- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- Engageny Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- enVision Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

Big Ideas Math Geometry Answers Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume
For better preparation and quality education, our team has shared the Big Ideas Math Book Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume for high school students. Provided Big Ideas Math Geometry Answers Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume are aligned topic-wise as per the latest common core curriculum. Students can easily understand the concepts of Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume. Learn how to solve the problems using the Circumference, Area, and Volume formulas in detail from here.
Big Ideas Math Book Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume
Step by Step Solutions explained for all the questions in the BIM Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume are easy to learn and understand as they are prepared by professional subject experts. After referring to the lesson-wise Big Ideas Math Geometry Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume Solution Key every high school student can become a pro in the concepts and gain better subject knowledge. So, click on the respective links and start preparing each topic of the BIM Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume efficiently.
Circumference, Area, and Volume Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Circumference, area, and volume monitoring progress, 11.1 circumference and arc length, lesson 11.1 circumference and arc length, exercise 11.1 circumference and arc length, 11.2 areas of circles and sectors, lesson 11.2 areas of circles and sectors, exercise 11.2 areas of circles and sectors, 11.3 areas of polygons, lesson 11.3 areas of polygons, exercise 11.3 areas of polygons, 11.4 three-dimensional figures, lesson 11.4 three-dimensional figures, exercise 11.4 three-dimensional figures, 11.1 – 11.4 quiz, 11.5 volumes of prisms and cylinders, lesson 11.5 volumes of prisms and cylinders, exercise 11.5 volumes of prisms and cylinders, 11.6 volumes of pyramids, lesson 11.6 volumes of pyramids, exercise 11.6 volumes of pyramids, 11.7 surface areas and volumes of cones, lesson 11.7 surface areas and volumes of cones, exercise 11.7 surface areas and volumes of cones, 11.8 surface areas and volumes of spheres, lesson 11.8 surface areas and volumes of spheres, exercise 11.8 surface areas and volumes of spheres, circumference, area, and volume review, circumference, area, and volume test, circumference, area, and volume cumulative assessment.
Find the surface area of the prism.
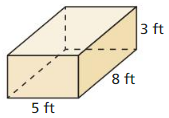
Answer: The surface area of the prism = 158.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, l = 5 ft, w = 8 ft, and h = 3 ft. where l = length, w = width, and h = height. The surface area of the rectangular prism = 2(lw + lh + wh). surface area = 2(5×8 + 5×3 + 8×3). surface area = 2(40 + 15 + 24). surface area = 2(79). surface area = 158.
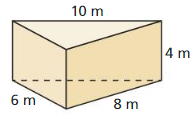
Answer: The surface area of the triangular prism = 68m.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, l = 10 m, p = 4 m, and h = 10. the surface area of the triangular prism = 2B + ph. b = base, p = perimeter, and h = height. surface area = 2(6 + 8) + 4(10). surface area = 2(14) + 40. surface area = 28 + 40. surface area = 68m.
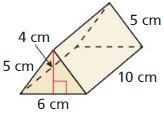
Answer: The surface area of the triangular prism = 42m.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, w = 10 cm, p = 4 cm, and h = 5 cm, l = 6 cm. the surface area of the triangular prism = 2B + ph. b = base, p = perimeter, and h = height. surface area = 2(6 + 5) + 4(5). surface area = 2(11) + 20. surface area = 22 + 20. surface area = 42cm.
Find the missing dimension.
Question 4. A rectangle has a perimeter 0f 28 inches and a width of 5 inches. What is the length of the rectangle?
Answer: The length of the rectangle = 9 in.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, A rectangle has a perimeter of 28 inches and a width of 5 inches. length of the rectangle = p/2 – w. length = 28/2 – 5. where perimeter = 28 in, and w = 5 in. length = 14 – 5. length = 9. so the length of the rectangle = 9 in.
Question 5. A triangle has an area of 12 square centimeters and a height of 12 centimeters. What is the base of the triangle?
Answer: The base of the triangle = 2 cm.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, A triangle has an area of 12 sq cm and a height of 12 cm. The base of the triangle = 2(A)/h. base = 2(12)/12. base = 24/12. base = 2cm. so the base of the triangle = 2 cm.
Question 6. A rectangle has an area of 84 square feet and a width of 7 feet. What is the length of the rectangle?
Answer: The length of the rectangle = 12 ft.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, A rectangle has an area of 84 sq ft and a width of 7 feet. area of the rectangle = l x b. 84 = l x 7. l = 84/7. l = 12. so the length of the rectangle = 12 ft.
Question 7. ABSTRACT REASONING Write an equation for the surface area of a Prism with a length, width, and height of x inches. What solid figure does the prism represent?
Answer: The surface area of a prism = 2(lw + wh + lh).
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, length = l, width = w, and height = x inches. the surface area of the prism = 2(lw + wh + lh). the solid figure does the prism represent the rectangular prism.
Draw a net of the three-dimensional figure. Label the dimensions.
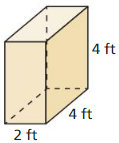
Answer: The surface area of the prism = 64 cm.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, l = 2 ft, w = 4 ft, and h = 4 ft. where l = length, w = width, and h = height. The surface area of the rectanguler prism = 2(lw + lh + wh). surface area = 2(2×4 + 4×4 + 4×2). surface area = 2(8 + 16 + 8). surface area = 2(32). surface area = 64.
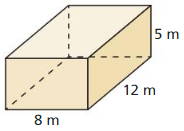
Answer: The surface area of the prism = 392 m.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, l =8 m, w = 12 m, and h = 5 m. where l = length, w = width, and h = height. The surface area of the rectanguler prism = 2(lw + lh + wh). surface area = 2(8×12 + 12×5 + 5×8). surface area = 2(96 + 60 + 40). surface area = 2(196). surface area = 392.
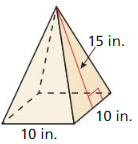
Answer: The surface area of the triangular prism = 170 in.
Explanation: In the above-given question, given that, B = 10 in, p = 15 in, and h = 15 in, l = 10 in. the surface area of the triangular prism = 2B + ph. b = base, p = perimeter, and h = height. surface area = 2(10) + 15(10). surface area = 2(10) + 150. surface area = 20 + 150. surface area = 170 in.
Exploration 1
Finding the Length of a Circular Arc
Work with a partner: Find the length of each red circular arc.
Answer: The Formula for the Arc Length is 2r(θ/360) r = 4 θ = 260 degrees Arc length = 2(4)(360/360) = 8(1) = 8 Therefore the Arc length is 8.
Exploration 2
Using Arc Length

Answer: C = πd C = 25π or 78.54 inch Half of revolution = 1/2 (78.54) = 39.27 inch No, the time has gone past the box by 3.27 inch
Communicate Your Answer
Question 3. How can you find the length of a circular arc? Answer: The length of a circular arc = 2 LOOKING FOR REGULARITY IN REPEATED REASONING To be proficient in math, you need to notice if calculations are repeated and look both for general methods and for shortcuts.
Question 4. A motorcycle tire has a diameter of 24 inches. Approximately how many inches does the motorcycle travel when its front tire makes three-fourths of a revolution? Answer: The diameter of the motorcycle is 24 inches. One revelation = 360 degrees. Three-fourths of one revelation = 270 degrees. The motorcycles travel = 2r(θ/360) Radius r = d/2 = 24/2 = 12 θ = 270 degrees. = 2(12)(270/360) = 24(270/360) = 18 Therefore the motorcycle travels 18 cm.
Monitoring Progress
Question 1. Find the circumference of a circle with a diameter of 5 inches.
Answer: Circumference C = πd C = 3.14x 5 = 15.7 in
Question 2. Find the diameter of a circle with a circumference of 17 feet.
Answer: Diameter d = C/π d = 17/π = 5.41 ft
Find the indicated measure.
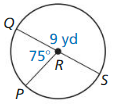
Answer: arc length of \(\widehat{P Q}\) is 5.887
Explanation: \(\widehat{P Q}\) = \(\frac { 75 }{ 360 } \) . π(9) = 5.887
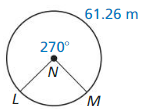
Answer: arc length of LM/C = LM/360 61.26/C = 270/360 C = 81.68
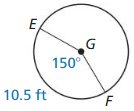
Answer: arc length of EF = \(\frac { 60 }{ 360 } \) • 2πr 10.5 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 6 } \) • 2πr r = 10.02
Question 6. A car tire has a diameter of 28 inches. How many revolutions does the tire make while traveling 500 feet?
Answer: The car tire have to make 69 revolutions to travel 500 ft.
Explanation: Circumference C = 2πr = πd C = 28π Distance travelled = number of revolutions x C 500 x 12 = number of revolutions x 28π number of revolutions = 68.2
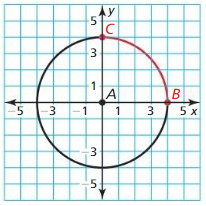
Question 7. In Example 4. the radius of the arc for a runner on the blue path is 44.02 meters, as shown in the diagram. About how far does this runner travel to go once around the track? Round to the nearest tenth of a meter.
Answer: Given that, The arc radius for a runner on the blue path is 44.02 meters. The diameter of the track is 2r = 2(44.02) = 88.04 The circumference of the track is πd = π(88.04) = 276.44 The runner travels around the track 276.44 cm.
Question 8. Convert 15° to radians.
Answer: 15° = 15 . \(\frac { π radians }{ 180° } \) = \(\frac { π }{ 12 } \) radians
Question 9. Convert \(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\) radians to degrees.
Answer: \(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\) radians = \(\frac{4 \pi}{3}\) radians . \(\frac { 180° }{ π radians } \) = 240 degrees
Vocabulary and Core Concept Check
Question 2. WRITING Describe the difference between an arc measure and an arc length.
Answer: An arc measure is measured in degrees while an arc length is the distance along an arc measured in linear units.
Monitoring Progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 10, find the indicated measure.

Question 4. diameter of a circle with a circumference of 63 feet
Answer: C = 63 ft πd = 63 d = 20.05

Question 6. exact circumference of a circle with a diameter of 5 inches
Answer: C = πd C = 5π = 15.707
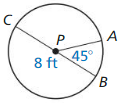
Answer: \(\frac { arc length of DE }{ 2πr } \) = \(\frac { DE }{ 360 } \) \(\frac { 8.73 }{ 2π(10) } \) = \(\frac { DE }{ 360 } \) DE = 50.01°
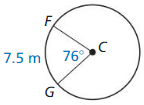
Answer: \(\frac { arc length of GH }{ 2πr } \) = \(\frac { m GH }{ 360 } \) \(\widehat{G H}\). = \(\frac { 5 }{ 24 } \) . 2π(10) = 13.08

Answer: Circumference of the front wheel = 2π(32.5) = 65π cm Distance covered = 40 m = 40 x 100 = 4000 cm Number of revolutions = \(\frac { 4000 }{ 65π } \) = 19.58
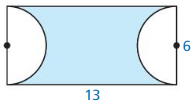
In Exercises 15-18 find the perimeter of the shaded region.
In Exercises 19 – 22, convert the angle measure.
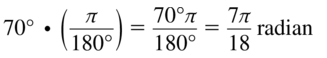
Question 20. Convert 300° to radians.
Answer: 300 • (\(\frac { π }{ 180 } \)) = \(\frac { 5π }{ 3 } \) radian
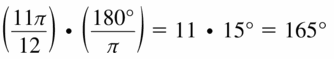
Question 22. Convert \(\frac{\pi}{8}\) radian to degrees.
Answer: \(\frac { π }{ 8 } \) • \(\frac { 180 }{ π } \)) = 22.5°
Answer: C = 38 ft 2πr = 38 r = 6.04
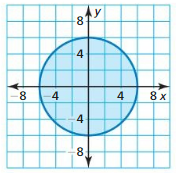
In Exercises 25 and 26, find the circumference of the circle with the given equation. Write the circumference in terms of π
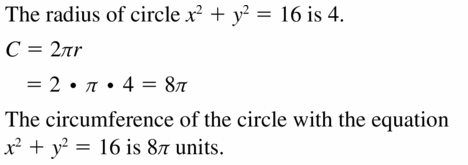
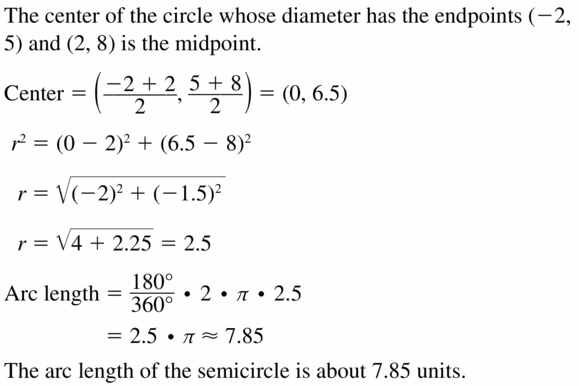
Question 26. (x + 2) 2 + (y – 3) 2 = 9
Answer: The radius of circle (x + 2)² + (y – 3)² = 9 is 3 C = 2πr = 2π(3) = 6π The circumference of the circle is 6π units.
Question 28. REASONING \(\widehat{E F}\) is an arc on a circle with radius r. Let x° be the measure of \(\widehat{E F}\). Describe the effect on the length of \(\widehat{E F}\) if you (a) double the radius of the circle, and (b) double the measure of \(\widehat{E F}\). Answer: Given x° is the measure of \(\widehat{E F}\) arc length of a circle = x/360 × 2πr arc length of \(\widehat{E F}\) = x/360 × 2πr a. double the radius of the circle x/360 × 2π(2r) = 2x/360 × 2πr x/360 × 2π(2r) = 2arc length of \(\widehat{E F}\) (b) double the measure of \(\widehat{E F}\) 2x/360 × 2πr = 2 × x/360 × 2πr 2x/360 × 2πr = 2arc length \(\widehat{E F}\)
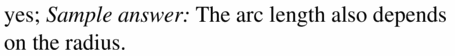
Question 32. ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS A 45° arc in ⊙C and a 30° arc in ⊙P have the same length. What is the ratio of the radius r 1 of ⊙C to the radius r 2 of ⊙P? Explain your reasoning. Answer: Given, A 45° arc in ⊙C and a 30° arc in ⊙P have the same length. r1/r2 = 45/30 = 3/2 So, the ratio of the radius r 1 of ⊙C to the radius r 2 of ⊙P is 3/2.

Question 38. MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS What is the measure (in radians) of the angle formed by the hands of a clock at each time? Explain your reasoning. a. 1 : 30 P.M.
Answer: 3π/4
b. 3:15 P.M.
Answer: π/24
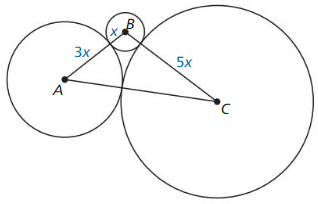
Question 40. THOUGHT PROVOKING Is π a rational number? Compare the rational number \(\frac{355}{113}\) to π. Find a different rational number that is even closer π.
Answer: π is not a rational number as it can not be represented as an equivalent fraction. π = 3.14 and 355/113 = 3.14. This fraction resembles that value of π. Therefore a more accurate fraction will be starting by the value of 7 decimal places of π, therefore 3.1415926 x x = a.
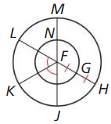
b. What would the sum of the arc lengths be if \(\overline{A B}\) was divided into 8 congruent segments? 16 congruent segments? n congruent segments? Explain your reasoning. Answer: 360/2 = 180 degrees Then the arc length of 1 semicircle is 180/360 × 2π(r/2) 1/2 × πr = πr/2 Therefore the arc length of 8 semicircles will be 8 × πr/2 = 4πr
Maintaining Mathematical Proficiency
Find the area of the polygon with the given vertices.
Question 44. L(- 3, 1), M(4, 1), N(4, – 5), P(- 3, – 5)
Finding the Area of a Sector of a Circle
Work with a partner: A sector of a circle is the region bounded by two radii of the circle and their intercepted arc. Find the area of each shaded circle or sector of a circle.
Finding the Area of a Circular Sector

Question 3. How can you find the area of a sector of a circle? Answer: The formula for sector area is simple, just multiply the central angle by the radius squared, and divide by 2 Area of a sector = θ/360 × πr²
Question 4. In Exploration 2, find the area of the sector that is irrigated in 2 hours. Answer:
Monitoring progress
Question 1. Find the area of a circle with a radius of 4.5 meters.
Answer: Circle area = πr² A = π(4.5)² = 20.25π
Question 2. Find the radius of a circle with an area of 176.7 square feet.
Answer: Circle area = πr² 176.7 = πr² r² = 56.24 r = 7.499
Question 3. About 58,000 people live in a region with a 2-mile radius. Find the population density in people per square mile.
Answer: The population density is about 4615.49 people per square mile.
Explanation: A = πr² = π • 2² = 4π Population density = \(\frac { number of people }{ area of land } \) = \(\frac { 58000 }{ 4π } \) = 4615.49
Question 4. A region with a 3-mile radius has a population density of about 1000 people per square mile. Find the number of people who live in the region.
Answer: The number of people who live in the region are 28274.
Explanation: A = πr² = π • 3² = 9π Population density = \(\frac { number of people }{ area of land } \) Number of people = 1000 x 9π = 28274
Find the indicated measure
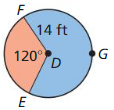
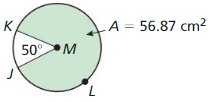
Question 5. area of red sector
Answer: The area of red sector = 205.25
Explanation: m∠FDE = 120°, FE = 120° and FGE = 360° – 120° = 240° Area of red sector = \(\frac { FE }{ 360° } \) • πr² = \(\frac { 120 }{ 360° } \) • π(14²) = 205.25
Question 6. area of blue sector
Answer: Area of blue sector = 410.5
Explanation: Area of blue sector = \(\frac { FGE }{ 360° } \) • πr² = \(\frac { 240 }{ 360° } \) • π(14²) = 410.5
Question 7. Find the area of ⊙H.
Answer: Area of ⊙H = 907.92 sq cm
Explanation: Area of sector FHG =\(\frac { FG }{ 360° } \) • Area of ⊙H 214.37 = \(\frac { 85 }{ 360° } \) • Area of ⊙H Area of ⊙H = 907.92 sq cm
Question 8. Find the area of the figure.
Answer: Area of triangle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \) • 7 • 7 = 24.5 sq m Area of semi circle = πr²/2 = π(3.5)²/2 = 19.242255 Area of the figure = 24.5 + 19.24 = 43.74 sq m
Question 9. If you know the area and radius of a sector of a circle, can you find the measure of the intercepted arc? Explain.
Answer: Yes, we can find the intercepted arc when we the area and the radius of the sector of the circle. Because the intercepted arc is the arc inside the inscribed angles and whose endpoints are on the angle.

Question 2. WRITING The arc measure of a sector in a given circle is doubled. will the area of the sector also be doubled? Explain our reasoning.
Answer: Yes
Explanation: Area of sector with arc measure x and radius r is s = π/180(xr) If x becomes doube, then s1 = π/180(2xr) = 2s This means that if the arc measure doubles, area of the sector also doubles.
In Exercise 3 – 10, find the indicated measure,
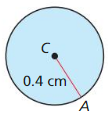
Answer: Area A = πr² A = π(10)² = 100π sq in
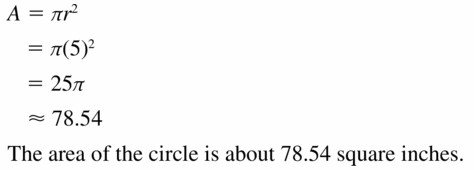
Question 6. area of a circle with a diameter of 16 feet
Answer: d = 2r Circle area = πr² = (π/4)d² = (π/4)16² = 64π

Question 8. radius of a circle with an area of 380 square inches
Answer: A = πr² 380 = πr² r = 10.99
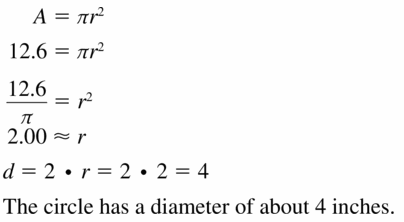
Question 10. diameter of a circle with an area of 676π square centimeters
Answer: Area A = 676π square centimeters (π/4)d² = 676π d² = 2704 d = 52
In Exercises 11 – 14, find the indicated measure.

Question 12. About 650,000 people live in a region with a 6-mile radius. Find the population density in people per square mile.
Answer: The population density is about 5747 people per square mile.
Explanation: Area of region = π(6)² = 36π Population density = \(\frac { Number of people }{ area of land } \) = \(\frac { 650,000 }{ 36π } \) = 5747.2
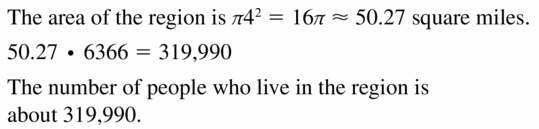
Question 14. About 79,000 people live in a circular region with a population density of about 513 people per square mile. Find the radius of the region.
Answer: The radius of the region is 7
Explanation: Population density = \(\frac { Number of people }{ area of land } \) 513 = \(\frac { 79,000 }{ πr² } \) πr² = 153.99 r = 7
In Exercises 15-18 find the areas of the sectors formed by∠DFE.
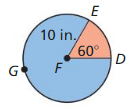
Answer: Area of sector = \(\frac { 104° }{ 360° } \) • π(14)² = 177.88 Area of red region is 177.88 sq cm Area of blue region = \(\frac { 256° }{ 360° } \) • π(14)² = 437.86 sq cm
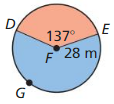
Answer: Area of red region is 10.471 sq ft Area of the blue region is 39.79 sq ft
Explanation: Area of sector = \(\frac { 75° }{ 360° } \) • π(4)² = 10.471 Area of red region is 10.471 sq ft Area of blue region = \(\frac { 285° }{ 360° } \) • π(4)² = 39.79 sq ft
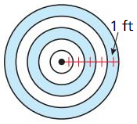
Answer: Area of ⊙Z is 255 square feet πr² = 255 r = 9 Area of sector XZY = \(\frac { 115 }{ 360 } \) • 255 n = 81.458 sq ft
In Exercises 21 and 22, the area of the shaded sector is show. Find the indicated measure.
Answer: radius of ⊙M = 3.98
Explanation: Area of region = \(\frac { 89 }{ 360 } \) . Area of ⊙M 12.36 = \(\frac { 89 }{ 360 } \) . Area of ⊙M Area of ⊙M = 49.99 πr² = 49.99 r = 3.98
In Exercises 23 – 28, find the area of the shaded region.
Answer: The area of the shaded region is 85.840 sq in.
Explanation: Area of square = 20² = 400 Diameter of one circle = 10 radius of one circle = 5 in Area of one circle = π(5)² = 78.53 Areas of four circle = 314.159 Area of shaded region = 400 – 314.159 = 85.840
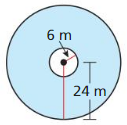
Answer: The area of shaded region is 301.59
Explanation: The radius of smaller circle is 8 cm The radius of bigger circle is 16 cm Area of smaller semicircle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(π(8)²) = 100.53 Area of lager semicircle = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(π(16)²) = 402.123 Area of shaded region = 402.123 – 100.53 = 301.59
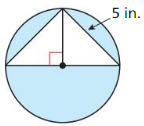
Explanation: c² = 3² + 4² = 25 c = 5 Radius = 2.5 Circle area = π(2.5)² = 19.63 Area of triangle = (3 x 4)/2 = 6 Area of shaded region = 19.63 – 12 = 7.63
Question 30. MAKING AN ARGUMENT Your friend claims that if the radius of a circle is doubled, then its area doubles. Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
Answer: The friend is not correct. doubling the radius quadruples the area.
Explanation: Area of circle with radius r = πr² Area of circle with radius 2r = π(2r)² = 4πr²
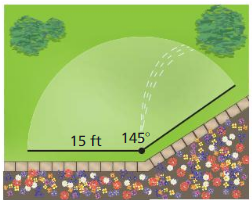
b. What is the area of land that can be covered by the light from the lighthouse? Answer: Area = \(\frac { 245 }{ 360 } \) x π(18)² = 692.72 sq mi

Question 34. ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS A square is inscribed in a circle. The same square is also circumscribed about a smaller circle. Draw a diagram that represents this situation. Then find the ratio of the area of the larger circle to the area of the smaller circle.
Answer: We start by assigning a variable to the radius of the inner circle. It is r, therefore the area of the circle is πr² It can be seen that the side length of square is twice this radius. Therefore it can be said that the side length of this square is 2r. Next, it can be seen that the diagonal of the square is diameter of outer circle. Therefore, length of the diagonal of the circle d = 2r√2. outer circle radius = r√2 Area of outer circle 2πr² The ratio of the area of larger circle to the smaller circle = 2.
Answer: Ellipse area = πab

Maintaining Mathematical proficiency
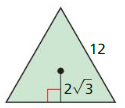
Find the area of the figure.
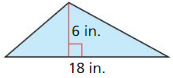
Answer: Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(base x height) Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(18 x 6) = 54 sq in
Finding the Area of a Regular Polygon
Writing a Formula for Area
Work with a partner: Generalize the steps you used in Exploration 1 to develop a formula for the area of a regular polygon. REASONING ABSTRACTLY To be proficient in math, you need to know and flexibly use different properties of operations and objects. Answer:
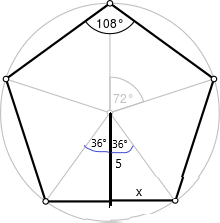
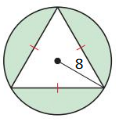
Question 3. How can you find the area of a regular polygon? Answer: You can find the area of the regular pentagon using the formulas. They are, The formula for the regular pentagon if only the side is known is A = 1/4 x square root of 5(5 + 2 square root(5) x (a)². The formula for the area of the regular pentagon is 1/2 x p x a. Where a = apothem P = perimeter
Question 4. Regular pentagon ABCDE has side lengths of 6 meters and an apothem of approximately 4.13 meters. Find the area of ABCDE. Answer: Given that, The side length of the regular pentagon ABCDE is 6 meters. The apothem of the regular pentagon is 4.13 meters. The formula for the area of the regular pentagon is 1/2 x p x a. Where a = apothem P = perimeter The formula for the perimeter of a regular pentagon is = 5a = 5(6) = 30 = 1/2 x 30 x 4.13 = 1/2 x 123.9 = 61.95 square cm
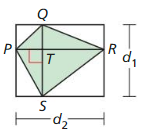
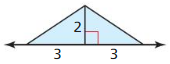
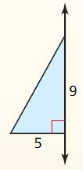
Question 1. Find the area of a rhombus with diagonals d 1 = 4 feet and d 2 = 5 feet.
Answer: Area of rhombus = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(4 x 5) = 5 sq ft
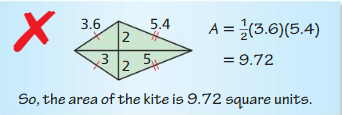
Question 2. Find the area of a kite with diagonals d 1 = 12 inches and d 1 = 9 inches.
Answer: Area of kite = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(12 x 9) = 27 sq in
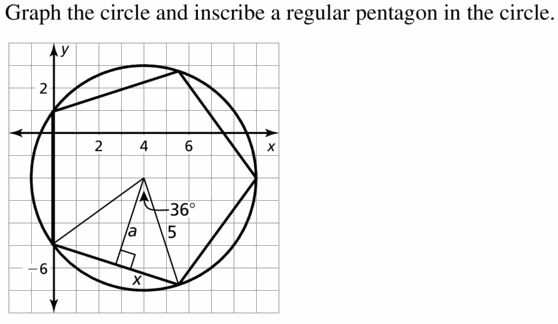
In the diagram. WXYZ is a square inscribed in ⊙P.
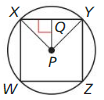
Question 3. Identify the center, a radius, an apothem, and a central angle of the polygon.
Answer: P is the center, PY or PX is the radius, PQ is apothem, ∠XPY is the central angle.
Question 4. Find m∠XPY, m∠XPQ, and m∠PXQ.
Answer: m∠XPY = \(\frac { 360 }{ 4 } \) = 90 m∠XPQ = 90/2 = 45 m∠PXQ = 180 – (90 + 45) = 45
Find the area of regular polygon
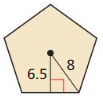
Answer: c = √(8² + 6.5²) = 10.3 a = 20.61 Area = 0.25(√5(5+2√5) a² Area = 0.25(√5(5+2√5) 20.61² = 730.8
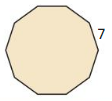
Answer: EF = radius = 6.8
Find the apothem of polygon ABCDE.
Answer: GF = apothem = 5.5
Answer: AF = √4² + 5.5² AF = 6.8
Find the radius of polygon ABCDE. Answer: AF = radius = 6.8
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the area of the kite or rhombus.
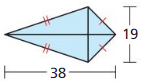
Answer: d₁ = 6 + 6 = 12 d₂ = 2 + 10 = 12 area A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(12 x 12) = 36
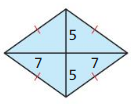
In Exercises 7 – 10, use the diagram
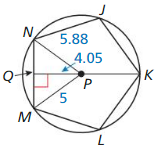
Question 8. Identify a central angle of polygon JKLMN.
Answer: ∠NPM is the central angle of polygon JKLMN
Question 10. What is the apothem of polygon JKLMN? Answer: QP is the apothem of polygon JKLMN
In Exercises 11 – 14, find the measure of a central angle of a regular polygon with the given number of sides. Round answers to the nearest tenth of a degree, if necessary.
Question 12. 18 sides
Answer: The measure of central angle = \(\frac { 360 }{ 18 } \) = 20

Question 14. 7 sides
Answer: The measure of central angle = \(\frac { 360 }{ 7 } \) = 51.42
In Exercises 15 – 18, find the given angle measure for regular octagon ABCDEFGH.
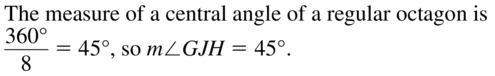
Question 16. m∠GJK
Answer: m∠GJK = m∠GJH/2 m∠GJK = 22.5
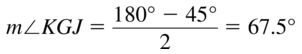
Question 18. m∠EJH Answer: m∠EJH = 3(45) = 135
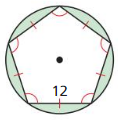
In Exercises 19 – 24, find the area of the regular polygon.
Question 24. a pentagon with an apothem of 5 units
Answer: A = 90.75
We know apothem a = and it divides pentagon into triangles, the central angle is divided into 360/5 = 72 After that, we halved this angle and got 2 right triangles with x = 44 and y = 36. Since we know one side and all three angles of the triangle, we can calculate p with the tangent function. tan y = p/a tan 36 = p/5 p = 3.63 Since p is just half of the length of the side, we have to multiply it by 2 2 . p = 2 . 3.63 = 7.26 = s Area = \(\frac { a . s. n }{ 2 } \) A = \(\frac { 15 x 7.26 x 5 }{ 2 } \) A = 90.75
Answer: s = √15² – 13² = 7.48 Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(a . ns) A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(13 x 6 x 7.48) A = 291.72
In Exercises 27 – 30, find the area of the shaded region.
Answer: Area of the shaded region = 223.75
Explanation: Square side = diagonal/√2 = 28/√2 = 19.79 Area of square = 19.79² = 392 Circle area = π(14)² = 615.75 Area of the shaded region = 615.75 – 392 = 223.75
CRITICAL THINKING In Exercises 33 – 35, tell whether the statement is true or false. Explain your reasoning

Question 34. The apothem of a regular polygon is always less than the radius.
Answer: true, the radius always reaches the end of the circle but the apothem never does

Explanation: (A) area = π(6.5)² = 132.73 (B) area = 139.25 (C) area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(18 x 15) = 135
Question 38. REASONING What happens to the area of a kite if you double the length of one of the diagonals? if you double the length of both diagonals? Justify your answer.
Answer: Area of a kite = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) If you double the length of one diagonal, then d₁ = 2d₁ Area of kite = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(d₁d₂) If you double length of both diagonals Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(2d₁2d₂) = d₁d₂ If you double the length of one diagonal, then the area becomes halve. If you double length of both diagonals, then area becomes 4 times.
MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS In Exercises 39 and 40, write and solve an equation to find the indicated lengths. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.

Question 40. One diagonal of a rhombus is four times the length of the other diagonal. The area of the rhombus is 98 square feet. Find the length of each diagonal.
Answer: The length of each diagonal is 9.89, 2.47.
Explanation: One diagonal of a rhombus is four times the length of the other diagonal. d₁ = 4d₂ Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) 98 = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁(4d₁)) d₁ = 9.89 d₂ = 2.47

Question 42. MAKING AN ARGUMENT Your friend claims that it is possible to find the area of any rhombus if you only know the perimeter of the rhombus. Is your friend correct? Explain your reasoning.
Answer: No; A rhombus is not a regular polygon.
Answer: Given that, The hexagon has 6 sides. The hexagon is divided into 6 equilateral triangles. The area of the equilateral triangle is (square root of 3)/4 x a² a = side length = (square root of 3)/4 x (6)² = (square root of 3)/4 x 36 = 15.588 square cm.
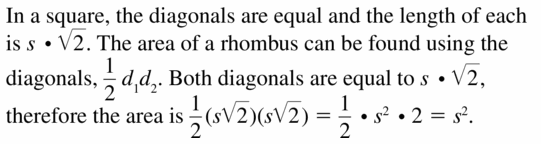
Question 48. CRITICAL THINKING The area of a dodecagon, or 12-gon, is 140 square inches. Find the apothem of the polygon.
Answer: Let the side length of dodecagon be 2x. The measure of each interior angle of a regular decagon is 150. This implies that the base angle C and A of the resulting isosceles triangle formed by the red sides is equal to 150/2 = 75. The adjacent to this angle is the length 2x/2 = x inches, while the opposite to it is the blue apothem in the right triangle BDC formed. Therefore a = x tan 75. Therefore, area of dodecagon is 140 = 1/2 (x tan75)(12 . 2x) 140 = 44.785 x² x² = 3.126 x = 1.768
Question 52. USING STRUCTURE Two regular polygons both have n sides. One of the polygons is inscribed in, and the other is circumscribed about, a circle of radius r. Find the area between the two polygons in terms of n and r.
Answer: The radius of the smaller polygon is equal to the apothem of the larger polygon. The central angle is 360/n, therefore the apothem makes an angle of 180/n. Use sine and cosine to find the apothem and side length of the smaller polygon. a small = r sin\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) s small = 2r cos\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) Use tangent to find the side length of the large polygon. S large = 2r tan\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) Use the formula to find the area of the smaller polygon. A small = 1/2 . a small . n . s small A small = 1/2 . r sin\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) . n . 2r cos\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) A small = nr² sin \(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) cos\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) Use the formula to find the area of the larger polygon. A Large = 1/2 . a large . n . slarge = nr² tan\(\frac { 180 }{ n } \) The area between the polygons is equal to the area of the larger polygon minus the area of the smaller polygon. Use some trig identities to simplify the expression. A = A large – A small A = nr² tan\(\frac { 180 }{ n } sin²[latex]\frac { 180 }{ n }
Determine whether the figure has line symmetry, rotational symmetry, both, or neither. If the figure has line symmetry. determine the number of lines of symmetry. It the figure has rotational symmetry, describe any rotations that map the figure onto itself.
Analyzing a Property of Polyhedra
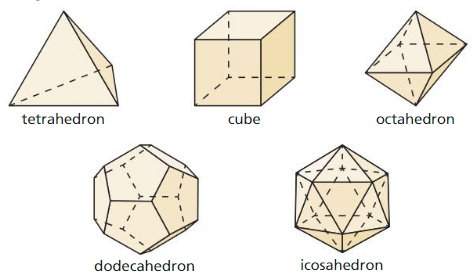
Question 2. What is the relationship between the numbers of vertices V, edges E, and faces F of a polyhedron? (Note: Swiss mathematician Leonhard Euler (1707 – 1783) discovered a formula that relates these quantities.) CONSTRUCTING VIABLE ARGUMENTS To be proficient in math, you need to reason inductively about data. Answer: The relationship between the vertices, edges, and faces of a polyhedron according to Euler’s formula is F + V = E + 2. Where F = number of faces. V = number of vertices. E = number of edges.
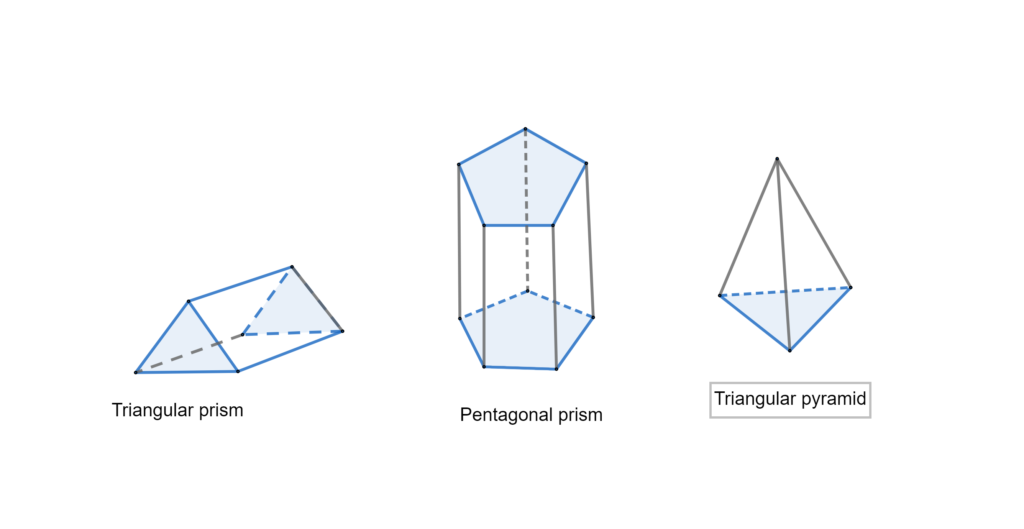
now we count vertices, edges, and faces in each solids A triangular prism has vertices 6, edges 9 and faces 5 6 – 9 + 5 = 2 A Pentagonal prism has vertices 10, edges 15 and faces 7 10 – 15 + 7 = 2 A triangular pyramid has vertices 4, edges6 and faces 4 – 6 + 2 = 2
Tell whether the solid is a polyhedron. If it is, name the polyhedron.
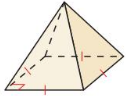
Answer: The solid is formed by polygons, so it is a polyhedron. The base is a square, it is a square pyramid.
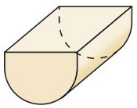
Describe the shape formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid.
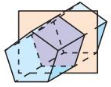
Sketch the solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis. Then identify and describe the solid.
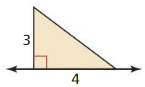
Answer: Cone does not belong with the other three as it has a curved surface and others not.
In Exercises 3 – 6, match the polyhedron with its name.
In Exercises 7 – 10, tell whether the solid is a polyhedron. If it is, name the polyhedron.
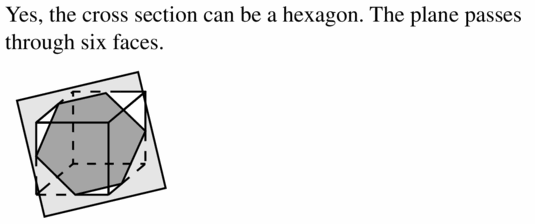
In Exercises 11 – 14, describe the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid.
In Exercises 15 – 18, sketch the solid produced by rotating the figure around the given axis. Then identify and describe the solid.
In Exercises 21 – 26, sketch the polyhedron.
Question 22. rectangular prism
Question 26. pentagonal pyramid
b. What is the perimeter of the cross section? Answer: The perimeter is 2(l + b)
c. What is the area of the cross section? Answer: Area is lb.
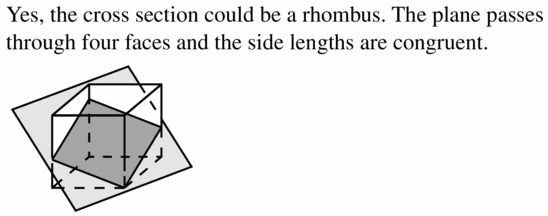
REASONING In Exercises 29 – 34, tell whether it is possible for a cross section of a cube to have the given shape. If it is, describe or sketch how the plane could intersect the cube.
Question 30. pentagon Answer: yes, cross-section of the cube can be a pentagon.
Question 32. isosceles triangle Answer: Yes, the cross-section can be an isosceles triangle.
Question 34. scalene triangle Answer: Yes, the cross-section can be scalene triangle.
Question 36. THOUGHT-PROVOKING Describe how Plato might have argued that there are precisely five Platonic Solids (see page 617). (Hint: Consider the angles that meet at a vertex.) Answer:
Decide whether enough information is given to prove that the triangles are congruent. It so, state the theorem you would use.
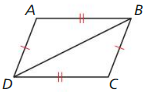
Answer: ∆JLK ≅ ∆JLM by SAS congruence theorem.
Question 4. Convert 26° to radians and \(\frac{5 \pi}{9}\) radians to degrees.
Answer: 26° = 26 . \(\frac { π }{ 180 } \) = \(\frac { 13π }{ 90 } \) radians \(\frac{5 \pi}{9}\) = \(\frac{5 \pi}{9}\) . \(\frac { 180 }{ π } \) = 100°
Use the figure to find the indicated measure.
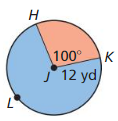
Answer: area of red sector = \(\frac { 100 }{ 360 } \) . π(12)² = 125.66
Answer: area of blue sector = \(\frac { 260 }{ 360 } \) . π(12)² = 326.72
In the diagram, RSTUVWXY is a reuIar octagon inscribed in ⊙C.
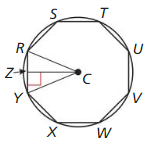
Question 7. Identify the center, a radius, an apothem, and a central angle of the polygon.
Answer: C is center, CY is radius, CZ is apothem, ∠YCR is central angle of the polygon
Question 8. Find m∠RCY, m∠RCZ, and m∠ZRC.
Answer: m∠RCY = 360/8 = 45 m∠RCZ = 45/2 = 22.5 m∠ZRC = 180 – (22.5 + 90) = 67.5
Question 9. The radius of the circle is 8 units. Find the area of the octagon.
Answer: Area of octagon = 0.5 x 8 x 8 sin 45 = 22.62
Answer: Area of yellow tile = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(15.7 x 11.4) = 44.745 area of red tile = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(18.5 x 6) = 27.75 Area of pattern = 32(44.745) + 23(27.75) = 2070.09 sq mm
Finding volume
Work with a partner: Consider a stack of square papers that is in the form of a right prism.
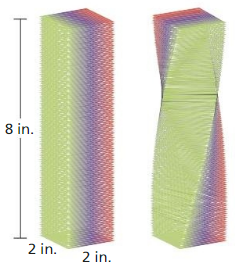
a. What is the volume the prism? Answer: The volume of the prism is B = 1/2 x h(b1 + b2) h = 8 b1 = 2 b2 = 2 = 1/2 x 8(2 + 2) = 1/2 x 8(4) = 1/2 x 32 = 16 cube inches. Therefore the volume of the prism is 16 cu. inches.
b. When you twist the slack of papers, as shown at the right, do you change the volume? Explain your reasoning. Answer: The volume of the prism and the twist of the slack of paper volume are the same. Because the different shapes of the prism have the same volume.
c. Write a carefully worded conjecture that describes the conclusion you reached in part (b). ATTENDING TO PRECISION To be proficient in math, you need to communicate precisely to others. Answer: The conjecture is that the different shapes of the prism have the same volume but are different in surface area.
d. Use your conjecture to find the volume of the twisted stack of papers. Answer: The volume of the twist of the slack of paper is B = 1/2 x h(b1 + b2) h = 8 b1 = 2 b2 = 2 = 1/2 x 8(2 + 2) = 1/2 x 8(4) = 1/2 x 32 = 16 cu. inches. Therefore the volume of the twist and the slack of the paper is 16 cu. inches. It is the same as the volume of the prism.
Work with a partner: Use the conjecture you wrote in Exploration I to find the volume of the cylinder.
Question 3. How can you find the volume of a prism or cylinder that is not a right prism or right cylinder? Answer: Using π we can find the volume of the prism or cylinder that is not a right prism of the right cylinder. The cylinder and the prism have the same cross-sectional area of πr². At every level and same height. Both the cylinder and prism have the same volume it is V = πr²h.
Question 4. In Exploration 1, would the conjecture you wrote change if the papers in each stack were not squares? Explain your reasoning. Answer:
Find the volume of the solid.
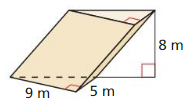
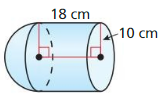
Answer: Area of circle = πr² = π(8)² = 64π Volume = 64π x 14 = 2814.86 cubic ft
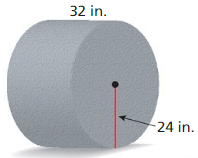
Question 4. WHAT IF? In Example 4, you want the length to be 5 meters, the width to be 3 meters. and the volume to be 60 cubic meters. What should the height be? Answer: volume = lbh 60 = 5 x 3 x h h = 4 m
Question 5. WHAT IF? In Example 5, you want the height to be 5 meters and the volume to be 75 cubic meters. What should the area of the base be? Give a possible length and width. Answer: volume V = base x height 75 = base x 5 Base = 15 sq m
Question 2. COMPLETE THE SENTENCE Density is the amount of _______ that an object has in a given unit of __________ .
Answer: Density is the mass of the object divided by its volume.
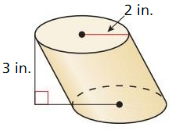
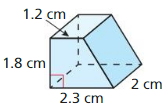
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the volume of the prism.
In Exercises 7 – 10. find the volume of the cylinder.
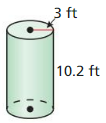
In Exercises 11 and 12. make a sketch of the solid and find its volume. Round your answer to the nearest hundredth.
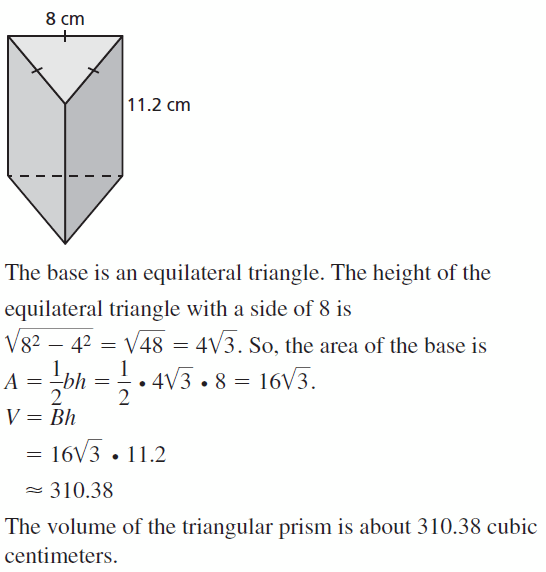
Question 12. A pentagonal prism has a height of 9 feet and each base edge is 3 feet.
Answer: volume is 139.32 ft³
explanation: Pentagon area = 15.48 Height h = 9 ft Volume V = area x height = 15.48 x 9 = 139.32

Answer: Density = mass / volume Density = \(\frac { 24 }{ 28.3 } \) Density = 0.8480
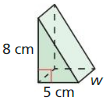
In Exercises 17 – 22, find the missing dimension of the prism or cylinder.
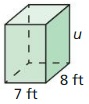
Answer: Volume = 2700 yd³ 12 x 5 x v = 2700 v = 15 yd
In Exercises 23 and 24, find the area of the base of the rectangular prism with the given volume and height. Then give a possible length and width.

Question 24. V = 27 m 3 ,h = 3m
Answer: V = Bh 27 = B x 3 B = 9
In Exercises 25 and 26, the solids are similar. Find the volume of solid B.
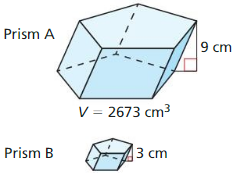
In Exercises 27 and 28, the solids are similar. Find the indicated measure.
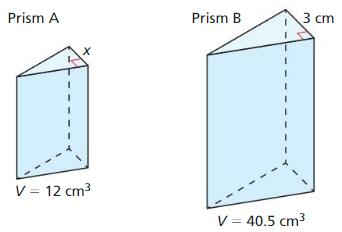
Explanation: \(\frac { 7π }{ 5 } \) = \(\frac { 56π }{ h } \) h = 40
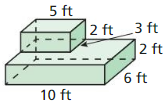
In Exercises 29 – 32. find the volume of the composite solid.
Explanation: Volume of square = 4³ = 64 Volume of semicircle = π(2)² x 4 = 8π
Answer: The volume of composite solid is 35 cubic ft
Explanation: Volume of larger prism = 4 x 2 x 5 = 40 Volume of the smaller prism = 1 x 1 x 5 = 5 Volume of larger prism – volume of the smaller prism = 40 – 5 = 35 cubic ft

Question 34. COMPARING METHODS The Volume Addition Postulate states that the volume of a solid is the sum of the volumes of all its non overlapping parts. Use this postulate to find the volume of the block of concrete in Example 7 by subtracting the volume of each hole from the volume of the large rectangular prism. Which method do you prefer? Explain your reasoning. Answer:
REASONING In Exercises 35 and 36, you are melting a rectangular block of wax to make candles. how many candles of the given shape can be made using a block that measures 10 centimeters by 9 centimeters by 20 centimeters?

Answer: 7 triangular prism candles with the given measures can be made.
Explanation: Volume of block = 1800 The volume of triangular prism = 4 x 6 x 10 = 240 1800/240 = 7.5

Question 38. PROBLEM SOLVING You drop an irregular piece of metal into a container partially filled with water and measure that the waler level rises 4.8 centimeters. The square base of the container has a side length of 8 centimeters. You measure the mass of the metal to be 450 grams. What is the density of the metal?
Answer: The density of metal is 1.4648
Explanation: Density = \(\frac { Mass }{ Volume } \) Volume V = 4.8 x 64 = 307.2 Density = \(\frac { 450 }{ 307.2 } \) = 1.4648
Answer: Volume = 2.5 x 3.5 x 6 Volume = 52.5
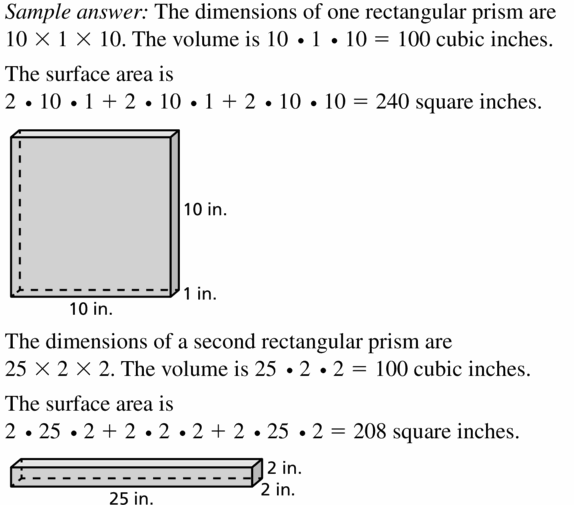
Answer: First one gives more cerel for your money.
Explanation: Bigger one volume = 16 x 4 x 10 = 640 Smaller one volume = 2 x 8 x 10 = 160 6 – 640 means 1 – 106.66 2 – 160 means 1 – 80
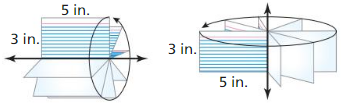
Question 46. CRITICAL THINKING The height of cylinder X is twice the height of cylinder Y. The radius of cylinder X is half the radius of cylinder Y. Compare the volumes of cylinder X and cylinder Y. Justify your answer.
Answer: Let the height of cylinder X be h, radius be r and its volume is πr²h So, the height of cylinder Y is h/2 and radius is 2r, then the volume is 2πr²h From both expressions, it can be seen that the volume of cylinder y is twice that of cylinder X.
Question 48. MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS You drill a circular hole of radius r through the base of a cylinder of radius R. Assume the hole is drilled completely through to the other base. You want the volume of the hole to be half the volume of the cylinder. Express r as a function of R.
Answer: r = √R²/2
Explanation: The radius of a solid cylinder without a hole is R. So its volume is πR²h As per the given condition, the volume of the hole must be half of that of the solid cylinder, hole volume is πR²h/2 Volume of cylinder V = πr²h πR²h/2 = πr²h R²/2 = r² r = √R²/2 r = \(\frac { R√2 }{ 2 } \)
Question 50. ANALYZING RELATIONSHIPS How can you change the edge length of a cube so that the volume is reduced by 40%?
Answer: Write the equation of volume of rectangular prism which can be used to evaluate the cube volume Volume = s x s x s The above equation shows that the volume of a cube is directly proportional to one of its side length, therefore, if the volume is to be reduced by 40%, then its the length of one of its side must be reduced by 40%, without changing the 2 other of its sides.
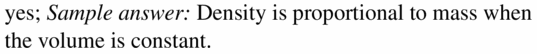
Find the surface area of the regular pyramid.
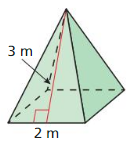
Finding the Volume of a Pyramid
Question 3. How can you find the volume of a pyramid? Answer: The volume of a pyramid is found using the formula V = (1/3) Bh, where ‘B’ is the base area and ‘h’ is the height of the pyramid. As we know the base of a pyramid is any polygon, we can apply the area of polygons formulas to find ‘B’.
Question 4. In Section 11 .7, you will study volumes of cones. How do you think you could use a method similar to the one presented in Exploration 1 to write a formula for the volume of a cone? Explain your reasoning. Answer:
Find the volume of the pyramid.
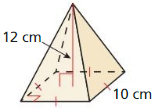
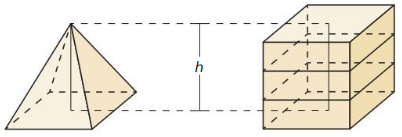
Explanation: Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(10 x 10 x 12) V = 400
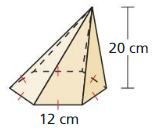
Answer: The volume of the pyramid is 2494.13 cm³
Explanation: Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(374.12 x 20) V = 2494.13
Question 3. The volume of a square pyramid is 75 cubic meters and the height is 9 meters. Find the side length of the square base.
Answer: The side length of the square base is 5 m
Explanation: Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 75 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)B(9) = 75 B = 25 s = 5
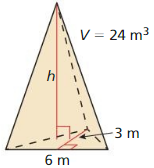
Answer: The height of the triangular pyramid is 8 m
Explanation: V = 24 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 24 B = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(3 x 6) = 9 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(9)h = 24 h = 8
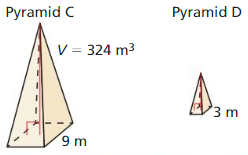
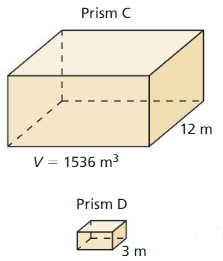
Answer: The volume of pyramid D is 12 m³
Explanation: \(\frac { volume of pyramid C }{ volume of pyramid D } \) = (\(\frac { pyramid C base }{ pyramid D base } \))³ \(\frac { 324 }{ V } \) = (\(\frac { 9 }{ 3 } \))³ V = 12
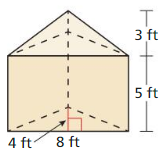
Answer: the volume of solid = 96
Explanation: Volume of prism = Bh B = 8 x 2 = 16 V = 16 x 5 = 80 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(16 x 3) = 16 the volume of solid = 16 + 80 = 96

Question 2. REASONING A square pyramid and a cube have the same base and height. Compare the volume of the square pyramid to the volume of the cube.
Answer: Square pyramid = 1/3 Bh Cube = BH So, the volume of the square pyramid is 1/3 of the volume of the cube.
In Exercises 3 and 4, find the volume of the pyramid.
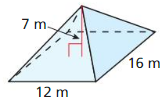
Answer: V = 6 in³
Explanation: V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh B = 2 x 3 = 6 V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(6 x 3)
In Exercises 5 – 8, find the indicated measure.
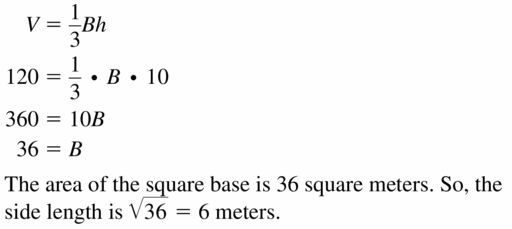
Question 6. A pyramid with a square base has a volume of 912 cubic feet and a height of 19 feet. Find the side length of the square base.
Answer: The side length of the square base is 12 ft
Explanation: A pyramid with a square base has a volume of 912 cubic feet h = 19 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 912 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)B(19) = 912 B = 144 s = 12
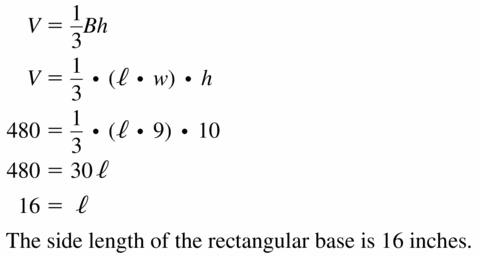
Question 8. A pyramid with a rectangular base has a volume of 105 cubic centimeters and a height of 15 centimeters. The length of the rectangular base is 7 centimeters. Find the width of the rectangular base.
Answer: The width of the rectangular base is 3 cm
Explanation: A pyramid with a rectangular base has a volume of 105 cubic centimeters h = 15 l = 7 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 105 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)lbh = 105 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(7 x 15 x b) = 105 b = 3
Question 10. OPEN-ENDED Give an example of a pyramid and a prism that have the same base and the same volume. Explain your reasoning. Answer: Let the rectangular prism have the base dimensions 4 x 2 nad a height of 5 so its volume is 4 x 2 x 5 = 40 cubic units Therefore the base of the rectangular prism also have the dimensions of 4 x 2 and a height of 5 x 3 = 15 units so its volume V = 1/3 x 4 x 2 x 15 = 40 cubic units
In Exercises 11 – 14, find the height of the pyramid.
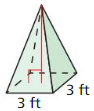
Answer: The height of the pyramid is 10.5 in
Explanation: Volume = 224 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 224 B = 8² = 64 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(64)h = 224 h = 10.5
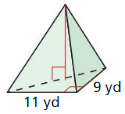
Answer: The height of the pyramid is 12 cm
Explanation: Volume = 392 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = 392 B = 14 x 7 = 98 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(98)h = 392 h = 12
In Exercises 15 and 16, the pyramids are similar. Find the volume of pyramid B.
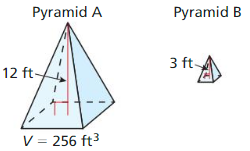
Answer: Volume of A = 80
Explanation: \(\frac { Volume of B }{ Volume of A } \) = (\(\frac { Side of B }{ side of A } \))³ \(\frac { V }{ 10 } \) = (\(\frac { 6 }{ 3 } \))³ V = 8 x 10 Volume of A = 80
In Exercises 17 – 20, find the volume of the composite solid.
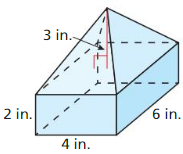
Answer: Composite solid volume = 306
Explanation: Base area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)bh = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(12 x 9) = 54 Bottom solid volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(54 x 10) V = 180 Top solid volume v = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(54 x 7) = 126 Composite solid volume = 180 + 126 = 306
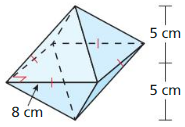
Answer: Composite solid volume = 1152
Explanation: Volume of Box = 12 x 12 x 12 = 1728 Square pyramid volume = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)Bh = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(144 x 12) = 576 Composite solid volume = 1728 – 576 = 1152
Question 21. ABSTRACT REASONING A pyramid has a height of 8 feet and a square base with a side length of 6 feet.
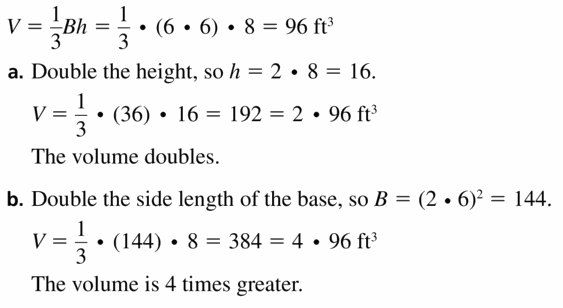
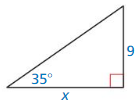
Find the value of X. Round your answer to the nearest tenth.
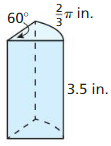
Finding the Surface Area of a Cone
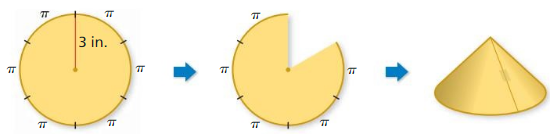
b. What is the area of the original circle? What is the area with one sector missing? Answer:
c. Describe the surface area of the cone, including the base. Use your description to find the surface area. Answer:
Finding the Volume of a Cone
Question 3. How can you find the surface area and the volume of a cone? Answer:
Question 4. In Exploration 1, cut another sector from the circle and make a cone. Find the radius of the base and the surface area of the cone. Repeat this three times, recording your results in a table. Describe the pattern. Answer:
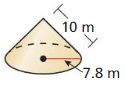
Answer: The surface area of the right cone is 436.17 m²
Explanation: r = 7.8 l = 10 S = πr² + πrl S = π(7.8)² + π(7.8 x 10) S = 436.17
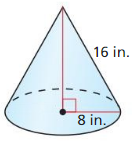
Find the volume of the cone.
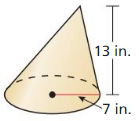
Answer: The volume of the cone is 2206.44 in³
Explanation: r = 7, h = 13 l = √13² – 7²= 10.95 S = πr² + πrl S = π7² + π(7 x 10.95) S = 394.74 Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 7² x 13) V = 2206.44
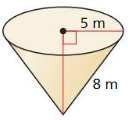
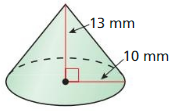
Answer: The volume of the cone is 163.4 m³
Explanation: h = √8² – 5² = 6.24 Volume V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 5² x 6.24) V = 163.4
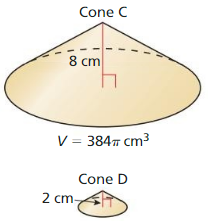
Answer: Volume of cone D = 18.84 cm³
Explanation: \(\frac { Volumeof cone C }{ Volume of cone D } \) = (\(\frac { height of C }{ height of D } \))³ \(\frac { 384π }{ Volume of cone D } \)= (\(\frac { 8 }{ 2 } \))³ Volume of cone D = 18.84
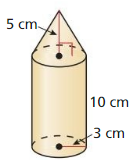
Answer: Composite solid volume = 329.86 cm³
Explanation: Volume of cylinder = πr²h = π(3)² x 10 = 90π Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 3² x 5) = 15π Composite solid volume = 15π + 90π = 105π

Question 2. COMPLETE THE SENTENCE The volume of a cone with radius r and height h is \(\frac{1}{3}\) the volume of a(n) __________ with radius r and height h. Answer:
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the surface area of the right cone.
Answer: The surface area of cone is 219.44 sq cm.
Explanation: S = πr² + πrl S = π(5.5)² + π(5.5 x 7.2) S = 219.44

Question 6. A right cone has a diameter of 11.2 feet and a height of 19.2 feet.
Answer: The surface area is 421.52 sq ft.
Explanation: r = 5.6 h = 19.2 l = √19.2² – 5.6² = 18.36 Surface area S = πr² + πrl S = π(5.6)² + π(5.6 x 18.36) S = 421.52
In Exercises 7 – 10, find the volume of the cone.
Answer: The volume is 2.09 cubic meter
Explanation: Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π(1)² x 2) V = 2.09
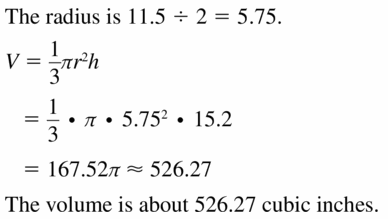
Question 10. A right cone has a radius of 3 feet and a slant height of 6 feet.
Answer: The volume is 56.54 cubic ft
Explanation: Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 3² x 6) V = 56.54
In Exercises 11 and 12, find the missing dimension(s).
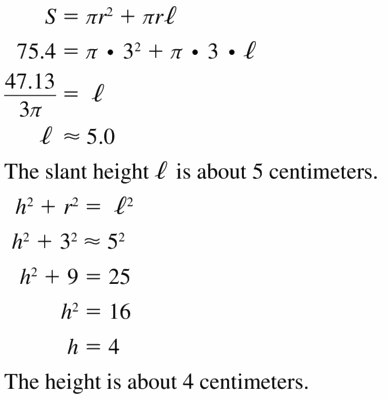
Question 12. Volume = 216π in. 3
Answer: The radius is 6.13 in
Explanation: Volume = 216π in. 3 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) = 216 \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr² x 18) = 216 r = 6.13
In Exercises 13 and 14, the cones are similar. Find the volume of cone B.
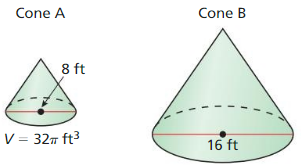
Answer: Volume of cone B = 24.127
Explanation: \(\frac { Volumeof cone A }{ Volume of cone B } \) = (\(\frac { height of A }{ height of B } \))³ \(\frac { 120π }{ Volume of cone B } \) = (\(\frac { 10 }{ 4 } \))³ Volume of cone B = 24.127
In Exercises 15 and 16, find the volume of the composite solid.
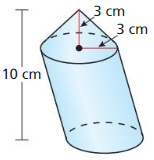
Answer: Volume of the composite solid = 97.93 cubic m
Explanation: Volume of box = lbh V = 51 x 5.1 x 5.1 = 132.651 Cone volume = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) v = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 2.55² x 5.1) v = 34.72 Volume of the composite solid = 132.651 – 34.72 = 97.93
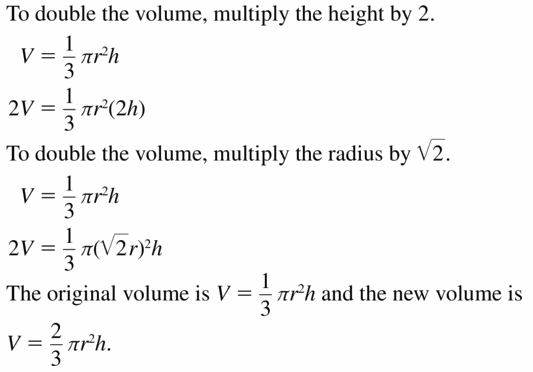
Answer: Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 3² x 8) = 75.39 Volume of cylinder = πr²h = π x 3² x 8 = 226.19 Volume of cylinder / Volume of cone = \(\frac { 226.19 }{ 75.39 } \) = 3 You have to buy 3 small containers of popcorn to equal the amount of popcorn in a large container.
b. Which container gives you more popcorn for your money? Explain. Answer: $1.25 -> 75.39 i.e $1 = 60.312 $2.50 -> 226.19 i.e $1 = 90.47 So, large containers gives you more popcorn for your money
In Exercises 19 and 20. find the volume of the right cone.
Answer: Volume of cone is 575.62 cubic yd
Explanation: tan 32 = \(\frac { 7 }{ h } \) h = 11.21 Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 7² x 11.21) V = 575.62

Question 22. MODELING WITH MATHEMATICS During a chemistry lab, you use a funnel to pour a solvent into a flask. The radius of the funnel is 5 centimeters and its height is 10 centimeters. You pour the solvent into the funnel at a rate of 80 milliliters per second and the solvent flows out of the funnel at a rate of 65 milliliters per second. How long will it be before the funnel overflows? (1 mL = 1 cm 3 ) Answer: 17.45 seconds
Explanation: Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 5² x 10) V = 261.8 \(\frac { 261.8 }{ 15 } \) = 17.45

Question 28. area of a circle with a diameter of 22 centimeters
Answer: d = 11 A = πr² A = 121π
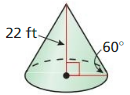
Question 30. radius of a circle with an area of 529 π square inches Answer: A = πr² 529π = πr² r = 23
Finding the Surface Area of a Sphere

Finding the volume of a sphere
Question 3. How can you find the surface area and the volume of a sphere? Answer:
Question 4. Use the results of Explorations 1 and 2 to find the surface area and the volume of a sphere with a radius of(a) 3 inches and (b) 2 centimeters. Answer:
Find the surface area of the sphere.
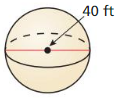
Answer: The surface area of the sphere is 5026.54 ft²
Explanation: D = 40 r = 20 The surface area of the sphere = 4πr² S = 4 x π x (20)² S = 5026.54 ft²
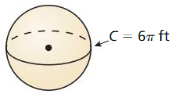
Answer: The surface area of the sphere is 113.09 ft²
Explanation: Circumference C = 6π 2πr = 6π r = 3 The surface area of the sphere = 4πr² S = 4π x 3² S = 113.09
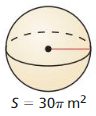
Answer: The radius of the sphere is 2.73 m
Explanation: The surface area of the sphere = 4πr² 30π = 4πr² r = 2.73
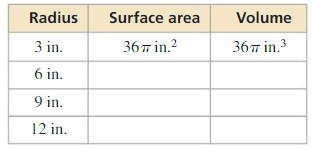
Question 4. The radius of a sphere is 5 yards. Find the volume of the sphere.
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 523.59 yards³
Explanation: r = 5 The volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 5³ V = 523.59 yards³
Question 5. The diameter of a sphere is 36 inches. Find the volume of the sphere.
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 24429.02 in³
Explanation: D = 36 r = 18 The volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 18³ V = 24429.02
Question 6. The surface area of a sphere is 576π square centimeters. Find the volume of the sphere.
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 2304π cm³
Explanation: The surface area of the sphere = 4πr² 576π = 4πr² r = 12 The volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 12³ V = 2304π
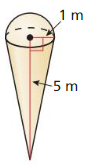
Answer: The volume of the composite solid is 7.324 m³
Explanation: The volume of cone = πr²\(\frac { h }{ 3 } \) = π x 1² x \(\frac { 5 }{ 3 } \) = 5.23 The volume of sphere = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 1³ = 4.188 The volume of the composite solid = The volume of cone + The volume of sphere/2 = 5.23 + 4.188/2 = 7.324 m³

Question 2. WRITING Explain the difference between a sphere and a hemisphere.
Answer: Hemisphere is a related term of the sphere. Sphere and hemisphere are three-dimensional solids. The volume of sphere is \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ and hemisphere volume is \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)πr³. The surface area of the sphere is 4πr² and hemisphere surface area is 3πr².
Monitoring progress and Modeling with Mathematics
In Exercises 3 – 6, find the surface area of the sphere.
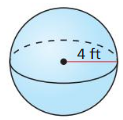
Answer: The surface area of the sphere is 225π cm²
Explanation: The surface area of the sphere = 4πr² S = 4π x 7.5² S = 225π
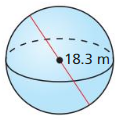
Answer: The surface area of the sphere is 8π ft²
Explanation: C = 4π 2πr = 4π r = 2 The surface area of the sphere = 4πr² S = 4π x 2² S = 8π
In Exercises 7 – 10. find the indicated measure.

Question 8. Find the radius of a sphere with a surface area of 1024π square inches.
Answer: The radius of a sphere is 16 in
Explanation: The surface area of the sphere = 1024π 4πr² = 1024π r = 16

Question 10. Find the diameter of a sphere with a surface area of 196π square centimeters.
Answer: The diameter of a sphere is 14 cm
Explanation: The surface area of the sphere = 196π 4πr² = 196π r = 7 D = 2(7) = 14
In Exercises 11 and 12, find the surface area of the hemisphere.
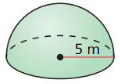
Answer: The surface area of the hemisphere is 108π in²
Explanation: D = 12, r = 6 The surface area of the sphere = 3πr² S = 3π x 6² S = 108π
In Exercises 13 – 18. find the volume of the sphere.
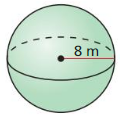
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 268.08 ft³
Explanation: r = 4 ft Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 4³ V = 268.08 ft
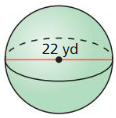
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 1436.75 ft³
Explanation: D = 14 ft r = 7 ft Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 7³ V = 1436.75 ft
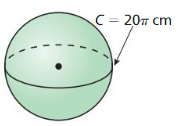
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 179.89 in³
Explanation: C = 7π 2πr = 7π r = 3.5 Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 3.5³ V = 179.89 in
In Exercises 19 and 20, find the volume of the sphere with the given surface area.

Question 20. Surface area = 484π cm 2
Answer: The volume of the sphere is 5575.27 cm³
Explanation: Surface area = 484π 4πr² = 484π r = 11 Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 11³ V = 5575.27
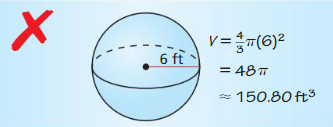
Answer: Diameter = 3 radius = 1.5 Volume of the sphere V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x (1.5)³ V = 14.137 cubic in
In Exercises 23 – 26, find the volume of the composite solid.
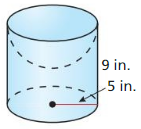
Answer: Volume is 288π ft³
Explanation: Volume of hemipshere = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)πr³ = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)π x 6³ = 144π volume of the cone = πr²\(\frac { h }{ 3 } \) = π x 6² x \(\frac { 12 }{ 3 } \) = 144π Area of circle = πr² = π x 6² = 36π Volume of hemipshere + volume of the cone = 144π + 144π = 288π
Answer: The volume of solid is 296π m³
Explanation: Volume of hemipshere = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)πr³ = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)π x 6³ = 144π Volume of cylinder = πr²h = π x 6² x 14 = 504π Volume of solid = 504π – 2(144π) = 296π
In Exercises 27 – 32, find the surface area and volume of the ball.

Answer: The surface area is 277 in², volume is 43212.27 in³
Explanation: C = 29.5 2πr = 29.5 r = 4.69 Surface area = 4πr² S = 4π x 4.69² = 277 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 4.69³ V = 43212.27

Answer: The surface area is 9.07 in², volume is 2.57 in³
Explanation: d = 1.7 r = 0.85 Surface area = 4πr² S = 4π x 0.85² = 9.07 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 0.85³ V = 2.57

Answer: The surface area is 25.78 in², volume is 12.24 in³
Explanation: C = 9 2πr = 9 r = 1.43 Surface area = 4πr² S = 4π x 1.43² S = 25.78 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 1.43³ V = 12.24

Question 34. REASONING A semicircle with a diameter of 18 inches is rotated about its diameter. Find the surface area and the volume of the solid formed.
Answer: The surface area is 1018 in², volume is 3054.02 in³
Explanation: Diameter = 18 radius r = 9 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 9³ V = 3054.02 Surface area = 4πr² S = 4π x 9² S = 1018

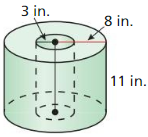
Answer: C = 8 in 2πr = 8 r = 1.27 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 1.27³ = 8.64 The volume of tennis ball = 8.64 in³
b. Find the amount of space within the cylinder not taken up by the tennis balls. Answer: The surface area of tennis ball S = 4πr² S = 4π x 1.27² = 20.26 Area of cylinder s = 2πrh+2πr² s = 2π x 1.43 x 8+2π x 1.43² s = 84.72 Remaining space = 84.72 – 20.26 = 64.46 in²
Question 38. MATHEMATICAL CONNECTIONS A sphere has a diameter of 4(x + 3) centimeters and a surface area of 784 π square centimeters. Find the value of x.
Answer: x =11
Explanation: Surface area = 4πr² 784π = πr² r = 28 2r = diameter = 4(x + 3) r = 2(x + 3) 28 = 2(x + 3) x = 11

b. A meteorite is equally likely to hit anywhere on Earth. Estimate the probability that a meteorite will land in the Torrid Zone. Answer: Probability of meteorites hitting the torrid zone = 80875080/197086348.8 = 0.4104

Explanation: Volume of hemisphere v = \(\frac { 2 }{ 3 } \)πr³ Volume of cone V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h If r = h Volume of cone V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr² x r = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr³ So, the hemisphere has the highest volume.
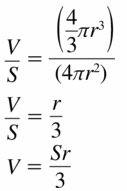
b. r = 34 cm, a = 30 cm Answer: The formula for the volume of the spherical cap is V = πh/6 x (3a² +h²). Where a is the radius h is the height of the cap. Where a = r = 34cm h = 30cm V = π(30)/6 x (3(34)² +(30)²) = π(30)/6 x (3(1156) + (900)) = π(30)/6 x 6,168 = 94.2/6 x 6,168 Therefore the volume of the spherical cap is 96,837.6 cu. cm.
c. r = 13 m, h = 8 m Answer: The formula for the volume of the spherical cap is V = πh/6 x (3a² +h²). Where a is the radius h is the height of the cap. Where a = r = 13cm h = 8cm V = π(8)/6 x (3(13)² +(8)²) = 8π/6 x (3(169 + 64)) = 8π/6 x (699) = 25.12/6 x 699 Therefore the volume of the spherical cap is 2,926.48 cu. cm
d. r=75 in., h = 54in. Answer: The formula for the volume of the spherical cap is V = πh/6 x (3a² +h²). Where a is the radius h is the height of the cap. Where r = 75in h = 54in V = π(54)/6 x (3(75)² +(54)²) = 54π/6 x (3(5,625 + 2,916) = 54π/6 x (25,623) = 169.56π/6 x 25,623 = 532.4184 x 25,623 Therefore the volume of the spherical cap is 13,642,156.66 cu. in.

Solve the triangle. Round decimal answers to the nearest tenth.
Question 48. A = 26°, C = 35°, b = 13
Answer: B = 119°, a = 7.16, c = 9.5
Explanation: B = 180 – (26 + 35) = 119 \(\frac { sin A }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) \(\frac { sin 26 }{ a } \) = \(\frac { sin 119 }{ 13 } \) a = 7.16 \(\frac { sin C }{ c } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ b } \) \(\frac { sin 35 }{ c } \) = \(\frac { sin 119 }{ 13 } \) c = 9.5
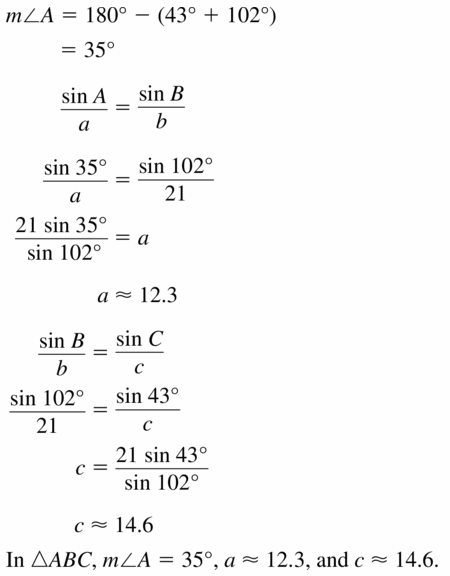
Question 50. a = 23, b = 24, c = 20
Answer: A = 62.2, B = 65.5, C = 49.4
Explanation: a² = b² + c² – 2bc cos A 23² = 24²+ 20² – 2(24 x 20) cos A A = 62.2 \(\frac { sin 62.2 }{ 23 } \) = \(\frac { sin B }{ 24 } \) B = 65.5 \(\frac { sin 62.2 }{ 23 } \) = \(\frac { sin C }{ 20 } \) C = 49.4

Answer: diameter of ⊙P is 29.99
Explanation: Circumference = 94.24 πd = 94.24 d = 29.99
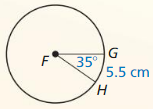
Answer: circumference of ⊙F = 56.57
Explanation: 5.5 = \(\frac { 35 }{ 360 } \) . C C = 56.57
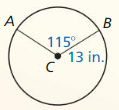
Answer: arc length of \(\widehat{A B}\) = 26.09
Explanation: arc length of \(\widehat{A B}\) = \(\frac { 115 }{ 360 } \) . 2π(13) = 26.09
Question 4. A mountain bike tire has a diameter of 26 inches. To the nearest foot, how far does the tire travel when it makes 32 revolutions?
Answer: The tire travels 2613.80 inches.
Explanation: D = 26 in r = 13 in Circumference C = 2π(13) = 81.68 32 revolutions = 32 x 81.68 = 2613.80
Find the area of the blue shaded region.
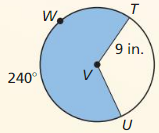
Answer: Area = \(\frac { 240 }{ 360 } \) . π(9)² = 169.64
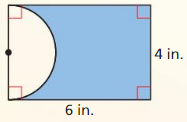
Answer: Area of shaded region = 11.43
Explanation: Area of rectangle = 6 x 4 = 24 Area of semicircle = π(2)² = 4π Area of shaded region = 24 – 4π = 11.43
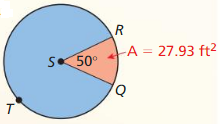
Answer: Area of shaded region = 173.13
Explanation: Area of small region = 27.93 = \(\frac { 50 }{ 360 } \) . πr² πr² = 201.096 r = 8 Area of shaded region = \(\frac { 310 }{ 360 } \) . π(8)² = 173.13
Find the area of the kite or rhombus.
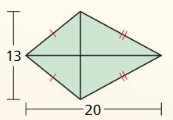
Explanation: Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(13 x 20) A = 65
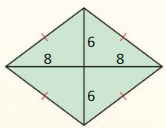
Explanation: Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(16 x 12) A = 48
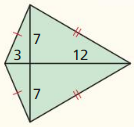
Explanation: Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(d₁d₂) A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)(14 x 15) A = 52.5
Find the area of the regular polygon.
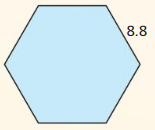
Question 14. A platter is in the shape of a regular octagon with an apothem of 6 inches. Find the area of the platter.
Answer: Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(n . a. s) A = \(\frac { 1 }{ 2 } \)(8 . 6 . sin 45) A = 16.97
Describe the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid.
Answer: Volume = lbh V = 3.6 x 2.1 x 1.5 = 113.4 m³
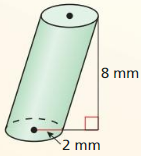
Answer: Volume = πr²h V = π(2)² x 8 = 100.53 mm³
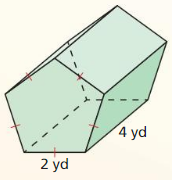
Answer: Pentagon area = 6.88 Volume = Area x height V = 6.88 x 4 = 27.52 yd³
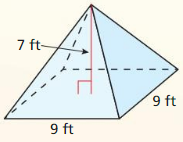
Answer: Volume V = Base area x height/3 Base Area = 9² = 81 V = 81 x 7/3 = 189 ft³
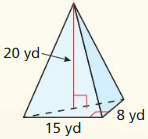
Answer: Volume V = Base area x height/3 base area = 18 x 10 = 180 V = 180 x 5/3 = 300 m³
Question 27. The volume of a square pyramid is 60 cubic inches and the height is 15 inches. Find the side length of the square base.
Answer: The side length of the square base is 3.46 in
Explanation: The volume of a square pyramid is 60 cubic inches V = 60 s²h/3 = 60 s² x 15/3 = 60 s² = 12 s = 3.46
Question 28. The volume of a square pyramid is 1024 cubic inches. The base has a side length of 16 inches. Find the height of the pyramid Answer: The volume of a square pyramid is 1024 cubic inches s²h/3 = 1024 16²h = 3072 h = 12
Find the surface area and the volume of the cone.
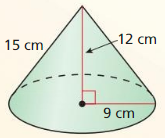
Explanation: Surface area of cone S = πr² + πrl S = π x 9² + π x 9 x 15 S = 678.58 Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 9² x 12) V = 1017.87
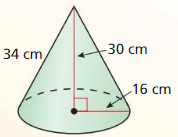
Answer: Surface area is 2513.27 cm² volume is 8042.47 cm³
Explanation: Surface area of cone S = πr² + πrl S = π x 16² + π x 16 x 34 S = 2513.27 Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 16² x 30) V = 8042.47
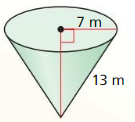
Answer: Surface area is 439.82 m² volume is 562.102 m³
Explanation: Surface area of cone S = πr² + πrl S = π x 7² + π x 7 x 13 S = 439.82 h = √13² – 7² = 10.95 Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) V = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 7² x 10.95) V = 562.102
Question 32. A cone with a diameter of 16 centimeters has a volume of 320π cubic centimeters. Find the height of the cone.
Answer: The height of the cone = 15 cm.
Explanation: r = 8 Volume V = 320π \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(πr²h) = 320π \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)(π x 8² x h) = 320π h = 15
Find the surface area and the volume of the sphere.
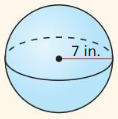
Answer: The surface area is 615.75 in², volume is 1436.75 in³
Explanation: Surface area S = 4πr² S = 4π x 7² S = 615.75 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 7³ V = 1436.75
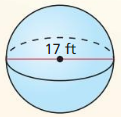
Answer: The surface area is 907.92 ft², volume is 2572.44 ft³
Explanation: d = 17 r = 8.5 Surface area S = 4πr² S = 4π x 8.5² S = 907.92 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 7³ V = 2572.44
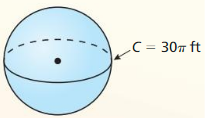
Answer: The surface area is 2827.43 ft², volume is 14137.16 ft³
Explanation: C = 30π 2πr = 30π r = 15 Surface area S = 4πr² S = 4π x 15² S = 2827.43 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 15³ V = 14137.16
Question 36. The shape of Mercury can be approximated by a sphere with a diameter of 4880 kilometers. Find the surface area and the volume of Mercury.
Answer: The surface area and the volume of Mercury is 23814400π, 19369045330π
Explanation: d = 4880 r = 2440 Surface area S = 4πr² S = 4π x 2440² = 23814400π Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 2440³ V = 19369045330π
Question 37. A solid is composed of a cube with a side length of 6 meters and a hemisphere with a diameter of 6 meters. Find the volume of the composite solid.
Answer: Volume of the composite solid = 272.52
Explanation: Volume of cube = a³ = 6³ = 216 Volume of hemisphere = \(\frac { 4 }{ 6 } \)πr³ = \(\frac { 4 }{ 6 } \)π x 3³ = 18π Volume of the composite solid = 216 + 18π = 272.52
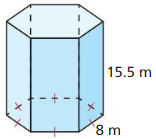
Answer: Volume = 2577.29 m³
Explanation: Volume = \(\frac { 3√3 }{ 2 } \)a²h = \(\frac { 3√3 }{ 2 } \) x 8² x 15.5 = 2577.29
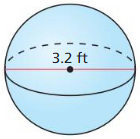
Answer: Volume is 17.157 ft³
Explanation: d = 3.2 r = 1.6 Volume V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)πr³ V = \(\frac { 4 }{ 3 } \)π x 1.6³ V = 17.157
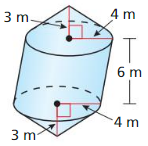
Answer: Volume of sloid = 402.11 m³
Explanation: Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)π x 4² x 3 = 50.26 Volume of cylinder = πr²h = π x 4² x 6 = 301.59 Volume of sloid = 2(50.26) + 301.59 = 402.11
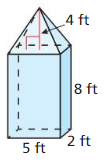
Answer: Volume of solid = 106.66
Explanation: Volume of rectangular box = 5 x 2 x 8 = 80 Volume of pyramid = 80/3 = 26.66 Volume of solid = 80 + 26.66 = 106.66
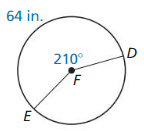
Answer: circumference of ⊙F is 109.71 in
Explanation: 64 = \(\frac { 210 }{ 360 } \) • C C = 109.7
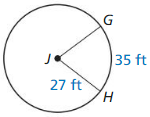
Answer: m\(\widehat{G H}\) = 74.27
Explanation: 35 = \(\frac { x }{ 360 } \) • 2π x 27 x = 74.27
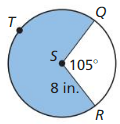
Answer: Area is 142.41 in²
Explanation: Area = \(\frac { 360 – 105 }{ 360 } \) • π x 8² Area = 142.41
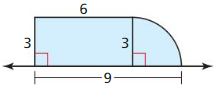
Question 9. Find the surface area of a right cone with a diameter of 10 feet and a height of 12 feet.
Answer: The surface area is 486.7 sq ft
Explanation: l² = r² + h² l² = 5² + 12² l = 13 Surface area S = πr² + 2πrl S = π x 5² + 2π x 5 x 13 S = 486.7
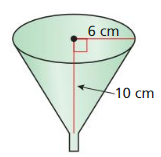
Answer: Volume = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)π x 6² x 10 = 376.99
b. You use the funnel to put oil in a ear. Oil flows out of the funnel at a rate of 45 milliliters per second. How long will it take to empty the funnel when it is full of oil? (1 mL = 1 cm 3 ) Answer: T = 376.8 ml/45 ml per sec T = 8.373 sec
c. How long would it take to empty a funnel with a radius of 10 centimeters and a height of 6 centimeters if oil flows out of the funnel at a rate of 45 milliliters per second? Answer: V = 1/3 πr²h = 1/3 (3.14 × 10² × 6) = 1/3(1884) = 628 cu. cm T = 628 ml/45 ml per sec T = 13.95 sec
d. Explain why you can claim that the time calculated in part (c) is greater than the time calculated in part (b) without doing any calculations. Answer:
- In cone type shaped object if the radius is large then the volume of the cone increases.
- In the b part of the funnel, the radius is smaller than the height and in the c part, the radius is larger than the height of the cone.
- V = 1/3 πr²h
- It means if radius increase volume also increases with the same rate. So, the time is taken by the c part (13.95 sec) is larger than the b part.
Question 11. A water bottle in the shape of a cylinder has a volume of 500 cubic centimeters. The diameter of a base is 7.5 centimeters. What is the height of the bottle? Justify your answer.
Answer: The height of the bottle is 11.3 cm
Explanation: Volume of cylinder = 500 πr²h = 500 π(3.75)²h = 500 h = 11.3 cm
Question 12. Find the area of a dodecagon (12 sides) with a side length of 9 inches.
Answer: Area is 237.31
Explanation: Area = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)πa²cot(π/n) = \(\frac { 1 }{ 4 } \)π x 9² x cot(π/12) = 237.31

Answer: Area of sector for fan of radius 9 cm = 120/360 × 3.14 × 9 × 9 = 1/3 × 254.57 = 84.85 sq. cm Area of sector of fan of radius 6 cm = 150/360 × 3.14 × 6 × 6 = 5/12 × 113.14 = 47.14 sq. cm
Question 1. Identify the shape of the cross section formed by the intersection of the plane and the solid.
b. Find the amount of space within the crayon box not taken up by the crayons. Answer: Volume of box = 94 x 28 x 71 = 186872 The volume of a crayon = 4650.21 Remaining space = 186872 – 24 x 4650.21 = 75266.96
Question 4. What is the equation ol the line passing through the point (2, 5) that is parallel to the line x + \(\frac{1}{2}\)y = – 1? (A) y = – 2x + 9 (B) y = 2x + 1 (C) y = \(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 4 (D) y = –\(\frac{1}{2}\)x + 6 Answer: (A) y = – 2x + 9
Explanation: x + \(\frac{1}{2}\)y = – 1 y = -2 – 2x The slope of the line is -2 The euation of line is y – 5 = -2(x – 2) y – 5 = -2x + 4 y = -2x + 9

Answer: (A) 22,019.63 ft 3
Explanation: Volume = a²\(\frac { h }{ 3 } \) = 34.5² x \(\frac { 55.5 }{ 3 } \) = 22019.62
Question 6. Prove or disprove that the point (1, √3 ) lies on the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). Answer: We consider the circle centered at the origin and containing the point (0, 2). Therefore, we canconclude that rdaius is 2 and points be (0, 0), (1, √3) distance = √(1 – 0)² + (√3 – 0)² = 2 As radius and distance are same. The point B(1, √3) lies on the circle.

Explanation: Volume of square pyramid = a²\(\frac { h }{ 3 } \) Square diagonal = √2a radius = √2a/2 a = 2r/√2 Volume of cone = \(\frac { 1 }{ 3 } \)πr²h

Answer: The number of people per square mile is 247
Explanation: S = πr² = π x 5² = 78.5 Number of people per square mile = 19400/78.5 = 247
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.
Chapter 11, Lesson 1: Areas of Parallelograms and Triangles
- Extra Examples
- Personal Tutor
- Self-Check Quizzes
The resource you requested requires you to enter a username and password below:
Please read our Terms of Use and Privacy Notice before you explore our Web site. To report a technical problem with this Web site, please contact the site producer .

- Texas Go Math
- Big Ideas Math
- enVision Math
- EngageNY Math
- McGraw Hill My Math
- 180 Days of Math
- Math in Focus Answer Key
- Math Expressions Answer Key
- Privacy Policy

Go Math Grade 5 Chapter 11 Answer Key Pdf Geometry and Volume
Go Math Grade 5 Chapter 11 Answer Key Pdf: Go Math Grade 5 Answer Key Chapter 11 Geometry and Volume contains the 5th standard solutions with brief explanations which helps the students to gain the highest marks in the exams. This chapter contains the concepts of Geometry and volume of rectangular prisms. We provide the Go Math Grade 5 Answer Key in such a way that the students will never feel difficulty in learning the geometry and volume.
Geometry and Volume Go Math Grade 5 Chapter 11 Answer Key Pdf
Every student has a chance to know how to find out the Geometry and Volume and how to find out the volume of shapes with the Go Math Grade 5 Key. Get quick solutions with Go Math Answer Key. Get the solutions to this chapter topic wise. Go through the topics mentioned below and start your preparation. The concepts in this chapter include polygons, triangles, quadrilaterals, estimate volume, understand volume, the volume of the rectangular prism
Lesson 1: Polygons
Share and Show – Lesson 1: Polygons – Page No. 639
Problem solving – lesson 1: polygons – page no. 640.
Lesson 2: Triangles
Share and Show – Lesson 2: Triangles – Page No. 645
Problem solving – lesson 2: triangles – page no. 646.
Lesson 3: Quadrilaterals
Share and Show – Lesson 3: Quadrilaterals – Page No. 651
Problem solving – lesson 3: quadrilaterals – page no. 652.
Lesson 4: Properties of Two-Dimensional Figures
Share and Show – Lesson 4: Properties of Two-Dimensional Figures – Page No. 455
On your own – lesson 4: properties of two-dimensional figures – page no. 456, share and show – lesson 4: properties of two-dimensional figures – page no. 656, problem solving – lesson 4: properties of two-dimensional figures – page no. 657.
Mid-Chapter Checkpoint
Mid-Chapter Review – Vocabulary – Page No. 661
Mid-chapter review – page no. 662.
Lesson 5: Unit Cubes and Solid Figures

Share and Show – Lesson 5: Unit Cubes and Solid Figures – Page No. 665
Lesson 5: unit cubes and solid figures – page no. 666.
Lesson 6: Understand Volume
Share and Show – Lesson 6: Understand Volume – Page No. 671
Problem solving – lesson 6: understand volume – page no. 672.
Lesson 7: Estimate Volume
Share and Show – Lesson 7: Estimate Volume – Page No. 677
Problem solving – lesson 7: estimate volume – page no. 678.
Lesson 8: Volume of Rectangular Prisms
Share and Show – Lesson 8: Volume of Rectangular Prisms – Page No. 683
Unlock the problem – lesson 8: volume of rectangular prisms – page no. 684.
Lesson 9: Algebra Apply Volume Formulas
Share and Show – Lesson 9: Algebra Apply Volume Formulas – Page No. 689
Problem solving – lesson 9: algebra apply volume formulas – page no. 690.
Lesson 10: Problem Solving Compare Volumes
Share and Show – Lesson 10: Problem Solving Compare Volumes – Page No. 695
On your own – lesson 10: problem solving compare volumes – page no. 696.
Lesson 11: Find Volume of Composed Figures
Share and Show – Lesson 11: Find Volume of Composed Figures – Page No. 701
Problem solving – lesson 11: find volume of composed figures – page no. 702.
Chapter Review/Test
Chapter Review/Test – Page No. 705
Chapter review/test – page no. 706, chapter review/test – page no. 707, chapter review/test – page no. 708, chapter review/test – page no. 709, chapter review/test – page no. 710.
- Chapter Review/Test – Page No. 4910
Chapter Review/Test – Page No. 4920
Chapter review/test – page no. 4930, chapter review/test – page no. 4940.

Answer: Triangle
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure consists of three sides. So, the name of the polygon is a triangle.
Question 1. b. Are all the sides and all the angles congruent? _____
Answer: Yes
Explanation: When line segments have the same length or when angles have the same measure, they are congruent. All sides are equal in the above figure. Thus the above figure is congruent.
Question 1. c. Is the polygon a regular polygon? _____
Explanation: In a regular polygon, all sides are congruent and all angles are congruent. The above figure has the same sides and same angles. Thus the above figure is a regular polygon.
Name each polygon. Then tell whether it is a regular polygon or not a regular polygon.

Answer: i. Hexagon ii. Regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure consists of 6 sides. So, the name of the polygon is Hexagon. In a regular polygon, all sides are congruent and all angles are congruent. The above figure has the same sides and same angles. Thus the above figure is a regular polygon.

Answer: i. Quadrilateral ii. Not regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure consists of 4 sides. So, the name of the polygon is Quadrilateral. The above figure doesn’t have the same sides thus the above figure is not a regular polygon.

Answer: i. Octagon ii. Regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure consists of 8 sides. So, the name of the polygon is Octagon. In a regular polygon, all sides are congruent and all angles are congruent. The above figure has the same sides and same angles. Thus the above Octagon is a regular polygon.

Answer: i. Quadrilateral ii. Regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure consists of 4 sides. So, the name of the polygon is Quadrilateral. In a regular polygon, all sides are congruent and all angles are congruent. The above figure has the same sides and same angles. Thus the above Quadrilateral is a regular polygon.

Answer: i. Triangle ii. Not regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure consists of three sides. So, the name of the polygon is a triangle. The above figure doesn’t have the same sides thus the above figure is not a regular polygon.

Answer: i. Heptagon ii. Regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure consists of 7 sides. So, the name of the polygon is Heptagon. In a regular polygon, all sides are congruent and all angles are congruent. The above figure has the same sides and same angles. Thus the above Heptagon is a regular polygon.

Answer: i. Hexagon ii. Not regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure consists of six sides. So, the name of the polygon is a Hexagon. The above figure doesn’t have the same sides and angles thus the above figure is not a regular polygon.

Answer: i. Pentagon ii. Not regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure consists of five sides. So, the name of the polygon is a pentagon. The above figure doesn’t have the same sides and angles thus the above figure is not a regular polygon.

Answer: i. Pentagon ii. Regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure consists of five sides. So, the name of the polygon is a pentagon. In a regular polygon, all sides are congruent and all angles are congruent. The above figure has the same sides and same angles. Thus the above Pentagon is a regular polygon.

Question 11. Which polygons in the floor plan have four equal sides and four congruent angles? How many of these polygons are there? polygon: __________ The number of polygons: __________
Answer: polygon: Quadrilateral The number of polygons: 8
Explanation: By seeing the above figure we can say that there are eight Quadrilaterals in the octagon. And the number of polygons is 8.
Question 12. Is there a quadrilateral in the floor plan that is not a regular polygon? Name the quadrilateral and tell how many of the quadrilaterals are in the floor plan. Name of quadrilateral: __________ The number of quadrilaterals: __________
Answer: Name of quadrilateral: Trapezoid The number of quadrilaterals: 8
Explanation: The name of the Quadrilateral for the above figure is Trapezoid. There is 8 number of quadrilaterals in the floor plan.
Question 13. Sketch eight points. Then connect the points to draw a closed plane figure. What kind of polygon did you draw? __________
Answer: Octagon
Question 14. Look at the angles for all regular polygons. As the number of sides increases, do the measures of the angles increase or decrease? What pattern do you see? angles measures __________
Answer: Increase
Explanation: As the number of sides increases, the measures of the angles increase. we know that The measure of the interior angle in a regular polygon is equal to x = (n-2)/n(180°) where n is the number of sides of the regular polygon. x is the measure of the interior angle in a regular polygon.

Classify each triangle. Write isosceles, scalene, or equilateral.
Then write acute, obtuse, or right.

Answer: △ – Scalene ∠ – Acute
Explanation: The 3 sides of the triangle are unequal. If three sides of the triangle are different it is known as Scalene. The angles are less than 90° thus the angle is known as an acute angle.

Answer: △ – Equilateral ∠ – Acute
Explanation: The 3 sides of the triangle are equal. If three sides of the triangle are equal it is known as the equilateral triangle. The angles are less than 90° thus the angle is known as an acute angle.

△ – Isosceles ∠ – Acute
Explanation: The 2 sides of the triangle are equal and the third side is not equal. If two sides of the triangle are different it is known as Isosceles. The angles are less than 90° thus the angle is known as an acute angle.
On Your Own

Answer: △ – Scalene ∠ – Right
Explanation: The 3 sides of the triangle are unequal. If three sides of the triangle are different it is known as Scalene. One of the angle is 90° thus the angle is known as a right angle.

Answer: △ – Isosceles ∠ – Acute

Answer: △ – Scalene ∠ – Obtuse
Explanation: The 3 sides of the triangle are unequal. If three sides of the triangle are different it is known as Scalene. The angles are more than 90° thus the angle is known as an obtuse angle.
A triangle has sides with the lengths and angle measures given.
Question 7. sides: 3.5 cm, 6.2 cm, 3.5 cm angles: 27°, 126°, 27° △ __________ ∠ __________
Answer: △ – Isosceles ∠ – Obtuse
Explanation: The 2 sides of the triangle are equal and the third side is not equal. If two sides of the triangle are different it is known as Isosceles. One of the angle is more than 90° thus the angle is known as an obtuse angle.
Question 8. sides: 2 in., 5 in., 3.8 in. angles: 43°, 116°, 21° △ __________ ∠ __________
Explanation: The 3 sides of the triangle are unequal. If three sides of the triangle are different it is known as Scalene. One of the angle is more than 90° thus the angle is known as an obtuse angle.

Question 10. Draw 2 equilateral triangles that are congruent and share a side. What polygon is formed? Is it a regular polygon? What polygon is formed? __________ Is it a regular polygon? __________
Answer: The name for the polygon is Quadrilateral. In a regular polygon, all sides are congruent and all angles are congruent.
Question 11. What’s the Error? Shannon said that a triangle with exactly 2 congruent sides and an obtuse angle is an equilateral obtuse triangle. Describe her error. Type below: __________
Answer: All angles of an equilateral triangle are acute. You cannot have an obtuse angle in an equilateral angle. And all of the angles must be congruent.
Question 12. Test Prep Which kind of triangle has exactly 2 congruent sides? Options: a. isosceles b. equilateral c. scalene d. right
Answer: isosceles
Explanation: An isosceles triangle, therefore, has both two equal sides and two equal angles. Thus the correct answer is option A.

Classify the triangles in the structures below. Write isosceles, scalene, or equilateral. Then write acute, obtuse, or right.

Answer: △ – Equilateral triangle ∠ – Acute
Explanation: From the figure, we can see an equilateral triangle. In an equilateral triangle, all sides will be less than 90°. So it is an acute angle.

Answer: △ – Scalene triangle ∠ – Right
Explanation: In the above figure, we can see a right-angle triangle. The three sides of the above triangle is different. So, it is known as the scalene triangle.

Explanation: The above figure consists of same sides. Thus the above Quadrilateral is congruent.
Question 1. b. How many right angles, if any, does the quadrilateral have? _____
The above figure doesn’t have any straight line. Thus the above figure has 0 right angles.
Question 1. c. How many pairs of parallel sides, if any, does the quadrilateral have? _____ pairs
Explanation: The above has two parallel sides. Yes, the Quadrilateral has the parallel sides.
Question 1. So, quadrilateral ABCD is a ______________ . _________
Answer: Parallelogram
Explanation: A parallelogram is a special trapezoid with opposite sides are equal.
Classify the quadrilateral in as many ways as possible.
Write quadrilateral, parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, square, or trapezoid.

Answer: The possible ways of Quadrilateral are: 1. Rectangle 2. Parallelogram 3. Quadrilateral

Answer: The possible ways of Quadrilateral are: 1. Quadrilateral 2. Trapezoid

Answer: The possible ways of Quadrilateral for the above figure are: 1. Square 2. Quadrilateral 3. Parallelogram 4. Rectangle 5. Rhombus

Answer: The possible ways of Quadrilateral for the above figure are: 1. Trapezoid 2. Parallelogram

Answer: The possible ways of Quadrilateral for the above figure are: 1. Rhombus 2. Parallelogram 3. Square

Answer: The possible ways of Quadrilateral for the above figure are: 1. Rectangle 2. Parallelogram
Solve the problems.
Question 8. A quadrilateral has exactly 2 congruent sides. Which quadrilateral types could it be? Which quadrilaterals could it not be? Type below: _________
Answer: A rectangle has 2 congruent sides.
Explanation: The type of quadrilateral that has two congruent sides is a rectangle.
Question 9. What’s the Error? A quadrilateral has exactly 3 congruent sides. Davis claims that the figure must be a rectangle. Why is his claim incorrect? Use a diagram to explain your answer. Type below: _________
Answer: Daviss’s claim is incorrect because a rectangle does not have three congruent sides.
Go Math Grade 5 Lesson 11.3 Homework Answers Question 10. The opposite corners of a quadrilateral are right angles. The quadrilateral is not a rhombus. What kind of quadrilateral is this figure? Explain how you know. Type below: _________

Question 11. I am a figure with four sides. I can be placed in the following categories: quadrilateral, parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, and square. Draw me. Explain why I fit into each category. Type below: _________

Question 12. Test Prep A quadrilateral has exactly 1 pair of parallel sides and no congruent sides. What type of quadrilateral is it? Options: a. rectangle b. rhombus c. parallelogram d. trapezoid
Answer: Trapezoid
Explanation: A quadrilateral with one pair of parallel sides is a trapezoid. Thus the correct answer is option D.

Question 1. Then, fold the triangle to match each pair of sides to determine if at least two of the sides are congruent. As you test the sides, record or draw the results for each pair to make sure that you have checked all pairs of sides. Possible drawings are shown. Type below: _________
Question 1. Finally, answer the question. ______
Question 2. What if Erica also wants to show, without using a protractor, that the triangle has one right angle and two acute angles? Explain how she can show this.
Answer: The sum of three angles = 180 If one of the angles is 90 then the other two angles will be acute angles.
Question 3. December, January, and February were the coldest months in Kristen’s town last year. February was the warmest of these months. December was not the coldest. What is the order of these months from coldest to warmest? Coldest: _________ _________ Warmest: _________ _________
Answer: Coldest: January December Warmest: February
Explanation: January and December are the coldest months of the year depending on the direction of the wind. February is the warmest month among these months.
Question 4. Jan enters a 20-foot by 30-foot rectangular room. The long sides face north and south. Jan enters the exact center of the south side and walks 10 feet north. Then she walks 8 feet east. How far is she from the east side of the room? ______ ft
Answer: 7 feet
Explanation: Given that, Jan enters a 20-foot by 30-foot rectangular room. The long sides face north and south. Jan enters the exact center of the south side and walks 10 feet north. Then she walks 8 feet east. Jan is 7 feet from the east wall in the room.

Answer: 3 lines
Explanation: From the above figure, we can see that there are 18 congruent squares. To find the least number of lines Max can draw we have to divide the number of squares by the number of congruent rectangles 18 ÷ 6 = 3 Thus the least number of lines that Max can Draw is 3 lines.
Geometry Chapter 11 Test Answer Key Go Math Grade 5 Workbook Question 6. Of the 95 fifth and sixth graders going on a field trip, there are 27 more fifth graders than sixth graders. How many fifth graders are going on the field trip? 5th graders = ______
Explanation: Since we are not told how many 6th graders are going on the trip let’s use a variable, the letter x. Now let’s understand the problem in the “math” language. x= the number of 6th graders. X+27= the number of 5th graders since there are 27 more fifth-graders than sixth graders. x+x+27 = 95 2x+27=95 -27 -27 2x+ 0 =68 2x=68 divide by 2 on both sides. x = 34 Now, remember how x+27 = the number of 5th graders going on the trip? Since we know that x=34, substitute the x as 34+27 which = 61 fifth graders going on the trip.

Question 7. Sam’s paper route begins and ends at the corner of Redwood Avenue and Oak Street. His route is made up of 4 streets, and he makes no 90° turns. What kind of polygon do the streets of Sam’s paper route form? Name the streets in Sam’s route. _________
Explanation: Given that, Sam’s paper route begins and ends at the corner of Redwood Avenue and Oak Street. His route is made up of 4 streets, and he makes no 90° turns. By following the route map we can say that the polygon is a parallelogram.
Question 8. Sam’s paper route includes all 32 houses on two pairs of parallel streets. If each street has the same number of houses, how many houses are on each street? Name the parallel streets. ______ houses on each street
Explanation: Given, Sam’s paper route includes all 32 houses on two pairs of parallel streets. If each street has same number of houses we have to divide 32 by 4 32 ÷ 4 = 8 Thus there are 8 houses on each street.

Explanation: A square is a type of quadrilateral that has opposite sides that are congruent and parallel. Thus the correct answer is option B.
Classify the solid figure. Write prism, pyramid, cone, cylinder, or sphere.

Answer: Triangular prism
Explanation: A triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides. A right triangular prism has rectangular sides, otherwise, it is oblique.

Answer: Sphere
Explanation: A sphere has no bases and 1 curved surface.
Answer: Hexagonal Base Pyramid
Explanation: A pyramid that has a hexagonal base, that is, a base with six sides and 6 triangular lateral faces, then it is a hexagonal pyramid.

Answer: Pentagonal prism
Explanation: A pentagonal prism is a prism that has two pentagonal bases top and bottom and five rectangular sides. It is a type of heptahedron with 7 faces, 10 vertices, and 15 edges.

Answer: Pentagonal Base Pyramid
Explanation: In geometry, a pentagonal pyramid is a pyramid with a pentagonal base upon which are erected five triangular faces that meet at a point.

Answer: Cylinder
Explanation: A cylinder has 2 congruent circular bases and 1 curved surface.

Answer: Rectangular prism
Explanation: A rectangular prism is a polyhedron with two congruent and parallel bases. It is also a cuboid. It has six faces, and all the faces are in a rectangle shape and have twelve edges. Because of its cross-section along the length, it is said to be a prism.

Answer: Cone
Explanation: A cone has 1 circular base and 1 curved surface.

Answer: Triangle base pyramid
Explanation: A triangle-based pyramid has four triangular sides. The base can be any shape or size of the triangle but usually, it is an equilateral triangle. This means the three sides of the pyramid are the same size as each other and the pyramid looks the same if you rotate it.

Explanation: A prism’s base shape is used to name the solid figure. The base shape of this prism is a triangle. The prism is a triangular prism.

Answer: Hexagonal Prism
Explanation: In geometry, the hexagonal prism is a prism with a hexagonal base. This polyhedron has 8 faces, 18 edges, and 12 vertices. Since it has 8 faces, it is an octahedron. However, the term octahedron is primarily used to refer to the regular octahedron, which has eight triangular faces.

Answer: Square Pyramid
Explanation: In geometry, a square pyramid is a pyramid having a square base. If the apex is perpendicularly above the center of the square, it is a right square pyramid and has symmetry. If all edges are equal, it is an equilateral square pyramid.

Answer: Octogonal Prism
Explanation: In geometry, the octagonal prism is the sixth in an infinite set of prisms, formed by square sides and two regular octagon caps. If the faces are all regular, it is a semiregular polyhedron.
Question 16. Mario is making a sculpture out of stone. He starts by carving a base with five sides. He then carves five triangular lateral faces that all meet at a point at the top. What three-dimensional figure does Mario make? _________
Answer: Pentagonal Pyramid
Explanation: Given, Mario is making a sculpture out of stone. He starts by carving a base with five sides. He then carves five triangular lateral faces that all meet at a point at the top. The polygon which has 5 sides is a pentagon. The three-dimensional figure which meets at the same point is the pyramid. The 3-dimensional figure that Mario makes is Pentagonal Pyramid So, the answer to the above question is Pentagonal Pyramid.
Question 17. What is another name for a cube? Explain your reasoning. Type below: _________
Answer: The cube can also be called a regular hexahedron. It is one of the five regular polyhedrons, which are also sometimes referred to as the Platonic solids.
Connect to Reading
Example Read the description. Underline the details you need to identify the solid figure that will name the correct building.

Identify the solid figure and name the correct building.
Question 18. Solve the problem in the Example. Solid figure: _________ Building: _________
Answer: i. Pyramid ii. Luxor Hotel-Las Vegas-Nevada
Explanation: The 3rd figure is in the form of a pyramid. The name of the pyramid-shaped building is Luxor Hotel Las Vegas-Nevada.
Go Math Grade 5 Chapter 11 Answer Key Pdf Question 19. This building was completed in 1902. It has a triangular foundation and a triangular roof that are the same size and shape. The three sides of the building are rectangles. Solid figure: _________ Building: _________
Answer: i. prism ii. Flatiron Building-New York City-New York
Explanation: The triangle-shaped figure is in the form of a prism. The name of the triangular prism building is Flatiron Building-New York, New York.

Question 1. A closed plane figure with all sides congruent and all angles congruent is called a ________ . _________
Answer: Regular Polygon
Question 2. Line segments that have the same length or angles that have the same measure are __________ . _________
Answer: Congruent
Concepts and Skills

Answer: i. Hexagon ii. Regular Polygon

Answer: i. Triangle ii. Non-Regular

Answer: i. Pentagon ii. Not Regular

Answer: i. Equilateral ii. Acute

Answer: i. Isosceles ii. Right
Answer: i. Isosceles ii. Obtuse
Classify the quadrilateral in as many ways as possible. Write quadrilateral, parallelogram, rectangle, rhombus, square, or trapezoid.

Answer: 1. Quadrilateral 2. Trapezoid
Answer: 1. Quadrilateral 2. Parallelogram 3. Rectangle

Answer: 1. Quadrilateral 2. Parallelogram 3. Rhombus 4. Rectangle 5. Square
Fill in the bubble completely to show your answer.
Answer: right isosceles
Explanation: The above figure is a right angle and the two sides of the triangle are equal. The above figure is a right isosceles. Thus the correct answer is option A.

Answer: quadrilateral, parallelogram, rhombus, rectangle, square

Explanation: The 3-dimensional figure of the above rectangle is a rectangular prism. Thus the correct answer is option C.
Count the number of cubes used to build each solid figure.
Explanation: By seeing the above figure we can say that the rectangular prism has 3 unit cubes.

Explanation: The above figure shows that there are 5 congruent squares of 3 lines. 5 × 3 = 15 unit cubes

Explanation: The above figure shows that there are 4 congruent squares of 3 lines. 4 × 3 = 12 unit cubes

Explanation: The above figure shows that there are 6 congruent squares of 2 lines. 6 × 2 = 12

Explanation: By seeing the above figure we can say that there are 5 unit cubes.

Explanation: There are 6 congruent squares in the above figure.

Explanation: The figure shows that there are 7 unit cubes.
Question 8. How are the rectangular prisms in Exercises 3–4 related? Can you show a different rectangular prism with the same relationship? Explain. Type below: _________

Compare the number of unit cubes in each solid figure. Use < , > or =.

Use the information to answer the questions.

Question 11. There are 38 Cube Houses. Each house could hold 1,000 unit cubes that are 1 meter by 1 meter by 1 meter. Describe the dimensions of a cube house using unit cubes. Remember that the edges of a cube are all the same length. Each dimension = ______ meters
Answer: 10 meters
Explanation: So each house can hold 1000 cubes that are 1 meter in length. The house is also shaped like a cube, so you need to cube-root 1000. The cube root of 1000 is 10. So the cube house has a length, width, and height of 10 meters. V = lbh V = 10 m × 10 m × 10 m = 1000 cu. meter Thus Each dimension is 10 meters.
Understanding Volume 5th Grade Geometry Answers Question 12. The Nakagin Capsule Tower has 140 modules and is 14 stories high. If all of the modules were divided evenly among the number of stories, how many modules would be on each floor? How many different rectangular prisms could be made from that number? Type below: _________
Answer: 10 modules on each floor
Explanation: The Nakagin Capsule Tower has 140 modules and is 14 stories high. Divide 140 modules by 14 140 ÷ 14 = 10 Thus 10 modules would be on each floor. The factors of 10 are 1, 2, 5. 1 × 10 = 10 2 × 5 = 10 Thus 2 different rectangular prisms can be made from 10 unit cubes.
Use the unit given. Find the volume.

Answer: 48 cu. cm
Explanation: Given that, L = 4cm B = 4cm H = 3 cm We know that, The volume of the cuboid is lbh V = 4 cm × 4 cm × 3 cm = 48 cubic cm Thus the volume for the above cube is 48 cubic cm.

Answer: 24 cu. in.
Explanation: Given that, L = 3 in B = 2 in H = 4 in. We know that, The volume of the cuboid is lb V = 3 in × 2 in × 4 in = 24 cubic inches Therefore the volume for the above cube is 24 cubic inches.

Answer: 36 cu. ft
Explanation: Given that, L = 6 ft B = 2 ft H = 3 ft We know that, The volume of the cuboid is lbh V = 6 ft × 2 ft × 3 ft = 36 cubic feet V = 36 cu. ft Therefore the volume for the above figure is 36 cu. ft

Answer: 60 cu. in
Given that, L = 5 in. B = 4 in. H = 3 in. We know that, The volume of the cuboid is lbh V = 5 in × 4 in × 3 in = 60 cubic inches Thus the volume for the above figure is 60 cu. in.
Compare the volumes. Write < , >, or =.

Question 7. What’s the Error? Jerry says that a cube with edges that measure 10 centimeters has a volume that is twice as much as a cube with sides that measure 5 centimeters. Explain and correct Jerry’s error. Type below: __________
Answer: Let v1 equal the 10 cm sided cube’s volume. Let v2 equal the 5 cm sided cube’s volume. v1 = 10 × 10 10 = 1000 cu. cm v2 = 5 × 5 × 5 = 125 cu. cm To find the relationship between the two volumes, divide the first volume by the second. r = v1 ÷ v2 r = 1000 ÷ 125 = 8 The volume differ by a factor of 8. Thus the volume differs by a factor of 8, not by a factor of 2.
Question 8. Pattie built a rectangular prism with cubes. The base of her prism has 12 centimeter cubes. If the prism was built with 108 centimeter cubes, how many layers does her prism have? What is the height of her prism? layers: ______ the height of the prism: ______ cm
Answer: 9 layers, the height of the prism is 9 cm
Explanation: Given: Pattie built a rectangular prism with cubes. The base of her prism has 12-centimeter cubes. The prism was built with 108 cm cubes. To find the layers divide the number of cubes by base of the prism That means 108 ÷ 12 108/12 = 9 Thus the prism has 9 layers. Now we have to find the base of the prism 108 = b × h 12 × h = 108 h = 108/12 = 9 Therefore the height of the prism = 9 cm
Question 9. A packing company makes boxes with edges each measuring 3 feet. What is the volume of the boxes? If 10 boxes are put in a larger, rectangular shipping container and completely fill it with no gaps or overlaps, what is the volume of the shipping container? volume of the boxes: __________ cu ft volume of the shipping container = __________ cu ft
Answer: the volume of the boxes: 27 cu ft the volume of the shipping container = 27 cu ft
Explanation: A packing company makes boxes with edges each measuring 3 feet. Volume of the cube = lbh V = 3 × 3 × 3 = 27 cubic feet Thus the volume of the boxes is 27 feet. The volume of the boxes for 10 boxes is 27 × 10 = 270 cubic feet Therefore the volume of the shipping container is 27 cu ft

Answer: 75 cubic centimeters
Explanation: L = 5 cm B = 3 cm H = 5 cm Volume of the rectangular prism is lbh V = 5 cm × 3 cm × 5 cm = 75 cubic centimeter V = 75 cu. cm Thus the correct answer is option D.
Estimate the volume.

Answer: Given that the volume of each box is 125 cubic inches. By seeing the above figure we can say that there are 9 boxes in the larger box. Thus there are 9 tissue boxes in the larger box. Now to find the volume of the tissue boxes. We have to multiply the number of boxes with the volume of the box V = 125 × 9 = 1125 cubic inches. Therefore The estimated volume of the box holding the tissue boxes is 1125 cubic inches.

Answer: Given that, the volume of the chalk box is 16 cubic inches. From the figure, we can see that there are 24 boxes. The volume of the large box is 24 × 16 = 384 cubic inches. Therefore the estimated volume of the large box is 384 cu in.

Answer: Given, the volume of the small jewelry box is 30 cu cm There are 10 small jewelry boxes. V = 30 × 10 = 300 cu. cm Thus the estimated volume of large box is 300 cu. cm

Answer: Given that, the volume of the book is 80 cu. in There are 12 books in the figure. Multiply the number of books with the volume of each book = 12 × 80 = 960 cu. inches Thus the estimated volume of large books is 960 cu in.

Answer: Volume of spaghetti box is 750 cu. cm Volume = 2 × 5 × 4 = 40 Number of boxes = 40 Now multiply 40 with 750 cu. cm to find the volume of large box V = 40 × 750 cu. cm V = 30000 cubic cm Therefore the estimated Volume of large box is 30000 cubic cm

Answer: Given the volume of a cereal box is 324 cu. in Number of boxes is 2 × 3 × 3 = 18 The volume of large box is 18 × 324 cu. in V = 18 × 324 cu. in = 5832 cubic inches Thus the estimated Volume of large box is 5832 cubic inches.

Answer: Volume of pencil box is 4500 cu cm Number of pencil boxes = 2 × 5 = 10 The volume of large box is 4500 × 10 = 45000 cu cm Thus the estimated volume of large box is 45000 cu cm
Sense or Nonsense?

Answer: Calculate the books in box 1 V = lbh V1 = 2 × 4 × 7 = 56 books Calculate the volume of books in box 2 V = lbh V2 = 1 × 4 × 14 = 56 books So, both boxes hold the same number of books. Thus Marcelle’s statement make sense.
Find the volume.

Answer: 120 cu. in
Explanation: From the figure, we can say that the length of the rectangular prism is 4 in The width of the rectangular prism is 5 in The height of the rectangular prism is 6 in. The volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 4 in × 6 in × 5 in = 120 cu. in So, the volume of the prism is 120 cu. in

Explanation: From the figure, we can say that the length of the rectangular prism is 2 cm The width of the rectangular prism is 3 cm The height of the rectangular prism is 3 cm The volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 2 cm × 3 cm × 3 cm = 18 cu. cm Thus the volume of the rectangular prism is 18 cu. cm

Explanation: From the figure, we can say that the length of the rectangular prism is 2 in. The width of the rectangular prism is 6 in. The height of the rectangular prism is 1 in. The volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 2 in × 6 in × 1 in V = 12 Cu in. Thus the volume of the rectangular prism is 12 Cu in.
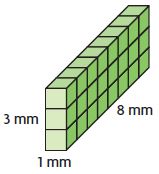
Explanation: From the figure, we can say that the length of the rectangular prism is 1 mm The width of the rectangular prism is 8 mm The height of the rectangular prism is 3 mm The volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 1 mm × 8 mm × 3 mm V = 24 Cu. mm Thus the volume of the rectangular prism is 24 Cu. mm

Answer: 160
Explanation: From the figure, we can say that the length of the rectangular prism is 10 cm The width of the rectangular prism is 4 cm The height of the rectangular prism is 4 cm The volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 10 cm × 4 cm × 4 cm = 160 Cu. cm Thus the volume of the rectangular prism is 160 Cu. cm

Answer: 150
Explanation: From the figure, we can say that the length of the rectangular prism is 5 ft The width of the rectangular prism is 6 ft The height of the rectangular prism is 5 ft The volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 5 ft × 6 ft × 5 ft V = 150 Cu. ft Thus the volume of the rectangular prism is 150 Cu. ft

Answer: 196
Explanation: From the figure, we can say that the length of the rectangular prism is 7 in. The width of the rectangular prism is 7 in. The height of the rectangular prism is 4 in. The volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 7 in × 7 in × 4 in = 196 Cu. in Thus the volume of the rectangular prism is 196 Cu. in

Answer: We need to find the volume of the travel crate that Rich should build.
Question 8. b. How can you use Thomas’s size to help you solve the problem? Type below: _________
Answer: Thomas’s size helps to find the length, width and height of the dog crate.
Question 8. c. What steps can you use to find the size of Thomas’s crate? Type below: _________
Answer: Rich is building a travel crate for his dog, Thomas, a beagle mix who is about 30 inches long, 12 inches wide, and 24 inches tall. For Thomas to travel safely, his crate needs to be a rectangular prism that is about 12 inches greater than his length and width, and 6 inches greater than his height. Length of the dog crate is 30 in + 12 in = 42 inches Width of the dog crate is 12 inches more than width of Thomas crate = 12 in + 12 in = 24 inches Height of the dog crate is 24 in + 6 in = 30 inches V = 42 in × 24 in × 30 in V = 30,240 cu in
Question 8. d. Fill in the blanks for the dimensions of the dog crate. length: _____ width: _____ height: _____ area of base: _____ Type below: _________
Answer: Crate length = 30 + 12 = 42 in Crate width = 12 + 12 = 24 in Crate height = 24 + 6 = 30 in Area of base = l × w A = 42 in × 24 in = 1008 sq in.
Question 8. e. Find the volume of the crate by multiplying the base area and the height. ______ × ______ = ______ So, Rich should build a travel crate for Thomas that has a volume of ______ . Type below: _________
Answer: Area of base = l × w A = 42 in × 24 in = 1008 sq in. Height = 30 in V = 1008 sq in × 30 in = 30240 cu. in So, Rich should build a travel crate for Thomas that has a volume of 30240 cu. in

Answer: 175 in. 3
Explanation: Length = 5 in Width = 7 in Height = 5 in Volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 5 in × 7 in × 5 in V = 175 in. 3 The volume of the rectangular prism is 175 in. 3 Therefore the correct answer is option D.

Explanation: length = 2 ft width = 4 ft height = 5 ft Volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 2 ft × 4 ft × 5 ft V = 40 cu ft Volume of the rectangular prism is 40 cu. ft

Answer: 144
Explanation: length = 4 cm width = 4 cm height = 9 cm Volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 4 cm × 4 cm × 9 cm V = 144 cu cm Volume of the rectangular prism is 144 cu cm

Answer: 216
Explanation: length = 6 in width = 6 in height = 6 in Volume of the prism is l × w × h V = 6 in × 6 in × 6 in V = 216 cu. in Thus the Volume of the prism is 216 cu. in.

Answer: 192
Explanation: length = 12 ft width = 4 ft height = 4 ft Volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 12 ft × 4 ft × 4 ft V = 192 cu ft Therefore, the Volume of the rectangular prism is 192 cu ft.
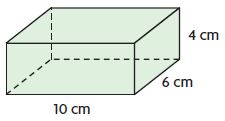
Answer: 240
Explanation: length = 10 cm width = 6 cm height = 4 cm Volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 10 cm × 6 cm × 4 cm V = 240 Cu. cm Therefore, the Volume of the rectangular prism is 240 Cu. cm.

Answer: 1008
Explanation: length = 14 in. width = 6 in. height = 12 in. Volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 14 in × 6 in × 12 in V = 1008 cu. in Thus the Volume of the rectangular prism is 1008 cu. in

Explanation: length = 7 ft width = 6 ft height = ■ ft Volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h 420 cu ft = 7 ft × 6 ft × ■ ■ × 42 sq ft = 420 cu ft ■ = 420 cu ft ÷ 42 sq ft ■ = 10 ft

Explanation: length = 6 cm width = 15 cm height = ■ cm Volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 900 cu cm 900 cu cm = 6 cm × 15 cm × ■ cm 900 cu cm = 90 sq cm × ■ cm ■ cm = 900 cu cm ÷ 90 sq cm ■ cm = 10 cm

Answer: 40 cu ft of water
Explanation: The Jade Restaurant has a large aquarium on display in its lobby. The base of the aquarium is 5 feet by 2 feet. The height of the aquarium is 4 feet. Volume = b × w × h V = 5 feet × 2 feet× 4 feet V = 40 Cu. ft Therefore, the volume of the aquarium is 40 cu ft of water.
Question 10. The Pearl Restaurant put a larger aquarium in its lobby. The base of their aquarium is 6 feet by 3 feet, and the height is 4 feet. How many more cubic feet of water does the Pearl Restaurant’s aquarium hold than the Jade Restaurant’s aquarium? ____ cu ft
Answer: 32 cu ft
Explanation: The Pearl Restaurant put a larger aquarium in its lobby. The base of their aquarium is 6 feet by 3 feet, and the height is 4 feet. Volume = b × w × h V = 6 feet × 3 feet × 4 feet = 72 cu. feet Thus the Volume of Pearl Restaurant’s aquarium is 72 cu. feet The volume of the Jade Restaurant’s aquarium is 40 cu ft of water V = Vp – Vj V = 72 – 40 = 32 cu feet
Question 11. Eddie measured his aquarium using a small fish food box. The box has a base area of 6 inches and a height of 4 inches. Eddie found that the volume of his aquarium is 3,456 cubic inches. How many boxes of fish food could fit in the aquarium? Explain your answer. ____ boxes
Answer: 144 boxes
Explanation: Volume = b × h V = 6 in × 4 in = 24 cu in To find out how many boxes will fit, divide the aquarium volume by the food box volume. numfit = Vaq/Vbox numfit = 3456/24 = 144 144 fish food boxes fir inside the aquarium.
Question 12. Describe the difference between area and volume. Type below: _________
Answer: The surface area is the sum of the areas of all the faces of the solid figure. It is measured in square units. Volume is the number of cubic units that make up a solid figure.

Answer: 1,050 cubic centimeters
Explanation: L = 15 cm W = 10 cm H = 7 cm V = lwh V = 15 cm × 10 cm × 7 cm = 1050 cubic centimeters Thus the correct answer is option C.
Question 1. Mr. Price makes cakes for special occasions. His most popular-sized cakes have a volume of 360 cubic inches. The cakes have a height, or thickness, of 3 inches, and have different whole number lengths and widths. No cakes have a length or width of 1 or 2 inches. How many different cakes, each with a different-size base, have a volume of 360 cubic inches? First, think about what the problem is asking you to solve, and the information that you are given. Next, make a table using the information from problem. Finally, use the table to solve the problem. Type below: _________
Answer: There are total of 8 different possible combination of length and width
Explanation: Volume = 360 cubic inches Height = 3 inches Volume = l x w x h 360 = l x w x 3 l x w = 120 The factors of 120 are, 1 x 120, 2x 60, 3 x 40, 4 x 30, 5 x 24, 6 x 20, 8 x 15, 10 x 12
Question 2. What if the 360 cubic-inch cakes are 4 inches thick and any whole number length and width are possible? How many different cakes could be made? Suppose that the cost of a cake that size is $25, plus $1.99 for every 4 cubic inches of cake. How much would the cake cost? Type below: _________
Answer: Since the store have a volume of 360 cu in and a height of 4 in. We need to find the number of different stones which have a base of 90 sq in. V = b × h B = 360 cu in/4 in B = 90 sq in. Consider the factors of 90. The factors of 90 are 1, 2, 3, 5, 6, 9, 10, 15, 18, 30, 45, 90 Make a table with the base, height and volume for each pair of factors Height = 4 in 1 × 90 × 4 = 360 cu in 2 × 45 × 4 = 360 cu in 3 × 30 × 4 = 360 cu in 5 × 18 × 4 = 360 cu in 6 × 15 × 4 = 360 cu in 9 × 10 × 4 = 360 cu in 6 different sized paving stones. Remember that each store has a volume of 360 cu in. Divide by 4 to find how many 4 cu in per stone Concrete = $0.18 × (360/4) = $0.18 × 90 = $18.70 The cost of the stone plus the concrete cost = $2.50 + concrete Cost = $2.50 + $16.20 = $18.70
Question 3. One company makes inflatable swimming pools that come in four sizes of rectangular prisms. The length of each pool is twice the width and twice the depth. The depth of the pools are each a whole number from 2 to 5 feet. If the pools are filled all the way to the top, what is the volume of each pool? Type below: _________
Answer: If the depth of the pool is 2 feet then the length of the pool is twice the width and twice the depth That means 2 feet × 2 × 2 = 8 feet Width is twice the depth W = 2 feet × 2 = 4 feet The volume of the rectangular swimming pool is l × w × h V = 8 ft × 4 feet × 2 ft V = 64 cu ft If the depth of the pool is 3 feet then the length of the pool is twice the width and twice the depth That means 3 feet × 2 × 2 = 12 feet Width is twice the depth W = 3 feet × 2 = 6 feet The volume of the rectangular swimming pool is l × w × h V = 12 ft × 6 feet × 2 ft V = 144 cu ft If the depth of the pool is 4 feet then the length of the pool is twice the width and twice the depth That means 4 feet × 2 × 2 = 16 feet Width is twice the depth W = 4 feet × 2 = 8 feet The volume of the rectangular swimming pool is l × w × h V = 16 ft × 8 feet × 2 ft V = 256 cu ft If the depth of the pool is 5 feet then the length of the pool is twice the width and twice the depth That means 5 feet × 2 × 2 = 20 feet Width is twice the depth W = 5 feet × 2 = 10 feet The volume of the rectangular swimming pool is l × w × h V = 20 ft × 10 feet × 2 ft V = 400 cu ft
Question 4. Ray wants to buy the larger of two aquariums. One aquarium has a base that is 20 inches by 20 inches and a height that is 18 inches. The other aquarium has a base that is 40 inches by 12 inches and a height that is 12 inches. Which aquarium has a greater volume? By how much? Type below: _________
Answer: 1440 cu. in
Explanation: Volume = l × w × h Volume of Aquarium 1 = 20 in × 20 in × 18 in V = 7200 cu. in Volume = l × w × h Volume of Aquarium 2 is 40 in × 12 in × 12 in V for A2 = 5760 cu in A1 > A2 A1 has a greater volume. Subtract A2 from A1 A1 – A2 = 7200 cu in – 5760 cu in = 1440 cu in The volume of Aquarium 1 is 1440 cu in more than Volume of Aquarium 2.
Question 5. Ken owns 13 CDs. His brother Keith has 7 more CDs than he does. Their brother, George, has more CDs than either of the younger brothers. Together, the three brothers have 58 CDs. How many CDs does George have? ______ CDs
Answer: 25 CDs
Explanation: Given that, Ken owns 13 CDs. His brother Keith has 7 more CDs than he does. Their brother, George, has more CDs than either of the younger brothers. Together, the three brothers have 58 CDs. Keith has 7 more CDs than Ken That means he has 7 + 13 = 20 CDs Now subtract Ken’s CDs, Keith CDs from the total number of CDs. = 58 – 20 – 13 = 25 CDs. Thus George has 25 CDs.
Question 6. Kathy has ribbons that have lengths of 7 inches, 10 inches, and 12 inches. Explain how she can use these ribbons to measure a length of 15 inches. Type below: _________
Answer: She could take the 10-inch ribbon and then use 5 inches from the 7-inch ribbon
Question 7. A park has a rectangular playground area that has a length of 66 feet and a width of 42 feet. The park department has 75 yards of fencing material. Is there enough fencing material to enclose the playground area? Explain. ______
Explanation: A park has a rectangular playground area that has a length of 66 feet and a width of 42 feet. The park department has 75 yards of fencing material. Area of the rectangular playground = l × w A = 66 feet × 42 feet A = 2772 sq. ft Perimeter of the rectangular playground = 2l + 2w P = 2 × 66 + 2 × 42 P = 216 ft Now convert from feet to yard We know that 1 yard = 3 feet 216 ft = 1/3 × 216 = 72 yard 72 yard is less than 75 yard Thus the park department has enough fencing material.
Question 8. Test Prep John is making a chest that will have a volume of 1,200 cubic inches. The length is 20 inches and the width is 12 inches. How many inches tall will his chest be? Options: a. 4 in. b. 5 in. c. 6 in. d. 7 in.
Answer: 5 in
Explanation: John is making a chest that will have a volume of 1,200 cubic inches. The length is 20 inches and the width is 12 inches. Volume = l × w × h 1200 cu in = 20 in × 12 in × h 240 sq in × h = 1200 cu in h = 1200 cu in ÷ 240 sq in h = 5 in Thus John’s chest will be 5 inches tall. The correct answer is option B.
Find the volume of the composite figure.

Answer: 88 cu in.
Explanation: Split the figure into 2 parts Volume of figure 1: b = 2 in h = 3 in w = 4 in V = 2 in × 4 in × 3 in V = 24 cu. in Volume of figure 2: b = 8 in w = 4 in h = 2 in V = 8 in × 4 in × 2 in V = 64 in Volume of the composite figure = 24 cu in + 64 cu. in = 88 cu. in

Answer: 48 cu cm
Explanation: Split the figure into 2 parts Volume of figure 1: b = 3 cm h = 1 cm w = 2 cm V = 3 cm × 2 cm × 1 cm V = 6 cu. cm Volume of figure 2: b = 7 cm w = 6 cm h = 1 cm V = 7 cm × 6 cm × 1 cm V = 42 cu. cm Volume of the composite figure = 42 cu. cm + 6 cu. cm = 48 cu cm

Answer: 52 cu ft
Explanation: Split the figure into 2 parts Volume of figure 1: b = 6 ft h = 2 ft w = 3 ft V = 6 ft × 3 ft × 2 ft V = 36 cu. ft Volume of figure 2: b = 4 ft w = 2 ft h = 2 ft V = 4 ft × 2 ft × 2 ft V = 16 cu. ft Volume of the composite figure = 36 cu. ft + 16 cu. ft = 52 cu ft

Answer: 108 cu. cm
Explanation: Split the figure into 2 parts Volume of figure 1: b = 3 cm w = 8 cm h = 2 cm V = 3 cm × 8 cm × 2 cm V = 48 cu cm Volume of figure 2: b = 10 cm w = 3 cm h = 2 cm V = 10 cm × 3 cm × 2 cm V = 60 cu cm Volume of the composite figure = 48 cu cm + 60 cu cm = 108 cu. cm

Answer: 204 cu. in
Explanation: Split the figure into 2 parts Volume of figure 1: b = 3 in h = 5 in w = 4 in V = 3 in × 4 in × 5 in V = 60 cu. in Volume of figure 2: b = 12 in w = 4 in h = 3 in V = 12 in × 4 in × 3 in V = 144 cu. in Volume of the composite figure = 60 cu in + 144 cu. in = 204 cu. in
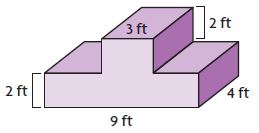
Answer: 96 cu ft
Explanation: Split the figure into 3 parts. Figure 1: V1 = 9 ft × 4 ft × 2 ft V1 = 72 cu. ft Figure 2: V2 = 3 ft × 4 ft × 2 ft V2 = 24 cu. ft V = V1 + V2 V = 72 cu. ft + 24 cu. ft = 96 cu. ft Thus the volume of the composite figure is 96 cu. ft

Answer: 300 cu. ft

Answer: 102 cu cm

Question 9. As part of a wood-working project, Jordan made the figure at the right out of wooden building blocks. How much space does the figure he made take up? ______ cu in.
Answer: 784 cu. in
Explanation: Split the figure into 2 parts Figure 1: V1 = 14 in × 4 in × 5 in V1 = 280 cu. in Figure 2: V2 = 12 in × 14 in × 3 in V2 = 504 cu. in V = V1 + V2 V = 280 cu. in + 504 cu. in V = 784 cu. in
Question 10. What are the dimensions of the two rectangular prisms you used to find the volume of the figure? What other rectangular prisms could you have used? Type below: ________
Answer: Dimensions for figure 1: Base = 14 in Width = 4 in Height = 5 in Dimensions for figure 2: Base = 12 in Width = 14 in Height = 3 in
Question 11. If the volume is found using subtraction, what is the volume of the empty space that is subtracted? Explain. ______ cu in.
Answer: 560 cu. in
Explanation: B = 8 in H = 5 in W = 14 in V = 8 in × 14 in × 5 in V = 560 cu. in Thus the volume of the empty space is 560 cu. in
Question 12. Explain how you can find the volume of composite figures that are made by combining rectangular prisms. Type below: ________

Answer: 476 cubic centimeters
Explanation: Split the figure into 2 parts Figure 1: V1 = 10 cm × 7 cm × 5 cm V1 = 350 cu. cm Figure 2: V2 = 3 cm × 7 cm × 6 cm V2 = 126 cu. cm V = V1 + V2 V = 350 cu. cm + 126 cu. cm V = 476 cu. cm
Question 1. Fran drew a triangle with no congruent sides and 1 right angle. Which term accurately describes the triangle? Mark all that apply. Options: a. isosceles b. scalene c. acute d. right
Answer: Right
Explanation: A right triangle is a type of triangle that has one angle that measures 90°. Right triangles, and the relationships between their sides and angles, are the basis of trigonometry. Thus the correct answer is option D.

Answer: Volume of the box is l × w × h V = 8 in × 10 in × 3 in V = 240 cu. in Thus the volume of the box is 240 cu. in

Answer: The figure has 3 sides and 3 angles.
Explanation: From the above figure we can say that there are three sides and three angles.

Answer: a regular polygon If all the sides are congruent then the polygon is a regular polygon.

Answer: 36 cubic feet
Explanation: Figure 1: length = 2 ft width = 3 ft height = 1 ft Volume of 1st figure = l × w × h V = 2 ft × 3 ft × 1 ft = 6 cu. ft Figure 2: length = 4 ft width = 3 ft height = 1 ft Volume of 1st figure = l × w × h V = 4 ft × 3 ft × 1 ft = 12 cu. ft Figure 3: length = 6 ft width = 3 ft height = 1 ft Volume of 1st figure = l × w × h V = 6 ft × 3 ft × 1 ft = 18 cu. ft Add all the volumes = 6 cu. ft + 12 cu. ft + 18 cu. ft Volume = 36 cu. ft

Explanation: Count the number of unit cubes in the first figure. There are 10 unit cubes in figure 1 so match the figure 1 to 10 unit cubes. Count the number of unit cubes in the second figure. There are 12 unit cubes in figure 2 so match figure 2 to 12 unit cubes. Count the number of unit cubes in the third figure. There are 9 unit cubes in figure 3 so match figure 3 to 9 unit cubes.
Question 6. Chuck is making a poster about polyhedrons for his math class. He will draw figures and organize them in different sections of the poster. Part A Chuck wants to draw three-dimensional figures whose lateral faces are rectangles. He says he can draw prisms and pyramids. Do you agree? Explain your answer. i. yes ii. no
Explanation: The lateral faces of a pyramid are triangles. The lateral faces of a prism are rectangles.
Question 6. Part B Chuck says that he can draw a cylinder on his polyhedron poster because it has a pair of bases that are congruent. Is Chuck correct? Explain your reasoning. i. yes ii. no
Explanation: A cylinder does have 2 congruent bases, but a cylinder is not a polyhedron. A cylinder has 1 curved surface, while a polyhedron has faces that are polygons

Answer: 8, 8 The above figure has 8 sides and 8 angles.

Answer: The polygon with 8 sides is known as the octagon. The above figure is congruent thus it is a regular octagon.

Explanation: Given, l = 6 in w = 3 in h = 4 in The volume of the rectangular prism is l × w × h V = 6 in × 3 in × 4in V = 72 cu in. Hence, the volume of the rectangular prism Victoria built is 72 cu. in.

Explanation: The above different have different sizes thus the triangle is scalene. The angle for the above triangle is more than 90° thus the angle is an obtuse angle. So, the answer is yes.

Explanation: The above different have different sizes thus the triangle is scalene. It has one right angle thus the statement is not correct.

Question 10. A shipping crate holds 20 shoeboxes. The dimensions of a shoebox are 6 inches by 4 inches by 12 inches. For 10a–10b, select True or False for each statement. a. Each shoebox has a volume of 22 cubic inches. i. True ii. False
Answer: False
Explanation: Shoebox volume: V = 6 in × 4 in × 12 in V = 288 cu. in Thus the statement is false.
Question 10. b. Each crate has a volume of about 440 cubic inches. i. True ii. False
Explanation: Crate Volume: V = 288 cu. in × 20 V = 5760 cu. in Thus the statement is false.
Question 10. c. If the crate could hold 27 shoeboxes the volume of the crate would be about 7,776 cubic inches. i. True ii. False
Answer: True
Explanation: Crate Volume: V = 288 cu. in × 27 V = 7776 cu. in Thus the statement is true.

Question 11. Part B Mario claims that a rhombus is sometimes a square, but a square is always a rhombus. Is he correct? Explain your answer. i. yes ii. no
Explanation: A square is a quadrilateral with all sides equal in length and all interior angles right angles. A square however is a rhombus since all four of its sides are of the same length.

Explanation: Prism: In geometry, a prism is a polyhedron comprising an n-sided polygonal base, a second base which is a translated copy of the first, and n other faces joining corresponding sides of the two bases. Figure B and C are prisms Pyramid: In geometry, a pyramid is a polyhedron formed by connecting a polygonal base and a point, called the apex. Each base edge and apex form a triangle called a lateral face. All the edges meet at the same point in the pyramid. Thus the figures A and D are pyramids.

Explanation: Mark packed 1-inch cubes into a box with a volume of 120 cubic inches. By seeing the figure we can say that there are 24 unit cubes. To find the number of layers we need to divide 120 by 24 = 120 ÷ 24 = 5 There are 5 layers of 1-inch cubes.

Answer: 312
Explanation: Split the figure into 2 parts. Figure 1: h = 3 cm w = 6 cm b = 4 cm V = 4 cm × 6 cm × 3 cm = 72 cu. cm Figure 2: b = 10 cm w = 6 cm h = 4 cm V = 10 cm × 6 cm × 4 cm = 240 cu. cm Now add the volume of 2 figures 72 cu. cm + 240 cu. cm = 312 cu cm Thus the volume of the composite figure is 312 cu. cm

Answer: rectangle
Explanation: Parallelograms are quadrilaterals with two sets of parallel sides. Since squares must be quadrilaterals with two sets of parallel sides, then all squares are parallelograms.

Answer: square
Explanation: A square is a quadrilateral with all sides equal in length and all interior angles right angles.

Answer: trapezoid
Explanation: A trapezoid has one pair of parallel sides and a parallelogram has two pairs of parallel sides. So a parallelogram is also a trapezoid.
Question 16. Megan’s aquarium has a volume of 4,320 cubic inches. Which could be the dimensions of the aquarium? Mark all that apply. Options: a. 16 in. by 16 in. by 18 in. b. 14 in. by 18 in. by 20 in. c. 12 in. by 15 in. by 24 in. d. 8 in. by 20 in. by 27 in.
Answer: C, D
Explanation: The volume of a prism = l × w × h 1. V = 16 in × 16 in × 16 in V = 4608 cu. in 2. V = 14 in × 18 in × 20 in = 5040 cu. in 3. V = 12 in × 15 in × 24 in = 4320 cu. in 4. V = 8 in × 20 in × 27 in = 4320 cu in Thus the suitable answers are C and D.
Question 17. Ken keeps paper clips in a box that is the shape of a cube. Each side of the cube is 3 inches. What is the volume of the box? ______ cubic inches
Explanation: Ken keeps paper clips in a box that is the shape of a cube. Each side of the cube is 3 inches. The volume of a cube = 3 in × 3 in × 3 in = 27 cu. in Therefore the volume of the box is 27 cubic inches.

Explanation: Monica used 1-inch cubes to make the rectangular prism Volume = 1 in × 1 in × 1 in = 1 cu. in. Each cube has a volume of 1 cubic inch.
Question 18. b. Each layer of the prism is made up of ____ cubes. ______ cubes
Explanation: We can calculate the layer by calculating the base and width 4 × 5 = 20 cubes Each layer of the prism is made up of 20 cubes.
Question 18. c. There are ____ layers of cubes. ______ layers
Answer: 3 By seeing the figure we can say that there are 3 layers of the cube. You can also find the layers of the cube by calculating the height of the figure.
Question 18. d. The volume of the prism is ____ cubic inches. ______ cubic inches
Explanation: The volume of a prism = l × w × h V = 4 in × 5 in × 3 in Volume = 60 cu. inches Therefore, the volume of the prism is 60 cubic inches.
Chapter Review/Test – Vocabulary – Page No. 4910

Question 1. A _____ has two congruent polygons as bases and rectangular lateral faces. __________
Answer: prism A prism has two congruent polygons as bases and rectangular lateral faces.
Question 2. A _____ has only one base and triangular lateral faces. __________
Answer: pyramid A pyramid has only one base and triangular lateral faces.

Answer: i. hexagon ii. regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure has six sides and 6 angles. Thus the name of the polygon is hexagon. Two polygons are congruent when they have the same size and the same shape. The above figure has same size and angles. Thus it is a regular polygon.

Answer: i. pentagon ii. regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure has five sides and 5 angles. Thus the name of the polygon is pentagon. Two polygons are congruent when they have the same size and the same shape. The above figure has same size and angles. Thus it is a regular polygon.

Answer: i. pentagon ii. not regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure has five sides and 5 angles. Thus the name of the polygon is the pentagon. Two polygons are congruent when they have the same size and the same shape. The above figure does not have the same size and angles. Thus it is not a regular polygon.

Answer: i. octagon ii. not regular
Explanation: A polygon is a closed plane figure formed by three or more line segments that meet at points called vertices. It is named by the number of sides and angles it has. The above figure has 8 sides and 8 angles. Thus the name of the polygon is octagon. Two polygons are congruent when they have the same size and the same shape. The above figure does not have same size and angles. Thus it is not a regular polygon.
Classify each figure in as many ways as possible.

Answer: 1. quadrilateral 2. trapezoid
Explanation: 1. A general quadrilateral has 4 sides and 4 angles. 2. A trapezoid is a 4-sided flat shape with straight sides that has a pair of opposite sides parallel.

Answer: △ – scalene ∠ – right
Explanation: The above triangle has different sides. Thus the triangle is a scalene triangle. The triangle with one right angle is known as a right angled triangle.

Answer: prism
Explanation: In geometry, a triangular prism is a three-sided prism; it is a polyhedron made of a triangular base, a translated copy, and 3 faces joining corresponding sides.

Answer: pyramid
Explanation: In geometry, a pentagonal pyramid is a pyramid with a pentagonal base upon which are erected five triangular faces that meet at a point (the vertex). Like any pyramid, it is self-dual.
Explanation: The figure shows that there are 4 unit cubes.

Explanation: By seeing the above figure we can say that there are 7 unit cubes.

Explanation: The figure above shows that there are 5 unit cubes.

Answer: obtuse; scalene
Explanation: The sides of the triangle is different. Thus it is a scalene triangle. The angle of the triangle is an obtuse angle. Thus the correct answer is option C.

Answer: 7 faces, 12 edges, 7 vertices
Explanation: In geometry, a hexagonal pyramid is a pyramid with a hexagonal base upon which are erected six isosceles triangular faces that meet at a point. The hexagonal pyramid has 7 faces, 12 edges and 7 vertices. Therefore the correct answer is option C.
Question 16. A manufacturing company constructs a shipping box to hold its cereal boxes. Each cereal box has a volume of 40 cubic inches. If the shipping box holds 8 layers with 4 cereal boxes in each layer, what is the volume of the shipping box? Options: a. 160 cu in. b. 320 cu in. c. 480 cu in. d. 1,280 cu in.
Answer: 1,280 cu in.
Explanation: A manufacturing company constructs a shipping box to hold its cereal boxes. Each cereal box has a volume of 40 cubic inches. If the shipping box holds 8 layers with 4 cereal boxes in each layer Multiply the number of layers with boxes = 8 × 4 = 32 The volume of 8 layers is 40 × 32 = 1280 cubic inches Thus the correct answer is option D.
Question 17. Sharri packed away her old summer clothes in a storage tote that had a length of 3 feet, a width of 4 feet, and a height of 3 feet. What was the volume of the tote that Sharri used? Options: a. 36 cu ft b. 24 cu ft c. 21 cu ft d. 10 cu ft
Answer: 36 cu ft
Explanation: Given, Sharri packed away her old summer clothes in a storage tote that had a length of 3 feet, a width of 4 feet, and a height of 3 feet. Volume = l × w × h V = 3 ft × 4 ft × 3 ft V = 36 cu. ft Thus the volume of the tote that Sharri used is 36 cu. ft. The correct answer is option A.

Explanation: The opposite sides of figure b are not parallel. Thus the figure b quadrilateral is NOT classified as a parallelogram.

Answer: Volume of 1st cube is 5 cm × 4 cm × 5 cm = 100 cu. cm Volume of 2nd cube is 5 cm × 4 cm × 8 cm = 160 cu. cm Volume of 3rd cube is 5 cm × 4 cm × 5 cm = 100 cu. cm Add all the volumes to find the volume of the composite figure That means 100 cu. cm + 160 cu. cm + 100 cu. cm = 360 cu. cm Therefore the volume of the composite figure is 360 cm 3 The correct answer is option C.
Constructed Response

Answer: 512 cu. ft
Explanation: length = 2 ft width = 2 ft height = 2 ft Volume of the display of game console boxes = 2 ft × 2 ft × 2 ft = 8 cu. ft Number of console boxes = 64 64 × 8 cu. ft = 512 cu ft The volume of the display of game console boxes = 512 cu ft
Question 20. b. On a busy Saturday, the video game store sold 22 game consoles. What is the volume of the game console boxes that are left? _____ cu ft.
Answer: 336 cu. ft
length = 2 ft width = 2 ft height = 2 ft The volume of the display of game console boxes = 2 ft × 2 ft × 2 ft = 8 cu. ft Number of console boxes = 22 The volume of the game console boxes that are left 22 × 8 cu. ft = 176 cu. ft The volume of the game console boxes that are left = 512 – 176 = 336 cu. ft
Performance Task
Question 21. Look for two pictures of three-dimensional buildings in newspapers and magazines. The buildings should be rectangular prisms. A. Paste the pictures on a large sheet of paper. Leave room to write information near the picture. B. Label each building with their name and location. C. Research the buildings, if the information is available. Find things that are interesting about the buildings or their location. Also find their length, width, and height to the nearest foot. If the information is not available, measure the buildings on the page in inches or centimeters, and make a good estimate of their width (such as 1/2 the height, rounded to the nearest whole number). Find their volumes. D. Make a class presentation, choosing one of the buildings you found.
Conclusion:
Follow our Go Math Grade 5 Answer Key Chapter 11 Geometry and Volume to get the step by step explanation. So, Download the pdf of HMH Go Math 5th Grade Solution Key Chapter 11 Geometry and Volume for free. Click on the above links and find the question and answers with images. Do not move to anywhere, stay on Go Math, and follow them each and every question of Geometry and Volume with explanation and strengthen your math skills.
Share this:
Leave a comment cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.

- school Campus Bookshelves
- menu_book Bookshelves
- perm_media Learning Objects
- login Login
- how_to_reg Request Instructor Account
- hub Instructor Commons
- Download Page (PDF)
- Download Full Book (PDF)
- Periodic Table
- Physics Constants
- Scientific Calculator
- Reference & Cite
- Tools expand_more
- Readability
selected template will load here
This action is not available.

11R: Chapter 11 Review Exercises
- Last updated
- Save as PDF
- Page ID 8639

For exercises 1 - 4, determine whether the statement is true or false. Justify the answer with a proof or a counterexample.
1) For vectors \(\vecs a\) and \(\vecs b\) and any given scalar \( c, \, c(\vecs a⋅\vecs b)=(c\vecs a)⋅\vecs b.\)
2) For vectors \(\vecs a\) and \(\vecs b\) and any given scalar \( c, \, c(\vecs a×\vecs b)=(c\vecs a)×\vecs b\).
3) The symmetric equation for the line of intersection between two planes \( x+y+z=2\) and \( x+2y−4z=5\) is given by \( −\frac{x−1}{6}=\frac{y−1}{5}=z.\)
4) If \(\vecs a⋅\vecs b=0,\) then \(\vecs a\) is perpendicular to \(\vecs b\).
For exercises 5 and 6, use the given vectors to find the quantities.
5) \(\vecs a=9\hat{\mathbf{i}}−2\hat{\mathbf{j}},\quad \vecs b=−3\hat{\mathbf{i}}+\hat{\mathbf{k}}\)
a. \( 3\vecs a+\vecs b\)
b. \( \|\vecs a\|\)
c. \(\vecs a×\|\vecs b×\vecs a\|\)
d. \( \|\vecs b×\vecs a\|\)
6) \(\vecs a=2\hat{\mathbf{i}}+\hat{\mathbf{j}}−9\hat{\mathbf{k}},\quad \vecs b=−\hat{\mathbf{i}}+2\hat{\mathbf{k}},\quad \vecs c=4\hat{\mathbf{i}}−2\hat{\mathbf{j}}+\hat{\mathbf{k}}\)
a. \( 2\vecs a−\vecs b\)
b. \( \|\vecs b×\vecs c\|\)
c. \( \vecs b×\left(\vecs b×\vecs c\right)\)
d. \( \vecs c×\|\vecs b×\vecs a\|\)
e. \( \text{Proj}_\vecs{a}\vecs b\)
7) Find the values of \(a\) such that vectors \( ⟨2,4,a⟩\) and \( ⟨0,−1,a⟩\) are orthogonal.
For exercises 8 and 9, find the unit vectors.
8) Find the unit vector that has the same direction as vector \(\vecs v\) that begins at \( (0,−3)\) and ends at \( (4,10).\)
9) Find the unit vector that has the same direction as vector \(\vecs v\) that begins at \( (1,4,10)\) and ends at \( (3,0,4).\)
For exercises 10 and 11, find the area or volume of the given shapes.
10) The parallelogram spanned by vectors \(\vecs a=⟨1,13⟩\) and \(\vecs b=⟨3,21⟩\)
11) The parallelepiped formed by \(\vecs a=⟨1,4,1⟩\) and \(\vecs b=⟨3,6,2⟩,\) and \(\vecs c=⟨−2,1,−5⟩\)
For exercises 12 and 13, find the parametric equations and the vector equation of the line with the given properties.
12) The line that passes through point \( (2,−3,7)\) that is parallel to vector \( ⟨1,3,−2⟩\)
13) The line that passes through points \( (1,3,5)\) and \( (−2,6,−3)\)
For exercises 14 and 15, find the equation of the plane with the given properties.
14) The plane that passes through point \( (4,7,−1)\) and has normal vector \(\vecs n=⟨3,4,2⟩\)
15) The plane that passes through points \( (0,1,5),(2,−1,6),\) and \( (3,2,5).\)
For exercises 16 and 17, find the traces for the surfaces in planes \( x=k,y=k\), and \( z=k.\) Then, describe and draw the surfaces.
16) \( 9x^2+4y^2−16y+36z^2=20\)
17) \( x^2=y^2+z^2\)

For exercises 18 and 19, write the given equation in cylindrical coordinates and spherical coordinates.
18) \( x^2+y^2+z^2=144\)
19) \( z=x^2+y^2−1\)
For exercises 20 and 21, convert the given equations from cylindrical or spherical coordinates to rectangular coordinates. Identify the given surface.
20) \( ρ^2(\sin^2(φ)−\cos^2(φ))=1\)
21) \( r^2−2r\cos(θ)+z^2=1\)
For exercises 22 and 23, consider a small boat crossing a river.
22) If the boat velocity is \( 5\) km/h due north in still water and the water has a current of \( 2\) km/h due west (see the following figure), what is the velocity of the boat relative to shore? What is the angle \( θ\) that the boat is actually traveling?

23) When the boat reaches the shore, two ropes are thrown to people to help pull the boat ashore. One rope is at an angle of \( 25°\) and the other is at \( 35°\). If the boat must be pulled straight and at a force of \( 500\) N, find the magnitude of force for each rope (see the following figure).

24) An airplane is flying in the direction of 52° east of north with a speed of 450 mph. A strong wind has a bearing 33° east of north with a speed of 50 mph. What is the resultant ground speed and bearing of the airplane?
25) Calculate the work done by moving a particle from position \( (1,2,0)\) to \( (8,4,5)\) along a straight line with a force \(\vecs F=2\hat{\mathbf{i}}+3\hat{\mathbf{j}}−\hat{\mathbf{k}}.\)
In problems 26 and 27, consider your unsuccessful attempt to take the tire off your car using a wrench to loosen the bolts. Assume the wrench is \( 0.3\) m long and you are able to apply a 200-N force.
26) Because your tire is flat, you are only able to apply your force at a \( 60°\) angle. What is the torque at the center of the bolt? Assume this force is not enough to loosen the bolt.
27) Someone lends you a tire jack and you are now able to apply a 200-N force at an \( 80°\) angle. Is your resulting torque going to be more or less? What is the new resulting torque at the center of the bolt? Assume this force is not enough to loosen the bolt.
Contributors
Gilbert Strang (MIT) and Edwin “Jed” Herman (Harvey Mudd) with many contributing authors. This content by OpenStax is licensed with a CC-BY-SA-NC 4.0 license. Download for free at http://cnx.org .

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
For better preparation and quality education, our team has shared the Big Ideas Math Book Geometry Answer Key Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume for high school students. Provided Big Ideas Math Geometry Answers Chapter 11 Circumference, Area, and Volume are aligned topic-wise as per the latest common core curriculum. Students can ...
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Big Ideas Geometry - 9781635988031, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Chapter 11:Circumference, Area, and Volume. Section 11.1: Circumference and Arc Length. ... you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Big Ideas Geometry ...
Calculus with Analytic Geometry. 7th Edition • ISBN: 9780618141807 (1 more) Bruce H. Edwards, Larson, Robert P. Hostetler. 11,568 solutions. Get your Geometry homework done with Quizlet! Browse through thousands of step-by-step solutions to end-of-chapter questions from the most popular Geometry textbooks.
The Chapter 11 Resource Masters includes the core materials needed for Chapter 11. These materials include worksheets, extensions, and assessment options. The answers for these pages appear at the back of this booklet. All of the materials found in this booklet are included for viewing and printing in the.
Our resource for Geometry: Homework Practice Workbook includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems, you can take the guesswork out of studying and move forward with confidence. Find step-by-step solutions and answers ...
Chapter 11:Two- and Three- Dimensional Models. Section 11-1: ... Now, with expert-verified solutions from enVision Geometry 1st Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for enVision Geometry includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by ...
CH11.4. Problem. 1CYU. Step-by-step solution. Step 1 of 3. The following figure is given. Step 2 of 3. The center of a regular polygon is the center of the polygon's circumscribed circle. So, the center of the square is .
Hotmath Homework Help Math Review Math Tools Multilingual Glossary Online Calculators Study to Go. Mathematics. Home > Chapter 11. Geometry. Chapter 11: Areas of Polygons and Circles. Chapter Readiness Quiz; Chapter Test; Concepts in Motion; Problem of the Week Cards; Real-World Careers;
11-27. The areas are all equal because the triangles have the same base and height. 11-28. a: x = 12.9 c: x=0 2.56 11-29. PA = PA (Reflexive Property), mLPBA = mZPCA = 900 (tangents are L to radii drawn to the point of tangency), PB = PC (radii of a circle must be equal), so APAB Therefore AB = AC (z As —¥ parts ). 11-30. a: 10 11-31. ±6 ...
Chegg's step-by-step geometry guided textbook solutions will help you learn and understand how to solve geometry textbook problems and be better prepared for class. Stuck on a geometry question that's not in your textbook? Chegg's geometry experts can provide answers and solutions to virtually any geometry problem, often in as little as 2 hours.
Chapter. CH11. Problem. 1CR. Step-by-step solution. Step 1 of 1. A set of points in space equidistant from a given point is called sphere. The reason the correct option is not a circle because this only applies for a two dimensional object and a sphere deals with any real point and a distance in all three dimensions.
Unit 1 Lines. Unit 2 Angles. Unit 3 Shapes. Unit 4 Triangles. Unit 5 Quadrilaterals. Unit 6 Coordinate plane. Unit 7 Area and perimeter. Unit 8 Volume and surface area. Unit 9 Pythagorean theorem.
Chapter Resources Chapter Readiness Quiz Chapter Test Math in Motion ... Personal Tutor Self-Check Quizzes. Common Core State Standards Supplement, SE Hotmath Homework Help Math Review Math Tools Multilingual eGlossary Study to Go Online Calculators. Mathematics. Home > Chapter 11 > Lesson 1. Geometry. Chapter 11, Lesson 1: Areas of ...
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Geometry Common Core - 9780133185829, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Chapter 1:Tools of Geometry. Section 1-1: Nets and Drawings for Visualizing Geometry. Section 1-2: Points, Lines, and Planes ... Chapter 11:Surface Area and Volume. Section 11-1: Space ...
John is making a chest that will have a volume of 1,200 cubic inches. The length is 20 inches and the width is 12 inches. Volume = l × w × h. 1200 cu in = 20 in × 12 in × h. 240 sq in × h = 1200 cu in. h = 1200 cu in ÷ 240 sq in. h = 5 in. Thus John's chest will be 5 inches tall. The correct answer is option B.
FREE Answers for McDougal Littell Jurgensen Geometry: Student Edition Geometry Chapter 1 Points, Lines, Planes, And Angles 2 Deductive Reasoning 3 Parallel Lines And Planes 4 Congruent Triangles 5 Quadrilaterals 6 Inequalities In Geometry 7 Similar Polygons 8 Right Triangles 9 Circles 10 Constructions And Loci 11 Areas Of Plane Figures 12 Areas ...
Now, with expert-verified solutions from Geometry, Volume 2 1st Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Geometry, Volume 2 includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the process step by step. With Expert Solutions for thousands of practice problems ...
Find step-by-step solutions and answers to Geometry - 9780395977279, as well as thousands of textbooks so you can move forward with confidence. ... Examinations: Chapter 11. Exercise 1. Exercise 2. Exercise 3. Exercise 4. Exercise 5. Exercise 6. Exercise 7. Exercise 8. Exercise 9. Exercise 10. Exercise 11. Exercise 12. Exercise 13. Exercise 14 ...
Step-by-step solution. Step 1 of 2. Considering the definition of a dilation, a dilation is a transformation that can change the size of a polygon but leaves the shape unchanged, the strategy is to say how the ratios of the measures of the corresponding sides related. Step 2 of 2. In dilation the ratios of the corresponding sides must be equal.
FREE Answers for Geometry: Homework Practice Workbook Chapter 0 Preparing For Geometry 1 Tools Of Geometry 2 Reasoning And Proof 3 Parallel And Perpendicular Lines 4 Congruent Triangles 5 Relationships In Triangles 6 Quadrilaterals 7 Proportions And Similarity 8 Right Triangles And Trigonometry 9 Transformations And Symmetry 10 Circles 11 Areas ...
Now, with expert-verified solutions from Geometry Common Core Practice and Problem Solving Workbook 1st Edition, you'll learn how to solve your toughest homework problems. Our resource for Geometry Common Core Practice and Problem Solving Workbook includes answers to chapter exercises, as well as detailed information to walk you through the ...
11) The parallelepiped formed by ⇀ a = 1, 4, 1 and ⇀ b = 3, 6, 2 , and ⇀ c = − 2, 1, − 5 . Answer. For exercises 12 and 13, find the parametric equations and the vector equation of the line with the given properties. 12) The line that passes through point (2, − 3, 7) that is parallel to vector 1, 3, − 2 .
Problem 1E. Chapter. CH11.1. Problem. 1E. Step-by-step solution. Step 1 of 1. Parallelogram has four sides in which opposite sides are parallel. Therefore, both pair of parallel sides of parallelogram can be called its bases and perpendicular distance between these sides is called the height.