An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- J Ayurveda Integr Med
- v.10(2); Apr-Jun 2019

How to plan and write a budget for research grant proposal?
Medical research can have an enormous positive impact on human health. Health research improves the quality of human lives and society which plays a vital role in social and economic development of the nation. Financial support is crucial for research. However, winning a research grant is a difficult task. A successful grant-winning application requires two key elements: one is an innovative research problem with best probable idea/plan for tackling it and appropriate planning of budget. The aim of the present paper is to give an insight on funding agencies providing funding for health research including traditional Indian medicine (from an Indian perspective) and key points for planning and writing budget section of a grant application.
1. Introduction
Why health science research is important and why should it to be funded? Science and technology innovations and health research can have an enormous impact on human health. They improve public health, quality of human lives, longevity and have made society better [1] , [2] . Healthy humans with better quality of life are crucial for the social and economical development of the nation [3] . Medical research led to the expansion of knowledge about health problems/conditions and their mechanism, risk factors, outcomes of treatments or interventions, preventive measures and proper management. Clinical studies or trials provide important information about the safety and efficacy of a drug/intervention. Innovative basic science research had led to the discovery of new technology, efficient diagnostic and therapeutic devices. So, currently, an effort with multidisciplinary approach is a demand for better understanding of clinical conditions and providing safest health care to the community [2] , [4] .
Whether it is basic or applied, clinical or non-clinical, all research needs financial support. Considering the importance of research in economic growth of a nation, many countries are increasing their budget for research and development in science. A study on impact of GDP (Gross Domestic Product) on research and development in science among Asian countries has found that one who spends more on research has more research outcomes in the form of total number of research documents, citations per documents and h-index [5] . About 95% of the NIH (National Institutes of Health, USA), budget goes directly to research awards, programs, and centers; training programs; and research and development contracts [6] . Total expenditure carried out for research in India is too less than USA and China. Percentage of GDP for research and development in India is 0.88%, while South Korea, USA and China have 4.292%, 2.742 and 2.1% respectively [7] .
Owing to the increasing competition among the researchers, especially the young ones, for their academic growth, preparing and planning a winning research proposal becomes very essential. A successful grant-winning application requires two key elements: (1) innovative research problem with best probable idea/plan for tackling it and (2) appropriate planning of budget. The aim of the present paper is to give an insight on funding agencies (from an Indian perspective) and key points for planning and writing budget section of a grant application.
2. What is the purpose of the budget plan in a grant application?
A budget is the quantitative expression of a financial plan for future expenses on the project in a given period of time [8] . Budget plan is a key element of a grant application. It demonstrates the required cost for the proposed project. It is a prediction of expenses and serves a plan for funders on how the organization will operate the project, spend the money in a given set of period and where their money will go. It shows the funders exactly what they can support and also helps the institution and investigating team in management of the project. Moreover, budget plan requires for accountability [9] .
3. Which are the funding agencies that sponsor health research in India?
Various national and international sponsoring agencies have identified health problems of priority for funding a research. Some of the leading funding agencies providing grant for health research including alternative systems of medicine in India are given in Table 1 . State Universities/deemed Universities also have a provision of funding for medical research.
Table 1
List of funding agencies those promote health research.
4. What constitutes a research project budget?
Proforma of the research grant applications and presentation of budget section may vary among the sponsoring agencies. However, major parts of budget plan in the applications of the above mentioned funding agencies are quite similar. The budget section is broadly divided into two categories: direct and indirect costs.
4.1. Direct costs:
These are the costs incurred specifically to carry out a project [10] . Direct costs include expenses towards personnel, materials, equipments, consumables and travel. These particulars are further categorized into recurring and non-recurring expenses on the basis of their occurrence during the study period. A brief description of the sub-sections under direct cost is given below:
4.1.1. Personnel:
Budget for personnel can be mentioned in this section in case human resources are required for the study and as per funding agency guidelines. Salaries with allowances can be budgeted for human resources such as site manager, research assistant, junior research fellow (JRF), senior research fellow (SRF), research associate, technician, data entry operator and attender. Most of the Indian funding agencies do not have a provision for salaries for the principal investigator (PI) and co-investigators (Co-PI). Ministry of AYUSH [11] and Rajiv Gandhi University of Health Science (RGUHS), Karnataka [12] provide one-time minimal fees for investigators and supporting staff respectively. There is a provision for salaries of investigators in Wellcome trust-DBT India alliance grants [13] .
4.1.2. Recurring expenses:
Recurring expenses are those which are variable and which keep on occurring throughout the entire project duration. Particulars categorized in this category are consumables, chemicals, glasswares, laboratory test charges, diagnostic kits, stationery, prints, photocopies, communication, postage, telephone charges, survey tools, questionnaires, publication charges, reprints, binding etc. Other expenses could be allowances for patients/participants, food charges and physician fees.
4.1.3. Non-recurring expenses:
Non-recurring expenses are those which are one-time in nature or which do not recur at regular intervals. Particulars included in this category are equipments or instruments with its accessories, software's, computer, printer, electrical and electronic items and accessories of the existing instrument in your lab. Percentage of budget allocated for equipment varies among the funding agencies from 25% to 90% of the entire budget. Some of the agencies do not have provision for equipment in budget. Vision Group on Science and Technology allocated their maximum grant (up to 90%) for development of infrastructure of laboratories [14] .
4.1.4. Traveling expenses:
Budget allocated for traveling can be used for attending meetings, conferences, workshops and training programs. Foreign travel is not allowed by any Indian funding agency. Traveling expenses for collection of data, survey and visit to other centers in multicentric study can be budgeted in this sub-section.
4.2. Indirect costs:
These are the costs which cannot be directly attributed to specific expenses of a project, but are required to run a project. It is also termed as overhead charges. Laboratory, electricity, water, library and other facilities are provided by the institution to run a proposed research project. Therefore, a fixed cost (usually) of about 5–15% of the total budget is provisioned as institutional overhead charges which goes to the institution directly. The range may, however, be flexible on the basis of the type of funding agency.
5. Budget justification
Most of the funding agencies require submission of a budget justification with all the items described above. Sometimes it is also called as budget narrative. Explanation of need for each line item in the budget with item-wise and year-wise breakdown has to be provided. Quantification of total costs of each line-item and document cost calculation should be done. When writing a budget justification, it is important to follow the same order as that in an itemized budget. For example, if equipment such as color doppler is required, then justify the need of a device with respect to the proposed methodology of the study. Similarly, for non-recurring expenses, breakdown the consumables item-wise and year-wise with its cost and calculation according to the protocol of the study and justify accordingly.
6. Budget summary
An item-wise and year wise summary of the total budget is usually required in most of the applications. Budget summary outlines the proposed grant and often (most of the format) appears at the beginning of the proposal. It should always be prepared at the end, after the grant proposal has been completely developed. A sample budget summary (as an example) for a proposed study for the duration of three years is shown in Table 2 . In the personnel section, a research fellow salary with allowances is budgeted year-wise. The salary of the research fellow for the first and second year is Rs. 2,30,000 per year (JRF) with an enhancement to Rs 2, 59,000 for the third year (SRF) as per the guidelines of the funding agency. As non-recurring expenses are one time in nature, a budget for equipment was budgeted only for the first year. Under the section of recurring expenses, more budgets are allocated in the second year for consumables because recruitment of subjects in large number will be done during the second year of the proposed study. Similarly, expenses toward travel, investigator fee and other miscellaneous costs year-wise have been budgeted. The emoluments and guidelines on service conditions for research personnel employed in research project by ICMR has been given in reference section [15] , [16] .
Table 2
Sample budget summary (year wise).
7. How to plan a simple research budget?
Planning of the research budget begins with an innovative research question, objectives and design of the study. Before starting to write a budget plan, it is essential to understand the expectations of funding agencies, University/Institute and the team of researchers. It is imperative to keep in mind that the research proposal will be reviewed by both scientific and financial (non-scientific) experts. Hence, the proposal should be prepared in such a way that it can be easily understood by even non-scientific experts.
Firstly, a list of what is essential and would add value for research such as focus of research, primary and secondary outcomes of the study, the source of the sample, study setting, sample design and sample size, techniques used to collect data, method of data analysis and available resources should be made [17] .
Secondly, the instructions, format of the application and rules of the funding agency should be read thoroughly. Budget specifications, limitations of recurring and non-recurring costs, and necessity of budget justification with cost breakdown should be checked. Note that one should not deviate or modify the proforma of the funding agency.
Thirdly, a list of items should be made and categorized into recurring and non-recurring expenses. Breakdown of the budget into item-wise and year-wise with cost calculation should be done. It should be ensured that costs are reasonable, allowable and related to the research proposal, so that the budget appears realistic. Travel expenses should be calculated as per the rules of the funding agency.
Fourthly, item-wise and year-wise justification of the requirement in a same sequence of format should be provided. A well-justified budget can enhance the evaluation of the research proposal by reviewers and funding body.
The last most important part is to review the budget and verify the costs and calculation. It is better, if other research team members can review the budget plan and re-calculate the costs thoroughly. Remember, too high budget and too low budget with respect to the research proposal are suspicious and chances of receiving a grant are less.
Sources of funding
Conflict of interest.
Peer review under responsibility of Transdisciplinary University, Bangalore.
The Research Whisperer
Just like the thesis whisperer – but with more money, how to make a simple research budget.

Every research project needs a budget*.
If you are applying for funding, you must say what you are planning to spend that funding on. More than that, you need to show how spending that money will help you to answer your research question .
So, developing the budget is the perfect time to plan your project clearly . A good budget shows the assessors that you have thought about your research in detail and, if it is done well, it can serve as a great, convincing overview of the project.
Here are five steps to create a simple budget for your research project.
1. List your activities
Make a list of everything that you plan to do in the project, and who is going to do it.
Take your methodology and turn it into a step-by-step plan. Have you said that you will interview 50 people? Write it on your list.
Are you performing statistical analysis on your sample? Write it down.
Think through the implications of what you are going to do. Do you need to use a Thingatron? Note down that you will need to buy it, install it, and commission it.
What about travel? Write down each trip separately. Be specific. You can’t just go to ‘South East Asia’ to do fieldwork. You need to go to Kuala Lumpur to interview X number of people over Y weeks, then the same again for Singapore and Jakarta.
Your budget list might look like this:
- I’m going to do 10 interviews in Kuala Lumpur; 10 interviews in Singapore; 10 interviews in Jakarta by me.
- I’ll need teaching release for three months for fieldwork.
- I’ll need Flights to KL, Singapore, Jakarta and back to Melbourne.
- I’ll need Accommodation for a month in each place, plus per diem.
- The transcription service will transcribe the 30 interviews.
- I’ll analysis the transcribed results. (No teaching release required – I’ll do it in my meagre research time allowance.)
- I’ll need a Thingatron X32C to do the trials.
- Thing Inc will need to install the Thingatron. (I wonder how long that will take.)
- The research assistant will do three trials a month with the Thingatron.
- I’ll need to hire a research assistant (1 day per week for a year at Level B1.)
- The research assistant will do the statistical analysis of the Thingatron results.
- I’ll do the writing up in my research allowance time.
By the end, you should feel like you have thought through the entire project in detail. You should be able to walk someone else through the project, so grab a critical friend and read the list to them. If they ask questions, write down the answers.
This will help you to get to the level of specificity you need for the next step.
2. Check the rules again
You’ve already read the funding rules, right? If not, go and read them now – I’ll wait right here until you get back.
Once you’ve listed everything you want to do, go back and read the specific rules for budgets again. What is and isn’t allowed? The funding scheme won’t pay for equipment – you’ll need to fund your Thingatron from somewhere else. Cross it off.
Some schemes won’t fund people. Others won’t fund travel. It is important to know what you need for your project. It is just as important to know what you can include in the application that you are writing right now.
Most funding schemes won’t fund infrastructure (like building costs) and other things that aren’t directly related to the project. Some will, though. If they do, you should include overheads (i.e. the general costs that your organisation needs to keep running). This includes the cost of basics like power and lighting; desks and chairs; and cleaners and security staff. It also includes service areas like the university library. Ask your finance officer for help with this. Often, it is a percentage of the overall cost of the project.
If you are hiring people, don’t forget to use the right salary rate and include salary on-costs. These are the extra costs that an organisation has to pay for an employee, but that doesn’t appear in their pay check. This might include things like superannuation, leave loading, insurance, and payroll tax. Once again, your finance officer can help with this.
Your budget list might now look like this:
- 10 interviews in Kuala Lumpur; 10 interviews in Singapore; 10 interviews in Jakarta by me.
- Teaching release for three months for fieldwork.
- Flights to KL, Singapore, Jakarta and back to Melbourne.
- Accommodation for a month in each place, plus per diem, plus travel insurance (rule 3F).
- Transcription of 30 interviews, by the transcription service.
- Analysis of transcribed results, by me. No teaching release required.
- Purchase and install Thingatron X32C, by Thing Inc . Not allowed by rule 3C . Organise access to Thingatron via partner organistion – this is an in-kind contribution to the project.
- Three trials a month with Thingatron, by research assistant.
- Statistical analysis of Thingatron results, by research assistant.
- Research assistant: 1 day per week for a year at Level B1, plus 25.91% salary on-costs.
- Overheads at 125% of total cash request, as per rule 3H.
3. Cost each item
For each item on your list, find a reasonable cost for it . Are you going to interview the fifty people and do the statistical analysis yourself? If so, do you need time release from teaching? How much time? What is your salary for that period of time, or how much will it cost to hire a replacement? Don’t forget any hidden costs, like salary on-costs.
If you aren’t going to do the work yourself, work out how long you need a research assistant for. Be realistic. Work out what level you want to employ them at, and find out how much that costs.
How much is your Thingatron going to cost? Sometimes, you can just look that stuff up on the web. Other times, you’ll need to ring a supplier, particularly if there are delivery and installation costs.
Jump on a travel website and find reasonable costs for travel to Kuala Lumpur and the other places. Find accommodation costs for the period that you are planning to stay, and work out living expenses. Your university, or your government, may have per diem rates for travel like this.
Make a note of where you got each of your estimates from. This will be handy later, when you write the budget justification.
- 10 interviews in Kuala Lumpur; 10 interviews in Singapore; 10 interviews in Jakarta by me (see below for travel costs).
- Teaching release for three months for fieldwork = $25,342 – advice from finance officer.
- Flights to KL ($775), Singapore ($564), Jakarta ($726), Melbourne ($535) – Blue Sky airlines, return economy.
- Accommodation for a month in each place (KL: $3,500; Sing: $4,245; Jak: $2,750 – long stay, three star accommodation as per TripAdviser).
- Per diem for three months (60 days x $125 per day – University travel rules).
- Travel insurance (rule 3F): $145 – University travel insurance calculator .
- Transcription of 30 interviews, by the transcription service: 30 interviews x 60 minutes per interview x $2.75 per minute – Quote from transcription service, accented voices rate.
- Analysis of transcribed results, by me. No teaching release required. (In-kind contribution of university worth $2,112 for one week of my time – advice from finance officer ).
- Purchase and install Thingatron X32C, by Thing Inc . Not allowed by rule 3C. Organise access to Thingatron via partner organistion – this is an in-kind contribution to the project. ($2,435 in-kind – quote from partner organisation, at ‘favoured client’ rate.)
- Research assistant: 1 day per week for a year at Level B1, plus 25.91% salary on-costs. $12,456 – advice from finance officer.
Things are getting messy, but the next step will tidy it up.
4. Put it in a spreadsheet
Some people work naturally in spreadsheets (like Excel). Others don’t. If you don’t like Excel, tough. You are going to be doing research budgets for the rest of your research life.
When you are working with budgets, a spreadsheet is the right tool for the job, so learn to use it! Learn enough to construct a simple budget – adding things up and multiplying things together will get you through most of it. Go and do a course if you have to.
For a start, your spreadsheet will multiply things like 7 days in Kuala Lumpur at $89.52 per day, and it will also add up all of your sub-totals for you.
If your budget doesn’t add up properly (because, for example, you constructed it as a table in Word), two things will happen. First, you will look foolish. Secondly, and more importantly, people will lose confidence in all your other numbers, too. If your total is wrong, they will start to question the validity of the rest of your budget. You don’t want that.
If you are shy of maths, then Excel is your friend. It will do most of the heavy lifting for you.
For this exercise, the trick is to put each number on a new line. Here is how it might look.
5. Justify it
Accompanying every budget is a budget justification. For each item in your budget, you need to answer two questions:
- Why do you need this money?
- Where did you get your figures from?
The budget justification links your budget to your project plan and back again. Everything item in your budget should be listed in your budget justification, so take the list from your budget and paste it into your budget justification.
For each item, give a short paragraph that says why you need it. Refer back to the project plan and expand on what is there. For example, if you have listed a research assistant in your application, this is a perfect opportunity to say what the research assistant will be doing.
Also, for each item, show where you got your figures from. For a research assistant, this might mean talking about the level of responsibility required, so people can understand why you chose the salary level. For a flight, it might be as easy as saying: “Blue Sky airlines economy return flight.”
Here is an example for just one aspect of the budget:
Fieldwork: Kuala Lumpur
Past experience has shown that one month allows enough time to refine and localise interview questions with research partners at University of Malaya, test interview instrument, recruit participants, conduct ten x one-hour interviews with field notes. In addition, the novel methodology will be presented at CONF2015, to be held in Malaysia in February 2015.
Melbourne – Kuala Lumpur economy airfare is based on current Blue Sky Airlines rates. Note that airfares have been kept to a minimum by travelling from country to country, rather than returning to Australia.
1 month accommodation is based on three star, long stay accommodation rates provided by TripAdvisor.
30 days per diem rate is based on standard university rates for South-East Asia.
Pro tip: Use the same nomenclature everywhere. If you list a Thingatron X32C in your budget, then call it a Thingatron X32C in your budget justification and project plan. In an ideal world, someone should be able to flip from the project plan, to the budget and to the budget justification and back again and always know exactly where they are.
- Project plan: “Doing fieldwork in Malaysia? Whereabouts?” Flips to budget.
- Budget: “A month in Kuala Lumpur – OK. Why a month?” Flips to budget justification.
- Budget justification: “Ah, the field work happens at the same time as the conference. Now I get it. So, what are they presenting at the conference?” Flips back to the project description…
So, there you have it: Make a list; check the rules; cost everything; spreadsheet it; and then justify it. Budget done. Good job, team!
This article builds on several previous articles. I have shamelessly stolen from them.
- Constructing your budget – Jonathan O’Donnell.
- What makes a winning budget ? – Jonathan O’Donnell.
- How NOT to pad your budget – Tseen Khoo.
- Conquer the budget, conquer the project – Tseen Khoo.
- Research on a shoestring – Emily Kothe.
- How to make a simple Gantt chart – Jonathan O’Donnell.
* Actually, there are some grant schemes that give you a fixed amount of money, which I think is a really great idea . However, you will still need to work out what you are going to spend the money on, so you will still need a budget at some stage, even if you don’t need it for the application.
Also in the ‘simple grant’ series:
- How to write a simple research methods section .
- How to make a simple Gantt chart .
Share this:
28 comments.
This has saved my day!
Happy to help, Malba.
Like Liked by 1 person
[…] you be putting in a bid for funding? Are there costs involved, such as travel or equipment costs? Research Whisperer’s post on research budgets may help you […]
I’ve posted a link to this article of Jonathan’s in the Australasian Research Management Society LinkedIn group as well, as I’m sure lots of other people will want to share this.
Thanks, Miriam.
This is great! Humorous way to talk explain a serious subject and could be helpful in designing budgets for outreach grants, as well. Thanks!
Thanks, Jackie
If you are interested, I have another one on how to do a timeline: https://theresearchwhisperer.wordpress.com/2011/09/13/gantt-chart/
[…] really useful information regarding budget development can be found on the Research Whisperer Blog here. Any other thoughts and suggestions are welcome – what are your tips to developing a good […]
[…] it gets you to the level of specificity that you need for a detailed methods section. Similarly, working out a budget for your workshops will force you to be specific about how many people will be attending (venue […]
A friend of mine recently commented by e-mail:
I was interested in your blog “How to make a simple research budget”, particularly the statement: “Think through the implications of what you are going to do. Do you need to use a Thingatron? Note down that you will need to buy it, install it, and commission it.”
From my limited experience so far, I’d think you could add:
“Who else is nearby who might share the costs of the Thingatron? If it’s a big capital outlay, and you’re only going to use it to 34% of it’s capacity, sharing can make the new purchase much easier to justify. But how will this fit into your grant? And then it’s got to be maintained – the little old chap who used to just do all that odd mix of electrickery and persuasion to every machine in the lab got retrenched in the last round. You can run it into the ground. But that means you won’t have a reliable, stable Thingatron all ready to run when you apply for the follow-on grant in two years.”
[…] (For more on this process, take a look at How to Write a Simple Project Budget.) […]
[…] Source: How to make a simple research budget […]
This is such a big help! Thank You!
No worries, Claudine. Happy to help.
Would you like to share the link of the article which was wrote about funding rules? I can’t find it. Many thanks!
Hello there – do you mean this post? https://theresearchwhisperer.wordpress.com/2012/02/14/reading-guidelines
Thank @tseen khoo, very useful tips. I also want to understand more about 3C 3F 3H. What do they stand for? Can you help me find out which posts talk about that. Thank again.
[…] mount up rapidly, even if you are in a remote and developing part of the world. Putting together a half decent budget early on and being aware of funding opportunities can help to avoid financial disaster half way […]
This is so amazing, it really helpful and educative. Happy unread this last week before my proposal was drafted.
Happy to help, Babayomi. Glad you liked it.
really useful! thanks kate
[…] “How to Make a Simple Research Budget,” by Jonathan O’Donnell on The Research Whisperer […]
[…] offering services that ran pretty expensive. until I found this one. It guided me through making a simple budget. The information feels sort of like a university graduate research paper but having analysed […]
[…] Advice on writing research proposals for industry […]
[…] research serves as the bedrock of informed budgeting. Explore the average costs of accommodation, transportation, meals, and activities in your chosen […]
Leave a comment Cancel reply
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar
- Vice-Chancellor
- Leadership and Governance
- Education Quality
- Sustainability
- Staff Directory
- Staff Profiles
- Staff Online
- Office of Human Resources
- Important Dates
- Accept and Enrol
- Student Forms
- Jobs for Students
- Future Students
- Scholarships
- Class Registration
- Online Courses
- Password Management
- Western Wifi - Wireless
- Accommodation
- The College
- Whitlam Institute
- Ask Western
- Staff Email
- WesternNow Staff Portal
- ResearchMaster
- Citrix Access
- Student Management System
- Exam Timetable
- Oracle Financials
- Casual Room Bookings
- Staff Profile Editor
- Vehicle Bookings
- Form Centre
- WSU SharePoint Portal
- Learning Guide Management System (LGMS)
- Student Email
- My Student Records (MySR)
- WesternLife
- WesternNow Student Portal
- My Exam Timetable
- Student Forms (eForms)
- Accept My Offer

Study with Us
- International
- Research Portal
- ResearchDirect
- Research Theme Program
- Researcher Development
- Funding Opportunities
- Preparing a Grant Application
- Research Ethics & Integrity
- Research Project Risk & Compliance
- Foreign Arrangements Scheme
- Managing Your Research Project
- Research Data Management
- Business Services
- Research Infrastructure
- Office of the DVC REI
- Research Services Update
- Contact Research Services
- Master of Research
- Research Degrees
- Find a Supervisor
- Graduate Research School
- Apply for a Research Degree
- Candidate Support and Resources
- HDR Knowledge Directory
- Research Ethics
- HDR Workshops
- Forms, Policies and Guidelines
- Giving to Western
- Bushfire and Natural Hazards
- Digital Health
- Future Food Systems
- RoZetta Institute
- Hawkesbury Institute for the Environment
- Ingham Institute
- Institute for Australian and Chinese Arts and Culture
- Institute for Culture and Society
- NICM Health Research Institute
- The MARCS Institute
- Translational Health Research Institute
- Australia India Water Centre
- Centre for Educational Research
- Centre for Infrastructure Engineering
- Centre for Research in Mathematics and Data Science
- Centre for Smart Modern Construction (c4SMC)
- Centre for Western Sydney
- Chinese Medicine Centre
- Global Centre for Land-Based Innovation
- International Centre for Neuromorphic Systems
- National Vegetable Protected Cropping Centre
- Transforming early Education And Child Health Research Centre (TeEACH)
- Urban Transformations Research Centre
- Writing and Society Research Centre
- Young and Resilient Research Centre
- Digital Humanities Research Group
- Humanitarian and Development Research Initiative (HADRI)
- Nanoscale Organisation and Dynamics Research Group
- Research at Western
- Research Impact
- - Research Portal
- - ResearchDirect
- - Researcher Development
- - Funding Opportunities
- - Definition of Research
- - Research or Consultancy Activity?
- - Writing a Project Description
- - Track Record Statement
- - Tips for ECRs
- - Developing a Budget
- - Budget Justification
- - Research Contracts
- - Research Codes
- - Research Project Risk and Compliance
- - Foreign Arrangements Scheme
- - Managing Your Project
- - Research Data Management
- Research Ethics and Integrity
- Research Management Solution (RMS)
- Research Participation Opportunities
Developing a Budget for Your Research Application
Budgets and budget justifications demonstrate feasibility, value for money and detail why you need an item for your project, as well as how you arrived at the costings.
Every research project has two budget categories: direct costs and indirect costs.
The University determines a set percentage for the indirect costs of funded research. Contact Grants Services for the correct figure to use.
Direct costs are costs integral to achieving the research objectives of a grant. The costs directly address the research objectives of the grant and relate to the research plan.
Direct cost examples:
- Personnel, e.g. research assistants, student stipends for PhDs, and staff costs. You need to factor in salary increases, on-costs (superannuation and payroll) and casual loadings . Always use the salary level and step corresponding with the skills and tasks required for the role. See the Position Descriptors in the relevant University Enterprise Agreement .
- Equipment, maintenance and travel (outline why you are going and for how long)
- Teaching relief
- Other (e.g. Consumables).
Indirect costs are institution costs that benefit and support research activities at the institution. Although they are necessary for the conduct of research and may be incurred during the project, they are costs that do not directly address the approved research objectives of a grant.
Indirect cost examples:
- Operations and maintenance of buildings (e.g. libraries, labs, meeting venues, IT such as computer access, specialist software, databases, secure cloud storage)
- Insurance, legal and financial services
- Hazardous waste disposal, and
- Regulatory and research compliance and administration of research services
All external research activities are expected to contribute to indirect costs except :
- Nationally competitive grants, such as ARC and NHMRC. This includes all Category 1 schemes.
- Registered charities listed on the ACNC register (opens in a new window)
- Grants transferred from another university
- Funding bodies that exclude or limit overheads or administrative costs (i.e. indirect costs) in their rules or guidelines
- Scholarships and internships
- Official Western Partnership projects
- Travel award type grants or facility usage type grants (e.g. Endeavour Fellowships, AINSE grants)
- Projects costed under $100,000 are discounted by waiving Western’s portion of the indirect costs.
Indirect costs are calculated by determining the direct costs first and then applying the indirect costs formula:
e.g. Direct costs = $50,000 x (indirect cost % figure) = Total project cost
Cash and in-kind support
Your project budget needs to include all cash and in-kind items it requires.
In-kind support is any non-cash contributions that a party gives to the project. In-kind can be contributed by Western Sydney University or by an external party, and can include:
- staff (e.g. time committed to the project which is not funded by the project)
- non-staff/infrastructure (e.g. if you are using lab space to conduct the project but are not receiving direct payment from the project to 'buy out' lab space)
- indirect costs
How to budget personnel and salaries
On-costs are direct costs associated with salary. These costs relate to superannuation, sick leave, payroll tax etc. and must be included your budget.
Access this link for more detail about Western on-costs
For the latest salary figures, please check with the Office of People
An example:
You are a Lead Chief Investigator (CI) on a non-Category 1 funding body project for one year. You commit 0.4 (FTE) of your time to the research = 2 days per week. You are paid at Academic Level E, Step 2, which is $188,944 per annum. You can calculate your salary inclusive of 28% on-costs as follows:
0.4 x 0.28 x 188,944 = 21,161.73
The budgeting of your salary, a direct cost of the research, should be listed as $21,161.73.
If your project covers three years, with the same or differing time commitments, you calculate this figure for each year of your project. Remember to factor in pay rises according to Step increases in multi-year grants.
You may also have a research assistant employed full-time for seven weeks at HEW Level 5, Step 3. You hire the assistant at the casual hourly rate of $48.97, which includes 25% leave loading. You add 16.5% on-costs to this figure:
48.97 x (35 x 7) = 11,997.65
11,997.65 x .165 = 1,979.50
1,979.50 + 11,997.65 = 13,977.15
The total cost to employ the research assistant is $13,977.15.
Note 1: the maximum period a person can be employed on a casual rate is 6 months.
Note 2: For some schemes, the funding provider stipulates a specific maximum rate for funding of salary on-costs, e.g. the Australian Research Council (ARC) funds on-costs at a rate of 30%, so you must use this figure.
- Grant Budget Calculator (Staff Login Required) (opens in a new window)
^ Back to top
Mobile options:
- Return to standard site
- Back to Top

International Students
Launch your career at UWS
- University Life
- Our Campuses
- Business and Community
- Undergraduate
- Postgraduate
- HDR Research
- Student Life
- Why Western
- The Academy
- Western Sydney University Online
- Misconduct Rule
- Study with Integrity
- Student Completions
- Student Support
- Services and Facilities
- Working with us
- Career Development
- Salary and Benefits
- Manager/Supervisor Toolkit
- Future Staff
- Staff Services
- Researchers
- Current Students
- Community and Industry
- Alumni Awards
- Alumni Spotlight
- Alumni Benefits
- Alumni Affinity Groups
- Alumni Publications
- Alumni Giving
Western Sydney University

- Emergency Help
- Right to Information
- Complaints Unit
- Accessibility
- Website Feedback
- Compliance Program
- Admissions Transparency

The scope of work should include the following sections: (1) introduction, (2) statement of objectives, (3) materials and methods, (4) expected results/format of report, and (5) literature citations. Your submitted scope of work should include the following:
1. The Cover Sheet . The cover sheet must include the tentative title, date, author(s), and MP advisor(s). The cover sheet must also include the author(s) and advisor(s) signature(s) to demonstrate faculty approval (Visit #1 on the Final Report page for more information on Cover Sheets or download the template ). 2. Introduction . Describe the problem you will be working on and why it is important. Include a concise literature review to relate your problem to previous work and set the stage for the approach you will take. If applicable, describe the client involved and their interest in the project. [2-4 pages] 3. Objectives . State the research questions your MP will answer or the hypotheses you will test. Be specific and succinct. You should be able to list your questions or hypotheses as a series of no more than 3 or 4 concrete bullet points. While you may fine-tune these questions after you begin your work, the initial description of your methods and expected results should follow directly from these objectives. [<1 page] 4. Methods and Sources of Support . Describe the methods/approach you plan to use including, as appropriate, your research approach, data or means of data collection, and plans for data analysis. Be specific and identify significant subtasks related to each part of your project. State any research support needed in terms of supplies, space, equipment and money. If needed, identify source(s) of financial support (e.g., case study funds, research project of professor, school support, grant, etc.). Note whether you will require Institutional Review Board (IRB) approval for data collection involving human subjects, or whether you will operate under a nondisclosure agreement . [2-3 pages] 5. Expected Results and Format of Report . Identify the expected results of the project and/or the deliverables to be produced (e.g., management plan, geospatial tool, scientific publication, policy recommendations, computer model, etc.). State the format of the final product and its intended audience. If appropriate, identify likely journals for publication of your research. [1-2 pages] 6. Literary Citations . Include full, standard citations for any references referred to in the text of your proposal. The Nicholas School does not require MPs to adhere to one specific citation style as long as citations are formatted consistently throughout the final document. Choose the appropriate manual of style for your project (for guidance, see Duke Libraries citation resources ). 7. Faculty . List all faculty who have agreed to serve as advisors or cooperators in your project, along with their affiliations (e.g., school or department). Indicate the primary adviser(s) responsible for evaluating the project.
Part II: Project Timeline
Part two should contain the timeline with anticipated deliverables, and may be attached as a separate document, if using Excel or other project management formats. Timeline of Tasks, Deliverables, and Events . Outline the various steps of project completion from start to finish. Include all significant milestones and recurring meetings with your teammates (if applicable) and MP advisor. For example, this could include completion of your literature review and other background research, as well as intermediate steps related to your data collection and planned analysis. It is highly recommended that you use a Gantt chart or an equivalent Excel spreadsheet (e.g. with individual tasks and milestones as rows and dates in columns), with ongoing tasks specified at a biweekly resolution. Your timeline should also include standing client meetings, if relevant.
Part III: Team Charter
The team charter should outline roles and responsibilities of the team and advisor. All students, including those completing an individual MPs, must include a team charter in the final Work Plan. If you are participating in an individual project, you and your MP advisor are considered a “team”.
Your team charter should include the following: 1. Team Roles and Responsibilities . Assign each team member a role and associated responsibilities to be fulfilled during completion of the MP. 2. Regular Meeting Schedule. Outline how often, in what way, and with whom your MP team will meet. This includes regular team meetings, as well as standing meetings with your advisor and, if relevant, client. Frequency and content of the meetings is up to the collective discretion of the team. 3. Team Expectations . Describe any additional agreements your MP team comes up with. (e.g., how to handle potential conflicts, preferred means of communication, data sharing and storage, etc.) 4. Team Purpose and Mission . Describe the top priorities and goals of each individual team member during the course of the project. 5. Team Cohesion and Conflict Resolution. Include a brief description that addresses these questions: How will your team resolve conflict? How can you most effectively handle scenarios in which team members are not pulling their weight or not living up to the expectations outlined in this charter? How will you have difficult conversations? What steps will you take to understand and know each other better? How do you want to promote ongoing integration and camaraderie within the team?
Site Login >
How to write a research plan: Step-by-step guide
Last updated
30 January 2024
Reviewed by
Today’s businesses and institutions rely on data and analytics to inform their product and service decisions. These metrics influence how organizations stay competitive and inspire innovation. However, gathering data and insights requires carefully constructed research, and every research project needs a roadmap. This is where a research plan comes into play.
There’s general research planning; then there’s an official, well-executed research plan. Whatever data-driven research project you’re gearing up for, the research plan will be your framework for execution. The plan should also be detailed and thorough, with a diligent set of criteria to formulate your research efforts. Not including these key elements in your plan can be just as harmful as having no plan at all.
Read this step-by-step guide for writing a detailed research plan that can apply to any project, whether it’s scientific, educational, or business-related.
- What is a research plan?
A research plan is a documented overview of a project in its entirety, from end to end. It details the research efforts, participants, and methods needed, along with any anticipated results. It also outlines the project’s goals and mission, creating layers of steps to achieve those goals within a specified timeline.
Without a research plan, you and your team are flying blind, potentially wasting time and resources to pursue research without structured guidance.
The principal investigator, or PI, is responsible for facilitating the research oversight. They will create the research plan and inform team members and stakeholders of every detail relating to the project. The PI will also use the research plan to inform decision-making throughout the project.
- Why do you need a research plan?
Create a research plan before starting any official research to maximize every effort in pursuing and collecting the research data. Crucially, the plan will model the activities needed at each phase of the research project.
Like any roadmap, a research plan serves as a valuable tool providing direction for those involved in the project—both internally and externally. It will keep you and your immediate team organized and task-focused while also providing necessary definitions and timelines so you can execute your project initiatives with full understanding and transparency.
External stakeholders appreciate a working research plan because it’s a great communication tool, documenting progress and changing dynamics as they arise. Any participants of your planned research sessions will be informed about the purpose of your study, while the exercises will be based on the key messaging outlined in the official plan.
Here are some of the benefits of creating a research plan document for every project:
Project organization and structure
Well-informed participants
All stakeholders and teams align in support of the project
Clearly defined project definitions and purposes
Distractions are eliminated, prioritizing task focus
Timely management of individual task schedules and roles
Costly reworks are avoided
- What should a research plan include?
The different aspects of your research plan will depend on the nature of the project. However, most official research plan documents will include the core elements below. Each aims to define the problem statement, devising an official plan for seeking a solution.
Specific project goals and individual objectives
Ideal strategies or methods for reaching those goals
Required resources
Descriptions of the target audience, sample sizes, demographics, and scopes
Key performance indicators (KPIs)
Project background
Research and testing support
Preliminary studies and progress reporting mechanisms
Cost estimates and change order processes
Depending on the research project’s size and scope, your research plan could be brief—perhaps only a few pages of documented plans. Alternatively, it could be a fully comprehensive report. Either way, it’s an essential first step in dictating your project’s facilitation in the most efficient and effective way.
- How to write a research plan for your project
When you start writing your research plan, aim to be detailed about each step, requirement, and idea. The more time you spend curating your research plan, the more precise your research execution efforts will be.
Account for every potential scenario, and be sure to address each and every aspect of the research.
Consider following this flow to develop a great research plan for your project:
Define your project’s purpose
Start by defining your project’s purpose. Identify what your project aims to accomplish and what you are researching. Remember to use clear language.
Thinking about the project’s purpose will help you set realistic goals and inform how you divide tasks and assign responsibilities. These individual tasks will be your stepping stones to reach your overarching goal.
Additionally, you’ll want to identify the specific problem, the usability metrics needed, and the intended solutions.
Know the following three things about your project’s purpose before you outline anything else:
What you’re doing
Why you’re doing it
What you expect from it
Identify individual objectives
With your overarching project objectives in place, you can identify any individual goals or steps needed to reach those objectives. Break them down into phases or steps. You can work backward from the project goal and identify every process required to facilitate it.
Be mindful to identify each unique task so that you can assign responsibilities to various team members. At this point in your research plan development, you’ll also want to assign priority to those smaller, more manageable steps and phases that require more immediate or dedicated attention.
Select research methods
Research methods might include any of the following:
User interviews: this is a qualitative research method where researchers engage with participants in one-on-one or group conversations. The aim is to gather insights into their experiences, preferences, and opinions to uncover patterns, trends, and data.
Field studies: this approach allows for a contextual understanding of behaviors, interactions, and processes in real-world settings. It involves the researcher immersing themselves in the field, conducting observations, interviews, or experiments to gather in-depth insights.
Card sorting: participants categorize information by sorting content cards into groups based on their perceived similarities. You might use this process to gain insights into participants’ mental models and preferences when navigating or organizing information on websites, apps, or other systems.
Focus groups: use organized discussions among select groups of participants to provide relevant views and experiences about a particular topic.
Diary studies: ask participants to record their experiences, thoughts, and activities in a diary over a specified period. This method provides a deeper understanding of user experiences, uncovers patterns, and identifies areas for improvement.
Five-second testing: participants are shown a design, such as a web page or interface, for just five seconds. They then answer questions about their initial impressions and recall, allowing you to evaluate the design’s effectiveness.
Surveys: get feedback from participant groups with structured surveys. You can use online forms, telephone interviews, or paper questionnaires to reveal trends, patterns, and correlations.
Tree testing: tree testing involves researching web assets through the lens of findability and navigability. Participants are given a textual representation of the site’s hierarchy (the “tree”) and asked to locate specific information or complete tasks by selecting paths.
Usability testing: ask participants to interact with a product, website, or application to evaluate its ease of use. This method enables you to uncover areas for improvement in digital key feature functionality by observing participants using the product.
Live website testing: research and collect analytics that outlines the design, usability, and performance efficiencies of a website in real time.
There are no limits to the number of research methods you could use within your project. Just make sure your research methods help you determine the following:
What do you plan to do with the research findings?
What decisions will this research inform? How can your stakeholders leverage the research data and results?
Recruit participants and allocate tasks
Next, identify the participants needed to complete the research and the resources required to complete the tasks. Different people will be proficient at different tasks, and having a task allocation plan will allow everything to run smoothly.
Prepare a thorough project summary
Every well-designed research plan will feature a project summary. This official summary will guide your research alongside its communications or messaging. You’ll use the summary while recruiting participants and during stakeholder meetings. It can also be useful when conducting field studies.
Ensure this summary includes all the elements of your research project. Separate the steps into an easily explainable piece of text that includes the following:
An introduction: the message you’ll deliver to participants about the interview, pre-planned questioning, and testing tasks.
Interview questions: prepare questions you intend to ask participants as part of your research study, guiding the sessions from start to finish.
An exit message: draft messaging your teams will use to conclude testing or survey sessions. These should include the next steps and express gratitude for the participant’s time.
Create a realistic timeline
While your project might already have a deadline or a results timeline in place, you’ll need to consider the time needed to execute it effectively.
Realistically outline the time needed to properly execute each supporting phase of research and implementation. And, as you evaluate the necessary schedules, be sure to include additional time for achieving each milestone in case any changes or unexpected delays arise.
For this part of your research plan, you might find it helpful to create visuals to ensure your research team and stakeholders fully understand the information.
Determine how to present your results
A research plan must also describe how you intend to present your results. Depending on the nature of your project and its goals, you might dedicate one team member (the PI) or assume responsibility for communicating the findings yourself.
In this part of the research plan, you’ll articulate how you’ll share the results. Detail any materials you’ll use, such as:
Presentations and slides
A project report booklet
A project findings pamphlet
Documents with key takeaways and statistics
Graphic visuals to support your findings
- Format your research plan
As you create your research plan, you can enjoy a little creative freedom. A plan can assume many forms, so format it how you see fit. Determine the best layout based on your specific project, intended communications, and the preferences of your teams and stakeholders.
Find format inspiration among the following layouts:
Written outlines
Narrative storytelling
Visual mapping
Graphic timelines
Remember, the research plan format you choose will be subject to change and adaptation as your research and findings unfold. However, your final format should ideally outline questions, problems, opportunities, and expectations.
- Research plan example
Imagine you’ve been tasked with finding out how to get more customers to order takeout from an online food delivery platform. The goal is to improve satisfaction and retain existing customers. You set out to discover why more people aren’t ordering and what it is they do want to order or experience.
You identify the need for a research project that helps you understand what drives customer loyalty. But before you jump in and start calling past customers, you need to develop a research plan—the roadmap that provides focus, clarity, and realistic details to the project.
Here’s an example outline of a research plan you might put together:
Project title
Project members involved in the research plan
Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan’s intent)
Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective)
Objective 2
Objective 3
Proposed timeline
Audience (detail the group you want to research, such as customers or non-customers)
Budget (how much you think it might cost to do the research)
Risk factors/contingencies (any potential risk factors that may impact the project’s success)
Remember, your research plan doesn’t have to reinvent the wheel—it just needs to fit your project’s unique needs and aims.
Customizing a research plan template
Some companies offer research plan templates to help get you started. However, it may make more sense to develop your own customized plan template. Be sure to include the core elements of a great research plan with your template layout, including the following:
Introductions to participants and stakeholders
Background problems and needs statement
Significance, ethics, and purpose
Research methods, questions, and designs
Preliminary beliefs and expectations
Implications and intended outcomes
Realistic timelines for each phase
Conclusion and presentations
How many pages should a research plan be?
Generally, a research plan can vary in length between 500 to 1,500 words. This is roughly three pages of content. More substantial projects will be 2,000 to 3,500 words, taking up four to seven pages of planning documents.
What is the difference between a research plan and a research proposal?
A research plan is a roadmap to success for research teams. A research proposal, on the other hand, is a dissertation aimed at convincing or earning the support of others. Both are relevant in creating a guide to follow to complete a project goal.
What are the seven steps to developing a research plan?
While each research project is different, it’s best to follow these seven general steps to create your research plan:
Defining the problem
Identifying goals
Choosing research methods
Recruiting participants
Preparing the brief or summary
Establishing task timelines
Defining how you will present the findings
Should you be using a customer insights hub?
Do you want to discover previous research faster?
Do you share your research findings with others?
Do you analyze research data?
Start for free today, add your research, and get to key insights faster
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 11 January 2024
Last updated: 15 January 2024
Last updated: 17 January 2024
Last updated: 12 May 2023
Last updated: 30 April 2024
Last updated: 18 May 2023
Last updated: 25 November 2023
Last updated: 13 May 2024
Latest articles
Related topics, .css-je19u9{-webkit-align-items:flex-end;-webkit-box-align:flex-end;-ms-flex-align:flex-end;align-items:flex-end;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-flex-direction:row;-ms-flex-direction:row;flex-direction:row;-webkit-box-flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-flex-wrap:wrap;-ms-flex-wrap:wrap;flex-wrap:wrap;-webkit-box-pack:center;-ms-flex-pack:center;-webkit-justify-content:center;justify-content:center;row-gap:0;text-align:center;max-width:671px;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}}@media (max-width: 799px){.css-je19u9{max-width:400px;}.css-je19u9>span{white-space:pre;}} decide what to .css-1kiodld{max-height:56px;display:-webkit-box;display:-webkit-flex;display:-ms-flexbox;display:flex;-webkit-align-items:center;-webkit-box-align:center;-ms-flex-align:center;align-items:center;}@media (max-width: 1079px){.css-1kiodld{display:none;}} build next, decide what to build next.

Users report unexpectedly high data usage, especially during streaming sessions.

Users find it hard to navigate from the home page to relevant playlists in the app.

It would be great to have a sleep timer feature, especially for bedtime listening.

I need better filters to find the songs or artists I’m looking for.
Log in or sign up
Get started for free
- Develop a research budget
- Research Expertise Engine
- Precursors to research
- Funding & award opportunities
- Grants vs contracts
- Sample Applications Library
- Factors to consider
- Internal Approval (formerly SFU Signature Sheet)
- Develop a research proposal
- Institutional support
- Review & submission
- Award & approval
- Award management
- Contracts & agreements
- Inventions & commercialization
- Ethics - human research
- Ethics - animal research
- Research safety
- Mobilizing Research
- Prizes & awards
- Training & events
- Forms & documents
On this page:
Basic components of a research budget, two models of budget development, other factors affecting your budget.
- Additional Resources
Budgets should provide the sponsor with an accurate assessment of all cost items and cost amounts that are deemed necessary and reasonable to carry out your project. They should be based upon your description or the statement of work. Budget justification provides more in-depth detail and reason for each cost and is often considered by reviewers as a good indicator of the feasibility of the research.
A research budget contains both direct costs and indirect costs (overhead), but the level of detail varies from sponsor to sponsor. The first step in developing a budget is to carefully read the guidelines of the funding opportunity being pursued.
There is no magic formula available for developing a budget but there are some basic steps to follow in order to develop an accurate budget:
- Define project tasks, timelines and milestones and determine the actual resources and costs required to complete these. Consider whether contingencies are needed (and confirm they are eligible expenses).
- Determine the eligible expense categories and maximum amount allowed by the sponsor. Adjust scope of the project to make sure proposed activities fit within the allowance.
- Categorize these costs (e.g., salaries, supplies, equipment…) per year, in some cases by quarter.
- Ensure that project scope and budget match. Include indirect costs of research as permitted by sponsor and the University policy.
The examples below developed by the University of British Columbia demonstrate two ways to include indirect costs in your budget.
- Price model: Indirect cost is built into each budget line item.
- Cost model: Indirect cost of research is presented as a separate line item.
Unless the sponsor specifies in writing that they require the indirect costs of research to be presented as a separate line item (Cost Model), the indirect cost should be built into each budget line item (Price Model). Indirect costs are normally included in the price of goods and services worldwide.
For example, you are developing a budget for a funding opportunity with an indirect cost rate of 25%. Your direct costs are $201,000 broken down by expense categories shown in the second column of the table below. The third and fourth colums present the two ways you can include the 25% overhead in your budget using the Price Model or the Cost Model, respectively:
In-kind and cash contributions, like other costs to the sponsored project, must be eligible and must be treated in a consistent and uniform manner in proposal preparation and in financial reporting.
Cash contributions
Cash contributions are actual cash transactions that can be documented in the accounting system. Examples of cash contributions include:
- allocation of compensated faculty and staff time to projects, or
- the purchasing of equipment by the university or other eligible sponsor for the benefit of the project.
In-kind contributions
In-kind contributions are both non-monetary or cash equivalent resources that can be given a cash value, such as goods and/or services in support of a research project or proposal. It is challenging to report on in-kind contribution, please make sure the numbers you use are well supported, consistent and easy to quantitate.
Examples of an in-kind contribution may include:
- Access to unique database or information
- Professional, analytical, and other donated services
- Employee salaries including benefits for time allocated to the project
- Study materials, technologies, or components
- Patents and licenses for use
- Use of facilities (e.g., lab or meeting spaces)
- Partner organization time spent participating in the project
- Eligible infrastructure items
Matching on sponsored projects
Some sponsored projects require the university and/or a third party to contribute a portion of the project costs–this contribution is known as matching.
Matching requirements may be in the form of an actual cash expenditure of funds or may be an “in-kind” match. For example:
- A 1:1 match would require $100 of a third-party matching for every $100 received from an agency.
- A 30% match would mean that of a total budget of $100, the agency would provide $70 and a third party would need to match $30.
Examples of agency programs that include some form of matching from a third party are:
- NSERC Collaborative Research and Development Grants
- NSERC Idea to Innovation Grants
- SSHRC Partnership Grants
- CIHR Industry Partnered Collaborative Research Program, and
- CIHR Proof of Principle Grants
Additional resources
- Current salary and benefit rates for graduate students and postdocs/research associates
- SFU Business and Travel Expense Policy
- Animal care services
As the nation’s largest public research university, the Office of the Vice President for Research (OVPR) aims to catalyze, support and safeguard U-M research and scholarship activity.
The Office of the Vice President for Research oversees a variety of interdisciplinary units that collaborate with faculty, staff, students and external partners to catalyze, support and safeguard research and scholarship activity.
ORSP manages pre-award and some post-award research activity for U-M. We review contracts for sponsored projects applying regulatory, statutory and organizational knowledge to balance the university's mission, the sponsor's objectives, and the investigator's intellectual pursuits.
Ethics and compliance in research covers a broad range of activity from general guidelines about conducting research responsibly to specific regulations governing a type of research (e.g., human subjects research, export controls, conflict of interest).
eResearch is U-M's site for electronic research administration. Access: Regulatory Management (for IRB or IBC rDNA applications); Proposal Management (eRPM) for the e-routing, approval, and submission of proposals (PAFs) and Unfunded Agreements (UFAs) to external entities); and Animal Management (for IACUC protocols and ULAM).
Sponsored Programs manages the post-award financial activities of U-M's research enterprise and other sponsored activities to ensure compliance with applicable federal, state, and local laws as well as sponsor regulations. The Office of Contract Administration (OCA) is also part of the Office of Finance - Sponsored Programs.
- Develop Proposal Overview
- Blue Pages: Find an RA
- Cost Accounting Standards
- Budget Table Sample
- Direct vs. F&A Costs
- Direct Costs Other Than Salaries
- Facilities & Administrative Rates
- Full Recovery of F&A Costs - Calculating Space
- NRSA Stipend Levels and GSRA Max
- NIH Modular Budgets
- Participant Support Costs
- Salaries in Sponsored Projects
Staff Benefits
- Uniform Guidance Monitored Costs
- Clinical Trials
- Create Biosketch
- OVPR Cost Sharing
- About the University of Michigan
- NIH - Other Support Reporting
- NSF and Other Sponsors - Current and Pending Support
- Principal Investigator Definition
- Cost / Price Analysis
- Working with Subrecipients / Subrecipient Forms / Letter of Commitment
You are here
- Develop Proposal
Budget and Cost Resources
Quick links.
- Budget & Cost Resources
- UG Monitored Costs
- Direct and Indirect Costs
- Indirect Cost Rates
- Full Recovery of Indirect Costs - Calculating space for certain private sponsor
- Direct Costs (other than salaries)
- Staff Fringe Benefits
- GSRA Cost Estimates
The Principal Investigator has primary responsibility for budget planning, in consultation with the department chair or director of the research unit. Budgets for all sponsored proposals are subject to review by ORSP.
A Special Note About NIH Grant-Related Data Sharing Costs
Certain funding agencies (e.g. the National Institutes of Health (NIH)) are increasingly allowing data management and sharing (DMS) costs to be included as direct costs in proposal budgets.
NIH DMS costs should be shared in the appropriate cost category, e.g., personnel, equipment, supplies, and other expenses, following the instructions and providing details as instructed within the applicable form (e.g., R&R Budget Form or PHS 398 Modular Budget Form).
In most cases, the DMS Plan oversight at U-M will be provided by the principal investigator (PI) and other study personnel. If help is needed, consider these resources:
- OVPR Research Data Stewardship page - NIH DMSP resources
- U-M Library - Research Guides - Research Data Management
- U-M Navigate Webinar - NIH Data Management & Sharing Policy (Nov 1, 2022)
Budget Format
Sponsors often prescribe the budget format that must accompany the proposal, including the specific cost categories that should be identified. The format shown on the sample budget page may be used, however, if one is not specified by the sponsor. Be sure to check with your department, unit, school or college administrator to determine the best practice.
The budget should be subdivided into periods of 12-month duration (unless partial year funding is anticipated). A "starting date" should be specified, since it is essential to ensure accurate budget calculations. If cost-sharing is included, each budget period should include columns for both "Sponsor" and "University" costs. A budget summary should be included for proposals with multi-year funding. All budget entries should be rounded to the nearest whole dollar.
Salary and Wages
The salary category in the proposed budget should include the names and/or titles for all personnel involved in the project. The number of person months or percent effort to be applied to the project should also be shown. Total salary costs can be determined by applying the percentage of effort to the current salary rates. An appropriate escalation rate (e.g., 3%) should be used to determine salary requirements beyond the current fiscal year. While standard percentages are applied to make these calculations, no commitment and no constraint on the rate of increase for a given individual is implied by this procedure.
If a faculty member is working on several sponsored projects, care must be exercised to ensure that no more than 100 percent of effort is committed to the aggregate of all projects and other University responsibilities.
Summer salary:
Summer salary for faculty with academic year (AY) appointments can be figured at one-ninth of their institutional base salary for each month of summer effort. A maximum of two and one-half months may be included for the whole summer. Some sponsors, however, impose specific limitations on summer salaries. The National Science Foundation, for example, usually will not pay for more than two months of summer research at a rate of one-ninth of the AY salary per month.
Technical staff
Costs incurred for the same purpose in like circumstances must be treated consistently. For example, salaries of technical staff should be treated as direct costs wherever the work to be undertaken can be identified with a particular sponsored project. Direct charging of these costs may be accomplished by specifying individual positions within the project budget or through the use of recharge rates or specialized service facilities, as appropriate under the circumstances.
Administrative and clerical support
The salaries of administrative and clerical support staff normally should be treated as indirect costs . However, it may be appropriate to charge these costs directly to a sponsored project when the participation of the administrative/clerical staff being charged to a federal project meet all four of the following conditions as set forth in §200.413 of the Uniform Guidance:
“(1) Administrative or clerical services are integral to a project or activity;
(2) Individuals involved can be specifically identified with the project or activity;
(3) Such costs are explicitly included in the budget or have the prior written approval of the Federal awarding agency; and
(4) The costs are not also recovered as indirect costs.”
The meaning of (4) is the same as that of 200.403(d) above. That is to say, the project must require support services beyond the normal scope necessary for the typical sponsored project (i.e., it is an unlike circumstance).
Personnel may be hired to work on a sponsored project on an hourly basis for periods up to 12 months. Individuals hired on this basis receive no staff benefits other than Social Security and should be advised accordingly. The Personnel Service Center should be consulted to obtain the appropriate hourly rates for various categories of employment.
Staff benefits are charged to sponsored project accounts on a real cost basis. Depending on the mix of personnel assigned to the project, the staff benefit rate may show significant variation. While it may be possible to apply an average benefit rate (30%), it may be more appropriate in some situations to calculate the staff benefits on an employee-by-employee basis. The range of applicable benefit rates are provided in Staff Benefits Table .
GSRA Compensation, Tuition, and Benefits
GSRA Cost Estimates are for budget estimating purposes only and may vary from school to school. A GSRA appointment may be held from May through August, even though the GSRA is not enrolled in the University during that time. If the appointment is for the winter and fall terms, the fringe benefit charges should be budgeted for the full year, since the student is eligible for coverage during the intervening summer even though he or she is not on a GSRA appointment at that time.
The non-resident tuition differential is provided by the University for out-of-state students appointed as GSRAs. In-state tuition should be charged to sponsored accounts for GSRAs with appointments of 25% or greater. However, Schools and Colleges may provide tuition fellowships to cover a portion of the in-state tuition for GSRAs (see GSRA Cost Estimates ). The portion of the in-state tuition that remains after the fellowship is applied must be included on the grant as a charge to the sponsor.
In-state tuition charges should not be included as part of the GSRA stipend. The modified total direct cost (MTDC) base on which the University's indirect cost rate is calculated must exclude tuition charges. Therefore, indirect costs are not recoverable on tuition charges included in proposals for which the indirect cost rate is based on MTDC. Please contact the appropriate ORSP Project Representative should you have any questions.
Consumable Supplies and Materials
Consumable supplies are items used exclusively in support of project objectives. If it can be demonstrated that such supplies are used only in the conduct of the project and not for other purposes and are consumed completely in the course of the project, such items can be included as direct costs. Laboratory supplies, laboratory notebooks, printer paper for research data and reports, and so forth usually can be justified as consumable supplies. However, when supply items are purchased to support the multiple activities of project personnel, they are considered office supplies and cannot be charged directly to federal funds. Such items would include University stationary, pens, tablets, file folders, staples, paper clips, etc.
The estimated costs of consumable supplies and materials should be indicated in the proposed budget. It is generally acceptable to sponsors to provide a breakdown of supplies and materials by broad categories as opposed to the detailed listing of individual items. Contracts awarded by industries holding a prime contract with a federal agency, however, may require detailed itemization of supplies.
Major items of equipment proposed for acquisition should be itemized by descriptive name and estimated cost, and an adequate justification should be provided in the proposal narrative. Items costing less than $5000 or with a useful life expectancy of less than one year normally should be included under "Supplies and Materials." Shipping and/or installation charges associated with equipment acquisitions should be included in the cost estimates but generally are not itemized.
Specialized Services
Charges for computing services should be budgeted whenever these costs are justified. It is essential, however, that the budget clearly differentiate between central computing services provided by Information Technology Services and other computing services.
Other specialized service centers that have an approved user rate should be included in the proposed budget on a cost basis that reflects the recharge rates with the anticipated number of hours or other units of service clearly indicated. Once established, the schedule of rates must be applied to all users of the services/facilities, including internal-university users. Recharge rates are designed to recover, over the long term, not more than the aggregate cost of the services provided. The recharge/user rate should be included as part of the modified total direct cost (MTDC) for the project and should carry the appropriate indirect cost rate .
Consultants and Subcontracts
Federal agencies frequently establish a maximum daily rate of pay for consultants--specific dollar limits for various agencies are available from ORSP. The University must enter into a formal agreement with the consultant prior to the initiation of his or her effort. Consultant agreements as subject to the full recovery of indirect costs at the rate applicable to other direct cost items in the proposed budget.
The entire cost of a subcontract is normally shown as a single line item under "Other Direct Costs." A formal proposal from the subcontractor--including a statement of work, a detailed budget, period of performance, and key personnel--should be included to support this cost element. The Project Director should provide an explanation of why and how the proposed sub-contractor was selected, including the number of bids obtained.
Subcontracted effort requires a formal agreement between the University and the subcontractor, signed by a University official authorized to enter into contractual agreements on behalf of the Board of Regents. See: the Subcontracts and Hybrid Purchase Orders web page for criteria and procedures. Indirect costs are recovered on the first $25,000 of each subcontract.
Indirect Costs
Indirect costs are real costs of University operations that are not readily assignable to a particular project. The sample budget illustrates the procedures for applying the indirect cost rate .
Human Subject Fees
Human subjects often are paid a fee for their participation in research projects. Protocols for the use of human beings in research, teaching, or testing are reviewed and approved, according to federal, state and university policies. (See: Human Research Protection Program )

Other Costs
Funds may be requested from the sponsor to cover travel costs associated with the proposed project. Sponsors often require a breakdown of such travel costs by trip, reflecting the purpose, point of travel, number of persons, number of days, air fare, lodging and meal costs (per diem), and so forth. If foreign travel is contemplated, the proposal should include relevant information (including names of countries to be visited) and justification. Some sponsors have special regulations (e.g., use of domestic air carriers) governing foreign travel.
Costs of preparing and publishing reports of project results should be included in proposed budgets. Since page charges often are billed well after the completion of the research, it may be necessary to secure time extensions to pay these charges prior to the time that the project is closed out.
Other anticipated direct costs should be itemized--for example, equipment rental, maintenance agreements, or off-campus space rental. Telephone services and postage should not be included unless these costs are expected to be major elements in the project (e.g., telephone surveys). "Miscellaneous" or "contingency" categories should not be included. Items normally considered indirect costs should not be included in the proposed budget unless they are extraordinary and for unlike circumstances (e.g., utility costs required to operate a high-energy particle accelerator).
Network costs, including the hardware, software, personnel services, public access sites, and other related costs required to enable University personnel to share software or data or to communicate electronically with other individuals, are generally considered to be part of the physical infrastructure of the University and should not be included as direct costs in the proposal budget, as these costs are indirect in nature and included as a component of the Facilities & Administrative rate. However, individual workstations and specialized hardware and software attached to the network, which are not available to all users, are not included as part of the network costs and therefore may be treated as direct costs and recovered from sponsored projects through the use of approved recharge rates.
Questions regarding the appropriate treatment of network costs as either direct costs or Facilities & Administrative costs in proposal budgets should be forwarded to the Office of Research and Sponsored Projects.
References and Resources
- Direct Cost Other than Salaries
- Graduate Student Salaries (GSRAs)
- Staff Fringe Benefits
- Rackham Cost Sharing for Federal Training Grants
- Sample Budget Table
- Contact your unit-level research administrator for the best practices for your department, school, college, or unit.
- Contact your ORSP Project Representative regarding any questions about University policies and procedures.
- Contact the Office of Contract Administration for further information on subcontracts and consulting agreements.
- For information on how to pay human subjects, please see the Treasurer's Office requester/study-coordinator resources and the HSIP (Human Subject Incentive Program .
- Budget Reallocation Process (formerly 7471)
- Direct Costs
- Facilities and Administrative Costs (F&A)
- HSIP (Human Subjects Incentives Program)

Thesis, major paper, and major project proposals
- Definitions
- Introductory section
- Literature review
- Methodology
Schedule/work plan
- Other potential elements
- Proposal references
- Ask for help

If you're unsure if your research proposal requires a schedule or work plan, please consult your project handbook and/or speak with your instructor, advisor, or supervisor.
The information about schedules or work plans in proposals was gathered from RRU thesis and major project handbooks, current in 2020, from programs in the Faculty of Social and Applied Sciences, the Faculty of Management, and the College of Interdisciplinary Studies. If the details here differ from the information provided in the handbook for your project, please follow the handbook's directions.
Image credit: Image by Gerd Altmann from Pixabay

- In RRU's Anxiety About Academic Writing guide, this resource is open to everyone.
How Do I Plan the Various Stages of My Research Project?
- In SAGE Research Methods: Planning and Practicalities, look for How Do I Plan the Various Stages of My Research Project? drop down option. Access via this link requires a RRU username and password.
Learning Skills: Time Management
- In RRU's Learning Skills guide, this resource is open to everyone.
What Do I Need to Know About Time and Timetabling?
- In SAGE Research Methods: Planning and Practicalities, look for the What Do I Need to Know About Time and Timetabling? drop down option. Access via this link requires a RRU username and password.
Image credit: Image by Mohamed Assan from Pixabay
- << Previous: Methodology
- Next: Other potential elements >>
- Last Updated: Jan 8, 2024 12:29 PM
- URL: https://libguides.royalroads.ca/proposals

- Schools & departments

Preparing your research project budget
What to consider in preparing your research project budget, and how we can help you
How we can help
Getting your budget as complete and realistic as possible will help your project go smoothly. Discuss it with us in good time to give you the best chance of having your project funded.
Full economic costing
An outline of Full Economic Costing.
Project costings and budget categories
Information about budget categories, what is covered in that category, and things to think about when preparing your research project costings.
A summary of the rules which apply when applying for equipment in UKRI grants
This article was published on 2024-01-24

Research Project Plan Template

What is a Research Project Plan?
A research project plan outlines the processes and activities that need to be completed to achieve the desired results of a research project. The plan should provide a timeline for the research activities and identify any potential risks. It should also specify the resources and personnel needed, as well as the budget and timeline for the project. The plan should be both comprehensive and flexible, so that it can be modified as needed throughout the project.
What's included in this Research Project Plan template?
- 3 focus areas
- 6 objectives
Each focus area has its own objectives, projects, and KPIs to ensure that the strategy is comprehensive and effective.
Who is the Research Project Plan template for?
The research project plan template is designed for research teams in academic, corporate, or non-profit sectors who need to plan and execute their research projects. The template provides a structure for outlining the processes and activities that must be completed in order to achieve the desired results of the research project. The template is designed to be comprehensive and flexible, allowing for modifications as needed throughout the project.
1. Define clear examples of your focus areas
A focus area is a specific area or topic that a research team is investigating. The focus area should be clearly defined and specific, so that the research team can develop objectives, projects, and KPIs that are relevant to the research project. Examples of focus areas could include developing new technologies, understanding customer behavior, or studying the effects of a particular policy.
2. Think about the objectives that could fall under that focus area
Objectives are the goals that a research team hopes to achieve by completing the research project. Objectives should be specific and measurable, and should be attainable within the timeline and budget of the research project. Examples of objectives could include developing a new technology, understanding customer behaviors, or studying the effects of a particular policy.
3. Set measurable targets (KPIs) to tackle the objective
Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) are measurable targets that are used to evaluate the progress of a research project. KPIs should be specific and measurable, and should be established in order to track progress towards the objectives of the research project. Examples of KPIs could include product development timelines, customer satisfaction surveys, or policy implementation reviews.
4. Implement related projects to achieve the KPIs
Projects are the activities that need to be completed in order to achieve the objectives of the research project. Projects should be specific and achievable, and should be completed within the timeline and budget of the research project. Examples of projects could include running customer surveys, conducting interviews, or collecting data.
5. Utilize Cascade Strategy Execution Platform to see faster results from your strategy
The Cascade Strategy Execution Platform is a comprehensive software that helps research teams plan, manage, and track their research projects. The platform provides tools for project management, tracking KPIs, and monitoring progress. It also helps teams visualize their data and collaborate on initiatives. With Cascade, teams can save time and resources, and get faster results from their strategies.
- Contact sales
Start free trial
What Is a Work Plan? How to Make a Work Plan In 7 Steps

Before you can accomplish your project goals, you need to plan how to reach them. A work plan creates a clear path project teams can follow to reach their desired goals and objectives. Along that path will be resources, constraints and other work management elements that need to be described in your work plan.
What Is a Work Plan?
As its name suggests, a work plan is an action plan that helps project teams achieve their goals. Work plans factor in key project planning elements such as tasks, milestones, deliverables, resources, budgetary requirements and a timeline to weave it all together.
The work plan won’t be written and initiated by a single person and it should be submitted to board members and stakeholders for approval. Once approved, you can continue building out the rest of your work plan.
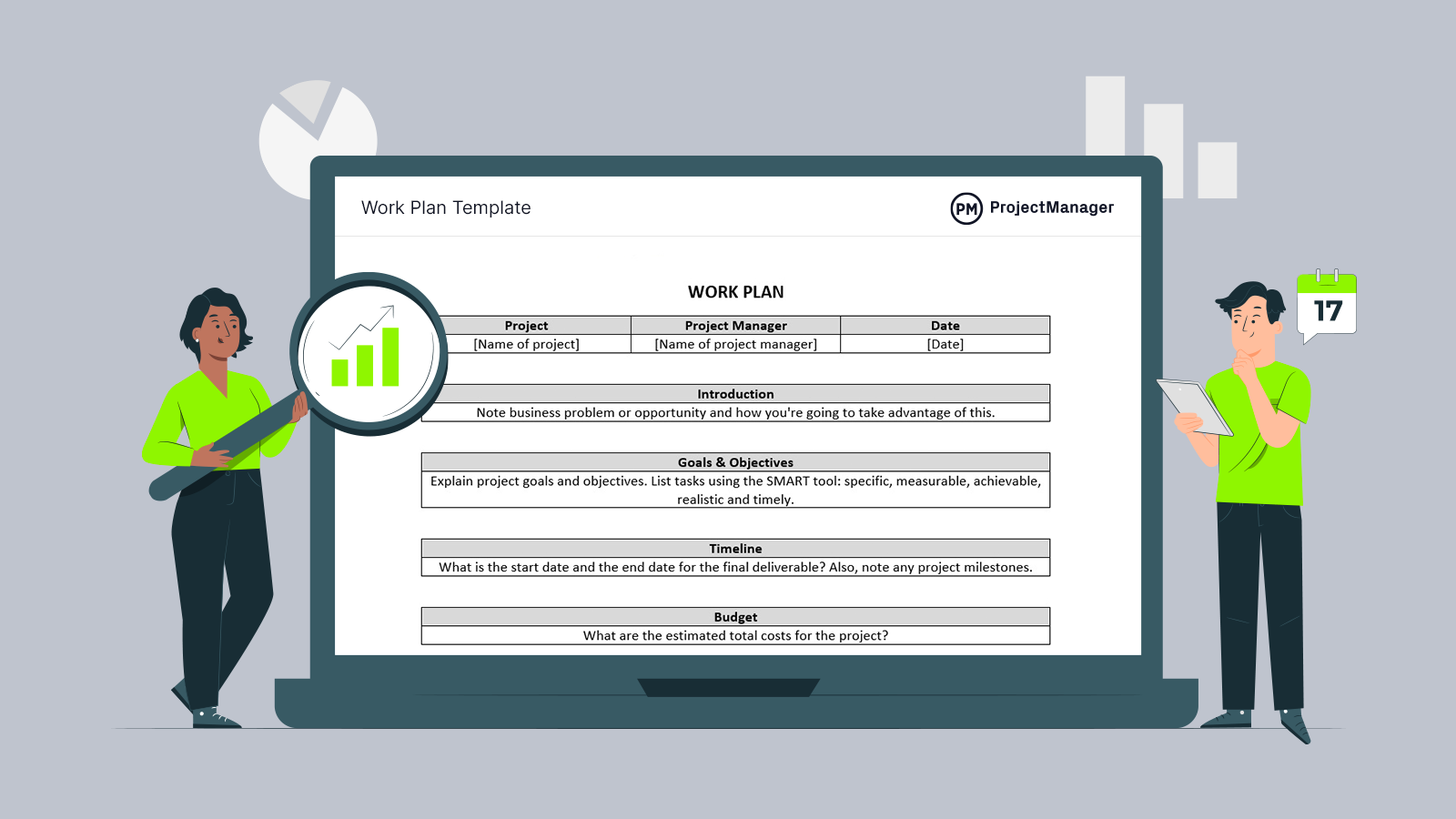
Get your free
Work Plan Template
Use this free Work Plan Template for Word to manage your projects better.
Why Do You Need a Work Plan?
As we mentioned, your work plan acts as your roadmap for the entire project execution. Not only will it keep you and your team organized, but it’ll ensure that you get buy-in from key stakeholders, related departments, relevant accountability/risk leaders and more.
Additionally, it helps manage expectations on both the stakeholder level as well as on the managerial and team member level—everyone that starts off on the right foot has a better chance of landing on the right foot, too.
Work plans guide project teams in a similar way project plans do. However, there’s a big difference between these two important project management documents .
Work Plan vs. Project Plan
Work plans are not as comprehensive as project plans , which have a wider scope and involve more components. The main difference between them is that project plans are created from a high-level view and address every aspect of project management. On the other hand, work plans focus on helping project teams achieve smaller objectives.
If you build your work plan in project management software like ProjectManager , then it’s easy to continue to iterate on your plan and make improvements over time. You can use robust project planning tools such as Gantt charts, kanban boards, project dashboards and much more. Get started today for free.
How to Make a Work Plan in 7 Steps
While work plans might take many forms, here are some simple work planning steps you can follow to make one.
1. Set Goals & Objectives
Before anything, it’s important to write down the goals and objectives that’ll be achieved through your work plan. These will describe the purpose of your plan. It’s important to use SMART goals : create goals that are specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-related. This should help you start your plan off on the right foot.
Your goals might sound like your purpose, but they’re more specific in that they’re more long-term oriented — i.e., your team learned more about the process of launching a bug fix or how to respond more directly to customer or market feedback.
Similarly, your project objectives should be measurable. For example, the objective of this project after launch is to create an increase of xx% of active monthly subscribers, or a certain dollar amount in revenue generated.
2. Define the Scope of Your Work Plan
Once you’ve identified your work plan goals, you should use a work breakdown structure (WBS) to identify all the tasks that must be executed to achieve them, which is your project scope. By breaking down your project scope, you can start assembling a team, estimating costs, creating a budget and drafting a project schedule.
3. Estimate What Resources Are Needed
When you break down your project scope using a WBS, you can better estimate what resources are needed for each task in your work plan. Make sure to include different types of project resources, such as human resources, raw materials, machinery, subcontractors or anything else that you might need for the execution of your work plan.
4. Assign Roles & Responsibilities
Now, assemble a project team and clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each member. Communicate with them and make sure they understand what their job is and how they can collaborate with each other.
5. Estimate Costs & Create a Budget
Once you have a clear idea of what resources are needed for your work plan, it’s time to estimate their costs and create a budget . To do so, simply establish a measurement unit for your labor, materials and other resources to then assign a price to them.
6. Create a Project Schedule
There are different tools and techniques you can use to create a project schedule for your work plan. In fact, most project managers use Gantt charts, project calendars, kanban boards
7. List Any Risks, Constraints and Assumptions
Remember that your work plan is the action plan that’ll guide your project, so the more details you have about constraints and potential risks, the better your team will perform their tasks to produce deliverables and achieve the goals and objectives.
Maybe some of your team members take a few sick days during this period of time; maybe unexpected tasks have to be executed; maybe some of your tools crash that requires more money pulled from the budget. Whatever your project constraints may be, factor in anything that might feel like a risk that can lead to a full-blown constraint, which may affect the completion of deliverables or even the goals and objectives of your project.
Free Work Plan Template
Our work plan template can help you document the steps explained above. Be sure to constantly monitor your template and update it as changes occur in your planning process. Or, if you’re looking for more dynamic project planning tools, you can use Gantt charts.
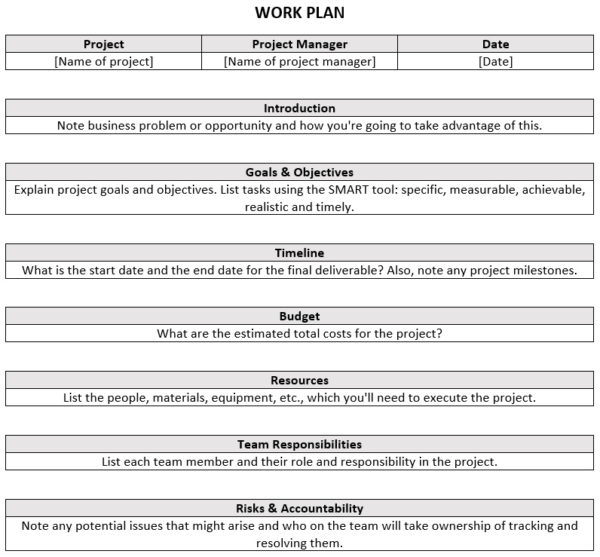
A work plan template can help you organize your thoughts, but in order to create your action plan and execute it, you’ll need dynamic project management software to help you throughout the planning, execution and monitoring phases.
Work Plan Example
Here’s a basic example to better illustrate how a work plan works. Let’s imagine you’re a business owner who wants to increase your production output by 25 percent by acquiring new machinery and hiring more production employees. While this project doesn’t involve producing tangible deliverables , you’ll still need a work plan.
Goals & Objectives It’s important to define one primary goal and then some smaller, more specific objectives needed for the completion of that goal.
Main Work Plan Goal Increase production output by 25 percent.
Work Plan Objectives
- Improve the company’s production capacity by acquiring new machinery
- Fill skill gaps in the production planning team
- Make sure machinery is well-maintained
Scope of the Work Plan Now, you should list individual activities that must be completed in order to achieve your goal and objectives. Here’s a simple breakdown of activities.
- Inspect the production line
- Perform preventive maintenance
- Optimize plant layout
- Acquire new machinery
- Assess the current team
- Hire new personnel
Resources/Roles & Responsibilities In this case, you’ll need a production manager, HR manager and maintenance team. They’re responsible for executing the tasks listed above.
Work Plan Budget Your budget should cover both the labor costs as well as the cost of the new equipment. Your labor costs will be the salaries of the production manager, HR manager and maintenance team. Make sure you estimate your project costs accurately before creating a budget.
Work Plan Schedule Define a timeframe for the analysis of your production line, the procurement of new machinery, preventive maintenance and hiring.
Risk, Assumptions & Constraints Think about any risks, assumptions or constraints that might affect your work plan. The best place to start is the triple constraint of time, budget and resources.
Creating a Work Plan With Project Management Software
To learn more about how project management tools such as Gantt charts , kanban boards and project dashboards can help you make the perfect work plan, watch the short video below. We’ll quickly show you all the ways that project planning software can improve your planning, execution and reporting—so you can make that work plan with confidence.
ProjectManager Can Help You With Your Work Plan
Getting every detail of a work plan sorted is no easy task—from managing your team to managing your stakeholders. It requires a delicate balance of understanding your project timeline, the tasks that make up the project scope, potential risks , balancing a budget and allocating resources. Not to mention, you’ll have to do this while keeping the customers’ ultimate needs and the project goals and objectives in mind.
With ProjectManager , our online Gantt charts let you schedule your entire project timeline, assign tasks, create dependencies and oversee tracking. Additionally, we have team collaboration features that allow your staff and managers to comment on tasks, attach necessary files, and interact with each other no matter where they’re located.
ProjectManager also features resource management tools that let you balance the hours worked across your team. This helps ensure that your time, tools and resources are balanced no matter what.
Related Work Management Content
- What Is Work Management? Creating a Work Management System
- Best Work Management Software of 2024 for Remote Teams
- What is a Statement of Work? Definition & Examples
- Work Breakdown Structure (WBS)
Creating a work plan and don’t know where to start? We’ve got you covered. With ProjectManager , you’ll get access to online software that helps you to better track your work plan from milestone to milestone. Start your free 30-day trial with ProjectManager today.

Deliver your projects on time and on budget
Start planning your projects.

Researched by Consultants from Top-Tier Management Companies

Powerpoint Templates
Icon Bundle
Kpi Dashboard
Professional
Business Plans
Swot Analysis
Gantt Chart
Business Proposal
Marketing Plan
Project Management
Business Case
Business Model
Cyber Security
Business PPT
Digital Marketing
Digital Transformation
Human Resources
Product Management
Artificial Intelligence
Company Profile
Acknowledgement PPT
PPT Presentation
Reports Brochures
One Page Pitch
Interview PPT
All Categories
Top 7 Research Budget Templates with Samples and Examples

Tejas Prasanna
There is no magic formula for creating a research budget. Depending on the kind of research and the potential changes it can bring about, careful planning and allocation is necessary. Budgets can, thus, vary depending on the sponsors, besides other factors. However, every research budget has some essential guidelines.
Research budgets depend on the project deliverables, timelines, and milestones. The resources required also depend on the scope of the projects and sponsors.
Best Templates for Planning Your Research Budget
Designing a research budget is not easy. You will need to consider the resources required and categorize them according to guidelines to ensure funding is not a problem. The categories may include the project’s necessary supplies and equipment and the wages you must pay your assistants. Research budgets are allocated for a year, but you can also plan for a quarter, depending on the project.
At SlideTeam, we have taken care of all these pain points and designed content-ready presentation templates that address each of these points. You save the time, the resources, and the tedium in having to make these presentations from scratch.
What is even better is that each of the templates is 100% editable and customizable. The content-ready nature means you get a starting point and a structure to guide your presentation; the editability feature means you can customize the template to audience profile.
Let’s explore these templates now.
Template 1 - Impact matrix evaluation research solution budget
This PPT Template is the perfect solution for your research budgeting needs. The matrix suggests what solutions are essential with the help of relevant keys that assign priority levels. Priorities go from low to highest influence with increasing importance. They are color-coded, with white being the lowest and red being the highest influence. For instance, Maintain Awareness and Evaluation are red in many cases, as shown in the slide. So, that means that they bear a significant impact on the research budget. Similarly, Strategic and Budget Planning are color-coded white, which means they don't impact the research budget as much in some cases.
With the impact matrix and heatmap, mapping out your research budget will be a breeze.
Get it now!
Template 2 Half-yearly research and development departmental budget
Research and Development departments can plan the budget required for projects for the two halves of the year using this PPT Template. The presentation template highlights areas for which you will need funding such as research and development, skills, innovation and patenting, and cooperation. You can also list your requirements for each area. For instance, under R&D and skills, you may need funding for medical research, chemical research, etc. Similarly, for innovation and patenting, you may need funding for product innovation and to cover patenting costs. Likewise, cooperation may involve setting up new laboratories and research centers. With this outlined, you can split the budget required for your research project for the two halves of the year.
Download now!
Template 3 - Budget Estimate for Research and Development Project
This presentation template for the budget estimate for your research and development project is apt for arriving at the calculation for the four quarters in a year. You can define and assign tasks as per the requirements of the project and allocate a set budget for each. The tasks may involve conducting market research and competitive analysis or be innovative or developmental. In either case, you can use this template to set a fixed budget for each task in the research project.

Get it today!
Template 4 Clinical Trial Phases with Communication and Budget Research Design for Clinical Trials
Clinical trials involve many phases, and you should let your research associates know about each step. For instance, you could post the information on the company website and provide relevant insights during the pre-trial phase. Similarly, you can offer the welcome letter and training materials during the trial start-up. During the trial, you can send newsletters to your associates, giving them relevant information and other valuable insights. All this requires funding, and you will need to allocate a budget. However, you don't need to worry, as this PPT Preset has you sorted, with dedicated sections for the pre-trial, trial start-up, during-trial, and trial-end phases. It also has communication, insights summary, and budget sections. You can use the budget section in the matrix to allot a budget for each trial phase and each section, including communication and insights.
Download here!
Template 5 Market research strategy with budget and area
The PPT Template has all the core elements required for your market research strategy, including the budget and area. This slide lets you list your clients, the items, and when to send them. You can also list background information related to your research, the aim and objectives of the project, the areas covered, and the budget.
The presentation template also provides a dedicated space to list your brands and products and a timeline for completing the research.
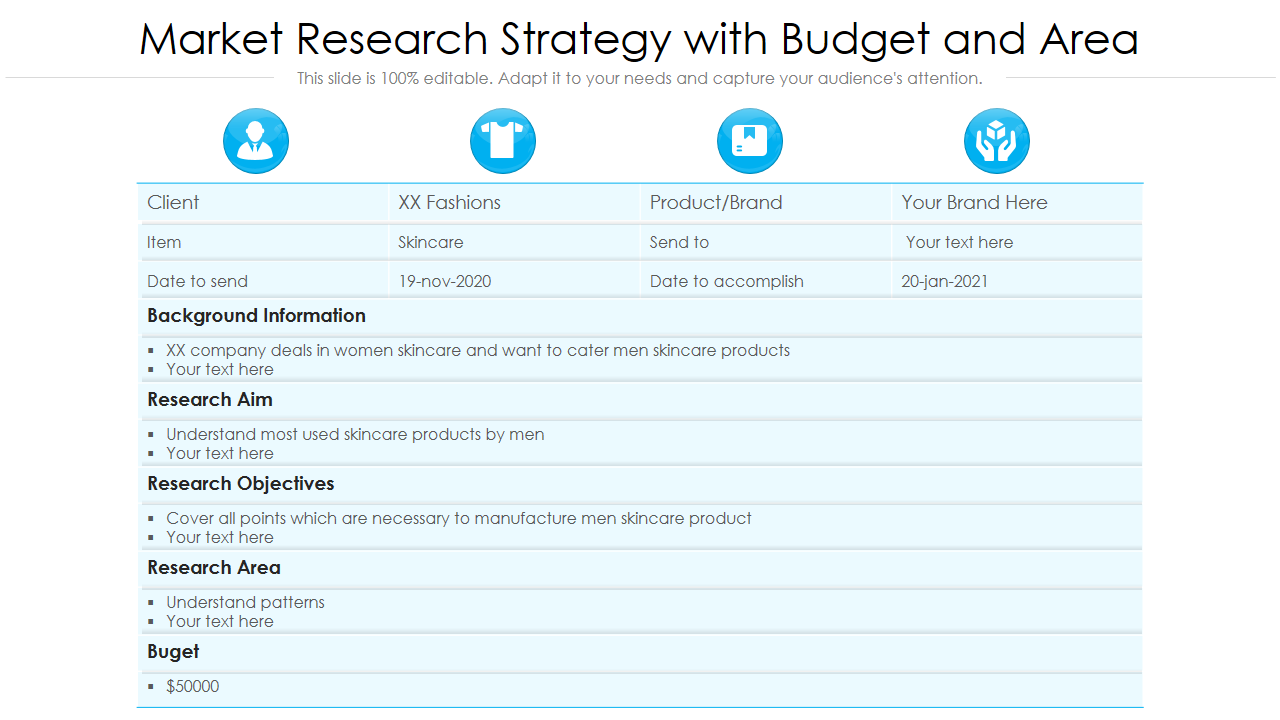
Template 6 - Determine Budget for Psychology Research Proposal One-Pager Sample Example Document
This presentation template is an easy-to-use tool for determining the budget required for psychology research. With this slide, you can allocate a budget for each area, including diagnostic assessment, training, technology and tools, supplies, travel, and workforce. It is a practical, hands-on template with information required to plan the budget for conducting psychological tests and evaluations. Please note that depending on your geography, taxes might or might not deserve a separate column.
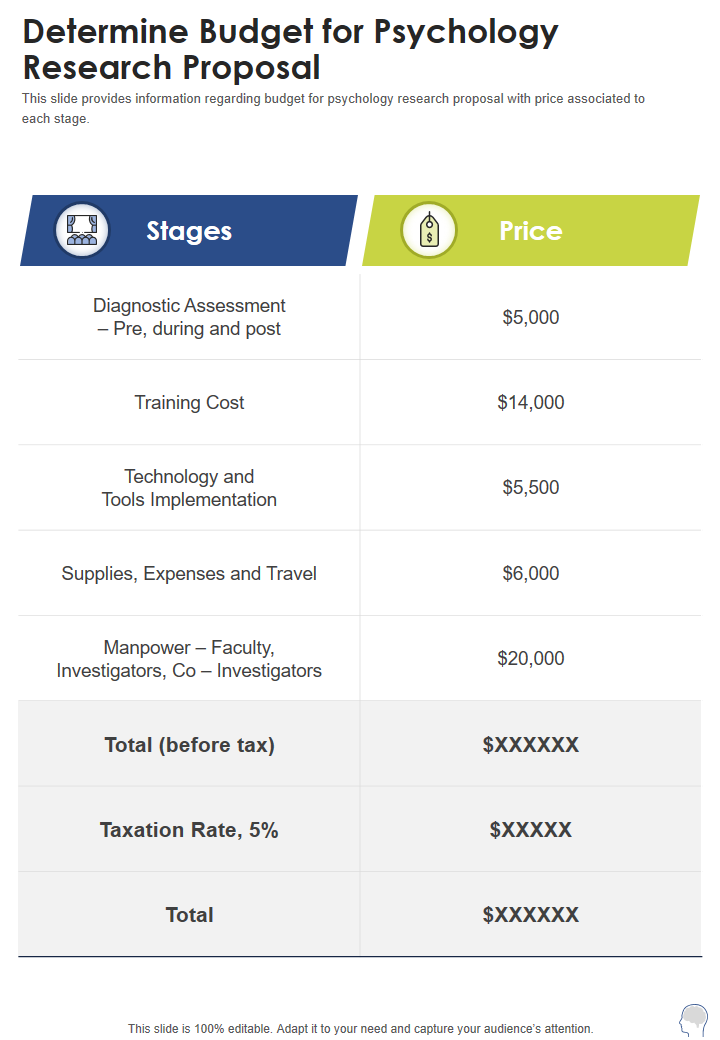
Template 7 - Budgeting for Product Launch Market Research
Every company needs to conduct market research before launching a new product. The PowerPoint Presentation that you have here can help you plan the budget required for conducting such market research. It includes necessary information, including business and research objectives, priorities, methodologies, and forecasts. The presentation template also has the metrics required for the research, such as improving customer engagement, introducing new products, and increasing market share. For example, to improve customer engagement, you may be looking to improve marketing approaches and gather customer feedback. The methods you may use include conducting marketing mix studies and tests. Similarly, you may want to optimize your social media posts and profiles and conduct A/B tests when introducing new products. Improving your market share may involve analyzing the competition. You may even use this handy template for conducting market research, estimating, and forecasting budgets.
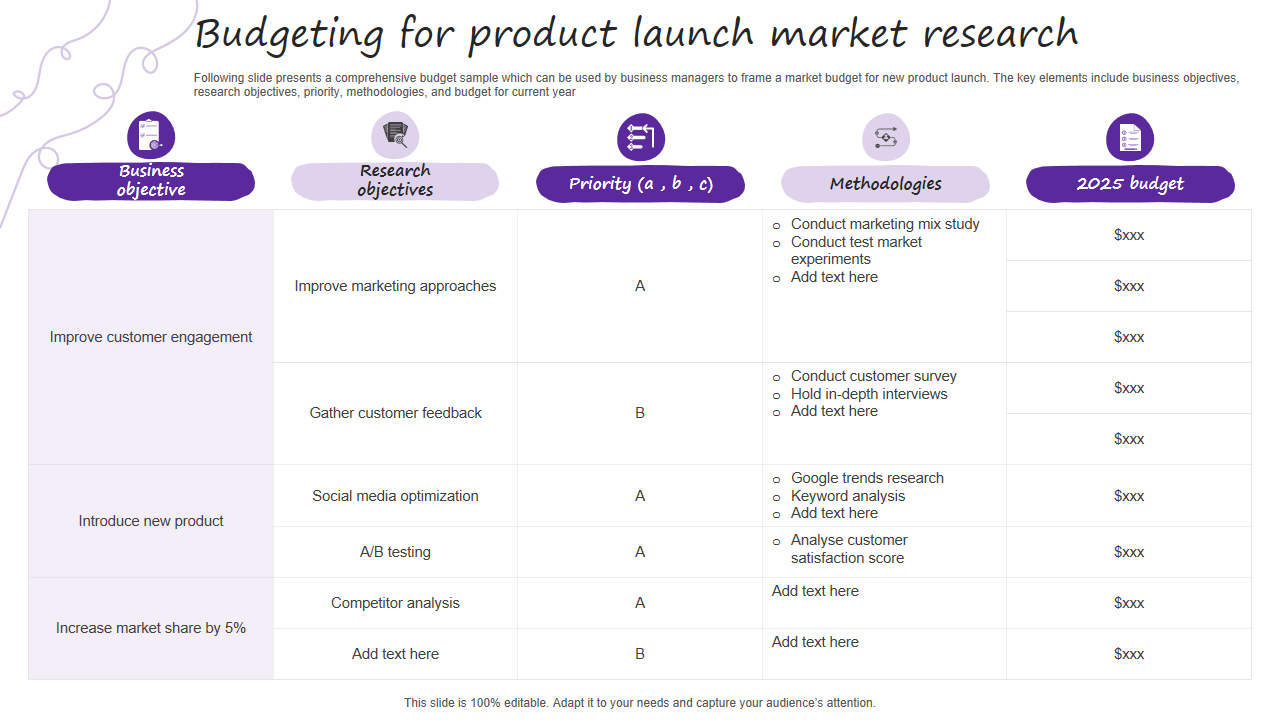
RESEARCH IS IMPORTANT BUSINESS
You can plan your research and the budget required using these templates. Remember that each new product launch has lots of research behind it. When going for a new launch, don’t just research the products and its uses, but also the markets – particularly, your target audience and how they will benefit from your brands. When allocating the budget for your research, don't forget to note your total resources and try to be as cost-effective as possible. You must consider the expected costs that you may incur and use these templates to work out a research budget that fits within your resources.
FAQs on Research Budget
What should be included in a research budget.
Research budgets should include all direct costs, and facilities and administrative costs (F&A). The facilities and administrative expenses are needed to achieve the primary objectives of the research. The project description should state the proposed budget and serve as a financial expression for the research. The idea is to ensure that the budget is comprehensive.
How do you create a research budget?
You can create a simple research budget by following these steps:
- List activities that will help you carry out the research.
- Check the rules for getting the funding required.
- Check all costs involved.
- Lay out the costs using a spreadsheet.
- Justify your budget by asking why and for what you need the money and where you got your figures.
What is the role of budget in research?
A budget can provide a detailed and clear picture of the structure of the research project, not to mention that it also lets you know how well it can be managed. The research project budget usually lets you see whether it will go according to plan and if it is feasible. So, it must be complete and reasonable.
What is the average budget for a research project?
The budget for a research project depends on the type of research and the proposed difference it could make to a field of study. For instance, the average budget for a market research project may vary between $20,000 and $50,000. Similarly, larger scientific research projects may cost millions or even billions of dollars, as in pharmaceuticals.
Related posts:
- Top 5 Startup Budget Templates with Samples and Examples
- Top 5 Construction Project Budget Templates With Examples And Samples
- Top 10 Cost Comparison Templates with Examples and Samples
- Top 5 Budget Planner Templates with Examples and Samples
Liked this blog? Please recommend us

Top 10 Purchasing Process Example Templates with Samples

Top 10 Banking Company Profile Templates for Crafting a Profile that Makes Money Talk!
This form is protected by reCAPTCHA - the Google Privacy Policy and Terms of Service apply.

Digital revolution powerpoint presentation slides

Sales funnel results presentation layouts
3d men joinning circular jigsaw puzzles ppt graphics icons

Business Strategic Planning Template For Organizations Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Future plan powerpoint template slide

Project Management Team Powerpoint Presentation Slides

Brand marketing powerpoint presentation slides

Launching a new service powerpoint presentation with slides go to market

Agenda powerpoint slide show

Four key metrics donut chart with percentage

Engineering and technology ppt inspiration example introduction continuous process improvement

Meet our team representing in circular format

All Formats
Table of Contents
Plan template bundle, what is a research work plan, what is the difference between a research plan and a research proposal, what is the purpose of a research plan, what are the good research questions, what are the components of a work plan, free 12+ research work plan templates in pdf | ms word, 1. research work plan format template, 2. research project communication plan template, 3. free project research work plan template, 4. free research work plan example, 5. free research work group plan template, 6. half yearly research work plan template, 7. sample research work plan template, 8. free research work plan template in pdf, 9. free business research work plan template, 10. free project research work plan example, 11. monthly project research work plan template, 12. transport research work plan template, 13. free research work plan template in doc, how to develop a work plan, advantages of developing a work plan, plan templates, 12+ research work plan templates in pdf | ms word.
A work plan is an overview of a series of objectives and procedures by which a team and/or entity can achieve those goals and provide the reader with a clearer picture of the project’s context. No matter if it is used in professional or academic life, work plans serve the purpose of helping you stay focused when working on a certain project. You disintegrate a process into tiny, manageable tasks by work schedules , and define the tasks you want to achieve.

- Google Docs

- Apple Pages

Step 1: Think About the Objectives
Step 2: introduction and background, step 3: list the resources, step 4: anticipate and define limitations, step 5: assign roles, step 6: write the strategy, determine goals and objectives, organize teams and leadership, establish project timelines, set project budget, quality assurance and control, more in plan templates, research template for kids, animal research paper template, quantitative research template, educational research template, artist research template, action research template, artistic research template, longitudinal research template, prediction research template, education qualitative research template.
- 7+ Financial Plan Templates
- 10+ Operational Plan Templates
- 9+ Training Plan Templates
- 5+ Shooting Schedule Template
- 11+ School Counselor Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | Word
- 9+ Interdisciplinary Lesson Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Business Continuity Plan Templates in Google Docs | Ms Word | Pages | PDF
- 18+ Compensation Plan Templates in Google Docs | MS Word | Pages | PDF
- 10+ Executive Bonus Plan Templates in PDF
- 8+ Facility Management Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Diversity Recruitment Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 11+ Audit Corrective Action Plan Templates in MS Word | Excel | PDF
- 9+ Recruitment Agency Marketing Plan Templates in PDF
- 10+ Recruitment Marketing Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
- 10+ Student Recruitment Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word
File Formats
Word templates, google docs templates, excel templates, powerpoint templates, google sheets templates, google slides templates, pdf templates, publisher templates, psd templates, indesign templates, illustrator templates, pages templates, keynote templates, numbers templates, outlook templates.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
A budget is a financial proposal that reflects the work proposed. It outlines the expected project costs in detail and should mirror the project description. A budget is presented as a categorical list of anticipated project costs representing the researcher's best estimate of the funds needed to support the proposed work.
the project will have, you will begin to outline the budget categories that will be included. As you have these conversations about what the project will entail, you will begin to develop a list of items for your budget. This list will be all of the things or people that the researcher will need for the project to be successfully completed.
Budget plan is a key element of a grant application. It demonstrates the required cost for the proposed project. It is a prediction of expenses and serves a plan for funders on how the organization will operate the project, spend the money in a given set of period and where their money will go.
A good budget shows the assessors that you have thought about your research in detail and, if it is done well, it can serve as a great, convincing overview of the project. Here are five steps to create a simple budget for your research project. 1. List your activities. Make a list of everything that you plan to do in the project, and who is ...
The budgeting of your salary, a direct cost of the research, should be listed as $21,161.73. If your project covers three years, with the same or differing time commitments, you calculate this figure for each year of your project. Remember to factor in pay rises according to Step increases in multi-year grants.
The completed work plan for your Master's Project should contain three parts: (1) scope of work, (2) project timeline, and (3) team charter. Guidelines for what to include in each section are outlined below. The full proposal should not exceed 15 pages in length, double-spaced, including the cover page.
Research Project Budget Guidelines Preparing your budget: • List your activities: Make a list of everything you plan to do on the project and who is going to do it. Take your methodology and turn it into a step -by-step plan. Examples: a. Do you plan to interview participants and give them a gift card as compensation for their time? Write it ...
Writing a research proposal can be quite challenging, but a good starting point could be to look at some examples. We've included a few for you below. Example research proposal #1: "A Conceptual Framework for Scheduling Constraint Management" Example research proposal #2: "Medical Students as Mediators of Change in Tobacco Use" Title page
Here's an example outline of a research plan you might put together: Project title. Project members involved in the research plan. Purpose of the project (provide a summary of the research plan's intent) Objective 1 (provide a short description for each objective) Objective 2. Objective 3. Proposed timeline
Adjust scope of the project to make sure proposed activities fit within the allowance. Categorize these costs (e.g., salaries, supplies, equipment…) per year, in some cases by quarter. Ensure that project scope and budget match. Include indirect costs of research as permitted by sponsor and the University policy. Two models of budget development
A good budget calculation requires some previous experience and repeatable processes. Because our projects typically involve research and some strategy, we developed a five-phased research ...
work. Initial workplans should be developed by the project team after the action plan, monitoring plan and operational plans have been completed. Workplans are shortterm by nature; one year is a typical period of coverage but they can be from 3 months to 3 years.
NIH DMS costs should be shared in the appropriate cost category, e.g., personnel, equipment, supplies, and other expenses, following the instructions and providing details as instructed within the applicable form (e.g., R&R Budget Form or PHS 398 Modular Budget Form). In most cases, the DMS Plan oversight at U-M will be provided by the ...
By identifying timelines, project goals, and due dates, both you and your advisor(s) will be able to evaluate if the proposed schedule is achievable within the required time frame of the project. If you're unsure if your research proposal requires a schedule or work plan, please consult your project handbook and/or speak with your instructor ...
A summary of the rules which apply when applying for equipment in UKRI grants. This article was published on 2024-01-24. What to consider in preparing your research project budget, and how we can help you.
BUDGET SUMMARY The budget summary will autopopulate based on the figures you have provided in the budget breakdown. Proposal title: [insert project title here] Duration of project: [insert project duration here] If you plan to collect primary data, please provide the expected sample size: [insert sample size here] Fees £0 Expenses £0
The template provides a structure for outlining the processes and activities that must be completed in order to achieve the desired results of the research project. The template is designed to be comprehensive and flexible, allowing for modifications as needed throughout the project. 1. Define clear examples of your focus areas.
1. Define the project purpose. The first step to creating a research plan for your project is to define why and what you're researching. Regardless of whether you're working with a team or alone, understanding the project's purpose can help you better define project goals.
Assign Roles & Responsibilities. Now, assemble a project team and clearly define the roles and responsibilities of each member. Communicate with them and make sure they understand what their job is and how they can collaborate with each other. 5. Estimate Costs & Create a Budget.
Budget Breakdown template Provide a detailed budget and how the funds will be used (use the templates). All expenses should be directly related to research projects. It may cover primarily personnel specifically hired for the project, travel cost, researcher perdiem and consumables. Budget narrative can be added as deemed necessary.
This presentation template is an easy-to-use tool for determining the budget required for psychology research. With this slide, you can allocate a budget for each area, including diagnostic assessment, training, technology and tools, supplies, travel, and workforce. It is a practical, hands-on template with information required to plan the ...
PROJECT WORK PLAN AND BUDGET MATRIX - Free download as Word Doc (.doc / .docx), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or read online for free.
12+ Research Work Plan Templates in PDF | MS Word. A work plan is an overview of a series of objectives and procedures by which a team and/or entity can achieve those goals and provide the reader with a clearer picture of the project's context. No matter if it is used in professional or academic life, work plans serve the purpose of helping you stay focused when working on a certain project.