Get science-backed answers as you write with Paperpal's Research feature

How to Write a Research Question: Types and Examples

The first step in any research project is framing the research question. It can be considered the core of any systematic investigation as the research outcomes are tied to asking the right questions. Thus, this primary interrogation point sets the pace for your research as it helps collect relevant and insightful information that ultimately influences your work.
Typically, the research question guides the stages of inquiry, analysis, and reporting. Depending on the use of quantifiable or quantitative data, research questions are broadly categorized into quantitative or qualitative research questions. Both types of research questions can be used independently or together, considering the overall focus and objectives of your research.
What is a research question?
A research question is a clear, focused, concise, and arguable question on which your research and writing are centered. 1 It states various aspects of the study, including the population and variables to be studied and the problem the study addresses. These questions also set the boundaries of the study, ensuring cohesion.
Designing the research question is a dynamic process where the researcher can change or refine the research question as they review related literature and develop a framework for the study. Depending on the scale of your research, the study can include single or multiple research questions.
A good research question has the following features:
- It is relevant to the chosen field of study.
- The question posed is arguable and open for debate, requiring synthesizing and analysis of ideas.
- It is focused and concisely framed.
- A feasible solution is possible within the given practical constraint and timeframe.
A poorly formulated research question poses several risks. 1
- Researchers can adopt an erroneous design.
- It can create confusion and hinder the thought process, including developing a clear protocol.
- It can jeopardize publication efforts.
- It causes difficulty in determining the relevance of the study findings.
- It causes difficulty in whether the study fulfils the inclusion criteria for systematic review and meta-analysis. This creates challenges in determining whether additional studies or data collection is needed to answer the question.
- Readers may fail to understand the objective of the study. This reduces the likelihood of the study being cited by others.
Now that you know “What is a research question?”, let’s look at the different types of research questions.
Types of research questions
Depending on the type of research to be done, research questions can be classified broadly into quantitative, qualitative, or mixed-methods studies. Knowing the type of research helps determine the best type of research question that reflects the direction and epistemological underpinnings of your research.
The structure and wording of quantitative 2 and qualitative research 3 questions differ significantly. The quantitative study looks at causal relationships, whereas the qualitative study aims at exploring a phenomenon.
- Quantitative research questions:
- Seeks to investigate social, familial, or educational experiences or processes in a particular context and/or location.
- Answers ‘how,’ ‘what,’ or ‘why’ questions.
- Investigates connections, relations, or comparisons between independent and dependent variables.
Quantitative research questions can be further categorized into descriptive, comparative, and relationship, as explained in the Table below.
- Qualitative research questions
Qualitative research questions are adaptable, non-directional, and more flexible. It concerns broad areas of research or more specific areas of study to discover, explain, or explore a phenomenon. These are further classified as follows:
- Mixed-methods studies
Mixed-methods studies use both quantitative and qualitative research questions to answer your research question. Mixed methods provide a complete picture than standalone quantitative or qualitative research, as it integrates the benefits of both methods. Mixed methods research is often used in multidisciplinary settings and complex situational or societal research, especially in the behavioral, health, and social science fields.
What makes a good research question
A good research question should be clear and focused to guide your research. It should synthesize multiple sources to present your unique argument, and should ideally be something that you are interested in. But avoid questions that can be answered in a few factual statements. The following are the main attributes of a good research question.
- Specific: The research question should not be a fishing expedition performed in the hopes that some new information will be found that will benefit the researcher. The central research question should work with your research problem to keep your work focused. If using multiple questions, they should all tie back to the central aim.
- Measurable: The research question must be answerable using quantitative and/or qualitative data or from scholarly sources to develop your research question. If such data is impossible to access, it is better to rethink your question.
- Attainable: Ensure you have enough time and resources to do all research required to answer your question. If it seems you will not be able to gain access to the data you need, consider narrowing down your question to be more specific.
- You have the expertise
- You have the equipment and resources
- Realistic: Developing your research question should be based on initial reading about your topic. It should focus on addressing a problem or gap in the existing knowledge in your field or discipline.
- Based on some sort of rational physics
- Can be done in a reasonable time frame
- Timely: The research question should contribute to an existing and current debate in your field or in society at large. It should produce knowledge that future researchers or practitioners can later build on.
- Novel
- Based on current technologies.
- Important to answer current problems or concerns.
- Lead to new directions.
- Important: Your question should have some aspect of originality. Incremental research is as important as exploring disruptive technologies. For example, you can focus on a specific location or explore a new angle.
- Meaningful whether the answer is “Yes” or “No.” Closed-ended, yes/no questions are too simple to work as good research questions. Such questions do not provide enough scope for robust investigation and discussion. A good research question requires original data, synthesis of multiple sources, and original interpretation and argumentation before providing an answer.
Steps for developing a good research question
The importance of research questions cannot be understated. When drafting a research question, use the following frameworks to guide the components of your question to ease the process. 4
- Determine the requirements: Before constructing a good research question, set your research requirements. What is the purpose? Is it descriptive, comparative, or explorative research? Determining the research aim will help you choose the most appropriate topic and word your question appropriately.
- Select a broad research topic: Identify a broader subject area of interest that requires investigation. Techniques such as brainstorming or concept mapping can help identify relevant connections and themes within a broad research topic. For example, how to learn and help students learn.
- Perform preliminary investigation: Preliminary research is needed to obtain up-to-date and relevant knowledge on your topic. It also helps identify issues currently being discussed from which information gaps can be identified.
- Narrow your focus: Narrow the scope and focus of your research to a specific niche. This involves focusing on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature or extending or complementing the findings of existing literature. Another approach involves constructing strong research questions that challenge your views or knowledge of the area of study (Example: Is learning consistent with the existing learning theory and research).
- Identify the research problem: Once the research question has been framed, one should evaluate it. This is to realize the importance of the research questions and if there is a need for more revising (Example: How do your beliefs on learning theory and research impact your instructional practices).
How to write a research question
Those struggling to understand how to write a research question, these simple steps can help you simplify the process of writing a research question.
Sample Research Questions
The following are some bad and good research question examples
- Example 1
- Example 2
References:
- Thabane, L., Thomas, T., Ye, C., & Paul, J. (2009). Posing the research question: not so simple. Canadian Journal of Anesthesia/Journal canadien d’anesthésie , 56 (1), 71-79.
- Rutberg, S., & Bouikidis, C. D. (2018). Focusing on the fundamentals: A simplistic differentiation between qualitative and quantitative research. Nephrology Nursing Journal , 45 (2), 209-213.
- Kyngäs, H. (2020). Qualitative research and content analysis. The application of content analysis in nursing science research , 3-11.
- Mattick, K., Johnston, J., & de la Croix, A. (2018). How to… write a good research question. The clinical teacher , 15 (2), 104-108.
- Fandino, W. (2019). Formulating a good research question: Pearls and pitfalls. Indian Journal of Anaesthesia , 63 (8), 611.
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: a key to evidence-based decisions. ACP journal club , 123 (3), A12-A13
Paperpal is a comprehensive AI writing toolkit that helps students and researchers achieve 2x the writing in half the time. It leverages 21+ years of STM experience and insights from millions of research articles to provide in-depth academic writing, language editing, and submission readiness support to help you write better, faster.
Get accurate academic translations, rewriting support, grammar checks, vocabulary suggestions, and generative AI assistance that delivers human precision at machine speed. Try for free or upgrade to Paperpal Prime starting at US$19 a month to access premium features, including consistency, plagiarism, and 30+ submission readiness checks to help you succeed.
Experience the future of academic writing – Sign up to Paperpal and start writing for free!
Related Reads:
- Scientific Writing Style Guides Explained
- Ethical Research Practices For Research with Human Subjects
- 8 Most Effective Ways to Increase Motivation for Thesis Writing
- 6 Tips for Post-Doc Researchers to Take Their Career to the Next Level
Transitive and Intransitive Verbs in the World of Research
Language and grammar rules for academic writing, you may also like, phd qualifying exam: tips for success , quillbot review: features, pricing, and free alternatives, what is an academic paper types and elements , 9 steps to publish a research paper, what are the different types of research papers, how to make translating academic papers less challenging, 6 tips for post-doc researchers to take their..., presenting research data effectively through tables and figures, ethics in science: importance, principles & guidelines , jenni ai review: top features, pricing, and alternatives.
Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
The “Golden Thread” Explained Simply (+ Examples)
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022
The research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
You Might Also Like:

39 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly
A Guide to Evidence Synthesis: 1. Draft your Research Question
- Meet Our Team
- Our Published Reviews and Protocols
- What is Evidence Synthesis?
- Types of Evidence Synthesis
- Evidence Synthesis Across Disciplines
- Finding and Appraising Existing Systematic Reviews
- 0. Develop a Protocol
- 1. Draft your Research Question
- 2. Select Databases
- 3. Select Grey Literature Sources
- 4. Write a Search Strategy
- 5. Register a Protocol
- 6. Translate Search Strategies
- 7. Citation Management
- 8. Article Screening
- 9. Risk of Bias Assessment
- 10. Data Extraction
- 11. Synthesize, Map, or Describe the Results
- Evidence Synthesis Institute for Librarians
- Open Access Evidence Synthesis Resources
Video: Formulating a research question (4:43 minutes)
Developing a Research Question
Developing your research question.
Developing your research question is one of the most important steps in the evidence synthesis process. At this stage in the process, you and your team have identified a knowledge gap in your field and are aiming to answer a specific question:
- If X is prescribed, then Y will happen to patients?
OR assess an intervention:
- How does X affect Y?
OR synthesize the existing evidence
- What is the nature of X?
Whatever your aim, formulating a clear, well-defined research question of appropriate scope is key to a successful evidence synthesis . The research question will be the foundation of your synthesis and from it your research team will identify 2-5 possible search concepts. These search concepts will later be used in step 5 to build your search strategy.
Search Concepts
Research question frameworks.
Formulating a research question takes time and your team may go through different versions until settling on the right research question. To help formulate your research question, some research question frameworks are listed below (there are dozen of different types of these frameworks--for a comprehensive overview, see this guide from the University of Maryland )
Think of these frameworks as you would for a house or building. A framework is there to provide support and to be a scaffold for the rest of the structure. In the same way, a research question framework can also help structure your evidence synthesis question. Probably the most common framework is PICO:
PICO for Quantitative Studies
- P Population/Problem
- I Intervention/Exposure
- C Comparison
- O Outcome
Example: Is gabapentin (intervention), compared to placebo (comparison), effective in decreasing pain symptoms (outcome) in middle aged male amputees suffering phantom limb pain (population)?
------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------------- While PICO is a helpful framework for clinical research questions, it may not be the best choice for other types of research questions, especially outside the health sciences. Here are a few others (for a comprehensive, but concise, overview of the almost 40 different types of research question frameworks, see this review from the British Medical Journal: Rapid review of existing question formulation frameworks)
PICo for Qualitative Studies
- P Population/Problem
- I Phenomenon of Interest
- Co Context
Example: What are the experiences (phenomenon of interest) of caregivers providing home based care to patients with Alzheimer's disease (population) in Australia (context)?
- S Setting
- P Perspective (for whom)
- I Intervention/Exposure
- C Comparison
- E Evaluation
Example: What are the benefits (evaluation) of a doula (intervention) for low income mothers (perspective) in the developed world (setting) compared to no support (comparison)?
- S Sample
- PI Phenomenon of Interest
- D Design
- E Evaluation
- R Study Type
Example: What are the experiences (evaluation) of women (sample) undergoing IVF treatment (phenomenon of interest) as assessed?
Design: questionnaire or survey or interview
Study Type: qualitative or mixed method
Inclusion/Exclusion Criteria
Inclusion and exclusion criteria.
Inclusion and exclusion criteria are developed after a research question is finalized but before a search is carried out. They determine the limits for the evidence synthesis and are typically reported in the methods section of the publication. For unfamiliar or unclear concepts, a definition may be necessary to adequately describe the criterion for readers.

From University of Melbourne Library LibGuide
How a Librarian Can Help
How librarians can help.
Librarians can help you learn how to search for existing information on your topic. Finding existing reviews on your topic will inform the development of your research question, identify gaps, and confirm that you are not duplicating the efforts of previous reviews. Email us at [email protected] to learn more about developing a research question.
- << Previous: 0. Develop a Protocol
- Next: 2. Select Databases >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 2:56 PM
- URL: https://guides.library.cornell.edu/evidence-synthesis
Research: From selecting a topic to writing the bibliography
- Selecting a Topic
- Developing a Research Question
- What Type of Source Do I Need?
- Selecting the Best Place to Search
- Search Like a Pro
- Evaluating Information
Research Questions Worth Asking
This video from the UMD, Global Campus gives a good introduction to research questions.
What is a research question?
Once you have selected a topic, you need to develop a research question. You may be used to working with a thesis statement, but a thesis statement is an answer. If you start your research with an answer, you might miss something important or your paper might be too one-sided. Starting with a question allows you to explore your topic while still having it clearly defined.
A good research question is specific and focused.
Topic : Netflix
Research Question : How has the rise of streaming television changed the nature of advertising during television shows?
Topic : the environmental impact of fracking
Research Question : What are some of the most effective ways of protecting local ground water from the waste water produced by fracking?
Tip: Beware of research questions that are too broad or too narrow.
Too Broad: Why is reality television so popular?
Too Narrow: What are the economic and social consequences of the popularity of Jersey Shore on the lives of teenagers living in Omaha, Nebraska?
Tip: be willing to tweak your research question as you go.
Research Question: How has the rise of streaming television changed the nature of advertising during television shows?
Potential Research Finding: Advertising during television hasn't changed much recently.
New Research Question: Why has advertising on television been able to remain the same when how we watch television has changed so much?
Examples of Research Questions
The assignment is a 10-15 page paper relying primarily on scholarly resources.
- How is malaria treated?
- Will tablet computing replace the need for laptops?
- How much has the popularity of Harry Potter improved the reading scores of second graders in Missouri?
- At what point in time will the need for nurses in pedatric wards outpace the graduation rates from nursing schools?
- In what ways have online communities changed the nature of support systems available for people with Attention Deficit Disorder?
- How has mountaintop removal mining in western Kentucky impacted the migratory habits of the local bird population?
- << Previous: Selecting a Topic
- Next: What Type of Source Do I Need? >>
- Last Updated: Apr 12, 2024 9:57 AM
- URL: https://libguides.gwu.edu/research
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Research process
- Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples
Published on 30 October 2022 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 12 December 2023.
A research question pinpoints exactly what you want to find out in your work. A good research question is essential to guide your research paper , dissertation , or thesis .
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly
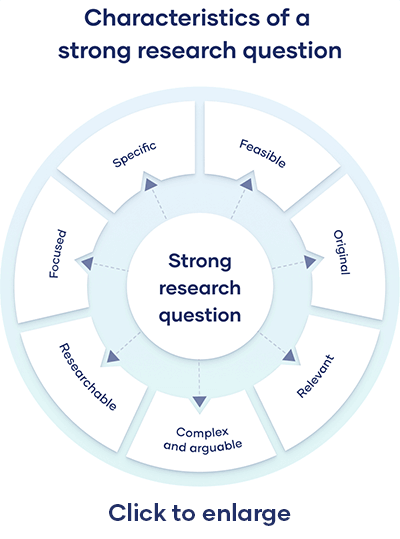
Table of contents
How to write a research question, what makes a strong research question, research questions quiz, frequently asked questions.
You can follow these steps to develop a strong research question:
- Choose your topic
- Do some preliminary reading about the current state of the field
- Narrow your focus to a specific niche
- Identify the research problem that you will address
The way you frame your question depends on what your research aims to achieve. The table below shows some examples of how you might formulate questions for different purposes.
Using your research problem to develop your research question
Note that while most research questions can be answered with various types of research , the way you frame your question should help determine your choices.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them. The criteria below can help you evaluate the strength of your research question.
Focused and researchable
Feasible and specific, complex and arguable, relevant and original.
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis – a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
As you cannot possibly read every source related to your topic, it’s important to evaluate sources to assess their relevance. Use preliminary evaluation to determine whether a source is worth examining in more depth.
This involves:
- Reading abstracts , prefaces, introductions , and conclusions
- Looking at the table of contents to determine the scope of the work
- Consulting the index for key terms or the names of important scholars
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarised in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
A research hypothesis is your proposed answer to your research question. The research hypothesis usually includes an explanation (‘ x affects y because …’).
A statistical hypothesis, on the other hand, is a mathematical statement about a population parameter. Statistical hypotheses always come in pairs: the null and alternative hypotheses. In a well-designed study , the statistical hypotheses correspond logically to the research hypothesis.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, December 12). Writing Strong Research Questions | Criteria & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 22 April 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/the-research-process/research-question/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, how to write a results section | tips & examples, what is a research methodology | steps & tips.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Sex Transm Dis AIDS
- v.31(1); Jan-Jun 2010
Formulating a researchable question: A critical step for facilitating good clinical research
Sadaf aslam.
Clinical and Translational Science Institute and Department of Internal Medicine, College of Medicine, University of South Florida, Tampa, FL, USA
Patricia Emmanuel
Developing a researchable question is one of the challenging tasks a researcher encounters when initiating a project. Both, unanswered issues in current clinical practice or when experiences dictate alternative therapies may provoke an investigator to formulate a clinical research question. This article will assist researchers by providing step-by-step guidance on the formulation of a research question. This paper also describes PICO (population, intervention, control, and outcomes) criteria in framing a research question. Finally, we also assess the characteristics of a research question in the context of initiating a research project.
INTRODUCTION
A researchable question is an uncertainty about a problem that can be challenged, examined, and analyzed to provide useful information.[ 1 ] A successful research project depends upon how well an investigator formulates the research question based on the problems faced in day-to-day research activities and clinical practice. The underlying questions of a research project provide important information to decide whether the topic is relevant, researchable, and significant. A well-formulated research question needs extreme specificity and preciseness which guides the implementation of the project keeping in mind the identification of variables and population of interest. Here we will present a clinical scenario and see how clinical questions arise and help us in finding the evidence to answer our question.
FORMULATING THE RESEARCH QUESTION
A 2-year-old boy presents in an outpatient clinic with fever and severe pain in his right ear. He has a history of recurrent ear infections, and his mother expresses a concern that he has been on the antibiotic amoxicillin for the past few weeks. She is worried about the consequences of the long-term antibiotic use. She is also concerned about the outcome associated with recurrent ear infections. She wants to know if the prescribed amoxicillin is effective, or it can be substituted with another antibiotic because of its side effects such as frequent diarrhea.
Several questions arise from this case which can be broadly classified into background and foreground questions. The general questions about a clinical problem or a disease are called “Background Questions.”[ 2 ] These questions generally ask what, when, how, and where about the disease, disorder, or treatment for instance, “What is otitis media?” or “How does amoxicillin work?” etc. These types of questions can be answered by going through review articles or text books.
The patient-oriented questions involving interpretation of a therapy or disease and consideration of risk vs. benefit for a patient or a group of patient are called “Foreground Questions.”[ 2 ] These types of complex clinical questions are best answered by primary or pre-assessed studies in the literature. These questions mostly compare the two, either two drugs or treatments or two diagnostic methods, etc.
The PICO (population, intervention, control, and outcomes) format [ Table 1 ] is considered a widely known strategy for framing a “foreground” research question.[ 3 ] Sackett et al . pointed out that breaking the question into four components will facilitate the identification of relevant information.
Considering PICO and FINER criteria for developing a research question[ 3 , 5 ]
Population or problem - addressing a specific population, its important characteristics and demographic information. From the above case, you can identify pediatric population with otitis media, the age range, sex, presenting complaint, and history.
Intervention or treatment of interest - the intervention can be a treatment, procedure, diagnostic test, and risk or prognostic factors. In this case, the intervention will be your plan to treat the patient which can be a new therapy, a diagnostic test, prognostic factor, or a procedure. For example, based on your observation in clinic, cefuroxime is another better treatment option as compared to amoxicillin in treating otitis media but you are not sure about its efficacy in pediatric population with otitis media.
Comparator or control -when a new therapy is compared with the existing one.
Outcome - is the effect of the intervention. For example, its effectiveness in controlling pain. Therefore, the outcome in the above case can be the relief of pain, the resolution of infection, or decreasing the risk of developing resistance. A good primary outcome should be easily quantifiable, specific, valid, reproducible, and appropriate to your research question.[ 4 ]
In a typical clinical setting, a clinician needs to know about background and foreground questions depending upon the experience about a particular disease and therapy. Once background questions are answered, more complex questions are addressed. The clinical questions arise from the central issues in a clinical work.[ 2 ] For example, identifying causes or risk factors (etiological questions), comparing diagnostic tests based on sensitivity and specificity (diagnostic query), identifying best treatment options (therapeutic question), and outcome of the treatment (prognostic question).
After determining a foreground question, the PICO approach is followed. Dissecting the question into parts makes it easy and searchable. As evident in this case, there are several relevant questions, for example: what are the outcomes associated with recurrent ear infection, what are the possible effects of long-term use of antibiotic, and what are the harms associated with current treatment? Now if you gather all the information from PICO approach, the following researchable questions can be formulated.
In children with acute otitis media (P), is cefuroxime (I) effective in reducing the duration of symptoms (O) as compared to amoxicillin (C)?
In children suffering from otitis media, will cefuroxime result in the improvement of symptoms and reduction in developing resistance?
Does treatment with amoxicillin increase the risk of developing resistance in children suffering from otitis media?
Does surgical procedure has better outcome for the treatment of otitis media in children after repeated antibiotic therapy?
From the above case, we have formulated multiple questions based on our patient’s illness and concerns. Now we can use the strategy of “selecting” the best question.[ 2 ] For example, which question has more significance for the patient’s well-being, which question is relevant to our knowledge needs and which question might lead to interesting answers for our patients and clinical query? Further, we need to consider the feasibility of finding the evidence in a short period.
ASSESSING THE RESEARCH QUESTION IN THE CONTEXT OF A STUDY DESIGN
As proposed by Hulley et al . [ Table 1 ], a research question should be formulated keeping in mind the FINER (feasible, interesting, novel, ethical, and relevant) criteria[ 5 ] and that the answer should fill gaps in the existing knowledge. The following points should be considered while assessing a research question.
Determining the required resources
The feasibility of conducting a research project is based on the research question and should be considered early in the process in order to avoid waste of resources and intellectual energy. This is sometimes difficult for a new investigator and they need guidance from their mentors.[ 4 ]
- Consider doing a pilot or proof of concept study to asses the feasibility;
- Consult a biostatistician early in the project in order to choose less costly design and common outcomes;
- Consider feasibility of enrolling the intended number of subjects from the population of your interest. Also, consider expanding your inclusion criteria and modifying exclusion criteria if it is difficult to enroll the intended number; and
- Consider cost of each element of the study design, research staff, and resources.
Significance of making it interesting and relevant
An important question may not seem interesting the way it is presented. It is a challenge to present a research question clearly and engage the interest and attention of the reviewers. Research is too much work to not have a passion for what you are investigating. You will have more support for your study, and it will be easier to publish if the topic is novel and also interests your collaborators, colleagues, and the community at large. It is important to pursue a research question with a passion of getting the truth out of the matter.[ 5 ] This is how we all perceive research; commitment to a high-quality systematic and unbiased completion of an innovative project. If your question can explain a given problem while pointing toward a specific aspect which is missing then your project can get a great deal of support.

Conducting literature review
The innovation of any research question is determined by a thorough literature search. Any replication of the study already existing in the literature is not worth repeating as it is. Depending upon the research question, sometimes the study can be replicated if your question approaches an existing problem in a refreshing way. This can be achieved by using a different populations, different techniques, new conceptual approaches, or linking two different studies in which outcomes did not solve the problem.[ 5 ] Once a preliminary question has been formulated, literature search should be done to find out what is known or unknown about the topic. The goal of the literature review is to determine what research has been conducted on the topic of interest? and how has it been conducted? and what are the gaps in the knowledge?. It is recommended to use PubMed, MedlinePlus, CINAHL, or Web of Science as the main search databases, but other databases can be used as well. PubMed clinical query is an easy and user-friendly database to search for evidence related to clinical practice. This also provides information to search MEDLINE by doing categorical searches, for example, therapeutic, diagnostic, etiological, and prognostic. The American College of Physicians (ACP) and clinical evidence from BMJ Publishing Group are excellent systems to find evidence on therapeutic questions. Other search engines such as OVID has a large selection of texts and journals which provides access to other databases such as Cochrane library in getting full text articles and systematic reviews. Gray et al . suggested 4 Ss for literature review: Systems : use of comprehensive resources, Synopses : extracting high-quality studies and abstracts, Syntheses: systematic reviews, and Studies : original research studies.[ 6 ] In the hierarchy of evidence-based medicine, systematic reviews are considered the best method for evidence. Systematic reviews are rigorous methods of collecting and synthesizing the results of many high-quality studies. Conducting a thorough literature search also helps in finding information on the methodology, calculating the sample size, and also the type of analysis as we are looking to find a difference. This information is necessary to help structure a new study and to identify gaps in the knowledge base of the scientific community.
Refining research question
A focused research question leads to a systematic planning of a research project. The difficulty in framing a research question is not due to the lack of ideas. The challenge is to transform a novel research question into a valid study design which is the next step in refining a research question.
Asking a well-formulated research question is a starting point in conducting a quality research project and in evidence-based clinical practice. The framework presented in this paper can be helpful for a clinician to formulate a question and search for an answer and for a researcher to develop a new research project. The classical approach is to identify a research question followed by a thorough literature search keeping in mind the PICO and FINER criteria. If it is a well-defined research question, it will lead to an appropriate study design and methodology. Discussing your research question with knowledgeable peers, department chair, mentor, and the biostatistician from the start will lead to the completion of a successful project. Other steps such as type and phase of the clinical trial, budget, informed consent, sites, resource constraints of both personnel and facilities, and timeline should also be considered while formulating a research question. We have introduced the concept of background and foreground questions and also the types of different questions that can arise (therapy, harm, diagnosis, and prognosis). We have described several strategies here while highlighting the major steps that will help investigators in framing a question with the goal of finding an answer based on evidence or initiation of a new research project. It is always good to focus on a single research question based on its relevance to patient’s health or one primary objective to drive the study design.[ 4 ] Once we have formulated our research question, we need to keep track of the progress toward finding an appropriate answer and then finally applying the results to a specific patient population. In short, a researchable question is what leads toward the facts rather than opinion[ 7 ] and is clearly linked to the overall research project goal.
Acknowledgments
The authors would like to acknowledge Dr. J.K Kosambiya, Dr. Eknath Naik, and Dr. Ambuj Kumar for their time in reviewing the paper and providing useful insights.
Source of Support: Nil
Conflict of Interest: None declared.
University of Tasmania, Australia
Systematic reviews for health: 1. formulate the research question.
- Handbooks / Guidelines for Systematic Reviews
- Standards for Reporting
- Registering a Protocol
- Tools for Systematic Review
- Online Tutorials & Courses
- Books and Articles about Systematic Reviews
- Finding Systematic Reviews
- Critical Appraisal
- Library Help
- Bibliographic Databases
- Grey Literature
- Handsearching
- Citation Tracking
- 1. Formulate the Research Question
- 2. Identify the Key Concepts
- 3. Develop Search Terms - Free-Text
- 4. Develop Search Terms - Controlled Vocabulary
- 5. Search Fields
- 6. Phrase Searching, Wildcards and Proximity Operators
- 7. Boolean Operators
- 8. Search Limits
- 9. Pilot Search Strategy & Monitor Its Development
- 10. Final Search Strategy
- 11. Adapt Search Syntax
- Documenting Search Strategies
- Handling Results & Storing Papers

Step 1. Formulate the Research Question
A systematic review is based on a pre-defined specific research question ( Cochrane Handbook, 1.1 ). The first step in a systematic review is to determine its focus - you should clearly frame the question(s) the review seeks to answer ( Cochrane Handbook, 2.1 ). It may take you a while to develop a good review question - it is an important step in your review. Well-formulated questions will guide many aspects of the review process, including determining eligibility criteria, searching for studies, collecting data from included studies, and presenting findings ( Cochrane Handbook, 2.1 ).
The research question should be clear and focused - not too vague, too specific or too broad.
You may like to consider some of the techniques mentioned below to help you with this process. They can be useful but are not necessary for a good search strategy.
PICO - to search for quantitative review questions
Richardson, WS, Wilson, MC, Nishikawa, J & Hayward, RS 1995, 'The well-built clinical question: A key to evidence-based decisions', ACP Journal Club , vol. 123, no. 3, pp. A12-A12 .
We do not have access to this article at UTAS.
A variant of PICO is PICOS . S stands for Study designs . It establishes which study designs are appropriate for answering the question, e.g. randomised controlled trial (RCT). There is also PICO C (C for context) and PICO T (T for timeframe).
You may find this document on PICO / PIO / PEO useful:
- Framing a PICO / PIO / PEO question Developed by Teesside University
SPIDER - to search for qualitative and mixed methods research studies
Cooke, A, Smith, D & Booth, A 2012, 'Beyond pico the spider tool for qualitative evidence synthesis', Qualitative Health Research , vol. 22, no. 10, pp. 1435-1443.
This article is only accessible for UTAS staff and students.
SPICE - to search for qualitative evidence
Cleyle, S & Booth, A 2006, 'Clear and present questions: Formulating questions for evidence based practice', Library hi tech , vol. 24, no. 3, pp. 355-368.
ECLIPSE - to search for health policy/management information
Wildridge, V & Bell, L 2002, 'How clip became eclipse: A mnemonic to assist in searching for health policy/management information', Health Information & Libraries Journal , vol. 19, no. 2, pp. 113-115.
There are many more techniques available. See the below guide from the CQUniversity Library for an extensive list:
- Question frameworks overview from Framing your research question guide, developed by CQUniversity Library
This is the specific research question used in the example:
"Is animal-assisted therapy more effective than music therapy in managing aggressive behaviour in elderly people with dementia?"
Within this question are the four PICO concepts :
S - Study design
This is a therapy question. The best study design to answer a therapy question is a randomised controlled trial (RCT). You may decide to only include studies in the systematic review that were using a RCT, see Step 8 .
See source of example
Need More Help? Book a consultation with a Learning and Research Librarian or contact [email protected] .
- << Previous: Building Search Strategies
- Next: 2. Identify the Key Concepts >>
- Last Updated: Apr 23, 2024 12:49 PM
- URL: https://utas.libguides.com/SystematicReviews


Think Like a Researcher: Instruction Resources: #6 Developing Successful Research Questions
- Guide Organization
- Overall Summary
- #1 Think Like a Researcher!
- #2 How to Read a Scholarly Article
- #3 Reading for Keywords (CREDO)
- #4 Using Google for Academic Research
- #4 Using Google for Academic Research (Alternate)
- #5 Integrating Sources
- Research Question Discussion
- #7 Avoiding Researcher Bias
- #8 Understanding the Information Cycle
- #9 Exploring Databases
- #10 Library Session
- #11 Post Library Session Activities
- Summary - Readings
- Summary - Research Journal Prompts
- Summary - Key Assignments
- Jigsaw Readings
- Permission Form
Course Learning Outcome: Develop ability to synthesize and express complex ideas; demonstrate information literacy and be able to work with evidence
Goal: Develop students’ ability to recognize and create successful research questions
Specifically, students will be able to
- identify the components of a successful research question.
- create a viable research question.
What Makes a Good Research Topic Handout
These handouts are intended to be used as a discussion generator that will help students develop a solid research topic or question. Many students start with topics that are poorly articulated, too broad, unarguable, or are socially insignificant. Each of these problems may result in a topic that is virtually un-researchable. Starting with a researchable topic is critical to writing an effective paper.
Research shows that students are much more invested in writing when they are able to choose their own topics. However, there is also research to support the notion that students are completely overwhelmed and frustrated when they are given complete freedom to write about whatever they choose. Providing some structure or topic themes that allow students to make bounded choices may be a way mitigate these competing realities.
These handouts can be modified or edited for your purposes. One can be used as a handout for students while the other can serve as a sample answer key. The document is best used as part of a process. For instance, perhaps starting with discussing the issues and potential research questions, moving on to problems and social significance but returning to proposals/solutions at a later date.
- Research Questions - Handout Key (2 pgs) This document is a condensed version of "What Makes a Good Research Topic". It serves as a key.
- Research Questions - Handout for Students (2 pgs) This document could be used with a class to discuss sample research questions (are they suitable?) and to have them start thinking about problems, social significance, and solutions for additional sample research questions.
- Research Question Discussion This tab includes materials for introduction students to research question criteria for a problem/solution essay.
Additional Resources
These documents have similarities to those above. They represent original documents and conversations about research questions from previous TRAIL trainings.
- What Makes a Good Research Topic? - Original Handout (4 pgs)
- What Makes a Good Research Topic? Revised Jan. 2016 (4 pgs)
- What Makes a Good Research Topic? Revised Jan 2016 with comments
Topic Selection (NCSU Libraries)
Howard, Rebecca Moore, Tricia Serviss, and Tanya K. Rodrigues. " Writing from sources, writing from sentences ." Writing & Pedagogy 2.2 (2010): 177-192.
Research Journal
Assign after students have participated in the Developing Successful Research Topics/Questions Lesson OR have drafted a Research Proposal.
Think about your potential research question.
- What is the problem that underlies your question?
- Is the problem of social significance? Explain.
- Is your proposed solution to the problem feasible? Explain.
- Do you think there is evidence to support your solution?
Keys for Writers - Additional Resource
Keys for Writers (Raimes and Miller-Cochran) includes a section to guide students in the formation of an arguable claim (thesis). The authors advise students to avoid the following since they are not debatable.
- "a neutral statement, which gives no hint of the writer's position"
- "an announcement of the paper's broad subject"
- "a fact, which is not arguable"
- "a truism (statement that is obviously true)"
- "a personal or religious conviction that cannot be logically debated"
- "an opinion based only on your feelings"
- "a sweeping generalization" (Section 4C, pg. 52)
The book also provides examples and key points (pg. 53) for a good working thesis.
- << Previous: #5 Integrating Sources
- Next: Research Question Discussion >>
- Last Updated: Sep 29, 2023 2:51 PM
- URL: https://libguides.ucmerced.edu/think_like_a_researcher


Market research
Research question: What is it and how do you do it correctly?

TRY OUT NOW
The Research question is the cornerstone of any study, whether it is market research or academic research in any field.
Although it is part of any research process, the aspects that allow it to be carried out correctly are not always known. That's why in this article we've put together everything you need to know when formulating the research question for your next project.
- 1 What is a research question?
- 2.1 Quantitative research question
- 2.2 Qualitative research questions
- 2.3 Mixed methods questions
- 3 What is the significance of the research question?
- 4.1 1. Start with a broad topic
- 4.2 2. carry out an initial review of the relevant literature
- 4.3 3. Narrow down your topic and identify possible research questions.
- 4.4 4. Evaluate the strength of your research question
- 5.1 PICOT model
- 5.2 PEO frame
- 6 Conclusion
- 7 1:1 Live Online Presentation: QUESTIONPRO MARKET RESEARCH SOFTWARE
- 8 Try software for market research and experience management now for 10 days free of charge!
What is a research question?
The research question is the central question that a study aims to answer. It is at the heart of systematic research and helps to clearly define the path for the research process.
The research question is usually the first step in the research methodology. It is the main point of the survey and determines the pace of the work.
This question usually refers to a problem or question that is answered by data analysis and interpretation in the conclusion of the study.
In most studies, the question is phrased in a way that highlights the various aspects of a study, including the problem the study is addressing, the population, and the variables being examined.
The research questions are often only determined during the course of the study. Therefore, these questions are dynamic, meaning researchers can change or refine the research question as they review the relevant literature and develop a framework for the study.
While many research projects focus on a single research question, larger studies may use more than one question.
Types of research questions
The type of research question depends on the focus and direction of the study being conducted and can therefore be different:
Quantitative research question
Quantitative research questions aim to understand processes that take place in specific contexts and locations. They generally fall into three types:
- Descriptive : They aim to obtain information about a variable or several variables in order to assign a size to the variable.
- Comparative : A comparison is made between two or more groups based on one or more reliable variables.
- Relational : These questions aim to understand the association, trends and causal relationship between two or more variables.
These questions are precise and typically include the population to be studied, the dependent and independent variables, and the research design to be used. They are usually formulated and defined at the beginning of the study. Check out these examples of quantitative questions for a survey
Qualitative research questions
These questions may cover broad areas of research or more specific areas of study. Like quantitative questions, these questions are also linked to the research design.
Unlike quantitative questions, qualitative research questions tend to be adaptive, non-directive, and more flexible, so studies with these types of questions generally aim to “discover,” “explain,” or “explore.”
Mixed methods questions
Mixed methods research requires a range of quantitative and qualitative questions. Separate research questions are appropriate when mixed studies focus on the importance and differences between quantitative and qualitative methods rather than the integrative factor of the study.
What is the significance of the research question?
The primary reason for asking a research question is that it narrows a broad topic of interest to a specific area of inquiry.
The research questions, along with the hypotheses, serve as a framework that guides the research. These questions also reveal the limitations of a study by establishing its boundaries and ensuring that it is coherent.
Most importantly, the research question has implications for the rest of the study and influences factors such as research methods, sample size, data collection and analysis.
How do you formulate a research question?
Now that you know what a research question is and how important it is, here are the key steps to consider when formulating a research question in a project:
1. Start with a broad topic
A broad topic provides researchers with a number of options to explore in finding a viable research question.
Brainstorming and concept mapping are some techniques that help develop a topic into subtopics and potential research questions.
These techniques help you organize your thoughts so you can identify relevant connections and subtopics within a broad topic.
When researching a topic, it makes sense to choose a subject area that really interests you, because your interest in the topic will affect your motivation during the research.
It is also worth considering the interests that have recently been expressed by the research community, as this may influence the chances of your research being published.
| See also: How to formulate a Research problem ?
2. carry out an initial review of the relevant literature
Once you have decided on a topic, you can begin to create a preliminary review of the relevant literature. With this first phase of research you can achieve two goals:
- You can find out what topics are currently being discussed by scientists and other researchers. In this way, you gain current and relevant knowledge on your topic.
- You identify gaps or limitations in existing knowledge about your topic. With some degree of fine-tuning, you can later use these gaps as the focus of your research question.
3. Narrow down your topic and identify possible research questions.
Once you have accumulated enough knowledge about the topic you want to work on, you can begin to focus on a more specific area of inquiry.
One option is to focus on gaps in existing knowledge or recent literature. This method involves developing research questions based on limitations identified in the literature that have been neglected in the past.
Similarly, researchers may choose research questions that extend or complement existing literature findings.
4. Evaluate the strength of your research question
The initial research and review of the relevant literature you have undertaken will have revealed some interesting questions that seem worth addressing.
However, are Not all interesting questions are also good research questions . Remember that research questions draw their answers or conclusions through an analysis of the evidence.
When formulating the research question, it is important to first consider relevance. A good strategy for this is to use the acronym FINER:
A good research question is feasible, meaning the question is within the researcher's capabilities. Researchers should be realistic about the scope of their research, as well as their ability to collect data and conduct the research within their skills and available resources.
Interesting
The ideal research question is interesting not only to the researcher, but also to his colleagues and the community. Novel The research question should be formulated in such a way that it provides new knowledge in the area under study.
The question and the subsequent study should be approved by the examination committees and the relevant authorities.
The research question should be relevant to the scientific community and the people working in your field of study. If possible, the question should also be relevant to the interest of the general public.
Recommendations for the appropriate formulation of a research question
Research questions should be appropriately structured to ensure clarity. There are several frameworks that can be used to correctly formulate a research question, the two most common are:
PICOT model
The PICOT framework allows research questions to be constructed to address important elements of the study, including the population to be studied, the expected results, and the time needed to achieve the result.
P : population, patient or problem. I: Intervention or indicator to be studied. C: Comparison group. O: Result of interest. T: Time frame of the study.
With these elements, the framework is commonly used in clinical research and evidence-based studies.
Example of a question constructed using the PICOT framework
Are children aged 5 to 20 of parents with addiction problems at a higher risk of developing depression or anxiety than children of parents without diagnosed mental health problems?
This question reflects the PICOT framework as follows:
P (population examined): Children I (indicator or intervention) : Parents with addiction problems C (comparison group) : Children of parents without addiction problems. O (result of interest) : Increased risk of depression T (interesting time frame) : Between the ages of 5 and 18
Like the PICOT framework, the PEO framework is also commonly used in clinical trials. However, this study is more suitable for conducting qualitative research questions.
This framework includes the following elements:
P: Population studied. E: Exposure to pre-existing conditions. O : result of interest.
Example of a question constructed using the PEO framework
How does exposure to classical music affect the development of emotional expression in infants and children under 8 years of age?
P (population examined): Infants and children under 8 years old E (exposure to given conditions) : exposure to classical music O (result of interest): Effects on the development of emotional expression
As you can see, the research question is the step you should pay the most attention to when conducting a study, as it will guide you for the rest of your work.
Once you have defined your research question, you can use QuestionPro's online surveys, which specialize in solving quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods research questions, to initiate the next phases of your project.
If you don't know them yet, we invite you to create a free account and explore all the options available to you by clicking the link below. We hope this article was of interest to you!
1:1 live online presentation: QUESTIONPRO MARKET RESEARCH SOFTWARE
Arrange an individual appointment and discover our market research software.
Try software for market research and experience management now for 10 days free of charge!
Do you have any questions about the content of this blog? Simply contact us via contact form . We look forward to a dialogue with you! You too can test QuestionPro for 10 days free of charge and without risk in depth!
Test the agile market research and experience management platform for qualitative and quantitative data collection and data analysis from QuestionPro for 10 days free of charge
FURTHER KEYWORDS
Types of research | Empirical research | Research topic
SHARE THIS ARTICLE
KEYWORDS OF THIS BLOG POST
Research question | Research | Question
FURTHER INFORMATION
- Applied Research: Definition, Types and Examples
- Research methods: what are they and how to choose them?
- Types of research and their features
- What is exploratory research?
- Mixed methods research: what it is and what types there are
- Research topic: what is it and how to choose it correctly?
- Data collection tools: which are the best?
- Big Data and Artificial Intelligence: How do they work together?
PRESS RELEASES

Ask a Librarian
How can I help you today?
A live human is ready to help.

Find & Cite | Research Help | Collections | Services | About
- Cook Library
- Research Guides
- Formulating a Research Question
- Information Literacy in Nursing
- Cultural Competency in Nursing
- Databases and Apps
- Books and Journals
- Clinical Skills
- Nursing Research Videos
Before You Start Searching
Clinical and epidemiological question frameworks.
- Basic Literature Searching
- Advanced Literature Searching
- Searching for Evidence with ABCDE
- Citation Management
- Citing Sources: APA and Other Styles
Step One: Start to formulate a research question or topic.
Aiming for clarity at the beginning of the project can help you get started right. It can be helpful to use one of the question frameworks detailed below.
Step Two: Do some background searching on the topic.
Taking a look in relevant resources to see what's already been written about your topic will help you understand how you can best contribute to the body of literature. It will also help you grasp the terminology around the topic, so that you'll be more prepared to do an effective literature search.
Step Three: Narrow down the question or topic if needed.
You may find that your original topic is too broad. After you have taken the time to evaluate what's already been written about your topic, you'll have a better understanding of what you're interested in.
Step Four: Meet with your librarian.
Try one of these tried and true clinical or quantitative research question frameworks. Not sure where to start? PICO is the most common clinical question framework. and PEO works well for public health and epidemiology.
- Condition, Context, Population
- Aromataris, E., & Munn, Z. (2017). Joanna Briggs Institute reviewer's manual. The Joanna Briggs Institute. Available from JBI Manual for Evidence Synthesis .
- Population, Exposure of Interest, Outcome or Response
- Population or Problem, Intervention or Exposure, Comparison or Control, Outcome
- Heneghan, C., & Badenoch, D. (2002). Evidence-based medicine toolkit. London: BMJ Books. https://www.worldcat.org/title/evidence-based-medicine-toolkit/oclc/62307845
- Population or Problem, Intervention or Exposure, Comparison or Control, Outcome, Study Type
- Methley, A. M., Campbell, S., Chew-Graham, C., McNally, R., & Cheraghi-Sohi, S. (2014). PICO, PICOS and SPIDER: a comparison study of specificity and sensitivity in three search tools for qualitative systematic reviews. BMC health services research, 14, 579. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12913-014-0579-0 .
- Population or Problem, Intervention or Exposure, Comparison or Control, Outcome, Time
- Richardson, W. S., Wilson, M. C., Nishikawa, J., & Hayward, R. S. (1995). The well-built clinical question: A key to evidence-based decisions. ACP Journal Club, 123(3), A12-A12. https://pubmed.ncbi.nlm.nih.gov/7582737/
- Population, Index Test, Reference Test, Diagnosis of Interest
- << Previous: Datasets
- Next: Searching for Evidence >>
- Last Updated: Mar 6, 2024 3:09 PM
- URL: https://towson.libguides.com/NURS
Numbers, Facts and Trends Shaping Your World
Read our research on:
Full Topic List
Regions & Countries
- Publications
- Our Methods
- Short Reads
- Tools & Resources
Read Our Research On:
Writing Survey Questions
Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions. Creating good measures involves both writing good questions and organizing them to form the questionnaire.
Questionnaire design is a multistage process that requires attention to many details at once. Designing the questionnaire is complicated because surveys can ask about topics in varying degrees of detail, questions can be asked in different ways, and questions asked earlier in a survey may influence how people respond to later questions. Researchers are also often interested in measuring change over time and therefore must be attentive to how opinions or behaviors have been measured in prior surveys.
Surveyors may conduct pilot tests or focus groups in the early stages of questionnaire development in order to better understand how people think about an issue or comprehend a question. Pretesting a survey is an essential step in the questionnaire design process to evaluate how people respond to the overall questionnaire and specific questions, especially when questions are being introduced for the first time.
For many years, surveyors approached questionnaire design as an art, but substantial research over the past forty years has demonstrated that there is a lot of science involved in crafting a good survey questionnaire. Here, we discuss the pitfalls and best practices of designing questionnaires.
Question development
There are several steps involved in developing a survey questionnaire. The first is identifying what topics will be covered in the survey. For Pew Research Center surveys, this involves thinking about what is happening in our nation and the world and what will be relevant to the public, policymakers and the media. We also track opinion on a variety of issues over time so we often ensure that we update these trends on a regular basis to better understand whether people’s opinions are changing.
At Pew Research Center, questionnaire development is a collaborative and iterative process where staff meet to discuss drafts of the questionnaire several times over the course of its development. We frequently test new survey questions ahead of time through qualitative research methods such as focus groups , cognitive interviews, pretesting (often using an online, opt-in sample ), or a combination of these approaches. Researchers use insights from this testing to refine questions before they are asked in a production survey, such as on the ATP.
Measuring change over time
Many surveyors want to track changes over time in people’s attitudes, opinions and behaviors. To measure change, questions are asked at two or more points in time. A cross-sectional design surveys different people in the same population at multiple points in time. A panel, such as the ATP, surveys the same people over time. However, it is common for the set of people in survey panels to change over time as new panelists are added and some prior panelists drop out. Many of the questions in Pew Research Center surveys have been asked in prior polls. Asking the same questions at different points in time allows us to report on changes in the overall views of the general public (or a subset of the public, such as registered voters, men or Black Americans), or what we call “trending the data”.
When measuring change over time, it is important to use the same question wording and to be sensitive to where the question is asked in the questionnaire to maintain a similar context as when the question was asked previously (see question wording and question order for further information). All of our survey reports include a topline questionnaire that provides the exact question wording and sequencing, along with results from the current survey and previous surveys in which we asked the question.
The Center’s transition from conducting U.S. surveys by live telephone interviewing to an online panel (around 2014 to 2020) complicated some opinion trends, but not others. Opinion trends that ask about sensitive topics (e.g., personal finances or attending religious services ) or that elicited volunteered answers (e.g., “neither” or “don’t know”) over the phone tended to show larger differences than other trends when shifting from phone polls to the online ATP. The Center adopted several strategies for coping with changes to data trends that may be related to this change in methodology. If there is evidence suggesting that a change in a trend stems from switching from phone to online measurement, Center reports flag that possibility for readers to try to head off confusion or erroneous conclusions.
Open- and closed-ended questions
One of the most significant decisions that can affect how people answer questions is whether the question is posed as an open-ended question, where respondents provide a response in their own words, or a closed-ended question, where they are asked to choose from a list of answer choices.
For example, in a poll conducted after the 2008 presidential election, people responded very differently to two versions of the question: “What one issue mattered most to you in deciding how you voted for president?” One was closed-ended and the other open-ended. In the closed-ended version, respondents were provided five options and could volunteer an option not on the list.
When explicitly offered the economy as a response, more than half of respondents (58%) chose this answer; only 35% of those who responded to the open-ended version volunteered the economy. Moreover, among those asked the closed-ended version, fewer than one-in-ten (8%) provided a response other than the five they were read. By contrast, fully 43% of those asked the open-ended version provided a response not listed in the closed-ended version of the question. All of the other issues were chosen at least slightly more often when explicitly offered in the closed-ended version than in the open-ended version. (Also see “High Marks for the Campaign, a High Bar for Obama” for more information.)
Researchers will sometimes conduct a pilot study using open-ended questions to discover which answers are most common. They will then develop closed-ended questions based off that pilot study that include the most common responses as answer choices. In this way, the questions may better reflect what the public is thinking, how they view a particular issue, or bring certain issues to light that the researchers may not have been aware of.
When asking closed-ended questions, the choice of options provided, how each option is described, the number of response options offered, and the order in which options are read can all influence how people respond. One example of the impact of how categories are defined can be found in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in January 2002. When half of the sample was asked whether it was “more important for President Bush to focus on domestic policy or foreign policy,” 52% chose domestic policy while only 34% said foreign policy. When the category “foreign policy” was narrowed to a specific aspect – “the war on terrorism” – far more people chose it; only 33% chose domestic policy while 52% chose the war on terrorism.
In most circumstances, the number of answer choices should be kept to a relatively small number – just four or perhaps five at most – especially in telephone surveys. Psychological research indicates that people have a hard time keeping more than this number of choices in mind at one time. When the question is asking about an objective fact and/or demographics, such as the religious affiliation of the respondent, more categories can be used. In fact, they are encouraged to ensure inclusivity. For example, Pew Research Center’s standard religion questions include more than 12 different categories, beginning with the most common affiliations (Protestant and Catholic). Most respondents have no trouble with this question because they can expect to see their religious group within that list in a self-administered survey.
In addition to the number and choice of response options offered, the order of answer categories can influence how people respond to closed-ended questions. Research suggests that in telephone surveys respondents more frequently choose items heard later in a list (a “recency effect”), and in self-administered surveys, they tend to choose items at the top of the list (a “primacy” effect).
Because of concerns about the effects of category order on responses to closed-ended questions, many sets of response options in Pew Research Center’s surveys are programmed to be randomized to ensure that the options are not asked in the same order for each respondent. Rotating or randomizing means that questions or items in a list are not asked in the same order to each respondent. Answers to questions are sometimes affected by questions that precede them. By presenting questions in a different order to each respondent, we ensure that each question gets asked in the same context as every other question the same number of times (e.g., first, last or any position in between). This does not eliminate the potential impact of previous questions on the current question, but it does ensure that this bias is spread randomly across all of the questions or items in the list. For instance, in the example discussed above about what issue mattered most in people’s vote, the order of the five issues in the closed-ended version of the question was randomized so that no one issue appeared early or late in the list for all respondents. Randomization of response items does not eliminate order effects, but it does ensure that this type of bias is spread randomly.
Questions with ordinal response categories – those with an underlying order (e.g., excellent, good, only fair, poor OR very favorable, mostly favorable, mostly unfavorable, very unfavorable) – are generally not randomized because the order of the categories conveys important information to help respondents answer the question. Generally, these types of scales should be presented in order so respondents can easily place their responses along the continuum, but the order can be reversed for some respondents. For example, in one of Pew Research Center’s questions about abortion, half of the sample is asked whether abortion should be “legal in all cases, legal in most cases, illegal in most cases, illegal in all cases,” while the other half of the sample is asked the same question with the response categories read in reverse order, starting with “illegal in all cases.” Again, reversing the order does not eliminate the recency effect but distributes it randomly across the population.
Question wording
The choice of words and phrases in a question is critical in expressing the meaning and intent of the question to the respondent and ensuring that all respondents interpret the question the same way. Even small wording differences can substantially affect the answers people provide.
[View more Methods 101 Videos ]
An example of a wording difference that had a significant impact on responses comes from a January 2003 Pew Research Center survey. When people were asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule,” 68% said they favored military action while 25% said they opposed military action. However, when asked whether they would “favor or oppose taking military action in Iraq to end Saddam Hussein’s rule even if it meant that U.S. forces might suffer thousands of casualties, ” responses were dramatically different; only 43% said they favored military action, while 48% said they opposed it. The introduction of U.S. casualties altered the context of the question and influenced whether people favored or opposed military action in Iraq.
There has been a substantial amount of research to gauge the impact of different ways of asking questions and how to minimize differences in the way respondents interpret what is being asked. The issues related to question wording are more numerous than can be treated adequately in this short space, but below are a few of the important things to consider:
First, it is important to ask questions that are clear and specific and that each respondent will be able to answer. If a question is open-ended, it should be evident to respondents that they can answer in their own words and what type of response they should provide (an issue or problem, a month, number of days, etc.). Closed-ended questions should include all reasonable responses (i.e., the list of options is exhaustive) and the response categories should not overlap (i.e., response options should be mutually exclusive). Further, it is important to discern when it is best to use forced-choice close-ended questions (often denoted with a radio button in online surveys) versus “select-all-that-apply” lists (or check-all boxes). A 2019 Center study found that forced-choice questions tend to yield more accurate responses, especially for sensitive questions. Based on that research, the Center generally avoids using select-all-that-apply questions.
It is also important to ask only one question at a time. Questions that ask respondents to evaluate more than one concept (known as double-barreled questions) – such as “How much confidence do you have in President Obama to handle domestic and foreign policy?” – are difficult for respondents to answer and often lead to responses that are difficult to interpret. In this example, it would be more effective to ask two separate questions, one about domestic policy and another about foreign policy.
In general, questions that use simple and concrete language are more easily understood by respondents. It is especially important to consider the education level of the survey population when thinking about how easy it will be for respondents to interpret and answer a question. Double negatives (e.g., do you favor or oppose not allowing gays and lesbians to legally marry) or unfamiliar abbreviations or jargon (e.g., ANWR instead of Arctic National Wildlife Refuge) can result in respondent confusion and should be avoided.
Similarly, it is important to consider whether certain words may be viewed as biased or potentially offensive to some respondents, as well as the emotional reaction that some words may provoke. For example, in a 2005 Pew Research Center survey, 51% of respondents said they favored “making it legal for doctors to give terminally ill patients the means to end their lives,” but only 44% said they favored “making it legal for doctors to assist terminally ill patients in committing suicide.” Although both versions of the question are asking about the same thing, the reaction of respondents was different. In another example, respondents have reacted differently to questions using the word “welfare” as opposed to the more generic “assistance to the poor.” Several experiments have shown that there is much greater public support for expanding “assistance to the poor” than for expanding “welfare.”
We often write two versions of a question and ask half of the survey sample one version of the question and the other half the second version. Thus, we say we have two forms of the questionnaire. Respondents are assigned randomly to receive either form, so we can assume that the two groups of respondents are essentially identical. On questions where two versions are used, significant differences in the answers between the two forms tell us that the difference is a result of the way we worded the two versions.

One of the most common formats used in survey questions is the “agree-disagree” format. In this type of question, respondents are asked whether they agree or disagree with a particular statement. Research has shown that, compared with the better educated and better informed, less educated and less informed respondents have a greater tendency to agree with such statements. This is sometimes called an “acquiescence bias” (since some kinds of respondents are more likely to acquiesce to the assertion than are others). This behavior is even more pronounced when there’s an interviewer present, rather than when the survey is self-administered. A better practice is to offer respondents a choice between alternative statements. A Pew Research Center experiment with one of its routinely asked values questions illustrates the difference that question format can make. Not only does the forced choice format yield a very different result overall from the agree-disagree format, but the pattern of answers between respondents with more or less formal education also tends to be very different.
One other challenge in developing questionnaires is what is called “social desirability bias.” People have a natural tendency to want to be accepted and liked, and this may lead people to provide inaccurate answers to questions that deal with sensitive subjects. Research has shown that respondents understate alcohol and drug use, tax evasion and racial bias. They also may overstate church attendance, charitable contributions and the likelihood that they will vote in an election. Researchers attempt to account for this potential bias in crafting questions about these topics. For instance, when Pew Research Center surveys ask about past voting behavior, it is important to note that circumstances may have prevented the respondent from voting: “In the 2012 presidential election between Barack Obama and Mitt Romney, did things come up that kept you from voting, or did you happen to vote?” The choice of response options can also make it easier for people to be honest. For example, a question about church attendance might include three of six response options that indicate infrequent attendance. Research has also shown that social desirability bias can be greater when an interviewer is present (e.g., telephone and face-to-face surveys) than when respondents complete the survey themselves (e.g., paper and web surveys).
Lastly, because slight modifications in question wording can affect responses, identical question wording should be used when the intention is to compare results to those from earlier surveys. Similarly, because question wording and responses can vary based on the mode used to survey respondents, researchers should carefully evaluate the likely effects on trend measurements if a different survey mode will be used to assess change in opinion over time.
Question order
Once the survey questions are developed, particular attention should be paid to how they are ordered in the questionnaire. Surveyors must be attentive to how questions early in a questionnaire may have unintended effects on how respondents answer subsequent questions. Researchers have demonstrated that the order in which questions are asked can influence how people respond; earlier questions can unintentionally provide context for the questions that follow (these effects are called “order effects”).
One kind of order effect can be seen in responses to open-ended questions. Pew Research Center surveys generally ask open-ended questions about national problems, opinions about leaders and similar topics near the beginning of the questionnaire. If closed-ended questions that relate to the topic are placed before the open-ended question, respondents are much more likely to mention concepts or considerations raised in those earlier questions when responding to the open-ended question.
For closed-ended opinion questions, there are two main types of order effects: contrast effects ( where the order results in greater differences in responses), and assimilation effects (where responses are more similar as a result of their order).
An example of a contrast effect can be seen in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in October 2003, a dozen years before same-sex marriage was legalized in the U.S. That poll found that people were more likely to favor allowing gays and lesbians to enter into legal agreements that give them the same rights as married couples when this question was asked after one about whether they favored or opposed allowing gays and lesbians to marry (45% favored legal agreements when asked after the marriage question, but 37% favored legal agreements without the immediate preceding context of a question about same-sex marriage). Responses to the question about same-sex marriage, meanwhile, were not significantly affected by its placement before or after the legal agreements question.
Another experiment embedded in a December 2008 Pew Research Center poll also resulted in a contrast effect. When people were asked “All in all, are you satisfied or dissatisfied with the way things are going in this country today?” immediately after having been asked “Do you approve or disapprove of the way George W. Bush is handling his job as president?”; 88% said they were dissatisfied, compared with only 78% without the context of the prior question.
Responses to presidential approval remained relatively unchanged whether national satisfaction was asked before or after it. A similar finding occurred in December 2004 when both satisfaction and presidential approval were much higher (57% were dissatisfied when Bush approval was asked first vs. 51% when general satisfaction was asked first).
Several studies also have shown that asking a more specific question before a more general question (e.g., asking about happiness with one’s marriage before asking about one’s overall happiness) can result in a contrast effect. Although some exceptions have been found, people tend to avoid redundancy by excluding the more specific question from the general rating.
Assimilation effects occur when responses to two questions are more consistent or closer together because of their placement in the questionnaire. We found an example of an assimilation effect in a Pew Research Center poll conducted in November 2008 when we asked whether Republican leaders should work with Obama or stand up to him on important issues and whether Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders or stand up to them on important issues. People were more likely to say that Republican leaders should work with Obama when the question was preceded by the one asking what Democratic leaders should do in working with Republican leaders (81% vs. 66%). However, when people were first asked about Republican leaders working with Obama, fewer said that Democratic leaders should work with Republican leaders (71% vs. 82%).
The order questions are asked is of particular importance when tracking trends over time. As a result, care should be taken to ensure that the context is similar each time a question is asked. Modifying the context of the question could call into question any observed changes over time (see measuring change over time for more information).
A questionnaire, like a conversation, should be grouped by topic and unfold in a logical order. It is often helpful to begin the survey with simple questions that respondents will find interesting and engaging. Throughout the survey, an effort should be made to keep the survey interesting and not overburden respondents with several difficult questions right after one another. Demographic questions such as income, education or age should not be asked near the beginning of a survey unless they are needed to determine eligibility for the survey or for routing respondents through particular sections of the questionnaire. Even then, it is best to precede such items with more interesting and engaging questions. One virtue of survey panels like the ATP is that demographic questions usually only need to be asked once a year, not in each survey.
U.S. Surveys
Other research methods, sign up for our weekly newsletter.
Fresh data delivered Saturday mornings
1615 L St. NW, Suite 800 Washington, DC 20036 USA (+1) 202-419-4300 | Main (+1) 202-857-8562 | Fax (+1) 202-419-4372 | Media Inquiries
Research Topics
- Age & Generations
- Coronavirus (COVID-19)
- Economy & Work
- Family & Relationships
- Gender & LGBTQ
- Immigration & Migration
- International Affairs
- Internet & Technology
- Methodological Research
- News Habits & Media
- Non-U.S. Governments
- Other Topics
- Politics & Policy
- Race & Ethnicity
- Email Newsletters
ABOUT PEW RESEARCH CENTER Pew Research Center is a nonpartisan fact tank that informs the public about the issues, attitudes and trends shaping the world. It conducts public opinion polling, demographic research, media content analysis and other empirical social science research. Pew Research Center does not take policy positions. It is a subsidiary of The Pew Charitable Trusts .
Copyright 2024 Pew Research Center
Terms & Conditions
Privacy Policy
Cookie Settings
Reprints, Permissions & Use Policy
- MyU : For Students, Faculty, and Staff
Hannah Kenagy and Melissa Ramirez join Department of Chemistry

MINNEAPOLIS / ST. PAUL (04/22/2024) – The Department of Chemistry will welcome Dr. Hannah Kenagy and Dr. Melissa Ramirez to the faculty in January 2025. Both chemists will enter the department as Assistant Professors.
Hannah S. Kenagy will join the department in January 2025 after completion of her postdoctoral training at the Massachusetts Institute of Technology (MIT), where she currently works as an NSF AGS Postdoctoral Fellow with Prof. Jesse Kroll and Prof. Colette Heald. Prior to her current position at MIT, Kenagy completed her PhD at the University of California Berkeley in 2021 with Ronald Cohen and her BS in Chemistry and the University of Chicago in 2016.
At the University of Minnesota, the Kenagy research group will focus on atmospheric chemistry. Kenagy’s research explores how emissions into the atmosphere get physically and chemically transformed into gases and particles with impacts on air quality and climate. “We will use an integrated toolset for thinking about these questions, including lab experiments, field observations, and multi-scale modeling,” Kenagy says. “In particular, we’ll focus on questions regarding how atmospheric chemistry and composition are changing as we reduce our reliance on fossil fuel combustion and as temperatures continue to rise with climate change. Integrating measurements and models together will enable us to push forward our understanding of this changing chemistry.”
Kenagy is passionate about integrating environmental chemistry learning opportunities in her classrooms to make real-world connections for students. “Because so much of my research is relevant to air quality and climate – things that impact people’s daily lives, often inequitably – outreach is a really key component of my group’s work,” Kenagy says. She also engages in ongoing efforts to make science more accessible, and to ensure all students have the resources they need to thrive and develop a sense of belonging in science.
The UMN Department of Chemistry’s strong focus on environmental chemistry and the opportunities to engage in interdisciplinary research make the move to Minnesota particularly exciting for Kenagy. “I’m looking forward to joining a university with atmospheric scientists in a variety of departments across both the Minneapolis and St. Paul campuses. I also plan to make some measurements of urban chemistry across the Twin Cities, a unique environment that is impacted by agricultural and biogenic emissions in addition to more typical urban emissions. This mix of emissions makes the Twin Cities an interesting place to study the air!”
When she’s not busy in the office and lab, Kenagy loves being outside, hiking and swimming. She also loves music – she plays piano and sings – and cooking. You can read more about Kenagy here.
Melissa Ramirez will also make her move to Minnesota in January of 2025. Currently, Ramirez is an NIH K99/R00 MOSAIC Scholar, NSF MPS-Ascend Fellow, and Caltech Presidential Postdoctoral Scholar in the laboratory of Prof. Brian Stoltz at the California Institute of Technology, where her research focuses on enantioselective quaternary center formation using experiments and computations. Before her postdoctoral position, Ramirez completed her PhD in Organic Chemistry at the University of California, Los Angeles with Prof. Ken Houk and Prof. Neil Garg in 2021 and her BA in Chemistry at the University of Pennsylvania in 2016.
The Ramirez laboratory at UMN will develop experimental and computational approaches to address challenges associated with efficiency in the synthesis of pharmaceutically relevant small molecules. “The mission of my research program will be to establish synthetic methods in the areas of main group catalysis, asymmetric organocatalysis, and transition metal photochemistry with the aid of computations,” Ramirez writes. “Students trained in my lab will develop strong skills in synthetic and computational organic chemistry with a focus on reaction development. This synergistic skillset in synthesis and computations will also give rise to a range of opportunities for collaboration with the broader scientific community.” Ramirez aims to bridge synthesis and catalysis research with computational chemistry at UMN.
Ramirez says an important goal for her as a professor will be to challenge students, support them, and make them feel connected to the classroom regardless of their background. “Throughout my academic career, some of the most effective teachers I have had are those who believed in my potential even when I experienced self-doubt or failure,” Ramirez says. She is also looking forward to collaborating with the Chemistry Diversity, Equity, and Inclusion Committee to explore ways to better connect students with resources to help remove barriers to their science education and career. “I am excited to help recruit a diverse student body by helping organize the CheMNext session and by continuing my close relationship with organizations such as the Alliance for Diversity in Science and Engineering and Científico Latino, which I have served on the organizational board for during my postdoc,” Ramirez says.
When she’s not on campus, Ramirez enjoys staying active. She’s an avid runner, loves Peloton, and likes taking high-intensity interval training (HIIT) classes. You can learn more about Ramirez here.
The hiring of Kenagy and Ramirez follows the recent announcement of Dr. Jan-Niklas Boyn and Dr. Kade Head-Marsden joining the faculty in Fall 2024 . These four incoming Gophers will bring the Department of Chemistry total of new faculty hires to nine over the past three years. We are excited for these outstanding chemists to join our community, and be part of the ongoing growth of the College of Science and Engineering on the UMN-TC campus.
Related news releases
- hUMNs of Chemistry #14
- hUMNs of Chemistry #13
- Jan-Niklas Boyn and Kade Head-Marsden join Department of Chemistry
- hUMNs of Chemistry #11
- Professor Peter Carr retires after over 45 years on Department of Chemistry faculty
- Future undergraduate students
- Future transfer students
- Future graduate students
- Future international students
- Diversity and Inclusion Opportunities
- Learn abroad
- Living Learning Communities
- Mentor programs
- Programs for women
- Student groups
- Visit, Apply & Next Steps
- Information for current students
- Departments and majors overview
- Departments
- Undergraduate majors
- Graduate programs
- Integrated Degree Programs
- Additional degree-granting programs
- Online learning
- Academic Advising overview
- Academic Advising FAQ
- Academic Advising Blog
- Appointments and drop-ins
- Academic support
- Commencement
- Four-year plans
- Honors advising
- Policies, procedures, and forms
- Career Services overview
- Resumes and cover letters
- Jobs and internships
- Interviews and job offers
- CSE Career Fair
- Major and career exploration
- Graduate school
- Collegiate Life overview
- Scholarships
- Diversity & Inclusivity Alliance
- Anderson Student Innovation Labs
- Information for alumni
- Get engaged with CSE
- Upcoming events
- CSE Alumni Society Board
- Alumni volunteer interest form
- Golden Medallion Society Reunion
- 50-Year Reunion
- Alumni honors and awards
- Outstanding Achievement
- Alumni Service
- Distinguished Leadership
- Honorary Doctorate Degrees
- Nobel Laureates
- Alumni resources
- Alumni career resources
- Alumni news outlets
- CSE branded clothing
- International alumni resources
- Inventing Tomorrow magazine
- Update your info
- CSE giving overview
- Why give to CSE?
- College priorities
- Give online now
- External relations
- Giving priorities
- Donor stories
- Impact of giving
- Ways to give to CSE
- Matching gifts
- CSE directories
- Invest in your company and the future
- Recruit our students
- Connect with researchers
- K-12 initiatives
- Diversity initiatives
- Research news
- Give to CSE
- CSE priorities
- Corporate relations
- Information for faculty and staff
- Administrative offices overview
- Office of the Dean
- Academic affairs
- Finance and Operations
- Communications
- Human resources
- Undergraduate programs and student services
- CSE Committees
- CSE policies overview
- Academic policies
- Faculty hiring and tenure policies
- Finance policies and information
- Graduate education policies
- Human resources policies
- Research policies
- Research overview
- Research centers and facilities
- Research proposal submission process
- Research safety
- Award-winning CSE faculty
- National academies
- University awards
- Honorary professorships
- Collegiate awards
- Other CSE honors and awards
- Staff awards
- Performance Management Process
- Work. With Flexibility in CSE
- K-12 outreach overview
- Summer camps
- Outreach events
- Enrichment programs
- Field trips and tours
- CSE K-12 Virtual Classroom Resources
- Educator development
- Sponsor an event

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
If you are looking for criteria for a good research question, Stone (2002) says that a good research question should be relevant, decided, and meaningful. Creating a research question can be a tricky process, but there is a specific method you can follow to ease the process. The following steps will guide you on how to formulate a research ...
Framing the research question is the first step in any research project, and you can learn how to write a research question that is focused, achievable, and answerable! Check this detailed article to know what a research question is, the different types, and a step-by-step process to formulate effective research questions, with examples.
Research questions should not be answerable with a simple "yes" or "no" or by easily-found facts. They should, instead, require both research and analysis on the part of the writer. They often begin with "How" or "Why.". Begin your research. After you've come up with a question, think about the possible paths your research ...
Abstract. Formulation of research question (RQ) is an essentiality before starting any research. It aims to explore an existing uncertainty in an area of concern and points to a need for deliberate investigation. It is, therefore, pertinent to formulate a good RQ. The present paper aims to discuss the process of formulation of RQ with stepwise ...
Focusing on the primary research question. The process of developing a new idea usually stems from a dilemma inherent to the clinical practice.[2,3,4] However, once the problem has been identified, it is tempting to formulate multiple research questions.Conducting a clinical trial with more than one primary study question would not be feasible.
In a research paper, the emphasis is on generating a unique question and then synthesizing diverse sources into a coherent essay that supports your argument about the topic. In other words, you integrate information from publications with your own thoughts in order to formulate an argument. Your topic is your starting place: from here, you will ...
Assess your chosen research question using the FINER criteria that helps you evaluate whether the research is Feasible, Interesting, Novel, Ethical, and Relevant. 1; Formulate the final research question, while ensuring it is clear, well-written, and addresses all the key elements of a strong research question. Examples of research questions
As the name suggests, these types of research questions seek to explore the relationships between variables. Here, an example could be something like "What is the relationship between X and Y" or "Does A have an impact on B". As you can see, these types of research questions are interested in understanding how constructs or variables ...
Formulating a Research Question. Every research project starts with a question. Your question will allow you to select, evaluate and interpret your sources systematically. The question you start with isn't set in stone, but will almost certainly be revisited and revised as you read. Every discipline allows for certain kinds of questions to be ...
Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives.
Formulating a research question takes time and your team may go through different versions until settling on the right research question. To help formulate your research question, some research question frameworks are listed below (there are dozen of different types of these frameworks--for a comprehensive overview, see this guide from the University of Maryland)
Formulating a research question is a crucial step in directing any scientific study. The classical evidence-based approach to formulating a question uses the PICO framework, consisting of population, intervention, comparison, and outcome. However, the PICO framework is not suitable for formulating research questions in some types of evidence ...
Once you have selected a topic, you need to develop a research question. You may be used to working with a thesis statement, but a thesis statement is an answer. If you start your research with an answer, you might miss something important or your paper might be too one-sided. Starting with a question allows you to explore your topic while ...
A good research question is essential to guide your research paper, dissertation, or thesis. All research questions should be: Focused on a single problem or issue. Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources. Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints. Specific enough to answer thoroughly.
Formulating Your Research Question (RQ) In a research paper, the emphasis is on generating a unique question and then synthesizing diverse sources into a coherent essay that supports your argument about the topic. In other words, you integrate information from publications with your own thoughts in order to formulate an argument.
Developing a researchable question is one of the challenging tasks a researcher encounters when initiating a project. Both, unanswered issues in current clinical practice or when experiences dictate alternative therapies may provoke an investigator to formulate a clinical research question.
Rapid review of 38 different frameworks for formulating questions. A question framework should (i) recognise setting, environment or context; (ii) acknowledge different stakeholder perspectives; (iii) accommodate time/timing and place; (iv) be sensitive to qualitative data.
- Is your research question clear? - Is your research question focused? (Research questions must be specific enough to be well covered in the space available.) - Is your research question complex? (Questions shouldn't have a simple yes/no answer and should require research and analysis.) • Hypothesize. After you've come up with a question ...
Step 1. Formulate the Research Question. A systematic review is based on a pre-defined specific research question (Cochrane Handbook, 1.1).The first step in a systematic review is to determine its focus - you should clearly frame the question(s) the review seeks to answer (Cochrane Handbook, 2.1).It may take you a while to develop a good review question - it is an important step in your review.
Course Learning Outcome: Develop ability to synthesize and express complex ideas; demonstrate information literacy and be able to work with evidence Goal: Develop students' ability to recognize and create successful research questions Specifically, students will be able to. identify the components of a successful research question. create a viable research question.
Remember that research questions draw their answers or conclusions through an analysis of the evidence. When formulating the research question, it is important to first consider relevance. A good strategy for this is to use the acronym FINER: Feasible. A good research question is feasible, meaning the question is within the researcher's ...
Step One: Start to formulate a research question or topic. Aiming for clarity at the beginning of the project can help you get started right. It can be helpful to use one of the question frameworks detailed below. Step Two: Do some background searching on the topic.
Writing Survey Questions. Perhaps the most important part of the survey process is the creation of questions that accurately measure the opinions, experiences and behaviors of the public. Accurate random sampling will be wasted if the information gathered is built on a shaky foundation of ambiguous or biased questions.
Here is a cover letter template you can use to create your own. [Your Full Name] [Company Name] Dear [Recipient's Name], I am writing in response to your recently advertised research fellowship position at [institution name]. As a highly motivated research professional with a [your degree] in [your field of study] and [number of years] of ...
Melissa Ramirez will also make her move to Minnesota in January of 2025. Currently, Ramirez is an NIH K99/R00 MOSAIC Scholar, NSF MPS-Ascend Fellow, and Caltech Presidential Postdoctoral Scholar in the laboratory of Prof. Brian Stoltz at the California Institute of Technology, where her research focuses on enantioselective quaternary center formation using experiments and computations.