organizing your writing.
Ethics Paper Introduction
An ethics essay introduction gives a synopsis of your main argument. One step on how to write an introduction for an ethics paper is telling about the topic and describing its background information. This paragraph should be brief and straight to the point. It informs readers what your position is on that issue. Start with an essay hook to generate interest from your audience. It can be a question you will address or a misunderstanding that leads up to your main argument. You can also add more perspectives to be discussed; this will inform readers on what to expect in the paper.
Ethics Essay Introduction Example
You can find many ethics essay introduction examples on the internet. In this guide, we have written an excellent extract to demonstrate how it should be structured. As you read, examine how it begins with a hook and then provides background information on an issue.
Imagine living in a world where people only lie, and honesty is becoming a scarce commodity. Indeed, modern society is facing this reality as truth and deception can no longer be separated. Technology has facilitated a quick transmission of voluminous information, whereas it's hard separating facts from opinions.
In this example, the first sentence of the introduction makes a claim or uses a question to hook the reader.
Ethics Essay Thesis Statement
An ethics paper must contain a thesis statement in the first paragraph. Learning how to write a thesis statement for an ethics paper is necessary as readers often look at it to gauge whether the essay is worth their time.
When you deviate away from the thesis, your whole paper loses meaning. In ethics essays, your thesis statement is a roadmap in writing, stressing your position on the problem and giving reasons for taking that stance. It should focus on a specific element of the issue being discussed. When writing a thesis statement, ensure that you can easily make arguments for or against its stance.
Ethical Paper Thesis Example
Look at this example of an ethics paper thesis statement and examine how well it has been written to state a position and provide reasons for doing so:
The moral implications of dishonesty are far-reaching as they undermine trust, integrity, and other foundations of society, damaging personal and professional relationships.
The above thesis statement example is clear and concise, indicating that this paper will highlight the effects of dishonesty in society. Moreover, it focuses on aspects of personal and professional relationships.
Ethics Essay Body
The body section is the heart of an ethics paper as it presents the author's main points. In an ethical essay, each body paragraph has several elements that should explain your main idea. These include:
- A topic sentence that is precise and reiterates your stance on the issue.
- Evidence supporting it.
- Examples that illustrate your argument.
- A thorough analysis showing how the evidence and examples relate to that issue.
- A transition sentence that connects one paragraph to another with the help of essay transitions .
When you write an ethics essay, adding relevant examples strengthens your main point and makes it easy for others to understand and comprehend your argument.
Body Paragraph for Ethics Paper Example
A good body paragraph must have a well-defined topic sentence that makes a claim and includes evidence and examples to support it. Look at part of an example of ethics essay body paragraph below and see how its idea has been developed:
Honesty is an essential component of professional integrity. In many fields, trust and credibility are crucial for professionals to build relationships and success. For example, a doctor who is dishonest about a potential side effect of a medication is not only acting unethically but also putting the health and well-being of their patients at risk. Similarly, a dishonest businessman could achieve short-term benefits but will lose their client’s trust.
Ethics Essay Conclusion
A concluding paragraph shares the summary and overview of the author's main arguments. Many students need clarification on what should be included in the essay conclusion and how best to get a reader's attention. When writing an ethics paper conclusion, consider the following:
- Restate the thesis statement to emphasize your position.
- Summarize its main points and evidence.
- Final thoughts on the issue and any other considerations.
You can also reflect on the topic or acknowledge any possible challenges or questions that have not been answered. A closing statement should present a call to action on the problem based on your position.
Sample Ethics Paper Conclusion
The conclusion paragraph restates the thesis statement and summarizes the arguments presented in that paper. The sample conclusion for an ethical essay example below demonstrates how you should write a concluding statement.
In conclusion, the implications of dishonesty and the importance of honesty in our lives cannot be overstated. Honesty builds solid relationships, effective communication, and better decision-making. This essay has explored how dishonesty impacts people and that we should value honesty. We hope this essay will help readers assess their behavior and work towards being more honest in their lives.
In the above extract, the writer gives final thoughts on the topic, urging readers to adopt honest behavior.
How to Write an Ethics Paper?
As you learn how to write an ethics essay, it is not advised to immediately choose a topic and begin writing. When you follow this method, you will get stuck or fail to present concrete ideas. A good writer understands the importance of planning. As a fact, you should organize your work and ensure it captures key elements that shed more light on your arguments. Hence, following the essay structure and creating an outline to guide your writing process is the best approach. In the following segment, we have highlighted step-by-step techniques on how to write a good ethics paper.
1. Pick a Topic
Before writing ethical papers, brainstorm to find ideal topics that can be easily debated. For starters, make a list, then select a title that presents a moral issue that may be explained and addressed from opposing sides. Make sure you choose one that interests you. Here are a few ideas to help you search for topics:
- Review current trends affecting people.
- Think about your personal experiences.
- Study different moral theories and principles.
- Examine classical moral dilemmas.
Once you find a suitable topic and are ready, start to write your ethics essay, conduct preliminary research, and ascertain that there are enough sources to support it.
2. Conduct In-Depth Research
Once you choose a topic for your essay, the next step is gathering sufficient information about it. Conducting in-depth research entails looking through scholarly journals to find credible material. Ensure you note down all sources you found helpful to assist you on how to write your ethics paper. Use the following steps to help you conduct your research:
- Clearly state and define a problem you want to discuss.
- This will guide your research process.
- Develop keywords that match the topic.
- Begin searching from a wide perspective. This will allow you to collect more information, then narrow it down by using the identified words above.
3. Develop an Ethics Essay Outline
An outline will ease up your writing process when developing an ethic essay. As you develop a paper on ethics, jot down factual ideas that will build your paragraphs for each section. Include the following steps in your process:
- Review the topic and information gathered to write a thesis statement.
- Identify the main arguments you want to discuss and include their evidence.
- Group them into sections, each presenting a new idea that supports the thesis.
- Write an outline.
- Review and refine it.
Examples can also be included to support your main arguments. The structure should be sequential, coherent, and with a good flow from beginning to end. When you follow all steps, you can create an engaging and organized outline that will help you write a good essay.
4. Write an Ethics Essay
Once you have selected a topic, conducted research, and outlined your main points, you can begin writing an essay . Ensure you adhere to the ethics paper format you have chosen. Start an ethics paper with an overview of your topic to capture the readers' attention. Build upon your paper by avoiding ambiguous arguments and using the outline to help you write your essay on ethics. Finish the introduction paragraph with a thesis statement that explains your main position. Expand on your thesis statement in all essay paragraphs. Each paragraph should start with a topic sentence and provide evidence plus an example to solidify your argument, strengthen the main point, and let readers see the reasoning behind your stance. Finally, conclude the essay by restating your thesis statement and summarizing all key ideas. Your conclusion should engage the reader, posing questions or urging them to reflect on the issue and how it will impact them.
5. Proofread Your Ethics Essay
Proofreading your essay is the last step as you countercheck any grammatical or structural errors in your essay. When writing your ethic paper, typical mistakes you could encounter include the following:
- Spelling errors: e.g., there, they’re, their.
- Homophone words: such as new vs. knew.
- Inconsistencies: like mixing British and American words, e.g., color vs. color.
- Formatting issues: e.g., double spacing, different font types.
While proofreading your ethical issue essay, read it aloud to detect lexical errors or ambiguous phrases that distort its meaning. Verify your information and ensure it is relevant and up-to-date. You can ask your fellow student to read the essay and give feedback on its structure and quality.
Ethics Essay Examples
Writing an essay is challenging without the right steps. There are so many ethics paper examples on the internet, however, we have provided a list of free ethics essay examples below that are well-structured and have a solid argument to help you write your paper. Click on them and see how each writing step has been integrated. Ethics essay example 1
Ethics essay example 2
Ethics essay example 3
Ethics essay example 4
College ethics essay example 5
Ethics Essay Writing Tips
When writing papers on ethics, here are several tips to help you complete an excellent essay:
- Choose a narrow topic and avoid broad subjects, as it is easy to cover the topic in detail.
- Ensure you have background information. A good understanding of a topic can make it easy to apply all necessary moral theories and principles in writing your paper.
- State your position clearly. It is important to be sure about your stance as it will allow you to draft your arguments accordingly.
- When writing ethics essays, be mindful of your audience. Provide arguments that they can understand.
- Integrate solid examples into your essay. Morality can be hard to understand; therefore, using them will help a reader grasp these concepts.
Bottom Line on Writing an Ethics Paper
Creating this essay is a common exercise in academics that allows students to build critical skills. When you begin writing, state your stance on an issue and provide arguments to support your position. This guide gives information on how to write an ethics essay as well as examples of ethics papers. Remember to follow these points in your writing:
- Create an outline highlighting your main points.
- Write an effective introduction and provide background information on an issue.
- Include a thesis statement.
- Develop concrete arguments and their counterarguments, and use examples.
- Sum up all your key points in your conclusion and restate your thesis statement.
Contact our academic writing platform and have your challenge solved. Here, you can order essays and papers on any topic and enjoy top quality.

Daniel Howard is an Essay Writing guru. He helps students create essays that will strike a chord with the readers.
You may also like

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Ethical Considerations in Research | Types & Examples
Ethical Considerations in Research | Types & Examples
Published on 7 May 2022 by Pritha Bhandari .
Ethical considerations in research are a set of principles that guide your research designs and practices. Scientists and researchers must always adhere to a certain code of conduct when collecting data from people.
The goals of human research often include understanding real-life phenomena, studying effective treatments, investigating behaviours, and improving lives in other ways. What you decide to research and how you conduct that research involve key ethical considerations.
These considerations work to:
- Protect the rights of research participants
- Enhance research validity
- Maintain scientific integrity
Table of contents
Why do research ethics matter, getting ethical approval for your study, types of ethical issues, voluntary participation, informed consent, confidentiality, potential for harm, results communication, examples of ethical failures, frequently asked questions about research ethics.
Research ethics matter for scientific integrity, human rights and dignity, and collaboration between science and society. These principles make sure that participation in studies is voluntary, informed, and safe for research subjects.
You’ll balance pursuing important research aims with using ethical research methods and procedures. It’s always necessary to prevent permanent or excessive harm to participants, whether inadvertent or not.
Defying research ethics will also lower the credibility of your research because it’s hard for others to trust your data if your methods are morally questionable.
Even if a research idea is valuable to society, it doesn’t justify violating the human rights or dignity of your study participants.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Before you start any study involving data collection with people, you’ll submit your research proposal to an institutional review board (IRB) .
An IRB is a committee that checks whether your research aims and research design are ethically acceptable and follow your institution’s code of conduct. They check that your research materials and procedures are up to code.
If successful, you’ll receive IRB approval, and you can begin collecting data according to the approved procedures. If you want to make any changes to your procedures or materials, you’ll need to submit a modification application to the IRB for approval.
If unsuccessful, you may be asked to re-submit with modifications or your research proposal may receive a rejection. To get IRB approval, it’s important to explicitly note how you’ll tackle each of the ethical issues that may arise in your study.
There are several ethical issues you should always pay attention to in your research design, and these issues can overlap with each other.
You’ll usually outline ways you’ll deal with each issue in your research proposal if you plan to collect data from participants.
Voluntary participation means that all research subjects are free to choose to participate without any pressure or coercion.
All participants are able to withdraw from, or leave, the study at any point without feeling an obligation to continue. Your participants don’t need to provide a reason for leaving the study.
It’s important to make it clear to participants that there are no negative consequences or repercussions to their refusal to participate. After all, they’re taking the time to help you in the research process, so you should respect their decisions without trying to change their minds.
Voluntary participation is an ethical principle protected by international law and many scientific codes of conduct.
Take special care to ensure there’s no pressure on participants when you’re working with vulnerable groups of people who may find it hard to stop the study even when they want to.
Informed consent refers to a situation in which all potential participants receive and understand all the information they need to decide whether they want to participate. This includes information about the study’s benefits, risks, funding, and institutional approval.
- What the study is about
- The risks and benefits of taking part
- How long the study will take
- Your supervisor’s contact information and the institution’s approval number
Usually, you’ll provide participants with a text for them to read and ask them if they have any questions. If they agree to participate, they can sign or initial the consent form. Note that this may not be sufficient for informed consent when you work with particularly vulnerable groups of people.
If you’re collecting data from people with low literacy, make sure to verbally explain the consent form to them before they agree to participate.
For participants with very limited English proficiency, you should always translate the study materials or work with an interpreter so they have all the information in their first language.
In research with children, you’ll often need informed permission for their participation from their parents or guardians. Although children cannot give informed consent, it’s best to also ask for their assent (agreement) to participate, depending on their age and maturity level.
Anonymity means that you don’t know who the participants are and you can’t link any individual participant to their data.
You can only guarantee anonymity by not collecting any personally identifying information – for example, names, phone numbers, email addresses, IP addresses, physical characteristics, photos, and videos.
In many cases, it may be impossible to truly anonymise data collection. For example, data collected in person or by phone cannot be considered fully anonymous because some personal identifiers (demographic information or phone numbers) are impossible to hide.
You’ll also need to collect some identifying information if you give your participants the option to withdraw their data at a later stage.
Data pseudonymisation is an alternative method where you replace identifying information about participants with pseudonymous, or fake, identifiers. The data can still be linked to participants, but it’s harder to do so because you separate personal information from the study data.
Confidentiality means that you know who the participants are, but you remove all identifying information from your report.
All participants have a right to privacy, so you should protect their personal data for as long as you store or use it. Even when you can’t collect data anonymously, you should secure confidentiality whenever you can.
Some research designs aren’t conducive to confidentiality, but it’s important to make all attempts and inform participants of the risks involved.
As a researcher, you have to consider all possible sources of harm to participants. Harm can come in many different forms.
- Psychological harm: Sensitive questions or tasks may trigger negative emotions such as shame or anxiety.
- Social harm: Participation can involve social risks, public embarrassment, or stigma.
- Physical harm: Pain or injury can result from the study procedures.
- Legal harm: Reporting sensitive data could lead to legal risks or a breach of privacy.
It’s best to consider every possible source of harm in your study, as well as concrete ways to mitigate them. Involve your supervisor to discuss steps for harm reduction.
Make sure to disclose all possible risks of harm to participants before the study to get informed consent. If there is a risk of harm, prepare to provide participants with resources, counselling, or medical services if needed.
Some of these questions may bring up negative emotions, so you inform participants about the sensitive nature of the survey and assure them that their responses will be confidential.
The way you communicate your research results can sometimes involve ethical issues. Good science communication is honest, reliable, and credible. It’s best to make your results as transparent as possible.
Take steps to actively avoid plagiarism and research misconduct wherever possible.
Plagiarism means submitting others’ works as your own. Although it can be unintentional, copying someone else’s work without proper credit amounts to stealing. It’s an ethical problem in research communication because you may benefit by harming other researchers.
Self-plagiarism is when you republish or re-submit parts of your own papers or reports without properly citing your original work.
This is problematic because you may benefit from presenting your ideas as new and original even though they’ve already been published elsewhere in the past. You may also be infringing on your previous publisher’s copyright, violating an ethical code, or wasting time and resources by doing so.
In extreme cases of self-plagiarism, entire datasets or papers are sometimes duplicated. These are major ethical violations because they can skew research findings if taken as original data.
You notice that two published studies have similar characteristics even though they are from different years. Their sample sizes, locations, treatments, and results are highly similar, and the studies share one author in common.
Research misconduct
Research misconduct means making up or falsifying data, manipulating data analyses, or misrepresenting results in research reports. It’s a form of academic fraud.
These actions are committed intentionally and can have serious consequences; research misconduct is not a simple mistake or a point of disagreement about data analyses.
Research misconduct is a serious ethical issue because it can undermine scientific integrity and institutional credibility. It leads to a waste of funding and resources that could have been used for alternative research.
Later investigations revealed that they fabricated and manipulated their data to show a nonexistent link between vaccines and autism. Wakefield also neglected to disclose important conflicts of interest, and his medical license was taken away.
This fraudulent work sparked vaccine hesitancy among parents and caregivers. The rate of MMR vaccinations in children fell sharply, and measles outbreaks became more common due to a lack of herd immunity.
Research scandals with ethical failures are littered throughout history, but some took place not that long ago.
Some scientists in positions of power have historically mistreated or even abused research participants to investigate research problems at any cost. These participants were prisoners, under their care, or otherwise trusted them to treat them with dignity.
To demonstrate the importance of research ethics, we’ll briefly review two research studies that violated human rights in modern history.
These experiments were inhumane and resulted in trauma, permanent disabilities, or death in many cases.
After some Nazi doctors were put on trial for their crimes, the Nuremberg Code of research ethics for human experimentation was developed in 1947 to establish a new standard for human experimentation in medical research.
In reality, the actual goal was to study the effects of the disease when left untreated, and the researchers never informed participants about their diagnoses or the research aims.
Although participants experienced severe health problems, including blindness and other complications, the researchers only pretended to provide medical care.
When treatment became possible in 1943, 11 years after the study began, none of the participants were offered it, despite their health conditions and high risk of death.
Ethical failures like these resulted in severe harm to participants, wasted resources, and lower trust in science and scientists. This is why all research institutions have strict ethical guidelines for performing research.
Ethical considerations in research are a set of principles that guide your research designs and practices. These principles include voluntary participation, informed consent, anonymity, confidentiality, potential for harm, and results communication.
Scientists and researchers must always adhere to a certain code of conduct when collecting data from others .
These considerations protect the rights of research participants, enhance research validity , and maintain scientific integrity.
Research ethics matter for scientific integrity, human rights and dignity, and collaboration between science and society. These principles make sure that participation in studies is voluntary, informed, and safe.
Anonymity means you don’t know who the participants are, while confidentiality means you know who they are but remove identifying information from your research report. Both are important ethical considerations .
You can only guarantee anonymity by not collecting any personally identifying information – for example, names, phone numbers, email addresses, IP addresses, physical characteristics, photos, or videos.
You can keep data confidential by using aggregate information in your research report, so that you only refer to groups of participants rather than individuals.
These actions are committed intentionally and can have serious consequences; research misconduct is not a simple mistake or a point of disagreement but a serious ethical failure.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Bhandari, P. (2022, May 07). Ethical Considerations in Research | Types & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 15 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/ethical-considerations/
Is this article helpful?

Pritha Bhandari
Other students also liked, a quick guide to experimental design | 5 steps & examples, data collection methods | step-by-step guide & examples, how to avoid plagiarism | tips on citing sources.
- Translators
- Graphic Designers
Please enter the email address you used for your account. Your sign in information will be sent to your email address after it has been verified.
25 Thesis Statement Examples That Will Make Writing a Breeze

Understanding what makes a good thesis statement is one of the major keys to writing a great research paper or argumentative essay. The thesis statement is where you make a claim that will guide you through your entire paper. If you find yourself struggling to make sense of your paper or your topic, then it's likely due to a weak thesis statement.
Let's take a minute to first understand what makes a solid thesis statement, and what key components you need to write one of your own.

A thesis statement always goes at the beginning of the paper. It will typically be in the first couple of paragraphs of the paper so that it can introduce the body paragraphs, which are the supporting evidence for your thesis statement.
Your thesis statement should clearly identify an argument. You need to have a statement that is not only easy to understand, but one that is debatable. What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute . An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic.
Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's cuteness is derived from its floppy ears, small body, and playfulness." These are three things that can be debated on. Some people might think that the cutest thing about puppies is the fact that they follow you around or that they're really soft and fuzzy.
All cuteness aside, you want to make sure that your thesis statement is not only debatable, but that it also actually thoroughly answers the research question that was posed. You always want to make sure that your evidence is supporting a claim that you made (and not the other way around). This is why it's crucial to read and research about a topic first and come to a conclusion later. If you try to get your research to fit your thesis statement, then it may not work out as neatly as you think. As you learn more, you discover more (and the outcome may not be what you originally thought).
Additionally, your thesis statement shouldn't be too big or too grand. It'll be hard to cover everything in a thesis statement like, "The federal government should act now on climate change." The topic is just too large to actually say something new and meaningful. Instead, a more effective thesis statement might be, "Local governments can combat climate change by providing citizens with larger recycling bins and offering local classes about composting and conservation." This is easier to work with because it's a smaller idea, but you can also discuss the overall topic that you might be interested in, which is climate change.
So, now that we know what makes a good, solid thesis statement, you can start to write your own. If you find that you're getting stuck or you are the type of person who needs to look at examples before you start something, then check out our list of thesis statement examples below.
Thesis statement examples
A quick note that these thesis statements have not been fully researched. These are merely examples to show you what a thesis statement might look like and how you can implement your own ideas into one that you think of independently. As such, you should not use these thesis statements for your own research paper purposes. They are meant to be used as examples only.
- Vaccinations Because many children are unable to vaccinate due to illness, we must require that all healthy and able children be vaccinated in order to have herd immunity.
- Educational Resources for Low-Income Students Schools should provide educational resources for low-income students during the summers so that they don't forget what they've learned throughout the school year.
- School Uniforms School uniforms may be an upfront cost for families, but they eradicate the visual differences in income between students and provide a more egalitarian atmosphere at school.
- Populism The rise in populism on the 2016 political stage was in reaction to increasing globalization, the decline of manufacturing jobs, and the Syrian refugee crisis.
- Public Libraries Libraries are essential resources for communities and should be funded more heavily by local municipalities.
- Cyber Bullying With more and more teens using smartphones and social media, cyber bullying is on the rise. Cyber bullying puts a lot of stress on many teens, and can cause depression, anxiety, and even suicidal thoughts. Parents should limit the usage of smart phones, monitor their children's online activity, and report any cyber bullying to school officials in order to combat this problem.
- Medical Marijuana for Veterans Studies have shown that the use of medicinal marijuana has been helpful to veterans who suffer from Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD). Medicinal marijuana prescriptions should be legal in all states and provided to these veterans. Additional medical or therapy services should also be researched and implemented in order to help them re-integrate back into civilian life.
- Work-Life Balance Corporations should provide more work from home opportunities and six-hour workdays so that office workers have a better work-life balance and are more likely to be productive when they are in the office.
- Teaching Youths about Consensual Sex Although sex education that includes a discussion of consensual sex would likely lead to less sexual assault, parents need to teach their children the meaning of consent from a young age with age appropriate lessons.
- Whether or Not to Attend University A degree from a university provides invaluable lessons on life and a future career, but not every high school student should be encouraged to attend a university directly after graduation. Some students may benefit from a trade school or a "gap year" where they can think more intensely about what it is they want to do for a career and how they can accomplish this.
- Studying Abroad Studying abroad is one of the most culturally valuable experiences you can have in college. It is the only way to get completely immersed in another language and learn how other cultures and countries are different from your own.
- Women's Body Image Magazines have done a lot in the last five years to include a more diverse group of models, but there is still a long way to go to promote a healthy woman's body image collectively as a culture.
- Cigarette Tax Heavily taxing and increasing the price of cigarettes is essentially a tax on the poorest Americans, and it doesn't deter them from purchasing. Instead, the state and federal governments should target those economically disenfranchised with early education about the dangers of smoking.
- Veganism A vegan diet, while a healthy and ethical way to consume food, indicates a position of privilege. It also limits you to other cultural food experiences if you travel around the world.
- University Athletes Should be Compensated University athletes should be compensated for their service to the university, as it is difficult for these students to procure and hold a job with busy academic and athletic schedules. Many student athletes on scholarship also come from low-income neighborhoods and it is a struggle to make ends meet when they are participating in athletics.
- Women in the Workforce Sheryl Sandberg makes a lot of interesting points in her best-selling book, Lean In , but she only addressed the very privileged working woman and failed to speak to those in lower-skilled, lower-wage jobs.
- Assisted Suicide Assisted suicide should be legal and doctors should have the ability to make sure their patients have the end-of-life care that they want to receive.
- Celebrity and Political Activism Although Taylor Swift's lyrics are indicative of a feminist perspective, she should be more politically active and vocal to use her position of power for the betterment of society.
- The Civil War The insistence from many Southerners that the South seceded from the Union for states' rights versus the fact that they seceded for the purposes of continuing slavery is a harmful myth that still affects race relations today.
- Blue Collar Workers Coal miners and other blue-collar workers whose jobs are slowly disappearing from the workforce should be re-trained in jobs in the technology sector or in renewable energy. A program to re-train these workers would not only improve local economies where jobs have been displaced, but would also lead to lower unemployment nationally.
- Diversity in the Workforce Having a diverse group of people in an office setting leads to richer ideas, more cooperation, and more empathy between people with different skin colors or backgrounds.
- Re-Imagining the Nuclear Family The nuclear family was traditionally defined as one mother, one father, and 2.5 children. This outdated depiction of family life doesn't quite fit with modern society. The definition of normal family life shouldn't be limited to two-parent households.
- Digital Literacy Skills With more information readily available than ever before, it's crucial that students are prepared to examine the material they're reading and determine whether or not it's a good source or if it has misleading information. Teaching students digital literacy and helping them to understand the difference between opinion or propaganda from legitimate, real information is integral.
- Beauty Pageants Beauty pageants are presented with the angle that they empower women. However, putting women in a swimsuit on a stage while simultaneously judging them on how well they answer an impossible question in a short period of time is cruel and purely for the amusement of men. Therefore, we should stop televising beauty pageants.
- Supporting More Women to Run for a Political Position In order to get more women into political positions, more women must run for office. There must be a grassroots effort to educate women on how to run for office, who among them should run, and support for a future candidate for getting started on a political career.
Still stuck? Need some help with your thesis statement?
If you are still uncertain about how to write a thesis statement or what a good thesis statement is, be sure to consult with your teacher or professor to make sure you're on the right track. It's always a good idea to check in and make sure that your thesis statement is making a solid argument and that it can be supported by your research.
After you're done writing, it's important to have someone take a second look at your paper so that you can ensure there are no mistakes or errors. It's difficult to spot your own mistakes, which is why it's always recommended to have someone help you with the revision process, whether that's a teacher, the writing center at school, or a professional editor such as one from ServiceScape .
Related Posts

201 Online Research Databases and Search Engines

Outlining and Writing an Analytical Essay
- Academic Writing Advice
- All Blog Posts
- Writing Advice
- Admissions Writing Advice
- Book Writing Advice
- Short Story Advice
- Employment Writing Advice
- Business Writing Advice
- Web Content Advice
- Article Writing Advice
- Magazine Writing Advice
- Grammar Advice
- Dialect Advice
- Editing Advice
- Freelance Advice
- Legal Writing Advice
- Poetry Advice
- Graphic Design Advice
- Logo Design Advice
- Translation Advice
- Blog Reviews
- Short Story Award Winners
- Scholarship Winners

Need an academic editor before submitting your work?
25 Thesis Statement Examples
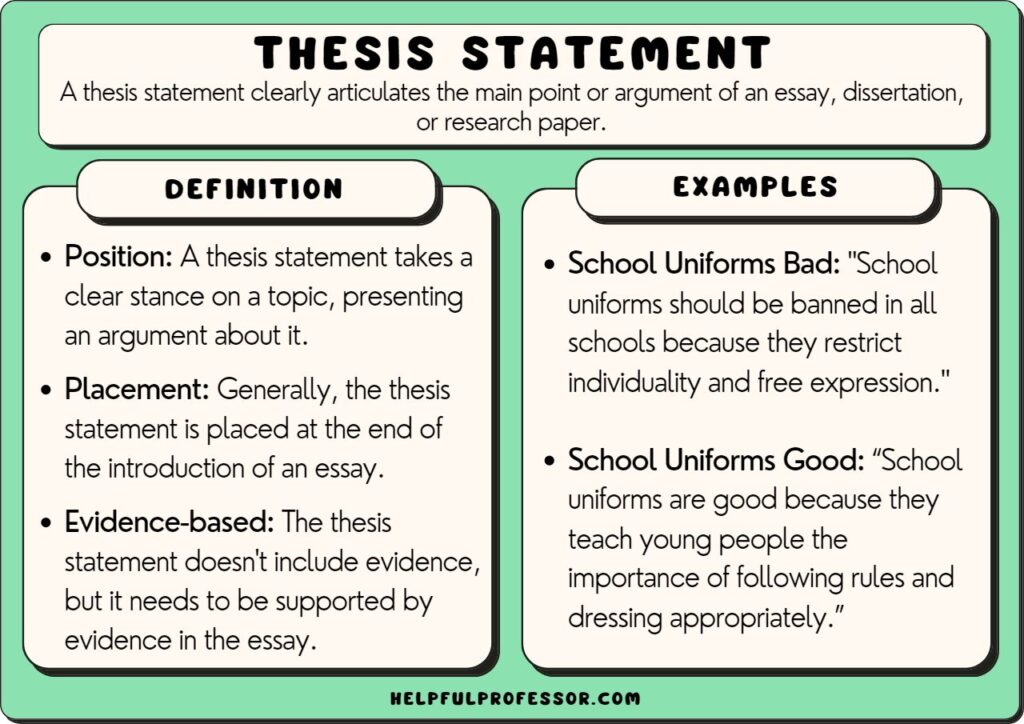
A thesis statement is needed in an essay or dissertation . There are multiple types of thesis statements – but generally we can divide them into expository and argumentative. An expository statement is a statement of fact (common in expository essays and process essays) while an argumentative statement is a statement of opinion (common in argumentative essays and dissertations). Below are examples of each.
Strong Thesis Statement Examples

1. School Uniforms
“Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate
Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons

2. Nature vs Nurture
“This essay will explore how both genetic inheritance and environmental factors equally contribute to shaping human behavior and personality.”
Best For: Compare and Contrast Essay
Read More: Nature vs Nurture Debate

3. American Dream
“The American Dream, a symbol of opportunity and success, is increasingly elusive in today’s socio-economic landscape, revealing deeper inequalities in society.”
Best For: Persuasive Essay
Read More: What is the American Dream?

4. Social Media
“Social media has revolutionized communication and societal interactions, but it also presents significant challenges related to privacy, mental health, and misinformation.”
Best For: Expository Essay
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Social Media

5. Globalization
“Globalization has created a world more interconnected than ever before, yet it also amplifies economic disparities and cultural homogenization.”
Read More: Globalization Pros and Cons

6. Urbanization
“Urbanization drives economic growth and social development, but it also poses unique challenges in sustainability and quality of life.”
Read More: Learn about Urbanization

7. Immigration
“Immigration enriches receiving countries culturally and economically, outweighing any perceived social or economic burdens.”
Read More: Immigration Pros and Cons

8. Cultural Identity
“In a globalized world, maintaining distinct cultural identities is crucial for preserving cultural diversity and fostering global understanding, despite the challenges of assimilation and homogenization.”
Best For: Argumentative Essay
Read More: Learn about Cultural Identity

9. Technology
“Medical technologies in care institutions in Toronto has increased subjcetive outcomes for patients with chronic pain.”
Best For: Research Paper

10. Capitalism vs Socialism
“The debate between capitalism and socialism centers on balancing economic freedom and inequality, each presenting distinct approaches to resource distribution and social welfare.”

11. Cultural Heritage
“The preservation of cultural heritage is essential, not only for cultural identity but also for educating future generations, outweighing the arguments for modernization and commercialization.”
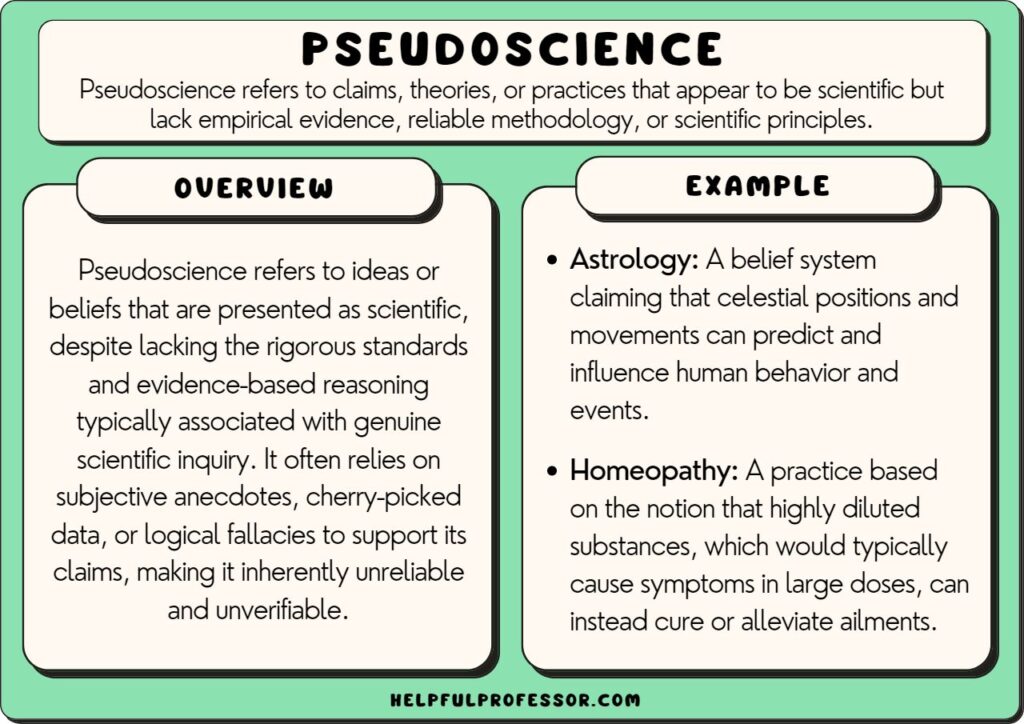
12. Pseudoscience
“Pseudoscience, characterized by a lack of empirical support, continues to influence public perception and decision-making, often at the expense of scientific credibility.”
Read More: Examples of Pseudoscience

13. Free Will
“The concept of free will is largely an illusion, with human behavior and decisions predominantly determined by biological and environmental factors.”
Read More: Do we have Free Will?

14. Gender Roles
“Traditional gender roles are outdated and harmful, restricting individual freedoms and perpetuating gender inequalities in modern society.”
Read More: What are Traditional Gender Roles?

15. Work-Life Ballance
“The trend to online and distance work in the 2020s led to improved subjective feelings of work-life balance but simultaneously increased self-reported loneliness.”
Read More: Work-Life Balance Examples
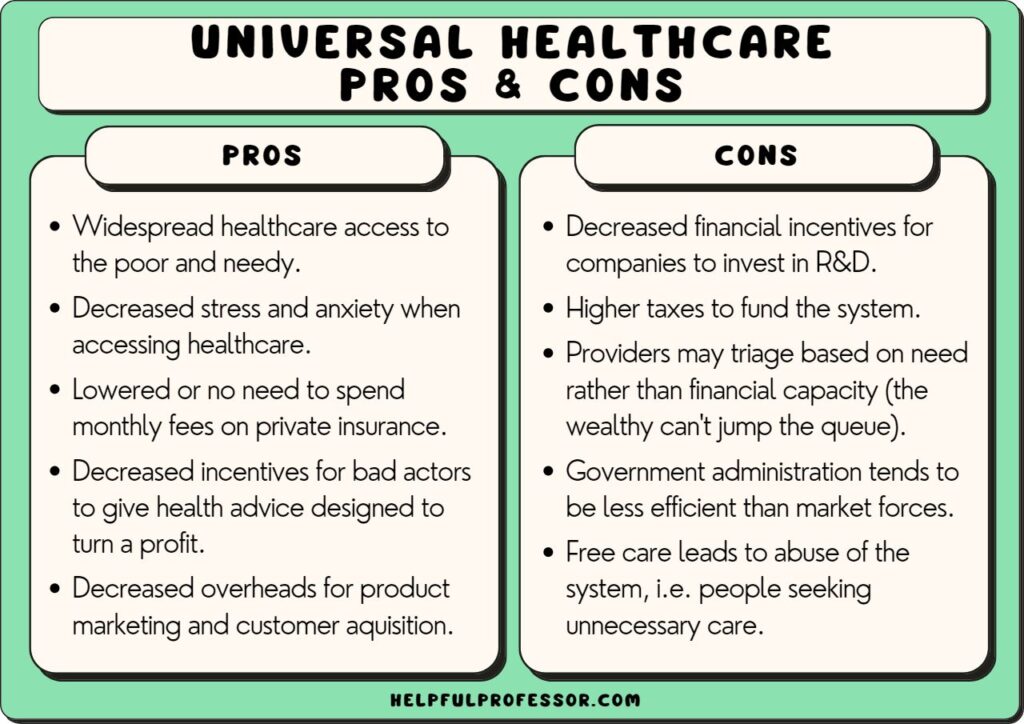
16. Universal Healthcare
“Universal healthcare is a fundamental human right and the most effective system for ensuring health equity and societal well-being, outweighing concerns about government involvement and costs.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Universal Healthcare

17. Minimum Wage
“The implementation of a fair minimum wage is vital for reducing economic inequality, yet it is often contentious due to its potential impact on businesses and employment rates.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Raising the Minimum Wage

18. Homework
“The homework provided throughout this semester has enabled me to achieve greater self-reflection, identify gaps in my knowledge, and reinforce those gaps through spaced repetition.”
Best For: Reflective Essay
Read More: Reasons Homework Should be Banned

19. Charter Schools
“Charter schools offer alternatives to traditional public education, promising innovation and choice but also raising questions about accountability and educational equity.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of Charter Schools

20. Effects of the Internet
“The Internet has drastically reshaped human communication, access to information, and societal dynamics, generally with a net positive effect on society.”
Read More: The Pros and Cons of the Internet

21. Affirmative Action
“Affirmative action is essential for rectifying historical injustices and achieving true meritocracy in education and employment, contrary to claims of reverse discrimination.”
Best For: Essay
Read More: Affirmative Action Pros and Cons

22. Soft Skills
“Soft skills, such as communication and empathy, are increasingly recognized as essential for success in the modern workforce, and therefore should be a strong focus at school and university level.”
Read More: Soft Skills Examples

23. Moral Panic
“Moral panic, often fueled by media and cultural anxieties, can lead to exaggerated societal responses that sometimes overlook rational analysis and evidence.”
Read More: Moral Panic Examples

24. Freedom of the Press
“Freedom of the press is critical for democracy and informed citizenship, yet it faces challenges from censorship, media bias, and the proliferation of misinformation.”
Read More: Freedom of the Press Examples

25. Mass Media
“Mass media shapes public opinion and cultural norms, but its concentration of ownership and commercial interests raise concerns about bias and the quality of information.”
Best For: Critical Analysis
Read More: Mass Media Examples
Checklist: How to use your Thesis Statement
✅ Position: If your statement is for an argumentative or persuasive essay, or a dissertation, ensure it takes a clear stance on the topic. ✅ Specificity: It addresses a specific aspect of the topic, providing focus for the essay. ✅ Conciseness: Typically, a thesis statement is one to two sentences long. It should be concise, clear, and easily identifiable. ✅ Direction: The thesis statement guides the direction of the essay, providing a roadmap for the argument, narrative, or explanation. ✅ Evidence-based: While the thesis statement itself doesn’t include evidence, it sets up an argument that can be supported with evidence in the body of the essay. ✅ Placement: Generally, the thesis statement is placed at the end of the introduction of an essay.
Try These AI Prompts – Thesis Statement Generator!
One way to brainstorm thesis statements is to get AI to brainstorm some for you! Try this AI prompt:
💡 AI PROMPT FOR EXPOSITORY THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTUCTIONS]. I want you to create an expository thesis statement that doesn’t argue a position, but demonstrates depth of knowledge about the topic.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR ARGUMENTATIVE THESIS STATEMENT I am writing an essay on [TOPIC] and these are the instructions my teacher gave me: [INSTRUCTIONS]. I want you to create an argumentative thesis statement that clearly takes a position on this issue.
💡 AI PROMPT FOR COMPARE AND CONTRAST THESIS STATEMENT I am writing a compare and contrast essay that compares [Concept 1] and [Concept2]. Give me 5 potential single-sentence thesis statements that remain objective.

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 5 Top Tips for Succeeding at University
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 50 Durable Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 100 Consumer Goods Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 30 Globalization Pros and Cons
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The following statements provide templates for the different types of ethical statements required for journal articles. Authors may use these as a guide when drafting their manuscripts. Please note there are many different types of statements and situations, so several examples are provided, but may not cover all cases. Ethics Approval 1.
Risk and benefit to researchers, participants and others (for example, potentially stigmatised or marginalised groups) as a result of the research and the potential impact, knowledge exchange, dissemination activity and future re-use of the data should also be considered as part of the ethical statement. If an ethics review is required at a ...
Broadly speaking, your dissertation research should not only aim to do good (i.e., beneficence ), but also avoid doing any harm (i.e., non-malfeasance ). The five main ethical principles you should abide by, in most cases, include: (a) minimising the risk of harm; (b) obtaining informed consent; (c) protecting anonymity and confidentiality; (d ...
When considering the research ethics in your dissertation, you need to think about: (a) the five basic ethical principles you need to take into account; and (b) how research ethics are influenced by your chosen research strategy. In addition, we set out some of the components that you will need to consider when writing an Ethics Consent Form ...
Revised on June 22, 2023. Ethical considerations in research are a set of principles that guide your research designs and practices. Scientists and researchers must always adhere to a certain code of conduct when collecting data from people. The goals of human research often include understanding real-life phenomena, studying effective ...
Identify the ethical principles and standards. 2. Describe your research design and methods. Be the first to add your personal experience. 3. Discuss the ethical implications and challenges. Be ...
Digital wildfire: (Mis)information flows, propagation and responsible governance. Digital wildfires (spread of dubious and dangerous information, hate speech and rumours, via social media) can seriously challenge the capacity of traditional media, civil society and government to report accurately and respond to events as they unfold.
Research Ethics. In the research context, ethics can be defined as "the standards of behaviour that guide your conduct in relation to the rights of those who become the subject of your work, or are affected by it" (Saunders, Lewis and Thornhill 2015, p239). The University itself is guided by the fundamental principle that research involving ...
Objectives of ethics statement. 2.1. Protect the dignity, rights, safety and wellbeing of all participants (including researchers). 2.2. Codify the principles governing the Bridge Group's research involving participants and personal data. 2.3. Establish the highest standards of research practice across the organisation to achieve high quality ...
Following the four steps outlined in this post will help you write an ethical and logistical considerations section in your dissertation: 1. Define your principles. 2. Evaluate the risks and implications of each stage of your research. 3. Record your practices carefully. 4. Write up your considerations in the appropriate format for the ...
Ethical considerations are the foundation of sound research practices. Ensuring that your dissertation adheres to ethical principles and guidelines is not just a formality; it's a fundamental aspect of maintaining the integrity and credibility of your research. Understanding Research Ethics: Research ethics encompass a set of principles and ...
At Newcastle University, researchers must complete an ethics application form, before any research commences, either by: completing the University Online Ethics Form or; by completing the HRA IRAS form (if NHS/HSC Research Ethics Committee approval required)* *Note, if you are unsure whether your study requires NHS/HSC REC approval, you should complete the University Online Ethics Form first ...
Dissertation ethics: Check your compliance with university regulations. ... For example, if you've interviewed budget holders about how they forecast their annual spend and your gatekeeper contact at the department was a research officer or someone in human resources, be sure to thank your contact as well as the subjects you interviewed. ...
In any research, the methodology chapter is one of the key components of your dissertation. It provides a detailed description of the methods you used to conduct your research and helps readers understand how you obtained your data and how you plan to analyze it. This section is crucial for replicating the study and validating its results.
While many. ethical concerns, by their nature, involve systematic concepts or metasystematic principles, ethical reasoning scored predominantly at lesser levels of complexity: abstract (6% of the dissertations), formal (84%) and. systematic (10%). Conclusions Research ethics are inadequately covered.
Step 2: Write your initial answer. After some initial research, you can formulate a tentative answer to this question. At this stage it can be simple, and it should guide the research process and writing process. The internet has had more of a positive than a negative effect on education.
Words: 550. Pages: 2. List of quality Ethics Dissertation Examples for writing your own work. Over 10,000 dissertation examples with references on your topic.
A Generic Example Of A Personal Ethics Statement The Oxford Dictionary defines 'ethics' as "Moral principles that govern a person's behavior or the conducting of an activity." Ethics are an important part of our daily lives, and our personal moral beliefs are responsible for several of our judgments and actions.
Ethics Essay Thesis Statement. An ethics paper must contain a thesis statement in the first paragraph. Learning how to write a thesis statement for an ethics paper is necessary as readers often look at it to gauge whether the essay is worth their time. When you deviate away from the thesis, your whole paper loses meaning.
Ethical considerations in research are a set of principles that guide your research designs and practices. Scientists and researchers must always adhere to a certain code of conduct when collecting data from people. The goals of human research often include understanding real-life phenomena, studying effective treatments, investigating ...
What that means is that you can't just put any statement of fact and have it be your thesis. For example, everyone knows that puppies are cute. An ineffective thesis statement would be, "Puppies are adorable and everyone knows it." This isn't really something that's a debatable topic. Something that would be more debatable would be, "A puppy's ...
Strong Thesis Statement Examples. 1. School Uniforms. "Mandatory school uniforms should be implemented in educational institutions as they promote a sense of equality, reduce distractions, and foster a focused and professional learning environment.". Best For: Argumentative Essay or Debate. Read More: School Uniforms Pros and Cons.
Dissertation Ethics Statement Example. REVIEWS HIRE. 100% Success rate. Undergraduate. Hire a Writer. Meet Robert! His research papers on information technology and design earn the highest scores. Robert is a safe pick for everyone who values quality, adherence to requirements, and custom approach. Total orders: 7428.