


How to Create a Law Firm Business Plan Aimed at Success
Want a successful law firm? Start with a solid business plan. Our guide covers everything that will help you create a roadmap for success.
A firm exists to serve people—so its business plan must take into account those it aims to help. A law firm's business plan lays out the key pillars that will support a practice, from operational details to marketing strategies to financial projections. Furthermore, it should provide a clear roadmap for where the firm hopes to be in the coming years.
In this blog, we will guide you through the process of creating a comprehensive law firm business plan that will help you achieve your goals . Additionally, in our latest Grow Law Firm podcast, our host Sasha Berson conversed with Omar Ochoa, the founding attorney of Omar Ochoa Law Firm, to discuss the topic of creating a law firm business plan aimed at success. Be sure to listen to another insightful episode featuring Tom Lenfestey, where he discusses crafting a sellable and profitable law firm.
Why Is a Business Plan Important for Law Firms?
A business plan is a vital tool for any law firm to achieve success. It outlines goals, strategies, and the feasibility of business ideas, providing a clear direction and focus for the firm. The plan can be used to secure funding from investors or financial institutions by demonstrating the potential for growth and profitability.

Moreover, a business plan supports decision-making by evaluating the feasibility of new ventures and assessing potential risks and rewards. It helps to manage resources effectively by setting financial goals and tracking progress, ensuring the firm is making the most of its resources and achieving objectives.
Lastly, a law firm's business plan enables growth by identifying new opportunities and developing strategies to capitalize on them. By planning for the future and setting realistic growth targets, law firms can take their businesses to the next level. Overall, a well-developed business plan is critical for success in the legal industry, providing direction and focus, supporting decision-making, managing resources effectively, and enabling growth.
General Tips for Creating an Attorney Business Plan

Building a business plan for law firms is not an easy or intuitive process. By considering the following issues before opening your doors to clients, you have a much better chance of having a stable firm that matches your values and has a clear set of goals.
— Stay Focused
Forming a law firm can feel overwhelming. You have a lot of freedom and can easily get sidetracked into issues that either can wait or do not deserve your attention.
If having a strong law firm website design is important enough for you to include in your plan, you will spend time on that instead of less important matters.
A plan also includes a budget. The process of planning your firm's finances can ensure that you do not overspend (or underspend) as you start your own firm.
The attention to detail that comes from having a plan will help you avoid spreading yourself too thin by focusing on every issue or the wrong issues. Instead, you will maintain your focus on the important issues.
Whether you have law partners or develop a solo law firm business plan, the plan will help you stay focused on your end goals.
— Keep Track of Goals and Results
It is easy to set goals when you start a law firm and then promptly forget about them.
Your plan will set out your goals and the metrics you will use to determine your progress toward meeting them. The plan should also explain how you will know when you have met them.
For example, you might have a growth goal of reaching five lawyers within two years. Or you might have a revenue goal of collecting $200,000 your first year.
Too many businesses, including law firms, meander on their developmental path. By setting goals and the path for meeting them, you will have guardrails to keep your firm on track.
"If you want to be the number one law firm in the country by revenue right in a 20 year time period, have that be your goal and everything that you do right is in service of that goal. You might not get there, but you're gonna find that you're gonna be very successful either way."
"If you want to be the number one law firm in the country by revenue right in a 20 year time period, have that be your goal and everything that you do right is in service of that goal. You might not get there, but you're gonna find that you're gonna be very successful either way." — Omar Ochoa
— Sort Out Your Own Law Firm Strategy
Developing a clear vision is important for establishing a strategic law firm plan aimed at long-term goals . As Omar Ochoa discusses in the podcast, having very specific milestone visions like where you want to be in five, ten, or fifteen years helps drive the strategy and actions needed to get there.
It's easy to say that you'll run your law firm better. But a plan actually helps you identify how to improve by articulating a concrete strategy. The process of creating the plan will help you pinpoint problems and solutions.
A plan forces consideration of operational details often overlooked. It equates to defining your firm's purpose and then pursuing that vision with purpose-driven strategies and actions. As Omar notes, marrying vision to action through knowledge of other successful law firm models is key to achieving goals.
One area that is frequently overlooked in plans is the inclusion of law firm marketing strategies . Developing this aspect is critical for attracting clients and sustaining growth.
Level Up Your Brand
Book a Free Consultation
— Move Forward
You should view your plan as a law firm business development plan that will guide the formation and growth of your firm .
You can review the document periodically to remind you and your law partners of your growth and expansion projections. After this review, you can ensure your growth and expansion remain on track to carry you to your goals.
The review will also tell you whether you need to update your firm's goals. When you started your law firm, you might have been unduly pessimistic or optimistic in your projections. Once you have some time to operate according to your plan, you can update your goals to keep them realistic. You can also update your processes to focus on what works and discard what does not.
The review can provide your projections for what you hope to accomplish and the roadmap for accomplishing it.
Law Firm Business Plan Template

Each of the websites below includes at least one attorney business development plan template:
- Business Plan Workbook
- PracticePro
- Smith & Jones, P.A.
- Wy'East Law Firm
You can use a law firm strategic plan example from these sites to start your firm's plan, then turn the plan into a document unique to your circumstances, goals, and needs.
What to Consider before Starting Law Firm Business Plans
Before starting a law firm business plan, think through a few key issues, including:
— Setting the Goals
Reflect deeply on your firm's purpose. Think about who you represent and how you can best meet their needs. A law firm exists for its clients. As you think about your law firm goals , think about goals for providing legal services to your clients.
"We continue to try to have the biggest impact that we can because ultimately, in my opinion at least, that's what lawyers are for, is to be able to help people and be able to move us forward." — Omar Ochoa
You need to set realistic and achievable goals. These goals should reflect your reasons for starting your law firm. Thus, if you started your law firm because you expected to make more money on your own than working for someone else, set some goals for collections.
While you are setting your goals, think about how you will reach them and the ways you will measure your success. For example, if you want to expand to include ten lawyers within three years, think about intermediate goals at the end of years one and two. This helps measure your progress.
— Choosing Partnership Structure
For lawyers considering a partnership structure, it's important to select partners that complement each other's strengths and weaknesses to help the firm function effectively.
There are 2 main partnership structure options:
- A single-tier model provides equal decision-making power and liability between partners.
- Meanwhile, a two-tier structure offers tiers like equity and non-equity partners, providing flexibility and career progression opportunities.
While similarly skilled individuals may clash, partners with differing abilities can succeed together. Some attorneys also choose to run their own firm for flexibility. This allows them to leverage different specialists through occasional joint ventures tailored for specific cases, without the constraints of a single long-term partnership. Furthermore, it highlights how the law firm partnership structures impacts freedom and sustainability.
— Thinking of the Revenue You Need
Calculate how much revenue you need to cover your overhead and pay your salary. Suppose your expenses include:
- $2,000 per month for office rent
- $36,000 per year for a legal assistant salary
- $600 per month for courier expenses
- $400 per month for a copier lease

Assume you want the median annual salary for lawyers of $127,990. You need $199,990 per year in revenue to cover your salary and expenses.
But revenue is not the end of the story. Your landlord, vendors, and employees expect to get paid monthly. So, you should also calculate how much cash flow you need each month to cover your hard expenses.
You also need a reserve. Clients expect you to front expenses like filing fees. Make sure you have a reserve to pay these costs and float them until clients reimburse you.
— Defining the Rate of Payment
You need to make some difficult decisions when it comes to setting your own fee structure. If you choose a higher billing rate, you will need to work less to meet your revenue goals. But you might not find many clients who are able to pay your fees.
Whether you charge a flat fee, contingent fee, or hourly fee, you should expect potential clients to compare your fees to those of your direct and indirect competitors. Remember, your firm competes against other lawyers, online services like LegalZoom , and do-it-yourself legal forms books.
Finally, you need to comply with your state's rules of professional conduct when setting your fees. The ABA's model rules give eight factors to determine the reasonableness of a fee. These factors include the customary fee for your location and the skill required to provide the requested legal services.
— Making the Cases in Your Law Practice Meet the Revenue Needs
Figure out how much you need to work to meet your revenue target . If you charge a flat fee, you can simply divide your revenue target by your flat fee.
Hourly fee lawyers can calculate the number of hours they need to bill and collect. However, law firm owners rarely bill 100% of the hours they work due to the administrative tasks they perform to run a firm. Also, you will probably not collect 100% of your billings, and clients could take 90 days or longer to pay.
Contingency fee lawyers will find it nearly impossible to project the cases they need. You have no way of knowing the value of your cases in advance. You also have no idea when your cases will settle. You could work on a case for years before you finally get paid.
The Founder of Omar Ochoa Law Firm
Omar Ochoa is a founding attorney with extensive experience in complex litigation, including antitrust, class actions, and securities cases. He has recovered hundreds of millions of dollars for clients and has been nationally recognized as one of the best young trial lawyers in the country.
Omar graduated from the University of Texas at Austin with degrees in business administration, accounting, and economics. He later earned his law degree from the university, serving as editor-in-chief of the Texas Law Review. He has clerked for two federal judges and has worked at the prestigious law firm Susman Godfrey L.L.P. Omar is dedicated to seeking excellence. He has been recognized for his outstanding achievements in antitrust litigation.
Parts of a Business Plan for Law Firm Formation: Structure
A law firm business plan is a written document that lays out your law firm goals and strategies.
For many businesses, a business plan helps secure investors. But the ethical rules prohibit law firms from seeking funding from outside investors or non-lawyer shareholders .

Your business plan is for you and your law partners. It will help you manage everyone's expectations and roles in the firm. Here is a law firm business plan example to help you see the parts and pieces in action.
— Executive Summary
An executive summary combines the important information in the business plan into a single-page overview. Your plan will include details like projections, budgets, and staffing needs. This section highlights the conclusions from those detailed analyses.
Your executive summary should include :
- A mission statement explaining the purpose of your firm in one or two sentences
- A list of the core values that your firm will use whenever it makes decisions about its future
- The firm's overarching goals for itself, its lawyers, and the clients it serves
- The unique selling proposition that sets your firm apart from other firms in the legal industry
You should think of this section as a quick way for people like lenders, potential law partners, and merger targets, to quickly understand the principles that drive your firm.
— Law Firm Description and Legal Structure
First, you will describe what your law firm does. You will describe your law practice and the clients you expect to serve.
Second, you will describe how your firm operates. The organization and management overview will explain your legal structure and the management responsibilities of you and your law partners.
This section should fill in the details about your firm's operation and structure by:
- Describing the scope of the legal services you offer and your ideal clients
- Restating your mission statement and core values and expanding upon how they will guide your firm
- Explaining your location and where your clients will come from
- Describing your business entity type and management structure
- Detailing your unique selling proposition , including the features that distinguish your firm from your competitors
When someone reads this section, they should have a clear picture of what you will create.
— Financial Calculations
Your attorney business plan explains where your firm's revenue comes from and where it goes. This is where your skills as a lawyer begin to diverge from your skills as a business owner. You may need to learn a few new accounting concepts so you can perform the analyses expected in a financial plan.
You will need a financial plan for at least the first year.
If you plan to seek a bank loan or line of credit, your bank may need a financial plan that covers three years or longer.
You will need more than a few rough numbers for a useful business plan. Instead, you will need to estimate your expenses and revenues as accurately as possible.
"Take some financial statements courses, take some managerial accounting courses that teach you how to track costs, how to frame costs in a way that you're looking at the important costs." — Omar Ochoa
You might need to contact vendors and service providers to get precise costs. You will probably need to track your billings with your prior firm to predict your revenues. If you are opening a law firm after law school or an in-house job, you may need a competitive analysis to show what similar law firms earn in your location and practice area.
Some reports you may need in your business plan include:
- Revenue analysis listing the fees you will collect each month
- Budget describing your monthly and annual expenses
- Financial projections combining the revenue analysis and budgeted expenses to predict your profit margins
- Cash flow statement showing how your revenues and expenses affect your cash on hand.
Your cash flow statement might be the most important financial report because it explains how your bank balance will fluctuate over time. If your clients take too long to pay their bills or you have too many accounts payable due at the same time, your cash flow statement will show you when money might get tight.
— Market Analysis
A market analysis will tell you where you fit into the legal market in your location and field. You need a competitive analysis to understand the other lawyers and law firms that will compete with you for potential clients. You can also analyze their marketing messages to figure out how to stand out from the competition.

A competitive analysis will tell you what services other firms offer, how much they charge, and what features help your competitors succeed.
Your analysis should include a discussion about your :
- Ideal clients and what you can do to help them
- Market size and whether you offer something clients need
- Competitors and what they offer to clients
- Competitive advantages and how you can market them to potential clients
You can also develop and hone your marketing strategy based on the benefits you offer to clients over your competitors. Finally, a market analysis can tell you the locations and practice areas in which your firm may expand in the future.
Your market analysis helps you focus your efforts on your legal niche.
— Marketing Plan
A marketing plan sets out the steps you will take to reach your target market. Your marketing strategy will take your market analysis and turn it into a plan of action.
You will start with the results of your market analysis identifying your clients, your competitors, and your competitive advantages. You will then discuss the message you can deliver to potential clients that captures the advantages you have over your competition.

Some advantages you might have over other lawyers and law firms might include tangible benefits like lower billing rates or local office locations. Other advantages might provide some intangible benefits like more years of experience or state-bar-certified specialists in those states that allow specialization.
You will then discuss your marketing plan. A marketing plan explains :
- Characteristics of the target market you want to reach
- What your competition offers
- The distinct benefits you offer
- A message you can use to explain what separates you from your competition
- Your action plan for delivering your message
- Your goals for your action plan, such as the number of client leads, new clients, or new cases per month
Your action plan will include the marketing channels you want to use to spread your message. Marketing specialists can help you identify the best channels for your marketing message and client base.
For example, if you practice intellectual property law, you need to reach business owners and in-house lawyers who want to protect their companies' brands, inventions, artistic works, and trade secrets. A marketing agency may help you create a marketing strategy geared toward trade publications and business magazines.
However, IP lawyers require an entirely different marketing strategy than firms that practice family law. Family lawyers need to market to individuals and will tailor their marketing efforts toward different marketing channels and messages.
Even if you expect most of your client leads to come from referrals, you still need brand recognition for those leads to find you. You should consider a website, basic SEO, legal directory, and bar association listings.
— Your Law Firm Services
You will outline the services your law firm offers to clients. Lawyers with established clients and an existing legal practice can simply describe what they already do.
Any new law firm or lawyer transitioning from other practice areas should consider:
- Practice areas you know and enjoy
- Overlapping practice fields that will not require extra staff, such as personal injury and workers' comp
- Related legal services your clients may need, such as wills and guardianship
By offering needed services you can competently provide, you can gain clients and avoid referring existing clients out to other lawyers.
— Your Law Firm Budget
You should approach your budget as a living document. You will spend more money as you add more lawyers and staff members to your firm. But you can also look for ways to reduce your operating costs through investments in technology services and other cost-saving measures .
Your budget should set out the amount you expect to initially spend on start-up expenses. As you create your start-up budget, remember many of these expenses are not recurring. Furniture, computers, and office space build-outs can last several years. In short, your budget should answer the question, "What do you need to open a law firm?"
It should also lay out the amount you plan to spend each month to operate your firm. Here, you will include your recurring expenses, such as rent, staff salaries, insurance premiums, and equipment leases.
Using your operating budget, you will determine the amount of money you need to start and run your firm. This, in turn, will tell you whether you need to take out a loan or tap into your savings to start your law firm. You will need a plan for paying your expenses and day-to-day costs while your firm gets onto its feet.

Let us help you create a digital marketing strategy and a growth plan
.webp)
Some Useful Tips on Creating a Business Plan for Law Firm Creation and Development
As you draft your law firm business plan, you should focus on the process. By putting your thoughts down in writing, you will often identify issues you had not previously considered.
Some other tips for drafting your business plan include:
— Describe Both Strengths and Weaknesses
You want to project confidence as you prepare your business plan. Remember, you will use this plan to approach potential law partners, lenders, and merger targets. You need to show that you have a solid plan backed up by your financial projections.
At the same time, you need to remain realistic. Write a business plan that describes your business challenges as well as your competitive advantages.
For example, if you have a strong competitor that has a solid law firm reputation management and many of the clients you will target, acknowledge the difficulty of getting those clients to switch law firms. Describe your marketing strategies for approaching and pitching your law firm to those clients.
— Think Ahead
Remember that your business plan sets out the roadmap for both the establishment and operation of your law firm . Think about issues that could arise as your firm grows and matures.
For example, you may have a goal of reaching ten lawyers in three years. But as your staff grows, you may need a human resources manager. You may also seek to handle your payroll in-house instead of outsourcing it to a payroll provider. These changes will create ripple effects throughout your business plans. You will incur costs when you add staff members. You will also realize benefits like increased attorney efficiency.
At the same time, any projections more than five years into the future will likely be useless. Your firm and its clients will evolve, and technology will change how you practice law.
"A law firm that actually does something in the unique way that is an actual measurable advantage to their clients or to their firm." — Tom Lenfestey
— Be Clear about Your Intentions
As you develop your plan, you should keep its purpose in mind. First, you want to outline your core values and goals for your law firm. Set out the reasons why you started your law firm and what you intend to accomplish with it.
"You can't just be doing something because you want prestige. There's gotta be more to that, right? You have to have a purpose that you're following. And if you've got that, that purpose is like gravity, right? You will always be grounded." — Omar Ochoa
Second, you set out your path to achieving those goals. This will include boring technical information like how much you spend on legal research every month. But it will also explain your approach to solving problems consistent with your mission statement and philosophy for law firm management.
— Consult and Update If Necessary
Your plan should guide you as you build your firm. It contains your goals and the roadmap for reaching them. But your plan is not carved in stone.
As you face challenges, you will consult your plan to make sure you approach these challenges in a way consistent with achieving your goals. But under some circumstances, you might find that the plan no longer provides the right solution.
As you work with your firm and your law partners, your goals, processes, and solutions to problems may evolve. The technology your firm uses may change. Your law firm's costs may go up with inflation or down as you realize economies of scale. You should update your plan when this happens.
— Develop a Succession Plan for Your Law Firm
Creating a succession plan for a law firm is essential for ensuring a smooth transition and preserving the firm’s value. Drawing from the experiences of professionals in other fields, it is clear that lawyers often face unique challenges in succession planning. A well-structured exit strategy can help lawyers realize the value of their practice, whether they plan to retire or pursue other interests.
Firms generating over $2 million in revenue typically have invested in systems that make them more attractive and easier to transition. These systems are crucial in creating value and attracting buyers. A transition-based sale, where the selling attorney remains involved for a period, ensures a smooth handover of clients and referral sources, reducing the risk of value loss. Additionally, specialized, systematized, and profitable firms command higher valuations. By investing in robust systems and considering your exit strategy early, you can create lasting value, financial security, and peace of mind, making your law firm more sellable in the future.
Building High-Value Law Firms with Tom Lenfestey, the CEO of Law Practice Exchange
This podcast episode features a discussion between Sasha Berson and Tom Lenfestey about the Law Practice Exchange, a marketplace for buying and selling law firms. Tom, an attorney and CPA, explains how his experience with other professionals inspired the creation of this marketplace. They discuss the importance of building systems to enhance a firm's value, the challenges of succession planning, and strategies for creating a smooth transition and maximizing value during a sale.
"You make more money with hopefully more consistency and less stress. And so that's also part of it is enjoy it. Build to better, right, overall, but build that firm that you want." — Tom Lenfestey
Tom Lenfestey
The CEO of Law Practice Exchange
Tom Lenfestey is an attorney and CPA who founded the Law Practice Exchange, a marketplace for buying and selling law firms. With a background in assisting dentists and CPAs in selling their practices, Tom identified the need for a similar platform for lawyers. His work focuses on helping attorneys realize the value of their practices, providing structured exit strategies, and facilitating smooth transitions.
Final Steps
There is no recipe for creating a business plan for law firm development. What goes into your mission statement and plan will depend on several factors, including your law firm's business model. But this is a feature, not a bug of developing a business plan.
The process of business planning will help you develop solutions to issues you might have overlooked. If you have law partners, just going through the process of creating a law firm business plan can ensure that everyone is on the same page.
As you create your plan, the process itself should provoke thoughts and ideas so you can have a unique law firm tailored to your goals and values. This will help you get exactly what you wanted when you started in the legal industry.
To learn how to expand your client base as your firm grows, check out Grow Law Firm, a professional law firm SEO agency .

- Easy steps you can take to bring in more clients and up this year’s revenue
- The top website and marketing mistakes holding your law firm back

Find out how much demand there is in your geographical area

To view the calculation tailored to your law firm's needs, please provide your email address

Consult with Sasha Berson, a legal marketing expert , to address your marketing needs.
You May Also Like

Law Firm Marketing Budget: How Much Should You Spend?

Unlocking the Secrets of Law Firm Partnership Structures: A Must-Read Guide for Success-Driven Lawyers

Lawyers Against Unbillable Hours: Joshua Lennon Maximizes Attorney Billable Hours

How to Start a Law Firm in 2024 and Succeed

Starting a Law Firm: LLP vs. PC

Don't just wait for clients, attract them!
Get our FREE Marketing Audit to find bold new ways to boost your caseload.
Contact us today to speak with one of our experts and learn more about how we can help you grow your firm.

Stay ahead of the competition!
Compare your law firm's performance to Local competitors with our instant assessment tool
Get a clear picture of your firm's performance
Boost your online presence
.webp)

Law Firm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Law Firm Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 lawyers to create business plans to start and grow their law firms. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a law firm business plan template step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is a Law Firm Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your law firm as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategy for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for a Law Firm
If you’re looking to start a law firm, or grow your existing law firm, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your law firm in order to improve your chances of success. Your law firm plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for Law Firms
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for a law firm are personal savings, credit cards and bank loans. With regards to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to confirm that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for a law firm.
If you want to start a law firm or expand your current one, you need a business plan. Below are links to each section of your law firm plan template:
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your Executive Summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the type of law firm you are operating and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have a law firm that you would like to grow, or are you operating law firms in multiple cities?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan. For example, give a brief overview of the law firm industry. Discuss the type of law firm you are operating. Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers. Provide a snapshot of your marketing plan. Identify the key members of your team. And offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Analysis
In your company analysis, you will detail the type of law firm you are operating.
For example, you might operate one of the following types of law firms:
- Commercial Law : this type of law firm focuses on financial matters such as merger and acquisition, raising capital, IPOs, etc.
- Criminal, Civil Negligence, and Personal Injury Law: this type of business focuses on accidents, malpractice, and criminal defense.
- Real Estate Law: this type of practice deals with property transactions and property use.
- Labor Law: this type of firm handles everything related to employment, from pensions/benefits, to contract negotiation.
In addition to explaining the type of law firm you will operate, the Company Analysis section of your business plan needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to question such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of clients served, number of cases won, etc.
- Your legal structure. Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry analysis, you need to provide an overview of the law firm industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the law firm industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your strategy, particularly if your research identifies market trends.
The third reason for market research is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your law firm plan:
- How big is the law firm industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential market for your law firm? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your law firm plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: businesses, households, and government organizations.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of law firm you operate. Clearly, households would respond to different marketing promotions than nonprofit organizations, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, include a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. Because most law firms primarily serve customers living in their same city or town, such demographic information is easy to find on government websites.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can understand and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your Law Firm Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other law firms.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t direct competitors. This includes accounting firms or human resources companies. You need to mention such competition as well.
With regards to direct competition, you want to describe the other law firms with which you compete. Most likely, your direct competitors will be law firms located very close to your location.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their businesses and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as:
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What types of cases do they accept?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you provide better legal advice and services?
- Will you provide services that your competitors don’t offer?
- Will you provide more responsive customer interactions?
- Will you offer better pricing or flexible pricing options?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For a law firm plan, your marketing plan should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of law firm company that you documented in your Company Analysis. Then, detail the specific products you will be offering. For example, in addition to in-person consultation, will you provide virtual meetings, or any other services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your marketing plan, you are presenting the products and services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the location of your law firm company. Document your location and mention how the location will impact your success. For example, is your law firm located in a busy business district, office building, etc. Discuss how your location might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your law firm marketing plan is the promotions section. Here you will document how you will drive customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertising in local papers and magazines
- Reaching out to local websites
- Social media marketing
- Local radio advertising
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your law firm, including filling and filing paperwork, researching precedents, appearing in court, meeting with clients, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to file your 100th lawsuit, or be on retainer with 25 business clients, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your law firm to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your law firm’ ability to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing law firms. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act like mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with legal experience or with a track record of successfully running small businesses.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet and cash flow statements.
Income Statement : an income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenues and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you file 25 lawsuits per month or sign 5 retainer contracts per month? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets : Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your law firm, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a bank writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement : Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and make sure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
In developing your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing a law firm:
- Location build-out including design fees, construction, etc.
- Cost of licensing, software, and office supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Taxes and permits
- Legal expenses
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your office location lease or your certificate of admission to the bar.
Putting together a business plan for your law firm is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert and know everything you need about starting a law firm business plan; once you create your plan, download it to PDF to show banks and investors. You will really understand the law firm industry, your competition, and your customers. You will have developed a marketing plan and will really understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful law firm.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your Law Firm business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

- Support Center
- System Status

A business plan for lawyers: How to write one and what to include

- June 21, 2024

Jennifer Anderson

If you’re reading this article, Congratulations! You must be thinking about starting a law firm and are looking for examples of a business plan for lawyers.
Of course, if you’re serious about this prospect, one of the first things you’ll need to do is sit down and draft a business plan. And, as luck would have it, that’s why we’re here today.
In this post, we’re going to walk you through the steps of creating a business plan for your new firm. As Aristotle once said, “For the things we have to learn before we can do them, we learn by doing them.”
Sound advice.
A simple guide for a business plan for lawyers
So, we’ll provide you with the key parts and pieces for creating a law firm business plan along with a sample plan intended to show you how to create your own plan.
Now, in order to walk you through this, we’ve created a hypothetical firm using certain assumptions, which we’ll list below. Your new firm almost certainly has different factors at play.
That’s alright. We trust you’ll be able to plug in the particulars that suit your business. For now, here’s what our fictional new law firm looks like:
- This California-based law firm is founded by four partners who were all business owners before going to law school. Using our fictional founders’ last names, we’ll call the firm Smith, Jones, Jackson, & Wyle, LLP.
- The firm aims to have multiple practice areas including business litigation, labor and employment, technology, and real estate.
- The target clients will be small-to-midsize regional businesses throughout the state.
- The partners’ goal is to hire up to 10 associates over the next five years.
- The firm’s main competitors are other small, regional business-focused firms.
- Initial marketing ideas include social media, networking with former business contacts, and becoming thought leaders in various areas of the law through blogging and public speaking.
- The partners envision being highly tech dependent, utilizing CRMs, AI, and other tech tools as much as possible.
- The founding partners’ goal is to launch the firm in 6 months and to be profitable within a year.
With those basic facts in mind, let’s break down the various components that we’ll include in our business plan:
1. Executive summary
A business plan for lawyers, like any plan, should start with an e xecutive summary . This section concisely outlines a business plan’s key points, goals, and strategies. Ultimately, it serves as a snapshot for quick understanding and decision-making and should include the following parts:
Mission statement
A Mission Statement is like the elevator speech for your new firm. It charts the course for your goals, objectives, clients – and also quickly lays out your proposed methods for reaching those goals. A sample Mission Statement for our firm might say:
At Smith, Jones, Jackson, & Wyle, LLP (“SJJW”) we are dedicated to empowering small-to-midsize businesses in California with comprehensive legal solutions. With a foundation built on the rich business acumen and legal expertise of our founding partners, we aim to bridge the gap between business challenges and legal success. Our mission is to provide personalized, effective, and technology-driven legal services that not only address today’s legal needs but also anticipate tomorrow’s challenges. We are committed to becoming trusted advisors to our clients who leverage our unique background as former business owners to offer practical, actionable legal advice. Through innovation, integrity, and a client-focused approach, SJJW strives to achieve excellence in all aspects of our service, fostering long-term partnerships with our clients and contributing to their success.
Here, you will outline the firm’s growth objectives and provide a snapshot of the firm’s operations.
SJJW aims to become the leading legal advisor for California’s small to mid-sized businesses, expand our team with 10 associates within five years, and leverage technology to enhance efficiency and client satisfaction.
Brief overview
Some business plans also include a brief overview of the business. Our hypothetical firm’s overview might look like this:
Founded by four partners with business ownership backgrounds, our California-based law firm specializes in serving small-to-midsize businesses, emphasizing technology-driven solutions and personalized legal services to navigate complex challenges.
2. Firm description
Your law firm description will provide a bit more detail about the make-up of your business. This section should include information on: (1) legal structure and history; (2) location and areas of practice; and (3) vision for the future:
SJJW is a dynamic legal partnership founded by four seasoned attorneys who are also experienced business owners. Based in California, our firm offers comprehensive legal services tailored to the needs and challenges of small-to-midsize businesses across the state. Our firm practices in four distinct areas: Business Litigation, Labor and Employment, Technology, and Real Estate. With a deep understanding of both the legal landscape and the entrepreneurial journey, our team is uniquely positioned to provide strategic, effective solutions across this range of legal disciplines. As an LLP, we emphasize collaboration, integrity, and innovation, leveraging cutting-edge technology to deliver exceptional service and outcomes for our clients. Our commitment to excellence, combined with our business-savvy approach, makes us a trusted partner for businesses seeking to navigate legal complexities with confidence.
3. Market analysis
The next part of our business plan for lawyers is the market analysis. Your market analysis is where you do the heavy lifting around how your firm fits into California’s extensive legal market. It should include information on your target market, a competitive analysis, and the need for your particular firm within the region.
Target market
SJJW’s primary target market consists of small-to-midsize businesses in California, spanning various industries such as technology, retail, real estate, energy, and manufacturing. These businesses often encounter unique legal challenges that require personalized attention and expertise. With the state’s diverse economic landscape, there is a substantial demand for legal services that cater specifically to the nuanced needs of these entities, from regulatory compliance and intellectual property protection to labor disputes and contract negotiations.
Competitive landscape
The legal services market in California is highly competitive, with numerous firms vying for the business sector’s attention. Small, regional law firms similar to ours form the bulk of this competition, offering a range of general and specialized services. However, our differentiation lies in the unique blend of legal expertise and real-world business experience possessed by our founding partners. This combination positions us to offer unparalleled insights and practical solutions that resonate with business owners.
Market trends
The increasing complexity of regulatory environments, coupled with the rapid evolution of technology and the digital economy, has led businesses to seek legal partners who are not only advisors but also innovators. There’s a growing trend towards legal services that are highly specialized yet broadly knowledgeable about the cross-functional impacts of legal decisions.
Opportunities
Given our firm’s unique positioning and expertise, significant opportunities exist to capture market share by:
- Offering specialized services that address the intersection of business operations and legal requirements, such as compliance, data privacy, and e-commerce.
- Developing niche expertise in emerging areas of law that are particularly relevant to California’s business environment, such as tech startups, renewable energy, and digital media.
- Leveraging technology to provide more efficient, transparent, and cost-effective legal services, appealing to the tech-savvy and cost-conscious small-to-midsize business sector.
- Building strong relationships through networking and thought leadership, establishing the founding partners as go-to experts in legal matters relating to business.
Key challenges include establishing a distinct brand in a crowded market, continually adapting to rapidly changing legal and technological landscapes, and ensuring the firm remains accessible and appealing to the target market’s cost and value expectations.
In summary, the market analysis underscores the potential for SJJW to carve out a significant presence in California’s legal services sector for small-to-midsize businesses. By focusing on our strengths and strategically addressing the market’s needs, we can achieve substantial growth and success.
4. Marketing and sales strategy
The marketing and sales strategy is a crucial but often neglected aspect of any business plan for lawyers. This is where you lay out how you’re going to attract clients, convince them to use your firm’s services, and – importantly – how you’re going to retain those clients long term:
Our objective is to establish SJJW as the premier legal service provider for small to mid-sized businesses in California, leveraging our unique blend of business acumen and legal expertise.
Marketing strategy
Brand positioning
Position the firm as not just legal experts, but as partners in our clients’ business success, emphasizing our founding partners’ background as business owners.
Digital marketing
- Website : Develop a professional website highlighting our expertise, services, and the unique value we bring to businesses.
- Content marketing : Regularly publish blogs, articles, and whitepapers on legal issues affecting our target market, positioning us as thought leaders.
- Social media : Engage with our audience on platforms like LinkedIn and Twitter, sharing insights, legal updates, and participating in discussions relevant to our target industries.
Networking and partnerships
- Leverage the existing business contacts of our founding partners and actively participate in industry events, seminars, and local business associations to build relationships and referrals.
- Establish partnerships with complementary service providers (e.g., accounting firms, business consultants) to offer bundled services or referrals.
Public relations
- Engage in speaking opportunities at industry conferences, webinars, and local business events to increase visibility and establish credibility.
- Utilize press releases for significant firm milestones, new service offerings, or significant case wins to build brand awareness.
Sales strategy
Client acquisition
- Implement a CRM system to manage leads and opportunities effectively and utilize personalized follow-up and engagement strategies.
- Offer free initial consultations to prospective clients that provide immediate value and foster trust from the first interaction.
Client retention
- Provide exceptional client service with a focus on transparency, regular communication, and technology-driven solutions for ease of access and efficiency.
- Implement a client feedback loop to continuously improve services and address client needs proactively.
Cross-selling and up-selling
Once a client relationship is established, SJJW will identify additional legal needs or areas where the firm can provide value. The goal is to make sure all clients are aware of the full range of services offered.
By executing this comprehensive marketing and sales strategy, SJJW aims to rapidly grow its client base while maintaining high levels of client satisfaction and loyalty.
5. Operations plan
An operations plan outlines the day-to-day activities required to run your law firm. It details things like processes, technology, staffing, and resources needed to achieve business objectives.
To ensure efficient, effective, and client-focused legal service delivery through advanced technology integration and streamlined processes.
Legal operations
Case managemen t: Implement a state-of-the-art Case Management System (CMS) to track and manage all cases efficiently, ensuring deadlines are met, and clients are kept informed.
Document management : Utilize a secure, cloud-based Document Management System (DMS) for storing, retrieving, and sharing documents with clients and within the team, enhancing collaboration and security.
Client communication : Adopt Customer Relationship Management (CRM) software to manage client interactions, ensuring personalized and timely communication across all touchpoints.
Technology integration
Artificial Intelligence (AI) : Leverage AI tools for legal research, document review, and predictive analytics to increase accuracy and reduce turnaround times.
Automation tools : Implement automation in routine tasks such as billing, client notifications, and document drafting to improve efficiency and reduce the risk of human error.
Human resources
Team structure : SJJW will initially be comprised of four partners and support staff, with plans to expand to up to 10 associates within five years. It is our goal to foster a culture of teamwork and continuous learning.
Professional development : Invest in ongoing training and professional development opportunities for all staff, ensuring the team remains at the forefront of legal and technological advancements.
Client service
Service delivery model : Offer flexible service models including traditional hourly billing and alternative arrangements like flat fees for defined services.
Client feedback system : Implement a system for collecting and acting on client feedback to continually refine and improve service offerings.
Compliance and quality assurance
Regulatory compliance : Ensure strict adherence to legal and ethical standards, with regular reviews of compliance protocols, especially regarding data protection and privacy laws.
Quality control : Establish a quality control framework to review legal work internally, guaranteeing the highest standards of legal service.
6. Financial plan
Your financial plan is one of the most critical aspects of a business plan for lawyers. There are too many factors at play here for us to create a meaningful sample plan for our hypothetical firm, but here are the details you definitely want to include in your plan:
Initial capital and use
Detail how the initial capital provided by the founding partners will be allocated (e.g., office space, technology, marketing, initial payroll).
Financial projections
Include projections for revenue, expenses, and profitability for the first 1-5 years. Use realistic assumptions based on the size of your target market, expected client acquisition rates, billing rates, and operational costs.
Revenue projections
Estimate potential earnings from client work, taking into account the growth in associate numbers and the capacity to handle more cases and matters.
Expense projections
Forecast expenses, including salaries, technology investments, office overhead, and marketing costs.
Profitability analysis
Calculate when the firm expects to become profitable. Our hypothetical firm, for example, aims to be profitable within the first year.
7. Legal and regulatory compliance
What kind of lawyers would you be if your plan didn’t include a section on legal and regulatory compliance ? A business plan for lawyers should always cover compliance, particularly in an environment where it is becoming increasingly important for firms to accommodate it .
This is where you’ll provide details regarding legal practice, data protection, and any relevant regulations for your areas of practice.
To uphold the highest standards of legal and ethical integrity by ensuring full compliance with all applicable laws, regulations, and professional guidelines governing the practice of law in California.
Compliance framework
State Bar of California : SJJW will strictly adhere to the rules and ethical standards set forth by the State Bar of California, including those related to client confidentiality, conflict of interest, and professional conduct.
Data protection and privacy : We will implement powerful data security measures compliant with the California Consumer Privacy Act (CCPA) and any relevant federal laws. We will also protect client information through encrypted storage and secure communication channels.
Business operations compliance : As an LLP, SJJW will maintain compliance with California’s business operation laws, including partnership registration requirements, financial reporting, and tax obligations.
Employment law : It is our steadfast aim to follow all state and federal employment laws, ensuring fair labor practices, workplace safety, and equal opportunity employment within the firm.
Continuous monitoring and education
Regular training : We will conduct or host ongoing legal education and training for all partners and staff on compliance matters, changes in the law, and best practices in legal ethics and data protection.
Compliance audits : The firm will perform regular internal audits to review and assess compliance with all legal, regulatory, and ethical standards, identifying and rectifying any potential issues proactively.
Risk management
Professional liability insurance : Before beginning operations, SJJW will secure comprehensive professional liability insurance to protect the firm and its clients against potential legal malpractice claims or other claims.
Conflict of interest checks : The firm will implement a rigorous system for conducting conflict of interest checks for every new client and case, with the goal of preventing ethical breaches and maintaining the firm’s integrity.
Client confidentiality and trust
Confidentiality protocols : SJJW will establish strict confidentiality protocols to protect client information, including secure document handling procedures and restricted access to sensitive data.
Client trust accounts : In accordance with California law, the firm will manage client funds with the utmost care, adhering to the State Bar’s guidelines for handling and accounting for trust accounts, ensuring transparency and accountability.
8. Milestones and timeline
Finally, a business plan for lawyers should include a section that details the timing involved in getting your law firm up and running. Again, there are probably too many details to give an effective sample here, but at the very least, your plan should include the following components:
Launch timeline
Here, you’ll plot out the key steps leading up to your launch date , including legal organization, the establishment of your office space, technology implementation, and initial marketing.
Growth milestones
Lawyers love deadlines and the growth milestones section is a good place to create them. Set specific goals for things like client acquisition, revenue targets, and team expansion to be reached within the first year and beyond.
Obviously, your firm’s business plan will include a lot more detail than our hypothetical plan for SJJW. We hope, however, that this sample plan gets you started on an enjoyable journey to starting a successful law firm.
Starting a law firm is a challenging yet rewarding endeavor. A well-crafted business plan for lawyers means getting all the essentials in place to guide your firm’s growth and success.
Get your executive summary, firm description, market analysis, marketing and sales strategy, operations plan, financial plan, and legal compliance all covered before embarking.
With careful planning and execution, you can build a firm that not only meets but exceeds your expectations, providing exceptional legal services to your clients.
One Legal: Delightfully easy eFiling

Share this article on social media:
More to explore.

A handy guide to legal due diligence

Tips and resources for handling international litigation

What you need to know about being a tech lawyer
What is one legal.
We’re California’s leading litigation services platform, offering eFiling, process serving, and courtesy copy delivery in all 58 California counties. Our simple, dependable platform is trusted by over 20,000 law firms to file and serve over a million cases each year.

All of your litigation support needs at your fingertips
© InfoTrack US, Inc.
- Accessibility statement
- Privacy policy
- Terms of service
You're invited!
Join us the second week of September for the next Beyond the Serves office hour session. Our One Legal customer success team will be on hand to answer all your questions. Don’t miss out on this opportunity to get the insights you need!
Legal Up Virtual Conference
Register now to get actionable strategies and inspiration to level up your legal career.

Client Management
Case management, billing & payments, accounting & report, e-signature.
- Help Center
Starting a law firm can be a rewarding and lucrative venture, but it requires careful planning and strategy. A well-crafted business plan is a crucial tool for any law firm looking to establish itself, secure funding, or grow its practice. The business plan will serve as a roadmap, outlining the law firm’s objectives, strategies, and unique selling proposition
Why Every Law Firm Needs a Business Plan
A well-structured business plan is imperative for every law firm, regardless of its size or specialization. While legal expertise is undoubtedly crucial, having a clear vision and strategic direction is equally essential. A business plan serves as a guiding light, defining the firm’s mission, values, and long-term goals. This clarity is vital for aligning the entire firm towards a common purpose, ensuring that everyone understands the objectives and the path to achieving them. Without a business plan, a law firm may find itself navigating uncertain waters, reacting to circumstances rather than proactively pursuing its ambitions.
The Key Components of a Law Firm Business Plan
A well-structured law firm business plan consists of several key components, each playing a crucial role in guiding the firm’s operations and ensuring its long-term success. Here are the essential elements of a comprehensive law firm business plan:
- Executive summary
- Law firm description
- Market analysis
- Organization and management
- Services
- Marketing Strategy
- Financial plan
- Start-up budget
Section One: Executive Summary
The executive summary is arguably the most critical section of your law firm’s business plan. While it appears at the beginning, it is often written last, as it serves as a concise yet comprehensive overview of your entire plan. This section should capture the reader’s attention, providing them with a clear understanding of your law firm’s essence, mission, and what to expect from the rest of the document. In your executive summary:
- Introduce your law firm: Briefly describe your law firm’s name, location, and legal specialization.
- Mission and vision: State your firm’s mission and vision, highlighting your commitment to serving clients’ legal needs effectively.
- Your unique selling proposition: Clearly state your USP, and present what is unique about your firm that will ensure success.
The executive summary sets the stage for your entire business plan. It should be a concise yet compelling introduction to your firm’s mission, values, and potential. If crafted well, it can grab the reader’s attention and encourage them to explore other sections in detail. If you feel overwhelmed by this, you can write this section last.
Section Two: Law Firm Description
This section of your business plan provides a deeper dive into your firm’s background, history, legal specializations, and legal structure and ownership. This section should provide a concise yet informative overview of your firm’s identity and history. Here’s what this section should cover:
- Mission Statement: Briefly reiterate your law firm’s mission statement. This statement should encapsulate your firm’s overarching purpose and guiding principles.
- Geographic Location: State out the physical location of your law firm’s office(s). This should include the city or region where your primary office is situated.
- Legal Structure and Ownership: State the legal structure of your law firm, whether it’s an LLC, S-Corp, or another legal entity. This choice is a fundamental aspect of your business model, influencing ownership, liability, and taxation. If your firm’s ownership is not that of a sole proprietorship, provide details on the ownership structure. Explain how the chosen structure aligns with your firm’s business model, decision-making processes, and long-term goals.
- Firm History: Provide the history of your law firm. Highlight key milestones, achievements, and notable moments in your firm’s journey. If your firm is well-established, briefly summarize its history, showcasing your accomplishments and contributions to the legal field.
Remember that brevity is key in this section. Don’t spend too much time, just touch on important points and achievements.
Section Three: Market Analysis
A well-conducted market analysis will not only demonstrate your understanding of the legal industry but also inform your law firm’s strategies and decision-making. It goes beyond understanding your competition; it delves deep into your potential clients’ needs and expectations.
Through market analysis, you can segment your target market based on demographics, industry, legal needs, and preferences. This segmentation allows you to tailor your services to meet the specific needs of different client groups. It also helps you identify the pain points and challenges that potential clients face. By understanding their concerns, you can offer solutions that directly address these pain points.
Your market analysis should also reveal the pricing strategies of your competitors. By benchmarking your pricing against theirs, you can position your services competitively. You can choose to price higher if you offer unique value or lower if you aim to attract price-sensitive clients. Your market analysis should reveal areas where your competitors may be falling short. Use this information to frame your services as the solution to these weaknesses. For example, if competitors have slow response times, emphasize your firm’s commitment to timely communication.
Showcase your firm’s USPs that directly address client needs and preferences. If you excel in a particular practice area, have a reputation for excellent client service, or offer innovative fee structures, use these strengths to attract your preferred clientele. Ultimately, a well-documented market analysis not only informs your law firm’s business model but also guides your approach to client acquisition, pricing, and service delivery. It ensures that your legal services align with client expectations and positions your firm for success in a competitive legal industry
Section Four: Organization and Management
Image Source – Creately
This section provides a clear picture of your firm’s internal structure and leadership. Name the key stakeholders in your law firm and what they bring to the table. Highlight any unique experiences or expertise that each partner brings to the firm. This could include prior work at prestigious law firms, involvement in landmark cases, or specialized knowledge in a specific area of law. Explain how these experiences set your firm apart and enhance its capabilities. You can also include an organizational chart that visually represents your law firm’s structure. This chart should showcase the hierarchy, roles, and reporting lines within the firm. By including the names, educational backgrounds, unique experiences, and organizational chart, you paint a comprehensive picture of your law firm’s leadership and structure. This not only builds confidence in your team’s capabilities but also showcases the depth and expertise of your staff to potential clients, partners, or investors.
Section Five: Services
This section is the core of your law firm business plan. Here, you will go into detail about all aspects of your services. Present in simple words:
- The problem(s) your law firm is addressing and your approach to how to alleviate those pain points? Answer these questions, and provide in detail how your firm is in the best position to tackle this problem.
- The solution(s) you are providing. This should describe how your law firm resolves your prospective market’s needs. This should include the work you do, and the benefits that each client will receive if they work with your firm.
- Your law firm competition. This should describe what advantages your law firm has over your competitors? What you do differently when providing your solutions and how your clients will gain additional benefits when they work with your law firm.
Section Six: Marketing Strategy
As you craft your business plan, keep these four essential questions in mind:
- What Is Your Firm’s Value Proposition? Clearly define what sets your law firm apart from others. This should guide your marketing and sales strategies, emphasizing the unique value you offer to clients.
- Who Is Your Target Audience? Identify your ideal client profile. Understanding your target audience helps tailor your marketing efforts to reach those most likely to benefit from your services.
- What Are Your Growth Goals? Set specific, measurable growth goals for your firm. These goals should inform your sales and marketing strategies, outlining how you plan to achieve them.
- How Will You Measure Success? Determine key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the success of your marketing and sales efforts. Whether it’s tracking client acquisition rates, website traffic, or revenue growth, having measurable metrics will help you gauge your progress and make informed adjustments.
It is also valuable to perform a SWOT analysis (Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats) to assess your law firm’s internal and external factors. Describe your online marketing efforts, including your website, social media presence, and email marketing campaigns. Explain how you plan to leverage marketing to reach and engage potential clients effectively. You should also define your pricing structure and fee arrangements. This may include hourly rates for specific legal services, retainer agreements for ongoing representation, or flat fees for standardized services.
Section Seven: Financial Plan
If you want to expand your law firm and ensure a steady income, it’s essential to create a financial strategy for your practice. While you might not have all the answers regarding your firm’s finances, provide comprehensive details. Your goal should be to establish a financial plan, particularly for the initial year of your firm’s operation.
Provide comprehensive financial projections that cover the anticipated income, expenses, and cash flow for your law firm. These forecasts should offer a clear picture of how your firm expects to perform financially. You should also Incorporate income statements, which show your firm’s revenue and expenses, balance sheets that detail your assets and liabilities, and cash flow projections, which illustrate how money moves in and out of your business. These financial statements offer a holistic view of your firm’s financial health.
Explain the assumptions underlying your financial projections. This may include factors like growth rates, market trends, client acquisition strategies, and pricing models. Describe your strategies for achieving growth and how they translate into financial outcomes. This section is critical for demonstrating your law firm’s financial preparedness and sustainability. Investors, lenders, or partners will scrutinize these sections to assess the viability of your firm, making it essential to provide detailed and well-supported financial information.
Section Eight: Start-up Budget
When developing a business plan for your law firm, it is essential to create a realistic startup budget. This involves carefully considering various initial and ongoing expenses and factoring them into your revenue objectives. Here are some instances of expenses to incorporate into your budget:
- Hardware costs, such as laptops, printers, scanners, and office furniture.
- Office space expenses, whether you plan to rent space or work from home.
- Malpractice insurance fees.
- Staff salaries, including potential hires like administrative assistants or paralegals.
- Utility expenses, covering phone and internet services, among others.
- Expenses on practice management software or other tech tools
After itemizing these costs, review them thoroughly. Clearly state the total amount of funding you require to start and sustain your law firm. Explain how this funding will be allocated, including how much goes into covering startup costs and how much is reserved for ongoing operations. Be specific about the purpose of each funding component.
Additionally, explore tools and solutions that can streamline non-billable tasks, freeing up more time for your legal practice. This not only enhances your overall productivity but also allows you to allocate more time to your legal practice. One exceptional solution that can significantly benefit your law firm operations is a legal practice management software.
DigitsLaw: The Legal Practice Management Software for Law Firms
DigitsLaw is an all-in-one practice management software that streamlines and simplifies the day-to-day operations of a law firm. Whether you are a small firm or you have law firms in major cities, DigitsLaw can meet the unique needs of your legal practice. Our simple and intuitive tool offers a wealth of features that can make a substantial difference in the success and efficiency of your firm.
Here’s how DigitsLaw can help your new law firm scale:
- Effortless Case Management: DigitsLaw simplifies case management by centralizing all your client information, documents, and communications in one secure location. This ensures that you have easy access to everything you need, right at your fingertips.
- Time Tracking and Billing: With DigitsLaw, tracking billable hours and generating invoices is seamless. You can accurately record your time, expenses, and activities, allowing for transparent and error-free billing processes.
- Conflict Check: DigitsLaw provides a robust conflict check system that assists law firms in maintaining ethical standards and preventing conflicts of interest. By incorporating DigitsLaw conflict check capabilities into your law firm’s workflow, you can enhance your due diligence processes, reduce the risk of conflicts of interest, and uphold the highest ethical standards in your legal practice.
- Client Collaboration: Foster better client relationships through DigitsLaw’s client portal . Clients can securely access case information, share documents, and communicate with your firm, enhancing transparency and trust.
- Legal Document Management: Say goodbye to the hassle of paper documents and disorganized files. DigitsLaw enables efficient document storage, organization, and collaboration, saving you time and reducing the risk of errors.
- Secure and Compliant: DigitsLaw prioritizes security and compliance, ensuring that your client data and sensitive information are protected at the highest standards.
By leveraging DigitsLaw’s capabilities, you can significantly reduce administrative overhead, minimize errors, and provide a more streamlined and responsive experience for your clients. It’s a strategic investment that will pay dividends as your firm grows and prospers.
Sample Business Plan and Fillable Template
If you’re in the early stages of creating your business plan, we’ve prepared an example that can serve as a reference. You can also download a blank version of our template here. Remember to tailor your plan to your specific requirements and objectives.
Download your copy of our law firm business plan template HERE
Final thoughts.
In conclusion, crafting a law firm business plan is not just a formality; it’s a roadmap that guides your firm toward success. Whether you’re launching a new law firm or seeking to revitalize an existing one, a well-thought-out plan helps you. From defining your firm’s mission and values to conducting a thorough market analysis every section of your plan plays a crucial role in shaping your law firm’s journey. It’s not just about impressing potential investors; it’s about setting clear goals, making informed decisions, and ensuring that your firm is well-prepared for the challenges and opportunities that lie ahead.
As you start planning, remember that your business plan is a living document. It should evolve and adapt as your firm grows and the legal industry changes. Regularly revisit and update your plan to stay aligned with your mission, serve your clients better, and achieve your long-term vision.

Share this post
Latest Writings
The latest news and resources from our team

Our Integrations
It is the easiest and most organized way to manage your law firm, clients, cases, billing, accounting and more.
Get the app
© 2023 Digitslaw. All rights reserved.
- Sample Business Plans
Law Firm Business Plan
If you are a lawyer, chances are you have thought of owning a law firm at least once if not more.
After all, having your firm gives you the freedom of taking up projects that you like and working at flexible hours.
But with freedom comes responsibility, and most of us find the thought of doing everything from onboarding clients to taking care of every detail of their case at least in the initial days quite overwhelming.
But don’t worry! It isn’t as scary as it looks. All you need to run a successful law firm is your sharp wit to deal with cases and a well-written law firm business plan to deal with the business side of your profession.

Free Law Firm Business Plan Template
Download our free business plan template now and pave the way to success. Let’s turn your vision into an actionable strategy!
- Fill in the blanks – Outline
- Financial Tables
Industry Overview
The global legal services market was valued at a whopping sum of 849.28 billion dollars in 2020 and is expected to rise at a high rate going forward too.
The main changes in the legal industry have been brought about by the introduction of AI which does proofreading and data research jobs with higher efficiency. This lets the lawyers focus on what really matters.
Also, the security and access systems have become loads better due to cloud computing.
What is Law Firm Business Plan?
A law firm business plan is a document that outlines your business goals and strategies to achieve those goals. It includes your law firm overview, your reason to start your firm, the services you will offer, a budget or funding requirements, and strategies to get and manage your clients.
Why Law Firm Business Plan is Important?
A business plan would help you understand what sets you apart from your competitors, and how you can market your USP to your clients.
It also helps you design strategies to reach out to your clients and manage them. It comes in extremely handy for analyzing the loopholes in your business structure.
Moreover, it helps you identify your strengths and work on your weaknesses.
All in all, It can make managing your business a hassle-free and less chaotic process.
Things to Consider Before Writing a Law Firm Business Plan
Focus on your expertise.
Between juggling business and practice, it is natural that practice gets neglected more often than not. But always keep in mind that though focusing on your business is important it shouldn’t come at the cost of skills you need to develop and upgrade to do well as a lawyer.
Also, it is important to decide on a niche so you can dig deeper and become an expert at handling cases of that kind.
Create a proper website
In today’s world being present and active on the internet is as important for your business as being good at what you do.
A strong web presence helps you reach out to your customers as well as builds your reliability for them.
Build your network
Networking is an important aspect of being a lawyer. From getting new customers, getting updates on the legal world, and even collecting evidence if you are a criminal lawyer, a good network can work wonders for your legal business.
The kind of circle you belong to also has an impact on your reputation and image as a lawyer.
Develop soft skills
We all know that confidence and intellect are a lawyer’s best friends. And although it is an ongoing process to develop these skills, it is good to get a head start before you start your business.
Intellect helps you upgrade and pay attention to detail, and confidence helps you sound more convincing and reliable. Both of which are foundational to a legal business.
How to Write a Law Firm Business Plan?
A law firm business plan would be a combination of segments common to all business plans and segments specific to a law firm.
Before you start writing your business plan for your new law firm, spend as much time as you can reading through some examples of consulting-related business plans .
Reading some sample business plans will give you a good idea of what you’re aiming for. It will also show you the different sections that different entrepreneurs include and the language they use to write about themselves and their business plans.
We have created this sample law firm business plan for you to get a good idea about how a perfect law firm business plan should look like and what details you will need to include in your stunning business plan.
Chalking out Your Business Plan
Starting your own law firm is an exciting prospect for any lawyer. Having your firm gives you more independence, lets you implement ideas you want to, and most importantly, you get to deal with clients firsthand.
And if you plan on starting your own, do so with a proper business plan.
But you might wonder, why do I need a business plan as a lawyer, isn’t my legal knowledge and years of work enough?
The answer is no.
To run a law firm you need a law degree, but to run a successful business you need a business plan alongside your degree.
Law Firm Business Plan Outline
This is the standard law firm business plan outline which will cover all important sections that you should include in your business plan.
- Mission Statement
- Vision Statement
- Financial Summary
- 3 Year profit forecast
- Business Structure
- Startup cost
- Market Analysis
- Market Trends
- Target Market
- Market Segmentation
- Sales Strategy
- Marketing Strategy
- Pricing Strategy
- Personnel Plan
- Financial Plan
- Important Assumptions
- Brake-even Analysis
- Profit Yearly
- Gross Margin Yearly
- Projected Cash Flow
- Projected Balance Sheet
- Business Ratios
Say goodbye to boring templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

Now, let’s understand how you can complete each section of your business plan.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary forms the first page of your business plan. It acts as a pitch for your business to potential investors and should consist of the following sections.
- Objective: This gives an overview of what you wish to accomplish with your business. The objective should be clear and solve an existing problem in the market.
- Vision Statement: This should state what vision you have for your business. How do you want it to function and how far do you expect to reach with it. You can also include how your vision sits with the current market situation.
- Financial Summary: This section should ideally consist of the history of your finances and their current state. A proper financial summary helps you gain an investor’s confidence and makes it easier for your business to get funded.
2. Company Summary
Next up we have the company summary section, this segment provides an overview of your company’s structure and its functioning.
This section provides a brief description of the following:
- Legal Structure: This section would describe the legal terms and conditions your firm functions on, as well as the ownership structure of your firm.
- USP: This would consist of points that set your firm apart from your competitor’s firm.
- Services: This section will include the services you offer, the legal procedures you are well versed in, all in all, the client base you cater to.
- Location: This segment covers your area of service and the location of your firm. A clearly stated area of service, helps you reach the right audience.
3. Market analysis
This segment consists of a thorough analysis of the market situation. It can be split up into the following sub-segments.
- Market Trends: This would consist of all the prevailing trends in the market. It is important to know market trends because it helps your business keep up with the evolving market.
- Target Market: This section would consist of a summary of the market you cater to. Clearly defining your niche helps you reach out to your desired customer base.
- Market Segmentation: In this section, note down the segments present in the market, as well as what segment of the market your business would fit in. This would help you narrow down the number of competitors you have, the strategies you must follow, and the major and additional services you should offer.
4. Strategy and implementations
In this section, you would include various business strategies like:
- Marketing strategy You can formulate a marketing strategy depending on your target audience and the easiest and most effective ways of reaching out to them. It is important to formulate your marketing strategy based on your USP and your vision statement.
- Pricing Strategy It is important to formulate a pricing strategy based on the market trends, the nature of the work, and your target audience.
- Milestones This segment would consist of the various milestones your business would have to reach to achieve your goal and the strategies to help you reach them.
5. Financial Plan
The financial section of your business plan would consist of the following information regarding your business.
- Financial history
- Current State of finances
- Profit and loss
Download a sample law firm business plan
Need help writing your business plan from scratch? Here you go; download our free law firm business plan pdf to start.
It’s a modern business plan template specifically designed for your law firm business. Use the example business plan as a guide for writing your own.
The Quickest Way to turn a Business Idea into a Business Plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
Law Firm Business Plan Summary
All of the above segments would help you in creating a well-rounded business plan. Starting your law firm with a well-written business plan can make your growth process faster and smoother.
After getting started with Upmetrics , you can copy this law firm business plan example into your business plan and modify the required information and download your law firm business plan pdf or doc file.
It’s the fastest and easiest way to start writing your business plan.
Related Posts
Law Firm Financial Plan
How to Write a Business Plan for Loan
Notary Business Plan
Bookkeeping Business Plan
About the Author
Upmetrics Team
Upmetrics is the #1 business planning software that helps entrepreneurs and business owners create investment-ready business plans using AI. We regularly share business planning insights on our blog. Check out the Upmetrics blog for such interesting reads. Read more

Turn your business idea into a solid business plan
Explore Plan Builder
Plan your business in the shortest time possible
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee

Create a great Business Plan with great price.
- 400+ Business plan templates & examples
- AI Assistance & step by step guidance
- 4.8 Star rating on Trustpilot
Streamline your business planning process with Upmetrics .

Free Download
Free law firm business plan template.
Whether you’re starting a law firm or developing a plan to grow an existing firm, it’s important to document your goals and how you’ll achieve them. This is why we created an easy-to-use business plan template for law firms.

This template includes sections for:
- Executive summary
- Market analysis
- Marketing strategy
- Financial plan
- Organization and management
How to Create a Law Firm Business Plan
What is in a law firm business plan.
A law firm business plan is an essential piece of document that outlines the goals and growth strategies of your venture. Ideally, it contains several components, such as an executive summary, company description, marketing strategy, financial plan, and organizational structure.
Why Your Law Firm Needs a Business Plan
Here are some of the biggest reasons why you need a law firm business plan:
- Establish your position in the market with unique value propositions.
- Set realistic goals to drive your marketing and business development forward.
- Better manage your law firm by guiding your decision-making process.
- Define an organizational structure for effective communication and collaboration workflows.
- Make better hiring decisions to keep your workforce as lean and efficient as possible.
- Ensure your capital is invested and allocated wisely.
- Create a profitable business model moving into the future.
Things to Consider Before Creating Your Business Plan
As a law firm, your business plan lays the foundation for a financially and professionally successful firm. It’s not something that you can go back to and revise whenever you want.
So, before creating your business plan, settle down and gather your thoughts on how you envision your firm’s success.
More specifically, you need to deliberate on your law firm’s goals, fee structure, and revenue targets.
Define Your Goals
How would you define success as far as running a law firm goes? What are the positive values you want to live by, and how will they benefit your future clients?
A well-defined goal may not seem as important initially, but it significantly impacts your decision-making as you flesh out your business plan.
Your goals can affect how you hire your staff, build your law firm website , plan your pricing, and so on. They will also help you plot out short- to mid-term goals, which serve as milestones that bring you closer to your long-term goals.
Some examples are:
- To have acquired 200 clients by the end of the first year in business.
- Build a solid law firm brand and grow online traffic by 200% in the first six months.
- Attain a case closure rate of at least 80% by the beginning of the third quarter.
Build Your Firm’s Fee Structure
Building your fee structure is an important step that also helps determine if your specified short-term objectives are realistic.
It’s generally a good idea to look at how competitors charge clients for their services. This should give you a baseline rate for similar services you offer.
You can also adopt policies like “no fee unless you win” over an hourly rate, which can attract clients by transferring risk to the firm.
Set Your Revenue Targets
Your annual revenue target is the last measurable piece of information you need to pin down before preparing your law firm business plan.
Don’t be afraid to aim high and exceed the average annual salary of attorneys in your law practice area. Keep in mind that, on top of essential expenses like student loan payments, office lease, insurance, and mortgages, you’ll need more funds for marketing your law firm and growing your team.
To put things into perspective, 2024 data from PayScale revealed that the average annual salary of lawyers in the United States is $97,720.
You can use the average salary as your baseline and increase your target revenue based on how much you’re willing to spend on marketing, advertising, and hiring.
Factor in your fee structure to determine how many clients you need. Of course, you should also consider the number of founding lawyers that your firm starts with.
Finally, use your own discretion and only lower the bar if you believe your target revenue is not humanly possible in terms of caseload. For example, if your target revenue requires you to handle over 150 active cases a month (which most lawyers would still consider attainable — depending on their practice area), you may need to readjust your expectations.
8-Point Law Firm Business Plan Checklist
Now that you have nailed your goals, fee structure, and target revenue, it’s time for the nitty-gritty of building a law firm business plan.
Here’s a rundown of all the key details you must include:
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary provides a concise, top-level overview of all the other elements of your business plan. It also encapsulates three points that give your law firm its unique identity, namely:
- Mission statement: A mission statement focuses on your firm’s purpose and guiding principles, including your commitment to new clients. It should ideally be two sentences at most.
- Core values: Your core values should reflect what you stand for as a legal professional — guiding your firm through tough decisions and challenging cases. Looking for employees who resonate with your core values also helps build a more productive, collaborative, and tightly-wound workplace culture.
- Unique value/selling proposition: A Unique Selling Proposition (USP) is a more direct statement that answers the question, “Why should clients pick you?” Try to capture the benefits and unique qualities that make your firm stand out.
2. Company Description
Next up, the company description summarizes the technical details of your business operations. This provides partners and potential investors a general idea of what your firm does on a day-to-day basis.
Below are the aspects that your firm description should cover:
- Services and target audience: What specific legal services do you offer, and who are they for?
- Legal structure: What is the legal structure of your firm (e.g., sole proprietorship, limited liability company (LLC), limited liability partnership)? If you’re forming a partnership, be sure to include the names and practice areas of each partner.
- Service locations: Where is your office’s location, and which areas do you serve?
3. Market Analysis
Every business plan — regardless of industry — needs preemptive market research to set initial financial projections on revenue and marketing performance.
Dig deep to gauge the demand for your services, how your target audience makes hiring decisions, who your competitors are, and your potential clients’ spending power. Your local bar association website should be a great place to start, along with local attorney directories and legal industry reports.
Be sure your line of inquiries encompasses the following details:
- Your ideal client: Who are you marketing your law firm to? Fill this information with demographic data, such as age, gender, occupation, and location.
- Client motivations: Why do prospects need your legal services? List down their pain points and the qualities they’re looking for in a law firm.
- Industry description: What is the projected size of your market? Are there any ongoing trends to consider?
- Competitive analysis: Build a list of known competitors in your area (similar practice areas serving the same location). You may also include indirect competitors that also compete for your target audience’s attention.
- Projections: How much are your ideal clients willing to pay for legal services? This will help you make fine adjustments to your fee structure.
4. Organization and Management Structure
The next section of your law firm business plan expands on the details of your partners and core staff members.
This process is as straightforward as it gets. Just write up their names, law school, experience, and primary roles in your new firm.
For bigger firms, you may need to create an organizational chart that visualizes who each member reports to.
5. Legal Services
After filling out the organization and management section, create summaries of the legal services your firm will provide.
For example, if you run a business law firm, are you going to cater to dispute resolution, intellectual property, contracts, estate planning, or corporate tax clients?
What specific problems do these services solve? What is your flat fee per hour or case?
More importantly, what are your firm’s unique advantages over competitors that offer similar services?
6. Marketing Strategy
Next comes the more challenging aspects of drawing up a law firm business plan.
In the marketing plan or strategy section, you need to determine a handful of details that play a critical role in your firm’s growth. This includes:
- Target client persona: Briefly describe the profile of your target market (as defined in your market analysis). Then, identify their media consumption preferences, like social media, magazines, and search engines.
- Marketing goals: Map out the marketing objectives you wish to accomplish within set timeframes. For example, are you looking to generate a specific number of leads through online marketing or securing more referral leads from local business partnerships?
- Key Performance Indicators (KPIs): Which KPIs will you use to measure law firm marketing success? You can set target values and brackets to rate the performance of your strategies (getting 10+ clients a month can be rated as excellent, whereas getting less than three clients can be rated as very poor).
- Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, and Threats (SWOT) analysis: An in-depth SWOT analysis can help you set campaign-level objectives for your marketing efforts. For example, having a lot of perfect, five-star reviews on your Google Business Profile is a strength you can leverage to boost your brand image.
- Marketing platforms: What content creation and distribution channels will you use to market your law firm? Depending on your answer, which tools and services do you need to make the most out of your channels?
- Marketing budget: Finally, you need to cook up a detailed law firm marketing budget . Itemize the platforms and strategies you want to use and allocate a budget accordingly (e.g., $3,000 for SEO, $4,000 for billboards, and $2,000 for PPC advertising ).
7. Financial Plan
A solid financial plan does two things: ensure your firm doesn’t run out of cash and create a positive profit margin needed for growth.
Since you’re still building your business plan, you only need to focus on your first year.
Here are the items you need to include:
- Monthly expenses: In addition to your marketing budget, you need to take into account other expenses. Some examples are office space, utilities, IT support, and salaries.
- Monthly target revenue (up to 12 months): Based on the fee structure and revenue goals you calculated earlier, determine the monthly revenue you need to be on track. This should be well above your firm’s monthly expenses.
- Cash flow statement: Attach a cash flow statement to the financial plan section of your law firm business plan. Update your revenue, expenses, and budget accordingly throughout the year.
8. Startup Budget
The startup budget section underlines everything you need to turn your law firm business plan into reality. With extra attention to detail, you can also use it to find opportunities to lower your overhead costs.
Wrap up your business plan by finalizing the following:
- Sources of capital: How will you fund your new law firm? Where is the money coming from?
- Capital allocation: Where will your firm’s initial funds be spent? This can be the same as the expenses table of your financial plan — with the addition of upfront costs like LLC formation and business registration fees.
5 Law Firm Business Plan Templates to Get You Started
Feel free to use the checklist above to create your law firm business plan from scratch. Or, you can streamline the process by using any of the templates below:
- Law Office Business Plan — This template was created by the Oregon State Bar Professional Liability Fund and includes guide questions to help you enter the required information.
- Practice Support Business Plan — This downloadable business plan template by the Law Society of Ireland helps you include specific details like your would-be business contact information, assets, and business continuity planning.
- Startup Business Plan — Canva is home to dozens of graphic business plan templates, including this one, which has all the important sections you need for your law firm.
- Law Firm Business Plan Outline — If you need pointers as you write your business plan, this simple template from practicePRO ensures you don’t miss important details.
- Attorney Business Plan — Lastly, this business plan sample by BCG Attorney Search is for individual lawyers looking to start a small firm or grow their legal practice as a solo attorney.
How About a Custom Marketing Strategy to Execute Your Business Plan?
With your business plan ready, the stage is set for a productive and profitable year for your own law firm. Let’s make sure you hit your goals . Contact us to get a custom marketing strategy crafted specifically for your firm’s needs .
Table of Contents

Related Articles

Employment Lawyer Marketing: Top 13 Strategies For 2024

SSDI Marketing for Lawyers: A Simple Guide

How to Create an Attorney Marketing Plan (With Example)
Dominate Your Market with Digital Marketing Services That Deliver
Talk to a certified professional today, and we will design a strategy specific to your case.

Log in to Lawyerist.com
Not a Subscriber yet? Register here. (It's free!)
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Forgot your password? Reset it here.
Subscribe to Lawyerist
Back to login.
- Hidden Date MM slash DD slash YYYY
- Name * First Last
- Password * Enter Password Confirm Password
- United States
- Which state is your firm's primary location? * Pick one. Alabama Alaska American Samoa Arizona Arkansas California Colorado Connecticut Delaware District of Columbia Florida Georgia Guam Hawaii Idaho Illinois Indiana Iowa Kansas Kentucky Louisiana Maine Maryland Massachusetts Michigan Minnesota Mississippi Missouri Montana Nebraska Nevada New Hampshire New Jersey New Mexico New York North Carolina North Dakota Northern Mariana Islands Ohio Oklahoma Oregon Pennsylvania Puerto Rico Rhode Island South Carolina South Dakota Tennessee Texas Utah U.S. Virgin Islands Vermont Virginia Washington West Virginia Wisconsin Wyoming Armed Forces Americas Armed Forces Europe Armed Forces Pacific State
- Which province is your firm's primary location? * Pick one. Alberta British Columbia Manitoba New Brunswick Newfoundland and Labrador Northwest Territories Nova Scotia Nunavut Ontario Prince Edward Island Quebec Saskatchewan Yukon Province
- What is the size of your firm? * Pick one. Solo practice Small firm (2–15 lawyers) Medium or large firm (16+ lawyers) I do not work at a law firm
- What is your role at your firm? * Pick one. Owner/partner Lawyer Staff Vendor (web designer, consultant, etc.) I do not work at a law firm
- What is your primary practice area? * Pick one. Bankruptcy Civil litigation (non-PI) Class Action Collections Corporate Criminal Education Employment Estate planning, probate, or elder Family General practice Immigration International Landlord/Tenant Mediation/ADR Personal injury Real estate Small business Sports/Entertainment Tax Trademark/IP Other I do not work in law
- Legal Technology Products and Services
- Building a Healthy Firm
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
You have read all five of your free articles this month. To read this article, log in or register.
- Email This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Legal product reviews and business guidance from industry experts.
19 Mar 2020
How to Write Your Law Firm Business Plan

By Cari Twitchell
News Articles Healthy Strategy
Every new law practice needs a business plan . This is a guide to creating one.
Here is what should go in your business plan once you’ve decided about your law firm business model.
Section One: Executive Summary
This section provides a succinct overview of your full plan. It should also include the following:
- Mission statement. This statement should be one or two sentences at most, so you can quickly state it off the top of your head at any given moment. It should clearly state your value and offer inspiration and guidance, while being plausible and specific enough to ensure relevancy. For further direction on how to write a mission statement, read this Entrepreneur article .
- Core values. Your core values outline the strategy that underpins your business. When written well, they help potential employees and clients understand what drives you every day. When written incorrectly, they include meaningless platitudes that become yet another thing forgotten or ignored during practice. To pack the most punch into your core values, write them as actionable statements that you can follow. And keep them to a minimum: two to four should do just fine. You can read more about writing core values at Kinesis .
- What sets you apart. If you are like every other attorney out there, how will you stand out? This is known as your unique selling proposition (USP). What is it that will convince clients to turn to you instead of your competition? By clearly stating your USP, you identify what it is about your firm that will ensure your success.
Are you feeling slightly overwhelmed by all of this? Then write this section last, as you’ll find much of what you write here is a summary of everything you include in subsequent sections.
Section Two: Company Description
Write a succinct overview of your company. Here is what it should cover:
- Mission statement and values. Reiterate your mission statement and core values here.
- Geographic location and areas served. Identify where your offices are located and the geographic areas that you serve.
- Legal structure and ownership. State whether you are an LLC, S-Corp or other legal entity. If you are something other than a sole proprietor, identify the ownership structure of your firm. How does your law firm business model influence the ownership type?
- Firm history. If you are writing or updating a plan for a law firm already in existence, write a brief history that summarizes firm highlights and achievements.
This section is often the shortest. Do not spend much time or space here. Touch on the major points and move on.
Section Three: Market Analysis
Done correctly, a well thought out market analysis will help you identify exactly what your potential clients are looking for and how much you should charge for your services. It also enables you to identify your competitors’ weaknesses, which in turn helps you best frame your services in a way that attracts your preferred clientele. You probably already considered some of these subjects when deciding on the small law firm business model, but you need to document them.
Elements of a market analysis include:
- Industry description. Draft up a summary that encompasses where your particular legal niche is today, where it has been, and which trends will likely affect it in the future. Identify everything from actual market size to project market growth.
- Target audience. Define your target audience by building your ideal client persona. Use demographics such as location, age, family status, occupation and more. Map out the motivations behind their seeking your services and then how it is you are best able to satisfy their requirements.
- Competitive analysis. This is where you dive into details about your competitors. What do they do well? Where do they fall short? How are they currently underserving your target market? What challenges do you face by entering legal practice in your field of choice?
- Projections. Provide specific data on how much your target audience has to spend. Then narrow that down to identify how much you can charge per service.
A proper market analysis includes actual data to support your analysis. If you are unsure of where to find data, Bplans has a great list of resources for you to use. And if you would like to read further about conducting a market analysis, check out this article from the Small Business Administration.
Section Four: Organization & Management
This section goes into detail about you and any others who may have ownership interest in the firm. The small law firm business model section here should incorporated into the management documentation. Do not be afraid to brag a bit!
- What is your educational background?
- What experience do you currently have?
- Why are you the right person to run your firm?
If there are other individuals involved, it is a good idea to insert your organizational chart here. Visuals help quickly convey information and break up otherwise blocky text.
Section Five: Services
The Services section is the heart of your law firm business model plan. It is where you dive into all aspects of your services, including:
- The problem(s) you are addressing. What pain points do your preferred clients experience? What can they do right now to alleviate those pain points? Answer these questions, and then take the extra step to explain how those current solutions fail to adequately address their problems.
- The solution(s) you are providing. This describes how your solutions better resolve your prospective market’s needs. This not only includes the actual work you do, but the benefits that each client will receive based on your work.
- An overview of your competition. Describe your competition here. For instance, which other solo attorneys and firms provide the same solutions as you? What are your advantages over these competitors? What do you differently when providing your solutions? How will clients gain additional benefits by seeking out your services instead of working with your competitors?
Section 6: Marketing Strategy
Your marketing strategy section needs to address the three P’s:
- Positioning. How will you position your law firm and your services? What will you say to present your practice in the best light? What short statements can you use to entice a potential client to pursue your services?
- Pricing. How much will you charge? How does that fit within the legal industry? Within your niche industry? What do clients receive for that price?
- Promotion. Which sales channels and marketing activities will you pursue to promote your practice? Who is in charge of these activities? Even if you plan to build your law firm on the basis of word-of-mouth referrals, you must remember that most referrals will still look for information about you before contacting you. Know where they will look and ensure you are there.
Section Seven: Financials
Last comes the financials section. It is the key component to your plan if you are going to seek funding to get your practice off the ground. It is imperative that you complete this section even if you are not seeking funding, however, as you need to paint a clear financial picture before opening your doors.
Two main items make up this section: budgeting and forecasting (sales and cash flow). Answer these questions to help you address these items:
- How much starting capital do you need?
- How much money will it cost to keep your practice operating on a month-to-month basis?
- How many cases will you need to close each month to break even?
- How many cases would you need to close to make a profit?
- What is your projected profit and loss for the year?
This section often incorporates graphs and other images, including profit-and-loss and cash-flow tables. The more specific you get with your numbers, the more likely you are to succeed!
One final note: If your goal is to submit your business plan to potential funders, you want to do everything you can to make sure your plan stands out. One good way to do this is to work with a designer to artfully format your plan. Great presentation can take you a long way.
Originally published 2017-09-23. Republished 2020-07-31.
Cari Twitchell
About the Author
@CariTwitchell
/in/caritwitchell/
Website: https://www.customcontentllc.com
Share Article
Last updated October 7th, 2022
Learn the Latest from Our Partners and Community
11 Jan 2023
On The Lawyerist Podcast: Top Episodes of 2022
By Kyle Harrington
Lawyerist News News Articles Healthy Clients Healthy Owner Healthy Strategy Healthy Team
Everett Hosts Interactive Strategic Planning Session at Alaska...
Lawyerist News News Articles Healthy Strategy
Lawyerist Media Launches Redesigned Website to Better Help...
By the Lawyerist editorial team
Lawyerist News News Articles Healthy Strategy Law Firm Finances Law Firm Websites Lawyerist News Starting a Law Firm
27 May 2022
Lawyerist Values: Grow as People
Lawyerist News News Articles Healthy Strategy Lawyerist Values
Lawyerist’s Seek Candor Value Is More Than...
Develop a healthy strategy, how to competently reinvent your practice.
By Megan Zavieh
31 Dec 2019
Year-End Law Practice Checklist
19 Dec 2019
How to Use Aged A/R Reports
By Mary Juetten
News Articles Healthy Strategy Law Firm Finances
26 Nov 2019
Small Firm Roadmap Stories: Vision and Values
News Articles Healthy Strategy Lawyerist Lab Roadmap Starting a Law Firm
18 Oct 2019
Design Thinking for Lawyers
By Marshall Lichty
News Articles Healthy Strategy Healthy Systems
19 Aug 2019
Strategic Planning for Law-Firm Success and Growth
25 Oct 2018
How to Promote a Unique Value Proposition to...
By Karin Conroy
News Articles Healthy Strategy Law Firm Clients
23 Jan 2018
Rethinking Law-Firm Productivity Measurement for the Post Billable...
By Jordan Furlong
23 Mar 2017
How to Calculate Client Acquisition Cost
- Product Reviews
The original content within this website is © 2024. Lawyerist, Lawyerist Lab, TBD Law, Small Firm Dashboard, and
The Small Firm Scorecard are trademarks registered by Lawyerist Media, LLC.
Privacy policy // XML sitemap // Page ID: 83157
Don't bother with copy and paste.
Get this complete sample business plan as a free text document.
Law Firm Business Plan
Start your own law firm business plan
Wy'East Law Firm
Executive summary executive summary is a brief introduction to your business plan. it describes your business, the problem that it solves, your target market, and financial highlights.">.
Wy’East Law Firm (WLF) is a boutique technology law firm located in Portland, Oregon. The firm will be lead by Richard Bloom, a seasoned attorney previously with (name omitted)’s e-group. WLF will service all needs generated by technology firms, with specialization on mergers and acquisitions and qualified stock option plans; and handles both start-up and established companies.
In addition to WLF’s technology practice, we will offer public interest legal work at subsidized rates. The technology practice will allow the firm to be able to provide public interest organizations legal help at the cost of overhead.
WLF is a limited liability company founded and lead by Richard Bloom.
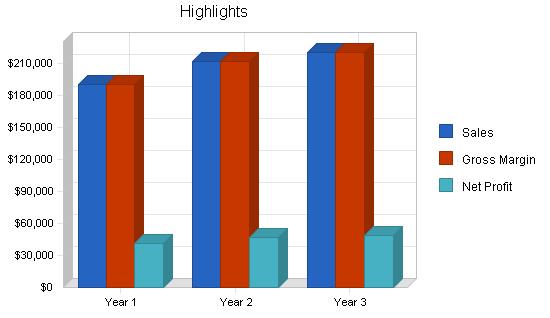
1.1 Objectives
The objectives for WLF for the first three years of operation include:
- To create a law firm whose primary goal is to exceed customer’s expectations.
- To develop a client list that includes at least 20 companies, each with revenues of over $3 million.
- To increase the ability to serve public interest organizations each year.
- To be able to offer each year some legal services at a subsidized rate.
1.2 Mission
The mission of Wy’East Law Firm is to provide the Portland community with technological and public interest legal guidance. We exist to attract and maintain customers and to support the public interest community. When we adhere to this maxim, everything else will fall into place.
Company Summary company overview ) is an overview of the most important points about your company—your history, management team, location, mission statement and legal structure.">
WLF is a law firm serving technology companies and public interest organizations, and will subsidize its public interest work with local companies. WLF specializes in mergers and acquisitions as well as stock option plans, but can handle most legal needs for a technology company.
The technology work will subsidize the company’s public interest work which will be billed out at the cost of overhead.
2.1 Company Ownership
WLF is a limited liability company, owned solely by Richard Bloom.
2.2 Start-up Summary
WLF’s start-up costs will include all equipment needed for the home office, website creation, and advertising.
The home office equipment will be the largest chunk of the start-up expenses. This equipment includes 4 computers, a fax machine, copier, cellular phone, office supplies, additional land line, a DSL connection, and office furniture.
Start-up expenses will also include advertising. Two methods will be used: a content-only website and the Yellow Pages.

| Start-up | |
| Requirements | |
| Start-up Expenses | |
| Legal | $0 |
| Stationery etc. | $100 |
| Website creation | $500 |
| DSL installation | $150 |
| Office equipment | $500 |
| Rent | $0 |
| Research and development | $0 |
| Expensed equipment | $0 |
| Other | $0 |
| Total Start-up Expenses | $1,250 |
| Start-up Assets | |
| Cash Required | $18,750 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 |
| Long-term Assets | $5,000 |
| Total Assets | $23,750 |
| Total Requirements | $25,000 |
| Start-up Funding | |
| Start-up Expenses to Fund | $1,250 |
| Start-up Assets to Fund | $23,750 |
| Total Funding Required | $25,000 |
| Assets | |
| Non-cash Assets from Start-up | $5,000 |
| Cash Requirements from Start-up | $18,750 |
| Additional Cash Raised | $0 |
| Cash Balance on Starting Date | $18,750 |
| Total Assets | $23,750 |
| Liabilities and Capital | |
| Liabilities | |
| Current Borrowing | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 |
| Accounts Payable (Outstanding Bills) | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $0 |
| Capital | |
| Planned Investment | |
| Investor 1 | $25,000 |
| Investor 2 | $0 |
| Other | $0 |
| Additional Investment Requirement | $0 |
| Total Planned Investment | $25,000 |
| Loss at Start-up (Start-up Expenses) | ($1,250) |
| Total Capital | $23,750 |
| Total Capital and Liabilities | $23,750 |
| Total Funding | $25,000 |
WLF will provide provide law services to two different groups of customers.
- Technology law services . WLF will provide legal services to high technology clients, to both start-up companies and established firms. While the firm excels in mergers, acquisitions, and qualified stock option plans, we also have experience in almost any legal field that a tech firm encounters. These clients, billed at market rate, will subsidize the public interest clients.
- Public interest law . WLF will serve regional public interest organizations, with a concentration on environmental and civil rights organizations. For most public interest organizations, good legal help is expensive. By using technology clients to subsidize the cost of legal fees for public interest firms, WLF is able to make significant contributions back to the community.
Market Analysis Summary how to do a market analysis for your business plan.">
WLF’s customers can be divided into two groups, technology firms and public interest organizations.
- Public interest organizations . These clients will be diversified, some are environmental organizations others are civil rights groups. While some public interest organizations receive their legal services for free (pro bono) from some attorneys, there is an extreme shortage of legal help for these organizations. Therefore, it is quite attractive to these organizations to have the possibility of receiving top legal help at a subsidized rate. Attracting these clients will not be the problem, the difficulty will be for Richard to select which organization will receive his help.

| Market Analysis | |||||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Year 4 | Year 5 | |||
| Potential Customers | Growth | CAGR | |||||
| Technology companies | 9% | 345 | 376 | 410 | 447 | 487 | 9.00% |
| Public interest organizations | 8% | 278 | 300 | 324 | 350 | 378 | 7.98% |
| Other | 0% | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0.00% |
| Total | 8.55% | 623 | 676 | 734 | 797 | 865 | 8.55% |
4.1 Target Market Segment Strategy
WLF will be targeting high technology companies for two reasons.
- Although the economy has taken a recent plummet, particularly technology firms, technology is still a growing sector of the economy. This is evidenced by the fact that 17 out of the top 25 fastest growing companies are technology firms, according to The Business Journal of Portland.
- Technology is Richard’s area of expertise. Richard practiced law at one of the top three law firms in Portland and was in their e-group, concentrating on technology firms. His experience, coupled with his network of colleagues within the industry, makes technology firms attractive customers.
WLF will be targeting public interest organizations for one simple reason, a desire to give back to the community. Public interest work is inherently altruistic to some degree. Generally, the person performing the work receives a good feeling for his/her contribution, but in today’s capitalistic society, someone who donates his/her time at far below market wages should be considered altruistic.
4.2 Service Business Analysis
The technology law practice is fairly competitive in Portland. Most larger, more prestigious firms have attorneys who specialize in technology. Some smaller firms also have attorneys who do work for technology companies. Lastly, there are boutique firms, like WLF. As a service-based industry, the practice of law is driven by personal relationships and reputation. Potential clients choose attorneys based on reputation and who they are familiar with or are recommended to. Therefore, if the attorney is providing better service to a client, the client is likely to form a long lasting business relationship with the client.

WLF has the advantage that when Richard left (name omitted) he brought 15 of his clients, which, for now, are almost enough to survive on.
Strategy and Implementation Summary
WLF will be courting new technology clients through networking and advertisements in the Yellow Pages, Business Journal of Portland, and other technology specific regional journals. As stated earlier, WLF has a sufficient amount of business at day one, however, more technology clients means the ability to perform more public interest work.
Richard will be attending the Portland Venture Group meetings as well as other informal gatherings of technology companies to network with the different technology firms in the region. These networking activities along with advertisements in appropriate media forms will allow WLF to steadily grow their list of clients.
5.1 Competitive Edge
WLF’s competitive advantage will be based on two factors, experience and specialization:
- Experience. Richard brings to WLF three years of practicing technology law at a top firm in Portland. Reputation carries a lot of weight and Richard’s time at (name omitted) means a lot in the Portland legal community and is very attractive to prospective clients. Additionally, beyond the reputation of working for a coveted firm, is the fact that the three years spent at (name omitted) provided Richard with big name clients.
- Specialization. As a boutique firm that concentrates on technology companies, WLF is in a desirable situation because it’s knowledge base is considerable, relative to other firms that practice a wide range of law.
5.2 Sales Strategy
WLF’s sales strategy will begin with months two through five with the goal of serving the existing customer base of clients. The absence of bringing in new clients during this time is purposeful, it allows WLF and the existing clients to form a new relationship at WLF, different from their previous relationship at (name omitted).
Month six will signal WLF’s conscious effort to generate new clients. Using the previously mentioned networking techniques, Richard, through personal communications, will convince prospective clients of the value of a boutique technology law firm, specifically the depth of knowledge and the close attention that the client will get when dealing with a small firm.
Regarding the public interest organizations, there will be less of a sale strategy, more of a choosing of the organizations that Richard wants to represent. There are so many needy public interest organizations that Richard will have to pick and choose those that he wishes to help out.
5.2.1 Sales Forecast
The first month will be spent setting up the home office. This will include setting up the office, a conference room, and all of the computer equipment. During the first month, Richard will also be serving some existing technology clients and some public interest clients. We project that if we spend 1/3 of our time on the technology clients, this would sufficiently subsidize the public interest clients so we would only have to cover overhead expenses.
By month six, Richard will begin actively soliciting new clients. Between months one and five he will continue networking, though will not be actively seeking customers. From month seven on and there will be a slight increase in clients taken aboard. There will be only a slight increase so as to create solid relationships with the new and existing clients. Richard will be cognizant of the possibility of growing too fast and not being able to offer the same quality service to his clients.
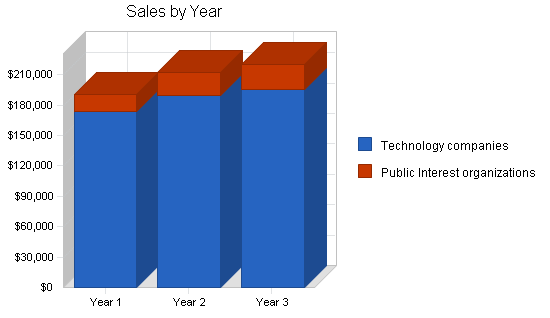
| Sales Forecast | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | |||
| Technology companies | $174,096 | $189,525 | $195,747 |
| Public Interest organizations | $16,839 | $22,578 | $24,547 |
| Total Sales | $190,935 | $212,103 | $220,294 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Technology companies | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Public Interest organizations | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 |
5.3 Milestones
WLF will have several milestones early on:
- Business plan completion.
- Set up home office.
- First month of total technology subsidy.
| Milestones | |||||
| Milestone | Start Date | End Date | Budget | Manager | Department |
| Business plan completion | 1/1/2001 | 1/1/2001 | $0 | Richard | Marketing |
| Set up ofifce | 1/1/2001 | 1/1/2001 | $0 | Richard | Department |
| First month of total technology subsidy | 4/1/2001 | 4/1/2001 | $0 | WLF | Department |
| Totals | $0 | ||||
Management Summary management summary will include information about who's on your team and why they're the right people for the job, as well as your future hiring plans.">
Wy’East Law Firm is an Oregon Corporation founded and run by Richard Bloom. Richard has a degree in Political Science from the University of Colorado, Boulder, and a J.D. from Lewis and Clark University. While at Lewis and Clark, Richard was the President of the school’s Public Interest Student Organization. It was through this organization that Richard became fond of public interest law. After graduation, Richard went to work for (name omitted) for three years in the e-group which concentrated on technology. While working in the e-group, Richard worked on technology issues with a number of well known start-up organizations and established companies.
One of the perks working at (name omitted) was his ability to do pro bono work which counted toward his required yearly billable hours requirement. Richard has spent a fair amount of time with 1000 Friends of Oregon and other public interest organizations. After three years however, Richard was feeling constrained and desired more autonomy. He decided to leave and start his own firm. Richard was able to bring a fair number of his clients from (name omitted) to his new firm, helping the transition from leaving an established practice to hanging out his own shingle and starting over.
6.1 Personnel Plan
The staff will consist of Richard working full time. In addition to Richard, a part-time secretary and part-time paralegal will join WLF by month two. Month four will bring WLF a law clerk, and a second law clerk by month eight.
| Personnel Plan | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Richard | $66,000 | $66,000 | $66,000 |
| Receptionist/ secretary | $11,550 | $12,500 | $13,500 |
| Paralegal | $22,000 | $23,000 | $24,000 |
| Law clerk | $8,100 | $11,000 | $12,000 |
| Law clerk | $4,500 | $11,000 | $12,000 |
| Total People | 5 | 5 | 5 |
| Total Payroll | $112,150 | $123,500 | $127,500 |

Financial Plan investor-ready personnel plan .">
The following sections will outline important financial information.
7.1 Important Assumptions
The following table details important assumptions.
| General Assumptions | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 |
| Current Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% |
| Tax Rate | 25.42% | 25.00% | 25.42% |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 |
7.2 Projected Profit and Loss
The following table and charts present the projected profit and loss.

| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Sales | $190,935 | $212,103 | $220,294 |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Gross Margin | $190,935 | $212,103 | $220,294 |
| Gross Margin % | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Expenses | |||
| Payroll | $112,150 | $123,500 | $127,500 |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $2,160 | $2,160 | $2,160 |
| Depreciation | $1,668 | $1,666 | $1,666 |
| Leased Equipment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Utilities | $1,500 | $1,500 | $1,500 |
| Rent | $2,400 | $2,400 | $2,400 |
| Payroll Taxes | $16,823 | $18,525 | $19,125 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Operating Expenses | $136,701 | $149,751 | $154,351 |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | $54,235 | $62,352 | $65,943 |
| EBITDA | $55,903 | $64,018 | $67,609 |
| Interest Expense | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Taxes Incurred | $13,210 | $15,588 | $16,761 |
| Net Profit | $41,024 | $46,764 | $49,182 |
| Net Profit/Sales | 21.49% | 22.05% | 22.33% |
7.3 Break-even Analysis
The Break-even Analysis indicates what WLF will need in hours and revenue a month to reach the break-even point.

| Break-even Analysis | |
| Monthly Revenue Break-even | $11,392 |
| Assumptions: | |
| Average Percent Variable Cost | 0% |
| Estimated Monthly Fixed Cost | $11,392 |
7.4 Projected Cash Flow
The following chart and table show anticipated cash flow.

| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Cash Received | |||
| Cash from Operations | |||
| Cash Sales | $47,734 | $53,026 | $55,074 |
| Cash from Receivables | $112,707 | $155,697 | $163,912 |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $160,441 | $208,722 | $218,986 |
| Additional Cash Received | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $160,441 | $208,722 | $218,986 |
| Expenditures | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||
| Cash Spending | $112,150 | $123,500 | $127,500 |
| Bill Payments | $31,394 | $41,570 | $41,800 |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $143,544 | $165,070 | $169,300 |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $143,544 | $165,070 | $169,300 |
| Net Cash Flow | $16,898 | $43,652 | $49,686 |
| Cash Balance | $35,648 | $79,300 | $128,986 |
7.5 Projected Balance Sheet
The following table displays the projected balance sheet.
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Assets | |||
| Current Assets | |||
| Cash | $35,648 | $79,300 | $128,986 |
| Accounts Receivable | $30,494 | $33,874 | $35,183 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $66,141 | $113,174 | $164,168 |
| Long-term Assets | |||
| Long-term Assets | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $1,668 | $3,334 | $5,000 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $3,332 | $1,666 | $0 |
| Total Assets | $69,473 | $114,840 | $164,168 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 |
| Current Liabilities | |||
| Accounts Payable | $4,699 | $3,302 | $3,448 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $4,699 | $3,302 | $3,448 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $4,699 | $3,302 | $3,448 |
| Paid-in Capital | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($1,250) | $39,774 | $86,538 |
| Earnings | $41,024 | $46,764 | $49,182 |
| Total Capital | $64,774 | $111,538 | $160,721 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $69,473 | $114,840 | $164,168 |
| Net Worth | $64,774 | $111,538 | $160,721 |
7.6 Business Ratios
Industry profile ratios based on the NAICS code 541110, Offices of Lawyers, are shown in the table below.
| Ratio Analysis | ||||
| Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | Industry Profile | |
| Sales Growth | 0.00% | 11.09% | 3.86% | 8.50% |
| Percent of Total Assets | ||||
| Accounts Receivable | 43.89% | 29.50% | 21.43% | 8.60% |
| Other Current Assets | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 66.90% |
| Total Current Assets | 95.20% | 98.55% | 100.00% | 75.50% |
| Long-term Assets | 4.80% | 1.45% | 0.00% | 24.50% |
| Total Assets | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Current Liabilities | 6.76% | 2.88% | 2.10% | 50.20% |
| Long-term Liabilities | 0.00% | 0.00% | 0.00% | 12.90% |
| Total Liabilities | 6.76% | 2.88% | 2.10% | 63.10% |
| Net Worth | 93.24% | 97.12% | 97.90% | 36.90% |
| Percent of Sales | ||||
| Sales | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% |
| Gross Margin | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 0.00% |
| Selling, General & Administrative Expenses | 78.70% | 77.95% | 77.55% | 58.20% |
| Advertising Expenses | 0.13% | 0.11% | 0.11% | 0.50% |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | 28.40% | 29.40% | 29.93% | 3.40% |
| Main Ratios | ||||
| Current | 14.08 | 34.28 | 47.62 | 1.54 |
| Quick | 14.08 | 34.28 | 47.62 | 1.09 |
| Total Debt to Total Assets | 6.76% | 2.88% | 2.10% | 63.10% |
| Pre-tax Return on Net Worth | 83.73% | 55.90% | 41.03% | 12.30% |
| Pre-tax Return on Assets | 78.07% | 54.29% | 40.17% | 33.40% |
| Additional Ratios | Year 1 | Year 2 | Year 3 | |
| Net Profit Margin | 21.49% | 22.05% | 22.33% | n.a |
| Return on Equity | 63.33% | 41.93% | 30.60% | n.a |
| Activity Ratios | ||||
| Accounts Receivable Turnover | 4.70 | 4.70 | 4.70 | n.a |
| Collection Days | 57 | 74 | 76 | n.a |
| Accounts Payable Turnover | 7.68 | 12.17 | 12.17 | n.a |
| Payment Days | 34 | 36 | 29 | n.a |
| Total Asset Turnover | 2.75 | 1.85 | 1.34 | n.a |
| Debt Ratios | ||||
| Debt to Net Worth | 0.07 | 0.03 | 0.02 | n.a |
| Current Liab. to Liab. | 1.00 | 1.00 | 1.00 | n.a |
| Liquidity Ratios | ||||
| Net Working Capital | $61,442 | $109,872 | $160,721 | n.a |
| Interest Coverage | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Additional Ratios | ||||
| Assets to Sales | 0.36 | 0.54 | 0.75 | n.a |
| Current Debt/Total Assets | 7% | 3% | 2% | n.a |
| Acid Test | 7.59 | 24.02 | 37.41 | n.a |
| Sales/Net Worth | 2.95 | 1.90 | 1.37 | n.a |
| Dividend Payout | 0.00 | 0.00 | 0.00 | n.a |
| Sales Forecast | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | |||||||||||||
| Technology companies | 0% | $0 | $8,005 | $9,514 | $13,587 | $16,547 | $16,874 | $16,854 | $17,525 | $18,547 | $18,752 | $18,887 | $19,004 |
| Public Interest organizations | 0% | $0 | $1,100 | $1,200 | $1,500 | $1,545 | $1,587 | $1,584 | $1,654 | $1,666 | $1,548 | $1,741 | $1,714 |
| Total Sales | $0 | $9,105 | $10,714 | $15,087 | $18,092 | $18,461 | $18,438 | $19,179 | $20,213 | $20,300 | $20,628 | $20,718 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Technology companies | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Public Interest organizations | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Direct Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Personnel Plan | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Richard | 0% | $5,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 | $5,500 |
| Receptionist/ secretary | 0% | $0 | $1,050 | $1,050 | $1,050 | $1,050 | $1,050 | $1,050 | $1,050 | $1,050 | $1,050 | $1,050 | $1,050 |
| Paralegal | 0% | $0 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 | $2,000 |
| Law clerk | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $900 | $900 | $900 | $900 | $900 | $900 | $900 | $900 | $900 |
| Law clerk | 0% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $900 | $900 | $900 | $900 | $900 |
| Total People | 1 | 3 | 3 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 4 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | 5 | |
| Total Payroll | $5,500 | $8,550 | $8,550 | $9,450 | $9,450 | $9,450 | $9,450 | $10,350 | $10,350 | $10,350 | $10,350 | $10,350 | |
| General Assumptions | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Plan Month | 1 | 2 | 3 | 4 | 5 | 6 | 7 | 8 | 9 | 10 | 11 | 12 | |
| Current Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | |
| Long-term Interest Rate | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | 10.00% | |
| Tax Rate | 30.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | 25.00% | |
| Other | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | 0 | |
| Pro Forma Profit and Loss | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Sales | $0 | $9,105 | $10,714 | $15,087 | $18,092 | $18,461 | $18,438 | $19,179 | $20,213 | $20,300 | $20,628 | $20,718 | |
| Direct Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Cost of Sales | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Gross Margin | $0 | $9,105 | $10,714 | $15,087 | $18,092 | $18,461 | $18,438 | $19,179 | $20,213 | $20,300 | $20,628 | $20,718 | |
| Gross Margin % | 0.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | 100.00% | |
| Expenses | |||||||||||||
| Payroll | $5,500 | $8,550 | $8,550 | $9,450 | $9,450 | $9,450 | $9,450 | $10,350 | $10,350 | $10,350 | $10,350 | $10,350 | |
| Sales and Marketing and Other Expenses | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | $180 | |
| Depreciation | $139 | $139 | $139 | $139 | $139 | $139 | $139 | $139 | $139 | $139 | $139 | $139 | |
| Leased Equipment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Utilities | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | $125 | |
| Rent | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | $200 | |
| Payroll Taxes | 15% | $825 | $1,283 | $1,283 | $1,418 | $1,418 | $1,418 | $1,418 | $1,553 | $1,553 | $1,553 | $1,553 | $1,553 |
| Other | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Operating Expenses | $6,969 | $10,477 | $10,477 | $11,512 | $11,512 | $11,512 | $11,512 | $12,547 | $12,547 | $12,547 | $12,547 | $12,547 | |
| Profit Before Interest and Taxes | ($6,969) | ($1,372) | $238 | $3,576 | $6,581 | $6,950 | $6,927 | $6,633 | $7,667 | $7,754 | $8,082 | $8,172 | |
| EBITDA | ($6,830) | ($1,233) | $377 | $3,715 | $6,720 | $7,089 | $7,066 | $6,772 | $7,806 | $7,893 | $8,221 | $8,311 | |
| Interest Expense | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxes Incurred | ($2,091) | ($343) | $59 | $894 | $1,645 | $1,737 | $1,732 | $1,658 | $1,917 | $1,938 | $2,020 | $2,043 | |
| Net Profit | ($4,878) | ($1,029) | $178 | $2,682 | $4,935 | $5,212 | $5,195 | $4,974 | $5,750 | $5,815 | $6,061 | $6,129 | |
| Net Profit/Sales | 0.00% | -11.30% | 1.66% | 17.77% | 27.28% | 28.23% | 28.17% | 25.94% | 28.45% | 28.65% | 29.38% | 29.58% | |
| Pro Forma Cash Flow | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Cash from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Sales | $0 | $2,276 | $2,679 | $3,772 | $4,523 | $4,615 | $4,610 | $4,795 | $5,053 | $5,075 | $5,157 | $5,180 | |
| Cash from Receivables | $0 | $0 | $228 | $6,869 | $8,145 | $11,390 | $13,578 | $13,845 | $13,847 | $14,410 | $15,162 | $15,233 | |
| Subtotal Cash from Operations | $0 | $2,276 | $2,906 | $10,641 | $12,668 | $16,006 | $18,188 | $18,640 | $18,900 | $19,485 | $20,319 | $20,413 | |
| Additional Cash Received | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Received | 0.00% | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| New Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Other Liabilities (interest-free) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Sales of Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| New Investment Received | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Received | $0 | $2,276 | $2,906 | $10,641 | $12,668 | $16,006 | $18,188 | $18,640 | $18,900 | $19,485 | $20,319 | $20,413 | |
| Expenditures | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Expenditures from Operations | |||||||||||||
| Cash Spending | $5,500 | $8,550 | $8,550 | $9,450 | $9,450 | $9,450 | $9,450 | $10,350 | $10,350 | $10,350 | $10,350 | $10,350 | |
| Bill Payments | ($761) | ($687) | $1,458 | $1,879 | $2,841 | $3,571 | $3,660 | $3,656 | $3,724 | $3,975 | $3,999 | $4,079 | |
| Subtotal Spent on Operations | $4,739 | $7,863 | $10,008 | $11,329 | $12,291 | $13,021 | $13,110 | $14,006 | $14,074 | $14,325 | $14,349 | $14,429 | |
| Additional Cash Spent | |||||||||||||
| Sales Tax, VAT, HST/GST Paid Out | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Principal Repayment of Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Other Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Long-term Liabilities Principal Repayment | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Purchase Long-term Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Dividends | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Subtotal Cash Spent | $4,739 | $7,863 | $10,008 | $11,329 | $12,291 | $13,021 | $13,110 | $14,006 | $14,074 | $14,325 | $14,349 | $14,429 | |
| Net Cash Flow | ($4,739) | ($5,587) | ($7,102) | ($688) | $376 | $2,985 | $5,078 | $4,634 | $4,826 | $5,160 | $5,970 | $5,984 | |
| Cash Balance | $14,011 | $8,424 | $1,322 | $634 | $1,010 | $3,995 | $9,073 | $13,707 | $18,533 | $23,693 | $29,663 | $35,648 | |
| Pro Forma Balance Sheet | |||||||||||||
| Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | ||
| Assets | Starting Balances | ||||||||||||
| Current Assets | |||||||||||||
| Cash | $18,750 | $14,011 | $8,424 | $1,322 | $634 | $1,010 | $3,995 | $9,073 | $13,707 | $18,533 | $23,693 | $29,663 | $35,648 |
| Accounts Receivable | $0 | $0 | $6,829 | $14,637 | $19,083 | $24,507 | $26,962 | $27,213 | $27,752 | $29,065 | $29,879 | $30,188 | $30,494 |
| Other Current Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Current Assets | $18,750 | $14,011 | $15,253 | $15,959 | $19,717 | $25,517 | $30,958 | $36,286 | $41,459 | $47,597 | $53,573 | $59,852 | $66,141 |
| Long-term Assets | |||||||||||||
| Long-term Assets | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 | $5,000 |
| Accumulated Depreciation | $0 | $139 | $278 | $417 | $556 | $695 | $834 | $973 | $1,112 | $1,251 | $1,390 | $1,529 | $1,668 |
| Total Long-term Assets | $5,000 | $4,861 | $4,722 | $4,583 | $4,444 | $4,305 | $4,166 | $4,027 | $3,888 | $3,749 | $3,610 | $3,471 | $3,332 |
| Total Assets | $23,750 | $18,872 | $19,975 | $20,542 | $24,161 | $29,822 | $35,124 | $40,313 | $45,347 | $51,346 | $57,183 | $63,323 | $69,473 |
| Liabilities and Capital | Month 1 | Month 2 | Month 3 | Month 4 | Month 5 | Month 6 | Month 7 | Month 8 | Month 9 | Month 10 | Month 11 | Month 12 | |
| Current Liabilities | |||||||||||||
| Accounts Payable | $0 | $0 | $2,132 | $2,521 | $3,458 | $4,184 | $4,273 | $4,268 | $4,327 | $4,577 | $4,598 | $4,677 | $4,699 |
| Current Borrowing | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Other Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Subtotal Current Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $2,132 | $2,521 | $3,458 | $4,184 | $4,273 | $4,268 | $4,327 | $4,577 | $4,598 | $4,677 | $4,699 |
| Long-term Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 |
| Total Liabilities | $0 | $0 | $2,132 | $2,521 | $3,458 | $4,184 | $4,273 | $4,268 | $4,327 | $4,577 | $4,598 | $4,677 | $4,699 |
| Paid-in Capital | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 | $25,000 |
| Retained Earnings | ($1,250) | ($1,250) | ($1,250) | ($1,250) | ($1,250) | ($1,250) | ($1,250) | ($1,250) | ($1,250) | ($1,250) | ($1,250) | ($1,250) | ($1,250) |
| Earnings | $0 | ($4,878) | ($5,907) | ($5,729) | ($3,047) | $1,888 | $7,100 | $12,295 | $17,270 | $23,019 | $28,835 | $34,896 | $41,024 |
| Total Capital | $23,750 | $18,872 | $17,843 | $18,021 | $20,703 | $25,638 | $30,850 | $36,045 | $41,020 | $46,769 | $52,585 | $58,646 | $64,774 |
| Total Liabilities and Capital | $23,750 | $18,872 | $19,975 | $20,542 | $24,161 | $29,822 | $35,124 | $40,313 | $45,347 | $51,346 | $57,183 | $63,323 | $69,473 |
| Net Worth | $23,750 | $18,872 | $17,843 | $18,021 | $20,703 | $25,638 | $30,850 | $36,045 | $41,020 | $46,769 | $52,585 | $58,646 | $64,774 |

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software

Latest Blogs
Assessing the accuracy and quality of answers from your legal....
By Simon Weierman Lawyers must rely on the accuracy and quality of their legal research when providing counsel to clients, drafting business agreements or writing legal documents for submission to the...
5 Keys for Monitoring Antitrust Compliance: A Guide for In-House...
U.S. District Judge Amit Mehta fired the latest shot in the recent acceleration of U.S. antitrust enforcement August 5 with a dramatic ruling that Google has violated federal antitrust law by monopolizing...
IP and Gen AI Technologies: Essential Guidance for In-House ...
The proliferation of generative artificial intelligence (AI) technology has taken most of the oxygen out of the room in corporate offices. Virtually every major company has aggressively investigated how...
New Revenue Streams: Time to Start Law Firm Business Innovat...
By Geoffrey D. Ivnik, Esq. | Director of Large Markets, LexisNexis Leaders of America’s largest law firms have decided to move full speed ahead with the adoption of generative artificial intelligence...
New Revenue Streams: Transform unprofitable practices into thriving...
By Geoffrey D. Ivnik, Esq. | Director of U.S. Large Markets, LexisNexis Law firm leaders perceive that generative artificial intelligence (Gen AI) technology is going to have a dramatic impact on how...
How to Draft a Law Firm Business Plan
Law firms are something more than a business. Law firms and the lawyers within them are engaged in a profession, with obligations that go beyond purely commercial concerns.
Listen to this article: Click here to play this audio clip
This truth can obscure the need for lawyers to pay attention to the business management side of their practices: their finances, marketing plans, business development efforts, IT purchases, lease terms and capital needs. For the highly trained lawyer, such concerns may feel at best like an afterthought, or at worst a nuisance that steals time from their true occupation: the “practice of law.”
And yet, those annoying business details are responsible for keeping the lights on. While law firms may be more than a business, there is, in fact, a large and necessary business element to them. For solo practices and small firms in particular, investing time into the business management side of legal practice can make a major difference in the financial rewards they derive from it—or even their survival. Firms that have failed to do so in the past (and even those that haven’t) can get a handle on their law practice business management by taking the step of drafting a business plan.
THE POINT OF A BUSINESS PLAN
We’ll discuss the components of a business plan in a moment, but first, let’s talk about why this exercise is valuable. For another type of business, a business plan may be useful in attracting investors or securing financing. Law firms should not think of their business plans as utilitarian documents in that sense (although someday one could prove helpful in obtaining a line of credit, say, or attracting lateral partners). Instead, the primary value of the business plan, particularly for the solo practice or small firm drafting one for the first time, lies in the fact that it forces the firm to think about business issues that it otherwise would not have considered.
As the D.C. Bar says in its advice to startup law offices : “The act of planning helps you think things through thoroughly, study and research if you are not sure of the facts, and look at your ideas critically. It takes time now, but avoids costly, perhaps disastrous, mistakes later.”
Of course, a business plan does little for anyone if it is quickly forgotten. But the mere act of generating a business plan gives a firm a direction to head in and goals to point toward. If the firm makes it a practice to revisit the business plan on an annual basis (if not more regularly), its business considerations will stay top-of-mind and the firm will continually refine them in ways that improve its performance.
THE CONTENTS OF A BUSINESS PLAN
Creating a strong business plan will require an investment of time and energy. At the same time, no one wants to write, or read, a massive document. To improve the chances that the project gets done, and gets read, it is best to keep a business plan to a reasonable length. Anything over 20 pages may stretch attention spans to the breaking point, and there’s no harm in going shorter if you have covered all the territory you need to by that point.
So, what, exactly, is the territory that you should cover? Most authorities agree that a sound business plan for a law firm should address the following broad areas:
- Overview of the Firm
This section should include basic information about the firm: its name, legal structure, practice areas and leadership positions. It should also contain some deeper information about the firm's identity and aspirations.
This would include:
A mission statement about the firm’s purpose
A vision statement or recitation of medium- and long-term goals for the firm
Important aspects of the firm’s history
Any important philosophies that the firm brings to legal practice
- Market Analysis
This section should discuss the business trends affecting the firm’s important practice areas and clients. It should evaluate any technologies that are affecting your practice area and consider how the firm may leverage or keep up with them. This section should also devote substantial energy to identifying the firm’s major competitors in each of its important practice areas and comparing their services to the firm’s.
In this section, identify the firm’s major clients, breaking them down by important characteristics like size, location, industry and practice groups used. Go through a similar exercise for major client prospects and targets. It’s worth examining how the firm can improve its relationships with both of these groups.
Important financial information includes the firm’s fixed and variable costs, backward- and forward-looking revenue, realization rate, collection rate, monthly overhead, assets and liabilities. A 12-month profit and loss projection should be included and could be considered the heart of the business plan.
There is a great amount of detail that any firm could get into on this front. Don’t get overwhelmed by it; at the same time, this is some of the most important information in the business plan, so it’s not advisable to gloss over it.
This section will address key operational issues like the office lease, equipment purchases and technology plans. You may assign roles to various staff members for operational issues.
Think about what marketing the firm currently performs, how it obtains clients and what marketing goals it wants to set for the future.
After completing these and any other sections the firm might want to address, then go back and draft an executive summary to be included at the beginning of the business plan document. The summary should be professional, but don’t be afraid to give it some optimistic energy. After all, with your eyes on the business management fundamentals of your firm, things should be looking up for the future.
- Growing Your Business
- Law Practice Management
Law Firm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Law Firm Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Law Firm business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Law Firms.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Law Firm business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
The Harris & Harris Law Firm is a startup up business that provides legal advice and services for clients located within the Scottsdale, Arizona region. The company is founded by Roger Harris and his son, Anthony. Roger Harris has been a partner in a well-established company, Foundations Law Firm, for over twenty years. Anthony Harris is a recent law school graduate who will begin his training under the scholarship of his father. With the extensive list of former clients in hand, Roger and Anthony are confident they can begin open their doors for business and grow the new law firm successfully.
Harris & Harris Law Firm will provide a comprehensive array of services for individuals or business entities who need advice and/or legal representation in court proceedings. Harris & Harris will provide a multi-prong approach to fashion specific solutions for each individual they represent; in that regard, all services are custom-packaged and provided for clients by the lawyers at Harris & Harris. This unique factor will set them above all other area lawyers, as most follow standard processes within the companies where they work.
Product Offering
The following are the services that Harris & Harris Law Firm will provide:
- Client-centric efforts in every case until resolution is found
- Unique process to fully explore client options in any dispute
- Creative and sustainable solutions on a case-by-case basis
- Prioritization of client needs above all else
- Dedication to professionalism and honesty
- Equally dedicated to securing the correct outcomes for our clients
- Team of highly-skilled lawyers who create winning solutions
Customer Focus
Harris & Harris will target the residents of Scottsdale, Arizona. They will also target medium-to-large businesses within Scottsdale, Arizona. They will target former associates and lawyers with whom they can collaborate in the future. They will target residents who have been served a summons for civil or criminal case appearances, whether as a witness, interested party or a potential defendant.
Management Team
Harris & Harris will be owned and operated by Roger Harris. He recruited his son, Anthony, to join the new firm upon Anthony’s recent graduation from law school. Within the next ten years, depending on performance, Anthony will receive incremental distributions of up to 49% of the company value in private stock. This will be based on Anthony’s performance and growth in the company as his role expands.
Roger Harris was formerly a partner in a well-established company, Foundations Law Firm, for over twenty years. He practiced law in the personal law arena, including wills and probates, trusts and other forms of personal law. He also managed the real estate law team at his former place of employment. Roger’s role in Harris & Harris will be the President, with the primary responsibility of driving new client traffic to the company. Roger has recruited Anthony, Richard Cummings, and Torey Crouch to begin their employment at Harris & Harris, as well.
Anthony Harris is a recent law school graduate who will begin his training under the scholarship of his father. Anthony will specialize in a unique processing of individual cases by creating algorithms that will specify which outcomes will best serve the client. Anthony will also represent clients in court and assist in defense appearances. With the extensive list of former clients in hand and the unique processes they’ve designed for clients going forward, Roger and Anthony are confident they can begin and grow the new law firm successfully.
Richard Cummings, a former associate of Roger Harris, will take on the role of Managing Partner in the launch of Harris & Harris. He will oversee all junior partners and staff, as the total number of lawyers grows expeditiously over the first few years.
Torey Crouch, a former law student with Anthony Cummings, will take on the role of Research & Records Manager, as she will form the background work necessary for all the other lawyers on staff.
Success Factors
Harris & Harris Law Firm will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Friendly, knowledgeable, and highly-qualified team of Harris & Harris Law Firm
- Comprehensive menu of services designed to provide specific customer-centric solutions
- Specializations in real estate, trusts, probate, civil and criminal law are all offered under this multi-pronged services of Harris & Harris Law Firm
- Harris & Harris offers family discounts and other forms of packages for clients.
- Harris & Harris offers a “monthly pay” program for clients who need to spread out payments over time.
Financial Highlights
Harris & Harris Law Firm is seeking $200,000 in debt financing to launch its Harris & Harris Law Firm. The funding will be dedicated toward securing the office space and purchasing office equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated toward three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the print ads and marketing costs. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Office space build-out: $20,000
- Office equipment, supplies, and materials: $10,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $10,000
- Working capital: $10,000
The following graph outlines the financial projections for Harris & Harris Law Firm.
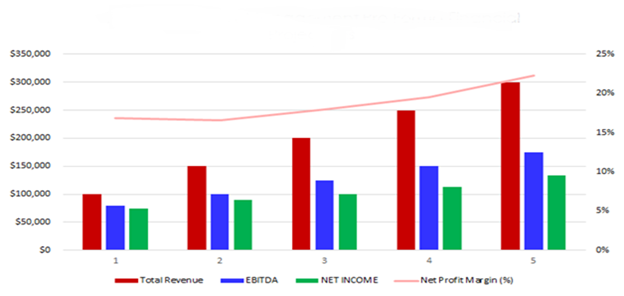
Company Overview
Who is harris & harris law firm.
Harris & Harris Law Firm is a newly established, full-service law firm in Scottsdale, Arizona. Harris & Harris Law Firm will be the most reliable, solution-centric and effective choice for clients in Scottsdale and the surrounding communities. Harris & Harris Law Firm will provide a comprehensive menu of attorney services for any individual, family or business to utilize. Their full-service approach includes a comprehensive array of services that are uniquely prepared for each client.
Harris & Harris Law Firm will be able to serve the residents and businesses of Scottsdale. The team of professionals are highly qualified and experienced in all aspects of the law and several permutations of legal representation. Harris & Harris Law Firm removes all headaches and issues of securing a comprehensive law firm that is reliable and dedicated to clients, and ensures all issues are taken care of expeditiously, while delivering the best customer service.
Harris & Harris Law Firm History
Since incorporation, Harris & Harris Law Firm has achieved the following milestones:
- Registered Harris & Harris Law Firm, LLC to transact business in the state of Arizona.
- Has a contract for 10,000 square feet of office space midtown Scottsdale office buildings
- Reached out to numerous former clients and contacts to consider Harris & Harris for all their legal representation needs.
- Began recruiting a staff of five lawyers and three office personnel to work at Harris & Harris.
Harris & Harris Law Firm Services
The following will be the services Harris & Harris Law Firm will provide:
- Dedication to professionalism and honest dialogue
Industry Analysis
The law firm industry is expected to grow over the next five years to over $75 billion. The growth will be driven by an increased population requiring legal representation The growth will be driven by the increase of income for individuals, which can support the decision to hire representation. The growth will be driven by the increase in faulty or misleading documents, agreements, and certifications. The growth will be driven by legal firms who collect fees for business mergers and negotiations. Costs will likely be reduced as current technology becomes dated and new, higher-performing technological advances are employed.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
| Total | Percent | |
|---|---|---|
| Total population | 1,680,988 | 100% |
| Male | 838,675 | 49.9% |
| Female | 842,313 | 50.1% |
| 20 to 24 years | 114,872 | 6.8% |
| 25 to 34 years | 273,588 | 16.3% |
| 35 to 44 years | 235,946 | 14.0% |
| 45 to 54 years | 210,256 | 12.5% |
| 55 to 59 years | 105,057 | 6.2% |
| 60 to 64 years | 87,484 | 5.2% |
| 65 to 74 years | 116,878 | 7.0% |
| 75 to 84 years | 52,524 | 3.1% |
Customer Segmentation
Harris & Harris Law Firm will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Residents of Scottsdale region
- Businesses within Scottsdale region
- Former associates and clients with whom they can collaborate
- Individuals or businesses that have been served with a summons to appear in court
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Harris & Harris Law Firm will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Diamond & Johnson Defense
Diamond & Johnson Defense is a law firm located in Phoenix, Arizona. The firm was established in 1998 and has three partners who oversee all cases: Robert Anderson, who is a lead criminal defense attorney; Lisa Martinez, who is a criminal appeals and post-conviction relief attorney, and David Collin, an investigations and trial preparation lawyer. The law firm has a total of six attorneys who specialize in criminal defense, and six office staff, who communicate directly with each lawyer on staff.
Diamond & Johnson Defense is known as “The Defendant’s Law Firm” in Scottsdale, as 99% of the law practice is focused on personal law representation in civil or criminal court cases. The law firm charges fees within the top 5% in the county for personal representation. The years of practice have proven to be winning ones for Diamond & Johnson Defense, as over 69% of their clients have been released without any prison time. The team at D & J Defense are known to be highly-skilled at investigations and trial preparation, with several team members who will take on a single case to thoroughly cover every possible defense for each client.
Legacy Law Associates
Legacy Law Associates is well-known as a “compassionate” team of attorneys, specializing in family wills and trusts. With a team of dedicated and experienced attorneys, the firm aims to provide comprehensive legal services that meet the goals of each client or family who need legal services during a difficult season of life. Legacy Law Associates consists of a partnership of two attorneys, Jonathan Dunlap and David Sessions, who established the law firm in 2005 in Phoenix after graduating from law school together. Together, the co-owners seek families who have legal needs after the death of a family member; such as estate negotiations, final documents and closures, trustee assistance, probate searches, and confidential proceedings per the will of any individual. The law firm has hired a private secretary for each partner and is housed in a small office in downtown Phoenix. The firm has not grown since 2007 and does not choose to make that a pivotal goal for their partnership, relying instead on the on-going legal processes of trusts, wills, probate and other related items.
Construction Defect Law Firm
The Construction Defect Law Firm is owned and operated by Chip Jackson and is located in Green Valley, Arizona. The focus of the law firm is to represent homeowners who have determined a new or nearly-new home contains construction defects. In most cases, the home builder has moved on from the geographic region and, even when contacted repeatedly, is unwilling to rectify the situation by repair or monetary refund.
Chip Jackson is a highly-skilled evaluator and contractor within the construction industry. He is able to determine the viability of most construction issues with merely a cursory examination and has proven over the past ten years to be a worthy adversary in the courtroom. He wins 98% of all cases he brings into the courtroom. Chip’s clients are always homeowners who have been victims of construction defects in homes that are typically new or less than ten years old. His skill set includes negotiation outside the courtroom, compelling videos of problematic construction processes, drone footage of damaged rooftops, chimneys and other areas not typically viewed by homeowners and other support graphics that demonstrate the defects of the property.
Competitive Advantage
Harris & Harris Law Firm will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Harris & Harris Law Firm will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Harris & Harris Law Firm is as follows:
Word of Mouth/Referrals
Harris & Harris Law Firm has built up an extensive list of contacts over the years by providing exceptional service and expertise to former clients and associates. This group will follow Roger and Anthony to their new company and help spread the word of Harris & Harris Law Firm.
Professional Associations and Networking
Harris & Harris Law Firm will take an active role in all community organizations and networking events, where they can spread the word about the launch and start of their company. The law firm will offer an Open House specifically for association members to acquaint the city of Scottsdale with their new services and location.
Website/SEO Marketing
Harris & Harris Law Firm will fully utilize their website. The website will be well organized, informative, and list all the services that Harris & Harris Law Firm provides. The website will also list their contact information and list their available reservation times to meet with one of the attorney’s for an initial consultation. The website will employ SEO marketing tactics so that anytime someone types in the Google or Bing search engine “law firm services” or “lawyer near me”, Harris & Harris Law Firm will be listed at the top of the search results.
The pricing of Harris & Harris Law Firm will be moderate and on par with competitors so customers feel they receive excellent value when purchasing their services.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Harris & Harris Law Firm. Operation Functions:
- Roger Harris will be the Owner and President of the company. He will engage and manage new client relations.
- Anthony Harris will be the Legal Outcomes & Research Manager for the company. He will work with clients to craft potential outcomes based on algorithms and research.
- Richard Cummings will take on the role of Managing Partner and, as such, will oversee junior partners and staff, as the total number of staff lawyers is expected to markedly grow in the coming five years.
- Torey Crouch will take on the role of Research & Records Manager, where she will support and provide research for all junior and senior attorney staff members. She will also oversee the office personnel.
Milestones:
Harris & Harris Law Firm will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
- 5/1/202X – Finalize contract to lease office space
- 5/15/202X – Finalize personnel and staff employment contracts for the Harris & Harris Law Firm
- 6/1/202X – Finalize contracts for Harris & Harris Law Firm clients
- 6/15/202X – Begin networking at association meetings and industry events
- 6/22/202X – Begin moving into Harris & Harris Law Firm office
- 7/1/202X – Harris & Harris Law Firm opens its office for business
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for Harris & Harris Law Firm are the fees they will charge to clients for the legal services and representation they provide.
The cost drivers will be the overhead costs required in order to staff Harris & Harris Law Firm. The expenses will be the payroll cost, rent, utilities, office supplies, and marketing materials.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Harris & Harris Law Firm is seeking $200,000 in debt financing to launch its law firm. The funding will be dedicated toward securing the office space and purchasing office equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated toward three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the print ads and association memberships. The breakout of the funding is below:
Key Assumptions
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and in order to pay off the startup business loan.
- Number of Clients Per Month: 125
- Average Revenue per Month: $325,000
- Office Lease per Year: $100,000
Financial Projections
Income statement.
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Total Revenues | $360,000 | $793,728 | $875,006 | $964,606 | $1,063,382 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $64,800 | $142,871 | $157,501 | $173,629 | $191,409 | |
| Lease | $50,000 | $51,250 | $52,531 | $53,845 | $55,191 | |
| Marketing | $10,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Salaries | $157,015 | $214,030 | $235,968 | $247,766 | $260,155 | |
| Initial expenditure | $10,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $291,815 | $416,151 | $454,000 | $483,240 | $514,754 | |
| EBITDA | $68,185 | $377,577 | $421,005 | $481,366 | $548,628 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| EBIT | $41,025 | $350,417 | $393,845 | $454,206 | $521,468 | |
| Interest | $23,462 | $20,529 | $17,596 | $14,664 | $11,731 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $6,147 | $115,461 | $131,687 | $153,840 | $178,408 | |
| NET INCOME | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 |
Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $30,000 | $33,072 | $36,459 | $40,192 | $44,308 | |
| Total Current Assets | $184,257 | $381,832 | $609,654 | $878,742 | $1,193,594 | |
| Fixed assets | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $54,320 | $81,480 | $108,640 | $135,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $153,790 | $126,630 | $99,470 | $72,310 | $45,150 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $315,831 | $270,713 | $225,594 | $180,475 | $135,356 | |
| Accounts payable | $10,800 | $11,906 | $13,125 | $14,469 | $15,951 | |
| Total Liability | $326,631 | $282,618 | $238,719 | $194,944 | $151,307 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| Total Equity | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 |
Cash Flow Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | ||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 | |
| Change in working capital | ($19,200) | ($1,966) | ($2,167) | ($2,389) | ($2,634) | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $19,376 | $239,621 | $269,554 | $310,473 | $355,855 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | ||||||
| Investment | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | ||||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from debt | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow | $154,257 | $194,502 | $224,436 | $265,355 | $310,736 | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | |
| Cash at End of Period | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 |
Law Firm Business Plan FAQs
What is a law firm business plan.
A law firm business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your law firm business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Law Firm business plan using our Law Firm Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Law Firm Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of law firm businesses , some examples include: Commercial Law, Criminal, Civil Negligence, and Personal Injury Law, Real Estate Law, and Labor Law.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Law Firm Business Plan?
Law Firm businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Law Firm Business?
Starting a law firm business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Law Firm Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed law firm business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your law firm business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your law firm business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Law Firm Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your law firm business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your law firm business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Law Firm Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your law firm business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your law firm business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful law firm business:
- How to Start a Law Firm

Home Committees, Members & Career Services Small Law Firm Center Overview Small Firm Resources Writing a Business Plan for Law Firm – Law Firm Business Plan Sample
Writing a Business Plan for Law Firm – Law Firm Business Plan Sample
Business plans for lawyers.
New York City Bar Association Small Law Firm Committee
Writing a Business Plans for Lawyers – The Non-Financial Side
1 Why write a law firm business plan?
First and foremost, it’s a Management Tool, It f orces you to think through important issues you may not otherwise consider The recipe to grow your law practice
- A roadmap, albeit a changing one, with milestones to help reach goals you already know and have yet to define
- A sales tool to obtain financing
- A sales tool when looking to form a partnership or join one
- Some parts of a business plan include stating the obvious, but should not be overlooked because they still form a part of the whole
- As you write it, ideas come, strategies unfold, beliefs you may have had change
- It also changes your mindset. You’re no longer thinking about starting a business, you’re now in the process of starting a business.
- If you write a business plan and put it away in a drawer you have not written one that is feasible or is going to do you any good. Continual updating – whether semi-annual, annual, biennial, whichever is best for you – is your own set of checks and balances.
If you are going to buy a book, look for one that offers general advice and suggestions applicable to all businesses. And, if you choose a software package, eliminate the “techy” things like their numbering system; that is a dead giveaway that you’re using a software program. Also, eliminate sections that are irrelevant!
Suggestion: Don’t just buy one from an online bookstore. Take the time go through a table of contents and thumb through.
Examples available from Barnes & Noble:
- Alpha Teach Yourself – Business Plans in 24 Hours by Michael Miller
- Successful Business Planning in 30 Days TM, 3/ed, Peter Patsula
- The Executive Summary
- Analysis of Your Market
- Description of Your Firm
- Competitors
- Your Marketing Strategy
No set formula for a successful practice
Before developing a plan for a lawyer, answer the following:
- Identify your practice niche(s)
- What skills and experience you bring to your practice
- What legal structure to use: sole proprietorship, PC, partnership, LLP, etc.
- What clients you currently have and might potentially acquire
- What clients you want
- What business and social contacts you have
- What other attorneys you can call upon to fill in practice gaps
- How your firm’s records will be kept
- What equipment and supplies will be needed
- What library and other information sources will be needed
- What insurance will be needed
- What other resources will be needed
- How you will compensate yourself
- Review your current finances re assets, current cash flow, expenses
- What financing may be needed
- What financial assets do you have
- What banking accounts will be needed
- Review your current non non-financial resources
- Identify your market
- Describe your startup plans
- Where will your office be located
- What will the name of your firm be
2 The Executive Summary
For some businesses this is the most important part of the business plan because it summarizes what the company does, where it is going and how to get there. Therefore, it must describe the company, the “product” and the market opportunities concisely.
It is written after the plan is complete but is the first and, sometimes, most important part read by investors.
How important this is for a legal business plan depends on your long and short term goals, e.g., whether they are to grow a partnership, join a firm, build up a practice that is enticing for acquisition by a larger firm, etc.
In order to provide that summary, go through a number of exercises:
- Mission statement – the firm’s purpose and what it will do
- Major goals
- Objectives/milestones needed to achieve those goals
- Vision statement – where you want to go and what you want your firm to become, not just 20 years down the road but where you want to be three or five years from now
- List what is out of your control e.g., nature of the law business, direction of the marketplace, competition, mergers and acquisitions among clients, and competitors, attorneys and firms already in place
- Analyze opportunities to face and threats
- List your firm’s specific capabilities and whatever you believe you can offer that is unique
- If you are not a solo practitioner, who is the management
- What is the legal organization
- What technology will you be capitalizing on
- What is the marketing potential
- Describe your basic strategies based on the information you have learned about the legal business, your competition and applicable markets within your field.
- Provide the basis for why you believe your strategy is the right one for your firm.
- What markers will you use to change direction
- Outline what your firm needs to make that strategy succeed
- Financial projections
- Back up of those projections with assumptions (so that they can be adjusted as necessary)
- Summary of revenues by month for at least three years
- Balance sheet
- Cash flow statement
- What actions you’re going to take to carry out the plan
- What changes will be needed or skills acquired to put the plan to work
3 Analysis of Your Market: The Legal “Business” that Affects You
Purpose: an accurate understanding of trends affecting law practice in general and your specializations, client demographics, client universe.
Keep track of impact factors, obstacles, opportunities and threats to better forecast and build the strategies.
- Identify who and what firms dominate and where they are
- What new technologies have already and may yet change the way your practice is done
- What laws and regulations have and may yet change your practice
- Describe the overall demand for your specialties
- What else besides price affects your client decisions to use your services
- What clients (people or companies) can influence your areas of practice
- Large firms, mid size, boutiques, solo practitioners
- In-house attorneys
- Government attorneys
- Divide into primary, secondary and, if necessary, tertiary levels
- Is there substitution, e.g., do it yourself or outsourcing to India
- List what is available and how it affects your practice
- Describe how technology is affecting your kind of practice
- Describe who controls the technologies that affect
- Describe how you keep up with new technology
- List all the things that will make it difficult for you to practice in your expertise and locale
- List the things that will make your exit from you area of expertise or your transition to a different one difficult
- What can relationships with suppliers do for you
- Could a supplier become a competitor, e.g.; for articles you write
- Colleagues and competitors
- Professional associations
- Community associations
- Social and business organizations
- Current and former clients
- Former employment colleagues
- Pro bono colleagues
- What ways improve your position with clients
- Does pricing affect
- What else affects your relationship
- What kind of follow up do you do after meeting someone who may be a potential client or who can introduce you
- Writing articles
- Giving speeches
- How can you use your other relationships
- What are the overall costs that affect your hourly, daily or matter rates?
- Profit margins
- What do suppliers of your technology, research, information, etc. offer by way of pricing, discounts
- Are there long term agreements that can be to your advantage/disadvantage
- Elasticity of demand for the rates you charge
- If on a regular retainer, are you realizing 100% of your hourly rate, or more/less
- Identify where the biggest costs of your practice come from
- Identify fixed and variable costs
- How to gain economies of scale
- Identify where you can lower costs
- Is the profit margin you’re working with the right one for your practice
- Describe the size of your primary market
- List the niche markets that can use your expertise
- Is your kind of practice a growing or shrinking market
- Identify new growth opportunities in your areas of expertise
- Economic slowdowns
- Changing statutes, regulations and decisions
- Social pressures
- By product, industry, size, geography
- Membership lists of trade organizations
- List of conference attendees
- By referral of current clients
- By referral of colleagues, bar association, etc.
- By referral from competitors with conflicts
- What untapped market is there
- What underserved market is there
- Trade associations made of small companies in the same field
- Part time general counsel for small companies
- Trade associations you can join and committees you can volunteer for
4 Describing and Analyzing Your Own Firm
- It’s not just a law firm.
- What’s the general history
- When was it formed and why
- What is your mission
- What are your goals
- What direct experience do you have? Your partners?
- How relevant is your experience to the current world?
- How often do you talk to prospective clients
- What do you current clients feel about you
- What is the maximum amount of business you can handle yourself without farming it out
- To whom can you farm
- Who is your backup when you are too busy, traveling on business, on vacation, sick
- What is unique about you or your practice
- Describe the areas you focus on and want to focus on
- What are the ancillary areas of law that often or usually involved or triggered by your focus area
- What need does your expertise serve
- What are the advantages and disadvantages of your areas of expertise
- Identify your own strengths and weaknesses
- Who are your clients
- Who among your clients makes the decisions to use your services
- What stage of business development are your clients in
- How sophisticated/knowledgeable are your clients
- Are your clients street smart and/or business savvy
- Do they use more than one lawyer at a time
- Long term objectives
- Short term objectives
- What problems do you face
- What problems do your clients face
- What do you consider milestones
- What are the legal (statutory, regulatory & case law) trends that will affect it
- What are the technological trends that will affect it
- What are the economic trends that will affect it
- What potential risks and opportunities to be faced?
- Do you use innovative technology
- Do you offer superior client care/service
- Is your hourly, daily, or matter pricing lower than the “norm”
- Is there a small group of firms or attorneys who offer the same expertise or specialization
- Are you well known for a book, a speech, an article, news coverage, etc.
- Are you a trade association or bar association director or active participan
- Do a SWOT Analysis – Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities, Threats
Strengths & Weaknesses are vis à vis your competitors, rather than your own history Focus on current competition and potential competition
- Are there advantages to your expertise areas
- What do you enjoy doing
- What resources to you have access to
- What do others see as your strengths
- What can you improve
- What don’t you do well
- What should you avoid
- Do others perceive a weakness you don’t agree with
- Are your competitors doing better than you
- How can you meet a potential client
- What are the good opportunities – are they new areas, new statutes & regulations, etc.
- How can changes in technology help you
- How can changes (or no changes) in government policy affect your area of expertise
- Are there changes in social patterns or lifestyle that can help
- What opportunities can open if a weakness is eliminated
- Family/emotional/physical challenges
- Technological challenges
- What is your competition doing you are not
- How can technological changes threaten you
5 Competitive Analysis and Target Market
- List law firm/solo practice trends
- List direct competition
- List indirect competition
- Describe the extent of the unserved market for your kind of legal services
- Who is your client/customer
- What is your price
- Profile your primary customer
- Traits: geographics, demographics, psychograhics
- List client needs
- Describe how your fill those needs
- List primary, secondary and tertiary competitors
- What services do they offer in addition to yours
- What do they charge
- How do competitor firms sell their services
- What are the competitor strengths
- What are the competitor weaknesses
- What size competes with you
- What other specialties do they offer
- Who are they representing
- What is their pricing
- What are their operational strengths and weaknesses
- Are they adequately financed
- How do your competitors advertise or promote themselves
- What are their conflicts
- How does your competition market itself
- Competitive Identification
- Direct competitor – offers the same benefit
- Indirect competitor – services the client can get instead of yours
- Visit and read competitor websites and their advertising, including separate websites by individual partners
- Subscribe to competitor law firm online or other newsletters
- Does it use innovative technology
- Does it offer superior client care/service
- Is its hourly, daily, or matter pricing lower than the “norm”
- Are they well known for a book, a speech, an article, news coverage, etc.
- Are they trade association or bar association directors or active participants
Generate similar info for potential clients to help identify the target that will be most interested in you
A marketing plan must have a detailed description of the target market for your services, an analysis of the trends and conditions of that marketplace and how the trends affect that marketplace
- Total size of targeted market
- Historical current and projected growth rates
- What social, economic &political changes could affect it and your services
- Describe recent developments in the law that affect your areas of expertise
- Are there identifiable niches
- What or will be your clients’ needs and wants
- How will potential customers find out about you
- What kind of marketing, if any, are your clients and potential clients receptive to
- What do existing clients like best about your services
- Are your target clients consumers, businesses or both
- Demographics, psychographics, legal service purchasing habits
- When and how does the client decide to use a lawyer & find a lawyer
- Does your potential client use the Internet, bar association, trade association, business referral, family referral, friend referral, etc. to find a lawyer
- What is your client’s level of education and occupation
- Are they Fortune 1000,500, 100, mid size or smaller
- Is your client industry specialized and do you know that industry
- Does the client use more than one lawyer or law firm
- How long does the client take to decide to use a lawyer
- Does more than one person at the client make the decisions to use a lawyer, and if so who are they
- Is the person who decides who is going to provide legal services the one who is going to receive those services
- What influences your client’s decision to retain a lawyer
- Is using a lawyer optional, a necessity or a luxury
- Is a lawyer needed all year round, seasonal or ad hoc
- How and how well do your clients market themselves
6 Marketing & Strategy
Once you analyze your client needs you can build a comprehensive marketing strategy,
- What is it you intend to accomplish
- What is the amount of increase in clients and/or billing that you want to achieve
- Make each goal measurable and explain each one specifically
- Set each goal to a planned schedule
- Be able and prepared to assess all components to revise when necessary
- Compare these goals to what you believe your competitors’ goals to be
- Tactical objectives = measurable tasks
- Create client value
- Name recognition among your clients and potential clients
- Client retention
- Attracting partners or merging into a bigger firm
- Create a timeline for the objectives or events
- Determine the time frame for the plan, e.g., every six months, every year, etc.
- Describe the need for your services from the client’s POV
- Define the impact on the client of your services
- Ask whether your clients currently obtain this service more cost-effectively than you can provide it
- Describe what would compel clients to change from the lawyers they are using to you or to add you to their lawyer rosters
- E.g., how you will use that list of relationships
- Marketing Mix – Networking, Advertising, Promotion, PR
- Inserts in papers
- Bus, taxi, etc. ads
- Space in professional and trade publications
- Street banners
- New resident welcome kits
- Trade and trade association show directories and handouts
- Trade and trade association show sponsorships
- Coupon mailers
- Press releases
- Sponsorship
- CRM (customer relationship marketing)
- Cost based = cost plus profit margin
- Cost plus profit = cost plus fixed percentage markup
- Market based = use the market norm and add or subtract
- Ask what the highest price your target market can bear
- Determine the price elasticity for your kind of legal services
- Should you offer an introductory rate
- Age of business
- Premises/location
- Competition
- Cost to acquire a client

- Privacy Overview
- Strictly Necessary Cookies
This website uses cookies so that we can provide you with the best user experience possible. Cookie information is stored in your browser and performs functions such as recognising you when you return to our website and helping our team to understand which sections of the website you find most interesting and useful.
Strictly Necessary Cookie should be enabled at all times so that we can save your preferences for cookie settings.
If you disable this cookie, we will not be able to save your preferences. This means that every time you visit this website you will need to enable or disable cookies again.

Law Firm Business Plan [Sample Template]
By: Author Tony Martins Ajaero
Home » Business ideas » Service Industry » Legal Services » Law Firm
Are you about starting a Law firm? If YES, here’s a complete sample Law firm business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE to get started .
Okay, so we have considered all the requirements for starting a law firm . We also took it further by analyzing and drafting a sample law firm marketing plan template backed up by actionable guerrilla marketing ideas for law firms. So let’s proceed to the business planning section.
Lawyers would always be in need by people, companies, schools, and what have you. This isn’t unique to any part of the world, because it is the same phenomenon all over the world. For as long as there are people still living on the face of the earth, there would be rancor and disputes, and the need to have lawyers trash out cases would always arise.
Suggested for You
- Personal Injury Law Firm Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Maid Service Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Snow Removal Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Coin Laundry Business Plan [Sample Template]
- Foreclosure Cleanup Business Plan [Sample Template]
It is for this reason that some lawyers have positioned themselves to take advantage of this trend, and have continued to make huge amount of money from the industry. Without mincing words, starting a law firm is a very profitable venture.
A Sample Law Firm Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
The services of lawyers are needed in every part of the united states of America. Statistics has it that the United States of America has about 165,000 law offices and they generate about $180 billion in annual revenue. These goes to show that starting a law firm is indeed a prosperous business in the U.S, because there is a large market for such business and the industry provides loads of job opportunities for lawyers and other professionals.
The United States Bureau of Labor Statistics predicts that job opportunities for legal practitioners will grow at the same rate as the average for all other occupations in coming years; the growth will be fastest in areas such as intellectual property, healthcare, antitrust, and environmental law et al.
No doubt, the growth of the U.S. population and the expansion of corporate America will definitely lead to the growth in the demand for legal services.
All over the globe, before anyone can be allowed to practice law, they are expected to pass the bar exams in the country or state in which they want to practice. In other words, the journey of starting your own private law firm starts when you eventual pass through a law school.
Although a large percentage of lawyers work for big, corporate law firms, but there are still many lawyers who are employed at mid-sized regional firms and even in one- man and two-person law firms. Just like most other industries in the U.S. and in other parts of the world, the legal services industry is globalizing at a swift pace.
Progressively more, bigger law firms are establishing offices in other countries, some are restructuring and repositioning their existing foreign offices, and others are merging or partnering with local law firms in order to position their organization to handle legal aspects of international trade and other related issues.
This recent trend is responsible for creating job opportunities for lawyers with expertise in international relations and cross-border transactions et al. In the U.S. and also in other parts of the world, lawyer firms who know how to position their organization will always be busy handling legal businesses for their clients.
Some law firms may decide to operate a general law business that cuts across various law practices, whilst others may choose to specialize in any of the two major areas of private sector law. They can choose to operate as a transactional (corporate) law firm or specialize in litigation.
Beyond every reasonable doubt, being a lawyer can be extremely challenging and demanding, but at the same time, it can also be quite rewarding. Lawyers have the privilege of providing a vital service to the business world and to individuals as well.
Lawyers serve as protectors, advisers, and advocates, which is why they are considered experts in communication, analysis, and persuasion, giving them prestige and leverage in society.
2. Executive Summary
Jefferson & MacArthur Law Firm LLP is a law firm that will be located in Inc. 268 13th Street, Suite 1110 Oakland, California 94612. The company will operate as a litigation law firm and also handle other related aspect of law as requested by our clients.
Our services will cover areas such as; breaches of contract, securities-law breaches, class-action lawsuits, antitrust actions, employment-related problems, white-collar crime, and any other related cases.
We are aware that businesses these days require diverse and sophisticated legal services. This is why we will position our law firm to offer a wide range of legal services as requested by our clients. We handle offer legal services ranging from mergers and acquisitions to Product liability, from intellectual property to real estate.
Jefferson & MacArthur Law Firm LLP is a client-focused business law firm that provides broad-based experience at an affordable fee that won’t in any way put a hole in the pocket of our clients.
We will offer a complete range of legal services to our local, state, national, and multi-national clients and we will ensure that we work hard to provide the legal services and counsel needed by our clients to accomplish their business goals and objectives.
At Jefferson & MacArthur Law Firm, our client’s best interests come first, and everything we do is guided by our values and professional ethics. We will ensure that we hire attorneys who are well experienced in a wide variety of transactional and litigation matters.
We will ensure that we hold ourselves accountable to the highest standards by meeting our client’s needs precisely and completely. We will cultivate a working environment that provides a human, sustainable approach to earning a living, and living in our world, for our partners, employees and for our clients.
Jefferson & MacArthur Law Firm will at all times demonstrate her commitment to sustainability, both individually and as a firm, by actively participating in our communities and integrating sustainable business practices wherever possible.
Jefferson & MacArthur Law Firm, LLP is founded by Jefferson Carson and his son MacArthur Carson. The organization will be managed by MacArthur Carson; he graduated from Cumberland School of Law and Brock School of Business at Stamford University.
He has extensive experience in a diverse range of transactional matters, and his legal practice is concentrated in the areas of commercial real estate, commercial finance, construction, and general business contracts.
3. Our Products and Services
Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP proposes to offer a variety of services within the scope of the law industry in the United States of America. Our intention of starting our law firm is to make profits from the industry and we will do all that is permitted by the law in the US to achieve our aim and ambition. Our business offering are listed below;
- Arbitration & Mediation
- Business Formation
- Business and Commercial Transaction
- Collections and Credit Matters
- Commercial Real Estate
- Construction
- Corporate Governance and Compliance
- Creditor’s Rights
- General Counsel Services
- Immigration
- Real Estate Consultancy and Advisory Services
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our vision is to provide our clients with skilled legal advice in a timely and efficient manner. We strive to handle each matter with accountability and responsiveness, as if we were representing ourselves. We focus our attention on the legal aspects of our client’s business so that our clients can focus their attention on the success of their business.
- Our vision reflects our values: integrity, service, excellence and teamwork.
- Our mission is to provide professional and trusted legal services that assist businesses and non-profit organizations in operating sustainably. We provide expert legal counsel in combination with our own business backgrounds, and deliver valuable services in a timely and cost-effective way.
Our Business Structure
Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP will build a solid business structure that can support the growth of our business. We will ensure that we hire competent hands to help us build the business of our dream. Below is the business structure that we will build Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP on;
- Founder and President
Patent Attorney
Legal Secretary
- Legal Assistant
Admin and HR Manager
Business Developer
Front Desk Officer
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Founder and President:
- Responsible for providing direction for the firm
- Creates, communicates, and implements the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy.
- Responsible for handling high profile clients and deals
- Responsible for fixing prices and signing business deals
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization
- Reports to the board
- Represents clients in criminal and civil litigation and other legal proceedings
- Draws up legal documents, or manage or advise clients on legal transactions.
- Attends court hearings (and doing the preparation beforehand)
- Responsible for negotiating (not all cases will end up in court)
- Explains the law and gives general legal advice
- Responsible for settling disputes and supervising any agreements
- Researching and gathering evidence
- Responsible for analyzing legal documents
- Supervises legal assistants.
- Discusses inventions and processes with inventors or manufacturers and ascertaining whether they are likely to succeed in being granted patents
- Studies and analyzes scientific or technical documents, including previously granted patents, to assess whether an invention is new and innovative
- Writes detailed descriptions of inventions in precise legal terms (patent drafts)
- Suggests modifications or extensions to the definition of the invention
- Applies for patents from the Intellectual Property Office (IPO) and the European Patent Office (EPO) , often presenting complicated technical arguments
- Prepares responses to reports from patent examiners
- Ensures application and renewal deadlines are met
- Works with solicitors and barristers to defend or enforce uk patents
- Conducts litigation in proceedings at the EPO or in the Intellectual Property Enterprise Court (IPEC), formerly the Patents County Court
- Advises overseas agents on applications for foreign patent applications
- Instructs on whether business activities will infringe someone else’s patent rights
- Deals with assignments of patent when a patent is sold or transferred
- Keeps up-to-date with legal developments in the intellectual property field
- Advises on other intellectual property rights, e.g. designs or trademarks
- Tutors and mentors trainee patent agents.
- Responsible for drawing up contracts and other legal documents for the company
- Welcomes guests and clients by greeting them in person or on the telephone; answering or directing inquiries.
- Produces information by transcribing, formatting, inputting, editing, retrieving, copying, and transmitting text, data, and graphics; coordinating case preparation.
- Conserves attorneys time by reading, researching, reviewing, verifying, and routing correspondence, reports and legal documents; drafting letters and documents; collecting and analyzing information; initiating telecommunications; organizing client conferences, and attorney meetings; scheduling couriers, court reporters, expert witnesses, and other special functions; coordinating preparation of charts, graphs, and other courtroom visuals; preparing expense reports.
- Maintains attorney calendar by planning and scheduling conferences, teleconferences, dispositions, and travel; recording and monitoring court appearance dates, pleadings, and filing requirements; monitoring evidence-gathering; anticipating changes in litigation or transaction preparation requirements.
- Represents attorney by communicating and obtaining information; following-up on delegated assignments; knowing when to act and when to refer matters to attorney.
- Generates revenues by documenting and inputting attorney billable time and reimbursable expenses; preparing invoices; tracking payments.
- Maintains client confidence by keeping client/attorney information confidential.
- Provides historical reference by developing and utilizing filing and retrieval systems; recording meeting discussions; maintaining transcripts; documenting and maintaining evidence.
- Maintains office supplies by checking stocks; placing and expediting orders; evaluating new products.
- Ensures operation of equipment by completing preventive maintenance requirements; calling for repairs.
- Updates job knowledge by participating in educational opportunities; reading professional publications; maintaining personal networks; participating in professional organizations.
- Enhances department and organization reputation by accepting ownership for accomplishing new and different requests; exploring opportunities to add value to job accomplishments.
- Assists attorneys in preparing for trials and court proceedings.
- Supports attorneys in a legal office.
- Investigates the facts of cases and ensure that all relevant information is considered.
- Identify appropriate laws, judicial decisions, legal articles, and other materials for assigned cases.
- Compiles, analyzes, and organizes information.
- Gathers exhibits.
- Prepares written reports.
- Prepares legal arguments for lawsuits.
- Drafts pleadings and motions filed in court.
- Secures affidavits.
- Assists attorneys during trials.
- Organizes and tracks files from case documents and make them available and easily accessible to attorneys.
- Drafts contracts, mortgages, and separation agreements.
- Prepares tax returns.
- Establishes trust funds.
- Plans estates.
- Supervises other law office employees.
- Delegates responsibilities.
- Maintains financial records.
- Searches legal literature stored in computer databases and on CD-ROM.
- Tracks hours and bill to clients.
Legal Office Assistant
- Works under the direction of lawyers and help them prepare for meetings, hearings and trials. Undertake research projects for multiple cases to determine precedent, drafts or completes legal documents and ensure the correct paperwork is filed with the courts within a specific time period.
- Works directly with clients in a non-advising capacity, such as answering questions, scheduling appointments and making sure all court requirements are met.
- Handles other routine tasks, such as processing and transcribing documents, entering data, scheduling and taking dictation are common duties of a legal office assistant.
- Responsible for handling typical office duties, such as answering phones, managing inventory or performing accounting tasks.
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Defines job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carries out staff induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Responsible for arranging travel, meetings and appointments
- Oversees the smooth running of the daily office activities.
- Identifies, prioritizes, and reaches out to new partners, and business opportunities et al
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts; participates in the structuring and financing of projects; assures the completion of development projects.
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with clients
- Develops, executes and evaluates new plans for expanding increase sales
- Documents all customer contact and information
- Represents the company in strategic meetings
- Helps increase sales and growth for the company
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- Provides managements with financial analyses, development budgets, and accounting reports; analyzes financial feasibility for the most complex proposed projects; conducts market research to forecast trends and business conditions.
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis.
- Performs cash management, general ledger accounting, and financial reporting for one or more properties.
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensures compliance with taxation legislation
- Handles all financial transactions for the company
- Serves as internal auditor for the company
- Receives Visitors / clients on behalf of the organization
- Receives parcels / documents for the company
- Handles enquiries via e-mail and phone calls for the organization
- Distributes mails in the organization
- Handles any other duties as assigned my the line manager
6. SWOT Analysis
Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP hired the services of a core professional in the area of business consulting and structuring to assist the firm in building a solid law firm that can favorably compete in the highly competitive law industry.
Part of what the business consultant did was to work with the management of the firm in conducting a SWOT analysis and preparing a law firm marketing plan for Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP. Here is a summary from the result of the SWOT analysis that was conducted on behalf of Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP;
Our core strength lies in the power of our team; our workforce. We have a team that can go all the way to give our clients value for their money. We are well positioned and we know we will attract loads of clients from the first day we open our doors for business.
As a new law firm, it might take some time for our firm to break into the market; that is perhaps our major weakness.
- Opportunities:
The opportunities in the law industry is massive and we are ready to take advantage of any opportunity that comes our way.
Some of the threats that we are likely going to face as a law firm operating in the United States are unfavorable government policies, and global economic downturn. There are hardly anything we could do as regards these threats other than to be optimistic that things will continue to work for our good.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
Quite a number of distinct trends have emerged in recent times in the legal industry, which is why law firms are positioning their organizations to survive the peaks and troughs of an ailing economy.
As a matter of fact, most of these trends aid law firms and organizations to become more creative, competitive, efficient, and productive in a global market. Some other trends in the legal industry could be attributed to changing demographics, attitudes and work styles.
Another trend that is gaining momentum in the legal industry is that clients have the options of seeking legal assistance from a growing number of non-lawyer professionals such as; paralegal technicians, legal document preparers, legal self-help sites, virtual assistants and offshore legal vendors.
As a result of this trend, the decisions about how legal services are delivered which include staffing, scheduling, strategies and most importantly how firms charge for their services – are increasingly being influenced by the clients, and not by the law firms as it used to be in time past.
No doubt, as the cost of legal services continues to increase and as corporate spending falls, new legal delivery methods will continue to emerge and gain momentum going forward. In addition, the market for legal services has shifted from a sellers’ market to a buyers’ market.
Lastly, it is now becoming trendy in the legal industry for smaller law firms to merge with bigger law firms and for bigger law firms to acquire smaller law firms; mergers and acquisitions. Many law firms all over the United States are coming to the conclusion that the bigger the better for them.
8. Our Target Market
Although Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP will initially serve small to medium sized businesses, from new ventures to well established businesses, but that does not in any way stop us from growing to be able to compete with the leading law firms in the United States.
We hope to someday merge or acquire other law firms and expand our legal services beyond the shores of the United States of America.
As a full service business law firm, Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP have a variety of practice areas to help startups grow.
While we works with a variety of organizations and industries, Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP will also specialize in working with startups, real estate investors, and contractors, manufacturers and distributors, banks, lending and financial institutions.
Our target market cuts across people of different classes and people from all walks of life, local and international organizations as well. We are coming into the industry with a business concept that will enable us work with the highly placed people and companies in the country and at the same with the lowly placed people and smaller businesses.
In other words, our target market is the whole of the United States of America and subsequently other parts of the world. Below is a list of the people and organizations that we have specifically design our products and services for;
- Businesses and Entrepreneurs
- Blue Chips Companies
- Corporate Counsel
- Manufacturers and Distributors
- Real Estate Owners, Developers, and Contractors
- Research and Development Companies
Our Competitive Advantage
A close study of the legal industry reveals that the law firm market has become much more intensely competitive over the past seven years. As a matter of fact, the supply of legal services has significantly exceeded demand. In other to position to take on the market, most law firms have begun to merger or acquire other law firms.
Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP might be a new entrant into the law industry in the United States of America, but the management staffs and board members are considered gurus. They are people who are core professionals and licensed legal practitioners in the US. These are part of what will count as a competitive advantage for us.
Lastly, our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be amongst the best within our category (startups law firm) in the industry – meaning that they will be more than willing to build the business with us and help deliver our set goals and achieve all our objectives.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
- Sources of Income
Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP is established with the aim of maximizing the profits in the law industry and we are going to go all the way to ensure that we do all it takes to attract clients on a regular basis. Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP we generate income by offering the following legal services for individuals and for organizations;
10. Sales Forecast
As long as there are people living in the United States of America and business starting and growing in the U.S., the services of law firms will always be needed.
We are well positioned to take on the available market in the U.S, and we are quite optimistic that we will meet our set target of generating enough income / profits from the first month or operations and grow the business and clientele beyond Oakland, CA to other states in the U.S. and even the global market
We have been able to critically examine the law market and we have analyzed our chances in the industry. We have been able to come up with the following sales forecast. The sales projection are based on information gathered on the field and some assumptions that are peculiar to startups in California.
Below is the sales projection for Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP, it is based on the location of our law firm and the wide range of legal services that we will be offering;
- First Year-: $500,000
- Second Year-: $1,000,000
- Third Year-: $2,500,000
N.B : This projection is done based on what is obtainable in the industry,
- Marketing Strategy and Sales Strategy
We are mindful of the fact that there is stiffer competition in the legal market in the United States of America; hence we have been able to hire some of the best business developer to handle our sales and marketing.
Our sales and marketing team will be recruited based on their vast experience in the industry and they will be trained on a regular basis so as to be well equipped to meet their targets and the overall goal of the organization. We will also ensure that our excellent job deliveries speaks for us in the market place; we want to build a legal business that will leverage on word of mouth advertisement from satisfied clients (both individuals and organizations).
Our goal is to grow our firm to become one of the top 20 law firms in California, which is why we have mapped out strategy that will help us take advantage of the available market and grow to become a major force in the. Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP is set to make use of the following marketing and sales strategies to attract clients;
- Introduce our business by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to organizations and key individuals in California and other parts of the U.S.
- Promptness in bidding for legal contracts
- List our business on yellow pages
- Attend expos, seminars, and business fairs et al
- Create different packages for different category of clients in order to work with their budgets and still deliver quality services to them
- Leverage on the internet to promote our business
- Direct marketing
- Encourage word of mouth marketing
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
We have been able to work with our consultants to help us map out publicity and advertising strategies that will help us walk our way into the heart of our target market.
We are set to take the law industry by storm which is why we have made provisions for effective publicity and advertisement of our firm. Below are the platforms we intend to leverage on to promote and advertise our property development business;
- Place adverts our law firm on both print and electronic media platforms
- Sponsor relevant TV shows
- Maximize our firm’s website to promote our business
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like; Instagram, Facebook ,Twitter, LinkedIn, Badoo, Google+ and other platforms (real estate online forums) to promote our business.
- Offer Pro Bono services as part of our community social responsibility
- Brand all our official cars
12. Our Pricing Strategy
Hourly billing for legal services is long – time tradition in the industry. However, for some types of work, flat fees make more sense because they allow clients to better predict legal costs. As a result of this, Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP will charge our clients a flat fee for many basic services such as; business formation and document drafting and review.
At Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP we will keep our fees below market rate for all of our clients by keeping our overhead low and by collecting payment in advance. In addition, we will also offer special discounted rates to disadvantaged individuals, nonprofits, cooperatives, and small social enterprises.
We are aware that there are some clients that would need regular access to legal advice and assistance; we will offer flat rate general counsel services that will be tailored to take care of such clients’ needs.
- Payment Options
At Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP, our payment policy will be all inclusive because we are quite aware that different people prefer different payment options as it suits them. Here are the payment options that we will make available to our clients;
- Payment by via bank transfer
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via check
- Payment via bank draft
- Payment with cash
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will help us achieve our plans without any itches.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
- The Total Fee for incorporating the Business in California: $750.
- The budget for Liability insurance, permits and license: $5,000
- The Amount needed to acquire a suitable Office facility with enough space in Oakland, California for 6 months (Re – Construction of the facility inclusive): $50,000.
- The Cost for equipping the office (computers, printers, fax machines, furniture, telephones, filing cabins, safety gadgets and electronics et al): $15,000
- Cost of accounting software, CRM software and Payroll Software – $3,000
- Other start-up expenses including stationery – $1000
- Phone and Utilities (gas, sewer, water and electric) deposits – ($3,500).
- Operational cost for the first 3 months (salaries of employees, payments of bills et al) – $40,000
- The Cost of Launching our official Website: $600
- Additional Expenditure (Business cards, Signage, Adverts and Promotions et al): $5,000
Going by the report from our research and feasibility studies, we will need about $200,000 to set up a law firm in Oakland, California.
Generating Funding / Startup Capital for At Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP
At Jefferson and MacArthur Law Firm, LLP is going to start as a private business that will be solely owned by Bar Jefferson Carson and family.
He will be the sole financial of the firm, but may likely welcome partners pretty much which is why he has decided to restrict the sourcing of his start – up capital to 3 major sources. These are the areas we intend generating our start – up capital;
- Generate part of the start – up capital from personal savings
- Source for soft loans from family members and friends
- Apply for loan from my Bank
N.B: We have been able to generate about $60,000 (Personal savings $40,000 and soft loan from family members $20,000) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $100,000 from our bank. All the papers and document has been signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
It is easier for businesses to survive when they have steady flow of business deals / customers patronizing their products and services. We are aware of this which is why we have decided to offer a wide range of legal services. We know that if we continue to deliver excellent legal services, there will be steady from of income for the organization.
Our key sustainability and expansion strategy is to ensure that we only hire competent employees, create a conducive working environment and employee benefits for our staff members. In the nearest future, we will explore the options of either merging with other law firms or acquire law firms in order for us to increase our market share.
We know that if we implement our business strategies, we will grow our law business beyond Oakland, California to other states in the U.S in record time.
Check List / Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check: Completed
- Business Incorporation: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts various banks in the United States: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of All form of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Generating part of the start – up capital from the founder: Completed
- Applications for Loan from our Bankers: In Progress
- writing of business plan: Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Drafting of Contract Documents: In Progress
- Design of The Company’s Logo: Completed
- Graphic Designs and Printing of Packaging Marketing / Promotional Materials: Completed
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Purchase of the Needed furniture, office equipment, electronic appliances and facility facelift: In progress
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business (Business PR): In Progress
- Health and Safety and Fire Safety Arrangement: In Progress
- Establishing business relationship with key players in the industry: In Progress

Item added to your cart
Here is a free business plan sample for a legal consulting services.

If you're passionate about the intricacies of the legal world and are considering launching your own legal consultancy, you've landed on the perfect page.
In the content that follows, we will present to you a comprehensive sample business plan tailored for a legal consultancy firm.
As an aspiring legal consultant, you're likely aware that a meticulously formulated business plan is a cornerstone of any successful venture. It serves as a roadmap, outlining your professional objectives, strategies, and the framework for your consulting services.
To streamline your planning process and ensure you're on the path to success, you can utilize our legal consultancy business plan template. Additionally, our team of experts is available to review and refine your plan at no extra cost.

How to draft a great business plan for your legal consulting services?
A good business plan for a legal consultancy must reflect the unique aspects of the legal industry.
To start, it is crucial to provide a comprehensive overview of the legal market. This includes current statistics and identifying emerging trends within the legal field, as illustrated in our legal consultancy business plan template .
Then, you must articulate your business concept effectively. This encompasses your mission, pinpointing your target clientele (such as small businesses, corporations, or individuals), and the distinctive services your legal consultancy offers (like specialized legal advice, compliance services, or intellectual property management).
The market analysis section should delve into a thorough understanding of the competitive landscape, legal service trends, and client needs.
For a legal consultancy, particular emphasis should be placed on the services you plan to provide. Detail your service offerings - contract drafting, legal audits, dispute resolution, etc. - and explain how they cater to the requirements and challenges faced by your target clients.
The operational plan is equally important. It should outline the location of your consultancy, the structure of your legal team, partnerships with other legal professionals, and your approach to case management.
In a legal consultancy, it is vital to highlight your team's expertise, confidentiality policies, and adherence to legal and ethical standards.
Then, address your marketing and client acquisition strategy. How will you build your client base and ensure client retention? Consider networking strategies, reputation management, and client service excellence.
Adopting digital strategies, such as a professional website or an online legal resource center, is also crucial in the modern marketplace.
The financial plan is another critical component. This should include your startup costs, revenue projections, operating expenses, and the point at which you expect to break even.
In a legal consultancy, understanding your cash flow is essential, as billing cycles can be lengthy and contingent on case outcomes. For this, you may refer to our financial forecast for a legal consultancy .
Compared to other business plans, a legal consultancy's plan must pay closer attention to regulatory compliance, professional liability insurance, and the potential for cyclical demand based on legal trends.
A well-crafted business plan will not only help you to define your strategy and approach but also to attract clients or secure funding.
Lenders and clients seek robust market analysis, sound financial projections, and a clear understanding of how the consultancy will manage its caseload and client relationships.
By presenting a detailed and substantiated plan, you showcase your professionalism and dedication to the success of your consultancy.
To achieve these goals while saving time, you are welcome to fill out our legal consultancy business plan template .

A free example of business plan for a legal consulting services
Here, we will provide a concise and illustrative example of a business plan for a specific project.
This example aims to provide an overview of the essential components of a business plan. It is important to note that this version is only a summary. As it stands, this business plan is not sufficiently developed to support a profitability strategy or convince a bank to provide financing.
To be effective, the business plan should be significantly more detailed, including up-to-date market data, more persuasive arguments, a thorough market study, a three-year action plan, as well as detailed financial tables such as a projected income statement, projected balance sheet, cash flow budget, and break-even analysis.
All these elements have been thoroughly included by our experts in the business plan template they have designed for a legal consultant .
Here, we will follow the same structure as in our business plan template.

Market Opportunity
Market data and figures.
The legal consulting market is a robust and essential sector within the professional services industry.
Recent estimates value the global legal services market at approximately 850 billion dollars, with projections indicating steady growth in the coming years. This is driven by an increase in legal complexities, regulatory changes, and the globalization of business operations.
In the United States, there are over 1.3 million licensed attorneys, contributing to a legal services market that generates an estimated annual revenue of over 300 billion dollars.
These figures underscore the critical role legal consultants play in the business ecosystem and their substantial contribution to the economy.
The legal industry is experiencing significant shifts, with trends that emphasize efficiency, accessibility, and specialization.
Technology adoption is on the rise, with law firms and legal consultants leveraging artificial intelligence, legal tech software, and online platforms to streamline operations and offer more cost-effective services.
There is also a growing demand for niche legal expertise, particularly in areas such as cybersecurity, data privacy, intellectual property, and environmental law, reflecting the evolving landscape of business risks and regulatory requirements.
Alternative legal service providers (ALSPs) are gaining traction, offering a range of services from legal process outsourcing to consultancy, challenging traditional law firm models.
Moreover, clients are increasingly seeking transparent billing practices and value-based pricing models, pushing legal consultants to innovate in their service delivery and client engagement strategies.
These trends indicate a transformation in how legal services are provided and consumed, aligning with the evolving expectations of 21st-century clients.
Success Factors
Several key elements contribute to the success of a legal consultant.
Expertise and specialization are paramount. Legal consultants who possess deep knowledge and experience in specific legal areas can offer more value to their clients and differentiate themselves in the market.
Building strong client relationships is also essential. Trust, confidentiality, and a track record of successful outcomes are crucial for client retention and referrals.
The ability to adapt to new technologies and incorporate them into legal practices can significantly enhance efficiency and client satisfaction.
Strategic networking and partnerships can expand a legal consultant's reach and resources, providing a competitive edge.
Lastly, effective business management, including cost control, marketing, and continuous professional development, is vital for sustaining and growing a legal consultancy practice in a dynamic market.
The Project
Project presentation.
Our legal consultancy project is designed to provide specialized legal services to individuals and businesses seeking expert advice and representation in various legal matters. Located in a business district with a high concentration of small to medium-sized enterprises, this consultancy will offer a comprehensive range of legal services, including contract law, intellectual property, employment law, and corporate compliance, all delivered with a commitment to professionalism and client satisfaction.
The focus will be on providing personalized legal solutions that are both effective and cost-efficient, ensuring that clients receive the best possible outcome for their legal issues.
This legal consultancy aims to become a trusted advisor and partner for clients, offering not just legal services but also proactive legal risk management and strategic advice to help them navigate the complexities of the law.
Value Proposition
The value proposition of our legal consultancy project is centered on delivering expert legal advice and representation tailored to the unique needs of each client. Our commitment to understanding our clients' businesses and challenges allows us to provide targeted legal solutions that protect their interests and facilitate their growth.
We are dedicated to maintaining the highest standards of integrity and transparency, ensuring that our clients are well-informed and confident in the legal strategies we pursue on their behalf.
Our consultancy aims to build long-term relationships with clients, becoming an integral part of their success by offering reliable, accessible, and forward-thinking legal services.
Project Owner
The project owner is a seasoned legal professional with a wealth of experience in providing legal counsel to a diverse clientele. With a background in both law firm and in-house settings, they possess a deep understanding of the legal challenges that businesses and individuals face.
Armed with a strong track record of successful case outcomes and a reputation for excellent client service, the project owner is committed to establishing a legal consultancy that stands out for its strategic approach, client-centric services, and innovative legal thinking.
With a dedication to the law and a passion for helping clients overcome their legal hurdles, the project owner is the driving force behind this project, aiming to deliver not just legal services, but peace of mind and a foundation for success.
The Market Study
Market segments.
The market segments for a legal consultancy are diverse and can be categorized as follows:
Firstly, there are small to medium-sized enterprises (SMEs) that require legal services but may not have the resources to maintain an in-house legal department.
Secondly, individual entrepreneurs and startups are in need of legal advice for business formation, intellectual property protection, and contract negotiations.
Additionally, larger corporations may seek specialized legal consulting for complex transactions, compliance issues, or litigation support.
Lastly, non-profit organizations and public sector entities also form a significant segment, often requiring legal expertise in regulatory, employment, and contractual matters.
SWOT Analysis
A SWOT analysis of the legal consultancy business reveals several key points:
Strengths include a deep understanding of legal frameworks, a reputation for professionalism and confidentiality, and the ability to offer personalized legal solutions.
Weaknesses might encompass the challenge of keeping up with rapidly changing laws and regulations, and the potential for high operational costs.
Opportunities can be found in the growing demand for legal services in emerging areas such as cyber law, data protection, and international trade.
Threats may include intense competition from established law firms and the increasing availability of online legal service platforms.
Competitor Analysis
Competitor analysis in the legal consultancy sector indicates a competitive landscape.
Direct competitors include other legal consultancies, full-service law firms, and online legal service providers.
These competitors vie for clients by offering a range of services, expertise, and pricing models.
Potential competitive advantages for a legal consultancy could be specialized knowledge in niche legal areas, flexible and client-focused service delivery, and a strong track record of successful case outcomes.
Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of competitors is crucial for carving out a unique position in the market and for client acquisition and retention.
Competitive Advantages
Our legal consultancy's competitive advantages lie in our personalized approach to client service and our commitment to staying at the forefront of legal innovation.
We offer tailored legal advice that addresses the specific needs of each client, whether they are navigating complex regulatory environments or seeking to protect their intellectual property.
Our dedication to continuous learning ensures that we are equipped to handle the latest legal challenges, providing our clients with cutting-edge solutions.
Moreover, our emphasis on building long-term client relationships is based on trust, transparency, and integrity, setting us apart in a competitive industry.
You can also read our articles about: - how to offer legal consulting services: a complete guide - the customer segments of a legal consulting services - the competition study for a legal consulting services
The Strategy
Development plan.
Our three-year development plan for the legal consultancy firm is designed to establish a strong foundation and expand our services.
In the first year, we will concentrate on building a robust client base by offering expert legal advice and personalized services. We will also invest in building our reputation for excellence and reliability.
The second year will focus on expanding our areas of expertise and introducing additional services such as online legal consultations and workshops for businesses on legal compliance.
In the third year, we aim to form strategic partnerships with other professional service providers and explore opportunities for mergers or acquisitions to broaden our market reach.
Throughout this period, we will remain dedicated to upholding the highest standards of legal practice, client confidentiality, and adapting to the evolving legal landscape to serve our clients effectively.
Business Model Canvas
The Business Model Canvas for our legal consultancy targets individuals and businesses in need of legal advice, representation, and compliance services.
Our value proposition is delivering expert legal solutions, personalized client care, and proactive risk management.
We offer our services through direct consultations, digital platforms, and client workshops, utilizing our key resources such as our legal expertise and professional network.
Key activities include legal research, client consultations, and continuous professional development.
Our revenue streams are derived from billable hours, retainer agreements, and flat-fee services, while our costs are primarily associated with professional staff, office operations, and marketing initiatives.
Find a complete and editable real Business Model Canvas in our business plan template .
Marketing Strategy
Our marketing strategy is centered on building a strong brand reputation and demonstrating our legal expertise.
We aim to engage our target audience through educational content on legal topics, free initial consultations, and client testimonials.
We will leverage online platforms, including our website and social media, to share valuable insights and case studies that showcase our success.
Networking events and partnerships with business associations will also play a crucial role in our strategy to gain referrals and build professional credibility.
Finally, we will monitor client satisfaction and feedback to continuously improve our services and client experience.
Risk Policy
The risk policy for our legal consultancy is focused on mitigating risks associated with legal practice, client data security, and professional liability.
We adhere to strict ethical standards and legal regulations, ensuring all client information is handled with the utmost confidentiality and security.
Regular training and audits are conducted to maintain compliance with the latest legal developments and to prevent any conflicts of interest.
We also maintain a comprehensive professional indemnity insurance policy to protect against potential legal claims.
Our priority is to provide reliable legal services while safeguarding our clients' interests and our firm's reputation.
Why Our Project is Viable
We are committed to establishing a legal consultancy that addresses the complex legal needs of our clients with precision and care.
With our focus on expertise, client service, and adaptability, we are confident in our ability to thrive in the competitive legal services market.
We are enthusiastic about the opportunity to support our clients' success and to grow a sustainable and respected legal practice.
We are prepared to make the necessary adjustments to navigate challenges and seize opportunities, looking forward to a prosperous future for our legal consultancy.
You can also read our articles about: - the Business Model Canvas of a legal consulting services - the marketing strategy for a legal consulting services
The Financial Plan
Of course, the text presented below is far from sufficient to serve as a solid and credible financial analysis for a bank or potential investor. They expect specific numbers, financial statements, and charts demonstrating the profitability of your project.
All these elements are available in our business plan template for a legal consultant and our financial plan for a legal consultant .
Initial expenses for our legal consultancy include setting up a professional office environment, investing in legal research databases and software, obtaining necessary licenses and insurance, developing a comprehensive website, and engaging in targeted marketing strategies to establish our brand within the legal services market.
Our revenue assumptions are based on a thorough analysis of the local demand for legal services, taking into account the increasing need for specialized legal advice in areas such as intellectual property, business law, and compliance.
We anticipate a steady growth in client acquisition, starting with a conservative client base and expanding as our reputation for expert legal consultation solidifies.
The projected income statement reflects expected revenues from our legal consulting fees, costs of services (research materials, office supplies, subcontracted expertise), and operating expenses (office lease, marketing, salaries, etc.).
This results in a forecasted net profit that is essential for assessing the long-term viability of our legal consultancy.
The projected balance sheet provides a snapshot of our consultancy's financial standing, including assets such as office equipment, legal libraries, and liabilities like business loans and accounts payable.
It demonstrates the overall financial health of our legal consultancy at the end of each fiscal period.
Our projected cash flow statement details the inflows and outflows of cash, enabling us to predict our financial needs. This is crucial for maintaining solvency and ensuring smooth operational management.
The projected financing plan outlines the specific sources of funding we intend to utilize to cover our initial costs and support growth.
The working capital requirement for our legal consultancy will be diligently managed to maintain sufficient liquidity for day-to-day operations, such as paying for office expenses, subscription services, and employee wages.
The break-even analysis for our consultancy will determine the volume of billable hours required to cover all our costs, including startup investments, and begin generating profits.
It will signal the point at which our business becomes financially sustainable.
Key performance indicators we will monitor include the average revenue per client, the ratio of billable hours to non-billable hours to gauge efficiency, and the client retention rate to measure our success in maintaining long-term relationships.
These metrics will assist us in evaluating the financial performance and overall success of our legal consultancy.
If you want to know more about the financial analysis of this type of activity, please read our article about the financial plan for a legal consulting services .
- Choosing a selection results in a full page refresh.
- Opens in a new window.
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
Legal Templates
Home Business Plan
Business Plan Templates
Use our template to make an investment-worthy business plan.

Updated December 8, 2023 Written by Sara Hostelley | Reviewed by Brooke Davis
A business plan is a document outlining a company’s operations, strategies, goals, and objectives. It’s crucial to guide you through each stage of starting and growing your business.
Templates (8)
What is a business plan, why is a business plan essential, components of a business plan, how to write a business plan, business plan sample.
Below, you can find free business plan templates for specific business types. You can also find more in-depth information on writing a plan for your business, whether it’s a food truck, restaurant, real estate business, or another entity:

Create a detailed plan that lays out the details of how your business will achieve it's objectives.
Traditional Business Plan

Create a simplified version of a traditional business plan.
One-Page Business Plan

Create a Non-Profit Business Plan and learn how to write one.

Create a Daycare Business Plan and learn how to write one.

Create a Restaurant Business Plan and learn how to write one.

Create a Real Estate Business Plan and learn how to write one.
Real Estate

Create a Food Truck Business Plan and learn how to write one.
A business plan is a document detailing how a business, whether it’s a new or existing company, will achieve its goals and objectives. It guides you through every step of starting and running a company.
A business plan can be the foundation of your business, serving as a written roadmap that covers all aspects of how to structure, run, and grow your business. You can also refer back to it as your business progresses to track its growth and success.
In addition to being a helpful document internally, a business plan is also vital for a company to communicate its success to external parties that may influence its future success.
Consider some of the main reasons why large and small business owners alike use business plans:
1. Use As a Roadmap
A business plan sets specific, measurable, and time-bound goals. Having these goals helps you track progress, evaluate performance, and adjust as necessary.
By laying out goals, you have a clear and attainable plan of action with the ability to see and monitor your progress.
2. Plan Strategies For Potential Challenges
A business plan can help you think objectively about your business’s key elements and inform your decision-making as you move forward.
A detailed plan can provide a semblance of control over a potentially cumbersome process. Formulating a plan can improve your ability to make choices and decisions for yourself and the business. This approach is much better than suddenly making a critical decision without time to evaluate or haphazardly letting others decide for you.
3. Get Funding or Bring on New Business Partners
An accurate business plan is essential whether or not you need to secure a business loan. Investors and lenders often require a business plan before they commit capital. A solid plan demonstrates your commitment, viability, and potential return on investment.
Create a business plan that grabs the attention of potential investors and provides them with enough structure and confidence that they will move forward and grant funding and support to your business.
You can use your business plan to highlight how the proposed business will be successful and profitable.
4. Discover Any Weaknesses
A business plan includes a strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats (SWOT) analysis that helps identify potential risks and challenges. It is essential to allocate resources and demonstrate monthly profit or loss. By recognizing these elements early, you can develop strategies to mitigate or address them.
5. Analyze the Market and Competition
Market research within the plan helps you better understand your target audience, competition, and industry trends. This knowledge is crucial for making informed business decisions.
By learning about your competition, you can help make your goods or services stand out and help validate your business idea.
You should update a business plan as you go, altering your goals as necessary and being mindful of any changes of direction in your business.
A typical business plan includes the following sections:
- Executive Summary
- Management Team
- Products and Services
- Customers and Marketing
- SWOT Analysis
Our business plan template includes all of the above, so you won’t have to worry about missing out on essential sections.
Step 1 – Create an Executive Summary
An executive summary is the first section of a traditional business plan, serving as the first impression of your business. Please give a brief overview of your company, including its mission, key goals, and a snapshot of your financial projections.
You can skip this step if you’re writing a lean business plan for a startup. Instead, replace it with a few sentences outlining the problem your startup aims to solve and the solution you will provide.
Executive Summary Example:
Market research indicates there are a growing number of dog owners in Tallahassee who want to train their animals. Consumer surveys indicate that most consumers don’t have the time or resources to train their animals themselves.
Consumers have also expressed a desire for combined dog walking and training services to help discipline their animals.
Pawsitive Strides Canine Coaching & Walks provides a convenient service for customers with furry friends and disposable incomes.
Tips for Writing an Executive Summary
- Define a problem in your market and state how your business will solve it.
- Limit your executive summary to one page.
- Use a tone appropriate for your audience.
Step 2 – Describe Your Company’s Team
A professional business plan will include a statement about your company’s team and management.
Describe your startup’s legal structure. After that, you can insert a chart to show the hierarchical structure of your company. Show and name your C-suite executives, management team, and key employees. Include short biographies and links to their resumes and LinkedIn profiles to give the reader a complete picture of your staff’s qualifications.
If you have a smaller staff, you can highlight the founder and CEO and your staff members who perform the services or create your business’s products.
Example for Company’s Team Statement:
Jamie Clayton, Founder and CEO
- Board-certified veterinarian.
Pawsitive Strides Canine Coaching & Walks’s dog walkers and trainers
- 14 full-time staff members.
- 26 part-time staff members.
- All staff members have the Certified Professional Dog Trainer-Knowledge and Skills Assessed (CPDT-KSA) credential from the Certification Council for Professional Dog Trainers.
Tips for Writing about Your Company Management and Team
- Include any roles you’d like to hire to grow your company, if applicable.
- Highlight expertise and awards one to show your staff’s capabilities.
Step 3 – Summarize Market Analysis and Potential
Your business plan must also thoroughly analyze your target market and customer base. The goal here is to show that you understand your market and target audience and that there is a viable market for your business.
Market Analysis Example:
Pawsitive Strides Canine Coaching & Walks’s ideal customer is a dog owner between the ages of 25 and 65 with a high disposable income. They’re ideally a working professional or have recently retired from the workplace. They love their dog (or dogs) and want them to be well-behaved and have an outlet for all their energy.
Market research shows that Pawsitive Strides Canine Coaching & Walks has ample opportunities in the Tallahassee area:
- The total revenue for dog walking services in the U.S. increased from $900 million in 2019 to $1.1 billion in 2023.
- Dog ownership has increased by 20% over the last five years.
- Online search volume for “dog walkers in Tallahassee” is up by 10% since last year.
- 19% of Tallahassee’s residents have a household income of $125,000 or more (compared to the average of 5% across the U.S.).
Tips for Writing a Market Analysis
- Use reliable sources for acquiring data.
- Conduct consumer surveys to hear from people in your target area.
- Focus on the demand in your area and the growth potential.
- Include revenue and expense projections based on market data.
Step 4 – Describe Your Product or Service
Describe the products and services you offer. Pinpoint the value they provide to current and future customers and share your plans for research and development.
The main goal of this section is to convince the reader and yourself that your business is viable and that you have enough resources, time, and energy to achieve your goals.
Product Description Example:
Pawsitive Strides Canine Coaching & Walks isn’t an ordinary dog walking service. When a customer signs up for our monthly subscription plan, we have one of our certified dog walkers go to their house 12 times a month on a schedule that works for them.
Our dog walker takes their dog on a 30-minute walk and corrects their behavior. Their dog learns how to walk on a leash calmly and be around cars and people. Not only does the dog get some exercise and fresh air, but they also learn discipline, meaning the customer doesn’t have to worry about training their dog in this sense.
Tips for Writing a Product/Service Description
- Highlight cross-sell and upsell opportunities, if applicable.
- Emphasize what distinguishes you from other companies providing similar services/products.
- Include details for updating your offerings in the future.
Step 5 – Plan Your Marketing Strategy
Discuss the brand vision you want to cultivate, the metrics you’ll track, and the channels you’ll use to reach your target audience. Outlining how you plan to collect and retain customers will help you experience growth in the long term.
Marketing Strategy Example:
Pawsitive Strides Canine Coaching & Walks will focus on social media and direct mail marketing as its two main forms of advertising. We’ll track customer referrals to determine how many current customers are satisfied with our services.
On our social media platforms, including Instagram and Facebook, we’ll track our audience growth rate, bounce rate, and click-through rate.
Tips for Writing a Marketing Strategy
- Add the budget/resources you have, if applicable.
- Create strategies for marketing to different segments within your main target audience.
Step 6 – Conduct SWOT Analysis
Organizations use SWOT analyses to determine how closely a business will adhere to its growth trajectories. This analysis involves looking at a company’s SWOTs, which are:
- Strengths: Strengths are things your company does well. Examples include having a unique selling proposition, standout brandings, or human resources, like your employees and C-class executives.
- Weaknesses: These barriers prevent your project or company from reaching certain milestones. Examples include financial limitations, a shortage of skilled professionals, and unclear selling propositions.
- Opportunities: These positive external factors could give you a competitive edge. For instance, if you’re a manufacturer and the federal government cuts tariffs, you can export your products into a new market to boost market share and sales.
- Threats: These are events, competitors, and situations that pose a risk to your company and the goals you’ve set for it. Typical threats include negative media coverage, changing customer demands, emerging competitors, and new rules and regulations.
SWOT Analysis Example:
- Appeals to people who don’t have the time or resources to train their pets.
- Low startup costs.
- Finding enough certified employees to meet the anticipated demand.
- Dealing with aggressive animals may be challenging for newer employees.
Opportunities
- Offering multiple subscription packages for customers who want more frequent training sessions for their pets.
- BehaviorBuddies is a dog walking service in Bradfordville that may take away customers.
Tips for Writing a SWOT Analysis
- Be honest with your business’s weaknesses and threats.
- Capitalize on opportunities you find through market analysis.
Step 7 – Develop a Strategy for Operations
Your business plan needs to include a thorough operations plan. This section reveals your manufacturing, fulfillment, managing, staffing, hiring strategies, and all the other processes you go through when running your business daily.
Operations Strategy Example:
Jamie Clayton will oversee the hiring of all employees, and the team lead will train all employees for at least one month to ensure they have the knowledge necessary to deal with animals of all temperaments.
The team lead will also organize the dog walking schedule to ensure all team members have enough time to arrive at customers’ houses and complete the dog walking/training sessions thoroughly.
Tips for Writing a Business Strategy
- Consider what your business needs to thrive on a daily basis.
- Account for inventory and supplies, even if your business is service-based.
Step 8 – Compile Your Business Financials
Create financial projections, including income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements for the first few years of operation. If you need funding, specify the amount and how you plan to use it.
Financial Statement Example:
Income Statement for the Year Ended December 31, 2023
- Revenue: $150,000
- Cost of Goods Sold: $30,000
- Gross Profit: $120,000
- Operating Expenses: $80,000
- Net Operating Income: $40,000
- Other Income/Expenses: -$2,000
- Net Income: $38,000
Tips for Writing a Financial Section
- Double-check the accuracy of financial information.
- Demonstrate how the proposed funding aligns with your company’s goals.
- Forecast future financial performance.
Step 9 – Explain Your Funding Request
If you’re seeking funding or investment for your business, explain the amount you need and how you intend to use it. Be transparent about the terms you’re offering to investors or lenders.
Funding Request Example:
Pawsitive Strides Canine Coaching & Walks has already hired a team to serve our existing customers. Once we scale to $500,000 in annual revenue over the next two years and at a 10% profit margin, our primary ongoing annual expenses (not including taxes) will total $350,000.
While already profitable, we are requesting $200,000 in the form of a business loan to buy two additional company vehicles. These vehicles will improve our employees’ ability to get to customers’ homes, and the remaining money will go toward maintaining current company vehicles.
Tips for Writing a Funding Request
- Add a timeline so investors know your goals and how you plan to use the money.
- If you seek funding in the form of an exchange for equity, an investor may expect to gain decision-making powers in your company. Plan for this situation accordingly.
Step 10 – Compile an Appendix for Official Documents
Include relevant documents, such as resumes of key team members, legal agreements, market research data, product design mock-ups, and your business’s legal structure documents.
Remember that each business plan is unique, so tailor your content to your venture and audience. Your business plan should effectively communicate your vision, strategy, and financial viability to potential investors, partners, and stakeholders.
Combine the appendix with a table of contents and footnotes section so you can reference it throughout your document.
You can download a free business plan template below in PDF or Word format:

Related Documents
- Business Continuity Plan : Outline how your business will run in the event of a range of disaster scenarios with a business continuity plan.
- One-Page Business Plan : A simplified version of a traditional business plan that outlines the basics of your business.
- LLC Operating Agreement : An internal written document among members of a Limited Liability Company (“LLC”).
- Business Proposal : Use this document to form new relationships with other businesses and organizations.
- Request for Proposal : Download this form to allow you to collect offers from various vendors who can provide goods or services your business needs.
- Legal Resources
- Partner With Us
- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Do Not Sell My Personal Information

The document above is a sample. Please note that the language you see here may change depending on your answers to the document questionnaire.
Thank you for downloading!
How would you rate your free template?
Click on a star to rate
Our Recommendations
- Best Small Business Loans for 2024
- Businessloans.com Review
- Biz2Credit Review
- SBG Funding Review
- Rapid Finance Review
- 26 Great Business Ideas for Entrepreneurs
- Startup Costs: How Much Cash Will You Need?
- How to Get a Bank Loan for Your Small Business
- Articles of Incorporation: What New Business Owners Should Know
How to Choose the Best Legal Structure for Your Business
Small business resources.
- Business Ideas
- Business Plans
- Startup Basics
- Startup Funding
- Franchising
- Success Stories
- Entrepreneurs
- The Best Credit Card Processors of 2024
- Clover Credit Card Processing Review
- Merchant One Review
- Stax Review
- How to Conduct a Market Analysis for Your Business
- Local Marketing Strategies for Success
- Tips for Hiring a Marketing Company
- Benefits of CRM Systems
- 10 Employee Recruitment Strategies for Success
- Sales & Marketing
- Social Media
- Best Business Phone Systems of 2024
- The Best PEOs of 2024
- RingCentral Review
- Nextiva Review
- Ooma Review
- Guide to Developing a Training Program for New Employees
- How Does 401(k) Matching Work for Employers?
- Why You Need to Create a Fantastic Workplace Culture
- 16 Cool Job Perks That Keep Employees Happy
- 7 Project Management Styles
- Women in Business
- Personal Growth
- Best Accounting Software and Invoice Generators of 2024
- Best Payroll Services for 2024
- Best POS Systems for 2024
- Best CRM Software of 2024
- Best Call Centers and Answering Services for Busineses for 2024
- Salesforce vs. HubSpot: Which CRM Is Right for Your Business?
- Rippling vs Gusto: An In-Depth Comparison
- RingCentral vs. Ooma Comparison
- Choosing a Business Phone System: A Buyer’s Guide
- Equipment Leasing: A Guide for Business Owners
- HR Solutions
- Financial Solutions
- Marketing Solutions
- Security Solutions
- Retail Solutions
- SMB Solutions
Business News Daily provides resources, advice and product reviews to drive business growth. Our mission is to equip business owners with the knowledge and confidence to make informed decisions. As part of that, we recommend products and services for their success.
We collaborate with business-to-business vendors, connecting them with potential buyers. In some cases, we earn commissions when sales are made through our referrals. These financial relationships support our content but do not dictate our recommendations. Our editorial team independently evaluates products based on thousands of hours of research. We are committed to providing trustworthy advice for businesses. Learn more about our full process and see who our partners are here .
Choosing the right legal structure is a necessary part of running a business. Whether you're just starting out or your business is growing, it's crucial to understand the options.

Table of Contents
Your business’s legal structure has many ramifications. It can determine how much liability your company faces during lawsuits. It can put up a barrier between your personal and business taxes – or ensure this barrier doesn’t exist. It can also determine how often your board of directors must file paperwork – or if you even need a board. [Related article: What to Do if Your Business Gets Sued ]
We’ll explore business legal structures and how to choose the right structure for your organization.
What is a business legal structure?
A business legal structure, also known as a business entity, is a government classification that regulates certain aspects of your business. On a federal level, your business legal structure determines your tax burden. On a state level, it can have liability ramifications.
Why is a business legal structure important?
Choosing the right business structure from the start is among the most crucial decisions you can make. Here are some factors to consider:
- Taxes: Sole proprietors, partnership owners and S corporation owners categorize their business income as personal income. C corporation income is business income separate from an owner’s personal income. Given the different tax rates for business and personal incomes, your structure choice can significantly impact your tax burden.
- Liability: Limited liability company (LLC) structures can protect your personal assets in the event of a lawsuit. That said, the federal government does not recognize LLC structures; they exist only on a state level. C corporations are a federal business structure that includes the liability protection of LLCs.
- Paperwork: Each business legal structure has unique tax forms. Additionally, if you structure your company as a corporation, you’ll need to submit articles of incorporation and regularly file certain government reports. If you start a business partnership and do business under a fictitious name, you’ll need to file special paperwork for that as well.
- Hierarchy: Corporations must have a board of directors. In certain states, this board must meet a certain number of times per year. Corporate hierarchies also prevent business closure if an owner transfers shares or exits the company, or when a founder dies . Other structures lack this closure protection.
- Registration: A business legal structure is also a prerequisite for registering your business in your state. You can’t apply for an employer identification number (EIN) or all your necessary licenses and permits without a business structure.
- Fundraising: Your structure can also block you from raising funds in certain ways. For example, sole proprietorships generally can’t offer stocks. That right is primarily reserved for corporations.
- Potential consequences for choosing the wrong structure: Your initial choice of business structure is crucial, although you can change your business structure in the future. However, changing your business structure can be a disorganized, confusing process that can lead to tax consequences and the unintended dissolution of your business.
Types of business structures
The most common business entity types are sole proprietorships, partnerships, limited liability companies, corporations and cooperatives. Here’s more about each type of legal structure.
Sole proprietorship
A sole proprietorship is the simplest business entity. When you set up a sole proprietorship , one person is responsible for all a company’s profits and debts.
“If you want to be your own boss and run a business from home without a physical storefront, a sole proprietorship allows you to be in complete control,” said Deborah Sweeney, vice president and general manager of business acquisitions at Deluxe Corp. “This entity does not offer the separation or protection of personal and professional assets, which could prove to become an issue later on as your business grows and more aspects hold you liable.”
Proprietorship costs vary by market. Generally, early expenses will include state and federal fees, taxes, business equipment leases , office space, banking fees, and any professional services your business contracts. Some examples of these businesses are freelance writers, tutors, bookkeepers , cleaning service providers and babysitters.
A sole proprietorship business structure has several advantages.
- Easy setup: A sole proprietorship is the simplest legal structure to set up. If you – and only you – own your business, this might be the best structure. There is very little paperwork since you have no partners or executive boards.
- Low cost: Costs vary by state, but generally, license fees and business taxes are the only fees associated with a proprietorship.
- Tax deduction: Since you and your business are a single entity, you may be eligible for specific business sole proprietor tax deductions , such as a health insurance deduction.
- Easy exit: Forming a proprietorship is easy, and so is ending one. As a single owner, you can dissolve your business at any time with no formal paperwork required. For example, if you start a day care center and wish to fold the business, refrain from operating the day care and advertising your services.
The sole proprietorship is also one of the most common small business legal structures. Many famous companies started as sole proprietorships and eventually grew into multimillion-dollar businesses. These are a few examples:
- Marriott Hotels
Partnership
A partnership is owned by two or more individuals. There are two types: a general partnership, where all is shared equally, and a limited partnership, where only one partner has control of operations and the other person (or persons) contributes to and receives part of the profits. Partnerships can operate as sole proprietorships, where there’s no separation between the partners and the business, or limited liability partnerships (LLPs), depending on the entity’s funding and liability structure.
“This entity is ideal for anyone who wants to go into business with a family member, friend or business partner – like running a restaurant or agency together,” Sweeney said. “A partnership allows the partners to share profits and losses and make decisions together within the business structure. Remember that you will be held liable for the decisions made as well as those actions made by your business partner.”
General partnership costs vary, but this structure is more expensive than a sole proprietorship because an attorney should review your partnership agreement. The attorney’s experience and location can affect the cost.
A business partnership agreement must be a win-win for both sides to succeed. Google is an excellent example of this. In 1995, co-founders Larry Page and Sergey Brin created a small search engine and turned it into the leading global search engine. The co-founders met at Stanford University while pursuing their doctorates and later left to develop a beta version of their search engine. Soon after, they raised $1 million in funding from investors, and Google began receiving thousands of visitors a day. Having a combined ownership of 11.4% of Google provides them with a total net worth of nearly $226.4 billion.
Business partnerships have many advantages.
- Easy formation: As with a sole proprietorship, there is little paperwork to file for a business partnership. If your state requires you to operate under a fictitious name ( “doing business as,” or DBA ), you’ll need to file a Certificate of Conducting Business as Partners and draft an Articles of Partnership agreement, both of which have additional fees. You’ll usually need a business license as well.
- Growth potential: You’re more likely to obtain a business loan with more than one owner. Bankers can consider two credit histories rather than one, which can be helpful if you have a less-than-stellar credit score.
- Special taxation: General partnerships must file federal tax Form 1065 and state returns, but they do not usually pay income tax. Both partners report their shared income or loss on their individual income tax returns. For example, if you opened a bakery with a friend and structured the business as a general partnership, you and your friend are co-owners. Each owner brings a certain level of experience and working capital to the business, affecting each partner’s business share and contribution. If you brought the most seed capital for the business, you and your partner may agree that you’ll retain a higher share percentage, making you the majority owner.
Partnerships are one of the most common business structures. These are some examples of successful partnerships:
- Warner Bros.
- Hewlett-Packard
- Ben & Jerry’s
Limited liability company
A limited liability company (LLC) is a hybrid structure that allows owners, partners or shareholders to limit their personal liabilities while enjoying a partnership’s tax and flexibility benefits. Under an LLC, members are shielded from personal liability for the business’s debts if it can’t be proven that they acted in a negligent or wrongful manner that results in injury to another in carrying out the activities of the business.
“Limited liability companies were created to provide business owners with the liability protection that corporations enjoy while allowing earnings and losses to pass through to the owners as income on their personal tax returns,” said Brian Cairns, CEO of ProStrategix Consulting. “LLCs can have one or more members, and profits and losses do not have to be divided equally among members.”
According to Wolters Kluwer , the cost of forming an LLC comprises the state filing fee and can vary depending on your state. For example, if you file an LLC in New York, you must pay a $200 filing fee, a $9 biennial fee, and file a biennial statement with the New York Department of State .
Although small businesses can be LLCs, some large businesses choose this legal structure. The structure is typical among accounting, tax, and law firms, but other types of companies also file as LLCs. One example of an LLC is Anheuser-Busch, one of the leaders in the U.S. beer industry. Headquartered in St. Louis, Anheuser-Busch is a wholly owned subsidiary of Anheuser-Busch InBev, a multinational brewing company based in Leuven, Belgium.
Here some other well-known examples of LLCs:
- Hertz Rent-a-Car
Corporation
The law regards a corporation as separate from its owners, with legal rights independent of its owners. It can sue, be sued, own and sell property, and sell the rights of ownership in the form of stocks. Corporation filing fees vary by state and fee category.
There are several types of corporations, including C corporations , S corporations, B corporations, closed corporations, and nonprofit corporations.
- C corporations: C corporations, owned by shareholders, are taxed as separate entities. JPMorgan Chase & Co. is a multinational investment bank and financial services holding company listed as a C corporation. Since C corporations allow an unlimited number of investors, many larger companies – including Apple, Bank of America and Amazon – file for this tax status.
- B corporations: B corporations, otherwise known as benefit corporations, are for-profit entities committed to corporate social responsibility and structured to positively impact society. For example, skincare and cosmetics company The Body Shop has proven its long-term commitment to supporting environmental and social movements, resulting in an awarded B corporation status. The Body Shop uses its presence to advocate for permanent change on issues like human trafficking, domestic violence, climate change, deforestation and animal testing in the cosmetic industry.
- Closed corporations: Closed corporations, typically run by a few shareholders, are not publicly traded and benefit from limited liability protection. Closed corporations, sometimes referred to as privately held companies, have more flexibility than publicly traded companies. For example, Hobby Lobby is a closed corporation – a privately held, family-owned business. Stocks associated with Hobby Lobby are not publicly traded; instead, the stocks have been allocated to family members.
- Open corporations: Open corporations are available for trade on a public market. Many well-known companies, including Microsoft and Ford Motor Co., are open corporations. Each corporation has taken ownership of the company and allows anyone to invest.
- Nonprofit corporations: Nonprofit corporations exist to help others in some way and are rewarded by tax exemption. Some examples of nonprofits are the Salvation Army, American Heart Association and American Red Cross. These organizations all focus on something other than turning a profit.
Corporations enjoy several advantages.
- Limited liability: Stockholders are not personally liable for claims against your corporation; they are liable only for their personal investments.
- Continuity: Corporations are not affected by death or the transferring of shares by their owners. Your business continues to operate indefinitely, which investors, creditors and consumers prefer.
- Capital: It’s much easier to raise large amounts of capital from multiple investors when your business is incorporated.
This structure is ideal for businesses that are further along in their growth, rather than a startup based in a living room. For example, if you’ve started a shoe company and have already named your business, appointed directors and raised capital through shareholders, the next step is to become incorporated. You’re essentially conducting business at a riskier, yet more lucrative, rate. Additionally, your business could file as an S corporation for the tax benefits. Once your business grows to a certain level, it’s likely in your best interest to incorporate it.
These are some popular examples of corporations:
- General Motors
- Exxon Mobil Corp.
- Domino’s Pizza
- JPMorgan Chase
Learn more about how to become a corporation .
Cooperative
A cooperative (co-op) is owned by the same people it serves. Its offerings benefit the company’s members, also called user-owners, who vote on the organization’s mission and direction and share profits.
Cooperatives offer a couple main advantages.
- Increased funding: Cooperatives may be eligible for federal grants to help them get started.
- Discounts and better service: Cooperatives can leverage their business size, thus obtaining discounts on products and services for their members.
Forming a cooperative is complex and requires you to choose a business name that indicates whether the co-op is a corporation (e.g., Inc. or Ltd.). The filing fee associated with a co-op agreement varies by state.
An example of a co-op is CHS Inc., a Fortune 100 business owned by U.S. agricultural cooperatives. As the nation’s leading agribusiness cooperative, CHS reported a net income of $422.4 million for fiscal year 2020. These are some other notable examples of co-ops:
- Land O’Lakes
- Navy Federal Credit Union
- Ace Hardware
Factors to consider before choosing a business structure
For new businesses that could fall into two or more of these categories, it’s not always easy to decide which structure to choose. Consider your startup’s financial needs, risk and ability to grow. It can be challenging to switch your legal structure after registering your business, so give it careful analysis in the early stages of forming your business.
Here are some crucial factors to consider as you choose your business’s legal structure. You should also consult a CPA for advice.
Flexibility
Where is your company headed, and which type of legal structure allows for the growth you envision? Turn to your business plan to review your goals and see which structure best aligns with those objectives. Your entity should support the possibility for growth and change, not hold it back from its potential. [Learn how to write a business plan with this template .]
When it comes to startup and operational complexity, nothing is more straightforward than a sole proprietorship. Register your name, start doing business, report the profits and pay taxes on it as personal income. However, it can be difficult to procure outside funding. Partnerships, on the other hand, require a signed agreement to define the roles and percentages of profits. Corporations and LLCs have various reporting requirements with state governments and the federal government.
A corporation carries the least amount of personal liability since the law holds that it is its own entity. This means creditors and customers can sue the corporation, but they can’t gain access to any personal assets of the officers or shareholders. An LLC offers the same protection but with the tax benefits of a sole proprietorship. Partnerships share the liability between the partners as defined by their partnership agreement.
An owner of an LLC pays taxes just as a sole proprietor does: All profit is considered personal income and taxed accordingly at the end of the year.
“As a small business owner, you want to avoid double taxation in the early stages,” said Jennifer Friedman, principal at Rivetr. “The LLC structure prevents that and makes sure you’re not taxed as a company, but as an individual.”
Individuals in a partnership also claim their share of the profits as personal income. Your accountant may suggest quarterly or biannual advance payments to minimize the effect on your return.
A corporation files its own tax returns each year, paying taxes on profits after expenses, including payroll. If you pay yourself from the corporation, you will pay personal taxes, such as those for Social Security and Medicare, on your personal return.
If you want sole or primary control of the business and its activities, a sole proprietorship or an LLC might be the best choice. You can negotiate such control in a partnership agreement as well.
A corporation is constructed to have a board of directors that makes the major decisions that guide the company. A single person can control a corporation, especially at its inception, but as it grows, so does the need to operate it as a board-directed entity. Even for a small corporation, the rules intended for larger organizations – such as keeping notes of every major decision that affects the company – still apply.
Capital investment
If you need to obtain outside funding from an investor, venture capitalist or bank, you may be better off establishing a corporation. Corporations have an easier time obtaining outside funding than sole proprietorships.
Corporations can sell shares of stock and secure additional funding for growth, while sole proprietors can obtain funds only through their personal accounts, using their personal credit or taking on partners. An LLC can face similar struggles, although, as its own entity, it’s not always necessary for the owner to use their personal credit or assets.
Licenses, permits and regulations
In addition to legally registering your business entity, you may need specific licenses and permits to operate. Depending on the type of business and its activities, it may need to be licensed at the local, state and federal levels.
“States have different requirements for different business structures,” Friedman said. “Depending on where you set up, there could be different requirements at the municipal level as well. As you choose your structure, understand the state and industry you’re in. It’s not ‘one size fits all,’ and businesses may not be aware of what’s applicable to them.”
The structures discussed here apply only to for-profit businesses. If you’ve done your research and you’re still unsure which business structure is right for you, Friedman advises speaking with a specialist in business law.
Max Freedman and Matt D’Angelo contributed to the writing and reporting in this article. Source interviews were conducted for a previous version of this article.

- Best CRM Software for Nonprofits

Building Better Businesses
Insights on business strategy and culture, right to your inbox. Part of the business.com network.
- Small Law Firms
- Legal Technology
- Legal Tech Non-Event
- Job Listings
- Newsletters
- Law Schools
- The Legal Tech Non-Event
- Law Firm Transparency Directory
- Law Firm Rankings
- Law School Rankings
- Resource Library
- Practice Management
- CRM for Law Firms
- Legal Operations
- Clio App Integrations
- Practice Mgmt. by Practice Area
- Document Management
- Time, Billing & Payments
- Law Firm KPIs
- Cybersecurity
- Spend Management Software
- Legal AI Software
- Legal Tech Directory
- Appellate Court Blog
Above The Law In your inbox
Subscribe and get breaking news, commentary, and opinions on law firms, lawyers, law schools, lawsuits, judges, and more.
Creating A Business Plan
The logistics of how lateral partners should sell themselves.
Ed. note: This is the latest installment in a series of posts Lateral Link’s team of expert contributors. Michael Allen is Managing Principal at Lateral Link, focusing exclusively on partner placements with Am Law 200 clients and placements for in-house attorneys.
A business plan is one of the most important tools to explain your practice, relationships, and strategy to another law firm. You should put together a business plan before even pursuing opportunities to preemptively answer questions that you anticipate encountering throughout the lateral placement process.
Why are business plans necessary in conjunction with their shorter brethren, LPQ’s (Lateral Partner Questionnaires), which deals almost exclusively with historical and projected business generations, conflicts, and key relationships? The answer is simply, the LPQ is your one-sheet resume, with just enough details to diligence a conversation on a lateral partner. The business plan on the other hand, is your opportunity to market your practice and walk the firm through your strategic process to achieving your goals.
There are a multitude of guidelines to adhere to when composing a business plan, but here are the six of the most crucial principles to consider:
1. The Format. There isn’t one set way to compose a business plan, but generally the best business plans we see follow this structure:
Summary: The summary highlights your practice and experience in a neat 100-200 word package, giving the firm an overview of your past achievements, and your expectations for your practice over the next few years. This is the time to brag about yourself, are you Chambers ranked? Did you win a high value or newsworthy case in the last year or two? These are eye-catching details that belong in the summary. The summary is your hook so be judicious about the material you include.
Strategy: Your strategy section should outline your vision for your practice at the firm. This is not the time for ambiguity; if your strategy calls for additional associates to service extra work, include this in your strategy. Context is vital to this section. Your strategy should detail current market trends and forecast future ones to synthesize a strategy that accounts for potential growth or decay in your practice.
Track Record: Your track record is simply a breakdown of clients by year and fee origination. This should be succinct, there is no need to delve into the fine details. A chart that lists your major clients and the revenue generated from them each year is sufficient.
Revenue Projection: This section is perhaps the most difficult and of the most interest to law firms. Completing this section requires straddling a fine line between over and under-projecting. The chart in this section should break down your work by category. For example, Outbound Lit, IP Lit and Inbound Lit, could be three sections under your category heading. Your next column should be projected revenue. If you anticipate an increase or decrease in your historic revenue, be sure to list why, as firms will examine this section carefully. The next column should list the percent of work serviced specifically by you. Your last column should be the amount you personally bill. As long as your projections are reasonable and you justify any projected growth then your business plan will be deemed credible.
Marketing Plan: The marketing plan is your opportunity to demonstrate your long-term plan for growth with the company. This section can easily span several pages and should include a market analysis across all your different specialties. In this section you want to identify trends in the market to anticipate legal demand. You should also list specific corporations and your plan for targeting them to gain their business. Structure matters here. It is easy to meander through two pages of epiphanies before you realize you have incoherent drivel. Outline this section before you write to save yourself an hour of revisions.
2. Identify The Why. Firms are looking for partners for different reasons. While some firms buy books for accretive growth, others have succession planning concerns in mind. Some have platform expansion on their minds or an appetite to build a practice that cross sells nicely with an existing client base. Whatever the reason, firms prioritize certain hires for various reasons. Determine the value you bring to the firm and vice versa. Connect the dots and communicate a strategy. For example, if you are nearing the retirement age, the firm may question your ability to pass down your business to the next generation of partners. If this is the case, your business plan should focus on the long-term viability of your practice and envision a seamless succession plan to help the firm retain the clients after your retirement.
3. Don’t Exaggerate. One of the biggest mistakes a lateral partner can make is to overestimate their potential. Your reputation and credibility are everything. Firms generally peg partner compensation at 33% of their business generation if under a $5mm practice. As the practice grows, there are more costs required to service the practice, and the percentage typically diminishes with scale. Given this formula it can be tempting to overestimate, or become overoptimistic of your chances to retain a client.
Firms run pro formas based on years of historical originations to determine future compensation. Since firms are not privy to every detail of your dealings, they might be unaware that your clients expect their demand to drop significantly—and in turn, diminish your book. If you fail to temper their expectations of future potential drops in earning potential, a disappointing year-end bonus could be the least of your problems.
Similarly, if your inflated estimations are the tipping point of your acceptance, you may find yourself being pushed back onto the market soon after if your business generation is comparatively disappointing to your estimations. You don’t want to start a job with a target on your back.
4. Don’t Understate. While the preceding section may sound unduly ominous, you do not want to underestimate your business potential out of fear of overshooting your true potential. Like any job interview, your goal is to communicate your potential, which means remaining cautiously optimistic while tastefully bombastic, i.e., credible to the decision maker who decides your compensation and role with the firm. Don’t expect firms to give you the benefit of the doubt. In fact, expect them to take a haircut off your numbers and poke holes in your strategy. That said, remain confident without exaggerating.
5 Give Them A Vision. Most AmLaw firms seek to expand their presence or influence around the globe by bringing on profitable partners. It is probably the main priority of a firm chair in his or her strategic plan. Figure out what the firm’s vision is and see how you can contribute and how the firm platform might increase the pie for everyone.
For example, if you have potential business in Mexico City and your current firm does not have a Mexico City office but the prospective firm has a strong Latin American practice, walk the prospective firm through how you plan to cross-sell an international platform to your current client base to service additional business you are leaving on the table. A business plan marries your past performance with your future potential, showing how you plan to continue to grow your practice given new synergies.
6. Address Issues Upfront. If you have something that needs explaining, you should take the opportunity to explain it upfront. Get ahead of the issue and make sure the firm understands what to expect. I am not suggesting that you should highlight your weaknesses, but at least, address issues that you can expect the firm to ask during the conversation. This can save major embarrassment later, and if the backlash is strong enough to push you from the partner ranks, it can be difficult to find another lateral job after that.
Writing a business plan is cumbersome, especially after a long day in the office. Between tailoring the message and the determining the structure, the whole affair can stretch out far longer than anticipated. My fellow recruiters and I at Lateral Link have ample experience to guide you through the process, help craft your motifs and structure your plan effectively. Feel free to reach out to me at [email protected] for more information.
Lateral Link is one of the top-rated international legal recruiting firms. With over 14 offices world-wide, Lateral Link specializes in placing attorneys at the most prestigious law firms and companies in the world. Managed by former practicing attorneys from top law schools, Lateral Link has a tradition of hiring lawyers to execute the lateral leaps of practicing attorneys. Click ::here:: to find out more about us.
Business Plan , Job Searches , Lateral Link , lateral partners , Lateral Partnership Questionnaire , Michael Allen
More From Above the Law

Readiness 2.0: What Does 'Readiness' Mean In 2024 And Beyond?

Biglaw Firm Pushes Out The Boat With Hiring Blitz

Ketanji Brown Jackson Launches Book Tour For Memoir Titled 'Lovely One'

Trump Files Hail Mary Motion Demanding Federal Judge Cancel NY Case
From the above the law network.
- Biglaw Professionals: We Want To Know About Your Dream Job Source: ABOVE THE LAW AND LATERAL LINK
- A Law Firm Checklist For Successful Client Portals Source: Thomson Reuters
- A Law Firm Checklist For Successful Transaction Management Source: Thomson Reuters
- Document Automation For Law Firms: The Definitive Guide Source: THOMSON REUTERS
- The Secrets Of Small Firm Success Source: Above The Law
- 5 Things To Consider Before Hiring A Legal Marketing Partner Source: THOMSON REUTERS
- How You Can Use Tech To Strengthen Client Ties Source: Thomson Reuters And Above The Law
- Differentiating Your Solo Firm In A Crowded Marketplace Source: Thomson Reuters & Above the Law
Love ATL? Let's make it official. Sign up for our newsletter.
Friend's Email Address
Your Email Address
- See our FAQs
- Send an email
- Chat online
- Call (877) 881-0947
MAKE YOUR FREE Business Plan

What we’ll cover
About business plans, business plan faqs, business plan checklist, what is a business plan.
A Business Plan outlines the financial, marketing and operational strategies a business will use to achieve its goals. Business Plans, when starting a business, especially when launching a startup with high growth expectations, can be critical to success.
Essentially, a Business Plan documents what your business is all about and how you’re going to make it grow. With a clear plan in writing, it’s easier to pitch your ideas to potential partners and investors, and to communicate your mission to your customers, clients, employees and leaders.
It does not need to be a laborious task. Using our Business Plan template you can build a professional plan, specific to your state, with minimal effort if you know your business well. You can even customize this Business Plan sample to include details about the company, product, or service, and provide information on the market, forecasts, and financial analyses.
When to use a Business Plan:
- You want to start a new business and want to set out the blueprint for the new venture.
- You will present your plan to potential investors to clearly outline the business goals, financials, and strategies.
- You are a business owner who wants all your employees and leaders to know the mission and goals for your business.
Take the next step: Register your business now
Many entrepreneurs opt to register a separate business entity (such as an LLC, corporation, or nonprofit) after creating a Business Plan. If this sounds like you, Rocket Lawyer can make your next step easy.
With Rocket Legal+, you can get fast, personalized support to start your business. Your first business registration is FREE*, and you can keep your business compliant with HALF OFF professional services for trademarks, taxes, and more. *See details
Register your business now
Sample Business Plan
The terms in your document will update based on the information you provide.
CONFIDENTIAL BUSINESS PLAN
| This __ day of ____________, ______. | ____________________________________ |
. EXECUTIVE SUMMARY
, (hereinafter "Business") is intended to be formed as a located at , , , poised for rapid growth in the industry. The Business seeks funding to take advantage of a window of opportunity for introducing a new product service , which has the potential to dominate the market.
Business Description. The Business is to be organized as a formed and authorized under the laws of the State of Commonwealth of , and will be led by , who will serve as .
New Product. New Service. The Business has developed a product service which has the following specifications:
The Business has a window of opportunity to introduce its products services and gain a significant piece of the market share.
. BUSINESS SUMMARY
The business is a start-up business, providing clients with .
Industry Overview. The industry in the United States currently generates in annual sales. Annual revenue for the regional market where the business is located is estimated at .
Position in the Industry.
Legal Issues. The promoters have secured the required patents and trademarks for the products services and processes of the business in accordance with the statutory requirements.
. MARKETING SUMMARY
Target Markets. The main target markets for the business include:
| - |
| - | __________________________________________________ |
It is estimated that there are potential customers within the Business defined trading area that are estimated to spend . To seek the most profitable market segments in the target markets overall, the Business will focus on the following areas within the target market:
Competition. Customer choice of services in this industry is based on
Services. The Business intends to provide exceptional, personalized service, which will be the crucial factor in building and protecting the Business's brand within the community. The Business intends to handle customer concerns and issues with a customer oriented focus with the intent of providing timely resolution and preventing the loss of customers.
. STRATEGY AND IMPLEMENTATION SUMMARY
The Business plans the following tactics as part of sales promotion:
| - | Develop a list of businesses in the neighborhood and send brochures by direct mail to the list. |
| - | Advertising through press releases to industry publications and local newspapers. |
| - | Internet marketing |
| - | Direct sales |
| - | Posting signage and flyers about the new business on bulletin boards in stores and public places. |
In addition, the Business will also engage in the following marketing campaigns:
| - |
| - | ______________________________________________________ |
| - | Sale of Equity |
| - | Public Offering |
| - | Strategic Sale/Merger with other similar enterprise |
| - | Management Buyout |
| - | Liquidate Assets |
. FINANCIAL PLAN
The Funding Request in this Business Plan outlines the major start-up costs associated with this business. Other costs include repair and maintenance, sales and production expenses. Regular monthly expenses are estimated at for paying the employee salaries and other regular business expenses. The Business is expected to generate in the first year, and gross profit is expected to be .
Business Plan Checklist
Make It Legal™
Find out next steps for your document
___ No signatures are required on this document.
___ Distribute copies. The Business Owner can share a copy of this Business Plan to business partners and potential investors.
Important Details
A copy is securely stored in your account. You can share your document from your account.
Learn about how to outline your business strategy
How to write a business plan.
Unlike what many people might think, a Business Plan is not simply a description of your business. It includes market analysis, marketing strategies, financial goals, funding and liability information, and company structure details.
Even if you are a sole proprietor, it will help you to set concrete goals and plan the future of your business. A Business Plan will also make it easy for the investors you approach to say yes. However, you'll need to do a bit of work before writing to be able to create a comprehensive plan. Below are the steps you need to take to write an effective Business Plan:
1. Identify your business's primary goals
What are your goals for the business within the next five years? This, along with what exactly you're offering as products or services, should be stated at the beginning of your Business Plan. Make it concise and easy to understand even to people who aren't familiar with industry jargon.
2. Provide an executive summary
The executive summary highlights all the information that you will present in the full-length Business Plan. This summary goes beyond the primary goals, but should be no more than two pages. If possible, make it no longer than one page.
3. Draft a business description
Write a description of your business, including information about your general industry, outlook, and current trends and competition within your niche, as well as what needs it fills for potential customers. Your business description shouldn’t be longer than one page unless you are citing specific statistics and research.
4. Develop general marketing strategies
How exactly do you plan on reaching your new customers? If it is a small local company, are you going to put up signage and attend local events? If your business is online, will you pay for ads or hire an online marketing or SEO company? Do you have strategic relationships with already established businesses? A good market analysis might also help you to see the potential weaknesses in your current marketing strategies so that you can set realistic goals. You can make your marketing plan as long as you need it to be. Here, the more detailed you are, the better.
5. Provide an analysis of your market and competition
What will you offer that is better than your competitors? Research your core competition. Analyze what your competitors are doing well and where they are failing. If you can find weaknesses that you can capitalize on, make note of those weaknesses in your Business Plan. Take the time to differentiate yourself in the areas in which you are similar. You should also be able to describe your market in quantifiable terms, like how many potential customers are in the market and what you expect them to spend. Remember that this part of the plan will be of as much interest to potential investors as it is to you.
6. Set out your general development and operation plan
It is important to plan how you will help your business to succeed. Lay out the general tasks and functions that your business engages in on a regular basis. Include the formal organization of the business, responsibilities of administrators and employees, and ongoing development plans. Here’s a tip: you'll get more investor confidence if your key members have a proven track record in running a business or working in the industry.
7. Examine your finances
Your financial analysis should be placed at the very end of your Business Plan. This section lays out your financial bottom line. List your financial assets and liabilities clearly. Be sure to also make it clear what you’re asking investors for, and the projected return investors can expect to receive for their investment.
Putting together the specific figures that you need as well as a clear plan for how the money will be paid back can be quite effective in this section. Because financial information can be quite complicated and confusing, you should consider putting it in chart format. You can create a basic pie chart or graph sheet. If possible, use colors to make your visuals easier to read. You want investors to be able to understand your company’s finances at a glance.
Ready to get started? With Rocket Lawyer, it’s as simple as answering a few questions.
How to make a SWOT analysis for my Business Plan
A SWOT analysis can increase your business awareness and provide a valuable addition to your Business Plan. It’s split into four sections - Strengths, Weaknesses, Opportunities and Threats - with each one detailing the various relevant attributes and downsides to your business and the industry.
This is where you can highlight the qualities of your particular business, whether it’s the skill set, industry knowledge or a specialist resource. Do you have any specific intellectual property rights? Have you secured a retail space with a particular high foot traffic? Think about all the potential advantages of your business compared to your key competitors.
if your business is lacking in a certain area you’ll need to specify how you plan to deal with it, as well as address any weaknesses compared to your competitors.
Opportunities
Make a general case as to why your business will succeed in a certain market, as well as detailing any specific opportunities and the possibility to claim a niche position.
Threats are any external factors that you have no control over and that may detrimentally affect and threaten your business. Try to be frank about any potential reasons your business may not succeed, particularly in light of existing or possible future market conditions.
Remember to detail contingency plans for dealing with such threats. Having in place contingency plans allows a business to plan for an outcome other than what was expected, as a result of any threats. As a result, contingency plans can help solve or alleviate any threats to the business by allowing the business to adjust to different circumstances and outcomes.
How to make a financial plan for your Business Plan
Investors like to see that you’ve done the math. Including detailed financial information proves that you have a grasp of the all-important monetary aspects of running a business. Unless you’re setting up a charity or social enterprise, you need to be aiming towards making a healthy profit.
Projections you must include in your proposal are:
- Employee salaries and overhead costs.
- Revenue and sales.
- Percentage of return you expect from your products or services.
- When your business will produce enough revenue to cover all costs (break-even point).
A cash flow forecast is one of the most important elements of a financial plan. The amount of capital you require can be determined largely from accurate predictions of cash flow. Even if your profit is high, a lack of readily available money can lead to major problems including insolvency. For example, if you’re waiting for substantial Invoices to be paid, while you may be owed a lot, without cash in the bank, you may not be able to manage your expenses, pay employees, or order new supplies.
The simplest way to forecast cash flow is to list monthly income and expenditure costs, preferably with annual totals. Try to think pragmatically and account for all kinds of variables. For example, you’ll probably need to use more heating over the winter months so your gas and electricity bills will increase. Similarly, if your product is seasonal (like an ice cream stand or snow plowing business) then you’ll need to revise your income for the relevant season.
A Profit and Loss (or P&L) Form indicates how well a business has performed overall. It differs from the cash flow forecast in that it shows how much profit has been made (or the amount of loss sustained) over a specified period (usually a year), but it doesn’t account for actual cash in the bank.
Overall, for this part of your Business Plan you'll need to map out how you plan to finance your business, even if all you have so far are projections. Do you have a business loan? Are you going to pay yourself a salary from the business? How much of the seed money will be from your own savings? Investors will also want to know if you plan to take on additional debt or if other investors are involved.
You'll also want to show how you plan to pay back debt and when you expect to be profitable. After all, the return on investment (ROI) is a key element of any Business plan, showing how much effect an investment will have upon the business.
State a realistic repayment period – it’s better to overstate the time required to avoid disappointment and show that you have taken various scenarios into account. You should also state how exactly your investors will make a profit. Will you repay them with interest? Do they get shares in the company?
An investor will want to know exactly why you need their money and what it will be spent on. You may have an excellent business idea but you’ll have to prove that the funding sought will directly lead to success. Get started on your Business Plan with Rocket Lawyer now!
How do I know if I should make a Business Plan?
- You are starting a business and want to outline your goals and strategies.
- You need to communicate your business concept to potential investors.
- You want to test your business idea for viability.
- You and your partners want to build a plan together.
Our Business Plan builder is suitable for most types of businesses from small to large, including online companies, service providers, nonprofits, side hustles and home-based businesses. Making a Business Plan helps you, and others, see the potential of your business.
What is the purpose of a Business Plan?
A Business Plan is extremely useful for any business seeking accountability or investment. It can serve as a roadmap to help business owners know which steps they need to take and when. It can also show potential investors why your product or service will be successful by setting out clear objectives and a strategy for growing your business. Writing a Business Plan will help you set a realistic timeline for repaying investments while conveying confidence to potential investors.
Remember that a Business Plan is unique to your business and depends on the specifics of your business. Do not hesitate to ask a lawyer for assistance with drafting or reviewing your plan.
How do I write an executive summary?
Writing a good executive summary for your Business Plan is important because it may be the only thing an investor reads to decide if they even want to bother with reading the rest of your plan. It should be able to grab the reader right away and entice them to want to learn more. Here are a few tips for writing an effective executive summary:
- Tailor it to your audience, change whenever needed.
- Add a sense of urgency, make it timely to the market and ideal to move on now.
- Include what needs it fills in the market, what real problem it solves.
- Make it more personable by using language like "us" and "we" rather than "the company."
- Use confident and positive words and remove indecisive language.
- Write it without worrying about the length and then shorten it as much as you can.
- Avoid cliché terms like "best in the world" or "industry disruptor."
- Show it rather than tell it.
- Test it before you send it.
- Write it after the rest of the plan is complete and well researched.
If you do not need to share your Business Plan with others, you may not need an executive summary. However, it is a good exercise for building your elevator pitch for times when you talk about your business with others.
How do I evaluate my business competition?
Often small business owners are so excited about their product that they forget to consider their competition. If you are planning on opening a local business, you likely know your competitors. But if you are starting an online business or are in a large city, you'll benefit from some market research.
One way to perform this analysis is to create a side-by-side comparison sheet. Using this type of document, you can compare pricing, product offerings, web presence, user review scores, size of business and market reach, customer profiles and more. If you are starting a restaurant, you could compare menus, pricing, customer loyalty and patron reviews. If it is an online business, you can compare keyword terms, social media presence, subscription pricing models, or customer service responsiveness to find a competitive angle.
You may even benefit from hiring someone to do the research for you since they might be more objective than you. Companies with large budgets may even hire a marketing agency to evaluate the market for them. Regardless of your budget, market research is not a step you'll want to skip in the business planning process.
What should I know about budgeting and financial planning?
Like evaluating your market, you also want to make sure you are realistic when it comes to your financial planning . For example, can you really afford to quit your day job and run your new business? Are your sales projections reasonable? Have you planned for issues that may arise?
If you plan to open a cafe, for example, you may need money to take care of unexpected compliance issues surrounding food service. Or, what if your location falls through? Can you afford a more expensive lease? Have you underestimated monthly expenses like water usage or employee salaries? And if business is good, what will you do with the profits?
If you are having trouble creating a realistic budget, you may want to consult with a business accountant. A working budget is needed to help run your business even if you do not plan to ask for funding, so it is important to create a realistic budget.
What should I do if I get stuck while making my Business Plan?
Sometimes it is hard to complete all the parts of your Business Plan in a single sitting. You may have to look at your business objectively to evaluate whether it makes sense or not. Is the market already saturated? Is there a market at all? Is there a way to test the market? Is there a certain segment of the market more suitable for your product? Do you have the time to run your business properly? Can you realistically afford to meet your objectives? Do you have the right partners? Is it the best time for your product or service to be launched? Are your goals realistic?
If you cannot answer these questions, it may be a good time to reevaluate your business idea and market. Perhaps somehow you are missing the mark, or maybe it just requires some more research. You may also benefit from reading through the Rocket Lawyer legal guides about starting a business . Also, try not to overthink it or avoid making a Business Plan. It is better to have a Business Plan that needs work rather than no plan at all.
A good Business Plan is not fabricated around your pie-in-the-sky dreams for your company to trick investors into buying into your vision. A good plan is a working document that proves you have a product or service that can be viable in the real market. Even if you are not seeking funding, making a functional Business Plan is an excellent tool for proving your business idea is a good one.
Who should review my Business Plan?
Looking at your business like an outsider is difficult for many small business owners. But your investors, unless they are family or friends, are going to look at it objectively to see how they might benefit from investing. This is one of the reasons you need a Business Plan capable of surviving intense scrutiny.
Once you have your Business Plan made, try to look at it as if you were a stranger to your business. Have a few respected colleagues read through it as well and tell them not to be nice, but to find as many weak areas as they can. If you need to keep your business information private, you can ask those reviewing your plan to sign a Non-Disclosure Agreement .
If you find information you need to change, you can easily edit your plan. In fact, a Business Plan is an evolving, working document, so change it as often as your business needs grow and evolve.

Our quality guarantee
We guarantee our service is safe and secure, and that properly executed Rocket Lawyer legal documents are legally enforceable under applicable US laws.
Need help? No problem!
Ask a question for free or get affordable legal advice when you connect with a Rocket Lawyer network attorney.
Complete your free Business Plan with our Make it Legal™ checklist
Make this document.
Customize your Business Plan by answering simple questions. We’ll help you along the way and build a document that fits your needs. Plus, you can always save and continue later after you start your document. Get started now!
Review your document
Look over your customized Business Plan to ensure it matches your intentions. If you'd like to make changes, you can make edits online, through the Rocket Lawyer app, or you can download this document in Microsoft Word. Remember that if you have any questions you can easily ask a lawyer or get affordable legal advice when you connect with a Rocket Lawyer network attorney .
Everyone gets a copy
Once completed, a business owner can print, download, and share this Business Plan through their Rocket Lawyer account to employees, leaders, business partners, and potential investors.
Important details
- No signatures are required on this document.
Create Your Document In Just 3 Easy Steps:
Build your document
Answer a few simple questions to make your document in minutes
Save now, finish later
Start now and save your progress, finish on any device
Download, print & share
Store securely, share online and make copies
Related documents
Rocket lawyer members who started a free business plan also made:, llc operating agreement.
Define and document how your business will be run
Limited Liability Company Worksheet
Keep track of important LLC information
Joinder Agreement
Add a party to an existing agreement
Single Member LLC Operating Agreement
Set forth a management plan for your LLC
Ask a lawyer
You've exceeded the character limit.
Start your Business Plan now and get Rocket Lawyer FREE for 7 days
Get legal services you can trust at prices you can afford. you'll get:.
All the legal documents you need—customize, share, print & more
Unlimited electronic signatures with RocketSign ®
Ask a lawyer questions or have them review your document
Dispute protection on all your contracts with Document Defense ®
30-minute phone call with a lawyer about any new issue
Discounts on business and attorney services
An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock Locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
Write your business plan
Business plans help you run your business.
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You’ll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It’s a way to think through the key elements of your business.
Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners. Investors want to feel confident they’ll see a return on their investment. Your business plan is the tool you’ll use to convince people that working with you — or investing in your company — is a smart choice.
Pick a business plan format that works for you
There’s no right or wrong way to write a business plan. What’s important is that your plan meets your needs.
Most business plans fall into one of two common categories: traditional or lean startup.
Traditional business plans are more common, use a standard structure, and encourage you to go into detail in each section. They tend to require more work upfront and can be dozens of pages long.
Lean startup business plans are less common but still use a standard structure. They focus on summarizing only the most important points of the key elements of your plan. They can take as little as one hour to make and are typically only one page.
Traditional business plan

Lean startup plan
Traditional business plan format
You might prefer a traditional business plan format if you’re very detail-oriented, want a comprehensive plan, or plan to request financing from traditional sources.
When you write your business plan, you don’t have to stick to the exact business plan outline. Instead, use the sections that make the most sense for your business and your needs. Traditional business plans use some combination of these nine sections.
Executive summary
Briefly tell your reader what your company is and why it will be successful. Include your mission statement, your product or service, and basic information about your company’s leadership team, employees, and location. You should also include financial information and high-level growth plans if you plan to ask for financing.
Company description
Use your company description to provide detailed information about your company. Go into detail about the problems your business solves. Be specific, and list out the consumers, organization, or businesses your company plans to serve.
Explain the competitive advantages that will make your business a success. Are there experts on your team? Have you found the perfect location for your store? Your company description is the place to boast about your strengths.
Market analysis
You'll need a good understanding of your industry outlook and target market. Competitive research will show you what other businesses are doing and what their strengths are. In your market research, look for trends and themes. What do successful competitors do? Why does it work? Can you do it better? Now's the time to answer these questions.
Organization and management
Tell your reader how your company will be structured and who will run it.
Describe the legal structure of your business. State whether you have or intend to incorporate your business as a C or an S corporation, form a general or limited partnership, or if you're a sole proprietor or limited liability company (LLC).
Use an organizational chart to lay out who's in charge of what in your company. Show how each person's unique experience will contribute to the success of your venture. Consider including resumes and CVs of key members of your team.
Service or product line
Describe what you sell or what service you offer. Explain how it benefits your customers and what the product lifecycle looks like. Share your plans for intellectual property, like copyright or patent filings. If you're doing research and development for your service or product, explain it in detail.
Marketing and sales
There's no single way to approach a marketing strategy. Your strategy should evolve and change to fit your unique needs.
Your goal in this section is to describe how you'll attract and retain customers. You'll also describe how a sale will actually happen. You'll refer to this section later when you make financial projections, so make sure to thoroughly describe your complete marketing and sales strategies.
Funding request
If you're asking for funding, this is where you'll outline your funding requirements. Your goal is to clearly explain how much funding you’ll need over the next five years and what you'll use it for.
Specify whether you want debt or equity, the terms you'd like applied, and the length of time your request will cover. Give a detailed description of how you'll use your funds. Specify if you need funds to buy equipment or materials, pay salaries, or cover specific bills until revenue increases. Always include a description of your future strategic financial plans, like paying off debt or selling your business.
Financial projections
Supplement your funding request with financial projections. Your goal is to convince the reader that your business is stable and will be a financial success.
If your business is already established, include income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements for the last three to five years. If you have other collateral you could put against a loan, make sure to list it now.
Provide a prospective financial outlook for the next five years. Include forecasted income statements, balance sheets, cash flow statements, and capital expenditure budgets. For the first year, be even more specific and use quarterly — or even monthly — projections. Make sure to clearly explain your projections, and match them to your funding requests.
This is a great place to use graphs and charts to tell the financial story of your business.
Use your appendix to provide supporting documents or other materials were specially requested. Common items to include are credit histories, resumes, product pictures, letters of reference, licenses, permits, patents, legal documents, and other contracts.
Example traditional business plans
Before you write your business plan, read the following example business plans written by fictional business owners. Rebecca owns a consulting firm, and Andrew owns a toy company.
Lean startup format
You might prefer a lean startup format if you want to explain or start your business quickly, your business is relatively simple, or you plan to regularly change and refine your business plan.
Lean startup formats are charts that use only a handful of elements to describe your company’s value proposition, infrastructure, customers, and finances. They’re useful for visualizing tradeoffs and fundamental facts about your company.
There are different ways to develop a lean startup template. You can search the web to find free templates to build your business plan. We discuss nine components of a model business plan here:
Key partnerships
Note the other businesses or services you’ll work with to run your business. Think about suppliers, manufacturers, subcontractors, and similar strategic partners.
Key activities
List the ways your business will gain a competitive advantage. Highlight things like selling direct to consumers, or using technology to tap into the sharing economy.
Key resources
List any resource you’ll leverage to create value for your customer. Your most important assets could include staff, capital, or intellectual property. Don’t forget to leverage business resources that might be available to women , veterans , Native Americans , and HUBZone businesses .
Value proposition
Make a clear and compelling statement about the unique value your company brings to the market.
Customer relationships
Describe how customers will interact with your business. Is it automated or personal? In person or online? Think through the customer experience from start to finish.
Customer segments
Be specific when you name your target market. Your business won’t be for everybody, so it’s important to have a clear sense of whom your business will serve.
List the most important ways you’ll talk to your customers. Most businesses use a mix of channels and optimize them over time.
Cost structure
Will your company focus on reducing cost or maximizing value? Define your strategy, then list the most significant costs you’ll face pursuing it.
Revenue streams
Explain how your company will actually make money. Some examples are direct sales, memberships fees, and selling advertising space. If your company has multiple revenue streams, list them all.
Example lean business plan
Before you write your business plan, read this example business plan written by a fictional business owner, Andrew, who owns a toy company.
Need help? Get free business counseling
The University of Chicago The Law School
Innovation clinic—significant achievements for 2023-24.
The Innovation Clinic continued its track record of success during the 2023-2024 school year, facing unprecedented demand for our pro bono services as our reputation for providing high caliber transactional and regulatory representation spread. The overwhelming number of assistance requests we received from the University of Chicago, City of Chicago, and even national startup and venture capital communities enabled our students to cherry-pick the most interesting, pedagogically valuable assignments offered to them. Our focus on serving startups, rather than all small- to medium-sized businesses, and our specialization in the needs and considerations that these companies have, which differ substantially from the needs of more traditional small businesses, has proven to be a strong differentiator for the program both in terms of business development and prospective and current student interest, as has our further focus on tackling idiosyncratic, complex regulatory challenges for first-of-their kind startups. We are also beginning to enjoy more long-term relationships with clients who repeatedly engage us for multiple projects over the course of a year or more as their legal needs develop.
This year’s twelve students completed over twenty projects and represented clients in a very broad range of industries: mental health and wellbeing, content creation, medical education, biotech and drug discovery, chemistry, food and beverage, art, personal finance, renewable energy, fintech, consumer products and services, artificial intelligence (“AI”), and others. The matters that the students handled gave them an unparalleled view into the emerging companies and venture capital space, at a level of complexity and agency that most junior lawyers will not experience until several years into their careers.
Representative Engagements
While the Innovation Clinic’s engagements are highly confidential and cannot be described in detail, a high-level description of a representative sample of projects undertaken by the Innovation Clinic this year includes:
Transactional/Commercial Work
- A previous client developing a symptom-tracking wellness app for chronic disease sufferers engaged the Innovation Clinic again, this time to restructure its cap table by moving one founder’s interest in the company to a foreign holding company and subjecting the holding company to appropriate protections in favor of the startup.
- Another client with whom the Innovation Clinic had already worked several times engaged us for several new projects, including (1) restructuring their cap table and issuing equity to an additional, new founder, (2) drafting several different forms of license agreements that the company could use when generating content for the platform, covering situations in which the company would license existing content from other providers, jointly develop new content together with contractors or specialists that would then be jointly owned by all creators, or commission contractors to make content solely owned by the company, (3) drafting simple agreements for future equity (“Safes”) for the company to use in its seed stage fundraising round, and (4) drafting terms of service and a privacy policy for the platform.
- Yet another repeat client, an internet platform that supports independent artists by creating short films featuring the artists to promote their work and facilitates sales of the artists’ art through its platform, retained us this year to draft a form of independent contractor agreement that could be used when the company hires artists to be featured in content that the company’s Fortune 500 brand partners commission from the company, and to create capsule art collections that could be sold by these Fortune 500 brand partners in conjunction with the content promotion.
- We worked with a platform using AI to accelerate the Investigational New Drug (IND) approval and application process to draft a form of license agreement for use with its customers and an NDA for prospective investors.
- A novel personal finance platform for young, high-earning individuals engaged the Innovation Clinic to form an entity for the platform, including helping the founders to negotiate a deal among them with respect to roles and equity, terms that the equity would be subject to, and other post-incorporation matters, as well as to draft terms of service and a privacy policy for the platform.
- Students also formed an entity for a biotech therapeutics company founded by University of Chicago faculty members and an AI-powered legal billing management platform founded by University of Chicago students.
- A founder the Innovation Clinic had represented in connection with one venture engaged us on behalf of his other venture team to draft an equity incentive plan for the company as well as other required implementing documentation. His venture with which we previously worked also engaged us this year to draft Safes to be used with over twenty investors in a seed financing round.
More information regarding other types of transactional projects that we typically take on can be found here .
Regulatory Research and Advice
- A team of Innovation Clinic students invested a substantial portion of our regulatory time this year performing highly detailed and complicated research into public utilities laws of several states to advise a groundbreaking renewable energy technology company as to how its product might be regulated in these states and its clearest path to market. This project involved a review of not only the relevant state statutes but also an analysis of the interplay between state and federal statutes as it relates to public utilities law, the administrative codes of the relevant state executive branch agencies, and binding and non-binding administrative orders, decisions and guidance from such agencies in other contexts that could shed light on how such states would regulate this never-before-seen product that their laws clearly never contemplated could exist. The highly varied approach to utilities regulation in all states examined led to a nuanced set of analysis and recommendations for the client.
- In another significant research project, a separate team of Innovation Clinic students undertook a comprehensive review of all settlement orders and court decisions related to actions brought by the Consumer Financial Protection Bureau for violations of the prohibition on unfair, deceptive, or abusive acts and practices under the Consumer Financial Protection Act, as well as selected relevant settlement orders, court decisions, and other formal and informal guidance documents related to actions brought by the Federal Trade Commission for violations of the prohibition on unfair or deceptive acts or practices under Section 5 of the Federal Trade Commission Act, to assemble a playbook for a fintech company regarding compliance. This playbook, which distilled very complicated, voluminous legal decisions and concepts into a series of bullet points with clear, easy-to-follow rules and best practices, designed to be distributed to non-lawyers in many different facets of this business, covered all aspects of operations that could subject a company like this one to liability under the laws examined, including with respect to asset purchase transactions, marketing and consumer onboarding, usage of certain terms of art in advertising, disclosure requirements, fee structures, communications with customers, legal documentation requirements, customer service and support, debt collection practices, arrangements with third parties who act on the company’s behalf, and more.
Miscellaneous
- Last year’s students built upon the Innovation Clinic’s progress in shaping the rules promulgated by the Financial Crimes Enforcement Network (“FinCEN”) pursuant to the Corporate Transparency Act to create a client alert summarizing the final rule, its impact on startups, and what startups need to know in order to comply. When FinCEN issued additional guidance with respect to that final rule and changed portions of the final rule including timelines for compliance, this year’s students updated the alert, then distributed it to current and former clients to notify them of the need to comply. The final bulletin is available here .
- In furtherance of that work, additional Innovation Clinic students this year analyzed the impact of the final rule not just on the Innovation Clinic’s clients but also its impact on the Innovation Clinic, and how the Innovation Clinic should change its practices to ensure compliance and minimize risk to the Innovation Clinic. This also involved putting together a comprehensive filing guide for companies that are ready to file their certificates of incorporation to show them procedurally how to do so and explain the choices they must make during the filing process, so that the Innovation Clinic would not be involved in directing or controlling the filings and thus would not be considered a “company applicant” on any client’s Corporate Transparency Act filings with FinCEN.
- The Innovation Clinic also began producing thought leadership pieces regarding AI, leveraging our distinct and uniquely University of Chicago expertise in structuring early-stage companies and analyzing complex regulatory issues with a law and economics lens to add our voice to those speaking on this important topic. One student wrote about whether non-profits are really the most desirable form of entity for mitigating risks associated with AI development, and another team of students prepared an analysis of the EU’s AI Act, comparing it to the Executive Order on AI from President Biden, and recommended a path forward for an AI regulatory environment in the United States. Both pieces can be found here , with more to come!
Innovation Trek
Thanks to another generous gift from Douglas Clark, ’89, and managing partner of Wilson, Sonsini, Goodrich & Rosati, we were able to operationalize the second Innovation Trek over Spring Break 2024. The Innovation Trek provides University of Chicago Law School students with a rare opportunity to explore the innovation and venture capital ecosystem in its epicenter, Silicon Valley. The program enables participating students to learn from business and legal experts in a variety of different industries and roles within the ecosystem to see how the law and economics principles that students learn about in the classroom play out in the real world, and facilitates meaningful connections between alumni, students, and other speakers who are leaders in their fields. This year, we took twenty-three students (as opposed to twelve during the first Trek) and expanded the offering to include not just Innovation Clinic students but also interested students from our JD/MBA Program and Doctoroff Business Leadership Program. We also enjoyed four jam-packed days in Silicon Valley, expanding the trip from the two and a half days that we spent in the Bay Area during our 2022 Trek.
The substantive sessions of the Trek were varied and impactful, and enabled in no small part thanks to substantial contributions from numerous alumni of the Law School. Students were fortunate to visit Coinbase’s Mountain View headquarters to learn from legal leaders at the company on all things Coinbase, crypto, and in-house, Plug & Play Tech Center’s Sunnyvale location to learn more about its investment thesis and accelerator programming, and Google’s Moonshot Factory, X, where we heard from lawyers at a number of different Alphabet companies about their lives as in-house counsel and the varied roles that in-house lawyers can have. We were also hosted by Wilson, Sonsini, Goodrich & Rosati and Fenwick & West LLP where we held sessions featuring lawyers from those firms, alumni from within and outside of those firms, and non-lawyer industry experts on topics such as artificial intelligence, climate tech and renewables, intellectual property, biotech, investing in Silicon Valley, and growth stage companies, and general advice on career trajectories and strategies. We further held a young alumni roundtable, where our students got to speak with alumni who graduated in the past five years for intimate, candid discussions about life as junior associates. In total, our students heard from more than forty speakers, including over twenty University of Chicago alumni from various divisions.
The Trek didn’t stop with education, though. Throughout the week students also had the opportunity to network with speakers to learn more from them outside the confines of panel presentations and to grow their networks. We had a networking dinner with Kirkland & Ellis, a closing dinner with all Trek participants, and for the first time hosted an event for admitted students, Trek participants, and alumni to come together to share experiences and recruit the next generation of Law School students. Several speakers and students stayed in touch following the Trek, and this resulted not just in meaningful relationships but also in employment for some students who attended.
More information on the purposes of the Trek is available here , the full itinerary is available here , and one student participant’s story describing her reflections on and descriptions of her experience on the Trek is available here .
The Innovation Clinic is grateful to all of its clients for continuing to provide its students with challenging, high-quality legal work, and to the many alumni who engage with us for providing an irreplaceable client pipeline and for sharing their time and energy with our students. Our clients are breaking the mold and bringing innovations to market that will improve the lives of people around the world in numerous ways. We are glad to aid in their success in any way that we can. We look forward to another productive year in 2024-2025!

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The lawyer or lawyers who will make up the firm at the time of launch. The location of the firm and the areas it serves. The general approach the firm takes when representing clients. 3. Market Analysis. A competitive analysis is one of the most compelling components of well-written business plans.
4. Determine how many cases you need to meet that revenue goal. If you are only handling two or three cases per month, the number you came up with above might look outrageous. It's not. For example, let's use the 2024 median pay of $176,470 a year in annual revenue as our goal, with a flat fee of $3,000 per client.
The plan should also explain how you will know when you have met them. For example, you might have a growth goal of reaching five lawyers within two years. Or you might have a revenue goal of collecting $200,000 your first year. Too many businesses, including law firms, meander on their developmental path.
Law Firm Plan. Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1,000 lawyers to create business plans to start and grow their law firms. On this page, we will first give you some background information with regards to the importance of business planning. We will then go through a law firm business plan template step-by-step so you can create your ...
1. Executive summary. A business plan for lawyers, like any plan, should start with an executive summary. This section concisely outlines a business plan's key points, goals, and strategies. Ultimately, it serves as a snapshot for quick understanding and decision-making and should include the following parts:
Download our law firm sample business plan for free right now and use it for reference as you write your own plan. You can even copy and paste sections from the sample plan and customize them for your business. ... You can also view other legal business plans, or browse the full Bplans library of over 550 sample business plans across numerous ...
Why Every Law Firm Needs a Business Plan. A well-structured business plan is imperative for every law firm, regardless of its size or specialization. While legal expertise is undoubtedly crucial, having a clear vision and strategic direction is equally essential. A business plan serves as a guiding light, defining the firm's mission, values ...
What is Law Firm Business Plan? A law firm business plan is a document that outlines your business goals and strategies to achieve those goals. It includes your law firm overview, your reason to start your firm, the services you will offer, a budget or funding requirements, and strategies to get and manage your clients.
Call 1-888-858-2546 or email [email protected]. Our sales team is available Monday to Friday from 8 a.m. to 8 p.m. EST. Download our free law firm business plan template. Start your law firm on the right foot with a clear plan that explains where you're going, and how you're getting there.
Follow these tips to quickly develop a working business plan from this sample. 1. Don't worry about finding an exact match. We have over 550 sample business plan templates. So, make sure the plan is a close match, but don't get hung up on the details. Your business is unique and will differ from any example or template you come across.
Cash flow statement: Attach a cash flow statement to the financial plan section of your law firm business plan. Update your revenue, expenses, and budget accordingly throughout the year. 8. Startup Budget. The startup budget section underlines everything you need to turn your law firm business plan into reality.
Write a succinct overview of your company. Here is what it should cover: Mission statement and values. Reiterate your mission statement and core values here. Geographic location and areas served. Identify where your offices are located and the geographic areas that you serve. Legal structure and ownership.
Explore a real-world law firm business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan. ... WLF will provide legal services to high technology clients, to both start-up companies and established firms. While the firm excels in mergers, acquisitions, and qualified stock option plans, we ...
It should also contain some deeper information about the firm's identity and aspirations. This would include: A mission statement about the firm's purpose. A vision statement or recitation of medium- and long-term goals for the firm. Important aspects of the firm's history. Any important philosophies that the firm brings to legal practice.
Business Overview. The Harris & Harris Law Firm is a startup up business that provides legal advice and services for clients located within the Scottsdale, Arizona region. The company is founded by Roger Harris and his son, Anthony. Roger Harris has been a partner in a well-established company, Foundations Law Firm, for over twenty years.
Before developing a plan for a lawyer, answer the following: What skills and experience you bring to your practice. What legal structure to use: sole proprietorship, PC, partnership, LLP, etc. What clients you currently have and might potentially acquire. What other attorneys you can call upon to fill in practice gaps.
A Sample Law Firm Business Plan Template 1. Industry Overview. The services of lawyers are needed in every part of the united states of America. Statistics has it that the United States of America has about 165,000 law offices and they generate about $180 billion in annual revenue.
A free example of business plan for a legal consulting services. Here, we will provide a concise and illustrative example of a business plan for a specific project. This example aims to provide an overview of the essential components of a business plan. It is important to note that this version is only a summary. As it stands, this business ...
Step 1 - Create an Executive Summary. An executive summary is the first section of a traditional business plan, serving as the first impression of your business. Please give a brief overview of your company, including its mission, key goals, and a snapshot of your financial projections.
If you want sole or primary control of the business and its activities, a sole proprietorship or an LLC might be the best choice. You can negotiate such control in a partnership agreement as well ...
The business plan on the other hand, is your opportunity to market your practice and walk the firm through your strategic process to achieving your goals. There are a multitude of guidelines to ...
A Business Plan outlines the financial, marketing and operational strategies a business will use to achieve its goals. Business Plans, when starting a business, especially when launching a startup with high growth expectations, can be critical to success. Essentially, a Business Plan documents what your business is all about and how you're ...
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business. Business plans can help you get funding or bring on new business partners.
General The Innovation Clinic continued its track record of success during the 2023-2024 school year, facing unprecedented demand for our pro bono services as our reputation for providing high caliber transactional and regulatory representation spread. The overwhelming number of assistance requests we received from the University of Chicago, City of Chicago, and even national startup and ...