
How Do You Draft the Personnel Section of the Business Plan? The Personnel Section of a Business Plan Explained.
Privacy Overview
Plan Smarter, Grow Faster:
25% Off Annual Plans! Save Now

0 results have been found for “”
Return to blog home
How to Create an Investor-Ready Personnel Plan and Forecast Employee Costs
Posted march 22, 2021 by noah parsons.

A personnel plan is a critical part of your business plan and financial forecast . In addition to helping you budget for current and future employees, your personnel plan enables you to think through who you should hire and when you should hire them.
If you’re pitching to angel investors or venture capitalists for funding, they will want to see why your team is uniquely suited to grow and scale your business, as well as your hiring plan.
Investors will want to know:
- What positions do you need to fill?
- When you plan on filling them?
- How much it’s going to cost to build the team you need??
What to include in the personnel section of your business plan
For many startups and small businesses, the people who do the work—your team—are both the most costly and most valuable asset. It makes sense that hiring the right person at the right time can have a significant impact on your ability to meet your company’s milestones and goals , not to mention your cash flow .
Thinking strategically about human resources — when to add positions, compensation levels, and whether to hire full-time or on a contract basis are all pieces of a healthy personnel plan.
So, whether you’re seeking investment or not, building a personnel plan and forecast is an essential part of business planning and strategic planning for the long-term viability of your company. Let’s dive right in and look at the five key steps to build an investor-ready personnel plan.
1. Describe your team
In the “team” section of your business plan, you will typically include an overview of the key positions in your company and the background of the people who will be in those critical roles. Usually, you’ll highlight each of the management positions in your company and then speak more generally about other departments and teams.
You don’t need to include full resumes for each team member—a quick summary of why each person is qualified to do the job is enough. Describe each person’s skills and experience and what they will be doing for the company.
Emphasize your team’s strengths. How do they make your team stronger? What specific expertise and experience do they have in your (or a related) industry? Assuming your market research identified a great opportunity, why are you the right team to capitalize on it?
For potential investors, this section helps qualify why each team member is necessary for the success of the business. It acts as a justification for their salary and equity share if they are part owners of the company.
2. Describe your organizational structure
The organizational structure of your company is frequently represented as an “org chart” that shows who reports to whom and who is responsible for what.
You don’t have to create a visual org chart, though—describing your organization in the text is just fine. Just make sure to show that you have a clear structure for your company.
Is authority adequately distributed among the team? Do you have the resources to get everything done that you need to grow your company?
You’ll also want to mention the various teams your company is going to have in the future. These might include sales, customer service, product development, marketing, manufacturing, and so on.
You don’t need to plan on hiring all of these people right away. Think of this section as an outline of what you plan to do in the future with your company.
3. Explain the gaps
It’s alright to have gaps on your team, especially if you’re a startup. You may not have identified all the “right” team members yet, or you may not have the funds available yet to hire for essential roles . That’s okay.
The key is to know that you do have gaps on your team—this is how you figure out who you need to hire and when you need to hire them. Also, it’s much better to define and identify weaknesses in your team than to pretend that you have all the key roles that you need. In your business plan , explain where your organization is weak and what your plans are to correct the problem as you grow.
It might be tempting to hide your potential weaknesses from investors, but they’ll see through that right away. It’s much better to be open and honest about where you have management gaps and your plans to solve those problems. You want them to know you have identified and made plans to mitigate risks .
You also need to keep in mind that employees might wear a lot of hats in the early days of a company, but that specialization will happen as the company grows.
For example, initially, the CEO might also be the VP of Sales. But, eventually, the VP of Sales role should be filled by a specialist to take on that responsibility. Include these types of changes in your personnel plan to explain to investors that you understand how your company is going to grow and scale.
4. List your advisors, consultants, and board members
For some companies, external advisors, board members , and even consultants can play a crucial role in setting business strategy. These people might even fill key positions temporarily as your company grows. If this is the case, you’ll want to list these people in your business plan. Like your management team, provide a brief background on each principal advisor that explains the value they provide.
If your advisors don’t hold key roles or are not critical to your success, you don’t necessarily have to list them. But, do list anyone that is adding substantial value to the company by providing advice, connections, or operational expertise.
5. Forecast your personnel costs
Most business plans should include a personnel table to forecast the expense of your employees. Here are the expenses you’ll need to be aware of when forecasting.
Direct and indirect labor expenses
You’ll want to include both direct expenses , which usually comprise salaries, as well as indirect expenses which include:
- Paid time off
- Healthcare and insurance
- Payroll costs
As well as any other costs you incur for each employee beyond their salary. Here’s an example of what a personnel forecast can look like using LivePlan .
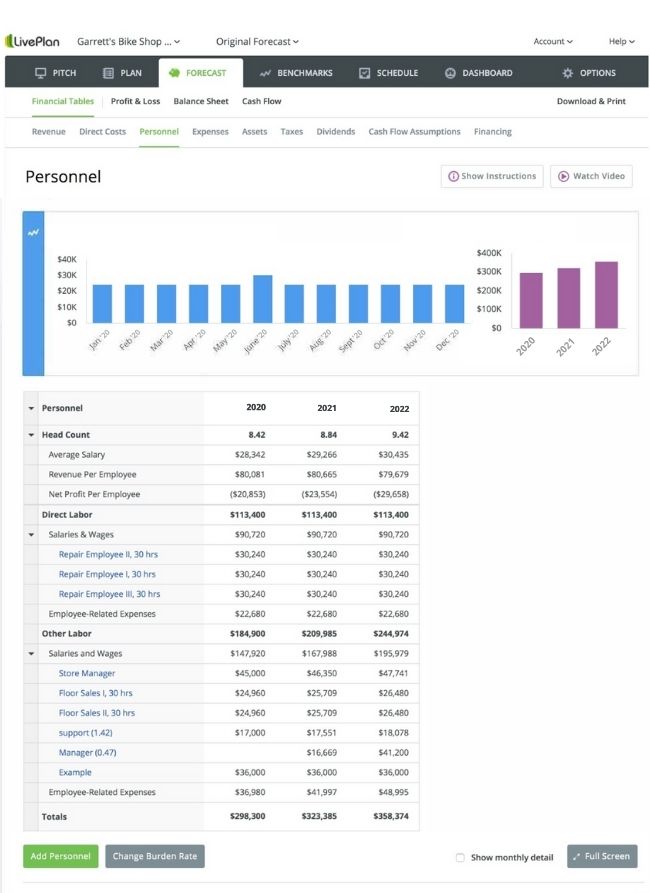
Burden rate and employee-related expenses
There are different names for the indirect expenses of personnel. Still, I like to call it “burden rate” or “employee-related expenses,” which is an expense over and above the direct wages and salaries. These expenses typically include payroll taxes, worker’s compensation insurance, health insurance, and other benefits and taxes.
For business planning purposes, don’t stress about coming up with the exact figure for the burden rate. Instead, estimate it using a percentage of total monthly salaries. Somewhere between 15 percent and 25 percent usually makes sense, but it depends on what kind of benefits you plan on offering.
In your personnel plan, you can list both individual people as well as groups of people. You’ll probably want to list out key people and other highly paid employees, but group together other departments or groups of people. For example, you might list out your management team, but then group together departments like Marketing, Customer Service, and Manufacturing.
Then, add in your personnel burden to cover benefits and insurance. In the example personnel table above, this is called “Employee-Related Expenses.”
You’ll then take the total number of your salaries plus personnel burden and include this in your profit and loss forecast as an expense. Suppose you’re using LivePlan to build your personnel forecast. In that case, this how-to article on entering personnel shows where you’ll see personnel costs appear on your cash flow statement, profit and loss (income statement), and your balance sheet.
Do you need a personnel plan if you have no employees?
If you are a sole proprietor and don’t have employees, you should still include your own salary as part of the business plan. Make sure to include your salary as an expense in your Profit & Loss Statement . Even if you, the business owner, don’t take the salary, so you can keep the cash in your business, you’ll want to record what you should have been paid.
In the case of a sole proprietor, you probably don’t need a full table for the personnel plan, like in the example above. But, when you do start planning to hire a team, you should use the format I’ve described here.
Personnel planning is a valuable part of the business planning process because it forces you to think about what needs to get done in your business and who’s going to do it. Take the time to work through this part of your financial forecast, and you’ll have a much better sense of what it’s going to take to make your business successful.
*Editors Note: This article was initially written in 2019 and updated for 2021.
Like this post? Share with a friend!
Noah Parsons
Posted in business plan writing, join over 1 million entrepreneurs who found success with liveplan, like this content sign up to receive more.
Subscribe for tips and guidance to help you grow a better, smarter business.
You're all set!
Exciting business insights and growth strategies will be coming your way each month.
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .

With our proven track record of exellence, we are confident that we are the perfect choice for businesses seeking for optimal performance and sustainable growth.
- Reasons to work with us
- Meet Our Leadership Team
- Why Outsource to Vietnam?
- Case Studies
Stay up-to-date with the latest news, industry trends, and valuable insights shared by our experts.
- BPO Trends & Updates
- Events and Podcasts
We are a Vietnam-based diverse, qualified and dedicated team that works to help clients in North America, Canada, Australia, and Asia-Pacific expand their global footprints.
- Innovaturer’s Activities
Guide to Developing a Personnel Plan
- May 12, 2023
- BPO Insights
- Finance and Accounting Services , Financial Analysis & Financial Planning

Table of Contents
A people plan is an essential component of your business strategy and Financial Planning . In addition to assisting you in budgeting for current and prospective employees, your personnel strategy allows you to consider who to hire and when to hire them.
What is a Personnel Plan?

A Personnel Plan is a document that details an organization’s staffing needs, goals, and workforce management practices. It is an essential component of human resource management and serves as a road map for employee recruitment, selection, training, development, retention, and management.
A Personnel Plan is an essential component of any start-up or entrepreneur’s business plan . It will aid you in your financial predictions, allowing you to anticipate the best periods to hire and expand.
When presenting for funding to angel investors or venture capitalists , they will want to see why your team is uniquely equipped to grow and scale your firm, as well as your hiring strategy.
Investors will be interested in learning:
- What positions do you require?
- When do you intend to fill them?
- How much will it cost to assemble the team you require?
What should you put in your Personnel Plan section?

The people who execute the work—your team—are both the most expensive and most important asset for many startups and small businesses . It stands to reason that hiring the appropriate individual at the right moment can have a big impact on your company’s ability to accomplish milestones and goals, not to mention cash flow.
A healthy Personnel Plan includes strategic thinking about human resources, such as whether to expand roles, and salary levels, and whether to hire full-time or on a contract basis.
So, whether you’re looking for investment or not, developing a people plan and forecast is an important aspect of business planning and strategic planning for your company’s long-term success. Look at the 9 critical phases of developing an investor-ready Personnel Plan .
What is the composition of your management team?
Typically, the “team” portion of your business plan will include an overview of the main jobs in your organization as well as the backgrounds of the people who will fill those critical responsibilities. You will highlight each of your company’s executive positions before speaking more broadly about other departments and teams.
Keep it brief .
You do not need to submit whole resumes for each team member; a brief overview of why each person is qualified for the position is sufficient. Describe each individual’s talents and expertise, as well as what they will do for the company.
Highlight your team’s strengths . How do they bolster your group’s strength? What is their special knowledge and experience in your (or a related) industry? If your market research uncovered a fantastic opportunity, why are you the best team to capitalize on it?
This part helps potential investors understand why each team member is critical to the company’s success. It serves as the rationale for their wage and ownership stake in the company if they are part owners.
How is the organizational structure defined?
Your company’s organizational structure is typically portrayed as an “org chart” that indicates who reports to whom and who is accountable for what.
However, you do not need to construct a graphic org chart; simply defining your organization in the text is sufficient . Simply demonstrate that your organization has a well-defined structure.
Is authority divided fairly among the team members? Do you have the resources to do all of the tasks required to expand your business?
You should also explain the many teams that your organization will have in the future . Sales, customer service, product development, marketing, production, and so on are examples.
You don’t have to hire all of these employees right away. Consider this section to be an outline of what you intend to do with your firm in the future.
Compile a list of your advisors, consultants, and board members
External advisers, board members, and even consultants can play an important role in determining a corporate strategy for some organizations. These individuals may even temporarily fill crucial positions as your company grows. You should include a list of these individuals in your Personnel Plan if this is the case. Give a brief background on each main advisor that outlines the value they give, just like you would for your management team.
You don’t have to include your advisors if they don’t play essential roles or aren’t critical to your achievement. However, i nclude anyone who adds significant value to the organization through advice, contacts, or operational skills.
Explain the gaps

It’s normal for your team to have gaps, especially if you’re a startup . You may not yet have identified all of the “right” team members, or you may not yet have the cash to hire for critical roles. That’s OK.
The trick is to recognize that you do have gaps on your team—this is how you determine who to employ and when to hire them . Furthermore, it is far better to describe and recognize team deficiencies than to pretend that you have all of the critical responsibilities that you require. Explain where your organization is weak and how you intend to address the issue as you develop in your business strategy.
Although it may be tempting to conceal potential weaknesses from investors, they will see right through you. It is far preferable to be open and honest about where you have management gaps and your Personnel Strategy to remedy those gaps. You want them to know you’ve identified and planned for dangers.
You should also bear in mind that your Personnel Plan may wear many hats in the early days of a company, but specialization will occur as the company expands.
For example, the CEO may initially also be the VP of Sales. However, the job of VP of Sales should eventually be filled by a specialist to take on that task. Include modifications like these in your personnel plan to show investors that you understand how your company will expand and scale.
What are your personnel requirements?
Outline the company’s personnel requirements, including the number and types of people required to run the business successfully . The credentials and skills required for each post should also be included.
Here you may identify your team’s shortcomings and vulnerabilities , ensuring that you have a competent grasp of the roles and duties that will be crucial to the business in the future – even if they are not currently in existence. Investors are ready to highlight “perfect” people strategies, so you should embrace the fact that you have recognized staffing hazards.
For example, your head of customer service may also be your head of sales, but these two responsibilities will need to be split in the future.
How will recruitment and training be carried out?
This section should explain how the company intends to recruit and train personnel, including any training programs or on-the-job training.
What are the remuneration and benefits?
Outline the salary and benefits packages that will be provided to employees, including salaries, bonuses, health insurance, retirement plans, and any other perks or incentives.
Describe your Human Resources policies
Explain the company’s policies on topics such as employee performance reviews, disciplinary procedures, and termination procedures.
Estimate your personnel costs
Most Personnel Plans should include a personnel table to anticipate labor costs . Here are some expenses to keep in mind when forecasting.
Labor costs, both direct and indirect
You should include both direct expenses, which are often salary, and indirect expenses, which include:
- Paid vacation
- Insurance and healthcare
- Payroll expenses
As well as any extra fees you incur for each employee in addition to their compensation. Here’s an example of a personnel prediction:

Employee-related expenses and the burden rate
The indirect costs of staff are known by various names . Still, Innovature BPO will refer to it as a “burden rate” or “employee-related expenses”, as it is an expense in addition to direct wages and salary . Payroll taxes, worker’s compensation insurance, health insurance, and other benefits and taxes are common examples of these costs.
Don’t worry about calculating the correct burden rate for company planning objectives. Estimate it instead as a proportion of total monthly compensation. A range of 15% to 25% is normally appropriate, but it depends on the type of benefits you intend to provide.
Individuals and groups of individuals can both be listed in your Personnel Plan . You should certainly mention key people and other highly paid employees but put other departments or groups of people together. For example, you may include your management team but then group departments such as marketing, customer service, and manufacturing together.
Then factor in your employee costs for benefits and insurance. In the example personnel table above, this is referred to as “Employee-Related Expenses.”
The whole quantity of your salary and personnel load will then be included as an item in your profit and loss prediction. Assume you’re using HR management software to create a Personnel Prediction. This software explains where you’ll see personnel costs on your cash flow statement, profit and loss (income statement), and balance sheet.
Is it necessary to Personnel Plan in a company strategy if you have no employees?
Even if you don’t currently have any employees, having a Personnel Plan is useful to your firm in the long run.
You may find it difficult to scale your firm or respond to changes in your sector or market if you do not have a Personnel Plan . For example, if you need to hire someone immediately to fill a key function, you may not know where to begin or what qualifications to search for.
Developing a Personnel Plan can also assist you in clarifying your company’s aims and objectives. You can better prioritize and focus on the critical tasks that must be completed by establishing the roles and responsibilities required to fulfill those goals.
As a result, even if you don’t currently have any employees, it’s a good idea to build a Personnel Plan to help you prepare for future growth and ensure that you have the correct team in place to support your business objectives.
Is there an easy approach to forecasting a Personnel Plan?
Personnel Plan is a time-consuming process that necessitates careful consideration of what needs to happen in your company and where you want it to go. Typically, this necessitates a lengthy process of spreadsheets and mathematics to determine who needs to work with you and at what expense.
A financial modeling tool can ensure that this component of your business strategy, along with other critical components, is easily constructed, requiring only a few data entries to be entered throughout the software. Currently, on the market, there are quite a few tools to support Personnel plans and personnel management . Let’s enjoy!
Personnel Plan is an important aspect of the business planning process because it forces you to consider what needs to be done in your company and who will do it. Take the time to work through this section of your financial plan, and you’ll have a lot better idea of what it will take to make your firm a success.
- What is Financial Analysis of a company and Financial Analysis Outsourcing Process you need to know
- What is Financial Planning for a business, and how to outsource Financial Planning?
- Mastering the Income Statement: A Beginner’s Guide to Financial Analysis
- The Role of Balance Sheet in Financial Analysis: Why It Matters
- Comparing the Financial Statements: Income Statement vs Balance Sheet
- A Beginner’s Guide to Cash Flow Statement: Examples and Explanation
- Understanding the Statement of Shareholder Equity: Key Concepts and Examples
- Risk Mitigation: Preparing for the Unexpected
- From Data to Insights: How to Build Accurate Sales Forecasts
- How Innovation Tools Change Financial Modeling for Strategic Success?
Are you ready to take your business to the next level?
- +84 28 2221 5580
- +1 201 862 8668
- +84 91 870 5429
- [email protected]

- Ree Tower 9 Doan Van Bo, District 4 Ho Chi Minh City, Viet Nam
- 15R, Avenir Building Archbishop Reyes Ave Lahug Cebu City, Philippines
- 5900 Balcones Drive #10422 Austin, Texas 78731
© Copyright by INNOVATURE BPO | All Rights Reserved.
- Business Planning
- Cash Flow Forecasting
- Scenario Planning
- Financial Reporting
- Financial Planning & Analysis
- For Enterprises
- For Franchises
- Case Studies
- Partnerships
- Software Integrations
- Templates & Downloads
A large update to Brixx has been released (15.04.24) - read about it here . Please clear cache/cookies in your browser if you encounter difficulties in loading the app.
How to Create a Personnel Plan for Investors

What is a personnel plan?
A personnel plan is a document that outlines an organization’s staffing needs, goals, and strategies for managing its workforce.
It is a key component of human resource management and provides a roadmap for the recruitment, selection, training, development, retention, and management of employees.
A personnel plan is critical within the business plan you would have created as a start-up or entrepreneur. It will help you in your financial forecasting, anticipating the right times to hire and expand.

What to include in the personnel section of your business plan
The personnel section of a business plan should include information about the management team and staff that will be involved in operating the business. The people who do the work are the most important asset, which of course comes with a cost. Understanding when to hire, when to think about human resources, and when to grow your business at the right time can be enormously important in meeting business objectives, setting yourself up for success with great personal benchmarks.
Building out a personnel plan within your business plan is going to be essential in planning for the long term success of your business. Forecasting this data can be the best way to ensure longevity.
Who is your management team?
This should include a brief introduction to the key members of the management team, including their backgrounds, experience, and relevant skills. It’s important to highlight their qualifications and how they will contribute to the success of the business.
This can be brief and doesn’t require a full resume for each member of the team. A simple explanation detailing qualifications and relevant experience applicable within the company is all that’s required.
What is the organizational structure?
This section should provide an overview of the organizational structure of the company, including who will be in charge of each department or functional area, as well as any outside consultants or advisors who will be involved.
In line with forecasting, you will want to illustrate the future of your company and who will be included. As you develop, you can anticipate your team growing from a just few employees into staff across multiple sectors, such as customer service, marketing, and support.
What are your staffing needs?
Outline the staffing needs of the business, including the number and types of employees needed to run the business successfully. This should also include the qualifications and skills required for each position.
Here you can identify the weaknesses and risks across your team, ensuring that you have a capable understanding of the roles and responsibilities that are important to the business in the future – though they may not be in place right now. Investors are quick to highlight “perfect” personnel plans, so you will want to embrace that you have identified risks in staffing.
As an example, your head of customer support may also be your head of sales, but in time these two roles will need to be separated.
What will recruitment and training look like?
This section should detail how the company plans to recruit and train employees, including any training programs or on-the-job training that will be provided.
What will the compensations and benefits be?
Outline the compensation and benefits packages that will be offered to employees, including salaries, bonuses, health benefits, retirement plans, and any other perks or incentives.
Outline the Human Resources policies
Detail the company’s policies on issues such as employee performance reviews, disciplinary procedures, and termination policies.

Does a business plan need personnel planning if I have no staff?
Even if you don’t have any employees right now, having a personnel plan is beneficial for your business in the long term.
Without a personnel plan, you may find it challenging to scale your business or adapt to changes in your industry or market. For example, if you suddenly need to hire someone to fill a critical role, you may not know where to start or what qualifications you should look for.
Creating a personnel plan can also help you to clarify your business goals and objectives. By determining the roles and responsibilities required to meet those goals, you can better prioritize and focus on the essential tasks that need to be done.
Therefore, even if you don’t have any employees currently, it’s still a good idea to develop a personnel plan to help you prepare for future growth and ensure that you have the right team in place to support your business objectives.
Is there an easy way to forecast a personnel plan?
Personnel planning is a long process as it requires dedicated thought as to what needs to happen in your business and where you want to take it. Typically, this require a lengthy process of spreadsheets and equations to figure out exactly who needs to be working with you, and at what cost.
Business planning software can ensure that this part of your business plan, alongside other key components, is created with ease – simply needing a few data entries to be entered throughout the software.

Related articles
- 10 Pitch Deck Mistakes to Avoid
- What are the Top 10 Business Plan Components?
- How To Find Potential Investors To Pitch To
- How to create financial projections for your business
Get started FREE with Brixx today
and take the first steps to planning your business’ future development

How to Write the Management Team Section of a Business Plan + Examples
Written by Dave Lavinsky

Over the last 20+ years, we’ve written business plans for over 4,000 companies and hundreds of thousands of others have used the best business plan template and our other business planning materials.
From this vast experience, we’ve gained valuable insights on how to write a business plan effectively , specifically in the management section.
What is a Management Team Business Plan?
A management team business plan is a section in a comprehensive business plan that introduces and highlights the key members of the company’s management team. This part provides essential details about the individuals responsible for leading and running the business, including their backgrounds, skills, and experience.
It’s crucial for potential investors and stakeholders to evaluate the management team’s competence and qualifications, as a strong team can instill confidence in the company’s ability to succeed.
Why is the Management Team Section of a Business Plan Important?
Your management team plan has 3 goals:
- To prove to you that you have the right team to execute on the opportunity you have defined, and if not, to identify who you must hire to round out your current team
- To convince lenders and investors (e.g., angel investors, venture capitalists) to fund your company (if needed)
- To document how your Board (if applicable) can best help your team succeed
What to Include in Your Management Team Section
There are two key elements to include in your management team business plan as follows:
Management Team Members
For each key member of your team, document their name, title, and background.
Their backgrounds are most important in telling you and investors they are qualified to execute. Describe what positions each member has held in the past and what they accomplished in those positions. For example, if your VP of Sales was formerly the VP of Sales for another company in which they grew sales from zero to $10 million, that would be an important and compelling accomplishment to document.
Importantly, try to relate your team members’ past job experience with what you need them to accomplish at your company. For example, if a former high school principal was on your team, you could state that their vast experience working with both teenagers and their parents will help them succeed in their current position (particularly if the current position required them to work with both customer segments).
This is true for a management team for a small business, a medium-sized or large business.
Management Team Gaps
In this section, detail if your management team currently has any gaps or missing individuals. Not having a complete team at the time you develop your business plan. But, you must show your plan to complete your team.
As such, describe what positions are missing and who will fill the positions. For example, if you know you need to hire a VP of Marketing, state this. Further, state the job description of this person. For example, you might say that this hire will have 10 years of experience managing a marketing team, establishing new accounts, working with social media marketing, have startup experience, etc.
To give you a “checklist” of the employees you might want to include in your Management Team Members and/or Gaps sections, below are the most common management titles at a growing startup (note that many are specific to tech startups):
- Founder, CEO, and/or President
- Chief Operating Officer
- Chief Financial Officer
- VP of Sales
- VP of Marketing
- VP of Web Development and/or Engineering
- UX Designer/Manager
- Product Manager
- Digital Marketing Manager
- Business Development Manager
- Account Management/Customer Service Manager
- Sales Managers/Sales Staff
- Board Members
If you have a Board of Directors or Board of Advisors, you would include the bios of the members of your board in this section.
A Board of Directors is a paid group of individuals who help guide your company. Typically startups do not have such a board until they raise VC funding.
If your company is not at this stage, consider forming a Board of Advisors. Such a board is ideal particularly if your team is missing expertise and/or experience in certain areas. An advisory board includes 2 to 8 individuals who act as mentors to your business. Usually, you meet with them monthly or quarterly and they help answer questions and provide strategic guidance. You typically do not pay advisory board members with cash, but offering them options in your company is a best practice as it allows you to attract better board members and better motivate them.
Management Team Business Plan Example
Below are examples of how to include your management section in your business plan.
Key Team Members
Jim Smith, Founder & CEO
Jim has 15 years of experience in online software development, having co-founded two previous successful online businesses. His first company specialized in developing workflow automation software for government agencies and was sold to a public company in 2003. Jim’s second company developed a mobile app for parents to manage their children’s activities, which was sold to a large public company in 2014. Jim has a B.S. in computer science from MIT and an M.B.A from the University of Chicago
Bill Jones, COO
Bill has 20 years of sales and business development experience from working with several startups that he helped grow into large businesses. He has a B.S. in mechanical engineering from M.I.T., where he also played Division I lacrosse for four years.
We currently have no gaps in our management team, but we plan to expand our team by hiring a Vice President of Marketing to be responsible for all digital marketing efforts.
Vance Williamson, Founder & CEO
Prior to founding GoDoIt, Vance was the CIO of a major corporation with more than 100 retail locations. He oversaw all IT initiatives including software development, sales technology, mobile apps for customers and employees, security systems, customer databases/CRM platforms, etc. He has a B.S in computer science and an MBA in operations management from UCLA.
We currently have two gaps in our Management Team:
A VP of Sales with 10 years of experience managing sales teams, overseeing sales processes, working with manufacturers, establishing new accounts, working with digital marketing/advertising agencies to build brand awareness, etc.
In addition, we need to hire a VP of Marketing with experience creating online marketing campaigns that attract new customers to our site.
How to Finish Your Business Plan in 1 Day!
Don’t you wish there was a faster, easier way to finish your business plan?
With Growthink’s Ultimate Business Plan Template you can finish your plan in just 8 hours or less!
Click here to finish your business plan today.
OR, Let Us Develop Your Plan For You
Since 1999, Growthink has developed business plans for thousands of companies who have gone on to achieve tremendous success.
Click here to see how Growthink’s professional business plan consulting services can create your business plan for you.
Other Resources for Writing Your Business Plan
- How to Write an Executive Summary
- How to Expertly Write the Company Description in Your Business Plan
- How to Write the Market Analysis Section of a Business Plan
- The Customer Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
- Completing the Competitive Analysis Section of Your Business Plan
- Financial Assumptions and Your Business Plan
- How to Create Financial Projections for Your Business Plan
- Everything You Need to Know about the Business Plan Appendix
- Business Plan Conclusion: Summary & Recap
Other Helpful Business Plan Articles & Templates

The Secrets of a Great Personnel Plan

Investing in human resources (HR) is a key element of healthy personnel planning and strategy. A hallmark of effective leadership is efficient HR which means hiring employees in a cost-effective manner and mostly when needed. Your business plan should always include an informative and up-to-date personnel plan section to provide direction for the company and help entrepreneurs stay focused.
At the heart of every business owner is the desire to excel. The best way to excel is to define your plans and proceed with purpose. Your business plan comprises a business description , a competition analysis, a marketing plan, a personnel section, the HR section and key financial information.
The personnel plan is designed to help company owners put their plans into action. It helps to clarify objectives for the current and forthcoming year. Thus, a good understanding of personnel plan and how to implement it in your business is vital.
What is a personnel plan?
A personnel plan is a vital part of every company plan and financial forecast, which aids future and current budgeting and defines the type of employee to hire and when to hire such employees.
When you are seeking funding, venture capitalists and angel investors will want a breakdown of your team. Who are they? What talents and skills do they bring to the table? What is your hiring plan for the first year, second year, and so on? How will your team drive business growth and success?
All this information will include the positions you will need employees for, the period in which the management intends to fill the plan, and the financial implications of the implementation of the plan. Just as you would assess if your business is financially feasible , you’ll need to apply this same sentiment when hiring employees.
The personnel plan represents a consolidated strategy for hiring the best people for all company positions, while keeping an eye on future expansion.
Michael E. Gerber, the author of The E-Myth Revisited, posited that an effective personnel plan designed as an efficient workplace game will help employers prime employees for organizational goals while creating job satisfaction. This means that an effective hiring process is vital to an efficient process of personnel planning.
The majority of employers find personnel planning difficult especially those whose staff work in shifts. Organizational challenges like these can easily be taken care of with TimeTrack Duty Roster which helps employers create a suitable overview of their workforce and personalize shifts according to any number of criteria, including their location and skills.
Features of the TimeTrack Duty Roster
Key elements of a personnel plan
Each company’s needs may differ, but in general, these are common elements that should form part of every personnel plan.
Job description
- Clearly explained requirements of the various job functions. Use easy-to-understand language and phrases.
Organizational chart and type of hiring
- The chart of the organization should show who works for whom and provide a good overview of the overall management and employee structure of the company.
- The plan should be clear on whether employees are independent contractors or receive salaries. This is essential for labor compliance issues and the workers’ tax.
Remuneration (salary amount and assumptions)
- Details of hourly or yearly payments are defined, including relevant assumptions that comprise estimates of salary increases over time. You also need to account for company benefits, including health insurance. This may be a percentage of salary costs employers pay to staff.
Time of recruitment
- The hiring of employees is often done over time and staggered. Thus, your plan must include details about when an employee will start and the end date for temporary staff.
Incorporate key personnel into the business plan
Employees are the most valuable assets any company can have. This means that hiring the right person should always be a key priority for every company. Your staff will have a significant impact on revenue, customer experience/satisfaction and the success of the company.
Incorporating the personnel section into your business plan is an important part of strategic planning for long-term viability. The information below serves as guide on how to implement a personnel plan in your business.
Team dynamics
This presents an overview of all the key positions in your business and the backgrounds of staff in their critical roles and departments. Add the total number of staff and their experiences. Emphasize the strengths of individuals and how to upskill where necessary. A great team is typically the fulcrum of business success because they have the responsibility of and possess the ability to translate policies into business success.
Organizational structure
The structure of your company is represented in the company’s organizational chart, which shows the hierarchy of duties and management. Is authority finely distributed and are the various company teams properly mentioned? This includes customer service, product development, marketing, manufacturing and sales.
When planning the company’s organizational details, you will need a strategy to manage absences and leave. TimeTrack Leave Management feature helps you to finetune these details so you can easily (and quickly!) oversee employee absences, vacation time and keep track of working hours for compliance management.
TimeTrack Leave Management
Gaps and stumbling blocks
While it may be difficult to identify gaps in your team, chances are that if you look closely, you will observe a section of your company in need of quality talent. You need to figure out how to fill this gap. Don’t hide the weakness of your team from potential investors. Always remember that specialization will evolve as the company grows.
Where advisors, board members and consultants are applicable to your company, list them. Where they will fill key positions as the business grows, you need to list them and provide background on the value they provide.
The fine print
Every personnel plan needs to include a section addressing employment benefits , rights and conditions, especially for managers. Design your company’s management personnel plan and include a table of staff expenses, including both direct and indirect labor expenses, a burden rate and employee-related expenses, while adding payroll tax, workers’ compensation, salaries and health insurance.

Checklist for personnel planning
Personnel improvement
Improving conditions for personnel involve the identification of gaps, developing and implementing action plans and taking follow-up actions. Managers should develop a performance improvement plan before taking disciplinary action against employees.
Identify skills or performance gaps
A gap analysis is designed to help you identify potential and current issues and is an essential part of the personnel process. Incorporate characteristics of human resource planning into your business planning.
Provide proof of a skills gap or underperformance of the workforce using a consistent format across all employment cadres. Design your format, including employee information and a description of performance discrepancies using expected and actual performance criteria.
Have a face-to-face meeting with your employees to share observed issues or concerns and gain insights into causal factors of underperformance. Use your documentation to share insights on performance challenges. Let the affected employees know they have committed specific policy infractions. Focus only on the outcomes of behaviors to help affected staff understand how their behaviors affect company success.
Develop action plans
Establish specific and measurable improvement goals for your workforce. Avoid generalizations and focus on key goals. Setting bit-sized goals is an effective way of working while monitoring task on time .
Provide detailed resources, including advanced tools that can help employees improve. This also means providing the management with essential tools that will help with the efficient oversight of the workforce.
Create a timeline for achieving performance improvement goals. This will help keep the staff on track towards achieving expectations. Don’t forget to identify metrics for measuring progress. Be specific about what you want employees to achieve and define the intended consequences in the event of failure to complete performance improvement plan. Be specific about actions you will take whether or not targets are met.
Schedule regular appointments to review the performance improvement plan with your employees and implement their feedback.
Incorporating a personnel plan into your business strategy is a key factor for efficient planning. To maximize the opportunity presented by personnel planning, use any of the effective and reliable TimeTrack planning and absence management software tools.

I am a researcher, writer, and self-published author. Over the last 9 years, I have dedicated my time to delivering unique content to startups and non-governmental organizations and have covered several topics, including wellness, technology, and entrepreneurship. I am now passionate about how time efficiency affects productivity, business performance, and profitability.
Time Tracking
- Absence Management Software
- Clock In System
- Time Attendance System
- Auto Scheduling
- Duty Roster
- Shift Planning
- Appointment Planning
- Task Planning
- Info Center
- Timesheet Templates
- Rota Templates
- Promotional Program
- Affiliate Program
- Success Stories


Free Download
Personnel Management Business Plan Template
Download this free personnel management business plan template, with pre-filled examples, to create your own plan..
Or plan with professional support in LivePlan. Save 50% today
Available formats:
What you get with this template
A complete business plan.
Text and financials are already filled out and ready for you to update.
- SBA-lender approved format
Your plan is formatted the way lenders and investors expect.
Edit to your needs
Download as a Word document and edit your business plan right away.
- Detailed instructions
Features clear and simple instructions from expert business plan writers.
All 100% free. We're here to help you succeed in business, no strings attached.
Get the most out of your business plan example
Follow these tips to quickly develop a working business plan from this sample.
1. Don't worry about finding an exact match
We have over 550 sample business plan templates . So, make sure the plan is a close match, but don't get hung up on the details.
Your business is unique and will differ from any example or template you come across. So, use this example as a starting point and customize it to your needs.
2. Remember it's just an example
Our sample business plans are examples of what one business owner did. That doesn't make them perfect or require you to cram your business idea to fit the plan structure.
Use the information, financials, and formatting for inspiration. It will speed up and guide the plan writing process.
3. Know why you're writing a business plan
To create a plan that fits your needs , you need to know what you intend to do with it.
Are you planning to use your plan to apply for a loan or pitch to investors? Then it's worth following the format from your chosen sample plan to ensure you cover all necessary information.
But, if you don't plan to share your plan with anyone outside of your business—you likely don't need everything.
More business planning resources

How to Create a Business Plan Presentation

Simple Business Plan Outline

How to Write a Business Plan for Investors

How to Start a Business With No Money

Industry Business Planning Guides

10 Qualities of a Good Business Plan

Business Plan Template

How to Write a Business Plan
Download your template now
Need to validate your idea, secure funding, or grow your business this template is for you..
- Fill-in-the-blank simplicity
- Expert tips & tricks
We care about your privacy. See our privacy policy .
Not ready to download right now? We'll email you the link so you can download it whenever you're ready.
Download as Docx
Download as PDF

Finish your business plan with confidence
Step-by-step guidance and world-class support from the #1 business planning software

From template to plan in 30 minutes
- Step-by-step guidance
- Crystal clear financials
- Expert advice at your fingertips
- Funding & lender ready formats
- PLUS all the tools to manage & grow

The quickest way to turn a business idea into a business plan
Fill-in-the-blanks and automatic financials make it easy.
No thanks, I prefer writing 40-page documents.

Discover the world’s #1 plan building software
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
- Building Your Business
- Becoming an Owner
- Business Plans
How To Write the Management Section of a Business Plan
Susan Ward wrote about small businesses for The Balance for 18 years. She has run an IT consulting firm and designed and presented courses on how to promote small businesses.
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/SusanWardLaptop2crop1-57aa62eb5f9b58974a12bac9.jpg)
Ownership Structure
Internal management team, external management resources, human resources, frequently asked questions (faqs).
When developing a business plan , the 'management section' describes your management team, staff, resources, and how your business ownership is structured. This section should not only describe who's on your management team but how each person's skill set will contribute to your bottom line. In this article, we will detail exactly how to compose and best highlight your management team.
Key Takeaways
- The management section of a business plan helps show how your management team and company are structured.
- The first section shows the ownership structure, which might be a sole proprietorship, partnership, or corporation.
- The internal management section shows the department heads, including sales, marketing, administration, and production.
- The external management resources help back up your internal management and include an advisory board and consultants.
- The human resources section contains staffing requirements—part-time or full-time—skills needed for employees and the costs.
This section outlines the legal structure of your business. It may only be a single sentence if your business is a sole proprietorship. If your business is a partnership or a corporation, it can be longer. You want to be sure you explain who holds what percentage of ownership in the company.
The internal management section should describe the business management categories relevant to your business, identify who will have responsibility for each category, and then include a short profile highlighting each person's skills.
The primary business categories of sales, marketing , administration, and production usually work for many small businesses. If your business has employees, you will also need a human resources section. You may also find that your company needs additional management categories to fit your unique circumstances.
It's not necessary to have a different person in charge of each category; some key management people often fill more than one role. Identify the key managers in your business and explain what functions and experience each team member will serve. You may wish to present this as an organizational chart in your business plan, although the list format is also appropriate.
Along with this section, you should include the complete resumés of each management team member (including your own). Follow this with an explanation of how each member will be compensated and their benefits package, and describe any profit-sharing plans that may apply.
If there are any contracts that relate directly to your management team members, such as work contracts or non-competition agreements, you should include them in an Appendix to your business plan.
While external management resources are often overlooked when writing a business plan , using these resources effectively can make the difference between the success or failure of your managers. Think of these external resources as your internal management team's backup. They give your business credibility and an additional pool of expertise.
Advisory Board
An Advisory Board can increase consumer and investor confidence, attract talented employees by showing a commitment to company growth and bring a diversity of contributions. If you choose to have an Advisory Board , list all the board members in this section, and include a bio and all relevant specializations. If you choose your board members carefully, the group can compensate for the niche forms of expertise that your internal managers lack.
When selecting your board members, look for people who are genuinely interested in seeing your business do well and have the patience and time to provide sound advice.
Recently retired executives or managers, other successful entrepreneurs, and/or vendors would be good choices for an Advisory Board.
Professional Services
Professional Services should also be highlighted in the external management resources section. Describe all the external professional advisors that your business will use, such as accountants, bankers, lawyers, IT consultants, business consultants, and/or business coaches. These professionals provide a web of advice and support outside your internal management team that can be invaluable in making management decisions and your new business a success .
The last point you should address in the management section of your business plan is your human resources needs. The trick to writing about human resources is to be specific. To simply write, "We'll need more people once we get up and running," isn't sufficient. Follow this list:
- Detail how many employees your business will need at each stage and what they will cost.
- Describe exactly how your business's human resources needs can be met. Will it be best to have employees, or should you operate with contract workers or freelancers ? Do you need full-time or part-time staff or a mix of both?
- Outline your staffing requirements, including a description of the specific skills that the people working for you will need to possess.
- Calculate your labor costs. Decide the number of employees you will need and how many customers each employee can serve. For example, if it takes one employee to serve 150 customers, and you forecast 1,500 customers in your first year, your business will need 10 employees.
- Determine how much each employee will receive and total the salary cost for all your employees.
- Add to this the cost of Workers' Compensation Insurance (mandatory for most businesses) and the cost of any other employee benefits, such as company-sponsored medical and dental plans.
After you've listed the points above, describe how you will find the staff your business needs and how you will train them. Your description of staff recruitment should explain whether or not sufficient local labor is available and how you will recruit staff.
When you're writing about staff training, you'll want to include as many specifics as possible. What specific training will your staff undergo? What ongoing training opportunities will you provide your employees?
Even if the plan for your business is to start as a sole proprietorship, you should include a section on potential human resources demands as a way to demonstrate that you've thought about the staffing your business may require as it grows.
Business plans are about the future and the hypothetical challenges and successes that await. It's worth visualizing and documenting the details of your business so that the materials and network around your dream can begin to take shape.
What is the management section of a business plan?
The 'management section' describes your management team, staff, resources, and how your business ownership is structured.
What are the 5 sections of a business plan?
A business plan provides a road map showing your company's goals and how you'll achieve them. The five sections of a business plan are as follows:
- The market analysis outlines the demand for your product or service.
- The competitive analysis section shows your competition's strengths and weaknesses and your strategy for gaining market share.
- The management plan outlines your ownership structure, the management team, and staffing requirements.
- The operating plan details your business location and the facilities, equipment, and supplies needed to operate.
- The financial plan shows the map to financial success and the sources of funding, such as bank loans or investors.
SCORE. " Why Small Businesses Should Consider Workers’ Comp Insurance ."
Manpower Requirements and Operations in a Business Proposal
- Small Business
- Running a Business
- Operating a Business
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Pinterest" aria-label="Share on Pinterest">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Reddit" aria-label="Share on Reddit">
- ')" data-event="social share" data-info="Flipboard" aria-label="Share on Flipboard">
How to Create a Business Plan as an Entrepreneur
How to write a proposal on the introduction & marketing of bakery products, 6 types of business plans.
- Professional Service Agreement
- How to Develop an Organizational Plan & Strategy to Get Project Staff
Writing a winning business proposal can be a critical part of expanding your business. An informal meeting with a potential new client sets the stage, but a thoughtful, personalized business proposal can help you seal the deal. As you craft your business proposal, two important areas to consider are the manpower requirements of the project and the operational requirements of the project. These areas will help inform the project deliverables, milestones and overall budget.
Writing a Business Proposal
The purpose of a business proposal is to win new business, so it should be written with sales in mind. Some industries have a specific template that’s commonly used, so if you’re uncertain of the correct format, connect with peers in your network to find out proposal specifics. In particular, federal and state governments bids may have specific requirements that you need to meet.
In general, business proposals have five to six sections. These include an introduction, an executive summary, details about the project, deliverables and project milestones, a breakdown of the budget for the project and the conclusion. In the introduction, you can provide a brief overview of your business and why it’s well-suited for this particular project. In the executive summary, you can provide an overview of the project itself. Next, give more details about the project, including your operational and manpower planning.
Your deliverables and project milestones can be spelled out in the simple table. Your budget breakdown can also be delivered in a table and should include your manpower proposal for the project. Overall, business proposals tend to be relatively short and easy-to-read.
Manpower Proposal Considerations
Before you write your business proposal, consider the manpower you’ll need for this project. Your manpower requirements definition may include managers, front-line employees and employees with special skill sets required for this project. Define the roles of each member of your proposed team and how they will interact with each other. Estimate how long it will take for each team member to complete their portion of the project. Use that estimate to determine your manpower costs, keeping in mind their salary, their employee benefits, payroll taxes and other costs associated with their employment.
When you address manpower requirements in your business proposal, you may not need to include this level of detail. This level of planning can help you develop an accurate budget, though. Be sure to include a cushion for unexpected costs such as overtime.
Operations Proposal Considerations
Your operational plan will influence several areas of your business proposal. For example, it will play a large role in the section where you spell out the details of your project. You may want to include a brief description of how your product is made, as well as your supply chain. You should also describe the quality control measures you have in place to ensure a high-quality product or service.
As you develop your project budget, keep in mind operational requirements such as the type of physical space you’ll need, any special equipment you will need to purchase, any special materials you’ll need to obtain, storage costs and delivery costs. You may not need to go into this level of detail in your proposed budget, but using a high level of detail for planning ensures a higher level of accuracy, which can help prevent cost overruns.
- Fundera: How to Write a Business Proposal in 6 Steps to Win Clients
- Inc.: Business Proposals
- The Balance Small Business: Including Management and Human Resources in Your Business Plan
- The Balance Small Business: The Operations Plan Section of the Business Plan
Melinda Hill Sineriz is a freelance writer with over a decade of experience. She specializes in business, personal finance, and career content. She has worked in sales and has managed her own small business for more than a decade. She has also written content for businesses in various industries, including restaurants, law firms, dental offices, and e-commerce companies. Learn more about her and her work at thatmelinda.com.
Related Articles
How to propose ideas to nonprofits, how to draw an outline for a business proposal, what is a project narrative, what are the components of a request for proposal, how to write a proposal for the workplace, how to write a grant for a nonprofit organization, how to convert boardmaker to pdf, how to write a bid rejection letter, how to write a wedding planning business plan, most popular.
- 1 How to Propose Ideas to Nonprofits
- 2 How to Draw an Outline for a Business Proposal
- 3 What Is a Project Narrative?
- 4 What Are the Components of a Request for Proposal?

How to develop a staffing plan
Lucid Content
Reading time: about 8 min
Your employees are one of your greatest assets. However, too often, organizations struggle to manage their human resources and plan for the future. In fact, according to a survey from the Society for Human Resource Management, 43% of HR professionals say human capital is the largest "investment challenge" for employers.
Plagued by turnover, skills gaps, over-employment, low productivity, and ever-changing business landscapes, it’s no wonder that businesses are struggling to keep up. But these issues can be mitigated with a strategic staffing plan.
Use the following tips to learn how to develop a staffing plan that puts the right people in the right place at the right time.
What is a staffing plan?
A staffing plan answers the questions:
- What work needs to be done?
- How many people do we need to employ?
- What skills and experience are necessary to do this work?
- What skills gaps need to be filled (and are there any areas of redundancies)?
Staffing plans can encompass the entire company or apply to smaller teams or departments and even individual projects.
For example, if your company’s business goals focus on expanding its salesforce in the coming year, a staffing plan can help prepare the sales department for that growth—so that the right people with the right skills are brought on board at the right times.
Additionally, a staffing plan helps your business to:
- Reduce labor costs and maximize productivity.
- Eliminate skills gaps.
- Increase employee engagement.
- Increase employee retention and reduce turnover.
- Improve customer experience.
- Streamline business growth.
Having a clear staffing plan helps prevent issues that could delay growth or hinder the quality of your products and services that could result in unhappy customers and lost business opportunities.
Not only do staffing plans help companies effectively recruit, hire, and develop employees, but they also help guide budgeting and financial decisions within the organization.

How to calculate staffing needs
A staffing plan involves three main steps:
- Determining current staffing levels
- Forecasting future staffing needs
- Identifying the gaps between the two
Once you’ve assessed your staffing needs, you can outline recommendations for how to address those needs, which might include recruiting and hiring new talent, promoting internally, focusing on training and employee development, or adding contractors to your staff. These forecasts and recommendations will help you develop your overall human resources plan for the organization.
Use the following steps to learn how to calculate staffing needs and make a plan for the future.
1. Identify the business goals
Before you dive into staffing plans and changes, you need to know what the overarching goals are for the business. These goals are typically outlined in a strategic business plan. Use this plan to clarify the company’s objectives and align the staffing plan accordingly.
What you do with your staff will affect business outcomes (for better or for worse), so you want to make sure the two plans align.
For instance, if the business plans to open a new location, you may need to move current staff around or hire new employees to fill those roles. The business plan will help inform those staffing decisions.
2. Determine your current staffing situation
To develop a staffing plan, you must first understand your current staffing environment.
If you have a robust HR database, this step could be reasonably straightforward. However, if you host personnel information on multiple sources, you will first need to consolidate that data into one source of truth. Work with business leaders and managers to help you ensure accurate and complete data on your human resources.
Once you have your staffing data in one place, you can assess the current staffing environment and begin to pull actionable insights from the data.
Pay particular attention to:
- The number of people on staff
- Staff distribution (team size and who works where)
- Skills and competencies within the workforce
- High performers and potential leaders
- Low performers or “flight risks” who could indicate turnover
- Staff age and tenure (to anticipate retirement numbers)
Pulling out these data will help you better understand the current staffing landscape and more accurately identify staffing needs and opportunities down the road.
Lucidchart can help you assess your current staff to glean new insights. Import employee data directly into Lucidchart to build an org chart or group employees in Smart Containers by role, competencies, performance, etc. Visualizing your workforce can help you identify important relationships, correlations, or gaps in the staffing.

3. Forecast future staffing needs
After you assess your current staffing landscape, it’s time to make some predictions about your future staffing needs.
As you conduct your staffing needs assessment, you will want to consider the factors that can affect staffing decisions and opportunities, including:
- Business goals
- Turnover rates and projections
- Expected mergers or acquisitions
- New product launches
- Business investments (e.g., new technology)
- Changes in the economy
- Competitors attracting key talent
- Industry labor costs
- Unemployment rate
All of these internal and external factors can influence the workforce and your staffing needs.
While forecasting will always involve some guesswork, you can make confident, educated, (and more accurate) predictions using the following methods.
Trend analysis
Trend analysis works well for established businesses with several years under their belt. Trend analysis uses historical data (i.e., past experience) to inform future needs.
To perform a trend analysis, start by gathering historical data. Focus on gathering information for at least the past five years—but you may want to go back as far as 10 years. (Keep in mind that the larger the sample size, the more accurate the results.)
Collect data on the following:
- Hiring and retirement patterns
- Transfers and promotions
- Employee turnover
- Years of service
- Employee demographics
- Skills and qualifications
- Past work experience
Once you have collected the data, you can analyze it to understand turnover rates over time as well as to discover trends or patterns between the data sets.
Ratio analysis
A ratio analysis is a dual-purpose forecasting method that both predicts staffing demand and compares forecasting results against an industry standard.
The beauty of the ratio analysis is that it doesn’t rely on historical data to predict future demand. This is an advantage for younger companies who don’t have the benefit of years of historical data to provide insight into future trends.
Here’s how it works.
A ratio establishes a relationship between two things. A business can calculate ratios between business factors like future sales revenue predictions and staffing requirements.
For example, let’s say your business plans to expand its sales in the coming year and predicts sales revenue at $500,000. You’ll need to estimate how many sales employees you will need to support that growth.
To calculate this, you need to determine the ratio between sales revenue and staff. To do this, divide current sales revenue by the current number of sales employees. If the ratio is 50:1 (with 50 representing $50,000 in sales), that means a sales revenue of $500,000 would require 10 employees.
Once you have that ratio, you can then identify gaps in your staffing. For instance, if you plan to increase your sales revenue to $500,000 but currently have only five employees, you know you will need to hire five more people to support that goal.
4. Do a gap analysis
With your current and future staffing assessments complete, you can compare the two reports for gaps. In other words, look at where your staff is now and where it needs to be. What discrepancies are there? Do you need more staff? Are there skills missing from your current workforce that you will need in the future to meet your business goals?
Note any gaps between the two assessments.
As you go through this process, our skills supply and demand chart can help you determine how many current employees and job candidates have the skills you need and whether you should hire or train to gain those competencies.
Make sure that your workforce has the skills and experience required to meet company goals. Learn how to conduct a skills gap analysis.
5. Make a staffing plan
With your staffing needs analysis completed, you can now make a plan.
Your staffing plan might include recommendations to implement a corporate training program to address skills gaps or to develop succession policies to streamline handoffs following retirements or promotions.
During this process, work with the business’s leaders to create a strategic action plan to address staffing needs that aligns with the organization’s goals, culture, and mission.

Learn how Lucidchart can help your organization plan for the future and hire employees with the right skills.
Lucidchart, a cloud-based intelligent diagramming application, is a core component of Lucid Software's Visual Collaboration Suite. This intuitive, cloud-based solution empowers teams to collaborate in real-time to build flowcharts, mockups, UML diagrams, customer journey maps, and more. Lucidchart propels teams forward to build the future faster. Lucid is proud to serve top businesses around the world, including customers such as Google, GE, and NBC Universal, and 99% of the Fortune 500. Lucid partners with industry leaders, including Google, Atlassian, and Microsoft. Since its founding, Lucid has received numerous awards for its products, business, and workplace culture. For more information, visit lucidchart.com.
Bring your bright ideas to life.
or continue with
- Skip to primary navigation
- Skip to main content
- Skip to footer
How to Write a Business Plan [Complete Guide]
Last Updated on – Aug 8, 2023 @ 3:22 pm
Preparing to write your business plan? You’re already one step ahead of other entrepreneurs who don’t see its value.
A well-thought-out and well-written plan for starting and running your business helps you focus on what you need to do to make your business idea work. It can also boost your chance of getting investments and loans to finance your business .
Did you know that half of small businesses fail in their first four years? Planning is such a crucial step to reducing the risks of managing an enterprise. Turn your business idea from something abstract and uncertain into a successful venture. It starts with drafting a good business plan.
Here’s your definitive guide to writing a business plan that speaks for itself.
What is a Business Plan?
A business plan is a written document that details what a business is, what direction it will take, and how you’ll get it there.
Practically speaking, the business plan evaluates your business’ viability. As the Department of Trade and Industry (DTI) puts it , the document allows entrepreneurs to find out whether or not their business idea will bring in more money than how much it costs to start and run it.
More than just a document, the business plan helps business owners to figure out the key aspects of an enterprise, including the following:
- Business goals and strategies to meet them
- Competitive edge and how to leverage it
- Potential problems and how to solve them
- Funding required to start the business
- Equipment, facilities, and manpower needed for operations
Who Needs a Business Plan and What Is It Used For?
Every aspiring entrepreneur who will spend a great amount of money, time, and energy to earn a profit needs a business plan.
Business planning is a crucial part of starting an entrepreneurial journey, no matter how small or big a business is. Never skip this step—as they say, failing to plan is planning to fail.
Here are some examples of business types that benefit much from business planning:
Founders of startup businesses seek funds to begin their new venture. Business plans help them persuade investors and lenders to provide the funding they need.
For startups, a business plan explains the nature of the new venture, how it will achieve its goals, and why the founders are the best people to lead the company. The startup business plan should also specify the capital needed to jumpstart the new business.
Related: Fast-Growing Startups in the Philippines
Existing Businesses
Not only do startups gain advantage from a business plan—existing enterprises need it, too.
But business plans for growing businesses serve a different purpose. Usually, a business plan helps a middle-stage business raise funds for additional facilities, equipment, manpower, and others needed for expansion. This document also defines strategies for growth and allocates resources based on strategic priorities.
Growing businesses also use business plans to communicate their vision to various stakeholders such as customers, business partners, potential investors and lenders, employees, and suppliers.
For such needs, a business plan for existing businesses lays out the goals, strategies, metrics to evaluate success, responsibilities, and resource allocation.
Social Enterprises
Social enterprises may not be as profit-driven as other business types, but that doesn’t mean they need business planning any less.
A social enterprise needs to prepare a business plan to achieve its social objectives and keep empowering the communities it’s supporting. This document is what government agencies and donor agencies require and evaluate when approving grants for funding a social project .
A social enterprise business plan determines the social issue that a business idea will solve, its beneficiaries, products or services, target market, and sales projections, among many others.
Non-Profit Organizations/NGOs
Like social enterprises, non-governmental organizations (NGOs) can also use business plans to source funds for their campaigns and projects.
A nonprofit business plan discusses the problems an NGO is trying to solve through a certain project, as well as how it will do that and how much resources are needed.
It also helps the organization and its board members to prepare for risks by making projections on how likely the activities will push through and how the current sources of funds will continue to yield a certain level of revenue. Most importantly, the business plan defines the Plan B if the original plan ends up failing.
Business Plan Format and Its Components
How does a business plan exactly look like? There’s no recommended universal format for business plans. Ideally, yours is customized according to the nature of your business and what you’re going to use the plan for.
However, all business plans have sections in common. Here’s a quick walkthrough of the six components that make up a business plan.
1. Executive Summary
Like an abstract of a college thesis or a foreword of a book, the executive summary is meant to provide a brief overview of the document. It presents the highlights of a business plan in a page or two.
The executive summary the first thing that readers see, so keep it short yet engaging and compelling enough to make them want to view more details in your plan.
2. Company Profile
The company profile is your chance to introduce yourself and your business to people outside your company. It’s also called the company summary, company information, business description, and business profile.
This section quickly answers the five Ws and one H of your business: who, what, when, where, why, and how.
Think of it as your business calling card. Being the shortest section of the business plan, the company profile provides a quick overview of the business—who the owner and founder is, management team, business goals, business address, product or service, and what makes it unique.
3. Operations Plan
The operations plan explains how you’ll run your business, focusing on the different aspects of manufacturing your product. This section includes the following information, among many others:
- Type of business (sole proprietorship, partnership, corporation , or non-profit)
- How the product is made or the service completed
- Necessary materials, equipment, and facilities to manufacture the product or complete the service
- Any subcontractors needed
- Quality control system
4. Organizational Plan
Your people should play a major role in your business plan, just as how they’re important to your business success . The organizational plan includes a chart that shows how your company is structured according to key departments or functions such as administration, production/manufacturing, marketing, and finance. This organizational chart not only presents the levels of authority in a company but also clarifies who is responsible for which people and function.
Aside from the organizational chart, the organizational plan also includes these details:
- Number of employees to hire
- Responsibilities of each job role
- Qualifications of workers who will perform each role
- Salaries and benefits per job assignment
5. Marketing Plan
The marketing plan and the succeeding chapters are the heart and soul of your business plan, explaining the things that will make your business work. This section details how you plan to promote your product or service in the market.
Specifically, the marketing plan covers the following:
- How the product or service will work and how it will benefit customers
- Target market and its profile
- Strategies for packaging, advertising, public relations, and distribution
- Competitive advantage
6. Financial Plan
A critical section in your business plan, the financial plan helps you assess how much money you’ll need to start or grow your enterprise and identify your funding sources to get your business off the ground and sustain its operations. This is where you’ll provide financial estimates that cover at least one year of running your business.
Investors and lenders specifically look for these financial details in business plans:
- How much you’re going to borrow, what you’ll use the loan for, and how you’ll pay it back
- How much profit you’re expecting to make (through an income statement and balance sheet)
- How you can finance your business operations (through a cash flow statement)
- Whether to keep the business going or close it down to cut losses (through a break-even analysis)
Related: How to Write a Business Proposal
Should You Use a Business Plan Template?
Business plan templates identify what information to put into each section and how it should be structured.
They provide instructions to guide entrepreneurs through the process. This way, nothing is missed out while writing the plan.
Thus, using a business plan template is a great idea, especially if this is your first time to prepare a plan for starting or growing your enterprise.
Helpful as it as may be, a business plan template doesn’t make business planning 100% effortless. While it provides the outline that makes writing the plan easy and quick, you still need to do your homework.
For example, a template won’t compute the financial projections for you—it’s a task you have to complete either on your own or with the help of a professional.
So before you use a business plan template, manage your expectations first and be prepared to do a lot of math!
8 Free Business Plan Templates
Yes, you read it right—you can download free online business plan templates. Some of these templates are designed for a specific niche, while others offer sample business plans for a wide range of business categories and industries.
Start off by choosing any of these free templates that suit your business planning needs.
1. Business Plan Format by the DTI
DTI has a wealth of useful information for micro, small, and medium businesses in the Philippines. Of course, it’s free to access since it comes from the government.
On the DTI website, simply look for the Business Planning section and download the business plan format in a PDF file. This document not only lists down all the information to be included in every section of a business plan, but it also provides guide questions per section—making business planning easier for first-timers.
If you want a more detailed discussion of what should go into each component of your business plan plus sample scenarios, check the DTI’s Negosyo Center e-book that fleshes out things for small business owners.
2. Simple Business Plan Template by The Balance Small Business
The Balance is an online resource for small business owners. It has a free business plan template that’s simple and easy to understand for beginners, with instructions on how to use it. Broken down into sections, the simple business plan template tells you what to include in each component of the plan.
Simply copy the free template and paste it into a word document or spreadsheet. From there, you can start drafting your business plan with the template as a guide.
3. Free Sample Business Plans by Bplans
This website features a collection of over 500 free business plan samples for various industries, including restaurants, e-commerce, real estate, services, nonprofit, and manufacturing.
Under each category are links to many sample business plans for specific types of business. Each sample comes with a plan outline, too. For example, under the Services category, you’ll find sample plans for businesses like auto repair shops, advertising agencies, catering companies, health spas, photography studios, and more.
4. Business Plan Samples by LivePlan
More than 500 free sample business plans are available at the LivePlan website, so you’re likely to find one that suits your business best. The samples allow users to know how other businesses structured and worded each component of their business plans. You can copy and paste the sections into your own plan.
To download a full business plan sample, you’ll have to sign up by submitting your name and email address through the website.
5. Business Plan Templates by PandaDoc
PandaDoc offers free business plan templates for NGOs, startups, restaurants, cafes, bakeries, hotels, and salons. These documents can be downloaded in PDF format.
But if you want a customizable template, you can download the PandaDoc template for a 14-day free trial. This template allows you to edit the document, choose a theme that matches your branding, and add pictures and videos.
The website also has free templates for executive summaries and business letters.
6. The One-Page Business Plan by The $100 Startup
If your business has a simple concept, then a one-page business plan template is ideal to use. This downloadable PDF file is a very simple outline made up of a few sections with questions that you have to answer in just a short sentence or two.
7. Business Plans by Microsoft
Microsoft provides a broad selection of templates for its users, including business plan templates in Word, business plan presentations in PowerPoint, and business plan checklists in Excel.
- Sample business plan template (Word) – Provides the steps in writing a complete business plan
- Business plan presentation template (PowerPoint) – Consists of slides for different sections of a business plan that highlight the key points for viewers
- Business plan checklist template (Excel) – Enumerates the important things to do when writing a business plan, using the Strength, Weakness, Opportunity, and Threat (SWOT) analysis framework
The advantage of using a template from Microsoft is having a professional-looking document, slideshow presentation, or spreadsheet. No need to do the formatting by yourself because the template is already formatted. All you have to do is enter the necessary information into the template to complete your business plan.
8. Social Business Plan Guidelines by the Ateneo de Manila
This free business plan format for social entrepreneurs comes from the Ateneo de Manila University’s John Gokongwei School of Management. In a glimpse, it provides the basic information you need to plan a social enterprise.
It also has more detailed business plan guidelines you can refer to. Simply click the link to the word document at the bottommost part of the page.
Related: 11 Best MBA Programs & Schools in the Philippines
How to Write a Business Plan
An outstanding business plan covers everything your stakeholders need to know about your business. So don’t just wing it—put a lot of thought into this critical document.
Let’s get down to the nitty-gritty of drafting a business plan, whether you’ll use a template or not.
1. Brainstorm about your business idea
You may have a very promising business idea, but it won’t fly unless you develop it into a clear-cut concept.
Brainstorm with your team about everything you can think of about starting and running the business. Then list them all down.
Be as creative as possible. No need to be too critical at this point.
While brainstorming, aim to answer these key questions:
- Why do you want to start the business? What has inspired you to go for it?
- What product or service do you plan to sell?
- Who will be your target customers? What are their problems that you’re hoping to solve through your product or service? How will you promote your offerings to them?
- What will be your business branding ? How will you position your brand in the industry?
- What is your competitive advantage? What makes your business unique?
- Where do you see your business within a year?
2. Validate your business idea
Research on the specifics of your business idea—paying special attention to your product or service, target market, and competitors.
According to entrepreneurship experts, it’s best to spend twice as much time on this step as spending the time to the actual drafting of the business plan.
Here are some ways to validate your business idea:
- Read studies and research to find information and trends about your industry .
- Conduct market research to gather insights from industry leaders, potential customers, and suppliers . You can do this through surveys, focus group discussions, and one-on-one interviews with your stakeholders.
- Collect data about your competitors , especially the product or service they offer and how they reach their customers. Consider buying from them or visiting their store to get a feel of their products and customer experience.
Gather all relevant information and analyze your findings to assess whether the business idea is feasible or not. You may need to tweak your business idea based on your evaluation of its feasibility.
3. Define the purpose of your business plan
It’s extremely difficult to carry out anything if you aren’t sure about why you’re doing it in the first place. Without a clear purpose, you’re like driving a car without knowing where you’re headed to.
When it comes to writing your business plan, you should have its purpose in mind from the get-go. It can be one or more of the following:
- Create a roadmap to provide the directions the business must take to achieve your goals and overcome challenges. This is ideal for bootstrapping or self-funding startups.
- Seek investments and loans to finance a business. If this is your purpose for making a business plan, it should be compelling enough to attract investors and lenders.
- Set your targets, budget, timelines, and milestones. When you put them all in writing, it’s so much easier to evaluate and measure your business’ actual performance versus your goals.
- Communicate your vision and strategic priorities with the management team. With this purpose, your business plan must establish specific goals for your managers so that they have something to commit to, you can track progress, and get them to follow through on their commitments. Also, having a business plan for this purpose ensures that everybody involved in running your business is on the same page.
- Minimize risks. Running a business in itself involves a lot of risks, and it gets riskier with a poorly researched business idea. A business plan can help entrepreneurs mitigate them by organizing activities and preparing for contingencies.
4. Create an outline for the executive summary
The first section of any business plan is the executive summary. You don’t have to draft it yet at this point, but it helps to write an outline for it before you proceed with the rest of the sections.
In a sentence or two, describe these key aspects of your business:
- Product or service
- Target market
- Competitors
- Unique value proposition (how you set your business apart from the competition)
- Management team
- Short-term and long-term business goals
- Possible sources of revenue
5. Describe your business
The next step is to write your company profile. Get your readers to become familiar with your business and realize why they should be interested in it.
If you have no idea what specifically goes into this crucial business plan section, you can check the company profiles of businesses in your industry. Usually, you can find them on their websites at the About Us or About the Company page. Take note of the information included and how they’re written.
Here are the must-haves of a great company profile:
- Brief history of the company
- Mission and vision
- Product or service lineup
- Target market and audience
- How the business will address the customers’ pain points
- What makes the business unique
6. Provide details about your operations and organizational structure
Anyone who will read your business plan needs to know what they should expect when they deal with you. They need to see a solid plan for your operations and the people who make up your team. So give your operations plan and organizational plan a careful thought.
For your operations plan, choose carefully the right legal structure for your business. Will you be a sole proprietor? Or will you partner with someone or form a corporation? Your choice will have an impact not only on your business operations but also on the taxes you’ll pay and your personal liability .
As for the organizational plan, it’s where you put your organizational chart that shows a glimpse of the hierarchy within your organization. You can easily create this chart in Microsoft Word, Excel, or PowerPoint.
Also introduce the people who comprise your management team—their relevant experience, qualifications, and expertise . The organizational plan must also include information of the support personnel, as well as who reports to whom and who manages whom.
If you’ll be outsourcing some of your business functions, add them to your organizational plan, too. These may include consultants , accountants , lawyers , logistics specialists, and IT specialists. This way, you’re showing that you’re planning to fill in any expertise and skill gaps in your in-house team.
Also Read: Business Process Outsourcing to the Philippines [Complete Guide]
7. Compose your marketing plan
Make this section of your business plan as comprehensive and detailed as possible. You’d want to prove that you’ll take a strategic and aggressive approach to reach your target customers and promote your brand and product or service to them.
Divide your marketing plan into five subsections: objectives, product/service description, target market profile, competition profile, and promotional activities.
A. Objectives
Zero in on the what and the why of your marketing activities. Under the marketing objectives section, list down all your goals and the strategies you’ll implement to meet them.
Your marketing goals can be any of the following:
- Raise brand awareness
- Introduce a new product or service
- Regain or get more customers for an existing product or service
- Secure long-term contracts with your ideal clients
- Increase sales in a certain market, product, or price point
- Improve product manufacturing or product/service delivery
- Increase prices without affecting sales
B. Product/Service Description
Describe each product or service you’ll offer, including its features and benefits. You can use storytelling , images, charts, tables, or any visual element that best illustrates how each item will work to the benefit of your target customers.
C. Target Market Profile
Present as much relevant data as you can about your potential customers. Make sure to include the following:
- Demographic profile: age range, gender, income level, education, interests, etc.
- Buying behaviors
- Factors that influence their buying decisions: purchasing power, personal preferences, economic conditions, marketing campaigns, social factors (such as peer pressure and social media influencers ), cultural factors, etc.
D. Competition Profile
Your marketing plan must focus not only on your own business but also those of your competitors. List down the similar products or services that they offer to your target customers.
Also, provide an assessment of your competitors’ performance. Which areas are they doing well? How can you improve on their strengths and weaknesses? How can your business stand out? Is it your more competitive pricing? Better customer service? Superior product quality?
To come up with a good competition profile, take the time to research about your competitors. When interviewing your target customers, ask them about the brands they use or businesses they deal with.
You can also do an online search of your competitors. For example, if you’ll run a pet supplies store in Pasig, search for “pet stores Pasig” on Google. The search engine results page may show you the different stores that sell the same products as the ones you plan to offer. Read customer reviews online to get deeper insights on how these businesses serve their clients.
Consider doing a “secret shopping” in your competitor’s store. This way, you can experience firsthand how they treat their customers and how they market and sell their products or services. You might even be able to get information about their product lineup and pricing.
E. Promotional Activities
The last subsection of your marketing plan must discuss how you’ll promote your brand and products or services and connect with customers. Also, be ready to allocate budget for each marketing activity you identify in your plan.
Create a list of marketing activities you plan to implement. Will you reach your audience through SEO (organic online search), paid advertising, and/or social media? Or will you go the traditional route through print and TV advertising or joining expos, exhibits, and trade shows? The right choice depends on the nature of your business and the type of audience you’re trying to reach.
8. Develop your financial plan
The financial plan is the section where you’ll crunch the numbers. Unless you’re really good at math, it’s best to hire an accountant or business consultant who will work with you to develop a foolproof financial plan.
Put simply, a financial plan explains how a business will spend money and make more money. It also estimates the amount of time it will take for the business to earn a profit.
Here are the specifics of a good financial plan:
- Total capital requirement
- Business financing plan and any loan requirement
- Collateral to put up for a business loan
- Schedule for loan repayment
- Financial statements : cash flow statement, income statement/profit and loss statement, and balance sheet
- Break-even analysis
- Return on investment (ROI)
- Financial analysis
Ultimately, these financial projections answer the question, “Is your business financially feasible?”
9. Back up your business plan with supporting documents
Books and theses have an appendix section at the end that provides additional resources. Your business plan should have one, too. This final section consists of documents, surveys, studies, charts, tables, images, and other elements that provide supporting data.
Depending on the information you’ve presented in the other sections of the plan, your appendix may include these things:
- Market research data and findings
- Resumes of the management team
- Relevant financial documents
- Lease agreements
- Bank statements
- Licenses and permits
10. Review and refine your business plan
Your business plan is almost done at this point. Now all you have to do is go over the document once more to ensure you’ve covered everything and nothing crucial is left out.
Check your final draft and be sure it has the following:
- Sound business idea – If you’ve done Step 2 properly (validating business idea), you can be confident that you have a sound business idea.
- Comprehensive and in-depth look into your business in a professional format
- Thorough understanding of your target customers , their behaviors, interests, and needs
- Competent management team – The people who make up your team must possess the skills and expertise that complement yours.
- Business focus or specialization
Aside from yourself, ask a business partner, proofreader, and accountant or financial expert to review your business plan and spot any errors and inconsistencies. You’d want to make sure that it looks professional and is accurate.
11. Write the executive summary
Lastly, get back to the outline you created in Step 4 and write it based on your final draft. Make sure to craft an engaging executive summary that hooks people into reading the rest of the plan.
6 Actionable Tips on Writing a Business Plan
Anyone can write a business plan—but it takes more than great writing skills to create an exceptional one.
Here are some tips to help you prepare an effective business plan that goes beyond the ordinary.
1. Write with your audience in mind
When drafting your business plan, you’re writing not for yourself but for people who will play key roles in starting and running your enterprise. This is why it’s important that you know whom you’re writing for and keep them in mind while preparing your business plan.
If you think you can’t create a plan that caters to all your audience groups, consider having different versions of the document. For example, you can come up with a business plan for investors, another for lenders, one for employees, and so on. But keep the data consistent across all versions.
To write a business plan that suits a particular audience, you have to use the right language, highlight the parts that interest them, and adjust the format accordingly.
A. Use the Right Language
One of the most important rules in business writing: use the language that your target audience easily understands. If you’re writing for engineers, finance people, or lawyers, your language can be technical—meaning you can use jargons and terminologies familiar to them.
However, if you’re writing for investors who barely have technical knowledge, tweak your language in simple terms that are easy to grasp and appreciate.
Likewise, if you’re writing a business plan to communicate internally with managers and employees your company’s direction and strategies, it’s best to use more casual language than you would when writing for high-level, external stakeholders.
B. Appeal to Your Audience’s Interests
It also helps to understand what interests your audience because they will influence how you’ll write your business plan.
Your management team, for instance, will be interested in knowing your business goals and strategies so that they can help you steer the company in the right direction.
Investors and lenders look at the business plan differently—they’ll be more interested in your financial statements to determine your financial health, like if your business is worth investing in or has the ability to pay back a loan.
C. Adopt a Suitable Business Plan Format
There’s no one-size-fits-all format for business plans because it depends mainly on your audience, aside from the nature of your business.
Let’s say you’ll set up a restaurant, and you’re drafting a business plan to apply for a business loan. To convince lenders that your business is viable, details such as your restaurant’s location and possible renovations are crucial.
Meanwhile, if you’re writing the plan for potential big-time investors, you’ll take a different approach. A good restaurant business plan focuses on the business aspects that will lead to growth and profitability (Remember that investors are interested in how they’ll make money from partnering with you).
2. Keep it concise
How long should a business plan be? According to the U.S. Small Business Administration (SBA) , it depends on various factors such as the specific audience it’s written for and the nature of a business. The SBA cites surveys that found the ideal length to be at least 25 to 100 pages.
Sounds a lot? If you have a simple business idea and you’re writing a business plan for busy people who don’t have time to pore over hundreds of pages, then one page up to 20 pages should be fine.
However, you may need to provide more explanation (which will take up more pages in your business plan) if you’re planning to build a new kind of business, and a risky one at that.
The size of your business also affects the length of your business plan. Business plans for small businesses need not exceed 30 pages. Corporate business plans are expected to be longer.
What matters more than length is how concise your business plan is. Meaning, it provides all the necessary information—including solid research and analysis—using the fewest words possible. No place for wordiness here!
3. Document everything related to your business
Support your claims in the business plan with solid facts and proof. Investors, for instance, need an assurance that they won’t lose their investment when they trust you with their money. This is where documenting your business thoroughly plays a crucial role.
What kinds of documentation can you include in your business plan?
- Industry forecast or projections
- Licensing agreements
- Location strategy
- Prototype of your product or service
- Survey and FGD results
- Resumes of your management team
4. Show your passion and dedication to your business
Although business plans have straightforward, matter-of-fact content, you can still establish an emotional connection with your readers through your plan. After all, your readers are humans with feelings and motivations.
No need to be dramatic about it—you can show your passion and dedication while still sounding professional in your business plan. Write about the mistakes you’ve had (like a failed business in the past), what you’ve learned from the experience, the values you hold, and the problems of your customers you want to solve through your product or service.
5. Know your competition and how you’ll stand out
Your business won’t be the single player in your industry. Other businesses in the same niche have started way ahead of you, and some new ones will also compete for business in the future.
Write your business plan in such a way that you know your competitors so well. Identify all of them and what makes your business unique compared with the rest without belittling them.
6. Be realistic and conservative in all your estimates
In any aspect of your business, it’s better to underpromise and overdeliver than the other way around. This also holds true when writing a business plan. You wouldn’t want to set unrealistic expectations that will lead to disappointments and worse, losses, when you fail to deliver on your promise.
There’s no place for too much optimism in your business plan. Your budget allocation, timelines, capital requirements, sales and revenue targets, and financial projections must be reasonable, realistic, and conservative. These will lend credibility to your business plan and yourself as an entrepreneur. Because there are a lot of factors beyond your control, always assume that things will get completed longer and cost more ( consider inflation over time! ).
This is where your research prior to writing the draft comes extremely helpful. You have something solid and factual to benchmark against. For example, if your analysis based on the facts you’ve gathered indicates that you’ll be able to get 40% share off the market in your first year of operations, consider making your estimates a bit more conservative and attainable.
Related: The Ultimate Guide to Business Valuation in the Philippines
10 Mistakes to Avoid When Writing a Business Plan
Now, let’s explore the mistakes entrepreneurs often commit when writing a business plan. Listing them all down here to let you know what to avoid.
1. Prioritizing Form Over Substance
Spend most of your time and energy on building solid research and facts rather than obsessing about which font type or background color will look best for your document.
2. Overthinking
Many entrepreneurs take too long to complete their business plans because they worry too much about it. Don’t get intimidated by business planning—you don’t have to be an expert or a degree holder in business management or business administration to be able to write an outstanding business plan. Overthinking will just lead to analysis paralysis and get nothing done.
As long as you know your business well and are passionate about it, then writing a business plan won’t be as difficult as you think, especially if you’re using a template.
3. Submitting the Document Without Proofreading It
If your business plan is filled with typos and grammatical errors, readers will get distracted even if you’re presenting substantial information. It may also give your audience an impression that you’re careless—and who wants to deal with a person who isn’t professional and careful enough?
Even if it costs you money, pay a professional proofreader to check your work and correct any errors so that the message you wanted to convey through your business plan will get across.
4. Making Empty Claims
Any statement that isn’t sufficiently supported by solid research or documentation has to go. For example, if you want to claim to be the top player in your industry but you don’t have any evidence to back it up, rethink about including it in your business plan.
5. Writing an Overly Long and Wordy Plan
Make sure that everything you put into your business plan is relevant and serves your purpose. Otherwise, remove unnecessary statements that just add fluff to the document.
Also, don’t waste your readers’ time by using too many words—including highfalutin ones. Remember, your goal is to make your audience understand your business, not to impress them with beautiful or complex prose.
6. Using Too Many Superlatives
Even if you really feel that your business, business idea, or projection is incredible, amazing, the best, great, fantastic, or one of a kind, avoid using these superlatives because they aren’t appropriate for formal documents like a business plan.
7. Doing the Financial Projections on Your Own
Unless you’re an accountant yourself, it’s best that you get a professional to do the job for you. It will save you time and the headache of dealing with numbers and formatting your financial plan properly.
8. Overestimating Your Projections
The business plan is not a place to make impossible promises—while they look good on paper, you might run into trouble fulfilling them. To avoid this mistake, always do your research. Find out how other businesses do it and what the typical timeframes and financial projections are before you come up with your estimates.
9. Long-Term Business Planning
As much as possible, limit your projections to only a year. A lot of things can happen and make your business different from how you initially planned it. Stick with your short-term or one-year targets and estimates, then just tweak your business plan as time goes by.
10. Including Unfounded Rumors About Your Competitors
Not only do rumors make your business plan look unprofessional, but they also distract your readers from your intended message, which is to highlight what makes your business different from the competition. Avoid including details based only on hearsay. Everything in your plan must be backed up by solid, quantifiable facts.
Key Takeaway
A business plan is more than just a document that you prepare once and will never look at again. Rather, it’s a strategic tool that you should use from time to time to guide your business operations, get the buy-in of your stakeholders, and grow your business over time.
Once you’re done with writing your business plan, make the most of it for your business. Use it and modify it as often as needed!
Ready and confident to start writing your business plan? Share your thoughts and questions below!
Other Useful Business Resources from Grit PH:
- How to Sell a Business in the Philippines
About Venus Zoleta
Venus Zoleta is an experienced writer and editor, specializing in personal finance and digital marketing.
She has been a regular columnist for some of the biggest business & finance publications in the Philippines, such as MoneyMax.ph and Filipiknow.net.
Hoping to retire early, she started investing and bought a home in her early 20s. This crazy cat mom eats ramen like there's no tomorrow.
Education: University of the Philippines (B.A. Journalism) Focus: Personal Finance, Personal Development, and Entrepreneurship
Reader Interactions
March 3, 2020 at 10:00 am
I like it, and i want to learn more about for business
March 6, 2020 at 9:46 am
Hello Ms. Venus, Rise Against Hunger Philippines, N.G.O. , branching out into a new high ways… and i am newly hired as a social enterprise development officer… whose main tasks to launch a product line; an up-cycled tarpaulin bags.. manufactured by a group of community women (skills training’s, coordinated by life coached; aiming w-holistic transformation and sustainability program.. . with such a big tasks, i need a step by step guides, and if possible a coach for i cannot do it alone… thank you, henry reandino chua
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
We need your help!
Our team is currently conducting research for an upcoming guide focusing on starting a business in the Philippines . We would greatly appreciate your contribution, which should only require a few seconds of your time.
Thank you in advance!
- Digital Marketing
- Search Engine Optimization (SEO)
- Digital PR & Link Building
- Social Media Marketing
- Digital Advertising (PPC & Social)
- Content Marketing
- Copywriting
- Email Marketing
- Conversion Optimization
- Web/App Development
- Ecommerce Development
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Name * Location of Business * Number of Employees * 1 - 10 11 -50 51 - 100 100 - 500 500+ Phone Number * Email * Insurance Company Standard Insurance AXA Philippines BDO AIG Submit
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Full Name * Company Name * Mobile Number * Email Address * Submit
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Name * Contact Number * Email Address * Target Location Preferred Developer * Ayala Land SM Prime Megaworld Alveo Land DMCI Homes Federal Land Robinsons Land Corp Vista Land and Lifescapes Filinvest Land Shang Properties Century Properties Empire East Rockwell Land Phone Submit
Disclosure: Your personal details will not be shared with any third-party companies. We’ll just need your contact details so our resident real estate agents can reach you to provide you with the details for any of the listed property developments you’re interested to invest in.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser to complete this form. Name * Age * Location* Phone Number * Email Address * Insurance Company Sun Life Financial Pru Life U.K. AXA Philippines AIA Philippines Manulife Insular Life BPI-AIA BDO Life Etiqa FWD Insurance Allianz PNB Life Name Get a Quote
Disclosure: Your personal details will not be shared with any third-party companies. We’ll just need your contact details so our resident financial advisors can reach you to provide you with the details for any of the listed insurance company you’re interested in.
Personnel Requirements Including Job Descriptions
- Open Access
- First Online: 20 February 2021
Cite this chapter
You have full access to this open access chapter

- Songul Tepebasi 6 &
- Ilknur Kozanoglu 7 , 8
5989 Accesses
1 Citations
Personnel are one of the most important parts of the quality management system within any haematopoietic stem cell transplantation and cellular therapy programme. Two main steps establish the quality management activities in relation to personnel. The first step is the creation of a well-defined organisational chart; the second step is the appointment of the correct employee for the correct job and responsibilities, with opportunities for continuous development of their competencies. Job descriptions for personnel should not be limiting and should support continuous professional development. In addition, accurate and frequent communication will increase cooperation within cellular therapy centres, minimise margins of error and contribute positively to patient care.
You have full access to this open access chapter, Download chapter PDF
Similar content being viewed by others

Human Resources

Informatics and Clinical Workforce Competencies and Education
- Key personnel
- Organisation
- Quality management
- Cellular therapy field
- Job description
Introductıon
Workforce is central to safe and effective delivery of cellular therapy. Staff organisation and collaboration are essential for successful outcomes [ 1 ]. It is important to define the roles of key personnel and their support personnel, thus ensuring that tasks are uninterrupted. The number of personnel should be determined in accordance with demand, as well as the nature of the respective centre’s activity. Cellular therapies are unique, in that they require many personnel with varying qualifications and competencies to work as a team. For these therapy centres to achieve their goals, employees must work together harmoniously; this requires communication and collaboration among employees [ 2 ].
To establish mutual understanding and cooperation between components of hematopoietic stem cell transplantation (HSCT) programs, it is imperative to establish a centralised and active communication network. Motivation is another factor that ensures effective and efficient employees. Training, organisation, management, and development of personnel should all be prioritised within the quality management plan, alongside regulations that ensure the occupational safety and health of workers for all processes [ 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ].
Organisational Structure and Organisational Chart
The organisational structure is a coordination system that enables individuals to realise their goals by combining their respective efforts, knowledge and abilities through collaborating with others, as well as through development and execution of a structure considered most suitable to achieve a specific goal. While developing the organisational structure in cellular therapy centres, the hierarchy, collaboration and communication of all units both within and outside the centre must be easily understood [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
The organisational chart should define, maintain and work with the optimal number of staff in the quality management system. Each level in the chart should consider the tasks, capabilities, responsibilities, and communication networks shaped within the framework of business processes and corporate systems. The scheme should reflect quality management, along with clearly defining the roles, authority, responsibilities and duties of all employees [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
In centres that provide cellular therapy services, organisational charts should never be made for individuals; they should be developed for units as a whole. This includes the organisational structure of all units involved, such as clinical units, cell processing, peripheral blood or bone marrow collection units, other disciplines (e.g., consultants), supporting units (e.g., medical/nutritionist) and administrative units (e.g., transportation unit and housekeeping), alongside all units with a service level agreement. Organisational charts should be developed in accordance with targets, systems and processes; staff should be chosen for positions within the chart, based on their qualifications, competencies and training. This is necessary, as the performance of a centre is directly influenced by its organisational structure [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
The quality management system should be able to accommodate fluctuations in personnel and cover planned and unplanned unavailability to maintain operations on a day-to-day basis, e.g. illness, annual leave and departures [ 1 , 2 , 3 , 4 , 5 ]. Succession planning for key position should also be considered, e.g. quality manager (1). Education, quality and motivation of personnel are the most important factors for ensuring well-organised human resources and quality awareness within cellular therapy centres.
Key Personnel
All personnel involved in the planning, management and control of critical activities, both directly and indirectly, in the field of cellular therapies should be defined as key personnel. For example, these personnel would include individuals performing stem cell collection, processing and freezing procedures. This definition will determine in advance when and what individual cellular therapy centres can provide, along with the personnel available within the centres.
It is necessary to ensure that personnel designated and appointed conform to the requirements and qualifications of the job to be undertaken. In addition, the experience and abilities of individuals should be considered during the selection; those selected should be trained in accordance with their duties. Designated key personnel should remain unchanged wherever possible; supervisors of key personnel should be trained to an equivalent standard, such that where key personnel are not available, those supervisors may step into the role as necessary [ 3 , 4 , 5 , 6 ].
Personnel Competency
Haematopoietic cellular therapies have complex and dynamic treatment pathways. All employees working in the field of cellular therapy should therefore be developing and improving skills and knowledge through continuous training [ 6 ]. As such, competencies of employees should be measured and recorded regularly within the quality management plan (Standards B3, C3, CM3, D3) [ 5 ]. The ability of employees to work effectively provides an indicator of the quality of training, its relevance to the requirements of employees in their respective roles and whether the system is working correctly with expected results. Various methods can be used to measure the adequacy of employees for a given role. A table completed through measurement or observation can be used; electrical monitoring systems can also be used (Table 7.1 ).
Responsibility and Task Awareness
Once recruited, personnel are given powers and responsibilities required to perform in their given roles. Individuals must know and understand their role, to whom and to what extent they have authority, and to what extent they can give instructions to others who rely on them. To achieve this, job descriptions should include relevant duties, necessary qualifications, responsibilities and authority.
Use of Effective Communication
Cellular therapy centres function as a multidisciplinary unit with other components within the same hospital and/or program, as well as with other centres both inside and outside of the country. To achieve this objective, interaction, cooperation between units and a common language are proven elements for success in the field. It is vital for all personnel involved in the process to possess good communication skills and be able to use communication resources effectively. Communication meetings with all personnel and key personnel involved in the processes should be scheduled regularly. These multi-unit meetings should be recorded and presented within annual reports [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
All personnel should undergo annual appraisal of performance and other key aspects of their work and relationships with others in the team, with appropriate action taken in order to promote team work and good practice and maximise quality for product safety and, ultimately, patient and donor benefit [ 7 – 8 ].
Job Descriptions
The roles of personnel included in the organisational chart of cellular therapy centres must be clearly defined in advance. Processes within cellular therapy centres are complex; as such, any errors that may occur must be minimised. Accordingly, European Union Directive 2006/86/EC states that all personnel working in the field of cellular therapies should have clear, documented and up-to-date job descriptions; moreover, their duties and responsibilities should be clearly documented and understandable [ 9 ].
International standards also require that current job descriptions be documented within the audits and that employees have received training for their respective job descriptions [ 5 ]. If employees have been given responsibility for a critical procedure, they must possess sufficient competencies to fulfil this responsibility . In addition, the level of authority should not be less than or greater than that required for the responsibility; the task designation of the employee should be sufficiently detailed in the job description. This should detail the positions of employees within the organisational chart [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
Job descriptions must be written, understandable, and clear. When employees read their job descriptions, they should not have to guess or interpret meanings beyond those which are written. Job descriptions should be concise, define the current position and possess a dynamic structure. They should not restrict the employees in their tasks, but should allow the employees’ experience to inform the work that each member performs. While creating a job definition, it is necessary to determine the nature of the proposed task and who will write the task description. The author should be competent and knowledgeable regarding the task and how it will function. When the definition of the task is initially formed, ideas should be collected from employees by means of interview or survey. It may also be useful to examine job descriptions created for similar positions in other institutions [ 10 ].
When a job definition is created, it should be properly documented. All job descriptions should be reviewed and approved by the relevant centre or unit director. The director should convey the final definition of the task to the relevant personnel; the relevant personnel should then be trained accordingly. The personnel must be confirmed to fully understand the content of the job description. An examination, observation or similar method can be used for this confirmation [ 10 ].
The structure of the job description may vary among centres; however, all job descriptions within an organisation should have a standardised appearance [ 10 ].
The following topics should be included:
Job title – name of the position.
Salary grade/level/range – compensation levels, groups or pay ranges, into which jobs of the same or similar worth are placed, including minimum and maximum pay bands.
Reports to – title of the position this job reports to.
Date – date when the job description was written or last reviewed.
Summary/objective – summary and overall objectives of the job.
Essential functions – essential functions, including how an individual is to perform them and the frequency with which the tasks are performed; the tasks must be part of the job function and be required to perform the job.
Competency – knowledge, skills and abilities.
Supervisory responsibilities – direct reports, if any, and the level of supervision.
Work environment – the work environment; temperature, noise level, inside or outside, or other factors that will affect the person’s working conditions while performing the job.
Physical demands – the physical demands of the job, including bending, sitting, lifting and driving.
Position type and expected hours of work – full time or part time, typical work hours and shifts, days of week and whether overtime is expected.
Required education and experience – required education and experience based on job-related requirements and consistent with the requirements of the centre.
Preferred education and experience – preferred education and experience based on job-related requirements and consistent with requirements of the centre.
Additional eligibility qualifications – additional requirements such as certifications, cellular therapy–specific experience and experience working with specific items of equipment.
Other duties –.
Signature lines
Signatures are important in validating the job description. They indicate that the job description has been approved and that the employee understands the requirements, essential functions and duties of the position. Signatures should include those of the supervisor and of the employee [ 10 ].
Personnel File
Personnel files should be created for uninterrupted monitoring of all key personnel in the quality management system. When no longer required, these files should be archived in a secure area for the period specified in the quality plan. Personnel files are confidential and should therefore be kept with controlled access. These files include personal education information, training participation and personnel qualification evaluations. Related documents should be included; when the employee leaves the unit, their file should be retained [ 3 , 4 , 5 ].
An important responsibility of directors working in cellular therapy centres is to understand and define the roles and responsibilities of employees so that their objectives are best met. This enables directors to better distribute workload to personnel appropriately, whilst maintaining safety and efficiency. The collection of personnel or staff satisfaction surveys at regular intervals is recommended. The results should be evaluated at the quality committee meetings or similar groups with the goal of optimising ongoing processes and operations as well as workforce well-being.
A continuously improving quality management system incorporating the correct personnel with clear roles, responsibilities, training, competency and working relationships will ensure that processes are effective and efficient and maintain safety and quality for the programme. Processes are numerous and diverse; personnel should have continuous development of skills and qualifications, and key personnel should continuously contribute to the training, competency and personal development of new and existing personnel. Continuity and robustness of operations should be supported by cross-cover arrangements and succession planning. All of these aspects are covered by FACT-JACIE standards and the accreditation process, which should be used as an opportunity to review personnel and their functions, and, where necessary, identify deficiencies or weaknesses, undertake corrective actions or highlight issues to the accreditation organisation and external inspectors during the accreditation process.
Kurt M, Ilhan O. JACIE: a 20 year-old voluntary body functioning worldwide. Transfus Apher Sci. 2018;57(2):153–8.
Article Google Scholar
Gratwohl A, Brand R, McGrath E, van Biezen A, Sureda A, Ljungman P, Baldomero H, Chabannon C, Apperley J. Use of the quality management system “JACIE” and outcome after hematopoietic stem cell transplantation. Haematologica. 2014;99(5):908–14.
Directive 2004/23/EC of The European Parliament and of The Council of 31 March 2004 on setting standards of quality and safety for the donation, procurement, testing, processing, preservation, storage and distribution of human tissues and cells.
Google Scholar
Commission Directive 2006/17/EC of 8 February 2006 implementing Directive 2004/23/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards certain technical requirements for the donation, procurement and testing of human tissues and cells.
International Standards For Hematopoietic Cellular Therapy Product Collection, Processing, And Administration Accreditatıon Manual Book Version 7.0 March 2018.
Babic A, Wannesson L, Trobia M, Lazzaro M. Transplant unit personnel competency maintanance: online testing by sharepoint application. EBMT.2015 (oral presentation N003).
Halter J, Kodera Y, Ispizua AU, Greinix HT, Schmitz N, Favre G, Baldomero H, Niederwieser N, Apperley JF, Gratwohl A. Severe events in donors after allogeneic hematopoietic stem cell donation. Haematologica. 2009;94:94–101.
Boga C, Kozanoglu I. JACIE accreditation from the perspective of an accredited centre. Bone Marrow Transplant. 2017;52(9):1352.
Article CAS Google Scholar
Commission Directive 2006/86/EC of 24 October 2006 implementing Directive 2004/23/EC of the European Parliament and of the Council as regards traceability requirements, notification of serious adverse reactions and events and certain technical requirements for the coding, processing, preservation, storage and distribution of human tissues and cells.
https://www.shrm.org/resourcesandtools/tools-and-samples/how-to-guides/pages/developajobdescription.aspx .
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Department of Quality Management, Adana Adult Bone Marrow Transplantation Centre, Adana, Turkey
Songul Tepebasi
Department of Physiology, Baskent University Medical Faculty, Ankara, Turkey
Ilknur Kozanoglu
Adana Adult Bone Marrow Transplantation Centre, University of Baskent, Adana, Turkey
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
King Faisal Specialist Hospital and Research Centre, Riyadh, Saudi Arabia
Mahmoud Aljurf
Sheffield Teaching Hospitals, NHS Foundation Trust and The University of Sheffield, Sheffield, UK
John A. Snowden
St. James’s Hospital and Trinity College Dublin, Dublin, Ireland
Patrick Hayden
University Hospital Southampton NHS FT and University of Southampton, Southampton, UK
Kim H. Orchard
JACIE Accreditation Office, EBMT, Barcelona, Spain
Eoin McGrath
Rights and permissions
Open Access This chapter is licensed under the terms of the Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License ( http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ ), which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons license and indicate if changes were made.
The images or other third party material in this chapter are included in the chapter's Creative Commons license, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the chapter's Creative Commons license and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder.
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2021 The Author(s)
About this chapter
Tepebasi, S., Kozanoglu, I. (2021). Personnel Requirements Including Job Descriptions. In: Aljurf, M., Snowden, J.A., Hayden, P., Orchard, K.H., McGrath, E. (eds) Quality Management and Accreditation in Hematopoietic Stem Cell Transplantation and Cellular Therapy. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64492-5_7
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-64492-5_7
Published : 20 February 2021
Publisher Name : Springer, Cham
Print ISBN : 978-3-030-64491-8
Online ISBN : 978-3-030-64492-5
eBook Packages : Medicine Medicine (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Starting a Business
- Growing a Business
- Small Business Guide
- Business News
- Science & Technology
- Money & Finance
- For Subscribers
- Write for Entrepreneur
- Entrepreneur Store
- United States
- Asia Pacific
- Middle East
- South Africa
Copyright © 2024 Entrepreneur Media, LLC All rights reserved. Entrepreneur® and its related marks are registered trademarks of Entrepreneur Media LLC
Create a Personal Business Plan That You'll Really Use Develop a customized tool that will serve to focus you on your most important objectives. Write it in user-friendly prose so you'll check it weekly.
By Marty Fukuda • Oct 7, 2014
Opinions expressed by Entrepreneur contributors are their own.
Every successful business leader I've encountered is in some way a prolific goal setter. For this reason, the single most important piece of advice I give any aspiring entrepreneur or business professional is to figure out exactly what you want, document it on paper and then attack it every day.
A personal business plan is something that I develop each year to help me put my own advice into action. Creating a plan can clarify your objectives for the coming year but don't just shove it in drawer. It is something that should become weekly, if not daily, reading material.
Related: Why Business Leaders Must Set a Personal Mission
1. Start with a simple brainstorming list.
Break down your role in the company into small parts and be sure it's comprehensive. This could mean taking each department that you oversee or are involved in, and breaking it down into further segments. For instance, for my company's graphic-design department, I would create separate objectives for its leadership development, equipment and software needs, anticipated hiring, the continued education plan and efficiency.
2. Prioritize objectives.
Your brainstorming list probably contains an overwhelming number of potential starting points. The key is narrowing them down into a manageable and realistic number of goals. Since you'll review the finished personal business plan often, don't write a novel.
I made the mistake of developing a massive 100-page personal business plan that I never looked at. The very thought of reviewing it was scary. A user-friendly one- to two-page document will do the trick.
Take your brainstorming list and organize it according to the biggest potential impact. You'll also have some must-dos (if not tackled business will fall apart). Then you'll have some items that aren't necessary or don't require much of your focus and perhaps can be delegated.
My company's CEO, Duane Hixon, does a wonderful job of narrowing down his list into what he refers to as his "rocks." These are the biggest areas of impact, the areas to which a person should offer most of his or her attention. These will make up the heart of the personal business plan.
Related: How to Build a Business Plan For Your Personal Brand
3. Be specific.
Once you've narrowed things down to a handful of rocks, be sure the plan includes specifics that will allow you to measure and track progress. For this year's plan, one of my rocks was maintaining company culture while building the team. Obviously, this is a broad, difficult-to-measure objective. For my plan, I developed a strategy for accomplishing the mission by including more details such as creating a company culture slide show and a plan for both current employees and new hires.
4. Set challenges but be realistic.
A goal that doesn't take much effort to accomplish isn't really a goal. Setting an objective that has a slim chance of realization, however, amounts to little more than a hope and can leave you feeling discouraged. Aim for a perfect balance between the two -- something that stretches you but doesn't break you.
Related: Write a Winning Business Plan With These 8 Key Elements
5. Set deadlines.
The beautiful thing about your personal business plan is that it's yours. You don't have to wait until the start of a new year to create one. While I create a plan annually, that doesn't mean that each objective has a deadline that's one year out. Set a deadline no matter what it is to keep you focused and provide a call to action (as opposed to adopting an open-ended objective).
6. Share the plan.
I recommend that you show your plan to a colleage whom you respect. Ask for feedback. This individual may think of an angle you have not. Equally important, this person will hold you accountable. It's a lot tougher to hit the eject button on a plan after you've shared it with someone you respect. And everyone can use a cheerleader in the workplace from time to time.
I personally love it when an employee shares a plan with me. It shows initiative and forward thinking. There are few things more impressive than when an employee has clear-cut objectives and works hard to meet them.
7. Revisit the plan weekly.
Creating the plan is just the first step. Put the plan in a prominent spot where you're going to remember to review it or place reminders in your calendar.If you've got a great plan, it can and will inspire you every time you see it.
Related: Your Mission Statement May Be Utterly Useless or a Gold Mine
Chief Operating Officer of N2 Publishing
Want to be an Entrepreneur Leadership Network contributor? Apply now to join.
Editor's Pick Red Arrow
- This 103-Year-Old Doctor Opened Her Medical Practice Before Women Could Have Bank Accounts — Here Are Her 6 Secrets to a Healthy, Successful Life
- Lock 5 Ways You Might Be Cheating on Your Taxes — And Why You Will Get Caught
- I've Had a Secret Side Hustle for Decades. It Keeps Tens of Thousands of Dollars in My Pocket — and Gets Me Into Places I Wouldn't Go Otherwise .
- Lock Here's How Steve Jobs Dealt With Negative Press and Avoided Brand Disasters
- One Factor Is Helping This Entrepreneur Tackle Business Ownership Later in Life. Now, She's Jumping Into a $20 Billion Industry .
- Lock Narcissism Can Help You Be Successful — Here's How to Harness It Without Going Too Far, According to an Ivy League-Trained Psychotherapist
Most Popular Red Arrow
Nike responds to criticism over u.s. women's olympic uniforms: 'everything's showing'.
The company is the official outfitter for the U.S. Olympic track and field athletes.
The 'Silver Tsunami' Meets 'Golden Handcuffs' as Past Low Mortgage Rates Lock in Homeowners — Whether They Like It or Not
The resulting lower supply of homes, and population growth outpacing construction, has led to a 7.2 million home shortage.
63 Small Business Ideas to Start in 2024
We put together a list of the best, most profitable small business ideas for entrepreneurs to pursue in 2024.
5 Entrepreneurial Mindsets That Drive Success
Here are the mindsets shared by the most successful entrepreneurs.
Elon Musk Informs Tesla Staff That Layoffs Will Affect at Least 14,000 Employees — Read the Leaked Email
The layoffs impact more than 10% of Tesla's 140,473-person workforce.
These Are the Busiest Airports in the World, According to a New Ranking
A surge in international and business travel has brought airports back to near pre-pandemic levels of passenger traffic.
Successfully copied link
Alexander Freeman

Finished Papers
Gombos Zoran

offers a great selection of professional essay writing services. Take advantage of original, plagiarism-free essay writing. Also, separate editing and proofreading services are available, designed for those students who did an essay and seek professional help with polishing it to perfection. In addition, a number of additional essay writing services are available to boost your customer experience to the maximum!
Advanced writer
Add more quality to your essay or be able to obtain a new paper within a day by requesting a top or premium writer to work on your order. The option will increase the price of your order but the final result will be totally worth it.
Top order status
Every day, we receive dozens of orders. To process every order, we need time. If you’re in a great hurry or seek premium service, then choose this additional service. As a result, we’ll process your order and assign a great writer as soon as it’s placed. Maximize your time by giving your order a top status!
SMS updates
Have you already started to write my essay? When it will be finished? If you have occasional questions like that, then opt-in for SMS order status updates to be informed regarding every stage of the writing process. If you’re pressed for time, then we recommend adding this extra to your order.
Plagiarism report
Is my essay original? How do I know it’s Turnitin-ready? Very simple – order us to attach a detailed plagiarism report when work is done so you could rest assured the paper is authentic and can be uploaded to Turnitin without hesitating.
1-page summary
World’s peace isn’t riding on essay writing. If you don’t have any intent on reading the entire 2000-word essay that we did for you, add a 1-page summary to your order, which will be a short overview of your essay one paragraph long, just to be in the loop.
Customer Reviews

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
The Personnel Section of a Business Plan Explained. One of the key sections of a Business Plan is the section that describes the plan to grow or scale the business. This often involves hiring staff and staff often represent the single largest ongoing expense that a company will have. As such, it is important to plan exactly who will be hired ...
Need real financials. We recommend using LivePlan as the easiest way to create automatic financials for your own business plan. Create your own business plan. Download This Plan. Explore a real-world personnel management business plan example and download a free template with this information to start writing your own business plan.
Think of this section as an outline of what you plan to do in the future with your company. 3. Explain the gaps. It's alright to have gaps on your team, especially if you're a startup. You may not have identified all the "right" team members yet, or you may not have the funds available yet to hire for essential roles.
Management and Human Resources Business Plans. By. Daniel Richards. Updated on September 13, 2022. Fact checked by J.R. Duren. In This Article. Photo: Georgijevic / Getty Images. A business plan should include plans for your company's management and human resources departments. Learn what each section should include and how to write them.
A Personnel Plan is a document that details an organization's staffing needs, goals, and workforce management practices. It is an essential component of human resource management and serves as a road map for employee recruitment, selection, training, development, retention, and management. A Personnel Plan is an essential component of any ...
A personnel plan is a document that outlines an organization's staffing needs, goals, and strategies for managing its workforce. It is a key component of human resource management and provides a roadmap for the recruitment, selection, training, development, retention, and management of employees. A personnel plan is critical within the ...
Your management team plan has 3 goals: To prove to you that you have the right team to execute on the opportunity you have defined, and if not, to identify who you must hire to round out your current team. To convince lenders and investors (e.g., angel investors, venture capitalists) to fund your company (if needed)
Investing in human resources (HR) is a key element of healthy personnel planning and strategy. A hallmark of effective leadership is efficient HR which means hiring employees in a cost-effective manner and mostly when needed. Your business plan should always include an informative and up-to-date personnel plan section to provide direction for the company and help entrepreneurs stay focused.
Recruiting personnel examples in your business plan. You've identified the positions you'll need both to start your business and to grow it. Now, describe your strategy for how you're going to land qualified candidates. Show potential lenders and investors that you know how to reach the people who are going to help you succeed.
Edit the text to make the plan your own and save hundreds of hours. A professional business plan template. All 550 of our business plans are in the SBA-approved format that's proven to raise money from lenders and investors. Instructions and help at every step. Get help with clear, simple instructions for each section of the business plan.
Here are the basic steps to take to create a staffing plan that aligns with your organizational objectives: 1. Identify your business goals. Identifying your business goals helps you anticipate staffing changes. They're usually outlined in a strategic business plan. Use this plan to clarify your company's objectives and evaluate how that ...
The management plan outlines your ownership structure, the management team, and staffing requirements. The operating plan details your business location and the facilities, equipment, and supplies needed to operate. The financial plan shows the map to financial success and the sources of funding, such as bank loans or investors.
Before you write your business proposal, consider the manpower you'll need for this project. Your manpower requirements definition may include managers, front-line employees and employees with ...
You'll first need to estimate the number and type of people you will require to run your plan. Startups can do this by looking at competitors' plants or by relying on the founders' prior ...
Here is a basic template that any business can use when developing its business plan: Section 1: Executive Summary. Present the company's mission. Describe the company's product and/or service offerings. Give a summary of the target market and its demographics.
Use the following steps to learn how to calculate staffing needs and make a plan for the future. 1. Identify the business goals. Before you dive into staffing plans and changes, you need to know what the overarching goals are for the business. These goals are typically outlined in a strategic business plan.
The key objective of personnel management is maintaining and being able to provide up-to-date, accurate personnel data. This ensures optimal internal communication within the company. Additionally, efficient administrative work is a prerequisite for smooth internal cooperation. In general, it is the personnel administrator's task to organize ...
This development plan each owner and key employee. i) Training - How method do you propose to obtain class, video, workshop,terms etc.) of You book need specific class title, video name, or learning associated with the training when specifying training methods. [For planning is one of our priorities.
To write a business plan that suits a particular audience, you have to use the right language, highlight the parts that interest them, and adjust the format accordingly. A. Use the Right Language. One of the most important rules in business writing: use the language that your target audience easily understands.
Personnel files should be created for uninterrupted monitoring of all key personnel in the quality management system. When no longer required, these files should be archived in a secure area for the period specified in the quality plan. Personnel files are confidential and should therefore be kept with controlled access.
A personal business plan is something that I develop each year to help me put my own advice into action. Creating a plan can clarify your objectives for the coming year but don't just shove it in ...
Personnel Requirements. All Contractor personnel shall comply with Safety Standards.Contractors shall comply with the Fair Labor Standards Act when employing persons under 18 years of age (Ref. 29 CFR 570).- Minimum Age for Firefighting Resources. Persons under 18 years of age shall not perform hazardous or arduous duties during wildland fire management operations, including execution of ...
Personnel Requirements In Business Plan Sample | Best Writing Service. Elliot Law. #19 in Global Rating. Essay (Any Type), Biology (and other Life Sciences), 7 pages by Mitrofan Yudin. We are quite confident to write and maintain the originality of our work as it is being checked thoroughly for plagiarism.