- Product overview
- All features
- Latest feature release
- App integrations

CAPABILITIES
- project icon Project management
- Project views
- Custom fields
- Status updates
- goal icon Goals and reporting
- Reporting dashboards
- workflow icon Workflows and automation
- portfolio icon Resource management
- Capacity planning
- Time tracking
- my-task icon Admin and security
- Admin console
- asana-intelligence icon Asana AI
- list icon Personal
- premium icon Starter
- briefcase icon Advanced
- Goal management
- Organizational planning
- Campaign management
- Creative production
- Content calendars
- Marketing strategic planning
- Resource planning
- Project intake
- Product launches
- Employee onboarding
- View all uses arrow-right icon
- Project plans
- Team goals & objectives
- Team continuity
- Meeting agenda
- View all templates arrow-right icon
- Work management resources Discover best practices, watch webinars, get insights
- Customer stories See how the world's best organizations drive work innovation with Asana
- Help Center Get lots of tips, tricks, and advice to get the most from Asana
- Asana Academy Sign up for interactive courses and webinars to learn Asana
- Developers Learn more about building apps on the Asana platform
- Community programs Connect with and learn from Asana customers around the world
- Events Find out about upcoming events near you
- Partners Learn more about our partner programs
- Support Need help? Contact the Asana support team
- Asana for nonprofits Get more information on our nonprofit discount program, and apply.
Featured Reads

- Project management |
- The 25 project management skills you ne ...
The 25 project management skills you need to succeed

Anyone who oversees projects is a project manager, but to become a more thoughtful manager (with a higher impact), you need to develop the right project management skills. Learn what skills are necessary to become a successful project manager and how to build them.
If you’re interested in honing and developing your project management skills, you’re in the right place. In this guide, we’ll cover 25 key skills you need to succeed as a project manager or project administrator , and how you can develop those skills over time.
What are project management skills (and why do they matter?)
Project management skills are the attributes you develop to become a more experienced project manager. Building a project management skill set includes learning technical and hard skills, such as portfolio management and project scoping, and soft skills (for example, adaptability).In honing these skills, you’re preparing yourself to more effectively perform in your role.
Project management is the practice of organizing and executing work efficiently—and helping your team do the same. For a while, project managers had to be trained and certified in complicated project management technology. Traditional project management tools were hard to set up and required constant maintenance, which is where the position “project manager” comes from.
Modern project management tools
Modern project management evolved from traditional project management in two distinct ways. As companies and teams democratized their project management processes, they needed more team members and team leads who were able to manage a process from conception to completion. In order to support those team leads, project management software has also evolved, from complex mechanisms to flexible and easy-to-use tools.
![management research project skills [Product UI] Work requests project example (Boards)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/4afbad21-f79b-4beb-86d1-6c12952d414f/inline-boards-work-requests-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Today, any team member may be called upon to run a project and become the de-facto project manager—which is why modern project management tools are built to be flexible enough for anyone to use on any project, so you’re able to jump in and hit the ground running.
These tools, like Asana , make it easy to track, manage, and organize work—without the learning curve associated with traditional tools. With today's project management tools , you can easily implement project management best practices and bring a new level of clarity and visibility to your project team.
How to use your project management skills
Project management tools do the heavy lifting when it comes to reducing silos, increasing visibility, and facilitating cross-functional collaboration. As the project manager, you can use these tools to give your team the insight they need to get their best work done. While you don’t need to learn complicated skills or tools in order to become a successful project manager , there are hard, soft, and technical skills you can develop in order to improve your management and collaboration skills.
Some of these skills might not apply to you—while others might be things you’re already seasoned in. Like everything in the five phases of project management , approach this list with flexibility and work on the skills that are most relevant to you.
10 soft skills for project managers
Soft skills are what we call “non-technical skills,” or skills that can help you improve your quality of work—without a specific tool or technical requirement. These are also called “people skills” or “interpersonal skills” because they often help you work with and relate to others in your workspace. These 10 skills are the most important soft skills for project management:
1. Collaboration
Collaboration is the cornerstone of all project management skills. In project management, collaboration helps you get work done quickly and more efficiently. When you can coordinate across teams, you gain valuable insights into your project that you might not find within your team. If more minds are involved in the work, projects are inherently more creative and well developed.
To improve your collaboration skills, practice having conversations. Use techniques like active listening , where you stay engaged and focused when others are speaking to you. It sounds simple, but learning how to have open communication, reduce boundaries, and co-create are critical for a collaborative team.
2. Teamwork
Everyone on your team has something to bring to the table, and your team is more effective working together than they would be alone. Teamwork ensures that everyone feels welcome, valued, and they are supported to contribute.
If you’re working to boost your teamwork skills, dig deeper into team brainstorms , 1:1 conversations, and ask for feedback from your team—how can you be a better team member? Notice if there’s someone who hasn’t spoken up in a while, and be supportive when another team member has a new idea.
3. Communication
Miscommunications are common when you’re working with a group of people. Learning how to communicate well and avoid these will make projects run more smoothly and be more enjoyable.
To develop your communication skills, practice being open and honest with your coworkers. This requires a lot of trust between you and your team members. To build this trust, encourage your team members to bring any thoughts into a discussion—even if you disagree with them.
4. Time management
Time management and organization skills go hand in hand. As you become better at organizing your tasks, you’ll also have a clearer sense of everything that’s on your plate and how long your upcoming tasks are going to take.
Still, it can be hard to buckle down and prioritize your work. To improve your time management skills and reduce procrastination, try prioritizing tasks. When you’re clear on which tasks are higher priority, you can tackle them first, to make sure nothing gets left behind or falls through the cracks.
5. Leadership
Even if you don’t think of yourself as a leader or have a role in team management, when you’re managing a project, your project team is looking to you for leadership, guidance, and support.
To develop your leadership skills, practice approaching situations with empathy and understanding. Good leaders bring everyone together and make them feel supported to foster teamwork and collaboration.
6. Organization
For a lot of project managers, organization is the most intimidating soft skill. You might think organization is either something you “have” or “don’t have.” But, like every other project management skill in this article, you can develop your organizational skills and become a Marie Kondo in your own right.
The best way to become a better organizer is to create (and maintain) a central source of truth for your work and your team’s work. We’re often disorganized because work is disconnected—in fact, the average employee switches between 10 tools per day . Instead of splitting your time between 10 tools, try using a digital organization tool to act as that one central source of truth for your team.
7. Problem solving
Problem solving skills are collaborative, iterative skills that help you approach a problem and, ultimately, solve it. Developing problem solving skills isn’t about always having the “right” answer to every problem—rather, people with great problem solving skills practice approaching problems from new perspectives and methodically working towards a solution.
To become a better problem solver, use data-driven decision-making frameworks or routine analyses. For example, if you need to solve for how to boost sales by 10% over your competition, you can run a competitive analysis to determine where you currently stand in the market. Then, use that information to solve the problem of lower sales. In this case, you could develop a new marketing strategy coordinated with the sales team.
8. Critical thinking
Critical thinking, like problem solving, doesn’t have a “solution.” You can’t “win” at critical thinking, but you can practice approaching problems logically instead of making decisions based on your emotions. Good critical thinkers practice analyzing information in front of them and forming their own conclusions based on the facts—the way Sherlock Holmes solves a mystery.
To practice critical thinking, always take a step back and ask yourself: how did I come to this conclusion? Could there be another answer? Am I being swayed by something other than factual information? Emotional decisions aren’t necessarily bad—in fact, some of the best decisions are those we’re passionate about. But critical thinking is a helpful way to make sure you’re approaching a situation from the right perspective.
9. Adaptability
At some point, whether it’s this project or the next one, aspects of your project plan will change. Maybe your deadline or priorities shifts, and you need to adapt your workflow accordingly. Great project managers are able to pivot and adapt to new situations to continue steering their project team in the right direction.
Becoming more adaptable is all about understanding when and how to shift gears. To do this, you need to understand yourself. Developing other soft skills, such as self-awareness and mindfulness, can help you be more in touch with and manage your emotions, which are often in flux during times of change.
10. Conflict resolution
Inevitably, conflict will arise during the projects you manage. It could be that a stakeholder wants to change the project scope. Or maybe you missed your budget or deadline. Conflict resolution is about addressing both sides of the conflict so everyone feels heard and supported. If there are harmed parties, take the time to listen to them and try to find a solution that works for everyone. Even when that can’t happen, approaching the conversation with patience and empathy can help defuse a potentially frustrating situation and lead to a better result.
7 hard skills for project managers
Unlike soft skills, hard skills are quantifiable abilities. While the soft skills mentioned above are applicable for many work skills, these seven hard skills are relevant specifically to project management. Developing these will help you become a more well rounded and efficient project manager.
1. Project planning
At its core, a project plan (sometimes called a project charter) is a blueprint of the key elements your project needs to succeed. Typically a project plan will include seven things:
Goals and project objectives
Success metrics
Stakeholders and roles
Scope and budget
Milestones , deliverables , and project dependencies
Timeline and schedule
Communication plan
Some of these things, like your goals or your milestones, might already be defined in your project roadmap or brief. But your project plan is where all of these project elements come together to create a cohesive picture of your upcoming work.
A lot of planning goes into the beginning of the year for what our vision is and where we will be by the end of that particular year. Once that is done, we summarize it in a project so it's visible to everyone... Having that visual representation in Asana makes it easier to move things around.”
2. Project scoping
![management research project skills [Product ui] Scope management project in Asana, spreadsheet-style project view (List)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/728f6575-937e-44bc-98b2-cf8cbc464d41/TG23-web-hero-51-scope-management-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Project scope is the size, goals, and limitations (i.e., deadlines and resources) for your project. Your project scope will define what you can achieve within a certain timeframe and budget. Setting and defining your project scope is important in order to prevent scope creep , which is when your project deliverables outgrow your original project scope.
In order to improve your project scoping skills, practice setting project scope early and often. Once you’ve set your project scope, share it with stakeholders and surface it frequently, so everyone is on the same page about the project’s aims and limitations. Use it as a point of reference, so you know when to say no to new asks.
We have been able to reduce the number of products that we’ve oversold and the number of times we have to contact the customer to push a ship date out.”
3. Writing a project brief
![management research project skills [Product UI] Example project brief in Asana (Project Brief)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/977bb6a3-07f4-498b-a9e7-c3fc9b82c9a1/inline-project-management-skills-2-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Your project brief outlines your general project objectives and how you plan to get there. This can serve as a helpful North Star to guide planning sessions.
The most important thing to remember about your project brief is that it’s a living document. As you develop your project plan and get input from stakeholders, you can adapt and update your project brief. In general, your project brief should contain a link to your project roadmap if you created one, a list of your project stakeholders and their responsibilities (sometimes called a RACI chart), other relevant documentation or files, and any other high-level information your team might need.
Having executive oversight and insight into projects is key so we can quickly get up to speed on what is happening at any point.”
4. Hosting a project kickoff meeting
![management research project skills [Product ui] Kickoff meeting project in Asana, spreadsheet-style view (List)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/9170a22c-5222-47e9-bc10-44edbe56e10e/TG23-web-hero-026-kickoff-meeting-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A kickoff meeting is an opportunity to align with your project stakeholders. This is your chance to clarify your project goals and scope, and share any documents you’ve already put together like your project roadmap, project brief, or supplemental documentation like a bill of materials for a marketing campaign or a creative brief for a design team.
To host a successful kickoff meeting, plan to share the documentation you have put together with project stakeholders. Then, host a brainstorming or Q&A session to align on any additional variables, like budget, resources , or final deliverables.
5. Project roadmapping
![management research project skills [product ui] milestone chart template in Asana (timeline view)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/46f9b6dc-a110-4348-9670-7e49f79b897e/TG23-web-hero-003-milestone-chart-static-2x-en?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
A project roadmap is a high-level overview of your project’s key deliverables and timeline. Project roadmaps are helpful for complex initiatives with a lot of stakeholders because they help the entire project team get on the same page before the project even starts.
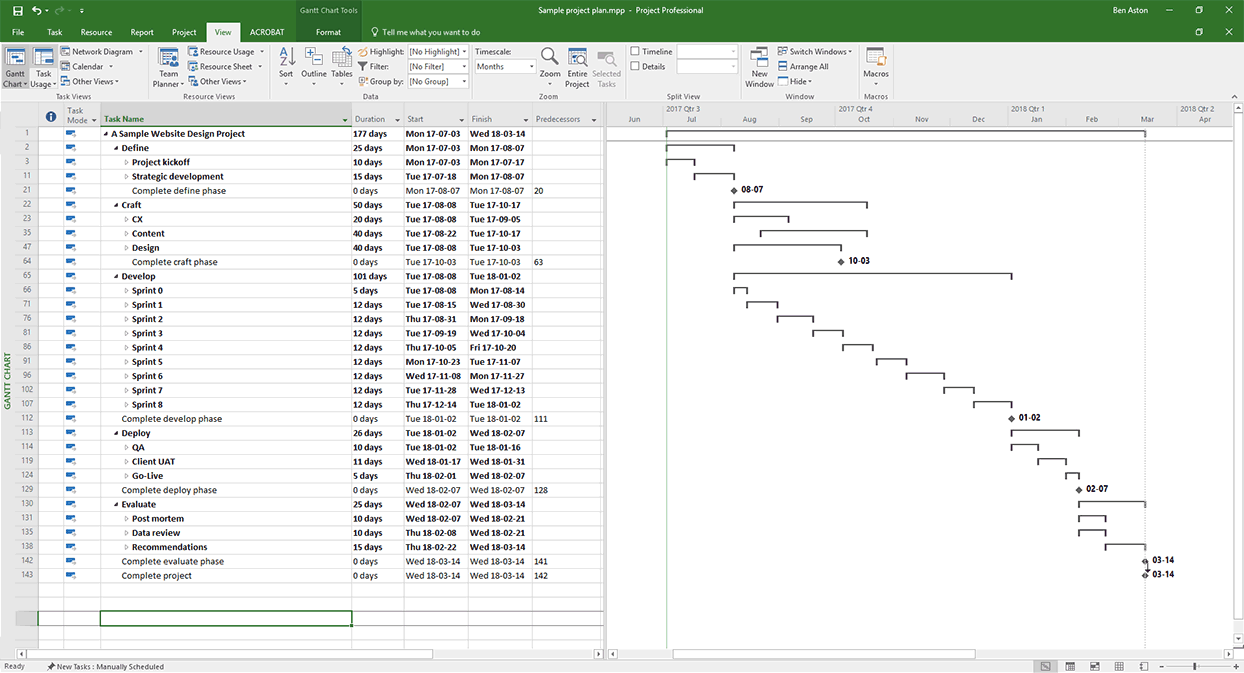
Traditionally, project roadmaps are created in Gantt chart-like software , in order to display a general schedule of your project as a horizontal bar chart. To create a project roadmap, use a tool like Timeline in Asana to create a rough timeline of your project, adding key milestones or important dependencies.
6. Mapping your project timeline
![management research project skills [Product ui] Timeline in Asana, Gantt chart-style view (Timeline)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/79f35737-4e03-4527-91cf-fb88073e11e2/TG23-web-hero-017-timeline-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Your project timeline is the order and duration of events during your project lifecycle. Knowing your project timeline helps your team track project success and deliver the right assets on time.
In order to build a great project timeline, make sure you clarify the start and end dates of your project, as well as any key milestones. As you continue building out individual tasks and deliverables, set dependencies between tasks, and clarify the start and end date of each piece of work.
7. Task management
Once your project is officially underway, task management refers to how well you manage your and your team’s time. The best project managers have visibility into what their team is working on in real-time, so they can help their team effectively prioritize and execute work.
But you don’t have to magically know everything that’s happening in your project—instead, use task management software. Task management software is more than a to-do list—it’s a way to get a holistic view of all of the work happening in your project. With effective task management, you can empower your team to work more productively, efficiently, and effectively.
With Asana, we can see project progress and blockers, plus feedback and action items, all in one place. We're now able to complete work more efficiently and effectively, which has become even more critical while working from home. We’d be lost without it!”
8 technical skills all project managers need
Soft skills: check. Hard skills: got it. The only thing you have left to master are technical skills!
Technical skills refer to your knowledge of specific tools and softwares within project management. These tools aren’t hard to learn—as we mentioned before, modern project management is built to be flexible and easy to use. These eight skills are aspects of project management roles you should become familiar with, so you know when and how to leverage them.
1. Project management software skills
Project management software has come a long way from legacy tools that were difficult to use and required a project management professional to implement. But like any tool, even easy-to-use ones, the software you choose takes time to learn and truly master. Make sure the tool you select has a written guide and helpful videos to teach you the ins and outs of how to use it.
2. Gantt charts
![management research project skills [Product ui] Product launch Gantt chart project in Asana (Timeline)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/d25dcaf2-e57e-4a6a-8528-0e429f95ff76/TG23-web-hero-025-gantt-chart-static-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Gantt charts are a way to visualize your project as a horizontal bar chart, where each bar represents a piece of work and the length of each bar represents the amount of time that work will take.
Project milestones
Dependencies
Real-time project progress
Start and end dates
Traditional Gantt chart technology can be tricky to use and limited in scope, which is why, at Asana, we took the best of Gantt chart technology and created Timeline , a Gantt-chart like tool that helps you see how all of the pieces fit together.
Launching an album has so many moving parts, and Asana helps us track every detail, who’s responsible for it, and when it needs to be completed.”
3. Kanban boards
![management research project skills [Product UI] Sprint plans project in Asana (Boards)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/9d21e8c7-9627-42eb-bda4-ac321d42c821/engineering-kanban-view?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
Another popular type of visual project management is the Kanban board . Each column in a Kanban board represents a stage of work, like New , In progress , or Done . Individual work is represented by cards, which move through the columns until they’re completed.
Kanban boards tools are a popular visual project management tool for lean project management teams, particularly product, engineering, and software development teams. They’re an Agile methodology , designed to be adaptable and flexible to adjust to development needs in real-time.
4. Agile management
Agile management is a lean project management methodology that’s particularly popular with product, engineering, and software development teams. Agile operates on a system of continuous improvement and incremental evolution, and it encompasses several lean methodologies, like lean portfolio management , Scrum , and Kanban .
In order to manage an Agile team, it's the project manager’s job to coordinate between team members and stay flexible. This can mean changing the project schedule, aligning with teams working on a different project, or just staying in touch with effective communication.
5. Workload management
![management research project skills [Product UI] Workload management in Asana (Workload)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/04f7d02f-1ce7-48dc-91d4-d17f2d3b3f9e/inline-generic-workload-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
If you’ve managed projects before, you know how hard it is to gain clarity on who is working on what—but it doesn’t have to be. Workload management helps you measure your team’s bandwidth and make sure they aren’t over- or under-worked. It’s an interactive process that doesn’t have a beginning or end state—rather, an effective project manager will continuously monitor their team’s workload to ensure no one is burning out.
There are two steps to using workload management software . First, start by figuring out your team’s capacity, competencies, and current workload. From there, allocate resources based on individual workload, or rebalance workloads as needed.
6. Cost management
In project management, cost management is considering how each task impacts your budget at every stage of the project. Cost management is a key part of project leadership, and an important element of whether or not your project is a success. Staying within budget is as important as hitting your project due date, and cost management can help you get there.
To manage cost effectively, good project managers define their costs and budget at the beginning of a project. Make sure project stakeholders and team members all understand the budget. Then, during the project, keep cost and budget in mind. Check in on your spending several times during the project to make sure you aren’t overshooting your budget. Once the project is completed, tally predicted cost vs. actual cost to determine how effective your cost management strategies were. This can also help you benchmark for future projects.
7. Project portfolio management
![management research project skills [Product UI] Project Management Skills - project portfolio management (Portfolios)](https://assets.asana.biz/transform/403373e9-e601-48c3-9fcc-5aac7847ee2d/inline-generic-portfolios-2x?io=transform:fill,width:2560&format=webp)
With project portfolio management (PMM), you can get a bird’s-eye view of your team’s work across multiple projects. Unlike traditional project management, PMM involves working on multiple projects or large-scale initiatives simultaneously. Project portfolio management tools help you get a holistic view of all of your team’s work in real-time, so you can connect strategy to execution.
Portfolios are also a key Asana feature for our team. It is a great tool for our executive team so they can see our big pieces of work all in a single place with the status, progress and ownership. Our CEO visits our portfolio daily and adds comments. He loves to be able to see what's going on in a snapshot.”
8. Change management
If you’ve ever rolled out a big organizational change, you’ve likely practiced change management, even if you didn’t know it. Change management is the process of introducing organizational change—like new processes or tools—over a set period of time to make them easier to adapt to.
At Asana, we use the Asana Way of Change, a six step process developed by our Customer Success team that incorporates proven change management strategies. To learn more, read our guide to change management .
The standard of our creative team, for a while, was just to react to work. But we’ll never do the best work we possibly can without a clear process.”
How to build your project management skills
Twenty five skills might feel like a lot, but remember that you don’t need to master every skill in this list. Some, like Agile, are only relevant for specific teams. Others, like organization, become virtually effortless with a little focus and great tools .
Keep in mind that developing your project management skills takes practice. Challenge yourself to focus on one or two new skills for each project—whether that’s trying out a new visual form of project management like Kanban, drafting your first ever project plan, or leaning into time-management.
There are also classes you can take to develop hard and soft project management skills. Though you no longer need certifications in order to be considered a project manager, the Project Management Institute (PMI) offers courses, learning events, and their famous Guide to the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK® Guide) , which was the first project management guide ever published.
Finally, once you’ve selected a project management tool , you can also take their classes to learn technical project management skills. At Asana, we’ve developed the Asana Academy and How to Asana series to help new project managers learn new soft, hard, and technical skills.
Build your project management toolkit
If you manage a project, you’re a project manager—and you likely already have some key project management skills. The most important thing is to be intentional, listen to your team, and collaborate with your team members. The rest will follow.
Project management doesn’t need to be complex. Asana was designed specifically to keep project manager’s organized, with tools, automations, and customizations built for collaborating and coordinating everything from a simple brainstorming session to a full-fledged product launch.
Related resources

Timesheet templates: How to track team progress

Scaling clinical trial management software with PM solutions

Data-driven decision making: A step-by-step guide

How Asana uses work management for employee onboarding
American Society for Microbiology
Project management tips for researchers.
Jan. 23, 2019
Project Monitoring and Control
Project closing.
- Undergraduate Student
- Graduate Student
- Management Skills
- Professional Development
Author: Caleb McKinney, Ph.D.

The 2024 Clinical Virology Symposium Registration Now Open!
Discover asm membership, get published in an asm journal.

- Share on Twitter
- Share on LinkedIn
- Share on Facebook
- Share on Pinterest
- Share through Email
21 Project Management Skills You Need For Your Resume In 2024
I’m Ben Aston, a digital project manager and founder of thedpm.com. I've been in the industry for more than 20 years working in the UK at London’s top digital agencies including Dare, Wunderman, Lowe and DDB. I’ve delivered everything from film to CMS', games to advertising and eCRM to eCommerce sites. I’ve been fortunate enough to work across a wide range of great clients; automotive brands including Land Rover, Volkswagen and Honda; Utility brands including BT, British Gas and Exxon, FMCG brands such as Unilever, and consumer electronics brands including Sony. I'm a Certified Scrum Master, PRINCE2 Practitioner and productivity nut!
The hard and soft project management skills required to be successful in this role are rapidly evolving. Discover and learn how to develop the PM skills required in 2024 to lead better teams and deliver more successful projects.

Project management is transforming quickly and drastically. Advancements in technology (looking at you, AI) and the evolution of project management tools, methodologies, frameworks, and best practices contribute to a similar change in the project management skills required to deliver successful projects.
In 2024, simply having hard project management skills is not enough. You need well developed soft skills and personal and professional traits. Where you're missing these skills, it's important to upskill yourself through project management training .
This is the definitive list of essential project management skills that are “in” right now and how you can best develop them to propel you along your project management career (or launch it!).
What Are Project Management Skills?
Project management skills are the capabilities and competencies that project managers need to have (and be good at) in order to do their jobs well and ensure their projects are successful. Common project management skills include project planning, requirements gathering, and risk management.
Complete Project Management Skills List
These are the hard and soft project management skills you’ll learn about in this article so you can add them to your resume and learn how to be an (even more) awesome project manager.
| Hard Skills | Soft Skills | Traits |
|---|---|---|
| Ordered | ||
| Visionary | ||
| Detail-oriented | ||
| Team-oriented | ||
| Cautiously Optimistic | ||
| Tenacious | ||
| Adaptable | ||
| Decisive | ||
| Responsible | ||
| Strong Work Ethic | ||
We've broken down these project management skills into hard skills, soft skills, and traits.
Click on any item within the skills list to understand what it is and how to develop it. You’ll also get a deep understanding of why they matter, and I’ll cover plenty of examples of when you’ll use them along the way.
Might I add: this is also the raison d’être for DPM Membership and the DPM School . Because having practical know-how and support to implement the skill set is really important!
11 Project Management Hard Skills
The hard skills of project management are all about competence, and speak to your practical technical ability: they are the tools, techniques, and methodologies you can apply.
Hard skills can be thought of as expert knowledge on how to operate that machine or make something work technically. You can do or make something. There are straightforward steps you follow that work. If you’re new to project management, hard skills are easiest to learn.
Hard Project Management Skills List
- Reading, Writing & Arithmetic
- Process Management
- Project Initiation
- Project Planning
- Project Scheduling
- Documentation
- Task Management
- Project Control
- Risk Management
- PM Tool Knowledge
- Technical Skills
1. Reading, Writing & Arithmetic
Any good project manager needs to be able to employ and activate quick, accurate, and clear reading, writing, and math skills .
- Can you read a proposal and immediately comprehend the technical or legal issues present in the text?
- Can you write a solid project brief that any team can understand and run with?
- Can you verify budget and expense math, catching errors before they become a bigger problem?
Reading, writing and arithmetic are hard skills that are repeatedly taught to us throughout grade school and even post-secondary. However, as we become adults these skills can stagnate if you don’t push yourself to use them regularly.
How To Develop Reading, Writing & Arithmetic
- Read often—you can read anything, just to keep your skill sharp—but I’d recommend any of these books for project managers . Even just 30 minutes of reading per day goes a long way to keeping that part of your brain exercised.
- Hone your writing. Invest in a program like Grammarly , which gives you customized feedback on your tone along with typical corrections for spelling, grammar, and wordiness. You can also check out these 5 tips for better writing .
- Practice basic arithmetic with apps like BBC Teach or Khan Academy . Nobody expects you to memorize advanced trigonometry equations, but it’s useful to know basic addition and subtraction and be able to puzzle out harder multiplication and division problems.
Return to the list of project management skills.
2. Process Management
Process management is the ability to map vital and control processes within a project ecosystem .
What are your most vital company and project management processes? For many, business processes include the likes of:
- Project launch
- Project delivery
- Reviews, reporting, and evaluations
Process management, then, is a way to catalog all of these processes, get a birds-eye-view of it all, and circulate knowledge about each item as needed. By its very nature, process management requires the balancing of a lot of spinning plates. Excelling in process management is a surefire way to stand out as a project manager, but it can be quite a daunting task.
How To Develop Process Management Skills
- There are plenty of process management training certifications that you can invest in. Consider night courses or a work-at-your-own-pace program that doesn’t interfere with your workday.
3. Project Initiation
Project initiation involves ensuring everyone's aligned on vision and approach , and it’s critical to starting projects effectively.
Before there can be a project, someone has to take the first step—be that a pitch, a formal project initiation document , a plan, a kickoff, a discovery session, or even simply being curious enough to notice an area of the business that could use some improvement.
As a project manager, initiating a project will often fall to you. It is to your benefit to learn how to instigate them and how to get them started on the right foot.
There are multiple sub-skills involved in initiating projects:
- Getting buy-in and alignment from the team and all stakeholders
- Setting up the project tools and documents
- Gathering or assigning the right resources
- Communicating a project vision to the right people
How To Develop Project Initiation Skills
- First, teach yourself how to write a stand-out project proposal . This is a big part in getting your ideas moving. Knowing how to build out an exemplary project proposal is going to teach you the basics of project initiation, namely the ability to identify a problem and then offer a solution that you are best equipped to handle.
- Next, learn how to kick off projects —how to plan for, lead, and follow up on a project kickoff meeting —so the project starts with the highest chance of success. There’s an entire workshop on mastering project kickoffs in DPM Membership .
- Learn more about which resource management skills to build up.
4. Project Planning
Project planning involves setting a course through the project that meets its objectives and adheres to its constraints . It spans both the meta and the micro.
There’s the large scale obvious planning we need to create things like meeting plans, statements of work , project estimates , timelines, resource plans, and briefs. There’s also the more mundane: planning out your day, who you’re going to talk to first, and how you are going to make time to keep your status documents up to date.
The extent to which you’re able to effectively plan will directly impact the project’s ability to be successful. No matter how good you are at executing, without a proper project plan , the project won’t succeed. Remember that you need to plan for both success and disaster, and that there’s always an element of trial-and-error when it comes to planning. Never be afraid to fail and learn.
How To Develop Project Planning Skills
- There is no one single way to do planning. Diversify your learning by consuming different materials and seeing what different experts have to say.
- To accompany the guide, there are templates and filled-in project plan samples available in DPM Membership .
5. Scheduling
Project scheduling is the ability to sequence the right people on your project at the right time .
This means building out a calendar that indicates who is doing what, and when. This could be a work breakdown structure in Excel, a Gantt chart in your project scheduling tool of choice, a dedicated project management calendar , or any other form of project schedule.
Project managers are responsible for determining project milestones, indicating when things need to be done, and what tasks are dependent on others, as well as who is representing your team at different hours, on different days, across different tasks and deliverables. You’ll need to account for all roles, tasks, and responsibilities when dividing up work amongst the project team.
Honing this skill will help you avoid common scheduling pitfalls, like last-minute adjustments, staff confusion, “clopen” shifts, and out-of-hand overtime/on-call practices.
How To Develop Scheduling Skills
- One of the best things you can do to learn the skill of project scheduling is to study your preferred project management methodology (whether it's waterfall or agile) and learn what “scheduling” means in that context.
6. Documentation Development
Project managers are often responsible for creating documentation for things like costs, timeline, scope, stakeholders, and the contract .
Documentation involves recording your process so that it can be accessed, checked, and repeated by others. For a PM, knowing HOW to do proper documentation is only half the battle—you must also know how much documentation is needed, to prevent excessive time and energy output.
The Manifesto for Agile Software Development states a preference for “working software over comprehensive documentation.” What does that mean? Well, documentation is needed, but don’t go overboard. A functional product is always the top priority.

Sign up to get weekly insights, tips, and other helpful content from digital project management experts.
- Your email *
- Yes, I want to sign up to receive regular emails filled with tips, expert insights, and more to build my PM practice.
- By submitting you agree to receive occasional emails and acknowledge our Privacy Policy . You can unsubscribe at any time. Protected by reCAPTCHA; Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
How To Develop Documentation Development Skills
- Use other people’s project documents to help you save time and use best practices without having to figure everything out the hard way. There are plenty of templates, charts, agendas, checklists, and the like in DPM Membership .
- If you’re totally new to project documentation you’ll be better off with training like The DPM School , which can help you learn when, why, and how to fill out the most important project documents.
Return to the list of project management skills .
7. Task Management
Task management involves scheduling, monitoring, and assessing project progress and quality of tasks so work flows smoothly.
Making lists, using text editors, using tools like Kanban boards, spreadsheet building, team-based approaches, and even simple pen-and-paper are all forms of task management.
Excellent task management can boost productivity, reduce errors, and keep everyone up-to-date, so it’s up to the project manager to use the best task management approach for the situation.
A lot of task management is trial-and-error. It's also having a willingness to scale to a more comprehensive solution if you are finding your current task management systems are becoming inadequate.
How To Develop Task Management Skills
- Don’t invest too much money into learning task management. It’s a skill that is nebulous and will change day-to-day as your project needs change. Work on this skill through simple practice and enhance your knowledge with free tutorials and guides to give you deeper insights.
- There are plenty of free resources that you can rely on to sharpen your tasking skills, including our own guide to task management here .
8. Project Control
Project control involves monitoring and managing critical aspects of the project such as cost, schedule, scope, and stakeholders .
It’s a project manager’s job to keep their project(s) from going over budget and over schedule. Almost every project will test these imposed limitations. Scope creep , unexpected bumps in the road, and other entanglements will try to push the boundaries of these time and cost constraints.
Project control involves gleaning data and analytics from your project tracking tools or project dashboard in order to predict and influence the financial and time expenditures required for a particular project.
Once limitations have been confirmed, it’s a project manager’s job to make sure things don’t run out of control on their way to completion.
Any project manager knows that no project is ever 100% complete. There is always more to do, more to build, more to finetune. Proper controls help to establish limitations around a project so that it doesn’t end up in developmental limbo.
How To Develop Project Control Skills
- A great resource is the DPM Podcast episode, Coloring In The Project Lines , which features Maik Stettner talking about his personal experience with delivering on budget, hitting timelines, and other areas of project control .
Return to the list of project management skills
9. Risk Management
Risk management is the process of identifying, evaluating, and mitigating against project snafus .
The skill for effective risk management is really experience—it’s knowing what could go wrong and having the humility to ask for your team’s input. The earlier you identify risks, the better your chances of avoiding the risk occurrence.
Risk identification must be followed by a risk plan that outlines how you’ll address them. This involves assigning a probability, a cost, and an owner, and using mitigation strategies that are suitable for the risk and the appetite of the client for things going wrong.
Whether you do these activities in a dedicated risk management tool or in a simple spreadsheet, RAID log , or risk register , the skill to master is the ability to identify risks well before they become issues and come up with effective mitigation plans to nullify the risk of them ever becoming issues.
How To Develop Risk Management Skills
- Rely on other people’s experiences and learn from their mistakes (and from their successes). Glean knowledge from the best-of-the-best and use their mistakes as lessons to fuel your own learning.
- There are plenty of books on risk management, which is a safe way to hone your practical skills before testing them out in the workplace. You can start with Fundamentals of Risk Management by Paul Hopkins or Implementing Enterprise Risk Management by James Lam.
10. Project Management Tool Knowledge
General knowledge of how project management tools work is useful, but there is no “one right project management tool”—you need the skills to learn them all.
A project manager can only do so much with their own two hands. That’s why it’s important for them to have a toolkit of software backing them up. There is a project management tool for every task, work style, team structure, and department need.
Over a quarter of survey participants from the Project Success Survey named “the use of project management tools” as a key component to project success. Software tools are not only useful for relieving an administrative workload burden, but they are a critical component to success.
How To Develop Your Skills In Using PM Tools
- There is no one-size-fits-all to learn the intricacies of every project management tool in existence. Instead, you are going to want to hone in on: what problem you need to solve, what tool can best do that, and how to best use that tool.
- If you want to understand the types of tools at your disposal, check out some of my favorites and get a deeper look at the project management software listed here.
11. Technical Skills
Technical skills include things like basic wireframing, copy, design, & coding , which can allow you to manage more effectively.
The number of technical skills a project manager brings to the table can elevate them from average to expert in a heartbeat.
- Can you wireframe a product using different techniques?
- Do you have basic design skills?
- Do you read or develop code at all?
These are some of the most valuable hard skills because they are tangible. If you know C++ or HTML5, you can easily prove it with a practical demonstration. However, these skills can also be incredibly difficult to master.
As a project manager, you will most likely be a jack-of-all-trades with a specialty in one or two items. A good practice to have is: make sure you have at least two unique and intersecting skills. That way, you stand out as a niche specialist that people who need your expertise cannot do without.
It’s up to you to decide how much guidance you need, how much of an expert you want to become, and how many technical skills you want to adopt.
How To Develop Technical Skills
Of course, technical project management skills can be learned online with:
- Myriad free resources, like these free coding resources
- Casual paid courses, like this Wireframe Overview on LinkedIn Learning, for example
- Traditional college/university courses, like the Computer Sciences program at the California Institute of Technology
10 Project Management Soft Skills
Soft skills (sometimes known as interpersonal skills) comprise other personal and professional skills. They’re soft because there aren't any specific steps to follow or a "correct" way to do them.
It requires intellectual engagement and personal interaction. These are harder to learn because they're developed through experience. These are also exceedingly valuable because machines and AI cannot recreate their effects.
Soft Project Management Skills List
- Organization
- Prioritization
- Critical Thinking
- Communication
1. Organization
Organization means bringing order to chaos, sorting things out, and staying on top of everything .
Whether you are mapping out resources or turning a messy project proposal into gold, organization is THE defining characteristic of a great project manager. You simply cannot be without it.
Bad organization wreaks havoc on your team’s motivation, morale, and ability to get things done. A project manager with a personal organization strategy will get more done, feel less stressed, and be an admirable leader.
Then, the hardest part: organizing your task list, team, thoughts, tools, workflow, errands, habits, and all the rest, while maintaining adaptability when the plan changes.
How To Develop Organization Skills
- There are whole communities dedicated to different organizational strategies. Just think about how wildly popular Marie Kondo’s “ tidying up ” self-help strategy became, with a best-selling book and a Netflix show. Organization has become a religion at this point.
2. Teamwork
Teamwork is the ability to make team members work together and to motivate them effectively . It’s something a project manager must learn and teach simultaneously, as you must flexibly and reliably work with employees, clients, suppliers, external contracts, customers, and anyone else who shows up in your inbox each morning.
The positive impact of teamwork is supported by behavior science and psychology. Working together is proven to spark innovation, foster happiness and personal growth, prevent burnout, grow specialized skills, improve productivity, promote taking worthwhile risks, reduce feelings of stress, and boost creativity.
How To Develop Teamwork
There are two approaches I suggest to “learning” teamwork skills:
- Theoretical knowledge about what it means to work as a team and the benefits of navigating teamwork successfully. Try seeing what cutting-edge research is being done in the areas of teamwork. My current suggestion is The Science of Teamwork .
- Fun, in-person exercises you can do with your team to promote trust, understanding, and comfort. Try these team building activities !
3. Prioritization
Prioritization is the ability to do the right thing, at the right time .
As project managers, a huge part of our job is determining and communicating how other people will spend their time. But it’s equally important to be aware of our own time management.
Steven Covey’s quote, “The enemy of the best is good,” applies really well when it comes to the project manager’s management of time (theirs and their team’s).
The problem is that important tasks usually get trumped by urgent tasks. If needed, do an 80/20 analysis of your current tasks . So if you’ve got a limited amount of time in your day, how can you make sure you set aside time for important tasks?
Successful project managers also respect their teammates’ time, so being able to read the body language of people in the room is also critical to ensuring that you’re staying on course.
How To Develop Prioritization Skills
- Understand where you are putting your time. If you’re not already, use a simple time-tracking tool to help you tag and analyze where you’re spending your time. Is that where your priorities are? If you’re not sure, remember this quote: “What is important is seldom urgent and what is urgent is seldom important.” Dwight D. Eisenhower
- Important and Urgent (Highest priority)
- Important but Not Urgent
- Not Important but Urgent
- Not important and Not Urgent (Lowest priority)
4. Research
Research is the ability to effectively investigate and understand the big picture . Effective project managers need to know ‘just enough to be dangerous’ about all the work that their teams execute.
You need to know the platforms and systems your teams use, and the possibilities and limitations of those so that you can have intelligent and informed conversations with clients, team, project stakeholders, and suppliers.
It’s worth trying to develop expertise across the full project life cycle : strategy, service design, product design, creative concept, user experience, design, content development, front end development, back end development, QA, hosting, content delivery networks, SEO, analytics, CMS, social media, or media (yes even banner ads).
How To Develop Research Skills
- You can always trust libraries, particularly post-secondary libraries, as being a great source for research practices. For example, read the 15 Steps to Good Research by the Georgetown University Library.
5. Creativity
Creativity involves the ability to see things differently and approach things uniquely .
Creativity is one skill that computers and AI cannot match. Machines might be able to build, entertain, and perform but there is nothing that channels creativity the way humankind does. This makes it an invaluable skill.
How To Develop Creativity
- There are plenty of ways to boost your creativity, like changing up a habit, spending time outdoors, indulging in a hobby, experimenting with art supplies, or listening to (or creating) music.
- I would also highly recommend you check out the TEDxDirigo presentation by John Paul Caponigro called “ You’re A Lot More Creative Than You Think You Are .” Caponigro is a renowned fine artist who has worked for Photoshop User, Apple.com, and The Huffington Post.
- Read more about how you can get involved in creative strategy here .
6. Critical Thinking
Critical thinking allows you to decide what to do when there’s no obvious choice and tackle problems with confidence .
You’ve most likely heard of the term “critical thinking” but can you describe it? Do you know what it is and how to access the parts of your brain that excel in it? According to the Oxford Dictionary, critical thinking is “the objective analysis and evaluation of an issue in order to form a judgment.”
Oftentimes, project managers are confronted with conflicting data, mismatched ideas and facts, and flaws in common reasoning. Being able to pick apart what we see, think, hear, and feel to decide what is best for the current situation at hand is the linchpin in what it means to be a critical thinker.
There are 7 critical thinking skills, which I’ve broken down into their most basic essence:
- Analysis : What information is present?
- Interpretation : What does the information suggest?
- Inference : What conclusion can be drawn?
- Explanation : An elevator pitch for the above.
- Self-regulation : Could I be wrong about something?
- Open-mindedness : What are other possibilities?
- Problem-solving : What is the next move?
How To Develop Critical Thinking Skills
- Harvard Business Review suggests that 3 habits can help you improve your critical thinking: questioning all assumptions, finding reason through logic, and diversifying your thought by trying to see things from an opposing point of view.
- You may want to try these INC.com exercises for better critical thinking . Udemy also has critical thinking exercises as well as an online course to go with it.
7. Communication
Communication is the ability to understand and be understood by people from varying backgrounds .
One of the essential skills for project management is the ability to communicate well—understanding and being understood.
The key communication skill to master is the ability to listen, to be clear, and to ensure you’re understood. When information flows with the right messaging, at the right time, to the right person, through the right channel, almost any hurdle can be overcome.
However, effective communication doesn’t just happen. It starts by putting in the time and effort required to get to know your team well and devising an appropriate communication plan and related communications tools that connect with the different personality types. It’s easy to communicate well under ideal conditions with perfect communicators—but projects rarely benefit from ideal conditions, and no one is a perfect communicator.
You’ll likely need to adapt the communications strategy from project to project, for the simple reason that you may have different team members for each project and a particular communication system or structure may not always work for everyone.
How To Develop Communication Skills
- I’ve focused on teaching the skills of communication in many contexts, whether it’s in troubleshooting client complaints to solve conflicts (get practice for that in The DPM School) or handling difficult conversations better ( DPM Member webinar).
- But beyond these dedicated communication-strengthening activities, I have to say: just put yourself out there. Go to events, meet new people, leave your comfort zone, and network enthusiastically. Every conversation you have is going to teach you something about effective communication.
Watch our video covering tips on improving your communication skills here:

8. Leadership
Leadership involves seeing what could be, seeing the big picture, and leading and inspiring others .
Great leadership is an essential skill for being a good project manager. Our leadership role means we lead and manage teams—setting the vision, motivating the team, and making your team’s life better by coaching them and inspiring others.
But being a leader isn’t just about creating a feel-good vibe for our teams—we have to enforce process and keep everyone on the team in line too.
We know that we have the final call about what our team works on next, as well as the final responsibility for whether the project fails or succeeds.
Make sure you’re leading, rather than just managing. That means providing a vision and roadmap for success, and serving and empowering your team to get there.
How To Develop Leadership Skills
- Leadership is one of those things that takes time, experience, and consistent effort. No book or course is going to turn you into a leader overnight. No online course can hand you true leadership qualifications.
- To get started, I suggest looking for leadership-oriented seminars by speakers that you feel have something worthwhile to say. There are whole conferences dedicated to developing leadership skills , and that’s a good place to start.
9. Diplomacy
Diplomacy is the ability to influence, negotiate, and collaborate in tricky situations .
Project management is somewhat like politics; it brings together a disparate group of people, often with competing interests, and our job is to get these different interests on the same page so that we can accomplish project goals. In other words, a good project manager must be an excellent negotiator.
Discussions about budgets, resource allocation , and timelines can become adversarial and counterproductive if not handled tactfully. The best project managers know how to find compromises where possible and how to hold a firm line without damaging their workplace relationships.
The key negotiation skill to master is finding that middle ground—working out compromises so everyone that matters feel like they’ve won!
How To Develop Diplomacy Skills
- There are plenty of books on diplomacy, some more theoretical and others more practical. You can start with a classic, The Power of Tact by Peter Legge. This book goes over how to keep your cool in tough situations, conflict resolution strategies , negotiation tactics, and being a positive influence on those around you.
- You should also check out Public Diplomacy by Nicholas J. Cull, which goes over five core areas of public diplomacy: listening, advocacy, cultural diplomacy, exchanges, and international broadcasting. This book focuses its advice through a lens of international relations, communication studies, psychology, and contemporary practice and highlights what this all means in a time of “Global Engagement in the Digital Age.”
10. Coaching
Coaching is the ability to simplify and complexity, and to build, drive, and encourage the team .
Every PM is a coach in the way that they must bring out the best in their team and their product. Coaching is an inverted form of teaching where the goal is to help the subject learn rather than convey information.
Coaching is meant to focus on a person’s individual needs and talents, drawing out their full potential. This may involve offering positive feedback, establishing positive expectations, identifying room to grow, listening to concerns, and allowing (even encouraging) mistakes.
How To Develop Coaching Skills
- Try being coached yourself. Work with a mentor or professional life/career coach and take note of what they do and how they do it. Pay special attention to what works well and what falls flat.
- TheCoachingToolsCompany.com has a series of free tools that you can access, including exercises, common questions, a newsletter, and templates for goal setting and the like.
- You could also consider looking up career coaches in your city and bringing one of them into your workplace for an all-day coaching session with your staff. You can also follow professional coaches online if they have a blog, videos, or podcasts.
Is Project Management A Soft or Hard Skill?
Project management is both a soft skill and hard skill. It's difficult to manage a project without both kinds of skills because they are so complementary to one another.
Trying to use project management hard skills without accompanying soft project management skills like team leadership will be largely ineffective. You might be able to create a great project plan, but the project is doomed if you aren’t able to effectively organize and lead the team to execute on the plan.
Similarly, trying to use soft skills without the hard skills required to properly plan and control the project will also lead to failure. Hard, technical skills allow you to ensure project stakeholders are aligned on the objectives and outputs, and that the plan to deliver them is feasible within the budget and timeline.
6 Traits of Successful Project Managers
The above list of key project management skills misses out on a crucial part of being a PM: personal and professional traits. Traits are the foundation for soft skills and the way you execute the hard skills.
In fact, when I’m hiring for project management roles, what I’m actually primarily trying to establish is the candidate’s character traits. These are hard—if not impossible—to teach, but in my experience, they really do set good PMs apart from the bad.
How many of these traits do you embody and practice on a daily basis?
- Ordered : your sock drawer, and everyone else’s
- Visionary : see what could be, potential and opportunity
- Detail-oriented : spot the gaps and mistakes
- Team-oriented : empathetic, enjoy working and communicating with people
- Cautiously optimistic : always careful, but positive about it
- Tenacious : keep going when things don’t go to plan
- Adaptable : love problem solving and can be flexible
- Decisive : ability to assess, anticipate, and make difficult decisions
- Responsible : take ownership, look after, and take the weight off the team
- Strong work ethic : hard-working, hustler, self-motivated, and on time
How To Build These Successful Project Manager Traits
- Be honest with yourself : Ask for feedback from your colleagues and be open and accepting about what they share. Learn how to gently and productively critique yourself and remember that it’s never about fault, it’s about a desire to constantly improve.
- Be humble : Humility is the beginning of wisdom. In order to build your character, you must be open to new ways. No one can ever be too humble, though those who aren't are sure to think so.
- Live out your principles and values : Whether it’s “love others,” or ”do the right thing,” living by your principles will make decision-making easier and your character more steadfast.
- Be intentional : Integrity does not happen by accident. We are all products of our thoughts and habits. Be intentional about filling your mind with good thoughts. Creating a habit of this internalizes principles and breeds high character.
- Practice self-discipline : Being of high character takes the ability to do what is right over what is easy. After all, as John Wooden says , “The true test of a man’s character is what he does when no one is watching.”
- Be accountable : Surround yourself with people who have high expectations. Be responsible for yourself first. Lose the pride. Open yourself up to accountability. Let others push you to a high character.
6 Key Agile Project Management Skills
Agile project management requires all of the above, as well as a few unique items I wanted to call attention to which are particularly important to methodologies that fall under the agile umbrella, such as Scrum or Kanban .
Here are a few additional traits you can count on a good agile PM to have mastered:
1. Facilitation
Help people understand common objectives and their part in the bigger picture. Effective facilitators are able to make overarching goals feel understandable and achievable.
Learn more on how to do this in our workshop with Annie MacLeod (you'll need to be a member to access this workshop).
2. Problem-solving
The ability to navigate conflict, errors, and unexpected roadblocks with poise and purpose. If something unexpected arises, you keep your cool and set a good example for others.
3. Issue resolution or escalation
Knowing when it is appropriate to internally resolve issues and when intervention is needed. It’s important to grasp what resources are available for when escalation is deemed necessary.
4. Team building
Understanding the social intricacies of project team management and properly providing guidance and encouragement. Make sure your team works well together, trusts one another, and feels satisfied as a unit.
5. Change management
Making natural and inevitable change within a business as easy, inclusive, and transparent as possible. No change, no matter how great, should disrupt your team to the extent they go into disarray.
6. Create the right environment
Know your “workplace culture” and make sure it aligns with your vision for the team and their work. Don’t let it become too strict or too casual and make sure everyone understands their freedoms and limitations.
How To Develop Your Project Management Skills Further
It might be getting more difficult to get a job as a PM , and just knowing what skills project management professionals need is not enough.
We must be knowledgeable and have the right tools; but critically, we must know how to apply the right techniques to our projects. Knowing theory without the skills to apply it is useless. Having the right tools without the practical skills to put them to good use is meaningless.
So, how should you go about improving your project management skills?
- Create a personal shortlist of skills you're missing. Include the technical skills you’d like to learn, as well as the soft skills and traits where you could develop further.
- Use your list to guide the development of your project management competencies.
- Take the DPM School course, Mastering Digital Project Management , to develop the hard and soft skills you need to succeed—the instinct, judgment, and leadership skills needed to deliver complex projects that revolve around people, pixels, and code.
- Join the vibrant DPM community where you'll discover even more ways to deepen and enhance your project management skills.
How To Become An Independent Project Management Consultant: 8 Steps
5 project management resume tips from an expert pm, jobs with purpose: my project management skills helped me build a career in sustainability.
23 Essential Project Management Skills You Need (+How to Get them)
Looking for a good project management tool? We built Upbase, an all-in-one workspace for teams. You can manage tasks, docs, files, messages, chats – all in one place. Click here to learn more and get started, it’s free.
Master these 23 project management skills, and you’ll be sure to get this job right away and take your career to the next level soon.
Here’s the deal:
You may not need to go to business school.
You may not need to get a project management degree.
You might be an engineer, a marketer, an editor, or a salesman.
No matter who you are or your background, you can pursue a career in project management. As long as you master essential skills in this area.
In this post, I’ll share with you 23 fundamental skills crucial to succeed in the project management career path.
You’ll learn:
- 10 must-have project management hard skills
- 13 key project management soft skills
- Useful resources to improve these skills on a solid foundation
- Plus, the best way to put your skills on a resume
Whether you’re looking for a project manager position or want to boost your career, these skills will help you get there.
But first, let’s cover some basics.
Two types of project management skills
Every employer looks for two kinds of skills: hard skills and soft skills.
Neither of them is better than the other. Employers want both.
See these quick facts, and you’ll understand why:
| – Skills that are defined for a specific job.
– They’re easy to measure. – They can be acquired through learning materials or using tools or on the job. – Examples are budgeting, coding, design, process management. – Hard skills show you’re a great fit for a specific job. | – Skills that aren’t unique to any job.
– They’re intangible and difficult to measure. – They can be employed without using any tool or software. – Examples are communication, leadership, or problem-solving. – Soft skills prove you’d be a great fit anywhere. |
Now that you understand the differences between hard skills and soft skills. Let’s dive deep into them.
Project management hard skills
Here are essential hard skills for a project manager position.
1. Process management
Every project requires a series of processes to bring it to fruition. It can include initiating, planning, executing, monitoring and control, and closing.
As a project manager, you should understand how a project works and break it down into processes. You should be knowledgeable of process management to ensure the fulfillment of a project.
For example, do you need to break the executing phase into ‘launch’ and ‘delivery’? Or do you need to add the resourcing phase? Mastering the process management skills will help you deal with this.

Also, you need to know how to monitor and evaluate project performance metrics. So you can gain insights into how many processes a project should have and improve it for better performance.
Courses to learn process management skills :
- BPM Essentials
- Association of Business Process Management Professionals (ABPMP)
- Object Management Group (OMG) BPM Certification
2. Project management methodologies
What’s exactly a project management methodology?
Simply put, a project management methodology gives you a structure to accomplish a project. It’s a set of principles and practices that show you how a project should be planned, managed, and executed from start to finish.
Waterfall, Scrum, Kanban, and Extreme Programming are the most widely-used project management methodologies.
According to a 2019 survey by Project Management Institute , organizations have implemented hybrid project management practices.
That means the more project methodologies you master, the better advantage you have.
How can you know which methodology you should learn?
There is no simple, short answer.
But you can use the following criteria to make a decision:
- Specific goals and complexity of the previous projects you joined and developed interests.
- The industry that you want to enter or are working in.
- The culture and work environment of your dream company.
- Your personal goal. Do you want to become a Kanban project manager expert? Or do you want to become a Scrum master?
Courses to learn project management methodologies:
- Project Management: The Basics for Success
- Agile Crash Course: Agile Project Management; Agile Delivery
- Project Management Principles and Practices Specialization
3. Budgeting
Budgeting or cost control skills in project management mean you know how to oversee and manage project expenses. You also know how to prepare for potential financial risks.
A project manager takes charge of developing a feasible budget to ensure money is allocated appropriately. It’s a skill that requires expertise and experience.

The more time you spent working on projects, the more financially savvy you’re. You’ll acquire valuable knowledge to help you contribute to the long-term financial success of your business.
Courses to improve your budgeting skills :
- Lean in Cost Control
- Cost Reduction: Cut Costs and Maximise Profits
- Projects Cost Management, Estimating, Budgeting and Control
4. Scheduling
In project management, scheduling indicates activities, deliverables, and milestones within a project. Scheduling isn’t an exact process. It’s more about estimating, predicting, and guessing.
When scheduling a project, you should review it regularly and revise it if necessary. It’s because when a project is in progress, it may face changes and new risks. Regular reviewing helps you ensure your project isn’t a vision but a time-based plan.
Mastering scheduling skills mean you:
- Know how to monitor and control project activities.
- Allocate resources efficiently to achieve project goals.
- Assess how time delays will impact a project.
- Identify where resources are redundant and re-allocate to other projects.
- Know how to track project progress.
Course to learn the scheduling skills :
- TILOS – Linear Projects Scheduling
- Project Management With MS Project – Scheduling Master Class
- Planning & Scheduling: Be the Professional from Scratch
5. Planning
Without planning, your project is just an idea. You need a plan that shows you how to take an intangible theory to a tangible result.

A project plan can be a formal, approved document. It includes assumptions and decisions, facilitates communication among stakeholders, clarifies budget, and schedule baselines.
Planning a project means you need to:
- Define the scope of the project.
- Describe the resources necessary to complete the project.
- Anticipate the time and financial requirements.
- Create a strategy for communicating regularly to stakeholders.
- Acquire and store the necessary documentation.
- Suggest a proposal for follow-up and maintenance.
- Assign tasks appropriately to team members.
- Schedule regular check-ins with team members.
- Plan a day-to-day management of the project, including making priorities.
A project plan should give answers to four basic questions: What work needs to be done? Why do they need to be done? Who will get it done? And when will it be done?
Tools to practice planning skills : Upbase .
6. Risk management
As a project manager, you’ll likely need to make a decision that involves an element of risk at some point.
Risk is an unexpected and uncertain event that might affect your team, processes, technology, or resources in a project. Risk can occur without you being noticed.
If you don’t know how to manage risks, you may face consequences that cost you a lot of time, effort, or even reputations.
Risk management skills include risk identification, risk analysis, risk prioritization, and risk control. When you master these skills, you know how to identify threats, estimate risks, and implement proper risk management strategies.
Courses to learn risk management skills :
- Project Risk Management
- Risk Management for Project Professionals
- Project risk management for PMP certification
7. Project management tools
Many great project management tools are available. Familiarize yourself with at least one of them.
Because a project management tool will help you master technical skills. You’ll learn how to manage projects, collaborate with your team, schedule your tasks, or control costs effectively.
Everything can be done using an all-in-one project management tool like Upbase . It gives you many features to implement and manage your project—No need to switch among tools.
8. Subject matter expertise
Being a subject matter expertise means you have a deep understanding of a particular job, process, department, function, and technology.
If you’re a subject matter expert in project management, you know the organization and what clients expect. You go out there and learn every day, explore a niche, and adjust your project to meet that niche’s needs as necessary.
You’re the key person to help your team solve highly specific problems where their general expertise proves insufficient.
For example, you may help your team assess whether a new application is compatible with others. Or you can help them extract and format data.
It takes time, effort, and intense research and study to become a subject matter expert. But if you can get it, you can level up your career at lightning speed.
Course to level up your project management knowledge :
- Mastering Agile Scrum Project Management
- Project Management Fundamentals: Run projects effectively
- The Complete Project Management Fundamentals Course + CERT
9. Task management
A project can consist of many tasks. That’s why you need to plan, track, test, monitor, and report all those tasks.
By doing so, you can complete the project efficiently and effectively. You also know where you need to improve for the next project.
Task management is different from project management. While project management aims to manage the whole project, task management focuses on the “task” level.

It shows you how to organize tasks, prioritize them, set deadlines, and delegate tasks. It also involves resource allocation, budgeting, and dependencies.
Mastering task management skills mean you know how to:
- Keep track of backlogs, bottlenecks, and completed tasks.
- Break down large tasks into smaller, manageable subtasks.
- Set a deadline for every single task and make sure your team sticks to it.
- Focus on one task at a time.
- Use dedicated task management software.
- Prioritize tasks for your whole team.
- Set up reminders when deadlines are approaching.
Tools to help manage your tasks : Upbase .
10. Change management
Changes can be planned or unplanned and inevitable.
In project management, change can be anything that transforms or impacts a project, processes, tasks, structures, or budget.
That’s where change management comes to play. You need to learn how to manage changes to always keep your team and project in control.
With Upbase , you can streamline documentation, improve communication, modify work styles, and track progress.
Also, Upbase gives you the flexibility to adjust the vision, timelines, or costs of your project, so you can be proactive in any situation. You can even develop a customized dashboard that works specifically for your team.
When you master the change management skills, you never resist changes. You’re always open to change and know how to adapt to it.
Courses to improve change management skills :
- Agile for Project, Iteration and Change Management
- Manage Change Through Collaboration and Teamwork
- Lean Leadership Skills, Lean Culture & Lean Management
Project management soft skills
Learning project management hard skills isn’t enough. You need to equip yourself with these soft skills as well:
11. Problem-solving
Problem-solving skills are much self-explanatory:
They mean you know how to solve problems.

When working on any project, you’ll encounter problems. Having problem-solving skills will help you detect those problems early enough to manage them in a timely and effective way.
Problem-solving skills can include several abilities, like:
- Break down problems into manageable parts.
- Do thorough research to identify the root causes of problems.
- Analyze strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
- Communicate and clarify the problems with your team members.
- Collect and arrange disparate information into a meaningful whole.
- Discover patterns in data and drive meaning from distinct pieces of data.
- Brainstorm possible solutions to tackle problems.
Courses to improve problem-solving skills :
- Introduction to Problem-Solving
- Lean Problem-Solving for Team Members and Leaders
- Effective Problem-solving and Decision-making under Pressure
12. Decision-making
What is decision-making?
Decision-making skills are the abilities to select between two or more possible solutions to reach the best outcome in the shortest time.
To become a good decision-maker, you need to master many sub-skills, for example, problem analysis, listening, and information gathering.
As a project manager, you need to make decisions every day. So, mastering decision-making skills will help you choose the best decision for your project and your organization.
Guidelines for decision-making:
- Focus on the goals and objectives to be served.
- Follow a decision-making process.
- Understand the internal and external environment factors.
- Collect and analyze available data.
- Listen to others’ opinions.
- Stimulate team creativity.
- Manage the risk.
Course to improve decision-making skills :
- Learn Effective Decision Making
- Master your Decision-Making, and Critical Thinking Skills!
- Decision Making: Solve Problems with Emotional Intelligence
13. Negotiation
Negotiation isn’t limited to “big decisions” or “big problems.” When you’re working with others, much of your time is spent negotiating.
Negotiation skills mean you have the ability to negotiate with clients or other stakeholders on a specific problem. It can be the scope of work, timeline, contract, payment terms, or budget.
When you master this skill, you can control the process and get your desired results.
Course to practice negotiation skills :
- Successful Negotiation: Master Your Negotiating Skills
- Negotiation Fundamentals: How To Negotiate Effectively
- The Complete Negotiation Skills & Strategies Course
14. Teamwork
Teamwork happens when at least two people cooperate and use their individual skills to achieve common goals.
Teamwork skills include interrelated abilities that let you work effectively with your team members.
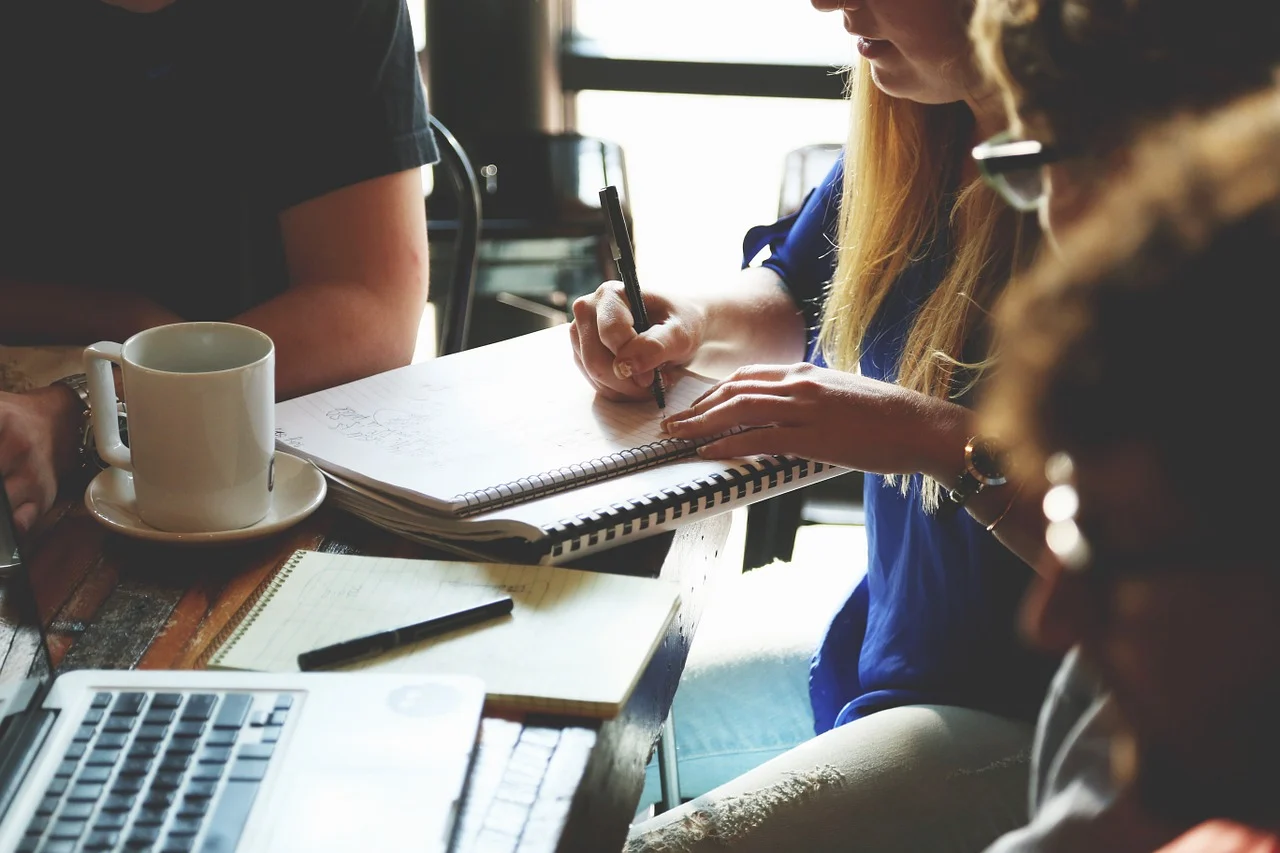

Mastering teamwork skills mean you can:
- Get your point across and truly understand what your team members want to tell you.
- Know how to manage conflicts.
- Have the ability to listen to others (also active listening).
- See the big picture, put your ego aside, and work towards the common goal.
- Look at an issue from multiple perspectives and utilize your skills to drive your team performance and success.
- Devise a master plan that everyone can understand and follow.
- Stick to deadlines and deliver your best work.
- Show respect, empathy, and sympathy to your team members.
Tools to help you improve teamwork skills : Upbase .
15. Organization
Organizational skills allow you to stay focused on different tasks and use your time, energy, strengths, mental capacity to achieve the desired outcome.
Employers always hunt for candidates who are effective and efficient. That means by mastering organizational skills, you make yourself stand out from the crowd.
The best part is organizational skills are transferable.
What does it mean?
If you’re a well-organized person, you’ll remain well-organized regardless of the job you’ll be doing—product owner, Scrum master, whatever.
Organizational skills are one of the soft skills you’ll bring with you to any position.
Mastering organizational skills mean you can:
- Effectively organize your collaboration with others. In other words, you can identify who to collaborate with and on what projects.
- Speak and write clearly so everyone can understand your message.
- Understand the strengths of each team member and build an exceptional team.
- Know what you can do on your own and what you need to assign to others.
- Plan your work effectively and efficiently.
- Give priority to your tasks and follow the schedule.
- Research and analyze situations, prepare documentation, and think strategically.
Organizational skills also include physical organization sub-skills like filing, office management, record keeping, and stock inventory.
Tools to get you organized : Upbase .
16. Business case writing
When starting a new project, you may need to write a business case to convince stakeholders if it’s worth continuing the project.
A business case isn’t similar to a project proposal.
A project proposal explains why you want a project. It contains an outline of the project, including vision, goals, expected results, market-product fit, estimated costs, and proposed timeline.
Meanwhile, a business case has many more details. It involves assessing business problems/opportunities, benefits, risks, costs, technical solutions, timescale, impact, and organizational capabilities to deliver project outcomes.
Mastering the business case writing skills mean you can:
- Make it interesting, clear, and concise.
- Convey the key points.
- Eliminate conjecture and minimize jargon.
- Clarify your vision of the future.
- Identify the values and benefits the project brings to the organization.
- Ensure consistent style and readability.
Courses to improve business case writing skills :
- 12 Steps Business Case Development
- Business Analysis & Scrum 4 Business analyst & Product Owner
- Business Analysis: Developing Irresistible Business Cases
17. Detail-oriented
As a project manager, you need to be detail-oriented.
What does that mean?
Detail-oriented means you can pay close attention and notice minor details.
You can give a task your undivided attention and catch mistakes, errors, or changes before they snowball into a bigger problem.
Being a detail-oriented person means you can:
- Create flawless deliverables that require little to no editing.
- Accomplish a project while following standards and protocols closely.
- Review the accuracy of documents and reports.
- Set up procedures to maintain high-quality standards.
- Provide full attention to every detail.
To be more detail-oriented, you can write your notes down or track your time. But the best way is using a task management system .
Take Upbase as an example. This tool allows you to manage tasks, and collaborate with your team easily.
In doing so, you can also improve your task management skill—an important hard skill of a great project manager.
18. Presentation
Presentation skills mean you can deliver compelling, engaging, informative, transformative, educational, enlightening, and/or instructive presentations.
Effective presentation skills are featured with public speaking, tone of voice, body language, creativity, and delivery.
As a project manager, you have many opportunities to practice and show your presentation skills. For example:
- Influence stakeholders regarding a decision.
- Communicate status and plans to business leaders and project board members.
- Brief and motivate your team members.
- Set the tone of your project at your kick-off meeting.
- The list goes on.
Useful resources to improve your presentation skills :
- Giving Presentations Worth Listening to
- TED’s Secret to Great Public Speaking
- The Surprising Secret to Speaking With Confidence
- How to Sound Smart in Your TEDx Talk
- The Secret Structure of Great Talks
- The Science of Stage Fright (and How to Overcome It)
19. Time management
Time management skills are precious, not just in project management but also in your everyday life.
Like organizational skills, time management skills are also transferable. In other words, these skills are beneficial to you in any circumstances.

No matter your job, being good at time management will greatly improve your hireability and performance.
Time management skills include several sub-skills, including:
- Prioritizing
- Goal setting
- Multitasking
- Managing appointments
- Record keeping
- Organization and filing
- Meeting deadlines
- Stress management and coping
- Strategic planning
Almost all project management tools integrate with time management features.
For example, tools like Upbase allow you to create to-do lists, set deadlines, reminders, notifications for tasks, so you don’t miss out on anything.
Believe it or not—using such a tool will help you improve your time management skills quickly.
20. Creative thinking
Some people think “creativity” is a skill useful only to artists, designers, writers, or marketers. It has nothing to do with project management.
The truth is, it’s indispensable for all professionals.
As a creative project manager, you can look at things in new, unorthodox ways and develop no one previously thought of.
Creative thinking also drives innovation and progress.
Here are some tips to help you practice creative thinking:
- Always wonder, question, and find out stuff. Take note of face value and investigate everything. Never be satisfied with your state of knowledge.
- Whenever you have an idea, note them down.
- Whenever you read or see something interesting, save them. Upbase is a great tool to store your knowledge and create wikis to share with team members.
- Talk with others to learn and pick their brain.
21. Critical thinking
Creative thinking means you think creatively—you come up with new ways to think about the surrounding world to make something innovative.
Critical thinking is different.

Critical thinking means you think about thinking. It means you can decode information and think in an organized and rational way. You understand the connections between ideas and/or facts and avoid bias.
To become a critical thinker, you need to practice a lot.
But why does a project manager need critical thinking skills?
The answer comes down to this: Critical thinking will help you try and identify new, better solutions so you can shorten the process and accomplish your project earlier.
In other words, critical thinking helps you work smarter.
Critical thinking skills can have the following sub-skills:
- Analysis: Collect and process information and knowledge.
- Interpretation: Conclude what the meaning of processed information is.
- Inference: Assess whether the knowledge you have is sufficient and reliable.
- Evaluation: Make decisions based on the available information.
- Explanation: Communicate your findings and reasoning clearly.
- Self-regulation: Constantly monitor and correct your ways of thinking.
- Open-mindedness: Take into account other possibilities and points of view.
- Problem-solving: Tackle unexpected problems and resolve conflicts.
22. Communication
When working on a project, you spend most of your time communicating with others: your teams, clients, functional managers, upper management, or other stakeholders.
It’s not just about face-to-face communication but also written communication and online communication through project management apps .
By mastering communication skills, you can convey your thoughts and ideas effectively. You know how to talk appropriately with different people from different cultures. You know when to stop, when to listen, and when to respond.
Mastering communication skills means you:
- Absorb, share, and understand the information presented.
- Communicate in a way that others can understand your message.
- Respect team members’ points of view through engagement and interest.
- Use relevant knowledge and skills to explain and clarify thoughts and ideas.
- Listen to others when they communicate and ask questions to better understand.
23. Leadership
As a project manager, you must influence your team members’ behaviors. You inspire and motivate them so everyone can continue working on the project.

Leadership skills can have the following sub-skills:
- Team management: Recruiting, hiring, training, mentoring, onboarding, team building.
- Collaboration leadership: Defining roles, facilitating discussion, employee engagement.
- Decision making: Prioritizing tasks, team decision making, problem analysis, consensus-building.
- Time management: Goal setting, self-awareness,self-motivation, stress management.
- Persuasion: Speaking, listening, empathy, emotional intelligence, empowerment.
- Ethical leadership: Accountability, professionalism, honesty, judgment.
- Motivating team: Rewards, recognition, feedback, expectations.
How to put project management skills in a resume
It’s one thing to master project management skills, another thing to put them in a resume rightly.
Two essential things when including skills in a resume:
- Relevance : The skills you list have to match the position you’re applying for.
- Specificity : The skills you list have to be as specific and credible as much as possible.
As someone says, “No one creates a perfect resume on their first try.”
You have to write, delete, write, delete until every skill you list makes sense. Don’t put your skills randomly.
To make your life easier, here are some steps you can follow to include project management skills in your resume:
Step 1 : List off all your project management skills and qualifications you’ve gained. Put them into a spreadsheet or doc, whatever.
Step 2 : Read the job description (especially the skills-related requirement section) of the position you’re applying for carefully.
Step 3 : Identify which of the required skills matches your acquired skills. Notice the keywords used to describe the skills requirements.
Step 4 : Put all the keywords you’ve filtered into a skills section of your resume.
Step 5 : Research the company. Look for how they implement project management. What methodology they use, the size of project teams, everything.
Step 6 : Go back to the skills section in your resume. Rewrite the skills section based on your acquired skills and all the insights you’ve collected. Remember to include both hard skills and soft skills.
A good example of listing project management skills :
- Agile tools: Employe Jira and Upbase to improve team velocity 40%.
- Strong written and verbal communication skills.
- Cost control: Saved $500,000 through a company-wide automation drive.
Read more: A Complete Guide to Agile Methodology in Project Management
A bad example of listing project management skills :
- Agile software
- Communication skills
The differences are apparent, right?
Learn how to show off your skills. Spend a significant amount of time and effort to make your skills section truly shine.
Key takeaways
Here’s everything you need to know about project management skills in a nutshell:
- Project management skills have hard skills and soft skills.
- Project management hard skills include process management, project management methodologies, budgeting, scheduling, planning, risk management, project management tools, subject matter expertise, task management, and change management.
- Project management soft skills include problem-solving, decision-making, negotiation, teamwork, organizational, business case writing, detail-oriented, presentation, time management, creative thinking, critical thinking, communication, and leadership.
- You can find a bunch of resources to practice these skills on the Internet. The best way to practice is by using an all-in-one project management tool like Upbase . It provides you with all the tools you need to become a project manager pro.
Are you ready to master these skills and reach a whole new level in your career? Sign up for an Upbase account to get full access to all the premium features. That’s a good step to start.
Happy learning!
Upbase Pro Tips: Interested to explore more PM tools for specific industries? Take a look at the articles below:
- Project Management For Architects | A Complete Guide (+Tips & Resources)
- Best Project Management Tools for Freelancers
- 12 Best Project Management Software With Client Portal for 2024
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
One place for all your work
Tasks, messages, docs, files, chats – all in one place.
- Help center
- Terms of service
- Privacy policy
- iOS mobile app
- Android mobile app
Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey
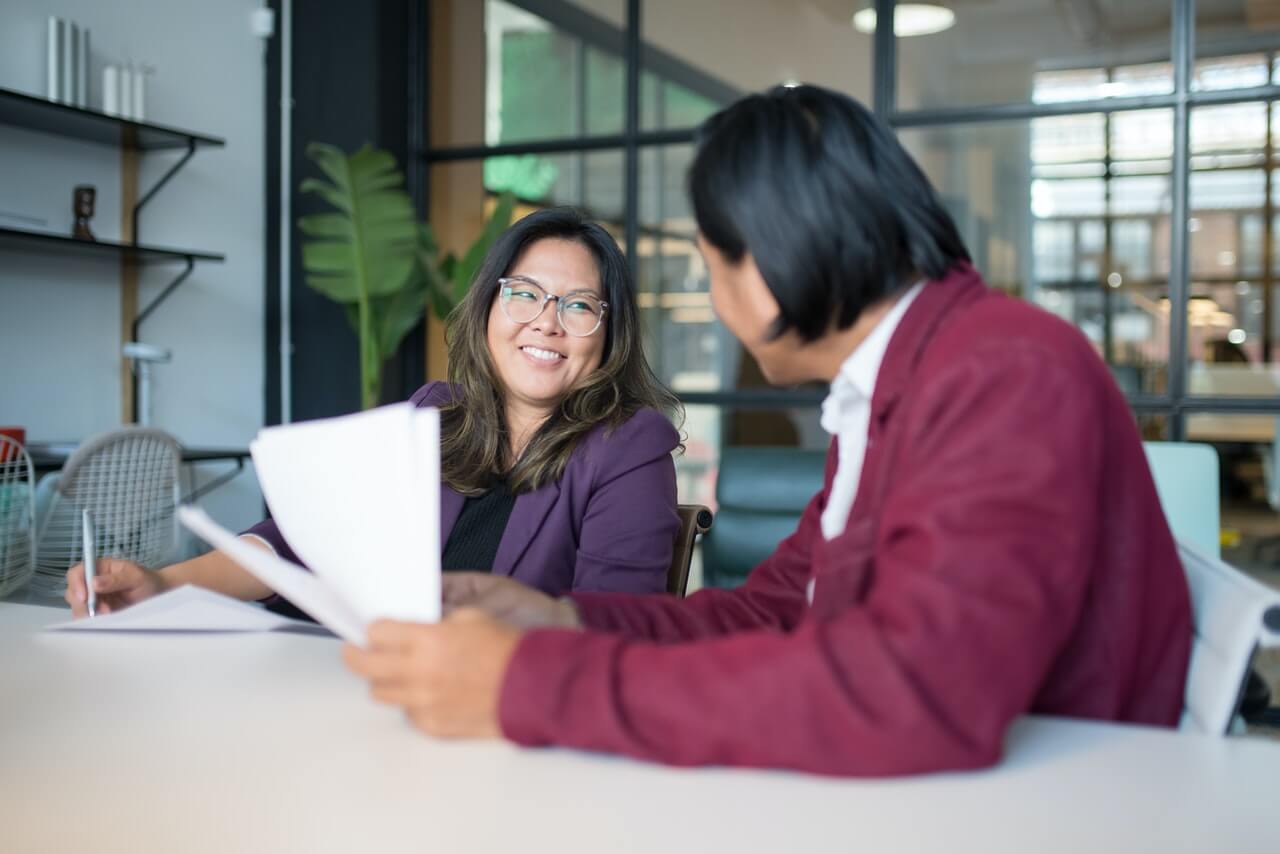

Research Project Management: 5 Project Management Tips for Researchers

Effective planning and a management of resources are essential prerequisites required for proper research project management and the successful completion of research projects. However, one of the biggest challenges researchers face while accomplishing these tasks is that these projects usually have varying lengths and unpredictable outcomes, so the research management techniques need to be redeveloped with every new project.
As a scientist, one is more inclined toward understanding the science and, hence, the leadership and organizational skills required for research project management need to be consciously acquired along the way. Furthermore, the ‘scientist mindset’ of adapting to unpredictability by making rapid changes in existing protocols can clash heavily with the ‘manager mindset’ of ensuring these changes align with the availability of resources. 1 Therefore, it’s understandable that many young researchers struggle with how to manage research projects, especially during the initial stages of their academic journey, often finding it difficult to incorporate such research management techniques.
If you are among those wondering how to manage your research projects effectively, this article will provide you with some useful tips to help you improve your research project management skills. But before having a closer look at these, let us have a short recap of the different aspects that are often associated with the successful management of any project.
Every new project ideally begins with preparation of a roadmap or a personal guide, which can be modified as required for the entire duration of the project. Here are some key steps that can help in better preparation of a roadmap for research project management. 2
Initiation and planning- The first step for research project management is typically defined as the initiation stage. In this stage, the feasibility of the project is assessed with respect to the different experiments to be performed and the availability of resources required for their completion. If any part of the project needs collaborative effort to be completed, an important research management technique would be to identify the relevant people required at this stage itself. The initiation stage is followed by the planning stage, which includes the preparation of necessary protocols, allocation of resources, and informing personnel involved about their specific roles and responsibilities.
Risk management- After the initiation and planning stage is complete, the next step in research project management is to identify potential roadblocks that may occur during the implementation of the roadmap and devise strategies to resolve them. This may include revisiting insufficiently standardized protocols and reconsidering the use of techniques depending on the limited availability of resources. Risk identification and mitigation planning saves time and ensures a smooth workflow and is, therefore, an essential component for effective research project management.

In spite of a perfectly planned project roadmap on paper, many researchers struggle to execute these research management techniques. This can be frustrating and demotivating for researchers, but there are some simple solutions that can be implemented to overcome these struggles and ensure successful research project management.
- Identify your core issue
If you’re struggling with implementing the roadmap in the desired manner, the first step or research management technique is to identify the core issue. For some researchers, the problems could range from a technical error that needs troubleshooting or a miscalculation while acknowledging the risks involved while preparing the roadmap. Identifying the core issue that is blocking the execution and finding solutions for it is an important aspect of improving your research project management skills.
- Simplify your timelines
To ensure a smooth workflow under any circumstances, a great research management technique would be to break down your envisioned timeline (especially when they involve new protocols) into smaller timelines with more attainable goals. This will allow you to revisit the ‘original’ roadmap on a more regular basis and ensure the better management of the funds and resources available.
- Refrain from perfectionism
Research is ‘work in progress’ and the outcome of any experiment may not always be the one that you envisioned in the roadmap. So how to manage such research projects? It is helpful to lower any expectations regarding a ‘perfect’ outcome; accepting ‘negative’ results and the learnings that come along with it is a critical research management technique. When one does not chase perfectionism, it becomes easier to accept and adapt to unpredictability, eventually leading to effective research project management and the successful completion of the project. 3
- Engage in regular communication with stakeholders
An important, yet underrated component of effective research project management is engaging in regular communication with all the relevant stakeholders. Whether it is the personnel involved directly in your project such as your advisor, peers, technicians or indirect stakeholders such as the funding agencies, it is important to keep the communication lines open at all times. Short meetings scheduled at defined intervals for the entire duration of the project is a good research management technique to discuss progress, pace, and troubleshooting strategies would help bring everyone on the same page regarding the outcome of the project.
- Maintain a record sheet for effective allocation of funds
If your project is funded by organizations that have stringent protocols regarding budget consumption, you need to pay extra attention to how you are using the funds. Using digital tools to maintain a record sheet as part of your research project management reduces your work load and makes it easier and convenient to share your spends with stakeholders whenever the need arises.
Lastly, before embarking upon any project, it is always important to get an external perspective on different aspects that are involved in the project. Discussing the roadmap with someone who is not directly involved in your project provides an objective overview and helps in better identification of loopholes, making it an important aspect of effective research project management.
We hope these research project management tips were useful and relevant in answering how to manage a research project, and will help you strengthen your research management techniques.
- Project Management for Scientists, Part 1: An Overview. https://www.science.org/content/article/project-management-scientists-part-1-overview.
- Project Management Tips for Researchers. ASM.org https://asm.org/Articles/2019/January/Project-Management-Tips-for-Researchers.
- 10 Project Management Tips for Non-Project Managers. Northeastern University Graduate Programs https://www.northeastern.edu/graduate/blog/project-management-tips/ (2019).
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

What is Cluster Sampling? Definition, Method, and Examples

What is Thematic Analysis and How to Do It (with Examples)
- News & Highlights
- Publications and Documents
- Education in C/T Science
- Browse Our Courses
- C/T Research Academy
- K12 Investigator Training
- Harvard Catalyst On-Demand
- Translational Innovator
- SMART IRB Reliance Request
- Biostatistics Consulting
- Regulatory Support
- Pilot Funding
- Informatics Program
- Community Engagement
- Diversity Inclusion
- Research Enrollment and Diversity
- Harvard Catalyst Profiles

Project Management Strategies for Research Team Members
Webinar series on the principles of project management
For more information:
- Understand the foundational principles of project management.
- Explore how project management principles and strategies can influence your work with colleagues and stakeholders on various projects.
Managing projects is a detailed and systematic process. Yet, the applications of this process vary across disciplines and teams. This webinar series will introduce how to troubleshoot, forecast, and problem solve using project management in various contexts while considering how these elements impact the work of teams. Each of the four independent sessions will be led by David Vincenti, PMP, a certified project management professional. This series will identify the principles of project management and how to apply templates and skills to your work and experiences in team settings. The last session will feature a panel of guest speakers who utilize successful project management strategies in their respective roles and professions. Those without official training in this area will gain skills and confidence in project management during this series.
Boundary-Crossing Skills for Research Careers
This session explores approaches to developing a broad range of competencies integral to establishing and maintaining a successful research career. The series delves into the following competencies: team science, mentorship, project management, communication, leadership, and funding research. For more information and to access other resources and webinars in the series, please visit Boundary-Crossing Skills for Research Careers.
Meet the Presenter

Vincenti has presented to academic and professional audiences on project management, professional development, and other topics, and has been recognized for his work with career planning for early-career technical professionals. He holds degrees in materials engineering and technology management from Stevens Institute of Technology.
Meet the Panelists
Sarita Patil, MD: Assistant Professor of Medicine, Harvard Medical School and Assistant Physician, Massachusetts General Hospital
Jane Shim, BA : Clinical Research Coordinator, Food Allergy Center, Massachusetts General Hospital
Neal Smith, MSc : Senior Computational Biologist, Center for Immunology and Inflammatory Diseases, Massachusetts General Hospital
Yamini Virkud, MD, MA, MPH : Pediatric Allergist/Immunologist and Assistant Professor, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Session dates
Session 1: Defining the Work November 1, 2022 | 12:00pm ET This session introduces basic project management principles. You will learn the definition of a project, how to manage project scope, and how to draft the baseline of a project while considering how projects can be connected.
Session 2: Creating the Plan November 3, 2022 | 12:00pm ET In this session, you will learn to apply project planning terms and understand how to break a project into manageable parts, sequence tasks, and manage time while considering how these components affect your work and the work of your team members.
Session 3: Finalizing the Plan November 8, 2022 | 12:00pm ET In this session, you will explore project management principles further by calculating risks, managing a process, reviewing a project plan, and forecasting the execution and completion of a project while considering how these elements impact your work and the work of your team members.
Session 4: Panel Discussion November 10, 2022 | 12:00pm ET This culminating session features a panel discussion with four successful project management practitioners. The panelists will share their experiences in their respective roles and professions, and discuss how they engage in project management work within team settings.
Time commitment
50-minute sessions on Zoom
This series is designed for team members in the clinical and translational (c/t ) workforce who are familiar with project management but have no formal training. Attendees are welcome to attend on their own or with their team members.
We believe that the research community is strengthened by understanding how a number of factors including gender identity, sexual orientation, race and ethnicity, socioeconomic status, culture, religion, national origin, language, disability, and age shape the environment in which we live and work, affect each of our personal identities, and impacts all areas of human health.
Eligibility
There are no eligibility requirements. Prior session attendees have included: PhD, MD, postdocs, junior faculty, and medical students.
Registration is currently closed. Please check back for future opportunities.
Related Courses
- Contact sales
Start free trial
Top 30 Project Management Skills: Soft and Hard Skills Included

Project management positions such as project manager, program manager and project portfolio manager aren’t easy. These roles require a variety of project management skills that are needed to guide project teams throughout the initiation, planning, executing , controlling, and closing of a project.
Project managers are responsible for planning projects, assembling a project team, and managing project tasks, time and costs. To do so, the best project managers use robust project management tools to keep all aspects of their projects organized.
Still, even with robust project management software, that’s a lot to ask of any individual, but project managers have a variety of project management skills to get the job done. But before we continue, what are project management skills?
What Are Project Management Skills?
As stated above, project managers need to plan and control many areas of a project. To do so requires a set of project management skills that consists of personality traits, soft skills and technical or hard skills.
Project Management Hard Skills
Hard skills, also known as technical skills are those project management skills that can be learned through education or training. In project management, hard skills are the most important because they’re the project management techniques that allow project managers to do their job. They’re also known as the technical skills or project management know-how that’s needed to plan, schedule and manage projects.

Get your free
Project Plan Template
Use this free Project Plan Template for Word to manage your projects better.

Project Management Soft Skills
Soft skills aren’t taught anywhere and are developed naturally by individuals. However, some of these can be improved through practice. Soft skills are all those which aren’t learned through formal education or training. Some of these are part of someone’s personality or are developed through the years.
Personality Traits of a Project Manager
As noted, these aren’t exactly skills but personality traits that benefit project managers and their teams. Some personality traits that serve project managers include being responsible and delivering on their commitments. They need to be proactive, problem solvers and, of course, be leaders . A project manager should also be open to feedback and even criticism, flexible, but decisive when they need to be.
30 Project Management Skills Every Project Manager Should Have
Below we’ve collected the top 30 personality traits, soft and hard skills every project manager should have. Realistically, there are certainly more than 30 project management skills to learn if you want to be a project manager, program manager or project portfolio manager, but if you have these, you have the foundation on which to build a successful career in project management .
These project management skills can be useful for several purposes. You can include them in your project manager resume and cover letter, and you can use them to prepare for your project manager interview . Or, you could simply study them to learn about technical skills to improve as a leader and project manager. First, let’s start with project management hard skills.
1. Knowledge of Project Management Methodologies
A project manager needs to know about the different project management methodologies that exist. That doesn’t mean that you need to be an expert in all of them, as they’re usually industry-specific and require certification. Here are some of the most common project management methodologies .
If you want to learn more about these and other approaches, check out our project management methodologies blog.
Pro tip: As a project manager, you should be familiar with the project management knowledge areas and project management process groups defined by the project management institute (PMI).
2. Proficient With Project Management Software
Having a working knowledge of project management software is a must-have technical skill for project managers in today’s world. There are many project management software alternatives available in the market, so you’ll need to determine which project management tools and features are best for you and your team’s workflow.
3. Project Planning
Project planning is a necessary project management skill because a project plan is the foundation of the project management cycle. It includes the project schedule, resources and costs. Traditional project management is all about planning ahead. Therefore, the planning stage of any project lays the foundation for everything that follows, including the success or failure of the project.
4. Project Scheduling
The project scheduling process is a vital part when writing your project plan. A project schedule organizes tasks, teams and time to complete a project. When people think about project management skills, they’re probably thinking about project scheduling, deadlines and deliverables. But project scheduling is more than that, as it also involves resource management and risk management.
There are many tools that can help with this process, chief among them a Gantt chart , which provides a visual of the schedule with tasks, durations of those tasks, dependencies, and milestones.
5. Project Scoping
Project scope is the documentation of the project’s goals, deliverables, tasks, costs and deadlines. This document is called a project scope statement and is sometimes referred to as the terms of reference. The purpose of project scoping is to set boundaries for the project, define the roles and responsibilities of the project team and determine the procedures that’ll be employed to execute, test and approve the work of the project.
6. Project Forecasting
Project forecasting is the process of trying to figure out potential outcomes in a project. It’s guesswork to an extent but guided by historical data and other research that can help with accuracy. The purpose of project forecasting is to reduce risk , which in turn will increase the probability of success. The process allows project managers to zero in on areas of the project that could be improved to avoid going over schedule, cost overruns and lacking resources when needed.
7. Project Tracking
Project tracking is used to measure progress in terms of the activities involved in a project. It monitors the project to determine if it’s meeting the schedule and, if not, identifies issues that are causing delays and resolves them. This process is important and begins early in the project. Both progress and performance are tracked in order to stay on schedule and uncover bottlenecks and other issues that are preventing the timely delivery of the project within its budget.
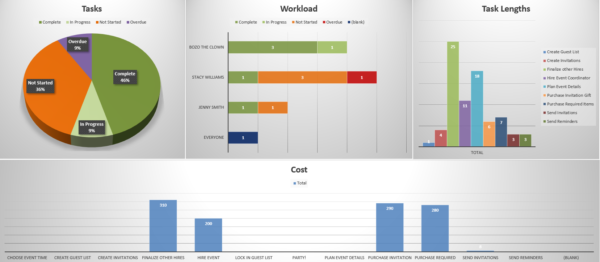
8. Project Reporting
Project reporting is the process of gathering data in an easily understandable format to make sure the project is meeting its goals. Project reports are also valuable tools in presenting information to stakeholders to keep them informed on the progress of the project. It’s a key tool for project managers in making sure the project is successfully delivered.
9. Project Budgeting
The project budget is the fuel that drives the project. Project management is all concepts and no action without a project budget. But having a project budget is one side of the project budgeting coin. There’s also budget management, which means tracking costs throughout the life cycle of the project and making sure your actual costs don’t exceed your planned budget.
10. Team Management
Project management is about teamwork, so project managers must have people skills to keep their teams working productively . That means understanding conflict management to keep everyone working together and morale high. It’s always helpful to start projects with team-building activities to help create relationships that will endure the thick and thin of a project.
11. Workload Management
Project managers are also responsible for workload management, which is the process of forecasting, planning, scheduling and monitoring the workload of an individual, team or organization. The goal is to balance workload evenly across your team to have them work at capacity and be more productive. It’s a discipline that involves project management, resource scheduling, capacity planning and much more.

12. Time Management
Time is one of the triple constraints and one of the most important technical skills. Not having time management skills can lead to delays and worse. Project management is about meeting deadlines and getting your deliverables out on time. Project managers have to be experts in managing their time, their team’s time and the overall time of the project.
13. Risk Management
Planning a project, big or small, is inherent with risk. Before executing the project, you have to create a risk management plan to identify, assess, and control risk. The more you can manage risk, the more likely your project is going to succeed.
14. Cost Management
Projects cost money. Estimating project costs and creating a budget is part of the planning stage of project management. Once you have a project budget, you have to use budget management to ensure that you control your costs through the execution stage.
15. Task Management
Tasks are little jobs that make up the execution phase of project management. They need to be created, organized, assigned to team members and tracked to make sure they meet the project constraints. This is done with task management . Project management software helps you manage tasks and fosters collaboration among your project team.
16. Leadership Skills
Some say that leadership is a personality trait or a soft skill that can’t be taught. While some project managers have better people skills than others, we think everyone has the potential to learn how to apply proven leadership skills and techniques.
As a project manager, you’re responsible not only for project success but also need to be a leader that applies leadership skills to guide and motivate team members to achieve their goals.
17. Communication Skills
Communication skills go hand-in-glove with leadership. You can’t be an effective project manager if you’re unable to articulate what it is you need your project team to do. But you’re not only going to be communicating with your team, you’ll need to have a clear communication plan for your customers, stakeholders and contractors.

18. Negotiation Skills
Being a strong negotiator is one of many communication skills, but it deserves its own space. In project management, negotiation is an important skill for conflict resolution and stakeholder management . For example, you’ll likely get demands from stakeholders that can impact the project scope. You’ll have to give them pushback, but diplomatically, so all project stakeholders feel they’re getting what they want.
19. Organizational Skills
The term organizational skills refer to the ability of an individual to manage time and tasks efficiently. As the name implies, organizational skills allow someone to work in an organized and efficient manner.
20. Interpersonal Skills
Teams are made of people and people have personalities. There are many different types of team members and they all have to get along. Having interpersonal skills brings the best out of your project team and helps with conflict resolution.
21. Problem-Solving Skills
Projects are problems, so having the skills to solve those problems means that your project is more likely to deliver success. Think of problems as puzzles that you have to figure out. There are many problem-solving tools out there to help you along the way.
Finally, let’s explore some personal qualities or personality traits that are important when pursuing a career in project management.
22. Adaptability
Change is a constant in project management. Being flexible is what keeps a project viable. If you’re not willing to adapt then the project will suffer. Of course, you have to have the wisdom to know when adaptability serves the project and when you have to bite the bullet and push through.
23. Decision-Making Skills
There are always decisions that must be made, often quickly, when managing a project. Project managers must process the situation and come to a decision that will positively impact the outcome of the project. This skill involves being able to properly evaluate whatever options are available, assessing the risks and benefits of those options and choosing the best course of action.
24. Attention to Detail
Projects are made up of tasks that must be completed on time and within budget. This requires a keen eye for detail. Project managers must pay close attention to detail, not only on the task but all the areas that are involved with that task. Being able to focus on those details, no matter how small, is key to project management.
25. Critical Thinking
Too many people understand the basics of project management but can’t think outside of the box. Critical thinking is all about not accepting everything you hear but taking the time to understand the issue and do the research that leads to an informed decision. A critical thinker is more likely to clear the hurdles that every project has to go through.
26. A Sense of Humor
Having a sense of humor is an essential project management skill, even if it’s a soft skill in project management. Humor relieves stress for you and your team, and only when tensions are lifted can smarter actions and ideas show themselves. Project team-building activities are a great example of how humor can be used by project managers.
27. Patience
Nothing is solved by rushing through a project or getting frustrated when things don’t go well. Projects need to be thoroughly planned in order to run smoothly, but that doesn’t mean there won’t be issues. Whether the issue is a change request or stakeholders having unrealistic expectations, if you don’t have patience, everything will be exponentially worse.
28. Personal Appearance
While it might not seem important, especially as the workforce embraces a more casual attire, a professional appearance is still a valuable asset for project managers. Presentation is important. It communicates responsibility, leadership and gives both stakeholders and team members a sense that they’re in good hands.
29. Delegation
Projects are complicated and involve the coordination of many people, places and things. One person can’t do it all by themselves. That’s why delegating is so important. A project manager must know what tasks can be delegated and to whom on the team in order to keep the work moving forward and distributed among everyone appropriately.
30. Collaboration
Collaboration in terms of project management is no different than the general definition: it’s a group of people working together towards a common goal. Specifically, for a project manager, that’s getting your project team , with its various project skills and experiences, to work better together. This is a discipline that extends across all projects and methodologies.
How to Develop Your Project Management Skills
As you can tell, the skills of a project manager are myriad. A project manager might have some of the hard and soft skills already, while others need to learn them. But everyone can improve their project management skills. Here are some ways to develop and improve your project management skills.
Project Management Certifications & Training Programs
There are many project management certifications and with good reason. Certification in any field is like a stamp of approval. It shows that you have learned and have passed a test on certain skills. Project management certification makes you a more valuable asset and is something employers will be looking for on job applicants’ resumes.
Hands-On Project Management Experience
There’s the old debate about which is better, book learning or real-life experience. The truth is that this isn’t an either/or answer. Both are important. You can learn on the job or in the classroom, but a combination of both is always more valuable. Being able to volunteer or work on any project in any capacity will provide you with experience that’ll make you a more effective project manager.
Project Management Events
Networking is one tool that professionals use to increase their position and knowledge. There are many project management events throughout the year and across the globe, such as those produced by the Project Management Institute (PMI), which offer networking opportunities and educational classes and exhibit new tools of the trade.
Use Project Management Software
Certification, hands-on experience and attending project management events are all going to help you become a better project manager. Project management software is going to help you apply that knowledge and be a more effective project manager. Project management tools help you plan, manage and track projects, manage teams and their tasks, risk and resources.
ProjectManager Puts Project Management Skills to Use
Now that you know what skills you need to be a successful project manager, it’s time to equip yourself with the right project management tools. ProjectManager has a suite of powerful tools that can improve the workflow of any project manager. Here are some of our main features.
Multiple Project Management Views
Project managers are going to use our robust Gantt charts , which can help them plan and schedule their tasks on a timeline. It also links all four types of task dependencies, which helps avoid costly delays, filters for the critical path, to identify critical tasks, and can set a baseline to track progress in real time. But teams don’t need all the features of a Gantt chart, which is why Gantt chart plans can be viewed on task lists, kanban boards and calendars to allow teams to work how they want. All the data across project views are shared in real time so everyone is always working on the same page.
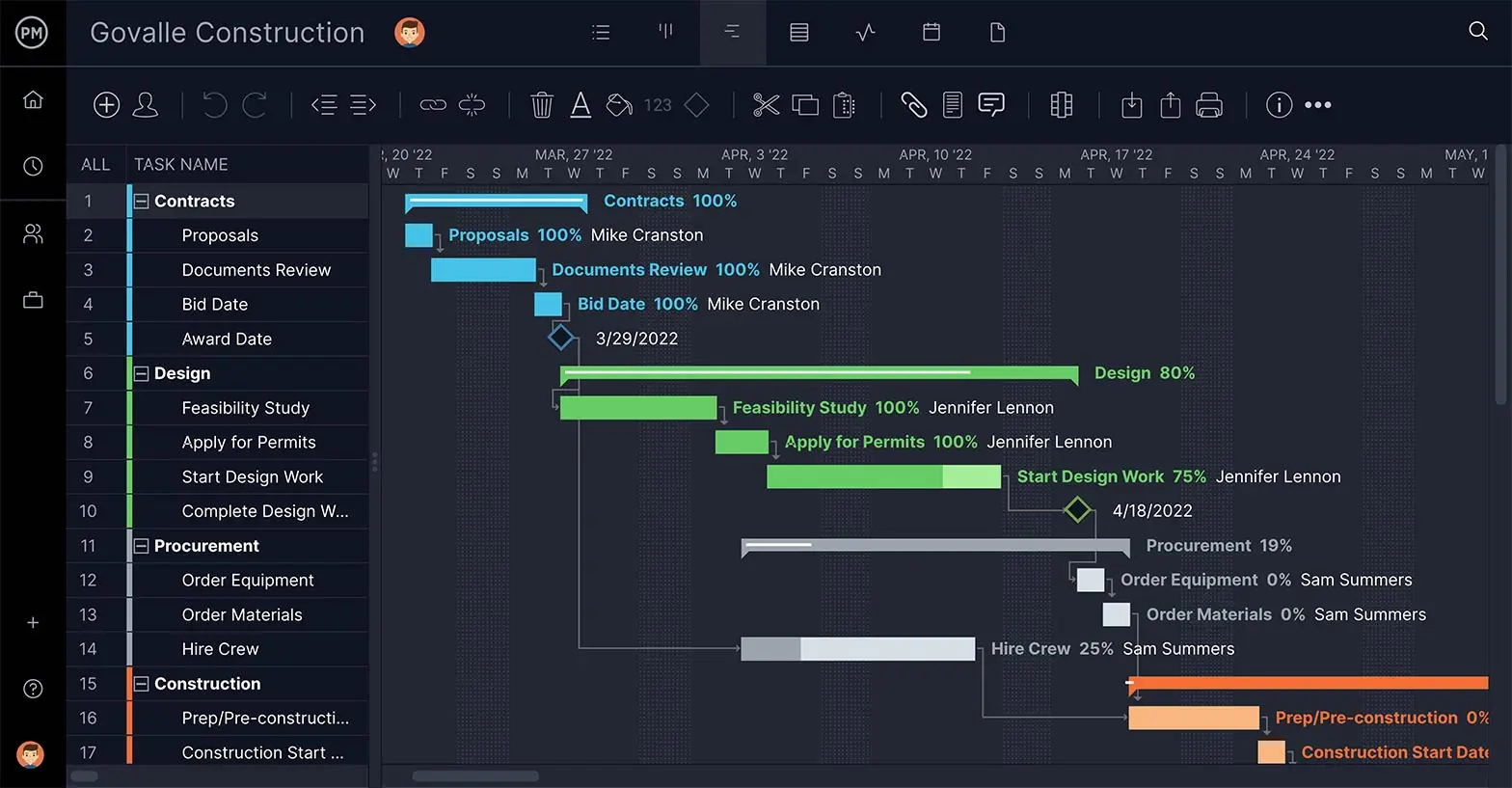
Real-Time Project Dashboards
Monitoring projects is one of a project manager’s main responsibilities. Our real-time project dashboard makes that easy. It automatically collects live project data and displays it on easy-to-read graphs and charts. Project managers get a high-level view of time, cost, workload and much more to keep track of project performance and catch issues quickly. Best of all, there’s no time-consuming configuration necessary as with lightweight project management software. Just toggle over to the dashboard and it’s already working for you.
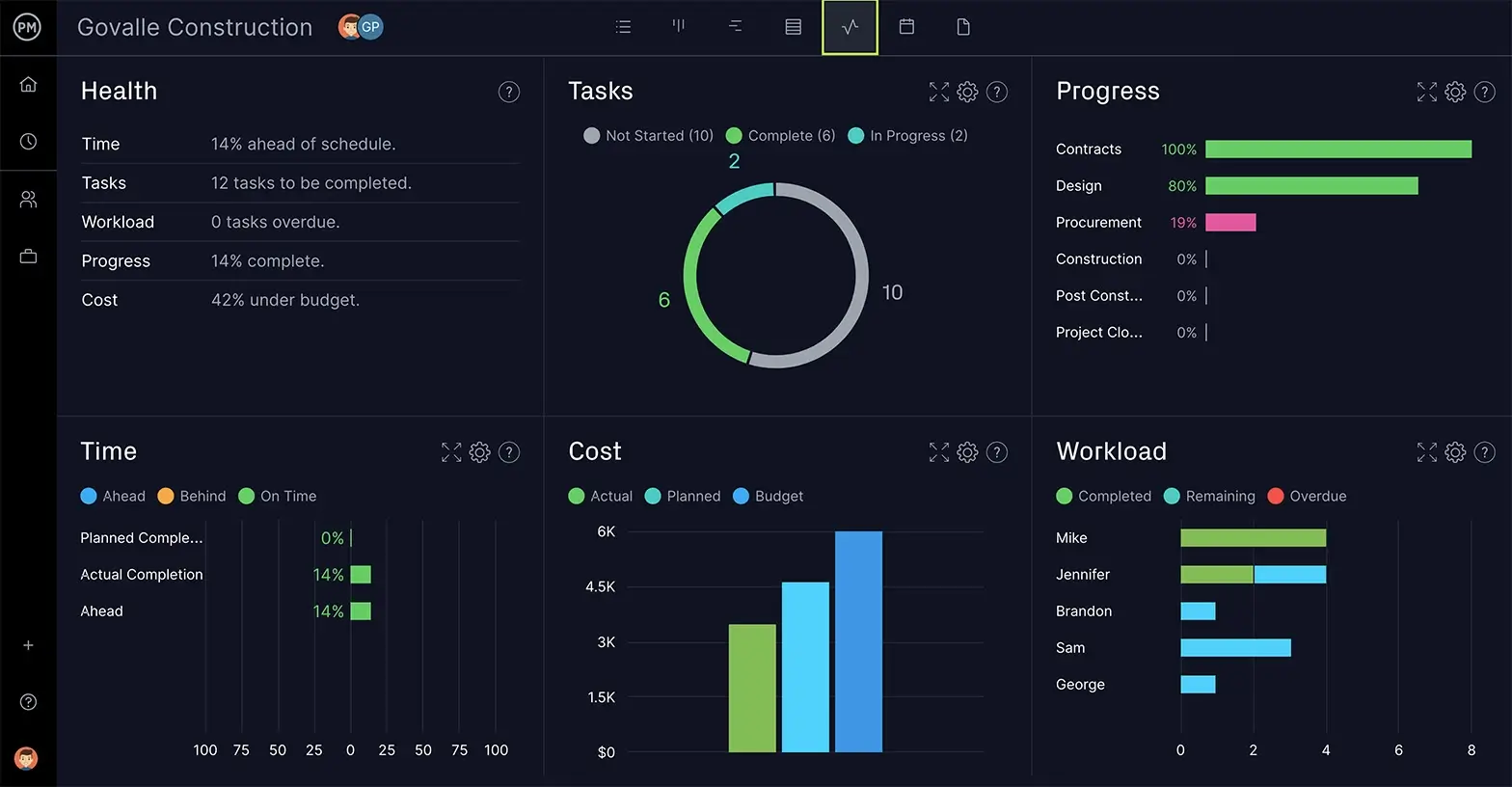
Project Timesheets & Reports
Our software also features secure timesheets that automate much of the process and streamline payroll. They’re also a tool to measure what percentage of your team’s tasks are complete. For more information, you can use our reporting tools. Each report is customizable so you can filter the results to show only what you’re interested in. There are reports on project status, portfolio status, variance and much more. Our reports can be shared in a variety of formats to keep your stakeholders updated.
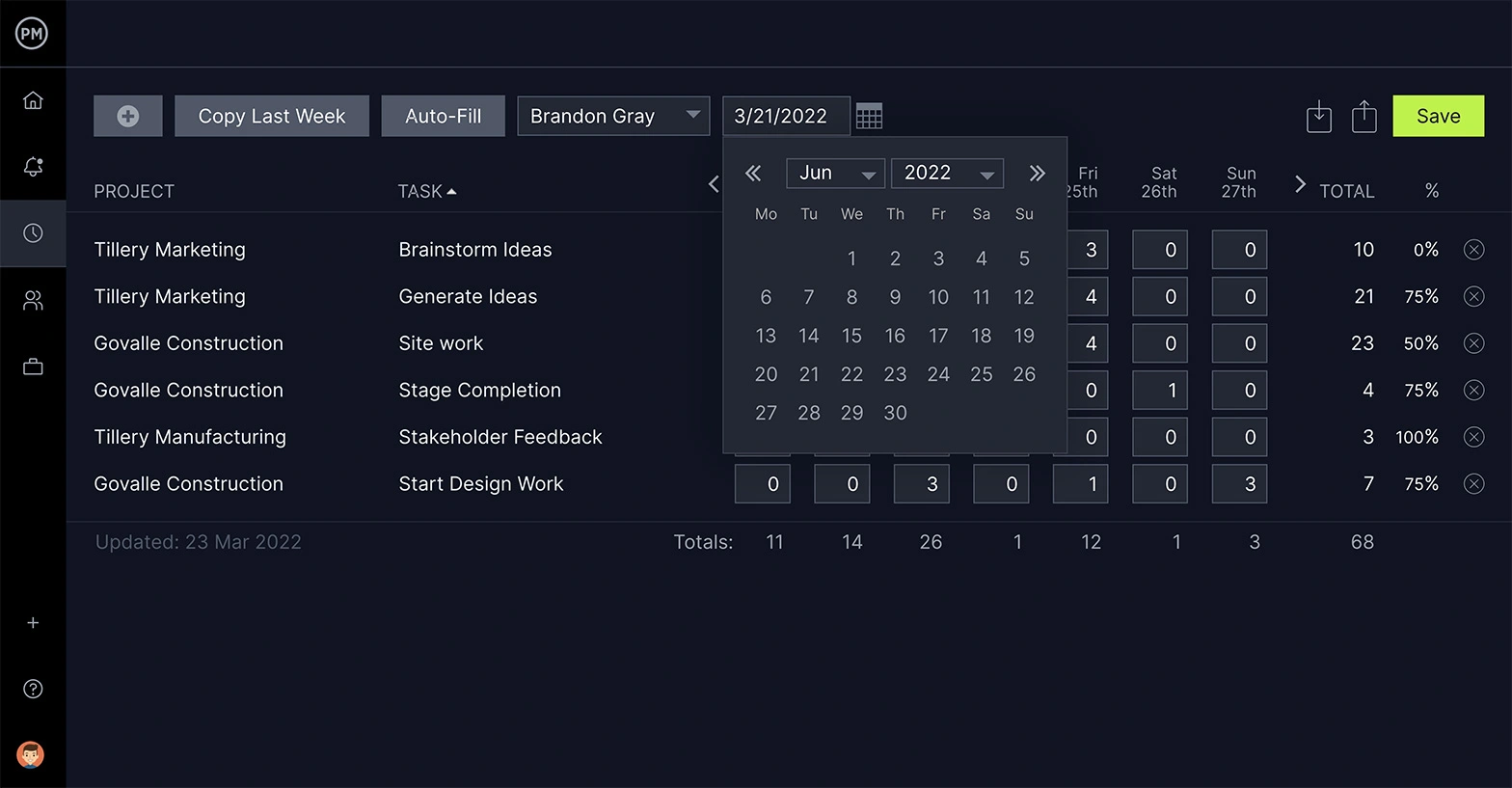
Related Project Management Content
ProjectManager isn’t only powerful project management software that empowers teams to plan, manage and track projects in real time and our website is a hub for online project management information. We publish weekly blogs, guides and videos and offer dozens of free project management templates for Excel and Word that you can download right now. Here’s a small sample of our project management-related content.
- Ultimate Guide to Project Management
- Project Manager Resume
- Project Manager Interview Questions
- Project Manager Job Description
You can have all the soft and technical skills in the world, but without project management software you’ll still be working at a disadvantage. Luckily, there are tools that enhance your skill set and make you even more efficient and productive. ProjectManager has features to help schedule, manage tasks and budget your project, as well as being online so it’s great for team collaboration. You’ll have to bring the sense of humor, but we’ve got the rest. Try it for yourself by taking this free 30-day trial.

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.

7 Essential Skills for Project Managers

Industry Advice Management
As companies strive to deliver complex projects in hyper-competitive environments, the demand for skilled project managers is incredibly high. In fact, according to our analysis of job postings data, the number of project management roles will increase by 11% by 2033.
This demand has resulted in continuous salary increases, with project managers earning an average salary of $98,580 in 2024 , according to the Bureau of Labor Statistics.
Despite this demand, however, organizations are facing talent shortages that leave them at significant risk. As such, career opportunities are abundant for project management professionals who possess the key skills these organizations need. Research shows that demand is highest for practitioners with the necessary mix of competencies—a combination of technical and leadership skills plus business acumen.
Are you ready to meet the demand? Read on to discover the seven essential project management skills you need to succeed, and learn how to refine these skills to stand out among the competition.

7 essential project management skills
Project managers need a wide range of competencies to successfully carry out their tasks. While specific responsibilities vary based on industry and job title, our analysis of job postings data shows that the top skills required across industries include:
- Communication
- Planning/coordinating
- Customer service
- Problem solving
Here’s an overview of each skill and its importance.

1. Communication
From project kickoffs to stakeholder meetings, project managers are constantly communicating. In fact, according to Cesar Abeid , host of the Project Management for the Masses podcast , project managers spend a whopping 90% of their time communicating in some way. As such, project managers must have excellent communication skills in order to successfully lead projects to completion. Poor communication, on the other hand, can lead to inefficiency and missed deadlines .
To mitigate this risk, project managers should prioritize learning how to communicate effectively. This includes knowing how to approach people, create meaningful relationships with co-workers, and articulate a clearly established vision of what you wish to achieve.
PMs who can “speak the language” of their organization’s subject matter experts will be able to communicate more effectively with their teams and have a better understanding of a project’s inherent risks and potential roadblocks. Taking the time to think about what you want to say—and how you want to say it—prior to communicating is a simple and productive first step toward honing this skill set.
Did you know: Most companies regard communication skills as extremely important, regardless of department or industry. In fact, recent studies show that 85% of job success comes from having well-developed soft skills.
2. Management
Project managers need effective management skills. Even if they haven’t had previous experience managing a team , they’re responsible for guiding their team throughout the life cycle of a project.
Many times, this requires familiarity with several project management tools and software, meaning project managers need intermediate technical expertise to effectively manage projects. These types of programs are frequently used to plan, organize, and communicate with teammates while simultaneously managing resources, budgets, and schedules.
Today, this means project managers must also constantly evolve, learning how to leverage the newest technologies available to successfully lead a project to completion.
According to our analysis of job postings data, the most common software skills project managers need include:
- Microsoft Office
- Microsoft Excel
- Microsoft PowerPoint
- Microsoft Project
- Microsoft Outlook
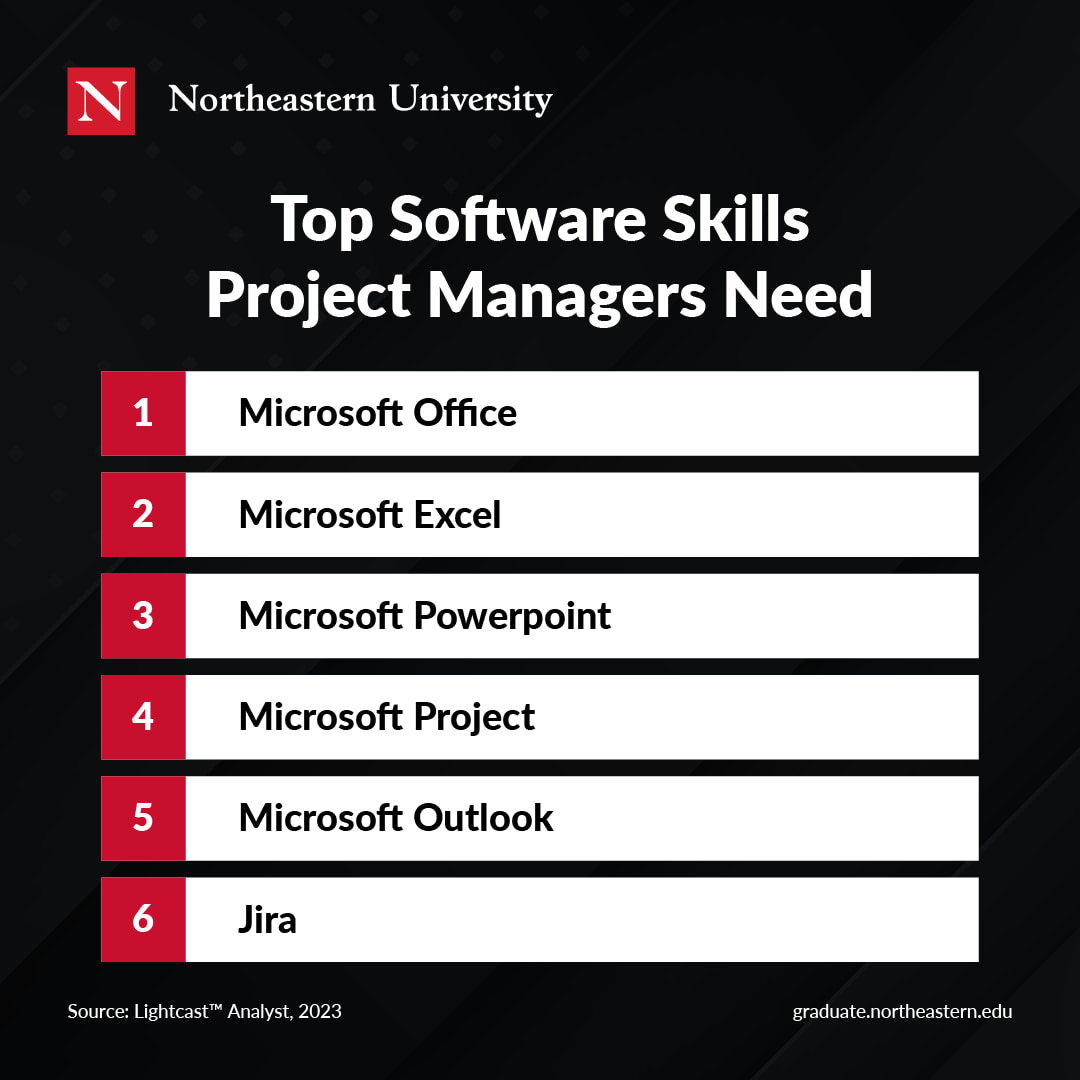
Read More: Project Management | Job Growth and Talent Gap Report
Risk management, which involves identifying and planning for potential risks, is another critical management competency. The most productive project managers are able to identify risks at the outset of a project and develop proper mitigation plans.
Since risks are, by definition, uncertain events, it’s easy for project managers to ignore them and assume they’ll never happen. But by knowing what positive or negative events may impact a project, managers can plan ahead to avoid major problems that could derail a project.
3 . Leadership
When managing a team or project, it’s crucial to have strong leadership skills . By effectively coaching, guiding, and motivating your co-workers, you can help move a project forward and deliver a positive outcome. Strong leaders also foster a productive work environment by communicating regularly with their teams and helping their employees develop important project management skills themselves.
Teams also work more efficiently when employees feel they are making a meaningful contribution to the project . You can help team members feel impactful by learning how to delegate tasks, provide constructive feedback, set goals, and evaluate individual and team performance. Be sure to recognize the achievements of your team members so they know you value their contributions, as well. Combining these elements with your own unique leadership style will help you to successfully manage projects while also becoming a more effective leader .
Leading a project also means constantly being involved in negotiations. An effective project manager is often a skillful negotiator with the ability to keep involved parties content and working toward a unified goal at all times.
Unavoidable discussions about budgets, scope creep, resources, and timelines can easily become adversarial if not handled tactfully, and savvy project managers instinctively know when—and how—to apply persuasive techniques that’ll encourage solutions and avoid damaging workplace relationships.
Depending on the situation at hand, project managers may choose to apply different negotiation styles, and it’s important they have the ability to choose which will be the most effective in each given scenario.
The following are examples of negotiation styles:
- Compromise: Reaching an agreement with the opposing party in which one or both sides make concessions.
- Collaboration: Reaching a win-win solution.
- Competition: One project, task, resource, etc. is chosen over another in a win-lose situation.
No matter what style, knowing how to effectively navigate these negotiation tactics is a vital tool for successful project managers.
4. Planning and coordinating
Planning is a key component of project management. The most common causes of project failure involve poor planning, along with:
- Changing priorities within an organization
- Inaccurate requirements
- Changes in project objectives
- Undefined project goals and risks
Naturally, scheduling is a core responsibility of project managers. However, if you’re adept at juggling multiple schedules and can anticipate roadblocks before they occur, you’ll increase your chances of delivering successful projects.
Chris Bolick , former lead faculty for Northeastern’s MS in Project Management and current associate dean of graduate programs, says the first step to effective time management for project managers starts with creating a well-defined project plan . At the fundamental level, a project plan captures business requirements and project scope , while sequencing activities and resources—all of which will go a long way in saving time and money.
5. Customer service
Customer dissatisfaction is one of the most common constraints project managers face . Even if the project doesn’t involve traditional customers, stakeholders still need to be satisfied in order for the project to ultimately succeed.
“When thinking about customer satisfaction as a constraint, project managers need to keep in mind that simply delivering a project on time, within budget and scope, does not mean the customer will be satisfied,” Bolick says.
It’s critical for project managers to be proficient at customer service and approach each project from the perspective of meeting stakeholders’ needs.
6. Operations
While project managers and operations managers have differing roles and responsibilities , they have several overlapping tasks as well. For this reason, project managers need to be familiar with operations in order for their projects to succeed.
According to Bolick, there are two primary operations-related tasks with which project managers need to be familiar:
- Business operations changes: When components of business operations require significant changes, project managers often need to manage these adjustments as projects before delivering them to operations managers.
- Closing projects: When a project is closing, project managers will collaborate with operations managers to ensure that there’s a plan for its maintenance and deliverability.
7. Problem solving
While critical thinking and problem solving are skills all professionals could benefit from learning , they’re particularly useful in the project management discipline. Rather than being reactive, the best project managers are proactive and use their critical thinking skills to navigate through tricky or ambiguous projects.
By remaining objective, analyzing the facts, and evaluating options without bias, project managers are able to solve complex problems for organizations while delivering results on time and within budget.
How to develop key project management skills
If you haven’t mastered all of these skills, don’t worry. The good news is that these skills can be learned. Here’s how.
1. Practice, practice, practice.
Like any new competency, these skills take time to learn. If you’re currently in a project management role, be cognizant of utilizing these tools in your day-to-day work. If you haven’t started a career in project management yet, try to seek out opportunities for hands-on learning that’ll allow you to harness and refine them.
2. Attend industry events and workshops.
Attending local and online events will allow you to learn best practices and stay abreast of the latest project management trends . For example, at Northeastern, each campus—including both the Boston and regional locations—is partnered with a local Project Management Institute chapter . The university encourages students to get involved with these local chapters, as doing so will give you a chance to expand your professional network to include other skilled project managers from whom you can learn.
3. Get involved.
Always be on the lookout for other opportunities to get involved in the project management community. Consider joining professional associations, which can be another way to meet and exchange knowledge with industry experts. The NUPM , for instance, is a project management student organization on Northeastern’s campuses and is a great option for students looking to get involved.
Advance your career by earning a degree or certificate in project management
One of the best ways to refine your project management skills is to earn a graduate certificate or degree. Programs like Northeastern’s Master of Science in Project Management provide students with the practical skills and technical expertise needed to lead complex projects to completion.
Not only will you master the above skills (and more), but you’ll also have the chance to obtain hands-on experience through an experiential learning program. Additionally, returning to school will connect you with industry experts from around the globe who can help to advance your career.
For more information on breaking into or advancing your career in project management, download our free guide below.

This article was originally published in July 2017. It has since been updated for accuracy and relevance.
Subscribe below to receive future content from the Graduate Programs Blog.
About shayna joubert, related articles.

Five Reasons a Master’s in Project Management Is Worth It

How to Create a Project Scope Management Plan

What Impact Will Artificial Intelligence Have on Project Management?
Did you know.
Employers will need to fill 2.2 million new project-oriented roles each year through 2027. (PMI, 2017)
Master of Science in Project Management
Behind every successful project is a leader who forged its path.
Most Popular:
Tips for taking online classes: 8 strategies for success, public health careers: what can you do with an mph, 7 international business careers that are in high demand, edd vs. phd in education: what’s the difference, 7 must-have skills for data analysts, in-demand biotechnology careers shaping our future, the benefits of online learning: 8 advantages of online degrees, how to write a statement of purpose for graduate school, the best of our graduate blog—right to your inbox.
Stay up to date on our latest posts and university events. Plus receive relevant career tips and grad school advice.
By providing us with your email, you agree to the terms of our Privacy Policy and Terms of Service.
Keep Reading:

Healthcare Leadership: What Is It and Why Is It Important?

How To Develop a Project Scope Statement in 8 Steps

What Do Pharmacists Do? Roles and Responsibilities

Should I Go to Grad School: 4 Questions To Consider
Evaluation Works
For all your research, evaluation and online course creation needs
Introduction to Research Project Management
ENJOY OUR CAREER-BUILDING ONLINE COURSE
If you’re an early career researcher or PhD student, you’ll be only too familiar with the pressures of developing your research career.
Drawing on more than 20 years’ experience, our online programme equips you to better manage any type of research – at whatever stage of your career – so you’re able to:
• Identify the key skills every research project/programme manager needs • Understand which skills are most in demand – inside and outside of academia • Explore the four core project management stages necessary for delivering research objectives on time and on budget • Find out how to get up to speed on any project – at whatever stage you join it • Learn which ‘buttons to press’ to help you convince potential funders your project will complete within your specified timeframe and resource limitations • Identify the Top 10 Research Project Management Challenges that can affect any project plus tried and tested strategies for resolving them.
Use our simple tools and templates – at absolutely no extra cost – to:
• Identify project stakeholders and prioritize their needs • Assess the impact of potential risks to your research and discover tried and tested strategies for overcoming the most common threats • Identify what skills and resources your project needs to achieve its objectives • Break your project into manageable tasks • Work out how long it should take to complete any given project • Identify the critical activities you’ll need to monitor closely to make sure you complete your research as planned.
- Eight modules and over 27 video lectures and tutorials
- Easy to use tools, templates and checklists
- After enrollment, you will have unlimited, ongoing access to this course – across any and all devices you own, plus FREE updates.
DON’T PUT YOUR CAREER ON HOLD. START TODAY!
COURSE START DATES
10 February
COURSE FEES Early Bird Rate £197 ( Standard Rate £297)
Doctoral Students £97
Who should take this course? • Designed for early career researchers, PhD and Professional Doctorate students and anyone responsible for day-to-day management or coordination of research projects or programmes. • Whether you’re putting together a research project proposal, getting ready to implement a project plan, working on your thesis or dissertation, figuring out how to budget, schedule tasks, manage time, work with colleagues, or co-ordinate a project or programme that is already underway, this course was designed with you in mind. • Because every research project is unique, we focus on the principles, choices and strategies that apply regardless of project size, content or research methodology. • The course is relevant to any research field; however, examples used reflect our experience in health care, social care, management, and social science. ___________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________ COURSE CURRICULUM The course is divided into eight sections. Each section contains a series of lectures or tutorials, together with resources relevant to each topic, including tools, templates, examples and checklists. Section 1: Course Overview Overview of the course and why successful project management is so important for researchers.
Section 2: Getting Started Definitions Research Project Manager Skills Research Project Management Lifecycle
Sections 3–6: Research Project Management Lifecycle We walk you through the whole project management lifecycle in depth, right from the beginning, so you’ll know what issues to consider and the topics that should be addressed at each stage, including the different entry points a Research Project Manager may have and their potential impact.
Section 3: Scoping/Design Setting Scope Stakeholders Roles/Responsibilities Research Design/Proposal Risk Management
Section 4: Planning Introduction Work Breakdown Structure Network Analysis Gantt Charts Resources Project Plans Revisited
Section 5: Implementation Implementation Monitoring Tools Managing the Budget Time Management Communication Leadership and Teamwork Managing Problems
Section 6: Completion Completion
Section 7: Top 10 Project Management Challenges (and what you can do about them)
Section 8: Further Resources
________________________________________________________________________________________________________________________
What do our students say about the course?
“A practical overview of research project management tasks, tips and tricks with useful planning tools you can use immediately!”
“This course covers everything you need to get started managing research. Tools, checklists and tips are very useful. I now have a way of monitoring projects that means I can focus on the most important tasks. Thanks!”
By the end of the course you should be able to: • Understand the essential principles of effective research project management • Identify the key skills every research project manager needs and how they can benefit your career – inside and outside of academia • Identify the resources a project needs to achieve its objectives on time and within budget • Break any project into manageable tasks so you can monitor them effectively and efficiently • Have tried and tested strategies at your fingertips to deal with the most frequently encountered challenges project managers face • Consider how to communicate, lead and work as a team with project stakeholders, staff and colleagues • Estimate how long it should take to complete any research project and the critical activities that can make or break it • Use our research proposal/plan template to include the key ingredients potential funders look for to convince them your project will complete within time and resource limitations • Use our simple but effective tools, templates and checklists to get your research project or programme off to a good start • Understand the core stages of the project lifecycle, so you’ll be better prepared to manage any research project or programme for success.
What does the course not cover? • We do not teach you how to use any particular proprietary project management software, e.g. Microsoft Project. Nor do we teach you how to use accounting software or systems.
What materials or software will I need before starting this course? • You will need access to a computer with an internet connection to view the online course and watch the video tutorials. • You will need only basic word processing and spreadsheet software and capabilities to use our tools, templates, and checklists.
START TODAY and give research project management the attention it deserves at the top of your career development agenda.
*Please note no refunds are available on this course due to immediate access to non-returnable course materials.
- Privacy Policy

- Project Management
Top 170 Project Management Research Topics to Work in 2024
Home Blog Project Management Top 170 Project Management Research Topics to Work in 2024
In the ever-evolving field of project management, staying ahead of the most recent research trends is essential for professionals who wish to enhance their skills and increase successful project outcomes. This article highlights the top ten project management research topics expected to impact the project management field in 2024 significantly.
Along with Project Management certification courses , this thorough list will be an invaluable tool for exploring the main research frontiers in the dynamic field of project management. Whether you are an aspiring project manager, an academic researcher, or an industry professional looking to optimize your project strategies, project management certifications will support your growth.
What is a Project Management Research Paper?
Project management research papers are academic documents that go deeply into a single topic or aspect of the field of project management. It is usually written by students, researchers, or professionals in the field of project management, and its goal is to add new knowledge, insights, or views to the field.
A research paper on project management will look at some aspects of project management, be it a theoretical framework, methodology, best practices, or case studies. It entails conducting a systematic investigation into the chosen topic, accumulating and analyzing relevant information, and drawing conclusions or making suggestions based on the findings. The study of the project management research topics 2024 will help budding project managers along with PMP certification training .
List of Project Management Research Topics and Ideas
Here is a list of project management research topics, for writing your project research paper.
| 1 | Impact of Global Leadership in Leading to the Success of a Project |
| 2 | Effects of Cultural Diversity on Project Performance |
| 3 | Popular Leadership Style Used by Project Managers |
| 4 | Evaluate PMBOK Guidelines |
| 5 | Stakeholder Approach to Successful Adoption of Projects |
| 6 | Effect of Change Mobilization on Companies |
| 7 | Impact of Reward System on Boosting Productivity |
| 8 | Relation Between Leadership and Change Management |
| 9 | How to Develop Cost-effective Projects in Developed Nations? |
| What is a Project Management Research Paper? |
Top 10 Project Management Research Topics
The following are the top project management thesis topics in 2024. Let us look into key points and overview of each project management research proposal:
1. Impact of Global Leadership in Leading to the Success of a Project
The following are the key points covered in the thesis on project management of “Impact of global leadership in leading to the success of a project”.
- Global Leadership in Leading Projects: Global leadership is the skill of project managers to lead and manage project teams that are from different cultures, different time zones, and different parts of the world. It means learning and adjusting to different cultural norms, ways of communicating, and ways of doing work.
- Communication and Working Together: Good communication and working together are key to the success of a project, especially when it's a global project.
- Team Building and Motivation: Global leaders must establish trust, develop a sense of a common goal, and provide adequate support and recognition to team members regardless of their geographic location.
- Knowledge Transfer and Learning: The importance of knowledge transfer and learning among project teams should be highlighted by global leadership.
The influence of global leadership on the success of a project has become an increasingly vital subject of research in the discipline of project management. Project teams are becoming more diverse, multicultural, and geographically dispersed as organizations continue to expand their global operations. This trend has created an urgent need for effective global leadership to navigate the complexities and challenges of managing projects across multiple countries, cultures, and time zones.
2. Effects of Cultural Diversity on Project Performance
.png&w=3840&q=75)
- Understanding Cultural Diversity: People from other cultures bring their own unique set of values, beliefs, behaviors, and modes of communication to the table, creating a rich stew of cultural diversity.
- Benefits of Cultural Diversity in Project Management: Cultural diversity has various advantages for project management in addition to highlighting differences.
- Challenges of Cultural Diversity in Project Management: Even though cultural diversity can have a lot of positive effects on a project, it also poses special difficulties that project managers must overcome to ensure project success.
- Effective Management of Culturally Diverse Teams: It can be difficult to manage a team with different cultural backgrounds, but with the correct strategy, project managers can capitalize on diversity's advantages and complete projects successfully.
This research topic, it is examined how cultural diversity affects project performance as well as how project managers may successfully lead a multicultural team to project success.
In today's globalized world, cultural diversity is more common than ever and has a big impact on project management. Project managers need to understand how cultural variations between the team, stakeholders, and clients might impact project performance.
3. Popular Leadership Style Used by Project Managers
The following are the key points discussed in the research paper “Popular leadership style used by project managers”.
- Qualities of Effective Leadership.
- Leadership Styles of Project Managers:
- Democratic leadership style
- Transformational leadership style
- Situational leadership style
- Comparative analysis
- Charismatic leadership style
- Summarizing the main findings and contributions of the research.
The paper begins by emphasizing the significance of effective project management leadership and its influence on project outcomes. It emphasizes that project managers require not only technical expertise but also the ability to inspire and lead their teams to deliver results. The purpose of this study is to identify the most prevalent leadership styles employed by project managers and cast light on their effectiveness within the context of project management.
Overall, the project management research paper offers insightful insights into the most prevalent leadership styles employed by project managers. It provides a thorough comprehension of the significance of leadership in project management and emphasizes the effectiveness of transformational leadership in motivating high-performance teams. The findings are a valuable resource for project managers and other professionals who wish to improve their leadership skills and project outcomes.
4. Evaluate PMBOK Guidelines
The following are the key points in “Evaluate the PMBOK guidelines”.
- Introduction to PMBOK Guidelines
- Evaluation of Strengths
- Identification of Weaknesses
- Areas for Improvement
- Suggestions for Enhancements
This research paper tries to evaluate the Project Management Body of Knowledge (PMBOK) guidelines, a widely accepted project management standard. The PMBOK provides a comprehensive framework and best practices for effectively managing projects. This study analyzes the strengths and weaknesses of the PMBOK guidelines, identifies areas for improvement, and proposes potential enhancements to increase its relevance and applicability in modern project management practices.
Delve into the most popular KnowledgeHut's Project Management Courses:
5. Stakeholder Approach to Successful Adoption of Projects
The following are the key points discussed in the research paper “Stakeholder Approach to Successful Adoption of Projects.”
- This paper examines the significance of stakeholder management to the successful adoption of projects.
- Understanding Stakeholders
- Significance of Stakeholder Management
- Stakeholder Analysis
- Engaging Stakeholders
- Stakeholder Engagement Strategies
- Managing Stakeholder Expectations
- Overcoming Challenges
- Benefits of the Stakeholder Approach
This research paper begins with an overview of stakeholders and their significance in project management. It emphasizes that stakeholders include individuals, groups, and organizations that can influence a project or be influenced by it. The paper emphasizes the necessity of identifying, analyzing, and ranking stakeholders based on their interests, power, and influence while acknowledging the wide variety of stakeholders involved in any given project.
The paper concludes by highlighting the importance of adopting a stakeholder-based approach to project management for attaining successful project outcomes. It prioritizes the need for project managers to recognize stakeholders as essential collaborators and engage them actively throughout the project lifecycle. By considering the interests of stakeholders, managing their expectations, and maintaining open communication channels, projects can increase their likelihood of successful adoption and long-term sustainability.
6. Effect of Change Mobilization on Companies
The following are the key points discussed in the research paper “Effects of change mobilization in Companies.”
- Importance of Change Mobilization
- Change Mobilization Strategies
- Impact on Organizational Performance
- Challenges and Barriers to Change Mobilization
- Overcoming Challenges and Enhancing Change Mobilization
The "Effect of Change Mobilization in Companies" research paper investigates the influence of change mobilization on organizational performance and employee engagement. The study investigates the numerous strategies and approaches utilized by businesses to successfully carry out and oversee initiatives to change. The findings demonstrate a positive relationship between effective change mobilization and increased productivity, innovation, and employee satisfaction. The paper highlights the significance of leadership, communication, and employee participation in facilitating organizational change.
7. Impact of Reward System on Boosting Productivity
The following are the key points included in the project management research paper “Impact of a reward system on boosting productivity”.
- This paper investigates the effect of a reward system on boosting productivity in a variety of contexts.
- Importance of Rewards in Motivation.
- Factors Affecting the Effectiveness of Reward Systems.
- Types of Rewards
- Case Studies and Empirical Evidence.
- Challenges and Limitations.
- The research paper also concludes that well-designed reward systems can have a positive impact on productivity by motivating individuals and fostering a sense of purpose and satisfaction.
The research paper investigates the effects of implementing a reward system on organizational productivity levels. The study investigates how incentives and recognition can positively impact employee motivation, engagement, and overall performance.
Overall, the research paper illuminates the significant influence of a reward system on increasing organizational productivity. It provides administrators and human resource professionals with valuable insights and recommendations that can be used to improve employee motivation and performance, leading to increased productivity and organizational success.
8. Relation Between Leadership and Change Management
The following are the key points discussed in the research paper “Relation between Leadership and Change Management”:
- Definition of leadership and change management in the project management context.
- Leadership's Role in Change Management.
- Leadership Styles and Change Management.
- Key Factors for Effective Leadership in Change Management.
- Case Studies and Examples.
- Challenges and Recommendations.
This project management research topic examines the vital connection between leadership and change management in the context of project management. It attempts to examine how effective leadership influences the success of organizational change initiatives. Examining various leadership styles and their influence on change management processes, the study identifies the important factors that contribute to effective leadership in driving successful change.
9. How to Develop Cost-effective Projects in Developed Nations?
The following are the key points discussed in the research paper “How to Develop Cost-effective Projects in Developed Nations”:
- A survey of project management in developed countries
- The significance of efficiency in project development.
- Objective and methodology of research.
- Cost-effectiveness factors in developed countries.
- Cost-Effective Project Management Strategies.
- Case Studies and Effective Methods.
- Cost-Effective Project Management Framework for Developed Nations.
This research paper concentrates on the identification of strategies and methods to build cost-effective projects in developed nations. The study acknowledges the challenges project managers experience in high-cost environments and aims to provide practical insights and suggestions for achieving optimal project outcomes while minimizing costs. The paper synthesizes current research and case studies to highlight key contributors to cost-effectiveness and presents a framework for project management in developed nations.
10. Analyze the Role of Soft Skills in Project Success Rates
The following are the key points included in the research paper “Analyze the Role of soft skills in project success rates”:
- Definition of soft skills
- Importance of soft skills in project management
- Relation between soft skills and project accomplishment
- Effective communication
- Leadership and team management
- Resolution of disagreements and problem-solving
- Importance of soft skills development
- Team composition and selection
- Integration of soft skills in project management practices
The "Analyze the Role of Soft Skills in Project Success Rates" research paper examines the significance of soft skills in determining project success rates. Soft skills are a collection of personal characteristics and interpersonal abilities that enable individuals to communicate, collaborate, and manage relationships in professional settings. This study seeks to investigate the effect of these abilities on project outcomes, shedding light on their contribution to project success.The paper begins with an introduction to the significance of soft skills in the contemporary workplace, emphasizing their increasing recognition alongside technical expertise. It emphasizes the growing complexity of initiatives and the need for effective teamwork, communication, and leadership skills to successfully navigate such complexity.
Software Project Management Research Topics
These topics cover a range of critical issues, tactics, risk management, AI integration, and agile methodologies in software project management.
- Software Project Management Challenges in Distributed and Remote Teams.
- Effective Software Project Risk Management Strategies.
- The Role of DevOps in Accelerating Software Project Delivery.
- Agile vs. Waterfall: Comparative Analysis in Software Project Management.
- Quality Assurance and Testing Practices in Software Project Management.
- Project Portfolio Management in Software Organizations.
- Managing Scope Changes and Requirements Volatility in Software Projects.
Construction Project Management Research Ideas
These topics cover sustainability, safety, technology adoption, and stakeholder engagement in construction project management.
- Risk Assessment and Mitigation in Large-Scale Construction Projects.
- The Role of Technology in Improving Construction Project Efficiency.
- Resource Allocation and Cost Control in Construction Methods.
- Safety Management and Accident Prevention in Construction.
- Optimizing Construction Project Scheduling and Time Management.
- Green Building Practices and Sustainable Construction Projects.
- Stakeholder Collaboration and Communication in Complex Construction Projects.
- Impact of Lean Construction Principles on Project Delivery.
Research Topics for Project Management in Healthcare
These topics cover various aspects of healthcare project management, facility construction, implementing technology, quality improvement, and crisis management.
- Healthcare Supply Chain Management and Project Efficiency.
- Managing Change in Healthcare Organizations: A Project Management Perspective.
- Optimizing Healthcare Facility Construction and Renovation Projects.
- Telemedicine Project Management and its Impact on Health care Delivery.
- Healthcare Project Risk Management: A Case Study Analysis.
- Patient-Centered Care Initiatives and Project Management Best Practices.
- Quality Improvement Projects in Healthcare: Challenges and Success Factors.
Research Topics in the Agile Project Management
- How can project managers survive the agile scare?
- Can a project manager be an effective scrum master?
- Agile leadership - Looking beyond the project management horizon
- Lean agile principles and project management - applying these constructively
- Zeroing down on the role of a functional manager in agile project management
- Measuring agile adoption across the organization
- Tips for being an effective impediment remover while driving projects successfully across the industries
- Scrum best practices with project management - creating high performing teams
- How utilization metrics help and what can project managers do to address low team utilization ratios?
- Beyond velocity - a look at key metrics for agile teams
- Roadmap planning - how does it help project managers?
- Understanding the overlapping roles of product and project management
- DevOps framework - explainer of the 4 pillars of DevOps
- Can a project manager be an effective impediment remover for teams
- How to manage risks effectively in case of distributed teams
- Changes in project management after the pandemic era
- Proven change management strategies for project managers
- Demystifying resource utilization to solve project problems
- How to drive effective retrospectives for any agile team
- Improving collaboration a key ingredient for project success
- Evolution of project lifecycle - from traditional to agile
- Avoiding pitfalls when scaling agile
- SAFe vs LeSS - understanding distinct agile methodologies
- Why is scrum the most popular agile methodology
- Product backlog - the key to agile project success
Project Management Research Topics in by Project Phases
A. project initiation .
- Explained - the art of choosing the right projects for the organization
- Mapping portfolio vision to project execution methods
- Understanding patterns of successful project selection methods
- What must project managers know about benefits management
- Project tradeoffs and how, what and when to make the choice
- The 4 quadrants of choosing the right projects
- Sunk costs - how to avoid hitting the tip of the iceberg
- The art of stakeholder management in project management
- Move stakeholders from unaware to leading - a guide for project managers
- Stakeholder engagement - the hidden truth of project management
- Identifying stakeholders - the first step to effective project management
- How to convert business documents to project documentation
B. Project Planning
- Peeling the agile planning onion layer by layer
- Shift left project planning from top-down to bottoms-up
- Understanding importance of Gantt charts in project planning
- Planning cross-vertical projects - Do’s and Don'ts
- Avoiding project planning pitfalls
- Project planning for dummies
- Passing the baton from project planning to implementation
- Planning projects as a servant leader
- Capacity planning and its applications across software development
- A guide to rolling-wave planning and its benefits
- Comparative analysis - project scheduling and planning tools
- Scope management - establishing clear boundaries for project success
C. Project Execution
- Handover from project planning to execution - A checklist
- Balancing the project management triangle in a chaotic environment
- Project documentation - the backbone of project management and execution
- Executing projects with the help of modern day GPTs
- Execute projects using AI - going beyond traditional project management
- How AI can change the way project managers think about project execution
- Different ways to capture unknown-unknowns in project management
- Contingency planning - how to plan for the worst and prepare for the best
- Executing cross-vertical projects - common challenges and pitfalls
- Linking themes, initiatives, and user stories - lessons for project managers
- Success stories on project communication - how to engage team members effectively
- Communication tools and strategies - chalking the project management path
D. Project Monitoring and Controlling
- What metrics must project managers see on a daily basis
- Fix the scope creep and gold plating problems the traditional way
- The art of project management - how to monitor and control projects effectively
- Effective risk management for project managers
- How to monitor projects using ChatGPT prompts
- Risk management 101 - 101 common risks every PM must know
- Patterns in risk management - how to uncover risks early and easily
- Quality control - the most effective methods for project success
- Impact of continuous improvement on project success and methods
- What cannot be fixed in projects - tips every project manager must know
- Triaging meetings - the lesser known project management gemstone
- Common project monitoring and control pitfalls every PM must avoid
E. Project Closure
- Simplifying project closure - ways to effectively close projects
- Why 90% project managers fail to close projects convincingly
- Balancing stakeholders during project closure
- Project closure - transitioning from project management to benefits management
- Project closure checklist - common handoffs to complete and close projects
- The what and how of post project evaluations
- How to perform effective retrospectives in any project
- Creating Organization Process Assets and lessons learned while closing projects
- Knowledge transfer - moving from project management to operations
- Establishing measures to address challenges when closing projects
- How can project managers learn from failures while closing projects
- Common project closure pitfalls every PM must avoid.
Project Research Topics by Domain
A. finance and accounting .
- A guide to key financial performance indicators (KPIs) to measure projects
- Cost benefit accounting and analysis in financial project selection
- Comparative analysis of project budgeting methods in finance and accounting projects
- Knowing what types of financial metrics are used in project evaluation
- Transparency and Accountability in project management reporting
- Project financial management - a guide to cost benefit analysis
- Key to project financial disclosures for project managers
- Risk mitigation and management in project financial analysis
- Key financial ratios to review project performance
- Project financial statements that a project manager must analyze during project closure
B. Sales and Marketing
- Borrowing techniques from project management for effective campaign planning
- Strategies for conducting comprehensive market research
- Product launch - creating a step-by-step path using project management practices
- How to add project management best practices to establish robust marketing management plans
- Project management in the digital age - tools to run digital marketing strategies
- Best practices and pitfalls for sales and marketing projects
- Project management practices to design and conduct impactful sales trainings
- Successful planning and control techniques experienced marketing managers must know
- How can project managers drive transition from sales management to service management
- How can project managers draft a successful CRM implementation plan
C. Manufacturing Industry
- TQM - the role of Total Quality Management in the manufacturing industry
- Getting the hands dirty - techniques PMs must employ for project management in factories
- Green manufacturing initiatives - how do they influence projects and project management
- Exploring project communication strategies and challenges in manufacturing project management
- How has six sigma and lean quality principles helped project management
- Waste reduction - the science every project manager in manufacturing must know
- Meeting labor needs - techniques for project managers to work with labor unions
- Project management and Internet of Things - driving innovation in industry 4.0
- Why quality is everyone’s responsibility in the project
- How can project managers create an effective documentation strategy for manufacturing industry
D. Service Industry
- Bridging the customer experience gap in project management
- Project management and customer satisfaction - making two ends meet
- Analysis of Agile adoption across industries and domains
- Embracing project management success strategies in the digital PM drive
- Risk management in service industry - an overview
- ChatGPT prompts that every project manager must know
- How ChatGPT can calculate Key Performance Indicators for any project
- Common project pitfalls that every project manager must know
- Applying agile techniques in service industry
- Enhancing digital adoption via various channels and techniques
Project Research Topics for the Non IT Industry
- Application of project management practices in Finance and Accounting
- Project management best practices for healthcare industry
- How project management can help optimize operations management
- Establishing measures for effective project management in primary industries
- Building effective project management strategies in secondary industries
- Improvising project management practices in tertiary industries
- Agile transformations in the retail space
- Harnessing project management practices for stock broking and trading
- Building engaging and successful team dynamics in the defense industry
- Creating meaningful OKRs for projects in the Non-IT industry
- How knowledge areas and processes of project management can help non-IT industries
- Creating meaningful metrics for measuring project performance
- Driving automobile sales and delivery using project management practices
- Insights for CRM based project applications
- PM best practices applied in non-IT based projects
How to Write a Project Management Research Paper?
It is suggested to get certified in PRINCE2 certification training for aspiring project managers, which will help them work on well-organized and logical project management topics for research papers. Here is a step-by-step guide to writing your research paper on project management:
- Select a topic of project management that sparks your interest.
- Utilize credible sources such as academic journals, books, Google research, websites, and scholarly articles to conduct extensive research on the selected topic.
- Create a plan to organize your primary ideas and thoughts.
- Write an appealing introduction that provides perspective and states your research question.
- Provide a comprehensive survey of the appropriate research by summarizing existing studies and theories.
- Clearly describe your method, including how you plan to collect and examine data.
- Use tables, charts, or graphs as necessary to present your findings or results.
- Consider any restrictions or limitations of your study and explain how they may have affected your findings.
- Your paper should be proofread and edited for clarity, coherence, grammar, and spelling.
- Format your paper according to the specific instructions provided by your institution or the journal to which you are submitting.
- To avoid plagiarism, cite your sources using the appropriate format (e.g., APA, MLA).
- To enhance the quality and rigor of your research paper, solicit feedback from peers or professors.
These topics for research in project management provide an excellent roadmap for project management academicians and practitioners to follow as we move forward. By focusing on these areas, we can obtain valuable insights, foster innovation, and elevate the project management discipline to new heights. The discipline of project management, such as construction project management research topics and ideas, is in a constant state of evolution, and researchers need to explore new avenues and address new challenges. Along with getting trained in these project management research proposal topics, it is suggested to enroll in KnowledgeHut Project Management courses for beginners and get globally recognized accreditations.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Project management for research is the process of planning, coordinating, and carrying out research tasks in a way that helps reach certain goals within certain limits.
The questions that a study or research project is trying to answer are the research questions. Most of the time, this question is about a problem or issue that is answered in the study's result through the analysis and interpretation of data.
The latest emerging project topics are Hybrid Project Management, Artificial Intelligence (AI) And Automation, Rise in remote working, Advanced Resource and Project Management Software, and Projects and Organizational strategy.

Kevin D.Davis
Kevin D. Davis is a seasoned and results-driven Program/Project Management Professional with a Master's Certificate in Advanced Project Management. With expertise in leading multi-million dollar projects, strategic planning, and sales operations, Kevin excels in maximizing solutions and building business cases. He possesses a deep understanding of methodologies such as PMBOK, Lean Six Sigma, and TQM to achieve business/technology alignment. With over 100 instructional training sessions and extensive experience as a PMP Exam Prep Instructor at KnowledgeHut, Kevin has a proven track record in project management training and consulting. His expertise has helped in driving successful project outcomes and fostering organizational growth.
Avail your free 1:1 mentorship session.
Something went wrong
Upcoming Project Management Batches & Dates
| Name | Date | Fee | Know more |
|---|
View or edit this activity in your CPD log.
What skills do you need to become a project manager?
Project management is a growing profession and changing fast. It has never been so important for project professionals to demonstrate their skills and for organisations to assess their capability. Project management skills are transferable. The tools and techniques of project management are universal and a good project manager should be able to add value in any environment.
A project manager should
- be effective at planning, monitoring and reviewing;
- be able to manage resources;
- be able to motivate and encourage others;
- be decisive and able to work well under pressure;
- be aware of who the project will affect and manage the effect it will have on them;
- command respect and trust;
- be able to resolve conflicts;
- be good at problem solving;
- have an understanding of health and safety;
- possess excellent communication skills both verbal and written;
- be able to co-ordinate work carried out by different people and organisations;
- be able to work as part of a team and on their own initiative;
- be able to control and monitor budgets;
- possess good IT skills.
It is also important to
- be interested in seeing a project through from start to finish
- enjoy taking responsibility
- be motivated by achieving set goals or targets.
The APM Competence Framework is a resource that reflects the complexity of the modern project management profession. It describes APM's new view of the competences necessary for effective project, programme, portfolio management and PMO in today's environment and in our view of the future needs of the profession. It allows professionals to measure their skills, knowledge and professional needs against specific roles and competencies. Now you can marry the skills you have to the skills you require.

Teaching Research Skills That Transfer to Future Projects
Exploratory research teaches skills that have lifelong use..
Updated August 1, 2024 | Reviewed by Monica Vilhauer
- Why Education Is Important
- Take our ADHD Test
- Find a Child Therapist

This post is the fourth in a series.
When helping students become researchers, the goal is not only to equip students to tackle a current research project but also to ensure the learned skills will stay with them for future endeavors. Students must understand which research staples must be applied under any circumstances (like critically evaluating sources or following ethical guidelines) while maintaining the flexibility to try different approaches and make new connections. Students at Laguna Beach High School (LBHS) are learning to do just that.
In Part I of this series I spoke to Jun Shen, the passionate teacher and ed-tech coordinator who runs LBHS’s Authentic Exploratory Research (AER) program . AER is an independent research course inspired by Palo Alto Unified School District’s Advanced Authentic Research program . The program pairs students with adult mentors (such as LBUSD staff, industry experts, and academics) who assist the teens in researching their big questions in fields of their choice.
Former LBHS student Carter Ghere was the third teenager to give us an account of his experience in AER and the findings that his AER research produced. A benefit to meeting with Ghere was that he has since moved on to projects outside the AER program, such as promoting physical and mental health . The research skills Ghere honed in AER, combined with his passion for his new endeavors, show us how students can learn research skills in a way that has lasting benefits.
Jenny Grant Rankin: What can teachers do to help students research effectively, not only for current projects but also for future research endeavors?
Carter Ghere: Teachers can encourage students to think about minor aspects of the project that greatly influence the thesis rather than just the thesis question itself. When I researched car design and why it varies, I had to consider each factor that could help me build a strong argument. What started as research on cars very quickly turned into research into socioeconomics, societal upbringing, and government involvement in diplomatic events and conflict. Automotive design changed because manufacturers were competing against each other to sell more cars or improve efficiency, but mass appeal is the biggest driving aspect of change, so I had to research what changes mass appeal and where interests originate from. Laterally, researching aspects of influence opens up much research to apply to your projects, instead of searching for the answer most people already know. Teachers can teach their students how to see the hidden influences, draw conclusions themselves to strengthen their arguments, and accelerate the research process. Knowing how to do research effectively carries over a lifetime, making every new learning endeavor exciting for students instead of monotonous.
JGR: What was the most significant thing you learned about conducting research?
CG: Relevance and impact. The biggest thing I learned while I was conducting research was keeping in mind how your study affects the current information already available. It’s easy to research and quote what most people know, but genuinely effective research isn’t commonly known or even thought of; the research is supposed to question the current knowledge to create new knowledge.
JGR: What was the most significant thing you learned about communicating research or other work?
CG: Knowing your audience is the biggest thing I learned about communicating my work. Putting myself in the shoes of someone reading my work helped me curate my research to better explain my findings to someone who may need to learn about my topic or why this is important. The last thing you want your audience to feel is confusion; a clear, simple explanation of your findings helps the reader draw their connections and relate them to what they already know.
JGR: What lessons learned in AER do you find yourself applying in your current efforts to promote mental health?
CG: The research experience I have from AER accelerated the work I’ve done beyond high school. In terms of research and the actual information I give out, I know that what I’m discovering isn’t new, but the personal opinion that I have is, and that’s what AER taught me. The thoughts that I have on the subject matter of lifestyle and self-development have more relevance than just plain information.
Learning through apprenticeship and embracing the guidance of a mentor profoundly expanded my understanding. This experience made me realize the vast opportunities I still have to learn and grow. At AER, I had the chance to engage in research, connect with experts in the field, develop personal convictions that I am passionate about, ensure these ideas resonate with others, and communicate them effectively.
Ghere demonstrates what we want students to be able to do with the knowledge and skills we teach: to remember, apply, and develop them perpetually. Ideally, as in Ghere’s case, students also use their research skills to help others and improve our world. To continue reading, look for Part V .

Jenny Grant Rankin, Ph.D., is a Fulbright Specialist for the U.S. Department of State.
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Psychiatrist
- Find a Support Group
- Find Online Therapy
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Self Tests NEW
- Therapy Center
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Sticking up for yourself is no easy task. But there are concrete skills you can use to hone your assertiveness and advocate for yourself.
- Emotional Intelligence
- Gaslighting
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience
TechRepublic
Account information.

Share with Your Friends
How to Become a Project Manager in 2024
Your email has been sent

| Course spotlight: Microsoft Project Management Professional Certificate Best for complete beginners. The Microsoft Project Management Professional Certificate from Coursera provides a cost-effective way of learning the basics of project management and getting a flavor of whether it is the career for you. It teaches the processes that professional project managers use on a daily basis over a four month period. Topics it covers include: |
Project managers are responsible for ensuring a team completes their projects on time, within budget and to a high standard. Specifically, this could involve organizing teams, setting outcomes, tracking progress and managing resources. The role suits someone who enjoys planning, setting goals and seeing projects through to completion.
Launching a career as a project manager does not require any specific qualifications or skills, but the path you choose to take into the role could determine the industry you end up in. Project managers are typically needed in construction, engineering, finance and IT.
As so many different organizations operate on a project-to-project basis, project managers are highly sought after. According to the Bureau of Labor Statistics , demand for the role will grow by 6% between 2022 and 2032 — faster than average. By 2027, employers will need nearly 88 million professionals in project management–oriented roles globally, according to a report from the Project Management Institute.
Whether you’re transitioning from a different field or embarking on a career change, this guide will give you all the information you need to set you on the path to success as a project manager.
Disclaimer: This article is sponsored by Coursera.
What does a project manager do?
A project manager is responsible for a number of tasks to ensure a project runs smoothly from its inception to the finish line, including:
- Creating and updating a project timeline.
- Selecting and training appropriate team members.
- Establishing deliverables and targets.
- Allocating and otherwise managing the budget or other resources.
- Keeping track of deadlines and performance metrics like number of errors and cost performance index.
- Communicating with team members, management and client, including updating on progress or delays.
SEE: 10 Best Free Project Management Software & Tools for 2024
What skills are required to be a project manager?
Many of the skills necessary to succeed as a project manager are nontechnical and can either be innate or gained through experience. They include:
- Leadership: Strong leadership ability enables a project manager to guide their team toward the project goals effectively.
- Time management: A good project manager efficiently allocates time to tasks, ensuring project milestones are met within deadlines.
- Knowledge of project management tools: Proficiency with Jira, Trello, Asana, Wrike and other common project management software is a huge asset.
- Communication: Strong communication skills, both oral and written, are essential for clearly conveying ideas, expectations and feedback to team members and stakeholders.
- Data analysis: Data-driven decisions are important for a project’s success, so a good project manager should be able to interpret project data with tools like Excel or PowerBI.
- Budgeting: Budgeting skills are crucial for managing project finances, ensuring resources are used effectively and costs are controlled.
Be sure to highlight these skills or experiences on your resume or CV, demonstrating them when applying for your first project manager role.
SEE: Project Management Reviews & Tutorials on TechRepublic
How do you launch a career as a project manager?
While many professional careers nowadays do require an undergraduate degree, a project manager is not necessarily one of them. What is most important is gaining experience managing projects, which can be obtained at university or in the workplace.
Manage projects in your existing role
Gaining project management experience can be achieved by volunteering to lead small projects or initiatives in your current job, which helps develop the essential skills highlighted in the last section. You may organize and lead team meetings, company events, training sessions or the implementation of new software. If you’re studying for a degree, participating in group projects can provide practical project management experience.
These scenarios can enable an aspiring project manager to exercise a number of transferable skills, including managing schedules, creating Gantt charts and developing risk mitigation strategies.
The industry in which you acquire a project manager role will likely be determined by where your experience lies. For example, if you are an engineering student and lead a group project as part of your studies, you will find it most easy to land your first job at an engineering firm.
Learn new technical skills
Certain technical skills are useful to project managers, but these can be difficult to obtain if you’re working in an unrelated field. Exploring self-study options outside of working hours, like books, video tutorials or short courses, could help lead to the first project manager job.
The following methodologies are the most widely used across industries, so mastering them could prove helpful:
- Agile: Agile project management focuses on iterative development and collaboration, allowing teams to react quickly to changes. It is a broad philosophy that guides how projects are managed and delivered.
- Scrum: Scrum is a defined framework within Agile for managing complex projects. It is characterized by its set of roles such as Scrum Master, ceremonies like spring planning and artifacts like product backlog.
- PRINCE2: Projects In Controlled Environments, or PRINCE2, is another structured project management methodology used widely in the U.K. It divides projects into stages and measures progress against six defined performance targets or ‘tolerances’.
SEE: 6 Best Agile Certifications for Project Managers in 2024
Take part in a project management course
There are a number of project management degrees and master’s degrees offered by universities that help students transition into a project manager role after graduation. However, the time and financial commitments that full-time courses of study require could be a luxury not all aspirants can afford.
Shorter and more flexible courses are available to professionals aiming to enhance their project management capabilities while retaining their existing job or other responsibilities. Industry-recognised certifications are delivered by the Project Management Institute, but many other relevant courses are offered by Coursera .
SEE: 5 Best Project Management Certifications for 2024
How long does it take to become a project manager?
Becoming a project manager can take different amounts of time depending on one’s career path. For university graduates, it typically requires about three years of gaining relevant experience, often starting in entry-level positions and progressively taking on more responsibilities.
If already employed at a company that hires project managers, the timeline can be shorter. It may take one or two years of gradually taking on more project management duties, supplemented by targeted training and certification. For those making a complete career change, the transition might take longer, as they need to acquire not only project management skills but also industry knowledge before they can land their first full-time role.
What are the best courses for aspiring project managers?
Microsoft project management professional certificate—coursera.
The Microsoft Project Management Professional Certificate program is designed to provide learners with the fundamental skills and knowledge needed for a project manager role. It requires no prerequisites, starting with defining commonly used terminology before moving into key areas like team development PMP formulas and Agile approaches. The course also teaches the basics of how to use Microsoft Excel for data preparation, analysis and visualization in the context of project scheduling. Content is delivered through a mix of videos, assessments and hands-on activities, which are regularly updated. The course is also designed to prepare learners to take the industry-recognized PMI Authorized PMP Exam, a global standard in project management certification.
$49/£39 a month after a 7-day free trial.
Four months at ten hours a week.
Google Project Management: Professional Certificate—Coursera
The Google Project Management certificate is slightly more in depth than the Microsoft version. On top of the fundamentals of project management and Agile methodologies, it has a particular emphasis on Scrum. The course covers implementing Scrum events, building Scrum artifacts and understanding Scrum roles. Upon finishing the course, learners will have completed over 100 hours of project management education so they qualify for the PMI Certified Associate in Project Management exam.
Six months at ten hours a week.
PRINCE2 7 Foundation—PRINCE2
The PRINCE2 project management courses were pioneered by the U.K. government in 1989 and quickly became popular worldwide. The PRINCE2 methodology involves dividing a project into smaller stages, defining team members’ roles and responsibilities and using seven processes to manage the project life cycle. There are also seven key principles that team members should adhere to continually and seven themes that provide guidance on how to apply the principles. The Foundation course is specifically designed for entry-level project managers with no experience with the PRINCE2 method.
Starting at $1,186/£1,725.
Three days.
Project Management Basics—PMI

The PMI is the most well-regarded project management body in the U.S. and offers a number of courses for project managers at different career stages. The Project Management Basics course covers fundamental concepts such as the language of projects and PMI standards and is perfect for those who want to see if a career in project management is for them. It also offers a solid starting point for those aiming to pursue PMI certifications like the Project Management Professional, but it is not an official exam prep course. The course, online and self-paced, teaches the very basics of project management as outlined in the PMBOK guide.
23 hours, divided into 20 minute modules.
PMP® Certification Training—Master of Project Academy

The PMP certification is globally recognised as a mark of excellence in project management, and this crash course from the Master of Project Academy is specifically designed to prepare candidates for the PMP exam. It offers over 300 video lectures, 740 practice exam questions, a sample exam and 20 real-world situational project cases—all of which can be completed at the learner’s own pace. The course also boasts a 99.6% first-time pass rate and has a 30-day money-back guarantee. As candidates looking to take the PMP exam must have at least three years of project experience, this course is most suitable for professionals with existing leadership experience.
$99/£78 per month.
Subscribe to the Project Management Insider Newsletter
Subscribe to Project Management Insider for best practices, reviews and resources. From project scheduling software to project planning apps, stay up to date with the latest in project management tools. Delivered Wednesdays
- 8 project management best practices
- 8 Best Scrum Master Certifications for 2024
- 7 Best Business Budgeting Software & Tools for 2024
- How to Become a Data Scientist: A Cheat Sheet
- Best software for businesses and end users

Create a TechRepublic Account
Get the web's best business technology news, tutorials, reviews, trends, and analysis—in your inbox. Let's start with the basics.
* - indicates required fields
Sign in to TechRepublic
Lost your password? Request a new password
Reset Password
Please enter your email adress. You will receive an email message with instructions on how to reset your password.
Check your email for a password reset link. If you didn't receive an email don't forgot to check your spam folder, otherwise contact support .
Welcome. Tell us a little bit about you.
This will help us provide you with customized content.
Want to receive more TechRepublic news?
You're all set.
Thanks for signing up! Keep an eye out for a confirmation email from our team. To ensure any newsletters you subscribed to hit your inbox, make sure to add [email protected] to your contacts list.
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
Research: How Passion Can Backfire at Work
- Erica R. Bailey,
- Kai Krautter,
- Adam D. Galinsky,
- Jon M. Jachimowicz

And how managers should handle this double-edged sword.
Passion has long been championed as a key to workplace success. However, scientific studies have found mixed results: On the one hand, some studies find evidence that passionate employees tend to perform better, while other research has documented null or even negative effects on performance. What’s the root of these inconsistent findings surrounding passion? And how can we reap the benefits of passion without falling prey to its downsides? Through a series of studies with more than 1,000 employees from the U.S. and China, researchers shed light on these questions by showing that passion is associated with overconfidence in our own performance. Although this passion-driven overconfidence is not necessarily harmful — and in certain contexts, it may even be helpful — their findings suggest that managers should take steps to mitigate the potential negative consequences of the overconfidence that may go hand in hand with passion.
From business leaders to athletes to everyday employees, passion is often cited as a key ingredient in the success of high achievers. Consider Elon Musk, whose passion is undeniable. He followed this drive and went on to popularize electric cars through Tesla and reinvigorate space transportation via SpaceX.
- EB Erica R. Bailey is an Assistant Professor in the Management of Organizations group at the Haas School of Business, University of California, Berkeley. Her research primarily focuses on authenticity and the self, asking questions like, how do we define who we are? When do we experience that sense of self in everyday life? What barriers prevent us from sharing that self fully with others?
- KK Kai Krautter is a PhD student in the Organizational Behavior Unit at the Harvard Business School. His research interests revolve around maintaining passion for work over time as well as flexibility in extraversion between different situations.
- WW Wen Wu is a professor at School of Economics and Management, Beijing Jiaotong University. His research focuses on leadership, emotions, and employee proactivity.
- Adam D. Galinsky is the chair of the Management Division at the Columbia Business School. He co-authored the critically acclaimed and best-selling book, Friend & Foe (Penguin Random House, 2015), and delivered a popular TED talk, How to Speak Up for Yourself .
- Jon M. Jachimowicz is an assistant professor in the Organizational Behavior Unit at the Harvard Business School. He received his PhD in management from Columbia Business School. He studies how people pursue their passion for work, how they perceive passion in others, and how leaders and organizations seek to manage for passion.
Partner Center
Work on some of the biggest tech projects in the world, coordinating overall performance, scope, cost and deliverables toward the success of any project team.
Featured stories
Learn about what type of work you'll be doing.
Working at IBM® means putting technology to work for good. See what kind of projects our IBMers are working on.
Get some insights from Georgi on working as a Project Management Officer.
We're sharing what we've learned from engaging in Agile projects, including what could go wrong, and tips to make your own projects succeed.
We aspire to make a lasting, positive global impact on business ethics, the environment and the communities where we work and live in.
We actively support initiatives like Call for Code that bring technology to communities in need. Working with partners like the United Nations and the Linux® Foundation on open source projects, we're able to fight systemic racism, improve clean water access and more.
We empower our IBMers to exemplify behavior that fosters a culture of conscious inclusion and belonging, where innovation can thrive. We're dedicated to promoting, advancing and celebrating plurality of thought from those of all backgrounds and experiences.
Not only has IBM pledged to skill 30 million people globally by 2030, our IBMers have also committed to achieve a minimum of 40 hours of personal learning every year through our skills programs.

Amy, Project Manager
Lead teams in delivering a solution to the customer using the appropriate business measurements.
Provide functional and management expertise managing programs, fostering delivery excellence, nurturing talent and improving project methodologies.
Help educate with methodologies like Scrum, Extreme Programming (XP), Kanban and SAFe, while acting as a servant leader and coach for an Agile team.
Identify, quantify and manage various risk for which the project, customer or company might have exposure.
Work with customers to understand their needs and liaise with SMEs to define solutions in more complex cases.
Lead the development and strategy of digital products, aligning business objectives with user needs and overseeing their implementation.
Stay up-to-date on career opportunities in Project and Product Management that match your skills and interests.
More From Forbes
Top 5 highest paying remote jobs of 2024, from research.
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to Linkedin
Remote work is having a comeback, gaining ground by 7% in the last quarter
What a year it's been for remote workers. If you look at most sources online, you would be forgiven for assuming that remote jobs are declining faster than you can apply for them.
But it's not over. Although employers are enforcing return-to-office mandates, there are still some positive signs of growth—although unlike pandemic figures—particularly in the high-paying jobs sectors.
Researchers at Ladders, a job search site that focuses exclusively on jobs that pay $100,000 or more, analyzed over half a million job postings on their platform from April through June of 2024 to compile the Q2 (second quarter) 2024 Ladders High Paying Jobs Report.
Their research revealed that although it plummeted somewhat in Q1, "remote work clawed back some ground, gaining about 7% in Q2. Hybrid roles reclaimed 40%," their report said.
Additionally, "the number of six-figure jobs available jumped 20% last quarter." John Mullinix, director of growth marketing at Ladders, explains: “As the economy rebounds, companies are expanding and investing in new projects, driving the need for higher-paying roles. With inflation on the rise, businesses are adjusting wages to attract and retain top talent, especially in specialized fields like tech, healthcare, and engineering. Industry growth in sectors like tech, finance, and healthcare also plays a big part, as these areas continue to boom. Additionally, increased investments in technology and sustainability are creating demand for skilled professionals, often with higher salaries.”
‘Say It To My Face’: Harris Issues New Trump Debate Challenge At Raucous Atlanta Rally
Today’s nyt mini crossword clues and answers for wednesday, july 31, nyt ‘strands’ hints, spangram and answers for wednesday, july 31st, highest paying jobs of q2 2024.
So what are the highest paying jobs of summer 2024?
- Nurse practitioner
- Project manager
- Physician assistant
- Software engineer
- Senior software engineer
- General manager
- Pharmacy manager
- Pharmacist (full or part time)
- Program manager
- Outside sales representative
5 Highest Paying Remote Jobs of Q2 2024
When considering their top 10 list of highest paying jobs for Q2 2024, one might be intrigued to learn which of these roles are remote or can be performed remotely.
From this list, it appears that at least half of them are reasonably popular as remote jobs:
There seems to be a clear trend here, with project and operational management, and tech leading the way in the highest paying remote jobs which are hiring right now.
Let's dig into the job projections and expected salary ranges for each of these in-demand remote jobs:
1. Remote Project Manager
Project managers have a bright future ahead. Almost every industry, every business, needs a project manager to ensure everything is kept at pace, running according to schedule, and that projects are delivered to client and stakeholder satisfaction. As such, they are indispensable.
Additionally, project management is a skill that is not easily replaced by AI, and at the same time, it is comparatively easy to learn as you do not need to have a degree to be a project manager. Although the training is rigorous and can be tough, especially if you're studying for a PMI certification, it certainly is more advantageous to spend six months studying for your certification than to spend years at university, expending money you cannot afford and drowning in debt. This signals good news for you if you've been laid off due to new technology taking over your job, or would like to explore a lucrative career path.
A word of warning: project managers tend to make the most money in the technology industry, so you may find that average salaries dwindle down a little in other industries, by comparison.
Average salary range: $128,376 to $160,574
High-paying jobs that pay over $100,000 have jumped by 20% in Q2
2. Remote Software Engineer
Software engineers are in a booming industry; the demand for their jobs is surging at 25% (much faster than average) according to the U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics , and they were listed by FlexJobs as being in the top 10 in-demand work-from-anywhere jobs too—talk about being a digital nomad!
Average salary range: $72,460 to $188,310
3. Remote Senior Software Engineer
As you progress in your career as a software engineer, there are multiple career paths to choose from, including freelance or contract software engineer, VP of engineering, and senior software engineer.
Becoming a senior software engineer entails some management responsibility, and as such, you will be required to not only be exceptionally proficient with your technical skills, but to also have strong leadership, decision-making, and team management skills.
Average salary range: $113,700 to $135,700
4. Remote General Manager
A general manager (also known as operations manager) runs several operations and departments at once and typically reports to the senior management team. You might also be handling an entire company branch. This role requires deep expertise and confidence in understanding many different business functions, and knowing the technical specifics of the business inside out.
Exceptional project management skills would go a long way in being successful with this role.
Average salary range: $78,356 to $105,170
5. Remote Program Manager
The role of a program manager, another management position, is very similar to that of a project manager in many ways, but in other ways, it can be totally different . This job can be exciting as you get involved in rolling out organizational-wide programs or programs that benefit the community in which you live. You're able to be a catalyst for change and ensure that resources are put to good use, for the benefit of the program's participants.
Demand for program managers, as project management professionals, is up by 6% according to the BLS, which is higher than the average job growth rate in the U.S. According to data from Salary.com, program managers tend to make slightly more money each year than their project manager counterparts.
Average salary range: $129,604 to $172,851
The highest paying remote jobs are in tech and project/operational management
So far, it seems that the best places to look for high-paying remote roles would be within project and operational management and technology.
With six-figure job availability up by 20%, and remote work regaining ground this last quarter by 7%, 2024 is beginning to look more optimistic for workers seeking high-paying remote jobs.

- Editorial Standards
- Reprints & Permissions
Join The Conversation
One Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts.
Forbes Community Guidelines
Our community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space.
In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil.
Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
- False or intentionally out-of-context or misleading information
- Insults, profanity, incoherent, obscene or inflammatory language or threats of any kind
- Attacks on the identity of other commenters or the article's author
- Content that otherwise violates our site's terms.
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
- Continuous attempts to re-post comments that have been previously moderated/rejected
- Racist, sexist, homophobic or other discriminatory comments
- Attempts or tactics that put the site security at risk
- Actions that otherwise violate our site's terms.
So, how can you be a power user?
- Stay on topic and share your insights
- Feel free to be clear and thoughtful to get your point across
- ‘Like’ or ‘Dislike’ to show your point of view.
- Protect your community.
- Use the report tool to alert us when someone breaks the rules.
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.
ACRP-PM Specialty
Acrp-pm® (acrp project manager) is a credential formally recognizing clinical research professionals with specialized knowledge in project management. candidates must be acrp certified to sit for this exam., this trusted mark of excellence in clinical research is awarded to clinical researchers who have demonstrated proficiency of specific knowledge and skills by passing the standardized acrp-pm® certification exam..
Apply for Your Exam

To be eligible for the ACRP-PM ® Specialty exam, you must currently hold one of the following ACRP Certifications
Certified clinical research coordinator (ccrc ® ) >, certified principal investigator (cpi ® ) >, acrp certified professional (acrp-cp ® ) >, acrp certified clinical research associate (ccra ® ) >.

The ACRP-PM ® exam consists of 60 multiple choice questions that must be answered within 90 minutes.
The exam is referenced only to the international conference on harmonization (ich) guidelines. no other regulatory framework is tested, including country-specific regulations (i.e, fda or ema)., the following are the only references for which the acrp certification exam content can be supported:, guideline for good clinical practice e6 (r2) >, definitions and standards for expedited reporting (e2a) >, general considerations for clinical trials (e8) >, statistical principles for clinical trials (e9) >, clinical trials in pediatric population (e11) >, the declaration of helsinki (doh) >, we strongly encourage you to also review the detailed content outline for the acrp-pm ® exam..

Review the Detailed Content Outline and make sure your experience and work hours are appropriate, as outlined in the Eligibility tab.
We also strongly encourage you to review the entire acrp certification handbook , which provides full details about every facet of acrp certification..

Create a free ACRP account so you can begin the application process. Follow the on-screen prompts to enter any requested information and documentation.
If you already have an acrp account, please proceed to step three., create account >.

You’re almost there! Please note, applications selected for audit will undergo a formal review by ACRP’s subject matter experts. In most instances, you will receive a status update about your application within 7 business days.
In accordance with the americans with disabilities act, acrp will provide reasonable accommodations for candidates with disabilities. please complete this special accommodations form for submission with your application before proceeding., acrp’s testing partner psi offers in-person testing, as well as on-demand remote testing available 24 hours a day, every day, during the testing windows., watch these videos to learn what to expect from each option before scheduling your exam..

Find Test Centers Near You >
Schedule your in-person exam >.

Schedule Your Remote Exam >
Check system requirements >.

The best way to prepare for the ACRP-PM ® exam is to fully understand the scope of the exam content and its references.
Please be sure to thoroughly review the following:, acrp-pm ® exam detailed content outline >, acrp certification handbook >, remember: the exam is referenced only to the international conference on harmonization guidelines. no other regulatory framework is tested, including country-specific regulations (i.e, fda or ema)..

Review the additional resources listed below to enhance your knowledge of the content area.
Improving recruitment, accrual, and retention in clinical trials, inspection readiness: best practices for managing clinical trial inspections, mastering budgeting at your site: building and negotiating clinical trial budgets that make sense, key skills for ensuring quality control through risk-based decision making, building quality management systems for sites and sponsors: root cause and capa.

Exam results are shared immediately at the conclusion of your exam, but PSI will send you an email with your full score report within 24 hours.
Your acrp account will reflect your results within 24 hours..

Congratulations! You just passed a major milestone on your professional journey and are now a member of the elite club of ACRP Certified clinical research professionals.
Keep an eye on your email because you will soon receive information from our digital badging partner credly about claiming your digital badge and how you can use it to tout your accomplishment. also learn how to use your new credential by reviewing the certification mark policy ..

Don’t worry. It happens to the best of us. Give it another try!
Refer to your acrp certification examination results email or the acrp certification handbook for guidance on the next steps in your certification journey., upcoming testing dates, spring 2024 testing february 15 – may 15, 2024, fall 2024 testing july 15 – october 15, 2024, 2024 registration dates and exam fees, acrp members – $250 nonmembers – $300, spring 2024: october 15, 2023 – april 30, 2024, fall 2024: may 15 – september 30, 2024, there are no application fees for the acrp-pm specialty., join acrp & save, joining acrp helps you save money. more importantly, acrp is where you will find the very best of what you need to design a career path that’s uniquely your own. connections through an engaged community. growth through gold-standard training. and elevation through rigorous certification., explore membership >, exam preparation, congratulations on your decision to earn the most recognized and respected endorsement of clinical research competency — acrp certification. as you start this important journey in your career, we’re here to support you every step of the way., learn more >.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
These are also called "people skills" or "interpersonal skills" because they often help you work with and relate to others in your workspace. These 10 skills are the most important soft skills for project management: 1. Collaboration. Collaboration is the cornerstone of all project management skills.
Research skills; Interpersonal skills; Project management methodologies; Policy knowledge; Conflict management; Related: Types of Project Management Certifications 1. Communication Project managers must have strong communication skills to be able to convey messages to clients and team members. They need this skill to effectively share their ...
Project management is also a key transferable skill that you can utilize within academia or the broader workforce. Lets review five stages of a typical project management life cycle and how you might apply these fundamentals to your own research projects. Initiation During the initiation stage, you determine the scope and feasibility of a project.
Return to the list of project management skills. 8. Project Control. Project control involves monitoring and managing critical aspects of the project such as cost, schedule, scope, and stakeholders. It's a project manager's job to keep their project (s) from going over budget and over schedule.
In your cover letter, choose one or two research skills, such as communication or project management skills, and mention them in the body of the letter. In an interview. You can portray your research skills before you get to the interview by researching the company and the job position and coming to the interview prepared with insightful ...
8. Subject matter expertise. Being a subject matter expertise means you have a deep understanding of a particular job, process, department, function, and technology. If you're a subject matter expert in project management, you know the organization and what clients expect.
3. Reading and Writing. Reading comprehension and clear writing are vital skills for project managers. Strong reading and writing skills are important for just about any job, and they play a ...
And leadership is more than the ability to run meetings and give orders. As Brantlee Underhill noted in a recent blog post, authentic leadership requires self-awareness, humility, empathy, and the ability to rally your team around a vision and a purpose. If you're new to management, you might want to check out CCL Boost ™ for New Leaders ...
When one does not chase perfectionism, it becomes easier to accept and adapt to unpredictability, eventually leading to effective research project management and the successful completion of the project. 3. Engage in regular communication with stakeholders. An important, yet underrated component of effective research project management is ...
Project Management Skills for Scientists. 1. Leadership. Proficiency in "the art and science of getting things done" is the most important skill for a project manager, says Christa Dhimo, professor of informatics and biotechnology at Northeastern University's College of Science. Leadership abilities in this industry are essential because ...
Krahn, J. & Hartment, F. (2006). Effective project leadership: a combination of project manager skills and competencies in context. Paper presented at PMI® Research Conference: New Directions in Project Management, Montréal, Québec, Canada. Newtown Square, PA: Project Management Institute. Jenny Krahn.
Project management skills are the competencies and traits a person needs in order to effectively coordinate a project from start to finish. A project manager leads a projects team using good communication, interpersonal skills, motivational skills, and organization. Project management is a simple term but it encompasses a wide range of skills ...
Success in project management requires a range of diverse skills spanning technical, strategic, business management, and leadership competencies. Examples of project management skills include negotiation, team-building, and technical proficiency in tools such as Microsoft Project, Asana, PowerPoint, Slack, and Trello.
In this session, you will explore project management principles further by calculating risks, managing a process, reviewing a project plan, and forecasting the execution and completion of a project while considering how these elements impact your work and the work of your team members. Session 4: Panel Discussion. November 10, 2022 | 12:00pm ET.
30. Collaboration. Collaboration in terms of project management is no different than the general definition: it's a group of people working together towards a common goal. Specifically, for a project manager, that's getting your project team, with its various project skills and experiences, to work better together.
Project management for academic research projects 15. to the two deliverables for a PM strategy applied to exploratory, complex and uncertain. projects: creati ve and diversified productivity ...
The NUPM, for instance, is a project management student organization on Northeastern's campuses and is a great option for students looking to get involved. Advance your career by earning a degree or certificate in project management. One of the best ways to refine your project management skills is to earn a graduate certificate or degree.
Research Project Manager Skills Research Project Management Lifecycle. Sections 3-6: Research Project Management Lifecycle We walk you through the whole project management lifecycle in depth, right from the beginning, so you'll know what issues to consider and the topics that should be addressed at each stage, including the different entry ...
Here is a list of project management research topics, for writing your project research paper. Sr. No. Top Project Management Research Topics. 1. Impact of Global Leadership in Leading to the Success of a Project. 2. Effects of Cultural Diversity on Project Performance. 3.
A project manager should. be effective at planning, monitoring and reviewing; be able to manage resources; be able to motivate and encourage others; be decisive and able to work well under pressure; be aware of who the project will affect and manage the effect it will have on them; command respect and trust; be able to resolve conflicts;
Research skills are the ability to find an answer to a question or a solution to a problem. They include your ability to gather information about a topic, review that information and analyze and interpret the details in a way to support a solution. Having research skills is necessary to advance your career as they directly relate to your ...
This post is the fourth in a series. When helping students become researchers, the goal is not only to equip students to tackle a current research project but also to ensure the learned skills ...
Course spotlight: Microsoft Project Management Professional Certificate. Our assessment: Best for complete beginners. The Microsoft Project Management Professional Certificate from Coursera ...
Passion has long been championed as a key to workplace success. However, scientific studies have found mixed results: On the one hand, some studies find evidence that passionate employees tend to ...
GenAI Adoption Research. A new report from Project Management Institute (PMI), the world's leading authority for project professionals, explores how high adopters of GenAI (or "trailblazers") are leading the charge in embracing GenAI, unlocking performance enhancements, advancing GenAI adoption, and sharing their learnings to propel business transformation.
In this article, we explore 6 uncommon project management concepts so that they can be used as a starting point for further research if any of the techniques fit your project management needs and ...
Get some insights from Georgi on working as a Project Management Officer. 10 ways to achieve Agile We're sharing what we've learned from engaging in Agile projects, including what could go wrong, and tips to make your own projects succeed. ... Stay up-to-date on career opportunities in Project and Product Management that match your skills and ...
Their research revealed that although it plummeted somewhat in Q1, "remote work clawed back some ground, gaining about 7% in Q2. ... Exceptional project management skills would go a long way in ...
ACRP-PM® (ACRP Project Manager) is a credential formally recognizing clinical research professionals with specialized knowledge in project management. Candidates must be ACRP Certified to sit for this exam.
Their curricula emphasize analytical skills such as statistical analysis, econometrics and policy evaluation. Graduates are equipped to conduct in-depth policy research and analysis. On the other hand, MPA programs focus more on the management and implementation of public policies and programs. MPA curriculums emphasize skills-based learning ...