

[Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Fish Farming Docx
In recent years, fish farming has gained significant popularity as a lucrative business opportunity. This comprehensive guide aims to provide you with a well-structured fish farming business plan in PDF format. Whether you’re a seasoned entrepreneur or a beginner in the industry, this article will equip you with the essential knowledge and insights to start and run a successful fish farming venture.
[Pdf Sample] Fish Farming Business Plan Proposal Docx
Table of Contents
To write a business plan, here is a breakdown of how it should be structured and what should be in each category. After this instruction, I will provide you with a sample of one I wrote for my farm, let us go:
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Sunflower Farming Docx
Executive Summary
The executive summary highlights the crucial elements of your fish farming business plan, providing a snapshot of the entire venture. It outlines the goals, objectives, and strategies required to achieve success in the industry.
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Onion Farming Docx
Market Analysis
Choosing the right fish species.
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Tomatoes Plantation Docx
Site Selection and Pond Construction
Choosing the right site for your fish farm is crucial. We discuss the criteria for selecting an ideal location, including water source, soil quality, accessibility, and environmental considerations. Additionally, we explore the construction process of fish ponds, ensuring they meet the necessary specifications.
Water Management and Quality
Read Also: [Pdf Sample] Business Plan For Potato Farming Docx
Fish Feeding and Nutrition
Disease prevention and management, harvesting and processing.
When it’s time to harvest your fish, proper techniques and handling are essential to maintain product quality. We discuss various harvesting methods, post-harvest handling practices, and processing options to ensure you deliver the best possible products to the market.
Marketing and Sales Strategies
Financial projections and budgeting.
Accurate financial projections and budgeting are essential for assessing the financial viability of your fish farming venture. This section guides you through the process of estimating costs, revenue projections, profit margins, and return on investment (ROI) analysis.
Legal and Regulatory Considerations
Complying with the legal and regulatory framework is vital for running a fish farming business. We discuss the necessary licenses, permits, and regulations you need to be aware of, ensuring your operation remains within the legal boundaries.
Sustainability Practices
Embracing sustainable practices in fish farming is not only environmentally responsible but also beneficial for long-term profitability. We highlight eco-friendly approaches, water conservation methods, waste management strategies, and the importance of social responsibility in the industry.
Risks and Challenges
Business model for agrolearner.com’s fish farming business.
Value Proposition: Agrolearner.com Farm aims to provide the local market with high-quality, sustainable, and locally-produced fish products. Our value proposition includes:
Traceability and Transparency: We provide full transparency regarding our farming methods , allowing customers to trace the origin and production process of our fish products.
Customer Education: We aim to educate consumers about the benefits of sustainable aquaculture and the importance of supporting local food systems.
Health-conscious individuals: Customers who prioritize nutritious and sustainably sourced food.
Channels: We utilize multiple channels to reach our target customers and distribute our fish products:
Partnerships: Collaborating with local markets, restaurants, and distributors to establish reliable sales channels.
Online Presence: Leveraging our website and social media platforms to engage with customers, share information, and promote our products.
Communication: Engaging with customers through social media, newsletters, and educational content.
Feedback and Support: Welcoming customer feedback and providing assistance to address inquiries and concerns.
Wholesale and Retail Sales: Selling fish directly to customers through various channels, including online and on-site.
Fish Farming: Cultivating fish species, such as tilapia and catfish, through proper management and nutrition.
Harvesting and Processing: Implementing efficient and humane harvesting techniques and processing fish to maintain quality.
Sustainability Practices: Implementing environmentally responsible practices, including water and energy conservation, waste management , and community engagement.
Fish Stock and Feed: Sourcing high-quality fish stock and formulating nutritious feed for optimal growth.
Key Partnerships: Agrolearner.com Farm establishes strategic partnerships to support its operations and enhance market reach:
Restaurants and Chefs: Building relationships with local restaurants and chefs to secure long-term partnerships for the supply of fresh fish.
Infrastructure Costs: Investments in land, pond construction, processing facilities, and equipment.
Compliance and Insurance: Costs associated with regulatory compliance and insurance coverage.
Key Metrics: Agrolearner.com Farm tracks the following key metrics to assess the performance and success of the business:
Production Efficiency: Assessing fish growth rates, feed conversion ratios, and other operational metrics to optimize production processes.
Sustainability Metrics: Monitoring water and energy consumption, waste management, and adherence to sustainability goals.
Required Capital to Start a Fish Farming Business
The required capital to start a fish farming business can vary depending on several factors, such as the scale of operation, the type of fish species being farmed, and the infrastructure needed. Generally, the capital required includes expenses for land or pond lease, construction or renovation of ponds, purchase of fingerlings (young fish), feed, equipment, water management systems , and other operational costs.
Time to Start Generating Profits from a Fish Farm
Some fast-growing fish species may allow for quicker returns on investment, while others with longer growth cycles may require more patience. Effective management practices, such as proper feeding, water quality management, and disease prevention, can help expedite the growth process and shorten the time to profitability.
Feasibility of Fish Farming in Landlocked Areas
Key factors affecting fish growth.
Genetics and the specific breed or strain of fish being farmed can also affect growth rates. Environmental factors like stocking density, availability of space, and light exposure can influence fish growth and overall health. Disease management and prevention, including timely vaccinations and biosecurity measures, are also critical for ensuring optimal fish growth.
Government Subsidies and Funding Options for Fish Farming Startups
Government support can come in the form of financial assistance, grants, low-interest loans, tax incentives, training programs, and technical guidance. These funding options and subsidies vary by region and country, and aspiring fish farmers should research and explore the opportunities provided by local government agencies, agricultural departments, and fisheries authorities.
Engaging with relevant industry associations and networking with experienced fish farmers can also provide valuable insights into available funding sources and support programs.
Share this:
Author: adewebs, you may also like:, [pdf sample] business plan for pig farming docx, starting a poultry farm with limited resources in ghana: a comprehensive guide for new farmers, how to register agribusiness company in kenya (see full guide), starting a poultry farm with limited resources in nigeria: guide for new farmers, leave a reply cancel reply.
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser or activate Google Chrome Frame to improve your experience.
Agriculture in Nepal
- Why organic
- What is organic farming
- Farming volunteer
- Agriculture internship
- Nepali cooking course
- Agricultural tours
- Agricultural research
- Program fee
- Gallery
- Contact us
Types & scope of fish farm in Nepal
Fish farming in Nepal is considered as one of the ancient farming system, there are lots of small scale fish farm in different villages in plain region started years ago. Commercial fish farming in Nepal provides many profitable opportunities; farmers are raising and selling the fish on commercial basis. There are more than 6000 rivers, fresh water resources suitable for fish farming in Nepal . Trout Fresh water fish farming is not expensive to produce and easy to sell in high price. Commercial fish farming at fresh water, natural lakes is a very emerging issue but it requires technical knowledge about aquaculture Nepal. Our fish farms are sustainable and environment friendly fishes are raised naturally and guaranteed free of diseases, pesticides and other harmful toxicants. Fish are an important source of food for people around the world, either caught wild or farmed. Consumption of fish products in Nepal is increasing dramatically because Fish is a healthy food, low in calories and cholesterol levels, but rich in protein. Organic farm Nepal started fish farm using the modern technology and raise fish on fresh water and pounds. We have different verities of fish on farm warm water species common crap, grass carp, big head carp and fresh water species trout etc. Catching fish from natural water resources started for tens of thousands of years, since the age of hunting. On the contest of Nepal there are some ethnic groups caught the fish as a profession from natural water resources and sell in market to generate the income to survive. Climate and nature of the soil is suitable to construct the fish ponds in different parts of Nepal . Before starting fish farming firstly to fix a location, choose proper verities of fish according to the climate, temperature and type of available water resources food and diseases control. Organic farm offers either fresh water or warm water fish farming training on these topics including practical knowledge for all interested farmers. If you interested for training, internship , volunteering and fish farm tours or would like to buy fresh water or warm water species of fish fell free to contact us .
Organic farming
- Agricultural tours
- Village volunteers
- Agricultural research
- Agriculture volunteer
- Village stay in Nepal
- Volunteer on organic farm
Organic farms Nepal
- Poultry farm
- Buffalo farm
- Avocado farm
- Mushroom farm
- Strawberry farm
Pasture raised poultry
- Turkey farm
- Ostrich farm
- Chicken farm
- Guinea fowl farm
- Farming volunteer
- Farm work abroad
- Agriculture internship
- Volunteer with Animals
- Volunteer in dairy farm
- Volunteer in coffee farm
Farming in Nepal info
- Farmer training
- Organic agriculture
- Traditional farming
- Farming techniques
- Cultural exchange programs
- Teaching volunteer
Agricultural tourism
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Production, marketing, and future prospects of fish farming in Nepal: National and global scenario

2020, Cogent Food and Agriculture
To ensure a food security in future for all, the fisheries sector is key. The world’s demands for fish products indicate sign of increasing. This study delves into the analysis of production, marketing, and strategies for enhancing production and marketing of the fishery products. Secondary data for production and trade value were collected from different organizations, websites, and journals and were analyzed in Microsoft Excel. Over the years, rearing of different fish species has been rising worldwide, including Nepal. Marine, along with inland fisheries is getting profitable market, globally. Being a landlocked country, Nepal’s fish farming is solely limited to inland water resources. So, the domestic fish production is very few which is unable to meet the national demand. The fisheries, at national level, remarkably expanded than the previous decades and total production, trade, and consumption reached an all-time record in 2018. It has provided employment to millions of people across the world. Still many challenges have often hindered the production and marketing. Climatic changes, technological constraints, disease outbreaks, water temperature fluctuations, high cost of inputs, marketing constraints such as unmanaged distribution networks, lack of storage facilities, etc., have lowered down the fishery development. Keeping this point in view, this review was performed to provide the relevant solution of production and marketing strategies to the fishery industry, helping them to enhance the production and make perfect level of distribution. Marketing mix of marketing strategies and SWOT analysis for both production and marketing was performed.
Related Papers
Aquaculture and Fisheries
Oliver Kaleem
Fish farming is considered an important agricultural activity that is capable of ending nutritional deficiencies of the world and contributing to poverty reduction. Its proponents argue that aquaculture will meet the food security needs of millions of people in developing countries who will benefit from relatively inexpensive protein, while depleted capture fisheries are allowed to replenish. Egypt is Africa’s leading aquaculture country, followed by Nigeria with similar production systems. The dominant species of fish cultured in Egypt and Nigeria are Tilapia and African catfish, respectively. The aquaculture industries in these two counties are very promising, as there is a presence of water bodies, some institutional commitment, and high demand for fish among others. Despite some gains made by the countries and the huge potential of the aquaculture sector, it is however bedeviled with constraints such as low technology adoption, inadequate supply of fingerlings, high cost of fish feed, etc. This work is an overview of the aquaculture sectors of Egypt and Nigeria, which includes the production systems, prospects, and potentials of the sector and the constraints that affect aquaculture
Soibam Ngasotter , Saumya Panda , David Waikhom
Space and Culture, India
Brajaballav Kar , sugato tripathy
Odisha’s economy is predominantly agriculture driven. Exports from mining industries remained a significant source of foreign exchange. However, over a period, aquaculture exports have also emerged as a lucrative possibility. It is a perfectly suitable sector considering the long coastline, rivers and water bodies and labour intensive nature of the industry. From an individual or community level of operation, aquaculture developed the characteristics of industry in the early 1970s. This descriptive research paper investigates the history of the aquaculture industry in Odisha over the past 50 years. The aquaculture industry in Odisha started two decades later than Kerala (another southern state of India), in the form of an experiential learning and opportunity-seeking process by the early players. The subsequent dominance of local players, consolidation, and expansion of the export market proves the natural resource advantage of the State. The study emphasises the contribution of the sector to the state economy. The adoption of healthy consumption habits, large untapped Indian market, value and values-addition in the product, and evolving traceability requirements for exports are some of the significant challenges facing the industry. Despite being an important sector for the State, this sector has not received due attention from academic research. Technology adoption practices, productivity improvement, internal competitions, development of industry structure, and role of policy could be some areas for future research.
Florence Poulain
Peertechz Journals
There is a huge potential in freshwater aquaculture in the EU and in other countries in the World. As for the World food demand fish had the second highest consumption levels, at 27.9 percent in 2014. There will be a sharp increase in demand for fish and aquaculture products as the UN FAO projects around 9 billion people living our planet by 2050. The economy has already started its adaptation. While the World aquaculture production has increased from 7 to 82 million tonnes per year from 1990, there is no rise in the EU where we can observe a stagnation in production around 1.26 million tonnes annually. The EU has its potential: coastline around 68 thousand km, 500 thousand natural lakes, etc. Next to seawater aquaculture there are several freshwater fish species such as trout, carp or catfish whose production could be radically increased by investing, innovating and creating many new jobs in the freshwater sector. A small country, Hungary can show good examples in pond and intensive fish farming despite the country has not reached its full potential yet. The boost could be managed by increased grants and other incentives for investments, innovation, cooperation and promotion. The valuable ecological services which fish farmers provide year to year have also to be rewarded. So, let’s start to act.
Musfiqur Rahman
We were given a task to select one of the sectors/aspects/industries pertaining to Bangladesh and create a report on it. In order to create this report we have selected Fisheries Industry of Bangladesh. Bangladesh is bestowed with a vast expanse of inland open waters. For example we can say rivers, canals, natural and man-made lakes, freshwater marshes, estuaries, brackish water impoundments floodplains etc. These resources have enabled Bangladesh to create a mammoth industry of fisheries. This sector is divided into 3 sub-sectors and they are: • Inland Capture Fishery • Inland Culture Fishery • Marine Fisheries In FY2017-18 fishing sector contributed 3.57 percent to the GDP and 25.30 percent to the country’s total agricultural products. A considerable part of the country’s export earning comes from this sector the second largest export industry in Bangladesh and produces 2.5% of the global production of shrimp. Bangladesh has been getting global recognition after being self-sufficient in fish production for the first time and she was ranked third in producing fish from inland water-bodies, behind China and India, according to a report of Food and Agriculture Organization in 2018. The growth rate of fish production f is 4.760208% in 2018. Blue economy can play a major part in the development of Bangladesh. Bangladesh has 118,813 square kilometers of the Bay of Bengal and the areas of resources include 200 nautical miles of exclusive economic zone and over 354 nautical miles of resources on seabed. As Bangladesh fisheries have ample scope of development to strengthen the national economy, many government and non-government institutions have been established for the research and development of this sector. This industry with the help of proper conservation method can create more positive impact on the economy of Bangladesh.
Journal of Agrarian Change
Irmak Ertor , Miquel Ortega Cerdà
Aquaculture is one of the fastest growing food‐producing sectors, and its share in global seafood production is rising significantly compared with capture fisheries. This transforms seafood production practices while allowing capital to expand to new marine commodity frontiers. Building on the conceptualization of aquaculture as a new frontier for capture fisheries, the article aims to uncover how commodity frontiers expand within the intensive marine aquaculture sector and shape the transformation of seafood production by focusing on its recent growth in Turkey. It analyses this transformation based on 22 in‐depth interviews with key social actors in Turkey, as well as a review of sector and state reports and the relevant legislations of Turkey and the European Union, and argues that the three‐pronged horizontal, vertical, and taxonomic expansion already observed in industrial capture fisheries has similarly taken place in intensive marine aquaculture through the commodity widening, deepening, and marketing strategies employed by aquaculture firms.
Freshwater biodiversity in the Lake Victoria Basin: Guidance for species conservation, site protection, climate resilience and sustainable livelihoods.
Cory Whitney
The Lake Victoria Basin is home to the most extensive wetlands in Eastern Africa and these wetlands support remarkably high levels of floral biodiversity. Freshwater plants have a diverse range of uses, with variations in use depending on the plant part and life stage. Medicinal use of plants is very common in rural communities, as there is often no access to modern medical facilities, and investigations of the medicinal properties of plants have been conducted for centuries. Given these attributes, Lake Victoria (and its basin) is uniquely central to curbing problems of both malnutrition and poverty if measures can be put in place to ensure sustainable use of its biodiversity. In this chapter, we provide a summary of our detailed assessment of the use and livelihoods value of the freshwater fishes and plants of the Lake Victoria Basin. The aim of this assessment was to collate information on the many and varied uses of these species, in order to increase awareness of their great importance to the livelihoods of the communities of the Lake Victoria Basin, and demonstrate that conservation of this biodiversity is of vital importance.
Norbert C Edomah
“Regional development is a broad term but can be seen as a general effort to reduce regional disparities by supporting (employment and wealth-generating) economic activities in regions. In the past, regional development policy tended to try to achieve these objectives by means of large-scale infrastructure development and by attracting inward investment” (OECD, 2014). A territorial and regional approach to development is crucial in addressing regional challenges, regional economic competitiveness, and reducing socio-economic discrepancies. This book provides a forum to articulate and discuss Africa’s regional development issues in view of the rising opportunities within the African region. This volume contains 14 chapters and is organized in four sections: Introduction; Industry, Trade and Investment in Africa; Agricultural Services and the Water-energy-food Nexus in Africa; and Environmental and Cultural Dimensions to Africa’s Regional Development.
Mary Anne Mandario
One of the factors that contribute to the success of shrimp hatchery operations is the availability of good quality broodstock diets. Polychaetes have been regarded as the best maturation diet for shrimps as they contain essential nutrients requisite for the reproduction of shrimps. Consequently, the demand for polychaetes increased with the intensification of shrimp farming and as a result, the natural stocks are depleting gradually and thus, could no longer provide sustainable supply for shrimp hatcheries. In addition, the issue on biosecurity concerning wild polychaetes prompted the shrimp farmers to obtain polychaetes from reputable sources, thus, the culture of polychaetes under controlled condition has become a sustainable alternative. The SEAFDEC Aquaculture Department (SEAFDEC/AQD) therefore initiated the “Refinement of rearing and feeding techniques for sustainable mass production of the polychaete Marphysa sp.” to address the gaps in polychaetes culture and ensure the sustainability of polychaetes production to supply the shrimp hatcheries at SEAFDEC/AQD, and where the potential mass production of the polychaetes (Marphysa sp.) in indoor tanks is being undertaken to ensure that these are pathogen-free.
RELATED PAPERS
Adekunle Mario
Archives of Agriculture and Environmental Science
Saugat Khanal , Mamata Shrestha
International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies 2020; 8(3): 384-394
Theophilus C H I N O N Y E R E M Nwokedi
Gap analysis evaluation of Nigeria’s fish demand and production: Empirical evidences for investment in and policy development for offshore mariculture practices
Nwokedi Theophilus
Masahiko Haraguchi
Pedro Bueno
Science of the Total Environment
Mostafa Hossain
Trudy Rood , Maurits van Den Berg
Sustainable Aquaculture
Meryl Williams , Marilyn B Porter , Kyoko Kusakabe
IPBES Global Assessment on Biodiversity and Ecosystem Services
Alfonso Langle
epheson sadebo
Rachel V E Cooper
Journal of AgriSearch (JAS) , Ashutosh Upadhyaya , prem k sundaram
INTERNATIONAL JOURNAL OF WATER RESOURCES DEVELOPMENT
Golam Rasul
Sandrine Dury
Journal of Economic and Social Policy
alistair mcilgorm
Yongkil Glen Cho
Chad L Hewitt
Phương Hoàng
Journal of cleaner production
Muhammad Amjad Bashir
Aquatic Invasions
ABDULWAKIL SABA , Shamarina Shohaimi , Syaizwan Zahmir Zulkifli
Maina Kumari
Christian Reinhard Vogl , Brojo Paul
BERNARD LAMA NGOTA
Reviews in Fisheries Science
Dominique Bureau
Journal of Industrial Ecology
Laura Saikku
Bijay Shrestha
Md Rony Golder
Shrestha, M.K. and J. Pant (eds.), Small-scale Aquaculture for Rural Livelihoods: Proceedings of the National Symposium on Small-scale Aquaculture for Increasing Resilience of Rural Livelihoods in Nepal.
Annette Breckwoldt
Poh Sze Choo
Alexander Shula Kefi
International Journal of Fisheries and Aquatic Studies
Olaganathan Rajee , Alicia Tang
Oluwafemi Ajayi
Manik Lal Bose
Meryl Williams , Kumi Soejima , Piyashi DebRoy , Mohammad Nuruzzaman , Marilyn B Porter , Farisal U Bagsit , Khalfan Alrashdi
RELATED TOPICS
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024

Rainbow Trout Business In Nepal
.jpg)
Related Post

Nepali RMG Waiting For Its Revival

Silver Lining On Silver Jewellery

Nepali Tea: Tea from the High Lands
Leave a comment, leave a facebook comment.
Hello, I am 21 years old. Recently living in Doha, Qatar. I'm planning to return back to Nepal after a year. I have done a small research about the Rainbow Trout fish and appear to have an interest to do once i'm back to Nepal. Recently my family is in Kathmandu. I would like to get some suggestion like, either i can start this business with 5-6 Lakhs along with the annual expenses or not. and also i would like to know a brief estimation or a small vision on how much profit could i get with my investment. I have realized that, working overseas will not help to grow on your own. So, i should start my own business from a young age. I would really appreciate your reply on my email. Regards, Sachin
Hello publisher, I have bit confusion on your calculation. You wrote 20 million required to produce 10 tons. could you please tell me how such is 20 million rupees.I think 1 million is equal to 10 lakhs.

No Laughing Matter
The sweet rewards of power.

Update: 2020-03-25 | Source: Nepal Rastra Bank (NRB)
Update : 2020-03-25
Source: Federation of Nepal Gold and Silver Dealers' Association

Biofloc Fish Farming in Nepal

Biofloc Fish Farming In Nepal
Introduction.
Biofloc fish farming is gaining popularity in Nepal as an effective and long-lasting technique for growing fish. This innovative technique involves creating an environment where microorganisms, such as bacteria and algae, form a bio floc to enhance water quality and provide a nutrient-rich environment for fish. In Nepal, where traditional aquaculture faces water scarcity and environmental concerns, bio floc fish farming offers a promising solution.
Biofloc fish farming is a kind of aquaculture that uses microbial communities to turn fish waste into a naturally occurring food source, enabling high-density, sustainable fish farming.
With its diverse topography and varying climate, Nepal presents opportunities and challenges for aquaculture. Implementing bio floc technology allows fish farmers to overcome some of these challenges. One of the critical advantages of bio floc fish farming in Nepal is its water-saving feature.
Traditional aquaculture often requires large amounts of water, which can be a limitation in regions with water scarcity. Biofloc systems significantly reduce water consumption, making it a sustainable option for farmers in Nepal.
Moreover, biofloc fish farming contributes to increased biosecurity. The closed and controlled environment minimizes the risk of diseases, providing a healthier and more secure environment for fish growth. This is particularly important in Nepal, where disease outbreaks can devastate aquaculture.
Also, Read: Depths of Sustainable Fish Farming Investigated
Is Biofloc Fish Farming Profitable?
Biofloc fish farming can be very profitable, but it’s not a guaranteed path to riches. Several factors influence its potential for success.
One key factor that makes biofloc fish farming profitable is the efficient use of resources. The technology allows farmers to optimize space, water, and feed, resulting in higher fish production with lower input costs. Additionally, the reduced risk of disease outbreaks enhances the survival rate of fish, further contributing to increased profitability.
The microbial flocs in biofloc systems provide a natural and cost-effective feed source for the fish.
The market demand for fish is another crucial factor. In Nepal, where fish is a staple food and demand is consistently high, biofloc fish farming can be lucrative. The controlled environment of biofloc systems ensures a steady supply of quality fish, meeting consumer preferences and fetching more money on the open market.
However, like any business venture, biofloc fish farming success requires careful planning, proper management, and adherence to best practices. Farmers need to invest in training and education to maximize the benefits of biofloc technology and ensure a profitable outcome.
Biofloc Fish Farming Guide
Implementing a successful biofloc fish farming system demands a thorough comprehension of the technology and its principles. Here is a step-by-step guide to help farmers in Nepal establish and manage a biofloc fish farm:
- Step 1: Selection of Site: Select a place that has access to water and adequate facilities. Think about things like availability, temperature, and water quality.
- Step 2: System Setup: Install a bio-floc system, including tanks or ponds, aeration systems, and a water recirculation system. Ensure proper design and sizing based on the planned fish production.
- Step 3: Microbial Inoculation: Introduce beneficial microorganisms like bacteria and algae to initiate bio floc formation. This microbial community will help maintain water quality and provide a nutrient-rich environment for fish.
- Step 4: Stocking the Fish: Select appropriate fish species based on market demand and local preferences. Stock the fish in the biofloc system at recommended densities.
- Step 5: Water Quality Management: Monitor and manage water parameters such as pH, dissolved oxygen, ammonia, and nitrite levels. Adjust water quality as needed to ensure optimal conditions for fish growth.
- Step 6: Feed Management: Implement a feeding strategy based on the nutritional requirements of the selected fish species. Use high-quality, balanced feed and adjust feeding rates based on fish growth.
- Step 7: Disease Prevention: Adopt biosecurity measures to prevent disease outbreaks. Implement quarantine protocols for new fish introductions and monitor health regularly.
- Step 8: Harvesting: Plan the harvesting process based on the growth rates of the fish. Use proper harvesting techniques to minimize stress and ensure product quality.
- Step 9: Marketing: Develop a marketing strategy to sell the harvested fish. Establish partnerships with local markets, restaurants, or distributors to guarantee a consistent item market.
- Step 10: Continuous Learning: Stay updated on advancements in biofloc technology and aquaculture best practices. Attend training programs and workshops and engage with the aquaculture community for continuous learning and improvement.
Biofloc Fish Farming Cost
While bio-floc fish farming offers numerous benefits, awareness of the setup and maintenance costs of a bio-floc system is crucial for farmers in Nepal considering this innovative method. The cost of biofloc fish farming can differ based on elements like the size of the operation, system design, and local conditions.
General range of estimated costs for Biofloc fish farming in Nepal:
Small backyard system (around 1000 liters): NPR 20,000 – NPR 50,000 Medium-scale system (around 5000 liters): NPR 50,000 – NPR 1,00,000 Large-scale commercial system (around 10,000 liters or more): NPR 1,00,000 – NPR 5,00,000 or more
Here’s a breakdown of critical expenses:
Infrastructure Costs:
Building bio floc ponds involves expenses such as excavation, pond liners, aeration systems, and other infrastructure components. The size and number of ponds will influence the overall infrastructure cost.
Microbial Inoculation:
Introducing beneficial microorganisms to initiate biofloc formation may require the purchase of microbial inoculants or probiotics.
Carbon sources, such as molasses, are often added to stimulate microbial growth in biofloc systems.
These additives contribute to developing a healthy microbial community in the pond.
Stocking Costs:
Acquiring quality fingerlings or juvenile fish for stocking the ponds is a significant upfront expense. The type of fish species chosen and the desired stocking density will impact the overall stocking cost.
Water Quality Management:
Invest in water quality monitoring tools to regularly assess parameters like pH, temperature, and ammonia levels. Quality testing kits and meters are essential for maintaining optimal conditions for fish growth.
Feed Costs:
While bio floc systems reduce reliance on external feed, farmers still need to provide supplementary feed to ensure proper nutrition for the fish. Calculate the cost of commercial feed based on the chosen feeding strategy.
Market Research and Marketing Costs:
Invest in market research to identify potential buyers and establish marketing channels. Budget for promotional activities and building relationships with local markets or distributors.
Labor Costs:
Consider the labor required for daily operations, including feeding, monitoring water quality, and general maintenance. Labor costs will depend on the farm scale and the level of automation implemented.
Farmers must conduct a thorough cost analysis based on their specific circumstances and local conditions. While the initial investment in bio floc fish farming may be higher than in traditional methods, the potential for increased efficiency, water savings, and higher yields can contribute to long-term profitability.
Here are some additional resources that you may find helpful:
- National Aquaculture Development Centre, Nepal: https://www.fao.org/fishery/countrysector/naso_nepal
- Biofloc Fish Farming Association of Nepal: https://vetnepal.com/article_details/Practices-of-Fish-farming-Biofloc-culture
Conclusion:
In conclusion, biofloc fish farming in Nepal holds excellent promise as a sustainable and profitable aquaculture method. With careful planning, proper management, and ongoing education, farmers can successfully implement and benefit from this innovative technology, contributing to the growth and sustainability of the aquaculture industry in Nepal.
Similarly: Sustainable Practices in Organic Fish Farming: Nurturing Healthier Aquatic Ecosystems

- Agriculture
Livestock Farming
Aquaculture
Poultry Farming

How to select the area for fish farming?
- Select the areas that clean and fertile. Don’t go for sloped lands.
- Don’t select the flooded and polluted lands, these can harm your business.
- Don’t select the land near the farming lands, as fertilizers and pesticides used in farming lands may mix with water and can the fishes.
- You should select the land that is slightly lower than the main water source. Areas near main water resources can reduce the cost of filling water to your farmland.
- Area your select should have a good transportation system that can be easy to market your products and other necessities.
Select the type of fish farm for your Fish Farming Business Plan:
Fish farming business can be started in many types, cage system, tank system, or pond system.
Cage System of Fish Farming Business Plan: Make a suitable cage and place it in lakes, ponds, bayous, or oceans and start feeding the fish until they grow for marketing.
Tank System of Fish Farming Business Plan: In this system fishes are raised in tanks, make of a few tanks, and grown fish in them .
Pond system of Fish Farming Business Plan: In this pond system, first you should construct the pond;
- Fish Farming Business Plan – Pond Construction: Construct the suitable pond in the area you selected for fishing. For that, you make a perfect design and construct the pond according to that. The design of the pond depends on the fish species you opted to raise. While designing the ponds, you should ensure the availability of all types of facilities for maintaining a profitable fish farming business. In designing the ponds, you take suggestions from the nearest fisheries institute to learn about the specific pond design. The pond environment should good and clean, which promotes the healthy growth of fish.
- Fish Farming Business Plan – Pond Management: Successful fish farming depends on the pond ecosystem. The source of water can be a river, lake, or other natural ways like rainwater and underground water. Ponds should have the facility to change water weekly or monthly. For high fish production, the pond water should be changed or replaced only when it would lose from evaporation or seepage. Changing the whole water more and more may reduce the reduce production. Small-sized and medium-sized ponds are easy to maintenance. Giant ponds are not suitable for good maintenance.
- Fish Farming Business Plan – Size of the Pond: The size of the farming depends on your farming type. If your cultivating fish commercially you must make a large one. The shape of the pond should be square or rectangular.
- Fish Farming Business Plan – The depth of the Pond: The water depth will be 30% in one corner and 100% in another corner. The depth of the water depends on the species of fish you are cultivating. The depth of the pond can be more if you want to use it for reserving water for the dry season .
The pond should be well-drained to remove all water while collecting the fish. The shore of the fish pond should be wide enough for reducing the erosion problem. Fishpond should be prevented from theft, so you should construct the pond near the residence or it should keep people for security. Another way is by keeping bamboo poles or tree branches with thorns in the ponds, it will make it impossible to collect fish with the net. The bamboo pole and tree branches not only prevent fish from theft but also serves fish come extra natural food.
For commercial fish farming you need some additional equipment:
- Aerations Devices.
- Net or seine reels.
- Handling and grading equipment.
- Water testing equipment.
Selecting the suitable species is very important that keeps your business in profits. You should select the breeds that have a huge market and high prices in your local and export markets. The most famous fish breeds that used in fish farming are carp, salmon, tilapia, and catfish. There are even many other fish species that have many varieties that are suitable for farming in all types of agro-climatic conditions. You should the fish species for farming, depending on your local climate, facilities, demand, and price.
Fishes that are grown in Saltwater: Prawn, Green Tiger shrimp, Indian White Shrimp, Horina Chingri, Bhetki, Bombay Duck, Rupchanda, Lalpoa, Hilsa, Tuna, Lakha, Dogfish, Ribbon Fish.
Fishes Grown InFresh Water: Katla, Ruli, Kalibaus, Ghonia, Mrigal, Nandina, Common crap, Sharpunti, Titpunti, Mola, Chela, Dankina, Boumach, Gutum, Aier, golsa Tangra, Rita, Pangas, Magur, African Catfish, Shing, Gozarm Taki, Kuche, Vheda, Nilotica, Koi, kholisa, Tepa, Chapila, FOli, Chotal, Lobster.

There are different fish species that are raised on fish farms, the most common fish species raised are salmon, carp, tilapia, catfish, catla, and cod, etc.
- Catfish Farming of a Fish Farming Business Plan: Catfish farming is suitable for the warm climate. These grown in freshwater ponds and fed with soybean, corn, and rice. This is more sustainable fish species for fish farming. It is popular for its health benefits. Harvesting periods for catfish are 18 months. There are a number of varieties of catfish some popular ones are blue catfish, channel catfish, and flathead catfish.
- Tilapia Farming of a Fish Farming Business Plan: One of the most popular fish used in fish farming in Asia. This fish has great demand for high protein, size, and production capability. Tilapia grow well in the warmer climate. Water temperature should be between 28 to 30 degreesCelsius of temperature. Tilapia fish require a cereal-based diet and don’t eat other fish. The reproduction rate in this fish species is very high so managing them is a bit challenging. These fish’s good resistance power in fighting the diseases.
- Salmon Farming of a Fish Farming Business Plan: One of the most popular fish farming species having great demand in the market. There are two other varieties of Pacific salmon that are also farmed-chinook and coho. These fish should be vaccinated to prevent diseases. Salmon feed is made to conserve wild fish stocks .
- Tuna farming of a Fish Farming Business Plan: These fish are saltwater fish and have great demand in the commercial fish farming business. Japan is having a great market for this fish species. Their many species of tuna are bluefin, yellowfin, and albacore. Tuna are carnivorous and eat other fishes, these are farmed in net pends offshore and recirculation systems.
- Eel Farming a Fish Farming Business Plan: These fishes have a huge export market. Eel fish farming majorly is done in Asia, Japan and Taiwan are leading producers of Eel fish. Eel fish live in freshwater they are young, and as they are mature they migrate to the sea for breeding.
Feeding the most important part of fish farming. You should always provide fish a high quality and nutritious food. As the quality of food leads to maximum production but also keeps the fish healthy with more weight. You should provide them both supplementary fish feed along with natural food. There are many brands of supplementary fish feed is available in the market depends on the specific fish species. The fish feed can be prepared on your own, you can learn preparation. You should take care that the feed should have all the necessary nutrients, vitamins, minerals, salt, etc. Feeding time depends on the fish species. Overfeeding may affect the fish .
- Natural Fish Feed: Water is the medium for surviving fish. There are much natural fish feeds available in the water. This natural feed depends upon water and soil fertility. This natural fish feed can be increased by using fertilizer. Natural fish feeds are Plankton(microscopic plants), Aquatic plants and insects, tiny moss, the organic substance of pons, various types of grasses in water.
- Supplementary Fish Feed:
- Rice Bran- A very common and cheap better fish feed. It contains 10 to 14% proteins, Vitamin B1, B2, B6, and many enzymes .
- Wheat Chaff: Contains more fiber, controls many types of fish diseases. The amount of protein is 10 to 15%.
- Maize: Best fish supplementary feed, it contains proteins, carbohydrates, fat, vitamin A, and E.
- Tiny moss: Floaty water plants, contain 14 to 20 % protein.
- Fish Powder: Easily digestible fish meal, contains 55 to 60% protein.
- Bone Powder: Best food for Fishbone, contains calcium and magnesium .
- Other supplementary feeds are Vitamins, animal blood, etc
For best fish production you provide both natural and supplementary fish feeds.

The food you provide to fish should be fresh and nutritious. Pond maintaining plays a major role in fish productions. Water in the pond can be changed occasionally or can use some necessary chemicals according to the suggestion of an expert. Fish health should be monitored regularly on a regular basis. All the necessary far tasks should be done timely. The pond environment should be maintained properly with timely maintenance for good fish production and growth. Regular soil and water quality test should be done on regular basis. You should keep stock of necessary drugs on your farm. Should take all necessary steps to prevent all types of predators, including frogs, snakes, etc.
Fish may get infected by diseases for many reasons. Some reasons for diseases in fishes:
- Bacterial, fungus, viral, and germ attack.
- Parasites like worms, leech, lice, etc.
- Malnutrition.
- Changes in water.
- Pollutions in water.
- Using excessive organic and chemical fertilizer.
Types of Diseases:
- Bacterial Diseases: Tail and fin rot diseases, gill rot diseases, etc.
- Fungus Diseases.
- Viral Diseases.
- Parasite Diseases: White spot diseases, argulosis fluke diseases, etc.
- Malnutrition’s Diseases: Caused due to lack of protein food.
Fish Farming Business Plan – Disease Symptoms in Fish:
- Fish stops consuming food.
- Losing physical balance.
- Floats over water.
- Rubbing their body to stones in water.
- Swimming restlessly.
- Head grows large.
- Losses bright looks.
- The natural color of fish get changes and becomes light or dark.
- Excessive release of mucus.
- Belly gets swelled and eyes come out.
- Fish become very sick.
- Rotation can be seen in the gill of the fish.
Fish Farming Business Plan – Prevention Method for Fish Diseases:
Some prevention methods to keep your fishes away from diseases:
- Pond or tank environments should be favorable for fish farming.
- Should maintain the quality of soul and water suitable for fish.
- Always stock healthy, strong, and high-quality minnow in the pond.
- Fishpond should in an open place and free from aquatic weeds.
- Ponds should be kept safe from harmful animals.
- Don’t allow floodwater to enter the pond.
- Supply sufficient quality fertilizer and food in the pond regularly.
- The pond should be germ-free by using lime in the pond 2-3 times a year.
- Test the fish health once a month.
- Diseases or infected fish should be removed from the pond.
- The net used for removing infected fish should not used to catching healthy fish.
- You should maintain the balance between the number of stocked fish and the stocking power of the pond.
- Should provide nutritious food at regular times .
Harvesting in Fish Farming Business Plan
Read this: tilapia fish farming ..

Fish takes a certain period of time to become suitable for harvesting. Each fish species take a different period to get ready for harvesting. You can start harvesting when fish start reaches a marketable weight for marketing. For harvesting, you can use nets or by removing water from the pond. Harvesting of the fish should be done during the morning or afternoon when the temperature is low. After harvesting, send the fish directly to the market as soon as possible.
Marketing is not a big task in fish farming. There are many markets available where you can market your products. All types of fishes are in great demand in the market. After harvesting, you can sell your fish at your nearest markets. Even there many companies that export the fish to other countries. So, there no matter to worry about marketing you just need to focus only on producing quality fish.
Commercial fish farming is really a very profitable and good source of earning living. If you are planning to enter into this business, you need to fish make a complete study of fish farms and fish breeds. For this, you need to visit nearby fish farms.
Indoor fish farming is the best alternative to cultivate fish outdoor in a cage system. Under many technological advances, raising fish indoor is now possible with proper control production methods. Indoor fish farming is a bit troublesome below are some advantages and disadvantages of fish farming.
Advantages:
- Fish will be safe from predators and weather changes.
- Fish are grown under suitable temperatures in good water with regular feeding.
- Fish escaping can be prevented and getting loose amongst wild fish populations.
- Allows higher stock densities and often saved farm labor input costs.
- Indoor fish farming is flexible and can save transportation costs .
Disadvantages:
- Huge maintenance like electricity, infrastructure.
- Huge investment.
- Fish raised indoors are carnivorous, they require a large amount of other fish for their diet.
In case if you miss this: Growing Vegetables Hydroponically .
Profitable Village Farming Business Ideas in 2024
High-yield aquaculture: fast-growing fish for farming, effective fish pond construction techniques for beginners, irrigation and water management in pineapple farming, blossom to harvest: mastering flowering and pollination in papaya farming, pig fattening essentials: from selection to sale for beginners, raising wagyu cattle: a complete guide for premium beef production, soil types and their water holding capacity, optimizing irrigation schedules for coconut groves for enhanced yield, espresso your garden: coffee grounds for healthier acid-loving plants.
- The Best Soil Mix for Snake Plants: How to Mix Your Own Snake Plant Soil
- Green Thumb Success: Expert Tips for Cultivating Greenhouse Beans All Year Round
- Bloom All Year Round: The Ultimate Guide to Indoor Hyacinth Care
Eco-Friendly Gardening: How to Make Liquid Fertilizer from Kitchen Waste
- Ultimate Guide to Grow Anise in Pots: Explore Seed Propagation to Harvesting
- Guide to Raising Chester White Pigs: Discover Breed Facts to Growth Management
- Mastering the Elegance: The Ultimate Guide to Weeping Cherry Tree Care, Planting, and Maintenance
- Ultimate Guide to Planting Garlic in Grow Bags: Growing Strategies for Beginners
Thanks, Mr. Reddy. I read your article on fish farming. It is a very insightful document for aspiring fish farmers. Thanks a lot
Thank you Mr Reddy for your effort to provide the required information related to the poultry and fish farming project. I am a newcomer in the farm sector but your articles reduced my doubts in this segment.
Thanks with regards
Thank you for your information,I love to start fish farming businesses in my compound Nigeria Delta state warri
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
The Best Soil Mix for Snake Plants: How to Mix...
Green thumb success: expert tips for cultivating greenhouse beans all..., bloom all year round: the ultimate guide to indoor hyacinth..., ultimate guide to grow anise in pots: explore seed propagation..., guide to raising chester white pigs: discover breed facts to..., mastering the elegance: the ultimate guide to weeping cherry tree..., ultimate guide to planting garlic in grow bags: growing strategies..., how to fix spider plant leaf-related problems: natural and organic..., 10 reasons why your tulsi plant is shedding leaves: home..., rice production in myanmar; paddy farming in myanmar, banana farming information guide, growing oats information for beginners, contract goat farming in india: how to earn an extra income from this long-term investment, chilli cultivation information guide, how to start and succeed with microgreens business plan.
Government of Nepal Ministry of Agricultural and Livestock Development Department of Livestock Services
Central fisheries promotion and conservation center, central fisheries building, balaju, kathmandu, government of nepal ministry of agriculture and livestock development department of livestock services.
- Introduction
- Organization Chart
- Old Organization Chart
- Technological Publication
- Annual Book
- Fishing Series
- Regulations
- Karyabidhi and Norms
- Annual Books
- Fisheries Series
- Fisheries Statistics
- Fish Production Technologies and Aspects
- Fisheries Bulletin
- Leaflet/ Booklet
- Technical Guides & Others
- Right to Information
- Grant Details
- Image Gallery
- Video Gallery
Sarita Gautam
Chief gazetted first (tech.) [email protected] The Government of Nepal gives priority on food security and poverty alleviation through developing various sectors of agriculture including fisheries and aquaculture. Nepal is an agricultural country having 66 percent people directly engaged in farming. Aquaculture and fishery is one of the fastest growing agriculture subsectors in Nepal. The current total national fish production is 113,736 Mt of which 20 % is contributed by capture fisheries while 80% is from aquaculture. Fisheries sector contributes about 1.83% in Agricultural Gross Domestic Production and 0.44% in Gross Domestic Production. History of Nepalese aquaculture is very short however; catching fish from nature is being practiced since ancient time. At present, the availability of fish in least developed country is 11 kg but in Nepal, it has very low 3.9kg. However, fish as a protein-rich food is acceptable to every level of the population. Domestically produced supplies of fish are primarily from simple traditional capture fisheries in rivers and lakes 21000 Mt and fish culture in the private and governmental sector 92,736 Mt. Thus, the production of fish in Nepal is still at a very low level, being very rich in water resources.
News & Notices
प्रथम त्रैमासिक बुलेटिन-२०८०.
Submited By : CFPCC
प्रशिक्षक रोष्टरमा सुचीकृत हुन आवश्यक बिषय बिज्ञको लागि Format
तालिम प्रशिक्षकको रोस्टरमा नामावली सूचीकृत हुन सम्बन्धी जरुरी सूचना, जानकारी सम्बन्धमा, publications, fisheries bulletin vol. 2, fisheries bulletin vol. 1, व्यवसायिक मत्स्य पालन प्रविधि, national fisheries statistics 2079/80, fish disease profile, rules & regulations, माछा भुरा बारे मापदण्ड, २०६१, trout development program, पशु क्वारेन्टाइन/मत्स्य कार्यविधि, आयात निर्यात सिफारिस, पशुजन्य उद्योग स्थापना तथा विक्री वितरण अनुमति सम्बन्धी कार्यविधि, 2073, माछा भुरा बारे मापदण्ड निर्धारण, २०६१, माछा बीमालेख, जलचर ठेक नियम - २०१९, feed regulation, 2041, नेपाल सरकारले जलचर संरक्षण ऐन, २०१७ को दफा ४ तथा ५ बमोजिमको आदेश, national parks and wildlife conservation act 2029(1973), aquatic animal protection act_ 2017(1960), feed act, 2033, animal health and livestock service act, 2055, fifth periodic plan (fiscal year 2076/77 - 2080/81), national fisheries development policy, 2079, national agricultural policy-2004, राष्ट्रिय सीमसार नीति २०५९, कृषि विकास रणनीति, पोखरीमा माछा पालन, related links.
- Ministry of Agricultural and Livestock Development
- Ministry of Federal Affairs and General Administration
- Ministry of Finance
- National Planning Commision
- Department of Livestock Services
- Nepal Agriculture Research Council
Fish Farm Business Plan Template
Written by Dave Lavinsky
Fish Farm Business Plan
You’ve come to the right place to create your Fish Farm business plan.
We have helped over 1,000 entrepreneurs and business owners create business plans and many have used them to start or grow their Fish Farms.
Below is a template to help you create each section of your Fish Farm business plan.
Executive Summary
Business overview.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm is an aquaculture business located 30 miles north of Madison, Wisconsin. The farm is owned by Jason Newcomb, a fish farm manager for over ten years, who had responsibility for all operations and customer supply in his former position. Now that Jason has garnered a sizable reputation as an experienced fish farmer, several former clients of his last employer are asking Jason if they can begin using his services to supply the fish they need. Jason plans on recruiting a team of professionals to help manage and operate the day-to-day activities found at the AcquaHarvest Fish Farm.
The AquaHarvest Fish Farm will provide high-quality, locally sourced fish to meet the growing demand for fresh and sustainable seafood in the region. By utilizing advanced aquaculture techniques and maintaining a focus on environmental stewardship, AquaHarvest Fish Farm aims to become a leading provider of farm-raised fish in Wisconsin.
Product Offering
The following are the products that AquaHarvest Fish Farm will provide:
- Fresh, locally-sourced, farm-raised trout and tilapia
- Fish products, such as smoked trout, fish jerky, fish for stocking ponds
- Sustainably produced farmed fish in a low-impact environment
Customer Focus
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will target a wide range of customers, including individual consumers, restaurants, grocery stores, and seafood distributors. Additionally, we will focus on promoting our fish as an alternative to wild-caught fish, emphasizing the traceability and sustainability of our farming practices.
Management Team
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be owned and operated by Jason Newcomb. He recruited his former marketing and sales manager, Tim Olsen, to be the new marketing and sales director for AcquaHarvest Fish Farm.
Jason Newcomb holds a certification from the National Institute of Fish Farming in Sustainable and Environmental Protections. He has been working at a well-known fish farm outside Madison for the past decade. Recently, he determined that he could take the best attributes of his former employer, apply them to his new business, and add several improvements to the fish farming process that would appeal to consumers and lower the environmental toll on the land he purchased.
Tim Olsen, who will be the new Marketing and Sales Director, has been working in his former position for over thirteen years and has won the “Outstanding Sales & Marketing Promotions” award multiple times within the fish farming community groups in Madison, Wisconsin. Tim is known for his ability to strategically market and sell long-term contracts from fish buyers on both a national and international level.
Success Factors
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be able to achieve success by offering the following competitive advantages:
- Friendly, knowledgeable, and highly-qualified team of AquaHarvest Fish Farm
- A selection of farmed fresh fish, sustainably raised and locally-sourced
- Fish products; including fish for stocking ponds, fish jerky, and smoked trout
- AquaHarvest Fish Farm will offer the best pricing in town. The pricing structure is the most cost-effective when compared to the competition.
Financial Highlights
AquaHarvest Fish Farm is seeking $200,000 in debt financing to launch its AquaHarvest Fish Farm. The funding will be dedicated toward securing the office building and purchasing office equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated toward three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the print ads and marketing costs. The breakout of the funding is below:
- Office space build-out: $20,000
- Office equipment, supplies, and materials: $10,000
- Three months of overhead expenses (payroll, rent, utilities): $150,000
- Marketing costs: $10,000
- Working capital: $10,000
The following graph outlines the financial projections for AquaHarvest Fish Farm.
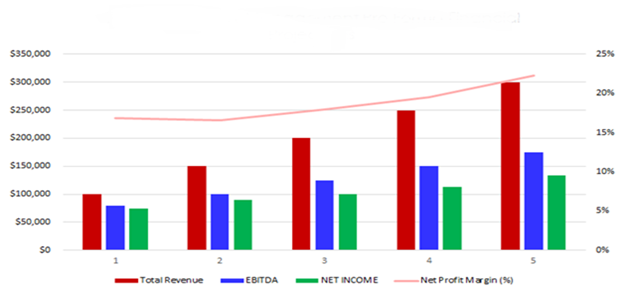
Company Overview
Who is aquaharvest fish farm.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm is a newly established, full-service fish farm 30 miles from Madison, Wisconsin. AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be the most reliable, cost-effective, and efficient choice for customers in Madison and the surrounding communities. AquaHarvest Fish Farm will provide a comprehensive menu of fish and fish products for multiple customer segments to utilize. Their full-service approach includes a comprehensive array of locally-sourced, sustainable fresh fish, smoked fish, fish jerky and other fish products.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be able to effectively provide 300 fresh fish each week, with fish products numbering 200-300 pounds per week. The team of professionals are highly qualified and experienced in the fish farming industry and the management and operations of a fish farm. AquaHarvest Fish Farm provides the perfect one-stop shop for all the fresh, locally-sourced fish customers may need, including filets, steaks, whole fish, fish for sushi, and other expanded customer uses. AquaHarvest will meet every customer expectation or offer refunds, if ever needed.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm History
Since incorporation, AquaHarvest Fish Farm has achieved the following milestones:
- Registered AquaHarvest Fish Farm, LLC to transact business in the state of Wisconsin.
- Has a contract in place at one of the office buildings, where the operations and management teams will set up office space within the 10,000 square foot area.
- Reached out to numerous former clients to include fish handlers, maintenance workers and other staff members for the new fish farm company.
- Began recruiting a staff of ten associates and office personnel to work at AquaHarvest Fish Farm.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm Services
The following will be the products AquaHarvest Fish Farm will provide:
Industry Analysis
- The fish farm industry is expected to grow over the next five years to over $202 billion.
- The growth will be driven by the increased need for regulated raising and harvesting of fresh fish and crustaceans.
- The growth will also be driven by the consumer demand for sustainable fish-farmed sources of fish.
- The growth will be driven by the increased interest by consumers in healthful eating practices, including fresh fish.
- Costs will likely be reduced as more fish farms are established and can provide fresh, locally-produced fish.
Customer Analysis
Demographic profile of target market.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will target customers within the Madison, Wisconsin region. They will target individual consumers, restaurants, grocery stores and seafood distributors.They will also target consumer groups focused on traceability and sustainability of food, including fish.
Customer Segmentation
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will primarily target the following customer profiles:
- Restaurants
- Grocery stores
- Seafood distributors
- Individual customers
Competitive Analysis
Direct and indirect competitors.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will face competition from other companies with similar business profiles. A description of each competitor company is below.
Fresh SeaPack Fish
The Fresh SeaPack Fish Company is located in Chicago, Illinois. The company is owned by Jerome Packson, a former restaurateur who now oversees the supply of fish and seafood into the finest Chicago restaurants. The company sources locally-raised fish, vacuum-packs and seals each filet, and ships the fish to regional and city-wide restaurants. With one-day service, the fish is as fresh as when it was shipped, which offers excellent flavors for consumers.
Jerome Packson established Fresh SeaPack Fish in 2000, when it became apparent the fish supplies coming in from Alaska were being depleted by wild-caught fishermen. This created in him a drive to change the process, so his company could guarantee a “fresh fish” result in restaurants, while processing and packing up to 24 hours in advance of shipment.
Sea & Land Distributors
Sea & Land Distributors are co-owned by brothers, Dean and Dave Lancaster, who have located their distribution company in Suamico, Wisconsin. From this location, vacuum packed fish can be flown to customers within a multi-state area, typically within 4 hours. The distribution company was formed in 2004 by Dean Lancaster, a former sales manager for a fish industry networking company, and Dave Lancaster, a former seafood salesman for the large, well-known fish and fish product provider.
In addition to fish and fish products, Sea & Land Distributors began distributing fresh beef to restaurants and grocery stores. Using the same processes and techniques, the beef filets, steaks, ribs and other choice cuts are sent to regional clients within 4-hours of processing. This addition to the company has resulted in a significant increase in revenue and the addition of staff to cover the beef portion of the business.
Harris Seafood Company
The Harris Seafood Company is a certified “organic and sustainable” seafood distributor, focusing on the Madison region of Wisconsin. Trent Harris is the owner and president of the company, while six employees process and pack seafood for delivery to Madison restaurants. The company was formed in 2021 and has an estimated 100 customers or clients, who are served weekly or monthly with vacuum-packed seafood.
The Harris Seafood Company has plans to open another processing center in Chicago within three years in order to grow the highly successful seafood sales industry into high-end Chicago restaurants. With demand rising, the Harris Seafood Company plans to meet that demand and exceed current company expectations.
Competitive Advantage
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be able to offer the following advantages over their competition:
Marketing Plan
Brand & value proposition.
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will offer the unique value proposition to its clientele:
- Highly-qualified team of skilled employees that is able to provide an array of fish and fish products, including smoked trout and fish jerky.
- Fresh locally-sourced fish farmed include: trout and tilapia. These two fish are the most sought-after and easily raised fish in the species, leading AquaHarvest to recognize their prominence in the restaurant industry and provide these two fish for all customers.
- Fish that is sustainably-raised and locally-sourced. Unlike other fish farms, AquaHarvest depends on aqua hydroponic techniques to successfully bring the oxygen and nutrients needed by the fish. These are not harmful to the environment; in fact, these elements enhance our environment over all.
- Unbeatable pricing for clients; AcquaHarvest will offer the lowest pricing in the region.
Promotions Strategy
The promotions strategy for AquaHarvest Fish Farm is as follows:
Word of Mouth/Referrals
AquaHarvest Fish Farm has built up an extensive list of contacts over the years by providing exceptional service and products to former clients. AquaHarvest Fish Farm will garner the former clients before they begin advertising and marketing to new clients. The former clients have already committed to referring associates to AquaHarvest Fish Farm, as well.
Professional Associations and Networking
Both Jason Newcomb and Tim Olsen are well-known in the fish farm industry and have extensive networking contacts. As such, they will work to secure long term contracts with their core target audience to raise the awareness of the new company as soon as possible.
Print Advertising
Two weeks prior to launch, a direct mail piece will be sent to every restaurant, grocery store, seafood distributor and related fishmonger to announce the opening of the company. A discount for clients to sign contracts in the first month will be announced and special packages of service and products will be offered at that time, as well.
Website/SEO Marketing
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will fully utilize their website. The website will be well-organized, informative, and list all the products and services that AquaHarvest Fish Farm provides. The website will also list their contact information and available fish and fish products each day. The sales and marketing director, Tim Olsen, will also manage AquaHarvest Fish Farm’s website presence with SEO marketing tactics. When someone searches in the Google or Bing search engine “fish farm” or “fresh fish near me”, AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be listed at the top of the search results.
The pricing of AquaHarvest Fish Farm will be moderate and on par with competitors so customers feel they receive excellent value when purchasing their services.
Operations Plan
The following will be the operations plan for AquaHarvest Fish Farm. Operation Functions:
- Jason Newcomb – will be the Owner and President of the company. He will oversee all staff and manage client relations. Jason has spent the past year recruiting the following staff:
- Nancy Dyce – will be the Office Manager, who will manage the office administration, client files, and accounts payable.
- Tina Stevens – whose role will be the Staff Accountant, providing all accounting, tax payments, and monthly financial reporting.
- Tim Olsen – Sales and Marketing Manager, who will provide all marketing for AquaHarvest Fish Farm and each product offered.
- John Quinten – Farm Manager, who will operate all fish tanks and facilities and provide all maintenance at the properties.
Milestones:
AquaHarvest Fish Farm will have the following milestones completed in the next six months.
- 5/1/202X – Finalize contract to lease office space
- 5/15/202X – Finalize personnel and staff employment contracts for the AquaHarvest Fish Farm
- 6/1/202X – Finalize contracts for AquaHarvest Fish Farm clients
- 6/15/202X – Begin networking at industry events
- 6/22/202X – Begin moving into AquaHarvest Fish Farm office
- 7/1/202X – AquaHarvest Fish Farm opens its office for business
Tina Stevens will be the Staff Accountant, providing all accounting, tax payments, and monthly financial reporting to Jason Newcomb.
Nancy Dyce will be the Office Manager, who will be responsible for the office administration, client files, and act as an executive assistant, upon request.
John Quinten, will take on the role of Farm Manager, in charge of the tank operations, cleaning, facilities oversight and all maintenance at the property buildings.
Financial Plan
Key revenue & costs.
The revenue drivers for AquaHarvest Fish Farm are the customer fees they will charge to the target audience for their services.
The cost drivers will be the overhead costs required in order to staff AquaHarvest Fish Farm. The expenses will be the payroll cost, rent, utilities, office supplies, and marketing materials.
Funding Requirements and Use of Funds
AquaHarvest Fish Farm is seeking $200,000 in debt financing to launch its fish farm. The funding will be dedicated towards securing the office space and purchasing office equipment and supplies. Funding will also be dedicated towards three months of overhead costs to include payroll of the staff, rent, and marketing costs for the print ads and association memberships. The breakout of the funding is below:
Key Assumptions
The following outlines the key assumptions required in order to achieve the revenue and cost numbers in the financials and in order to pay off the startup business loan.
- Number of Customers Per Month: 185
- Average Revenue per Month: $44,500
- Office Lease per Year: $100,000
Financial Projections
Income statement, balance sheet, cash flow statement, fish farm business plan faqs, what is a fish farm business plan.
A fish farm business plan is a plan to start and/or grow your fish farm business. Among other things, it outlines your business concept, identifies your target customers, presents your marketing plan and details your financial projections.
You can easily complete your Fish Farm business plan using our Fish Farm Business Plan Template here .
What are the Main Types of Fish Farm Businesses?
There are a number of different kinds of fish farm businesses , some examples include: Inland pond fish farm, Open-net pen and cage system fish farm, and Mariculture fish farms.
How Do You Get Funding for Your Fish Farm Business Plan?
Fish Farm businesses are often funded through small business loans. Personal savings, credit card financing and angel investors are also popular forms of funding.
What are the Steps To Start a Fish Farm Business?
Starting a fish farm business can be an exciting endeavor. Having a clear roadmap of the steps to start a business will help you stay focused on your goals and get started faster.
1. Develop A Fish Farm Business Plan - The first step in starting a business is to create a detailed fish farm business plan that outlines all aspects of the venture. This should include potential market size and target customers, the services or products you will offer, pricing strategies and a detailed financial forecast.
2. Choose Your Legal Structure - It's important to select an appropriate legal entity for your fish farm business. This could be a limited liability company (LLC), corporation, partnership, or sole proprietorship. Each type has its own benefits and drawbacks so it’s important to do research and choose wisely so that your fish farm business is in compliance with local laws.
3. Register Your Fish Farm Business - Once you have chosen a legal structure, the next step is to register your fish farm business with the government or state where you’re operating from. This includes obtaining licenses and permits as required by federal, state, and local laws.
4. Identify Financing Options - It’s likely that you’ll need some capital to start your fish farm business, so take some time to identify what financing options are available such as bank loans, investor funding, grants, or crowdfunding platforms.
5. Choose a Location - Whether you plan on operating out of a physical location or not, you should always have an idea of where you’ll be based should it become necessary in the future as well as what kind of space would be suitable for your operations.
6. Hire Employees - There are several ways to find qualified employees including job boards like LinkedIn or Indeed as well as hiring agencies if needed – depending on what type of employees you need it might also be more effective to reach out directly through networking events.
7. Acquire Necessary Fish Farm Equipment & Supplies - In order to start your fish farm business, you'll need to purchase all of the necessary equipment and supplies to run a successful operation.
8. Market & Promote Your Business - Once you have all the necessary pieces in place, it’s time to start promoting and marketing your fish farm business. This includes creating a website, utilizing social media platforms like Facebook or Twitter, and having an effective Search Engine Optimization (SEO) strategy. You should also consider traditional marketing techniques such as radio or print advertising.

BagBazar, Ktm
Opposite to PK Campus
- +9779804495818
24/7 SMS support
Sun - Fri: 9:00 - 17:30
Saturdays: 10am-2pm

All About Agriculture Business in Nepal
Table of contents.
Nepal is a predominantly agricultural country, with agriculture representing a significant portion of its economy. The main crops grown in Nepal include rice, wheat, maize, millet, and barley. In addition, various fruits and vegetables are also grown in the country. The mountainous terrain of Nepal makes it well-suited for terrace farming, which is a common method of cultivation in the country. However, Nepal’s agriculture sector faces challenges such as poor infrastructure and limited access to markets, technology, and credit, which hinder its growth and productivity. Despite these challenges, the government of Nepal is working to improve the agriculture sector and increase its contribution to the country’s economy. So, with a proper planning and innovation, investment in agriculture sector can provide a good return in long run.

Objectives of Agriculture Business in Nepal
The objectives of agriculture business can vary depending on the specific goals and priorities of the business. Some common objectives of agriculture businesses include:
- Maximizing profits: Like any other business, agriculture businesses aim to generate profits by selling their products for more than they cost to produce.
- Increasing productivity: Agriculture businesses often focus on improving their production processes and techniques in order to increase the amount of crops or livestock they are able to produce.
- Expanding markets: Agriculture businesses may seek to expand their market reach by selling their products to new customers or in new geographic areas.
- Improving sustainability: Many agriculture businesses are focused on improving their sustainability by using environmentally friendly farming practices and reducing their impact on the environment.
- Providing food security: Agriculture businesses play a crucial role in providing food security for their communities and for the country as a whole.
Ultimately, the specific objectives of an agriculture business will depend on the business’s goals and priorities.
Some general factors to consider before starting an Agribusiness in Nepal
There are several important factors to consider before starting an agriculture business. Some of these factors include:
- The type of agriculture business: There are many types of agriculture businesses, such as crop production, animal husbandry, and aquaculture. It is essential to carefully consider which type of agriculture business is right for you and your goals.
- Location: The location of your agriculture business will play a significant role in its success. Consider factors such as climate, soil quality, access to markets and suppliers, and proximity to customers.
- Capital and financing: Starting an agriculture business can require significant capital, especially if you need to purchase land, equipment, and other resources. It is important to carefully plan your financing strategy and secure the necessary funding.
- Regulations and licenses: Agriculture businesses are subject to various regulations and may require specific licenses or permits. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the regulations that apply to your business and obtain the necessary licenses and permits.
- Market demand: Before starting an agriculture business, it is important to carefully research the market demand for your products. This will help you determine whether there is a market for your products and how to position your business to meet that demand.
Starting an agriculture business requires careful planning and consideration of various factors to ensure success. It is important to thoroughly research and understand the market, regulations, competition and other aspects of the business before launching and constantly monitor the business environment after starting the agriculture business in Nepal.
The Future of Agriculture Business in Nepal
The future of agriculture business in Nepal is likely to be shaped by a number of factors, including technological advancements, changing consumer preferences, and shifts in global economic and political conditions. Some potential developments that could impact the agriculture business in the future include:
- Advances in technology: Advances in technology, such as precision agriculture and automation, are likely to continue to transform the agriculture industry. These technologies can increase productivity, reduce costs, and improve sustainability.
- Changing consumer preferences: Consumers are increasingly demanding healthier, more sustainable, and more ethically produced food. This is likely to drive changes in the agriculture industry, as businesses adapt to meet these changing preferences.
- Global economic and political conditions: Economic and political conditions in different parts of the world can impact the agriculture industry. For example, changes in trade policies or fluctuations in global demand can affect the prices and availability of agricultural products.
- Climate change: Climate change is likely to have significant impacts on the agriculture industry, including changes in weather patterns, water availability, and pests and diseases. Adapting to these changes will be an important challenge for the industry in the future.
Overall, the future of agriculture business is likely to be influenced by a range of factors, and businesses will need to adapt and innovate in order to succeed in this rapidly changing environment.
Agro-Tourism Business in Nepal
Agro-tourism, also known as agritourism or rural tourism, is a type of tourism that involves visiting a working farm or agricultural operation. Agro-tourism businesses offer a range of activities and experiences that give tourists a glimpse into the world of farming and agriculture. These activities can include farm tours, workshops, hands-on activities, and the opportunity to stay on the farm or visit a rural community.
Agro-tourism businesses can be a great way to promote local agriculture, provide educational experiences for tourists, and generate income for farmers and rural communities. However, starting an agro-tourism business can be challenging and requires careful planning. Some key factors to consider when starting an agro-tourism business include:
- Location: Agro-tourism businesses often rely on their location and proximity to tourist destinations in order to attract visitors. Carefully consider the location of your business and how it will appeal to potential tourists.
- Activities and experiences: Agro-tourism businesses need to offer unique and engaging activities and experiences that will attract tourists. Consider what activities and experiences your business will offer, and how you will differentiate yourself from other agro-tourism businesses.
- Marketing and promotion: Agro-tourism businesses need to be marketed and promoted effectively in order to attract visitors. Consider how you will market your business and what channels you will use to reach potential customers.
- Regulations and licenses: Agro-tourism businesses may be subject to various regulations and may require specific licenses or permits. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the regulations that apply to your business and obtain the necessary licenses and permits.
Starting an agro-tourism business can be a great long term investment in Nepal and also a way to promote local agriculture and support rural communities. However, to make the agro-tourism business successful in Nepal, it requires careful planning and consideration of various factors in order to succeed.
Animal Husbandry Business in Nepal
Animal husbandry is the practice of breeding and caring for farm animals, such as cows, pigs, chickens, and sheep. Animal husbandry businesses are involved in various aspects of animal production, including breeding, feeding, and caring for animals. These businesses may focus on a specific type of animal, such as dairy cows or meat chickens, or they may raise a variety of animals.

Animal husbandry businesses in Nepal can be a profitable and sustainable way to produce food and other products. However, like any other businesses, starting an animal husbandry business can be challenging in the beginning and requires careful planning. Some key factors to consider when starting an animal husbandry business in Nepal include:
- Type of animals: The type of animals you raise will impact many aspects of your business, including the type of facilities and equipment you need, the feed and other inputs you require, and the market for your products. Carefully research and consider the type of animals that are right for your business.
- Location: The location of your animal husbandry business will impact factors such as the availability of land, access to markets and suppliers, and the cost of inputs. Consider the location of your business carefully.
- Capital and financing: Animal husbandry businesses can require significant capital, especially if you need to purchase land, buildings, and equipment. Carefully plan your financing strategy and secure the necessary funding.
- Regulations and licenses: Animal husbandry businesses are subject to various regulations and may require specific licenses or permits. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the regulations that apply to your business and obtain the necessary licenses and permits.
- Market demand: Before starting an animal husbandry business, it is important to carefully research the market demand for your products. This will help you determine whether there is a market for your products and how to position your business to meet that demand.
Cash-crop farming in Nepal
Cash-crop farming is the practice of growing crops that are sold for profit, rather than being used for the farmer’s own consumption. Common examples of cash crops include cotton, coffee, tobacco, and sugar. Cash-crop farming is a type of commercial agriculture that is focused on producing crops for sale in the global market.
Starting a cash-crop farming business can be a profitable way to earn a living from the land. However, starting a cash crop business in Nepal requires careful planning and consideration of various factors. Some key factors to consider when starting a cash-crop farming business include:
- Type of crops: The type of crops you grow will impact many aspects of your business, including the type of land and climate required, the inputs you need, and the market for your products. Carefully research and consider the type of crops that are right for your business.
- Location: The location of your cash-crop farming business will impact factors such as the availability of land, access to markets and suppliers, and the cost of inputs. Consider the location of your business carefully.
- Capital and financing: Cash-crop farming can require significant capital, especially if you need to purchase land, equipment, and other resources. It is important to carefully plan your financing strategy and secure the necessary funding.
- Regulations and licenses: Cash-crop farming is subject to various regulations and may require specific licenses or permits. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the regulations that apply to your business and obtain the necessary licenses and permits.
- Market demand: Before starting a cash-crop farming business, it is important to carefully research the market demand for your products. This will help you determine whether there is a market for your products and how to position your business to meet that demand.
Horticulture business in Nepal
Horticulture is the practice of growing fruits, vegetables, flowers, and other plants. Horticulture businesses are involved in various aspects of plant production, including planting, cultivating, and harvesting. These businesses may focus on a specific type of plant, such as fruits or vegetables, or they may grow a variety of plants.
Starting a horticulture business in Nepal can be a profitable venture if done with the right strategy and sustainable way to produce fresh, healthy foods and other products. However, starting a horticulture business in Nepal requires careful planning as a lot of technicalities are involved. Some key factors to consider when starting a horticulture business in Nepal include:
- Type of plants: The type of plants you grow will impact many aspects of your business, including the type of land and climate required, the inputs you need, and the market for your products. Carefully research and consider the type of plants that are right for your business.
- Location: The location of your horticulture business will impact factors such as the availability of land, access to markets and suppliers, and the cost of inputs. Consider the location of your business carefully.
- Capital and financing: Horticulture businesses can require significant capital, especially if you need to purchase land, equipment, and other resources. It is important to carefully plan your financing strategy and secure the necessary funding.
- Regulations and licenses: Horticulture businesses are subject to various regulations and may require specific licenses or permits. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the regulations that apply to your business and obtain the necessary licenses and permits.
- Market demand: Before starting a horticulture business, it is important to carefully research the market demand for your products. This will help you determine whether there is a market for your products and how to position your business to meet that demand.
Starting a Fishery Business in Nepal
A fishery is a business that involves breeding, raising, and harvesting fish and other aquatic animals. Fishery businesses can be involved in various aspects of fish production, including breeding, feeding, and caring for fish. These businesses may focus on a specific type of fish, such as salmon or tilapia, or they may raise a variety of fish species.
Some key factors to consider when starting a fishery business in Nepal include:
- Type of fish: The type of fish you raise will impact many aspects of your business, including the type of facilities and equipment you need, the feed and other inputs you require, and the market for your products. Carefully research and consider the type of fish that are right for your business.
- Location: The location of your fishery business will impact factors such as the availability of water, access to markets and suppliers, and the cost of inputs. Consider the location of your business carefully.
- Capital and financing: Fishery businesses can require significant capital, especially if you need to purchase land, buildings, and equipment. Carefully plan your financing strategy and secure the necessary funding.
- Regulations and licenses: Fishery businesses are subject to various regulations and may require specific licenses or permits. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the regulations that apply to your business and obtain the necessary licenses and permits.
- Market demand: Before starting a fishery business, it is important to carefully research the market demand for your products. This will help you determine whether there is a market for your products and how to position your business to meet that demand.
Beekeeping Business in Nepal
Beekeeping is the practice of breeding and caring for bees in order to produce honey and other products. Beekeeping businesses are involved in various aspects of bee production, including breeding, feeding, and caring for bees. These businesses may also produce and sell other bee-related products, such as beeswax, pollen, and royal jelly.

Starting a beekeeping business can be a good option to invest in Agriculture sector in Nepal. Diverse flora and fauna found in Nepalese jungles can provide free resources for the beekeeping business in Nepal. Also, Nepali honey is quite popular overseas too. However, starting a beekeeping business requires careful planning and a clear vision. One needs to be persistent and patient because returns may not arrive immediately from the beekeeping business. Some key factors to consider when starting a beekeeping business in Nepal include:
- Location: The location of your beekeeping business will impact factors such as the availability of land, access to markets and suppliers, and the health of your bees. Consider the location of your business carefully.
- Capital and financing: Beekeeping businesses can require significant capital, especially if you need to purchase land, equipment, and other resources. It is important to carefully plan your financing strategy and secure the necessary funding.
- Regulations and licenses: Beekeeping businesses are subject to various regulations and may require specific licenses or permits. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the regulations that apply to your business and obtain the necessary licenses and permits.
- Market demand: Before starting a beekeeping business, it is important to carefully research the market demand for your products. This will help you determine whether there is a market for your products and how to position your business to meet that demand.
- Hive management: Proper hive management is crucial for the health and productivity of your bees. Consider factors such as hive placement, bee nutrition, and pest and disease control when planning your beekeeping business.
Overall, starting a beekeeping business can be a rewarding and fulfilling way to produce healthy, natural products from bees. However, it requires careful planning and consideration of various factors in order to succeed.
Aquaponics Business in Nepal
Aquaponics is a type of agriculture that combines aquaculture (the breeding and raising of aquatic animals) with hydroponics (the cultivation of plants in water). In an aquaponics system, fish produce waste that is converted into nutrients for the plants, and the plants help to clean the water for the fish. This symbiotic relationship allows for the efficient and sustainable production of both fish and plants.
Some key factors to consider when starting an aquaponics business include:
- Location: The location of your aquaponics business will impact factors such as the availability of land, access to markets and suppliers, and the cost of inputs. Consider the location of your business carefully.
- Capital and financing: Aquaponics businesses can require significant capital, especially if you need to purchase land, equipment, and other resources. It is important to carefully plan your financing strategy and secure the necessary funding.
- Regulations and licenses: Aquaponics businesses are subject to various regulations and may require specific licenses or permits. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the regulations that apply to your business and obtain the necessary licenses and permits.
- Market demand: Before starting an aquaponics business, it is important to carefully research the market demand for your products. This will help you determine whether there is a market for your products and how to position your business to meet that demand.
- System design and management: Proper design and management of your aquaponics system are crucial for the health and productivity of your fish and plants. Consider factors such as water quality, plant and fish nutrition, and pest and disease control when planning your aquaponics business.
Hydroponics Business in Nepal
Hydroponics is a type of agriculture that involves growing plants in nutrient-rich water rather than soil. In a hydroponics system, plants are supported by a growing medium, such as gravel or sand, and are supplied with the necessary nutrients through the water. This allows for the efficient and sustainable production of a variety of crops.
Starting a hydroponics involves a lot of technical aspects and requires careful planning and implementation to be successful and sustainable. Some key factors to consider when starting a hydroponics business include:
- Type of crops: The type of crops you grow will impact many aspects of your business, including the type of facilities and equipment you need, the nutrients and other inputs you require, and the market for your products. Carefully research and consider the type of crops that are right for your hydroponics business.
- Location: The location of your hydroponics business will impact factors such as the availability of land, access to markets and suppliers, and the cost of inputs. Consider the location of your business carefully.
- Capital and financing: Hydroponics businesses can require significant capital, especially if you need to purchase land, equipment, and other resources. It is important to carefully plan your financing strategy and secure the necessary funding.
- Regulations and licenses: Hydroponics businesses are subject to various regulations and may require specific licenses or permits.
Plant breeding and genetics in Nepal
Plant breeding and genetics is a field of agriculture that involves the development and improvement of plants through the application of genetic principles and techniques. Plant breeders and geneticists work to create new plant varieties with desirable traits, such as improved yield, disease resistance, and taste.
Some key factors to consider when starting a plant breeding and genetics business include:
- Type of crops: The type of crops you work with will impact many aspects of your business, including the facilities and equipment you need, the market for your products, and the regulations and licenses that apply to your business. Carefully research and consider the type of crops that are right for your business.
- Location: The location of your plant breeding and genetics business will impact factors such as the availability of land, access to markets and suppliers, and the cost of inputs. Consider the location of your business carefully.
- Capital and financing: Plant breeding and genetics businesses can require significant capital, especially if you need to purchase land, equipment, and other resources. It is important to carefully plan your financing strategy and secure the necessary funding.
- Regulations and licenses: Plant breeding and genetics businesses are subject to various regulations and may require specific licenses or permits. Be sure to familiarize yourself with the regulations that apply to your business and obtain the necessary licenses and permits.
- Market demand: Before starting a plant breeding and genetics business, it is essential to carefully research the market demand for your products. This will help you determine whether there is a market for your products and how to position your business to meet that demand.
Overall, starting a plant breeding and genetics business can not only be a profitable business but will also add value to the agriculture sector of Nepal and globe by contributing to the development of new and improved plant varieties.
- [email protected]
- Yeti Plaza, Bagbazar, Kathmandu
- Company Registration
- Marketing Plan
- Bookkeeping
- Management Consulting
- StudentsNepal
- Best Consultancy
- Developables

© All rights reserved
Quick Support
♠ 9804495818
- Agriculture Farming
- Livestock Farming
Project Reports
- Hydroponics
- Best Fertilizers
- Vertical Farming
- Sheep Farming
- Goat Farming
- Poultry Farming
- Fish Farming
- Pig Farming
- Dairy Farming
- Rabbit Farming
- Success Stories of Farmers
- Boost Fruit Yield
- District Wise Crop Production
- Schemes & Subsidies
- Agriculture Colleges
- Farm Insurance
- Disease Control And Management
Agriculture
Aquaculture
Horticulture
Agri Business
Poultry Farming in Nepal: How to Start, A Step-By-Step Guide for Beginners
Table of contents, is poultry farming profitable in nepal , cost to start a poultry farm in nepal, scope of poultry farming in nepal, poultry breeds in nepal, types of poultry are reared in nepal, housing for poultry birds , why is poultry important in nepal , management of poultry farm for profitable business, government policy for poultry production in nepal, poultry production systems in nepal, scavenging system.
- Semi-scavenging system
- Deep litter (intensive) system
Chicken farm in Nepal
Sustainable prospects of poultry production in nepal , health management for poultry farming in nepal, problems faced by poultry farmers in nepal.
Poultry is produced all over Nepal. However, production can vary in agro-ecological and politically distinct geographical areas. Production depends directly on market facilities, seasonal actors, etc. Production is generally higher in the lowlands and the urban regions, while consumption is lower in less favored hilly and mountainous areas. Assuming that meat production is low in the highlands, there is room for increased egg production in this environment.

According to the Ministry of Agriculture, Nepal produces 1.61 billion eggs and 548,000 tons of meat annually. The poultry farming business is an emerging industry in Nepal. Healthy poultry production can pave the way for better income and sustainable development. Let’s check out more information about poultry farming in Nepal.
Livestock, including poultry, is an integral part of the agricultural production system in Nepal, providing draft power for human consumption, fertilizers, and high-value animal proteins such as meat, milk, and eggs, which account for approximately 32% of agricultural GDP. Poultry farms use modern equipment, and organic chickens are raised on natural free-range land.
Due to high demand, poultry is growing rapidly in Nepal’s meat business sector. This refining system of chicken production provides high-quality animal protein in easy-to-use units for smallholders in dietary protein-deficient areas. In addition, extra eggs and birds are sold in the market, which generates cash to meet the immediate household needs of the family.
However, the organization of poultry production is changing rapidly as attitudes towards eggs and poultry are changing in response to better education and easing religious and social restrictions. Social groups, which previously did not allow chickens to be crushed near home, now enjoy eggs and poultry and understand the potential for raising poultry for economic gain. According to the survey, 75% of commercial chicken producers are making a profit.
Poultry farms can be a good business in Nepal with proper care, a balanced diet, and regularly vaccinated chickens. These can cost around INR 5-7 lakhs per thousand chickens (including the price of chickens, vaccination, feeding, etc.
In case you missed it: Poultry Farming in Uttar Pradesh, How to Start, Schemes, and Loans

The poultry farming business is an emerging industry in Nepal. Healthy poultry production can pave the way for better income and sustainable development. There are a wide scope and marketing opportunities for poultry farming in Nepal. The marketing of poultry is also increasing daily due to the change in eating meat and eggs. Nepal has an annual production of 114,058 tons, while egg production is 1.20 billion per year. A Nepali eats 4.1 kg per hen and 44 eggs annually.
With increasing consumer demand, the need to increase the productivity of individual birds is becoming clearer. Improvement in breeding, nutrition, disease control, marketing, and management can all play a role. However, achieving this requires a new approach so poultry farming can become profitable for families in mountainous villages and households close to urban centers. Nepal’s poultry population is estimated at 9.8 million birds, of which about 20% are improved breed, and the remaining 80% are considered an indigenous breed, Sakini.
There are 3.3 million laying birds in the country, producing an estimated 265 million eggs, an average of 80 eggs/hen/year. It means an annual per capita consumption of 15 eggs. With 180 eggs per capita with large regional variations in egg supply and nutritional requirements for the population, it can be seen that in less popular mountainous areas, there is great potential for increasing egg production.
Annual meat production in Nepal is about 140,000mt, providing an average of 20 grams/head/day to the total population. Poultry accounts for only 4.5%. Again, there is a big difference in production, distribution, and consumption in the physiographic region.
Various exotic breeds have been introduced in Nepal, such as New Hampshire, Rhode Island Red, White Leghorn, Australop, Black Minorka, and other synthetic breeds. They are raised under an intensive management system with proper housing, nutrition, and health control. This more intensive production usually occurs near cities where a good, regular market is assured. On the other hand, indigenous breeds are reared under hygienic or semi-hygienic systems with less control and consequently higher levels of mortality and lower levels of production.
- Shakini – Shakini is the largest breed of chicken in the country. They are suitable for hard and dual-purpose meats (famous for delicious meats) and eggs.
- Ghanti Khuile – It is tough and suitable for dual-purpose meat and eggs. They are hard and suitable for cleaning.
- Pwankhulte or Dumse chicken is challenging and suitable for dual-purpose meat and eggs. Their feathers are torn. They are found in small numbers all over the country. They are rare and require immediate attention to their protection. This breed of chickens is a common bird with outward growth of feathers. The average adult body weight of a male is 1.0 kg, and that of a female is 0.9 kg.
The major commercial poultry breeds are Cobb 100, Cobb 500, Kashila, Lohmann, H & N, Hyline, Marshall, and Rose308.
In case you missed it: Poultry Farming in Tamil Nadu, How to Start, Schemes, Loans, and Subsidy

Housing for chickens should be protected from predators, theft, etc. Still, in Nepal, domestic chickens are generally reared in the free-range system in addition to deep litter and battery cage systems. However, animals are brought back to walled houses for protection. The use of bamboo to make chicken housing in Nepal.
It was found that 79% of rural households shared shelters with chickens and other animals such as goats and cats. Free-range chickens weighed more than captives and were more challenging because they ate the natural ingredients found around them. In the deep litter system, the chicken was fed twice daily with the recommended amount of commercial feed with fresh and clean drinking water.
In Nepal, chickens are traditionally raised by lower caste farmers, and their husbandry is part of the entire farming system. Poultry farming in remote areas of Nepal is still limited to the poor and lower castes, who are primarily a source of income by selling a common source of animal protein and extra poultry eggs and birds.
Poultry farming is the commercial rearing of domestic birds such as chickens, ducks, turkeys, etc. Poultry farming in Nepal and its popularity among local farmers is increasing. They regularly raise chickens for meat or eggs, which provides a quick return on our investment. Poultry is growing rapidly in the meat business sector in Nepal due to high demand. Poultry farming has become an essential aspect of agriculture for profitable business because,
- It creates business opportunities for traders.
- It also employs job-seeking citizens.
- This is the kind of business that can never be dry.
- It generates a lot of income.
Poultry production in Nepal plays an important role in generating cash income and improving people’s food quality. However, the lack of a national policy on poultry production in the country is an obstacle to improvement. A small number of artificial poultry birds are reared in private urban areas to produce meat and eggs commercially under high management.
However, in the hills and mountains where 80% of the birds are reared, no attention is paid to the improvement of native birds under the scavenging management system. New Hampshire has a general government policy to divide dual-purpose breeds into mountainous areas. Still, lack of health care, poor nutrition, and high hunting rates mean this distribution policy has suffered negatively. Nevertheless, New Hampshire’s policy of distributing chickens continues.
Modern farming methods can not only improve the current pattern of development of the poultry industry but also control production prices and, consequently, lower prices and increase population consumption. May increase demand for poultry products. New investment is also rising with the growing demand for poultry products and expanding existing farmers’ activities.
In case you missed it: Poultry Farm Insurance in India, Companies, Policy, and Premium

One billion Nepali rupees (NPR) is in the pipeline for investment in different parts of the country in the coming year. Poultry production systems in Nepal – Poultry production systems in Nepal can be classified into scavenging, semi-scavenging, and intensive.
The majority of farmers in mountain villages keep birds under the free-range system. During the day, they scrape for food, and at night they are kept indoors to protect them from theft and predation. In this farming, chickens roam freely and pick up various foods such as insects, household waste, grass, and pebbles. They are less likely to be malnourished if a small amount of grain supplement is supplemented.
Nepali farmers, especially hill farmers, are busy most of the year, so keeping a few birds under a hygienic system gives them extra income in the form of eggs and meat. Native birds dominate this poultry rearing system in the village, but exotic breeds such as New Hampshire, Black Australorp, and Light Sussex are commonly seen. New Hampshire is the most famous of these.
In hill and mountainous areas, where food is deficient, sanitation is an effective way of raising chickens. The flock usually has three to four indigenous birds per household. Family members eat the eggs, and any surplus is sold locally. Local consumers prefer eggs and meat made from Sakini hens, which are kept under the scavenging system, even if they are more expensive. Therefore, the system rarely encounters a marketing problem.
The small-scale poultry production scavenging system is suitable for the fragile ecosystem of the hill as poultry birds may be present in the waste products, which help keep the environment clean. Therefore, in less desirable mountainous areas where access to roads is limited, it is preferable to keep resident chickens under sanitation.
Semi- scavenging system
This system means that the birds are allowed to roam freely for some part of the day, but, when necessary, they are stopped and supplemented with extra food. Many factors may be responsible for farmers adopting this system in village committees. Poultry can be protected from bad weather and can also be protected from predators by shutting them down when family members are engaged in activities away from home.
Farmers can also collect fertilizer to maintain soil fertility where chemical fertilizers are not feasible. It is a relatively new system; only a few farmers have adopted it. It requires the construction of a small house depending on the size of the flock. The house is usually low cost, built on the porch or erected separately, and is made of local materials such as bamboo.
While this system is common with indigenous birds, the availability of better breeds in the countryside means that the system is becoming more popular, as the sanitation system is better suited to birds and susceptibility to diseases. This system adapts to a range of herd sizes and can produce more eggs than a scavenging system if supplemental feed is provided. Therefore, it is especially suitable for farmers with surplus grain or regular access to supplementary food.
Deep litter (intensive) system
It is a method in which chickens are reared entirely on deep dung. High-quality rearing is required to realize the full potential of chickens in this system. In the village, a relatively large investment of money will be required for housing and food for keeping deep-litters chickens. Birds are raised indoors, so they need to be provided with a well-balanced diet. In mountainous areas, deep management requires a grain supply for raising chickens, which is already in deficit.
Under this type of management, foreign, more productive commercial breeds must be bred under a high input / high output system. Therefore, this type of farm is found in large cities and peri-urban areas where the market is secure and is generally not recommended for mountain farming situations. However, improved technologies in agriculture and expanded irrigation facilities in rural areas have increased crop intensity and resulted in increased grain production.
In case you missed it: Poultry Farming in West Bengal, How to Start, Schemes, and Loans

It has made it possible to run small-scale (10-20 hens) deep litter poultry production in some villages. One beneficial by-product is that deep litter poultry farming produces high-quality fertilizers, which, when added to the soil, increase soil fertility in areas where the purchase of chemical fertilizers may be limited in terms of availability and cost. Therefore, in areas with high crop intensity, it is considered that small-scale intensive poultry farming can be maintained where the local market is available.
Chicken farming in Nepal is very popular among Nepal’s urban and rural farmers. Poultry farming is one of the best ways for the villagers to get the most out of their pastures. There are many commercial chicken farms in Nepal; they started free-range chicken farming using the latest technology. Chickens live in a natural environment, provide a healthy supply of grass and grain, and raise chickens on a farm for meat, eggs, and down.
Chickens reared for eggs are generally called layers, while chickens reared for meat are often called broilers, but Nepali native hens are growing steadily in the country. Chicken farm controls all aspects of nutrition, breeding, selection, incubation, hatching, and breeding in the natural environment to produce high-quality poultry products.
Free-range chicken meat is healthier and tastier than industrial chicken. Many ethnic groups have been raising chickens naturally for a long time. Still, the trend of chicken farming is gradually changing, and most families have accepted chicken socially and culturally due to urbanization.
Naturally, raising chickens is more complicated than other types of poultry farming. Before starting organic chicken farming, it is important to know the facts, such as food, care, diseases, breed, and management of the chicken farm. Organic farm Nepal provides chicken farming training and practical information for all farmers interested in chicken farming.
Nepal is currently unable to produce excess food in surpluses of the needs of the human population. Therefore, the poultry industry has become a responsibility rather than an asset. The production of smallholder rural poultry, if adequately developed, has the potential to produce sustainable poultry. The program should establish projects to understand the rural poultry production system and its weaknesses. Develop and test new methods that will not only overcome these vulnerabilities but also be affordable and sustainable.
The unsustainable nature of heavy poultry production requires a quick search for locally grown low-grain feedstuffs for chicken. In well-organized pasture systems, producers use very little medication, as proper hygiene and a healthy growing environment help prevent health problems before they begin. When using the low-quality feed, vitamins obtained from birds feeding on grass can balance nutritional deficiencies in feed rations.
Poultry health management is important due to the emergence of highly pathogenic diseases in different parts of the world. Biosecurity measures are essential for better poultry production performance and quality in a competitive world. The latest technological advances can help adopt biosecurity measures and environmentally friendly practices in poultry production systems. A biosecurity policy can be developed with the participation of stakeholders. It will provide new dimensions to poultry farming in different clusters in Nepal.
In addition, the participatory response of poultry entrepreneurs will be invaluable for programs that prioritize poultry disease research, eradication, and poultry industry protection. Poultry health management is an emerging issue with the biosecurity initiative. It promotes organic farming in rural areas. Biological conservation measures, poultry farm management, and organic farming become a cycle of sustainable development in rural areas.
Farmers used to keep a few birds in the villages’ sanitation system and the native chickens in the backyard. Therefore, due to close contact, poultry disease is at risk in cattle and human populations. It should be avoided in the long run for better hygiene practices. Poultry farming has made tremendous progress in the last six decades and generates income in urban and per urban areas. Demand for poultry has increased due to tourism and changing food habits.
Poultry farmers face many challenges due to the high cost of feed and medicines, emerging new diseases, and lack of biosecurity measures. Bird flu often spreads in South and East Asia, causing panic among stakeholders. Government policies on biosecurity are not enough. Poultry farmers and small business owners in the backyard will feel the burden of biosecurity. However, it is also a helpful and cost-effective method for businesses in the long run.
The District Livestock Services Office (DLSO) disease reporting system comes from various service centers in Nepal. They gather information from district backyard poultry farms and small commercial farms. They do not know large commercial farms. So epidemiological surveillance reporting is incomplete and cannot be properly interpreted.
Biosecurity is one of the proposed methods on farm premises, which initially costs some extra investment but will be cheaper in the long run. Biosecurity is essential for effective disease control. Involvement in treatment and safety measures and their cost will be reduced. In addition, biosecurity measures should include awareness and training programs.
Nepal produces various vaccines for livestock and poultry on its own, and vaccination of poultry birds as per schedule is one of the measures to strengthen biosecurity in poultry farms. Poultry diseases are a significant cause of underdeveloped poultry farming. Farmers are not aware of various diseases and how to control them. Major infectious diseases include Brussels, Newcastle, mycoplasmosis, coccidiosis, etc. There is a lack of vaccination and administrative methods in these cases. This results in poor production.
In case you missed it: Common Mistakes Everyone Makes in Poultry Farming

Lack of modern diagnostic laboratories: The lack of modern laboratories for diagnosing diseases in chicken and testing the quality of feed and meat are some of the major setbacks facing the poultry industry in Nepal. It has created an unfavorable business environment for poultry farmers and sellers. Compared to mutton and buffalo meat, chicken meat is less prone to contamination, so proper inspection and construction of storage laboratories can help reduce diseases in chickens.
Wrong types of chickens and indiscriminate breeding methods – The chickens may have originally come from another country. In rural conditions, local chickens are often the most reliable and profitable. There are no good breeding methods for poultry production on demand. Indigenous peoples are declining sharply. The production and improvement of these native breeds can result in better production.
Poultry farming in Nepal and its growing popularity among local farmers regularly raise chickens for meat or eggs, which provides a quick return on your investment. Organic farm Nepal has set up the first pasture-rearing poultry farming business in Nepal, which has increased poultry production in Nepal for free. You should follow the above steps for better production in poultry farming in Nepal.
Types of Pesticides Used in Agriculture: A Beginner’s Guide
Economical aquaculture: a guide to low-budget fish farming, 15 common planting errors that can doom your fruit trees, how to make houseplants bushy: effective tips and ideas, innovative strategies for boosting coconut pollination and yield, pollination strategies for maximum pumpkin yield, the complete guide to chicken fattening: strategies for maximum growth.
- Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Bulb-Related Issues
Revolutionizing Citrus Preservation: Towards a Healthier, Greener Future
- Natural Solutions for Peony Leaf and Flower Problems: 100% Effective Remedies
- Maximizing Profits with Avocado Contract Farming in India: A Comprehensive Guide
- Natural Solutions for Hydrangea Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf and Flowers
- The Ultimate Guide to Choosing the Perfect Foliage Friend: Bringing Life Indoors
- From Sunlight to Sustainability: 15 Ways to Use Solar Technology in Agriculture
- The Ultimate Guide to Dong Tao Chicken: Exploring from History to Raising
- The Eco-Friendly Makeover: How to Convert Your Unused Swimming Pool into a Fish Pond
- Mastering the Art of Delaware Chicken Farming: Essentials for Healthy Backyard Flocks
- 20 Best Homemade Fertilizers for Money Plant: DIY Recipes and Application Methods
How to Craft a Comprehensive Free-Range Chicken Farming Business Plan
- Brighten Your Flock: Raising Easter Egger Chickens for Beauty and Bounty
- How to Optimize Your Poultry Egg Farm Business Plan with These Strategies
- Subsidy for Spirulina Cultivation: How Indian Government Schemes Encouraging Spirulina Farmers
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Dominique Chickens: Breeding, Feeding, Egg-Production, and Care
- Mastering the Art of Raising Jersey Giant Chickens: Care, Feeding, and More
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Legbar Chickens: Breeding, Farming Practices, Diet, Egg-Production
- How to Raise Welsummer Chickens: A Comprehensive Guide for Beginners
- How to Protect Indoor Plants in Winter: A Comprehensive Guide
- Ultimate Guide to Grow Bag Gardening: Tips, Tricks, and Planting Ideas for Urban Gardeners
- Guide to Lotus Cultivation: How to Propagate, Plant, Grow, Care, Cost, and Profit
- Agriculture Drone Subsidy Scheme: Government Kisan Subsidy, License, and How to Apply Online
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Araucana Chickens: Breed Profile, Farming Economics, Diet, and Care
- Bringing Hydroponics to Classroom: Importance, Benefits of Learning for School Students
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Polish Chickens: Breed Profile, Farming Economics, Diet, and Care
- Ultimate Guide to Raising Australorp Chickens: Profile, Farming Economics, Egg Production, Diet, and Care
- Silkie Chicken Farming: Raising Practices, Varieties, Egg Production, Diet, and Care
- Sussex Chicken Farming: Raising Practices, Varieties, Egg Production, Diet and Care
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name and email in this browser for the next time I comment.
Natural Solutions for Tulip Problems: 100% Effective Remedies for Leaf...
Natural solutions for peony leaf and flower problems: 100% effective..., maximizing profits with avocado contract farming in india: a comprehensive..., natural solutions for hydrangea problems: 100% effective remedies for leaf..., the ultimate guide to choosing the perfect foliage friend: bringing..., from sunlight to sustainability: 15 ways to use solar technology..., the ultimate guide to dong tao chicken: exploring from history..., the eco-friendly makeover: how to convert your unused swimming pool..., mastering the art of delaware chicken farming: essentials for healthy..., 20 best homemade fertilizers for money plant: diy recipes and..., brighten your flock: raising easter egger chickens for beauty and..., borewell drilling cost, pump price, and pipe cost, polyhouse subsidy, cost, profit, project report, tractor subsidy, bank loan, eligibility, schemes, process, malabar neem project report details guide, cold storage project report, cost and subsidy, mushroom farming project report, cost and profit analysis.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The copious availability of water resources makes Nepal a country with potentiality for fish farming. The Nepal Agriculture Perspective Plan (APP) has assumed fisheries and aquaculture in Nepal as a minor but indispensable and potential sub-sector of agriculture (FAOa, Citation 2020). Fish is often supposed as good luck (Sagun) in Nepal.
The abstract of your fish farming business plan provides a concise overview of the key aspects covered in the article. It serves as a quick reference for readers interested in specific sections. Executive Summary. The executive summary highlights the crucial elements of your fish farming business plan, providing a snapshot of the entire venture.
Being a landlocked country, Nepal's fish farming is solely limited to inland water resources. So, the domestic fish production is very few which is unable to meet the national demand.
Being a landlocked country, Nepal's fish farming is solely limited to inland water resources. So, the domestic fish production is very few which is unable to meet the national demand. The fisheries, at national level, remarkably expanded than the previous decades and total production, trade, and consumption reached an all-time record in 2018. ...
Types & scope of fish farm in Nepal. Fish farming in Nepal is considered as one of the ancient farming system, there are lots of small scale fish farm in different villages in plain region started years ago. Commercial fish farming in Nepal provides many profitable opportunities; farmers are raising and selling the fish on commercial basis. There are more than 6000 rivers, fresh water ...
The copious availability of water resources makes Nepal a country with potentiality for fish farming. The Nepal Agriculture Perspective Plan (APP) has assumed fisheries and aquaculture in Nepal as a minor but indispensable and potential sub-sector of agriculture (FAOa, 2020). Fish is often supposed as good luck (Sagun) in Nepal.
Status of Fish Production and Import in Nepal . Aquaculture production is mainly from pond fish farming of terai region. The major fish production districts are Bara, Dhanusha, Saptari, Rupandehi, Mahottari, and Chitwan of terai region of Nepal. The cultured species includes seven carp species: Bighead carp (Aristichthys nobilis), Silver carp
Fish consumption per capita in 2013 was 2.10 kg in Nepal. There are several fish and fishery product that are consumed by the consumer. In the market mostly live fishes, iced fishes, frozen fishes, dried fishes and canned fishes are consumed. Beside these fishes are also keep in aquarium for recreational purpose.
Most fisheries and aquaculture production in Nepal is consumed mostly by the domestic market (Labh et al., 2017). The marketing channel of fish in Nepal has not been systematic (Karki, 2016) and ...
Rainbow Trout fish farming is a profit generating business, which has a wide scope in the Nepali market. Rainbow Trout, one of the many species of trout fishes, is a freshwater fish of the salmon family. ... In Nepal, it is generally perceived that fish farming is possible only in the Terai region of the nation. However, recent developments ...
Fish Farming I - Pond Plan As mentioned in the Strategy section, the fish farming income generation program in Sarlahi can be broken down into two main sections: skill development training and seed funds required for scaling, which go hand in hand. The fish farming income generation program will be operated by Hoste Hainse under the
the modern fish farming was initiated around 1947 in Nepal. Since then, fisheries sector started to receive investment under the government plans especially during 1983-90, when Asian Development Bank supported the fisheries development in Nepal. Later there was slackness in investment in the fisheries subsector.
In Nepal, peripheral trench is commonly practiced for rice-fish farming and are of 50cm width and 30 cm depth [18]. For the maximum yield of rice, trench should not account more than 10% of the paddy area. 3.4 Pond refuse construction: It may be circular, square or rectangular shape with about 1 m of depth.
Biofloc Fish Farming Cost. While bio-floc fish farming offers numerous benefits, awareness of the setup and maintenance costs of a bio-floc system is crucial for farmers in Nepal considering this innovative method. The cost of biofloc fish farming can differ based on elements like the size of the operation, system design, and local conditions.
Organic farm Nepal started fish farm using modern technology and fish raise on fresh water and pounds. There are different varieties of fish on-farm warm water species common carp, grass carp, bighead carp, and freshwater species trout, etc. In Nepal, fish farming is considered a profitable, occupation and source of income for people.
The trend of fish production in Nepal is increasing. Mrigal carp (Cirrhinus cirrhosus) with a production of 29.2 percent is the fish with the highest production in Nepal. Nepal imports fish and ...
and information are very limited for the fish and fisheries of Nepal, the proposed investment looks worthwhile. There are clearly identifiable opportunities to stimulate and sustain growth in benefits, over and above the current (baseline) value of fish production of USD 204 million per year.
If your cultivating fish commercially you must make a large one. The shape of the pond should be square or rectangular. Fish Farming Business Plan - The depth of the Pond: The water depth will be 30% in one corner and 100% in another corner. The depth of the water depends on the species of fish you are cultivating.
The future prospects of fish farming can also be seen as a part of providing employment to millions of people worldwide. While global fish production for inland water resources was 63 million ...
Aquaculture and fishery is one of the fastest growing agriculture subsectors in Nepal. The current total national fish production is 113,736 Mt of which 20 % is contributed by capture fisheries while 80% is from aquaculture. Fisheries sector contributes about 1.83% in Agricultural Gross Domestic Production and 0.44% in Gross Domestic Production.
The fish farm industry is expected to grow over the next five years to over $202 billion. The growth will be driven by the increased need for regulated raising and harvesting of fresh fish and crustaceans. The growth will also be driven by the consumer demand for sustainable fish-farmed sources of fish.
Nepal is a predominantly agricultural country, with agriculture representing a significant portion of its economy. The main crops grown in Nepal include rice, wheat, maize, millet, and barley. In addition, various fruits and vegetables are also grown in the country. The mountainous terrain of Nepal makes it well-suited for terrace farming ...
Dhanusha is one of the leading fish farming districts of Nepal with. increasing numbers of farmers involved in commercial fish farming. According to the data of 2018/2019, there was total of 2442 ...
There are a wide scope and marketing opportunities for poultry farming in Nepal. The marketing of poultry is also increasing daily due to the change in eating meat and eggs. Nepal has an annual production of 114,058 tons, while egg production is 1.20 billion per year. A Nepali eats 4.1 kg per hen and 44 eggs annually.