Advertisement

Identifying factors for employee retention using computational techniques: an approach to assist the decision-making process
- Research Article
- Published: 31 August 2020
- Volume 2 , article number 1612 , ( 2020 )
Cite this article
- Zahid Halim ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0003-3094-3483 1 ,
- Muhammad Waqas 1 , 3 ,
- Cedric A. Edwin 4 &
- Ahsan Shah 1
17k Accesses
3 Citations
Explore all metrics
In the today’s competitive environment, employee retention is a challenge faced by many industries. This work aims to identify the factors that influence employee retention. This is done using employees’ feedback and various computational techniques. A survey is conducted within multiple sectors to collect data. The questionnaire is divided into two parts: the first part includes demographic information, whereas the second part contains questions pertaining to employees’ job description and their satisfaction. The questions on the second portion are based on theories like Herzberg’s duality theory, expectancy theory, social cognitive theory, and sociocultural theory. These theories are further linked with factors like motivation, recognition and reward, bullying and work harassment. Later, the frequent items mining technique from the domain of data mining is utilized to identify the frequent factors from an employee perspective toward better retention rates. A test is also conducted to ensure the reliability of the data. The obtained results indicate it to be 87% reliable. A comparison between two frequent items mining methods indicates four times quicker performance of the k Direct Count and Intersect (kDCI) method in identifying key retention aspects from the data. A tool is utilized for analysis of variance (ANOVA) and exploratory factor analysis (EFA) tests to find factors crucial for retaining employees. The result identifies that work environment, reward and recognition, work performance, supervisory support, and income have high impact on employee retention.
Similar content being viewed by others
Reskilling and Upskilling the Future-ready Workforce for Industry 4.0 and Beyond

Reporting reliability, convergent and discriminant validity with structural equation modeling: A review and best-practice recommendations
Gordon W. Cheung, Helena D. Cooper-Thomas, … Linda C. Wang
The four-day work week: a chronological, systematic review of the academic literature
Timothy T. Campbell
Avoid common mistakes on your manuscript.
1 Introduction
Human resource is generally the most valuable asset for an organization. Skilled human recourses enable an organization to excel and achieve its objectives efficiently [ 1 , 2 ]. To classify an employee as skillful, her experience acts as a key indicator in addition to other basic credentials [ 3 ]. Organizations prefer to retain their existing skilled employees by offering multiple perks and benefits [ 4 ]. They also try to attract skilled resources using similar measures. At times, such skilled resources are attracted by the competitor organizations. This results in the issue of employee retention [ 5 ]. The issue is dependent on the country’s culture, its economic growth, the number of companies operating in public/private sectors and the availability of skilled human resource [ 6 ]. Interestingly, today`s corporate sector has seen an increased number of employees leaving the previous job to find better opportunities [ 7 ]. Organizations facing this challenge need to adopt new strategies and identify factors to motivate their skilled resources. Human resource (HR) departments maintain an employee retention policy for this task. Such policies are highly dependent on the data from their current staff, organization’s functions, and other previous experiences. Identification of key factors that influence employee retention is an important research undertaking. These factors do depend on the study domain. Previous studies have suggested multiple reasons for an employee to leave an organization. These can be low current pay, competitor offering better career opportunity, organization’s environment, organization’s culture or employees being bullied by the coworkers. On the contrary, an organization can also ask its employees to leave their job due to poor performance, attitude issues or financial crises. All this results in affecting overall health of an organization since new human resource needs to be evaluated, hired, trained, and transferred the domain knowledge. Therefore, skilled employee retention is crucial to many organizations. If an organization fails to retain its current employees, they must invest a considerable amount of money for training new employees again and over again.
Most of the organizations strive to keep their employees satisfied to reduce their turnover rate. Loosing skilled and experienced workers reduces organization's productivity and profitability. Previous studies [ 8 , 9 ] show that to keep “employee happy,” organizations should consider some key factors like knowing the employee well, creating an interactive, innovative, and cultural environment that indirectly keeps reminding your employees to stay loyal to their organization, offering reward, and recognizing best performers. Providing workers with a better leadership also works well in retaining the staff [ 9 ]. Few of the rapidly growing sectors like telecom, information technology and higher education need to know the key factors specific to them that can assist in retaining skilled work force. The work presented here deals with this issue by utilizing computational techniques and the emerging concepts of data mining. The key aim of this study is to find the factors that can increase employee retention in various working sectors. This work uses frequent items mining (FIM) techniques from the domain of data mining to identify factors that commonly exist together to influence employee retention. Finding frequently occurring items in a transactional database is an active research problem. The problem is commonly known as market basket analysis. The applications of finding frequently occurring items range from core computer science problems to a range of multidisciplinary areas of research. The aim of market basket analysis is to find all items in a dataset that occur together above a certain frequency [ 10 ]. Later, these frequently occurring patterns are analyzed to find associations between various factors. This study is based on following research questions.
RQ1: Which factors do the computational techniques identify as crucial for retaining employees and what is the relationship between those factors across multiple sectors in the developing countries?
RQ2: Which demographic and organizational environmental factors influence employee retention across multiple sectors in the developing countries and how these factors rank against each other?
To address the abovementioned questions, this research uses a qualitative approach. The research questions are answered through a questionnaire in this work. A survey was distributed in the major cities of Pakistan such as Karachi, Lahore, Rawalpindi, and Islamabad. The survey questions were built based on the factors such as recognition and reward, advancement and growth, relationship with supervisors, work conditions, income, ethical behavior, organizational satisfaction and commitment, bullying and work harassment. These factors helped to identify the features and their correlation for employee retention. The data analysis was divided into six stages: These include (a) loading raw data from the survey forms to a text file, (b) analysis of data through one-way ANOVA, (c) identification of correlating factors through frequent items mining (FIM), (d) analysis of data through exploratory factor analysis (EFA), (e) analysis of data through Pearson correlation (PC), and (f) analysis of data through regression analysis (RA). The association rule mining technique, which is preceded by the FIM method, is used to analyze and interpret the data. The ARM is a tool that identifies the frequently occurring factors in the responses with other features. The Statistics Package for Social Science Software (SPSS) is also used to analyze the data. One-way ANOVA is used to see a significant difference in data, and the EFA is used to interpret the variables. The Pearson correlation is used to observe the correlation between independent and dependent variables, and regression analysis is used to study the impact of independent variables on the dependent ones. A combinational approach is applied to the data that helps in analyzing the responses.
1.1 Present work aim and motivation
The employee retention is a growing problem in today's modern world, and it needs to be solved using various retention strategies to improve the employees' turnover rate. There is a demand for skilled workers in areas such as hospitals, software industry, universities, banks, and many other emerging sectors. However, unfortunately, the number of qualified employees at times remains low. Organizations are therefore in a need to find ways to reduce their turnover rate. This study aims to determine the factors that can reduce such organizational problems. Specifically, the task here is to determine what factors are used for higher employee retention in various organizations. This study is focused to find the features that influence employee retention and the relationship between independent factors and employee retention. The findings will be useful for many organizations to enhance their retention strategies. This work is motivated by the employees’ perspective rather than the organizational point of view. Therefore, the finds of this work are based on the data collected from various mid- to early-career individuals instead of taking the decisions-makers’ perspective.
The rest of the paper is organized as follows. Section 2 contains a detailed literature review on employee retention and other important factors for the same. Section 3 lists the methodology utilized in this work. Section 4 contains the results obtained. Section 5 lists the policy implications. Finally, Sect. 6 concludes this work and also mentions a few of the further research directions.
2 Related work
This section covers the previous work on employee retention. The section is organized factorwise where the previous work on each factor that can help retain employees is described. The section also contains relevant theories that can help build a conceptual framework for this or other such studies. Previous studies have shown the following factors that influence employee motivation to continue working with the same organization, working environment, organization commitment, reward and recognition, work performance, supervisor support, and income.
2.1 Working environment
The working environment is a factor in an organization where employee tends to show their positive abilities and leadership skills. Authors in [ 11 ] suggest that a positive working environment can have good impact on the employees. They state that different organizations may have dissimilar working environment depending on the clients the organization deals with. Ritter et al. [ 12 ] suggest a working environment that includes a culture where it involves good communication between co-workers, leadership style, and professional growth. In retaining employees, one needs to have a healthy working environment. The good working environment requires an appreciation for others, a strong relationship between colleagues, and no harassment [ 13 ]. Christmas et al. [ 14 ] suggest retaining an employee with good professional skills by improving the organization’s working environment. In order to improve their working environment, organizations should facilitate their employees and provide them necessary equipment that can help the organization in better management. The work in [ 15 ] presents a study on employee engagement. Their aim is to find correlation between purpose and joy in a work environment among the managers and their employee engagement. The domain of study is medical profession, and the data are collected from nurses. The authors use Cronbach's alpha to gauge internal consistency in a population sample. The obtained results do not find any significant correlation between nurse manager meaning and joy in their work and the employee engagement. Their study is limited to a specific set of individuals, and the same method if applied to a different dataset may yield diverse results. The work in [ 16 ] presents a study on employees’ perception on formulation of human resource policies. They also cover the implementation of various human resource retention plans in their work. The focus domain of their work is the hospitality industry. The data in their work are primarily obtained through personal interviews of employees in a specific region within a few cities.
2.2 Organization commitment
Studies have shown that employees with higher commitment stay with the organization for a longer period, whereas those having low commitment leave the organization during early stages. The employees with higher commitment also desire to stay in the organization and work hard with a positive attitude. Previous work identifies that organization's commitment is related to employees’ turnover. Higher rate of commitment level of the organization results in lower turnover. Bashir et al. [ 17 ] represented three dimensions of organizational commitment. Affective commitment is the sense of attachment toward the organization and relation with employee’s characteristics, work performance, and structure of the organization [ 18 ]. For example, an employee stays in the organization because she knows their value in the organization [ 19 ]. Continuance commitment is the realization of a cost that is related to the organization [ 20 ]. For instance, employees will stay in the organization because they know if they leave, they have to face a higher risk of not getting a new job [ 18 ]. The normative commitment deals with an emotional feeling of employees [ 17 ].
2.3 Reward/recognition and work performance
The terms reward and recognition have high impact on employee retention. These factors are used by organizations to motivate their employees. A reward is given by the organizations to the employees for their best performance, which keeps them motivated. The work in Silbert et al. [ 21 ] suggests that organizations can offer reward in the form of cash, bonuses, promotion, recognition, or announcing a worker as an employee of the month, offer trip, and other benefits. According to the authors, organizations present reward to employees so that they keep giving their best performance. Such organizations believe that reward and recognition keep employees motivated for future performance. It is important that employee should think that their perceptions are valued by the organization when they are rewarded.
Work performance is another factor that has an impact on employees and the organization. It is a critical factor for retaining employees. Reviewing the performance of employees can help both the organization and the employees. Employees can be assisted by telling them where they stand in the organization and what are their strengths and weaknesses. In a few cases where employees are highly talented, an increased pay or other benefit does not motivate them; however, performance appraisal does. The organization implies factors like performance appraisal, leadership, reward and recognition, training, and development in order to keep employees motivated to work harder .
2.4 Supervisor support
Supervisor support is defined as a relationship between employees and managers, and it is a factor that has huge impact on the employee retention. The employees tend to stay in an organization when they have good communication skills and strong support from supervisors. When employees have a supportive environment that increases their ability and comfort level of working, they tend to produce excellent results. The authors mention that an organization should be a place where the employee tends to stay. For this, the supervisors should be trained so that they can build a comfortable working environment for the staff [ 22 ]. A study suggested that improved employee’s performance results in a tendency to improve the capabilities of their work [ 23 ].
2.5 Income-related benefits
The work in [ 24 ] stated that employees and supervisors are motivated to work effectively when they are paid and provided with other benefits. There are a number of reasons for employees to be dissatisfied with a job. In addition to an individual’s domestic issues, income is one of the reasons when employees feel dissatisfied [ 25 ]. To improve retention strategies, organizations should periodically increase income scales and other benefits such as good working environment, leadership skills, the workload that employee can bear, and flexible timings. Deery et al. [ 26 ] find other factors such as flexibility in work, learning, and training, provision of resources to employees and reward system to improve employee retention. Gevrek et al. [ 27 ] explore the Schadenfreude effect in employee retention. They study five different salary rises in their work. Their study is based on a dataset constructed over a period of five years by obtaining data from university employees. The obtained results suggest that a one-time, small increase in compensation does not influence employee retention. The work in [ 28 ] aims to identify the retention strategies that have an actual effect on the employee turnover. They present a procedure to build an uplift model for testing the effectiveness of the different strategies for the task at hand. Their uplift model is based on a machine learning classifier, i.e., random forest. It is used for personal treatment learning estimation.
2.6 Bullying and work harassment
Bullying is considered as one of the serious problems at the workplace. Studies conducted worldwide identify increased bullying factor in organizations [ 29 ]. There are direct negative effects of bullying. It is stated that violence in the workplace also increases the factors such as bullying, workplace harassment, and emotional abuse [ 30 ]. The work in [ 31 ] examines the correlation between workplace bullying and high-performance work practices (HPWPs). They also suggest a few possible solutions. The obtained results suggest a positive effect of HPWPs on employee well-being. They also observe that reduced role conflict has an influence of HPWPs and less bullying. A limitation of their work is reliance on single-source, self-reported data. This may have caused biased views.
2.7 Factors that improve retention
There are a few other factors that can improve employee retention. These have been identified by an assortment of research contributions. Past work states that retaining talented employees should be the organization's primary focus. In their work, health, success and safety are correlated with retaining the employees. The studies in [ 32 ] and [ 33 ] identified some strategies for retaining employees and improving employee productivity by including factors in organizations such as appreciating employee on a good performance, mentoring, management, morale, and employee development training. Work in [ 34 ] identifies factors such as leadership skills, utilization of skill, compensation, safety and security and professional success to improve employee retention. A study [ 35 ] conducted in five companies of India on hundred managers and staff concludes that the factors such as income, training possibilities and careful selection of employee improve job satisfaction and commitment. It also has an influence on retaining employees. Another study on middle managers of Nigeria concludes three factors: compensation, advancement growth and affiliation, to be the reason to stay within the organization [ 36 ]. A research on hotel employees discovered that employee tends to stay in an organization for a longer period if they are satisfied with their job and the environment of the organization. The communication has always been a factor through which one can understand the employees better. Studies have shown that poor communication between co-workers leads to a poor employee retention. The economic circumstances and market forces in the world have an impact on the employee’s decision to stay or leave an organization. The certainty of an employee leaving a job and finding another job is when economic conditions are better. A research study found that the better the economic surroundings, the higher are the chances for an employee to leave the organization. Somewhat similar work that utilizes computational methods [ 37 , 38 , 39 , 40 , 41 ] to predict customer churn can be seen in past works. Similar computational methods [ 42 ] can be utilized to predict the retention period of a particular employee in an organization. However, for this, the historical data related to the employee and the company will be required to train the model.
2.8 Employee retention factors in the developing countries
Compensation is considered to be a key factor to retain employees in the developing countries. In this context, the work in [ 43 ] presents a case study of Hong Kong and China. The data are collected from 704 respondents to identify the important compensation components by various organizations. The study also identifies the six most important compensation components from an employee perspective. In Hong Kong, these five factors are salary, merit pay, end-year bonus, annual leaves, mortgage loan, and profit sharing, whereas for China the first three factors are the same as those for the Hong Kong and the remaining three include housing provision, overtime allowance, and individual bonus. This suggests that the employee retention factors vary between various countries and economies. Lall et al. [ 44 ] evaluate the analytical framework of the globalization–employment relationship in the developing countries. The focus of their study is on the manufacturing sector employees. It is observed in the study that globalization may cause an outflux of the talent pool from the developing/underdeveloped countries to the developed nations. Lowell et al. [ 45 ] present a report on the impact of high-skilled mobility from the developing countries. The report focuses on eight countries, namely Bulgaria, South Africa, Argentina, Uruguay, Jamaica, India, Philippines, and Sri Lanka. They identify four issues yet to be researched about. First is to evaluate the particular channels of impact generated by highly skilled emigration. Second is to study the range of feedback effects on the total emigration impact. Third and fourth are how high-skilled migration increases country trade and the need for documentation. Bhatnagar et al. [ 27 ] present talent management strategies for employee retention in a developing country, i.e., India. The author finds that low factor loadings indicate low engagement scores at the beginning of the career. However, high factor loadings at intermediate stages of employment are indicative of high engagement levels. A key finding is that good engagement results in higher retention in the developing countries. The work in [ 46 ] utilizes a new Cultural Intelligence (CI) measure to empirically study the evidence on several key antecedents of CI across five countries. The measure is named as Business Cultural Intelligence Quotient (BCIQ). This or a similar measure can be adopted for employee retention.
Based on the abovementioned literature survey, the conceptual framework developed for the current study is demonstrated in Fig. 1 . As evident from this literature review, a detailed study that identifies key employee retention factors and correlates them with each other using a computational technique for the developing countries is needed. This work aims to bridge this gap.
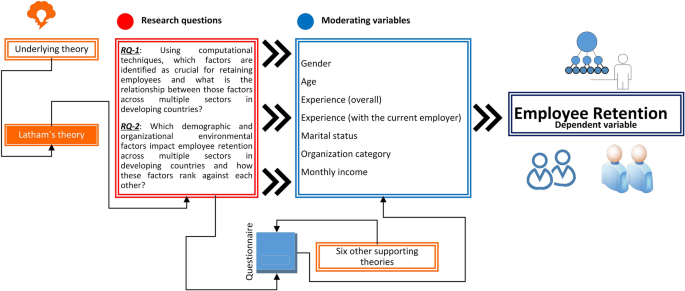
Conceptual framework of the proposed work
3 Methodology
This section describes the methodology used to collect and analyze the data. Moreover, the section also describes the research design, area and population selected for the study, its sampling procedure/size, and the data collection procedure. This work presents a quantitative research that will answer questions asked from multiple organizations. The queries are related to factors such as work environment, work performance and motivation, organization commitment, and satisfaction, reward and recognition, income, supervisors support and bullying, and work harassment.
3.1 Research design
For the current research study, a quantitative research mechanism is carried out via questioner distribution to a targeted population. The responses were measured through the statistical instrument. Quantitative research is to be carried out for a huge number of population, and they are tested by mathematical and statistical instruments. On the contrary, qualitative research is not appropriate for this research study as qualitative research deals with data related to observation and a specific style. It does not statistically describe findings. The exploratory research answers the “why” and “how” questions, whereas descriptive research focuses on four Ws, namely “what,” “where,” “when,” and “who.” Therefore, the exploratory research methodology is also not applied here because of the close-ended nature of the questioner.
3.2 Theoretical framework
The concept of employee retention falls under the theoretical framework of leadership, motivation theory and practice. The theoretical framework of this research is specifically based on the work of Latham [ 47 ]. Latham’s theory not only provides a chronological history of motivation theory and practice, but also presents an “insider view” on leadership and motivation. He presents six distinct eras of how motivation theory and practice has evolved over the past 110 years. The first era, according to Latham, presents the birth of behavioral theory in management and motivation. Industrial and Organizational (I/O) psychologists in this era were not interested in studying inner motivations and considered money to be the primary motivator at the workplace. The second era is marked with the trend of measuring the impact of attitudes on work and employee motivation. This era placed emphasis on the decision-maker and revealed the importance of identifying variables in building theoretical frameworks. The first and second eras are deemed obsolete for the current research due to their unidimensional approach toward measuring employee motivation. However, both these eras are fed into the proposed work indirectly. In the third era, the focus turned toward assessing and forecasting factors that influence employee motivation. This era had the strongest impact on organizational practices in the developing countries. The fourth era introduced the notion of scientific theories and methods in leadership and motivation research. The present research is based on the leadership and motivation theories of the third and the fourth era due to their relevance in the developing countries. According to Latham, we are currently in the fifth era and this period is marked with putting the practitioner at the center and devising frameworks that proactively and holistically aid in taking well-informed decisions. However, the sixth era is the era of the future. Latham predicts that the future of leadership and motivation theory will take deeper roots in psychology and consider the emotions and beliefs of employees. This research aims to provide crucial lessons for practitioners in the fifth and sixth eras.
3.3 Geographical zones
This study is carried out in four major cities of Pakistan, namely Karachi, Lahore, Rawalpindi, and Islamabad. The choice of these sites is made based on their population and availability of larger number of public and private organizations. Karachi is one of the biggest business hubs and also has many other service-oriented companies. Lahore is one of the known cities of the Punjab province, the populationwise largest province of Pakistan, where people are struggling to be retained in their organization, and most of the research data were collected from this zone. Islamabad, which is the capital city of Pakistan, has many organizations, and data were also collected from here. Figure 2 shows an overview of the general research design.
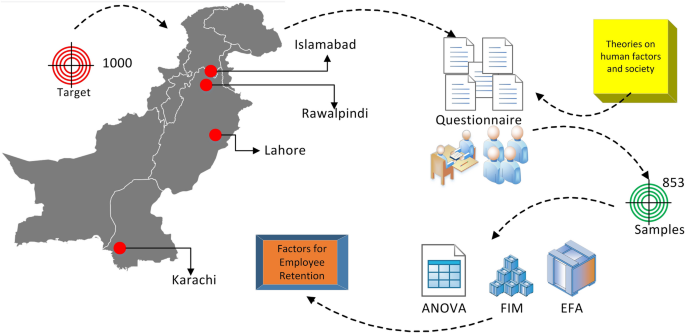
Overall research design
3.4 Population of the study
For this study, the target group was all categories of sectors where we could get a significant number of employees. This was done to analyze the factors which are generally applicable to all possible working classes instead of focusing on just any particular group. The organizations in which this study is carried out are large appliances venders, corporate sector, schools, universities, banking sector, government organizations, hotel industry, information technology companies, hospitals, professional engineers, and telecommunication sector.
3.5 Sampling size and data collection
The sample size is an illustration which tells about the targeted population in the research. To carry this research, a target of 1000 was set and 853 responses were received. However, to achieve more responses, the targeted population could have been increased. For the current study, enough samples were received, i.e., 85.3% turnout rate; therefore, the target was not further increased. Figure 3 lists an overall summary of the data collected. Both primary and secondary methods were used for data collection. It is important for the researchers to test the result of hypothesis, and it is also important to collect data through secondary methods to save time.
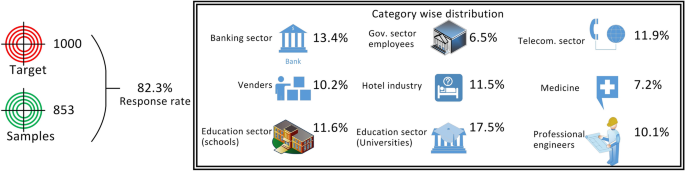
Summary of the collected data
3.5.1 Primary data collection
Primary data collection is a method of collecting genuine data. Questioners are the primary data source in this research. These were developed based on existing theories on employee retention. The collected data help to analyze patterns through FIM technique and Statistical Package for the Social Sciences (SPSS). Questioners are the best way to gather data, and it is the most effective and efficient mechanism through which one can measure various factors. This study was conducted on many individuals in diverse organizations. Firstly, all forms were distributed in multiple organizations and within one-month the forms were returned. The data were recorded in a Microsoft excel sheet for further process. Moreover, data analysis was performed through FIM and SPSS.
3.5.2 Secondary data collection
Secondary data collection method was used for reviewing theories and literature from many sources such as research papers, articles, and thesis reports. These sources were used to relate the factors that influence employee retention and learn employee retention strategies.
3.6 Hypothesis
Properly formalized hypothesis enables to guide the research toward appropriate simulation and experiments in order to answer key research questions. For this study, seven initial hypotheses were formed. These are listed as follows:
H1: Better work environment will result in higher employee retention.
H2: Higher organizational commitment results in higher employee retention.
H3: Increase in reward and recognition system results in higher employee retention.
H4: Increase in the individual’s work performance results in increased employee retention.
H5: Higher support and supervision by managers result in higher employee retention.
H6: Increase in employee income results in increased employee retention.
H7: Higher rate of bullying and work harassment results in lower employee retention.
3.7 Research instrument
When large amount of data is needed for a study, a survey seems the most effective way to do the needful. The questionnaire for this study was designed using Google forms Footnote 1 , and also a few instances were printed in the hard copy. The survey form was divided into two sections: the first section asked for the demographic information such as gender, age, experience (overall), experience (with the current organization), organization name, organization category, and monthly income range, whereas the second section asked for the factors affecting employee retention. Moreover, the second section was comprised of 54 questions and these questions were measured by a five-point Likert scale ranging from one to five, where 1 showed strongly agree, 2 showed agree, 3 indicated neutral, 4 showed disagree, and 5 showed strongly disagree. The questions contained in the survey are listed in “ Appendix .”
A few constraints and problems were faced while conducting this study. Some companies refused to fill the survey because they thought that the survey was a bit lengthy and it will take their time. Few did not return the required number of forms requested from them. There were a very few people who did not understand English. For such individuals, questions translated into their local language were used.
4 Results and findings
This section presents the experiments conducted and their results. These experiments are mainly conducted using SPSS as a tool and FIM as a data mining technique. The demographic profile utilized here includes gender, age, overall experience, experience with the current employer, marital status, and income. The experiments are conducted mainly to answer the following questions.
Using computational techniques, which factors are crucial for retaining employees and what is the relationship between those factors across multiple sectors in developing countries?
Using computational techniques, what is the impact of motivation, recognition and reward, advancement and growth, commitment and satisfaction, work environment, individual’s performance, support and supervision by managers, employee income, bullying and work harassment on employee retention across multiple sectors in developing countries?
How do these factors improve the organization’s overall environment and increase the rate of retaining employees?
4.1 Demographic profile
Getting key information about the respondents is important before drawing conclusions about any finding. For the current study, 36% of the participants were female and 64% were male. For this study, age was categorized into five ranges: less than 20 years, between 20 and 30 years, between 30 and 40 years, between 40 and 50 years, and greater than 60 years. According to this categorization, the highest response was obtained from the 20–30-year bracket, whereas the second highest response was from 30–40 category. Based on experience, the highest number of responses came from those who had work experience of less than five years and the lowest number of responses was from individuals having work experience greater than 10 years. Among the respondents, 45.6% were single and 54.1% were married. The highest response rate, i.e., 17.5%, was from the individuals working in the higher education sector. From the salary perspective, maximum responses were from those having annual income between 4329 and 8658 USD and the lowest response rate was from those respondents who had an annual income greater than 16,500 USD.
4.2 Factor analysis
This study focuses on various factors such as working environment, organization commitment, reward and recognition, work performance, supervisor support, income, bullying, and work harassment for employee retention. Table 1 lists the mean, standard deviation, and significant difference between male and female respondents using one-way ANOVA for the employee retention factors. When both male and female were asked about the working environment in their organization, the mean for males was 1.75 and for females, this was 2.10. This indicates that male agrees on working environment to be important for employee retention, whereas females neither agree nor disagree. There was no significant difference between male and female considering organization commitment. Considering this factor, the mean for male participants is 2.52 and for female it is 2.55 indicating their disagreement. The reward and recognition factor has a significant difference. The male participants have a mean of 2.00, and females have a mean of 2.34 which lies in the agreeing range. The factor work performance has a significant difference where the mean value for males is 2.45 indicating their agreement and females have a mean of 2.90 that shows they neither agree nor disagree. When questions related to the supervisor’s administration were asked, the results indicate no significant difference between males and females. For the factor of income, there is a significant difference observed in the male and female groups, where the mean for men is 2.44 and for women it is 3.21, indicating their disagreement.
Table 2 lists the results when considering all factors and grouping these by age. The results show the highest mean for bullying factor and work harassment, considering the age-group greater than 60. The work environment has the lowest mean, i.e., 1.41 for the age-group of 40–50, whereas the highest standard deviation of 1.672 is for the factor work performance considering participants having age less than 20 years. The lowest standard deviation is 0.840 for the factor work environment within the age-group of 40–50. A significant difference is observed for the factors of working environment, reward and recognition, supervisors support, and income within the various group of ages. As shown in Table 3 , all single and married respondents have the highest mean and standard deviation in bullying and work harassment factors and the lowest mean and standard deviation in working environment factor.
Table 4 lists the results grouped professionwise. The factor work environment here got the highest mean in the domain of medicine, and the lowest mean is obtained for the individuals working in telecommunication sector. The highest standard deviation is for hotel industry, while the lowest standard deviation is for the vender category. The organizational commitment has the highest mean value in the education sector (schools) and the lowest mean in the banking sector. However, the highest standard deviation is noted in government employees and the lowest standard deviation is observed in employees of the professional engineering companies. The reward/recognition being the third factor has the highest mean and standard deviation in hotel industry, and that has the lowest mean and standard deviation in telecommunication sector employees. The factor work performance has the highest mean in medicine sector and professional engineering, while it has the lowest mean in the field of education sector (schools). The highest standard deviation of work performance is observed in the hotel industry, and the lowest standard deviation is in the professional engineering sector employees. The highest mean and standard deviation of supervisor support are also for the hotel industry, and the lowest mean and standard deviation are that of the telecommunication department. The highest mean of income is observed in the telecommunication department, whereas the lowest mean is observed for the individuals working in the hotel industry. The income factor has the highest standard deviation in medicine domain and the lowest standard deviation in the government employee. The highest mean of the factor bullying and work harassment is observed in the education sector (schools), and the lowest mean is observed for the hotel industry. There is no indication of a significant difference in factors except for bullying and work harassment.
Table 5 lists the results grouped salarywise. The work environment factor has the highest mean between those respondents who earn more than 27,166 USD annually and the lowest mean for those respondents who earn between 8767 USD and 16,235 USD. The exploratory factor analysis is used here to uncover the underlying patterns. By applying EFA on two categories of experience, the results show that these factors can further be divided into three groups. Table 6 summarizes the results of this.
4.3 Hypothesis
To test the hypothesis formed in Sect. 1 , a correlation between various employee retention factors is computed (see Table 7 ) and the regression analysis is performed (see Table 8 ). Based on these, the formed hypothesis is either accepted or rejected.
4.3.1 H1: Better work environment will result in higher employee retention
The findings for hypothesis H1 indicate that the working environment is positively correlated with employee retention, which means a better working environment in an organization results in higher employee retention. The p value is less than 0.05 which means that there is a significant relationship between working environment and employee retention. The working environment`s B value is 0.294, which means that this factor has 29.4% of an impact on employee retention. The t value also shows that it has high impact on employee retention. Based on these results, H1 is accepted.
4.3.2 H2: Higher organizational commitment results in higher employee retention
The results in Tables 7 and 8 indicate that organizational commitment is slightly correlated with employee retention. The p value for this suggests that there is no significant relationship between organizational commitment and employee retention. The organizational commitment`s B value is 0.034, which means that this factor has 3.4% influence on employee retention. The t value also shows that it has low impact on employee retention. Therefore, H2 is rejected.
4.3.3 H3: Increase in reward and recognition system results in higher employee retention
The findings in Tables 7 and 8 for hypothesis H3 indicate that reward and recognition is positively correlated with employee retention. The p value for this is less than 0.05, which means that there is a significant relationship between reward/recognition and employee retention. For this factor, B value is 0.330, which means that this factor has 33% impact on employee retention. The t value also shows that it has a significant impact on employee retention. Therefore, this results in accepting H3.
4.3.4 H4: Increase in the individual’s work performance results in increased employee retention
The findings for hypothesis H4 indicate that work performance is positively correlated with employee retention. The p value is less than 0.05, which means that there is a significant relationship between work performance and employee retention. The work performance's B value is 0.311, which means that this factor has 31% of an impact on employee retention. The t value also shows that it has significant impact on employee retention. Based on these figures, H4 is accepted.

Accepted or rejected hypothesis
4.3.5 H5: Higher support and supervision by managers result in higher employee retention
The findings for hypothesis H5 in Tables 7 and 8 indicate that supervisor support is positively correlated with employee retention. The p value is less than 0.05, which means that there is a significant relationship between supervisor support and employee retention. The B value of supervisor support is 0.253, which means that this factor has 25.3% of an impact on employee retention. Therefore, H5 is accepted.
4.3.6 H6: Increase in employee income results in increased employee retention
The findings for hypothesis H6 indicate that income is positively correlated with employee retention. The p value of this factor is also less than 0.05, which means that there is a significant relationship between income and employee retention. The B value for income is 0.299, which means that this factor has 29.9% impact on employee retention. The t value also shows that it has high impact on employee retention. Based on these figures, H6 is accepted.
4.3.7 H7: Higher rate of bullying and work harassment results in lower employee retention
Finally, the findings for hypothesis H7 indicate that bullying and work harassment is slightly correlated with employee retention. The p value for this factor is not greater than 0.05, which means that there is no significant relationship between bullying and work harassment and employee retention. Therefore, H7 is rejected. Figure 4 pictorially represents the acceptance or rejection of the seven hypothesis.
4.4 Frequent items identification
The FIM technique [ 48 ] from the domain of data mining is utilized here to find factors that frequently occur together to influence employee retention. The FIM is used over transactional databases to find all those items that occur together above a certain frequency, known as the minimum support. In order to utilize FIM in this work, first all responses were converted in a database transaction format. Each row of the database represented all responses from a unique respondent. This formed a dataset with 853 records. Later, this dataset was partitioned into various categories to identify frequently occurring job retention factors for a specific group. This categorization was done for the following attributes: gender, marital status, overall experience, job description (organization), and income. Table 9 lists the results of this experiment. There are a number of algorithms available to extract the frequent items from a dataset. The output of all these algorithms is the same. However, they consume different amounts of execution time. From an application point of view, it does not matter which FIM algorithm is utilized as long as the dataset size is not extremely large. This work utilizes the AIM Footnote 2 (Another Itemset Miner) implementation of the FIM technique to extract patterns. For the sake of completeness, Fig. 5 shows a comparison of time consumed by AIM against another FIM algorithm, i.e., k DCI ( k Direct Count and Intersect) for various minimum support (minSup) values. The figure indicates that k DCI is quicker that AIM in finding the frequent itemsets.
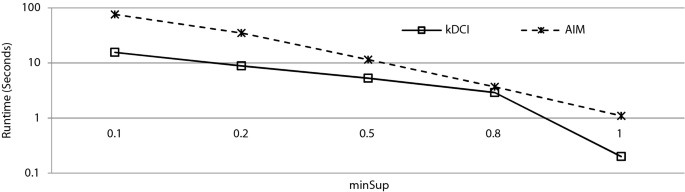
Performance comparison between kDCI and AIM in finding frequent items
4.5 Reliability test
A reliability test was conducted before any other test to make sure that the data are reliable. The Cronbach’s Alpha test was performed for the reliability of the data, and results indicated that the collected data were 87% reliable. Table 10 lists the results of this. The value of Cronbach’s alpha ranges between 0 and 1. A Cronbach’s alpha value greater than 0.6 is considered reliable. As shown in Table 10 , the value obtained for the collected data is 0.874 indicating the reliability of the collected data.
4.6 Comparison
This section presents a qualitative comparison between the present work and past contributions regarding the identification of factors that influence employee retention. The comparison is based on seven factors, i.e., has the work considered multiple sectors, are the data mining methods utilized, is there the use of computational methods in drawing conclusions, what is the sample size, what is the geographic location of the study, is the study employee centric or organizational centric, and does the survey contain open-ended questions. The choice of comparison methods is made here due to their closeness to the task at hand and recency. Table 11 lists the quantitative comparison. It can be observed that the present work utilizes data mining methods and covers multiple domains as compared to the past works. Additionally, the majority of the past work utilizes the computational methods to gain insights about the employee retention. The table also indicates that the use of open-ended questions is rare while collecting the data. A few works have not mentioned their sample size; therefore, this field is left blank in the table.
5 Policy implications
Labor laws in many developing countries are at a nascent stage. Debates on employee rights, such as medical cover [ 49 , 50 ], provisions of sabbaticals, data protection, diversity management, investing in human resource through training and development programs, etc., are still isolated practices only functional in a handful of multinational organizations in the developing world. This research provided an in-depth understanding of the impact of demographics on employee retention across multiple sectors, which will enable policymakers to (a) develop retention strategies in the backdrop of severe competition, (b) improve organizational long-term sustainability, (c) improve organizational brand name through providing better working conditions to employees, and (d) understand the dynamics of employee retention across multiple sectors and industries.
Increased global competition has inevitably led to a severe competition in talent acquisition and retention. Organizations, today, are not only competing for customers, but also for employees. Thus, losing a resourceful human talent can be devastating for an organization. If an organization is facing quick turnover, this can adversely affect its long-term sustainability. Talented employees are not only hard to find; they exist in clusters. Therefore, if an organization loses a dissatisfied employee, a bad word-of-mouth gets spread about the specific organization, which may then find it extremely hard to attract talented employees. Conversely, if an organization has a low employee turnover, the organization shall be able to contest and survive in highly competitive markets, ensure long-term sustainability, and celebrate a good brand name.
For policymakers, this research provides the basis to understand and re-evaluate the systems and practices of motivation; recognition and reward; and advancement and growth, by placing a strong emphasis on organizational justice. Policymakers shall be able improve their decision making through this research by considering numerous variables, which may impact employee behavior, specifically retention. This work enables policymakers to systematically diagnose and comprehend organizational structures and communicational channels in light of employees’ relationship and authority dynamics with the supervisor, thus redefining organizational esprit de corps in the developing world across multiple sectors. Through this research, policymakers shall be able to decipher the complexities of work conditions and highlight aspects which contribute to or pose a challenge to employee retention. Policymakers are interested in developing customized policies for clusters of employees who have similar ethical behavior and income level. This research dived deep into how ethical behavior and income level impact employee retention and how policymakers should distinguish between employees of varying ethical behaviors and income levels. Another policy implication of this research is that it shall enable policymakers to develop policies and practices which place emphasis on organizational commitment and satisfaction. The results revealed a strong relationship between organizational commitment and satisfaction, and employee retention. Policies and practices addressing organizational commitment and satisfaction shall not only ensure that talented employees are retained in the organization, but shall also attract new and budding talent more effectively and efficiently. Finally, bullying and work harassment has become a serious concern for several organizations in the developing countries. Gender discrimination discourages several women in the developing countries to either quit or switch their workplace. Bullying, harassment and gender discrimination are not only severely unethical, but also bring the organization in the limelight for the wrong reasons. Thus, this research provides policymakers with the insight and tools to develop proactive policies to discourage bullying and work harassment and encourage fair and equal treatment of all employees.
In a nutshell, at a microlevel, this research delivers policymakers with the right variables and tools to assess the state of employee retention in an organization. At the macrolevel, however, this research provides an in-depth analysis of trends and patterns of employee retention across multiple sectors. The research sheds light on how policymakers can encourage organizations to improve employee retention through training and development programs, medical cover, sabbatical, flexible working hours, etc. Through these techniques, policymakers can benchmark best practices for employee retention. Moreover, this work highlighted which sectors are severely suffering from low employee retention, thus allowing policymakers to target specific sectors/industries on a high-priority basis.
Like any other research, there were a few limitations of this study. The aspect of training and development was not considered in this work. Another limitation was that few respondents thought that survey forms were too lengthy and even some organizations rejected to fill out these. This study was only limited to the boundaries of Pakistan. The findings may be different if applied to a different country or may vary if considered different demographic variables.
6 Conclusion
Retaining skilled employees has always been a major concern for any organization across the globe. Organizations spend a significant amount on their training and development programs for this purpose. This work presented computational methods to identify factors for employee retention using their feedback collected through a questionnaire. The focus here was to identify factors to improve employee retention strategies based on the computational methods. A survey was conducted mainly within four sectors, namely health care, business, academics, and banking sector, to collect the data. The survey was divided into two parts: the first part included demographic information and the second part contained questions pertaining to employees’ job description and their satisfaction. The questions on the second portion were based on theories such as Herzberg's duality theory, expectancy theory, social cognitive theory, self-determination theory, social bonding theory, and sociocultural theory. The findings showed that the factors such as work environment, organization commitment, reward and recognition, work performance, supervisor support, income and bullying and work harassment have an impact on demographic profile. When these factors were correlated with employee retention, the statistical tests illustrated that, except organization commitment and bullying, all variables were identified to be strongly linked with employee retention. These factors have tended to have a power through which organization can improve the working environment and facilitate not only their client but also the employees.
From the extension point of view, there are many other factors that can be used for employee retention other than those utilized here. These may include training and development, medical cover, sabbatical and paid leaves, to name a few. This research can extend to multiple countries, and the effect of various cultures on the employee retention can be studied. The survey form can also have a few open-ended questions so that the investigation can better identify what an employee feels like when given an option to mention any factor of her choice.
Data availability
The data that support the findings of this study are available on request from the corresponding author. The data are not publicly available due to containing information that could compromise the privacy of research participants.
https://www.google.com/forms/about/ .
https://fimi.ua.ac.be/src/ .
Papa A, Dezi L, Gregori GL, Mueller J, Miglietta N (2018) Improving innovation performance through knowledge acquisition: the moderating role of employee retention and human resource management practices. J Knowl Manag 24(3):589–605
Article Google Scholar
Roslender R, Monk L, Murray N (2020) Promoting greater levels of employee health and well-being in the UK: how much worse do the problems have to get? In: Virtuous cycles in humanistic management, pp 135–149.
Silva HC, Lima F (2017) Technology, employment and skills: a look into job duration. Res Policy 46(8):1519–1530
Nekoei A, Weber A (2017) Does extending unemployment benefits improve job quality? Am Economic Rev 107(2):527–561
Aruna M, Anitha J (2015) Employee retention enablers: generation Y employees. SCMS J Indian Manag 12(3):94
Google Scholar
Deery M, Jago L (2015) Revisiting talent management, work-life balance and retention strategies. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 27(3):453–472
Ahammad MF, Tarba SY, Liu Y, Glaister KW (2016) Knowledge transfer and cross-border acquisition performance: the impact of cultural distance and employee retention. Int Bus Rev 25(1):66–75
Eisenberger R, Stinglhamber F, Vandenberghe C, Sucharski IL, Rhoades L (2002) Perceived supervisor support: contributions to perceived organizational support and employee retention. J Appl Psychol 87(3):565
Oswald AJ, Proto E, Sgroi D (2015) Happiness and productivity. J Labor Econ 33(4):789–822
Halim Z, Ali O, Khan G (2020) On the efficient representation of datasets as graphs to mine maximal frequent itemsets. IEEE Trans Knowl Data Eng. https://doi.org/10.1109/TKDE.2019.2945573
Tourangeau AE, Cummings G, Cranley LA, Ferron EM, Harvey S (2010) Determinants of hospital nurse intention to remain employed: broadening our understanding. J Adv Nurs 66(1):22–32
Ritter D (2011) The relationship between healthy work environments and retention of nurses in a hospital setting. J Nurs Manag 19(1):27–32
Tummers LG, Groeneveld SM, Lankhaar M (2013) Why do nurses intend to leave their organization? A large-scale analysis in long-term care. J Adv Nurs 69(12):2826–2838
Christmas K (2008) How work environment impacts retention. Nurs Econ 26(5):316
Deetz JM, Davidson JE, Daugherty J, Graham P, Carroll DM (2020) Exploring correlation of nurse manager meaning and joy in work with employee engagement. Appl Nurs Res. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apnr.2020.151297
Aggarwal N, Satyam MK (2020) The employees’ perception on formulation and implementation of HR retention strategies-an analytical study in hospitality industry of Garhwal and Kumaun Region of Uttarakhand. Stud Indian Place Names 40(3):4103–4111
Bashir S, Ramay MI (2008) Determinants of organizational commitment: a study of information technology professionals in Pakistan. J Behav Appl Manag 9(2):226
Nafei WA (2014) Assessing employee attitudes towards organizational commitment and change: the case of King Faisal Hospital in Al-Taif Governorate, Kingdom of Saudi Arabia. J Manag Sustain 4(1):204
Moynihan DP, Pandey SK (2007) Finding workable levers over work motivation: comparing job satisfaction, job involvement, and organizational commitment. Adm Soc 39(7):803–832
Aydogdu S, Asikgil B (2011) An empirical study of the relationship among job satisfaction, organizational commitment and turnover intention. Int Rev Manag Mark 1(3):43
Silbert L (2005) The effect of tangible rewards on perceived organizational support. Master's thesis, University of Waterloo.
Sankar M (2015) Impact of hygiene factors on employee retention: experimental study on paper industry. Indian J Manag Sci 5(1):58–61
Camps J, Oltra V, Aldás-Manzano J, Buenaventura-Vera G, Torres-Carballo F (2016) Individual performance in turbulent environments: the role of organizational learning capability and employee flexibility. Human Resour Manag 55(3):363–383
Maccoby M (1984) Helping labor and management set up a quality-of-worklife program. Mon Labor Rev 107(3):28–32
Bhatnagar J (2007) Talent management strategy of employee engagement in Indian ITES employees: key to retention. Empl Relat 29(6):640–663
Deery M (2008) Talent management, work-life balance and retention strategies. Int J Contemp Hosp Manag 20(7):792–806
Gevrek D, Hudgins D, Spencer MK (2020) Detecting a shade of schadenfreude in employee satisfaction with salary raises. Appl Econ Lett. https://doi.org/10.1080/13504851.2020.1711506
Rombaut E, Guerry MA (2020) The effectiveness of employee retention through an uplift modeling approach. Int J Manpower. https://doi.org/10.1108/IJM-04-2019-0184
Hoel H, Cooper CL, Faragher B (2001) The experience of bullying in Great Britain: the impact of organizational status. Eur J Work Org Psychol 10(4):443–465
Halim Z, Atif M, Rashid A, Edwin CA (2019) Profiling players using real-world datasets: clustering the data and correlating the results with the big-five personality traits. IEEE Trans Affect Comput 10(4):586–584
Salin D, Notelaers G (2020) Friend or foe? The impact of high-performance work practices on workplace bullying. Human Resour Manag J 30(2):312–326
Klippert I (2014) Employee retention management. Instruments of Human Resources in the view of current developments.
Armstrong-Stassen M, Schlosser F (2010) When hospitals provide HR practices tailored to older nurses, will older nurses stay? It may depend on their supervisor. Human Resour Manag J 20(4):375–390
Odubanjo D (2015) Employee retention strategies in Gauff Consultants (Nigeria) Limited. A case study on Gauff Consultants Nigerial Limited (Doctoral dissertation, Dublin Business School).
Mahal PK (2012) HR practices as determinants of organizational commitment and employee retention. IUP J Manag Res 11(4):37
Ovadje F, Muogboh O (2009) Exploring the motivation to stay and to perform among managers in Nigeria. Int J Bus Res 9(3):1555–1296
Halim Z, Waqas M, Baig AR, Rashid A (2017) Efficient clustering of large uncertain graphs using neighborhood information. Int J Approx Reason 90:274–291
Article MathSciNet MATH Google Scholar
Halim Z, Muhammad T (2017) Quantifying and optimizing visualization: an evolutionary computing-based approach. Inf Sci 385:284–313
Halim Z, Baig AR, Abbas G (2015) Computational Intelligence-based Entertaining Level Generation for Platform Games. Int J Comput Intell Syst 8(6):1128–1143
Muhammad T, Halim Z (2016) Employing artificial neural networks for constructing metadata-based model to automatically select an appropriate data visualization technique. Appl Soft Comput 49:365–384
Zafar K, Baig AR, Bukhari N, Halim Z (2011) Route planning and optimization of route using Simulated ant agent system. J Circuits Syst Comput 20(30):457–478
Iqbal S, Halim Z (2020) Orienting conflicted graph edges using genetic algorithms to discover pathways in protein-protein interaction networks. IEEE/ACM Trans Comput Biol Bioinf. https://doi.org/10.1109/TCBB.2020.2966703
Chiu RK, Wai-Mei Luk V, Li-Ping Tang T (2002) Retaining and motivating employees: compensation preferences in Hong Kong and China. Personnel Rev 31(4):402–431
Lall S (2004) The employment impact of globalization in developing countries. Understanding globalization, employment and poverty reduction. Palgrave Macmillan, New York, pp 73–101
Lowell BL, Findlay A (2001) Migration of highly skilled persons from developing countries: impact and policy responses. Int Migr Papers 44:25
Alon I, Boulanger M, Elston JA, Galanaki E, Martínez de Ibarreta C, Meyers J, Muñiz-Ferrer M, Vélez-Calle A (2018) Business cultural intelligence quotient: a five-country study. Thunderbird Int Bus Rev 60(3):237–250
Latham GP (2012) Work motivation: history, theory, research, and practice. Sage, Thousand Oaks
Book Google Scholar
Bashir S, Halim Z, Baig A (2008) Mining fault-tolerant frequent patterns using pattern growth approach. In: 6th ACS/IEEE international conference on computer systems and applications, pp 172–179
Amina T, Shanchita RK, Basharat A (2020) Internet use, ehealth literacy, and dietary supplement use among young adults in Pakistan: cross-sectional study. J Med Internet Res 22(6):e17014
Hyde LL, Boyes AW, Evans TJ, Mackenzie LJ, Sanson-Fisher R (2018) Three-factor structure of the eHealth literacy scale among magnetic resonance imaging and computed tomography outpatients: a confirmatory factor analysis. JMIR Human Factors 5(1):66
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
The Machine Intelligence Research Group (MInG), Faculty of Computer Science and Engineering, Ghulam Ishaq Khan Institute of Engineering Sciences and Technology, Topi, 23460, Pakistan
Zahid Halim, Muhammad Waqas & Ahsan Shah
Projects and Creative Department, Lead360, Karachi, 74600, Pakistan
Faculty of Information Technology, Beijing University of Technology, Beijing, 100000, China
Muhammad Waqas
Department of Management Sciences, CECOS University of Information Technology and Emerging Sciences, Peshawar, 25000, Pakistan
Cedric A. Edwin
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Zahid Halim .
Ethics declarations
Conflict of interest.
The authors declare that they have no conflict of interest.
Additional information
Publisher's note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Halim, Z., Maria, Waqas, M. et al. Identifying factors for employee retention using computational techniques: an approach to assist the decision-making process. SN Appl. Sci. 2 , 1612 (2020). https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03415-5
Download citation
Received : 10 April 2020
Accepted : 23 August 2020
Published : 31 August 2020
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/s42452-020-03415-5
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Employee retention
- Frequent items mining
- Retention strategies
- Organizational environment
- Find a journal
- Publish with us
- Track your research
Examining employee retention and motivation: the moderating effect of employee generation
Evidence-based HRM
ISSN : 2049-3983
Article publication date: 18 April 2022
Issue publication date: 20 September 2022
This study explored moderating effects of employee generations on factors related to employee retention and motivation in the workplace.
Design/methodology/approach
The authors developed a survey instrument and collected the survey data via Amazon Mechanical Turk. After filtering out bad responses, the authors ended up with 489 sample cases for this study. The authors used structural equation modeling for data analysis.
Evidence showed that only transformational leadership was significantly related to retention of Generation X employees and only work–life balance had a significant relationship with intrinsic motivation. For Generation Y employees, transformational leadership was the only factor affecting their retention while both transformational leadership and autonomy showed significant impacts on their intrinsic motivation. Generation Z employees reported that only transformation leadership affected their retention while transformational leadership, corporate social responsibility and autonomy were significantly related to their intrinsic motivation in the workplace. All three generations showed statistical significance between intrinsic motivation and employee retention.
Practical implications
This study could help business practitioners increase employees' work motivation and retention.
Originality/value
First, our results revealed interesting similarities and differences between generations in terms of the factors that affected employees' retention and motivation. Second, this study proved that employees' generation affects the impacts of transformational leadership, CSR, autonomy, WLB and technology on their motivation and retention in the workplace. Third, the results of our study also showed that employees of different generations are intrinsically motivated by different factors, proving the importance of considering generational differences in motivation literature.
- Employee generation
- Generational differences
Lee, C.C. , Lim, H.S. , Seo, D.(J). and Kwak, D.-H.A. (2022), "Examining employee retention and motivation: the moderating effect of employee generation", Evidence-based HRM , Vol. 10 No. 4, pp. 385-402. https://doi.org/10.1108/EBHRM-05-2021-0101
Emerald Publishing Limited
Copyright © 2022, Emerald Publishing Limited
1. Introduction
For the past several decades, employee retention has been an important topic to both scholars and practitioners because employees, the most valuable assets of an organization, are the ones who add to its value, quantitatively and qualitatively ( Anitha, 2016 ). Therefore, employers have taken steps to ensure that employees stay with the organization for as long as possible ( Alferaih et al. , 2018 ). Doing so is challenging because the workforce is becoming more confident and demanding due to changes in markets and demographics ( Anitha, 2016 ). A disengaged workforce leads to higher turnover rates that increase the costs of recruiting and selecting new employees ( Malinen et al. , 2013 ).
The objective of this study is to examine the moderating effects of employee generations on factors related to employee retention and motivation in the workplace. In doing so, this study makes a significant contribution to literature in several ways. First, although there have been numerous studies on factors that affect employees' retention such as a manger's leadership style (e.g. Khan and Wajidi, 2019 ), a firm's commitment to corporate social responsibility (e.g. Valentine and Godkin, 2017 ), autonomy (e.g. Kim and Stoner, 2008 ), work–life balance (e.g. Koubova and Buchko, 2013 ) and technology (e.g. Haar and White, 2013 ), there are no studies that have examined the effect of these five factors on employee retention and the underlying mechanism of these relationships. Second, few studies have examined effects of these five factors on different generations of employees – Gen X, Gen Y (also known as the Millennials) and Gen Z. Studies have focused on certain generations such as Gen Y (e.g. García et al. , 2019 ) or Gen X (e.g. Westerman and Yamamura, 2007 ), but no studies have been conducted to understand the different effects of the five factors on employee retention spanning three different generations. According to the US Bureau of Labor Statistics (2021) , while 40% of the 2020 American workforce comprises Gen X and 44% of Gen Y, Gen Z represented 15% of the American workforce. This indicates that Gen Z has also become an important generation to consider when examining generational differences of employee retention. Finally, no studies have reported the effects of these variables on retaining employees from these various generations during the pandemic. Retaining employees is a challenge at the best of times, but it has become even more challenging during the pandemic. A recent survey of working age people in various industries found that about 40% of respondents expressed strong intention to quit their current job in the next three to six months ( De Smet et al. , 2021 ).
2. Literature review and hypotheses
2.1 employee generations.
Based on the generational theory originated from the work of Mannheim (1970) , generations refer to groups of individuals (i.e. cohorts) born in the same period, sharing similar historical events and social experiences. This means that a cohort of individuals who shared common historical and social experiences are more likely to share similar characteristics, attitudes and behaviors ( Strauss and Howe, 1991 ). Given that the main objective of this study is to examine generational differences in effects of leadership styles, corporate social responsibility, autonomy, work–life balance and technology on intrinsic motivation and employee retention, we will use the generational theory as our theoretical framework to develop hypotheses in the next sections.
2.2 Effects of leadership across generations
Transformational leadership is defined as transforming the values and priorities of followers and motivating them to perform beyond their expectations ( Kark et al. , 2003 ). Concurrently, Wilkesmann and Schmid (2014) reported that one characteristic of strong leaders is the ability to motivate and influence people. Motivation was also found to be a complex act that had several factors involved. Employees, who were proactive both at work and in their personal lives, were positively affected by both their employer's leadership style and ability to foster a team and showed stronger motivation ( Felfe and Schyns, 2014 ; Khan and Wajidi, 2019 ). Gerhold and Whiting (2020) explored the motivations of employees over several generations, from Boomers to Gen Z, and the leadership skills that inspired them. They found no significant differences among generations. Rather the differences were driven more by an employee's stage of life and career than age. They reported that leadership fundamentals were a constant. These fundamentals, building strong teams, providing feedback and understanding employees' motivations, were multi-generationally relevant skills. In addition, Diskiene et al. (2019) found that the relationship between a leader's emotional and social intelligence and an employee's motivation to work was undeniable, although there was some variance depending on the latter's age. Interestingly, younger workers relied less on their leader's emotional stability to motivate them than older, more experienced workers.
The generation of employees will moderate the effect of leadership on their intrinsic motivation in the workplace, such that transformational leadership is more positively related to the workplace motivation of younger generation employees.
The generation of employees will moderate the effect of leadership on employees' retention in the workplace, such that transformational leadership is more positively related to the workplace retention of younger generation employees.
2.3 Effects of corporate social responsibility across generations
The generation of employees will moderate the effect of CSR on employees' intrinsic motivation in the workplace, such that greater CSR is more positively related to the workplace motivation of younger generation employees.
The generation of employees will moderate the effect of CSR on employees' retention in the workplace, such that a CSR policy is more positively related to the retention of younger generation employees.
2.4 Effects of autonomy across generations
The generation of employees will moderate the effect of autonomy on employees' motivation in the workplace, such that greater autonomy in one's job role is more positively related to the workplace motivation of younger generation employees.
The generation of employees will moderate the effect of autonomy on employees' retention in the workplace, such that greater autonomy is more positively related to the retention of younger generation employees.
2.5 Effects of work–life balance across generations
The generation of employees will moderate the effect of WLB on employees' motivation in the workplace, such that greater WLB is more positively related to the workplace motivation of a younger generation of employees.
The generation of employees will moderate the effect of WLB on employees' retention in the workplace, such that greater WLB is positively related to the retention of a younger generation of employees.
2.6 Effects of technology across generations
The generation of employees will moderate the effect of technology on employees' motivation in the workplace, such that more technology is more positively related to the workplace motivation of younger generation employees.
Companies competent with IT knowledge, objects and entrepreneurship had better chances of attracting loyal prospects and retaining their employees, especially those of Gen Z ( Haar and White, 2013 ). In addition to attracting employees, digital communication created two-way channels of dialogue and helped employees understand how their roles were helping the company. This increases possible retention rates ( Kick et al. , 2015 ).
The generation of employees will moderate the effect of technology on employees' retention in the workplace, such that more technology is more positively related to the retention of younger generation employees.

2.7 Motivation and retention
Employees' intrinsic motivation is positively related to their retention in all generations.
3.1 Sample data and questionnaire
The definition of generations in terms of the birth year varies across studies. As a compromise, we used the middle value. Thus, for the purpose of this study, three generations (Gen X, Y and Z) are defined based on the age as of August 2020. Specifically, Gen X is between 40 and 55 years old; Gen Y is between 25 and 39 years old; and Gen Z is between 18 and 24 years old. We created a survey questionnaire with the items that measured our variables and posted it on Google Forms. To take the survey, we required members of Amazon's Mechanical Turk to be employed and ages 18–55 years old. The survey was first run for a week in the third week of April 2020 and received 570 responses. We deleted 9 responses due to repeat responses and 24 due to multiple missing values, which reduced the total number of valid responses to 537. Furthermore, 48 responses were deleted due to poor response quality. Poor responses were identified using items that were reverse coded. After removing the poor responses, we were left with 489 useable and valid sample cases for this research. Regarding the sample size per each generation group, Gen Z is 120 (24%), Gen Y is 278 (56%) and Gen X is 91 (18%).
3.2 Measures
Our participants indicated their responses to all items on a 7-point Likert-type scales, ranging from 1 (strongly disagree) to 7 (strongly agree). Note that Cronbach's alpha for all variables exceeded the 0.70 cutoff value ( Greco et al. , 2018 ), indicating that all of the variables were reliable and could be used in the analysis. Examples of each item for each category are in Table 1 .
3.2.1 Retention
We used three items from Armstrong-Stassen and Schlosser (2008) to measure the employees' intention to remain with their company.
3.2.2 Transformational leadership
We used the Vera and Crossan (2004) 12-item scale to assess transformational leadership, consisting of four dimensions – charismatic leadership, inspirational motivation, intellectual stimulation and individual consideration.
3.2.3 Corporate social responsibility
We chose items from Woo (2013) to measure, which assessed five dimensions of CSR: environment, human rights and labor issues, product responsibility, society and economics. We excluded the product responsibility category because of low factor loading problems.
3.2.4 Autonomy
We used three items from Hackman and Oldham (1976) to assess autonomy.
3.2.5 Work–life balance
To measure this variable, we used five items from Brett and Stroh (2003) .
3.2.6 Technology
To measure this variable, we picked three items from Nambisan et al. (1999) .
3.2.7 Intrinsic motivation
We used items from Grant (2008) to measure intrinsic motivation.
3.3 Analytical models
In this study, we created three analytical models to test our hypotheses that examine the generational differences in the relationships between five independent variables and three dependent variables. The first model was the intrinsic motivation model in which intrinsic motivation was the dependent variable and transformational leadership, CSR, autonomy, WLB and technology were the independent variables. Y 1 = β 0 + β 1 X 1 + β 2 X 2 + β 3 X 3 + β 4 X 4 ( w h e r e Y = I n t r i n s i c M o t i v a t i o n ; X 1 = T r a n s f o r m a t i o n a l L e a d e r s h i p ; X 2 = C o r p o r a t e S o c i a l R e s p o n s i b i l i t y ; X 3 = A u t o n o m y , X 4 = W o r k - L i f e B a l a n c e ; X 5 = T e c h n o l o g y )
The second model was the retention model in which retention was the dependent variable and the five independent variables were the same as the first model. Y 2 = β 0 + β 1 X 1 + β 2 X 2 + β 3 X 3 + β 4 X 4 ( w h e r e Y 2 = R e t e n t i o n ; s a m e f o r X 1 t o 4 )
The third model examined whether intrinsic motivation affects retention. Retention was the dependent variable and intrinsic motivation was an independent variable. Y 2 = β 0 + β 1 Y 1 ( w h e r e Y 2 = R e t e n t i o n ; Y 1 = I n t r i n s i c M o t i v a t i o n )
Figure 1 describes our analytical models with the results. When conducting three analytical models, we used a subsample analysis instead of a two-way interaction design to examine generational differences in the relationships as we hypothesized. This method allows us to compare the impact of each independent variable on dependent variables among different generations of employees. This approach is preferable because it reduces the possibility that noise will be introduced into the model ( Stone-Romero and Anderson, 1994 ).
4.1 Descriptive statistics and correlations
Table 2 summarizes descriptive statistics for the variables used in our study.
4.2 Measurement model
To evaluate the fit of our measurement model, we conducted a series of confirmatory factor analyses (CFA). We used several fit indices such as chi-square ( χ 2 ) values, the Comparative Fit Index (CFI), the Root Mean Square Error of Approximation (RMSEA) and the Standardized Root Mean Square Residual (SRMR). As shown in Table 3 , the results of CFA suggest an excellent fit ( χ 2 = 757.41, p < 0.01; CFI = 0.95, RMSEA = 0.06, SRMR = 0.07) for our hypothesized seven-factor model ( Hooper et al. , 2008 ). In addition to our focal seven-factor model, we further assessed the fit of alternative models. The results proved that the hypothesized seven-factor model fits the data significantly better than the other possibilities.
Several statistical indictors were used to assess the reliability and the convergent and discriminant validity of our constructs. As shown in Table 4 , composite reliability (CR) estimated our constructs to be from 0.885 to 0.946, which were all above the threshold value of 0.7 ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981 ). Therefore, internal consistency was validated. Convergent validity of the constructs was also acceptable. All estimated factor loadings were significant at p < 0.001, and all estimates are above 0.6 and most estimates are above 0.7. Furthermore, average variance extracted (AVE) for all constructs are above 0.5, the acceptable threshold level ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981 ). Given that the AVE for each construct was greater than the squared correlations between two constructs ( Fornell and Larcker, 1981 ), discriminant validity of the constructs was achieved. Hence, these results provided support for using the seven constructs as reliable and distinctive variables in our analysis.
4.3 Test for the potential common method bias
Given the nature of our data using a single source of information, we tried to control for common method bias with both procedural and statistical remedies. In terms of procedural remedies, we ensured respondent anonymity, provided a guidance with detailed instruction, added reversed items and minimized the length of the survey following guidelines provided by Podsakoff and Organ (1986) . In terms of statistical remedies, we conducted Harman's single-factor test to examine potential common method bias ( Harman, 1967 ; Podskoff and Organ, 1986 ). Our results of the Harman's single-factor test indicated that the single factor accounted for 43.37% of the total variance, not exceeding 50% ( Podsakoff and Organ, 1986 ). Thus, common method bias does not appear to be an issue in this study.
4.4 Testing hypotheses using structural equation model
The results of the testing using structural equation modeling showed that the hypothesized model yielded an excellent fit ( χ 2 = 2,194.49). In order to further assess the validity of the hypothesized model, we tested a more parsimonious model that removed the direct paths from the independent variables to retention. This would be an alternative model. According to the principle of model parsimony, an alternative model would fit the data better if the χ 2 value of the hypothesized model did not drop significantly. If the χ 2 value of the hypothesized model dropped significantly, however, the hypothesized model would fit the data better. Although the alternative model also yielded an excellent fit ( χ 2 = 2,316.78), our hypothesized model provided a significantly better model fit compared to the alternative model (Δ χ 2 = 122.29). Table 5 presents a summary of the fit indices for the hypothesized and alternative models.
Consistent with H1a , the effects of transformational leadership on the employees' intrinsic motivation were different among the generations. They were significant for Gen Y ( β = 0.50, p < 0.01) and Gen Z ( β = 0.37, p < 0.01), but not for Gen X ( β = 0.18, n.s. ), supporting H1a . Although transformational leadership had a significant effect on all employees' retention ( β = 0.30, p < 0.01 for Gen X; β = 0.33, p < 0.01 for Gen Y; β = 0.29, p < 0.01 for Gen Z), the effects were not different across generation groups. Therefore, H1b was not supported.
Consistent with H2a , CSR was positively and significantly related to employees' intrinsic motivation for Gen Z ( β = 0.23, p < 0.05), but not for Gen X ( β = 0.03, n.s. ) or Gen Y ( β = −0.02, n.s. ). However, the effects of CSR on employees' retention were not significant in any of the generation groups ( β = 0.03, n.s. for Gen X; β = 0.03, n.s. for Gen Y; β = 0.02, n.s. for Gen Z), failing to support H2b .
Supporting H3a , autonomy was positively and significantly related to employees' intrinsic motivation for Gen Y ( β = 0.28, p < 0.01) and for Gen Z ( β = 0.24, p < 0.05), but not for Gen X ( β = 0.18, n.s. ). H3b was not supported because autonomy did not have a significant impact on employees' retention in any of the generation groups ( β = 0.01, n.s. for Gen X; β = 0.01, n.s. for Gen Y; β = 0.01, n.s. for Gen Z).
Hypotheses 4a proposed that the effect of WLB on employees' intrinsic motivation would be more significant to younger generations while Hypothesis 4b proposed that the effect of WLB on employees' retention would be more significant to younger generations. The results revealed that WLB was positively and significantly related to employees' intrinsic motivation for Gen X ( β = 0.42, p < 0.01), but not for Gen Y ( β = 0.04, n.s. ) and Gen Z ( β = 0.05, n.s. ). However, WLB did not have a significant effect on employees' retention in any of the generation groups ( β = 0.01, n.s. for Gen X; β = 0.04, n.s. for Gen Y; β = 0.02, n.s. for Gen Z). H4a was not supported because the effect of WLB on intrinsic motivation was not significant among younger generations, Gen Y and Gen Z. In addition, H4b was not supported because no significant difference was found among the three generations.
Hypotheses 5a and 5b proposed that the effect of technology on employees' intrinsic motivation ( H5a ) and their retention ( H5b ) would differ by generation. However, technology had no significant effect on employees' intrinsic motivation in any generation groups ( β = 0.08, n.s. for Gen X; β = 0.07, n.s. for Gen Y; β = 0.05, n.s. for Gen Z). Furthermore, technology had no significant effect on employees' retention in any generation groups ( β = 0.03, n.s. for Gen X; β = 0.05, n.s. for Gen Y; β = 0.04, n.s. for Gen Z). Based on these findings, neither H5a nor H5b was supported.
Hypothesis 6 proposed that employees' intrinsic motivation would be positively related to their retention in all generations. Our findings supported this contention ( β = 0.54, p < 0.01 for Gen X; β = 0.48, p < 0.01 for Gen Y; β = 0.49, p < 0.01 for Gen Z).
5. Discussion
5.1 theoretical contributions.
The results of this study provided several theoretical contributions to management literature. First, our results revealed interesting similarities and differences between generations in terms of the factors that affected employees' retention and motivation. For Gen X employees, transformational leadership was significantly related to retention and only WLB had a significant relationship with their intrinsic motivation. For Gen Y employees, transformational leadership was also the only factor affecting their retention, while both transformational leadership and autonomy had a significant impact on their intrinsic motivation. Finally, for Gen Z employees, only transformation leadership also mattered for their retention while transformational leadership, corporate social responsibility and autonomy were significantly related to their intrinsic motivation. For all three generations, there was a statistically significant relationship between intrinsic motivation and employee retention.
Second, this study proved that employees' generation affects the impacts of transformational leadership, CSR, autonomy, WLB and technology on their motivation and retention in the workplace. As motivating and retaining employees becomes more challenging and workforces become more diverse in terms of generation, understanding generational differences in employee motivation and retention becomes a very important topic to explore. Only a few studies looked at generational differences in either employee motivation ( Andrade and Westover, 2018 ) or employee's retention ( Roman-Calderon et al. , 2019 ) and no studies have examined the different effects of transformational leadership, CSR, autonomy, WLB and technology on employee motivation and retention spanning three different generations.
Third, the results of our study also showed that employees of different generations are intrinsically motivated by different factors, proving the importance of considering generational differences in motivation literature. However, our results did not provide empirical support for generational differences in retaining employees. Interestingly, only transformational leadership significantly affected employees of all generations. This finding would emphasize the critical role of leadership in retaining employees regardless of their generation.
5.2 Practical implications
The retention of an employee, especially younger generation employees, is pivotal in ensuring that organizations will be able to maintain sustained competitive advantages during the period of the pandemic since many companies have been experiencing serious younger generation employee retention issue. For instance, major retail companies, such as Target and Walmart, have been confronted with challenging managerial decisions because of the workforce shortage and have been forced to decrease their operation hours. To resolve this challenge, many companies have tried to increase the retention rate of their employees, especially those of the younger generation, by offering competitive financial and non-financial packages such as signing bonuses, healthcare benefits and/or opportunities for a college education. Despite all these endeavors, many companies have still been experiencing serious employee retention problems, which they have never experienced before. The findings of this study could be highly useful for organizations that are experiencing serious employee retention issues, many of whom are younger generation employees who are quitting their jobs during the pandemic.
First, these findings suggest reasons why so many organizations have had a challenging time managing low employee retention rates by showing that the impact of major factors (transformational leadership, CSR, autonomy, WLB and technology) on employee retention could vary depending on an employee's generation. For instance, our study's findings show that organizations actively implementing CSR policies may positively affect the retention of younger generation employees relative to older generations by intrinsically motivating younger generation employees more. Therefore, organizations should consider generational differences in employee motivation and retention when implementing employee retention strategies since an effective strategy for one employee generation may not be effective (or even harmful) for another employee generation.
Second, these results illustrate that employee retention is not a simple function, but rather a result of interactions between employee motivation and the specific generation. For instance, for Gen X, even though job autonomy does not directly affect employee retention, job autonomy still plays a crucial role in affecting employee retention by affecting employee motivation. Therefore, organizations should take care of factors affecting employee motivation as well because employee motivation works as a significant pathway to boost employee retention.
5.3 Limitations and future research directions
While the study advances our understanding in these areas, it has several limitations that future studies could explore. First, given that our study was a cross-sectional study with all responses collected from a single period, strong causality arguments cannot be made. Considering that our study collected the sample during the period of pandemic, it would have been a more interesting study if we deployed a longitudinal design because longitudinal data would have allowed us to examine how our independent variables affected employee motivation and retention as employee worked through the pandemic. Future studies should implement longitudinal design by collecting samples at different time points to provide greater insight into the causality argument as well as into the impact of the pandemic. Second, although this study examined the impact of employee motivation on employee retention as a significant pathway, we didn’t test the mediating effect of employee motivation on employee retention. Further studies could be done to investigate the mediating effect of employee motivation on employee retention in the context of different employee generations. Furthermore, regarding employee generation as a moderator, even though we used sub-sample design to examine the moderating impact of an employee's generation on employee motivation and retention, further studies could test the effect of the interaction between our independent variables and employee generation. Third, future studies could extend our study by examining whether our findings could change depending on the industry (e.g. retail, manufacturing) as well as firm characteristics (e.g. size). For instance, stronger impact of CSR on employee motivation in Gen Z may not exist in the financial industry wherein competitive environment and culture dominates.
Research framework
Summary of measure
Means, standard deviations and correlations of the variables
Summary of the reliability and the convergent and discriminant validity of constructs
Aboramadan , M. ( 2021 ), “ Servant leadership and followers' creativity: does climate for creativity matter? ”, Evidence-Based HRM , Vol. 9 No. 1 , pp. 78 - 94 .
Ahsan , R. , Hossain , M.S. and Akter , S. ( 2016 ), “ The strategic interplay among work life balance, age, employee experience and employee retention: evidence from the pharmaceutical industry in Bangladesh ”, Independent Business Review , Vol. 9 No. 1 , pp. 87 - 103 .
Al-Asfour , A. and Lettau , L. ( 2014 ), “ Strategies for leadership styles for multi-generational workforce ”, Journal of Leadership, Accountability and Ethics , Vol. 11 No. 2 , pp. 58 - 69 .
Alatawi , M.A. ( 2017 ), “ Can transformational managers control turnover intention? ”, SA Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 15 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 6 .
Alferaih , A. , Sarwar , S. and Eid , A. ( 2018 ), “ Talent turnover and retention research: the case of tourism sector organisations in Saudi Arabia ”, Evidence-based HRM , Vol. 6 No. 2 , pp. 166 - 186 .
Andrade , M. and Westover , J. ( 2018 ), “ Generational differences in work quality characteristics and job satisfaction ”, Evidence-based HRM , Vol. 6 No. 3 , pp. 287 - 304 .
Anitha , J. ( 2016 ), “ Role of organisational culture and employee commitment in employee retention ”, ASBM Journal of Management , Vol. 9 No. 1 , pp. 17 - 28 .
Armstrong-Stassen , M. and Schlosser , F. ( 2008 ), “ Benefits of a supportive development climate for older workers ”, Journal of Managerial Psychology , Vol. 23 No. 4 , pp. 419 - 437 .
Bornman , D. ( 2019 ), “ Gender-based leadership perceptions and preferences of Generation Z as future business leaders in South Africa ”, Acta Commercii , Vol. 19 No. 1 , pp. 1 - 11 .
Brett , J. and Stroh , L. ( 2003 ), “ Working 61 plus hours a week: why do managers do it? ”, Journal of Applied Psychology , Vol. 88 No. 1 , pp. 67 - 78 .
Bui , H. , Liu , G. and Footner , S. ( 2016 ), “ Perceptions of HR practices on job motivation and work-life balance ”, International Journal of Manpower , Vol. 37 No. 6 , pp. 1004 - 1023 .
Chaudhary , R. ( 2018 ), “ Can green human resource management attract young talent? An empirical analysis ”, Evidence-Based HRM , Vol. 6 No. 3 , pp. 305 - 319 .
Clausen , S. ( 2009 ), Why People Stay: Exploring the Relationship between Leadership and Retention , Unpublished doctoral dissertation , Alliant International University .
Cohen , M. , de Souza Costa Neves Cavazotte , F. , da Costa , T. and Ferreira , K. ( 2017 ), “ Corporate social-environmental responsibility as an attraction and retention factor for young professionals ”, Brazilian Business Review , Vol. 14 No. 1 , pp. 21 - 41 .
Coldwell , D. , Billsberry , J. , van Meurs , N. and Marsh , P. ( 2008 ), “ The effects of person-organization ethical fit on employee attraction and retention: towards a testable explanatory model ”, Journal of Business Ethics , Vol. 78 No. 4 , pp. 611 - 622 .
De Smet , A. , Dowling , B. , Mugayar-Baldocchi , M. and Schaninger , B. ( 2021 ), Great Attrition' or 'great Attraction'? the Choice Is Yours , McKinsey & Company .
Deery , M. ( 2008 ), “ Talent management, work-life balance and retention strategies ”, International Journal of Contemporary Hospitality Management , Vol. 20 No. 7 , pp. 792 - 806 .
Dex , S. and Bond , S. ( 2005 ), “ Measuring work–life balance and its covariates ”, Work, Employment and Society , Vol. 19 No. 3 , pp. 627 - 637 .
Diskiene , D. , Pauliene , R. and Ramanauskaite , D. ( 2019 ), “ Relationships between leadership competencies and employees' motivation, initiative and interest to work ”, Montenegrin Journal of Economics , Vol. 15 No. 1 , pp. 113 - 129 .
Dizaho , E. , Salleh , R. and Abdullah , A. ( 2017 ), “ Achieving work life balance through flexible work schedules and arrangements ”, Global Business and Management Research: An International Journal , Vol. 9 No. 1 , pp. 455 - 465 .
Elias , S. , Smith , W. and Barney , C. ( 2012 ), “ Age as a moderator of attitude towards technology in the workplace: work motivation and overall job satisfaction ”, Behaviour and Information Technology , Vol. 31 No. 5 , pp. 453 - 467 .
Farr-Wharton , R. , Brunetto , Y. and Shacklock , K. ( 2011 ), “ Professionals' supervisor-subordinate relationships, autonomy and commitment in Australia: a leader-member exchange theory perspective ”, The International Journal of Human Resource Management , Vol. 22 No. 17 , pp. 3496 - 3512 .
Felfe , J. and Schyns , B. ( 2014 ), “ Romance of motivation and leadership to lead ”, Journal of Managerial Psychology , Vol. 29 No. 7 , pp. 1 - 17 .
Fiaz , M. , Su , Q. , Amir , I. and Saqib , A. ( 2017 ), “ Leadership styles and employees' motivation: perspective from an emerging economy ”, The Journal of Developing Areas , Vol. 51 No. 4 , pp. 143 - 156 .
Fornell , C. and Larcker , D. ( 1981 ), “ Evaluating structural equation models with unobservable variables and measurement error ”, Journal of Marketing Research , Vol. 18 No. 1 , pp. 39 - 50 .
García , G. , Gonzales-Miranda , D. , Gallo , O. and Roman-Calderon , J. ( 2019 ), “ Employee involvement and job satisfaction: a tale of the millennial generation ”, Employee Relations , Vol. 41 No. 3 , pp. 374 - 388 .
George , C. ( 2014 ), “ Retaining professional workers: what makes them stay? ”, Employee Relations , Vol. 37 No. 1 , pp. 102 - 121 .
Gerhold , C. and Whiting , A. ( 2020 ), “ From boomers to gen z: leading across generations ”, Leadership Excellence , Vol. 37 No. 3 , pp. 11 - 14 .
Ghosh , P. , Satyawadi , R. , Joshi , J. and Shadman , M. ( 2012 ), “ Who stays with you? Factors predicting employees' intention to stay ”, International Journal of Organizational Analysis , Vol. 21 No. 3 , pp. 288 - 312 .
Grant , A. ( 2008 ), “ Does intrinsic motivation fuel the prosocial fire? Motivational synergy in predicting persistence, performance, and productivity ”, Journal of Applied Psychology , Vol. 93 No. 1 , pp. 48 - 58 .
Greco , L. , O'Boyle , E. , Cockburn , B. and Yuan , Z. ( 2018 ), “ Meta‐analysis of coefficient alpha: a reliability generalization study ”, Journal of Management Studies , Vol. 55 No. 4 , pp. 583 - 618 .
Haar , J. and White , B. ( 2013 ), “ Corporate entrepreneurship and information technology towards employee retention: a study of New Zealand firms ”, Human Resource Management Journal , Vol. 23 No. 1 , pp. 109 - 125 .
Hackman , J. and Oldham , G. ( 1976 ), “ Motivation through the design of work: test of a theory ”, Organizational Behavior and Human Performance , Vol. 16 No. 2 , pp. 250 - 279 .
Harman , H. ( 1967 ), Modern Factor Analysis , University of Chicago Press , Chicago, IL .
Hicks , M. ( 2018 ), “ How HR execs can use technology to connect a divided workforce ”, Strategic HR Review , Vol. 17 No. 1 , pp. 23 - 28 .
Hooper , D. , Coughlan , J. and Mullen , M. ( 2008 ), “ Structural equation modelling: guidelines for determining model fit ”, Electronic Journal of Business Research Methods , Vol. 6 No. 1 , pp. 53 - 60 .
Kark , R. , Shamir , B. and Chen , G. ( 2003 ), “ The two faces of transformational leadership: empowerment and dependency ”, Journal of Applied Psychology , Vol. 88 No. 2 , p. 246 .
Kaur , R. and Randhawa , G. ( 2021 ), “ Supportive supervisor to curtail turnover intentions: do employee engagement and work–life balance play any role? ”, Evidence-based HRM , Vol. 9 No. 3 , pp. 241 - 257 .
Khan , M. and Wajidi , A. ( 2019 ), “ Role of leadership and team building in employee motivation in the workplace ”, Global Management Journal for Academic and Corporate Studies , Vol. 9 No. 1 , pp. 39 - 49 .
Kick , A. , Contacos-Sawyer , J. and Thomas , B. ( 2015 ), “ How Generation Z's reliance on digital communication can affect future workplace relationships ”, Competition Forum , Vol. 13 No. 2 , pp. 214 - 222 .
Kim , H. and Stoner , M. ( 2008 ), “ Burnout and turnover intention among social workers: effects of role stress, job autonomy and social support ”, Administration in Social Work , Vol. 32 No. 3 , pp. 5 - 25 .
Koubova , V. and Buchko , A.A. ( 2013 ), “ Life‐work balance: emotional intelligence as a crucial component of achieving both personal life and work performance ”, Management Research Review , Vol. 36 No. 7 , pp. 700 - 719 .
Kundu , S.C. and Lata , K. ( 2017 ), “ Effects of supportive work environment on employee retention: mediating role of organizational engagement ”, International Journal of Organizational Analysis , Vol. 25 No. 4 , pp. 703 - 722 .
Lanier , K. ( 2017 ), “ 5 things HR professionals need to know about Generation Z: though leaders share their views on the HR profession and its direction for the future ”, Strategic HR Review , Vol. 16 No. 6 , pp. 288 - 290 .
Malinen , S. , Wright , S. and Cammock , P. ( 2013 ), “ What drives organisational engagement? A case study on trust, justice perceptions and withdrawal attitudes ”, Evidence-based HRM , Vol. 1 No. 1 , pp. 96 - 108 .
Mannheim , K. ( 1970 ), “ The problem of generations ”, Psychoanalytic Review , Vol. 57 No. 3 , pp. 378 - 404 .
Mohammed Sayed Mostafa , A. and Shen , J. ( 2020 ), “ Ethical leadership, internal CSR, organisational engagement and organisational workplace deviance ”, Evidence-based HRM , Vol. 8 No. 1 , pp. 113 - 127 .
Nambisan , S. , Agarwal , R. and Tanniru , M. ( 1999 ), “ Organizational mechanisms for enhancing user innovation in information technology ”, MIS Quarterly , Vol. 23 No. 3 , pp. 365 - 395 .
Parkes , L. and Langford , P. ( 2008 ), “ Work–life balance or work–life alignment? A test of the importance of work-life balance for employee engagement and intention to stay in organisations ”, Journal of Management and Organization , Vol. 14 No. 3 , pp. 267 - 284 .
Pierce , L. and Snyder , J. ( 2015 ), “ Unethical demand and employee turnover ”, Journal of Business Ethics , Vol. 131 No. 4 , pp. 853 - 869 .
Podsakoff , P. and Organ , D. ( 1986 ), “ Self-reports in organizational research: problems and prospects ”, Journal of Management , Vol. 12 No. 4 , pp. 531 - 544 .
Pulevska-Ivanovska , L. , Postolov , K. , Janeska-Iliev , A. and Magdinceva Sopova , M. ( 2017 ), “ Establishing balance between professional and private life of generation Z ”, Research in Physical Education, Sport and Health , Vol. 6 No. 1 , pp. 3 - 10 .
Ramlall , S. ( 2004 ), “ A review of employee motivation theories and their implications for employee retention within organizations ”, Journal of American Academy of Business , Vol. 5 No. 1 , pp. 52 - 63 .
Roman-Calderon , J. , Gonzales-Miranda , D. , García , G. and Gallo , O. ( 2019 ), “ Colombian millennials at the workplace ”, Evidence-based HRM , Vol. 7 No. 3 , pp. 249 - 261 .
Rothmann , S. , Diedericks , E. and Swart , J. ( 2013 ), “ Manager relations, psychological need satisfaction and intention to leave in the agricultural sector ”, SA Journal of Industrial Psychology , Vol. 39 No. 2 , pp. 1 - 11 .
Shah , M. and Asad , M. ( 2018 ), “ Effect of motivation on employee retention: mediating role of perceived organizational support ”, European Online Journal of Natural and Social Sciences , Vol. 7 No. 2 , p. 511 .
Shin , Y. , Hur , W. , Moon , T. and Lee , S. ( 2019 ), “ A motivational perspective on job insecurity: relationships between job insecurity, intrinsic motivation, and performance and behavioral outcomes ”, International Journal of Environmental Research and Public Health , Vol. 16 No. 10 , p. 1812 .
Sobotka , B. ( 2019 ), “ CSR and the competences of employees from generations Y and Z. Scientific papers of Silesian University of technology ”, Organization and Management , Vol. 134 , pp. 225 - 235 .
Stone-Romero , E. and Anderson , L. ( 1994 ), “ Relative power of moderated multiple regression and the comparison of subgroup correlation coefficients for detecting moderating effects ”, Journal of Applied Psychology , Vol. 79 No. 3 , p. 354 .
Strauss , W. and Howe , N. ( 1991 ), Generations: The History of America's Future, 1584 to 2069 , William Morrow , New York .
U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics ( 2021 ), Employment Projections , available at: https://www.bls.gov .
Vadvilavičius , T. and Stelmokienė , A. ( 2019 ), “ The consequences of ‘dark’ leadership: perspective of Generation Z ”, Management of Organizations: Systematic Research , Vol. 82 No. 1 , pp. 97 - 110 .
Valentine , S. and Godkin , L. ( 2017 ), “ Banking employees' perceptions of corporate social responsibility, value-fit commitment, and turnover intentions: ethics as social glue and attachment ”, Employee Responsibilities and Rights Journal , Vol. 29 No. 2 , pp. 51 - 71 .
Vera , D. and Crossan , M. ( 2004 ), “ Strategic leadership and organizational learning ”, Academy of Management Review , Vol. 29 No. 2 , pp. 222 - 240 .
Westerman , J. and Yamamura , J. ( 2007 ), “ Generational preferences for work environment fit: effects on employee outcomes ”, Career Development International , Vol. 12 No. 2 , pp. 150 - 161 .
Wilkesmann , U. and J Schmid , C. ( 2014 ), “ Intrinsic and internalized modes of teaching motivation ”, Evidence-based HRM , Vol. 2 No. 1 , pp. 6 - 27 .
Woo , H. ( 2013 ), Do Consumers Want a “Good” Apparel Brand? The Effects of Apparel Brands' CSR Practices on Brand Equity Moderated by Culture , Master’s thesis , University of North Carolina at Greensboro .
Corresponding author
Related articles, we’re listening — tell us what you think, something didn’t work….
Report bugs here
All feedback is valuable
Please share your general feedback
Join us on our journey
Platform update page.
Visit emeraldpublishing.com/platformupdate to discover the latest news and updates
Questions & More Information
Answers to the most commonly asked questions here
- Browse All Articles
- Newsletter Sign-Up
Retention →

- 04 Mar 2024
- What Do You Think?
Do People Want to Work Anymore?
Surveys indicate that US employee engagement and job satisfaction are down. To what degree are attitudes toward work to blame? asks James Heskett. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 02 Jan 2024
- Research & Ideas
10 Trends to Watch in 2024
Employees may seek new approaches to balance, even as leaders consider whether to bring more teams back to offices or make hybrid work even more flexible. These are just a few trends that Harvard Business School faculty members will be following during a year when staffing, climate, and inclusion will likely remain top of mind.

- 14 Sep 2023
Working Moms Are Mostly Thriving Again. Can We Finally Achieve Gender Parity?
The pandemic didn't destroy the workplace advancements moms had achieved. However, not all of the positive changes forced by the crisis and remote work have stuck, says research by Kathleen McGinn and Alexandra Feldberg.

- 20 Dec 2022
Employee Feedback: The Key to Retention During the Great Resignation
Employees need to feel that they're on the same team as managers—not adversaries in a zero-sum game. Michael Beer offers six guiding principles for senior leaders who are ready to listen to and act on employee feedback.

- 09 Jun 2022
From Truck Driver to Manager: US Foods’ Novel Approach to Staff Shortages
Restaurant closures, supply disruptions, and now, worker shortages. The pandemic has been hard on food suppliers. A case study by David Bell looks at the innovative thinking that helped one of the industry's biggest companies stabilize staffing—and grow.

- 03 Jun 2022
In a Work-from-Anywhere World, How Remote Will Workers Go?
Will professionals still choose cities if they have the option to work from the beach? Research by Prithwiraj Choudhury considers the radical ripple effects of remote work.

- 03 May 2022
Desperate for Talent? Consider Advancing Your Own Employees First
What would it take to build the skills your company needs in your current workforce? Joseph Fuller and Manjari Raman offer a new playbook for a historic talent crunch with no end in sight.

- 01 Feb 2022
Is Concierge Management an Answer to the “Big Quit”?
Are employees more likely to be forgotten in remote settings, leaving without so much as a goodbye? Should companies do more to give them a voice? asks James Heskett. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 18 Jan 2022
How Eliminating Non-Competes Could Reshape Tech
President Biden says non-compete agreements threaten innovation, but the tech industry leans on them to protect trade secrets. Andy Wu discusses what a potential ban on these legal pacts could mean for business. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 19 Aug 2021
Don't Ignore Your Employees' Misery—TAKE Control
Many workers are unhappy with their companies' return-to-work policies. Rather than risk losing productive people, managers should confront employee dissatisfaction head on, says Hise O. Gibson. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 07 Jul 2019
Walmart's Workforce of the Future
A case study by William Kerr explores Walmart's plans for future workforce makeup and training, and its search for opportunities from digital infrastructure and automation. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 18 Mar 2019
Stuck in Commuter Hell? You Can Still Be Productive
Commuters who listen to music or browse social media might be increasing their chance of a stressful workday. Research by Francesca Gino and colleagues offers better ways to cope with a bad commute. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 17 Jan 2019
Why Business Should Support Employees Who Are Caregivers
Shifting demographics are causing an increasing number of people to act as caregivers for family and friends—but employers seem hardly to notice the trend. Joseph Fuller discusses why companies should support them. Open for comment; 0 Comments.

- 16 Jul 2018
Kids of Working Moms Grow into Happy Adults
In earlier research, Kathleen McGinn and colleagues discovered that adult kids of working moms are high achievers at work. Now it turns out they are happy, too. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 01 Apr 2013
First Minutes are Critical in New-Employee Orientation
Employee orientation programs ought to be less about the company and more about the employee, according to new research by Daniel M. Cable, Francesca Gino, and Bradley R. Staats. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 21 Nov 2011
- Lessons from the Classroom
The New Challenge of Leading Financial Firms
Running a financial organization, never easy to begin with, has quickly become one of the most difficult leadership challenges that an executive can undertake, requiring mastery of talent management, change management, and ethics. An interview with Professor Boris Groysberg, who teaches a new HBS Executive Education program on the subject with Professor Paul M. Healy. Key concepts include: Leading a financial firm is very different from leading any other kind of institution, requiring deep skills in a multitude of areas. Financial firms make expensive bets on top talent, but often make hiring decisions without enough deliberation. Risk management, strategy for growth, and competing in emerging markets are especially critical for financial firms to get right. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 11 Jul 2011
Non-competes Push Talent Away
California is among several states where non-compete agreements are essentially illegal. Is it a coincidence that so many inventors flock to Silicon Valley? New research by Lee Fleming, Matt Marx, and Jasjit Singh investigates whether there is a "brain drain" of talented engineers and scientists who leave states that allow non-competes and move to states that don't. Key concepts include: The research shows that inventors are leaving states that allow non-competes and moving to states that don't. The results are most pronounced among those inventors with the most patent citations—that is, those who are most productive, collaborative, and valuable to their firms. The researchers hope that their study will induce state legislators to consider regional rules regarding non-compete agreements. Open for comment; 0 Comments.
- 25 May 2011
QuikTrip’s Investment in Retail Employees Pays Off
Instead of treating low-paid staffers as commodities, a new breed of retailers such as QuikTrip assigns them more responsibility and invests in their development, says professor Zeynep Ton. The result? Happy customers and even happier employees. Key concepts include: Unusual for a retailer, QuikTrip offers its operational employees above-average wages, job security, and significant benefits. By using operational efficiencies and standardization, QuikTrip reduces complexity to create higher employee productivity and fewer errors. By investing in employees and giving them more responsibility, QuikTrip enjoys a competitive advantage in service and benefits from continuous process improvement. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
- 19 Sep 2005
Rethinking Company Loyalty
These days, your best workers are likely to show more loyalty to their careers than the company. What's needed, says this Harvard Management Update article, is a new view of loyalty and its meaning to employers and employees. Closed for comment; 0 Comments.
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Front Psychol
Employee Retention and Change Management During Times of Uncertainty
Introduction.
Human resource management is a type of management that focuses on maximizing the abilities of its employees or members through a number of strategic steps in order to improve employee performance and help the company achieve its goals. According to Mathis et al. ( 2015 ). Human resource management has a decisive role in the life of an organization, namely how well the organization performs, how well the organization's strategy can be implemented, and how far the predetermined goals can be achieved. There is a good way to tell how well a company is able to deal with problems if there is a company. Research and discussion on organizational behavior (OB) have been around for about half a century. However, as OB points out, in reality, things never really change, which clearly shows the problems facing managers in an organization have been around since the dawn of civilization (Luthans, 2012 ). Although the problems in an organization and the solutions provided have not changed much, the emphasis and context of the surrounding environment have certainly changed. For example, from the 1980's to the mid-1990's, managers were busy restructuring their organizations to increase productivity and meet competitive challenges in international markets and increase customer buying interest. A case in point, an analysis of Fortune 500 companies between 1995 and 2005 found the most prominent initiatives were restructuring (downsizing), cost reduction programs, creating shared services, and Six Sigma quality programs (Luthans, 2012 ).
Based on the literature review, both theoretically and empirically (can be seen in Table 1 ), this study comes up with hypotheses that will lead to an empirical research model. In his explanation, Wayne ( 2014 ) explains that there is a significant influence between employer branding, management performance, and employee retention. This finding is supported by research conducted by Sutherland et al. ( 2002 ) that employer branding has a direct influence on employee retention. Even in research conducted by Chhabra and Sharma ( 2014 ), employer branding is one of the corporate strategies in modern times that is used to reduce costs from company employee search. Oladapo ( 2014 ) explains that talent management has a positive and significant influence on employee retention. This is supported by research conducted by Deery ( 2008 ), which states that talent management and work-life balance have a strong enough influence on employee retention. The research conducted by Fahlevi et al. ( 2020 ) is limited to companies engaged in hospitality. However, there are previous studies that have obtained quite the same results regarding the relationship between talent management and employee retention in companies as the research conducted by Hughes and Rog ( 2008 ).
Path analysis.
Figurska and Matuska ( 2013 ) found that there is a positive and significant influence between employer branding and employee engagement. Their research reveals that employer branding is one of the company's strategies for maintaining their human resources in order to improve the performance of individuals in a company so that its reputation is enhanced. from the company will make the employee bond better. Kennedy and Daim ( 2010 ) explain that there is a significant effect between employee engagement and employee retention. In their research, it is explained that employee engagement can be a major force in maintaining employee resilience and causing a decrease in turnover, but this research is limited to companies that operate in the IT industry. Kashyap and Rangnekar ( 2016 ) found that there is a positive and significant relationship between employer branding and organizational trust. It is explained that the perception of a company's reputation has a significant influence in reducing employees' willingness to switch companies. I can mediate between the two relationships. Organizational trust is seen as the output of good employer branding in a company.
Al-Hussaini et al. ( 2019 ) explain that there is a significant influence between talent management and employee engagement. This also applies to individual performance variables. This study specifically explains how companies develop talent management to increase bonds between employees, which will have an impact on increasing individual performance. This study also explains the role of talent management as a strategy and the role of employee engagement as a mediator between the two relationships. Özçelik ( 2015 ) explains the determinants of organizational trust in talent management in an organization. In this case, talent management can also be interpreted as talent management regarding how the company's efforts to maintain fuel retention of its employees will reduce recruitment costs. Research conducted using nurses in a hospital found that there is a direct influence between organizational trust and employee retention. Researchers not only used organizational trust variables but also added job satisfaction variables in measuring the effect on employee retention.
Suikkanen ( 2010 ) explained that employee branding can have a direct and indirect effect on employee retention. The role of employee engagement in mediating the effect of these two variables has a significant and positive influence, so employee engagement is needed to increase employee retention. The same thing was also found by Özçelik ( 2015 ) in his research. Backhaus and Tikoo ( 2004 ) explain the role of organizational trust in mediating the relationship between employer branding and employee retention, but the research conducted by Backhaus and Tikoo ( 2004 ) is only conceptual, and there are no empirical findings that explain the role of organizational trust as a mediator. Research conducted by Biswas and Suar ( 2016 ) also explains the factors and impacts of employer branding on organizational trust and employee retention. In support of this hypothesis, no in-depth research has been conducted on the role of organizational trust in mediating the effect of employer branding on employee retention.
Bhatnagar ( 2007 ) explains that employee engagement can mediate the influence of employer branding on employee retention. The explanation used by the researcher is that talent supported by work ties will have a greater influence on employee retention. This is in line with research conducted by Hughes and Rog ( 2008 ), although the research is limited to companies in the hotel industry. Chitsaz-Isfahani and Boustani ( 2014 ) explain that organizational trust can mediate between employer branding and employee retention, but that much like the relationship between employer branding and employee retention, there is no research that clearly states organizational trust has a positive and significant influence in mediating the influence between these two variables.
The subjects of this research are employees of one of the largest manufacturing companies in Indonesia, which is a company engaged in the automotive sector. This company is the only one in Indonesia that has the right to be the sole agent for the world's leading motorcycle brand. How many samples will be used in this study will be based on Hair et al. ( 2010 ) which uses more than 100 samples as the minimum number in the use of this study. Formula by Slovin et al. ( 1993 ) this is the minimum recommended size for this research survey.
Based on the formula above, from a total of 23,953 employees, the minimum sample size is 394 employees. Part-time workers and employees of manufacturing companies comprise the sample unit in this study. Considering the number of samples to be studied, which can be done randomly, the researchers used random sampling in their research at this company.
At the data processing stage, validity, reliability, and discriminant validity tests have been carried out so that in the model there are several indicator items that are removed from the model because they do not meet the criteria that have been set to measure or explain the constructs in the model. Figure 1 shows the result of bootstrapping the final modified model.

Bootstrapping.
The results of the bootstrapping above are used to test the hypothesis that all of the indicator items in all constructs have a statistical value >1.96. In conclusion, all of the indicator items above are able to measure the existing constructs. Meanwhile, to test the effect between variables, the statistical values from the Smart PLS analysis were compared with the table values. The following is a table that provides the results of the relationship between the constructs.
An important contribution to this research is the use of employee engagement and organizational trust as mediating variables based on consideration of the results of previous studies. This study found that employee engagement can positively mediate the influence of employer branding on employee retention. In contemporary research, which is characterized by intense business competition, engagement has received attention from both academics and practitioners and has been established as an important human resource intervention for the survival and growth of companies (Rai and Maheshwari, 2021 ). Many studies have been conducted to explore the various antecedents of engagement. Job-related antecedents are constructs, strategies, and conditions applied at the job or task level to develop engagement. It has been said in theories like the JCM (Job Characteristics Model) that work has a big impact on an employee's overall motivational potential by affecting their psychological states.
In this study, the contribution to organizational theory regarding organizational trust is an important element of social relations in an organization. At the interpersonal level, employees' trust in managers affects the results of their attitudes, behavior, and performance (Ozmen, 2019 ). Knowledge-based organizational trust among peers and commitment mediates the effect of employer branding on employee retention and also finds that trust in management partially mediates the relationship between employee-oriented HRM and employee behavior. Employer branding and employee retention are both important parts of this dissertation. One of the new things about adding organizational trust variables between these two things is that this model is used for companies in the automotive industry. From the psychological point of view of employee retention as a future factor for the company to retain talented employees in the future, human resource assets become a valuable asset but are often not visible in the eyes of management (Fahlevi, 2021 ). Understanding the psychology of employees to stay with the company is something that is rare in today's companies even though it is very much needed now.
This research contributes as input to the automotive industry's business practices in increasing employee retention rates. The automotive industry, which has a high turnover rate, must innovate in the organization related to several main variables. The results obtained in this study are quite high, namely employee engagement and organizational trust. With the increase in these two variables, employer branding and talent management can be improved, which will have an impact on employees. Retention will increase as several variables in this research model will have a direct or indirect impact on the company's employee retention. The benefits of high employee retention for the company will reduce costs, be they recruitment costs or training costs. It is known that the automotive industry requires a large amount of training costs, especially on the part of production employees, which is a must for companies to provide training to their employees so that training costs can be reduced by increasing employee retention.
Author Contributions
All authors listed have made a substantial, direct, and intellectual contribution to the work and approved it for publication.
Conflict of Interest
The authors declare that the research was conducted in the absence of any commercial or financial relationships that could be construed as a potential conflict of interest.
Publisher's Note
All claims expressed in this article are solely those of the authors and do not necessarily represent those of their affiliated organizations, or those of the publisher, the editors and the reviewers. Any product that may be evaluated in this article, or claim that may be made by its manufacturer, is not guaranteed or endorsed by the publisher.
- Al-Hussaini S. H., Turi J. A., Altamimi A. N. A., Khan M. A., Ahmad M. (2019). Impact of talent management strategies on employee performance behaviour with the mediating role of talent management outputs . Arch. Bus. Res . 7 , 116–124. 10.14738/abr.73.6309 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Backhaus K., Tikoo S. (2004). Conceptualizing and researching employer branding . Career Develop. Int . 9 , 501–517. 10.1108/13620430410550754 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Bhatnagar J.. (2007). Predictors of organizational commitment in India: strategic HR roles, organizational learning capability and psychological empowerment . Int. J. Hum. Resour. Manag . 18 , 1782–1811. 10.1080/09585190701570965 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Biswas M. K., Suar D. (2016). Antecedents and consequences of employer branding . J. Bus. Ethics 136 , 57–72. 10.1007/s10551-014-2502-3 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chhabra N. L., Sharma S. (2014). Employer branding: strategy for improving employer attractiveness . Int. J. Organ. Anal . 22 , 48–60. 10.1108/IJOA-09-2011-0513 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Chitsaz-Isfahani A., Boustani H. R. (2014). Effects of talent management on employees retention: the mediate effect of organizational trust . Int. J. Acad. Res. Eco. Manag. Sci. 3 , 114. 10.6007/IJAREMS/v3-i5/1196 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Deery M.. (2008). Talent management, work-life balance and retention strategies . Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag . 20 , 792–806. 10.1108/09596110810897619 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Fahlevi M.. (2021). “Corporate branding in banking environment: evidence from acquisition process,” in Paper Presented at the IOP Conference Series: Earth and Environmental Science (Boston, MA: ). [ Google Scholar ]
- Fahlevi M., Rabiah A. S., Pradipta I. A., Marta A. (2020). Tourism and absorption of the labor force in Indonesia: a strategy for development . E3S Web Conf. 16001 , 2–6. 10.1051/e3sconf/202020216001 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Figurska I., Matuska E. (2013). Employer branding as a human resources management strategy . Hum. Resour. Manag. Ergonom . 7 , 35–51. Available online at: https://frcatel.fri.uniza.sk/hrme/files/2013/2013_2_03.pdf [ Google Scholar ]
- Hair J., Black W., Babin B., Anderson R. (2010). Multivariate Data Analysis: A Global Perspective . London: Pearson. [ Google Scholar ]
- Hughes J. C., Rog E. (2008). Talent management: A strategy for improving employee recruitment, retention and engagement within hospitality organizations . Int. J. Contemp. Hosp. Manag. International . 7 , 743–757. 10.1108/09596110810899086 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kashyap V., Rangnekar S. (2016). Servant leadership, employer brand perception, trust in leaders and turnover intentions: a sequential mediation model . Rev. Manag. Sci . 10 , 437–461. 10.1007/s11846-014-0152-6 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Kennedy E., Daim T. U. (2010). A strategy to assist management in workforce engagement and employee retention in the high tech engineering environment . Eval. Program Plann. 33 , 468–476. 10.1016/j.evalprogplan.2009.12.001 [ PubMed ] [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Luthans F.. (2012). “Organizational behavior: an evidence-based approach,” in Organizational behavior: An Edivence-Based Approach, 12th Edn (McGraw Hill: ). [ Google Scholar ]
- Mathis R. L., Jackson J. H., Valentine S. R., Meglich P. A. (2015). Human Resource Management, 15th Edn (Cengage Learning: ). [ Google Scholar ]
- Oladapo V.. (2014). The impact of talent management on retention . J. Bus. Stud. Q . 5 , 19–36. [ Google Scholar ]
- Özçelik G.. (2015). Engagement and retention of the millennial generation in the workplace through internal branding . Int. J. Bus. Manag. 10 , 99. 10.5539/ijbm.v10n3p99 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Ozmen Y. S.. (2019). How the exchange relationship affects employee commitment: the mediating role of organizational trust . J. Manag. Dev. 38 , 501–516. 10.1108/JMD-08-2018-0220 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Rai A., Maheshwari S. (2021). Exploring the mediating role of work engagement between the linkages of job characteristics with organizational engagement and job satisfaction . Manag. Res. Rev . 44 , 133–157. 10.1108/MRR-10-2019-0442 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Slovin M. B., Sushka M. E., Polonchek J. A. (1993). The value of bank durability: borrowers as bank stakeholders . J. Finance 48 , 247–266. 10.1111/j.1540-6261.1993.tb04708.x [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Suikkanen E.. (2010). How does employer branding increase employee retention? (Ph. D. dissertation: ). Metropolia University of Applied Sciences, Helsinki, Finland. [ Google Scholar ]
- Sutherland M. M., Torricelli D. G., Karg R. F. (2002). Employer-of-choice branding for knowledge workers . South Afr. J. Bus. Manag . 33 , 13–20. 10.10520/EJC22210 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]
- Wayne F. C.. (2014). Leveraging employer branding, performance management and human resource development to enhance employee retention ,. Hum. Resour. Dev. Int. 17: 2 , 121–128, 10.1080/13678868.2014.886443 [ CrossRef ] [ Google Scholar ]

Employee Retention Research: Questions, Topics, & Objectives
Topics covered ✅.
- Employee retention research topics
- Employee retention program
- Why employee retention is important
- Employee retention examples
- Employee retention articles
- Factors affecting employee retention research
- Employee retention in HRM
Employee retention is a common issue in the modern workplace. In fact, employee turnover rates are high in most organizations, and this can have a negative impact on companies' profitability.
In order to retain employees, it's important to conduct employee retention research and how key factors can be addressed in your company culture.
This article provides an overview of employee retention research and the key considerations it should include.
1. Employees
When it comes to building a great culture, there are few things as valuable as employee retention research.
When you can understand the motivations, experiences, and needs of your employees, you can make real changes that will help them stay with your company longer.
To help businesses retain their best workers and reduce turnover costs, Kahana conducts ongoing research into the factors that contribute to employee retention—including stress levels and voluntary turnover.
Claim My Free Team Onboarding Template
This free team onboarding hub comes ready-made with welcome messages, instructions, spaces for important links, plus more.
2. Employee Turnover
Two factors to consider for employee retention research are work-life balance and seniority.
Work-Life Balance
The most important factor in employee retention is work-life balance.
According to Forbes, 66% of employees say they would "likely leave their job if they didn't feel appreciated."
Significantly, this figure has increased from 51% of employees who felt this way in 2012.
Companies need to be aware of this issue and take steps to ensure their employees are not being overworked or under-appreciated by management.
Senior Employees
Another key impact on employee retention is seniority levels among employees: those with more experience tend to stay at their current company longer than those who have less.
This may be because they feel more secure in their positions, they have more responsibilities than newer employees do, or they are more likely to receive raises during their tenure with a company, which helps them feel more valued and appreciated by management.
3. Company Costs
Employee turnover is a major concern for companies.
Based on this SHRM Report on Retaining Talent , replacement costs can be as high as 50%-60% with overall costs ranging anywhere from 90%-200%.
In a nutshell, this means that if an employee makes $60,000 per year in salary, then it would cost an average of $30,000 - $45,000 just to replace that employee and roughly $54,000 - $120,000 in overall costs to the company.
This is especially true when it comes to senior employees, who are more expensive to replace than their junior counterparts.
Not to mention, a workforce with high turnover rates tends to be less engaged in their work and more prone to stress and burnout, which can lead to other issues like absenteeism or workplace violence.
4. Questions
As a human resources manager, it's important to have a good handle on employee turnover rates.
- What about those employees who voluntarily leave your company?
- Why do they do it?
- How can you keep them around?
When you know how many employees leave your company voluntarily and involuntarily each month, you can make calculated decisions that will help you retain more talent.
Many companies are struggling to find new employees who possess the skills needed to fill these vacant positions.
This shortage has created an environment where talented people are in demand and are able to negotiate their salaries higher than they would have been able to do just five years ago.
With so many unemployed or underemployed people looking for work, it would seem like companies should be able to easily fill their open positions with qualified applicants even without paying them top dollar—but this isn't happening.
Many companies are creating cultures that drive away talented employees who want to feel valued and supported by their employers.
6. Cost of Turnover Relative to Career Length
Employee turnover can be expensive.
According to Built in, the true costs of employee turnover are extremely high.
It’s estimated that losing an employee can cost a company 1.5-2 times the employee’s salary .
Depending on the individual’s level of seniority, the financial burden fluctuates.
- Hourly workers can cost an average of $1,500 per employee .
- Technical positions can cost between 100-150 percent of the salary.
- C-suite turnover can cost 213 percent of salary.
7. Development of Employee Turnover
Stress levels and age also have a significant impact on voluntary employee turnover rates.
High-stress environments often lead to increased absenteeism and lower productivity, which contribute to higher turnover rates.
For example, senior employees may leave a company because of the lack of flexibility and remote options, especially during a pandemic.
They will look for companies that are adopting a more hybrid work schedule.
Companies can better retain these valuable workers through improved communication channels between management and staff members or by offering more flexible policies related specifically to older workers.
8. Employee Experiences
If employees have positive experiences at their job, there will most likely be a lower turnover rate.
However, when it comes to identifying signs of negative employee experiences within your own company culture, you should look for low staff morale or frequent absences from work due to illness or personal issues.
If you notice these types of behaviors among your employees, you should consider implementing more flexible work schedules or other policies that might help reduce their stress levels and improve productivity overall.
Claim My Free Community Building Template
This free community-building template comes pre-built with the structures you need to get started, including process documentation, goal-setting guides, plus more.
9. Management
Another common reason why people leave their jobs is that they don't feel like they're getting enough support from management.
Employees may be unhappy at work due to a bad manager or a toxic culture within the organization.
It is important to make a note of employees' attitudes and feelings at work so that improvements can be made in the workplace.
10. Feedback
If you want to retain your employees longer than usual, you can do a couple of things.
One thing is that there's no harm in asking for feedback from your employees .
You could have meetings with individual employees or a brainstorming session with your whole team to come up with ideas that can improve employee experiences.
If you want to make sure your employees will stay with you for a long time, you should look at hiring people who have been with other companies for a long time and will likely stay with yours as well.
However, this is not the only route to ensuring long-lasting employment.
The key factor in retaining employees is treating them well and appreciating them.
For more insights on building culture, check out our article on employee satisfaction research .
- SUGGESTED TOPICS
- The Magazine
- Newsletters
- Managing Yourself
- Managing Teams
- Work-life Balance
- The Big Idea
- Data & Visuals
- Reading Lists
- Case Selections
- HBR Learning
- Topic Feeds
- Account Settings
- Email Preferences
3 Ways to Boost Retention Through Professional Development
- Erica Keswin

Data suggests it’s one of the best ways to improve company culture.
People’s lives and priorities are changing in dramatic ways before our very eyes. While increasing compensation, promoting from within, offering flexible schedules, and making remote work easier are always good talent strategies, there’s one lever leaders can pull that’s highly accessible, doesn’t have to be expensive, and gives employees something they really want: on-the-job professional development. The author offers three ways for leaders to prioritize learning and development in their organizations. First, incorporate learning into onboarding and give employees time for it regularly. Second, make learning a ritual. Finally, offer coaching to all your employees — not just executives.
With Americans continuing to quit their jobs at a record pace , leaving companies with more openings than candidates, it’s no surprise that attracting and retaining talent tops many leaders’ priority lists this year. While increasing compensation, promoting from within, offering flexible schedules, and making remote work easier are always good talent strategies, there’s one lever leaders can pull that’s highly accessible, doesn’t have to be expensive, and gives employees something they really want.
- EK Erica Keswin is a bestselling author, internationally sought-after speaker, and workplace strategist. She helps top-of-the-class businesses, organizations, and individuals improve their performance by honoring relationships in every context, always with an eye toward high-tech for human touch. She was named one of Marshall Goldsmith’s Top 100 Coaches in 2020, as well as one of Business Insider ’s most innovative coaches of 2020 . Her first book, Bring Your Human to Work: 10 Sure-Fire Ways to Design a Workplace That’s Good for People, Great for Business, and Just Might Change the World was published in 2018 by McGraw Hill. Her second book, Rituals Roadmap: The Human Way to Transform Everyday Routines Into Workplace Magic was published by McGraw Hill in January 2021. Both books debuted as Wall Street Journal bestsellers. You can learn more about her on her website: ericakeswin.com
Partner Center

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
It's Time to Reimagine Employee Retention. by. Helen Tupper. and. Sarah Ellis. July 04, 2022. Steven Puetzer/Getty Images. Summary. According to Gartner, the pace of employee turnover is ...
Employee Retention can be defined as the ability of an organization to retain its employees (Awolaja, 2023). It is also seen as a process, in which employees are motivated and encouraged to stay ...
The moderating role of transformational leadership on the work environment-employee retention relationship was not supported. This result is a clear indicator of the rejection of hypothesis H5. Similarly, there is no study regarding leadership as a contingent variable on the work environment-employee retention association.
Theoretical Background and Hypothesis. Past research has examined employees' behavior predicted by several factors, such as the creation of a positive organizational climate to stimulate safe work behavior in employees (Smith-Crowe et al., 2003).Employees' behavior, including OCB, was positively affected by the ethical climate through the social identity approach (Pagliaro et al., 2018).
factors affecting employee retention, four commonly identified factors; compensation, work-. life-balance, working-environment and superior-subordinate relationship in past researches. were ...
In the today's competitive environment, employee retention is a challenge faced by many industries. This work aims to identify the factors that influence employee retention. This is done using employees' feedback and various computational techniques. A survey is conducted within multiple sectors to collect data. The questionnaire is divided into two parts: the first part includes ...
1. Introduction. For the past several decades, employee retention has been an important topic to both scholars and practitioners because employees, the most valuable assets of an organization, are the ones who add to its value, quantitatively and qualitatively (Anitha, 2016).Therefore, employers have taken steps to ensure that employees stay with the organization for as long as possible ...
Talent management has been advocated as an important strategy to retain talented employees, but academic studies exploring their relationship are limited. Building on the Resource-Based View (RBV) theory and Social Exchange Theory (SET), the present article studies the relationship between talent management and employee retention.
Retention. New research on retention from Harvard Business School faculty on issues including how to use employee orientation to improve retention, the importance of investing in employees, and what it means that a company's best workers are more likely to show loyalty to their careers than the company. Page 1 of 19 Results.
As a result, factors that promoted employees' job satisfaction, organisational commitment and suitable work conditions are fundamental elements to staff retention. Keywords: Employee Retention Strategies, literature review, future research. DOI: 10.7176/EJBM/13-1-03. Publication date: January 31st 2021.
strategies to manage employee retention because they focus on day-to-day operations (Adams et al., 2015). Banerjee (2019) explained that lack of effective employee retention strategies might impact customer satisfaction, sales volumes, productivity, and profitability. Human resources strategies not focusing on employee engagement and a
Besides that, according to Kamalaveni et al. (2019), an SME with a work-life balance culture with flexible working schedules also undoubtedly positively impacts employee retention. But, on the ...
this article attempts to find strategies for employee retention (ER). According to Guchait and Cho (2010), more than 80% of employees would like to work in a healthy and supportive environment. Thereby, it is becoming important to provide a supportive work environment (SWE) to retain talented per-sonnel (Ghosh & Sahney, 2011).
The chapter reviews research linking work-life balance to retention-related outcomes. It then discussed the role of formal and informal work-family support policies in improving work-life outcomes as well as retention-related outcomes. Empirical evidence supports the theoretical association between work-life conflict and withdrawal-related ...
Transparency and Employee Engagement at Unstructure 2010. I'm in Orlando at HCL Technology's annual "Unstructure" conference — informally known as the global customer meet. HCL, the ...
employee turnover, they can implement employee retention strategies to reduce employee turnover (Garibay, 2015; Sandhya & Kumar, 2014). In this qualitative case study, I explored employee retention strategies university leaders use to reduce employee turnover in U.S. colleges and universities. Background of the Problem
This is supported by research conducted by Deery , which states that talent management and work-life balance have a strong enough influence on employee retention. The research conducted by Fahlevi et al. ( 2020 ) is limited to companies engaged in hospitality.
Read more on Employee retention or related topics Work-life balance and Talent management Ron Carucci is co-founder and managing partner at Navalent , working with CEOs and executives pursuing ...
Two factors to consider for employee retention research are work-life balance and seniority. Work-Life Balance. The most important factor in employee retention is work-life balance. According to Forbes, 66% of employees say they would "likely leave their job if they didn't feel appreciated."
One HR strategy they should embrace is to make themselves so attractive that employees won't want to leave. These six measures can help accomplish that: (1) add monetary incentives for staying ...
Together, these two areas of dissatisfaction make up 69% of the total reasons employees left their employer in 2023. That means four times as many people left their job due to "Engagement and ...
The author offers three ways for leaders to prioritize learning and development in their organizations. First, incorporate learning into onboarding and give employees time for it regularly. Second ...