- Preferences


The different types of electrical insulators - PowerPoint PPT Presentation

The different types of electrical insulators
Insulation is an important element for receiving safe electricity within homes and offices. learn about the various types of insulators commonly used, and the materials used to build them, in this blog. – powerpoint ppt presentation.
PowerShow.com is a leading presentation sharing website. It has millions of presentations already uploaded and available with 1,000s more being uploaded by its users every day. Whatever your area of interest, here you’ll be able to find and view presentations you’ll love and possibly download. And, best of all, it is completely free and easy to use.
You might even have a presentation you’d like to share with others. If so, just upload it to PowerShow.com. We’ll convert it to an HTML5 slideshow that includes all the media types you’ve already added: audio, video, music, pictures, animations and transition effects. Then you can share it with your target audience as well as PowerShow.com’s millions of monthly visitors. And, again, it’s all free.
About the Developers
PowerShow.com is brought to you by CrystalGraphics , the award-winning developer and market-leading publisher of rich-media enhancement products for presentations. Our product offerings include millions of PowerPoint templates, diagrams, animated 3D characters and more.
Academia.edu no longer supports Internet Explorer.
To browse Academia.edu and the wider internet faster and more securely, please take a few seconds to upgrade your browser .
Enter the email address you signed up with and we'll email you a reset link.
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center

Related Papers
Decoraciones Curari
Zohaib Latif
Vikas Kumar
ahmed jalil
Yasir shehzad
gideon ukam
Raihanul Islam
Raja Agarwal
MANISH BISHNOI
400 KV GSS RRVPNL , Surpura , Jodhpur
Loading Preview
Sorry, preview is currently unavailable. You can download the paper by clicking the button above.
RELATED PAPERS
GJESR Journal
EE8402 -TRANSMISSION AND DISTRIBUTION 2 Marks And 16 Marks-Question Bank UNIT I TRANSMISSION LINE PARAMETERS Two marks Q&A
Sampath Kaliavarathan
Dave Kurniawan
Sameer Bodre
Vi truong van
Asaph Adigue
Chathuranga Basnayaka
DIVYANGSINH RANA
mezo mohmmed
Rishu Arora
Julien Camara
VINOD KUMAR MEENA
European Transactions on Electrical Power
Marco Ricca
Guzman Murillo
lanyuy elvis
Harsha Talluri
kabir Durowoju
Ravalika Vadduri
- We're Hiring!
- Help Center
- Find new research papers in:
- Health Sciences
- Earth Sciences
- Cognitive Science
- Mathematics
- Computer Science
- Academia ©2024
- YouTube Thumbnail Downloader
- Image Compressor
- QR Code Generator
- Environment
- Submit An Article
- Privacy Policy
- Terms and Conditions
What is Insulation Material and its Uses
- by Refresh Science
- January 15, 2022 January 15, 2022
Many people make the mistake of not taking insulation seriously. They think that they only need the insulation layer to work just fine. They severely underestimate the materials and maintenance cost.
Several insulation materials are essential for a building . They are thermal and sound. And if you plan to have a studio, you should look for acoustic insulation.
What is insulation materials?
In short, it is the material that works as a buffer inside the walls. It acts as extra protection for your house from the temperature outside. These materials can help you stay warm in the winter and cool during summer.

Benefits of insulation
Having insulation can provide several benefits. Here are to name a few.
- Controlling the temperature inside the house
You may still need to install a heater and air conditioner for your house. But in general, your place will stay warm enough to keep you comfortable.
- Fire-proofing your house
Some insulators also have fire-retardant qualities. But keep in mind that it doesn’t mean it’s total fireproof. It only means that your walls and roof will last a little longer during the fire.
- Keeping the maintenance cost low
Having a good insulator means you don’t have to spend a lot of money on the heater and air conditioners. You can save up to 75% on maintenance costs for one year.
- Adding the house value
You can have a higher ROI value by installing the right insulation material. On average, the initial cost from the installation will return within six months to two years.
Which is the example of insulating material?
Many materials can work as insulation. However, you still need to know which materials can give you the best result for the price. Here are several insulation materials that you may have encountered.
- Polyurethane Foam
- Mineral Wool
- Foam boards
- Polystyrene (EPS)
What is the most common insulating material?
There are some materials that you can find in any building supply store. As some of them are affordable and you can install them yourself.
- polystyrene
- Mineral wool
Download Insulation Materials PowerPoint Presentation:
What are the 4 main types of insulation used in homes.
Depending on how big a house is, there are various types of insulation that you can choose. However, four main types are popular, especially in a residential area.
- Rigid foam or fiber
- Sprayed foam
- Structural Insulation Panels
Several insulation materials are applicable through multiple types. For example, fiberglass and mineral wool. You can install them using the blanket type or a rigid fiber type.
Please remember that some types require a professional HVAC to do the installation. As it’s common to wear protective gear when installing an insulation layer.
What are thermal insulation materials?
Thermal insulation works to control the temperature inside the room. As you know, 25% of the heat goes inside your house through the roof, and 15% is from the walls.
These materials can block most of the heat from getting inside the house. In general, most insulation materials can do this. But the most affordable ones are fiberglass and Polystyrene foam (EPS).
What are sound insulation materials?
Unlike heat, sound requires a different type of insulation. With heat, it is only a matter of transferring the energy to a comfortable level. But sound requires a complete block of sound.
Most common sound insulations are great for soundproofing. Depending on how much noise cancellation you need, you can choose from the options below.
- Mass loaded vinyl
- Soundproof sheetrock
- Green glue vibration dampening compound

What are acoustic insulation materials?
One thing to keep in mind is the difference between soundproofing and acoustic insulation. People often use both terms interchangeably when they refer to different usage. Here are some examples.
- Foam panels
- acoustical panels
As you can see, they are different from the sound insulation ones. That is because these materials only absorb instead of blocking the sound. Thus it has a different effect in the room.
What insulation material is most efficient?
So far, the most efficient insulation material is the Pyrogel XT. This industrial insulation works with less than 80% thickness of other materials. To illustrate, people usually have to install 1-inch thick fiberglass as insulation. With Pyrogel XT, they only need to do 0.5-0.2 inches.
Is Copper an insulating material?
Copper is a conductor and not an insulator. It transfers heat and electricity throughout the material. That is why you see copper as the main material for cables and other wiring products.
What is the best insulator?
The best insulator is the one that can work the best within your budget. But it doesn’t mean that you can trim some edges by cutting down the insulation budget.
This is the best insulator that money can buy. It can hold up to 2000 degrees Fahrenheit. And even essential to NASA spaceships.
This gel can be difficult to attain, but it’s very effective and efficient. It’s great for large buildings since it can cover a lot of space for a small amount.
This insulation is lightweight and fire-retardant. It uses non-CFC gas as a blowing agent to fill the space. This material works as a sound insulator as well. However, it can be expensive to have and install.
Eco-friendly and fireproof. This natural material is one of the favorite insulators to many. However, it can be difficult to apply on an uneven surface.
This is the most popular option since it’s affordable, eco-friendly, fire-retardant, and easy to work with. Many people often choose to install fiberglass insulation by themselves.

Thermal insulation materials for buildings
A larger building requires a different type of insulation from a house. It requires a different technique, and perhaps a different set of materials as well.
However, it also needs to comply with the regulation on the climate zone. You need to check if the location requires extra or specific insulation.
Insulation covers a wide array of options. Keep in mind that a residential building has different needs than a larger commercial one. Therefore, it needs different insulation to install.
And if you’re looking to build a studio in the house, you can start looking for which acoustic insulation you want to add to the room.

CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS
Nov 12, 2014
1.02k likes | 3.77k Views
CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS. CONDUCTORS. Conductor is an object or type of material which permits the flow of electric charges in one or more directions. For example, a wire is an electrical conductor that can carry electricity along its length.
Share Presentation
- electrical conductor
- electrical wiring
- electric charges
- practical electrical conductors
- maximum conductor temperature rating

Presentation Transcript
CONDUCTORS Conductor is an object or type of material which permits the flow of electric charges in one or more directions. For example, a wire is an electrical conductor that can carry electricity along its length. In metals such as copper or aluminum, the movable charged particles are electrons. Positive charges may also be mobile, such as the cationic electrolyte(s) of a battery, or the mobile protons of the proton conductor of a fuel cell. Insulators are non-conducting materials with few mobile charges and which support only insignificant electric currents. Conductors contain electrical charges, which will move when an electric potential difference (measured in volts) is applied across separate points on the material. This flow of charge (measured in amperes) is what is meant by electric current. In most materials, the direct current is proportional to the voltage (as determined by Ohm's law), provided the temperature remains constant and the material remains in the same shape and state.
Copper is the most common material used for electrical wiring . Silver is the best conductor, but it is expensive. It has a resistivity of1.6×10−8Ω⋅m. Because gold does not corrode, it is used for high-quality surface-to-surface contacts. However, there are also many non-metallic conductors, including graphite, solutions of salts, and all plasmas. There are even conductive polymers. All non-superconducting materials offer some resistance and warm up during electric currents. Proper design of an electrical conductor takes into account the temperature of the conductor as well as the value of electric current. The motion of charges creates an electromagnetic field around the conductor that exerts a mechanical radial squeezing force on the conductor. The current carrying capacity of a conductor is limited by its ability to dissipate heat. This effect is especially critical in printed circuits, where conductors are relatively small and close together, and inside an enclosure: the heat produced can melt the tracks.
Thermal and electrical conductivity often go together. For instance the sea of electrons causes most metals to act both as electrical and thermal conductors. However, some non-metallic materials are practical electrical conductors without being good thermal conductors. One of the best conductors is lead. The best, is also expensive, is Silver.
EXAMPLES OF CONDUCTORS IRON COPPER
ALUMINUM GOLD
GRAPHITE SILVER
INSULATORS Anelectrical insulator is a material whose internal electric charges do not flow freely, and therefore does not conduct an electric current under the influence of an electric field. A perfect insulator does not exist, but some materials such as glass, paper and Teflon, which have high resistivity, are very good electrical insulators. A much larger class of materials, even though they may have lower bulk resistivity, are still good enough to insulate electrical wiring and cables. Examples include rubber-like polymers and most plastics. Such materials can serve as practical and safe insulators for low to moderate voltages (hundreds, or even thousands, of volts). Insulators are used in electrical equipment to support and separate electrical conductors without allowing current through themselves. An insulating material used in bulk to wrap electrical cables or other equipment is called insulation. The term insulator is also used more specifically to refer to insulating supports used to attach electric power distribution or transmission lines to utility poles and transmission towers.
Insulators are commonly used as a flexible coating on electric wire and cable. Since air is an insulator, in principle no other substance is needed to keep power where it should be. High-voltage power lines commonly use just air, since a solid (e.g., plastic) coating is impractical. However, wires that touch each other produce cross connections, short circuits, and fire hazards. In coaxial cable the center conductor must be supported exactly in the middle of the hollow shield in order to prevent EM wave reflections. Finally, wires that expose voltages higher than 60V can cause human shock and electrocution hazards. Insulating coatings help to prevent all of these problems. Some wires have a mechanical covering with no voltage rating—e.g.: service-drop, welding, doorbell, thermostat wire. An insulated wire or cable has a voltage rating and a maximum conductor temperature rating. It may not have an ampacity (current-carrying capacity) rating, since this is dependent upon the surrounding environment (e.g. ambient temperature). In electronic systems, printed circuit boards are made from epoxy plastic and fiber glass. The nonconductive boards support layers of copper foil conductors. In electronic devices, the tiny and delicate active components are embedded within nonconductive epoxy or phenolic plastics, or within baked glass or ceramic coatings.
In microelectronic components such as transistors and ICs, the silicon material is normally a conductor because of doping, but it can easily be selectively transformed into a good insulator by the application of heat and oxygen. Oxidised silicon is quartz, i.e. silicon dioxide, the primary component of glass. • In high voltage systems containing transformers and capacitors, liquid insulator oil is the typical method used for preventing arcs. The oil replaces air in spaces that must support significant voltage without electrical breakdown. Other high voltage systems insulation materials include ceramic or glass wire holders, gas, vacuum, and simply placing wires enough far apart to use air as insulation. • Types of Insulators • Dead End Suspension Insulators • Pin Type Insulators • Line Post Insulators • Station Post Insulators • Cut Outs
EXAMPLES OF INSULATORS GLASS PORCELAINE
CLAY QUARTZ
- More by User

Conductors and Insulators
Conductors and Insulators. A conductor is a substance that allows electrons to move freely from one atom to another . Name 3 things that are good conductors: Silver Copper Gold. An insulator is a substance that electrons cannot move freely from one atom to another .
392 views • 5 slides
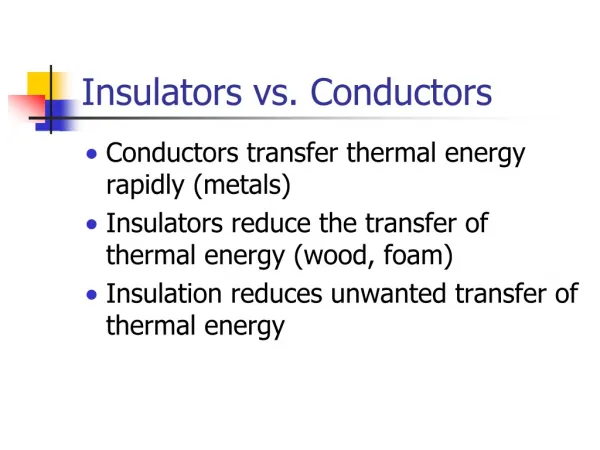
Insulators vs. Conductors
Insulators vs. Conductors. Conductors transfer thermal energy rapidly (metals) Insulators reduce the transfer of thermal energy (wood, foam) Insulation reduces unwanted transfer of thermal energy. R-value of insulating materials. Which materials are the best insulators?
388 views • 22 slides
Insulators and Conductors
Insulators and Conductors. 9.6. How would you feel if someone asked you to grab a live power line? Knowledge of insulators and conductors allows us to approach these situations. Insulators.
474 views • 9 slides

Insulators and Conductors. 9.6. Task 1: Design a safety poster telling people at least two ways of how to be safe during a thunderstorm and to avoid lightning. Insulators and Conductors. In order to use electricity to our advantage, we have need both insulators and conductors .
557 views • 6 slides

18.3 Conductors and Insulators
18.3 Conductors and Insulators. Electric charge can exist on an object and can move through an object. Different materials have different abilities to allow electric charge to move or be conducted through them. Electrical conductors.
473 views • 25 slides

Conductors & Insulators
Conductors & Insulators. Physics 2/4/13-2/8/13 Coach Stephens. Conductors. The behavior of an object that has been charged is dependent upon whether the object is made of a conductive or a non-conductive material.
1.08k views • 74 slides

Conductors, insulators and induces charges
Conductors, insulators and induces charges. Conductors, insulators . We show experimentally that there are : materials which allow to move charge from one region to another . Conductors. Materials which don’t allow to move charge from one region to another . Insulators. Experiment : .
198 views • 5 slides

Conductors vs Insulators
Conductors vs Insulators. Sofia Valentina Grisales Aranguen, Juliana Giraldo Carvajal, Matthias Neira Velasquez. Question. Hypothesis. Procedure. Materials. Charts and Tables. Results And Conclusion . Pictures. QUESTION.
365 views • 8 slides

Conductors & Insulators. How do these words relate to conductors and insulators?. Protection Aluminum Plastic Copper Slow flow of electrons Glass Metals Transfer electric charge Lamp cord. What is a conductor?.
1.11k views • 6 slides

Insulators and Conductors. Hi, Slippery again. Some materials conduct electricity and are called conductors and some materials do not conduct electricity and are called insulators . So Remember: Conductors allow electricity to flow quite easily and will compete a circuit.
374 views • 7 slides
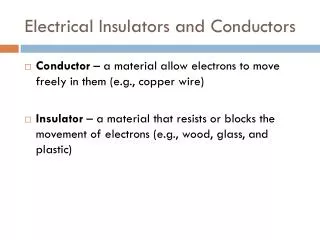
Electrical Insulators and Conductors
Electrical Insulators and Conductors. Conductor – a material allow electrons to move freely in them (e.g., copper wire) Insulator – a material that resists or blocks the movement of electrons (e.g., wood, glass, and plastic). Water as a Conductor. Water is an insulator only if its pure.
298 views • 2 slides

Conductors and Insulators. What are conductors ?. They allow the electricity to pass through the circuit. What are insulators?. They stop the flow of electricity through the circuit. . Conductors and Insulators Song. Experiment. Conductor =. Insulator=. Results. Conductors.
434 views • 15 slides

Conductors and Insulators. What does it mean?. Conductors allow charge (electrons) to flow through them freely Insulators DO NOT allow charge (electrons) to flow through them freely. It’s a Gradient!. strong insulator. strong conductor. Water: A Special Case.
381 views • 11 slides

Conductors and insulators
Conductors and insulators. Conductors = materials that transfer thermal energy easily. Insulators = materials that slows or stops thermal energy from flowing. Conductors. Allows thermal energy to travel easily through them. Solids liquids gases
1.28k views • 5 slides
Conductors vs. Insulators
Conductors vs. Insulators. Focus Question. Which material is the best conductor of heat? Styrofoam Plastic Glass. Hypothesis. I think ______________________ will be the best conductor because. Materials. 3 cups for each lab group – one plastic, one styrofoam , one glass
307 views • 9 slides

ELECTRICITY: Conductors and Insulators
ELECTRICITY: Conductors and Insulators. ATOMS and MOLECULES. An atom is the smallest unit of an element that has the properties of the element.
323 views • 9 slides
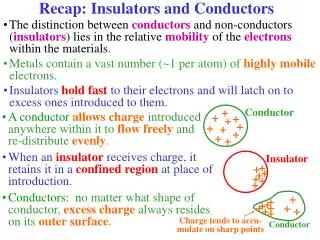
Recap: Insulators and Conductors
Recap: Insulators and Conductors. +. Conductor. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. Insulator. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. +. Charge tends to accu-mulate on sharp points. +. Conductor.
326 views • 14 slides

Conductors, insulators and induces charges. Conductors, insulators. We show experimentally that there are : materials which allow to move charge from one region to another. Conductors. Materials which don’t allow to move charge from one region to another. Insulators. Experiment :. e.g.
203 views • 5 slides

Types of Conductors & Insulators
Electricity flows on an atomic level from electrons traveling between atoms in a substance. These valence, or free, electrons vary between substances, causing them to exhibit varied electrical properties. To know more details please visit www.waferpro.com
499 views • 7 slides

Insulators and Conductors. Objective: Describe insulators and conductors. Identify materials that are good insulators and conductors. Heat Transfer. Heat always moves from a warmer place to a cooler place.
839 views • 52 slides

Chapter. 11. Conductors and Insulators. Topics Covered in Chapter 11 11-2: Standard Wire Gage Sizes 11-8: Wire Resistance 11-9: Temperature Coefficient of Resistance. 11-2: Standard Wire Gage Sizes. Sizes are specified by the American Wire Gage (AWG) system (p. 317, Table 11-1).
143 views • 10 slides

Insulators and Conductors. Objective: Describe insulators and conductors. Identify materials that are good insulators and conductors. What are Insulators?. Insulators are materials that do not allow heat to move easily through them. Using your booklet, name materials that are insulators.
215 views • 12 slides

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
There are several types of insulators but the most commonly used are : 1) Pin Insulator 2) Suspension Insulator 3) Strain Insulator and 4) Shackle insulator. 4. 6. Fig.) Pin Insulator. 7. Fig.) Glass suspension insulator. 8. For high voltages (>33 kV), it is a usual practice to use suspension type insulators consist of a number of porcelain ...
The device, therefore, provides insulation between the line conductors and the Earth. Types of Insulators • ESP Insulators • The technicians utilise it for high voltage power lines and insulation. • The major applications are in cement works, power and coal industry. • The types are shaft insulator, conical support, cylindrical support etc.
How are conductors and insulators different? Conductors Insulators A material that allows electricity to flow Ex. Metals, copper, water, human body, silver Materials that resist the flow of electricity Ex. Rubber, plastic, cardboard, foam, wood, glass Used for safety
Insulator — Any material that does not allow electric current to pass through it 'like the protective coating on wires 'plastic 'rubber 'glas 'Cloth 'wood 'copper 'aluminum 'steel 'any metal . Conductor Temperature . Metal Dirac material Insulator particle— hole excitations . Title: PowerPoint Presentation Author: Steven Mark Anlage
Learning Objectives. Describe the key characteristics of the four basic market types used in economic analysis.Compare and contrast the degree of price competition among the four market types.Provide specific actual examples of the four types of markets.Explain why the P=MC rule leads firms to th. 1.31k views • 21 slides
An insulator is an electronic device that gives support to the poles and overhead line conductors. Its main purpose is to prevent the current flow toward the Earth. In transmission lines, it has an integral role to play. The manufacturers design the insulator using rubber, mica, wood or even plastic. They use special materials like glass, PVC, ceramic, polymer, steatite etc. However, the ...
Insulation is an important element for receiving safe electricity within homes and offices. Learn about the various types of insulators commonly used, and the materials used to build them, in this blog. - A free PowerPoint PPT presentation (displayed as an HTML5 slide show) on PowerShow.com - id: 897c9f-NDJhY
Insulators.ppt - Free download as Powerpoint Presentation (.ppt), PDF File (.pdf), Text File (.txt) or view presentation slides online. This document discusses different types of insulators used in electric systems. It describes three main types of dielectric materials - solid, liquid, and gaseous dielectrics - that are used for insulation.
This teaching presentation was designed to introduce and discuss the concepts of: Thermal Energy. Electrical Energy. Conduction and conductors. Insulation and insulators. By looking at examples of how energy is transferred, students will walk away from this lesson with the ability to differentiate between insulators and conductors of thermal ...
Some examples of insulators include: glass; paper; wood; rubber; With this teaching presentation, students will take an in-depth look at not only what insulators are, but also how they work, the difference between electrical and thermal insulators, and why these materials are important in our world. Tips for Differentiation + Scaffolding
Download Free PPT. Download Free PDF. Insulators. Insulators. Insulators. Insulators. Insulators. Smita Jana ... or wood. As the name suggests, the pin type insulator is secured to the cross-arm on the pole. There is a groove on the upper end of the insulator for housing the conductor. The conductor passes through this groove and is bound by ...
Pin Type Insulators • This is one of the earliest designs. • Can be used for voltages upto 33kV. • Mounted on a pin which is secured on cross-arm of pole. • Conductor placed in groove and tied down with soft Cu or soft Al according to conductor material. • Bottom shell is protected by top shell. • Beyond 33kV, pin type insulators become bulky and uneconomical.
7. Material Insulators used for high-voltage power transmission are made from glass, porcelain or composite polymer materials. Porcelain insulators are made from clay, quartz or alumina and feldspar, and are covered with a smooth glaze to shed water. Insulators made from porcelain rich in alumina are used where high mechanical strength is a criterion. Porcelain has a dielectric strength of ...
D" ú ÷ ppt/presentation.xmlì˜moÚ: €¿_éþ‡(_'š÷ Pa‚q³;©WªVö Lb ªcG¶i¡Óþû=v )붮û† >çø¼9ÄŽ¯ßï*b=`.JFǶwåÚ ¦9+Jº Û_ Ù µ-! - a í= öûÉß ]×£šc ©D ¦Zà†Š Û )ë'ãˆ|ƒ+$®X )èVŒWH ¯ ‚£Gp_ ÇwÝØ©PIm3ŸÿÌ|¶Z•9ž³|[AøÆ ÇDç!6e- ÞêŸñÖâ4%\-q±à[¼Ø×8cT dO rAŠÿ ...
History Approx 1970 - present • Domestic manufacturing of insulators decreases, shift to offshore (all types) • Engineers need to develop knowledge and skills necessary to evaluate and compare suppliers and products from many different countries • An understanding of the basics of insulator manufacturing, design and application is more ...
insulation. a material that reduces or prevents the transmission of heat or sound or electricity. INSULATOR. A . material. or an object that does not easily allow heat, electricity, light, or sound to pass through it. Air, cloth and rubber are good electrical . insulators. ; feathers and wool make good thermal .
Thermal insulation works to control the temperature inside the room. As you know, 25% of the heat goes inside your house through the roof, and 15% is from the walls. These materials can block most of the heat from getting inside the house. In general, most insulation materials can do this. But the most affordable ones are fiberglass and ...
CONDUCTORS AND INSULATORS. CONDUCTORS. Conductor is an object or type of material which permits the flow of electric charges in one or more directions. For example, a wire is an electrical conductor that can carry electricity along its length. Slideshow 6493799 by mallory-good