

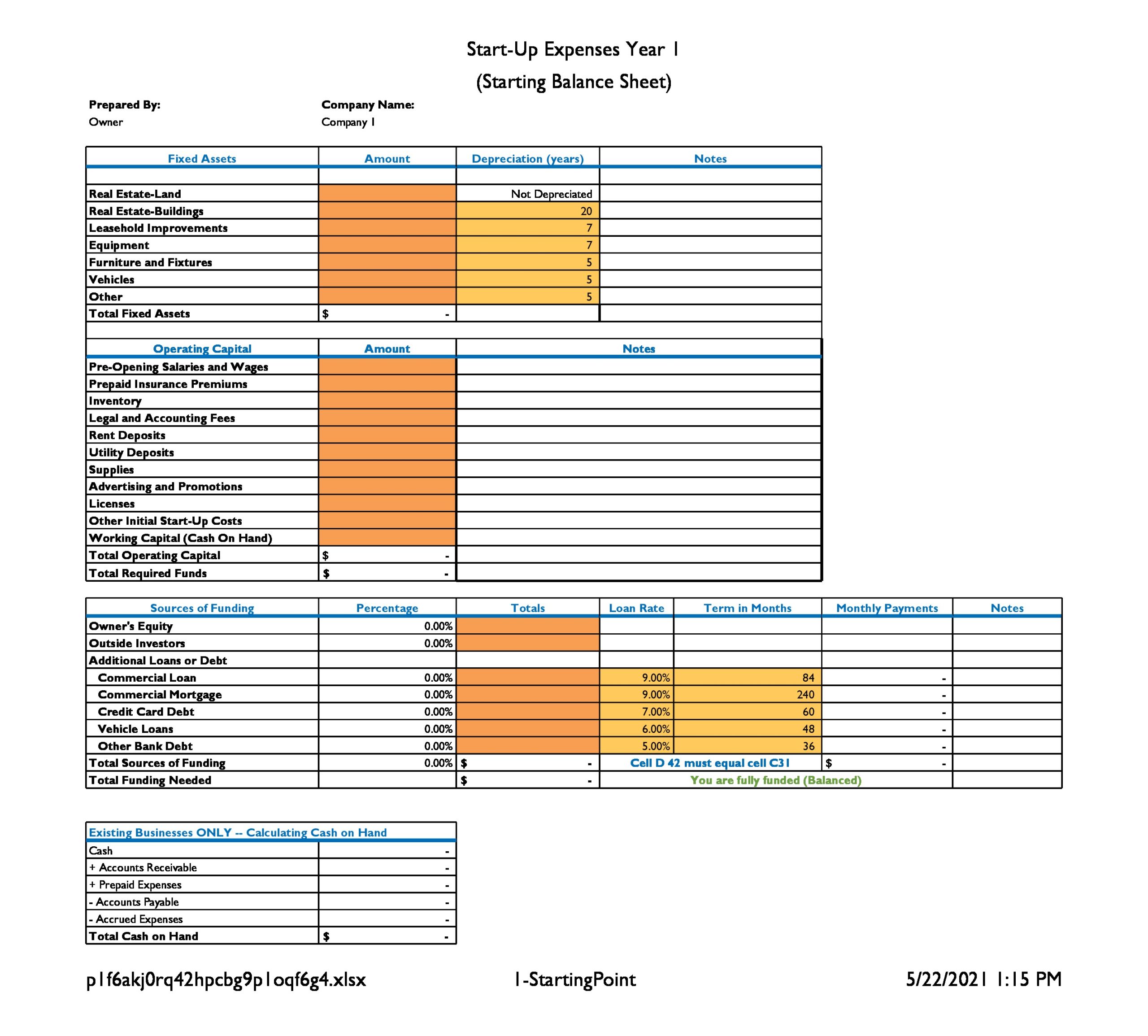
Free Business Plan Excel Template [Excel Download]
Written by Dave Lavinsky

A business plan is a roadmap for growing your business. Not only does it help you plan out your venture, but it is required by funding sources like banks, venture capitalists and angel investors.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
The body of your business plan describes your company and your strategies for growing it. The financial portion of your plan details the financial implications of your business: how much money you need, what you project your future sales and earnings to be, etc.
Below you will be able to download our free business plan excel template to help with the financial portion of your business plan. You will also learn about the importance of the financial model in your business plan.
Download the template here: Financial Plan Excel Template
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less! It includes a simple, plug-and-play financial model and a fill-in-the-blanks template for completing the body of your plan.
What’s Included in our Business Plan Excel Template
Our business plan excel template includes the following sections:
Income Statement : A projection of your business’ revenues, costs, and expenses over a specific period of time. Includes sections for sales revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, and net profit or loss.
Example 5 Year Annual Income Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Revenues | $368,306 | $402,786 | $440,494 | $481,732 | $526,831 | |
| Direct Costs | ||||||
| Direct Costs | $10,475 | $10,901 | $11,343 | $11,804 | $12,283 | |
| Salaries | $58,251 | $60,018 | $61,839 | $63,715 | $65,648 | |
| Marketing Expenses | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Rent/Utility Expenses | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Other Expenses | $12,135 | $12,503 | $12,883 | $13,274 | $13,676 | |
| Depreciation | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | |
| Amortization | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Interest Expense | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $273,443 | $305,362 | $340,428 | $378,938 | $421,222 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $95,705 | $106,877 | $119,149 | $132,628 | $147,427 | |
| Net Profit Margin (%) | 48.3% | 49.3% | 50.2% | 51.1% | 52% |
Cash Flow Statement : A projection of your business’ cash inflows and outflows over a specific period of time. Includes sections for cash inflows (such as sales receipts, loans, and investments), cash outflows (such as expenses, salaries, and loan repayments), and net cash flow.
Example 5 Year Annual Cash Flow Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Net Income (Loss) | $177,738 | $198,485 | $221,278 | $246,310 | $273,794 | |
| Change in Working Capital | ($24,912) | ($2,754) | ($3,025) | ($2,052) | ($3,523) | |
| Plus Depreciation | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | $6,000 | |
| Plus Amortization | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Fixed Assets | ($30,000) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Intangible Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from Equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from Debt financing | $80,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | ($80,000) | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $208,826 | $410,557 | $634,809 | $885,067 | |
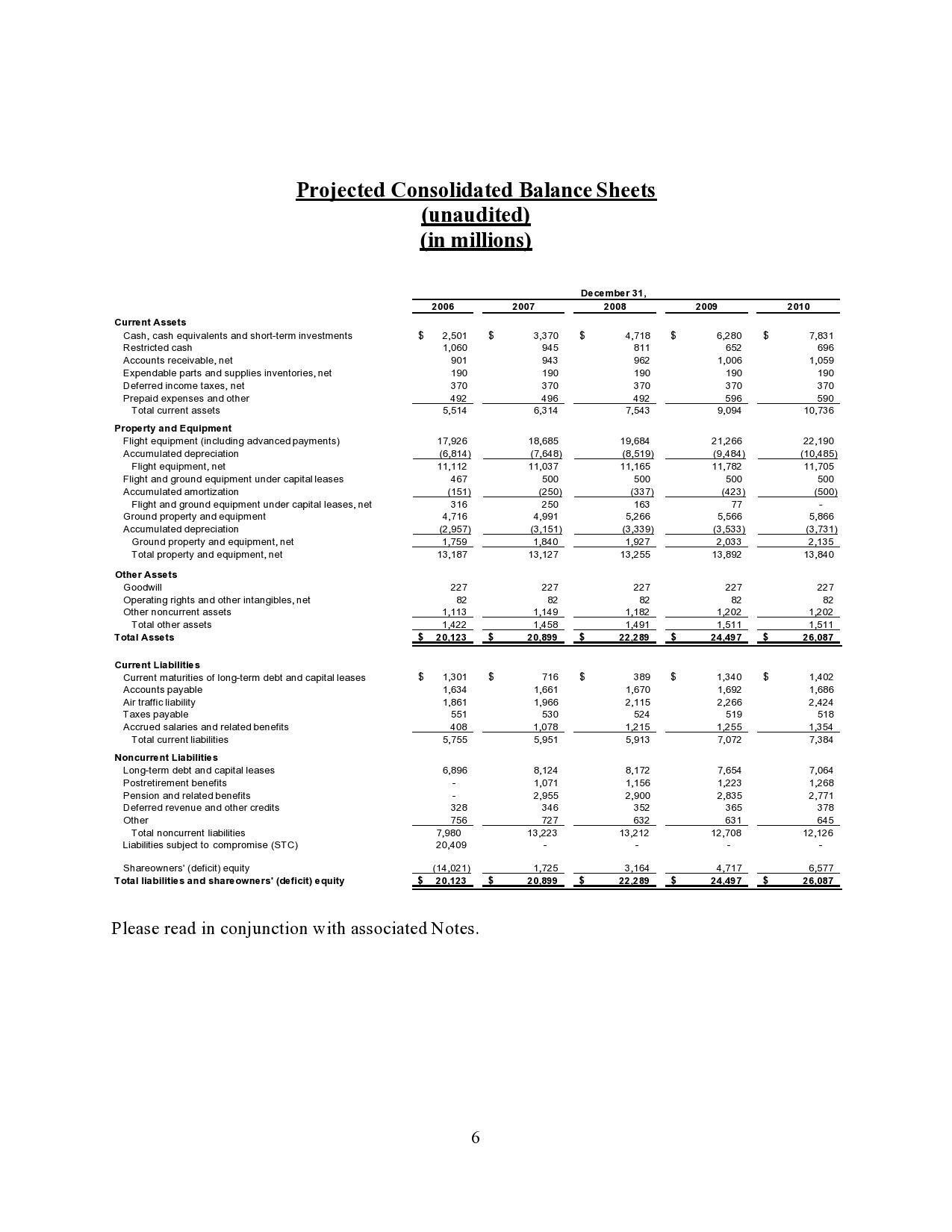
Balance Sheet : A snapshot of your business’ financial position at a specific point in time. Includes sections for assets (such as cash, inventory, equipment, and property), liabilities (such as loans, accounts payable, and salaries payable), and owner’s equity (such as retained earnings and capital contributions).
Example 5 Year Annual Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Cash | $208,826 | $410,557 | $634,809 | $885,067 | $1,081,338 | |
| Other Current Assets | $31,729 | $34,700 | $37,948 | $40,144 | $43,902 | |
| Intangible Assets | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Acc Amortization | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Fixed Assets | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | $30,000 | |
| Accum Depreciation | $6,000 | $12,000 | $18,000 | $24,000 | $30,000 | |
| Preliminary Exp | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Current Liabilities | $6,817 | $7,033 | $7,256 | $7,399 | $7,634 | |
| Debt outstanding | $80,000 | $80,000 | $80,000 | $80,000 | $0 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $177,738 | $376,224 | $597,502 | $843,812 | $1,117,606 | |
Download the template here: Business Plan Excel Template
The template is easy to customize according to your specific business needs. Simply input your own financial data and projections, and use it as a guide to create a comprehensive financial plan for your business. Remember to review and update your financial plan regularly to track your progress and make informed financial decisions.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
The importance of the financial model in your business plan.
A solid financial model is a critical component of any well-prepared business plan. It provides a comprehensive and detailed projection of your business’ financial performance, including revenue, expenses, cash flow, and profitability. The financial model is not just a mere set of numbers, but a strategic tool that helps you understand the financial health of your business, make informed decisions, and communicate your business’ financial viability to potential investors, lenders, and other stakeholders. In this article, we will delve into the importance of the financial model in your business plan.
- Provides a roadmap for financial success : A well-structured financial model serves as a roadmap for your business’ financial success. It outlines your revenue streams, cost structure, and cash flow projections, helping you understand the financial implications of your business strategies and decisions. It allows you to forecast your future financial performance, set financial goals, and measure your progress over time. A comprehensive financial model helps you identify potential risks, opportunities, and areas that may require adjustments to achieve your financial objectives.
- Demonstrates financial viability to stakeholders : Investors, lenders, and other stakeholders want to see that your business is financially viable and has a plan to generate revenue, manage expenses, and generate profits. A robust financial model in your business plan demonstrates that you have a solid understanding of your business’ financials and have a plan to achieve profitability. It provides evidence of the market opportunity, pricing strategy, sales projections, and financial sustainability. A well-prepared financial model increases your credibility and instills confidence in your business among potential investors and lenders.
- Helps with financial decision-making : Your financial model is a valuable tool for making informed financial decisions. It helps you analyze different scenarios, evaluate the financial impact of your decisions, and choose the best course of action for your business. For example, you can use your financial model to assess the feasibility of a new product launch, determine the optimal pricing strategy, or evaluate the impact of changing market conditions on your cash flow. A well-structured financial model helps you make data-driven decisions that are aligned with your business goals and financial objectives.
- Assists in securing funding : If you are seeking funding from investors or lenders, a robust financial model is essential. It provides a clear picture of your business’ financials and shows how the funds will be used to generate revenue and profits. It includes projections for revenue, expenses, cash flow, and profitability, along with a breakdown of assumptions and methodology used. It also provides a realistic assessment of the risks and challenges associated with your business and outlines the strategies to mitigate them. A well-prepared financial model in your business plan can significantly increase your chances of securing funding as it demonstrates your business’ financial viability and growth potential.
- Facilitates financial management and monitoring : A financial model is not just for external stakeholders; it is also a valuable tool for internal financial management and monitoring. It helps you track your actual financial performance against your projections, identify any deviations, and take corrective actions if needed. It provides a clear overview of your business’ cash flow, profitability, and financial health, allowing you to proactively manage your finances and make informed decisions to achieve your financial goals. A well-structured financial model helps you stay on top of your business’ financials and enables you to take timely actions to ensure your business’ financial success.
- Enhances business valuation : If you are planning to sell your business or seek investors for an exit strategy, a robust financial model is crucial. It provides a solid foundation for business valuation as it outlines your historical financial performance, future projections, and the assumptions behind them. It helps potential buyers or investors understand the financial potential of your business and assess its value. A well-prepared financial model can significantly impact the valuation of your business, and a higher valuation can lead to better negotiation terms and higher returns on your investment.
- Supports strategic planning : Your financial model is an integral part of your strategic planning process. It helps you align your financial goals with your overall business strategy and provides insights into the financial feasibility of your strategic initiatives. For example, if you are planning to expand your business, enter new markets, or invest in new technologies, your financial model can help you assess the financial impact of these initiatives, including the investment required, the expected return on investment, and the timeline for achieving profitability. It enables you to make informed decisions about the strategic direction of your business and ensures that your financial goals are aligned with your overall business objectives.
- Enhances accountability and transparency : A robust financial model promotes accountability and transparency in your business. It provides a clear framework for setting financial targets, measuring performance, and holding yourself and your team accountable for achieving financial results. It helps you monitor your progress towards your financial goals and enables you to take corrective actions if needed. A well-structured financial model also enhances transparency by providing a clear overview of your business’ financials, assumptions, and methodologies used in your projections. It ensures that all stakeholders, including investors, lenders, employees, and partners, have a clear understanding of your business’ financial performance and prospects.
In conclusion, a well-prepared financial model is a crucial component of your business plan. It provides a roadmap for financial success, demonstrates financial viability to stakeholders, helps with financial decision-making, assists in securing funding, facilitates financial management and monitoring, enhances business valuation, supports strategic planning, and enhances accountability and transparency in your business. It is not just a set of numbers, but a strategic tool that helps you understand, analyze, and optimize your business’ financial performance. Investing time and effort in creating a comprehensive and robust financial model in your business plan is vital for the success of your business and can significantly increase your chances of achieving your financial goals.


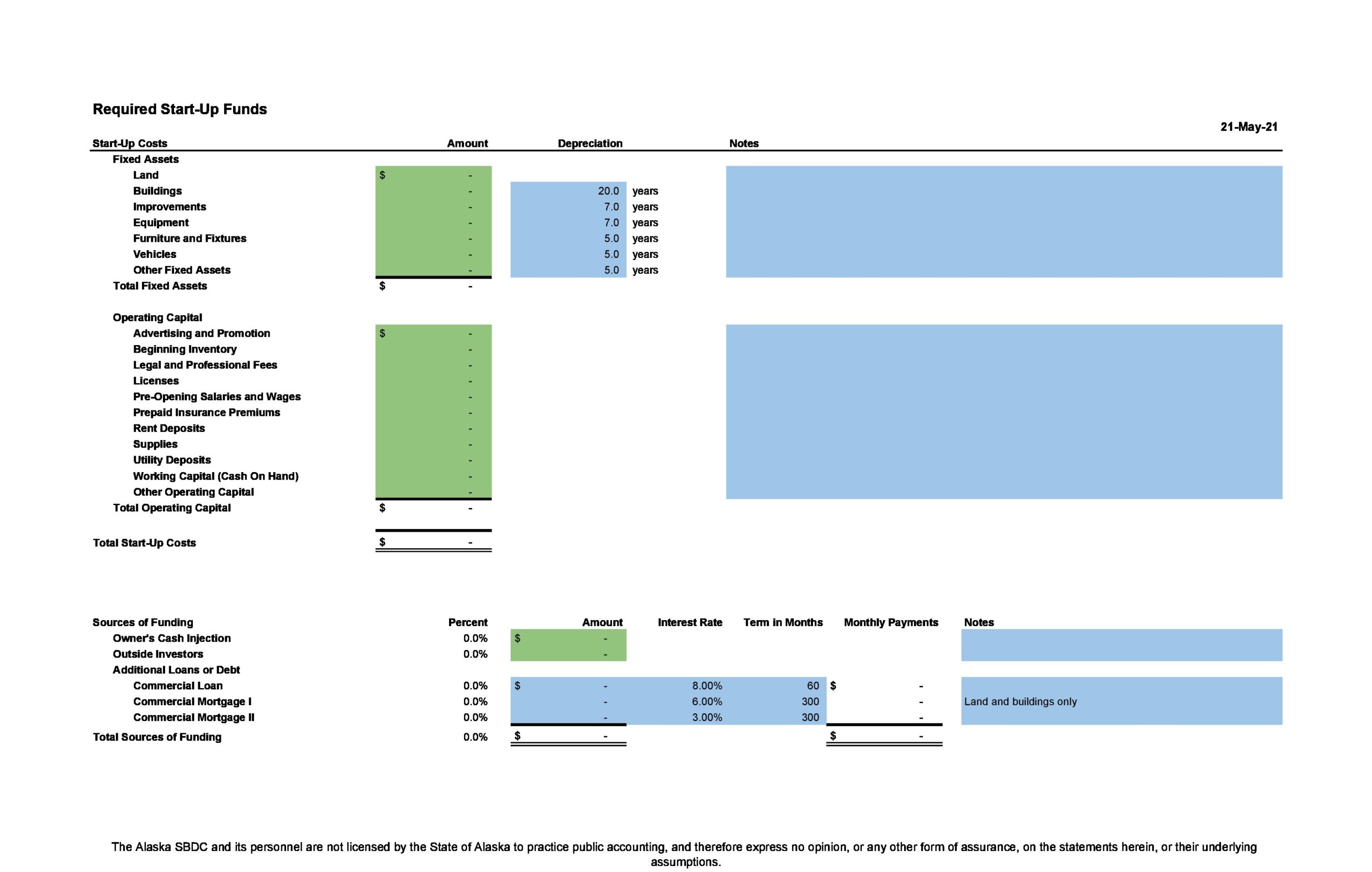
5-Year Financial Plan Template
Whether you are already running a business, or making plans to start one up, financial planning is a vital part of ensuring your success. Not knowing your expected income and expenditure will make it difficult to plan, and hard to find investors.
This 5-Year Financial Plan spreadsheet will make it easy for you to calculate profit and loss, view your balance sheet and cash flow projections, as well as calculate any loan payments you may have. Whilst the wording on this spreadsheet is focussed around products, it can just as easily be used for businesses who largely provide services to their customers.
5-Year Financial Plan Projection

How to use Financial Plan
Model inputs.
Use the Model Inputs sheet to enter information about your business that will be used to model results seen on the other pages.
Forecasted Revenue
The forecasted revenue section allows you to estimate your revenue for 4 different products. Simply use the white boxes to enter the number of units you expect to sell, and the price you expect to sell them for, and the spreadsheet will calculate the total revenue for each product for the year. If you want to give your products names, simply type over the words "Product 1", "Product 2" etc. and these names will be carried through to the rest of the spreadsheet.
Cost of Goods Sold
Your margins are unlikely to be the same on all of your products, so the cost of goods sold allows you to enter your expected gross margin for each product into the white boxes in Column B. The spreadsheet will automatically calculate the annual cost of goods sold based on this information, along with your forecasted revenue.
Annual Maintenance, Repair and Overhaul
As the cost of annual maintenance, repair and overhaul is likely to increase each year, you will need to enter a percentage factor on your capital equipment in the white box in Column B. This will be used to calculate your operating expenses in the profit and loss sheet.
Asset Depreciation
Use the white box to enter the number of years you expect your assets to depreciate over. This may vary greatly from business to business, as assets in some sectors depreciate much more quickly than they do in others.
In most parts of the world, you will have to pay income on your earnings. Enter the annual tax rate that applies to your circumstances in the white box in Column B. If you have to pay any other taxes, these can be entered later on the Profit and Loss sheet.
Although you cannot be certain of the level of inflation, you will still need to try and plan for it when coming up with a 5-year financial plan. The International Monetary Fund provide forecasts for a number of countries, so is a good place to look if you are unsure what to enter here. Simply enter your inflation rate in the white box.
Product Price Increase
As a consumer, you are no doubt aware that the price of products goes up over time. Enter a number in the white box to show the expected annual price increase of your products to enable the spreadsheet to calculate income in future years. If you are unsure what to put here, increasing your product price in line with inflation is a good starting point. If your business is just starting out, you may be able to command higher prices for your products or services as the years go on, as you build up brand recognition and a good reputation.
The funding section allows you to enter information about your business loan. To use this section, simply fill in the three white boxes representing the amount of the loan, the annual interest rate and the term of the loan in months - for example, 12 for 1 year, 24 for 2 years, 36 for 3 years, 48 for 4 years, or 60 for a 5 year loan.
Profit and loss
This sheet calculates your profit and loss for each year over a 5 year period. The profit and loss assumptions, along with income, are automatically calculated using information entered in the model inputs sheet.
Non-Operation Income
You may have, or be expecting some income in addition to your operating income. These can be entered manually in the white cells in Column B for Year 1, Column C for Year 2 and so on. There are pre-entered categories for rental, lost income and loss (or gain) on the sale of assets, as well as an additional row where you can enter your own non-operation income.
Operating Expenses
Some parts of this are already filled in based on information you put on the Model Inputs, for example, depreciation, maintenance and interest on long-term debt. Years 2-5 are also filled in for you across all categories based on the inflation information entered in the Model Inputs sheet. You therefore only need to enter your Sales and Marketing, Insurance, Payroll and Payroll Tax, Property Taxes, Utilities, Administration Fees and any Other Expenses into the white cells in Column B for Year 1.
Non-recurring Expenses
This section is for entering any expenses that you will not be paying on an annual basis. The Unexpected Expenses row allows you to enter a contingency for unexpected expenses, whilst the Other Expenses row allows you to enter any other one off expenses you may be expecting to make, for example the purchase of new equipment part way into your 5 year plan.
Income Tax is filled in based on the information you enter into the model inputs. Depending on where your business is based, you may find yourself having to pay other taxes. These can be entered in the Other Tax row. You can rename this row by typing over the "Other Tax (specify)" text.
Balance Sheet
The annual balances for Years 1-5 are, in most cases, filled in for you, based on the information you have entered on the Model Inputs sheet and in the Initial Balance column of the Balance Sheet column itself. This makes it very easy to use.
Current Assets
This is where you can enter the value of any of your current assets, with spaces to enter information about Cash and Short-term Investments, Accounts Receivable, Inventory, Prepaid Expenses and Deferred Income Tax. At the bottom of this section is a space for you to enter any other current assets you may have that do not fall into any of these categories.
Property and Equipment
Depending on the nature of your business, you may have assets such as Buildings, Land, Capital Improvements and Machinery. Enter the value of these assets into Column B, and these values will be copied over to each of the 5 years of the plan. The depreciation information entered into the Model Inputs sheet will be used to calculate the depreciation expenses, which allows a total for property and equipment to be calculated automatically.
Other Assets
This section is for entering information on any assets that don't fit in the other sections. These could be Goodwill Payments, Deferred Income Tax, Long-term Investments, Deposits, or any Other long-term assets. Enter the information into Column B, and it will be carried across to the yearly columns automatically.
Current Liabilities
As well as assets, your business is likely to have liabilities. There are spaces to enter Accounts Payable, Accrued Expenses, Notes Payable and Short-term Debt, Capital Leases and Other current liabilities. Just leave blank any rows where you do not have any liabilities, and the totals will be calculated for you.
Your long-term debt/loan information will have already been entered in the Model Inputs sheet, so the only thing to do here is to enter any other long-term debt. Unlike much of the rest of the Balance Sheet, you can manually enter different amounts for each year, as you may, for example, be expecting to take on another loan to purchase some new equipment in Year 3 as your business expands.
Other Liabilities
Use this section to enter any liabilities not covered by the pre-defined labels. You can amend the text in Column A, in order to specify the liabilities, and then enter the cost of these liabilities in Column B.
Your business is likely to have some equity, and this can be entered into this section. You can fill out the Owner's Equity, Paid-in Capital and Preferred Equity in Column B. Your retained earnings are automatically calculated based on the Profit and Loss sheet.
Much of the information on the cash flow sheet is based on calculations in the Balance Sheet. It is important to plan your cash flow carefully, so that you know what funds you will have available to buy new stock and equipment.
Operating Activities
Much of this section is automatically filled in based on your balance sheet. There are only three rows to fill out, which are Amortization, Other Liabilities and Other Operating Cash Flow. You only need to fill out the white boxes in Column B for Year 1, as these values will automatically be carried over into subsequent years for you.
Investing Activities
Your capital expenditures and sale of fixed assets will be automatically populated if you have filled out the relevant sections of the Balance Sheet. They will be blank if they do not apply. As investing activities can vary year on year, you will need to fill out any investment activities for each of the 5 years in the appropriate columns for Acquisition of Business, and any Other Investing Cash Flow items.
Financing Activities
The long-term debt/financing row will be pre-filled based on the loan information previously entered. Use Column B to fill out your Preferred Stock, Total Cash Dividends Paid, Common Stock and Other Financing Cash Flow items for Year 1. This information will automatically carried over to Years 2-5.
Loan Payment Calculator
There is nothing to enter on this sheet, as it is for information only. Whether or not you already have a loan, or are using this spreadsheet as a part of a business plan to help you obtain one, it allows you to easily see how much you will be paying each month, showing how much you are paying off your loan, and how much you are paying in interest. This will allow you to get an idea of whether or not you can afford to borrow a bit extra, if you feel it would allow you to push your business into higher places, or whether you need to shop around for a better interest rate or adjust the loan term in order to afford the loan payments.
Related Templates

- TemplateLab
Financial Projections Templates
34 simple financial projections templates (excel,word).
A financial projections template is a tool that is an essential part of managing businesses as it serves as a guide for the various team to achieve the desired goals. The preparation of these projections seems like a difficult task, especially for small businesses. If you can come up with financial statements , then you can also make financial projections.
Table of Contents
- 1 Financial Projections Templates
- 2 When do you need a financial projections template?
- 3 Business Projections Templates
- 4 What to include in financial projections?
- 5 Financial Forecast Templates
- 6 How do I make a financial projection?
- 7 Revenue Projection Templates
When do you need a financial projections template?
A financial projections template uses estimated or existing financial information to forecast the future expenses and income of your business. These projections don’t just consider a single scenario but different ones so you can determine how the changes in one part of your finances might affect the profitability of your company.
If you have to create a financial business projections template for your business, you can download a template to make the task easier. Financial projection has become an important tool in business planning for the following reasons:
- If you’re starting a business venture, a financial projection helps you plan your start-up budget.
- If you already have a business, a financial projection helps you set your goals and stay on track.
- If you’re thinking about getting outside financing, you need a financial projection to convince investors or lenders of the potential of your business.
Business Projections Templates
What to include in financial projections?
A financial projections template usually includes a few financial statements that will help you achieve better financial performance for your business:
- Income Statement Also called the Profit and Loss Statement , this focuses on your company’s expenses and revenues generated for a specific period of time. A typical income statement includes expenses, revenue, losses, and gains. The sum of all these is the net income, a measure of your company’s profitability.
- Cash Flow Statement Taking a look at a cash flow statement makes you understand how your company’s operations work. The statement explains in detail how much money goes in and out of your business in the form of either expense or income. This document includes the following: Operating Activities The cash flow from operating activities reports cash outflows and inflows from your company’s daily operations. This includes changes in accounts receivable, cash, inventory, accounts payable, and depreciation. Investing Activities You use the cash flows from investing activities for your company’s investments into the long-term future. This includes cash outflows for purchases of fixed assets like equipment and property and cash inflows for sales of assets. Financing Activities The financial activities in a cash flow statement show your business’ sources of cash from either banks or investors along with expenditures of cash you have paid to your shareholders. Total these at the end of each period to determine either a loss or a profit. The cash flow statement gets connected to the income statement through net income. To make this document, it requires the reconciliation of the two documents. You can calculate net profitability or income in the income statement which you then use to start the cash flow from the operations category in your cash flow statement.
- Balance Sheet This is a statement of your business’ liabilities, assets, and capital at a specific point in time. It details the balance of expenditure and income over the preceding period. This document provides you with a general overview of your business’ financial health. Here is an overview of these components: Assets These are your business’ resources with economic value that your business owns and which you believe will provide some benefit in the future. Examples of such future benefits include reducing expenses, enhancing sales, or generating cash flow. Assets typically include inventory, property, and cash. Liabilities In general, these refer to the obligations of your business to other entities. In more common terms, these are the debts that your business incurs in your daily operations. It typically includes loans and accounts payable. You can classify liabilities either as short-term or long-term. Owner’s Equity This is the amount you have left after you have paid off your liabilities. It is usually classified as retained earnings – the sum of your net income earned minus all the dividends you have paid since the start of your business.
Together with your break-even analysis and financial statements, you can include any other document that will help explain the assumptions behind your cash flow and financial forecast template.
Financial Forecast Templates
How do I make a financial projection?
The creation of a financial projections template requires the same information to use whether your business is still in its planning stages or it’s already up and running. The difference is whether you’re creating your revenue projection template using historical financial information or if you need to start from scratch.
This includes the creation of projections based on your own experiences or by conducting market research in the industry in which your business will operate. Here are some tips for creating an effective business plan financial projections template:
- Create the sales projection An important component of your business projections template is the sales projections. A business that’s already running can base its projections on its past performance, which you can derive from financial statements. When creating your sales projections, you must consider some external factors like the projected and current health of your company, if your inventory will get affected by additional tariffs, or if there is a downturn in your industry. Even if you want to remain optimistic about your business, you have to make realistic plans.
- Create the expense projection At the onset, the creation of an expense projection seems simpler because it’s much easier to predict the possible expenses of your business than it is to predict potential customers or their buying habits. If you have experience working in a certain industry, you can predict with some degree of accuracy what your fixed expenses are and any recurring expenses. But when it comes to one-time expenses that have the potential to bring down your business, these are much harder to predict. The best thing you can do in this scenario is to project expenses to the best of your ability then increase this value by 15%.
- Come up with a balance sheet for your financial projections template If you have a business that has been in operation for a couple of months, you can come up with a balance sheet using accounting software. The balance sheet shows your business’ financial status, listing its liabilities, equity, and assets balance for a certain time period. Use the current totals in your balance sheet when making your financial projections, In doing so, you will make better predictions on where your business will be a few years in the future. If you’re still in the planning stage of a business, you can create a balance sheet based on the data you’ve gathered from industry research.
- Create the income statement projection If you have a business that is currently in operation, you can create an income statement projection using your existing income statements to create an estimate of your business’ projected numbers. This is a logical move since an income statement provides a picture of your business’s net income after subtracting things like taxes, cost of goods, and other expenses. One of the main purposes of the income statement is to provide an idea of your business’ current performance. It also serves as the basis for estimating your net income for the next couple of years. If your business is still in the planning stages, the creation of a potential income statement shows that you have conducted extensive research and created a diligent and well-crafted estimate of your income in the next couple of years. If you have uncertainties on how to start creating an income statement projection, you can consult with market research firms in your locale. They can provide you with an overview of your targeted industry which includes target markets, expected and current industry growth levels, and sales.
- Come up with a cash flow projection The creation of this document is the final step leading to the completion of your financial projection. The cash flow statement is directly connected to the balance sheet and the net income statement, showing any cash-related or cash activities that can affect your industry. One of the purposes of this statement is to show how much money your business spends. This is a must for businesses obtaining financing or looking for investors. You can use this cash flow statement if your business has been in operation for a minimum of six months, but if your business is still in the planning stages, you can use the information you have gathered to create a credible projection. To make things easier for you, consider using spreadsheet software. Chances are, you’re already using spreadsheets. Using a spreadsheet will be the starting point for your financial projections. In addition, it offers flexibility that allows you to quickly judge alternative scenarios or change assumptions. Be as clear and reasonable as possible with your financial projections. Remember that financial projection is as much science as art. At some point, you will have to make assumptions on certain things like how administrative costs and raw materials will grow, revenue growth, and how efficient you will be at gathering accounts receivable for your business.
Revenue Projection Templates
More Templates
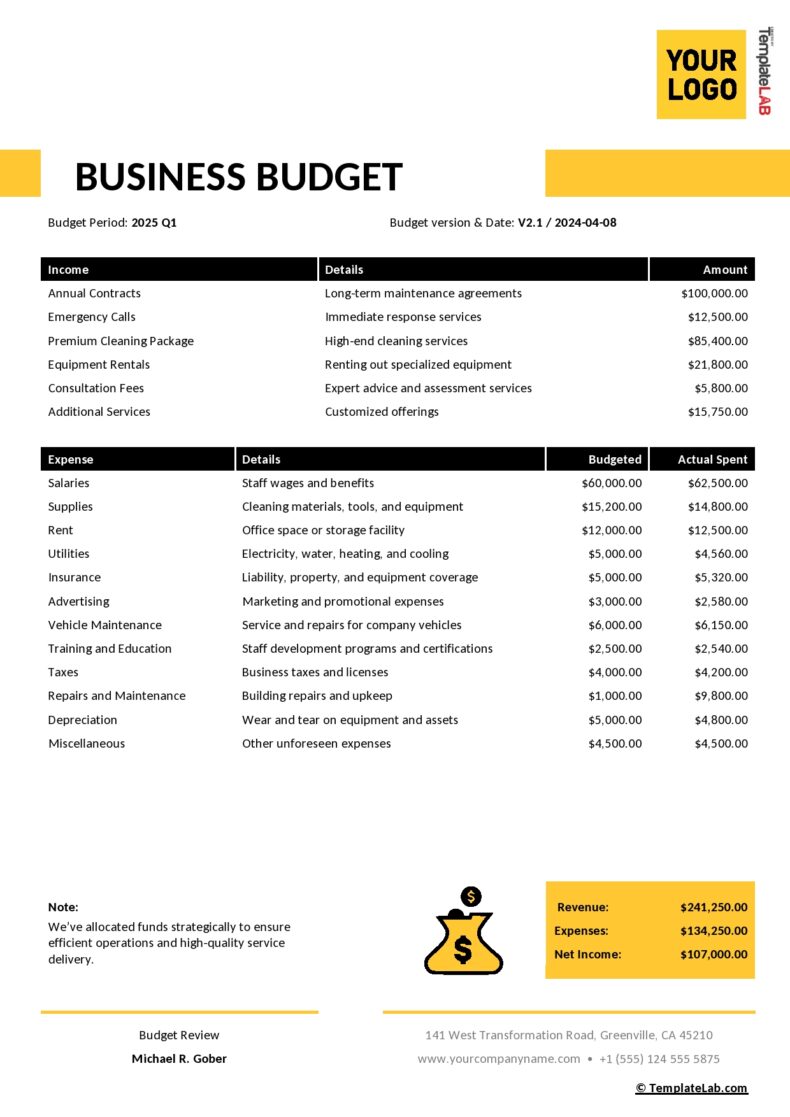
Business Budget Templates
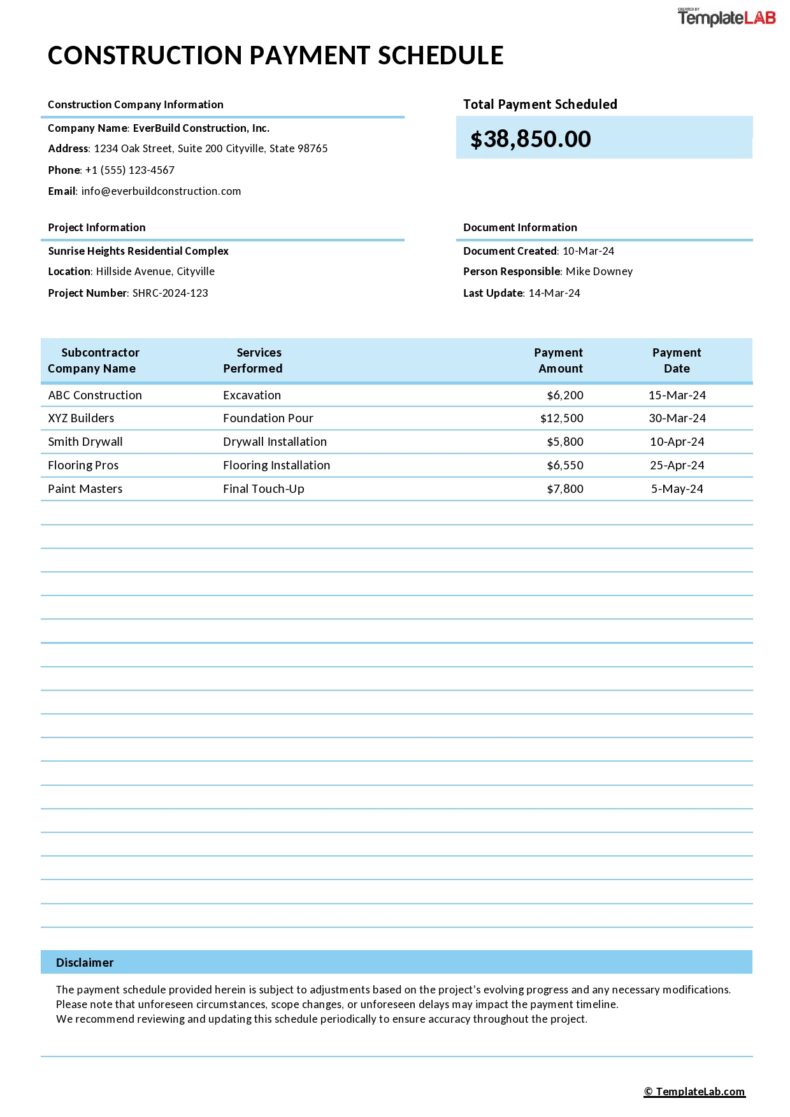
Payment Schedule Templates
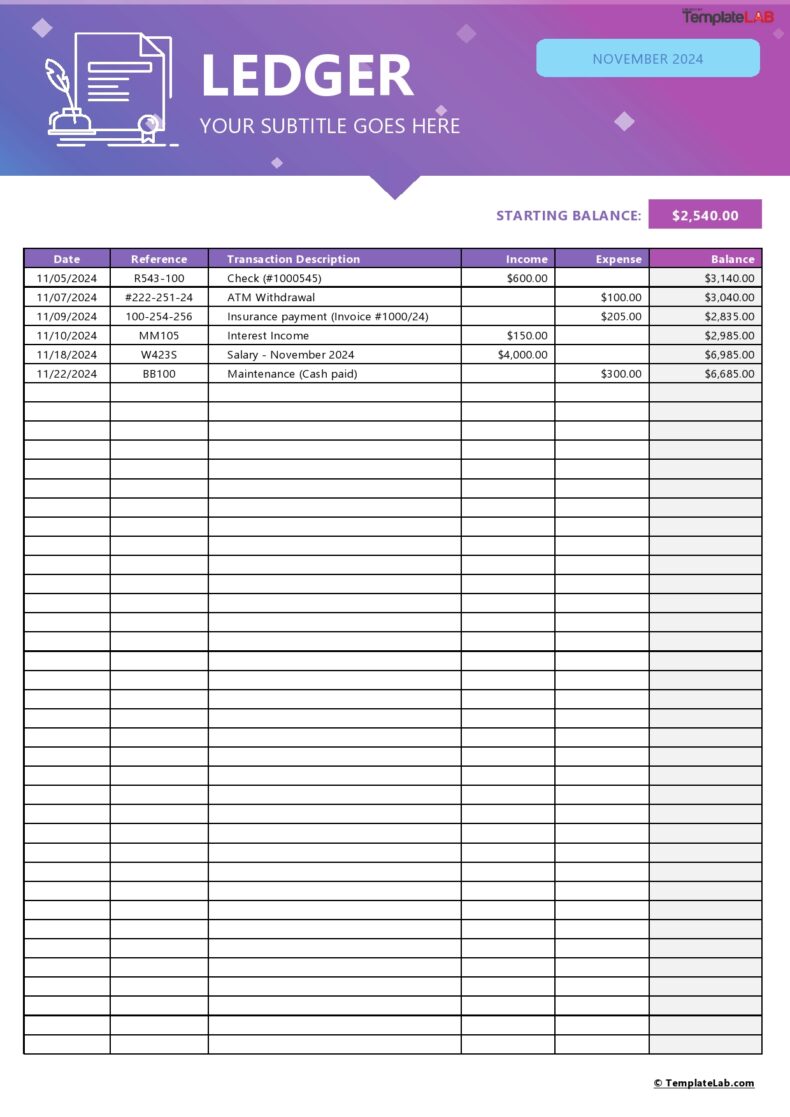
General Ledger Templates

Bill Pay Checklists

Collection Letter Templates
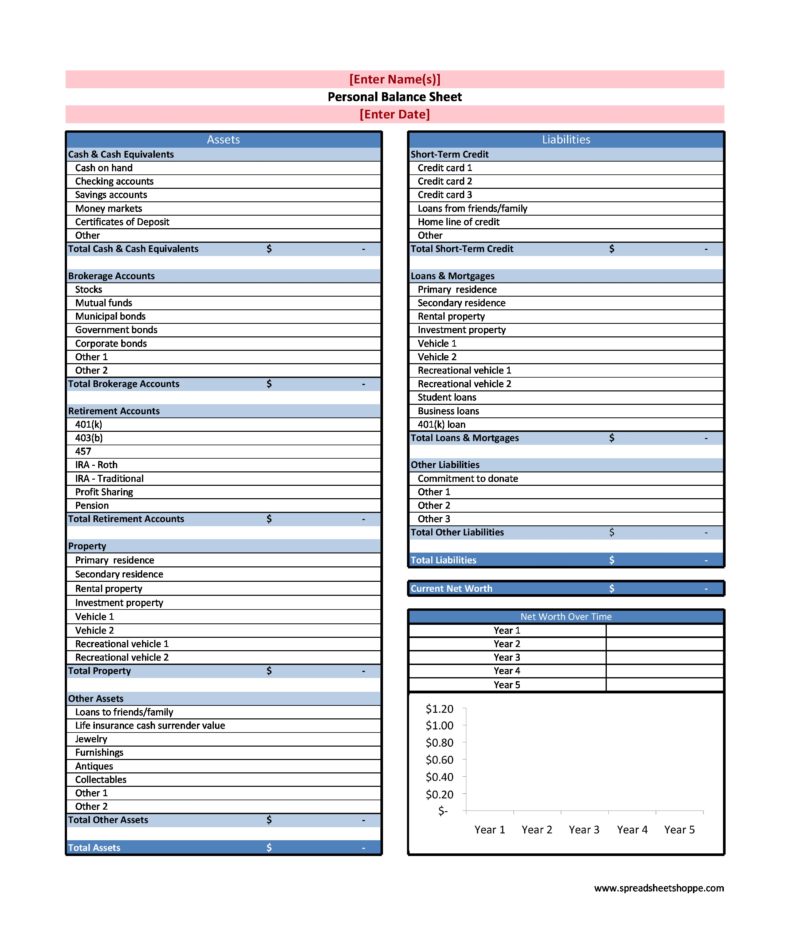
Personal Balance Sheets
Free Business Plan Templates in Excel
By Joe Weller | September 27, 2020
- Share on Facebook
- Share on LinkedIn
Link copied
In this article, we’ve rounded up an extensive list of free business plan templates and samples for organizations of all sizes. You can download all of the plans in Excel.
Included on this page, you’ll find business plan templates in Excel , business plan checklists in Excel , business plan financial templates in Excel , and more.
Business Plan Templates in Excel
These Excel business plan templates are designed to guide you through each step of a well-rounded strategy that supports your marketing, sales, financial, and operational goals.
Business Plan Template in Excel

This Excel business plan template has all the traditional components of a standard business plan, with each section divided into tabs. This template includes space to provide the executive summary, target audience characteristics, product or service offering details, marketing strategies, and more. The plan also offers built-in formulas to complete calculations for sales forecasting, financial statements, and key business ratios.
Download Business Plan Template
Excel | Smartsheet
One-Page Business Plan in Excel
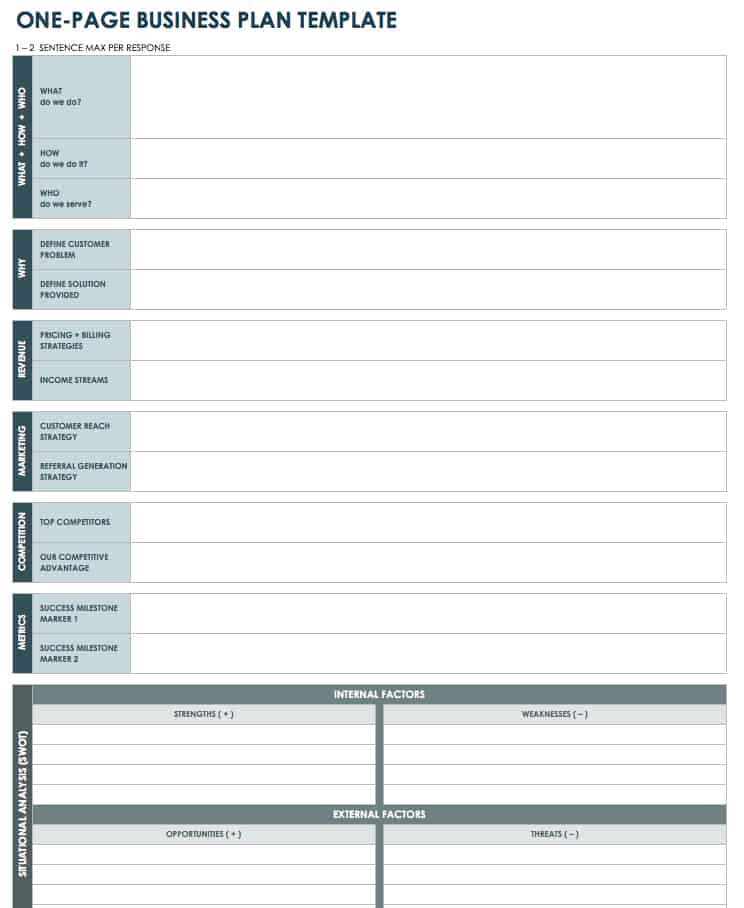
To check the feasibility of your business concept, use this single-page business plan template. The template allows you to jot down the core details related to your idea. This template also includes room for you to provide concise information about what you do, how you do it, why you do it, who your idea serves, your competitive advantage, your marketing strategies, and your success factors. At the bottom of this one-page plan, you’ll find a table to conduct a SWOT (strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats) analysis. Find more downloadable single-page plans and examples at “ One-Page Business Plan Templates with a Quick How-To Guide .”
Download One-Page Business Plan
Excel | Word | PDF | Smartsheet
Sample 30-60-90-Day Business Plan for Startup in Excel
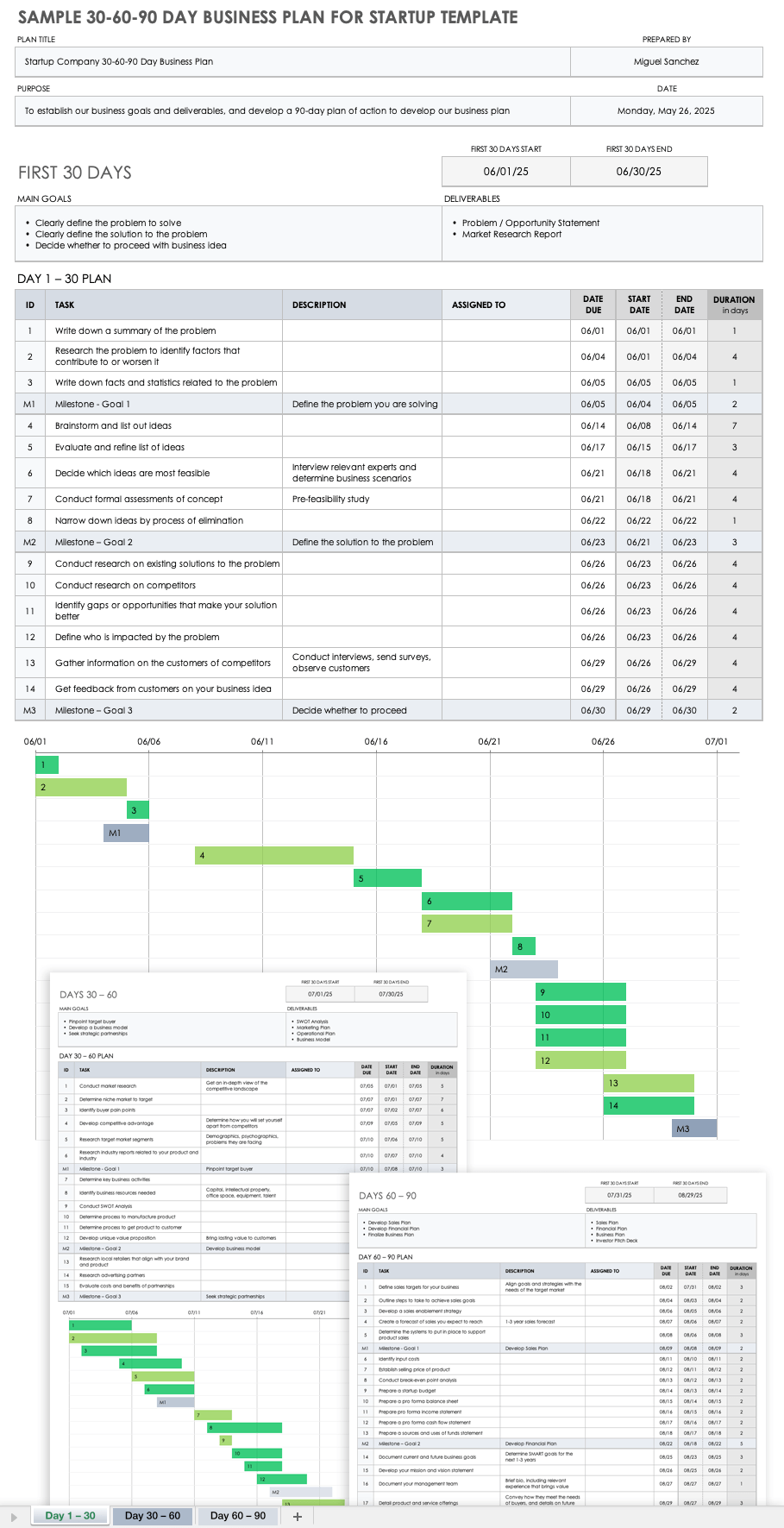
This 90-day business plan is designed for startup companies to develop a 90-day action plan. This template gives you room to outline the following: main goals and deliverables for each 30-day increment; key business activities; task ownership; and deadlines. This template also includes a built-in Gantt chart that adjusts as you enter dates. Visit “ 30-60-90-Day Business Plan Templates and Samples ” to download more free plans.
Download 30-60-90-Day Business Plan for Startup
For more free business plans in a wider variety of formats, visit “ Simple Business Plan Templates .”
Business Plan Checklists in Excel
These business plan checklists are useful for freelancers, entrepreneurs, and business owners who want to organize and track the progress of key business activities.
Business Planning Checklist with Timeline in Excel
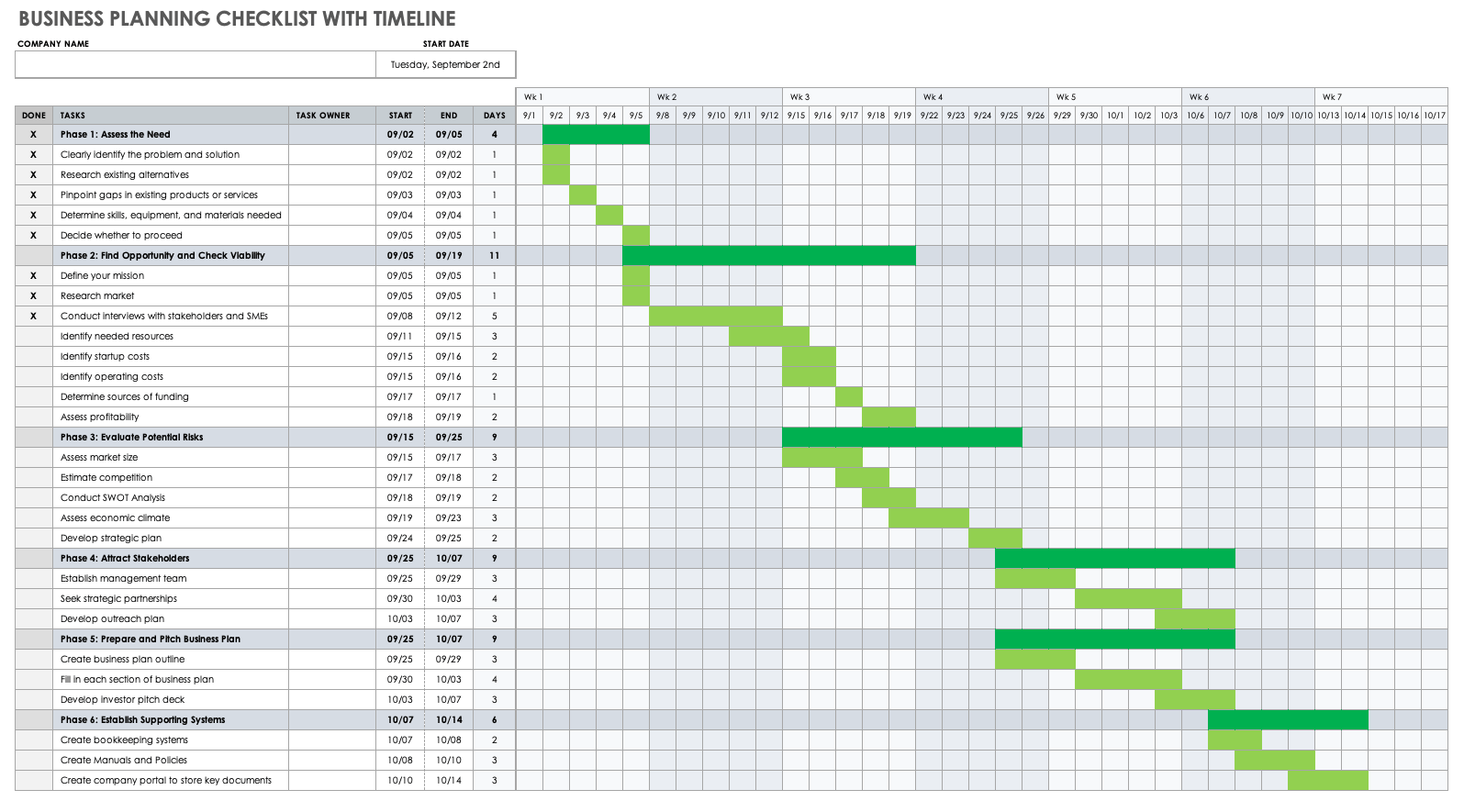
Use this checklist to keep your business planning efforts on track. This template enables you to add tasks according to each phase of your plan, assign an owner to each task, and enter the respective start and end dates. The checklist also enables you to create and color-code a visual timeline when you highlight the start and end dates for each task.
Download Business Planning Checklist with Timeline Template
Business Plan Checklist with SWOT Analysis in Excel

Use this business plan checklist to develop and organize your strategic plan. Add the name of the business activity, along with its status, due date, and pertinent notes. This template also includes a separate tab with a SWOT analysis matrix, so you can evaluate and prioritize your company’s strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats.
Download Business Plan Checklist with SWOT Analysis - Excel
Business Startup Checklist in Excel
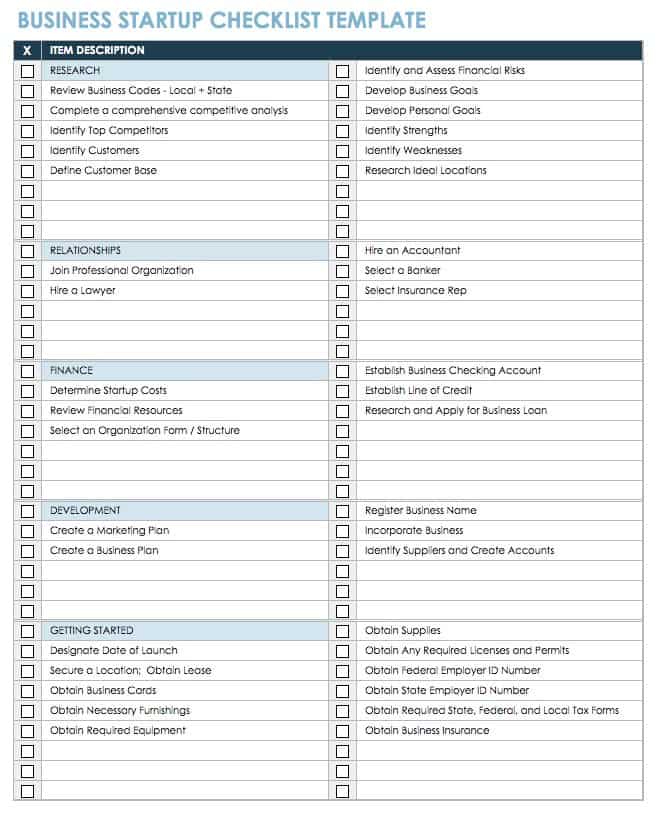
This checklist template is ideal for startup organizations. It allows you to list and categorize key tasks that you need to complete, including items related to research, strategic relationships, finance, development, and more. Check off each task upon completion to ensure you haven’t missed or overlooked any important business activities. Find additional resources by visiting “ Free Startup Plan, Budget & Cost Templates .”
Download Business Startup Checklist Template
Business Plan Financial Templates in Excel
Use these customizable templates to develop your organization’s financial plan.
Business Startup Costs Template in Excel
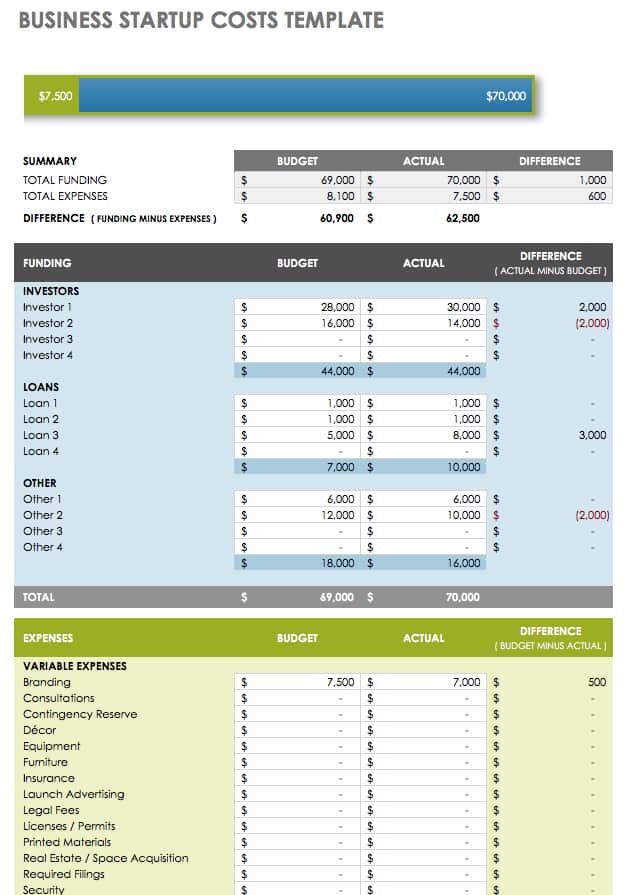
Use this template to estimate and track your startup and operational costs. This template gives you room to list line items for both funding and expenses; you can automatically calculate totals using the built-in formulas. To avoid overspending, compare budgeted amounts against actual amounts to determine where you can cut costs or find additional funding.
Download Business Startup Costs Template
Small-Business Budget Template in Excel
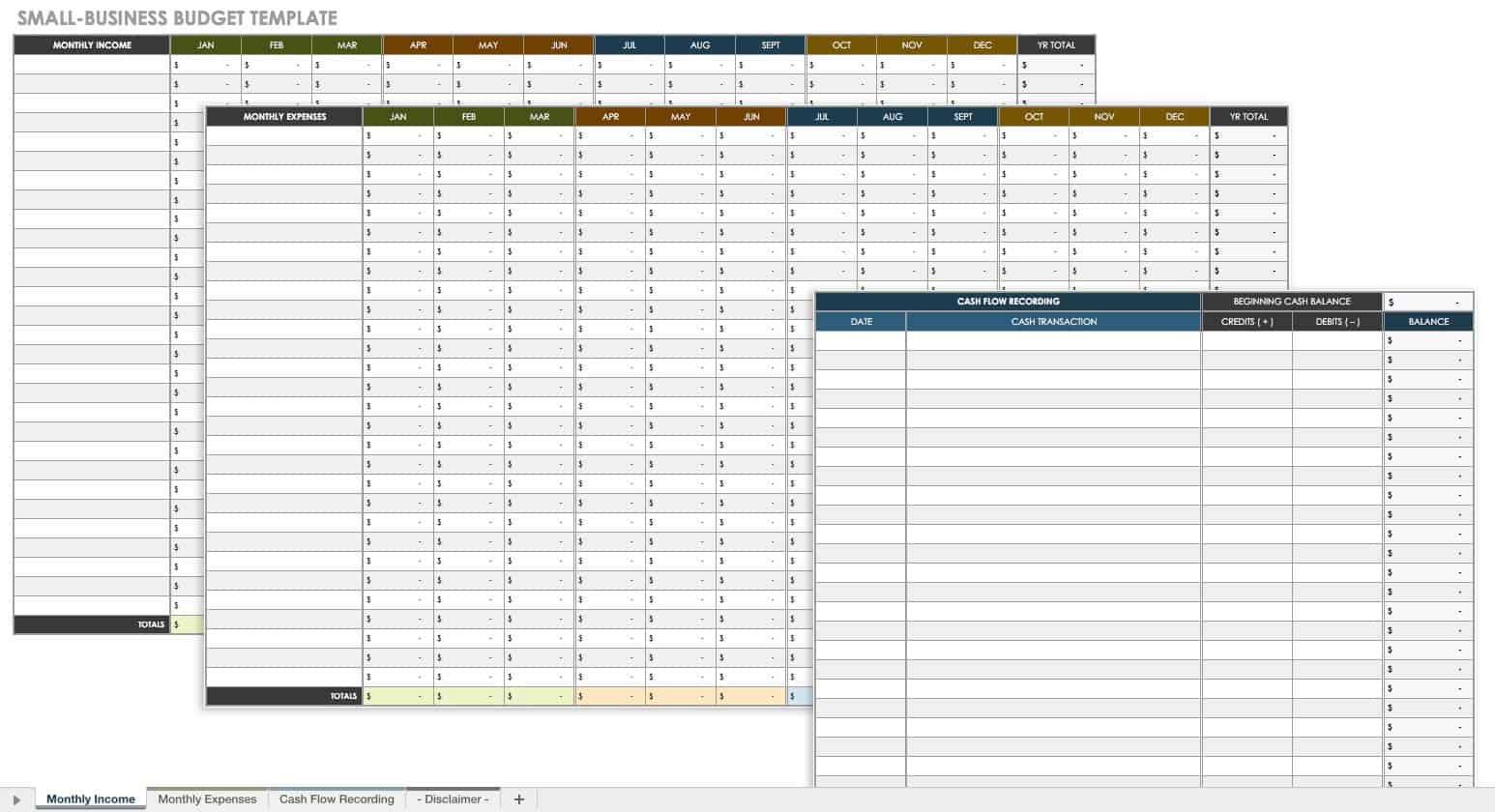
This simple business budget template is designed with small businesses in mind. The template helps you track the income and expenses that you accrue on a monthly and yearly basis. To log your cash balances and transactions for a given time frame, use the tab for cash flow recording.
Download Small-Business Budget Template - Excel
Startup Financial Statement Projections Template
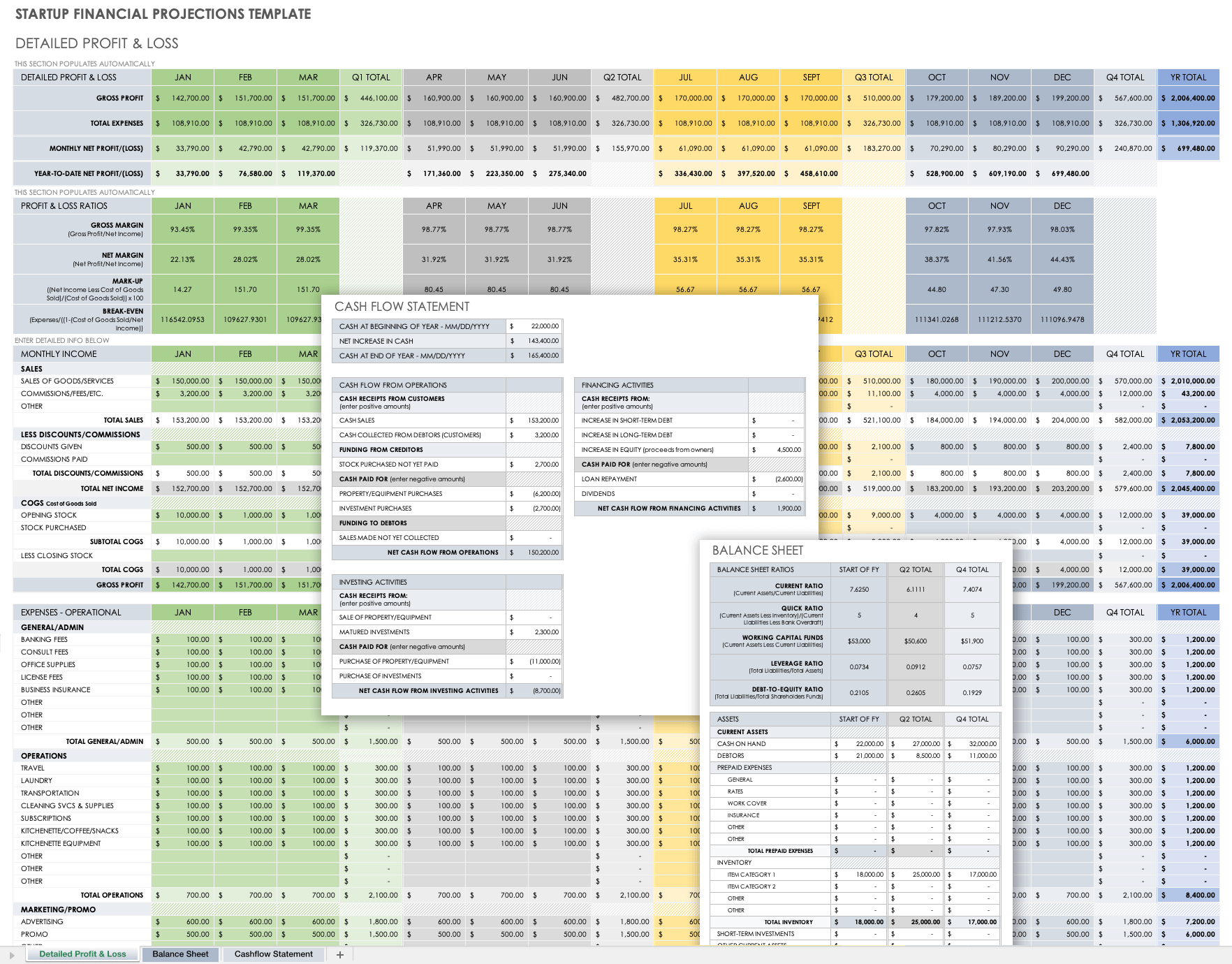
This financial statement projections template includes a detailed profit and loss statement (or income statement), a balance sheet with business ratios, and a cash flow statement to analyze your company’s current and future financial position. This template also comes with built-in formulas, so you can calculate totals as you enter values and customize your statement to fit the needs of your business.
Download Startup Financial Statement Projections Template
For additional templates to help you produce a sound financial plan, visit “ Free Financial Templates for a Business Plan .”
Business Plan Marketing and Sales Templates in Excel
Use these downloadable templates to support and reinforce the marketing and sales objectives in your business plan.
Sales Forecast Template in Excel
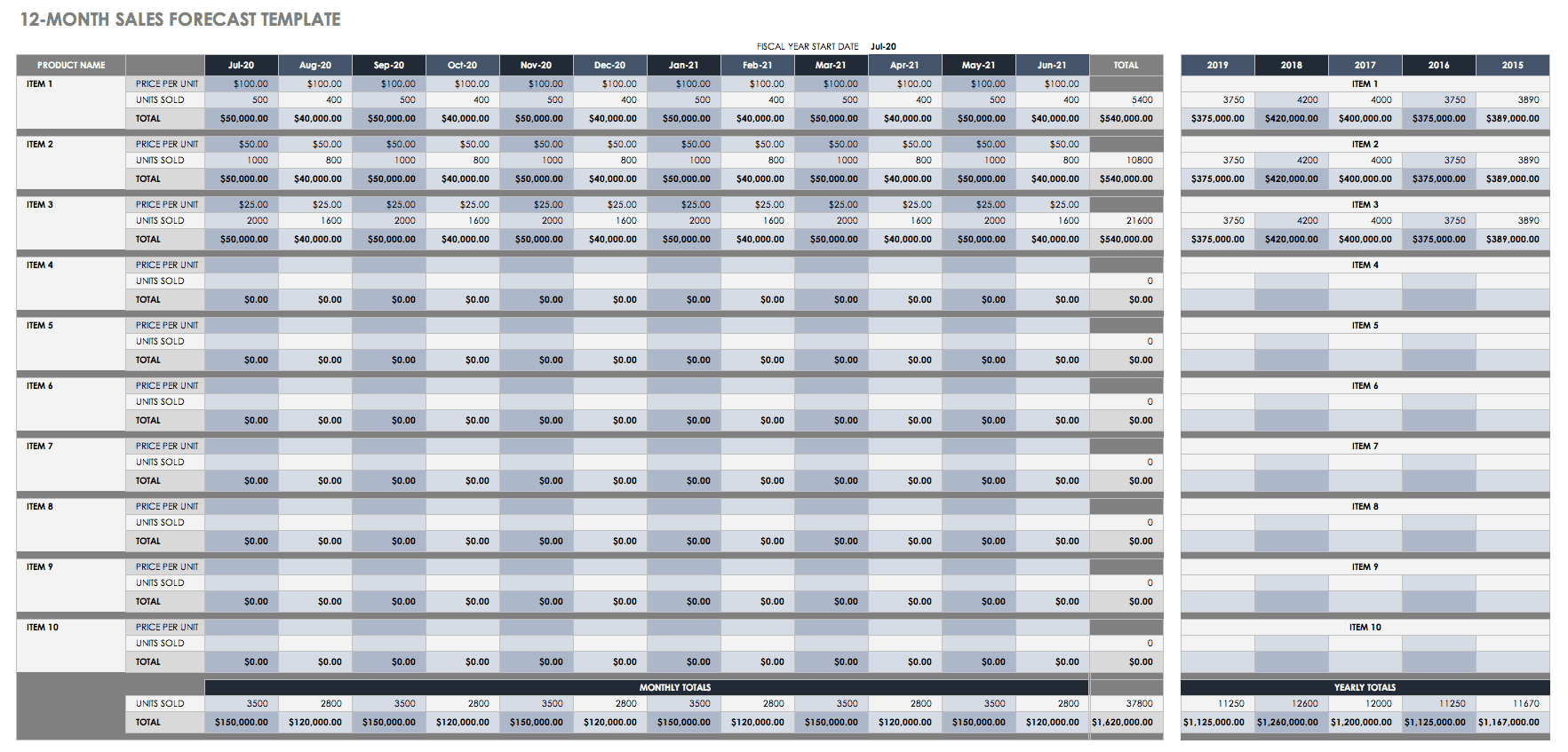
This sales forecast template allows you to view the projected sales of your products or services at both individual and combined levels over a 12-month period. You can organize this template by department, product group, customer type, and other helpful categories. The template has built-in formulas to calculate monthly and yearly sales totals. For additional resources to project sales, visit “ Free Sales Forecasting Templates .”
Download Sales Forecast Template
Marketing Budget Plan in Excel
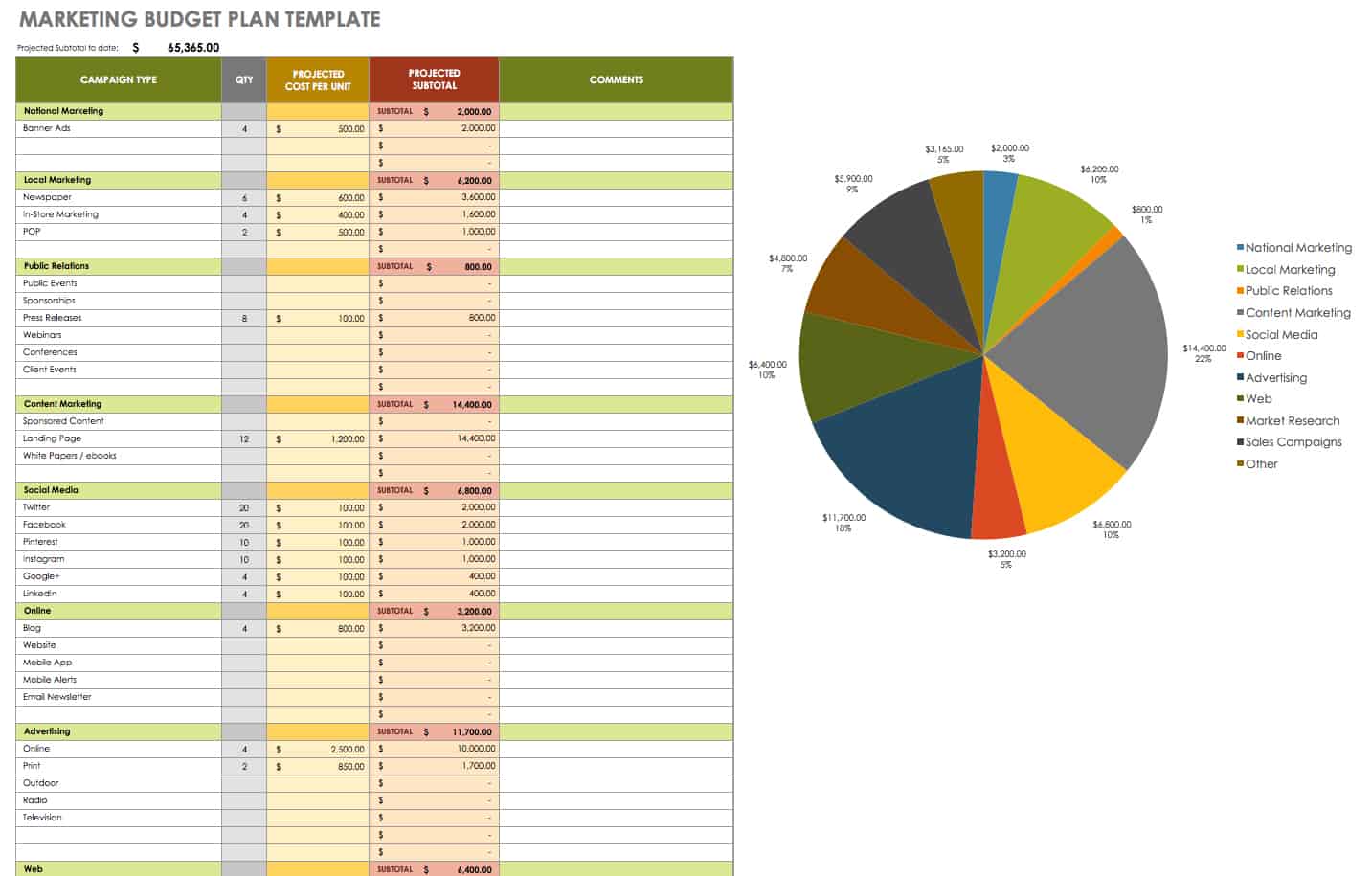
This marketing budget plan template helps you organize and plan your campaign costs for key marketing activities, such as market research, advertising, content marketing , and public relations. Enter the projected quantity and cost under each campaign category; the built-in formulas enable you to calculate projected subtotals automatically. This template also includes a graph that auto-populates as you enter values, so you can see where your marketing dollars are going.
Download Marketing Budget Plan Template
Other Business Plans in Excel
Use these business plan templates to conduct analyses and develop a plan of action that aligns your strategy with your main business objectives.
Business Action Plan Template in Excel
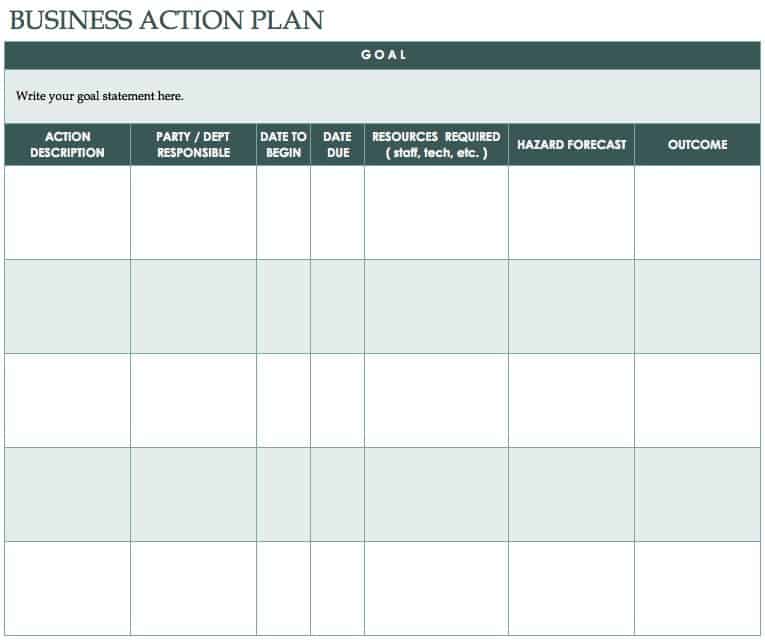
Use this basic action plan template to develop a roadmap for reaching your goals. Add a description of each action item, assign the responsible party, and list the required resources, potential hazards, key dates, and desired outcome. You can use this template to develop an action plan for marketing, sales, program development, and more.
Download Business Action Plan Template
Business Plan Rubric in Excel
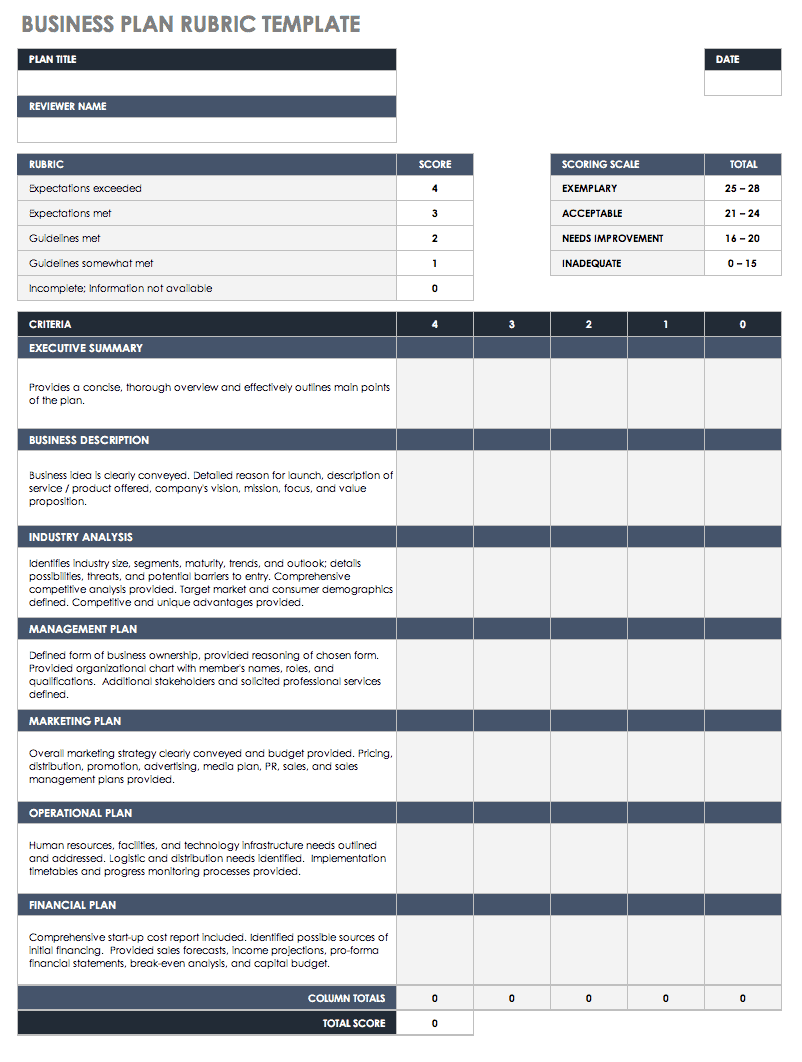
Once you complete your business plan, use this rubric template to score each section to ensure you include all the essential information. You can customize this rubric to fit the needs of your organization and provide insight into the areas of your plan where you want to delve more deeply or remove unnecessary details. By following these steps, you can make certain that your final business plan is clear, concise, and thorough.
Download Simple Business Plan Rubric
Competitive Analysis Template in Excel
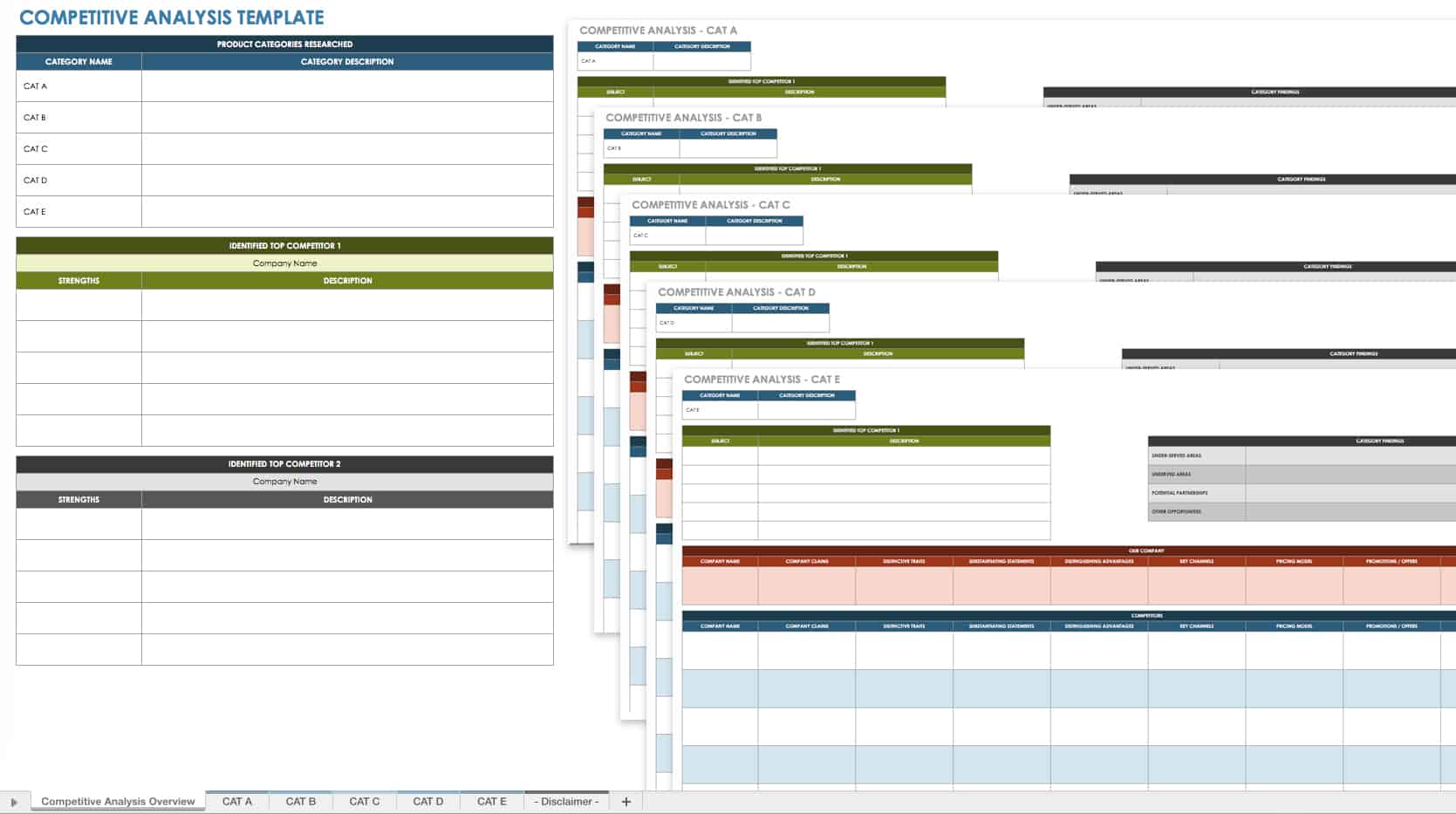
This template enables you to analyze the competitive landscape and industry for your business. By providing details related to your company and competitors, you can assess and compare all key areas, including the target market, marketing strategies, product or service offerings, distribution channels, and more.
Download Competitive Analysis Template
Excel | Smartsheet
For additional free templates for all aspects of your business, visit “ Free Business Templates for Organizations of All Sizes .”
Turbo-Charge Your Business Plans with Templates from Smartsheet
Empower your people to go above and beyond with a flexible platform designed to match the needs of your team — and adapt as those needs change.
The Smartsheet platform makes it easy to plan, capture, manage, and report on work from anywhere, helping your team be more effective and get more done. Report on key metrics and get real-time visibility into work as it happens with roll-up reports, dashboards, and automated workflows built to keep your team connected and informed.
When teams have clarity into the work getting done, there’s no telling how much more they can accomplish in the same amount of time. Try Smartsheet for free, today.
Discover why over 90% of Fortune 100 companies trust Smartsheet to get work done.
Free 1-year Financial Projection Template
Complete the form to get your copy of this free resource!
Free excel template to create financial projections for any business startup and first year. Forecast revenue, expenses, employee costs and generate an income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow pro forma automatically

Join 15,000+ founders and consultants who have used our free resources and tools

Free 1 Year Pro Forma Template
Download our 12 months financial projection template for free. This tool will allow you to:
- Forecast startup costs
- Project your first 12 months of product or service revenue
- Forecast your operating expenses
- Add Salary Forecasts for your employees
Once you have input all of your own assumptions, you will be able to generate:
- 12 month pro forma income statement
- 12 month cash flow forecast
- 12 month balance sheet projection
- Basic graphs and charts
This free financial model is industry agnostic. If you need an industry specific financial model you can check out ProjectionHub’s premium pro forma templates .
Below you will be able to see some examples of the input and outputs of the projection spreadsheet.
Financial Model Input Examples
Below you will be able to see examples of the input tabs for startup costs, fixed assets, revenue, operating expenses and salaries.
Example of Startup Cost Forecast
The financial model input assumptions tab will include general assumptions and startup costs like your fixed assets like buildings, equipment, leasehold improvements and vehicles. On the input assumptions tab you will also be able to include startup cost assumptions like initial inventory.

12 Month Revenue Forecast Example
Our revenue assumptions tab will allow you to forecast your number of customers, the products or services they purchase, the purchase price and the percentage of total units sold represented by each product. You can see a quick example of our revenue model below:

Startup Operating Expense Projections Example
You can enter in your operating expense projections for your startup in the table below. It will allow you to add expenses as a fixed monthly expense or a percentage of revenue.

Startup Salary Forecasting Example
The last input tab is our salary forecast assumptions. You can set a salary, employer taxes, benefits, the month the employee starts and ends, and the number of the particular employee.

Projection Template Output Examples
Our free financial model spreadsheet will produce 12 months of income statement, cash flow and balance sheet projections. You can see examples of each of these outputs below along with some of the basic charts and graphs that will be included.
Example of a 12 Month Pro Forma P&L
Below you will see an example of our income statement pro forma output.

Cash Flow Forecast 12 Month Example
Next you will see an example of our cash flow forecast output with cash from operating activities, financing and investing activities.

Balance Sheet Forecast Example for 12 Months
The balance sheet forecast output will include 12 months of forecasted assets and liabilities as seen below:

Pro Forma Graphs
Finally, our free template includes a profit and loss at a glance, a monthly sales forecast and graph to display monthly sales, gross profit and net income.

If you are needing a more tailored template to your industry as well as 5 years of projections, we have 100+ different industry templates to choose from as well:
Examples: Restaurant, Trucking, SaaS, Airbnb, Brewery, Dentist, etc.
Check out our Highly Rated Financial Projection Templates

Cash Flow - Business Plan Forecast Template
Use our business plan financial projections template to create financial projections for a business plan which includes 12 monthly periods and 5 annual periods. The template includes a detailed income statement, cash flow statement and balance sheet in Excel. Cash flow projections are based on user defined turnover, gross profit and expense values and automated calculations based on a series of assumptions.
- Includes 12 monthly & 5 annual periods
- Suitable for service and trade based businesses
- Reporting periods based on a single user input cell
- User input limited to basic template assumptions
- Expense accounts can be customized & more accounts added
- Automated income statement, cash flow statement & balance sheet
- Accommodates loan amortization or interest-only loans
- Includes sales tax, income tax, payroll accruals & dividends
How to use the Cash Flow - Business Plan Forecast template
This template enables users to create cash flow projections for a business plan which includes 12 monthly periods and five annual periods. The template includes a monthly income statement, cash flow statement and balance sheet. The cash flow projections are based on turnover, gross profit and expense values that are entered by the user as well as a number of default assumptions which are used to create an automated balance sheet. These assumptions include opening balance sheet balances, working capital ratios, payroll accruals, sales tax, income tax, dividends and loans. The monthly reporting periods are based on any user defined start date.
Note: We have included 12 monthly and 5 annual reporting periods in this template because this format is frequently required by financial institutions when submitting business plans. If you only require annual cash flow projections, refer to our Annual Cash Flow Projections template and if you only require monthly cash flow projections, refer to our Monthly Cash Flow Projections template.
The following sheets are included in the template: Assumptions - this sheet includes the default assumptions on which the monthly & annual cash flow projections are based. IncState - this sheet includes a detailed monthly income statement for 12 monthly periods and 5 annual periods. All the rows that are highlighted in yellow in column A require user input and the codes in column A are mainly used in the sales tax, receivables & payables calculations. The rows that do not contain yellow highlighting in column A contain formulas and are therefore calculated automatically. CashFlow - as with the income statement, only the rows with yellow highlighting in column A require user input. All the other rows contain formulas and are therefore calculated automatically. BalanceSheet - all balance sheet calculations are based on the template assumptions and the income statement & cash flow statement calculations. No user input is therefore required on this sheet. Loans1 to Loans3 & Leases - these sheets include detailed amortization tables which are used to calculate the interest charges and capital repayment amounts that are included on the income statement and cash flow statement. Each sheet provides for a different set of loan repayment terms to be specified.
Note: If you do not want to include any of the line items that are listed on the income statement, cash flow statement or balance sheet, we recommend hiding these items instead of deleting them. If you delete items which are used in other calculations, these calculations will result in errors which you then need to fix or remove.
Business Name & Reporting Periods
The business name and the start date for the cash flow projections need to be entered at the top of the Assumptions sheet. The business name is included as a heading on all the sheets and the reporting periods which are included in the template are determined based on the start date that is specified. This date is used as the first month and the 11 subsequent months and four subsequent years are added to form the 5 year projection period.
The income statement and cash flow statement only require user input where there is yellow highlighting in column A and the user input only relates to the 12 monthly periods. All annual totals are calculated automatically and all rows without yellow highlighting are calculated automatically in both the monthly and annual columns.
Income Statement
All monthly income statement projections need to be entered exclusive of any sales tax that may be applicable.
Turnover & Gross Profits
Monthly turnover values need to be entered on the IncState sheet for the first 12 months. The projected monthly gross profit percentages also need to be entered on this sheet and are used in order to calculate the gross profit values. The monthly cost of sales projections are calculated by simply deducting the gross profit values from the monthly turnover values.
The year 2 to 5 turnover amounts are calculated based on the totals for the first year and adjusted by the annual turnover growth rates that are specified on the Assumptions sheet. Gross profit percentages for each turnover line need to be entered on the IncState sheet. Gross profit values and cost of sales totals are calculated automatically.
The template includes two default lines in each of these sections - one for a typical product based item and one for a typical service based item. The template can therefore be used for both service and trade based businesses. There are no cost of sales and gross profit values in service based businesses and a gross profit percentage of 100% can therefore be specified. You can also hide the cost of sales and gross profit sections if you do not want to include them in your cash flow projections.
Note: You can insert as many additional line items as required by inserting the required number of items in each section and then entering the appropriate values where user input is required or copying the formulas from one of the existing lines. We recommend inserting additional line items between the two existing default line items.
Note: The codes in column A are used in the sales tax and trade receivables calculations. The first two characters represent the sales tax code and the last two characters represent the payment status. Refer to the Balance Sheet - Sales Tax and Balance Sheet - Trade Receivables sections for more information on these codes.
Other Income
Monthly projections of other income should be entered in this row. Note that other income may consist of items like interest or dividends received and this line item is therefore not included in trade receivables and sales tax calculations. If you want to include other income in the trade receivables or sales tax calculations, you need to add the income to the Turnover section as an additional line item.
The year 2 to 5 totals for other income are calculated by applying the annual turnover growth percentages on the Assumptions sheet to the previous year's total.
Operating Expenses
All the monthly operating expense projections need to be entered in the operating expenses section of the income statement. The template contains 22 default operating expense line items but you can add as many additional items as required or delete the line items that you do not need. When adding additional line items, remember to copy the formulas in the total columns from one of the existing line items.
The year 2 to 5 totals for operating expenses are calculated by applying the annual expense inflation percentages on the Assumptions sheet to the previous year's total.
Note: The codes in column A are used in the sales tax and trade payables calculations. The first two characters represent the sales tax code and the last two characters represent the payment status. Refer to the Balance Sheet - Sales Tax and Balance Sheet - Trade Payables sections for more information on these codes.
Staff Costs
All the monthly staff cost projections need to be entered in the staff costs section of the income statement. The template contains 2 default staff cost line items but you can add as many additional items as required or delete the line items that you do not need.
The year 2 to 5 totals for staff costs are calculated by applying the annual expense inflation percentages on the Assumptions sheet to the previous year's total.
Note: Staff costs have been included in a separate section on the income statement in order to be able to calculate payroll accruals. If you do not need to include payroll accruals in your cash flow projections, we recommend entering nil values and hiding these rows. If you delete the section, some of the payroll accrual formulas may result in errors and you therefore may need to delete them as well.
Depreciation & Amortization
Monthly & annual projections for depreciation and amortization charges need to be calculated independently of the template and included in this section. We unfortunately cannot include default depreciation or amortization calculations because some businesses may have very different asset bases than others with existing assets which may already have been depreciated over a number of years. Any calculation which is based on a percentage of the balance sheet asset value may therefore not be accurate.
If you already have a sheet which is used for depreciation or amortization calculations, you can include it in this template and add formulas in the depreciation & amortization section of the income statement to include your calculations in the appropriate line items.
The monthly depreciation & amortization charges for the first 12 months need to be included on the IncState sheet and the totals for year 2 to 5 need to be included on the Assumptions sheet.
We also realize that some users may want to include depreciation and amortization as part of their operating expenses. We have therefore provided for this in that the depreciation and amortization calculations on the cash flow statement are based on the default code which is included in column A. You can therefore enter nil values in the depreciation & amortization section on the income statement, hide the section and include these line items in the operating expenses section and as long as you also include the default codes in column A, the cash flow statement values for depreciation and amortization will be calculated correctly.
Interest Paid
All interest paid calculations are automated and based on the amortization tables on the Loans1 to Loans3 and Leases sheets. The template accommodates the inclusion of loans & leases based on four different sets of loan repayment terms which need to be specified on the Assumptions sheet.
Opening loan balances are based on the balance sheet opening balances section on the Assumptions sheet and additional loan amounts can be entered in column C of the appropriate amortization table.
You do not need to use all four loan amortization sheets - if you only need to include loans based on one set of repayment terms, you can delete the other loan amortization sheets, delete the other interest paid rows on the income statement, delete the other proceeds from loans rows on the cash flow statement, delete the other repayment of loans rows on the cash flow statement and delete the other loan balances from the balance sheet.
The template provides for four sets of loan repayment terms - the same amortization table can basically be used for all loans with the same repayment terms by adding additional loan amounts as proceeds to the cash flow statement in order to add new loans to the appropriate amortization table.
If you need to add more than four sets of loan repayment terms, you will need to copy one of the amortization sheets, change it to reflect the appropriate loan terms and then change the formulas in the amortization table to be based on the correct loan repayment terms at the top of the sheet. This means that you need to add another set of repayment terms to the Assumptions sheet and link the fields at the top of the new amortization table to the appropriate cells on the Assumptions sheet.
If there is an opening balance for the required additional loan terms, you need to include a new code in the balance sheet opening balances section on the Assumptions sheet and base the opening balance calculation in the first period of the amortization schedule on this code. You also need to add new rows to the interest paid section on the income statement, the loan proceeds section on the cash flow statement, the loan repayment section on the cash flow statement and the loan balances section on the balance sheet. The appropriate formulas can be copied from one of the existing items and the sheet reference in the copied formula can then just be replaced by the sheet name of the new amortization table that you've added.
The taxation line item on the income statement is automatically calculated based on the profit before tax and the income tax assumptions which are specified on the Assumptions sheet. If you do not want to include income tax in the cash flow projections, simply enter an income tax rate of 0%. This will result in no income tax being calculated.
If you do want to include income tax calculations, the appropriate income tax percentage needs to be entered in the Income Tax section on the Assumptions sheet. You can also enter a value for an assessed loss (as a positive value) which may have been carried over from a previous tax year which would result in income tax only being calculated after profits exceed the value of the assessed loss.
You also need to specify the payment frequency in months and the first calendar month in which a payment needs to be included. The template automatically provides for income tax based on what is due and includes the income statement amount and a provision for taxation on the balance sheet. The payment frequency and month of payment assumptions are then used to determine when the income tax liability will be settled which will result in the appropriate cash outflow being recorded on the cash flow statement and the provision for taxation being reduced.
The template can accommodate income tax calculations based on current and subsequent month payments. If you select the Current option, the income tax payment amount will be calculated based on all amounts that have accrued up to and including the month of payment. If you select the Subsequent option, the income tax payment amount will only be calculated based on all amounts which have accrued up to the previous month end.
Example: If you select the Current option in the Income Tax section of the Assumptions sheet, all income tax amounts up to and including the current month will be included in the income tax payment amount. This means that the provision for taxation at the end of the particular month will be nil. The Current setting is therefore usually appropriate for provisional taxpayers.
Example: If you select the Subsequent option, all amounts up to and including the previous month end will be included in the income tax payment amount. The provision for taxation balance on the balance sheet will therefore not be nil at the end of the month of payment and include the current month's income tax charge.
The template also includes automated dividends calculations. If you do not want to include any dividends in your cash flow projections, you can simply specify a dividend percentage of zero percent.
If you want to include dividend calculations, you need to specify a dividend percentage which will be applied to the profit for the period in order to calculate the dividend value. You also need to specify the frequency in months of dividend payments and the first payment month. The frequency of dividends determines when the dividends are included on the income statement and the first month of payment determines when the dividend payment is included on the cash flow statement (only has an effect if the dividend payment option is Subsequent).
You can also specify whether the dividend is paid in the month of calculation (Cash option), the month after calculation (Next option) or in a subsequent month. When you elect the subsequent month option, the payment of the dividend will be included based on the relative position of the first month of payment in relation to the year-end period (which is determined based on the template start date at the top of the Assumptions sheet).
Example: If you want to include a dividend in the last month of each financial year, select a payment frequency of 12 months and month 12 as the first payment month. Then select the Cash option in order to include both the dividend on the income statement and the payment in the last month of the year.
Example: If you want to include a dividend in the last month of each financial year but delay payment to the first month of the next financial year, select a payment frequency of 12 months and month 12 as the first payment month. Then select the Next option in order to include the dividend on the income statement in the last month of the financial year and the payment in the first month of the next financial year. A dividend payable amount will then automatically be included on the balance sheet at year-end.
Balance Sheet
All the calculations on the balance sheet are automated and no user input is therefore required.
Opening Balances
If you need to compile cash flow projections for an existing business, you will need to include the opening balance sheet balances at the start of the cash flow projection period. This is facilitated in the Balance Sheet Opening Balances section on the Assumptions sheet. The opening balances that are entered here are included in the first column on the balance sheet.
You can use the trial balance as at the end of the period immediately before the start of the cash flow projection period for this purpose. All assets should have positive balances and all equity & liabilities should have negative balances. The opening balances should also balance to a total of nil as with any accounting system trial balance. If you enter balances and the total of all balances is not nil, the entire opening balances section on the Assumptions sheet will be highlighted in orange.
You then need to fix the imbalance by adjusting the opening balances so that the total comes to a total of nil. The orange highlighting will then be removed automatically. Also note that the cash flow projection balance sheet cannot balance if the opening balances do not balance.
Note: If you are preparing a cash flow projection for a new business, you can include zero balances for all the balance sheet items in the opening balances section.
Non-Current Assets
The property, plant & equipment balances on the balance sheet are calculated by adding the purchases of property, plant & equipment (entered on the cash flow statement for the first 12 months and on the Assumptions sheet for year 2 to 5) and then deducting the appropriate depreciation charges that are included on the income statement.
Intangible assets balances are calculated in much the same way by adding the purchases of intangible assets (as per the cash flow statement for the first 12 months and the Assumptions sheet for year 2 to 5) and deducting the appropriate amortization charges as per the income statement. The calculation of the investments balances on the balance sheet is a bit simpler in that only the purchases of new investments (as per the cash flow statement for the first 12 months and the Assumptions sheet for your 2 to 5) are added to the previous period's balance and there is no depreciation or amortization on investments.
Note: Purchases of property, plant & equipment, intangible assets and investments all need to be entered as negative values. The purchases for the first 12 months need to be entered on the cash flow statement and the purchases for year 2 to 5 need to be entered on the Assumptions sheet.
Current Assets - Inventory
The inventory balances on the balance sheet are calculated based on the inventory days assumption which is specified on the Assumptions sheet. The number of days that are entered here is applied to the monthly cost of sales in order to calculate the appropriate inventory balance. This calculation is based on the actual number of days in each month if the inventory days assumption is greater than the number of days in the appropriate month.
Example: If you enter an inventory days assumption of 60 days and the month is April, the entire cost of sales value for April will be included in the inventory balance because April only has 30 days. After including the 30 days in April, there is a difference of 30 days between the 60 days assumption and the 30 days in April. The March cost of sales balance will therefore be used, divided by the 31 days in March and multiplied by the 30 remaining days. The inventory balance at the end of April will therefore consist of the cost of sales total for April and an equivalent of 30 days of the 31 day cost of sales of March.
Note: The above calculation principle is applied regardless of the number of days which are entered as the inventory days assumption on the Assumptions sheet even if the value of the inventory days assumption requires the inclusion of more than 2 months. This method of calculation is the most accurate way of projecting inventory balances even for businesses where there is significant sales volatility.
Note: If your business does not carry inventory, you can simply enter a nil value in the inventory days assumption on the Assumptions sheet. The inventory line on the balance sheet will then also contain nil values.
If you want to include variable monthly inventory days, you can do so by changing the inventory days assumption in the Workings section of the balance sheet which has been included below the section with the ratios. Simply replace the formula which links the inventory days assumption to the value on the Assumptions sheet by overwriting it with the appropriate inventory days value.
The year 2 to 5 inventory balances are calculated by applying the annual turnover growth percentage to the inventory balance at the end of year 1. This method ensures that the monthly trend in year 1 is reflected in the year 2 to 5 balances. If you amend the inventory days in the Workings section of the balance sheet, the amended days for the appropriate year will be used in the calculation.
Current Assets - Trade Receivables
The trade receivables balances on the balance sheet are calculated based on the debtors days assumption which is specified on the Assumptions sheet. The debtors days number can be determined based on the average trading terms which has been negotiated with customers. The debtors days is applied to the monthly turnover in order to calculate the appropriate trade receivables balance. This calculation is based on the actual number of days in each month if the debtors days assumption is greater than the number of days in the appropriate month.
Example: If you enter a debtors days assumption of 60 days and the month is April, the entire turnover value for April will be included in the trade receivables balance because April only has 30 days. After including the 30 days in April, there is a difference of 30 days between the 60 days assumption and the 30 days in April. The March turnover balance will therefore be used, divided by the 31 days in March and multiplied by the 30 remaining days. The trade receivables balance at the end of April will therefore consist of the turnover total for April and an equivalent of 30 days of the 31 day turnover of March.
Note: The above calculation principle is applied regardless of the number of days which are entered in the debtors days assumption on the Assumptions sheet even if the value of the debtors days assumption requires the inclusion of more than 2 months. This method of calculation is the most accurate way of projecting trade receivable balances even for businesses where there is significant sales volatility.
Where sales tax is applicable, the appropriate sales tax value relating to monthly turnover will be added to the trade receivables balance. Sales tax codes are defined on the Assumptions sheet and the codes in column A next to the turnover amounts on the income statement are used to determine the appropriate rate of sales tax to be used.
The trade receivables calculation will also only include lines that are coded with a sales tax rate code (in the first two characters) and a "C1" at the end of the code. The C1 part of the code refers to credit sales while the inclusion of a C0 code at the end refers to cash sales. Cash sales do not need to be included in the trade receivables calculation and turnover lines with C0 or no code in column A are therefore ignored when calculating trade receivable balances.
Example: If the standard rate sales tax code is V1 and the appropriate turnover line needs to be included in the calculation of trade receivables, the code V1C1 needs to be added in column A of the appropriate turnover line on the income statement. If you do not want to add sales tax in the trade receivables calculation but you do want a trade receivables line to be included in the balance sheet, you can add a code which refers to a 0% sales tax calculation as well as the C1 credit sales indicator.
Example: If you do not want a particular turnover line to be included in the trade receivables calculation, you can include any sales tax rate followed by C0 in order to exclude the line in the trade receivables calculations. For example, a turnover line with a code of V1C0 would not form part of the trade receivables calculations.
Note: If your business has no trade receivables, you can simply enter a nil value in the debtors days assumption on the Assumptions sheet. The trade receivables line on the balance sheet will then also contain nil values.
If you want to include variable monthly debtors days, you can do so by changing the debtors days assumption in the Workings section of the balance sheet which has been included below the section with the ratios. Simply replace the formula which links the debtors days assumption to the value on the Assumptions sheet by overwriting it with the appropriate debtors days value.
The year 2 to 5 trade receivables balances are calculated by applying the annual turnover growth percentage to the trade receivables balance at the end of year 1. This method ensures that the monthly trend in year 1 is reflected in the year 2 to 5 balances. If you amend the debtors days in the Workings section of the balance sheet, the amended days for the appropriate year will be used in the calculation.
Current Assets - Loans & Advances, Other Receivables
The loans and advances & other receivables balances cannot be calculated by basing them on specific income statement items and they are therefore calculated by adding the movements in these balances (as per the cash flow statement for the first 12 months and the Assumptions sheet for year 2 to 5) to the balances of the previous month. If you therefore want to increase or decrease these balances, you need to add the amount of the increase or decrease to the line with a matching description on the cash flow statement (under the changes in operating assets section) for the first 12 months or the Assumptions sheet for year 2 to 5.
Current Assets - Cash & Cash Equivalents
The cash & cash equivalents balances on the balance sheet are linked to the closing cash balances on the cash flow statement. If the resulting cash & cash equivalents balance has a negative value, it will automatically be included in the bank overdraft line in the Current Liabilities section of the balance sheet.
Equity - Shareholders Contributions, Reserves
The shareholders contributions & reserves balances cannot be calculated by basing them on income statement items and they are therefore calculated by adding the movements in these balances (as per the cash flow statement for the first 12 months and the Assumptions sheet for year 2 to 5) to the balances of the previous month. If you therefore want to increase or decrease these balances, you need to add the amount of the increase or decrease to the line with a matching description on the cash flow statement or Assumptions sheet.
Note: The shareholders contribution line on the cash flow statement can be found under the cash flow from financing activities and the reserves line on the cash flow statement under the non-cash adjustments.
Equity - Retained Earnings
The retained earnings balances on the balance sheet are linked to the retained earnings for the year which is calculated on the income statement.
Non-Current Liabilities - Loans 1 to 3, Leases
The template provides for loans & leases to be included based on 4 different sets of loan repayment terms. Loans with the same repayment terms can be grouped together in the appropriate line item. There is no difference between the treatment of loans 1 to 3 and leases. If you do not have finance leases and have loans with 4 different sets of repayment terms, you can use the Leases sheet and rename the appropriate line items accordingly.
Note: The loan repayment period in years is limited to a maximum period of 30 years. If you want to include a loan repayment period which exceeds this period, you need to change the data validation settings in the appropriate input cell by selecting the data validation feature from the Data tab on the Excel ribbon and editing the maximum value of 30 which has been set in the loan repayment period cells.
Each of the loan repayment terms can be specified in the Loan Terms section on the Assumptions sheet. The loan terms include the annual interest rate, loan repayment period in years and a selection field which can be used to indicate interest-only loans. These loan repayment terms are then included at the top of the appropriate loan amortization sheet on the Loans1 to Loans3 and Leases sheets.
Note: A set of loan terms can be specified as interest-only by selecting the "Yes" option from the interest-only drop-down list in the appropriate loan terms on the Assumptions sheet. If this selection is made, the loan will be interest only and not include any loan repayments.
All the calculations on the amortization sheets are fully automated. The only user input that is required on these sheets is entering the additional loan amounts in column C. The loan terms are taken from the Assumptions sheet and the opening balances in the first row of the amortization table are based on the opening balances that are entered in the balance sheet opening balances section of the Assumptions sheet.
The loan repayments, interest charged and capital repayments are calculated based on the outstanding balances at the beginning of each period. The outstanding loan or lease balances at the end of the appropriate monthly or annual period are then included in the appropriate lines on the balance sheet.
Current Liabilities - Bank Overdraft
The bank overdraft as well as cash & cash equivalents are based on the closing cash balances which are calculated on the cash flow statement. If the appropriate monthly closing balance is negative, the balance is included as a bank overdraft and if it is positive, it is included as cash under current assets on the balance sheet.
Current Liabilities - Trade Payables
The trade payables balances on the balance sheet are calculated based on the creditors days assumption which is specified on the Assumptions sheet. The number of days that are included here can be determined based on the average trading terms which has been negotiated with suppliers.
The monthly cost of sales, operating expenses and staff costs on the income statement are added together in order to determine a monthly value on which the trade payables calculations should be based. Expenses and costs which are paid on a cash basis can be excluded from the trade payables calculation by entering a code which ends in C0 in column A on the income statement. The codes in column A start with the appropriate two character sales tax code and end with the two character payables code.
Example: The expense codes in column A for all line items that need to be included in the trade payables calculation and which need to be subject to sales tax at a standard rate should be V1C1. If the expense item is settled on a cash basis and also subject to the standard sales tax rate, the code in column A should be V1C0 which will then result in the item not being included in the trade payables calculation.
If you want to also include purchases of property, plant & equipment in the trade payables calculation, the standard code of PPE in column A on the cash flow statement needs to be amended to the appropriate code which starts with the sales tax code and ends with C1. For standard sales tax, the code will therefore be V1C1.
Like the calculation of inventory and trade receivables balances, the trade payables balances on the balance sheet are based on the actual number of days in each month if the creditors days assumption is greater than the days in the appropriate month.
Example: If you enter a creditors days assumption of 60 days and the month is April, the entire cost of sales & expense value for April will be included in the trade payables balance because April only has 30 days. After including the 30 days in April, there is a difference of 30 days between the 60 days assumption and the 30 days in April. The March cost of sales & expense balance will therefore be used, divided by the 31 days in March and multiplied by the 30 remaining days. The trade payables balance at the end of April will therefore consist of the cost of sales & expenses total for April and an equivalent of 30 days of the 31 day cost of sales & expense values of March.
Note: The above calculation principle is applied regardless of the number of days which are entered as the creditors days assumption on the Assumptions sheet even if the value of the creditors days assumption requires the inclusion of more than 2 months. This method of calculation is the most accurate way of projecting trade payables balances even for businesses where there is significant sales or expense volatility.
Where sales tax is applicable, the appropriate sales tax value relating to monthly cost of sales & expenses will be added to the trade payables balance. Sales tax codes are defined on the Assumptions sheet and the code in column A next to the cost of sales & expense amounts on the income statement are used to determine the appropriate rate of sales tax to be used.
The trade payables calculation will also only include lines that are coded with a sales tax rate code (in the first two characters) and a "C1" at the end of the code. The C1 part of the code refers to purchases on credit while the inclusion of a C0 code at the end refers to cash purchases. Cash purchases do not need to be included in the trade payables calculation and cost of sales & expense lines with C0 or no code in column A are therefore ignored when calculating trade payables balances.
Example: If the standard rate sales tax code is V1 and the appropriate cost of sales or expense line needs to be included in the calculation of trade payables, the code V1C1 needs to be added in column A of the appropriate line on the income statement. If you do not want to add sales tax in the trade payables calculation but you do want a trade payables line to be included in the balance sheet, you can add a code which refers to a 0% sales tax calculation as well as the C1 credit purchases indicator.
Example: If you do not want a particular cost of sales or expense line to be included in the trade payables calculation, you can include any sales tax rate followed by C0 in order to exclude the line in the trade payables calculations. For example, an expense or cost of sales line item with a code of V1C0 in column A on the income statement would not form part of the trade payables calculations.
Note: If your business has no trade payables, you can simply enter a nil value in the creditors days assumption on the Assumptions sheet. The trade payables line on the balance sheet will then also contain nil values.
If you want to include variable monthly creditors days, you can do so by changing the creditors days assumption in the Workings section of the balance sheet which has been included below the section with the ratios. Simply replace the formula which links the creditors days assumption to the value on the Assumptions sheet by overwriting it with the appropriate creditors days value.
The year 2 to 5 trade payables balances are calculated by applying the annual expense inflation percentage to the trade payables balance at the end of year 1. This method ensures that the monthly trend in year 1 is reflected in the year 2 to 5 balances. If you amend the creditors days in the Workings section of the balance sheet, the amended days for the appropriate year will be used in the calculation.
Current Liabilities - Sales Tax
The template accommodates the inclusion of sales tax in all relevant calculations based on four default sales tax calculation codes and any sales tax period. All income statement and cash flow statement items need to be entered exclusive of any sales tax that may be applicable and the trade receivables and trade payables balances on the balance sheet will be calculated inclusive of sales tax. The net sales tax liability is included in the Sales Tax line on the balance sheet.
The template can be used for general sales tax (GST) and value added tax (VAT) purposes. Where there is no sales tax input which reduces the sales tax liability, the codes in column A on the income statement can simply be changed to contain a sales tax code (in the first two characters of the code) which has a zero percentage. Only the sales tax codes that are included next to the turnover lines will then be included in sales tax calculations (as required by some general sales tax calculations).
The appropriate sales tax percentages can be entered in the Sales Tax section of the Assumptions sheet. The template provides for 4 default sales tax codes, each with its own sales tax percentage. The sales tax codes are numbered from V1 to V4.
The income statement contains codes in column A which affects the calculations of sales tax and trade receivables or trade payables. The first two characters of these codes determine which sales tax percentage is used in the sales tax calculations. If an income statement item needs to be excluded from sales tax calculations, you should use a sales tax code with a zero percentage on the Assumptions sheet.
Note: Each line on the income statement can therefore only be linked to one sales tax percentage. If more than one sales tax percentage needs to be applied to the same income statement item, you need to split the income statement amount into two lines and enter the appropriate sales tax codes in column A for each of the lines.
Note: If you are preparing cash flow projections for a business which is not subject to sales tax, simply enter zero percentages for all four sales tax codes.
The sales tax assumptions that need to be specified on the Assumptions sheet also include the frequency of sales tax payments (in months) and the calendar month of the first payment period. You can therefore calculate sales tax based on any period frequency from one to twelve months.
Example: If your business is subject to sales tax payments of every two months and the first payment is due in February, a frequency of 2 needs to be specified and the first payment month should be set to 2 for February. Similarly, if your business is subject to sales tax payments of every 6 months with payments due in March and August, the frequency should be set to 6 and the first payment month should be set to 3. If your business is subject to monthly sales tax payment periods, the frequency should be 1 and the first payment month should also be 1.
The Current or Subsequent setting in the Sales Tax section on the Assumptions sheet determines how the calculated sales tax amounts of the current period are handled. If you select the Current option, the sales tax amounts of the current period will be included in the calculation of the payment amount which is due in the particular month and the sales tax liability at the end of the payment month will be nil.
If you select the Subsequent setting, the sales tax amount of the current period is not included in the calculation of the payment amount and the sales tax liability at the end of the appropriate payment month will always include at least one month.
Note: The Subsequent setting is usually the appropriate setting to use for sales tax purposes. The Current settings is more applicable to tax types which are subject to provisional tax.
Example: If you set a payment frequency of 1 month, first payment month of 1 and select the Current option, the sales tax liability on the balance sheet will always be nil because the current month's sales tax will be included in the sales tax payment. If you have the same period settings and select the Subsequent option, the sales tax liability on the balance sheet will always include the current month's sales tax because the payment amount will be based on the previous month's sales tax.
Note: The first payment month setting refers to the month of payment and not the sales tax period end. There is a difference - a sales tax period may end in February with payment in March which means that the first payment month of the calendar year is actually January or month 1 (if the payment frequency is two months).
The year 2 to 5 balances for sales tax are calculated by calculating the total sales tax for the appropriate year, dividing it by twelve and then multiplying the value by the number of months that are included in the sales tax balance at the end of the first year.
Current Liabilities - Payroll Accruals
The payroll accrual on the balance sheet is based on the payroll accrual assumptions in the Working Capital section of the Assumptions sheet and the amounts in the staff costs section of the income statement. If payroll deductions are paid in the same month as they are incurred, you can set the payroll accrual percentage to zero and the payroll accrual balances on the balance sheet will also be zero.
Staff costs have been included in a separate section on the income statement to make it easier to calculate payroll accrual balances. You can however include staff costs in operating expenses but you need to ensure that you also include the "PAY" code in column A for all the staff costs that you want to include in the payroll accrual calculations.
You also need to specify the appropriate percentage of staff costs which needs to be included in your payroll accruals. This percentage should be based on the percentage of staff costs which are paid in a subsequent month and is based on the current month's staff costs. Payroll accruals usually consist of salary & wage deductions which need to be paid over to third parties and differ from entity to entity. You therefore need to calculate the appropriate payroll accrual percentage based on the composition of the salary or wage structures of all employees.
The payroll accrual assumptions that need to be specified on the Assumptions sheet also include the frequency of payroll accrual payment periods (in months) and the payment month of the first payroll accrual period. You can therefore calculate payroll accruals based on any payment period frequency from one to twelve months. The calculated payroll accruals are added together in the payroll accrual balance until the month of payment.
Example: If you need to settle payroll accruals every two months and the first payment is due in February, a frequency of 2 needs to be specified and the first payment month should be set to 2 for February. Similarly, if you settle payroll accruals every 6 months with payments due in March and August, the frequency should be set to 6 and the first payment month should be set to 3. If you settle payroll accruals on a monthly basis, the frequency should be 1 and the first payment month should also be 1.
The Current or Subsequent setting in the Payroll Accruals section on the Assumptions sheet determines how the calculated payroll accrual amounts of the current period are handled. If you select the Current option, the payroll accrual amounts of the current period will be included in the calculation of the payment amount which is due in the particular month and the payroll accrual balance at the end of the payment month will be nil.
If you select the Subsequent setting, the payroll accrual amounts of the current period are not included in the calculation of the payment amount and the payroll accrual balances on the balance sheet at the end of the appropriate payment month will always include at least one month.
Note: The Subsequent setting is usually the appropriate setting to use for payroll accrual purposes. The Current setting is more applicable to tax types which are subject to provisional tax payments where payment occurs in the same month as the tax calculation.
Example: If you set a payment frequency of 1 month, first payment month of 1 and select the Current option, the payroll accruals on the balance sheet will always be nil because the current month's payroll accruals will be included in the payment calculation. If you have the same period settings and select the Subsequent option, the payroll accruals on the balance sheet will always include the current month's payroll accrual because the payment amount will be based on the previous month's payroll accrual.
Note: The first payment month setting refers to the month of payment and not the payroll accrual period end. There is a difference - a payroll accrual period may end in February with payment in March which means that the first payment month of the calendar year is actually January or month 1 (if the payment frequency is two months).
If you want to include payroll accruals based on variable monthly payroll accrual percentages, you can do so by changing the payroll accrual percentage assumption in the Workings section of the balance sheet which has been included below the section with the ratios. Simply replace the formula which links the payroll accrual percentage assumption to the value on the Assumptions sheet by overwriting it with the appropriate payment accrual percentage.
The year 2 to 5 payroll accrual balances are calculated by adjusting the previous year's balance by the appropriate expense inflation percentage on the Assumptions sheet.
Current Liabilities - Other Accruals, Other Provisions
The other accrual & other provisions balances cannot be calculated by basing them on specific income statement items and they are therefore calculated by adding the movements in these balances (as per the cash flow statement for the first 12 months and the Assumptions sheet for year 2 to 5) to the balances of the previous period. If you therefore want to increase or decrease these balances, you need to add the amount of the increase or decrease to the line with a matching description on the cash flow statement (under the changes in operating assets section) for the first 12 months or the Assumptions sheet for years 2 to 5.
Current Liabilities - Provision for Taxation
The calculation of income tax on the income statement is based on the profit before tax on the income statement and the assumptions that are specified in the Income Tax section on the Assumptions sheet.
The profit before tax amount is multiplied by the income tax percentage on the Assumptions sheet in order to calculate the monthly or annual income tax value. If there is a loss before tax on the income statement, no income tax will be calculated but if there were profits before the period with the loss, the income tax that was calculated in previous periods will be reversed in the period with the loss.
The template also makes provision for the inclusion of an assessed loss which has been carried over from previous financial periods and income tax will only be calculated after the assessed loss has been fully reduced by profits in the projection periods.
The income tax assumptions on the Assumptions sheet also include the frequency of payment of income tax (in months) and the calendar month of the first income tax payment. You can therefore calculate a provision for income tax based on any payment period frequency from one to twelve months. The calculated income tax amounts are added together in the provision for income tax balance on the balance sheet until the month of payment.
Example: If you need to settle income tax liabilities every six months and the income tax payments are due in February and August of each year, a frequency of 6 needs to be specified and the first calendar month should be set to 2 for February. Similarly, if you settle income tax liabilities at the end of each quarter with payments due in March, June, September and December, the frequency should be set to 3 and the first payment month should also be set to 3. If you need to settle income tax liabilities 9 months after each year-end and the cash flow projection year-end is February, the frequency should be set to 12 months and the first payment month should be set to 11.
The Current or Subsequent setting in the Income Tax section on the Assumptions sheet determines how the income tax amounts of the current period are handled. If you select the Current option, the income tax amounts of the current period will be included in the calculation of the payment amount which is due in the particular month and the provision for income tax balance on the balance sheet at the end of the payment month will be nil.
If you select the Subsequent setting, the income tax amounts of the current period are not included in the calculation of the payment amount and the provision for income tax balance on the balance sheet at the end of the appropriate payment month will always include income tax for at least one month.
Note: The Current setting is usually the appropriate setting to use for income tax purposes if the entity is a provisional taxpayer which effectively means that income tax is paid in advance. If the entity is not a provisional taxpayer, the Subsequent setting should be used because income tax will be settled after being incurred.
The year 2 to 5 balances are calculated by calculating the income tax amount for the appropriate year, dividing it by 12 and multiplying the value by the number of months which needs to be included in the provision. This is determined based on the year-end period and the income tax assumptions on the Assumptions sheet.
Current Liabilities - Dividends Payable
The calculation of dividends on the income statement is based on the profit for the year on the income statement and the assumptions that are specified in the Dividends section on the Assumptions sheet. Dividends will only be calculated if you enter a dividend percentage on the Assumptions sheet - if you therefore do not want to include dividends in your cash flow projections, you can simply enter a zero value as the dividend percentage.
The dividend percentage that is specified on the Assumptions sheet is applied to the profit for the year on the income statement which can be found directly above the dividends line. Dividends will also only be calculated if there is a cumulative profit for the year.
The dividends assumptions on the Assumptions sheet also include the frequency of payment of dividends (in months) and the first calendar month of the dividend payment. You can therefore calculate dividends based on any payment period frequency from one to twelve months (although 6 or 12 months is the norm). The calculated dividends amounts are added together in the dividends payable balance on the balance sheet until the month of payment.
Example: If dividends are declared every six months, you need to specify a frequency of 6 months on the Assumptions sheet and then select the appropriate payment basis. Dividends will be reflected on the income statement every 6 months and the dividends payable balances on the balance sheet will be determined based on the first payment month and the payment option which is selected (Cash, Next or Subsequent). Similarly, if the payment frequency is set to 12 months, dividends will be included on the income statement every 12 months and the dividends payable balance will be determined based on the first payment month and the payment option.
The Cash, Next or Subsequent setting in the Dividends section on the Assumptions sheet determines how the dividends payable balances on the balance sheet are calculated and therefore also when the dividend payment will be included on the cash flow statement.
If you select the Cash option, the dividend payable balances on the balance sheet will always be nil and what this means is that the dividend payment is effectively included in the same month as the month in which the dividend is declared. The month in which the declared dividend is included is based on the payment frequency (in months) and the cash flow projection year-end.
If you select the Next option, the dividend payment will be included in the month after the month in which the dividend amount is included on the income statement. The dividend payable balance on the balance sheet will therefore only contain a balance in the dividend declaration month.
If you select the Subsequent option, dividends will be included on the income statement based on the frequency setting on the Assumptions sheet and the payment of the dividend will be delayed until the first payment month (also as per the Assumptions sheet) is reached. A dividends payable balance will be reflected on the balance sheet in all months until the payment month is reached.
Example: If you set the dividend payment frequency to 12 months, a dividend amount will be included on the income statement in the last month of the appropriate cash flow projection year. If the payment option is set to Cash, no dividend payable amount will be included on the balance sheet and the dividend payment will be included on the cash flow statement in the same month.
Example: If you set the dividend payment frequency to 12 months and the payment option is set to Next, the dividend will be included on the income statement in the last month of the appropriate cash flow projection year, the dividend payable at the end of the financial year will equal the income statement amount and the dividend payment will be included in the first month of the next financial year.
Example: If you set the dividend payment frequency to 12 months and the payment option is set to Subsequent, the dividend will be included on the income statement in the last month of the appropriate cash flow projection year and the dividend payable at the end of the financial year and all subsequent months in the new financial year until the first payment month is reached will equal the income statement amount. The dividend payment will be included in the first payment month as set on the Assumptions sheet but in the year after inclusion on the income statement.
If the cash flow projection year-end as per the above example is February, the first payment month is set to 9 for September and the Subsequent payment option is selected, the dividend will be included in February on the income statement and the same amount will be included as a dividend payable on the balance sheet from February to August of the next financial year. The dividend payment will then be included in September on the cash flow statement and the dividend payable at the end of September will be nil.
The year 2 to 5 balances are calculated based on the profit for the year, the dividend percentage and the payment status of Cash, Next or Subsequent.
Balance Sheet Errors
If the balance sheet for any monthly or annual period does not balance, the amount of the imbalance will be included in the row below the total equities & liabilities and displayed in red. The template has been designed in such a way that the balance sheet should always be in balance as long as the total of the balance sheet opening balances which are included on the Assumptions sheet is nil.
If you see an imbalance on the balance sheet, you therefore need to check the opening balance sheet balances on the Assumptions sheet and ensure that the total of all the opening balances in this section is nil.
If fixing the opening balances does not resolve your imbalance, you can e-mail our Support function and let us know what changes you have made to the formulas in the template so that we can assist you. If you have made a lot of changes, you may need to start over with the downloaded copy of the template.
Balance Sheet Workings
We have included all the calculations which form part of the calculation of balance sheet balances in the Workings section below the balance sheet ratios. These workings will not be printed and are for information purposes only. You can therefore hide this section if you do not want to see it on the sheet but do not delete any of these formulas because it will result in calculation errors if you do!
Cash Flow Statement
All the rows on the cash flow statement which require user input are indicated with yellow highlighting in column A. User input is only required in the monthly columns - the user input for the annual columns need to be included on the Assumptions sheet in the first balance sheet section. All the rows on the cash flow statement which do not contain yellow highlighting contain formulas which automate the calculations of these items.
The input rows on the cash flow statement are all related to balance sheet items where the calculations on the balance sheet are based on adding the movement on the cash flow statement to the previous month's balance on the balance sheet. If you need more guidance on any of these items, refer to the appropriate section for the particular item under the Balance Sheet section of these instructions.
Note: The colour of the codes in column A on the cash flow statement indicate whether positive or negative values need to be entered in order to increase the appropriate balance sheet item's balance. If the code is green, positive input values increase the balance sheet balance and if the code is red, you need to enter negative values in order to increase the balance sheet balances.
Loan Amortization Tables (Loans1 to Loans3 & Leases sheets)
The template makes provision for including loans with up to four different sets of repayment terms in the cash flow projections. The amortization tables that are used to calculate the interest charges, loan repayments and outstanding balances have been included on the Loans1, Loans2, Loans3 and Leases sheets. The only user input that is required on these sheets is the additional loan amounts in column C.
Note: Refer to the instructions in the income statement - interest paid section and the balance sheet - non-current liabilities section for guidance on how these amortization tables have been compiled and where to include user input for each of these amortization tables.
Free Business Plan Template for Excel
Ajay Jagtap
- October 31, 2023

With 1 in 8 people using Excel, I’d be hard-pressed to believe that anyone has never used it at some point in life.
While we have all used it at least once—be it for school homework, college assignments, or travel planning—we never really got the hang of it.
(Excel formulas are tough!)
Preparing a business plan from scratch using Excel is not a joke; we get that. That’s why we created this business plan template in Excel .
So, no more worrying about Excel formulas or plan structure—download the document and follow the instructions in the article for successful business planning.
Sounds good? Let’s start with understanding the pros and cons of using Excel for planning:
Pros and Cons of Using Excel for Business Plans
Before we head to discussing the Excel business plan template, let’s understand the pros and cons of using Excel for business planning:
- Free to use: MS Excel is 100% free for all its users, making it a cost-effective choice.
- Data Analysis: Excel is a powerful tool for performing various financial and data analyses and calculations.
- Collaboration: Collaborating with your team while working on a project using Excel is easier.
- Lack of automation: Excel may not help create dynamic business plans with automated features.
- Limited presentation: Excel cannot create an appealing business plan like a business plan software.
- Complex formulas: Excel’s formulas are complex and require a significant learning curve to master.
So these were the pros and cons. Let’s cut to the chase and discuss the key components of our free business plan Excel template.
Key Components of Our Excel Business Plan Template
It’s a fact—you cannot use Excel to create the entire plan from scratch, no! Excel is a powerful tool for complex calculations and analyses; let’s use it for that only.
So, we’ll use this business plan Excel template only to perform complex financial analyses and calculations—to prepare financial projections.
Following are the critical components of a good business plan template you must include in your financial plan:
1. Income Statement
The income statement is one of the key financial statements of your financial plan that highlights its profit and loss over a given period of time.
The critical components of your income statement include—revenue/sales, Cost of Goods Sold (COGS), operational costs, EBITDA, interest, and others.
Say goodbye to old-school Excel sheets & templates
Build your business plan faster and easier with AI
Plans starting from $7/month

2. Balance Sheet
Your balance sheet is a statement that reports your company’s assets, liabilities, and shareholder equity, providing a snapshot of its financial position at a specific period of time.
The statement helping you calculate financial ratios includes the following:
- Assets—e.g. Inventory, cash, property.
- Liabilities—e.g. Accounts payable, loans, salaries to be paid.
- Owners equity—e.g. Capital investment/contribution.
3. Cash Flow Statement
The cash flow statement of your financial plan is the projection of your cash in and outflows over a certain period of time.
As one of three key components of your financial plan, the cash flow statement summarizes the amount of cash or cash equivalents entering or leaving your company.
4. Break-Even Analysis
A break-even analysis helps you determine the number of units you need to sell to cover all fixed and variable costs.
The break-even point is considered a measure of safety margin, and anything you sell beyond the point will result in profit.
While your balance sheet already highlights the assets, liabilities, and owner’s equity, assets are considered critical for investors to assess the company’s financial health. So, our simple business plan template (Excel) has a separate sheet for business assets.
6. Accounts Payable & Receivable
The accounts payable refer to the amount due to vendors or suppliers for services or goods received, whereas accounts receivable represent the money due to the company.
The increase or decrease in your accounts payable or receivable can be seen in your cash flow statement.
7. Working Capital
Working capital is the subtraction of your current liabilities from your current assets. As a critical element in identifying your company’s health, it helps investors understand if it has enough capital to pay employees and fund operations to meet short-term goals.
Download the Financial Forecast Template In Excel
We discussed all the critical statements to be covered in your financial plan. Now what? It’s time for you to download the financial forecast template and start preparing your financial plan.
Unlike other free Excel templates, this template has all the reports with the suggested revenue streams, expenses, and other details.
You can directly download and use the template to forecast cash flow, create balance sheets, and prepare income statements that provide detailed information about your revenue and expenses. So what are you waiting for?
How to Use an Excel Business Plan Template
We’re hoping you’ve already downloaded the business plan template. So, the question arises: How can this Excel template be used to prepare realistic forecasts?
Let’s get this over with:
Understand the template structure
Before you start planning, you must understand the structure of the financial portion of your business plan. Get a thorough review of the template and understand:
- What critical statements does it include?
- What are the revenue streams?
- What are considered to be assets and liabilities?
- What does the taxation structure look like?
And others. Once you thoroughly understand the structure, you can move ahead with the next step.
Analyze historical data
Financial forecasting is about assumptions—a lot of them, but accurate ones. If you’re a total stranger to financial forecasting, analyzing historical data will help you get off on the right foot.
Analyze the historical data and try to gain insights about your business financials:
- Monthly revenue over the last year?
- How much you’re spending on day-to-day operations?
- What is your sales growth rate? How fast is it increasing over time?
And others. These historical figures will be of massive help in the next step.
Make pre-assumptions
As I said before, financial forecasts heavily rely on certain assumptions like sales forecasts, operational expenses, revenue growth, and others.
So, in this step, you’ll make assumptions about these variables based on the historical data to make them realistic and accurate.
Prepare key financial reports
Once you have made pre-assumptions, it’s time to prepare forecasts. Don’t overwhelm yourself with a lot of numbers; start by preparing critical financial reports that include—a cash flow statement, balance sheet, and income statement.
Other statements of your plan rely heavily on these reports, so the process will become much easier after having prepared these three beforehand.
Monitor and track progress
After preparing your financial reports, the next step is timely monitoring these reports and tracking progress.
You can compare your assumptions with actual results to see if your projections are accurate and relevant to the changing market trends.
Analyzing metrics like customer acquisition rate, acquisition costs, net profit, and gross margin will help track progress.
If you follow these steps rigorously, you can surely make a decent plan to support your business strategies and achieve financial goals.
Still, it was just about financial planning. What about the entire business plan? Excel is a no-go for business planning; let’s see why.
How Excel may not be the best choice for business planning?
Since Excel doesn’t offer all the necessary features for business planning that a business plan software like Upmetrics would, it is not the tool to be used to create a comprehensive business plan.
Following are a few reasons why Excel may not be a better choice for business planning compared to a tool like Upmetrics:
- Limited features: Since it is not designed specifically for planning, it has limited business planning features compared to software like Upmetrics. A business planning software may include features like business plan builder, financial forecasting, and pitch deck creator.
- Limited collaboration: Everyone knows Excel isn’t the tool with the best collaboration features. Business plan software offers collaboration features, allowing multiple team members to work on a business plan simultaneously.
- No Automation: Upmetrics comes with many automation features like AI assistant and financial forecasting tool, helping entrepreneurs and small businesses save time and reduce human errors.
- No customizable templates: Upmetrics has 400+ business plan examples and templates that make it easier for new users to get started, which has not been the case with Excel.
These were just a few of many reasons why a planning tool is a better alternative than Excel to create a comprehensive plan to support their business strategy.
Improve Your Business Financial Plan with Upmetrics
I’d surely have recommended Excel for financial planning if you had asked maybe a decade ago.
Today? There’s no way Excel stands a chance when competing with a cutting-edge AI business planning solution like Upmetrics.
Upmetrics simplifies business planning with its library of business templates, financial forecasting tool, and AI-powered assistant, making it a much more efficient alternative to Excel.
What are you waiting for? Start planning today!
Make your plan in half the time & twice the impact with Upmetrics
Fill-in-the-blanks, AI-assistance, and automatic financials make it easy.
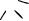
Frequently Asked Questions
How do i create a business plan in excel.
It’s challenging to draft an entire business plan in Excel. However, you can use Excel to create the financial portion of your plan using a free business plan Excel template. A ready-made template is always better and faster than preparing your financial reports from scratch.
Are there any alternatives to Excel for creating a business plan?
Yes, there are a few alternatives to Excel for creating a business plan. However, using a business plan software like Upmetrics would be a better alternative to creating a business plan than others.
Why should I use an Excel template for my business financial plan?
You cannot certainly master Excel formulas in one day, and preparing advanced financial reports from scratch means you must be very good at accounting, budgeting, and Excel sheets and ready to spare some intense hours.
So, considering the complexity of Excel—using a ready-made template seems like a great starting point for budding entrepreneurs with no financial planning experience.
Are there any free business plan templates available in Excel?
Although it’s tough to create the entire business plan in Excel from scratch, Upmetrics offers a free business plan Excel template to help you gain inspiration and make the financial portion of your business plan.
Can I share my financial plan online with others using Excel?
Yes, you can share your financial plan online with others using Excel. To share your document with others, simply click on the “Share with People” option and enter their email addresses, and you have shared the doc.
About the Author

Ajay is a SaaS writer and personal finance blogger who has been active in the space for over three years, writing about startups, business planning, budgeting, credit cards, and other topics related to personal finance. If not writing, he’s probably having a power nap. Read more
Reach Your Goals with Accurate Planning
No Risk – Cancel at Any Time – 15 Day Money Back Guarantee
Ready to Kickstart Your Business Planning?

– Don’t Miss It
Original text

Financial projections use existing or estimated financial data to forecast your business’s future income and expenses. They often include different scenarios to see how changes to one aspect of your finances (such as higher sales or lower operating expenses) might affect your profitability.
If you need to create financial projections for a startup or existing business, this free, downloadable template includes all the necessary tools.
What Are Financial Projections Used for?
Financial projections are an essential business planning tool for several reasons.
- If you’re starting a business, financial projections help you plan your startup budget, assess when you expect the business to become profitable, and set benchmarks for achieving financial goals.
- If you’re already in business, creating financial projections each year can help you set goals and stay on track.
- When seeking outside financing, startups and existing businesses need financial projections to convince lenders and investors of the business’s growth potential.
What’s Included in Financial Projections?
This financial projections template pulls together several different financial documents, including:
- Startup expenses
- Payroll costs
- Sales forecast
- Operating expenses for the first 3 years of business
- Cash flow statements for the first 3 years of business
- Income statements for the first 3 years of business
- Balance sheet
- Break-even analysis
- Financial ratios
- Cost of goods sold (COGS), and
- Amortization and depreciation for your business.
You can use this template to create the documents from scratch or pull in information from those you’ve already made. The template also includes diagnostic tools to test the numbers in your financial projections and ensure they are within reasonable ranges.
These areas are closely related, so as you work on your financial projections, you’ll find that changes to one element affect the others. You may want to include a best-case and worst-case scenario for all possibilities. Make sure you know the assumptions behind your financial projections and can explain them to others.
Startup business owners often wonder how to create financial projections for a business that doesn’t exist yet. Financial forecasts are continually educated guesses. To make yours as accurate as possible, do your homework and get help. Use the information you unearthed in researching your business plans, such as statistics from industry associations, data from government sources, and financials from similar businesses. An accountant with experience in your industry can help fine-tune your financial projections. So can business advisors such as SCORE mentors.
Once you complete your financial projections, don’t put them away and forget about them. Compare your projections to your financial statements regularly to see how well your business meets your expectations. If your projections turn out to be too optimistic or too pessimistic, make the necessary adjustments to make them more accurate.
*NOTE: The cells with formulas in this workbook are locked. If changes are needed, the unlock code is "1234." Please use caution when unlocking the spreadsheets. If you want to change a formula, we strongly recommend saving a copy of this spreadsheet under a different name before doing so.
We recommend downloading the Financial Projections Template Guide in English or Espanol .
Do you need help creating your financial projections? Take SCORE’s online course on-demand on financial projections or connect with a SCORE mentor online or in your community today.
Simple Steps for Starting Your Business: Financial Projections In this online module, you'll learn the importance of financial planning, how to build your financial model, how to understand financial statements and more.
Business Planning & Financial Statements Template Gallery Download SCORE’s templates to help you plan for a new business startup or grow your existing business.
Why Projected Financial Statements Are Essential to the Future Success of Startups Financial statements are vital to the success of any company but particularly start-ups. SCORE mentor Sarah Hadjhamou shares why they are a big part of growing your start-up.
Copyright © 2024 SCORE Association, SCORE.org
Funded, in part, through a Cooperative Agreement with the U.S. Small Business Administration. All opinions, and/or recommendations expressed herein are those of the author(s) and do not necessarily reflect the views of the SBA.
Financial Projection Template
Building up forecast from payroll schedules, operating expenses schedules and sales forecast to the three financial statements
Our financial projection template will help you forecast future revenues and expenses by building up from payroll schedules, operating expenses schedules, and sales forecast to the three financial statements.
Below is a screenshot of the financial projection template:
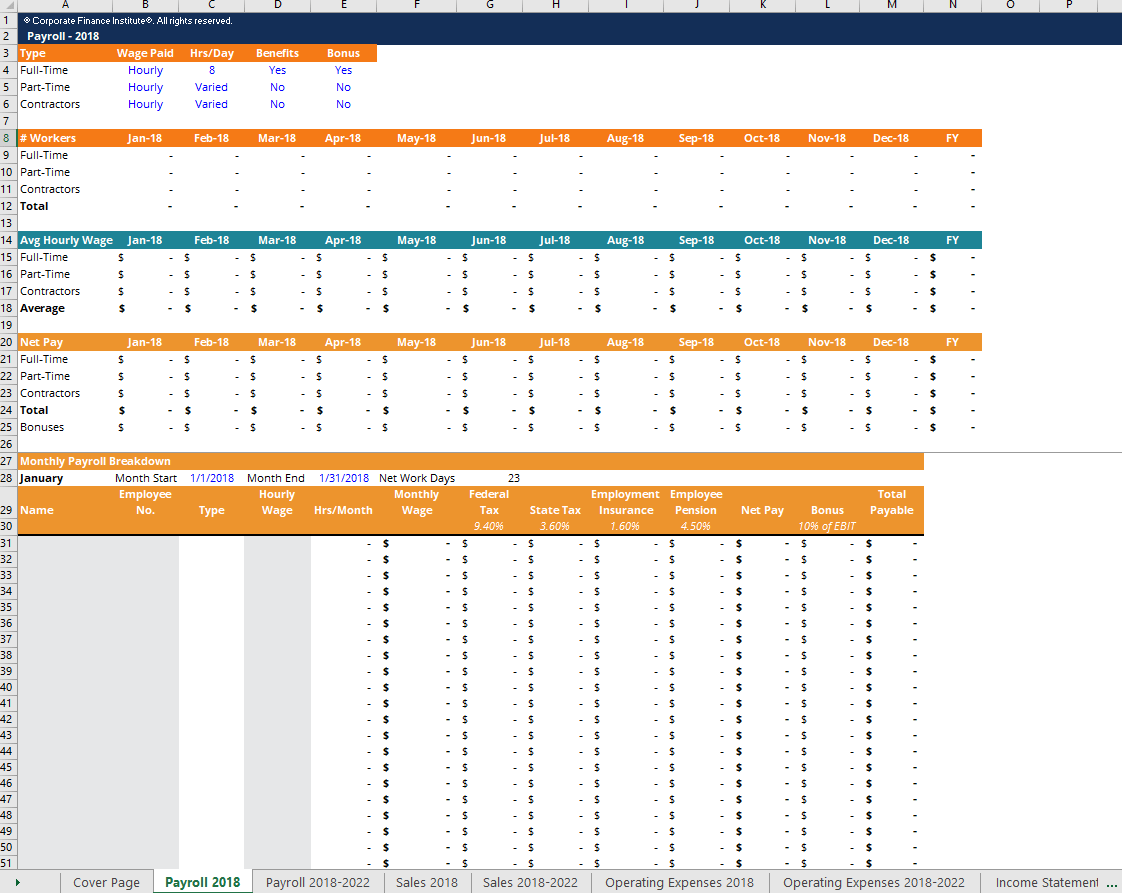
Download the Free Financial Projection Template
Enter your name and email in the form below and download the free template now!
Components of a financial projection template
This financial projection template contains the following sections:
#1 Payroll (current year)
In the payroll (current year) worksheet, you will input the payroll expenses for each of the full-time employees, part-time employees, and contractors. The model helps you break down the salary, taxes, employee insurance, pension, and employee bonus expenses so you can easily track the total amount for each of the items. These individual monthly payrolls then roll up to the summary tables, which automatically calculate the average hourly wage and net pay for each month (all expenses except bonuses) by staff type.
#2 Payroll (forecast)
In the payroll ( forecast ) worksheet, you will put your own assumptions for the growth rate of the number of workers for the period of forecast. These are the only manual inputs required for the model. Once the assumptions are filled in, the pre-entered formulas will generate the payroll forecast for the rest of the period and calculate average hourly wages by staff type. You’ll also be able to estimate the total amount of taxes, employee insurance, and pension expenses for each of the years.
#3 Sales (current year)
In the sales (current year) worksheet, you’ll input the per-unit sales price, the number of units sold, and the per-unit cost of goods sold for each product line under the “sales breakdown” section. The model will automatically calculate the monthly revenue , COGS , and gross margin for each product line, which are linked to the summary tables at the top of the worksheet. You’ll be able to quickly understand the sales and margin for each product for the current year.
#4 Sales (forecast)
In the sales (current year) worksheet, assumptions on sales growth rate are entered for the forecast period to generate the predicted revenue, COGS, and gross margin for the following years.
#5 Operating expenses (current year)
The operating expenses (current year) worksheet is for you to enter the actual operating expenses for the current year. These will help build up the forecast for operating expenses and the income statement.
#6 Operating expenses (forecast)
In the operating expenses (forecast) worksheet, the operating expenses forecast for the next few years will be calculated using the assumptions for each of the expense items.
#7 Income statement (current & forecast)
The income statements for the current year and forecast period are built up by linking to values in the sales worksheets and operating expenses worksheets.
#8 Balance sheet (current year)
This balance sheet worksheet consists of two main sections: balance sheet and supporting schedules. Balance sheet items such as accounts receivable , inventory , accounts payable , and retained earnings will be manually input, while items such as cash, property and equipment , and long-term debt will be linked to other parts of this financial projection template. For example, the debt & interest schedule under the supporting schedules section will help you compute the amount of debt closing and interest expenses , which will then be linked back up to the balance sheet as long-term debt and to the income statement as interest expense.
#9 Balance sheet (forecast)
This balance sheet forecast worksheet is built up by taking the current year’s balance sheet and calculating the following years’ values using assumptions such as accounts receivable days, inventory days , accounts payable days , and capital expenditures .
#10 Cash flow statement (current year & forecast)
The cash flow statements for the current year and forecast period are constructed using figures calculated in the income statement, balance sheet, and supporting schedules. The closing cash balance for each month will be linked back to the balance sheet, shown as cash under current assets .
#11 Financial ratio analysis
The final section of this financial projection template is the financial ratio analysis. This worksheet will show you the list of all commonly used financial ratios including profitability ratios , efficiency ratios, liquidity ratios, leverage ratios , and coverage ratios , which are calculated using all the worksheets previously built. The ratios will allow you to understand the financial stability of the company and its expected performance in the following years.

More Free Templates
For more resources, check out our business templates library to download numerous free Excel modeling, PowerPoint presentations, and Word document templates.
- Excel Modeling Templates
- PowerPoint Presentation Templates
- Transaction Document Templates
- Word Document Templates
- See all financial modeling resources
- See all Excel resources
Additional Resources
CFI is a global provider of financial modeling courses and of the FMVA Certification . CFI’s mission is to help all professionals improve their technical skills. If you are a student or looking for a career change, the CFI website has many free resources to help you jumpstart your Career in Finance. If you are seeking to improve your technical skills, check out some of our most popular courses. Below are some additional resources for you to further explore:
- Careers
- CFI’s Most Popular Courses
- All CFI Resources
- Finance Terms
The Financial Modeling Certification
Excel tutorial.
Launch CFI’s Excel Course now
to take your career to the next level and move up the ladder!
- Share this article

Create a free account to unlock this Template
Access and download collection of free Templates to help power your productivity and performance.
Already have an account? Log in
Supercharge your skills with Premium Templates
Take your learning and productivity to the next level with our Premium Templates.
Upgrading to a paid membership gives you access to our extensive collection of plug-and-play Templates designed to power your performance—as well as CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs.
Already have a Self-Study or Full-Immersion membership? Log in
Access Exclusive Templates
Gain unlimited access to more than 250 productivity Templates, CFI's full course catalog and accredited Certification Programs, hundreds of resources, expert reviews and support, the chance to work with real-world finance and research tools, and more.
Already have a Full-Immersion membership? Log in
- Start free trial
Start selling with Shopify today
Start your free trial with Shopify today—then use these resources to guide you through every step of the process.

How To Create Financial Projections for Your Business Plan
Building a financial projection as you write out your business plan can help you forecast how much money your business will bring in.

Planning for the future, whether it’s with growth in mind or just staying the course, is central to being a business owner. Part of this planning effort is making financial projections of sales, expenses, and—if all goes well—profits.
Even if your business is a startup that has yet to open its doors, you can still make projections. Here’s how to prepare your business plan financial projections, so your company will thrive.
What are business plan financial projections?
Business plan financial projections are a company’s estimates, or forecasts, of its financial performance at some point in the future. For existing businesses, draw on historical data to detail how your company expects metrics like revenue, expenses, profit, and cash flow to change over time.
Companies can create financial projections for any span of time, but typically they’re for between one and five years. Many companies revisit and amend these projections at least annually.
Creating financial projections is an important part of building a business plan . That’s because realistic estimates help company leaders set business goals, execute financial decisions, manage cash flow , identify areas for operational improvement, seek funding from investors, and more.
What are financial projections used for?
Financial forecasting serves as a useful tool for key stakeholders, both within and outside of the business. They often are used for:
Business planning
Accurate financial projections can help a company establish growth targets and other goals . They’re also used to determine whether ideas like a new product line are financially feasible. Future financial estimates are helpful tools for business contingency planning, which involves considering the monetary impact of adverse events and worst-case scenarios. They also provide a benchmark: If revenue is falling short of projections, for example, the company may need changes to keep business operations on track.
Projections may reveal potential problems—say, unexpected operating expenses that exceed cash inflows. A negative cash flow projection may suggest the business needs to secure funding through outside investments or bank loans, increase sales, improve margins, or cut costs.
When potential investors consider putting their money into a venture, they want a return on that investment. Business projections are a key tool they will use to make that decision. The projections can figure in establishing the valuation of your business, equity stakes, plans for an exit, and more. Investors may also use your projections to ensure that the business is meeting goals and benchmarks.
Loans or lines of credit
Lenders rely on financial projections to determine whether to extend a business loan to your company. They’ll want to see historical financial data like cash flow statements, your balance sheet , and other financial statements—but they’ll also look very closely at your multi-year financial projections. Good candidates can receive higher loan amounts with lower interest rates or more flexible payment plans.
Lenders may also use the estimated value of company assets to determine the collateral to secure the loan. Like investors, lenders typically refer to your projections over time to monitor progress and financial health.
What information is included in financial projections for a business?
Before sitting down to create projections, you’ll need to collect some data. Owners of an existing business can leverage three financial statements they likely already have: a balance sheet, an annual income statement , and a cash flow statement .
A new business, however, won’t have this historical data. So market research is crucial: Review competitors’ pricing strategies, scour research reports and market analysis , and scrutinize any other publicly available data that can help inform your projections. Beginning with conservative estimates and simple calculations can help you get started, and you can always add to the projections over time.
One business’s financial projections may be more detailed than another’s, but the forecasts typically rely on and include the following:
True to its name, a cash flow statement shows the money coming into and going out of the business over time: cash outflows and inflows. Cash flows fall into three main categories:
Income statement
Projected income statements, also known as projected profit and loss statements (P&Ls), forecast the company’s revenue and expenses for a given period.
Generally, this is a table with several line items for each category. Sales projections can include the sales forecast for each individual product or service (many companies break this down by month). Expenses are a similar setup: List your expected costs by category, including recurring expenses such as salaries and rent, as well as variable expenses for raw materials and transportation.
This exercise will also provide you with a net income projection, which is the difference between your revenue and expenses, including any taxes or interest payments. That number is a forecast of your profit or loss, hence why this document is often called a P&L.
Balance sheet
A balance sheet shows a snapshot of your company’s financial position at a specific point in time. Three important elements are included as balance sheet items:
- Assets. Assets are any tangible item of value that the company currently has on hand or will in the future, like cash, inventory, equipment, and accounts receivable. Intangible assets include copyrights, trademarks, patents and other intellectual property .
- Liabilities. Liabilities are anything that the company owes, including taxes, wages, accounts payable, dividends, and unearned revenue, such as customer payments for goods you haven’t yet delivered.
- Shareholder equity. The shareholder equity figure is derived by subtracting total liabilities from total assets. It reflects how much money, or capital, the company would have left over if the business paid all its liabilities at once or liquidated (this figure can be a negative number if liabilities exceed assets). Equity in business is the amount of capital that the owners and any other shareholders have tied up in the company.
They’re called balance sheets because assets always equal liabilities plus shareholder equity.
5 steps for creating financial projections for your business
- Identify the purpose and timeframe for your projections
- Collect relevant historical financial data and market analysis
- Forecast expenses
- Forecast sales
- Build financial projections
The following five steps can help you break down the process of developing financial projections for your company:
1. Identify the purpose and timeframe for your projections
The details of your projections may vary depending on their purpose. Are they for internal planning, pitching investors, or monitoring performance over time? Setting the time frame—monthly, quarterly, annually, or multi-year—will also inform the rest of the steps.
2. Collect relevant historical financial data and market analysis
If available, gather historical financial statements, including balance sheets, cash flow statements, and annual income statements. New companies without this historical data may have to rely on market research, analyst reports, and industry benchmarks—all things that established companies also should use to support their assumptions.
3. Forecast expenses
Identify future spending based on direct costs of producing your goods and services ( cost of goods sold, or COGS) as well as operating expenses, including any recurring and one-time costs. Factor in expected changes in expenses, because this can evolve based on business growth, time in the market, and the launch of new products.
4. Forecast sales
Project sales for each revenue stream, broken down by month. These projections may be based on historical data or market research, and they should account for anticipated or likely changes in market demand and pricing.
5. Build financial projections
Now that you have projected expenses and revenue, you can plug that information into Shopify’s cash flow calculator and cash flow statement template . This information can also be used to forecast your income statement. In turn, these steps inform your calculations on the balance sheet, on which you’ll also account for any assets and liabilities .
Business plan financial projections FAQ
What are the main components of a financial projection in a business plan.
Generally speaking, most financial forecasts include projections for income, balance sheet, and cash flow.
What’s the difference between financial projection and financial forecast?
These two terms are often used interchangeably. Depending on the context, a financial forecast may refer to a more formal and detailed document—one that might include analysis and context for several financial metrics in a more complex financial model.
Do I need accounting or planning software for financial projections?
Not necessarily. Depending on factors like the age and size of your business, you may be able to prepare financial projections using a simple spreadsheet program. Large complicated businesses, however, usually use accounting software and other types of advanced data-management systems.
What are some limitations of financial projections?
Projections are by nature based on human assumptions and, of course, humans can’t truly predict the future—even with the aid of computers and software programs. Financial projections are, at best, estimates based on the information available at the time—not ironclad guarantees of future performance.
Keep up with the latest from Shopify
Get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
popular posts

The point of sale for every sale.

Subscribe to our blog and get free ecommerce tips, inspiration, and resources delivered directly to your inbox.
Unsubscribe anytime. By entering your email, you agree to receive marketing emails from Shopify.
Latest from Shopify
Aug 23, 2024
Aug 22, 2024
Learn on the go. Try Shopify for free, and explore all the tools you need to start, run, and grow your business.
Try Shopify for free, no credit card required.

Expert-built business plan and financial model templates

Download the template for your business. Customise it. Get funded.
Try restaurant business plan ecommerce financial model
Trusted by 12,000+ entrepreneurs, consultants and investors
Vetted by professionals at leading organizations

BuSINESS PLANS
Professional powerpoint business plan templates to raise funding.
- 30+ slides already completed
- Business overview
- Updated market research
- Sales & marketing plan
- SWOT, competitive landscape

Financial models
Easy-to-use excel financial models for serious entrepreneurs.
- Profit and loss
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
- Business valuation (DCF)
- 20+ charts and metrics

Start free. Upgrade if you need to.
Start here if you need a solid yet simple financial plan, one-size-fits-all starter 3-year financial model.
This is our 3-year financial model for entrepreneurs who need a rock-solid template to get started.
Works for most businesses.
- One-size-fits-all
- 3-year Excel financial model
- Break-even analysis
- Return on investment
- Business valuation report
- No email support
or UPGRADE TO A CUSTOMIZED ADVANCED FINANCIAL PLAN
200+ advanced 5-year financial models.
200+ financial models for entrepreneurs who need more flexibility by using a template made specifically for their business .
200+ businesses. Choose yours.
- Choose from 200+ businesses
- 5-year Excel financial model
- Free email support
Privacy Overview
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| BIGipServerwww_ou_edu_cms_servers | session | This cookie is associated with a computer network load balancer by the website host to ensure requests are routed to the correct endpoint and required sessions are managed. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-advertisement | 1 year | Set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin, this cookie is used to record the user consent for the cookies in the "Advertisement" category . |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-analytics | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Analytics". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-functional | 11 months | The cookie is set by GDPR cookie consent to record the user consent for the cookies in the category "Functional". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-necessary | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookies is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Necessary". |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-others | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Other. |
| cookielawinfo-checkbox-performance | 11 months | This cookie is set by GDPR Cookie Consent plugin. The cookie is used to store the user consent for the cookies in the category "Performance". |
| CookieLawInfoConsent | 1 year | Records the default button state of the corresponding category & the status of CCPA. It works only in coordination with the primary cookie. |
| elementor | never | This cookie is used by the website's WordPress theme. It allows the website owner to implement or change the website's content in real-time. |
| viewed_cookie_policy | 11 months | The cookie is set by the GDPR Cookie Consent plugin and is used to store whether or not user has consented to the use of cookies. It does not store any personal data. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| __cf_bm | 30 minutes | This cookie, set by Cloudflare, is used to support Cloudflare Bot Management. |
| language | session | This cookie is used to store the language preference of the user. |
| Cookie | Duration | Description |
|---|---|---|
| _ga | 2 years | The _ga cookie, installed by Google Analytics, calculates visitor, session and campaign data and also keeps track of site usage for the site's analytics report. The cookie stores information anonymously and assigns a randomly generated number to recognize unique visitors. |
| _ga_QP2X5FY328 | 2 years | This cookie is installed by Google Analytics. |
| _gat_UA-189374473-1 | 1 minute | A variation of the _gat cookie set by Google Analytics and Google Tag Manager to allow website owners to track visitor behaviour and measure site performance. The pattern element in the name contains the unique identity number of the account or website it relates to. |
| _gid | 1 day | Installed by Google Analytics, _gid cookie stores information on how visitors use a website, while also creating an analytics report of the website's performance. Some of the data that are collected include the number of visitors, their source, and the pages they visit anonymously. |
| browser_id | 5 years | This cookie is used for identifying the visitor browser on re-visit to the website. |
| WMF-Last-Access | 1 month 18 hours 11 minutes | This cookie is used to calculate unique devices accessing the website. |

Financial Projection Excel Template

A financial projection is an approach used to forecast the future income, revenue, costs, and expenses of a business or proposal.
Typically, there are several methods used for the forecasting of a business’s financial position at any point in the future. For this purpose, internal historic data is used by developed businesses.
While for new business proposals, external market analysis is conducted to evaluate the financial sustainability of the business.
Financial Projection Template in Excel
The analysis of current financial data that helps to forecast a company or project/business’s future financial position is called financial projection. Basically, this projection has some limitations i.e; projection for 5 years or 10 years.
This forecasting may wrong too because there are always remain risk factors too.
A financial projection excel template can be used to develop short, mid, or long-term financial projections of any business.
A short-term financial project is usually a yearly forecast of the business containing month-by-month projects. The mid-term financial project of the business is calculated for the coming three years of the business. While for more than three years of projects, a long-term financial projection excel template is used.
Why Using Financial Projection Excel Template
There are several reasons for using the financial projection excel template for new startups or developed businesses.
However, a few of the most fundamental ones are;
- It is easy to use and helps beginners to effectively forecast the financial position of their startup.
- It helps the businesses to adopt the right approach for the projection of their financial stability in the future.
- It can be used to forecast the financial position of a business from short to long-term plans.
- It helps the businesses to set targets out of the business goals.
- It helps businesses to get feedback about the situation at any point in the future.
- It helps to forecast the problems and allows to control them.
The financial projection excel template can be used in different situations such as;
- While creating a new business model.
- Looking for investors to generate funds for business growth plans.
- To better anticipate the financial stability of the business at any point in the future.
Essential Elements of Financial Projection Excel Template
There are three fundamental financial sheets used by businesses. So, the financial projection also includes all of these to completely evaluate the financial position of the business in the future.
It includes the income statement, which covers the financial aspects such as revenue, expenses, other expenses, income, other income, net income.
The 2 nd sheet is a cash flow projection that involves cash revenues, cash disbursements, and reconciliation.
Finally, the last balance sheet project covers the assets, liabilities, and equity of the business.
Below are some important elements that must be included;
- An initial amount of investment
- Employee Payroll Expenses
- Expected Sales Forecast
- Operating expenses in terms of 2-3 years
- Cash flow statements for the first 2-3 years
- Income statements for the first 2-3 years
- Balance sheet
- Breakeven analysis
- Financial ratios and Percentage
- Cost of goods sold
- Cost-Benefit Analysis
- Rate of Amortization
- Rate of Depreciation
Steps to Create Financial Projection Excel Template
There is a simple five-step approach that can be used to create a financial projection excel template;
Step 1: Create the sales projection of the business for a specified period
Step 2: Create the projection of expenses/costs
Step 3: Create the projection of the business income statement
Step 4: Create the projection of the business balance sheet
Step 5: Create the projection of the business cash flow statement
The above steps can be followed for any new startup or for a small business to make an effective financial projection sheet for any point in the future to check the financial position of the business.
The financial projection Excel template helps the business to constantly evaluate the company’s core competencies, weaknesses, markets, and competition. So, it enables the business to better analyze the problems and business opportunities. Also, provide new growth opportunities for business.
Financial Projection Template Used For?
This financial projection is part of basic business planning and below there are important reasons of it used;
- We need this project management documentation tool when we are going to launch a new project. It helps to make a complete budget plan , provides statistical data that shows when we may be able to get profit from this project or business, and most importantly helps to set up financial achievement goals.
- However, if we already launched a project or business, this projection provides us sufficient financial data on the basis of, we set our financial planning and procurement plan.
- It also helps us to get on track in the pursuit of our goals.
- As we know that, a financial projection is part of financial planning, so when we need investment, clients, or any other stakeholders, these projections are very helpful to show the company’s position on the scale of years.
How can we get this template?
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

Privacy Policy
Terms & Conditions
Recent Posts
- Resilience in Project Management: Strategies To Handle Setbacks & Challenges 01/07/2024
- Project Portfolio Management Dashboard Templates Excel 19/02/2024
- Advanced Project Pipeline Tracker Template Excel 31/01/2024
The Enlightened Mindset
Exploring the World of Knowledge and Understanding
Welcome to the world's first fully AI generated website!
Making Financial Projections in Excel: A Step-by-Step Guide
By Happy Sharer

Introduction
Financial projections are essential for any business or organization. They provide an estimate of future income and expenses, helping you plan ahead and make informed decisions. Making financial projections in Excel is an effective way to create accurate projections and track them over time. In this article, we’ll explore the benefits of making financial projections in Excel and provide a step-by-step guide on how to do it.
What are Financial Projections?
Financial projections are estimates of future financial performance, based on past performance and current trends. They help businesses and organizations set realistic goals, plan for growth, and make sound financial decisions. Typically, financial projections cover a period of one to five years, but can be longer or shorter depending on the situation. They include estimates of revenue, expenses, cash flow, capital investments, and other financial variables.

Benefits of Making Financial Projections in Excel
Excel is a powerful tool for making financial projections. It allows you to easily enter, organize, and analyze data. You can also use formulas and functions to automate calculations, as well as create graphs and charts to visualize the results. Excel also makes it easy to update your projections as new information becomes available.
Step-by-Step Guide on How to Make Financial Projections in Excel
Making financial projections in Excel involves several steps. Here’s a step-by-step guide on how to do it.
Setting Up the Spreadsheet
The first step is to create a spreadsheet in Excel. Set up columns for each type of financial data you want to track, such as revenue, expenses, and cash flow. If you’re projecting multiple years, add one column for each year. If you’re projecting quarterly or monthly, add one column for each period.
Entering Financial Data
Next, enter your financial data into the spreadsheet. This includes historical data, such as actual revenue and expenses from previous years, as well as projected data, such as estimated revenue and expenses for the future. Be sure to double-check your entries to ensure accuracy.
Formatting the Spreadsheet
Once you’ve entered your data, format the spreadsheet so it’s easier to read and understand. Add headers to the columns, color-code rows and columns, and adjust the font size and style. You can also use built-in features such as conditional formatting to highlight important data points.
Calculating Projected Values
Now that you have your data entered and formatted, you can begin calculating the projected values. Use formulas and functions to add, subtract, multiply, and divide numbers in order to calculate the projected values. Excel has a wide range of built-in formulas and functions that you can use to make your calculations.
Exploring the Power of Excel for Financial Projections
Excel provides a variety of tools and features that you can use to make financial projections. Here are some of the ways you can use Excel to make more accurate projections.
Understanding Formulas
Formulas are fundamental to making accurate financial projections in Excel. They allow you to quickly and accurately calculate the projected values based on your input data. Spend some time familiarizing yourself with the different types of formulas available in Excel, and practice using them to make projections.
Using Functions and Macros
Functions and macros are pre-written formulas that you can use to automate calculations. Excel has hundreds of built-in functions that you can use to make projections. You can also create custom macros to perform complex calculations with minimal effort.
Analyzing Data with Graphs and Charts
Graphs and charts are useful for visualizing your data and analyzing trends over time. Excel has a variety of built-in chart types that you can use to display your data in an easy-to-understand format. You can also customize the charts to make them more visually appealing.

Crafting Accurate Financial Projections with Excel
In addition to understanding formulas and using functions and macros, there are other steps you can take to make more accurate projections. Here are some tips for crafting accurate financial projections in Excel.
Estimating Revenue and Expenses
Revenue and expenses are key components of financial projections. Estimate your revenue and expenses by researching industry trends, analyzing competitor data, and considering potential changes in the market. Make sure to factor in inflation when estimating future expenses.
Calculating Ratios and Breakeven Points
Ratios and breakeven points are useful metrics for evaluating financial performance. Calculate these metrics by dividing one number by another. For example, to calculate the breakeven point, divide total fixed costs by the difference between unit selling price and variable costs per unit.
Setting Goals and Benchmarks
Goals and benchmarks provide targets to strive for when making projections. Set realistic goals and benchmarks based on your research and analysis. Monitor progress towards these goals and adjust them as needed.

Excel Tips and Tricks to Make Financial Projections Easier
Making financial projections in Excel doesn’t have to be difficult. Here are some tips and tricks for making the process easier.
Automating Tasks
You can use macros and scripts to automate tedious tasks, such as entering data or calculating formulas. This can save you time and reduce errors, allowing you to focus on more important tasks.
Streamlining Data Entry
Data entry is an important part of making financial projections. To make the process easier, use templates and shortcuts to quickly enter data into the spreadsheet. You can also use data validation to ensure that only valid data is entered.
Adding Visual Elements
Visual elements, such as graphs and charts, make it easier to understand and interpret data. In Excel, you can add visual elements to your projections to make them more informative and engaging. Consider using icons, images, and other visual elements to make your projections stand out.
Making financial projections in Excel is a powerful way to plan for the future and make informed decisions. It allows you to easily enter, organize, and analyze data, as well as automate calculations and visualize results. With the right knowledge and tools, you can craft accurate financial projections in Excel.
In this article, we explored the benefits of making financial projections in Excel and provided a step-by-step guide on how to do it. We also discussed the power of Excel for financial projections, including understanding formulas, using functions and macros, analyzing data with graphs and charts, estimating revenue and expenses, calculating ratios and breakeven points, setting goals and benchmarks, and tips and tricks for making the process easier.
(Note: Is this article not meeting your expectations? Do you have knowledge or insights to share? Unlock new opportunities and expand your reach by joining our authors team. Click Registration to join us and share your expertise with our readers.)
Hi, I'm Happy Sharer and I love sharing interesting and useful knowledge with others. I have a passion for learning and enjoy explaining complex concepts in a simple way.
Related Post
Making croatia travel arrangements, make their day extra special: celebrate with a customized cake, top 4 most asked questions when applying for etias, leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Expert Guide: Removing Gel Nail Polish at Home Safely
Trading crypto in bull and bear markets: a comprehensive examination of the differences.
Everything that you need to know to start your own business. From business ideas to researching the competition.
Practical and real-world advice on how to run your business — from managing employees to keeping the books
Our best expert advice on how to grow your business — from attracting new customers to keeping existing customers happy and having the capital to do it.
Entrepreneurs and industry leaders share their best advice on how to take your company to the next level.
- Business Ideas
- Human Resources
- Business Financing
- Growth Studio
- Ask the Board
Looking for your local chamber?
Interested in partnering with us?
Run » finance, how to create a financial projection in excel.
Do you want to forecast your sales and revenue? Here's how Microsoft Excel can help.

Financial forecasting helps predict future surpluses and deficits. It also allows you to make critical insights to support business decisions. Small business owners return to their forecasts frequently to update data and ensure any predictions about growth rates or expenses are reasonable. Having an editable template in Microsoft Excel can save a significant amount of time.
Excel’s forecasting tool automatically generates a chart from your data. You can also use an Excel template from Microsoft or through SCORE. Below we'll list the documents used to create your financial projection in Excel and offer three options for building your forecasting template.
Gather financial statements and forms
Regardless of the method chosen to create a financial forecast in Excel, you need to enter data from various sources. You may already house this information in Excel spreadsheets or use accounting, point-of-sale (POS) or payroll software. Third-party tools often let you download your financial statements as an .xls extension so you can use them in your financial forecast template.
To create a financial projection, you need:
- Balance sheet .
- Cost of goods sold (COGS).
- Startup expenses .
- Sales forecast.
- Payroll costs.
- Income statements.
- Operating expenses.
- Cash flow statements .
- Break-even analysis.
- Financial ratios.
- Amortization and depreciation for your business.
[Read more: Creating a Financial Accounting Report With the Four Basic Statements ]
Third-party tools often let you download your financial statements as an .xls extension so you can use them in your financial forecast template.
Create a financial projection in Excel from scratch
Get a quick view of what to expect in the coming year using Excel's Forecast Sheet tool. It creates a chart based on any data sets in your spreadsheet. For instance, you can pull up your net revenue for the previous years and instantly generate a forecast.
Follow these steps to predict future revenue:
- Open an Excel sheet with your historical sales data.
- Select data in the two columns with the date and net revenue data.
- Click on the Data tab and pick "Forecast Sheet."
- Enter the date your forecast will end and click "Create."
- Title and save your financial projection.
Likewise, you can use this method to forecast cash flow and operating profit. Developing a financial projection in Excel from scratch can be time-consuming, and data entry or formula errors will return inaccurate results. Learn more by viewing Microsoft's tutorial on creating a forecast in Excel.
Use a small business cash flow projection template
If you're familiar with Microsoft Excel and don't want to start from scratch, consider one of Microsoft's pre-built templates. The Small Business Cash Flow Projection template is a free download that includes a forecasting spreadsheet and chart showing your predicted monthly balances. Instructions don't accompany the template, so this spreadsheet can be difficult to navigate if you're unfamiliar with accounting or Excel formulas.
Here's how to get your Excel financial projection template:
- Go to the Small Business Cash Flow Projection template.
- Download and save a copy of it to your computer.
- Open the file in your browser's download bar or the file folder.
The financial forecast template opens automatically in your Excel software. From there, customize your spreadsheet by adding your company name and starting date. Also, be sure to include the minimum monthly amount you need to meet your obligations. This way, Excel will flag any projections that don't reach your minimum.
Get help from SCORE
SCORE provides a complete financial projection template that pulls data from various financial documents and creates financial forecasts for cash flow, operating profit, balance sheet and income statements. It also provides a sales forecast, financial ratios and a breakeven analysis.
SCORE walks you through each step, making this the best option if you're new to financial forecasting or Excel. Through SCORE or other small business resource centers, business mentors can also help you understand financial forecasting. Plus, SCORE offers an on-demand online course on financial projections .
Here's how to create a financial projection using the SCORE template:
- Click "Download Template" on SCORE's Financial Projections Template page.
- Select the download link in your browser bar or file, and it'll open in Excel.
- Read the instructions page and fill out the information about your company.
This method requires more effort initially than projecting one financial statement. But, it provides a complete set of documents needed by investors and lenders and gives you a clear view of your future finances.
CO— aims to bring you inspiration from leading respected experts. However, before making any business decision, you should consult a professional who can advise you based on your individual situation.
Follow us on Instagram for more expert tips & business owners’ stories.
CO—is committed to helping you start, run and grow your small business. Learn more about the benefits of small business membership in the U.S. Chamber of Commerce, here .
Subscribe to our newsletter, Midnight Oil
Expert business advice, news, and trends, delivered weekly
By signing up you agree to the CO— Privacy Policy. You can opt out anytime.
For more finance tips
Types of credit card machines and terminals: a business guide, what is a credit card authorization, and who needs a form, payment gateways vs. payment processors: what's the difference.
By continuing on our website, you agree to our use of cookies for statistical and personalisation purposes. Know More
Welcome to CO—
Designed for business owners, CO— is a site that connects like minds and delivers actionable insights for next-level growth.
U.S. Chamber of Commerce 1615 H Street, NW Washington, DC 20062
Social links
Looking for local chamber, stay in touch.
Financial modeling spreadsheets and templates in Excel & Google Sheets
- Your cart is empty.

Pro Financial Forecast – Dynamic and Advanced Financial Projections
Unleash the power of precise, customizable forecasting with Pro Financial Forecast, the advanced yet user-friendly financial modeling template that can be used for any business regardless of the sector.

| , , |
| , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , , |
Pro Financial Forecast Model – Advanced and Dynamic Financial Forecasting
Unleash the power of precise, customizable forecasting with Pro Financial Forecast , the advanced yet user-friendly financial modeling template that can be used for any business regardless of the sector.
Key Features:
- Dynamic Flexibility: Forecast up to 10 years to navigate evolving landscapes and achieve long-term goals.
- Granular Insights: Track 10+ distinct revenue streams for a comprehensive view of your income potential.
- Engage with dynamic charts and graphs that translate your financial story into clear, actionable insights.
- Caters to any business or industry
- Robust Analysis Suite: Dive deep with Forecast vs. Actuals, Breakeven Analysis, Financial Ratios, and Business Valuation , supported by sophisticated charts .
Model Structure:
- Timing: This sheet includes detailed calculations of periods that may affect financial projections, such as fiscal years or quarters
- Input: The primary data entry sheet where initial assumptions, variables, and raw data are entered.
- Actual: This sheet contains historical financial data used as a basis for forecasting.
- Calculations: This sheet is dedicated to intermediate calculations that feed into the final outputs, such as detailed expense calculations or revenue build-ups.
- FinST_Forecast: The output sheet presents the financial statements projected based on the inputs.
- Actual + Forecast: A combined output sheet that merges actual historical data with projected figures
- Q_FinST: Quarterly financial statements output, which includes income statements, balance sheets, and cash flows on a quarterly basis, aggregated from the Actuals+Plan Sheet.
- Ann_FinST: Annual financial statements output, showing the yearly aggregated financial position and performance, aggregated from Actuals + Plan Sheet.
- Performance: Encompasses KPIs, ratios, and other metrics for evaluating financial health. Users can set KPI ranges to match company objectives, and conditional formatting quickly highlights strengths and weaknesses in performance.
- Breakeven: Output sheet that calculates the point at which revenues equal expenses and the project will start to generate profit.
- TTM_FinST: Trailing twelve months’ financial statements output, providing a rolling annual perspective on economic performance
- Dashboard: A dashboard output visually presents the financial data and metrics through charts, graphs, and summaries for quick reference.
- Mo_Dashboard: A specialized dashboard output focused on YTD and trailing twelve months of data, offering a dynamic view of the latest full-year financials.
- DCF_Val: An output sheet where the Discounted Cash Flow valuation method is applied to estimate the present value of the business or project.
- Checks: This documentation sheet tracks errors, assumptions that need review, or any inconsistencies within the model.
- Excel Model – $60.00 Version 1
- PDF Demo – $0.00 Version 1
Similar Products
Other customers were also interested in....
10 Years Financial Forecast and Valuation Excel Mo...
This is a generic financial model that allows the user to forecast the Company's profit and loss acc... Read more
- Excel Template – $60.00
- PDF Demo – $0.00

Private Equity Fund Model (Investor Cashflows)
Private Equity Financial Model to analyze fund cashflows and returns available to Limited Partners (... Read more
- PDF Demo version – $0.00 Version 1
- American Waterfall – $155.00 Version 2
- European Waterfall – $115.00 Version 2

Jason Varner
All my financial models, spreadsheets, templates, ....
Lifetime access to all future templates as well! Here is a set of spreadsheets that have some of the... Read more
- All My Excel Tools – $999.00 Version 1

Startup Company Financial Model – 5 Year Fin...
Highly-sophisticated and user-friendly financial model for Startup Companies providing a 5-Year adva... Read more
- Financial Model - Light Version – $119.00 Version 1
- Financial Model - Standard Version – $159.00 Version 1
- Financial Model - Premium Version – $219.00 Version 1
- PDF Free Demo – $0.00 Version 1

Pierre-AlexandreHeur...
Due diligence p&l – exhaustive revenue a....
Model for in depth understanding of high level profit and loss and revenue analysis. Big-4 like chec... Read more

Joint Venture and Fund Cash Flow Waterfall Templat...
Here are all the spreadsheets I've built that involve cash flow distributions between GP/LP. Include... Read more
- Template Bundle – $199.00 Version 1

ECF Consultancy
Corporate finance toolkit – 25 financial mod....
The toolkit is an essential resource for any organization, providing a comprehensive collection of t... Read more
- All Excel Model Templates – $249.00 Version 1
- PDF Demo & Excel Free Download – $0.00 Version 1

3 Statement Financial Modeling with DCF & Rel...
Financial Modeling Tutorial guides user via step by step approach on how to build financial models w... Read more

Advanced Financial Model with DCF & Valuation
General Overview Advanced Financial Model suitable for any type of business/industry and fully cu... Read more
- Excel Financial Model – $129.00 Version 1

Leveraged Buyout (LBO) Model
Leveraged Buy Out (LBO) Model presents the business case of the purchase of a company by using a hig... Read more
- Free PDF – $0.00
- Paid Excel Model – $119.00
You must log in to submit a review.
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Request submitting Please wait...
Vendor Contact Form
- Log into Your Account
- Register New Account
Please register to contact the author.
Receive regular updates on new model templates
Attachments
(Maximum file upload limit is 10MB)
The 8 best free project management and planner templates for Microsoft Excel

Your changes have been saved
Email is sent
Email has already been sent
Please verify your email address.
You’ve reached your account maximum for followed topics.
Key Takeaways
- Templates in Excel are essential for efficient project planning, tracking milestones, and performance reporting.
- Using Gantt charts, project trackers, and performance reports can streamline collaboration and goal achievement.
- Excel templates like to-do lists, party planning, and school planners help organize tasks and budgets effectively.
While Microsoft Excel is an excellent tool for project managers and planners, unlocking its full potential can be daunting without the right templates. Make no mistake, you can always create a workbook from scratch and share it with team members, but a dedicated template speeds up the entire process and streamlines your planning.
Whether you need to oversee a client’s project, organize a celebration for a loved one, monitor milestones, or create efficient to-do lists for your tasks, explore the best templates available to track and execute your projects like a pro.

3 reasons you should learn to use Python for data analysis with Excel
If you want to do data analysis and you're using Excel, there are a few reasons why you may want to learn Python, too.
8 Gantt project planner
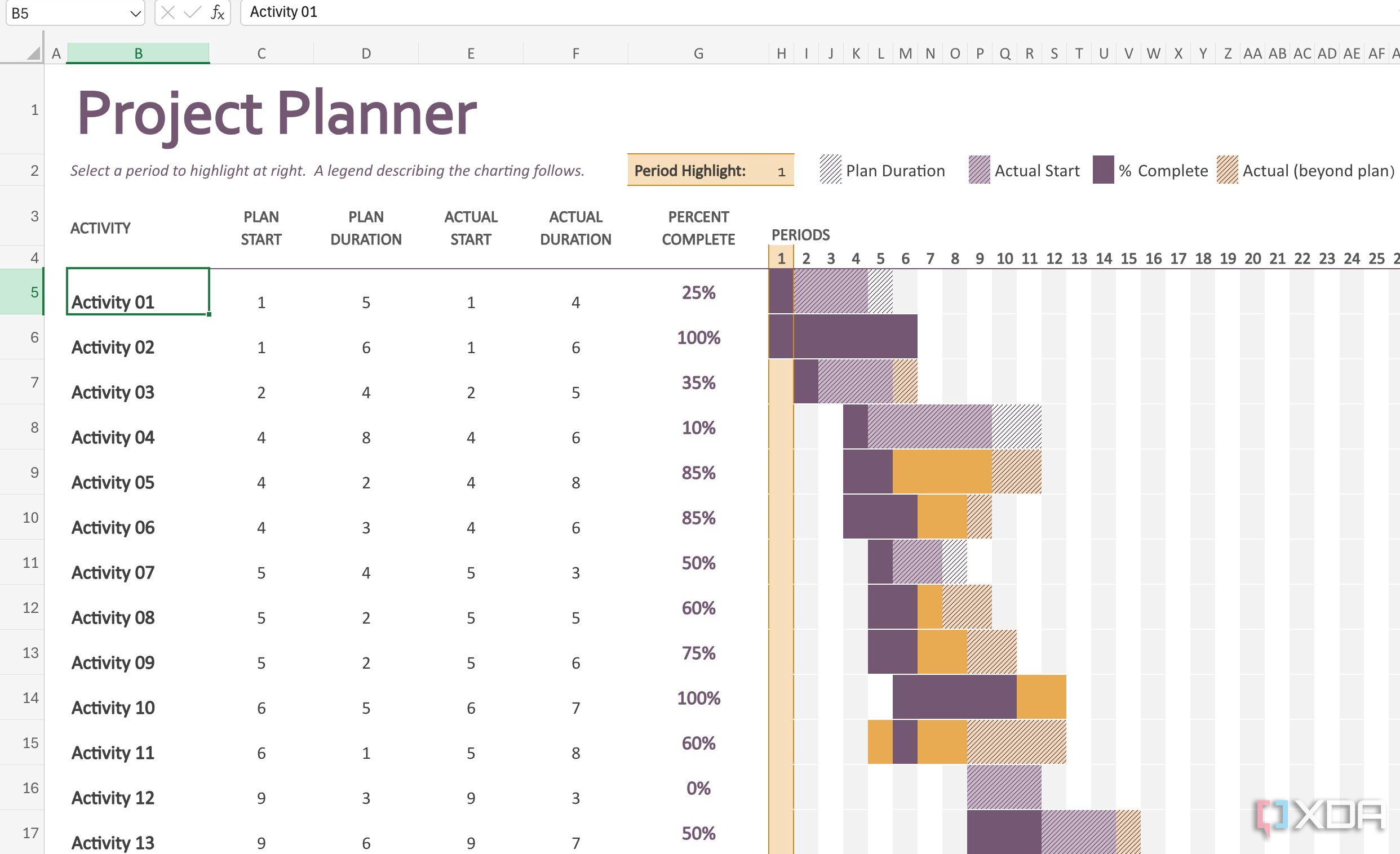
As the name suggests, this project planner template follows the Gantt chart model to let you track and plan all activities in detail. It uses easy-to-understand visual charts to display how a project will be managed over time. You can set the plan start date, the intended duration, and track the actual duration. Plus, you can add relevant activities and monitor the progress in real-time using the Gantt chart.
While it may seem simple at first glance, this template can accommodate both large and small projects for professionals, providing transparency to the collaboration and achievement towards a goal.
Gantt project planner
7 project tracker.
Here is another simple project tracker template designed for Microsoft Excel users. This template is perfect for those wishing to divide large projects into smaller, more manageable stages. For example, if you are an interior designer, you can use this template to divide every stage of furniture planning and assign relevant category, employee name, estimated start and end date, number of hours, cost, duration in days, and more. The possibilities are endless here.
Project tracker
6 project performance report.
Project performance report template is suitable for advanced users. If you are responsible for handling multiple projects, you can use this to report high-level status on them. It uses a table and conditional formatting for easy customization.
You can enter item descriptions and track the overall budget, actual costs, schedule, performance index, forecast, and overall project status. It employs charts and graphs to display essential performance metrics such as schedule variance, cost variance, and earned value. This allows stakeholders to understand the project's status at a glance.
Project performance report
5 milestone and task project timeline.
Do you prefer to track your projects in a timeline view? Look no further and get this milestone and task project template from Microsoft. This template employs a scatter chart featuring data labels and error bars to craft a project timeline showcasing milestones and tasks with their durations.
Unlike a Gantt chart, where each task appears on a distinct row, this allows you to manage the vertical placement of tasks within the timeline. Additionally, you have the option to set the length of the vertical leader line to illustrate task dependencies. It is mostly useful for project overview rather than assigning and tracking specific tasks.
Milestone and task project timeline
4 to-do lists for projects.
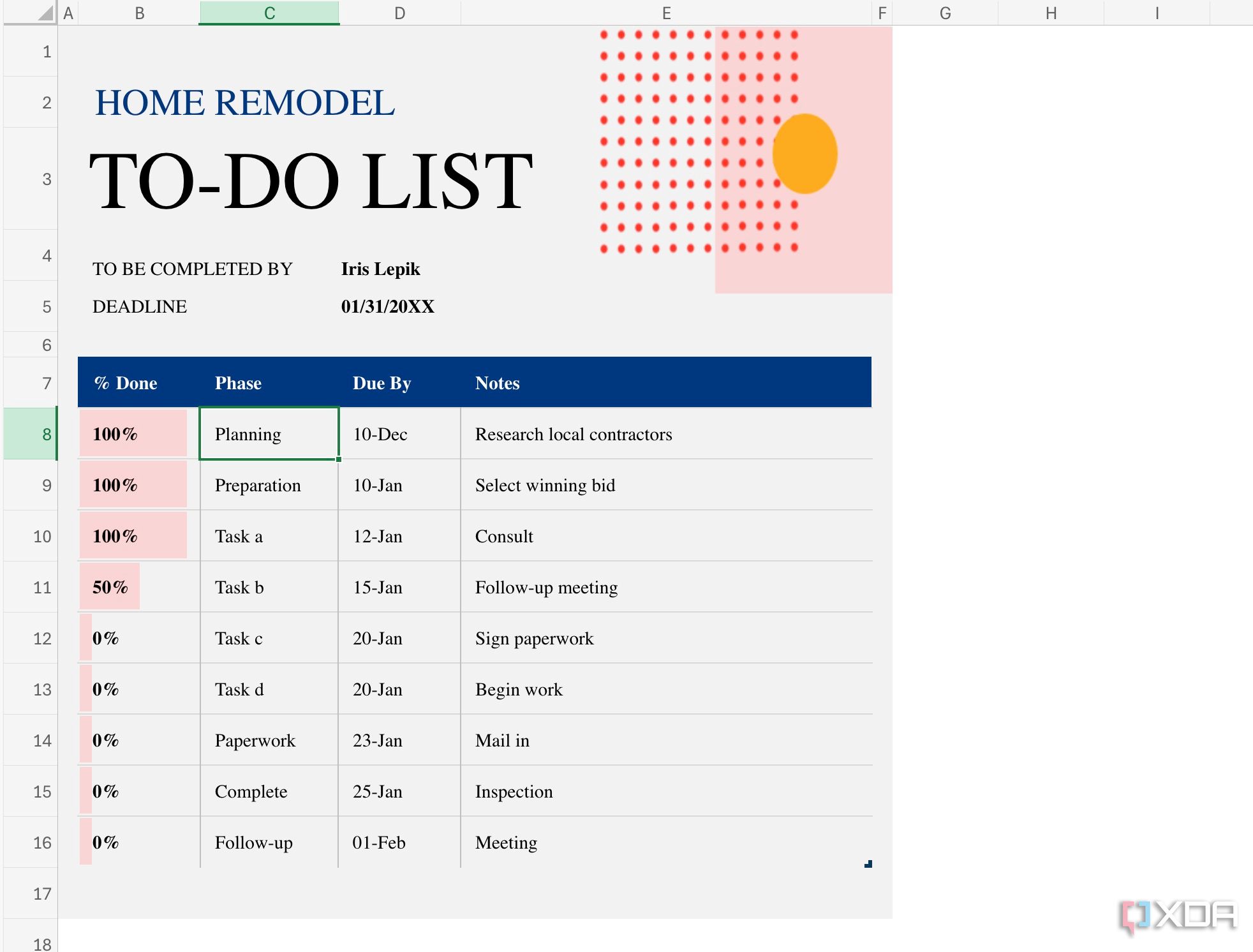
Are you planning a home remodel or other large project? You need an effective planner that helps you track every part of the entire process without breaking a sweat. This to-do list template is a simple Excel template to get the job done. You can enter phase names, due dates, notes, project deadlines, and project completion percentages in different columns. You can even get creative and add more relevant columns to the sheet.
To-do lists for projects
How to automate microsoft excel with macros.
Dive into the world of macros to stream your workflow with Excel
3 Party planner and checklist
Organizing a party often comes with both exhilaration and stress. Using an Excel party planning template can serve as your essential tool, helping you remain organized and manage all the details effectively. It’s a must-have template for event managers.
You can enter party name, venue, date, time, client name, create a party planning checklist, guest list, and track their attendance. You can split your party budget into different categories, track spending, and more to transform party planning from a daunting task into a fun and enjoyable experience.
Party planner and checklist
2 simple gantt chart.
Yes, this is another Gantt chart template on the list. But unlike the previous one, this Excel template goes into greater detail and lets you evaluate, plan, design, and execute your projects like a pro. You can divide the entire project into different stages, enter tasks for every section, assignee, progress, start and end date, and more. The Gantt chart bars show task durations with conditional formatting. An 'About' sheet is even included to help you use the template to its fullest.
Simple Gantt chart
10 cool projects you can do with just Microsoft Excel
Excel-erate your creativity beyond boring spreadsheets
1 Back to school planner
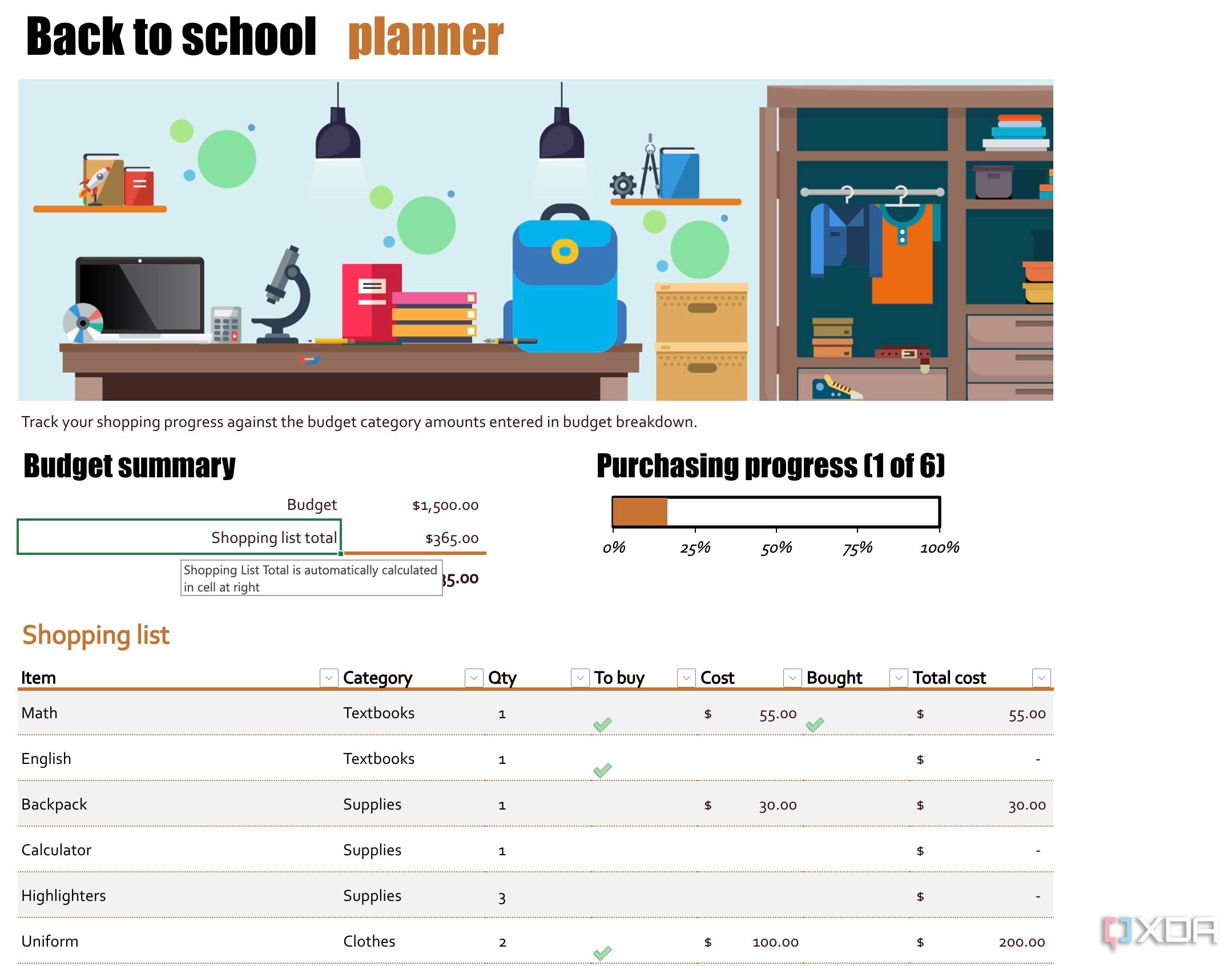
As the name suggests, this one is an ideal school planner template for students. Before the next term starts, you can keep everything ready and organized. You can enter budget details, create a shopping list, categories, costs, and more. There are also a few more sheets to track budget breakdowns and to-do lists. Once you fill in the data, the workbook shows the purchasing progress at the top.
Back-to-school planner
Apart from the templates above, you can also find more top project management templates from third-party sources like Etsy .
Streamline your project planning and tracking
Starting with the right template can set a positive tone and make a significant difference in your project. What are you waiting for? Download your preferred template into your Excel account and plan, track, and execute projects of all sizes.
Microsoft has done a splendid job with the Excel template library. Almost any requirement you might have is likely covered by one of their templates. For further exploration, refer to our detailed guide on the best free Excel templates available .
- Software and Services
- Microsoft 365
Cookies on GOV.UK
We use some essential cookies to make this website work.
We’d like to set additional cookies to understand how you use GOV.UK, remember your settings and improve government services.
We also use cookies set by other sites to help us deliver content from their services.
You have accepted additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
You have rejected additional cookies. You can change your cookie settings at any time.
- HM Treasury
Agile digital and IT projects: clarification of business case guidance
Published 23 August 2024

© Crown copyright 2024
This publication is licensed under the terms of the Open Government Licence v3.0 except where otherwise stated. To view this licence, visit nationalarchives.gov.uk/doc/open-government-licence/version/3 or write to the Information Policy Team, The National Archives, Kew, London TW9 4DU, or email: [email protected] .
Where we have identified any third party copyright information you will need to obtain permission from the copyright holders concerned.
This publication is available at https://www.gov.uk/government/publications/agile-digital-and-it-projects-clarification-of-business-case-guidance/agile-digital-and-it-projects-clarification-of-business-case-guidance
To help with efficient planning and approval of spending proposals for agile digital and IT projects, the following clarification of business case guidance has been produced in collaboration between HM Treasury and the Central Digital and Data Office. This should realise the potential of the agile approach to produce better systems more quickly and cheaply than conventional IT planning and project management while maintaining effective business planning and spending control processes.
This should enable a controlled early release of resources for the Discovery and Alpha phases of agile projects and enable a proportionate process of planning and control that delivers value for money without excessive bureaucracy.
1. Existing guidance
All current Treasury guidance on production and approval of business cases , the guidance on Treasury approval processes , the Treasury’s Departmental Spending Limits rules and the supplementary Cabinet Office controls on digital and technology operated through the spending mechanism remain unaffected by this.
Although this supplementary business case guidance focuses on projects that require HMT spending approval, it is expected (as with all current HMT business case guidance) that it will be understood as best practice and applied to all projects requiring spending approval including those falling within DEL .
2. Agile spending project approval process
The approval process for agile projects should be adapted to suit each project’s spend and the risk to the programme within which it sits. There are 3 categories for which different variants of the approval and business case process are appropriate as follows:
3. Initial research and scoping stages of all Agile projects – Discovery and Alpha
All agile Discovery and Alpha work is regarded as initial research and, subject to a limit of £750,000, would normally be undertaken from departments’ DEL budgets subject only to CO controls. Agile projects are frequently part of wider business programmes to be delivered for reasons of either business transformation or business continuity. Even before Discovery and Alpha, departments should have a clear justification for why such scoping is financially and strategically worthwhile. This should be assured via the CO pipeline process.
The Discovery and subsequent stages are learning phases that feed back into the evolving project business case and into the wider Programme Business Case of which the project is a part.
The relatively low level of spending involved, the need for CDDO approval of digital projects and the existence of an overarching programme business case (which defines the business scope, the outputs, their timing and the likely resource allocation of the agile project), allows the business case and approval to be streamlined and tailored to suit the needs of the programme and project. Thus, the classical three stage approval process ( SOC , OBC , FBC ) can be adapted to support something more suited to agile. This guidance clarification recommends more use of PBCs for programmes and project approvals using a light touch OBC only (this may be iterative).
HMT and CDDO have agreed that departments can spend up to £750,000 from within their own DEL budget on Discovery and Alpha as a research and scoping activity subject only to CO digital and technology controls. If a particular project requires more than £750,000 this can be agreed by the overarching programme, in consultation with the relevant approving authority, which in many cases will be the HMT spending team.
Projects that are above DEL spending limits or which are novel or contentious require Treasury approval at these stages but the process should be adapted to suit the case and set out in the PBC .
4. Larger projects costing above £10 million
Larger projects costing above £10 million (for the whole life of the project to the end of two years live running) or which pose significant risk to the programme should be approved by the Treasury through the project approval process but using an agreed plan of monitoring and approval points set out in the management plan of the PBC rather than through a classic three stage process.
5. Smaller projects costing below £10 million
Smaller projects costing below £10 million that are not high risk to the overall programme can be approved and managed against the PBC without needing a separate OBC .
Project level approval for larger agile projects should use a light touch OBC and try to minimise traditional detailed IT planning documents. Instead, they should focus on user needs, business outcomes, costs and milestones within the context of a wider programme business case. This project approval process should be agreed as part of the wider management plan of the wider PBC . We recommend that management review meetings should use digital service demonstrations and agile artefacts (e.g. burn charts , backlogs ).
Relatively inexpensive agile projects, which are not high risk to the programme within which they sit, can be approved as part of the programme approval process. That approval process should be planned as a part of the PBC .
In some cases a programme will have numerous agile projects, each of which is below £10 million spend but which in aggregate cost over £10 million (this typically happens in a department wide transformation programme). In this case, a PBC should be used rather than multiple OBCs, but the PBC should contain a significant degree of economic scrutiny proportionate to the spend. It is also particularly crucial when managing a programme of agile work to schedule regular reviews and to use the service demonstration, burn charts and backlogs to give the approving authority a high level of visibility and control over the speed of progress and the prioritisation of tasks.
Using the PBC process has the advantage that as well as being relatively light touch for the agile project it also highlights clearly how the agile work fits into a wider programme by flagging dependencies.
Walkthrough of the process to obtain agile spend approval

How to do spend approvals in parallel with early agile work
1. Before business case
- apply for Cabinet Office spend approval (for Discovery & Alpha build)
2. Discovery (8 weeks)
- notify HMT spend team about agile work
- plan MPA Review
3. ALPHA build (8 weeks)
- MPA Review, Approvals Plan
- submit business case to HMT (at least 4 weeks before end of Alpha)
- HM Treasury approve business case
- digital service assessment (on Alpha build)
- apply Cabinet Office spend approvals (for Beta build)
4. BETA build (Business case required before starting Beta build)
- MPA Review before Beta release
- Digital service assessment
When signing off the business case, HMT will generally agree to release the funding in tranches and agree when HMT / MPA reviews will take place. This could align to delivery milestones or be periodic (e.g. every six months). Generally, MPA will want to have one its major reviews shortly before Beta release.
5.1 Apply to CO Spend Controls for Alpha and Discovery funding
This can be done before the business case for approval is complete based on an outline brief containing the business outputs required, the timing needed and likely scale of funding available because it qualifies as research and feeds back to inform the options appraisal in the business case.
5.2 Do Discovery and Alpha
At the start of Discovery, if external approval will eventually be required departments should contact the HMT spend team and IPA (if they haven’t already done so) to plan the engagement described in the next paragraph.
5.3 Develop and write a project business case and/or input to a PBC (in parallel with, and informed by, Discovery and Alpha)
Low Spending projects: where spending on agile is relatively low and external approval of the project business case is not likely to be required, the PBCs provides a more streamlined vehicle for managing external spending and approval where project spending is below £10 million.
Higher Spending projects: alternatively, if the whole life agile project spending is likely to be above £10 million an OBC is needed. The programme team should work on the business case and the IPA Project Validation Review at the same time as the agile team complete Discovery and Alpha phases. The completion of the PVR and PBC is not a pre-condition for this work to begin. The programme business case should include an agile spend envelope with some sensible allowance for contingency. HMT must sign off a business case before you can move into Beta. If the expected project cost is £10 million or if the project poses high risk to the delivery of the programme, a project business case is required, but it does not need to take the form of the Full or Final Business where procurement is taken care of through the use of pre-competed digital frameworks .
5.4 Alpha digital service assessment
This assesses the service against the Service Standard . Depending the service you will assessed by an internal panel or a CDDO -led one .
5.5 Apply to CO Spend Controls to release Beta funding
CO Spend Controls and HMT (for projects above delegated spend limits) both look at the proposed agile Beta spend. In general, HMT ’s main focus is economic / financial (especially affordability, delivery and value for money); CO ’s focus is more on the appropriateness of the technology choices being made. CO Spend Controls will only approve Beta funding to projects for which a working Alpha can be demonstrated.
5.6 Beta and Live agile delivery
During Beta and Live agile delivery, updates by the department to HMT and IPA should normally focus on a digital service demonstration accompanied by agile artefacts (e.g. burn chart, backlog) rather than conventional technically detailed and lengthy IT project documents. The department should agree with HMT and IPA what arrangements are appropriate to monitor, review and approve Beta and Live spend in each particular project. Review and approval points should be planned and agreed at the outset as part of the programme management plan and be aligned to selected reporting points and delivery appropriate to the particular service (e.g. every 6-12 months).
5.7 Digital service assessments
Assessments take place before a service is available publicly on the internet in Beta, and again before the service can be branded as “live”. These assess whether the service achieves all the points of the Service Standard , and hence give a sufficiently high quality user experience to enable that service to become digital by default.
If departments have further questions about how to apply this guidance, please contact your HMT spending team (or CDDO / IPA as applicable).
Is this page useful?
- Yes this page is useful
- No this page is not useful
Help us improve GOV.UK
Don’t include personal or financial information like your National Insurance number or credit card details.
To help us improve GOV.UK, we’d like to know more about your visit today. Please fill in this survey (opens in a new tab) .

IMAGES
COMMENTS
Our business plan excel template includes the following sections: Income Statement: A projection of your business' revenues, costs, and expenses over a specific period of time. Includes sections for sales revenue, cost of goods sold (COGS), operating expenses, and net profit or loss. Example 5 Year Annual Income Statement.
On this page, you'll find many helpful, free, customizable financial projection and forecasting templates, including a 1 2-month financial projection template, a startup financial projection template, a 3-year financial projection template, and a small business financial forecast template, among others. You'll also find details on the ...
Financial Projections Template Excel. This free 4 page Excel business plan financial projections template produces annual income statements, balance sheets and cash flow projections for a five year period for any business. The financial projections template is available for free download below.
Whether you are already running a business, or making plans to start one up, financial planning is a vital part of ensuring your success. Not knowing your expected income and expenditure will make it difficult to plan, and hard to find investors.. This 5-Year Financial Plan spreadsheet will make it easy for you to calculate profit and loss, view your balance sheet and cash flow projections, as ...
Here are some tips for creating an effective business plan financial projections template: Create the sales projection An important component of your business projections template is the sales projections. A business that's already running can base its projections on its past performance, which you can derive from financial statements ...
This financial plan projections template comes as a set of pro forma templates designed to help startups. The template set includes a 12-month profit and loss statement, a balance sheet, and a cash flow statement for you to detail the current and projected financial position of a business. Download Startup Financial Projections Template.
Sample 30-60-90-Day Business Plan for Startup in Excel. This 90-day business plan is designed for startup companies to develop a 90-day action plan. This template gives you room to outline the following: main goals and deliverables for each 30-day increment; key business activities; task ownership; and deadlines.
The Plan Projections template is free, easy to set up and customize, and loaded with great features. Everything you need to create perfect business financial projections for startups. The Plan Projections template produces the three main financial statements, income statements, balance sheets, and cash flow statements for the next five years.
At Projection Hub, our Excel-based financial plan templates allow you to create an effective plan for informing your business decisions. To be effective at raising capital or just building an informed self-sustaining company, you can utilize a financial plan template as a general guide to help you reach financial objectives.
Free 1 Year Pro Forma Template. Download our 12 months financial projection template for free. This tool will allow you to: Forecast startup costs. Project your first 12 months of product or service revenue. Forecast your operating expenses. Add Salary Forecasts for your employees.
Use our business plan financial projections template to create financial projections for a business plan which includes 12 monthly periods and 5 annual periods. The template includes a detailed income statement, cash flow statement and balance sheet in Excel. Cash flow projections are based on user defined turnover, gross profit and expense ...
Excel is a powerful tool for complex calculations and analyses; let's use it for that only. So, we'll use this business plan Excel template only to perform complex financial analyses and calculations—to prepare financial projections. Following are the critical components of a good business plan template you must include in your financial ...
Download Template. Financial projections use existing or estimated financial data to forecast your business's future income and expenses. They often include different scenarios to see how changes to one aspect of your finances (such as higher sales or lower operating expenses) might affect your profitability.
Financial Projection Template. Building up forecast from payroll schedules, operating expenses schedules and sales forecast to the three financial statements. Over 1.8 million professionals use CFI to learn accounting, financial analysis, modeling and more. Start with a free account to explore 20+ always-free courses and hundreds of finance ...
Open Excel and set up your columns with headings like "Income," "Expenses," and "Net Cash Flow. " Estimate monthly incomes and expenses, entering these under appropriate headings. Subtract expenses from income to calculate net cash flow for each month. Summarize to project future cash balances.
Collect relevant historical financial data and market analysis. Forecast expenses. Forecast sales. Build financial projections. The following five steps can help you break down the process of developing financial projections for your company: 1. Identify the purpose and timeframe for your projections.
USD 179. 200+ financial models for entrepreneurs who need more flexibility by using a template made specifically for their business . 200+ businesses. Choose yours. Download more than 500+ expert-built business plan and Excel financial model templates. For startups, franchises and small businesses.
Steps to Create Financial Projection Excel Template. There is a simple five-step approach that can be used to create a financial projection excel template; Step 1: Create the sales projection of the business for a specified period. Step 2: Create the projection of expenses/costs. Step 3: Create the projection of the business income statement.
Setting Up the Spreadsheet. The first step is to create a spreadsheet in Excel. Set up columns for each type of financial data you want to track, such as revenue, expenses, and cash flow. If you're projecting multiple years, add one column for each year. If you're projecting quarterly or monthly, add one column for each period.
Business Plan Projections for Excel is a range of powerful, easy-to-use template packages for preparing comprehensive financial projections for business plans and budgets, strategic and corporate planning, business restructuring, financial appraisals and performance monitoring. Based on a user's assumptions, Excel Business Plan Projections ...
Follow these steps to predict future revenue: Open an Excel sheet with your historical sales data. Select data in the two columns with the date and net revenue data. Click on the Data tab and pick "Forecast Sheet." Enter the date your forecast will end and click "Create." Title and save your financial projection.
Pro Financial Forecast - Dynamic and Advanced Financial Projections. Unleash the power of precise, customizable forecasting with Pro Financial Forecast, the advanced yet user-friendly financial modeling template that can be used for any business regardless of the sector. Share On: All Industries, Financial Model, General Excel Financial Models.
Using regression analysis the past data has been used to calculate values for the variable cost per unit and the fixed cost. Our cost forecast equation using these two values can be stated as follows. Cost forecast = Variable cost per unit x Users + Fixed cost. Cost forecast = 0.0528 x Users + 1,938.
Download your preferred template into your Excel account and plan, track, and execute projects of all sizes. Microsoft has done a splendid job with the Excel template library.
Based in Odessa, Texas, the Odessa American was founded in 1940. Odessa American 700 N. Grant Ave., Suite 800 Odessa, TX 79761-4590 (432) 337-4661
The road project is estimated to cost $20,600 million. Columbia has received $16 million from South Carolina budget earmarks over the last two budget cycles. The other $4.6 million will come from ...
MPA Review, Approvals Plan; submit business case to ... 5.3 Develop and write a project business case and/or input to a ...