

Why Is It Important to Study Psychology?
Psychology sheds light on human behavior and helps us understand why we act the way we do. The field offers insights into our human experiences, helps us connect with others, and can mean the difference between a life well-lived and a life of challenges.
A psychology degree can lead to a rewarding career in social science. Let's explore why psychology is an essential part of your studies and how you can transition to a career if you find out it's right for you.
What is psychology and why is psychology important?

Psychology is the study of human behavior. It has roots in healthcare and the scientific method, helping uncover the processes of the mind. Through research and observation, psychologists can help answer questions about the brain's mysteries and improve mental health standards for communities.
Psychology studies offer new perspectives on human development, and it's not all about the physical process. Students in the field explore:
- How the physical development of the body and brain work together.
- The role of environmental influences on human development and behavior.
- Causes and treatments of mental illness
The field is important because it offers answers to the question, “What makes humans tick?” Studying psychology can mean walking away with a greater understanding of how humans handle everyday life.
What are the fields of psychology?

Psychology studies fall into a few different subcategories:
- Counseling psychology: A focus on the developmental, interpersonal, and personal functions across the lifespan.
- Clinical psychology: Integration of psychology and medical treatment methods for mental health issues.
- Educational psychology: Integration of psychology and the learning process.
- Forensic psychology: Supports the judicial system and criminal recovery.
- Social psychology: The application of psychology to understand how humans perceive themselves within larger society.
- Developmental psychology: A focus on the development of human beings and human behavior across the lifespan.
- Quantitative psychology: The integration of psychology with quantitative research methods.
- Organizational psychology: The study of human behavior in the workplace, including critical thinking and decision making as an organization.
While not an exhaustive list, these subfields offer insight into different aspects of the psychology discipline. Students can align their unique interests with a particular specialization.
Why study psychology?

There is so much we don't know about human behavior and the brain that powers it. The more we understand human brains, the more we can unlock the inner lives of other animals and even plant life.
Psychology is also helping in other fields as well—for instance, artificial intelligence and cognitive science . Learning about how brains process data, respond to stimuli, and take in information can help us build efficient machines with human-like characteristics. We may even crack the final barrier between humans and machines.
Some psychology specializations offer insight into human well-being in communities:
- Social work
- Workplace wellness
- Individual mental health
Many specializations help individual psychological health via medical interventions, counseling , and coaching . Other specializations involve engaging in psychological research to answer questions and find solutions to challenges.
Why do so many students study psychology?

People love to learn about themselves and the people around them. Many students are drawn to psychology because of the opportunity to learn about others while discovering more about their own lives. The field’s many subfields and specializations are also designed to match a student’s unique strengths and interests.
With the right education and training, whether that means an online certification or a graduate degree, students become equipped with the knowledge and skills to:
- Help themselves and others overcome challenges in mental processes.
- Aid in psychology research.
- Make a difference in everyday life.
Is psychology right for me?

Psychology may be a fascinating subject, but depending on your goals, many positions require graduate degrees, certifications, and even some time in residency:
- Clinical psychologists, for example, must complete a doctorate level degree or a medical degree to practice.
- A counseling psychologist may need a master's degree to find a suitable position.
- A researcher may need a bachelor’s degree to contribute to the field.
If higher education doesn't intimidate you, psychology may be a suitable career. In addition, a love of continuous learning helps because psychologists have professional development requirements to maintain certification.
There are other options for students who don't want to complete graduate work to practice in psychology. Subject matter expertise or an undergraduate degree in psychology can help students:
- Develop communication and empathy skills needed in a variety of fields ranging from education to marketing.
- Engage in research, applying data science or computer programming principles to create data-driven research tools.
If you want to dip your toes and figure out whether you enjoy psychology, consider taking free online psychology courses .
Where can I learn psychology online?

Psychology is a common online major for undergraduate students. They may also have online options for graduate degrees in the field.
edX offers online psychology courses . Learners can explore different specializations in the field of psychology for free or take official credit. Courses take place online, and students can begin their studies for free or pay a fee to earn verified certificates.
Other options include XSeries pathways and a MicroMasters program in Organizational Psychology. These are designed and delivered in partnership with leaders in the field of psychology and education.
Explore careers in psychology with edX
Students can learn to be better communicators, understand human behavior , and build foundational knowledge of their own brains. The psychology field offers research opportunities and the chance to grow as knowledge improves. It's an opportunity to help others and contribute to critical research . There's no better way to start exploring psychology than with the edX platform.
Related Posts
Best programming languages for web development, professional math: what jobs use math, why is it important to study a foreign language.
edX is the education movement for restless learners. Together with our founding partners Harvard and MIT, we’ve brought together over 35 million learners, the majority of top-ranked universities in the world, and industry-leading companies onto one online learning platform that supports learners at every stage. And we’re not stopping there—as a global nonprofit, we’re relentlessly pursuing our vision of a world where every learner can access education to unlock their potential, without the barriers of cost or location.
© 2021 edX. All rights reserved. Privacy Policy | Terms of Service


5 Reasons Why Psychology Matters
Understanding behavior is no longer just nice; it's essential..
Posted October 17, 2022 | Reviewed by Jessica Schrader
- What Is Therapy?
- Find a therapist near me
- Millions of students around the globe study in the field of psychology.
- These days, studying psychology has all kinds of critical applications and it leads to various career options.
- Therapy has demonstrated not only its importance, but, over the past several decades, it has also demonstrated its efficacy.

A lot has happened since I first started teaching courses in psychology in 1994.
At that time, studying in the field of psychology was considered nice , but only partly practical. Jobs related to therapy were difficult to get, and they often required doctoral-level degrees. Research experience in statistics and in the behavioral sciences was considered to essentially be nice transferable skills , with few career paths sitting there at the ready.
Research on the efficacy of therapy, which is a primary career goal of people who major in psychology, was mixed at the time. And large-scale, societal implications for the work of behavioral scientists were somewhat difficult to pinpoint.
When it comes to psychology education , a lot has changed since 1994. Having been immersed in the field of behavioral science since that time, I've come to see an increasing need for people with education related to the applied and research-focused areas of psychology.
At this point, there is little argument regarding the utility of an advanced education in psychology (as I discuss in detail in my book, Own Your Psychology Major! ).
Below are five reasons that, in the current day and age, psychology matters.
1. There is a mental health crisis in the industrialized world.
The proportion of people in industrialized nations, such as the United States, who are diagnosed with any number of mental health problems has increased dramatically in the past few decades (see Twenge, 2019). Disorders related to depression , anxiety , and mood instability, for instance, have increased significantly in prevalence over the past decade—and this increase shows no sign of slowing down anytime soon.
This trend is particularly common among adolescents and emerging adults, but it's a problem that affects all of us. The field of psychology is nothing short of necessary when it comes to this problem.
2. Therapy is often extremely helpful.
When I was a college student studying psychology in the '80s and '90s, the textbooks and cutting -edge research at the time tended to speak to ambiguity as to whether therapy was, on average, across various populations, helpful for people. The amount of research and work that has gone into understanding the efficacy of various forms of therapy since that time has been nothing short of profound (see Munder et al., 2019).
In short, based on extensive scientific data collected over the past several decades, it's clear that, in general, on average, psychotherapeutic treatments of various kinds tend to be helpful when it comes to addressing depression and other issues related to mental health. The advances in such fields as clinical psychology, psychiatry , and mental health counseling in the past few decades have, simply, been extraordinary.
3. Modern technologies often have unintended adverse outcomes when it comes to psychological well-being.
A good deal of research in the modern behavioral sciences is rooted in the evolutionary perspective, which largely focuses on how the ancestral conditions that surrounded the evolutionary history of our ancestors are extremely mismatched with modern, industrialized conditions that surround so many of us. So many modern technologies, such as social media platforms, are strongly mismatched from ancestral conditions, often leading to a broad array of psychological problems.
One pronounced example pertains to cyberbullying, which is largely an outcome associated with advances in social media technology and, in the same breath, is strongly related to adverse mental health outcomes among adolescents and young adults today (see my and Nicole Wedberg's book, Positive Evolutionary Psychology , for a detailed summary of this topic).
4. The internet age requires experts in the behavioral sciences.
It used to be the case that getting an advanced education in behavioral science was considered nice and something that would help someone in some abstract sense. Wow, have times changed.
These days, some of the most notable companies that host products used by so many of us (Google, Instagram, Facebook, Tinder, Spotify, etc.) have their products rooted in human behavioral science. These companies desperately need experts in research design, survey development, data analysis, data interpretation, research translation, and the presentation of research in the behavioral sciences. As an example, Instagram needs behavioral-science-based statisticians and researchers to help figure out algorithms that affect what you will see in your feed when you check your Instagram after you read this post.

Behavioral science has arrived. And it is going to become only more important with time. A degree in behavioral science is no longer a that's nice degree. It is now a degree in a critical body of skills that is strongly needed by some of the world's top corporations and organizations.
5. Understanding our evolved psychology sheds light on many problems of the modern world.
The field of evolutionary psychology , which surrounds my particular area of interest, has proven to shed dramatically important light on such critical issues as physical health, mental health, education, politics , religion, warfare, love, relationships, and prosocial behavior. And more (see Geher & Wedberg, 2020). Understanding the evolutionary processes that surround our psychology has extremely important implications regarding the entirety of the human experience. And only the surface of this profound area of psychological science has been scratched.
Bottom Line
Millions of people around the globe spend years of their life earning an advanced education in psychology. For a broad array of reasons, this is a good thing. Applied psychology has led to dramatic improvements in therapy and in the helping professions in general. The behavioral sciences now provide foundational skills for some of the world's most important industries. And the field of evolutionary psychology provides us with a framework so that we can understand how our ancestral past has profound implications for understanding all aspects of our lives today.
For a variety of reasons, at this point in our history, the field of psychology matters. And it will only matter more moving forward.
Facebook image: Bricolage/Shutterstock
LinkedIn image: VH-studio/Shutterstock
Geher, G. (2019). Own Your Psychology Major! A Guide to Student Success. Washington, DC: American Psychological Association.
Geher, G. & Wedberg, N. (2020). Positive Evolutionary Psychology: Darwin’s Guide to Living a Richer Life. New York: Oxford University Press.
Munder, T., Flückiger, C., Leichsenring, F., Abbass, A. A., Hilsenroth, M. J., Luyten, P., Rabung, S., Steinert, C., & Wampold, B. E. (2019). Is psychotherapy effective? A re-analysis of treatments for depression. Epidemiology and psychiatric sciences, 28(3), 268–274. https://doi.org/10.1017/S2045796018000355
Twenge, J. M., Cooper, A. B., Joiner, T. E., Duffy, M. E., & Binau, S. G. (2019). Age, period, and cohort trends in mood disorder indicators and suicide-related outcomes in a nationally representative dataset, 2005-2017. Journal of Abnormal Psychology, 128, 185-199.

Glenn Geher, Ph.D. , is professor of psychology at the State University of New York at New Paltz. He is founding director of the campus’ Evolutionary Studies (EvoS) program.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Teletherapy
- United States
- Brooklyn, NY
- Chicago, IL
- Houston, TX
- Los Angeles, CA
- New York, NY
- Portland, OR
- San Diego, CA
- San Francisco, CA
- Seattle, WA
- Washington, DC
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
1.1 Psychology as a Science
Learning objectives.
- Explain why using our intuition about everyday behavior is insufficient for a complete understanding of the causes of behavior.
- Describe the difference between values and facts and explain how the scientific method is used to differentiate between the two.
Despite the differences in their interests, areas of study, and approaches, all psychologists have one thing in common: They rely on scientific methods. Research psychologists use scientific methods to create new knowledge about the causes of behavior, whereas psychologist-practitioners , such as clinical, counseling, industrial-organizational, and school psychologists, use existing research to enhance the everyday life of others. The science of psychology is important for both researchers and practitioners.
In a sense all humans are scientists. We all have an interest in asking and answering questions about our world. We want to know why things happen, when and if they are likely to happen again, and how to reproduce or change them. Such knowledge enables us to predict our own behavior and that of others. We may even collect data (i.e., any information collected through formal observation or measurement ) to aid us in this undertaking. It has been argued that people are “everyday scientists” who conduct research projects to answer questions about behavior (Nisbett & Ross, 1980). When we perform poorly on an important test, we try to understand what caused our failure to remember or understand the material and what might help us do better the next time. When our good friends Monisha and Charlie break up, despite the fact that they appeared to have a relationship made in heaven, we try to determine what happened. When we contemplate the rise of terrorist acts around the world, we try to investigate the causes of this problem by looking at the terrorists themselves, the situation around them, and others’ responses to them.
The Problem of Intuition
The results of these “everyday” research projects can teach us many principles of human behavior. We learn through experience that if we give someone bad news, he or she may blame us even though the news was not our fault. We learn that people may become depressed after they fail at an important task. We see that aggressive behavior occurs frequently in our society, and we develop theories to explain why this is so. These insights are part of everyday social life. In fact, much research in psychology involves the scientific study of everyday behavior (Heider, 1958; Kelley, 1967).
The problem, however, with the way people collect and interpret data in their everyday lives is that they are not always particularly thorough. Often, when one explanation for an event seems “right,” we adopt that explanation as the truth even when other explanations are possible and potentially more accurate. For example, eyewitnesses to violent crimes are often extremely confident in their identifications of the perpetrators of these crimes. But research finds that eyewitnesses are no less confident in their identifications when they are incorrect than when they are correct (Cutler & Wells, 2009; Wells & Hasel, 2008). People may also become convinced of the existence of extrasensory perception (ESP), or the predictive value of astrology, when there is no evidence for either (Gilovich, 1993). Furthermore, psychologists have also found that there are a variety of cognitive and motivational biases that frequently influence our perceptions and lead us to draw erroneous conclusions (Fiske & Taylor, 2007; Hsee & Hastie, 2006). In summary, accepting explanations for events without testing them thoroughly may lead us to think that we know the causes of things when we really do not.
Research Focus: Unconscious Preferences for the Letters of Our Own Name
A study reported in the Journal of Consumer Research (Brendl, Chattopadhyay, Pelham, & Carvallo, 2005) demonstrates the extent to which people can be unaware of the causes of their own behavior. The research demonstrated that, at least under certain conditions (and although they do not know it), people frequently prefer brand names that contain the letters of their own name to brand names that do not contain the letters of their own name.
The research participants were recruited in pairs and were told that the research was a taste test of different types of tea. For each pair of participants, the experimenter created two teas and named them by adding the word stem “oki” to the first three letters of each participant’s first name. For example, for Jonathan and Elisabeth, the names of the teas would have been Jonoki and Elioki.
The participants were then shown 20 packets of tea that were supposedly being tested. Eighteen packets were labeled with made-up Japanese names (e.g., “Mataku” or “Somuta”), and two were labeled with the brand names constructed from the participants’ names. The experimenter explained that each participant would taste only two teas and would be allowed to choose one packet of these two to take home.
One of the two participants was asked to draw slips of paper to select the two brands that would be tasted at this session. However, the drawing was rigged so that the two brands containing the participants’ name stems were always chosen for tasting. Then, while the teas were being brewed, the participants completed a task designed to heighten their needs for self-esteem, and that was expected to increase their desire to choose a brand that had the letters of their own name. Specifically, the participants all wrote about an aspect of themselves that they would like to change.
After the teas were ready, the participants tasted them and then chose to take a packet of one of the teas home with them. After they made their choice, the participants were asked why they chose the tea they had chosen, and then the true purpose of the study was explained to them.
The results of this study found that participants chose the tea that included the first three letters of their own name significantly more frequently (64% of the time) than they chose the tea that included the first three letters of their partner’s name (only 36% of the time). Furthermore, the decisions were made unconsciously; the participants did not know why they chose the tea they chose. When they were asked, more than 90% of the participants thought that they had chosen on the basis of taste, whereas only 5% of them mentioned the real cause—that the brand name contained the letters of their name.
Once we learn about the outcome of a given event (e.g., when we read about the results of a research project), we frequently believe that we would have been able to predict the outcome ahead of time. For instance, if half of a class of students is told that research concerning attraction between people has demonstrated that “opposites attract” and the other half is told that research has demonstrated that “birds of a feather flock together,” most of the students will report believing that the outcome that they just read about is true, and that they would have predicted the outcome before they had read about it. Of course, both of these contradictory outcomes cannot be true. (In fact, psychological research finds that “birds of a feather flock together” is generally the case.) The problem is that just reading a description of research findings leads us to think of the many cases we know that support the findings, and thus makes them seem believable. The tendency to think that we could have predicted something that has already occurred that we probably would not have been able to predict is called the hindsight bias , or the tendency to think that we could have predicted something that has already occurred that we probably would not have been able to predict.
Why Psychologists Rely on Empirical Methods
All scientists, whether they are physicists, chemists, biologists, sociologists, or psychologists, use empirical methods to study the topics that interest them. Empirical methods include the processes of collecting and organizing data and drawing conclusions about those data. The empirical methods used by scientists have developed over many years and provide a basis for collecting, analyzing, and interpreting data within a common framework in which information can be shared. We can label the scientific method as the set of assumptions, rules, and procedures that scientists use to conduct empirical research .
Psychologists use a variety of techniques to measure and understand human behavior.
Tim Sheerman-Chase – “Volunteer Duty” Psychology Testing – CC BY 2.0 CAFNR – CC BY-NC 2.0
Although scientific research is an important method of studying human behavior, not all questions can be answered using scientific approaches. Statements that cannot be objectively measured or objectively determined to be true or false are not within the domain of scientific inquiry. Scientists therefore draw a distinction between values and facts. Values are personal statements such as “Abortion should not be permitted in this country,” “I will go to heaven when I die,” or “It is important to study psychology.” Facts are objective statements determined to be accurate through empirical study. Examples are “There were more than 21,000 homicides in the United States in 2009,” or “Research demonstrates that individuals who are exposed to highly stressful situations over long periods of time develop more health problems than those who are not.”
Because values cannot be considered to be either true or false, science cannot prove or disprove them. Nevertheless, as shown in Table 1.1 “Examples of Values and Facts in Scientific Research” , research can sometimes provide facts that can help people develop their values. For instance, science may be able to objectively measure the impact of unwanted children on a society or the psychological trauma suffered by women who have abortions. The effect of capital punishment on the crime rate in the United States may also be determinable. This factual information can and should be made available to help people formulate their values about abortion and capital punishment, as well as to enable governments to articulate appropriate policies. Values also frequently come into play in determining what research is appropriate or important to conduct. For instance, the U.S. government has recently supported and provided funding for research on HIV, AIDS, and terrorism, while denying funding for research using human stem cells.
Although scientists use research to help establish facts, the distinction between values and facts is not always clear-cut. Sometimes statements that scientists consider to be factual later, on the basis of further research, turn out to be partially or even entirely incorrect. Although scientific procedures do not necessarily guarantee that the answers to questions will be objective and unbiased, science is still the best method for drawing objective conclusions about the world around us. When old facts are discarded, they are replaced with new facts based on newer and more correct data. Although science is not perfect, the requirements of empiricism and objectivity result in a much greater chance of producing an accurate understanding of human behavior than is available through other approaches.
Levels of Explanation in Psychology
The study of psychology spans many different topics at many different levels of explanation which are the perspectives that are used to understand behavior . Lower levels of explanation are more closely tied to biological influences, such as genes, neurons, neurotransmitters, and hormones, whereas the middle levels of explanation refer to the abilities and characteristics of individual people, and the highest levels of explanation relate to social groups, organizations, and cultures (Cacioppo, Berntson, Sheridan, & McClintock, 2000).
The same topic can be studied within psychology at different levels of explanation, as shown in Figure 1.3 “Levels of Explanation” . For instance, the psychological disorder known as depression affects millions of people worldwide and is known to be caused by biological, social, and cultural factors. Studying and helping alleviate depression can be accomplished at low levels of explanation by investigating how chemicals in the brain influence the experience of depression. This approach has allowed psychologists to develop and prescribe drugs, such as Prozac, which may decrease depression in many individuals (Williams, Simpson, Simpson, & Nahas, 2009). At the middle levels of explanation, psychological therapy is directed at helping individuals cope with negative life experiences that may cause depression. And at the highest level, psychologists study differences in the prevalence of depression between men and women and across cultures. The occurrence of psychological disorders, including depression, is substantially higher for women than for men, and it is also higher in Western cultures, such as in the United States, Canada, and Europe, than in Eastern cultures, such as in India, China, and Japan (Chen, Wang, Poland, & Lin, 2009; Seedat et al., 2009). These sex and cultural differences provide insight into the factors that cause depression. The study of depression in psychology helps remind us that no one level of explanation can explain everything. All levels of explanation, from biological to personal to cultural, are essential for a better understanding of human behavior.
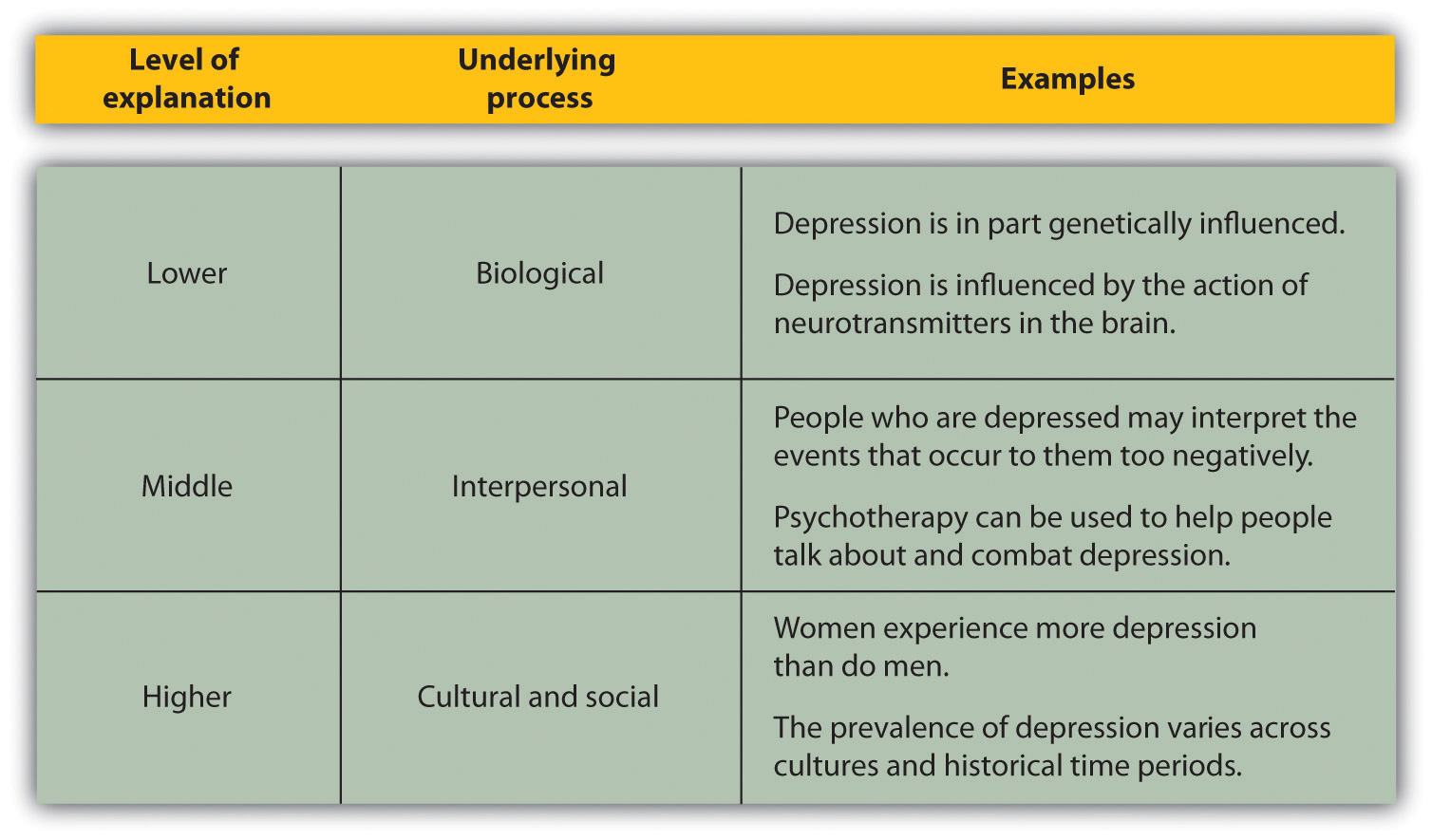
Figure 1.3 Levels of Explanation
The Challenges of Studying Psychology
Understanding and attempting to alleviate the costs of psychological disorders such as depression is not easy, because psychological experiences are extremely complex. The questions psychologists pose are as difficult as those posed by doctors, biologists, chemists, physicists, and other scientists, if not more so (Wilson, 1998).
A major goal of psychology is to predict behavior by understanding its causes. Making predictions is difficult in part because people vary and respond differently in different situations. Individual differences are the variations among people on physical or psychological dimensions. For instance, although many people experience at least some symptoms of depression at some times in their lives, the experience varies dramatically among people. Some people experience major negative events, such as severe physical injuries or the loss of significant others, without experiencing much depression, whereas other people experience severe depression for no apparent reason. Other important individual differences that we will discuss in the chapters to come include differences in extraversion, intelligence, self-esteem, anxiety, aggression, and conformity.
Because of the many individual difference variables that influence behavior, we cannot always predict who will become aggressive or who will perform best in graduate school or on the job. The predictions made by psychologists (and most other scientists) are only probabilistic. We can say, for instance, that people who score higher on an intelligence test will, on average, do better than people who score lower on the same test, but we cannot make very accurate predictions about exactly how any one person will perform.
Another reason that it is difficult to predict behavior is that almost all behavior is multiply determined , or produced by many factors. And these factors occur at different levels of explanation. We have seen, for instance, that depression is caused by lower-level genetic factors, by medium-level personal factors, and by higher-level social and cultural factors. You should always be skeptical about people who attempt to explain important human behaviors, such as violence, child abuse, poverty, anxiety, or depression, in terms of a single cause.
Furthermore, these multiple causes are not independent of one another; they are associated such that when one cause is present other causes tend to be present as well. This overlap makes it difficult to pinpoint which cause or causes are operating. For instance, some people may be depressed because of biological imbalances in neurotransmitters in their brain. The resulting depression may lead them to act more negatively toward other people around them, which then leads those other people to respond more negatively to them, which then increases their depression. As a result, the biological determinants of depression become intertwined with the social responses of other people, making it difficult to disentangle the effects of each cause.
Another difficulty in studying psychology is that much human behavior is caused by factors that are outside our conscious awareness, making it impossible for us, as individuals, to really understand them. The role of unconscious processes was emphasized in the theorizing of the Austrian neurologist Sigmund Freud (1856–1939), who argued that many psychological disorders were caused by memories that we have repressed and thus remain outside our consciousness. Unconscious processes will be an important part of our study of psychology, and we will see that current research has supported many of Freud’s ideas about the importance of the unconscious in guiding behavior.
Key Takeaways
- Psychology is the scientific study of mind and behavior.
- Though it is easy to think that everyday situations have commonsense answers, scientific studies have found that people are not always as good at predicting outcomes as they think they are.
- The hindsight bias leads us to think that we could have predicted events that we actually could not have predicted.
- People are frequently unaware of the causes of their own behaviors.
- Psychologists use the scientific method to collect, analyze, and interpret evidence.
- Employing the scientific method allows the scientist to collect empirical data objectively, which adds to the accumulation of scientific knowledge.
- Psychological phenomena are complex, and making predictions about them is difficult because of individual differences and because they are multiply determined at different levels of explanation.
Exercises and Critical Thinking
- Can you think of a time when you used your intuition to analyze an outcome, only to be surprised later to find that your explanation was completely incorrect? Did this surprise help you understand how intuition may sometimes lead us astray?
- Describe the scientific method in a way that someone who knows nothing about science could understand it.
- Consider a behavior that you find to be important and think about its potential causes at different levels of explanation. How do you think psychologists would study this behavior?
Brendl, C. M., Chattopadhyay, A., Pelham, B. W., & Carvallo, M. (2005). Name letter branding: Valence transfers when product specific needs are active. Journal of Consumer Research, 32 (3), 405–415.
Cacioppo, J. T., Berntson, G. G., Sheridan, J. F., & McClintock, M. K. (2000). Multilevel integrative analyses of human behavior: Social neuroscience and the complementing nature of social and biological approaches. Psychological Bulletin, 126 (6), 829–843.
Chen, P.-Y., Wang, S.-C., Poland, R. E., & Lin, K.-M. (2009). Biological variations in depression and anxiety between East and West. CNS Neuroscience & Therapeutics, 15 (3), 283–294.
Cutler, B. L., & Wells, G. L. (2009). Expert testimony regarding eyewitness identification. In J. L. Skeem, S. O. Lilienfeld, & K. S. Douglas (Eds.), Psychological science in the courtroom: Consensus and controversy (pp. 100–123). New York, NY: Guilford Press.
Fiske, S. T., & Taylor, S. E. (2007). Social cognition: From brains to culture . New York, NY: McGraw-Hill.
Gilovich, T. (1993). How we know what isn’t so: The fallibility of human reason in everyday life . New York, NY: Free Press.
Heider, F. (1958). The psychology of interpersonal relations . Hillsdale, NJ: Erlbaum.
Hsee, C. K., & Hastie, R. (2006). Decision and experience: Why don’t we choose what makes us happy? Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 10 (1), 31–37.
Kelley, H. H. (1967). Attribution theory in social psychology. In D. Levine (Ed.), Nebraska symposium on motivation (Vol. 15, pp. 192–240). Lincoln: University of Nebraska Press.
Nisbett, R. E., & Ross, L. (1980). Human inference: Strategies and shortcomings of social judgment . Englewood Cliffs, NJ: Prentice Hall.
Seedat, S., Scott, K. M., Angermeyer, M. C., Berglund, P., Bromet, E. J., Brugha, T. S.,…Kessler, R. C. (2009). Cross-national associations between gender and mental disorders in the World Health Organization World Mental Health Surveys. Archives of General Psychiatry, 66 (7), 785–795.
Wells, G. L., & Hasel, L. E. (2008). Eyewitness identification: Issues in common knowledge and generalization. In E. Borgida & S. T. Fiske (Eds.), Beyond common sense: Psychological science in the courtroom (pp. 159–176). Malden, NJ: Blackwell.
Williams, N., Simpson, A. N., Simpson, K., & Nahas, Z. (2009). Relapse rates with long-term antidepressant drug therapy: A meta-analysis. Human Psychopharmacology: Clinical and Experimental, 24 (5), 401–408.
Wilson, E. O. (1998). Consilience: The unity of knowledge . New York, NY: Vintage Books
Introduction to Psychology Copyright © 2015 by University of Minnesota is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial-ShareAlike 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
What Is Psychology?
Saul Mcleod, PhD
Editor-in-Chief for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MRes, PhD, University of Manchester
Saul Mcleod, PhD., is a qualified psychology teacher with over 18 years of experience in further and higher education. He has been published in peer-reviewed journals, including the Journal of Clinical Psychology.
Learn about our Editorial Process
Olivia Guy-Evans, MSc
Associate Editor for Simply Psychology
BSc (Hons) Psychology, MSc Psychology of Education
Olivia Guy-Evans is a writer and associate editor for Simply Psychology. She has previously worked in healthcare and educational sectors.
On This Page:
Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and behavior, according to the American Psychological Association. Psychology is a multifaceted discipline and includes many sub-fields of study such areas as human development, sports, health, clinical, social behavior and cognitive processes.
Psychology is a new science, with most advances happening over the past 150 years. However, its origins can be traced back to ancient Greece, 400 – 500 BC.
The emphasis was a philosophical one, with great thinkers such as Socrates (470 BC – 399 BC) influencing Plato (428/427 BC – 348/347 BC), who in turn influenced Aristotle (384 BC – 322 BC).
Philosophers used to discuss many topics now studied by modern psychology, such as memory , free will vs. determinism , nature vs. nurture , attraction, etc.
Psychology is a vast and multifaceted field. Over time, as our understanding of the human mind and behavior has expanded, various specialized areas or branches of psychology have emerged, such as clinical psychology, social psychology, and developmental psychology.
The Beginnings of Psychology as a Discipline
In the early days of psychology, there were two dominant theoretical perspectives regarding how the brain worked, structuralism and functionalism.
Structuralism was the name given to the approach pioneered by Wilhelm Wundt (1832-1920), which focused on breaking down mental processes intro the most basic components.
The term originated from Edward Titchener, an American psychologist who had been trained by Wundt. Wundt was important because he separated psychology from philosophy by analyzing the workings of the mind in a more structured way, with the emphasis being on objective measurement and control.
Structuralism relied on trained introspection, a research method whereby subjects related what was going on in their minds while performing a certain task.
However, introspection proved to be an unreliable method because there was too much individual variation in the experiences and reports of research subjects.
Despite the failure of introspection Wundt is an important figure in the history of psychology as he opened the first laboratory dedicated to psychology in 1879, and its opening is usually thought of as the beginning of modern experimental psychology.
An American psychologist named William James (1842-1910) developed an approach which came to be known as functionalism, that disagreed with the focus of Structuralism.
James argued that the mind is constantly changing and it is pointless to look for the structure of conscious experience. Rather, he proposed the focus should be on how and why an organism does something, i.e. the functions or purpose of the brain.
James suggested that psychologists should look for the underlying cause of behavior and the mental processes involved. This emphasis on the causes and consequences of behavior has influenced contemporary psychology.
The Perspectives of Psychology
Structuralism and functionalism have since been replaced by several dominant and influential approaches to psychology , each underpinned by a shared set of assumptions of what people are like, what is important to study, and how to study it.
Behavioral Perspective : Emerging around the 1910s and 1920s with John Watson’s work, it gained prominence with B.F. Skinner in the 1930s and 1940s. This perspective emphasizes observable behaviors and the environment’s role.
Psychodynamic Perspective : Developed in the early 1900s with the work of Sigmund Freud (1856-1939), emphasizing the unconscious mind and early experiences. Freud’s psychoanalysis was the original psychodynamic theory, but the psychodynamic approach as a whole includes all theories that were based on his ideas, e.g., Jung (1964), Adler (1927), and Erikson (1950).
Humanistic Perspective : Emerged in the 1950s and 1960s as a reaction to behaviorism and psychoanalysis. Carl Rogers and Abraham Maslow are primary figures.
- Cognitive Perspective : Became prominent around the 1950s and 1960s as a response to behaviorism. Key figures include Jean Piaget and Aaron Beck.
- Biological Perspective : While physiological psychology dates back to early experimental psychology, the more integrative biological/neuroscientific perspective emphasizing genetics and brain structures became dominant in the latter part of the 20th century.
Evolutionary Perspective : While Charles Darwin’s evolutionary theory dates to the 19th century, its application to psychology as an “evolutionary psychology” perspective gained traction in the 1980s and 1990s.
Sociocultural Perspective : Gained prominence in the latter half of the 20th century, emphasizing the influence of social interactions, cultural practices, and environmental contexts on individual behavior and cognitive processes.
Ecological Systems Perspective : Introduced by Urie Bronfenbrenner in the 1970s, this perspective examines the multi-layered influences on an individual’s development.
The Goals of Psychology
The four main goals of psychology are to describe, explain, predict and change the behavior and mental processes of others
To Describe
Describing a behavior or cognition is the first goal of psychology. This can enable researchers to develop general laws of human behavior.
For example, by describing the response of dogs to various stimuli, Ivan Pavlov helped develop laws of learning known as classical conditioning theory.
Once researchers have described general laws behavior, the next step is to explain how or why this trend occurs. Psychologists will propose theories which can explain a behavior.
Psychology aims to be able to predict future behavior from the findings of empirical research. If a prediction is not confirmed, then the explanation it is based on might need to be revised.
For example, classical conditioning predicts that if a person associates a negative outcome with a stimuli they may develop a phobia or aversion of the stimuli.
Once psychology has described, explained and made predictions about behavior, changing or controlling a behavior can be attempted.
For example, interventions based on classical conditioning, such as systematic desensitization, have been used to treat people with anxiety disorders including phobias.
Critical Evaluation
Kuhn (1962) argues that a field of study can only legitimately be regarded as a science if most of its followers subscribe to a common perspective or paradigm.
Kuhn believes that psychology is still pre-paradigmatic, while others believe it’s already experienced scientific revolutions (Wundt’s structuralism being replaced by Watson’s behaviorism, in turn, replaced by the information-processing approach ).
The crucial point here is: can psychology be considered a science if psychologists disagree about what to study and how to study it?
Frequently Asked Questions
What are some of the major subfields within psychology.
Major branches of psychology include clinical, developmental, social, cognitive, neuroscience, and educational psychology. They study mental health, development, social interaction, cognition, brain function, and learning.
What is the difference between a psychologist and a psychiatrist?
Psychologists and psychiatrists both work in the mental health field, but their training and approach differ.
Psychologists typically hold a doctoral degree in psychology and provide therapy, conduct research, and administer psychological tests.
Psychiatrists are medical doctors who specialize in mental health and can prescribe medication to manage mental health conditions. They often work with more complex cases and those requiring medication management.
How do researchers in psychology gather and analyze data?
Researchers in psychology gather and analyze data using a variety of methods such as surveys, observations, experiments, and case studies.
They use statistical analysis to identify patterns and relationships in the data and draw conclusions. Some researchers also use brain imaging techniques to study the neural basis of behavior.
Ethical considerations are taken into account when conducting research with human or animal participants. The results of research are often published in academic journals to advance knowledge in the field.
How is psychology used in everyday life?
Psychology can help you in your everyday life by improving your communication skills, relationships, and ability to manage stress. It can also be used to make better decisions in school, healthcare, and work, and improve your mental health and well-being.
By learning about psychology, you can understand people and the world around you better and use that knowledge to improve your own life and the lives of others.
What is reverse psychology?
Reverse psychology is a persuasion technique where an individual encourages another person to adopt a certain behavior or attitude by suggesting the opposite, often because they anticipate a resistant or contrary response.
It’s essentially a method of getting someone to do what you want by suggesting they do the opposite.

Psychological Foundations
Why It Matters: Psychological Foundations

Clive Wearing is an accomplished musician who lost his ability to form new memories when he became sick at the age of 46. While he can remember how to play the piano perfectly, he cannot remember what he ate for breakfast just an hour ago (Sacks, 2007). James Wannerton experiences a taste sensation that is associated with the sound of words. His former girlfriend’s name tastes like rhubarb (Mundasad, 2013). John Nash is a brilliant mathematician and Nobel Prize winner. However, while he was a professor at MIT, he would tell people that the New York Times contained coded messages from extraterrestrial beings that were intended for him. He also began to hear voices and became suspicious of the people around him. Soon thereafter, Nash was diagnosed with schizophrenia and admitted to a state-run mental institution (O’Connor & Robertson, 2002). Nash was the subject of the 2001 movie A Beautiful Mind .
Why did these people have these experiences? How does the human brain work? And what is the connection between the brain’s internal processes and people’s external behaviors? This course will introduce you to various ways that the field of psychology has explored these questions. Psychology is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes—in this course, we will examine the connection between thoughts and actions and better understand how and why people think and behave.
This module will introduce you to what psychology is and what psychologists do. You’ll learn the basic history of the discipline and about the major domains and subdivisions that exist within modern psychology. Lastly, you’ll consider what it means to study psychology and what career options are available for those who do.
American Board of Forensic Psychology. (2014). Brochure. Retrieved from http://www.abfp.com/brochure.asp
American Psychological Association. (2014). Retrieved from www.apa.org
American Psychological Association. (2014). Graduate training and career possibilities in exercise and sport psychology. Retrieved from http://www.apadivisions.org/division-47/about/resources/training.aspx?item=1
American Psychological Association. (2011). Psychology as a career. Retrieved from http://www.apa.org/education/undergrad/psych-career.aspx
Ashliman, D. L. (2001). Cupid and Psyche. In Folktexts: A library of folktales, folklore, fairy tales, and mythology. Retrieved from http://www.pitt.edu/~dash/cupid.html
Betancourt, H., & López, S. R. (1993). The study of culture, ethnicity, and race in American psychology. American Psychologist, 48, 629–637.
Black, S. R., Spence, S. A., & Omari, S. R. (2004). Contributions of African Americans to the field of psychology. Journal of Black Studies, 35, 40–64.
Bulfinch, T. (1855). The age of fable: Or, stories of gods and heroes. Boston, MA: Chase, Nichols and Hill.
Buss, D. M. (1989). Sex differences in human mate preferences: Evolutionary hypotheses tested in 37 cultures. Behavioral and Brain Sciences, 12, 1–49.
Carlson, N. R. (2013). Physiology of Behavior (11th ed.). Boston, MA: Pearson.
Confer, J. C., Easton, J. A., Fleischman, D. S., Goetz, C. D., Lewis, D. M. G., Perilloux, C., & Buss, D. M. (2010). Evolutionary psychology. Controversies, questions, prospects, and limitations. American Psychologist, 65, 100–126.
Crawford, M., & Marecek, J. (1989). Psychology reconstructs the female 1968–1988. Psychology of Women Quarterly, 13, 147–165.
Danziger, K. (1980). The history of introspection reconsidered. Journal of the History of the Behavioral Sciences, 16, 241–262.
Darwin, C. (1871). Thedescent of man and selection in relation to sex. London: John Murray.
Darwin, C. (1872). The expression of the emotions in man and animals. London: John Murray.
DeAngelis, T. (2010). Fear not. gradPSYCH Magazine, 8, 38.
Department of Health and Human Services. (n.d.). Projected future growth of the older population. Retrieved from http://www.aoa.gov/Aging_Statistics/future_growth/future_growth.aspx#age
Endler, J. A. (1986). Natural Selection in the Wild. Princeton, NJ: Princeton University Press.
Fogg, N. P., Harrington, P. E., Harrington, T. F., & Shatkin, L. (2012). College majors handbook with real career paths and payoffs (3rd ed.). St. Paul, MN: JIST Publishing.
Franko, D. L., et al. (2012). Racial/ethnic differences in adults in randomized clinical trials of binge eating disorder. Journal of Consulting and Clinical Psychology, 80, 186–195.
Friedman, H. (2008), Humanistic and positive psychology: The methodological and epistemological divide. The Humanistic Psychologist, 36, 113–126.
Gordon, O. E. (1995). A brief history of psychology. Retrieved from http://www.psych.utah.edu/gordon/Classes/Psy4905Docs/PsychHistory/index.html#maptop
Greek Myths & Greek Mythology. (2014). The myth of Psyche and Eros. Retrieved from http://www.greekmyths-greekmythology.com/psyche-and-eros-myth/
Green, C. D. (2001). Classics in the history of psychology. Retrieved from http://psychclassics.yorku.ca/Krstic/marulic.htm
Greengrass, M. (2004). 100 years of B.F. Skinner. Monitor on Psychology, 35, 80.
Halonen, J. S. (2011). White paper: Are there too many psychology majors? Prepared for the Staff of the State University System of Florida Board of Governors. Retrieved from http://www.cogdop.org/page_attachments/0000/0200/FLA_White_Paper_for_cogop_posting.pdf
Hock, R. R. (2009). Social psychology. Forty studies that changed psychology: Explorations into the history of psychological research (pp. 308–317). Upper Saddle River, NJ: Pearson.
Hoffman, C. (2012). Careers in clinical, counseling, or school psychology; mental health counseling; clinical social work; marriage & family therapy and related professions. Retrieved from http://www.indiana.edu/~psyugrad/advising/docs/Careers%20in%20Mental%20Health%20Counseling.pdf
Jang, K. L., Livesly, W. J., & Vernon, P. A. (1996). Heritability of the Big Five personality dimensions and their facets: A twin study. Journal of Personality, 64, 577–591.
Johnson, R., & Lubin, G. (2011). College exposed: What majors are most popular, highest paying and most likely to get you a job. Business Insider.com. Retrieved from http://www.businessinsider.com/best-college-majors-highest-income-most-employed-georgetwon-study-2011-6?op=1
Knekt, P. P., et al. (2008). Randomized trial on the effectiveness of long- and short-term psychodynamic psychotherapy and solution-focused therapy on psychiatric symptoms during a 3-year follow-up. Psychological Medicine: A Journal of Research In Psychiatry And The Allied Sciences, 38, 689–703.
Landers, R. N. (2011, June 14). Grad school: Should I get a PhD or Master’s in I/O psychology? [Web log post]. Retrieved from http://neoacademic.com/2011/06/14/grad-school-should-i-get-a-ph-d-or-masters-in-io-psychology/#.UuKKLftOnGg
Macdonald, C. (2013). Health psychology center presents: What is health psychology? Retrieved from http://healthpsychology.org/what-is-health-psychology/
McCrae, R. R. & Costa, P. T. (2008). Empirical and theoretical status of the five-factor model of personality traits. In G. J. Boyle, G. Matthews, & D. H. Saklofske (Eds.), The Sage handbook of personality theory and assessment. Vol. 1 Personality theories and models. London: Sage.
Michalski, D., Kohout, J., Wicherski, M., & Hart, B. (2011). 2009 Doctorate Employment Survey. APA Center for Workforce Studies. Retrieved from http://www.apa.org/workforce/publications/09-doc-empl/index.aspx
Miller, G. A. (2003). The cognitive revolution: A historical perspective. Trends in Cognitive Sciences, 7, 141–144.
Munakata, Y., McClelland, J. L., Johnson, M. H., & Siegler, R. S. (1997). Rethinking infant knowledge: Toward an adaptive process account of successes and failures in object permanence tasks. Psychological Review, 104, 689–713.
Mundasad, S. (2013). Word-taste synaesthesia: Tasting names, places, and Anne Boleyn. Retrieved from http://www.bbc.co.uk/news/health-21060207
Munsey, C. (2009). More states forgo a postdoc requirement. Monitor on Psychology, 40, 10.
National Association of School Psychologists. (n.d.). Becoming a nationally certified school psychologist (NCSP). Retrieved from http://www.nasponline.org/CERTIFICATION/becomeNCSP.aspx
Nicolas, S., & Ferrand, L. (1999). Wundt’s laboratory at Leipzig in 1891. History of Psychology, 2, 194–203.
Norcross, J. C. (n.d.) Clinical versus counseling psychology: What’s the diff? Available at http://www.csun.edu/~hcpsy002/Clinical%20Versus%20Counseling%20Psychology.pdf
Norcross, J. C., & Castle, P. H. (2002). Appreciating the PsyD: The facts. Eye on Psi Chi, 7, 22–26.
O’Connor, J. J., & Robertson, E. F. (2002). John Forbes Nash. Retrieved from http://www-groups.dcs.st-and.ac.uk/~history/Biographies/Nash.html
O’Hara, M. (n.d.). Historic review of humanistic psychology. Retrieved from http://www.ahpweb.org/index.php?option=com_k2&view=item&layout=item&id=14&Itemid=24
Person, E. S. (1980). Sexuality as the mainstay of identity: Psychoanalytic perspectives. Signs, 5, 605–630.
Rantanen, J., Metsäpelto, R. L., Feldt, T., Pulkkinen, L., & Kokko, K. (2007). Long-term stability in the Big Five personality traits in adulthood. Scandinavian Journal of Psychology, 48, 511–518.
Riggio, R. E. (2013). What is industrial/organizational psychology? Psychology Today. Retrieved from http://www.psychologytoday.com/blog/cutting-edge-leadership/201303/what-is-industrialorganizational-psychology
Sacks, O. (2007). A neurologists notebook: The abyss, music and amnesia. The New Yorker. Retrieved from http://www.newyorker.com/reporting/2007/09/24/070924fa_fact_sacks?currentPage=all
Shedler, J. (2010). The efficacy of psychodynamic psychotherapy. American Psychologist, 65(2), 98–109.
Soldz, S., & Vaillant, G. E. (1999). The Big Five personality traits and the life course: A 45-year longitudinal study. Journal of Research in Personality, 33, 208–232.
Thorne, B. M., & Henley, T. B. (2005). Connections in the history and systems of psychology (3rd ed.). Boston, MA: Houghton Mifflin Company.
Tolman, E. C. (1938). The determiners of behavior at a choice point. Psychological Review, 45, 1–41.
U.S. Department of Education, National Center for Education Statistics. (2013). Digest of Education Statistics, 2012 (NCES 2014-015).
Weisstein, N. (1993). Psychology constructs the female: Or, the fantasy life of the male psychologist (with some attention to the fantasies of his friends, the male biologist and the male anthropologist). Feminism and Psychology, 3, 195–210.
Westen, D. (1998). The scientific legacy of Sigmund Freud, toward a psychodynamically informed psychological science. Psychological Bulletin, 124, 333–371.
CC licensed content, Original
- Modification, adaptation, and original content. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
CC licensed content, Shared previously
- Psychology Introduction. Authored by : OpenStax College. Located at : https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction . License : CC BY: Attribution . License Terms : Download for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
General Psychology Copyright © by OpenStax and Lumen Learning is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book
- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2023 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
The Origins of Psychology
From Philosophical Beginnings to the Modern Day
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Adah Chung is a fact checker, writer, researcher, and occupational therapist.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Adah-Chung-1000-df54540455394e3ab797f6fce238d785.jpg)
Verywell / Madelyn Goodnight
- Importance of History
- Structuralism
Functionalism
- Psychoanalysis
- Behaviorism
- The Third Force
Cognitive Psychology
While the psychology of today reflects the discipline's rich and varied history, the origins of psychology differ significantly from contemporary conceptions of the field. In order to gain a full understanding of psychology, you need to spend some time exploring its history and origins.
How did psychology originate? When did it begin? Who were the people responsible for establishing psychology as a separate science?
Why Study Psychology History?
Contemporary psychology is interested in an enormous range of topics, looking at human behavior and mental process from the neural level to the cultural level. Psychologists study human issues that begin before birth and continue until death. By understanding the history of psychology, you can gain a better understanding of how these topics are studied and what we have learned thus far.
From its earliest beginnings, psychology has been faced with a number of questions. The initial question of how to define psychology helped establish it as a science separate from physiology and philosophy.
Additional questions that psychologists have faced throughout history include:
- Is psychology really a science?
- Should psychologists use research to influence public policy, education, and other aspects of human behavior?
- Should psychology focus on observable behaviors, or on internal mental processes?
- What research methods should be used to study psychology?
- Which topics and issues should psychology be concerned with?
Background: Philosophy and Physiology
While psychology did not emerge as a separate discipline until the late 1800s, its earliest history can be traced back to the time of the early Greeks. During the 17th-century, the French philosopher Rene Descartes introduced the idea of dualism, which asserted that the mind and body were two entities that interact to form the human experience.
Many other issues still debated by psychologists today, such as the relative contributions of nature vs. nurture , are rooted in these early philosophical traditions.
So what makes psychology different from philosophy? While early philosophers relied on methods such as observation and logic, today’s psychologists utilize scientific methodologies to study and draw conclusions about human thought and behavior.
Physiology also contributed to psychology’s eventual emergence as a scientific discipline. Early physiological research on the brain and behavior had a dramatic impact on psychology, ultimately contributing to applying scientific methodologies to the study of human thought and behavior.
Psychology Emerges as a Separate Discipline
During the mid-1800s, a German physiologist named Wilhelm Wundt was using scientific research methods to investigate reaction times. His book published in 1873, "Principles of Physiological Psychology," outlined many of the major connections between the science of physiology and the study of human thought and behavior.
He later opened the world’s first psychology lab in 1879 at the University of Leipzig. This event is generally considered the official start of psychology as a separate and distinct scientific discipline.
How did Wundt view psychology? He perceived the subject as the study of human consciousness and sought to apply experimental methods to studying internal mental processes. While his use of a process known as introspection is seen as unreliable and unscientific today, his early work in psychology helped set the stage for future experimental methods.
An estimated 17,000 students attended Wundt’s psychology lectures, and hundreds more pursued degrees in psychology and studied in his psychology lab. While his influence dwindled as the field matured, his impact on psychology is unquestionable.
Structuralism: Psychology’s First School of Thought
Edward B. Titchener , one of Wundt’s most famous students, would go on to found psychology’s first major school of thought . According to the structuralists , human consciousness could be broken down into smaller parts. Using a process known as introspection, trained subjects would attempt to break down their responses and reactions to the most basic sensation and perceptions.
While structuralism is notable for its emphasis on scientific research, its methods were unreliable, limiting, and subjective. When Titchener died in 1927, structuralism essentially died with him.
The Functionalism of William James
Psychology flourished in America during the mid- to late-1800s. William James emerged as one of the major American psychologists during this period and publishing his classic textbook, "The Principles of Psychology," established him as the father of American psychology.
His book soon became the standard text in psychology and his ideas eventually served as the basis for a new school of thought known as functionalism.
The focus of functionalism was about how behavior actually works to help people live in their environment. Functionalists utilized methods such as direct observation to study the human mind and behavior.
Both of these early schools of thought emphasized human consciousness, but their conceptions of it were significantly different. While the structuralists sought to break down mental processes into their smallest parts, the functionalists believed that consciousness existed as a more continuous and changing process.
While functionalism quickly faded a separate school of thought, it would go on to influence later psychologists and theories of human thought and behavior.
The Emergence of Psychoanalysis
Up to this point, early psychology stressed conscious human experience. An Austrian physician named Sigmund Freud changed the face of psychology in a dramatic way, proposing a theory of personality that emphasized the importance of the unconscious mind.
Freud’s clinical work with patients suffering from hysteria and other ailments led him to believe that early childhood experiences and unconscious impulses contributed to the development of adult personality and behavior.
In his book "The Psychopathology of Everyday Life " Freud detailed how these unconscious thoughts and impulses are expressed, often through slips of the tongue (known as "Freudian slips" ) and dreams . According to Freud, psychological disorders are the result of these unconscious conflicts becoming extreme or unbalanced.
The psychoanalytic theory proposed by Sigmund Freud had a tremendous impact on 20th-century thought, influencing the mental health field as well as other areas including art, literature, and popular culture. While many of his ideas are viewed with skepticism today, his influence on psychology is undeniable.
The Rise of Behaviorism
Psychology changed dramatically during the early 20th-century as another school of thought known as behaviorism rose to dominance. Behaviorism was a major change from previous theoretical perspectives, rejecting the emphasis on both the conscious and unconscious mind . Instead, behaviorism strove to make psychology a more scientific discipline by focusing purely on observable behavior.
Behaviorism had its earliest start with the work of a Russian physiologist named Ivan Pavlov . Pavlov's research on the digestive systems of dogs led to his discovery of the classical conditioning process, which proposed that behaviors could be learned via conditioned associations.
Pavlov demonstrated that this learning process could be used to make an association between an environmental stimulus and a naturally occurring stimulus.
An American psychologist named John B. Watson soon became one of the strongest advocates of behaviorism. Initially outlining the basic principles of this new school of thought in his 1913 paper Psychology as the Behaviorist Views It , Watson later went on to offer a definition in his classic book "Behaviorism " (1924), writing:
"Behaviorism...holds that the subject matter of human psychology is the behavior of the human being. Behaviorism claims that consciousness is neither a definite nor a usable concept. The behaviorist, who has been trained always as an experimentalist, holds, further, that belief in the existence of consciousness goes back to the ancient days of superstition and magic."
The impact of behaviorism was enormous, and this school of thought continued to dominate for the next 50 years. Psychologist B.F. Skinner furthered the behaviorist perspective with his concept of operant conditioning , which demonstrated the effect of punishment and reinforcement on behavior.
While behaviorism eventually lost its dominant grip on psychology, the basic principles of behavioral psychology are still widely in use today.
Therapeutic techniques such as behavior analysis , behavioral modification, and token economies are often utilized to help children learn new skills and overcome maladaptive behaviors, while conditioning is used in many situations ranging from parenting to education.
The Third Force in Psychology
While the first half of the 20th century was dominated by psychoanalysis and behaviorism, a new school of thought known as humanistic psychology emerged during the second half of the century. Often referred to as the "third force" in psychology, this theoretical perspective emphasized conscious experiences.
American psychologist Carl Rogers is often considered to be one of the founders of this school of thought. While psychoanalysts looked at unconscious impulses and behaviorists focused on environmental causes, Rogers believed strongly in the power of free will and self-determination.
Psychologist Abraham Maslow also contributed to humanistic psychology with his famous hierarchy of needs theory of human motivation. This theory suggested that people were motivated by increasingly complex needs. Once the most basic needs are fulfilled, people then become motivated to pursue higher level needs.
During the 1950s and 1960s, a movement known as the cognitive revolution began to take hold in psychology. During this time, cognitive psychology began to replace psychoanalysis and behaviorism as the dominant approach to the study of psychology. Psychologists were still interested in looking at observable behaviors, but they were also concerned with what was going on inside the mind.
Since that time, cognitive psychology has remained a dominant area of psychology as researchers continue to study things such as perception, memory, decision-making, problem-solving, intelligence, and language.
The introduction of brain imaging tools such as MRI and PET scans have helped improve the ability of researchers to more closely study the inner workings of the human brain.
Psychology Continues to Grow
As you have seen in this brief overview of psychology’s history, this discipline has seen dramatic growth and change since its official beginnings in Wundt’s lab. The story certainly does not end here.
Psychology has continued to evolve since 1960 and new ideas and perspectives have been introduced. Recent research in psychology looks at many aspects of the human experience, from the biological influences on behavior on the impact of social and cultural factors.
Today, the majority of psychologists do not identify themselves with a single school of thought. Instead, they often focus on a particular specialty area or perspective, often drawing on ideas from a range of theoretical backgrounds. This eclectic approach has contributed new ideas and theories that will continue to shape psychology for years to come.
Women in Psychology History
As you read through any history of psychology, you might be particularly struck by the fact that such texts seem to center almost entirely on the theories and contributions of men. This is not because women had no interest in the field of psychology, but is largely due to the fact that women were excluded from pursuing academic training and practice during the early years of the field.
There are a number of women who made important contributions to the early history of psychology, although their work is sometimes overlooked.
A few pioneering women psychologists included:
- Mary Whiton Calkins , who rightfully earned a doctorate from Harvard, although the school refused to grant her degree because she was a woman. She studied with major thinkers of the day like William James, Josiah Royce, and Hugo Munsterberg. Despite the obstacles she faced, she became the American Psychological Association's first woman president.
- Anna Freud , who made important contributions to the field of psychoanalysis. She described many of the defense mechanisms and is known as the founder of child psychoanalysis. She also had an influence on other psychologists including Erik Erikson.
- Mary Ainsworth , who was a developmental psychologist, made important contributions to our understanding of attachment . She developed a technique for studying child and caregiver attachments known as the "Strange Situation" assessment.
A Word From Verywell
In order to understand how psychology became the science that it is today, it is important to learn more about some of the historical events that have influenced its development.
While some of the theories that emerged during the earliest years of psychology may now be viewed as simplistic, outdated, or incorrect, these influences shaped the direction of the field and helped us form a greater understanding of the human mind and behavior.
Mehta N. Mind-body Dualism: A critique from a health perspective . Mens Sana Monogr . 2011;9(1):202-209. doi:10.4103/0973-1229.77436
Blumenthal AL. A Wundt Primer . In: Rieber RW, Robinson DK, eds. Wilhelm Wundt in History. Boston: Springer; 2001. doi:10.1007/978-1-4615-0665-2_4
Patanella D. Titchener, Edward Bradford . In: Goldstein S, Naglieri JA, eds. Encyclopedia of Child Behavior and Development . Boston: Springer; 2011. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-79061-9
De Sousa A. Freudian theory and consciousness: A conceptual analysis . Mens Sana Monogr . 2011;9(1):210-217. doi:10.4103/0973-1229.77437
Wolpe J, Plaud JJ. Pavlov's contributions to behavior therapy. The obvious and not so obvious . Am Psychol . 1997;52(9):966-972. doi:10.1037//0003-066x.52.9.966
Staddon JE, Cerutti DT. Operant Conditioning . Annu Rev Psychol . 2003;54:115-144. doi:10.1146/annurev.psych.54.101601.145124
Koole SL, Schlinkert C, Maldei T, Baumann N. Becoming who you are: An integrative review of self-determination theory and personality systems interactions theory . J Pers . 2019;87(1):15-36. doi:10.1111/jopy.12380
Block M. Maslow’s hierarchy of needs . In: Goldstein S, Naglieri JA, eds. Encyclopedia of Child Behavior and Development . Boston: Springer; 2011. doi:10.1007/978-0-387-79061-9
Russo NF, Denmark FL. Contributions of Women to Psychology . Ann Rev Psychol . 1987;38:279-298. doi:10.1146/annurev.ps.38.020187.001431
Fancher RE, Rutherford A. Pioneers of Psychology . New York: W.W. Norton; 2016.
Lawson RB, Graham JE, Baker KM. A History of Psychology . New York: Routledge; 2007.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Why is psychology important?
The mind is amazing. As an engine for all consciousness and thought, it can solve some of the most complicated problems we face and yet, from time to time, it can feel like our brains are actively working against us. We have a need to make sense of things, so it’s only natural we seek to understand the most powerful tool we have at our disposal. Below, we explore what psychology is, why it’s important, and how it can help us become better versions of ourselves.
By Grant Longstaff . Published 30 May 2023.
What is psychology?
Psychology is the scientific study of the mind and human behaviour. It’s a discipline based on research and experimentation, and psychologists draw on a long history of psychological theory to inform modern approaches and practices.
When we asked Dr Julie Prescott, our head of Psychology, why the discipline is important she said: “Psychology is everywhere and covers all aspects of life. It’s about humans and the human mind. Studying psychology is so varied and as a student, you get to learn a range of theories and topics and how they can be applied to real situations and settings.”
Psychology is such a vast field the benefits are wide ranging, it could include researching mental health to help enhance wellbeing, better understanding the relationships we form, self-improvement, or battling addiction. There can also be benefits to our communication with, and understanding of, other people.
It goes beyond the individual and can help improve society too, by helping shape and inform areas including education, justice, employment, medicine, and business to name just a few. It can even improve technology, for instance, our BSc (Hons) Computer Science includes optional psychology modules so students can explore the interaction between human behaviour and technological advancement.
What are the different types of psychology?
There are many different types of psychology. Below we’ve offered a brief overview of some of the most common types of psychology around today.
Clinical psychology involves the evaluation and treatment of psychological challenges, including mental illnesses, psychological disorders, learning disabilities, and relationships.
Sports psychology is focused on supporting athletes, either individually or as a team, with various aspects of their personal development and professional performance.
Educational psychology uses the principles of psychology to develop and improve learning for children, schools, and their wider communities.
Counselling psychology can help with complex emotional challenges and the work involves clinical research and study.
Occupational psychology is focused on improving business through employee care and development.
Forensic psychology examines the impact of criminality on both the individual and society.
This list barely scratches the surface of the types of psychology in which people could study and work. For more information on the scope of psychology in the world today, explore the British Psychological Society (BPS) website. It offers information and advice on education and careers and hosts the latest news in psychology.

Why study psychology?
Studying psychology goes beyond helping you understand yourself and others. There are many psychology careers where a qualification is either necessary or, at the very least, desirable and the transferrable skills gained can benefit you in any workplace. If you’re interested in learning more about how the mind works, then our BSc (Hons) Psychology is an excellent starting point. Moreover, if you already hold an undergraduate degree and you’re looking for a career in psychology, our MSc Psychology (Conversion) course is for you. You can read our guide - what to know before you study psychology – for more information.
There are many reasons why a student might choose to study psychology, and it’s impossible to say exactly why with any certainty, but we can perhaps look for answers in the fundamentals of the subject for clues. At its core, psychology is about further understanding human nature and behaviour. Maybe those who choose to study psychology are ultimately seeking to better comprehend themselves and those around them.
Are you interested in a career in psychology but unable to commit to full-time study? Explore our online MSc Psychology (Conversion) and take your first steps toward a new career today.
resources Our Recent Blogs

What is case law?

Stress Awareness Month – Little by Little

Reddit Roundup: March 2024
PSYCH101: Introduction to Psychology
Why research is important.
Read this text, which introduces the scientific method, which involves making a hypothesis or general premise, deductive reasoning, making empirical observations, and inductive reasoning,
Scientific research is a critical tool for successfully navigating our complex world. Without it, we would be forced to rely solely on intuition, other people's authority, and blind luck. While many of us feel confident in our abilities to decipher and interact with the world around us, history is filled with examples of how very wrong we can be when we fail to recognize the need for evidence in supporting claims. At various times in history, we would have been certain that the sun revolved around a flat earth, that the earth's continents did not move, and that mental illness was caused by possession (Figure 2.2). It is through systematic scientific research that we divest ourselves of our preconceived notions and superstitions and gain an objective understanding of ourselves and our world.

Figure 2.2 Some of our ancestors, across the world and over the centuries, believed that trephination - the practice of making a hole in the skull, as shown here - allowed evil spirits to leave the body, thus curing mental illness and other disorders.
Use of Research Information
Trying to determine which theories are and are not accepted by the scientific community can be difficult, especially in an area of research as broad as psychology. More than ever before, we have an incredible amount of information at our fingertips, and a simple internet search on any given research topic might result in a number of contradictory studies. In these cases, we are witnessing the scientific community going through the process of reaching a consensus, and it could be quite some time before a consensus emerges. For example, the explosion in our use of technology has led researchers to question whether this ultimately helps or hinders us. The use and implementation of technology in educational settings has become widespread over the last few decades.
Researchers are coming to different conclusions regarding the use of technology. To illustrate this point, a study investigating a smartphone app targeting surgery residents (graduate students in surgery training) found that the use of this app can increase student engagement and raise test scores. Conversely, another study found that the use of technology in undergraduate student populations had negative impacts on sleep, communication, and time management skills. Until sufficient amounts of research have been conducted, there will be no clear consensus on the effects that technology has on a student's acquisition of knowledge, study skills, and mental health. In the meantime, we should strive to think critically about the information we encounter by exercising a degree of healthy skepticism. When someone makes a claim, we should examine the claim from a number of different perspectives: what is the expertise of the person making the claim, what might they gain if the claim is valid, does the claim seem justified given the evidence, and what do other researchers think of the claim? This is especially important when we consider how much information in advertising campaigns and on the internet claims to be based on "scientific evidence" when in actuality it is a belief or perspective of just a few individuals trying to sell a product or draw attention to their perspectives. We should be informed consumers of the information made available to us because decisions based on this information have significant consequences. One such consequence can be seen in politics and public policy. Imagine that you have been elected as the governor of your state. One of your responsibilities is to manage the state budget and determine how to best spend your constituents' tax dollars. As the new governor, you need to decide whether to continue funding early intervention programs. These programs are designed to help children who come from low-income backgrounds, have special needs, or face other disadvantages. These programs may involve providing a wide variety of services to maximize the children's development and position them for optimal levels of success in school and later in life.
While such programs sound appealing, you would want to be sure that they also proved effective before investing additional money in these programs. Fortunately, psychologists and other scientists have conducted vast amounts of research on such programs and, in general, the programs are found to be effective. While not all programs are equally effective, and the short-term effects of many such programs are more pronounced, there is reason to believe that many of these programs produce long-term benefits for participants. If you are committed to being a good steward of taxpayer money, you would want to look at research. Which programs are most effective? What characteristics of these programs make them effective? Which programs promote the best outcomes? After examining the research, you would be best equipped to make decisions about which programs to fund. Ultimately, it is not just politicians who can benefit from using research in guiding their decisions. We all might look to research from time to time when making decisions in our lives. Imagine you just found out that your sister Maria's child, Umberto, was recently diagnosed with autism. There are many treatments for autism that help decrease the negative impact of autism on the individual. Some examples of treatments for autism are applied behavior analysis (ABA), social communication groups, social skills groups, occupational therapy, and even medication options. If Maria asked you for advice or guidance, what would you do? You would likely want to review the research and learn about the efficacy of each treatment so you could best advise your sister. In the end, research is what makes the difference between facts and opinions. Facts are observable realities, and opinions are personal judgments, conclusions, or attitudes that may or may not be accurate. In the scientific community, facts can be established only using evidence collected through empirical research.
Notable Researchers
Psychological research has a long history involving important figures from diverse backgrounds. While the introductory chapter discussed several researchers who made significant contributions to the discipline, there are many more individuals who deserve attention in considering how psychology has advanced as a science through their work (Figure 2.3). For instance, Margaret Floy Washburn (1871–1939) was the first woman to earn a PhD in psychology. Her research focused on animal behavior and cognition. Mary Whiton Calkins (1863–1930) was a preeminent first-generation American psychologist who opposed the behaviorist movement, conducted significant research into memory, and established one of the earliest experimental psychology labs in the United States. Francis Sumner (1895–1954) was the first African American to receive a PhD in psychology in 1920. His dissertation focused on issues related to psychoanalysis. Sumner also had research interests in racial bias and educational justice. Sumner was one of the founders of Howard University's department of psychology, and because of his accomplishments, he is sometimes referred to as the "Father of Black Psychology". Thirteen years later, Inez Beverly Prosser (1895–1934) became the first African American woman to receive a PhD in psychology. Prosser's research highlighted issues related to education in segregated versus integrated schools, and ultimately, her work was very influential in the hallmark Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court ruling that segregation of public schools was unconstitutional.

Figure 2.3 (a) Margaret Floy Washburn was the first woman to earn a doctorate degree in psychology. (b) The outcome of Brown v. Board of Education was influenced by the research of psychologist Inez Beverly Prosser, who was the first African American woman to earn a PhD in psychology.
The Process of Scientific Research
Scientific knowledge is advanced through a process known as the scientific method. Basically, ideas (in the form of theories and hypotheses) are tested against the real world (in the form of empirical observations), and those empirical observations lead to more ideas that are tested against the real world, and so on. In this sense, the scientific process is circular. The types of reasoning within the circle are called deductive and inductive. In deductive reasoning , ideas are tested in the real world; in inductive reasoning , real-world observations lead to new ideas (Figure 2.4). These processes are inseparable, like inhaling and exhaling, but different research approaches place different emphasis on the deductive and inductive aspects.

In the scientific context, deductive reasoning begins with a generalization - one hypothesis - that is then used to reach logical conclusions about the real world. If the hypothesis is correct, then the logical conclusions reached through deductive reasoning should also be correct. A deductive reasoning argument might go something like this: All living things require energy to survive (this would be your hypothesis). Ducks are living things. Therefore, ducks require energy to survive (logical conclusion). In this example, the hypothesis is correct; therefore, the conclusion is correct as well. Sometimes, however, an incorrect hypothesis may lead to a logical but incorrect conclusion. Consider this argument: all ducks are born with the ability to see. Quackers is a duck. Therefore, Quackers was born with the ability to see. Scientists use deductive reasoning to empirically test their hypotheses. Returning to the example of the ducks, researchers might design a study to test the hypothesis that if all living things require energy to survive, then ducks will be found to require energy to survive. Deductive reasoning starts with a generalization that is tested against real-world observations; however, inductive reasoning moves in the opposite direction. Inductive reasoning uses empirical observations to construct broad generalizations. Unlike deductive reasoning, conclusions drawn from inductive reasoning may or may not be correct, regardless of the observations on which they are based. For instance, you may notice that your favorite fruits - apples, bananas, and oranges - all grow on trees; therefore, you assume that all fruit must grow on trees. This would be an example of inductive reasoning, and, clearly, the existence of strawberries, blueberries, and kiwi demonstrate that this generalization is not correct despite it being based on a number of direct observations. Scientists use inductive reasoning to formulate theories, which in turn generate hypotheses that are tested with deductive reasoning. In the end, science involves both deductive and inductive processes. For example, case studies, which you will read about in the next section, are heavily weighted on the side of empirical observations. Thus, case studies are closely associated with inductive processes as researchers gather massive amounts of observations and seek interesting patterns (new ideas) in the data. Experimental research, on the other hand, puts great emphasis on deductive reasoning. We've stated that theories and hypotheses are ideas, but what sort of ideas are they, exactly? A theory is a well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation for observed phenomena. Theories are repeatedly checked against the world, but they tend to be too complex to be tested all at once; instead, researchers create hypotheses to test specific aspects of a theory. A hypothesis is a testable prediction about how the world will behave if our idea is correct, and it is often worded as an if-then statement (e.g., if I study all night, I will get a passing grade on the test). The hypothesis is extremely important because it bridges the gap between the realm of ideas and the real world. As specific hypotheses are tested, theories are modified and refined to reflect and incorporate the result of these tests Figure 2.5.

Figure 2.5 The scientific method involves deriving hypotheses from theories and then testing those hypotheses. If the results are consistent with the theory, then the theory is supported. If the results are not consistent, then the theory should be modified and new hypotheses will be generated.

Figure 2.6 Many of the specifics of (a) Freud's theories, such as (b) his division of the mind into id, ego, and superego, have fallen out of favor in recent decades because they are not falsifiable. In broader strokes, his views set the stage for much of psychological thinking today, such as the unconscious nature of the majority of psychological processes.

- Career Advisor
- Career Coach
- Career Counselling
- What Should I Study?
- Business School
- Best MBA Schools
- Business Analytics
- Business Degrees
- Management Courses
- Marketing Courses
- MBA Online Courses
- Project Management
- Education Masters
- Health Management
- Mental Health
- Mental Health Nursing
- Nursing Degrees
- Nurse Postgraduate
- Psychology Courses
- Psychology Degree
- Social Work
- Cyber Security
- Data Analytics
- Data Science
- Masters Degrees
- Legal Overview

Why I Study Psychology (10 Essays)
Why I Study Psychology is a collection of short essays. Each student explains their motivation for choosing psychology.
Psychology students are often motivated by personal experiences and a wish for healthier, happier communities. The essays demonstrate the value from having a vision for your career – whether it’s detailed or “big picture” – before you start a psychology degree . Having a long-term goal in mind offers a reliable source of study motivation.
Why I Chose Psychology Essays

As part of a national essay competition, current and future psychology students were asked to explain their study motivation. Each student describes in 250 words or less (a) why I chose psychology as a major and (b) how I’m motivated to succeed at psychology studies. The best, most inspiring essays are published here.
1. Motivation
We all know that there will almost always be something to do that sounds much more appealing than our studies, so why do we study if there is something better? Motivation, that’s why. Everyone has their own motivating factor that keeps them in line with studying. Mine is pretty general and that is my future.
I have dreams of becoming a psychologist and helping people throughout my life. I also have a huge passion for American Sign Language. I plan to merge these two goals into one for my future career . I don’t want to be just any psychologist, I want to be a psychologist that is open to Deaf people and hearing people alike. I want Deaf people to feel comfortable coming to me without the need of a third person interpreter who is usually a stranger . Many Deaf people feel uncomfortable visiting a psychologist because of the need for a third person. I plan to make a step towards breaking that barrier by being able to signor speak with any patient who comes to me.
With all these huge goals I know that I have to be very on top of studies and make sure I continue to stay on track and do my best. All of these reasons put together make up my ideal future and therefore my motivation to study.
~ Hannah Reis, Palomar College
2. My Dream
We live in a world filled with hurt and suffering, and a place that is not equal for all. My dream is to leverage my unique set of skills, abilities, privileges, resources, and knowledge in a way that increases equality and privilege for all (not just people with white skin). I am pursuing a degree in Industrial and Organizational Psychology which combines psychology and business.
I feel most alive when I am volunteering with my family at The Christian Children’s Home of Ohio (CCHO) which is a non-profit orphanage for children. I love working with the children there, and it hurts my heart when I see them being forced to leave once they are eighteen without any further aid or support. Due to this fact, I have decided that after I get several years of work experience applying psychology principles to the business world, I want to start my own non-profit organization that aids young adults who grew up in foster care or orphanages . Once they have turned eighteen the government will no longer provide very much aid to them; I want to supply them with the additional skills and services that they need to make it in the real world, and give them the emotional support that they may not have.
One of the main services I want to provide them is taking them to do mission work because the best way to grow as a person and gain perspective is through service and travel. When college gets hard, I hold on tight to this dream because I know my studies will help me achieve this dream.
~ Alyssa Powers, The University of Akron
3. A Catalyst for Change
The incredible transformation I have experienced in my own life from the power of the therapeutic relationship motivates me to immerse myself in my studies and move closer towards my goal of becoming a psychologist. Recognizing how the quality of my own life has been profoundly enhanced by self-reflection, the invaluable lesson of how to learn from suffering, and coming to a deeper understanding of who I am, encourages me to try and be a catalyst for this kind of change in other’s lives. I’m motivated to empower people to feel confident enough in who they are that they don’t feel the need to bring others down.
When life as a student feels exceptionally challenging, I remind myself of the impact that the work I wish to practice has on people’s lives and those around them. I strongly believe large scale change happens on the individual level first, and if we want to see a world where we value the earth and all the people living on it, we have to do the work with ourselves first. I want to help people in their transformation towards becoming more unconditionally loving, tolerant, and compassionate people . I think when people are more comfortable with, and accepting of, who they are, they are consequently kinder and more loving towards those around them. Encouraging this kind of growth first on an individual level, and ultimately on a global level, motivates me to not only get through, but thrive within my program.
~ Hannah Freund, California Institute of Integral Studies
4. Reshaping Mental Health
People who are given psychiatric diagnoses experience some of the worst prejudice and discrimination. They are more likely to be the victims of violence, have a harder time securing jobs and housing, and constantly come face-to-face with the harmful stereotypes that state that these individuals are violent and unpredictable. As such, much research needs to be done to understand the cause of such distress, as well as to develop effective interventions and achieve healthy minds.
Our current mental health paradigm positions mental distress as biological in origin and best treated with medical interventions. However this paradigm has conversely led to an increase in stigma and an increase in the number of people on disability for mental health related reasons. I was one of the fortunate few who was able to pursue a college degree despite being given a severe diagnosis and a hopeless prognosis. However, I know that much of my success has been due to luck and privilege, and the opportunities that I have been afforded are an exception, not a rule. I am striving to change that.
It is my hope that, through increased research and advocacy, society can come to understand that extreme distress is often a message about something that is wrong in a person’s world, and as such, is profoundly meaningful and can be understood. Furthermore, by understanding the psychosocial origins of distress – trauma, poverty, inequality, etc. – we can refocus upstream and create policies that protect against these stressors in the first place.
~ name withheld, Mount Holyoke College
5. C’s Get Degrees
It is said that “C’s get degrees”, but that isn’t enough for me. C’s show an average amount of work, an average amount of time, an average amount of effort. “Average” is not something that I want to be known as. I want to be known as the girl who kept moving forward, went above and beyond, and never looked back. My driving force is making my family proud and reaching my ultimate goal—becoming a school psychologist.
I am the very first in my family to attend college. Every time the topic of school or my future is mentioned, I can see on their faces that they are overwhelmed with pride. When I received my Associate’s degree, seeing my grandpa cry made me realize how special my academic journey is to them. They have given up so much and have supported me in every way, making them proud is the very least I could do in return.
Becoming a school psychologist has been my dream career since I was in middle school. The thought of being able to connect and help a child grow both academically and socially is the greatest reward I could ever receive . Every time I am procrastinating typing a paper, not studying when I know I should have, or wanting to give up on a difficult problem, I think about my end goal. Making a difference to even just one child with make all of school worth it.
~ Haleigh Cordeiro, California Polytechnic State University
6. Find Your Unconscious
Psychologists have discovered reasons, stages, and correlations among our biopsychosocial make-up. Over the centuries, they have managed to explain why humans experience what occurs in everyday life. They provide answers when we have questions about ourselves; it is for this reason that I strive to major in psychology.
I believe that I can make people in my environment, as well as myself, healthier by providing some sense of clarity whenever life situations become foggy. My dream is to someday become a successful industrial-psychologist. Why not a clinical psychologist? Working one-on-one with individuals who are struggling would definitely bring me pleasure. However, I believe that I would have a greater impact within my society by helping larger groups . This dream of mine to become an industrial-psychologist would allow me to make the environment of common day people the most comfortable and enjoyable one.
Through the study of psychology, I will be able to know what qualities are the most necessary to enrich the daily lives of people and ensure that I apply them to my work. What drives me? The fact that I have seen psychologists help my family make sense of one of the most difficult things that we have gone through. Psychologists helped my sister facing anorexia nervosa deal with her disorder and helped my family become a strong support system to aid my sister’s recuperation. I want to know that I can help other people, psychology will open the doors to this dream of mine.
~ Iridian, Cal State University of Long Beach
7. My Dream
Over 22 million children in the United States do not live with their biological mother and father and reside with their grandparents. This means that 3 percent of children living in America face the same situation as me. My father and mother were teenagers when they had me, so raising a baby girl was a difficult task for them. Neither of my parents went to college either, so having me took a toll on their lives. For the both of them, college was an opportunity to better their education and be successful, but with me, that would have been harder for them. Living with my grandparents was the best option for me.
I am currently experiencing teenage life and I can understand why raising a child, when you are only a child yourself, is a daunting responsibility. I commend my parents because they choose to provide a better life for me. They wanted to prevent me from facing adversity, they shielded me from their struggles. When I enter college, my goal is not just to pass my classes, it is to make something of myself . I know my parents would want that for me.
My dream is to work up to my doctorate and become a psychiatrist, fulfilling every opportunity and experience that comes my way. Psychiatrist Carl Gustav Jung once said “I am not what happened to me, I am what I choose to become”, and through my hardship, I choose to overcome and prepare for my destiny.
~ Nina Grizzle
8. Art Therapy
My love for psychology began my junior year when I took the AP course. What was supposed to be a schedule-filling elective credit accidentally grew into a genuine fascination. I found myself going above and beyond the curriculum purely out of curiosity . My interest in what we were discussing in class every day would often send me down long, thought-provoking paths that motivated me to hunt down explanations to the answers of questions I didn’t know I had. But once I had the answers, they seemed to be demanding further explanation, and I was always more than happy to oblige.
With my future education in this field, I hope to further develop new methods of art therapy that will aid those suffering from different mental disorders and cognitive declines. I feel that experimenting with the effects that art has on people’s brain chemistry will open up a new type of therapy that can be clinically prescribed. According to the National Alliance on Mental Illness, approximately 52.9 million adults in the United States suffer from mental illnesses. This new form of therapy could possibly improve the mental state of the millions of people impacted while inspiring the creation of art.
~ Taylor Himes, University of Texas San Antonio
9. If You Put Your Mind To It
For as long as I can remember, I knew that I wanted to make a difference in the world. I knew that the first step was to attend an accredited university, and that university happens to be Michigan State. I went into college with the dream of becoming a doctor, however, I had a change of heart.
At the beginning of my freshmen year, the unthinkable happened. My dad committed suicide. My world came crashing down. It was a complete shock. My dad always kept all his feelings masked. I never knew what he was going through, and everyday I regret not paying closer attention. Not a day goes by where I don’t think about him. If only I had known. I could’ve done something. That experience then motivated me to change my major to psychology.
I always wanted to make a difference, and now I know just how I am going to be able to accomplish that dream. I want to help people who are going through what my dad endured. I want to be there for them, to help them overcome their inner demons. I want to let them know that their lives are worth living. Losing a family member to suicide is one of the most detrimental events that anyone can ever endure, and if I can one day prevent someone from experiencing that, then I would have accomplished my goal; I will make a difference.
~ Kayla Harper, Michigan State University
10. Motivated by God to Help Others
I’ve heard from so many different people how difficult college can be. Late nights, big tests, difficult and early classes, that doesn’t even sound like fun. The only thing that keeps me moving towards college is the idea of being able to help other people when I graduate.
In December of 2016 I travelled halfway around the world to the Philippines. While I was there I met 15 wonderful children with horrible backgrounds. The love these children missed out on for so many years is heartbreaking. My future goal is to study Psychology and Religion at Liberty University .
The dream that keeps me motivated to go back to school is the idea that I could help so many people , not just children, but anyone who needs someone willing to listen and talk about their problems. People need more people to care and who want to listen. If people would feel the love that God made for them this world would be a much better place.
~ Trinity Rake, Liberty University
How Long Does It Take to Get a Psychology Degree?
- About Author
- Latest Posts

Writing Team
Latest posts from writing team.
- Study Planner and Timetable Template - March 30, 2024
- Can International Students Study Online in Australia? - February 4, 2024
- Upskillist / Shaw Academy | Reviews, Complaints, Scam, Not Legit - September 27, 2023
2.1 Why Is Research Important?
Learning objectives.
By the end of this section, you will be able to:
- Explain how scientific research addresses questions about behavior
- Discuss how scientific research guides public policy
- Appreciate how scientific research can be important in making personal decisions
Scientific research is a critical tool for successfully navigating our complex world. Without it, we would be forced to rely solely on intuition, other people’s authority, and blind luck. While many of us feel confident in our abilities to decipher and interact with the world around us, history is filled with examples of how very wrong we can be when we fail to recognize the need for evidence in supporting claims. At various times in history, we would have been certain that the sun revolved around a flat earth, that the earth’s continents did not move, and that mental illness was caused by possession ( Figure 2.2 ). It is through systematic scientific research that we divest ourselves of our preconceived notions and superstitions and gain an objective understanding of ourselves and our world.
The goal of all scientists is to better understand the world around them. Psychologists focus their attention on understanding behavior, as well as the cognitive (mental) and physiological (body) processes that underlie behavior. In contrast to other methods that people use to understand the behavior of others, such as intuition and personal experience, the hallmark of scientific research is that there is evidence to support a claim. Scientific knowledge is empirical : It is grounded in objective, tangible evidence that can be observed time and time again, regardless of who is observing.
While behavior is observable, the mind is not. If someone is crying, we can see behavior. However, the reason for the behavior is more difficult to determine. Is the person crying due to being sad, in pain, or happy? Sometimes we can learn the reason for someone’s behavior by simply asking a question, like “Why are you crying?” However, there are situations in which an individual is either uncomfortable or unwilling to answer the question honestly, or is incapable of answering. For example, infants would not be able to explain why they are crying. In such circumstances, the psychologist must be creative in finding ways to better understand behavior. This chapter explores how scientific knowledge is generated, and how important that knowledge is in forming decisions in our personal lives and in the public domain.
Use of Research Information
Trying to determine which theories are and are not accepted by the scientific community can be difficult, especially in an area of research as broad as psychology. More than ever before, we have an incredible amount of information at our fingertips, and a simple internet search on any given research topic might result in a number of contradictory studies. In these cases, we are witnessing the scientific community going through the process of reaching a consensus, and it could be quite some time before a consensus emerges. For example, the explosion in our use of technology has led researchers to question whether this ultimately helps or hinders us. The use and implementation of technology in educational settings has become widespread over the last few decades. Researchers are coming to different conclusions regarding the use of technology. To illustrate this point, a study investigating a smartphone app targeting surgery residents (graduate students in surgery training) found that the use of this app can increase student engagement and raise test scores (Shaw & Tan, 2015). Conversely, another study found that the use of technology in undergraduate student populations had negative impacts on sleep, communication, and time management skills (Massimini & Peterson, 2009). Until sufficient amounts of research have been conducted, there will be no clear consensus on the effects that technology has on a student's acquisition of knowledge, study skills, and mental health.
In the meantime, we should strive to think critically about the information we encounter by exercising a degree of healthy skepticism. When someone makes a claim, we should examine the claim from a number of different perspectives: what is the expertise of the person making the claim, what might they gain if the claim is valid, does the claim seem justified given the evidence, and what do other researchers think of the claim? This is especially important when we consider how much information in advertising campaigns and on the internet claims to be based on “scientific evidence” when in actuality it is a belief or perspective of just a few individuals trying to sell a product or draw attention to their perspectives.
We should be informed consumers of the information made available to us because decisions based on this information have significant consequences. One such consequence can be seen in politics and public policy. Imagine that you have been elected as the governor of your state. One of your responsibilities is to manage the state budget and determine how to best spend your constituents’ tax dollars. As the new governor, you need to decide whether to continue funding early intervention programs. These programs are designed to help children who come from low-income backgrounds, have special needs, or face other disadvantages. These programs may involve providing a wide variety of services to maximize the children's development and position them for optimal levels of success in school and later in life (Blann, 2005). While such programs sound appealing, you would want to be sure that they also proved effective before investing additional money in these programs. Fortunately, psychologists and other scientists have conducted vast amounts of research on such programs and, in general, the programs are found to be effective (Neil & Christensen, 2009; Peters-Scheffer, Didden, Korzilius, & Sturmey, 2011). While not all programs are equally effective, and the short-term effects of many such programs are more pronounced, there is reason to believe that many of these programs produce long-term benefits for participants (Barnett, 2011). If you are committed to being a good steward of taxpayer money, you would want to look at research. Which programs are most effective? What characteristics of these programs make them effective? Which programs promote the best outcomes? After examining the research, you would be best equipped to make decisions about which programs to fund.
Link to Learning
Watch this video about early childhood program effectiveness to learn how scientists evaluate effectiveness and how best to invest money into programs that are most effective.
Ultimately, it is not just politicians who can benefit from using research in guiding their decisions. We all might look to research from time to time when making decisions in our lives. Imagine that your sister, Maria, expresses concern about her two-year-old child, Umberto. Umberto does not speak as much or as clearly as the other children in his daycare or others in the family. Umberto's pediatrician undertakes some screening and recommends an evaluation by a speech pathologist, but does not refer Maria to any other specialists. Maria is concerned that Umberto's speech delays are signs of a developmental disorder, but Umberto's pediatrician does not; she sees indications of differences in Umberto's jaw and facial muscles. Hearing this, you do some internet searches, but you are overwhelmed by the breadth of information and the wide array of sources. You see blog posts, top-ten lists, advertisements from healthcare providers, and recommendations from several advocacy organizations. Why are there so many sites? Which are based in research, and which are not?
In the end, research is what makes the difference between facts and opinions. Facts are observable realities, and opinions are personal judgments, conclusions, or attitudes that may or may not be accurate. In the scientific community, facts can be established only using evidence collected through empirical research.
NOTABLE RESEARCHERS
Psychological research has a long history involving important figures from diverse backgrounds. While the introductory chapter discussed several researchers who made significant contributions to the discipline, there are many more individuals who deserve attention in considering how psychology has advanced as a science through their work ( Figure 2.3 ). For instance, Margaret Floy Washburn (1871–1939) was the first woman to earn a PhD in psychology. Her research focused on animal behavior and cognition (Margaret Floy Washburn, PhD, n.d.). Mary Whiton Calkins (1863–1930) was a preeminent first-generation American psychologist who opposed the behaviorist movement, conducted significant research into memory, and established one of the earliest experimental psychology labs in the United States (Mary Whiton Calkins, n.d.).
Francis Sumner (1895–1954) was the first African American to receive a PhD in psychology in 1920. His dissertation focused on issues related to psychoanalysis. Sumner also had research interests in racial bias and educational justice. Sumner was one of the founders of Howard University’s department of psychology, and because of his accomplishments, he is sometimes referred to as the “Father of Black Psychology.” Thirteen years later, Inez Beverly Prosser (1895–1934) became the first African American woman to receive a PhD in psychology. Prosser’s research highlighted issues related to education in segregated versus integrated schools, and ultimately, her work was very influential in the hallmark Brown v. Board of Education Supreme Court ruling that segregation of public schools was unconstitutional (Ethnicity and Health in America Series: Featured Psychologists, n.d.).
Although the establishment of psychology’s scientific roots occurred first in Europe and the United States, it did not take much time until researchers from around the world began to establish their own laboratories and research programs. For example, some of the first experimental psychology laboratories in South America were founded by Horatio Piñero (1869–1919) at two institutions in Buenos Aires, Argentina (Godoy & Brussino, 2010). In India, Gunamudian David Boaz (1908–1965) and Narendra Nath Sen Gupta (1889–1944) established the first independent departments of psychology at the University of Madras and the University of Calcutta, respectively. These developments provided an opportunity for Indian researchers to make important contributions to the field (Gunamudian David Boaz, n.d.; Narendra Nath Sen Gupta, n.d.).
When the American Psychological Association (APA) was first founded in 1892, all of the members were White males (Women and Minorities in Psychology, n.d.). However, by 1905, Mary Whiton Calkins was elected as the first female president of the APA, and by 1946, nearly one-quarter of American psychologists were female. Psychology became a popular degree option for students enrolled in the nation’s historically Black higher education institutions, increasing the number of Black Americans who went on to become psychologists. Given demographic shifts occurring in the United States and increased access to higher educational opportunities among historically underrepresented populations, there is reason to hope that the diversity of the field will increasingly match the larger population, and that the research contributions made by the psychologists of the future will better serve people of all backgrounds (Women and Minorities in Psychology, n.d.).
The Process of Scientific Research
Scientific knowledge is advanced through a process known as the scientific method . Basically, ideas (in the form of theories and hypotheses) are tested against the real world (in the form of empirical observations), and those empirical observations lead to more ideas that are tested against the real world, and so on. In this sense, the scientific process is circular. The types of reasoning within the circle are called deductive and inductive. In deductive reasoning , ideas are tested in the real world; in inductive reasoning , real-world observations lead to new ideas ( Figure 2.4 ). These processes are inseparable, like inhaling and exhaling, but different research approaches place different emphasis on the deductive and inductive aspects.
In the scientific context, deductive reasoning begins with a generalization—one hypothesis—that is then used to reach logical conclusions about the real world. If the hypothesis is correct, then the logical conclusions reached through deductive reasoning should also be correct. A deductive reasoning argument might go something like this: All living things require energy to survive (this would be your hypothesis). Ducks are living things. Therefore, ducks require energy to survive (logical conclusion). In this example, the hypothesis is correct; therefore, the conclusion is correct as well. Sometimes, however, an incorrect hypothesis may lead to a logical but incorrect conclusion. Consider this argument: all ducks are born with the ability to see. Quackers is a duck. Therefore, Quackers was born with the ability to see. Scientists use deductive reasoning to empirically test their hypotheses. Returning to the example of the ducks, researchers might design a study to test the hypothesis that if all living things require energy to survive, then ducks will be found to require energy to survive.
Deductive reasoning starts with a generalization that is tested against real-world observations; however, inductive reasoning moves in the opposite direction. Inductive reasoning uses empirical observations to construct broad generalizations. Unlike deductive reasoning, conclusions drawn from inductive reasoning may or may not be correct, regardless of the observations on which they are based. For instance, you may notice that your favorite fruits—apples, bananas, and oranges—all grow on trees; therefore, you assume that all fruit must grow on trees. This would be an example of inductive reasoning, and, clearly, the existence of strawberries, blueberries, and kiwi demonstrate that this generalization is not correct despite it being based on a number of direct observations. Scientists use inductive reasoning to formulate theories, which in turn generate hypotheses that are tested with deductive reasoning. In the end, science involves both deductive and inductive processes.
For example, case studies, which you will read about in the next section, are heavily weighted on the side of empirical observations. Thus, case studies are closely associated with inductive processes as researchers gather massive amounts of observations and seek interesting patterns (new ideas) in the data. Experimental research, on the other hand, puts great emphasis on deductive reasoning.
We’ve stated that theories and hypotheses are ideas, but what sort of ideas are they, exactly? A theory is a well-developed set of ideas that propose an explanation for observed phenomena. Theories are repeatedly checked against the world, but they tend to be too complex to be tested all at once; instead, researchers create hypotheses to test specific aspects of a theory.
A hypothesis is a testable prediction about how the world will behave if our idea is correct, and it is often worded as an if-then statement (e.g., if I study all night, I will get a passing grade on the test). The hypothesis is extremely important because it bridges the gap between the realm of ideas and the real world. As specific hypotheses are tested, theories are modified and refined to reflect and incorporate the result of these tests Figure 2.5 .
To see how this process works, let’s consider a specific theory and a hypothesis that might be generated from that theory. As you’ll learn in a later chapter, the James-Lange theory of emotion asserts that emotional experience relies on the physiological arousal associated with the emotional state. If you walked out of your home and discovered a very aggressive snake waiting on your doorstep, your heart would begin to race and your stomach churn. According to the James-Lange theory, these physiological changes would result in your feeling of fear. A hypothesis that could be derived from this theory might be that a person who is unaware of the physiological arousal that the sight of the snake elicits will not feel fear.
A scientific hypothesis is also falsifiable , or capable of being shown to be incorrect. Recall from the introductory chapter that Sigmund Freud had lots of interesting ideas to explain various human behaviors ( Figure 2.6 ). However, a major criticism of Freud’s theories is that many of his ideas are not falsifiable; for example, it is impossible to imagine empirical observations that would disprove the existence of the id, the ego, and the superego—the three elements of personality described in Freud’s theories. Despite this, Freud’s theories are widely taught in introductory psychology texts because of their historical significance for personality psychology and psychotherapy, and these remain the root of all modern forms of therapy.
In contrast, the James-Lange theory does generate falsifiable hypotheses, such as the one described above. Some individuals who suffer significant injuries to their spinal columns are unable to feel the bodily changes that often accompany emotional experiences. Therefore, we could test the hypothesis by determining how emotional experiences differ between individuals who have the ability to detect these changes in their physiological arousal and those who do not. In fact, this research has been conducted and while the emotional experiences of people deprived of an awareness of their physiological arousal may be less intense, they still experience emotion (Chwalisz, Diener, & Gallagher, 1988).
Scientific research’s dependence on falsifiability allows for great confidence in the information that it produces. Typically, by the time information is accepted by the scientific community, it has been tested repeatedly.
As an Amazon Associate we earn from qualifying purchases.
This book may not be used in the training of large language models or otherwise be ingested into large language models or generative AI offerings without OpenStax's permission.
Want to cite, share, or modify this book? This book uses the Creative Commons Attribution License and you must attribute OpenStax.
Access for free at https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Authors: Rose M. Spielman, William J. Jenkins, Marilyn D. Lovett
- Publisher/website: OpenStax
- Book title: Psychology 2e
- Publication date: Apr 22, 2020
- Location: Houston, Texas
- Book URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/1-introduction
- Section URL: https://openstax.org/books/psychology-2e/pages/2-1-why-is-research-important
© Jan 6, 2024 OpenStax. Textbook content produced by OpenStax is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution License . The OpenStax name, OpenStax logo, OpenStax book covers, OpenStax CNX name, and OpenStax CNX logo are not subject to the Creative Commons license and may not be reproduced without the prior and express written consent of Rice University.

What's happening at UDC!
Aspire. Accomplish. Take on the World.

The Importance of Psychology in Today’s World
Psychology is the scientific study of human behavior and mental processes. It’s existed since the ancient civilizations of Egypt and Greece, mostly as a branch of philosophy, but broke out as an independent branch of scientific study in the 1870s. The effects of psychological studies are more relevant and respected than any period in the past, and new discoveries and applications for psychology are always being uncovered by top researchers.
For example, consider the initial reaction to World War I veterans by the psychological and medical professionals of the early 20 th Century. An initial theory written by physician Charles Myers in 1915 posited soldiers were experiencing “shell shock” due to exposure to repeated concussive blasts, resulting in brain damage. When this theory was disproven, the prevailing wisdom at the time was the people suffering from “shell shock” were simply weak or cowardly, despite the fact that some estimates suggest nearly 20 percent of surviving WWI veterans developed the condition. There is near unanimous agreement among modern psychologists that shell shock was in fact what we commonly refer to today as post-traumatic stress disorder (PTSD). 1
Many of the primary modern applications for psychology revolve around protecting people from emotional and physical harm while providing them with the necessary mental bandwidth to handle the psychological perils many people face daily. Issues like relationships, workplace stress and financial difficulties all can be affected by psychological symptoms that require diagnosing and managing, which is where modern psychology comes into play and why it’s so important.
Despite the popular stereotype of the private practice therapist popularized by the media, psychology professionals actually have access to a wide variety of industries and fields, from education and criminal justice to marketing and politics.
How Does Psychology Help People?
Essentially, psychology helps people in large part because it can explain why people act the way they do. With this kind of professional insight, a psychologist can help people improve their decision making, stress management and behavior based on understanding past behavior to better predict future behavior. All of this can help people have a more successful career, better relationships, more self-confidence and overall better communication.
Sub-Disciplines of Psychology
The study of psychologically is so widespread today, different sub-disciplines or branches of psychology are widely recognized and frequently leveraged in an array of industries. Some psychology sub-disciplines include:
- Family – Family psychology, sometimes known as family therapy, focuses on the interpersonal systems found with the family.
- Sports – Sports psychology focuses on how psychology factors can affect an athlete’s performance.
- Business – Business psychology focuses on the effectiveness of a workplace or organization through the study of people and overall behavior in the workplace.
- Media – Media psychology focuses on the complex relationship between media and its effect on human behavior.
- Forensic – Forensic psychology is the practice of studying individuals who are involved in the legal system, such as expert witnesses or those under criminal investigation.
Modern Psychology Careers
A career in psychology could take multiple trajectories. For example, a modern psychology career could be completely researched-based and non-public facing, or it could be as a family counselor who works with people of all ages each day. Here are some of the common careers people enjoy after they’ve earned their bachelors of science in psychology .
Professors – A career as a psychology professor can be rewarding for two reasons: First, professors are often at the forefront of new discoveries made in the field by attending conferences and keeping up on new research. Second, psychology professors often cite the joy of shaping young, curious minds as one of the most rewarding aspects of their work.
Working at Hospitals – Licensed psychologists often work in hospitals or in clinics where they can use their knowledge to help people who are experiencing psychological trauma of some kind. It could be in a children’s hospital, a rehab clinic or any number of health care establishments.
Government Agencies – All sorts of government agencies employ psychologists. Some of the top government psychology jobs include correctional counselors, military psychologists, criminal profilers and veteran counselors.
Working in Schools – Psychologists commonly work in schools as well, where their expertise can be used to help students who are dealing with any sort of emotional, behavioral or learning difficulties that may be impairing their education. Psychology jobs in schools could be in primary, secondary or even on college campuses.
Business – Large businesses frequently consult psychologists to better understand things like their clientele’s practices and habits. Elsewhere, businesses may tap into industrial-organization psychology to increase productivity by improving workplace organization and structure while also refining training and employee screening processes.
Are You Interested in a Career in Psychology?
If so, consider applying for the Bachelor of Science in Psychology program offered at the University of the District of Columbia. At UDC, the psychology program allows students to explore a wide array of disciplines and sub-fields to ensure graduates are prepared for entry-level employment or to continue their education to a masters or doctoral degree. Begin your journey toward making a difference in people’s lives by calling (202) 274-5787 or by visiting us online and applying today!
1 http://theconversation.com/from-shell-shock-to-ptsd-a-century-of-invisible-war-trauma-74911
The Study Blog
Term Paper Writing Help

If you aren't sure whether you are good at expressing yourself through writing, then if you find it difficult to do so (e.g., when trying to write an english essay), we can help you overcome those obstacles by assisting you in improving your communication through writing. We help students compose essays or other types of papers for their courses. Now is the time to come visit us!
How to Overcome the Complexity of a Nursing Essay
There aren't many alternatives for professional translations. Before writing a good summary of something, you need to know your subject well enough to be able to write an accurate one. A research paper requires mastery of research language, a deep understanding of their subjects to be able to write about them clearly, and a careful consideration of possible problems before proposing solutions. Students often have trouble understanding medical terminology when they first encounter it, because they have never heard of these words before. When writing a cohesive psychology essay, students must be familiar with some psychological concepts. We have a wealth of experience under our belt, so we know where they need help. Although you may be able to find better deals elsewhere, there is no way to tell if these sites offer superior customer service and top-quality results. Read customer reviews before making any online purchases. If you don't think there's a market for them, it's perhaps best to skip them.
Professional Help from Copywriters
If you would like us to write anything from an essay in history to a term paper for you, we’d be happy to oblige. When writing something, there's a precise formula for choosing the best word. You can rest assured that you'll receive an expertly written paper from those who know exactly what they're doing. No need to write anything down today; there are no reasons why you shouldn't let others edit your document for you. Don't waste your time trying to convince them to do it for you, instead, invest it in something more productive! Order term papers online and go there! Founded in a simple belief that we are capable of delivering top-quality content to you, we offer a range of guarantees. Test it out yourself! The results must be presented after all the research has been completed.
Cheap Business Essay Writing Services
Before being accepted into our company, we underwent extensive background checks. Check their credentials to confirm that they have been writing professionally for some time. If they are members of professional associations, check, for instance.

Fun Tips to Spend Orthodox Easter Away from Home
In "Student Life"
Welcome to the New Bloggers
In "Degree Essentials"
Mastering Warwick as a Postgraduate
In "Looking After You"
Comments are closed.
Copyright, 2023
Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Writing in Psychology Overview

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
Written for undergraduate students and new graduate students in psychology (experimental), this handout provides information on writing in psychology and on experimental report and experimental article writing.
Psychology is based on the study of human behaviors. As a social science, experimental psychology uses empirical inquiry to help understand human behavior. According to Thrass and Sanford (2000), psychology writing has three elements: describing, explaining, and understanding concepts from a standpoint of empirical investigation.
Discipline-specific writing, such as writing done in psychology, can be similar to other types of writing you have done in the use of the writing process, writing techniques, and in locating and integrating sources. However, the field of psychology also has its own rules and expectations for writing; not everything that you have learned in about writing in the past works for the field of psychology.
Writing in psychology includes the following principles:
- Using plain language : Psychology writing is formal scientific writing that is plain and straightforward. Literary devices such as metaphors, alliteration, or anecdotes are not appropriate for writing in psychology.
- Conciseness and clarity of language : The field of psychology stresses clear, concise prose. You should be able to make connections between empirical evidence, theories, and conclusions. See our OWL handout on conciseness for more information.
- Evidence-based reasoning: Psychology bases its arguments on empirical evidence. Personal examples, narratives, or opinions are not appropriate for psychology.
- Use of APA format: Psychologists use the American Psychological Association (APA) format for publications. While most student writing follows this format, some instructors may provide you with specific formatting requirements that differ from APA format .
Types of writing
Most major writing assignments in psychology courses consists of one of the following two types.
Experimental reports: Experimental reports detail the results of experimental research projects and are most often written in experimental psychology (lab) courses. Experimental reports are write-ups of your results after you have conducted research with participants. This handout provides a description of how to write an experimental report .
Critical analyses or reviews of research : Often called "term papers," a critical analysis of research narrowly examines and draws conclusions from existing literature on a topic of interest. These are frequently written in upper-division survey courses. Our research paper handouts provide a detailed overview of how to write these types of research papers.
7-Week SSP & 2-Week Pre-College Program are still accepting applications until April 10, or earlier if all course waitlists are full. 4-Week SSP Application is closed.
Celebrating 150 years of Harvard Summer School. Learn about our history.
Why Choose Psychology as Your College Major
Choosing a psychology major can lead to many different pathways.
Pamela Reynolds
Psychology is one of the most popular college majors today. Here’s why it might be the right major for you.
If you’ve ever been curious why you—and those around you—act and think in seemingly inexplicable ways, you might consider majoring in psychology.
Many people, it turns out, are doing just that.
According to a Niche ranking , psychology was the third most popular major among college students in the classes of 2022 and 2023 . The share of college students majoring in psychology now hovers around 6 percent , up from 4 to 5 percent in the 1980s.
And it’s easy to understand what the attraction is. A psychology major offers students an opportunity to learn more about themselves and others on a very personal level. It can also lead to an array of interesting careers, sometimes in unexpected places.
Let’s take a look at why students are choosing to study psychology, potential career paths for psychology majors, as well as what to expect if you choose this field as your major. You’re likely to be surprised by the choice that a degree in psychology can offer.
Why Should I Choose Psychology?
Psychology is the scientific study of the human mind and behavior. There are several reasons why so many college students opt to major in psychology:
- There is great potential for personal growth , as you learn more about the factors that influence human behavior and development. On a personal level, you will gain insight into yourself, but will also better understand your family, friends, classmates, and people you interact with in everyday life.For this reason alone, many students are drawn to this subject. A good grasp of psychology can be useful in a variety of situations, whether it be in resolving a conflict you are having with a friend, negotiating a raise at your job, or persuading your parents to help fund that new car you’ve been wanting.
- It can open up the door to many different types of careers. More than some other majors you might choose, a psychology degree can lead to many diverse career paths in sectors you may have never considered. You might decide to focus on psychology in a theoretical setting, as a researcher at a university, for example, or you might turn to applied research in a clinical or corporate setting. Other options include counseling, social work, human resources, marketing, workforce development, or education.
Specific career options range from advertising agent to career counselor, case manager, human resources specialist, lab assistant, market researcher, rehabilitation specialist, or youth counselor. Even if you choose a line of work that seems quite distant from the psychology field, chances are you will be able to put to use many of the concepts you learned as a psychology student.
- A bachelor’s degree in psychology can lay the groundwork for graduate level study in psychology, education, law, medicine, and business. If you opt to continue your education, your career path widens even more. It’s a major that can be applied to multiple fields, so your career options are wide-ranging.
What Would I Study as a Psychology Major?
Psychology programs usually include introductory courses such as:
- General psychology
- Research methods in psychology
- Statistical methods in psychology
- A lab course like psychology as a natural science
Foundational courses might include cognitive neuroscience, social psychology, developmental psychology, psychopathology, and the neurobiology of behavior. These introductory courses usually delve into the core types of psychology, the history of this field of study, and the relationship between the brain, behavior, and experience.
Psychology lab courses , on the other hand, give students experience conducting research, designing experiments, learning observation and measurement techniques, and analyzing behavioral data.
Once you’ve met the prerequisite requirements in the major, you’re free to take more specific courses. Examples of potential psychology elective courses include:
- Developmental psychology
- Learning and behavior
- Social psychology
- Theories of personality
- Drugs and behavior
- Affective neuroscience
- Child psychology
- Introduction to clinical psychology
Most schools offer course credit for independent research projects, too, although they often will require a certain GPA and approval of a student’s topic through the psychology department. Many schools will also require psychology students to take courses in math, social science, and physical science.
Is Psychology a Hard Major?
If you research this question, you’ll find a range of opinions on both sides of the question.
On one hand, it might be considered “hard” because students are required, as with any subject, to do lots of reading and analysis. In particular, many students may have difficulty with subjects like advanced mathematics, statistics, and research methods . You will also be expected to conduct experiments.
On the other hand, a high level of interest in a subject can make it easier to focus on and learn. If a student is deeply interested in how humans relate both individually and in groups, the coursework, reading and experimentation may be easier to get through, even when it involves more difficult subjects in science or math. Psychology also easily allows you to contextualize concepts you learn to real-life, which may also help with learning material.
Explore Our Secondary School Program.
What Jobs Are Available With a Bachelor’s Degree in Psychology?
If you pursue a bachelor’s degree in this field, you can qualify for jobs in the human or social services sector. Typical jobs for psychology majors include:
- Career counselor
- Childcare worker
- Psychiatric technician
- Lab assistant
- Rehabilitation specialist
- Case manager
- Human resources assistant
- Market researcher
- Substance abuse counselor
- Probation or parole officer
- Sales representative
- Social service specialist
Because many of these jobs are in social services, candidates will be required to evaluate the needs of clients, keep accurate records and express empathy and compassion. These roles can be challenging as they are not typically well paid, and it can be discouraging to work with people who have severe needs.
However, it should be noted that many people who graduate with a bachelor’s degree in psychology, never go on to apply their degree in the subject itself.
Psychology majors develop a number of skills which can be applied to many other occupations, particularly because of the amount of writing and research required. This means that career paths for psychology majors are wide open.
About three quarters of students earning a bachelor’s degree in psychology never pursue a graduate degree in psychology. Only about a quarter of psychology undergraduates actually end up working in psychology or a related field. Even so, many find they can apply what they learned as an undergrad to their field of choice.
Do You Need an Advanced Degree to Work in the Field of Psychology?
While you do not necessarily require an advanced psychology degree to find work, you will find your career options broaden, as well as the potential to earn more.
With more education comes the opportunity to help people in more substantial ways than you might with only a bachelor’s degree. Not only can you help people overcome the effects of trauma or deal with a mental illness, but you can help make advances toward better treatments for diseases, disorders or illnesses that affect mental health or cognitive function.
Potential jobs with a master’s degree in the field include:
- Program managers
- School psychologists
- Adjunct faculty members
- Licensed clinical social workers
- Adjunct instructors
- Medical social workers
- Mental health professionals
- UX Designer
- Academic advisors
Those interested in becoming a psychologist or psychiatrist require more education. For example, a psychologist needs a PhD or PsyD , while a psychiatrist must earn a Doctor of Medicine (MD) degree.
The Final Word
If you’re psyched about choosing psychology as a major, you probably already know why. You want to help others. Choosing a psychology major can potentially give you the tools to do exactly that.
Interested in a summer at Harvard? Learn more about our summer programs.
Request Information
About the Author
Pamela Reynolds is a Boston-area feature writer and editor whose work appears in numerous publications. She is the author of “Revamp: A Memoir of Travel and Obsessive Renovation.”
Why College Professors Want You to Talk to Them
Talking with your professors is an important part of college. Here's why you should reach out—and why they want you to.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

- Study Guides
- Homework Questions
Historyofpsychology Exam 1 Essay

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Psychology is the study of people's behavior, performance, and mental operations. It also refers to the application of that knowledge, which can be used to understand events, treat mental health, and improve education, employment, and relationships. The subject lies at the intersection of applied, educational, and theoretical sciences.
Psychology is all around you and touches on every aspect of your life. Who you are now, how you will be in the future, how you interact with family, friends, and strangers; these are all things that psychology can help you better understand. Here are 10 reasons we we think everyone should learn at least a little bit about psychology.
Psychology sheds light on human behavior and helps us understand why we act the way we do. The field offers insights into our human experiences, helps us connect with others, and can mean the difference between a life well-lived and a life of challenges. A psychology degree can lead to a rewarding career in social science.
First, in How to Read Sources Critically, we will discuss why it is important to for you to be a discerning reader of the work of other psychologists, and we will present guide-lines to help you read critically. In Writing a Conceptually Coherent Paper, we will go through, step by step, the process of writing an essay or term paper in psychology.
At this point, there is little argument regarding the utility of an advanced education in psychology (as I discuss in detail in my book, Own Your Psychology Major! ). Below are five reasons that ...
Psychology is very important to mankind in that it is important in understanding the world we live in. Psychology helps us and allows us to better understand the emotional and behavioral effects of our surroundings. According to Taylor (1988), many prominent researchers believe a healthy mental outlook on the world and what we perceive it to be ...
The science of psychology is important for both researchers and practitioners. In a sense all humans are scientists. We all have an interest in asking and answering questions about our world. We want to know why things happen, when and if they are likely to happen again, and how to reproduce or change them. Such knowledge enables us to predict ...
Identify the subject of the essay and define the key terms. Highlight the major issues which "lie behind" the question. Let the reader know how you will focus your essay by identifying the main themes to be discussed. "Signpost" the essay's key argument, (and, if possible, how. this argument is structured).
The science of psychology generates knowledge about the nature and development of human thoughts, emotions, and behaviors at both individual and societal levels. Psychology is an autonomous scientific discipline that applies to nearly every aspect of our boundless experience.
The discipline of psychology is broadly divisible into two parts: a large profession of practitioners and a smaller but growing science of mind, brain, and social behaviour. The two have distinctive goals, training, and practices, but some psychologists integrate the two. (Read Sigmund Freud's 1926 Britannica essay on psychoanalysis.) Early ...
Psychology is a multifaceted discipline and includes many sub-fields of study such areas as human development, sports, health, clinical, social behavior and cognitive processes. Psychology is a new science, with most advances happening over the past 150 years. However, its origins can be traced back to ancient Greece, 400 - 500 BC.
Psychology is the scientific study of behavior and mental processes—in this course, we will examine the connection between thoughts and actions and better understand how and why people think and behave. This module will introduce you to what psychology is and what psychologists do. You'll learn the basic history of the discipline and about ...
Background: Philosophy and Physiology. While psychology did not emerge as a separate discipline until the late 1800s, its earliest history can be traced back to the time of the early Greeks. During the 17th-century, the French philosopher Rene Descartes introduced the idea of dualism, which asserted that the mind and body were two entities that ...
Psychology is such a vast field the benefits are wide ranging, it could include researching mental health to help enhance wellbeing, better understanding the relationships we form, self-improvement, or battling addiction. There can also be benefits to our communication with, and understanding of, other people.
Why Research Is Important. Read this text, which introduces the scientific method, which involves making a hypothesis or general premise, deductive reasoning, making empirical observations, and inductive reasoning, Scientific research is a critical tool for successfully navigating our complex world. Without it, we would be forced to rely solely ...
Psychology writing, like writing in the other sciences, is meant to inform the reader about a new idea, theory or experiment. Toward this end, academic psychologists emphasize the importance of clarity and brevity in writing while minimizing descriptive language and complex sentence structure. The best writers of psychology have
Abstract. Psychology has traditionally seen itself as the science of universal human cognition, and has only recently begun seriously grappling with the issue of cross-cultural variation. Here we argue that the roots of cross-cultural variation often lie in the past. Therefore, to understand not just the way, but also why psychology varies, we ...
Psychology students are often motivated by personal experiences and a wish for healthier, happier communities. The essays demonstrate the value from having a vision for your career - whether it's detailed or "big picture" - before you start a psychology degree. Having a long-term goal in mind offers a reliable source of study motivation.
Discuss how scientific research guides public policy. Appreciate how scientific research can be important in making personal decisions. Scientific research is a critical tool for successfully navigating our complex world. Without it, we would be forced to rely solely on intuition, other people's authority, and blind luck.
Essentially, psychology helps people in large part because it can explain why people act the way they do. With this kind of professional insight, a psychologist can help people improve their decision making, stress management and behavior based on understanding past behavior to better predict future behavior. All of this can help people have a ...
Cheap Business Essay Writing Services. Before being accepted into our company, we underwent extensive background checks. Check their credentials to confirm that they have been writing professionally for some time. If they are members of professional associations, check, for instance. Some students may have difficulty completing their research ...
Writing in Psychology Overview. Psychology is based on the study of human behaviors. As a social science, experimental psychology uses empirical inquiry to help understand human behavior. According to Thrass and Sanford (2000), psychology writing has three elements: describing, explaining, and understanding concepts from a standpoint of ...
Psychology is the scientific study of the human mind and behavior. There are several reasons why so many college students opt to major in psychology: There is great potential for personal growth, as you learn more about the factors that influence human behavior and development. On a personal level, you will gain insight into yourself, but will ...
Essay Exam I (Chapters 1-5) 1. Explain why it is important to study (a) history in general, and (b) psychology's history in particular. Studying history enables us to understand human nature while preventing us from believing the idea that things in the past were better. Studying history, in general, also aids us in understanding the present better. . The history of psychology improves our ...
41%. Percentage of teens with the highest social media use who rate their overall mental health as poor or very poor, compared with 23% of those with the lowest use. For example, 10% of the highest use group expressed suicidal intent or self-harm in the past 12 months compared with 5% of the lowest use group, and 17% of the highest users expressed poor body image compared with 6% of the lowest ...