What is GPA?
Considering studying abroad in the us you will read a lot about gpa, so here is how to calculate your gpa and when you might need to use it for applications..


Grace McCabe
GPA is a system used in high schools and universities, mainly in the US, to measure a student’s performance and academic achievement. GPA is calculated by converting grades or percentages you receive for an assignment (A, B, C etc) to a corresponding point on the GPA scale (more information on this below).
There are some ways to calculate your GPA – if you have been studying at a school in the UK for example – for your university application to the US, by using a GPA calculator.
What does GPA stand for?
GPA stands for “grade point average” and is usually calculated using a scale of 0 to 4. Four is usually the highest GPA you can receive and corresponds to an A grade, and 0 corresponds to an F grade.
How to calculate GPA?
Students receive a grade or a percentage for each assignment, project and exam. Those grades are then converted to the corresponding GPA points which are added together and divided by the number of units or credits in each class to calculate the average score for the semester. This provides the average GPA.
Some institutions award GPAs higher than 4 using a weighted scale, taking difficulty of coursework and assignments into account rather than just considering the final grade. More information on a weighted vs unweighted GPA can be found below.
What is a weighted GPA?
A weighted GPA is the grade point average that takes into account the difficulty of the course alongside the student’s grades. As more and more students are taking advanced programmes, the weighted GPA aims to reflect a student’s work in these courses.
While the unweighted GPA scale can only go up to a 4, the weighted GPA scale is between 0 and 5. So students that take more difficult and advanced courses might find that they score a higher GPA than the perfect 4.
Having a weighted GPA can show employers and universities that you are willing to take on more challenging courses.
How do you calculate a weighted GPA? One of the easier ways to calculate a weighted GPA is to calculate your average unweighted GPA and then divide that by the number of classes you took. Then add 0.5 for each mid-level class and 1 for each advanced class (you can check with your teachers if you aren’t sure). Then divide that result by the number of classes you took.
There are also GPA calculators that can help you calculate your weighted and unweighted GPAs.
What is the highest GPA?
GPA is calculated on a scale between 0 and 4, so 4 is the highest GPA you can achieve in most classes.. However, if you take some advanced level classes you may be able to achieve a GPA of 5.
How can you convert your UK school grades to a GPA?
This table helps you convert your grades and percentages to the closest GPA point for each individual class or assignment.
What is a good GPA?
This will very much depend on where you are applying too and which classes you have taken.
Different universities and different schools will have varying levels of what constitutes a good GPA, but it's generally advisable to keep your GPA around 3 or more.
What is a good GPA for high school?
GPA is often one of the entry requirements for US universities . A high GPA along with a strong GRE or SAT score , can help a student’s chances of being considered for the top universities in the country. It is also important because it’s a measure of a candidate’s academic skill, unlike the SAT, ACT and GRE exams, which test aptitude.
Top universities may have a minimum GPA requirement of 3 for admission to undergraduate programmes. This may be higher for postgraduate studies. However, there will be many universities that do accept students with GPAs lower than 3.
If you find your standardised test score is lower than you hoped, a higher GPA can help raise your overall impression and make you stand out more during university applications.
Generally, the higher your GPA, the more choice you will have in which universities you can apply to.
Ivy League universities such as Harvard University , Columbia University , Yale University and Princeton University do not have a minimum GPA, however the average GPA of many of the applicants are above 3.5.
While it is always advisable to put time and effort into getting the best grades you can, do remember that universities will also look at your extracurricular activities, work experience and overall academic performance when considering your application.
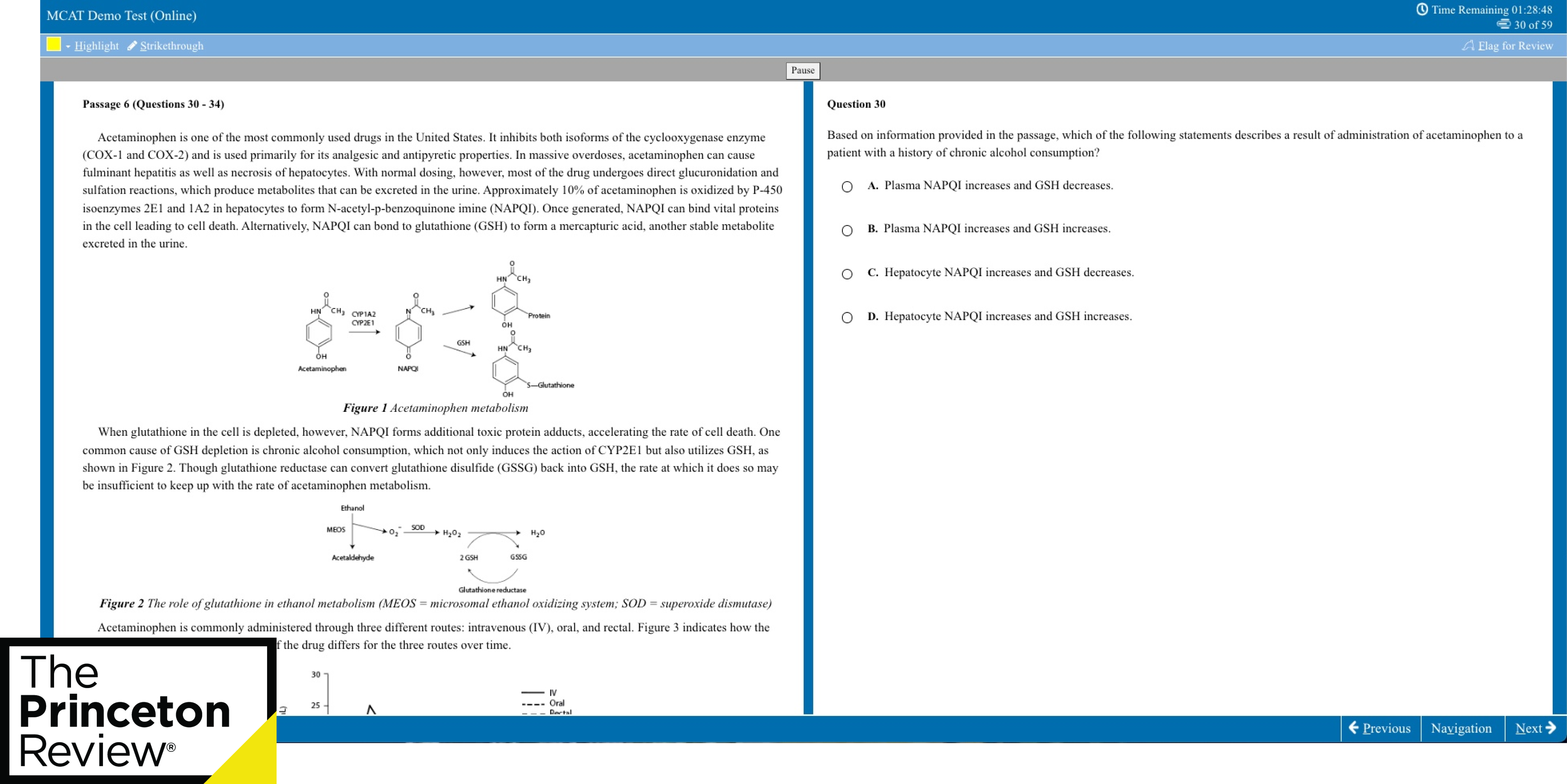
What is a good GPA for university?
Your GPA at university will depend a lot on which university you attend and which major you are studying.
The average GPA for a course that is considered fairly challenging is usually 2.75 upwards.
When applying for jobs after university, employers may or may not ask for your GPA, but having a higher GPA will show your future employers that you are hard-working and motivated.
It is also worth remembering that some scholarship programmes and some university courses require you to keep your GPA up in order to continue to receive financial aid. So be sure to check if there are any GPA requirements that you need to adhere to throughout your time at university.
Your GPA for your undergraduate degree will also be looked at if you choose to apply for a master’s or PhD programme. Some postgraduate programmes may look for a GPA of 3 or above, but again this will vary based on the course and the university you are applying to.
What does test-optional mean for US university applications? Finding your university: UK versus US Best universities in the United States
What is cumulative GPA?
A cumulative GPA is the average of all the GPAs you have achieved while at high school or university. In other words, it combines all the GPAs you have received for each semester to create one representative GPA of your time at high school or university.
The higher your semester GPAs are, the higher your cumulative GPA will be.
Prospective universities will often ask for your high school cumulative GPA as part of the application process. Prospective employers may also ask for your cumulative university GPA, as it is a good measure of a student’s academic grades.
Cumulative GPA is also sometimes known as the overall GPA or average GPA.
Are there ways to improve your GPA?
A student’s GPA is calculated using all the grades they receive throughout their time at high school or university. If you are concerned about your GPA, you can do a few things to improve:
– Ask for help: your teachers might be able to assist you by explaining a topic in another way to help you gain better marks in a course.
– Changing your study habits : altering your focus can help you retain more information and do better in assessments.
– Taking on more of a challenge: a lower score in a top-tier class has a stronger weighting than a high score in a lower-tier class.
– Extra credit: some teachers will assign additional tests or assignments to give students a chance to improve. But remember that overall grades are still divided by the number of units of work you complete.
How important is a good GPA?
A good GPA can show employers and universities that you are hard-working and motivated to do well in your studies. It is a good measure of how you perform academically, but it is not the only factor that universities will look at in your application.
Universities will also look at your personal statement and the commitment that you show to your chosen course or any extracurriculars or work experience you carried out. Everything that you do at school paints a picture of the kind of student you will be, so it’s important to ensure that you take all the opportunities that come your way while at school and university.
Some clubs and societies in the US will require students to maintain a particular GPA in order to join them. Fraternities and sororities in the US are an example of some societies in the US that require students to maintain their grades in order to remain a member.
You may also like

.css-185owts{overflow:hidden;max-height:54px;text-indent:0px;} Everything international students need to know about US student visas

The cost of studying at a university in the United States

Scholarships available in the US for international students
Seeta Bhardwa
Register free and enjoy extra benefits
Created by the Great Schools Partnership , the GLOSSARY OF EDUCATION REFORM is a comprehensive online resource that describes widely used school-improvement terms, concepts, and strategies for journalists, parents, and community members. | Learn more »

Grade Point Average
A grade point average is a number representing the average value of the accumulated final grades earned in courses over time. More commonly called a GPA , a student’s grade point average is calculated by adding up all accumulated final grades and dividing that figure by the number of grades awarded. This calculation results in a mathematical mean—or average—of all final grades. The most common form of GPA is based on a 0 to 4.0 scale (A = 4.0, B = 3.0, C = 2.0, D = 1.0, and F = 0), with a 4.0 representing a “perfect” GPA—or a student having earned straight As in every course. Schools may also assign partial points for “plus” or “minus” letter grades, such as a 3.7 for an A–, a 3.3 for a B+, and so on. GPAs may be calculated at the end of a course, semester, or grade level, and a “cumulative GPA” represents an average of all final grades individual students earned from the time they first enrolled in a school to the completion of their education.
In some schools, weighted-grade systems are used in GPA calculations, and they give students a numerical advantage for grades earned in higher-level courses, such as honors courses or Advanced Placement courses, or for completing more challenging learning experiences. In weighted-grade systems, an A in a higher-level course might be awarded a 4.5 or 5.0, for example, while an A in a lower-level course is awarded a 4.0 (yet weighted grading systems vary widely in design and methodology).
A student’s GPA is often used to determine academic honors, such as honor roll, class rank , or Latin honors. GPAs have been one of several major factors used by colleges, postsecondary programs, and employers to assess a student’s overall academic record.
In public schools, grading systems and GPA scales may vary significantly from one school or school district to the next. When investigating or reporting on grading systems, class rank, or other academic honors, it is important to determine specifically how grades and GPAs are calculated, and what evaluation criteria was used to measure academic performance and award grades.
While the use of grade point averages has been common in public schools for decades, critics of the practice may argue that averaging grades over a semester, year, or school tenure can misrepresent student learning, particularly learning growth over time, and that it can adversely affect a student’s academic performance, educational confidence, and sense of self-worth. Since the arguments against the use of GPAs are complex and nuanced, see class rank , grade averaging , weighted grades , and proficiency-based learning for more detailed discussions.

Alphabetical Search
Explainer: what is a GPA and what use is it?
Senior Assessment Scholar, School of Education, The University of Queensland
Disclosure statement
Royce Sadler does not work for, consult, own shares in or receive funding from any company or organisation that would benefit from this article, and has disclosed no relevant affiliations beyond their academic appointment.
University of Queensland provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners

A Grade Point Average (GPA) is a summary statistic that represents a student’s average performance in their studies over a stated period of time, such as one semester. Being numerical, GPAs are often calculated to two decimals. They are used as indicators of whether levels of student performance meet some fixed criterion, and for sorting groups of students into rank order.
However, grading scales differ considerably across institutions and countries. Conversion tables are usually available for comparing grades and GPAs within countries and internationally.
When an entire study program is organised as a collection of “units”, each period of time gives rise to its own GPA. The most common study period for a course is one semester, usually 12-15 weeks of class. If a full-time student enrols in four courses in a particular semester, the GPA is calculated as the average performance over those four courses.
How is a GPA calculated?
A student’s level of attainment in a course is typically represented by a grade chosen from a set of approved ordered symbols. Depending on the institution’s preferences, the grade labels may take the form of letters (A, B, C, D…), descriptive terms (Distinction, Honour, Credit, Pass, Fail), or numerals on an arbitrary scale (7, 6,…, 1).
For a GPA to be calculated, all letter and word labels must be given numerical equivalents, such as A = 4.0, B = 3.0, C = 2.0; D = 1.0 and F = 0.0. The numerals are deemed to represent genuine measurements and, under this assumption, facilitate the calculation of GPAs.
The GPA is the “weighted average” of course grades calculated over the defined period of study. The weights reflect the relative contributions of courses to the program measured in arbitrary units, called “credit value”, based on contact hours or presumed total student workload. Each course has a credit value or “weight” approved by the institution.
As an example of how a GPA is calculated, suppose a student enrols in four courses in a particular semester. Three of these are designated as “five credit” courses but the fourth is designated a “ten credit” course because the academic demands involved are about double those of the other courses. The student receives grades of A, B and B in the three five-credit courses and an A in the ten-credit course.
The first step in calculating the GPA is to multiply the credit value of each course by the respective grade’s numerical equivalent.
Symbolically, using the equivalence scale above, this is as follows:
The second step is to divide that aggregate (90.0) by the total number of credits for all the courses studied in that semester (25) to give a GPA of (90.0/25) = 3.6.
Only the relativities of the weights assigned to the various courses matter in a GPA calculation. Suppose the student had studied exactly the same courses at another institution and received the same grades – the same grade scale with the same numerical equivalents. The GPA would come out exactly the same (3.6) even if the second institution used 20, 20, 20, and 40 to represent its course weights instead of 5, 5, 5 and 10.
A related statistic, the “cumulative GPA”, uses the same calculation formula but takes into account all studies completed from the time of enrolment in an academic program up to the time of calculation. Many academic transcripts show details of the grade scale used, a GPA for each semester and a running (cumulative) GPA for all studies up to that point. Institutions differ in how they treat pass/fail courses, fail grades and transfer credits.
What use are GPAs?
GPAs often serve as input data for decisions on: progression through degree programs; admission to advanced studies; rankings for prizes, medals, honours and scholarships; determinations of degree classification; and accreditation and quality assurance. Too low a GPA, or too many marginal or failing grades, may prevent a student from continuing. Consistently poor performance may lead to a period of exclusion from the degree program or the institution.
It is hard to find clear evidence that potential employers place significant emphasis on GPAs in hiring decisions, although in general they like to know the GPA. Probably more important would be the graduate’s pattern of grades attained in courses that make up the major.
Basing decisions on grades gives the appearance of being both objective and meritocratic. A notable weakness of GPAs is that their basic input data are derived from course grades. The relationship between the grade awarded and a student’s actual level of achievement is not assured.
This means there is no guarantee that course grades are comparable. Pooling grades (for a GPA) does nothing to improve that. However, using GPAs almost always delivers administrative solutions when required, so there usually is in practice little incentive to place the grades themselves under close scrutiny.

Audience Development Coordinator (fixed-term maternity cover)

Data and Reporting Analyst

Lecturer (Hindi-Urdu)

Director, Defence and Security

Opportunities with the new CIEHF
- Create Account
What is a GPA?

When you’re enrolled in the United States for a bachelor’s or master’s degree , your GPA is one of the most important numbers to keep an eye on. It is key to your status as a student in "good standing,” continued enrollment in your major, future financial aid, which requires satisfactory academic progress, maybe scholarship eligibility, future employment opportunities, eligibility for college athletic teams, and more.
GPA stands for “grade point average” and is a standardized way of measuring academic achievement in the U.S on a scale of 0 to 4. If your country's grading system is percentage-based or letter-based, you may be able to calculate your GPA — however, most systems outside the U.S. do not use this scale.

What do these numbers mean?
Each course is given a certain number of "units" or "credits," as designated by your school, depending on the importance of the course. In secondary school, most courses carry the same number of units, but this is not true at the college level.
Most college courses have a value of 3 units (approximately three hours of lecture and six hours of homework per week for each semester), but that number can hold a value from 1 to 5 depending on the course. GPA assumes a grading scale of A, B, C, D, and F. Each grade is assigned a number of grade points. An A grade receives 4 points, a B=3, a C=2, a D=1, and an F=0.
Here are other articles you may find helpful:
- Tips for International Students Who Have a Low GPA
- How to Write an Illustrative Essay to Get an A+ Grade
- Understanding the American Education System
- Handling Grade Disputes: A Guide
How do I calculate my GPA?
If you take a 3-unit class and receive an A grade, you receive 3 units times 4 points (for the A), which gives a total of 12-grade points for the course. Let's say you also take a 4-unit class (common in mathematics, for example) and receive a C grade. That's 4 units times 2 points for a total of 8 points.
So for your two classes, you have accumulated 20-grade points for the 7 units. You then divide the cumulative grade points by the number of units and you have your GPA. (20/7 = 2.86), so your GPA is 2.86, which is slightly less than a B average.
What are the GPA requirements for admission into U.S. institutions?
The minimum GPA requirement to study abroad varies depending on the school, but a 2.0 GPA is typically the lowest you will find. However, finding admission with such low averages will prove difficult. To be a competitive candidate at most American institutions, we recommend maintaining at least a 3.0 GPA — and making it 3.5 if you’re looking for admission into prestigious universities.
That is not to say that if you don’t have a high GPA you won’t get accepted into an American institution. Your grade point average is only one part of the criteria that you will be measured on. The culmination of your experiences, your standardized test scores, and a number of other factors will be used to determine your eligibility.
If you lack in one area (i.e. low standardized test scores) but make up for it in another, such as maintaining a consistently high GPA, it can help mitigate any negative aspects of your candidacy.
How does my GPA affect me as an international student in the U.S.?
Your GPA is not only important in helping you gain admission into U.S. colleges and universities, but it’s also vital in helping you stay there. If you are unable to maintain a minimum 2.0 GPA over the course of a semester, you will be placed on academic probation. Failure to raise your GPA to above 2.0 within the time frame that your school provides will lead to the termination of your study abroad. You will be notified that you will have to leave the U.S. within a designated period.
On the other hand, maintaining a high GPA can open opportunities for you during your study abroad experience and beyond. Your GPA is a testament to your work ethic and inspires trust in your ability to lead the next generation. With high scores, you can apply to and receive a number of performance-based scholarships, position yourself to further your studies, find quality internships, or gain the experiences necessary to make a seamless transition into post-graduate life.
How do I raise my GPA?
Raising your GPA requires earning consistently better grades than your current average. Here are a few strategies you can use to do that:
Retake old classes: Your GPA is more than likely being weighed down by classes in which you performed poorly. Certain colleges and universities will allow you to retake credits, giving you the opportunity to turn a bad grade into a good one.
Build a better schedule: Don’t take all of your required, challenging classes at once. You have the ability to make your own schedule, so build in a healthy mix of hard classes with easier ones.
Get organized: Between school, work, and extracurricular activities, being a student can take up a lot of your time. As stressful as a packed schedule can be, it is possible to succeed if you have the right strategy.
Speak with your teachers: Struggling to understand the material? Have a reason you didn’t perform to the best of your abilities? Teachers want you to succeed, and they’ll work with you to find a solution to your problems.
For more tips, see other related articles below:
- Having A Studious Roommate May Raise Your Grades
- More Sleep Means Higher Grades
- Common Grad School Tests and Tips for Success
- Improve Test-Taking Scores: Learn From Your Mistakes

Charles Varghese
By Charles Varghese
Get matched to the best program for you
Let us know what you're looking for so we can find the best school for you.
Useful Articles

Check Out These Schools

Chaffey College
$5,000—$10,000 Year

Los Angeles City College Language Academy
$1,000—$5,000 Session

Study Oregon
Featured programs.

Southwestern Community College District
Typical cost per Semester: $5,000—$10,000

Golden West College
Typical cost per Year: $5,000—$10,000

Mohawk Valley Community College
Related stories.

Start your U.S. adventure with Study in the USA

Learn About U.S. education financing, housing, and more

Uniplaces is an accommodation provider with a large choice of verified rooms, entire flats and residences. The platform offers an easy, fast and safe way of booking a place to live. Check out the thousands of properties in the best cities and book a...

Education Insurance Plans in partnership with InsureMyTrip offers...
These plans provide refund insurance coverage for program costs in the event the student has to interrupt their trip for unforeseen covered reasons and withdraw from the program. We offer plans that are available to both K-12 and College Students.

The Intern Group
Summer plans suspended because of COVID-19? The deadline's approaching for TheInternGroup's virtual/remote global internship program. Gain professional experience, grow your network and make your resume shine from wherever you are this summer.
Learn about American culture and education direct from our experts at Study in the USA. Read more
Achieving Your Goal
Admissions and placement testing, beyond the basics, education system in the usa, financing your u.s. education, frequently asked questions, life in the usa, student experiences, for students age 10-18, study in canada, student voices, ask studyusa.com, subscribe to get the latest from study in the usa.
You can unsubscribe at any time.
What a Good College GPA Is and Why It Matters
A college GPA factors into financial aid and scholarships eligibility, program admission and graduation.
Why Your College GPA Matters

Getty Images
Repeating a course is one way for college students to boost their GPA.
Grade-point average can be a critical determinant in what comes next for a high school student, with college admissions and financial aid often on the line. The same holds true for a college student, as minimum grades are often necessary for getting into certain majors and graduate school and for maintaining scholarships and other aid.
Students' primary focus in college should be on the process of learning and not just on their GPA, says Susan Whorton, director of the Academic Success Center at Clemson University in South Carolina. But maintaining a high GPA can make life easier for students while they're in college, and after they graduate and apply for jobs or graduate school.
“GPA isn’t really a reflection of learning, it’s a reflection of how a student did on the assessments in that course,” Whorton says. “It’s about navigating the academic environment that currently exists." At minimum, experts say, students must generally meet a GPA standard of 2.0, or a C average, on a 4.0 scale to graduate and remain eligible for federal financial aid. Institutional scholarships and program enrollment at many colleges often hinge on academic achievement above a C average. For students with a GPA below 2.0, the fallout can be dire, and students can end up on academic probation .
"As soon as a student is placed on probation, they’re invited to meet with an academic adviser to start working on a plan to get back into good academic standing," Luke Wood, vice president of student affairs and campus diversity at San Diego State University in California, wrote in an email. "There is risk of disqualification if a student’s cumulative GPA does not improve, so we want to be sure the student understands the potential repercussions, but more importantly, that we can work with them on a sustainable plan to improve their academic performance."
What Is a Good GPA in College?
In general, colleges operate on a standard grading scale similar to what students are used to in K-12, though certain programs may operate on a stricter scale.
At SDSU, for example, students are considered "in good academic standing" when their overall cumulative GPA is 2.0 or higher, Wood says. Wood describes academic probation as a period when "a student's academic performance is below the state minimum required for graduation" and "improvement is required." Students at SDSU are placed on probation at the end of the semester when their GPA is less than 2.0, or below a C average.
In addition to potential dismissal from the university, federal financial aid may also be rescinded if a student continues to fall short of minimum GPA standards.
For students in danger of academic punishment, SDSU offers a "Bounce Back" retention program – a one-unit course that helps students improve time management, test taking, study skills and dealing with adversity, Wood says.
The U.S. Department of Education website notes that students who failed to meet GPA requirements and lost their financial aid should contact their school to determine whether they can appeal the decision to withhold financial aid. To have aid restored, a student must meet the "school's standards for satisfactory academic progress toward a degree or certificate offered by that institution," the website states.
Some Scholarships, Programs May Require Higher GPAs
While experts say a 2.0 GPA is generally the minimum to receive federal aid and meet graduation requirements, individual scholarships and programs often demand more from a student.
At West Virginia University , for example, a 2.0 GPA isn't high enough for students to graduate from or even gain admission into certain undergraduate programs, such as pre-nursing.
SDSU requires its nursing students to maintain a 3.0 GPA, which is at least a B average, in general education courses as well as certain science classes.
"It can depend on student level, program and various circumstances, but we generally like to see students with 3.0+ GPAs at a minimum," Wood says.
Some colleges offer direct admission into programs but may require a strong high school GPA . Experts say prior to applying to colleges, students should focus on making their GPA as strong as possible. A low mark in certain areas could require students to take remedial classes at the college level, which often don't count toward credits but still take up time and cost money.
While anything above a 2.0 at the college level might show satisfactory academic progress, students must earn higher marks to qualify for the dean's list and honors programs , notes Patrick Register, director of the financial aid and scholarships office at the University of California—Santa Cruz .
To be named to the dean's list at SDSU, for example, a student "must be in good academic standing and achieve a 3.50 GPA or greater based on a minimum of 12 units of credit for courses in which letter grades were assigned," Wood says.
Experts say a 4.0 GPA, which is straight A's, can be difficult to maintain throughout college.
"Unless a student is very focused from the beginning … that is going to be a difficult challenge," says Sherry Tignor, executive director of the Center for Academic Success and Student Life at Union University in Tennessee.
For college students with graduate school ambitions, a low GPA can be problematic, experts say, with many graduate programs having minimum standards for admission. Entering graduate school with a high GPA can open doors for potential awards and scholarships, Register says.
While requirements aren't universal, with individual schools setting varying standards, many require a minimum GPA of 3.0 for admission into a graduate program. "Many grad school programs are very competitive," Tignor says.
Ways to Raise Your College GPA
Students looking to boost their college GPA have options, though sometimes those can include repeating courses and making sacrifices.
“It’s about a student asking themselves, ‘What are my priorities?’” Whorton says. “What’s most important to me? If I want to get into that major that has a GPA requirement, then what do I need to do to attain that GPA? How do I set myself up to achieve the GPA that I need?"
For some students, that might mean prioritizing studying over social events, seeing a tutor or academic coach, or making changes to how they manage their time, she says. Depending on the academic hole a student is in, it might require some digging.
“It’s really about understanding their goals and what steps they’re willing to take to get there,” Whorton says.
A good way for students to rehabilitate a GPA is to retake courses they received a low grade in, Register says, though there are some conditions. For example, Register says, some courses may be repeated only a certain number of times, particularly if a student has earned a passing grade such as a D. Policies governing how many times coursework can be repeated may vary by school.
Another good corrective plan is to attend tutoring regularly, Whorton says, adding that it can also serve as a preventive measure for students already in good academic standing.
“A good analogy would be college athletics,” she says. "The top athletes get coaching every single day. The best quarterbacks, or the best linebackers, they want to get better every single day. They get coaching. They partner with somebody who can help them achieve their fullest potential."
Experts cite numerous reasons students may have a low GPA, such as struggling to adapt to the faster pace and higher workload of college academics, attempting difficult combinations of classes in the same semester, illness, family issues, employment and the adjustment to college from a highly structured high school environment.
While much of the responsibility falls on students to either maintain their grades or seek help when needed, Wood says universities need to make sure plenty of support is offered to those who are struggling.
"Sometimes student performance is a result of gaps in university support systems, and effective teaching and learning practices at the university or college may well not be in place for all student groups," he says.
Experts say struggling students should proactively reach out for help . Whorton says students should view it as "productive struggle" and challenges students to embrace opportunities to improve.
Likewise, Wood encourages students to look past whatever stigma they might feel about seeking help from campus resources, whether that is tutoring, advising or one-on-one discussions with faculty and staff members.
"One of the most important lessons that we eventually learn in life is that asking for help is not a sign of weakness, but one of strength," he says.
Searching for a college? Get our complete rankings of Best Colleges.
Facts About Merit Aid Scholarships

Tags: education , colleges , students , scholarships , financial aid
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
College Admissions: Get a Step Ahead!
Sign up to receive the latest updates from U.S. News & World Report and our trusted partners and sponsors. By clicking submit, you are agreeing to our Terms and Conditions & Privacy Policy .
Ask an Alum: Making the Most Out of College
You May Also Like
How to decide if an mba is worth it.
Sarah Wood March 27, 2024

What to Wear to a Graduation
LaMont Jones, Jr. March 27, 2024

FAFSA Delays Alarm Families, Colleges
Sarah Wood March 25, 2024

Help Your Teen With the College Decision
Anayat Durrani March 25, 2024

Toward Semiconductor Gender Equity
Alexis McKittrick March 22, 2024

March Madness in the Classroom
Cole Claybourn March 21, 2024

20 Lower-Cost Online Private Colleges
Sarah Wood March 21, 2024

How to Choose a Microcredential
Sarah Wood March 20, 2024

Basic Components of an Online Course
Cole Claybourn March 19, 2024

Can You Double Minor in College?
Sarah Wood March 15, 2024

TR Bursa Province
Recently viewed courses
Recently viewed.
Find Your Dream School
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
COVID-19 Update: To help students through this crisis, The Princeton Review will continue our "Enroll with Confidence" refund policies. For full details, please click here.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., calculate your gpa with our gpa scale, what is a gpa.
Your grade point average (GPA) is the sum of all your course grades throughout your high school career divided by the total number of credits. Most high schools (and colleges) report grades on a 4.0 scale. The top grade, an A, equals a 4.0.
Why is a Good GPA Important?
We receive data from schools every year, and from that we know there are two factors that weigh most heavily in college admission:

- Your high school GPA
- Rigor of your high school curriculum
( Standardized test scores, like those from the SAT and ACT, are a close third.)
What is a Good GPA?
The answer to this depends on where you want to go to college. Check out the GPA ranges for accepted students to the schools on your wishlist, and see how your grades compare. Use our college search to research schools that interest you or grab a copy of our book Best 384 Colleges to help you find your best-fit school.
Colleges will also consider the rigor of your high school schedule . Did you take Honors and AP courses when they were available? Were you enrolled in your high school’s IB program? Besides doing well in the courses you took, colleges want to see that you are challenging yourself academically.
Since GPA is so important, here's a simple chart that shows how to convert your letter grades to the 4.0 scale
Weighted vs. Unweighted GPA
An unweighted GPA is the average of all your grades on the 4.0 scale above.
Some high schools use a weighted GPA scale, which gives more points (greater "weight") to grades in accelerated courses like Honors Biology or AP French. So, while a B might normally equal a 3.0, a B in an AP class would be more like a 3.3 on a weighted scale.
Free SAT Practice Tests & Events
Evaluate and improve your SAT score.
Great Grades Can Equal Financial Aid
Your GPA will help you get in, but in these budget-tight times, great grades can also translate directly into dollars and cents. As Kal Chaney attests in our book Paying for College , “Every tenth of a point a student raises her high school GPA can save her thousands of dollars in student loans she won’t have to pay back later.”
Even at schools where students are awarded aid based only on their financial need , applicants with high academic achievement get preferential packaging. (Their award packages have a higher percentage of grants and a lower percentage of loans.) Some colleges offer full scholarships for great GPAs. There are other schools (more and more in recent years) that give out large merit-based grants, regardless of need. These grants are not necessarily just for 4.0 students, either! We know of several colleges that award merit-based grants for students with B averages.
Get Your Grades Up—and Keep Them That Way!
Senioritis is real, but colleges keep an eye on your grades even after you’re accepted. So don't think you can let your grades sink once that acceptance letter hits your mailbox! Plus, if you were waitlisted for your dream school, keeping your GPA up could boost your chances of getting off of it .

Test Your College Knowledge
How well do you understand the college admissions process? Find out with our quiz.
Take the Quiz
- College
- Applying to College

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
Free MCAT Practice Test
Thank you! Look for the MCAT Review Guide in your inbox.
I already know my score.
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- Local Offices
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
The Ultimate Guide What is GPA and Why Is it Important
Link Copied
Share on Facebook
Share on Twitter
Share on LinkedIn

Score smarter, not harder - calculate your GPA with ease!
GPA, or a grade point average, is a figure that reflects the typical value of all combined final grades obtained over the duration of a course. Of course, the grading system wasn’t already complicated enough for students to understand that they decided to add one more point system. You must be familiar with the A, B, C, D, and F grading systems. But GPA is a whole different ball game.
However, it is essential for your "good standing" as a student, continued enrollment in your major, future financial aid eligibility, which depends on maintaining a satisfactory GPA, potential eligibility for scholarships, potential employment opportunities, eligibility for collegiate athletic teams, and more. So you might wanna have to read this carefully and clearly understand what GPA is.
What Is GPA
“Hey, how much did you get?”
“ I got 50."
”Damn! That's nice.”
“Yeah, it would’ve been if the exam was out of 50 or 60 or even a 70".
”So how much was it out of?”
“Well, how much?”
“ A hundred”
Remember when we used to discuss our marks like this, not in letters, not in points and certainly in “averages”, but in numbers, simple times, huh? But well, such is the way of life that no one likes simply. Fancy and complexity are the way to go for everything, be it technology, travel, food, or entertainment. So why should the grading system fall behind? Let's make that complex, too. And in came the GPA system. So what is GPA exactly?
The grade point average, or GPA, as it's commonly known, is a figure that represents the average grade you have received for each of your courses. Your GPA monitors your academic achievement on a scale from 1.0 to 4.0 . This figure is used to determine whether you satisfy the requirements and criteria established by the degree programme or university.
Ezra Stiles, the president of Yale, first used GPA when he established the first grading system in the country in 1785 using the terms Optimi, Second Optimi, Inferiores, and Perjores. In 1817, other universities, including William and Mary, adopted comparable strategies.
Let's say you get an A+ in a subject, then the 4 points obtained from an A+ in a class during the semester count toward your cumulative GPA. The average of the grades you received over the course of a semester or academic year is your GPA.
How To Calculate Your GPA?
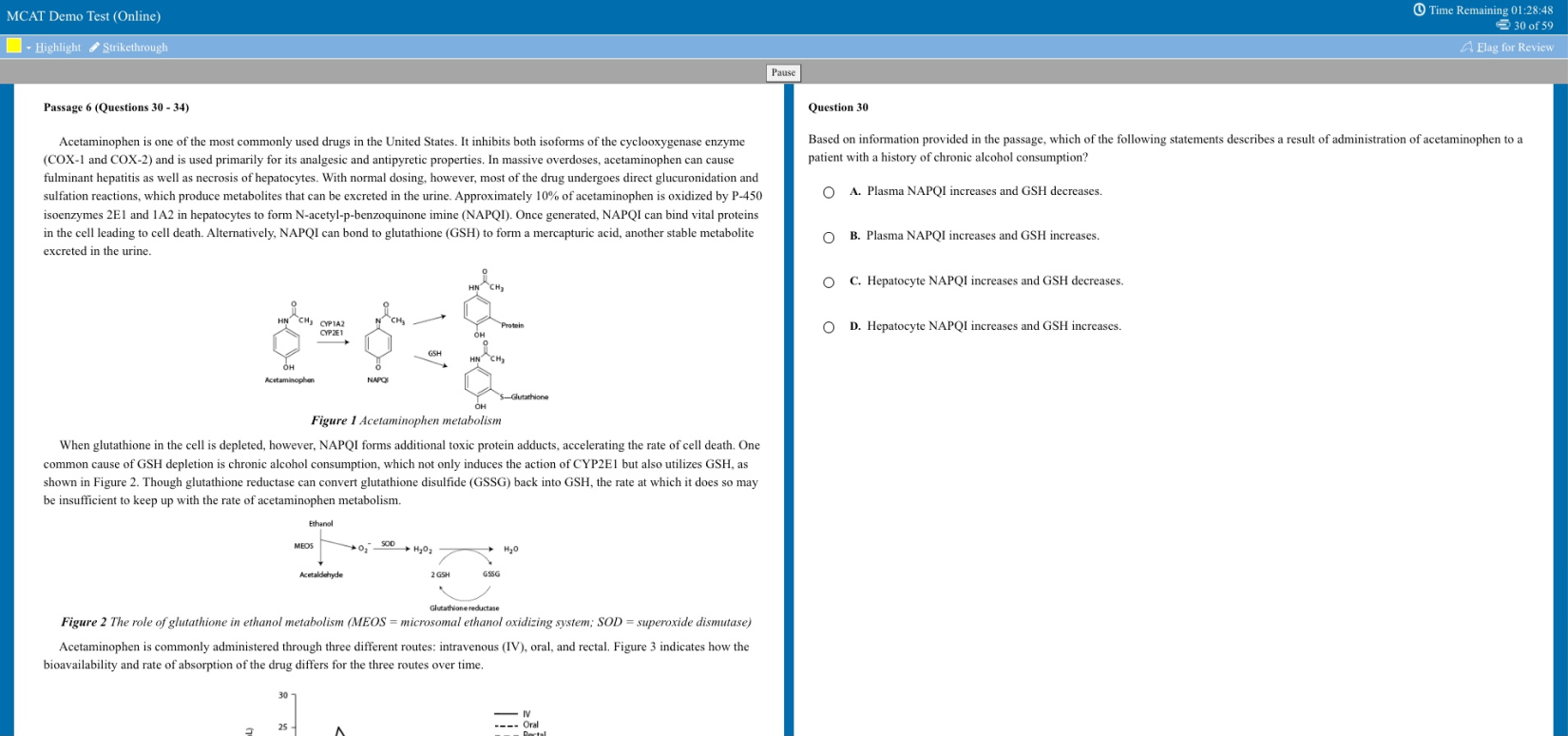
You know what GPA is. But now stands one more question: how to calculate GPA? The basic formula for calculating GPA is dividing the total number of programme points obtained by the total number of attempted credits. Converting UK school grades to GPA can be a bit tricky, but don't worry; we’ll guide you through it in simple terms.
To calculate your GPA or convert your UK Grades to GPA, you need to know these things:
- Credits attempted - This is the total number of credits you've attempted for the courses you have taken.
- Final grades earned - You can view your final grades in your program's coursework using your unofficial transcript.
- Point values for specific grades - A point value is given to each grade. The point values for your grades are assigned like this.
Suppose you take four courses: English, Maths, Biology and History. You manage to rack up 5, 1, 5, and 5 credit hours in them, respectively. That gives you a total of 16 hours of credit attempted. Now, you are graded A, B, C, and F (remember this is hypothetical) in the courses, respectively. So, going by the point values assigned to each of the grades, your grade points are 20, 3, 10, and 0, respectively. That equals 33 total grade points. Now, referring to the GPA calculator formula, the Total grade points earned(33) divided by the number of credits attempted (16). That gives you 2.06, which is your GPA. We know, not exactly a simple formula, but hey, we aren't the ones who came up with it. So until some genius comes up with an easier and smarter way to calculate GPA, this is your best bet.
Converting CGPA To GPA
CGPA is a popular grading scheme used in many countries like Pakistan, India, and other regions of the world. The grading scheme employed in the US is called GPA, on the other hand. Let's get into it! You have to carry out the following steps in order to convert your CGPA to GPA:
Step 1: Understanding your CGPA scale
CGPA scales might differ depending on the institution or country. The CGPA may be measured on a scale of 4.0 in some instances or a scale of 10.0 or another range. Verify the scale on which your CGPA is calculated.
Step 2 : Determine the corresponding GPA scale
In the US, the GPA scale normally runs from 0.0 to 4.0. Some colleges, however, might have their own modifications. You must inquire about the GPA scale directly with the particular university you are considering.
Step 3: Calculate the conversion
You can determine the equivalent GPA once you are familiar with both the CGPA and GPA scales. A general formula you can use is as follows:
- GPA is equal to (CGPA / CGPA scale) x GPA scale.
If you wish to convert your CGPA from 8.5 on a 10.0 scale to 4.0 on a GPA scale. The calculation is as follows:
- GPA = (8.5 / 10.0) * 4.0 = 3.4
Therefore, in this instance, your CGPA of 8.5 would roughly be equivalent to a GPA of 3.4. Just keep in mind that there can be a few minor differences depending on the exact conversion scale employed by the school you're applying to. This is a typical method for converting CGPA to GPA. To get correct information based on the university's criteria, it's always a good idea to get in touch with them or speak with an academic advisor.
Why GPA Matters?
In universities and colleges, your eligibility for financial assistance programmes, scholarships, and other help is based on your average GPA. You risk losing financial assistance if your GPA drops below the required level (often 2.0, but this varies from institution to institution). Additionally, GPAs are a prerequisite for joining a particular club or organisation or participating in extracurricular activities. You could miss many chances if your academic efforts aren't up to grade. Your GPA is equally crucial if you wish to continue your education and apply for a Master's or PhD degree. Some schools will accept applicants with GPAs of 2.75, 3.0, or 3.5. But one thing is sure: having a good GPA certainly does more good than harm.
Ready to GPA-nalyze? Unleash Your Excellence with Our Ultimate Guide!
Book through amber today!
Ways To Improve GPA
We hope you don't need to read this section, but if you do, there is no need to worry if your GPA is lower than what you desired. It can be improved in different ways. Some ways that students can improve their GPA are:
1. Make sure to attend classes regularly
It seems like a no-brainer, right? You signed up for the class, so it's evident that you would attend it. But we know this is easier said than done for university/college students. You might be skipping classes for various reasons, and they might be genuine more often than not.
But you won't be helping your case if you're not regular. So be sure to attend classes regularly.
2. Be active in classes.
Now that you're attending classes, it's better to be active and contribute to the class than be a silent spectator. Not only does this help you retain information and remember things taught to you to the professor's notice, but it can also assist you in improving your points for the particular class.
3. Hand in your assignments on time (before, even if possible)
Assignments must be submitted by a specific date; if you miss the deadline, you will not receive credit for the project. If you're wondering how to improve your GPA, make a schedule that will give you enough time to do all of your tasks by the due date.
4. Choose your subjects carefully.
Avoid choosing subjects that are too difficult or take up a large amount of your time. If you are not doing well in an elective, talk to your professor, and if there is an option, either change it to a class or drop it altogether.
If you want more help regarding this, head to our blog on How to Improve GPA , which solely focuses on this aspect.
GPA Requirement For US And UK Universities
In the United States, GPA (Grade Point Average) requirements for universities can vary depending on the institution and the program you are applying to. Generally speaking, most universities will look for a GPA of 3.0 or higher on a 4.0 scale, although some highly competitive programs may require a higher GPA. However, it's important to keep in mind that GPA is just one factor that universities consider when making admissions decisions, and other factors like test scores, extracurricular activities, and essays can also play a significant role. Here's everything you need to know about the US grading system .
In the United Kingdom, GPA is not typically used as a measure of academic achievement in the same way as it is in the US. Instead, universities will typically look at your overall academic record, including the grades you have earned on specific exams like the A-levels or International Baccalaureate. The specific requirements for admission will vary depending on the university and program you are applying to, so it's important to research the requirements carefully and consult with admissions staff if you have questions.
Difference Between Unweighted vs. Weighted GPA
Unweighted GPA is calculated on a standard 4.0 scale, where each letter grade is assigned a numerical value (A=4, B=3, C=2, D=1, F=0). Your unweighted GPA is simply the average of all your grades on this scale, with no additional weight given to any particular course or assignment.
On the other hand, a weighted GPA takes into account the level of difficulty of the courses you have taken. For example, if you have taken honours or Advanced Placement (AP) courses, these may be assigned a higher numerical value (such as A=5, B=4, etc.) to reflect the additional rigour and challenge of these courses. Your weighted GPA is calculated by averaging your grades on this scale, with the higher numerical values given to the more challenging courses.
Difference Between Cumulative GPA Vs Overall GPA
To explain this in short, Cumulative GPA measures academic performance over a specific period of time, while overall GPA measures academic performance across a student's entire high school or college career. Overall, GPA is often used as a key factor in college and university admissions decisions, as it provides a broad overview of a student's academic performance over time. Cumulative GPA, on the other hand, is more focused on specific periods of time and can be used by students to track their progress and identify areas where they may need to improve.
So now you know what GPA is and that GPA is not as complicated as it seems, and moreover, why is it so important? It does seem a bit complex at first, but hopefully, we've simplified it for you. Since it's hard to sum up someone's background, personality, and skills in a single figure, your GPA doesn't determine who you are. It does, however, give colleges and employers a clear sense of how seriously you treated your education and how consistently you maintained your grades. You can also read our blog on the simple guide for a percentage to GPA converter .
Frequently Asked Questions
What is gpa, how do i calculate my gpa, is 3.5 a good gpa, what is the highest gpa, can you get a 5.0 gpa.
Your ideal student home & a flight ticket awaits
Follow us on :

amber © 2023. All rights reserved.
4.8/5 on Trustpilot
Rated as "Excellent" • 4700+ Reviews by Students

Easily convert your letter grade or percentage grade to a 4-point system with our easy to use GPA converter and handy GPA scale.
GPA Converter
List of common gpa conversions, what is the gpa scale.
You’ve probably heard the term, GPA or Grade Point Average, and discovered how important it is during high school, college, and your early career.
A person’s GPA can affect what colleges are likely to accept him or her. It can also open or close doors to what graduate or advanced degree programs might be available. An individual’s GPA can affect the availability of grants or scholarships for financial aid. Finally, job opportunities can be dependent on a person’s GPA.
GPA’s are actually calculations, based on a person’s letter grade. For example, the letter grade of an “A” has a number value. Likewise, calculating a letter grade is usually done by looking at a particular percentage.
These three factors, together, make up the GPA scale.
Let’s take a closer look.
Percentages to Letter Grades to Grade Points and Back Again
Calculating your percentage.
Most of us are familiar with “letter grades.” Since early childhood, we’ve most likely received grades on our report cards that are based on the letter grade system. We know, for example, that an “A” is great! An “F,” not so much.
But, what’s the breakdown of a letter grade, as it relates to the GPA scale in particular?
Basically, to calculate a letter grade, your teacher figured out your class percentage grade, and converted that to a letter grade.
Let’s say you’ve taken the following class, and you have 10 grades for the final report card. We’ll look at how many points you received, how many were available, what your percentage grade was, and how that translates to a letter grade.
As we see, you earned 340 points out of 380 available. Let’s first figure out your percentage, in other words, what percentage of the total points you earned.
We take the total points earned (340), and divide them by the total points available (380).
340 ÷ 380 = 0.89
To convert that to a percentage, we move the decimal point to the right two spaces, giving us a percentage grade of 89%.
Figuring out your letter grade
Now, we take that percentage, and convert it into a letter grade. Here is a typical conversion table:
(NOTE - not all schools or teachers use this exact scale, but this is pretty standard)
So, in this example, with a grade percentage of 89%, that translates or converts to a “B+.”
Let’s now figure out how those letter grades get converted into a GPA.
Converting your letter grade to a grade point average (GPA)
As a reminder, your GPA is a number that colleges and universities look at to determine if you’re eligible to attend. The higher your GPA, the better. If you take classes that are particularly difficult, Advanced Placement (AP), or Honors coursework that’s even better. (We’ll talk about AP and Honors classes and how they affect your GPA, in just a bit).
To figure out your GPA, we have to look at the GPA Scale, which changes your letter grade into a point system. Here’s a typical scale, for regular (not AP or Honors coursework) at the high school or college level.
For AP and Honors classes, these are calculated with an “A” being worth 5 points (instead of 4); a “B” is worth 4 points, a “C” is worth 3 points, and so on.
In our example, an 89% grade converts to a “B+” letter grade; what does that do for your GPA? As the above table shows, a “B+” is worth 3.3 points on the GPA Scale. Not too bad!
Calculating GPA
To figure out your overall GPA at the high school level (college is a little different—we’ll take a look at that in a second), you convert your class letter grades to grade points using a GPA Scale. Then you add all of your classes up, and average them. Confused?
Let’s do a quick example to make some sense out of it. Let’s say during your first semester of senior year in high school you had these grades, and GPA scale values.
First, let’s add up all the GPA Scale points: 4.0 + 3.0 + 3.0 + 4.0 + 4.0 = 18.
Now, we average that sum by dividing the total by how many classes you took, or “5”:
18 ÷ 5 = 3.6
Your average for that semester is a 3.6 GPA . To figure out your cumulative GPA , or high school career GPA, we simply add up all your semester GPAs, divide them by how many semesters completed, and get your average GPA. Here’s a quick look at that:
Now, we divide that total by the number of semesters (7) to get your cumulative GPA:
24.8 ÷ 7 = 3.4
The result? A 3.4 GPA . Pretty easy, right? But, if you want to skip the calculations altogether, head on over to our wonderful high school GPA calculator which will perform the same math but behind the scenes, letting you focus on getting those grades where you want them.
How AP and Honors Classes Affect GPA
As mentioned above, if you take an AP or Honors class, your “A” is converted to a 5.0, instead of a 4.0.
So, when you take an AP or Honors class, your GPA scale for that class is higher than for a regular class. This will increase your GPA, almost automatically—so, it’s a great idea to take AP and Honors classes whenever you can.
Let’s look at a quick example of this. Let’s say you took two honors classes this semester:
Summing up the grade points (19) and dividing by the number of classes (5) yields:
19 ÷ 5 = 3.8
A 3.8 GPA is very good! See how the 5.0 scale for the Honors and AP classes increased the GPA to an “A-” range, even though you earned 3 “B” grades? If you're taking Honors or AP classes and want to see what your current weighted class grades are, try our weighted grade calculator which lets you select different weights for each of your high school class assignments.
How to Calculate College GPA
We won’t get into too much detail, but let’s quickly look at college GPAs, because they’re calculated a little differently.
Each college class has a certain number of credit usually 3, but they can sometimes be 4–5 if the class is particularly difficult, or requires extra time, like lab work.
The credit hours are multiplied by the course grade point, and then divided accordingly. Let’s take a look at an example college semester to help understand it better.
For each course we multiply the grade points received by the course's credit hours to determine the total points awarded. Finally, we divide the total points by total credit hours to get the semester grade point average , like so:
43 ÷ 13 = 3.3
Not too shabby! A 3.3 GPA , when converted back into a letter grade, is a solid “B+.” Could use a little work, but impressive nonetheless. Again, this is just an example to demonstrate the underlying how of college GPA calculation; if you're interested in calculating your own college GPA, check out our easy to use college GPA calculator which will handle all of the math for you, no questions asked.
So, Why Do You Need to Know This?
This might seem kind of like Algebra! You might be saying to yourself, “When am I ever going to need to know how to convert my GPA to a letter grade, or understand a college grading scale.”
Well, believe it or not, you WILL need Algebra in your life (at least figuring for “x”)! And, it does help to know this information.
For example, let’s say that you are shooting for a 3.8 GPA , but your professors don’t hand back assignments on that grading scale. You won’t, for instance, get a final exam back with a score of “3.8 GPA.” So, you need to know how your percentage grade will affect your GPA.
If you get a test back that has a percentage grade of 94%, you can safely assume that you just earned an “A.” But, how is that calculated in relation to your GPA on your final grade?
As we learned above, a 94% is a 4.0 GPA , and a solid “A.” So, if you are shooting for a cumulative GPA of 3.8, your 94% will work its magic and help you out.
If, however, your grade for that final is an 89%, which translates to a “B+” or 3.3-3.6 GPA, you can see how that will fall short of your 3.8 GPA goal.
Your GPA Scale and You
Knowing how your grades are converted from a percentage to a letter grade, and then into your GPA can really help you plan your future to meet your needs and goals. Knowing how each individual class grade is either going to help or hurt you can make a big difference. It might, for example, help you understand that you need to study for a particular final much more than another in a different class.
Remember, colleges, universities, scholarship committees and future employers are looking at your GPA as an indicator of how good a student you are. Aim high!
- Letter A+ A A- B+ B B- C+ C C- D+ D D- F Percent 100 99 98 97 96 95 94 93 92 91 90 89 88 87 86 85 84 83 82 81 80 79 78 77 76 75 74 73 72 71 70 69 68 67 66 65 64 63 62 61 60
- Grade A+ A A- B+ B B- C+ C C- D+ D D- F Weight Regular Honors AP / IB College

GPA: What it is and How to Calculate it
What Does GPA Stand For?
How is a gpa calculated, is there a gpa converter, gpa to percentage conversion, what does a gpa of 4.0 mean, history of the gpa, gpa use in education.
Most high school students in the United States get graded through a letter system that is familiar to anyone who has been to a traditional school. Using a scale of A, B, C, D and F, teachers mark students assignments, tests, papers and overall progress. A GPA is the value of all of these marks converted to a number, by which a student's overall academic status can be measured and evaluated.
A GPA is the value of all of these marks converted to a number, by which a student's overall academic status can be measured and evaluated.
The acronym "GPA" stands for grade point average . A grade point average is the numerical equivalent of a letter grade assessment designed to evaluate student's academic performance.
Though letter grades are most common in the classroom, the GPA has become the standard measurement for comparing academic assessment in the United States. GPAs are used in a variety of areas, but mostly to rank student performance in discrete academic subjects and in school overall.
The acronym "GPA" stands for grade point average.
A GPA is calculated by assigning a number from 0.0 to 4.0 to each letter grade. A 4.0 is the highest possible grade point average and 0.0 is the lowest possible grade point average. The system takes a letter or percentage grade and converts it to a number between the 0.0 and 4.0 scale.
Once this is done, the value assessed is then multiplied by the number of credit units the course is worth. This is where GPAs help to differentiate high-weight classes like primary major subjects, from lower weight classes like sports or electives. An elective or a gym class, for example, rarely carries the same weight as a class in the sciences or the humanities.
Within the scale, an A= 4 points, a B= 3 points, a C = 2 points, a D=1 point and an F=0 points. These values are consistent throughout secondary and college educational environments. GPAs are calculated by multiplying the number of your letter grade in a course by the number of course credit units each class carries.
For example
So if your science course carries 4 credit units, and your grade is a B, 3 x 4 =12. You have 12-grade points in that particular course.
Your grade point average is calculated by adding up all the grade points you have earned in all of your courses and dividing it by the number of credit units you have, thereby assessing your average.
If you have a B which equals 12 points in science, and an A which equals 16 points in English and a C which equals 8 points in math, your GPA would be 12 + 16 + 8 divided by 12, the number of credit units you have, to equal a grade point average of 3.0, or a B average.
There are GPA converters online , but it is very easy to turn letter grades into numerical grades and calculate a GPA from there. By following the simple formula the grade point total for any grade for any course can be found. Although the A, B, C system seems fairly straightforward, there are small nuances which can change the outcome of a GPA calculation. For example, within the letter grading system, there are also + and - signs that are often administered that need to be taken into account. A B+ and an B- have different grade point values than a B, for example. The grade and GPA scale is:
- A+ = 4.0, A = 4.0, A- = 3.7
- B+ = 3.3, B = 3.0, B- = 2.7
- C+ =2.3, C = 2.0, C- = 1.7
- D+ = 1.3, D = 1.0
When you have identified all of the grades that you need to asses your GPA, including pluses or minuses for particular letters, you simply write down the equivalent numerical assessment. Once this is recorded you can multiply the numbers by the number of credit units each course holds, and then do the rest of the necessary calculations to tabulate your grade point average.
Some institutions or professors prefer to evaluate work on a scale of a percentage of 100. These percentage grades can be converted into letter grades and thus into grade points. However, you do not need to convert from a percentage into a letter grade. The formula is applicable to any grading system that has a score that can be converted into a percentage or a letter.
When converting from a percentage into GPA points, there is a formula similar to the one used to convert letter grades to GPA points. The conversion and some GPA examples are:
- 97-100 = 4.0,
- 93-96 = 4.0,
- 90-92 = 3.7
- 87-89 = 3.3,
- 83-86, 3.0,
- 80-82 = 2.7
- 77-79 = 2.3,
- 73-76 = 2.0,
- 70-72 = 1.7
- 67-69 = 1.3,
- 65-66 = 1.0,
- Below 65 = 0.0
A GPA of 4.0 is equivalent to an A average. This doesn't necessarily mean that the student in question has an A in every class, but that the overall number of As he or she has earned helps to outweigh any lesser grades and bring the average up. GPAs can be deceptive because depending on the number of courses one is taking, a GPA can either be dramatically affected by one low grade or hardly at all.
Imagine that Kim is taking 6 classes at 4 credits apiece, and Terry is taking 3 credits at 5 credits apiece. Kim and Terry both have a C in one class, but in every other class, they are getting an A. This gives Kim a GPA of 3.0 and Terry a GPA of 3.33. So even though Kim is getting As in more classes than Terry is, Terry's GPA is less affected by the C grade than Kim's is, because Terry's GPA is calculated using a lower number of credits.
The history of grading, in general, can be credited to William Farish, a professor of philosophy at Cambridge University. Prior to the industrial revolution, education was about a mentor relationship. Teachers worked with students, spent time with them, got to know them and their learning styles and made it their job to ensure that all children that passed through their instruction left with a solid understanding of the material.
This was the responsibility of the educator, and any student who left a teacher's classroom without having demonstrably learned what the teacher had taught would have reflected poorly on the teacher. This all changed at the turn of the 19th century when the Industrial Revolution came about. As factory labor and piece-work labor began to be more popular, universities began to pay their teachers based on the number of children they had in their classes rather than a flat salary based on the job they had to do.
William Farish, a professor at Cambridge found that if he were able to evaluate student performance more quickly and disseminate information in a one-size-fits-all manner, he would be able to process more students more quickly and thus increase his income. Farish's system of grading caught on, and as many educators were eager to process as many students as possible so that they might join the new labor workforce, the practice spread.
The letter grading system Farish adopted was similar to the grading system that evaluated the quality of goods on a factory floor. An item being "up to grade" meant that it could be sold and that the maker could be paid for it. This is the basis of the system that was then put in place to evaluate student learning.
In retrospect, the grading system was less about ensuring that students left classes with a solid grasp of the material and a complete education. Rather, the focus was on getting as many students through the system as possible.
An item being "up to grade" meant that it could be sold and that the maker could be paid for it.
This was done at first to line the pockets of the teacher, but as the industrial revolution progressed and more and more factory labor was required, the system was useful in getting large numbers of students taught the exact same material, graded and then ready to enter the workforce. This system, while lacking in qualities and metrics that have been deemed critical by educators, has persisted into the 21st century. The GPA is the natural evolution of the grading system, wherein letter grades are converted to points, and students courses are weighted by credit hours.
the grading system was useful in getting large numbers of students taught the exact same material, graded and then ready to enter the workforce.
There are many criticisms of the system, but the greatest is that the model wherein the teacher grades the student on his or her demonstrated grasp of the material places the onus on the student and not the teacher. Students with low GPAs are often assumed to be less intelligent, less hardworking and less capable than their counterparts with higher GPAs.
However, research indicates that only a certain type of student thrives in the lecture format of most education spaces and that many students who are intelligent, motivated and hardworking may simply not be well served by the traditional format:
- which is less devoted to inculcating students with knowledge
- more devoted to imparting information to as many as possible,
- places the responsibility for being able to understand, interpret and apply the information being disseminated squarely on the student.
For many high school students, the GPA is a topic of stress and concern . The GPA is used, most critically, for college admissions. Some universities have a GPA threshold that they do not go below, while other universities use the GPA as only a piece of a student's academic portfolio. Traditionally, a high GPA is seen as indicative of intelligence and ability to perform well academically. As the main college admissions criteria, this can understandably cause a lot of stress for student populations who are worried about their standing.
An issue with GPAs is that there is no truly standardized way of evaluating what an A is or what a B is. Schools vary widely on their perceptions of quality of work, and often the grading happens on a curve, meaning that a student's work is considered "A" work compared to the work of the student's peers.
In certain elite private schools with highly rigorous academic programs, the work that constitutes an "A" grade could be very different from work that earns an "A" grade in a larger less academically rigorous school with a large student population, less personal attention and more students to compare the work against. This is what can cause problems for students during the college admissions process.
Students who have high GPAs but who are not necessarily prepared for college-level work may find themselves admitted to a competitive university solely based on the strength of their GPA. A GPA's meaning is subject to interpretation, which is why many colleges and universities use it only as a piece of a student's academic background.
In addition to a GPA, most colleges and universities make their admissions decisions based on additional criteria like:
- extracurricular activities,
- a student's independent work,
- letters of recommendation
- and a personal essay or statement.
Related Articles

The Disadvantages of a Letter Grading System

How to Curve Grades Fairly

Grade Point Average Vs. Percentile System
How does a gpa work, how to calculate a report card grade.

How to Know If You Are in the Top 10% of Your Graduation Class

Victorian Boarding Schools

What Does a GPA of 2.4 Mean?
- STUDY USA: What is a GPA?
- CollegeBoard: How to Convert Your GPA to a 4.0 Scale
Ashley Friedman is a freelance writer with experience writing about education for a variety of organizations and educational institutions as well as online media sites. She has written for Pearson Education, The University of Miami, The New York City Teaching Fellows, New Visions for Public Schools, and a number of independent secondary schools. She lives in Los Angeles.

Choose Your Test
Sat / act prep online guides and tips, how do you calculate your gpa step-by-step instructions.
Coursework/GPA

How exactly do you take a document that's as complicated as your transcript and shrink it all down to a single number? If you're wondering how to use the final grades you've gotten in high school to determine your GPA, then you've come to the right place. This article will show you how to make this calculation, step by step. But first, what exactly is a GPA?
What Is a GPA?
Most likely, in your high school classes, your final grades are awarded either as letters (A-, B+, etc.) or percents (92%, 85%, etc. out of 100%).
A GPA, or grade point average, converts those letters or percents into numbers and then averages these numbers together. Because it's made up of all your grades, your GPA is one of the most important factors for college admission. It's a good indicator of your intelligence, work ethic, perseverance, and willingness to push yourself.
GPAs are useful for colleges to easily compare you with other students who graduated from your school and with all the other applicants. But why?
Imagine you're an admissions officer who has to look at thousands of college applications. Would you rather go through each transcript individually, add up all the As and all the Bs, and then compare that to the next person, and so on? Or, would you rather have an easy summary number that could be used for a quick comparison across the board?
Your GPA is that quick summary number.

The Difference Between Weighted and Unweighted GPA
There are two main types of GPAs: weighted and unweighted.
An unweighted GPA is when a school uses a scale that goes from 0.0 to 4.0 and does not take into account the difficulty level of classes.
By contrast, a weighted GPA is when a school uses a scale that goes from 0.0 all the way up to 5.0 (or sometimes 6.0) and does take into account class difficulty. In this model, the school gives higher numerical values to grades earned in honors , AP , and/or IB classes .
Here's an example to help clarify the differences here. Say Jeremy gets an A in a standard-level US History class, whereas Lakshmi gets an A in AP US History . In the unweighted GPA model, both As are treated the same way, with each translating to a 4.0 .
But in the weighted GPA model, Jeremy's A would convert to a 4.0 and Lakshmi's A would convert to a 5.0 to show that her class took a lot more effort to ace .
See the difference?
Before we continue, it's important to understand that this article focuses mainly on explaining and calculating unweighted GPAs. (For more information on weighted GPAs, check out our other guide .)

How Do You Calculate Your Unweighted GPA?
The first thing to do in order to calculate a grade point average is to convert each of the final class grades you've gotten so far in high school into the correct decimal.
Here is the standard unweighted scale for doing this:
Next, perform the following calculation :
- Add all the converted decimal grades together—this is your sum
- Count the number of classes you've taken
- Divide the sum by the number of classes , and you have your unweighted GPA
In the following section, we'll go through an example calculation of an unweighted GPA.
Step-by-Step Example of an Unweighted GPA Calculation
Let me show you an example of how to calculate an unweighted GPA so you can see how this will look in practice. (To see how to calculate a weighted GPA, check out our other article .) We'll use a sample transcript for incognito CIA operative John Doe.
Be aware that for this example, we are assuming that all classes are worth the same number of credits (in other words, you can ignore the credit column in the transcript below).
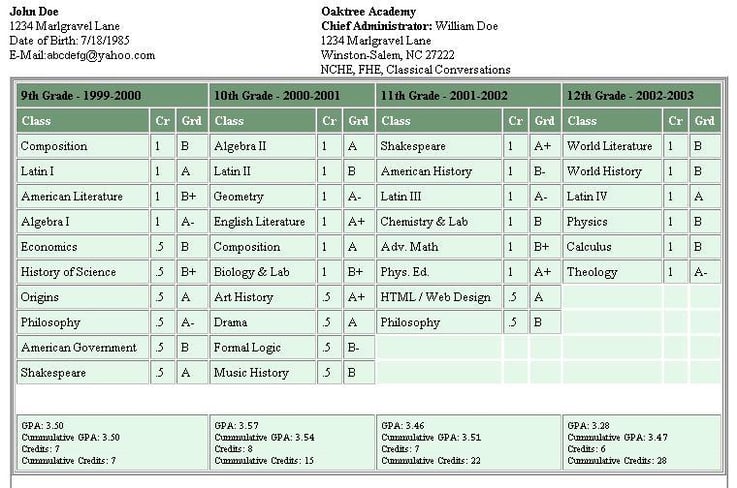
Step 1: Convert Grades Into Decimals
In order to learn how to calculate a GPA, let's first convert John's letter grades into numbers:
Let's also count how many classes he took each of those school years:
Step 2: Calculate Individual Year GPAs
To get each individual year's GPA, all we need to do is divide the sum by the number of classes . If this division ends up with a long decimal, simply round to the nearest hundredth:
Step 3: Calculate Cumulative High School GPA
To get a cumulative GPA for John's entire high school career, we simply add up the sums for all the years and divide by the number of classes he took over all those years:
35 + 35.7 + 27.7 + 19.7 = 118.1 (sum of all final grades)
10 + 10 + 8 + 6 = 34 (total number of classes taken)
118.1 / 34 = 3.47 (GPA)
So, his GPA for all of high school is 3.47.
Pro tip: The cumulative GPA is not an average of each year because the number of classes taken each year is different.
Step 4: Calculate GPA Submitted to Colleges (Optional)
Finally, if we wanted to figure out the GPA that John would send out on his college applications, we would do the same process, but leave off senior year. Since applications go out in the beginning of 12th grade, those final grades won't make it into the application GPA:
35 + 35.7 + 27.7 = 98.4 (sum of final grades from 9th to 11th grade)
10 + 10 + 8 = 28 (number of classes taken from 9th to 11th grade)
98.4 / 28 = 3.51 (college application GPA)
As you can see, John's college application GPA would be 3.51 .

What If My Classes Are Worth Different Amounts of Credits?
In the example above, we calculated John's GPA with the assumption that every took was worth the same amount of credits. If this isn't the case for you, you'll need to add in an extra step.
To calculate your GPA when your classes are worth different amounts of credits, you'll need to multiply your grade for each class by the number of credits it was worth and sum those together (instead of just summing all your grades together) and divide that sum by the total number of credits you took (rather than just the total number of classes you took).
As a quick example, let's take another look at John's junior year grades, this time with the number of credits each class was worth.
Here we can see that the last two classes John took were each only worth half a credit. In the table, the third column, "Quality Points," shows the product of John's GPA in each class with the number of credits that class was worth.
To find John's GPA (based solely on these eight classes), all you need to do now is sum the number of quality points and divide them by the number of credits John took:
GPA = (4.0+2.7+3.7+3.0+3.3+4.0+2.0+1.5) / (1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 1 + 0.5 + 0.5)
GPA = 24.2/7 = 3.46 .
What's Next?
Interested in diving even deeper into the differences between weighted and unweighted GPA? Then check out our guide to the benefits and drawbacks of both .
Want to see step-by-step weighted GPA calculation? Let us show you how it's done .
Curious how your GPA compares? Learn what a good or bad GPA is and then see how you stack up against the average high school student .

Anna scored in the 99th percentile on her SATs in high school, and went on to major in English at Princeton and to get her doctorate in English Literature at Columbia. She is passionate about improving student access to higher education.
Student and Parent Forum
Our new student and parent forum, at ExpertHub.PrepScholar.com , allow you to interact with your peers and the PrepScholar staff. See how other students and parents are navigating high school, college, and the college admissions process. Ask questions; get answers.

Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
Improve With Our Famous Guides
- For All Students
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 160+ SAT Points
How to Get a Perfect 1600, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 800 on Each SAT Section:
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading
Score 800 on SAT Writing
Series: How to Get to 600 on Each SAT Section:
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading
Score 600 on SAT Writing
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
What SAT Target Score Should You Be Aiming For?
15 Strategies to Improve Your SAT Essay
The 5 Strategies You Must Be Using to Improve 4+ ACT Points
How to Get a Perfect 36 ACT, by a Perfect Scorer
Series: How to Get 36 on Each ACT Section:
36 on ACT English
36 on ACT Math
36 on ACT Reading
36 on ACT Science
Series: How to Get to 24 on Each ACT Section:
24 on ACT English
24 on ACT Math
24 on ACT Reading
24 on ACT Science
What ACT target score should you be aiming for?
ACT Vocabulary You Must Know
ACT Writing: 15 Tips to Raise Your Essay Score
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
Is the ACT easier than the SAT? A Comprehensive Guide
Should you retake your SAT or ACT?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!
Looking for Graduate School Test Prep?
Check out our top-rated graduate blogs here:
GRE Online Prep Blog
GMAT Online Prep Blog
TOEFL Online Prep Blog
Holly R. "I am absolutely overjoyed and cannot thank you enough for helping me!”

Grades and Grade Point Average (GPA) Calculation
Grade-point-average (gpa) calculation.
The grade point average (GPA) is the arithmetic mean of the grade points earned for all credits taken at the University of Arizona for University Credit or by Special Examination for Grade, where regular grades are awarded. Ordinarily, cumulative GPAs are calculated using only the courses at the career level of the student. For example, the undergraduate GPA is based on undergraduate courses only (see Graduate Credit for Seniors , Grade Replacement Opportunity , and Second Start , Academic Renewal for undergraduates or graduates for exceptions).
A term GPA reflects only the courses taken in that term. A cumulative GPA represents all courses taken in the student's career program (i.e., undergraduate and graduate programs will have a separate GPA). Classes taken for Pass/Fail, or classes transferred from another college or university are not factored into the GPA.
Many colleges calculate a GPA based on the core or major courses for that program and will have GPA minimums to satisfy program requirements.
Undergraduate, graduate, pharmacy, veterinary medicine, and medicine programs use regular grades (A, B, C, D, E) that are included in the calculation of the grade point average. (Law, J.D. uses the regular scale with the addition of +/- grades).
Grade Point Values
Grade points for undergraduate, graduate, and professional programs (except Law J.D. grades) are assigned to each regular grade as follows: A = 4, B=3, C=2, D=1, E=0. A complete list of possible regular and alternative grades (including +/- Law J.D. grades), with their grade point values, can be found in the Grades and the Grading Systems policy.
How to Calculate a GPA
Grade points are calculated by multiplying the number of credits by the numeric value of the grade for each course. the sum of the grade points is then divided by the sum of the attempted graded units to get the gpa., for example , this is the calculation of the term gpa for these completed courses:, units x grade point value = class grade points, add the class grade points from each class, take that sum and: , total grade points ÷ total units = term gpa , example with above coursework: 45 ÷ 15 = 3.0 term gpa, example with above coursework: 41 ÷ 16 = 2.56 term gpa, this example shows an alternate process to calculate gpa, to find the cumulative gpa for the above fall and spring terms. here we multiply the units represented by each grade by the number of points for that grade: , or, you can enter your classes and grades into the:.
ADVISING RESOURCE CENTER GPA CALCULATOR
TOTAL GRADE POINTS ÷ TOTAL UNITS = CUMULATIVE GPA In this example: 86 GRADE POINTS ÷ 31 UNITS = 2.77 Cumulative GPA
Repeating courses, replacing grades.
Students may attempt the same course no more than twice. Credit will be applied only once to the degree program unless the course is designated as repeatable for credit in the catalog. Courses that may be attempted again include courses completed with a passing or failing grade (i.e., C, D, E, S, P, F, I grades) or courses that were audited or withdrawn from (i.e., O, W, E, WO, XO grades).
Repeating a Course
When a completed course with a passing or failing grade is repeated, the cumulative grade point average (GPA) will reflect the grades earned in both the first and second attempts . Credit will be applied only once to the degree program, unless the course is designated repeatable for credit by the department.
Undergraduate Grade Replacement Opportunity (GRO)
Grade Replacement Opportunity (GRO) offers undergraduate students the chance to replace grades of C, D, or E by repeating the course. Grades earned using the GRO will replace one previous grade for the course in calculating the grade point average (GPA) , even if the grade from the repeated attempt is lower than the first attempt. Both the original grade and the grade from the repeated attempt remain on the academic record. Courses eligible for GRO will be listed in the student's UAcces Student Center.
Programs such as Second Start Readmission (undergraduate), and Academic Renewal (graduate or undergraduate ) allow for an opportunity to have previous coursework excluded from the student’s GPA.
Transfer Credit Grades and GPA
Grades for coursework transferred from another institution are not included in the University of Arizona GPA.
For information on coursework eligible for transfer to the University of Arizona, see the undergraduate , general education , and graduate transfer policies.
Credit or Grade by Special Examination
Special Examinations are constructed and administered by the department . There are two types of special examination:
- Special Examinations for Credit : Passing grades, recorded as "CR" (credit), become a permanent part of the student's record but are not used in computing the cumulative grade point average (GPA). Failing grades are not recorded.
Special Examination for Grade : All grades, whether passing or failing, are permanently recorded and are used in computing the cumulative grade average.
Grades FAQs
The grade of I may be awarded only at the end of a term, when the following criteria is met:
- all but a minor portion of the course work has been satisfactorily completed
- the student is unable to finish due to extenuating circumstances
it would be possible for the student to earn a passing grade once the remaining coursework is completed
Learn more about the Incomplete Grade process.
Yes, but you will have to change your degree date to the term in which you will complete the coursework for that course. All coursework (required or elective) must be complete on the day before the graduation date. Taking an incomplete in a course in your final semester means that you did not finish all coursework in time for your degree date.
Yes, but you will have to change your degree date to the term in which you will complete the coursework for that course. All coursework (required or elective) must be completed on the day before the graduation date. Taking an incomplete in a course in your final semester means that you did not finish all coursework in time for your degree date.
For most classes, a grade of D is the lowest passing grade that will earn course credit. Some colleges require a grade of C or better to receive credit for core or upper-division courses, or courses taken as a prerequisite.
Students should contact an academic advisor for specific requirements for their program.
Graduate and professional programs have specific requirements for passing grades.
A student may appeal their final course grade by using the following procedures. The current process, deadlines, and the grade appeal form are defined by the Office of the Registrar .
Prior to filing an official grade appeal, the student should discuss the concerns with the course instructor or faculty member responsible for the course. It is important for a student to initiate this conversation as soon as possible in order to meet the deadline should they choose to file an appeal.
If concerns over a course grade are not resolved satisfactorily after speaking with the instructor, students may file a grade appeal. Valid reasons for appeal include:
- violation of university policy
- failure to follow published course policies
- inconsistent grading within the student’s course section
- disagreement over factual accuracy of graded work
Invalid reasons for appeal include:
- disagreement with published course policies
- differences in grading policies between other courses or sections of the same course
- impact of disputed grade on student’s academic progress or eligibility
The steps of the grade appeal process are available at this link: Grade Appeal .
You may be eligible for a Grade Replacement Opportunity (GRO) or to repeat the class.
Review our GRO & Repeats page for information.
Learn more about viewing grades
An "I" grade does not affect GPA unless it is changed to another letter grade once the remainder of the coursework is completed. For more information about the “I” grade please visit the webpage: https://catalog.arizona.edu/policy/courses-credit/grading/grading-system
Please contact [email protected] .
Courses such as directed research, dissertation, or a thesis are for ongoing projects. Students are likely to enroll in multiple units across multiple terms. The grading of these types of units must follow the grading basis of the course, usually S/P/F.
- S = Superior (superior achievement and progress on said project has been made)
- P = Passing (student has made appropriate progress on their project)
- F = Failure (Student did not make progress on the project)
In most cases, students will earn a ‘P’ indicating the project is continuing and the student is making satisfactory progress.
Per policy, instructors have 48 hours after the final has been administered. Review our Reporting Final Grades page for information.
Related Grade Policies
Grades & the Grading System
Academic Distinction, Dean's List, Honors & Awards
Grade Replacement Opportunity
Credit by Exam
University of Arizona Credit Requirement
Graduate Credit for Seniors
Second Start Readmission
Academic Renewal For Undergraduate Students

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
GPA stands for grade point average and is a system used to measure a student's performance and academic achievement in the US. It is calculated by converting grades or percentages to a scale of 0 to 4, with 4 being the highest. Learn how to calculate your GPA, when you might need it for applications, and how to convert it from UK to US or vice versa.
GPA stands for grade point average, a number that indicates your academic success in college. Learn what is a good GPA, how it is calculated, and when it matters for employers, graduate school and financial aid.
Find out how your high school calculates your GPA. High schools can calculate GPAs based on your letter grades in different ways. Following a standard 4.0 scale for example, A=4, B=3, C=2, D=1, F=0. However, some high schools count pluses and minuses differently. For example, B+=3.3, B=3.0, B-=2.7.
The Grade Point Average, or GPA, is a system used to quantify a student's academic performance. This system provides an average of the grades a student has obtained in their courses. These grades are converted to a standardized scale, typically ranging between 0 to 4.0 or 0 to 5.0, making it easier to compare the academic performances of ...
A grade point average (GPA) is a number representing the average value of the accumulated final grades earned in courses over time. It is often used to calculate academic honors, such as honor roll, class rank, or Latin honors. Learn how GPAs are calculated, weighted, and debated in education.
A GPA is a numerical summary of a student's average performance in their studies over a period of time, such as one semester. GPAs are used for various purposes, such as progression, admission, ranking, and quality assurance, but they may not reflect the actual level of achievement.
GPA is a way of converting your grades into a numerical scale that colleges use to judge your academic potential and engagement. Learn how GPA can help or hurt you in the college admissions process, what factors affect it, and how to improve it.
GPA stands for grade point average and is a standardized way of measuring academic achievement in the U.S. Learn how to calculate your GPA, what it means for your admission and financial aid, and how to raise your GPA if you are an international student.
The most common GPA structure is the 4.0 scale, in which an A equals 4.0 and an F equals 0.0. Some schools use a variation of that but amend it with a weighted scale that includes added credit for ...
Each grade is weighted to a specific number of points so that the sum total makes up your grade point average (GPA), which in turn reflects your overall academic performance. A good college GPA on a standard 4.0 scale can fall between 3.0 and 4.0—or between a B and an A+. However, "good" often depends on context.
The GPA, or Grade Point Average, is a number that indicates how high you scored in your courses on average. Using a scale from 1.0 to 4.0, your GPA tracks your progress during your studies. ... Throughout your university education, your average GPA is really the only metric or calculation showing how good a student you are. Although you will ...
Grade-point average can be a critical determinant in what comes next for a high school student, with college admissions and financial aid often on the line. The same holds true for a college ...
Your grade point average (GPA) is the sum of all your course grades throughout your high school career divided by the total number of credits. Most high schools (and colleges) report grades on a 4.0 scale. ... TPR Education, LLC (doing business as "The Princeton Review") is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese ...
Today, the GPA system is widely used by middle schools, high schools, and colleges throughout the U.S. Most schools calculate GPA on a 0.0-4.0 scale. Each of your letter grades (or percentage grades, depending on the school) receives a numeric equivalent. The average of those equivalencies becomes your cumulative GPA.
Grading in education is the process of applying standardized measurements for varying levels of achievements in a course. Grades can be assigned as letters (usually A to F), as a range (for example, 1 to 6), as a percentage, or as a number out of a possible total (often out of 100). ... A cumulative grade point average (CGPA), sometimes ...
The grade point average, or GPA, as it's commonly known, is a figure that represents the average grade you have received for each of your courses. Your GPA monitors your academic achievement on a scale from 1.0 to 4.0. This figure is used to determine whether you satisfy the requirements and criteria established by the degree programme or ...
GPA is a measure of academic success in high school that colleges consider in admissions. Learn how unweighted and weighted GPA scales work, what they mean, and how to calculate them.
The Grade Point Average, or GPA, is a standardized measure used to evaluate the overall academic performance of students. It reduces a student's grades from all their subjects into a single number that provides a broad view of their academic achievements. It serves as a universal metric that allows colleges, universities, and other ...
Learn how to use the 4-point GPA scale to convert your letter grade or percentage to a grade point average (GPA) for education. Find out the meaning of GPA, the 4.0 scale, and how to raise your GPA with examples and tips.
A GPA is calculated by assigning a number from 0.0 to 4.0 to each letter grade. A 4.0 is the highest possible grade point average and 0.0 is the lowest possible grade point average. The system takes a letter or percentage grade and converts it to a number between the 0.0 and 4.0 scale. Once this is done, the value assessed is then multiplied by ...
Step 3: Calculate Cumulative High School GPA. To get a cumulative GPA for John's entire high school career, we simply add up the sums for all the years and divide by the number of classes he took over all those years: 35 + 35.7 + 27.7 + 19.7 = 118.1 (sum of all final grades)
Most community colleges only require a high school diploma or GED® certificate for admission. If you want to attend a four-year school, however, having a GPA higher than 3.0 is ideal. Schools ...
It depends on the school and program. In general, graduate schools look for a minimum 3.0 GPA, but programs admit applicants with lower GPAs, too. Grades aren't the only way grad schools measure ...
Grade-Point-Average (GPA) Calculation. The grade point average (GPA) is the arithmetic mean of the grade points earned for all credits taken at the University of Arizona for University Credit or by Special Examination for Grade, where regular grades are awarded. Ordinarily, cumulative GPAs are calculated using only the courses at the career level of the student.
When it comes to listing your degree on your resume, it's important to make sure it is prominent and integral to the document and that you include any relevant details about your degree that will sell you to an employer or college. Review the steps below to discover how to list your degree for maximum effect. 1. Create a resume education section.
Brenna Swanston is an education-focused editor and writer with a particular interest in education equity and alternative educational paths. As a newswriter in her early career, Brenna's education ...
Norwalk High student with 4.5 GPA is 'truly honored' to win $120K college scholarship. NHS senior Kiera Cunniffe is the recipient of the Kevin M. Eidt Norwalk High School Scholarship this year ...