Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Parts of speech

The 8 Parts of Speech | Chart, Definition & Examples

A part of speech (also called a word class ) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence. Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing.
The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns , pronouns , verbs , adjectives , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and interjections . Some modern grammars add others, such as determiners and articles .
Many words can function as different parts of speech depending on how they are used. For example, “laugh” can be a noun (e.g., “I like your laugh”) or a verb (e.g., “don’t laugh”).
Table of contents
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Other parts of speech
Interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
A noun is a word that refers to a person, concept, place, or thing. Nouns can act as the subject of a sentence (i.e., the person or thing performing the action) or as the object of a verb (i.e., the person or thing affected by the action).
There are numerous types of nouns, including common nouns (used to refer to nonspecific people, concepts, places, or things), proper nouns (used to refer to specific people, concepts, places, or things), and collective nouns (used to refer to a group of people or things).
Ella lives in France .
Other types of nouns include countable and uncountable nouns , concrete nouns , abstract nouns , and gerunds .
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
A pronoun is a word used in place of a noun. Pronouns typically refer back to an antecedent (a previously mentioned noun) and must demonstrate correct pronoun-antecedent agreement . Like nouns, pronouns can refer to people, places, concepts, and things.
There are numerous types of pronouns, including personal pronouns (used in place of the proper name of a person), demonstrative pronouns (used to refer to specific things and indicate their relative position), and interrogative pronouns (used to introduce questions about things, people, and ownership).
That is a horrible painting!
A verb is a word that describes an action (e.g., “jump”), occurrence (e.g., “become”), or state of being (e.g., “exist”). Verbs indicate what the subject of a sentence is doing. Every complete sentence must contain at least one verb.
Verbs can change form depending on subject (e.g., first person singular), tense (e.g., simple past), mood (e.g., interrogative), and voice (e.g., passive voice ).
Regular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participle are formed by adding“-ed” to the end of the word (or “-d” if the word already ends in “e”). Irregular verbs are verbs whose simple past and past participles are formed in some other way.
“I’ve already checked twice.”
“I heard that you used to sing .”
Other types of verbs include auxiliary verbs , linking verbs , modal verbs , and phrasal verbs .
An adjective is a word that describes a noun or pronoun. Adjectives can be attributive , appearing before a noun (e.g., “a red hat”), or predicative , appearing after a noun with the use of a linking verb like “to be” (e.g., “the hat is red ”).
Adjectives can also have a comparative function. Comparative adjectives compare two or more things. Superlative adjectives describe something as having the most or least of a specific characteristic.
Other types of adjectives include coordinate adjectives , participial adjectives , and denominal adjectives .
An adverb is a word that can modify a verb, adjective, adverb, or sentence. Adverbs are often formed by adding “-ly” to the end of an adjective (e.g., “slow” becomes “slowly”), although not all adverbs have this ending, and not all words with this ending are adverbs.
There are numerous types of adverbs, including adverbs of manner (used to describe how something occurs), adverbs of degree (used to indicate extent or degree), and adverbs of place (used to describe the location of an action or event).
Talia writes quite quickly.
Other types of adverbs include adverbs of frequency , adverbs of purpose , focusing adverbs , and adverbial phrases .
A preposition is a word (e.g., “at”) or phrase (e.g., “on top of”) used to show the relationship between the different parts of a sentence. Prepositions can be used to indicate aspects such as time , place , and direction .
I left the cup on the kitchen counter.
A conjunction is a word used to connect different parts of a sentence (e.g., words, phrases, or clauses).
The main types of conjunctions are coordinating conjunctions (used to connect items that are grammatically equal), subordinating conjunctions (used to introduce a dependent clause), and correlative conjunctions (used in pairs to join grammatically equal parts of a sentence).
You can choose what movie we watch because I chose the last time.
An interjection is a word or phrase used to express a feeling, give a command, or greet someone. Interjections are a grammatically independent part of speech, so they can often be excluded from a sentence without affecting the meaning.
Types of interjections include volitive interjections (used to make a demand or request), emotive interjections (used to express a feeling or reaction), cognitive interjections (used to indicate thoughts), and greetings and parting words (used at the beginning and end of a conversation).
Ouch ! I hurt my arm.
I’m, um , not sure.
The traditional classification of English words into eight parts of speech is by no means the only one or the objective truth. Grammarians have often divided them into more or fewer classes. Other commonly mentioned parts of speech include determiners and articles.
- Determiners
A determiner is a word that describes a noun by indicating quantity, possession, or relative position.
Common types of determiners include demonstrative determiners (used to indicate the relative position of a noun), possessive determiners (used to describe ownership), and quantifiers (used to indicate the quantity of a noun).
My brother is selling his old car.
Other types of determiners include distributive determiners , determiners of difference , and numbers .
An article is a word that modifies a noun by indicating whether it is specific or general.
- The definite article the is used to refer to a specific version of a noun. The can be used with all countable and uncountable nouns (e.g., “the door,” “the energy,” “the mountains”).
- The indefinite articles a and an refer to general or unspecific nouns. The indefinite articles can only be used with singular countable nouns (e.g., “a poster,” “an engine”).
There’s a concert this weekend.
If you want to know more about nouns , pronouns , verbs , and other parts of speech, make sure to check out some of our language articles with explanations and examples.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Types of verbs
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
A is an indefinite article (along with an ). While articles can be classed as their own part of speech, they’re also considered a type of determiner .
The indefinite articles are used to introduce nonspecific countable nouns (e.g., “a dog,” “an island”).
In is primarily classed as a preposition, but it can be classed as various other parts of speech, depending on how it is used:
- Preposition (e.g., “ in the field”)
- Noun (e.g., “I have an in with that company”)
- Adjective (e.g., “Tim is part of the in crowd”)
- Adverb (e.g., “Will you be in this evening?”)
As a part of speech, and is classed as a conjunction . Specifically, it’s a coordinating conjunction .
And can be used to connect grammatically equal parts of a sentence, such as two nouns (e.g., “a cup and plate”), or two adjectives (e.g., “strong and smart”). And can also be used to connect phrases and clauses.
Is this article helpful?
Other students also liked, what is a collective noun | examples & definition.
- What Is an Adjective? | Definition, Types & Examples
- Using Conjunctions | Definition, Rules & Examples
More interesting articles
- Definite and Indefinite Articles | When to Use "The", "A" or "An"
- Ending a Sentence with a Preposition | Examples & Tips
- What Are Prepositions? | List, Examples & How to Use
- What Is a Determiner? | Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Adverb? Definition, Types & Examples
- What Is an Interjection? | Examples, Definition & Types
Get unlimited documents corrected
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

Parts of Speech
What are the parts of speech, a formal definition.
Table of Contents
The Part of Speech Is Determined by the Word's Function
Are there 8 or 9 parts of speech, the nine parts of speech, (1) adjective, (3) conjunction, (4) determiner, (5) interjection, (7) preposition, (8) pronoun, why the parts of speech are important, video lesson.

- You need to dig a well . (noun)
- You look well . (adjective)
- You dance well . (adverb)
- Well , I agree. (interjection)
- My eyes will well up. (verb)
- red, happy, enormous
- Ask the boy in the red jumper.
- I live in a happy place.
- I caught a fish this morning! I mean an enormous one.
- happily, loosely, often
- They skipped happily to the counter.
- Tie the knot loosely so they can escape.
- I often walk to work.
- It is an intriguingly magic setting.
- He plays the piano extremely well.
- and, or, but
- it is a large and important city.
- Shall we run to the hills or hide in the bushes?
- I know you are lying, but I cannot prove it.
- my, those, two, many
- My dog is fine with those cats.
- There are two dogs but many cats.
- ouch, oops, eek
- Ouch , that hurt.
- Oops , it's broken.
- Eek! A mouse just ran past my foot!
- leader, town, apple
- Take me to your leader .
- I will see you in town later.
- An apple fell on his head .
- in, near, on, with
- Sarah is hiding in the box.
- I live near the train station.
- Put your hands on your head.
- She yelled with enthusiasm.
- she, we, they, that
- Joanne is smart. She is also funny.
- Our team has studied the evidence. We know the truth.
- Jack and Jill went up the hill, but they never returned.
- That is clever!
- work, be, write, exist
- Tony works down the pit now. He was unemployed.
- I will write a song for you.
- I think aliens exist .
Are you a visual learner? Do you prefer video to text? Here is a list of all our grammar videos .
Video for Each Part of Speech
The Most Important Writing Issues
The top issue related to adjectives.
| Don't write... | Do write... |
|---|---|
| very happy boy | delighted boy |
| very angry | livid |
| extremely posh hotel | luxurious hotel |
| really serious look | stern look |
The Top Issue Related to Adverbs
- Extremely annoyed, she stared menacingly at her rival.
- Infuriated, she glared at her rival.
The Top Issue Related to Conjunctions
- Burger, Fries, and a shake
- Fish, chips and peas
The Top Issue Related to Determiners
The Top Issue Related to Interjections
The top issue related to nouns, the top issue related to prepositions, the top issue related to pronouns, the top issue related to verbs.
| Unnatural (Overusing Nouns) | Natural (Using a Verb) |
|---|---|
| They are in agreement that he was in violation of several regulations. | They agree he violated several regulations. |
| She will be in attendance to present a demonstration of how the weather will have an effect on our process. | She will attend to demonstrate how the weather will affect our process. |
- Crack the parts of speech to help with learning a foreign language or to take your writing to the next level.

This page was written by Craig Shrives .
You might also like...
Help us improve....

Was something wrong with this page?

Use #gm to find us quicker .

Create a QR code for this, or any, page.
mailing list
grammar forum
teachers' zone
Confirmatory test.
This test is printable and sendable
expand to full page
show as slides
download as .doc
print as handout
send as homework
display QR code
The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
- Ph.D., Rhetoric and English, University of Georgia
- M.A., Modern English and American Literature, University of Leicester
- B.A., English, State University of New York
A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences, such as nouns or verbs. Also known as word classes, these are the building blocks of grammar.
Every sentence you write or speak in English includes words that fall into some of the nine parts of speech. These include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. (Some sources include only eight parts of speech and leave interjections in their own category.)
Parts of Speech
- Word types can be divided into nine parts of speech:
- prepositions
- conjunctions
- articles/determiners
- interjections
- Some words can be considered more than one part of speech, depending on context and usage.
- Interjections can form complete sentences on their own.
Learning the names of the parts of speech probably won't make you witty, healthy, wealthy, or wise. In fact, learning just the names of the parts of speech won't even make you a better writer. However, you will gain a basic understanding of sentence structure and the English language by familiarizing yourself with these labels.
Open and Closed Word Classes
The parts of speech are commonly divided into open classes (nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs) and closed classes (pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections). Open classes can be altered and added to as language develops, and closed classes are pretty much set in stone. For example, new nouns are created every day, but conjunctions never change.
In contemporary linguistics , parts of speech are generally referred to as word classes or syntactic categories. The main difference is that word classes are classified according to more strict linguistic criteria. Within word classes, there is the lexical, or open class, and the function, or closed class.
The 9 Parts of Speech
Read about each part of speech below, and practice identifying each.
Nouns are a person, place, thing, or idea. They can take on a myriad of roles in a sentence, from the subject of it all to the object of an action. They are capitalized when they're the official name of something or someone, and they're called proper nouns in these cases. Examples: pirate, Caribbean, ship, freedom, Captain Jack Sparrow.
Pronouns stand in for nouns in a sentence . They are more generic versions of nouns that refer only to people. Examples: I, you, he, she, it, ours, them, who, which, anybody, ourselves.
Verbs are action words that tell what happens in a sentence. They can also show a sentence subject's state of being ( is , was ). Verbs change form based on tense (present, past) and count distinction (singular or plural). Examples: sing, dance, believes, seemed, finish, eat, drink, be, became.
Adjectives describe nouns and pronouns. They specify which one, how much, what kind, and more. Adjectives allow readers and listeners to use their senses to imagine something more clearly. Examples: hot, lazy, funny, unique, bright, beautiful, poor, smooth.
Adverbs describe verbs, adjectives, and even other adverbs. They specify when, where, how, and why something happened and to what extent or how often. Many adjectives can be turned into adjectives by adding the suffix - ly . Examples: softly, quickly, lazily, often, only, hopefully, sometimes.
Preposition
Prepositions show spatial, temporal, and role relations between a noun or pronoun and the other words in a sentence. They come at the start of a prepositional phrase , which contains a preposition and its object. Examples: up, over, against, by, for, into, close to, out of, apart from.
Conjunction
Conjunctions join words, phrases, and clauses in a sentence. There are coordinating, subordinating, and correlative conjunctions. Examples: and, but, or, so, yet.
Articles and Determiners
Articles and determiners function like adjectives by modifying nouns, but they are different than adjectives in that they are necessary for a sentence to have proper syntax. Articles and determiners specify and identify nouns, and there are indefinite and definite articles. Examples of articles: a, an, the ; examples of determiners: these, that, those, enough, much, few, which, what.
Some traditional grammars have treated articles as a distinct part of speech. Modern grammars, however, more often include articles in the category of determiners , which identify or quantify a noun. Even though they modify nouns like adjectives, articles are different in that they are essential to the proper syntax of a sentence, just as determiners are necessary to convey the meaning of a sentence, while adjectives are optional.
Interjection
Interjections are expressions that can stand on their own or be contained within sentences. These words and phrases often carry strong emotions and convey reactions. Examples: ah, whoops, ouch, yabba dabba do!
How to Determine the Part of Speech
Only interjections ( Hooray! ) have a habit of standing alone; every other part of speech must be contained within a sentence and some are even required in sentences (nouns and verbs). Other parts of speech come in many varieties and may appear just about anywhere in a sentence.
To know for sure what part of speech a word falls into, look not only at the word itself but also at its meaning, position, and use in a sentence.
For example, in the first sentence below, work functions as a noun; in the second sentence, a verb; and in the third sentence, an adjective:
- Bosco showed up for work two hours late.
- The noun work is the thing Bosco shows up for.
- He will have to work until midnight.
- The verb work is the action he must perform.
- His work permit expires next month.
- The attributive noun (or converted adjective) work modifies the noun permit .
Learning the names and uses of the basic parts of speech is just one way to understand how sentences are constructed.
Dissecting Basic Sentences
To form a basic complete sentence, you only need two elements: a noun (or pronoun standing in for a noun) and a verb. The noun acts as a subject, and the verb, by telling what action the subject is taking, acts as the predicate.
In the short sentence above, birds is the noun and fly is the verb. The sentence makes sense and gets the point across.
You can have a sentence with just one word without breaking any sentence formation rules. The short sentence below is complete because it's a verb command with an understood "you" noun.
Here, the pronoun, standing in for a noun, is implied and acts as the subject. The sentence is really saying, "(You) go!"
Constructing More Complex Sentences
Use more parts of speech to add additional information about what's happening in a sentence to make it more complex. Take the first sentence from above, for example, and incorporate more information about how and why birds fly.
- Birds fly when migrating before winter.
Birds and fly remain the noun and the verb, but now there is more description.
When is an adverb that modifies the verb fly. The word before is a little tricky because it can be either a conjunction, preposition, or adverb depending on the context. In this case, it's a preposition because it's followed by a noun. This preposition begins an adverbial phrase of time ( before winter ) that answers the question of when the birds migrate . Before is not a conjunction because it does not connect two clauses.
- What Is a Phrase? Definition and Examples in Grammar
- Closed Class Words
- Reduced Relative Clauses
- Word Class in English Grammar
- Open Class Words in English Grammar
- Telegraphic Speech
- Parts of Speech Printable Worksheets
- How to Diagram a Sentence
- Content or Lexical Word in English
- Adverbio o Adjetivo
- Sentence Parts and Sentence Structures
- What are 'Wh- Words' in Grammar?
- How Does Concord Apply to English Grammar?
- Understanding Anthimeria in Language
- Meaning and Examples of Inflectional Morphemes
- Passed vs. Past: How to Choose the Right Word
- Parts of Speech
- Sentence Structure
- Sentence Types
- Rules & Usage
- Punctuation
- How to Diagram
- Diagramming Index
- Diagramming Together
- Contact & FAQ
- Stream the Documentary
- Testimonials
Download your free grammar guide here.
What are the parts of speech?
Today's the day for you to learn about this important grammatical concept! But first...let's see what the parts of speech have to do with your clothes.

Imagine that it's laundry day, and you've just finished washing and drying your clothes. You dump the contents of the laundry basket onto your bed, and you begin to organize everything. You fold matching socks together, you create a pile of perfectly folded shirts that you would be proud to show Marie Kondo, and you do the same thing with your pants, jackets, and everything else.
In the same way that we organize our clothes into groups based on each item's function and features, we organize our words into categories based on each word's function and features. We call these categories of words the parts of speech .
Some people categorize words into eight parts of speech, and some people categorize them into nine parts of speech. Neither one is wrong; they're just two ways of looking at things. We'll go over these categories below. Here at English Grammar Revolution, we categorize words into eight groups, but I'll tell you about the ninth one as well.
There's one important thing for you to know before we look at these categories: most words can function as more than one part of speech . They will only do one job at a time, but they can do different things in different sentences. Look at the word love in the following sentences.
My love of grammar inspired me to make this website.
Here, love is functioning as a noun. It's the subject of the sentence.
I love you.
Now, love is acting as a verb ! It's telling us an action.
The only way we can know how to categorize a word is to look at how it's acting within a sentence.
Okay, let's check out the parts of speech!
The 8 Parts of Speech
Nouns name people, places, things, or ideas. They're important parts of our sentences because they perform important jobs (subjects, direct objects, predicate nouns, etc.).
A peacock walked through our yard .
The dog howled during the night , and it woke up our whole family .
Sometimes people get bogged down with this part of speech because there are also many subcategories of nouns. This is similar to the way that we have subcategories for our clothes. You may have a whole drawer full of pants, but you may also have different types of pants that you use for different purposes (workout pants, lounge pants, work pants, etc.). This is similar to the way that we can further categorize nouns into smaller groups.
Here are a few of the subcategories of nouns: proper nouns, common nouns , collective nouns , possessive nouns , and compound nouns.
Tip : Other parts of speech also have subcategories. If you're studying this information for the first time, ignore the subcategories and focus on learning about each broader category.
2. Pronouns
Pronouns take the place of nouns. When most people hear the word pronoun , they think of words like I, we, me, he, she, and they . These are indeed all pronouns, but they're a part of a subcategory called personal pronouns. Know that there are other kinds of pronouns out there as well. Here are some examples: myself, his, someone , and who .
Here are a few of the subcategories of pronouns: reflexive pronouns , indefinite pronouns , possessive pronouns , and relative pronouns .
When we walked across the bridge, we saw someone who knows you .
I will fix the dishwasher myself .
Verbs show actions or states of being. They are integral elements of sentences .
The shuttle will fly into space.
The loving mother comforted and soothed the baby.
In the Montessori tradition of education, they use a large red circle or ball to symbolize a verb, and they often teach children to think of verbs as a sun providing the energy of a sentence. Isn't that a lovely way to think of verbs?
I know that you're getting tired of hearing about subcategories, but linking verbs, action verbs, and helping verbs are described on the verb page here .
Modal verbs are described on that link, and you can learn even more about action verbs and linking verbs from those links.
4. Adjectives
Adjectives describe, or modify , nouns and pronouns. I like to think of them as adding color to language. It would be hard to describe a beautiful sunset or the way a touching story makes us feel without using adjectives.
The wise, handsome owl had orange eyes.
The caring father rocked the baby.
One helpful strategy for learning about and identifying adjectives is to learn how they are diagrammed . Sentence diagrams are pictures of sentences that help us see how all of the words are grammatically related. Since adjectives modify nouns and pronouns, we diagram them on slanted lines under the nouns/pronouns that they are modifying.
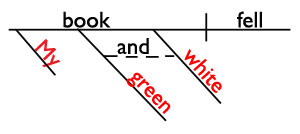
My green and white book fell.
Book is a noun. It's the subject of this sentence. My, green , and white are all adjectives describing book , so we diagram them on slanted lines underneath book . Isn't that a great way to SEE what adjectives do?
Nine Parts of Speech
When people categorize words into eight parts of speech, they say that articles/determiners ( a, an, the, this, that, etc. ) are subcategories of adjectives.
When people categorize words into nine parts of speech, they say that articles/determiners make up their own category and are not a part of the adjective category.
Adverbs modify (describe) verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs. Adverbs are similar to adjectives in that they both modify things.
The extremely cute koala hugged its mom very tightly .
The dog howled loudly .
Sentence diagrams also make it really easy to see what adverbs do. Take a look at this diagram. What do you notice about the way the adverbs are diagrammed?
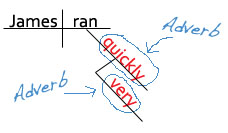
James ran very quickly.
Did you notice that the adverbs are diagrammed on slanted lines under the words that they are modifying?
Ran is a verb. Quickly is an adverb telling us more about the verb ran . Very is an adverb telling us more about the adverb quickly .
Doesn't the diagram make it easier to SEE what adverbs do?
6. Prepositions
Prepositions are probably the most difficult part of speech to explain, but people generally have an easier time understanding them when they look at lots of examples. So...let's start with some examples of commonly used prepositions!
in, for, of, off, if, until
The frog sat in the flower.
The baby cried for a long time.
I'm so convinced that memorizing some of the prepositions will be helpful to you that I'll teach you a preposition song .
Okay, now that we've looked at some examples, let's look at the definition of a preposition.
Prepositions show the relationship between a noun or a pronoun and some other word in the rest of the sentence.
Sentence diagrams will come to the rescue again to help us visualize what prepositions do. Think of prepositions as "noun hooks" or "noun bridges." In the diagram below, notice how the preposition down links the noun tree to the rest of the sentence.
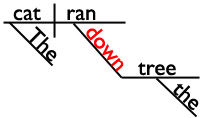
The cat ran down the tree.
Since prepositions always function as "noun hooks," they'll always be accompanied by a noun. The preposition plus its noun is called a prepositional phrase .
If you find a word from the preposition list that's not a part of a prepositional phrase, it's not functioning as a preposition. (You remember that words can function as different parts of speech , right?)
7. Conjunctions
Conjunctions join things together. They can join words or groups of words (phrases and clauses).
The hummingbird sat and waited .
The conjunction and is joining the words sat and waited .
Do you live near the park or near the hospital ?
The conjunction or is joining the phrases near the park and near the hospital.
The two conjunctions we just looked at ( and and or ) belong to a subcategory called coordinating conjunctions, but there are other subcategories of conjunctions as well. The other one that we use most often is subordinating conjunctions . Subordinating conjunctions are a little trickier to learn because they involve a more complicated concept ( dependent adverb clauses ).
For now, just know that all conjunctions, no matter what type they are, connect things together. In fact, let's LOOK at how they do this by looking at a sentence diagram.
Here is a sentence diagram showing how the coordinating conjunction and connects two clauses.

She cooked, and he cleaned.
8. Interjections
Interjections show excitement or emotion.
Wow ! That jump was amazing!
Phew , the baby finally fell asleep.
They are different from the other parts of speech in that they're not grammatically related to the rest of the sentence, and the way that we diagram them reflects that. Look at how we diagram interjections :
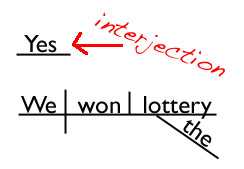
Yes ! We won the lottery!
The interjection yes sit sits there on its own line floating above the rest of the sentence. This helps show that it's not grammatically related to the other words in the sentence.
It's time to review what we covered on this page.
- We can categorize the words that we use into groups based on their functions and features. We call these groups the parts of speech.
- Many words can function as multiple parts of speech. You need to look at each word in the context of a sentence in order to say what part of speech it is.
- The eight parts of speech are nouns, pronouns, adjectives, verbs, adverbs, conjunctions, prepositions, and interjections.
- You just learned about all of the parts of speech. Give yourself a high five!
If you'd like to teach or learn grammar the easy way—with sentence diagrams—check out our Get Smart Grammar Program .
It starts from the very beginning and teaches you grammar and sentence diagramming in easy, bite-size lessons.

Hello! I'm Elizabeth O'Brien, and my goal is to get you jazzed about grammar.
This is original content from https://www.english-grammar-revolution.com/parts-of-speech.html

Our Free Guide Gives You A Fun Way
To Teach And Learn The Basics v

Elizabeth O'Brien is the creator of Grammar Revolution.
Her lessons are guaranteed to give you more confidence in your communication skills and make you smile. :)
Other Helpful Resources
- Learn more about how Montessori classrooms teach the parts of speech .
Sentences & Diagrams
Shop & log in.
|
|
|
|
Home BLOG SHOP Contact PRIVACY POLICY Your Purchases
Copyright © 2009 - 2024 Grammar Revolution. All Rights Reserved.
JOIN OUR PRIVATE FACEBOOK GROUP RSS INSTAGRAM
- Words With Friends Cheat
- Word Finder
- Crossword Top Picks
- Anagram Solver
- Word Descrambler
- Word Unscrambler
- Scrabble Cheat
- Unscrambler
- Scrabble Word Finder
- Word Scramble
- Scrabble Go Word Finder
- Word Solver
- Jumble Solver
- Blossom Answer Finder
- Crossword Solver
- NYT Spelling Bee Answers
- Wordscapes Answers
- Word Cookies Answers
- Words Of Wonders
- 4 Pics 1 Word
- Word Generator
- Anagramme Expert
- Apalabrados Trucos
- Today's NYT Wordle Answer
- Today's NYT Connections Answers
- Today's Connections Hints
- Today's NYT Mini Crossword Answers
- Today's NYT Spelling Bee Answers
- Today's Contexto Answer
- Today's NYT Strands Answer
- Grammar Rules And Examples
- Misspellings
- Confusing Words
- Scrabble Dictionary
- Words With Friends Dictionary
- Words Ending In
- Words By Length
- Words With Letters
- Words Start With
- 5-letter Words With These Letters
- 5-letter Words Start With
- 5-letter Words Ending In
- All Consonant Words
- Vowel Words
- Words With Q Without U
- Username Generator
- Password Generator
- Random Word Generator
- Word Counter
Parts Of Speech: Breaking Them Down With Examples
Author: sarah perowne, more content, why understanding parts of speech is important , the 8 parts of speech: definitions, examples, and rules, 2. pronouns, 3. adjectives, 6. prepositions, 7. conjunctions, 8. articles, takeaways - tips.
Parts of speech are like Legos. Instead of being made into houses or spaceships, they’re the building blocks we use to form written and spoken language.
Every word you speak or write is a part of speech. In the English language, there are 8 parts of speech: nouns , pronouns , adjectives , verbs , adverbs , prepositions , conjunctions , and articles (determiners). These parts of speech represent categories of words according to their grammatical function.

Having a basic understanding of the parts of speech in the English language gives you a specific terminology and classification system to talk about language. It can help you correctly punctuate a sentence, capitalize the right words, and even understand how to form a complete sentence to avoid grammatical errors.
| Part Of Speech | Function | Example Vocabulary | Example Sentences |
|---|---|---|---|
| Part Of Speech Noun | Function is a person or thing. | Example Vocabulary Birthday, cake, Paris, flat | Example Sentences Today is my birthday. I like cake. I have a flat; It's in Paris. |
| Part Of Speech Pronoun | Function is a noun substitute. | Example Vocabulary I, you, she, her, him, some, and them. | Example Sentences Susan is my neighbor; She is charming. |
| Part Of Speech Adjective | Function describes the noun in a sentence. | Example Vocabulary Happy, small, cozy, hungry, and warm. | Example Sentences She lives in a small cottage. Her home is cozy and warm. |
| Part Of Speech Verb | Function is an action word or state of being. | Example Vocabulary Run, jump, sleep, can, do, (to) be, or like | Example Sentences The teacher is happy; she likes her students. |
| Part Of Speech Adverb | Function describes a verb, adverb, or adjective. | Example Vocabulary Merrily, slowly, softly, or quickly | Example Sentences The girl spoke softly. She walked away slowly. |
| Part Of Speech Preposition | Function connects a noun or pronoun to another word. Shows the direction, location, or movement. | Example Vocabulary In, on, at, to, after. | Example Sentences We left by bus in the morning. Conjunction,"connects words, sentences, or clauses. |
| Part Of Speech Article | Function shows whether a specific identity is known or unknown. | Example Vocabulary A, an, and the. | Example Sentences A man called today. The cat is on the table; get it off! |
Still with us? Now, we will break down each of these English grammar categories and give some examples.
Nouns are words that name a person, place, thing, or idea. They can be further classified into different types of nouns .
Proper Nouns Vs. Common Nouns
There are some nouns we can count and others we cannot. Take a look at this table.
| Type Of Noun | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Type Of Noun Proper Nouns | Definition Name a specific person, place, or thing. Always start with a capital letter. | Examples Egypt, Paul, Eiffel Tower, Chicago |
| Type Of Noun Common Nouns | Definition Don’t name a specific person, place, or thing. Don’t start with a capital letter unless they are placed at the beginning of a sentence. | Examples dog, houses, sleep, homes, cup |
Concrete Nouns Vs. Abstract Nouns
| Type Of Noun | Definition | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Type Of Noun Concrete Nouns | Definition Identify material things. | Examples apple, boy, clock, table, window |
| Type Of Noun Abstract Nouns | Definition Express a characteristic or idea. | Examples happiness, tranquility, war, danger, friendship |
Singular Nouns Vs. Plural Nouns
| Rule | Add | Singular Noun Examples | Plural Noun Examples |
|---|---|---|---|
| Rule For most common nouns… | Add -s | Singular Noun Examples Chair | Plural Noun Examples Chairs |
| Rule For nouns that end in -ch, -s, -ch, or x… | Add -es | Singular Noun Examples Teach | Plural Noun Examples Teaches |
| Rule For nouns ending with -y and a vowel… | Add -s | Singular Noun Examples Toy | Plural Noun Examples Toys |
| Rule For nouns ending with -y and a consonant… | Add Remove -y and add -ies | Singular Noun Examples Lady | Plural Noun Examples Ladies |
| Rule For nouns ending in -o and a vowel… | Add -es or -s | Singular Noun Examples Tomato | Plural Noun Examples Tomatoes |
| Rule For nouns ending in -f or -fe… | Add Remove -fe or -f and add -v and -es | Singular Noun Examples Leaf | Plural Noun Examples Leaves |
| Rule For nouns ending in o- and consonant… | Add -es | Singular Noun Examples Echo | Plural Noun Examples Echoes |
Exceptions To The Rule
Some nouns are irregular, and it’s a case of learning their plural form as they don’t always follow specific rules. Here are some examples:
| Singular Irregular Noun | Plural Form |
|---|---|
| Singular Irregular Noun Man | Plural Form Men |
| Singular Irregular Noun Woman | Plural Form Women |
| Singular Irregular Noun Tooth | Plural Form Teeth |
| Singular Irregular Noun Child | Plural Form Children |
| Singular Irregular Noun Person | Plural Form People |
| Singular Irregular Noun Buffalo | Plural Form Buffalo |
Countable Vs. Uncountable Nouns
| Countable Nouns | Uncountable of Mass Nouns | Countable and Uncountable Nouns |
|---|---|---|
| Countable Nouns Singular and Plural | Uncountable of Mass Nouns Cannot be pluralized | Countable and Uncountable Nouns Depends on the context of the sentence |
| Countable Nouns Table / Tables | Uncountable of Mass Nouns Hair | Countable and Uncountable Nouns Chicken / A chicken |
| Countable Nouns Chair / Chairs | Uncountable of Mass Nouns Air | Countable and Uncountable Nouns Coffee / Two coffees |
| Countable Nouns Dog / Dogs | Uncountable of Mass Nouns Information | Countable and Uncountable Nouns Paper / Sheet of paper |
| Countable Nouns Quantifiers: some, many, a few, a lot, numbers | Uncountable of Mass Nouns Quantifiers: some, any, a piece, a lot of, much, a little | Countable and Uncountable Nouns |
Other Types of Nouns
Possessive nouns.
Possessive nouns possess something and usually have ‘s or simply ‘ at the end. When the noun is singular, we add an ‘s. When the noun is plural, we add an apostrophe.
Here are examples of possessive nouns :
- David’s sister has a dog.
- His sister’s dog is named Max.
Collective Nouns
Collective nouns refer to a group or collection of things, people, or animals. Such as,
- Choir of singers
- Herd of sheep
Noun Phrases
A noun phrase is two or more words that function as a noun in a sentence. It also includes modifiers that can come before or after the noun.
Here are examples of noun phrases:
- The little brown dog is mine.
- The market down the street has the best prices.
If you want to know where to find nouns in a sentence, look for the subject or a direct object, and they will stand right out. For example:
- Mary ate chocolate cake and ice cream .
(Mary = Subject) (Chocolate cake, and ice cream = direct objects)
This is an easy way to identify nouns in a sentence.
Pronouns are words used in the place of a noun or noun phrase. They can be further classified into different types of pronouns , such as personal, reflexive, and possessive.
Personal Pronouns
| Subject | Person Pronoun | Examples |
|---|---|---|
| Subject 1st Person Singular | Person Pronoun I | Examples I am walking. |
| Subject 2nd Person Singular | Person Pronoun You | Examples You are walking. |
| Subject 3rd Person Singular | Person Pronoun She, He, and It | Examples It is walking. |
| Subject 1st Person Plural | Person Pronoun We | Examples We are walking. |
| Subject 2nd Person Plural | Person Pronoun You (all) | Examples You are walking. |
| Subject 3rd Person Plural | Person Pronoun They | Examples They are walking. |
Reflexive Pronouns
Some examples of reflexive pronouns are myself, yourself, herself, and itself.
Here are examples of reflexive pronouns in sentences:
- I helped myself to an extra serving of gravy.
- She didn’t do the cooking herself.
- The word itself is pretty easy to spell but hard to pronounce.
Reflexive pronouns can also be used for emphasis, as in this sentence:
- Joe himself baked the cake.
Possessive Pronouns
Some examples of possessive pronouns are my, mine, your, yours, his, hers, its, ours, and theirs. We use these words when we want to express possession. Such as,
- Is this your car?
- No, it’s his .
- It’s not mine .
Mine, yours, and his are examples of the independent form of possessive pronouns , and when showing possession, these pronouns never need an apostrophe.
Adjectives are words that describe nouns or pronouns. They make the meaning more definite. When we want to talk about what kind of a house we have, we can use adjectives to describe it, such as big, red, or lovely.
We can use adjectives to precede the word it modifies, like this;
- She wore a beautiful , blue dress.
Or we can use adjectives following the word they modify, like this;
- The athlete, tall and thin , was ready to win the race.
There are many types of adjectives, one being possessive . The seven possessive adjectives are my, your, his, her, its, our, and their. These words modify a noun or pronoun and show possession. Such as,
- Their dog is brown.
- How old is your brother?
- That was my idea.
Verbs are words that express an action or a state of being. All verbs help to make a complete statement. Action verbs express a physical action, for example:
Other verbs express a mental action, for example:
These can also be called lexical verbs .
Lexical Verbs and Auxiliary Verbs
Sometimes lexical verbs need the help of another type of verb . That’s where helping verbs , or auxiliary verbs , come into action; they help to make a statement or express action.
Examples of auxiliary verbs are am, are, is, has, can, may, will be, and might have.
When we use more than one verb when writing or speaking to express an action or state of being, it’s a verbal phrase consisting of the main verb, lexical verb, and one or more auxiliary verbs.
Some examples of verbal phrases:
- Should have done
- Must have been broken
- Will be following
Here are examples of verbal phrases used in a sentence.
- You should have gone to the concert last night. It was amazing!
- I may go to the concert next time if I have the money for a ticket.
- I might have missed out this time, but I certainly won’t next time.
Adverbs are used to describe an adjective, verb, or even another adverb . They can express how something is done, as in splendidly or poorly .
Here are some examples of adverbs in use:
- She was running extremely fast during that race .
The adverb extremely modifies the adjective fast , expressing just how rapid the runner was.
- I can hardly see it in the distance.
The adverb hardly modifies the verb see , expressing how much is visible, which in this case is not much at all.
- It’s been surprisingly poorly cleaned.
The adverb surprisingly modifies the adverb poorly, expressing the surprise at how badly the car has been cleaned.
They are used to show relationships between words, such as nouns or pronouns, with other words in the sentence. They can indicate spatial or time relationships. Some common prepositions are about, at, before, behind, but, in, off, on, to, and with.
Here are some examples of common prepositions in sentences:
- She sat behind me in class.
- Her mother was from Vietnam.
- The two of us worked together on the project.
Prepositions are followed by objects of prepositions, a noun, or a noun phrase that follows to give it meaning.
- Julie goes to school with Mark . (With whom? Mark.)
Groups of words can also act as prepositions together, such as in spite of .
- In spite of all the traffic, we arrived just on time.
Conjunctions link words or groups of words together. We often use them to create complex sentences. There are three types of conjunctions: coordinating conjunctions , correlative conjunctions , and subordinating conjunctions.
Coordinating Conjunctions
Examples of coordinating conjunctions are and, but, or, nor, for, so, and yet. Such as:
- He wanted apple pie and ice cream.
- She offered him fruit or cookies.
- He ate the fruit but still wanted apple pie.
Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions are used in pairs. Some examples are;
- and neither/ nor.
Here is an example of the conjunctions above in use:
- He wanted neither fruit nor cookies for dessert.
Subordinating Conjunctions
We use subordinating conjunctions to begin subordinate clauses or sentences.
Some examples of common subordinating conjunctions are after, before, then, when, provided, unless, so that, and while. Such as,
- He left the house before it turned dark.
- He realized he had forgotten a gift when he arrived at the party.
- The party was better than he had imagined.
There are three articles in the English language: a, an, and the. Articles can indicate whether a specific identity is known or not.
A and an are called indefinite articles and refer to a general group. Such as,
- A woman is at the front door.
- She stood there for a minute.
- She had a book in her hand.
The is a definite article and refers to a specific thing or person. Such as,
- The woman at the door is my friend Tracy.
- She’s returning the book she borrowed last week.
Getting these right to know if we’re talking about a specific item, person, or thing, in general, is important.
How many parts of speech are there in the English language? Are there 8, 9, or 10?
Many words can also be used as more than one part of speech..
Once you get the hang of it, identifying the various parts of speech in a sentence will be second nature, like riding a bike. And just think, it can help you craft stronger sentences!
More Parts of Speech Topics:
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Popular Pages
- Top Searches
- External Resources
- Definitions
- WordFinderX
- Letter Solver

Parts of Speech
What is a Part of Speech?
We can categorize English words into 9 basic types called "parts of speech" or "word classes". It's quite important to recognize parts of speech. This helps you to analyze sentences and understand them. It also helps you to construct good sentences.
Parts of Speech Table
Parts of speech examples.
- Parts of Speech Quiz
This is a summary of the 9 parts of speech*. You can find more detail if you click on each part of speech.
| part of speech | function or "job" | example words | example sentences |
|---|---|---|---|
| action or state | (to) be, have, do, like, work, sing, can, must | EnglishClub a website. I EnglishClub. | |
| thing or person | pen, dog, work, music, town, London, teacher, John | This is my . He lives in my . We live in . | |
| describes a noun | good, big, red, well, interesting | My dogs are . I like dogs. | |
| limits or "determines" a noun | a/an, the, 2, some, many | I have dogs and rabbits. | |
| describes a verb, adjective or adverb | quickly, silently, well, badly, very, really | My dog eats . When he is hungry, he eats quickly. | |
| replaces a noun | I, you, he, she, some | Tara is Indian. is beautiful. | |
| links a noun to another word | to, at, after, on, but | We went school Monday. | |
| joins clauses or sentences or words | and, but, when | I like dogs I like cats. I like cats dogs. I like dogs I don't like cats. | |
| short exclamation, sometimes inserted into a sentence | oh!, ouch!, hi!, well | ! That hurts! ! How are you? , I don't know. |
- lexical Verbs ( work, like, run )
- auxiliary Verbs ( be, have, must )
- Determiners may be treated as adjectives, instead of being a separate part of speech.
Here are some examples of sentences made with different English parts of speech:
| verb |
|---|
| Stop! |
| noun | verb |
|---|---|
| John | works. |
| noun | verb | verb |
|---|---|---|
| John | is | working. |
| pronoun | verb | noun |
|---|---|---|
| She | loves | animals. |
| noun | verb | noun | adverb |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tara | speaks | English | well. |
| noun | verb | adjective | noun |
|---|---|---|---|
| Tara | speaks | good | English. |
| pronoun | verb | preposition | determiner | noun | adverb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| She | ran | to | the | station | quickly. |
| pron. | verb | adj. | noun | conjunction | pron. | verb | pron. |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| She | likes | big | snakes | but | I | hate | them. |
Here is a sentence that contains every part of speech:
| interjection | pron. | conj. | det. | adj. | noun | verb | prep. | noun | adverb |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Well, | she | and | my | young | John | walk | to | school | slowly. |
Words with More Than One Job
Many words in English can have more than one job, or be more than one part of speech. For example, "work" can be a verb and a noun; "but" can be a conjunction and a preposition; "well" can be an adjective, an adverb and an interjection. In addition, many nouns can act as adjectives.
To analyze the part of speech, ask yourself: "What job is this word doing in this sentence?"
In the table below you can see a few examples. Of course, there are more, even for some of the words in the table. In fact, if you look in a good dictionary you will see that the word " but " has six jobs to do:
- verb, noun, adverb, pronoun, preposition and conjunction!
| word | part of speech | example |
|---|---|---|
| work | noun | My is easy. |
| verb | I in London. | |
| but | conjunction | John came Mary didn't come. |
| preposition | Everyone came Mary. | |
| well | adjective | Are you ? |
| adverb | She speaks . | |
| interjection | ! That's expensive! | |
| afternoon | noun | We ate in the . |
| noun acting as adjective | We had tea. |
People often ask
FAQ: frequently asked parts of speech questions
Instantly enhance your writing in real-time while you type. With LanguageTool
Get started for free
Understanding the Parts of Speech in English
Yes, the parts of speech in English are extensive and complex. But we’ve made it easy for you to start learning them by gathering the most basic and essential information in this easy-to-follow and comprehensive guide.

Parts of Speech: Quick Summary
Parts of speech assign words to different categories. There are eight different types in English. Keep in mind that a word can belong to more than one part of speech.
Learn About:
- Parts of Speech
- Prepositions
- Conjunctions
- Interjections
Using the Parts of Speech Correctly In Your Writing
Knowing the parts of speech is vital when learning a new language.
When it comes to learning a new language, there are several components you should understand to truly get a grasp of the language and speak it fluently.
It’s not enough to become an expert in just one area. For instance, you can learn and memorize all the intricate grammar rules, but if you don’t practice speaking or writing colloquially, you will find it challenging to use that language in real time.
Conversely, if you don’t spend time trying to learn the rules and technicalities of a language, you’ll also find yourself struggling to use it correctly.
Think of it this way: Language is a tasty, colorful, and nutritious salad. If you fill your bowl with nothing but lettuce, your fluency will be bland, boring, and tasteless. But if you spend time cultivating other ingredients for your salad—like style, word choice, and vocabulary— then it will become a wholesome meal you can share with others.
In this blog post, we’re going to cover one of the many ingredients you’ll need to build a nourishing salad of the English language—the parts of speech.
Let’s get choppin’!
What Are the Parts of Speech in English?
The parts of speech refer to categories to which a word belongs. In English, there are eight of them : verbs , nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
Many English words fall into more than one part of speech category. Take the word light as an example. It can function as a verb, noun, or adjective.
Verb: Can you please light the candles?
Noun: The room was filled with a dim, warm light .
Adjective: She wore a light jacket in the cool weather.
The parts of speech in English are extensive. There’s a lot to cover in each category—much more than we can in this blog post. The information below is simply a brief overview of the basics of the parts of speech. Nevertheless, the concise explanations and accompanying example sentences will help you gain an understanding of how to use them correctly.

What Are Verbs?
Verbs are the most essential parts of speech because they move the meaning of sentences along.
A verb can show actions of the body and mind ( jump and think ), occurrences ( happen or occur ), and states of being ( be and exist ). Put differently, verbs breathe life into sentences by describing actions or indicating existence. These parts of speech can also change form to express time , person , number , voice , and mood .
There are several verb categories. A few of them are:
- Regular and irregular verbs
- Transitive and intransitive verbs
- Auxiliary verbs
A few examples of verbs include sing (an irregular action verb), have (which can be a main verb or auxiliary verb), be , which is a state of being verb, and would (another auxiliary verb).
My little sister loves to sing .
I have a dog and her name is Sweet Pea.
I will be there at 5 P.M.
I would like to travel the world someday.
Again, these are just the very basics of English verbs. There’s a lot more that you should learn to be well-versed in this part of speech, but the information above is a good place to start.
What Are Nouns?
Nouns refer to people ( John and child ), places ( store and Italy ), things ( firetruck and pen ), and ideas or concepts ( love and balance ). There are also many categories within nouns. For example, proper nouns name a specific person, place, thing, or idea. These types of nouns are always capitalized.
Olivia is turning five in a few days.
My dream is to visit Tokyo .
The Supreme Court is the highest court in the United States.
Some argue that Buddhism is a way of life, not a religion.
On the other hand, common nouns are not specific to any particular entity and are used to refer to any member of a general category.
My teacher is the smartest, most caring person I know!
I love roaming around a city I’ve never been to before.
This is my favorite book , which was recommended to me by my father.
There’s nothing more important to me than love .
Nouns can be either singular or plural. Singular nouns refer to a single entity, while plural nouns refer to multiple entities.
Can you move that chair out of the way, please? (Singular)
Can you move those chairs out of the way, please? (Plural)
While many plural nouns are formed by adding an “–s” or “–es,” others have irregular plural forms, meaning they don’t follow the typical pattern.
There was one woman waiting in line.
There were several women waiting in line.
Nouns can also be countable or uncountable . Those that are countable refer to nouns that can be counted as individual units. For example, there can be one book, two books, three books, or more. Uncountable nouns cannot be counted as individual units. Take the word water as an example. You could say I drank some water, but it would be incorrect to say I drank waters. Instead, you would say something like I drank several bottles of water.
What Are Pronouns?
A pronoun is a word that can take the place of other nouns or noun phrases. Pronouns serve the purpose of referring to nouns without having to repeat the word each time. A word (or group of words) that a pronoun refers to is called the antecedent .
Jessica went to the store, and she bought some blueberries.
In the sentence above, Jessica is the antecedent, and she is the referring pronoun. Here’s the same sentence without the proper use of a pronoun:
Jessica went to the store, and Jessica bought some blueberries.
Do you see how the use of a pronoun improves the sentence by avoiding repetitiveness?
Like all the other parts of speech we have covered, pronouns also have various categories.
Personal pronouns replace specific people or things: I, me, you, he, she, him, her, it, we, us, they, them.
When I saw them at the airport, I waved my hands up in the air so they could see me .
Possessive pronouns indicate ownership : mine, ours, yours, his, hers, theirs, whose.
I think that phone is hers .
Reflexive pronouns refer to the subject of a sentence or clause. They are used when the subject and the object of a sentence refer to the same person or thing: myself, yourself, himself, herself, itself, ourselves, yourselves, themselves.
The iguanas sunned themselves on the roof of my car.
Intensive pronouns have the same form as reflexive pronouns and are used to emphasize or intensify the subject of a sentence.
I will take care of this situation myself .
Indefinite pronouns do not refer to specific individuals or objects but rather to a general or unspecified person, thing, or group. Some examples include someone, everybody, anything, nobody, each, something, and all.
Everybody enjoyed the party. Someone even said it was the best party they had ever attended.
Demonstrative pronouns are used to identify or point to specific pronouns: this, that, these, those.
Can you pick up those pens off the floor?
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions and seek information: who, whom, whose, which, what.
Who can help move these heavy boxes?
Relative pronouns connect a clause or a phrase to a noun or pronoun: who, whom, whose, which, that, what, whoever, whichever, whatever.
Christina, who is the hiring manager, is the person whom you should get in touch with.
Reciprocal pronouns are used to refer to individual parts of a plural antecedent. They indicate a mutual or reciprocal relationship between two or more people or things: each other or one another.
The cousins always giggle and share secrets with one another .
What Are Adjectives?
Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, usually by describing, identifying, or quantifying them. They play a vital role in adding detail, precision, and imagery to English, allowing us to depict and differentiate the qualities of people, objects, places, and ideas.
The blue house sticks out compared to the other neutral-colored ones. (Describes)
That house is pretty, but I don’t like the color. (Identifies)
There were several houses I liked, but the blue one was unique. (Quantifies)
We should note that identifying or quantifying adjectives are also referred to as determiners. Additionally, articles ( a, an, the ) and numerals ( four or third ) are also used to quantify and identify adjectives.
Descriptive adjectives have other forms (known as comparative and superlative adjectives ) that allow for comparisons. For example, the comparative of the word small is smaller, while the superlative is smallest.
Proper adjectives (which are derived from proper nouns) describe specific nouns. They usually retain the same spelling or are slightly modified, but they’re always capitalized. For example, the proper noun France can be turned into the proper adjective French.
What Are Adverbs?
Adverbs are words that modify or describe verbs, adjectives, other adverbs, or entire clauses. Although many adverbs end in “–ly,” not all of them do. Also, some words that end in “–ly” are adjectives, not adverbs ( lovely ).
She dances beautifully .
In the sentence above, beautifully modifies the verb dances.
We visited an extremely tall building.
Here, the adverb extremely modifies the adjective tall.
He had to run very quickly to not miss the train.
The adverb very modifies the adverb quickly.
Interestingly , the experiment yielded unexpected results that left us baffled.
In this example, the word interestingly modifies the independent clause that comprises the rest of the sentence (which is why they’re called sentence adverbs ).
Like adjectives, adverbs can also have other forms when making comparisons. For example:
strongly, more strongly, most strongly, less strongly, least strongly
What Are Prepositions?
Prepositions provide context and establish relationships between nouns, pronouns, and other words in a sentence. They indicate time, location, direction, manner, and other vital information. Prepositions can fall into several subcategories. For instance, on can indicate physical location, but it can also be used to express time.
Place the bouquet of roses on the table.
We will meet on Monday.
There are many prepositions. A few examples include: about, above, across, after, before, behind, beneath, beside, during, except, for, from, in, inside, into, like, near, of, off, onto, past, regarding, since, through, toward, under, until, with, without.
Prepositions can contain more than one word, like according to and with regard to.
What Are Conjunctions?
Conjunctions are words that join words, phrases, or clauses together within a sentence and provide information about the relationship between those words. There are different types of conjunctions.
Coordinating conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses of equal importance: and, but, for, not, or, so, yet.
I like to sing, and she likes to dance.
Correlative conjunctions come in pairs and join balanced elements of a sentence: both…and, just as…so, not only…but also, either…or, neither…nor, whether…or.
You can either come with us and have fun, or stay at home and be bored.
Subordinating conjunctions connect dependent clauses to independent clauses. A few examples include: after, although, even though, since, unless, until, when , and while.
They had a great time on their stroll, even though it started raining and they got soaked.
Conjunctive adverbs are adverbs that function as conjunctions, connecting independent clauses or sentences. Examples of conjunctive adverbs are also, anyway, besides, however, meanwhile, nevertheless, otherwise, similarly, and therefore .
I really wanted to go to the party. However , I was feeling sick and decided to stay in.
I really wanted to go to the party; however , I was feeling sick and decided to stay in.
What Are Interjections?
Interjections are words that express strong emotions, sudden reactions, or exclamations. This part of speech is usually a standalone word or phrase, but even when it is part of a sentence, it does not relate grammatically to the rest of .
There are several interjections. Examples include: ahh, alas, bravo, eww, hello, please, thanks, and oops.
Ahh ! I couldn’t believe what was happening.
When it comes to improving your writing skills, understanding the parts of speech is as important as adding other ingredients besides lettuce to a salad.
The information provided above is indeed extensive, but it’s critical to learn if you want to write effectively and confidently. LanguageTool—a multilingual writing assistant—makes comprehending the parts of speech easy by detecting errors as you write.
Give it a try—it’s free!

Unleash the Professional Writer in You With LanguageTool
Go well beyond grammar and spell checking. Impress with clear, precise, and stylistically flawless writing instead.
Works on All Your Favorite Services
- Thunderbird
- Google Docs
- Microsoft Word
- Open Office
- Libre Office
We Value Your Feedback
We’ve made a mistake, forgotten about an important detail, or haven’t managed to get the point across? Let’s help each other to perfect our writing.
Applied Grammar by Gail Brubaker

Understanding the 8 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
Are you trying to master the grammatical rules of English? If so, understanding the 8 parts of speech is crucial. But what exactly are the parts of speech? How many are there? And how do you know which words fall into each category? Don’t worry, we’ve got you covered. In this comprehensive guide, we will break down the definitions and examples of the 8 parts of speech, making it easier for you to navigate the intricacies of the English language.
English can be a challenging language to learn, but by understanding the parts of speech, you’ll gain a solid foundation for constructing sentences with clarity and precision. Whether you’re a student, a writer, or simply someone looking to improve your language skills, this article will provide you with a clear understanding of each part of speech. So, let’s immerse and explore the definitions and examples of the 8 parts of speech, empowering you to communicate effectively and confidently in English.
Key Takeaways
- Understanding the 8 parts of speech is crucial for mastering English grammar.
- The 8 parts of speech are: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
- Nouns represent people, places, things, or ideas.
- Pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition.
- Verbs describe actions or states of being.
- Adjectives provide additional details about nouns.
- Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
- Prepositions show relationships between words in a sentence.
- Conjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses together.
- Interjections express strong emotions or surprise.
What Are Parts of Speech?
When it comes to understanding the intricacies of English grammar, learning the different parts of speech is crucial. But what exactly are parts of speech? How many are there? And how do you determine which words belong to each part of speech? In this comprehensive guide, we’ll provide clear definitions and examples for each part of speech, helping you navigate the complexities of the English language.
Nouns are words that represent people, places, things, or ideas. They can be common or proper, singular or plural. Examples of nouns include “dog,” “New York City,” and “love.”
Pronouns are words used in place of nouns to avoid repetition. They can refer to individuals or groups. Examples of pronouns include “he,” “she,” “it,” and “they.”
Verbs are action words that describe what a subject does or the state of being. They can be in different tenses and forms. Examples of verbs include “run,” “jump,” and “is.”
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns, giving more details or information about them. They can describe qualities, size, shape, color, and more. Examples of adjectives include “beautiful,” “large,” and “blue.”
Adverbs modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, providing information on how, when, where, or to what extent. They often end in “-ly.” Examples of adverbs include “quickly,” “happily,” and “very.”
Prepositions
Prepositions show a relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. They indicate position, direction, time, or manner. Examples of prepositions include “in,” “on,” “at,” and “from.”
Conjunctions
Conjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses together. They can be coordinating or subordinating. Examples of conjunctions include “and,” “but,” “or,” and “because.”
Interjections
Interjections are short exclamations used to express emotions or surprise. They are often followed by exclamation marks. Examples of interjections include “Wow,” “Yay,” and “Ouch!”
Parts of Speech
Understanding the different parts of speech is crucial for building a strong foundation in English grammar. Each part of speech plays a unique role in the construction of sentences, providing clarity and meaning to our language. In this section, we will explore the definitions and examples of the eight parts of speech: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
A noun is a word that identifies a person, place, thing, or idea. It can refer to both concrete objects, such as “book” or “dog,” and abstract concepts, such as “love” or “happiness.” Nouns are often referred to as “persons, places, or things,” but it is essential to recognize that they encompass much more than that. Here are some examples of nouns used in sentences:
- The cat is sleeping on the couch.
- I love to read a good book .
- She has a beautiful voice .
Pronouns are words that are used to replace nouns in a sentence. They help avoid repetitive use of nouns and add fluency to our language. Personal pronouns, such as “he,” “she,” or “they,” refer to specific individuals or groups of people. Here are some examples of pronouns used in sentences:
- She is going to the store.
- We had an amazing time at the party.
- Please give me the book.
Verbs are action words that express an action, occurrence, or state of being. They are the backbone of a sentence and provide information about what is happening. Verbs can be either transitive or intransitive, depending on whether they require an object to complete their meaning. Here are some examples of verbs used in sentences:
- The dog ran in the park.
- I love to swim in the ocean.
- They are studying for the exam.
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns. They provide additional information about the nouns they accompany, such as their size, color, or quality. Adjectives help make our language more vivid and expressive. Here are some examples of adjectives used in sentences:
- She has a beautiful smile.
- The blue sky is clear today.
- He is a talented musician.
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They provide information about how, when, where, or to what extent an action is performed. Adverbs enhance the meaning of a sentence and add precision to our language. Here are some examples of adverbs used in sentences:
- He quickly finished his assignments.
- She sings beautifully .
- They went outside to play.
Preposition
Prepositions are words that indicate the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. They often express location, direction, time, or manner. Prepositions are essential for understanding spatial and temporal relationships. Here are some examples of prepositions used in sentences:
- The cat is under the table.
- We walked through the park.
- The book is on the shelf.
Conjunction
Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses within a sentence. They help establish relationships between different parts of a sentence, coordinating or subordinating their meaning. Conjunctions are essential for creating complex sentences. Here are some examples of conjunctions used in sentences:
- I will go to the store, but I need to buy milk.
- Because it was raining, we stayed indoors.
- He likes both chocolate and vanilla ice cream.
Interjection
Interjections are words or phrases used to convey strong emotions or reactions. They are often standalone expressions and can add emphasis or express surprise, joy, or frustration. Interjections bring life and emotion to our language. Here are some examples of interjections used in sentences:
- Wow , that’s an impressive performance!
- Ouch , that hurt!
- Alas , I lost my wallet.
Understanding and mastering the eight parts of speech will greatly enhance your language skills and enable you to effectively communicate in English. From nouns that identify people and things to verbs that express actions, each part of speech contributes to the overall structure and meaning of a sentence. Keep practicing and exploring the various functions of these parts of speech to become a confident English speaker and writer.
Examples of Each Part of Speech
Nouns play a crucial role in sentence construction as they represent people, places, things, or ideas. Here are some examples of nouns:
Pronouns, on the other hand, replace nouns to avoid repetition. Here are a few examples for better understanding:
- If you leave now, only James and I will remain behind.
- Their feet ached more than ours .
Verbs express actions, feelings, or states of being. Check out these verb examples:
- We sang songs , danced all night , and by the morning had fallen in love .
- Can you bring me something from the kitchen?
Adjectives add descriptions to nouns. Here are a few examples:
- The tall building stood out in the city skyline.
Adverbs add meaning to verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Take a look at these examples:
- The car drove quickly down the street.
- She performed very well in the competition.
Prepositions express the relationship between nouns, pronouns, and other words. Here are some examples:
- The book is on the table.
- The cat jumped over the fence.
Conjunctions connect words, phrases, or clauses within a sentence. Check out these examples:
- He likes tea and coffee.
- She is tired, but she is determined to finish the project.
Interjections convey strong emotions or sudden reactions. Here are a few examples:
- Wow , what a beautiful sunset!
- Oh no , I forgot to bring my umbrella.
Remember, understanding the different parts of speech and their functions is crucial in constructing meaningful sentences. Keep practicing and exploring the various examples to strengthen your language skills.
Now that you have a clear understanding of the eight parts of speech in English grammar, you are equipped with the knowledge to construct sentences with precision and clarity. By mastering the definitions and examples of nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections, you can effectively communicate in English.
Each part of speech serves a unique purpose in sentence construction, providing meaning and structure to our language. Nouns name people, places, things, or ideas, while pronouns replace nouns to avoid repetition. Verbs express actions or states of being, while adjectives and adverbs provide descriptions and modify other words. Prepositions indicate relationships between words, conjunctions connect words or phrases, and interjections express strong emotions.
By practicing and exploring the functions of these parts of speech, you will become a confident English speaker and writer. Remember to apply this knowledge in your daily conversations and written communication to enhance your language skills.
Continue to refine your understanding and usage of the eight parts of speech, and watch as your language abilities flourish.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

The Parts of Speech – Definitions and Examples
The different parts of speech are the breakdown and classification of words in English that show their unique functions and properties. In core language, a single word can function as two or more parts of speech.
Differentiating between the 9 parts of speech is the first step to building your grammar skills and writing tools. Keep reading to learn the definitions and examples of each category!
What are the 9 Basic Parts of Speech?
A noun is any place, person, idea, or thing. Some examples of nouns include:
There are various classifications of nouns you can use in your writing. Proper nouns are specific names for places, persons, ideas, or things. Meanwhile, common nouns are generic class nouns. A possessive noun is another type of noun that demonstrates belonging.
We can also classify this part of speech as an abstract noun, concrete noun, count noun, and uncountable noun.
The placement of the noun in a sentence also determines its function. A noun can be in the nominative or objective case. The nominative functions include subject and subject complement. And the types of objects are direct object, indirect object, and object of a preposition.
A quick introduction to pronouns shows they are classes of words that take the place of nouns. Some examples of pronouns include he, that, whoever, myself.
This quick guide to pronouns shows they can be classified as:
- Personal pronoun (I, he, she, you, etc.)
- Demonstrative pronouns (that, those, these, this, etc.).
- Interrogative pronouns (what, when, why, how, etc.).
- Relative pronouns (who/whom, whose, which, etc.).
- Indefinite pronouns (anybody, everybody, somebody, everything, etc.).
- Reflexive pronouns (myself, yourself, herself, etc.).
- Intensive pronouns (myself, yourself, herself, etc.).
Pronouns can further be divided into first-person pronoun, second-person pronoun, and third-person pronoun.
A verb is a word that conveys time while showing a condition, an action, or the fact that something exists. All complete sentences should contain at least one verb unless using an interjection.
Verbs can be treated as either lexical verbs/action verbs (study, love, drink) or auxiliary verbs (seem, is, have).
A verb phrase combines verbs with linking verbs and lexical categories of verbs. Some examples include:
- Has become.
Phrasal verbs are forms of verbs that consist of two or more words. Here are some examples:
- Put up with.
When you add “up with” after the simple verb “put,” you create a brand-new verb with a new meaning. Therefore, phrasal verbs should be treated as complete verbs because of their unique definitions.
Some verbs are reflexive. A reflexive verb is where the subject and object are one since the sentence uses reflexive pronouns like “himself” or “itself.”
Whether you’re using a lexical or auxiliary verb, this part of the speech always expresses time through the different tenses. For instance, the verb “eats” is a present-tense verb, and its past form is “ate.”
4. Adjective
Another part of speech is the adjective , which modifies or describes a noun or a pronoun. It typically answers the questions “what kind,” “which one,” or “how much.” For example:
The articles “a,” “an,” and “the” are sometimes categorized as adjectives. “The” is a definite article, and “a” and “an” are indefinite articles.
Adjective classes include:
- Absolute adjectives.
- Appositive adjectives.
- Attributive adjectives.
- Predicative adjectives.
- Compound adjectives.
- Qualitative adjectives.
- Denomial adjectives.
- Participial adjectives.
- Demonstrative adjectives.
Adverbs are a word class that modifies adjectives, verbs, and fellow adverbs. One frequent adverb marker is the suffix -ly, such as “healthily,” “badly,” and “swiftly.”
But the discussion of adverbs goes beyond words that describe actions. There are also adverbs of degree, place, time, and frequency. The English language also considers “most days,” “to visit my friend,” “very loudly,” and other adverbial phrases as adverbs.
Adverbial phrases are under the phrasal categories, including verb phrases, adjective phrases, etc.
6. Conjunction
A conjunction is a word that binds words, clauses, and phrases. “And,” “but,” “because,” and “consequently” are some examples of conjunctions.
Conjunctions make it easy to construct more complex sentences because you can easily add new clauses. The category distinctions of this part of speech are:
- Coordinating conjunctions (for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so, etc.)
- Subordinating conjunctions (after, although, unless, since, if, etc.)
- Correlative conjunctions (not only… but also, either… or, etc.)
7. Preposition
Prepositions show relations of space, time, and role between nouns, pronouns, and other words. They are at the start of prepositional phrases. Here are some examples of prepositions:
- Apart from.
8. Determiner
A determiner is like an adjective because it also modifies nouns. However, these words are essential for proper syntax as opposed to adjectives. They can be classified as indefinite and definite. New grammar rules now treat articles as determiners. Examples of determiners include:
- Which.
9. Interjection
The last part of speech is the interjection which may have standalone functions in sentences. “Whoops,” “ouch,” “ah,” and “hooray” can be an entire sentence on their own.
Parts of Speech Chart
Analyzing the parts of speech is different for every individual language. Here’s an overview of the different categories in English.
| Noun | Person, thing, place, or event | She is the new . |
| Pronoun | Replaces a noun | is the new assistant. bag is missing. |
| Verb | Expresses time while demonstrating a condition, action, or the fact that something exists | She the new assistant. I what she that day. |
| Adjective | Modifies a noun or a pronoun | She is the assistant. Jane is selling her apartment. |
| Adverb | Modifies a verb, adjective, or fellow adverb. | remove your makeup. |
| Conjunction | Connects clauses, words, or sentences | I like candles I like reed diffusers. She asked me not to attend she won’t be there. |
| Preposition | Connects a noun to another word | My dog went the neighbor’s house. |
| Determiner | Determines a noun | buzzcut suits your face shape. |
| Interjection | Short exclamation | ! That was an impressive performance. |
When A Word is Also Two Different Kinds of Speech
Sometimes, words have more than one role in the English language. For example, some nouns can also act as adjectives called adjectival nouns. In the phrase “race car,” “race” modifies “car,” so its usage is as an adjective instead of a noun.
A noun can be used in verbal senses. Consider the word “work” in these sentences.
- My new work is more promising than the old one. (noun)
- Shew works in a new industry. (verb)
Open and Closed Word Classes
The two classifications of the parts of speech include open and closed classes. The open classes can be changed and added as the language changes.
- Adjectives.
Meanwhile, closed classes are parts of speech that do not change. These include:
- Prepositions.
- Conjunctions.
- Articles and determiners.
- Interjections.
In some languages, verbs and adjectives form closed classes. This closedness of verbs is common in Basque and Persian verbs .
Linguistics , or the study of language, does not recommend the label “part of speech” anymore. Instead, the discipline favors “syntactic category” or “word class.”
What Part of Speech is With?
In the stricter sense, the only use of “with” is as a preposition. You can find it before a noun or a pronoun to form prepositional phrases. Use it to show togetherness, associations, and connections between people and objects.
What Part of Speech is And?
The conjunction “and” connects words, clauses, and phrases. It can also combine sentences that need to be presented at once.
What Part of Speech is My?
“My” is a possessive pronoun that can also act as an adjective, determiner, or interjection.
Are You Using the Parts of Speech the Right Way?
This guide has shown you the nine parts of speech and their grammatical functions. By now, you should already be able to give definitions and examples of each category, so they make sense.
To correctly use the parts of speech, ask yourself, “what is the function of this word in the sentence?” Keep practicing until you master the traditional grammar rules of English!
Grammarist is a participant in the Amazon Services LLC Associates Program, an affiliate advertising program designed to provide a means for sites to earn advertising fees by advertising and linking to Amazon.com. When you buy via the links on our site, we may earn an affiliate commission at no cost to you.
2024 © Grammarist, a Found First Marketing company. All rights reserved.
- English Grammar
- Parts of Speech
Parts of Speech - Definition, 8 Types and Examples
In the English language , every word is called a part of speech. The role a word plays in a sentence denotes what part of speech it belongs to. Explore the definition of parts of speech, the different parts of speech and examples in this article.
Table of Contents
Parts of speech definition, different parts of speech with examples.
- Sentences Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
A Small Exercise to Check Your Understanding of Parts of Speech
Frequently asked questions on parts of speech, what is a part of speech.
Parts of speech are among the first grammar topics we learn when we are in school or when we start our English language learning process. Parts of speech can be defined as words that perform different roles in a sentence. Some parts of speech can perform the functions of other parts of speech too.
- The Oxford Learner’s Dictionary defines parts of speech as “one of the classes into which words are divided according to their grammar, such as noun, verb, adjective, etc.”
- The Cambridge Dictionary also gives a similar definition – “One of the grammatical groups into which words are divided, such as noun, verb, and adjective”.
Parts of speech include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections.
8 Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples:
1. Nouns are words that are used to name people, places, animals, ideas and things. Nouns can be classified into two main categories: Common nouns and Proper nouns . Common nouns are generic like ball, car, stick, etc., and proper nouns are more specific like Charles, The White House, The Sun, etc.
Examples of nouns used in sentences:
- She bought a pair of shoes . (thing)
- I have a pet. (animal)
- Is this your book ? (object)
- Many people have a fear of darkness . (ideas/abstract nouns)
- He is my brother . (person)
- This is my school . (place)
Also, explore Singular Nouns and Plural Nouns .
2. Pronouns are words that are used to substitute a noun in a sentence. There are different types of pronouns. Some of them are reflexive pronouns, possessive pronouns , relative pronouns and indefinite pronouns . I, he, she, it, them, his, yours, anyone, nobody, who, etc., are some of the pronouns.
Examples of pronouns used in sentences:
- I reached home at six in the evening. (1st person singular pronoun)
- Did someone see a red bag on the counter? (Indefinite pronoun)
- Is this the boy who won the first prize? (Relative pronoun)
- That is my mom. (Possessive pronoun)
- I hurt myself yesterday when we were playing cricket. (Reflexive pronoun)
3. Verbs are words that denote an action that is being performed by the noun or the subject in a sentence. They are also called action words. Some examples of verbs are read, sit, run, pick, garnish, come, pitch, etc.
Examples of verbs used in sentences:
- She plays cricket every day.
- Darshana and Arul are going to the movies.
- My friends visited me last week.
- Did you have your breakfast?
- My name is Meenakshi Kishore.
4. Adverbs are words that are used to provide more information about verbs, adjectives and other adverbs used in a sentence. There are five main types of adverbs namely, adverbs of manner , adverbs of degree , adverbs of frequency , adverbs of time and adverbs of place . Some examples of adverbs are today, quickly, randomly, early, 10 a.m. etc.
Examples of adverbs used in sentences:
- Did you come here to buy an umbrella? (Adverb of place)
- I did not go to school yesterday as I was sick. (Adverb of time)
- Savio reads the newspaper everyday . (Adverb of frequency)
- Can you please come quickly ? (Adverb of manner)
- Tony was so sleepy that he could hardly keep his eyes open during the meeting. (Adverb of degree)
5. Adjectives are words that are used to describe or provide more information about the noun or the subject in a sentence. Some examples of adjectives include good, ugly, quick, beautiful, late, etc.
Examples of adjectives used in sentences:
- The place we visited yesterday was serene .
- Did you see how big that dog was?
- The weather is pleasant today.
- The red dress you wore on your birthday was lovely.
- My brother had only one chapati for breakfast.
6. Prepositions are words that are used to link one part of the sentence to another. Prepositions show the position of the object or subject in a sentence. Some examples of prepositions are in, out, besides, in front of, below, opposite, etc.
Examples of prepositions used in sentences:
- The teacher asked the students to draw lines on the paper so that they could write in straight lines.
- The child hid his birthday presents under his bed.
- Mom asked me to go to the store near my school.
- The thieves jumped over the wall and escaped before we could reach home.
7. Conjunctions are a part of speech that is used to connect two different parts of a sentence, phrases and clauses . Some examples of conjunctions are and, or, for, yet, although, because, not only, etc.
Examples of conjunctions used in sentences:
- Meera and Jasmine had come to my birthday party.
- Jane did not go to work as she was sick.
- Unless you work hard, you cannot score good marks.
- I have not finished my project, yet I went out with my friends.
8. Interjections are words that are used to convey strong emotions or feelings. Some examples of interjections are oh, wow, alas, yippee, etc. It is always followed by an exclamation mark.
Examples of interjections used in sentences:
- Wow ! What a wonderful work of art.
- Alas ! That is really sad.
- Yippee ! We won the match.
Sentence Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
- Noun – Tom lives in New York .
- Pronoun – Did she find the book she was looking for?
- Verb – I reached home.
- Adverb – The tea is too hot.
- Adjective – The movie was amazing .
- Preposition – The candle was kept under the table.
- Conjunction – I was at home all day, but I am feeling very tired.
- Interjection – Oh ! I forgot to turn off the stove.
Let us find out if you have understood the different parts of speech and their functions. Try identifying which part of speech the highlighted words belong to.
- My brother came home late .
- I am a good girl.
- This is the book I was looking for.
- Whoa ! This is amazing .
- The climate in Kodaikanal is very pleasant.
- Can you please pick up Dan and me on your way home?
Now, let us see if you got it right. Check your answers.
- My – Pronoun, Home – Noun, Late – Adverb
- Am – Verb, Good – Adjective
- I – Pronoun, Was looking – Verb
- Whoa – Interjection, Amazing – Adjective
- Climate – Noun, In – Preposition, Kodaikanal – Noun, Very – Adverb
- And – Conjunction, On – Preposition, Your – Pronoun
What are parts of speech?
The term ‘parts of speech’ refers to words that perform different functions in a sentence in order to give the sentence a proper meaning and structure.
How many parts of speech are there?
There are 8 parts of speech in total.
What are the 8 parts of speech?
Nouns, pronouns, verbs, adverbs, adjectives, prepositions, conjunctions and interjections are the 8 parts of speech.
| ENGLISH Related Links | |
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.
The 8 Parts Of Speech In English
There are eight major parts of speech .
- Nouns name persons, places, things, ideas, or qualities, e.g., Franklin, boy, Yangtze River, shoreline, Bible, desk, fear, happiness.
- Pronouns usually substitute for nouns and function as nouns, e.g., I, you, he, she, it, we, they, myself, this, that, who, which, everyone.
- Verbs express actions, occurrences, or states of being, e.g., be, become, bunt, inflate, run.
- Adjectives describe or modify nouns or pronouns, e.g., gentle, helpful, small.
- Adverbs describe or modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, e.g., almost, gently, helpfully, someday.
- Prepositions relate nouns or pronouns to other words in a sentence, e.g., about, at, down, for, of, with.
- Conjunctions link words, clauses, and phrases. There are coordinating conjunctions that link words, clauses, or phrases of equal importance, and there are subordinating conjunctions that introduce subordinate clauses and link them to main clauses.
- Interjections express feeling or command attention, either alone or in a sentence, e.g., darn, hey, oh, wow.
Some words ( adjectives , adverbs , interjections , nouns , verbs ) are productive classes allowing new members; others, with functional rather than lexical meaning ( articles , conjunctions , prepositions ) are nonproductive and have a limited number of members.
Some grammarians consider articles , quantifiers , and numerals to also be parts of speech.
Trending Words

Current Events
Hobbies & Passions
[ vap -id ]
- By clicking "Sign Up", you are accepting Dictionary.com Terms & Conditions and Privacy policies.
- Phone This field is for validation purposes and should be left unchanged.
Parts of Speech: A Guide to Learning English Grammar
By: Author English Study Online
Posted on Last updated: December 27, 2023
Sharing is caring!
In this page, we will break down each part of speech and provide examples to help you understand their usage. We will also discuss how to identify the different parts of speech in a sentence and provide tips on how to use them correctly. Whether you are a beginner or an advanced English learner, this article will provide valuable insights into the parts of speech and improve your language skills. Let’s get started!
Table of Contents
Overview of Parts of Speech
In this section, we will provide a brief overview of the eight parts of speech in English. Understanding the parts of speech is essential for anyone learning the English language, as it enables them to construct meaningful sentences and communicate effectively.
The eight parts of speech are:
Prepositions
Conjunctions, interjections.
Each part of speech has a specific function in a sentence. For example, nouns are used to name people, places, things, or ideas, while verbs are used to describe an action or state of being. Adjectives are used to describe nouns, while adverbs are used to describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs.
Pronouns are used to replace nouns in a sentence, while prepositions are used to indicate the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. Conjunctions are used to connect words, phrases, or clauses, while interjections are used to express emotions or feelings.

Nouns are words that represent people, places, things, or ideas. They are one of the most important parts of speech in English and are used in nearly every sentence. In this section, we will explore the different types of nouns and their functions.
Common Nouns
Common nouns are general names for people, places, or things. They are not capitalized unless they appear at the beginning of a sentence.
- Examples of common nouns include “book,” “city,” and “teacher.”
Proper Nouns
Proper nouns are specific names for people, places, or things. They are always capitalized.
- Examples of proper nouns include “Harry Potter,” “New York City,” and “Ms. Johnson.”
Abstract Nouns
Abstract nouns are names for ideas, concepts, or emotions. They are intangible and cannot be seen, heard, or touched.
- Examples of abstract nouns include “love,” “happiness,” and “freedom.”
Collective Nouns
Collective nouns are names for groups of people or things. They can be singular or plural, depending on the context.
- Examples of collective nouns include “team,” “family,” and “herd.”
In this section, we will discuss the different types of pronouns used in English grammar. Pronouns are words that replace nouns in a sentence. They help to avoid repetition and make sentences more concise.
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns refer to specific people or things. They can be used as the subject or object of a sentence. Here are the personal pronouns in English:
| I | me | my | mine |
| you | you | your | yours |
| he | him | his | his |
| she | her | her | hers |
| it | it | its | its |
| we | us | our | ours |
| they | them | their | theirs |
Demonstrative Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns are used to point to specific people or things. They can be used to indicate distance or location. Here are the demonstrative pronouns in English:
| this | refers to something nearby |
| that | refers to something farther away |
| these | refers to multiple things nearby |
| those | refers to multiple things farther away |
Interrogative Pronouns
Interrogative pronouns are used to ask questions. They are typically used at the beginning of a sentence. Here are the interrogative pronouns in English:
| who | refers to a person |
| whom | refers to a person (object of a verb) |
| whose | refers to possession |
| what | refers to a thing or idea |
| which | refers to a specific thing or idea |
Indefinite Pronouns
Indefinite pronouns refer to non-specific people or things. They can be used as the subject or object of a sentence. Here are the indefinite pronouns in English:
| anybody | refers to any person |
| anyone | refers to any person |
| anything | refers to any thing or idea |
| each | refers to individual members of a group |
| either | refers to one of two things |
| everybody | refers to every person |
| everyone | refers to every person |
| everything | refers to every thing or idea |
| neither | refers to none of two things |
| nobody | refers to no person |
| no one | refers to no person |
| nothing | refers to no thing or idea |
| one | refers to a singular person or thing |
| some | refers to an unspecified number or amount |
| somebody | refers to some person |
| someone | refers to some person |
| something | refers to some thing or idea |
Verbs are one of the most important parts of speech in English. They are used to describe an action, state, or occurrence. In this section, we will cover the three types of verbs: action verbs, linking verbs, and helping verbs.
Action Verbs
Action verbs are used to describe an action that is being performed by the subject of the sentence. They can be used in the present, past, or future tense. Here are a few examples of action verbs:
Linking Verbs
Linking verbs are used to connect the subject of the sentence to a noun, pronoun, or adjective that describes it. They do not show action. Here are a few examples of linking verbs:
Helping Verbs
Helping verbs are used in conjunction with the main verb to express tense, voice, or mood. They do not have a meaning on their own. Here are a few examples of helping verbs:
In conclusion, verbs are an essential part of English grammar. Understanding the different types of verbs and how they are used in a sentence can help you communicate more effectively in both written and spoken English.
In this section, we will discuss adjectives, which are an important part of speech in English. Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns. They provide more information about the noun or pronoun, such as its size, shape, color, or quality.
Descriptive Adjectives
Descriptive adjectives are the most common type of adjectives. They describe the physical or observable characteristics of a noun or pronoun. For example, in the sentence “The red car is fast,” “red” is a descriptive adjective that describes the color of the car, and “fast” is another descriptive adjective that describes its speed.
Here are some examples of descriptive adjectives:
Quantitative Adjectives
Quantitative adjectives are used to describe the quantity or amount of a noun or pronoun. They answer the question “how much” or “how many.” For example, in the sentence “I have two apples,” “two” is a quantitative adjective that describes the number of apples.
Here are some examples of quantitative adjectives:
Demonstrative Adjectives
Demonstrative adjectives are used to point out or indicate a specific noun or pronoun. They answer the question “which one” or “whose.” For example, in the sentence “This book is mine,” “this” is a demonstrative adjective that indicates the specific book that belongs to the speaker.
Here are some examples of demonstrative adjectives:
In conclusion, adjectives are an important part of speech in English. They provide more information about nouns and pronouns, and they help to make our language more descriptive and precise. By understanding the different types of adjectives, we can use them effectively in our speaking and writing.
In this section, we will discuss adverbs, which are words that modify or describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Adverbs give more information about the action, manner, place, time, frequency, degree, or intensity of a verb.
Adverbs of Manner
Adverbs of manner describe how an action is performed. They answer the question “how?” and usually end in “-ly”, but not always. Here are some examples:
- She sings beautifully.
- He speaks softly.
- They ran quickly.
- The dog barked loudly.
Adverbs of manner can also be formed by adding “-ly” to some adjectives. For example:
- She is a quick learner. (adjective: quick)
- He is a careful driver. (adjective: careful)
Adverbs of Place
Adverbs of place describe where an action takes place. They answer the question “where?” and usually come after the verb or object. Here are some examples:
- She looked everywhere.
- He lives nearby.
- They went outside.
- The cat hid underneath the bed.
Adverbs of Time
Adverbs of time describe when an action takes place. They answer the question “when?” and can come at the beginning, middle, or end of a sentence. Here are some examples:
- She wakes up early every day.
- He arrived yesterday.
- They will leave soon.
- The concert starts tonight.
Adverbs of time can also be used to show the duration of an action. For example:
- She studied for hours.
- He worked all day.
- They talked for a long time.
In this section, we will discuss prepositions and their usage in English. Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence. They usually indicate the position or direction of the noun or pronoun in relation to other elements in the sentence.
Prepositions of Time
Prepositions of time are used to indicate when an action took place. They include words such as “at,” “in,” and “on.”
- “At” is used for specific times, such as “at 2 pm” or “at midnight.”
- “In” is used for longer periods of time, such as “in the morning” or “in October.”
- “On” is used for dates, such as “on Monday” or “on July 4th.”
Prepositions of Place
Prepositions of place are used to indicate where something is located. They include words such as “in,” “on,” and “at.”
- “In” is used for enclosed spaces, such as “in the house” or “in the car.”
- “On” is used for surfaces, such as “on the table” or “on the floor.”
- “At” is used for specific locations, such as “at the park” or “at the beach.”
Prepositions of Direction
Prepositions of direction are used to indicate movement. They include words such as “to,” “from,” and “towards.”
- “To” is used to indicate movement towards a specific destination, such as “I am going to the store.”
- “From” is used to indicate movement away from a specific location, such as “I am coming from the park.”
- “Towards” is used to indicate movement in the direction of a specific location, such as “I am walking towards the museum.”
In this section, we will discuss the different types of conjunctions and their functions in English grammar. Conjunctions are words that connect words, phrases, or clauses in a sentence. They are essential in creating complex sentences and conveying relationships between ideas.
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions join words, phrases, or clauses that are of equal importance. They are easy to remember using the mnemonic device FANBOYS: for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so. Here are some examples:
- I like pizza and pasta.
- She is neither tall nor short.
- He wanted to go to the beach, but it was raining.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions connect dependent clauses to independent clauses and establish a relationship between them. They are used to show cause and effect, time, condition, and contrast. Some examples of subordinating conjunctions are:
Here are some examples:
- Because it was raining, we stayed inside.
- Although she was tired, she stayed up to finish her work.
- While I was studying, my roommate was watching TV.
Correlative Conjunctions
Correlative conjunctions are pairs of words that work together to connect words, phrases, or clauses. They are used to show a relationship between two elements. Here are some examples:
- both…and
- either…or
- neither…nor
- not only…but also
- Both my sister and I like to read.
- Either you come with us or you stay here.
- Not only was he late, but he also forgot his homework.
In conclusion, conjunctions are important in creating complex sentences and conveying relationships between ideas. By understanding the different types of conjunctions and their functions, you can improve your writing and communication skills.
In English grammar, interjections are words or phrases that express strong emotions or feelings. They are also known as exclamations and are one of the eight parts of speech in English. Interjections are grammatically independent from the words around them, and they can often be removed from a sentence or context without affecting its basic meaning.
Interjections can be used to express a wide range of emotions, including surprise, joy, anger, frustration, and pain. Some common examples of interjections include “ wow ,” “ ouch ,” “ yay ,” “ oh no ,” and “ oops .” They can be used to add emphasis to a sentence or to convey a particular tone or mood.
It is important to note that interjections do not have any grammatical function in a sentence. They are not nouns, verbs, adjectives, or any other part of speech. Instead, they simply stand alone as a way to express emotion.
When using interjections in writing, it is important to consider the context in which they are being used. While they can be a useful tool for adding emphasis or conveying emotion, they can also be overused or misused, which can detract from the overall effectiveness of the writing.
Articles/Determiners
In English grammar, articles and determiners are words that are used with nouns to provide more information about them. They help us to understand the context and meaning of a sentence.
There are three articles in the English language: “ the ,” “ a, ” and “ an. ” “The” is known as the definite article because it refers to a specific noun that has already been mentioned or is known to the reader. For example, “The cat is sleeping on the sofa.” In this sentence, “the” refers to a specific cat that has already been mentioned or is known to the reader.
“A” and “an” are known as indefinite articles because they refer to any member of a group or class of nouns. “A” is used before words that begin with a consonant sound, while “an” is used before words that begin with a vowel sound. For example, “I need a pen” and “She ate an apple.”
Determiners
Determiners are words that come before a noun to provide more information about it. They can include articles, as well as words like “ this ,” “ that ,” “ these ,” and “ those .”
In addition to these, there are other types of determiners such as possessive determiners (e.g. “my,” “your,” “his,” “her,” “its,” “our,” and “their”), demonstrative determiners (e.g. “this,” “that,” “these,” and “those”), and quantifying determiners (e.g. “some,” “any,” “many,” “few,” “several,” etc.).
Determiners can also be used with adjectives to provide more information about a noun. For example, “She ate the delicious apple” and “I saw that beautiful sunset.”
Understanding articles and determiners is crucial for mastering English grammar. By using them correctly, you can convey your thoughts and ideas more clearly and effectively.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the 8 parts of speech in English?
In English, there are eight parts of speech: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Each part of speech serves a different function in a sentence and helps to convey meaning.
What are some examples of different parts of speech?
Here are a few examples of different parts of speech:
- Noun: dog, cat, book, table
- Pronoun: he, she, it, they
- Verb: run, jump, sing, dance
- Adjective: happy, sad, tall, short
- Adverb: quickly, slowly, loudly, softly
- Preposition: in, on, at, under
- Conjunction: and, but, or, so
- Interjection: wow, oh, ouch, hooray
What is the difference between a noun and a verb?
A noun is a word that represents a person, place, thing, or idea. A verb is a word that represents an action, occurrence, or state of being. In other words, a noun is a subject or object in a sentence, while a verb is the action or occurrence that takes place.
What are the different types of nouns?
There are several different types of nouns, including:
- Common nouns: refer to general, non-specific people, places, things, or ideas (e.g. dog, city, book)
- Proper nouns: refer to specific people, places, things, or ideas and are always capitalized (e.g. John, Paris, The Great Gatsby )
- Concrete nouns: refer to tangible, physical objects (e.g. table, chair, car)
- Abstract nouns: refer to intangible concepts or ideas (e.g. love, happiness, freedom)
- Recent Posts
- Juridical Process vs. Judicial Process: Understanding the Crucial Differences - December 14, 2023
- Compound Nouns: How to Use Them Effectively in English - November 9, 2023
- English Tenses: A Beginner’s Guide in English - November 6, 2023
Understanding Parts of Speech (9 Types With Examples)

What are parts of speech? In the American English language, parts-of-speech is a category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions. They exist under the verb , noun, pronoun, interjection , adjective , conjunction, adverb, and preposition forms.
Learn more about parts of the speech in this comprehensive worksheet…
What are parts of speech?
“Parts of speech” refers to the essential words used in sentence formation in the English language.
Every word used in a sentence structure plays an important role in defining the sentence’s meaning. These words use and placement give proper intentions in sentence structures.
Parts of speech are the basic grammar lessons taught during the primary phases of learning English.
Any word used in sentence formation falls into one of these categories for proper sentence structure.
Some of those words can be a part of one or more parts of speech. This topic further explores the essential parts of speech used in the English language.
Watch this as a video lesson
In total, there are nine categories of parts of speech
These nine parts of speech are namely: Verbs, Nouns , Adjectives, Determiners, Adverbs , Pronouns, Prepositions , Conjunctions, and Interjections.
Another additional classification is used as a part of speech, i.e. , Articles, a subprogram of determiners.
To comprehend the meaning and use of each word in the English language, it is essential to clearly understand the various parts of speech and select the right parts of speech form at the appropriate place in the sentence.
What are the 9 parts of speech with their functions?
Here are the nine parts of speech and how they impact the English language.
| Noun | name a place, person, thing, or idea. | California, man, park |
| Pronoun | Used to replace the name of a person, place, thing or idea. | He, she, it, they |
| Verb | A verb expresses what the does. | Leave, do, work put, |
| Adverb | Used to describe verb, adverb, or adjective. | Always, silently, quickly |
| Adjective | Words that are used to describe qualities or things. | Long, short, tiny, bright, dark |
| Preposition | Shows the relationship between other words in a sentence. | In, on, at, with, |
| Interjection | Words that express emotions or feelings. | Wow, oh, ah, yikes |
| Conjunction | Words that join words or groups of words together. | And, but, , , also |
‘Verbs’ are the words used in a sentence to define the action/state of action being performed. Most of the sentences in sentence formation require the inclusion of verbs.
Some examples of verbs used in the English language are Love, Break, Fall , and Cry . These are the basic forms of verbs and are known as infinitives .
Most of the verbs used have two other major forms called participles . The use of these participles is for the formation of various verb-tense combinations.
These participles define the forms of verbs concerning the time of action/performance. These verb-tense combinations can be used in two types: Active voice and passive voice .
A ‘noun’ are words used in a sentence to give recognition or the name of an object, individual, or animal.
Nouns can be sub-classified into two major categories: Common nouns , which give generic descriptor names to things, and common items, such as a bat, a bicycle , etc. The other category of nouns is Proper nouns , which have specific descriptor names to refer to a specialized object, place, or individual, such as Charley, The Empire State Building, The Telegraph , etc.
Additionally, nouns can be classified as singular nouns and plural nouns based on the number of individuals/objects.
Singular Nouns
The definition of a Singular Noun is the same as that of a noun when used commonly. It carries the same definition as the noun: “A word referring towards an individual/object/event/material/place.”
Plural Nouns
The word plural relates to “more than one in certain languages or more than two in certain languages.”
Thus singular nouns can be converted to their plural noun format when there is an implication of more than one or two objects/individuals/places.
A general Singular/Common Noun can be turned into the appropriate form of a Plural Noun by adding a ‘s’/’es’/’ ies’/’ves.’ It is also initiated by changing ‘us’ to ‘i’, ‘is’ to ‘es’ , or ‘on’ to ‘a’ .
Some common nouns do not change when interchanged between their singular and plural noun forms. Some other common nouns do not fall under plural nouns and are called irregular nouns, which are made plural by changing the spelling or adding a suffix to the word.
‘Adjectives’ are words that give a description or modify the scope of nouns/pronouns by being specific. For example, adjectives used to define a noun can be red, small, hot, common, etc.
An adjective is usually placed before a noun or after the verb that it modifies. Three forms of adjectives are used to compare similar characteristics of different individuals/objects. These three degrees of comparison are:
- Positive/Absolute form
This comparison of adjectives defines the original form of the adjective as stated in English. For example, “this candy is tasty .” This degree of comparison states that no relative subject is available for comparison.
- Comparative form
This form of the adjective gives a relative comparison between two objects performing similar actions with identical characteristics. For example, “the candy we had today is tastier than the one we received yesterday.”
- Superlative form
This form of the adjective gives the superiority declaration of one object over similar objects possessing similar characteristics. For example, “this candy is the tastiest I have ever had in the last two years .”
Adjectives can be sub-classified based on their function in sentence formation. This sub-classification is:
- Possessive Adjectives
These adjectives show/represent the possessiveness of an object. For example, mine, my, his/her, their, its, etc.
- Interrogative Adjectives
These adjectives modify the noun/pronoun by interrogation. Only a select few adjectives are available in this form. For example, whose, which, what, and where.
- Demonstrative Adjectives
These adjectives describe the current state/position of the noun/pronoun concerning space/time. For example, this, these, those, that.
- Compound Adjectives
These adjectives are a result of the combination of two or more adjectives. The resulting adjective modifies the subject in the sentence. For example, hand-dried, heavy-weighted, spike-haired, etc.
‘Determiners’ are the words placed before a noun/pronoun group terms to refer to a single/multiple things. Some commonly used determiners in English are ‘a’, ‘the’, ‘some’, ‘any’, and ‘this.’ Determiners are generally placed before descriptive adjectives . It tells the reader more about the description of the noun being referred to.
Determiners are classified into sub-categories, articles, and demonstratives.
An ‘Article’ can be either definite or indefinite. An article modifies a noun/pronoun without specifying any description of the object. In English, an example of a ‘definite article’ is the , whereas examples of two ‘indefinite articles’ are a and an .
Here, the refers to specific things or things that are identified beforehand. A or a refer to non-specific things that have not been identified beforehand.
Demonstratives
A ‘Demonstrative’ is defined as a demonstrative adjective/pronoun based on its usage in the sentence. Some examples of demonstratives are ‘this’, ‘that’, and ‘those’ .
A determiner has the same rules of use as in the case of adjectives in sentence formation. Thus, confusion takes place when carefully choosing the type of parts of speech to assign when given a choice of either a determiner or adjective.
An ‘Adverb’ defines essential information about the verb, similar to what an adjective is to a noun. It provides a descriptor for a verb used in a sentence and some cases, can also describe an adjective or another adverb.
Some adverbs used in sentences with verbs are ‘slowly’, ‘hastily’, ‘unfortunately’, and ‘angrily’.
Adverbs are further sub-classified into various types based on their application in a sentence.
- Adverbs of Time (to inform about the occurrence of a verb), For example, ‘now’, ‘tomorrow’, and ‘soon’.
- Adverbs of Manner (to describe the action of a verb), For example, ‘hastily’, ‘slowly’, and ‘minutely’.
- Adverbs of Place (to indicate the place of action of the verb),
- Adverbs of Frequency (to describe the frequency of a verb action),
- Adverbs of Degree (to describe the intensity of an action),
- Conjunctive Adverbs (are used to link/act as a conjunction to two sentences).
A ‘Pronoun’ is a word used in specifically providing an alternate name for a non/noun phrase. They are alternate words for referring to an object/individual when the requirement of a noun is unnecessary, as the noun has been mentioned previously in some parts of the sentence.
Some examples of pronouns are ‘it’, ‘he/she’, and ‘himself/herself’.
Pronouns are sub-classified into different categories based on their use in the sentence.
Some of these sub-categories are:
- Relative Pronouns (to relate a part of a sentence with the other)
- Possessive Pronouns (to show possessiveness)
- Reflexive Pronouns (to refer back to the subject of discussion)
- Demonstrative Pronouns (to refer to specific objects/individuals)
- Interrogative Pronouns (to ask questions)
- Indefinite Pronouns (to avoid reference to any specific object/individual/place)
- Personal Pronouns (to use as substitutes for proper names)
- Subject Pronouns (to assign acting on an object)
- Object Pronouns (to assign receiving action towards an object)
- Reciprocal Pronouns (to express two-way/mutual relationship)
- Preposition
A ‘Preposition’ is a word used as a connective between a noun, a noun phrase, or a pronoun with another word.
Prepositions are used in sentence formations to convey these meanings:
- To show the direction towards/of something/someone
- To refer to the period of an action taking place
- To specify the location/position of an object
- To present the space and time relationship between objects
Based on their use and function, prepositions are classified into four subtypes:
- Prepositions of Time (to indicate the happening of an action/event)
- Preposition of Place (to indicate the location of an object)
- Preposition of Direction (to indicate the direction/orientation of an object)
- Prepositions of Spatial Relationship (to indicate an object moving away/towards a source)
- Conjunction
A ‘Conjunction’ is a word that combines two/more objects and behaves as connectives in a sentence. These can appear in the beginning/middle/end of the sentence following the location of the objects.
There are three types of conjunctions used in sentence formation:
- Coordinate conjunction (to combine two independent clauses )
- Subordinate conjunction (to combine an independent with a dependent clause)
- Correlation conjunction (to combine two phrases having equal weightage)
Interjection
An ‘Interjection’ is a word to convey the expression of a variety of emotions/feelings. As such, there is no specific rule for the use of interjection and where it is to be placed.
However, in most cases, it is placed at the beginning of the sentence. For example, some of the most commonly used interjections are ‘ouch’, ‘phew’, and ‘well’.
| Noun | The howled. |
| Pronoun | It woke the baby. |
| Verb | The loving mother the child. |
| Adjective | The father rocked the baby. |
| Adverb | The dog howled |
| Preposition | The baby cried a long time. |
| Conjunction | The baby gazed at his mother father. |
| Interjection | , the baby fell back asleep. |
Parts of speech examples
Here are some examples of the parts of speech used in sentences. Note the placement and its relation with other parts of speech present in the sentence format.
- John is cutting a pipe.
- John intends to come to the office this Monday .
- Jogging regularly is good for health.
- Drinking and driving put other motorists in danger.
- Would you want to wear a suit?
- I love to sing in between classes.
See another example in the image below.
- Juno ran towards the classroom.
- The janitor requested the students to clear their lockers.
- The monkey was caged after being sedated.
- I gifted my brother a phone .
- Why did you purchase the book ?
- I misplaced the manuscript .
- Do you want to eat some ice cream ?
- Mum loved my new car .
- Daniel gifted his brother a Porsche.

- I purchased a blue suit for the reception.
- Mary purchased two oranges from the fruit seller.
- The curry is tasty .
- Juno’s brother is arrogant .
- The documentary that premiered on television was fascinating .
- Giovanni Giorgio is a great music composer.
- My house is currently under lease.
- This novel is lengthy.
- I purchased some fruits and vegetables.
- She sent me an expensive watch.
- Velma loved the dress gifted by her parents.
- Joyce and Jill watched a movie together.
- Grandma gave us materials to prepare the dessert.

- Typically , we visit Mom on Mondays.
- Don’t you taste the coffee to be too bitter?
- Do not be nervous. You will eventually get the hang of it.
- The movie I watched was very scientific.
- It is scorching hot inside the workshop.
- Can I visit the office today ?
- His aunt will be staying at the apartment for a while .
- He is the man I was referring to.
- I found my missing luggage outside the airport.

- I won’t be coming to the office in the afternoon.
- He arranged the cutlery on the table.
- Bhaskar made the dog hide under its bed.
- I enjoy strolling by the lake in the mornings.
- James and I trekked to the hilltop today.
- I stayed back home because I felt uneasy.
- He did not enjoy the yogurt , yet he finished it.

- Interjection
- Hurray! We got the funding.
- Ouch! That wound looks severe.
- Wow! You look great in the wedding gown.
- Oh my God ! I hope he is safe.
See an example in the image below.
Words with more than one job
Many parts of speech can have more than one function/job in the sentence. This improves the versatility of the words being used and makes the use more situational in its placement and conveyance of meaning.
- Myers can shift for herself (Preposition)
- Give prayers to the Almighty; for He is the one above all (Conjunction)
- We require more women to have the same vigor. (Adjective)
- More of the women died in the operating room than in the cabin. (Pronoun)
- Agatha needs to shut the gossiping and work more (Adverb)
To see how all the objects work together, see the table below.
| She | likes | big | but | I | hate | them |
Here is a chart showing the parts of speech:
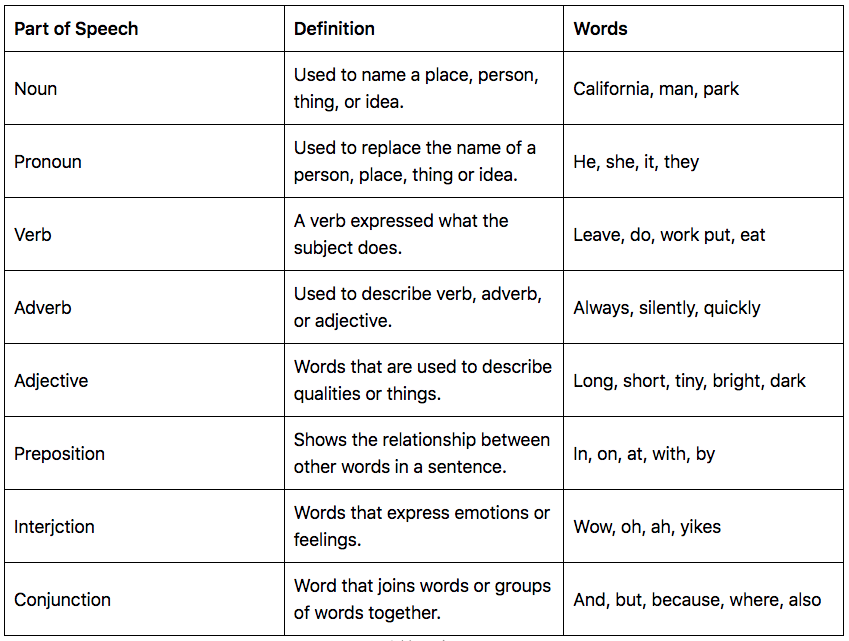
How to identify parts of speech
In sentence formation, it often becomes difficult to ascertain the parts of speech represented by each word. To help out and to make the process of identification easier, follow these steps:
- Identify any word which names an object/individual/place in a generalized form as a noun .
- To identify a specific noun, use pronouns .
- Any words which describe/identify actions/performance are verbs .
- Any word that modifies or gives a greater definition to nouns is an adjective.
- Any word that modifies or gives meaning to the actions of verbs, are adverbs.
- It is easy to pick out prepositions as they describe relationships between a noun/pronoun with other nouns/pronouns.
- Any joiner used to join two clauses is a conjunction .
- Exclamations generally follow any interjections in the text.

- Parts of speech
More parts of speech:
- Conjunctions
- Prepositions
- Possessive nouns
- Irregular plural nouns
- Proper nouns
- Concrete nouns
- Collective nouns
- Possessive and plural nouns
- Verbs: The Definitive Guide
- Nouns | Explore Definition, Examples & Types with Examples
- What Are Pronouns? Definitions and Examples
- What Are Adverbs? (with Examples)
- Interjections – Explore Meaning, Definition, Usage and Examples
- What Is A Conjunction? Types & Examples
- The 9 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
- What Is a Determiner?
- The 8 Parts of Speech: Examples and Rules
- Adverbs – What is It? Explore the Meaning, Definition, Types, Usage and Examples
Inside this article
Fact checked: Content is rigorously reviewed by a team of qualified and experienced fact checkers. Fact checkers review articles for factual accuracy, relevance, and timeliness. Learn more.

About the author
Dalia Y.: Dalia is an English Major and linguistics expert with an additional degree in Psychology. Dalia has featured articles on Forbes, Inc, Fast Company, Grammarly, and many more. She covers English, ESL, and all things grammar on GrammarBrain.
Core lessons
- Abstract Noun
- Accusative Case
- Active Sentence
- Alliteration
- Adjective Clause
- Adjective Phrase
- Adverbial Clause
- Appositive Phrase
- Body Paragraph
- Compound Adjective
- Complex Sentence
- Compound Words
- Compound Predicate
- Common Noun
- Comparative Adjective
- Comparative and Superlative
- Compound Noun
- Compound Subject
- Compound Sentence
- Copular Verb
- Collective Noun
- Colloquialism
- Conciseness
- Conditional
- Concrete Noun
- Conjugation
- Conditional Sentence
- Comma Splice
- Correlative Conjunction
- Coordinating Conjunction
- Coordinate Adjective
- Cumulative Adjective
- Dative Case
- Declarative Statement
- Direct Object Pronoun
- Direct Object
- Dangling Modifier
- Demonstrative Pronoun
- Demonstrative Adjective
- Direct Characterization
- Definite Article
- Doublespeak
- Equivocation Fallacy
- Future Perfect Progressive
- Future Simple
- Future Perfect Continuous
- Future Perfect
- First Conditional
- Gerund Phrase
- Genitive Case
- Helping Verb
- Irregular Adjective
- Irregular Verb
- Imperative Sentence
- Indefinite Article
- Intransitive Verb
- Introductory Phrase
- Indefinite Pronoun
- Indirect Characterization
- Interrogative Sentence
- Intensive Pronoun
- Inanimate Object
- Indefinite Tense
- Infinitive Phrase
- Intensifier
- Indicative Mood
- Juxtaposition
- Linking Verb
- Misplaced Modifier
- Nominative Case
- Noun Adjective
- Object Pronoun
- Object Complement
- Order of Adjectives
- Parallelism
- Prepositional Phrase
- Past Simple Tense
- Past Continuous Tense
- Past Perfect Tense
- Past Progressive Tense
- Present Simple Tense
- Present Perfect Tense
- Personal Pronoun
- Personification
- Persuasive Writing
- Parallel Structure
- Phrasal Verb
- Predicate Adjective
- Predicate Nominative
- Phonetic Language
- Plural Noun
- Punctuation
- Punctuation Marks
- Preposition of Place
- Parts of Speech
- Possessive Adjective
- Possessive Determiner
- Possessive Case
- Possessive Noun
- Proper Adjective
- Proper Noun
- Present Participle
- Quotation Marks
- Relative Pronoun
- Reflexive Pronoun
- Reciprocal Pronoun
- Subordinating Conjunction
- Simple Future Tense
- Stative Verb
- Subjunctive
- Subject Complement
- Subject of a Sentence
- Sentence Variety
- Second Conditional
- Superlative Adjective
- Slash Symbol
- Topic Sentence
- Types of Nouns
- Types of Sentences
- Uncountable Noun
- Vowels and Consonants
Popular lessons


Stay awhile. Your weekly dose of grammar and English fun.

The world's best online resource for learning English. Understand words, phrases, slang terms, and all other variations of the English language.
- Abbreviations
- Editorial Policy

- History & Society
- Science & Tech
- Biographies
- Animals & Nature
- Geography & Travel
- Arts & Culture
- Games & Quizzes
- On This Day
- One Good Fact
- New Articles
- Lifestyles & Social Issues
- Philosophy & Religion
- Politics, Law & Government
- World History
- Health & Medicine
- Browse Biographies
- Birds, Reptiles & Other Vertebrates
- Bugs, Mollusks & Other Invertebrates
- Environment
- Fossils & Geologic Time
- Entertainment & Pop Culture
- Sports & Recreation
- Visual Arts
- Demystified
- Image Galleries
- Infographics
- Top Questions
- Britannica Kids
- Saving Earth
- Space Next 50
- Student Center
- Introduction
Conjunctions
Prepositions, interjections, categorizing the parts of speech.

part of speech
Our editors will review what you’ve submitted and determine whether to revise the article.
- College of Saint Rose - Parts of Speech
- Butte College - TIP Sheets - The Eight Parts of Speech
- Humanities LibreTexts - Parts of Speech
- Pressbooks Create - The Simple Math of Writing Well - Part of speech
- Table Of Contents
part of speech , lexical category to which a word is assigned based on its function in a sentence.
There are eight parts of speech in traditional English grammar: noun, pronoun, verb , adjective , adverb , conjunction, preposition , and interjection . In linguistics , parts of speech are more typically called word classes .

A noun names a person, place, thing, or idea. There are many subcategories of nouns, including common nouns, proper nouns, collective nouns, and abstract nouns.
Common nouns name basic things that can be seen and touched. Examples of common nouns include dog , banana , table , and book .
- The dog ate a banana .
- The book was on the table .
Proper nouns name specific people, places, and things, and they begin with a capital letter . Examples of proper nouns include George, New York City , Empire State Building , and Atlantic Ocean .
- George sailed the Atlantic Ocean .
- The Empire State Building is in New York City .
Collective nouns name groups of people or things. Examples of collective nouns include team , flock , litter , and batch .
- The team won the game.
- The flock flew south for the winter.
Abstract nouns name things that cannot be seen or touched. Examples of abstract nouns include happiness , truth , friendship , and beauty .
- He brings her so much happiness .
- The friendship is a strong one.
A pronoun is used in place of a noun. There are many subcategories of pronouns, including but not limited to personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, and reflexive pronouns.
Personal pronouns replace names of people, places, things, and ideas. Examples of personal pronouns include she , he , it , and they .
- They enjoyed the party.
- Mikey likes it .
Possessive pronouns replace nouns and indicate ownership. Because they modify nouns, they are also frequently categorized as adjectives. Examples of possessive pronouns include his , its , mine , and theirs .
- The house is theirs .
- The parrot knows its name.
Reflexive pronouns replace nouns when the subject and object in a sentence are the same. Examples of reflexive pronouns include myself , herself , themselves , and oneself .
- She baked a cake all by herself .
- They prepared themselves for the adventure.
A verb indicates a state of doing, being, or having. There are three main subcategories of verbs: doing verbs, being verbs, and having verbs.
Doing verbs indicate actions. Examples of doing verbs include run , wash , explain , and wonder .
- Oliver washed the windows.
- I wonder where the cat is hiding.
Being and having verbs do not indicate action and are considered relating (or linking) verbs because they connect one piece of information to another. Examples of being and having verbs include am , are , has , and own .
- We are at the store.
- John has a red baseball cap.
An adjective describes or modifies a noun or pronoun.
Adjectives provide information about the qualities or classifications of a person or thing. Examples of adjectives include tall , purple , funny , and antique .
- The Willis Tower is a tall building.
- There were several antique cars in the parade.
An adverb describes or modifies verbs, adjectives, and other adverbs.
Adverbs provide information about the manner in which things are done, as well as when, where, and why they are done. Examples of adverbs include quickly , extremely , fiercely , and yesterday .
- The boy ran quickly through the rainstorm.
- That was a fiercely competitive game yesterday.
A conjunction links words, phrases, and clauses. There are two main subcategories of conjunctions: coordinating conjunctions and subordinating conjunctions.
Coordinating conjunctions link words, phrases, and clauses that are equally important in a sentence. Examples of coordinating conjunctions include and , but , or , and so .
- The students read short stories and novels.
- Liz went to the movies but not to dinner.
Subordinating conjunctions link subordinate clauses to a sentence. Examples of subordinating conjunctions include because , although , before , and since .
- The team is cheering because it is excited.
- Henry had Swiss cheese on his burger although he preferred cheddar.
A preposition provides information about the relative position of a noun or pronoun. Prepositions can indicate direction, time, place, location, and spatial relationships of objects. Examples of prepositions include on , in , across , and after .
- The cat ran across the road.
- The pencil is in the drawer.
An interjection acts as an exclamation. Interjections typically express emotional reactions to information in an adjoining sentence. Examples of interjections include eek , wow , oops , and phew .
- Eek ! That was a huge spider.
- Oops ! I didn’t mean to slam the door.
Although the number of parts of speech is traditionally fixed at eight, some grammarians consider there to be additional parts of speech. For example, determiners (also called determinatives) modify nouns and are therefore generally considered to be adjectives, but they differ from other adjectives in that their exact meaning is supplied by context . They include articles, demonstrative pronouns, possessive pronouns, and quantifiers. Examples of determiners include the , an , that , your , and many .
Over the years grammarians have also proposed changes in how parts of speech are categorized. The 2002 edition of the Cambridge Grammar of the English Language , for example, placed pronouns as a subcategory of nouns.

Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
Understanding the 8 Parts of Speech: Definitions and Examples
General Education
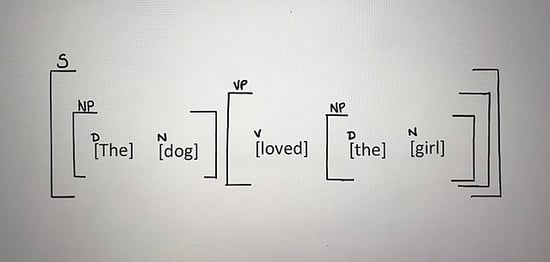
If you’re trying to learn the grammatical rules of English, you’ve probably been asked to learn the parts of speech. But what are parts of speech and how many are there? How do you know which words are classified in each part of speech?
The answers to these questions can be a bit complicated—English is a difficult language to learn and understand. Don’t fret, though! We’re going to answer each of these questions for you with a full guide to the parts of speech that explains the following:
- What the parts of speech are, including a comprehensive parts of speech list
- Parts of speech definitions for the individual parts of speech. (If you’re looking for information on a specific part of speech, you can search for it by pressing Command + F, then typing in the part of speech you’re interested in.)
- Parts of speech examples
- A ten question quiz covering parts of speech definitions and parts of speech examples
We’ve got a lot to cover, so let’s begin!
Feature Image: (Gavina S / Wikimedia Commons)

What Are Parts of Speech?
The parts of speech definitions in English can vary, but here’s a widely accepted one: a part of speech is a category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences.
To make that definition even simpler, a part of speech is just a category for similar types of words . All of the types of words included under a single part of speech function in similar ways when they’re used properly in sentences.
In the English language, it’s commonly accepted that there are 8 parts of speech: nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, pronouns, conjunctions, interjections, and prepositions. Each of these categories plays a different role in communicating meaning in the English language. Each of the eight parts of speech—which we might also call the “main classes” of speech—also have subclasses. In other words, we can think of each of the eight parts of speech as being general categories for different types within their part of speech . There are different types of nouns, different types of verbs, different types of adjectives, adverbs, pronouns...you get the idea.
And that’s an overview of what a part of speech is! Next, we’ll explain each of the 8 parts of speech—definitions and examples included for each category.

There are tons of nouns in this picture. Can you find them all?
Nouns are a class of words that refer, generally, to people and living creatures, objects, events, ideas, states of being, places, and actions. You’ve probably heard English nouns referred to as “persons, places, or things.” That definition is a little simplistic, though—while nouns do include people, places, and things, “things” is kind of a vague term. I t’s important to recognize that “things” can include physical things—like objects or belongings—and nonphysical, abstract things—like ideas, states of existence, and actions.
Since there are many different types of nouns, we’ll include several examples of nouns used in a sentence while we break down the subclasses of nouns next!
Subclasses of Nouns, Including Examples
As an open class of words, the category of “nouns” has a lot of subclasses. The most common and important subclasses of nouns are common nouns, proper nouns, concrete nouns, abstract nouns, collective nouns, and count and mass nouns. Let’s break down each of these subclasses!
Common Nouns and Proper Nouns
Common nouns are generic nouns—they don’t name specific items. They refer to people (the man, the woman), living creatures (cat, bird), objects (pen, computer, car), events (party, work), ideas (culture, freedom), states of being (beauty, integrity), and places (home, neighborhood, country) in a general way.
Proper nouns are sort of the counterpart to common nouns. Proper nouns refer to specific people, places, events, or ideas. Names are the most obvious example of proper nouns, like in these two examples:
Common noun: What state are you from?
Proper noun: I’m from Arizona .
Whereas “state” is a common noun, Arizona is a proper noun since it refers to a specific state. Whereas “the election” is a common noun, “Election Day” is a proper noun. Another way to pick out proper nouns: the first letter is often capitalized. If you’d capitalize the word in a sentence, it’s almost always a proper noun.
Concrete Nouns and Abstract Nouns
Concrete nouns are nouns that can be identified through the five senses. Concrete nouns include people, living creatures, objects, and places, since these things can be sensed in the physical world. In contrast to concrete nouns, abstract nouns are nouns that identify ideas, qualities, concepts, experiences, or states of being. Abstract nouns cannot be detected by the five senses. Here’s an example of concrete and abstract nouns used in a sentence:
Concrete noun: Could you please fix the weedeater and mow the lawn ?
Abstract noun: Aliyah was delighted to have the freedom to enjoy the art show in peace .
See the difference? A weedeater and the lawn are physical objects or things, and freedom and peace are not physical objects, though they’re “things” people experience! Despite those differences, they all count as nouns.
Collective Nouns, Count Nouns, and Mass Nouns
Nouns are often categorized based on number and amount. Collective nouns are nouns that refer to a group of something—often groups of people or a type of animal. Team , crowd , and herd are all examples of collective nouns.
Count nouns are nouns that can appear in the singular or plural form, can be modified by numbers, and can be described by quantifying determiners (e.g. many, most, more, several). For example, “bug” is a count noun. It can occur in singular form if you say, “There is a bug in the kitchen,” but it can also occur in the plural form if you say, “There are many bugs in the kitchen.” (In the case of the latter, you’d call an exterminator...which is an example of a common noun!) Any noun that can accurately occur in one of these singular or plural forms is a count noun.
Mass nouns are another type of noun that involve numbers and amount. Mass nouns are nouns that usually can’t be pluralized, counted, or quantified and still make sense grammatically. “Charisma” is an example of a mass noun (and an abstract noun!). For example, you could say, “They’ve got charisma, ” which doesn’t imply a specific amount. You couldn’t say, “They’ve got six charismas, ” or, “They’ve got several charismas .” It just doesn’t make sense!

Verbs are all about action...just like these runners.
A verb is a part of speech that, when used in a sentence, communicates an action, an occurrence, or a state of being . In sentences, verbs are the most important part of the predicate, which explains or describes what the subject of the sentence is doing or how they are being. And, guess what? All sentences contain verbs!
There are many words in the English language that are classified as verbs. A few common verbs include the words run, sing, cook, talk, and clean. These words are all verbs because they communicate an action performed by a living being. We’ll look at more specific examples of verbs as we discuss the subclasses of verbs next!
Subclasses of Verbs, Including Examples
Like nouns, verbs have several subclasses. The subclasses of verbs include copular or linking verbs, intransitive verbs, transitive verbs, and ditransitive or double transitive verbs. Let’s dive into these subclasses of verbs!
Copular or Linking Verbs
Copular verbs, or linking verbs, are verbs that link a subject with its complement in a sentence. The most familiar linking verb is probably be. Here’s a list of other common copular verbs in English: act, be, become, feel, grow, seem, smell, and taste.
So how do copular verbs work? Well, in a sentence, if we said, “Michi is ,” and left it at that, it wouldn’t make any sense. “Michi,” the subject, needs to be connected to a complement by the copular verb “is.” Instead, we could say, “Michi is leaving.” In that instance, is links the subject of the sentence to its complement.
Transitive Verbs, Intransitive Verbs, and Ditransitive Verbs
Transitive verbs are verbs that affect or act upon an object. When unattached to an object in a sentence, a transitive verb does not make sense. Here’s an example of a transitive verb attached to (and appearing before) an object in a sentence:
Please take the clothes to the dry cleaners.
In this example, “take” is a transitive verb because it requires an object—”the clothes”—to make sense. “The clothes” are the objects being taken. “Please take” wouldn’t make sense by itself, would it? That’s because the transitive verb “take,” like all transitive verbs, transfers its action onto another being or object.
Conversely, intransitive verbs don’t require an object to act upon in order to make sense in a sentence. These verbs make sense all on their own! For instance, “They ran ,” “We arrived ,” and, “The car stopped ” are all examples of sentences that contain intransitive verbs.
Finally, ditransitive verbs, or double transitive verbs, are a bit more complicated. Ditransitive verbs are verbs that are followed by two objects in a sentence . One of the objects has the action of the ditransitive verb done to it, and the other object has the action of the ditransitive verb directed towards it. Here’s an example of what that means in a sentence:
I cooked Nathan a meal.
In this example, “cooked” is a ditransitive verb because it modifies two objects: Nathan and meal . The meal has the action of “cooked” done to it, and “Nathan” has the action of the verb directed towards him.

Adjectives are descriptors that help us better understand a sentence. A common adjective type is color.
#3: Adjectives
Here’s the simplest definition of adjectives: adjectives are words that describe other words . Specifically, adjectives modify nouns and noun phrases. In sentences, adjectives appear before nouns and pronouns (they have to appear before the words they describe!).
Adjectives give more detail to nouns and pronouns by describing how a noun looks, smells, tastes, sounds, or feels, or its state of being or existence. . For example, you could say, “The girl rode her bike.” That sentence doesn’t have any adjectives in it, but you could add an adjective before both of the nouns in the sentence—”girl” and “bike”—to give more detail to the sentence. It might read like this: “The young girl rode her red bike.” You can pick out adjectives in a sentence by asking the following questions:
- Which one?
- What kind?
- How many?
- Whose’s?
We’ll look at more examples of adjectives as we explore the subclasses of adjectives next!
Subclasses of Adjectives, Including Examples
Subclasses of adjectives include adjective phrases, comparative adjectives, superlative adjectives, and determiners (which include articles, possessive adjectives, and demonstratives).
Adjective Phrases
An adjective phrase is a group of words that describe a noun or noun phrase in a sentence. Adjective phrases can appear before the noun or noun phrase in a sentence, like in this example:
The extremely fragile vase somehow did not break during the move.
In this case, extremely fragile describes the vase. On the other hand, adjective phrases can appear after the noun or noun phrase in a sentence as well:
The museum was somewhat boring.
Again, the phrase somewhat boring describes the museum. The takeaway is this: adjective phrases describe the subject of a sentence with greater detail than an individual adjective.
Comparative Adjectives and Superlative Adjectives
Comparative adjectives are used in sentences where two nouns are compared. They function to compare the differences between the two nouns that they modify. In sentences, comparative adjectives often appear in this pattern and typically end with -er. If we were to describe how comparative adjectives function as a formula, it might look something like this:
Noun (subject) + verb + comparative adjective + than + noun (object).
Here’s an example of how a comparative adjective would work in that type of sentence:
The horse was faster than the dog.
The adjective faster compares the speed of the horse to the speed of the dog. Other common comparative adjectives include words that compare distance ( higher, lower, farther ), age ( younger, older ), size and dimensions ( bigger, smaller, wider, taller, shorter ), and quality or feeling ( better, cleaner, happier, angrier ).
Superlative adjectives are adjectives that describe the extremes of a quality that applies to a subject being compared to a group of objects . Put more simply, superlative adjectives help show how extreme something is. In sentences, superlative adjectives usually appear in this structure and end in -est :
Noun (subject) + verb + the + superlative adjective + noun (object).
Here’s an example of a superlative adjective that appears in that type of sentence:
Their story was the funniest story.
In this example, the subject— story —is being compared to a group of objects—other stories. The superlative adjective “funniest” implies that this particular story is the funniest out of all the stories ever, period. Other common superlative adjectives are best, worst, craziest, and happiest... though there are many more than that!
It’s also important to know that you can often omit the object from the end of the sentence when using superlative adjectives, like this: “Their story was the funniest.” We still know that “their story” is being compared to other stories without the object at the end of the sentence.
Determiners
The last subclass of adjectives we want to look at are determiners. Determiners are words that determine what kind of reference a noun or noun phrase makes. These words are placed in front of nouns to make it clear what the noun is referring to. Determiners are an example of a part of speech subclass that contains a lot of subclasses of its own. Here is a list of the different types of determiners:
- Definite article: the
- Indefinite articles : a, an
- Demonstratives: this, that, these, those
- Pronouns and possessive determiners: my, your, his, her, its, our, their
- Quantifiers : a little, a few, many, much, most, some, any, enough
- Numbers: one, twenty, fifty
- Distributives: all, both, half, either, neither, each, every
- Difference words : other, another
- Pre-determiners: such, what, rather, quite
Here are some examples of how determiners can be used in sentences:
Definite article: Get in the car.
Demonstrative: Could you hand me that magazine?
Possessive determiner: Please put away your clothes.
Distributive: He ate all of the pie.
Though some of the words above might not seem descriptive, they actually do describe the specificity and definiteness, relationship, and quantity or amount of a noun or noun phrase. For example, the definite article “the” (a type of determiner) indicates that a noun refers to a specific thing or entity. The indefinite article “an,” on the other hand, indicates that a noun refers to a nonspecific entity.
One quick note, since English is always more complicated than it seems: while articles are most commonly classified as adjectives, they can also function as adverbs in specific situations, too. Not only that, some people are taught that determiners are their own part of speech...which means that some people are taught there are 9 parts of speech instead of 8!
It can be a little confusing, which is why we have a whole article explaining how articles function as a part of speech to help clear things up .

Adverbs can be used to answer questions like "when?" and "how long?"
Adverbs are words that modify verbs, adjectives (including determiners), clauses, prepositions, and sentences. Adverbs typically answer the questions how?, in what way?, when?, where?, and to what extent? In answering these questions, adverbs function to express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty . Adverbs can answer these questions in the form of single words, or in the form of adverbial phrases or adverbial clauses.
Adverbs are commonly known for being words that end in -ly, but there’s actually a bit more to adverbs than that, which we’ll dive into while we look at the subclasses of adverbs!
Subclasses Of Adverbs, Including Examples
There are many types of adverbs, but the main subclasses we’ll look at are conjunctive adverbs, and adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency.
Conjunctive Adverbs
Conjunctive adverbs look like coordinating conjunctions (which we’ll talk about later!), but they are actually their own category: conjunctive adverbs are words that connect independent clauses into a single sentence . These adverbs appear after a semicolon and before a comma in sentences, like in these two examples:
She was exhausted; nevertheless , she went for a five mile run.
They didn’t call; instead , they texted.
Though conjunctive adverbs are frequently used to create shorter sentences using a semicolon and comma, they can also appear at the beginning of sentences, like this:
He chopped the vegetables. Meanwhile, I boiled the pasta.
One thing to keep in mind is that conjunctive adverbs come with a comma. When you use them, be sure to include a comma afterward!
There are a lot of conjunctive adverbs, but some common ones include also, anyway, besides, finally, further, however, indeed, instead, meanwhile, nevertheless, next, nonetheless, now, otherwise, similarly, then, therefore, and thus.
Adverbs of Place, Time, Manner, Degree, and Frequency
There are also adverbs of place, time, manner, degree, and frequency. Each of these types of adverbs express a different kind of meaning.
Adverbs of place express where an action is done or where an event occurs. These are used after the verb, direct object, or at the end of a sentence. A sentence like “She walked outside to watch the sunset” uses outside as an adverb of place.
Adverbs of time explain when something happens. These adverbs are used at the beginning or at the end of sentences. In a sentence like “The game should be over soon,” soon functions as an adverb of time.
Adverbs of manner describe the way in which something is done or how something happens. These are the adverbs that usually end in the familiar -ly. If we were to write “She quickly finished her homework,” quickly is an adverb of manner.
Adverbs of degree tell us the extent to which something happens or occurs. If we were to say “The play was quite interesting,” quite tells us the extent of how interesting the play was. Thus, quite is an adverb of degree.
Finally, adverbs of frequency express how often something happens . In a sentence like “They never know what to do with themselves,” never is an adverb of frequency.
Five subclasses of adverbs is a lot, so we’ve organized the words that fall under each category in a nifty table for you here:
It’s important to know about these subclasses of adverbs because many of them don’t follow the old adage that adverbs end in -ly.
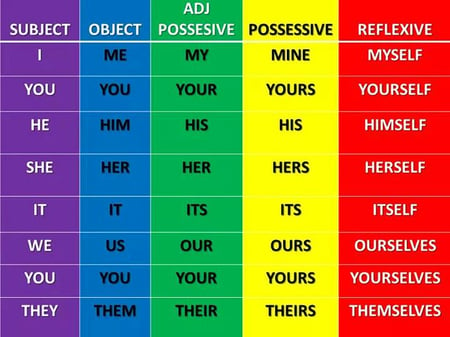
Here's a helpful list of pronouns. (Attanata / Flickr )
#5: Pronouns
Pronouns are words that can be substituted for a noun or noun phrase in a sentence . Pronouns function to make sentences less clunky by allowing people to avoid repeating nouns over and over. For example, if you were telling someone a story about your friend Destiny, you wouldn’t keep repeating their name over and over again every time you referred to them. Instead, you’d use a pronoun—like they or them—to refer to Destiny throughout the story.
Pronouns are typically short words, often only two or three letters long. The most familiar pronouns in the English language are they, she, and he. But these aren’t the only pronouns. There are many more pronouns in English that fall under different subclasses!
Subclasses of Pronouns, Including Examples
There are many subclasses of pronouns, but the most commonly used subclasses are personal pronouns, possessive pronouns, demonstrative pronouns, indefinite pronouns, and interrogative pronouns.
Personal Pronouns
Personal pronouns are probably the most familiar type of pronoun. Personal pronouns include I, me, you, she, her, him, he, we, us, they, and them. These are called personal pronouns because they refer to a person! Personal pronouns can replace specific nouns in sentences, like a person’s name, or refer to specific groups of people, like in these examples:
Did you see Gia pole vault at the track meet? Her form was incredible!
The Cycling Club is meeting up at six. They said they would be at the park.
In both of the examples above, a pronoun stands in for a proper noun to avoid repetitiveness. Her replaces Gia in the first example, and they replaces the Cycling Club in the second example.
(It’s also worth noting that personal pronouns are one of the easiest ways to determine what point of view a writer is using.)
Possessive Pronouns
Possessive pronouns are used to indicate that something belongs to or is the possession of someone. The possessive pronouns fall into two categories: limiting and absolute. In a sentence, absolute possessive pronouns can be substituted for the thing that belongs to a person, and limiting pronouns cannot.
The limiting pronouns are my, your, its, his, her, our, their, and whose, and the absolute pronouns are mine, yours, his, hers, ours, and theirs . Here are examples of a limiting possessive pronoun and absolute possessive pronoun used in a sentence:
Limiting possessive pronoun: Juan is fixing his car.
In the example above, the car belongs to Juan, and his is the limiting possessive pronoun that shows the car belongs to Juan. Now, here’s an example of an absolute pronoun in a sentence:
Absolute possessive pronoun: Did you buy your tickets ? We already bought ours .
In this example, the tickets belong to whoever we is, and in the second sentence, ours is the absolute possessive pronoun standing in for the thing that “we” possess—the tickets.
Demonstrative Pronouns, Interrogative Pronouns, and Indefinite Pronouns
Demonstrative pronouns include the words that, this, these, and those. These pronouns stand in for a noun or noun phrase that has already been mentioned in a sentence or conversation. This and these are typically used to refer to objects or entities that are nearby distance-wise, and that and those usually refer to objects or entities that are farther away. Here’s an example of a demonstrative pronoun used in a sentence:
The books are stacked up in the garage. Can you put those away?
The books have already been mentioned, and those is the demonstrative pronoun that stands in to refer to them in the second sentence above. The use of those indicates that the books aren’t nearby—they’re out in the garage. Here’s another example:
Do you need shoes? Here...you can borrow these.
In this sentence, these refers to the noun shoes. Using the word these tells readers that the shoes are nearby...maybe even on the speaker’s feet!
Indefinite pronouns are used when it isn’t necessary to identify a specific person or thing . The indefinite pronouns are one, other, none, some, anybody, everybody, and no one. Here’s one example of an indefinite pronoun used in a sentence:
Promise you can keep a secret?
Of course. I won’t tell anyone.
In this example, the person speaking in the second two sentences isn’t referring to any particular people who they won’t tell the secret to. They’re saying that, in general, they won’t tell anyone . That doesn’t specify a specific number, type, or category of people who they won’t tell the secret to, which is what makes the pronoun indefinite.
Finally, interrogative pronouns are used in questions, and these pronouns include who, what, which, and whose. These pronouns are simply used to gather information about specific nouns—persons, places, and ideas. Let’s look at two examples of interrogative pronouns used in sentences:
Do you remember which glass was mine?
What time are they arriving?
In the first glass, the speaker wants to know more about which glass belongs to whom. In the second sentence, the speaker is asking for more clarity about a specific time.

Conjunctions hook phrases and clauses together so they fit like pieces of a puzzle.
#6: Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that are used to connect words, phrases, clauses, and sentences in the English language. This function allows conjunctions to connect actions, ideas, and thoughts as well. Conjunctions are also used to make lists within sentences. (Conjunctions are also probably the most famous part of speech, since they were immortalized in the famous “Conjunction Junction” song from Schoolhouse Rock .)
You’re probably familiar with and, but, and or as conjunctions, but let’s look into some subclasses of conjunctions so you can learn about the array of conjunctions that are out there!
Subclasses of Conjunctions, Including Examples
Coordinating conjunctions, subordinating conjunctions, and correlative conjunctions are three subclasses of conjunctions. Each of these types of conjunctions functions in a different way in sentences!
Coordinating Conjunctions
Coordinating conjunctions are probably the most familiar type of conjunction. These conjunctions include the words for, and, nor, but, or, yet, so (people often recommend using the acronym FANBOYS to remember the seven coordinating conjunctions!).
Coordinating conjunctions are responsible for connecting two independent clauses in sentences, but can also be used to connect two words in a sentence. Here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two independent clauses in a sentence:
He wanted to go to the movies, but he couldn’t find his car keys.
They put on sunscreen, and they went to the beach.
Next, here are two examples of coordinating conjunctions that connect two words:
Would you like to cook or order in for dinner?
The storm was loud yet refreshing.
The two examples above show that coordinating conjunctions can connect different types of words as well. In the first example, the coordinating conjunction “or” connects two verbs; in the second example, the coordinating conjunction “yet” connects two adjectives.
But wait! Why does the first set of sentences have commas while the second set of sentences doesn’t? When using a coordinating conjunction, put a comma before the conjunction when it’s connecting two complete sentences . Otherwise, there’s no comma necessary.
Subordinating Conjunctions
Subordinating conjunctions are used to link an independent clause to a dependent clause in a sentence. This type of conjunction always appears at the beginning of a dependent clause, which means that subordinating conjunctions can appear at the beginning of a sentence or in the middle of a sentence following an independent clause. (If you’re unsure about what independent and dependent clauses are, be sure to check out our guide to compound sentences.)
Here is an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears at the beginning of a sentence:
Because we were hungry, we ordered way too much food.
Now, here’s an example of a subordinating conjunction that appears in the middle of a sentence, following an independent clause and a comma:
Rakim was scared after the power went out.
See? In the example above, the subordinating conjunction after connects the independent clause Rakim was scared to the dependent clause after the power went out. Subordinating conjunctions include (but are not limited to!) the following words: after, as, because, before, even though, one, since, unless, until, whenever, and while.
Correlative Conjunctions
Finally, correlative conjunctions are conjunctions that come in pairs, like both/and, either/or, and neither/nor. The two correlative conjunctions that come in a pair must appear in different parts of a sentence to make sense— they correlate the meaning in one part of the sentence with the meaning in another part of the sentence . Makes sense, right?
Here are two examples of correlative conjunctions used in a sentence:
We’re either going to the Farmer’s Market or the Natural Grocer’s for our shopping today.
They’re going to have to get dog treats for both Piper and Fudge.
Other pairs of correlative conjunctions include as many/as, not/but, not only/but also, rather/than, such/that, and whether/or.

Interjections are single words that express emotions that end in an exclamation point. Cool!
#7: Interjections
Interjections are words that often appear at the beginning of sentences or between sentences to express emotions or sentiments such as excitement, surprise, joy, disgust, anger, or even pain. Commonly used interjections include wow!, yikes!, ouch!, or ugh! One clue that an interjection is being used is when an exclamation point appears after a single word (but interjections don’t have to be followed by an exclamation point). And, since interjections usually express emotion or feeling, they’re often referred to as being exclamatory. Wow!
Interjections don’t come together with other parts of speech to form bigger grammatical units, like phrases or clauses. There also aren’t strict rules about where interjections should appear in relation to other sentences . While it’s common for interjections to appear before sentences that describe an action or event that the interjection helps explain, interjections can appear after sentences that contain the action they’re describing as well.
Subclasses of Interjections, Including Examples
There are two main subclasses of interjections: primary interjections and secondary interjections. Let’s take a look at these two types of interjections!
Primary Interjections
Primary interjections are single words, like oh!, wow!, or ouch! that don’t enter into the actual structure of a sentence but add to the meaning of a sentence. Here’s an example of how a primary interjection can be used before a sentence to add to the meaning of the sentence that follows it:
Ouch ! I just burned myself on that pan!
While someone who hears, I just burned myself on that pan might assume that the person who said that is now in pain, the interjection Ouch! makes it clear that burning oneself on the pan definitely was painful.
Secondary Interjections
Secondary interjections are words that have other meanings but have evolved to be used like interjections in the English language and are often exclamatory. Secondary interjections can be mixed with greetings, oaths, or swear words. In many cases, the use of secondary interjections negates the original meaning of the word that is being used as an interjection. Let’s look at a couple of examples of secondary interjections here:
Well , look what the cat dragged in!
Heck, I’d help if I could, but I’ve got to get to work.
You probably know that the words well and heck weren’t originally used as interjections in the English language. Well originally meant that something was done in a good or satisfactory way, or that a person was in good health. Over time and through repeated usage, it’s come to be used as a way to express emotion, such as surprise, anger, relief, or resignation, like in the example above.

This is a handy list of common prepositional phrases. (attanatta / Flickr)
#8: Prepositions
The last part of speech we’re going to define is the preposition. Prepositions are words that are used to connect other words in a sentence—typically nouns and verbs—and show the relationship between those words. Prepositions convey concepts such as comparison, position, place, direction, movement, time, possession, and how an action is completed.
Subclasses of Prepositions, Including Examples
The subclasses of prepositions are simple prepositions, double prepositions, participle prepositions, and prepositional phrases.
Simple Prepositions
Simple prepositions appear before and between nouns, adjectives, or adverbs in sentences to convey relationships between people, living creatures, things, or places . Here are a couple of examples of simple prepositions used in sentences:
I’ll order more ink before we run out.
Your phone was beside your wallet.
In the first example, the preposition before appears between the noun ink and the personal pronoun we to convey a relationship. In the second example, the preposition beside appears between the verb was and the possessive pronoun your.
In both examples, though, the prepositions help us understand how elements in the sentence are related to one another. In the first sentence, we know that the speaker currently has ink but needs more before it’s gone. In the second sentence, the preposition beside helps us understand how the wallet and the phone are positioned relative to one another!
Double Prepositions
Double prepositions are exactly what they sound like: two prepositions joined together into one unit to connect phrases, nouns, and pronouns with other words in a sentence. Common examples of double prepositions include outside of, because of, according to, next to, across from, and on top of. Here is an example of a double preposition in a sentence:
I thought you were sitting across from me.
You see? Across and from both function as prepositions individually. When combined together in a sentence, they create a double preposition. (Also note that the prepositions help us understand how two people— you and I— are positioned with one another through spacial relationship.)
Prepositional Phrases
Finally, prepositional phrases are groups of words that include a preposition and a noun or pronoun. Typically, the noun or pronoun that appears after the preposition in a prepositional phrase is called the object of the preposition. The object always appears at the end of the prepositional phrase. Additionally, prepositional phrases never include a verb or a subject. Here are two examples of prepositional phrases:
The cat sat under the chair .
In the example above, “under” is the preposition, and “the chair” is the noun, which functions as the object of the preposition. Here’s one more example:
We walked through the overgrown field .
Now, this example demonstrates one more thing you need to know about prepositional phrases: they can include an adjective before the object. In this example, “through” is the preposition, and “field” is the object. “Overgrown” is an adjective that modifies “the field,” and it’s quite common for adjectives to appear in prepositional phrases like the one above.
While that might sound confusing, don’t worry: the key is identifying the preposition in the first place! Once you can find the preposition, you can start looking at the words around it to see if it forms a compound preposition, a double preposition of a prepositional phrase.

10 Question Quiz: Test Your Knowledge of Parts of Speech Definitions and Examples
Since we’ve covered a lot of material about the 8 parts of speech with examples ( a lot of them!), we want to give you an opportunity to review and see what you’ve learned! While it might seem easier to just use a parts of speech finder instead of learning all this stuff, our parts of speech quiz can help you continue building your knowledge of the 8 parts of speech and master each one.
Are you ready? Here we go:
1) What are the 8 parts of speech?
a) Noun, article, adverb, antecedent, verb, adjective, conjunction, interjection b) Noun, pronoun, verb, adverb, determiner, clause, adjective, preposition c) Noun, verb, adjective, adverb, pronoun, conjunction, interjection, preposition
2) Which parts of speech have subclasses?
a) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, and adverbs b) Nouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, conjunctions, and prepositions c) All of them! There are many types of words within each part of speech.
3) What is the difference between common nouns and proper nouns?
a) Common nouns don’t refer to specific people, places, or entities, but proper nouns do refer to specific people, places, or entities. b) Common nouns refer to regular, everyday people, places, or entities, but proper nouns refer to famous people, places, or entities. c) Common nouns refer to physical entities, like people, places, and objects, but proper nouns refer to nonphysical entities, like feelings, ideas, and experiences.
4) In which of the following sentences is the emboldened word a verb?
a) He was frightened by the horror film . b) He adjusted his expectations after the first plan fell through. c) She walked briskly to get there on time.
5) Which of the following is a correct definition of adjectives, and what other part of speech do adjectives modify?
a) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns and noun phrases. b) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify verbs and adverbs. c) Adjectives are describing words, and they modify nouns, verbs, and adverbs.
6) Which of the following describes the function of adverbs in sentences?
a) Adverbs express frequency, degree, manner, time, place, and level of certainty. b) Adverbs express an action performed by a subject. c) Adverbs describe nouns and noun phrases.
7) Which of the following answers contains a list of personal pronouns?
a) This, that, these, those b) I, you, me, we, he, she, him, her, they, them c) Who, what, which, whose
8) Where do interjections typically appear in a sentence?
a) Interjections can appear at the beginning of or in between sentences. b) Interjections appear at the end of sentences. c) Interjections appear in prepositional phrases.
9) Which of the following sentences contains a prepositional phrase?
a) The dog happily wagged his tail. b) The cow jumped over the moon. c) She glared, angry that he forgot the flowers.
10) Which of the following is an accurate definition of a “part of speech”?
a) A category of words that serve a similar grammatical purpose in sentences. b) A category of words that are of similar length and spelling. c) A category of words that mean the same thing.
So, how did you do? If you got 1C, 2C, 3A, 4B, 5A, 6A, 7B, 8A, 9B, and 10A, you came out on top! There’s a lot to remember where the parts of speech are concerned, and if you’re looking for more practice like our quiz, try looking around for parts of speech games or parts of speech worksheets online!

What’s Next?
You might be brushing up on your grammar so you can ace the verbal portions of the SAT or ACT. Be sure you check out our guides to the grammar you need to know before you tackle those tests! Here’s our expert guide to the grammar rules you need to know for the SAT , and this article teaches you the 14 grammar rules you’ll definitely see on the ACT.
When you have a good handle on parts of speech, it can make writing essays tons easier. Learn how knowing parts of speech can help you get a perfect 12 on the ACT Essay (or an 8/8/8 on the SAT Essay ).
While we’re on the topic of grammar: keep in mind that knowing grammar rules is only part of the battle when it comes to the verbal and written portions of the SAT and ACT. Having a good vocabulary is also important to making the perfect score ! Here are 262 vocabulary words you need to know before you tackle your standardized tests.
Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Ashley Sufflé Robinson has a Ph.D. in 19th Century English Literature. As a content writer for PrepScholar, Ashley is passionate about giving college-bound students the in-depth information they need to get into the school of their dreams.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
- Phrases and Clauses
- Parts of a Sentence
- Modal Verbs
- Relative Clauses
- Confusing Words
- Online Grammar Quizzes
- Printable Grammar Worksheets
- Courses to purchase
- Grammar Book
- Grammar Blog
8 Parts of Speech
The 8 parts of speech in English are: Nouns, Adjectives, Adverbs, Verbs, Prepositions, Pronouns, Conjunctions, and Interjections.
A part of speech is a category of words that have similar grammatical functions or properties. In other words, they play similar roles in a sentence. For instance, a verb shows the action of a subject or the subject's state of being.

We'll now look in more detail at the function of each of these parts of speech.
Understanding the 8 Parts of Speech
Nouns are words used to talk about people, places, things, or ideas/concepts. Here are some examples:
- Person: The President
- Place: London
- Thing: Table
- Idea/concept: Neo-liberalism
So it may be naming something we can touch ( e.g. table; book; car ) or something we cannot touch ( e.g. Neo-liberalism; happiness; wish ).
There are both common nouns, used for classes of people, places, things, or ideas/concepts, and proper nouns, which is their given name, always with a capital letter.
Common Nouns
- political party
Proper Nouns
- Chester Avenue
Learn more about the various types of noun >>
Another of the 8 parts of speech are adjectives. They describe nouns or pronouns. They can come before or after the noun/pronoun they describe:
Absolute Adjectives
- The large shopping complex
- The excited child
- She is happy
- It was a shocking film
- Her dress was lovely
- He's a good-looking man
These are absolute adjectives , but they can also be comparative (comparing two or more things) or superlative (showing degree or quality):
Comparative Adjectives
- She's fitter than the others
- Their house is bigger
- I ran faster than you
- Cats are more agile than dogs
- Sue's more tired than Tim
Superlative Adjectives
- She's the fittest
- Their house is the biggest
- I ran the fastest
- Cats are the most agile
- Sue's the most tired
There are various other types of adjective. Learn more about the different types of adjectives >>
Adverbs modify verbs, other adverbs, and adjectives. There are adverbs of manner, time, place and degree . Here are examples of each being modified in relation to verbs, adverbs, and adjectives (the word being modified is underlined):
Adverbs Modifying Verbs
- He runs fast
- Ian quickly left the room
- She spoke slowly
Adverbs Modifying Other Adverbs
- He runs exceptionally fast
- Ian very quickly left the room
- She spoke extremely slowly
Adverbs Modifying Adjectives
- She's really excited
- He's happily married
- The elegantly designed dress is mine
Verbs form part of the predicate of a sentence.
In relation to the subject, they are used to express a physical action (e.g. walk; speak; show) or a mental action (e.g. think; feel; want). They can also express a state of being , mainly with the verb 'to be' but also some others.
Here are some examples:
Physical Action
- He ran home
- They chose the blue one
Mental Activity
- I am thinking about it
- Ian guessed the answer
- She believes in ghosts
State of Being
- She is a police woman
- They seem worried
These though are main verbs. They have many other uses in a sentence so you should read about all the types of verbs further.
Prepositions
Another of the 8 parts of speech are prepositions. These show the relationship between two words or phrases in a sentence. They precede a noun or pronoun.
Commons examples of prepositions are above, up, upon, at, before, behind, since, to, through, under, until, with, within, about, against, along, around, beside, between, down, during, below, by, except, for, from, in, into, like, near, of, off, on, toward.
In these example sentences with prepositions, the two words whose relationship is being expressed are underlined and the prepositions are in bold:
- The book is on the table
- He is the leader of the conservative party
- The boy picked up the toy under the sofa
- This is a present for your mother
Pronouns replace nouns and they prevent us from repeating the noun in a sentence. These are the types of pronouns with some examples:
- Personal e.g. I; you; they; she
- Possessive e.g. mine; yours; his; theirs
- Relative e.g. who; which; that; whom
- Demonstrative e.g. this; these; those
- Reciprocal e.g. one another; each other
- Emphatic / Reflexive e.g. myself; herself; itself; ourselves
- Interrogative e.g. what; which; whom; whose
Here are some examples of these words used in sentences:
- Martha decided she would leave
- Why don't you use his car instead of mine
- Mick is a person who learns quickly
- Shall we buy some of these ?
- They began to argue with each other
- Jenny is pleased with herself
- What time is he coming?
Conjunctions
Conjunctions are the of the 8 parts of speech responsible for joining together words, phrases, or clauses. There are three types:
- Coordinating: and; or; but; so; yet; for; nor
- Correlative: neither/nor; either/or; not only/but also
- Subordinating: e.g. although; because; while; which; where; until
Coordinating Conjunctions
Used to connect like for like words (e.g. noun+noun):
- I like apples and oranges ( 2 nouns )
- His speech was slow but effective ( 2 adjectives )
- Shall I say it loudly or quietly? ( 2 adverbs )
Or simple sentences (independent clauses):
- I find the music annoying but she finds It pleasant
- She came to the lecture late so she missed everything important
- She took her umbrella for it was raining hard
Correlative Conjunctions
Used to join alternative or equal elements:
- He felt neither happy nor sad about it
- Sue had to decide to either quit or carry on
- I went not only to Australia but also to New Zealand
Subordinating Conjunctions
Used to join subordinate clauses to main clauses:
- The government won't vote on the bill until both parties agree
- I'm still not tired although it is late
- I'll eat the dish which you don't like
Interjections
Interjections are words used to express an emotion or a sentiment such as surprise, joy, disgust, fear, excitement, pain, or enthusiasm.
They usually appear at the start of a sentence and are not connected to it grammatically. Here are some examples of interjections in sentences:
- Wow , that's an amazing score!
- Oh , I didn't know you failed the exam
- Well , we better not leave too late
- Ow , that really hurt!
- Ah , I understand now
- Oops , I've forgotten to bring the sandwiches
Learn more about interjections >>
Are there only 8 Parts of Speech?
Sometimes rather than 8 parts of speech, you may see 9 or 10 listed. This is because some people treat articles and determiners as separate categories.
However, when there are only 8 parts of speech considered (as above), this is because as these two types of word modify nouns, they are classified under adjectives.
Now practice what you have learned in our identifying parts of speech quiz
More on Sentence Structure:

Types of Clauses in English Grammar - Independent and Dependent Clause
The two types of clauses in English grammar are the independent and dependent clause. Both have a subject and verb which makes them clauses, but while independent clauses express a complete thought, dependent clauses do not. This is the main distinction.

Nominalisation in English Grammar: High Level Writing Tips
Nominalisation is an important aspect of academic writing. This lesson teachers you what this is and how you can use it effectively in your writing.

Subject Complements: Predicate Adjectives and Predicate Nominatives
Here we demystify subject complements, predicate adjectives, and predicate nominatives with simple explanations and examples.

Examples of Parallelism in English Grammar
View examples of parallelism in English grammar that show you correct and incorrect parallel sentences.

How to Use Either and Neither with Examples
Advice on how to use either and neither in English grammar. They can be adjectives, adverbs, pronouns and conjunctions.

Parts of a Sentence: Subject, Verbs, Objects, Predicates, Complements
The main parts of a sentence are subjects, verbs, objects, predicates, and subject complements. All of these have a specific purpose within the structure of a sentence.

Using Object Complements in a Sentence
Using object complements in a sentence enhances your ability to convey specific information about actions and their outcomes.

Parallelism Grammar Rules (Parallel Structure)
Parallelism is about balancing the grammatical structure of words, phrases and clauses in your sentences. Parallel structure will improve your writing's coherence.

Phrases and Clauses - Building good sentences
Phrases and clauses are the key building blocks of sentences. A clause contains a subject and a verb and can express a complete thought. A phrase does not contain a subject or verb.

Direct and Indirect Objects: The Differences
Direct and indirect objects are key parts of most sentences. A direct object is the receiver of action while indirect object identifies to or for whom or what the action of the verb is performed.
New! Comments
Any questions or comments about the grammar discussed on this page?
Post your comment here.

Sign up for free grammar tips, quizzes and lessons, straight into your inbox
Grammar Rules
Subscribe to grammar wiz:, grammar ebook.

This is an affiliate link
Recent Articles
Future continuous tense quiz: yes/no questions.
Jun 29, 24 11:04 AM
Future Continuous Affirmative Tense Quiz
Future continuous interrogative tense quiz.
Jun 29, 24 11:03 AM
Important Pages
Online Quizzes Grammar Lessons Courses Blog
Connect with Us
Search Site
Privacy Policy / Disclaimer / Terms of Use
Parts of Speech: Essential Components of Language
Understanding the parts of speech is essential for anyone looking to improve their grasp on the English language. There are traditionally eight parts of speech, each serving a distinct function within a sentence. By familiarizing oneself with the functions and rules governing each part of speech, one can develop better communication skills, whether it’s through written or spoken language.
Overview of Parts of Speech

Nouns are words that denote a person, place, or thing. In a sentence, nouns answer the questions who and what. For example, in the sentence “The dog ran after the ball,” there are two nouns: “dog” and “ball.” Nouns can be further classified into common nouns, proper nouns, and collective nouns.
- Common nouns: general names for people, places, or things (e.g., dog, city)
- Proper nouns : specific names of a particular person, place, or thing (e.g., John, London)
- Collective nouns: names for groups of things (e.g., flock, team)
2. Pronouns
Pronouns are words that replace nouns in a sentence. They help avoid repetition and make sentences less monotonous. For example, in the sentence “She gave her book to him,” the pronouns “she,” “her,” and “him” replace the respective nouns. Pronouns can be classified as:
- Personal pronouns : I, you, he, she
- Demonstrative pronouns : this, that, these, those
- Possessive pronouns: mine, yours, his, hers
- Reflexive pronouns: myself, yourself, himself, herself
3. Adjectives
Adjectives are words that describe or modify nouns or pronouns. They provide additional information about the noun/pronoun, such as size, color, or emotion. For example, in the sentence “The red ball is big,” “red” and “big” are adjectives.
Verbs are words that express an action, occurrence, or state of being. They usually indicate what the subject (noun or pronoun) of the sentence is doing. For example, in the sentence “The dog barks,” “barks” is the verb. Verbs can be classified as:
- Action verbs: run, jump, eat, think
- Linking verbs : be, seem, become, appear
- Helping/auxiliary verbs : have, do, will, should
Adverbs are words that modify or describe verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. They provide additional information about the action or quality of an action, such as how, when, or where it took place. For example, in the sentence “The dog barks loudly,” “loudly” is an adverb.
6. Prepositions
Prepositions are words that show the relationship between a noun or a pronoun and other words in a sentence. They usually indicate direction, location, or time. Common prepositions include:
- Direction : to, from, across, through, towards
- Location : in, on, at, under, above
- Time : before, after, during, since, until
7. Conjunctions
Conjunctions are words that connect words or groups of words in sentences. They help form complex sentences and provide a flow of ideas. There are three main types of conjunctions:
- Coordinating conjunctions : and, but, or, for, so (connect words, phrases, or clauses of equal importance)
- Subordinating conjunctions : because, if, although, when (introduce dependent clauses)
- Correlative conjunctions : either…or, neither…nor, both…and (work in pairs to connect similar elements)
8. Interjections
Interjections are short, abrupt words or phrases that express strong emotion or surprise. They are usually set apart from the rest of the sentence by punctuation, such as an exclamation mark or a comma. Examples of interjections include:
- Surprise: oh, wow, ouch
- Agreement: yes, indeed, exactly
- Disagreement: no, nonsense, definitely not
9. Articles
Articles are a type of determiner that precede nouns to specify the noun’s definiteness (whether it is specific or general) and can be classified as:
- Definite article: the (refers to a specific noun)
- Indefinite articles : a, an (refers to a non-specific noun)
Sentence Examples for the 8 Parts of Speech
In this section, we will provide examples of sentences that illustrate the 8 parts of speech in English. The parts of speech include nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
| Parts of Speech | Examples |
|---|---|
| Dog | The chased the mailman down the street. |
| Books | Sarah loves reading in the library. |
| She | decided to take up swimming lessons. |
| They | went to the movies together. |
| Jumps | The cat onto the couch. |
| Is | Helen an excellent musician. |
| Happy | The child played with the new toy. |
| Beautiful | She wore a dress to the event. |
| Quickly | The car sped down the road. |
| Softly | She spoke during the presentation. |
| On | The pen is the table. |
| Through | She walked the park. |
| And | She likes pizza pasta. |
| But | I want to go for a run, it’s raining outside. |
| Ouch | That hurt. |
| Wow | What an incredible view. |
Word Classes and Categories
Parts of speech in a language can be subcategorized into word classes and categories, making it easier to study and understand grammar. Word classes can be defined as groups of words that share similar linguistic properties, while categories refer to the roles they play in sentences.
There are generally two basic types of word classes: open and closed. Open word classes are the ones that regularly acquire new words as the language evolves. These include nouns, adjectives, adverbs, and verbs. On the other hand, closed word classes comprise pronouns, prepositions, conjunctions, articles/determiners, and interjections. Closed classes usually remain constant over time, with new words being infrequent additions.
Some major word class categories are:
- Nouns : These represent people, places, things, or ideas. Examples include “dog,” “city,” and “happiness.”
- Verbs : These express actions, states, or occurrences. Examples include “run,” “is,” and “become.”
- Adjectives : These describe qualities or characteristics of nouns. Examples include “tall,” “red,” and “happy.”
- Adverbs : These modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs. Examples include “quickly,” “very,” and “well.”
Word classes can be further divided into subcategories based on their specific functions or forms. For instance, nouns can be categorized as proper nouns (e.g., “John”) or common nouns (e.g., “man”), while verbs can be classified as transitive (e.g., “eat”) or intransitive (e.g., “sleep”).
Dictionaries play a crucial role in defining word classes by providing definitions, grammatical information, and usage examples for each word. It helps users understand which category a word belongs to and how it functions in a sentence.
English Language Grammar and Structure
Sentence structure.
In the English language, the foundation of grammar lies in the structure of sentences. A sentence consists of words arranged in a specific order, following a set of rules to convey a complete thought. The basic structure of an English sentence consists of a subject, a verb, and an object. For example:
Furthermore, sentences can be simple, compound, or complex, depending on the number of independent and dependent clauses they contain.
Parts of Speech Relationships
English grammar can be broken down into eight primary parts of speech, each with a unique function in the structure of sentences. These parts of speech are as follows:
- Nouns : They represent people, animals, things, or ideas. Examples: dog, city, love, time.
- Pronouns : These words replace nouns to avoid repetition, such as he, she, they, it, and their.
- Verbs : They describe actions, states, or occurrences, like eat, think, and know.
- Adjectives : Adjectives modify nouns or pronouns, providing more details or descriptions, for instance, red, happy, or large.
- Adverbs : They modify verbs, adjectives, or other adverbs, giving more information about the manner, place, time, or degree. Examples: quickly, very, well.
- Prepositions : These words show the relationship between a noun or pronoun and other words in a sentence, including location or time. Examples: in, on, at, between.
- Conjunctions : They connect words, phrases, or clauses, providing coherence and fluency to sentences. Examples: and, but, because, although.
- Interjections : They express emotions or reactions, often followed by an exclamation point. Examples: oh, wow, ouch, great.
Frequently Asked Questions on Parts of Speech
What are the parts of speech.
The parts of speech are different categories of words based on their usage and role in a sentence. In the English language, there are eight traditional parts of speech: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections.
Can you provide examples of each part of speech?
Certainly! Here are examples for each part of speech:
- Nouns : cat, book, happiness, city
- Pronouns : he, she, they, whose
- Verbs : run, think, be, have
- Adjectives : happy, large, warm, yellow
- Adverbs : quickly, very, almost, gently
- Prepositions : in, on, of, with
- Conjunctions : and, but, or, yet
- Interjections : ouch, hooray, wow, oh
Related Posts:

So interesting page
I love this , let me know can we connect
Parts of Speech – Word Classes
What is an adverb? What is a preposition? What is a…?
These are questions that students sometimes ask when a teacher is explaining a grammar point.
The different parts of speech (or all of those “grammar words” as some students call them) are important to know when learning English, or any other language.
In order to help solve doubts about what the different parts of speech are and what functions they have, I created a summary chart and a video explaining the main differences between each one.
Parts of Speech in English – ESL Video
In our ESL video, we look at the eight parts of speech in traditional English grammar. These parts of speech, sometimes called word classes, include: Nouns, Pronouns, Adjectives, Verbs, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions, and Interjections .
We give an explanation of how each word class is used and have included example sentences. For some of the parts of speech we also look at sub-classes such as subject pronouns and possessive pronouns, the different types of adverbs such as adverbs of manner, adverbs of frequency, etc.
In the final section we talk about how some teachers sometimes include a 9th part of speech which can be either Articles or Determiners. Again, we include examples.
This ESL video to ideal to give students a general overview of the different parts of speech in English.
Summary Chart
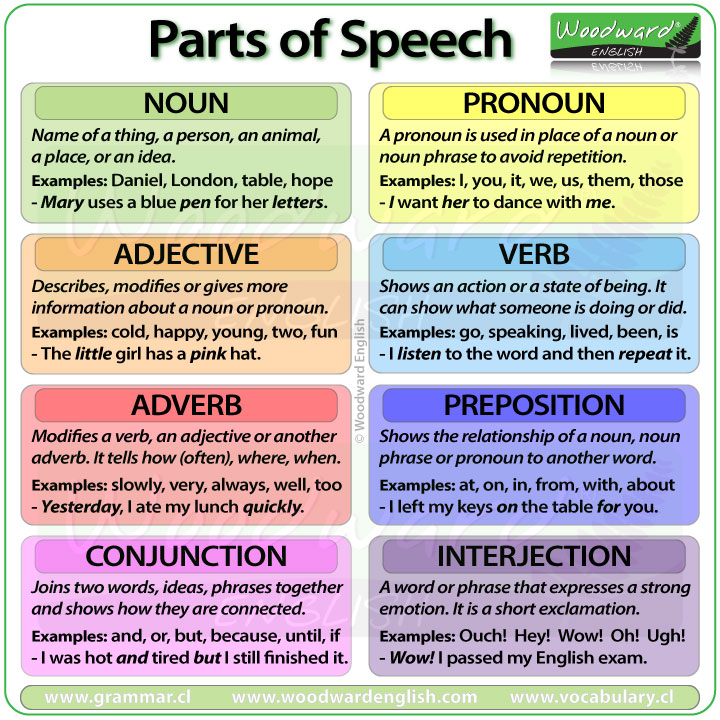
English Teacher Resource

- 934k Followers
- 214k Followers
- 104k Followers
FREE English Courses

Pin It on Pinterest
- More from M-W
- To save this word, you'll need to log in. Log In
part of speech
noun phrase
Definition of part of speech, examples of part of speech in a sentence.
These examples are programmatically compiled from various online sources to illustrate current usage of the word 'part of speech.' Any opinions expressed in the examples do not represent those of Merriam-Webster or its editors. Send us feedback about these examples.
Word History
1517, in the meaning defined above
Articles Related to part of speech

A Comprehensive Guide to Forming...
A Comprehensive Guide to Forming Compounds
Everything you need to know

The Adverb: A Most Fascinating POS
'POS' means "part of speech," obviously
Dictionary Entries Near part of speech
partnership life insurance
part of the package
Cite this Entry
“Part of speech.” Merriam-Webster.com Dictionary , Merriam-Webster, https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/part%20of%20speech. Accessed 27 Jul. 2024.
Kids Definition
Kids definition of part of speech, more from merriam-webster on part of speech.
Nglish: Translation of part of speech for Spanish Speakers
Britannica.com: Encyclopedia article about part of speech
Subscribe to America's largest dictionary and get thousands more definitions and advanced search—ad free!

Can you solve 4 words at once?
Word of the day, jurisprudence.
See Definitions and Examples »
Get Word of the Day daily email!
Popular in Grammar & Usage
Plural and possessive names: a guide, your vs. you're: how to use them correctly, every letter is silent, sometimes: a-z list of examples, more commonly mispronounced words, how to use em dashes (—), en dashes (–) , and hyphens (-), popular in wordplay, it's a scorcher words for the summer heat, flower etymologies for your spring garden, 12 star wars words, 8 words for lesser-known musical instruments, birds say the darndest things, games & quizzes.

Part 2: Select the word that select the word that matches each part of speech - noun A. Thanksgiving b, and C. exist d. awesome
Explanation:
A. Thanksgiving
Related Questions
The poem “Father William” is
It is a poem by Lewis Carroll that appears in Alice's Adventures in Wonderland, his 1865 novel.
Read the passage. (1) Universal health care should be adopted by every country around the world. (2) Over 100 million people become poor every year because of healthcare bills. (3) Imagine how it feels to be afraid to go to the doctor for fear of plunging into debt. (4) That is a really terrible thing, and governments need to act. (5) The World Health Organization (WHO) says that universal health care is achievable, even in poor countries. (6) The WHO recommends spreading the costs of health care across the population, so no one is overly burdened. (7) If a responsible organization like the WHO says it is possible, then worldwide governments should implement universal healthcare immediately. Which revision is the best way to strengthen the argument? A sentence stating the claim should be added before sentence 1. Sentence 2 should be deleted because it does not clearly support the claim. Sentence 4 should be revised to incorporate strong supporting evidence. A sentence that includes a strong rebuttal should be added after sentence 7.
The revision that is the best way to strengthen the argument is:
Sentence 4 should be revised to incorporate strong supporting evidence.
In order to defend his claims, an author needs to offer his audience strong arguments. Strong arguments need support, which comes for providing evidence of what is being claimed. Having that in mind, let's take a look at sentence 4:
4) That is a really terrible thing, and governments need to act.
Even though sentence 4 is addressing what was said in sentence 3, it is still a weak sentence to be included. It does not support the argument with evidence at all. It simply conveys the author's personal opinion and feelings, which is not enough to help strengthen this argument. The best way to revise it would be by adding evidence that truly conveys the idea that not having healthcare is a terrible thing.
He was betrayed by his partner. He suffered a huge lose.
fill in the blancks below to complete the sentences AYUDA
Answer: 2. doesn't walk
3.i was really surprised when my friend cooked dinner
4. A: you ordered your food? B: Yes we did.
5. Don't play tennis
6. Troy wanted to study for the final exam
7.First we boiled the water, and then we poured it into a cup.
8. They laughed at your joke? B: No they didn't
9. What time do you arrive at school?
Match each character to the most appropriate description Cecily fantasizes about the perfect courtship Jack forbids Jack from proposing to Gwendolen Lady Bracknell creates a fake brother, Ernest Algernon creates a fake friend, Bunbury
The character is said to be match to the most appropriate description below
Lady Bracknell : is known to be the mother to Gwendolen and also the aunt to Algernon. She is known to be hypocritic.
Gwendolyn Fairfax: is said to accepts the proposal of Jack (as Ernest). She is said to only want to marry the man who has the name Ernest.
Jack Worthing : is known as the man who is said to remain a moral role model towards Cecily. He did proposed to Gwendolen and formed a fake brother called Ernest .
Cecily Cardew: is said to accepts Ernest's proposal due to the fact that they had been engaged 3 months before it was called off once. She is known to loves ' wicked ' boys.
Algernon Moncrieff: He was said to went to the city and pretends to be Ernest so as to have Cecily like him. He is nephew to Lady Bracknell and he creates a fake friend named Bunbury .
Learn more about play from
https://brainly.com/question/19599489
What is the goal of Brutus' speech? Did he achieve it?
Brutus feels that the people will understand that he did not kill Caesar just for power and not consider him a killer. He wanted to be considered a tyrant slayer instead.
brutus goal is to persuades his audience (common people) that he had good and noble reasons to kill Caesar, so i think brutus achieve his speech after killing caesar....
04 The boy dog dog was hit by a car has not been to school for 3 days.
The boy's dog was hit by a car and has not been to school for 3 days.
Q: The aim of research is to obtain power A to increase ranks D to gain social status to produce knowledge
to produce knowledge.
Science can be defined as a branch of intellectual and practical study which systematically observe a body of fact in relation to the structure and behavior of non-living and living organisms (animals, plants and humans) in the natural world through experiments.
Research can be defined as the systematic investigation and careful study or analysis of materials and sources through the use of scientific techniques in order to establish facts and accurate conclusions.
The aim of research is to produce knowledge. Once the knowledge has been produced (acquired), it is then taught to the knowledge seekers and applied in real life scenarios or fields.
what kind of tone do the underlined worlds give this passage
because those are joyful words
Match each sentence part to the question is answers
I got it!!!!!
Here is the pic...
Hope this helps!! :)
1. 50 yrs 2.cost more
Does this sentence have a plural subject/verb? Apples have seeds in their cores
apples is a plural subject
"have" could be a verb?
Can someone please help me with Im begging you I Will mark brainless please help me
what motivated the African Americans during World War II
The civil rights movement was a fight for equal rights under the law for African Americans during the 1950s and 1960s.
how do i make college free?
Get a scholarship but its still not fully free so i dont know sneak in
WILL MARK BRAINLIEST Help me with these questions for it 1.Choose all the right answers. The skeletons of fossilized animals are put together by: facts recorded position in the ground inferences comparison with similar living animals 2. Why is it important that the location of fossils found in the ground is recorded? The location in which they are found provides the age of the fossil. The locations in which they are found provide clues to what type of animals lived in that area. The location in which they are found can provide clues on how to reconstruct the fossil. The location in which they are found provides clues on what time they were fossilized. 3. Brontosaurus is no longer considered a dinosaur because: its reconstruction was incorrect it was renamed after new data was discovered scientist have changed their conclusions all of the above 4. The hair, color, and skin of a reconstructed fossil animal is usually based on: inference photographs fact observation 5. The hair, color, and skin of a reconstructed fossil animal is usually based on: inference photographs fact observation 6. How can scientists predict the muscle size of an animal? Scientist can make inferences based on the location fossils are found. Some fossils contain muscle tissues. Scientists can make inferences based on the type of climate that animal lived in. Bone scars give clues about the muscle size.
1.) Comparison with similar living animals
2.)The location in which they are found provide clues to hat type of animals lived in that area.
3.)All of the above
4.)Inference
5.)Inference
6.)Some fossils contain muscle tissues.
Try These questions out and I’ll give you brainliest
Which belief did Frederick Douglass and the slaveholders NOT share? O Africans are inherently inferior. O Education and slavery are incompatible. O Sometimes a master was benevolent. O A mother will try to protect her own child.
The belief that Frederick Douglass and the slaveholders did NOT share is: Africans are inherently inferior.
Frederick Douglass was an African slave who later regained his freedom in America. Unlike the slaveholders, Douglass believed that the Africans were not inferior .
He believed that if they were given the same chances as the whites, they would excel.
Learn more about Frederick Douglass here:
https://brainly.com/question/16024772
EXERCISE B: Identifying verbal and non-verbal phrases. Fill in the grid below using expressions inside the box. 1. Shut up and let me finish! 2. (Derisive laughter). 3. (Move closer to the speaker) 4. Just a minute, please. 5. Signal "stop" with hand. 6. (Tiger look) 7. (Talk louder) 8. Please don't interrupt me. 9. (Angry face) 10. How are you today? Non-verbal Verba!
How is the poem "On the Bus with Rosa Parks" different from the memoir My Story? Check all that apply. The poem describes a single scene, the memoir describes many scenes. The poem uses few words, the memoir uses many words. The poem has short lines and stanzas; the memoir is written in prose paragraphs. * The poem places the bus ride in historical perspective, the memoir does not. * The poem explains why Rosa Parks stayed seated, the memoir does not. The poem shows an outsider's point of view of Rosa Parks; the memoir does not. The poem compares Rosa Parks's gaze to a flame, the memoir does not.
A,B,C,F,and G
Explanation:i got 100 on the test
ANSWER FAST PLS FOR 30 POINTSone example of when Margaret Bourke-White’s hardworking attitude helped advance her career
Margaret Bourke-White (1904-1971)
Introduction & Biographical Essay | Resources
Introduction & Biographical Essay
Introduction
Margaret Bourke-White, half-length portrait, facing left, holding camera.
Margaret Bourke-White,
holding camera (detail), 1940.
Photo by Acme Newspictures, Inc.
LC-USZ62-109633
Margaret Bourke-White was a woman of firsts: the first photographer for Fortune, the first Western professional photographer permitted into the Soviet Union, Life magazine's first female photographer, and the first female war correspondent credentialed to work in combat zones during World War II.
Help please need asap
the answer is C I believe
sorry if I'm wrong
Benito lived in many cities before settling down, such as Mexico City, Monterrey, as well as Puebla. Which revision corrects the structure? Benito lived in many cities before settling down, such as Mexico City, Monterrey too, and in Puebla. Benito lived in many cities before settling down, such as Mexico City, also Monterrey, as well as Puebla. Benito lived in many cities before settling down, such as Mexico City, Monterrey, and Puebla. Benito lived in many cities before settling down, in Mexico City, in Monterrey, in Puebla,
Psychology is the _____ study of behavior and mental processes. A. clinical B. social C. scientific D. medical
The correct answer is C
The goal of a psychology is to describe,explain,predict,and control the behaviors and mental process of both humans and animals.
In other words, Psychology focuses on all aspects of the human experiences while it also encompasses the understanding of behavior, more presicely, the factors that motivate behavior.
When quoting directly from sources you must blank each source correctly
Author's name, Title of Article or Book, Title of Journal, Publisher, Page Number(s), URL or DOI, Date of Publication
Read the excerpt from Roosevelt’s State of the Union address and the poster below it. Fortunately, there are only a few Americans who place appetite above patriotism. The overwhelming majority realize that the food we send abroad is for essential military purposes, for our own and Allied fighting forces, and for necessary help in areas that we occupy. Poster about rationing. Both the speech and the poster convey the importance of conserving resources at home so troops can have more. making sure that all citizens receive a fair share. displaying patriotism in all facets of one’s daily life. donating money to provide supplies for the troops.
I believe the correct answer is: diction to convey their message.
Both this excerpt from Roosevelt’s State of the Union address and the poster use the particular diction, a style of enunciation in speaking or singing, to convey their message. In his speech Roosevelt uses words such as patriotism, essential and necessary to put an emphasis on the need to send more food to the soldiers, so they could win a war. On the poster, the emphasis is realized by using the dash and by underlining “they”.
what are the significance of communication theory to the effectiveness communication
body language
displaying effective listening skills
benefits of effective communication.
hope it helps you a little....
Use the writing process to compose an essay on the following topic: “Diseases of the present age are very different from diseases of the past. Discuss.” INSTRUCTIONS Show your outline at the beginning of your essay. Your essay should be 450-500 words.
Diseases have been present in the world since antiquity, being a problem that directly causes many harm to society and human beings.
It is unfair to compare current illnesses with those of yesteryear. This is because, first, today we know diseases better, we have more advanced ways of treating them, we know the organisms than the causes and we can promote ways to avoid them. The people of old, did not have this type of information, which made illnesses stronger and more violent, causing many deaths and problems.
But this is not the only difference between old and current diseases. That's because we currently have a stronger immune system than people in the past. This is because our immune system is strengthened with vaccines that we have taken throughout our lives, which did not previously exist. In addition, with the more globalized and interconnected world, disease transmission becomes faster than it used to be.
Therefore, we can say that the diseases are different according to the time when they are being analyzed. These differences prevent them from being compared, since they have such different variables.
If you fraternize with your friends that means that you __ with them A) disagree B) argue C) feed D) associate Please real answers only
to fraternize means to associate
is our gain also our loss whats the central idea of the story
i am very smart
characteristics of hypertext
Hypertext is defined as a form of writing with three characteristics: discernable free standing content nodes, links between nodes, and the expectation of active choice by readers
Stephen Colbert Nails 'Absolutely Chilling' Part Of Marjorie Taylor Greene's RNC Speech

Overnight Editor, HuffPost

“Late Show” host Stephen Colbert began Monday night’s show from behind his desk with an appeal for civility after this weekend’s attempted assassination of Donald Trump .
“My immediate reaction when I saw this on Saturday were horror at what was unfolding, relief that Donald Trump had lived and frankly grief for my beautiful country,” he said.
Colbert appealed for calm.
“Our job as American citizens is to reject violence and violent rhetoric in this time of crisis, however hard we want to fight for our ideas,” he said, calling violence “the last refuge of the incompetent.”
Then, he took on Day One of the Republican National Convention , promising to talk about ideas and even deliver some fart jokes.
Colbert looked at some of the day’s speakers, including conspiracy theorist Rep. Marjorie Taylor Greene (R-Ga.).
“She said something absolutely chilling,” Colbert said, then rolled footage of Greene calling Trump “the leader America deserves.”
“Why?” Colbert shot back. “Did we run over a witch’s cat? Did someone make a wish on a cursed chicken foot?”
Check it out in his Monday night monologue:
From Our Partner
More in entertainment.
Paris 2024 Olympics Opening Ceremony: All you need to know

Picture by Florian Hulleu/Paris 2024
Ambitious, historic, spectacular – these are some of the words used to describe the Paris 2024 Opening Ceremony since the first plans were unveiled three years ago.
Set to be the first Olympic Games Opening Ceremony held outside a stadium , the 26 July celebration will transform the French capital into a stadium and theatre as the traditional parade of athletes takes place in boats along the Seine, passing the most iconic Parisian landmarks.
Here is all you need to know about the Opening Ceremony.
- Paris 2024 day-by-day highlights: When to catch the top moments from the Olympic Games
- Twelve of the biggest athletes to watch at Paris 2024
When will the Opening Ceremony be held?
The Opening Ceremony of the Paris 2024 Olympic Games will take place on Friday, 26 July .
The event will start at 19:30 CEST and is expected to last more than three hours.
Why is this ceremony historic?
Paris 2024 will mark the first time in history of the Olympic Summer Games that the Opening Ceremony is held outside a stadium.
Instead of familiar images of athletes marching out along an athletics track, guests and viewers will be treated to a colourful river parade through the heart of the French capital.
The Seine , the city’s main water artery, will substitute for the traditional track, the quays will become spectator stands , while the setting sun reflecting off famous Parisian landmarks will provide the backdrop for the event.
This outdoor concept also makes Paris 2024 the largest Opening Ceremony in terms of audience and geographical coverage .
What is the route of the parade?
The parade route along the Seine is a visual journey through Parisian history and architecture.
The Austerlitz Bridge next to the Jardin des Plantes is the starting point for the flotilla, which will then continue west for 6 kilometres along the Seine, passing under historic bridges and by iconic landmarks, such as the Notre-Dame and the Louvre , as well as some Games venues, including the Esplanade des Invalides and the Grand Palais .
Grouped on the boats with their national teams, the athletes will ultimately arrive opposite the Trocadero – the esplanade across from the Eiffel Tower – where the official protocols will be carried out, the Olympic cauldron lit, and the Paris 2024 Games officially declared open.
How many athletes will take part?
Almost 100 boats carrying an estimated 10,500 athletes will float along the Seine during the parade. The larger of the 206 National Olympic Committees (NOCs) represented in the parade will have boats to themselves, while the smaller ones will share boats.
Camera equipment set up on the decks will allow spectators to see the athletes up close and witness their emotions.
What entertainment performances can we expect?
Thomas Jolly , a French theatre director and actor, is overseeing the Paris 2024 Olympic and Paralympic ceremonies as artistic director .
While most of the entertainment acts remain under wraps, based on the hints so far, we can expect a show on a grand scale with an eclectic mash up of the old and the new. Speaking to the media in January, Jolly said that he wants to showcase the contrasting cultures of France, be that opera or rap, thus bringing together all the pieces that form the nation's diverse cultural identity.
For his part, ceremonies choreographer Maud Le Pladec promised that every bridge along the parade route will have dancers on it. Le Pladec will lead 400 dancers out of the total 3,000 artists who are set to take part in the Paris 2024 Opening and Closing Ceremonies, all decked out in one-of-a-kind costumes by Daphne Burki .
The French television presenter serves as the costume director for the show, leading a team of hundreds of dressmakers, hair stylists and makeup artists. Burki’s focus on sustainability also means there will be many vintage and upcycled pieces used in the ceremonies, mixed in with newer creations.
What will the athletes be wearing?
Artists will not be the only ones showing their style at the Opening Ceremony. With a line-up of luxury brands designing athlete uniforms, expect the Olympians to shine as well.
Team USA mix preppy jackets with jeans for a cool, all-American look, while Italian athletes will show up in casual, dark blue sets . Hosts France worked with a luxury brand to come up with vests and jackets that tie in with the general Paris 2024 look.
Other teams, such as Canada, Great Britain and Sweden , opted for a more athleisure look, all evoking the colour palettes of their national flags.
Some nations went even further with the patriotic details. Mongolian outfits have already created a buzz on social networks for their intricate embroidery and traditional silhouettes .
Brazil and Guatemala ’s looks are also sure to turn heads. Brazil’s denim jackets feature animals that are native to the country, while the Guatemalan athletes are dressed up in folkloric hats and bags to make a colourful statement on the Seine.
What are the different ways to watch the Opening Ceremony?
Almost 600,000 people will be able to enjoy the Opening Ceremony in person. True to its slogan, “Games Wide Open”, Paris 2024 tried to make the event accessible to as many people as possible by taking it outside of the traditional stadium setting.
There were 222,000 free tickets available to watch the parade from the upper banks of the Seine, in addition to 104,000 paid tickets on the lower quays. This marks the first Opening Ceremony where most spectators will not pay an admission fee – another historic milestone for Paris 2024.
Those in Paris who could not get tickets will be able to watch the Opening Ceremony on 80 giant screens set up throughout the city.
An additional 1.5 billion people from around the world are expected to tune into the television broadcasts of the ceremony.
Find the Paris 2024 Media Rights Holders in your country here .
Related content
- Share full article
Advertisement
Read the Transcript of Donald J. Trump’s Convention Speech
He spoke for just over 90 minutes.

By The New York Times
- July 19, 2024
Thank you very much. Thank you very, very much. And thank you, Dana. Thank you, Kid Rock, sometimes referred to as “Bob.” And thank you, Lee, right from the beginning, thank you very much. What a talent. What a beautiful, beautiful song. Thank you.
Friends, delegates and fellow citizens. I stand before you this evening with a message of confidence, strength and hope. Four months from now, we will have an incredible victory, and we will begin the four greatest years in the history of our country.
Together, we will launch a new era of safety, prosperity and freedom for citizens of every race, religion, color and creed.
The discord and division in our society must be healed. We must heal it quickly. As Americans, we are bound together by a single fate and a shared destiny. We rise together. Or we fall apart.
I am running to be president for all of America, not half of America, because there is no victory in winning for half of America.
So tonight, with faith and devotion, I proudly accept your nomination for president of the United States. Thank you. Thank you very much.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .
Fact-checking RNC Day 4: What Trump, other speakers got right and wrong

Donald Trump's first public speech since the failed assassination attempt against him highlighted the final night of the Republican National Convention, and we were there to let you know when he and other speakers strayed from the truth.
The 78-year-old former president spoke five days after a gunman opened fire during his rally in Butler, Pennsylvania, leaving one attendee dead, two others seriously injured and Trump with a wounded ear . Other speakers joining him in Milwaukee tonight included Eric Trump, Tucker Carlson and Hulk Hogan.
More from the Fact-Check Team: How we pick and research claims | Email newsletter | Facebook page
Fact-checking the Republican convention : What Vance, Trump Jr., others got right (and wrong) on Day 3
Donald Trump claim: Household costs rose $28,000 per family
“The total household costs have increased an average of $28,000 per family under this administration.”
Trump's figure is largely in line with a study from Republicans on the Joint Economic Committee that has tracked inflation since President Joe Biden took office in January 2021. From that date through January 2024, the study found the average household has paid $27,007 more in household costs due to inflation.
That includes cumulative increases of $9,366 for transportation, $4,678 for shelter, $4,562 for energy and $3,640 more for food, according to the study.
– Joedy McCreary
Donald Trump claim: There was no inflation during his presidency
“We had no inflation.”
This is wrong, according to consumer price index data from the Bureau of Labor Statistics .
The year-over-year inflation rate between February 2017 and February 2018, which would have been entirely under the Trump administration, was 2.2%.
The highest rate during his presidency was 2.9% in both June and July 2018 – the highest in more than six years .
By contrast, Biden’s inflation rate peaked at 9.1% in June 2022, the highest rate in four decades . The highest rate during former President Barack Obama's administration was 3.9% in September 2011 .
The inflation rate did dip below 1% for three months of Trump’s presidency, amid the COVID-19 pandemic.
– BrieAnna Frank
Donald Trump claim: US crime rate going up
“Our crime rate is going up while crime statistics all over the world are going down.”
This isn’t what the latest data shows.
A report from the FBI found violent crime in the U.S. dropped in 2023 .
Many U.S. cities also reported declines in homicides from 2023 to 2024, Axios reported in April. The number of murders fell by nearly 20% in the first three months of 2024 in 204 cities analyzed by criminal justice consulting firm AH Datalytics .
And FBI crime data showed sharp declines in violent crime in the first three months of 2024 compared to a year earlier, the Associated Press reported in June. Murder and rape were both down 26%, robbery was down 18% and aggravated assault fell by 13%, the AP said, noting the declines were in line with improvements following a surge in crime during the COVID-19 pandemic.
– Andre Byik and Chris Mueller
Trump claim: I’ve already built most of the border wall
“I will end the illegal immigration crisis by closing the border and finishing the wall, most of which I’ve already built.”
This is inaccurate. While it is true that under the Trump administration 458 miles of barriers were added to the southern border, the vast majority of this construction occurred where some kind of barrier was already in place, according to U.S. News .
These 458 miles of barrier account for about two-thirds of the total amount of barrier along the border, according to the Cato Institute . In all, the U.S. has 354 miles of pedestrian barriers and 300 miles of vehicle barriers, for a total of 654 miles, according to Customs and Border Protection’s website .
But the U.S.-Mexico border is 1,933 miles long , so the current wall only accounts for a fraction of that expanse. USA TODAY’s interactive border wall map shows there are vast swaths of land on the border with no barrier of any sort.
- Brad Sylvester
Donald Trump claim: Inflation under Biden was worst in U.S. history
“We’ve suffered the worst inflation we’ve ever had”
Inflation under President Joe Biden has certainly been higher than under former President Donald Trump, but it is far from the highest in the lifetimes of many Americans – much less ever.
Under Biden, the average annual inflation rate is about 5.7%, according to an analysis by Investopedia based on the seasonally adjusted consumer price index.
However, that rate was higher under both Jimmy Carter (9.9% average from 1977 to 1981) and Gerald Ford (average 8% from 1974 to 1977).
On an annual level this claim is also wrong, Investopedia reports . The highest annual increase under Biden was 7% in 2021. Inflation topped double digits in 1980 and twice in the 1970s.
– Nate Trela
Donald Trump claim: Democrats ‘cheating on elections’
“We don’t have fierce people. We have people that are a lot less than fierce except when it comes to cheating on elections, and a couple of other things. Then they’re fierce.”
Trump’s comment came as he reflected on the domestic and international problems facing the U.S., such as immigration and wars.
But his assertion that Democrats have engaged in widespread voter fraud – a claim he’s made repeatedly since his 2020 defeat to Joe Biden – is false.
There’s an overwhelming amount of evidence that shows Biden won the presidency that year. And no credible evidence of widespread voter fraud has been uncovered. Recounts, reviews and lawsuits have ultimately shown Biden’s win was legitimate.
Trump’s attorney general, William Barr, also said in December 2020 that the Justice Department had "not seen fraud on a scale that could have effected a different outcome in the election."
And in a statement released shortly after the election, the Cybersecurity and Infrastructure Security Agency said it was "the most secure in American history," and there was "no evidence that any voting system deleted or lost votes, changed votes or was in any way compromised."
Donald Trump claim: His administration passed nation’s largest tax cut
“We gave you the largest tax cut.”
This is false, and it’s a claim Trump has made before .
The Tax Cuts and Jobs Act that Trump championed ranks as the eighth-largest tax cut since 1918 as a percentage of gross domestic product , according to a 2017 analysis from the Committee for a Responsible Federal Budget.
The largest tax cut during that time frame was enacted in 1981, early in Ronald Reagan’s presidency, according to the think tank’s analysis.
The 2017 act overhauled the tax code , cutting the corporate tax rate from 35% to 21% and increasing the standard deduction, among other provisions, several of which are set to expire in 2025 .
Donald Trump claim: Grocery prices have risen by 57%
Grocery prices are up, but not this much.
From 2019 to 2023, the all-food Consumer Price Index rose by 25%, according to the U.S. Department of Agriculture.
The USDA said increases from 2020-21 were “largely driven by shifting consumption patterns and supply chain disruptions resulting from the Coronavirus (COVID-19) pandemic.
-Eric Litke
Eric Trump claim: Gas prices under Trump were the lowest in decades
“Trump made the United States energy independent with the lowest gas prices in decades.”
This is false. Gas prices fell precipitously late in Donald Trump's term in the White House, coinciding with stay-at-home restrictions at the start of the COVID-19 pandemic. During Trump's term, the Energy Information Administration's data on the average weekly price of gasoline (based on all grades and formulations) bottomed out the week of April 27, 2020, at $1.87 per gallon.
While significantly lower than a couple months earlier, it certainly was not the lowest in decades. During the week of Feb. 15, 2016, gas averaged $1.83 per gallon under President Barack Obama.
- Nate Trela
Eric Trump claim: Obama administration ‘handed’ Iran $150 billion
On why Donald Trump ran for office: “(Donald Trump) could no longer tolerate an inept administration that handed $150 billion to Iran.”
This is false, and it’s a claim Trump has also repeatedly made about his predecessor, Barack Obama.
It references the 2015 international agreement to curb Iran’s nuclear weapons program, the Joint Comprehensive Plan of Action .
While the agreement lifted some sanctions, it did not involve the Obama White House handing $150 billion to Iran. That money belonged to Iran – not the U.S. – and had been frozen in financial institutions around the globe as part of sanctions designed to curb the nation’s push for nuclear weapons, The Washington Post reported .
Much of the money was held in Asian and Turkish banks, not American ones, and many countries that received waivers to buy Iranian fossil fuels placed their payments in accounts resembling escrow accounts that remained inaccessible to Iran.
Additionally, the $150 billion figure is an upper-range estimate of the unfrozen funds. According to Treasury Department figures cited by The Washington Post, Tehran would have about $55 billion left once it fulfills its other obligations.
Eric Trump claim: Donald Trump made the U.S. energy independent
“My father made the U.S. energy independent.”
This is accurate, if you define energy independence as producing more energy than you consume . The U.S. most recently reached this mark in 2019 under Trump’s presidency when it became an "annual net total energy exporter,” according to the Energy Information Administration .
This was a reversal of the prior seven decades.
"Up to the early 1950s, the United States produced most of the energy it consumed," the administration's website says. "U.S. energy consumption was higher than U.S. energy production in every year from 1958 (to) 2018."
The U.S. has remained a net energy exporter since 2019, according to the available data.
-Brad Sylvester
Tucker Carlson claim: US drug deaths in last four years outnumbered US World War II casualties
“We’ve lost more Americans from drugs in the past four years than we lost in World War II.”
The two numbers are very close, but drug deaths are indeed higher than military deaths in WWII.
There were 418,500 American deaths during World War II, including both military members and civilians, according to the National World War II Museum . The Department of Veterans Affairs puts the number of military deaths at 405,000.
Data from the last four full years, 2020 through 2023, shows 419,849 Americans have died from drug overdoses in that period.
That includes 93,655 deaths in 2020 , 107,622 in 2021 , 111,029 in 2022 and 107,543 in 2023 , according to news releases from the CDC’s National Center for Health Statistics.
Tucker Carlson claim: WWII was America’s bloodiest war
“We’ve lost more Americans from drugs in the past four years than we lost in World War II. Yeah. Our bloodiest war.”
Though figures vary , the U.S. Department of Veterans Affairs says the American Civil War resulted in more U.S. military deaths than World War II.
Nearly 500,000 military personnel were killed in the Civil War (1861-1865), according to the VA. The total includes both Union and Confederate battle deaths and other in-theater deaths. Other estimates pin the total at over 600,000 deaths .
About 405,000 U.S. military deaths were tallied in World War II (1941-1945), according to the VA . The National World War II Museum puts the figure at 418,500 American deaths including civilians.
– Andre Byik
Alina Habba claim: The only crime Donald Trump has committed is loving America
“The only crime president Trump has committed is loving America.” - Trump attorney
A jury in New York disagrees. Former president Donald Trump and his legal team have maintained his innocence in the face of criminal indictments in multiple jurisdictions, but on May 30 he was convicted of 34 counts of falsifying business records in connection with a hush money payment to a porn actress. State prosecutors said it was an illegal scheme to interfere with the 2016 presidential election.
Trump has asked to have the conviction thrown out , pointing to the Supreme Court’s ruling that a sitting president has immunity from criminal prosecution for official acts .
Trump’s other cases likely will not be resolved before the election. Federal charges over Trump’s possession of classified materials after leaving the White House were thrown out this month, although that action has been appealed . An election interference case in Atlanta has been put on hold until a hearing on whether DA Fani Willis can remain on the case. And his federal election interference case in Washington was put on hold before the Supreme Court ruling and likely cannot be completed before the election.
RNC video claim: Income fell three consecutive years under Biden
“Under Biden, Americans’ income has gone down three straight years.”
This is misleading and oversimplifies the effect of the COVID-19 pandemic on the economy.
The claim is an apparent reference to reports such as a September 2023 House Budget Committee analysis that tracked the inflation-adjusted median household incomes and found three consecutive yearly declines.
But it fails to point out that the decline started during the final year of Donald Trump’s presidency. After reaching a high of $78,250 in 2019, the real median household income fell to $76,660 in 2020 – the first full year of the COVID-19 pandemic, a fact noted in the House committee analysis but not the video. It fell to $76,330 in 2021, the year Joe Biden took office, and dropped to $74,580 in 2022, the most recent data available.
But other datasets show increases under Biden. Bureau of Labor Statistics data show full-time workers’ median weekly earnings rising from $983 at the end of 2020 to $1,142 in the fourth quarter of 2023.
RNC video claim: Credit card fees soared under Biden
“Credit card fees surged 50% since Biden became president.” -narration of a video played at RNC
The Financial Times reported in March that U.S. consumers paid nearly 50% more in credit card expenses in 2023 than in 2020, the year before Joe Biden became president.
Citing data provided by U.S. banks to the Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation, FT reported credit card interest and fees increased by $51 billion in that time, to $157 billion. The change amounts to about a 48% increase.
The Biden administration has tried to implement new rules to address what it characterizes as “junk fees,” such as late fees and overdraft fees, the Associated Press reported . A federal judge in May temporarily halted a plan by Biden’s administration to lower late fees on credit cards to $8 from the current average of $32, the AP reported .
Linda McMahon claim: Trump tariffs on China raised billions
“Donald Trump put tariffs on China that raised billions of dollars and protected American industries.”
The numbers here are accurate. Beginning in 2018, Trump levied tariffs on thousands of products being imported from China valued at approximately $380 billion in 2018 and 2019, according to the Tax Foundation . The intention of these tariffs was to protect American domestic production. The tariffs resulted in nearly $80 billion in taxes paid to the U.S. government, according to the foundation.
However, it is worth noting that much of the revenue generated from these tariffs was paid by American importers, not the Chinese, according to the foundation and the Council on Foreign Relations . Most economists agree the increased cost of business is typically passed on to the consumer. The Tax Foundation estimated the tariffs, most of which have been kept in place under the Biden administration, have had a negative impact on U.S. gross domestic product in the long run.
Mike Pompeo claim: No Chinese spy balloons during Trump’s presidency
“Not a single Chinese spy balloon flew across the United States of America, four years.”
This false claim came up for a second straight night . Multiple news outlets reported in 2023 that Chinese surveillance balloons flew over the U.S. at least three different times during former President Donald Trump's administration, but military officials didn’t know it at the time.
Those spy balloons went undetected because of what Gen. Glen D. VanHerck , the commander of the Pentagon’s Northern Command, described to The New York Times as an “awareness gap.” Objects originally classified as U.F.O.s were later reclassified as Chinese spy balloons.
That report came shortly after a Chinese balloon was shot down off the coast of South Carolina in February 2023 , during the Biden administration. Trump, for his part, called it “ fake disinformation .”
– Joedy McCreary and Kim Breen
RNC background: Rally shooting looms over Trump’s closing address
The assassination attempt that left Donald Trump with an injured ear dominated the headlines during the days leading up to the former president’s keynote speech tonight.
In the wake of the July 13 shooting in Pennsylvania that left one dead and two others seriously injured , Trump said he rewrote his closing remarks to “bring the whole country, even the whole world, together,” he told the Washington Examiner.
The FBI identified the gunman as 20-year-old Thomas Matthew Crooks of Bethel Park, Pennsylvania , and said Secret Service agents killed him at the scene . But officials have been unable to determine his motive, one of the key unanswered questions sparking a significant amount of misinformation.
USA TODAY has debunked an array of false claims stemming from the assassination attempt.
- Fact check roundup: False claims about rally attack spread online
- Claim: Image shows Trump's suit jacket was pierced with a bullet during Pennsylvania rally shooting (False)
- Claim: Thomas Matthew Crooks is not the suspected Trump rally shooter (False)
- Claim: Image shows Trump rally shooter Thomas Matthew Crooks (False)
- Claim: Alejandro Mayorkas denied requests for additional security at Trump rally (False)
- Claim: Butler, Pennsylvania, police identified Trump shooter as Mark Violets, arrested him at scene (False)
- Claim: Video shows Trump assassination attempt was 'staged,' there were 'no bullets flying’ (False)
RNC background: Trump faces election interference charges as he tries to reclaim White House
As former President Donald Trump wages his campaign for re-election, he continues to face criminal charges for his alleged role in the Jan. 6, 2021, attack on the U.S. Capitol.
Trump is accused in a federal indictment of directing his supporters to march on the Capitol in an effort to pressure former Vice President Mike Pence to reject the certification of Joe Biden’s election victory.
The former president took to his Truth Social social media platform on July 15 – just two days after he was injured in an assassination attempt in Pennsylvania – to call for the case's dismissal, characterizing it as the “January 6th Hoax.”
More than 1,200 defendants have been charged in the attack on the Capitol. Trump’s case was overseen by Justice Department special counsel Jack Smith . Trump has pleaded not guilty .
USA TODAY has debunked numerous claims about the Jan. 6 attack on the Capitol.
- Fact check roundup: What's real and not three years after the Jan. 6 Capitol riot
- Claim: Video shows comedian, not liberal Jan. 6 rioter, posing as Trump supporter
- Claim: No evidence January 6 committee destroyed records, contrary to online claims
- Claim: Image shows man later convicted for role in Jan. 6 riot, not federal agent
- Claim: Video shows a pro-Trump mob with floor plans inside Capitol building on Jan. 6
RNC background: Biden’s age, gaffes a frequent theme
Joe Biden’s fitness to serve as president became a frequent Republican talking point when he and Donald Trump first faced off in 2020, and recent events have only fed that narrative in their second matchup.
The specter of his age was elevated in February by a special counsel report describing the 81-year-old Biden as an elderly man with "diminished capacities," including memory loss. His abominable performance in June’s presidential debate against Trump exacerbated the issue to the point where some leading Democrats are asking him to drop out of the race. Biden at one point chalking up the performance to exhaustion did not ease those concerns.
Biden insists he is fit to serve another term , but his actions and comments are being examined closely for clues about his capabilities – and sometimes they are misrepresented.
USA TODAY has debunked several false claims about Biden’s mental acuity and physical stamina:
- Claim : Joe Biden was declared 'mentally unfit' to stand trial
- Claim : Biden had a medical emergency on Air Force One on July 5
- Claim : Biden mistakenly read 'end of quote' prompt on teleprompter
- Claim : Video shows Biden talking about resigning as president in 2024
- Claim : Biden fell asleep during debate
- Claim : Biden said he’s running for president to 'reduce the prospect of war in Vietnam'
– Nate Trela
RNC background: Project 2025 stirs debate
Democratic lawmakers have in recent weeks sought to turn voters’ attention to Project 2025, also known as the Presidential Transition Project.
It’s an effort by the Heritage Foundation and other conservative organizations that resulted in a 900-page playbook for the next Republican president. A full implementation of the guidance in the document would effectively overhaul the federal government .
A slew of Trump’s allies are involved in the project, though Trump has maintained that he is not.
He wrote in a July 5 Truth Social post that “some of the things they’re saying are absolutely ridiculous and abysmal,” though he did not specify what elements of Project 2025 he objected to.
His campaign has instead presented “Agenda47” as its policy plan in a second Trump presidency. It includes a day-one executive order ending automatic citizenship for children of undocumented immigrants who are born in the U.S. and closing the U.S. Department of Education .
The Republican Party's 2024 policy platform echoes Trump’s vision for the country , calling for the “largest deportation program in American history” and penalizing school districts that expose children to what it deems “inappropriate racial, sexual or political content,” USA TODAY reported .
USA TODAY has debunked claims about Project 2025:
- Claim: Project 2025 is an effort by the Heritage Foundation, not Donald Trump
- Claim: Claim of ‘period passports’ under Project 2025 is from satire
-BrieAnna Frank
RNC background: Trump’s baseless claims of rigged 2020 election persist
With the 2024 election drawing near, former President Donald Trump continues to baselessly – but repeatedly – claim the one four years earlier was rigged against him .
He even dropped this claim in a video shown during Wednesday’s Republican National Convention.
His campaign and the Republican National Committee led by his daughter-in-law have said they will mobilize 100,000 people in battleground states to ensure “transparency and fairness” in a move that has drawn criticism from opponents saying it has the potential to lead to voter intimidation .
State-level recounts, reviews and audits of the 2022 midterm elections found no indication of systemic problems with voter fraud.
That’s significant because the baseless allegations from Trump and his allies have penetrated the Republican Party and eroded confidence in the process. Sen. Tim Scott of South Carolina and other top Republicans have refused to commit to accepting the outcome of the election.
USA TODAY has debunked numerous false claims about the integrity of the elections:
- Fact check roundup: False claims about election fraud, candidates swirl amid 2022 midterms
- Claim: 105% of Michigan’s population is registered to vote (False)
- Claim: A software company's contract allows officials to override election results (False)
- Claim: Malware, remote access caused printer problems; 200,000 'ejected' ballots in Arizona (False)
- Claim: A chart shows election fraud in the Michigan AG’s race (False)
- Claim: Blackout in live stream in Nevada points to election theft (False)
- Claim: Fraud due to Texas voting machine adding voters as polls close (False)
- Claim: Photo showing ballots from 2022 midterms in the trash is evidence of fraud (False)
- Claim: Democrats used 47 million mail-in ballots to steal every election (False)
- Claim: Joe Biden did not legally win the presidential election (False)
Fact check : Facts about Trump assassination attempt: What's real, what's not and how we know
Thank you for supporting our journalism. You can subscribe to our print edition, ad-free app or e-newspaper here .
USA TODAY is a verified signatory of the International Fact-Checking Network, which requires a demonstrated commitment to nonpartisanship, fairness and transparency. Our fact-check work is supported in part by a grant from Meta .
3 takeaways from Trump’s speech, final night of the Republican convention
Trump delivered an initially powerful but ultimately bizarrely meandering speech, as the convention played up the assassination attempt against him.

MILWAUKEE — Welcome to The Campaign Moment. This week, we’re running through the big moments and trends from the Republican National Convention.
(Did a friend forward this to you, or are you seeing this on the website? If so, sign up for this newsletter here . And make sure to check out the Campaign Moment podcast .)
The big moment
The 2024 GOP convention came to a close Thursday night, with former president Donald Trump formally accepting his party’s nomination just five days after surviving an assassination attempt.
But even that story wasn’t necessarily the biggest of Thursday, as the potential exit of the opponent Republicans had spent four days attacking — President Biden — loomed larger and larger .
Here’s our final set of takeaways from the convention week that was.
1. A tale of two Trump speeches: powerful and perplexing
The first 15 minutes of Trump’s speech were powerful, as he recounted Saturday’s assassination attempt.
The rest of the more than 90-minute-long speech was thoroughly confusing. It meandered between points, often going off-script with ad-libs that left a standard-issue Trump campaign speech without the kind of coherent, lofty theme that defines traditional presidential convention fare. And Trump’s initially subdued manner and calls for unity didn’t match the content of an often-divisive speech.
Trump grabbed the audience with a promise to discuss what happened Saturday, but qualified it by saying he would only do it once, “because it’s actually too painful to tell.”
He celebrated slain firefighter Corey Comperatore and two others who were shot.
Perhaps the most powerful moment came when Trump said, “I’m not supposed to be here tonight.” The crowd began chanting, “Yes you are!” Trump ultimately responded, “Thank you, but I’m not.”
“Despite such a heinous attack, we unite this evening more determined than ever,” Trump wrapped up that section. “I am more determined than ever. So are you. So is everybody. … Our resolve is unbroken, and our purpose is unchanged.”
Also unchanged: Virtually the rest of his speech, undifferentiated from a normal Trump stump speech.
Despite the call for unity, Trump soon referred to “crazy Nancy Pelosi,” repeatedly cited false allegations of stolen elections, called for the firing of the head of the United Auto Workers, cited the “China virus” and the “invasion” at the Southern border. He called a Democratic senator a “total lightweight.” He even repeated a puzzling allusion to “ the late, great Hannibal Lecter ,” from “The Silence of the Lambs,” which he’s used before.
All of it was familiar from Trump’s speeches — as was the extensive ad-libbing. But this wasn’t just any Trump speech. This was a different venue, his introduction to many more casual voters who might not eat up his many musings.
The assassination attempt probably drew even more eyeballs to him, and it’s not clear what those new viewers took away, beyond that Trump was nearly killed five days ago.
“So I’d better finish strong,” Trump said at one point. “Otherwise we’ll blow it. And we can’t let that happen.”
2. Republicans trolled Democrats on replacing Biden
As Democrats appeared to inch closer to replacing their 2024 standard-bearer, Republicans decided now would be a good time to stir the pot.
Previously, some high-profile Republicans made clear their preference for facing Biden and began attacking Vice President Harris more . But Wednesday, their move was to try to stoke Democratic divisions, casting any attempt to replace the nominee as a brazen and even undemocratic one.
Top Trump campaign adviser Chris LaCivita, at a CNN/Politico event, called it an attempted “coup” and an effort to “ depose ” Biden “that’s going to create a whole host of different issues.”
At another event, former Trump acting director of national intelligence Richard Grenell called efforts to switch nominees “ outrageous ” and urged the media to declare that “you don’t get to dump this [president]. This is what happens in other countries, not in America.”
On X, Rep. Matt Gaetz (R-Fla.) labeled it an “ insurrection .”
None of these descriptions actually fit; Democrats are trying to persuade Biden to drop out, not overturn the primary results themselves. But as the Biden loyalists get a little quieter , there’s certainly value for Republicans in framing things this way in hopes of riling them (or perhaps even Biden) up.
At the very least, Republicans seemed to be having some fun trolling Democrats over their discord.
3. They leaned in on the assassination attempt — and maybe God’s favoritism
Trump wasn’t the only one to focus extensively on the assassination attempt.
Speakers repeatedly pitched it and Trump’s response as evidence of Trump’s resolve, courage — and possibly even God’s will that he be president.
Eric Trump focused on it, calling Trump “a man who survived a bullet that was intended to eliminate him permanently from our future and from our family.”
“You wiped the blood off your face,” Eric Trump said. “And you put your fist in the air, in a moment that will be remembered as one of the most courageous acts in the history of American politics.”
Trump lawyer Alina Habba said Trump “did not just take a bullet in Butler, Pennsylvania. He has and will continue to take them for each and every one of us.”
While other Trump supporters have posited that God intervened to save Trump, a couple of speakers seemed to go a little further to suggest it showed God’s favoritism.
Evangelical leader Franklin Graham, unlike many others pointing to possible divine intervention, noted that firefighter Corey Comperatore was not spared.
“I cannot explain why God would save one life and allow another one to be taken,” Graham said. “I don’t have the answer for that.”
Former Fox News host Tucker Carlson suggested that he did have that answer.
“When he stood up after being shot in the face, bloodied, and put his hand up, I thought at that moment that was a transformation. This was no longer a man. Well, I think that I think it was divine intervention,” Carlson said, adding: “This was the leader of a nation.”
Carlson added: “I think a lot of people are wondering, what is this? This doesn’t look like politics. Something bigger is going on here. I think even people who don’t believe in God are beginning to think, well, maybe there’s something to this, actually.”
Take a moment to read:
- “ What happens if Biden drops out of the presidential race? ” (Washington Post)
- “ Pelosi has told House Democrats that Biden may soon be persuaded to exit race ” (Washington Post)
- “ Obama tells allies Biden’s path to winning reelection has greatly diminished ” (Washington Post)
- “ The right is attacking the Secret Service’s women agents. Trump hasn’t joined in. ” (Politico)
- “ Pelosi, Long Fixated on Winning, Is in No Mood to Lose With Biden ” (New York Times)


COMMENTS
A part of speech (also called a word class) is a category that describes the role a word plays in a sentence.Understanding the different parts of speech can help you analyze how words function in a sentence and improve your writing. The parts of speech are classified differently in different grammars, but most traditional grammars list eight parts of speech in English: nouns, pronouns, verbs ...
A Formal Definition A "part of speech" is a category to which a word is assigned in accordance with its syntactic functions. In English, the main parts of speech are noun, pronoun, adjective, determiner, verb, adverb, preposition, conjunction, and interjection.
A part of speech is a term used in traditional grammar for one of the nine main categories into which words are classified according to their functions in sentences, such as nouns or verbs. Also known as word classes, these are the building blocks of grammar.
Now, love is acting as a verb!It's telling us an action. The only way we can know how to categorize a word is to look at how it's acting within a sentence. Okay, let's check out the parts of speech!
Part Of Speech Function Example Vocabulary Example Sentences Part Of Speech Noun Function is a person or thing. Example Vocabulary Birthday, cake, Paris, flat Example Sentences Today is my birthday. I like cake.
Words with More Than One Job. Many words in English can have more than one job, or be more than one part of speech. For example, "work" can be a verb and a noun; "but" can be a conjunction and a preposition; "well" can be an adjective, an adverb and an interjection.
What Are the Parts of Speech in English? The parts of speech refer to categories to which a word belongs. In English, there are eight of them : verbs , nouns, pronouns, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Many English words fall into more than one part of speech category.
The 8 parts of speech are: nouns, pronouns, verbs, adjectives, adverbs, prepositions, conjunctions, and interjections. Nouns represent people, places, things, or ideas.
Part of Speech: Function: Sentence examples: Noun: Person, thing, place, or event: She is the new assistant.: Pronoun: Replaces a noun: She is the new assistant.My bag is missing.: Verb: Expresses time while demonstrating a condition, action, or the fact that something exists
In the English language, every word is called a part of speech.The role a word plays in a sentence denotes what part of speech it belongs to. Explore the definition of parts of speech, the different parts of speech and examples in this article.
There are eight major parts of speech. Nouns name persons, places, things, ideas, or qualities, e.g., Franklin, boy, Yangtze River, shoreline, Bible, desk, fear ...
Verbs. Verbs are one of the most important parts of speech in English. They are used to describe an action, state, or occurrence. In this section, we will cover the three types of verbs: action verbs, linking verbs, and helping verbs.
Parts of speech are categories of words that perform similar grammatical roles in phrase and sentence structures. But what exactly are the different parts of speech and how do you know which words correspond to different grammatical categories?
In total, there are nine categories of parts of speech. These nine parts of speech are namely: Verbs, Nouns, Adjectives, Determiners, Adverbs, Pronouns, Prepositions, Conjunctions, and Interjections. Another additional classification is used as a part of speech, i.e., Articles, a subprogram of determiners. To comprehend the meaning and use of each word in the English language, it is essential ...
Part of speech, lexical category to which a word is assigned based on its function in a sentence. There are eight parts of speech in traditional English grammar: noun, pronoun, verb, adjective, adverb, conjunction, preposition, and interjection. In linguistics, parts of speech are more typically
Though some of the words above might not seem descriptive, they actually do describe the specificity and definiteness, relationship, and quantity or amount of a noun or noun phrase. For example, the definite article "the" (a type of determiner) indicates that a noun refers to a specific thing or entity.The indefinite article "an," on the other hand, indicates that a noun refers to a ...
Prepositions are words that express a relationship between a noun or pronoun (known as the object of the preposition) and another part of the sentence.Together, these form prepositional phrases, which can function as adjectives or as adverbs in a sentence.Some examples of prepositional phrases are: on the table, in the shed, and across the field. (The prepositions are in bold.)
Knowing the different parts of speech is essential for good grammar. Become an expert at knowing when and what parts of speech to use with these examples.
The 8 parts of speech in English are: Nouns, Adjectives, Adverbs, Verbs, Prepositions, Pronouns, Conjunctions, and Interjections. A part of speech is a category of words that have similar grammatical functions or properties.
Parts of Speech Examples; Nouns: Dog: The dog chased the mailman down the street.: Books: Sarah loves reading books in the library.: Pronouns: She: She decided to take up swimming lessons.: They: They went to the movies together.: Verbs: Jumps: The cat jumps onto the couch.: Is: Helen is an excellent musician.: Adjectives: Happy: The happy child played with the new toy.: Beautiful: She wore a ...
We look at the eight different parts of speech in English including: Nouns, Pronouns, Adjectives, Verbs, Adverbs, Prepositions, Conjunctions, and Interjection. We also mention Articles and Determiners which some teachers consider a 9th word class.
The meaning of PART OF SPEECH is a traditional class of words (such as adjectives, adverbs, nouns, and verbs) distinguished according to the kind of idea denoted and the function performed in a sentence. How to use part of speech in a sentence.
The belief that Frederick Douglass and the slaveholders did NOT share is: Africans are inherently inferior.. Who was Frederick Douglass? Frederick Douglass was an African slave who later regained his freedom in America.Unlike the slaveholders, Douglass believed that the Africans were not inferior.. He believed that if they were given the same chances as the whites, they would excel.
"Late Show" host Stephen Colbert began Monday night's show from behind his desk with an appeal for civility after this weekend's attempted assassination of Donald Trump. "My immediate reaction when I saw this on Saturday were horror at what was unfolding, relief that Donald Trump had lived ...
Ambitious, historic, spectacular - these are some of the words used to describe the Paris 2024 Opening Ceremony since the first plans were unveiled three years ago.. Set to be the first Olympic Games Opening Ceremony held outside a stadium, the 26 July celebration will transform the French capital into a stadium and theatre as the traditional parade of athletes takes place in boats along the ...
He spoke for just over 90 minutes. By The New York Times Thank you very much. Thank you very, very much. And thank you, Dana. Thank you, Kid Rock, sometimes referred to as "Bob." And thank you ...
Donald Trump's first public speech since the failed assassination attempt against him highlighted the final night of the Republican National Convention, and we were there to let you know when he ...
The rest of the more than 90-minute-long speech was thoroughly confusing. It meandered between points, often going off-script with ad-libs that left a standard-issue Trump campaign speech without ...