- The Open University
- Guest user / Sign out
- Study with The Open University

My OpenLearn Profile
Personalise your OpenLearn profile, save your favourite content and get recognition for your learning
EPQs: writing up your dissertation
The Extended Project Qualification (EPQ) is an opportunity for you to work independently on a topic that really interests you or that you think is important. It is equivalent to an A-level qualification. These articles are designed to help you if you are enrolled on an EPQ.
See previous article in series: Finding and using evidence
Writing up your dissertation.
Being able to communicate well is an essential skill for both university and working life. One of the aims of the EPQ is to help you develop your skills in using different communication tools, so you can communicate what you have found clearly and appropriately for different audiences.
Communication is also a vital part of the research cycle. The progress of research thrives on the exchange, review and discussion of ideas. Writing is one of the ways in which we communicate what we have found out and share it with others.
Sharing the results of your research by writing well and effectively gives your readers the opportunity to learn from the work you have done.
This article offers suggestions and support for developing your skills in writing in the academic style that is needed for your EPQ dissertation.
Getting organised .
It’s worth considering a few practical points first. The start of writing is a good time to gather your material together and get yourself organised.
- Don’t lose your work
- Timings & deadlines
- Organise your records
- Laying out the document
- Tables, graphs and charts
You don’t want to find yourself a few days – or hours – from the submission deadline when a computer breakdown or accident means you lose everything you’ve done.
It has happened before, and you don’t want it to happen to you!
Build a routine for backups into your work pattern. For example, when you sit down to write, save a copy (named, for example, Version 1, Version 2 ... Version 25 ...) of the existing document before you make any changes.
And back up your backup. Once a week, make a backup copy of your files (your dissertation, your notes and the resources you have collected) to an external hard drive, memory stick or cloud storage.
Work out how much time you have to write your dissertation, and how much time you want to allocate to each section. (There’ll be more on this shortly under ‘Structuring the dissertation – Start with the structure’.)
Make sure you know – and have written down! – the deadlines for submitting your dissertation, including deadlines for any draft versions your teacher might want to see. Use these to help plan your writing time.
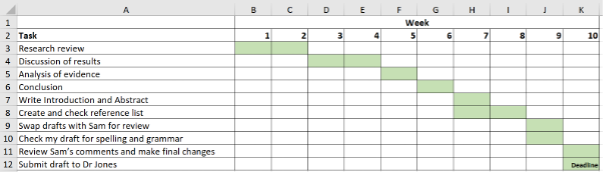
There are many tools to choose from to keep yourself on track. For example, you could create a table with a list of tasks.
Or you could make a simple Gantt chart, using a spreadsheet. If you use Microsoft Excel, it has some Gantt chart templates. The advantage of a Gantt chart is that it makes it easier to see how you can overlap some tasks, and you can mark important milestones such as submission deadlines .
As you have gone through the process of collecting and analysing the evidence you need to answer your research question, you will have gathered records of:
- what you looked for (the search terms you used in your searches)
- where you looked (search engines, websites, etc.)
- what you read / watched / listened to (academic papers, articles, videos, podcasts, etc.)
- the notes you made on your reading, listening and watching
- the data you have gathered.
All these sources contribute to the content of your written dissertation. Hopefully you have good records, but if you got a bit behind, now is the time to sort them out and remind yourself what you did and what you found out.
If you need a reminder of what information you need to keep, look back at Article 2 – Finding and using evidence .
Organising your records and keeping a note of the sources you mention in the text as you write helps you build a comprehensive reference list.
There is more information on how to set out your reference list later in this article (see ‘Structuring the dissertation – Referencing styles’ ).
Laying out your document in a clear and neat style helps make your readers’ life easier.
For the text , use a classic font such as Arial, Helvetica or Times New Roman. It’s best to avoid quirky fonts such as Comic Sans, or difficult to read fonts such as Lucida handwriting.
For easy reading, the font shouldn’t be too small. 11 or 12 point is a popular choice for the main (or body) text, which is usually black in colour. You can use larger fonts for headings and sub-headings, and perhaps make them bold or a different colour.
Generous margins also make the document easier to read. As a guide, around half the area of the page should be white space; on an A4 page, that means margins of about 2cm all round.
Use the paragraph styling tool . It’s well worth investing some time learning to use paragraph styling in Microsoft Word and Mac Pages ; it can really speed up the creation of long documents and help you produce good-looking work.
This tool gives you control over the appearance of the text in your document. For example, you can use it to include automatic numbering for your headings ( Word or Pages ). This means you don’t have to manually change all the numbering if you insert a new heading or delete one that is no longer useful. You can also use automatic numbering for figure and table captions. Or, if you decide you don’t like the font you have used, you can change it in the paragraph style and it will be changed throughout the document.
Some kinds of evidence – such as numeric data – work well when displayed as graphs, charts and tables.
Readers should be able to make sense of the graph, chart or table without explanation.
Look at Table 2. Is it clear what information the creator wanted to share?
A better example can be seen below in Table 3:
Graphs and charts need titles too. They should also have axis titles (naming what is plotted on each axis, with the relevant units) and axis labels (the values plotted).
When it comes to plotting graphs, using different shapes or line styles can help readers distinguish different data points or collections of data on a single graph. You can use contrasting colours, but keep in mind that too many colours can be distracting for the reader. And some readers – for example, people who are colour-blind or have vision problems – might not be able to distinguish between certain colours, so choose carefully.
Look at Figure 3. Does it have all the elements of a good graph? Could anything be improved?
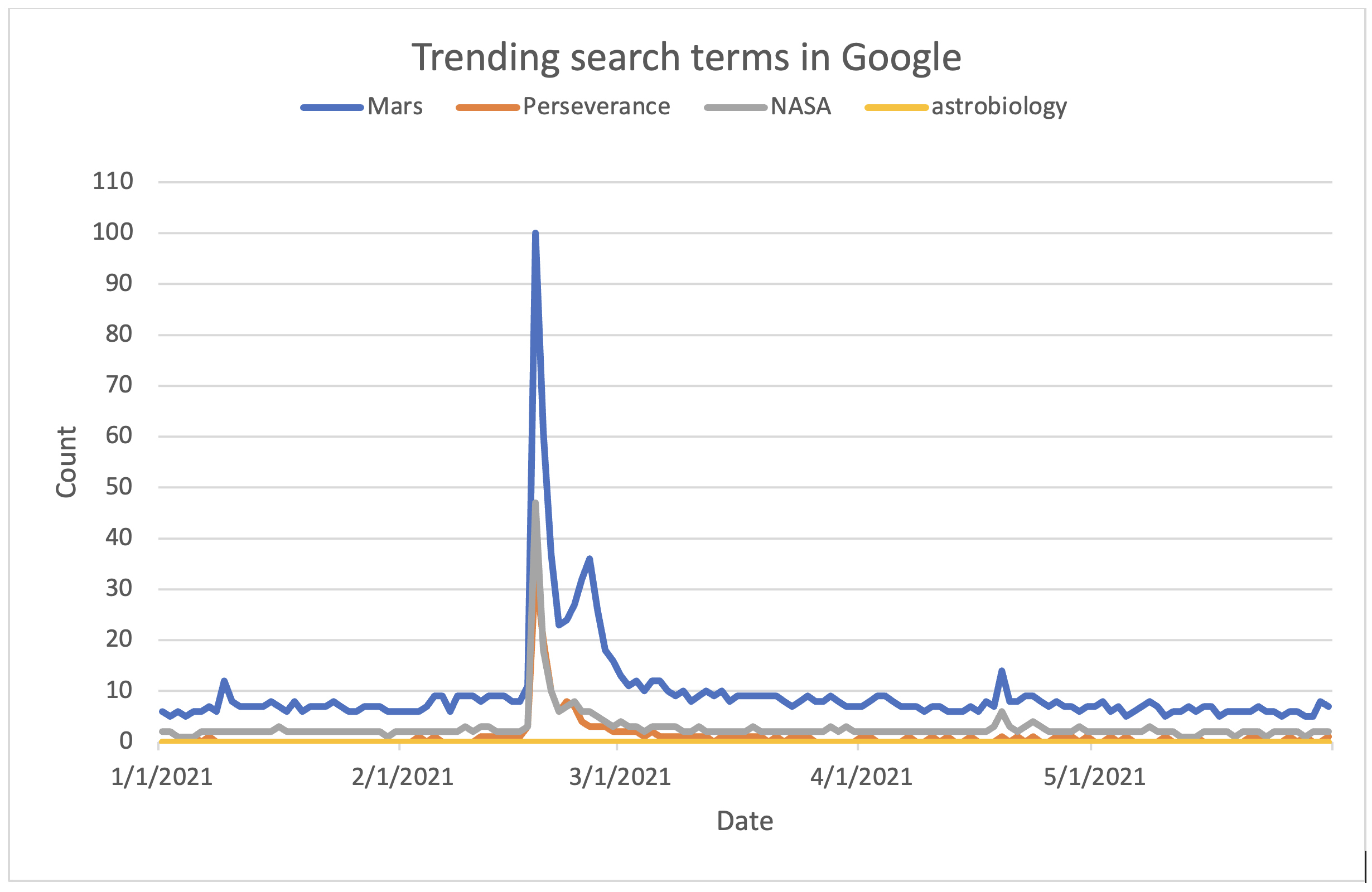
This has many of the requirements of a good graph. The title explains what the graph is about, the axes are labelled and the four search terms are each given their own colour, with a key to show which is which.
It could be made better by:
- making the graph larger, so that the four lines are more separate
- choosing different colours – the orange for ‘Perseverance’ and the yellow for ‘astrobiology’ are difficult to distinguish from each other.
Evidently, something interesting must have happened in mid-February to cause this spike in searches – you might remember that on 18 February 2021, the NASA Mars Perseverance Rover mission landed on Mars!
Structuring the dissertation .
Facing a blank page and the prospect of writing 5000 or so words can feel daunting. But you can structure the way you write to help make the task easier.
- Start with the structure
- Facing the blank page
- The narrative arc
- Finishing things off
- Referencing styles
Starting with the structure will help you consider how you want the dissertation to flow, and how to allocate your time and effort.
This example, taken from the Edexcel documentation, gives a suggested word count for the different sections of a ‘research review’ dissertation. All the exam boards publish their requirements, so you should check the requirements for your board and the type of EPQ you are doing .
A ‘research review’ dissertation would probably follow something like the structure above. For other kinds of project, check with your teacher or look at the exam board’s requirements. Knowing what structure the exam board is expecting helps you to know where to focus your effort.
In Table 4, you can see that the biggest section of the dissertation is the discussion/development/analysis of the argument, so it would make sense to spend the largest part of your writing time on this section. Look back at the Gantt chart under ‘Getting organised – Tables, graphs and charts’ for an example of time allocated in this way.
You’ve opened a new document. You know the sections you need to include.
How do you get started on the sentences that will fill the gaps in between? Two researchers offered suggestions from their experience.

Robert, a space scientist, says he usually works out the first paragraph in his head before sitting down to write.
- Ann’s summary
This is how Charlotte described her approach. First step, open a Word document!
Second step, write titles and sub-headings on the page. These can be working titles that you can come back to and polish once you have developed the document. But getting that structure down on the page is a key step for Charlotte in building the document and working out how the manuscript is going to flow. Once she’s broken the document up into sections, it feels much less daunting for her. Instead of starting at word one of six thousand, she’s working on smaller, more manageable chunks – word one of a hundred, or two hundred.
Step three is to write down the aims, objectives and scope of the document. And then she goes on to write the conclusions. And she says yes, that’s not a typo – if you’ve done a good job of researching the topic, developing the aims and objectives and making your notes, then writing the conclusion first should be relatively easy. The benefit of writing the end of your manuscript before the beginning is that you’re less likely to go off on tangents when you’re writing the rest of the manuscript, because you know where you’re heading.
If you feel you’ve thoroughly researched your topic and you’re still finding it hard to work out what your conclusions are, then it may be a good idea to turn your research notes into a presentation, during which you can ask yourself ‘what key message do I want the audience to walk away with?’, and that will be your conclusion.
Step five: write the remaining sections of the dissertation, justifying and building your arguments for each conclusion.
Charlotte’s main points

Charlotte’s steps are:
- Open a Word document!
- Write titles and sub-headings on the page.
- Write down the aims, objectives and scope of the document.
- Write the conclusion – ask yourself ‘what key message do I want the audience to walk away with?’
- Write the remaining sections, justifying and building your arguments for each conclusion.
Headings and sub-headings
Charlotte described how she likes to set up the headings and sub-headings that structure her writing, even though she knows they might change as the document develops.
Using descriptive headings, such as ‘The history of ...’ tells the reader what to expect in that section or chapter. This is sometimes called ‘signposting’, because the headings and sub-headings guide the reader around your work.
As well as descriptive headings, you can number your headings and sub-headings:
- Section 1: An introduction to…
- Section 1.1 : The history of ...
This means you can refer the reader back and forth (e.g. ‘see Section 1.2’), which cuts down repetition and wasted words.
Both approaches have the merit of getting something on to the blank page, which makes it look much less scary.
Whether you start with an opening paragraph, a set of headings, or another method that works for you, getting those first few words on the page is one of the biggest hurdles to clear.
Narrative – the story thread that runs through any piece of work we create – is important in any piece of writing. Stories keep people’s attention, as storytellers have known for hundreds of years. Writers, broadcasters and podcasters continue to make use of this fact today.
One way to think about how you shape your story is to consider its narrative arc. Yes, even the most ‘science-y’ of dissertations has a story.
Click on the crosses on Figure 6 to find out more about the components of the narrative arc.
Figure 6 The narrative arc
Points on the narrative arc
Description : A parabolic curve representing the narrative arc of a story. The first half of the curve rises to a peak, showing the points that build interest in the story. The second half falls back to the baseline, showing how we reflect on the details of the story and bring it to a close.
– In the Introduction , attract the reader’s attention at the start, perhaps by telling them what got you interested in the question; a personal interest, an ambition or a desire to know more about a topic.
– In the Introduction , describe the journey to your research question. Make sure you do actually tell your reader what your question is (you’d be surprised how often people forget that!)
Information
– In the Research Review section, you show the reader how you found your evidence; tell them about the keywords you used, the mindmaps, flowcharts, tables you made; what information was important and what was not; what stayed in and what didn’t.
– This is your analysis of the material you found, showing how you pulled together the information you uncovered in your review and what it meant for your question. However, this isn’t an absolute rule; where you put the analysis depends on the kind of dissertation you are writing.
– Tell the reader what you found out and how it relates to what is already known.
– Use the Conclusion to round off your story. What’s the answer to your research question? What did you discover? What’s still not known?
There are a couple of sections of the dissertation that are best dealt with towards the end of the writing process: abstract and bibliography.
The abstract
At the beginning of the dissertation, you should provide a short summary or abstract.
An abstract is like a trailer for a film or television programme. It gives the reader a sense of what’s in the dissertation. However, unlike a trailer, it’s OK to give away the ending! Someone who only reads the abstract, and never looks at the dissertation, should still understand the scope of your work.
For this reason, it’s easier to write the abstract towards the end of your writing time, when you have a complete picture of your work in your mind.
The abstract is usually quite short (perhaps only 200 words) and is written in one paragraph. That’s not much space, so what should you include?
A typical abstract would tell the reader:
- why you did this research – the question you set out to answer
- how you did the research – the methods you used to collect the data and where you looked for it
- what you found out – a summary of your main findings
- the key message – the answer to your question; if your readers could remember just one thing from your dissertation, this would be it.
One way to approach writing the abstract is to read through your dissertation section by section. For each section, write one or two sentences that summarise the main point. Click on ‘example’ to see what we mean.
The use of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is growing rapidly among young people, but the usefulness and safety of some therapies is controversial. Therefore, I investigated the question: what are the best places to reach young people with information about CAM?
Using Google Scholar, I searched for articles using different combinations of these search terms: ‘alternative medicine’, ‘complementary medicine’, understanding, knowledge, motivation, CAM. I filtered the results to keep only articles that related to the use of CAM by young people. I defined ‘young’ as people under the age of 25. I downloaded twenty complete papers, articles and other resources from open access sources and the Open University research repository.
Use of CAM by young people has increased since 2000. Young women use CAM more than young men. The most common sources for getting information about CAM are friends and family and social media.
Key message
The best way to provide information for young people about CAM is through social media.
Take away the headings and polish the sentences and you have an abstract:
The use of complementary and alternative medicine (CAM) is growing rapidly among young people, but the usefulness and safety of some therapies is controversial. Therefore, I investigated the question: what are the best places to reach young people with information about CAM? Using Google Scholar, I searched for articles using different combinations of these search terms: ‘alternative medicine’, ‘complementary medicine’, understanding, knowledge, motivation, CAM. I filtered the results to keep only articles that related to the use of CAM by young people. I defined ‘young’ as people under the age of 25. My search found twenty relevant papers, articles and other resources, which I downloaded from open access sources and the Open University research repository. My results show that young people’s most common sources for information about CAM are friends and family and social media. Therefore, I believe that using social media is the best way to provide information about CAM for young people.
The bibliography or reference list
The last thing to include in your dissertation is the bibliography or reference list * .
Your reference list shows the people who read (and mark!) your dissertation how well you have researched your subject and how your arguments are supported by evidence from other people’s research.
It is also evidence of how you have been open and honest in your work. Readers can use it to find the sources that you used and check that you have read and used them correctly.
Using your reference list, a reader should be able to find that source for themselves if they want to follow up an idea or check something you have written. Including a reference list helps you avoid plagiarism (passing off someone else’s work as your own), because readers can check the original source if they have any doubts.
If you need a reminder of what information you should keep, look back at ‘Finding and using evidence – Keeping track’ .
* A reference list is a list of all references to other people’s work that you have mentioned in your dissertation. A bibliography is a list of references, plus the background readings or other material that you have read but not actually mentioned.
The Open University Library Services’ Referencing and plagiarism page has lots of help and pointers to further information about references and referencing styles.
If you go on to study at university, and have to write essays, assignments and reports, you will be asked to set out – or ‘style’ – reference lists in a specific way. There are many different referencing styles; which one you are asked to use will depend on the subject you are studying and the university’s requirements.
For the EPQ, check the requirements of your exam board or ask your teacher what these are.
Even if you aren’t asked to use a specific style, you should aim to include as much information about the sources as possible. The minimum information would be:
- the authors’ (or creators’) names
- the year the source was published
- the title of the article or book chapter, or the name of the artwork, film or video
- the title of the journal or the book in which the article/chapter appeared
- for books – the name of the publisher
- for online sources – the name of the website and the page on which the article appeared, the URL of the website, and the date on which you read the article*.
*The date you found the article is important for online sources, as websites sometimes disappear or are changed. If the reader can’t find the same article but knows when you found it, that suggests they can trust the source.
These examples are laid out in the Harvard referencing style, which is a style used in many university subjects.
Books and ebooks
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) Title . Edition if later than first. Place of publication: publisher. Series and volume number if relevant.
Mukherjee, S. (2011) The Emperor of all Maladies . London: Fourth Estate.
Article from an academic journal
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) ‘Title of article’, Title of Journal , volume number (issue number), page reference. Doi: doi number if available OR Available at: URL (Accessed date)
Ungar, S. (2008) ‘Global bird flu communication: hot crisis and media reassurance’, Science Communication , 29(4), 472-497. DOI: 10.1177/1075547008316219
Article from a newspaper or magazine
Surname, Initial. (Year of publication) ‘Title of article’, Title of Newspaper , Day and month, Page reference if available. Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
Rice-Oxley, M. (2021) ‘Do good things come to those who wait?’, The Guardian , 26 February. Available at https://www.theguardian.com/world/2021/feb/26/do-good-things-come-to-those-who-wait (Accessed 26 February 2021).
Organisation (Year that the page was last updated) Title of web page . Available at: URL (Accessed: date).
BBC Online (2020) How New Zealand relied on science and empathy . Available at: bbc.co.uk/news/world-asia-52344299 (Accessed 17 September 2020).
Writing clearly .
Good writing takes time, effort and energy. Being able to produce clear, readable, logical and well-argued pieces of writing is important in both university and in your working life.
- Precise & concise
- Keep it simple
- A word about style
- Quoting others

Blaise Pascal was a seventeenth-century mathematician, physicist, inventor, philosopher and writer. He once wrote:
‘ Je n’ai fait celle-ci plus longue que parce que je n’ai pas eu le loisir de la faire plus courte ’ .
–Blaise Pascal, Provincial Letters, Letter XVI, December 1656.
Translation: ‘I wrote this very long [letter] because I didn’t have the time to make it shorter’.
What do you think Pascal meant by this?

Claire, whose research looks for evidence of how we might ‘ sniff’ for life , produced a mind map of what she thinks Pascal meant (Figure 9). The audio below describes her process.
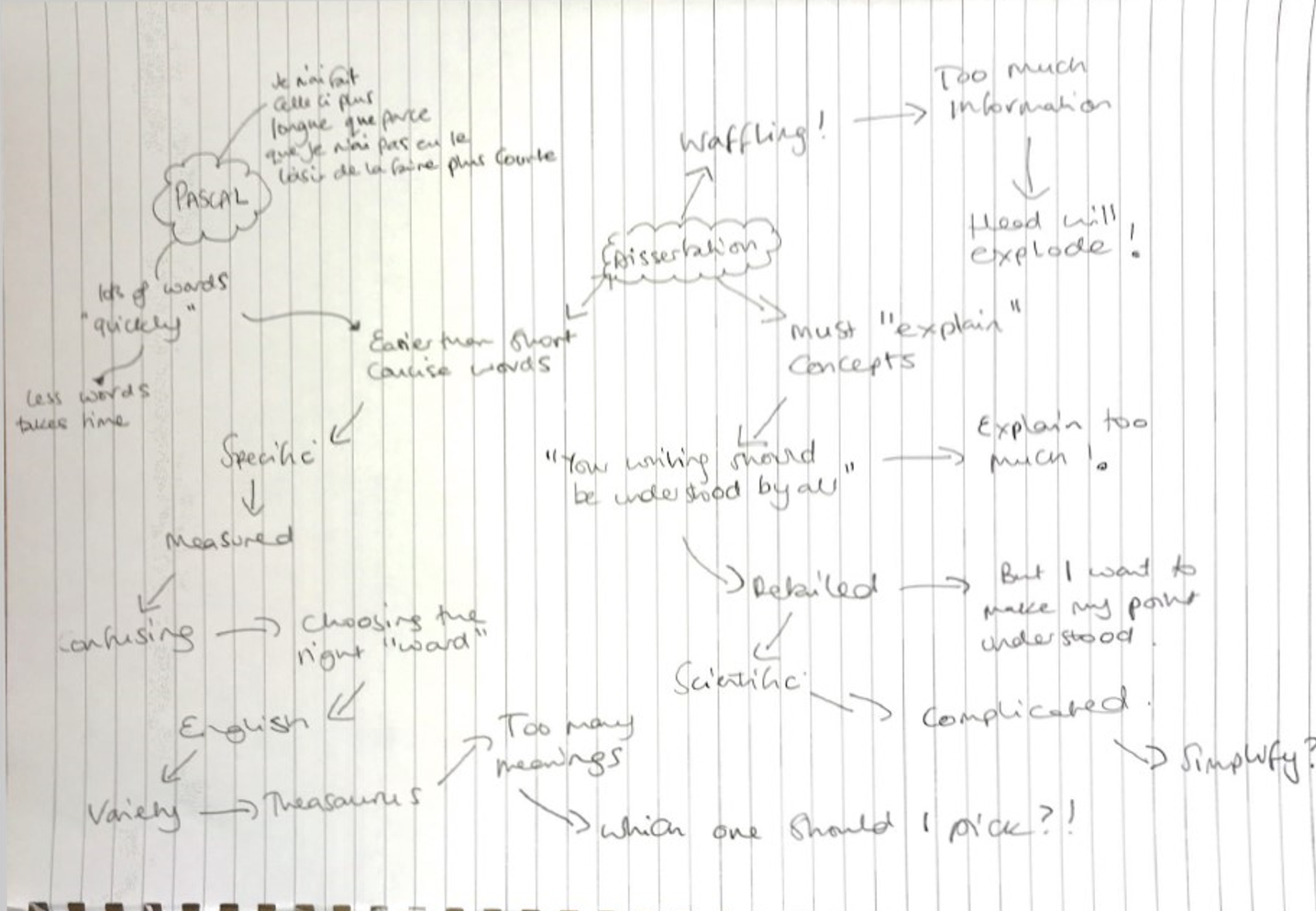
Claire’s mind map takes us on quite a journey. Starting from Pascal’s premise that it’s better to write short than long, slower than quicker, makes her think about the need for concision, to look for concise words, words that are specific and measured, not being confusing, the need to choose the right word. Not always easy in English, where one word can have a variety of meanings.
She suggest perhaps using a thesaurus, but that could lead down the pathway of having too many words to choose from and not being able to decide which one to pick. Thinking about the dissertation, she introduces a word we all dread – waffling! No one wants to be a waffler, and giving too much information might make your readers’ heads explode.
And yet we must explain our concepts, because we want our writing to be understood by everyone but that means a balance with explaining too much. We need to give enough detail to make our point understood, and scientific, if it’s that kind of research question, without being too complicated. All in all, it comes down to the need to simplify.
More tips from Ann
As Pascal – and Claire – suggest, taking out what isn’t needed is as important as putting in what is.
Writing clearly and to the point takes time, effort and energy. Allow yourself plenty of time to draft, review, get feedback, edit ... draft again, review again, get more feedback, edit again … … check, proof-read, finish.
As we established earlier, your dissertation will have a word allowance. EdExcel, for example, suggests a research review dissertation should be around 6000 words. That sounds like a lot, but then, you’ve done a lot of work that needs to be included.
The exact figure will depend on the exam board’s requirements and the kind of EPQ you have carried out, so check before you start writing, or ask your teacher.
The best writers keep things as simple as possible. It’s a way of being kind to your readers and making the task of reading easier.
However, keeping things simple isn’t simple. As Steve Jobs, the designer and co-founder of Apple said: ‘Simple can be harder than complex: you have to work hard to get your thinking clean to make it simple’. The same applies to writing.
When you’ve done a complex piece of work, it’s tempting to think you can only describe it in complex language. But you should try to avoid the pitfall of using over-complicated language. You don’t want to run the risk of sounding pompous or making your text too difficult to understand.
You’ve almost certainly come across simple questions with unnecessarily complicated answers before. Here’s an example. Which is the best answer to this question?
The Up Goer Five challenge
To practise writing in simple language, you can take the Up Goer Five challenge. This is a project by the artist Randall Monroe, creator of XKCD .
The challenge is to explain a hard idea using only the ‘ten hundred’ most common words in the English language. As an example, how might we explain ‘astrobiology’?:
We think about where we might find living things. We take stuff from places – dry places, cold places, hot places – and we put it in stuff that we think has what living things need to grow. We wait, then we use a seeing-small-things tool to look for the living things. At the moment, we look at stuff from here but one day, we want to look at stuff from other stars.

Have a go at using the Up Goer Five text editor (which has a link to the ten hundred most common words ) to explain an idea related to your research topic. If you find it tricky to think of an idea, here are a few to get you started:
- global warming and its consequences
- what causes earthquakes
- the problems caused by the misuse of antibiotics.
You wouldn’t write your dissertation in this style, but experimenting with writing like this helps develop skills in keeping things simple, avoiding jargon and complicated language and writing in short sentences and paragraphs.
We all write in different ways every day, depending on who we’re writing for. The style of a textbook is different from the style of a WhatsApp message; we write an email to a family member in a different style from the way we would write a personal statement for a university application.
When we write anything, we start by thinking about our readers and the kind of writing they are expecting to see.
For the EPQ dissertation, start by checking the requirements of the exam board you are studying with. It is very likely that the exam board will want the dissertation to be written in a formal style; the kind of style you will have seen in the academic articles and books you drew on in your research.
Plagiarism is presenting someone else’s work as your own. It is, essentially, theft of someone else’s work.
Learning alongside a friend, discussing ideas or sharing your thoughts can be helpful and valuable. We have also encouraged you to take notes on everything that you find. So, it is likely that you have ideas you want to present in your report that are not entirely your own.
Plagiarism can occur in a variety of ways. It can mean copying someone else’s text and passing it off as your own, or copying and pasting text/images from a web page and pretending they are your own work. It can also overlap with what is called ‘collusion’, which means collaborating with someone to share work on a task that you are expected to complete by yourself.
Try this interactive resource from OpenLearn to understand some of the challenges and ways to avoid plagiarism. This is aimed at university students, but it will be relevant for the EPQ.

All my own work
Plagiarism comes in all shapes and forms. Step into the shoes of a university student to learn the challenges and temptations facing her during her assignment, and help make it all her own work.
Level: 1 Introductory
There will be points in your dissertation when you want to present ideas that have come from someone else’s work. How can you do this while avoiding plagiarism?
Identify your sources
If you have used an image, graph or chart created by someone else, identify where the image has come from and who made it.

You might remember this image from Article 1 , in the section on dealing with feedback.
This image comes from an online picture library, creazilla.com. They have placed it in the ‘public domain’, which means it can be re-used freely. Show this information in the image caption within your work.
If you create a graph, chart or table yourself, identify the source of the data, as you saw earlier in ‘ Getting organised – Tables, graphs and charts ’.
If you find a phrase or a sentence in a source that helpfully illustrates a point you are trying to make, you can quote that in your work. You must quote it exactly as the authors wrote it. After the quote, you give the name of the author, the date of publication and the page where the quote is from. Then give the full reference in your reference list (see ‘ Structuring the dissertation – Referencing styles ’). For example:
This shows that the format of an infographic can influence people’s responses to the evidence. For example, ‘ graphs commonly used to show descriptive statistics, such as line or area graphs, may also appear “scientific” and create a pseudo sense of trustworthiness ’ (Li et al., 2018, p. 4).
The quote marks (‘…’) show which words are the quote.
We use the Latin phrase ‘et al.’ (meaning ‘and others’) when an article has more than three authors, so that the reader doesn’t have to read through a long list of names. In the reference list, you would see the full list of authors along with the other source details:
Li, N., Brossard, D., Scheufele, D., Wilson, P. and Rose, K. (2018) ‘Communicating data: interactive infographics, scientific data and credibility’, Journal of Science Communication, 17(2), A06. DOI: 10.22323/2.17020206
When you paraphrase, you express an idea that has come from someone else in your own words. You might do this to re-state the idea in simpler language, or to bring together the ideas of several writers on the same topic. Paraphrasing can also help you show that any new ideas you’ve put together from your research are supported by earlier research.
You should show where the ideas you have paraphrased came from, but because you are not directly quoting, you need only give the authors’ names and the date of publication. For example:
My survey of fifty young people aged 16 to 18 showed that their social media posts were most often connected with current events. This is supported by earlier research, which shows that the most common topics for young people’s posts are current events, health and fitness, and celebrity and entertainment news, closely followed by science and technology (Hargittai, Füchslin & Schäfer, 2018) .
In the reference list, you would see:
Hargittai, E., Füchslin, T. and Schäfer, M. (2018) ‘How do young adults engage with science and research on social media?’, Social Media + Society, July-September 2018, 1-10, DOI: 10.1177/205630511879772
Although your dissertation must be all your own work, you can ask for help to review what you have written.
How do you ask for help, then, while keeping the dissertation all your own work and avoiding plagiarism?
Reviews – who and when?
Before you ask someone to review your work, you can check some things for yourself.
Check the spelling and grammar . Microsoft Word has built-in tools, or you can use online ones such as Grammarly . The more technically correct your writing is, the more your reviewers will be able to focus their energy on the content.
Then read it all through yourself . Some people like to read through silently, line by line, others prefer to read the text out loud. You can record yourself and listen back later, or use the Read Aloud function in Word, if you’re using that software. This has the advantage of using a different part of your brain – when you listen, you hear mistakes that you just don’t see in writing.
After you have reviewed it yourself, ask others to do the same. Getting someone else’s feedback on your work is immensely valuable. This is where you can collaborate with friends or classmates – if you ask them to review your work, you can offer to review theirs. And families can help too; even if they don’t know anything about your topic, the questions they ask will help you review your work.
- Michael asks for help
- Who could you ask for help?

Listen to the audio in the next tab about how Michael, who is a microbiologist, asks for help. When does he do this, and who does he ask?
Michael turns to his colleagues, his family and his senior colleagues at work. He asks for help at different stages: perhaps when he’s struggling a little, when he’s written the first draft and later on at the final stages, when he’s finished editing.
For Michael, feedback is incredibly important, not only for the actual content of the work, but for assessing how easy it is to understand. And he felt it’s always important to consider reviews of our writing from the viewpoint that the reviewer wants to help us improve our work, not criticise it. In terms of who he asks, first he calls on his peers; when he was at school, friends in his class and year, and now his colleagues, who can comment on the content of the work and how easy it is for them to follow. When he was at school, he also turned to his parents. During high school, his parents helped with input on grammar, spelling and how easy it was to understand. Now, his wife performs that role. As he says, by having someone from outside the field review your work, you can gain valuable insights. He also thinks about his seniors – in his current job, his senior colleagues will read multiple drafts of a manuscript before it’s complete. This is always an advantage – it allows him to get input from someone more experienced and means the work is improved.
In terms of when, he asks for help when he’s struggling, perhaps to find the right direction for a piece of work. Discussing the work with a friend or a teacher can start him developing insights on where it should start. Certainly after completing and spell-checking a first draft, he’ll ask for help.
And of course it’s always important to go back and review after editing, because when you change a piece of work, it’s easy to introduce errors, as well as fix them.
Conclusion.

Other articles in this series...

EPQs: designing your research question
You’ve already decided to do an EPQ, so it might seem a little odd to start this resource by asking you to consider why you want to do a research project. People do an EPQ for all sorts of reasons. Why do you want to do an EPQ?

EPQs: finding and using evidence
Finding the evidence that will help you understand a topic or answer a question is an important stage in the research process. And once you have found it, you will need to examine it closely and carefully, to judge how reliable it is and whether it is useful to help you answer your question.

EPQs: why give a presentation?
What are the guidelines for the presentation?
Become an OU student
Ratings & comments, share this free course, copyright information, publication details.
- Originally published: Friday, 3 March 2023
- Body text - Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 : The Open University
- Image 'Graph of the EPQ cycle' - Copyright: Ann Grand
- Image 'Comparison of four search terms used in Google in the UK from Jan to May 2021.' - Copyright: Ann Grand
- Image 'Robert, a space scientist.' - Copyright: Robert from AstrobiologyOU
- Image 'Sketch of Blaise Pascal' - Copyright: Wikimedia Commons
- Image 'Photo of Claire' - Copyright: Claire Batty
- Image 'Claire's mind map' - Copyright: Claire Batty
- Image 'Screenshot from the UpGoer project' - Copyright: XKCD
- Image 'Responses to feedback ' - Copyright: creazilla.com Public Domain boy crying angry woman happy man
- Image 'Photo of Michael' - Copyright: Michael Macey
- Image 'Extended Project Qualification banner' - Copyright: © Betta0147 | Dreamstime.com
- Image 'All my own work' - The Open University under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
- Image 'EPQs: why give a presentation?' - Alphabet Yellow © Betta0147 | Dreamstime.com under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
- Image 'EPQs: writing up your dissertation' - © Betta0147 | Dreamstime.com under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
- Image 'EPQs: finding and using evidence' - Alphabet Yellow © Betta0147 | Dreamstime.com under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
- Image 'EPQs: designing your research question' - © Betta0147 | Dreamstime.com under Creative Commons BY-NC-SA 4.0 license
Rate and Review
Rate this article, review this article.
Log into OpenLearn to leave reviews and join in the conversation.
Article reviews
For further information, take a look at our frequently asked questions which may give you the support you need.

How To Write An EPQ Essay & Dissertation (9 Steps)
Writing an EPQ essay involves several steps to ensure a well-structured and compelling piece.
Here is a 9-step guide to help you write an effective EPQ essay:
- Brainstorm EPQ topic ideas : Choose an engaging topic that interests you and is relevant to your academic or career goals.
- Conduct research : Gather information from various sources to support your arguments and provide evidence.
- Create a structure : Organise your essay with a clear introduction, main body, and conclusion. Outline the main points and arguments you will cover in each section.
- Write an introduction : Begin your essay with an introductory paragraph that introduces the topic, outlines the scope of the essay, and provides an overview of the structure 4 .
- Develop the main body : Write the main body of the essay, focusing on presenting your arguments, evidence, and analysis. Ensure each paragraph has a clear topic sentence and flows logically from one point to the next.
- Use proper referencing : Cite your sources correctly to avoid plagiarism and demonstrate your research skills.
- Write a conclusion : Summarise your main points and answer the question you posed at the beginning of the essay.
- Review and revise : Proofread your essay for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors. Ensure your arguments are clear, coherent, and well-supported 1 .
- Seek feedback : Ask a teacher, tutor, or peer to review your essay and provide constructive feedback to help you improve your work
The article below is designed to help you develop a strong foundation for writing your EPQ essay by providing practical tips and guidance from an expert in the field.
You’ll learn about key elements such as structure, formatting, research methods, argumentation techniques and more so that you can craft a compelling paper that stands out from the crowd.
By following these steps, you’ll have all the tools necessary to make sure your EPQ essay stands out and meets its desired goals.
- 1 Understanding The EPQ Essay Requirements
- 2.1 Organizing Ideas
- 2.2 Outlining Content
- 3 Formatting Your Essay
- 4 Researching For Your Essay
- 5 Developing Your Argument
- 6 Crafting A Compelling Conclusion
- 7 Writing a good EPQ essay
Understanding The EPQ Essay Requirements
Navigating the world of EPQ essay writing can be intimidating, and even overwhelming at times! But never fear – with a little bit of knowledge and preparation you’ll find yourself soaring towards success.
At its core, crafting an effective EPQ essay comes down to analyzing expectations and exploring options. It’s important to take into account the specific requirements for your topic or course; many professors will have different standards that need to be met.
Once you’re clear on what needs to be accomplished, it’s time to get creative – start brainstorming ideas and looking for relevant sources that support them. Be sure to record everything as you go along so you don’t forget any key details later on in the process.
Research is essential here, but make sure not to lose sight of the bigger picture: Your paper should still reflect your unique perspective and originality. With this approach, you can create an engaging work that will stand out from the crowd — one which takes readers on a journey of exploration through freedom-filled imagination!
Structuring Your EPQ Essay
Organizing your ideas is an important part of writing an EPQ essay.
Start by making a list of the main points you want to make and then organize them into groups that fit with your argument.
Once you have your ideas organized, you can start outlining the content. This will help you create a logical flow of information and ensure that your essay is structured in a clear and concise way.
It’ll also make it easier to write the actual essay, and make sure that you haven’t skipped any important points.
Organizing Ideas
Organizing your ideas is an important part of writing a successful EPQ essay. Before you start jotting down notes or typing away on your computer, identify the sources that will be most useful in completing your project.
Ask yourself questions like “what do I already know?” and “where can I find more information?” By identifying these sources early on, you’ll ensure that all the research needed to write a quality paper has been done ahead of time.
Once you’ve identified the best source material for your project, it’s time to develop a structure for your essay. Think about how each point should flow logically from one to another and what order would make the most sense when reading through your work.
As with any type of academic writing, having an outline helps keep everything organized and makes it easier to create well-structured argument points throughout your paper.
Additionally, if there are sections where multiple topics require further discussion, consider breaking them up into separate paragraphs so readers can easily digest each idea independently.
Writing an EPQ essay doesn’t have to be overwhelming; by taking proactive steps to organize ideas before starting the actual writing process, you’re sure to craft an impressive piece of work!
Outlining Content
Once you’ve identified the sources and outlined your structure, it’s time to start brainstorming techniques for what content should be included in your essay.
This is an important step to ensure that all the key points are covered in a logical order. Brainstorming can include anything from writing down ideas as they come to mind or even mapping out each section with bullet points.
Additionally, if there are any specific topics you’d like to discuss further, consider breaking them up into separate paragraphs so readers can easily digest each idea independently.
No matter which strategy works best for you, it’s essential to make sure that each point has been thoroughly researched beforehand—this will guarantee that only quality information is presented throughout your paper.
Writing an EPQ essay doesn’t have to be daunting; by taking proactive steps such as outlining the content of your project ahead of time, you’re sure to craft an impressive piece!
Formatting Your Essay
The formatting of your essay is as important as the structure. When structuring, you made sure all the pieces were in place and ready to go; now it’s time to make them look nice.
You should consider several stylistic choices when formatting:
- Word choice – Use precise language that adds power and meaning to each sentence without detracting from its original intent
- Font size – Choose a font size that looks professional yet comfortable for reading
- Headers/subheaders – Create visual breaks between sections using headers or subheaders with interesting titles that capture readers’ attention
- Margins – Establish margins so your reader can easily find where one section ends and another begins
By implementing these subtle but powerful formatting techniques, you will improve the overall quality of your EPQ essay and ensure a successful submission!
Researching For Your Essay
The research phase of an EPQ essay is one of the most important steps to ensure you can write a quality paper. Defining your objectives clearly and citing sources accurately are essential for success. As such, it’s important to take your time during this step, as any mistakes here will be difficult to recover from later on in the writing process.
When researching for your essay, begin by getting organized. Gather all pertinent information related to your topic and compile them into separate folders or files so they’re easy to access when needed.
Once that’s completed, start reading up on relevant materials and taking notes along the way – summarize each source and make sure you properly cite authors at the end of each note taken. Doing so will help you save valuable time looking back through books or articles once you move onto actually putting pen to paper (or fingers to keys).
Ultimately, if done correctly, research should provide a solid foundation which allows you to create an innovative and unique piece of work without having to worry about accuracy or plagiarism issues!
Developing Your Argument
Having completed your research, it’s time to develop your argument.
To do this, start by brainstorming ideas about the topic and evaluating sources for their relevance and suitability. Consider which evidence is best placed to support your position on a particular issue or idea.
After gathering all of your information from various sources, try to identify the common themes that emerge in relation to the topic you are researching. In order to form an effective argument, you will need to assess how each piece of evidence fits together in order to demonstrate its relevance and importance.
This could include looking at different perspectives on an issue or comparing multiple results of research studies into a specific field. Additionally, make sure that when forming your argument you take note of any counter arguments which may be presented as these can help strengthen your overall conclusion.
Once you have identified all relevant points related to your argument, consider how they work together and analyse them more deeply – this will allow you to draw meaningful conclusions from the data available.
Crafting A Compelling Conclusion
The conclusion of your EPQ essay is essential to summarizing all the points you have made and discussing their implications. It’s important to remember that this section should be both succinct and clear, so as not to confuse or distract from the main message of your paper.
When writing a compelling conclusion, start by restating your thesis statement in a different way than you did at the beginning of your paper.
Take some time to review each point discussed throughout the body paragraphs and summarize them briefly. This will help remind readers what they just read and why it matters.
Additionally, make sure to tie up loose ends, such as unanswered questions, by either providing an answer or referring back to prior sections.
Finally, conclude with a strong sentence that drives home the importance of your topic while offering insight into future research possibilities or other relevant discussions.
Writing a good EPQ essay
In conclusion, writing an EPQ essay is a unique challenge that requires serious attention and hard work.
With the right structure, research, argumentation, and conclusion in place however, you can put together a compelling piece of writing that will impress even the most discerning master’s student.
One interesting statistic to consider when crafting your essay is that only 50% of students who submit an EPQ are successful in achieving their desired grade.
This serves as a reminder to emphasise quality over quantity in your work: focus on making sure each element of your essay is thoroughly researched and well-written before submitting it for review.
What Is The 11 Plus Exam?
The Ultimate Guide to A-Levels for Psychology
Leave a comment Cancel reply
Reach out to us for career and sponsorship opportunities.
© 2024 Acrosophy Excellence in Application
A Medical MBA Company The Medical MBA Ltd Company number: 13561401 86-90 Paul Street, London, England, United Kingdom, EC2A 4NE
How To Write An EPQ Essay (Step-by-Step Guide)
In A-Level by Think Student Editor March 29, 2019 8 Comments
Whatever the reasons were for you choosing to write an EPQ, the grade you get is most definitely important to you. That is why I have written this (hopefully) detailed guide on how to write an EPQ.
1. Think Of An EPQ Topic That Genuinely Interests You

It’s important to choose an EPQ you’re interested in, or you may run into some problems . Many students take EPQs each year, and many students fail because they make this mistake.
If you don’t take an EPQ you’re interested in, you’ll have no motivation to work on it . This will be because you start to want to do other things, anything instead of your EPQ.
Think about revision, for example. Is it interesting? Nope. Would you rather be playing videogames, watching Netflix, or literally anything else? Yeah, me too.
If you’re not motivated to write your EPQ essay, then you’ll either not do it or do it badly. If you don’t work hard for it, you won’t get good marks – and therefore there’s less point in even taking it in the first place .
If you find an EPQ topic to write your essay on that genuinely peaks your interest, you’ll find it much easier to get better grades in it.
A more interesting EPQ essay topic will mean that your focus is better . This will result in a better EPQ, meaning more marks when you hand it in.
You’ll also enjoy the EPQ a lot more if you find it interesting . You’ll find the whole experience a lot more fun, and therefore a lot easier too.
To find an EPQ topic that genuinely interests you, you just have to think about what you like. There are lots of different things you can do, but you only get to choose once – so choose carefully.
And if you’re really stuck on ideas, take a look at this list of 600+ EPQ ideas that guarantee an A* . Any of these ideas will be great for your EPQ, so just choose one that interests you and that you’ll actually enjoy.
2. Create A Mind Map Surrounding Your EPQ Topic

A mind map is where you write down everything you know about a topic . In this case, you’d be writing down all the ideas and concepts surrounding your EPQ topic.
That way you can see everything you need to write about in your EPQ essay. You’re essentially making a mood board for whatever EPQ idea you’ve chosen, and it will help you get in the right mindset for the task ahead.
Mind maps are most commonly used to identify gaps in your knowledge . Students tend to use them when revising to work out what they don’t know, whilst also helping them consolidate what they do know.
In terms of your EPQ essay, a mind map will provide a loose structure for you to follow . You’ll come up with lots of different things you can write about, and that will make the essay a lot easier.
In addition to this, whilst creating your mind map you may even decide to change your topic entirely. You might find that the topic you’ve chosen isn’t giving you any idea inspiration, and so you move on to a different topic.
To make sure you get your mind maps right, you might want to follow this helpful guideline . It’s mainly about studying, but the same things can be said for planning your EPQ essay.
Don’t try rushing in to your EPQ essay without first creating a mind map . Mind maps are more useful than most students think…
Mind maps will help you avoid getting lost in what you’ve written, what you’ve missed, and what you’re planning on doing. You can use your EPQ topic mind maps as a sort of checklist as you write your EPQ essay.
3. Use Your Mind Map To Think Of A Question Related To Your Main EPQ Topic

Many students forget to think about this, but it’s probably the most important part of your EPQ . If you get this bit wrong, you can say goodbye to a good grade in your EPQ.
The question relating to your EPQ topic of choice is what you’ll spend your time working on . The 5000 words you write will be about this question, and so it really needs to be a good one.
If you don’t make it a question that interests you, then you’ll find it harder to write as much about it. Find a question that genuinely peaks your interest (relating to your EPQ of course) and the rest will come naturally.
It’s also important, however, that you choose a question where there’s a lot to write about . If you choose a question with lots to write about, you can use that to your advantage when trying to reach those 5000 words.
However, if you don’t choose a question where there’s a lot to write about, you’ll find that your EPQ is slow and drains you. Not only that, but it’ll probably be worse in terms of grade too.
I’d suggest doing a little background research into your question before you start writing your EPQ essay . Just check that there’s lots to write about and then you can avoid starting something you can’t finish.
As a general rule, you’ll want questions that don’t have definitive answers. If you can find a question that is inconclusive, you’re onto a winner.
If you can’t be bothered to look up EPQ questions, then there’s an alternative . Take a look at this list of 600+ EPQ ideas that guarantee an A* .
4. Write Down Subtitles That Relate To Your Main EPQ Question

Writing down subtitles for your EPQ question means that you’ll have a better idea of what’s actually going into your EPQ essay .
When you create your subtitles for your EPQ essay, you’re essentially writing down all the mini-topics you’ll write about. You split up the massive 5000 word count into smaller, more manageable parts.
I’d suggest making as many subtitles as you can that relate to your main EPQ question. Just go for a massive brainstorm ( potentially using your mind map ) to try and come up with lots of subtitles.
That way you maximize the chances of you making some actually good subtitles. You’ll have lots of options to choose from, and your EPQ will benefit from having such a varied range of points.
You also put yourself in the right mindset for your EPQ essay . You’ll be much more open to different ideas and approaches whilst actually writing the EPQ, and examiners will see this and give you extra credit.
However, you need to make sure that the subtitles you’re writing actually relate to your EPQ question . If they don’t, you could run into some serious problems.
If you choose to work on a subtitle that doesn’t wholly relate to your EPQ question, you risk filling up your word count with irrelevant information. That means less room for the important stuff, and less marks for you.
Make sure you check all your subtitles before you start writing . Work out what the plan is before you start writing, so that you don’t have to rewrite a large portion of your EPQ essay.
So grab a pen and paper, sit down, put on some nice music, and get to writing those subtitles.
5. Triple Check That Every Subtitle Question Actually Relates To The Main EPQ Topic

By this point, you should have around 16 subtitles that you want to include in your EPQ essay . 16 subtitles will give you a nice 300 word per subtitle guide, give or take a few.
Any more subtitles, and you run the risk of overcomplicating your EPQ. Any fewer, and you’ll struggle to reach that gargantuan 5000 word count.
It’s essential that you break down your EPQ essay into smaller modules like this, to make it easier for you in the long term. 16 subtitles will mean the best productivity for you when you actually come to write your EPQ essay .
The next step is to order your subtitles, for easier reading. You’ll want to make the layout of your subtitles as sensible and as easy to follow as possible for your examiner .
If you please your examiner like this, they’ll be more inclined to give you more marks. They mark you on your written communication, and therefore you’ll want to make sure you’re communicating the most effective way.
Try ordering your subtitles by the order of most important to least important . Laying out your subtitles this way will show your examiner that you’ve really thought about your EPQ and understand what they want to see.
Alternatively, you could lay out your subtitles chronologically . What I mean by this is that you start with your question, move onto research, then explanations, and finally a conclusion.
This is probably the best way to lay out your EPQ essay subtitles . It’s the easiest way to follow the process you went through, and examiners like to see EPQ essays that are laid out like this.
It’s how I laid my EPQ essay subtitles out, and I got an A* – so I’d suggest doing the same.
6. Allocate A Word Count To Each Element Of Your EPQ Structure

You’ll want an introductory paragraph to start with, and that should only take about 200-300 words . Don’t go overboard with your introduction, as you should aim to make the bulk of your essay about your EPQ question.
I’ve already mentioned it, but you want to write about 300 words per subtitle . This is the perfect amount of words to write if you want the EPQ essay to go as smoothly as possible.
16 subtitles at 300 words each will put you at just under 5000 words – 4800, to be exact. That will leave you just enough room to add a short introduction too.
You can go for less subtitles, but that means a higher word count for each individual subtitle . If you make your word count per subtitle too high, then you’ll struggle when it comes to actually writing your EPQ essay.
You could also try more subtitles if you want, but that then means you’d write less per subtitle . That means there’s less room for all your explanation, and less marks when you hand it in.
I’d recommend keeping your subtitle count between 14 and 18 . That way you give yourself the best chances of your EPQ being easier to write.
You also make it easier for you to enjoy, too. Making your EPQ essay subtitles this long means you’ll find it easier and less monotonous, and therefore you’ll enjoy it more.
The word count of each element in your EPQ essay has an impact on your productivity and focus, too . Generally, the shorter the piece of writing you have to do, the more productive you’ll be.
Setting yourself short-term goals like this will help you stay focused and make your EPQ that little bit better. It’s worth setting effective word counts for your EPQ essay elements for those extra marks .
7. Research, Research ( And A Little Bit More Research )

Research should make up about 40%-50% of your total EPQ essay . That’s a lot of research, and you can see from this figure that quality research is crucial to your success.
The reason research takes up so much space is because you need to explore all opportunities within your question. Research will help you develop ideas and improve your knowledge of the subject, helping you to better answer your EPQ essay question.
And besides, who doesn’t want help reaching the massive 5000 word count?
There are many ways to research, with the most common being the internet, and books . Both ways of researching are valid and useful, but you still need to be careful.
Especially with the internet, you may come across facts and information that isn’t entirely accurate. This is because anybody can access anything, and usually the information you see online is edited by people who aren’t professionals.
Try to stay away from websites like Wikipedia, where anybody can change the information you see . There are much better alternatives out there, like Google Scholar for example.
Whereas with books, they have to go through a long-winded process to ensure they’re accurate . Books tend to be slightly more reliable than the internet, especially if they have an ‘exam-board approved’ label on them.
I’d also recommend keeping track of all the sources of your information, as you’ll have to write a bibliography at the end of your EPQ .
What that basically means is that you have to reference each individual source of information after you’ve written your EPQ essay. That’s just so examiners can check to see if you’re plagiarising any content, in case you were wondering.
8. Check That Your EPQ Structure Still Makes Sense

You should have around 16 subtitles ready to go, in chronological order or order of importance . I’d suggest chronological order, but that’s up to you.
You should also have space to add an introduction and conclusion paragraphs . They shouldn’t take up too much space, but still leave some room for you to add them in.
You’ll actually want to wait until the end of your EPQ essay to write either of these paragraphs, so it might help to add placeholders until you get to writing them.
Around 7 of your subtitles should be based on research . You’ll want to leave yourself a nice amount of in-depth research, whilst also allowing room for all that explanation.
If you don’t give the right proportions for your research and explanation subtitles, your EPQ can become lopsided. Examiners will easily spot this and take away precious marks.
You’ll want your conclusion to be longer than your introduction, as you’re essentially summing up all that you’ve written . Your conclusion should be about the same size as your subtitles, but maybe just a little bit bigger.
If all else fails, just read through your structure and think about it from an examiners’ point of view. Does it all make sense? Are the subtitles in a sensible order? Have you left space for your introduction and conclusion paragraphs?
If you reckon you’ve got all these elements in the right order and the right sizes, you should be good to go. Just keep a clear focus on your EPQ essay question, and you can’t go wrong.
9 . Write Down The Answers To Each Of Your Subtitles

Start with your subtitles to get the main bulk of your EPQ essay underway . The quicker you get your subtitles done, the sooner you can finish your EPQ.
Starting your subtitles first is a good idea, as they make up most of your EPQ. You’ll want to get them done first, and then you have time after that to work on the finer details.
As I’ve said, your subtitles should be around 300 words long . This will allow you just enough space to answer the subtitle, without repeating yourself or going overboard.
If you go too far over 300 words, you risk either repeating yourself or just extending your points so much that your words become empty. Empty words = no marks, which is what you definitely don’t want.
If you don’t write 300 words, the points you make are likely to be underdeveloped. This means you can’t get into the top band of marks no matter how good what you’re saying is – there’s just simply not enough of it.
Of course, if you think you can express yourself in more or less than 300 words, go for it . Everybody’s different, and some people have better writing skills than others.
The amount of words you write per subtitle can also depend on how many subtitles you have . If you have less subtitles, you write more words per subtitle, and vice versa – simple maths.
Try to explore every possibility within your subtitle. The more routes you go down and the further the detail you go into, the more marks you’ll get from the examiner.
10 . Write The Introduction And Conclusion Paragraphs

Your introduction paragraph needs to be slightly shorter than your average subtitle paragraph . Usually about 200-300 words, the introduction will basically talk about what’s to come in your EPQ essay.
If you make your introduction too long, you waste space that you might need for your research/explanations. You also take up space that could be used for your conclusion, which is very important.
It’s a good idea to write your introduction paragraph after you’ve written all of your subtitles . It may sound odd, but there’s method to the madness.
If you write your introductory paragraph last, it’ll be a lot more accurate than if you’d have done it at the start. You’ll know exactly what’s in your EPQ, and therefore your introduction can accurately ‘introduce’ your essay .
Your conclusion paragraph should be slightly longer than your average subtitle, and definitely longer than your introduction . I’d say about 400 words, your conclusion should sum up everything you’ve talked about in your EPQ essay.
Your conclusion should essentially answer the question you asked at the start of your EPQ essay. You should aim to include everything you talked about in your other subtitles (that’s why it’s a little bit longer).
You’ll obviously want to write your conclusion paragraph after everything else, or you’ll have nothing to conclude. Once you get on to your conclusion, you’re on the home stretch.
11. Get Someone To Proof Read It To Make Sure There Are No Errors

Proof reading your EPQ essay is so, so, SO important to your success . If you don’t proof read your EPQ essay, you may miss some pretty crucial mistakes…
I’m not just talking about the spelling mistakes you may have made (although you might want to fix those too). I mean the mistakes where you contradict yourself, go off topic, or even just get your facts wrong.
I’m sure I don’t need to explain it, but these mistakes will cost you dearly when your EPQ gets examined . Sometimes just a few marks can be the difference between an A and an A*, so you need to maximize your chances of success.
A good way to ensure your EPQ essay is perfect is to get someone else to look through it. Having a second opinion ensures that everything you’ve written is accurate and concise, and it’s better than just checking through it yourself.
If you rely on your own methods of checking through your work, you’re more likely to miss mistakes . Having a fresh perspective on your work broadens the chances of catching every mistake you make.
It doesn’t matter who you get to check your work . You can ask friends, family, or even your teachers/tutor – just get it proof read before you send it off to be marked .
If you need to check through it for spelling mistakes or wording issues, there’s a handy little trick I used for my EPQ essay. Paste your entire essay into google translate, and have it read out to you .
That way you can listen and check for anything that’s not quite right, and sort it out in time for your EPQ essay to be examined.
Thanks so much for the help !
This is so, so helpful, thanks so much!
How many resources should I have for my EPQ?
20-25 should be the right number
Hi, thanks for the cool tips! I will definitely keep it for myself
Hello, thanks for the cool advice, but the most difficult thing for me is 1 point – to think through the topic itself. Therefore, already at the first stage, I give up and turn to the college essay writing service. This service helped me more than once or twice. My friends also use it. Also, it is difficult for me to create a mental map, which is in point 2. Therefore, I would rather spend my writing time on purposes that are useful to me.
This is so useful! I have been working on my EPQ over the past few weeks and have had a few big quandries about how I should go about forming an answer to my question and this has made it much clearer. Thank you!

EPQ Guide: Expressing your ideas
- The Inquiry Process
- Developing a line of inquiry
- Finding and selecting sources
- Working with ideas
Expressing your ideas

This is the stage you have been building towards - writing your report. Although that is largely the focus of this page , it is not all there is to the EPQ.
Your EPQ will be assessed on:
- Your completed Production Log
- if your project is a research based written report of any kind (e.g. a science investigation or an essay) it should be approximately 5,000 words long
- If your project is an artefact, it must be accomapanied by a research based written report of a minimum of 1,000 words. For artefacts, you may include photos showing various stages of the production process as well as the final product. You do not need to submit a large artefact as evidence - photographs or other media are fine.
- If your product was itself a presentation then you still need to produce a presentation about the process of producing it!
- Your presentation must be delivered live to a non-specialist audience and might use flipcharts or posters, presentation tools such as PowerPoint or Prezi or short video clips. The evidence for your presentation will include a record in your Production Log of questions your supervisor asked and how you responded.
Am I ready?
Am I ready to start writing my essay?
Before you start writing, think:
- Is my investigation largely complete? As you write you may find that you need a few additional resources or information to support your argument, but you should not sta rt to write until you are largely sure where your argument is going.
- Have I filled in a Research Organiser (which you will find on the Working with Ideas tab)? This will help you to organise your thoughts and make sure you understand the argument you intend to make and have the evidence to support it. While not compulsory, it makes writing your final essay significantly easier.
- Do I understand how to write in an appropriate academic style? Guidance is given in the Academic Writing box below.
- Do I know how to import my sources from my Investigative Journal? Don't waste time putting all your citation data in again! Import all your sources as you set up your document. There are helpsheets in the Resources for PC / Mac users boxes to the right.
You should use the Oakham APAv3 Academic Writing Template (below) rather than a generic Word template to set up your essay.
(The image below is taken from the EE LibGuide, but the template is just as useful for EPQs)

Citing and referencing
There are many different ways to acknowledge the sources you use. These are called referencing styles . You are free to use any recognised referencing style you wish for your EPQ, but Oakham's 'house style' is APA. We suggest you use this because we already have a lot of support in place for it. APA is an 'Author-date' system, meaning that you show which source you have used by putting the author and date in brackets after it in your text, and then put the full reference in an alphabetical list at the end of the essay. The Library does not support 'footnote referencing', where you put all the information in a footnote at the bottom of the page. If you want help with this then please talk to the member of staff who suggested that you use it.
For detailed information and guidance on how to use sources in your writing and how to cite and reference them accurately using the tools in Microsoft Word, consult the Citing and Referencing LibGuide . This site includes information about how to reference all sorts of different kinds of sources, including videos and works of art, and what to do if you are using a source written in a language that is not the language of your essay. It also gives some examples of how to use in-text citations , whether quoting, paraphrasing or just referring to a source more generally, and how to use the automatic citing and referencing tools in Word .

Academic writing
Stages in an academic essay

Your thesis is the point you want to make. It emerges from your research and your task is to use the evidence you have found to establish it as the most reasonable response to that research.
In both approaches, you must state the research question in your introduction, and make sure you return to it in your conclusion .
Sections required in your essay
Have a look at the Formal Presentation guide in the sidebar for a guide to laying out your essay.
Paragraph Structure
Paragraphs themselves have a structure - the most common you will have come across is likely to be PEEL. The letters often stand for slightly different things in different subjects, but the idea is largely the same - introduce your main idea for the paragraph ( Point ), justify it with Evidence and/or Examples , and Evaluate this evidence. Finally, Link back to the Research Question and/or Link forward to the next paragraph.
This is not the only way to write a paragraph and, with experience, you will soon find that your argument develops a flow of its own that does not require a formula - indeed, your essay would be very dull if every paragraph followed exactly the same structure. However, this structure can be a useful scaffold to get you started and make sure you don't miss anything important.

The structure of academic writing
Note that the following graphic was originally produced for the IB Extended Essay, but is equally applicable to the EPQ.

Planning your essay
It is vital to plan your essay before you start writing. An essay plan provides an outline of your argument and how it develops.
What sections and subsections do you need?
Although this might change as you write your essay, you should not start writing until you have your overall structure. Then think about roughly how you are going to divide your 5000 words between the different sections. 5000 words seems like a lot before you start writing, but it is much easier to write to the limit, section by section, than to try to cut your essay down once it is written.
What will the reader will expect to see and where?
Look back at your checklist and think about where in your essay you are planning to include the required information. Make sure the flow of your essay makes sense to a reader who may be a subject expert but knows little about your topic. Have you included background information? Details of experimental methods? Arguments and counter arguments?
Now get writing!
You've read all the guidance. You've made your plan. Now you have a blank screen in front of you and you just need to get started! Start with the section you think you will find easiest to write and work outwards from there, or follow the steps below to get started. Don't forget to write with the word limit in mind though.

What if you are writing lots of paragraphs but your essay just doesn't seem to be coming together?
1. Condense each paragraph into a short statement or bullet point. This is the skeleton structure of your essay.
2. Look at the order of the statements.
- Is the order logical?
- Does each point follow another in a sensible order?
- Do you need to change the order?
- Do you need to add paragraphs?
- Do you need to remove paragraphs?
3. Add, subtract and rearrange the paragraphs until your structure makes sense.
4. Redraft using your new paragraph order.
Image by OpenClipart-Vectors from Pixabay
Willard, D. (2003) My journey to and b eyond tenure in a secular university . Retrieved from: www.dwillard.org/articles/individual/my-journey-to-and-beyond-tenure-in-a-secular-university . Accessed: 9th May 2020
Oh no! It's too long!!
If you haven't managed to write to the word limit and are suddenly faced with cutting down an essay that is over the word limit, try these tips on concise writing from Purdue Online Writing Lab.

Use the menu on the left of this page from Purdue OWL to browse the four very practical pages on writing concisely and one on the Paramedic Method for reducing your word count.
AQA Guide to completing the Production Log: Expressing your ideas

AQA copyright notice
The presentation above contains slides from the AQA presentation Teaching slides: how to complete the production log (available from the AQA EPQ Teaching and Learning Resources website ). These slides are Copyright © 2020 AQA and its licensors. All rights reserved.
A downloadable copy of the Production Log can be found here , on the Home tab of this guide.
Formal presentation

Guides for PC users
- Citing and Referencing in Word 2016 for Windows
- Managing Sources in Word 2016 for Windows
- Creating a Table of Contents in Word 2016 for Windows
Guides for Mac users
- Managing Sources in Word 2016 for Mac
- Citing and Referencing in Word 2016 for Mac
- << Previous: Working with ideas
- Next: Reflecting >>
- Last Updated: Feb 27, 2023 2:28 PM
- URL: https://oakham-rutland.libguides.com/EPQ
Smallbone Library homepage
Search the Library Catalogue
Access our Subscription Databases
Normal term-time Library opening hours: Mon-Fri: 08:30-21:15 Sat: 08:00-16:00 Sun: 14:00-18:00 (Summer Term only)
EPQ resources
- Study with us
- Information for:
- Young people
- Extended Project Qualification
- Extended Project Qualification Resources
- Preparing for University MOOC
- Subject Taster Sessions
Our resources are designed to support you every step of the way - from setting your question to presenting your findings.
Your epq plan, setting your question, introduction.
Kristina and Becca will take you through the thoughts behind setting a question and how to go about choosing your project title/question. They will consider why you choose your topic, whether or not you will undertake the artefact or essay, aims and objectives and how to make the project manageable.
- A study of mental wellbeing in older people
- Does the WAP dance craze endanger children?
- Criminology
- Create a series of online lessons for a local Cub Scout group
- Is the use of Stop and Search by the Police discriminatory?
- What are the long-term health impacts of COVID-19?
- Build a robot
- Assess the impact of the 2020 Green Recovery
- For any you have identified as either too big or too small, how could they be adapted?
Useful links
- 'Setting Your Question' presentation
- Bryman, Bell and Harley: Research Project Guide
Getting started on research
Introduction.
Kristina and Rebecca take you through starting your research, finding reliable sources, considering primary and secondary research, and thinking about bias.
Harvard referencing
Kristina and Becca will take you through Harvard Referencing. This is one form of referencing you can use for your project.
- Read the article Care home deaths: the untold and largely unrecorded tragedy of COVID-19
- Use the CARS ( C redibility, A ccuracy, R easonableness, S upport) method to review the source.
- 'Getting Started with Research' presentation
- 'Harvard Referencing' presentation
- University of Toronto: Research Using the Internet
The production log
Rebecca and Kristina discuss how and when to build you Production Log, and the different levels of content required.
Think about a learning experience and identify the different factors that were present within the experience. It can be a formal experience or an informal one. You may find the following questions helpful:
- What was your reaction?
- Were there any issues?
- Did you find anything challenging?
- What have you learned?
- 'Production Log' presentation
- Real example: Ed
- Real example: Sophie
Academic writing
Rebecca and Kristina will take you through reviewing your reading, considering reliable sources, questioning the sources you have, and linking them to build the themes and topics of your project.
Rebecca and Kristina lead you through building your extended essay, considering the components, and how to include all the necessary information.
Rebecca and Kristina will take you through an example of structuring your academic writing for your practical project or artefact, drawing on the information you have learnt about your Literature Review and Production Log.
- Write a 300 word summary of the key arguments of your EPQ project. This summary must contain at least two in-text citations. You should use the Harvard Referencing style to reference the sources and evidence used.
- Write out a plan of what information you are going to put in each section. Make a note of the key literature that will support the points you’re making in each paragraph.
- 'Literature Review' presentation
- 'Structuring Your Writing: Extended Essay' presentation
- 'Structuring Your Writing: Artefact or Practical Project' presentation
- University of Manchester: Academic Phrasebook
Presentation skills
Heather will take you through what makes a great presentation, structure and content, design and tackling nerves.
Think about something you love. This could be your favourite film, favourite band, or a hobby you enjoy. Spend 5-10 minutes jotting down some notes about it. You could think about:
- Why do you enjoy it?
- When did you first get into them?
You will then have 2 minutes to talk non-stop about something you love to another individual. Ask someone to time you during this exercise.
Reflection: How did you find this exercise? Did it go quickly or slowly? Did you need more time to prep? Ask for feedback from your audience: How engaged were they? What did you do well? What could you improve on?
- 'Presentation Skills' presentation
- David JP Phillips: 'The 110 Techniques of Communication and Public Speaking' (TEDxZagreb)
Additional resources
- Study Skills booklet - A handy guide to support you in completing the EPQ, covering topics such as academic language, referencing and time management.
Places on our 2024 summer school are filling fast. Don’t miss out. Enrol now to avoid disappointment
- 600 EPQ Ideas – The Ultimate List For an A*

So, this is it. You’ve decided to do an EPQ and now you’re sitting at a blank computer screen with the entire spectrum of human knowledge at your disposal. You could write about any topic on any subject in the dizzying realms of the known universe. But there’s just one problem… how do you begin?
An EPQ (Extended Project Qualification) allows A-Level students to write either a 5,000 word essay on any question or subject of their choice. Alternatively, students can create an artefact or product, and write a shorter essay explaining it. The EPQ is equivalent to half an A-Level.
EPQs are a fantastic way of proving to universities that you are the best prospective student for them, and that you deserve a place on one of their courses. An EPQ requires a huge amount of independent research (which proves that you can handle university-style work) and allows you to showcase your original thoughts and academic rigour, which is exactly what universities are looking for.
Even more importantly, an EPQ counts for extra UCAS points . This means that if you don’t get the grades you expect at A-Level, a strong EPQ grade could help you meet the conditions of a university place offer. Feeling inspired now? We’ve got 600 EPQ ideas for multiple different subjects, to get those ideas rolling.
What are some top EPQ ideas for a guaranteed A*?
Some strong EPQ ideas for a guaranteed A* are specific and original topics like “Should parents be allowed to genetically change their child’s gender” for an EPQ in medicine, and “Is the media making suicide aspirational?”, for a psychology EPQ.
You could also consider EPQ questions like, “Was the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki justified?” for History, and “Should we legalise human organ trade?” for Economics.
We’ve got a list of 600 EPQ ideas for a guaranteed A*, so scroll down and get inspired. We’ve searched all over the internet and interviewed students to get the most pressing topics for each subject. You should just use these EPQ ideas to give you an idea of what you could research, and it’s up to you to come up with your own title.
EPQ Ideas For Medicine
- Is gene therapy ethical?
- Should parents be allowed to genetically alter their child’s gender?
- Can cannabis use in adolescence cause schizophrenia?
- To what extent does the sugar tax reduce sugar consumption in the UK?
- Why are the death-rates from Covid-19 worse in places with higher air pollution?
- Why does emetophobia primarily affect women?
- Could the legalisation of cannabis improve mental health?
- Should we allow only UK citizens to use the NHS?
- Can plastic surgery ever solve body dysmorphic disorder?
- Do care home environments worsen the affects of Dementia and Alzheimer’s?
- What are the links between obesity and parents criticizing their children’s bodies?
- If a woman who wanted a child freezes her eggs and then happens to die, should a relative be allowed to use her eggs to conceive a child?
- Is it right that mothers of Down’s syndrome babies are allowed to abort them up until birth?
- Are anti-depressants a quick fix problem in an overwhelmed healthcare system?
- Should the NHS provide IVF for women over 40?
- To what extent are Black women discriminated against when giving birth?
- Should counsellors have a qualification in psychology before being allowed to practice?
- Why are girls so chronically misdiagnosed when it comes to autism?
- Did the ancient Egyptians have a comprehensive understanding of mental health and illness?
- Could electroshock therapy be the most effective method of treating depression?
- Should we prioritise ICU places to people with children and dependents?
- What are the similarities between Reactive Attachment Disorder and Autism?
- A study of medical practices in North Korea
- A comparison of different cancer treatments: surgical removals and chemotherapy to immunotherapies.
- Is hypnotherapy ever a viable anaesthetic for surgery?
Students interested in taking medicine further should consider studying at one of our award winning Medicine Summer Schools to strengthen their application.
EPQ Ideas for Psychology
- Is the media making suicide aspirational for young people?
- To what extent does having social workers intervene in a family affect a child’s life outcomes?
- Is talking therapy nearly ineffective for treating panic disorder?
- Should children be allowed to decide if they can be taken into care?
- Are the children of alcoholics more likely to become hoarders?
- Is there a link between undiagnosed Autism Spectrum Disorder (ASD) and alcoholism?
- Can non-violent psychopaths have successful relationships?
- Given how they change behaviour, should advertising and marketing be made illegal?
- How has social media altered our brains since its inception?
- Does the Stanford Prison Experiment prove that we should promote rehabilitation over punitive incarceration?
- Are attachment issues in neglected children irreversible?
- Can unschooling be classed as child neglect?
- Can authoritarian parenting styles lead to overeating in adulthood?
- Is technology making us more depressed?
- Do gender-neutral toys lead to children with less stereotypical views of gender roles?
- Can music help ease the effects of Dementia?
- What are the long term effects of bullying?
- Can studying people’s behaviours pre-suicide help prevent suicide?
- Should crime-predicting algorithms be banned for their bias?
- A study of the effects of living in an overcrowded household during Covid-19 lockdown.
- Do memories alter when we recall them?
- How does intergenerational trauma effect cortisol levels?
- Do the negative affects of racism begin in the womb?
- What can Savant Syndrome tell us about the multi-faceted nature of intelligence?
- Do all humans have some level of body dysmorphia?
EPQ ideas for Law
- Should defendants be allowed to represent themselves?
- Is the internet an ungovernable wilderness when it comes to Law?
- Why secret trials are a form of abuse
- Should CCTV be made illegal?
- Is the use of juries inevitably flawed when it comes to reaching a just verdict?
- Should mass media be banned from high profile investigations?
- Should we replace juries with AI-powered robots?
- Should Donald Trump go to prison?
- Could the police be classed as a gang in America?
- How we can stop criminalising victims of sex trafficking.
- Should we bring back the death penalty?
- How much should a child’s desire to live with one parent or another affect the court’s decision?
- Should people who see child abuse but don’t report it be subject to the law?
- Should male partners sue their female partners for abortion?
- Should organ donation be mandatory for everyone?
- When should one country legally intervene in another, when it comes to human rights abuses?
- Should marriage be banned until the age of 21?
- Should lie detector results be legalised in UK courts?
- Could the government be legally obliged to pay women for their unpaid labour that contributes to the economy?
- If embryos are capable of feelings and sensations, should abortion be forbidden at any stage?
- Should minors trafficked to the UK from a dangerous country or situation be given immediate residency?
- Could euthanasia be legalised, whether or not someone is critically ill and close to death?
- Should parents be legally obliged to leave money to their children?
- Should the inheritance tax be abolished?
- Should people with dual citizenship automatically receive diplomatic protection from both countries?
Students interested in becoming a lawyer should consider studying at one of our Law Summer Schools on campus at top UK and US universities.
EPQ ideas for primary school teaching
- Should boys receive exclusive lessons on feminism in primary school?
- How can we teach primary school students about internet safety?
- How can we teach primary school students about their rights over their own bodies?
- Is the way we teach obesity in school harmful to overweight or obese children?
- Is the Education system indoctrinating students?
- The importance of girls in primary school having role models in STEM.
- Why banning mobile phones in school does more harm than good.
- Why our education system fails to pick up students with dyspraxia.
- Why we should allow students to move around the classroom as they learn.
- Is the Montessori childrearing method of any use in mainstream primary school?
- Should every school have access to a Forest School?
- Why primary schools should teach skills such as cooking and home management to every child.
- Are school uniforms too institutionalising for children?
- Should school uniforms be enforced as a way of giving children routine?
- The importance of failing well.
- Should school be only three days a week?
- Should children be able to choose what subjects they want to study at any time?
- How exams unfairly disadvantage girls in primary school.
- Should we abolish sets in primary school?
- How can we teach healthy eating to children?
- How can we teach anti-racism to primary school students?
- A study of anxiety disorders in primary school students due to Covid-19.
- How the education system can better accommodate students with high-functioning autism.
- Why we need a better understanding of selective mutism in primary school.
- Should primary schools in the UK become bilingual to enhance language learning?
EPQ ideas for Secondary School Teaching
- Should school start and end later for teenagers?
- Why students should never have to ask to go the bathroom.
- Could a four day school week improve mental health among secondary school students?
- Is the secondary school curriculum creative enough?
- Why we should be teaching healthy communication to secondary school students.
- Should parents be allowed to choose for their children not to receive sex education?
- Should sports be compulsory at secondary school?
- When does strict teaching become bullying?
- Should modern languages be compulsory at secondary school?
- Could Pathological Demand Avoidance explain why students who are bright aren’t meeting their potential?
- Should we ban school uniform in secondary school?
- Should we decolonise the secondary school curriculum?
- Are their enough teachers of colour in secondary schools?
- What is the effect of divorce on a student’s learning and development?
- How to narrow the technology poverty gap among secondary school students.
- How to create educational support for looked-after children.
- How does having less money than your peers affect your identity as a secondary school student?
- The effects of overcrowded and poor housing on educational attainment.
- The effects of homelessness and insecure housing on educational attainment.
- What effect does the assessment and exam structure in UK schools have on students’ mental health?
- Are exams an unfair form of assessment for students with a specific learning difficulty like dyslexia or dyspraxia?
- How does ADHD link to cleverness and giftedness in students?
- Is our method of diagnosing autism in students informed enough?
- How can we tackle perfectionism and fear of failure in female students?
- Do exams unfairly advantage boys, and why?
EPQ ideas for Biology
- Why we don’t have enough evidence for evolution.
- Is Covid-19 more deadly than Ebola?
- Are animals as intelligent as humans?
- Is abortion murder?
- Is homosexuality genetic or social?
- What can the oldest living creature on earth teach us about biological immortality?
- Does incest always create biological issues?
- The use of parasites in weight loss attempts
- How long would it take you to die if you ate the same thing and nothing else for years?
- What causes diseases in trees?
- Could we ever grow food on walls?
- If your spouse died, what would the ethical implications be of cloning them?
- A study on identity crises in identical twins.
- Is obesity a genetic issue?
- How does sepsis attack the body?
- Will artificial hearts ever be a viable solution to chronic heart problems?
- Could brain transplants ever be a viable option?
- How do certain drugs affect cellular interactions?
- A study of courting behaviours in different species.
- How did different cellular mechanisms regulate different physiological processes?
- Is obesity a modern phenomenon?
- Can gene therapy cure Cystic Fibrosis?
- Can gut microbiota influence host appetite?
- What is the impact of invasive species on ecosystems?
- What is the biology of laughter?
EPQ Ideas for History
- Why poor dental hygiene in the middle ages was a myth.
- Was the bombing of Hiroshima and Nagasaki Justified?
- Is it right to topple the statues of slave owners, in order to erase history?
- Who does history belong to?
- Why did the USA join World War Two so late?
- How have male and female romantic relationships changed over time?
- How has the role of marriage changed over time?
- Should a country be allowed to teach its own history?
- How did the British Empire expand so much?
- Should museums return all their historical artefacts to their country of origin?
- Were the Suffragettes the biggest force in women getting the vote?
- Is religious warfare ever Justified?
- How medieval fashion influences our outfits today
- Was Anne Boleyn the main reason that Henry VII left the Catholic church?
- Did Henry VII suffer from a genetic disease that prevented him from conceiving healthy children?
- Why do we hold on to so many myths in History?
- A study of propaganda in History textbooks in UK history.
- Why is History important to the future?
- To what extent did the purchase of commissions affect the fighting power of the British army between 1760-1860?
- What is the validity of historical fiction and romance?
- How did secret churches operate in Mao’s China?
- How did 19th Century attitudes towards madness affect society’s treatment of ‘hysterical’ women?
- What is the holocaust’s relationship with literature?
- Were the liquidators who helped clean up the Chernobyl explosion used as human collateral?
- How did the pill help women’s liberation?
EPQ Ideas For Economics
- From an economic perspective, should we legalise human organ trade?
- Can an increase of wealth directly influence happiness levels?
- Could stock analysts be replaced by artificial intelligence?
- How do socio-economic factors determine someone’s health in adulthood?
- Who is to blame for the 2008 financial crisis?
- Is illicit trade with China the only factor preventing the North Korean economy from total collapse?
- How would we recover economically if the internet ceased to exist?
- How did the 2008 financial crisis make house buying impossible for the majority of millennials?
- Is the poverty trap impossible to get out of?
- Can we compare the trickle-down economy to a pyramid scheme?
- Does a lack of wealth in childhood really hold you back in life?
- Is the gig economy leading to job insecurity a myth?
- To what extent does women’s unpaid labour prop up the UK economy?
- How has Brexit affected the UK economy?
- Should we legalise a Universal Basic Income?
- How quickly did the UK economy recover from the effects of World War Two?
- Are all socialist economies doomed to fail?
- How would the legalisation of Marijuana affect the world economy?
- How does a lack of free speech negatively affect China’s economy?
- Should there be a minimum wage?
- Should there be a maximum wage?
- Should billionaires be allowed to exist?
- How has the global demand for oil changed over time?
- What effect does illegal immigration have on the UK economy?
- Why a lack of childcare support for women hurts the economy.

EPQ Ideas for Business Studies
- Should businesses expanding to developing countries be forced to pay their employees the same amount they would at home?
- What does Foxconn show about the human cost of business?
- How should we hold businesses to account for unethical behaviour?
- Should we have a single, global currency?
- How can companies become more eco-friendly?
- Should we lower the corporate income tax?
- Will Google kill the journalism industry?
- Why apprenticeships should pay more
- Why every business leader should take a course in empathy.
- How successful is it when businesses rebrand?
- Should companies interfere in their employees’ private lives?
- How churches like Hillsong became multi-million pound businesses.
- Should CEOs have a salary limit?
- Is the American government a big business?
- How has e-commerce affected bookshops?
- Does corporate social responsibility have an impact on company sales and profits?
- A study of businesswomen in the 18th Century
- When do business marketing practices become unethical?
- Should multi-million pound businesses have taken advantage of the government’s furlough scheme during the Covid-19 lockdown?
- How do corporations influence politics?
- Should a business ever own a town or city?
- Start your own small business – perhaps on eBay or Etsy – and write your EPQ on an aspect of it.
- Should private healthcare be allowed to exist?
- Could marketing be considered a mass human experiment?
- To what extent does colour effect audience response to branding and logos?
If you want to study economics, business or marketing to a higher level, consider joining Oxford Royale this summer for a Business Summer School .
EPQ Ideas for English Literature
- The evil stepmothers in fairy tales were actually mothers in the original texts. What does this tell us about society’s anxieties and perspectives on motherhood?
- To what extent is the state of Gilead in The Handmaid’s Tale based on real life?
- Is writing an act of magic?
- Can works of literature oppress their fictional, female characters?
- Can the mistranslation of literature create a liminal world – a place that is not quite one thing and not quite another?
- What does the rise of the digital book teach us about literature?
- Can we ever ‘eat’ literature?
- Do you need to be able to read and write to be an author?
- Are stories living things?
- Discuss the gender politics in George Eliot’s Middlemarch.
- How is the sensory experience of dyslexia presented in literature?
- Is English Literature considered a ‘feminine’ subject?
- As an English student, is it your job to always work out what an author means?
- Is the author dead?
- Could journalists be replaced by AI-reporters?
- Do we need to overhaul the literary canon?
- Do we really need spelling and punctuation in literature?
- Should mass media be allowed to be biased?
- How helpful is the idea of literary genres to understanding a text?
- How George Orwell hid his dissenting view of communism in Animal Farm.
- Why learning to read is a human right.
- Can a novel ever be timeless?
- Does literary form exist just so that writers can subvert it?
- Is rhythm in a poem a separate language?
- Explore Plath’s portrayal of depression in The Bell Jar.
EPQ ideas for Art
- Should Banksy be allowed to graffiti on walls?
- Who decides the value of art, and should we standardise it?
- Has photography always been a form of art?
- To what extent is mathematics art?
- Why do people consider art to be an easy subject?
- Can art reverse the effects of mental illness?
- Can anything be art?
- Is all graffiti a form of art?
- Why the common perception of medieval people being bad at art is misguided.
- How does the commercialisation of the art industry change art itself?
- How does the perception of a career in art as worthless affect the life choices of students?
- Does an audience’s gaze change a piece of art?
- Are art and beauty essentially related?
- Is art supposed to be a visual and sensory experience, or something that we think about and define a meaning for?
- Who decides that a piece of art is ‘good’?
- Does art have a purpose?
- Can art help fight climate change?
- Why does it matter that children are exposed to art?
- What is the effect of producing art on a child’s brain?
- If nobody ever saw your artwork, would it be worth creating?
- Does a piece of art necessarily have a relationship with its creator, or can it detach itself?
- Is art a language?
- What does the disdain for modern art teach us about people’s stereotypes of art?
- Are philosophers artists?
- Could the world itself count as a work of art?
EPQ Ideas for Foreign Languages
- Where did language come from?
- Do idioms prove that languages can never truly be translated?
- Is body language universal across all countries?
- Should everyone be made to learn sign language?
- Why did Esperanto fail as a language policy?
- Which is the hardest language to learn and why?
- Do multi-lingual children grow up to be more economically successful?
- Why does having dyspraxia make language learning difficult?
- Should the whole world be made to speak one language?
- How does an influx of immigration alter the language of a region?
- What is the effect of trading on local dialects?
- Should everyone be made to learn a foreign language at school?
- What does the Korean language, when compared in North and South Korea, teach us about the evolution of language?
- Is there such a thing as a ‘correct’ way of speaking a language, when languages never stop evolving with culture?
- Could a language be classed as a living thing?
- Why is English such a dominant language across the world?
- Is Latin a dead language?
- What caused the English language to evolve so drastically over time?
- What is the hardest language to learn, and why?
- What does baby-talk in different foreign countries teach us about the acquisition of language?
- Why does China have several dialects, but only one alphabet?
- Did grammar always exist?
- What is the link between being good at maths and being good at language learning?
- Why are young children such natural language learners?
- Is learning a language cultural appropriation?
EPQ Ideas for Sport
- How sports stars experience an identity crisis after they retire
- Should soldiers be paid more than footballers?
- How do psychological factors influence performance in sport?
- What do fans react to their team winning a football match as though they won it themselves?
- Are national and international sports a misuse of resources?
- How does struggling with sports in primary school affect children’s self esteem?
- Should women be allowed to compete against men in professional sports?
- Is the ability to run fast purely a genetic advantage?
- Why do we fail to take women’s sports seriously as a society?
- Should children be forced to do sports in school?
- How can the presence of media affect the outcome of a game?
- Should referees be replaced by AI-powered robots, to decrease bias?
- How does a lack of female representation in sport prevent girls from seeking it out as a career?
- What is the effect of parents’ motivation a child’s enjoyment of sport?
- What are the long term effects of the Olympics on the host country’s tourism?
- How does a lack of ability at sports correlate to bullying?
- Why do we have less interest in women’s sports?
- A history of sport in pandemics
- How does a long-term sports injury affect an athlete’s mental health?
- Can a star athlete succeed without a coach?
- Should cheerleaders be banned?
- Is racism being taken seriously in sport?
- Can you still be a top athlete with a poor diet?
- Who decides when something is a sport?
- Why is netball predominantly considered to be a sport for women?
EPQ Ideas for Architecture
- How does the design of a building influence its inhabitants emotions?
- Should city-dwellers without gardens be given free access to national parks at all times?
- What is the link between Brutalist style architecture and anxiety and depression?
- What is the link between mathematics and art in Architecture?
- How is a building affected by the people who live in it?
- How does the style of council housing feed into class stereotypes?
- Can architecture cause social dysfunction?
- Would smart cities be a breach of privacy?
- Could we create a building the size of a city, to house an entire population?
- Make an architectural model of a zero-carbon home and write an essay describing how its functions avoid the use of carbon.
- Should the local government have the right to pull down a building if the community who live there oppose it?
- Is it ethical to spend millions of pounds creating a building in a city with high levels of quality?
- Were houses built in the 1930s of superior quality?
- Should councils have been allowed to remove tenement dwellers from their homes in the post-war era, when the enforced move was traumatic?
- Can we adapt Japanese smart space efficient buildings to western buildings?
- What were the influences on architecture in China?
- How did communism during Mao’s China change the country’s cityscapes?
- How can we build environmentally-friendly housing in LEDCs?
- Can zero carbon housing ever really exist?
- Should public playgrounds exist for people of every age?
- Was Grenfell tower a total architectural failure?
- What house styles in different areas tell us about gender forms of the time.
- How does technology affect architecture?
- What was the effect of feminism on architecture?
- Should houses worth over a million pounds be built with some benefit to the whole neighbourhood?
Join our Oxford Architecture Summer School for the chance to learn architecture amongst the dreaming spires of the city of Oxford.
EPQ ideas for Maths
- Is the golden ratio a racist idea?
- What is the maths behind cryptocurrencies?
- What are the links between foreign language learning and maths?
- What are the links between mathematics and art?
- Has maths always existed?
- How can we use statistical analysis to predict a child’s outcomes in life?
- Should children be forced to take maths at A-Level in the UK?
- Should maths be optional at secondary school in the UK?
- Why do some people say that maths is beautiful?
- Does money really exist?
- An exploration of chaos theory.
- Can maths explain how the universe came into existence?
- How can calculations improve the safety of commuters who cycle in Oxford over the next 5 years?
- Explore conflict and co-operation in The Prisoner’s Dilemma.
- Which is more important, e or pi?
- Can we calculate infinity?
- An exploration of orbital mechanics.
- Is maths a pointless subject if we don’t apply it to something?
- Is learning Maths more important than learning English in primary school?
- What was the role of maths in the code-breaking of Bletchley Park?
- How do fractals work in modelling systems?
- Can we reverse dyscalculia?
- Can mathematical systems ever be illogical?
- Did people discover maths?
- Could maths ever prove the existence of a parallel universe?
Those keen on studying maths in the heart of the silicon valley can join our Mathematics programme for 15-18 year olds on campus at our Berkeley Summer School in 2024.
EPQ ideas for Physics
- How does String Theory explain the universe?
- How can physics help us prevent climate change?
- What is the relationships between maths and physics?
- What was the role of Mileva Maric Einstein, Albert Einstein’s wife, in his scientific findings?
- Build a quadcopter with remote control.
- How can emergency whistles be optimised for design and use in rural environments?
- What would happen to the solar system when the sun dies?
- How can physics help us provide electricity to parts of rural India?
- Is time an illusion?
- Discuss the different interpretations of quantum mechanics.
- Could humans ever live on Mars?
- Design and build a functioning robot.
- How soon will we have flying cars?
- What are some feasible methods for cleaning up space junk?
- Where did the universe come from?
- How can physics prove the existence of God?
- How did Einstein’s theory of relativity influence Physics?
- Now that NASA has confirmed there is water on the moon, could it be a feasible tourist destination?
- Given their devastating effects, should we eliminate nuclear weapons from the earth?
- What contributed to the Cleddau bridge disaster?
- How can we solve the pay gap in the field of physics?
- A study of star formation and star death.
- Is time travel possible?
- How far can humans realistically explore space?
- Mathematical knot theory and its applications.
EPQ ideas for Chemistry
- What was the impact of optical isomerism in the drug Thalidomide, which led to fetal abnormalities?
- An assessment of the safety of fluoride in water.
- To what extent did the government in Louisiana cover up the danger of the petrochemical plants in Louisiana’s ‘cancer alley’?
- Should Aspartame (E951) be allowed in our food and drink?
- When do chemicals become hallucinogens?
- An assessment of hydrogen storage within Metal-Organic Frameworks (MOFs).
- An extraction of limonene from citrus fruits.
- Make a collection of esters that smell pleasant.
- Will graphene have a significant influence on the future?
- To what extent have inventions in Chemical Engineering impacted our lives?
- As assessment of the total synthesis of natural products.
- An experiment in polymer chemistry.
- An assessment of molecular dynamics
- An assessment of solid state structure
- Could we ever create a plastic that decomposes?
- A research project on hydrogen fuel cells
- Why doesn’t plastic decompose?
- What are the chemical processes behind purifying water?
- An exploration of the chemistry behind food allergies in humans?
- What are the chemicals involved in human attraction?
- How does cortisol affect the human body?
- Should pesticides be ethically permissible?
- What are the advantages of computer aided fragment based drug design?
- How can click chemistry be used to improve drug synthesis?
- How has the discovery of pharmaceutical chemicals changed over the past 200 years?
EPQ ideas for Engineering
- Should we teach Engineering in primary school?
- Why is there a gender imbalance in Engineering, and how can we fix it?
- Is there an oversaturation of engineers in India, and if so, why?
- Was everything in the world built by an engineer?
- Do we need to expand our definition of engineer?
- Can Engineering solve the mystery of Malaysian Airlines flight 370?
- Can Engineering explain the disappearance of Emilia Earhart?
- Did Engineering faults contribute to the sinking of the titanic.
- Build your own model plane, boat or high altitude balloon.
- Could hot air balloons become a mainstream method of travel?
- Discuss the hydraulics paradox.
- How have innovations in airframe design increased safety in commercial aircraft?
- How do architects and engineers collaborate?
- Should we be allowed to develop robots that can mimic human emotion?
- What would it mean for an engineer to be ethical when building something?
- How has Civil Engineering changed over time?
- How can chemical engineers improve energy efficiency?
- How could alterations in chemical Engineering have prevented the Deepwater Horizon oil spill?
- As assessment of the sustainability of London’s tube system.
- How much of our countryside should we sacrifice for better transport links?
- Will we have enough oil for future generations?
- Would energy provided entirely by a wind farm system run the UK economy?
- What are the reasons for the pay gap in Engineering, and how can we solve them?
- How can we get pre-school children interested in Engineering?
- Design a system to enhance plastic recycling.
Prospective engineers can join our Engineering Summer Schools for a two-week immersion in the core principles of the subject.
EPQ ideas for Computer Science
- Why we should teach children how to code at the same time we teach them to write.
- Create a website design and code it.
- Is one coding language superior to another?
- How can we reduce computer illiteracy in poorer areas?
- Why internet access is a human right.
- Are AI-driven robots responsible for their own actions?
- Are Ai-assessed job interviews inevitably biased?
- How soon will handwriting become totally irrelevant?
- Are companies upskilling fast enough to cope with the digital demands of Covid-19?
- It’s more important to learn to code than to learn to write
- Is Computer Science a more relevant subject than Physics?
- How will quantum computers change our way of life?
- Should silicon valley companies be criminalised for our widespread addiction to technology?
- What would happen if all technology was wiped out?
- Will we ever be able to search Google through a microchip in our brains?
- What new jobs will Ai create in the next ten years?
- What is increased automation doing to our jobs?
- Develop your own game.
- Should we allow AI-writing assistants like Grammarly to change the way we express ourselves?
- What are the positive effects of machine learning on healthcare?
- How does AI differ from human intelligence?
- Is it ethical to use social care robots to alleviate loneliness?
- Is it ethical to create an app which offers you an AI friend?
- What is the most efficient way to track down cyber criminals?
- How do cyber criminals cover their tracks on the internet?
EPQ ideas for Ethics
- Should people be able to sue their parents for bringing them into the world?
- Do men automatically have the right to be present at their child’s birth?
- Should we be allowed to dispose of spare embryos in IVF?
- Should we be allowed to use embryos for stem cell research?
- Should machines with AI have their own rights?
- Are Siri and Alexa slaves?
- Should we be allowed to mix human and animal DNA?
- Should we be allowed to clone humans?
- Do we have the right to experiment on animals?
- Do we have the right to visit other planets and the moon?
- Should a father have rights over an unborn child?
- Should there be an assessment process before people have children?
- Is sterilisation unethical in every circumstance?
- Should we be allowed to cuddle babies if they can’t give verbal consent?
- Should an embryo have protected rights under the law?
- Do we have the right to prevent someone from committing suicide?
- The disturbing eugenics around birth control
- Should parents be allowed to edit out genetic conditions before a child’s birth?
- Should testing fetuses for Down’s Syndrome be legal?
- Are our moral decisions innate or socially conditioned?
- Should we have the right to decide when life begins?
- If you need a heart transplant and you’re hoping for a heart, does that mean you’re hoping for someone else to die?
- Should we put a limit on the number of children people have?
- Does the means justify the end?
EPQ ideas for Politics
- Why has the USA never had a female president?
- If we colonised Mars, who would govern it?
- Has Great Britain lost its status as a world power?
- Are the government’s counter-terror policies effective?
- Is it acceptable to teach British values in primary schools?
- How does nepotism negatively affect politics?
- How has Donald Trump changed politics?
- Should there be universal freedom of information?
- Why did Brexit happen?
- What are the dangerous effects of conspiracy theories like Q-Anon on the public?
- Should it be illegal to publicly shame politicians?
- Will there ever be a viable mid-ground between socialism and capitalism?
- Would global governance be a better policy than individual governments?
- How are female politicians and prime ministers perceived?
- Should there be freedom of speech at all costs?
- Should countries be allowed to ban religion?
- An assessment of the case for anarchy.
- Should the UK’s land belong to everyone?
- An analysis of political cartoons in the UK
- Should everyone have to vote by law?
- Should politics be taught in primary school?
- Should everyone be made to take politics in secondary school?
- Should National Service be mandatory in Singapore?
- How did the war on drugs affect inner city US communities?
- How was Twitter revolutionised politics?
Sociology EPQ ideas
- How can we reverse stereotypes over drug use and misuse in different communities?
- What is the impact of the media on our perception of women from Muslim communities?
- Evaluate Marx’s account on the origins of the industrial revolution in Britain?
- Is it fair for today’s feminists to criticise the lack of gender commentary in classical sociology?
- How do human ideas, customs and behaviour come together to make culture?
- How do gender, class, race and sexuality affect us and our social relations today?
- A study of the effects of polyamorous family settings on children.
- Have sociologists neglected emotion in their studies of human behaviour?
- Do emotions come from society, or from within us?
- How do different models of socialisation affect children?
- Are eating disorders a social phenomenon?
- Should we ban face-altering apps?
- Should teenage pregnancy be so vilified?
- Can upbringing create a narcissist?
- Is perfectionism more prevalent in girls than boys, and how does that relate to the way we socialise either gender?
- Should we ban gendered toys?
- How can we assuage the social causes of substance abuse?
- An exploration of the sociology of food.
- Is it right to try and get someone out of a cult?
- How racial segregation in cities enforces poverty, and prevents upward mobility.
- What is the relationship between race and class?
- The effects of interracial marriage in the 1950s.
- The cultural diaspora of mixed race children.
- How Disney made princesses key role models for girls.
- Should weddings have to be registered to be legal?
EPQ ideas for Geography
- How did Hurricane Catrina change the New Orleans community?
- Is there such a thing as collective trauma after a natural disaster?
- Does the earth belong more to humans than animals?
- To what extent should be allow deforestation?
- A study on how we will survive and adapt to climate change in 3020.
- Does the way we categorise developing countries increase stereotypes?
- How have the demand for super-crops impacted the agricultural systems in the countries where we grow them?
- Should companies be allowed to expand to developing countries if they won’t pay workers the same wage as at home?
- How does tourism affect a country’s culture?
- Should all new houses be built with solar panels?
- How can we reduce the effects of coastal erosion?
- How has global warming changed the world’s physical features?
- What are the socio-economic and political implications of migration policies for the UK?
- Should borders between countries exist?
- Are countries doing enough to meet their MDG targets?
- Can a country ever become fully developed?
- How does living as an illegal immigrant affect mental and physical health?
- To what extent is global warming caused by human beings?
- Was the civil war in Syria caused by climatic factors?
- Could the National Geographic be considered exploitative?
- A comparison of two earthquakes in different decades. to observe how advances in technology have impacted responses.
- How does climate change affect different biomes and ecosystems around the world?
- What are the environmental and social impacts of natural gas fracking?
- A prototype for the generation of sustainable energy.
- The effects of littering on marine health.
EPQ ideas for Religious Studies
- Why materialism can’t disprove the existence of God.
- Why science and religion are part of the same entity.
- Paley provides the best argument to issues surrounding the existence of God.
- To what extent can Freud’s view of religion and God be said to be accurate?
- Is C.S Lewis’ claim that atheism is weaker than theism correct?
- Is the belief in nothing still a belief?
- Can we reach God through the via negativa?
- Is atheism just ignorance?
- Can we prove that the universe exists outside our mind?
- Is the Catholic catechism biblical truth?
- How did the history of the church shape our society today?
- Should Religious Studies be compulsory in primary school?
- The existence of life on earth is evidence of the existence of a higher being.
- How do you explain the goodness of God in the light of the world’s evil?
- What are the boundaries between a cult and a religion?
- Should the church always be subject to the government?
- Should the Queen be head of the protestant church?
- Should the church form its own political party?
- Are expensive religious buildings insensitive to those living in poverty?
- Does baptising a baby save its soul?
- Should politicians interfere in religious conflicts?
- Is religion nothing more than a comfort blanket against death?
- Can you ever justify taking a life?
- Is religion the same as morality?
- Is religion just a set of rules disguised as something greater?
So, there you have it. 600 EPQ ideas to enhance your passion and imagination for this exciting qualification. Now get ready to kickstart your academic future with an amazing EPQ idea of your own. Don’t forget to fill out that activity log as you go along!
Press ESC to close
How to Conduct an Effective Literature Review for Your EPQ: A Step-by-Step Guide
- backlinkworks
- Writing Articles & Reviews
- September 23, 2023

Introduction
A literature review is an important component of any Extended Project Qualification (EPQ) project. IT involves researching and analyzing existing literature and scholarly works relevant to your topic. A well-conducted literature review can provide a solid foundation for your EPQ, helping you to identify gaps in the research, establish the context for your study, and build a strong theoretical framework.
Why is a literature review important?
Conducting an effective literature review is crucial for several reasons:
- Identifying existing knowledge: A literature review enables you to familiarize yourself with the existing research and theories related to your topic. This helps you understand what is already known, what gaps exist in the literature, and how your project can contribute to the field.
- Guiding your research: A well-constructed literature review can help you determine the direction and scope of your EPQ project. IT serves as a roadmap, assisting you in identifying the key concepts, theories, and methodologies that are relevant to your research.
- Building a theoretical framework: A literature review allows you to identify and analyze different theories and perspectives related to your topic. This helps you establish a strong theoretical foundation for your project and provides a basis for your analysis and interpretation of the data.
- Supporting your arguments: By citing relevant literature, you can support your arguments and claims with evidence from authoritative sources. This enhances the credibility and reliability of your EPQ project.
Step-by-Step Guide to Conducting an Effective Literature Review
1. define your research question.
The first step in conducting a literature review is to clearly define your research question or objective. This will help you narrow down your search and focus on the most relevant sources.
2. Develop a search strategy
Once you have defined your research question, you need to develop a search strategy to identify relevant literature. Start by brainstorming keywords and phrases related to your topic. Use synonyms and variations of these terms to broaden your search.
Next, identify the most appropriate sources for your research. These may include academic databases, libraries, online journals, books, and relevant websites. Consider both primary and secondary sources to ensure comprehensive coverage of your topic.
3. Conduct a literature search
Using your search strategy, begin exploring the identified sources. Start with academic databases like PubMed, Google Scholar, or JSTOR, as they provide access to a wide range of scholarly articles and research papers.
Make use of advanced search tools and filters to refine your search results. Take note of the relevant sources, including the title, authors, and abstracts, for further evaluation and analysis.
4. Evaluate the literature
After conducting the initial search, IT is important to critically evaluate the literature to determine its relevance, reliability, and credibility. Consider the following criteria:
- Publication date: Ensure that the sources you use are up-to-date and relevant to your research. However, older articles can be included to provide historical context or trace the development of a particular theory.
- Author credentials: Evaluate the expertise, qualifications, and reputation of the authors. Look for authors who are recognized authorities in the field.
- Research design and methodology: Assess the rigor and validity of the research methods used in the studies. Consider whether the sample size, data collection techniques, and analysis methods are appropriate and reliable.
- Consistency and relevance: Look for common themes, findings, and arguments across the literature. Ensure that the sources you select directly address your research question and contribute to the overall understanding of your topic.
5. Organize and synthesize the literature
Once you have evaluated the literature, IT is important to organize and synthesize the information. Create a clear structure for your literature review, categorizing the sources according to themes, theories, or methodologies.
Identify the main arguments, theories, and findings from each source, and compare and contrast them. Look for patterns and connections that emerge across the literature. This will help you build a coherent narrative and identify any gaps or debates in the existing research.
6. Write your literature review
With a clear synthesis of the literature, you can now begin writing your literature review. Follow a logical structure, starting with an introduction that provides an overview of the topic and states your research question or objective.
Organize the body of your literature review according to the themes, theories, or methodologies you have identified. Present the key findings and arguments from each source, critically analyzing and synthesizing the information.
Finally, conclude your literature review by summarizing the main points and highlighting the gaps or areas for further research. Make sure to cite all the sources you have referenced in a consistent citation style, such as APA or MLA.
A well-conducted literature review is a crucial step in any EPQ project. IT helps you identify and analyze the existing knowledge related to your topic, guides your research, builds a theoretical framework, and supports your arguments with credible evidence. By following the step-by-step guide outlined in this article, you can conduct an effective literature review that enhances the quality and impact of your EPQ project.
Q: How many sources should I include in my literature review?
The number of sources you include in your literature review largely depends on the scope of your research and the depth of existing literature on your topic. Aim for a balance between comprehensiveness and relevance. Include enough sources to demonstrate a comprehensive understanding of the topic, but also focus on the most influential and recent works.
Q: How do I avoid plagiarism in my literature review?
To avoid plagiarism, IT is essential to properly attribute the ideas, opinions, and findings of other authors. Make sure to cite all the sources you have referenced in a consistent citation style, such as APA or MLA. Paraphrase and summarize the information in your own words, and use quotation marks for direct quotations. Always provide a clear citation whenever you use someone else’s work.
Q: Can I include non-academic sources in my literature review?
While academic sources are generally preferred for a literature review, IT might be relevant to include some non-academic sources, such as government reports, industry publications, or reputable websites. However, ensure that these sources are reliable, authoritative, and directly contribute to your research question.
Q: How do I determine the quality of a source?
When evaluating the quality of a source, consider the publication date, author credentials, research design and methodology, consistency and relevance to your research question. Look for peer-reviewed articles from reputable journals and books from renowned publishers. Assess the reliability and credibility of the sources by checking the reputation of the authors and the publication venues.
Q: Does the literature review come before or after the data collection?
The literature review usually comes before data collection in the research process. IT provides the theoretical and conceptual background for your study, helping you design your research methodology and data collection instruments. However, IT is important to continuously review and update the literature as your project progresses, as new studies and findings might emerge.
Introduction to Maya 3D: A Beginner’s Guide
10 best free one page wordpress themes for a stunning website.

Recent Posts
- Driving Organic Growth: How a Digital SEO Agency Can Drive Traffic to Your Website
- Mastering Local SEO for Web Agencies: Reaching Your Target Market
- The Ultimate Guide to Unlocking Powerful Backlinks for Your Website
- SEO vs. Paid Advertising: Finding the Right Balance for Your Web Marketing Strategy
- Discover the Secret Weapon for Local SEO Success: Local Link Building Services
Popular Posts

Shocking Secret Revealed: How Article PHP ID Can Transform Your Website!

Uncovering the Top Secret Tricks for Mastering SPIP PHP – You Won’t Believe What You’re Missing Out On!

Unlocking the Secrets to Boosting Your Alexa Rank, Google Pagerank, and Domain Age – See How You Can Dominate the Web!

The Ultimate Collection of Free Themes for Google Sites

Discover the Shocking Truth About Your Website’s Ranking – You Won’t Believe What This Checker Reveals!
Explore topics.
- Backlinks (2,425)
- Blog (2,744)
- Computers (5,318)
- Digital Marketing (7,741)
- Internet (6,340)
- Website (4,705)
- Wordpress (4,705)
- Writing Articles & Reviews (4,208)
Extended Project Qualification Level 3
Back to courses
About this course
What is it.
The Extended Project Qualification (EPQ) is a nationally recognised and fully resourced qualification at Level 3. It carries up to 18 performance table points, or 28 UCAS points towards entry into higher education.
ASDAN’s EPQ is a single piece of work that requires a high degree of planning, preparation, research and autonomous working. This can be a 5,000 word dissertation or an artefact or performance accompanied by a 1,000 word report. The EPQ provides a unique opportunity to build the project around a work experience placement, offering a clear line of sight to employment and training.
Available for delivery in England and Northern Ireland, ASDAN’s EPQ has the same specification as those offered by other awarding organisations with an additional focus on completing the EPQ as part of a work placement.
We introduced the suggested delivery model, fully planned and resourced sessions to help learners develop the study skills required to complete their project. Access to all resources is included in ASDAN membership cost and are available to download on this page.
Read the abridged EPQ specification and view key dates .
"The new EPQ ASDAN is delivering gives students the opportunity to gain valuable employability skills through attendance at a work placement and completing a work-based project. We believe that successful completion of this qualification will prepare learners for further study and employment."
Katie Jenkins, Director, Marketing and Future Students, UWE Bristol
- Qualifications
Already a member? Sign in
Who is it for?
The EPQ is for students aged 16+ on a full-time programme of study.
ASDAN's EPQ can be used to complement vocational or academic learning; it provides learners with the skills that employers and higher education are looking for. The EPQ encourages independent study, critical thinking and teamwork – it is ideal for improving transferable skills such as planning, research, analysis and evaluation.
Facts and figures
- Available to centres in England and Northern Ireland only
- 120 hours total qualification time, including a pre-project taught element (30 hours)
- UCAS Tariff points are available on the Extended Project Qualification. For more information, please refer to ASDAN Qualifications key dates and performance information 2023-2024 .
- Students choose the topic for their project – it can be linked to their programme of study or a work placement
- Develops study skills and employability skills for progression to higher education and employment
- Supported by high quality teaching and learning resources
Students are free to choose the topic for their project, however they must show that it is useful for their progression and is linked to their programme of study or their future career.
ASDAN’s EPQ has the same specification as those offered by other awarding organisations with an additional focus on completing the EPQ as part of a work placement. This could be a dissertation linked to a work placement, or an artefact and report created as part of a work placement.
Assessment objectives
Students’ projects are graded based on four assessment objectives:
- AO1. Manage (20%)
- AO2. Use resources (20%)
- AO3. Develop and realise (40%)
- AO4. Review (20%)
Taught element
The ASDAN EPQ begins with a taught element (30 hours) to support learners in designing and carrying out their project.
Key documents
High quality resources are available to support learners, teachers, parents and employers involved in the ASDAN EPQ:
- EPQ specification (abridged)
EPQ key dates for centres
- EPQ Teacher guide
- EPQ What's in it for me? learner guide
- EPQ What's in it for them? parent guide
Other high quality key documents are available for registered centres to download via the members area . These additional resources include learner guides, a guide for employers, resources to support the pre-project taught element and mandatory forms.
The following documents are available to download for free:
- EPQ Suggested delivery model
Getting started
New to ASDAN?
Your first step is to become a member of ASDAN. Read more about our membership tiers and the benefits of being a member.
Already a member?
If you are on our qualifications membership and your centre has been approved to deliver qualifications, you can get started by purchasing materials below.
Please note that someone from your centre must have attended a mandatory training session or INSET prior to delivering this course.
You can upgrade your membership at any time under account settings .
ASDAN members' area
You can manage your courses, learners, orders and account settings in the members’ area . This also contains all the essential documents, forms and updates that you will need to deliver your course.
After students' work has been internally moderated, centres must submit candidate marks and send projects for external moderation, which is carried out by post. ASDAN will issue certificates following successful external moderation.
ASDAN training events are delivered by experts to enable your centre to successfully run our courses. They provide an introduction to the course, along with guidance on the processes involved, course delivery and moderation.
Training is mandatory for the Extended Project Qualification.
Book training
All candidate registration costs shown below are per candidate, unless otherwise stated.
Public funding for ASDAN qualifications delivered in the UK
Many ASDAN qualifications are fully funded by the UK Government.
Whether you are an employer, a learner or a training provider, the following websites will provide you with more information on the different types of public funding in the UK for ASDAN qualifications.
- England - Education and Skills Funding Agency, ESFA
- Wales - Qualifications in Wales, QiW
- Northern Ireland - Department for the Economy
Course resources
EPQ specification (full)
EPQ centre handbook
EPQ forms 1–12
EPQ centre declaration form
Qualifications EQA/external moderation sample centre checklist
EPQ teacher guide
EPQ suggested delivery model (taught element)
EPQ learner guide: areas of interest
EPQ learner guide: work experience
EPQ graded exemplar project
EPQ exemplar project with supervisor/assessor marks: dissertation
EPQ exemplar project with supervisor/assessor marks: artefact
EPQ exemplar project with supervisor/assessor marks: mandatory paperwork
EPQ internal moderation report template
Extended Project Qualification grade boundaries (most recent awarding period)
EPQ post results and appeal policy
EPQ application form for post results review and appeals
Principal Moderator report (most recent awarding period)
EPQ What's in it for them? parent guide
EPQ What's in it for me? learner guide
EPQ employer guide
Success stories
“asdan’s extended project qualification made me realise that university is an attainable goal.”, similar courses.
- International
- Schools directory
- Resources Jobs Schools directory News Search

A* EPQ Dissertation Example
Subject: English
Age range: 16+
Resource type: Assessment and revision
Last updated
30 April 2020
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

This is an A* EPQ dissertation example. This is 36 page, and approximately 10000 word document. This is an example of an EPQ dissertation fully meeting every criteria outlined in mark scheme, clearly laid out and includes a fully descriptive and analytical activity log, which is the bulk of the marks for the EPQ. The question I answered was: ‘Investigating the Dark Side of Beauty: What is the basis behind the skin whitening industry in India?’.
Tes paid licence How can I reuse this?
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
This resource hasn't been reviewed yet
To ensure quality for our reviews, only customers who have purchased this resource can review it
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, automatically generate references for free.
- Knowledge Base
- Dissertation
- How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples
Published on 1 March 2019 by Shona McCombes . Revised on 10 October 2022 by Eoghan Ryan.
An abstract is a short summary of a longer work (such as a dissertation or research paper ). The abstract concisely reports the aims and outcomes of your research, so that readers know exactly what your paper is about.
Although the structure may vary slightly depending on your discipline, your abstract should describe the purpose of your work, the methods you’ve used, and the conclusions you’ve drawn.
One common way to structure your abstract is to use the IMRaD structure. This stands for:
- Introduction
Abstracts are usually around 100–300 words, but there’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check the relevant requirements.
In a dissertation or thesis , include the abstract on a separate page, after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents .
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Be assured that you'll submit flawless writing. Upload your document to correct all your mistakes.

Table of contents
Abstract example, when to write an abstract, step 1: introduction, step 2: methods, step 3: results, step 4: discussion, tips for writing an abstract, frequently asked questions about abstracts.
Hover over the different parts of the abstract to see how it is constructed.
This paper examines the role of silent movies as a mode of shared experience in the UK during the early twentieth century. At this time, high immigration rates resulted in a significant percentage of non-English-speaking citizens. These immigrants faced numerous economic and social obstacles, including exclusion from public entertainment and modes of discourse (newspapers, theater, radio).
Incorporating evidence from reviews, personal correspondence, and diaries, this study demonstrates that silent films were an affordable and inclusive source of entertainment. It argues for the accessible economic and representational nature of early cinema. These concerns are particularly evident in the low price of admission and in the democratic nature of the actors’ exaggerated gestures, which allowed the plots and action to be easily grasped by a diverse audience despite language barriers.
Keywords: silent movies, immigration, public discourse, entertainment, early cinema, language barriers.
Prevent plagiarism, run a free check.
You will almost always have to include an abstract when:
- Completing a thesis or dissertation
- Submitting a research paper to an academic journal
- Writing a book proposal
- Applying for research grants
It’s easiest to write your abstract last, because it’s a summary of the work you’ve already done. Your abstract should:
- Be a self-contained text, not an excerpt from your paper
- Be fully understandable on its own
- Reflect the structure of your larger work
Start by clearly defining the purpose of your research. What practical or theoretical problem does the research respond to, or what research question did you aim to answer?
You can include some brief context on the social or academic relevance of your topic, but don’t go into detailed background information. If your abstract uses specialised terms that would be unfamiliar to the average academic reader or that have various different meanings, give a concise definition.
After identifying the problem, state the objective of your research. Use verbs like “investigate,” “test,” “analyse,” or “evaluate” to describe exactly what you set out to do.
This part of the abstract can be written in the present or past simple tense but should never refer to the future, as the research is already complete.
- This study will investigate the relationship between coffee consumption and productivity.
- This study investigates the relationship between coffee consumption and productivity.
Next, indicate the research methods that you used to answer your question. This part should be a straightforward description of what you did in one or two sentences. It is usually written in the past simple tense, as it refers to completed actions.
- Structured interviews will be conducted with 25 participants.
- Structured interviews were conducted with 25 participants.
Don’t evaluate validity or obstacles here — the goal is not to give an account of the methodology’s strengths and weaknesses, but to give the reader a quick insight into the overall approach and procedures you used.
The only proofreading tool specialized in correcting academic writing
The academic proofreading tool has been trained on 1000s of academic texts and by native English editors. Making it the most accurate and reliable proofreading tool for students.

Correct my document today
Next, summarise the main research results . This part of the abstract can be in the present or past simple tense.
- Our analysis has shown a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
- Our analysis shows a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
- Our analysis showed a strong correlation between coffee consumption and productivity.
Depending on how long and complex your research is, you may not be able to include all results here. Try to highlight only the most important findings that will allow the reader to understand your conclusions.
Finally, you should discuss the main conclusions of your research : what is your answer to the problem or question? The reader should finish with a clear understanding of the central point that your research has proved or argued. Conclusions are usually written in the present simple tense.
- We concluded that coffee consumption increases productivity.
- We conclude that coffee consumption increases productivity.
If there are important limitations to your research (for example, related to your sample size or methods), you should mention them briefly in the abstract. This allows the reader to accurately assess the credibility and generalisability of your research.
If your aim was to solve a practical problem, your discussion might include recommendations for implementation. If relevant, you can briefly make suggestions for further research.
If your paper will be published, you might have to add a list of keywords at the end of the abstract. These keywords should reference the most important elements of the research to help potential readers find your paper during their own literature searches.
Be aware that some publication manuals, such as APA Style , have specific formatting requirements for these keywords.
It can be a real challenge to condense your whole work into just a couple of hundred words, but the abstract will be the first (and sometimes only) part that people read, so it’s important to get it right. These strategies can help you get started.
Read other abstracts
The best way to learn the conventions of writing an abstract in your discipline is to read other people’s. You probably already read lots of journal article abstracts while conducting your literature review —try using them as a framework for structure and style.
You can also find lots of dissertation abstract examples in thesis and dissertation databases .
Reverse outline
Not all abstracts will contain precisely the same elements. For longer works, you can write your abstract through a process of reverse outlining.
For each chapter or section, list keywords and draft one to two sentences that summarise the central point or argument. This will give you a framework of your abstract’s structure. Next, revise the sentences to make connections and show how the argument develops.
Write clearly and concisely
A good abstract is short but impactful, so make sure every word counts. Each sentence should clearly communicate one main point.
To keep your abstract or summary short and clear:
- Avoid passive sentences: Passive constructions are often unnecessarily long. You can easily make them shorter and clearer by using the active voice.
- Avoid long sentences: Substitute longer expressions for concise expressions or single words (e.g., “In order to” for “To”).
- Avoid obscure jargon: The abstract should be understandable to readers who are not familiar with your topic.
- Avoid repetition and filler words: Replace nouns with pronouns when possible and eliminate unnecessary words.
- Avoid detailed descriptions: An abstract is not expected to provide detailed definitions, background information, or discussions of other scholars’ work. Instead, include this information in the body of your thesis or paper.
If you’re struggling to edit down to the required length, you can get help from expert editors with Scribbr’s professional proofreading services .
Check your formatting
If you are writing a thesis or dissertation or submitting to a journal, there are often specific formatting requirements for the abstract—make sure to check the guidelines and format your work correctly. For APA research papers you can follow the APA abstract format .
Checklist: Abstract
The word count is within the required length, or a maximum of one page.
The abstract appears after the title page and acknowledgements and before the table of contents .
I have clearly stated my research problem and objectives.
I have briefly described my methodology .
I have summarized the most important results .
I have stated my main conclusions .
I have mentioned any important limitations and recommendations.
The abstract can be understood by someone without prior knowledge of the topic.
You've written a great abstract! Use the other checklists to continue improving your thesis or dissertation.
An abstract is a concise summary of an academic text (such as a journal article or dissertation ). It serves two main purposes:
- To help potential readers determine the relevance of your paper for their own research.
- To communicate your key findings to those who don’t have time to read the whole paper.
Abstracts are often indexed along with keywords on academic databases, so they make your work more easily findable. Since the abstract is the first thing any reader sees, it’s important that it clearly and accurately summarises the contents of your paper.
An abstract for a thesis or dissertation is usually around 150–300 words. There’s often a strict word limit, so make sure to check your university’s requirements.
The abstract is the very last thing you write. You should only write it after your research is complete, so that you can accurately summarize the entirety of your thesis or paper.
Avoid citing sources in your abstract . There are two reasons for this:
- The abstract should focus on your original research, not on the work of others.
- The abstract should be self-contained and fully understandable without reference to other sources.
There are some circumstances where you might need to mention other sources in an abstract: for example, if your research responds directly to another study or focuses on the work of a single theorist. In general, though, don’t include citations unless absolutely necessary.
The abstract appears on its own page, after the title page and acknowledgements but before the table of contents .
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the ‘Cite this Scribbr article’ button to automatically add the citation to our free Reference Generator.
McCombes, S. (2022, October 10). How to Write an Abstract | Steps & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved 6 May 2024, from https://www.scribbr.co.uk/thesis-dissertation/abstract/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, how to write a thesis or dissertation introduction, thesis & dissertation acknowledgements | tips & examples, dissertation title page.

COMMENTS
9) EPQ series: Charlotte on facing the blank page. Writing clearly. Good writing takes time, effort and energy. Being able to produce clear, readable, logical and well-argued pieces of writing is important in both university and in your working life. Precise & concise. Keep it simple. A word about style. Plagiarism.
9 steps to write your EPQ essay. 1. Come up with an idea. One of the main reasons students fail their EPQ is because they've chosen the wrong subject matter. It's vital that you choose a topic you're genuinely interested in, otherwise you won't have any motivation to work on it.
Here is a 9-step guide to help you write an effective EPQ essay: Brainstorm EPQ topic ideas: Choose an engaging topic that interests you and is relevant to your academic or career goals. Conduct research: Gather information from various sources to support your arguments and provide evidence. Create a structure: Organise your essay with a clear ...
Work out what the plan is before you start writing, so that you don't have to rewrite a large portion of your EPQ essay. So grab a pen and paper, sit down, put on some nice music, and get to writing those subtitles. 5. Triple Check That Every Subtitle Question Actually Relates To The Main EPQ Topic.
Reflecting. Expressing your ideas. This is the stage you have been building towards - writing your report. Although that is largely the focus of this page , it is not all there is to the EPQ. Your EPQ will be assessed on: Your completed Production Log. A written report (sometimes referred to in this guide as an essay)
EPQ Checklist & Guidance. Completed Projects must have: ) Proposal Form - signed by teacher and supervisor. ) Activity Log. ) Candidate Record - p1 signed by student and teacher p2 showing the record of marks allocated. ) Record of oral presentation (Powerpoint plus record sheet signed by SDS). ) Dissertation.
Additional resources. . Study Skills booklet - A handy guide to support you in completing the EPQ, covering topics such as academic language, referencing and time management. Check out the resources we offer to help you plan your extended project qualification, designed to help you every step of the way.
An EPQ (Extended Project Qualification) allows A-Level students to write either a 5,000 word essay on any question or subject of their choice. Alternatively, students can create an artefact or product, and write a shorter essay explaining it. The EPQ is equivalent to half an A-Level. EPQs are a fantastic way of proving to universities that you ...
Merchant Taylors' EPQ Presentation Evening - Wednesday 16th March 2016 . 11 Keep you Extended Project under control - don't get side-tracked or think 'I'll put it off until next week'. The summer holidays are a vital time to get the bulk of your research
This is an an EPQ dissertation fully meeting every criteria outlined in mark scheme, clearly laid out and includes a fully descriptive and analytical activity log, which is the bulk of the marks for the EPQ. The question I answered was: 'Public offenders deserve the right to rehabilitative programs in preference of being punished in prison or ...
Introduction. A literature review is an important component of any Extended Project Qualification (EPQ) project. IT involves researching and analyzing existing literature and scholarly works relevant to your topic. A well-conducted literature review can provide a solid foundation for your EPQ, helping you to identify gaps in the research, establish the context for your study, and build a ...
Level 3 Extended Project H856 Exemplar Folder 1. ocr.org.uk/extendedproject. Extended Project Exemplar 1 - 49/60 A* Palladium Catalysts. AO1 -Some reservations at the start, with the abstract, introduction approach etc, so seemed to be more concerned with dissertation than with project management. PPR had good evidence of choice and planning ...
ASDAN's EPQ is a single piece of work that requires a high degree of planning, preparation, research and autonomous working. This can be a 5,000 word dissertation or an artefact or performance accompanied by a 1,000 word report. The EPQ provides a unique opportunity to build the project around a work experience placement, offering a clear ...
Module. Unit 1 - Social psychology. Institution. PEARSON (PEARSON) Book. The God of Small Things. This is an A* EPQ dissertation example. This is a 36 page, and approximately 10000 word document. This is an example of an EPQ dissertation fully meeting every criteria outlined in mark scheme, clearly laid out and includes a fully descriptive and ...
File previews. docx, 4 MB. This is an A* EPQ dissertation example. This is 36 page, and approximately 10000 word document. This is an example of an EPQ dissertation fully meeting every criteria outlined in mark scheme, clearly laid out and includes a fully descriptive and analytical activity log, which is the bulk of the marks for the EPQ.
How to write an EPQ introduction. The first thing to do is to establish the purpose of the essay - in doing this, we want to break down the question that is being answered and examine the components of it. This sounds like it is just an exercise in definitions, and to an extent it is, but it's more complicated than it may appear because it ...
You will almost always have to include an abstract when: Completing a thesis or dissertation. Submitting a research paper to an academic journal. Writing a book proposal. Applying for research grants. It's easiest to write your abstract last, because it's a summary of the work you've already done.
Epq presentation template. Jan 21, 2013 • Download as PPTX, PDF •. 16 likes • 155,077 views. Matthew Jones. 1 of 8. Download now. Epq presentation template - Download as a PDF or view online for free.