
Technology Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Technology Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your own Technology business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Technology businesses.
Technology Business Plan Example & Template
Below is a Technology business plan template and sample to help you create each section of your own business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
Kearney Tech Inc., located in Houston, Texas is a tech startup that focuses on developing and commercializing new artificial intelligence (AI) technology applications designed for small-to-medium sized businesses. The company has created proprietary technology that helps businesses improve their profitability by using AI to increase customer engagement. We offer multiple products, including AI hardware, marketing AI software, and CRM AI software. Many of our most basic services are free, but the rest can be accessed by paying a subscription fee. By providing flexible and affordable subscription options for our clients, Kearney Tech Inc. aims to be the next big technology company in the AI space for small and medium-sized businesses.
Kearney Tech Inc. was founded and is led by Abigail Kearney. Abigail has been a senior software engineer for nearly 10 years and has extensive experience in artificial intelligence and machine learning. In addition to her experience, she has a bachelor’s degree in computer science and an MBA. Her education and experience are sure to lead Kearney Tech Inc. to success.
Product Offering
Kearney Tech Inc. will showcase a variety of different applications for its AI technology that companies can utilize to increase their customer engagement from day one. Businesses can choose the platform package that works for them, based on a freemium subscription pricing structure.
The following are the services that Kearney Tech Inc. will provide:
- AI Hardware
- Marketing AI Software
- Customer Relationship Management AI Software
- Customer Support AI Software
- Technology Training: Training sessions on how to use our AI solutions and integrate them into their businesses
Customer Focus
Kearney Tech Inc. will serve small to medium-sized businesses within a 30-mile radius of Houston, Texas. Many of the businesses in our target demographic are startups looking to expand their reach and thus would benefit from technology that can increase their customer base.
Management Team
Kearney Tech Inc. will also employ an experienced assistant to work as a business analyst and help with various administrative duties around the office. She will also hire several developers, salesmen, and other administrative staff to assist her.
Success Factors
Kearney Tech Inc. will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Management: Abigail Kearney has been extremely successful working in the technology industry and will be able to use her previous experience to provide the best service experience. Her unique qualifications will serve customers in a much more sophisticated manner than Kearney Tech Inc.’s competitors.
- Relationships: Abigail Kearney knows many of the local leaders, business managers, and other influencers within Houston, Texas. With her 10 years of experience and good relationships with business leaders in the area, she will be able to develop an initial client base.
- Proprietary technology : The company has developed proprietary AI technology that will be used to add new data sources, expand on valuable insights, launch advanced features like benchmarking, provide predictive and prescriptive analytics, and ensure self-guided data discovery.
- Client-oriented service: Kearney Tech Inc. will have full-time customer service and sales managers to keep in contact with clients and answer their everyday questions.
Financial Highlights
Kearney Tech Inc. is seeking a total funding of $400,000 of debt capital to open its office. The funding will be dedicated to office design, software development, marketing, and working capital. Specifically, these funds will be used as follows:
- Office design/build: $50,000
- Software development: $150,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $25,000
- Working capital: $25,000
The following graph below outlines the pro forma financial projections for Kearney Tech Inc.:
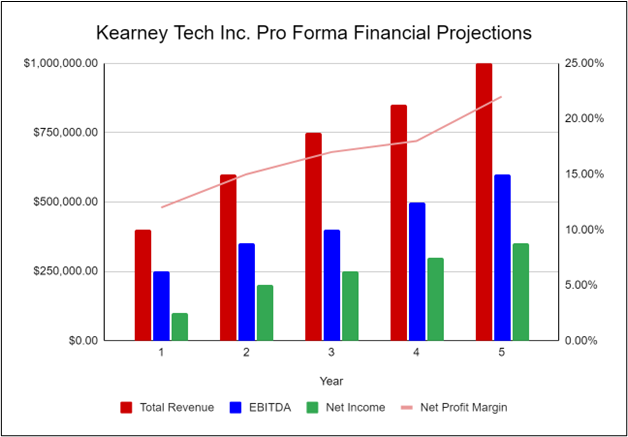
Company Overview
Who is kearney tech inc..
Abigail began researching what it would take to create her own technology company and did a thorough analysis of the costs, market, demographics, and competition. Abigail has compiled enough information to develop her business plan in order to approach investors.
Kearney Tech Inc.’s History
Once her market analysis was complete, Abigail Kearney began surveying the local vacant office space and located an ideal location to house the technology company. Abigail Kearney incorporated Kearney Tech Inc. as a Limited Liability Corporation in April 2023.
Since incorporation, the company has achieved the following milestones:
- Located available office space for rent
- Developed the company’s name, logo, and website
- Determined equipment and necessary supplies
- Began recruiting key employees
Kearney Tech Inc. Services
Industry analysis.
As of 2021, the global technology industry was valued at approximately $5.2T. Of all countries worldwide, the United States currently has the largest technology market, with 32% of the market share at $1.7T. The technology industry in the U.S. accounts for a large part of the nation’s economy.
The Information Technology market can be segmented by categories such as software, devices, infrastructure IT and business services, emerging technology, and telecom services. In the United States, IT and business services hold the greatest market share (30%), followed by software (20%) and telecom services (20%).
Market drivers include the economy, employment rates, and the digital transformation of daily life for a growing number of people and businesses worldwide. Corporations and organizations are seeking IT service providers that can help improve their software, cybersecurity, data, and infrastructure. Technology companies that can provide products and services that cater to these issues can be competitive in the constantly evolving market.
Technology is an integral part of society. Developments in AI and machine learning are essential to keep society moving forward and make businesses more efficient. Therefore, businesses will always be in need of AI solutions to bring in more customers and streamline their services and products. According to Market Watch, the Technology industry is set to grow at a CAGR of 25.73% from now until 2027. Very few industries see this growth, which shows how much demand there is for technological solutions. Therefore, we expect Kearney Tech Inc. to see great success in our local market.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
Kearney Tech Inc. will serve the small and medium-sized businesses of Houston, Texas, and the surrounding areas.
Many small businesses in the community are startups or established enterprises looking to expand their reach and thus would benefit from technology that can increase their customer engagement.
Customer Segmentation
Kearney Tech Inc. will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Small businesses
- Medium-sized businesses
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
Kearney Tech Inc. will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Tekuserv has been a reliable technology company in Houston, Texas for more than fifteen years. The company is known for its wide range of technology solutions that serve many small-to-medium-sized businesses. With its large number of experts focused on delivering customer satisfaction, the organization maintains its high standard of developing quality products and providing exceptional customer service. Tekuserv provides business software on a freemium subscription basis. It develops enterprise technology solutions with a focus on customer relationship management.
Prime AI Business Solutions
Prime AI Business Solutions is a technology development company in Houston, Texas. In business for several years, the company has developed highly-rated AI solutions used by many well-known businesses in a variety of industries. Prime AI Business Solutions now offers a range of AI hardware and software products geared toward helping businesses of all sizes increase their customer base. The company has also introduced a “pay-as-you-grow” pricing model that scales to provide users with more support as they scale up.
AICE Developments
AICE stands for Artificial Intelligence for Customer Engagement. AICE Developments is also a local technology company that manufactures and distributes a variety of technology products. AICE Developments was established in 2009 in Houston, Texas, providing integrated AI applications and platform services. Its products include applications and infrastructure offerings delivered through various IT deployment models, including on-premise deployments, cloud-based deployments, and hybrid deployments. The company serves automotive, financial services, healthcare, hospitality, retail, utilities, construction, etc. It provides AI solutions for enterprise marketing and customer engagement.
Competitive Advantage
Kearney Tech Inc. will be able to offer the following advantages over the competition:
- Proprietary technology: The company has developed proprietary AI technology that will be used to add new data sources, expand on valuable insights, launch advanced features like benchmarking, provide predictive and prescriptive analytics, and ensure self-guided data discovery.
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
Kearney Tech Inc. will offer a unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Service built on long-term relationships
- Big-firm expertise in a small-firm environment
- Thorough knowledge of the clients and their varying needs
- Proprietary technology developed by skilled software engineers
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for Kearney Tech Inc. is as follows:
Kearney Tech Inc. understands that the best promotion comes from satisfied customers. The company will encourage its clients to refer other businesses by providing economic or financial incentives for every new client produced. This strategy will increase in effectiveness after the business has already been established.
Social Media
Kearney Tech Inc. will invest heavily in a social media advertising campaign. The brand manager will create the company’s social media accounts and invest in ads on all social media platforms. It will use targeted marketing to appeal to the target demographics.
Website/SEO
Kearney Tech Inc. will invest heavily in developing a professional website that displays all of the features and benefits of the technology company. It will also invest heavily in SEO so that the brand’s website will appear at the top of search engine results.
Direct Mail
Kearney Tech Inc. will blanket businesses with direct mail pieces. These pieces will provide general information on Kearney Tech Inc., offer discounts, and/or provide other incentives for companies to use the AI platform.
Kearney Tech Inc.’s pricing will be on par with competitors so clients feel they receive great value when purchasing the technology.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for Kearney Tech Inc.:
Operation Functions:
- Abigail Kearney will be the Owner and CEO of the company. She will oversee all the operations and executive functions of the company. In the beginning, she will also provide customer support and market/sell AI products to potential clients.
- Abigail will employ an experienced assistant to work as a business analyst and help with various administrative duties around the office.
- Abigail will also hire several developers to maintain and develop AI products and services.
- Abigail will also hire a solid sales team to sell our products to potential clients. As the company grows, she will also hire a team that is solely dedicated to customer service.
Milestones:
Kearney Tech Inc. will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
5/2023 – Finalize lease agreement
6/2023 – Design and build out Kearney Tech Inc.
7/2023 – Hire and train initial staff
8/2023 – Kickoff of promotional campaign
9/2023 – Launch Kearney Tech Inc.
10/2023 – Reach break-even
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
Kearney Tech Inc.’s revenues will come primarily from its technology solution subscription sales. The company will use a freemium subscription model, in which basic functions can be used by any company for free. Additional solutions and support will be available in a tiered package model based on the enterprises’ size and the number of users.
The office lease, equipment, supplies, and labor expenses will be the key cost drivers of Kearney Tech Inc. Ongoing marketing expenditures are also notable cost drivers for Kearney Tech Inc.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
Key assumptions.
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and pay off the startup business loan.
- Average number of clients per month
- Annual rent: $20,000
Financial Projections
Income statement.
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| Revenues | ||||||
| Total Revenues | $360,000 | $793,728 | $875,006 | $964,606 | $1,063,382 | |
| Expenses & Costs | ||||||
| Cost of goods sold | $64,800 | $142,871 | $157,501 | $173,629 | $191,409 | |
| Lease | $50,000 | $51,250 | $52,531 | $53,845 | $55,191 | |
| Marketing | $10,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | $8,000 | |
| Salaries | $157,015 | $214,030 | $235,968 | $247,766 | $260,155 | |
| Initial expenditure | $10,000 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Total Expenses & Costs | $291,815 | $416,151 | $454,000 | $483,240 | $514,754 | |
| EBITDA | $68,185 | $377,577 | $421,005 | $481,366 | $548,628 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| EBIT | $41,025 | $350,417 | $393,845 | $454,206 | $521,468 | |
| Interest | $23,462 | $20,529 | $17,596 | $14,664 | $11,731 | |
| PRETAX INCOME | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Use of Net Operating Loss | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Taxable Income | $17,563 | $329,888 | $376,249 | $439,543 | $509,737 | |
| Income Tax Expense | $6,147 | $115,461 | $131,687 | $153,840 | $178,408 | |
| NET INCOME | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 |
Balance Sheet
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| ASSETS | ||||||
| Cash | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 | |
| Accounts receivable | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Inventory | $30,000 | $33,072 | $36,459 | $40,192 | $44,308 | |
| Total Current Assets | $184,257 | $381,832 | $609,654 | $878,742 | $1,193,594 | |
| Fixed assets | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | $180,950 | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $54,320 | $81,480 | $108,640 | $135,800 | |
| Net fixed assets | $153,790 | $126,630 | $99,470 | $72,310 | $45,150 | |
| TOTAL ASSETS | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 | |
| LIABILITIES & EQUITY | ||||||
| Debt | $315,831 | $270,713 | $225,594 | $180,475 | $135,356 | |
| Accounts payable | $10,800 | $11,906 | $13,125 | $14,469 | $15,951 | |
| Total Liability | $326,631 | $282,618 | $238,719 | $194,944 | $151,307 | |
| Share Capital | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Retained earnings | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| Total Equity | $11,416 | $225,843 | $470,405 | $756,108 | $1,087,437 | |
| TOTAL LIABILITIES & EQUITY | $338,047 | $508,462 | $709,124 | $951,052 | $1,238,744 |
Cash Flow Statement
| FY 1 | FY 2 | FY 3 | FY 4 | FY 5 | ||
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| CASH FLOW FROM OPERATIONS | ||||||
| Net Income (Loss) | $11,416 | $214,427 | $244,562 | $285,703 | $331,329 | |
| Change in working capital | ($19,200) | ($1,966) | ($2,167) | ($2,389) | ($2,634) | |
| Depreciation | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | $27,160 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Operations | $19,376 | $239,621 | $269,554 | $310,473 | $355,855 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM INVESTMENTS | ||||||
| Investment | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Net Cash Flow from Investments | ($180,950) | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| CASH FLOW FROM FINANCING | ||||||
| Cash from equity | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | $0 | |
| Cash from debt | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow from Financing | $315,831 | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | ($45,119) | |
| Net Cash Flow | $154,257 | $194,502 | $224,436 | $265,355 | $310,736 | |
| Cash at Beginning of Period | $0 | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | |
| Cash at End of Period | $154,257 | $348,760 | $573,195 | $838,550 | $1,149,286 |
Technology Business Plan FAQs
What is a technology business plan.
A technology business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your technology business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections. You can easily complete your Technology business plan using our Technology Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Technology Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of technology businesses, some examples include: Network technology, Software technology, and Customer relationship technology.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Technology Business Plan?
Technology businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Technology Business?
Starting a technology business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Technology Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed technology business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your technology business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your technology business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Technology Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your technology business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your technology business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Technology Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your technology business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your technology business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.
Learn more about how to start a successful Technology business: How to Start a Tech Company
MassChallenge

Innovation Blog
7 steps to create a technology startup business plan.
- Published on: April 26, 2022
- Author: masschallenge

Many entrepreneurs still overlook the importance of a technology startup business plan. In a space as competitive as the tech industry, a lack of preparation will surely pave the way to disappointment.
Instead of diving in without any concrete strategy, a plan provides a foundation for sustainable business growth.
In this article, we’ll explore the essential elements of a tech startup business plan, and provide the insights you need to create a plan for success.
What Is A Business Plan?
A tech startup business plan is a document that details the premise of your technology business, summarizing vital financial objectives and operational goals, as well as details on how you will accomplish these goals.
Put simply:
It’s a road map that describes what you intend to do, and how you intend to do it.
A typical business plan will comprise the following seven elements:
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
Market Research
- Description of Products and/or Services
- Management & Operational Structure
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Plan
3 Reasons You Need a Business Plan
Before we dive into the individual aspects of a startup business plan, let’s first consider why you need one.
Just what are the benefits of a business plan?
1. It Offers Greater Clarity
Having a business plan will give you a much better understanding of your business and the objectives you are trying to achieve. Even the most basic technology startup business plan example will seek to define your goals in more objective terms.
For example, you can set specific targets for website traffic, sales volumes, or profit margins. This makes it easier to track and measure success and aligns your decision-making with sales and marketing initiatives.
2. It Increases the Chances of Success
A report from the Harvard Business Review found that companies with a business plan are 16% more likely to succeed.
Furthermore, companies that have a business plan also enjoy higher growth rates than companies without a plan.
3. You Are More Likely to Get Investment
Angel investors and venture capitalists aren’t in the habit of making bad bets. When they part with large sums of money, it’s a carefully considered decision they base on the likelihood of earning a positive return on investment (ROI). When you have a business plan, you give your startup strategic focus, which helps you create an identity that is built to succeed. This makes for a more attractive prospect in the eyes of investors, so it’s easier to raise capital for your startup when you have a plan.
How to Write a Business Plan for Your Tech Startup (7-Steps)
So, now that you understand the motivation behind creating a tech startup business plan, it’s time to see how it’s done. By including the seven elements below, you’ll have a plan that gives your company a much stronger footing.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is, without a doubt, the most critical element of your tech startup business plan. Despite this, a lot of plans fail here because the summary doesn’t captivate readers. If you can’t hook prospective investors, partners, or employees with your executive summary, they may never read the rest of your business plan.

Source: The Balance
This section should be compelling yet concise, giving people enough to understand what makes your startup unique, and how it will be able to offer solutions in an existing, competitive market.
While you want to keep it brief, there is a lot to pack into this opening section of your business plan. Here are the crucial components of an executive summary:
- Business Model – What is your product or service? How will you make money?
- Target Market – Who will benefit from this product or service?
- Business Opportunity – Why do consumers need your product or service?
- Marketing Strategy – How will these consumers learn more about your product or service?
- Competition – What other companies are competing for market share?
- Goals – How will your startup transform the marketplace with this product or service?
As the executive summary is such a vital aspect, it’s a smart move to write it last. By waiting until you have finished the rest of the business plan, you can draw from the other sections to craft an excellent executive summary.
2. Company Summary
The company summary essentially boils down to a single sentence, otherwise known as a headline statement. When it’s done right, this summary can be the perfect elevator pitch to capture the imagination of would-be financial backers or partners, and it will serve as a natural lead-in to your more detailed business plan.

Source: Gusto (credit: LivePlan)
The company summary or headline statement should do the following:
- Give people a brief overview of what your company does.
- Communicate the value you offer.
- Highlight the opportunity in the market.
Here is a good template to create your company summary:
<Your company> is a <type of business> who sells <product or service> to <target customer> , who needs <solution> , but doesn’t get it from <competition> .
Don’t worry if you can’t create the perfect summary now. When you develop your business plan, you will get a better understanding of what this headline statement should be, and then you can refine it to reflect your vision and value proposition.
We’re sure you have a great idea, but that’s no guarantee that everyone is going to love it as much as you do. No matter how good you think your startup may be, you still need to conduct proper market research to learn more about your ideal customers and competitors.
Identify your Target Market
Without a viable market for your product or service, your business is doomed.
Many startups have failed quickly because the owners were so obsessed with their own product that they were effectively blind to the fact that nobody else cared about it.

Source: CB Insights Image: Cleveroad
Initially, you can adopt a broad scope to get a sense of your total addressable market (TAM), which is the potential revenue opportunity your new product or service could generate. Of course, with the competition, and changing consumer interests, it’s unlikely you will dominate the entire TAM.
Once you have this broad idea, you can hone your sights to go more niche. While this presents a smaller audience, it is more effective. By narrowing your targeting, you can market to a more engaged audience that will be more receptive and likely to purchase your product or service.
Consider the following factors when segmenting your audience:
- Demographic – What age group? What gender?
- Geographic – In what country or city do your prospects live?
- Behavior – What websites/blogs/news sources do they use? What are their purchasing habits? What retail sites or brands do they buy from?
With in-depth data analysis and evaluation of your prospective customers, you can create detailed buyer personas that help you refine your marketing strategies.
Perform Competitor Analysis
During the market research stage of your tech startup business plan, you should also carry out a thorough competitor analysis.
This will help you determine the key differentiators between your company and the competition.
Ask yourself these questions:
- Why should people choose my product or service?
- How can I improve on the existing solutions in the market?
- Why do people not already buy the products in the market?
By thinking about current trends or flaws in existing products, you can identify opportunities for innovation so that your business can connect with customers on a deeper level.
Knowing your audience is crucial, and therefore, your business plan must demonstrate a deep understanding of your target market, and your competitors.
3. Description of Products and/or Services
Here, you must highlight the link between what you are offering, and what people need, so you can prove that people are ready and willing to pay for your product or service.
Research Problems in Market
It helps to conduct some face-to-face research, asking potential customers about the problems they have. Don’t try to usher the conversation in any direction or shoehorn their answers to fit your product – instead, look to learn from their honest responses about the solutions they need.
You should do this research before creating the product. After all, it makes more sense to create a product for an existing problem, instead of trying to find a problem for your product.

Source: ProductTribe
Tailor Product to Problems
After doing your research on the existing problems in the market, trim your list to focus on a few of the most important issues. Describe how your product or service will be the ultimate solution to these problems.
For instance, if people believe the existing solutions are too expensive, you can offer a product with a more attractive price point.
By matching up consumer problems with specific solutions, you can develop a product or service that has a more significant value proposition.
4. Management & Operational Structure
The next stage of the traditional technology startup business plan template delves into the people that make up your company. You must highlight the strengths and experience of your existing team, as new partners effectively invest their money in the team as much as the business idea.
Ideally, your team will consist of several experts whose respective skill-sets complement one another. For example, your tech startup may have a coder, a graphic designer, an inbound marketing expert, and a sales professional. Discuss the merits of each team member to convey the value they add to the business.
You can also speculate about prospective new hires and the key attributes you will seek in future team members. If you haven’t already got a chief financial officer (CFO), it’s a smart move to mention adding one soon. This will add backbone to your business plan by reassuring people that you have good financial sense.
Organizational Chart
Here, your plan should clearly define the organizational structure of your startup. For now, it may just be you and a couple of business partners.
However, by including a graphic that visualizes the structure you intend to build, people will get a clear understanding of the distribution of power and chain of command.
For example, it may look something like this:

Having a hierarchy prepared before starting helps prevent any debates about who is in charge of each department, and makes it easier to understand who reports to who.
5. Marketing and Sales plan
No tech startup business plan would be complete without mentioning the marketing and sales strategies you intend to use.
Sales channels
To clarify the difference, marketing channels are used to promote your business, and its products or services, whereas sales channels are the mediums that enable people to purchase those products or services.
You may only have one direct sales channel to begin with, such as an online e-commerce store. Make sure you explain it in your business plan.
Marketing activities
In this section, you must detail how you will acquire leads and customers.
At the base level, you should do the following:
- Launch a company website
- Develop strategy to get organic traffic (i.e. visitors from search engines like Google)
- Develop a PPC strategy to get immediate online exposure for your most important product/service keywords
- Develop channel partnerships
- Build an email subscriber list

Over time, you can use marketing to nurture stronger customer relationships, which in turn, help you build an audience of loyal followers that will, hopefully, become customers.
The marketing section of your business plan will need to account for several factors, including your goals, risks in the market, and your budget. Which brings us to the final aspect of your tech startup business plan.
6. Financial Plan
Lastly, any good business plan must include pertinent details about your company budget and sales goals.
This can be daunting for many new entrepreneurs and is all the more challenging when you have no balance sheets, cash flow reports, or even any stable income on which to base your projections.
That being said, it’s still possible to make educated projections – so long as you have done solid market research.
When it comes to financial matters, your business plan should include details about:
- Revenue streams – how will the company generate income?
- Major expenses – What high costs do you anticipate in the year ahead?
- Salary demands – Are you still bootstrapping or are you and the partners taking a salary? If so, how much?
- Financial milestones – Detail your expansion strategy by considering future hires or store openings that will impact the books.
Many startups aren’t profitable in the first year. Your financial projections should maintain a long-term view for success, keeping ambitions realistic and honest. That way, you’ll be able to produce a more accurate break-even analysis .

With these long-term projections, you must consider the financial impact of expanding. You may be making more money in Year 3, but opening a new store will set you back.
Keep everything in perspective and make sure you don’t set yourself or your investors up for any nasty shocks down the road.
5 Tech Startup Business Plan Templates
When you have all the elements above in place, your business plan will be in good shape. However, presentation matters. If you want to make the best first impression, getting creative with your technology startup business plan template can make a big difference.
Not only will your research and expertise shine through, but you will have a visually stunning presentation that catches the eye of investors.
Here are five tech business plan examples to inspire you.
Business Plan Infographic PowerPoint
This plan allows you to present in-depth market analysis, statistics, and projections in a professional visual infographic. With several hundred editable slide options, it’s well worth the $16 fee for the license.

Source: Medium
Emaze Business Planning With Analytics
This is more than the average technology startup business plan template. Emaze has a diverse array of creative collaboration tools, making it easy and enjoyable for teams to create unique plans together from any of the built-in templates. Furthermore, you can incorporate analytics, which is perfect for impressing investors. That said, $19 per month for the premium version may seem a little steep for some small businesses.

Source: Emaze
Lean Canvas 1-Page Business Plan
A tech startup business plan doesn’t need to take weeks to create. In fact, with this template, you can have a basic – yet brilliant – business plan all together on a single page in just 20 minutes.

Source: Lean Stack
StartUp Pitch
For $15, you can access the full array of colorful slides in this presentation, which are all customizable to your needs. This template includes many ready-made aspects of the typical business plan, such as SWOT analysis, competitor analysis, and project timelines.

Source: Envato
This is another user-friendly tool for creating short business plans. You enter the information, and then LivePlan will generate a one-page plan in an infographic style.

Source: LivePlan
Make Your Tech Startup Business Plan a Priority
It’s not enough to have a great startup idea.
If you want to stand out from the pack, secure investment, and build a successful company that can earn real profits, growth, and customer loyalty, then you absolutely must have a solid tech startup business plan.
It’s time to create yours.

New to MassChallenge?
Visit the join section of our site to learn more about the organization and how you may benefit by getting involved., upcoming events, masschallenge uk: awards ceremony 2024 and ceo roundtable.
- November 21, 2024
- London, United Kingdom
MassChallenge Switzerland: Awards Ceremony
- October 31, 2024
- Lausanne, Switzerland
MassChallenge Switzerland: Mentor-Matching 3
- September 3, 2024
Let's get in touch
Kindly fill out the form below, and our team will get back to your inquiries ASAP.
Required(*)
Email Address
I'm interested in:
Please fill all the required fields!
*By submitting this form, you have read and agreed to Orient Software's Term of Use and Privacy Statement
+84 28 3812 0101
OTHER ENQUIRIES
7 Elements to Successfully Write a Tech Startup Business Plan

Vy Le | 18/05/2023

When it comes to starting a tech business, having a well-crafted tech business plan is crucial to attract investors and succeed in the competitive market landscape. A business plan outlines your company’s vision, strategy, and financial plan over time, giving potential investors insight into your business model and growth potential.
However, writing a tech startup business plan can be a daunting task, especially for new entrepreneurs that lack experience in the tech industry. In this article, we’ll provide you with a comprehensive guide on writing a tech startup business plan that will impress investors and help you succeed in the fast-paced tech startup world.
What is a Tech Startup Business Plan?

A tech startup business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the goals, objectives, and strategies of a technology-based startup company. It is a crucial tool that helps entrepreneurs in the tech industry to define and organize their ideas, demonstrate the feasibility of their business concept, and present a clear plan for how they intend to build and grow their company.
Generally, most business plans typically include a summary of the company history, the problem it is solving, the target audience, competitive analysis, the marketing and sales strategy, the development strategy, and the financial plan. Also, such a document may include details about the management team, operations, and product development roadmap.
Particularly for the technology sector, the tech startup business plan also includes more specialized elements. Specifically, it is important to focus on the e-commerce technology trends being developed and how it addresses a gap or problem in the market while building such a document. This includes details such as the software or hardware being constructed, the technology stack being used, its technical architecture, and how it will improve or disrupt existing technology solutions.
Overall, a well-crafted business plan can help secure funding from potential investors or lenders, attract top talent, and ultimately guide the company toward success.
10 Core Questions to Answer When Conducting a Tech Startup Business Plan
For a tech startup business to build a good business plan, keep in your mind these questions and find the answers for yourself along the way. Answering these questions will help your startup team formulate a clear and compelling business plan/business idea, which can be used to guide the tech startup founder toward success.
1. Which product or service does your tech startup offer?
2. What is the team structure, and who are the key members?
3. Who is your target audience for the product or service?
4. Who are the competitors?
5. What are your competitive advantages?
6. What is your marketing strategy, and how do you leverage marketing channels?
7. What is your sales plan, and how do you leverage sales channels?
8. What is your financial plan, including projections for revenue, expenses, and funding needed?
9. What are the risks and challenges the business may face?
10. What is your timeline for product development, launch, and growth?
3 Reasons Why You Need a Technology Startup Business Plan
But why do businesses compose a tech startup business plan at the beginning of the software development process? There must be reasons. Check them out now!

Providing a Blueprint for Success
According to a Harvard Business Review study , startups that write a detailed business plan have a 16% chance to achieve viability than businesses that don’t. This metric proves the usefulness of this action.
By systematizing the business idea into a complete tech startup business plan, you give the business itself and each team member a clear picture of the company’s goals, vision, and strategies. While people are a prerequisite for an organization’s success, understanding the product’s direction will help each individual in the development team structure closely link together throughout the software development process and shorten product completion time.
Raising Capital from Investors
In the tech industry, startups often require significant amounts of capital to fund product development, hire staff, and invest in marketing and sales efforts. Raising such funds from investors is often necessary for startups’ future growth and success.
However, among the hundreds of thousands of startups out there, what sets your business apart from all of them? It is a specific technology startup business plan that is well-written to demonstrate.
Prospective investors and venture capitalists do not spend their money arbitrarily on poorly invested projects because, ultimately, they care about the return on investment (ROI). Investors are usually drawn to companies that understand their market and have a plan to tackle the market gap, and a well-curated business plan can make a tech startup stand out from the crowd.
Attract Top Talent
Suppose you don’t intend to use outsourced software development services to quickly build a development team of professionals and want to recruit developers for your startup yourself . A tech startup business plan can help in this situation.
A technology startup business plan can showcase the unique features of the business and its competitive advantage in a crowded market. Therefore, it can become a valuable tool for convincing top talent to join the team, especially if the company’s plans align with professionals’ aspirations and career goals.
7 Essential Elements to Write a Business Plan for Your Tech Startup
Your business idea can be good. But to easily realize it and stick to the outlined roadmap, you must present them in a systematic document. To do this, don’t skip the seven key elements to conduct a tech startup business plan below.

Executive Summary
The executive summary is the most critical component of a tech startup business plan as it gives the reader a first-hand look at your product/service. An executive summary is a brief overview of your entire tech startup business plan, providing context for the reader and summarizing all the key points. It is usually the first section of the business plan and is customized to reflect the company’s goals, values, and unique selling points in a way that inspires the reader’s confidence in the startup.
An excellent executive summary in a software startup business plan typically includes the general situation of the target market or related industry based on conducted market research and an overview of the software solution you offer. Other information, such as unique value proposition (UVP), competitors in the same segment, and the company’s goal, can also be included in the executive summary as an optional option.
The advice is not to write the executive summary too long and vague, lacking focus on the main ideas. It is recommended to keep it within two pages to optimize visual efficiency and avoid boring the reader. Use the executive summary as an opportunity to showcase your tech startup’s strengths before diving into the details later on.
Company Description
If the executive summary is the section that presents all the overview data about your product or service, the company description in a technology startup business plan is the part that gives the reader a clearer view of your entire tech startup, or what we call a company overview.
This section should provide a clear understanding of the business to potential partners or customers and inspire confidence in the startup . There are many primary elements that make up a complete company description. So, it will be hard if tech startup founders don’t start small. Draft fundamental ideas and gradually develop them into complete content until they meet all the needs of a business plan.
Here are some main elements to consider when writing a company description: tech company’s name, company history, business model, vision, mission, legal structure (whether it is a sole proprietorship, partnership, LLC, or corporation.), management team structure (each role and responsibilities) and competitive advantage.
Target Market Research
By doing target market research, a tech startup is able to figure out three key elements for a tech startup’s business plan. These are the total addressable market (TAM), technology market trends, target customer groups, and competitor analysis.
- The total addressable market (TAM) is the target market’s total size that helps assess potential future revenue streams and justify the business case.
- Market trends help tech startups stay up to date with market demand, ever-changing information technology, and changes in perspective customers’ behavior.
- Target audience gives tech startups a better understanding of their potential customers by gathering demographic, geographic, and behavior factors.
- The competitor analysis section of your business plan helps tech company in identifying their direct competitors and understand their own strengths and weaknesses to promote competitive advantage better.
Target market research not only benefits the startup company but also shows your investment and determination in the product or service.
Product/Service Line
It’s time to be more descriptive of the product or service your company offers rather than just general, like in the executive summary. Because the purpose of a startup business plan is generally still to introduce products to potential customers, this section should be written carefully and go into detail to demonstrate the product’s uniqueness and promising growth potentials.
Some elements to consider when writing a business plan include:
- Product or service explanation: This includes key features and benefits, how it works, and how it is different from other solutions in the market.
- Value proposition: Clearly stating how your product fulfills a customer need and backing it up with evidence.
- Product development: Providing a product development roadmap by outlining your timeline and steps to achieve further development goals.
Team Structure
The team structure is an essential part of a tech startup business plan. It gives investors and stakeholders insight into the management team’s ability to execute the business plan and the team’s capacity to bring the idea to fruition.
In this part of the business plan, it is vital to highlight the leadership team and their roles. Start by introducing your founders and executive team and describe their previous experience and expertise with a proven track record that makes them qualified to lead the company. For investors to easily visualize the development team of your startup business, using a graphic, such as an organizational chart, can help.
Next, outline the roles and responsibilities of each member of your team , including any advisors or board members. Remember to describe carefully how each team member will contribute and cooperate to the successful company and how their respective skill sets complement, and experience are relevant to the tech industry.
Goals and plans for the future of the leadership team and development team members can also be written in the business plan as a supplement. For example, you expect to expand your team within one year by hiring additional staff or bringing on new partners or investors. All must be written in a clear, concise, and focused manner.
Marketing and Sales Plan
A product or service with good quality is only part of it when marketing and sales plans are exactly the activities that bring users and profits to the company. The marketing and sales plan section of a tech startup business plan will serve as a critical component that outlines how your company plans to acquire and retain customers, generate revenue, and achieve sustainable growth.
Regarding the marketing strategy, since you have already defined the target audience in the target market research section of the business plan, you only need to briefly repeat this section to once again help investors develop a comprehensive understanding of your ideal customer and their buying behavior. Next, don’t forget to differentiate your product or service from competitors and effectively manage your marketing plan by describing your unique value proposition. Consider using social media advertising, SEO, content marketing, email marketing, and public relations as tactics to reach your audience and successfully execute a marketing plan.
After your marketing efforts, it’s time to build your business plan and a suitable sales strategy. The basic elements of sales strategies adopted by many startups include sales approach, pricing strategy, sales channels, and sales team structure, which provides a clear path for converting leads into paying customers.
To measure the success of your marketing and sales efforts, track progress, and make data-driven decisions, you should identify key performance indicators (KPIs) such as website traffic, conversion rates, customer acquisition cost, and revenue generated.
Financial Projections
Running out of cash is one of the primary reasons why many businesses fail. Building a financial plan right from the start will make it easier to manage expenses and manage risks for your software solution. There is no fixed financial plan of the business plan as each startup has different business orientations and goals.
However, one of the most vital aspects of this section is the sales forecast, which details how your company plans to generate revenue, including the sales channels you will use, your pricing strategy, and your projected customer acquisition rate.
The cash flow statement and the balance sheet are also important elements in a basic financial plan. The balance sheet provides a snapshot of the company’s financial health and helps you make informed decisions about your operations and growth strategies. The cash flow statement identifies how much money you expect to have on hand each month, taking into account both revenue and expense forecasts.
Final Thought

As for business plans, there is no single startup business plan template that is a perfect fit for your project since there is no startup like any other in the technology market. Each startup has different characteristics and different product businesses. Some companies set up a business plan to raise capital for a banking product . Meanwhile, there are companies that are working on human resources software.
So, start a business plan from small things. Take note of all your ideas on paper and discuss them in turn with the development team is Orient Software ’s advice.
With years of experience in the field of information technology, Orient is confident of having the ability to advise you on all problematic aspects of the industry. Contact us for more details !
Content Map
Related articles.

Software Development Plan: Benefits & Steps to Craft Your Efficient Project Plan
Learn how software development planning can help you create an efficient and successful project. Find out the benefits and how to develop your own plan.
Trung Tran | 28/05/2024
Ten Programming Languages for Web Development in 2024
Øyvind Forsbak | 09/02/2024
Best Cloud Certifications: Which Ones Are in High Demand and Why?
Tan Dang | 24/01/2024
Salesforce Service Cloud Vs. Sales Cloud: The Comparison
Shannon Jackson-Barnes | 25/12/2023
Assemble a Competent Web Development Team: Roles, Skills, and Qualities
Hieu Nguyen | 18/12/2023
Disclose the Astonishing Use Cases of Robotic Process Automation in Healthcare
Trung Tran | 19/10/2023
Why Outsource Web Application Development? - All the Practical Benefits to Take Action
Trung Tran | 06/08/2023

The Most Common Software Development Challenges & How to Solve Them
Here are the ten most common software development challenges and how to address them properly.
Trung Tran | 23/05/2024

Software Release Planning Process Made Easy: A Comprehensive Approach
Mastering software release planning is crucial for success in software development. It's the key to gaining a significant competitive edge for your business.
Quynh Pham | 17/05/2024

Is Your Recruitment Process Costing You? Check out Recruitment ROI!
Is your hiring process a budget drain? Discover recruitment ROI & learn how to optimize for top talent and cost savings.
Tan Dang | 23/04/2024
Deciphering Project Management Tools: Airtable Vs. Jira Comparison
Here is what you need to know to choose between Airtable and Jira - two popular project management tools.
Quynh Pham | 05/04/2024
Looking for an IT partner?
Contact us today for a free quote within 3 business days


Having a great business idea and having the willingness and ability to jump into the entrepreneurial or intrapreneurial journey are the stepping stones to a successful journey. Next, you will develop expertise on how to write a business plan for a tech startup step by step.
You may like to start a business venture on your own or start a new business initiative within the firm that you work for. Whatever the case may be; you need to start your journey by writing a tech startup business plan proposal.
Like they say, a job well begun is half done. So, knowing how to write a well thought out business plan wins half the battle for you.
You also need to follow the “Keep it Simple, Silly” doctrine and come up with a simple business plan. Following a step-by-step business plan template, in this case, helps.
Sounds interesting? Let’s start the journey.
How do you begin a tech startup business plan?
To begin a tech startup business plan, you need to ask yourself the following questions:
“What to do?” “How to do it?” “When to do it?” and ” Who will do it?”
These questions will help in starting to plan how to take your business idea to executable action. Planning will help you bridge the gap between where you are right now and where you want to reach, concerning your business idea.

What are the 5 elements of a tech startup business plan?
There is no sacrosanct format of a good business plan or a business plan pdf, and also the ingredients of a business plan proposal would depend on your experience in business and knowledge in that particular field.
However, a good startup business plan consists of the following:
1. Your background
In case you have partners, their background too
2. Description of the business idea
It should consist of Utility of the Product / Service and the Unique Selling Proposition, i.e., USP
3. Production plan
In case of a product, how would you produce the product, in case of a service, how will you deliver the service
4. Operational plan
How would you smoothly coordinate the day to day work, how would you ensure the desired quality, where would you set up your factory/office, at what price will you sell
5. Organizational plan
This contains details of how many people you will employ to produce or deliver the service, what your marketing set up will be, who will manage your accounting and liaison with the various stakeholders and authorities
6. Financial plan
Now we come to an essential part of your business plan, where you need to spend considerable time and effort. It is the Financial Plan .
Your financial plan should spell out the investment required for the business. Where would the funds come from, and when are the funds needed? How much cash is needed to carry on day to day operations?
This section would also describe the economic feasibility of the business. This would include the revenue forecast for the next year, or three years or even further.
How do you write a one-page business plan for a tech startup?
You need an elaborate plan to be successful in your business. However, at the same time, you also need to keep in mind that the business plan is needed for the potential investor to consider investing in your business.
Given the lack of time the potential investor has, you need to make a one-page business plan which has a concise description of your plans but gives details on why she/he should invest in your business. It should motivate the potential investor to spend time and read a more elaborate business plan.
The one-page business plan is also your means of communication with the external stakeholders like the government, the public at large when you need to do any statutory filing of information of the company or present in various conferences.
You may also like to term this one-page plan as a written “elevator pitch.”
You may like to start a business venture on your own or start a new business initiative within the firm that you work for. Whatever the case may be; you need to start your journey by writing a tech startup business plan proposal.
Like they say, a job well begun is half done. So, knowing how to write a well thought out business plan wins half the battle for you.
You also need to follow the “Keep it Simple, Silly” doctrine and come up with a simple business plan. Following a step-by-step business plan template, in this case, helps.
What does a tech startup business plan consist of?
A startup business plan consists of an internal roadmap elaborating on the most important aspects of your business (i.e., the background, the production, operational, organizational, and financial aspects).
At the same time, it consists of the purpose, and the financial returns your business will generate, which acts as a written marketing document for external stakeholders.
However, given the uncertainties in modern times, business plans are increasingly focusing on the risks, and the fall back plans that would be in place if the original plan fails.
A significant point that gives confidence to the investor about the long term viability of the business plan is the interest that the target market will show in the product or service. So, it is worthwhile to add as a Business plan annexure pdf, any primary research done by a reputed marketing agency of the market potential of the product or service.
When the business plan involves a new product or service, it is effortless to fall into the trap of looking at the product from your point of view and taking the market for granted. What is required at this stage is to focus exclusively on how you conceptualized the idea and how you are planning to bring the concept to execution.
Researchers from MIT suggested successful business plan examples where users were invited to pre-test the products or services. Their feedback is of interest to the investor and needs to be included in your startup business plan.
8 Steps to Create a Business Plan for Your Tech Startup
Step 1: executive summary.
The first step in writing a startup business plan for your new tech business is to create an executive summary.
The executive summary doesn’t need to be lengthy and tedious; around two to three pages should suffice.
Although a short document, the executive summary one of the most important elements of your business plan.
Your executive summary should be concise and clear as it should be successful in communicating everything about your business.
Some investors might only ask for your executive summary — so be sure to craft it well and pepper it with all the right bits of information. you’ll want to ensure it can stand on its own.
Stick to the following:
1. Mission Statement: In one crisp paragraph, explain the mission of your business and what you want to accomplish.
2. General Company Information: Next, include general information like when your business was formed, the name of the other founders, their roles, the number of employees, office locations, and so on.
3. Visual Highlights: Include graphs and charts pertaining to any key milestones of the business or any growth you’ve seen since starting the business.
4. Products and Services: Without getting overly passionate or verbose, briefly describe your product, the technology that powers it, and your target customer base.
5. Financial Information: If you’re looking for startup fundraising , include your funding goals. You can also include any information on previous loans or about banks or lenders you’ve worked with before.
6. Future plans: Don’t forget to include where you plan on taking your business in the future.
Pro tip: Write your executive summary after you’ve completed creating your business plan.
This way you’ll have all your facts in place and all your information and details sorted so you will be better equipped to summarize them.
Step 2: Company Overview
Many entrepreneurs confuse the company overview with the executive summary. However, there is a stark difference between the two.
The company overview is a more detailed top-level view of the structure of your tech business and what you do.
Here’s how you can go about drafting your startup overview:
1. Begin your company overview section by describing what your business specializes in and the technology behind it. This part of the company overview is intended to give readers and investors a general idea of your business.
2. Next, proceed to explain the nature of the industry and marketplace.
3. Lay out the legal structure of your business and provide the ownership structure.
Step 3: Market Analysis
The next step along the process of creating your startup business plan is to perform in-depth research and analysis of your niche, target market, and primary competitors.
This is the first part of your startup business plan where you dive into the details.
Your market analysis will give readers and investors enough proof about the level of understanding you have about the dynamics of your industry.
Your market analysis should include the following sections:
1. Industry Description: Start by including a detailed view of your industry. How big is it? How much has it grown in the past few years? What are its growth predictions from industry experts? Who are your competitors? How have they performed? And so on.
2. Target Market Details: Dive into the details of your target market . And include your target market’s characteristics and target market size and growth.
3. Your Market Share Potential: Chart out what your market share could look like along with how much market share you expect to gain.
4. Market Pricing: Include an estimated cost of your products and how you will distribute them.
5. Challenges: Don’t shy away from including any challenges that you may across. This could be legal issues to shifting technologies to capital issues to lack of talented or skilled human resources.
6. Competitor Research: Study your competitors by analyzing their strengths, market share, weaknesses, challenges they pose to you, and so on.
Step 4: Business Organization
This next section of your startup business plan provides insights and information on your tech business’s management structure clearly defining and explaining what everyone does.
You will also have to go a step further to include everyone’s business background and past experiences.
Here’s what you need to break down:
1. Organizational Structure: Start this section by creating an organizational chart that depicts how your business is structured.
2. Ownership Structure: Although you’ll repeat this information in your company overview, you have the liberty to go in-depth allowing you to talk about the ownership structure of your company, who owns how much, and so on.
3. Background of Owners: Categorically explain the background of your team. This includes information on directors, senior management members, and managers.
4. Talent Requirement: Clearly make a list of all hiring needs.
Step 5: Products and Services
This section of your startup business plan is all about laying out the details and plans for positioning your product, the utility it provides, the technology behind it, and so on.
For instance, if you are offering Internet of Things (IoT) based solutions or Artificial Intelligence-powered services, then give details about how these products work and how you wish to promote and sell it.
Here’s exactly what this section should include:
1. General Description: Highlight the USP of your product or service and the value it provides to potential customers.
2. Status of products: Paint an honest picture of the status of your product. Is your product in the idea stage? Is it already selling? Or is it ready to go to market?
3. Product goals: If you are still in the ideation phase, map out a journey that talks about how you plan to launch the product and bring it to life. Include details on the research and development activities required. You can also include new versions or new products or any new features you wish to include in the future.
4. Intellectual property: As a tech business, it is imperative to have proprietary intellectual property . Make mention of this and any other patent or trademark that you own or are in the process of owning.
5. Sourcing and fulfillment: If you are dependent on third-party vendors to fulfill or your product or service creation, mention it here.
This section is crucial for your startup business plan as it defines everything about your products and services.
It will work as a bible for product managers and for you in the development stages and go to market phase.
Step 6: Marketing and Sales Plan
Once you’ve explained everything about your product, it’s time to delve into explaining how you are going to go about marketing and selling your product or service.
When it comes to marketing, this is what this section should look like:
1. Positioning: This first part of your marketing plan should talk about how you’re positioning your business and products. What price bracket are you targeting? Are you offering any free service? What guarantees and warranties are you offering? Answering these questions and more will help you determine where you are positioning your products and services.
2. Promotion: This part involves explaining marketing channels and plans you have for advertising your product, PR strategies, SEO plans, content marketing practices, social media marketing, etc.
Next, your sales plan:
1. Salesforce: How do you plan to sell your product? Do you need a sales force? How big a team do you need? Who will train your sales team? These parameters need to be addressed in your sales plan.
2. Selling strategy: Give an overview of how you will sell your product or service. Define the process you will follow as a technology business. Will you start with cold-calling potential customers? Or attending events? Or appointing channel partners? Clearly describe what your sales funnel should look like.
Step 7: Financial Plan and Projections
This is a supremely important section of your business plan.
Investors and VCs will want to look at your financial plans and projections before parting with their money.
Ideally, this section uses financial data from past performances or forecasts.
Include the following as part of your financial plan:
1. Income statements
2. Cash flow statements
3. Balance sheets
Additionally, if applicable, include the accounts of receivable statements, accounts of payable statements, and details or documents of debts.
Ideally, your financial projections should be supported either by past performances or future projections and estimations.
Include statements of projected income, cash flow forecasts, forecasted balance statements, capital expenditure budgets, and miscellaneous expenses.
Your startup business plan should include projections for the first year of business but should include a vision for the coming 3 to 5 years.
Step 8: Appendix
The appendix should be included towards the end of your business plan. This section includes all additional information that you didn’t include in the sections above of your business plan.
Any data, statistics, strategic points, charts, footnotes, or further explanations that you think are necessary to be included as part of your startup business plan but has been skipped should be included here.
As an entrepreneur or founder, you can also consider including your own resume and resumes of other founders or senior management team members.
Ideally, the appendix should begin with a table of contents that categorically breaks down your business plan into relevant, followed by the additional information that corresponds to each section.
199 Resources for Startup Business Plan Templates, Business Plan Examples, and Business Plan Samples
| 1 | bussinessplanpro.com | Business Plan Examples |
| 2 | mynewoffice.com | Business Plan Examples |
| 3 | kaufmanschedule.com | Business Plan Examples |
| 4 | businessplanexamples.net | Business Plan Examples |
| 5 | business-plan-examples.com | Business Plan Examples |
| 6 | ovucscanexel.tk | Business Plan Examples |
| 7 | wheretogetanessay.club | Business Plan Examples |
| 8 | allusionexamples.com | Business Plan Examples |
| 9 | financemart.net | Business Plan Examples |
| 10 | hoodcleaningschool.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 11 | aspencapgroup.net | Business Plan Sample |
| 12 | iiiventures.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 13 | vztap.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 14 | capitalsystemwebgroup.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 15 | ridgecrestinvestments.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 16 | restaurantbplans.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 17 | lifemasterpreneur.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 18 | agplan.umn.edu | Business Plan Sample |
| 19 | baincapitalscrewsthepoor.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 20 | bochferns.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 21 | dayohub.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 22 | paneracares.ca | Business Plan Sample |
| 23 | practicalbusinessideas.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 24 | acceletv.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 25 | jwindustrialpartners.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 26 | joplinregionalbizcenter.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 27 | crainsclevelandevents.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 28 | beallinc.org | Business Plan Sample |
| 29 | signalhillcapital.info | Business Plan Sample |
| 30 | moneilpatel.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 31 | internationalschoolofsiliconvalley.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 32 | ctinnovations.us | Business Plan Sample |
| 33 | morebusiness.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 34 | thestartupjitters.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 35 | pragatimaidaan.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 36 | startgreennow.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 37 | elevatelake.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 38 | bainhypocrisy.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 39 | bestpracticesfoundation.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 40 | appraisalbestpractices.org | Business Plan Sample |
| 41 | allianceventures.info | Business Plan Sample |
| 42 | lumenityventures.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 43 | businessplanpro.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 44 | truventureholdings.org | Business Plan Sample |
| 45 | baincapitalblows.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 46 | meritechnic.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 47 | mch-zuerich.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 48 | csokolozas.info | Business Plan Sample |
| 49 | glassbuildamerica.us | Business Plan Sample |
| 50 | nextviews.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 51 | theedusystems.info | Business Plan Sample |
| 52 | reddottemasek.co.uk | Business Plan Sample |
| 53 | voicemetrics.net | Business Plan Sample |
| 54 | baincapitalscrewspeople.net | Business Plan Sample |
| 55 | eduproperessays.info | Business Plan Sample |
| 56 | tisemadigital.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 57 | bplanexperts.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 58 | namgioi.info | Business Plan Sample |
| 59 | myemploymentexpresspro.com | Business Plan Sample |
| 60 | rainbow9.org | Business Plan Template |
| 61 | fastbusinessplans.com | Business Plan Template |
| 62 | howtowritebusinessplan.com | Business Plan Template |
| 63 | pattyenright.com | Business Plan Template |
| 64 | planmagic.com | Business Plan Template |
| 65 | meetpartnertoprofit.com | Business Plan Template |
| 66 | riffstation.co | Business Plan Template |
| 67 | navigatesmallbusiness.ca | Business Plan Template |
| 68 | businessplantemplate.com | Business Plan Template |
| 69 | kcfi.ca | Business Plan Template |
| 70 | start-my-own-business-now.com | Business Plan Template |
| 71 | isolveconsulting.ca | Business Plan Template |
| 72 | inbizz.ca | Business Plan Template |
| 73 | marketingandbusinessplanning.com | Business Plan Template |
| 74 | wabusinessassist.com | Business Plan Template |
| 75 | blukfoundation.com | Business Plan Template |
| 76 | minorityownedbusiness.com | Business Plan Template |
| 77 | businessplancompanies.com | Business Plan Template |
| 78 | d1college.com | Business Plan Template |
| 79 | spathium.com | Business Plan Template |
| 80 | transformyourlawfirm.com | Business Plan Template |
| 81 | aft-fx.jp | Business Plan Template |
| 82 | business-plan-example.com | Business Plan Template |
| 83 | 519businessplans.ca | Business Plan Template |
| 84 | wazup.me | Business Plan Template |
| 85 | pvgtranslation.com | Business Plan Template |
| 86 | shannonmenard.com | Business Plan Template |
| 87 | fdcdubai.website | Business Plan Template |
| 88 | inspiredlifeproject.com | Business Plan Template |
| 89 | creationchurch.co | Business Plan Template |
| 90 | b2bvault.com | Business Plan Template |
| 91 | businessexponow.co.uk | Business Plan Template |
| 92 | profitmakingventures.org | Business Plan Template |
| 93 | officetemplatesonline.com | Business Plan Template |
| 94 | charlotteopenforbusiness.org | Business Plan Template |
| 95 | hempcbdbusinessplans.com | Business Plan Template |
| 96 | fitnessbusinessschool.com | Business Plan Template |
| 97 | parissbdc.com | Business Plan Template |
| 98 | carmaconnect.in | Business Plan Template |
| 99 | newbusinessplantemplates.com | Business Plan Template |
| 100 | legal-timber.info | Business Plan Template |
| 101 | chrisessentials.com | Business Plan Template |
| 102 | tecfx.co | Business Plan Template |
| 103 | scaleyourserviceonline.com | Business Plan Template |
| 104 | pozycjoner.org | Business Plan Template |
| 105 | business.laws.com | Business Plan Template |
| 106 | imari.com.au | Business Plan Template |
| 107 | jabcob.com | Business Plan Template |
| 108 | smef.gov.bd | Business Plan Template |
| 109 | londonbizreport.com | Business Plan Template |
| 110 | felices-prado.com | Business Plan Template |
| 111 | tatforum.org | Business Plan Template |
| 112 | koopalia.com | Business Plan Template |
| 113 | startminer.co | Business Plan Template |
| 114 | abusinessplantemplate.com | Business Plan Template |
| 115 | cakintl.com | Business Plan Template |
| 116 | jackijacobs.shop | Business Plan Template |
| 117 | blackboxbusinessplans.com | Business Plan Template |
| 118 | bizplandb.com | Business Plan Template |
| 119 | whitelighteducation.com | Business Plan Template |
| 120 | businessplandownload.net | Business Plan Template |
| 121 | bolatogel.net | Business Plan Template |
| 122 | bizplans4u.com | Business Plan Template |
| 123 | 7makemoneyonline.com | Business Plan Template |
| 124 | jaysetconsulting.com | Business Plan Template |
| 125 | sbrss.com | Business Plan Template |
| 126 | secob.co.za | Business Plan Template |
| 127 | paydayloanslts.com | Business Plan Template |
| 128 | startuplab.co.nz | Business Plan Template |
| 129 | russaliana.me | Business Plan Template |
| 130 | specimenplanner.co.uk | Business Plan Template |
| 131 | endtoendhrsolutions.com | Business Plan Template |
| 132 | yourplanplace.com | Business Plan Template |
| 133 | capturethefracture.org | Business Plan Template |
| 134 | stansmithpascher.club | Business Plan Template |
| 135 | savvystartupclub.com | Business Plan Template |
| 136 | aspiher.com | Business Plan Template |
| 137 | baodaipad.biz | Business Plan Template |
| 138 | coffeeshopstartups.com | Business Plan Template |
| 139 | bpplans.com | Business Plan Template |
| 140 | alphaunit.com | Business Plan Template |
| 141 | a-formula.com | Business Plan Template |
| 142 | thepolicylibrarymembership.co.uk | Business Plan Template |
| 143 | tvlentrepreneur.com | Business Plan Template |
| 144 | greenskiing.co | Business Plan Template |
| 145 | kpfunds.net | Business Plan Template |
| 146 | virginstartup.org | Business Plan Template |
| 147 | lavenderllewellyn.com | Business Plan Template |
| 148 | grandbusinessplan.com | Business Plan Template |
| 149 | bayanescorts.net | Business Plan Template |
| 150 | free-directory-online.com | Business Plan Template |
| 151 | lanarkshire-business.co.uk | Business Plan Template |
| 152 | marketingandbusinessplanning.co.uk | Business Plan Template |
| 153 | hrjkkj.icu | Business Plan Template |
| 154 | 150startups.com | Business Plan Template |
| 155 | arthurmandell.com | Business Plan Template |
| 156 | filmproposals.com | Business Plan Template |
| 157 | bplanshop.com | Business Plan Template |
| 158 | realmoneyinvestors.com | Business Plan Template |
| 159 | moneylendingpros.com | Business Plan Template |
| 160 | atozerp.com | Business Plan Template |
| 161 | getcharismatic.com | Business Plan Template |
| 162 | sampleplan.com | Business Plan Template |
| 163 | startupcrest.com | Business Plan Template |
| 164 | goairban.com | Business Plan Template |
| 165 | cacatalano.com | Business Plan Template |
| 166 | paydayloansnow24h.com | Business Plan Template |
| 167 | thelaundrybiz.com | Business Plan Template |
| 168 | klarititemplateshop.com | Business Plan Template |
| 169 | theglobal.co.za | Business Plan Template |
| 170 | businessplanjournal.com | Business Plan Template |
| 171 | jocuri888.com | Business Plan Template |
| 172 | thefinanceresource.com | Business Plan Template |
| 173 | leanaplummer.com | Business Plan Template |
| 174 | pittsburghbusiness.biz | Business Plan Template |
| 175 | wheretowriteapaper.live | Business Plan Template |
| 176 | stayli.com | Business Plan Template |
| 177 | startupprofessionals.com | Business Plan Template |
| 178 | mawazoafrica.org | Business Plan Template |
| 179 | gremmy-gr.host | Business Plan Template |
| 180 | 2eu.org | Business Plan Template |
| 181 | businessplanscentral.com | Business Plan Template |
| 182 | businessplantemplate.net | Business Plan Template |
| 183 | essayflooor.site | Business Plan Template |
| 184 | business-plan.co.za | Business Plan Template |
| 185 | dispensarypermits.com | Business Plan Template |
| 186 | contractorhub.com | Business Plan Template |
| 187 | dorchesterbayloans.org | Business Plan Template |
| 188 | businesschecklist.org | Business Plan Template |
| 189 | officialbuddoctor.com | Business Plan Template |
| 190 | bargerveen.info | Business Plan Template |
| 191 | bizdevczar.com | Business Plan Template |
| 192 | cbdbizplan.com | Business Plan Template |
| 193 | freelancetofounder.space | Business Plan Template |
| 194 | helm-group.com | Business Plan Template |
| 195 | perfectlittlebusinessplan.com | Business Plan Template |
| 196 | bestfunnywifinames.club | Business Plan Template |
| 197 | bpiplans.com | Business Plan Template |
| 198 | planmagic.org | Business Plan Template |
| 199 | plusacademics.org | Business Plan Template |
Final Thoughts
Although creating a startup business plan seems daunting and arduous, when you break it down into a step by step process, it gets easy to create one.
And with these 8 steps, you can create a killer tech business plan for your tech startup that will help you catapult to success and leave investors mesmerized.
Starting a tech business? Build it on a .tech domain!
Leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
In this blog...
How to Write A Tech Startup Business Plan
Whether you’re just starting out or have been in business for a while, creating a tech startup business plan is valuable. It will help you clarify your idea, assess its feasibility, and determine what resources you need to make it a reality. Here are some tips on how to write a tech startup business plan to will help you get started.
What is a business plan, and why do you need one for your tech startup?
A business plan is a written document describing in detail how a business will achieve its goals. This document lays out a written plan from a marketing, financial, and operational standpoint.
Sometimes, business plans are prepared for investors or as a requirement for a small business loan . But even if you don’t need outside funding, preparing a business plan is still a good exercise to ensure your ducks are all in one row.
If you’re considering starting a tech startup, having a business plan helps you to stay on track. When you have an idea for a new tech product or service, it’s easy to get caught up in the excitement and overlook the importance of creating a solid foundation for your business. A solid business plan will allow you to take a step back and think critically about your concept. At the same time, you’ll perceive how your concept will be received by the marketplace.
Furthermore, a good business plan keeps you focused on your goals and helps you track your progress as your tech startup grows. As your business evolves, you can refer back to your original business plan and adjust it accordingly. This document should be living and breathing, just like your tech startup.
Elements of a good business plan
The contents of your tech startup business plan will vary depending on your company’s specific needs , but certain elements should always be present. Here are the five key elements that every good business plan includes.
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary is a brief overview of your business plan. It should include your company’s mission statement, a brief description of your products or services, an overview of your target market, a summary of your financial projections , and your goals for the next three to five years.
Even though the executive summary should be the first section of your business plan document, it would be a good idea to write it last. This is because you’ll find all the important information from the other sections to complete the executive summary.
2. Company Description
The company description section of your business plan should provide an overview of your company’s history, mission statement, and core values. This section should also describe your company’s structure and how it will operate going forward. If you have any patents or proprietary technology, this is the place to mention it.
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section of your business plan should research and describe your industry and the specific market segment you’re targeting. This information will be useful in developing your sales and marketing strategy later on in the business plan. Include information about your target customer’s needs, buying habits, and demographics.
4. Competitive Analysis
In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll need to identify and research your competitors—both direct and indirect. This portion is where you indicate their strengths and weaknesses relative to yours. Knowing what your competition is up to will help you develop strategies to stay ahead in the marketplace.
5. Sales and Marketing Plan
Your sales and marketing plan will detail how you plan to reach and sell to your target market segment. This part of the business plan should include information about your pricing strategy, promotional activities, distribution channels, and sales methods. You’ll also need to provide realistic financial projections for sales revenue over the next three to five years.
Tips for making your business plan stand out from the competition
Business plans are a dime a dozen. You need to go above and beyond the basics to make yours stand out from competitors. Here are a few tips on how to make your business plan shine:
1. Do your research
This may seem like a no-brainer, but you would be surprised how many people try to wing it when it comes to their business plan. Before you even start writing, take some time to research the industry, your competition, and your target market. This will give you a solid foundation to work from and will help you make your plan as comprehensive and impressive as possible.
2. Keep it concise
Nobody wants to read a 50-page business plan. Get to the point and be as concise as possible. This doesn’t mean that you should skimp on the details, but rather that you should focus on including only the most important information. The executive summary is a great place to start when it comes to being concise; make sure that you include everything!
3. Make it visually appealing
Remember, first impressions matter. Even if your business plan is top-notch, potential investors or partners will likely gloss over it if it’s boring or difficult to read. Use infographics, charts, and other visuals to break up the text and make your plan more enjoyable (and memorable) to read.
4. Proofread the document many times!
Last but not least, be sure to proofread your business plan before sending it off into the world. Nothing screams “unprofessional” louder than a poorly written document. So, take the time to edit and revise until your plan is error-free. Better yet, have someone else look at it for you. Sometimes, it’s easier for someone else to catch errors we overlook.
Final Thoughts: Writing A Tech Startup Business Plan
You now have a basic understanding of the components that make up a tech startup business plan. This is just a starting point, and your specific business will require more detail. But following these guidelines should give you a good foundation on which to build.
Besides a well-written business plan, you will also need the right team to help execute all the necessary actions to solidify your business strategy. When it comes to the tech talent side, Full Scale is the right match for any tech startup or even scale-up.
Full Scale houses the best and brightest software engineers, developers, and QA testers that you can find. You can forego the tedious process of finding, recruiting, and hiring developers for your tech team. We do all that for you and enjoy watching our client partners achieve great results.
Find out what Full Scale can do for you and your tech company!
Learn More about Offshore Development
Copyright 2024 © Full Scale

IT Services Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
IT Services Business Plan
Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 500 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans to start and grow their IT companies.
If you’re unfamiliar with creating an IT business plan, you may think creating one will be a time-consuming and frustrating process. For most entrepreneurs it is, but for you, it won’t be since we’re here to help. We have the experience, resources, and knowledge to help you create a great business plan.
In this article, you will learn some background information on why business planning is important. Then, you will learn how to write an IT business plan step-by-step so you can create your plan today.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
What is an IT Services Business Plan?
A business plan provides a snapshot of your IT business as it stands today, and lays out your growth plan for the next five years. It explains your business goals and your strategies for reaching them. It also includes market research to support your plans.
Why You Need a Business Plan for IT Company
If you’re looking to start an IT business or grow your existing IT company, you need a business plan. A business plan will help you raise funding, if needed, and plan out the growth of your IT business to improve your chances of success. Your IT business plan is a living document that should be updated annually as your company grows and changes.
Sources of Funding for IT Businesses
With regards to funding, the main sources of funding for an IT business are personal savings, credit cards, bank loans, and angel investors. When it comes to bank loans, banks will want to review your business plan and gain confidence that you will be able to repay your loan and interest. To acquire this confidence, the loan officer will not only want to ensure that your financials are reasonable, but they will also want to see a professional plan. Such a plan will give them the confidence that you can successfully and professionally operate a business. Personal savings and bank loans are the most common funding paths for IT companies.
Finish Your Business Plan Today!
How to write a business plan for an it services business.
If you want to start an IT business or expand your current one, you need a business plan. The guide below details the necessary information for how to write each essential component of your IT business plan.
Executive Summary
Your executive summary provides an introduction to your business plan, but it is normally the last section you write because it provides a summary of each key section of your plan.
The goal of your executive summary is to quickly engage the reader. Explain to them the kind of IT business you are running and the status. For example, are you a startup, do you have an IT business that you would like to grow, or are you operating a chain of IT businesses?
Next, provide an overview of each of the subsequent sections of your plan.
- Give a brief overview of the IT industry.
- Discuss the type of IT business you are operating.
- Detail your direct competitors. Give an overview of your target customers.
- Provide a snapshot of your marketing strategy. Identify the key members of your team.
- Offer an overview of your financial plan.
Company Overview
In your company overview, you will detail the type of IT business you are operating.
For example, you might specialize in one of the following types of IT businesses:
- Computer repair: This type of IT business provides computer maintenance and repair services.
- Computer training: This type of IT professional specializes in teaching others how to use computers as well as various software and computer programs.
- IT support: This type of IT professional provides services for businesses such as setting up a network, backing up data, and systems management.
- Cloud computing: This type of IT specialist helps individuals and businesses establish cloud platforms and tools, or may help to migrate their information to the cloud.
In addition to explaining the type of IT business you will operate, the company overview needs to provide background on the business.
Include answers to questions such as:
- When and why did you start the business?
- What milestones have you achieved to date? Milestones could include the number of new clients served, the number of repeat clients, reaching $X amount in revenue, etc.
- Your legal business Are you incorporated as an S-Corp? An LLC? A sole proprietorship? Explain your legal structure here.
Industry Analysis
In your industry or market analysis, you need to provide an overview of the IT industry.
While this may seem unnecessary, it serves multiple purposes.
First, researching the IT industry educates you. It helps you understand the market in which you are operating.
Secondly, market research can improve your marketing strategy, particularly if your analysis identifies market trends.
The third reason is to prove to readers that you are an expert in your industry. By conducting the research and presenting it in your plan, you achieve just that.
The following questions should be answered in the industry analysis section of your IT business plan:
- How big is the IT industry (in dollars)?
- Is the market declining or increasing?
- Who are the key competitors in the market?
- Who are the key suppliers in the market?
- What trends are affecting the industry?
- What is the industry’s growth forecast over the next 5 – 10 years?
- What is the relevant market size? That is, how big is the potential target market for your IT business? You can extrapolate such a figure by assessing the size of the market in the entire country and then applying that figure to your local population.
Customer Analysis
The customer analysis section of your IT business plan must detail the customers you serve and/or expect to serve.
The following are examples of customer segments: individuals, schools, families, and corporations.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of IT business you operate. Clearly, individuals would respond to different marketing promotions than corporations, for example.
Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations, and income levels of the potential customers you seek to serve.
Psychographic profiles explain the wants and needs of your target customers. The more you can recognize and define these needs, the better you will do in attracting and retaining your customers.
Finish Your IT Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Competitive Analysis
Your competitive analysis should identify the indirect and direct competitors your business faces and then focus on the latter.
Direct competitors are other IT businesses.
Indirect competitors are other options that customers have to purchase from that aren’t directly competing with your product or service. This includes other types of IT consultants, in-house IT support, or do-it-yourself IT tutorials. You need to mention such competition as well.
For each such competitor, provide an overview of their business and document their strengths and weaknesses. Unless you once worked at your competitors’ businesses, it will be impossible to know everything about them. But you should be able to find out key things about them such as
- What types of customers do they serve?
- What type of IT business are they?
- What is their pricing (premium, low, etc.)?
- What are they good at?
- What are their weaknesses?
With regards to the last two questions, think about your answers from the customers’ perspective. And don’t be afraid to ask your competitors’ customers what they like most and least about them.
The final part of your competitive analysis section is to document your areas of competitive advantage. For example:
- Will you make it easier for clients to acquire your product or service?
- Will you offer products or services that your competition doesn’t?
- Will you provide better customer service?
- Will you offer better pricing?
Think about ways you will outperform your competition and document them in this section of your plan.
Marketing Plan
Traditionally, a marketing plan includes the four P’s: Product, Price, Place, and Promotion. For an IT business plan, your marketing strategy should include the following:
Product : In the product section, you should reiterate the type of IT company that you documented in your company overview. Then, detail the specific products or services you will be offering. For example, will you provide cloud computing, data center management, or network setup services?
Price : Document the prices you will offer and how they compare to your competitors. Essentially in the product and price sub-sections of your plan, you are presenting the products and/or services you offer and their prices.
Place : Place refers to the site of your IT company. Document where your company is situated and mention how the site will impact your success. For example, is your IT business located in a busy retail district, a business district, a standalone office, or purely online? Discuss how your site might be the ideal location for your customers.
Promotions : The final part of your IT marketing plan is where you will document how you will drive potential customers to your location(s). The following are some promotional methods you might consider:
- Advertise in local papers, radio stations and/or magazines
- Reach out to websites
- Distribute flyers
- Engage in email marketing
- Advertise on social media platforms
- Improve the SEO (search engine optimization) on your website for targeted keywords
Operations Plan
While the earlier sections of your business plan explained your goals, your operations plan describes how you will meet them. Your operations plan should have two distinct sections as follows.
Everyday short-term processes include all of the tasks involved in running your IT business, including answering calls, meeting with new clients, billing and collecting payments from clients, etc.
Long-term goals are the milestones you hope to achieve. These could include the dates when you expect to acquire your Xth client, or when you hope to reach $X in revenue. It could also be when you expect to expand your IT business to a new city.
Management Team
To demonstrate your IT business’ potential to succeed, a strong management team is essential. Highlight your key players’ backgrounds, emphasizing those skills and experiences that prove their ability to grow a company.
Ideally, you and/or your team members have direct experience in managing IT businesses. If so, highlight this experience and expertise. But also highlight any experience that you think will help your business succeed.
If your team is lacking, consider assembling an advisory board. An advisory board would include 2 to 8 individuals who would act as mentors to your business. They would help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. If needed, look for advisory board members with experience in managing an IT business or successfully running a small IT consulting service.
Financial Plan
Your financial plan should include your 5-year financial statement broken out both monthly or quarterly for the first year and then annually. Your financial statements include your income statement, balance sheet, and cash flow statements.
Income Statement
An income statement is more commonly called a Profit and Loss statement or P&L. It shows your revenue and then subtracts your costs to show whether you turned a profit or not.
In developing your income statement, you need to devise assumptions. For example, will you charge your clients an hourly rate of $250 per hour, and will you work 5 hours per day? And will sales grow by 2% or 10% per year? As you can imagine, your choice of assumptions will greatly impact the financial forecasts for your business. As much as possible, conduct research to try to root your assumptions in reality.
Balance Sheets
Balance sheets show your assets and liabilities. While balance sheets can include much information, try to simplify them to the key items you need to know about. For instance, if you spend $50,000 on building out your IT business, this will not give you immediate profits. Rather it is an asset that will hopefully help you generate profits for years to come. Likewise, if a lender writes you a check for $50,000, you don’t need to pay it back immediately. Rather, that is a liability you will pay back over time.
Cash Flow Statement
Your cash flow statement will help determine how much money you need to start or grow your business, and ensure you never run out of money. What most entrepreneurs and business owners don’t realize is that you can turn a profit but run out of money and go bankrupt.
When creating your Income Statement and Balance Sheets be sure to include several of the key costs needed in starting or growing an IT business:
- Cost of equipment and office supplies
- Payroll or salaries paid to staff
- Business insurance
- Other start-up expenses (if you’re a new business) like legal expenses, permits, computer software, and equipment
Attach your full financial projections in the appendix of your plan along with any supporting documents that make your plan more compelling. For example, you might include your office location lease or a list of your IT credentials.
Writing a business plan for your IT business is a worthwhile endeavor. If you follow the template above, by the time you are done, you will truly be an expert on IT business planning. You will understand the IT industry, your competition, and your customers. You will develop a marketing strategy and will understand what it takes to launch and grow a successful IT business.
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your IT business plan?
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success. Click here to see how Growthink’s business plan services can give you a winning business plan.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

- Services Product Management Product Ideation Services Product Design Design Design Web Design Mobile Application Design UX Audit Web Development Web Development Web Development in Ruby on Rails Backend API Development in Ruby on Rails Web Applications Development on React.js Web Applications Development on Vue.js Mobile Development Mobile Development Mobile app Development on React Native iOS Applications Development Android Applications Development Software Testing Software Testing Web Application Testing Mobile Application Testing Technology Consulting DevOps Maintenance Source Code Audit HIPAA security consulting
- Solutions Multi-Vendor Marketplace Multi-Vendor Marketplace B2B - Business to Business B2C - Business to Customer C2C - Customer to Customer Online Store Create an online store with unique design and features at minimal cost using our MarketAge solution Custom Marketplace Get a unique, scalable, and cost-effective online marketplace with minimum time to market Telemedicine Software Get a cost-efficient, HIPAA-compliant telemedicine solution tailored to your facility's requirements Chat App Get a customizable chat solution to connect users across multiple apps and platforms Custom Booking System Improve your business operations and expand to new markets with our appointment booking solution Video Conferencing Adjust our video conferencing solution for your business needs For Enterprise Scale, automate, and improve business processes in your enterprise with our custom software solutions For Startups Turn your startup ideas into viable, value-driven, and commercially successful software solutions
- Industries Fintech Automate, scale, secure your financial business or launch innovative Fintech products with our help Edutech Cut paperwork, lower operating costs, and expand your market with a custom e-learning platform E-commerce Streamline and scale your e-commerce business with a custom platform tailored to your product segments Telehealth Upgrade your workflow, enter e-health market, and increase marketability with the right custom software

- Case Studies

- Entrepreneurship
- Business Plan for a Technology Startup
Writing a Business Plan for a Technology Startup and the Benefits for Your Company
- 13481 views
- Jul 17, 2020

Business Analyst

Anastasiia S.
- Tech Navigator

Have a business idea but don’t know where to start? Consider creating a business plan first! An extensive and informative business plan allows you to understand your goals, opportunities, and threats, assess the market situation, and get a lot of insights to successfully launch your startup. Moreover, it can help you interest your investors.
Read our article to find out what a business plan is, what its benefits are, and how to create one. Let’s start with a definition.
What’s a business plan?
A business plan presents a detailed vision of your business idea. This document usually consists of 30 to 35 pages and several sections that cover vital topics for your business development such as goals, management, marketing, and funding.
A business plan is usually created before setting up a new business. It projects up to five years into the future to ensure you know where you’re headed at the beginning of your entrepreneurial journey. It’s advisable to revise this plan every month or two to check whether you’re sticking to your goals.
Benefits of creating a business plan
Although creating a business plan requires a lot of time and research, it’s sensible to make one before launching your startup. A business plan helps you realistically assess your opportunities and provides more benefits that we’ll describe below.
Detect weaknesses in your startup idea
When preparing a business plan, you should carry out a SWOT analysis to understand your chances of success.
To perform a SWOT analysis, you need to determine your business’s s trengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threat s. Take into account that strengths and weaknesses are internal characteristics of your company that you can control, while opportunities and threats are external factors out of your control.
Once you’ve completed SWOT analysis, pay close attention to your weaknesses. By being aware of your soft spots, you can transform them into workable solutions to make your business successful.
- Set goals and milestones
Setting goals is one of the core ideas behind creating a business plan, since by knowing your short- and long-term goals you can clearly understand where your business is heading.
Milestones allow you to track progress toward achieving your goals. Setting milestones is a strategic step that allows you to stick to your plan and not get distracted on your way.
Once you’ve listed your goals, you need to choose the path to achieve them. There are several options to choose from. For instance, you can map a long but predictable path with minimum risks and a short path full of challenges.
Let’s consider different options for launching your MVP as an example. You can choose a soft launch: a careful step-by-step presentation of your product to your target audience. When you use a soft launch approach, you reveal your product to a limited number of users, gather feedback from them, and fix bugs quickly. Thus, we can define a soft launch as a long yet predictable way to reach your goals.
A hard launch, on the other hand, is a short and risky path, since it means presenting a new product to a large number of people at once. It can bring you immediate revenue, but at the same time it can cause a lot of problems if your product isn’t perfect.
Once you’ve distinguished two different paths to reach your goals, which one to choose is up to you.
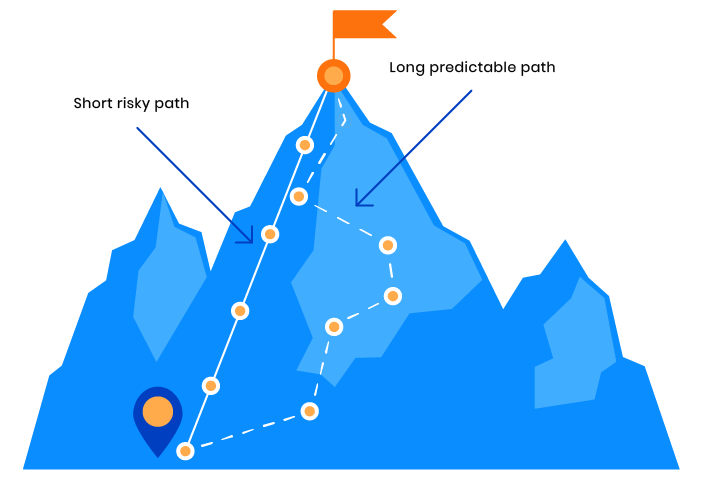
- Make data-driven decisions
Preparing a business plan entails carrying out a lot of research. To make a realistic business plan, you should dive deep into marketing, finance, and management. You should also perform a comprehensive analysis of your direct and indirect competitors to get a full picture of the market situation.
By gathering information about other market players, you can learn about their strengths and weaknesses along with your own. This gives you a chance to better determine your company’s unique value proposition (UVP) and stand out from the competition.
With this information, your business plan is not merely a suggestion but a realistic view of your startup, the challenges you might face, and the ways you can overcome them.
- Obtain an effective management tool
With a business plan in hand, it’s easier to manage your progress. Since a business plan includes a map with milestones, you can use it to keep track of how well you stick to and achieve your goals.
A business plan also helps you check whether you’re keeping within your budget and how profitable your business is. Plus, it allows you to monitor other financial aspects such as your employees’ incomes, pay raises, and your bonus system.
- Get more information than with a Lean Canvas
Creating a Lean Canvas is a fast way to assess business opportunities. A Lean Canvas is a one-page document with 10 to 12 fields that gives a general overview of the current state of your business, your opportunities, and your goals. Although it’s a nice option for a quick assessment, a Lean Canvas is not very informative.
Here’s an example of how a Lean Canvas looks and what information it can present:

A business plan, in turn, is an extensive document that covers a long period of time (usually up to five years). Consequently, it requires a more comprehensive approach to business analysis than a Lean Canvas does and includes more detailed information about your business idea.
Use your plan as a pitch deck
Once you create your business plan, you can use it as the basis for your pitch deck. Just select the most important information and you’ll have a ready presentation for your investors, business partners, or whoever you want to interest in your business idea.
An informative pitch deck based on your business plan can lead investors to consider your business worth supporting.
How to create a technology startup business plan
Once you understand the benefits a business plan can give you, it’s time to move to developing one. Here are the must-have sections for your business plan.
#1 Executive summary
An executive summary presents your overall business plan. Its aim is to capture your readers’ attention and make them interested in reading through all the details.
This summary should be written in clear language and be understandable even for people who don’t have specific knowledge of your business area.
Do your best to outline the maximum relevant information within a five- to ten-minute read.

To make your executive summary informative and captivating, it’s best to write this section after you’ve finished all the other sections. Also, you should answer all these questions briefly in the summary since you’ll cover them in detail in the following sections.
#2 Business idea
This section is a detailed presentation of your product or service. You should include the following information:
- Product/service description. Cover all the characteristics of your product, its uniqueness in the market, patent issues and compliance requirements (e.g. PCI DSS for payment systems, HIPAA for healthcare, or GDPR compliance), and a description of the development process.
- Benefits for customers. Explain why your product is outstanding, how it reflects the needs of your target audience, and how it will solve your customers’ problems.
- Pricing. Calculate how much it will cost to create your product and decide what monetization approach to choose (for instance, a subscription-based model or one-time payments). Make sure your revenue will cover your expenses.


#3 Business sector and market analyses
In this section, you’ll present the results of your research that show how successfully you can penetrate the desired market.
First of all, analyze your preferred business sector. Pay attention to the current situation in the sector, predicted trends, sources of profit, and entry barriers.
Then, carry out market analysis including geographical, socio-demographic, socio-economic, and behavior-oriented segmentation of your potential customers. These criteria will help you better understand your target audience and attract more customers in the short term.
Finally, perform competition and location analyses. Competition analysis will help you determine your and your competitors’ strengths and weaknesses while location analysis will help you decide on the location for your company.

#4 Marketing strategy
This section demonstrates how you will build your marketing campaign. You already know your target audience, your competitors’ weaknesses, and the strengths of your product, so it’s time to sell it. At this stage, it’s important to decide if your marketing campaign will be extensive or targeted, what steps it will include, how many customers you need to attract to make your campaign successful, etc.

#5 Management
In this section, you should provide information about the key roles inside your company and your legal situation.
When introducing your team, it’s important to mention roles and responsibilities and the qualities that make each person a valuable team member.
By legal situation, we mean the legal structure of your company and the legal framework that determines how your startup operates. You should state whether your business is a one-person startup or a partnership, for instance.

#6 Opportunities and threats
This section describes external opportunities and challenges you can face when starting and expanding your business. To present this information as accurately as possible, you should create both positive and negative forecasts based on detailed research concerning your business sector, the current market situation, upcoming trends, your competitors, etc. Use the results of your SWOT analysis to provide information in this section.

#7 Financial plan
You should prepare a financial plan for the first five years of your business activity. It should include:
- Staff costs. This is the money you’ll spend on human resources at the beginning of your business and as it grows.
- Investment and depreciation information. In this section of the financial plan, you should enumerate any kinds of material investments you plan to make (vehicles, furniture, PCs, etc.) and their predicted service life.
- A profitability plan that includes your revenue and expenses. Make sure that planned revenue exceeds your expenses. There’s no point in starting a business that isn’t profitable.

#8 Funding opportunities
This section should list sources of investment and include the amount of money you need to start your business. You should also list investment options that you’re going to use. You can choose among local banks, venture capitalists, public funding schemes, business angels, and other options.
Once you decide how you’ll fund your business ‒ take out a loan or find investors ‒ include a repayment plan or mention the conditions of cooperation with your financiers.

#9 Map for the future with milestones
In this section, you should describe the step-by-step implementation of your plan. It’s important to set priorities, divide the whole plan into small scopes of tasks, and set realistic deadlines. By doing this, you’ll get milestones that lead to your business success.
It can be a sensible idea to present milestones graphically so it’s easier for your readers to perceive the information and track your progress.

Final thoughts
With an elaborate business plan, you’ll have a clear understanding of your business opportunities and a chance to get into the desired market. Once you’ve created a comprehensive business plan, it’s time to create an MVP to attract your first customers.
What benefits does a business plan provide?
Writing a business plan is an important step before launching a startup. With a detailed business plan, you can:
- Detect weaknesses in your startup
- Have a starting point for creating a pitch deck
What sections should I include in a business plan?
There are nine main sections you should include in a business plan:
- Executive summary
- Business idea
- Business sector and market analyses
- Marketing strategy
- Opportunities and threats
- Financial plan
- Funding opportunities
- Map for the future with milestones
Is it necessary to create a business plan for my technology startup?
Writing a business plan isn’t obligatory, but you might want to do it since having a plan gives a lot of benefits. A business plan can help you understand your opportunities and threats, analyze the current market situation, learn more about your competitors, attract investors, and more.
If you already have a business plan and need help creating your MVP, contact us for professional assistance .
Rate this article!

Share article with
RubyGarage Blog
Please identify yourself to leave comments and connect with other readers
There are no comments yet
Subscribe via email and know it all first!
Thanks for your subscription!
- 16890 views

- 27349 views

- 16763 views
ZenBusinessPlans
Home » Sample Business Plans » Technology
How to Write an IT Tech Startup Business Plan [Sample Template]
Are you about starting an IT tech startup? If YES, here is a detailed sample IT tech startup business plan template & feasibility report you can use for FREE . If you are a software developer or you have a background in the ICT industry and you are looking for An IT business to start, then you need to look far because there are loads of businesses in the industry and one of them is software as a service (or SaaS) company.
Software as a service (or SaaS) is an emerging paradigm business that enables software to be delivered as a service. This is an arrangement that enables companies to expand their network capacity, and run applications directly on a vendor’s network, offer a host of advantages with the most primary being radically lowering IT costs.
The lower budgetary requirements and commitments allow even smaller companies to piece together an IT project without spending on purchasing legacy server, and storage systems. However, due to the technical nature of this business, it would be wise to consult with a business consultant before starting off.
If your business concept is a great one, the business consultant would offer you tips and suggestions on the way forward. Below is a sample IT tech startup company business plan template that can help you successfully write your own with little or no stress.
A Sample IT Tech Startup Business Plan Template
1. industry overview.
An IT technology company (often tech company) is a type of business entity that focuses on the development and manufacturing of technology products, or providing technology as a service. “Technology”, in this context, has come to mean electronics-based technology. This can include businesses relating to digital electronics, software, and internet-related services, such as e-commerce.
For the purpose of this business plan, we will be looking at software development as a service. Software as a service (or SaaS) is part of the Business Analytics and Enterprise Software Publishing industry and players in this industry consist of companies that are into ERP software, bi software, crm software, scm software and other software development and they may decide to strictly adopt the Software as a services (SaaS) Business model.
A recent report published by IBISWorld shows that the Business Analytics and Enterprise Software Publishing industry has grown steadily due to favorable demand conditions caused by high corporate profit and investment. Over the five years to 2018, industry revenue rose at an annualized rate of 7.1 percent, driven by businesses’ increased technological complexity and the eagerness to adopt efficiency-enhancing software.
The report also shows that many industry products, such as customer relationship management and enterprise resource planning software systems, have become basic tools in the management of large companies. In 2018, industry revenue is expected to rise 2.6 percent to $55.4 billion. The world’s largest software companies have spent the past five years acquiring high-performing enterprise software vendors, cloud companies and data.
The report further states that over the past five years, the Business Analytics & Enterprise Software Publishing in the US industry has grown by 7.1 percent to reach revenue of $55bn in 2018. In the same timeframe, the number of businesses has grown by 10.0 percent and the number of employees has grown by 10.2 percent.
The Business Analytics and Enterprise Software Publishing industry is indeed a growing industry and is gaining ground in most countries of the world. Statistics has it that in the united states of America alone, there are about 2,869 registered and licensed business analytics and enterprise software publishing companies (Software as a services (SaaS) business model inclusive) responsible for employing about 139,347 people and the industry rakes $55 billion annually.
The industry is projected to grow at 7.1 percent annual growth within 2013 and 2018. The companies holding the largest market share in the Business Analytics & Enterprise Software Publishing in the US industry include SAP SE, International Business Machines Corporation, Salesforce.com Inc. and Oracle Corporation.
Some of the factors that encourage entrepreneurs to start their own Software as a service (SaaS) business could be the growing recognition of economic and operational benefits and the efficiency of this business model. As companies ease out gradually from the economic uncertainties and financial shackles, widespread adoption of Software as a service is in the offing.
The successful adoption of this technology concept will pave the way for mass enterprise adoption of Software as a service in the upcoming years. The transition of enterprises from virtual machines to the cloud will additionally extend the impetus required for strong growth of Software as a service (SaaS).
Poised to score the maximum gains will be end-to end cloud-computing solutions that offer complete functionalities ranging from integration of internal and external clouds, automation of business-critical tasks, and streamlining of business processes and workflow, among others.
Over and above, starting a software as a services (SaaS) company requires professionalism and good grasp of how the ICT industry works. Besides, you would need to get the required certifications and license and also meet the standard security expected for players in the industry in the United States.
2. Executive Summary
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is an IT tech startup that will specialize in offering software as a service (SaaS). The business will be based in Overland Park – Kansas and we were able to secure a well – positioned and standard office facility.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is a client – focused and result driven IT tech startup company that is into ERP software, bi software, crm software, scm software and other software development. We will provide broad – based software development services at an affordable fee that won’t in any way put a hole in the pocket of our clients. We will offer standard and professional services to all to our clients.
At Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc., our client’s best interest would always come first, and everything we do is guided by our values and professional ethics. We will ensure that we hire professionals who are experienced in the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry in general.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will at all times demonstrate her commitment to sustainability, both individually and as a firm, by actively participating in our communities and integrating sustainable business practices wherever possible. We will ensure that we hold ourselves accountable to the highest standards by meeting our client’s needs precisely and completely.
Our plan is to position the business to become the leading brand in software as a service (SaaS) business in the whole of Overland Park – Kansas, and also to be amongst the top 10 IT tech startup companies in the United States of America within the first 10 years of operation. This might look too tall a dream but we are optimistic that this will surely be realized.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will be owned and managed by Joel Rogers. He has a Bachelor of Technology. He is a certified SOC 2 – Trust (SOC 2 is designed specifically for SaaS operations) and has over 10 years’ experience working in related industry as a senior software engineer prior to starting Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc.
3. Our Products and Services
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is going to offer varieties of services within the scope of the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry in the United States of America. We are well prepared to make profits from the industry and we will do all that is permitted by the law in the United States to achieve our business goals, aim and ambition.
Our business offerings are listed below;
- ERP software development
- BI software development
- CRM software development
- SCM software development
- Other software development
4. Our Mission and Vision Statement
- Our vision is to build an IT tech startup company that will be among the forerunners when it comes to offering software as a service (SaaS) in the world.
- Our mission is as an IT tech startup with bias in software as a services (SaaS) is to help a wide range of clients develop customized software that will help them simplify their businesses and operations.
Our Business Structure
Ordinarily we would have settled for two or three staff members, but as part of our plan to build a standard IT tech startup company in Overland Park – Kansas, we have perfected plans to get it right from the beginning which is why we are going to ensure that we have competent, honest and hardworking employees to occupy all the available positions in our firm.
The kind of IT tech startup company we intend building and the business goals we want to achieve is what informed the amount we are ready to pay for the best hands available in and around Overland Park – Kansas as long as they are willing and ready to work with us.
Below is the business structure that we will build Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. on;
- Chief Executive Officer
- Programmers and Software Developers
Admin and HR Manager
- Digital Marketers (Marketing and Sales Executive)
- Customer Care Executive / Front Desk Officer
5. Job Roles and Responsibilities
Chief Executive Office:
- Increases management’s effectiveness by recruiting, selecting, orienting, training, coaching, counseling, and disciplining managers; communicating values, strategies, and objectives; assigning accountabilities; planning, monitoring, and appraising job results
- Creating, communicating, and implementing the organization’s vision, mission, and overall direction – i.e. leading the development and implementation of the overall organization’s strategy.
- Responsible for fixing prices and signing business deals
- Responsible for providing direction for the business
- Responsible for signing checks and documents on behalf of the company
- Evaluates the success of the organization
Programmers and Software Developer
- Responsible for designing, installing, testing and maintenance of software systems for the organization
- Identifying areas for modification in existing programs and subsequently developing these modifications
- Writing and implementing efficient code
- Determining operational practicality
- Developing quality assurance procedures
- Training users
- Working closely with other developers, UX designers, business and systems analysts
- Presenting ideas for system improvements, including cost proposals
- Working closely with analysts, designers and staff
- Producing detailed specifications and writing the programme codes
- Maintaining and upgrading existing systems once they are up and running
- Responsible for overseeing the smooth running of HR and administrative tasks for the organization
- Regularly hold meetings with key stakeholders to review the effectiveness of HR Policies, Procedures and Processes
- Maintains office supplies by checking stocks; placing and expediting orders; evaluating new products.
- Ensures operation of equipment by completing preventive maintenance requirements; calling for repairs.
- Defining job positions for recruitment and managing interviewing process
- Carrying out induction for new team members
- Responsible for training, evaluation and assessment of employees
- Responsible for arranging travel, meetings and appointments
- Oversee the smooth running of the daily office activities.
Marketing and Sales Executive
- Identify, prioritize, and reach out to new partners, and business opportunities et al
- Identifies development opportunities; follows up on development leads and contacts
- Writing winning proposal documents, negotiate fees and rates in line with company policy
- Responsible for handling business research, marker surveys and feasibility studies for clients
- Responsible for supervising implementation, advocate for the customer’s needs, and communicate with clients
- Document all customer contact and information
- Represent the company in strategic meetings
- Help increase sales and growth for the company
- Responsible for preparing financial reports, budgets, and financial statements for the organization
- create reports from the information concerning the financial transactions as recorded
- Prepare the income statement and balance sheet using the trial balance and ledgers
- Provides managements with financial analyses, development budgets, and accounting reports
- Responsible for financial forecasting and risks analysis.
- Performs cash management, general ledger accounting, and financial reporting for one or more properties.
- Responsible for developing and managing financial systems and policies
- Responsible for administering payrolls
- Ensuring compliance with taxation legislation
- Handles all financial transactions for the company
- Serves as internal auditor for the company
Technical Help Desk Officer
- Provide technical assistance and support for incoming queries and issues related to our software
- Identifies problems and issues by performing relevant research using the appropriate tools and by following established procedures.
- Through interaction with clients on the phone, uses every opportunity to build client’s interest in the company’s services
- Consistently stays abreast of any new information on the company’s promotional campaigns etc. to ensure accurate and helpful information is supplied to clients
6. SWOT Analysis
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. engaged the services of a professional in the area of business consulting and structuring to assist the firm in building a well – structured IT tech startup company that can favorably compete in the highly competitive business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry.
Part of what the business consultant did was to work with the management of our organization in conducting a SWOT analysis for Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. Here is a summary from the result of the SWOT analysis that was conducted on behalf of Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc.;
We can boast of a competent technical team that has analytical and critical thinking skills that can help them find creative solutions for our clients. Aside from the synergy that exists in our carefully selected workforce, we have a very strong online presence and we are well positioned to attract loads of clients from the first day we open our doors for business.
One of the weaknesses that is obvious to us is the lack of capacity and inability to compete with big players in the industry especially as it relates to economy of scales.
- Opportunities:
The opportunities in the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry is massive considering the fact that the world is going the way of technology, and software as a service (SaaS) is indispensable in the value chain of the info tech industry.
Some of the threats that we are likely going to face as an IT tech startup business operating in the United States are hosting issues, installation or upkeep troubles, piracy, unfavorable government policies , and global economic downturn which usually affects purchasing/spending power.
7. MARKET ANALYSIS
- Market Trends
The advancement we are enjoying in our world today can be attributed to the advancement of technology. Technology has indeed given leverage to all aspects of human endeavor. To start with, it is the advancement of technology that landed man in the moon.
It is the advancement of technology that made communication either via the telephone or computer easier and faster. It is the advancement of technology that made transportation faster and perhaps cheaper. It is the advancement of technology that made the manufacturing of goods faster and cheaper, etc.
The technology industry is so wide and vibrant and there is still room large enough for those who are interested in the industry to come in and create their own impact. One thing is certain, the world will always celebrate any inventor who is able to invent machines or devices that can ease the process of doing things.
8. Our Target Market
We are aware that the nature of our business is geared to words serving B2B clients, hence Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will initially serve small to medium sized business, from new ventures to well established businesses and individual clients, but that does not in any way stop us from growing to compete with the leading IT tech startup companies that offer software as a services (SaaS) in the United States.
As a standard and licensed IT tech startup company that offers software as a service (SaaS), Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will develop software apps for the following clients;
- Financial services providers
- Insurance companies
- Businesses in the health sector
- Supply chain businesses
- Other related businesses that may need software as a services (SaaS) technology
Our competitive advantage
The level of competition in the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry does not in any way depend on the location of the business since most companies that offer software as a service (SaaS), can operate from any part of the world and still effectively compete in the industry.
We are quite aware that to be highly competitive in the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry means that we should be able to develop software apps that will help simplify business and operation process for clients.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. might be a new entrant into the industry in the United States of America, but the management staff are considered gurus. They are highly qualified software programmers and developers in the United States. These are part of what will count as a competitive advantage for us.
Lastly, our employees will be well taken care of, and their welfare package will be among the best within our category in the industry meaning that they will be more than willing to build the business with us and help deliver our set goals and achieve all our aims and objectives.
9. SALES AND MARKETING STRATEGY
We are mindful of the fact that there is fast – growing competition amongst IT tech startup companies and other players in the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry in the United States of America and around the globe; hence we have been able to hire some of the best business developer cum digital marketers to handle our sales and marketing.
Our sales and marketing team will be recruited base on their vast experience in the industry and they will be trained on a regular basis so as to be well equipped to meet their targets and the overall goal of the organization. We will also ensure that our excellent job deliveries speak for us in the market place; we want to build a standard IT tech startup company that offer software as a services (SaaS), that will leverage on word of mouth advertisement from satisfied clients.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is set to make use of the following marketing and sales strategies to attract clients;
- Introduce our business by sending introductory letters alongside our brochure to all the companies, institutions and organizations within and outside the United States
- Promptness in bidding for software as a service (SaaS) contracts from companies, and organizations within and outside the United States
- Advertise our business in relevant programming magazines, radio and TV stations
- List our business on local directories/yellow pages
- Attend international software as a services (SaaS) developers related, seminars, and business fairs et al
- Create different packages for different category of clients in order to work with their budgets
- Leverage on the internet to promote our business
- Join related associations around us with the main aim of networking and marketing our services; we are likely going to get referrals from such networks.
Sources of Income
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is established with the aim of maximizing profits in the business analytics and enterprise software publishing industry and we are going to ensure that we do all it takes to attract clients on a regular basis.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will generate income by offering the following services and products
10. Sales Forecast
We are well positioned to take on the available market in Overland Park – Kansas and in the cyberspace and we are quite optimistic that we will meet our set target of generating enough income / profits from the first six months of operation and grow the business and our clientele base beyond Overland Park to other cities in the United States of America and in the cyberspace.
We have been able to examine the business analytics and enterprise software publishing market, we have analyzed our chances in the industry and we have been able to come up with the following sales forecast. Below are the sales projections for Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc., it is based on the location of our business and the services we will be offering;
- First Fiscal Year (FY1): $300,000
- Second Fiscal Year (FY2): $550,000
- Third Fiscal Year (FY3): $1.5 million
N.B : This projection was done based on what is obtainable in the industry and with the assumption that there won’t be any major economic meltdown and internet shutdown within the period stated above. Please note that the above projection might be lower and at the same time it might be higher.
11. Publicity and Advertising Strategy
We have been able to work with our brand and publicity consultants to help us map out publicity and advertising strategies that will help us walk our way into the heart of our target market. We are set to take the software as a services (SaaS) industry by storm which is why we have made provisions for effective publicity and advertisement of our IT tech startup company.
Below are the platforms we intend to leverage on to promote and advertise Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc.;
- Place adverts on both print (community – based newspapers and magazines) and electronic media platforms
- Sponsor relevant community – based events/programs
- Leverage on the internet and social media platforms like; Instagram, Facebook, twitter, YouTube, Google + et al to promote our brand
- Install our billboards in strategic locations all around Overland Park
- Ensure that all our workers wear our branded shirts and all our vehicles are well branded with our company’s logo et al.
12. Our Pricing Strategy
At Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. we will keep our product and service fees a little bit below the average market rate by keeping our overhead low and by collecting payment in advance. In addition, we will also offer special discounted rates to startups, nonprofits, cooperatives, and small social enterprises who want to develop software apps for their business.
- Payment Options
The payment policy adopted by Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is all inclusive because we are quite aware that different customers prefer different payment options as it suits them but at the same time, we will ensure that we abide by the financial rules and regulation of the United States of America.
Here are the payment options that Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will make available to her clients;
- Payment via bank transfer
- Payment with cash
- Payment via online bank transfer
- Payment via mobile money
- Payment via Point of Sales Machines (POS Machines)
- Payment via check
In view of the above, we have chosen banking platforms that will enable our client make payment without any stress on their part.
13. Startup Expenditure (Budget)
These are the areas we are looking towards spending our startup capital on;
- The total fee for incorporating the Business in the United States of America – $750.
- Legal expenses for obtaining licenses and permits as well as the accounting services P.O.S machines – $3,300.
- The total cost for payment of insurance policy covers (general liability, workers’ compensation and property casualty) coverage at a total premium – $9,400.
- The amount needed to acquire a suitable Office facility in a business district for 6 months (Re – Construction of the facility inclusive) – $40,000.
- Marketing expenses for the grand opening of Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. in the amount of $3,500 and as well as flyer printing (2,000 flyers at $0.04 per copy) for the total amount of $3,580.
- The total cost for hiring Business Consultant – $2,500
- The cost for equipping the office (computers, software apps and hardware such as Application-specific integrated circuit (ASIC) machines, internet server, printers, fax machines, furniture, telephones, filing cabins, safety gadgets and electronics et al) – $25,000
- The cost of launching our official website – $800
- Budget for paying at least two employees for 3 months and utility bills – $75,000
- Additional expenditure (Business cards, Signage, Adverts and Promotions et al) – $2,500
- Miscellaneous – $10,000
Going by the report from the research and feasibility studies, we will need about Two Hundred and Fifty Thousand US Dollars ($250,000) to set up a small scale but standard IT tech startup company in the United States of America.
Generating Funds/Startup Capital for Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is owned and managed by Joel Rogers. He may likely welcome partners later which is why he has decided to restrict the sourcing of the startup capital for the business to just three major sources.
- Generate part of the startup capital from personal savings
- Source for soft loans from family members and friends
- Apply for loan from the bank
N.B: We have been able to generate about $50,000 (Personal savings $40,000 and soft loan from family members $10,000) and we are at the final stages of obtaining a loan facility of $200,000 from our bank. All the papers and documents have been duly signed and submitted, the loan has been approved and any moment from now our account will be credited.
14. Sustainability and Expansion Strategy
The future of a business lies in the number of loyal customers that they have, the capacity and competence of their employees, their investment strategy and the business structure. If all of these factors are missing from a business (company), then it won’t be too long before the business closes shop.
One of our major goals of starting Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. is to build a business that will survive off its own cash flow without injecting finance from external sources once the business is officially running. We know that one of the ways of gaining approval and winning customers over is to offer our software as a services (SaaS) a little bit cheaper than what is obtainable in the market and we are prepared to survive on lower profit margin for a while.
Joel Rogers® Technologies, Inc. will make sure that the right foundation, structures and processes are put in place to ensure that our staff welfare are well taken of. Our company’s corporate culture is designed to drive our business to greater heights and training and retraining of our workforce is at the top burner of our business strategy.
As a matter of fact, profit-sharing arrangement will be made available to all our management staff and it will be based on their performance for a period of three years or more as determined by the board of the organization. We know that if that is put in place, we will be able to successfully hire and retain the best hands we can get in the industry; they will be more committed to help us build the business of our dreams.
Check List/Milestone
- Business Name Availability Check : Completed
- Business Incorporation: Completed
- Opening of Corporate Bank Accounts: Completed
- Opening Online Payment Platforms: Completed
- Application and Obtaining Tax Payer’s ID: In Progress
- Application for business license and permit: Completed
- Purchase of Insurance for the Business: Completed
- Conducting Feasibility Studies: Completed
- Leasing a standard and well positioned office facility in the heart of Overland Park – Kansas: Completed
- Generating part of the start up capital from the founder: Completed
- Applications for Loan from our Bankers: In Progress
- Writing of Business Plan: Completed
- Drafting of Employee’s Handbook: Completed
- Drafting of Contract Documents: In Progress
- Design of The Company’s Logo: Completed
- Printing of Promotional Materials: Completed
- Recruitment of employees: In Progress
- Purchase of the needed software applications, internet server, furniture, office equipment, electronic appliances and facility facelift: In progress
- Creating Official Website for the Company: In Progress
- Creating Awareness for the business (Business PR): In Progress
- Health and Safety and Fire Safety Arrangement: In Progress
- Establishing business relationship with vendors and key players in the industry: In Progress.
More on Technology
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Tips White Papers
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
- Write Your Business Plan | Part 1 Overview Video
- The Basics of Writing a Business Plan
- How to Use Your Business Plan Most Effectively
- 12 Reasons You Need a Business Plan
- The Main Objectives of a Business Plan
- What to Include and Not Include in a Successful Business Plan
- The Top 4 Types of Business Plans
- A Step-by-Step Guide to Presenting Your Business Plan in 10 Slides
- 6 Tips for Making a Winning Business Presentation
- 3 Key Things You Need to Know About Financing Your Business
- 12 Ways to Set Realistic Business Goals and Objectives
- How to Perfectly Pitch Your Business Plan in 10 Minutes
- Write Your Business Plan | Part 2 Overview Video
- How to Fund Your Business Through Friends and Family Loans and Crowdsourcing
- How to Fund Your Business Using Banks and Credit Unions
- How to Fund Your Business With an SBA Loan
- How to Fund Your Business With Bonds and Indirect Funding Sources
- How to Fund Your Business With Venture Capital
- How to Fund Your Business With Angel Investors
- How to Use Your Business Plan to Track Performance
- How to Make Your Business Plan Attractive to Prospective Partners
- Is This Idea Going to Work? How to Assess the Potential of Your Business.
- When to Update Your Business Plan
- Write Your Business Plan | Part 3 Overview Video
- How to Write the Management Team Section to Your Business Plan
- How to Create a Strategic Hiring Plan
- How to Write a Business Plan Executive Summary That Sells Your Idea
- How to Build a Team of Outside Experts for Your Business
- Use This Worksheet to Write a Product Description That Sells
- What Is Your Unique Selling Proposition? Use This Worksheet to Find Your Greatest Strength.
- How to Raise Money With Your Business Plan
- Customers and Investors Don't Want Products. They Want Solutions.
- Write Your Business Plan | Part 4 Overview Video
- 5 Essential Elements of Your Industry Trends Plan
- How to Identify and Research Your Competition
- Who Is Your Ideal Customer? 4 Questions to Ask Yourself.
- How to Identify Market Trends in Your Business Plan
- How to Define Your Product and Set Your Prices
- How to Determine the Barriers to Entry for Your Business
- How to Get Customers in Your Store and Drive Traffic to Your Website
- How to Effectively Promote Your Business to Customers and Investors
- Write Your Business Plan | Part 5 Overview Video
- What Equipment and Facilities to Include in Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Income Statement for Your Business Plan
- How to Make a Balance Sheet
- How to Make a Cash Flow Statement
- How to Use Financial Ratios to Understand the Health of Your Business
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Retail and Sales Businesses
- How to Make Realistic Financial Forecasts
- How to Write an Operations Plan for Manufacturers
- What Technology Needs to Include In Your Business Plan
- How to List Personnel and Materials in Your Business Plan
- The Role of Franchising
- The Best Ways to Follow Up on a Buisiness Plan
- The Best Books, Sites, Trade Associations and Resources to Get Your Business Funded and Running
- How to Hire the Right Business Plan Consultant
- Business Plan Lingo and Resources All Entrepreneurs Should Know
- How to Write a Letter of Introduction
- What To Put on the Cover Page of a Business Plan
- How to Format Your Business Plan
- 6 Steps to Getting Your Business Plan In Front of Investors
What Technology Needs to Include In Your Business Plan Listing tech infrastructure, software, and digital tools showcases your ability to streamline processes and enhance efficiency.
By Eric Butow Oct 27, 2023
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
This is part 10 / 12 of Write Your Business Plan: Section 5: Organizing Operations and Finances series.
Whatever business you are in, technology most likely plays a key role. Retailers place their orders faster and more accurately using computers and track their inventory, while other business owners make international deals thanks to computers and communication technology.
Related: Business Plan Tips
Other key technology that fits into your operations, such as that of a medical equipment manufacturer, should be included in the business plan. Explain how this technology is significant to your business and how it can separate you from your competitors.
Related: How to Write an Operations Plan for Retail and Sales Businesses
How much detail should you include about the technology you employ? We're living in a highly technical environment. That means you should explain some of the key technology that comes into play during your operations—in lay terms. You need to go into greater detail only if your business relies heavily on technology, sells technology, or utilizes some unique technology that is uncommon in your industry.
A Note of Caution
Stay up on technology, but also be careful. There are numerous ways unscrupulous folks can tap into intellectual property, such as recorded music or films. It is harder than ever to catch those who pirate—or steal—such protected properties. But if you are caught, you can get in real trouble. So be careful not to inadvertently use other people's music, images, and so on. Conversely, protect intellectual properties, and if you see your original material showing up elsewhere, contact an attorney.
Related: What Equipment and Facilities to Include in Your Business Plan
More in Write Your Business Plan
Section 1: the foundation of a business plan, section 2: putting your business plan to work, section 3: selling your product and team, section 4: marketing your business plan, section 5: organizing operations and finances, section 6: getting your business plan to investors.
Successfully copied link
- Business Process Improvement
- Data Driven Decision Making
- Data Migration
- Actionable Insights
- Data Integration
- Business Documents
- Streamline Process
- What Is Business Intelligence
- Data Transformation
- Software Integration
- Cloud Based
- Business Process Automation
- System Integration
- EDI Transactions
- Digital Transformation Strategy
- IT Strategy
- API Integration
- Enterprise Application
- Data Security
How To Create A Technology Plan In 8 Steps

Hanh Truong
Introduction to technology plan.
Many modern businesses are evolving technologically as the digital world continues to grow. To keep up with new demands and markets, brands are investing in online tools to streamline specific business functions. This includes digital platforms , such as inventory management software and data reporting systems. These solutions can help businesses of all sizes reach their goals and stay competitive in their industry. However, before allocating capital to these technologies, management teams need to strategize a technology plan.
What is Technology Planning?

Technology planning refers to the process of outlining the technical evolution of a business or its processes to achieve goals. Management teams and program directors will typically collaborate to decide which digital tools are beneficial for the business. For example, they may look for solutions that will help increase employee morale, improve customer service, or boost productivity. Generally, technology planning will also encompass technology forecasting, scheduling projections, and creating a technology roadmap. These activities will help top leaders identify what objectives the technical tools will achieve and when. It will also give brands insight into how their existing systems can evolve technologically to address future needs. By planning what tools are appropriate for a company, management teams can ensure that they are making the right investment. Additionally, planning will effectively empower the organization with key information about its performance.
8 Steps to Create a Technology Plan
Organizations that want to revamp their technology usage or upgrade to new digital tools should follow these steps to create a technology plan.
1. Create A Technology Planning Team
A technology plan should have ideas that reflect the entire organization. Therefore, creating a planning team that includes a wide range of employees across all departments is important. A typical planning committee will include a project manager, executive director, administrative assistant, accountant, and system administrator. When beginning the planning process, leaders should assign responsibilities and goals for each member. The team should also have a regular meeting schedule so they can collaborate and review the technology plan.
2. Examine Existing Technology
- What system works well?
- How does the company benefit from its current technology?
- Do the tech operations need improvements?
- What parts are replaceable and which are not?
- Are any repairs needed?
3. Outline Priorities of the Technology Plan
The team needs to identify the main goals of their technology plan. Generally, companies will prioritize their strategy to solve a problem, like replacing an obsolete legacy system. Sometimes, a brand may focus its plan on leveraging new opportunities. Businesses can determine what their priorities are by using their assessment from the previous step. That audit will help teams gain insight into issues in their existing tech infrastructure.
4. Identify Tech Solutions

Now that the team has an idea of what their tech goals are, they can explore different solutions. This step requires extensive research into various hardware, software, and other digital tools. A restaurant, for example, may look for specific inventory management software that can accommodate their growing list of ingredients.
5. Create A Budget for the Plan
A budget for the new tools needs to be created to protect the business's bottom line. It is recommended that the team breaks down the various costs of a system to accurately plan a budget. The team should consider the different long-term and short-term expenses. For example, most systems will have costs related to data storage, network, IT labor, and add-on features. The budget should have capital reserved for these various expenses.
6. Find a Tech Vendor

The team can then look for a vendor or tech tool that aligns with their needs and budget. Typically, software providers have scalable packages, in which brands can purchase specific features that will help them achieve their objectives. It is important that the team does comprehensive research and compares different vendors. This will ensure that the organization will invest in the right tools and prevent delays in its technology plan.
7. Develop a Timeline
After a vendor or technology partner is selected, the team needs to outline a timeline for implementation. This involves setting deadlines or benchmarks for integrating software and training employees on how to use it. A date should also be set for the assessment of the new technologies . On these days, the team should meet and examine the effectiveness of the system and their goal achievement progress.
8. Draft and Implement the Technology Plan

- Overview of the current tech system
- List of tools the company needs to purchase
- Vendor names
- Employee training process

3 Core Business Integration Strategies

4 Different Types of Cloud Computing Models and Services

6 Expert Tips for Small Business Record Keeping

Breaking Down Data Silos - 4 Key Tips

What Is Software Integration? Everything to Know

What is Trend Analysis in Business?
- CASE STUDIES

A Step-by-step Guide to Building Your Technology Implementation Plan
Time to leverage digital transformation for growth and competitive advantage read our 7-step guide to creating an enterprise technology implementation plan..
Niket Ashesh
In the world of enterprise business, stakes (and complexities) are high. When it comes to a new technology implementation plan , you need to make sure your implementation partner understands the unique challenges that large-scale organizations face.
When integrating new technologies and implementing new systems and software, the approach must be meticulously tailored to cater to the intricate dynamics of your specific enterprise.
We’re talking details, here.
As a leading digital tech consultancy , we are experts when it comes to guiding enterprises through the complexities of digital transformation in a way that ensures growth and competitive advantage .
This article outlines a step-by-step technology implementation plan , shedding light on the nuances of composable technology versus non-composable technology. Plus, how a holistic approach can facilitate seamless integration for enterprise businesses .

Understanding the Enterprise Ecosystem
The first step in your technology implementation plan is to understand the needs of your enterprise ecosystem.
Enterprise businesses most often operate with
multiple layers of management,
diverse departments, and
a broad spectrum of stakeholders.
A lot of moving pieces!
As you can imagine, this level of complexity requires a strategic approach that acknowledges and integrates all of these operational elements.
In our experience, the following are the most critical focus areas for enterprises implementing new systems: Stakeholder Alignment You will want to make sure all stakeholders are aligned, from C-level executives to department heads, ensuring that the technology implementation plan resonates across all levels of your organization.
Complex System Integration Enterprises typically have established systems in place. This requires careful integration of new technologies so they work with existing systems, ensuring minimal disruption and maximum efficiency.
Scalability and Flexibility Given the size and scope of enterprise businesses, we recommend that you emphasize scalable and flexible solutions. This approach allows for growth and adaptation as an enterprise evolves.
Data Security and Compliance Enterprises are often subject to stringent data security and regulatory compliance requirements. Our technology implementation plans are designed to meet these high standards, and we suggest that your implementation partner take the same approach.
Customized Solutions for Diverse Needs No two enterprises are the same, so your implementation partner should offer customized solutions that cater to your enterprise's specific needs, challenges, and goals.

Having taken all of this into consideration, we then move through the following seven-step technology implementation plan.
Step 1: Initial Assessment and Strategy Development
What are your business needs?
The first step in any new technology implementation plan should involve a thorough assessment of your enterprise's current digital landscape.
You’ll want your implementation partner to
study your business model,
understand your existing technology stack, and
clarify your long-term goals.
This assessment is crucial in aligning your new technology implementation plan with your business objectives.
Key activities in your initial assessment and strategy development:
Conduct workshops and interviews with key stakeholders
Analyze current technology infrastructure and capabilities
Identify gaps and potential areas for digital enhancement
|
Get our free accessibility checklist to guide your efforts for getting compliant and doing the right thing. Plus, receive real feedback from us to help you on your next steps.
 Step 2: Choosing Composable vs Non-Composable Technologies What type of technology do you need? As part of our digital technology consultancy, we make sure that our clients understand the importance of choosing between composable and non-composable technologies based on their enterprise's unique needs. Spoiler alert: It’s not just about making the choice between either composable or non-composable. If you’re building a system from scratch, that may be the exception. But who is actually doing that these days? Make the components of your system composable where it has value in these two areas- It solves issues you have It gives you a competitive advantage This is the core of composable technology; it’s faster, less risky, and adds value quickly. In essence, here’s the differences between the two: Composable Technology Composable technologies are modular and flexible. They can be easily integrated or replaced without affecting the entire system, making them ideal for businesses looking for agility and scalability in a fast-paced market. ➡️ Composable technology is ideal for businesses undergoing rapid transformation or those that need to quickly adjust to market changes. Non-Composable Technology Non-composable technologies are often more stable and rigid (monolithic) than composable technologies. ➡️ Non-composable technology is generally preferred for enterprises with unchanging processes where consistency is the key priority. Your implementation partner may… Evaluate your business's adaptability and future growth plans. Recommend composable technologies for dynamic, fast-evolving enterprises. Suggest non-composable solutions for businesses with fixed, well-established processes. Choosing between composable and monolithic technology is an important piece of your technology implementation plan, and there are many factors that should play into the decision. Remember though - it’s not either/or. Your solution does not have to be 100% composable vs non-composable. READ MORE: A 5-Step Process for Shifting to a Composable Commerce Platform  Step 3: Crafting a Customized Technology Implementation Plan (aka Digital Transformation Roadmap) What do you want to achieve? Developing a new technology implementation plan (or digital transformation roadmap ) means considering every facet of your business to ensure that your final plan is comprehensive, achievable, and aligned with the strategic goals of your enterprise. Let’s look at an implementation plan example: The following areas are key pieces to a well-organized plan that can be implemented cost-effectively. Scope Definition : Clearly outline the project's scope, including the technologies to be implemented and the business areas they will impact. Timeline and Milestones : Develop a realistic timeline with key milestones, ensuring timely progress and accountability. Budgeting : Set a budget that reflects the project's scope and your enterprise's financial capacity. Resource Allocation : Identify and allocate internal and external resources necessary for the project. Risk Management Plan : Anticipate potential challenges and devise strategies to mitigate them.  Step 4: Employee Training and Change Management What do you need for the transition? One critical and often overlooked aspect of the software implementation process and integration is managing the human element. Our consultancy provides comprehensive training and change management support to ensure our clients’ teams are well-equipped to adapt to the new technologies being integrated into the enterprise. Your implementation partner should offer the same service. The following are some of the key activities for employee training and change management: Develop customized training programs for different user groups. Establish a change management team to guide employees through the transition. Create communication plans to keep all stakeholders informed and engaged throughout the digital transformation process.  Step 5: Implementation and Continuous Monitoring How will you stay on track? With a solid plan in place, you’re ready to move towards the implementation phase. Your implementation partner should be willing to become an extension of your enterprise to ensure the integration is smooth and disruption-free. There are steps to be taken during and following implementation: During Implementation Monitor progress. Make adjustments as necessary to stay on track. Provide ongoing support to resolve any technical or operational issues. Post-Implementation Conduct regular reviews to ensure the technology aligns with your business goals. Offer continuous monitoring and support services.  Step 6: Evaluation and Iterative Improvement What will you need to measure? Post-implementation, the focus should move to evaluating the impact of your new technologies. Our goal is always to ensure that the new technology integration not only meets, but exceeds our clients’ expectations, driving growth and efficiency. The steps we take for our evaluation include: Measuring performance against pre-defined KPIs. Gathering feedback from users and stakeholders. Identifying areas for improvement and planning iterative enhancements. How will you stay ahead? The final step in your technology implementation plan is to prepare your enterprise for future technological advancements. As your implementation partner, we would help you to establish a framework for scaling your new technologies and integrating future innovations seamlessly. On an ongoing basis, as your digital consultancy partner, we would: Conduct regular technology trend analyses. Develop a scalable and adaptable IT architecture. Foster a culture of continuous innovation and learning.  For enterprise businesses, integrating new technologies is not just an IT initiative; it's a strategic move that impacts the entire organization . Your strategic implementation partner should demonstrate a commitment to ensuring your enterprise not only integrates new technologies effectively but also is poised to thrive in today’s ever-evolving digital landscape . At Alpha Solutions, we take a holistic approach that considers the strategic business goals of your enterprise at each step of your digital transformation journey. We recommend you follow these seven steps, and answer the following questions: ✅ Step 1: Initial Assessment and Strategy Development What are your business needs? ✅ Step 2: Choosing Composable vs Non-Composable Technologies What type of technology do you need? ✅ Step 3: Crafting a Customized Technology Implementation Plan What do you want to achieve? ✅ Step 4: Employee Training and Change Management What do you need for the transition? ✅ Step 5: Implementation and Continuous Monitoring How will you stay on track? ✅ Step 6: Evaluation and Iterative Improvement What will you need to measure? ✅ Step 7: Scaling and Future-Proofing How will you stay ahead? Going lightyears beyond mere technology integration, we focus on how your software implementation plan may strategically drive business growth, enhance operational efficiency, and give your enterprise business a competitive edge in your industry. Let us lead your enterprise toward a strategic advantage for sustainable growth and success. Contact us for a chat today.  A 5-STEP PROCESS FOR SHIFTING TO A COMPOSABLE COMMERCE PLATFORM THE ROLE OF AN IMPLEMENTATION PARTNER (+ HOW TO FIND ONE) HOW TO CREATE A SUSTAINABLE DIGITAL TRANSFORMATION ROADMAPAlpha Solutions 221 River St., 9th Fl Hoboken NJ 07030 USA +1 (347) 338-2220 [email protected] Alpha Solutions 16415 Addison Road Suite 400 Addison, TX 75001 USA +1 (347) 338-2220 [email protected] LOS ANGELES Alpha Solutions 15303 Ventura Boulevard Suite 900 Sherman Oaks CA 91403 USA +1 (347) 338-2220 [email protected] Alpha Solutions Gothersgade 14, 4th floor DK-1123 Copenhagen K Denmark +45 70 20 65 38 [email protected] Alpha Solutions Drammensveien 130, C19 0277 Oslo Norway +47 900 54 940 [email protected]  Privacy policy LinkedIn US
What Is a Business Plan?Understanding business plans, how to write a business plan, common elements of a business plan, the bottom line, business plan: what it is, what's included, and how to write one. Adam Hayes, Ph.D., CFA, is a financial writer with 15+ years Wall Street experience as a derivatives trader. Besides his extensive derivative trading expertise, Adam is an expert in economics and behavioral finance. Adam received his master's in economics from The New School for Social Research and his Ph.D. from the University of Wisconsin-Madison in sociology. He is a CFA charterholder as well as holding FINRA Series 7, 55 & 63 licenses. He currently researches and teaches economic sociology and the social studies of finance at the Hebrew University in Jerusalem. :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/adam_hayes-5bfc262a46e0fb005118b414.jpg)
A business plan is a document that outlines a company's goals and the strategies to achieve them. It's valuable for both startups and established companies. For startups, a well-crafted business plan is crucial for attracting potential lenders and investors. Established businesses use business plans to stay on track and aligned with their growth objectives. This article will explain the key components of an effective business plan and guidance on how to write one. Key Takeaways
Investopedia / Ryan Oakley Any new business should have a business plan in place before beginning operations. Banks and venture capital firms often want to see a business plan before considering making a loan or providing capital to new businesses. Even if a company doesn't need additional funding, having a business plan helps it stay focused on its goals. Research from the University of Oregon shows that businesses with a plan are significantly more likely to secure funding than those without one. Moreover, companies with a business plan grow 30% faster than those that don't plan. According to a Harvard Business Review article, entrepreneurs who write formal plans are 16% more likely to achieve viability than those who don't. A business plan should ideally be reviewed and updated periodically to reflect achieved goals or changes in direction. An established business moving in a new direction might even create an entirely new plan. There are numerous benefits to creating (and sticking to) a well-conceived business plan. It allows for careful consideration of ideas before significant investment, highlights potential obstacles to success, and provides a tool for seeking objective feedback from trusted outsiders. A business plan may also help ensure that a company’s executive team remains aligned on strategic action items and priorities. While business plans vary widely, even among competitors in the same industry, they often share basic elements detailed below. A well-crafted business plan is essential for attracting investors and guiding a company's strategic growth. It should address market needs and investor requirements and provide clear financial projections. While there are any number of templates that you can use to write a business plan, it's best to try to avoid producing a generic-looking one. Let your plan reflect the unique personality of your business. Many business plans use some combination of the sections below, with varying levels of detail, depending on the company. The length of a business plan can vary greatly from business to business. Regardless, gathering the basic information into a 15- to 25-page document is best. Any additional crucial elements, such as patent applications, can be referenced in the main document and included as appendices. Common elements in many business plans include:
Investors want to see a clear exit strategy, expected returns, and a timeline for cashing out. It's likely a good idea to provide five-year profitability forecasts and realistic financial estimates. 2 Types of Business PlansBusiness plans can vary in format, often categorized into traditional and lean startup plans. According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Why Do Business Plans Fail?A business plan isn't a surefire recipe for success. The plan may have been unrealistic in its assumptions and projections. Markets and the economy might change in ways that couldn't have been foreseen. A competitor might introduce a revolutionary new product or service. All this calls for building flexibility into your plan, so you can pivot to a new course if needed. How Often Should a Business Plan Be Updated?How frequently a business plan needs to be revised will depend on its nature. Updating your business plan is crucial due to changes in external factors (market trends, competition, and regulations) and internal developments (like employee growth and new products). While a well-established business might want to review its plan once a year and make changes if necessary, a new or fast-growing business in a fiercely competitive market might want to revise it more often, such as quarterly. What Does a Lean Startup Business Plan Include?The lean startup business plan is ideal for quickly explaining a business, especially for new companies that don't have much information yet. Key sections may include a value proposition , major activities and advantages, resources (staff, intellectual property, and capital), partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources. A well-crafted business plan is crucial for any company, whether it's a startup looking for investment or an established business wanting to stay on course. It outlines goals and strategies, boosting a company's chances of securing funding and achieving growth. As your business and the market change, update your business plan regularly. This keeps it relevant and aligned with your current goals and conditions. Think of your business plan as a living document that evolves with your company, not something carved in stone. University of Oregon Department of Economics. " Evaluation of the Effectiveness of Business Planning Using Palo Alto's Business Plan Pro ." Eason Ding & Tim Hursey. Bplans. " Do You Need a Business Plan? Scientific Research Says Yes ." Harvard Business Review. " Research: Writing a Business Plan Makes Your Startup More Likely to Succeed ." Harvard Business Review. " How to Write a Winning Business Plan ." U.S. Small Business Administration. " Write Your Business Plan ." SCORE. " When and Why Should You Review Your Business Plan? " :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/GettyImages-1456193345-2cc8ef3d583f42d8a80c8e631c0b0556.jpg)
How To Write the Operations Plan Section of the Business PlanSusan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses. :max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg) Stage of Development SectionProduction process section, the bottom line, frequently asked questions (faqs). The operations plan is the section of your business plan that gives an overview of your workflow, supply chains, and similar aspects of your business. Any key details of how your business physically produces goods or services will be included in this section. You need an operations plan to help others understand how you'll deliver on your promise to turn a profit. Keep reading to learn what to include in your operations plan. Key Takeaways
In your business plan , the operations plan section describes the physical necessities of your business's operation, such as your physical location, facilities, and equipment. Depending on what kind of business you'll be operating, it may also include information about inventory requirements, suppliers, and a description of the manufacturing process. Keeping focused on the bottom line will help you organize this part of the business plan. Think of the operating plan as an outline of the capital and expense requirements your business will need to operate from day to day. You need to do two things for the reader of your business plan in the operations section: show what you've done so far to get your business off the ground and demonstrate that you understand the manufacturing or delivery process of producing your product or service. When you're writing this section of the operations plan, start by explaining what you've done to date to get the business operational, then follow up with an explanation of what still needs to be done. The following should be included: Production WorkflowA high-level, step-by-step description of how your product or service will be made, identifying the problems that may occur in the production process. Follow this with a subsection titled "Risks," which outlines the potential problems that may interfere with the production process and what you're going to do to negate these risks. If any part of the production process can expose employees to hazards, describe how employees will be trained in dealing with safety issues. If hazardous materials will be used, describe how these will be safely stored, handled, and disposed. Industry Association MembershipsShow your awareness of your industry's local, regional, or national standards and regulations by telling which industry organizations you are already a member of and which ones you plan to join. This is also an opportunity to outline what steps you've taken to comply with the laws and regulations that apply to your industry. Supply ChainsAn explanation of who your suppliers are and their prices, terms, and conditions. Describe what alternative arrangements you have made or will make if these suppliers let you down. Quality ControlAn explanation of the quality control measures that you've set up or are going to establish. For example, if you intend to pursue some form of quality control certification such as ISO 9000, describe how you will accomplish this. While you can think of the stage of the development part of the operations plan as an overview, the production process section lays out the details of your business's day-to-day operations. Remember, your goal for writing this business plan section is to demonstrate your understanding of your product or service's manufacturing or delivery process. When writing this section, you can use the headings below as subheadings and then provide the details in paragraph format. Leave out any topic that does not apply to your particular business. Do an outline of your business's day-to-day operations, including your hours of operation and the days the business will be open. If the business is seasonal, be sure to say so. The Physical PlantDescribe the type, site, and location of premises for your business. If applicable, include drawings of the building, copies of lease agreements, and recent real estate appraisals. You need to show how much the land or buildings required for your business operations are worth and tell why they're important to your proposed business. The same goes for equipment. Besides describing the equipment necessary and how much of it you need, you also need to include its worth and cost and explain any financing arrangements. Make a list of your assets , such as land, buildings, inventory, furniture, equipment, and vehicles. Include legal descriptions and the worth of each asset. Special RequirementsIf your business has any special requirements, such as water or power needs, ventilation, drainage, etc., provide the details in your operating plan, as well as what you've done to secure the necessary permissions. State where you're going to get the materials you need to produce your product or service and explain what terms you've negotiated with suppliers. Explain how long it takes to produce a unit and when you'll be able to start producing your product or service. Include factors that may affect the time frame of production and describe how you'll deal with potential challenges such as rush orders. Explain how you'll keep track of inventory . FeasibilityDescribe any product testing, price testing, or prototype testing that you've done on your product or service. Give details of product cost estimates. Once you've worked through this business plan section, you'll not only have a detailed operations plan to show your readers, but you'll also have a convenient list of what needs to be done next to make your business a reality. Writing this document gives you a chance to crystalize your business ideas into a clear checklist that you can reference. As you check items off the list, use it to explain your vision to investors, partners, and others within your organization. What is an operations plan?An operations plan is one section of a company's business plan. This section conveys the physical requirements for your business's operations, including supply chains, workflow , and quality control processes. What is the main difference between the operations plan and the financial plan?The operations plan and financial plan tackle similar issues, in that they seek to explain how the business will turn a profit. The operations plan approaches this issue from a physical perspective, such as property, routes, and locations. The financial plan explains how revenue and expenses will ultimately lead to the business's success. Want to read more content like this? Sign up for The Balance's newsletter for daily insights, analysis, and financial tips, all delivered straight to your inbox every morning! Inc. Power Partner Awards Application Deadline This Friday, July 12 Apply Now
Inc. Premium How to Write the Perfect Business Plan: A Comprehensive GuideThinking of starting a business here's the best step-by-step template for writing the perfect business plan when creating your startup..  Maybe you think you don't need a step-by-step guide to writing a great business plan . Maybe you think you don't need a template for writing a business plan. After all, some entrepreneurs succeed without writing a business plan. With great timing, solid business skills, entrepreneurial drive, and a little luck , some founders build thriving businesses without creating even an informal business plan . But the odds are greater that those entrepreneurs will fail. Does a business plan make startup success inevitable? Absolutely not. But great planning often means the difference between success and failure. Where your entrepreneurial dreams are concerned, you should do everything possible to set the stage for success. And that's why a great business plan is one that helps you succeed . The following is a comprehensive guide to creating a great business plan. We'll start with an overview of key concepts. Then we'll look at each section of a typical business plan: Executive SummaryOverview and objectives, products and services, market opportunities, sales and marketing.
Management TeamFinancial analysis. So first let's gain a little perspective on why you need a business plan. Key ConceptsMany business plans are fantasies. That's because many aspiring entrepreneurs see a business plan as simply a tool--filled with strategies and projections and hyperbole--that will convince lenders or investors the business makes sense. That's a huge mistake. First and foremost, your business plan should convince you that your idea makes sense--because your time, your money, and your effort are on the line. So a solid business plan should be a blueprint for a successful business . It should flesh out strategic plans, develop marketing and sales plans, create the foundation for smooth operations, and maybe--just maybe--persuade a lender or investor to jump on board. For many entrepreneurs, developing a business plan is the first step in the process of deciding whether to actually start a business. Determining if an idea fails on paper can help a prospective founder avoid wasting time and money on a business with no realistic hope of success. So, at a minimum, your plan should:
A good business plan delves into each of the above categories, but it should also accomplish other objectives. Most of all, a good business plan is convincing . It proves a case. It provides concrete, factual evidence showing your idea for a business is in fact sound and reasonable and has every chance of success. Who must your business plan convince? First and foremost, your business plan should convince you that your idea for a business is not just a dream but can be a viable reality. Entrepreneurs are by nature confident, positive, can-do people. After you objectively evaluate your capital needs, products or services, competition, marketing plans, and potential to make a profit, you'll have a much better grasp on your chances for success. And if you're not convinced, fine: Take a step back and refine your ideas and your plans. Who can your business plan convince? 1. Potential sources of financing. If you need seed money from a bank or friends and relatives, your business plan can help you make a great case. Financial statements can show where you have been. Financial projections describe where you plan to go. Your business plan shows how you will get there. Lending naturally involves risk, and a great business plan can help lenders understand and quantity that risk, increasing your chances for approval. 2. Potential partners and investors. Where friends and family are concerned, sharing your business plan may not be necessary (although it certainly could help). Other investors--including angel investors or venture capitalists--generally require a business plan in order to evaluate your business. 3. Skilled employees . When you need to attract talent, you need something to show prospective employees since you're still in the startup phase. Early on, your business is more of an idea than a reality, so your business plan can help prospective employees understand your goals--and, more important, their place in helping you achieve those goals. 4. Potential joint ventures. Joint ventures are like partnerships between two companies. A joint venture is a formal agreement to share the work--and share the revenue and profit. As a new company, you will likely be an unknown quantity in your market. Setting up a joint venture with an established partner could make all the difference in getting your business off the ground. But above all, your business plan should convince you that it makes sense to move forward. As you map out your plan, you may discover issues or challenges you had not anticipated. Maybe the market isn't as large as you thought. Maybe, after evaluating the competition, you realize your plan to be the low-cost provider isn't feasible since the profit margins will be too low to cover your costs. Or you might realize the fundamental idea for your business is sound, but how you implement that idea should change. Maybe establishing a storefront for your operation isn't as cost-effective as taking your products directly to customers--not only will your operating costs be lower, but you can charge a premium since you provide additional customer convenience. Think of it this way. Successful businesses do not remain static. They learn from mistakes, and adapt and react to changes: changes in the economy, the marketplace, their customers, their products and services, etc. Successful businesses identify opportunities and challenges and react accordingly. Creating a business plan lets you spot opportunities and challenges without risk. Use your plan to dip your toe in the business water. It's the perfect way to review and revise your ideas and concepts before you ever spend a penny. Many people see writing a business plan as a "necessary evil" required to attract financing or investors. Instead, see your plan as a no-cost way to explore the viability of your potential business and avoid costly mistakes. Now let's look at the first section of your business plan: The Executive Summary. The Executive Summary is a brief outline of the company's purpose and goals. While it can be tough to fit on one or two pages, a good Summary includes:
I know that seems like a lot, and that's why it's so important you get it right. The Executive Summary is often the make-or-break section of your business plan. A great business solves customer problems. If your Summary cannot clearly describe, in one or two pages, how your business will solve a particular problem and make a profit, then it's very possible the opportunity does not exist--or your plan to take advantage of a genuine opportunity is not well developed. So think of it as a snapshot of your business plan. Don't try to "hype" your business--focus on helping a busy reader get a great feel for what you plan to do, how you plan to do it, and how you will succeed. Since a business plan should above all help you start and grow your business, your Executive Summary should first and foremost help you do the following. 1. Refine and tighten your concept. Think of it as a written elevator pitch (with more detail, of course). Your Summary describes the highlights of your plan, includes only the most critical points, and leaves out less important issues and factors. As you develop your Summary, you will naturally focus on the issues that contribute most to potential success. If your concept is too fuzzy, too broad, or too complicated, go back and start again. Most great businesses can be described in several sentences, not several pages. 2. Determine your priorities. Your business plan walks the reader through your plan. What ranks high in terms of importance? Product development? Research? Acquiring the right location? Creating strategic partnerships? Your Summary can serve as a guide to writing the rest of your plan. 3. Make the rest of the process easy. Once your Summary is complete, you can use it as an outline for the rest of your plan. Simply flesh out the highlights with more detail. Then work to accomplish your secondary objective by focusing on your readers. Even though you may be creating a business plan solely for your own purposes, at some point you may decide to seek financing or to bring on other investors, so make sure your Summary meets their needs as well. Work hard to set the stage for the rest of the plan. Let your excitement for your idea and your business shine through. In short, make readers want to turn the page and keep reading. Just make sure your sizzle meets your steak by providing clear, factual descriptions. How? The following is how an Executive Summary for a bicycle rental store might read. Introduction Blue Mountain Cycle Rentals will offer road and mountain bike rentals in a strategic location directly adjacent to an entrance to the George Washington National Forest. Our primary strategy is to develop Blue Mountain Cycle Rentals as the most convenient and cost-effective rental alternative for the thousands of visitors who flock to the area each year. Once underway, we will expand our scope and take advantage of high-margin new equipment sales and leverage our existing labor force to sell and service those products. Within three years we intend to create the area's premier destination for cycling enthusiasts. Company and Management Blue Mountain Cycle Rentals will be located at 321 Mountain Drive, a location providing extremely high visibility as well as direct entry and exit from a primary national park access road. The owner of the company, Marty Cycle, has over 20 years experience in the bicycle business, having served as a product manager for Acme Cycles as well as the general manager of Epic Cycling. Because of his extensive industry contacts, initial equipment inventory will be purchased at significant discounts from OEM suppliers as well by sourcing excess inventory from shops around the country. Because of the somewhat seasonal nature of the business, part-time employees will be hired to handle spikes in demand. Those employees will be attracted through competitive wages as well as discounts products and services. 460,000 people visited the George Washington National Forest during the last 12 months. While the outdoor tourism industry as a whole is flat, the park expects its number of visitors to grow over the next few years.
The market potential inherent in those visitors is substantial. According to third-party research data, approximately 30 percent of all cyclists would rather rent than transport their own bicycles, especially those who are visiting the area for reasons other than cycling. Competitive Advantages The cycling shops located in Harrisonburg, VA, are direct and established competitors. Our two primary competitive advantages will be location and lower costs. Our location is also a key disadvantage where non-park rentals are concerned. We will overcome that issue by establishing a satellite location in Harrisonburg for enthusiasts who wish to rent bicycles to use in town or on other local trails. We will also use online tools to better engage customers, allowing them to reserve and pay online as well as create individual profiles regarding sizes, preferences, and special needs. Financial Projections Blue Mountain Cycle Rentals expects to earn a modest profit by year two based on projected sales. Our projections are based on the following key assumptions:
We project first-year revenue of $720,000 and a 10 percent growth rate for the next two years. Direct cost of sales is projected to average 60 percent of gross sales, including 50 percent for the purchase of equipment and 10 percent for the purchase of ancillary items. Net income is projected to reach $105,000 in year three as sales increase and operations become more efficient. And so on ... Keep in mind this is just a made-up example of how your Summary might read. Also keep in mind this example focused on the rental business, so a description of products was not included. (They'll show up later.) If your business will manufacture or sell products, or provide a variety of services, then be sure to include a Products and Services section in your Summary. (In this case the products and services are obvious, so including a specific section would be redundant.) Bottom line: Provide some sizzle in your Executive Summary, but make sure you show a reasonable look at the steak, too. Providing an overview of your business can be tricky, especially when you're still in the planning stages. If you already own an existing business, summarizing your current operation should be relatively easy; it can be a lot harder to explain what you plan to become . So start by taking a step back. Think about what products and services you will provide, how you will provide those items, what you need to have in order to provide those items, exactly who will provide those items, and most important, whom you will provide those items to. Consider our bicycle rental business example. It's serves retail customers. It has an online component, but the core of the business is based on face-to-face transactions for bike rentals and support. So you'll need a physical location, bikes, racks and tools and supporting equipment, and other brick-and-mortar related items. You'll need employees with a very particular set of skills to serve those customers, and you'll need an operating plan to guide your everyday activities. Sound like a lot? It boils down to:
In our example, defining the above is fairly simple. You know what you will provide to meet your customer's needs. You will of course need a certain quantity of bikes to service demand, but you will not need a number of different types of bikes. You need a retail location, furnished to meet the demands of your business. You need semi-skilled employees capable of sizing, customizing, and repairing bikes. And you know your customers: cycling enthusiasts. In other businesses and industries, answering the above questions can be more difficult. If you open a restaurant, what you plan to serve will in some ways determine your labor needs, the location you choose, the equipment you need to purchase. And, most important, it will help define your customer. Changing any one element may change other elements; if you cannot afford to purchase expensive kitchen equipment, you may need to adapt your menu accordingly. If you hope to attract an upscale clientele, you may need to invest more in purchasing a prime location and creating an appealing ambience. So where do you start? Focus on the basics first:
If you are still stuck, try answering these questions. Some may pertain to you; others may not.
Once you work through this list you will probably end up with a lot more detail than is necessary for your business plan. That is not a problem: Start summarizing the main points. For example, your Business Overview and Objectives section could start something like this: History and Vision Blue Mountain Cycle Rentals is a new retail venture that will be located at 321 Mountain Drive, directly adjacent to an extremely popular cycling destination. Our initial goal is to become the premier provider for bicycle rentals. We will then leverage our customer base and position in the market to offer new equipment sales as well as comprehensive maintenance and service, custom equipment fittings, and expert trail advice.
Keys to Success
You could certainly include more detail in each section; this is simply a quick guide. And if you plan to develop a product or service, you should thoroughly describe the development process as well as the end result. The key is to describe what you will do for your customers--if you can't, you won't have any customers. In the Products and Services section of your business plan, you will clearly describe--yep--the products and services your business will provide. Keep in mind that highly detailed or technical descriptions are not necessary and definitely not recommended. Use simple terms and avoid industry buzzwords. On the other hand, describing how the company's products and services will differ from the competition is critical. So is describing why your products and services are needed if no market currently exists. (For example, before there was Federal Express, overnight delivery was a niche business served by small companies. FedEx had to define the opportunity for a new, large-scale service and justify why customers needed--and would actually use --that service.) Patents, copyrights, and trademarks you own or have applied for should also be listed in this section. Depending on the nature of your business, your Products and Services section could be very long or relatively short. If your business is product-focused, you will want to spend more time describing those products. If you plan to sell a commodity item and the key to your success lies in, say, competitive pricing, you probably don't need to provide significant product detail. Or if you plan to sell a commodity readily available in a variety of outlets, the key to your business may not be the commodity itself but your ability to market in a more cost-effective way than your competition. But if you're creating a new product (or service), make sure you thoroughly explain the nature of the product, its uses, and its value, etc.--otherwise your readers will not have enough information to evaluate your business. Key questions to answer:
In the cycling rental business example we've been using, products and services could be a relatively simple section to complete or it could be fairly involved. It depends on the nature of the products the company plans to rent to customers. If Blue Mountain Cycling Rentals plans to market itself as a provider of high-end bikes, describing those bikes--and the sources for those bikes--is important, since "high-end cycling rentals" is intended to be a market differentiation. If the company plans to be the low-cost provider, then describing specific brands of equipment is probably not necessary. Also, keep in mind that if a supplier runs out of capacity--or goes out of business altogether--you may not have a sufficient supply to meet your demand. Plan to set up multiple vendor or supplier relationships, and describe those relationships fully. Remember, the primary goal of your business plan is to convince you that the business is viable--and to create a road map for you to follow. The Products and Services section for our cycling rental business could start something like this: Product Description Blue Mountain Cycle Rentals will provide a comprehensive line of bicycles and cycling equipment for all ages and levels of ability. Since the typical customer seeks medium-quality equipment and excellent services at competitive prices, we will focus on providing brands like Trek bikes, Shimano footwear, and Giro helmets. These manufacturers have a widespread reputation as mid- to high-level quality, unlike equipment typically found in the rental market. The following is a breakdown of anticipated rental price points, per day and per week:
Competition Blue Mountain Cycle Rentals will have clear advantages over its primary competitors, the bike shops located in Harrisonburg, VA:
Future Products Expansion will allow us to move product offerings into new equipment sales. We will also explore maintenance and fitting services, leveraging our existing maintenance staff to provide value-added services at a premium price. When you draft your Products and Services section, think of your reader as a person who knows little to nothing about your business. Be clear and to the point. Think of it this way: The Products and Services section answers the "what" question for your business. Make sure you fully understand the "what" factor; you may run the business, but your products and services are its lifeblood. Market research is critical to business success. A good business plan analyzes and evaluates customer demographics, purchasing habits, buying cycles, and willingness to adopt new products and services. The process starts with understanding your market and the opportunities inherent in that market. And that means you'll need to do a little research. Before you start a business you must be sure there is a viable market for what you plan to offer. That process requires asking, and more importantly answering, a number of questions. The more thoroughly you answer the following questions, the better you will understand your market. Start by evaluating the market at a relatively high level, answering some high-level questions about your market and your industry:
Fortunately, you've already done some of the legwork. You've already defined and mapped out your products and services. The Market Opportunities section provides a sense-check of that analysis, which is particularly important since choosing the right products and services is such a critical factor in business success. But your analysis should go further: Great products are great, but there still must be a market for those products. (Ferraris are awesome, but you're unlikely to sell many where I live.) So let's dig deeper and quantify your market. Your goal is to thoroughly understand the characteristics and purchasing ability of potential customers in your market. A little Googling can yield a tremendous amount of data. For the market you hope to serve, determine:
The key is to understand the market in general terms and then to dig deeper to understand whether there are specific segments within that market--the segments you plan to target--that can become customers and support the growth of your business. Also keep in mind that if you plan to sell products online the global marketplace is incredibly crowded and competitive. Any business can sell a product online and ship that product around the world. Don't simply assume that just because "the bicycle industry is a $62 billion business" (a number I just made up) that you can capture a meaningful percentage of that market. On the other hand, if you live in an area with 50,000 people and there's only one bicycle shop, you may be able to enter that market and attract a major portion of bicycle customers in your area. Always remember it's much easier to serve a market you can define and quantify. After you complete your research you may feel a little overwhelmed. While data is good, and more data is great, sifting through and making sense of too much data can be daunting. For the purposes of your business plan, narrow your focus and focus on answering these main questions:
The Market Opportunities section for our cycling rental business could start something like this: Market Summary Consumer spending on cycling equipment reached $9,250,000 in the states of VA, WV, MD, and NC last year. While we expect sales to rise, for the purposes of performing a conservative analysis we have projected a zero growth rate for the next three years. In those states 2,500,000 people visited a national forest last year. Our target market includes customers visiting the Shenandoah National Forest; last year 120,000 people visited the area during spring, summer, and fall months. Over time, however, we do expect equipment rentals and sales to increase as the popularity of cycling continues to rise. In particular we forecast a spike in demand in 2015 since the national road racing championships will be held in Richmond, VA. Market Trends Participation and population trends favor our venture:
Market Growth According to the latest studies, recreation spending in our target market has grown by 14 percent per year for the past three years. In addition, we anticipate greater than industry-norm growth rates for cycling in the area due to the increase in popularity of cycling events like the Alpine Loop Gran Fondo. Market Needs Out target market has one basic need: The availability to source bicycle rentals at a competitive price. Our only other competition are the bike shops in Harrisonburg, VA, and our location will give us a competitive advantage over those and other companies who try to serve our market. You may want to add other categories to this section based on your particular industry. For example, you might decide to provide information about Market Segments. In our case, the cycling rental business does not require much segmentation. Rentals are typically not broken down into segments like "inexpensive," "midrange," and "high-end." For the most part rental bikes are more of a commodity. (Although you'll notice in our Products and Services section, we decided to provide "high-end" rentals.) But say you decide to open a clothing store. You could focus on high fashion, or children's clothes, or outdoor wear, or casual--you could segment the market in a number of ways. If that's the case, provide detail on segmentation that supports your plan. The key is to define your market--and then show how you will serve your market. Providing great products and services is wonderful, but customers must actually know those products and services exist. That's why marketing plans and strategies are critical to business success. (Duh, right?) But keep in mind marketing is not just advertising. Marketing--whether advertising, public relations, promotional literature, etc.--is an investment in the growth of your business. Like any other investment you would make, money spent on marketing must generate a return. (Otherwise why make the investment?) While that return could simply be greater cash flow, good marketing plans result in higher sales and profits. So don't simply plan to spend money on a variety of advertising efforts. Do your homework and create a smart marketing program . Here are some of the basic steps involved in creating your marketing plan:
Then focus on providing detail and backup for your marketing plan.
The Sales and Marketing section for our cycling rental business could start something like this: Target Market The target market for Blue Mountain Cycling Rentals is western VA, eastern WV, southwestern MD, and northern NC. While customers in the counties surrounding the George Washington National Forest make up 35 percent of our potential customer base, much of our market travels from outside that geographic area. Marketing Strategy Our marketing strategy will focus on three basic initiatives:
Pricing Strategy We will not be the low-cost provider for our target market. Our goal is to provide mid- to high-end equipment. However, we will create web-based loyalty programs to incent customers to set up online profiles and reserve and renew equipment rentals online, and provide discounts for those who do. Over time we will be able to market specifically to those customers. Just as in the Market Opportunity section, you may want to include a few more categories. For example, if your business involves a commission-compensated sales force, describe your Sales Programs and incentives. If you distribute products to other companies or suppliers and those distribution efforts will impact your overall marketing plans, lay out your Distribution Strategy. The key is to show you understand your market and you understand how you will reach your market. Marketing and promotions must result in customers--your goal is to thoroughly describe how you will acquire and keep your customers. Also keep in mind you may want to include examples of marketing materials you have already prepared, like website descriptions, print ads, web-based advertising programs, etc. While you don't need to include samples, taking the time to create actual marketing materials might help you better understand and communicate your marketing plans and objectives. Make sure your Sales and Marketing section answers the "How will I reach my customers?" question. Competitive AdvantageThe Competitive Analysis section of your business plan is devoted to analyzing your competition--both your current competition and potential competitors who might enter your market. Every business has competition. Understanding the strengths and weaknesses of your competition--or potential competition--is critical to making sure your business survives and grows. While you don't need to hire a private detective, you do need to thoroughly assess your competition on a regular basis even if you plan to run only a small business. In fact, small businesses can be especially vulnerable to competition, especially when new companies enter a marketplace. Competitive analysis can be incredibly complicated and time-consuming, but it doesn't have to be. Here is a simple process you can follow to identify, analyze, and determine the strengths and weaknesses of your competition. Profile Current Competitors First, develop a basic profile of each of your current competition. For example, if you plan to open an office supply store, you may have three competing stores in your market. Online retailers will also provide competition, but thoroughly analyzing those companies will be less valuable unless you also decide you want to sell office supplies online. (Although it's also possible that they--or, say, Amazon--are your real competition. Only you can determine that.) To make the process easier, stick to analyzing companies you will directly compete with. If you plan to set up an accounting firm, you will compete with other accounting firms in your area. If you plan to open a clothing store, you will compete with other clothing retailers in your area. Again, if you run a clothing store, you also compete with online retailers, but there is relatively little you can do about that type of competition other than to work hard to distinguish yourself in other ways: great service, friendly salespeople, convenient hours, truly understanding your customers, etc. Once you identify your main competitors, answer these questions about each one. And be objective. It's easy to identify weaknesses in your competition, but less easy (and a lot less fun) to recognize how they may be able to outperform you:
While these questions may seem like a lot of work to answer, in reality the process should be fairly easy. You should already have a feel for the competition's strengths and weaknesses--if you know your market and your industry. To gather information, you can also:
Keep in mind competitive analysis does more than help you understand your competition. Competitive analysis can also help you identify changes you should make to your business strategies. Learn from competitor strengths, take advantage of competitor's weaknesses, and apply the same analysis to your own business plan. You might be surprised by what you can learn about your business by evaluating other businesses. Identify Potential Competitors It can be tough to predict when and where new competitors may pop up. For starters, regularly search for news on your industry, your products, your services, and your target market. But there are other ways to predict when competition may follow you into a market. Other people may see the same opportunity you see. Think about your business and your industry, and if the following conditions exist, you may face competition does the road:
In general terms, if serving your market seems easy you can safely assume competitors will enter your market. A good business plan anticipates and accounts for new competitors. Now distill what you've learned by answering these questions in your business plan:
The Competitive Analysis section for our cycling rental business could start something like this: Primary Competitors Our nearest and only competition is the bike shops in Harrisonburg, VA. Our next closest competitor is located over 100 miles away. The in-town bike shops will be strong competitors. They are established businesses with excellent reputations. On the other hand, they offer inferior-quality equipment and their location is significantly less convenient. Secondary Competitors We do not plan to sell bicycles for at least the first two years of operation. However, sellers of new equipment do indirectly compete with our business since a customer who buys equipment no longer needs to rent equipment. Later, when we add new equipment sales to our operation, we will face competition from online retailers. We will compete with new equipment retailers through personalized service and targeted marketing to our existing customer base, especially through online initiatives. Opportunities
While your business plan is primarily intended to convince you that your business makes sense, keep in mind most investors look closely at your competitive analysis. A common mistake made by entrepreneurs is assuming they will simply "do it better" than any competition. Experienced businesspeople know you will face stiff competition: showing you understand your competition, understand your strengths and weaknesses relative to that competition, and that you understand you will have to adapt and change based on that competition is critical. And, even if you do not ever plan to seek financing or bring in investors, you absolutely must know your competition. The Competitive Analysis section helps you answer the "Against whom?" question. The next step in creating your business plan is to develop an Operations Plan that will serve your customers, keep your operating costs in line, and ensure profitability . Your ops plan should detail strategies for managing, staffing, manufacturing, fulfillment, inventory--all the stuff involved in operating your business on a day-to-day basis. Fortunately, most entrepreneurs have a better handle on their operations plan than on any other aspect of their business. After all, while it may not seem natural to analyze your market or your competition, most budding entrepreneurs tend to spend a lot of time thinking about how they will run their businesses. Your goal is to answer the following key questions:
Operations plans should be highly specific to your industry, your market sector, and your customers. Instead of providing an example like I've done with other sections, use the following to determine the key areas your plan should address: Location and Facility Management In terms of location, describe:
Daily Operations
Personnel Requirements
Sound like a lot? It can be, but not all of the above needs to be in your business plan. You should think through and create a detailed plan for each category, but you won't need to share the results with the people who read your business plan Working through each issue and developing concrete operations plans helps you in two major ways:
Think of Operations as the "implementation" section of your business plan. What do you need to do? How will you get it done? Then create an overview of that plan to make sure your milestones and timeline make sense. That way the operations section answers the "How?" question. Many investors and lenders feel the quality and experience of the management team is one of the most important factors used to evaluate the potential of a new business. But putting work into the Management Team section will not only benefit people who may read your plan. It will also help you evaluate the skills, experiences, and resources your management team will need . Addressing your company's needs during implementation will make a major impact on your chances for success.
The Management Team section for our cycling rental business could start something like this: Jim Rouleur, Owner and Manager Joe has over 20 years experience in the cycling business. He served for 10 years as a product manager for Acme Bikes. After that he was the operations manager of Single Track Cycles, a full-service bike shop located in Bend, Oregon. He has an undergraduate degree in marketing from Duke University and an MBA from Virginia Commonwealth University. (A complete resume for Mr. Rouleur can be found in the Appendix.) Mary Gearset, Assistant Manager Mary was the 2009 U.S. Mountain Biking National Champion. She worked in product development for High Tec frames, creating custom frames and frame modifications for professional cyclists. She also has extensive customer service and sales experience, having worked for four years as the online manager of Pro Parts Unlimited, an online retailer of high-end cycling equipment and accessories. In some instances you may also wish to describe your staffing plans. For example, if you manufacture a product or provide a service and will hire a key skilled employee, describe that employee's credentials. Otherwise, include staffing plans in the Operations section. One key note: Don't be tempted to add a "name" to your management team in hopes of attracting investors. Celebrity management team members may attract the attention of your readers, but experienced lenders and investors will immediately ask what role that person will actually play in the running of the business--and in most cases those individuals won't play any meaningful role. If you don't have a lot of experience--but are willing to work hard to overcome that lack of experience--don't be tempted to include people in your plan who will not actually work in the business. If you can't survive without help, that's okay. In fact, that's expected; no one does anything worthwhile on their own. Just make plans to get help from the right people. Finally, when you create your Management section, focus on credentials but pay extra attention to what each person actually will do . Experience and reputation are great, but action is everything. That way your Management section will answer the "Who is in charge?" question. Numbers tell the story. Bottom line results indicate the success or failure of any business. Financial projections and estimates help entrepreneurs, lenders, and investors or lenders objectively evaluate a company's potential for success. If a business seeks outside funding, providing comprehensive financial reports and analysis is critical. But most important, financial projections tell you whether your business has a chance of being viable--and if not let you know you have more work to do. Most business plans include at least five basic reports or projections:
It's easy to find examples of all of the above. Even the most basic accounting software packages include templates and samples. You can also find templates in Excel and Google Docs. (A quick search like "google docs profit and loss statement" yields plenty of examples.) Or you can work with an accountant to create the necessary financial projections and documents. Certainly feel free to do so, but first play around with the reports yourself. While you don't need to be an accountant to run a business, you do need to understand your numbers, and the best way to understand your numbers is usually to actually work with your numbers. But ultimately the tools you use to develop your numbers are not as important as whether those numbers are as accurate as possible--and whether those numbers help you decide whether to take the next step and put your business plan into action. Then Financial Analysis can help you answer the most important business question: "Can we make a profit?" Some business plans include less essential but potentially important information in an Appendix section. You may decide to include, as backup or additional information:
Keep in mind creating an Appendix is usually only necessary if you're seeking financing or hoping to bring in partners or investors. Initially the people reading your business plan don't wish to plow through reams and reams of charts, numbers, and backup information. If one does want to dig deeper, fine--he or she can check out the documents in the Appendix. That way your business plan can share your story clearly and concisely. Otherwise, since you created your business plan, you should already have the backup. Tying It All TogetherWhile you may use your business plan to attract investors, partners, suppliers, etc., never forget that the goal of your business plan is to convince you that your idea makes sense. Because ultimately it's your time, your money, and your effort on the line. The Daily Digest for Entrepreneurs and Business Leaders Privacy Policy  Our Team Just Got Bigger! dPrism is now part of Mod Op. LEARN MORE → Inside this GuideIntroduction, foundations of technology planning, what is a strategic technology plan.
Remaining considerationsKey contributors.  The CEO’s Definitive Guide to Strategic Technology PlanningIt’s an inescapable fact of today’s business environment: Growth and efficiency depend on how effectively your organization leverages data and technology. For centuries, management of cash and physical assets have been central to building a growing, sustainable, successful business. Today, our technology systems that underpin the lifecycle of data are just as critical an asset as the cash and physical components. Key Takeaways
Technology: The bedrock of modern businessData and technology provide the lifeblood of every aspect of a modern business, including driving internal process improvements, maximizing marketing impacts, building sustainable customer relationships , accelerating sales and providing effective customer support. There is now a clear imperative for all CEOs and boards to have a strategic understanding of the technology strategies, choices and investments their organizations need to make. Vistage International found that 40 percent of small- and medium-business CEOs surveyed plan to increase their technology investments for 2021. We’ve found a similar result among the clients and markets we serve. The CEO’s challenge is to develop an appropriate strategic perspective on the choices to be made, so effective guidance and decisions can determine budgeting, investment priorities and talent strategies across the organization.  All modern organizations require a strategic investment plan for technology. This plan should be sponsored and championed by the CEO and executive leadership, and ultimately reviewed and approved by the board where appropriate.But that is often easier said than done. In this guide, you’ll discover the process of creating a strategic technology plan that aligns with your business’s key growth and performance objectives. In the simplest terms, a technology plan addresses the data and underlying technical capabilities needed to enable the organization to achieve its strategic objectives. It can be boiled down to:
An effective technology plan, then, does not simply encompass future needs based on your current operating framework. It must accommodate the evolution of the operating model and be driven by a handful of future scenarios. A real-life example of technology planning in actionConsider the case of one of our past clients, a publisher who sold a series of highly valuable annual reference books with lots of tabular data. A thorough review with the customers of the books found most only bought them every two to three years and used them mainly for reference. After converting to a web-based annual subscription model, combined with an Excel plug-in, the publisher more than tripled its revenue. Considerations from the C-suiteThe six elements above are required for any effective strategic technology plan. But success in these areas will depend on embracing some core principles. One is to place an “outside-in” customer perspective at the core of the design of all digital products and services. Another is to ensure the strategic technology plan is closely aligned with the business’s strategic operating plan and is owned by the entire executive leadership team. Most important, however, is effective communication. The plan must be written in plain language and be understandable by the entire organization, including the board. Technical details should be placed in the appendix 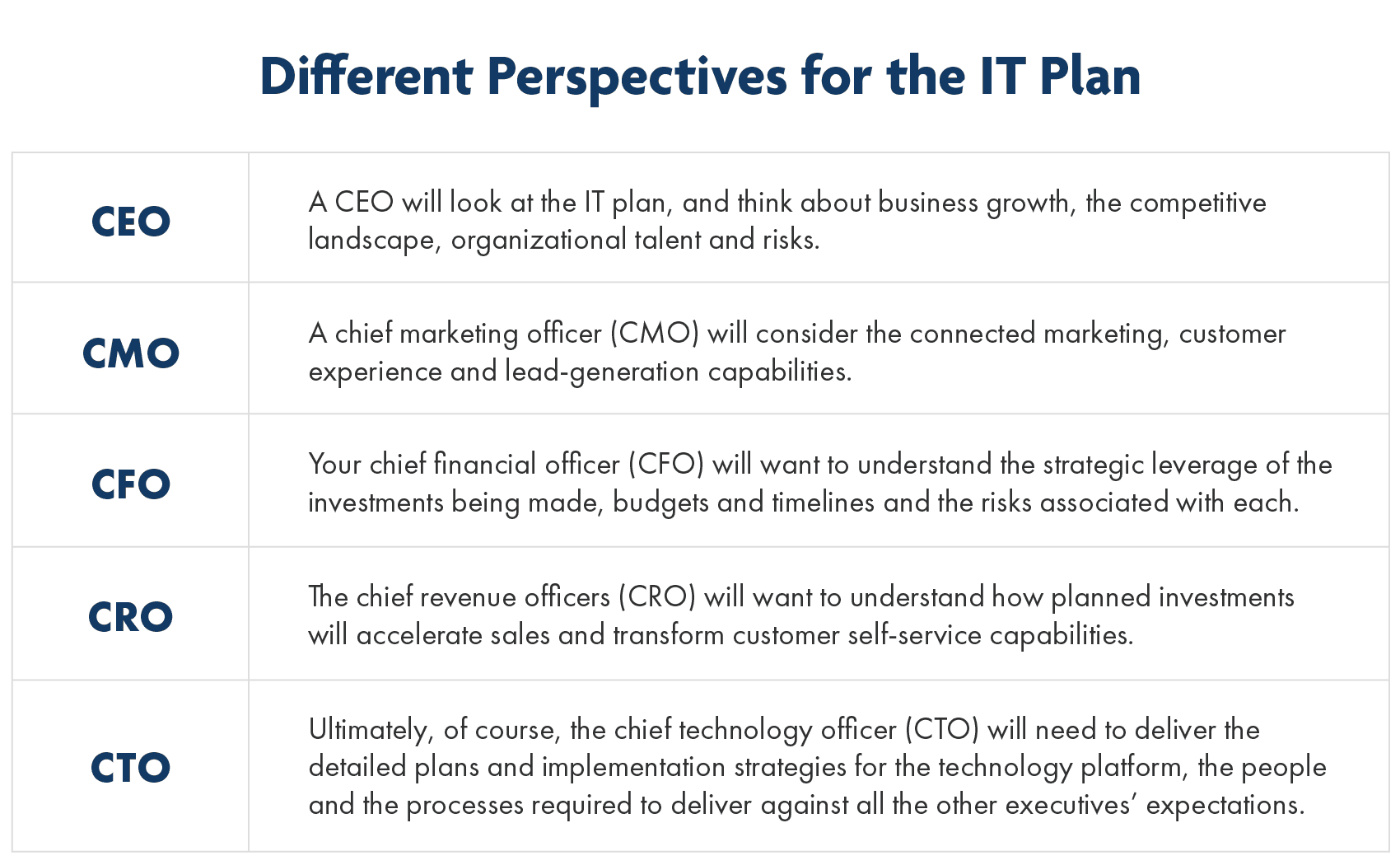 Steps to creating an effective technology planBased on our work in technology strategy over the last several years, it’s safe to say you’ll require a master technology plan and then several smaller functional-specific plans for key strategic investments or operating transformations. Here are three key steps to creating an effective plan: 1. Analyze your current technology stateEnsure you have the proper experience and expertise to conduct the technology assessment , either with in-house skills and expertise or by enlisting an external consulting firm . External partners should be able to demonstrate the depth of expertise in real-world technology operations valid for assessing your needs. Interview key technology and business stakeholders to understand the current state of their technology landscape, capabilities and operational alignment with strategic objectives and – most importantly – perceived gaps and deficiencies in current capabilities. Particular focus should be placed on the following functional domains:
2. Develop your technology roadmapIdentify any functional gaps between your defined forward-looking business strategy and your current enabling technology landscape. Quantify the costs and investments associated with addressing prioritized investments. Analysis should include engineering costs, third-party consulting, software licensing or cloud-based operating expenses, new staffing required to fill skills gaps, etc. Define priorities and sequencing based on alignment to high-impact strategic requirements and the level of investment and associated risk. Make sure your plan adopts the following principles:
3. Manage the technology implementationEstablish a small, dedicated team to manage the implementation. This also can be handled internally, but key staff should still be closely involved if the job is outsourced to a consulting firm . The team will define implementation options and create a phased schedule that addresses dependencies and linkages between each investment stream. Adopt an agile approach to carrying out the project, with success measured in short, manageable sprints and frequent value delivery of value.
Developing your technology budget for growthOnce you have your plan, it is time to establish budgets. While it’s often contemplated in terms of which one comes first, it is difficult to budget without knowing what type of growth and change you want your technology to drive. Working with so many organizations and technology budgets, we’ve seen a lot of dos and don’ts when it comes to budgeting. Too often, budgets and reviews are focused simply on line-items such as hardware, software, security, networking, data center and staffing costs. But these don’t tell the whole story of the business, nor do they speak to the rationale for how technology investments are supporting the business today or paving the way for future growth.  Technology budget size and scopeUnderstanding your industry benchmarks is a good way to begin determining the size and scope of your technology plan. Start by defining your industry as narrowly as possible. Map the industry leaders, followers, mainstream and laggards and map your own place on this continuum today and in the future. Then, you’ll want to define and benchmark each of your technology spending platforms and categories such as end-user computing, security, networking, e-commerce and customer relationship management (CRM) . You can obtain benchmark data from such sources as Gartner, Forrester and IDC, among others. Don’t stop at benchmarking. Once you have the data, analyze where in the range your technology budgets fall, and where the opportunity may be to make allocations both more efficient and effective for growth. A final reminder when looking at your budget is the importance of teamwork. As a CEO, your job is to bring together the plans between operations, finance, product, technology and service departments. A reserve, a capital spending plan or some other flexible approach to reallocate budgets based on changing priorities may be necessary to create future products. This may also be necessary to seize new market opportunities and improve the customer experience in a changing competitive landscape.
Planning for changes and “what if” scenariosWhile change is the only constant in our world today, it’s a component we must consider as we plan and manage technology. Many companies establish three- to five-year cycles for their in-depth business strategy review, with annual review and update cycles. The technology plan cycle should match this business strategy cycle. The majority of growth-minded, mid-market organizations revisit their technology plans on an annual basis and monitor spending throughout the course of the year, whether monthly or quarterly. Major accomplishments or events can lead to the update of the plan. For example, if a new CRM platform has been implemented, or a cloud policy has been established, these events should trigger a review of the plan to ensure any consequences are accurately reflected in the plan. Obviously, there is no one single approach to developing and implementing a strategic technology plan. But we hope the guidance above sparks some thinking about how to tackle the problem in manageable pieces. Developing a plan in a way that makes all stakeholders feel included is key. Keeping the customers’ needs in mind, as well as the business’s imperatives, is also a core part of our message. And, when budgeting, deciding which functions you want to run, grow and transform will help you allocate your spending in a way that keeps current business operations intact while finding new revenue and staying current with customers fast-changing technology demands.  How to Write a Business Plan Outline in 9 Steps (Example Included!) Starting a business often begins with writing a business plan , especially if you need funding . It acts as a roadmap, guiding you through each stage of launching and managing your company, and it presents a clear, compelling case to potential investors and partners. But here's the thing: not everyone finds this step intuitive. That's where a business plan outline can be incredibly helpful. Creating a detailed business plan outline helps you organize your thoughts and ensure you cover all the key aspects of your business strategy. Plus, it might be just what you need to overcome that blank page and start typing. Below, you'll find an easy-to-follow guide on how to craft your business plan outline, and an example to show you what it should look like. Build your dream business with the help of a high-paying job—browse open jobs on The Muse » What is an outline of a business plan?Think of a business plan outline as the skeleton of your entire business plan. It gives a high-level overview of the main sections you'll need to flesh out later. It's not the final document but a crucial step in getting you there. Simply put, it's like creating a detailed table of contents for your business plan, showing you exactly what information to include and how everything fits together. A well-structured business plan outline also helps you plan things ahead, saving time and effort. Writing a business plan outline in 9 stepsFollow these steps to build your business plan outline and learn exactly what each section should include. (Bear in mind that every business plan is unique, tailored to the specific needs and goals of the business. While the structure below is common, the order of sections may vary—only the executive summary will always come first.) 1. Executive summaryImagine you have just 60 seconds to convince someone to invest in your business. That's the essence of a strong executive summary. Although it appears first on your business plan, this section is often written last because it sums up the entire plan. Think of it as your elevator pitch . This section gives a quick overview of your entire business plan, highlighting key points that grab the reader's attention. Keep it clear and concise. Start with a brief overview of your business, including its name and what it offers. Summarize your mission statement and objectives, and don’t forget to mention crucial aspects like financial projections and competitive advantages. 2. Company descriptionHere's where you provide detailed information about your company. Begin with the business name and location. Describe the legal structure (e.g., sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation) and ownership. If your business already exists, share a brief history. For new ventures, explain the business's nature and the problems you aim to solve. Go into more detail about your vision and mission statements, outlining your goals and the principles guiding your business. This section helps potential investors and stakeholders grasp your company’s identity and purpose. 3. Market research and analysisThis section shares insights into your company’s industry. Start with a landscape analysis to give an overview of the market, including its size, growth rate, and key players. Next, define your target market and customer demographics—age, location, income, and interests—detailing who your ideal customers are. Identify market needs and trends your business will address, and highlight customer pain points your product or service aims to solve. Consider conducting a SWOT analysis to evaluate your business's strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats, and gain a strategic view of where your business stands in the competitive landscape. 4. Organization and managementDescribe how your business is structured and who runs it. Outline the organizational structure, and if helps, include a chart. Introduce the leadership team and key personnel, highlighting their qualifications and roles. If you have a board of directors, mention them and briefly explain their involvement. Then, outline your production processes, detailing how your product or service is (or will be) created—from sourcing materials to delivery—to give a comprehensive view of your operational capabilities. 5. Products and servicesThis section of your business plan outline is crucial for showing potential investors what makes your products and services unique and valuable. Clearly describe what your business offers, emphasizing your unique selling propositions (USPs) and the benefits and features that set you apart from the competition. Talk about the product life cycle, including any plans for future updates. If your business holds any intellectual property or proprietary technologies, detail them here to underscore your competitive advantages. 6. Marketing strategyHaving a fantastic product or service is just half the battle. The marketing plan section should outline how you'll reach your target market and convert them into customers. Begin with market positioning and branding, explaining how you want your brand perceived. Detail your marketing and promotional strategies, including specific tactics to reach your target audience. Discuss your sales strategy, focusing on how you'll convert leads into customers. Lastly, include your pricing strategy and provide a sales forecast, projecting your expected revenue over a certain period. 7. Operations planHere, the goal is to give a detailed overview of the physical and logistical aspects of your company. Start with the business location and facilities, describing where it operates and any significant physical assets. Detail the technology and equipment needed for daily operations. Briefly describe your supply chain and logistics processes to illustrate how you manage inventory, procurement, and distribution. Finish it by outlining your production process and quality control measures to ensure your products or services consistently meet high standards. 8. Financial planUse this section of the business plan to show how your company will succeed financially. Include financial projections like income statements and cash flow statements. Specify how much capital you need and how you plan to use it, discussing funding sources. Conduct a break-even analysis to estimate when your business will become profitable. Be transparent and address any financial risks and assumptions, outlining how you plan to mitigate them. 9. Appendices and exhibitsIn this section, include any additional information that supports your business plan. This might be resumes of key personnel to highlight your team's expertise and experience, or even legal documents and agreements. Include market research data and surveys to back up your market analysis. Add financial statements for a detailed look at your financial plan. Also, provide detailed product specifications to give a clear understanding of your products and services. Here's a business plan outline exampleNot quite there yet? Take a look at this business plan outline example—it will make everything clear for you. 3.1 Executive Summary
3.2 Company Description
3.3 Market Research and Analysis
3.4 Organization and Management
3.5 Products and Services
3.6 Marketing Strategy
3.7 Operations Plan
3.8 Financial Plan
3.9 Appendices and Exhibits (if applicable)
Bonus tips on how to write a winning business planOnce you've done your business plan outline, it's time to fill in the gaps and craft a winning business plan. Here are some bonus tips to keep in mind:
Read this next: How to Start a Business in 8 Steps: A Comprehensive Guide from Concept to Launch More From ForbesHow To Start A Business Plan: A Step-By-Step Guide
Creating a business plan is a critical first step for any entrepreneur. Knowing how to start a business plan will help you create a roadmap, guiding your business from startup to growth and beyond. Whether you're looking for investment, trying to set clear goals, or simply organizing your thoughts, a solid business plan can make all the difference. Here is a guide to help you get started on your business plan:1. executive summary. What It Is: This section summarizes your business plan as a whole and outlines your company profile and goals. What to Include:
Tip: Keep it concise. Although it's the first section, it's often best to write it last, after you’ve detailed everything else. 2. Company DescriptionWhat It Is: This section provides detailed information about your company, including who you are, what you do, and what markets you serve. ‘House Of The Dragon’ Season 2, Episode 5 Recap And Review: The Seeds Of The DragonTrump says rewritten gop convention speech will call for unity after assassination attempt, will smith’s ‘bad boys: ride or die’ gets digital streaming date.
Tip: Use this section to highlight your company’s strengths and what makes you unique. 3. Market ResearchWhat It Is: Market research demonstrates your understanding of the industry and target market.
Tip: Include data and statistics to back up your findings and show that you’ve done your homework. 4. Organization and ManagementWhat It Is: This section outlines your business’s organizational structure and management team.
Tip: Highlight the skills and experiences of your team that will help the business succeed. 5. Products or Services LineWhat It Is: Here, you detail the products or services you offer or plan to offer.
Tip: Focus on the benefits your products or services bring to your customers. 6. Marketing and Sales StrategyWhat It Is: This section explains how you will attract and retain customers.
Tip: Ensure your marketing and sales strategies are aligned with your market research findings. 7. Funding RequestWhat It Is: If you’re seeking funding , this section outlines your requirements.
Tip: Be specific and realistic about how much funding you need and how it will be used. 8. Financial Projections What It Is: Financial projections provide a forecast of your business’s financial future.
Tip: Use realistic and conservative estimates. Consider hiring a financial professional to help with this section if needed. 9. AppendixWhat It Is: The appendix includes any additional information that supports your business plan.
Tip: Only include essential information that adds value to your business plan. Final Tips for Creating a Business PlanCreating a business plan requires clarity and precision. First and foremost, keep your business plan clear and concise. Avoid using jargon or complex language that could make the plan difficult to read or understand. Your aim should be to communicate your ideas effectively and efficiently. Next, be realistic in your approach. Ensure that your goals and financial projections are attainable based on your research and understanding of the market. Overly ambitious projections can undermine your credibility and potentially lead to unrealistic expectations. It's also essential to remember that a business plan is a dynamic document. As your business grows and market conditions change, you should revisit and revise your plan regularly. This helps you stay aligned with your goals and adapt to new challenges and opportunities. Finally, seek feedback from experienced business professionals. Having someone with business experience review your plan can provide valuable insights and help identify any potential issues or areas for improvement. Their feedback can enhance the overall quality and effectiveness of your business plan. By following these tips, you'll be better equipped to create a robust and effective business plan that can guide your business towards success. The bottom line is that starting a business plan may seem challenging, but with careful planning and attention to detail, you can create a comprehensive guide to steer your business toward success. Use this step-by-step guide to ensure that all essential components are covered, giving your business the best possible start. Melissa Houston, CPA is the author of Cash Confident: An Entrepreneur’s Guide to Creating a Profitable Business and the founder of She Means Profit . As a Business Strategist for small business owners, Melissa helps women making mid-career shifts, to launch their dream businesses, and I also guide established business owners to grow their businesses to more profitably. The opinions expressed in this article are not intended to replace any professional or expert accounting and/or tax advice whatsoever. 
Join The ConversationOne Community. Many Voices. Create a free account to share your thoughts. Forbes Community GuidelinesOur community is about connecting people through open and thoughtful conversations. We want our readers to share their views and exchange ideas and facts in a safe space. In order to do so, please follow the posting rules in our site's Terms of Service. We've summarized some of those key rules below. Simply put, keep it civil. Your post will be rejected if we notice that it seems to contain:
User accounts will be blocked if we notice or believe that users are engaged in:
So, how can you be a power user?
Thanks for reading our community guidelines. Please read the full list of posting rules found in our site's Terms of Service.

START Planning Steps To Develop Your Digital Marketing Success Plan – S For StrategyFind out how to achieve ROI and business outcomes with a documented digital marketing success plan. Get tips from Corey Morris' new book.  This excerpt is from The Digital Marketing Success Plan, the new book from SEJ VIP Contributor Corey Morris. In what is the most distracted and disrupted era in digital marketing–especially SEO–history, we’re testing and trying things out faster than ever. While change is coming at us fast, it is critically important to still have a documented, actionable, and accountable plan for your digital marketing efforts . In his new book, Corey Morris, details a five-step START Planning process to help brands arrive at their own digital marketing success plans to ensure ROI and business outcomes are at the heart of every effort while allowing plenty of room and agility for the rapid changes we’re experiencing in digital and search marketing. Search Engine Journal has an exclusive feature of the first step in the START Planning process–”S for Strategy”–unpacking the four steps in this first and most critical phase. Chapter 3: S For StrategyThe Strategy Phase is the most comprehensive part of the START planning process. The subsequent phases are all dependent on the work done and defined in this phase. Strategy works through profiling, auditing, research, and goal setting. Knowing what marketing has been done in the past, where things stand currently, and—most importantly—where you want to go is critical at this juncture and overall for any digital marketing success plan. The strategy phase has four steps, the first of which is profile. This could be considered a simple step, as we’re just gathering information and definitions. However, it could also be misinterpreted, and it is challenging because it requires an expert to ask the right questions. That includes detailing the team involved in the effort and defining the product (services) we must sell, the brand, and the target audiences. In short, we’re putting the details on the table about who we are, our resources, and our capabilities. We are identifying what we’re selling, what value it has, how we deliver it, and the pricing model. We also must know what our brand is in terms of positioning, differentiation, and equity that it holds. And, as important as anything, we must know who our target audience personas are, their customer behaviors, and the funnels or journeys they take to buy. Anyone can ramble off some demographics or targets. But, as companies grow, having a mutually agreed understanding of what the business sells, who it sells to, and the money it costs to do so is extremely hard. I say all of this in hopes that you don’t get stuck here on some of the hard details, and also knowing that if it is easy, you might want to challenge some things and see if you can go deeper and ensure that you truly have the agreement and buy-in that you seem to. The second step in the strategy phase is audit. We need to know what we’ve done in the past and are currently doing so we have a full picture of what has worked, what hasn’t, and why. Audits are important at this juncture, and this step might be one of the most time-consuming in the entire digital marketing success plan development journey. As you obtain or create documentation of historical activities, you’ll need access to all the past and present networks and platforms. Then, you can deep dive into audits , including technical paid search , technical SEO , content SEO , web systems, email marketing systems , and more, based on what has been done in the past and what is available for you at this juncture. The third step in the strategy phase is research. So far, the focus has been on who we are and what we’ve done leading up to where we currently stand with our efforts. This phase is where we get perspectives beyond our own data and understanding. This is where we seek out internal perspectives from marketing, sales, ops, product, and other relevant teams and stakeholders—as well as from our customers or clients. Additionally, we’re doing external research to learn new insights or validate what we think when it comes to competitors, target audiences, and what the future opportunity forecasts or models out for us. The final step in strategy is goals. With a thorough picture of who we are, where we stand, and what opportunities are out there for us, we can workshop to arrive at a realistic set of goals . Maybe we came into the process with our own goals, or maybe at this point, we’re starting from scratch. Regardless, this step is critical to the rest of the process and arriving at a plan that can drive success. This is where we look at business goals and how marketing can affect them and ensure we set proper expectations before we move the strategy from ideas to action. “WE HAVE A PROBLEM” Premium Roofing Manufacturer StoryA high-end roofing manufacturing company came to us with a unique problem. Marcy, their marketing manager, had a lot of past success with SEO, their website and email marketing, and extensive campaigns driving traffic to their websites for homeowners and contractors alike–fueling their sales operations. Marcy had gone through several different agencies over the past few years. She had varying experiences with them, had a great one for a while, and then had a couple that didn’t value or know as much about SEO. She didn’t realize that, at the time, it was a line item to some of those agencies. It was getting done, and rankings and traffic were fine. Nothing was sticking out of the ordinary. One day, Marcy noticed a problem in Google Analytics. Traffic is starting to drop overall. She dives in and, as she is very familiar with the reports and channels and diagnoses this as an SEO problem within a minute. SEO traffic is dropping, but she can’t tell why. The agency says everything looks good on their end. Marcy can’t find any errors on the site. However, there’s this mysterious drop where she can see they’re not where they used to be in the Google rankings. Subsequent drops in traffic, conversions, and form submissions going through to their sales team validate it. She remembered her work with me a few years prior at a different agency and reached out. She thought of me as someone she could trust to fix any SEO problem, which I take as high praise. I was at a conference in Silicon Valley, getting ready to take the stage to speak about SEO troubleshooting. And so that was the ironic part of it to me. I gave my speech and immediately after had a longer conversation with Marcy over the phone. I could dive in and see the same things she saw, and I knew that we needed to do a full audit very quickly and understand what was going on. I brought the rest of my team back home into the challenge. Within two days, we had diagnosed two very acute issues that were hidden and that most people wouldn’t see. We wouldn’t have found them unless we had gone through our analysis auditing process to get that deep. We presented those findings to Marcy and her CEO, who both knew how big of a negative impact this would have on their business if they didn’t get this corrected. We presented three options. One was to fix the issues technically within their current site. Still, being forward-thinking and ROI-driven, we didn’t want just to offer to patch the holes and wait for the next problem to come. So, we presented two other plans. They included a midrange plan and a long-range plan to build a new website and not only fix the issues but also strategically amplify some other things. They opted to invest in the new website, and that turned into an ongoing relationship with us to monitor and amplify their SEO and take it to new heights, not just reclaiming what they had lost but making new ground. And I’m excited that we saw that all the way through. It played out exactly as we had projected and was validated by growth for them. The company eventually sold for a record amount and won awards from our peers for that work. The moral of the story is not just to accept the status quo but to realize that not all professionals who have SEO in their title have an equal set of skills. Auditing is an important tool in getting to the root cause, not just for fixing an immediate problem but even more critically for long-term success. “WE HAVE TO GET THIS RIGHT” Continuing Care Retirement Community StoryJamaal found us through Google. He was the director of admissions and marketing for a high-end retirement facility that serves as a continuing care community. They had everything: independent living, dining in chef-inspired restaurants, activities, a pub, and anything that active senior living would want through the continuum of care, including assisted living and skilled nursing. They have an excellent reputation in their city and are well known; however, that’s with the community at large. They needed help to reach their target audience, who could be potential residents or adult child influencers in their lives—the next generation down. When something happens, and it’s time to look for this type of living situation, the people at that important step are less aware and less prepared for the conversations they must have with their loved ones in a critical phase of life. These people were supposed to be moving into research and action toward admission. Also, while it was a wealthy, high-end property, it was nonprofit, very benevolent, and gave back so much. The margins were tight, and there wasn’t a large marketing budget, but they knew they needed to do something. Jamaal’s challenge when he came to us was, “I know you can do everything. I know I probably need all the things under the digital marketing umbrella. I even need a new website, but I don’t have the budget.” We said, “That’s not a problem. We start small with many of our clients and find the areas where we can have the greatest ROI and impact. Then, we build from there and create budgets, opening up dollars for investment in other opportunities.” So, we came into the situation, and we analyzed their audience. They had a wealth of data. They knew their business inside and out, and it was fantastic for us to see that. Still, they needed help understanding digital marketing and couldn’t connect the dots. They had talked to three or four other providers who gave them high-ticket products or service offerings and didn’t want to work with them to find the right solution or where they should get the most bang for their buck. We returned to them and recommended, “You should start with SEO.” Jamaal laughed because he said that was the opposite recommendation that several of the other agencies had made. They had said, “No, you should start with $100,000 a month in Google Ads.” I said, “You should start on SEO at a fraction of that,” even though we knew the challenges were there with being unable to build a new website. We’d have to navigate their antiquated website and optimize what they had. We knew that telling the story, getting the content right, and even optimizing a lousy website would get us further along in the long-term journey of driving new leads to the website. We knew we only needed a handful of people to find the site to understand what they did at the right moment, get the right story, and come through the doors and experience this wonderful place. After building momentum, one lead at a time, we could start talking about a new website, activate additional marketing channels, and layer in aspects of the digital marketing success plan to see success in the long term. Ultimately, they grew as a business and their marketing investment grew respectively. Eventually, they were acquired by a large hospital system, where everyone could flourish and get the mission and the word out. The moral of the story is it’s always better to do something rather than nothing. But if you’re on a limited budget, understand that the obvious answers or the expensive ones aren’t necessarily the best ones. Be willing to dig into the data, do the hard work, and see the opportunity to create new budgets. By seeing small successes, one at a time, you can build toward bigger things. To learn more about why digital marketing planning is so important, Corey’s START Planning process, and how to implement which he details in the full book (including more real stories and “how to” sections for each phase of the process), download the book now on Amazon . For a limited time through July 17, the Kindle version is only 99 cents. You can also find out more information and free resources at https://thedmsp.com More resources:
Featured Image: nuruddean/Shutterstock Corey is the owner and President/CEO of Voltage. He has spent nearly 20 years working in strategic and leadership roles ... Subscribe To Our Newsletter.Conquer your day with daily search marketing news. How to Write a Business Plan: Step-by-Step Guide + Examples Noah Parsons 24 min. read Updated May 7, 2024 Writing a business plan doesn’t have to be complicated. In this step-by-step guide, you’ll learn how to write a business plan that’s detailed enough to impress bankers and potential investors, while giving you the tools to start, run, and grow a successful business.
If you’re reading this guide, then you already know why you need a business plan . You understand that planning helps you:
As you start to write your plan, it’s useful to zoom out and remember what a business plan is . At its core, a business plan is an overview of the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy: how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are. Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It’s also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can use it as a management tool to track your progress toward your goals. Updating and adjusting your forecasts and budgets as you go is one of the most important steps you can take to run a healthier, smarter business. We’ll dive into how to use your plan later in this article. There are many different types of plans , but we’ll go over the most common type here, which includes everything you need for an investor-ready plan. However, if you’re just starting out and are looking for something simpler—I recommend starting with a one-page business plan . It’s faster and easier to create. It’s also the perfect place to start if you’re just figuring out your idea, or need a simple strategic plan to use inside your business. Dig deeper : How to write a one-page business plan Brought to you by Create a professional business planUsing ai and step-by-step instructions. Secure funding Validate ideas Build a strategy
Executive summaryThe executive summary is an overview of your business and your plans. It comes first in your plan and is ideally just one to two pages. Most people write it last because it’s a summary of the complete business plan. Ideally, the executive summary can act as a stand-alone document that covers the highlights of your detailed plan. In fact, it’s common for investors to ask only for the executive summary when evaluating your business. If they like what they see in the executive summary, they’ll often follow up with a request for a complete plan, a pitch presentation , or more in-depth financial forecasts . Your executive summary should include:
Dig Deeper: How to write an effective executive summary Products and services descriptionThis is where you describe exactly what you’re selling, and how it solves a problem for your target market. The best way to organize this part of your plan is to start by describing the problem that exists for your customers. After that, you can describe how you plan to solve that problem with your product or service. This is usually called a problem and solution statement . To truly showcase the value of your products and services, you need to craft a compelling narrative around your offerings. How will your product or service transform your customers’ lives or jobs? A strong narrative will draw in your readers. This is also the part of the business plan to discuss any competitive advantages you may have, like specific intellectual property or patents that protect your product. If you have any initial sales, contracts, or other evidence that your product or service is likely to sell, include that information as well. It will show that your idea has traction , which can help convince readers that your plan has a high chance of success. Market analysisYour target market is a description of the type of people that you plan to sell to. You might even have multiple target markets, depending on your business. A market analysis is the part of your plan where you bring together all of the information you know about your target market. Basically, it’s a thorough description of who your customers are and why they need what you’re selling. You’ll also include information about the growth of your market and your industry . Try to be as specific as possible when you describe your market. Include information such as age, income level, and location—these are what’s called “demographics.” If you can, also describe your market’s interests and habits as they relate to your business—these are “psychographics.” Related: Target market examples Essentially, you want to include any knowledge you have about your customers that is relevant to how your product or service is right for them. With a solid target market, it will be easier to create a sales and marketing plan that will reach your customers. That’s because you know who they are, what they like to do, and the best ways to reach them. Next, provide any additional information you have about your market. What is the size of your market ? Is the market growing or shrinking? Ideally, you’ll want to demonstrate that your market is growing over time, and also explain how your business is positioned to take advantage of any expected changes in your industry. Dig Deeper: Learn how to write a market analysis Competitive analysisPart of defining your business opportunity is determining what your competitive advantage is. To do this effectively, you need to know as much about your competitors as your target customers. Every business has some form of competition. If you don’t think you have competitors, then explore what alternatives there are in the market for your product or service. For example: In the early years of cars, their main competition was horses. For social media, the early competition was reading books, watching TV, and talking on the phone. A good competitive analysis fully lays out the competitive landscape and then explains how your business is different. Maybe your products are better made, or cheaper, or your customer service is superior. Maybe your competitive advantage is your location – a wide variety of factors can ultimately give you an advantage. Dig Deeper: How to write a competitive analysis for your business plan Marketing and sales planThe marketing and sales plan covers how you will position your product or service in the market, the marketing channels and messaging you will use, and your sales tactics. The best place to start with a marketing plan is with a positioning statement . This explains how your business fits into the overall market, and how you will explain the advantages of your product or service to customers. You’ll use the information from your competitive analysis to help you with your positioning. For example: You might position your company as the premium, most expensive but the highest quality option in the market. Or your positioning might focus on being locally owned and that shoppers support the local economy by buying your products. Once you understand your positioning, you’ll bring this together with the information about your target market to create your marketing strategy . This is how you plan to communicate your message to potential customers. Depending on who your customers are and how they purchase products like yours, you might use many different strategies, from social media advertising to creating a podcast. Your marketing plan is all about how your customers discover who you are and why they should consider your products and services. While your marketing plan is about reaching your customers—your sales plan will describe the actual sales process once a customer has decided that they’re interested in what you have to offer. If your business requires salespeople and a long sales process, describe that in this section. If your customers can “self-serve” and just make purchases quickly on your website, describe that process. A good sales plan picks up where your marketing plan leaves off. The marketing plan brings customers in the door and the sales plan is how you close the deal. Together, these specific plans paint a picture of how you will connect with your target audience, and how you will turn them into paying customers. Dig deeper: What to include in your sales and marketing plan Business operationsThe operations section describes the necessary requirements for your business to run smoothly. It’s where you talk about how your business works and what day-to-day operations look like. Depending on how your business is structured, your operations plan may include elements of the business like:
Some businesses distribute their products and reach their customers through large retailers like Amazon.com, Walmart, Target, and grocery store chains. These businesses should review how this part of their business works. The plan should discuss the logistics and costs of getting products onto store shelves and any potential hurdles the business may have to overcome. If your business is much simpler than this, that’s OK. This section of your business plan can be either extremely short or more detailed, depending on the type of business you are building. For businesses selling services, such as physical therapy or online software, you can use this section to describe the technology you’ll leverage, what goes into your service, and who you will partner with to deliver your services. Dig Deeper: Learn how to write the operations chapter of your plan Key milestones and metricsAlthough it’s not required to complete your business plan, mapping out key business milestones and the metrics can be incredibly useful for measuring your success. Good milestones clearly lay out the parameters of the task and set expectations for their execution. You’ll want to include:
If you have a budget, you can include projected costs to hit each milestone. You don’t need extensive project planning in this section—just list key milestones you want to hit and when you plan to hit them. This is your overall business roadmap. Possible milestones might be:
You should also discuss the key numbers you will track to determine your success. Some common metrics worth tracking include:
It’s perfectly fine to start with just a few metrics and grow the number you are tracking over time. You also may find that some metrics simply aren’t relevant to your business and can narrow down what you’re tracking. Dig Deeper: How to use milestones in your business plan Organization and management teamInvestors don’t just look for great ideas—they want to find great teams. Use this chapter to describe your current team and who you need to hire . You should also provide a quick overview of your location and history if you’re already up and running. Briefly highlight the relevant experiences of each key team member in the company. It’s important to make the case for why yours is the right team to turn an idea into a reality. Do they have the right industry experience and background? Have members of the team had entrepreneurial successes before? If you still need to hire key team members, that’s OK. Just note those gaps in this section. Your company overview should also include a summary of your company’s current business structure . The most common business structures include:
Be sure to provide an overview of how the business is owned as well. Does each business partner own an equal portion of the business? How is ownership divided? Potential lenders and investors will want to know the structure of the business before they will consider a loan or investment. Dig Deeper: How to write about your company structure and team Financial planLast, but certainly not least, is your financial plan chapter. Entrepreneurs often find this section the most daunting. But, business financials for most startups are less complicated than you think, and a business degree is certainly not required to build a solid financial forecast. A typical financial forecast in a business plan includes the following:
A strong business plan will include a description of assumptions about the future, and potential risks that could impact the financial plan. Including those will be especially important if you’re writing a business plan to pursue a loan or other investment. Dig Deeper: How to create financial forecasts and budgets This is the place for additional data, charts, or other information that supports your plan. Including an appendix can significantly enhance the credibility of your plan by showing readers that you’ve thoroughly considered the details of your business idea, and are backing your ideas up with solid data. Just remember that the information in the appendix is meant to be supplementary. Your business plan should stand on its own, even if the reader skips this section. Dig Deeper : What to include in your business plan appendix Optional: Business plan cover pageAdding a business plan cover page can make your plan, and by extension your business, seem more professional in the eyes of potential investors, lenders, and partners. It serves as the introduction to your document and provides necessary contact information for stakeholders to reference. Your cover page should be simple and include:
Just remember, the cover page is optional. If you decide to include it, keep it very simple and only spend a short amount of time putting it together. Dig Deeper: How to create a business plan cover page How to use AI to help write your business planGenerative AI tools such as ChatGPT can speed up the business plan writing process and help you think through concepts like market segmentation and competition. These tools are especially useful for taking ideas that you provide and converting them into polished text for your business plan. The best way to use AI for your business plan is to leverage it as a collaborator , not a replacement for human creative thinking and ingenuity. AI can come up with lots of ideas and act as a brainstorming partner. It’s up to you to filter through those ideas and figure out which ones are realistic enough to resonate with your customers. There are pros and cons of using AI to help with your business plan . So, spend some time understanding how it can be most helpful before just outsourcing the job to AI. Learn more: 10 AI prompts you need to write a business plan
To help streamline the business plan writing process, here are a few tips and key questions to answer to make sure you get the most out of your plan and avoid common mistakes . Determine why you are writing a business planKnowing why you are writing a business plan will determine your approach to your planning project. For example: If you are writing a business plan for yourself, or just to use inside your own business , you can probably skip the section about your team and organizational structure. If you’re raising money, you’ll want to spend more time explaining why you’re looking to raise the funds and exactly how you will use them. Regardless of how you intend to use your business plan , think about why you are writing and what you’re trying to get out of the process before you begin. Keep things concise Probably the most important tip is to keep your business plan short and simple. There are no prizes for long business plans . The longer your plan is, the less likely people are to read it. So focus on trimming things down to the essentials your readers need to know. Skip the extended, wordy descriptions and instead focus on creating a plan that is easy to read —using bullets and short sentences whenever possible. Have someone review your business planWriting a business plan in a vacuum is never a good idea. Sometimes it’s helpful to zoom out and check if your plan makes sense to someone else. You also want to make sure that it’s easy to read and understand. Don’t wait until your plan is “done” to get a second look. Start sharing your plan early, and find out from readers what questions your plan leaves unanswered. This early review cycle will help you spot shortcomings in your plan and address them quickly, rather than finding out about them right before you present your plan to a lender or investor. If you need a more detailed review, you may want to explore hiring a professional plan writer to thoroughly examine it. Use a free business plan template and business plan examples to get startedKnowing what information to include in a business plan is sometimes not quite enough. If you’re struggling to get started or need additional guidance, it may be worth using a business plan template. There are plenty of great options available (we’ve rounded up our 8 favorites to streamline your search). But, if you’re looking for a free downloadable business plan template , you can get one right now; download the template used by more than 1 million businesses. Or, if you just want to see what a completed business plan looks like, check out our library of over 550 free business plan examples . We even have a growing list of industry business planning guides with tips for what to focus on depending on your business type. Common pitfalls and how to avoid themIt’s easy to make mistakes when you’re writing your business plan. Some entrepreneurs get sucked into the writing and research process, and don’t focus enough on actually getting their business started. Here are a few common mistakes and how to avoid them: Not talking to your customers : This is one of the most common mistakes. It’s easy to assume that your product or service is something that people want. Before you invest too much in your business and too much in the planning process, make sure you talk to your prospective customers and have a good understanding of their needs.
The planning process forces you to think through every aspect of your business and answer questions that you may not have thought of. That’s the real benefit of writing a business plan – the knowledge you gain about your business that you may not have been able to discover otherwise. With all of this knowledge, you’re well prepared to convert your business plan into a pitch presentation to present your ideas. A pitch presentation is a summary of your plan, just hitting the highlights and key points. It’s the best way to present your business plan to investors and team members. Dig Deeper: Learn what key slides should be included in your pitch deck Use your business plan to manage your businessOne of the biggest benefits of planning is that it gives you a tool to manage your business better. With a revenue forecast, expense budget, and projected cash flow, you know your targets and where you are headed. And yet, nothing ever goes exactly as planned – it’s the nature of business. That’s where using your plan as a management tool comes in. The key to leveraging it for your business is to review it periodically and compare your forecasts and projections to your actual results. Start by setting up a regular time to review the plan – a monthly review is a good starting point. During this review, answer questions like:
Now that you see whether you’re meeting your goals or are off track, you can make adjustments and set new targets. Maybe you’re exceeding your sales goals and should set new, more aggressive goals. In that case, maybe you should also explore more spending or hiring more employees. Or maybe expenses are rising faster than you projected. If that’s the case, you would need to look at where you can cut costs. A plan, and a method for comparing your plan to your actual results , is the tool you need to steer your business toward success. Learn More: How to run a regular plan review Free business plan templates and examplesKickstart your business plan writing with one of our free business plan templates or recommended tools.  Free business plan template Download a free SBA-approved business plan template built for small businesses and startups. Download Template  One-page plan template Download a free one-page plan template to write a useful business plan in as little as 30-minutes.  Sample business plan library Explore over 500 real-world business plan examples from a wide variety of industries. View Sample Plans How to write a business plan FAQ What is a business plan? A document that describes your business , the products and services you sell, and the customers that you sell to. It explains your business strategy, how you’re going to build and grow your business, what your marketing strategy is, and who your competitors are. What are the benefits of a business plan? A business plan helps you understand where you want to go with your business and what it will take to get there. It reduces your overall risk, helps you uncover your business’s potential, attracts investors, and identifies areas for growth. Having a business plan ultimately makes you more confident as a business owner and more likely to succeed for a longer period of time. What are the 7 steps of a business plan? The seven steps to writing a business plan include:
What are the 5 most common business plan mistakes? There are plenty of mistakes that can be made when writing a business plan. However, these are the 5 most common that you should do your best to avoid:
What questions should be answered in a business plan? Writing a business plan is all about asking yourself questions about your business and being able to answer them through the planning process. You’ll likely be asking dozens and dozens of questions for each section of your plan. However, these are the key questions you should ask and answer with your business plan:
How long should a business plan be? The length of your business plan fully depends on what you intend to do with it. From the SBA and traditional lender point of view, a business plan needs to be whatever length necessary to fully explain your business. This means that you prove the viability of your business, show that you understand the market, and have a detailed strategy in place. If you intend to use your business plan for internal management purposes, you don’t necessarily need a full 25-50 page business plan. Instead, you can start with a one-page plan to get all of the necessary information in place. What are the different types of business plans? While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering. Traditional business plan: The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used when applying for funding or pitching to investors. This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. Business model canvas: The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea. One-page business plan: This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences. It’s most useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business. Lean Plan: The Lean Plan is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance. It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date. What’s the difference between a business plan and a strategic plan? A business plan covers the “who” and “what” of your business. It explains what your business is doing right now and how it functions. The strategic plan explores long-term goals and explains “how” the business will get there. It encourages you to look more intently toward the future and how you will achieve your vision. However, when approached correctly, your business plan can actually function as a strategic plan as well. If kept lean, you can define your business, outline strategic steps, and track ongoing operations all with a single plan. Noah is the COO at Palo Alto Software, makers of the online business plan app LivePlan. He started his career at Yahoo! and then helped start the user review site Epinions.com. From there he started a software distribution business in the UK before coming to Palo Alto Software to run the marketing and product teams.  Table of Contents
Related Articles  5 Min. Read How To Write a Business Plan for a Life Coaching Business + Free Example  7 Min. Read How to Write a Bakery Business Plan + Sample  3 Min. Read What to Include in Your Business Plan Appendix  1 Min. Read How to Calculate Return on Investment (ROI) The Bplans Newsletter The Bplans WeeklySubscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business. We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .  The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business planFill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy. No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.  Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
Tax preparation company Intuit to lay off 1,800 as part of an AI-focused reorganization planFILE - Intuit TurboTax packages are seen on display in a Costco Warehouse, Jan. 26, 2023, in Pittsburgh. Tax preparation and financial software company Intuit announced an AI-focused reorganization plan Wednesday, July 10, 2024, that includes laying off about 10% of its workforce. (AP Photo/Gene J. Puskar, File)
WASHINGTON (AP) — Tax preparation and financial software company Intuit announced an AI-focused reorganization plan Wednesday that includes laying off about 10% of its workforce. The company behind QuickBooks and TurboTax said it was laying off 1,800 employees, but that it expects to hire at least that many in fiscal 2025 as it accelerates its focus on incorporating artificial intelligence into its products and services. In an email to employees, CEO Sasan Goodarzi said more than 1,000 of the layoffs were employees that were not meeting the company’s elevated expectations. Another 300 positions are being eliminated “to streamline work and reallocate resources toward key growth areas,” the email said. Mountain View, California-based Intuit will also close offices in Boise, Idaho and Edmonton in Alberta, Canada where more than 250 employees work. Some of those workers will transfer to new locations, the company said. “The era of AI is one of the most significant technology shifts of our lifetime,” Goodarzi said in the opening of his email to staff. ”Companies that aren’t prepared to take advantage of this AI revolution will fall behind and, over time, will no longer exist.” As for severance, Intuit said that all its laid off U.S. employees will get a minimum of 16 weeks of pay, plus two additional weeks for every year of service and “at least” six months of health insurance coverage. U.S. employees received 60 days notice of their termination, with a last day of Sept. 9. In a regulatory filing, Intuit estimated the reorganization plan will incur between $250 million and $260 million in charges, mostly coming in its fiscal fourth quarter ending July 31. Intuit shares fell 3.6% in morning trading to $626.29 per share.
 Elon Musk’s Plan to Put a Million Earthlings on Mars in 20 YearsSpaceX employees are working on designs for a Martian city, including dome habitats and spacesuits, and researching whether humans can procreate off Earth. Mr. Musk has volunteered his sperm. Credit... Gica Tam Supported by  By Kirsten Grind Reporting from San Francisco
For more than two decades, Elon Musk has focused SpaceX , his rocket company, on his lifelong goal of reaching Mars. Over the last year, he has also ramped up work on what will happen if he gets there. Mr. Musk, 53, has directed SpaceX employees to drill into the design and details of a Martian city, according to five people with knowledge of the efforts and documents viewed by The New York Times. One team is drawing up plans for small dome habitats, including the materials that could be used to build them. Another is working on spacesuits to combat Mars’s hostile environment, while a medical team is researching whether humans can have children there. Mr. Musk has volunteered his sperm to help seed a colony, two people familiar with his comments said. The initiatives, which are in their infancy, are a shift toward more concrete planning for life on Mars as Mr. Musk’s timeline has hastened. While he said in 2016 that it would take 40 to 100 years to have a self-sustaining civilization on the planet, Mr. Musk told SpaceX employees in April that he now expects one million people to be living there in about 20 years.  “There’s high urgency to making life multi-planetary,” he said, according to a publicly posted video of his remarks. “We’ve got to do it while civilization is so strong.” Mr. Musk has long tried to defy the impossible and has often managed to beat tough odds. But his vision for life on Mars takes his seemingly limitless ambitions to their most extreme — and some might say absurdist — point. No one has ever set foot on the planet. NASA doesn’t expect to land humans on Mars until the 2040s. And if people get there, they will be greeted by a barren terrain, icy temperatures, dust storms, and air that is impossible to breathe. We are having trouble retrieving the article content. Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings. Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times. Thank you for your patience while we verify access. Already a subscriber? Log in . Want all of The Times? Subscribe . Advertisement We've detected unusual activity from your computer networkTo continue, please click the box below to let us know you're not a robot. Why did this happen?Please make sure your browser supports JavaScript and cookies and that you are not blocking them from loading. For more information you can review our Terms of Service and Cookie Policy . For inquiries related to this message please contact our support team and provide the reference ID below. India's Cyient rises on plan to set up semiconductor unit** CYIE on Thursday said it approved setting up separate unit for end to end turnkey ASIC semiconductor business ** More than 1 mln shares change hands, 2.6x the 30-day avg ** Average analyst rating on stock is "Buy"; median PT at 2,210 rupees, a 16% premium to day's high - LSEG data ** Stock last up 4.2%, set to snap 4 straight weeks of losses  |
IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
PlanBuildr's Technology business plan template will help you to quickly and easily complete your Technology business plan.
Learn how to create a business plan for a technology business with this step-by-step guide and template. Find out the importance, sources of funding, and key sections of a technology business plan.
A tech startup business plan is a document that details the premise of your technology business, summarizing vital financial objectives and operational goals, as well as details on how you will accomplish these goals.
A tech startup business plan is a comprehensive document that outlines the goals, objectives, and strategies of a technology-based startup company. It is a crucial tool that helps entrepreneurs in the tech industry to define and organize their ideas, demonstrate the feasibility of their business concept, and present a clear plan for how they intend to build and grow their company.
Explore our library of Technology Business Plan Templates and find inspiration for your own business.
Often, a business plan introduces a new technology that needs explaining. Learn how to write about it to fit your audience and get the point across.
Here's an 8-step guide to creating a tech startup business plan with over 199 resources for business plan templates, examples, and samples to help you!
Explore a real-world information technology business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan.
In this guide, you'll discover the process of creating a strategic technology plan that aligns with your business's key growth and performance objectives.
Writing a business plan is tedious but it helps investors understand your startup and win them over. Here are tips on how to write a tech startup business plan!
Get Growthink's IT company business plan template & step-by-step instructions to quickly & easily create your IT business plan.
If you want your technology startup to be successful, you should start with planning. In our article, you'll find out how to reveal the strengths of your startup idea, define clear goals, and make data-driven decisions with a business plan.
A Sample IT Tech Startup Business Plan Template. 1. Industry Overview. An IT technology company (often tech company) is a type of business entity that focuses on the development and manufacturing of technology products, or providing technology as a service. "Technology", in this context, has come to mean electronics-based technology.
What Technology Needs to Include In Your Business Plan Listing tech infrastructure, software, and digital tools showcases your ability to streamline processes and enhance efficiency.
A technology plan is often created by senior managers and top leaders of an organization to understand the best technological tools for their operations.
The first step in any new technology implementation plan should involve a thorough assessment of your enterprise's current digital landscape. You'll want your implementation partner to. study your business model, understand your existing technology stack, and. clarify your long-term goals.
Business Plan: A business plan is a written document that describes in detail how a business, usually a new one, is going to achieve its goals. A business plan lays out a written plan from a ...
How to write the operations plan section of the business plan, including details on writing the development and production process sections.
Thinking of starting a business? Here's the best step-by-step template for writing the perfect business plan when creating your startup.
The CEO's Definitive Guide to Strategic Technology Planning. It's an inescapable fact of today's business environment: Growth and efficiency depend on how effectively your organization leverages data and technology. For centuries, management of cash and physical assets have been central to building a growing, sustainable, successful business.
Download a free information technology business plan template that includes pre-written examples for every section to help you write your own plan.
A good business plan guides you through each stage of starting and managing your business. You'll use your business plan as a roadmap for how to structure, run, and grow your new business. It's a way to think through the key elements of your business.
A well-structured business plan outline also helps you plan things ahead, saving time and effort. Writing a business plan outline in 9 steps. Follow these steps to build your business plan outline and learn exactly what each section should include.
Knowing how to start a business plan will help you create a roadmap, guiding your business from startup to growth and beyond.
Find out how to achieve ROI and business outcomes with a documented digital marketing success plan. Get tips from Corey Morris' new book.
A simple, step-by-step guide to writing a compelling business plan with real-world examples and a free downloadable template.
Tax preparation and financial software company Intuit announced an AI-focused reorganization plan Wednesday that includes laying off about 10% of its workforce.
SpaceX employees are working on designs for a Martian city, including dome habitats and spacesuits, and researching whether humans can procreate off Earth. Mr. Musk has volunteered his sperm.
International Business Machines Corp.'s proposed $6.4 billion takeover of software maker HashiCorp Inc. will undergo an in-depth antitrust review by the US Federal Trade Commission.
TradingView India. ** Shares of technology solutions provider Cyient NSE:CYIENT rise as much as 7.4% at 1,905 rupees** CYIE on Thursday said it approved setting up separate unit for end to end turnkey ASIC semiconductor business** More than 1 mln shares change hands, 2.6x the 30-day avg** Average analyst rating on st…