How to Write a Critique Paper: Format, Tips, & Critique Essay Examples
A critique paper is an academic writing genre that summarizes and gives a critical evaluation of a concept or work. Or, to put it simply, it is no more than a summary and a critical analysis of a specific issue. This type of writing aims to evaluate the impact of the given work or concept in its field.
Want to learn more? Continue reading this article written by Custom-writing experts! It contains:
- best tips on how to critique an article or a literary work,
- a critique paper example with introduction, body, and conclusion.

💁 What Is a Critique Paper?
- 👣 Critical Writing Steps
👀 Critical Essay Types
📝 critique paper format, 📑 critique paper outline, 🔗 references.
A critique is a particular academic writing genre that requires you to carefully study, summarize, and critically analyze a study or a concept. In other words, it is nothing more than a critical analysis. That is all you are doing when writing a critical essay: trying to understand the work and present an evaluation. Critical essays can be either positive or negative, as the work deserves.
👣 How to Write a Critique Essay: Main Steps
Starting critique essays is the most challenging part. You are supposed to substantiate your opinion with quotes and paraphrases, avoiding retelling the entire text. A critical analysis aims to find out whether an article or another piece of writing is compelling. First, you need to formulate the author’s thesis: what was the literary work supposed to convey? Then, explore the text on how this main idea was elaborated. Finally, draft your critique according to the structure given below.
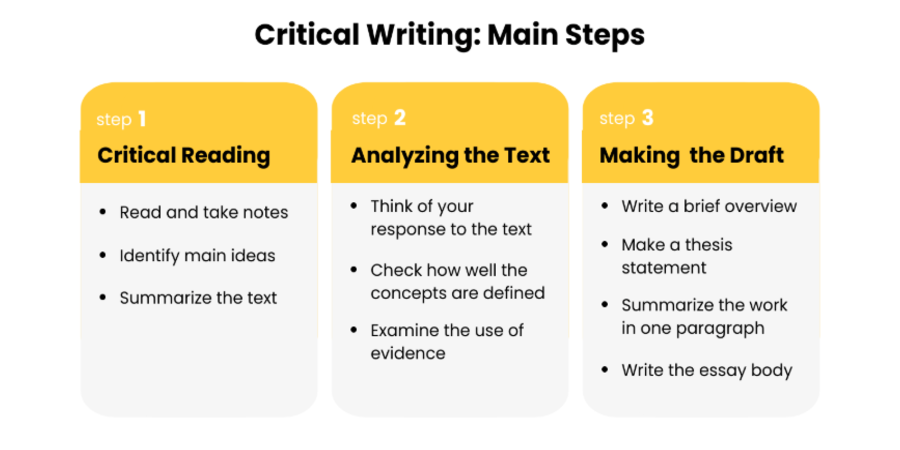
Step 1: Critical Reading
1.1. Attentively read the literary work. While reading, make notes and underline the essentials.
- Try to come into the author’s world and think why they wrote such a piece.
- Point out which literary devices are successful. Some research in literary theory may be required.
- Find out what you dislike about the text, i.e., controversies, gaps, inconsistency, or incompleteness.
1.2. Find or formulate the author’s thesis.
- What is the principal argument? In an article, it can be found in the first paragraph.
- In a literary work, formulate one of the principal themes, as the thesis is not explicit.
- If you write a critique of painting, find out what feelings, emotions, or ideas, the artist attempted to project.
1.3. Make a summary or synopsis of the analyzed text.
- One paragraph will suffice. You can use it in your critique essay, if necessary.
- The point is to explore the gist.
Step 2: Analyzing the Text
After the reading phase, ask yourself the following questions :
- What was your emotional response to the text? Which techniques, images, or ideas made you feel so?
- Find out the author’s background. Which experiences made them raise such a thesis? What other significant works have they written that demonstrate the general direction of thought of this person?
- Are the concepts used correctly in the text? Are the references reliable, and do they sufficiently substantiate the author’s opinion?
Step 3: Drafting the Essay
Finally, it is time to draft your essay. First of all, you’ll need to write a brief overview of the text you’re analyzing. Then, formulate a thesis statement – one sentence that will contain your opinion of the work under scrutiny. After that, make a one-paragraph summary of the text.
You can use this simple template for the draft version of your analysis. Another thing that can help you at this step is a summary creator to make the creative process more efficient.
Critique Paper Template
- Start with an introductory phrase about the domain of the work in question.
- Tell which work you are going to analyze, its author, and year of publication.
- Specify the principal argument of the work under study.
- In the third sentence, clearly state your thesis.
- Here you can insert the summary you wrote before.
- This is the only place where you can use it. No summary can be written in the main body!
- Use one paragraph for every separate analyzed aspect of the text (style, organization, fairness/bias, etc.).
- Each paragraph should confirm your thesis (e.g., whether the text is effective or ineffective).
- Each paragraph shall start with a topic sentence, followed by evidence, and concluded with a statement referring to the thesis.
- Provide a final judgment on the effectiveness of the piece of writing.
- Summarize your main points and restate the thesis, indicating that everything you said above confirms it.
You can evaluate the chosen work or concept in several ways. Pick the one you feel more comfortable with from the following:
- Descriptive critical essays examine texts or other works. Their primary focus is usually on certain features of a work, and it is common to compare and contrast the subject of your analysis to a classic example of the genre to which it belongs.
- Evaluative critical essays provide an estimate of the value of the work. Was it as good as you expected based on the recommendations, or do you feel your time would have been better spent on something else?
- Interpretive essays provide your readers with answers that relate to the meaning of the work in question. To do this, you must select a method of determining the meaning, read/watch/observe your analysis subject using this method, and put forth an argument.
There are also different types of critiques. The University of North Carolina-Chapel Hill, in the article “ Writing critiques ,” discusses them as well as the appropriate critique language.
Critique Paper Topics
- Critique of the article Is Google Making Us Stupid? by Nicholas Carr .
- Interpret the symbolism of Edgar Alan Poe’s The Black Cat .
- Examine the topicality of the article Impact of Racial/Ethnic Differences on Child Mental Health Care .
- Critical essay on Alice Walker’s short story Everyday Use .
- Discuss the value of the essay The Hanging by George Orwell.
- A critique on the article Stocks Versus Bonds: Explaining the Equity Risk Premium .
- Explore the themes Tennessee Williams reveals in The Glass Menagerie.
- Analyze the relevance of the article Leadership Characteristics and Digital Transformation .
- Critical evaluation of Jonathan Harvey’s play Beautiful Thing .
- Analyze and critique Derek Raymond’s story He Died with His Eyes Open .
- Discuss the techniques author uses to present the problem of choice in The Plague .
- Examine and evaluate the research article Using Evidence-Based Practice to Prevent Ventilator-Associated Pneumonia .
- Explore the scientific value of the article Our Future: A Lancet Commission on Adolescent Health and Wellbeing .
- Describe the ideas E. Hemingway put into his A Clean, Well-Lighted Place .
- Analyze the literary qualities of Always Running La Vida Loca: Gang Days in L. A .
- Critical writing on The Incarnation of Power by Wright Mills.
- Explain the strengths and shortcomings of Tim Kreider’s article The Busy Trap .
- Critical response to Woolf’s novel Mrs. Dalloway .
- Examine the main idea of Richard Godbeer’s book Escaping Salem .
- The strong and weak points of the article The Confusion of Tongues by William G. Bellshaw .
- Critical review of Gulliver’s Travels .
- Analyze the stylistic devices Anthony Lewis uses in Gideon’s Trumpet.
- Examine the techniques Elie Wiesel uses to show relationship transformation in the book Night .
- Critique of the play Fences by August Wilson.
- The role of exposition in Achebe’s novel Things Fall Apart.
- The main themes John Maxwell discusses in his book Disgrace .
- Critical evaluation of Ray Bradbury’s Fahrenheit 451 .
- The ideas and concept of the book The Vegetarian Imperative .
- Different points of view on one historical figure in the book Two Lives of Charlemagne .
Since the APA critique paper format is one of the most common, let’s discuss it in more detail. Check out the information below to learn more:
The APA Manual recommends using the following fonts:
- 11-point Calibri,
- 11-point Arial,
- 10-point Lucida Sans Unicode,
- 12-point Times New Roman,
- 11-point Georgia,
- 10-point Computer Modern.
Add 1-inch margins on all sides.
📌 Page numbers
Page numbers should appear at the top right-hand corner, starting with the title page.
📌 Line spacing
The entire document, including the title page and reference list, should be double-spaced.
📌 Title page
The title page should include the following information:
- page number 1 in the top right-hand corner of the page header,
- paper title,
- the student’s name,
- the name of the department and the college or university,
- course number and name,
- the instructor’s name,
- due date (the date format used in your country).
📌 Critique paper title
The title of your critique paper should be no more than 12 words. In addition, it should be centered and typed in bold using title case.
📌 In-text citations
For the in-text citation, provide the author’s last name and publication year in brackets. If you are using direct citation, add the page number after the year.
📌 References
The last page of your paper should include a list of all sources cited in your essay. Here’s a general format of book and journal article citations you should use:
Book: Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year). Book title: Subtitle . Publisher.
Journal article: Last name, First initial. Middle initial. (Year). Title of the article. Journal Title, volume (issue number), start page–end page.
The main parts of good critical response essays are:
- Introduction. The introduction is the most essential part of the critical response. It should be concise and include the author and title of the work being analyzed, its main idea, and a strong thesis statement.
- Summary. This should be brief and to the point. Only the author’s/creator’s main ideas and arguments should be included.
- Analysis/interpretation. Discuss what the author’s/creator’s primary goal was and determine whether this goal was reached successfully. Use the evidence you have gathered to argue whether or not the author/creator achieved was adequately convincing (remember there should be no personal bias in this discussion).
- Evaluation/response. At this point, your readers are ready to learn your objective response to the work. It should be professional yet entertaining to read. Do not hesitate to use strong language. You can say that the work you analyzed was weak and poorly-structured if that is the case, but keep in mind that you have to have evidence to back up your claim.
- Conclusion. The last paragraph of your work should restate the thesis statement, summarize the key points, and create a sense of closure for the readers.
Critique Paper Introduction
The introduction is setting the stage for your analysis. Here are some tips to follow when working on it:
- Provide the reader with a brief synopsis of the main points of the work you are critiquing .
- State your general opinion of the work , using it as your thesis statement. The ideal situation is that you identify and use a controversial thesis.
- Remember that you will uncover a lot of necessary information about the work you are critiquing. You mustn’t make use of all of it, providing the reader with information that is unnecessary in your critique. If you are writing about Shakespeare, you don’t have to waste your or your reader’s time going through all of his works.
Critique Paper Body
The body of the critique contains the supporting paragraphs. This is where you will provide the facts that prove your main idea and support your thesis. Follow the tips below when writing the body of your critique.
- Every paragraph must focus on a precise concept from the paper under your scrutiny , and your job is to include arguments to support or disprove that concept. Concrete evidence is required.
- A critical essay is written in the third-person and ensures the reader is presented with an objective analysis.
- Discuss whether the author was able to achieve their goals and adequately get their point across.
- It is important not to confuse facts and opinions . An opinion is a personal thought and requires confirmation, whereas a fact is supported by reliable data and requires no further proof. Do not back up one idea with another one.
- Remember that your purpose is to provide the reader with an understanding of a particular piece of literature or other work from your perspective. Be as specific as possible.
Critique Paper Conclusion
Finally, you will need to write a conclusion for your critique. The conclusion reasserts your overall general opinion of the ideas presented in the text and ensures there is no doubt in the reader’s mind about what you believe and why. Follow these tips when writing your conclusion:
- Summarize the analysis you provided in the body of the critique.
- Summarize the primary reasons why you made your analysis .
- Where appropriate, provide recommendations on how the work you critiqued can be improved.
For more details on how to write a critique, check out the great critique analysis template provided by Thompson Rivers University.
If you want more information on essay writing in general, look at the Secrets of Essay Writing .
Example of Critique Paper with Introduction, Body, and Conclusion
Check out this critical response example to “The Last Inch” by James Aldridge to show how everything works in practice:
Introduction
In his story “The Last Inch,” James Aldridge addresses the issue of the relationship between parents and children. The author captured the young boy’s coming into maturity coinciding with a challenging trial. He also demonstrated how the twelve-year-old boy obtained his father’s character traits. Aldridge’s prose is both brutal and poetic, expressing his characters’ genuine emotions and the sad truths of their situations.
Body: Summary
The story is about Ben Ensley, an unemployed professional pilot, who decides to capture underwater shots for money. He travels to Shark Bay with his son, Davy. Ben is severely injured after being attacked by a shark while photographing. His last hope of survival is to fly back to the little African hamlet from where they took off.
Body: Analysis
The story effectively uses the themes of survival and fatherhood and has an intriguing and captivating plot. In addition, Ben’s metamorphosis from a failing pilot to a determined survivor is effectively presented. His bond with his son, Davy, adds depth and emotional importance to the story. At the same time, the background information about Ben’s past and his life before the shark attack could be more effectively integrated into the main story rather than being presented as separate blocks of text.
Body: Evaluation
I find “The Last Inch” by James Aldridge a very engaging and emotional story since it highlights the idea of a father’s unconditional love and determination in the face of adversity. I was also impressed by the vivid descriptions and strong character development of the father and son.
Conclusion
“The Last Inch” by James Aldridge is an engaging and emotional narrative that will appeal to readers of all ages. It is a story of strength, dedication, and the unbreakable link between father and son. Though some backstory could be integrated more smoothly, “The Last Inch” impresses with its emotional punch. It leaves the readers touched by the raw power of fatherly love and human will.
📚 Critique Essay Examples
With all of the information and tips provided above, your way will become clearer when you have a solid example of a critique essay.
Below is a critical response to The Yellow Wallpaper by Charlotte Perkins Gilman.
When speaking of feminist literature that is prominent and manages to touch on incredibly controversial issues, The Yellow Wallpaper is the first book that comes to mind. Written from a first-person perspective, magnifying the effect of the narrative, the short story by Charlotte Perkins Gilman introduces the reader to the problem of the physical and mental health of the women of the 19th century. However, the message that is intended to concern feminist ideas is rather subtle. Written in the form of several diary entries, the novel offers a mysterious plot, and at the same time, shockingly realistic details.
What really stands out about the novel is the fact that the reader is never really sure how much of the story takes place in reality and how much of it happens in the psychotic mind of the protagonist. In addition, the novel contains a plethora of description that contributes to the strain and enhances the correlation between the atmosphere and the protagonist’s fears: “The color is repellent, almost revolting; a smoldering unclean yellow, strangely faded by the slow-turning sunlight” (Gilman).
Despite Gilman’s obvious intent to make the novel a feminist story with a dash of thriller thrown in, the result is instead a thriller with a dash of feminism, as Allen (2009) explains. However, there is no doubt that the novel is a renowned classic. Offering a perfect portrayal of the 19th-century stereotypes, it is a treasure that is certainly worth the read.
If you need another critique essay example, take a look at our sample on “ The Importance of Being Earnest ” by Oscar Wilde.
And here are some more critique paper examples for you check out:
- A Good Man Is Hard to Find: Critique Paper
- Critique on “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman
- “When the Five Rights Go Wrong” Article Critique
- Homer’s Iliad and Odyssey — Comparison & Critique
- “The TrueBlue Study”: Qualitative Article Critique
- Ethical Conflict Associated With Managed Care: Views of Nurse Practitioners’: Article Critique
- Benefits and Disadvantages of Prone Positioning in Severe Acute Respiratory Distress: Article Critique
- Reducing Stress in Student Nurses: Article Critique
- Management of Change and Professional Safety – Article Critique
- “Views of Young People Towards Physical Activity”: Article Critique
Seeing an example of a critique is so helpful. You can find many other examples of a critique paper at the University of Minnesota and John Hopkins University. Plus, you can check out this video for a great explanation of how to write a critique.
- Critical Analysis
- Writing an Article Critique
- The Critique Essay
- Critique Essay
- Writing a Critique
- Writing A Book Critique
- Media Critique
- Tips for an Effective Creative Writing Critique
- How to Write an Article Critique
- Share to Facebook
- Share to Twitter
- Share to LinkedIn
- Share to email

What is a creative essay, if not the way to express yourself? Crafting such a paper is a task that allows you to communicate your opinion and tell a story. However, even using your imagination to a great extent doesn’t free you from following academic writing rules. Don’t even get...

A compare and contrast essay — what is it? In this type of paper, you compare two different things or ideas, highlighting what is similar between the two, and you also contrast them, highlighting what is different. The two things might be events, people, books, points of view, lifestyles, or...

What is an expository essay? This type of writing aims to inform the reader about the subject clearly, concisely, and objectively. The keyword here is “inform”. You are not trying to persuade your reader to think a certain way or let your own opinions and emotions cloud your work. Just stick to the...
![critique paper essay example Short Story Analysis: How to Write It Step by Step [New]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/man-sits-end-trolltunga-before-mountains-284x153.jpg)
Have you ever tried to write a story analysis but ended up being completely confused and lost? Well, the task might be challenging if you don’t know the essential rules for literary analysis creation. But don’t get frustrated! We know how to write a short story analysis, and we are...

Have you ever tried to get somebody round to your way of thinking? Then you should know how daunting the task is. Still, if your persuasion is successful, the result is emotionally rewarding. A persuasive essay is a type of writing that uses facts and logic to argument and substantiate...
![critique paper essay example Common Essay Mistakes—Writing Errors to Avoid [Updated]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/avoid-mistakes-ccw-284x153.jpg)
One of the most critical skills that students gain during their college years is assignment writing. Composing impressive essays and research papers can be quite challenging, especially for ESL students. Nonetheless, before learning the art of academic writing, you may make numerous common essay mistakes. Such involuntary errors appear in:...

You’re probably thinking: I’m no Mahatma Gandhi or Steve Jobs—what could I possibly write in my memoir? I don’t even know how to start an autobiography, let alone write the whole thing. But don’t worry: essay writing can be easy, and this autobiography example for students is here to show...
![critique paper essay example Why I Want to Be a Teacher Essay: Writing Guide [2024]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/senior-male-professor-writing-blackboard-with-chalk3-284x153.jpg)
Some people know which profession to choose from childhood, while others decide much later in life. However, and whenever you come to it, you may have to elaborate on it in your personal statement or cover letter. This is widely known as “Why I Want to Be a Teacher” essay.
![critique paper essay example Friendship Essay: Writing Guide & Topics on Friendship [New]](https://custom-writing.org/blog/wp-content/uploads/2020/12/smiley-female-friends-fist-bumping-284x153.jpg)
Assigned with an essay about friendship? Congrats! It’s one of the best tasks you could get. Digging through your memories and finding strong arguments for this paper can be an enjoyable experience. I bet you will cope with this task effortlessly as we can help you with the assignment. Just...

When you are assigned an autobiography to write, tens, and even hundreds of questions start buzzing in your head. How to write autobiography essay parts? What to include? How to make your autobiography writing flow? Don’t worry about all this and use the following three simple principles and 15 creative...

A life experience essay combines the elements of narration, description, and self-reflection. Such a paper has to focus on a single event that had a significant impact on a person’s worldview and values. Writing an essay about life experience prompts students to do the following: You may struggle with such...

Who has made a significant impact in your life and why? Essay on the topic might be challenging to write. One is usually asked to write such a text as a college admission essay. A topic for this paper can be of your choice or pre-established by the institution. Either...
May I know who’s the author? For my citation activity.

Hello, Kriszha! You can reference it as a web source/web page.
Wow…great work… kindly can you assist me in writing a critique about indiscipline in a school
That’s an interesting demonstration I watched. However, my weakness is that I’m very poor in language and analysing issues.
Hi, can you help me for my assignment about article critiquing?
I need your help if you can send me a full written dissertation..thank you
This is gud
Can you help me to my activities
Thank you so much! This really helped me!
- Essay Topic Generator
- Summary Generator
- Thesis Maker Academic
- Sentence Rephraser
- Read My Paper
- Hypothesis Generator
- Cover Page Generator
- Text Compactor
- Essay Scrambler
- Essay Plagiarism Checker
- Hook Generator
- AI Writing Checker
- Notes Maker
- Overnight Essay Writing
- Topic Ideas
- Writing Tips
- Essay Writing (by Genre)
- Essay Writing (by Topic)
How to Write a Critique Paper: Guide + Steps & Tips
Critical thinking is an essential life skill taught in academia. Critique essays help us develop this skill. However, it’s challenging to figure out how to write one independently. Our team has created this comprehensive guide to teach you how to express opinions in an academically correct manner. Here, you’ll discover step-by-step guidelines to help you write an essay. We’ve also addressed the proper essay critique format structure and provided several practical examples of how it should look. So, if you are interested and wish to learn more, start reading ASAP!
📃 What Is a Critique Paper?
A critique paper is a piece of writing that provides an in-depth analysis of another work. These include books, poems, articles, songs, movies, works of art, or podcast episodes. Aside from these, a critique may also cover arguments, concepts, and artistic performances. For example, a student may evaluate a book they’ve read or the merit of the First Amendment.
In a critique essay , one addresses the subject of the analysis, its source, intent, and purpose, in addition to its structure and content. You may present your own opinion on the analyzed work or include alternative points of view. Your paper can consist of an interpretation of what a piece of work means and an assessment of its worth.
🔍 Discover All Critique Essay Types
Now, we will detail everything you need to know about the main types of critique papers. Use the table below to determine which one will suit your essay best.

| This critique essay type examines texts and other written papers. It usually focuses on specific characteristics of a piece. Sometimes, a work can be compared to other examples in its genre. Descriptive essays often provide detailed insight into the examined works. | |
| These essays estimate the value of a work. In them, a writer tells the readers if something was as good as they had hoped for or failed to meet their expectations. Such essays should avoid baseless personal bias. Its authors are required to provide evidence-backed personal opinions. | |
| An interpretive paper explains the work’s meaning to the readers. It involves selecting the right approach to discovering this meaning. Writing an interpretive essay requires one to understand its subject fully. |
🥇 19 Best Critique Essay Topics
This segment has some of the best topics for critical essays that you can use in your assignments. Make sure to look through them and find some inspiration! Some of them are sure to catch your attention.
- Analyze the effectiveness of the justice system in curbing drug use.
- Why are people reluctant to change their views on the Second Amendment?
- Critical review of the moral lessons in contemporary young adult novels.
- Is critical thinking still relevant in the modern world?
- Analyze the health effects of fast food on the human body.
- Describe the effects of racism on underrepresented groups.
- Build a case for the causes of the homeless crisis in the US.
- Unraveling motivational factors: a critique of psychological theories in the workplace.
- Analyze the shifting of gender roles in modern society.
- What is the impact of corruption on the economy?
- The impact of setting and atmosphere on the reader’s experience of a book.
- Investigate the role of mass media in decreasing racial tension in the US.
- Analyze the use of symbolism and imagery in Edgar Allan Poe’s short stories.
- Ethical dilemmas in medical study: critical analysis of journal articles on human trials.
- Which themes are the most common in current TV shows?
- Explain how fashion choices impact one’s identity.
- Build a case for a free higher education.
- What are the effects of social media on human communication?
- From page to screen: A comparative critique of the book and movie versions of The Lord of the Rings.
🗝 How to Write a Critique Paper: 5 Key Steps
We recognize that tackling a critique paper without proper guidance can be time-consuming and daunting. That’s why we have outlined the steps you should take to make a detailed plan for your future essay. These five steps will guide you in analyzing work successfully and creating quality papers.

- Explore the work. Before writing your essay, carefully examine the text you will be critiquing. Take notes relevant to your paper’s topic along the way. Pay attention to details and try noting the strengths and weaknesses of a piece of work.
- Conduct research. Aside from inspecting the work itself, you should also thoroughly study the surrounding context. Learn everything relevant about its author, background, and cultural and historical factors. So, you will receive essential information about the research subject, allowing you to understand it better.
- Create a thesis statement. This part usually includes a concise summary of the analysis of the work and conducted research. Students must carefully write their thesis statements to present their main argument or the work’s brief evaluation.
- Write the critical paper. After you have composed a solid thesis statement, it’s time to write your essay. Begin by providing background data in the introductory paragraph. Follow with analysis and evidence that supports the paper’s intent. Finish with a conclusion that gives a summary of the key points and reinforcing the thesis statement.
- Edit and revise to perfection. When you have the first draft, carefully review and edit its segments. See if the paper is structurally sound, easy to follow, and has a coherent format. Good writing provides its arguments logically, with clear connections between evidence and analysis. Pay close attention to segments that make you stumble and reread all sentences twice.
📝 Critique Paper Format & Structure
Before attempting to write your critique essay, you should familiarize yourself with its structure and form. We’ll examine each part in-depth and describe which elements they should have. It will give you an idea of how to structure your essay correctly.
| The beginning of your critique should state the author’s name, the work’s title, and its publication date. It includes one or two sentences that summarize the examined work and a central argument that will be the basis of your critique. | |
| The second part of the paper provides evidence and analysis based on your thesis statement. For example, you may use it to explain why director did an excellent job with the movie. It may cover such aspects as actors, cinematography, writing, and the film’s satirical tone. | |
| The essay’s final part gives critical takeaways from a piece of work. They usually involve summarizing the paper’s arguments and thesis statement. In the case of a film critique, it should tell people why it’s good or bad based on the conducted analysis. |
Examining each component is essential after you get acquainted with the basic structure of a critique paper. We have detailed for you below.
Critique Essay: Introduction
You probably already know how essential the introduction is in a critique paper. This is why it’s vital to understand its proper structure. One should consider all elements that must be present in this part of the paper.
- Provide the name of the critiqued work, when it was first published, and by whom.
- Describe the thesis statement or the main idea of the paper.
- Give the context of the work, political or social, and its importance in a discipline or an academic field.
- Finish with a sentence that briefly evaluates the examined work and transitions into the main body.
Critique Essay: Main Body
We’ve finally arrived at the analysis, the most crucial part of creating a critique. Here, we’ll look at the structure of the main body paragraphs . This part of the article will explain what to include in your critical paper.
The body starts with a summary that explains:
- The main points of the work.
- How the points were achieved through characters, symbols, and various techniques.
- The aim of the research, how it was conducted, and based on what.
The rest of the body is a detailed critical evaluation of the work that includes:
- A systematic and thorough approach to assessing different elements.
- An assessment of the author’s ability or lack thereof to achieve their goals with these components.
- Supporting evidence for your arguments and evaluation.

Critique Essay: Conclusion
Lastly, let’s consider the conclusion of your critique paper. It is the time to summarize and reiterate what you have discussed in your work. An essay conclusion should contain the following elements:
- A concise statement that summarizes the entire work.
- A rundown of key points identified and covered in the evaluation.
- If necessary, the conclusion may provide recommendations for others interested in getting acquainted with the work.
🏆 Great Critique Paper Examples
We believe a good sample is one of the best aids in writing a quality essay. After all, theory can be insufficient and it’s best to see something done in practice. We’ve provided several great essay examples below for you to consider.
- Critique Against Orwell’s Style in “Animal Farm.” Orwell’s Animal Farm is a witty commentary on society and the cycle of power. To this day, the work is one of the strongest anti-Stalinist novels. Despite its themes, one of his most famous novels is often criticized for its mediocre writing style. This essay wants to advocate for this opinion through literary analysis.
- Critique of an Adidas Promotional Strategy. Adidas is one of the world’s most fabulous clothes, shoes, and equipment producers. The corporation registers hundreds of patterns on new tech for its products every year. But this doesn’t mean that Adidas does everything right. This paper demonstrates the unethical practices the company uses in its advertising campaigns.
- A Reader Response Critique of “A Rose for Emily.” Written in 1892, The Yellow Wallpaper is a short story by Charlotte Perkins Gilman. It talks about the role of women in the late 1800s. Back then, they were regarded as passive individuals who couldn’t think independently. This paper critically examines the text’s effectiveness as a psychological horror story.
- Organizational Personnel Policy Critique. Personnel management covers many aspects of a company’s daily operations. It helps create a harmonious work environment that benefits all participants. However, some of the current policies are outdated and need to be adjusted. This paper critically analyzes policies that drive and evaluate performance. It also shows which changes can be applied to standard HR guidelines.
We are confident that our tips and instructions will make it easier for you to achieve great results. Besides, you can try our helpful essay topic maker to come up with writing ideas! Consider forwarding this article to your friends who may be looking for a quality guide on critical papers.
🔗 References
- What Makes a Critique a Critique? – Tara Horkoff, Writing for Success, OpenTextBC
- How to write a critique – CiteWrite, Queensland University of Technology
- Writing a Critique – Tiffin University, Pfeiffer Library
- Writing a Critique Paper: Seven Easy Steps – Patrick A. Regoniel, Simple Educate
- How to Write a Critical Analysis Essay – Dan Brown, MasterClass

Writing a Critique
- About this Guide
- What Is a Critique?
- Getting Started
- Components of a Critique Essay
Further Reading
This article provides additional guidance for writing critiques:
Vance DE, Talley M, Azuero A, Pearce PF, & Christian BJ. (2013). Conducting an article critique for a quantitative research study: perspectives for doctoral students and other novice readers. Nursing : Research and Reviews , 2013 , 67–75.
Parts of a Critique Essay
There are 4 distinct components to a critique, and those are the:
Introduction
Each of these components is described in further detail in the boxes on this page of the guide.
An effective introduction:
- Provides a quick snapshot of background information readers may need in order to follow along with the argument
- Defines key terminology as needed
- Ends with a strong argument (thesis)
For additional guidance on writing introduction paragraphs, librarians recommend:
Need some extra help on thesis statements? Check out our Writing Effective Thesis Statements guide .
A summary is a broad overview of what is discussed in a source. In a critique essay, writers should always assume that those reading the essay may be unfamiliar with the work being examined. For that reason, the following should be included early in the paper:
- The name of the author(s) of the work
- The title of the work
- Main ideas presented in the work
- Arguments presented in the work
- Any conclusions presented in the work
Depending on the requirements of your particular assignment, the summary may appear as part of the introduction, or it may be a separate paragraph. The summary should always be included before the analysis, as readers need a base-level familiarity of the resource before you can effectively present an argument about what the source does well and where improvements are needed.
More information about summaries can be found on our Writing an Effective Summary guide .
The critique is your evaluation of the resource. A strong critique:
- Discusses the strengths of the resource
- Discusses the weaknesses of the resource
- Provides specific examples (direct quotes, with proper citation) as needed to support your evaluation
- The accuracy of the resource
- Any bias found within the resource
- The relevance of the resource
- The clarity of the resource
A critique is your opinion of the text, supported by evidence from the text.
If you need further guidance on how to evaluate your source, you can also consult our Evaluating Your Sources guide .
Need help with citation?
Compose papers in pre-formatted APA templates. Manage references in forms that help craft APA citations. Learn the rules of APA style through tutorials and practice quizzes.
Academic Writer will continue to use the 6th edition guidelines until August 2020. A preview of the 7th edition is available in the footer of the resource's site. Previously known as APA Style Central.
- APA Style Help Learn more about APA style through our research guide.
A conclusion has three main functions in an essay. A conclusion will:
- Summarize the main ideas presented in the essay
- Remind readers of the thesis (argument)
- Draw the paper to a close
For additional guidance, the library recommends:
- << Previous: Getting Started
- Next: Examples >>
- Last Updated: May 22, 2023 10:46 AM
- URL: https://library.tiffin.edu/critique
How to Structure and Write an Effective Critique Paper
Critique papers are an essential part of academic writing, especially in the fields of humanities and social sciences. They involve analyzing a piece of work and objectively evaluating its strengths and weaknesses. Writing a critique paper can be challenging, requiring careful reading, research, and analysis. Yet, it is possible to produce a high-quality essay with careful planning and attention to detail.
This article will teach you how to write an article critique by explaining the types of critique essays, their structure, and the steps involved in how to write a critique essay. The article also provides essay tips for producing a well-written and effective critique.
What is a Critique Paper?
A critique paper is an academic paper as a response to a body of work, such as a play, concept, scholarly article, poetry, book, or research paper. Its purpose is to objectively assess the work in question, highlighting its strengths and weaknesses. But also to provide a detailed analysis of its content, structure, and methodology.
This kind of essay can be one of the trickiest assignments, and not everyone can produce a well-scrutinized, original piece of writing. That’s why many students reach for assistance from analytical essay writing services that guarantee to handle the job with the help of professional writers and experts. These services proved to be of high quality and effective support to many schoolers who chose to try them in a variety of different disciplines.
Knowing how to write an article critique requires careful reading, analysis, and an evaluative approach. A well-written critique paper example demonstrates the writer’s ability to analyze and evaluate works. It should also be organized logically, guiding the reader through the analysis. Additionally, writers should be aware of their biases and assumptions and strive to critique objectively. On a final note, it’s essential to review the guidelines and follow the required structure. This is to ensure that the article critique meets the assignment’s expectations.
Types of Critical Essays
There are several types of essays of this kind, each with its approach and focus. To follow we have a list of the most common ones.
Descriptive
A descriptive critical essay combines elements of descriptive writing with a thorough analysis. In this type of essay, the writer describes a particular work in detail and then evaluates it based on certain criteria. They can provide a deep and insightful understanding of the work using sensory details and descriptive language.
An evaluative essay consists of a personal judgment to evaluate the value or effectiveness of a particular work or idea. In this type of essay, the writer analyzes the work and expresses their opinion on its merits or shortcomings. At the same time, they must avoid personal bias and focus on facts rather than one’s opinions or feelings. However, it’s also essential to provide a personal perspective and interpretation of the work as long as it’s supported by evidence.
Interpretive
This type of essay involves analyzing and interpreting the meaning and significance of the work being evaluated. It delves deeper into the themes, symbolism, and underlying conveyed messages. When writing an interpretive essay, it’s important to be clear and concise. Avoid confusing the reader by using jargon or unnecessarily complex language.
Structure of Critique Paper
The structure of a typical critique essay example includes an introduction, a summary, an analysis, and a conclusion. The paper format is a crucial element. Just like when you write your research papers , a critique benefits from a clear one to guide the reader. Therefore, work on defining the critique essay outline before starting the writing process. One of the most common formatting styles to adopt is the APA format (APA: American Psychological Association), which has specific rules and guidelines. And keep in mind that some specific elements should be included in each section:
Introduction: The introduction’s function is to provide background relevant information. It should also include the thesis statement, which is the writer’s main argument or position on the topic. The thesis statement should be clear and specific and presented in a way that engages the reader.
Summary: The summary provides an overview of the text. It must be objective, unbiased, and accurately summarize the piece’s main points. The summary has to be brief and to the point and should only include the most important details of the work.
Analysis: The analysis is where the writer provides their evaluation of the text being critiqued. This section is the most detailed and extensive part of the paper, containing the facts that prove your main argument and support your thesis. The analysis should focus on the thesis statement and provide a clear and logical argument.
Conclusion: In the conclusion, the paper’s main points are summarized, and the thesis statement is restated to emphasize the writer’s main position. It should provide a final evaluation of the work and include recommendations for improvement.
Essential Steps to Write a Critique Essay
Critique writing requires a thoughtful and detailed approach. You can find below the essential steps to follow:
Read and observe the work:
Before beginning the essay, you should read and observe the work, taking notes on its relevant elements. It is crucial to pay attention to details and to identify both strengths and weaknesses.
Conduct research:
In addition to analyzing the work, you need to research the author, director, or artist and the work’s historical and cultural context. This step can be time and effort-consuming. That’s why as a student who’s probably stuck with many assignments, you can consider to pay for research paper , which will solve the problem most efficiently. The research can provide valuable insights into the work and help you develop a more informed critique.
Develop a thesis statement:
Based on the analysis of the work and any research conducted, you should develop a clear and specific thesis statement that accurately presents your main argument or evaluation of the piece.
Write your critique:
Once you have your thesis statement, you can begin writing your critique essay. Begin by providing some background information on the work in an introduction. In the body of your essay, provide evidence and analysis to support your evaluation. Use specific examples and quotes from the text to support your arguments. Consider including external sources to provide additional context or compare the work to similar works. Finally, end your essay with a conclusion summarizing your main points and restating your thesis statement.
Revise and edit:
After completing the first draft of your essay, you should revise and edit it carefully. Pay attention to your argument’s structure, clarity, and coherence. Also, ensure that your essay logically progresses from one concept to the next. It’s important to note that when you format an essay , considerations may vary depending on the assignment’s specific requirements. Some may require additional sections, such as a discussion of the author’s background or a comparison to other works.
How to start a critique paper?
Starting a critique paper requires careful consideration and preparation. It is important to read and understand the subject thoroughly, including its purpose, structure, and context. Once you have a clear understanding of the subject, you should identify specific criteria to use in your evaluation, such as style, structure, effectiveness, relevance, and accuracy. Taking notes on the subject’s strengths, weaknesses, and areas for improvement will help you organize your thoughts, and creating an outline that includes the introduction, analysis, and conclusion will ensure a well-structured paper. Finally, a strong thesis statement that clearly states your evaluation of the subject and the criteria you will use to evaluate it is crucial to the success of your critique paper.
How can I write a critique paper on a research article?
To write a critique paper on a research article, it is essential to consider key areas such as the research question and hypothesis, methodology, results, and overall evaluation. Firstly, determine whether the research question is clear, relevant, and testable. Secondly, evaluate the methodology used in the study to determine whether it’s appropriate for the research question. Thirdly, analyze the results presented in the research article to determine whether they are consistent with the research question and hypothesis. Lastly, evaluate the overall quality and contribution of the research article to the field. By considering these areas, you can provide a comprehensive critique of the research article.
What is the difference between summarizing and critiquing an article?
Many students struggle to distinguish between the two. They often summarize the work, neglecting to adopt a personal approach and use analytical skills. In such cases, custom essay writing service Edusson is the best option to handle the job for you. It also helps you improve your critical thinking and practical skills.
Related posts:
- 6 Step Process for Essay Writing
- How to Write a Diagnostic Essay (Without Fail)
- The Full Guide to Writing Comparison Essays with Point-by-Point Method
- Footnotes 101: A Guide to Proper Formatting
Improve your writing with our guides

How to Write a Scholarship Essay

Definition Essay: The Complete Guide with Essay Topics and Examples

Critical Essay: The Complete Guide. Essay Topics, Examples and Outlines
Get 15% off your first order with edusson.
Connect with a professional writer within minutes by placing your first order. No matter the subject, difficulty, academic level or document type, our writers have the skills to complete it.
100% privacy. No spam ever.

- Bipolar Disorder
- Therapy Center
- When To See a Therapist
- Types of Therapy
- Best Online Therapy
- Best Couples Therapy
- Best Family Therapy
- Managing Stress
- Sleep and Dreaming
- Understanding Emotions
- Self-Improvement
- Healthy Relationships
- Student Resources
- Personality Types
- Guided Meditations
- Verywell Mind Insights
- 2024 Verywell Mind 25
- Mental Health in the Classroom
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board
- Crisis Support
How to Write an Article Critique
Tips for Writing a Psychology Critique Paper
Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/IMG_9791-89504ab694d54b66bbd72cb84ffb860e.jpg)
Emily is a board-certified science editor who has worked with top digital publishing brands like Voices for Biodiversity, Study.com, GoodTherapy, Vox, and Verywell.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Emily-Swaim-1000-0f3197de18f74329aeffb690a177160c.jpg)
Cultura RM / Gu Cultura / Getty Images
- Steps for Writing a Critique
Evaluating the Article
- How to Write It
- Helpful Tips
An article critique involves critically analyzing a written work to assess its strengths and flaws. If you need to write an article critique, you will need to describe the article, analyze its contents, interpret its meaning, and make an overall assessment of the importance of the work.
Critique papers require students to conduct a critical analysis of another piece of writing, often a book, journal article, or essay . No matter your major, you will probably be expected to write a critique paper at some point.
For psychology students, critiquing a professional paper is a great way to learn more about psychology articles, writing, and the research process itself. Students will analyze how researchers conduct experiments, interpret results, and discuss the impact of the results.
At a Glance
An article critique involves making a critical assessment of a single work. This is often an article, but it might also be a book or other written source. It summarizes the contents of the article and then evaluates both the strengths and weaknesses of the piece. Knowing how to write an article critique can help you learn how to evaluate sources with a discerning eye.
Steps for Writing an Effective Article Critique
While these tips are designed to help students write a psychology critique paper, many of the same principles apply to writing article critiques in other subject areas.
Your first step should always be a thorough read-through of the material you will be analyzing and critiquing. It needs to be more than just a casual skim read. It should be in-depth with an eye toward key elements.
To write an article critique, you should:
- Read the article , noting your first impressions, questions, thoughts, and observations
- Describe the contents of the article in your own words, focusing on the main themes or ideas
- Interpret the meaning of the article and its overall importance
- Critically evaluate the contents of the article, including any strong points as well as potential weaknesses
The following guidelines can help you assess the article you are reading and make better sense of the material.
Read the Introduction Section of the Article
Start by reading the introduction . Think about how this part of the article sets up the main body and how it helps you get a background on the topic.
- Is the hypothesis clearly stated?
- Is the necessary background information and previous research described in the introduction?
In addition to answering these basic questions, note other information provided in the introduction and any questions you have.
Read the Methods Section of the Article
Is the study procedure clearly outlined in the methods section ? Can you determine which variables the researchers are measuring?
Remember to jot down questions and thoughts that come to mind as you are reading. Once you have finished reading the paper, you can then refer back to your initial questions and see which ones remain unanswered.
Read the Results Section of the Article
Are all tables and graphs clearly labeled in the results section ? Do researchers provide enough statistical information? Did the researchers collect all of the data needed to measure the variables in question?
Make a note of any questions or information that does not seem to make sense. You can refer back to these questions later as you are writing your final critique.
Read the Discussion Section of the Article
Experts suggest that it is helpful to take notes while reading through sections of the paper you are evaluating. Ask yourself key questions:
- How do the researchers interpret the results of the study?
- Did the results support their hypothesis?
- Do the conclusions drawn by the researchers seem reasonable?
The discussion section offers students an excellent opportunity to take a position. If you agree with the researcher's conclusions, explain why. If you feel the researchers are incorrect or off-base, point out problems with the conclusions and suggest alternative explanations.
Another alternative is to point out questions the researchers failed to answer in the discussion section.
Begin Writing Your Own Critique of the Paper
Once you have read the article, compile your notes and develop an outline that you can follow as you write your psychology critique paper. Here's a guide that will walk you through how to structure your critique paper.
Introduction
Begin your paper by describing the journal article and authors you are critiquing. Provide the main hypothesis (or thesis) of the paper. Explain why you think the information is relevant.
Thesis Statement
The final part of your introduction should include your thesis statement. Your thesis statement is the main idea of your critique. Your thesis should briefly sum up the main points of your critique.
Article Summary
Provide a brief summary of the article. Outline the main points, results, and discussion.
When describing the study or paper, experts suggest that you include a summary of the questions being addressed, study participants, interventions, comparisons, outcomes, and study design.
Don't get bogged down by your summary. This section should highlight the main points of the article you are critiquing. Don't feel obligated to summarize each little detail of the main paper. Focus on giving the reader an overall idea of the article's content.
Your Analysis
In this section, you will provide your critique of the article. Describe any problems you had with the author's premise, methods, or conclusions. You might focus your critique on problems with the author's argument, presentation, information, and alternatives that have been overlooked.
When evaluating a study, summarize the main findings—including the strength of evidence for each main outcome—and consider their relevance to key demographic groups.
Organize your paper carefully. Be careful not to jump around from one argument to the next. Arguing one point at a time ensures that your paper flows well and is easy to read.
Your critique paper should end with an overview of the article's argument, your conclusions, and your reactions.
More Tips When Writing an Article Critique
- As you are editing your paper, utilize a style guide published by the American Psychological Association, such as the official Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association .
- Reading scientific articles can be challenging at first. Remember that this is a skill that takes time to learn but that your skills will become stronger the more that you read.
- Take a rough draft of your paper to your school's writing lab for additional feedback and use your university library's resources.
What This Means For You
Being able to write a solid article critique is a useful academic skill. While it can be challenging, start by breaking down the sections of the paper, noting your initial thoughts and questions. Then structure your own critique so that you present a summary followed by your evaluation. In your critique, include the strengths and the weaknesses of the article.
Archibald D, Martimianakis MA. Writing, reading, and critiquing reviews . Can Med Educ J . 2021;12(3):1-7. doi:10.36834/cmej.72945
Pautasso M. Ten simple rules for writing a literature review . PLoS Comput Biol . 2013;9(7):e1003149. doi:10.1371/journal.pcbi.1003149
Gülpınar Ö, Güçlü AG. How to write a review article? Turk J Urol . 2013;39(Suppl 1):44–48. doi:10.5152/tud.2013.054
Erol A. Basics of writing review articles . Noro Psikiyatr Ars . 2022;59(1):1-2. doi:10.29399/npa.28093
American Psychological Association. Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (7th ed.). Washington DC: The American Psychological Association; 2019.
By Kendra Cherry, MSEd Kendra Cherry, MS, is a psychosocial rehabilitation specialist, psychology educator, and author of the "Everything Psychology Book."
Writing a Critique Paper: Seven Easy Steps
Were you assigned or asked by your professor to write a critique paper? It’s easy to write one. Just follow the following four steps in writing a critique paper and three steps in presenting it, then you’re ready to go.
One of the students’ requirements I specified in the course module is a critique paper. Just so everyone benefits from the guide I prepared for that class, I share it here.
Since they are graduate students, more is expected of them. Hence, most of the verbs I use in writing the lesson’s objectives reside in the domain of higher thinking skills or HOTS. Developing the students’ critical thinking skills will help them analyze future problems and propose solutions that embody environmental principles thus resonate desirable outcomes aligned with the goal of sustainable development.
Table of Contents
Step-by-step procedure in writing a critique paper, the four steps in writing a critique paper.
To write a good critique paper, it pays to adhere to a smooth flow of thought in your evaluation of the piece. You will need to introduce the topic, analyze, interpret, then conclude it.
Introduce the Discussion Topic
Introduce the topic of the critique paper. To capture the author’s idea, you may apply the 5Ws and 1H approach in writing your technical report.
The news article by John Doe was a narrative about a bank robbery. Accordingly, a masked man (Who) robbed a bank (What) the other day (When) next to a police station (Where) . He did so in broad daylight (How) . He used a bicycle to escape from the scene of the crime (How) . In his haste, he bumped into a post. His mask fell off; thus, everyone saw his face, allowing witnesses to describe him. As a result, he had difficulty escaping the police, who eventually retrieved his loot and put him in jail because of his wrongdoing (Why) .
Is the essay written to inform, entertain, educate, raise an issue for debate, and so on? Don’t parrot or repeat what the writer wrote in his paper. And write a paragraph or a few sentences as succinctly as you can.
Analyze means to break down the abstract ideas presented into manageable bits.
We can use an analogy here to clearly explain the analysis portion.
Thus, it would be best if you defined the tools of your analysis. Tools facilitate understanding and allow you to make an incisive analysis.
Now, you are ready to interpret the article, book, or any composition once the requisites of analysis are in place.
That fact confirms the first observation that he was not ready at all. Escaping the scene of the crime using a bicycle with nothing to defend himself once pursued? He’s insane. Unimaginable. He’s better off sleeping at home and waiting for food to land on his lap if food will come at all.
What? With bare knuckles? It makes little sense.
Assess or Evaluate
Finally, judge whether the article was a worthwhile account after all. Did it meet expectations? Was it able to convey the information most efficiently? Or are there loopholes or flaws that should have been mentioned?
Format of Presenting the Critique Paper
Introduction.
You can find the thesis in the paper’s hypothesis section. That’s because a hypothesis is a tentative thesis. Hypo means “below or under,” meaning it is the author’s tentative explanation of whatever phenomenon he tackles.
This section is similar to the results and discussion portion of a scientific paper. It describes the outcome of your analysis and interpretation.
I mention the gender issue because the literature says that there is a difference in how a person sees things based on gender. For example, Ragins & Sundstrom (1989) observed that it would be more difficult for women to obtain power in the organization than men. And there’s a paper on gender and emotions by Shields et al. (2006) , although I wouldn’t know the outcome of that study as it is behind a paywall. My point is just that there is a difference in perspective between men and women. Alright.
Read More : How to Write an Article with AI: A Guide to Using AI for Article Creation and Refinement
Related Reading
Related posts, high-end mobile devices: mobile learning made easy in six ways, why publish research findings, how to use research tools in managing your finances, about the author, patrick regoniel.
Dr. Regoniel, a faculty member of the graduate school, served as consultant to various environmental research and development projects covering issues and concerns on climate change, coral reef resources and management, economic valuation of environmental and natural resources, mining, and waste management and pollution. He has extensive experience on applied statistics, systems modelling and analysis, an avid practitioner of LaTeX, and a multidisciplinary web developer. He leverages pioneering AI-powered content creation tools to produce unique and comprehensive articles in this website.
SimplyEducate.Me Privacy Policy
45 Critique Examples

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

A critique is an in-depth analysis and evaluation of a work, idea, or event. Critical evaluation is considered a higher-order thinking skill necessary for logical reasoning and development of new ideas.
Critique not only includes critical evaluation of content, but also an assessment of the structure, style, and effectiveness of a work or idea in achieving its purpose.
The importance of critique lies in its capacity to challenge assumptions, illuminate underlying ideologies, and promote critical thinking.
We need critical thinking skills in order to make sound judgments, develop well-formed opinions, and enhance our understanding of our world.
As such, critique is a valuable tool for academic, artistic, and professional contexts, driving innovation, improvement, and progress.
Critique Examples
1. assessing relevance.
Relevance is all about whether the point being made is valuable for the broader discussion or debate.
For example, bringing up stars in an astrology discussion is relevant; discussing the price of fish at the supermarket, on the other hand, is completely irrelevant to an astrology discussion!
In a critique, it is essential to evaluate whether the presented arguments and statements are pertinent to the core theme or purpose.If the content is irrelevant, it detracts from the main message, undermining the overall credibility and effectiveness of the work.
Assessing Relevance Example : The lecture on marine biology seemed out of place at a conference primarily focused on space exploration and astrophysics.
2. Evaluating Accuracy
Evaluating accuracy involves scrutinizing the factual correctness and reliability of the information or arguments presented in a work or idea.
Meticulous fact-checking is central to this evaluation process, ensuring that the claims made are based on accurate information.
Inaccurate or misrepresented facts can compromise the integrity of the work, and undermine its value to its audience or stakeholders. So, evaluating accuracy is a fundamental task in critique, contributing to the credibility and trustworthiness of the work.
Evaluating Accuracy Example : During the review of a book on World War II history, discrepancies were found between the dates mentioned in the book and the accepted historical timeline, bringing into question the book’s accuracy.

3. Analyzing Structure
Analyzing structure refers to the process of examining the arrangement or plan of a work or idea. This is common, for example, in the critical analysis of art and fashion.
This process could involve looking at how the various elements are organized and interlinked to form a coherent whole.
There are different conventions about what a well-structured work or idea looks like, depending on the discipline. For example, in fashion, it may have to do with how the clothing accentuates body features, whereas in non-fiction, it might be able how well a text presents logically ordered elements that enable easier understanding and following of the topic.
Analyzing Structure Example: In a film critique, the reviewer noted how the narrative structure, with flashbacks interspersed at strategic points, amplified the emotional impact and depth of the story.
4. Considering Originality
Originality refers to the creativity, novelty, or freshness brought to a work or an idea.
For a critique, weighing originality involves exploring whether the work or idea offers new perspectives, unique themes, or innovative methods. Or, in contrast, does the work simply repeat tired old tropes ?
The level of originality can greatly enhance the value of a work or idea by stimulating thought, provoking discussion, or advancing knowledge.
In many fields, such as art, literature, and academia, originality is a highly sought characteristic since it identifies works or ideas that break from convention and inspire progress.
Originality Example: In a critique of a music album, it was noted that the artiste successfully incorporated a blend of traditional folk and modern electronic music in their compositions, enhancing the album’s originality.
5. Questioning Sources
Questioning sources involves scrutinizing the origin and credibility of the evidence supporting a work or an idea.
Sources provide the foundation for arguments and assertions in a work, and their reliability and relevance are crucial for validity.
In a critique, evaluating sources helps ascertain the accuracy and integrity of the work, ensuring the information is well-founded and correctly attributed.
This is particularly important in academic and journalistic works wherein the veracity and reliability of sources significantly affect the overall validity and strength of the work.
Questioning Sources Example: During the peer-review of a scientific paper, one reviewer questioned the credibility of a non-peer reviewed website that the author had used extensively to support their arguments.
6. Examining Clarity
Examining clarity refers to checking the transparency, simplicity, and comprehensibility of a work or an idea.
Clarity ensures that the message or argument is effectively communicated to and understood by the audience. It helps avoid misunderstandings and misinterpretations.
In a critique, clarity examination entails assessing the work’s language, terminology, and style, evaluating whether these elements facilitate understanding.
A work displaying a high degree of clarity allows its audience to comprehend and engage with its content with relative ease.
Examining Clarity Example: The reviewer of a mystery novel observed that the author’s clear and concise writing style made the complex plot twists and clues easy to follow throughout the story.
7. Appraising Depth
Appraising depth is the examination of how profound a work or an idea is. In other words, has this person said something of meaning, or only scraped the surface of the concept?
A deep and thorough treatment of the subject matter suggests nuanced understanding, and often adds value to the work or idea.
I often tell my students that to achieve depth in essays, they need to consider the level of detail, context, compare-and-contrast, and insight they have provided. Furthermore, they might want to consider various perspectives related to the topic, not just one.
Appraising Depth Example: Upon analyzing an analysis of economic policy, it was recognized that the author’s in-depth exploration of varying socioeconomic impacts showed their deep understanding and research into the subject matter.
8. Reviewing Consistency
Reviewing consistency entails checking for the uniformity and reliability of the arguments, facts, and tone within a work or an idea.
Consistency is important because it lends credibility and cohesiveness to a work or idea. It shows that the author has a clear understanding and thoughtful execution of their topic or theme.
In a critique, consistency is assessed by observing the steadiness of the work’s arguments, use of evidence, and tone. Any inconsistencies detract from the overall quality and reliability of the work.
Reviewing Consistency Example : In a politician’s speech critique, it was noted that their stance concerning environmental policies remained consistent, maintaining the same core arguments throughout each policy discussion, lending strength to their overall position.
9. Assessing Feasibility
When we assess feasibility, we’re assessing whether something is really practical or viable. Quite simply, we’re asking: “will this actually work?”
Assessing feasibility can include exploring aspects such as financial considerations, available resources, and time factors.
This method is particularly useful for the critique of a proposal, business plan, or research project. A feasible work or idea has a much higher chance of achieving its intended outcome, making it more reliable and, in the case of business, attractive to stakeholders such as investors.
Exploring Feasibility Example: The critique of an ambitious development plan included an assessment of its feasibility. Given the budget constraints and tight timeframe, the plan was determined to be unrealistic in its current form.
10. Scrutinizing Aesthetic Appeal
Scrutinizing aesthetic appeal involves assessing the visual or sensory attractiveness of a work or idea.
This is significant especially in fields such as art, design, and literature where aesthetic attractiveness can greatly enhance the appeal and appreciation of the work.
In a critique, this might involve reviewing elements such as color, composition, style, form, and intricacy to determine how well they harmonize to create an appealing visual or sensory output.
Scrutinizing Aesthetic Appeal Example: In a review of a new architectural structure, the critic lauded the creative blending of traditional and modern design elements, which added to the aesthetic appeal of the building.
11. Measuring Efficiency
Measuring efficiency relates to the examination of how optimally resources were utilized.
In a critique, efficiency measurement can relate to various elements including workflow, process design, time allocation, use of labor, or use of technology, among other things. A highly efficient operation minimizes waste, reduces costs, and maximizes results.
Measuring Efficiency Example : In a critique of a production process, it was observed that by adopting automation, the company significantly improved its efficiency, allowing it to produce more units in less time.
12. Gauging Effectiveness
Gauging effectiveness is about determining the success of a work or an idea in achieving its intended purpose or objective.
This requires an examination of the outcomes, results, or impact of the work or idea relative to its stated goals.
In a critique, this will often require a summative assessment of performance measures. An advertising campaign, for example, may require a poll or consumer survey to get the results of how effective it was in increasing brand awareness.
Gauging Effectiveness Example: A critique of an educational program looked at student test scores, classroom engagement, and teacher feedback to gauge how effectively the program was in improving student learning outcomes.
13. Investigating Methodology
Investigating methodology refers to the critical examination of the strategies, techniques, or procedures employed in the formulation of a work or an idea. This is particularly common in academic critique.
For example, this means examining the soundness and relevancy of the chosen methods in achieving the objective or producing the required results. Why did the person choose qualitative over quantitative methods? Was that a good idea, or did they miss an opportunity in this choice? Did they defend their choice sufficiently?
A well-chosen and properly executed methodology supports the conclusions and enhances the integrity and trustworthiness of a work or idea.
Investigating Methodology Example: In a critique of a psychological study, the peer-review process involved questioning the appropriateness of the chosen experimental design and statistical analysis techniques, thus investigating the research methodology.
14. Probing Author Bias
Probing author bias deals with uncovering and examining the unstated beliefs, values, or principles of the author which influence their claims.
Take, for example, a media critique, where you realize that the person writing a newspaper article has an underlying self-interest in what they’re saying. For example, someone who writes an article denying climate change may also have a lot of shares in a coal company, so they’ve got self-interest and bias inherent in their writing.
Probing Bias Example: In a critique of an economic policy proposal, the critic highlighted the underlying assumption that economic growth always leads to improved social welfare, provoking a deeper debate on the correlation between growth and welfare.
15. Judging Coherence
Judging coherence involves assessing how well the different parts of a work or an idea logically fit together to form a meaningful whole.
Coherence is vital in ensuring that a work or idea makes sense to the audience and that the overall message or argument is clear and consistent.
In a critique, examining coherence may include looking at how arguments are structured, how information is sequenced, and how concepts relate to each other.
A highly coherent work or idea effectively communicates its message or purpose, making it easy for its audience to understand and follow.
Judging Coherence Example : While critiquing an academic essay, the evaluator noted high coherence since the arguments were logically ordered, well connected, and systematically built up to support the overall thesis.
Other Techniques for Critique
Media Critique
- Evaluating cultural sensitivity.
- Analyzing representation and inclusivity.
- Examining bias and objectivity.
- Considering emotional resonance.
- Assessing narrative flow.
- Investigating technical proficiency (e.g., in films: cinematography, editing).
- Evaluating character development and depth.
- Probing thematic depth and complexity.
- Gauging audience reception and feedback.
- Analyzing historical context and accuracy.
Academic Critique
- Evaluating research methodology .
- Assessing the adequacy of literature review.
- Analyzing the validity of conclusions.
- Inspecting the rigor of data analysis.
- Questioning the reliability of the instruments used.
- Investigating potential conflicts of interest.
- Examining the relevance and recency of cited sources.
- Gauging the scope and limitations of the study.
- Evaluating the theoretical framework and its application.
- Assessing the generalizability of the findings to broader populations.
Business Critique
- Analyzing financial viability and profitability.
- Evaluating the effectiveness of marketing strategies.
- Assessing organizational structure and hierarchy.
- Investigating ethical business practices.
- Gauging scalability and growth potential.
- Reviewing talent acquisition and retention strategies.
- Examining stakeholder and shareholder relations.
- Scrutinizing supply chain and operational efficiencies.
- Evaluating product or service innovation and differentiation.
- Analyzing competitive positioning and market share.
The Difference Between Critique and Criticism
Critique is a good-faith evaluation of a range of factors, positive and negative, to provide constructive feedback on a topic. Criticism is a fully negative evaluation that’s often interpreted as an attack in bad faith.
- Critique is generally viewed as a detailed, analytical assessment aimed at understanding and improving a work or idea. This process usually involves constructive feedback, evaluating the strengths and the weaknesses while offering enlightening perspectives for enhancement. Sometimes, we call it ‘ constructive criticism ‘.
- Criticism often bears a negative connotation, focusing mainly on pointing out faults and shortcomings, often without providing considerable insight for improvement or recognizing the positive aspects of the work or idea.
| Aspect | Critique | Criticism |
|---|---|---|
| A detailed analysis and assessment of something, often emphasizing its positive and negative aspects. | Expressing disapproval or pointing out the faults or weaknesses in something or someone. | |
| Usually constructive and often involves a thorough examination. | Can be either constructive or negative. However, in everyday usage, it’s often perceived as negative. | |
| To provide feedback, enhance understanding, and promote improvement. | To highlight problems, mistakes, or flaws. Might be used to guide correction, but can also just be an expression of disapproval. | |
| More neutral, balanced, and analytical. | Can be neutral, but often tends toward being negative or disapproving. | |
| Common in academic, artistic, and professional settings. | Used in both formal and informal settings. | |
| Typically invites discussion and improvement based on the feedback. | Might lead to defensiveness or denial, especially if it’s perceived as an attack or overly negative. |
The act of critique is a powerful tool that adds depth to our understanding and interpretation of works or ideas. The multilayered aspects of critique, ranging from analyzing the structure to questioning underlying assumptions, work together to provide a holistic evaluation. It allows us to identify strengths, expose weaknesses, and ultimately discover ways to improve. Therefore, honing critique skills is critical for intellectual growth, creativity, and progression in numerous fields of study and professional arenas.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 119 Bloom’s Taxonomy Examples
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ All 6 Levels of Understanding (on Bloom’s Taxonomy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 15 Self-Actualization Examples (Maslow's Hierarchy)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ Forest Schools Philosophy & Curriculum, Explained!
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

- Writing well
How to write a critique
- Starting well
- How to write an annotated bibliography
- How to write a case study response
- How to write an empirical article
- How to write an essay
- How to write a literature review
- How to write a reflective task
- How to write a report
- Finishing well
Before you start writing, it is important to have a thorough understanding of the work that will be critiqued.
- Study the work under discussion.
- Make notes on key parts of the work.
- Develop an understanding of the main argument or purpose being expressed in the work.
- Consider how the work relates to a broader issue or context.
Example template
There are a variety of ways to structure a critique. You should always check your unit materials or Canvas site for guidance from your lecturer. The following template, which showcases the main features of a critique, is provided as one example.
Introduction
Typically, the introduction is short (less than 10% of the word length) and you should:
- name the work being reviewed as well as the date it was created and the name of the author/creator
- describe the main argument or purpose of the work
- explain the context in which the work was created - this could include the social or political context, the place of the work in a creative or academic tradition, or the relationship between the work and the creator’s life experience
- have a concluding sentence that signposts what your evaluation of the work will be - for instance, it may indicate whether it is a positive, negative, or mixed evaluation.
Briefly summarise the main points and objectively describe how the creator portrays these by using techniques, styles, media, characters or symbols. This summary should not be the focus of the critique and is usually shorter than the critical evaluation.
Critical evaluation
This section should give a systematic and detailed assessment of the different elements of the work, evaluating how well the creator was able to achieve the purpose through these. For example: you would assess the plot structure, characterisation and setting of a novel; an assessment of a painting would look at composition, brush strokes, colour and light; a critique of a research project would look at subject selection, design of the experiment, analysis of data and conclusions.
A critical evaluation does not simply highlight negative impressions. It should deconstruct the work and identify both strengths and weaknesses. It should examine the work and evaluate its success, in light of its purpose.
Examples of key critical questions that could help your assessment include:
- Who is the creator? Is the work presented objectively or subjectively?
- What are the aims of the work? Were the aims achieved?
- What techniques, styles, media were used in the work? Are they effective in portraying the purpose?
- What assumptions underlie the work? Do they affect its validity?
- What types of evidence or persuasion are used? Has evidence been interpreted fairly?
- How is the work structured? Does it favour a particular interpretation or point of view? Is it effective?
- Does the work enhance understanding of key ideas or theories? Does the work engage (or fail to engage) with key concepts or other works in its discipline?
This evaluation is written in formal academic style and logically presented. Group and order your ideas into paragraphs. Start with the broad impressions first and then move into the details of the technical elements. For shorter critiques, you may discuss the strengths of the works, and then the weaknesses. In longer critiques, you may wish to discuss the positive and negative of each key critical question in individual paragraphs.
To support the evaluation, provide evidence from the work itself, such as a quote or example, and you should also cite evidence from related sources. Explain how this evidence supports your evaluation of the work.
This is usually a very brief paragraph, which includes:
- a statement indicating the overall evaluation of the work
- a summary of the key reasons, identified during the critical evaluation, why this evaluation was formed
- in some circumstances, recommendations for improvement on the work may be appropriate.
Reference list
Include all resources cited in your critique. Check with your lecturer/tutor for which referencing style to use.
- Mentioned the name of the work, the date of its creation and the name of the creator?
- Accurately summarised the work being critiqued?
- Mainly focused on the critical evaluation of the work?
- Systematically outlined an evaluation of each element of the work to achieve the overall purpose?
- Used evidence, from the work itself as well as other sources, to back and illustrate my assessment of elements of the work?
- Formed an overall evaluation of the work, based on critical reading?
- Used a well structured introduction, body and conclusion?
- Used correct grammar, spelling and punctuation; clear presentation; and appropriate referencing style?
Further information
- University of New South Wales: Writing a Critical Review
- University of Toronto: The Book Review or Article Critique
Global links and information
- Referencing and using sources
- Background and development
- Changes to QUT cite|write
- Need more help?
- Current students
- Current staff
- TEQSA Provider ID: PRV12079 (Australian University)
- CRICOS No. 00213J
- ABN 83 791 724 622
- Last modified: 28-May-2024
- Accessibility
- Right to Information
- Feedback and suggestions

Acknowledgement of Traditional Owners
QUT acknowledges the Traditional Owners of the lands where QUT now stands.

Critique Paper
Ai generator.

A critique paper is an analytical essay focusing on evaluating and interpreting a piece of work, such as an article, book , film, or painting. The aim is to assess the work’s strengths and weaknesses, often comparing it to relevant standards or other works in the field. The writer should provide a balanced analysis, supporting their observations with evidence, to inform readers about the work’s value and significance.
Critique Paper Free PDF Bundle
What is a critique paper.
A critique paper is an analytical evaluation of a work, focusing on its strengths and weaknesses. It requires critical thinking to assess and discuss the work’s effectiveness and provide recommendations for improvement, often backed by evidence.
Types of Critique Paper
Critique papers can vary widely in focus and approach, depending on the subject and purpose. Here are some common types:
- Literature Critique : Evaluates books, articles, and other written materials, focusing on theme , style, and contribution to the field.
- Art Critique : Analyzes artworks in terms of technique, style, symbolism, and emotional impact.
- Film Critique : Examines films, discussing elements like narrative, directing, acting, and cinematography.
- Performance Critique : Reviews live performances such as plays, concerts, or dance shows, commenting on the performance, direction, and production values.
- Research Article Critique : Assesses scientific studies or academic research, focusing on methodology, data analysis, and the validity of conclusions.
- Business Critique : Looks at business practices, products , or company strategies to evaluate effectiveness and suggest improvements.
Purpose of Critique Paper
A critique paper serves several important academic and intellectual purposes, contributing to both the writer’s understanding and the broader scholarly community’s discussion on a subject. Here are the primary purposes of a critique paper:
- Analytical Thinking: Writing a critique paper encourages deep analytical thinking. It requires the writer to not only summarize the content of a work—be it a book, article, film, or art piece—but also to analyze its components critically. This process involves assessing the strengths and weaknesses of the work, understanding its structure, and evaluating its impact.
- Critical Engagement: A critique paper fosters engagement with ideas and arguments presented by others. Through critique, a writer interacts with the work’s themes, methodologies, and conclusions, providing a personal interpretation and positioning it within a larger scholarly context .
- Developing Arguments: One of the main goals of a critique paper is to develop and articulate a coherent and reasoned argument. The writer must present a clear thesis or main argument about the work being critiqued and support this thesis with evidence, logical reasoning, and systematic analysis.
- Enhancing Understanding: Writing a critique helps in deepening the writer’s understanding of the subject matter. By analyzing different aspects of a work and connecting them to broader themes and knowledge, the writer gains a more comprehensive insight into the topic.
- Scholarly Contribution: Critique papers contribute to academic discourse by adding to the diversity of interpretations and perspectives on a particular work or topic. This can influence how a work is understood in academic and professional fields, potentially leading to new insights and developments.
- Improving Writing and Research Skills: The process of writing a critique paper enhances a writer’s research and writing skills. It involves gathering information, synthesizing insights, formulating arguments, and composing a structured document—all essential skills in academic and professional settings.
- Preparation for Professional Activities: Especially in fields like literature, art , and film studies, critique papers prepare students and professionals to engage in critiques and discussions, which are common professional activities. This preparation can be crucial for career in academia, criticism, journalism, and beyond.
Critique Paper Format
A critique paper generally follows a structured format to ensure a thorough evaluation and clear presentation of thoughts. Here’s an outline of the typical format along with an example for a research article critique:
1. Introduction
- Background : Provide context for the work being critiqued.
- Thesis Statement : Present your main argument or overall impression of the work.
- Overview of the Work : Briefly describe the main points of the work.
In this critique, I evaluate the article “The Impact of Daily Exercise on Wellbeing” by Dr. Jane Smith, published in the 2020 edition of Health & Lifestyle. The article claims that daily exercise significantly improves mental health. This critique assesses the validity of Dr. Smith’s research methods and findings.
- Key Points : Summarize the main arguments, findings, or artistic elements of the work.
Dr. Smith’s article outlines a study conducted over 12 months involving 300 participants, exploring the effects of various exercise routines on mental health indicators such as stress, happiness, and overall life satisfaction.
3. Critique
- Methodology Evaluation : Analyze the methods used to determine their adequacy and fairness.
- Evidence Review : Discuss the evidence presented and whether it supports the claims.
- Bias and Limitations : Point out any biases or limitations within the work.
While Dr. Smith’s methodology of tracking participant wellbeing through self-reported surveys is insightful, the reliance on self-reporting can introduce bias and affect the reliability of the data. Furthermore, the study lacks a control group, which is crucial for comparing the effects observed.
4. Conclusion
- Summary of Critique : Recap your main points of critique.
- Final Assessment : Provide your final thoughts on the work’s overall validity and effectiveness.
- Recommendations : Suggest ways to improve or further areas for research.
In conclusion, although Dr. Smith’s findings provide valuable insights into the positive effects of daily exercise on mental health, the study’s methodologies could be strengthened by incorporating a control group and using more objective data collection methods. Future research should address these limitations to build on Dr. Smith’s work.
5. References
- Citation of the Work : Include all necessary citation information according to the academic style required.
Smith, J. (2020). The Impact of Daily Exercise on Wellbeing. Health & Lifestyle Journal, 15(4), 234-248.
Examples of Critique Paper
Here are the Examples of critique papers provide structured analyses and evaluations of various works, including books, films, and artworks. They illustrate how to critically assess themes, techniques, and overall impact.
Critique of a Novel
Critique of a film, critique of a scientific research article.


Critique Paper Examples for Students
Providing students with examples of critique papers can help them understand how to effectively analyze and evaluate different types of work, such as literature, films, research articles, and more. Here are three examples of critique paper topics, each tailored to a specific subject, that could be useful for students learning to write critiques:
- Critique of a Literary Work
- Critique of a Scientific Research Article: “Effects of Plastic Pollution on Marine Life”
- Critique of a Film: “Inception” Directed by Christopher Nolan
Critique Paper Examples for Short Story
Creating a critique for a short story involves analyzing elements such as plot, characters, setting, themes, and the author’s writing style. Here are three examples of critique papers for short stories that can help students learn to evaluate and interpret literature effectively:
- Critique of “The Lottery” by Shirley Jackson
- Critique of “Harrison Bergeron” by Kurt Vonnegut
- Critique of “The Yellow Wallpaper” by Charlotte Perkins Gilman
Feminist Critique Paper Examples
Feminist critique papers provide insightful analyses on literature, media, or cultural practices through the lens of feminist theory, highlighting issues of gender equality, representation, and the experiences of women. Here are three examples of feminist critique paper topics, each tailored to examine different subjects with a focus on feminist perspectives:
- Feminist Critique of “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen
- Feminist Analysis of “Mad Men”: A Look at Gender Roles in 1960s America
- Gender and Power in “Game of Thrones”: A Feminist Perspective
Art Critique Paper Examples
Art critique paper examples offer structured evaluations of various artworks, including paintings, sculptures, and photographs. These examples analyze themes, techniques, and emotional impact, providing insights into the artist’s intentions and the work’s significance. They serve as guides for understanding and articulating critical perspectives on art.
- Critique of “Starry Night” by Vincent van Gogh
- Critique of “The Thinker” by Auguste Rodin
- Critique of “Migrant Mother” by Dorothea Lange
Critique Paper Examples for Books
Critique paper examples for books provide detailed analyses and evaluations of various literary works, including novels, non-fiction, and classics. They examine themes, character development, writing style, and overall impact, offering insights into the strengths and weaknesses of each book. These examples guide readers in developing their own critical perspectives.
- Critique of “To Kill a Mockingbird” by Harper Lee
- Critique of “Sapiens: A Brief History of Humankind” by Yuval Noah Harari
- Critique of “Pride and Prejudice” by Jane Austen
Critique Paper Examples for Novel
Critique paper examples for novels offer in-depth analyses and evaluations of fictional works across genres. They explore themes, character development, plot structure, and writing style. These examples help readers understand the novel’s strengths and weaknesses, providing a framework for developing thoughtful, balanced critiques of literary fiction.
- Critique of “1984” by George Orwell
- Critique of “The Great Gatsby” by F. Scott Fitzgerald
- Critique of “Beloved” by Toni Morrison
Characteristics of Critique Paper
A critique paper is a detailed analysis and evaluation of a work, such as a book, article, film, or painting. It goes beyond merely summarizing the work by also providing a critical discussion regarding the quality and impact of the work. Here are some essential characteristics of a well-crafted critique paper:
- Analytical Focus: A critique paper primarily analyzes and evaluates the subject matter rather than just summarizing it. It discusses what the work does, how it does it, and how effectively the purpose of the work is achieved.
- Evidence-Based: Critiques are not just based on opinion; they are supported by evidence from the work itself. This might include quotations, examples, and detailed observations that back up the critique’s claims and conclusions.
- Balanced Argumentation: While it’s important to discuss what you perceive as the weaknesses of the work, a good critique also acknowledges its strengths. This balanced view helps to avoid bias and gives the paper credibility.
- Clear Structure: Like any formal piece of writing, a critique paper should be well-organized. It typically includes an introduction that states the work being critiqued and the main points of the critique, a body that discusses each point in detail, and a conclusion that summarizes the critique and may suggest broader implications or future directions.
- Critical Perspective: The critique should offer a distinct perspective that reflects critical thinking. It should engage with the work’s themes, techniques, and impact, providing a deeper understanding or new insights that go beyond the surface.
- Contextual Awareness: A critique considers the work in its broader context. This might include the historical, cultural, or academic context of the work, discussing how these elements influence the creation and reception of the work.
- Objective Tone: While personal responses can be included in a critique, the tone should remain objective and professional. The critique should focus on the work itself and its merits or faults, rather than on the author or creator as an individual.
- Thesis Statement: A strong critique paper features a clear thesis statement that guides the analysis. This statement typically outlines the main argument or viewpoint of the critique and sets the tone for the discussion.
- Engaging Writing: Effective critiques not only provide insights but are also engaging to read. They use persuasive language to make their points and maintain the reader’s interest throughout the paper.
- Reflective Insight: Beyond evaluating the work, a critique often reflects on its significance within a larger context or discipline. It may discuss how the work contributes to ongoing debates, trends, or theories within the field.
How to Write Critique Paper

Writing a critique paper involves a systematic analysis of a work (like an article, book, film, or painting), focusing on evaluating its various components and expressing your point of view. Here’s a structured guide on how to write a high-quality critique paper that’s SEO-friendly and well-suited for readability:
Understand the Assignment
Before you start writing, make sure you fully understand the requirements of your critique. Know whether you need to provide a general analysis or focus on a specific aspect of the work
Read or View the Work
Engage with the work thoroughly. If it’s a book or an article, read it multiple times. For films or exhibitions, consider multiple viewings. Take notes on key points, themes, and elements that stand out.
Develop a Thesis Statement
Your thesis is the central argument of your critique. It should state your main point clearly and concisely, expressing your overall opinion of the work. For instance, “John Doe’s ‘Modern Society’ effectively argues its point about social media addiction through compelling data and relatable personal stories, though it sometimes lacks sufficient counterarguments.”
Write an Introduction
Start with an engaging introduction that provides essential information about the work (title, author, type of work, and publication date) and ends with your thesis statement. This section sets the stage for your critique.
Summarize the Work
Briefly summarize the main points of the work to provide context for your analysis. Keep this part factual and neutral, covering key points that are relevant to your critique without going into excessive detail.
Critically Analyze the Work
In the body paragraphs, discuss your analysis of the work, supporting your thesis with evidence. Break down your critique into organized sections, such as: Content Evaluation: Analyze the accuracy, depth, and relevance of the information presented. Structure: Evaluate the organization and clarity of the work. Style: Consider the author’s writing style, use of language, and the appropriateness for the intended audience. Impact: Discuss the effectiveness and impact of the work on its audience.
Use Effective Transitions
Smooth transitions between paragraphs help guide the reader and improve the flow of your essay. Use transitional words and phrases to connect ideas.
Conclude Your Critique
Summarize your points briefly and restate your thesis in a new way in the conclusion. You might also discuss the broader implications of the work or suggest areas for further research or consideration.
Revise and Edit
Ensure your critique is clear and concise. Check for grammar and spelling errors, and make sure your arguments are logically structured. Compliance with SEO standards such as using familiar words, maintaining appropriate sentence length, and avoiding passive voice will enhance the readability and effectiveness of your critique.
Cite Your Sources
If you’ve used additional sources to support your critique or to understand the work, make sure to cite them appropriately to avoid plagiarism.
What is a critique paper?
A critique paper analyzes and evaluates the quality and significance of a work, such as an article, book, film, or painting.
How do I start a critique paper?
Begin with an engaging introduction that includes the work’s basic information and your thesis statement expressing your main evaluation.
What should be included in the body of a critique paper?
The body should include your detailed analysis, supported by evidence from the work, covering content, structure, style, and impact.
How do I conclude a critique paper?
Summarize the main points, restate your thesis in a new light, and possibly suggest areas for further research or implications.
How long should a critique paper be?
The length varies based on assignment requirements but typically ranges from 500 to 2000 words.
Do I need a thesis statement for a critique paper?
Yes, a clear thesis statement is crucial as it guides your analysis and states your overarching opinion of the work.
Can I include personal opinions in a critique paper?
Yes, personal opinions are valid as long as they are supported by evidence and reasoned analysis.
How do I cite sources in a critique paper?
Use the citation style specified by your instructor, typically APA, MLA, or Chicago, to cite all referenced materials.
What is the difference between a critique and a summary?
A critique offers a detailed evaluation and analysis, whereas a summary only provides a concise recap of the work’s main points.
How can I make my critique paper stand out?
Offer unique insights, engage deeply with the text, and provide a balanced evaluation that includes both strengths and weaknesses.
Text prompt
- Instructive
- Professional
10 Examples of Public speaking
20 Examples of Gas lighting

Writing Critiques
Writing a critique involves more than pointing out mistakes. It involves conducting a systematic analysis of a scholarly article or book and then writing a fair and reasonable description of its strengths and weaknesses. Several scholarly journals have published guides for critiquing other people’s work in their academic area. Search for a “manuscript reviewer guide” in your own discipline to guide your analysis of the content. Use this handout as an orientation to the audience and purpose of different types of critiques and to the linguistic strategies appropriate to all of them.
Types of critique
Article or book review assignment in an academic class.
Text: Article or book that has already been published Audience: Professors Purpose:
- to demonstrate your skills for close reading and analysis
- to show that you understand key concepts in your field
- to learn how to review a manuscript for your future professional work
Published book review
Text: Book that has already been published Audience: Disciplinary colleagues Purpose:
- to describe the book’s contents
- to summarize the book’s strengths and weaknesses
- to provide a reliable recommendation to read (or not read) the book
Manuscript review
Text: Manuscript that has been submitted but has not been published yet Audience: Journal editor and manuscript authors Purpose:
- to provide the editor with an evaluation of the manuscript
- to recommend to the editor that the article be published, revised, or rejected
- to provide the authors with constructive feedback and reasonable suggestions for revision
Language strategies for critiquing
For each type of critique, it’s important to state your praise, criticism, and suggestions politely, but with the appropriate level of strength. The following language structures should help you achieve this challenging task.
Offering Praise and Criticism
A strategy called “hedging” will help you express praise or criticism with varying levels of strength. It will also help you express varying levels of certainty in your own assertions. Grammatical structures used for hedging include:
Modal verbs Using modal verbs (could, can, may, might, etc.) allows you to soften an absolute statement. Compare:
This text is inappropriate for graduate students who are new to the field. This text may be inappropriate for graduate students who are new to the field.
Qualifying adjectives and adverbs Using qualifying adjectives and adverbs (possible, likely, possibly, somewhat, etc.) allows you to introduce a level of probability into your comments. Compare:
Readers will find the theoretical model difficult to understand. Some readers will find the theoretical model difficult to understand. Some readers will probably find the theoretical model somewhat difficult to understand completely.
Note: You can see from the last example that too many qualifiers makes the idea sound undesirably weak.
Tentative verbs Using tentative verbs (seems, indicates, suggests, etc.) also allows you to soften an absolute statement. Compare:
This omission shows that the authors are not aware of the current literature. This omission indicates that the authors are not aware of the current literature. This omission seems to suggest that the authors are not aware of the current literature.
Offering suggestions
Whether you are critiquing a published or unpublished text, you are expected to point out problems and suggest solutions. If you are critiquing an unpublished manuscript, the author can use your suggestions to revise. Your suggestions have the potential to become real actions. If you are critiquing a published text, the author cannot revise, so your suggestions are purely hypothetical. These two situations require slightly different grammar.
Unpublished manuscripts: “would be X if they did Y” Reviewers commonly point out weakness by pointing toward improvement. For instance, if the problem is “unclear methodology,” reviewers may write that “the methodology would be more clear if …” plus a suggestion. If the author can use the suggestions to revise, the grammar is “X would be better if the authors did Y” (would be + simple past suggestion).
The tables would be clearer if the authors highlighted the key results. The discussion would be more persuasive if the authors accounted for the discrepancies in the data.
Published manuscripts: “would have been X if they had done Y” If the authors cannot revise based on your suggestions, use the past unreal conditional form “X would have been better if the authors had done Y” (would have been + past perfect suggestion).
The tables would have been clearer if the authors had highlighted key results. The discussion would have been more persuasive if the authors had accounted for discrepancies in the data.
Note: For more information on conditional structures, see our Conditionals handout .

Make a Gift

How to Critique an Article: Mastering the Article Evaluation Process

Did you know that approximately 4.6 billion pieces of content are produced every day? From news articles and blog posts to scholarly papers and social media updates, the digital landscape is flooded with information at an unprecedented rate. In this age of information overload, honing the skill of articles critique has never been more crucial. Whether you're seeking to bolster your academic prowess, stay well-informed, or improve your writing, mastering the art of article critique is a powerful tool to navigate the vast sea of information and discern the pearls of wisdom.
How to Critique an Article: Short Description
In this article, we will equip you with valuable tips and techniques to become an insightful evaluator of written content. We present a real-life article critique example to guide your learning process and help you develop your unique critique style. Additionally, we explore the key differences between critiquing scientific articles and journals. Whether you're a student, researcher, or avid reader, this guide will empower you to navigate the vast ocean of information with confidence and discernment. Still, have questions? Don't worry! We've got you covered with a helpful FAQ section to address any lingering doubts. Get ready to unleash your analytical prowess and uncover the true potential of every article that comes your way!
What Is an Article Critique: Understanding The Power of Evaluation
An article critique is a valuable skill that involves carefully analyzing and evaluating a written piece, such as a journal article, blog post, or news article. It goes beyond mere summarization and delves into the deeper layers of the content, examining its strengths, weaknesses, and overall effectiveness. Think of it as an engaging conversation with the author, where you provide constructive feedback and insights.
For instance, let's consider a scenario where you're critiquing a research paper on climate change. Instead of simply summarizing the findings, you would scrutinize the methodology, data interpretation, and potential biases, offering thoughtful observations to enrich the discussion. Through the process of writing an article critique, you develop a critical eye, honing your ability to appreciate well-crafted work while also identifying areas for improvement.
In the following sections, our ' write my paper ' experts will uncover valuable tips on and key points on how to write a stellar critique, so let's explore more!
Unveiling the Key Aims of Writing an Article Critique
Writing an article critique serves several essential purposes that go beyond a simple review or summary. When engaging in the art of critique, as when you learn how to write a review article , you embark on a journey of in-depth analysis, sharpening your critical thinking skills and contributing to the academic and intellectual discourse. Primarily, an article critique allows you to:
%20(3).webp)
- Evaluate the Content : By critiquing an article, you delve into its content, structure, and arguments, assessing its credibility and relevance.
- Strengthen Your Critical Thinking : This practice hones your ability to identify strengths and weaknesses in written works, fostering a deeper understanding of complex topics and critical evaluation skills.
- Engage in Scholarly Dialogue : Your critique contributes to the ongoing academic conversation, offering valuable insights and thoughtful observations to the existing body of knowledge.
- Enhance Writing Skills : By analyzing and providing feedback, you develop a keen eye for effective writing techniques, benefiting your own writing endeavors.
- Promote Continuous Learning : Through the writing process, you continually refine your analytical abilities, becoming an avid and astute learner in the pursuit of knowledge.
How to Critique an Article: Steps to Follow
The process of crafting an article critique may seem overwhelming, especially when dealing with intricate academic writing. However, fear not, for it is more straightforward than it appears! To excel in this art, all you require is a clear starting point and the skill to align your critique with the complexities of the content. To help you on your journey, follow these 3 simple steps and unlock the potential to provide insightful evaluations:
%20(4).webp)
Step 1: Read the Article
The first and most crucial step when wondering how to do an article critique is to thoroughly read and absorb its content. As you delve into the written piece, consider these valuable tips from our custom essay writer to make your reading process more effective:
- Take Notes : Keep a notebook or digital document handy while reading. Jot down key points, noteworthy arguments, and any questions or observations that arise.
- Annotate the Text : Underline or highlight significant passages, quotes, or sections that stand out to you. Use different colors to differentiate between positive aspects and areas that may need improvement.
- Consider the Author's Purpose : Reflect on the author's main critical point and the intended audience. Much like an explanatory essay , evaluate how effectively the article conveys its message to the target readership.
Now, let's say you are writing an article critique on climate change. While reading, you come across a compelling quote from a renowned environmental scientist highlighting the urgency of addressing global warming. By taking notes and underlining this impactful quote, you can later incorporate it into your critique as evidence of the article's effectiveness in conveying the severity of the issue.
Step 2: Take Notes/ Make sketches
Once you've thoroughly read the article, it's time to capture your thoughts and observations by taking comprehensive notes or creating sketches. This step plays a crucial role in organizing your critique and ensuring you don't miss any critical points. Here's how to make the most out of this process:
- Highlight Key Arguments : Identify the main arguments presented by the author and highlight them in your notes. This will help you focus on the core ideas that shape the article.
- Record Supporting Evidence : Take note of any evidence, examples, or data the author uses to support their arguments. Assess the credibility and effectiveness of this evidence in bolstering their claims.
- Examine Structure and Flow : Pay attention to the article's structure and how each section flows into the next. Analyze how well the author transitions between ideas and whether the organization enhances or hinders the reader's understanding.
- Create Visual Aids : If you're a visual learner, consider using sketches or diagrams to map out the article's key points and their relationships. Visual representations can aid in better grasping the content's structure and complexities.
Step 3: Format Your Paper
Once you've gathered your notes and insights, it's time to give structure to your article critique. Proper formatting ensures your critique is organized, coherent, and easy to follow. Here are essential tips for formatting an article critique effectively:
- Introduction : Begin with a clear and engaging introduction that provides context for the article you are critiquing. Include the article's title, author's name, publication details, and a brief overview of the main theme or thesis.
- Thesis Statement : Present a strong and concise thesis statement that conveys your overall assessment of the article. Your thesis should reflect whether you found the article compelling, convincing, or in need of improvement.
- Body Paragraphs : Organize your critique into well-structured body paragraphs. Each paragraph should address a specific point or aspect of the article, supported by evidence and examples from your notes.
- Use Evidence : Back up your critique with evidence from the article itself. Quote relevant passages, cite examples, and reference data to strengthen your analysis and demonstrate your understanding of the article's content.
- Conclusion : Conclude your critique by summarizing your main points and reiterating your overall evaluation. Avoid introducing new arguments in the conclusion and instead provide a concise and compelling closing statement.
- Citation Style : If required, adhere to the specific citation style guidelines (e.g., APA, MLA) for in-text citations and the reference list. Properly crediting the original article and any additional sources you use in your critique is essential.
How to Critique a Journal Article: Mastering the Steps
So, you've been assigned the task of critiquing a journal article, and not sure where to start? Worry not, as we've prepared a comprehensive guide with different steps to help you navigate this process with confidence. Journal articles are esteemed sources of scholarly knowledge, and effectively critiquing them requires a systematic approach. Let's dive into the steps to expertly evaluate and analyze a journal article:
Step 1: Understanding the Research Context
Begin by familiarizing yourself with the broader research context in which the journal article is situated. Learn about the field, the topic's significance, and any previous relevant research. This foundational knowledge will provide a valuable backdrop for your journal article critique example.
Step 2: Evaluating the Article's Structure
Assess the article's overall structure and organization. Examine how the introduction sets the stage for the research and how the discussion flows logically from the methodology and results. A well-structured article enhances readability and comprehension.
Step 3: Analyzing the Research Methodology
Dive into the research methodology section, which outlines the approach used to gather and analyze data. Scrutinize the study's design, data collection methods, sample size, and any potential biases or limitations. Understanding the research process will enable you to gauge the article's reliability.
Step 4: Assessing the Data and Results
Examine the presentation of data and results in the article. Are the findings clear and effectively communicated? Look for any discrepancies between the data presented and the interpretations made by the authors.
Step 5: Analyzing the Discussion and Conclusions
Evaluate the discussion section, where the authors interpret their findings and place them in the broader context. Assess the soundness of their conclusions, considering whether they are adequately supported by the data.
Step 6: Considering Ethical Considerations
Reflect on any ethical considerations raised by the research. Assess whether the study respects the rights and privacy of participants and adheres to ethical guidelines.
Step 7: Identifying Strengths and Weaknesses
Identify the article's strengths, such as well-designed experiments, comprehensive, relevant literature reviews, or innovative approaches. Also, pinpoint any weaknesses, like gaps in the research, unclear explanations, or insufficient evidence.
Step 8: Offering Constructive Feedback
Provide constructive feedback to the authors, highlighting both positive aspects and areas for improvement for future research. Suggest ways to enhance the research methods, data analysis, or discussion to bolster its overall quality.
Step 9: Presenting Your Critique
Organize your critique into a well-structured paper, starting with an introduction that outlines the article's context and purpose. Develop a clear and focused thesis statement that conveys your assessment. Support your points with evidence from the article and other credible sources.
By following these steps on how to critique a journal article, you'll be well-equipped to craft a thoughtful and insightful piece, contributing to the scholarly discourse in your field of study!
Got an Article that Needs Some Serious Critiquing?
Don't sweat it! Our critique maestros are armed with wit, wisdom, and a dash of magic to whip that piece into shape.
An Article Critique: Journal Vs. Research
In the realm of academic writing, the terms 'journal article' and 'research paper' are often used interchangeably, which can lead to confusion about their differences. Understanding the distinctions between critiquing a research article and a journal piece is essential. Let's delve into the key characteristics that set apart a journal article from a research paper and explore how the critique process may differ for each:
Publication Scope:
- Journal Article: Presents focused and concise research findings or new insights within a specific subject area.
- Research Paper: Explores a broader range of topics and can cover extensive research on a particular subject.
Format and Structure:
- Journal Article: Follows a standardized format with sections such as abstract, introduction, methodology, results, discussion, and conclusion.
- Research Paper: May not adhere to a specific format and allows flexibility in organizing content based on the research scope.
Depth of Analysis:
- Journal Article: Provides a more concise and targeted analysis of the research topic or findings.
- Research Paper: Offers a more comprehensive and in-depth analysis, often including extensive literature reviews and data analyses.
- Journal Article: Typically shorter in length, ranging from a few pages to around 10-15 pages.
- Research Paper: Tends to be longer, spanning from 20 to several hundred pages, depending on the research complexity.
Publication Type:
- Journal Article: Published in academic journals after undergoing rigorous peer review.
- Research Paper: May be published as a standalone work or as part of a thesis, dissertation, or academic report.
- Journal Article: Targeted at academics, researchers, and professionals within the specific field of study.
- Research Paper: Can cater to a broader audience, including students, researchers, policymakers, and the general public.
- Journal Article: Primarily aimed at sharing new research findings, contributing to academic discourse, and advancing knowledge in the field.
- Research Paper: Focuses on comprehensive exploration and analysis of a research topic, aiming to make a substantial contribution to the body of knowledge.
Appreciating these differences becomes paramount when engaging in the critique of these two forms of scholarly publications, as they each demand a unique approach and thoughtful consideration of their distinctive attributes. And if you find yourself desiring a flawlessly crafted research article critique example, entrusting the task to professional writers is always an excellent option – you can easily order essay that meets your needs.
Article Critique Example
Our collection of essay samples offers a comprehensive and practical illustration of the critique process, granting you access to valuable insights.
Tips on How to Critique an Article
Critiquing an article requires a keen eye, critical thinking, and a thoughtful approach to evaluating its content. To enhance your article critique skills and provide insightful analyses, consider incorporating these five original and practical tips into your process:
1. Analyze the Author's Bias : Be mindful of potential biases in the article, whether they are political, cultural, or personal. Consider how these biases may influence the author's perspective and the presentation of information. Evaluating the presence of bias enables you to discern the objectivity and credibility of the article's arguments.
2. Examine the Supporting Evidence : Scrutinize the quality and relevance of the evidence used to support the article's claims. Look for well-researched data, credible sources, and up-to-date statistics. Assess how effectively the author integrates evidence to build a compelling case for their arguments.
3. Consider the Audience's Perspective : Put yourself in the shoes of the intended audience and assess how well the article communicates its ideas. Consider whether the language, tone, and level of complexity are appropriate for the target readership. A well-tailored article is more likely to engage and resonate with its audience.
4. Investigate the Research Methodology : If the article involves research or empirical data, delve into the methodology used to gather and analyze the information. Evaluate the soundness of the study design, sample size, and data collection methods. Understanding the research process adds depth to your critique.
5. Discuss the Implications and Application : Consider the broader implications of the article's findings or arguments. Discuss how the insights presented in the article could impact the field of study or have practical applications in real-world scenarios. Identifying the potential consequences of the article's content strengthens your critique's depth and relevance.
Wrapping Up
In a nutshell, article critique is an essential skill that helps us grow as critical thinkers and active participants in academia. Embrace the opportunity to analyze and offer constructive feedback, contributing to a brighter future of knowledge and understanding. Remember, each critique is a chance to engage with new ideas and expand our horizons. So, keep honing your critique skills and enjoy the journey of discovery in the world of academic exploration!
Tired of Ordinary Critiques?
Brace yourself for an extraordinary experience! Our critique geniuses are on standby, ready to unleash their extraordinary skills on your article!
What Steps Need to Be Taken in Writing an Article Critique?
What is the recommended length for an article critique.

is an expert in nursing and healthcare, with a strong background in history, law, and literature. Holding advanced degrees in nursing and public health, his analytical approach and comprehensive knowledge help students navigate complex topics. On EssayPro blog, Adam provides insightful articles on everything from historical analysis to the intricacies of healthcare policies. In his downtime, he enjoys historical documentaries and volunteering at local clinics.

- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
- English Grammar
- Writing Paragraphs
How to Write a Critique in Five Paragraphs
Last Updated: January 20, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Diane Stubbs . Diane Stubbs is a Secondary English Teacher with over 22 years of experience teaching all high school grade levels and AP courses. She specializes in secondary education, classroom management, and educational technology. Diane earned a Bachelor of Arts in English from the University of Delaware and a Master of Education from Wesley College. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 974,692 times.
A critique is usually written in response to a creative work, such as a novel, a film, poetry, or a painting. However, critiques are also sometimes assigned for research articles and media items, such as news articles or features. A critique is slightly different than a traditional 5-paragraph theme, as it is usually focused on the overall effectiveness and usefulness of the work it is critiquing, rather than making a strictly analytical argument about it. Organizing your critique into 5 paragraphs can help you structure your thoughts.
Laying the Groundwork

- Does the creator clearly state her/his main point or goal? If not, why do you think that is?
- Who do you think is the creator’s intended audience? This can be crucial to determining the success of a work; for example, a movie intended for young children might work well for its intended audience but not for adult viewers.
- What reactions do you have when reading or viewing this work? Does it provoke emotional responses? Do you feel confused?
- What questions does the work make you think of? Does it suggest other avenues of exploration or observation to you?

- For example, if you're critiquing a research article about a new treatment for the flu, a little research about other flu treatments currently available could be helpful to you when situating the work in context.
- As another example, if you're writing about a movie, you might want to briefly discuss the director's other films, or other important movies in this particular genre (indie, action, drama, etc.).
- Your school or university library is usually a good place to start when conducting research, as their databases provide verified, expert sources. Google Scholar can also be a good source for research.
Writing the Introductory Paragraph

- For a work of fiction or a published work of journalism or research, this information is usually available in the publication itself, such as on the copyright page for a novel.
- For a film, you may wish to refer to a source such as IMDb to get the information you need. If you're critiquing a famous artwork, an encyclopedia of art would be a good place to find information on the creator, the title, and important dates (date of creation, date of exhibition, etc.).

- For example, if you’re assessing a research article in the sciences, a quick overview of its place in the academic discussion could be useful (e.g., “Professor X’s work on fruit flies is part of a long research tradition on Blah Blah Blah.”)
- If you are evaluating a painting, giving some brief information on where it was first displayed, for whom it was painted, etc., would be useful.
- If you are assessing a novel, it could be good to talk about what genre or literary tradition the novel is written within (e.g., fantasy, High Modernism, romance). You may also want to include details about the author’s biography that seem particularly relevant to your critique.
- For a media item, such as a news article, consider the social and/or political context of the media outlet the item came from (e.g., Fox News, BBC, etc.) and of the issue it is dealing with (e.g., immigration, education, entertainment).

- The authors of research articles will often state very clearly in the abstract and in the introduction to their work what they are investigating, often with sentences that say something like this: "In this article we provide a new framework for analyzing X and argue that it is superior to previous methods because of reason A and reason B."
- For creative works, you may not have an explicit statement from the author or creator about their purpose, but you can often infer one from the context the work occupies. For example, if you were examining the movie The Shining, you might argue that the filmmaker Stanley Kubrick's goal is to call attention to the poor treatment of Native Americans because of the strong Native American themes present in the movie. You could then present the reasons why you think that in the rest of the essay.

- For example, if you were writing about The Shining, you could summarize the main points this way: "Stanley Kubrick uses strong symbolism, such as the placement of the movie's hotel on an Indian burial ground, the naming of the hotel "Overlook," and the constant presence of Native American artwork and representation, to call viewers' attention to America's treatment of Native Americans in history."

- For a research article, you will probably want to focus your thesis on whether the research and discussion supported the authors' claims. You may also wish to critique the research methodology, if there are obvious flaws present.
- For creative works, consider what you believe the author or creator's goal was in making the work, and then present your assessment of whether or not they achieved that goal.
Writing the 3 Body Paragraphs

- If you have three clear points about your work, you can organize each paragraph by point. For example, if you are analyzing a painting, you might critique the painter’s use of color, light, and composition, devoting a paragraph to each topic.
- If you have more than three points about your work, you can organize each paragraph thematically. For example, if you are critiquing a movie and want to talk about its treatment of women, its screenwriting, its pacing, its use of color and framing, and its acting, you might think about the broader categories that these points fall into, such as “production” (pacing, color and framing, screenwriting), “social commentary” (treatment of women), and “performance” (acting).
- Alternatively, you could organize your critique by “strengths” and “weaknesses.” The aim of a critique is not merely to criticize, but to point out what the creator or author has done well and what s/he has not.

- For example, if you are critiquing a song, you could consider how the beat or tone of the music supports or detracts from the lyrics.
- For a research article or a media item, you may want to consider questions such as how the data was gathered in an experiment, or what method a journalist used to discover information.

- Does the author use primary sources (e.g., historical documents, interviews, etc.)? Secondary sources? Quantitative data? Qualitative data? Are these sources appropriate for the argument?
- Has evidence been presented fairly, without distortion or selectivity?
- Does the argument proceed logically from the evidence used?

- If the work is a creative work, consider whether it presents its ideas in an original or interesting way. You can also consider whether it engages with key concepts or ideas in popular culture or society.
- If the work is a research article, you can consider whether the work enhances your understanding of a particular theory or idea in its discipline. Research articles often include a section on “further research” where they discuss the contributions their research has made and what future contributions they hope to make.

Writing the Conclusion Paragraph and References

Sample Critiques

Community Q&A
- Before you begin writing, take notes while you are watching or reading the subject of your critique. Keep to mind certain aspects such as how it made you feel. What was your first impression? With deeper examination, what is your overall opinion? How did you come to this opinion? Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0
- While the 5-paragraph form can work very well to help you organize your ideas, some instructors do not allow this type of essay. Be sure that you understand the assignment. If you’re not sure whether a 5-paragraph format is acceptable to your teacher, ask! Thanks Helpful 0 Not Helpful 0

- Avoid using first and second person pronouns such as, “you”, “your”, “I”, “my”, or “mine.” State your opinion objectively for a more credible approach. Thanks Helpful 39 Not Helpful 14
You Might Also Like

- ↑ https://www.indeed.com/career-advice/career-development/how-to-write-a-critique
- ↑ https://writingcenter.uagc.edu/writing-article-critique
- ↑ https://www.citewrite.qut.edu.au/write/writing-well/critique.html
- ↑ http://www.writing.utoronto.ca/advice/specific-types-of-writing/book-review
- ↑ https://www.hunter.cuny.edu/rwc/handouts/the-writing-process-1/invention/Writing-a-Critique
- ↑ https://writingcenter.unc.edu/esl/resources/writing-critiques/
About This Article

To write a 5-paragraph critique, provide the basic information about the work you're critiquing in the first paragraph, including the author, when it was published, and what its key themes are. Then, conclude this paragraph with a statement of your opinion of the work. Next, identify 3 central positive or negative issues in the work and write a paragraph about each one. For example, you could focus on the color, light, and composition of a painting. In the final paragraph, state your overall assessment of the work, and give reasons to back it up. For tips on how to take notes on the piece your critiquing, read on! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
Lura Norton
Feb 7, 2017
Did this article help you?

Ahmed Misry
Sep 30, 2017
Celia Seecharan
Feb 11, 2017
Sep 23, 2017
Lusady Taylor
Jul 28, 2016

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Don’t miss out! Sign up for
wikiHow’s newsletter

- Spartanburg Community College Library
- SCC Research Guides
- Writing a Critique
- Parts of a Critique
Depending on the source you are critiquing, your critique may not follow this exact format below. However, in general, critiques will be formatted in a similar way.
Introduction
- The name of the source or event
- What kind of source it is (book, film, lecture, etc.)
- The name of the author or the speaker
- The author or speaker's experience/expertise on the topic
- The main argument in the source (or the thesis statement of the source)
- The intended (target) audience for the source or event
- The purpose of the source or the event
- Did the author/speaker well-support their thesis statement?
- Did the author use any interest supports (stories, humor, examples, interactions, personal experience, etc.). Were they effective?
- What kind of evidence did the author/speaker use in the source (statistics, facts, quotations, surveys, studies, interviews, expert opinions). Are these resources credible/reliable? Did the evidence add to or contradict the author/speaker's argument?
- Did the source have quality content (avoiding fillers, presented newsworthy information, kept audiences interested)?
- Did the source use any visual aids (PowerPoint, images, artwork, etc.). Did the visual aids match or enhance what the author/speaker was discussing? Were the visual aids clearly organized, spell-checked, and included citations?
- Did the speaker move well through different topics?
- If the source was a live event or a recording, was the speaker energetic? Did they talk to the crowd or did they look at their notes too much? Were you able to hear and understand the speaker?
- If you're critiquing a film, were the film techniques used effective?
Conclusion/Recommendation
- What was your overall impression of the source?
- Would you recommend this source to others? Why or why not?
- What are your final thoughts about the source?
Helpful Handouts
- Sample Critique Paper Check out a sample critique essay of an event a student attended.
- How to Critique for a Live Performance (WOW) This worksheet will provide an outline of how to write a critique for the Wonders of Writing (WOW) event at SCC.
- How to Critique a Live/Zoom Presentation (Informational Presentation) This worksheet will show the outline for writing a critique for a live or a Zoom informational presentation.
- << Previous: Writing a Critique
- Next: Recommended Videos >>
- Recommended Videos
- Recommended Websites
Questions? Ask a Librarian

- Last Updated: May 8, 2024 9:31 AM
- URL: https://libguides.sccsc.edu/writingacritique
Giles Campus | 864.592.4764 | Toll Free 866.542.2779 | Contact Us
Copyright © 2024 Spartanburg Community College. All rights reserved.
Info for Library Staff | Guide Search
Return to SCC Website
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to write a literary analysis essay | A step-by-step guide
How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide
Published on January 30, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on August 14, 2023.
Literary analysis means closely studying a text, interpreting its meanings, and exploring why the author made certain choices. It can be applied to novels, short stories, plays, poems, or any other form of literary writing.
A literary analysis essay is not a rhetorical analysis , nor is it just a summary of the plot or a book review. Instead, it is a type of argumentative essay where you need to analyze elements such as the language, perspective, and structure of the text, and explain how the author uses literary devices to create effects and convey ideas.
Before beginning a literary analysis essay, it’s essential to carefully read the text and c ome up with a thesis statement to keep your essay focused. As you write, follow the standard structure of an academic essay :
- An introduction that tells the reader what your essay will focus on.
- A main body, divided into paragraphs , that builds an argument using evidence from the text.
- A conclusion that clearly states the main point that you have shown with your analysis.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
Step 1: reading the text and identifying literary devices, step 2: coming up with a thesis, step 3: writing a title and introduction, step 4: writing the body of the essay, step 5: writing a conclusion, other interesting articles.
The first step is to carefully read the text(s) and take initial notes. As you read, pay attention to the things that are most intriguing, surprising, or even confusing in the writing—these are things you can dig into in your analysis.
Your goal in literary analysis is not simply to explain the events described in the text, but to analyze the writing itself and discuss how the text works on a deeper level. Primarily, you’re looking out for literary devices —textual elements that writers use to convey meaning and create effects. If you’re comparing and contrasting multiple texts, you can also look for connections between different texts.
To get started with your analysis, there are several key areas that you can focus on. As you analyze each aspect of the text, try to think about how they all relate to each other. You can use highlights or notes to keep track of important passages and quotes.
Language choices
Consider what style of language the author uses. Are the sentences short and simple or more complex and poetic?
What word choices stand out as interesting or unusual? Are words used figuratively to mean something other than their literal definition? Figurative language includes things like metaphor (e.g. “her eyes were oceans”) and simile (e.g. “her eyes were like oceans”).
Also keep an eye out for imagery in the text—recurring images that create a certain atmosphere or symbolize something important. Remember that language is used in literary texts to say more than it means on the surface.
Narrative voice
Ask yourself:
- Who is telling the story?
- How are they telling it?
Is it a first-person narrator (“I”) who is personally involved in the story, or a third-person narrator who tells us about the characters from a distance?
Consider the narrator’s perspective . Is the narrator omniscient (where they know everything about all the characters and events), or do they only have partial knowledge? Are they an unreliable narrator who we are not supposed to take at face value? Authors often hint that their narrator might be giving us a distorted or dishonest version of events.
The tone of the text is also worth considering. Is the story intended to be comic, tragic, or something else? Are usually serious topics treated as funny, or vice versa ? Is the story realistic or fantastical (or somewhere in between)?
Consider how the text is structured, and how the structure relates to the story being told.
- Novels are often divided into chapters and parts.
- Poems are divided into lines, stanzas, and sometime cantos.
- Plays are divided into scenes and acts.
Think about why the author chose to divide the different parts of the text in the way they did.
There are also less formal structural elements to take into account. Does the story unfold in chronological order, or does it jump back and forth in time? Does it begin in medias res —in the middle of the action? Does the plot advance towards a clearly defined climax?
With poetry, consider how the rhyme and meter shape your understanding of the text and your impression of the tone. Try reading the poem aloud to get a sense of this.
In a play, you might consider how relationships between characters are built up through different scenes, and how the setting relates to the action. Watch out for dramatic irony , where the audience knows some detail that the characters don’t, creating a double meaning in their words, thoughts, or actions.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Your thesis in a literary analysis essay is the point you want to make about the text. It’s the core argument that gives your essay direction and prevents it from just being a collection of random observations about a text.
If you’re given a prompt for your essay, your thesis must answer or relate to the prompt. For example:
Essay question example
Is Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” a religious parable?
Your thesis statement should be an answer to this question—not a simple yes or no, but a statement of why this is or isn’t the case:
Thesis statement example
Franz Kafka’s “Before the Law” is not a religious parable, but a story about bureaucratic alienation.
Sometimes you’ll be given freedom to choose your own topic; in this case, you’ll have to come up with an original thesis. Consider what stood out to you in the text; ask yourself questions about the elements that interested you, and consider how you might answer them.
Your thesis should be something arguable—that is, something that you think is true about the text, but which is not a simple matter of fact. It must be complex enough to develop through evidence and arguments across the course of your essay.
Say you’re analyzing the novel Frankenstein . You could start by asking yourself:
Your initial answer might be a surface-level description:
The character Frankenstein is portrayed negatively in Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
However, this statement is too simple to be an interesting thesis. After reading the text and analyzing its narrative voice and structure, you can develop the answer into a more nuanced and arguable thesis statement:
Mary Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as.
Remember that you can revise your thesis statement throughout the writing process , so it doesn’t need to be perfectly formulated at this stage. The aim is to keep you focused as you analyze the text.
Finding textual evidence
To support your thesis statement, your essay will build an argument using textual evidence —specific parts of the text that demonstrate your point. This evidence is quoted and analyzed throughout your essay to explain your argument to the reader.
It can be useful to comb through the text in search of relevant quotations before you start writing. You might not end up using everything you find, and you may have to return to the text for more evidence as you write, but collecting textual evidence from the beginning will help you to structure your arguments and assess whether they’re convincing.
To start your literary analysis paper, you’ll need two things: a good title, and an introduction.
Your title should clearly indicate what your analysis will focus on. It usually contains the name of the author and text(s) you’re analyzing. Keep it as concise and engaging as possible.
A common approach to the title is to use a relevant quote from the text, followed by a colon and then the rest of your title.
If you struggle to come up with a good title at first, don’t worry—this will be easier once you’ve begun writing the essay and have a better sense of your arguments.
“Fearful symmetry” : The violence of creation in William Blake’s “The Tyger”
The introduction
The essay introduction provides a quick overview of where your argument is going. It should include your thesis statement and a summary of the essay’s structure.
A typical structure for an introduction is to begin with a general statement about the text and author, using this to lead into your thesis statement. You might refer to a commonly held idea about the text and show how your thesis will contradict it, or zoom in on a particular device you intend to focus on.
Then you can end with a brief indication of what’s coming up in the main body of the essay. This is called signposting. It will be more elaborate in longer essays, but in a short five-paragraph essay structure, it shouldn’t be more than one sentence.
Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein is often read as a crude cautionary tale about the dangers of scientific advancement unrestrained by ethical considerations. In this reading, protagonist Victor Frankenstein is a stable representation of the callous ambition of modern science throughout the novel. This essay, however, argues that far from providing a stable image of the character, Shelley uses shifting narrative perspectives to portray Frankenstein in an increasingly negative light as the novel goes on. While he initially appears to be a naive but sympathetic idealist, after the creature’s narrative Frankenstein begins to resemble—even in his own telling—the thoughtlessly cruel figure the creature represents him as. This essay begins by exploring the positive portrayal of Frankenstein in the first volume, then moves on to the creature’s perception of him, and finally discusses the third volume’s narrative shift toward viewing Frankenstein as the creature views him.
Some students prefer to write the introduction later in the process, and it’s not a bad idea. After all, you’ll have a clearer idea of the overall shape of your arguments once you’ve begun writing them!
If you do write the introduction first, you should still return to it later to make sure it lines up with what you ended up writing, and edit as necessary.
The body of your essay is everything between the introduction and conclusion. It contains your arguments and the textual evidence that supports them.
Paragraph structure
A typical structure for a high school literary analysis essay consists of five paragraphs : the three paragraphs of the body, plus the introduction and conclusion.
Each paragraph in the main body should focus on one topic. In the five-paragraph model, try to divide your argument into three main areas of analysis, all linked to your thesis. Don’t try to include everything you can think of to say about the text—only analysis that drives your argument.
In longer essays, the same principle applies on a broader scale. For example, you might have two or three sections in your main body, each with multiple paragraphs. Within these sections, you still want to begin new paragraphs at logical moments—a turn in the argument or the introduction of a new idea.
Robert’s first encounter with Gil-Martin suggests something of his sinister power. Robert feels “a sort of invisible power that drew me towards him.” He identifies the moment of their meeting as “the beginning of a series of adventures which has puzzled myself, and will puzzle the world when I am no more in it” (p. 89). Gil-Martin’s “invisible power” seems to be at work even at this distance from the moment described; before continuing the story, Robert feels compelled to anticipate at length what readers will make of his narrative after his approaching death. With this interjection, Hogg emphasizes the fatal influence Gil-Martin exercises from his first appearance.
Topic sentences
To keep your points focused, it’s important to use a topic sentence at the beginning of each paragraph.
A good topic sentence allows a reader to see at a glance what the paragraph is about. It can introduce a new line of argument and connect or contrast it with the previous paragraph. Transition words like “however” or “moreover” are useful for creating smooth transitions:
… The story’s focus, therefore, is not upon the divine revelation that may be waiting beyond the door, but upon the mundane process of aging undergone by the man as he waits.
Nevertheless, the “radiance” that appears to stream from the door is typically treated as religious symbolism.
This topic sentence signals that the paragraph will address the question of religious symbolism, while the linking word “nevertheless” points out a contrast with the previous paragraph’s conclusion.
Using textual evidence
A key part of literary analysis is backing up your arguments with relevant evidence from the text. This involves introducing quotes from the text and explaining their significance to your point.
It’s important to contextualize quotes and explain why you’re using them; they should be properly introduced and analyzed, not treated as self-explanatory:
It isn’t always necessary to use a quote. Quoting is useful when you’re discussing the author’s language, but sometimes you’ll have to refer to plot points or structural elements that can’t be captured in a short quote.
In these cases, it’s more appropriate to paraphrase or summarize parts of the text—that is, to describe the relevant part in your own words:
The conclusion of your analysis shouldn’t introduce any new quotations or arguments. Instead, it’s about wrapping up the essay. Here, you summarize your key points and try to emphasize their significance to the reader.
A good way to approach this is to briefly summarize your key arguments, and then stress the conclusion they’ve led you to, highlighting the new perspective your thesis provides on the text as a whole:
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
By tracing the depiction of Frankenstein through the novel’s three volumes, I have demonstrated how the narrative structure shifts our perception of the character. While the Frankenstein of the first volume is depicted as having innocent intentions, the second and third volumes—first in the creature’s accusatory voice, and then in his own voice—increasingly undermine him, causing him to appear alternately ridiculous and vindictive. Far from the one-dimensional villain he is often taken to be, the character of Frankenstein is compelling because of the dynamic narrative frame in which he is placed. In this frame, Frankenstein’s narrative self-presentation responds to the images of him we see from others’ perspectives. This conclusion sheds new light on the novel, foregrounding Shelley’s unique layering of narrative perspectives and its importance for the depiction of character.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, August 14). How to Write a Literary Analysis Essay | A Step-by-Step Guide. Scribbr. Retrieved June 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/literary-analysis/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis statement | 4 steps & examples, academic paragraph structure | step-by-step guide & examples, how to write a narrative essay | example & tips, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
Home — Essay Samples — Literature — Harrison Bergeron — Harrison Bergeron: A Dystopian Critique of Equality
Harrison Bergeron: a Dystopian Critique of Equality
- Categories: Harrison Bergeron Kurt Vonnegut
About this sample

Words: 690 |
Published: Jun 13, 2024
Words: 690 | Pages: 2 | 4 min read
Table of contents
The concept of equality in harrison bergeron, character analysis, societal implications.

Cite this Essay
Let us write you an essay from scratch
- 450+ experts on 30 subjects ready to help
- Custom essay delivered in as few as 3 hours
Get high-quality help

Dr. Heisenberg
Verified writer
- Expert in: Literature

+ 120 experts online
By clicking “Check Writers’ Offers”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy . We’ll occasionally send you promo and account related email
No need to pay just yet!
Related Essays
3 pages / 1490 words
2 pages / 851 words
4 pages / 1725 words
3.5 pages / 1498 words
Remember! This is just a sample.
You can get your custom paper by one of our expert writers.
121 writers online
Still can’t find what you need?
Browse our vast selection of original essay samples, each expertly formatted and styled
Related Essays on Harrison Bergeron
Imagine living in a society where everyone is equal in every aspect of their being. In Kurt Vonnegut's dystopian short story, "Harrison Bergeron," this is precisely the reality. Set in a future America where the government [...]
Kurt Vonnegut's story "Harrison Bergeron" is a satirical portrayal of a dystopian society where equality is enforced through extreme measures. The story is filled with instances of hyperbole, or exaggerated statements or claims [...]
What is the author's point of view in "Harrison Bergeron?" This question arises a few times throughout the text, as Kurt Vonnegut presents a dystopian society where everyone is forced to be equal in every aspect. In this essay, [...]
In Kurt Vonnegut's dystopian short story, "Harrison Bergeron," the author employs metaphors to convey a deeper meaning and critique certain aspects of society. Through the use of metaphors, Vonnegut explores themes of equality, [...]
Ancient German Philosopher, Georg Christoph once said, “Equality which we demand is the most tolerant degree of inequality.” For centuries, humankind has diligently worked towards an equal society, but what happens when such [...]
While the short film, 2081, has many common similarities with its adapted version of the short story, Harrison Bergeron, they differ from each other to the point where it can change our whole view on who Harrison Bergeron [...]
Related Topics
By clicking “Send”, you agree to our Terms of service and Privacy statement . We will occasionally send you account related emails.
Where do you want us to send this sample?
By clicking “Continue”, you agree to our terms of service and privacy policy.
Be careful. This essay is not unique
This essay was donated by a student and is likely to have been used and submitted before
Download this Sample
Free samples may contain mistakes and not unique parts
Sorry, we could not paraphrase this essay. Our professional writers can rewrite it and get you a unique paper.
Please check your inbox.
We can write you a custom essay that will follow your exact instructions and meet the deadlines. Let's fix your grades together!
Get Your Personalized Essay in 3 Hours or Less!
We use cookies to personalyze your web-site experience. By continuing we’ll assume you board with our cookie policy .
- Instructions Followed To The Letter
- Deadlines Met At Every Stage
- Unique And Plagiarism Free
The Ideal of “A City Upon a Hill”: Vision and Reality
This essay about “A City Upon a Hill” explores the evolution of the ideal from John Winthrop’s 1630 sermon to its role in American exceptionalism. It examines the successes and contradictions in living up to this vision, highlighting achievements in education and morality, but also addressing issues of exclusivity, racism, and foreign policy. The metaphor remains a powerful tool for reflection and aspiration in America’s ongoing quest to align its practices with its ideals.
How it works
The phrase “A City Upon a Hill” has resonated through American history, encapsulating a vision of exceptionalism and moral leadership. This ideal, rooted in the early days of the American colonies, has evolved into a complex symbol of both aspiration and critique. It draws from John Winthrop’s 1630 sermon aboard the Arbella, where he articulated a vision for the Massachusetts Bay Colony as a model society that others would look up to. Winthrop’s use of the biblical metaphor from the Sermon on the Mount envisioned a society that, through its virtue and godliness, would illuminate a path for others.
However, the reality of this vision has been a nuanced journey, with instances of profound success and glaring contradictions.
Winthrop’s vision was grounded in the Puritan belief in a covenant with God, which obligated the colonists to live righteous lives. The idea was that their community would be so exemplary in its adherence to divine principles that it would attract admiration and emulation. This vision underscored the Puritan’s self-perception as chosen people destined to create a new, more pious society that would contrast with the perceived moral failings of England.
In practice, the Massachusetts Bay Colony did achieve significant milestones that aligned with Winthrop’s vision. It became known for its relatively high literacy rates, established institutions of higher learning like Harvard College, and a complex legal system that reflected its Puritan values. The community’s emphasis on education and moral rectitude set a high standard that influenced the broader development of American society.
However, the ideal of “A City Upon a Hill” also harbored exclusivity and rigidity. The Puritan’s vision of a model society was not inclusive; it was predicated on conformity to a specific religious and moral code. Those who deviated from Puritan orthodoxy faced persecution, as seen in the banishment of dissenters like Roger Williams and Anne Hutchinson. The stringent adherence to their religious and social norms often led to a lack of tolerance for differing viewpoints and practices, revealing a stark contrast between the inclusive rhetoric of a model society and the exclusive reality.
As America grew, the metaphor of “A City Upon a Hill” persisted, evolving to reflect the nation’s expanding ambitions. The idea was secularized and integrated into the broader narrative of American exceptionalism, suggesting that the United States had a unique destiny to lead and uplift the world. This belief became particularly prominent in the 20th century, influencing foreign policy and domestic attitudes. Presidents from John F. Kennedy to Ronald Reagan invoked the metaphor to inspire and justify actions, projecting an image of America as a beacon of freedom, democracy, and opportunity.
Yet, the reality has often been at odds with this idealized vision. The United States’ history is marred by contradictions, such as slavery, segregation, and systemic racism, which starkly contrast with the principles of equality and justice that the metaphor espouses. The civil rights movement, for instance, highlighted the gap between the nation’s self-image and the lived experiences of many of its citizens. Despite the progress made, the struggle for racial equality and social justice continues, underscoring the ongoing challenge of reconciling the vision of “A City Upon a Hill” with reality.
Moreover, America’s foreign interventions, justified by the belief in its exceptional role, have sometimes resulted in controversy and backlash. The Vietnam War, the invasion of Iraq, and other interventions have sparked debates about the ethical implications and effectiveness of America’s self-appointed mission to spread democracy and freedom. These actions often exposed the complexities and unintended consequences of attempting to live up to the ideal of being a global exemplar.
The metaphor also endures in contemporary discussions about immigration, economic inequality, and social policies. The United States is often viewed as a land of opportunity, attracting immigrants who seek a better life. However, debates over immigration policies reveal tensions between this aspirational identity and the realities of border enforcement, refugee crises, and integration challenges. Similarly, economic inequality and access to healthcare and education are critical issues that question whether America truly lives up to its ideal as a model society.
In the face of these contradictions, the ideal of “A City Upon a Hill” remains a powerful aspirational tool. It encourages continuous reflection and striving towards a society that embodies its highest values. The metaphor serves as both a guide and a critique, reminding Americans of the potential to lead by example and the imperative to address shortcomings.
In conclusion, the ideal of “A City Upon a Hill” has been a dynamic and multifaceted symbol throughout American history. It originated as a religious vision of moral exemplarity but has evolved into a broader narrative of American exceptionalism. The reality, however, has been marked by both achievements and significant challenges. The ongoing endeavor to align the nation’s practices with its lofty ideals reflects the complex and evolving nature of the American experiment. As a guiding light, the metaphor continues to inspire and challenge the nation to live up to its highest potential, even as it grapples with its imperfections.
Cite this page
The Ideal of "A City Upon a Hill": Vision and Reality. (2024, Jun 17). Retrieved from https://papersowl.com/examples/the-ideal-of-a-city-upon-a-hill-vision-and-reality/
"The Ideal of "A City Upon a Hill": Vision and Reality." PapersOwl.com , 17 Jun 2024, https://papersowl.com/examples/the-ideal-of-a-city-upon-a-hill-vision-and-reality/
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Ideal of "A City Upon a Hill": Vision and Reality . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-ideal-of-a-city-upon-a-hill-vision-and-reality/ [Accessed: 19 Jun. 2024]
"The Ideal of "A City Upon a Hill": Vision and Reality." PapersOwl.com, Jun 17, 2024. Accessed June 19, 2024. https://papersowl.com/examples/the-ideal-of-a-city-upon-a-hill-vision-and-reality/
"The Ideal of "A City Upon a Hill": Vision and Reality," PapersOwl.com , 17-Jun-2024. [Online]. Available: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-ideal-of-a-city-upon-a-hill-vision-and-reality/. [Accessed: 19-Jun-2024]
PapersOwl.com. (2024). The Ideal of "A City Upon a Hill": Vision and Reality . [Online]. Available at: https://papersowl.com/examples/the-ideal-of-a-city-upon-a-hill-vision-and-reality/ [Accessed: 19-Jun-2024]
Don't let plagiarism ruin your grade
Hire a writer to get a unique paper crafted to your needs.

Our writers will help you fix any mistakes and get an A+!
Please check your inbox.
You can order an original essay written according to your instructions.
Trusted by over 1 million students worldwide
1. Tell Us Your Requirements
2. Pick your perfect writer
3. Get Your Paper and Pay
Hi! I'm Amy, your personal assistant!
Don't know where to start? Give me your paper requirements and I connect you to an academic expert.
short deadlines
100% Plagiarism-Free
Certified writers

Reference Examples
More than 100 reference examples and their corresponding in-text citations are presented in the seventh edition Publication Manual . Examples of the most common works that writers cite are provided on this page; additional examples are available in the Publication Manual .
To find the reference example you need, first select a category (e.g., periodicals) and then choose the appropriate type of work (e.g., journal article ) and follow the relevant example.
When selecting a category, use the webpages and websites category only when a work does not fit better within another category. For example, a report from a government website would use the reports category, whereas a page on a government website that is not a report or other work would use the webpages and websites category.
Also note that print and electronic references are largely the same. For example, to cite both print books and ebooks, use the books and reference works category and then choose the appropriate type of work (i.e., book ) and follow the relevant example (e.g., whole authored book ).
Examples on these pages illustrate the details of reference formats. We make every attempt to show examples that are in keeping with APA Style’s guiding principles of inclusivity and bias-free language. These examples are presented out of context only to demonstrate formatting issues (e.g., which elements to italicize, where punctuation is needed, placement of parentheses). References, including these examples, are not inherently endorsements for the ideas or content of the works themselves. An author may cite a work to support a statement or an idea, to critique that work, or for many other reasons. For more examples, see our sample papers .
Reference examples are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Chapter 10 and the Concise Guide Chapter 10
Related handouts
- Common Reference Examples Guide (PDF, 147KB)
- Reference Quick Guide (PDF, 225KB)
Textual Works
Textual works are covered in Sections 10.1–10.8 of the Publication Manual . The most common categories and examples are presented here. For the reviews of other works category, see Section 10.7.
- Journal Article References
- Magazine Article References
- Newspaper Article References
- Blog Post and Blog Comment References
- UpToDate Article References
- Book/Ebook References
- Diagnostic Manual References
- Children’s Book or Other Illustrated Book References
- Classroom Course Pack Material References
- Religious Work References
- Chapter in an Edited Book/Ebook References
- Dictionary Entry References
- Wikipedia Entry References
- Report by a Government Agency References
- Report with Individual Authors References
- Brochure References
- Ethics Code References
- Fact Sheet References
- ISO Standard References
- Press Release References
- White Paper References
- Conference Presentation References
- Conference Proceeding References
- Published Dissertation or Thesis References
- Unpublished Dissertation or Thesis References
- ERIC Database References
- Preprint Article References
Data and Assessments
Data sets are covered in Section 10.9 of the Publication Manual . For the software and tests categories, see Sections 10.10 and 10.11.
- Data Set References
- Toolbox References
Audiovisual Media
Audiovisual media are covered in Sections 10.12–10.14 of the Publication Manual . The most common examples are presented together here. In the manual, these examples and more are separated into categories for audiovisual, audio, and visual media.
- Artwork References
- Clip Art or Stock Image References
- Film and Television References
- Musical Score References
- Online Course or MOOC References
- Podcast References
- PowerPoint Slide or Lecture Note References
- Radio Broadcast References
- TED Talk References
- Transcript of an Audiovisual Work References
- YouTube Video References
Online Media
Online media are covered in Sections 10.15 and 10.16 of the Publication Manual . Please note that blog posts are part of the periodicals category.
- Facebook References
- Instagram References
- LinkedIn References
- Online Forum (e.g., Reddit) References
- TikTok References
- X References
- Webpage on a Website References
- Clinical Practice References
- Open Educational Resource References
- Whole Website References

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
How to write a critique. When you're ready to begin writing your critique, follow these steps: 1. Determine the criteria. Before you write your critique, it's helpful to first determine the criteria for the critique. If it's an assignment, your professor may include a rubric for you to follow. Examine the assignment and ask questions to verify ...
Before you start writing, you will need to take some steps to get ready for your critique: Choose an article that meets the criteria outlined by your instructor. Read the article to get an understanding of the main idea. Read the article again with a critical eye. As you read, take note of the following: What are the credentials of the author/s?
The critique essay is not about concerned with the content of the article - but whether or not the AUTHOR of the article presented an effective (or ineffective) argument. EXAMPLE - Dr. John Stamos writes an article about polka music (he's in favor of more polka music on the radio). Do not focus on polka music - you can love it or hate ...
Step 3: Drafting the Essay. Finally, it is time to draft your essay. First of all, you'll need to write a brief overview of the text you're analyzing. Then, formulate a thesis statement - one sentence that will contain your opinion of the work under scrutiny. After that, make a one-paragraph summary of the text.
A critique paper is a piece of writing that provides an in-depth analysis of another work. These include books, poems, articles, songs, movies, works of art, or podcast episodes. Aside from these, a critique may also cover arguments, concepts, and artistic performances. For example, a student may evaluate a book they've read or the merit of ...
1. Use these guidelines to critique your selected research article to be included in your research proposal. You do not need to address all the questions indicated in this guideline, and only include the questions that apply. 2. Prepare your report as a paper with appropriate headings and use APA format 5th edition.
The critique is your evaluation of the resource. A strong critique: Discusses the strengths of the resource. Discusses the weaknesses of the resource. Provides specific examples (direct quotes, with proper citation) as needed to support your evaluation. Discusses anything else pertinent to your evaluation, including.
Structure of Critique Paper. The structure of a typical critique essay example includes an introduction, a summary, an analysis, and a conclusion. The paper format is a crucial element. Just like when you write your research papers, a critique benefits from a clear one to guide the reader. Therefore, work on defining the critique essay outline ...
Guidelines for Writing a Research Critique. 1. Begin your critique by identifying the article's title, author(s), date of publication, and the name of the journal or other publication in which it appeared. In your introduction, you should also briefly describe the purpose and nature of the study and, if applicable, its theoretical framework ...
To write an article critique, you should: Read the article, noting your first impressions, questions, thoughts, and observations. Describe the contents of the article in your own words, focusing on the main themes or ideas. Interpret the meaning of the article and its overall importance. Critically evaluate the contents of the article ...
When writing an article critique, you should follow a few formatting guidelines. The importance of using a proper format is to make your review clear and easy to read. Make sure to use double spacing throughout your critique. It will make it easy to understand and read for your instructor. Indent each new paragraph.
1) Procedure in Writing a Critique Paper, and the. 2) Format of the Critique Paper. First, you will need to know the procedure that will guide you in evaluating a paper. Second, the format of the critique paper refers to how you present it so that it becomes logical and scholarly in tone. The Four Steps in Writing a Critique Paper
Analyzing Structure Example: In a film critique, the reviewer noted how the narrative structure, with flashbacks interspersed at strategic points, amplified the emotional impact and depth of the story. 4. Considering Originality. Originality refers to the creativity, novelty, or freshness brought to a work or an idea.
How to write a critique. Before you start writing, it is important to have a thorough understanding of the work that will be critiqued. Study the work under discussion. Make notes on key parts of the work. Develop an understanding of the main argument or purpose being expressed in the work. Consider how the work relates to a broader issue or ...
Here are three examples of critique papers for short stories that can help students learn to evaluate and interpret literature effectively: Critique of "The Lottery" by Shirley Jackson. Critique of "Harrison Bergeron" by Kurt Vonnegut. Critique of "The Yellow Wallpaper" by Charlotte Perkins Gilman.
Writing Critiques. Writing a critique involves more than pointing out mistakes. It involves conducting a systematic analysis of a scholarly article or book and then writing a fair and reasonable description of its strengths and weaknesses. Several scholarly journals have published guides for critiquing other people's work in their academic area.
Writing a Critique. To critique a piece of writing is to do the following: describe: give the reader a sense of the writer's overall purpose and intent. analyze: examine how the structure and language of the text convey its meaning. interpret: state the significance or importance of each part of the text. assess: make a judgment of the work ...
Step 9: Presenting Your Critique. Organize your critique into a well-structured paper, starting with an introduction that outlines the article's context and purpose. Develop a clear and focused thesis statement that conveys your assessment. Support your points with evidence from the article and other credible sources.
1. Give the basic information about the work. The first paragraph is your introduction to the work, and you should give the basic information about it in this paragraph. This information will include the author's or creator's name (s), the title of the work, and the date of its creation.
Using specific examples from the source, you might consider talking about the following points. Keep in mind, depending on the source you are critiquing, some points may be more relevant than others. ... Sample Critique Paper. Check out a sample critique essay of an event a student attended. How to Critique for a Live Performance (WOW)
of the main points of the paper you chose to critique!) If you cannot write a clear summary, you absolutely cannot begin to critique the paper. 2) Example summary and critique of primary research paper The fertilized eggs of marine snails are often enclosed in complex, leathery egg capsules with 30 or more embryos being confined within each ...
Table of contents. Step 1: Reading the text and identifying literary devices. Step 2: Coming up with a thesis. Step 3: Writing a title and introduction. Step 4: Writing the body of the essay. Step 5: Writing a conclusion. Other interesting articles.
The results wer e discussed appropriat ely- No misinterpretation. 11. Streng ths motioned are the true strengths. 12. Limitations are r eported do not aff ec t the applicability of the study-. 13 ...
Published in 1961, Kurt Vonnegut's short story Harrison Bergeron presents a chilling dystopian vision of a future society obsessed with enforced equality. Set in the year 2081, the narrative explores the consequences of extreme egalitarianism, where the government imposes physical and mental handicaps on individuals to ensure that everyone is equal "every which way."
Essay Example: The phrase "A City Upon a Hill" has resonated through American history, encapsulating a vision of exceptionalism and moral leadership. This ideal, rooted in the early days of the American colonies, has evolved into a complex symbol of both aspiration and critique. It draws from
An author may cite a work to support a statement or an idea, to critique that work, or for many other reasons. For more examples, see our sample papers. Learn more. Reference examples are covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Chapter 10 and the Concise Guide Chapter 10.