
Verbs are direct, vigorous communicators. Use a chosen verb tense consistently throughout the same and adjacent paragraphs of a paper to ensure smooth expression.
Use the following verb tenses to report information in APA Style papers.
|
|
|
|
|---|---|---|
| Literature review (or whenever discussing other researchers’ work) | Past | Martin (2020) addressed |
| Present perfect | Researchers have studied | |
| Method Description of procedure | Past | Participants took a survey |
| Present perfect | Others have used similar approaches | |
| Reporting of your own or other researchers’ results | Past | Results showed Scores decreased Hypotheses were not supported |
| Personal reactions | Past | I felt surprised |
| Present perfect | I have experienced | |
| Present | I believe | |
| Discussion of implications of results or of previous statements | Present | The results indicate The findings mean that |
| Presentation of conclusions, limitations, future directions, and so forth | Present | We conclude Limitations of the study are Future research should explore |
Verb tense is covered in the seventh edition APA Style manuals in the Publication Manual Section 4.12 and the Concise Guide Section 2.12

From the APA Style blog

Check your tone: Keeping it professional
When writing an APA Style paper, present ideas in a clear and straightforward manner. In this kind of scholarly writing, keep a professional tone.

The “no second-person” myth
Many writers believe the “no second-person” myth, which is that there is an APA Style guideline against using second-person pronouns such as “you” or “your.” On the contrary, you can use second-person pronouns in APA Style writing.
The “no first-person” myth
Whether expressing your own views or actions or the views or actions of yourself and fellow authors, use the pronouns “I” and “we.”

Navigating the not-so-hidden treasures of the APA Style website
This post links directly to APA Style topics of interest that users may not even know exist on the website.

Welcome, singular “they”
This blog post provides insight into how this change came about and provides a forum for questions and feedback.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- PLoS Comput Biol
- v.9(7); 2013 Jul

Ten Simple Rules for Writing a Literature Review
Marco pautasso.
1 Centre for Functional and Evolutionary Ecology (CEFE), CNRS, Montpellier, France
2 Centre for Biodiversity Synthesis and Analysis (CESAB), FRB, Aix-en-Provence, France
Literature reviews are in great demand in most scientific fields. Their need stems from the ever-increasing output of scientific publications [1] . For example, compared to 1991, in 2008 three, eight, and forty times more papers were indexed in Web of Science on malaria, obesity, and biodiversity, respectively [2] . Given such mountains of papers, scientists cannot be expected to examine in detail every single new paper relevant to their interests [3] . Thus, it is both advantageous and necessary to rely on regular summaries of the recent literature. Although recognition for scientists mainly comes from primary research, timely literature reviews can lead to new synthetic insights and are often widely read [4] . For such summaries to be useful, however, they need to be compiled in a professional way [5] .
When starting from scratch, reviewing the literature can require a titanic amount of work. That is why researchers who have spent their career working on a certain research issue are in a perfect position to review that literature. Some graduate schools are now offering courses in reviewing the literature, given that most research students start their project by producing an overview of what has already been done on their research issue [6] . However, it is likely that most scientists have not thought in detail about how to approach and carry out a literature review.
Reviewing the literature requires the ability to juggle multiple tasks, from finding and evaluating relevant material to synthesising information from various sources, from critical thinking to paraphrasing, evaluating, and citation skills [7] . In this contribution, I share ten simple rules I learned working on about 25 literature reviews as a PhD and postdoctoral student. Ideas and insights also come from discussions with coauthors and colleagues, as well as feedback from reviewers and editors.
Rule 1: Define a Topic and Audience
How to choose which topic to review? There are so many issues in contemporary science that you could spend a lifetime of attending conferences and reading the literature just pondering what to review. On the one hand, if you take several years to choose, several other people may have had the same idea in the meantime. On the other hand, only a well-considered topic is likely to lead to a brilliant literature review [8] . The topic must at least be:
- interesting to you (ideally, you should have come across a series of recent papers related to your line of work that call for a critical summary),
- an important aspect of the field (so that many readers will be interested in the review and there will be enough material to write it), and
- a well-defined issue (otherwise you could potentially include thousands of publications, which would make the review unhelpful).
Ideas for potential reviews may come from papers providing lists of key research questions to be answered [9] , but also from serendipitous moments during desultory reading and discussions. In addition to choosing your topic, you should also select a target audience. In many cases, the topic (e.g., web services in computational biology) will automatically define an audience (e.g., computational biologists), but that same topic may also be of interest to neighbouring fields (e.g., computer science, biology, etc.).
Rule 2: Search and Re-search the Literature
After having chosen your topic and audience, start by checking the literature and downloading relevant papers. Five pieces of advice here:
- keep track of the search items you use (so that your search can be replicated [10] ),
- keep a list of papers whose pdfs you cannot access immediately (so as to retrieve them later with alternative strategies),
- use a paper management system (e.g., Mendeley, Papers, Qiqqa, Sente),
- define early in the process some criteria for exclusion of irrelevant papers (these criteria can then be described in the review to help define its scope), and
- do not just look for research papers in the area you wish to review, but also seek previous reviews.
The chances are high that someone will already have published a literature review ( Figure 1 ), if not exactly on the issue you are planning to tackle, at least on a related topic. If there are already a few or several reviews of the literature on your issue, my advice is not to give up, but to carry on with your own literature review,

The bottom-right situation (many literature reviews but few research papers) is not just a theoretical situation; it applies, for example, to the study of the impacts of climate change on plant diseases, where there appear to be more literature reviews than research studies [33] .
- discussing in your review the approaches, limitations, and conclusions of past reviews,
- trying to find a new angle that has not been covered adequately in the previous reviews, and
- incorporating new material that has inevitably accumulated since their appearance.
When searching the literature for pertinent papers and reviews, the usual rules apply:
- be thorough,
- use different keywords and database sources (e.g., DBLP, Google Scholar, ISI Proceedings, JSTOR Search, Medline, Scopus, Web of Science), and
- look at who has cited past relevant papers and book chapters.
Rule 3: Take Notes While Reading
If you read the papers first, and only afterwards start writing the review, you will need a very good memory to remember who wrote what, and what your impressions and associations were while reading each single paper. My advice is, while reading, to start writing down interesting pieces of information, insights about how to organize the review, and thoughts on what to write. This way, by the time you have read the literature you selected, you will already have a rough draft of the review.
Of course, this draft will still need much rewriting, restructuring, and rethinking to obtain a text with a coherent argument [11] , but you will have avoided the danger posed by staring at a blank document. Be careful when taking notes to use quotation marks if you are provisionally copying verbatim from the literature. It is advisable then to reformulate such quotes with your own words in the final draft. It is important to be careful in noting the references already at this stage, so as to avoid misattributions. Using referencing software from the very beginning of your endeavour will save you time.
Rule 4: Choose the Type of Review You Wish to Write
After having taken notes while reading the literature, you will have a rough idea of the amount of material available for the review. This is probably a good time to decide whether to go for a mini- or a full review. Some journals are now favouring the publication of rather short reviews focusing on the last few years, with a limit on the number of words and citations. A mini-review is not necessarily a minor review: it may well attract more attention from busy readers, although it will inevitably simplify some issues and leave out some relevant material due to space limitations. A full review will have the advantage of more freedom to cover in detail the complexities of a particular scientific development, but may then be left in the pile of the very important papers “to be read” by readers with little time to spare for major monographs.
There is probably a continuum between mini- and full reviews. The same point applies to the dichotomy of descriptive vs. integrative reviews. While descriptive reviews focus on the methodology, findings, and interpretation of each reviewed study, integrative reviews attempt to find common ideas and concepts from the reviewed material [12] . A similar distinction exists between narrative and systematic reviews: while narrative reviews are qualitative, systematic reviews attempt to test a hypothesis based on the published evidence, which is gathered using a predefined protocol to reduce bias [13] , [14] . When systematic reviews analyse quantitative results in a quantitative way, they become meta-analyses. The choice between different review types will have to be made on a case-by-case basis, depending not just on the nature of the material found and the preferences of the target journal(s), but also on the time available to write the review and the number of coauthors [15] .
Rule 5: Keep the Review Focused, but Make It of Broad Interest
Whether your plan is to write a mini- or a full review, it is good advice to keep it focused 16 , 17 . Including material just for the sake of it can easily lead to reviews that are trying to do too many things at once. The need to keep a review focused can be problematic for interdisciplinary reviews, where the aim is to bridge the gap between fields [18] . If you are writing a review on, for example, how epidemiological approaches are used in modelling the spread of ideas, you may be inclined to include material from both parent fields, epidemiology and the study of cultural diffusion. This may be necessary to some extent, but in this case a focused review would only deal in detail with those studies at the interface between epidemiology and the spread of ideas.
While focus is an important feature of a successful review, this requirement has to be balanced with the need to make the review relevant to a broad audience. This square may be circled by discussing the wider implications of the reviewed topic for other disciplines.
Rule 6: Be Critical and Consistent
Reviewing the literature is not stamp collecting. A good review does not just summarize the literature, but discusses it critically, identifies methodological problems, and points out research gaps [19] . After having read a review of the literature, a reader should have a rough idea of:
- the major achievements in the reviewed field,
- the main areas of debate, and
- the outstanding research questions.
It is challenging to achieve a successful review on all these fronts. A solution can be to involve a set of complementary coauthors: some people are excellent at mapping what has been achieved, some others are very good at identifying dark clouds on the horizon, and some have instead a knack at predicting where solutions are going to come from. If your journal club has exactly this sort of team, then you should definitely write a review of the literature! In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense.
Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure
Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical. It also needs a good structure. With reviews, the usual subdivision of research papers into introduction, methods, results, and discussion does not work or is rarely used. However, a general introduction of the context and, toward the end, a recapitulation of the main points covered and take-home messages make sense also in the case of reviews. For systematic reviews, there is a trend towards including information about how the literature was searched (database, keywords, time limits) [20] .
How can you organize the flow of the main body of the review so that the reader will be drawn into and guided through it? It is generally helpful to draw a conceptual scheme of the review, e.g., with mind-mapping techniques. Such diagrams can help recognize a logical way to order and link the various sections of a review [21] . This is the case not just at the writing stage, but also for readers if the diagram is included in the review as a figure. A careful selection of diagrams and figures relevant to the reviewed topic can be very helpful to structure the text too [22] .
Rule 8: Make Use of Feedback
Reviews of the literature are normally peer-reviewed in the same way as research papers, and rightly so [23] . As a rule, incorporating feedback from reviewers greatly helps improve a review draft. Having read the review with a fresh mind, reviewers may spot inaccuracies, inconsistencies, and ambiguities that had not been noticed by the writers due to rereading the typescript too many times. It is however advisable to reread the draft one more time before submission, as a last-minute correction of typos, leaps, and muddled sentences may enable the reviewers to focus on providing advice on the content rather than the form.
Feedback is vital to writing a good review, and should be sought from a variety of colleagues, so as to obtain a diversity of views on the draft. This may lead in some cases to conflicting views on the merits of the paper, and on how to improve it, but such a situation is better than the absence of feedback. A diversity of feedback perspectives on a literature review can help identify where the consensus view stands in the landscape of the current scientific understanding of an issue [24] .
Rule 9: Include Your Own Relevant Research, but Be Objective
In many cases, reviewers of the literature will have published studies relevant to the review they are writing. This could create a conflict of interest: how can reviewers report objectively on their own work [25] ? Some scientists may be overly enthusiastic about what they have published, and thus risk giving too much importance to their own findings in the review. However, bias could also occur in the other direction: some scientists may be unduly dismissive of their own achievements, so that they will tend to downplay their contribution (if any) to a field when reviewing it.
In general, a review of the literature should neither be a public relations brochure nor an exercise in competitive self-denial. If a reviewer is up to the job of producing a well-organized and methodical review, which flows well and provides a service to the readership, then it should be possible to be objective in reviewing one's own relevant findings. In reviews written by multiple authors, this may be achieved by assigning the review of the results of a coauthor to different coauthors.
Rule 10: Be Up-to-Date, but Do Not Forget Older Studies
Given the progressive acceleration in the publication of scientific papers, today's reviews of the literature need awareness not just of the overall direction and achievements of a field of inquiry, but also of the latest studies, so as not to become out-of-date before they have been published. Ideally, a literature review should not identify as a major research gap an issue that has just been addressed in a series of papers in press (the same applies, of course, to older, overlooked studies (“sleeping beauties” [26] )). This implies that literature reviewers would do well to keep an eye on electronic lists of papers in press, given that it can take months before these appear in scientific databases. Some reviews declare that they have scanned the literature up to a certain point in time, but given that peer review can be a rather lengthy process, a full search for newly appeared literature at the revision stage may be worthwhile. Assessing the contribution of papers that have just appeared is particularly challenging, because there is little perspective with which to gauge their significance and impact on further research and society.
Inevitably, new papers on the reviewed topic (including independently written literature reviews) will appear from all quarters after the review has been published, so that there may soon be the need for an updated review. But this is the nature of science [27] – [32] . I wish everybody good luck with writing a review of the literature.
Acknowledgments
Many thanks to M. Barbosa, K. Dehnen-Schmutz, T. Döring, D. Fontaneto, M. Garbelotto, O. Holdenrieder, M. Jeger, D. Lonsdale, A. MacLeod, P. Mills, M. Moslonka-Lefebvre, G. Stancanelli, P. Weisberg, and X. Xu for insights and discussions, and to P. Bourne, T. Matoni, and D. Smith for helpful comments on a previous draft.
Funding Statement
This work was funded by the French Foundation for Research on Biodiversity (FRB) through its Centre for Synthesis and Analysis of Biodiversity data (CESAB), as part of the NETSEED research project. The funders had no role in the preparation of the manuscript.
- Resources Home 🏠
- Try SciSpace Copilot
- Search research papers
- Add Copilot Extension
- Try AI Detector
- Try Paraphraser
- Try Citation Generator
- April Papers
- June Papers
- July Papers

How To Write A Literature Review - A Complete Guide

Table of Contents
A literature review is much more than just another section in your research paper. It forms the very foundation of your research. It is a formal piece of writing where you analyze the existing theoretical framework, principles, and assumptions and use that as a base to shape your approach to the research question.
Curating and drafting a solid literature review section not only lends more credibility to your research paper but also makes your research tighter and better focused. But, writing literature reviews is a difficult task. It requires extensive reading, plus you have to consider market trends and technological and political changes, which tend to change in the blink of an eye.
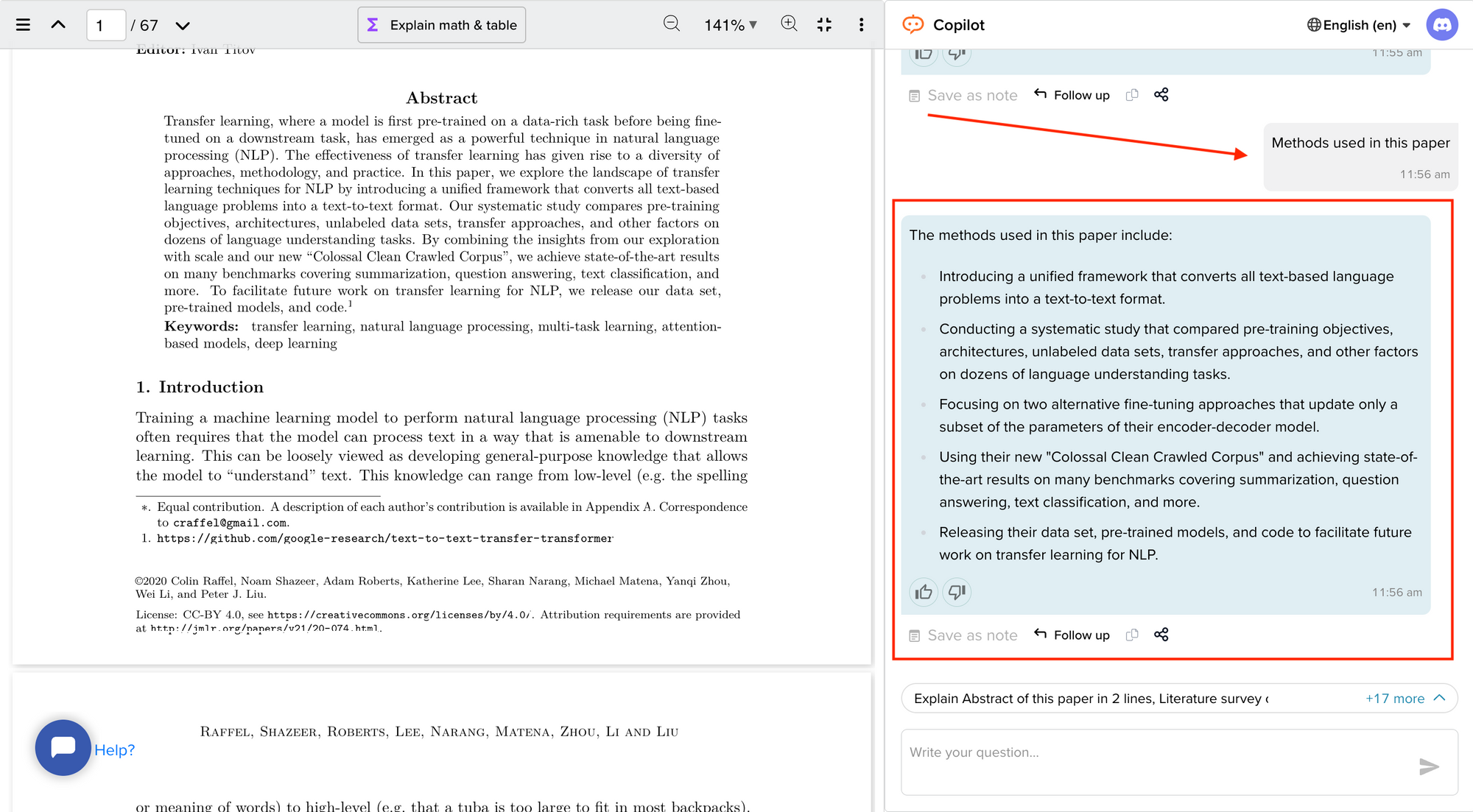
Now streamline your literature review process with the help of SciSpace Copilot. With this AI research assistant, you can efficiently synthesize and analyze a vast amount of information, identify key themes and trends, and uncover gaps in the existing research. Get real-time explanations, summaries, and answers to your questions for the paper you're reviewing, making navigating and understanding the complex literature landscape easier.
In this comprehensive guide, we will explore everything from the definition of a literature review, its appropriate length, various types of literature reviews, and how to write one.
What is a literature review?
A literature review is a collation of survey, research, critical evaluation, and assessment of the existing literature in a preferred domain.
Eminent researcher and academic Arlene Fink, in her book Conducting Research Literature Reviews , defines it as the following:
“A literature review surveys books, scholarly articles, and any other sources relevant to a particular issue, area of research, or theory, and by so doing, provides a description, summary, and critical evaluation of these works in relation to the research problem being investigated.
Literature reviews are designed to provide an overview of sources you have explored while researching a particular topic, and to demonstrate to your readers how your research fits within a larger field of study.”
Simply put, a literature review can be defined as a critical discussion of relevant pre-existing research around your research question and carving out a definitive place for your study in the existing body of knowledge. Literature reviews can be presented in multiple ways: a section of an article, the whole research paper itself, or a chapter of your thesis.
A literature review does function as a summary of sources, but it also allows you to analyze further, interpret, and examine the stated theories, methods, viewpoints, and, of course, the gaps in the existing content.
As an author, you can discuss and interpret the research question and its various aspects and debate your adopted methods to support the claim.
What is the purpose of a literature review?
A literature review is meant to help your readers understand the relevance of your research question and where it fits within the existing body of knowledge. As a researcher, you should use it to set the context, build your argument, and establish the need for your study.
What is the importance of a literature review?
The literature review is a critical part of research papers because it helps you:
- Gain an in-depth understanding of your research question and the surrounding area
- Convey that you have a thorough understanding of your research area and are up-to-date with the latest changes and advancements
- Establish how your research is connected or builds on the existing body of knowledge and how it could contribute to further research
- Elaborate on the validity and suitability of your theoretical framework and research methodology
- Identify and highlight gaps and shortcomings in the existing body of knowledge and how things need to change
- Convey to readers how your study is different or how it contributes to the research area
How long should a literature review be?
Ideally, the literature review should take up 15%-40% of the total length of your manuscript. So, if you have a 10,000-word research paper, the minimum word count could be 1500.
Your literature review format depends heavily on the kind of manuscript you are writing — an entire chapter in case of doctoral theses, a part of the introductory section in a research article, to a full-fledged review article that examines the previously published research on a topic.
Another determining factor is the type of research you are doing. The literature review section tends to be longer for secondary research projects than primary research projects.
What are the different types of literature reviews?
All literature reviews are not the same. There are a variety of possible approaches that you can take. It all depends on the type of research you are pursuing.
Here are the different types of literature reviews:
Argumentative review
It is called an argumentative review when you carefully present literature that only supports or counters a specific argument or premise to establish a viewpoint.
Integrative review
It is a type of literature review focused on building a comprehensive understanding of a topic by combining available theoretical frameworks and empirical evidence.
Methodological review
This approach delves into the ''how'' and the ''what" of the research question — you cannot look at the outcome in isolation; you should also review the methodology used.
Systematic review
This form consists of an overview of existing evidence pertinent to a clearly formulated research question, which uses pre-specified and standardized methods to identify and critically appraise relevant research and collect, report, and analyze data from the studies included in the review.
Meta-analysis review
Meta-analysis uses statistical methods to summarize the results of independent studies. By combining information from all relevant studies, meta-analysis can provide more precise estimates of the effects than those derived from the individual studies included within a review.
Historical review
Historical literature reviews focus on examining research throughout a period, often starting with the first time an issue, concept, theory, or phenomenon emerged in the literature, then tracing its evolution within the scholarship of a discipline. The purpose is to place research in a historical context to show familiarity with state-of-the-art developments and identify future research's likely directions.
Theoretical Review
This form aims to examine the corpus of theory accumulated regarding an issue, concept, theory, and phenomenon. The theoretical literature review helps to establish what theories exist, the relationships between them, the degree the existing approaches have been investigated, and to develop new hypotheses to be tested.
Scoping Review
The Scoping Review is often used at the beginning of an article, dissertation, or research proposal. It is conducted before the research to highlight gaps in the existing body of knowledge and explains why the project should be greenlit.
State-of-the-Art Review
The State-of-the-Art review is conducted periodically, focusing on the most recent research. It describes what is currently known, understood, or agreed upon regarding the research topic and highlights where there are still disagreements.
Can you use the first person in a literature review?
When writing literature reviews, you should avoid the usage of first-person pronouns. It means that instead of "I argue that" or "we argue that," the appropriate expression would be "this research paper argues that."
Do you need an abstract for a literature review?
Ideally, yes. It is always good to have a condensed summary that is self-contained and independent of the rest of your review. As for how to draft one, you can follow the same fundamental idea when preparing an abstract for a literature review. It should also include:
- The research topic and your motivation behind selecting it
- A one-sentence thesis statement
- An explanation of the kinds of literature featured in the review
- Summary of what you've learned
- Conclusions you drew from the literature you reviewed
- Potential implications and future scope for research
Here's an example of the abstract of a literature review
Is a literature review written in the past tense?
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present perfect tenses.
How many sources for a literature review?
There are multiple approaches to deciding how many sources to include in a literature review section. The first approach would be to look level you are at as a researcher. For instance, a doctoral thesis might need 60+ sources. In contrast, you might only need to refer to 5-15 sources at the undergraduate level.
The second approach is based on the kind of literature review you are doing — whether it is merely a chapter of your paper or if it is a self-contained paper in itself. When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. In the second scenario, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
Quick tips on how to write a literature review
To know how to write a literature review, you must clearly understand its impact and role in establishing your work as substantive research material.
You need to follow the below-mentioned steps, to write a literature review:
- Outline the purpose behind the literature review
- Search relevant literature
- Examine and assess the relevant resources
- Discover connections by drawing deep insights from the resources
- Structure planning to write a good literature review
1. Outline and identify the purpose of a literature review
As a first step on how to write a literature review, you must know what the research question or topic is and what shape you want your literature review to take. Ensure you understand the research topic inside out, or else seek clarifications. You must be able to the answer below questions before you start:
- How many sources do I need to include?
- What kind of sources should I analyze?
- How much should I critically evaluate each source?
- Should I summarize, synthesize or offer a critique of the sources?
- Do I need to include any background information or definitions?
Additionally, you should know that the narrower your research topic is, the swifter it will be for you to restrict the number of sources to be analyzed.
2. Search relevant literature
Dig deeper into search engines to discover what has already been published around your chosen topic. Make sure you thoroughly go through appropriate reference sources like books, reports, journal articles, government docs, and web-based resources.
You must prepare a list of keywords and their different variations. You can start your search from any library’s catalog, provided you are an active member of that institution. The exact keywords can be extended to widen your research over other databases and academic search engines like:
- Google Scholar
- Microsoft Academic
- Science.gov
Besides, it is not advisable to go through every resource word by word. Alternatively, what you can do is you can start by reading the abstract and then decide whether that source is relevant to your research or not.
Additionally, you must spend surplus time assessing the quality and relevance of resources. It would help if you tried preparing a list of citations to ensure that there lies no repetition of authors, publications, or articles in the literature review.
3. Examine and assess the sources
It is nearly impossible for you to go through every detail in the research article. So rather than trying to fetch every detail, you have to analyze and decide which research sources resemble closest and appear relevant to your chosen domain.
While analyzing the sources, you should look to find out answers to questions like:
- What question or problem has the author been describing and debating?
- What is the definition of critical aspects?
- How well the theories, approach, and methodology have been explained?
- Whether the research theory used some conventional or new innovative approach?
- How relevant are the key findings of the work?
- In what ways does it relate to other sources on the same topic?
- What challenges does this research paper pose to the existing theory
- What are the possible contributions or benefits it adds to the subject domain?
Be always mindful that you refer only to credible and authentic resources. It would be best if you always take references from different publications to validate your theory.
Always keep track of important information or data you can present in your literature review right from the beginning. It will help steer your path from any threats of plagiarism and also make it easier to curate an annotated bibliography or reference section.
4. Discover connections
At this stage, you must start deciding on the argument and structure of your literature review. To accomplish this, you must discover and identify the relations and connections between various resources while drafting your abstract.
A few aspects that you should be aware of while writing a literature review include:
- Rise to prominence: Theories and methods that have gained reputation and supporters over time.
- Constant scrutiny: Concepts or theories that repeatedly went under examination.
- Contradictions and conflicts: Theories, both the supporting and the contradictory ones, for the research topic.
- Knowledge gaps: What exactly does it fail to address, and how to bridge them with further research?
- Influential resources: Significant research projects available that have been upheld as milestones or perhaps, something that can modify the current trends
Once you join the dots between various past research works, it will be easier for you to draw a conclusion and identify your contribution to the existing knowledge base.
5. Structure planning to write a good literature review
There exist different ways towards planning and executing the structure of a literature review. The format of a literature review varies and depends upon the length of the research.
Like any other research paper, the literature review format must contain three sections: introduction, body, and conclusion. The goals and objectives of the research question determine what goes inside these three sections.
Nevertheless, a good literature review can be structured according to the chronological, thematic, methodological, or theoretical framework approach.
Literature review samples
1. Standalone
2. As a section of a research paper
How SciSpace Discover makes literature review a breeze?
SciSpace Discover is a one-stop solution to do an effective literature search and get barrier-free access to scientific knowledge. It is an excellent repository where you can find millions of only peer-reviewed articles and full-text PDF files. Here’s more on how you can use it:
Find the right information
Find what you want quickly and easily with comprehensive search filters that let you narrow down papers according to PDF availability, year of publishing, document type, and affiliated institution. Moreover, you can sort the results based on the publishing date, citation count, and relevance.
Assess credibility of papers quickly
When doing the literature review, it is critical to establish the quality of your sources. They form the foundation of your research. SciSpace Discover helps you assess the quality of a source by providing an overview of its references, citations, and performance metrics.
Get the complete picture in no time
SciSpace Discover’s personalized suggestion engine helps you stay on course and get the complete picture of the topic from one place. Every time you visit an article page, it provides you links to related papers. Besides that, it helps you understand what’s trending, who are the top authors, and who are the leading publishers on a topic.
Make referring sources super easy
To ensure you don't lose track of your sources, you must start noting down your references when doing the literature review. SciSpace Discover makes this step effortless. Click the 'cite' button on an article page, and you will receive preloaded citation text in multiple styles — all you've to do is copy-paste it into your manuscript.
Final tips on how to write a literature review
A massive chunk of time and effort is required to write a good literature review. But, if you go about it systematically, you'll be able to save a ton of time and build a solid foundation for your research.
We hope this guide has helped you answer several key questions you have about writing literature reviews.
Would you like to explore SciSpace Discover and kick off your literature search right away? You can get started here .
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. how to start a literature review.
• What questions do you want to answer?
• What sources do you need to answer these questions?
• What information do these sources contain?
• How can you use this information to answer your questions?
2. What to include in a literature review?
• A brief background of the problem or issue
• What has previously been done to address the problem or issue
• A description of what you will do in your project
• How this study will contribute to research on the subject
3. Why literature review is important?
The literature review is an important part of any research project because it allows the writer to look at previous studies on a topic and determine existing gaps in the literature, as well as what has already been done. It will also help them to choose the most appropriate method for their own study.
4. How to cite a literature review in APA format?
To cite a literature review in APA style, you need to provide the author's name, the title of the article, and the year of publication. For example: Patel, A. B., & Stokes, G. S. (2012). The relationship between personality and intelligence: A meta-analysis of longitudinal research. Personality and Individual Differences, 53(1), 16-21
5. What are the components of a literature review?
• A brief introduction to the topic, including its background and context. The introduction should also include a rationale for why the study is being conducted and what it will accomplish.
• A description of the methodologies used in the study. This can include information about data collection methods, sample size, and statistical analyses.
• A presentation of the findings in an organized format that helps readers follow along with the author's conclusions.
6. What are common errors in writing literature review?
• Not spending enough time to critically evaluate the relevance of resources, observations and conclusions.
• Totally relying on secondary data while ignoring primary data.
• Letting your personal bias seep into your interpretation of existing literature.
• No detailed explanation of the procedure to discover and identify an appropriate literature review.
7. What are the 5 C's of writing literature review?
• Cite - the sources you utilized and referenced in your research.
• Compare - existing arguments, hypotheses, methodologies, and conclusions found in the knowledge base.
• Contrast - the arguments, topics, methodologies, approaches, and disputes that may be found in the literature.
• Critique - the literature and describe the ideas and opinions you find more convincing and why.
• Connect - the various studies you reviewed in your research.
8. How many sources should a literature review have?
When it is just a chapter, sources should equal the total number of pages in your article's body. if it is a self-contained paper in itself, you need at least three times as many sources as there are pages in your work.
9. Can literature review have diagrams?
• To represent an abstract idea or concept
• To explain the steps of a process or procedure
• To help readers understand the relationships between different concepts
10. How old should sources be in a literature review?
Sources for a literature review should be as current as possible or not older than ten years. The only exception to this rule is if you are reviewing a historical topic and need to use older sources.
11. What are the types of literature review?
• Argumentative review
• Integrative review
• Methodological review
• Systematic review
• Meta-analysis review
• Historical review
• Theoretical review
• Scoping review
• State-of-the-Art review
12. Is a literature review mandatory?
Yes. Literature review is a mandatory part of any research project. It is a critical step in the process that allows you to establish the scope of your research, and provide a background for the rest of your work.
But before you go,
- Six Online Tools for Easy Literature Review
- Evaluating literature review: systematic vs. scoping reviews
- Systematic Approaches to a Successful Literature Review
- Writing Integrative Literature Reviews: Guidelines and Examples
You might also like

Consensus GPT vs. SciSpace GPT: Choose the Best GPT for Research

Literature Review and Theoretical Framework: Understanding the Differences

Types of Essays in Academic Writing - Quick Guide (2024)
Training videos | Faqs

Mastering Verb Tenses in Literature Reviews
In this blog, we will see what tense you should use in the literature review section of your research paper. We will look at some examples of literature review excerpts from published research papers and understand the tenses used in them.
1. Which Tense to Use?
You may have to use multiple tenses in your literature review depending on what you are saying. The present tense is generally used in statements to introduce the literature review, and the past tense is typically used when you are talking about specific papers. The following table summarizes different types of statements you might typically include in your literature review and the corresponding tenses you should use.
| (2003) | ||
2. Usage Example #1
In the first statement, we make a general statement about the topic by saying that this topic has been studied extensively in the literature, and therefore we have used the present tense. In the second sentence, we say that although there has been a lot of research on this topic, it is still relevant today and therefore we have used the present perfect tense.
✔ Example of simple present & present perfect tense use This is widely reported and extensively explored in the literature. This has been of interest for a considerable period, ranging from the early 90s. _ Broad summary (Simple Present) _ Ongoing situation (Present Perfect)
3. Usage Example #2
In the first statement, we begin the literature review by saying that there are many techniques available in the literature to combat weight gain. This statement is only a general summary of previous research on this topic. So we used the present perfect tense. Then, when we then talk about individual works from the literature, we present their results in the past tense.
✔ Example of present perfect & past tense use A number of solutions have been proposed to deal with the problem of weight gain and obesity. He simplest approach was proposed by Lee et al. (2003) which involves fasting. Wang et al. (2010) proposed an alternative solution of using an intragastric balloon. _ Broad summary (Present Perfect) _ Specific papers from past (Past Tense)
4. Usage Example #3
In the following example, in the first sentence we are talking about a collective finding that is generally accepted in the field, and therefore we have used the present perfect tense. In the second statement, we are talking about a finding from a specific work conducted in the past and have therefore used the past tense.
✔ Example of present perfect & past tense use It has been shown that there is a direct correlation between social media and children’s mental health[1-10]. Recently, Elan et al. [11] showed that these findings also applies to teenagers and older population. _ Accepted findings (Present Perfect) _ Specific paper from past (Past Tense)
5. Usage Example #4
In the example below, we talk about past research papers and that’s why we have used the past tense.
✔ Example of past tense use In the initial work presented by Kim et al. (2004), they showed that there is a direct link between Vitamin C and obesity. Smith et al. (2006) replicated this finding in a much larger study. Recently, it was pointed out by Young et al. (2010) that Vitamin C is also related to many other diseases. _ Specific papers from past (Past Tense)
If you have any questions, please drop a comment below, and we will answer as soon as possible. We also recommend you to refer to our other blogs on academic writing tools , academic writing resources , academic writing phrases and research paper examples which are relevant to the topic discussed in this blog.
Similar Posts

How to Make Your Study Limitations Sound Positive?
In this blog, we will look at some clever techniques to present the study limitations without reducing the impact of your work.

Paraphrasing – Techniques for Rephrasing, Rewording, and Rewriting.
In this blog, we explain good paraphrasing techniques. We also discuss how paraphrasing tools and plagiarism checkers can be used to avoid academic misconduct.

3 Costly Mistakes to Avoid in the Research Introduction
In this blog, we will discuss three common mistakes that beginner writers make while writing the research paper introduction.

Limitations in Research – A Simplified Guide with Examples
In this blog, we provide tips for presenting study limitations in your paper and provide some real-world examples.

How to Write Catchy Research Paper Titles with Examples
The title of your paper should be catchy yet informative. Let’s dive into some tips and tricks to ensure your title stands out in the academic crowd.

Technical Terms, Notations, and Scientific Jargon in Research Papers
In this blog, we will teach you how to use specialized terminology in your research papers with some practical examples.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- 10 Share Facebook
- 0 Share Twitter
- 1 Share LinkedIn
- 0 Share Email
Dissertations & projects: Tenses
- Research questions
- The process of reviewing
- Project management
- Literature-based projects
On this page:
“You will use a range of tenses depending on what you are writing about . ” Elizabeth M Fisher, Richard C Thompson, and Daniel Holtom, Enjoy Writing Your Science Thesis Or Dissertation!
Tenses can be tricky to master. Even well respected journals differ in the guidance they give their authors for their use. However, their are some general conventions about what tenses are used in different parts of the report/dissertation. This page gives some advice on standard practice.
What tenses will you use?

There are exceptions however, most notably in the literature review where you will use a mixture of past , present and present perfect tenses (don't worry, that is explained below), when discussing the implications of your findings when the present tense is appropriate and in the recommendations where you are likely to use the future tense.
The tenses used as standard practice in each of these sections of your report are given and explained below.
In your abstract
You have some leeway with tense use in your abstract and guidance does vary which can sometimes be confusing. We recommend the following:
Describing the current situation and reason for your study
Mostly use the present tense, i.e. "This is the current state of affairs and this is why this study is needed."
Occasionally, you may find the need to use something called the present perfect tense when you are describing things that happened in the past but are still relevant. The present perfect tense uses have/has and then the past participle of the verb i.e. Previous research on this topic has focused on...
Describing the aims of your study
Here you have a choice. It is perfectly acceptable to use either the present or past tense, i.e. "This study aims to..." or "This study aimed to..."
Describing your methodology
Use the past tense to describe what you did, i.e. "A qualitative approach was used." "A survey was undertaken to ...". "The blood sample was analysed by..."
Describing your findings
Use the past tense to describe what you found as it is specific to your study, i.e. "The results showed that...", "The analysis indicated that..."
Suggesting the implications of your study
Use the present tense as even though your study took place in the past, your implications remain relevant in the present, i.e. Results revealed x which indicates that..."
Example abstract
An example abstract with reasoning for the tenses chosen can be found at the bottom of this excellent blog post:
Using the Present Tense and Past Tense When Writing an Abstract
In your methodology
The methodology is one of the easiest sections when it comes to tenses as you are explaining to your reader what you did. This is therefore almost exclusively written in the past tense.
Blood specimens were frozen at -80 o C.
A survey was designed using the Jisc Surveys tool.
Participants were purposefully selected.
The following search strategy was used to search the literature:
Very occasionally you may use the present tense if you are justifying a decision you have taken (as the justification is still valid, not just at the time you made the decision). For example:
Purposeful sampling was used to ensure that a range of views were included. This sampling method maximises efficiency and validity as it identifies information-rich cases and ... (Morse & Niehaus, 2009).
In your discussion/conclusion
This will primarily be written in the present tense as you are generally discussing or making conclusions about the relevance of your findings at the present time. So you may write:
The findings of this research suggest that.../are potentially important because.../could open a new avenue for further research...
There will also be times when you use the past tense , especially when referring to part of your own research or previous published research research - but this is usually followed by something in the present tense to indicate the current relevance or the future tense to indicate possible future directions:
Analysis of the survey results found most respondents were not concerned with the processes, just the outcome. This suggests that managers should focus on...
These findings mirrored those of Cheung (2020), who also found that ESL pupils failed to understand some basic yet fundamental instructions. Addressing this will help ensure...
In your introduction
The introduction generally introduces what is in the rest of your document as is therefore describing the present situation and so uses the present tense :
Chapter 3 describes the research methodology.
Depending on your discipline, your introduction may also review the literature so please also see that section below.
In your literature review
The findings of some literature may only be applicable in the specific circumstances that the research was undertaken and so need grounding to that study. Conversely, the findings of other literature may now be accepted as established knowledge. Also, you may consider the findings of older literature to be still relevant and relatively recent literature be already superseded. The tenses you write in will help to indicate a lot of this to the reader. In other words, you will use a mix of tenses in your review depending on what you are implying.
Findings only applicable in the specific circumstances
Use the past tense . For example:
In an early study, Sharkey et al. (1991) found that isoprene emissions were doubled in leaves on sunnier sides of oak and aspen trees.
Using the past tense indicates that you are not implying that isoprene emissions are always doubled on the sunnier side of the trees, just that is what was found in the Sharkey et al. study.
Findings that are still relevant or now established knowledge
Mostly use the present tense , unless the study is not recent and the authors are the subject of the sentence (which you should use very sparingly in a literature review) when you may need to use a mixture of the past and present. For example:
A narrowing of what 'graduateness' represents damages students’ abilities to thrive as they move through what will almost certainly be complex career pathways (Holmes, 2001).
Holmes (2001) argued strongly that a narrowing of what 'graduateness' represents damages students’ abilities to thrive as they move through what will almost certainly be complex career pathways
Both of these imply that you think this is still the case (although it is perhaps more strongly implied in the first example). You may also want to use some academic caution too - such as writing 'may damage' rather than the more definite 'damages'.
Presenting your results
As with your methodology, your results section should be written in the past tense . This indicates that you are accepting that the results are specific to your research. Whilst they may have current implications, that part will not be considered until your discussion/conclusions section(s).
Four main themes were identified from the interview data.
There was a significant change in oxygen levels.
Like with the methodology, you will occasionally switch to present tense to write things like "Table 3.4 shows that ..." but generally, stick to the past tense.

In your recommendations
Not everyone will need to include recommendations and some may have them as part of the conclusions chapter. Recommendations are written in a mixture of the present tense and future tense :
It is recommended that ward layout is adapted, where possible, to provide low-sensory bays for patients with autism. These will still be useable by all patients but...
Useful links
- Verb tenses in scientific manuscripts From International Science Editing
- Which Verb Tenses Should I Use in a Research Paper? Blog from WordVice
- << Previous: Writing style
- Next: Voice >>
- Last Updated: Apr 24, 2024 1:09 PM
- URL: https://libguides.hull.ac.uk/dissertations
- Login to LibApps
- Library websites Privacy Policy
- University of Hull privacy policy & cookies
- Website terms and conditions
- Accessibility
- Report a problem

Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates
Published on January 2, 2023 by Shona McCombes . Revised on September 11, 2023.
What is a literature review? A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources on a specific topic. It provides an overview of current knowledge, allowing you to identify relevant theories, methods, and gaps in the existing research that you can later apply to your paper, thesis, or dissertation topic .
There are five key steps to writing a literature review:
- Search for relevant literature
- Evaluate sources
- Identify themes, debates, and gaps
- Outline the structure
- Write your literature review
A good literature review doesn’t just summarize sources—it analyzes, synthesizes , and critically evaluates to give a clear picture of the state of knowledge on the subject.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
What is the purpose of a literature review, examples of literature reviews, step 1 – search for relevant literature, step 2 – evaluate and select sources, step 3 – identify themes, debates, and gaps, step 4 – outline your literature review’s structure, step 5 – write your literature review, free lecture slides, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions, introduction.
- Quick Run-through
- Step 1 & 2
When you write a thesis , dissertation , or research paper , you will likely have to conduct a literature review to situate your research within existing knowledge. The literature review gives you a chance to:
- Demonstrate your familiarity with the topic and its scholarly context
- Develop a theoretical framework and methodology for your research
- Position your work in relation to other researchers and theorists
- Show how your research addresses a gap or contributes to a debate
- Evaluate the current state of research and demonstrate your knowledge of the scholarly debates around your topic.
Writing literature reviews is a particularly important skill if you want to apply for graduate school or pursue a career in research. We’ve written a step-by-step guide that you can follow below.

Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Writing literature reviews can be quite challenging! A good starting point could be to look at some examples, depending on what kind of literature review you’d like to write.
- Example literature review #1: “Why Do People Migrate? A Review of the Theoretical Literature” ( Theoretical literature review about the development of economic migration theory from the 1950s to today.)
- Example literature review #2: “Literature review as a research methodology: An overview and guidelines” ( Methodological literature review about interdisciplinary knowledge acquisition and production.)
- Example literature review #3: “The Use of Technology in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Thematic literature review about the effects of technology on language acquisition.)
- Example literature review #4: “Learners’ Listening Comprehension Difficulties in English Language Learning: A Literature Review” ( Chronological literature review about how the concept of listening skills has changed over time.)
You can also check out our templates with literature review examples and sample outlines at the links below.
Download Word doc Download Google doc
Before you begin searching for literature, you need a clearly defined topic .
If you are writing the literature review section of a dissertation or research paper, you will search for literature related to your research problem and questions .
Make a list of keywords
Start by creating a list of keywords related to your research question. Include each of the key concepts or variables you’re interested in, and list any synonyms and related terms. You can add to this list as you discover new keywords in the process of your literature search.
- Social media, Facebook, Instagram, Twitter, Snapchat, TikTok
- Body image, self-perception, self-esteem, mental health
- Generation Z, teenagers, adolescents, youth
Search for relevant sources
Use your keywords to begin searching for sources. Some useful databases to search for journals and articles include:
- Your university’s library catalogue
- Google Scholar
- Project Muse (humanities and social sciences)
- Medline (life sciences and biomedicine)
- EconLit (economics)
- Inspec (physics, engineering and computer science)
You can also use boolean operators to help narrow down your search.
Make sure to read the abstract to find out whether an article is relevant to your question. When you find a useful book or article, you can check the bibliography to find other relevant sources.
You likely won’t be able to read absolutely everything that has been written on your topic, so it will be necessary to evaluate which sources are most relevant to your research question.
For each publication, ask yourself:
- What question or problem is the author addressing?
- What are the key concepts and how are they defined?
- What are the key theories, models, and methods?
- Does the research use established frameworks or take an innovative approach?
- What are the results and conclusions of the study?
- How does the publication relate to other literature in the field? Does it confirm, add to, or challenge established knowledge?
- What are the strengths and weaknesses of the research?
Make sure the sources you use are credible , and make sure you read any landmark studies and major theories in your field of research.
You can use our template to summarize and evaluate sources you’re thinking about using. Click on either button below to download.
Take notes and cite your sources
As you read, you should also begin the writing process. Take notes that you can later incorporate into the text of your literature review.
It is important to keep track of your sources with citations to avoid plagiarism . It can be helpful to make an annotated bibliography , where you compile full citation information and write a paragraph of summary and analysis for each source. This helps you remember what you read and saves time later in the process.
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
To begin organizing your literature review’s argument and structure, be sure you understand the connections and relationships between the sources you’ve read. Based on your reading and notes, you can look for:
- Trends and patterns (in theory, method or results): do certain approaches become more or less popular over time?
- Themes: what questions or concepts recur across the literature?
- Debates, conflicts and contradictions: where do sources disagree?
- Pivotal publications: are there any influential theories or studies that changed the direction of the field?
- Gaps: what is missing from the literature? Are there weaknesses that need to be addressed?
This step will help you work out the structure of your literature review and (if applicable) show how your own research will contribute to existing knowledge.
- Most research has focused on young women.
- There is an increasing interest in the visual aspects of social media.
- But there is still a lack of robust research on highly visual platforms like Instagram and Snapchat—this is a gap that you could address in your own research.
There are various approaches to organizing the body of a literature review. Depending on the length of your literature review, you can combine several of these strategies (for example, your overall structure might be thematic, but each theme is discussed chronologically).
Chronological
The simplest approach is to trace the development of the topic over time. However, if you choose this strategy, be careful to avoid simply listing and summarizing sources in order.
Try to analyze patterns, turning points and key debates that have shaped the direction of the field. Give your interpretation of how and why certain developments occurred.
If you have found some recurring central themes, you can organize your literature review into subsections that address different aspects of the topic.
For example, if you are reviewing literature about inequalities in migrant health outcomes, key themes might include healthcare policy, language barriers, cultural attitudes, legal status, and economic access.
Methodological
If you draw your sources from different disciplines or fields that use a variety of research methods , you might want to compare the results and conclusions that emerge from different approaches. For example:
- Look at what results have emerged in qualitative versus quantitative research
- Discuss how the topic has been approached by empirical versus theoretical scholarship
- Divide the literature into sociological, historical, and cultural sources
Theoretical
A literature review is often the foundation for a theoretical framework . You can use it to discuss various theories, models, and definitions of key concepts.
You might argue for the relevance of a specific theoretical approach, or combine various theoretical concepts to create a framework for your research.
Like any other academic text , your literature review should have an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion . What you include in each depends on the objective of your literature review.
The introduction should clearly establish the focus and purpose of the literature review.
Depending on the length of your literature review, you might want to divide the body into subsections. You can use a subheading for each theme, time period, or methodological approach.
As you write, you can follow these tips:
- Summarize and synthesize: give an overview of the main points of each source and combine them into a coherent whole
- Analyze and interpret: don’t just paraphrase other researchers — add your own interpretations where possible, discussing the significance of findings in relation to the literature as a whole
- Critically evaluate: mention the strengths and weaknesses of your sources
- Write in well-structured paragraphs: use transition words and topic sentences to draw connections, comparisons and contrasts
In the conclusion, you should summarize the key findings you have taken from the literature and emphasize their significance.
When you’ve finished writing and revising your literature review, don’t forget to proofread thoroughly before submitting. Not a language expert? Check out Scribbr’s professional proofreading services !
This article has been adapted into lecture slides that you can use to teach your students about writing a literature review.
Scribbr slides are free to use, customize, and distribute for educational purposes.
Open Google Slides Download PowerPoint
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Sampling methods
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A literature review is a survey of scholarly sources (such as books, journal articles, and theses) related to a specific topic or research question .
It is often written as part of a thesis, dissertation , or research paper , in order to situate your work in relation to existing knowledge.
There are several reasons to conduct a literature review at the beginning of a research project:
- To familiarize yourself with the current state of knowledge on your topic
- To ensure that you’re not just repeating what others have already done
- To identify gaps in knowledge and unresolved problems that your research can address
- To develop your theoretical framework and methodology
- To provide an overview of the key findings and debates on the topic
Writing the literature review shows your reader how your work relates to existing research and what new insights it will contribute.
The literature review usually comes near the beginning of your thesis or dissertation . After the introduction , it grounds your research in a scholarly field and leads directly to your theoretical framework or methodology .
A literature review is a survey of credible sources on a topic, often used in dissertations , theses, and research papers . Literature reviews give an overview of knowledge on a subject, helping you identify relevant theories and methods, as well as gaps in existing research. Literature reviews are set up similarly to other academic texts , with an introduction , a main body, and a conclusion .
An annotated bibliography is a list of source references that has a short description (called an annotation ) for each of the sources. It is often assigned as part of the research process for a paper .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, September 11). How to Write a Literature Review | Guide, Examples, & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved July 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/dissertation/literature-review/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, what is a theoretical framework | guide to organizing, what is a research methodology | steps & tips, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
| GUIDELINES FOR WRITING THE LITERATURE REVIEW Reference to Published Sources of Information
|
|
|
|
the speed needed to …
|
Present Perfect Tense is often used when the focus of the work is on several authors.
|
Present Perfect Tense may also be used when you want to refer to how much or how little research has been carried out on a particular topic.
Present Tense is often used to refer to generally accepted scientific facts.
Modal Verbs may be used if you wish to introduce a degree of tentativeness into your comments about the work of an author. In this situation the reporting verb will be in the passive voice and the addition of a modal verb will indicate the degree of confidence attributed to the information.
|






















COMMENTS
Learn when to use past, present or present perfect tense in a literature review, depending on your focus and context. See examples, tips and links to external reading on the topic.
Learn how to use verb tenses consistently in APA Style papers, especially in literature reviews. See examples of past, present, and future tenses for different paper sections.
Learn how to use past, present, and past perfect tenses correctly in literature reviews. See examples, explanations, and tips from a nursing journal editor.
In addition to critical thinking, a literature review needs consistency, for example in the choice of passive vs. active voice and present vs. past tense. Rule 7: Find a Logical Structure Like a well-baked cake, a good review has a number of telling features: it is worth the reader's time, timely, systematic, well written, focused, and critical.
8. Generally speaking any are acceptable. If you focus on the authors then "did show" or "have shown" feels about right. But if you take the citation to mean the paper itself, then the present tense is fine since the paper still exists and does still show... However, advisors can be a bit picky on some such things, so it would be good to ask ...
Yes, the literature review should ideally be written in the past tense. You should not use the present or future tense when writing one. The exceptions are when you have statements describing events that happened earlier than the literature you are reviewing or events that are currently occurring; then, you can use the past perfect or present ...
The present tense is generally used in statements to introduce the literature review, and the past tense is typically used when you are talking about specific papers. The following table summarizes different types of statements you might typically include in your literature review and the corresponding tenses you should use.
There are exceptions however, most notably in the literature review where you will use a mixture of past, present and present perfect tenses (don't worry, that is explained below), when discussing the implications of your findings when the present tense is appropriate and in the recommendations where you are likely to use the future tense.
Identify the most appropriate verb tense for each sentence in the literature review section of a manuscript. Although past tense is the most common one, past perfect and present perfect tenses may be appropriate for sentences describing something that occurred earlier than another study or something that is still occurring. Author's Background
Examples of literature reviews. Step 1 - Search for relevant literature. Step 2 - Evaluate and select sources. Step 3 - Identify themes, debates, and gaps. Step 4 - Outline your literature review's structure. Step 5 - Write your literature review.
The tenses often used are simple past, present perfect and simple present. Such a range is perfectly acceptable and there are several reasons that influence the choice of tense. Simple Past Tense tends to be the most frequently used tense to refer to the findings of another author's research. The past tense is also most commonly used when the ...
Answer: By 'literature write-up,' we understand you mean 'literature review.'. Now, do you mean an entire paper that is a literature review or only the literature review section of the paper that typically comes in the Introduction? Anyway, the answer is: it depends, and it's quite possible to have multiple tenses in the literature ...
Referring to the ideas of other researchers (e.g. in a literature review) No matter how long ago the work was published, the present tense is used, and even a deceased author 'argues' or 'claims'. Simple present tense. Vasquez and Lopez argue that… Present perfect tense. Bailey has outlined… Discussing the actions of characters in ...
Literature review verb tense. For the literature review, most academic editors recommend using the past simple or present perfect when talking about past research. Use the past simple to discuss what was done in the past (the authors collected, investigated, analyzed, etc.). Use present perfect to talk about findings from previous studies that ...
Ideally, Chapter 1 (introduction) should be past tense, chapter 2 (literature) can be present or past depending on how you quote, chapter 3( methodology) definitely past tense, chapter 4( results ...
2. Either past or present tense is reasonable for a literature survey. You could argue for the past tense since the work was already completed, or use the present tense because the papers currently exist and describe something that can be found now. The main issue is to be consistent in your usage throughout the review. Share. Improve this answer.
Use the past tense (e.g., researchers presented) or the present perfect (e.g., researchers have presented) for the literature review and the description of the procedure if discussing past events. Use the past tense to describe the results (e.g., test scores improved significantly).
Literary works, paintings, films, and other artistic creations are assumed to exist in an eternal present. Therefore, when you write about writers or artists as they express themselves in their work, use the present tense. The Basic Rule: You should use the past tense when discussing historical events, and you should use the literary present ...
Literature Review Guide: What tense should I use? How to create Literature reviews. What is a Literature Review? How to start? Search strategies and Databases. Examples of Literature Reviews.
The most commonly used verb tenses in academic writing, however, are the simple present, simple past, present perfect, and simple future tenses. APA (2010) says that, in an academic paper: The simple past tense or present perfect tense is appropriate for the literature review and the description of the procedure if the discussion is of past ...
Use the past tense (e.g., researchers presented) or the present perfect (e.g., researchers have presented) for the literature review and the description of the procedure if discussing past events. Use the past tense to describe the results (e.g., test scores improved significantly). Use the present tense to discuss implications of the results ...
A recent flurry of tweets, seemingly initiated by @thesiswhisperer, discussed the use of tense in literature review. There doesn't seem to be a definitive rule to using either present or past tense (i.e. Smith (1989) argues… vs. Smith (1989) argued… etc.), though switching from one to the other can be problematic and should only be done ...
It is customary to use the present tense when discussing a literary work: Othello is a play by Shakespeare. It begins on a street in Venice, where Roderigo and Iago are arguing.. Some of the themes of Othello are racism, love, jealousy, and betrayal.. Like other Shakespearean tragedies, Othello has five acts. The play ends with Othello's murder of Desdemona and with the revelation of Iago ...