What Are the Functions of a Business Plan?
by Deb McLeod
Published on 26 Sep 2017
A business plan can help you to define and classify the goals you have for your business. Devoid of fluff, a business plan is a business document that is written for a variety of audiences. You might send your business plan to investors or it might be written for the benefit of your employees. Generally, the audience should have no bearing on the content. In the end, the business plan is about the business, its goals and how to achieve those goals.

Short-term goals
A business plan helps you to define, for the short term, where you want your business to go. Because most people write a business plan when the business is new--or even still in the formative stages--providing immediate goals can be one solid method for defining exactly how you want your business to run right out of the box.
Long-term goals
A good business plan will define in an unequivocal manner where you want your business to go. Some business plans will outline a two-, five- and 10-year plan, while others will simply identify long-term goals. The goals should be realistic; this part of the business plan should be the one that you give the most attention to. Having a solid long-term plan helps you to define how to operate now.
A good business plan will identify costs, sources of funding and expected income. Consider doing proper research before you add this element of the business plan; it’s important that your numbers are accurate, especially if you will be presenting your business plan to the bank or potential investors.
Business Strategy
Use the business plan to identify your overall business strategy. You can identify how you plan to get and retain customers, get funding, improve your technology, deal with difficulties, send shipments, grow your business, hire employees and any other aspects of running your business.
Though it might not be read often, at its core, your business plan helps you to define what you want out of your business. Writing it down helps you to refine those goals and make them real.
Communication
Your business plan communicates to readers--who might be customers, investors or employees--what exactly your business is about. It’s likely you don’t have time to communicate these things verbally, so the business plan gives you a forum and a mechanism for communicating what matters to you about your business.
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
What Is a Business Plan? Definition and Planning Essentials Explained
Posted february 21, 2022 by kody wirth.

What is a business plan? It’s the roadmap for your business. The outline of your goals, objectives, and the steps you’ll take to get there. It describes the structure of your organization, how it operates, as well as the financial expectations and actual performance.
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. It’s more than just a stack of paper and can be one of your most effective tools as a business owner.
Let’s explore the basics of business planning, the structure of a traditional plan, your planning options, and how you can use your plan to succeed.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a document that explains how your business operates. It summarizes your business structure, objectives, milestones, and financial performance. Again, it’s a guide that helps you, and anyone else, better understand how your business will succeed.
Why do you need a business plan?
The primary purpose of a business plan is to help you understand the direction of your business and the steps it will take to get there. Having a solid business plan can help you grow up to 30% faster and according to our own 2021 Small Business research working on a business plan increases confidence regarding business health—even in the midst of a crisis.
These benefits are directly connected to how writing a business plan makes you more informed and better prepares you for entrepreneurship. It helps you reduce risk and avoid pursuing potentially poor ideas. You’ll also be able to more easily uncover your business’s potential. By regularly returning to your plan you can understand what parts of your strategy are working and those that are not.
That just scratches the surface for why having a plan is valuable. Check out our full write-up for fifteen more reasons why you need a business plan .
What can you do with your plan?
So what can you do with a business plan once you’ve created it? It can be all too easy to write a plan and just let it be. Here are just a few ways you can leverage your plan to benefit your business.
Test an idea
Writing a plan isn’t just for those that are ready to start a business. It’s just as valuable for those that have an idea and want to determine if it’s actually possible or not. By writing a plan to explore the validity of an idea, you are working through the process of understanding what it would take to be successful.
The market and competitive research alone can tell you a lot about your idea. Is the marketplace too crowded? Is the solution you have in mind not really needed? Add in the exploration of milestones, potential expenses, and the sales needed to attain profitability and you can paint a pretty clear picture of the potential of your business.
Document your strategy and goals
For those starting or managing a business understanding where you’re going and how you’re going to get there are vital. Writing your plan helps you do that. It ensures that you are considering all aspects of your business, know what milestones you need to hit, and can effectively make adjustments if that doesn’t happen.
With a plan in place, you’ll have an idea of where you want your business to go as well as how you’ve performed in the past. This alone better prepares you to take on challenges, review what you’ve done before, and make the right adjustments.
Pursue funding
Even if you do not intend to pursue funding right away, having a business plan will prepare you for it. It will ensure that you have all of the information necessary to submit a loan application and pitch to investors. So, rather than scrambling to gather documentation and write a cohesive plan once it’s relevant, you can instead keep your plan up-to-date and attempt to attain funding. Just add a use of funds report to your financial plan and you’ll be ready to go.
The benefits of having a plan don’t stop there. You can then use your business plan to help you manage the funding you receive. You’ll not only be able to easily track and forecast how you’ll use your funds but easily report on how it’s been used.
Better manage your business
A solid business plan isn’t meant to be something you do once and forget about. Instead, it should be a useful tool that you can regularly use to analyze performance, make strategic decisions, and anticipate future scenarios. It’s a document that you should regularly update and adjust as you go to better fit the actual state of your business.
Doing so makes it easier to understand what’s working and what’s not. It helps you understand if you’re truly reaching your goals or if you need to make further adjustments. Having your plan in place makes that process quicker, more informative, and leaves you with far more time to actually spend running your business.
What should your business plan include?
The content and structure of your business plan should include anything that will help you use it effectively. That being said, there are some key elements that you should cover and that investors will expect to see.
Executive summary
The executive summary is a simple overview of your business and your overall plan. It should serve as a standalone document that provides enough detail for anyone—including yourself, team members, or investors—to fully understand your business strategy. Make sure to cover the problem you’re solving, a description of your product or service, your target market, organizational structure, a financial summary, and any necessary funding requirements.
This will be the first part of your plan but it’s easiest to write it after you’ve created your full plan.
Products & Services
When describing your products or services, you need to start by outlining the problem you’re solving and why what you offer is valuable. This is where you’ll also address current competition in the market and any competitive advantages your products or services bring to the table. Lastly, be sure to outline the steps or milestones that you’ll need to hit to successfully launch your business. If you’ve already hit some initial milestones, like taking pre-orders or early funding, be sure to include it here to further prove the validity of your business.
Market analysis
A market analysis is a qualitative and quantitative assessment of the current market you’re entering or competing in. It helps you understand the overall state and potential of the industry, who your ideal customers are, the positioning of your competition, and how you intend to position your own business. This helps you better explore the long-term trends of the market, what challenges to expect, and how you will need to initially introduce and even price your products or services.
Check out our full guide for how to conduct a market analysis in just four easy steps .
Marketing & sales
Here you detail how you intend to reach your target market. This includes your sales activities, general pricing plan, and the beginnings of your marketing strategy. If you have any branding elements, sample marketing campaigns, or messaging available—this is the place to add it.
Additionally, it may be wise to include a SWOT analysis that demonstrates your business or specific product/service position. This will showcase how you intend to leverage sales and marketing channels to deal with competitive threats and take advantage of any opportunities.
Check out our full write-up to learn how to create a cohesive marketing strategy for your business.
Organization & management
This section addresses the legal structure of your business, your current team, and any gaps that need to be filled. Depending on your business type and longevity, you’ll also need to include your location, ownership information, and business history. Basically, add any information that helps explain your organizational structure and how you operate. This section is particularly important for pitching to investors but should be included even if attempted funding is not in your immediate future.
Financial projections
Possibly the most important piece of your plan, your financials section is vital for showcasing the viability of your business. It also helps you establish a baseline to measure against and makes it easier to make ongoing strategic decisions as your business grows. This may seem complex on the surface, but it can be far easier than you think.
Focus on building solid forecasts, keep your categories simple, and lean on assumptions. You can always return to this section to add more details and refine your financial statements as you operate.
Here are the statements you should include in your financial plan:
- Sales and revenue projections
- Profit and loss statement
- Cash flow statement
- Balance sheet
The appendix is where you add additional detail, documentation, or extended notes that support the other sections of your plan. Don’t worry about adding this section at first and only add documentation that you think will be beneficial for anyone reading your plan.
Types of business plans explained
While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it’s best to find a format that suits your needs. Here are a few common business plan types worth considering.
Traditional business plan
The tried-and-true traditional business plan is a formal document meant to be used for external purposes. Typically this is the type of plan you’ll need when applying for funding or pitching to investors. It can also be used when training or hiring employees, working with vendors, or any other situation where the full details of your business must be understood by another individual.
This type of business plan follows the outline above and can be anywhere from 10-50 pages depending on the amount of detail included, the complexity of your business, and what you include in your appendix. We recommend only starting with this business plan format if you plan to immediately pursue funding and already have a solid handle on your business information.
Business model canvas
The business model canvas is a one-page template designed to demystify the business planning process. It removes the need for a traditional, copy-heavy business plan, in favor of a single-page outline that can help you and outside parties better explore your business idea.
The structure ditches a linear structure in favor of a cell-based template. It encourages you to build connections between every element of your business. It’s faster to write out and update, and much easier for you, your team, and anyone else to visualize your business operations. This is really best for those exploring their business idea for the first time, but keep in mind that it can be difficult to actually validate your idea this way as well as adapt it into a full plan.
One-page business plan
The true middle ground between the business model canvas and a traditional business plan is the one-page business plan. This format is a simplified version of the traditional plan that focuses on the core aspects of your business. It basically serves as a beefed-up pitch document and can be finished as quickly as the business model canvas.
By starting with a one-page plan, you give yourself a minimal document to build from. You’ll typically stick with bullet points and single sentences making it much easier to elaborate or expand sections into a longer-form business plan. This plan type is useful for those exploring ideas, needing to validate their business model, or who need an internal plan to help them run and manage their business.
Now, the option that we here at LivePlan recommend is the Lean Plan . This is less of a specific document type and more of a methodology. It takes the simplicity and styling of the one-page business plan and turns it into a process for you to continuously plan, test, review, refine, and take action based on performance.
It holds all of the benefits of the single-page plan, including the potential to complete it in as little as 27-minutes . However, it’s even easier to convert into a full plan thanks to how heavily it’s tied to your financials. The overall goal of Lean Planning isn’t to just produce documents that you use once and shelve. Instead, the Lean Planning process helps you build a healthier company that thrives in times of growth and stable through times of crisis.
It’s faster, keeps your plan concise, and ensures that your plan is always up-to-date.
Try the LivePlan Method for Lean Business Planning
Now that you know the basics of business planning, it’s time to get started. Again we recommend leveraging a Lean Plan for a faster, easier, and far more useful planning process.
To get familiar with the Lean Plan format, you can download our free Lean Plan template . However, if you want to elevate your ability to create and use your lean plan even further, you may want to explore LivePlan.
It features step-by-step guidance that ensures you cover everything necessary while reducing the time spent on formatting and presenting. You’ll also gain access to financial forecasting tools that propel you through the process. Finally, it will transform your plan into a management tool that will help you easily compare your forecasts to your actual results.
Check out how LivePlan streamlines Lean Planning by downloading our Kickstart Your Business ebook .
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Posted in Business Plan Writing
Join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
What is a Business Plan? Definition, Tips, and Templates
Published: June 07, 2023
In an era where more than 20% of small enterprises fail in their first year, having a clear, defined, and well-thought-out business plan is a crucial first step for setting up a business for long-term success.

Business plans are a required tool for all entrepreneurs, business owners, business acquirers, and even business school students. But … what exactly is a business plan?

In this post, we'll explain what a business plan is, the reasons why you'd need one, identify different types of business plans, and what you should include in yours.
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a documented strategy for a business that highlights its goals and its plans for achieving them. It outlines a company's go-to-market plan, financial projections, market research, business purpose, and mission statement. Key staff who are responsible for achieving the goals may also be included in the business plan along with a timeline.
The business plan is an undeniably critical component to getting any company off the ground. It's key to securing financing, documenting your business model, outlining your financial projections, and turning that nugget of a business idea into a reality.
What is a business plan used for?
The purpose of a business plan is three-fold: It summarizes the organization’s strategy in order to execute it long term, secures financing from investors, and helps forecast future business demands.
Business Plan Template [ Download Now ]

Working on your business plan? Try using our Business Plan Template . Pre-filled with the sections a great business plan needs, the template will give aspiring entrepreneurs a feel for what a business plan is, what should be in it, and how it can be used to establish and grow a business from the ground up.
Purposes of a Business Plan
Chances are, someone drafting a business plan will be doing so for one or more of the following reasons:
1. Securing financing from investors.
Since its contents revolve around how businesses succeed, break even, and turn a profit, a business plan is used as a tool for sourcing capital. This document is an entrepreneur's way of showing potential investors or lenders how their capital will be put to work and how it will help the business thrive.
All banks, investors, and venture capital firms will want to see a business plan before handing over their money, and investors typically expect a 10% ROI or more from the capital they invest in a business.
Therefore, these investors need to know if — and when — they'll be making their money back (and then some). Additionally, they'll want to read about the process and strategy for how the business will reach those financial goals, which is where the context provided by sales, marketing, and operations plans come into play.
2. Documenting a company's strategy and goals.
A business plan should leave no stone unturned.
Business plans can span dozens or even hundreds of pages, affording their drafters the opportunity to explain what a business' goals are and how the business will achieve them.
To show potential investors that they've addressed every question and thought through every possible scenario, entrepreneurs should thoroughly explain their marketing, sales, and operations strategies — from acquiring a physical location for the business to explaining a tactical approach for marketing penetration.
These explanations should ultimately lead to a business' break-even point supported by a sales forecast and financial projections, with the business plan writer being able to speak to the why behind anything outlined in the plan.
.webp)
Free Business Plan Template
The essential document for starting a business -- custom built for your needs.
- Outline your idea.
- Pitch to investors.
- Secure funding.
- Get to work!
You're all set!
Click this link to access this resource at any time.
Free Business Plan [Template]
Fill out the form to access your free business plan., 3. legitimizing a business idea..
Everyone's got a great idea for a company — until they put pen to paper and realize that it's not exactly feasible.
A business plan is an aspiring entrepreneur's way to prove that a business idea is actually worth pursuing.
As entrepreneurs document their go-to-market process, capital needs, and expected return on investment, entrepreneurs likely come across a few hiccups that will make them second guess their strategies and metrics — and that's exactly what the business plan is for.
It ensures an entrepreneur's ducks are in a row before bringing their business idea to the world and reassures the readers that whoever wrote the plan is serious about the idea, having put hours into thinking of the business idea, fleshing out growth tactics, and calculating financial projections.
4. Getting an A in your business class.
Speaking from personal experience, there's a chance you're here to get business plan ideas for your Business 101 class project.
If that's the case, might we suggest checking out this post on How to Write a Business Plan — providing a section-by-section guide on creating your plan?
What does a business plan need to include?
- Business Plan Subtitle
- Executive Summary
- Company Description
- The Business Opportunity
- Competitive Analysis
- Target Market
- Marketing Plan
- Financial Summary
- Funding Requirements
1. Business Plan Subtitle
Every great business plan starts with a captivating title and subtitle. You’ll want to make it clear that the document is, in fact, a business plan, but the subtitle can help tell the story of your business in just a short sentence.
2. Executive Summary
Although this is the last part of the business plan that you’ll write, it’s the first section (and maybe the only section) that stakeholders will read. The executive summary of a business plan sets the stage for the rest of the document. It includes your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
3. Company Description
This brief part of your business plan will detail your business name, years in operation, key offerings, and positioning statement. You might even add core values or a short history of the company. The company description’s role in a business plan is to introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way.
4. The Business Opportunity
The business opportunity should convince investors that your organization meets the needs of the market in a way that no other company can. This section explains the specific problem your business solves within the marketplace and how it solves them. It will include your value proposition as well as some high-level information about your target market.

5. Competitive Analysis
Just about every industry has more than one player in the market. Even if your business owns the majority of the market share in your industry or your business concept is the first of its kind, you still have competition. In the competitive analysis section, you’ll take an objective look at the industry landscape to determine where your business fits. A SWOT analysis is an organized way to format this section.
6. Target Market
Who are the core customers of your business and why? The target market portion of your business plan outlines this in detail. The target market should explain the demographics, psychographics, behavioristics, and geographics of the ideal customer.
7. Marketing Plan
Marketing is expansive, and it’ll be tempting to cover every type of marketing possible, but a brief overview of how you’ll market your unique value proposition to your target audience, followed by a tactical plan will suffice.
Think broadly and narrow down from there: Will you focus on a slow-and-steady play where you make an upfront investment in organic customer acquisition? Or will you generate lots of quick customers using a pay-to-play advertising strategy? This kind of information should guide the marketing plan section of your business plan.
8. Financial Summary
Money doesn’t grow on trees and even the most digital, sustainable businesses have expenses. Outlining a financial summary of where your business is currently and where you’d like it to be in the future will substantiate this section. Consider including any monetary information that will give potential investors a glimpse into the financial health of your business. Assets, liabilities, expenses, debt, investments, revenue, and more are all useful adds here.
So, you’ve outlined some great goals, the business opportunity is valid, and the industry is ready for what you have to offer. Who’s responsible for turning all this high-level talk into results? The "team" section of your business plan answers that question by providing an overview of the roles responsible for each goal. Don’t worry if you don’t have every team member on board yet, knowing what roles to hire for is helpful as you seek funding from investors.
10. Funding Requirements
Remember that one of the goals of a business plan is to secure funding from investors, so you’ll need to include funding requirements you’d like them to fulfill. The amount your business needs, for what reasons, and for how long will meet the requirement for this section.
Types of Business Plans
- Startup Business Plan
- Feasibility Business Plan
- Internal Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Business Acquisition Plan
- Business Repositioning Plan
- Expansion or Growth Business Plan
There’s no one size fits all business plan as there are several types of businesses in the market today. From startups with just one founder to historic household names that need to stay competitive, every type of business needs a business plan that’s tailored to its needs. Below are a few of the most common types of business plans.
For even more examples, check out these sample business plans to help you write your own .
1. Startup Business Plan

As one of the most common types of business plans, a startup business plan is for new business ideas. This plan lays the foundation for the eventual success of a business.
The biggest challenge with the startup business plan is that it’s written completely from scratch. Startup business plans often reference existing industry data. They also explain unique business strategies and go-to-market plans.
Because startup business plans expand on an original idea, the contents will vary by the top priority goals.
For example, say a startup is looking for funding. If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture.
2. Feasibility Business Plan
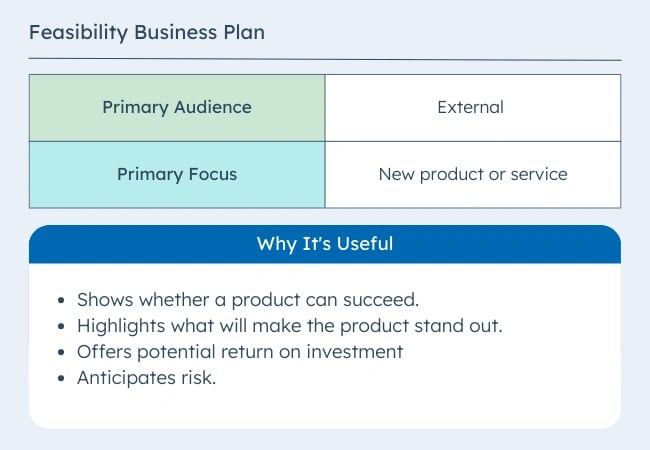
This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing organization. This comprehensive plan may include:
- A detailed product description
- Market analysis
- Technology needs
- Production needs
- Financial sources
- Production operations
According to CBInsights research, 35% of startups fail because of a lack of market need. Another 10% fail because of mistimed products.
Some businesses will complete a feasibility study to explore ideas and narrow product plans to the best choice. They conduct these studies before completing the feasibility business plan. Then the feasibility plan centers on that one product or service.
3. Internal Business Plan

Internal business plans help leaders communicate company goals, strategy, and performance. This helps the business align and work toward objectives more effectively.
Besides the typical elements in a startup business plan, an internal business plan may also include:
- Department-specific budgets
- Target demographic analysis
- Market size and share of voice analysis
- Action plans
- Sustainability plans
Most external-facing business plans focus on raising capital and support for a business. But an internal business plan helps keep the business mission consistent in the face of change.
4. Strategic Business Plan

Strategic business plans focus on long-term objectives for your business. They usually cover the first three to five years of operations. This is different from the typical startup business plan which focuses on the first one to three years. The audience for this plan is also primarily internal stakeholders.
These types of business plans may include:
- Relevant data and analysis
- Assessments of company resources
- Vision and mission statements
It's important to remember that, while many businesses create a strategic plan before launching, some business owners just jump in. So, this business plan can add value by outlining how your business plans to reach specific goals. This type of planning can also help a business anticipate future challenges.
5. Business Acquisition Plan

Investors use business plans to acquire existing businesses, too — not just new businesses.
A business acquisition plan may include costs, schedules, or management requirements. This data will come from an acquisition strategy.
A business plan for an existing company will explain:
- How an acquisition will change its operating model
- What will stay the same under new ownership
- Why things will change or stay the same
- Acquisition planning documentation
- Timelines for acquisition
Additionally, the business plan should speak to the current state of the business and why it's up for sale.
For example, if someone is purchasing a failing business, the business plan should explain why the business is being purchased. It should also include:
- What the new owner will do to turn the business around
- Historic business metrics
- Sales projections after the acquisition
- Justification for those projections
6. Business Repositioning Plan
.webp?width=650&height=450&name=businessplan_6%20(1).webp)
When a business wants to avoid acquisition, reposition its brand, or try something new, CEOs or owners will develop a business repositioning plan.
This plan will:
- Acknowledge the current state of the company.
- State a vision for the future of the company.
- Explain why the business needs to reposition itself.
- Outline a process for how the company will adjust.
Companies planning for a business reposition often do so — proactively or retroactively — due to a shift in market trends and customer needs.
For example, shoe brand AllBirds plans to refocus its brand on core customers and shift its go-to-market strategy. These decisions are a reaction to lackluster sales following product changes and other missteps.
7. Expansion or Growth Business Plan
When your business is ready to expand, a growth business plan creates a useful structure for reaching specific targets.
For example, a successful business expanding into another location can use a growth business plan. This is because it may also mean the business needs to focus on a new target market or generate more capital.
This type of plan usually covers the next year or two of growth. It often references current sales, revenue, and successes. It may also include:
- SWOT analysis
- Growth opportunity studies
- Financial goals and plans
- Marketing plans
- Capability planning
These types of business plans will vary by business, but they can help businesses quickly rally around new priorities to drive growth.
Getting Started With Your Business Plan
At the end of the day, a business plan is simply an explanation of a business idea and why it will be successful. The more detail and thought you put into it, the more successful your plan — and the business it outlines — will be.
When writing your business plan, you’ll benefit from extensive research, feedback from your team or board of directors, and a solid template to organize your thoughts. If you need one of these, download HubSpot's Free Business Plan Template below to get started.
Editor's note: This post was originally published in August 2020 and has been updated for comprehensiveness.

Don't forget to share this post!
Related articles.

24 of My Favorite Sample Business Plans & Examples For Your Inspiration
![functions of the business plan How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/executive-summary-example_5.webp)
How to Write a Powerful Executive Summary [+4 Top Examples]

Maximizing Your Social Media Strategy: The Top Aggregator Tools to Use

The Content Aggregator Guide for 2023
![functions of the business plan 7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/gantt-chart-example.jpg)
7 Gantt Chart Examples You'll Want to Copy [+ 5 Steps to Make One]
![functions of the business plan The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]](https://blog.hubspot.com/hubfs/flowchart%20templates.jpg)
The 8 Best Free Flowchart Templates [+ Examples]

16 Best Screen Recorders to Use for Collaboration

The 25 Best Google Chrome Extensions for SEO

Professional Invoice Design: 28 Samples & Templates to Inspire You
Customers’ Top HubSpot Integrations to Streamline Your Business in 2022
2 Essential Templates For Starting Your Business
Marketing software that helps you drive revenue, save time and resources, and measure and optimize your investments — all on one easy-to-use platform
How To Write A Business Plan (2024 Guide)

Updated: Apr 17, 2024, 11:59am

Table of Contents
Brainstorm an executive summary, create a company description, brainstorm your business goals, describe your services or products, conduct market research, create financial plans, bottom line, frequently asked questions.
Every business starts with a vision, which is distilled and communicated through a business plan. In addition to your high-level hopes and dreams, a strong business plan outlines short-term and long-term goals, budget and whatever else you might need to get started. In this guide, we’ll walk you through how to write a business plan that you can stick to and help guide your operations as you get started.
Featured Partners
ZenBusiness
$0 + State Fees
Varies By State & Package

On ZenBusiness' Website

On LegalZoom's Website
Northwest Registered Agent
$39 + State Fees

On Northwest Registered Agent's Website
Drafting the Summary
An executive summary is an extremely important first step in your business. You have to be able to put the basic facts of your business in an elevator pitch-style sentence to grab investors’ attention and keep their interest. This should communicate your business’s name, what the products or services you’re selling are and what marketplace you’re entering.
Ask for Help
When drafting the executive summary, you should have a few different options. Enlist a few thought partners to review your executive summary possibilities to determine which one is best.
After you have the executive summary in place, you can work on the company description, which contains more specific information. In the description, you’ll need to include your business’s registered name , your business address and any key employees involved in the business.
The business description should also include the structure of your business, such as sole proprietorship , limited liability company (LLC) , partnership or corporation. This is the time to specify how much of an ownership stake everyone has in the company. Finally, include a section that outlines the history of the company and how it has evolved over time.
Wherever you are on the business journey, you return to your goals and assess where you are in meeting your in-progress targets and setting new goals to work toward.
Numbers-based Goals
Goals can cover a variety of sections of your business. Financial and profit goals are a given for when you’re establishing your business, but there are other goals to take into account as well with regard to brand awareness and growth. For example, you might want to hit a certain number of followers across social channels or raise your engagement rates.
Another goal could be to attract new investors or find grants if you’re a nonprofit business. If you’re looking to grow, you’ll want to set revenue targets to make that happen as well.
Intangible Goals
Goals unrelated to traceable numbers are important as well. These can include seeing your business’s advertisement reach the general public or receiving a terrific client review. These goals are important for the direction you take your business and the direction you want it to go in the future.
The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you’re offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit in the current market or are providing something necessary or entirely new. If you have any patents or trademarks, this is where you can include those too.
If you have any visual aids, they should be included here as well. This would also be a good place to include pricing strategy and explain your materials.
This is the part of the business plan where you can explain your expertise and different approach in greater depth. Show how what you’re offering is vital to the market and fills an important gap.
You can also situate your business in your industry and compare it to other ones and how you have a competitive advantage in the marketplace.
Other than financial goals, you want to have a budget and set your planned weekly, monthly and annual spending. There are several different costs to consider, such as operational costs.
Business Operations Costs
Rent for your business is the first big cost to factor into your budget. If your business is remote, the cost that replaces rent will be the software that maintains your virtual operations.
Marketing and sales costs should be next on your list. Devoting money to making sure people know about your business is as important as making sure it functions.
Other Costs
Although you can’t anticipate disasters, there are likely to be unanticipated costs that come up at some point in your business’s existence. It’s important to factor these possible costs into your financial plans so you’re not caught totally unaware.
Business plans are important for businesses of all sizes so that you can define where your business is and where you want it to go. Growing your business requires a vision, and giving yourself a roadmap in the form of a business plan will set you up for success.
How do I write a simple business plan?
When you’re working on a business plan, make sure you have as much information as possible so that you can simplify it to the most relevant information. A simple business plan still needs all of the parts included in this article, but you can be very clear and direct.
What are some common mistakes in a business plan?
The most common mistakes in a business plan are common writing issues like grammar errors or misspellings. It’s important to be clear in your sentence structure and proofread your business plan before sending it to any investors or partners.
What basic items should be included in a business plan?
When writing out a business plan, you want to make sure that you cover everything related to your concept for the business, an analysis of the industry―including potential customers and an overview of the market for your goods or services―how you plan to execute your vision for the business, how you plan to grow the business if it becomes successful and all financial data around the business, including current cash on hand, potential investors and budget plans for the next few years.
- Best VPN Services
- Best Project Management Software
- Best Web Hosting Services
- Best Antivirus Software
- Best LLC Services
- Best POS Systems
- Best Business VOIP Services
- Best Credit Card Processing Companies
- Best CRM Software for Small Business
- Best Fleet Management Software
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Best Business Loans
- Best Business Software
- Best Business Apps
- Best Free Software For Business
- How to Start a Business
- How To Make A Small Business Website
- How To Trademark A Name
- What Is An LLC?
- How To Set Up An LLC In 7 Steps
- What is Project Management?

What Is a Proxy Server?
How To Get A Business License In North Dakota (2024)
How To Write An Effective Business Proposal
Best New Hampshire Registered Agent Services Of 2024
Employer Staffing Solutions Group Review 2024: Features, Pricing & More
How To Sell Clothes Online In 2024
Julia is a writer in New York and started covering tech and business during the pandemic. She also covers books and the publishing industry.
Kelly Main is a Marketing Editor and Writer specializing in digital marketing, online advertising and web design and development. Before joining the team, she was a Content Producer at Fit Small Business where she served as an editor and strategist covering small business marketing content. She is a former Google Tech Entrepreneur and she holds an MSc in International Marketing from Edinburgh Napier University. Additionally, she is a Columnist at Inc. Magazine.

- Customer Reviews
- Net 30 Account
- Wise Services
- Steps & Timeline
- Work at a Glance
- Market Research at a Glance
- Business Plan Writing Services
- Bank Business Plan
- Investor Business Plan
- Franchise Business Plan
- Cannabis Business Plan
- Strategic Business Plan
- Corporate Business Plan
- Merge and Acquisition Business Plan (M&A)
- Private Placement Memorandums (PPM)
- Sample Business Plans
- Professional Feasibility Study
- PowerPoint Presentations
- Pitch Deck Presentation Services
- Business Plan Printing
- Market Research
- L-1 Business Plan
- E-2 Business Plan
- EB-5 Business Plan
- EB-5 Regional Centers
- Immigration Attorneys
- Nonprofit Business Plan
- Exit Business Planning
- Business Planning
- Business Formation
- Business License
- Business Website
- Business Branding
- Business Bank Account
- Digital Marketing
- Business Funding Resources
- Small Business Loans
- Venture Capital
- Net 30 Apply

What is a business plan? Definition, Purpose, and Types
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company’s goals, strategies , and financial projections. Whether you’re starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.
As a business plan writer and consultant , I’ve crafted over 15,000 plans for a diverse range of businesses. In this article, I’ll be sharing my wealth of experience about what a business plan is, its purpose, and the step-by-step process of creating one. By the end, you’ll have a thorough understanding of how to develop a robust business plan that can drive your business to success.
What is a business plan?
Purposes of a business plan, what are the essential components of a business plan, executive summary, business description or overview, product and price, competitive analysis, target market, marketing plan, financial plan, funding requirements, types of business plan, lean startup business plans, traditional business plans, how often should a business plan be reviewed and revised, what are the key elements of a lean startup business plan.
- What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?
A business plan is a roadmap for your business. It outlines your goals, strategies, and how you plan to achieve them. It’s a living document that you can update as your business grows and changes.
Looking for someone to write a business plan?
Find professional business plan writers for your business success.
These are the following purpose of business plan:
- Attract investors and lenders: If you’re seeking funding for your business , a business plan is a must-have. Investors and lenders want to see that you have a clear plan for how you’ll use their money to grow your business and generate revenue.
- Get organized and stay on track: Writing a business plan forces you to think through all aspects of your business, from your target market to your marketing strategy. This can help you identify any potential challenges and opportunities early on, so you can develop a plan to address them.
- Make better decisions: A business plan can help you make better decisions about your business by providing you with a framework to evaluate different options. For example, if you’re considering launching a new product, your business plan can help you assess the potential market demand, costs, and profitability.

The executive summary is the most important part of your business plan, even though it’s the last one you’ll write. It’s the first section that potential investors or lenders will read, and it may be the only one they read. The executive summary sets the stage for the rest of the document by introducing your company’s mission or vision statement, value proposition, and long-term goals.
The business description section of your business plan should introduce your business to the reader in a compelling and concise way. It should include your business name, years in operation, key offerings, positioning statement, and core values (if applicable). You may also want to include a short history of your company.
In this section, the company should describe its products or services , including pricing, product lifespan, and unique benefits to the consumer. Other relevant information could include production and manufacturing processes, patents, and proprietary technology.
Every industry has competitors, even if your business is the first of its kind or has the majority of the market share. In the competitive analysis section of your business plan, you’ll objectively assess the industry landscape to understand your business’s competitive position. A SWOT analysis is a structured way to organize this section.
Your target market section explains the core customers of your business and why they are your ideal customers. It should include demographic, psychographic, behavioral, and geographic information about your target market.
Marketing plan describes how the company will attract and retain customers, including any planned advertising and marketing campaigns . It also describes how the company will distribute its products or services to consumers.
After outlining your goals, validating your business opportunity, and assessing the industry landscape, the team section of your business plan identifies who will be responsible for achieving your goals. Even if you don’t have your full team in place yet, investors will be impressed by your clear understanding of the roles that need to be filled.
In the financial plan section,established businesses should provide financial statements , balance sheets , and other financial data. New businesses should provide financial targets and estimates for the first few years, and may also request funding.
Since one goal of a business plan is to secure funding from investors , you should include the amount of funding you need, why you need it, and how long you need it for.
- Tip: Use bullet points and numbered lists to make your plan easy to read and scannable.
Access specialized business plan writing service now!
Business plans can come in many different formats, but they are often divided into two main types: traditional and lean startup. The U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) says that the traditional business plan is the more common of the two.
Lean startup business plans are short (as short as one page) and focus on the most important elements. They are easy to create, but companies may need to provide more information if requested by investors or lenders.
Traditional business plans are longer and more detailed than lean startup business plans, which makes them more time-consuming to create but more persuasive to potential investors. Lean startup business plans are shorter and less detailed, but companies should be prepared to provide more information if requested.
Need Guidance with Your Business Plan?
Access 14 free business plan samples!
A business plan should be reviewed and revised at least annually, or more often if the business is experiencing significant changes. This is because the business landscape is constantly changing, and your business plan needs to reflect those changes in order to remain relevant and effective.
Here are some specific situations in which you should review and revise your business plan:
- You have launched a new product or service line.
- You have entered a new market.
- You have experienced significant changes in your customer base or competitive landscape.
- You have made changes to your management team or organizational structure.
- You have raised new funding.
A lean startup business plan is a short and simple way for a company to explain its business, especially if it is new and does not have a lot of information yet. It can include sections on the company’s value proposition, major activities and advantages, resources, partnerships, customer segments, and revenue sources.
What are some of the reasons why business plans don't succeed?

- Unrealistic assumptions: Business plans are often based on assumptions about the market, the competition, and the company’s own capabilities. If these assumptions are unrealistic, the plan is doomed to fail.
- Lack of focus: A good business plan should be focused on a specific goal and how the company will achieve it. If the plan is too broad or tries to do too much, it is unlikely to be successful.
- Poor execution: Even the best business plan is useless if it is not executed properly. This means having the right team in place, the necessary resources, and the ability to adapt to changing circumstances.
- Unforeseen challenges: Every business faces challenges that could not be predicted or planned for. These challenges can be anything from a natural disaster to a new competitor to a change in government regulations.
What are the benefits of having a business plan?
- It helps you to clarify your business goals and strategies.
- It can help you to attract investors and lenders.
- It can serve as a roadmap for your business as it grows and changes.
- It can help you to make better business decisions.
How to write a business plan?
There are many different ways to write a business plan, but most follow the same basic structure. Here is a step-by-step guide:
- Executive summary.
- Company description.
- Management and organization description.
- Financial projections.
How to write a business plan step by step?
Start with an executive summary, then describe your business, analyze the market, outline your products or services, detail your marketing and sales strategies, introduce your team, and provide financial projections.
Why do I need a business plan for my startup?
A business plan helps define your startup’s direction, attract investors, secure funding, and make informed decisions crucial for success.
What are the key components of a business plan?
Key components include an executive summary, business description, market analysis, products or services, marketing and sales strategy, management and team, financial projections, and funding requirements.
Can a business plan help secure funding for my business?
Yes, a well-crafted business plan demonstrates your business’s viability, the use of investment, and potential returns, making it a valuable tool for attracting investors and lenders.
Quick Links

- Investor Business Plans
- M&A Business Plan
- Private Placement
- Feasibility Study
- Hire a Business Plan Writer
- Business Valuation Calculator
- Business Plan Examples
- Real Estate Business Plan
- Business Plan Template
- Business Plan Pricing Guide
- Business Plan Makeover
- SBA Loans, Bank Funding & Business Credit
- Finding & Qualifying for Business Grants
- Leadership for the New Manager
- Content Marketing for Beginners
- All About Crowdfunding
- EB-5 Regional Centers, A Step-By-Step Guide
- Logo Designer
- Landing Page
- PPC Advertising

- Business Entity
- Business Licensing
- Virtual Assistant
- Business Phone
- Business Address
- E-1 Visa Business Plan
- EB1-A Visa Business Plan
- EB1-C Visa Business Plan
- EB2-NIW Business Plan
- H1B Visa Business Plan
- O1 Visa Business Plan
- Business Brokers
- Merger & Acquisition Advisors
- Franchisors
Proud Sponsor of
- 1-800-496-1056

- (613) 800-0227

- +44 (1549) 409190

- +61 (2) 72510077

- Sources of Business Finance
- Small Business Loans
- Small Business Grants
- Crowdfunding Sites
- How to Get a Business Loan
- Small Business Insurance Providers
- Best Factoring Companies
- Types of Bank Accounts
- Best Banks for Small Business
- Best Business Bank Accounts
- Open a Business Bank Account
- Bank Accounts for Small Businesses
- Free Business Checking Accounts
- Best Business Credit Cards
- Get a Business Credit Card
- Business Credit Cards for Bad Credit
- Build Business Credit Fast
- Business Loan Eligibility Criteria
- Small-Business Bookkeeping Basics
- How to Set Financial Goals
- Business Loan Calculators
- How to Calculate ROI
- Calculate Net Income
- Calculate Working Capital
- Calculate Operating Income
- Calculate Net Present Value (NPV)
- Calculate Payroll Tax
12 Key Elements of a Business Plan (Top Components Explained)
Starting and running a successful business requires proper planning and execution of effective business tactics and strategies .
You need to prepare many essential business documents when starting a business for maximum success; the business plan is one such document.
When creating a business, you want to achieve business objectives and financial goals like productivity, profitability, and business growth. You need an effective business plan to help you get to your desired business destination.
Even if you are already running a business, the proper understanding and review of the key elements of a business plan help you navigate potential crises and obstacles.
This article will teach you why the business document is at the core of any successful business and its key elements you can not avoid.
Let’s get started.
Why Are Business Plans Important?
Business plans are practical steps or guidelines that usually outline what companies need to do to reach their goals. They are essential documents for any business wanting to grow and thrive in a highly-competitive business environment .
1. Proves Your Business Viability
A business plan gives companies an idea of how viable they are and what actions they need to take to grow and reach their financial targets. With a well-written and clearly defined business plan, your business is better positioned to meet its goals.
2. Guides You Throughout the Business Cycle
A business plan is not just important at the start of a business. As a business owner, you must draw up a business plan to remain relevant throughout the business cycle .
During the starting phase of your business, a business plan helps bring your ideas into reality. A solid business plan can secure funding from lenders and investors.
After successfully setting up your business, the next phase is management. Your business plan still has a role to play in this phase, as it assists in communicating your business vision to employees and external partners.
Essentially, your business plan needs to be flexible enough to adapt to changes in the needs of your business.
3. Helps You Make Better Business Decisions
As a business owner, you are involved in an endless decision-making cycle. Your business plan helps you find answers to your most crucial business decisions.
A robust business plan helps you settle your major business components before you launch your product, such as your marketing and sales strategy and competitive advantage.
4. Eliminates Big Mistakes
Many small businesses fail within their first five years for several reasons: lack of financing, stiff competition, low market need, inadequate teams, and inefficient pricing strategy.
Creating an effective plan helps you eliminate these big mistakes that lead to businesses' decline. Every business plan element is crucial for helping you avoid potential mistakes before they happen.
5. Secures Financing and Attracts Top Talents
Having an effective plan increases your chances of securing business loans. One of the essential requirements many lenders ask for to grant your loan request is your business plan.
A business plan helps investors feel confident that your business can attract a significant return on investments ( ROI ).
You can attract and retain top-quality talents with a clear business plan. It inspires your employees and keeps them aligned to achieve your strategic business goals.
Key Elements of Business Plan
Starting and running a successful business requires well-laid actions and supporting documents that better position a company to achieve its business goals and maximize success.
A business plan is a written document with relevant information detailing business objectives and how it intends to achieve its goals.
With an effective business plan, investors, lenders, and potential partners understand your organizational structure and goals, usually around profitability, productivity, and growth.
Every successful business plan is made up of key components that help solidify the efficacy of the business plan in delivering on what it was created to do.
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan.
1. Executive Summary
One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
In the overall business plan document, the executive summary should be at the forefront of the business plan. It helps set the tone for readers on what to expect from the business plan.
A well-written executive summary includes all vital information about the organization's operations, making it easy for a reader to understand.
The key points that need to be acted upon are highlighted in the executive summary. They should be well spelled out to make decisions easy for the management team.
A good and compelling executive summary points out a company's mission statement and a brief description of its products and services.

An executive summary summarizes a business's expected value proposition to distinct customer segments. It highlights the other key elements to be discussed during the rest of the business plan.
Including your prior experiences as an entrepreneur is a good idea in drawing up an executive summary for your business. A brief but detailed explanation of why you decided to start the business in the first place is essential.
Adding your company's mission statement in your executive summary cannot be overemphasized. It creates a culture that defines how employees and all individuals associated with your company abide when carrying out its related processes and operations.
Your executive summary should be brief and detailed to catch readers' attention and encourage them to learn more about your company.
Components of an Executive Summary
Here are some of the information that makes up an executive summary:
- The name and location of your company
- Products and services offered by your company
- Mission and vision statements
- Success factors of your business plan
2. Business Description
Your business description needs to be exciting and captivating as it is the formal introduction a reader gets about your company.
What your company aims to provide, its products and services, goals and objectives, target audience , and potential customers it plans to serve need to be highlighted in your business description.
A company description helps point out notable qualities that make your company stand out from other businesses in the industry. It details its unique strengths and the competitive advantages that give it an edge to succeed over its direct and indirect competitors.
Spell out how your business aims to deliver on the particular needs and wants of identified customers in your company description, as well as the particular industry and target market of the particular focus of the company.
Include trends and significant competitors within your particular industry in your company description. Your business description should contain what sets your company apart from other businesses and provides it with the needed competitive advantage.
In essence, if there is any area in your business plan where you need to brag about your business, your company description provides that unique opportunity as readers look to get a high-level overview.

Components of a Business Description
Your business description needs to contain these categories of information.
- Business location
- The legal structure of your business
- Summary of your business’s short and long-term goals
3. Market Analysis
The market analysis section should be solely based on analytical research as it details trends particular to the market you want to penetrate.
Graphs, spreadsheets, and histograms are handy data and statistical tools you need to utilize in your market analysis. They make it easy to understand the relationship between your current ideas and the future goals you have for the business.
All details about the target customers you plan to sell products or services should be in the market analysis section. It helps readers with a helpful overview of the market.
In your market analysis, you provide the needed data and statistics about industry and market share, the identified strengths in your company description, and compare them against other businesses in the same industry.
The market analysis section aims to define your target audience and estimate how your product or service would fare with these identified audiences.

Market analysis helps visualize a target market by researching and identifying the primary target audience of your company and detailing steps and plans based on your audience location.
Obtaining this information through market research is essential as it helps shape how your business achieves its short-term and long-term goals.
Market Analysis Factors
Here are some of the factors to be included in your market analysis.
- The geographical location of your target market
- Needs of your target market and how your products and services can meet those needs
- Demographics of your target audience
Components of the Market Analysis Section
Here is some of the information to be included in your market analysis.
- Industry description and statistics
- Demographics and profile of target customers
- Marketing data for your products and services
- Detailed evaluation of your competitors
4. Marketing Plan
A marketing plan defines how your business aims to reach its target customers, generate sales leads, and, ultimately, make sales.
Promotion is at the center of any successful marketing plan. It is a series of steps to pitch a product or service to a larger audience to generate engagement. Note that the marketing strategy for a business should not be stagnant and must evolve depending on its outcome.
Include the budgetary requirement for successfully implementing your marketing plan in this section to make it easy for readers to measure your marketing plan's impact in terms of numbers.
The information to include in your marketing plan includes marketing and promotion strategies, pricing plans and strategies , and sales proposals. You need to include how you intend to get customers to return and make repeat purchases in your business plan.

5. Sales Strategy
Sales strategy defines how you intend to get your product or service to your target customers and works hand in hand with your business marketing strategy.
Your sales strategy approach should not be complex. Break it down into simple and understandable steps to promote your product or service to target customers.
Apart from the steps to promote your product or service, define the budget you need to implement your sales strategies and the number of sales reps needed to help the business assist in direct sales.
Your sales strategy should be specific on what you need and how you intend to deliver on your sales targets, where numbers are reflected to make it easier for readers to understand and relate better.

6. Competitive Analysis
Providing transparent and honest information, even with direct and indirect competitors, defines a good business plan. Provide the reader with a clear picture of your rank against major competitors.
Identifying your competitors' weaknesses and strengths is useful in drawing up a market analysis. It is one information investors look out for when assessing business plans.

The competitive analysis section clearly defines the notable differences between your company and your competitors as measured against their strengths and weaknesses.
This section should define the following:
- Your competitors' identified advantages in the market
- How do you plan to set up your company to challenge your competitors’ advantage and gain grounds from them?
- The standout qualities that distinguish you from other companies
- Potential bottlenecks you have identified that have plagued competitors in the same industry and how you intend to overcome these bottlenecks
In your business plan, you need to prove your industry knowledge to anyone who reads your business plan. The competitive analysis section is designed for that purpose.
7. Management and Organization
Management and organization are key components of a business plan. They define its structure and how it is positioned to run.
Whether you intend to run a sole proprietorship, general or limited partnership, or corporation, the legal structure of your business needs to be clearly defined in your business plan.
Use an organizational chart that illustrates the hierarchy of operations of your company and spells out separate departments and their roles and functions in this business plan section.
The management and organization section includes profiles of advisors, board of directors, and executive team members and their roles and responsibilities in guaranteeing the company's success.
Apparent factors that influence your company's corporate culture, such as human resources requirements and legal structure, should be well defined in the management and organization section.
Defining the business's chain of command if you are not a sole proprietor is necessary. It leaves room for little or no confusion about who is in charge or responsible during business operations.
This section provides relevant information on how the management team intends to help employees maximize their strengths and address their identified weaknesses to help all quarters improve for the business's success.
8. Products and Services
This business plan section describes what a company has to offer regarding products and services to the maximum benefit and satisfaction of its target market.
Boldly spell out pending patents or copyright products and intellectual property in this section alongside costs, expected sales revenue, research and development, and competitors' advantage as an overview.
At this stage of your business plan, the reader needs to know what your business plans to produce and sell and the benefits these products offer in meeting customers' needs.
The supply network of your business product, production costs, and how you intend to sell the products are crucial components of the products and services section.
Investors are always keen on this information to help them reach a balanced assessment of if investing in your business is risky or offer benefits to them.
You need to create a link in this section on how your products or services are designed to meet the market's needs and how you intend to keep those customers and carve out a market share for your company.
Repeat purchases are the backing that a successful business relies on and measure how much customers are into what your company is offering.
This section is more like an expansion of the executive summary section. You need to analyze each product or service under the business.
9. Operating Plan
An operations plan describes how you plan to carry out your business operations and processes.
The operating plan for your business should include:
- Information about how your company plans to carry out its operations.
- The base location from which your company intends to operate.
- The number of employees to be utilized and other information about your company's operations.
- Key business processes.
This section should highlight how your organization is set up to run. You can also introduce your company's management team in this section, alongside their skills, roles, and responsibilities in the company.
The best way to introduce the company team is by drawing up an organizational chart that effectively maps out an organization's rank and chain of command.
What should be spelled out to readers when they come across this business plan section is how the business plans to operate day-in and day-out successfully.
10. Financial Projections and Assumptions
Bringing your great business ideas into reality is why business plans are important. They help create a sustainable and viable business.
The financial section of your business plan offers significant value. A business uses a financial plan to solve all its financial concerns, which usually involves startup costs, labor expenses, financial projections, and funding and investor pitches.
All key assumptions about the business finances need to be listed alongside the business financial projection, and changes to be made on the assumptions side until it balances with the projection for the business.
The financial plan should also include how the business plans to generate income and the capital expenditure budgets that tend to eat into the budget to arrive at an accurate cash flow projection for the business.
Base your financial goals and expectations on extensive market research backed with relevant financial statements for the relevant period.
Examples of financial statements you can include in the financial projections and assumptions section of your business plan include:
- Projected income statements
- Cash flow statements
- Balance sheets
- Income statements
Revealing the financial goals and potentials of the business is what the financial projection and assumption section of your business plan is all about. It needs to be purely based on facts that can be measurable and attainable.
11. Request For Funding
The request for funding section focuses on the amount of money needed to set up your business and underlying plans for raising the money required. This section includes plans for utilizing the funds for your business's operational and manufacturing processes.
When seeking funding, a reasonable timeline is required alongside it. If the need arises for additional funding to complete other business-related projects, you are not left scampering and desperate for funds.
If you do not have the funds to start up your business, then you should devote a whole section of your business plan to explaining the amount of money you need and how you plan to utilize every penny of the funds. You need to explain it in detail for a future funding request.
When an investor picks up your business plan to analyze it, with all your plans for the funds well spelled out, they are motivated to invest as they have gotten a backing guarantee from your funding request section.
Include timelines and plans for how you intend to repay the loans received in your funding request section. This addition keeps investors assured that they could recoup their investment in the business.
12. Exhibits and Appendices
Exhibits and appendices comprise the final section of your business plan and contain all supporting documents for other sections of the business plan.
Some of the documents that comprise the exhibits and appendices section includes:
- Legal documents
- Licenses and permits
- Credit histories
- Customer lists
The choice of what additional document to include in your business plan to support your statements depends mainly on the intended audience of your business plan. Hence, it is better to play it safe and not leave anything out when drawing up the appendix and exhibit section.
Supporting documentation is particularly helpful when you need funding or support for your business. This section provides investors with a clearer understanding of the research that backs the claims made in your business plan.
There are key points to include in the appendix and exhibits section of your business plan.
- The management team and other stakeholders resume
- Marketing research
- Permits and relevant legal documents
- Financial documents
Was This Article Helpful?
Martin luenendonk.
Martin loves entrepreneurship and has helped dozens of entrepreneurs by validating the business idea, finding scalable customer acquisition channels, and building a data-driven organization. During his time working in investment banking, tech startups, and industry-leading companies he gained extensive knowledge in using different software tools to optimize business processes.
This insights and his love for researching SaaS products enables him to provide in-depth, fact-based software reviews to enable software buyers make better decisions.
7 Different Types of Business Plans Explained

11 min. read
Updated April 10, 2024
Business plans go by many names: Strategic plans, traditional plans , operational plans, feasibility plans, internal plans, growth plans, and more.
Different situations call for different types of plans.
But what makes each type of plan unique? And why should you consider one type over another?
In this article, we’ll uncover a quick process to find the right type of business plan, along with an overview of each option.
Let’s help you find the right planning format.
- What type of business plan do you need?
The short answer is… it depends.
Your current business stage, intended audience, and how you’ll use the plan will all impact what format works best.
Remember, just the act of planning will improve your chances of success . It’s important to land on an option that will support your needs. Don’t get too hung up on making the right choice and delay writing your plan.
So, how do you choose?
1. Know why you need a business plan
What are you creating a business plan for ? Are you pitching to potential investors? Applying for a loan? Trying to understand if your business idea is feasible?
You may need a business plan for one or multiple reasons. What you intend to do with it will inform what type of plan you need.
For example: A more robust and detailed plan may be necessary if you seek investment . But a shorter format could be more useful and less time-consuming if you’re just testing an idea.
2. Become familiar with your options
You don’t need to become a planning expert and understand every detail about every type of plan. You just need to know the basics:
- What makes this type of plan unique?
- What are its benefits?
- What are its drawbacks?
- Which types of businesses typically use it?
By taking the time to review, you’ll understand what you’re getting into and be more likely to complete your plan. Plus, you’ll come away with a document built with your use case(s) in mind—meaning you won’t have to restart to make it a valuable tool.
Brought to you by
Create a professional business plan
Using ai and step-by-step instructions.
Secure funding
Validate ideas
Build a strategy
3. Start small and grow
When choosing a business plan format, a good tactic is to opt for a shorter option and build from there. You’ll save time and effort and still come away with a working business plan.
Plus, you’ll better understand what further planning you may need to do. And you won’t be starting from scratch.
Read More: How to identify the right type of plan for your business
Again, the type of business plan you need fully depends on your situation and use case. But running through this quick exercise will help you narrow down your options.
Now let’s look at the common business plan types you can choose from.

- Traditional business plan
The traditional (or standard) business plan is an in-depth document covering every aspect of your business. It’s the most common plan type you’ll come across.
A traditional business plan is broken up into 10 sections:
- Executive summary
- Description of products and services
- Market analysis
- Competitive analysis
- Marketing and sales plan
- Business operations
- Key milestones and metrics
- Organization and management team
- Financial plan
- Appendix
Why use this type of plan?
A traditional business plan is best for anyone approaching specific business planning events—such as presenting a business plan to a bank or investor for funding.
A traditional plan can also be useful if you need to add more details around specific business areas.
For example: You start as a solopreneur and don’t immediately need to define your team structure. But eventually you hit a threshold where you need more staff in order to keep growing. A great way to explore which roles you need and how they will function is by fleshing out the organization and management section .
That’s the unseen value of a more detailed plan like this. While you can follow the structure outlined above and create an in-depth plan ready for funding, you can also choose which sections to prioritize.
Read More: How to write a traditional business plan
- One-page plan
The one-page business plan is a simplified (but just as useful) version of a traditional business plan. It follows the same structure, but is far easier to create. It can even be used as a pitch document.
Here’s how you’ll organize information when using a one-page plan:
- Value proposition
- Market need
- Your solution
- Competition
- Target market
- Sales and marketing
- Budget and sales goals
- Team summary
- Key partners
- Funding needs
A one-page plan is faster and easier to assemble than a traditional plan. You can write a one-page plan in as little as 30 minutes .
You’ll still cover the crucial details found in a traditional plan, but in a more manageable format.
So, if you’re exploring a business idea for the first time or updating your strategy—a one-page plan is ideal. You can review and update your entire plan in just a few minutes.
Applying for a loan with this type of plan probably wouldn’t make sense. Lenders typically want to see a more detailed plan to accurately assess potential risk.
However, it is a great option to send to investors.
“Investors these days are much less likely to look at a detailed plan,” says Palo Alto Software COO Noah Parsons. “An executive summary or one-page plan, pitch presentation, and financials are all a VC is likely to look at.”
Creating a more detailed plan is as much about being prepared as anything else. If you don’t dig into everything a traditional plan covers, you’ll struggle to land your pitch .
If you don’t intend to seek funding, a one-page plan is often all you need. The key is regularly revisiting it to stay on top of your business.
Let’s explore two unique processes to help you do that:
Read More: How to write a one-page business plan
Lean planning process
Lean planning is a process that uses your one-page plan as a testing tool. The goal is to create a plan and immediately put it into action to see if your ideas actually work. You’ll typically be focusing on one (or all) of the following areas:
- Strategy – What you will do
- Tactics – How you will do it
- Business Model – How you make money
- Schedule – Who is responsible and when will it happen
Why use this process?
Lean planning is best for businesses that need to move fast, test assumptions, revise, and get moving again. It’s short and simple, and meant to get everyone on the same page as quickly as possible.
That’s why it’s so popular for startups. They don’t necessarily need a detailed plan, since they’re mostly focused on determining whether or not they have a viable business idea .
The only drawback is that this planning process is built primarily around early-stage businesses. It can be a useful tool for established businesses looking to test a strategy, but it may not be as helpful for ongoing management.
Read More: The fundamentals of lean planning
Growth planning
Growth planning is a financials-focused planning process designed to help you make quick and strategic decisions.
Again, it starts with a one-page plan outlining your strategy, tactics, business model, and schedule. The next step is to create a working financial forecast that includes projected sales, expenses, and cash flows.
From there, you run your business.
As you go, track your actual financial performance and carve out time to compare it to your forecasts . If you spot any differences, these discrepancies may indicate problems or opportunities that call for adjusting your current strategy.
Growth planning combines the simplicity of the one-page plan and the speed of lean planning, with the power of financial forecasting.
This makes the process useful for every business stage and even allows you to skip to the forecasting step if you already have a plan.
With growth planning, you’ll:
- Regularly revisit your financials
- Better understand how your business operates
- Make quick and confident decisions
This process focuses on growing your business. If diving into your financials isn’t a priority right now, that’s okay. Start with a one-page plan instead, and revisit growth planning when you’re ready.
Read More: How to write a growth-oriented business plan
- Internal plan
Sometimes you just need a business plan that works as an internal management tool.
Something to help you:
- Set business goals
- Provide a high-level overview of operations
- Prepare to create budgets and financial projections
You don’t need an overly long and detailed business plan for this. Just a document that is easy to create, useful for developing or revisiting your strategy, and able to get everyone up to speed.
The internal plan is a great option if you’re not planning to present your plan to anyone outside your business. Especially if you’re an up-and-running business that may have created a plan previously. You might just need something simple for day-to-day use.
Read More: 8 steps to write a useful internal business plan
- 5-year business plan
Some investors or stakeholders may request a long-term plan stretching up to five years. They typically want to understand your vision for the future and see your long-term goals or milestones.
To be honest, creating a detailed long-term business plan is typically a waste of time. There are a few exceptions:
- A long-term plan is specifically asked for
- You want to outline your long-term vision
- Real estate development
- Medical product manufacturing
- Transportation, automotive, aviation, or aerospace development
The reality is, you can’t predict what will happen in the next month, let alone the next one, three, or five years.
So, when creating a long-term plan, don’t dig too deep into the details. Focus on establishing long-term goals , annual growth targets, and aspirational milestones you’d like to hit.
Then supplement these with a more focused one-page plan that actually describes your current business, which you can use in your business right now.
Read More: How to write a five-year business plan
- Nonprofit business plan
A nonprofit business plan is not too different from a traditional plan. You should still cover all of the sections I listed above to help you build a sustainable business.
The main differences in a nonprofit plan are tied to funding and awareness. You need to account for:
- Fundraising sources and activities.
- Alliances and partnerships.
- Promotion and outreach strategies.
You also need to set goals, track performance, and demonstrate that you have the right team to run a fiscally healthy organization. You’re just not pursuing profits, you’re trying to fulfill a mission. But you cannot serve your community if your organization isn’t financially stable.
If you can use your business plan to show that you’re a well-organized nonprofit organization, you are more likely to attract donors and convince investors to provide funding.
Read More: How to write a nonprofit business plan
Resources to help write your business plan
Don’t get too hung up on the type of business plan you choose. Remember, you can always start small and expand if you need to.
To help you do that, I recommend downloading our free one-page business plan template . It’s especially useful if you’re exploring an idea and need a quick way to document how your business will operate.
If you know you’ll pursue funding, download our free traditional business plan template . It’s already in an SBA-lender-approved format and provides detailed instructions for each section. And if you want to explore other options, check out our roundup of the 8 best business plan templates you can download for free.
Lastly, check out our library of over 550 sample business plans if you need inspiration. These can provide specific insight into what you should focus on in a given industry.
Remember, just by deciding to write a business plan, you are increasing your likelihood of success. Pick a format and start writing!
Types of business plans FAQ
Which type of planning should be done for a business?
The type of planning fully depends on your business stage and how you intend to use the plan. Generally, whatever format you choose should help you outline your strategy, business model, tactics, and timeline.
How many types of business plans are there?
There are seven common types of business plans, including: traditional, one-page, lean, growth, internal, 5-year, and nonprofit plans.
See why 1.2 million entrepreneurs have written their business plans with LivePlan
Tim Berry is the founder and chairman of Palo Alto Software , a co-founder of Borland International, and a recognized expert in business planning. He has an MBA from Stanford and degrees with honors from the University of Oregon and the University of Notre Dame. Today, Tim dedicates most of his time to blogging, teaching and evangelizing for business planning.
.png?format=auto)
Table of Contents
- Plan writing resources
Related Articles

16 Min. Read
How to Write a Mission Statement + 10 Great Examples

12 Min. Read
How to Write a Food Truck Business Plan (2024 + Template)

6 Min. Read
How to Write a Fast Food Restaurant Business Plan + Free Template

7 Min. Read
How to Write a Brewery Business Plan + Free Sample Plan
The Bplans Newsletter
The Bplans Weekly
Subscribe now for weekly advice and free downloadable resources to help start and grow your business.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Setting up in the UK
- Start-up business
- A growing business
- Maturing company considering exit strategy
- An individual
- Bookkeeping & accounting
- Choosing the right structure
- Corporate finance
- Forensic accounting & litigation
- Mergers, acquisitions & disposals
- Profit & cashflow forecasting
- Raising finance
- Share schemes
- Strategic planning
- Corporate tax planning
- Estate planning
- Personal tax planning
- R&D tax credits
- Self assessment
- The patent box
- Trust & executorships
- VAT planning and compliance
- Agriculture
- Contracting
- Estate & letting agents
- Family enterprise
- Hospitality
- Legal practices
- Pension schemes
- Property & construction
- Our Approach
- There are no suggestions because the search field is empty.
In this post we cover:
A business plan is used to help manage an organisation by stating ambitions, how they will be achieved, and exactly when. The plan will also help summarise what the business is about, why it exists, and where it will get to.
Your business plan will serve as a key point of reference for investors, partners, employees and management to gauge progress against objectives.
Provide a road map
A detailed plan will help you as the owner and founder to manage your business effectively. Writing down and illustrating both your ideas and tactics will establish a path and course of action, akin to a road map. This will give you something concrete by which to monitor and assess the progress you make.
It may seem like an odd suggestion but you should look to work with your accountant on this task even at an early stage. Why? Well, a quality professional advisor will have helped many early stage businesses. Given how close a good accountant is to the operations and strategic direction of a company, they’ll be able to draw upon their experience of what’s worked and what hasn’t with other clients.
This means they’ll be well placed to help you test your assumptions. Remember you want your business concept to be as well thought through as possible. Having a fresh set of eyes reviewing your ideas from a different perspective could make all the difference as to the viability of your business model . An accountant will know what success looks like along with what’s required and when to achieve it.
In charting a potential course of action you may find your business is faced with multiple different potential paths. It would therefore be wise to plot the most likely scenarios and strategies for these different circumstances. If, for example, your business is heavily reliant upon exporting then you may need to consider potential global and political events. How would that impact on currencies in your chosen markets in the near future?
What does a 10% currency appreciation or depreciation mean for sales, revenues, profits and cashflow? Working through this with your accountant will ensure you can ascertain the impact of such events from a financial perspective. You’ll then be able to craft solutions accordingly to deal with such events.
Developing a clear plan and strategy will focus your mind. What resources will you need and when to achieve each of your goals? This provides you with clarity as to how much needs to be invested at each stage of the business lifecycle . You'll then know when you're going to need cash injections based on likely cashflow.
Understand what to focus on
As an entrepreneur, where should your efforts and concentrations be centred on? It’s a common issue. The early days of starting out can be very chaotic. There’s so much to set up, think about, implement and develop. It’s an emotional roller coaster of mass excitement and sharp shots of anxiety. Amid all this and with an ever mounting in-tray of to do’s, you can fast lose track of what’s important.
When writing a business plan you’re defining exactly what your organisation is today and then intends to become tomorrow. This coherence concerning the purpose of your business and direction in which you’re heading is invaluable. Doing this means you’ll understand what needs to be implemented to move forward.
As an example, your plan should describe your ideal customer and include their needs and wants. Then you’d expand on this as to how your products or services address their requirements. How are you going to market to these potential customers? How will you get your name out there? What approach will you adopt to make sales and generate revenue?
These are vital matters to address early on. Growth primarily comes through new customers and achieving repeat custom. This then determines your progress towards profitability. By mapping this all out on paper you’re giving yourself yardsticks to work towards. This means all tasks that you as the entrepreneur should focus on should be geared towards achieving your next goal. In a nutshell that’s where your focus should be.
Projections and the need for an accountant
Raise finance.
The likelihood is to support your growth will require an injection of funding. That's unless you have an extremely cash generative business model. More often than not you probably won’t have enough customers and thus free cash flow to finance the next opportunity. You'll have a working capital requirement and thus need investment beyond the reach of your business.
You’ll likely have to approach potential sources of finance and they’ll want to assess the your income statements/profit and loss statements, and business plan. If you’re still at concept stage, or haven’t begun making sales, then their decision will rest solely on the strength of you and your business plan.
The statements help prospective lenders and investors understand the history of the organisation to date. The business plan provides them with a view of your future direction. They’ll look for many things in your plan. Ultimately their interest will focus on whether the expansion or development of your business will generate sufficient cash to both operate effectively while also fulfilling debt obligations.
This means you’re going to need to detail both profit and cashflow projections. Good forecasting and planning is seen as a way of understanding income and expenditure. This is particularly useful as a means to prevent payment issues over things like suppliers and staff wages. Many businesses close when such issues arise.
The likelihood is unless you’ve done this before, and know what you’re doing, then you’re going to need the help of an accountant. They’ll work with you to model the probable amount of cash in the business over time. This will then act as evidence to potential investors and financiers. They'll see if sufficient money will be generated by the activities of the business, to both fund future growth, while meeting financial commitments.
Manage your business effectively
The usefulness of a cashflow forecast doesn’t end there though. Managing your cash position , as you may have already gathered, is fundamental to the long term future of your business. There’s a common quote that “most businesses fail because they run out of money”. This means they’re no longer able to pay their debts when they’re due.
You should reference your cashflow projections in your business plan regularly. When you invest in your business, there will be significant out flows of money before any cash comes in. The timing of your investments thus needs to be considered against your projections and statements. Consider trading patterns, seasonal variations and the likely impact on cash flows.
If, for example, you sell through a credit extension then you’re going to receive payment in the future. That means after the goods or services have changed hands. The likelihood then is you’ll have to make payments in relation to the usual operations of your business before that income comes in from your customer.
So you can then see how poor cash management creates real issues. Make sure you work with your accountant, in the creation of your business plan and monitoring performance in relation to it. The documentation of well thought through ideas, combined with a shrewd strategy, and carefully planned projections will markedly improve your chances of long term survival and growth.

This post was created on 03/11/2016 and updated on 24/02/2022.
Please be aware that information provided by this blog is subject to regular legal and regulatory change. We recommend that you do not take any information held within our website or guides (eBooks) as a definitive guide to the law on the relevant matter being discussed. We suggest your course of action should be to seek legal or professional advice where necessary rather than relying on the content supplied by the author(s) of this blog.

Related posts -
Leave a comment -, subscribe to email updates, popular posts, posts by topic.
- Business insight (78)
- Personal Tax (48)
- Hospitality (44)
- Tax developments (42)
Click below for office location details
Wellers London
Wellers Oxford
Wellers Thame
Wellers Banbury
- Business Services
- Specialist Sectors
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
subscribe to newsletter
Connect with us.

The 10 Key Components of a Business Plan
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Over the past 20+ years, we have helped over 1 million entrepreneurs and business owners write business plans. These plans have been used to raise funding and grow countless businesses.
Download our Ultimate Business Plan Template here >
From working with all these businesses, we know what the 10 elements in any great business plan. Providing a comprehensive assessment of each of these components is critical in attracting lenders, angel investors, venture capitalists or other equity investors.
Get started with a title page that includes your company name, logo and contact information, since interested readers must have a simple way to find and reach out to you. After that be sure to include the 10 parts of a business plan documented below.
What are the 10 Key Components of a Business Plan?
The 10 sections or elements of a business plan that you must include are as follows:
1. Executive Summary
The executive summary provides a succinct synopsis of the business plan, and highlights the key points raised within. It often includes the company’s mission statement and description of the products and services. It’s recommended by me and many experts including the Small Business Administration to write the executive summary last.
The executive summary must communicate to the prospective investor the size and scope of the market opportunity, the venture’s business and profitability model, and how the resources/skills/strategic positioning of the company’s management team make it uniquely qualified to execute the business plan. The executive summary must be compelling, easy-to-read, and no longer than 2-4 pages.
2. Company Analysis
This business plan section provides a strategic overview of the business and describes how the company is organized, what products and services it offers/will offer, and goes into further detail on the business’ unique qualifications in serving its target markets. As any good business plan template will point out, your company analysis should also give a snapshot of the company’s achievements to date, since the best indicator of future success are past accomplishments.
3. Industry or Market Analysis
This section evaluates the playing field in which the company will be competing, and includes well-structured answers to key market research questions such as the following:
- What are the sizes of the target market segments?
- What are the trends for the industry as a whole?
- With what other industries do your services compete?
To conduct this market research, do research online and leverage trade associations that often have the information you need.
4. Analysis of Customers
The customer analysis business plan section assesses the customer segment(s) that the company serves. In this section, the company must convey the needs of its target customers. It must then show how its products and services satisfy these needs to an extent that the customer will pay for them.
The following are examples of customer segments: moms, engaged couples, schools, online retailers, teens, baby boomers, business owners, etc.
As you can imagine, the customer segment(s) you choose will have a great impact on the type of business you operate as different segments often have different needs. Try to break out your target customers in terms of their demographic and psychographic profiles. With regards to demographics, including a discussion of the ages, genders, locations and income levels of the customers you seek to serve. With regards to psychographic variables, discuss whether your customers have any unique lifestyles, interests, opinions, attitudes and/or values that will help you market to them more effectively.
5. Analysis of Competition
All capable business plan writers discuss the competitive landscape of your business. This element of your plan must identify your direct and indirect competitors, assesses their strengths and weaknesses and delineate your company’s competitive advantages. It’s a crucial business plan section.
Direct competitors are those that provide the same product or service to the same customer. Indirect competitors are those who provide similar products or services. For example, the direct competitors to a pizza shop are other local pizza shops. Indirect competitors are other food options like supermarkets, delis, other restaurants, etc.
The first five components of your business plan provide an overview of the business opportunity and market research to support it. The remaining five business plan sections focus mainly on strategy, primarily the marketing, operational, financial and management strategies that your firm will employ.
6. Marketing, Sales & Product Plan
The marketing and sales plan component of your business plan details your strategy for penetrating the target markets. Key elements include the following:
- A description of the company’s desired strategic positioning
- Detailed descriptions of the company’s product and service offerings and potential product extensions
- Descriptions of the company’s desired image and branding strategy
- Descriptions of the company’s promotional strategies
- An overview of the company’s pricing strategies
- A description of current and potential strategic marketing partnerships/ alliances
7. Operations Strategy, Design and Development Plans
These sections detail the internal strategies for building the venture from concept to reality, and include answers to the following questions:
- What functions will be required to run the business?
- What milestones must be reached before the venture can be launched?
- How will quality be controlled?
8. Management Team
The management team section demonstrates that the company has the required human resources to be successful. The business plan must answer questions including:
- Who are the key management personnel and what are their backgrounds?
- What management additions will be required to make the business a success?
- Who are the other investors and/or shareholders, if any?
- Who comprises the Board of Directors and/or Board of Advisors?
- Who are the professional advisors (e.g., lawyer, accounting firm)?
9. Financial Plan
The financial plan involves the development of the company’s revenue and profitability model. These financial statements detail how you generate income and get paid from customers,. The financial plan includes detailed explanations of the key assumptions used in building the business plan model, sensitivity analysis on key revenue and cost variables, and description of comparable valuations for existing companies with similar business models.
One of the key purposes of your business plan is to determine the amount of capital the firm needs. The financial plan does this along with assessing the proposed use of these funds (e.g., equipment, working capital, labor expenses, insurance costs, etc.) and the expected future earnings. It includes Projected Income Statements, Balance Sheets (showing assets, liabilities and equity) and Cash Flow Statements, broken out quarterly for the first two years, and annually for years 1-5.
Importantly, all of the assumptions and projections in the financial plan must flow from and be supported by the descriptions and explanations offered in the other sections of the plan. The financial plan is where the entrepreneur communicates how he/she plans to “monetize” the overall vision for the new venture. Note that in addition to traditional debt and equity sources of startup and growth funding that require a business plan (bank loans, angel investors, venture capitalists, friends and family), you will probably also use other capital sources, such as credit cards and business credit, in growing your company.
10. Appendix
The appendix is used to support the rest of the business plan. Every business plan should have a full set of financial projections in the appendix, with the summary of these financials in the executive summary and the financial plan. Other documentation that could appear in the appendix includes technical drawings, partnership and/or customer letters, expanded competitor reviews and/or customer lists.
Find additional business plan help articles here.
Expertly and comprehensively discussing these components in their business plan helps entrepreneurs to better understand their business opportunity and assists them in convincing investors that the opportunity may be right for them too.
In addition to ensuring you included the proper elements of a business plan when developing your plan always think about why you are uniquely qualified to succeed in your business. For example, is your team’s expertise something that’s unique and can ensure your success? Or is it marketing partnerships you have executed? Importantly, if you don’t have any unique success factors, think about what you can add to make your company unique. Doing so can dramatically improve your success. Also, whether you write it on a word processor or use business plan software , remember to update your plan at least annually. After several years, you should have several business plans you can review to see what worked and what didn’t. This should prove helpful as you create future plans for your company’s growth.
Download The 10 Key Components of a Business Plan Here
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies that have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink business plan consultants can create your business plan for you.
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

Do you REALLY need a business plan?
The top three questions that I get asked most frequently as a professional business plan writer will probably not surprise you:
- What is the purpose of a business plan – why is it really required?
- How is it going to benefit my business if I write a business plan?
- Is a business plan really that important – how can I actually use it?
Keep reading to get my take on what the most essential advantages of preparing a business plan are—and why you may (not) need to prepare one.
The importance, purpose and benefit of a business plan is in that it enables you to validate a business idea, secure funding, set strategic goals – and then take organized action on those goals by making decisions, managing resources, risk and change, while effectively communicating with stakeholders.
Let’s take a closer look at how each of the important business planning benefits can catapult your business forward:
1. Validate Your Business Idea
The process of writing your business plan will force you to ask the difficult questions about the major components of your business, including:
- External: industry, target market of prospective customers, competitive landscape
- Internal: business model, unique selling proposition, operations, marketing, finance
Business planning connects the dots to draw a big picture of the entire business.
And imagine how much time and money you would save if working through a business plan revealed that your business idea is untenable. You would be surprised how often that happens – an idea that once sounded so very promising may easily fall apart after you actually write down all the facts, details and numbers.
While you may be tempted to jump directly into start-up mode, writing a business plan is an essential first step to check the feasibility of a business before investing too much time and money into it. Business plans help to confirm that the idea you are so passionate and convinced about is solid from business point of view.
Take the time to do the necessary research and work through a proper business plan. The more you know, the higher the likelihood that your business will succeed.
2. Set and Track Goals
Successful businesses are dynamic and continuously evolve. And so are good business plans that allow you to:
- Priorities: Regularly set goals, targets (e.g., sales revenues reached), milestones (e.g. number of employees hired), performance indicators and metrics for short, mid and long term
- Accountability: Track your progress toward goals and benchmarks
- Course-correction: make changes to your business as you learn more about your market and what works and what does not
- Mission: Refer to a clear set of values to help steer your business through any times of trouble
Essentially, business plan is a blueprint and an important strategic tool that keeps you focused, motivated and accountable to keep your business on track. When used properly and consulted regularly, it can help you measure and manage what you are working so hard to create – your long-term vision.
As humans, we work better when we have clear goals we can work towards. The everyday business hustle makes it challenging to keep an eye on the strategic priorities. The business planning process serves as a useful reminder.
3. Take Action
A business plan is also a plan of action . At its core, your plan identifies where you are now, where you want your business to go, and how you will get there.
Planning out exactly how you are going to turn your vision into a successful business is perhaps the most important step between an idea and reality. Success comes not only from having a vision but working towards that vision in a systematic and organized way.
A good business plan clearly outlines specific steps necessary to turn the business objectives into reality. Think of it as a roadmap to success. The strategy and tactics need to be in alignment to make sure that your day-to-day activities lead to the achievement of your business goals.
4. Manage Resources
A business plan also provides insight on how resources required for achieving your business goals will be structured and allocated according to their strategic priority. For example:
Large Spending Decisions
- Assets: When and in what amount will the business commit resources to buy/lease new assets, such as computers or vehicles.
- Human Resources: Objectives for hiring new employees, including not only their pay but how they will help the business grow and flourish.
- Business Space: Information on costs of renting/buying space for offices, retail, manufacturing or other operations, for example when expanding to a new location.
Cash Flow It is essential that a business carefully plans and manages cash flows to ensure that there are optimal levels of cash in the bank at all times and avoid situations where the business could run out of cash and could not afford to pay its bills.
Revenues v. Expenses In addition, your business plan will compare your revenue forecasts to the budgeted costs to make sure that your financials are healthy and the business is set up for success.
5. Make Decisions
Whether you are starting a small business or expanding an existing one, a business plan is an important tool to help guide your decisions:
Sound decisions Gathering information for the business plan boosts your knowledge across many important areas of the business:
- Industry, market, customers and competitors
- Financial projections (e.g., revenue, expenses, assets, cash flow)
- Operations, technology and logistics
- Human resources (management and staff)
- Creating value for your customer through products and services
Decision-making skills The business planning process involves thorough research and critical thinking about many intertwined and complex business issues. As a result, it solidifies the decision-making skills of the business owner and builds a solid foundation for strategic planning , prioritization and sound decision making in your business. The more you understand, the better your decisions will be.
Planning Thorough planning allows you to determine the answer to some of the most critical business decisions ahead of time , prepare for anticipate problems before they arise, and ensure that any tactical solutions are in line with the overall strategy and goals.
If you do not take time to plan, you risk becoming overwhelmed by countless options and conflicting directions because you are not unclear about the mission , vision and strategy for your business.
6. Manage Risk
Some level of uncertainty is inherent in every business, but there is a lot you can do to reduce and manage the risk, starting with a business plan to uncover your weak spots.
You will need to take a realistic and pragmatic look at the hard facts and identify:
- Major risks , challenges and obstacles that you can expect on the way – so you can prepare to deal with them.
- Weaknesses in your business idea, business model and strategy – so you can fix them.
- Critical mistakes before they arise – so you can avoid them.
Essentially, the business plan is your safety net . Naturally, business plan cannot entirely eliminate risk, but it can significantly reduce it and prepare you for any challenges you may encounter.
7. Communicate Internally
Attract talent For a business to succeed, attracting talented workers and partners is of vital importance.
A business plan can be used as a communication tool to attract the right talent at all levels, from skilled staff to executive management, to work for your business by explaining the direction and growth potential of the business in a presentable format.
Align performance Sharing your business plan with all team members helps to ensure that everyone is on the same page when it comes to the long-term vision and strategy.
You need their buy-in from the beginning, because aligning your team with your priorities will increase the efficiency of your business as everyone is working towards a common goal .
If everyone on your team understands that their piece of work matters and how it fits into the big picture, they are more invested in achieving the objectives of the business.
It also makes it easier to track and communicate on your progress.
Share and explain business objectives with your management team, employees and new hires. Make selected portions of your business plan part of your new employee training.
8. Communicate Externally
Alliances If you are interested in partnerships or joint ventures, you may share selected sections of your plan with the potential business partners in order to develop new alliances.
Suppliers A business plan can play a part in attracting reliable suppliers and getting approved for business credit from suppliers. Suppliers who feel confident that your business will succeed (e.g., sales projections) will be much more likely to extend credit.
In addition, suppliers may want to ensure their products are being represented in the right way .
Professional Services Having a business plan in place allows you to easily share relevant sections with those you rely on to support the organization, including attorneys, accountants, and other professional consultants as needed, to make sure that everyone is on the same page.
Advisors Share the plan with experts and professionals who are in a position to give you valuable advice.
Landlord Some landlords and property managers require businesses to submit a business plan to be considered for a lease to prove that your business will have sufficient cash flows to pay the rent.
Customers The business plan may also function as a prospectus for potential customers, especially when it comes to large corporate accounts and exclusive customer relationships.
9. Secure Funding
If you intend to seek outside financing for your business, you are likely going to need a business plan.
Whether you are seeking debt financing (e.g. loan or credit line) from a lender (e.g., bank or financial institution) or equity capital financing from investors (e.g., venture or angel capital), a business plan can make the difference between whether or not – and how much – someone decides to invest.
Investors and financiers are always looking at the risk of default and the earning potential based on facts and figures. Understandably, anyone who is interested in supporting your business will want to check that you know what you are doing, that their money is in good hands, and that the venture is viable in the long run.
Business plans tend to be the most effective ways of proving that. A presentation may pique their interest , but they will most probably request a well-written document they can study in detail before they will be prepared to make any financial commitment.
That is why a business plan can often be the single most important document you can present to potential investors/financiers that will provide the structure and confidence that they need to make decisions about funding and supporting your company.
Be prepared to have your business plan scrutinized . Investors and financiers will conduct extensive checks and analyses to be certain that what is written in your business plan faithful representation of the truth.
10. Grow and Change
It is a very common misconception that a business plan is a static document that a new business prepares once in the start-up phase and then happily forgets about.
But businesses are not static. And neither are business plans. The business plan for any business will change over time as the company evolves and expands .
In the growth phase, an updated business plan is particularly useful for:
Raising additional capital for expansion
- Seeking financing for new assets , such as equipment or property
- Securing financing to support steady cash flows (e.g., seasonality, market downturns, timing of sale/purchase invoices)
- Forecasting to allocate resources according to strategic priority and operational needs
- Valuation (e.g., mergers & acquisitions, tax issues, transactions related to divorce, inheritance, estate planning)
Keeping the business plan updated gives established businesses better chance of getting the money they need to grow or even keep operating.
Business plan is also an excellent tool for planning an exit as it would include the strategy and timelines for a transfer to new ownership or dissolution of the company.
Also, if you ever make the decision to sell your business or position yourself for a merger or an acquisition , a strong business plan in hand is going to help you to maximize the business valuation.
Valuation is the process of establishing the worth of a business by a valuation expert who will draw on professional experience as well as a business plan that will outline what you have, what it’s worth now and how much will it likely produce in the future.
Your business is likely to be worth more to a buyer if they clearly understand your business model, your market, your assets and your overall potential to grow and scale .
Related Questions
Business plan purpose: what is the purpose of a business plan.
The purpose of a business plan is to articulate a strategy for starting a new business or growing an existing one by identifying where the business is going and how it will get there to test the viability of a business idea and maximize the chances of securing funding and achieving business goals and success.
Business Plan Benefits: What are the benefits of a business plan?
A business plan benefits businesses by serving as a strategic tool outlining the steps and resources required to achieve goals and make business ideas succeed, as well as a communication tool allowing businesses to articulate their strategy to stakeholders that support the business.
Business Plan Importance: Why is business plan important?
The importance of a business plan lies in it being a roadmap that guides the decisions of a business on the road to success, providing clarity on all aspects of its operations. This blueprint outlines the goals of the business and what exactly is needed to achieve them through effective management.
Sign up for our Newsletter
Get more articles just like this straight into your mailbox.
Related Posts
Recent Posts
10 Characteristics Of A Business Plan, its Functions, Features and Benefits
We explain what a business plan is, its functions, and the benefits it provides. Also, what are its features and methods it uses?
What is a business plan?
A business plan is a written document that expresses a formal declaration of the objectives of the initiatives that a company has in the projection and evaluation phase.
These initiatives can be new projects within the company's activities or the start of the company itself. Therefore, a business plan describes a series of interrelated activities aimed at achieving certain goals.
This allows a planning of the tasks and the evaluation of the resources that will be necessary to achieve those goals (for example, resorting to banks or investors for financing).
In addition, its function is to transmit to current or potential investors (investors, shareholders, financiers, etc.) how the investment will be recovered and the guarantees they have. It differs from an investment project in that a business plan is more focused on the strategies that will be carried out.
Characteristics of a business plan :
Flexibility.

- It allows errors to be detected and difficulties to be anticipated before the start of the investment . In this way solutions can be planned.
- By including the economic and financial forecast of the business, it facilitates access to bank financing, as well as attracting new partners and collaborators.
- It allows the measurement of results of each stage, through short and medium-term goals that allow establishing measurement criteria.
- It allows detecting the most promising business opportunities in terms of markets of interest, products and services.
- It allows an evaluation of the company's situation in the context of its competitors, and the identification of tasks and areas that need improvement.
- It facilitates the rational use of resources, including personnel, since planning facilitates the assignment of responsibilities and coordinated work .
- Once the goals of the company have been established, it allows evaluating various strategies according to their effectiveness .
- Establishes the financial framework.
Executive Summary

After the cover and table of contents, the executive summary gives an overall impression of the project . For that, you must highlight the key data of the same and include all the relevant information .
Among this information should not be missing the needs and objectives of the business , the advantages offered by the product or service and the opportunity offered by the market, as well as the history of the company and its management team.
Most of this information will be expanded upon in the rest of the document.
Insertion in the market
The projected product or service must be described in detail and its possible insertion in the market explained. For that, it is necessary to make a comparison with similar products or services that already exist in the market.
The project arises to cover an existing need in the market, which is why potential consumers must be identified and what advantages or weak points they will find in the proposed product or service.
The relationship between the product and the market must include a SWOT analysis (strengths, opportunities, weaknesses, threats).
Market Characteristics

Once the market that will be the context of the business has been identified, said market is described in depth. This includes:
- Size, rate of growth and potential benefits offered.
- What segments does it include?
- Locate it geographically.
- Identify possible competitors, substitutes and complements.
- Define means of audience research.
It details who makes up the management team , but also the characteristics of the work team: how the company will be managed, the history of the personnel involved, the general experience of the company, the various areas of management, sales, stock control and quality.
Marketing plan
Promotional strategies are described, taking into account "the four P's" : product , price, advertising , points of sale.
Business system and schedule

All the necessary steps are described from the manufacture of the product to the moment of purchase or completion of the service. It includes the areas of human resources , sales, commercial, management and organizational culture .
The schedule must specify when each of the necessary steps will be activated (hiring or relocation of personnel, start of production, purchase of raw material , etc.).

The accounting-financial area allows detailing the structure and composition of social capital , as well as calculating capital flows and valuing the investment.
Sources of income are analyzed and a plan is created that determines how profits and losses will be managed . If it is a search for risk capital, what are exit alternatives for investors should be included?
The above content published at Collaborative Research Group is for informational and educational purposes only and has been developed by referring to reliable sources and recommendations from technology experts. We do not have any contact with official entities nor do we intend to replace the information that they emit.
Luke Wigman
Luke is passionate about fostering student involvement and connection. He studied psychology for his major and likes learning about the past. Luke aims to specialize in artificial intelligence and cybersecurity. .
Leave a reply
Social media, entertainment, recent post.

Sport: What Is It, Types, Risks, Features, Characteristics and Examples

Dogs: Emergence, Features, Characteristics, Feeding and Breeds

Story: Definition, Elements, Structure, Features and Characteristics

Essay: Definition, Structure, Features, Characteristics, How to Do It

Narrative Text: What It Is, Structure, Features, Characteristics and Examples
Module 1: Role of Business
Functional areas of business, learning objectives.
- Identify the primary functional areas within a business
- Identify key people and explain the activities within each functional area

One of the reasons for separating business operations into functional areas is to allow each to operate within its area of expertise, thus building efficiency and effectiveness across the business as a whole. Functional areas in a business vary according to the nature of the market and the size of the business. For example, manufacturing companies like Nike and Apple have significant Research and Development (R&D) departments in order to stay in the lead in their respective business segments. On the other hand, retail companies may have no R&D functional area per se, but will be heavily invested in Operations areas surrounding Supply Chain Management.
In general, the key functional areas of a business are the following:
Marketing/Sales
- Research and Development
Each of these functional areas is represented in the following organization chart.

The primary role of managers in business is to supervise other people’s performance. Most management activities fall into the following categories:
- Planning : Managers plan by setting long-term goals for the business, as well as short-term strategies needed to execute those goals.
- Organizing: Managers are responsible for organizing the operations of a business in the most efficient way—enabling the business to use its resources effectively.
- Controlling: A large percentage of a manager’s time is spent controlling the activities within the business to ensure that it’s on track to achieve its goals. When people or processes stray from the path, managers are often the first ones to notice and take corrective action.
- Leading : Managers serve as leaders for the organization, in practical as well as symbolic ways. The manager may lead work teams or groups through a new process or the development of a new product. The manager may also be seen as the leader of the organization when it interacts with the community, customers, and suppliers.
Operations is where inputs, or factors of production, are converted to outputs, which are goods and services. Operations is the heart of a business—providing goods and services in a quantity and of a quality that meets the needs of the customers. Operations controls the supply chain, including procurement and logistics.
Marketing consists of all that a company does to identify customers’ needs and design products and services that meet those needs. The marketing function also includes promoting goods and services, determining how the goods and services will be delivered and developing a pricing strategy to capture market share while remaining competitive. In today’s technology-driven business environment, marketing is also responsible for building and overseeing a company’s Internet presence (e.g., the company website, blogs, social media campaigns, etc.). Today, social media marketing is one of the fastest growing sectors within the marketing function.
The goal of Sales is to close the revenue the company needs in order to operate profitably, especially in B2B businesses. Again, depending on the nature of the market and the company size, Sales functional areas can vary in structure and approach: inside/outside representation, vertical/horizontal focus, direct, etc. Sales works to exploit the leads created by Marketing and activities generated by the sales force itself.
The Finance function involves planning for, obtaining, and managing a company’s funds. Finance managers plan for both short-term and long-term financial capital needs and analyze the impact that borrowing will have on the financial well-being of the business. A company’s finance department answers questions about how funds should be raised (loans vs. stocks), the long-term cost of borrowing funds, and the implications of financing decisions for the long-term health of the business.
Accounting is a crucial part of the Finance functional area. Accountants provide managers with information needed to make decisions about the allocation of company resources. This area is ultimately responsible for accurately representing the financial transactions of a business to internal and external parties, government agencies, and owners/investors. Financial accountants are primarily responsible for the preparation of financial statements to help entities both inside and outside the organization assess the financial strength of the company. Managerial accountants provide information regarding costs, budgets, asset allocation, and performance appraisal for internal use by management for the purpose of decision-making.
Key People Within Functional Areas
Here is an example of the functional areas of a large technology manufacturing corporation and the key functions and people within.
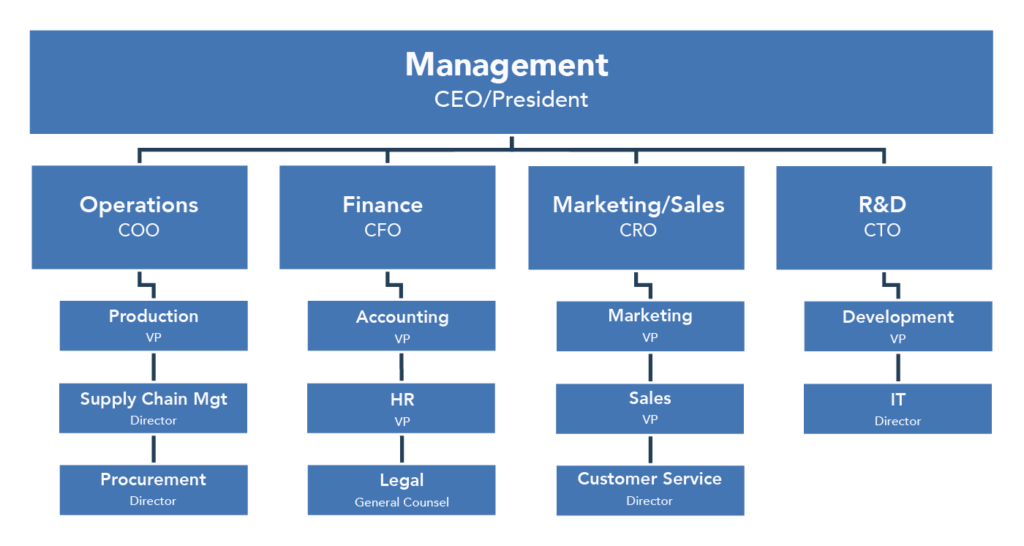
The Management functional area in most large corporations is led by the Chief Executive Officer (CEO). Depending on company size, there may be a President in position as well.
The Operations functional area is managed by the Chief Operations Officer (COO). In this example, Operations consists of Production, led by a Vice President (VP), a Supply Chain department, and a Procurement area with Director-level people in charge.
The Finance functional area is led by the Chief Financial Officer (CFO), who is one of the most important “C-level” executives. In addition to running Finance and Accounting, the CFO is responsible for reporting company results to the financial community. Finance also contains Human Resources (HR) in many companies and the Legal department as well. It is common for the CFO to have VPs of HR, Accounting, and Legal as direct reports. HR contains functions like employee training, compensation and benefits, and recruiting. Accounting has multiple functions, such as Accounts Payable, Receivable, record-keeping, and cash flow. The Legal department is responsible for contracts, copyrights, and various negotiations on behalf of the company.
The Marketing/Sales functional area is managed by the Chief Revenue Officer (CRO), which is a relatively new addition to C-level executives. The CRO may have a Sales VP and Marketing VP as direct reports, but in some cases, the CRO may act as VP of Sales or Marketing. This functional area may also contain Customer Service (and Support) with a Director-level manager in charge. Marketing has specialized functions, such as communications (press releases), social media, data science analysis, and product marketing. Customer Service is usually responsible for Customer Relationship Management (CRM) and problem resolution and support.
Finally, the Research and Development functional area is the lifeblood of manufacturing businesses. R&D is staffed with scientists, thought leaders, subject matter experts, and industry analysts striving to provide the organization with knowledge and ideas to keep up with, and ahead of, the competition. R&D is led by the Chief Technology Officer (CTO), who manages a Development VP or similar title, depending on what technology products are being produced: semiconductors, software systems, or dental appliances. In many organizations, the Information Technology area (IT), responsible for providing internal technology tools to the company’s employees, is housed in the R&D organization.
Practice Questions
- Reading: Functional Areas of Business. Authored by : Linda Williams and Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Revision and adaptation. Authored by : Robert Danielson. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Practice Questions. Authored by : Robert Danielson. Provided by : Lumen Learning. License : CC BY: Attribution
- Worker Bees. Authored by : Scott Kidder. Located at : https://www.flickr.com/photos/skidder/434622114/ . License : CC BY-NC-ND: Attribution-NonCommercial-NoDerivatives

- Get Started
- Another Item
- Sub-menu Item 2
- Yet Another Item
- Menu Item 3
- Menu Item 4
Org Design , Org structure
A Brief Explanation of Business Functions
Every organization launches with the goal of providing a product, service, or some collection of those to customers or clients. The overarching function of a business is to fulfill its reason for existing. What these items are and how they are prioritized can vary significantly from one business to another.
What Are Business Functions?
Business functions are the things a business does to provide the product or service that it offers. At the highest level is the primary business function. This principal function reflects why the company exists.
Examples of a primary business function include:
- Providing tutoring services to college students
- Manufacturing precision parts for airplanes
- Building custom homes
Some businesses have one primary business function, while others may have more than one. However, it’s possible to articulate these as a single function. For example, a business that provides computer security and help desk management might have a primary function of providing comprehensive IT services.
As you drill down into your own business, you will probably uncover that its primary function is supported by other mission-critical functions.
The primary function of building customized homes may be split into:
- Construction
- Quality control
- User consultation
To figure out your organization’s primary function, start with a simple question: “What do we do?” The answer is your primary function.
What are the Five Core Business Functions?
Core business functions are five key areas that you must execute in addition to your primary function. They are human resources, finance, marketing, sales, and strategy. These are universal functions, which means that they are necessary for the success of any business.
Human Resources
HR is the function of building and maintaining a successful team of employees who have the skills and experience to achieve the company’s primary and core functions.
Finance is the function of handling the company’s money. This core function exists to ensure that the business spends and invests money properly so that it can continue to operate successfully.
Every business needs its target audience to:
- Know that it exists
- Understand what it does
- Regard it as being trustworthy
- View it as a provider of products or services they need
The core function of marketing creates brand awareness and engages potential customers.
Ultimately, all businesses have products or services to sell. The sales function helps prospective customers see the benefits and features of products and services and then make a purchase.
The strategy function involves all of the necessary planning required for growth and success. This function is what businesses use to make choices on product development and workforce planning . Strategy helps ensure that a business has a plan for the future and can remain competitive.
In addition to these core functions, other functions are also important to your business. Building upkeep and maintenance, IT, and customer service are just a few examples. You may determine that additional proprietary functions are necessary for your business operations.
Interactive template: Functionly includes a pre-loaded Functional Chart for the most typical business functions. These can be assigned to roles within Functionly.
Functions and Responsibilities
Once a business has clearly defined its functions, leaders must determine which teams or individuals are responsible for them. This is a complex process that influences organizational design, team structures, and eventually, the assignment of roles and responsibilities .
Consider the core function of human resources. The role of chief human resources officer (CHRO) may be created with HR as its assigned responsibility.
Next, that role may break down into smaller functions, such as:
- Recruiting and hiring
- Payroll and benefits
- Training and development
These functions may be assigned as responsibilities for individuals or team leaders within HR. The functions and responsibilities may be divided as follows:
The CHRO is responsible for the core function of human resources. They are also responsible for the sub-functions of recruiting, training, and payroll.
Payroll and Benefits Administrator
This role is responsible for the HR function of paying employees and ensuring that appropriate benefits are available to them. Although training and recruiting are also HR functions, this role is not responsible for these.
What Is the Relationship Between Functions and Processes?
Business processes are a series of related activities that contribute to a specific function. Some processes create a direct functional outcome. One example is the process of demonstrating a product to a customer, helping them overcome doubts, and convincing them to make a purchase.
Other processes provide input that supports a function. The HR process of providing sales training gives the salesperson the skills they need to execute the processes they use to sell products.
How Do Business Functions Work Together?
All of the functions within a business impact one another. If a primary or core function isn’t being executed, then others will also fail. Because of this, it’s important to understand where lines of communication must exist between business areas and where shared responsibilities exist.
Additionally, as part of organizational planning, businesses can use org chart software to document the relationships among functional areas. The software can increase understanding of how communication and reporting need to flow from one area to another.
What Is the Most Important Function of a Business?
The primary function of your business is the most important because it allows you to deliver your product or service to your customers. It is your company’s reason for existing.
However, that doesn’t mean this will always be the function that has the highest priority. Different functions within an organization will require more or less focus, depending on your goals, challenges that have emerged, changes in the market, or high-demand projects.
A Solution for Documenting Business Functions
An accountability chart is a document that business leaders can create in addition to a traditional org chart. It illustrates the key business functions necessary for the business to operate successfully. It also details the employee roles supporting those functions along with areas of responsibility.
Functionly is the tool that many businesses use to create org and accountability charts. These documents ensure that all responsibilities get properly recorded so that mission-critical functions get completed. Start for free with Functionly .
Org Design Org structure
Related articles

Leadership , Org Design
Navigating the Maze: Strategies for Gaining Stakeholder Buy-in During Company Reorganizations

Org Design , Org Strategy
Reshaping the Future: Tools and Tactics for Organizational Adaptability
Get started now.
Your first step towards a more effective organization.
Start trial
Subscribe to our newsletter
- Integrations
- Trial for 22 days
- Business Functions
- Workforce Transformation
- Org Chart Templates
- Org Design Podcast
- Orginometry Blog
- Org Design Cards
- Functionly TV
- Knowledge Base
© Copyright 2024 Functionly
- Privacy Policy
- Terms of Service

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

16.3: Functions of the Marketing Plan
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 16068

Learning Objectives
- Understand the functions of a marketing plan.
- Write a marketing plan.
In Chapter 1, we introduced the marketing plan and its components. Recall that a marketing plan should do the following:
- Identify customers’ needs.
- Evaluate whether the organization can meet those needs in some way that allows for profitable exchanges with customers to occur.
- Create offerings that are the result of meticulous market research.
- Form operations and supply chains that advance the successful delivery of those offerings.
- Pursue advertising, promotional, and public relations campaigns that lead to continued successful exchanges between the company and its customers.
- Engage in meaningful communications with customers on a regular basis.
The Marketing Plan’s Outline
The actual marketing plan you create will be written primarily for executives, who will use the forecasts in your plan to make budgeting decisions. These people will make budgeting decisions not only for your marketing activities but also for the firm’s manufacturing, ordering, and production departments, and other functions based on your plan.
In addition to executives, many other people will use the plan. Your firm’s sales force will use the marketing plan to determine its sales strategies and how many salespeople are needed. The entire marketing staff will rely on the plan to determine the direction and nature of their activities. The advertising agency you hire to create your promotional campaigns will use the plan to guide its creative team. Figure 16.2 shows a complete outline of a marketing plan (you may also want to go to http://www.morebusiness.com/templates_worksheets/bplans/printpre.brc for an example). Next, we will discuss the elements in detail so you will know how to prepare a marketing plan.

The Executive Summary
A marketing plan starts with an executive summary. An executive summary should provide all the information your company’s executives need to make a decision without reading the rest of the plan. The summary should include a brief description of the market, the product to be offered, the strategy behind the plan, and the budget. Any other important information, such as how your competitors and channel partners will respond to the actions your firm takes, should also be summarized. Because most executives will be reading the plan to make budgeting decisions, the budgeting information you include in the summary is very important. If the executives want more detail, they can refer to the “budget” section, which appears later in the plan. The executive summary should be less than one page long; ideally, it should be about a half page long. Most marketing plan writers find it easier to write a plan’s summary last, even though it appears first in the plan. A summary is hard to write when you don’t know the whole plan, so waiting until the plan is complete makes writing the executive summary easier.
The Business Challenge
In the “business challenge” section of the plan, the planner describes the offering and provides a brief rationale for why the company should invest in it. In other words, why is the offering needed? How does it fit in with what the company is already doing and further its overall business goals? In addition, the company’s mission statement should be referenced. How does the offering and marketing plan further the company’s mission?

Richter Frank-Jurgen – Horasis Global China Business Meeting 2013 – CC BY-SA 2.0.
Remember that a marketing plan is intended to be a persuasive document. You are trying not only to influence executives to invest in your idea but also to convince other people in your organization to buy into the plan. You are also trying to tell a compelling story that will make people outside your organization—for example, the director of the advertising agency you work with, or a potential supplier or channel partner—invest money, time, and effort into making your plan a success. Therefore, as you write the plan you should constantly be answering the question, “Why should I invest in this plan?” Put your answers in the business challenge section of the plan.
The market section of the plan should describe your customers and competitors, any other organizations with which you will collaborate, and the state of the market. We suggest that you always start the section by describing the customers who will purchase the offering. Why? Because customers are central to all marketing plans. After that, discuss your competitors, the climate, and your company in the order you believe readers will find most persuasive. In other words, discuss the factor you believe is most convincing first, followed by the second-most convincing factor, and so on.

Vladimir Pustovit – Family – CC BY 2.0.
Who does your market consist of? What makes these people decide to buy the products they do, and how do they fulfill their personal value equations? What is their buying process like? Which of their needs does your offering meet?
Break the market into customer segments and describe each segment completely, answering those questions for each segment. When you write your plan, begin with the most important segment first and work your way to the least important segment. Include in your discussion the market share and sales goals for each segment.
For example, Progresso Soups’ primary market segments might include the following:
- Families in colder regions
- People who need a good lunch but have to eat at their desks
- Busy young singles
- Older, perhaps retired, empty-nesters
These segments would be based on research that Progresso has completed showing that these are the groups that eat the most soup.
Your discussion of each segment should also include how to reach the customers within it, what they expect or need in terms of support (both presales and postsales support), and other information that helps readers understand how each segment is different from the others. After reading the section, a person should have a good grasp of how the segments differ yet understand how the needs of each are satisfied by the total offering.
Katie Scallan-Sarantakes
http://app.wistia.com/embed/medias/4e5cbb5411
A marketing plan has to account for many factors: customers, competitors, and more. Listen as Katie Scallan-Sarantakes describes how she had to consider these factors when creating marketing plans for Toyota.
Company Analysis
Include the results of your analysis of your company’s strengths and weaknesses in this section. How is the company perceived by the customers you described earlier? Why is the company uniquely capable of capitalizing on the opportunity outlined in the plan? How sustainable is the competitive advantage you are seeking to achieve?
You will also need to identify any functional areas in which your company might need to invest for the plan to succeed. For example, money might be needed for new production or distribution facilities and to hire new marketing or sales employees and train existing ones.
One tool that is useful for framing these questions is the SWOT analysis. SWOT stands for strengths, weaknesses, opportunities, and threats. Strengths and weaknesses are internal, meaning they are conditions of the company. Either these conditions are positive (strengths) or negative (weaknesses). Opportunities and threats are external to the company, and could be due to potential or actual actions taken by competitors, suppliers, or customers. Opportunities and threats could also be a function of government action or changes in technology and other factors.
When working with executives, some consultants have noted the difficulty executives have in separating opportunities from strengths, weaknesses from threats. Statements such as “We have an opportunity to leverage our strong product features” indicate such confusion. An opportunity lies in the market, not in a strength. Opportunities and threats are external; strengths and weaknesses are internal. Assuming demand (an external characteristic) for a strength (an internal characteristic) is a common marketing mistake. Sound marketing research is therefore needed to assess opportunity.
Other factors that make for better SWOT analysis are these:
- Honest. A good SWOT analysis is honest. A better way to describe those “strong” product features mentioned earlier would be to say “strong reputation among product designers,” unless consumer acceptance has already been documented.
- Broad. The analysis has to be broad enough to capture trends. A small retail chain would have to look beyond its regional operating area in order to understand larger trends that may impact the stores.
- Long term. Consider multiple time frames. A SWOT analysis that only looks at the immediate future (or the immediate past) is likely to miss important trends. Engineers at Mars (makers of Skittles, M&Ms, and Snickers) visit trade shows in many fields, not just candy, so that they can identify trends in manufacturing that may take a decade to reach the candy industry. In this way, they can shorten the cycle and take advantage of such trends early when needed.
- Multiple perspectives. SWOT analyses are essentially based on someone’s perception. Therefore, a good SWOT should consider the perspective of all areas of the firm. Involve people from shipping, sales, production, and perhaps even from suppliers and channel members.
The SWOT analysis for a company, or for any organization, is both internal and external in focus. Some of the external areas for focus are collaborators (suppliers, distributors, and others), competitors, and the business climate.
Collaborators
Along with company strengths and weaknesses, identify any actual or potential partners needed to pull the plan off. Note that collaborators are more than just a list of suppliers and distributors. Collaborators are those organizations, either upstream or downstream in the value chain, you need to partner with to cocreate value.
For example, AT&T collaborated with Apple to develop the iPhone. AT&T is downstream in the value chain, providing the needed cell service and additional features that made the iPhone so revolutionary. At the same time, however, AT&T was a part of the development of the iPhone and the attendant marketing strategy; the partnership began well before the iPhone was launched.
Competitors
Your marketing plan, if it is any good at all, is likely to spark retaliation from one or more competitors. For example, Teradata and Unica operate in the same market. Both sell data-warehousing products to companies. Teradata primarily focuses on the information technology departments that support the data warehouse, whereas Unica focuses on the marketing departments that actually use the data warehouse. Nonetheless, Teradata is well aware of Unica’s marketing strategy and is taking steps to combat it by broadening its own market to include data-warehousing users in marketing departments. One step was to teach their salespeople what marketing managers do and how they would use a data warehouse as part of their job so that when these salespeople are talking to marketing managers, they can know what they’re talking about.
Teradata marketing planners also have to be aware of potential competitors. What if IBM or HP decided to enter the market? Who is most likely to enter the market, what would their offering look like, and how can we make it harder for them to want to enter the market? If your company captures their market before they can enter, then they may choose to go elsewhere.
Identify your competitors and be honest about both their strengths and weaknesses in your marketing. Remember that other people, and perhaps other organizations, will be using your plan to create their own plans. If they are to be successful, they have to know what competition they face. Include, too, in this section of the plan how quickly you expect your competitors to retaliate and what the nature of that retaliation will be. Will they lower their prices, create similar offerings, add services to drive up the value of their products, spend more on advertising, or a combination of these tactics?
A complete competitive analysis not only anticipates how the competition will react; it also includes an analysis of the competition’s financial resources. Do your competitors have money to invest in a competitive offering? Are they growing by acquiring other companies? Are they growing by adding new locations or new sales staff? Or are they growing simply because they are effective? Maybe they are not growing at all. To answer these questions, you will need to carefully review your competitors’ financial statements and all information publicly available about them. This can include an executive quoted in an article about a company’s growth for a particular product or an analyst’s projection for future sales within a specific market.
Business Climate
You may have already addressed some of the factors in the business environment that are creating the opportunity for your offering. For example, when you discussed customers, you perhaps noted a new technology they are beginning to use.
A complete coverage of the climate would include the following (the PEST analysis):
- Political climate
- Economic climate
- Social and cultural environment
- Technological environment
A scan of the political climate should include any new government regulations as well as legislation. For example, will changes in the tax laws make for more or less disposable income among our customers? Will the tightening of government regulations affect how salespeople can call on doctors, for example, hindering your marketing opportunity? Will federal policies that affect exchange rates or tariffs make global competitors stronger or weaker? For example, the government introduced the Cash for Clunkers program to encourage people to buy new cars. Within only a few weeks, 250,000 new cars were sold through the program and it ran out of money. Auto dealers were caught unprepared and many actually ran out of popular vehicles.
The economic climate is also important to consider. While 2008 saw tremendous swings in gas prices, other factors such as the subprime lending crisis and decline of the housing market affected everything from the price of corn to the sales of movie tickets. Such volatility is unusual, but it is important nonetheless to know what the economy is doing.

Jeff Turner – Sign Of The Times – Foreclosure – CC BY 2.0.
The social and cultural environment is also important to watch. Marketers, for example, may note the rise in the Hispanic population as a market segment, but it is also important to recognize the influence of the Hispanic culture. Understanding the Hispanic culture is important in reaching this market segment with the right marketing mix. In creating marketing campaigns for something such as a financial product, it’s very important to understand the history that Hispanics have had with financial institutions in their home countries. Understanding that culturally Hispanics might not trust financial institutions and developing campaigns that generate positive word of mouth, such as refer-a-friend and influencer tactics, can be explosive once the wall has been torn down.
Finally, the technological environment should be considered. Technology is the application of science to solve problems. It encompasses more than just information (computer) technology. For example, when Ted Schulte (profiled in Chapter 13) discusses a pacemaker with a cardiac surgeon, Ted is describing the latest technology available. The new technology could be related to the battery used to power the pacemaker, the materials used in the leads (the wires that connect the pacemaker to the body), or even the material that encases the pacemaker. Understanding the technological environment can provide you with a greater understanding of a product’s life cycle and the direction the market is taking when it comes to newer technologies.

Steven Rodriguez – Pacemaker – CC BY-NC-ND 2.0.
Many of the environmental factors we mentioned impact other factors. For example, technological changes are altering the social and cultural environment. Instead of writing letters to one another, families and friends use e-mail and social networking sites to communicate and maintain relationships. Online communication has affected any number of businesses, including the greeting card business and the U.S. Postal Service, which recently announced it was closing many facilities.
Likewise, the economic environment influences the political environment and vice versa. The huge bailout of the banks by the government is an example of how the economic environment affects the political environment. The laws passed as a result of the bank bailout, which include more-restrictive lending practices, are affecting banks, businesses, and consumers. Any looming changes in the business climate such as this need to be included in your marketing plan.
The Strategy
The next section of the plan details the strategy your organization will use to develop, market, and sell the offering. This section is your opportunity to create a compelling argument as to what you intend to do and why others should invest in the strategy. Your reader will be asking, “Why should we adopt this strategy?” To answer that question, you may need to include a brief discussion of the strategic alternatives that were considered and discarded. When readers complete the section, they should conclude that the strategy you proposed is the best one available.
The Offering
Provide detail on the features and benefits of the offering, including pricing options, in this section. For example, in some instances, your organization might plan for several variations of the offering, each with different pricing options. The different options should be discussed in detail, along with the market segments expected to respond to each option. Some marketing professionals like to specify the sales goals for each option in this section, along with the associated costs and gross profit margins for each. Other planners prefer to wait until the budget section of the plan to provide that information.
The plan for the offering should also include the plan for introducing offerings that will follow the initial launch. For example, when should Progresso introduce new soup flavors? Should there be seasonal flavors? Should there be smaller sizes and larger sizes, and should they be introduced all at the same time or in stages?
Part of an offering is the service support consumers need to extract the offering’s full value. The support might include presales support as well as postsales support. For example, Teradata has a team of finance specialists who can help customers document the return on investment they would get from purchasing and implementing a Teradata data warehouse. This presales support helps potential buyers make a stronger business case for buying Teradata’s products with executives who control their companies’ budgets.
Postsales support can include technical support. In B2B (business-to-business) environments, sellers frequently offer to train their customers’ employees to use products as part of their postsales support. Before you launch an offering, you need to be sure your firm’s support services are in place. That means training service personnel, creating the appropriate communication channels for customers to air their technical concerns, and other processes.

CWCS Managed Hosting – customer service assistant on phone – CC BY 2.0.
The Communication Plan
How will the offering be launched? Will it be like Dow Corning’s launch of a new silicon acrylate copolymer, a product used to add color to cosmetics? That product was announced at the In-Cosmetics trade show in Barcelona. Or will you invite customers, media, and analysts from around the globe to your company’s offices for the launch, as SAS did with its SAS 9 software product?
In addition to the announcement of the new product, the communication plan has to specify how ongoing customer communications will be conducted. The mechanisms used to gather customer feedback as well as how the offering will be promoted to customers need to be spelled out. For example, will you create an online community like Laura Carros did with the JCPenney Ambrielle line?
The discussion of the communication plan can be fairly broad. You can put additional details in a separate planning document that outlines the product’s advertising strategies, event strategies (such as trade shows and special events like customer golf tournaments that will be used to promote the product), and sales strategies.
Distribution
This section should answer questions about where and how the offering will be sold. Who will sell it? Who will ship it? Who will service and support it? In addition, the distribution section should specify the inventories that need to be maintained in order to meet customer expectations for fast delivery and where those inventories should be kept.
The budget section is more than just a discussion of the money needed to launch the new offering. A complete budget section will cover all the resources, such as new personnel, new equipment, new locations, and so forth, for the launch to be a success. Of course, these resources have costs associated with them. In some instances, the budget might require that existing resources be redeployed and a case made for doing so.
The first portion of the budget will likely cover the investment required for the launch. The plan might point out that additional funds need to be allocated to the offering to make it ready for the market. For example, perhaps additional beta testing or product development over and above what the firm normally commits to new products is needed. Certainly, marketing funds will be needed to launch the offering and pay for any special events, advertising, promotional materials, and so forth. Funds might also be needed to cover the costs of training salespeople and service personnel and potentially hiring new staff members. For example, Teradata introduced a new offering that was aimed at an entirely new market. The new market was so different that it required a new sales force. Details for the sales force, such as how many salespeople, sales managers, and support personnel will be needed, would go in this section.
The budget section should include the costs associated with maintaining the amount of inventory of the product to meet customers’ needs. The costs to provide customers with support services should also be estimated and budgeted. Some products will be returned, some services will be rejected by the consumer, and other problems will occur. The budget should include projections and allowances for these occurrences.
The budget section is also the place to forecast the product’s sales and profits. Even though the plan likely mentioned the sales goals set for each market segment, the budget section is where the details go. For example, the cost for advertising, trade shows, special events, and salespeople should be spelled out. The projections should also include timelines. The sales costs for one month might be estimated, as well as two months, six months, and so forth, as Figure 16.8 shows.
Note that Figure 16.8 shows that the product’s costs are high early on and then decrease before leveling out. That cost line assumes there is a heavy upfront investment to launch the offering, which is usually true for new products. The sales of the offering should grow as it gathers momentum in the market. However, the market potential stays the same, assuming that the potential number of customers stays the same. That might not always be the case, though. If we were targeting mothers of babies, for example, the market potential might vary based on the projected seasonality in birth rates because more babies tend to be born in some months than others.

In the conclusion, repeat the highlights. Summarize the target market, the offer, and the communication plan. Your conclusion should remind the reader of all the reasons why your plan is the best choice.
Of course, the written plan is itself a marketing tool. You want it to convince someone to invest in your ideas, so you want to write it down on paper in a compelling way. Figure 16.9 offers some tips for effectively doing so. Also, keep in mind that a marketing plan is created at a single point in time. The market, though, is dynamic. A good marketing plan includes how the organization should respond to various scenarios if the market changes. In addition, the plan should include “triggers” detailing what should happen under the scenarios. For example, it might specify that when a certain percentage of market share is reached, then the price of the product will be reduced (or increased). Or the plan might specify the minimum amount of the product that must be sold by a certain point in time—say, six months after the product is launched—and what should happen if the mark isn’t reached. Also, it should once again be noted that the marketing plan is a communication device. For that reason, the outline of a marketing plan may look somewhat different from the order in which the tasks in the outline are actually completed.

Key Takeaway
The budget section of the marketing plan covers all the resources, such as new personnel, new equipment, new locations, and so forth, needed to successfully launch the product, as well as details about the product’s costs and sales forecasts.
Review Questions
- What is a marketing plan and how is it used?
- Which section of the marketing plan is most important? Why? The least important?
- What is the purpose of scenario planning?

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Get A Professional Business Plan W/ Our Easy Builder. Erase Errors, Save & Print In Mins! Business Planning Made Easy. Create A Winning Business Plan In Half The Time - Start Now!
Fill In Professional Business Plan Templates. Download & Print Instantly- 100% Free! Answer Easy Questions & Create In Minutes - Save To PDF & Word - Jumpstart Your Business!
A business plan can help you to define and classify the goals you have for your business. Devoid of fluff, a business plan is a business document that is written for a variety of audiences. You might send your business plan to investors or it might be written for the benefit of your employees. Generally, the audience should have no bearing on ...
A Harvard Business Review study found that the ideal time to write a business plan is between 6 and 12 months after deciding to start a business. But the reality can be more nuanced - it depends on the stage a business is in, or the type of business plan being written. Ideal times to write a business plan include: When you have an idea for a ...
A business plan can help you explore ideas, successfully start a business, manage operations, and pursue growth. In short, a business plan is a lot of different things. ... While all business plans cover similar categories, the style and function fully depend on how you intend to use your plan. So, to get the most out of your plan, it's best ...
If capital is a priority, this business plan might focus more on financial projections than marketing or company culture. 2. Feasibility Business Plan. This type of business plan focuses on a single essential aspect of the business — the product or service. It may be part of a startup business plan or a standalone plan for an existing ...
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan: Section 1: Executive Summary. Present the company's mission. Describe the company's product and/or service offerings. Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
Describe Your Services or Products. The business plan should have a section that explains the services or products that you're offering. This is the part where you can also describe how they fit ...
Most business plans also include financial forecasts for the future. These set sales goals, budget for expenses, and predict profits and cash flow. A good business plan is much more than just a document that you write once and forget about. It's also a guide that helps you outline and achieve your goals. After completing your plan, you can ...
In the world of business, a well-thought-out plan is often the key to success. This plan, known as a business plan, is a comprehensive document that outlines a company's goals, strategies, and financial projections.Whether you're starting a new business or looking to expand an existing one, a business plan is an essential tool.. As a business plan writer and consultant, I've crafted over ...
Here are some of the components of an effective business plan. 1. Executive Summary. One of the key elements of a business plan is the executive summary. Write the executive summary as part of the concluding topics in the business plan. Creating an executive summary with all the facts and information available is easier.
A business plan typically explores the competitive landscape of an industry, analyzes a market and different customer segments within it, describes the products and services, lists business strategies for success, and outlines financial planning. ... and your vision for building teams to perform various functions, such as graphic design ...
Business functions are the foundation of a company's structure and operations. They include all the divisions, departments, and other components involved in creating a product or service. Within an organization, the main functional groups include manufacturing, sales & marketing, accounts & finance, and human resources.
7 Different Types of Business Plans Explained. Business plans go by many names: Strategic plans, traditional plans, operational plans, feasibility plans, internal plans, growth plans, and more. Different situations call for different types of plans. But what makes each type of plan unique?
A business plan is an executive document that acts as a blueprint or roadmap for a business. It is quite necessary for new ventures seeking capital, expansion activities, or projects requiring additional capital. It is also important to remind the management, employees, and partners of what they represent. You are free to use this image on your ...
A business plan is used to help manage an organisation by stating ambitions, how they will be achieved, and exactly when. The plan will also help summarise what the business is about, why it exists, and where it will get to. Your business plan will serve as a key point of reference for investors, partners, employees and management to gauge ...
The 10 sections or elements of a business plan that you must include are as follows: 1. Executive Summary. The executive summary provides a succinct synopsis of the business plan, and highlights the key points raised within. It often includes the company's mission statement and description of the products and services.
The business plan may also function as a prospectus for potential customers, especially when it comes to large corporate accounts and exclusive customer relationships. 9. Secure Funding ... Business plan is also an excellent tool for planning an exit as it would include the strategy and timelines for a transfer to new ownership or dissolution ...
Effective business plans contain several key components that cover various aspects of a company's goals. The most important parts of a business plan include: 1. Executive summary. The executive summary is the first and one of the most critical parts of a business plan. This summary provides an overview of the business plan as a whole and ...
Function. The main function of a business plan is to define the model and the strategic actions to achieve the goals. Once defined, you must establish the economic viability of the project. This requires analyzing the different areas involved , which allows supporting the project conceptually and observing it from all dimensions.
Before you write a business plan, consider the function of a business plan document to a new business or company changing direction. Investopedia defines a business plan as "[a] written document that describes in detail how a new business is going to achieve its goals.". A comprehensive legal business plan includes sections about the company's budget, financing, projected revenue ...
Management. The primary role of managers in business is to supervise other people's performance. Most management activities fall into the following categories: Planning: Managers plan by setting long-term goals for the business, as well as short-term strategies needed to execute those goals. Organizing: Managers are responsible for organizing ...
Core business functions are five key areas that you must execute in addition to your primary function. They are human resources, finance, marketing, sales, and strategy. ... Strategy helps ensure that a business has a plan for the future and can remain competitive. In addition to these core functions, other functions are also important to your ...
15 examples of business functions. Here is a list of 15 examples of business functions, whether they are the primary focus of a company or a department within it: 1. Strategy. A strategy firm or department develops the strategy, approach and way to implement change for a company. Strategy-based businesses help others reach their goals and ...
Figure 16.3: Your marketing plan has to convince busy executives and other stakeholders that your idea is worth investing in. Richter Frank-Jurgen - Horasis Global China Business Meeting 2013 - CC BY-SA 2.0. Remember that a marketing plan is intended to be a persuasive document.