University Libraries
- Research Guides
- Blackboard Learn
- Interlibrary Loan
- Study Rooms
- University of Arkansas

Literature Reviews
- Qualitative or Quantitative?
- Getting Started
- Finding articles
- Primary sources? Peer-reviewed?
- Review Articles/ Annual Reviews...?
- Books, ebooks, dissertations, book reviews
Qualitative researchers TEND to:
Researchers using qualitative methods tend to:
- t hink that social sciences cannot be well-studied with the same methods as natural or physical sciences
- feel that human behavior is context-specific; therefore, behavior must be studied holistically, in situ, rather than being manipulated
- employ an 'insider's' perspective; research tends to be personal and thereby more subjective.
- do interviews, focus groups, field research, case studies, and conversational or content analysis.

Image from https://www.editage.com/insights/qualitative-quantitative-or-mixed-methods-a-quick-guide-to-choose-the-right-design-for-your-research?refer-type=infographics
Qualitative Research (an operational definition)
Qualitative Research: an operational description
Purpose : explain; gain insight and understanding of phenomena through intensive collection and study of narrative data
Approach: inductive; value-laden/subjective; holistic, process-oriented
Hypotheses: tentative, evolving; based on the particular study
Lit. Review: limited; may not be exhaustive
Setting: naturalistic, when and as much as possible
Sampling : for the purpose; not necessarily representative; for in-depth understanding
Measurement: narrative; ongoing
Design and Method: flexible, specified only generally; based on non-intervention, minimal disturbance, such as historical, ethnographic, or case studies
Data Collection: document collection, participant observation, informal interviews, field notes
Data Analysis: raw data is words/ ongoing; involves synthesis
Data Interpretation: tentative, reviewed on ongoing basis, speculative
- Qualitative research with more structure and less subjectivity
- Increased application of both strategies to the same study ("mixed methods")
- Evidence-based practice emphasized in more fields (nursing, social work, education, and others).
Some Other Guidelines
- Guide for formatting Graphs and Tables
- Critical Appraisal Checklist for an Article On Qualitative Research
Quantitative researchers TEND to:
Researchers using quantitative methods tend to:
- think that both natural and social sciences strive to explain phenomena with confirmable theories derived from testable assumptions
- attempt to reduce social reality to variables, in the same way as with physical reality
- try to tightly control the variable(s) in question to see how the others are influenced.
- Do experiments, have control groups, use blind or double-blind studies; use measures or instruments.

Quantitative Research (an operational definition)
Quantitative research: an operational description
Purpose: explain, predict or control phenomena through focused collection and analysis of numberical data
Approach: deductive; tries to be value-free/has objectives/ is outcome-oriented
Hypotheses : Specific, testable, and stated prior to study
Lit. Review: extensive; may significantly influence a particular study
Setting: controlled to the degree possible
Sampling: uses largest manageable random/randomized sample, to allow generalization of results to larger populations
Measurement: standardized, numberical; "at the end"
Design and Method: Strongly structured, specified in detail in advance; involves intervention, manipulation and control groups; descriptive, correlational, experimental
Data Collection: via instruments, surveys, experiments, semi-structured formal interviews, tests or questionnaires
Data Analysis: raw data is numbers; at end of study, usually statistical
Data Interpretation: formulated at end of study; stated as a degree of certainty
This page on qualitative and quantitative research has been adapted and expanded from a handout by Suzy Westenkirchner. Used with permission.
Images from https://www.editage.com/insights/qualitative-quantitative-or-mixed-methods-a-quick-guide-to-choose-the-right-design-for-your-research?refer-type=infographics.
- << Previous: Books, ebooks, dissertations, book reviews
- Last Updated: Jan 8, 2024 2:51 PM
- URL: https://uark.libguides.com/litreview
- See us on Instagram
- Follow us on Twitter
- Phone: 479-575-4104
You are now being redirected to go-pdf.net....
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods
Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods
Published on April 12, 2019 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on June 22, 2023.
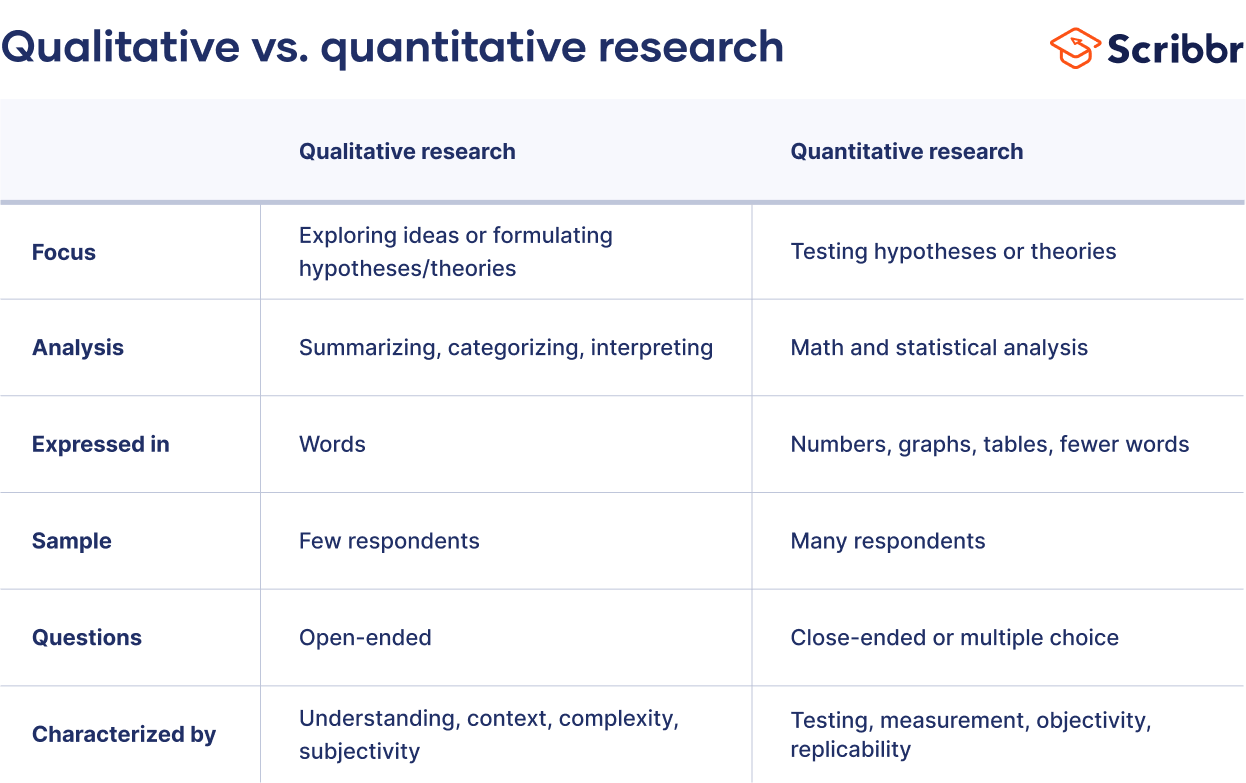
When collecting and analyzing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge.
Common quantitative methods include experiments, observations recorded as numbers, and surveys with closed-ended questions.
Quantitative research is at risk for research biases including information bias , omitted variable bias , sampling bias , or selection bias . Qualitative research Qualitative research is expressed in words . It is used to understand concepts, thoughts or experiences. This type of research enables you to gather in-depth insights on topics that are not well understood.
Common qualitative methods include interviews with open-ended questions, observations described in words, and literature reviews that explore concepts and theories.
Table of contents
The differences between quantitative and qualitative research, data collection methods, when to use qualitative vs. quantitative research, how to analyze qualitative and quantitative data, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about qualitative and quantitative research.
Quantitative and qualitative research use different research methods to collect and analyze data, and they allow you to answer different kinds of research questions.
Quantitative and qualitative data can be collected using various methods. It is important to use a data collection method that will help answer your research question(s).
Many data collection methods can be either qualitative or quantitative. For example, in surveys, observational studies or case studies , your data can be represented as numbers (e.g., using rating scales or counting frequencies) or as words (e.g., with open-ended questions or descriptions of what you observe).
However, some methods are more commonly used in one type or the other.
Quantitative data collection methods
- Surveys : List of closed or multiple choice questions that is distributed to a sample (online, in person, or over the phone).
- Experiments : Situation in which different types of variables are controlled and manipulated to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Observations : Observing subjects in a natural environment where variables can’t be controlled.
Qualitative data collection methods
- Interviews : Asking open-ended questions verbally to respondents.
- Focus groups : Discussion among a group of people about a topic to gather opinions that can be used for further research.
- Ethnography : Participating in a community or organization for an extended period of time to closely observe culture and behavior.
- Literature review : Survey of published works by other authors.
A rule of thumb for deciding whether to use qualitative or quantitative data is:
- Use quantitative research if you want to confirm or test something (a theory or hypothesis )
- Use qualitative research if you want to understand something (concepts, thoughts, experiences)
For most research topics you can choose a qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods approach . Which type you choose depends on, among other things, whether you’re taking an inductive vs. deductive research approach ; your research question(s) ; whether you’re doing experimental , correlational , or descriptive research ; and practical considerations such as time, money, availability of data, and access to respondents.
Quantitative research approach
You survey 300 students at your university and ask them questions such as: “on a scale from 1-5, how satisfied are your with your professors?”
You can perform statistical analysis on the data and draw conclusions such as: “on average students rated their professors 4.4”.
Qualitative research approach
You conduct in-depth interviews with 15 students and ask them open-ended questions such as: “How satisfied are you with your studies?”, “What is the most positive aspect of your study program?” and “What can be done to improve the study program?”
Based on the answers you get you can ask follow-up questions to clarify things. You transcribe all interviews using transcription software and try to find commonalities and patterns.
Mixed methods approach
You conduct interviews to find out how satisfied students are with their studies. Through open-ended questions you learn things you never thought about before and gain new insights. Later, you use a survey to test these insights on a larger scale.
It’s also possible to start with a survey to find out the overall trends, followed by interviews to better understand the reasons behind the trends.
Qualitative or quantitative data by itself can’t prove or demonstrate anything, but has to be analyzed to show its meaning in relation to the research questions. The method of analysis differs for each type of data.
Analyzing quantitative data
Quantitative data is based on numbers. Simple math or more advanced statistical analysis is used to discover commonalities or patterns in the data. The results are often reported in graphs and tables.
Applications such as Excel, SPSS, or R can be used to calculate things like:
- Average scores ( means )
- The number of times a particular answer was given
- The correlation or causation between two or more variables
- The reliability and validity of the results
Analyzing qualitative data
Qualitative data is more difficult to analyze than quantitative data. It consists of text, images or videos instead of numbers.
Some common approaches to analyzing qualitative data include:
- Qualitative content analysis : Tracking the occurrence, position and meaning of words or phrases
- Thematic analysis : Closely examining the data to identify the main themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying how communication works in social contexts
If you want to know more about statistics , methodology , or research bias , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Chi square goodness of fit test
- Degrees of freedom
- Null hypothesis
- Discourse analysis
- Control groups
- Mixed methods research
- Non-probability sampling
- Quantitative research
- Inclusion and exclusion criteria
Research bias
- Rosenthal effect
- Implicit bias
- Cognitive bias
- Selection bias
- Negativity bias
- Status quo bias
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to systematically measure variables and test hypotheses . Qualitative methods allow you to explore concepts and experiences in more detail.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyze a large amount of readily-available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how it is generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organizations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organize your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2023, June 22). Qualitative vs. Quantitative Research | Differences, Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved June 29, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/qualitative-quantitative-research/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk
Other students also liked, what is quantitative research | definition, uses & methods, what is qualitative research | methods & examples, mixed methods research | definition, guide & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
Table of Contents
Collaboration, information literacy, writing process, how to frame research questions, literature reviews, & citations: qualitative vs. quantitative.
- © 2023 by Joseph M. Moxley - University of South Florida
This assignment will guide you through the analysis of how qualitative , quantitative , and mixed-methods researchers frame research questions, construct literature reviews, and integrate citations. You will engage in discourse analysis, rhetorical analysis, and citation analysis of one qualitative study and one quantitative or mixed-methods research study. This creative challenge will help you understand the different methodologies and the scholarly conventions in Professional and Technical Communication.
- Research Questions: Explore how the formulation of research questions differs between qualitative and quantitative or mixed-methods studies. Consider whether these questions are open-ended or specific, reflecting the underlying methodologies.
- Literature Reviews: Analyze how authors frame their literature reviews, emphasizing themes and sources. Consider how these reviews set the stage for the research questions or hypotheses.
- Citation Analysis: Evaluate how researchers use citations to support their arguments and research questions, noting the conventions followed and their alignment with audience expectations.
- Methodological Alignment: Assess how research questions align with qualitative or quantitative approaches, and how literature reviews and citations support the formulation of hypotheses.
Why Do Different Research Methodologies Frame Research Questions, Literature Reviews, and Citations Differently?
In research methods, understanding why different methodologies frame research questions, literature reviews, and citations differently is crucial. These differences are deeply rooted in contrasting epistemological assumptions about knowledge construction. Qualitative research, informed by interpretivist and constructivist epistemologies, explores subjective meanings and interpretations through methods like interviews, observations, and textual analysis. Researchers using these approaches view knowledge as socially constructed, emphasizing the contextual and subjective nature of understanding.
Conversely, quantitative research, rooted in positivist or post-positivist epistemologies, seeks objective measurement and hypothesis testing. Positivist epistemology emphasizes empirical observation and hypothesis verification, assuming an objective reality that can be measured and confirmed. Post-positivist epistemology extends this by acknowledging the role of interpretation and multiple perspectives in constructing knowledge, integrating critical perspectives into empirical inquiry.
These methodological differences significantly influence how researchers approach and interpret their findings in academic and professional contexts. Language practices, such as the formulation of research questions, the construction of literature reviews, and the use of citations, reflect these underlying epistemological assumptions. Qualitative researchers frame open-ended questions to delve into complex phenomena, reflecting their belief in the constructed nature of knowledge. Their literature reviews emphasize thematic analysis and the interpretation of texts to uncover underlying meanings, often citing sources that contribute to theoretical understanding.
In contrast, quantitative researchers frame specific, measurable questions aimed at testing hypotheses and generalizing findings. Their literature reviews synthesize empirical studies and statistically analyze data to validate or refute hypotheses, prioritizing citations that provide empirical evidence and support for their claims.
By understanding these epistemological foundations and their influence on language practices, researchers can navigate and critically evaluate different methodological approaches to research in Professional and Technical Communication and beyond.
Writing Prompt
Choose one qualitative and quantitative or mixed-methods research study from Jason Tham’s list of PTC Journals, listed below. Reflect on the differences and similarities in how qualitative and quantitative or mixed-methods researchers frame their research questions, literature reviews, and use of citations.
Guidelines:
- Do not engage in methodological critique for this assignment.
- Demonstrate an awareness of the research terms and conventions defined in the assigned readings and from the first creative challenge
- Adopt a professional writing style.
- Before each of the studies you analyze, provide a full bibliographic reference in APA 7 style
Recommended Readings:
- Scholarship as a Conversation – Explores the ongoing dialogues shaping scholarly research.
- Credibility & Authority – Guides on establishing credibility and authority in academic writing and research.
- Citation – How to Connect Evidence to Your Claims
- Citation & Voice – How to Distinguish Your Ideas from Your Sources
- Citation Conventions – What is the Role of Citation in Academic & Professional Writing?
- Citation Conventions – When Are Citations Required in Academic & Professional Writing?
- Paraphrasing – How to Paraphrase with Clarity & Concision
- Block Quotations
- Summary – Learn How To Summarize Sources in Academic & Professional Writing
Deliverables
- A comparative analysis paper of 4-5 pages
- A reflection on your processes responding to this creative challenge, including a summary of how you used AI tools.
Step 1 – Select Two Studies to Analyze
Review the list of academic and professional journals below, which has been compiled and annotated by Professor Jason Tham, an associate professor of technical communication and rhetoric at Texas Tech. To log on to many of these journals, because they are locked behind a paywall, you may need to log on to the University’s Library Services portal.
Journal of Business and Technical Communication (SAGE)
- Nature: Theory driven; seems to balance qualitative and quantitative research
- Focus: Technical and business communication practices and pedagogy; discussions about training students to be professionals; some useful teaching strategies and cases
- Notes: Currently one of the top journals in technical communication; arguably most cited; has a strong tie to Iowa State’s professional communication program
Journal of Technical Writing and Communication (SAGE)
- Nature: Slightly less theoretical than JBTC and TCQ but still heavy academic-speak
- Focus: Trends and approaches in technical communication practices and research
- Notes: One of the oldest technical communication journals in the US
Technical Communication (Society for Technical Communication)
- Nature: Arguably more practical than JTWC, JBTC, TCQ, and IEEE Transactions; caters to STC’s professional audience… and it’s associated with the STC’s annual summit
- Focus: Emerging topics, methods, and practices in technical communication; content management, information architecture, and usability research
- Notes: It’s behind a paywall some university libraries may not even access; there is an online version of the journal called Technical Communication Online… but it’s not as prominent as the print journal; seems to have a strong association with Texas Tech’s technical communication program
Technical Communication Quarterly (Association for Teachers of Technical Writing) (Taylor & Francis)
- Nature: Theoretical + pedagogical
- Focus: Teaching methods and exemplary approaches to research; features many exemplary qualitative research cases
- Notes: Another top journal in technical communication; produces many award-winning pieces; associated with ATTW so it has a huge academic following… especially those who also attend the annual Conference on College Composition and Communication (CCCC)
IEEE Transactions on Professional Communication (Institute of Electrical & Electronics Engineers – Professional Communication Society)
- Nature: 50-50 theory and practice
- Focus: Engineering communication as professional communication; empirical research
- Notes: Another old journal that has a lot of history; seems to have a strong tie to the University of North Texas’s technical communication department
IEEE Transactions on Technology and Society (IEEE Society on Social Implications of Technology)
- Nature: 30% technical, 70% philosophical discussions about social technologies
- Focus: Computers science, CS education, technical design, social computing
- Notes: Good for interdisciplinary work, digital humanities, and digital education
Communication Design Quarterly (Association for Computing Machinery – Special Interest Group on Design of Communication)
- Nature: Theoretical, methodological
- Focus: Offers many accessible (comprehensible) research reports on design methods, research practices, teaching approaches, and industry trends
- Notes: Open access…yay! Recently pursued an “online first” model where articles are published on a rolling basis; it’s considered the second-tier journal in the academic circle but it’s surely becoming more popular among technical communication scholars
Journal of Usability Studies (User Experience Professionals Association)
- Nature: For academics, this is highly practical
- Focus: Empirical research; mostly quantitative
- Notes: Independent journal not associated with an academic institution
Behaviour and Information Technology (Taylor & Francis)
- Nature: Computer science emphasis… so, experimental + theoretical
- Focus: Human-computer interaction; information design, behavioral science
- Notes: This is a UK journal… provides a nice juxtaposition to US journals and perspectives
Human Factors: The Journal of the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society (SAGE)
- Nature: Similar to BIT, experimental and theoretical
- Focus: Puts emphasis on the human factors and ergonomics discipline; draws from psychology
- Notes: As shown in its name… it’s a journal for the Human Factors and Ergonomics Society
Ergonomics in Design: The Quarterly of Human Factors Applications (SAGE)
- Nature: Slightly more theoretical than Human Factors
- Focus: Theoretical discussions, experiments, and demonstrations
- Notes: Also an HFES journal
International Journal of Human-Computer Studies (Elsevier)
- Nature: Theoretical
- Focus: More interdisciplinary than EID and Human Factors
- Notes: May be one that technical communication researchers feel more comfortable publishing in even if they are not working directly in HCI or computer science fields
Human Technology (Independent journal)
- Nature: Theoretical, philosophical
- Focus: Discusses technological futures and human-computer interaction
- Notes: It’s got less prestige compared to EID and Human Factors
Human Communication & Technology (Independent journal)
- Nature: Theoretical, empirical
- Focus: Communication studies and social technologies
- Notes: It’s fairly new and doesn’t seem to publish multiple issues a year
Journal of Computer-Mediated Communication (International Communication Association) (Oxford)
- Nature: Empirical; qualitative; quantitative
- Focus: Social scientific approach to computer-based communication; media studies and politics; social media research
- Notes: Top journal for solid communication technologies research
International Journal of Sociotechnology and Knowledge Development (IGI Global)
- Nature: Empirical; qualitative; quantitative; practical
- Focus: Social scientific approach to technology studies and professional communication; seems catered to practitioner audience
- Notes: Has an interdisciplinary feel to it; one or two special issues are of specific interest to technical communication design
Business and Professional Communication Quarterly (SAGE)
- Nature: Theoretical, pedagogical
- Focus: Workplace communication studies and teaching cases
- Notes: A journal of the Association for Business Communication (ABC); top tiered for business writing and communication research
International Journal of Business Communication (SAGE)
- Nature: Practical, pedagogical, experimental
- Focus: Similar focus to BPCQ
- Notes: Also an ABC journal (I am not sure why there is this other journal)
Programmatic Perspectives (Council for Programs in Technical and Scientific Communication)
- Nature: Programmatic, pedagogical
- Focus: Program and curriculum design; teaching issues; professional development of teachers
- Notes: Smaller journal… not sure how big is the readership but it’s got a good reputation
Xchanges: An Interdisciplinary Journal of Technical Communication, Rhetoric, and Writing across the Curriculum (Independent journal)
- Nature: Pedagogical, beginner research, experimental, teaching cases
- Focus: Technical communication, writing studies, rhet/comp, and everything in between!
- Notes: Open access journal with pretty good editorial support; provides mentorship to undergrad and graduate writing; multimedia friendly
RhetTech Undergraduate Journal (Independent journal)
- Nature: Beginner research, undergraduate research
- Focus: Writing studies, rhet/comp, technical communication
Notes: Open access; print based (PDF) so not very multimedia-friendly
Step 2 – Engage in Critical Analysis
Consider These Heuristic Questions to Guide Your Analysis
a) Research Question Analysis (discourse analysis)
- How do the investigators present their research question(s)? Do they present their research question in the abstract and intro and throughout the study?
- How do the investigators clarify the significance of their research question(s)?
- Based on the research question and definition of its significance and scholarly roots, what methodological community is the researching targeting as its primary audience?
- How do the research questions differ in their formulation between the qualitative and quantitative or mixed-methods studies?
- Are the research questions open-ended or specific? How does this reflect the study’s methodology?
- Identify and discuss the research questions or hypotheses in both studies.
- Explain how the research questions align with the qualitative or quantitative approach.
- Reflect on how the literature review supports the formulation of these research questions or hypotheses.
b) Types of Literature Cited (Citation Analysis):
- How do the researchers use citations to build their arguments and support their research questions?
- What citation conventions are followed, and how do they reflect the expectations of the target audience?
- Theoretical works (conceptual frameworks, models, theories)
- quantitative studies?
- qualitative studies?
- Past scholarly conversations?
- Policy documents or industry reports (especially in applied research)
- Original research?
c) Information Literacy Conventions (Rhetorical Analysis)
Authority is constructed & contextual:.
- How do the authors address the authority of the sources they cite or use to develop their study or argument?
- Do they evaluate and present the credibility of their sources?
Information Creation as a Process:
- How do the authors describe the research and information creation process?
- Do they acknowledge the iterative nature of research and knowledge development?
- How do they present different formats of information (e.g., raw data, analyzed results, interpretations)?
Information Has Value :
- How do the authors give credit to secondary sources through proper attribution and citation?
Research as Inquiry :
- How do the authors formulate questions based on information gaps or existing conflicting information?
- Do they explain how they determined the scope of their investigation?
- Do they employ research methods appropriate to their inquiry/research questions?
- How do the research questions align with the qualitative, quantitative, or mixed-methods approach?
- How do the literature reviews and citations support the formulation of these research questions or hypotheses?
Scholarship as Conversation :
- How do the authors situate their work within the larger scholarly conversation?
- Do they cite and build upon contributing work of others in their field?
- How do they identify the contribution their work makes to the disciplinary knowledge?
- Do they acknowledge competing perspectives on the issue?
Searching as Strategic Exploration :
- Do the authors describe their search strategies and how they refined them based on initial results?
- How do they demonstrate the use of different types of searching language (e.g., controlled vocabulary, keywords, natural language)?
- Do they discuss how they determined the initial scope of their literature review and adjusted it as necessary?
- How do they show persistence and flexibility in their information gathering process?
d) Rhetorical Appeals
- Appeals to ethos (credibility) fallacious ethos ?
- Appeals to pathos (emotion)
- Appeals to logos (logic)
- Overall rhetorical strategies used to persuade the audience
e) Literature Reviews
- How do the authors of each study frame their literature review? What themes and sources are emphasized?
- How does the literature review set the stage for the research questions or hypotheses?
Scholarly Conversations:
- How do the investigators root their research questions in existing scholarly conversations?
- What hermeneutic methods are used to interpret and integrate prior research?
Literature Review Analysis:
- Identify the main themes and sources cited in the literature review sections of both studies.
- Discuss how the literature review sets the stage for the research questions or hypotheses.
- Compare the depth and breadth of the literature reviews in both types of studies.
Citation Analysis:
- Analyze how the researchers use citations to support their arguments and research questions.
- Discuss the citation conventions followed and their alignment with the expectations of the target audience.
Evaluation Criteria:
- Depth of Analysis: Thorough identification and discussion of key themes, sources, research questions, and citations.
- Comparative Insight: Ability to compare and contrast framing of research questions, literature reviews, and citations.
- Clarity and Coherence: Clear and coherent presentation of ideas with logical flow.
- Reflective Thought: Depth of reflection on implications of research paradigm differences.
Step 2 – Choose 2 Articles from the List of PTC Journals below — 1 Qualitative Study & 1 Quantitative Study.
Step 2 – engage in discourse, rhetorical, and citation analysis, for each study in parts 1 and 2, analyze:, 3. comparison.
Compare and contrast the two articles, considering
- differences in how quantitative vs. qualitative studies engage with literature
- variations in presenting research questions and their significance
- variations in how each study type uses literature to interpret results
- differences in rhetorical strategies employed.
4. Evaluation
Score each article on:
- Authority (1-4 scale): Assess how well the authors establish their credibility and the legitimacy of their sources
- Clarity (1-4 scale): Evaluate how clearly the authors present their research questions and engage with existing literature. Did the investigators use visual language / data visualizations to clarify and emphasize key concepts?
- Rhetorical Effectiveness (1-4 scale): Evaluate how well the authors use rhetorical strategies to inform and persuade their audience
Featured Articles

Academic Writing – How to Write for the Academic Community

Professional Writing – How to Write for the Professional World

Credibility & Authority – How to Be Credible & Authoritative in Research, Speech & Writing
'Qualitative' and 'quantitative' methods and approaches across subject fields: implications for research values, assumptions, and practices
- Open access
- Published: 30 September 2023
- Volume 58 , pages 2357–2387, ( 2024 )
Cite this article
You have full access to this open access article

- Nick Pilcher ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5093-9345 1 &
- Martin Cortazzi 2
12k Accesses
Explore all metrics
There is considerable literature showing the complexity, connectivity and blurring of 'qualitative' and 'quantitative' methods in research. Yet these concepts are often represented in a binary way as independent dichotomous categories. This is evident in many key textbooks which are used in research methods courses to guide students and newer researchers in their research training. This paper analyses such textbook representations of 'qualitative' and 'quantitative' in 25 key resources published in English (supported by an outline survey of 23 textbooks written in German, Spanish and French). We then compare these with the perceptions, gathered through semi-structured interviews, of university researchers (n = 31) who work in a wide range of arts and science disciplines. The analysis of what the textbooks say compared to what the participants report they do in their practice shows some common features, as might be assumed, but there are significant contrasts and contradictions. The differences tend to align with some other recent literature to underline the complexity and connectivity associated with the terms. We suggest ways in which future research methods courses and newer researchers could question and positively deconstruct such binary representations in order to free up directions for research in practice, so that investigations can use both quantitative or qualitative approaches in more nuanced practices that are appropriate to the specific field and given context of investigations.
Similar content being viewed by others

Qualitative Research and Content Analysis

Designing a Research Question

“Qualitative Research” Is a Moving Target
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction: qualitative and quantitative methods, presentations, and practices
Teaching in research methods courses for undergraduates, postgraduates and newer researchers is commonly supported or guided through textbooks with explanations of 'qualitative' and 'quantitative' methods and cases of how these methods are employed. Student dissertations and theses commonly include methodology chapters closely aligned with these textbook representations. Unexceptionally, dissertations and theses we supervise and examine internationally have methodology chapters and frequently these consider rationales and methods associated with positivist or interpretivist paradigms. Within such positivist or interpretivist frameworks, research approaches are amplified with elaborations of the rationale, the methods, and reasons for their choice over likely alternatives. In an apparent convention, related data are assigned as quantitative or qualitative in nature, with associated labelling as ‘numerical’ or ‘textual'. The different types of data yield different values and interpretive directions, and are clustered conceptually with particular research traditions, approaches, and fields or disciplines. Frequently, these clusters are oriented around 'quantitative' and 'qualitative' conceptualizations.
This paper seeks to show how ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’, whether stereotyped or more nuanced, as binary divisions as presented in textbooks and published resources describing research methods may not always accord with the perceptions and day-to-day practices of university researchers. Such common binary representations of quantitative and qualitative and their associated concepts may hide complexities, some of which are outlined below. Any binary divide between ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’ needs caution to show complexity and awareness of disparities with some researchers’ practices.
To date, as far as the present authors are aware, no study has first identified a range of binary representations of ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ methods and approaches in a literature review study of the many research methods textbooks and sources which guide students and then, secondly, undertaken an interview study with a range of established participant researchers in widely divergent fields to seek their understandings of ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ in their own fields. The findings related here complement and extend the complexities and convergences of understanding the concepts in different disciplines. Arguably, this paper demonstrates how students and novice researchers should not be constrained in their studies by any binary representations of ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ the terms. They should feel free to use either (or neither) or both in strategic combinations, as appropriate to their fields.
1.1 Presentations
Characteristically, presentations in research methods textbooks distinguish postivist and interpretivist approaches or paradigms (e.g. Guba and Lincoln 1994 ; Howe 1988 ; Denzin and Lincoln 2011 ) or ‘two cultures’ (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ) with associated debates or ‘wars’ (e.g. Creswell 1995 ; Morse 1991 ). Quantitative data are shown as ‘numbers’ gathered through experiments (Moore 2006 ) or mathematical models (Denzin and Lincoln 1998 ), whereas qualitative data are usually words or texts (Punch 2005 ; Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ), characteristically gathered through interviews or life stories (Denzin and Lincoln 2011 ). Regarding analysis, some sources claim that establishing objective causal relationships is key in quantitative analysis (e.g. Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ) whereas qualitative analysis uses more discursive and interpretative procedures.
Thus, much literature presents research in terms of two generally distinct methods—quantitative and qualitative—which many students are taught in research methods courses. The binary divide may seem to be legitimated in the titles of many academic journals. This division prevails as designated strands of separated research methods in courses which apparently handle both (cf. Onwuegbuzie and Leech 2005 ). Consequently, students may follow this seemingly stereotyped binary view or feel uncomfortable to deviate from it. Arguably, PhD candidates need to demonstrate understanding of such concepts and procedures in a viva—or risk failure (cf. Trafford and Leshem 2002 ). The Cambridge Dictionary defines ‘quality’ as “how good or bad something is”; while ‘quantity' is “the amount or number of something, especially that can be measured” (Cambridge 2022 ). But definitions of ‘Qualitative' can be elusive, since “a precise definition of qualitative research, and specifically… its distinctive feature of being “qualitative”, the literature is meager” (Aspers and Corte 2019 , p.139). Some observe a “paradox… that researchers act as if they know what it is, but they cannot formulate a definition” and that “there is no consensus about specific qualitative methods nor… data” (Aspers and Corte 2019 , p40). In general, ‘qualitative research’ is an iterative process to discover more about a phenomenon (ibid.). Elsewhere, 'qualitative’ is defined negatively: "It is research that does not use numbers” (Seale 1999b , p.119). But this oversimplifies and hides possible disciplinary variation. For example, when investigating criminal action, numeric information (quantity) always follows an interpretation (De Gregorio 2014 ), and consequently this is a quantity of a quality (cf. Uher 2022 ).
Indeed, many authorities note the presence of elements of one in the other. For example, in analysis specifically, that what are considered to be quantitative elements such as statistics are used in qualitative analysis (Miles and Huberman 1994 ). More generically, that “a qualitative dimension is present in quantitative work as well” (Aspers and Corte 2019 , p.139). In ‘mixed methods’ research (cf. Tashakkori et al. 1998 ; Johnson et al. 2007 ; Teddlie and Tashakkori 2011 ) many researchers ‘mix’ the two approaches (Seale 1999a ; Mason 2006 ; Dawson 2019 ), either using multiple methods concurrently, or doing so sequentially. Mixed method research logically depends on prior understandings of quantitative and qualitative concepts but this is not always obvious (e.g. De Gregorio 2014 ); for instance Heyvaert et al. ( 2013 ) define mixed methods as combining quantitative and qualitative items, but these key terms are left undefined. Some commentators characterize such mixing as a skin, not a sweater to be changed every day (Marsh and Furlong 2002 , cited in Grix 2004 ). In some disciplines, these terms are often blurred, interchanged or conjoined. In sociology, for instance, “any quality can be quantified. Any quantity is a quality of a social context, quantity versus quality is therefore not a separation” (Hanson 2008 , p.102) and characterizing quantitative as ‘objective’ and qualitative as ‘subjective’ is held to be false when seeking triangulation (Hanson 2008 ). Additionally, approaches to measuring and generating quantitative numerical information can differ in social sciences compared to physics (Uher 2022 ). Indeed, quantity may consist of ‘a multitude’ of divisible aspects and a ‘magnitude’ for indivisible aspects (Uher 2022 ). Notably, “the terms ‘measurement’ and ‘quantification’ have different meanings and are therefore prone to jingle-jangle fallacies” (Uher 2022 ) where individuals use the same words to denote different understandings (cf. Bakhtin 1986 ). Comparatively, the words ‘unit’ and ‘scale’ are multitudinous in different sciences, and the key principles of numerical traceability and data generation traceability arguably need to be applied more to social sciences and psychology (Uher 2022 ). The interdependence of the terms means any quantity is grounded in a quality of something, even if the inverse does not always apply (Uher 2022 ).
1.2 Practices
The present paper compares representations found in research methods textbooks with the reported practices of established researchers given in semi-structured interviews. The differences revealed between what the literature review of methods texts showed and what the interview study showed both underlines and extends this complexity, with implications for how such methodologies are approached and taught. The interview study data (analysed below) show that many participant researchers in disciplines commonly located within an ostensibly ‘positivist’ scientific tradition (e.g. chemistry) are, in fact, using qualitative methods as scientific procedures (contra Tashakkori et al 1998 ; Guba and Lincoln 1994 ; Howe 1988 ; Lincoln and Guba 1985 ; Teddlie and Tashakkori 2011 ; Creswell 1995 ; Morse 1991 ). These interview study data also show that many participant researchers use what they describe as qualitative approaches to provide initial measurements (geotechnics; chemistry) of phenomena before later using quantitative procedures to measure the quantity of a quality (cf. Uher 2022 ). Some participant researchers also say they use quantitative procedures to reveal data for which they subsequently use qualitative approaches to interpret and understand (biology; dendrology) through their creative imaginations or experience (contra e.g. Hammersley, 2013 ). Participant researchers in ostensibly ‘positivist’ areas describe themselves as doubting ‘facts’ measured by machines programmed by humans (thus showing they feel researchers are not outside the world looking in (contra. e.g. Punch 2005 )) or doubting the certainty of quantitative data over time (contra e.g. Punch 2005 ). Critically, the interview study data show that these participant researchers often engage in debate over what a ‘number’ is and the extent to which ‘numbers’ can be considered ‘quantitative’. For example the data show how a mathematician considers that many individuals do not know what they mean by the word ‘quantitative’, and an engineer interprets any numbers involving human judgements as ‘qualitative’. Further, both a chemist and a geotechnician routinely define and use ‘qualitative’ methods and analysis to arrive at numerical values (contra. Davies and Hughes 2014 ; Denzin and Lincoln 2011 ).
Such data refute many textbook and key source representations of quantitative and qualitative as being binary and separately ringfenced entities as shown in the literature review study below (contra e.g. Punch 2005 ; Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ). Nevertheless, they resonate with much recent and current literature in the field (e.g. Uher 2022 ; De Gregorio 2014 ). They also arguably extend the complexities of the terms and approaches. In some disciplines, these participant researchers only do a particular type of research and never need anything other than clear ‘quantitative’ definitions (Mathematics), and some only ever conduct research involving text and never numbers (Literature). Moreover, some participant researchers consider certain aspects lie outside the ‘qualitative’ or ‘quantitative’ (the theoretical in German Literature), or do research which they maintain does not contain ‘knowledge’ (Fine-Art Sculpture), while others outline how they feel they do foundational conceptual research which they believe comes at a stage before any quantity or quality can be assessed (Philosophy). Indeed, of the 31 participant researchers we spoke to, nine of them considered the terms ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ to be of little relevance for their subject.
1.3 Outline of the two studies
This paper reports and discusses findings from a constructivist grounded approach interview study that interviewed experienced participant researchers (N = 31) in various disciplines (see Table 1 below) about their understandings of ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’ in their subject areas. Findings from this interview study were compared with findings from a research methods literature review study that revealed many disparities with received and often binary presentations of the concepts in much key literature that informs student research methods courses. In this section we outline the review criteria, the method of analysis, and our findings. The findings are grouped according to how the sources reviewed consider ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ approaches the aspects of positivism and constructivism; the nature of research questions; research methods; analysis; issues of reliability, validity and generalizability; and the value and worth of the different approaches. Following this. We outline the approach, method, and procedure adopted for the interviews with research participants; sampling and saturation; and analysis; beside details of the participant researchers. Subsequently, Theme 2 focuses on contrasts of the interview data with ‘binary’ textbook and key source representations. Theme 3 focuses on what the interview data show about participant researcher perceptions of the value of ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ methods and approaches. This section outlines where, how, and sometimes why, participant researchers considered ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ methods approaches to be (or to not be) useful to them. These interview study findings show a surprising range of understandings, usage, and often perceived irrelevance of the terms. In the Discussion section, these findings form the focus of comparison with the literature as well as a consideration of possible implications for approaching and teaching research methods. In the conclusion we summarise the implications for research methods courses, for researchers in different disciplines and interdisciplinary contexts and discuss limitations and suggest future research. Besides adding to the debate on how ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ are conceptualized and how they are related, the paper appeals to those delivering research methods courses and to novice researchers to consider the concepts as highly complex and overlapping, to loosen constraints, and elaborate nuances of the commonplace binary representations of the terms.
2 Literature review study: some key textbooks and sources for teaching Research Methods.
2.1 review criteria.
To identify how concepts are presented in key materials we undertook a literature review study by consulting research methods course reading lists, library search engines, physically available shelves in institutional libraries, and Google Scholar. We wanted to encompass textbooks and some key texts which are recommended to UG, PG Masters and PhD students., for example, ‘textbooks’ like ‘Doing Your Research Project: A Guide for first-time researchers’ (Bell and Waters 2014 ) and ‘Introduction to Research Methods: A Practical Guide for Anyone Undertaking a Research project (5th Edition)’ (Dawson 2019 ). Such sources were frequently mentioned on reading lists and are freely available in many institutional libraries. We consulted seminal thinkers who have published widely on research methods, such as Denzin and Lincoln, or Cresswell, but we also considered texts which are likely less known such as ‘A tale of two cultures’ (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ) and key articles such as ‘Five misunderstandings about case-study research’ (Flyvbjerg 2006 ). Students can freely find such sources, and are easily directed to them by supervisors. Although a more comprehensively robust search is possible, we nevertheless followed procedures and standard criteria for literature reviews (Atkinson et al. 2015 ).
3 Method of analysis
We assembled a total of 25 sources to look for a number of key tenets. We examined the sources for occurrence of the following: whether quantitative was described as positivist and qualitative was described as constructivist; whether quantitative was said to be science-based and qualitative was more reflective and non-science based; whether the research questions were presented as predetermined in quantitative methods and initially less focused in qualitative methods; whether quantitative methods were structured and qualitative methods were discussed as less structured; whether quantitative analysis focused on cause-effect type relationships and qualitative analysis was more exploratory; whether reliability, validity and generalizability were achieved through large numbers in quantitative research and through in-depth study in qualitative research; whether for particular subjects such as the sciences quantitative approaches were perceived to be of value (and qualitative was implied to have less value) and whether the converse was the case for other subjects such as history and anthropology; and whether mixed methods were considered possible or not possible. The 25 sources are detailed in Appendix 1 . As a confirmatory but less detailed exercise, and also detailed in Appendix 1 , we checked a further 23 research methods textbooks in German, Spanish and French, authored in those languages (rather than translations from English).
3.1 Findings
Overall, related to what quantitative and qualitative approaches, methods and analysis are, we found many key, often binary representations in this literature review. We outline these here below.
3.2 Positivism and constructivism
Firstly, 20 of the sources we reviewed stated that quantitative is considered positivist, and qualitative constructivist (e.g. Tashakkori et al 1998 ; Guba and Lincoln 1994 ; Howe 1988 ; Lincoln and Guba 1985 ; Teddlie and Tashakkori 2011 ; Creswell 1995 ; Morse 1991 ). Even if not everyone doing quantitative research (e.g. in sociology) consider themselves positivists (Marsh 1979 ), it is generally held quantitative research is positivist. Here, 12 of the sources noted that quantitative is considered ‘scientific’, situating observers outside the world looking in, e.g. through gathering numerical data (Punch 2005 ; Davis and Hughes 2014 ) whereas qualitative “locates the observer in the world” (Denzin and Lincoln 2011 , p.3). Quantitative researchers “collect facts and study the relationship of one set of facts to another”, whereas qualitative researchers “doubt whether social ‘facts’ exist and question whether a ‘scientific’ approach can be used when dealing with human beings” (Bell and Waters 2014 , p. 9).
3.3 The nature of research questions
Secondly, regarding research questions, “qualitative research… typically has… questions and methods… more general at the start, and… more focused as the study progresses” (Punch 2005 , p.28). In contrast, quantitative research uses “numerical data and typically… structured and predetermined research questions, conceptual frameworks and designs” (Punch 2005 , p.28). Of the sources we reviewed, 16 made such assertions. This understanding relates to type, and nature, of data, which is in turn anchored to particular worldviews. Punch ( 2005 , p 3–4) writes of how “in teaching about research, I find it useful to approach the qualitative-quantitative distinction primarily through…. the nature of the data. Later, the distinction can be broadened to include …. ways of conceptualising the reality being studied, and methods.” Here, the nature of data influences approach: numbers are for quantitative, and not-numbers (commonly words) for qualitative. Similarly, for Miles et al. ( 2018 ) “the nature of qualitative data” is “primarily on data in the form of words, that is, language in the form of extended text” (Miles et al. 2018 , no page). These understandings in turn relate to methods used.
Commonly, specific types of methods are said to be related to the type of approach adopted, and 18 of the sources we reviewed presented quantitative methods as being structured, and qualitative methods as less structured. For example, Davies and Hughes ( 2014 , p.23) claim “there are two principal options open to you: 1… quantitative research methods, using the traditions of science. 2… qualitative research, employing a more reflective or exploratory approach.” Here, quantitative methods are “questionnaires or structured interviews” whereas qualitative methods are “such as interviews or focus groups” (Dawson 2019 , no page given). Quantitative methods are more scientific, involve controlling a set of variables, and may involve experiments, something which, “qualitative researchers are agreed in their opposition to this definition of scientific research, or at least its application to social inquiry” (Hammersley 2013 , p. ix). As Punch notes ( 2005 , p.208), “the experiment was seen as the basis for establishing cause-effect relationships between variables, and its outcome (and control) variables had to be measured.”
4.1 Analysis
Such understandings often relate to analysis, and 16 of the sources we reviewed presented quantitative analysis as being statistical and number related, and qualitative analysis as being text based. With quantitative methods, “the data is subjected to statistical analysis, using techniques… likely to produce quantified, and, if possible, generalizable conclusions” (Bell and Waters 2014 , p.281). With qualitative research, however, this “calls for advanced skills in data management and text-driven creativity during the analysis and write-up” (Davies and Hughes 2014 ). Again, the data’s nature is key, and whilst qualitative analysis may condense data, it does not seek numbers. Indeed, “by data condensation, we do not necessarily mean quantification”, however, “occasionally, it may be helpful to convert the data into magnitudes… but this is not always necessary” (Miles et al. 2018 , npg). Qualitative analysis may involve stages such as assigning codes, subsequently sorting and sifting them, isolating patterns, then gradually refining any assertions made and comparing them to other literature (Miles et al. 2018 ). This could involve condensing, displaying, then drawing conclusions from the data (Miles et al. 2018 ). In this respect, some sources consider qualitative and quantitative analysis broadly similar in overall goals, yet different because quantitative analyses use “well-defined, familiar methods; are guided by canons; and are usually more sequential than iterative or cyclical” (Miles et al. 2018 , npg). In contrast, “qualitative researchers are… more fluid and… humanistic” in meaning making (Miles et al. 2018 , npg). Here, both approaches seek causation and may attempt to reveal ‘cause and effect’ but qualitative approaches often seek multiple and interacting influences, and effects and are less rigid (Miles et al. 2018 ). In quantitative inquiry search for causation relates to “causal mechanisms (i.e. how did X cause Y)” whereas in “the human sciences, this distinction relates to causal effects (i.e. whether X causes Y)” (Teddlie and Tashakkori 2011 , p.286). Similarly, that “scientific research in any area… seeks to trace out cause-effect relationships” (Punch 2005 , p.78). In contrast, qualitative research seeks interpretative understandings of human behaviour, “not ‘caused’ in any mechanical way, but… continually constructed and reconstructed” (Punch 2005 , p.126).
4.2 Issues of reliability, validity and generalizability
Regarding reliability, validity and generalizability, 19 of the sources we reviewed presented ideas along the lines that quantitative research is understood to seek large numbers, so quantitative researchers, “use techniques… likely to produce quantified and, if possible, generalizable conclusions (Bell and Waters 2014 , p.9). This means quantitative “research researches many more people” (Dawson 2019 , npg). Given quantitative researchers aim, “to discover answers to questions through the application of scientific procedures” it is anticipated these procedures will “increase the likelihood that the information… will be reliable and unbiased” (Davies and Hughes 2014 , p.9). Conversely, qualitative researchers are considered “more concerned to understand individuals’ perceptions of the world” (Bell and Waters 2014 , p.281) and consequently aim for in-depth data with smaller numbers, “as it is attitudes, behaviour and experiences that are important” (Dawson 2019 , npg). Consequently, generalizability of data is not key, as qualitative research has its “emphasis on a specific case, a focused and bounded phenomenon embedded in its context” (Miles et al. 2018 , npg). Yet, such research is considered generalizable in theoretical insight if not actual data (Flyvbjerg 2006 ).
4.3 The value and worth of the different approaches
Regarding ‘value’ and ‘worth’, many see this related with appropriacy to the question being researched. Thus, if questions involve more quantitative approaches, then these are of value, and if more qualitative, then these are of value, and 6 of the sources we reviewed presented these views (e.g. Bell and Waters 2014 ; Punch 2005 ; Dawson 2019 ). This resonates with disciplinary orientations where choices between given approaches are valued more in specific disciplines. History and Anthropology are seen more qualitative, whereas Economics and Epidemiology may be more quantitative (Kumar 1996 ). Qualitative approaches are valuable to study human behaviour and reveal in-depth pictures of peoples’ lived experience (e.g. Denzin and Lincoln 2011 ; Miles et al. 2018 ). Many consider there to be no real inherent superiority for one approach over another, and “asking whether quantitative or qualitative research is superior to the other is not a useful question” (Goertz and Mahoney 2012 , p.2).
Nevertheless, some give higher pragmatic value to quantitative research for studying individuals and people; neoliberal governments consistently value quantitative over qualitative research (Barone 2007 ; Bloch 2004 ; St Pierre 2004 ). Concomitantly, data produced by qualitative research is criticised by quantitative proponents “because of their problematic generalizability” (Bloor and Wood 2006 , p.179). However, other studies find quantitative researchers see qualitative methods and approaches positively (Pilcher and Cortazzi 2016 ). Some even question the qualitative/quantitative divide, and suggest “a more subtle and realistic set of distinctions that capture variation in research practice better” (Hammersley 2013 , p.99).
The above literature review study of key texts is hardly exhaustive, but shows a general outline of the binary divisions and categorizations that exist in many sources students and newer researchers encounter. Thus, despite the complex and blurred picture as outlined in the introduction above, many key texts students consult and that inform research methods courses often present a binary understanding that quantitative is positivist, focused on determining cause and effect, numerical or magnitude focused, uses experiments, and is grounded in an understanding the world can be observed from the outside in. Conversely, qualitative tends to be constructivist, focused on determining why events occur, is word or textual based (even if these elements are measured by their magnitude in a number or numerical format) and grounded in understanding the researcher is part of the world. The sciences and areas such as economics are said to tend towards the quantitative, and areas such as history and anthropology towards the qualitative.
We also note that in our literature review study we focused on English language textbooks, but we also looked at outline details, descriptions, and contents lists of texts in the languages of German, Spanish and French. We find that these broadly confirm the perception of a division between quantitative and qualitative research, and we detail a number of these in Appendix 1 . These examples are all research methods handbooks and student guides intended for under and post-graduates in social sciences and humanities; many are inter-disciplinary but some are more specifically books devoted to psychology, health care, education, politics, and management. Among the textbooks and handbooks examined in other languages, more recent books pay attention to online research and uses of the internet, social media and sometimes to big data and software for data analysis.
In these sources in languages other than English we find massive predominance of two (quantitative/qualitative) or three approaches (mixed). These are invariably introduced and examined with related theories, examples and cases in exactly that order: quantitative; qualitative; mixed. Here there is perhaps the unexamined implication that this is a historical order of research method development and also of acceptability of use (depending on research purposes). Notably, Molina Marin (2020) is oriented to Latin America and makes the point that most European writing about research methods is in English or German, while there are far fewer publications in Spanish and few with Latin American contextual relevance, which may limit epistemological perspectives. This point is evident in French and Spanish publications (much less the case in German) where bibliographic details seem dominated by English language publications (or translations from them). We now turn to outline our interview study.
5 Interview study
5.1 approach and choice of method.
We approached our interview study from a constructivist standpoint of exploring and investigating different subject specialists’ understandings of quantitative and qualitative. Critically, we were guided by the key constructivist tenet that knowledge is not independent of subjects seeking it (Olssen 1996 ), nor of subjects using it. Extending from this we considered interviews more appropriate than narratives or focus groups. Given the exploratory nature of our study, we considered interviews most suited as we wanted to have a free dialogue (cf. Bakhtin 1981 ) regarding how the terms are understood in their subject contexts as opposed to their neutral dictionary definitions (Bakhtin 1986 ), and not to focus on a specific point with many individuals. Specifically, we used ‘semi’-structured interviews. ‘Semi’ can mean both ‘half in quantity or value’ but also ‘to some extent: partly: incompletely’ (e.g. Merriam Webster 2022 ). Our interviews, following our constructionist and exploratory approach, aligned with the latter definition (see Appendix 2 for the Interview study schedule). This loose ‘semi’ structure was deliberately designed to (and did) lead to interviews directed by the participants, who themselves often specifically asked what was meant by the questions. This created a highly technical dialogue (Buber, 1947) focused on the subject.
5.2 Sampling and saturation
Our sampling combined purposive and snowball sampling (Sharma 2017 ; Levitt et al. 2018 ). Initially, participants were purposively identified by subject given the project sought to understand different subject perspectives of ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative.’ Later, a combined purposive and snowball sampling technique was used whereby participants interviewed were asked if they knew others teaching particular subjects. Regarding priorities for participant eligibility, this was done according to subject, although generally participants also had extensive experience (see Table 1 ). For most, English was their first language, where it was not, participants were proficient in English. The language of interview choice was English as it was most familiar to both participants and interviewer (Cortazzi et al. 2011 ).
Regarding saturation, some argue saturation occurs within 12 interviews (Guest et al. 2006 ), others within 17 (Francis et al. 2010 ). Arguably, however, saturation cannot be determined in advance of analysis and is “inescapably situated and subjective” (Braun and Clarke 2021 , p.201). This critical role of subjectivity and context guided how we approached saturation, whereby it was “operationalized in a way consistent with the research question(s) and the theoretical position and analytic framework adopted” (Saunders et al. 2018 , p.1893). We recognise that more could always be found but are satisfied that 31 participants provided sufficient data for our investigation. Indeed, our original intention was to recruit 20 participants, feeling this would provide sufficient saturation (Francis et al. 2010 ; Guest et al. 2006 ) but when we reached 20, and as we had already started analysis (cf. Braun and Clarke 2021 ) as we ourselves transcribed the interviews (Bird 2005 ) we wanted to explore understandings of ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’ with other subject fields. As Table 1 shows, ‘English Literature’, ‘Philosophy, and ‘Sculpture’ were only explored after interview 20. These additional subject fields added significantly (see below) to our data.

5.3 Analysis and participant researcher details
Our analysis followed Braun and Clarke’s ( 2006 ) thematic analysis. Given the study’s exploratory constructionist nature, we combined ‘top down’ deductive type analysis for anticipated themes, and ‘bottom up’ inductive type analysis for any unexpected themes. The latter was similar to a constructivist grounded theory analysis (Charmaz 2010 ) whereby the transcripts were explored through close repeated reading for themes to emerge from the bottom up. We deliberately did not use any CAQDAS software such as NVivo as we wanted to manually read the scripts in one lengthy word document. We recognise that such software could allow us to do this but we were familiar with the approach we used and have found it effective for a number of years. We thus continued to use it here as well. We counted instances of themes through cross-checking after reading transcripts and discussing them, thereby heightening reliability and validity (Golafshani 2003 ). All interviews were undertaken with informed consent and participants were assured all representation was anonymous (Christians 2011 ). The study was approved by relevant ethics committees. Table 1 above shows the subject area, years of experience, and first language of the participant researchers. We also bracket after each subject area whether we consider it to be ‘Science’ or ‘Arts’ or whether we consider them as ‘Arts/Science’ or ‘Science/Arts’. This is of course subjective and in many ways not possible to do, but we were guided in how we categorised these subjects by doing so according to how we feel the methodology sources form the literature review study would categorize them.
5.4 Presentation of the interview study data compared with data from the literature review study
We present our interview study data in the three broad areas that emerged through analysis. Our approach to thematic analysis was to deductively code the interview transcripts manually under the three broad areas of: where data aligns with textbook and key source ‘binary’ representations; where the data contrasts with such representations; and where the data relates to interviewee perceptions of the value of ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’. The latter relates to whether participant researchers expressed views that suggested they considered each approach to be useful, valuable, or not. We also read through the transcripts inductively with a view to being open to emerging and unanticipated themes. For each data citation, we note the subject field to show the range of subject areas. We later discuss these data in terms of their implications for research values, assumptions and practices and for their use when teaching about different methods. We provide illustrative citations and numbers of participant researchers who commented in relation to the key points below, but first provide an overview in Table 2 .
5.4.1 Theme 1: Alignments with ‘binary’ textbook and key source representations
The data often aligned with textbook representations. Seven participant researchers explicitly said, or alluded to the representation that ‘quantitative’ is positivist and seeks objectivity whereas ‘qualitative’ is more constructivist and subjective. For example: “the main distinction… is that qualitative is associated with subjectivity and quantitative being objective.” This was because “traditionally quantitative methods they’ve been associated with the positivist scientific model of research whereas qualitative methods are rooted in the constructivist and interpretivist model” (Psychology). Similarly, “quantitative methods… I see that as more… logical to a scientific mode of generating knowledge so… largely depends on numbers to establish causal relations… qualitative, I want to more broadly summarize that as anything other than numbers” (Communication Studies). One Statistics researcher had “always associated quantitative research more with statistics and numbers… you measure something… I think qualitative… you make a statement… without saying to what extent so… so you run fast but it’s not clear how fast you actually run…. that doesn’t tell you much because it doesn’t tell you how fast.” One mathematics participant researcher said mathematics was “ super quantitative… more beyond quantitative in the sense that not only is there a measurement of size in everything but everything is defined in… really careful terms… in how that quantity kind of interacts with other quantities that are defined so in that sense it’s kind of beyond quantitative.” Further, this applied at pre-data and data integration stages. Conversely, ‘qualitative’ “would be more a kind of verbalistic form of reasoning or… logic.”
Another representation four participant researchers noted was that ‘quantitative ‘ has structured predetermined questions whereas ‘qualitative’ has initially general questions that became more focused as research proceeded. For example, in Tourism, “with qualitative research I would go with open ended questions whereas with quantitative research I would go with closed questions.” This was because ‘qualitative’ was more exploratory: “quantitative methods… I would use when the parameters… are well understood, qualitative research is when I’m dealing with topics where I’m not entirely sure about… the answers.” As one Psychology participant researcher commented: “the main assumption in quantitative… is one single answer… whereas qualitative approaches embrace… multiplicity.”
Nineteen participant researchers considered ‘quantitative’ numbers whereas ‘qualitative’ was anything except numbers. For example, “quantitative research… you’re generating numbers and the analysis is involving numbers… qualitative is… usually… text-based looking for something else… not condensing it down to numbers” (Psychology). Similarly, ‘quantitative’ was “largely… numeric… the arrangement of larger scale patterns” whereas, “in design field, the idea of qualitative…is about the measure… people put against something… not [a] numerical measure” (Design). One participant researcher elaborated about Biology and Ecology, noting that “quantitative it’s a number it’s an amount of something… associated with a numerical dimension… whereas… qualitative data and… observations… in biology…. you’re looking at electron micrographs… you may want to describe those things… purely in… QUALitative terms… and you can do the same in… Ecology” (Human Computer Interaction). One participant researcher also commented on the magnitude of ‘quantitative’ data often involving more than numbers, or having a complex involvement with numbers: “I was thinking… quantitative… just involves numbers…. but it’s not… if… NVivo… counts the occurrence of a word… it’s done in a very structured way…. to the point that you can even… then do statistical analysis” (Logistics).
Regarding mixed methods, data aligned with the textbook representations that there are two distinct ‘camps’ but also that these could be crossed. Six participants felt opposing camps and paradigms existed. For example, in Nursing, that “it does feel quite divided in Nursing I think you’re either a qualitative or a quantitative researcher there’s two different schools… yeah some people in our school would be very anti-qualitative.” Similarly, in Music one participant researcher felt “it is very split and you’ll find… some people position themselves in one or the other of those camps and are reluctant to consider the other side. In Psychology, “yes… they’re quite… territorial and passionately defensive about the rightness of their own approaches so there’s this… narrative that these two paradigms… of positivistic and interpretivist type… cannot be crossed… you need to belong to one camp.” Also, in Communication Studies, “I do think they are kind of mutually exclusive although I accept… they can be combined… but I don’t think they, they fundamentally… speak to each other.” One Linguistics participant researcher felt some Linguists were highly qualitative and never used numbers, but “then you have… the corpus analysts who quantify everything and always under the headline ‘Corpus linguistics finally gets to the point… where we get rid of researcher bias; it objectifies the analysis’ because you have big numbers and you have statistical values and therefore… it’s led by the data not by the researcher.” This participant researcher found such striving for objectivity a “very strange thing” as any choice was based on previously argued ideas, which themselves could not be objective: “because all the decisions that you need to put into which software am I using, which algorithm am I using, which text do I put in…. this is all driven by ideas.”
Nevertheless, three participant researchers felt the approaches not diametrically opposed. For example, the same Psychology participant researcher cited immediately above felt people’s views could change: “some people although highly defensive over time… may soften their view as mixed method approaches become more prominent.” Comparatively flexibly, a Historian commented “I don’t feel very concerned by the division between qualitative and quantitative; I think they’re just two that are separate sometimes complementary approaches to study history.” In Translation and Interpreting, one participant researcher said methods could be quantitative, but have qualitative analysis, saying one project had: “an excellent use of quantitative tools… followed by not a qualitative method but qualitative analysis of what that implied.” Thus, much of the data did align with the binary representations of the key textbooks reviewed above and also the representation that approaches could be combined.
5.4.2 Theme 2: Contrasts with ‘binary’ textbook and key source representations
One recurrent contrast with common textbook representations was where both qualitative and quantitative were used in some sciences; nine participant researchers felt this. For example, in Geotechnics, when ascertaining soil behaviour: “the first check, the Qualitative check is to look whether those [the traditional and new paths of soil direction] bear resemblance, [be] coz if that doesn’t have that shape how can I expect there to be a quantitative comparison or… fit.” Both qualitative and quantitative approaches combined helped “rule out coincidence” and using both represented “a check which moves through qualitative… to quantitative.” Quantitative was a “capital Q for want of a better expression” and consisted of ‘bigger numbers’, which constituted “the quantitative or calculated strength.” However, this ‘capital Q’ quantitative data aimed to quantify a qualitatively measured numerically estimated phenomenon. So both were numerical. Nevertheless, over the long-term, even the quantitative became less certain because: “when you introduce that time element… you create… circumstances in which you need to be careful with the way you define the strength… different people have come up with different values… so the quantitative match has to be done with an element of uncertainty.”
Similarly, in Chemistry, both qualitative and quantitative methods and analysis were used, where “ the qualitative is the first one, and after you have the other ones [I—Right to kind of verify] if… if you need that.” Both were used because, “we need to know what is there and how much of each component is there… and a knowledge of what is there is a qualitative one, how much of each one is a quantitative one.” Moreover, “they are analysed sometimes by the same technique ” which could be quantitative or qualitative: “[I—and chromatography, again… would that be qualitative or quantitative or both?] Both, both… the quantitative is the area of the peak, the qualitative is the position in which this characteristic appears.” Here, both were key, and depending on the research goal: “we… use them according to what we need… sometimes it’s enough to detect [qualitative] … other times you need to know how much [quantitative] ”.
For Biology also, both were key: “quantitative is the facts and… qualitative is the theory you’re trying to make fit to the facts you can’t do it the other way around… the quantitative data… just doesn’t tell you anything without the qualitative imagination of what does it mean?” Inversely, in an area commonly understood as quantitative, Statistics, the qualitative was an initial, hypothetical stage requiring later quantitative testing. For example: “very often the hypothesis is a qualitative hypothesis” and then, “you would test it by putting in all sorts of data and then the test result would give you a p-value… and the p-value of course is quantitative because that’s a number.”
In Engineering, both helped research sound frequencies: “we need to measure the spectrum of the different frequencies… created… all those things were quantifiable, but then we need to get participants to listen and tell us… which one do you prefer?… this is a qualitative answer.” Mathematical Biology also used both: qualitative for change in nature of a state, and quantitative for the magnitude of that change. Here: “quantitative changes the numerical value of the steady state but it doesn’t change its stability… but qualitative change is when you… change the parameters and you either change its stability or you change whether it exists or not… and that point over which you cross to change it from being stable to unstable is called a bifurcation point… that’s where I use quantitative and qualitative the most in my research.”
The idea of ‘quantitative’ involving large data sets was expressed; however, the ‘qualitative’ could help represent these. In Computing Mathematics one participant researcher commented that: “quantitative… I do almost 90% of the time…. calculating metrics… and using significance testing to determine whether the numbers mean anything.” Yet, this participant researcher also used qualitative representations for simplified visual representation of large number sets: “I think for me QUALitative work is almost always about visualizing things in a way that tries to illustrate the trends… so I’m not actually calculating numbers but I’m just saying if I somehow present it in in this way.” Concomitantly, ‘quantitative’ could be smaller scale. For example, in Architecture: “my expectation is it wouldn’t be valid until you have a certain quantity of response but that said [I] have had students use… quantitative analysis on a small sample.” Similarly, in History: “you could have a quantitative study of a small data set or a small… number of statistics I really think it’s determined by the questions… you’re asking.”
Interestingly, two participant researchers questioned their colleagues’ understandings of ‘quantitative’ and of ‘numbers’. For example, one Mathematician considered some researchers did not know what ‘quantitative’ meant, because “when they say quantitative… I think what they mean is the same as qualitative except it’s got numbers in it somewhere.” For example, “I’m talking to a guy who does research in pain and, so I do know now what he means by quantitative research, and what he means is that he doesn’t know what he means [both laugh] and he wants me to define what it means… I think he means he wants some form of modelling with data and… he’s not quite sure how to go about doing that.” For this Mathematician, engineers would, “Mean that purposefully when they talk about quantitative modelling” whereas, “generically you know when politicians [consider these things] quantitative just means there’s a number in it somewhere.”
Three participant researchers felt that when ‘quantitative’ involved human elements or decisions, subjectivity was inevitable. One Logistics participant researcher felt someone doing materials research was “Doing these highly quantitative analyses still there is a degree of subjectivity because… this involves human assessment… they’re using different photometric equipment… taking photos… what is the angle.” Another researcher in Sciences similarly noted, “I don’t know why people believe in machines so much because they’re built by humans and there’s so many errors.” An Engineer commented: “To me, just the involvement of humans… gives it a qualitative element no matter what.” For this researcher, with people’s ‘quantitative’ reaction times and memory recall, “I would call that again qualitative you know… yes we did quantify the reaction time… the correct number of answers, but… it’s a person… I could get somebody else now doing it and not get exactly the same answer, so that uncertainty of human participants to me make it a qualitative approach.” For this participant researcher, anything involving human participants was ‘qualitative’: “I would say anything that is measurable, but by measurable I mean physically measurable… or predictable through numbers is quantitative [and] anything that involves a judgment, therefore human participants… is qualitative.”
‘Qualitative’ was often highly subject-specific. For example, in Film Studies and Media—English, ‘qualitative’ was: “about… the qualities of particular texts…. I’ve read a lot about silence as a texture and a technique in cinema… so silence is a quality, and also what are the qualities of that silence.” One Sciences researcher felt ‘qualitative’ involved experience applied to interpreting data: “Qualitative I would define as using your own experience to see if the data makes sense… and… something that… cannot be measured so far by machine… like the shape of a tree.” One Historian also highlighted the importance of subject-sub-branches, saying, “I’d situate myself in history but I guess you’d probably get a different response depending on… whether that historian saw themselves as a cultural historian or as a social and economic historian or… an intellectual historian.”
A fluidity regarding ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ was characterized. One Human Computer Interaction participant researcher commented, “I think sometimes people can use both terms quite loosely without really sort of thinking about [them] .” Comparatively, one Psychology participant researcher commented that “even within the Qual[itative] people they disagree about how to do things [laughs] … so you have people talking about doing IPA [Interpretative Phenomenological Analysis] and they’re doing… and presenting it in completely different ways.” Another Psychologist felt using ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ as an ‘either/or’ binary division erroneously suggested all questions were answerable, whereas: “no method… can… answer this question… and this is something… many people I don’t think are getting is that those different methodologies come with huge limitations… and as a researcher you need… to appreciate… how far your work can go.” One Communication Studies participant researcher even perceived the terms were becoming less used in all disciplines, and that, “we’re certainly in a phase where even these labels now are becoming so arbitrary almost… that they’re not, not carrying a lot of meaning.” However, the terms were considered very context dependent: “I think I’d be very hesitant about… pigeonholing any particular method I’d want to look very closely at the specific context in which that particular method or methodology is being used.” Further, some concepts were considered challenging to align with textbook representations. One German Literature participant researcher, reflecting on how the ‘theoretical’ worked, concluded, “… the theoretical… I’m not sure whether… that is actually within the terms quantitative or qualitative or whether that’s a term… on a different level altogether .” Indeed, many participant researchers (nine in total across many subject areas e.g. Design, Film and Media, Philosophy, Mathematical Biology) confirmed they were fully aware of the commonplace representations, but felt they did not apply to their own research, only using them to communicate with particular audiences (see below).
5.4.3 Theme 3: Perceptions on the value of ‘Quantitative’ and ‘Qualitative’ methods and approaches
As the data above show, many participant researchers valued both ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’, including many scientists (in Geotechnics; Biology, Chemistry, Engineering). Many considered the specific research question key. For example: “I certainly don’t think quantitative bad, qualitative good: it’s horses for courses, yeah” (Tourism). Participant researchers in History and Music Education felt similarly; the latter commenting how “I do feel it’s about using the right tools which is why I wouldn’t want to… enter into this kind of vitriolic negative mud-slinging thing that does happen within the fields because I think people… get too entrenched in one or the other and forget about the fact that these are just various ways to approach inquiry.” Similarly, one Psychologist observed, “I’m always slightly irritated [laughs] when I hear people you know say ‘Oh I’m only doing… qualitative research’ or ‘I’m only doing quantitative research’… I think it’s the research question that should drive the methodological choices.” This participant researcher had “seen good quality in both quantitative and qualitative research.”
Five participant researchers considered quantitative approaches to be of little value if they were applied inappropriately. For example, a Translation and Interpreting participant researcher felt quantitative data-generating eye tracking technology was useful “for marketing,… product placement,… [or] surgeons.” However, for Translation and Interpreting, “I don’t think… it is a method that would yield results… you could find better in a more nuanced manner through other methods, interviews or focus groups, or even ethnographic observation.” One Chemist questioned the value of quantitative methods when the sample was too small. For example, when students were asked about their feedback on classes, and one student in 16 evaluated the classes badly, “4% it was one person [laughs] in 16, one person, but I received that evaluation and I think this is not correct… because sometimes…. I think that one person probably he or she didn’t like me… well, it’s life, so I think these aspects… may happen also but it’s with the precision of the system… the capacity of the system to detect and to measure.” Meaningfulness was held to be key: “When we do the analysis the sample has meaning” . Similarly, a Theoretical Physicist felt quantitative approaches unsuited to education: “in the context of education… we all produce data all the time… we grade students… we assess creativity… people will say… ‘you measure somebody's IQ using this made-up test and you get this kind of statis[tic]..’ and then you realize that all of those things are just bogus… or at least… doesn't measure anything of any real serious significance.” Comparatively, one participant researcher in Design felt ‘quantitative’ had a danger to “lead to stereotypes”; for example, when modern search engines use quantitative data to direct people to particular choices, “There’s potential there to constrain kind of broader behaviours and thinking… and therefore it can become a programmer in its own right.” One Mathematical Biologist commented how statistics can be misused, and how a popular Maths book related “How statistics are a light shone on a particular story from a particular angle to paint a picture that people want you to see but… it’s almost never the whole picture, it’s a half-truth, if you like, at best.”
Seven participant researchers considered that their disciplines valued quantitative over qualitative. This could be non-judgmental, and perhaps inherent in major areas of a discipline, as in Theoretical Physics, where precision is crucial, although this was said not to be ‘disparaging’: “theoretical physics… or physics in general… we… tend to think of ourselves as being very, very quantitative and very precise, and we think of qualitative, I guess… as being a bit vague, right?… which is not disparaging, because sometimes… we have to be a bit vague… and we're working things out.” In Psychology, however, despite “a call to advocate for more qualitative methods”, there, “definitely… is a bias toward quantitative… measures in psychology; all the high impact factor journals advocate for quantitative measures.” In Nursing, quantitative was also deemed paramount, with “the randomized control trial seen as being… you know the apex and… some researchers in our school would absolutely say it’s the only reliable thing… would be very anti-qualitative.”
Yet, four participant researchers were positively oriented towards anything qualitative. For example, one Tourism researcher felt that, “in an uncertain world, such as the one we’re living in today, qualitative research is the way forward.” Also, an Architect highlighted that in one of their studies, “I think the most important finding of my questionnaires was in the subjective comments.” One Music education participant researcher personally favoured qualitative approaches but regretted how their field was biased toward quantitative data, saying they had been informed: “ ‘what journals really care about is that p-value…’ and I remember… thinking… that’s a whole area of humanity… you’re failing to acknowledge.”
Nevertheless, side-stepping this debate, nine researchers considered the terms of little value, and simply irrelevant for their own research. One Film and Media—English participant researcher commented: “I have to say… these are terms I’m obviously familiar with, but… not terms… I… tend to really use in my own research… to describe what I do … mainly because everything that I do is qualitative.” As an English Literature participant researcher noted in email correspondence: “they are not terms we use in literary research, probably because most of what we do is interpretation of texts and substantiating arguments through examples. I have really only encountered these terms in the context of teaching and have never used them myself.” In the interview, this participant researcher commented that “I can imagine… they would be terms… quite common in the sciences and mathematics, but not Social Sciences and Arts.” A German Literature participant researcher felt similarly, commenting that in “German Literature… the term quantitative hadn’t even entered my vocabulary all the way through the PhD [laughs] … because… you could argue the methods in literary research are always qualitative.”
Complementing such perspectives, in Theoretical Physics ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’ was: “not something that ever comes up… I don’t think I read a paper ever that will say we do qualitative research in any way, but I never… or hardly ever handle any data… I just have a bunch of principles that are sort of either taken to be true or are… a model… we’re exploring.” In Mathematics, ‘quantitative’ was simply never used as all mathematics research was quantitative: “I never use the word in the company of my colleagues, never, it’s a non-vocabulary word, for the simple reason that when everything is so well defined why do you need a generic term when you’ve got very specific reference points in the language that you’re using?”.
One Philosopher felt the terms did not fit conceptual analysis in philosophy, given that the object of consideration was uncertain: “I guess… I thought it didn’t fit conceptual analysis… you need to know what you’re dealing with in order to then do the quantitative or qualitative whereas in philosophy it feels like… you don’t quite know what you’re dealing with you’re trying to work out… what are rights?… What is knowledge? What is love?… and then look at its qualities.” For this researcher, Philosophy was tentatively pre-quantitative or pre-qualitative, because philosophy “feels like it’s before then.” The terms were not considered valuable for Philosophy or for the humanities generally: “in philosophy we wouldn’t use the term qualitative or quantitative research… you just use the tools… you need… to develop your argument and so you don’t see the distinction… I would say in the humanities that’s relatively similar.” Further, a Fine Art—Sculpture participant researcher said: “they’re not words I would use… partly because… I’m engaged with… through… research and… teaching… what I’d call practice research… and… my background’s in fine art, predominantly in making sculpture and that doesn’t contain knowledge.” Here, the participant researcher related how they may consider a student’s work hideous but if the student had learned a lot through creating the work, they should be rewarded. This participant researcher spoke of a famous sound artist, concluding, “if you asked him about qualitative and quantitative… it just wouldn’t come into his thing at all…. He doesn’t need to say well there were a thousand visitors plus you know it’s just ‘bang’… he wouldn’t think about those things… not as an artist.”
Six participant researchers said they only ever used the terms for particular audiences. For example, for ‘quantitative’ in Film and Media: “the only time is when it’s been related to public engagement that we’ve ever sort of produced anything that is more along quantitative lines,” and that “it was not complex data we were giving them.” In Fine-Art Sculpture, too, the terms were solely used with a funder, for example, to measure attendance at an exhibition for impact, but “that’s not the type of research that I’m involved with necessarily.” One Logistics participant researcher commented that “it really depends on the audience how you define qualitative or quantitative.” For this researcher, if communicating with “statisticians econometricians or a bunch of people who are number crunchers” then “they will be very precise on what quantitative is and what qualitative is” and would only recognise mathematical techniques as quantitative. Indeed, “they wouldn’t even recognize Excel as quantitative because it’s not that hard.” In contrast, for social scientists, Excel would be quantitative, as would “anything to do with numbers… I suppose you know a questionnaire where you have to analyse responses would be probably classed as quantitative.”
Conversely, a Mathematical Biology participant researcher commented they had been doing far more public outreach work, “using quantitative data so numbers… even with things that might often be treated in a qualitative way… so stuff which… is often treated I think qualitatively we try to quantify… I think partly because it’s easier to make those comparisons when you quantify something.” One researcher in Communication Studies said they advised a student that “it depends on your research objectives; if you are focusing on individual experiences… I think naturally that’s going towards qualitative, but if you’re … doing this research oriented to a leader of … [a] big number of people… for informing policy… then you need some sort of insights that can be standardized… so it’s a choice.”
Another Communication participant researcher felt political shifts in the 1990s and 2000s meant that a ‘third way’ now dominated with a move towards hybridity and a breakdown in ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’ with everything now tied to neoliberalism. Therefore, since “the late 90s and early noughties I’ve seen this kind of hybridity in research methods almost as being in parallel with the third way there seems to be… no longer opposition between left and right everything… just happens to buy into neoliberalism so likewise… with research methods… there’s a breakdown of qual and quant.” Comparatively, a Historian felt underpinning power structures informed approaches, commenting that “the problem is not the terminology it’s the way in which power is working in the society in which we live in that’s the root problem it seems to me and what’s valued and what’s not.” A Philosopher felt numbers appealed to management even when qualitative data were more suitable: “I think management partly… are always more willing to listen to numbers… finding the right number can persuade people of things that actually… you think really a better persuasion would do something more qualitative and in context.” One Fine Art participant researcher felt ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ only became important when they focused on processes related to the Research Excellence Framework but not for their research as such: “I guess we are using qualitative and quantitative things in the sense of moving ourselves through the process as academics but that’s not what I’d call research.”
6 Discussion: implications for teaching research methods
Research Methods teaching for undergraduate, postgraduate and newer researchers is commonly guided by textbook and seminal text understandings of what constitutes ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’. Often, the two are treated in parallel, or interlinked, and used in combination or sequentially in research. But the relations between these are complex. The above analysis of the interview study with established participant researchers underlines and often extends this complexity, with implications for how such methodologies are approached and taught. Many of these participant researchers in disciplines commonly located within an ostensibly ‘positivist’ scientific tradition are, in fact, using qualitative methods as scientific procedures. They do so to provide initial measurements of phenomena before later using quantitative procedures to measure the quantity of a quality. They also use quantitative procedures to reveal data for which they subsequently use qualitative approaches to interpret and understand through their creative imaginations or experience. Participant researchers in ostensibly positivist disciplines describe themselves as doubting ‘facts’ measured by machines programmed by humans or doubting the certainty of quantitative data over time. Critically, these participant researchers engage in debate over what a ‘number’ is and the extent to which ‘numbers’ can be considered ‘quantitative’. One mathematician spoke of how many individuals do not know what they mean by the word ‘quantitative’, and an engineer interpreted any numbers involving human judgements as ‘qualitative’. Both a chemist and a geotechnician routinely defined and use ‘qualitative’ methods and analysis to arrive at numerical values.
Although this analysis of participant researchers’ reported practices refutes many textbook and key research methods source representations of quantitative and qualitative as being binary and separately ringfenced entities (contra e.g. Punch 2005 ; Goertz and Mahoney 2012 ), they resonate with much recent and current literature in the field (e.g. Uher 2022 ; De Gregorio 2014 ). In some disciplines, participant researchers only do a particular type of research and never need anything other than clear ‘quantitative’ definitions (Mathematics); others only ever conduct research involving text and never numbers (Literature). Further, other participant researchers considered how certain aspects lie outside the ‘qualitative’ or ‘quantitative’ (the ‘theoretical’ in German Literature), or they did research which they maintain does not contain ‘knowledge’ (Fine-Art Sculpture), while others do foundational ‘conceptual’ research which they claim comes at a stage before any quantity or quality can be assessed (Philosophy). Nine researchers considered the terms of little relevance at all to their subject areas.
This leads to subsequent questions. Firstly, do the apparently emerging tensions and contradictions between commonplace textbook and key source presentations and on-the-ground participant researcher practices matter? Secondly, what kind of discourse might reframe the more conventional one?
Regarding whether tensions and contradictions matter: in one practical way, perhaps not, since participant researchers in all these areas continue to be productive in their current research practices. Nevertheless, the foundations of the binary quantitative and qualitative divide are discourse expressions common to research methods courses. These expressions frame how the two terms are understood as the guide for novices to do research. This guiding discourse is evident in specifically designated chapters in research handbooks, in session titles in university research methods modules, and in entries for explanations of research terms within glossaries. The literature review study detailed above illustrates this. ‘Quantitative’ means numbers, ‘qualitative’ means words. ‘Quantitative’ connotes positivist, objective, scientific; ‘qualitative’ implies constructivist, subjective, non-science-based. Arguably, any acceptance of the commonplace research method understanding gives an apparent solidity which can sometimes be a false basis that masks the complexities or inadequacies involved. Such masking can, in turn, allow certain agencies or individuals to claim their policies and practices are based on ‘objective’ numerical data when they are merely framing something as ‘quantitative’ when, as a cited Mathematician participant researcher observed above, it is simply something with a number in it somewhere. Conventionally, limitations are mentioned in research studies, but often they seem ritualized remarks which refer to insufficient numbers, or restricted types of participants, or a constrained focus on a particular area. Rarely do research studies (let alone handbooks and guides for postgraduates) question a taken-for-granted understanding, such as whether the very idea of using numbers with human participants may mean the number is not objective. Ironically, it is the field of Qualitative Inquiry itself in which occasionally some of these issues are mentioned. Concurrently, while the quantitative is promoted as ‘scientific’ and ‘objective evidence’, we find some scientists researching in sciences often question the terms, or consciously set them aside in their practices.
Concerning what could replace the commonplace terms and reframe the research discourse environment: arguably, any discussion of ‘quantitative’/‘qualitative’ should be preceded by key questions of how they are understood by researchers. Hammersley ( 2013 ) has suggested the value of a more nuanced approach. As the Communication Studies participant researcher here commented, the two terms seem to be breaking down somewhat. Nevertheless, alongside the data and arguments here, we see some value in considering things as being ‘quantitative’ or ‘qualitative’, and other value in viewing them as separate. The terms can still be simply outlined, not just as methodological listings of characteristics, but as a critical point, Outlines of methods should include insider practitioner views—illustrations of how they are used and understood by practising researchers in different disciplines (as in Table 2 above). This simple suggestion has benefits. When outlining approaches as qualitative or quantitative, we suggest space is devoted to how this is understood in disciplines, together with the opportunity to question the issues raised by these understandings. This would help to position the understandings of qualitative and quantitative within specific disciplinary contexts, especially in inter-disciplinary fields and, implicitly, it encourages reflection on the objectivity and subjectivity evoked by the terms. Such discussion can be included in research methods texts and in research methods courses, dissertations and frameworks for viva examinations (Cortazzi and Jin 2021 ). Here, rather than start with outlining what the terms mean by using concrete definitions such as ‘Quantitative means X’ the terms should be outlined using subject contextualised phrases such as ‘In the field of X quantitative is understood to mean Y’. In this way, quantitative and qualitative methods and approaches can be seen, understood and contextualised within their subject areas, rather than prescriptively outlined in a generic or common form. Furthermore, if the field is one that has no use for such terms, this can also be stated, to prevent any unnecessary need for their use. Discourse around the terms can be extended if they are seen in line with much current literature and the data above that shows their complexities and overlaps, and goes beyond the binary choices and representations of many textbooks.
7 Conclusion
This paper has presented and discussed data from an interview study with experienced participant researchers (n = 31) regarding their perceptions of ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’ in their research areas. This interview study data was compared with findings from a literature review study of common textbooks and research methods publications (n = 25) that showed often binary and reified representations of the terms and related concepts. The interview study data show many participant researcher understandings do in some ways align with the binary and commonplace representations of ‘qualitative ‘and ‘quantitative’ as shown to be presented in many research methods textbooks and sources from the literature review study. However, the interview study data more often illustrate how such representations are somewhat inaccurate regarding how research is undertaken in the different areas researched by the participant researchers. Rather, they corroborate much of the current literature that shows the blurring and complexity of the terms. Often, they extend this complexity. Sometimes they bypass complexity when these terms are considered irrelevant to their research fields by many researcher participants. For some researchers, the terms are simply valueless. We propose that future research methods courses could present and discuss the data above, perhaps using something akin to Table 2 as a starting point, so that students and novice researchers are able to loosen or break free of the chains of any stereotypical representations of such terms or use them reflectively with awareness of disciplinary specific usage. This could help them to advance their research, recognizing complex caveats related to the boundaries of what they do, what methods they use, and how to conduct research using both quantitative and qualitative approaches, as interpreted and used in their own fields. In multi- or inter-disciplinary research, such reflective awareness seems essential. Future research could also study the impact of the use of the data here in research methods courses so that such courses encompass both qualitative and quantitative methods (cf. Onwuegbuzie and Leech 2005 ) yet also question and contextualise such terms in specific subject areas order to free research from any constraints created by binary representations of the terms.
Whilst we interviewed 31 participant researchers to approach what seems a reasonable level of saturation, clearly future research could add to what we have found here by speaking to a wider range and larger number of researchers. The 25 research methods sources in English (supplemented by 23 sources in German, Spanish and French) examined here can clearly be expanded for a wider analysis of ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ in other languages for a more comprehensive European perspective. This strategy might ascertain likely asymmetries between the numerous English language texts (and their translations) and relatively smaller numbers of texts written by national or local experts in other languages. As a world-wide consideration, given the relative paucity of published research guidance in many languages, this point is especially significant related to fitting research methods to local contexts and cultures without imposition. Translating and discussing the terms ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’, in and beyond European languages, will need care to avoid binary stereotyped or formulaic expression and to maintain some of the insight, resonances and complexities shown here.
Aspers, P., Corte, U.: What is qualitative in qualitative research. Qual. Sociol. 42 (2), 139–160 (2019)
Article Google Scholar
Atkinson, K.M., Koenka, A.C., Sanchez, C.E., Moshontz, H., Cooper, H.: Reporting standards for literature searches and report inclusion criteria: making research syntheses more transparent and easy to replicate. Res. Synth. Methods 6 (1), 87–95 (2015)
Autran, D., Bassel, G.W., Chae, E., Ezer, D., Ferjani, A., Fleck, C., Wolf, S.: What is quantitative plant biology? Quant. Plant Biol. (2021). https://doi.org/10.1017/qpb.2021.8
Bakhtin, M.: The dialogic imagination. University of Texas Press, Austin (1981)
Google Scholar
Bakhtin, M. M. Speech genres and other late essays. In: Trans. Vern W. McGee; Ed. Caryl Emerson and Michael Holquist. University of Texas Press, Austin, (1986)
Barone, T.: A return to the gold standard? Questioning the future of narrative construction as educational research. Qual. Inq. 13 (4), 454–470 (2007)
Bell, J., Waters, S.: Doing your research project: a guide for first-time researchers (6 th edit.). McGraw-Hill Education, London, (2014)
Bird, C.M.: How I stopped dreading and learned to love transcription. Qual. Inq. 11 (2), 226–248 (2005)
Bloch, M.: A discourse that disciplines, governs, and regulates: The national research c report on scientific research in education. Qual. Inq. 10 (1), 96–110 (2004)
Bloor, M., Wood, F.: Keywords in qualitative methods: A vocabulary of research concepts. Sage, London (2006)
Book Google Scholar
Braun, V., Clarke, V.: Using thematic analysis in psychology. Qual. Res. Psychol. 3 (2), 77–101 (2006). https://doi.org/10.1191/1478088706qp063oa
Braun, V., Clarke, V.: To saturate or not to saturate? Questioning data saturation as a useful concept for thematic analysis and sample-size rationales. Qualit. Res. Sport Exer. Health 13 (2), 201–216 (2021)
Cambridge: Cambridge Dictionary. English Dictionary. Available at: https://dictionary.cambridge.org/dictionary/english/ Last Accessed January 2023. (2022)
Chan, E.S., Okumus, F., Chan, W.: What hinders hotels’ adoption of environmental technologies: a quantitative study. Int. J. Hosp. Manag. 84 , 102324 (2020)
Charmaz, K.: Grounded theory. Objectivist and constructivist methods. In W. Luttrell (Ed.), Qualitative educational research: Readings in reflexive methodology and transformative practice (pp. 183–207). Routledge, New York. (2010)
Christians, C.G.: Ethics and politics in qualitative research. In: Denzin, N.K., Lincoln, Y.S. (eds.) The Sage handbook of qualitative research, pp. 61–80. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA (2011)
Cortazzi, M., Pilcher, N., Jin, L.: Language choices and ‘blind shadows’: investigating interviews with Chinese participants. Qual. Res. 11 (5), 505–535 (2011)
Cortazzi, M., Jin, L.: The doctoral viva: questions for, with and to candidates (or supervisors). Int. J. Educat. Lit. Stud. 9 (4), 2–15 (2021)
Creswell, J.W.: Research design: Qualitative & quantitative approaches. Sage, Thousand Oaks, CA (1995)
Davies, M.B., Hughes, N.: Doing a successful research project: Using qualitative or quantitative methods. Macmillan International Higher Education, London (2014)
Dawson, C.: Introduction to Research Methods: A Practical Guide for Anyone Undertaking a Research Project, 5th edn. Robinson, London (2019)
De Gregorio, E.: Bridging “quality” and “quantity” in the study of criminal action. Qual. Quant. 48 (1), 197–215 (2014)
Denzin, N.K., Lincoln, Y.S. (eds.): The landscape of qualitative research: Theories and issues. Sage, Thousand Oaks (1998)
Denzin, N.K., Lincoln, Y.S. (eds.): The SAGE handbook of qualitative research (4th edit). Sage, Thousand Oaks (2011)
Flyvbjerg, B.: Five misunderstandings about case-study research. Qual. Inq. 12 (2), 219–245 (2006)
Francis, J.J., Johnston, M., Robertson, C., Glidewell, L., Entwistle, V., Eccles, M.P., Grimshaw, J.M.: What is an adequate sample size? Operationalising data saturation for theory-based interview studies. Psychol. Health 25 (10), 1229–1245 (2010)
Goertz, G., Mahoney, J.: A tale of two cultures. Princeton University Press, New Jersey (2012)
Golafshani, N.: Understanding reliability and validity in qualitative research the qualitative report, vol. 8 no. 4 597–607. (2003). http://www.nova.edu/ssss/QR/QR8-4/golafshani.pd
Grix, J.: The undations of research. Palgrave Macmillan, New York (2004)
Guba, E.G, Lincoln, Y.S: Competing paradigms in qualitative research. In: Denzin, N.K. Lincoln, Y.S. (eds.) Handbook of qualitative research, pp. 105–117. Sage, Thousand Oaks, 1994
Guest, G., Bunce, A., Johnson, L.: How many interviews are enough? An experiment with data saturation and variability. Field Methods 18 (1), 59–82 (2006)
Hammersley, M.: What is qualitative research? Bloomsbury Academic, London (2013)
Hanson, B.: Wither qualitative/quantitative? Grounds for methodological convergence. Qual. Quant. 42 , 97–111 (2008)
Heyvaert, M., Maes, B., Onghena, P.: Mixed methods research synthesis: definition, framework, and potential. Qual. Quant. 47 (2), 659–676 (2013)
Howe, K.R.: Against the quantitative-qualitative incompatibility thesis or dogmas die hard. Educ. Res. 17 (8), 10–16 (1988)
Johnson, R.B., Onwuegbuzie, A.J., Turner, L.A.: Toward a definition of mixed methods research. J. Mixed Methods Res. 1 (2), 112–133 (2007)
Kumar, R.: Research methodologies: a step-by-step guide for beginners. Sage, London (1996)
Levitt, H.M., Bamberg, M., Creswell, J.W., Frost, D.M., Josselson, R., Suarez-Orozco, C.: Journal article reporting standards for qualitative research in psychology: The APA publications and communications board task force report. Am. Psychol. 73 (1), 26–46 (2018)
Lincoln, Y.S., Guba, E.G.: Naturalistic inquiry. Sage, Thousand Oaks (1985)
Marsh, C.: Problems with surveys: method or epistemology? Sociology 13 (2), 293–305 (1979)
Marsh, D., Furlong, P.: A skin, not a sweater: ontology and epistemology in political science. Theory Methods Polit. Sci. 2 (1), 17–41 (2002)
Mason, J.: Mixing methods in a qualitatively driven way. Qual. Res. 6 (1), 9–25 (2006)
Miles, M. B., Huberman, A. M., Saldaña, J.: Qualitative data analysis: A methods sourcebook (4th edit.). Sage, Los Angeles, (2018)
Miles, M.B., Huberman, A.M.: Qualitative data analysis: An expanded sourcebook. Sage, Thousand Oaks (1994)
Moore, N.: How to do research: a practical guide to designing and managing research projects, 3rd edn. Facet, London (2006)
Morse, J.M.: Approaches to qualitative-quantitative methodological triangulation. Nurs. Res. 40 (2), 120–123 (1991)
Olssen, M.: Radical constructivism and its failings: anti-realism and individualism. Br. J. Educ. Stud. 44 (3), 275–295 (1996)
Onwuegbuzie, A.J., Leech, N.L.: Taking the “Q” out of research: teaching research methodology courses without the divide between quantitative and qualitative paradigms. Qual. Quant. 39 (3), 267–295 (2005)
Pilcher, N., Cortazzi, M.: Dialogues: QUANT researchers on QUAL methods. Qual. Report 21 (3), 450–473 (2016)
Punch, K.: Introduction to social research quantitative and qualitative approaches. Sage, Thousand Oaks (2005)
Saunders, B., Sim, J., Kingstone, T., Baker, S., Waterfield, J., Bartlam, B., Jinks, C.: Saturation in qualitative research: exploring its conceptualization and operationalization. Qualit. Quant. 52 (4), 1893–1907 (2018)
Seale, C.: Quality in qualitative research. Qual. Inq. 5 , 465–478 (1999a)
Seale, C.: The Quality of Qualitative Research. Sage, London (1999b)
Sharma, G.: Pros and cons of different sampling techniques. Int. J. Appl. Res. 3 (7), 749–752 (2017)
St Pierre, E.A.: Refusing alternatives: a science of contestation. Qual. Inq. 10 (1), 130–139 (2004)
Tashakkori, A., Teddlie, C., Teddlie, C.B.: Mixed methodology: Combining qualitative and quantitative approaches. Sage, Thousand Oaks (1998)
Teddlie, C., Tashakkori, A. Mixed methods research. Contemporary Issues in an emerging Field. In Denzin, N.K., Lincoln, Y.S. (eds.) The Sage handbook of qualitative research (4 th edit.), pp. 285–300. Sage, Thousand Oaks, (2011)
Trafford, V., Leshem, S.: Starting at the end to undertake doctoral research: predictable questions as stepping stones. High. Educ. Rev. 35 (1), 31–49 (2002)
Uher, J.: Functions of units, scales and quantitative data: fundamental differences in numerical traceability between sciences. Qual. Quant. 56 (4), 2519–2548 (2022)
Merriam Webster: Definition of ‘semi’. (2022). Available at https://www.merriam-webster.com/dictionary/semi
Download references
The authors declare that no funds, grants, or other support were received during the preparation of this manuscript.
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Business School, Edinburgh Napier University, Edinburgh, UK
Nick Pilcher
University of Warwick, Coventry, UK
Martin Cortazzi
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
All authors contributed to the study conception and design. Material preparation, data collection and analysis were performed by Nick Pilcher and Martin Cortazzi. The first draft of the manuscript was written by NP along with MC and all authors commented on previous versions of the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Nick Pilcher .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors have no relevant financial or non-financial interests to disclose.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Appendix 1: Literature review study
The table below contains details of the binary representations and possibilities in the two columns on the left and in the right it contains the numbers of the key sources that conveyed or adhered to these binary representations. The details of these sources and their respective numbers are listed below.
Table: Textbook and key source binary representations
Quantitative | Qualitative | Sources |
|---|---|---|
Positivist | Constructivist | 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 13, 14, 15, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25 |
Using traditions of Science | Not science based; reflective/exploratory | 3, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 14, 15, 19, 20, 25 |
Structured & predetermined questions | Initially general questions, more focused later | 1, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 14, 19, 20, 22, 23, 25 |
Structured methods: Surveys, questionnaires, experiments | Less structured methods: Interviews, focus groups, narratives | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 14, 18, 19, 20, 22, 23, 25 |
Analysis to establish cause-effect and type information—well defined methods of analysis Generate statistics and numbers for analysis | Analysis to establish interpretative causal explanatory reasons—goes iteratively through data Condense, display, and conclude from data—focus not numbers | 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 9, 11, 14, 17, 18, 19, 20, 22, 23, 25 |
Reliability, Validity and Generalizability achieved through large scale research & numbers | Reliability, Validity and Generalizability achieved through in-depth small-scale research & numbers | 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 11, 13, 14, 18, 19, 20, 21, 22, 23, 25 |
Value: for specific subjects and approaches—for e.g. Economics, the Sciences and to research large numbers—may see Qualitative of little value | Value: for specific subjects and approaches—for e.g. History, Anthropology and to research individuals’ lived experiences—may see Quantitative of little value | 5, 7, 9, 19, 20, 25 |
Mixed methods—possible | 1, 2, 3, 6, 7, 8, 9, 16, 17, 18, 19, 21, 22, 23, 24, 25 | |
Mixed Method—not possible | 4, 5, 11, 12, 14 | |
Bell, J., & Waters, S. (2014). Doing your research Project: A Guide for first-time researchers. McGraw-Hill Education (UK). 6 th edn
Bloor, M., & Wood, F. (2006). Keywords in qualitative methods: A vocabulary of research concepts. London, UK: Sage Publications.
Bryman, A. (2008). Social research methods. Oxford, UK: Oxford University Press. [with caveats for many but still using the divide as ‘useful’]
Bryman, A., & Cramer, D. (2009). Quantitative data analysis with SPSS 14, 15 and 16: A guide for social scientists. London, UK: Routledge.
Ceglowski, D., Bacigalupa, C., & Peck, E. (2011). Aced out: Censorship of qualitative research in the age of "scientifically based research." Qualitative Inquiry, 17(8), 679–686.
Daly, K. J. (2007). Qualitative Methods for Family Studies and Human Development. London, UK: Sage.
Davies, M. B., & Hughes, N. (2014). Doing a successful research project: Using qualitative or quantitative methods . Bloomsbury Publishing.
Dawson, C. (2019). Introduction to Research Methods 5th Edition: A Practical Guide for Anyone Undertaking a Research Project . Robinson.
Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (Eds.). (1998). The landscape of qualitative research: Theories and issues. Thousand Oaks, CA: Sage Publications. [with caveat that original qual was positivist in root but not now]
Denzin and Lincoln (2011) Introduction: The Discipline and Practice of Qualitative Research. In Denzin, N. K., & Lincoln, Y. S. (2011). The Sage handbook of qualitative research . Thousand Oaks, Calif: Sage. Pp1-20
Goertz, G., & Mahoney, J. (2012). A tale of two cultures . Princeton University Press.
Grix, J. (2004). The foundations of research. New York, NY: Palgrave Macmillan.
Hammersley, M. (2007). The issue of quality in qualitative research. International Journal of Research & Method in Education, 30(3), 287–305.
Hammersley, M. (2013). What is qualitative research? London, UK: Bloomsbury Academic. [caveat that some qual do use causal analysis – and if you mix you abandon key assumptions associated with qualitative work]
Harman, W. W. (1996). The shortcomings of western science. Qualitative Inquiry, 2(1), 30–38.
Howe, K. R. (2011). Mixed methods, mixed causes? Qualitative Inquiry, 17(2), 166–171.
Mason, J. (2006). Mixing methods in a qualitatively driven way. Qualitative Research, 6(1), 9–25.
Miles, M. B., Huberman, A. M., & Saldaña, J. (2018). Qualitative data analysis: A methods sourcebook . Sage publications.
Punch, K. (2005). Introduction to Social Research Quantitative and Qualitative Approaches. Sage.
Sandelowski, M. (1997). "To be of use": Enhancing the utility of qualitative research. Nursing Outlook, 45(3), 125–132 [caveat – does rebut many of the ideas but nevertheless outlines them as how the two are seen – e.g. of generalizability]
Seale, C. (1999). Quality in qualitative research. Qualitative Inquiry, 5, 465–478.
Silverman, D. (2016). Introducing qualitative research. Qualitative research , 3 (3), 14–25.
Tashakkori, A., Teddlie, C., & Teddlie, C. B. (1998). Mixed methodology: Combining qualitative and quantitative approaches (Vol. 46). sage. [with the caveat that they talk about the differences as existing even though say they are not that wide]
Teddlie, C., & Tashakkori, A. (2011). Mixed methods research. Contemporary Issues in an emerging Field. in The Sage handbook of qualitative research , 4 , 285–300.
Torrance, H. (2008). Building confidence in qualitative research: Engaging the demands of policy. Qualitative Inquiry, 14(4), 507–527.
1.1 Sources in languages other than English, and brief notes regarding their focus and content
Whilst not part of the literature review study, we also consulted the outline details, abstracts and contents lists of a number of sources in languages other than English. We put brief notes about after each source. Each source, unless specifically noted, adhered to similar binary treatment of quantitative and qualitative methods and approaches as the English language sources outlined above.
1.1.1 German
Blandz, M. (2021) Forschungsmethoden und Statistik für die Soziale Arbeit : Grundlage und Anwendingen. 2 nd . edit. Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag. – this is a multidisciplinary source that focuses mostly on quantitative and mixed methods. It follows the suggestion that a qualitative study can be a preliminary study for the main quantitative study.
Caspari, D; Klippel, F; Legutke, M. & Schram, K. (2022) Forschungsmethoden: in der Fremdsprachendidaktik; Ein Handbuch. Tübingen: Narr Franke Altempo Verlag. [Focused on foreign language teaching, details quantitative, then qualitative and then mixed; all separately]
Dōring, N. (2023) Forschungsmethoden und Evaluation in den Sozial- und Humanwissenschaften. 6. th edit. Berlin: Springer. [Focused on the Social Sciences and humanities; as with the previous source it has separate chapters on quantitative and qualitative and a section on mixed, and contains some critical commentary]
Frankenberger, N. (Ed.) (2022) Grundlagen der Politikwissenschaft : Forschungsmethoden und Forschendes Lernen. Stuttgart: Kohlhammer Verlag. [Political science focused and based around distinctions between quantitative and qualitative approaches, each of which is elaborated with different methods; there is no obvious section on mixed methods]
Hussy, W; Schiener, M; Echterhoff, G. (2013) Forschungsmethoden in Psychologie und Sozialwissenschaften für Bachelor. Berlin: Springer. [This book is focused on psychology and social sciences for undergraduates. It has separate parts to focus on quantitative and on qualitative and then a chapter on mixed, identifying mixed methods as an emerging trend]
Niederberger, M. & Finne, E. (Eds.) (2021) Forschungsmethoden in der Gesundsheitsfōrderung und Prävention. Berlin: Springer. [Focused on Health and wellbeing; develops the roles of quantitative, qualitative and mixed (in combinations) in multidisciplinary, interdisciplinary and transdisciplinary research. Notes much research is exclusively quantitative and that social sciences are more qualitative or mixed. Makes the argument that the quantitative versus qualitative divide was surpassed by ‘post-positivist’ versus ‘combined’ thinking and that integrated approaches are now widely accepted]
1.1.2 Spanish
Campos-Arenas, A. (2014) Métodos mixtos de investigación. Bogota: Magisterio Editorial. [Social science focused; devoted to mixed or combined approaches in Latin American contexts]
Hernandez-Sampieri, R. & Mendoza Torres, C. P. (2018) Metodología de investigación: Las rutas cuantitativa , cualitativa y mixta. Mexico: McGrw-Hill. [Social science focused with an introduction and conclusion focused on ‘three routes to research’ that are exceptionally and thoroughly elaborated; quantitative given 8 chapters; qualitative 3 and mixed just one]
Léon-García, O. G. & Carda-Celay, I. M. (2020) Méthodos de investigación en psicología y educación: Las tradiciones cuantitativas y qualitativas. 5. th edit. Barcelona : McGraw-Hill, España. [Psychology and education focused; based on relatively clearly cut distinctinos between ‘the two traditions’ of quantitative and qualitative]
Molina Marin, G. (Ed.) (2020) Integración de métodos de investigación : Estrategias metodológicas u experiencias en salud pública. Bogotá: Universidad de Antioquia. [Public health focused; gives most attention to multi-method combinations and asks questions about the epistemological integrity of integrating different approaches]
Ortega-Sanchez, D, (Ed.) (2023) ¿Como investigar en didáctica de las ciencias sociales? Fundamentos metodológicos , técnicas e instrumentos de investigación. Barcelona: Octaedro. [Education, research, pedagogy of teaching social sciences; focused on quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods in Spanish contexts]
Páramo-Reales, D. (2020) Métodos de investigación caulitativa : Fundamentos y aplicaciones . Bogota: Editorial Unimagdalena. [Social sciences: basic applications of qualitative approaches in Latin America]
Ponce, O. A. (2014) Investigación de métodos mixtos en educación, 2. nd edit. San Jaun: Publicaciones Puertoriqueñas. [Education and Pedagogy; Puerto Rican context and entirely about mixed methods]
Vasilachis de Giradino, I. (Ed.) (2009) Estrategias de investigación cauitativa. Barcelona: Editorial Gedisa. [Social sciences; much detail on research design; focus exclusively on qualitative methods in Spanish contexts]
1.1.3 French
Bouchard, S. & Cyr, C. (Eds.) (2005) Reserche psycosocial pour harmoniser reserche st pratique. Quebec: Prese de la Université de Quebec. [Focused on psychology and sociology. Despite its title about ‘harmonizing’ research it is mainly focused on quantitative approaches, with a small section on qualitative and nothing on mixed approaches]
Corbière, M. & Lamviere, N. (2021) Méthodes quantitatives , qualitatives et mixtes , dans la reserche en sciences humaines et de la santé. 2. nd edit. Quebec : PU Quebec. [Focused on Humanities and health care; highlights the division between quantitative, qualitative and mixed methods]
Devin, G. (Ed.) (2016) Méthodes de recherche en relations internationals. Paris: Sciences Po. [Focused on politics and international relations; mostly wholly focused on quantitative; only a little on qualitative]
Gavard-Perret, M.L; Gotteland, D; Haon, C. & Jolibert, A. (2018) Methodologie de la recherche en sciences de gestion : Réussir son mémoire ou sa these. Paris: Pearson. [Business and management focused and geared towards thesis research; notes clear distinctions between quantitative and qualitative approaches with nothing on mixed]
Komu, S. C. S. (2020) Le receuil des méthodes en sciences sociales : Mèthodo;ogies en reserche. Manitoba: Sciences Script. [Social sciences focused; mostly quantitative methods with some attention to focus groups and participatory research]
Lepillier, O; Fournier, T; Bricas, N. & Figuié, M. (2011 ) Méthodes d’investigation de l’alimentation et des mangeurs. Versailles: Editions Quae. [Focused on nutrition, health studies and diet; details quantitative and qualitative methods and has very little on mixed]
Millette, M; Millerand, F; Myles, D. & Latako-Toth, T. (2021) Méthodes de reserches en contexte humanique , une orientation qualiificative. Montreal: PU Montreal. [Humanities focused; outlines quantitative and qualitative methods and, unusually, attends to ‘qualitative investigations in numerical contexts’ in Canada]
Moscarda, J. (2018) Faire parler les donées: Méthodologies quantitatives et qualitatives. Caen: Editions EMS. [Has a multidisciplinary focus on ‘let the data talk’; deals with quantitative methods and then qualitative methods and also mixed]
Vallerand, R. J. (2000) Méthodes de recherche en psychologie. Quebec: Gaetan Morin. [Focused on psychology; emphasis on quantitative research; brief section on qualitative; Canadian contexts]
Appendix 2: Interview study schedule
2.1 understandings of ‘qualitative’ and ‘quantitative’.
This research project is exploratory and intends to delve into understandings of the specific terms ‘quantitative’ and ‘qualitative’ as they are perceived, used, and interpreted by researchers in very different fields. Such research is intended to shed light on the fields of quantitative and qualitative research. The idea for the research arises from a previous project where the researcher interviewed quantitative focused researchers and saw the use of qualitative and quantitative being used and interpreted very differently to how the terms are presented and understood in the research methods literature. It is expected that exploring these understandings further will add to the field by shedding light on the subtleties of how they are used and also in turn help researchers make informed decisions about the optimum approaches and methods to use in their own research.
2.2 Interview questions

Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article's Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article's Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Pilcher, N., Cortazzi, M. 'Qualitative' and 'quantitative' methods and approaches across subject fields: implications for research values, assumptions, and practices. Qual Quant 58 , 2357–2387 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-023-01734-4
Download citation
Accepted : 21 August 2023
Published : 30 September 2023
Issue Date : June 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s11135-023-01734-4
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Qualitative
- Quantitative
- Assumptions
- Disciplines
- Semi-structured interviews
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- BMJ Glob Health
- v.4(Suppl 1); 2019

Synthesising quantitative and qualitative evidence to inform guidelines on complex interventions: clarifying the purposes, designs and outlining some methods
1 School of Social Sciences, Bangor University, Wales, UK
Andrew Booth
2 School of Health and Related Research (ScHARR), University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK
Graham Moore
3 School of Social Sciences, Cardiff University, Wales, UK
Kate Flemming
4 Department of Health Sciences, The University of York, York, UK
Özge Tunçalp
5 Department of Reproductive Health and Research including UNDP/UNFPA/UNICEF/WHO/World Bank Special Programme of Research, Development and Research Training in Human Reproduction (HRP), World Health Organization, Geneva, Switzerland
Elham Shakibazadeh
6 Department of Health Education and Promotion, School of Public Health, Tehran University of Medical Sciences, Tehran, Iran
Associated Data
bmjgh-2018-000893supp001.pdf
bmjgh-2018-000893supp002.pdf
bmjgh-2018-000893supp003.pdf
bmjgh-2018-000893supp005.pdf
bmjgh-2018-000893supp004.pdf
Guideline developers are increasingly dealing with more difficult decisions concerning whether to recommend complex interventions in complex and highly variable health systems. There is greater recognition that both quantitative and qualitative evidence can be combined in a mixed-method synthesis and that this can be helpful in understanding how complexity impacts on interventions in specific contexts. This paper aims to clarify the different purposes, review designs, questions, synthesis methods and opportunities to combine quantitative and qualitative evidence to explore the complexity of complex interventions and health systems. Three case studies of guidelines developed by WHO, which incorporated quantitative and qualitative evidence, are used to illustrate possible uses of mixed-method reviews and evidence. Additional examples of methods that can be used or may have potential for use in a guideline process are outlined. Consideration is given to the opportunities for potential integration of quantitative and qualitative evidence at different stages of the review and guideline process. Encouragement is given to guideline commissioners and developers and review authors to consider including quantitative and qualitative evidence. Recommendations are made concerning the future development of methods to better address questions in systematic reviews and guidelines that adopt a complexity perspective.
Summary box
- When combined in a mixed-method synthesis, quantitative and qualitative evidence can potentially contribute to understanding how complex interventions work and for whom, and how the complex health systems into which they are implemented respond and adapt.
- The different purposes and designs for combining quantitative and qualitative evidence in a mixed-method synthesis for a guideline process are described.
- Questions relevant to gaining an understanding of the complexity of complex interventions and the wider health systems within which they are implemented that can be addressed by mixed-method syntheses are presented.
- The practical methodological guidance in this paper is intended to help guideline producers and review authors commission and conduct mixed-method syntheses where appropriate.
- If more mixed-method syntheses are conducted, guideline developers will have greater opportunities to access this evidence to inform decision-making.
Introduction
Recognition has grown that while quantitative methods remain vital, they are usually insufficient to address complex health systems related research questions. 1 Quantitative methods rely on an ability to anticipate what must be measured in advance. Introducing change into a complex health system gives rise to emergent reactions, which cannot be fully predicted in advance. Emergent reactions can often only be understood through combining quantitative methods with a more flexible qualitative lens. 2 Adopting a more pluralist position enables a diverse range of research options to the researcher depending on the research question being investigated. 3–5 As a consequence, where a research study sits within the multitude of methods available is driven by the question being asked, rather than any particular methodological or philosophical stance. 6
Publication of guidance on designing complex intervention process evaluations and other works advocating mixed-methods approaches to intervention research have stimulated better quality evidence for synthesis. 1 7–13 Methods for synthesising qualitative 14 and mixed-method evidence have been developed or are in development. Mixed-method research and review definitions are outlined in box 1 .
Defining mixed-method research and reviews
Pluye and Hong 52 define mixed-methods research as “a research approach in which a researcher integrates (a) qualitative and quantitative research questions, (b) qualitative research methods* and quantitative research designs, (c) techniques for collecting and analyzing qualitative and quantitative evidence, and (d) qualitative findings and quantitative results”.A mixed-method synthesis can integrate quantitative, qualitative and mixed-method evidence or data from primary studies.† Mixed-method primary studies are usually disaggregated into quantitative and qualitative evidence and data for the purposes of synthesis. Thomas and Harden further define three ways in which reviews are mixed. 53
- The types of studies included and hence the type of findings to be synthesised (ie, qualitative/textual and quantitative/numerical).
- The types of synthesis method used (eg, statistical meta-analysis and qualitative synthesis).
- The mode of analysis: theory testing AND theory building.
*A qualitative study is one that uses qualitative methods of data collection and analysis to produce a narrative understanding of the phenomena of interest. Qualitative methods of data collection may include, for example, interviews, focus groups, observations and analysis of documents.
†The Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods group coined the term ‘qualitative evidence synthesis’ to mean that the synthesis could also include qualitative data. For example, qualitative data from case studies, grey literature reports and open-ended questions from surveys. ‘Evidence’ and ‘data’ are used interchangeably in this paper.
This paper is one of a series that aims to explore the implications of complexity for systematic reviews and guideline development, commissioned by WHO. This paper is concerned with the methodological implications of including quantitative and qualitative evidence in mixed-method systematic reviews and guideline development for complex interventions. The guidance was developed through a process of bringing together experts in the field, literature searching and consensus building with end users (guideline developers, clinicians and reviewers). We clarify the different purposes, review designs, questions and synthesis methods that may be applicable to combine quantitative and qualitative evidence to explore the complexity of complex interventions and health systems. Three case studies of WHO guidelines that incorporated quantitative and qualitative evidence are used to illustrate possible uses of mixed-method reviews and mechanisms of integration ( table 1 , online supplementary files 1–3 ). Additional examples of methods that can be used or may have potential for use in a guideline process are outlined. Opportunities for potential integration of quantitative and qualitative evidence at different stages of the review and guideline process are presented. Specific considerations when using an evidence to decision framework such as the Developing and Evaluating Communication strategies to support Informed Decisions and practice based on Evidence (DECIDE) framework 15 or the new WHO-INTEGRATE evidence to decision framework 16 at the review design and evidence to decision stage are outlined. See online supplementary file 4 for an example of a health systems DECIDE framework and Rehfuess et al 16 for the new WHO-INTEGRATE framework. Encouragement is given to guideline commissioners and developers and review authors to consider including quantitative and qualitative evidence in guidelines of complex interventions that take a complexity perspective and health systems focus.
Designs and methods and their use or applicability in guidelines and systematic reviews taking a complexity perspective
| Case study examples and references | Complexity-related questions of interest in the guideline | Types of synthesis used in the guideline | Mixed-method review design and integration mechanisms | Observations, concerns and considerations |
| A. Mixed-method review designs used in WHO guideline development | ||||
| Antenatal Care (ANC) guidelines ( ) | What do women in high-income, medium-income and low-income countries want and expect from antenatal care (ANC), based on their own accounts of their beliefs, views, expectations and experiences of pregnancy? | Qualitative synthesis Framework synthesis Meta-ethnography | Quantitative and qualitative reviews undertaken separately (segregated), an initial scoping review of qualitative evidence established women’s preferences and outcomes for ANC, which informed design of the quantitative intervention review (contingent) A second qualitative evidence synthesis was undertaken to look at implementation factors (sequential) Integration: quantitative and qualitative findings were brought together in a series of DECIDE frameworks Tools included: Psychological theory SURE framework conceptual framework for implementing policy options Conceptual framework for analysing integration of targeted health interventions into health systems to analyse contextual health system factors | An innovative approach to guideline development No formal cross-study synthesis process and limited testing of theory. The hypothetical nature of meta-ethnography findings may be challenging for guideline panel members to process without additional training See Flemming for considerations when selecting meta-ethnography |
| What are the evidence-based practices during ANC that improved outcomes and lead to positive pregnancy experience and how should these practices be delivered? | Quantitative review of trials | |||
| Factors that influence the uptake of routine antenatal services by pregnant women Views and experiences of maternity care providers | Qualitative synthesis Framework synthesis Meta-ethnography | |||
| Task shifting guidelines ( ) | What are the effects of lay health worker interventions in primary and community healthcare on maternal and child health and the management of infectious diseases? | Quantitative review of trials | Several published quantitative reviews were used (eg, Cochrane review of lay health worker interventions) Additional new qualitative evidence syntheses were commissioned (segregated) Integration: quantitative and qualitative review findings on lay health workers were brought together in several DECIDE frameworks. Tools included adapted SURE Framework and post hoc logic model | An innovative approach to guideline development The post hoc logic model was developed after the guideline was completed |
| What factors affect the implementation of lay health worker programmes for maternal and child health? | Qualitative evidence synthesis Framework synthesis | |||
| Risk communication guideline ( ) | Quantitative review of quantitative evidence (descriptive) Qualitative using framework synthesis | A knowledge map of studies was produced to identify the method, topic and geographical spread of evidence. Reviews first organised and synthesised evidence by method-specific streams and reported method-specific findings. Then similar findings across method-specific streams were grouped and further developed using all the relevant evidence Integration: where possible, quantitative and qualitative evidence for the same intervention and question was mapped against core DECIDE domains. Tools included framework using public health emergency model and disaster phases Very few trials were identified. Quantitative and qualitative evidence was used to construct a high level view of what appeared to work and what happened when similar broad groups of interventions or strategies were implemented in different contexts | Example of a fully integrated mixed-method synthesis. Without evidence of effect, it was highly challenging to populate a DECIDE framework | |
| B. Mixed-method review designs that can be used in guideline development | ||||
| Factors influencing children’s optimal fruit and vegetable consumption | Potential to explore theoretical, intervention and implementation complexity issues New question(s) of interest are developed and tested in a cross-study synthesis | Mixed-methods synthesis Each review typically has three syntheses: Statistical meta-analysis Qualitative thematic synthesis Cross-study synthesis | Aim is to generate and test theory from diverse body of literature Integration: used integrative matrix based on programme theory | Can be used in a guideline process as it fits with the current model of conducting method specific reviews separately then bringing the review products together |
| C. Mixed-method review designs with the potential for use in guideline development | ||||
| Interventions to promote smoke alarm ownership and function | Intervention effect and/or intervention implementation related questions within a system | Narrative synthesis (specifically Popay’s methodology) | Four stage approach to integrate quantitative (trials) with qualitative evidence Integration: initial theory and logic model used to integrate evidence of effect with qualitative case summaries. Tools used included tabulation, groupings and clusters, transforming data: constructing a common rubric, vote-counting as a descriptive tool, moderator variables and subgroup analyses, idea webbing/conceptual mapping, creating qualitative case descriptions, visual representation of relationship between study characteristics and results | Few published examples with the exception of Rodgers, who reinterpreted a Cochrane review on the same topic with narrative synthesis methodology. Methodology is complex. Most subsequent examples have only partially operationalised the methodology An intervention effect review will still be required to feed into the guideline process |
| Factors affecting childhood immunisation | What factors explain complexity and causal pathways? | Bayesian synthesis of qualitative and quantitative evidence | Aim is theory-testing by fusing findings from qualitative and quantitative research Produces a set of weighted factors associated with/predicting the phenomenon under review | Not yet used in a guideline context. Complex methodology. Undergoing development and testing for a health context. The end product may not easily ‘fit’ into an evidence to decision framework and an effect review will still be required |
| Providing effective and preferred care closer to home: a realist review of intermediate care. | Developing and testing theories of change underpinning complex policy interventions What works for whom in what contexts and how? | Realist synthesis NB. Other theory-informed synthesis methods follow similar processes | Development of a theory from the literature, analysis of quantitative and qualitative evidence against the theory leads to development of context, mechanism and outcome chains that explain how outcomes come about Integration: programme theory and assembling mixed-method evidence to create Context, Mechanism and Outcome (CMO) configurations | May be useful where there are few trials. The hypothetical nature of findings may be challenging for guideline panel members to process without additional training. The end product may not easily ‘fit’ into an evidence to decision framework and an effect review will still be required |
| Use of morphine to treat cancer-related pain | Any aspect of complexity could potentially be explored How does the context of morphine use affect the established effectiveness of morphine? | Critical interpretive synthesis | Aims to generate theory from large and diverse body of literature Segregated sequential design Integration: integrative grid | There are few examples and the methodology is complex. The hypothetical nature of findings may be challenging for guideline panel members to process without additional training. The end product would need to be designed to feed into an evidence to decision framework and an intervention effect review will still be required |
| Food sovereignty, food security and health equity | Examples have examined health system complexity To understand the state of knowledge on relationships between health equity—ie, health inequalities that are socially produced—and food systems, where the concepts of 'food security' and 'food sovereignty' are prominent Focused on eight pathways to health (in)equity through the food system: (1) Multi-Scalar Environmental, Social Context; (2) Occupational Exposures; (3) Environmental Change; (4) Traditional Livelihoods, Cultural Continuity; (5) Intake of Contaminants; (6) Nutrition; (7) Social Determinants of Health; (8) Political, Economic and Regulatory context | Meta-narrative | Aim is to review research on diffusion of innovation to inform healthcare policy Which research (or epistemic) traditions have considered this broad topic area?; How has each tradition conceptualised the topic (for example, including assumptions about the nature of reality, preferred study designs and ways of knowing)?; What theoretical approaches and methods did they use?; What are the main empirical findings?; and What insights can be drawn by combining and comparing findings from different traditions? Integration: analysis leads to production of a set of meta-narratives (‘storylines of research’) | Not yet used in a guideline context. The originators are calling for meta-narrative reviews to be used in a guideline process. Potential to provide a contextual overview within which to interpret other types of reviews in a guideline process. The meta-narrative review findings may require tailoring to ‘fit’ into an evidence to decision framework and an intervention effect review will still be required Few published examples and the methodology is complex |
Supplementary data
Taking a complexity perspective.
The first paper in this series 17 outlines aspects of complexity associated with complex interventions and health systems that can potentially be explored by different types of evidence, including synthesis of quantitative and qualitative evidence. Petticrew et al 17 distinguish between a complex interventions perspective and a complex systems perspective. A complex interventions perspective defines interventions as having “implicit conceptual boundaries, representing a flexible, but common set of practices, often linked by an explicit or implicit theory about how they work”. A complex systems perspective differs in that “ complexity arises from the relationships and interactions between a system’s agents (eg, people, or groups that interact with each other and their environment), and its context. A system perspective conceives the intervention as being part of the system, and emphasises changes and interconnections within the system itself”. Aspects of complexity associated with implementation of complex interventions in health systems that could potentially be addressed with a synthesis of quantitative and qualitative evidence are summarised in table 2 . Another paper in the series outlines criteria used in a new evidence to decision framework for making decisions about complex interventions implemented in complex systems, against which the need for quantitative and qualitative evidence can be mapped. 16 A further paper 18 that explores how context is dealt with in guidelines and reviews taking a complexity perspective also recommends using both quantitative and qualitative evidence to better understand context as a source of complexity. Mixed-method syntheses of quantitative and qualitative evidence can also help with understanding of whether there has been theory failure and or implementation failure. The Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group provide additional guidance on exploring implementation and theory failure that can be adapted to address aspects of complexity of complex interventions when implemented in health systems. 19
Health-system complexity-related questions that a synthesis of quantitative and qualitative evidence could address (derived from Petticrew et al 17 )
| Aspect of complexity of interest | Examples of potential research question(s) that a synthesis of qualitative and quantitative evidence could address | Types of studies or data that could contribute to a review of qualitative and quantitative evidence |
| What ‘is’ the system? How can it be described? | What are the main influences on the health problem? How are they created and maintained? How do these influences interconnect? Where might one intervene in the system? | Quantitative: previous systematic reviews of the causes of the problem); epidemiological studies (eg, cohort studies examining risk factors of obesity); network analysis studies showing the nature of social and other systems Qualitative data: theoretical papers; policy documents |
| Interactions of interventions with context and adaptation | Qualitative: (1) eg, qualitative studies; case studies Quantitative: (2) trials or other effectiveness studies from different contexts; multicentre trials, with stratified reporting of findings; other quantitative studies that provide evidence of moderating effects of context | |
| System adaptivity (how does the system change?) | (How) does the system change when the intervention is introduced? Which aspects of the system are affected? Does this potentiate or dampen its effects? | Quantitative: longitudinal data; possibly historical data; effectiveness studies providing evidence of differential effects across different contexts; system modelling (eg, agent-based modelling) Qualitative: qualitative studies; case studies |
| Emergent properties | What are the effects (anticipated and unanticipated) which follow from this system change? | Quantitative: prospective quantitative evaluations; retrospective studies (eg, case–control studies, surveys) may also help identify less common effects; dose–response evaluations of impacts at aggregate level in individual studies or across studies included with systematic reviews (see suggested examples) Qualitative: qualitative studies |
| Positive (reinforcing) and negative (balancing) feedback loops | What explains change in the effectiveness of the intervention over time? Are the effects of an intervention are damped/suppressed by other aspects of the system (eg, contextual influences?) | Quantitative: studies of moderators of effectiveness; long-term longitudinal studies Qualitative: studies of factors that enable or inhibit implementation of interventions |
| Multiple (health and non-health) outcomes | What changes in processes and outcomes follow the introduction of this system change? At what levels in the system are they experienced? | Quantitative: studies tracking change in the system over time Qualitative: studies exploring effects of the change in individuals, families, communities (including equity considerations and factors that affect engagement and participation in change) |
It may not be apparent which aspects of complexity or which elements of the complex intervention or health system can be explored in a guideline process, or whether combining qualitative and quantitative evidence in a mixed-method synthesis will be useful, until the available evidence is scoped and mapped. 17 20 A more extensive lead in phase is typically required to scope the available evidence, engage with stakeholders and to refine the review parameters and questions that can then be mapped against potential review designs and methods of synthesis. 20 At the scoping stage, it is also common to decide on a theoretical perspective 21 or undertake further work to refine a theoretical perspective. 22 This is also the stage to begin articulating the programme theory of the complex intervention that may be further developed to refine an understanding of complexity and show how the intervention is implemented in and impacts on the wider health system. 17 23 24 In practice, this process can be lengthy, iterative and fluid with multiple revisions to the review scope, often developing and adapting a logic model 17 as the available evidence becomes known and the potential to incorporate different types of review designs and syntheses of quantitative and qualitative evidence becomes better understood. 25 Further questions, propositions or hypotheses may emerge as the reviews progress and therefore the protocols generally need to be developed iteratively over time rather than a priori.
Following a scoping exercise and definition of key questions, the next step in the guideline development process is to identify existing or commission new systematic reviews to locate and summarise the best available evidence in relation to each question. For example, case study 2, ‘Optimising health worker roles for maternal and newborn health through task shifting’, included quantitative reviews that did and did not take an additional complexity perspective, and qualitative evidence syntheses that were able to explain how specific elements of complexity impacted on intervention outcomes within the wider health system. Further understanding of health system complexity was facilitated through the conduct of additional country-level case studies that contributed to an overall understanding of what worked and what happened when lay health worker interventions were implemented. See table 1 online supplementary file 2 .
There are a few existing examples, which we draw on in this paper, but integrating quantitative and qualitative evidence in a mixed-method synthesis is relatively uncommon in a guideline process. Box 2 includes a set of key questions that guideline developers and review authors contemplating combining quantitative and qualitative evidence in mixed-methods design might ask. Subsequent sections provide more information and signposting to further reading to help address these key questions.
Key questions that guideline developers and review authors contemplating combining quantitative and qualitative evidence in a mixed-methods design might ask
Compound questions requiring both quantitative and qualitative evidence?
Questions requiring mixed-methods studies?
Separate quantitative and qualitative questions?
Separate quantitative and qualitative research studies?
Related quantitative and qualitative research studies?
Mixed-methods studies?
Quantitative unpublished data and/or qualitative unpublished data, eg, narrative survey data?
Throughout the review?
Following separate reviews?
At the question point?
At the synthesis point?
At the evidence to recommendations stage?
Or a combination?
Narrative synthesis or summary?
Quantitising approach, eg, frequency analysis?
Qualitising approach, eg, thematic synthesis?
Tabulation?
Logic model?
Conceptual model/framework?
Graphical approach?
- WHICH: Which mixed-method designs, methodologies and methods best fit into a guideline process to inform recommendations?
Complexity-related questions that a synthesis of quantitative and qualitative evidence can potentially address
Petticrew et al 17 define the different aspects of complexity and examples of complexity-related questions that can potentially be explored in guidelines and systematic reviews taking a complexity perspective. Relevant aspects of complexity outlined by Petticrew et al 17 are summarised in table 2 below, together with the corresponding questions that could be addressed in a synthesis combining qualitative and quantitative evidence. Importantly, the aspects of complexity and their associated concepts of interest have however yet to be translated fully in primary health research or systematic reviews. There are few known examples where selected complexity concepts have been used to analyse or reanalyse a primary intervention study. Most notable is Chandler et al 26 who specifically set out to identify and translate a set of relevant complexity theory concepts for application in health systems research. Chandler then reanalysed a trial process evaluation using selected complexity theory concepts to better understand the complex causal pathway in the health system that explains some aspects of complexity in table 2 .
Rehfeuss et al 16 also recommends upfront consideration of the WHO-INTEGRATE evidence to decision criteria when planning a guideline and formulating questions. The criteria reflect WHO norms and values and take account of a complexity perspective. The framework can be used by guideline development groups as a menu to decide which criteria to prioritise, and which study types and synthesis methods can be used to collect evidence for each criterion. Many of the criteria and their related questions can be addressed using a synthesis of quantitative and qualitative evidence: the balance of benefits and harms, human rights and sociocultural acceptability, health equity, societal implications and feasibility (see table 3 ). Similar aspects in the DECIDE framework 15 could also be addressed using synthesis of qualitative and quantitative evidence.
Integrate evidence to decision framework criteria, example questions and types of studies to potentially address these questions (derived from Rehfeuss et al 16 )
| Domains of the WHO-INTEGRATE EtD framework | Examples of potential research question(s) that a synthesis of qualitative and/or quantitative evidence could address | Types of studies that could contribute to a review of qualitative and quantitative evidence |
| Balance of benefits and harms | To what extent do patients/beneficiaries different health outcomes? | Qualitative: studies of views and experiences Quantitative: Questionnaire surveys |
| Human rights and sociocultural acceptability | Is the intervention to patients/beneficiaries as well as to those implementing it? To what extent do patients/beneficiaries different non-health outcomes? How does the intervention affect an individual’s, population group’s or organisation’s , that is, their ability to make a competent, informed and voluntary decision? | Qualitative: discourse analysis, qualitative studies (ideally longitudinal to examine changes over time) Quantitative: pro et contra analysis, discrete choice experiments, longitudinal quantitative studies (to examine changes over time), cross-sectional studies Mixed-method studies; case studies |
| Health equity, equality and non-discrimination | How is the intervention for individuals, households or communities? How —in terms of physical as well as informational access—is the intervention across different population groups? | Qualitative: studies of views and experiences Quantitative: cross-sectional or longitudinal observational studies, discrete choice experiments, health expenditure studies; health system barrier studies, cross-sectional or longitudinal observational studies, discrete choice experiments, ethical analysis, GIS-based studies |
| Societal implications | What is the of the intervention: are there features of the intervention that increase or reduce stigma and that lead to social consequences? Does the intervention enhance or limit social goals, such as education, social cohesion and the attainment of various human rights beyond health? Does it change social norms at individual or population level? What is the of the intervention? Does it contribute to or limit the achievement of goals to protect the environment and efforts to mitigate or adapt to climate change? | Qualitative: studies of views and experiences Quantitative: RCTs, quasi-experimental studies, comparative observational studies, longitudinal implementation studies, case studies, power analyses, environmental impact assessments, modelling studies |
| Feasibility and health system considerations | Are there any that impact on implementation of the intervention? How might , such as past decisions and strategic considerations, positively or negatively impact the implementation of the intervention? How does the intervention ? Is it likely to fit well or not, is it likely to impact on it in positive or negative ways? How does the intervention interact with the need for and usage of the existing , at national and subnational levels? How does the intervention interact with the need for and usage of the as well as other relevant infrastructure, at national and subnational levels? | Non-research: policy and regulatory frameworks Qualitative: studies of views and experiences Mixed-method: health systems research, situation analysis, case studies Quantitative: cross-sectional studies |
GIS, Geographical Information System; RCT, randomised controlled trial.
Questions as anchors or compasses
Questions can serve as an ‘anchor’ by articulating the specific aspects of complexity to be explored (eg, Is successful implementation of the intervention context dependent?). 27 Anchor questions such as “How does intervention x impact on socioeconomic inequalities in health behaviour/outcome x” are the kind of health system question that requires a synthesis of both quantitative and qualitative evidence and hence a mixed-method synthesis. Quantitative evidence can quantify the difference in effect, but does not answer the question of how . The ‘how’ question can be partly answered with quantitative and qualitative evidence. For example, quantitative evidence may reveal where socioeconomic status and inequality emerges in the health system (an emergent property) by exploring questions such as “ Does patterning emerge during uptake because fewer people from certain groups come into contact with an intervention in the first place? ” or “ are people from certain backgrounds more likely to drop out, or to maintain effects beyond an intervention differently? ” Qualitative evidence may help understand the reasons behind all of these mechanisms. Alternatively, questions can act as ‘compasses’ where a question sets out a starting point from which to explore further and to potentially ask further questions or develop propositions or hypotheses to explore through a complexity perspective (eg, What factors enhance or hinder implementation?). 27 Other papers in this series provide further guidance on developing questions for qualitative evidence syntheses and guidance on question formulation. 14 28
For anchor and compass questions, additional application of a theory (eg, complexity theory) can help focus evidence synthesis and presentation to explore and explain complexity issues. 17 21 Development of a review specific logic model(s) can help to further refine an initial understanding of any complexity-related issues of interest associated with a specific intervention, and if appropriate the health system or section of the health system within which to contextualise the review question and analyse data. 17 23–25 Specific tools are available to help clarify context and complex interventions. 17 18
If a complexity perspective, and certain criteria within evidence to decision frameworks, is deemed relevant and desirable by guideline developers, it is only possible to pursue a complexity perspective if the evidence is available. Careful scoping using knowledge maps or scoping reviews will help inform development of questions that are answerable with available evidence. 20 If evidence of effect is not available, then a different approach to develop questions leading to a more general narrative understanding of what happened when complex interventions were implemented in a health system will be required (such as in case study 3—risk communication guideline). This should not mean that the original questions developed for which no evidence was found when scoping the literature were not important. An important function of creating a knowledge map is also to identify gaps to inform a future research agenda.
Table 2 and online supplementary files 1–3 outline examples of questions in the three case studies, which were all ‘COMPASS’ questions for the qualitative evidence syntheses.
Types of integration and synthesis designs in mixed-method reviews
The shift towards integration of qualitative and quantitative evidence in primary research has, in recent years, begun to be mirrored within research synthesis. 29–31 The natural extension to undertaking quantitative or qualitative reviews has been the development of methods for integrating qualitative and quantitative evidence within reviews, and within the guideline process using evidence to decision-frameworks. Advocating the integration of quantitative and qualitative evidence assumes a complementarity between research methodologies, and a need for both types of evidence to inform policy and practice. Below, we briefly outline the current designs for integrating qualitative and quantitative evidence within a mixed-method review or synthesis.
One of the early approaches to integrating qualitative and quantitative evidence detailed by Sandelowski et al 32 advocated three basic review designs: segregated, integrated and contingent designs, which have been further developed by Heyvaert et al 33 ( box 3 ).
Segregated, integrated and contingent designs 32 33
Segregated design.
Conventional separate distinction between quantitative and qualitative approaches based on the assumption they are different entities and should be treated separately; can be distinguished from each other; their findings warrant separate analyses and syntheses. Ultimately, the separate synthesis results can themselves be synthesised.
Integrated design
The methodological differences between qualitative and quantitative studies are minimised as both are viewed as producing findings that can be readily synthesised into one another because they address the same research purposed and questions. Transformation involves either turning qualitative data into quantitative (quantitising) or quantitative findings are turned into qualitative (qualitising) to facilitate their integration.
Contingent design
Takes a cyclical approach to synthesis, with the findings from one synthesis informing the focus of the next synthesis, until all the research objectives have been addressed. Studies are not necessarily grouped and categorised as qualitative or quantitative.
A recent review of more than 400 systematic reviews 34 combining quantitative and qualitative evidence identified two main synthesis designs—convergent and sequential. In a convergent design, qualitative and quantitative evidence is collated and analysed in a parallel or complementary manner, whereas in a sequential synthesis, the collation and analysis of quantitative and qualitative evidence takes place in a sequence with one synthesis informing the other ( box 4 ). 6 These designs can be seen to build on the work of Sandelowski et al , 32 35 particularly in relation to the transformation of data from qualitative to quantitative (and vice versa) and the sequential synthesis design, with a cyclical approach to reviewing that evokes Sandelowski’s contingent design.
Convergent and sequential synthesis designs 34
Convergent synthesis design.
Qualitative and quantitative research is collected and analysed at the same time in a parallel or complementary manner. Integration can occur at three points:
a. Data-based convergent synthesis design
All included studies are analysed using the same methods and results presented together. As only one synthesis method is used, data transformation occurs (qualitised or quantised). Usually addressed one review question.
b. Results-based convergent synthesis design
Qualitative and quantitative data are analysed and presented separately but integrated using a further synthesis method; eg, narratively, tables, matrices or reanalysing evidence. The results of both syntheses are combined in a third synthesis. Usually addresses an overall review question with subquestions.
c. Parallel-results convergent synthesis design
Qualitative and quantitative data are analysed and presented separately with integration occurring in the interpretation of results in the discussion section. Usually addresses two or more complimentary review questions.
Sequential synthesis design
A two-phase approach, data collection and analysis of one type of evidence (eg, qualitative), occurs after and is informed by the collection and analysis of the other type (eg, quantitative). Usually addresses an overall question with subquestions with both syntheses complementing each other.
The three case studies ( table 1 , online supplementary files 1–3 ) illustrate the diverse combination of review designs and synthesis methods that were considered the most appropriate for specific guidelines.
Methods for conducting mixed-method reviews in the context of guidelines for complex interventions
In this section, we draw on examples where specific review designs and methods have been or can be used to explore selected aspects of complexity in guidelines or systematic reviews. We also identify other review methods that could potentially be used to explore aspects of complexity. Of particular note, we could not find any specific examples of systematic methods to synthesise highly diverse research designs as advocated by Petticrew et al 17 and summarised in tables 2 and 3 . For example, we could not find examples of methods to synthesise qualitative studies, case studies, quantitative longitudinal data, possibly historical data, effectiveness studies providing evidence of differential effects across different contexts, and system modelling studies (eg, agent-based modelling) to explore system adaptivity.
There are different ways that quantitative and qualitative evidence can be integrated into a review and then into a guideline development process. In practice, some methods enable integration of different types of evidence in a single synthesis, while in other methods, the single systematic review may include a series of stand-alone reviews or syntheses that are then combined in a cross-study synthesis. Table 1 provides an overview of the characteristics of different review designs and methods and guidance on their applicability for a guideline process. Designs and methods that have already been used in WHO guideline development are described in part A of the table. Part B outlines a design and method that can be used in a guideline process, and part C covers those that have the potential to integrate quantitative, qualitative and mixed-method evidence in a single review design (such as meta-narrative reviews and Bayesian syntheses), but their application in a guideline context has yet to be demonstrated.
Points of integration when integrating quantitative and qualitative evidence in guideline development
Depending on the review design (see boxes 3 and 4 ), integration can potentially take place at a review team and design level, and more commonly at several key points of the review or guideline process. The following sections outline potential points of integration and associated practical considerations when integrating quantitative and qualitative evidence in guideline development.
Review team level
In a guideline process, it is common for syntheses of quantitative and qualitative evidence to be done separately by different teams and then to integrate the evidence. A practical consideration relates to the organisation, composition and expertise of the review teams and ways of working. If the quantitative and qualitative reviews are being conducted separately and then brought together by the same team members, who are equally comfortable operating within both paradigms, then a consistent approach across both paradigms becomes possible. If, however, a team is being split between the quantitative and qualitative reviews, then the strengths of specialisation can be harnessed, for example, in quality assessment or synthesis. Optimally, at least one, if not more, of the team members should be involved in both quantitative and qualitative reviews to offer the possibility of making connexions throughout the review and not simply at re-agreed junctures. This mirrors O’Cathain’s conclusion that mixed-methods primary research tends to work only when there is a principal investigator who values and is able to oversee integration. 9 10 While the above decisions have been articulated in the context of two types of evidence, variously quantitative and qualitative, they equally apply when considering how to handle studies reporting a mixed-method study design, where data are usually disaggregated into quantitative and qualitative for the purposes of synthesis (see case study 3—risk communication in humanitarian disasters).
Question formulation
Clearly specified key question(s), derived from a scoping or consultation exercise, will make it clear if quantitative and qualitative evidence is required in a guideline development process and which aspects will be addressed by which types of evidence. For the remaining stages of the process, as documented below, a review team faces challenges as to whether to handle each type of evidence separately, regardless of whether sequentially or in parallel, with a view to joining the two products on completion or to attempt integration throughout the review process. In each case, the underlying choice is of efficiencies and potential comparability vs sensitivity to the underlying paradigm.
Once key questions are clearly defined, the guideline development group typically needs to consider whether to conduct a single sensitive search to address all potential subtopics (lumping) or whether to conduct specific searches for each subtopic (splitting). 36 A related consideration is whether to search separately for qualitative, quantitative and mixed-method evidence ‘streams’ or whether to conduct a single search and then identify specific study types at the subsequent sifting stage. These two considerations often mean a trade-off between a single search process involving very large numbers of records or a more protracted search process retrieving smaller numbers of records. Both approaches have advantages and choice may depend on the respective availability of resources for searching and sifting.
Screening and selecting studies
Closely related to decisions around searching are considerations relating to screening and selecting studies for inclusion in a systematic review. An important consideration here is whether the review team will screen records for all review types, regardless of their subsequent involvement (‘altruistic sifting’), or specialise in screening for the study type with which they are most familiar. The risk of missing relevant reports might be minimised by whole team screening for empirical reports in the first instance and then coding them for a specific quantitative, qualitative or mixed-methods report at a subsequent stage.
Assessment of methodological limitations in primary studies
Within a guideline process, review teams may be more limited in their choice of instruments to assess methodological limitations of primary studies as there are mandatory requirements to use the Cochrane risk of bias tool 37 to feed into Grading of Recommendations Assessment, Development and Evaluation (GRADE) 38 or to select from a small pool of qualitative appraisal instruments in order to apply GRADE; Confidence in the Evidence from Reviews of Qualitative Research (GRADE-CERQual) 39 to assess the overall certainty or confidence in findings. The Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group has recently issued guidance on the selection of appraisal instruments and core assessment criteria. 40 The Mixed-Methods Appraisal Tool, which is currently undergoing further development, offers a single quality assessment instrument for quantitative, qualitative and mixed-methods studies. 41 Other options include using corresponding instruments from within the same ‘stable’, for example, using different Critical Appraisal Skills Programme instruments. 42 While using instruments developed by the same team or organisation may achieve a degree of epistemological consonance, benefits may come more from consistency of approach and reporting rather than from a shared view of quality. Alternatively, a more paradigm-sensitive approach would involve selecting the best instrument for each respective review while deferring challenges from later heterogeneity of reporting.
Data extraction
The way in which data and evidence are extracted from primary research studies for review will be influenced by the type of integrated synthesis being undertaken and the review purpose. Initially, decisions need to be made regarding the nature and type of data and evidence that are to be extracted from the included studies. Method-specific reporting guidelines 43 44 provide a good template as to what quantitative and qualitative data it is potentially possible to extract from different types of method-specific study reports, although in practice reporting quality varies. Online supplementary file 5 provides a hypothetical example of the different types of studies from which quantitative and qualitative evidence could potentially be extracted for synthesis.
The decisions around what data or evidence to extract will be guided by how ‘integrated’ the mixed-method review will be. For those reviews where the quantitative and qualitative findings of studies are synthesised separately and integrated at the point of findings (eg, segregated or contingent approaches or sequential synthesis design), separate data extraction approaches will likely be used.
Where integration occurs during the process of the review (eg, integrated approach or convergent synthesis design), an integrated approach to data extraction may be considered, depending on the purpose of the review. This may involve the use of a data extraction framework, the choice of which needs to be congruent with the approach to synthesis chosen for the review. 40 45 The integrative or theoretical framework may be decided on a priori if a pre-developed theoretical or conceptual framework is available in the literature. 27 The development of a framework may alternatively arise from the reading of the included studies, in relation to the purpose of the review, early in the process. The Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group provide further guidance on extraction of qualitative data, including use of software. 40
Synthesis and integration
Relatively few synthesis methods start off being integrated from the beginning, and these methods have generally been subject to less testing and evaluation particularly in a guideline context (see table 1 ). A review design that started off being integrated from the beginning may be suitable for some guideline contexts (such as in case study 3—risk communication in humanitarian disasters—where there was little evidence of effect), but in general if there are sufficient trials then a separate systematic review and meta-analysis will be required for a guideline. Other papers in this series offer guidance on methods for synthesising quantitative 46 and qualitative evidence 14 in reviews that take a complexity perspective. Further guidance on integrating quantitative and qualitative evidence in a systematic review is provided by the Cochrane Qualitative and Implementation Methods Group. 19 27 29 40 47
Types of findings produced by specific methods
It is highly likely (unless there are well-designed process evaluations) that the primary studies may not themselves seek to address the complexity-related questions required for a guideline process. In which case, review authors will need to configure the available evidence and transform the evidence through the synthesis process to produce explanations, propositions and hypotheses (ie, findings) that were not obvious at primary study level. It is important that guideline commissioners, developers and review authors are aware that specific methods are intended to produce a type of finding with a specific purpose (such as developing new theory in the case of meta-ethnography). 48 Case study 1 (antenatal care guideline) provides an example of how a meta-ethnography was used to develop a new theory as an end product, 48 49 as well as framework synthesis which produced descriptive and explanatory findings that were more easily incorporated into the guideline process. 27 The definitions ( box 5 ) may be helpful when defining the different types of findings.
Different levels of findings
Descriptive findings —qualitative evidence-driven translated descriptive themes that do not move beyond the primary studies.
Explanatory findings —may either be at a descriptive or theoretical level. At the descriptive level, qualitative evidence is used to explain phenomena observed in quantitative results, such as why implementation failed in specific circumstances. At the theoretical level, the transformed and interpreted findings that go beyond the primary studies can be used to explain the descriptive findings. The latter description is generally the accepted definition in the wider qualitative community.
Hypothetical or theoretical finding —qualitative evidence-driven transformed themes (or lines of argument) that go beyond the primary studies. Although similar, Thomas and Harden 56 make a distinction in the purposes between two types of theoretical findings: analytical themes and the product of meta-ethnographies, third-order interpretations. 48
Analytical themes are a product of interrogating descriptive themes by placing the synthesis within an external theoretical framework (such as the review question and subquestions) and are considered more appropriate when a specific review question is being addressed (eg, in a guideline or to inform policy). 56
Third-order interpretations come from translating studies into one another while preserving the original context and are more appropriate when a body of literature is being explored in and of itself with broader or emergent review questions. 48
Bringing mixed-method evidence together in evidence to decision (EtD) frameworks
A critical element of guideline development is the formulation of recommendations by the Guideline Development Group, and EtD frameworks help to facilitate this process. 16 The EtD framework can also be used as a mechanism to integrate and display quantitative and qualitative evidence and findings mapped against the EtD framework domains with hyperlinks to more detailed evidence summaries from contributing reviews (see table 1 ). It is commonly the EtD framework that enables the findings of the separate quantitative and qualitative reviews to be brought together in a guideline process. Specific challenges when populating the DECIDE evidence to decision framework 15 were noted in case study 3 (risk communication in humanitarian disasters) as there was an absence of intervention effect data and the interventions to communicate public health risks were context specific and varied. These problems would not, however, have been addressed by substitution of the DECIDE framework with the new INTEGRATE 16 evidence to decision framework. A d ifferent type of EtD framework needs to be developed for reviews that do not include sufficient evidence of intervention effect.
Mixed-method review and synthesis methods are generally the least developed of all systematic review methods. It is acknowledged that methods for combining quantitative and qualitative evidence are generally poorly articulated. 29 50 There are however some fairly well-established methods for using qualitative evidence to explore aspects of complexity (such as contextual, implementation and outcome complexity), which can be combined with evidence of effect (see sections A and B of table 1 ). 14 There are good examples of systematic reviews that use these methods to combine quantitative and qualitative evidence, and examples of guideline recommendations that were informed by evidence from both quantitative and qualitative reviews (eg, case studies 1–3). With the exception of case study 3 (risk communication), the quantitative and qualitative reviews for these specific guidelines have been conducted separately, and the findings subsequently brought together in an EtD framework to inform recommendations.
Other mixed-method review designs have potential to contribute to understanding of complex interventions and to explore aspects of wider health systems complexity but have not been sufficiently developed and tested for this specific purpose, or used in a guideline process (section C of table 1 ). Some methods such as meta-narrative reviews also explore different questions to those usually asked in a guideline process. Methods for processing (eg, quality appraisal) and synthesising the highly diverse evidence suggested in tables 2 and 3 that are required to explore specific aspects of health systems complexity (such as system adaptivity) and to populate some sections of the INTEGRATE EtD framework remain underdeveloped or in need of development.
In addition to the required methodological development mentioned above, there is no GRADE approach 38 for assessing confidence in findings developed from combined quantitative and qualitative evidence. Another paper in this series outlines how to deal with complexity and grading different types of quantitative evidence, 51 and the GRADE CERQual approach for qualitative findings is described elsewhere, 39 but both these approaches are applied to method-specific and not mixed-method findings. An unofficial adaptation of GRADE was used in the risk communication guideline that reported mixed-method findings. Nor is there a reporting guideline for mixed-method reviews, 47 and for now reports will need to conform to the relevant reporting requirements of the respective method-specific guideline. There is a need to further adapt and test DECIDE, 15 WHO-INTEGRATE 16 and other types of evidence to decision frameworks to accommodate evidence from mixed-method syntheses which do not set out to determine the statistical effects of interventions and in circumstances where there are no trials.
When conducting quantitative and qualitative reviews that will subsequently be combined, there are specific considerations for managing and integrating the different types of evidence throughout the review process. We have summarised different options for combining qualitative and quantitative evidence in mixed-method syntheses that guideline developers and systematic reviewers can choose from, as well as outlining the opportunities to integrate evidence at different stages of the review and guideline development process.
Review commissioners, authors and guideline developers generally have less experience of combining qualitative and evidence in mixed-methods reviews. In particular, there is a relatively small group of reviewers who are skilled at undertaking fully integrated mixed-method reviews. Commissioning additional qualitative and mixed-method reviews creates an additional cost. Large complex mixed-method reviews generally take more time to complete. Careful consideration needs to be given as to which guidelines would benefit most from additional qualitative and mixed-method syntheses. More training is required to develop capacity and there is a need to develop processes for preparing the guideline panel to consider and use mixed-method evidence in their decision-making.
This paper has presented how qualitative and quantitative evidence, combined in mixed-method reviews, can help understand aspects of complex interventions and the systems within which they are implemented. There are further opportunities to use these methods, and to further develop the methods, to look more widely at additional aspects of complexity. There is a range of review designs and synthesis methods to choose from depending on the question being asked or the questions that may emerge during the conduct of the synthesis. Additional methods need to be developed (or existing methods further adapted) in order to synthesise the full range of diverse evidence that is desirable to explore the complexity-related questions when complex interventions are implemented into health systems. We encourage review commissioners and authors, and guideline developers to consider using mixed-methods reviews and synthesis in guidelines and to report on their usefulness in the guideline development process.
Handling editor: Soumyadeep Bhaumik
Contributors: JN, AB, GM, KF, ÖT and ES drafted the manuscript. All authors contributed to paper development and writing and agreed the final manuscript. Anayda Portela and Susan Norris from WHO managed the series. Helen Smith was series Editor. We thank all those who provided feedback on various iterations.
Funding: Funding provided by the World Health Organization Department of Maternal, Newborn, Child and Adolescent Health through grants received from the United States Agency for International Development and the Norwegian Agency for Development Cooperation.
Disclaimer: ÖT is a staff member of WHO. The author alone is responsible for the views expressed in this publication and they do not necessarily represent the decisions or policies of WHO.
Competing interests: No financial interests declared. JN, AB and ÖT have an intellectual interest in GRADE CERQual; and JN has an intellectual interest in the iCAT_SR tool.
Patient consent: Not required.
Provenance and peer review: Not commissioned; externally peer reviewed.
Data sharing statement: No additional data are available.
Supplemental material: This content has been supplied by the author(s). It has not been vetted by BMJ Publishing Group Limited (BMJ) and may not have been peer-reviewed. Any opinions or recommendations discussed are solely those of the author(s) and are not endorsed by BMJ. BMJ disclaims all liability and responsibility arising from any reliance placed on the content. Where the content includes any translated material, BMJ does not warrant the accuracy and reliability of the translations (including but not limited to local regulations, clinical guidelines, terminology, drug names and drug dosages), and is not responsible for any error and/or omissions arising from translation and adaptation or otherwise.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Methodology
- Qualitative vs Quantitative Research | Examples & Methods
Qualitative vs Quantitative Research | Examples & Methods
Published on 4 April 2022 by Raimo Streefkerk . Revised on 8 May 2023.
When collecting and analysing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge.
Common quantitative methods include experiments, observations recorded as numbers, and surveys with closed-ended questions. Qualitative research Qualitative research is expressed in words . It is used to understand concepts, thoughts or experiences. This type of research enables you to gather in-depth insights on topics that are not well understood.
Table of contents
The differences between quantitative and qualitative research, data collection methods, when to use qualitative vs quantitative research, how to analyse qualitative and quantitative data, frequently asked questions about qualitative and quantitative research.
Quantitative and qualitative research use different research methods to collect and analyse data, and they allow you to answer different kinds of research questions.
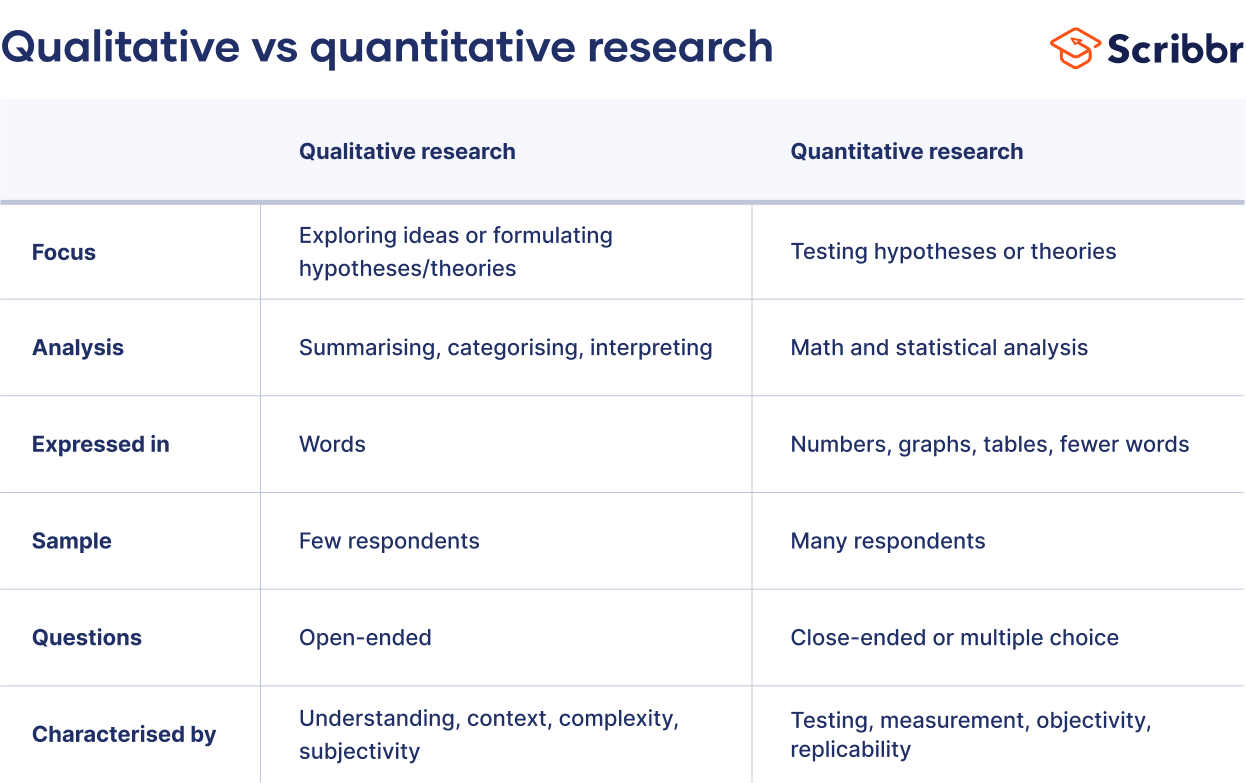
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
Quantitative and qualitative data can be collected using various methods. It is important to use a data collection method that will help answer your research question(s).
Many data collection methods can be either qualitative or quantitative. For example, in surveys, observations or case studies , your data can be represented as numbers (e.g. using rating scales or counting frequencies) or as words (e.g. with open-ended questions or descriptions of what you observe).
However, some methods are more commonly used in one type or the other.
Quantitative data collection methods
- Surveys : List of closed or multiple choice questions that is distributed to a sample (online, in person, or over the phone).
- Experiments : Situation in which variables are controlled and manipulated to establish cause-and-effect relationships.
- Observations: Observing subjects in a natural environment where variables can’t be controlled.
Qualitative data collection methods
- Interviews : Asking open-ended questions verbally to respondents.
- Focus groups: Discussion among a group of people about a topic to gather opinions that can be used for further research.
- Ethnography : Participating in a community or organisation for an extended period of time to closely observe culture and behavior.
- Literature review : Survey of published works by other authors.
A rule of thumb for deciding whether to use qualitative or quantitative data is:
- Use quantitative research if you want to confirm or test something (a theory or hypothesis)
- Use qualitative research if you want to understand something (concepts, thoughts, experiences)
For most research topics you can choose a qualitative, quantitative or mixed methods approach . Which type you choose depends on, among other things, whether you’re taking an inductive vs deductive research approach ; your research question(s) ; whether you’re doing experimental , correlational , or descriptive research ; and practical considerations such as time, money, availability of data, and access to respondents.
Quantitative research approach
You survey 300 students at your university and ask them questions such as: ‘on a scale from 1-5, how satisfied are your with your professors?’
You can perform statistical analysis on the data and draw conclusions such as: ‘on average students rated their professors 4.4’.
Qualitative research approach
You conduct in-depth interviews with 15 students and ask them open-ended questions such as: ‘How satisfied are you with your studies?’, ‘What is the most positive aspect of your study program?’ and ‘What can be done to improve the study program?’
Based on the answers you get you can ask follow-up questions to clarify things. You transcribe all interviews using transcription software and try to find commonalities and patterns.
Mixed methods approach
You conduct interviews to find out how satisfied students are with their studies. Through open-ended questions you learn things you never thought about before and gain new insights. Later, you use a survey to test these insights on a larger scale.
It’s also possible to start with a survey to find out the overall trends, followed by interviews to better understand the reasons behind the trends.
Qualitative or quantitative data by itself can’t prove or demonstrate anything, but has to be analysed to show its meaning in relation to the research questions. The method of analysis differs for each type of data.
Analysing quantitative data
Quantitative data is based on numbers. Simple maths or more advanced statistical analysis is used to discover commonalities or patterns in the data. The results are often reported in graphs and tables.
Applications such as Excel, SPSS, or R can be used to calculate things like:
- Average scores
- The number of times a particular answer was given
- The correlation or causation between two or more variables
- The reliability and validity of the results
Analysing qualitative data
Qualitative data is more difficult to analyse than quantitative data. It consists of text, images or videos instead of numbers.
Some common approaches to analysing qualitative data include:
- Qualitative content analysis : Tracking the occurrence, position and meaning of words or phrases
- Thematic analysis : Closely examining the data to identify the main themes and patterns
- Discourse analysis : Studying how communication works in social contexts
Quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings.
Quantitative methods allow you to test a hypothesis by systematically collecting and analysing data, while qualitative methods allow you to explore ideas and experiences in depth.
In mixed methods research , you use both qualitative and quantitative data collection and analysis methods to answer your research question .
The research methods you use depend on the type of data you need to answer your research question .
- If you want to measure something or test a hypothesis , use quantitative methods . If you want to explore ideas, thoughts, and meanings, use qualitative methods .
- If you want to analyse a large amount of readily available data, use secondary data. If you want data specific to your purposes with control over how they are generated, collect primary data.
- If you want to establish cause-and-effect relationships between variables , use experimental methods. If you want to understand the characteristics of a research subject, use descriptive methods.
Data collection is the systematic process by which observations or measurements are gathered in research. It is used in many different contexts by academics, governments, businesses, and other organisations.
There are various approaches to qualitative data analysis , but they all share five steps in common:
- Prepare and organise your data.
- Review and explore your data.
- Develop a data coding system.
- Assign codes to the data.
- Identify recurring themes.
The specifics of each step depend on the focus of the analysis. Some common approaches include textual analysis , thematic analysis , and discourse analysis .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
Streefkerk, R. (2023, May 08). Qualitative vs Quantitative Research | Examples & Methods. Scribbr. Retrieved 24 June 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/research-methods/quantitative-qualitative-research/
Is this article helpful?
Raimo Streefkerk

How to write a Literature Review: Quantitative vs qualitative method
- Literature review process
- Purpose of a literature review
- Evaluating sources
- Managing sources
- Request a literature search
- Selecting the approach to use
Quantitative vs qualitative method
- Summary of different research methodologies
- Research design vs research methodology
- Diagram: importance of research
- Attributes of a good research scholar
|
|
| ||
|
|
|
|
|
| Reliability | Same findings upon replication? Test-retest & interrater reliability | Dependability; Trustworthiness; Consistency | Similar context yields similar findings? Inquiry audit |
| Internal validity | Measured what intention was? Experimental control; statistical triangulation | Credibility | Compatibility between respondents’ and reported perceptions? Prolonged engagement; member checks; quality record; narrative triangulation |
| External validity | Generalisability to population? Random sampling | Transferability | Applicable to other cases and contexts? Purposive sampling; detailed descriptions of process |
| ‘Objectivity’ | Reflecting own views? Control over subjective factors | Confirmability | Findings not function of biases of researcher? Audit trail; trust & rapport with subject; intersubjectivity |
| Replicability | Can next researcher replicate the study? Peer reviewed publication | Replicability | Clear description of procedures? Appropriate peer-reviewed publication |
Source : Golafshani, 2003
- << Previous: Selecting the approach to use
- Next: Summary of different research methodologies >>
- Last Updated: Apr 30, 2024 1:19 PM
- URL: https://libguides.unisa.ac.za/literature_review

About Systematic Reviews
Are Systematic Reviews Qualitative or Quantitative?

Automate every stage of your literature review to produce evidence-based research faster and more accurately.
A systematic review is designed to be transparent and replicable. Therefore, systematic reviews are considered reliable tools in scientific research and clinical practice. They synthesize the results using multiple primary studies by using strategies that minimize bias and random errors. Depending on the research question and the objectives of the research, the reviews can either be qualitative or quantitative. Qualitative reviews deal with understanding concepts, thoughts, or experiences. Quantitative reviews are employed when researchers want to test or confirm a hypothesis or theory. Let’s look at some of the differences between these two types of reviews.
To learn more about how long it takes to do a systematic review , you can check out the link to our full article on the topic.
Differences between Qualitative and Quantitative Reviews
The differences lie in the scope of the research, the methodology followed, and the type of questions they attempt to answer. Some of these differences include:
Research Questions
As mentioned earlier qualitative reviews attempt to answer open-ended research questions to understand or formulate hypotheses. This type of research is used to gather in-depth insights into new topics. Quantitative reviews, on the other hand, test or confirm existing hypotheses. This type of research is used to establish generalizable facts about a topic.
Type of Sample Data
The data collected for both types of research differ significantly. For qualitative research, data is collected as words using observations, interviews, and interactions with study subjects or from literature reviews. Quantitative studies collect data as numbers, usually from a larger sample size.
Data Collection Methods
To collect data as words for a qualitative study, researchers can employ tools such as interviews, recorded observations, focused groups, videos, or by collecting literature reviews on the same subject. For quantitative studies, data from primary sources is collected as numbers using rating scales and counting frequencies. The data for these studies can also be collected as measurements of variables from a well-designed experiment carried out under pre-defined, monitored conditions.
Data Analysis Methods
Data by itself cannot prove or demonstrate anything unless it is analyzed. Qualitative data is more challenging to analyze than quantitative data. A few different approaches to analyzing qualitative data include content analysis, thematic analysis, and discourse analysis. The goal of all of these approaches is to carefully analyze textual data to identify patterns, themes, and the meaning of words or phrases.
Quantitative data, since it is in the form of numbers, is analyzed using simple math or statistical methods. There are several software programs that can be used for mathematical and statistical analysis of numerical data.
Presentation of Results
Learn more about distillersr.
(Article continues below)
Final Takeaway – Qualitative or Quantitative?
3 reasons to connect.

Systematic & scoping reviews
Systematic reviews.
From Munn et al (2018): “Systematic reviews can be broadly defined as a type of research synthesis that are conducted by review groups with specialized skills, who set out to identify and retrieve international evidence that is relevant to a particular question or questions and to appraise and synthesize the results of this search to inform practice, policy and in some cases, further research. .. Systematic reviews follow a structured and pre-defined process that requires rigorous methods to ensure that the results are both reliable and meaningful to end users. .. A systematic review may be undertaken to confirm or refute whether or not current practice is based on relevant evidence, to establish the quality of that evidence, and to address any uncertainty or variation in practice that may be occurring. .. Conducting a systematic review may also identify gaps, deficiencies, and trends in the current evidence and can help underpin and inform future research in the area. .. Indications for systematic reviews are:
- Uncover the international evidence
- Confirm current practice/ address any variation/ identify new practices
- Identify and inform areas for future research
- Identify and investigate conflicting results
- Produce statements to guide decision-making”
Scoping reviews
From Munn et al (2018): “Scoping reviews are an ideal tool to determine the scope or coverage of a body of literature on a given topic and give clear indication of the volume of literature and studies available as well as an overview (broad or detailed) of its focus. Scoping reviews are useful for examining emerging evidence when it is still unclear what other, more specific questions can be posed and valuably addressed by a more precise systematic review. They can report on the types of evidence that address and inform practice in the field and the way the research has been conducted. The general purpose for conducting scoping reviews is to identify and map the available evidence . Purposes for conducting a scoping review:
- To identify the types of available evidence in a given field
- To clarify key concepts/ definitions in the literature
- To examine how research is conducted on a certain topic or field
- To identify key characteristics or factors related to a concept
- As a precursor to a systematic review
- To identify and analyse knowledge gaps”
Munn, Z., Peters, M. D. J., Stern, C., Tufanaru, C., McArthur, A., & Aromataris, E. (2018). Systematic review or scoping review? Guidance for authors when choosing between a systematic or scoping review approach. BMC Medical Research Methodology , 18(1), 143. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12874-018-0611-x
Reviews can be quantitative or qualitative
A quantitative review will include studies that have numerical data. A qualitative review derives data from observation, interviews, or verbal interactions and focuses on the meanings and interpretations of the participants. It will include focus groups, interviews, observations and diaries. See the qualitative research section for more information.
PRISMA Statement
PRISMA: Preferred Reporting Items for Systematic Reviews and Meta-Analyses is an evidence-based minimum set of items for reporting in systematic reviews and meta-analyses.
The PRISMA 2020 statement was published in 2021 and comprises a 27-item checklist addressing the introduction, methods, results and discussion sections of a systematic review report. It is intended to be accompanied by the PRISMA 2020 Explanation and Elaboration document .
The PRISMA extension for scoping reviews (PRISMA-ScR) was published in 2018. The checklist contains 20 essential reporting items and 2 optional items to include when completing a scoping review.
Steps in a systematic review
A systematic review involves the following steps:
- Check for existing reviews/protocols . If a systematic review answering your question has been conducted, or is being undertaken, you may need to amend or refine your question
- Formulate a specific research question that is clear and focused. Use the PICO tool (for quantitative reviews) or PICo (for qualitative reviews)
- Develop and register your protocol , including the rationale for the review, and eligibility criteria
- Design a robust search strategy that is explicit and reproducible
- Conduct a comprehensive search of the literature by searching the relevant databases and other sources
- Select and critically appraise the quality of included studies
- Extract relevant data from individual studies and use established methods to synthesise the data
- Interpret your results and prepare a comprehensive report on all aspects of your systematic review. Present your findings so that they can be translated into clinical practice.
Comparison of different types of reviews
This table outlines the differences between a systematic review and a literature review:
| Focused on a single question | Not necessarily focused on a single question, but may describe an overview | |
| Includes a peer review protocol or plan | No protocol is included | |
| Provides summaries of the available literature on a topic | Provides summaries of the available literature on a topic | |
| Clear objectives are identified | Objectives may or may not be identified | |
| Criteria is stated before review is conducted | Criteria is not specified | |
| Comprehensive search conducted in a systematic way | Strategy not explicitly stated | |
| Process usually clear and explicit | Not described in a literature review | |
| Comprehensive evaluation of study quality | Evaluation of study quality may or may not be included | |
| Clear summaries based on high quality evidence | Summary based on studies where the quality of the articles may not be specified. May also be influenced by the reviewer’s theories, needs and beliefs | |
| Written by an expert or group of experts with a detailed and well grounded knowledge of the issues | Written by an expert or group of experts with a well grounded knowledge of the issues |
Adapted from: University of Newcastle Australia Library
This table outlines the differences between a systematic review and a scoping review:
| Systematic Review | Scoping Review | |
|---|---|---|
| Attempts to identify, appraise and synthesize all empirical evidence that meets pre-specified eligibility criteria to answer a given research question | A rapid gathering of literature in a given area, aiming to provide an overview of the type, extent and quantity of research available | |
| To address a clearly focused review question by finding the best available, relevant studies and synthesizing the results | To capture the breadth of literature; identify gaps in a research area; occasionally used as a precursor to a systematic review | |
| Focused research question with narrow parameters | The research question is often broad | |
| Inclusion/exclusion usually defined at outset | Inclusion/exclusion can be developed | |
| Rigorous critical appraisal and evaluation of study quality | Appraisal can be variable; typically not done, or may be done in a narrative form | |
| Clear summaries of studies based on high quality evidence. May include a meta-analysis | The summary is usually descriptive | |
| Evidence based | Evidence based |
Adapted from: University of South Australia
References:
Pollock, D., Davies, E. L., Peters, M. D. J., et al. (2021). Undertaking a scoping review: A practical guide for nursing and midwifery students, clinicians, researchers, and academics. J Adv Nurs, 77, 2102-2113. https://doi.org/10.1111/jan.14743
“Rapid reviews have emerged as a streamlined approach to synthesizing evidence-typically for informing emergent decisions faced by decision makers in health care setting”.
| Often a focused clinical question (focused PICOS) | Narrow question (may use PICOS) | |
| Comprehensive sources searched and explicit strategies | Sources may be limited but sources and strategies made explicit | |
| Criterion-based | Criterion-based; uniformly applied | |
| Rigorous; critical appraisal | Rigorous, critical appraisal (SRs only) | |
| Qualitative summary with/without meta-analysis | Descriptive summary/categorisation of data | |
| Evidence-based | Limited/cautious interpretation of findings |
Source: Khangura, S., Konyu, K., Cushman, R., Grimshaw, J. & Moher, D. (2012). Evidence summaries: the evolution of a rapid review approach. Systematic Review, 1-10. https://doi.org/10.1186/2046-4053-1-10
Examples of different types of reviews:
Literature review: A Literature review of mentorship programs in academic nursing https://doi.org/10.1016/j.profnurs.2017.02.007
Narrative review: A silent burden—prolapse, incontinence, and infertility in Australian Aboriginal and Torres Strait Islander women: A systematic search and narrative review https://doi.org/10.1002/ijgo.13920
Rapid review: Blended foods for tube-fed children: a safe and realistic option? A rapid review of the evidence https://doi.org/10.1136/archdischild-2016-311030
Scoping review: How do patients experience caring? Scoping review https://doi.org/10.1016/j.pec.2017.03.029
Systematic review: Barriers and facilitators to health screening in men: A systematic review https://doi.org/10.1016/j.socscimed.2016.07.023
A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies (2009) https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1471-1842.2009.00848.x

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Quantitative research. Quantitative research is 'explaining phenom enon by collection numerical data that are. analyzed using mathematically based methods (in particular statistics)' (Aliaga and ...
Unlike in quantitative research where hypotheses are usually developed to be tested, qualitative research can lead to both hypothesis-testing and hypothesis-generating outcomes.2 When studies require both quantitative and qualitative research questions, this suggests an integrative process between both research methods wherein a single mixed ...
Qualitative Research and the Review of Related Literature Unlike quantitative researchers, who spend a great deal of time examining the research on their topic at the outset of the study, some qualitative researchers will not delve deeply into their literature until their topic has emerged over time. There is disagreement among qualitative
between qualitative and quantitative research designs is about the question of scale or depth versus. breath (Sayer, 1992). There are limited preliminary changes between both re search designs ...
Quantitative Research (an operational definition) Quantitative research: an operational description. Purpose: explain, predict or control phenomena through focused collection and analysis of numberical data. Approach: deductive; tries to be value-free/has objectives/ is outcome-oriented. Hypotheses: Specific, testable, and stated prior to study.
0 Qualitative main traditions1. 0 Quantitative Qualitative research. 0 sampling different = = research: Quantitative inferential interpretive. 0 one another i.e., in mixed Although procedures, different, of of be applications, methods2 complementary data analysis, of. Introduction.
Each approach offers distinct frameworks, tools, and philosophies that researchers employ to. investigate and comprehend diverse aspects of the wo rld [1 ]. Qualitative research involves a nuanced ...
The Difference Between Qualitative And Quantitative Jennifer Cleland,Steven J. Durning Qualitative Research for Quantitative Researchers Helen Kara,2022-01-12 Approaching qualitative research for the first time and unsure how to get started? This book captures what you need to know to jump into effective qualitative or mixed methods research.
Literature review: Survey of published works by other authors. When to use qualitative vs. quantitative research. A rule of thumb for deciding whether to use qualitative or quantitative data is: Use quantitative research if you want to confirm or test something (a theory or hypothesis)
This paper describes a broad framework of critical appraisal of published research literature that covers both quantitative and qualitative methodologies. The aim is the heart of a research study. It should be robust, concisely stated and specify a study factor, outcome factor(s) and reference population. Quantitative study designs, including ...
Learning Objectives for Chapter 4. Upon completion of this chapter, the reader should be able to: Understand the differences between quantitative and qualitative research, including: d. the differing assumptions underlying the two approaches; d. the methods typical of each approach; and. d Understand and discuss how these two approaches to ...
Summary This assignment will guide you through the analysis of how qualitative, quantitative, and mixed-methods researchers frame research questions, construct literature reviews, and integrate citations. You will engage in discourse analysis, rhetorical analysis, and citation analysis of one qualitative study and one quantitative or mixed-methods research study. This creative challenge will ...
Quantitative methodology is the dominant research framework in the social sciences. It refers to a set of strategies, techniques and assumptions used to study psychological, social and economic processes through the exploration of numeric patterns. Quantitative research gathers a range of numeric data.
There is considerable literature showing the complexity, connectivity and blurring of 'qualitative' and 'quantitative' methods in research. Yet these concepts are often represented in a binary way as independent dichotomous categories. This is evident in many key textbooks which are used in research methods courses to guide students and newer researchers in their research training. This paper ...
Chapter 3 of the dissertation provides the reader with a detailed description of the components of the method that will be used in the research. This chapter helps the reader to judge if the method used in the research provided an adequate opportunity to examine the research questions and hypotheses.
Pluye and Hong 52 define mixed-methods research as "a research approach in which a researcher integrates (a) qualitative and quantitative research questions, (b) qualitative research methods* and quantitative research designs, (c) techniques for collecting and analyzing qualitative and quantitative evidence, and (d) qualitative findings and quantitative results".A mixed-method synthesis ...
Learn how to choose and apply quantitative and qualitative methods for evidence-based outcomes. A comprehensive guide for young researchers.
investigations. Therefore, the purpose of current literature review is to distinguish the imperative comparison of quantitative and qualitative in the research methodology and determining the brilliant differences between these research factors. Furthermore, realizing the accurate appr oach and apply it
When collecting and analysing data, quantitative research deals with numbers and statistics, while qualitative research deals with words and meanings. Both are important for gaining different kinds of knowledge. Quantitative research. Quantitative research is expressed in numbers and graphs. It is used to test or confirm theories and assumptions.
3. How do I structuring my literature review? Turning circles into a triangle Your research Aims The text of the literature review Stepped out argument Leading to the aims The literature to review 1 1 3 2 2 3 What methods are available? 1.Traditional narrative 2.Meta‐analysis 3.Systematic quantitative literature review
Literature review process; Purpose of a literature review; Evaluating sources; Managing sources; Request a literature search; Sage Research Methods Toggle Dropdown. Selecting the approach to use ; Quantitative vs qualitative method ; Summary of different research methodologies ; Research design vs research methodology ; Diagram: importance of ...
A systematic review can be qualitative, quantitative, or a combination of the two. The approach that is chosen is determined by the research question and the scope of the research. When qualitative and quantitative techniques are used together in a given study, it is called a mixed method. In a mixed-method study, synthesis for the quantitative ...
Difference Between Qualitative and Quantitative Literature Review - Free download as PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free. difference between qualitative and quantitative literature review
A typology of reviews: an analysis of 14 review types and associated methodologies (2009) A systematic literature review is a review of a clearly formulated question that uses systematic and reproducible methods to identify, select and critically appraise all relevant research. A scoping search is a search of the existing literature which will ...
The search dates for identifying literature were from September 2001 to September 2021. The review's search strategy identified 3208 articles from 4 databases and 9 studies from web and citation search, of which 11 met the inclusion criteria for the review. Quality appraisal was conducted using the Critical Appraisal Skills Programme (CASP).