Created by the Great Schools Partnership , the GLOSSARY OF EDUCATION REFORM is a comprehensive online resource that describes widely used school-improvement terms, concepts, and strategies for journalists, parents, and community members. | Learn more »


Formative Assessment
Formative assessment refers to a wide variety of methods that teachers use to conduct in-process evaluations of student comprehension, learning needs, and academic progress during a lesson, unit, or course. Formative assessments help teachers identify concepts that students are struggling to understand, skills they are having difficulty acquiring, or learning standards they have not yet achieved so that adjustments can be made to lessons, instructional techniques, and academic support .
The general goal of formative assessment is to collect detailed information that can be used to improve instruction and student learning while it’s happening . What makes an assessment “formative” is not the design of a test, technique, or self-evaluation, per se, but the way it is used—i.e., to inform in-process teaching and learning modifications.
Formative assessments are commonly contrasted with summative assessments , which are used to evaluate student learning progress and achievement at the conclusion of a specific instructional period—usually at the end of a project, unit, course, semester, program, or school year. In other words, formative assessments are for learning, while summative assessments are of learning. Or as assessment expert Paul Black put it, “When the cook tastes the soup, that’s formative assessment. When the customer tastes the soup, that’s summative assessment.” It should be noted, however, that the distinction between formative and summative is often fuzzy in practice, and educators may hold divergent interpretations of and opinions on the subject.
Many educators and experts believe that formative assessment is an integral part of effective teaching. In contrast with most summative assessments, which are deliberately set apart from instruction, formative assessments are integrated into the teaching and learning process. For example, a formative-assessment technique could be as simple as a teacher asking students to raise their hands if they feel they have understood a newly introduced concept, or it could be as sophisticated as having students complete a self-assessment of their own writing (typically using a rubric outlining the criteria) that the teacher then reviews and comments on. While formative assessments help teachers identify learning needs and problems, in many cases the assessments also help students develop a stronger understanding of their own academic strengths and weaknesses. When students know what they do well and what they need to work harder on, it can help them take greater responsibility over their own learning and academic progress.
While the same assessment technique or process could, in theory, be used for either formative or summative purposes, many summative assessments are unsuitable for formative purposes because they do not provide useful feedback. For example, standardized-test scores may not be available to teachers for months after their students take the test (so the results cannot be used to modify lessons or teaching and better prepare students), or the assessments may not be specific or fine-grained enough to give teachers and students the detailed information they need to improve.
The following are a few representative examples of formative assessments:
- Questions that teachers pose to individual students and groups of students during the learning process to determine what specific concepts or skills they may be having trouble with. A wide variety of intentional questioning strategies may be employed, such as phrasing questions in specific ways to elicit more useful responses.
- Specific, detailed, and constructive feedback that teachers provide on student work , such as journal entries, essays, worksheets, research papers, projects, ungraded quizzes, lab results, or works of art, design, and performance. The feedback may be used to revise or improve a work product, for example.
- “Exit slips” or “exit tickets” that quickly collect student responses to a teacher’s questions at the end of a lesson or class period. Based on what the responses indicate, the teacher can then modify the next lesson to address concepts that students have failed to comprehend or skills they may be struggling with. “Admit slips” are a similar strategy used at the beginning of a class or lesson to determine what students have retained from previous learning experiences .
- Self-assessments that ask students to think about their own learning process, to reflect on what they do well or struggle with, and to articulate what they have learned or still need to learn to meet course expectations or learning standards.
- Peer assessments that allow students to use one another as learning resources. For example, “workshopping” a piece of writing with classmates is one common form of peer assessment, particularly if students follow a rubric or guidelines provided by a teacher.
In addition to the reasons addressed above, educators may also use formative assessment to:
- Refocus students on the learning process and its intrinsic value, rather than on grades or extrinsic rewards.
- Encourage students to build on their strengths rather than fixate or dwell on their deficits. (For a related discussion, see growth mindset .)
- Help students become more aware of their learning needs, strengths, and interests so they can take greater responsibility over their own educational growth. For example, students may learn how to self-assess their own progress and self-regulate their behaviors.
- Give students more detailed, precise, and useful information. Because grades and test scores only provide a general impression of academic achievement, usually at the completion of an instructional period, formative feedback can help to clarify and calibrate learning expectations for both students and parents. Students gain a clearer understanding of what is expected of them, and parents have more detailed information they can use to more effectively support their child’s education.
- Raise or accelerate the educational achievement of all students, while also reducing learning gaps and achievement gaps .
While the formative-assessment concept has only existed since the 1960s, educators have arguably been using “formative assessments” in various forms since the invention of teaching. As an intentional school-improvement strategy, however, formative assessment has received growing attention from educators and researchers in recent decades. In fact, it is now widely considered to be one of the more effective instructional strategies used by teachers, and there is a growing body of literature and academic research on the topic.
Schools are now more likely to encourage or require teachers to use formative-assessment strategies in the classroom, and there are a growing number of professional-development opportunities available to educators on the subject. Formative assessments are also integral components of personalized learning and other educational strategies designed to tailor lessons and instruction to the distinct learning needs and interests of individual students.
While there is relatively little disagreement in the education community about the utility of formative assessment, debates or disagreements may stem from differing interpretations of the term. For example, some educators believe the term is loosely applied to forms of assessment that are not “truly” formative, while others believe that formative assessment is rarely used appropriately or effectively in the classroom.
Another common debate is whether formative assessments can or should be graded. Many educators contend that formative assessments can only be considered truly formative when they are ungraded and used exclusively to improve student learning. If grades are assigned to a quiz, test, project, or other work product, the reasoning goes, they become de facto summative assessments—i.e., the act of assigning a grade turns the assessment into a performance evaluation that is documented in a student’s academic record, as opposed to a diagnostic strategy used to improve student understanding and preparation before they are given a graded test or assignment.
Some educators also make a distinction between “pure” formative assessments—those that are used on a daily basis by teachers while they are instructing students—and “interim” or “benchmark” assessments, which are typically periodic or quarterly assessments used to determine where students are in their learning progress or whether they are on track to meeting expected learning standards. While some educators may argue that any assessment method that is used diagnostically could be considered formative, including interim assessments, others contend that these two forms of assessment should remain distinct, given that different strategies, techniques, and professional development may be required.
Some proponents of formative assessment also suspect that testing companies mislabel and market some interim standardized tests as “formative” to capitalize on and profit from the popularity of the idea. Some observers express skepticism that commercial or prepackaged products can be authentically formative, arguing that formative assessment is a sophisticated instructional technique, and to do it well requires both a first-hand understanding of the students being assessed and sufficient training and professional development.

Alphabetical Search
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- Professional learning
Teach. Learn. Grow.
Teach. learn. grow. the education blog.

What is formative assessment?

Human-centered formative assessment drives long-term, holistic success for students. Because there is still confusion around this type of assessment, let’s explore what it is and why it should be a part of our responsive teaching and learning cycles.
“Formative assessment” defined
As an organization, NWEA subscribes to the revised definition from CCSSO : “Formative assessment is a planned, ongoing process used by all students and teachers during learning and teaching to elicit and use evidence of student learning to improve student understanding of intended disciplinary learning outcomes and support students to become self-directed learners .”
Let’s take a closer look at the key phrases in that definition:
- “Planned, ongoing process.” Formative assessment is a continuous, low- or no-stakes, responsive process comprised of practices, methods, and tools that are selected to support all students in reaching challenging learning goals. Teachers and students collaborate to use this kind of assessment in responsive ways that positively impact learners and learning. They partner to know and respond to strengths, interests, and needs.
- “All students and teachers during learning and teaching.” Formative assessment is a collaborative learning process happening “with” students, not “to” students .
- “Elicit and use evidence of student learning.” Formative assessment processes capture levels of knowledge and skill along the learning journey so teachers and students can make small, immediate, impactful decisions to support well-being, learning-goal achievement, and self-efficacy. Using formative assessment evidence is appropriate for making decisions during the practice phases of learning; formative assessment scores are not appropriate for calculating grades or for making placement decisions.
- “Support students to become self-directed learners.” This type of assessment includes students as active agents in the learning journey, which fuels learning and agency in learning environments and beyond. Engaging students in goal setting is a great way to do this.
What does formative assessment look like?
Little is required to start formative assessment processes because they can begin with a variety of methods and tools . Instead of specific programs, supplies, or resources, effective processes involve partnering with students to incorporate the following five practices into cycles of responsive teaching and learning.
- Clarifying learning goals and success criteria within a broader progression of learning. Students should have context for what they’re learning: why they’re learning it, how it connects to previous lessons and their own interests, and what success looks like. Having goal clarity, purpose, and a path promotes student motivation and agency.
- Eliciting and analyzing evidence of student thinking. Whether it’s capturing ideas on a whiteboard, responding to an online survey, or giving a thumbs-up or down in response to a check for understanding, an effective process centers on knowing learning goals, then gathering, interpreting, and responding to learning-goal evidence.
- Engaging in self-assessment and peer feedback. This type of assessment is more than providing feedback from teacher to student. As I explained in “The importance of student self-assessment,” having students reflect on their progress helps them become active participants in their learning. The process should also involve students collaborating with each other, asking questions, making observations, celebrating successes, and suggesting improvements in ways that support them in attaining challenging learning goals.
- Using actionable feedback. Once learning evidence is collected, teachers work with students to ensure that they have both the time and processes to apply feedback in ways that move learning forward.
- Responding by adjusting learning strategies or next instructional steps. This practice is the “why” of formative assessment. To make the process effective, we must collaborate with students to use evidence and insights to propel learners toward shared and personal short- and long-term goals.
Why formative assessment is so important
As my colleague Chase Nordengren noted , “[f]ormative assessment is [critical] for educators looking to unlock in-depth information on student learning. […] Using strategies that expose misconceptions, support higher-level thinking within a subject, and engage students in academic discourse, formative assessment provides the real-time feedback necessary to dynamically adjust instruction to meet learner needs as they emerge and change.”
In short, formative assessment helps us evaluate whether our plans and responsive “moves” are working, while there’s still time to do something about it. It celebrates that learning is an ongoing process, complete with stretches of success and periods of struggle, and it helps us remember that learning is not linear but, instead, an endeavor that rewards effort, persistence, and dedication. Best of all, it helps us collaborate with students as co-partners in the entire learning experience. Together we are a learning team, one that makes anything possible.
Ready for more?
There is no shortage of information and resources available on formative assessment. For easy-to -implement, research-based strategies, check out our eBook, Making it work: How formative assessment can supercharge your practice , and our article “27 easy formative assessment strategies for gathering evidence of student learning.” Our professional learning team also offers five workshops that can engage you and your colleagues in deep dives designed and delivered by expert educators.
Recommended for you

Six commonly used MAP Growth terms worth knowing

12 common questions parents ask about MAP Growth

Educator assessment literacy can be strengthened by professional development

Helping students grow
Students continue to rebound from pandemic school closures. NWEA® and Learning Heroes experts talk about how best to support them here on our blog, Teach. Learn. Grow.
See the post

Put the science of reading into action
The science of reading is not a buzzword. It’s the converging evidence of what matters and what works in literacy instruction. We can help you make it part of your practice.
Get the guide

Support teachers with PL
High-quality professional learning can help teachers feel invested—and supported—in their work.
Read the article

STAY CURRENT by subscribing to our newsletter
You are now signed up to receive our newsletter containing the latest news, blogs, and resources from nwea..
Formative Assessment of Teaching
What is formative assessment of teaching.
How do you know if your teaching is effective? How can you identify areas where your teaching can improve? What does it look like to assess teaching?
Formative Assessment
Formative assessment of teaching consists of different approaches to continuously evaluate your teaching. The insight gained from this assessment can support revising your teaching strategies, leading to better outcomes in student learning and experiences. Formative assessment can be contrasted with summative assessment, which is usually part of an evaluative decision-making process. The table below outlines some of the key differences between formative and summative assessment:
By participating in formative assessment, instructors connect with recent developments in the space of teaching and learning, as well as incorporate new ideas into their practice. Developments may include changes in the students we serve, changes in our understanding of effective teaching, and changes in expectations of the discipline and of higher education as a whole.
Formative assessment of teaching ultimately should guide instructors towards using more effective teaching practices. What does effectiveness mean in terms of teaching?
Effectiveness in Teaching
Effective teaching can be defined as teaching that leads to the intended outcomes in student learning and experiences. In this sense, there is no single perfect teaching approach. Effective teaching looks will depend on the stated goals for student learning and experiences. A course that aims to build student confidence in statistical analysis and a course that aims to develop student writing could use very different teaching strategies, and still both be effective at accomplishing their respective goals.
Assessing student learning and experiences is critical to determining if teaching is truly effective in its context. This assessment can be quite complex, but it is doable. In addition to measuring the impacts of your teaching, you may also consider evaluating your teaching as it aligns with best practices for evidence-based teaching especially in the disciplinary and course context or aligns with your intended teaching approach. The table below outlines these three approaches to assessing the effectiveness of your teaching:
What are some strategies that I might try?
There are multiple ways that instructors might begin to assess their teaching. The list below includes approaches that may be done solo, with colleagues, or with the input of students. Instructors may pursue one or more of these strategies at different points in time. With each possible strategy, we have included several examples of the strategy in practice from a variety of institutions and contexts.
Teaching Portfolios
Teaching portfolios are well-suited for formative assessment of teaching, as the portfolio format lends itself to documenting how your teaching has evolved over time. Instructors can use their teaching portfolios as a reflective practice to review past teaching experiences, what worked and what did not.
Teaching portfolios consist of various pieces of evidence about your teaching such as course syllabi, outlines, lesson plans, course evaluations, and more. Instructors curate these pieces of evidence into a collection, giving them the chance to highlight their own growth and focus as educators. While student input may be incorporated as part of the portfolio, instructors can contextualize and respond to student feedback, giving them the chance to tell their own teaching story from a more holistic perspective.
Teaching portfolios encourage self-reflection, especially with guided questions or rubrics to review your work. In addition, an instructor might consider sharing their entire teaching portfolio or selected materials for a single course with colleagues and engaging in a peer review discussion.
Examples and Resources:
Teaching Portfolio - Career Center
Developing a Statement of Teaching Philosophy and Teaching Portfolio - GSI Teaching & Resource Center
Self Assessment - UCLA Center for Education, Innovation, and Learning in the Sciences
Advancing Inclusion and Anti-Racism in the College Classroom Rubric and Guide
Course Design Equity and Inclusion Rubric
Teaching Demos or Peer Observation
Teaching demonstrations or peer classroom observation provide opportunities to get feedback on your teaching practice, including communication skills or classroom management.
Teaching demonstrations may be arranged as a simulated classroom environment in front of a live audience who take notes and then deliver summarized feedback. Alternatively, demonstrations may involve recording an instructor teaching to an empty room, and this recording can be subjected to later self-review or peer review. Evaluation of teaching demos will often focus on the mechanics of teaching especially for a lecture-based class, e.g. pacing of speech, organization of topics, clarity of explanations.
In contrast, instructors may invite a colleague to observe an actual class session to evaluate teaching in an authentic situation. This arrangement gives the observer a better sense of how the instructor interacts with students both individually or in groups, including their approach to answering questions or facilitating participation. The colleague may take general notes on what they observe or evaluate the instructor using a teaching rubric or other structured tool.
Peer Review of Course Instruction
Preparing for a Teaching Demonstration - UC Irvine Center for Educational Effectiveness
Based on Peer Feedback - UCLA Center for Education, Innovation, and Learning in the Sciences
Teaching Practices Equity and Inclusion Rubric
Classroom Observation Protocol for Undergraduate STEM (COPUS)
Student Learning Assessments
Student learning can vary widely across courses or even between academic terms. However, having a clear benchmark for the intended learning objectives and determining whether an instructor’s course as implemented helps students to reach that benchmark can be an invaluable piece of information to guide your teaching. The method for measuring student learning will depend on the stated learning objective, but a well-vetted instrument can provide the most reliable data.
Recommended steps and considerations for using student learning assessments to evaluate your teaching efficacy include:
Identify a small subset of course learning objectives to focus on, as it is more useful to accurately evaluate one objective vs. evaluating many objectives inaccurately.
Find a well-aligned and well-developed measure for each selected course learning objective, such as vetted exam questions, rubrics, or concept inventories.
If relevant, develop a prompt or assignment that will allow students to demonstrate the learning objective to then be evaluated against the measure.
Plan the timing of data collection to enable useful comparison and interpretation.
Do you want to compare how students perform at the start of your course compared to the same students at the end of your course?
Do you want to compare how the same students perform before and after a specific teaching activity?
Do you want to compare how students in one term perform compared to students in the next term, after changing your teaching approach?
Implement the assignment/prompt and evaluate a subset or all of the student work according to the measure.
Reflect on the results and compare student performance measures.
Are students learning as a result of your teaching activity and course design?
Are students learning to the degree that you intended?
Are students learning more when you change how you teach?
This process can be repeated as many times as needed or the process can be restarted to instead focus on a different course learning objective.
List of Concept Inventories (STEM)
Best Practices for Administering Concept Inventories (Physics)
AAC&U VALUE Rubrics
Rubric Bank | Assessment and Curriculum Support Center - University of Hawaiʻi at Mānoa
Rubrics - World Languages Resource Collection - Kennesaw State University
Student Surveys or Focus Groups
Surveys or focus groups are effective tools to better understand the student experience in your courses, as well as to solicit feedback on how courses can be improved. Hearing student voices is critical as students themselves can attest to how course activities made them feel, e.g. whether they perceive the learning environment to be inclusive, or what topics they find interesting.
Some considerations for using student surveys in your teaching include:
Surveys collect individual and anonymous input from as many students as possible.
Surveys can gather both quantitative and qualitative data.
Surveys that are anonymous avoid privileging certain voices over others.
Surveys can enable students to share about sensitive experiences that they may be reluctant to discuss publicly.
Surveys that are anonymous may lend to negative response bias.
Survey options at UC Berkeley include customized course evaluation questions or anonymous surveys on bCourses, Google Forms, or Qualtrics.
Some considerations for using student focus groups in your teaching include:
Focus groups leverage the power of group brainstorming to identify problems and imagine possible solutions.
Focus groups can gather both rich and nuanced qualitative data.
Focus groups with a skilled facilitator tend to have more moderated responses given the visibility of the discussion.
Focus groups take planning, preparation, and dedicated class time.
Focus group options at UC Berkeley include scheduling a Mid-semester Inquiry (MSI) to be facilitated by a CTL staff member.
Instructions for completing question customization for your evaluations as an instructor
Course Evaluations Question Bank
Student-Centered Evaluation Questions for Remote Learning
Based on Student Feedback - UCLA Center for Education, Innovation, and Learning in the Sciences
How Can Instructors Encourage Students to Complete Course Evaluations and Provide Informative Responses?
Student Views/Attitudes/Affective Instruments - ASBMB
Student Skills Inventories - ASBMB
How might I get started?
Self-assess your own course materials using one of the available rubrics listed above.
Schedule a teaching observation with CTL to get a colleague’s feedback on your teaching practices and notes on student engagement.
Schedule an MSI with CTL to gather directed student feedback with the support of a colleague.
Have more questions? Schedule a general consultation with CTL or send us your questions by email ( [email protected] )!
References:
Evaluating Teaching - UCSB Instructional Development
Documenting Teaching - UCSC Center for Innovations in Teaching and Learning
Other Forms of Evaluation - UCLA Center for Education, Innovation, and Learning in the Sciences
Evaluation Of Teaching Committee on Teaching, Academic Senate
Report of the Academic Council Teaching Evaluation Task Force
Teaching Quality Framework Initiative Resources - University of Colorado Boulder
Benchmarks for Teaching Effectiveness - University of Kansas Center for Teaching Excellence
Teaching Practices Instruments - ASBMB
- Subject List
- Take a Tour
- For Authors
- Subscriber Services
- Publications
- African American Studies
- African Studies
- American Literature
- Anthropology
- Architecture Planning and Preservation
- Art History
- Atlantic History
- Biblical Studies
- British and Irish Literature
- Childhood Studies
- Chinese Studies
- Cinema and Media Studies
- Communication
- Criminology
- Environmental Science
- Evolutionary Biology
- International Law
- International Relations
- Islamic Studies
- Jewish Studies
- Latin American Studies
- Latino Studies
- Linguistics
- Literary and Critical Theory
- Medieval Studies
- Military History
- Political Science
- Public Health
- Renaissance and Reformation
- Social Work
- Urban Studies
- Victorian Literature
- Browse All Subjects
How to Subscribe
- Free Trials
In This Article Expand or collapse the "in this article" section Formative Assessment
Introduction, the evolution of formative assessment.
- Theory and Formative Assessment
- Formative Assessment and Student Achievement
- The Role of Feedback in Formative Assessment
- Formative Assessment Process and Practice in the Classroom?
- Formative Assessment as Part of a Balanced Assessment System
- Developing Teacher Capacity for Formative Assessment
- National and International Reports
Related Articles Expand or collapse the "related articles" section about
About related articles close popup.
Lorem Ipsum Sit Dolor Amet
Vestibulum ante ipsum primis in faucibus orci luctus et ultrices posuere cubilia Curae; Aliquam ligula odio, euismod ut aliquam et, vestibulum nec risus. Nulla viverra, arcu et iaculis consequat, justo diam ornare tellus, semper ultrices tellus nunc eu tellus.
- Academic Achievement
- Performance Objectives and Measurement
Other Subject Areas
Forthcoming articles expand or collapse the "forthcoming articles" section.
- Gender, Power, and Politics in the Academy
- Girls' Education in the Developing World
- Non-Formal & Informal Environmental Education
- Find more forthcoming articles...
- Export Citations
- Share This Facebook LinkedIn Twitter
Formative Assessment by Leslie W. Grant , Christopher R. Gareis , Sarah P. Hylton LAST REVIEWED: 29 July 2020 LAST MODIFIED: 26 May 2021 DOI: 10.1093/obo/9780199756810-0062
Formative assessment has received international attention as an instructional approach that has great potential to improve teaching and learning. The concept has roots in educational evaluation practices and has evolved over time, from a focus on formative evaluation to formative assessment or assessment for learning. Although one singular definition has not emerged among researchers, scholars, and practitioners, shared themes across the sources suggest the emergence of common elements of formative assessment: Formative assessment is a cyclical process that involves interactions among teachers and students. Those interactions include prompting thinking and eliciting information. The information is then gathered and analyzed by both the teacher and the students. Finally, teachers and students provide feedback, and the student makes use of the feedback to either confirm or improve their understandings and/or skills. Research into these common elements will continue to inform our evolving understanding of the formative assessment process. This article first addresses the evolution of formative assessment and the theories that have informed the conceptualization of and research into the formative assessment process. The work of the Assessment Reform Group in the 1990s catapulted formative assessment into the spotlight for teacher education programs, teacher professional development, and educational research primarily due to claims of the impact on student achievement. This article provides often cited, seminal research studies claiming to provide evidence of a link between formative assessment and student achievement. Being central to the formative assessment process, works addressing the role of feedback are explored. The next two sections focus on works that have emerged to support implementation of the formative assessment process in the classroom and works to support the development of balanced assessment systems that include formative assessment at both the classroom and the school system levels. Over time, professional organizations have developed and revised standards to address both uses of assessments, to include formative assessments, in the classroom as well as standards for the development of educator knowledge, skills, and dispositions. The standards provided in this article represent the most referenced standards in the assessment and evaluation field. Finally, national reports from the United States and international reports noted in the final section provide insight into evolving policies and practices and signal the emergence over time of agreement on common elements of the formative assessment process.
Formative assessment has become a mainstay in educational discourse and practice. The first reference to the term “formative” has roots in curriculum development and evaluation. Cronbach 1963 refers to the idea of using evaluation as a tool for improving curricular programs. Scriven 1967 builds on Cronbach’s work in proposing the term “formative” as a way of clarifying the roles of evaluation. Bloom 1971 applies Scriven’s definition to the process of teaching and learning, by using the term to describe a way of improving student learning. Bloom, et al. 1971 links the idea of formative evaluation to the instructional approach of mastery learning as an instructional process that includes the use of data to improve both teaching and learning. During the 1980s and 1990s, educational researchers continued to expand on the ideas and theories proposed, and use of the term “formative evaluation” was replaced by the term “formative assessment.” Sadler 1989 builds on the definitions previously offered, highlighting the role of the student in the assessment process and viewing student self-assessment as critical to improved student learning. First published in 1994, Gipps 2012 documents the shift in how the educational community views assessment, including a shift from a psychometric view to the development of assessments and use of assessment data by teachers to guide instruction. The is distinguished as a classic text and it was thus reprinted in 2012. During the 1990s and the early 2000s, the Assessment Reform Group in the United Kingdom focused on the development of formative assessment practices and provided a definition of formative assessment. Written by Assessment Reform Group members, Harlen and James 1997 affirms that a distinction between formative and summative assessment is needed due to the confluence of these two roles of assessment in the field. The term “assessment for learning” was first coined in Assessment Reform Group 1999 to further delineate the differences between the goals and roles of summative and formative assessment and extended by the vision of assessment not only for learning but also of learning and as learning found in Earl 2003 . Stiggins and Chappuis 2012 highlights the importance of assessment for learning and situates it as the key practice of classroom assessment.
Assessment Reform Group. 1999. Assessment for learning: Beyond the black box . Cambridge, UK: Cambridge Univ., School of Education.
In this text, the authors first coin the term “assessment for learning” to distinguish it from the more conventional and long-standing notion of “assessment of learning.” The purpose of assessment of learning is to verify student learning, whereas the purpose of assessment for learning is to contribute to the acquisition, or forming, of learning.
Bloom, B. S. 1971. Learning for mastery. In Handbook on formative and summative evaluation of student learning . Edited by B. S. Bloom, J. T. Hastings, and G. F. Madaus, 43–57. New York: McGraw-Hill.
This book chapter connects the concept of mastery learning with formative evaluation. The author indicates that formative tests are used to gauge student learning, to diagnose difficulties, and to design interventions so that the student achieves mastery of a unit of instruction.
Bloom, B. S., J. T. Hastings, and G. F. Madaus. 1971. Formative evaluation. In Handbook on formative and summative evaluation of student learning . Edited by B. S. Bloom, J. T. Hastings, and G. F. Madaus, 117–138. New York: McGraw-Hill.
A book chapter that builds on Scriven’s definition of formative evaluation in curriculum development and implementation. The authors apply this definition to planning, instructional delivery, and student learning, with guidance on how to create assessments and use assessment data.
Cronbach, L. J. 1963. Course improvement through evaluation. Teacher’s College Record 64.8: 672–683.
In perhaps the earliest intimations of the concept of formative evaluation, Cronbach calls for an evaluation process that focuses on gathering and reporting information to use in guiding decisions in an educational program and in curriculum development while the program can be modified.
Earl, L.?M. 2003. Assessment as learning: Using classroom assessment to maximize student learning . Thousand Oaks, CA: Corwin.
The author describes a vision for the future of assessment as being composed of assessment of,for , and as learning. Principles of assessment for learning are illustrated with examples from multiple subject areas and grade levels. Assessment as learning focuses on the role of students as active participants in their own learning, which the author describes as virtually absent from most classrooms at the time of publication of the text.
Gipps, C. V. 2012. Beyond testing: Towards a theory of educational assessment . Classic ed. London: Routledge.
First published in 1994 in London by the Falmer publishing house, this book explores the evolution of how assessment is viewed. The author delineates the move from the psychometric view of assessment and a focus on testing to a classroom view of assessment that includes the development of a culture of assessment and a wider range of assessment tools and uses.
Harlen, W., and M. James. 1997. Assessment and learning: Differences and relationships between formative and summative assessment. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice 4.3: 365–379.
DOI: 10.1080/0969594970040304
In this article, the authors focus on providing clarity on the differences between formative and summative assessment. In addition, the authors provide conditions by which formative assessments can be used for summative purposes. These conditions include the use of external criteria for assessing student learning, viewing the results of formative assessment holistically across a period of instruction, and ensuring inter-rater reliability across teachers.
Sadler, D. R. 1989. Formative assessment and the design of instructional systems. Instructional Science 18.2: 119–144.
DOI: 10.1007/BF00117714
In this article, Sadler focuses on the judgments made about the quality of student work, discussing not only who makes such judgments but also how they are made and used. He posits that students must be able to appraise their own work and draw on their own skills to make modifications to their learning, thus alluding to the intersection of formative and self-assessment. The importance of feedback is emphasized.
Scriven, M. 1967. The methodology of evaluation. In Perspectives of curriculum evaluation . Edited by R. W. Tyler, R. M. Gagné, and M. Scriven, 39–85. Rand McNally Education. Chicago: Rand McNally.
In this monograph, Scriven proposes the use of the terms “formative” and “summative” to provide clarity about roles and goals within the evaluation community. The role of formative evaluation is to make improvements while the focus of the evaluation can still be improved. By comparison, summative evaluation is used to determine the merit or worth of an educational program.
Stiggins, R. J., and J. Chappuis. 2012. An introduction to student-involved assessment FOR learning . 6th ed. Boston: Pearson.
This classic textbook on classroom assessment may be the earliest example of a text that uses assessment for learning as the organizing conceptual framework for the principles, strategies, and techniques that it presents. This textbook is written for pre-service teachers, and it accentuates the intentional involvement of students in gauging their own learning.
back to top
Users without a subscription are not able to see the full content on this page. Please subscribe or login .
Oxford Bibliographies Online is available by subscription and perpetual access to institutions. For more information or to contact an Oxford Sales Representative click here .
- About Education »
- Meet the Editorial Board »
- Academic Audit for Universities
- Academic Freedom and Tenure in the United States
- Action Research in Education
- Adjuncts in Higher Education in the United States
- Administrator Preparation
- Adolescence
- Advanced Placement and International Baccalaureate Courses
- Advocacy and Activism in Early Childhood
- African American Racial Identity and Learning
- Alaska Native Education
- Alternative Certification Programs for Educators
- Alternative Schools
- American Indian Education
- Animals in Environmental Education
- Art Education
- Artificial Intelligence and Learning
- Assessing School Leader Effectiveness
- Assessment, Behavioral
- Assessment, Educational
- Assessment in Early Childhood Education
- Assistive Technology
- Augmented Reality in Education
- Beginning-Teacher Induction
- Bilingual Education and Bilingualism
- Black Undergraduate Women: Critical Race and Gender Perspe...
- Blended Learning
- Case Study in Education Research
- Changing Professional and Academic Identities
- Character Education
- Children’s and Young Adult Literature
- Children's Beliefs about Intelligence
- Children's Rights in Early Childhood Education
- Citizenship Education
- Civic and Social Engagement of Higher Education
- Classroom Learning Environments: Assessing and Investigati...
- Classroom Management
- Coherent Instructional Systems at the School and School Sy...
- College Admissions in the United States
- College Athletics in the United States
- Community Relations
- Comparative Education
- Computer-Assisted Language Learning
- Computer-Based Testing
- Conceptualizing, Measuring, and Evaluating Improvement Net...
- Continuous Improvement and "High Leverage" Educational Pro...
- Counseling in Schools
- Critical Approaches to Gender in Higher Education
- Critical Perspectives on Educational Innovation and Improv...
- Critical Race Theory
- Crossborder and Transnational Higher Education
- Cross-National Research on Continuous Improvement
- Cross-Sector Research on Continuous Learning and Improveme...
- Cultural Diversity in Early Childhood Education
- Culturally Responsive Leadership
- Culturally Responsive Pedagogies
- Culturally Responsive Teacher Education in the United Stat...
- Curriculum Design
- Data Collection in Educational Research
- Data-driven Decision Making in the United States
- Deaf Education
- Desegregation and Integration
- Design Thinking and the Learning Sciences: Theoretical, Pr...
- Development, Moral
- Dialogic Pedagogy
- Digital Age Teacher, The
- Digital Citizenship
- Digital Divides
- Disabilities
- Distance Learning
- Distributed Leadership
- Doctoral Education and Training
- Early Childhood Education and Care (ECEC) in Denmark
- Early Childhood Education and Development in Mexico
- Early Childhood Education in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Childhood Education in Australia
- Early Childhood Education in China
- Early Childhood Education in Europe
- Early Childhood Education in Sub-Saharan Africa
- Early Childhood Education in Sweden
- Early Childhood Education Pedagogy
- Early Childhood Education Policy
- Early Childhood Education, The Arts in
- Early Childhood Mathematics
- Early Childhood Science
- Early Childhood Teacher Education
- Early Childhood Teachers in Aotearoa New Zealand
- Early Years Professionalism and Professionalization Polici...
- Economics of Education
- Education For Children with Autism
- Education for Sustainable Development
- Education Leadership, Empirical Perspectives in
- Education of Native Hawaiian Students
- Education Reform and School Change
- Educational Statistics for Longitudinal Research
- Educator Partnerships with Parents and Families with a Foc...
- Emotional and Affective Issues in Environmental and Sustai...
- Emotional and Behavioral Disorders
- Environmental and Science Education: Overlaps and Issues
- Environmental Education
- Environmental Education in Brazil
- Epistemic Beliefs
- Equity and Improvement: Engaging Communities in Educationa...
- Equity, Ethnicity, Diversity, and Excellence in Education
- Ethical Research with Young Children
- Ethics and Education
- Ethics of Teaching
- Ethnic Studies
- Evidence-Based Communication Assessment and Intervention
- Family and Community Partnerships in Education
- Family Day Care
- Federal Government Programs and Issues
- Feminization of Labor in Academia
- Finance, Education
- Financial Aid
- Formative Assessment
- Future-Focused Education
- Gender and Achievement
- Gender and Alternative Education
- Gender-Based Violence on University Campuses
- Gifted Education
- Global Mindedness and Global Citizenship Education
- Global University Rankings
- Governance, Education
- Grounded Theory
- Growth of Effective Mental Health Services in Schools in t...
- Higher Education and Globalization
- Higher Education and the Developing World
- Higher Education Faculty Characteristics and Trends in the...
- Higher Education Finance
- Higher Education Governance
- Higher Education Graduate Outcomes and Destinations
- Higher Education in Africa
- Higher Education in China
- Higher Education in Latin America
- Higher Education in the United States, Historical Evolutio...
- Higher Education, International Issues in
- Higher Education Management
- Higher Education Policy
- Higher Education Research
- Higher Education Student Assessment
- High-stakes Testing
- History of Early Childhood Education in the United States
- History of Education in the United States
- History of Technology Integration in Education
- Homeschooling
- Inclusion in Early Childhood: Difference, Disability, and ...
- Inclusive Education
- Indigenous Education in a Global Context
- Indigenous Learning Environments
- Indigenous Students in Higher Education in the United Stat...
- Infant and Toddler Pedagogy
- Inservice Teacher Education
- Integrating Art across the Curriculum
- Intelligence
- Intensive Interventions for Children and Adolescents with ...
- International Perspectives on Academic Freedom
- Intersectionality and Education
- Knowledge Development in Early Childhood
- Leadership Development, Coaching and Feedback for
- Leadership in Early Childhood Education
- Leadership Training with an Emphasis on the United States
- Learning Analytics in Higher Education
- Learning Difficulties
- Learning, Lifelong
- Learning, Multimedia
- Learning Strategies
- Legal Matters and Education Law
- LGBT Youth in Schools
- Linguistic Diversity
- Linguistically Inclusive Pedagogy
- Literacy Development and Language Acquisition
- Literature Reviews
- Mathematics Identity
- Mathematics Instruction and Interventions for Students wit...
- Mathematics Teacher Education
- Measurement for Improvement in Education
- Measurement in Education in the United States
- Meta-Analysis and Research Synthesis in Education
- Methodological Approaches for Impact Evaluation in Educati...
- Methodologies for Conducting Education Research
- Mindfulness, Learning, and Education
- Mixed Methods Research
- Motherscholars
- Multiliteracies in Early Childhood Education
- Multiple Documents Literacy: Theory, Research, and Applica...
- Multivariate Research Methodology
- Museums, Education, and Curriculum
- Music Education
- Narrative Research in Education
- Native American Studies
- Note-Taking
- Numeracy Education
- One-to-One Technology in the K-12 Classroom
- Online Education
- Open Education
- Organizing for Continuous Improvement in Education
- Organizing Schools for the Inclusion of Students with Disa...
- Outdoor Play and Learning
- Outdoor Play and Learning in Early Childhood Education
- Pedagogical Leadership
- Pedagogy of Teacher Education, A
- Performance-based Research Assessment in Higher Education
- Performance-based Research Funding
- Phenomenology in Educational Research
- Philosophy of Education
- Physical Education
- Podcasts in Education
- Policy Context of United States Educational Innovation and...
- Politics of Education
- Portable Technology Use in Special Education Programs and ...
- Post-humanism and Environmental Education
- Pre-Service Teacher Education
- Problem Solving
- Productivity and Higher Education
- Professional Development
- Professional Learning Communities
- Program Evaluation
- Programs and Services for Students with Emotional or Behav...
- Psychology Learning and Teaching
- Psychometric Issues in the Assessment of English Language ...
- Qualitative Data Analysis Techniques
- Qualitative, Quantitative, and Mixed Methods Research Samp...
- Qualitative Research Design
- Quantitative Research Designs in Educational Research
- Queering the English Language Arts (ELA) Writing Classroom
- Race and Affirmative Action in Higher Education
- Reading Education
- Refugee and New Immigrant Learners
- Relational and Developmental Trauma and Schools
- Relational Pedagogies in Early Childhood Education
- Reliability in Educational Assessments
- Religion in Elementary and Secondary Education in the Unit...
- Researcher Development and Skills Training within the Cont...
- Research-Practice Partnerships in Education within the Uni...
- Response to Intervention
- Restorative Practices
- Risky Play in Early Childhood Education
- Scale and Sustainability of Education Innovation and Impro...
- Scaling Up Research-based Educational Practices
- School Accreditation
- School Choice
- School Culture
- School District Budgeting and Financial Management in the ...
- School Improvement through Inclusive Education
- School Reform
- Schools, Private and Independent
- School-Wide Positive Behavior Support
- Science Education
- Secondary to Postsecondary Transition Issues
- Self-Regulated Learning
- Self-Study of Teacher Education Practices
- Service-Learning
- Severe Disabilities
- Single Salary Schedule
- Single-sex Education
- Single-Subject Research Design
- Social Context of Education
- Social Justice
- Social Network Analysis
- Social Pedagogy
- Social Science and Education Research
- Social Studies Education
- Sociology of Education
- Standards-Based Education
- Statistical Assumptions
- Student Access, Equity, and Diversity in Higher Education
- Student Assignment Policy
- Student Engagement in Tertiary Education
- Student Learning, Development, Engagement, and Motivation ...
- Student Participation
- Student Voice in Teacher Development
- Sustainability Education in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Early Childhood Education
- Sustainability in Higher Education
- Teacher Beliefs and Epistemologies
- Teacher Collaboration in School Improvement
- Teacher Evaluation and Teacher Effectiveness
- Teacher Preparation
- Teacher Training and Development
- Teacher Unions and Associations
- Teacher-Student Relationships
- Teaching Critical Thinking
- Technologies, Teaching, and Learning in Higher Education
- Technology Education in Early Childhood
- Technology, Educational
- Technology-based Assessment
- The Bologna Process
- The Regulation of Standards in Higher Education
- Theories of Educational Leadership
- Three Conceptions of Literacy: Media, Narrative, and Gamin...
- Tracking and Detracking
- Traditions of Quality Improvement in Education
- Transformative Learning
- Transitions in Early Childhood Education
- Tribally Controlled Colleges and Universities in the Unite...
- Understanding the Psycho-Social Dimensions of Schools and ...
- University Faculty Roles and Responsibilities in the Unite...
- Using Ethnography in Educational Research
- Value of Higher Education for Students and Other Stakehold...
- Virtual Learning Environments
- Vocational and Technical Education
- Wellness and Well-Being in Education
- Women's and Gender Studies
- Young Children and Spirituality
- Young Children's Learning Dispositions
- Young Children's Working Theories
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Legal Notice
- Accessibility
Powered by:
- [66.249.64.20|185.148.24.167]
- 185.148.24.167
Skip to Content
Other ways to search:
- Events Calendar
- Formative Assessments
Formative assessments are assessments implemented during the course of instruction, while learning is in progress. Whereas summative assessments evaluate what students have learned by the end of a period of instruction, formative assessments are typically designed for the purpose of providing feedback on student learning that is immediate, continuous, specific, and action-oriented (Suskie 2004). This feedback can be used by students to adjust their approach to learning–for example, helping them to identify areas on which they need to focus more attention, while also promoting metacognition more generally (reflection on their own thinking and learning processes). The feedback gathered through formative assessments can also be used by educators to adjust their teaching methods during the semester or even during a class period–for example, helping them to identify concepts in need of further clarification. Formative assessments are typically “no stakes” or “low stakes,” meaning that they are often ungraded or worth a relatively small proportion of a student’s grade.
Formative assessment plays a crucial role in equity-minded assessment, which strives to achieve equal outcomes for all students–that is, outcomes that are unrelated to students’ race, ethnicity, socioeconomic background, or other backgrounds or identities. Equitable assessments are typically learning-focused, inclusive, relevant, rigorous, and transparent (Artze-Vega et al., 2023). By providing ample opportunity to practice and actionable feedback to improve, formative assessments support all students in being able to achieve the high expectations set for rigorous courses. Portraying learning as an iterative process can also boost student motivation by focusing their attention on the learning process instead of on an outcome, such as a credential or grade (Nicol and McFarlane-Dick, 2007). Student motivation, in turn, can promote engagement, a sense of belonging, and ultimately, success in the classroom.
Formative assessments may include:
1. Classroom Assessment Techniques (CATs)
Classroom Assessment Techniques, also known as CAT(s), are a set of ungraded, quick, and effective techniques that can be implemented during class to gauge student preparedness or comprehension of topics as learning is in progress. Explore our webpage on different types of CATs to learn more.
2. Classroom Polls
Classroom polls are also a great way to gauge student comprehension of course topics and identify and address misconceptions as they arise. Classroom polls may be particularly helpful in large classes or other contexts in which students are hesitant to speak up. Visit iClickers and Real-Time Polls to explore CU-supported polling systems.
3. Low-stakes homework assignments or quizzes
Low-stakes (low point value) assignments or assessments completed outside of class are another way to gauge student comprehension and provide students with timely feedback as they learn new skills or topics. This might, for example, involve students completing brief problem sets or quizzes on a weekly basis that are graded but have little impact on their final grade. Explore the DePaul Teaching Commons’ webpage on low-stakes assignments to learn more.
4. Self-assessments
Self-assessments encourage students to reflect on their own learning and their progress in the course. Self-assessments can help students identify gaps in their own understanding, while promoting their development of broader metacognitive skills. Some examples of self-assessment techniques include students grading their own essays or quizzes using rubrics , student-designed quizzes , reflective writing , or exam-wrappers . To understand why and how to incorporate self-assessments in class, visit University of New South Wales’ resource on student self-assessments .
5. Peer-assessments
Peer-assessments are an additional method for providing students with feedback on their learning as it occurs. When students provide feedback on the work of their peers, it can promote collaboration, communication, community-building, and skills for providing and receiving constructive feedback. In addition, peer assessments can be an effective method to provide detailed feedback to students in contexts in which providing individual feedback by instructors is impractical (e.g. large classes). Explore some of our tips on designing rubrics for peer-assessment .
You can find a full list of linked resources and additional references below to learn more about incorporating formative assessments and feedback in your class. For individualized support, you may also schedule a consultation with our team .
References:
Artze-Vega, I., Darby, F., Dewsbury, B., & Imad, M. (2023). The Norton Guide to Equity-Minded Teaching , New York, NY: W.W. Norton & Company, Inc.
Eberly Center. Formative vs Summative Assessments . Carnegie Mellon University.
Nicol, D.J., & Macfarlane‐Dick, D. (2007). Formative assessment and self‐regulated learning: A model and seven principles of good feedback practice . Studies in Higher Education , 31( 2), 199-218.
Poorvu Center for Teaching and Learning. (2021). Formative and summative assessments . Yale University.
Suskie, L. (2004). Assessing student learning: A common sense guide . Bolton, MA. Anker Publishing.
Teaching Commons. Low Stakes-Assignments . DePaul University.
Further reading & resources:
Angelo, T. A. & Cross, K. P. (1993). Classroom assessment techniques: A handbook for college teachers (2nd ed.). Jossey-Bass Publishing.
Andrade, H. L. (2019). A Critical Review of Research on Student Self-Assessment. Frontiers in Education . 4(87).
Barkley, E. & Major, C. H. (2020). Student Engagement Techniques: A Handbook for College Faculty (2nd ed.). Jossey-Bass Publishing.
Center for Teaching Innovation. Incorporating Peer Assessments . Cornell University.
Center for Teaching and Learning. Rubrics . University of Colorado, Boulder.
Center for Teaching and Learning. Incorporating Peer Assessments . University of Colorado, Boulder.
Formative Assessment Insights. Basics of Peer Assessment . Projects at WestEd.
Genova, L., Armstrong, K., Greenlee, J. W. & Samuel, D. (2021). Teaching Gradually: Practical Pedagogy for Graduate Students, by Graduate Students . Stylus Publishing: Sterling, VA.
Lovett, M. C. (2013). Make exams worth more than the grade: Using exam wrappers to promote metacognition . In Kaplan, M., Silver, N, Lavaque-Manty, D., & Meizlish, D. Using reflection and metacognition to improve student learning. Stylus Publishing: Sterling, VA., pp. 18-52.
Office of Information Technology. CUClickers/iClickers . University of Colorado, Boulder.
Office of teaching and Learning. Assignment/Exam Wrappers . University of Denver.
Research & Innovation Office. Real-Time Polls . University of Colorado, Boulder.
The Teaching Gateway. Student Self-Assessment . University of New South Wales.
Techniques Video Library. Classroom Assessment Techniques . The K. Patricia Cross Academy.
Writing Across the curriculum. Using Reflective Writing to Deepen learning . University of Minnesota.
- Assessment in Large Enrollment Classes
- Classroom Assessment Techniques
- Creating and Using Learning Outcomes
- Early Feedback
- Five Misconceptions on Writing Feedback
- Frequent Feedback
- Online and Remote Exams
- Student Learning Outcomes Assessment
- Student Peer Assessment
- Student Self-assessment
- Summative Assessments: Best Practices
- Summative Assessments: Types
- Assessing & Reflecting on Teaching
- Departmental Teaching Evaluation
- Equity in Assessment
- Glossary of Terms
- Attendance Policies
- Books We Recommend
- Classroom Management
- Community-Developed Resources
- Compassion & Self-Compassion
- Course Design & Development
- Course-in-a-box for New CU Educators
- Enthusiasm & Teaching
- First Day Tips
- Flexible Teaching
- Grants & Awards
- Inclusivity
- Learner Motivation
- Making Teaching & Learning Visible
- National Center for Faculty Development & Diversity
- Open Education
- Student Support Toolkit
- Sustainaiblity
- TA/Instructor Agreement
- Teaching & Learning in the Age of AI
- Teaching Well with Technology
This site belongs to UNESCO's International Institute for Educational Planning

IIEP Learning Portal

Search form
- issue briefs
- Monitor learning
- Formative assessment
This brief explains how formative assessment can contribute to improving learning and what recurring challenges affect its implementation. It then provides policy recommendations that may help educators and policy-makers overcome these obstacles.
Formative assessment, often referred to as ‘assessment for learning’, classroom, or continuous assessment, encompasses ‘all those activities undertaken by teachers, and/or by students which provide information to be used as feedback to modify the teaching and learning activities in which they are engaged’ (Black and Wiliam, 1998: 7–8). Whether formal or informal, they can take various forms such as quizzes and tests, written essays, self/peer assessment, oral questioning, learning logs, and so on. While traditionally opposed to summative assessment or ‘assessment of learning’, which is used to ‘certify or select learners in a given grade or age for further schooling’ (UNESCO, 2019: 16), the distinction has become blurred, with a growing number of hybrid assessments mixing both purposes. Additionally, although generally low-stake, formative assessments can count for students’ final grades. Thus, it is worth noting that classifying an assessment as formative should consider both its characteristics and the use of the information generated (Dunn and Mulvenon, 2009).
During the COVID-19 crisis formative assessments gained more relevance due to uncertainty about whether students were acquiring the necessary skills. With summative and high-stake examinations often being cancelled or postponed, formative assessments may provide better options and solutions in measuring learner progress (Bawane and Sharma, 2020). Although the education sector globally was unprepared for the crisis, some countries managed to find alternative modes of formative assessment through innovative means. For instance, in the United Arab Emirates, a smart measurement policy enabled the assessment of students’ academic performance using artificial intelligence (IIEP-UNESCO, 2020).
What we know
Evidence about the benefits of formative assessments on learning is mixed. A review of the literature in Clarke (2012) suggests that they can yield promising learning gains (especially for low achievers) if frequent and of high quality. Meaningful feedback is central to the efficiency of formative assessments (OECD, 2005a; Muskin, 2017). Hill argues that ‘when used to provide feedback on a daily basis to both teacher and students’, they are ‘one of the most powerful interventions ever recorded in educational research literature’ (Hill, 2013: 65). To be effective, feedback needs to be based on sound data, performed well (Hill, 2013), and followed by appropriate corrective measures (Allal and Mottier Lopez, 2005). However, Browne (2016) makes the nuance that while research clearly points to the inefficient implementation of formative assessments in sub-Saharan Africa and South Asia, the only rigorous experimental study conducted in these regions found no positive effects on learning even with appropriate implementation. Moreover, some authors raise methodological concerns or concerns related to definitions in the literature supportive of formative assessments (see for example Dunn and Mulvenon, 2009; Bennett, 2011).
Nevertheless, if ‘valid, timely, constructive, and specific to the learning needs of the child’, formative assessments can be particularly helpful in advancing teaching and learning (READ, 2020: 3). By providing feedback to teachers and students, they can help educators to plan instructional activities (Allal and Mottier Lopez, 2005), including differentiated instruction (OECD, 2008), and enable adjustment and remediation targeted to a student or group of students (Muskin, 2017). They may also help identify areas for improvement in teacher professional development, and may be crucial for teachers in motivating and engaging their students (Muskin, 2017).
Challenges
Many education systems are moving towards more formative assessments, acknowledging the limitations of high-stake examinations (e.g. the limited range of skills assessed and techniques used). However, their implementation in classrooms remains problematic, especially in developing contexts.
Teaching conditions
Poor teaching conditions may affect the effective implementation of formative assessments. Large class sizes may cause teachers difficulties in providing individualized attention to their students (Browne, 2016). Moreover, fears that formative assessments might be time-consuming and resource-intensive, especially alongside extensive curriculum requirements, contribute to their perception as an ‘administrative burden’ for teachers (OECD, 2005b; Browne, 2016). Teachers may conform to policies but do not use assessment results to improve teaching or learning (Browne, 2016).
School- and system-level support
Although policy changes initiated a shift towards formative assessments in Africa, minimal institutional support, such as additional teacher training and materials, has been provided to operate this shift (Browne, 2016).
Moreover, school culture may not always be supportive of formative assessments. In many countries, the focus remains on more visible summative assessments conducted for accountability purposes (OECD, 2005a; Browne, 2016). Additionally, school directors, inspectors, or the wider system may not grant teachers enough freedom to make decisions based on assessment results by adjusting their teaching methods and moving away from traditional teaching practices (Muskin, 2017). Teachers’ autonomy is all the more imperative as the current pandemic creates unprecedented situations in which teachers’ ability to adapt and innovate is essential (UNICEF, 2021).
Lack of trained teachers
In some countries, many teachers need capacity development in test construction, administration, record-keeping of test marks, and assessment of soft skills (Muskin, 2017). Consequently, teachers may use poorly constructed tests or may copy tests from textbooks (Kellaghan and Greaney, 2004). However, Browne (2016) notes that even when trained and equipped with adequate resources, teachers may return to previous practices if they lack confidence, do not understand the purpose of formative assessments, or are not encouraged by a supportive school culture.
Inclusion and equity
Formative assessments are central to the teaching-learning process. They can help improve student outcomes if part of a fair, valid, and reliable process of gathering, interpreting and using information generated throughout the student learning process (Global Education Monitoring Report Team, 2020).
Equity preoccupations are at the center of the debate between proponents of formative and summative assessments. Arguments against formative assessments include that they can penalize disadvantaged students, for instance because of patronage risks or potential biases in teacher assessments linked to gender, ethnicity, or socio-economic background (Kellaghan and Greaney, 2004; Bennett, 2011; IIEP-UNESCO, 2020).
However, formative assessments can foster equity and inclusion if they are used through a variety of assessment methods that take into account the diversity of students’ abilities (Muskin, 2017) and if teachers are aware of, and address, any potential preconceptions they might have (OECD, 2005a).
Students with disabilities may require alternative forms of assessment. They are more likely to access the curriculum in inclusive environments when teachers use a universal design approach and are already capable and competent to modify, adapt, or accommodate the needs of students within their assessment plans (Manitoba Education, Citizenship, and Youth, 2006; Wagner, 2011). Accommodations may include extra time to complete assignments, the use of scribes, oral instruction, and so on.
Policy and planning
Linking formative assessments to sector planning.
Whereas summative assessments often dominate the political debate on education (OECD, 2008), it is not evident how formative assessments can inform sector planning. An OECD study points to ‘a lack of coherence between assessments and evaluations at the policy, school and classroom levels’ as a major barrier to wider practice (OECD, 2005b: 4). It means that information gathered at regional or national levels is often judged unhelpful in informing classroom practices; vice versa, classroom-based assessments may be perceived as irrelevant for policy-making. This may also come from the fact that, in the absence of standardization within or across schools, formative assessment data cannot be aggregated into system-level information in the way large-scale standardized assessments are (World Bank, 2018).
However, the importance of classroom-level variables in student learning variations still makes it necessary to look ‘inside the black box’ of classroom practice (OECD, 2005a: 88). International organizations such as OECD and UNESCO advocate for a better alignment between, or combination of, formative and summative assessments (OECD, 2005a; Muskin, 2017). For instance, in Uruguay, large-scale national assessment results were used for formative purposes to advance both student learning and in-service teacher training (Ravela, 2005). Additionally, the Early Grade Reading Assessment (EGRA), a ‘hybrid assessment’, offers an example of how a large-scale assessment, whose data inform decision-makers, can also help identify the need for early instruction improvement in classrooms (Wagner, 2011; IIEP-UNESCO, 2019).
Investing in teacher training
Investments in initial and in-service training, as well as materials for formative assessments, are essential for teachers’ confidence and the effective implementation of formative assessments (OECD, 2005a; Muskin, 2017), especially in regions such as sub-Saharan Africa where they are relatively new (Browne, 2016). Ensuring teachers understand the purpose of formative assessments is key to fostering their ownership of these pedagogical changes (Browne, 2016). Such efforts, combined with the provision of tools and incentives to use the results of formative assessments, proved effective in Malawi, Liberia and India (World Bank, 2018).
Strengthening schools and the education system’s support
Schools play a major role in stimulating and guiding teachers while conducting and using formative assessments. For instance, the Framework for Improving Student Outcomes (FISO) implementation guide of the state of Victoria, Australia, encourages schools to obtain school-wide agreement on the use of formative assessments and to establish consistent processes for analyzing the data generated.
Implementing formative assessment requires a system which follows up, monitors the quality of assessment practices, and supports teachers when needed (Browne, 2016; World Bank, 2018). It is also important that teachers are not overwhelmed with assessments while they juggle dense curricula. Some countries, such as Morocco, have dedicated time in the calendar for continuous assessments, while others, such as Tanzania, have simply opted for a dramatic simplification of the curriculum (Muskin, 2017). The COVID-19 crisis has rendered the latter option relevant, as UNICEF recommends prioritizing some curriculum components and identifying those that are currently unachievable (UNICEF, 2021).
Creating a culture of evaluation
Instilling a culture of evaluation throughout the system is crucial. It signifies that ‘teachers and school leaders use information on students to generate new knowledge on what works and why, share their knowledge with colleagues, and build their ability to address a greater range of their students’ learning needs’ (OECD, 2005a: 25). Moreover, teachers are more likely to conduct formative assessments if schools and education systems alike encourage them to innovate, for example through peer support or pilot projects which test new assessment methods (OECD, 2005a).
Plans and policies
- Liberia: National learning assessment policy (2021)
- Zambia: National learning assessment framework (2017)
- READ (Russian Education Aid for Development). 2020. ‘Formative Assessment and Student Learning: How to Ensure Students Continue to Learn Outside of the Classroom’. Newsletter 13 .
- Soland, J.; Hamilton, L. S.; Stecher, B. M. 2013. Measuring 21st Century Competencies: Guidance for Educators. Asia Society and RAND Corporation.
Allal, L.; Mottier Lopez, L. 2005. 'Formative assessment of learning: A review of publications in French.' In: Formative Assessment: Improving Learning in Secondary Classrooms , (pp. 241–264). Paris: OECD Publishing.
Bennett, R. E. 2011. 'Formative assessment: A critical review.' In: Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice 18 (1) : 5–25.
Black, P.; Wiliam, D. 1998. 'Assessment and classroom learning.' Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy & Practice 5 (1) : 7–74.
Browne, E. 2016. Evidence on formative classroom assessment for learning. K4D Helpdesk Report. Brighton: Institute of Development Studies.
Bawane, J.; Sharma, R, 2020. Formative assessments and the continuity of learning during emergencies and crises. NEQMAP 2020 Thematic Review. Paris: UNESCO.
Clarke, M. 2012. What matters most for student assessment systems: A framework paper. Washington DC: World Bank.
Dunn, K. E.; Mulvenon, S. W. 2009. 'A critical review of research on formative assessment: The limited scientific evidence of the impact of formative assessment in education. In: Practical Assessment, Research & Evaluation 14 (7) : 11.
Global Education Monitoring Report Team. 2020. Global Education Monitoring Report, 2020: Inclusion and Education: All Means All. Paris: UNESCO.
Hill, P. W. 2013. ‘ The Role of assessment in measuring outcomes'. In: M. Barber and S. Rizvi (eds), Asking More: The Path to Efficacy . London: Pearson.
IIEP-UNESCO. 2019. 'Student learning assessments'. IIEP Policy Toolbox.
———. 2020. 'Will we ever go back to normal when it comes to student assessments?' Education for Safety, Resilience and Social Cohesion ,. Last accessed June 10 2021.
Kellaghan, T.; Greaney, V. 2004. Assessing student learning in Africa. Directions in Development. Washington, D.C: World Bank.
Manitoba Education, Citizenship, and Youth (Canada). 2006. Rethinking Classroom Assessment with Purpose in Mind: Assessment for Learning, Assessment as Learning, Assessment of Learning. Manitoba Education, Citizenship, and Youth.
Muskin, J. A. 2017. Continuous Assessment for Improved Teaching and Learning: A Critical Review to Inform Policy and Practice. Current and critical issues in curriculum, learning and assessment, 13. Geneva: UNESCO International Bureau of Education.
OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development). 2005a. Formative Assessment: Improving Learning in Secondary Classrooms. Paris: OECD.
———. 2005b. Formative Assessment: Improving Learning in Secondary Classrooms. Policy brief. Paris: OECD.
OECD (Organisation for Economic Co-operation and Development). 2008. Assessment for Learning. The Case for Formative Assessment. OECD/CERI International Conference 'Learning in the 21st Century: Research, Innovation and Policy'.
Ravela, P. 2005. 'A formative approach to national assessments: The Case of Uruguay.' In: Prospects 35 (1) : 21–43.
READ (Russian Education Aid for Development). 2020. 'Formative assessment and student learning: How to ensure students continue to learn outside of the classroom.' Newsletter 13 .
UNESCO. 2019. The Promise of Large-Scale Learning Assessments: Acknowledging Limits to Unlock Opportunities. Paris: UNESCO.
Wagner, D. A. 2011. Smaller, Quicker, Cheaper: Improving Learning Assessments for Developing Countries. Paris: IIEP-UNESCO.
World Bank. 2018. Learning to Realize Education’s Promise. World Development Report 2018. Washington, DC: World Bank.
Related information
- Are students still learning during COVID-19? Formative assessment can provide the answer
Maths Tutoring Built for Schools
"This is one of the most effective interventions I have come across in my 27 years of teaching."
Hundreds of FREE online maths resources
Daily activities, ready-to-go lesson slides, SATs revision packs, video CPD and more!

What Is Formative Assessment: A Practical Guide To When And How To Use It
Zoe Benjamin
Read this guide to formative assessment to find out what it means, how to use it most effectively and what challenges and pitfalls to look out for.
Dylan Wiliam has described formative assessment as a cornerstone of outstanding lessons and an essential area for ongoing professional development. So, if you are keen to unlock the full potential of your teaching and help your students excel, it’s time to embrace the power of formative assessment!
What is formative assessment?
Formative assessment vs summative assessment, what are the benefits of formative assessment, how formative assessment raises student achievement, examples of formative assessment , the importance of formative feedback, examples of formative feedback, challenges associated with formative assessment processes , formative assessment faqs.
Formative assessment is the process of monitoring and assessing students’ learning and understanding in order to adapt your teaching methods to better address students’ individual needs. The result of this continual formative feedback is that both teacher and student know the areas of greatest strength and the areas for improvement. Formative assessment is by its nature a low stakes form of assessment.
One way to view formative assessment is that it is a way for pupils to provide feedback to their teacher about whether they are on track to achieve the learning outcomes for the lesson.
Although the feedback is provided by pupils, it is the responsibility of the teacher to ensure that pupils are given access to formative assessment opportunities that provide the teacher with accurate and ongoing feedback. The feedback must then also be used carefully to inform the teacher’s next steps.
Formative assessment is often, but not always relatively quick and in the moment eg asking children to hold up mini whiteboards to assess their understanding of a concept; it can also be much more extensive such as a diagnostic maths test .
Some people will use the term formative assessment as synonymous with assessment for learning or assessment as learning because it utilises assessment to ultimately help the learning process.
Diagnostic Year 6 Maths Quizzes
Identify and plug gaps with your Year 6 class on key maths topics with these formative diagnostic quizzes
The difference between formative assessment and summative assessment is best seen in terms of their goals.
The goal of formative assessment is to guide the next stage of teaching and learning and inform the teacher and student on their gaps in skills knowledge.
In contrast, the goal of summative assessment is a snapshot or record of what a pupil has learnt by a particular point in time, often benchmarked against school, trust or national standards.
Looking for your own summative maths tests?
The following are all free to download:
- Year 6 maths test
- Year 7 maths test
- Year 8 maths test
- Year 9 maths test
Formative assessment strategies offer assessment for learning; they provide teachers with the information they need to enhance and track student progress .
Summative assessment provides an assessment of learning and a measure of student performance.
Summative assessments are more likely to take the form of high stakes classroom assessments like SATs, GCSEs or even end of year tests in a school. Examples of formative assessments will include low stakes quizzes or exit tickets. However, you cannot rely on the format of the assessment alone – it’s all about how it’s used.
Read more: Formative and Summative Assessment: The Differences Explained
Wiliam and Leahy (2016) conducted a two-year study in 57 schools to measure the impact that formative assessment has on students’ learning experience. At the end of the study, students in 85% of the schools were responding significantly more to their teachers’ feedback than before the study started.
The five strategies promoted by Wiliam and Leahy were:
- Clarifying, sharing and understanding learning intentions and success criteria
- Engineering effective discussions, tasks, and activities that elicit evidence of learning
- Providing feedback that moves learners forward
- Activating students as learning resources for one another
- Activating students as owners of their own learning.
The benefits of formative assessment include:
- Encourages a culture of reflection and adaptation in students, empowering them to reflect on and adapt their own learning.
- Facilitates teachers in evaluating and refining their teaching strategies based on formative assessment insights.
- Promotes self-evaluation and metacognition, enabling students to effectively plan, monitor, and evaluate their learning progress.
- Improves students’ academic performance by providing teachers with valuable feedback on student understanding.
- Enables teachers to implement whole class or small group interventions as necessary, ensuring personalised instruction and enhanced learning outcomes .
- Formative assessment raises student achievement by allowing more targeted teaching. By analysing the results of carefully planned formative assessment, teachers can develop an accurate picture of their pupil’s current understanding of a given topic. Using this information to inform the next steps in the lesson and future lesson planning can allow gaps in understanding to be closed and improved pupil outcomes.
- Formative assessment can raise pupil achievement through improving their self-evaluation. If the results of formative assessment are shared with pupils and appropriate targeted teaching strategies are implemented, they can begin to identify whether a solution is accurate, which methods are most effective and when it is appropriate to use them. However due to the Dunning-Kruger effect – a cognitive bias causing students to overestimate their own achievement – it is vital that the ability of a student to accurately self-evaluate their understanding is itself continually assessed and monitored.
- Formative assessment encourages students metacognitive skills as they receive ongoing feedback as they are exposed to a range of formative assessment techniques and become more involved in their learning; metacognition is a proven technique to raise student achievement.
The formative assessment technique you choose will depend on the situation, your current knowledge of the student, and what outcome you require from your assessment. The most reliable information about pupil knowledge comes from formative assessment activities consciously designed to uncover what students do and don’t know and and expose misconceptions.
Some of these formative assessment examples by their nature will be diagnostic i.e. with the primary goal of identifying and evaluating students’ current knowledge and understanding in a specific content domain.
The most effective examples of formative assessment are:
- Diagnostic questions
- Low stakes quizzes
- Mini whiteboards
- Problem pairs
- Examples and non-examples
- Exit tickets or exit slips
- Shadow tests
- Comment-only marking
- Metacognitive prompts
- One-minute papers
- Always, sometimes, never
- Directed questioning
- Open-ended questions
- Identifying misconceptions
- Concept map
- Mark scheme or rubric
- Homework tasks
Read more: The best formative assessment examples .
How to use formative assessment as part of your intervention
We recommend every intervention should have some level of formative assessment at the end or beginning to inform the next lesson. This is because the best interventions by their nature are targeted and focused on an individual student’s needs as is the case for our one to one online maths tuition .
At Third Space Learning, pupils complete post session questions after their online one to one maths tutoring sessions. Pupils will be asked questions related to the Learning Objective(s) they’ve covered with their tutor in that session, as well as Learning Objectives they’ve not yet covered. This helps us understand both how well they’ve understood the content of the lesson, and which Learning Objectives they still need to cover in future tutoring sessions. Teachers can access the results of pupils’ post session questions anytime on our online platform.
The success of formative assessment relies on teachers being able to give clear and concise feedback that helps students move from their current level of understanding to the next level.
When feedback gives pupils explicit instructions that move their learning forward, it is called formative feedback. Formative assessments that are not followed by effective formative feedback will not improve student attainment.
Formative feedback is crucial for students to improve their academic performance by gaining insights into their strengths and weaknesses.
This can be given on an individual basis, either verbal or written, or it may be given to a whole class following a low-stakes quiz or at the start of a lesson in response to the information gained from the previous lesson’s exit ticket.
The following examples illustrate the types of formative feedback seen in maths lessons:
1. Verbal formative feedback
A teacher explains to a student that they have mixed up the definitions of factors and multiples.
They might remind the pupil that the word multiple means ‘lots of’ something to help them remember that they can use their times tables to identify the multiples of a number.
2. Written formative feedback
In response to the work shown below in a student’s exercise book, a teacher writes: ‘Remember that the denominators do not need to be the same when multiplying fractions. Try this question again by multiplying the numerators and denominators together for the original question’.
3. Whole class formative feedback
Following the completion of the nth term exit ticket shown in the examples above, the teacher begins the next lesson with a recap for finding the nth term of a quadratic sequence emphasising the need to divide the common difference by two.
Formative assessment is a crucial aspect of evaluating student work and adjusting instruction to meet their needs. Nevertheless, teachers encounter challenges in implementing effective practices:
1. Ensuring accurate reflection of student learning
David Didau has argued that there must be a period of time between the new knowledge acquired and the formative assessment. Otherwise the assessment becomes a measure of student performance rather than student learning.
He argues that when students are shown a new method during a lesson, say expanding double brackets, any assessment of their ability to do that during the same lesson is a measure of memory and performance rather than learning and understanding.
If we consider learning to be a permanent change in students’ long-term memories, then it is difficult to argue that any assessment completed soon after a new method has been taught can accurately predict whether it has been successfully learnt.
As Wiliam and others have pointed out, the point of eliciting evidence of learning via formative techniques is to incrementally increase the probability that the learning that has taken place matches the initial learning intentions – the more you check and correct, the more likely this becomes. No formative assessment technique can definitively confirm that learning has occurred.
Despite this criticism, it is still important to know whether pupils can independently reproduce a new method during the lesson in which it has first been taught.
Even if we are only measuring performance at this stage in the learning process, being able to successfully perform a new skill is still a prerequisite to being able to do it at a future date.
If a student is not able to demonstrate understanding of a new topic during the lesson it is important that the teacher has that information and adjusts their teaching strategy accordingly.
Testing previously learnt material through a low stakes quiz at the start of a lesson is likely to be an accurate assessment of learning rather than performance, particularly if the material being tested was taught in the previous month or term.
Providing students with retrieval practice in this way will strengthen the connections in their long-term memory, activate prior knowledge, and allow teachers to know whether previously learnt material needs to be retaught.
2. Selecting effective questions to identify specific learning gaps
Another challenge associated with formative assessment is selecting the right questions to include in the assessment materials.
Poorly chosen questions can identify that a student has not fully understood a topic but will not be able to identify which specific part has been misunderstood.
It is much more effective to include diagnostic questions when creating formative assessments. Diagnostic questions are specifically designed to give a greater insight into students’ cognitive processes and produce answers that allow the teacher to know which specific part of the topic has not been understood.
In the example below, each incorrect answer will reveal the nature of students’ misunderstanding.
B is the correct answer. Each incorrect answer reveals the learner’s misconception :
- Answer A: triangle is isosceles.
- Answer C: 85° and x add to 180.°
- Answer D: 105° and x are corresponding angles.
You may also be interested in:
- What NEW KS1 Assessment Frameworks Mean For KS2 [Maths]
- Pupil Progress: Measuring The Impact Of The Affective Domain Across 1,750 Schools
- Primary School Grades Explained: Levels, Attainment, Achievement & Progress
- The Myth of Expected Progress in Primary Schools
- Embedding Formal Assessment by Dylan Wiliam and Siobhan Leahy
Summative assessments produce a measure of student attainment; they are usually presented in the form of a high stakes assessment. The results have little or no impact on subsequent teaching. Formative assessments produce a measure of attainment and are designed to identify students’ misconceptions. Teachers use the results of formative assessments to adapt their teaching and improve pupil progress.
Formative assessment allows teachers to quickly check their pupils’ understanding and identify how they should adapt their teaching to improve student attainment. Ongoing formative feedback also helps pupils to develop metacognitive skills which supports them to become self-regulated learners.
Use formative assessment to test prior knowledge to ensure you are testing learning rather than performance. Design your formative assessment questions so that each incorrect answer reveals students’ specific misunderstanding.
DO YOU HAVE STUDENTS WHO NEED MORE SUPPORT IN MATHS?
Every week Third Space Learning’s maths specialist tutors support thousands of students across hundreds of schools with weekly maths intervention programmes designed to plug gaps and boost progress.
Since 2013 these personalised one to one lessons have helped over 150,000 primary and secondary students become more confident, able mathematicians.
Learn about the diagnostic assessment or request a personalised quote for your school to speak to us about your school’s needs and how we can help.
Related articles

A Teacher’s Guide To Spaced Repetition And Creating An Effective Spaced Repetition Schedule

Retrieval Practice: A Foolproof Method To Improve Student Retention and Recall

A Practical Guide To Rosenshine’s Principles of Instruction: How To Apply Them to Maths Lessons

Cognitive Load Theory: A Practical Guide And Tips For Teachers
FREE Guide to Hands on Manipulatives
Download our free guide to manipulatives that you can use in the maths classroom.
Includes 15 of the best concrete resources every KS1 and KS2 classroom should have.
Privacy Overview
Formative Assessment and Improving Learning
- Reference work entry
- pp 1318–1320
- Cite this reference work entry

- Janet Looney 2
423 Accesses
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Durable hardcover edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
Allal, L., & Lopez, M. L. (2005). Formative assessment of learning: A review of publications in French. In OECD (Ed.), Formative assessment: Improving learning in secondary classrooms (pp. 241 – 265). Paris: OECD.
Google Scholar
Black, P., & Wiliam, D. (1998). Assessment and classroom learning. Assessment in Education: Principles, Policy and Practice, 5 , 7–74.
Bloom, B. S. (1968). Learning for mastery. Evaluation Comment, 1 , 1–12.
OECD. (2005). Formative assessment: Improving learning in secondary classrooms . Paris: OECD.
Sadler, R. (1989). Formative assessment and the design of instructional systems. Instructional Science, 18 , 119–144.
Scriven, M. (1967). The methodology of evaluation. AERA Monograph Series on Evaluation, 1 , 39–83.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Vital Insight, 14 Rue de l'Ecole Polytechnique, Paris, 75005, France
Janet Looney
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Janet Looney .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Faculty of Economics and Behavioral Sciences, Department of Education, University of Freiburg, 79085, Freiburg, Germany
Norbert M. Seel
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2012 Springer Science+Business Media, LLC
About this entry
Cite this entry.
Looney, J. (2012). Formative Assessment and Improving Learning. In: Seel, N.M. (eds) Encyclopedia of the Sciences of Learning. Springer, Boston, MA. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1428-6_1831
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-1-4419-1428-6_1831
Publisher Name : Springer, Boston, MA
Print ISBN : 978-1-4419-1427-9
Online ISBN : 978-1-4419-1428-6
eBook Packages : Humanities, Social Sciences and Law
Share this entry
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
You are using an outdated browser. Upgrade your browser today or install Google Chrome Frame to better experience this site.
- Assessment Basics
- Policy & Leadership
- Classroom Tips
- Teacher Voices
Teach. Learn. Grow.
Teach. learn. grow. the education blog.

What is formative assessment?

“Formative assessment” defined
As an organization, NWEA subscribes to the CCSSO revised definition of formative assessment : “Formative assessment is a planned, ongoing process used by all students and teachers during learning and teaching to elicit and use evidence of student learning to improve student understanding of intended disciplinary learning outcomes and support students to become self-directed learners .”
Let’s take a closer look at the key phrases in that definition:
- “Planned, ongoing process.” Formative assessment is a continuous, low- or no-stakes, responsive process comprised of practices, methods, and tools that are selected to support all students in reaching challenging learning goals. Teachers and students collaborate to use formative assessment in responsive ways that positively impact learners and learning. They partner to know and respond to strengths, interests, and needs.
- “All students and teachers during learning and teaching.” Formative assessment is a collaborative learning process happening “with” students, not “to” students .
- “Elicit and use evidence of student learning.” Formative assessment processes capture levels of knowledge and skill along the learning journey so teachers and students can make small, immediate, impactful decisions to support well-being, learning-goal achievement, and self-efficacy. Using formative assessment evidence is appropriate for making decisions during the practice phases of learning; formative assessment scores are not appropriate for calculating grades or for making placement decisions.
- “Support students to become self-directed learners.” Formative assessment includes students as active agents in the learning journey, which fuels learning and agency in learning environments and beyond. Engaging students in goal setting is a great way to do this.
What does formative assessment look like?
Little is required to start formative assessment processes because they can begin with a variety of methods and tools . Instead of specific programs, supplies, or resources, effective formative assessment processes involve partnering with students to incorporate the following five practices into cycles of responsive teaching and learning.
- Clarifying learning goals and success criteria within a broader progression of learning. Students should have context for what they’re learning: why they’re learning it, how it connects to previous lessons and their own interests, and what success looks like. Having goal clarity, purpose, and a path promotes student motivation and agency.
- Eliciting and analyzing evidence of student thinking. Whether it’s capturing ideas on a whiteboard, responding to an online survey, or giving a thumbs-up or down in response to a check for understanding, an effective formative assessment process centers on knowing learning goals, then gathering, interpreting, and responding to learning-goal evidence.
- Engaging in self-assessment and peer feedback. Formative assessment is more than providing feedback from teacher to student. As I explained in “The importance of student self-assessment,” having students reflect on their progress helps them become active participants in their learning. The process should also involve students collaborating with each other, asking questions, making observations, celebrating successes, and suggesting improvements in ways that support them in attaining challenging learning goals.
- Using actionable feedback. Once learning evidence is collected, teachers work with students to ensure that they have both the time and processes to apply feedback in ways that move learning forward.
- Responding by adjusting learning strategies or next instructional steps. This practice is the “why” of formative assessment. To make the process effective, we must collaborate with students to use evidence and insights to propel learners toward shared and personal short- and long-term goals.
Why formative assessment is so important
As my colleague Chase Nordengren noted in “The power of formative assessment when the only constant is change,” “[f]ormative assessment is [critical] for educators looking to unlock in-depth information on student learning. […] Using strategies that expose misconceptions, support higher-level thinking within a subject, and engage students in academic discourse, formative assessment provides the real-time feedback necessary to dynamically adjust instruction to meet learner needs as they emerge and change.”
In short, formative assessment helps us evaluate whether our plans and responsive “moves” are working, while there’s still time to do something about it. It celebrates that learning is an ongoing process, complete with stretches of success and periods of struggle, and it helps us remember that learning is not linear but, instead, an endeavor that rewards effort, persistence, and dedication. Best of all, it helps us collaborate with students as co-partners in the entire learning experience. Together we are a learning team, one that makes anything possible.
Ready for more?
There is no shortage of information and resources available on formative assessment. For easy-to -implement, research-based strategies, check out our formative assessment eBook, Making it work: How formative assessment can supercharge your practice , or the formative assessment archive here on Teach. Learn. Grow. Our professional learning team also offers five workshops on formative practice , which can engage you and your colleagues in deep dives designed and delivered by expert educators.
Recommended for you

3 tips for understanding when—and how—to use formative assessment

75 digital tools and apps teachers can use to support formative assessment in the classroom

The importance of student self-assessment

Build math confidence
Lots of kids dread math. You can help them love it. Get advice on how from our Teach. Learn. Grow. math experts in our latest ebook.

For policymakers
There’s a lot policymakers can do to support schools during COVID-19. We talked with experts Evan Stone and LaTanya Pattillo about what to focus on during SY21–22.
Read the post

The ABCs of reading
Effective literacy instruction must rely on the science of reading and best practices in balanced literacy.
STAY UPDATED
Sign up for our newsletter and get recent blog posts—and more—delivered right to your inbox.

STAY CURRENT by subscribing to our newsletter
You are now signed up to receive our newsletter containing the latest news, blogs, and resources from nwea..
Use Formative Assessments to Enhance Student Performance
Formative assessments: a valuable tool to support student achievement.
Formative assessments are a critical tool for teachers to monitor student progress, optimize their teaching methods, and enhance student learning.
Education leaders share strategies for measuring student learning throughout the year to inform instruction.

What is Formative Assessment?
The Council of Chief State School Officers defines formative assessment as “a planned, ongoing process used by all students and teachers during learning and teaching to elicit and use evidence of student learning to improve student understanding of intended disciplinary learning outcomes and support students to become self-directed learners.”
Performance assessments must be…


Planned and Ongoing
As the definition states, formative assessment is planned and ongoing . It involves using practices, methods, and tools that support all students in achieving challenging learning goals. This type of assessment is continuous, low-stakes, and responsive. Teachers and students collaborate to use the data from formative assessments to positively impact learning. They work together to identify and respond to strengths, interests, and needs.

A Collaborative Learning Process
Formative assessment is a collaborative learning process that happens “with” students, rather than “to” students. The process aims to make students active participants in their own learning, rather than passive recipients of information. Through this approach, teachers and students work together to develop a shared understanding of the students’ current learning status and what they need to do to move forward. This strategy encourages self-regulation and helps students adapt their learning strategies to meet their individual learning needs.

A Tool to Make Informed Decisions
Teachers and students can use formative assessment to know how well students understand the material they are learning and make decisions about additional instruction that may be needed during the practice phases of learning. Note that formative assessments are not intended to be used for calculating grades or for making placement decisions. Formative assessments are designed to provide insights into where students are at in their learning and to guide the teaching process as students continue their knowledge building.

Formative Assessment Examples
Examples of formative assessments include:
- Class discussions
- Self-assessments
- Performance-based assessments
- Peer assessments
The goal of formative assessments is to help teachers and students to identify areas of strength and areas where continued learning is needed. Teachers also use the data to adjust their teaching methods and ultimately improve learning outcomes.
“Formative assessment data can offer more than just a retrospective measure of student academic performance, rather it can be a powerful tool to help educators improve student learning and skills in real time.” ~ Doris Zahner, Ph.D., CAE Chief Academic Officer
Formative assessment benefits.
There are many ways formative assessments enhance student learning. Here are some of the chief benefits for educators and students:
Focused and Targeted Feedback
Formative assessments promote teacher-student communication, enabling individualized support for students.
Addresses Learning Gaps
Formative assessments help teachers identify and address student misconceptions and gaps in understanding.
Increased Student Engagement
Research shows that w hen formative assessments are used well, students become active participants in the learning process. This fosters learning, cultivates responsibility, and boosts intrinsic motivation.
Clear Learning Goals
Formative assessments measure student progress toward teacher-specified goals. Once students understand what they need to know or be able to do, formative assessments allow them to see how close they are to meeting those goals.
Self-Regulation
Studies show that formative assessments can boost self-regulation, which is crucial for lifelong learning. Self-regulated learning helps students identify their learning goals, manage their learning process, and evaluate their performance against goals.
Personalized Learning
Providing students with a personalized path for learning starts with an understanding of their strengths and areas for growth. Embedding formative assessments within lessons provides immediate feedback and enhances learning.
Rigorous Learning Environments
Teachers can use formative assessment data to determine student needs and create a more challenging learning environment that fosters student growth and success.
Five Formative Assessment Strategies
To get the most out of formative assessments, create a plan so you can implement them seamlessly and in a low-stakes way. Here are five tips to get started:
1. Define Clear Metrics and Goals Start by defining clear performance criteria and discuss these with students to ensure understanding.
2. Assess Early and Often Formative assessment requires frequent monitoring of student performance through current data. It is best to assess early and often to ensure optimal results.
3. Encourage Peer Discussions Teachers should encourage group discussions among students to gain insights into their concerns and define learning goals.
4. Encourage Student Self-Evaluation Asking students to evaluate their progress will help identify areas for improvement and can increase engagement in their learning. It will also save time and make the formative assessment more manageable.
5. Provide Comprehensive Feedback Feedback should be constructive and focused on helping students correct mistakes. This means providing specific advice and guidance on how to overcome the problem.
Build Higher-Order Skills with CAE’s Formative Assessments
Preparing all students for success is a complex task that requires a multifaceted approach. While content knowledge is essential, equally important are higher-order skills .
Higher-order skills are a set of personal attributes and abilities that allow individuals to thrive academically, professionally, and personally. These skills include being able to think critically, communicate effectively, collaborate with others, and solve problems. A large body of research confirms the need to teach students higher-order skills alongside traditional academic content to prepare them for future success. In response, school districts, higher education institutions, and even the Department of Education are shifting instructional and assessment approaches to be more competency based.
CAE’s Formative Assessments for K–12 and Higher Education

CCRA+ and CLA+ can be used as a formative assessment tool, and students may take them several times throughout the school year to give teachers more information about what students know and can do. The assessment results—along with other schoolwork and classroom observations—help teachers identify where students are flourishing and where they need more help.
CAE also offers actionable data reports that can be utilized for both formative and summative purposes. These reports are helpful in evaluating a student’s progress in developing higher-order skills at the start and/or end of a specific class or academic year. Additionally, they can be used to measure growth over multiple years.
Preview CAE’s Formative Assessments
CAE’s CCRA+ and CLA+ assessments evaluate students’ proficiency in higher-order skills. These performance-based assessments present real-world scenarios that require students to apply critical thinking, problem-solving, and written communication skills to recommend solutions. Take a look at these samples to get a better understanding of how these assessments work.

CAE’s Custom Formative Assessments
In addition to CCRA+ and CLA+, CAE provides a wide range of custom assessment services . From initial design and development to test delivery, scoring, and analyses, we provide innovative assessments that measure the constructs most important to students, educators, and institutions.
These assessments cover all subject areas, as well as non-content areas such as higher-order skills like critical thinking, problem solving, and written communication. Additionally, they provide insights into social-emotional competence, collaboration, creativity, and more.
CAE’s custom assessments focus on knowledge application and are available for formative, interim, and summative purposes, using various testing methods.
Learn more about CAE’s custom formative assessments and our Higher-Order Skills Solution. Schedule a time to chat with us!
Eberly Center
Teaching excellence & educational innovation, what is the difference between formative and summative assessment, formative assessment.
The goal of formative assessment is to monitor student learning to provide ongoing feedback that can be used by instructors to improve their teaching and by students to improve their learning. More specifically, formative assessments:
- help students identify their strengths and weaknesses and target areas that need work
- help faculty recognize where students are struggling and address problems immediately
Formative assessments are generally low stakes , which means that they have low or no point value. Examples of formative assessments include asking students to:
- draw a concept map in class to represent their understanding of a topic
- submit one or two sentences identifying the main point of a lecture
- turn in a research proposal for early feedback
Summative assessment
The goal of summative assessment is to evaluate student learning at the end of an instructional unit by comparing it against some standard or benchmark.
Summative assessments are often high stakes , which means that they have a high point value. Examples of summative assessments include:
- a midterm exam
- a final project
- a senior recital
Information from summative assessments can be used formatively when students or faculty use it to guide their efforts and activities in subsequent courses.
CONTACT US to talk with an Eberly colleague in person!
- Faculty Support
- Graduate Student Support
- Canvas @ Carnegie Mellon
- Quick Links
- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
How do You Use Social Media? Be entered to win a $50 gift card!
Formative, Summative, and More Types of Assessments in Education
All the best ways to evaluate learning before, during, and after it happens.

When you hear the word assessment, do you automatically think “tests”? While it’s true that tests are one kind of assessment, they’re not the only way teachers evaluate student progress. Learn more about the types of assessments used in education, and find out how and when to use them.
Diagnostic Assessments
Formative assessments, summative assessments.
- Criterion-Referenced, Ipsative, and Normative Assessments
What is assessment?
In simplest terms, assessment means gathering data to help understand progress and effectiveness. In education, we gather data about student learning in variety of ways, then use it to assess both their progress and the effectiveness of our teaching programs. This helps educators know what’s working well and where they need to make changes.
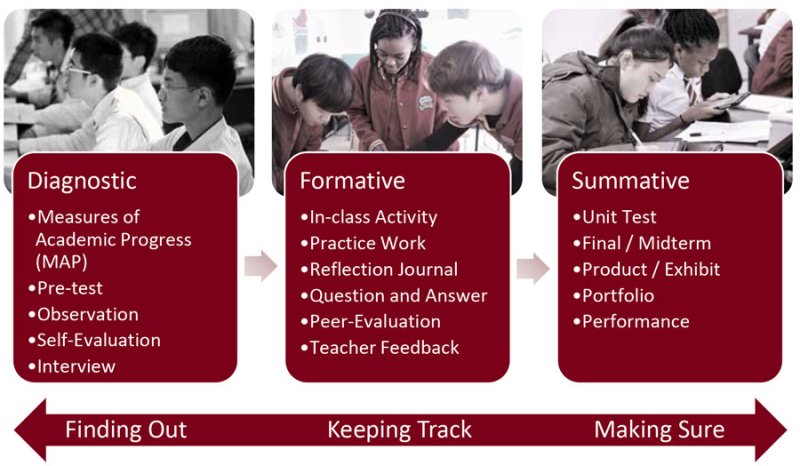
There are three broad types of assessments: diagnostic, formative, and summative. These take place throughout the learning process, helping students and teachers gauge learning. Within those three broad categories, you’ll find other types of assessment, such as ipsative, norm-referenced, and criterion-referenced.
What’s the purpose of assessment in education?
In education, we can group assessments under three main purposes:
- Of learning
- For learning
- As learning
Assessment of learning is student-based and one of the most familiar, encompassing tests, reports, essays, and other ways of determining what students have learned. These are usually summative assessments, and they are used to gauge progress for individuals and groups so educators can determine who has mastered the material and who needs more assistance.
When we talk about assessment for learning, we’re referring to the constant evaluations teachers perform as they teach. These quick assessments—such as in-class discussions or quick pop quizzes—give educators the chance to see if their teaching strategies are working. This allows them to make adjustments in action, tailoring their lessons and activities to student needs. Assessment for learning usually includes the formative and diagnostic types.
Assessment can also be a part of the learning process itself. When students use self-evaluations, flash cards, or rubrics, they’re using assessments to help them learn.
Let’s take a closer look at the various types of assessments used in education.

Diagnostic assessments are used before learning to determine what students already do and do not know. This often refers to pre-tests and other activities students attempt at the beginning of a unit.
How To Use Diagnostic Assessments
When giving diagnostic assessments, it’s important to remind students these won’t affect their overall grade. Instead, it’s a way for them to find out what they’ll be learning in an upcoming lesson or unit. It can also help them understand their own strengths and weaknesses, so they can ask for help when they need it.
Teachers can use results to understand what students already know and adapt their lesson plans accordingly. There’s no point in over-teaching a concept students have already mastered. On the other hand, a diagnostic assessment can also help highlight expected pre-knowledge that may be missing.
For instance, a teacher might assume students already know certain vocabulary words that are important for an upcoming lesson. If the diagnostic assessment indicates differently, the teacher knows they’ll need to take a step back and do a little pre-teaching before getting to their actual lesson plans.
Examples of Diagnostic Assessments
- Pre-test: This includes the same questions (or types of questions) that will appear on a final test, and it’s an excellent way to compare results.
- Blind Kahoot: Teachers and kids already love using Kahoot for test review, but it’s also the perfect way to introduce a new topic. Learn how Blind Kahoots work here.
- Survey or questionnaire: Ask students to rate their knowledge on a topic with a series of low-stakes questions.
- Checklist: Create a list of skills and knowledge students will build throughout a unit, and have them start by checking off any they already feel they’ve mastered. Revisit the list frequently as part of formative assessment.

Formative assessments take place during instruction. They’re used throughout the learning process and help teachers make on-the-go adjustments to instruction and activities as needed. These assessments aren’t used in calculating student grades, but they are planned as part of a lesson or activity. Learn much more about formative assessments here.
How To Use Formative Assessments
As you’re building a lesson plan, be sure to include formative assessments at logical points. These types of assessments might be used at the end of a class period, after finishing a hands-on activity, or once you’re through with a unit section or learning objective.
Once you have the results, use that feedback to determine student progress, both overall and as individuals. If the majority of a class is struggling with a specific concept, you might need to find different ways to teach it. Or you might discover that one student is especially falling behind and arrange to offer extra assistance to help them out.
While kids may grumble, standard homework review assignments can actually be a pretty valuable type of formative assessment . They give kids a chance to practice, while teachers can evaluate their progress by checking the answers. Just remember that homework review assignments are only one type of formative assessment, and not all kids have access to a safe and dedicated learning space outside of school.
Examples of Formative Assessments
- Exit tickets : At the end of a lesson or class, pose a question for students to answer before they leave. They can answer using a sticky note, online form, or digital tool.
- Kahoot quizzes : Kids enjoy the gamified fun, while teachers appreciate the ability to analyze the data later to see which topics students understand well and which need more time.
- Flip (formerly Flipgrid): We love Flip for helping teachers connect with students who hate speaking up in class. This innovative (and free!) tech tool lets students post selfie videos in response to teacher prompts. Kids can view each other’s videos, commenting and continuing the conversation in a low-key way.
- Self-evaluation: Encourage students to use formative assessments to gauge their own progress too. If they struggle with review questions or example problems, they know they’ll need to spend more time studying. This way, they’re not surprised when they don’t do well on a more formal test.
Find a big list of 25 creative and effective formative assessment options here.

Summative assessments are used at the end of a unit or lesson to determine what students have learned. By comparing diagnostic and summative assessments, teachers and learners can get a clearer picture of how much progress they’ve made. Summative assessments are often tests or exams but also include options like essays, projects, and presentations.
How To Use Summative Assessments
The goal of a summative assessment is to find out what students have learned and if their learning matches the goals for a unit or activity. Ensure you match your test questions or assessment activities with specific learning objectives to make the best use of summative assessments.
When possible, use an array of summative assessment options to give all types of learners a chance to demonstrate their knowledge. For instance, some students suffer from severe test anxiety but may still have mastered the skills and concepts and just need another way to show their achievement. Consider ditching the test paper and having a conversation with the student about the topic instead, covering the same basic objectives but without the high-pressure test environment.
Summative assessments are often used for grades, but they’re really about so much more. Encourage students to revisit their tests and exams, finding the right answers to any they originally missed. Think about allowing retakes for those who show dedication to improving on their learning. Drive home the idea that learning is about more than just a grade on a report card.
Examples of Summative Assessments
- Traditional tests: These might include multiple-choice, matching, and short-answer questions.
- Essays and research papers: This is another traditional form of summative assessment, typically involving drafts (which are really formative assessments in disguise) and edits before a final copy.
- Presentations: From oral book reports to persuasive speeches and beyond, presentations are another time-honored form of summative assessment.
Find 25 of our favorite alternative assessments here.
More Types of Assessments
Now that you know the three basic types of assessments, let’s take a look at some of the more specific and advanced terms you’re likely to hear in professional development books and sessions. These assessments may fit into some or all of the broader categories, depending on how they’re used. Here’s what teachers need to know.
Criterion-Referenced Assessments
In this common type of assessment, a student’s knowledge is compared to a standard learning objective. Most summative assessments are designed to measure student mastery of specific learning objectives. The important thing to remember about this type of assessment is that it only compares a student to the expected learning objectives themselves, not to other students.
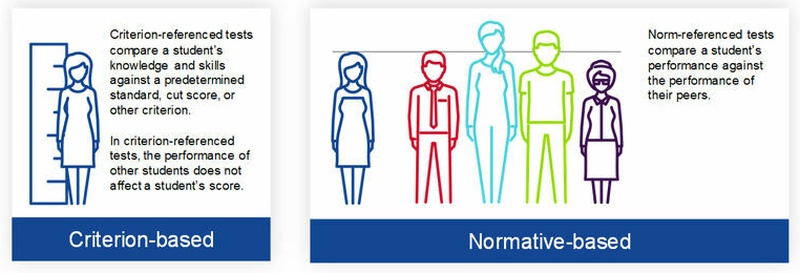
Many standardized tests are criterion-referenced assessments. A governing board determines the learning objectives for a specific group of students. Then, all students take a standardized test to see if they’ve achieved those objectives.
Find out more about criterion-referenced assessments here.
Norm-Referenced Assessments
These types of assessments do compare student achievement with that of their peers. Students receive a ranking based on their score and potentially on other factors as well. Norm-referenced assessments usually rank on a bell curve, establishing an “average” as well as high performers and low performers.
These assessments can be used as screening for those at risk for poor performance (such as those with learning disabilities) or to identify high-level learners who would thrive on additional challenges. They may also help rank students for college entrance or scholarships, or determine whether a student is ready for a new experience like preschool.
Learn more about norm-referenced assessments here.
Ipsative Assessments
In education, ipsative assessments compare a learner’s present performance to their own past performance, to chart achievement over time. Many educators consider ipsative assessment to be the most important of all , since it helps students and parents truly understand what they’ve accomplished—and sometimes, what they haven’t. It’s all about measuring personal growth.
Comparing the results of pre-tests with final exams is one type of ipsative assessment. Some schools use curriculum-based measurement to track ipsative performance. Kids take regular quick assessments (often weekly) to show their current skill/knowledge level in reading, writing, math, and other basics. Their results are charted, showing their progress over time.
Learn more about ipsative assessment in education here.
Have more questions about the best types of assessments to use with your students? Come ask for advice in the We Are Teachers HELPLINE group on Facebook.
Plus, check out creative ways to check for understanding ..

You Might Also Like

What Is Formative Assessment and How Should Teachers Use It?
Check student progress as they learn, and adapt to their needs. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256
- Terms and Conditions

Professional Learning
Formative assessment modules, pre-assessment , self-assessment, peer feedback, feedback breaks, quick links.
Already know your way around? Head straight to our resources for:
PRE-ASSESSMENT
SELF-ASSESSMENT
PEER FEEDBACK
FEEDBACK BREAKS
About this Resource
Would you like to make a contribution to this content? Contribute here . If you use these materials in your teaching, please provide feedback about them here .

19 Mantua Road Mt. Royal, NJ 08061 Phone: (856) 284-3700 Fax: (856) 423-3420 Email: [email protected] Professionally managed by Talley Management Group
National Council on Measurement in Education
14 Examples of Formative Assessment [+FAQs]

Traditional student assessment typically comes in the form of a test, pop quiz, or more thorough final exam. But as many teachers will tell you, these rarely tell the whole story or accurately determine just how well a student has learned a concept or lesson.
That’s why many teachers are utilizing formative assessments. While formative assessment is not necessarily a new tool, it is becoming increasingly popular amongst K-12 educators across all subject levels.
Curious? Read on to learn more about types of formative assessment and where you can access additional resources to help you incorporate this new evaluation style into your classroom.
What is Formative Assessment?
Online education glossary EdGlossary defines formative assessment as “a wide variety of methods that teachers use to conduct in-process evaluations of student comprehension, learning needs, and academic progress during a lesson, unit, or course.” They continue, “formative assessments help teachers identify concepts that students are struggling to understand, skills they are having difficulty acquiring, or learning standards they have not yet achieved so that adjustments can be made to lessons, instructional techniques, and academic support.”
The primary reason educators utilize formative assessment, and its primary goal, is to measure a student’s understanding while instruction is happening. Formative assessments allow teachers to collect lots of information about a student’s comprehension while they’re learning, which in turn allows them to make adjustments and improvements in the moment. And, the results speak for themselves — formative assessment has been proven to be highly effective in raising the level of student attainment, increasing equity of student outcomes, and improving students’ ability to learn, according to a study from the Organization for Economic Co-operation and Development (OECD).
On the flipside of the assessment coin is summative assessments, which are what we typically use to evaluate student learning. Summative assessments are used after a specific instructional period, such as at the end of a unit, course, semester, or even school year. As learning and formative assessment expert Paul Black puts it, “when the cook tastes the soup, that’s formative assessment. When a customer tastes the soup, that’s summative assessment.”
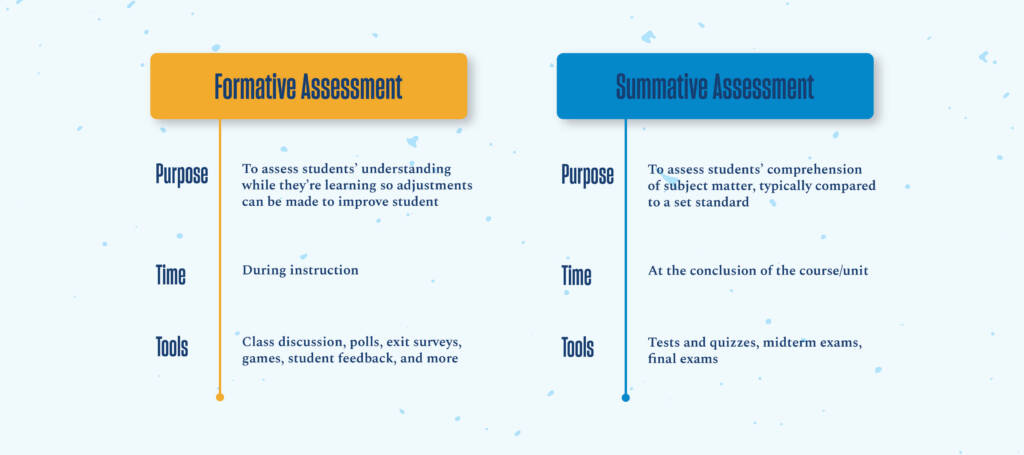
14 Examples of Formative Assessment Tools & Strategies
There are many types of formative assessment tools and strategies available to teachers, and it’s even possible to come up with your own. However, here are some of the most popular and useful formative assessments being used today.
- Round Robin Charts
Students break out into small groups and are given a blank chart and writing utensils. In these groups, everyone answers an open-ended question about the current lesson. Beyond the question, students can also add any relevant knowledge they have about the topic to their chart. These charts then rotate from group to group, with each group adding their input. Once everyone has written on every chart, the class regroups and discusses the responses.
- Strategic Questioning
This formative assessment style is quite flexible and can be used in many different settings. You can ask individuals, groups, or the whole class high-level, open-ended questions that start with “why” or “how.” These questions have a two-fold purpose — to gauge how well students are grasping the lesson at hand and to spark a discussion about the topic.
- Three-Way Summaries
These written summaries of a lesson or subject ask students to complete three separate write-ups of varying lengths: short (10-15 words), medium (30-50 words), and long (75-100). These different lengths test students’ ability to condense everything they’ve learned into a concise statement, or elaborate with more detail. This will demonstrate to you, the teacher, just how much they have learned, and it will also identify any learning gaps.
- Think-Pair-Share
Think-pair-share asks students to write down their answers to a question posed by the teacher. When they’re done, they break off into pairs and share their answers and discuss. You can then move around the room, dropping in on discussions and getting an idea of how well students are understanding.
- 3-2-1 Countdown
This formative assessment tool can be written or oral and asks students to respond to three very simple prompts: Name three things you didn’t know before, name two things that surprised you about this topic, and name one you want to start doing with what you’ve learned. The exact questions are flexible and can be tailored to whatever unit or lesson you are teaching.
- Classroom Polls
This is a great participation tool to use mid-lesson. At any point, pose a poll question to students and ask them to respond by raising their hand. If you have the capability, you can also use online polling platforms and let students submit their answers on their Chromebooks, tablets, or other devices.
- Exit/Admission Tickets
Exit and admission tickets are quick written exercises that assess a student’s comprehension of a single day’s lesson. As the name suggests, exit tickets are short written summaries of what students learned in class that day, while admission tickets can be performed as short homework assignments that are handed in as students arrive to class.
- One-Minute Papers
This quick, formative assessment tool is most useful at the end of the day to get a complete picture of the classes’ learning that day. Put one minute on the clock and pose a question to students about the primary subject for the day. Typical questions might be:
- What was the main point?
- What questions do you still have?
- What was the most surprising thing you learned?
- What was the most confusing aspect and why?
- Creative Extension Projects
These types of assessments are likely already part of your evaluation strategy and include projects like posters and collage, skit performances, dioramas, keynote presentations, and more. Formative assessments like these allow students to use more creative parts of their skillset to demonstrate their understanding and comprehension and can be an opportunity for individual or group work.
Dipsticks — named after the quick and easy tool we use to check our car’s oil levels — refer to a number of fast, formative assessment tools. These are most effective immediately after giving students feedback and allowing them to practice said skills. Many of the assessments on this list fall into the dipstick categories, but additional options include writing a letter explaining the concepts covered or drawing a sketch to visually represent the topic.
- Quiz-Like Games and Polls
A majority of students enjoy games of some kind, and incorporating games that test a student’s recall and subject aptitude are a great way to make formative assessment more fun. These could be Jeopardy-like games that you can tailor around a specific topic, or even an online platform that leverages your own lessons. But no matter what game you choose, these are often a big hit with students.
- Interview-Based Assessments
Interview-based assessments are a great way to get first-hand insight into student comprehension of a subject. You can break out into one-on-one sessions with students, or allow them to conduct interviews in small groups. These should be quick, casual conversations that go over the biggest takeaways from your lesson. If you want to provide structure to student conversations, let them try the TAG feedback method — tell your peer something they did well, ask a thoughtful question, and give a positive suggestion.
- Self Assessment
Allow students to take the rubric you use to perform a self assessment of their knowledge or understanding of a topic. Not only will it allow them to reflect on their own work, but it will also very clearly demonstrate the gaps they need filled in. Self assessments should also allow students to highlight where they feel their strengths are so the feedback isn’t entirely negative.
- Participation Cards
Participation cards are a great tool you can use on-the-fly in the middle of a lesson to get a quick read on the entire classes’ level of understanding. Give each student three participation cards — “I agree,” “I disagree,” and “I don’t know how to respond” — and pose questions that they can then respond to with those cards. This will give you a quick gauge of what concepts need more coverage.
5 REASONS WHY CONTINUING EDUCATION MATTERS FOR EDUCATORS
The education industry is always changing and evolving, perhaps now more than ever. Learn how you can be prepared by downloading our eBook.

List of Formative Assessment Resources
There are many, many online formative assessment resources available to teachers. Here are just a few of the most widely-used and highly recommended formative assessment sites available.
- Arizona State Dept of Education
FAQs About Formative Assessment
The following frequently asked questions were sourced from the Association for Supervision and Curriculum Development (ASCD), a leading education professional organization of more than 100,000 superintendents, principals, teachers, and advocates.
Is formative assessment something new?
No and yes. The concept of measuring a student’s comprehension during lessons has existed for centuries. However, the concept of formative assessment as we understand it didn’t appear until approximately 40 years ago, and has progressively expanded into what it is today.
What makes something a formative assessment?
ASCD characterized formative assessment as “a way for teachers and students to gather evidence of learning, engage students in assessment, and use data to improve teaching and learning.” Their definition continues, “when you use an assessment instrument— a test, a quiz, an essay, or any other kind of classroom activity—analytically and diagnostically to measure the process of learning and then, in turn, to inform yourself or your students of progress and guide further learning, you are engaging in formative assessment. If you were to use the same instrument for the sole purpose of gathering data to report to a district or state or to determine a final grade, you would be engaging in summative assessment.”
Does formative assessment work in all content areas?
Absolutely, and it works across all grade levels. Nearly any content area — language arts, math, science, humanities, and even the arts or physical education — can utilize formative assessment in a positive way.
How can formative assessment support the curriculum?
Formative assessment supports curricula by providing real-time feedback on students’ knowledge levels and comprehension of the subject at hand. When teachers regularly utilize formative assessment tools, they can find gaps in student learning and customize lessons to fill those gaps. After term is over, teachers can use this feedback to reshape their curricula.
How can formative assessment be used to establish instructional priorities?
Because formative assessment supports curriculum development and updates, it thereby influences instructional priorities. Through student feedback and formative assessment, teachers are able to gather data about which instructional methods are most (and least) successful. This “data-driven” instruction should yield more positive learning outcomes for students.
Can formative assessment close achievement gaps?
Formative assessment is ideal because it identifies gaps in student knowledge while they’re learning. This allows teachers to make adjustments to close these gaps and help students more successfully master a new skill or topic.
How can I help my students understand formative assessment?
Formative assessment should be framed as a supportive learning tool; it’s a very different tactic than summative assessment strategies. To help students understand this new evaluation style, make sure you utilize it from the first day in the classroom. Introduce a small number of strategies and use them repeatedly so students become familiar with them. Eventually, these formative assessments will become second nature to teachers and students.
Before you tackle formative assessment, or any new teaching strategy for that matter, consider taking a continuing education course. At the University of San Diego School of Professional and Continuing Education, we offer over 500 courses for educators that can be completed entirely online, and many at your own pace. So no matter what your interests are, you can surely find a course — or even a certificate — that suits your needs.
Be Sure To Share This Article
- Share on Twitter
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Your Salary
Browse over 500+ educator courses and numerous certificates to enhance your curriculum and earn credit toward salary advancement.
Related Posts

What Teachers Should Know About Integrating Formative Tests With Instruction

- Share article
Teachers need more support to move testing from a “necessary evil” to a classroom tool, experts say.
While summative tests—like unit quizzes or annual state assessments—are used for evaluation and accountability, research shows formative assessments—like puzzles, projects, and class error analyses—can help teachers and students identify misunderstandings and reflect on students’ progress as they’re learning.
While most teachers use at least some formative testing in daily classroom practice, experts at the American Educational Research Association conference here last week argued they need more support to integrate daily assessments with overall classroom instruction.

“We need to think about assessment more holistically,” said E. Caroline Wylie, a senior associate at the National Center for the Improvement of Educational Assessment and co-author of the National Academy of Education’s new report on assessment released last week. “Certainly we’ve got to be sharing learning goals for students, assessment, and learning in ways that are recognizable.”
For example, in one study, Dustin Van Orman, a STEM education research associate at Western Washington University, asked a national sample of more than 100 elementary student-teachers who participated in simulations of English, science, and math classes. The teachers were asked how much experience they had in using formative assessment, and then were asked to use information about students in the simulated classes to plan tasks and other formative assessments over three class periods.
About 1 in 5 of the preservice teachers had little to no prior training in formative assessment, and a third had experience only with formal testing, rather than informal assessment through tasks and activities. One preservice teacher reported that her mentor-teacher downplayed the usefulness of classroom assessment and “only likes to do assessment if it’s like something she kind of has to do.”
While a majority of preservice teachers in the study could identify tasks students should be able to do as they learn particular academic content, Van Orman and his colleagues found many student-teachers did not set learning goals with their students or set criteria for tests and tasks based on learning goals. Rather, tests and tasks often could be disconnected from overarching instructional goals. Teachers less experienced in assessment also tended to give more static feedback—praising or correcting students—but not providing information on which students were expected to act.
How to use formative tests effectively
“Assessment shouldn’t be dropped in from the sky, disconnected from student experience,” said Wylie, who was not part of the preservice teacher study. It’s also important for teachers to understand their own and students’ cultural backgrounds when designing assessments, she noted.
Van Orman and Erin Riley-Lepo, a visiting assistant professor at the College of New Jersey, have been working with researchers, teachers, and principals to develop a framework for teachers’ own assessment literacy.
To effectively use formative testing in class, they recommended:
- Teachers and students develop a shared understanding of the goal of tests.
- Assessments focus on what students are learning in ways that the students can recognize, so that they can understand their own progress.
- Students should engage in self- and peer-assessments, to help take ownership of their learning.
- Assessments should make students’ thinking visible to both the teacher and students, to correct misconceptions and build on students’ strengths.
- Assessments should directly inform teachers’ instruction.
Building better classroom assessment practice also requires support from principals and district leaders.
“We talk about teachers, but the reality is, teachers are embedded in schools and districts with particular approaches and constraints on their assessment that may or may not be—and often is not—supportive of active and focused assessments,” Wylie said.
For example, Wylie noted that in the last four months, she and her research team repeatedly had to cancel professional development for teachers because the principals could not secure enough substitute teachers to cover their classes.
Sign Up for EdWeek Update
Edweek top school jobs.

Sign Up & Sign In

- (855) 776-7763
Training Maker
Collaborate
Webinar Ninja
ProProfs.com
Knowledge Base
Survey Maker
All Products
- Sign Up Free
Do you want a free Quiz Software?
We have the #1 AI-powered Quiz Maker Software for complete learning & assessment.
Guide to Diagnostic Assessments in Education: Definition, Types & Examples

Matthew Tang
eLearning & Instructional Design Expert
Review Board Member
Matthew Tang is a highly skilled eLearning consultant with over two decades of experience in delivering exceptional learning products. He has taught students in public schools and online, led online ... Read more
Matthew Tang is a highly skilled eLearning consultant with over two decades of experience in delivering exceptional learning products. He has taught students in public schools and online, led online education for a Fortune 50 company, partnered with university researchers to pioneer new learning technologies, and delivered expert learning solutions to clients of all sizes. With a genuine passion for helping individuals succeed and reach their academic or business goals, Matthew continually improves and innovates educational technology solutions, making him a trusted authority in eLearning. Read less
Author & Editor at ProProfs
Vipul is a seasoned e-learning expert, specializing in crafting impactful learning experiences and designing employee training assessments. His passion lies in writing about tools that enhance online learning and training outcomes.

Have you ever wondered why some students excel in new topics almost immediately while others seem to struggle? The secret might not lie in the content being taught but in understanding the starting point of each learner.
This is where the power of diagnostic assessment comes into play.
Think of it as the GPS for the educational journey; it helps you pinpoint exactly where your students are so that you can guide them to where they need to be.
Join us as we explore the what, why, and how of diagnostic assessments, unraveling their potential to transform teaching and learning experiences.
What Is Diagnostic Assessment?
Diagnostic assessment serves as a crucial tool in education, utilized before embarking on new lessons or units. It captures a clear picture of students’ existing knowledge and areas of uncertainty regarding a subject.
This process goes beyond mere grading to deeply understanding students’ initial knowledge levels. With this valuable insight, educators are empowered to tailor their teaching strategies to specifically address the unique needs and knowledge gaps of their students, thereby significantly enhancing the effectiveness of learning from the very beginning.
Such assessments often take the form of pre-tests, skills checklists, and introductory surveys, each aimed at crafting a customized learning journey for every student.
The Purpose of Educational Diagnostic Assessment
The main goal of educational diagnostic assessment is to guide educators in creating a personalized learning experience. By identifying students’ knowledge base and uncovering any learning gaps at the outset, teachers can tailor their instruction to address these areas effectively.
This ensures that teaching strategies are not only targeted but also inclusive, catering to the diverse learning needs within a classroom.
Ultimately, diagnostic assessments aim to enhance student engagement, improve learning outcomes, and make the educational process more efficient by focusing on areas that require the most attention.
Types of Diagnostic Assessment
Diagnostic assessments come in various forms, each designed to uncover specific learning needs and strengths.
- Formal Diagnostic Assessments: These are structured tests or evaluations designed to systematically measure students’ skills, knowledge, or competencies in a specific area.
They often come in the form of standardized tests with predetermined criteria and are used to identify learning needs, strengths, and areas for improvement.
- Informal Diagnostic Assessments: Unlike formal assessments, these are less structured and can be adapted by educators to fit the context of their classroom. Informal assessments include observations, discussions, and ungraded quizzes.
Informal assessments provide immediate feedback and insights into students’ learning processes, misconceptions, and individual learning needs.
- Peer Assessment: In peer assessments, students evaluate each other’s work or performance. This type can help students develop critical thinking and self-reflection skills, and it offers insights into how students understand and apply concepts in relation to their peers.
- Self-Assessment: This type involves students assessing their own understanding and skills. Through self-reflection activities such as surveys, journals, and checklists, students identify their own learning preferences, strengths, and areas that require more attention.
Examples of Diagnostic Assessments
Using a diverse set of diagnostic tools allows educators to pinpoint exactly where each student stands, offering a clear roadmap for personalized learning.
- Pre-Tests: These are administered before introducing new content to gauge the students’ prior knowledge and readiness. They enable educators to tailor their lessons to address the learning needs of their class effectively.
- Skills Checklists: Teachers use these to systematically assess and document each student’s proficiency in specific skills. This method helps in identifying areas where individual students or the class may need additional support or advanced challenges.
- Concept Maps: By creating visual representations of how concepts are related, students demonstrate their understanding and identify misconceptions. Educators can use these maps to adjust instruction and clarify misunderstandings.
- Introductory Surveys: These questionnaires gather insights into students’ interests and previous exposure to the topic, allowing teachers to make the curriculum more relevant and engaging. They can also highlight collective areas of interest or concern.
- KWL Charts: Students list what they Know, what they Want to find out, and what they Learned about a topic, promoting active engagement. This tool guides educators in focusing their teaching on filling knowledge gaps and expanding on students’ interests.
- Self-Assessment Forms: Students evaluate their own learning, identifying areas of strength and those needing improvement. This encourages self-reflection and responsibility for their learning journey.
- Peer Reviews: Students assess their peers’ work, providing feedback that can offer new perspectives and insights. This process encourages critical thinking and helps students learn from each other.
- Diagnostic Quizzes: Short quizzes assess students’ grasp of specific concepts, providing a quick check on understanding. Results from these quizzes inform teachers about topics that may require more detailed instruction or review.
Watch: How to Create an Online Quiz in Under 5 Mins
Benefits of Diagnostic Assessments in Education
Diagnostic assessments serve as a cornerstone in modern education, empowering teachers to tailor their instruction to meet the diverse needs and abilities of their students. These tools offer a multi-faceted approach to enhancing the learning experience by offering these benefits:
- Tailored Instruction: Utilizing diagnostic assessments, such as pre-tests, enables educators to understand the varying knowledge levels within a subject, fostering an environment where teaching methods are customized to each student’s needs.
- Early Intervention: Early detection of learning gaps through diagnostics allows for precise interventions. This targeted support ensures foundational concepts are mastered, setting the stage for more complex learning.
- Enhanced Engagement: Through surveys and initial assessments, teachers can tap into students’ interests, making lessons more engaging and relevant. This approach not only boosts motivation but also deepens students’ connection to the subject matter.
- Immediate Feedback: The use of exit tickets and similar tools provides educators with instant insights into student understanding, allowing for agile adjustments to teaching strategies to better address classroom needs.
- Inclusive Learning: Diagnostic assessments acknowledge and adapt to the diverse ways students learn, ensuring instructional methods are accessible and resonate with every learner, thus promoting a more inclusive classroom environment.
Incorporating diagnostic assessments into teaching practices not only enriches the educational journey for students but also elevates the teaching experience, creating a dynamic and responsive learning environment.
How to Create a Diagnostic Assessment Quiz
Here’s how to create a diagnostic assessment quiz with ProProfs Quiz Maker in five quick and easy steps:
Step 1: Click “Create a Quiz” on your dashboard.
Step 2: Pick a ready-to-use quiz, create a quiz with ProProfs AI, or build it from scratc
Step 3: Add/edit the quiz title, description & cover image.
Step 4: Add/edit questions.
Utilize a mix of question types to probe different areas of knowledge and skills, ensuring you cover a broad spectrum of the subject matter.
ProProfs offers various question types, such as multiple-choice, fill-in-the-blanks, drag & drop, hotspot, audio/video response, and more, allowing for a comprehensive evaluation of students’ understanding.
Watch: 15+ Question Types for Online Learning & Assessment
You can add new questions by:
- importing them from the quiz library with over a million ready-to-use questions
- generating them using ProProfs AI .
- creating them scratch
You can add images, videos, audio clips, and docs to your quiz.
You can also provide answer explanations every time a quiz taker answers a question. Such instant feedback not only aids in learning but also helps students self-identify areas they need to work on.
Step 5: Configure settings.
You can configure various security and anti-cheating settings, such as:
- Making your quiz private and password-protected
- Randomizing the order of questions and/or answer options
- Creating a question bank and using it to present a randomly selected set of questions to each quiz taker
- Proctoring the assessment via screen share, webcam, and microphone
- Disabling tab switching, printing, copying, downloading, and repeat attempts
Watch: How to Customize & Configure Your Quiz Settings
You can also customize the quiz theme by changing the background, colors, fonts, button text, and more. There’s also an option to change the interface language to the quiz taker’s native tongue.
That’s it. Your diagnostic assessment quiz is ready.
Analyzing the Results
Upon completion, ProProfs Quiz Maker offers detailed analytics that give you a clear picture of class-wide and individual student performance. This data is invaluable for adjusting your teaching strategy to meet the students where they are.
Use the diagnostic data to fine-tune lesson plans, ensuring that you address common misconceptions and reinforce areas where students are struggling.
Maximize Learning Impact With Diagnostic Assessments
In conclusion, the strategic implementation of diagnostic assessments, particularly through tools like ProProfs Quiz Maker, empowers educators to precisely map out students’ knowledge and areas for growth at the course outset.
This process ensures that instruction is directly aligned with student needs, optimizing learning outcomes.
With ProProfs Quiz Maker, educators can craft engaging, informative assessments that pave the way for customized learning experiences.
Take the step towards enriched education by signing up for a free trial or requesting a demo of ProProfs Quiz Maker today.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is an example of a diagnostic assessment in teaching?
An example of a diagnostic assessment in teaching is a pre-test given before starting a new unit to gauge students’ prior knowledge and identify areas that need focus.
What are the disadvantages of diagnostic assessment?
Disadvantages of diagnostic assessment include the potential for increased anxiety among students, the time required for administration and analysis, and possibly not reflecting all students’ abilities accurately due to its typically one-time nature.
What is the difference between formative and diagnostic assessment?
The difference between formative and diagnostic assessments lies in their purpose and timing. Diagnostic assessments are used at the beginning to understand students’ existing knowledge and skills, while formative assessments are ongoing, supporting learning by providing continuous feedback throughout the instructional process.
Do you want free Quiz Software?
We have the #1 Online Quiz Maker Software for complete learning & assessment
About the author
Vipul bhagia.
Vipul Bhagia is an e-learning expert and content creator, specializing in instructional design. He excels in crafting compelling e-learning modules and designing effective employee training assessments. He is passionate about leveraging digital solutions to transform work culture and boost productivity. Vipul enjoys exploring emerging tech innovations and sharing his insights with fellow industry professionals.
Popular Posts in This Category
8 Best Fun Quiz Maker Software in 2024: A Definitive List

How to Create a Quiz Using Hotspot Questions

How to Create a Video Quiz for Business or Education

How to Use Quizzes for Last-Minute Revision

How to Use Online Quizzes for Your Marketing Strategy

Leadership Assessment Guide for Succession Planning, Hiring & Training

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Formative assessment refers to a wide variety of methods that teachers use to conduct in-process evaluations of student comprehension, learning needs, and academic progress during a lesson, unit, or course. Formative assessments help teachers identify concepts that students are struggling to understand, skills they are having difficulty acquiring, or learning standards they have not yet achieved so that adjustments can be made to lessons, instructional techniques, and academic support.
Formative assessment is a type of assessment that occurs during the learning process, focuses on improvement and is often informal and low-stakes. It helps instructors and students adjust instruction, assess knowledge, prevent overconfidence and enhance learning.
Formative assessment is a planned, ongoing process of eliciting and using evidence of student learning to improve student understanding and support self-directed learning. Learn how to implement formative assessment in responsive teaching and learning cycles with five key practices and the benefits of human-centered formative assessment.
Formative assessment is a low-stakes, planned, and ongoing way to check student progress and adjust teaching. Learn what it is, how it differs from other assessments, and how to use it effectively in the classroom.
Learn how to continuously evaluate your teaching and improve your effectiveness using formative assessment approaches. Find out the key differences between formative and summative assessment, and explore various strategies and resources for assessing your teaching.
Formative assessment, formative evaluation, formative feedback, or assessment for learning, including diagnostic testing, is a range of formal and informal assessment procedures conducted by teachers during the learning process in order to modify teaching and learning activities to improve student attainment.The goal of a formative assessment is to monitor student learning to provide ongoing ...
A formative assessment is a teaching practice—a question, an activity, or an assignment—meant to gain information about student learning. It's formative in that it is intentionally done for the purpose of planning or adjusting future instruction and activities. Like we consider our formative years when we draw conclusions about ourselves, a ...
Formative assessment is a cyclical process that involves interactions among teachers and students, feedback, and student learning. The article traces the evolution of formative assessment from a focus on formative evaluation to formative assessment or assessment for learning, and its role in improving teaching and learning. It also covers the theories, standards, and reports that support the concept and practice of formative assessment.
Formative assessments are assessments implemented during the course of instruction, while learning is in progress. Whereas summative assessments evaluate what students have learned by the end of a period of instruction, formative assessments are typically designed for the purpose of providing feedback on student learning that is immediate, continuous, specific, and action-oriented (Suskie 2004).
Formative assessment is a set of activities that provide feedback to modify teaching and learning. Learn how it can improve learning, what challenges affect its implementation, and how to overcome them.
The goal of formative assessment is to guide the next stage of teaching and learning and inform the teacher and student on their gaps in skills knowledge. In contrast, the goal of summative assessment is a snapshot or record of what a pupil has learnt by a particular point in time, often benchmarked against school, trust or national standards.
1. Introduction. Using assessment for a formative purpose is intended to guide students' learning processes and improve students' learning outcomes (Van der Kleij, Vermeulen, Schildkamp, & Eggen, 2015; Bennett, 2011; Black & Wiliam, 1998).Based on its promising potential for enhancing student learning (Black & Wiliam, 1998), formative assessment has become a "policy pillar of educational ...
Formative assessment moves out of strategies and into classroom interaction with roots in disciplinary activities and goals (Coffey et al. 2011, p. 1131). 'Formative assessment takes place day by day and allows the teacher and the student to adapt their respective actions to the teaching/learn-ing situation in question.
The use of assessment to provide feedback to teach- ers and students in the course of learning is called formative assessment. Information gained through informal assessments provides opportunities for teachers to make adjustments to the ways in which they deliver instruction. For example, they may re- teach a concept, use alternative ...
Definition. Formative assessment refers to the frequent assessment of student progress to identify learning needs and shape teaching (OECD 2005 ). Formative assessment is sometimes referred to as assessment for learning, while summative assessment - that is, tests and examinations that are intended to provide summary statements of student ...
Formative assessment is a collaborative learning process happening "with" students, not "to" students. "Elicit and use evidence of student learning.". Formative assessment processes capture levels of knowledge and skill along the learning journey so teachers and students can make small, immediate, impactful decisions to support well ...
The Council of Chief State School Officers defines formative assessment as "a planned, ongoing process used by all students and teachers during learning and teaching to elicit and use evidence of student learning to improve student understanding of intended disciplinary learning outcomes and support students to become self-directed learners.".
Learn the difference between formative and summative assessment in education, and how they can help students and instructors improve their learning and teaching. Formative assessment is low stakes and ongoing, while summative assessment is high stakes and final.
The process of formative assessment is a key way that reflectivity can be enhanced (Citation Hadrill, 1995, p.169). Regular formative assessment can be motivational, as continuous feedback is integral to the learning experience, stimulating and challenging students (Citation Leach et al., 1998, p.204).
St. Paul American School. There are three broad types of assessments: diagnostic, formative, and summative. These take place throughout the learning process, helping students and teachers gauge learning. Within those three broad categories, you'll find other types of assessment, such as ipsative, norm-referenced, and criterion-referenced.
FACT. Formative assessment practices are those that provide teachers and students with information about learning as it develops—not just at the end of a project, unit, or year. The information is formative because it enables adjustments that deepen learning: Teachers use formative assessment to make adjustments to instruction, and students ...
ASCD characterized formative assessment as "a way for teachers and students to gather evidence of learning, engage students in assessment, and use data to improve teaching and learning." Their definition continues, "when you use an assessment instrument— a test, a quiz, an essay, or any other kind of classroom activity—analytically ...
Formative assessment contrasts with summative assessment. Formative assessments aim at improving education, while summative assessments aim at measuring education (Pryor, 2015). Summative assessments are examinations and formal tests which determine whether a student has passed or failed.
Teachers need more support to move testing from a "necessary evil" to a classroom tool, experts say. While summative tests—like unit quizzes or annual state assessments—are used for ...
Such assessments often take the form of pre-tests, skills checklists, and introductory surveys, each aimed at crafting a customized learning journey for every student. The Purpose of Educational Diagnostic Assessment. The main goal of educational diagnostic assessment is to guide educators in creating a personalized learning experience.
engaged with formative assessments: students, teachers, school leaders, families/caregivers, and others who support learners. In the definition below, please note the overlap between definitions of AI and formative assessment; both have to do with detecting patterns and choosing a future course of action (that adapts to learner strengths and ...