9 Creative Problem Solving Tools For Your Next Breakthrough Idea
This is a suite of 9 creative problem solving tools from Erik op ten Berg. He’s an expert in creative thinking or applying creativity from the Netherlands.
He’s been working in this field for 25 years and has a Master of Science from Buffalo State University in New York.
His creative problem solving process takes a challenge and finds ideas that are new, useful and meaningful. I guarantee you this process will help you mobilise your group’s creative thinking skills.
You and your group will find original ideas which are always there. This helps you get to the holy grail of breakthrough thinking and quite possibly the ‘next big thing’.
Download free slides... enter your email address at the bottom to get this team building activity in your inbox

Interview with Erik op ten Berg
Watch this video to see Erik describe in detail how each tool / activity works with examples.
Please note that the video and audio quality is a little shaky in places. Sorry about that! We had some technical issues with Skype that were difficult to overcome.
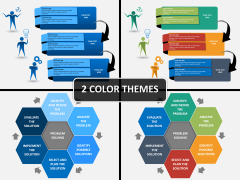
Four Stages of Creative Problem Solving
The first two stages help you and your group ‘explore ideas’. The third stage helps you select the best ideas and the fourth tests the feasibility of your best ideas.
These are the four stages you need to go through (no skipping a stage please):
- Idea generation
- Idea expansion
- Idea selection
- Idea feasibility
Always start with the ABC Avalanche and then use 1 or 2 of the next 5 tools to expand the list of possible solutions.
1. ABC Avalanche (3:55sec on video)
A very basic brainstorming technique but extremely powerful.
This tool asks people to generate at least 26 ideas for a specific challenge sorting them by their first letters. It takes about 10-15 minutes.
- Write down the central question.
- Write down the letters of the alphabet.
- Generate many ideas sorting them by their first letters.
- Complete the alphabet.
Because participants focus on generating a specific number of ideas they postpone their judgments.
These attitudes are core to creative problem solving:
- Generating many alternative ideas.
- Postponing judgments.
- Moving past the first few (obvious) ideas.
Depending on the number of people in the session you can split into sub-groups. Feel free to build in a little competition between the groups if you like.
From this stage you have at least 26 starting ideas and people won’t have jumped into judging whether they are good ideas or not.
2. Breaking Assumptions (7:38min on video)
This is a second stage to an ABC Avalanche.
One of the very classical thinking techniques because to be truly creative you need to break patterns.
Once you’re aware of a pattern or an assumption in your idea generation so far you can deliberately break this assumption and new ideas will come forward and present themselves.
- List 5 assumptions present in the question or in the list of ideas.
- Take the opposite of each assumption.
- Imagine new solutions that run opposite to the initial assumptions.
- Add these to your list of ideas.
You ask the group to identify any patterns or assumptions that are built into either the challenge or list of ideas they’ve generated so far.
Then you ask them to take the opposite view (i.e. break that assumption) and come up with any new solutions and add them to your list of ideas.
3. Association Flower (11:13min on video)
Also a second stage technique after ABC Avalanche giving you and your group extra ‘access points’ from which to consider the challenge and generate more ideas.
This technique will generate a long list of associated keywords that can be used to generate even more ideas related to the original challenge.
- Write down a keyword about the challenge in the centre of the flower and four words that are associated with the keyword around it (see template on next page).
- Write around this keyword four associations.
- Then follow each of the 4 words in turn up its branch writing associated keywords as you go.
- Then use all these words to think in a new way about your challenge and generate even more ideas.
- Make the list of ideas as large as possible.
4. Visual Connections (15:33min on video)
Another way to create new ‘access points’ from which to generate new ideas.
- Focus on an interesting object, picture or an article in a newspaper.
- Write down your thoughts, reactions, impressions and observations.
- Make connections to the central topic and write these down as new ideas.
- Repeat this several times and expand your list of ideas.
You could bring a deck of pictures with you, or a set of magazines, or even ask the participants to bring their own magazines so they’re an integral part of the process.
5. SCAMPER (18:31min on video)
Use the 8 words from the acronym to approach the challenge from a different angle and generate a larger list of creative ideas.
SCAMPER is the summary of 72 questions used by Alex Osborn who is the man that founded the concept of brainstorming in the early 40s.
- SUBSTITUTE: parts, the whole, material…
- COMBINE: functions, material, just different…
- ADAPT: other color, place, use, form, timing…
- MAXIMIZE: bigger, stronger, longer, more time, macro level, use more often…
- MINIMIZE: smaller, lighter, shorter, micro level, less important…
- PUT TO OTHER USES: other context…
- ELIMINATE: parts, functions, material…
- REVERSE: sequence, upside down, inside out…
There’s no need to do all these words. Let them go wherever they want to go to create more productive access points to tackle the original challenge.
6. Analogy with nature (22:32min on video)
Sometimes people are using this technique as biomimicry .
Your question to the group: what kind of animals are you thinking about when you use your imagination?
Get them to list lots of animals quickly and ask them to select one. What is it that makes this an extraordinary animal?
Once you have that list of characteristics about the animal use those words as access points to generate more ideas about the challenge. What you’re doing here is using the beauty of nature and bringing that connection back to the challenge.
- List several names of animals.
- Choose a special animal with no link to the problem.
- List 10 characteristics about this animal.
- Use each characteristic as a stimulus for new ideas.
- Make a force-to-fit to the problem and boost your list of ideas.
Next step is to select ideas through a process of prioritization that you want to go deeper into and do further work on to develop them further.
7. Selecting ideas & COCD Box (24:37min on video)
Using a combination of dots (or hits as Erik calls them) and his COCD box you’re looking to boil down your grand list of ideas down to about 15 really good ones (5 in each color – blue, red and yellow).
- 5-15 IDEAS: everybody selects his or her 1-3 favorite hits; make out of these a top 3.
- 15-40 IDEAS: 5 sparkling ideas per person; focus on these and define an overall top 5 using dots or hits.
- >40 IDEAS: select individually 5-8 blue-red-yellow ideas (COCD-box); define the BIG 5 in each color.
Once you have 5 good ideas in each of the coloured boxes look for themes across them to try and boil everything down to a Top 5 by making some smart combinations.
If you’re looking for breakthrough ideas (and most often you will be) the ideas in the red box will be the ones you want to focus on in the next stage.
8. Concepting (30:07min on video)
What you’re looking to do now is enrich your ideas into concepts. You do this by combining your headline ideas with other ideas that are closely related from your overall list.
Take each red idea in turn and see if you can bundle in other ideas from the grand list.
- Focus on the selected ideas.
- Take one idea and add on different ideas (with and without dots) from the idea list, to enrich the original idea.
- Do this for all the selected ideas.
- Give the enriched ideas an attractive title.
- Go on with these results.
Then give the enriched ideas a more attractive title.
9. PPCO (33:38min on video)
This is one of Erik’s little gems he got out of his Master of Science in Buffalo.
At this stage you’re looking to expand and test your best ideas or concepts for feasibility.
- Pluses : what is good, positive about the idea.
- Potentials : what are the possibilities if the idea were pursued.
- Concerns : phrase shortcomings or limitations of the idea as questions.
- Overcomes : generate ideas to overcome the ‘burning’ concerns.
PPCO is like a SWOT analysis but in a more positive end. A moving towards approach instead of getting away approach. Facing truth and reality in a way of opportunities.
Pluses : Let’s see why we should do this idea. Potentials : What are the extra potentials of this idea that you haven’t considered before? These are extra or super pluses. Concerns : ‘how can I overcome (insert negative point here) …” Overcomes : your last stage of creative thinking where you’re generating answers of how to overcome your concerns.
You end with a triple positive state with very realistic backgrounds. That’s the kind of creativity you need when you have a good idea and you want to move it further whilst trying to taste a bit of the potential of it.
Creative problem solving is a process that, if you have the right tools and activities at hand, you can consistently achieve fantastic results from.
For your session to be a success you need to make sure you move past the first few obvious ideas, you generate tonnes of alternatives and that you postpone judgment on the quality of each idea until the appropriate moment.
How does your experience stack up? Do you have any secrets you’d like to share in the comments below?
Free Download Files
Download your creative problem solving slides (free).
Subscribe to our newsletter to receive a new team activity every couple of weeks & get your slides instantly.
About the Author
Erik op ten Berg (1963) holds a Master of Science Degree in Creativity and Change Leadership, and is educated in Innovation Management at Delft Technical University in The Netherlands. He is a well-known trainer in Creative Problem Solving, and moderator of hundreds of change focused brainstorm workshops. Besides his own company Pioen consult he is also partner at the “Center for the Development of Creative Thinking” (COCD) in Belgium.
Thanks great would like to communicate with Erik Op Ten Berg
dear Rakesh! send me an email at [email protected] ; I will appologize for the delays in my answer because of some Summer holiday trips until August 22…
Thanks for sharing all these ideas. Very interesting and it generates a lots of ideas. One of them is the potential use of istock or getty image platform to search visuals using key words for Visual connections exercises. Wonder if you have try something like this in the past.
Great idea Dany. You need to be careful of potential copyright infringements obviously but there are loads of free stock image repositories out there too you can use in the way you suggest.
hi Dany! visual connections are an “easy way” to create access to thoughts that didn’t came up before; you can do this offline and also online; my experience with group thinking is better with offline pictures then online; bur for individual practice the online inspiration can be very productive and provocative; I wish you lots of creative detours in your own thinking; best wishes, Erik op ten Berg
Very educative, very informative, very useful for a trainer/coach. Thanks for great help to trainer community. World owes you a lot.
excellent approach
Session expired
Please log in again. The login page will open in a new tab. After logging in you can close it and return to this page.

- My presentations
Auth with social network:
Download presentation
We think you have liked this presentation. If you wish to download it, please recommend it to your friends in any social system. Share buttons are a little bit lower. Thank you!
Presentation is loading. Please wait.
Creative Problem Solving
Published by Darrell Brown Modified over 6 years ago
Similar presentations
Presentation on theme: "Creative Problem Solving"— Presentation transcript:

Objectives Identify the differences between Analytical Decision Making and Intuitive Decision Making Demonstrate basic design and delivery requirements.

‘ the 6 thinking styles’ by Dr. Edward de Bono (Ch. 8, the team handbook, p 6-7) Pooja Kishore Emily Vaughn Team: Fo’Sho!

Divergent Thinking Creative Thinking Terry A. Ring Chemical Engineering University of Utah.

Basic Problem Solving Tools Mark Pitman. Contents Topics/issues to be covered include: 1.Brainstorming 2.Cause and Effect diagrams 3.Pareto Charts 2.

Group Techniques John A. Cagle California State University, Fresno.

Brainstorming - Creative Problem Solving Method Halka Baláčková, MBA Masaryk Institute of Advanced Studies, Czech Technical University in Prague

Chapter 2: Creativity1 Copyright 2002 Prentice Hall Publishing Company Inside the Entrepreneurial Mind: From Ideas to Reality.

Use of Process Tools One of the main tasks in facilitation is the effective generation and management of information. Process Tools help to manage information.

UNIT 9. CLIL THINKING SKILLS

Chapter 4 – Concept Generation & Evaluation

Mantova 18/10/2002 "A Roadmap to New Product Development" Supporting Innovation Through The NPD Process and the Creation of Spin-off Companies.

Creativity Tools Prepared by Jamal Yousef

Copyright © 2006 by The McGraw-Hill Companies, Inc. All rights reserved. McGraw-Hill Technology Education Logic and Problem Solving Advanced Computer Programming.

1 Train the Trainer 2 HostFacilitator u Be prepared u Be available.

T 7.0 Chapter 7: Questioning for Inquiry Chapter 7: Questioning for Inquiry Central concepts: Questioning stimulates and guides inquiry Teachers use.

Chapter 7: A Summary of Tools Focus: This chapter outlines all the customer-driven project management tools and techniques and provides recommendations.

Brainstorm Solutions Problem Solving Module Session 4.

EENG 1920 Chapter 4 Concept Generation and Evaluation 1.

Lecture : 5 Problem Identification And Problem solving.

/0904 © Business & Legal Reports, Inc. BLR’s Training Presentations Creative Problem-Solving.
About project
© 2024 SlidePlayer.com Inc. All rights reserved.
Newly Launched - AI Presentation Maker

- Customer Favourites
Creative Problem Solving
AI PPT Maker
Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories

- You're currently reading page 1
Stages // require(['jquery'], function ($) { $(document).ready(function () { //removes paginator if items are less than selected items per page var paginator = $("#limiter :selected").text(); var itemsPerPage = parseInt(paginator); var itemsCount = $(".products.list.items.product-items.sli_container").children().length; if (itemsCount ? ’Stages’ here means the number of divisions or graphic elements in the slide. For example, if you want a 4 piece puzzle slide, you can search for the word ‘puzzles’ and then select 4 ‘Stages’ here. We have categorized all our content according to the number of ‘Stages’ to make it easier for you to refine the results.
Category // require(['jquery'], function ($) { $(document).ready(function () { //removes paginator if items are less than selected items per page var paginator = $("#limiter :selected").text(); var itemsperpage = parseint(paginator); var itemscount = $(".products.list.items.product-items.sli_container").children().length; if (itemscount.
- Business Plans (2)
- Business Slides (609)
- Circular (40)
- Cluster (9)
- Complete Decks (21)

JavaScript seems to be disabled in your browser. For the best experience on our site, be sure to turn on Javascript in your browser.
Exclusive access to over 200,000 completely editable slides.
- Diagram Finder
- Free Templates
- Human Resources
- Project Management
- Timelines & Planning
- Health & Wellness
- Environment
- Cause & Effect
- Executive Summary
- Customer Journey
- 30 60 90 Day Plan
- Social Media
- Escalation Matrix
- Communication
- Go to Market Plan/Strategy
- Recruitment
- Pros and Cons
- Business Plan
- Risk Management
- Roles and Responsibilities
- Mental Health
- ISO Standards
- Process Diagrams
- Puzzle Diagrams
- Organizational Charts
- Arrow Diagrams
- Infographics
- Tree Diagrams
- Matrix Charts
- Stage Diagrams
- Text Boxes & Tables
- Data Driven Charts
- Flow Charts
- Square Puzzle
- Circle Puzzle
- Circular Arrows
- Circle Segments
- Matrix Table
- Pillar Diagrams
- Triangle Puzzle
- Compare Diagrams
- Ladder Diagrams
- Google Slides
- North America Maps
- United States (US) Maps
- Europe Maps
- South America Maps
- Apple Keynote
- People & Objects
- Trending Products
- PowerPoint Templates
Creative Problem Solving PowerPoint and Google Slides Template
(8 Editable Slides)

Download Now
This template is part of our Pro Plan.
Gain access to over 200,000 slides with pro plan..
Upgrade Now
Already a Pro customer? Login

Related Products
Problem Solving PowerPoint and Google Slides Template
(11 Editable Slides)
8D Problem Solving PowerPoint and Google Slides Template

Systematic Problem Solving PowerPoint and Google Slides Template
(14 Editable Slides)

Problem Solving Cycle PowerPoint and Google Slides Template
(7 Editable Slides)
Six Step Problem Solving Model PowerPoint and Google Slides Template
(2 Editable Slides)
4 Step Problem Solving PowerPoint and Google Slides Template
(3 Editable Slides)
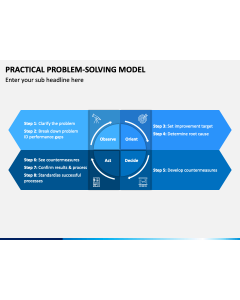
Practical Problem-Solving Model
(1 Editable Slide)

Problem Solving Checklist
Creative Problem Solving Process refers to a distinct approach taken to resolve any issue via new and innovative ideas. This process is conducted on varied stages to handle and solve organizational problems efficiently. As a senior executive or team leader, promoting your fellow employees to develop creative ideas and innovative approaches to address any operational issues can help gain growth opportunities. To help you with this, we offer you a ready-to-use Creative Problem Solving Process PPT template. In this set, you will find graphical and relevant content depicting the process of identifying an issue, its analyses, and finding the best solution to resolve it. So, download this amazing deck of slides to educate your employees on this subject.
Relevant Content
To offer our users high-quality content on this subject, we have included well-researched topics relevant to this subject. Our expert designers have strategically placed all the content in a sequence to understand the flow of information easily. The topics we have included in this set are listed below:
- Creative Problem Solving Process: OSBORN
- Steps Involved
- Its Framework
- Major Roles
Other than these topics, if you wish to insert additional information or remove any slide, you can easily do it with this customizable PowerPoint template.
Easily Editable Slides and Elements
We understand that you would need to customize this deck of slides as per your requirements and would want to do it without investing much of your time. Therefore, we have designed this set to let you easily personalize the slides with its user-friendly editing features. Here, you will get complete access to:
- Modify every element without any designing experience
- Resize, recolor, add and remove any visual element or content easily
- Even pick individual slide or visual aspects, and use it in any of your presentations
Useful for Training Purposes
Using creative ideas while addressing any issue can let you solve it more efficiently and quickly. So, you can also motivate your fellow employees to have a creative mindset while solving any problem with this amazing presentation template. Since its slides contain all the relevant information with HD and vector-based infographics, your audience will understand the concept and importance of adopting it.
Accessible on Varied Platforms
We offer you this PPT in two distinct color layouts (blue and multicolor), which you can easily modify on different platforms, like MS PowerPoint, Apple Keynote, and Google Slides. You can also display it on different screen sizes (Standard 4:3 and Widescreen 16:9) without worrying about the visual quality of the graphics and objects. So, download this PPT right now to share a compelling presentation on this subject.
Create compelling presentations in less time
- All PowerPoint Templates
- Highly Recommended Templates
- Multipurpose PowerPoint Templates
- PowerPoint Profession Templates
- PowerPoint Diagrams
- PowerPoint Shapes
- PowerPoint Image Layouts
- PowerPoint Data Charts
- PowerPoint Maps
- PowerPoint Infographics
- PowerPoint Mockups Layouts
- PowerPoint Bundles
- All Google Slides Templates
- Multipurpose Google Slides Templates
- Google Slides Profession Templates
- Google Slides Diagrams
- Google Slides Shapes
- Google Slides Image Layouts
- Google Slides Maps
- Google Slides Infographics
- Google Slides Mockups Layouts
- Google Slides Bundles
- Keynote Templates
- Templates on Sale
- Featured Templates
- All Free Templates
- PowerPoint Free Templates
- Google Slides Free Templates
- Keynote Free Templates
20+ Best Problem Solving Models and Techniques PowerPoint Templates for 2024
In powerpoint templates ,.
Decision making is a crucial part of any business or organization, and the ability to make effective decisions can mean the difference between success and failure. Of course, making the right decision isn’t always easy, which is why it’s essential to have a strong problem-solving process in place. This blog post discusses the definition of problem solving and some of the recommended problem solving models and techniques PowerPoint templates .
What is Problem Solving?
Problem solving is the process of identifying and resolving issues or challenges. It can be done individually or as part of a team. Problem solving usually requires a systematic approach and often includes steps such as: identifying the problem, generating potential solutions, evaluating the options, selecting the solution, and implementing the plan. Of course, not every problem will require all of these steps. But in general, taking a systematic and structured approach to problem solving will increase the chances of finding a successful resolution. With practice, problem solving can become second nature – something that we do automatically and effortlessly. When faced with an issue or challenge, our first instinct will be to quickly find a solution that works.
The Problem Solving Process
The first step in the problem solving process is to identify the source of the problem. Once the source has been identified, it is important to gather information about the problem. This may include conducting research, observing the situation, or speaking to those who are affected by the problem . Once enough information has been gathered, it is time to start brainstorming solutions. Possible solutions should be evaluated based on their feasibility and potential impact. After a solution has been chosen, it is important to implement it in a way that is efficient and effective. Finally, it is necessary to monitor the situation to ensure that the chosen solution is having the desired effect. If not, then the problem solving process will need to begin anew in order to find a different solution.

Best Problem Solving Models and Techniques PowerPoint Templates from SlideSalad
If you are looking for some helpful PPT templates to Create Problem solving Model PowerPoint presentations, then look no further! Here are some of the best problem solving models and techniques PowerPoint templates that you can use to make your next presentation. This clean template come with easy-to-follow instructions and plenty of sample slides to get you started. With these multipurpose PowerPoint templates , you’ll be able to create a professional, engaging presentation that will help your audience understand the problem solving process and how to apply it in real-world situations. So check out these great problem solving models and techniques PowerPoint templates today and get started on your next presentation!
1. PDCA Cycle Diagrams PowerPoint Template – Best PDCA Cycle Diagram Illustrations in PowerPoint
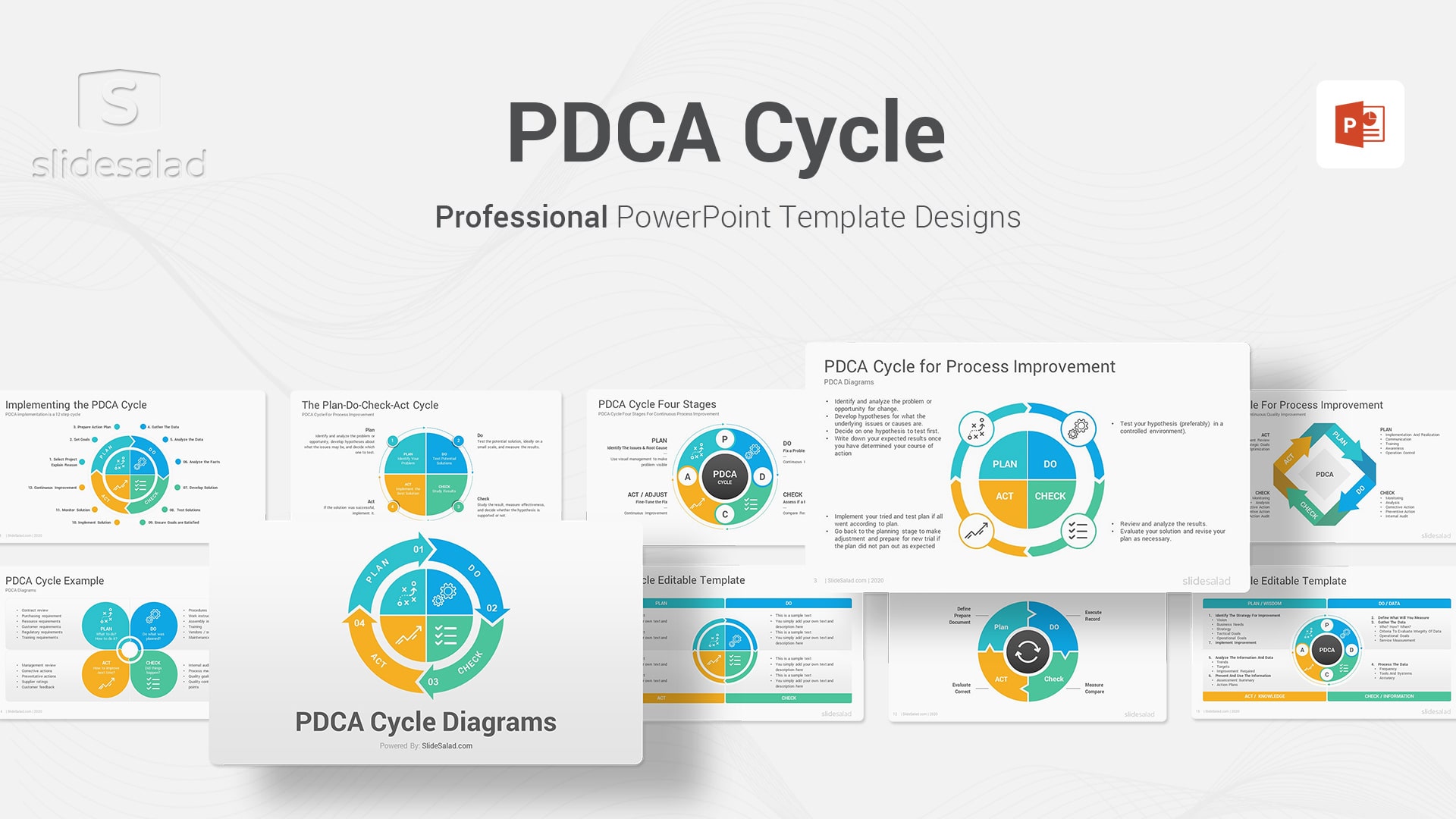
The PDCA cycle is also known as the Deming Wheel , named after Dr. William Edwards Deming who introduced the concept in the 1950s. The PDCA cycle is a quality control method that can be used to continually improve processes and systems. The four steps of the cycle are: Plan, Do, Check (study), and Act. The Plan step involves identifying the problem and developing a plan to address it. The Do step involves implementing the plan. The Check (study) step involves monitoring the results of the implementation and determining whether they are effective. The Act step involves taking action to make permanent changes based on the findings of the study. By following this cycle, organizations can improve their processes and systems on an ongoing basis.
2. 5 whys PowerPoint Template PPT Slides – Effective Way to Uncover the Root of Problems in Problem Solving
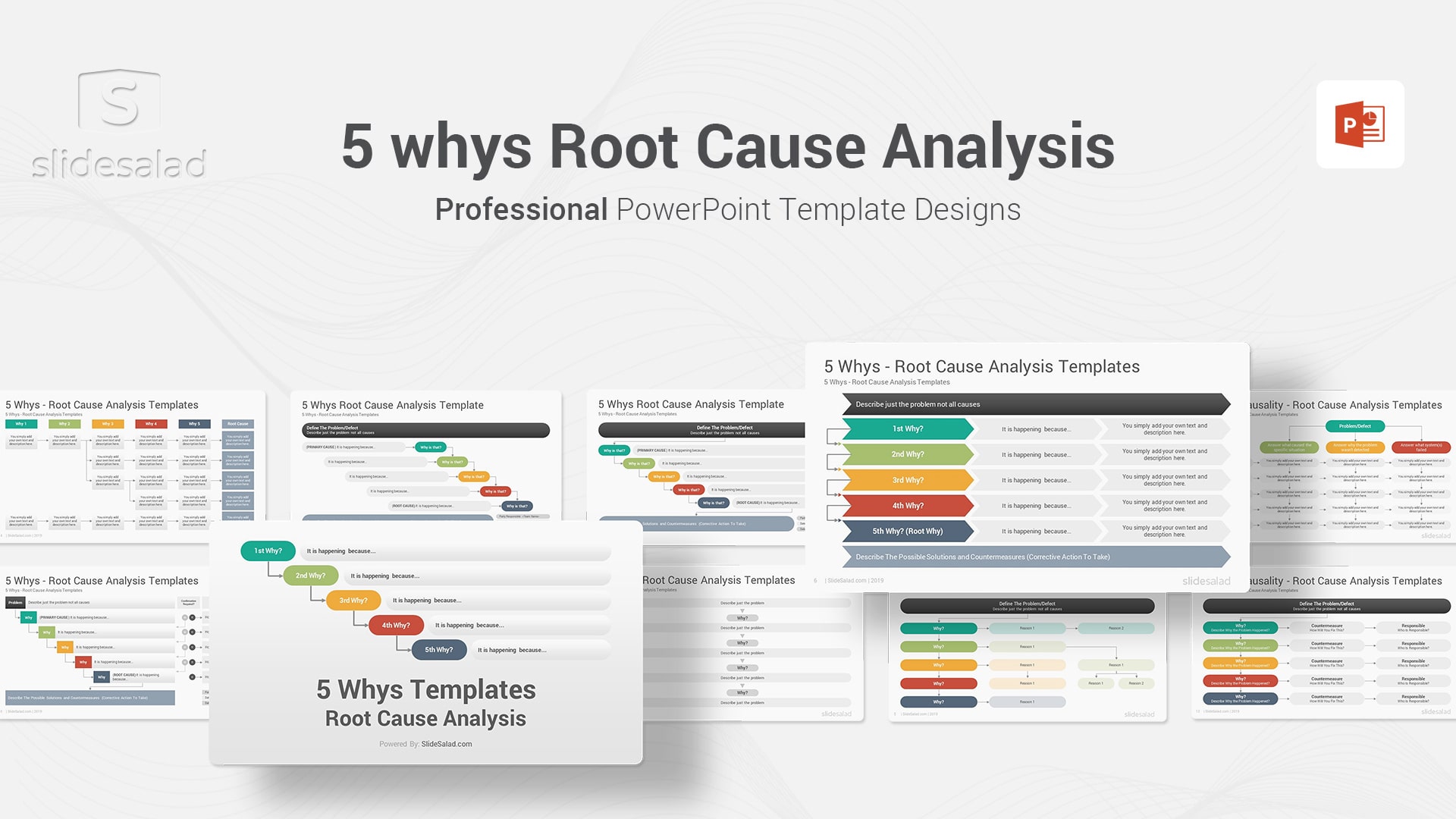
Five Why’s is a simple and effective root cause analysis tool that can be used to identify the underlying cause of an issue. The Five Why’s Framework is based on the premise that for every problem, there are five whys that need to be asked in order to get to the root cause. Asking why five times gets to the heart of the matter and helps to ensure that all possible causes are considered. The Five Why’s tool can be used for both individual and team problem-solving exercises. It is a helpful tool for preventing issues from recurring because it gets everyone thinking about all the potential causes of a problem, not just the most obvious ones. Buy and download this best problem solving PowerPoint template and get started illustrating the 5 Whys in your presentation.
3. CATWOE Analysis PowerPoint Template Diagrams – The Ultimate Guide for Understanding Your Customers
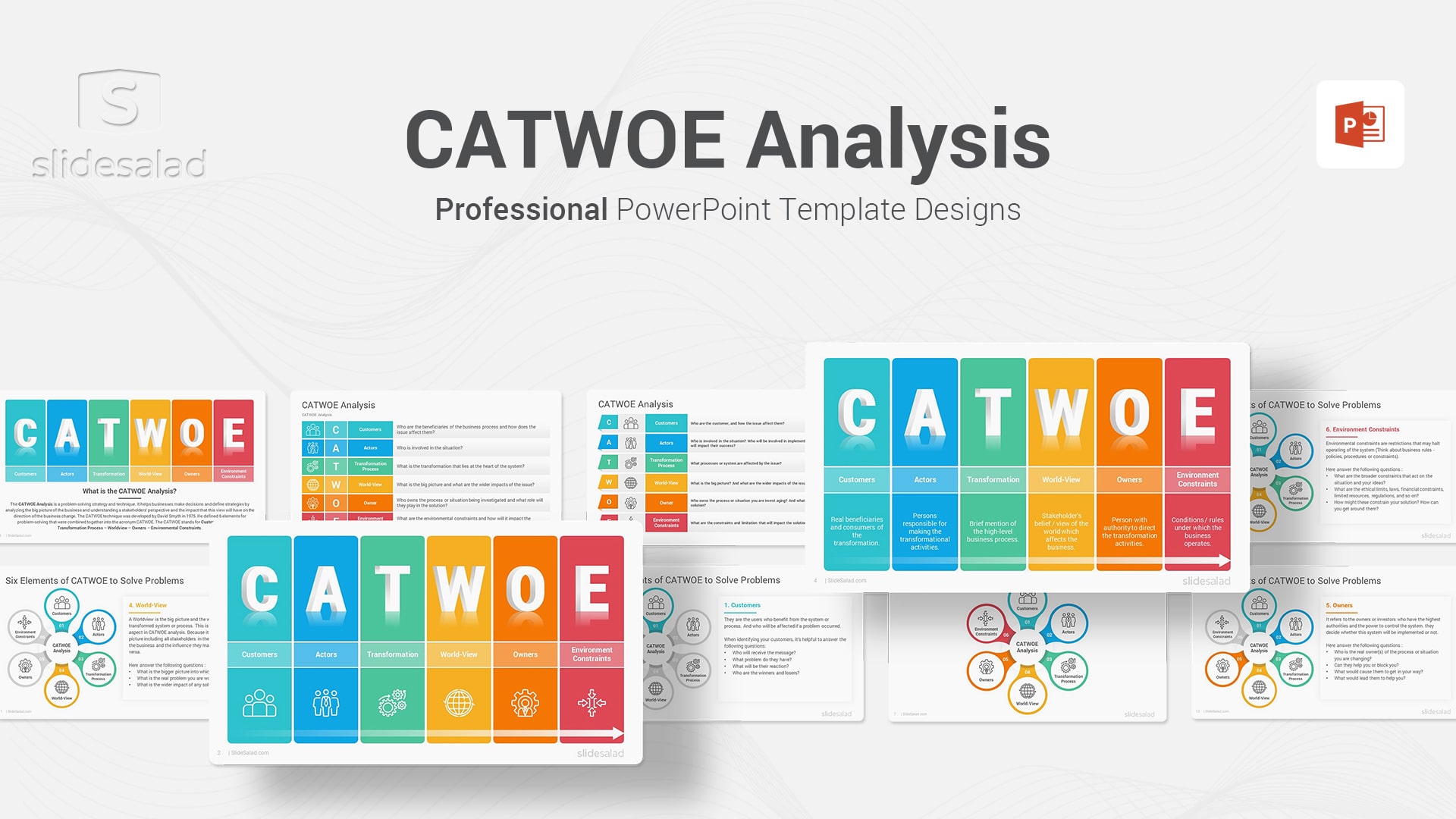
David Smyth first introduced the CATWOE Analysis in 1975 as a tool for business and systems analysis.
The acronym CATWOE stands for:
- Transformation Process
- Environmental Constraints
This framework can be used to identify and understand the key elements of a system under consideration. By taking into account the needs of customers, the people who will be affected by the system, the process that will be used to implement it, and the worldview that it represents, CATWOE Analysis provides a comprehensive way to understand complex systems. In addition, by considering environmental constraints and identifying who will be responsible for operating and maintaining the system, CATWOE Analysis can help to ensure that a proposed system is viable and sustainable.
4. Fishbone Ishikawa Diagrams PowerPoint Template Designs – Give a Compelling Presentation on How Fishbone Ishikawa Can Help You Solve Problems

Fishbone Ishikawa diagrams also called cause and effect diagrams or Fishikawa , are a graphical tool used to identify possible causes of a problem. The name “fishbone” comes from the fact that the diagram resembles the skeleton of a fish . The main purpose of the fishbone diagram is to help identify all of the possible causes of a problem so that it can be more effectively addressed. The diagram is often used in quality management and Six Sigma initiatives as a way to brainstorm about potential causes and identify root causes. It can also be used in other business settings as a tool for identifying problems and their causes. While the fishbone diagram is most commonly used in manufacturing and service industries, it can be applied to any type of problem-solving situation. You can also use this recommended template for decision making presentations. To test our template quality, download some of our free PowerPoint templates .
5. Kepner-Tregoe Method PowerPoint Template – Creative PPT Template to Discover the Practical way to Make the Best Decisions Under Pressure
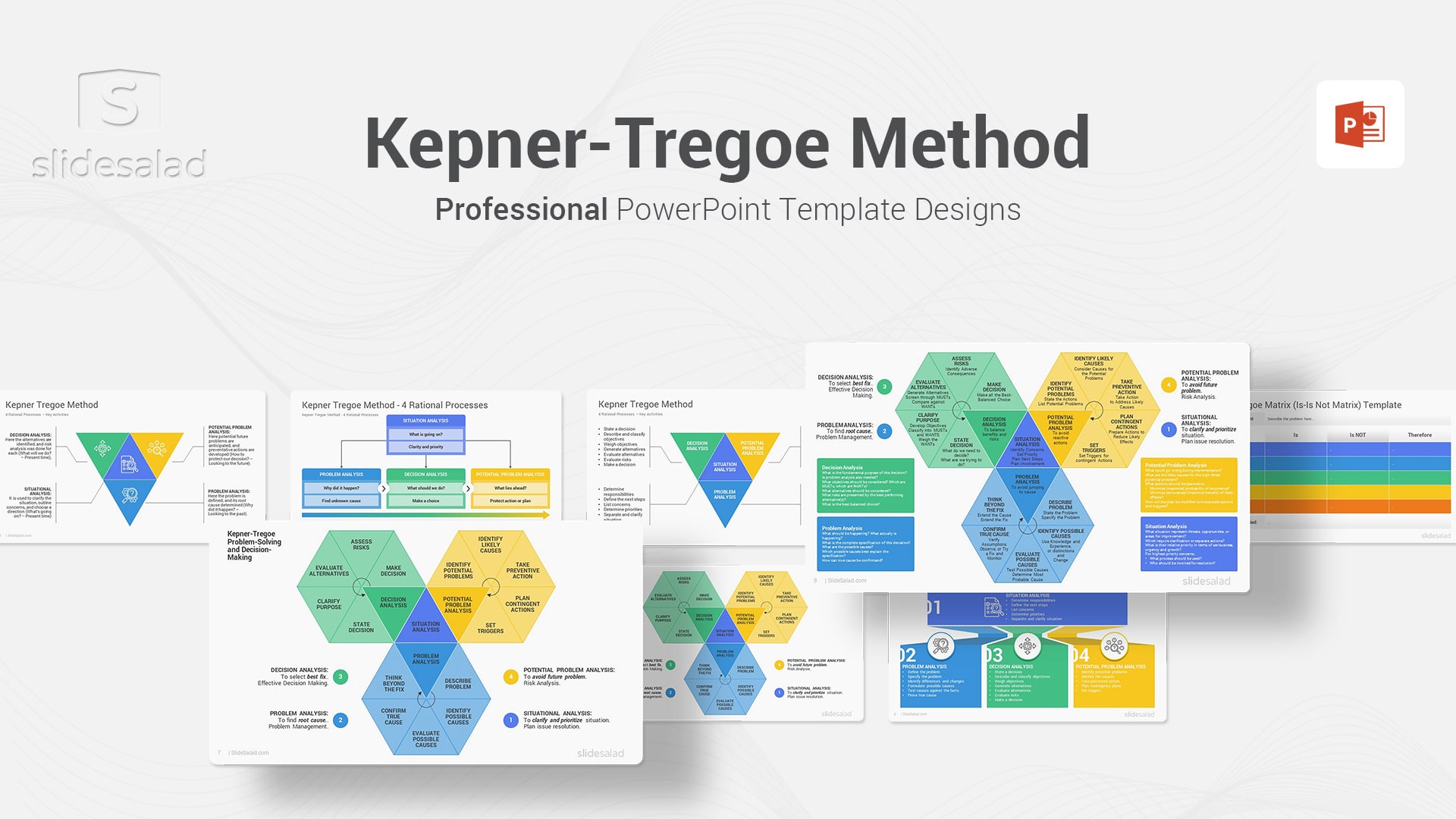
The Kepner-Tregoe method is a problem-solving and decision-making technique developed in the 1960s by Charles H. Kepner and Benjamin B. Tregoe.
The KT methodology is based on four fundamental elements:
- Situation Analysis
- Problem Analysis
- Decision Analysis
- Potential Problem (Opportunity) Analysis
These elements are designed to help individuals and organizations systematically identify, assess, and resolve problems in a rational and efficient manner. In each step, specific tools and techniques are used to help identify the cause of a problem or opportunity, generate possible solutions, select the best solution, and implement it effectively. The KT approach has been used successfully in a variety of industries, including manufacturing, healthcare, government, and service. While the method is not without its critics, it continues to be one of the most popular problem-solving tools available today.
6. Six Sigma and DMAIC Model PowerPoint Templates Diagrams – Rapidly Improve Your Business Performance with Six Sigma and DMAIC Model
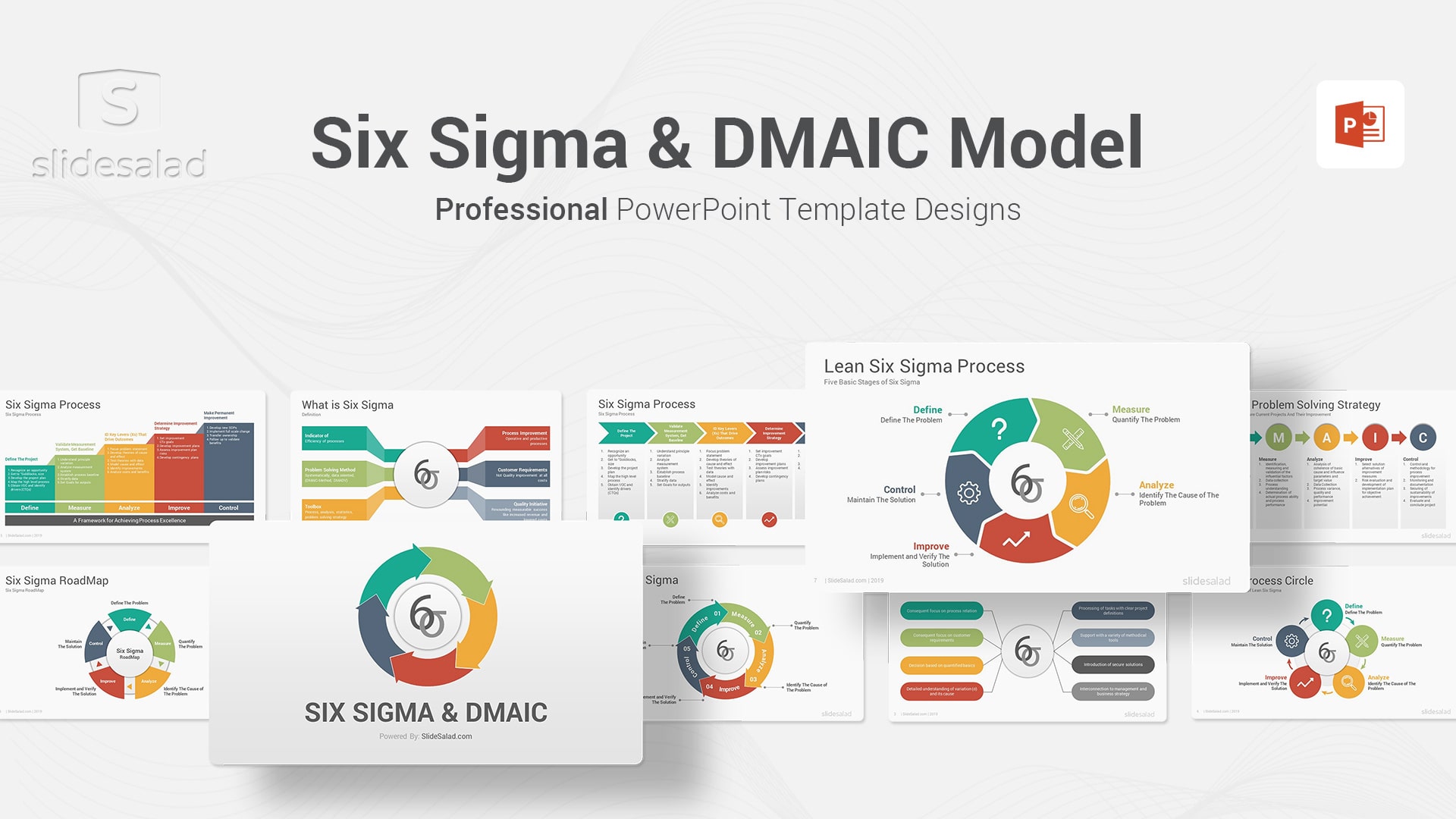
Six Sigma is a quality refinement strategy that aims to reduce defects by minimizing variation in manufacturing and business processes. The DMAIC model, which stands for Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, and Control , is a framework for Six Sigma projects. The Define phase involves identifying the problem to be addressed and setting objectives. In the Measure phase, data is gathered to quantify the problem. In the Analyze phase, the data is analyzed to identify the root causes of variation. The Improve phase involves implementing solutions to address the root causes. Finally, in the Control phase, process control plans are put in place to ensure that the improvements are sustainable. By following the DMAIC model, Six Sigma projects can achieve substantial improvements in quality and productivity.
Features of SlideSalad’s Top Problem Solving PowerPoint Templates:
- Fully editable unique slides
- Unlimited premade color themes
- 100% Resizable vector icons, objects, and image layouts
- Completely editable Vector infographics
- Royalty-free stock photos
- Editable data charts, graphs, shapes, smart art, and tables
- Vector country map for representing locations
- Attractive image backgrounds
- Drag and drop ready elements
- One-time purchase
- Free lifetime updates
- Free lifetime support
7. Design Thinking PowerPoint Templates – Innovative PPT Template to Discover How Design Thinking Helps Companies Become Creative

Design Thinking is a method for approaching problems with empathy, creativity, and a focus on real-world solutions. The process begins with empathizing with those who will be using the product or solution. This step helps to ensure that the final product meets the needs of the end users. Once the problem has been clearly defined, the next step is to ideate or generate ideas for potential solutions. These ideas are then prototyped or put into a form that can be tested in the real world. Finally, the prototypes are tested with users to get feedback and refine the design. The Design Thinking process is an iterative one, meaning that each step is automatically followed by another round of refinement. This cycle continues until the problem is solved in a way that is both effective and efficient.
8. Simplex Problem-Solving Process PowerPoint Template – Professional Presentation Examples of Simplifying Complex Problems with the Simplex Method
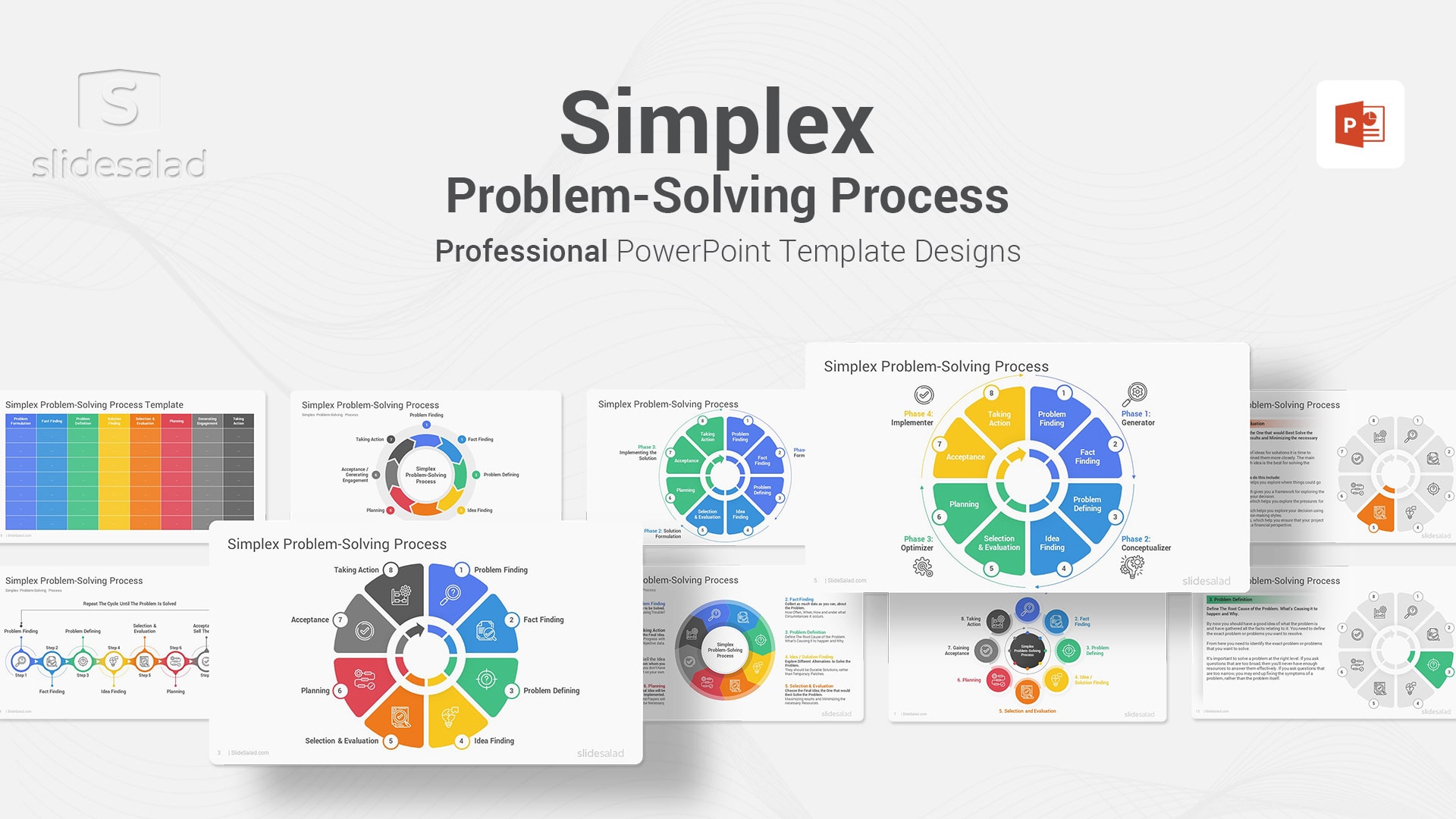
The Simplex Problem-Solving Process, developed by Min Basadur , is a systematic and comprehensive approach to problem solving that can be applied to both individual and organizational problems . The process begins with problem finding, followed by fact-finding and problem definition. Once the problem has been adequately defined, the focus shifts to idea/solution finding; this involves generating and evaluating potential solutions to the problem. Once a satisfactory solution has been found, it is then necessary to sell the idea/gain acceptance from those who will be affected by it. Finally, taking action to implement the solution and monitoring its effectiveness completes the process. Throughout the process, it is important to maintain open communication and keep all stakeholders involved and informed of progress. The Simplex Problem-Solving Process is an effective tool for addressing both simple and complex problems in an organized and efficient manner. Purchase this elegant presentation theme to professionally present the Simplex problem solving process.
9. SCAMPER Technique PowerPoint Template Designs – Powerful Creative Tool to Create New Ideas Using This Proven Technique
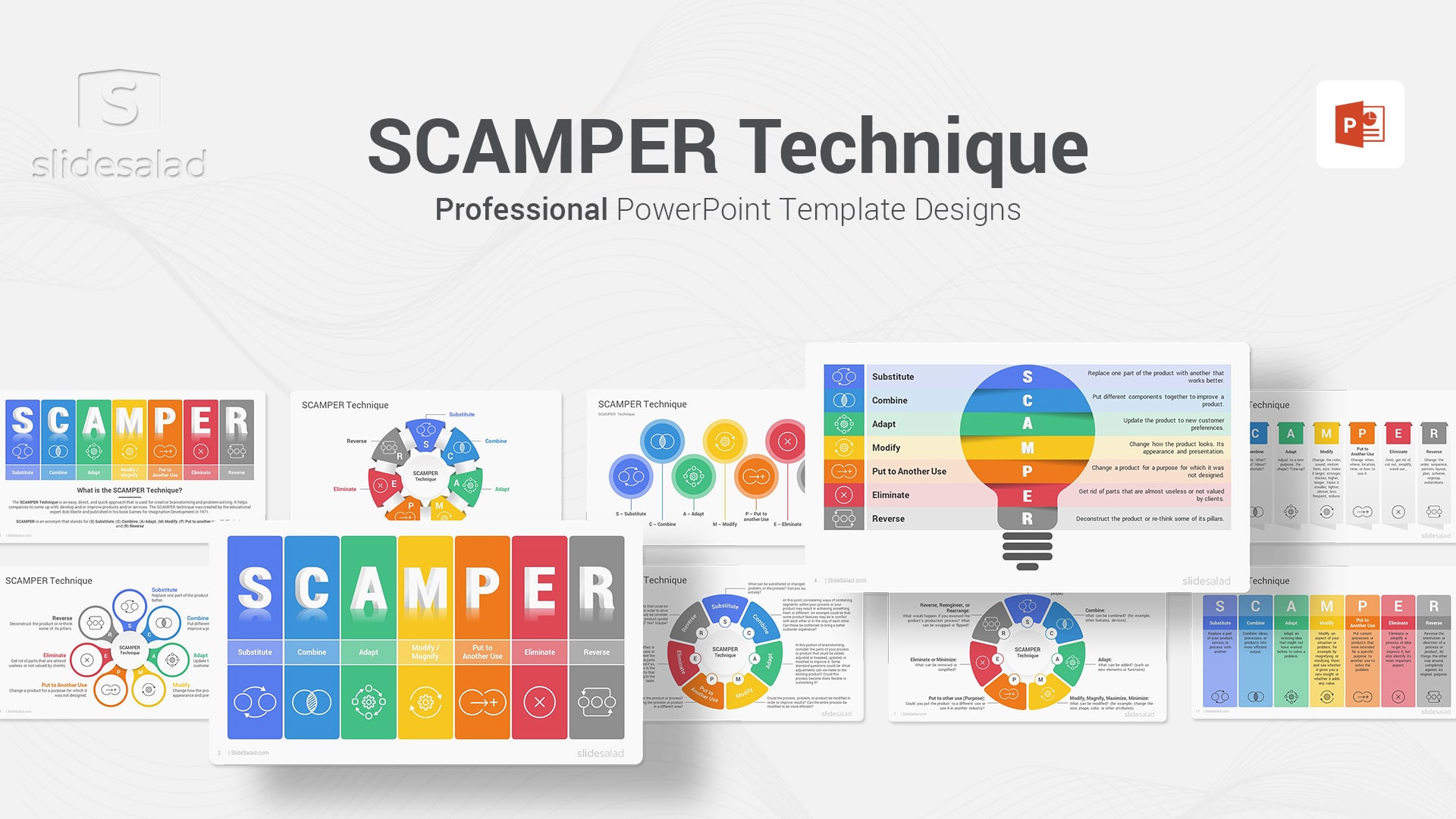
The SCAMPER technique is a powerful tool for generating new ideas. It was developed by Bob Eberle in 1971 as a way to help people develop their imagination.
The technique involves seven different steps:
- Put to another use
Each step provides a different way of looking at a problem or challenge and can help to spark new ideas. For example, the “substitute” step asks you to consider what you could use instead of the existing element. This can lead to new ways of solving problems or creating entirely new products or services. The “combine” step asks you to consider two or more elements and how they could be combined. This can lead to new combinations of products or services or new ways of using existing products or services. The other steps provide similarly powerful ways of generating new ideas, and all together, they can help you to overcome creative blocks and come up with fresh solutions.
10. Innovation Management Models and Practices PowerPoint Templates – Minimalist PPT Theme That Illustrates Innovation Management Models to Help You Be More Productive

Innovation management is a combination of strategic and operational activities that are necessary for an organization to introduce and deliver new products, services, or processes. The goal of innovation management is to create value through the development and commercialization of new ideas. There are many different models and practices that can be used to achieve this goal, but they all share some common elements. First, innovation management must identify and assess opportunities for a new product or service development. Second, it must create a plan for how to develop and commercialize these new ideas. Finally, it must monitor progress and make adjustments as necessary to ensure that the goals are met. By following these steps, organizations can increase their chances of successful innovation. All our multipurpose presentation templates include fully customizable slides, beautiful slide designs , awesome vector icons, objects and image layouts, resizable shapes , color schemes, colorful infographics , 4:3 and 16:9 widescreen resolutions, and more.
11. Productive Thinking Model PowerPoint Template – The Best Problem Solving PPT Template to Discover the Best Way to Think for Maximum Output
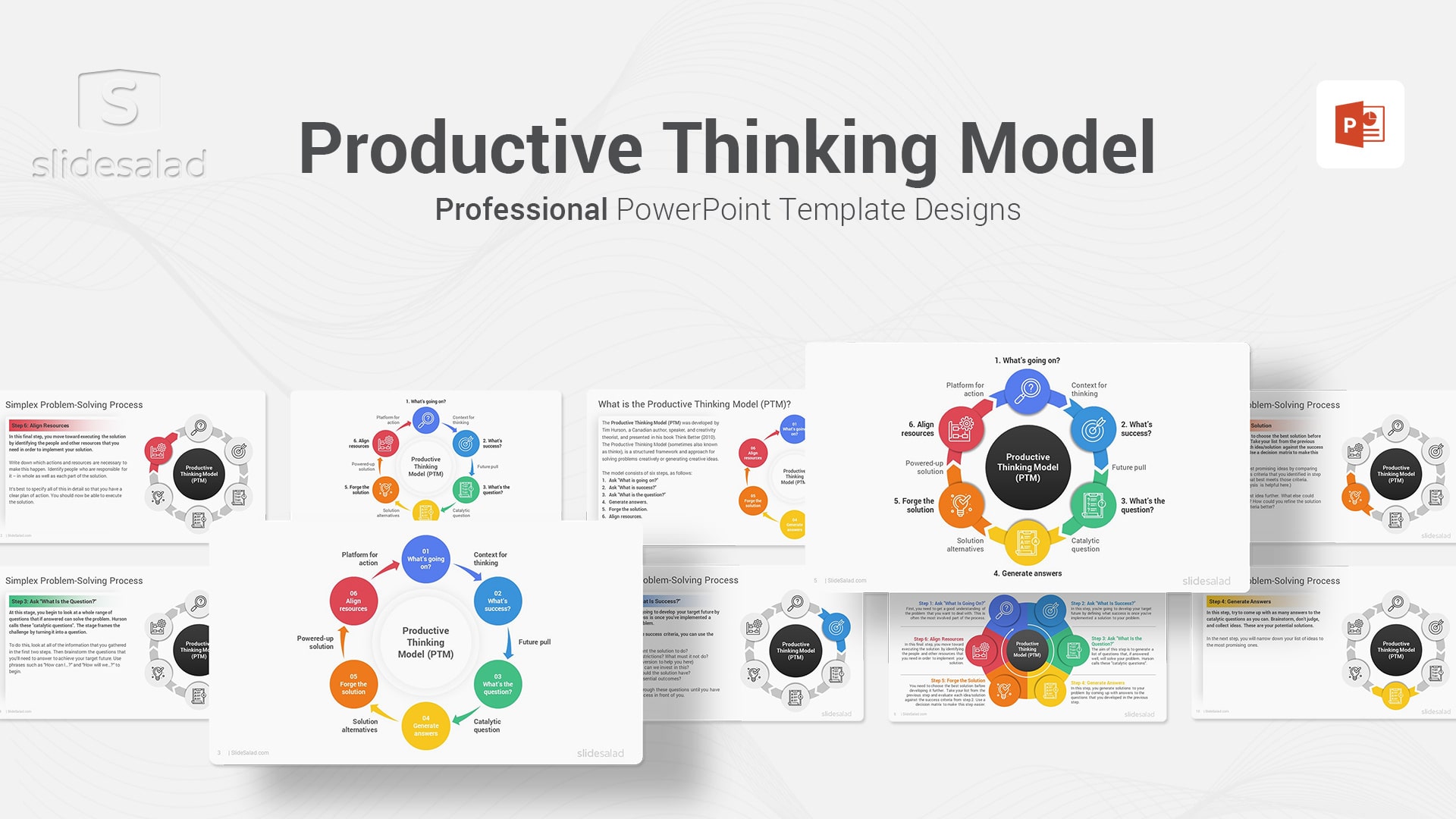
Tim Hurson developed the Productive Thinking Model in his book, Think Better (2010) , and it is based on the premise that, in order to be successful, we need to understand what is going on, what success looks like, and what the question is. Once we have a clear understanding of these three things, we can then generate answers, forge the solution, and align resources. The model is designed to help individuals and organizations think more effectively so that they can achieve their desired outcomes. The Productive Thinking Model has been used by a variety of organizations, including Fortune 500 companies, government agencies, and non-profit organizations. When applied correctly, it can help individuals and organizations to achieve success. Once you are done with the presentation, you can save it on OneDrive or Google Drive for remote access.
12. 8D Problem Solving Report PowerPoint Template – Create a Stunning Presentation for Learning the 8D Problem Solving Report Process to Save Your Business

8D (Eight Disciplines) is a problem-solving methodology used in engineering primarily for corrective action and preventive action. It includes specific steps for identifying, analyzing, and correcting root causes of defects/issues. The method was developed by Ford Motor Company in the 1980s but has since been adopted by other companies across various industries.
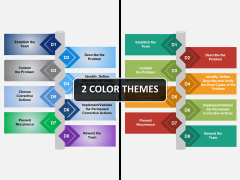
The 8D methodology follows a logical sequence of 8 steps:
- Define the problem.
- Form a cross-functional team.
- Describe the current situation.
- Identify and implement short-term containment actions.
- Identify root causes and verify their effects.
- Develop and implement permanent corrective actions.
- Prevent the recurrence of the problem by implementing systemic improvements.
- Congratulate the team on a job well done.
Following these steps helps to ensure that problems are properly identified and addressed at the root cause level, preventing them from recurring in the future. Additionally, involving a cross-functional team in the problem-solving process ensures that all relevant stakeholders have a chance to provide input and improve the chances of success. Ultimately, 8D is an effective tool for improving quality and preventing them from happening again in the future.
13. PPDAC Cycle PowerPoint Template Diagrams – Make a Complete PowerPoint Presentation on the Top Problem Solving Methodology for Solving the Real-World Problems With PPDAC Cycle

The PPDAC cycle is a five-step process for solving problems and making decisions introduced by R.J. McKay and R.W. Oldford . It is commonly used in business and government, as well as in personal decision-making.
The steps in the cycle are:
- Conclusions
- The first step in the cycle is to identify the problem. This involves understanding what the problem is and why it is important to solve.
- The second step is to develop a plan for how to solve the problem. This plan should take into account the resources available and the potential risks and benefits of different courses of action.
- The third step is to gather data. This data can come from research, surveys, interviews, or observation. Once the data has been gathered, it must be analyzed to identify trends and patterns.
- The fourth step is to reach conclusions based on the data analysis. These conclusions should be supported by evidence and should be clear and concise.
- The fifth and final step is to take action based on the conclusions. This action may involve implementing a plan or making a decision.
The PPDAC cycle is a useful tool for solving problems and making decisions. It helps to ensure that all relevant information is considered and that decisions are based on evidence.
14. Straw Man Proposal PowerPoint Template Diagrams – Modern PPT Presentation for Showing McKinsey Method for Problem Solving
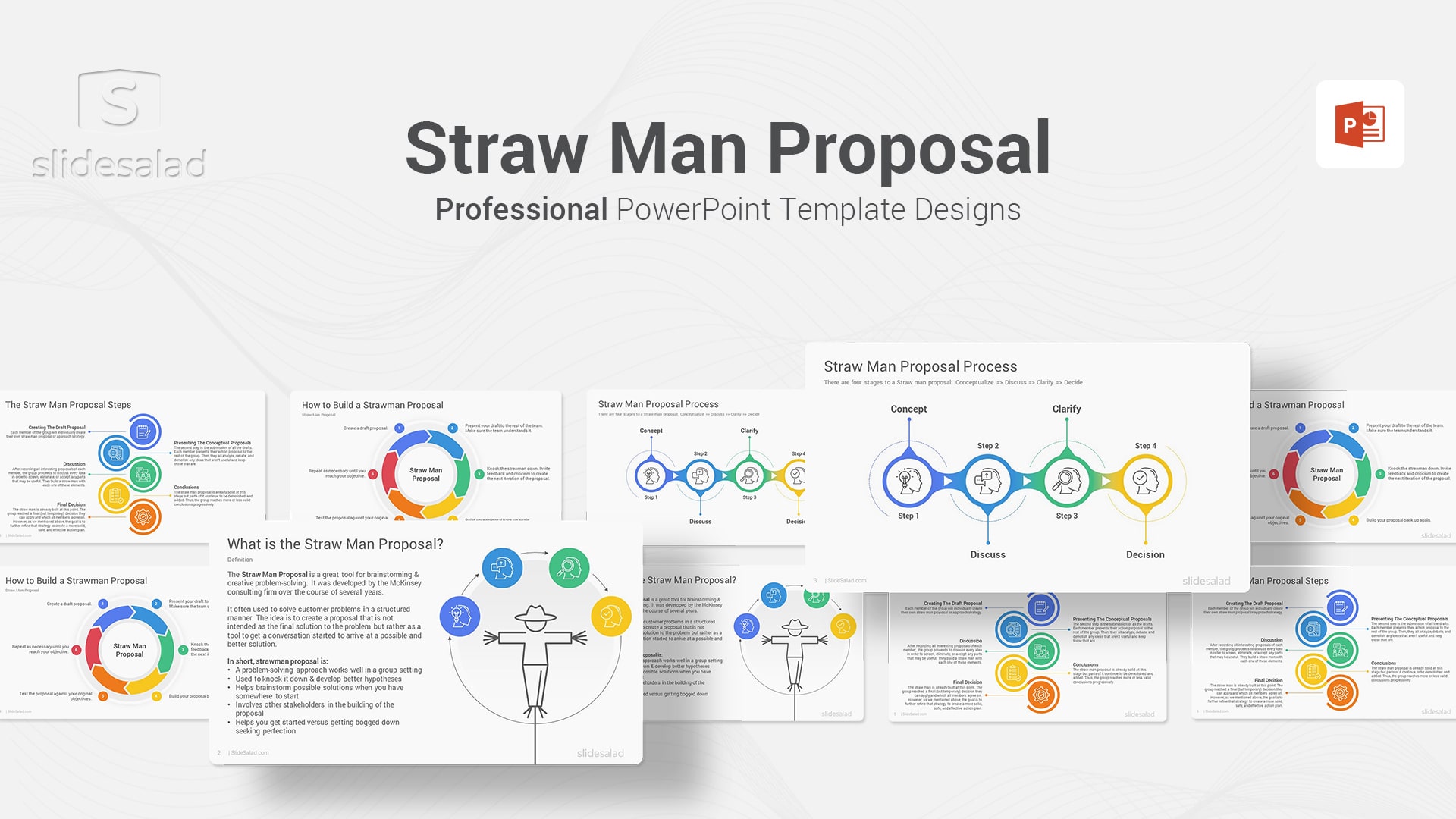
The Straw Man Proposal is a brainstorming-like method for problem solving developed by McKinsey. It involves rapidly generating a large number of potential solutions to a problem, then evaluating and selecting the best one. The goal is to come up with an innovative solution that is feasible and superior to existing solutions. The technique is named after the “straw man” used in legal arguments, which is a weak or easily refuted opponent that is used to make the argument look stronger . In the same way, the Straw Man Proposal allows ideas to be quickly evaluated and rejected if they are not viable, leaving only the strongest ones remaining. This makes it an effective tool for finding creative solutions to complex problems. While it is often used by businesses, the Straw Man Proposal can be adapted for use in any situation where problem solving is needed.
15. ACHIEVE Coaching Model PowerPoint Template – Clean Slide Designs to Show Best Results to Your Clients by Following a Measurable and Sustainable Methodology

The ACHIEVE coaching model is a framework that can be used by coaches to help their clients assess their current situation, identify their goals, and generate and implement a plan of action. The model was developed by the Coaching Centre (Dombkowski and Eldridge) in 2003 , a UK-based organization that provides training and resources for coaches. The acronym ACHIEVE stands for Assess, Creative brainstorming, Hone goals, Initiate option generation, Evaluate options, Valid Action Programme Design, and Encourage momentum . The seven steps of the model can be applied to any coaching situation, and each step can be further customized to meet the specific needs of the client. The ACHIEVE coaching model is a flexible and comprehensive approach that can be used to help individuals achieve their personal and professional goals.
16. STEPPA Coaching Model PowerPoint Template – Premium Presentation Examples to Present a Topic About the STEPPA Coaching Model

The STEPPA Coaching Model was developed by Dr. Angus McLeod as a way to help people identify and achieve their goals. The acronym STEPPA stands for Subject, Target Identification, Emotion, Perception, Plan, Pace, and Action . Each of these components is essential for successful goal-setting and achievement. The first step, Subject, involves identifying what area of your life you want to improve. The second step, Target Identification, helps you to zero in on specific goals that you would like to achieve. The third step, Emotion, involves exploring the feelings that are associated with your goals. The fourth step, Perception, is about how you see yourself achieving your goals. The fifth step, Plan, helps you to develop a specific plan of action for achieving your goals. And finally, the sixth and seventh steps, Pace and Action, involve taking concrete steps towards achieving your goals. By following the STEPPA Coaching Model, you can set and achieve any goal that you desire.
17. ESH Framework PowerPoint Template – Deliver a Presentation About How ESH Framework Aids Organizations in Reducing Costs and Meeting Deadlines

The ESH Framework is a systems approach to organizational management and change that was developed by Dutch organizational theorists Mathieu Weggeman and Geert Hofstede . The framework is based on the premise that organizations are composed of five interrelated subsystems: strategy, structure, personnel, culture, and management styles . Each of these subsystems exerts a unique influence on organizational behavior and performance. To be effective, organizations must maintain a balance between these subsystems ( evenwicht ), as well as a sense of cohesion ( samenhang ) and diversity ( heterogeneity ). The ESH Framework provides a comprehensive and systematic way of understanding how organizations function and how they can be managed effectively. It is a useful tool for both practitioners and researchers alike.
18. David Rock’s Focus Model PowerPoint Template – Most Popular Presentation PPT Template on Problem Solving: David Rock’s ‘Choose Your Focus’ Model
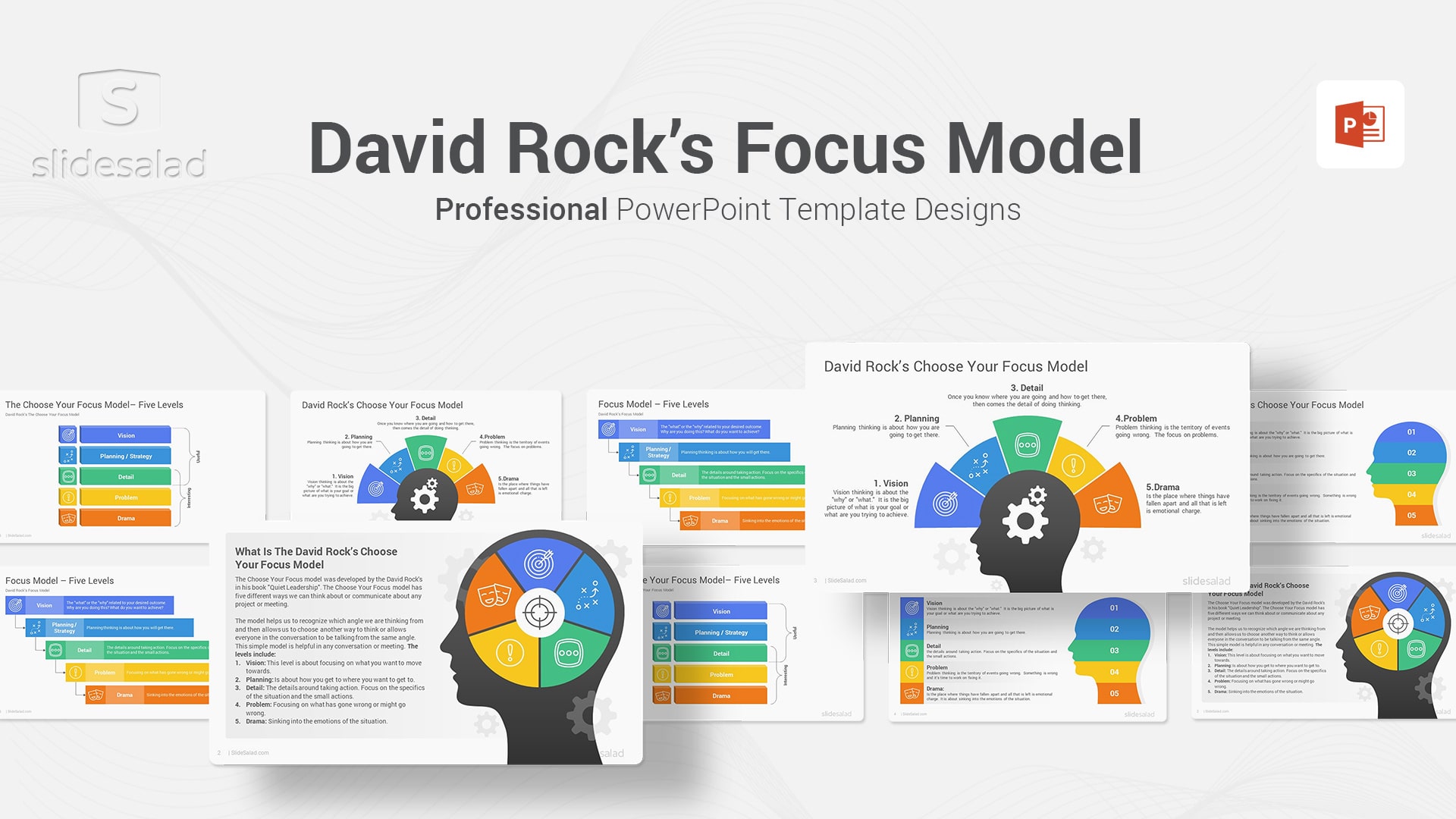
In his book “ Quiet Leadership ,” David Rock discusses the importance of focusing on what is most important.
He divided this focus into six different areas:
Vision refers to having a clear idea of what you want to achieve, and planning refers to taking the time to develop a detailed plan of how you will achieve it. Detail refers to ensuring that all the small details are taken care of, and problem refers to solving any problems that arise along the way. Drama refers to managing any difficult situations that may arise, and finally, quiet leadership refers to maintaining your composure and keeping your head during times of stress. By focusing on these six areas, you can increase your chances of success and achieving your goals. Buy and download a business PPT presentation template for an instant presentation.
19. 5E Learning Model PowerPoint Template Designs – A Forward-Thinking Way to Learn and Implement the 5E Model in Your Organization

The 5E learning model is a constructivist approach to teaching that emphasizes the learner’s experience and prior knowledge as the foundation for new learning. The model was developed by the Biological Sciences Curriculum Study in 1987 and has since been adopted by many school districts across the United States.
The 5E model is comprised of five stages:
The first stage, Engage, is designed to capture students’ attention and interest in the topic. The second stage, Explore, allows students to investigate the topic and form their own hypotheses. In the third stage, Explain, students share their hypotheses with the class and receive feedback from the teacher. The fourth stage, Elaborate, gives students an opportunity to practice what they have learned. Finally, in the fifth stage, Evaluate, students reflect on their learning and assess their understanding of the material. The 5E learning model is an effective way to engage students in active learning and promote a deep understanding of content.
20. The Stepladder Technique PowerPoint Template Diagrams – Well-Designed PowerPoint Slide Layouts to How to Use the Step Ladder Technique for an Effective Decision Making
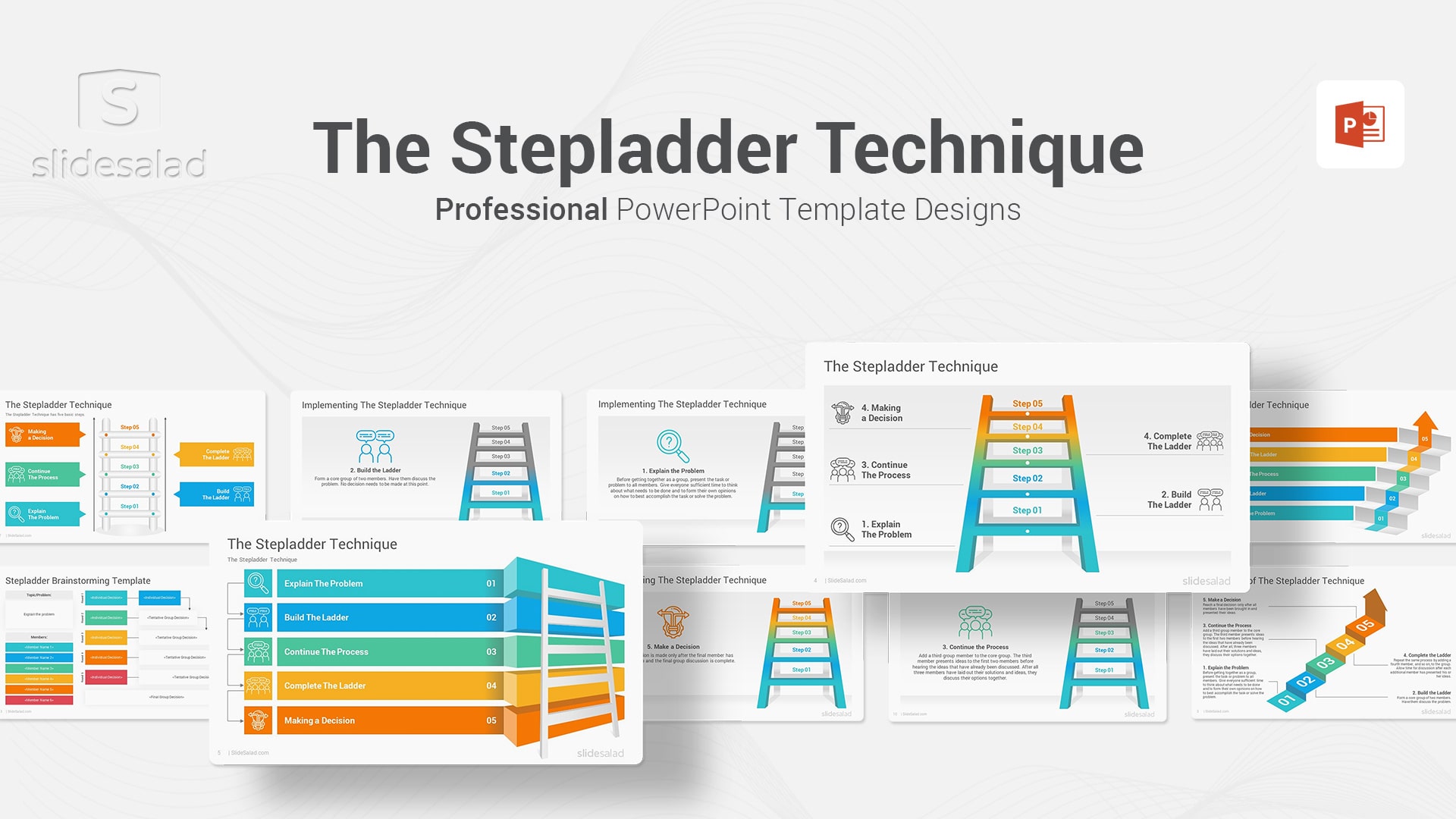
The Stepladder Technique is a structured brainstorming method that can be used by groups of people to generate ideas and solve problems. The technique was first developed by Steven Rogelberg, Janet Barnes-Farrell, and Charles Lowe in 1992 . The process involves each member of the group working individually to generate ideas on a topic or problem. Once all members have generated their ideas, they then share their ideas with the person next to them and build on those ideas to create a “ladder” of solutions. This process is then repeated until all members of the group have had a chance to contribute. Once the ladder is complete, the group can then discuss the options and make a decision. The Stepladder Technique is an effective way to generate a large number of ideas and find creative solutions to problems. Try this corporate presentation template for your next successful problem solving PPT presentation. Also, consider purchasing some of our professional Google Slides and Keynote templates if needed.
21. Perceptual Positions PowerPoint Template – Well-Organized PPT Template for Showcasing a Compelling Presentation About the Reframing Exercise Perceptual Positions

Perceptual positions are a neuro-linguistic programming and psychology term that refers to the three different ways we can view a situation. The first position is the ‘I, self’ position, where we view the situation from our own perspective. The second position is the ‘the other’ position, where we view the situation from the perspective of another person. The third position is the ‘the observer’ position, where we view the situation from an objective, detached perspective. By understanding and utilizing all three positions, we can gain a complete understanding of a situation and make more effective decisions.
Conclusion: Buying the Best Problem Solving Models and Techniques PowerPoint Templates
No matter which problem solving model you choose, Modern Premium PowerPoint templates can be a valuable tool for communicating your findings to others. SlideSalad’s problem solving models and techniques PPT templates come in a variety of styles and can be customized to fit your needs . Choose a template that includes all of the elements you need to present your data clearly and effectively. With just a few clicks, you’ll be able to create an engaging and professional presentation that will help your team solve problems more efficiently.
Share This Story:

Recent Posts
- Best Human Resources Models and Practices PowerPoint Template Designs for 2024
- Best Digital Business Models PowerPoint Template Designs for 2024
- Best Timeline and Roadmap Infographics and Diagrams PowerPoint Templates for 2024
- Best Software Development Life Cycle (SDLC) Models PowerPoint Templates
- 30+ Best Coaching Models and Personal Development PowerPoint Templates for 2024
- Google Slide Themes
- PowerPoint Templates

- Preferences

Problem Solving and Creative Thinking - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

Problem Solving and Creative Thinking
A problem arises when a living creature has a goal but does not know how this ... don't give a joke answer (e.g. depends if we get chuck norris to help) ... – powerpoint ppt presentation.
- What is a Problem?
- A problem arises when a living creature has a goal but does not know how this goal is to be reached.
- A problem exists whenever one cannot go from the given situation to the desired situation simply by action. K. Dunker, On Problem Solving, (1945) p. 1
- What is Problem Solving?
- Problem Solving is the process of working out or discovering how to reach such a goal.
- Creative thinking is the process of generating novel ideas and alternative courses of action, no matter how good those ideas and alternatives might be.
- Creative thinking should not be seen as an alternative to critical thinking
- When you have recognised a problem, then you should employ creative thinking to produce some options for solving the problem, then you should employ critical thinking
- If you havent come up with enough options to begin with, then your critical thinking decision procedure might produce the wrong result a dangerous result!
- Creative thinking supports critical thinking While critical thinking focuses on step-by-step, linear processes aimed at arriving at a correct answer, creative thinking begins with possibility, multiple ideas, and suspended judgement. It might be said that creative thinking supports the ideas with which critical thinking works. Thus, even though these two kinds of thinking work in different ways, they actually support one another and aim at the same ultimate goal, which is to solve a problem At the beginning of the process, creative methods are used to examine the problem environment, generate ideas, and make associations. Then the analysis and judgment faculties are brought into play, and the possibilities are analyzed for a possible solution. Robert Harris, CB pp. 115-6
- Did the smithy replace some of the kings gold with silver?
- How did Archimedes find out?
- (Not Archimedes style to torture the smithy)
- The solution, which occurred when he stepped into a public bath and caused it to overflow, was to put a weight of gold equal to the crown, and known to be pure, into a bowl which was filled with water to the brim. Then the gold would be removed and the kings crown put in, in its place. An alloy of lighter silver would increase the bulk of the crown and cause the bowl to overflow. Vitruvius, De Architectura
- And the wreath was impure!
- It was very useful to Archimedes
- He was well respected and treated in Syracuse
- Marcellus, the Roman general, ordered his life to be spared when Syracuse finally fell
- But his obsession with maths was ultimately his downfall!
- Can we be like Archimedes?
- Can we learn to be creative thinkers?
- Associative Techniques
- Analytic Techniques
- Brainstorming
- Role Playing
- Compare something familiar to something unfamiliar.
- Close analogy e.g. apples and pears
- Remote analogy e.g. Pringles
- Forced analogy
- The problem recreating that dazzling 360 degree panoramic holiday view
- The forced analogy a wreath
- The answer!
- The problem vertigo
- The forced analogy swimming
- The problem Carrying lots of shopping when its raining
- The forced analogy a tennis player
- Breaking a problem down into smaller parts
- E.g. How can I make the All Blacks win the Rugby World Cup?
- Vital components of the problem
- Henry Just one ensuring the ABs perform to their capacity
- Hence the 4 Rs of Henrys regime
- Relationships within team are friendly
- Really discreet signaling during matches
- Unfortunately (as we know), Henry didnt analyse the problem thoroughly.
- He missed a vital component of the problem
- The Barnes Factor
- Good analytic techniques will help to ensure that all of the important components of the problem are addressed
- Deliberately set about coming up with alternatives, and write them all down, no matter what.
- No idea is a bad idea (at least just yet)
- Edward de Bono 6 hats green hat time
- One company generated 2,200 ideas in one day!
- Roleplaying. Attempt to simulate aspects of the problem and proposed solutions. Try to imagine details of the relevant outcomes after your choice has been made, and attempt to put yourself in the shoes of other people.
- A good method for gathering information and gaining perspective
- E.g. Theoretical vs. practical lecturing
- E.g. Customers-eye-view of displays
- E.g. Hand-out-of-the-car-window aerodynamics
- He was also a prolific problem solver
- So, how can we harness these 4 idea creation techniques to help us solve problems?
- Ideas should be generated after the problem has been properly understood and represented
- One and only one of the switches (A, B C) on the outside of the room turns on all of the lights (x, y z) in the room
- From outside, you cannot see into the room
- The wiring is hidden from view
- You are not allowed to damage any of the property
- Is there a way of knowing for sure which switch turns the lights on?
- Once you enter the room, you cannot leave again to rearrange the switches
- Station 1 and Station 2 are 50 miles apart on a straight train track
- Train 1 leaves Station 1 at the same time that Train 2 leaves Station 2
- Both trains travel at 25 miles per hour toward the other station
- The bird starts directly above Train 1 and flies above the track until it reaches Train 2. Then it flies back to Train 1 etc.
- The bird flies at 230 miles per hour
- How far has the bird flown by the time the trains meet?
- What will happen to the block of wood when the person lets go of it?
- The block will drop down as it is drawn to earth by gravity
- so long as the person is on earth.
- It will float up if the person is under water.
- And it will go nowhere (or a little bit sideways?!) if the person is in space.
- Suggestion 1 Drop presuppositions that arent explicit in the original statement of the problem
- Can you connect all of the dots with just 4 straight lines?
- You cannot take your pen off the paper
- You cant use a ridiculously big pen
- The second line must start where the first line finished. The third line must start where the second line finished etc.
- Imagine the dots are drawn on a flat an immovable surface
- The solution
- Suggestion 1 Drop presuppositions that arent explicit in the original statement of the problem.
- There was a terrible accident on the motorway coming into Wellington
- A man was killed on impact and his son was rushed to hospital with life-threatening injuries
- At the hospital, the surgeon saw the boy and said I cant operate, thats my son
- What is going on here?
- Many of us assume that surgeons have to be male, making us come up with crazy answers for a simple question
- Suggestion 2 Make sure you represent everything explicit in the original statement of the problem.
- Age of the first son x
- Age of the second son y
- Age of the third son z
- Safe assumption x y z
- Suggestion 3 When thinking about how you could represent a problem, look for structural similarities between this problem and one you know the answer to..
- Suggestion 3 When thinking about how you could represent a problem, look for structural similarities between this problem and one you know the answer to.
- This certainly works with IQ tests and brainteasers
- But also with (real life!) problem solving in general
- Radiotherapy treatment for stomach cancer
- - A structurally similar dictator analogy helped 1 20
- - The analogy with an answer helped 1 75
- An ability to solve logic puzzles is thought to be positively correlated with an ability to think creatively and solve problems of any kind.
- Whether or not such a correlation really exist, it is commonly believed to exist.
- Employers care more about creative thinking and problem solving abilities in the workforce more than any other general skill..
- Creative thinking and problem solving abilities are among the most important skills sought after by universities..
- Hence, universities and employers will screen candidates on the basis of their ability to solve logic puzzles.
- You have twenty blue socks, twenty brown socks, and two black sock in a drawer in your room. If it is night time, and the room is completely dark, how many would you have to take out to be sure you have 2 of the same colour?
- A mother sent her child to the lake and told him to bring back exactly 7 litres of water. She gave him a 5 litre bucket and a 3 litre bucket. How can the child measure out exactly 7 litres of water using nothing but the two buckets.
- You've got someone working for you for seven days and a gold bar to pay them. The gold bar is segmented into seven connected pieces. You must give them a piece of gold at the end of every day. If you are only allowed to make two breaks in the gold bar, how do you pay your worker?
- An Impossible Interview Question is one that has no single acceptable answer.
- How many piano tuners are there in the world?
- How long would it take to move Mount Fuji?
- Dont freak out!
- Dont give a joke answer (e.g. depends if we get Chuck Norris to help)
- Suggest a potential approach
- Ask them questions
- How to solve problems creatively
- Make sure you represent the problem in the right way!
- Dont assume restrictions that arent stipulated
- Do represent everything explicit in the question
- Do compare the structure of the problem with similar ones
- Then generate lots of creative ideas with
- Associative techniques
- Analytic techniques
- Roleplaying
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.


Problem Solving and Creative Thinking
Jun 14, 2012
1.06k likes | 2.26k Views
Problem Solving and Creative Thinking. Problem Solving. What is a Problem? A problem arises when a living creature has a goal but does not know how this goal is to be reached.
Share Presentation
- roman general
- ridiculously big
- step process
- correct answer
- rugby world cup

Presentation Transcript
Problem Solving What is a Problem? A problem arises when a living creature has a goal but does not know how this goal is to be reached. [A problem exists] whenever one cannot go from the given situation to the desired situation simply by action. [K. Dunker, On Problem Solving, (1945) p. 1] What is Problem Solving? Problem Solving is the process of working out or discovering how to reach such a goal.
What is creative thinking? Creative thinking is the process of generating novel ideas and alternative courses of action, no matter how good those ideas and alternatives might be. Creative thinking should not be seen as an alternative to critical thinking When you have recognised a problem, then you should employ creative thinking to produce some options for solving the problem, then you should employ critical thinking If you haven’t come up with enough options to begin with, then your critical thinking decision procedure might produce the wrong result… a dangerous result!
Creative Thinking, Critical Thinking, and Problem Solving Creative thinking supports critical thinking … While critical thinking focuses on step-by-step, linear processes aimed at arriving at a correct answer, creative thinking begins with possibility, multiple ideas, and suspended judgement. It might be said that creative thinking supports the ideas with which critical thinking works. Thus, even though these two kinds of thinking work in different ways, they actually support one another and aim at the same ultimate goal, which is to solve a problem … At the beginning of the process, creative methods are used to examine the problem environment, generate ideas, and make associations. Then the analysis and judgment faculties are brought into play, and the possibilities are analyzed for a possible solution. [Robert Harris, CB pp. 115-6]
Who is this man?
Archimedes Great inventor, mathematician etc. The Screw The Lever
Archimedes Helped protect Syracuse from the Romans in the siege of 213BC The Mirror The Claw
Archimedes’ puzzle • Did the smithy replace some of the kings gold with silver? • How did Archimedes find out? • (Not Archimedes style to torture the smithy)
Solution to Archimedes’ puzzle. • The solution, which occurred when he stepped into a public bath and caused it to overflow, was to put a weight of gold equal to the crown, and known to be pure, into a bowl which was filled with water to the brim. Then the gold would be removed and the king’s crown put in, in its place. An alloy of lighter silver would increase the bulk of the crown and cause the bowl to overflow. [Vitruvius, De Architectura] • And the wreath was impure!
Creative thinking! • It was very useful to Archimedes • He was well respected and treated in Syracuse • Marcellus, the Roman general, ordered his life to be spared when Syracuse finally fell • But his obsession with maths was ultimately his downfall! • Can we be like Archimedes? • Can we learn to be creative thinkers?
4 Methods for Generating Ideas • Associative Techniques • Analytic Techniques • Brainstorming • Role Playing
Associative Techniques • Compare something familiar to something unfamiliar. • Close analogy e.g. apples and pears • Remote analogy e.g. Pringles • Forced analogy…
Forced Analogy 1 • The problem: recreating that dazzling 360 degree panoramic holiday view • The forced analogy: a wreath • The answer!
Forced Analogy 2 • The problem: vertigo • The forced analogy: swimming • The answer!
Forced Analogy 3 • The problem: Carrying lots of shopping when its raining • The forced analogy: a tennis player • The answer!
Analytic Techniques • Breaking a problem down into smaller parts • E.g. How can I make the All Blacks win the Rugby World Cup? • Vital components of the problem: • Henry: Just one:ensuring the ABs perform to their capacity • Hence the 4 Rs of Henry’s regime • Rest • Rotation • Relationships within team are friendly • Really discreet signaling during matches
Analytic Techniques • Unfortunately (as we know), Henry didn’t analyse the problem thoroughly. • He missed a vital component of the problem: • The Barnes Factor
Analytic Techniques • Good analytic techniques will help to ensure that all of the important components of the problem are addressed
Brainstorming • Deliberately set about coming up with alternatives, and write them all down, no matter what. • No idea is a bad idea (at least just yet) • Edward de Bono 6 hats – green hat time • One company generated 2,200 ideas in one day!
Roleplaying • Roleplaying. Attempt to simulate aspects of the problem and proposed solutions. Try to imagine details of the relevant outcomes after your choice has been made, and attempt to put yourself in the shoes of other people. • A good method for gathering information and gaining perspective • E.g. Theoretical vs. practical lecturing • E.g. Customers-eye-view of displays • E.g. Hand-out-of-the-car-window aerodynamics
But Archimedes was not just a creative thinker... • He was also a prolific problem solver • So, how can we harness these 4 idea creation techniques to help us solve problems? • Ideas should be generated after the problem has been properly understood and represented
The Main Message Solving real problems is a two step process: Model Solution Problem In order to generate potentially fruitful ideas, and thereby make it more likely that you solve your problem, make sure you represent the problem in the right way.
The Lights Example • One and only one of the switches (A, B & C)on the outside of the room turns on all of the lights (x, y & z) in the room • From outside, you cannot see into the room • The wiring is hidden from view • You are not allowed to damage any of the property • Is there a way of knowing for sure which switch turns the lights on? • Once you enter the room, you cannot leave again to rearrange the switches xyz C B A
The Lights Example Switches: Possible arrangements: A 1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0 B 1 1 0 0 1 1 0 0 C 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 0 1 – on, 0 – off
The Bird-Train Problem (Posner, 1973) • Station 1 and Station 2 are 50 miles apart on a straight train track • Train 1 leaves Station 1 at the same time that Train 2 leaves Station 2 • Both trains travel at 25 miles per hour toward the other station • The bird starts directly above Train 1 and flies above the track until it reaches Train 2. Then it flies back to Train 1 etc. • The bird flies at 230 miles per hour • How far has the bird flown by the time the trains meet?
The Bird-Train Problem (Posner, 1973)
The Drop Block Problem What will happen to the block of wood when the person lets go of it?
The Drop Block Problem The block will drop down as it is drawn to earth by gravity
The Drop Block Problem … so long as the person is on earth.
The Drop Block Problem It will float up if the person is under water.
The Drop Block Problem And it will go nowhere (or a little bit sideways?!) if the person is in space.
So, how can I best represent a problem? Suggestion 1: Drop presuppositions that aren’t explicit in the original statement of the problem
The Nine Dot Problem (Maier, 1931) • Can you connect all of the dots with just 4 straight lines? • You cannot take your pen off the paper • You can’t use a ridiculously big pen • The second line must start where the first line finished. The third line must start where the second line finished etc. • Imagine the dots are drawn on a flat an immovable surface • The solution…
Solution to The Nine Dot Problem (Maier, 1931)
How can I best represent a problem? Suggestion 1: Drop presuppositions that aren’t explicit in the original statement of the problem.
A Terrible Accident • There was a terrible accident on the motorway coming into Wellington • A man was killed on impact and his son was rushed to hospital with life-threatening injuries • At the hospital, the surgeon saw the boy and said: “I can’t operate, that’s my son” • What is going on here? • Many of us assume that surgeons have to be male, making us come up with crazy answers for a simple question
How can I best represent a problem? Suggestion 1: Drop presuppositions that aren’t explicit in the original statement of the problem. Suggestion 2: Make sure you represent everything explicit in the original statement of the problem.
2 old high school math club pals meet up after many years On a street somewhere: Ted: All three of my sons celebrate their birthday today. Can you tell me how old each one is? (Ted is a bit weird) Fred: Yes, but you have to tell me something about them… Ted: The product of their ages is 36. Fred: I need more info… Ted: The sum of their ages is equal to the number of windows in the building next to us… Fred: I need more info… Ted: My oldest son has blue eyes. Fred: That is sufficient! Can Fred really know how old Ted’s sons are? How?
2 old high school math club pals meet up after many years • Age of the first son: x • Age of the second son: y • Age of the third son: z • Safe assumption: x ≥ y ≥ z
2 old high school math club pals meet up after many years “The product of their ages is 36”: xyz • 1 1 • 2 1 • 3 1 • 9 4 1 • 9 2 2 • 6 6 1 • 6 3 2 • 4 3 3
2 old high school math club pals meet up after many years “The sum of their ages is equal to the number of windows in the building next to us…” xyz • + 1 + 1 = 38 • + 2 + 1 = 21 • + 3 + 1 = 16 • 9 + 4 + 1 = 14 • 9 + 2 + 2 = 13 • 6 + 6 + 1 = 13 • 6 + 3 + 2 = 11 • 4 + 3 + 3 = 10
How can I best represent a problem? Suggestion 2: Make sure you represent everything explicit in the original statement of the problem.
There are five houses, each of a different color and inhabited by men of different nationalities, with one unique pet, drink, and car. Some facts are given: 1. The Englishman lives in the red house. 2. The Spaniard owns the dog. 3. The man in the green house drinks cocoa. 4. The Ukrainian drinks eggnog. 5. The green house is immediately to the right (your right) of the ivory house. 6. The owner of the Oldsmobile also owns snails. 7. The owner of the Ford lives in the yellow house. 8. The man in the middle house drinks milk. 9. The Norwegian lives in the first house on the left. 10. The man who owns the Chevrolet lives in the house next to the house where the man owns a fox. 11. The Ford owner's house is next to the house where the horse is kept. 12. The Mercedes-Benz owner drinks orange juice. 13. The Japanese drives a Volkswagen. 14. The Norwegian lives next to the blue house. Who owns the Zebra?
- More by User

Creativity Creative Thinking & Creative Problem-solving
Creativity Creative Thinking & Creative Problem-solving. 2 Models of Creative Problem Solving plus The Incubation Model of Teaching: 13 Additional Creative “Qualities”. Creativity is not : . The domain of a few individuals Not known to be linked to specific factors or traits
1.1k views • 26 slides

Creative Problem Solving with Six Thinking Hats
Creative Problem Solving with Six Thinking Hats. How to use Edward deBono’s parallel thinking in problem solving. Gary Dichtenberg CyberSkills, Inc. Goals of this program. Define parallel thinking Identify each of the six hats Learn how to ask a good question
954 views • 30 slides

Creative Problem Solving
Creative Problem Solving. Chapter 13. “ Make it a practice to keep on the lookout for novel and interesting ideas that others have used successfully. Your idea only has to be original in its adaptation to the problem you are working on.” —Thomas Alva Edison.
422 views • 13 slides

CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING. Prof. Vidyanand Jha IIM Calcutta December 7, 2000. PROBLEM SOLVING. Problem - a discrepancy current state-desired state Decisions- Choices Two or more alternatives Decision Making process of choice making. General model of problem solving. Identify problem
783 views • 36 slides

CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING. CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING. Introductions Purpose Learning Objectives. CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING. PURPOSE: To develop the awareness and the skills necessary to solve problems creatively. LEARNING OBJECTIVES. 1. Define creative problem solving.
781 views • 51 slides

Creative Problem Solving. Visualization. Visualization. “Seeing with the mind’s eye” can expand creative thinking and problem solving. Dorothy A. Sisk, Professor, Lamar University. Memory. Human Brain: Short-term memory Long-term memory Information processor
407 views • 14 slides

Thinking and Problem Solving
Thinking and Problem Solving. What is thinking?. Thinking is the mental activity that is involved in the manipulation and understanding of information. Units of Thought: Concept : group of objects, events, or ideas that share similar characteristics Concept of “mom,” “dad,” “soccer game”
274 views • 6 slides

Thinking and Problem Solving. The Basics of Thinking. Thinking: changing reorganizing, and using info stored in your memory to create new information Convergent Thinking : systematic attempt to reach a specific goal/answer. Used to solve math problems and accomplish personal goals.
282 views • 12 slides

Thinking and Problem Solving. Week 2: Making Connections . The TAP TM System Training Portal. Objective. Teachers will connect thinking and problem solving and develop a lesson incorporating both the process and the product. . Agenda. Evaluation Long Range Plan & Thinking Evaluation
911 views • 18 slides

Creative Problem Solving. Adapted from “CPS For Kids” written by Bob Eberle and Bob Stanish.
372 views • 17 slides

Thinking and Problem Solving. “Our job is not to make up anyone’s mind, but to open minds and to make the agony of decision-making so intense, you can only escape by thinking.” - Author Unknown. The TAP TM System Training Portal. Reflective Thinking… How did you implement?.
398 views • 16 slides

Skills critical analysis, problem solving, and creative thinking
Ria Hanewald, School of Education Title: “Developing graduate attributes through collaborative online concept mapping”.
286 views • 6 slides

Creative Thinking, Strategic Thinking, Innovative Thinking & Creative Problem Solving
Creative Thinking, Strategic Thinking, Innovative Thinking & Creative Problem Solving. Robert Alan Black, Ph.D., CSP, DLA. Intro/ Overview. Day One. Don ’ t Just Sit There. Intro/ Overview. Day One. Don ’ t Just Sit There. Tools & Techniques. Intro/ Overview. Day One.
829 views • 35 slides

Creative problem solving
Creative problem solving. The art and mindset of hacking. WHO?. ME. WHO?. ?. YOU. Hacking. Hacking. creative solution illegal computer access neat trick …. Right and wrong. Legality Ethics. Problem 1. Solve each equation by adding one straight line. history. Phreaks Morris Worm.
355 views • 12 slides

Thinking and Problem Solving. Fact #1. The brain is awesome – and we know nothing about it. No, but really… there are reasons she will be forever alone. Girl’s got some moves?. How is all that possible – and you can speak and pick up a pencil “…without thinking about it?”.
398 views • 24 slides

Creative Problem Solving. Adeyl Khan (Ayn) BPS 440. We are managers!. Why CPS? Tackle complex problems Encourage innovation Implement new solutions Is creativity the key to management success?. successful managers. The Goal: Understand CPS. Introduction to the essential skills
411 views • 11 slides

Creative Problem Solving. TRIZ. Problem Solving Methods. DMAIC – Define, Measure, Analyze, Improve, Control DFSS – Design for Six Sigma PDCA – Plan, Do, Check, Act PDSA – Plan, Do, Study, Act TQM, PR, Kaizen, Pugh, WB, . . . . TRIZ – Theory of Inventive Problem Solving.
382 views • 15 slides

Creative Problem Solving. Brainstorming & Nominal Group Technique. Brainstorming :. Introduced by Alex Osborn, 1939 Creative problem-solving technique Atmosphere free of criticism All members must participate Implemented during the “solutions step” of the Standard Agenda.
813 views • 4 slides

Creative Thinking, Strategic Thinking & Creative Problem Solving
Creative Thinking, Strategic Thinking & Creative Problem Solving. Robert Alan Black, Ph.D. Intro/ Overview. Don ’ t Just Sit There. Tools & Techniques Divergent. 1. Summary & Integration. 2. 8. Learning Teaching Training C.T. Creative Thinking Styles. 3. 7. 4. 6. Creative
682 views • 25 slides
Our Creative Problem Solving course will help you to come up with many innovative ideas, to crafi those ideas and apply them in your own life. You will also develop your skills in creative expression, both verbally and visually and learn how to see problems from diGerent perspectives. The Creative Problem Solving course will equip you with a creative process that you can apply in academic and work contexts or when pursuing your own personal creative projects.
58 views • 3 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
• Creative problem solving requires an attitude that allows you to search for new ideas and use your knowledge and experience. • Change perspective and use knowledge to make the ordinary extraordinary and the usual commonplace.
9 Creative Problem Solving Tools For Your Next Breakthrough Idea This is a suite of 9 creative problem solving tools from Erik op ten Berg. He's an expert in creative thinking or applying creativity from the Netherlands.
Creative Problem Solving The connection between critical thinking and creative problem solving. Critical thinking is necessary for analyzing arguments and for rational decision making. Creative thinking is necessary for developing alternatives to our ways of life. Convergent & divergent thinking. We move back and forth quite often.
Different Problem Solving Process ANALYTICAL What is the problem? Plan the solution. Look for ways of getting there. Carry out the plan. Check the results. CREATIVE What is the real problem? Brainstorm many ideas. Make the ideas better; pick the best solution. Implement the best solution. How does the solution work? What have you learned? What else can you do?
Creative Problem Solving found in: Present a solution for a problem bulb and puzzle, Problem solving skills creative thinking concept idea generation, Creative problem solving process ppt powerpoint presentation model infographic..
Problem Solving Powerpoint Templates and Google Slides Themes Unlock your creative problem-solving skills with our collection of visually stunning and highly versatile presentation templates designed to captivate your audience.
CREATIVE PROBLEM SOLVING PURPOSE: To develop the awareness and the skills necessary to solve problems creatively. LEARNING OBJECTIVES 1. Define creative problem solving. 2. Be familiar with common mental blocks to creative thinking process. 3. Explore ways to be more creative. 4.
Our pre-designed Creative Problem Solving Process PowerPoint and Google Slides template. The set will help you educate your audience about the nitty-gritty of the topic. It is incorporated with high definition vector-based graphics.
Problem Solving and Creativity. Chapter 11. Outline. The Problem-Solving Cycle Types of Problems Well-Structured Problems Ill-Structured Problems and the Role of Insight Creativity. 1. The Problem-Solving Cycle. Problem Solving Download Presentation gestaltist view creative work early gestaltist view incubation small town computer simulations ...
Creative Problem Solving Visualization Visualization Seeing with the mind s eye can expand creative thinking and problem solving. Dorothy A. Sisk, Professor ... - A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as an HTML5 slide show) on PowerShow.com - id: 42ab75-ZDBmM
Make your next business presentation stand out from the rest with these best-in-class problem solving models and techniques PowerPoint PPT templates in 2024.
Easily plan a problem solving class with this template designed to help you organise discussion topics with problems and soutions. Free and easy to use.
Our Problem Solving Training Program focuses on problem solving strategies and tools that help to analyze, structure and solve business issues. It is an important element in Management Skills training.
4. Creative Thinking, Critical Thinking, and Problem. Solving. Creative thinking supports critical thinking. While critical thinking focuses on step-by-step, linear processes aimed at arriving at a correct. answer, creative thinking begins with. possibility, multiple ideas, and suspended. judgement.
It can generate, edit, and iterate with users on creative and technical writing tasks, such as composing songs, writing screenplays, or learning a user's writing style.
Problem Solving is the process of working out or discovering how to reach such a goal. What is creative thinking? Creative thinking is the process of generating novel ideas and alternative courses of action, no matter how good those ideas and alternatives might be. Creative thinking should not be seen as an alternative to critical thinking When ...