

Top 40 Most Popular Case Studies of 2017
We generated a list of the 40 most popular Yale School of Management case studies in 2017 by combining data from our publishers, Google analytics, and other measures of interest and adoption. In compiling the list, we gave additional weight to usage outside Yale
We generated a list of the 40 most popular Yale School of Management case studies in 2017 by combining data from our publishers, Google analytics, and other measures of interest and adoption. In compiling the list, we gave additional weight to usage outside Yale.
Case topics represented on the list vary widely, but a number are drawn from the case team’s focus on healthcare, asset management, and sustainability. The cases also draw on Yale’s continued emphasis on corporate governance, ethics, and the role of business in state and society. Of note, nearly half of the most popular cases feature a woman as either the main protagonist or, in the case of raw cases where multiple characters take the place of a single protagonist, a major leader within the focal organization. While nearly a fourth of the cases were written in the past year, some of the most popular, including Cadbury and Design at Mayo, date from the early years of our program over a decade ago. Nearly two-thirds of the most popular cases were “raw” cases - Yale’s novel, web-based template which allows for a combination of text, documents, spreadsheets, and videos in a single case website.
Read on to learn more about the top 10 most popular cases followed by a complete list of the top 40 cases of 2017. A selection of the top 40 cases are available for purchase through our online store .
#1 - Coffee 2016
Faculty Supervision: Todd Cort
Coffee 2016 asks students to consider the coffee supply chain and generate ideas for what can be done to equalize returns across various stakeholders. The case draws a parallel between coffee and wine. Both beverages encourage connoisseurship, but only wine growers reap a premium for their efforts to ensure quality. The case describes the history of coffee production across the world, the rise of the “third wave” of coffee consumption in the developed world, the efforts of the Illy Company to help coffee growers, and the differences between “fair” trade and direct trade. Faculty have found the case provides a wide canvas to discuss supply chain issues, examine marketing practices, and encourage creative solutions to business problems.
#2 - AXA: Creating New Corporate Responsibility Metrics
Faculty Supervision: Todd Cort and David Bach
The case describes AXA’s corporate responsibility (CR) function. The company, a global leader in insurance and asset management, had distinguished itself in CR since formally establishing a CR unit in 2008. As the case opens, AXA’s CR unit is being moved from the marketing function to the strategy group occasioning a thorough review as to how CR should fit into AXA’s operations and strategy. Students are asked to identify CR issues of particular concern to the company, examine how addressing these issues would add value to the company, and then create metrics that would capture a business unit’s success or failure in addressing the concerns.
#3 - IBM Corporate Service Corps
Faculty Supervision: David Bach in cooperation with University of Ghana Business School and EGADE
The case considers IBM’s Corporate Service Corps (CSC), a program that had become the largest pro bono consulting program in the world. The case describes the program’s triple-benefit: leadership training to the brightest young IBMers, brand recognition for IBM in emerging markets, and community improvement in the areas served by IBM’s host organizations. As the program entered its second decade in 2016, students are asked to consider how the program can be improved. The case allows faculty to lead a discussion about training, marketing in emerging economies, and various ways of providing social benefit. The case highlights the synergies as well as trade-offs between pursuing these triple benefits.
#4 - Cadbury: An Ethical Company Struggles to Insure the Integrity of Its Supply Chain
Faculty Supervision: Ira Millstein
The case describes revelations that the production of cocoa in the Côte d’Ivoire involved child slave labor. These stories hit Cadbury especially hard. Cadbury's culture had been deeply rooted in the religious traditions of the company's founders, and the organization had paid close attention to the welfare of its workers and its sourcing practices. The US Congress was considering legislation that would allow chocolate grown on certified plantations to be labeled “slave labor free,” painting the rest of the industry in a bad light. Chocolate producers had asked for time to rectify the situation, but the extension they negotiated was running out. Students are asked whether Cadbury should join with the industry to lobby for more time? What else could Cadbury do to ensure its supply chain was ethically managed?
#5 - 360 State Real Options
Faculty Supervision: Matthew Spiegel
In 2010 developer Bruce Becker (SOM ‘85) completed 360 State Street, a major new construction project in downtown New Haven. Just west of the apartment building, a 6,000-square-foot pocket of land from the original parcel remained undeveloped. Becker had a number of alternatives to consider in regards to the site. He also had no obligation to build. He could bide his time. But Becker worried about losing out on rents should he wait too long. Students are asked under what set of circumstances and at what time would it be most advantageous to proceed?
#6 - Design at Mayo
Faculty Supervision: Rodrigo Canales and William Drentell
The case describes how the Mayo Clinic, one of the most prominent hospitals in the world, engaged designers and built a research institute, the Center for Innovation (CFI), to study the processes of healthcare provision. The case documents the many incremental innovations the designers were able to implement and the way designers learned to interact with physicians and vice-versa.
In 2010 there were questions about how the CFI would achieve its stated aspiration of “transformational change” in the healthcare field. Students are asked what would a major change in health care delivery look like? How should the CFI's impact be measured? Were the center's structure and processes appropriate for transformational change? Faculty have found this a great case to discuss institutional obstacles to innovation, the importance of culture in organizational change efforts, and the differences in types of innovation.
This case is freely available to the public.
#7 - Ant Financial
Faculty Supervision: K. Sudhir in cooperation with Renmin University of China School of Business
In 2015, Ant Financial’s MYbank (an offshoot of Jack Ma’s Alibaba company) was looking to extend services to rural areas in China by providing small loans to farmers. Microloans have always been costly for financial institutions to offer to the unbanked (though important in development) but MYbank believed that fintech innovations such as using the internet to communicate with loan applicants and judge their credit worthiness would make the program sustainable. Students are asked whether MYbank could operate the program at scale? Would its big data and technical analysis provide an accurate measure of credit risk for loans to small customers? Could MYbank rely on its new credit-scoring system to reduce operating costs to make the program sustainable?
#8 - Business Leadership in South Africa’s 1994 Reforms
Faculty Supervision: Ian Shapiro
This case examines the role of business in South Africa's historic transition away from apartheid to popular sovereignty. The case provides a previously untold oral history of this key moment in world history, presenting extensive video interviews with business leaders who spearheaded behind-the-scenes negotiations between the African National Congress and the government. Faculty teaching the case have used the material to push students to consider business’s role in a divided society and ask: What factors led business leaders to act to push the country's future away from isolation toward a "high road" of participating in an increasingly globalized economy? What techniques and narratives did they use to keep the two sides talking and resolve the political impasse? And, if business leadership played an important role in the events in South Africa, could they take a similar role elsewhere?
#9 - Shake Shack IPO
Faculty Supervision: Jake Thomas and Geert Rouwenhorst
From an art project in a New York City park, Shake Shack developed a devoted fan base that greeted new Shake Shack locations with cheers and long lines. When Shake Shack went public on January 30, 2015, investors displayed a similar enthusiasm. Opening day investors bid up the $21 per share offering price by 118% to reach $45.90 at closing bell. By the end of May, investors were paying $92.86 per share. Students are asked if this price represented a realistic valuation of the enterprise and if not, what was Shake Shack truly worth? The case provides extensive information on Shake Shack’s marketing, competitors, operations and financials, allowing instructors to weave a wide variety of factors into a valuation of the company.
#10 - Searching for a Search Fund Structure
Faculty Supervision: AJ Wasserstein
This case considers how young entrepreneurs structure search funds to find businesses to take over. The case describes an MBA student who meets with a number of successful search fund entrepreneurs who have taken alternative routes to raising funds. The case considers the issues of partnering, soliciting funds vs. self-funding a search, and joining an incubator. The case provides a platform from which to discuss the pros and cons of various search fund structures.
40 Most Popular Case Studies of 2017
Click on the case title to learn more about the dilemma. A selection of our most popular cases are available for purchase via our online store .
7 Favorite Business Case Studies to Teach—and Why
Explore more.
- Case Teaching
- Course Materials
FEATURED CASE STUDIES
The Army Crew Team . Emily Michelle David of CEIBS
ATH Technologies . Devin Shanthikumar of Paul Merage School of Business
Fabritek 1992 . Rob Austin of Ivey Business School
Lincoln Electric Co . Karin Schnarr of Wilfrid Laurier University
Pal’s Sudden Service—Scaling an Organizational Model to Drive Growth . Gary Pisano of Harvard Business School
The United States Air Force: ‘Chaos’ in the 99th Reconnaissance Squadron . Francesca Gino of Harvard Business School
Warren E. Buffett, 2015 . Robert F. Bruner of Darden School of Business
To dig into what makes a compelling case study, we asked seven experienced educators who teach with—and many who write—business case studies: “What is your favorite case to teach and why?”
The resulting list of case study favorites ranges in topics from operations management and organizational structure to rebel leaders and whodunnit dramas.
1. The Army Crew Team
Emily Michelle David, Assistant Professor of Management, China Europe International Business School (CEIBS)

“I love teaching The Army Crew Team case because it beautifully demonstrates how a team can be so much less than the sum of its parts.
I deliver the case to executives in a nearby state-of-the-art rowing facility that features rowing machines, professional coaches, and shiny red eight-person shells.
After going through the case, they hear testimonies from former members of Chinese national crew teams before carrying their own boat to the river for a test race.
The rich learning environment helps to vividly underscore one of the case’s core messages: competition can be a double-edged sword if not properly managed.
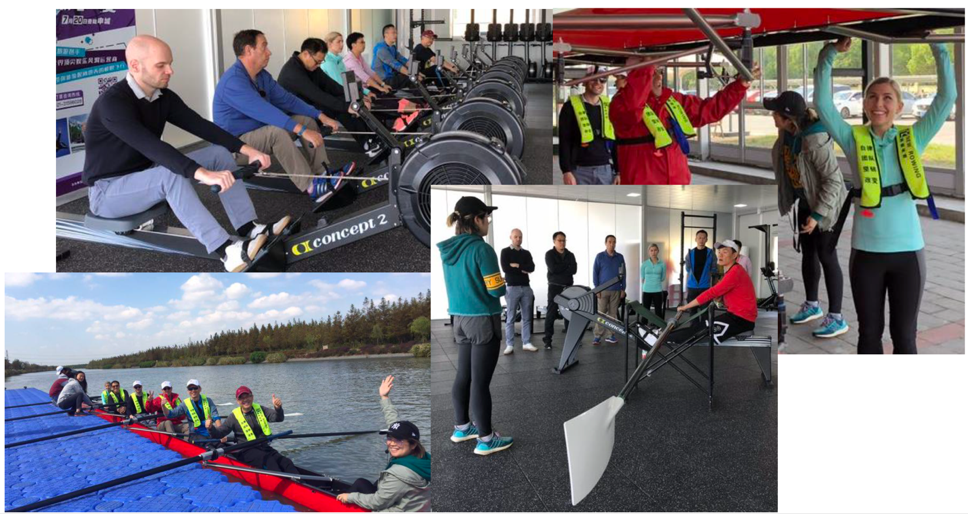

Executives in Emily Michelle David’s organizational behavior class participate in rowing activities at a nearby facility as part of her case delivery.
Despite working for an elite headhunting firm, the executives in my most recent class were surprised to realize how much they’ve allowed their own team-building responsibilities to lapse. In the MBA pre-course, this case often leads to a rich discussion about common traps that newcomers fall into (for example, trying to do too much, too soon), which helps to poise them to both stand out in the MBA as well as prepare them for the lateral team building they will soon engage in.
Finally, I love that the post-script always gets a good laugh and serves as an early lesson that organizational behavior courses will seldom give you foolproof solutions for specific problems but will, instead, arm you with the ability to think through issues more critically.”
2. ATH Technologies
Devin Shanthikumar, Associate Professor of Accounting, Paul Merage School of Business

“As a professor at UC Irvine’s Paul Merage School of Business, and before that at Harvard Business School, I have probably taught over 100 cases. I would like to say that my favorite case is my own, Compass Box Whisky Company . But as fun as that case is, one case beats it: ATH Technologies by Robert Simons and Jennifer Packard.
ATH presents a young entrepreneurial company that is bought by a much larger company. As part of the merger, ATH gets an ‘earn-out’ deal—common among high-tech industries. The company, and the class, must decide what to do to achieve the stretch earn-out goals.
ATH captures a scenario we all want to be in at some point in our careers—being part of a young, exciting, growing organization. And a scenario we all will likely face—having stretch goals that seem almost unreachable.
It forces us, as a class, to really struggle with what to do at each stage.
After we read and discuss the A case, we find out what happens next, and discuss the B case, then the C, then D, and even E. At every stage, we can:
see how our decisions play out,
figure out how to build on our successes, and
address our failures.
The case is exciting, the class discussion is dynamic and energetic, and in the end, we all go home with a memorable ‘ah-ha!’ moment.
I have taught many great cases over my career, but none are quite as fun, memorable, and effective as ATH .”
3. Fabritek 1992
Rob Austin, Professor of Information Systems, Ivey Business School

“This might seem like an odd choice, but my favorite case to teach is an old operations case called Fabritek 1992 .
The latest version of Fabritek 1992 is dated 2009, but it is my understanding that this is a rewrite of a case that is older (probably much older). There is a Fabritek 1969 in the HBP catalog—same basic case, older dates, and numbers. That 1969 version lists no authors, so I suspect the case goes even further back; the 1969 version is, I’m guessing, a rewrite of an even older version.
There are many things I appreciate about the case. Here are a few:
It operates as a learning opportunity at many levels. At first it looks like a not-very-glamorous production job scheduling case. By the end of the case discussion, though, we’re into (operations) strategy and more. It starts out technical, then explodes into much broader relevance. As I tell participants when I’m teaching HBP's Teaching with Cases seminars —where I often use Fabritek as an example—when people first encounter this case, they almost always underestimate it.
It has great characters—especially Arthur Moreno, who looks like a troublemaker, but who, discussion reveals, might just be the smartest guy in the factory. Alums of the Harvard MBA program have told me that they remember Arthur Moreno many years later.
Almost every word in the case is important. It’s only four and a half pages of text and three pages of exhibits. This economy of words and sparsity of style have always seemed like poetry to me. I should note that this super concise, every-word-matters approach is not the ideal we usually aspire to when we write cases. Often, we include extra or superfluous information because part of our teaching objective is to provide practice in separating what matters from what doesn’t in a case. Fabritek takes a different approach, though, which fits it well.
It has a dramatic structure. It unfolds like a detective story, a sort of whodunnit. Something is wrong. There is a quality problem, and we’re not sure who or what is responsible. One person, Arthur Moreno, looks very guilty (probably too obviously guilty), but as we dig into the situation, there are many more possibilities. We spend in-class time analyzing the data (there’s a bit of math, so it covers that base, too) to determine which hypotheses are best supported by the data. And, realistically, the data doesn’t support any of the hypotheses perfectly, just some of them more than others. Also, there’s a plot twist at the end (I won’t reveal it, but here’s a hint: Arthur Moreno isn’t nearly the biggest problem in the final analysis). I have had students tell me the surprising realization at the end of the discussion gives them ‘goosebumps.’
Finally, through the unexpected plot twist, it imparts what I call a ‘wisdom lesson’ to young managers: not to be too sure of themselves and to regard the experiences of others, especially experts out on the factory floor, with great seriousness.”
4. Lincoln Electric Co.
Karin Schnarr, Assistant Professor of Policy, Wilfrid Laurier University

“As a strategy professor, my favorite case to teach is the classic 1975 Harvard case Lincoln Electric Co. by Norman Berg.
I use it to demonstrate to students the theory linkage between strategy and organizational structure, management processes, and leadership behavior.
This case may be an odd choice for a favorite. It occurs decades before my students were born. It is pages longer than we are told students are now willing to read. It is about manufacturing arc welding equipment in Cleveland, Ohio—a hard sell for a Canadian business classroom.
Yet, I have never come across a case that so perfectly illustrates what I want students to learn about how a company can be designed from an organizational perspective to successfully implement its strategy.
And in a time where so much focus continues to be on how to maximize shareholder value, it is refreshing to be able to discuss a publicly-traded company that is successfully pursuing a strategy that provides a fair value to shareholders while distributing value to employees through a large bonus pool, as well as value to customers by continually lowering prices.
However, to make the case resonate with today’s students, I work to make it relevant to the contemporary business environment. I link the case to multimedia clips about Lincoln Electric’s current manufacturing practices, processes, and leadership practices. My students can then see that a model that has been in place for generations is still viable and highly successful, even in our very different competitive situation.”
5. Pal’s Sudden Service—Scaling an Organizational Model to Drive Growth
Gary Pisano, Professor of Business Administration, Harvard Business School

“My favorite case to teach these days is Pal’s Sudden Service—Scaling an Organizational Model to Drive Growth .
I love teaching this case for three reasons:
1. It demonstrates how a company in a super-tough, highly competitive business can do very well by focusing on creating unique operating capabilities. In theory, Pal’s should have no chance against behemoths like McDonalds or Wendy’s—but it thrives because it has built a unique operating system. It’s a great example of a strategic approach to operations in action.
2. The case shows how a strategic approach to human resource and talent development at all levels really matters. This company competes in an industry not known for engaging its front-line workers. The case shows how engaging these workers can really pay off.
3. Finally, Pal’s is really unusual in its approach to growth. Most companies set growth goals (usually arbitrary ones) and then try to figure out how to ‘backfill’ the human resource and talent management gaps. They trust you can always find someone to do the job. Pal’s tackles the growth problem completely the other way around. They rigorously select and train their future managers. Only when they have a manager ready to take on their own store do they open a new one. They pace their growth off their capacity to develop talent. I find this really fascinating and so do the students I teach this case to.”
6. The United States Air Force: ‘Chaos’ in the 99th Reconnaissance Squadron
Francesca Gino, Professor of Business Administration, Harvard Business School

“My favorite case to teach is The United States Air Force: ‘Chaos’ in the 99th Reconnaissance Squadron .
The case surprises students because it is about a leader, known in the unit by the nickname Chaos , who inspired his squadron to be innovative and to change in a culture that is all about not rocking the boat, and where there is a deep sense that rules should simply be followed.
For years, I studied ‘rebels,’ people who do not accept the status quo; rather, they approach work with curiosity and produce positive change in their organizations. Chaos is a rebel leader who got the level of cultural change right. Many of the leaders I’ve met over the years complain about the ‘corporate culture,’ or at least point to clear weaknesses of it; but then they throw their hands up in the air and forget about changing what they can.
Chaos is different—he didn’t go after the ‘Air Force’ culture. That would be like boiling the ocean.
Instead, he focused on his unit of control and command: The 99th squadron. He focused on enabling that group to do what it needed to do within the confines of the bigger Air Force culture. In the process, he inspired everyone on his team to be the best they can be at work.
The case leaves the classroom buzzing and inspired to take action.”
7. Warren E. Buffett, 2015
Robert F. Bruner, Professor of Business Administration, Darden School of Business

“I love teaching Warren E. Buffett, 2015 because it energizes, exercises, and surprises students.
Buffett looms large in the business firmament and therefore attracts anyone who is eager to learn his secrets for successful investing. This generates the kind of energy that helps to break the ice among students and instructors early in a course and to lay the groundwork for good case discussion practices.
Studying Buffett’s approach to investing helps to introduce and exercise important themes that will resonate throughout a course. The case challenges students to define for themselves what it means to create value. The case discussion can easily be tailored for novices or for more advanced students.
Either way, this is not hero worship: The case affords a critical examination of the financial performance of Buffett’s firm, Berkshire Hathaway, and reveals both triumphs and stumbles. Most importantly, students can critique the purported benefits of Buffett’s conglomeration strategy and the sustainability of his investment record as the size of the firm grows very large.
By the end of the class session, students seem surprised with what they have discovered. They buzz over the paradoxes in Buffett’s philosophy and performance record. And they come away with sober respect for Buffett’s acumen and for the challenges of creating value for investors.
Surely, such sobriety is a meta-message for any mastery of finance.”
More Educator Favorites

Emily Michelle David is an assistant professor of management at China Europe International Business School (CEIBS). Her current research focuses on discovering how to make workplaces more welcoming for people of all backgrounds and personality profiles to maximize performance and avoid employee burnout. David’s work has been published in a number of scholarly journals, and she has worked as an in-house researcher at both NASA and the M.D. Anderson Cancer Center.

Devin Shanthikumar is an associate professor and the accounting area coordinator at UCI Paul Merage School of Business. She teaches undergraduate, MBA, and executive-level courses in managerial accounting. Shanthikumar previously served on the faculty at Harvard Business School, where she taught both financial accounting and managerial accounting for MBAs, and wrote cases that are used in accounting courses across the country.

Robert D. Austin is a professor of information systems at Ivey Business School and an affiliated faculty member at Harvard Medical School. He has published widely, authoring nine books, more than 50 cases and notes, three Harvard online products, and two popular massive open online courses (MOOCs) running on the Coursera platform.

Karin Schnarr is an assistant professor of policy and the director of the Bachelor of Business Administration (BBA) program at the Lazaridis School of Business & Economics at Wilfrid Laurier University in Waterloo, Ontario, Canada where she teaches strategic management at the undergraduate, graduate, and executive levels. Schnarr has published several award-winning and best-selling cases and regularly presents at international conferences on case writing and scholarship.

Gary P. Pisano is the Harry E. Figgie, Jr. Professor of Business Administration and senior associate dean of faculty development at Harvard Business School, where he has been on the faculty since 1988. Pisano is an expert in the fields of technology and operations strategy, the management of innovation, and competitive strategy. His research and consulting experience span a range of industries including aerospace, biotechnology, pharmaceuticals, specialty chemicals, health care, nutrition, computers, software, telecommunications, and semiconductors.

Francesca Gino studies how people can have more productive, creative, and fulfilling lives. She is a professor at Harvard Business School and the author, most recently, of Rebel Talent: Why It Pays to Break the Rules at Work and in Life . Gino regularly gives keynote speeches, delivers corporate training programs, and serves in advisory roles for firms and not-for-profit organizations across the globe.

Robert F. Bruner is a university professor at the University of Virginia, distinguished professor of business administration, and dean emeritus of the Darden School of Business. He has also held visiting appointments at Harvard and Columbia universities in the United States, at INSEAD in France, and at IESE in Spain. He is the author, co-author, or editor of more than 20 books on finance, management, and teaching. Currently, he teaches and writes in finance and management.
Related Articles

We use cookies to understand how you use our site and to improve your experience, including personalizing content. Learn More . By continuing to use our site, you accept our use of cookies and revised Privacy Policy .
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
HBS Case Selections
OpenAI: Idealism Meets Capitalism
- Shikhar Ghosh
- Shweta Bagai
Generative AI and the Future of Work
- Christopher Stanton
- Matt Higgins
Copilot(s): Generative AI at Microsoft and GitHub
- Frank Nagle
- Shane Greenstein
- Maria P. Roche
- Nataliya Langburd Wright
- Sarah Mehta
Innovation at Moog Inc.
- Brian J. Hall
- Ashley V. Whillans
- Davis Heniford
- Dominika Randle
- Caroline Witten
Innovation at Google Ads: The Sales Acceleration and Innovation Labs (SAIL) (A)
- Linda A. Hill
- Emily Tedards
Juan Valdez: Innovation in Caffeination
- Michael I. Norton
- Jeremy Dann
UGG Steps into the Metaverse
- Shunyuan Zhang
- Sharon Joseph
- Sunil Gupta
- Julia Kelley
Metaverse Wars
- David B. Yoffie
Roblox: Virtual Commerce in the Metaverse
- Ayelet Israeli
- Nicole Tempest Keller
Timnit Gebru: "SILENCED No More" on AI Bias and The Harms of Large Language Models
- Tsedal Neeley
- Stefani Ruper
Hugging Face: Serving AI on a Platform
- Kerry Herman
- Sarah Gulick
SmartOne: Building an AI Data Business
- Karim R. Lakhani
- Pippa Tubman Armerding
- Gamze Yucaoglu
- Fares Khrais
Honeywell and the Great Recession (A)
- Sandra J. Sucher
- Susan Winterberg
Target: Responding to the Recession
- Ranjay Gulati
- Catherine Ross
- Richard S. Ruback
- Royce Yudkoff
Hometown Foods: Changing Price Amid Inflation
- Julian De Freitas
- Jeremy Yang
- Das Narayandas
Elon Musk's Big Bets
- Eric Baldwin
Elon Musk: Balancing Purpose and Risk
Tesla's ceo compensation plan.
- Krishna G. Palepu
- John R. Wells
- Gabriel Ellsworth
China Rapid Finance: The Collapse of China's P2P Lending Industry
- William C. Kirby
- Bonnie Yining Cao
- John P. McHugh
Forbidden City: Launching a Craft Beer in China
- Christopher A. Bartlett
- Carole Carlson
Booking.com
- Stefan Thomke
- Daniela Beyersdorfer
Innovation at Uber: The Launch of Express POOL
- Chiara Farronato
- Alan MacCormack
Racial Discrimination on Airbnb (A)
- Michael Luca
- Scott Stern
- Hyunjin Kim
Unilever's Response to the Future of Work
- William R. Kerr
- Emilie Billaud
- Mette Fuglsang Hjortshoej
AT&T, Retraining, and the Workforce of Tomorrow
- Joseph B. Fuller
- Carl Kreitzberg
Leading Change in Talent at L'Oreal
- Lakshmi Ramarajan
- Vincent Dessain
- Emer Moloney
- William W. George
- Andrew N. McLean
Eve Hall: The African American Investment Fund in Milwaukee
- Steven S. Rogers
- Alterrell Mills
United Housing - Otis Gates
- Mercer Cook
The Home Depot: Leadership in Crisis Management
- Herman B. Leonard
- Marc J. Epstein
- Melissa Tritter
The Great East Japan Earthquake (B): Fast Retailing Group's Response
- Hirotaka Takeuchi
- Kenichi Nonomura
- Dena Neuenschwander
- Meghan Ricci
- Kate Schoch
- Sergey Vartanov
Insurer of Last Resort?: The Federal Financial Response to September 11
- David A. Moss
- Sarah Brennan
Under Armour
- Rory McDonald
- Clayton M. Christensen
- Daniel West
- Jonathan E. Palmer
- Tonia Junker
Hunley, Inc.: Casting for Growth
- John A. Quelch
- James T. Kindley
Bitfury: Blockchain for Government
- Mitchell B. Weiss
- Elena Corsi
Deutsche Bank: Pursuing Blockchain Opportunities (A)
- Lynda M. Applegate
- Christoph Muller-Bloch
Maersk: Betting on Blockchain
- Scott Johnson
Yum! Brands
- Jordan Siegel
- Christopher Poliquin
Bharti Airtel in Africa
- Tanya Bijlani
Li & Fung 2012
- F. Warren McFarlan
- Michael Shih-ta Chen
- Keith Chi-ho Wong
Sony and the JK Wedding Dance
- John Deighton
- Leora Kornfeld
United Breaks Guitars
David dao on united airlines.
- Benjamin Edelman
- Jenny Sanford
Marketing Reading: Digital Marketing
- Joseph Davin
Social Strategy at Nike
- Mikolaj Jan Piskorski
- Ryan Johnson
The Tate's Digital Transformation
Social strategy at american express, mellon financial and the bank of new york.
- Carliss Y. Baldwin
- Ryan D. Taliaferro
The Walt Disney Company and Pixar, Inc.: To Acquire or Not to Acquire?
- Juan Alcacer
- David J. Collis
Dow's Bid for Rohm and Haas
- Benjamin C. Esty
Finance Reading: The Mergers and Acquisitions Process
- John Coates
Apple: Privacy vs. Safety? (A)
- Henry W. McGee
- Nien-he Hsieh
- Sarah McAra
Sidewalk Labs: Privacy in a City Built from the Internet Up
- Leslie K. John
Data Breach at Equifax
- Suraj Srinivasan
- Quinn Pitcher
- Jonah S. Goldberg
Apple's Core
- Noam Wasserman
Design Thinking and Innovation at Apple
- Barbara Feinberg
Apple Inc. in 2012
- Penelope Rossano
Iz-Lynn Chan at Far East Organization (Abridged)
- Anthony J. Mayo
- Dana M. Teppert
Barbara Norris: Leading Change in the General Surgery Unit
- Boris Groysberg
- Nitin Nohria
- Deborah Bell
Adobe Systems: Working Towards a "Suite" Release (A)
- David A. Thomas
- Lauren Barley
Home Nursing of North Carolina
Castronics, llc, gemini investors, angie's list: ratings pioneer turns 20.
- Robert J. Dolan
Basecamp: Pricing
- Frank V. Cespedes
- Robb Fitzsimmons
J.C. Penney's "Fair and Square" Pricing Strategy
J.c. penney's 'fair and square' strategy (c): back to the future.
- Jose B. Alvarez
Osaro: Picking the best path
- James Palano
- Bastiane Huang
HubSpot and Motion AI: Chatbot-Enabled CRM
- Thomas Steenburgh
GROW: Using Artificial Intelligence to Screen Human Intelligence
- Ethan S. Bernstein
- Paul D. McKinnon
- Paul Yarabe
Arup: Building the Water Cube
- Robert G. Eccles
- Amy C. Edmondson
- Dilyana Karadzhova
(Re)Building a Global Team: Tariq Khan at Tek
Managing a global team: greg james at sun microsystems, inc. (a).
- Thomas J. DeLong
Organizational Behavior Reading: Leading Global Teams
Ron ventura at mitchell memorial hospital.
- Heide Abelli
Anthony Starks at InSiL Therapeutics (A)
- Gary P. Pisano
- Vicki L. Sato
Wolfgang Keller at Konigsbrau-TAK (A)
- John J. Gabarro
Midland Energy Resources, Inc.: Cost of Capital
- Timothy A. Luehrman
- Joel L. Heilprin
Globalizing the Cost of Capital and Capital Budgeting at AES
- Mihir A. Desai
- Doug Schillinger
Cost of Capital at Ameritrade
- Mark Mitchell
- Erik Stafford
Finance Reading: Cost of Capital
David Neeleman: Flight Path of a Servant Leader (A)
- Matthew D. Breitfelder
Coach Hurley at St. Anthony High School
- Scott A. Snook
- Bradley C. Lawrence
Shapiro Global
- Michael Brookshire
- Monica Haugen
- Michelle Kravetz
- Sarah Sommer
Kathryn McNeil (A)
- Joseph L. Badaracco Jr.
- Jerry Useem
Carol Fishman Cohen: Professional Career Reentry (A)
- Myra M. Hart
- Robin J. Ely
- Susan Wojewoda
Alex Montana at ESH Manufacturing Co.
- Michael Kernish
Michelle Levene (A)
- Tiziana Casciaro
- Victoria W. Winston
John and Andrea Rice: Entrepreneurship and Life
- Howard H. Stevenson
- Janet Kraus
- Shirley M. Spence
Partner Center
Case Studies in Business, Management, and Organizations
Case studies - full text as part of library subscription.
- Sage Business Cases This link opens in a new window SAGE Business Cases is a digital collection of business cases tailored to library needs – providing faculty, students and researchers with unlimited access to more than 4,850 authoritative cases from over 120 countries. SAGE curates interdisciplinary cases on in-demand subjects such as entrepreneurship, accounting, healthcare management, leadership, social enterprise, and more. Publishing partners include Yale University, Kellogg School of Management, Society of Human Resource Management, and more. For Instructors: additional teaching note material is available; please contact the library for more information on how to access this content.
- HS Talks Business & Management Collection This link opens in a new window Specially commissioned talks from leading experts in industry, commerce, the professions and academia. The collection also includes 20 peer reviewed vocational journals.
Case Studies - summary collections available at low/no cost
- Business Source Premier --Abstracts for Harvard Business School Case Studies from 1942 to the present are available as part of Business Source Premier. Full text of the case is not available.
- Harvard Business School Case Studies The case method forms the basis of learning at Harvard Business School. It is a method designed to provide an "immersion" experience, challenging students by bringing them as close as possible to the business situations of the real world. Harvard Business School Publishing makes these cases and related materials available to improve and enhance business education around the world. They are available to purchase online for around $7.00.
- Case Depositories Page at GlobalEdge This section of the GlobalEdge database provides information about publishers or depositories of cases. Some sites list cases by that institution. Other sites act as clearinghouses and feature cases from a variety of sources.
- LearningEdge The case studies available on LearningEdge are teaching case studies, narratives that facilitate class discussion about a particular business or management issue.
- Darden Case Collection The Darden case collection provides numerous business and management case studies.
- European Case Clearing House The Clearing House distributes the European Collection from the Babson College Office including case collections of IMD, INSEAD, IESE, London Business School, Cranfield School of Management, Babson College and cases from independent authors. Cases cost about $3.50.
- Kellogg School of Management Case Study Abstracts The Kellogg School of Management is making available to academic practitioners and corporate trainers selected cases and teaching materials, developed by Kellogg faculty and taught in the Kellogg classroom. Information on how to order the case studies is included on the web site.
- Stanford Graduate School of Business Case Studies Abstracts This database contains abstracts and ordering information for case studies written and published by the Stanford Graduate School of Business. You may search by authors name, title, keyword, etc. Most cases in this collection are distributed by Harvard Business School Publishing and you will find a link to the HBSP site to place your order. Contact them for availability of other cases.
- Case Research Journal Available in Print: Case research journal. Published: [United States] : The North American Case Research Association (NACRA), 1980--present. Availability: TC Wilson Periodicals --Basement The Index to the cases in the print journal is available at the link shown above. This site from the North American Case Research Association also shows how to purchase the cases available in the journal.
- NASPAA Publicases Publicases is an online repository and marketplace developed by NASPAA (Network of Schools of Public Policy, Affairs, and Administration) as platform connecting students and faculty in public affairs schools around the world with simulations, case studies, data, and other experiential learning opportunities. Currently, case content is developed by the Evans School and the Humphrey School and is available without charge to member schools.
Writing Case Studies - teaching and research
Find Case Studies in Books by using MNCAT :
- Search for a subject term, such as marketing, and add the phrase: case studies. See below for examples:
- Books on the case method: Search our MNCAT catalog using the subject term: Case method.
Business growth
Marketing tips
16 case study examples (+ 3 templates to make your own)
I like to think of case studies as a business's version of a resume. It highlights what the business can do, lends credibility to its offer, and contains only the positive bullet points that paint it in the best light possible.
Imagine if the guy running your favorite taco truck followed you home so that he could "really dig into how that burrito changed your life." I see the value in the practice. People naturally prefer a tried-and-true burrito just as they prefer tried-and-true products or services.
To help you showcase your success and flesh out your burrito questionnaire, I've put together some case study examples and key takeaways.
What is a case study?
A case study is an in-depth analysis of how your business, product, or service has helped past clients. It can be a document, a webpage, or a slide deck that showcases measurable, real-life results.
For example, if you're a SaaS company, you can analyze your customers' results after a few months of using your product to measure its effectiveness. You can then turn this analysis into a case study that further proves to potential customers what your product can do and how it can help them overcome their challenges.
It changes the narrative from "I promise that we can do X and Y for you" to "Here's what we've done for businesses like yours, and we can do it for you, too."
16 case study examples
While most case studies follow the same structure, quite a few try to break the mold and create something unique. Some businesses lean heavily on design and presentation, while others pursue a detailed, stat-oriented approach. Some businesses try to mix both.
There's no set formula to follow, but I've found that the best case studies utilize impactful design to engage readers and leverage statistics and case details to drive the point home. A case study typically highlights the companies, the challenges, the solution, and the results. The examples below will help inspire you to do it, too.
1. .css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class]{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;cursor:pointer;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class]{all:unset;box-sizing:border-box;-webkit-text-decoration:underline;text-decoration:underline;cursor:pointer;-webkit-transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;transition:all 300ms ease-in-out;outline-offset:1px;-webkit-text-fill-color:currentColor;outline:1px solid transparent;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']{color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='ocean']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='white']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']{color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']:hover{color:#2b2358;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='primary']:focus{color:#3d4592;outline-color:#3d4592;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']{color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']:hover{color:#a8a5a0;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-color='secondary']:focus{color:#fffdf9;outline-color:#fffdf9;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='inherit']{font-weight:inherit;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='normal']{font-weight:400;}.css-1l9i3yq-Link[class][class][class][class][class][data-weight='bold']{font-weight:700;} Volcanica Coffee and AdRoll

People love a good farm-to-table coffee story, and boy am I one of them. But I've shared this case study with you for more reasons than my love of coffee. I enjoyed this study because it was written as though it was a letter.
In this case study, the founder of Volcanica Coffee talks about the journey from founding the company to personally struggling with learning and applying digital marketing to finding and enlisting AdRoll's services.
It felt more authentic, less about AdRoll showcasing their worth and more like a testimonial from a grateful and appreciative client. After the story, the case study wraps up with successes, milestones, and achievements. Note that quite a few percentages are prominently displayed at the top, providing supporting evidence that backs up an inspiring story.
Takeaway: Highlight your goals and measurable results to draw the reader in and provide concise, easily digestible information.
2. Taylor Guitars and Airtable

This Airtable case study on Taylor Guitars comes as close as one can to an optimal structure. It features a video that represents the artistic nature of the client, highlighting key achievements and dissecting each element of Airtable's influence.
It also supplements each section with a testimonial or quote from the client, using their insights as a catalyst for the case study's narrative. For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail.
Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail.
3. EndeavourX and Figma

My favorite part of Figma's case study is highlighting why EndeavourX chose its solution. You'll notice an entire section on what Figma does for teams and then specifically for EndeavourX.
It also places a heavy emphasis on numbers and stats. The study, as brief as it is, still manages to pack in a lot of compelling statistics about what's possible with Figma.
Takeaway: Showcase the "how" and "why" of your product's differentiators and how they benefit your customers.
4. ActiveCampaign and Zapier

Zapier's case study leans heavily on design, using graphics to present statistics and goals in a manner that not only remains consistent with the branding but also actively pushes it forward, drawing users' eyes to the information most important to them.
The graphics, emphasis on branding elements, and cause/effect style tell the story without requiring long, drawn-out copy that risks boring readers. Instead, the cause and effect are concisely portrayed alongside the client company's information for a brief and easily scannable case study.
Takeaway: Lean on design to call attention to the most important elements of your case study, and make sure it stays consistent with your branding.
5. Ironclad and OpenAI
In true OpenAI fashion, this case study is a block of text. There's a distinct lack of imagery, but the study features a narrated video walking readers through the product.
The lack of imagery and color may not be the most inviting, but utilizing video format is commendable. It helps thoroughly communicate how OpenAI supported Ironclad in a way that allows the user to sit back, relax, listen, and be impressed.
Takeaway: Get creative with the media you implement in your case study. Videos can be a very powerful addition when a case study requires more detailed storytelling.
6. Shopify and GitHub

GitHub's case study on Shopify is a light read. It addresses client pain points and discusses the different aspects its product considers and improves for clients. It touches on workflow issues, internal systems, automation, and security. It does a great job of representing what one company can do with GitHub.
To drive the point home, the case study features colorful quote callouts from the Shopify team, sharing their insights and perspectives on the partnership, the key issues, and how they were addressed.
Takeaway: Leverage quotes to boost the authoritativeness and trustworthiness of your case study.
7 . Audible and Contentful

Contentful's case study on Audible features almost every element a case study should. It includes not one but two videos and clearly outlines the challenge, solution, and outcome before diving deeper into what Contentful did for Audible. The language is simple, and the writing is heavy with quotes and personal insights.
This case study is a uniquely original experience. The fact that the companies in question are perhaps two of the most creative brands out there may be the reason. I expected nothing short of a detailed analysis, a compelling story, and video content.
Takeaway: Inject some brand voice into the case study, and create assets that tell the story for you.
8 . Zoom and Asana
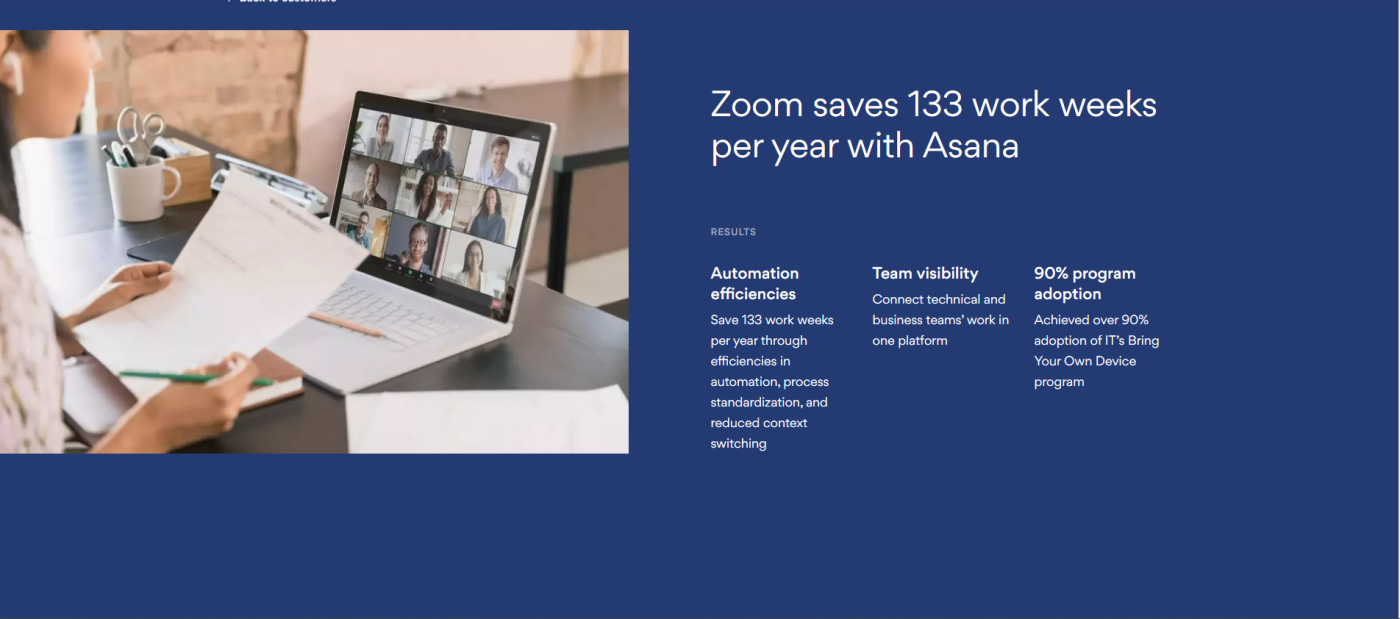
Asana's case study on Zoom is longer than the average piece and features detailed data on Zoom's growth since 2020. Instead of relying on imagery and graphics, it features several quotes and testimonials.
It's designed to be direct, informative, and promotional. At some point, the case study reads more like a feature list. There were a few sections that felt a tad too promotional for my liking, but to each their own burrito.
Takeaway: Maintain a balance between promotional and informative. You want to showcase the high-level goals your product helped achieve without losing the reader.
9 . Hickies and Mailchimp

I've always been a fan of Mailchimp's comic-like branding, and this case study does an excellent job of sticking to their tradition of making information easy to understand, casual, and inviting.
It features a short video that briefly covers Hickies as a company and Mailchimp's efforts to serve its needs for customer relationships and education processes. Overall, this case study is a concise overview of the partnership that manages to convey success data and tell a story at the same time. What sets it apart is that it does so in a uniquely colorful and brand-consistent manner.
Takeaway: Be concise to provide as much value in as little text as possible.
10. NVIDIA and Workday
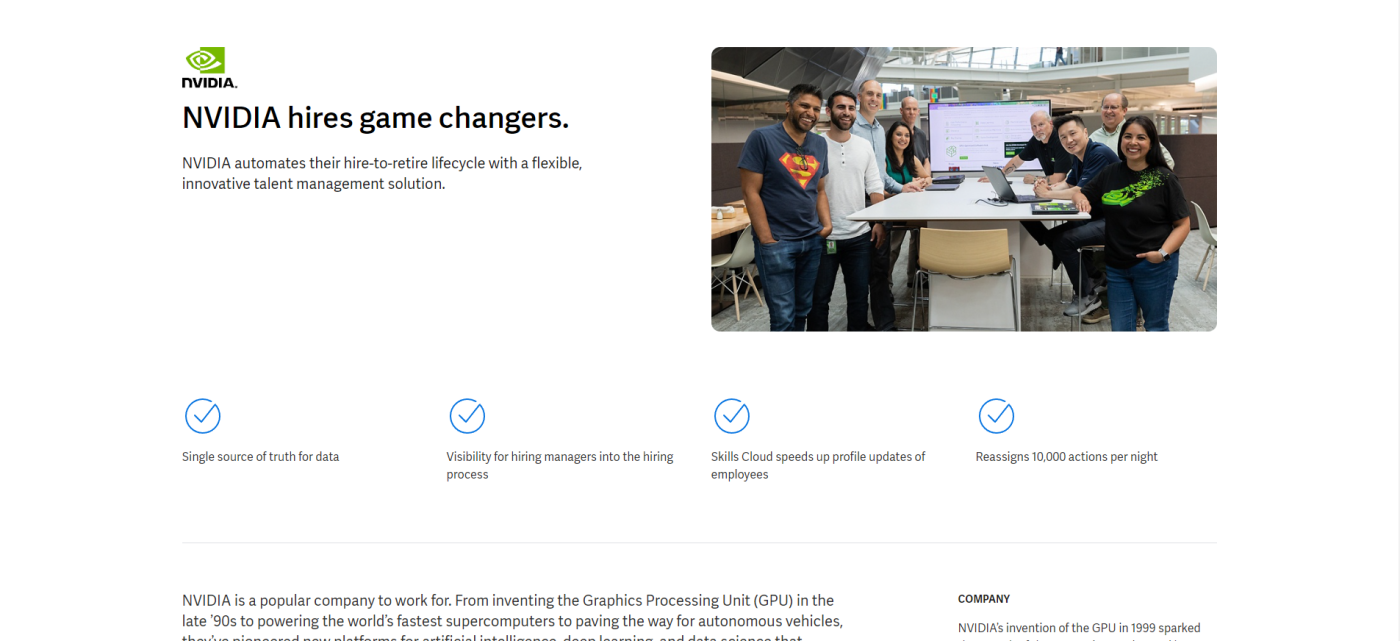
The gaming industry is notoriously difficult to recruit for, as it requires a very specific set of skills and experience. This case study focuses on how Workday was able to help fill that recruitment gap for NVIDIA, one of the biggest names in the gaming world.
Though it doesn't feature videos or graphics, this case study stood out to me in how it structures information like "key products used" to give readers insight into which tools helped achieve these results.
Takeaway: If your company offers multiple products or services, outline exactly which ones were involved in your case study, so readers can assess each tool.
11. KFC and Contentful
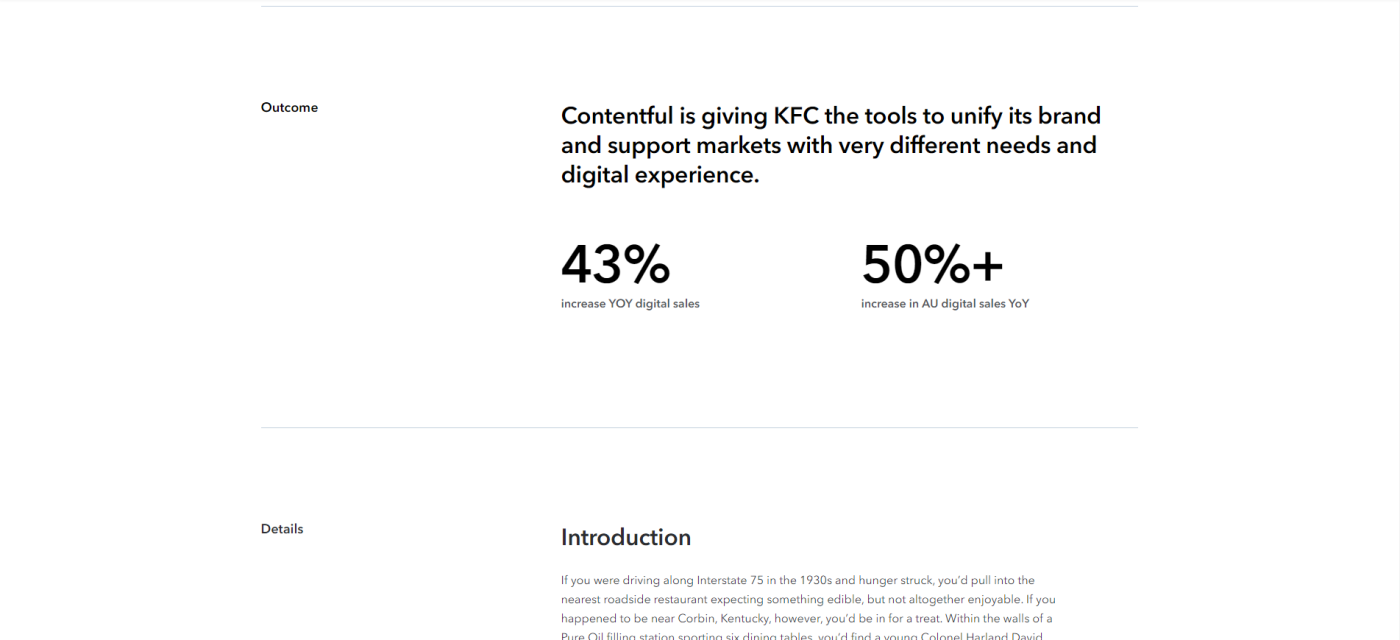
I'm personally not a big KFC fan, but that's only because I refuse to eat out of a bucket. My aversion to the bucket format aside, Contentful follows its consistent case study format in this one, outlining challenges, solutions, and outcomes before diving into the nitty-gritty details of the project.
Say what you will about KFC, but their primary product (chicken) does present a unique opportunity for wordplay like "Continuing to march to the beat of a digital-first drum(stick)" or "Delivering deep-fried goodness to every channel."
Takeaway: Inject humor into your case study if there's room for it and if it fits your brand.
12. Intuit and Twilio

Twilio does an excellent job of delivering achievements at the very beginning of the case study and going into detail in this two-minute read. While there aren't many graphics, the way quotes from the Intuit team are implemented adds a certain flair to the study and breaks up the sections nicely.
It's simple, concise, and manages to fit a lot of information in easily digestible sections.
Takeaway: Make sure each section is long enough to inform but brief enough to avoid boring readers. Break down information for each section, and don't go into so much detail that you lose the reader halfway through.
13. Spotify and Salesforce

Salesforce created a video that accurately summarizes the key points of the case study. Beyond that, the page itself is very light on content, and sections are as short as one paragraph.
I especially like how information is broken down into "What you need to know," "Why it matters," and "What the difference looks like." I'm not ashamed of being spoon-fed information. When it's structured so well and so simply, it makes for an entertaining read.
Takeaway: Invest in videos that capture and promote your partnership with your case study subject. Video content plays a promotional role that extends beyond the case study in social media and marketing initiatives .
14. Benchling and Airtable

Benchling is an impressive entity in its own right. Biotech R&D and health care nuances go right over my head. But the research and digging I've been doing in the name of these burritos (case studies) revealed that these products are immensely complex.
And that's precisely why this case study deserves a read—it succeeds at explaining a complex project that readers outside the industry wouldn't know much about.
Takeaway: Simplify complex information, and walk readers through the company's operations and how your business helped streamline them.
15. Chipotle and Hubble

The concision of this case study is refreshing. It features two sections—the challenge and the solution—all in 316 words. This goes to show that your case study doesn't necessarily need to be a four-figure investment with video shoots and studio time.
Sometimes, the message is simple and short enough to convey in a handful of paragraphs.
Takeaway: Consider what you should include instead of what you can include. Assess the time, resources, and effort you're able and willing to invest in a case study, and choose which elements you want to include from there.
16. Hudl and Zapier
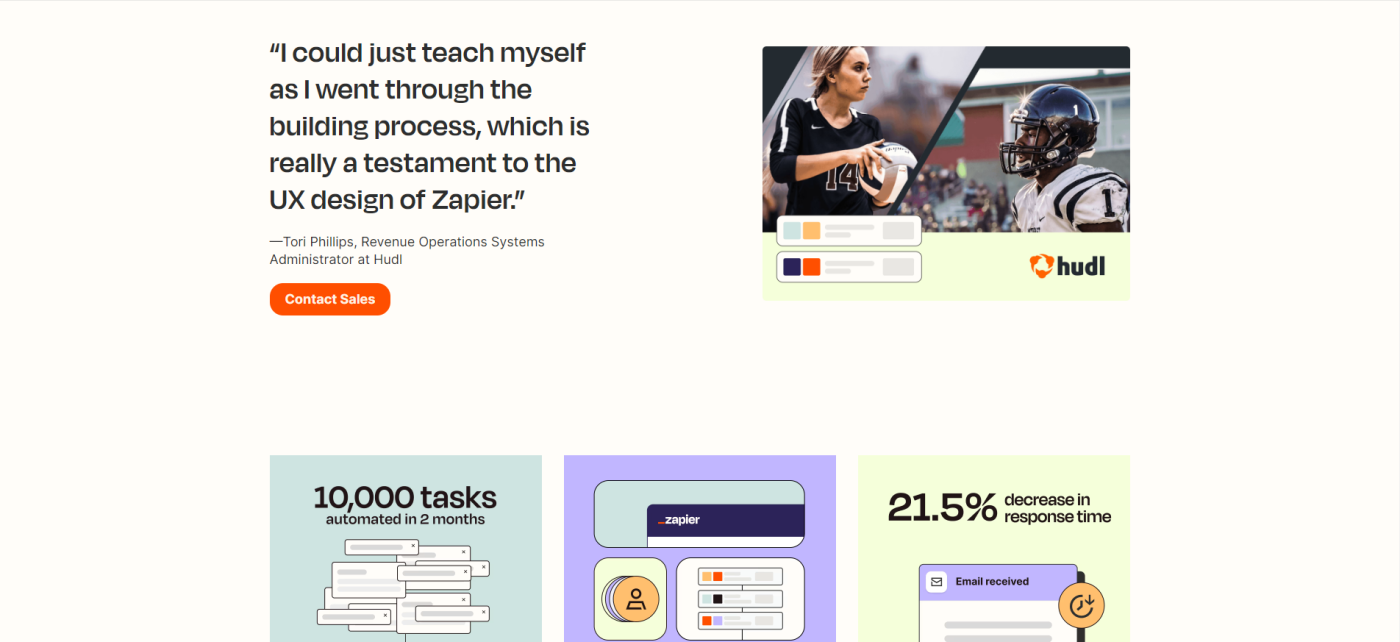
I may be biased, but I'm a big fan of seeing metrics and achievements represented in branded graphics. It can be a jarring experience to navigate a website, then visit a case study page and feel as though you've gone to a completely different website.
The Zapier format provides nuggets of high-level insights, milestones, and achievements, as well as the challenge, solution, and results. My favorite part of this case study is how it's supplemented with a blog post detailing how Hudl uses Zapier automation to build a seamless user experience.
The case study is essentially the summary, and the blog article is the detailed analysis that provides context beyond X achievement or Y goal.
Takeaway: Keep your case study concise and informative. Create other resources to provide context under your blog, media or press, and product pages.
3 case study templates
Now that you've had your fill of case studies (if that's possible), I've got just what you need: an infinite number of case studies, which you can create yourself with these case study templates.
Case study template 1

If you've got a quick hit of stats you want to show off, try this template. The opening section gives space for a short summary and three visually appealing stats you can highlight, followed by a headline and body where you can break the case study down more thoroughly. This one's pretty simple, with only sections for solutions and results, but you can easily continue the formatting to add more sections as needed.
Case study template 2

For a case study template with a little more detail, use this one. Opening with a striking cover page for a quick overview, this one goes on to include context, stakeholders, challenges, multiple quote callouts, and quick-hit stats.
Case study template 3

Whether you want a little structural variation or just like a nice dark green, this template has similar components to the last template but is designed to help tell a story. Move from the client overview through a description of your company before getting to the details of how you fixed said company's problems.
Tips for writing a case study
Examples are all well and good, but you don't learn how to make a burrito just by watching tutorials on YouTube without knowing what any of the ingredients are. You could , but it probably wouldn't be all that good.
Writing a good case study comes down to a mix of creativity, branding, and the capacity to invest in the project. With those details in mind, here are some case study tips to follow:
Have an objective: Define your objective by identifying the challenge, solution, and results. Assess your work with the client and focus on the most prominent wins. You're speaking to multiple businesses and industries through the case study, so make sure you know what you want to say to them.
Focus on persuasive data: Growth percentages and measurable results are your best friends. Extract your most compelling data and highlight it in your case study.
Use eye-grabbing graphics: Branded design goes a long way in accurately representing your brand and retaining readers as they review the study. Leverage unique and eye-catching graphics to keep readers engaged.
Simplify data presentation: Some industries are more complex than others, and sometimes, data can be difficult to understand at a glance. Make sure you present your data in the simplest way possible. Make it concise, informative, and easy to understand.

Use automation to drive results for your case study
A case study example is a source of inspiration you can leverage to determine how to best position your brand's work. Find your unique angle, and refine it over time to help your business stand out. Ask anyone: the best burrito in town doesn't just appear at the number one spot. They find their angle (usually the house sauce) and leverage it to stand out.
In fact, with the right technology, it can be refined to work better . Explore how Zapier's automation features can help drive results for your case study by making your case study a part of a developed workflow that creates a user journey through your website, your case studies, and into the pipeline.
Case study FAQ
Got your case study template? Great—it's time to gather the team for an awkward semi-vague data collection task. While you do that, here are some case study quick answers for you to skim through while you contemplate what to call your team meeting.
What is an example of a case study?
An example of a case study is when a software company analyzes its results from a client project and creates a webpage, presentation, or document that focuses on high-level results, challenges, and solutions in an attempt to showcase effectiveness and promote the software.
How do you write a case study?
To write a good case study, you should have an objective, identify persuasive and compelling data, leverage graphics, and simplify data. Case studies typically include an analysis of the challenge, solution, and results of the partnership.
What is the format of a case study?
While case studies don't have a set format, they're often portrayed as reports or essays that inform readers about the partnership and its results.
Related reading:
How Hudl uses automation to create a seamless user experience
How to make your case studies high-stakes—and why it matters
How experts write case studies that convert, not bore
Get productivity tips delivered straight to your inbox
We’ll email you 1-3 times per week—and never share your information.

Hachem Ramki
Hachem is a writer and digital marketer from Montreal. After graduating with a degree in English, Hachem spent seven years traveling around the world before moving to Canada. When he's not writing, he enjoys Basketball, Dungeons and Dragons, and playing music for friends and family.
- Content marketing
Related articles

14 types of email marketing to experiment with
14 types of email marketing to experiment...
8 business anniversary marketing ideas and examples worth celebrating
8 business anniversary marketing ideas and...
A guide to verticalization: What it is, when to try it, and how to get started
A guide to verticalization: What it is, when...

12 Facebook ad copy examples to learn from
Improve your productivity automatically. Use Zapier to get your apps working together.


- Onsite training
3,000,000+ delegates
15,000+ clients
1,000+ locations
- KnowledgePass
- Log a ticket
01344203999 Available 24/7
Business Management Case Study: A Complete Breakdown
Gain a comprehensive understanding of the "Business Management Case Study" as we break down the concept from start to finish. Discover the incredible journeys of companies like Apple Inc., Tesla and Netflix as they navigate innovation, global expansion, and transformation. This detailed analysis will provide insights into the dynamic world of business management.

Exclusive 40% OFF
Training Outcomes Within Your Budget!
We ensure quality, budget-alignment, and timely delivery by our expert instructors.
Share this Resource
- PMP® Certification Training Course
- Introduction to Management
- Introduction to Managing People
- CAPM® Certification Training Course
- Business Management Training Course

Case studies play a pivotal role in understanding real-world challenges, strategies, and outcomes in the ever-evolving field of Business Management. This blog dives into the intricacies of a compelling Business Management Case Study, dissecting its components to extract valuable insights for aspiring managers, entrepreneurs, and students alike. Learn the study behind some of the most significant Business Management Case Studies & how an online business degree can help you learn more in this article.
Table of Contents
1) What is Business Management?
2) Case Studies in Business Management
a) Apple Inc. Innovation
b) Tesla’s EV revolution
c) Amazon retailer to e-commerce giant
d) McDonald’s global expansion
e) Netflix’s transformation
3) Conclusion
What is Business Management?
Business Management refers to the set of activities, strategies, and practices employed to oversee and coordinate an organisation's operations, resources, and personnel to achieve specific goals and objectives. It encompasses a wide range of responsibilities to ensure an organisation's efficient and effective functioning across various functional areas.
Try our Business Case Training Course today and start your career!
Case Studies in Business Management
Here are some of the notable case studies in the field of Business Management that have garnered attention due to their complexity, innovative strategies, and significant impact on their respective industries:
Apple Inc. innovation
a) Background: Apple Inc. is a global technology giant noted for its innovative products and design-driven approach. In the early 2000s, Apple faced intense competition and declining market share. The company needed to reinvent itself to remain relevant and competitive.
b) Problem statement: Apple's challenge was revitalising its product line and regaining market leadership while navigating a rapidly changing technological world.
c) Analysis of the situation: The Case Study dives into Apple's design thinking and customer-centric innovation to develop products that seamlessly blend form and function. The company's focus on user experience, ecosystem integration, and attention to detail set it apart from its competitors.
d) Proposed solutions: Apple's strategy involved launching breakthrough products like the iPod, iPhone, and iPad that redefined their respective markets. The company also invested heavily in creating a robust ecosystem through iTunes and the App Store.
e) Chosen strategy: Apple's commitment to user-centred design and innovation became the cornerstone of its success. The strategy encompassed cutting-edge technology, minimalist design, and exceptional user experience.
f) Implementation process: Apple's implementation involved rigorous research and development, collaboration among various teams, and meticulous attention to detail. The company also established a loyal customer base through iconic product launches and marketing campaigns.
g) Results and outcomes: Apple's strategy paid off immensely, leading to a resurgence in its market share, revenue, and brand value. The company's products became cultural touchstones, and its ecosystem approach set new standards for the technology industry.
Tesla’s EV revolution
a) Background: Tesla, led by Elon Musk, aimed to disrupt the traditional automotive industry by introducing electric vehicles (EVs) that combined sustainability, performance, and cutting-edge technology.
b) Problem statement: Tesla faced challenges related to the production, scalability, and market acceptance of electric vehicles in an industry dominated by internal combustion engine vehicles.
c) Analysis of the situation: This Case Study examines Tesla's unique approach, which combines innovation in electric powertrains, battery technology, and software. The company also adopted a direct-to-consumer sales model, bypassing traditional dealership networks.
d) Proposed solutions: Tesla's solutions included building a network of Supercharger stations, developing advanced autonomous driving technology, and leveraging over-the-air software updates to improve vehicle performance and features.
e) Chosen strategy: Tesla focused on high-quality engineering, creating a luxury brand image for EVs, and promoting a community of passionate supporters. The company also bet on long-term sustainability and energy innovation beyond just manufacturing cars.
f) Implementation process: Tesla faced production challenges, supply chain issues, and scepticism from traditional automakers. The company's determination to continuously refine its vehicles and technology resulted in incremental improvements and increased consumer interest.
g) Results and outcomes: Tesla's innovative approach catapulted it into the forefront of the EV market. The Model S, Model 3, Model X, and Model Y gained popularity for their performance, range, and technology. Tesla's market capitalisation surged, and the company played a significant part in changing the perception of electric vehicles.
Amazon retailer to e-commerce giant
a) Background: Amazon started as an online bookstore in the 1990s and quickly expanded its offerings to become the world's largest online retailer. However, its journey was riddled with challenges and risks.
b) Problem statement: Amazon faced difficulties in achieving profitability due to its aggressive expansion, heavy investments, and price competition. The company needed to find a way to sustain its growth and solidify its position in the e-commerce market.
c) Analysis of the situation: This Case Study explores Amazon's unique business model, which prioritises customer satisfaction, convenience, and diversification. The company continuously experimented with new ideas, services, and technologies.
d) Proposed solutions: Amazon's solutions included the introduction of Amazon Prime, the Kindle e-reader, and the development of its third-party seller marketplace. These initiatives aimed to enhance customer loyalty, expand product offerings, and increase revenue streams.
e) Chosen strategy: Amazon's strategy revolved around long-term thinking, customer obsession, and a willingness to invest heavily in innovation and infrastructure, even at the expense of short-term profits.
f) Implementation process: Amazon's implementation involved building a vast network of fulfilment centres, investing in advanced technology for logistics and supply chain management, and expanding its services beyond e-commerce into cloud computing (Amazon Web Services) and entertainment (Amazon Prime Video).
g) Results and outcomes: Amazon's strategy paid off as it transformed from an online bookstore to an e-commerce behemoth. The company not only achieved profitability but also diversified into various sectors, making Jeff Bezos the richest person in the world for a time.
McDonald’s global expansion
a) Background: McDonald's is one of the world's largest and most recognisable fast-food chains. The Case Study focuses on the company's global expansion strategy and challenges in adapting to diverse cultural preferences and market conditions.
b) Problem statement: McDonald's challenge was maintaining its brand identity while tailoring its menu offerings and marketing strategies to suit different countries' preferences and cultural norms.
c) Analysis: The Case Study analyses McDonald's localisation efforts, menu adaptations, and marketing campaigns in different countries. It explores how the company balances standardisation with customisation to appeal to local tastes.
d) Solutions and outcomes: McDonald's successfully combines global branding with localized strategies, resulting in sustained growth and customer loyalty in various markets. The Case Study demonstrates the importance of understanding cultural nuances in international business.
Netflix’s evolution
a) Background: Netflix started as a DVD rental-by-mail service and became a leading global streaming platform. The Case Study explores Netflix's strategic evolution, content production, and influence on the entertainment industry.
b) Problem statement: Netflix's challenge was transitioning from a traditional DVD rental business to a digital streaming service while competing with established cable networks and other streaming platforms.
c) Analysis: The Case Study analyses Netflix's shift to online streaming, its investment in original content production, and its use of data analytics to personalise user experiences and content recommendations.
d) Solutions and outcomes: Netflix's strategic pivot and focus on content quality and user experience contributed to its dominance in the streaming market. The Case Study illustrates how embracing digital disruption and customer-centric strategies can drive success.

Conclusion
These case studies offer valuable insights into different facets of Business Management, including innovation, strategic decision-making, customer-centric approaches, and market disruption. Analysing these cases provides aspiring managers and entrepreneurs with real-world examples of how effective strategies, risk-taking, and adaptability can lead to remarkable success in the dynamic business world.
Try our Business Analyst Training today for a rewarding career!
Frequently Asked Questions
Upcoming business skills resources batches & dates.
Fri 31st May 2024
Fri 26th Jul 2024
Fri 27th Sep 2024
Fri 29th Nov 2024
Get A Quote
WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
My employer
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry
- Business Analysis
- Lean Six Sigma Certification
Share this course
Our biggest spring sale.

We cannot process your enquiry without contacting you, please tick to confirm your consent to us for contacting you about your enquiry.
By submitting your details you agree to be contacted in order to respond to your enquiry.
We may not have the course you’re looking for. If you enquire or give us a call on 01344203999 and speak to our training experts, we may still be able to help with your training requirements.
Or select from our popular topics
- ITIL® Certification
- Scrum Certification
- Change Management Certification
- Business Analysis Courses
- Microsoft Azure Certification
- Microsoft Excel Courses
- Microsoft Project
- Explore more courses
Press esc to close
Fill out your contact details below and our training experts will be in touch.
Fill out your contact details below
Thank you for your enquiry!
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go over your training requirements.
Back to Course Information
Fill out your contact details below so we can get in touch with you regarding your training requirements.
* WHO WILL BE FUNDING THE COURSE?
Preferred Contact Method
No preference
Back to course information
Fill out your training details below
Fill out your training details below so we have a better idea of what your training requirements are.
HOW MANY DELEGATES NEED TRAINING?
HOW DO YOU WANT THE COURSE DELIVERED?
Online Instructor-led
Online Self-paced
WHEN WOULD YOU LIKE TO TAKE THIS COURSE?
Next 2 - 4 months
WHAT IS YOUR REASON FOR ENQUIRING?
Looking for some information
Looking for a discount
I want to book but have questions
One of our training experts will be in touch shortly to go overy your training requirements.
Your privacy & cookies!
Like many websites we use cookies. We care about your data and experience, so to give you the best possible experience using our site, we store a very limited amount of your data. Continuing to use this site or clicking “Accept & close” means that you agree to our use of cookies. Learn more about our privacy policy and cookie policy cookie policy .
We use cookies that are essential for our site to work. Please visit our cookie policy for more information. To accept all cookies click 'Accept & close'.
- Browse Topics
- Executive Committee
- Affiliated Faculty
- Harvard Negotiation Project
- Great Negotiator
- American Secretaries of State Project
- Awards, Grants, and Fellowships
- Negotiation Programs
- Mediation Programs
- One-Day Programs
- In-House Training and Custom Programs
- In-Person Programs
- Online Programs
- Advanced Materials Search
- Contact Information
- The Teaching Negotiation Resource Center Policies
- Frequently Asked Questions
- Negotiation Journal
- Harvard Negotiation Law Review
- Working Conference on AI, Technology, and Negotiation
- 40th Anniversary Symposium
- Free Reports and Program Guides
Free Videos
- Upcoming Events
- Past Events
- Event Series
- Our Mission
- Keyword Index
PON – Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School - https://www.pon.harvard.edu
Team-Building Strategies: Building a Winning Team for Your Organization

Discover how to build a winning team and boost your business negotiation results in this free special report, Team Building Strategies for Your Organization, from Harvard Law School.
- Case Study of Conflict Management: To Resolve Disputes and Manage Conflicts, Assume a Neutral 3rd Party Role
Here is a case study of conflict management emphasizing the importance of hearing all sides in a dispute
By PON Staff — on May 13th, 2024 / Conflict Resolution
In their book Difficult Conversations: How to Discuss What Matters Most (Penguin Putnam, 2000), authors Douglas Stone , Bruce Patton , and Sheila Heen tell us how to engage in the conversations in our professional or personal lives that make us uncomfortable by examining a case study of conflict management. Tough, honest conversations are critical for managers, whether they need to change the group culture, manage conflict within a team, give a negative performance evaluation, disagree with others in a group, or offer an apology.
To set the stage for a productive discussion, open a difficult conversation with the “Third Story,” advise the authors of Difficult Conversations . The Third Story is one an impartial observer, such as a mediator, would tell; it’s a version of events both sides can agree on. “The key is learning to describe the gap—or difference—between your story and the other person’s story. Whatever else you may think and feel, you can at least agree that you and the other person see things differently,” Stone, Patton, and Heen write.

Claim your FREE copy: The New Conflict Management
In our FREE special report from the Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School - The New Conflict Management: Effective Conflict Resolution Strategies to Avoid Litigation – renowned negotiation experts uncover unconventional approaches to conflict management that can turn adversaries into partners.
Suppose two regional sales reps share responsibility for sending weekly updates to their manager. Brad always submits them on time, but Frank often turns them in late. Saying, “Frank, you’ve turned in the sales reports late again” would only put Frank on the defensive. Instead, Brad opens the conversation this way: “Frank, you and I place a different value on deadlines. I want to explain why meeting them is important to me, and then I’d like to hear your take on them.”
Brad learns that Frank, when faced with the choice of possibly making a sale or compiling the report, thinks he should focus on the sale. With this insight, Brad proposes another way to share responsibilities: Brad will complete the report when it’s Frank’s turn to do so, as long as Frank gives Brad two hours’ notice and a share in any commission Frank earns as a result of being able to continue pursuing a lead.
What are your favorite conflict management methods?
Related Conflict Resolution Article: Conflict Management Skills When Dealing with an Angry Public – Here is some negotiation advice drawn from a case study of conflict management dealing with an angry public.
Adapted from “How to Say What Matters Most,” by Susan Hackley (former managing director, Program on Negotiation), first published in the Negotiation newsletter.
Originally published in 2010.
Related Posts
- The Pitfalls of Negotiations Over Email
- 3 Types of Conflict and How to Address Them
- Negotiation with Your Children: How to Resolve Family Conflicts
- What is Conflict Resolution, and How Does It Work?
- Conflict Styles and Bargaining Styles
Click here to cancel reply.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Negotiation and Leadership
- Learn More about Negotiation and Leadership

NEGOTIATION MASTER CLASS
- Learn More about Harvard Negotiation Master Class

Negotiation Essentials Online
- Learn More about Negotiation Essentials Online

Beyond the Back Table: Working with People and Organizations to Get to Yes
- Learn More about Beyond the Back Table

Select Your Free Special Report
- Beyond the Back Table September 2024 and February 2025 Program Guide
- Negotiation and Leadership Fall 2024 Program Guide
- Negotiation Essentials Online (NEO) Spring 2024 Program Guide
- Negotiation Master Class May 2024 Program Guide
- Negotiation and Leadership Spring 2024 Program Guide
- Make the Most of Online Negotiations
- Managing Multiparty Negotiations
- Getting the Deal Done
- Salary Negotiation: How to Negotiate Salary: Learn the Best Techniques to Help You Manage the Most Difficult Salary Negotiations and What You Need to Know When Asking for a Raise
- Overcoming Cultural Barriers in Negotiation: Cross Cultural Communication Techniques and Negotiation Skills From International Business and Diplomacy
Teaching Negotiation Resource Center
- Teaching Materials and Publications
Stay Connected to PON
Preparing for negotiation.
Understanding how to arrange the meeting space is a key aspect of preparing for negotiation. In this video, Professor Guhan Subramanian discusses a real world example of how seating arrangements can influence a negotiator’s success. This discussion was held at the 3 day executive education workshop for senior executives at the Program on Negotiation at Harvard Law School.
Guhan Subramanian is the Professor of Law and Business at the Harvard Law School and Professor of Business Law at the Harvard Business School.
Articles & Insights
- Negotiation Examples: How Crisis Negotiators Use Text Messaging
- BATNA Examples—and What You Can Learn from Them
- What is BATNA? How to Find Your Best Alternative to a Negotiated Agreement
- For Sellers, The Anchoring Effects of a Hidden Price Can Offer Advantages
- Taylor Swift: Negotiation Mastermind?
- Individual Differences in Negotiation—and How They Affect Results
- Winner’s Curse: Negotiation Mistakes to Avoid
- Solutions for Avoiding Intercultural Barriers at the Negotiation Table
- Top Negotiation Case Studies in Business: Apple and Dispute Resolution in the Courts
- Sales Negotiation Techniques
- Crisis Negotiation Skills: The Hostage Negotiator’s Drill
- Police Negotiation Techniques from the NYPD Crisis Negotiations Team
- Famous Negotiations Cases – NBA and the Power of Deadlines at the Bargaining Table
- Negotiating Change During the Covid-19 Pandemic
- AI Negotiation in the News
- Dealing with Hardball Tactics in Negotiation
- Dealing with Difficult People: Coping with an Insulting Offer in Contract Negotiations
- When Dealing with Difficult People, Look Inward
- Ethics in Negotiations: How to Deal with Deception at the Bargaining Table
- How to Manage Difficult Staff: Gen Z Edition
- MESO Negotiation: The Benefits of Making Multiple Equivalent Simultaneous Offers in Business Negotiations
- 7 Tips for Closing the Deal in Negotiations
- How Does Mediation Work in a Lawsuit?
- Dealmaking Secrets from Henry Kissinger
- Writing the Negotiated Agreement
- The Importance of Power in Negotiations: Taylor Swift Shakes it Off
- Settling Out of Court: Negotiating in the Shadow of the Law
- How to Negotiate with Friends and Family
- What is Dispute System Design?
- What are the Three Basic Types of Dispute Resolution? What to Know About Mediation, Arbitration, and Litigation
- The Importance of Relationship Building in China
- A Top International Negotiation Case Study in Business: The Microsoft-Nokia Deal
- India’s Direct Approach to Conflict Resolution
- International Negotiations and Agenda Setting: Controlling the Flow of the Negotiation Process
- Overcoming Cultural Barriers in Negotiations and the Importance of Communication in International Business Deals
- Advantages and Disadvantages of Leadership Styles: Uncovering Bias and Generating Mutual Gains
- Leadership and Decision-Making: Empowering Better Decisions
- The Contingency Theory of Leadership: A Focus on Fit
- Directive Leadership: When It Does—and Doesn’t—Work
- How an Authoritarian Leadership Style Blocks Effective Negotiation
- Negotiations and Logrolling: Discover Opportunities to Generate Mutual Gains
- Using E-Mediation and Online Mediation Techniques for Conflict Resolution
- Undecided on Your Dispute Resolution Process? Combine Mediation and Arbitration, Known as Med-Arb
- Alternative Dispute Resolution (ADR) Training: Mediation Curriculum
- What Makes a Good Mediator?
- The Anchoring Bias: Consumers, Beware!
- Collective Bargaining Negotiations and the Risk of Strikes
- Identify Your Negotiation Style: Advanced Negotiation Strategies and Concepts
- The Inseparable Link Between Effective Leadership and Communication
- Communication in Negotiation: How Hard Should You Push?
- Use a Negotiation Preparation Worksheet for Continuous Improvement
- The Importance of a Relationship in Negotiation
- Collaborative Negotiation Examples: Tenants and Landlords
- Ethics and Negotiation: 5 Principles of Negotiation to Boost Your Bargaining Skills in Business Situations
- Negotiation Journal celebrates 40th anniversary, new publisher, and diamond open access in 2024
- How to Negotiate a Higher Salary
- Setting Standards in Negotiations
- Negotiating a Salary When Compensation Is Public
- How to Negotiate a Higher Salary after a Job Offer
- How to Negotiate Pay in an Interview
- Bidding in an International Business Negotiation: Euro-Idol
- Check Out the All-In-One Curriculum Packages!
- Teaching the Fundamentals: The Best Introductory Negotiation Role Play Simulations
- Check Out Videos from the PON 40th Anniversary Symposium on Negotiation Pedagogy, Practice, & Research
- Teach Your Students to Negotiate a Management Crisis
- What is a Win-Win Negotiation?
- Win-Win Negotiation: Managing Your Counterpart’s Satisfaction
- Win-Lose Negotiation Examples
- How to Negotiate Mutually Beneficial Noncompete Agreements
- How to Win at Win-Win Negotiation
PON Publications
- Negotiation Data Repository (NDR)
- New Frontiers, New Roleplays: Next Generation Teaching and Training
- Negotiating Transboundary Water Agreements
- Learning from Practice to Teach for Practice—Reflections From a Novel Training Series for International Climate Negotiators
- Insights From PON’s Great Negotiators and the American Secretaries of State Program
- Gender and Privilege in Negotiation
Remember Me This setting should only be used on your home or work computer.
Lost your password? Create a new password of your choice.
Copyright © 2024 Negotiation Daily. All rights reserved.
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
ChangeManagement →
No results found in working knowledge.
- Were any results found in one of the other content buckets on the left?
- Try removing some search filters.
- Use different search filters.
Short Case Study on Change Management
A short case study on change management can be very helpful in learning how to manage change effectively. In today’s business world, change is constantly happening and it can be very difficult to keep up.
Having a solid understanding of change management is essential for any manager or business owner.
A good case study will show you how one company successfully managed a major change and what lessons can be learned from their experience.
By studying short case study on change management, you will gain valuable insights into the importance of planning, communication, and employee involvement when managing change.
You will also learn about the different stages of change and how to overcome resistance to change.
These are all important topics that any manager or business owner should be familiar with. Learning about them through a short case study is an excellent way to gain a better understanding of these concepts.
Here are 05 short case studies on change management that offer you valuable insights on managing change.
1. Adobe- a transformation of HR functions to support strategic change
Many a times external factors lead to changes in organisational structures and culture. This truly happened at Adobe which has 11,000 employees worldwide with 4.5 billion $ yearly revenue.
Acrobat, Flash Player, and Photoshop are among the well-known products of Abode.
Due to new emerging technologies and challenges posed by small competitors Adobe had to stop selling its licensed goods in shrink-wrapped containers in 2011 and switched to offering digital services through the cloud. They gave their customers option of downloading the necessary software for free or subscribing to it every month rather than receiving a CD in a box.
The human resource (HR) function also took on a new role, which meant that employees had to adjust to new working practices. A standard administrative HR function was housed at Adobe’s offices. However, it was less suitable for the cloud-based strategy and performed well when Adobe was selling software items.
HR changed its role and became more human centric and reduced its office based functions.
The HR personnel did “walk-ins,” to see what assistance they might offer, rather than waiting for calls. With a focus on innovation, change, and personal growth, Adobe employed a sizable percentage of millennials.
Instead of having an annual reviews, staff members can now use the new “check-in” method to assess and define their own growth goals whenever they find it necessary, with quick and continuous feedback.
Managers might receive constructive criticism from HR through the workshops they conduct. The least number of employees have left since this changed approach of HR.
Why did Adobe’s HR department make this change? Since the company’s goals and culture have changed, HR discovered new ways to operate to support these changes.
2. Intuit – applying 7s framework of change management
Steve Bennett, a vice president of GE Capital, was appointed CEO of Intuit in 2000. Intuit is a provider of financial software solutions with three products: Quicken, TurboTax, and QuickBooks, which have respective market shares of 73 percent, 81 percent, and 84 percent.
Despite this market domination, many observers believed Intuit was not making as much money as it could.
Additionally, the business was known for making decisions slowly, which let rivals take advantage of numerous market opportunities. Bennett desired to change everything.
In his first few weeks, he spoke with each of the top 200 executives, visited the majority of Intuit’s offices, and addressed the majority of its 5,000 employees.
He concluded that although employees were enthusiastic about the company’s products, internal processes weren’t given any thought (based on Higgins, 2005).
He followed the famous Mckinsey 7S Model for Change Management to transform the organization. Let’s see what are those changes that he made:
By making acquisitions, he increased the products range for Intuit.
He established a flatter organizational structure and decentralized decision-making, which gave business units more authority and accountability throughout the whole product creation and distribution process.
To accomplish strategic goals, the rewards system was made more aligned to strategic goals.
He emphasized the necessity of a performance-oriented focus and offered a vision for change and also made every effort to sell that vision.
He acknowledged the commitment of staff to Intuit’s products and further strengthened process by emphasizing on quality and efficiency of his team.
Resources were allotted for learning and development, and certain selected managers were recruited from GE in particular skill categories, all to enhance staff capabilities concerning productivity and efficiency.
Superordinate goals:
Bennett’s strategy was “vision-driven” and he communicated that vision to his team regularly to meet the goals.
Bennett’s modifications led to a 40–50% rise in operating profits in 2002 and 2003.
8,000 people worked for Intuit in the United States, Canada, the United Kingdom, India, and other nations in 2014, and the company generated global revenues of nearly $5 billion.
3. Barclays Bank – a change in ways of doing business
The financial services industry suffered heavily during mortgage crisis in 2008. In addition to significant losses, the sector also had to deal with strict and aggressive regulations of their investing activities.
To expand its business, more employees were hired by Barclays Capital under the leadership of its former chief executive, Bob Diamond, who wanted to make it the largest investment bank in the world.
But Barclays Capital staff was found manipulating the London Inter-Bank Offered Rate (LIBOR) and Barclays was fined £290 million and as a result of this the bank’s chairman, CEO, and COO had to resign.
In an internal review it was found that the mindset of “win at all costs” needed to be changed so a new strategy was necessary due to the reputational damage done by the LIBOR affair and new regulatory restrictions.
In 2012, Antony Jenkins became new CEO. He made the following changes in 2014, which led to increase of 8% in share price.
Aspirations
The word “Capital” was removed from the firm name, which became just Barclays. To concentrate on the U.S. and UK markets, on Africa, and on a small number of Asian clients, the “world leader” goal was dropped.
Business model
Physical commodities and obscure “derivative” products would no longer be traded by Barclays. It was decided that rather than using its customers’ money, the business would invest its own.
Only thirty percent of the bank’s profits came from investment banking. Instead of concentrating on lending at high risk, the focus was on a smaller range of customers.
In place of an aggressive, short-term growth strategy that rewarded commercial drive and success and fostered a culture of fear of not meeting targets, “customer first,” clarity, and openness took precedence. Investment bankers’ remuneration was also reduced.
Beginning in 2014, branches were shut, and 19,000 jobs were lost over three years, including 7,000 investment banking employees, personnel at high-street firms, and many in New York and London headquarters. £1.7 billion in costs were reduced in 2014.
There was an increase in customers’ online or mobile banking, and increased automation of transactions to lower expenses. To assist customers in using new computer systems, 30 fully automated branches were established by 2014, replacing the 6,500 cashiers that were lost to this change with “digital eagles” who used iPads.
These changes were made to build an organization that is stronger, more integrated, leaner, and more streamlined, leading to a higher return on equity and better returns for shareholders. This was also done to rebuild the bank’s credibility and win back the trust of its clients.
4. Kodak – a failure to embrace disruptive change
The first digital camera and the first-megapixel camera were both created by Kodak in 1975 and 1986 respectively.
Why then did Kodak declare bankruptcy in 2012?
When this new technology first came out in 1975, it was expensive and had poor quality of images. Kodak anticipated that it would be at least additional ten years until digital technology started to pose a threat to their long-standing business of camera, film, chemical, and photo-printing paper industries.
Although that prediction came true, Kodak chose to increase the film’s quality through ongoing advances rather than embracing change and working on digital technology.
Kodak continued with old business model and captured market by 90% of the film and 85% of the cameras sold in America in 1976. With $16 billion in annual sales at its peak, Kodak’s profits in 1999 was around $2.5 billion. The brand’s confidence was boosted by this success but there was complete complacency in terms of embracing new technology.
Kodak started experiencing losses in 2011 as revenues dropped to $6.2 billion.
Fuji, a competitor of Kodak, identified the same threat and decided to transition to digital while making the most money possible from film and creating new commercial ventures, such as cosmetics based on chemicals used in film processing.
Even though both businesses had the same information, they made different judgments, and Kodak was reluctant to respond. And when it started to switch towards digital technology, mobile phones with in-built digital camera had arrived to disrupt digital cameras.
Although Kodak developed the technology, they were unaware of how revolutionary digitalization would prove to be, rendering their long-standing industry obsolete.
You can read here in detail Kodak change management failure case study.
5. Heinz – a 3G way to make changes
Warren Buffett’s Berkshire Hathaway and the Brazilian private equity business 3G Capital paid $29 billion in 2013 to acquire Heinz, the renowned food manufacturer with $11.6 billion in yearly sales.
The modifications were made right away by the new owners. Eleven of the top twelve executives were replaced, 600 employees were let go, corporate planes were sold, personal offices were eliminated, and executives were required to stay at Holiday Inn hotel rather than the Ritz-Carlton when traveling and substantially longer work hours were anticipated.
Each employee was given a monthly copy restriction of 200 by micromanagement, and printer usage was recorded. Only 100 business cards were permitted each year for executives.
Numerous Heinz workers spoke of “an insular management style” where only a small inner circle knows what is truly going on.
On the other side, 3G had a youthful team of executives, largely from Brazil, who moved from company to company as instructed across nations and industries. They were loyal to 3G, not Heinz, and were motivated to perform well to earn bonuses or stock options.
“The 3G way,” a theory that 3G has applied to bring about change in prior acquisitions like Burger King, was the driving reason behind these modifications. Everything was measured, efficiency was paramount, and “nonstrategic costs” were drastically reduced.
From this vantage point, “lean and mean” prevails, and human capital was not regarded as a crucial element of business success. It was believed that rather than being driven by a feeling of purpose or mission, employees were motivated by the financial gains associated with holding company stock.
Because it had been well-received by the 3G partners, those who might be impacted by a deal frequently saw a “how to” guide published by consultant Bob Fifer as a “must read.”
However, many food industry experts felt that while some of 3G’s prior acquisitions would have been ideal candidates for a program of cost-cutting, Heinz was not the most appropriate choice to “hack and slash.” The company had already undergone several years of improved efficiency and it was already a well-established player in the market.
In summarizing the situation, business journalists Jennifer Reingold and Daniel Roberts predicted that “the experiment now underway will determine whether Heinz will become a newly invigorated embodiment of efficiency—or whether 3G will take the cult of cost-cutting so far that it chokes off Heinz’s ability to innovate and make the products that have made it a market leader for almost a century and a half.”
Final Words
A short case study on change management can be a helpful tool in learning how to effectively manage change. These case studies will show you how one company successfully managed a major change and what lessons can be learned from their experience. By studying these case studies, you will gain valuable insights into the importance of planning, communication, and employee involvement when managing change. These are all vital elements that must be considered when implementing any type of change within an organization.
About The Author
Tahir Abbas
Related posts.

ITIL Change Management Roles and Responsibilities

Change Management and Continuous Improvement – Connection and Benefits

The Power of KPIs for Social Media Engagement

- University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Subject Guides
Organizational Studies
- Case Studies
- Articles & Journals
- Books & References
- Corporate Responsibility
- Country Profiles
- Business Etiquette
- Public Companies
- Doing International Business
Case Studies Collections
The library provides access to many case studies, but NOT Harvard Business Review studies. Below are a list of studies provided via the library and free sites.
- The Case Centre (free) A growing range of free cases produced by a number of prominent schools and organisations across the globe. Must register to access .
Login only with UNM NetID. For more information visit https://libguides.unm.edu/Safari
- Ivey Business School (free) Ivey at the University of Western Ontario provides Complimentary Cases.
- MIT LearningEdge (free) Cases cover the subjects: entrepreneurship, leadership/ethics, operations management, strategy, sustainability, and system dynamics.
- Stanford Business (some free) Use the Narrow Your Results option to select subjects and "Available to download at no charge."
Case Study Journals
- Case Studies in Business, Industry & Government Statistics (free) Open Journal via Societe Francaise de Statistique. Cases are in English.
- << Previous: Doing International Business
- Last Updated: Mar 25, 2024 11:47 AM
- URL: https://libguides.unm.edu/org

Want to create or adapt books like this? Learn more about how Pressbooks supports open publishing practices.
Case Studies
Robert j. glushko.
We now fulfill the promise of this book, with a set of case study examples that apply the concepts and phases of the roadmap. (The first four case studies appeared in the first print edition of the book. All the others have been contributed by students or other readers of the book and edited for consistency.——Ed.)
Navigating This Chapter
Case study template.
For the sake of consistency, we employ the questions posed in Design Decisions in Organizing Systems as a template for the case studies. We remind you of six groups of design decisions, itemizing the most important dimensions in each group:
What is being organized? What is the scope and scale of the domain? What is the mixture of physical things , digital things, and information about things in the organizing system? Is the organizing system being designed to create a new resource collection, catalog an existing and closed resource collection, or manage a collection in which resources are continually added or deleted? Are the resources unique, or are they interchangeable members of a category? Do they follow a predictable “ life cycle ” with a “ useful life ”? Does the organizing system use the interaction resources created through its use, or are these interaction resources extracted and aggregated for use by another organizing system? ( “What Is Being Organized?” )
Why is it being organized? What interactions or services will be supported, and for whom? Are the uses and users known or unknown? Are the users primarily people or computational processes? Does the organizing system need to satisfy personal, social, or institutional goals? ( “Why Is It Being Organized?” )
How much is it being organized? What is the extent, granularity, or explicitness of description, classification, or relational structure being imposed? What organizing principles guide the organization? Are all resources organized to the same degree, or is the organization sparse and non-uniform? ( “How Much Is It Being Organized?” )
When is it being organized? Is the organization imposed on resources when they are created, when they become part of the collection, when interactions occur with them, just in case, just in time, all the time? Is any of this organizing mandated by law or shaped by industry practices or cultural tradition? ( “When Is It Being Organized?” )
How or by whom, or by what computational processes, is it being organized? Is the organization being performed by individuals, by informal groups, by formal groups, by professionals, by automated methods? Are the organizers also the users? Are there rules or roles that govern the organizing activities of different individuals or groups? ( “How (or by Whom) Is It Organized?” )
Where is it being organized? Is the resource location constrained by design or by regulation? Are the resources positioned in a static location? Are the resources in transit or in motion? Does their location depend on other parameters, such as time? ( “Where is it being Organized?” )
As we discussed in “Where is it being Organized?” , when location is a constraint, it will typically be identified as such in the other questions. As result, we will only examine “ Where? ” as distinct design dimension in cases where it is warranted.
The Discipline of Organizing: 4th Professional Edition Copyright © 2020 by Robert J. Glushko is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution-NonCommercial 4.0 International License , except where otherwise noted.
Share This Book

Taking BioPhorum value back into your organization: case study examples from BioPhorum Drug Substance

Taking BioPhorum Value Back into your Organization: Case Study Examples from BioPhorum Drug Substance
There are many benefits to a BioPhorum membership – from productivity and cost improvements to workforce enablement. A crucial factor in delivering these is a member’s interaction with BioPhorum, so we wanted to understand how different companies approach the governance of their membership and how they gain value from it.
We looked at two examples within BioPhorum Drug Substance (DS) that illustrate approaches based on different levels of membership maturity – one is a relatively new member and the other is more established.
We spoke with Jennifer Hanson, BioPhorum Drug Substance Leadership Team member and a Quality Systems Specialist 3 at Partner Therapeutics, a company with less than 200 employees and which has been a member of BioPhorum Drug Substance since 2020. We also spoke with Guido Kremer van der Kamp, Albin Simoni, Pascal Valax and Sofia Meyer, who are members of BioPhorum Leadership teams from Merck, which has been a BioPhorum Drug Substance member since 2008
Jennifer Hanson – Partner Therapeutics
What is your personal experience of being a member of BioPhorum? It has been great. I have always had good feedback from the subject matter experts (SMEs) involved and learned a lot personally.
We decided that more structured internal governance around our membership would be useful to maximize the learnings from the SMEs who participated in the BioPhorum activities and meetings. That would give us more return on our investment and offer people opportunities to share, lead, network, and provide more experience for junior employees. BioPhorum Account Managers provided us with some case studies of companies that had set up their internal governance, which were very, very helpful. They included Merck’s governance model (see below). Now that we are established, it is even more important to understand where we can go.
How did you set up a governance structure to maximize value?
I reviewed the models supplied by BioPhorum and surveyed our SMEs to understand their needs, interests, and levels of engagement. This work fed into the goals I set for us. I opened up channels of communication to share information, including a SharePoint site, and we are creating onboarding training to show what is expected of participation, etc. Our goals for 2024 include measuring the impact of setting up the governance model.
So far, this activity has contributed to doubling the participation from our SMEs. And people are proactively seeking to join, which ensures that the individuals are the right people to be involved.
How are you structured to maximize value from BioPhorum?
We are setting up a scoring/assessment tool to measure value and rank what is of most importance. We can consider which publications apply to us, if we need to adopt recommendations, are we already doing what is suggested, etc. This early evaluation saves us time.
What is your biggest personal benefit from participating in BioPhorum?
I have learned general leadership skills from leading the program. I am not a manager and do not have direct reports, but this is really giving me the opportunity to lead. Process improvement is my passion and working with BioPhorum has given me the opportunity to improve what we are doing.
For our SMEs, the community exists to support and answer our questions, and feedback from others gives them the courage to ask more questions. So much information and guidance exist, and BioPhorum has been a tremendous help for our company to help focus our attention.
The Merck team
What is the Merck Governance model?
Our model consists of layers. At the bottom is a series of Community of Practice leads in our Life Science business for E-data and Supply Chain, Single Use, Raw Materials, Cell and Gene Therapy, Regulatory and Biocontinuum. These can operate across any Phorum. For example, Biocontinuum is about the future of manufacturing, so the team is involved with workstreams from BioPhorum IT, Cell and Gene Therapy, and Technology Strategy. Then there are levels for Phorum Leaders and Sponsors, both covering the Life Science and Healthcare parts of our business. Above these, we have the Governance Board, which includes governance support and cross-Phorum communication. This is because we saw the need to foster collaboration and communication across the Phorums, both for specific topics and for the whole involvement of the Merck group with BioPhorum. This mirrors our ‘One Merck’ approach of having people from both sides of the business communicating and sitting together. We are looking at applying this approach to the other levels of our governance model.

This structure allows us to create maximum value by supporting people development, cross-communication, thought leadership activities, etc. Ultimately, we try to allow people to be the most efficient in what they do and we are creating tools around that approach.
How have responsibilities changed?
Before implementing our new governance structure, we did not have a clear definition of responsibilities. We now have a RACI (Responsible, Accountable, Consulted, and Informed) matrix for all the levels of involvement of people – from an SME to a community leader to a Phorum leader to a sponsor. Even the governance people have job descriptions.
The RACI matrix is also used for onboarding new members. It is linked to one of our most important pillars – for people to understand not only their role and see how they fit into the organization, but also what they can expect from a Phorum lead, from a sponsor, etc.
Has onboarding new members changed?
Yes. Originally, anyone who was interested just reached out to a BioPhorum contact and they were onboarded straight away without any review or selection. This has completely changed. Now, we get proposals from potential new members from SMEs in a workstream, community practice leaders, Phorum leaders or even sponsors. Then, we make a conscious decision on whether somebody joins or not, which is driven by the RACI. Joining must be aligned with the individual’s work objectives within the Merck strategy and/or the development plan of the person. We do not ask for people to join anymore. If someone is motivated to join and they have checked with their line management, then they have a good chance of being accepted. Being proactive in joining is much more indicative of someone’s likelihood to stay engaged and be committed.
We have also built an online training program where every new member has to pass the course as part of their onboarding. This covers areas such as the RACI matrix and responsibilities, what BioPhorum is, what our collaboration strategy is, why we are collaborating with BioPhorum in terms of value assessment and return on investment, what the rules of communication are, etc. It is a nice summary of what we have been doing to improve and increase value and decrease administrative time. We believe we now have a more professional image internally.
How was it implemented across your business?
Once everything was prepared, we launched the new process through scheduled calls, which are now ongoing. We have a series of invitations that are set up for communities of practice (monthly) and Phorum leaders, sponsors, and governance (quarterly). We are in the process of combining those calls to bring together the Healthcare and Life Science parts of our business.
How do you track and report the value of your membership?
We have a dashboard with defined value points, such as people, finances, and thought leadership. We also track the engagement of our people in the BioPhorum workstreams; for example, how often they attend, how much time they spend on a project, etc. And also the publications produced, conference participation, etc. This is the type of information we show to management and we are trying to automate this reporting. We also do phone surveys, e.g., to see how much a BioPhorum white paper has been used across Merck. We would like to see improved tracking of how many BioPhorum papers published in scientific publications have been read, referenced, etc.
One key message?
This is about collaboration and communication. Collaboration is how people deliver their RACI responsibilities, which therefore need to be clear. And communication is letting people know about the value of implementing our governance model. Our collaboration and communication approach runs through our organization regardless of the Phorum. This was a big discussion at the very start of our collaboration with BioPhorum and is a key part of breaking down silos where they exist.
These case studies show that companies can have a different approach to the governance model around their BioPhorum membership, which is often determined by the size of the company, how long they have been members, and their level of engagement. However, whatever approach is taken, there are many benefits – both at personal and company levels.
For individuals, they can gain experience in sharing and networking and developing their leadership skills. Companies, meanwhile, can benefit from easier onboarding of new staff, letting SMEs share their experience with other parts of the business, and helping people be efficient at what they do. A structured approach to governance – with communication, collaboration, and measurement at its core – will help to maximize the value of a BioPhorum membership, whatever the size of your company.

The Future of the Inbound Supply Chain – Implementing Electronic Data Exchange

How biomanufacturers can drive SUS standardization

Cross industry collaboration for carbon transparency at product level

Welcome BioPhorum Quality

A view from industry on the implication of the new Annex 1 requirements on visual inspection process
Advanced therapy medicinal products.
Advanced Therapy Medicinal Products support the quest for better and faster development of cell, gene and RNA therapies through connecting therapy developers, contract manufacturing, and testing organizations to gain an understanding and respond to the challenges faced by the advanced therapeutics industry.
Development Group
Development Group accelerates and improves the development process of biopharmaceutical medicines for the benefit of the patient. Replacing isolation with collaboration by providing a “safe” space where subject matter experts can work on sharing solutions and best practice on emerging industry trends, implementation of new technologies and common issues whilst ensuring their intellectual property and confidentiality is protected.
Drug Substance
Drug Substance advances excellence in drug substance manufacturing and testing, acting as an industry voice to accelerate technology adoption, implement post-approval change more rapidly and increase confidence in maintaining compliance.
Fill Finish
Fill Finish accelerates development and acceptance of sustainable world-class filling and packaging operations for drug product which meets the future needs of patients. Through innovative solutions resulting from the sharing of expertise, we can overcome common performance challenges and deliver on quality and regulatory compliance.
Information Technology
Information Technology accelerates digital maturity across the global pharmaceutical manufacturing industry.
BioPhorum Quality provides a dedicated, safe space for quality professionals from biomanufacturers and contract organizations to coalesce and enhance effective collaboration to address shared industry challenges.
Regulatory-CMC
Regulatory CMC brings leaders together who have a common goal – to improve access to medicines through innovation in the Regulatory ecosystem. It provides a dedicated space for strategic leadership and a coordinated industry voice, to move from divergence to convergence.
Supply Chain to Patient
Supply Chain to Patient transforms the performance of global pharmaceutical clinical and commercial outbound supply chains through industry collaboration by creating transparent patient-centric, resilient and agile E2E supply chains, that consistently deliver high-quality medicines ensuring an uninterrupted supply to patients.
Supply Resilience
Supply Resilience is a trusted advisory group and collaboration that is the engine for driving change across the global industry for all things relevant to the inbound supply chain. Addressing the challenges of complexity, resilience, cost, sustainability, and innovation.
Sustainability
Sustainability enables the industry’s transition to a low carbon, circular future – supporting members to improve patient health while respecting the planet. We activate multi-disciplinary teams drawn from our network to deliver environmental sustainability improvements across the value chain.
Technology Strategy
Technology Strategy acts as one voice of the industry to define strategy, accelerate technology transformation and support technology translation and adoption. With a purpose of enabling the future state of flexible, resilient, sustainable end-to-end biomanufacturing.

An industry perspective on understanding AAV capsid content variants

An intercompany perspective on practical experiences of predicting, optimizing and analyzing high concentration biologic therapeutic formulations

BioPhorum’s holistic approach to container closure integrity

Answering the ‘why’ and ‘what’ questions around MES integration

Inaugural BioPhorum Quality face to face – get involved

The next step in building regulatory as a capability to enable strategic innovation across the BioPhorum community

A launchpad for an improved CGT outbound supply chain

Building a resilient business means adopting water stewardship

BioPhorum Technology Roadmapping roadmap vision 2.0

Publications Webinars Podcasts Tools Benchmarks and surveys Browse all
Publications
Documents including best practices, vision statements and peer reviewed papers to help you take value back to your business.
BioPhorum Connect is our podcast series that keeps you up to date with the latest news and trends in the biopharmaceutical industry. From experienced professionals to thought leaders, these podcasts bring you the insights and perspectives of experts from around the world.
A variety of resources including design tools and user requirement specifications to help you improve and streamline your business processes.
Benchmarks and Surveys
Research conducted among the BioPhorum membership providing evidence to support change and identify best practice.
Access a variety of free tools and papers and other resources designed to provide you with up-to-date information and insights to help you make informed decisions and maximize your success. Access our resources today and start making improving and streamlining your business processes.

Bioreactivity testing in single-use system biomanufacturing

Digital Plant Maturity Model V3
Top 10 Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024
1. nasa's mars exploration rover: innovative project management in space exploration., 2. apple's iphone development: delivering revolutionary products with precision., 3. tesla's gigafactory construction: exemplary project execution in renewable energy., 4. netflix's content expansion: agile management in the entertainment industry., 5. amazon's prime air drone delivery: pioneering logistics project management., 6. google's waymo self-driving cars: cutting-edge technology meets project efficiency., 7. mcdonald's digital transformation: adaptive project management in fast food., 8. ikea's sustainable store design: eco-friendly project implementation in retail., 9. unicef's vaccine distribution: humanitarian project management at scale., 10. spacex's starlink satellite network: revolutionizing global connectivity with project prowess., discover more stories.
- Become a Partner
- Product Overview Know more about our products
- OKR Management Strategy-execution made easy
- Performance Management Build a high performance team
- Task Management Increase day-to-day productivity
- Employee Engagement Engage, align and inspire your team
- Integrations Integrate easily with all your favorite apps
- Case Study Know why 1000s of brands trust Profit.co
- Why Profit.co? Know what customers like you think about us.
- OKR Certification Iterate Faster with OKRs Coaching & Certification Programs
- OKR University OKR resources for beginners and experts
- eBooks Books sharing our OKR expertise, ideas and insights
- KPI Library Find the Most Effective KPIs for your business
- OKR Examples Collection of OKR examples for your business
- OKR Webinars Discover current trends and expert insights
- Answers (FAQs) Get instant solutions to your queries
- OKR Canvas Kick start your OKR implementation right away
- Help Center Endless support in case you are stuck
- Release Updates Outlined feature updates from our last releases
- Try it Free
- Schedule Demo
Mastering Conflict Management with Strategies and Solutions in the Workplace

Category: Task Management .
Introduction
Conflict is the disagreement or difference of opinions between individuals that can potentially harm any organization. In the workplace setting, it often involves personal agendas, insights, or goals versus those of the group or team. Conflict management seeks to resolve these disagreements positively, with outcomes that satisfy everyone involved or benefit the group.
However, the perception of conflict is often negative.
The reality is that conflict can be positive if managed properly, promoting team-building skills, critical thinking, new ideas, and alternative solutions. Leaders must master conflict management to ensure team success.
In this blog, we’ll look into the essentials of conflict management, explore different styles and strategies, and provide practical tips and FAQs.
The Importance of Conflict Management
Conflict management is crucial in ensuring that team members work harmoniously towards common goals. Managed effectively, conflict can encourage learning and growth in an organization.
Benefits of Conflict Management
- Enhanced Team Cohesion: Teams can build stronger bonds and trust by resolving conflicts collaboratively.
- Increased Innovation: Differing viewpoints often lead to new ideas and creative solutions.
- Improved Communication: Conflict resolution fosters open dialogue and effective listening.
- Reduced Workplace Stress: Properly managed conflict minimizes tension, improving overall morale.
To learn how you can optimize your organization’s performance!
Sign up with Profit.co
Conflict Management Styles

In this style, individuals involved in the conflict simply avoid the situation or ignore its existence. This approach may be useful temporarily to de-escalate a tense situation. However, it’s a losing situation in the long run as unresolved conflict festers and creates more tension.
Accommodative
In this style, one party wins, and one party loses. The losing party easily gives in when the problem is not so important to them or when they want to keep the peace. The resolution benefits one side but can leave others feeling resentful and dissatisfied.
Competitive
In the competitive style, one party wins at the expense of the other. Although the conflict is resolved, this style can foster resentment and hinder teamwork.
In compromise, each party sacrifices a portion of their solution, leading to a resolution that partially satisfies both sides. However, the best outcome might not always prevail, potentially leaving some parties feeling shortchanged.
Collaborative
The collaborative style aims to bring all parties together to find a resolution that benefits everyone involved. It incorporates active listening, respectful communication, and open-mindedness to reach the best possible solution.
“To get something new done you have to be stubborn and focused, to the point that others might find unreasonable.” Jeff Bezos
7 Steps in Conflict Management
1. set communication rules.
Establish ground rules for respectful communication before discussions begin. For cross-cultural conflicts, it’s important to consider cultural nuances in communication styles and norms.
2. Set Aside Preconceived Opinions
Ask all parties to approach the conflict with an open mind. In virtual team settings, be mindful of potential misunderstandings due to lack of non-verbal cues.
3. Active Listening
Encourage active listening without interruptions. Having emotional intelligence skills like empathy and self-awareness can greatly aid in truly understanding different perspectives during conflicts.
4. Define the Problem
Write down and restate the problem to ensure mutual understanding. Use collaboration tools or online platforms to document the issue for virtual teams.
5. Propose Solutions
Have each party suggest potential solutions. Online whiteboards or ideation tools can facilitate this process for remote teams.
6. Customer Lifetime Value (CLTV)
Evaluate the positive and negative aspects of each solution. Involve legal or HR departments if the conflict has potential legal or policy implications.
7. Agree on a Resolution
Choose a solution that benefits everyone involved or is beneficial to the group. Establish metrics like employee satisfaction, productivity or turnover rates to measure the effectiveness of the resolution.
Proactive conflict prevention strategies, such as clear communication, setting expectations, and building trust, can also help avoid conflicts from arising or escalating.
Conflict Management in Organizations
- Party-Directed Mediation (PDM): Suitable for disputes between co-workers, it involves pre-mediation coaching and role-playing before a joint session.
- Negotiated Performance Appraisal (NPA): Improves communication between supervisors and subordinates, preserving hierarchical power while encouraging dialogue.
- International Conflict Management: When managing conflicts across cultures, it’s essential to understand cultural differences in communication, traditions, and thought processes. A Confrontational style may not work well in cultures where harmony is prioritized.
- Inter-Organizational Conflict Management: In inter-organizational relationships, conflicts involve both individuals and organizations. Formal and informal governance mechanisms influence the type of conflicts and how they’re managed.
Conflict Resolution Case Study
Google vs. antitrust regulators.
In response to antitrust charges, Google followed its principle “ Don’t litigate, negotiate .” By engaging in direct negotiations with regulators, Google adapted its practices and provided settlements to affected parties, avoiding litigation and improving relations.
Apple vs. Samsung
Apple and Samsung ended their long-running patent dispute with a settlement, concluding a seven-year legal battle over whether Samsung copied the iPhone. While settlement terms remain undisclosed, Apple emphasized the case was always about protecting innovation beyond monetary compensation. The settlement between Apple and Samsung shows how compromise and collaboration can help resolve long-standing disputes while protecting core business interests.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
Q1: what are the five styles of conflict management.
A1: The five styles of conflict management are Avoidance, Accommodative, Competitive, Compromise, and Collaborative.
Q2: How can conflict management benefit an organization?
A2: Conflict management can enhance team cohesion, improve communication, foster innovation, and reduce workplace stress.
Q3: What is Party-Directed Mediation (PDM)?
A3: PDM is a mediation approach suitable for disputes between colleagues. It involves coaching and role-playing before a joint mediation session.
Q4: How can leaders effectively manage international conflicts?
A4: Leaders should understand cultural differences in communication, traditions, and thought processes to navigate international conflicts.
Q5: What are the key steps to resolving workplace conflicts?
A5: The key steps include setting communication rules, actively listening, defining the problem, proposing solutions, discussing pros and cons, and agreeing on a resolution.
Conflict management is the process of limiting the negative aspects of conflict while increasing the positive aspects to enhance learning and group outcomes. Properly managed conflict can improve organizational performance and foster innovation, communication, and team cohesion. Leaders must be well-versed in conflict management styles and strategies to create a harmonious and productive workplace.
To learn more about Profit.co and deploy it within your organization
Book a free demo
Related Articles
How to master stakeholder analysis for project success.
Introduction Picture yourself at the helm of an important project with high stakes. The atmosphere is charged, the team is... Read more
10 Essential Task Delegation Tips Every Manager Should Know
Ah, delegation—the age-old management dilemma. On one hand, it's the key to unlocking team potential, driving efficiency, and fostering professional... Read more
Dynamics of Cost-Benefit Analysis for Business Success
Picture yourself standing at the crossroads, weighing whether to introduce groundbreaking technology into your startup or to initiate a significant... Read more
A Guide to Implementing Scrum for Agile Project Management
Scrum is a popular Agile framework developed to help run complex projects. While it originated and is widely used across... Read more

What is Iterative Business Execution?
Get a Personalized Demo
Execute your strategy with the industry’s most preferred and intuitive software
Artificial intelligence in strategy
Can machines automate strategy development? The short answer is no. However, there are numerous aspects of strategists’ work where AI and advanced analytics tools can already bring enormous value. Yuval Atsmon is a senior partner who leads the new McKinsey Center for Strategy Innovation, which studies ways new technologies can augment the timeless principles of strategy. In this episode of the Inside the Strategy Room podcast, he explains how artificial intelligence is already transforming strategy and what’s on the horizon. This is an edited transcript of the discussion. For more conversations on the strategy issues that matter, follow the series on your preferred podcast platform .
Joanna Pachner: What does artificial intelligence mean in the context of strategy?
Yuval Atsmon: When people talk about artificial intelligence, they include everything to do with analytics, automation, and data analysis. Marvin Minsky, the pioneer of artificial intelligence research in the 1960s, talked about AI as a “suitcase word”—a term into which you can stuff whatever you want—and that still seems to be the case. We are comfortable with that because we think companies should use all the capabilities of more traditional analysis while increasing automation in strategy that can free up management or analyst time and, gradually, introducing tools that can augment human thinking.
Joanna Pachner: AI has been embraced by many business functions, but strategy seems to be largely immune to its charms. Why do you think that is?
Subscribe to the Inside the Strategy Room podcast
Yuval Atsmon: You’re right about the limited adoption. Only 7 percent of respondents to our survey about the use of AI say they use it in strategy or even financial planning, whereas in areas like marketing, supply chain, and service operations, it’s 25 or 30 percent. One reason adoption is lagging is that strategy is one of the most integrative conceptual practices. When executives think about strategy automation, many are looking too far ahead—at AI capabilities that would decide, in place of the business leader, what the right strategy is. They are missing opportunities to use AI in the building blocks of strategy that could significantly improve outcomes.
I like to use the analogy to virtual assistants. Many of us use Alexa or Siri but very few people use these tools to do more than dictate a text message or shut off the lights. We don’t feel comfortable with the technology’s ability to understand the context in more sophisticated applications. AI in strategy is similar: it’s hard for AI to know everything an executive knows, but it can help executives with certain tasks.
When executives think about strategy automation, many are looking too far ahead—at AI deciding the right strategy. They are missing opportunities to use AI in the building blocks of strategy.
Joanna Pachner: What kind of tasks can AI help strategists execute today?
Yuval Atsmon: We talk about six stages of AI development. The earliest is simple analytics, which we refer to as descriptive intelligence. Companies use dashboards for competitive analysis or to study performance in different parts of the business that are automatically updated. Some have interactive capabilities for refinement and testing.
The second level is diagnostic intelligence, which is the ability to look backward at the business and understand root causes and drivers of performance. The level after that is predictive intelligence: being able to anticipate certain scenarios or options and the value of things in the future based on momentum from the past as well as signals picked in the market. Both diagnostics and prediction are areas that AI can greatly improve today. The tools can augment executives’ analysis and become areas where you develop capabilities. For example, on diagnostic intelligence, you can organize your portfolio into segments to understand granularly where performance is coming from and do it in a much more continuous way than analysts could. You can try 20 different ways in an hour versus deploying one hundred analysts to tackle the problem.
Predictive AI is both more difficult and more risky. Executives shouldn’t fully rely on predictive AI, but it provides another systematic viewpoint in the room. Because strategic decisions have significant consequences, a key consideration is to use AI transparently in the sense of understanding why it is making a certain prediction and what extrapolations it is making from which information. You can then assess if you trust the prediction or not. You can even use AI to track the evolution of the assumptions for that prediction.
Those are the levels available today. The next three levels will take time to develop. There are some early examples of AI advising actions for executives’ consideration that would be value-creating based on the analysis. From there, you go to delegating certain decision authority to AI, with constraints and supervision. Eventually, there is the point where fully autonomous AI analyzes and decides with no human interaction.
Because strategic decisions have significant consequences, you need to understand why AI is making a certain prediction and what extrapolations it’s making from which information.
Joanna Pachner: What kind of businesses or industries could gain the greatest benefits from embracing AI at its current level of sophistication?
Yuval Atsmon: Every business probably has some opportunity to use AI more than it does today. The first thing to look at is the availability of data. Do you have performance data that can be organized in a systematic way? Companies that have deep data on their portfolios down to business line, SKU, inventory, and raw ingredients have the biggest opportunities to use machines to gain granular insights that humans could not.
Companies whose strategies rely on a few big decisions with limited data would get less from AI. Likewise, those facing a lot of volatility and vulnerability to external events would benefit less than companies with controlled and systematic portfolios, although they could deploy AI to better predict those external events and identify what they can and cannot control.
Third, the velocity of decisions matters. Most companies develop strategies every three to five years, which then become annual budgets. If you think about strategy in that way, the role of AI is relatively limited other than potentially accelerating analyses that are inputs into the strategy. However, some companies regularly revisit big decisions they made based on assumptions about the world that may have since changed, affecting the projected ROI of initiatives. Such shifts would affect how you deploy talent and executive time, how you spend money and focus sales efforts, and AI can be valuable in guiding that. The value of AI is even bigger when you can make decisions close to the time of deploying resources, because AI can signal that your previous assumptions have changed from when you made your plan.
Joanna Pachner: Can you provide any examples of companies employing AI to address specific strategic challenges?
Yuval Atsmon: Some of the most innovative users of AI, not coincidentally, are AI- and digital-native companies. Some of these companies have seen massive benefits from AI and have increased its usage in other areas of the business. One mobility player adjusts its financial planning based on pricing patterns it observes in the market. Its business has relatively high flexibility to demand but less so to supply, so the company uses AI to continuously signal back when pricing dynamics are trending in a way that would affect profitability or where demand is rising. This allows the company to quickly react to create more capacity because its profitability is highly sensitive to keeping demand and supply in equilibrium.
Joanna Pachner: Given how quickly things change today, doesn’t AI seem to be more a tactical than a strategic tool, providing time-sensitive input on isolated elements of strategy?
Yuval Atsmon: It’s interesting that you make the distinction between strategic and tactical. Of course, every decision can be broken down into smaller ones, and where AI can be affordably used in strategy today is for building blocks of the strategy. It might feel tactical, but it can make a massive difference. One of the world’s leading investment firms, for example, has started to use AI to scan for certain patterns rather than scanning individual companies directly. AI looks for consumer mobile usage that suggests a company’s technology is catching on quickly, giving the firm an opportunity to invest in that company before others do. That created a significant strategic edge for them, even though the tool itself may be relatively tactical.
Joanna Pachner: McKinsey has written a lot about cognitive biases and social dynamics that can skew decision making. Can AI help with these challenges?
Yuval Atsmon: When we talk to executives about using AI in strategy development, the first reaction we get is, “Those are really big decisions; what if AI gets them wrong?” The first answer is that humans also get them wrong—a lot. [Amos] Tversky, [Daniel] Kahneman, and others have proven that some of those errors are systemic, observable, and predictable. The first thing AI can do is spot situations likely to give rise to biases. For example, imagine that AI is listening in on a strategy session where the CEO proposes something and everyone says “Aye” without debate and discussion. AI could inform the room, “We might have a sunflower bias here,” which could trigger more conversation and remind the CEO that it’s in their own interest to encourage some devil’s advocacy.
We also often see confirmation bias, where people focus their analysis on proving the wisdom of what they already want to do, as opposed to looking for a fact-based reality. Just having AI perform a default analysis that doesn’t aim to satisfy the boss is useful, and the team can then try to understand why that is different than the management hypothesis, triggering a much richer debate.
In terms of social dynamics, agency problems can create conflicts of interest. Every business unit [BU] leader thinks that their BU should get the most resources and will deliver the most value, or at least they feel they should advocate for their business. AI provides a neutral way based on systematic data to manage those debates. It’s also useful for executives with decision authority, since we all know that short-term pressures and the need to make the quarterly and annual numbers lead people to make different decisions on the 31st of December than they do on January 1st or October 1st. Like the story of Ulysses and the sirens, you can use AI to remind you that you wanted something different three months earlier. The CEO still decides; AI can just provide that extra nudge.
Joanna Pachner: It’s like you have Spock next to you, who is dispassionate and purely analytical.
Yuval Atsmon: That is not a bad analogy—for Star Trek fans anyway.
Joanna Pachner: Do you have a favorite application of AI in strategy?
Yuval Atsmon: I have worked a lot on resource allocation, and one of the challenges, which we call the hockey stick phenomenon, is that executives are always overly optimistic about what will happen. They know that resource allocation will inevitably be defined by what you believe about the future, not necessarily by past performance. AI can provide an objective prediction of performance starting from a default momentum case: based on everything that happened in the past and some indicators about the future, what is the forecast of performance if we do nothing? This is before we say, “But I will hire these people and develop this new product and improve my marketing”— things that every executive thinks will help them overdeliver relative to the past. The neutral momentum case, which AI can calculate in a cold, Spock-like manner, can change the dynamics of the resource allocation discussion. It’s a form of predictive intelligence accessible today and while it’s not meant to be definitive, it provides a basis for better decisions.
Joanna Pachner: Do you see access to technology talent as one of the obstacles to the adoption of AI in strategy, especially at large companies?
Yuval Atsmon: I would make a distinction. If you mean machine-learning and data science talent or software engineers who build the digital tools, they are definitely not easy to get. However, companies can increasingly use platforms that provide access to AI tools and require less from individual companies. Also, this domain of strategy is exciting—it’s cutting-edge, so it’s probably easier to get technology talent for that than it might be for manufacturing work.
The bigger challenge, ironically, is finding strategists or people with business expertise to contribute to the effort. You will not solve strategy problems with AI without the involvement of people who understand the customer experience and what you are trying to achieve. Those who know best, like senior executives, don’t have time to be product managers for the AI team. An even bigger constraint is that, in some cases, you are asking people to get involved in an initiative that may make their jobs less important. There could be plenty of opportunities for incorporating AI into existing jobs, but it’s something companies need to reflect on. The best approach may be to create a digital factory where a different team tests and builds AI applications, with oversight from senior stakeholders.
The big challenge is finding strategists to contribute to the AI effort. You are asking people to get involved in an initiative that may make their jobs less important.
Joanna Pachner: Do you think this worry about job security and the potential that AI will automate strategy is realistic?
Yuval Atsmon: The question of whether AI will replace human judgment and put humanity out of its job is a big one that I would leave for other experts.
The pertinent question is shorter-term automation. Because of its complexity, strategy would be one of the later domains to be affected by automation, but we are seeing it in many other domains. However, the trend for more than two hundred years has been that automation creates new jobs, although ones requiring different skills. That doesn’t take away the fear some people have of a machine exposing their mistakes or doing their job better than they do it.
Joanna Pachner: We recently published an article about strategic courage in an age of volatility that talked about three types of edge business leaders need to develop. One of them is an edge in insights. Do you think AI has a role to play in furnishing a proprietary insight edge?
Yuval Atsmon: One of the challenges most strategists face is the overwhelming complexity of the world we operate in—the number of unknowns, the information overload. At one level, it may seem that AI will provide another layer of complexity. In reality, it can be a sharp knife that cuts through some of the clutter. The question to ask is, Can AI simplify my life by giving me sharper, more timely insights more easily?
Joanna Pachner: You have been working in strategy for a long time. What sparked your interest in exploring this intersection of strategy and new technology?
Yuval Atsmon: I have always been intrigued by things at the boundaries of what seems possible. Science fiction writer Arthur C. Clarke’s second law is that to discover the limits of the possible, you have to venture a little past them into the impossible, and I find that particularly alluring in this arena.
AI in strategy is in very nascent stages but could be very consequential for companies and for the profession. For a top executive, strategic decisions are the biggest way to influence the business, other than maybe building the top team, and it is amazing how little technology is leveraged in that process today. It’s conceivable that competitive advantage will increasingly rest in having executives who know how to apply AI well. In some domains, like investment, that is already happening, and the difference in returns can be staggering. I find helping companies be part of that evolution very exciting.
Explore a career with us
Related articles.

Strategic courage in an age of volatility

Bias Busters Collection
Evaluation of online job portals for HR recruitment selection using AHP in two wheeler automotive industry: a case study
- ORIGINAL ARTICLE
- Published: 12 May 2024
Cite this article

- S. M. Vadivel ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5287-3693 1 &
- Rohan Sunny ORCID: orcid.org/0009-0002-2347-3081 2
Automotive companies are booming worldwide in the economy. In order to sustain in the highly competitive world, every organization tries to create itself a trademark in the market. In our research, we looked at how two wheelers automotive company's selection enhances an organizational performance, which ensures the company's future growth. In today's fast-paced, globally integrated world, human resources are one of the most important production variables. It is critical to preserve and improve economic competitiveness by properly selecting and developing these resources. The main aim of this study is to identify the best online job portal website for recruitment at Two Wheeler Company and to suggest an HR strategy which resonates company’s values and culture. In this study, we have selected 6 criteria and 6 online popular job portals for recruitment with a sample of 15 candidates have been selected. Findings reveal that, AHP method has significant results on the selection of best employer, which helps HR Manager to finalize the decision making process/strategies. Towards the managerial implications section, the researcher aims to design an functional and effective HR strategy that can grasp, engage and retain the top talent in the organization.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this article
Price includes VAT (Russian Federation)
Instant access to the full article PDF.
Rent this article via DeepDyve
Institutional subscriptions
Availability of data and material
'Not applicable' in this section.
Abbreviations
Analytic hierarchy process
Artificial intelligence
Analysis of variance
Chief Human Resources Officer
Consistency index
Curriculum vitae
Consistency ratio
Decision making
Faculty Development Programme
Hierarchical linear modelling
Human resources
Research and Development
Randomized index
Structural equation modelling
Search engine optimization
Triple bottom line
Technique for order preference by similarity
Maximum Eigen value
The normalized value of ith criterion for the jth alternative
The normalized value of jth criterion for the ith alternative
The number of alternatives for a certain MCDM problem
The number of criteria for a certain MCDM problem
Avinash Kapse S, Vishal Patil S, Nikhil PV (2021) E-Recruitment. Int J Eng Adv Technol (IJEAT) 1(4):82–86
Google Scholar
Chahar B, Jain SR, Hatwal V (2021) Mediating role of employee motivation for training, commitment, retention, and performance in higher education institutions. Probl Perspect Manag 19(3):95
Chauhan P (2019) Impact of training and development programs on motivation of employees in “A” graded commercial bank of Nepal. Int J Res Anal Rev 6(3):850–857
Elsafty A, Oraby M (2022) The impact of training on employee retention: an empirical research on the Private Sector in Egypt. Int J Bus Manage 17(5):58–74
Article Google Scholar
Habibie M, Mustika I (2020) The effect of training on work motivation and its impact on employee performance (Case Study at BPJS Ketenagakerjaan Headquarters). Int J Innovat Sci Res Technol 5(7):51–57
Haryono S, Supardi S, Udin U (2020) The effect of training and job promotion on work motivation and its implications on job performance: evidence from Indonesia. Manage Sci Lett 10(9):2107–2112
Horodyski P (2023a) Recruiter’s perception of artificial intelligence (AI)-based tools in recruitment. Comp Human Behav Reports 10:100298
Horodyski P (2023b) Applicants’ perception of artificial intelligence in the recruitment process. Comp Human Behav Reports 11:100303
Jack Walker H, Feild HS, Giles WF, Bernerth JB, Short JC (2011) ‘so what do you think of the organization? a contextual priming explanation for recruitment web site characteristics as antecedents of job seekers’ organizational image perceptions. Organ Behav Human Decis Process 2(2011):165–178
Khan N (2018) Does training & employee commitment predict employee retention. In: International Conference on Management and Information Systems (Vol. 21, pp. 120–124)
Lee I (2005) The evolution of E-Recruiting. A content analysis of Fortune 100 Career Websites. J Electronic Commerce Organ 3(3):57–68
Lievens F, Harris MM (2003) Research on Internet recruiting and testing: current status and future directions. Int Rev Ind Organ Psychol 16:131–165
Lin CY, Huang CK (2021) Employee turnover intentions and job performance from a planned change: the effects of an organizational learning culture and job satisfaction. Int J Manpow 42(3):409–423
Martins D, Diaconescu LM (2014) Expatriates recruitment and selection for long-term international assignments in Portuguese companies. Tékhne 12:48–57
RoyChowdhury T, Srimannarayana M (2013) Applicants’ perceptions on online recruitment procedures. Manage Labour Stud 38(3):185–199
Ryu G, Moon SG (2019) The effect of actual workplace learning on job satisfaction and organizational commitment: The moderating role of intrinsic learning motive. J Workplace Learn 31(8):481–497
Saaty TL (1990) How to make a decision: the analytic hierarchy process. Eur J Oper Res 48(1):9–26
Sengazhani Murugesan V, Sequeira AH, Shetty DS, Jauhar SK (2020) Enhancement of mail operational performance of India post facility layout using AHP. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manage 11(2):261–273
Sigalingging H, Pakpahan ME (2021) The Effect of training and work environment on employee performance with motivation as an intervening variable At PT Intraco Agroindustry. South East Asia Journal of Contemporary Business. Econ Law 24(6):130–139.
Sharawat K, Dubey SK (2018) An approach to vendor selection on usability basis by AHP and fuzzy topsis method. In: Soft computing: theories and applications: proceedings of SoCTA 2016, vol 2. Springer, Singapore, pp 595–604
Steil AV, de Cuffa D, Iwaya GH, Pacheco RCDS (2020) Perceived learning opportunities, behavioral intentions and employee retention in technology organizations. J Work Learn 32(2):147–159
Sugiarti E (2022) The influence of training, work environment and career development on work motivation that has an impact on employee performance at PT. Suryamas Elsindo Primatama In West Jakarta. Int J Artif Intell Res 6(1.2).
Sumrit D (2020) Supplier selection for vendor-managed inventory in healthcare using fuzzy multi-criteria decision-making approach. Decis Sci Lett 9(2):233–256
Thompson LF, Braddy PW, Wuensch KL (2008) E-recruitment and the benefits of organizational web appeal. Comp Human Behav 24(5):2384–2398
Turan FK, Scala NM, Sacre MB, Needy KL (2009) An Analytic Network Process (ANP) approach to the project portfolio management for Organizational Sustainability. In: Proceedings of the Industrial Engineering Research Conference. Institute of Industrial Engineers.
Wadhawan S, Sinha S (2018) Factors Influencing Young Job Seekers Perception towards Job Portals. AIMS Int J Manage 12(3).
Weerarathna RS, Somawardana WSD (2021) Impact on training and employee motivation in an electricity company. Future Work, 497.
Zusman R, Landis R (2002) Applicant preferences for Web-based versus traditional job postings. Comput Hum Behav 18(3):285–329
Download references
Acknowledgements
The authors would like to express their gratitude to two wheeler Automotive Industries in Chennai, Tamil Nadu, India, for their invaluable assistance and cooperation. We greatly acknowledge Ms. Ruchi Mishra, Research scholar from NIT Karnataka, for editing this manuscript in better form.
There is no funding provided in this research.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Operations Management Division, Vellore Institute of Technology Chennai, Vandalur-Kelambakkam Road, Chennai, 600127, India
S. M. Vadivel
Vellore Institute of Technology Chennai, Vandalur-Kelambakkam Road, Chennai, 600127, India
Rohan Sunny
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
S M Vadivel: Methodology, Writing—review & editing, Supervision. Rohan Sunny: Data Curation, Writing—original draft preparation.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to S. M. Vadivel .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interests.
The authors declare that they have no competing interests.
Ethics approval and consent to participate
This manuscript has a research study involves human participants (Interview Candidates) for studying job portal evaluations in Indian two wheeler company running in Chennai, Tamil Nadu.
Consent for publication
‘ Not applicable’ in this section.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Springer Nature or its licensor (e.g. a society or other partner) holds exclusive rights to this article under a publishing agreement with the author(s) or other rightsholder(s); author self-archiving of the accepted manuscript version of this article is solely governed by the terms of such publishing agreement and applicable law.
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Vadivel, S.M., Sunny, R. Evaluation of online job portals for HR recruitment selection using AHP in two wheeler automotive industry: a case study. Int J Syst Assur Eng Manag (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-024-02358-z
Download citation
Received : 04 December 2023
Revised : 07 April 2024
Accepted : 25 April 2024
Published : 12 May 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s13198-024-02358-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Analytical hierarchy process (AHP)
- Online job portals
- Automobile two wheeler industries
- Artificial intelligence (AI)
- HR recruitment
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research

Salesforce is closed for new business in your area.

COMMENTS
Fifty four percent of raw case users came from outside the U.S.. The Yale School of Management (SOM) case study directory pages received over 160K page views from 177 countries with approximately a third originating in India followed by the U.S. and the Philippines. Twenty-six of the cases in the list are raw cases.
Case Study Research & Development (CRDT) | December 19, 2017. We generated a list of the 40 most popular Yale School of Management case studies in 2017 by combining data from our publishers, Google analytics, and other measures of interest and adoption. In compiling the list, we gave additional weight to usage outside Yale.
1. The Army Crew Team. Emily Michelle David, Assistant Professor of Management, China Europe International Business School (CEIBS) EMILY MICHELLE DAVID Assistant Professor, CEIBS. "I love teaching The Army Crew Team case because it beautifully demonstrates how a team can be so much less than the sum of its parts.
Case Library Control Panel. Welcome to the Case Library, Management Consulted's repository of over 600 cases, organized by firm, difficulty, and subject matter. Right now, you're looking at the Limited Case Library, a free version that lets users see one whole case and preview another. If you should have access to the whole course, but are ...
HBS Case Selections. Get the perspectives and context you need to solve your toughest work problems with these immersive sets of real-world scenarios from Harvard Business School.
Providing a complete portal to the world of case study research, the Fifth Edition of Robert K. Yin′s bestselling text offers comprehensive coverage of the design and use of the case study method as a valid research tool. The book offers a clear definition of the case study method as well as discussion of design and analysis techniques.
For example, the case study quotes the social media manager and project manager's insights regarding team-wide communication and access before explaining in greater detail. Takeaway: Highlight pain points your business solves for its client, and explore that influence in greater detail. 3. EndeavourX and Figma.
Revised on November 20, 2023. A case study is a detailed study of a specific subject, such as a person, group, place, event, organization, or phenomenon. Case studies are commonly used in social, educational, clinical, and business research. A case study research design usually involves qualitative methods, but quantitative methods are ...
These case studies offer valuable insights into different facets of Business Management, including innovation, strategic decision-making, customer-centric approaches, and market disruption. Analysing these cases provides aspiring managers and entrepreneurs with real-world examples of how effective strategies, risk-taking, and adaptability can ...
Rather than discussing case study in general, a targeted step-by-step plan with real-time research examples to conduct a case study is given. Introduction In recent years, a great increase in the number of students working on their final dissertation across business and management disciplines has been noticed ( Lee & Saunders, 2017 ).
15 Real-Life Case Study Examples. Now that you understand what a case study is, let's look at real-life case study examples. In this section, we'll explore SaaS, marketing, sales, product and business case study examples with solutions. Take note of how these companies structured their case studies and included the key elements.
In their book Difficult Conversations: How to Discuss What Matters Most (Penguin Putnam, 2000), authors Douglas Stone, Bruce Patton, and Sheila Heen tell us how to engage in the conversations in our professional or personal lives that make us uncomfortable by examining a case study of conflict management. Tough, honest conversations are critical for managers, whether they need to change the ...
Change Management. New research on change management from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including how to plan for opportunities, how to effect change in the workplace, and case studies on how business leaders managed the economic crisis. Page 1 of 66 Results →. 12 Dec 2023.
Learning about them through a short case study is an excellent way to gain a better understanding of these concepts. Here are 05 short case studies on change management that offer you valuable insights on managing change. 1. Adobe- a transformation of HR functions to support strategic change. Many a times external factors lead to changes in ...
Over 500 cases from Marketline/Datamonitor, among other publishers. Ivey at the University of Western Ontario provides Complimentary Cases. Cases cover the subjects: entrepreneurship, leadership/ethics, operations management, strategy, sustainability, and system dynamics. Use the Narrow Your Results option to select subjects and "Available to ...
Overview. We now fulfill the promise of this book, with a set of case study examples that apply the concepts and phases of the roadmap. (The first four case studies appeared in the first print edition of the book. All the others have been contributed by students or other readers of the book and edited for consistency.——Ed.)
An operations management example that well-illustrates all three of these strengths is the case study conducted by Gerwin (1981) on one of the first flexible manufacturing systems (FMSs). Yin (2017) , McCutcheon and Meredith (1993) , and Eisenhardt (1989) identify other advantages of the case method, such as the richness of its explanations and ...
Taking BioPhorum Value Back into your Organization: Case Study Examples from BioPhorum Drug Substance There are many benefits to a BioPhorum membership - from productivity and cost improvements to workforce enablement. A crucial factor in delivering these is a member's interaction with BioPhorum, so we wanted to understand how different companies approach the governance of… Read More »
Top 10 Project Management Case Studies with Examples 2024. 1. NASA's Mars Exploration Rover: Innovative project management in space exploration. 2. Apple's iPhone Development: Delivering revolutionary products with precision. 3. Tesla's Gigafactory Construction: Exemplary project execution in renewable energy.
Nueva Ecija University of Science and Technology, Cabanatuan, Philippines. Abstract. This study described the Case of the Organization and Management of Bon- gabon Market Vendors Multi-Purpose Cooperative (BMVMPC). Specifically, it looked into the problems encountered of the Bongabon Market Vendor and analyzed how four Functions of Management ...
ORGANIZATION AND MANAGEMENT. Performance task 1 CASE STUDY In June 2012, Zeta Furniture Company, a leading furniture store in the Philippines, hired a salesman who looked perfect for the job opening based on the application form which he filled out and submitted to the company's human resources department. After working in the company for a few months, the man raped female customer in her home ...
For cross-cultural conflicts, it's important to consider cultural nuances in communication styles and norms. 2. Set Aside Preconceived Opinions. Ask all parties to approach the conflict with an open mind. In virtual team settings, be mindful of potential misunderstandings due to lack of non-verbal cues. 3.
Joanna Pachner: Do you think this worry about job security and the potential that AI will automate strategy is realistic? Yuval Atsmon: The question of whether AI will replace human judgment and put humanity out of its job is a big one that I would leave for other experts. The pertinent question is shorter-term automation. Because of its complexity, strategy would be one of the later domains ...
Automotive companies are booming worldwide in the economy. In order to sustain in the highly competitive world, every organization tries to create itself a trademark in the market. In our research, we looked at how two wheelers automotive company's selection enhances an organizational performance, which ensures the company's future growth. In today's fast-paced, globally integrated world ...
Shift from reactive to proactive service with real-time asset tracking. Monitor service outcomes and create preventive maintenance plans based on asset use, condition, and specific criteria. For example, you can schedule service if an asset's temperature exceeds a set threshold — ensuring smooth operations and preventing downtime
The online survey was emailed to a sample of marketers using lists from CMI and MarketingProfs. This article presents the findings from the 894 respondents, mostly from North America, who indicated their organization is primarily B2B and that they are either content marketers or work in marketing, communications, or other roles involving content.