Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment. These harmful materials are called pollutants.
Biology, Ecology, Health, Earth Science, Geography

Loading ...
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment . These harmful materials are called pollutants . Pollutants can be natural, such as volcanic ash . They can also be created by human activity, such as trash or runoff produced by factories. Pollutants damage the quality of air, water, and land. Many things that are useful to people produce pollution. Cars spew pollutants from their exhaust pipes. Burning coal to create electricity pollutes the air. Industries and homes generate garbage and sewage that can pollute the land and water. Pesticides —chemical poisons used to kill weeds and insects— seep into waterways and harm wildlife . All living things—from one-celled microbes to blue whales—depend on Earth ’s supply of air and water. When these resources are polluted, all forms of life are threatened. Pollution is a global problem. Although urban areas are usually more polluted than the countryside, pollution can spread to remote places where no people live. For example, pesticides and other chemicals have been found in the Antarctic ice sheet . In the middle of the northern Pacific Ocean, a huge collection of microscopic plastic particles forms what is known as the Great Pacific Garbage Patch . Air and water currents carry pollution. Ocean currents and migrating fish carry marine pollutants far and wide. Winds can pick up radioactive material accidentally released from a nuclear reactor and scatter it around the world. Smoke from a factory in one country drifts into another country. In the past, visitors to Big Bend National Park in the U.S. state of Texas could see 290 kilometers (180 miles) across the vast landscape . Now, coal-burning power plants in Texas and the neighboring state of Chihuahua, Mexico have spewed so much pollution into the air that visitors to Big Bend can sometimes see only 50 kilometers (30 miles). The three major types of pollution are air pollution , water pollution , and land pollution . Air Pollution Sometimes, air pollution is visible . A person can see dark smoke pour from the exhaust pipes of large trucks or factories, for example. More often, however, air pollution is invisible . Polluted air can be dangerous, even if the pollutants are invisible. It can make people’s eyes burn and make them have difficulty breathing. It can also increase the risk of lung cancer . Sometimes, air pollution kills quickly. In 1984, an accident at a pesticide plant in Bhopal, India, released a deadly gas into the air. At least 8,000 people died within days. Hundreds of thou sands more were permanently injured. Natural disasters can also cause air pollution to increase quickly. When volcanoes erupt , they eject volcanic ash and gases into the atmosphere . Volcanic ash can discolor the sky for months. After the eruption of the Indonesian volcano of Krakatoa in 1883, ash darkened the sky around the world. The dimmer sky caused fewer crops to be harvested as far away as Europe and North America. For years, meteorologists tracked what was known as the “equatorial smoke stream .” In fact, this smoke stream was a jet stream , a wind high in Earth’s atmosphere that Krakatoa’s air pollution made visible. Volcanic gases , such as sulfur dioxide , can kill nearby residents and make the soil infertile for years. Mount Vesuvius, a volcano in Italy, famously erupted in 79, killing hundreds of residents of the nearby towns of Pompeii and Herculaneum. Most victims of Vesuvius were not killed by lava or landslides caused by the eruption. They were choked, or asphyxiated , by deadly volcanic gases. In 1986, a toxic cloud developed over Lake Nyos, Cameroon. Lake Nyos sits in the crater of a volcano. Though the volcano did not erupt, it did eject volcanic gases into the lake. The heated gases passed through the water of the lake and collected as a cloud that descended the slopes of the volcano and into nearby valleys . As the toxic cloud moved across the landscape, it killed birds and other organisms in their natural habitat . This air pollution also killed thousands of cattle and as many as 1,700 people. Most air pollution is not natural, however. It comes from burning fossil fuels —coal, oil , and natural gas . When gasoline is burned to power cars and trucks, it produces carbon monoxide , a colorless, odorless gas. The gas is harmful in high concentrations , or amounts. City traffic produces highly concentrated carbon monoxide. Cars and factories produce other common pollutants, including nitrogen oxide , sulfur dioxide, and hydrocarbons . These chemicals react with sunlight to produce smog , a thick fog or haze of air pollution. The smog is so thick in Linfen, China, that people can seldom see the sun. Smog can be brown or grayish blue, depending on which pollutants are in it. Smog makes breathing difficult, especially for children and older adults. Some cities that suffer from extreme smog issue air pollution warnings. The government of Hong Kong, for example, will warn people not to go outside or engage in strenuous physical activity (such as running or swimming) when smog is very thick.
When air pollutants such as nitrogen oxide and sulfur dioxide mix with moisture, they change into acids . They then fall back to earth as acid rain . Wind often carries acid rain far from the pollution source. Pollutants produced by factories and power plants in Spain can fall as acid rain in Norway. Acid rain can kill all the trees in a forest . It can also devastate lakes, streams, and other waterways. When lakes become acidic, fish can’t survive . In Sweden, acid rain created thousands of “ dead lakes ,” where fish no longer live. Acid rain also wears away marble and other kinds of stone . It has erased the words on gravestones and damaged many historic buildings and monuments . The Taj Mahal , in Agra, India, was once gleaming white. Years of exposure to acid rain has left it pale. Governments have tried to prevent acid rain by limiting the amount of pollutants released into the air. In Europe and North America, they have had some success, but acid rain remains a major problem in the developing world , especially Asia. Greenhouse gases are another source of air pollution. Greenhouse gases such as carbon dioxide and methane occur naturally in the atmosphere. In fact, they are necessary for life on Earth. They absorb sunlight reflected from Earth, preventing it from escaping into space. By trapping heat in the atmosphere, they keep Earth warm enough for people to live. This is called the greenhouse effect . But human activities such as burning fossil fuels and destroying forests have increased the amount of greenhouse gases in the atmosphere. This has increased the greenhouse effect, and average temperatures across the globe are rising. The decade that began in the year 2000 was the warmest on record. This increase in worldwide average temperatures, caused in part by human activity, is called global warming . Global warming is causing ice sheets and glaciers to melt. The melting ice is causing sea levels to rise at a rate of two millimeters (0.09 inches) per year. The rising seas will eventually flood low-lying coastal regions . Entire nations, such as the islands of Maldives, are threatened by this climate change . Global warming also contributes to the phenomenon of ocean acidification . Ocean acidification is the process of ocean waters absorbing more carbon dioxide from the atmosphere. Fewer organisms can survive in warmer, less salty waters. The ocean food web is threatened as plants and animals such as coral fail to adapt to more acidic oceans. Scientists have predicted that global warming will cause an increase in severe storms . It will also cause more droughts in some regions and more flooding in others. The change in average temperatures is already shrinking some habitats, the regions where plants and animals naturally live. Polar bears hunt seals from sea ice in the Arctic. The melting ice is forcing polar bears to travel farther to find food , and their numbers are shrinking. People and governments can respond quickly and effectively to reduce air pollution. Chemicals called chlorofluorocarbons (CFCs) are a dangerous form of air pollution that governments worked to reduce in the 1980s and 1990s. CFCs are found in gases that cool refrigerators, in foam products, and in aerosol cans . CFCs damage the ozone layer , a region in Earth’s upper atmosphere. The ozone layer protects Earth by absorbing much of the sun’s harmful ultraviolet radiation . When people are exposed to more ultraviolet radiation, they are more likely to develop skin cancer, eye diseases, and other illnesses. In the 1980s, scientists noticed that the ozone layer over Antarctica was thinning. This is often called the “ ozone hole .” No one lives permanently in Antarctica. But Australia, the home of more than 22 million people, lies at the edge of the hole. In the 1990s, the Australian government began an effort to warn people of the dangers of too much sun. Many countries, including the United States, now severely limit the production of CFCs. Water Pollution Some polluted water looks muddy, smells bad, and has garbage floating in it. Some polluted water looks clean, but is filled with harmful chemicals you can’t see or smell. Polluted water is unsafe for drinking and swimming. Some people who drink polluted water are exposed to hazardous chemicals that may make them sick years later. Others consume bacteria and other tiny aquatic organisms that cause disease. The United Nations estimates that 4,000 children die every day from drinking dirty water. Sometimes, polluted water harms people indirectly. They get sick because the fish that live in polluted water are unsafe to eat. They have too many pollutants in their flesh. There are some natural sources of water pollution. Oil and natural gas, for example, can leak into oceans and lakes from natural underground sources. These sites are called petroleum seeps . The world’s largest petroleum seep is the Coal Oil Point Seep, off the coast of the U.S. state of California. The Coal Oil Point Seep releases so much oil that tar balls wash up on nearby beaches . Tar balls are small, sticky pieces of pollution that eventually decompose in the ocean.
Human activity also contributes to water pollution. Chemicals and oils from factories are sometimes dumped or seep into waterways. These chemicals are called runoff. Chemicals in runoff can create a toxic environment for aquatic life. Runoff can also help create a fertile environment for cyanobacteria , also called blue-green algae . Cyanobacteria reproduce rapidly, creating a harmful algal bloom (HAB) . Harmful algal blooms prevent organisms such as plants and fish from living in the ocean. They are associated with “ dead zones ” in the world’s lakes and rivers, places where little life exists below surface water. Mining and drilling can also contribute to water pollution. Acid mine drainage (AMD) is a major contributor to pollution of rivers and streams near coal mines . Acid helps miners remove coal from the surrounding rocks . The acid is washed into streams and rivers, where it reacts with rocks and sand. It releases chemical sulfur from the rocks and sand, creating a river rich in sulfuric acid . Sulfuric acid is toxic to plants, fish, and other aquatic organisms. Sulfuric acid is also toxic to people, making rivers polluted by AMD dangerous sources of water for drinking and hygiene . Oil spills are another source of water pollution. In April 2010, the Deepwater Horizon oil rig exploded in the Gulf of Mexico, causing oil to gush from the ocean floor. In the following months, hundreds of millions of gallons of oil spewed into the gulf waters. The spill produced large plumes of oil under the sea and an oil slick on the surface as large as 24,000 square kilometers (9,100 square miles). The oil slick coated wetlands in the U.S. states of Louisiana and Mississippi, killing marsh plants and aquatic organisms such as crabs and fish. Birds, such as pelicans , became coated in oil and were unable to fly or access food. More than two million animals died as a result of the Deepwater Horizon oil spill. Buried chemical waste can also pollute water supplies. For many years, people disposed of chemical wastes carelessly, not realizing its dangers. In the 1970s, people living in the Love Canal area in Niagara Falls, New York, suffered from extremely high rates of cancer and birth defects . It was discovered that a chemical waste dump had poisoned the area’s water. In 1978, 800 families living in Love Canal had to a bandon their homes. If not disposed of properly, radioactive waste from nuclear power plants can escape into the environment. Radioactive waste can harm living things and pollute the water. Sewage that has not been properly treated is a common source of water pollution. Many cities around the world have poor sewage systems and sewage treatment plants. Delhi, the capital of India, is home to more than 21 million people. More than half the sewage and other waste produced in the city are dumped into the Yamuna River. This pollution makes the river dangerous to use as a source of water for drinking or hygiene. It also reduces the river’s fishery , resulting in less food for the local community. A major source of water pollution is fertilizer used in agriculture . Fertilizer is material added to soil to make plants grow larger and faster. Fertilizers usually contain large amounts of the elements nitrogen and phosphorus , which help plants grow. Rainwater washes fertilizer into streams and lakes. There, the nitrogen and phosphorus cause cyanobacteria to form harmful algal blooms. Rain washes other pollutants into streams and lakes. It picks up animal waste from cattle ranches. Cars drip oil onto the street, and rain carries it into storm drains , which lead to waterways such as rivers and seas. Rain sometimes washes chemical pesticides off of plants and into streams. Pesticides can also seep into groundwater , the water beneath the surface of the Earth. Heat can pollute water. Power plants, for example, produce a huge amount of heat. Power plants are often located on rivers so they can use the water as a coolant . Cool water circulates through the plant, absorbing heat. The heated water is then returned to the river. Aquatic creatures are sensitive to changes in temperature. Some fish, for example, can only live in cold water. Warmer river temperatures prevent fish eggs from hatching. Warmer river water also contributes to harmful algal blooms. Another type of water pollution is simple garbage. The Citarum River in Indonesia, for example, has so much garbage floating in it that you cannot see the water. Floating trash makes the river difficult to fish in. Aquatic animals such as fish and turtles mistake trash, such as plastic bags, for food. Plastic bags and twine can kill many ocean creatures. Chemical pollutants in trash can also pollute the water, making it toxic for fish and people who use the river as a source of drinking water. The fish that are caught in a polluted river often have high levels of chemical toxins in their flesh. People absorb these toxins as they eat the fish. Garbage also fouls the ocean. Many plastic bottles and other pieces of trash are thrown overboard from boats. The wind blows trash out to sea. Ocean currents carry plastics and other floating trash to certain places on the globe, where it cannot escape. The largest of these areas, called the Great Pacific Garbage Patch, is in a remote part of the Pacific Ocean. According to some estimates, this garbage patch is the size of Texas. The trash is a threat to fish and seabirds, which mistake the plastic for food. Many of the plastics are covered with chemical pollutants. Land Pollution Many of the same pollutants that foul the water also harm the land. Mining sometimes leaves the soil contaminated with dangerous chemicals. Pesticides and fertilizers from agricultural fields are blown by the wind. They can harm plants, animals, and sometimes people. Some fruits and vegetables absorb the pesticides that help them grow. When people consume the fruits and vegetables, the pesticides enter their bodies. Some pesticides can cause cancer and other diseases. A pesticide called DDT (dichlorodiphenyltrichloroethane) was once commonly used to kill insects, especially mosquitoes. In many parts of the world, mosquitoes carry a disease called malaria , which kills a million people every year. Swiss chemist Paul Hermann Muller was awarded the Nobel Prize for his understanding of how DDT can control insects and other pests. DDT is responsible for reducing malaria in places such as Taiwan and Sri Lanka. In 1962, American biologist Rachel Carson wrote a book called Silent Spring , which discussed the dangers of DDT. She argued that it could contribute to cancer in humans. She also explained how it was destroying bird eggs, which caused the number of bald eagles, brown pelicans, and ospreys to drop. In 1972, the United States banned the use of DDT. Many other countries also banned it. But DDT didn’t disappear entirely. Today, many governments support the use of DDT because it remains the most effective way to combat malaria. Trash is another form of land pollution. Around the world, paper, cans, glass jars, plastic products, and junked cars and appliances mar the landscape. Litter makes it difficult for plants and other producers in the food web to create nutrients . Animals can die if they mistakenly eat plastic. Garbage often contains dangerous pollutants such as oils, chemicals, and ink. These pollutants can leech into the soil and harm plants, animals, and people. Inefficient garbage collection systems contribute to land pollution. Often, the garbage is picked up and brought to a dump, or landfill . Garbage is buried in landfills. Sometimes, communities produce so much garbage that their landfills are filling up. They are running out of places to dump their trash. A massive landfill near Quezon City, Philippines, was the site of a land pollution tragedy in 2000. Hundreds of people lived on the slopes of the Quezon City landfill. These people made their living from recycling and selling items found in the landfill. However, the landfill was not secure. Heavy rains caused a trash landslide, killing 218 people. Sometimes, landfills are not completely sealed off from the land around them. Pollutants from the landfill leak into the earth in which they are buried. Plants that grow in the earth may be contaminated, and the herbivores that eat the plants also become contaminated. So do the predators that consume the herbivores. This process, where a chemical builds up in each level of the food web, is called bioaccumulation . Pollutants leaked from landfills also leak into local groundwater supplies. There, the aquatic food web (from microscopic algae to fish to predators such as sharks or eagles) can suffer from bioaccumulation of toxic chemicals. Some communities do not have adequate garbage collection systems, and trash lines the side of roads. In other places, garbage washes up on beaches. Kamilo Beach, in the U.S. state of Hawai'i, is littered with plastic bags and bottles carried in by the tide . The trash is dangerous to ocean life and reduces economic activity in the area. Tourism is Hawai'i’s largest industry . Polluted beaches discourage tourists from investing in the area’s hotels, restaurants, and recreational activities. Some cities incinerate , or burn, their garbage. Incinerating trash gets rid of it, but it can release dangerous heavy metals and chemicals into the air. So while trash incinerators can help with the problem of land pollution, they sometimes add to the problem of air pollution. Reducing Pollution Around the world, people and governments are making efforts to combat pollution. Recycling, for instance, is becoming more common. In recycling, trash is processed so its useful materials can be used again. Glass, aluminum cans, and many types of plastic can be melted and reused . Paper can be broken down and turned into new paper. Recycling reduces the amount of garbage that ends up in landfills, incinerators, and waterways. Austria and Switzerland have the highest recycling rates. These nations recycle between 50 and 60 percent of their garbage. The United States recycles about 30 percent of its garbage. Governments can combat pollution by passing laws that limit the amount and types of chemicals factories and agribusinesses are allowed to use. The smoke from coal-burning power plants can be filtered. People and businesses that illegally dump pollutants into the land, water, and air can be fined for millions of dollars. Some government programs, such as the Superfund program in the United States, can force polluters to clean up the sites they polluted. International agreements can also reduce pollution. The Kyoto Protocol , a United Nations agreement to limit the emission of greenhouse gases, has been signed by 191 countries. The United States, the world’s second-largest producer of greenhouse gases, did not sign the agreement. Other countries, such as China, the world’s largest producer of greenhouse gases, have not met their goals. Still, many gains have been made. In 1969, the Cuyahoga River, in the U.S. state of Ohio, was so clogged with oil and trash that it caught on fire. The fire helped spur the Clean Water Act of 1972. This law limited what pollutants could be released into water and set standards for how clean water should be. Today, the Cuyahoga River is much cleaner. Fish have returned to regions of the river where they once could not survive. But even as some rivers are becoming cleaner, others are becoming more polluted. As countries around the world become wealthier, some forms of pollution increase. Countries with growing economies usually need more power plants, which produce more pollutants. Reducing pollution requires environmental, political, and economic leadership. Developed nations must work to reduce and recycle their materials, while developing nations must work to strengthen their economies without destroying the environment. Developed and developing countries must work together toward the common goal of protecting the environment for future use.
How Long Does It Last? Different materials decompose at different rates. How long does it take for these common types of trash to break down?
- Paper: 2-4 weeks
- Orange peel: 6 months
- Milk carton: 5 years
- Plastic bag: 15 years
- Tin can: 100 years
- Plastic bottle: 450 years
- Glass bottle: 500 years
- Styrofoam: Never
Indoor Air Pollution The air inside your house can be polluted. Air and carpet cleaners, insect sprays, and cigarettes are all sources of indoor air pollution.
Light Pollution Light pollution is the excess amount of light in the night sky. Light pollution, also called photopollution, is almost always found in urban areas. Light pollution can disrupt ecosystems by confusing the distinction between night and day. Nocturnal animals, those that are active at night, may venture out during the day, while diurnal animals, which are active during daylight hours, may remain active well into the night. Feeding and sleep patterns may be confused. Light pollution also indicates an excess use of energy. The dark-sky movement is a campaign by people to reduce light pollution. This would reduce energy use, allow ecosystems to function more normally, and allow scientists and stargazers to observe the atmosphere.
Noise Pollution Noise pollution is the constant presence of loud, disruptive noises in an area. Usually, noise pollution is caused by construction or nearby transportation facilities, such as airports. Noise pollution is unpleasant, and can be dangerous. Some songbirds, such as robins, are unable to communicate or find food in the presence of heavy noise pollution. The sound waves produced by some noise pollutants can disrupt the sonar used by marine animals to communicate or locate food.
Media Credits
The audio, illustrations, photos, and videos are credited beneath the media asset, except for promotional images, which generally link to another page that contains the media credit. The Rights Holder for media is the person or group credited.
Illustrators
Educator reviewer, last updated.
March 6, 2024
User Permissions
For information on user permissions, please read our Terms of Service. If you have questions about how to cite anything on our website in your project or classroom presentation, please contact your teacher. They will best know the preferred format. When you reach out to them, you will need the page title, URL, and the date you accessed the resource.
If a media asset is downloadable, a download button appears in the corner of the media viewer. If no button appears, you cannot download or save the media.
Text on this page is printable and can be used according to our Terms of Service .
Interactives
Any interactives on this page can only be played while you are visiting our website. You cannot download interactives.
Related Resources

An official website of the United States government
Here’s how you know
Official websites use .gov A .gov website belongs to an official government organization in the United States.
Secure .gov websites use HTTPS A lock ( Lock A locked padlock ) or https:// means you’ve safely connected to the .gov website. Share sensitive information only on official, secure websites.
JavaScript appears to be disabled on this computer. Please click here to see any active alerts .
Lesson Plans, Teacher Guides and Online Environmental Resources for Educators
Find an array of environmental and science based lesson plans, activities and ideas below from EPA, other federal agencies and external organizations. Encontrar recursos para estudiantes y maestros.
Topics: Air | Climate Change | Ecosystems | Energy | Health | Waste | Water
Acid Rain: A Teacher's Guide (PDF 56 pp, 4.6 MB) Lesson plan and activities from EPA for teachers on acid rain. Grades: 6-8 Type of Resource: Lesson plan
Acid Rain Student Pages Find the acid rain student pages, as well as general information for older students or adults. Grades: K-12 Type of Resource: Lesson plans and experiments
AIRNOW Get up-to-the-minute information about air pollution in your community, through a joint project from EPA, the National Oceanic and Atmospheric Administration, the National Park Service and other partners. The AIRNOW website includes maps, forecasts, and information about the health effects of air pollution. Grades: 9-12 Type of Resource: Website
AIRNOW Air Quality Resources Find air quality curriculum materials and activities from AIRNOW, including a toolkit and workshop opportunities for teachers. Grades: K-8 Type of Resource: Curriculum guide
Measuring Air Quality Improvements from Vegetative Barriers This unit has been designed by EPA as a teaching aid on the topic of air quality; particularly, investigating the role vegetative barriers play in improving air quality for surrounding areas. Grades: K-5 Type of Resource: Lesson Plan
Carl Gets Some Rest (PDF 12 pp, 765 KB) This EPA coloring and story book, for children in pre-school through 2nd grade, teaches a simple lesson: there are many transportation alternatives to using a car. Grades: K-2 Type of Resource: Coloring Book
Creating Healthy Indoor Air Quality in Schools This EPA page provides information on indoor air quality in school buildings and how to order the Tools for Schools Action Kit. The kit shows how to carry out a practical plan of action to improve indoor air quality at little or no cost using common-sense activities and in-house staff. Grades: K-12 Type of Resource: Toolkit
EnviroAtlas Educational Materials These ready-made lesson plans can be used in formal and informal education settings and are aligned with Next Generation and State Science Standards. Grades: K-12 Type of Resource: Lesson Plans
Noise Pollution for Kids (PDF 15 pp, 6.54 MB) This EPA booklet for your students will teach you how to identify which sounds are loud and ways to protect your hearing and health. Grades: K-5 Type of Resource: Activity book
Particulate Matter (PM) Air Sensor Kits Particle pollution known as particulate matter (PM) is one of the major air pollutants regulated by EPA to protect public health and the environment. A PM air sensor kit has been developed by EPA researchers as an educational tool to teach children about air quality and air science. Grades: 5-12 Type of Resource: Hands-on activity guide
Basic Ozone Layer Science Find a straightforward explanation of the ozone layer and ozone depletion. Grades: 9-12 Type of Resource: Website
AIRNOW's Ozone: Good Up High, Bad Nearby (PDF 4 pp) Ozone acts as a protective layer high above the Earth, but it can be harmful to breathe. This publication provides basic information about ground-level and high-altitude ozone. Grades:6-12 Type of Resource: Booklet/Brochure
Plain English Guide to the Clean Air Act A brief introduction to the 1990 version of the Clean Air Act, to help you understand what is in the law and how it may affect you. Grades: 9-12 Type of Resource: Booklet
RadTown USA EPA's RadTown USA is a virtual community that aims to educate students about the sources of radiation in our daily lives. Grades: 9-12 Type of Resource: Virtual activity
Teaching Kids to Conserve Energy at Home: Resources for K-12 teachers and parents This 11-minute presentation focuses on an introduction to energy and the environment, energy saving tips, how to use the Energy Star home energy yardstick, and homework ideas. Grades: K-12 Type of Resource: Video
Village Green Project These lessons provide a unique opportunity for students to learn about air quality as it relates to various topics of science appropriate to their grade level. The purpose of these lessons is to engage students of varying ability levels through hands-on and minds-on thinking. Each lesson is designed to focus around the topic of air quality; from issues of human health to career and 21st century skills. Grades: K-8 Type of Resource: Lesson Plan (PDF) (52 pp)
Lea en español: ¿Por qué Coco es de color naranja?
Why is Coco Orange? Coco has a problem. He is a chameleon, but he cannot change colors, and his asthma is acting up. Read how Coco and his friends at Lizard Lick Elementary solve this mystery as they learn about air quality and how to stay healthy when the air quality is bad. Grades: Pre K-2 Type of Resource: Book
Other resources
NOAA's Education Resources Website Explore this site to find the information you need to teach students about weather, climate change, and oceans. You'll find activities, background information, and much more! Grades: 6-12
National Park Service Education Resources Classroom materials, field trip opportunities and professional development programs for educators from the National Park Service. Grades: All
Climate and Health Lesson Plan and Toolkit by The American Public Health Association This lesson adopts materials developed by the National Institute for Environmental Health Sciences (NIH) to make it easy for public health professionals to guest teach at local high schools. For more resources aimed directly at teachers, see Climate Change and Human Health Lesson Plans by NIH. Grades: 9-12
EPA Publications
EPA has many publications on every environmental subject that you can download or order. See our predefined searches below on specific search terms to help you view our publication offerings from the National Service Center for Environmental Publications (NSCEP).
Predefined Search Terms:
- Activity Book
- Coloring Books
- Environmental Education
- Science Fair
- Students Home
- Community Service Project Ideas
- Science Fair Projects
- Homework Help and Activities for K-12 Students
Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- Environmental Pollution Essay

Essay on Environmental Pollution
The environment is the surrounding of an organism. The environment in which an organism lives is made up of various components like air, water, land, etc. These components are found in fixed proportions to create a harmonious balance in the environment for the organism to live in. Any kind of undesirable and unwanted change in the proportions of these components can be termed as pollution. This issue is increasing with every passing year. It is an issue that creates economic, physical, and social troubles. The environmental problem that is worsening with each day needs to be addressed so that its harmful effects on humans as well as the planet can be discarded.
Causes of Environmental Pollution
With the rise of the industries and the migration of people from villages to cities in search of employment, there has been a regular increase in the problem of proper housing and unhygienic living conditions. These reasons have given rise to factors that cause pollution.
Environmental pollution is of five basic types namely, Air, Water, Soil, and Noise pollution.
Air Pollution: Air pollution is a major issue in today’s world. The smoke pouring out of factory chimneys and automobiles pollute the air that we breathe in. Gases like carbon dioxide, carbon monoxide, and sulphur dioxide are emitted with this smoke which mixes with air and causes great harm to the human body, flora, and fauna. The dry-farm waste, dry grass, leaves, and coal used as domestic fuels in our villages also produce harmful gases. Acid rain occurs due to an excess of sulphur dioxide in the air.
The Main Sources of Air Pollution are as Follows:
Automobile pollution
Industrial air pollution
Burning garbage
Brick kilns
Indoor air pollution
Decomposed animals and plants
Radioactive elements
Water Pollution: Water pollution is one of the most serious environmental issues. The waste products from the growing industries and sewage water are not treated properly before disposing of the wastewater into the rivers and other water bodies, thus leading to water pollution. Agricultural processes with excess fertilizers and pesticides also pollute the water bodies.
The Main Sources of Water Pollution as Follows:
Marine commerce.
Industrial effluents joining seas and oceans.
Dumping of radioactive substances into seawater.
Sewage is disposed of into the sea by rivers.
Offshore oil rigs.
Recreational activities.
Agricultural pollutants are disposed of into the water bodies.
Soil or Land Pollution: Soil pollution or land pollution results from the deposition of solid waste, accumulation of biodegradable material, deposition of chemicals with poisonous chemical compositions, etc on the open land. Waste materials such as plastics, polythene, and bottles, cause land pollution and render the soil infertile. Moreover, the dumping of dead bodies of animals adds to this issue. Soil pollution causes several diseases in man and animals like Cholera, Dysentery, Typhoid, etc.
The Main Causes of Soil Pollution are as Follows:
Industrial waste
Urban commercial and domestic waste
Chemical fertilizers
Biomedical waste
Noise Pollution: With an increasing population, urbanization, and industrialization, noise pollution is becoming a serious form of pollution affecting human life, health, and comfort in daily life. Horns of vehicles, loudspeakers, music systems, and industrial activities contribute to noise pollution.
The Main Sources of Noise Pollution as Follows:
The machines in the factories and industries produce whistling sounds, crushing noise, and thundering sounds.
Loudspeakers, horns of vehicles.
Blasting of rocks and earth, drilling tube wells, ventilation fans, and heavy earth-moving machinery at construction sites.
How Pollution Harms Health and Environment
The lives of people and other creatures are affected by environmental pollution, both directly and indirectly. For centuries, these living organisms have coexisted with humans on the planet.
1. Effect on the Environment
Smog is formed when carbon and dust particles bind together in the air, causing respiratory problems, haze, and smoke. These are created by the combustion of fossil fuels in industrial and manufacturing facilities and vehicle combustion of carbon fumes.
Furthermore, these factors impact the immune systems of birds, making them carriers of viruses and diseases. It also has an impact on the body's system and organs.
2. Land, Soil, and Food Effects
The degradation of human organic and chemical waste harms the land and soil. It also releases chemicals into the land and water. Pesticides, fertilisers, soil erosion, and crop residues are the main causes of land and soil pollution.
3. Effects on water
Water is easily contaminated by any pollutant, whether it be human waste or factory chemical discharge. We also use this water for crop irrigation and drinking. They, too, get polluted as a result of infection. Furthermore, an animal dies as a result of drinking the same tainted water.
Furthermore, approximately 80% of land-based pollutants such as chemical, industrial, and agricultural waste wind up in water bodies.
Furthermore, because these water basins eventually link to the sea, they contaminate the sea's biodiversity indirectly.
4. Food Reaction
Crops and agricultural produce become poisonous as a result of contaminated soil and water. These crops are laced with chemical components from the start of their lives until harvest when they reach a mass level. Due to this, tainted food has an impact on our health and organs.
5. Climate Change Impact
Climate change is also a source of pollution in the environment. It also has an impact on the ecosystem's physical and biological components.
Ozone depletion, greenhouse gas emissions, and global warming are all examples of environmental pollution. Because these water basins eventually link to the sea, they contaminate the sea's biodiversity indirectly. Furthermore, their consequences may be fatal for future generations. The unpredictably cold and hot climate impacts the earth’s natural system.
Furthermore, earthquakes, starvation, smog, carbon particles, shallow rain or snow, thunderstorms, volcanic eruptions, and avalanches are all caused by climate change, caused entirely by environmental pollution.
How to Minimise Environmental Pollution?
To minimise this issue, some preventive measures need to be taken.
Principle of 3R’s: To save the environment, use the principle of 3 R’s; Reuse, Reduce and Recycle.
Reuse products again and again. Instead of throwing away things after one use, find a way to use them again. Reduce the generation of waste products.
Recycle: Paper, plastics, glass, and electronic items can be processed into new products while using fewer natural resources and lesser energy.
To prevent and control air pollution, better-designed equipment, and smokeless fuels should be used in homes and industries. More and more trees should be planted to balance the ecosystem and control greenhouse effects.
Noise pollution can be minimised by better design and proper maintenance of vehicles. Industrial noise can be reduced by soundproofing equipment like generators, etc.
To control soil pollution, we must stop the usage of plastic. Sewage should be treated properly before using it as fertilizers and as landfills. Encourage organic farming as this process involves the use of biological materials and avoiding synthetic substances to maintain soil fertility and ecological balance.
Several measures can be adopted to control water pollution. Some of them are water consumption and usage that can be minimized by altering the techniques involved. Water should be reused with treatment.
The melting icebergs in Antarctica resulted in rising sea levels due to the world's environmental pollution, which had become a serious problem due to global warming, which had become a significant concern. Rising carbon pollution poses a risk for causing natural disasters such as earthquakes, cyclones, and other natural disasters.
The Hiroshima-Nagasaki and Chernobyl disasters in Russia have irreversibly harmed humanity. Different countries around the world are responding to these calamities in the most effective way possible.
Different countries around the world are responding to these calamities in the most effective way possible. More public awareness campaigns are being established to educate people about the hazards of pollution and the importance of protecting our environment. Greener lifestyles are becoming more popular; for example, energy-efficient lighting, new climate-friendly autos, and the usage of wind and solar power are just a few examples.
Governments emphasise the need to plant more trees, minimise the use of plastics, improve natural waste recovery, and reduce pesticide use. This ecological way of living has helped humanity save other creatures from extinction while making the Earth a greener and safer ecology.
Conclusion
It is the responsibility of every individual to save our planet from these environmental contamination agents. If preventive measures are not taken then our future generation will have to face major repercussions. The government is also taking steps to create public awareness. Every individual should be involved in helping to reduce and control pollution.

FAQs on Environmental Pollution Essay
1. What do you understand by ‘Environmental Pollution’?
Environmental pollution is the contamination of the environment and surroundings like air, water, soil by the discharge of harmful substances.
2. What preventive measures should be taken to save our environment?
Some of the preventive measures that should be taken to save our environment are discussed below.
We can save our environment by adopting the concept of carpooling and promoting public transport to save fuel. Smoking bars are public policies, including criminal laws and occupational safety and health regulations that prohibit tobacco smoking in workplaces and other public places.
The use of Fossil fuels should be restricted because it causes major environmental issues like global warming.
Encourage organic farming to maintain the fertility of the soil.
3. What are the main sources of soil pollution?
The main sources of soil pollution as follows:
Industrial waste
Urban commercial and domestic waste
Chemical fertilizers
Biomedical waste
4. What is organic farming?
It is a farming method that involves growing and nurturing crops without the use of synthetic fertilizers and pesticides.
Environmental Pollution [Environmental Studies Notes BCOM/BA/BSC 2nd SEM CBCS Pattern]
Unit 5: environmental pollution (8 lectures), environmental studies notes for ba, b.com and bsc cbcs pattern.
• Environmental pollution: types, causes, effects and controls; Air, water, soil and noise pollution
• Nuclear hazards and human health risks
• Solid waste management: Control measures of urban and industrial waste.
• Pollution case studies – Bharalu river, Deepor Beel, Kolong river
**************

Table of Contents
Soil Pollution
Land is an important component of environment because soil is vital for the substances of life on earth. An inch of soil takes about 500 to 1000 years to be build. It is estimated that the total surface area of earth is 3,15,14,640 square km out of which only about one third is land surface. It is a resource for which there is no substitute. So, it becomes necessary to protect soil from pollutants.
Soil pollution can be more dangerous than other types of pollution. Soil pollution is defined as the presence of toxic chemicals (pollutants or contaminants) in soil, in high enough concentrations to pose risk to human health and ecosystem. Soil pollution is the adverse alternation in the properties of the soil due to dumping of solid and semi-solid waste from agriculture, industry and urban areas. It also results because of washing down of pollutants by rain and faulty sanitation in the soil.
Sources of Soil Pollution
a) Agrochemicals: The application of inorganic fertilisers to crop lands and the use of toxic insecticides, pesticides, fungicides etc. for controlling diseases have an adverse impact of soil.
b) Industrial waste: The rapid growth of industries has resulted in the release of a lot of industrial waste on the land surface. The quality of those wastes depends on the types of raw materials and chemicals used in the industries. The toxic chemicals are absorbed by the green plants along with the nutrients and enter into the food chain and finally reaching the human being causing health hazards.
c) Domestic Garbage: Plastics are mainly used as packing materials which are normally thrown away as garbage. This garbage is pile up at public places which creates disposal problem.
d) Petroleum wastes: Contamination of soil by petroleum products is a major cause of soil pollution in several countries in the world.
e) Electric Waste: Electronic waste like cell phones, computers, gadgets, printers, radio, camera, video games, scanners, DVDs, Land phones etc. are non-biodegradable waste which is generally dumped in soil.
Measures to Control Soil Pollution
Since soil is vital for life, these should be protected from pollution. Some important measures to control soil pollution are:
a) Agro-chemicals should be used with caution in the field. Organic manure should be used instead of agro-chemicals.
b) Use of bio-fertilizers should be encouraged instead of chemical fertilizers.
c) Industrial effluents should be properly treated before discharging them on the soil. The effluents released should be subjected to proper treatment before their release into land mass.
d) The garbage produced should be dumped in closed chamber.
e) Adequate latrine facility should be provided in rural and urban areas.
f) Public awareness programmes should be implemented to educate people on health hazards due to soil pollution. Prevention of erosion and silting.
g) People should be trained regarding proper sanitary practices.
h) Application of pesticides should be controlled.
i) Bioremediation can be adopted for degradation of toxic chemicals present in soil.
Effects of Soil Pollution
a) Industrial wastes consist of a variety of chemicals which are extremely toxic. Chemical like acids, alkalis, pesticides, heavy metals etc. affect soil fertility and ultimately affect human health.
b) Nitrogen and phosphorus from the fertilizers in soil reach nearby water bodies with agricultural run-off and cause eutrophication.
c) Excess use of chemical fertilizers may result in reducing the ability of plants to fix nitrogen.
d) Pollutants in soil cause alteration in soil structure, causing death of many soil organisms which can affect the food chain.
e) Decline in the microorganisms found in the soil creating additional problems of soil erosion.
f) Contamination of underground and surface drinking water.
Water Pollution
Water is undoubtedly the most precious natural resource that exists on our planet. It is essential for the survival of any form of life. Lakes, rivers, seas and groundwater are the main source of water. Water pollution is the pollution of bodies of water , such as lakes, rivers, seas, the oceans, as well as groundwater. It occurs when pollutants reach these bodies of water , without treatment. Waste from homes, factories and other buildings are main pollutant of the water bodies.
Sources of Water Pollution:
a) Domestic wastes if they are not properly treated and released into water bodies cause serious water pollution.
b) Industrial wastes such as Toxic chemicals, acids, alkalis, metallic salts, phenols, cyanides are released into water bodies causes thermal pollution of water.
c) Agricultural pollutants such as excessive nutrients, ammonia and nitrates, pathogens, antibiotics and hormones.
d) Run off from urban areas such as rainfall and snowmelt can wash natural and man-made pollutants into rivers, lakes, wetlands, and coastal waters.
e) Oil pollution
f) Radioactive waste produced during industrial, medical and scientific processes.
Effects of Water Pollution
Domestic and hospital sewage contain many undesirable pathogenic microorganisms, and its disposal into a water without proper treatment may cause outbreak of serious diseases, such as, amoebiasis dysentery, typhoid, jaundice, cholera, etc. Metals like lead, zinc, arsenic, copper, mercury and cadmium in industrial waste waters adversely affect humans and other animals. Some of the serious effects of water pollution are listed below:
a) Drinking contaminated water causes health problems like cancer, reproductive problems, typhoid fever, stomach sickness and skin rashes in humans.
b) Excess fluoride in water causes defects in teeth and bones called fluorosis, while arsenic can cause significant damage to the liver and nervous system.
c) Oil spills in the water cause animals to die when they ingest or encounter it.
d) Excess radioactive materials in water cause genetic mutations, birth defects and cancer.
e) Excess sediments in water cause cloudiness reducing photosynthetic ability, which disrupts the aquatic food chain.
Control of water pollution
a) The first and most important step in controlling water pollution is to Increase public education and awareness around the world concerning the causes and impacts of water pollution.
b) Government initiatives like Swachh Bharat Mission helps in reducing domestic wastes.
c) Setting up effluent treatment plants to treat waste water.
d) Laws, standards and practices should be established to prevent water pollution and these laws should be modified from time to time based on current requirements and technological advancements.
e) Planting more trees will reduce the amount of sulphur dioxide and nitric oxide.
f) Industrial plants should be based on recycling operations as it helps prevent disposal of wastes into natural waters but also extraction of products from waste.
g) Thermal pollution can be reduced by employing techniques like cooling ponds, wet/dry cooling towers etc.
Air Pollution
We all breathe in air, we can feel, and even smell the air and say whether it is fresh or stale. The pollution in air may not be noticed until we see smoke coming out from some source. All human activities from cooking at home to activities in highly mechanized industries contribute to air pollution.
The World Health Organization defines air pollution as “the presence of materials in the air in such concentration which are harmful to man and his environment.”
In Simple words, it is the occurrence or addition of foreign particles, gases and other pollutants into the air which have an adverse effect on human beings, animals, vegetation, buildings, etc.
Air Pollutants
Pollutants are classified into primary and secondary pollutants.
Primary pollutants: they are emitted into the atmosphere directly from the source and retains the same chemical form. Examples are carbon monoxide, sulphur oxides, nitrogen oxides, hydrocarbons, suspended particulate matter(SPM).
Secondary pollutants: they are formed by the inter mingling and reactions of primary pollutants. Examples are photochemical smog, acid rain, PAN etc.
Sources and causes of Air Pollution
The sources of air pollution are classified into two groups: Natural and Man- made sources.
(a) Natural sources:
1) Volcanic eruption: releasing poisonous gases like SO2, H2S, CO etc.
2) Forest fires: Very large quantities of smoke and particulate matter are liberated during their breakout.
3) Decomposition of organic and inorganic substances: Methane gas, carbon dioxide is released into the air.
4) Dust: Dust is always present in the atmosphere in varying amount.
(b) Manmade sources:
1) Deforestation.
2) Burning of fossil fuels.
3) Emission from vehicles.
4) Rapid industrialization.
5) Modern agricultural practices.
Effects of Air Pollution
Air pollution is very dangerous for health. Some of the adverse effects of air pollution are given below:
1. Air pollution affects our respiratory system and causes breathing difficulties.
2. Diseases such as bronchitis, asthma, lung cancer, tuberculosis and pneumonia caused due to air pollution.
3. Increased concentration of carbon dioxide in atmosphere causes global warming.
4. Air pollution causes acid rain which damages crop plants, trees and buildings. It also makes the soil acidic.
5. Ozone layer depletion due to air pollution which allows ultraviolet radiation to reach the earth. Such radiation causes various skin and eye diseases.
6. Excess nitrogen oxides in the atmosphere results in respiratory problems and bronchitis.
Measures to Control Air Pollution
Air pollution can control from the following points:
1. A raw material for feedstock should be renewable rather than depleting.
2. Better designed equipment and smokeless fuels should be used in houses and industries. Less polluting fuels should be used.
3. Growing plants capable of fixing carbon monoxide. Example: Phaseolus vulgaris, Daucus carota.
4. Growing plants capable of metabolizing nitrogen oxides and other gaseous pollutants. Example: Vitis, Pimis, Pyrus etc.
5. Use of non-conventional sources of energy should be encouraged.
6. Use of public transport to control fuel consumption.
7. Automobiles should be properly maintained and adhere to emission control standards.
8. Proper Environmental Impact Assessment for any developmental work must be done.
Environmental Studies MCQs Multiple Choice Questions and Answers
➡ Top 100 Environmental Studies MCQs
Environmental Studies Chapterwise Notes
➡ Unit 1: Introduction to Environmental Studies
➡ Unit 2: Ecosystems
➡ Unit 3: Natural Resources: Types, Renewable and Non-renewable Resources
➡ Unit 4: Biodiversity and Conservation (Available in DTS App – Only for Members)
➡ Unit 5: Environmental Pollution
➡ Unit 6: Social Issues and the Environment
➡ Unit 7: Environmental Policies & Practices
➡ Unit 8: Human Communities and the Environment
➡ Unit 9: Field work
Environmental Studies Question Papers
➡ Dibrugarh University 2022
➡ Gauhati University 2022
➡ Assam University 2019 2021
➡ Kolkata University (Coming Soon)
Environmental Studies Solved Question Papers
Noise pollution.
Noise is one of the most pervasive pollutant. A musical clock may be nice to listen during the day, but may be an irritant during sleep at night. Noise by definition is “sound without value” or “any noise that is unwanted by the recipient”.
Noise in industries such as stone cutting and crushing, steel forgings, loudspeakers, shouting by hawkers selling their wares, movement of heavy transport vehicles, railways and airports leads to irritation and an increased blood pressure, loss of temper, decrease in work efficiency, loss of hearing which may be first temporary but can become permanent in the noise stress continues. It is therefore of utmost importance that excessive noise is controlled.
Noise level is measured in terms of decibels (dB). W.H.O. (World Health Organization) has prescribed optimum noise level as 45 dB by day and 35 dB by night. Anything above 80 dB is hazardous.
Causes and Sources of Noise Pollution
There are several sources of noise that contribute to both indoor and outdoor noise pollution which are listed below:
a) Cutting and Crushing in Industries/ Factories.
b) M ovement of heavy transport vehicles, railways and airports etc.
c) Sound generated during Construction activities.
d) Household chores such as washing and cleaning.
e) Playing of loud speakers during festivals/ social events and also hearing loud music in home.
f) Fire crackers burning during festivals and celebrations.
g) Microphones, Television and radio run in loud voice.
h) Loudspeakers in religious places.
h) Some noises are also caused by nature which are called a tmospheric noise which arises due to spurious radio frequency waves due to lightning and other natural disturbances occurring in the atmosphere. Natural phenomena like lightning, thunder, volcanic eruption, earthquake, sound of the ocean waves, etc.
Effects of Noise Pollution
a) Hearing Problems: Exposure to noise can damage one of the most vital organs of the body, the ear.
b) Poor Cognitive Function: With regular exposure to loud noise, the ability to read, learn and understand decreases significantly over time.
c) Serious diseases: High noise pollution can cause high blood pressure and loss of temperament.
d) Sleep disorders – exposure to noise reduces duration of sleep, diminish quality of sleep, Psychic disorders.
e) Wild life issues – noise bring about changes in the behavioural aptitude of birds and animals. They become inefficient in hunting and hence disturb the balance of ecosystem.
Thermal Pollution
The excessive heat dissipated into air or water from the industries increases the temperatures of the entire ecosystem and hence causes thermal pollution. Industrial waste and heat not only causes widespread climatological changes but also it can cause the damage of aquatic and terrestrial life. The effect of thermal pollution is more prominently marked in aquatic system.
The industries like iron and steel plants, petroleum refineries, nuclear reactor, electronic power plants etc. use large amount of water for cooling purposes. The water carries a lot of heat which when released into nearby bodies leads to thermal power pollution. Such an increase in temperature of the aquatic bodies by 8 to 10 degree celcius becomes injuries to the aquatic life.
When an increase in temperature of the aquatic body affects and disrupts the normal activities of the aquatic living organisms, the process is known as thermal pollution.
Sources of Thermal Pollution
a) Nuclear reactor
b) Industrial Wastes
c) Hydro-electric Power Plant
d) Thermal Power
e) Domestic Sewage
Effects of thermal pollution
Thermal pollution affects the living organism in the following ways:
a) It reduces the dissolved oxygen content of water.
b) It changes the characteristics properties of water.
c) It influences reproductive cycle, digestion rate, respiration rate and many enzymatic activities of living organism.
d) It favours the growth of certain bacteria and pathogens.
e) The egg of fish may hatch early or fail to hatch at all.
f) Thermal pollution results in low dissolved oxygen levels thereby perishing aquatic organisms.
Measures to Control Thermal Pollution
1. Colling of Pond’s water is the simplest and cheapest method to control thermal pollution.
2. Plantation of trees upon the banks of rivers, seas and other water bodies. Trees not only help in controlling thermal pollution but also aid in a better environment.
3. Creating artificial lakes for cooling of ponds.
4. Recycling of used water of factories.
5. Co-generation of heat from hot water and used in different tasks of industries.
Solid Waste Management
Industrialization across the world has brought a lot of good as well as bad things as well. One of the negative effects of industrialization is the creation of solid waste and consequent environmental degradation.
According to Britannica, “Solid-waste management is the collecting, treating and disposing of solid material that is discarded because it has served its purpose or is no longer useful. Improper disposal of municipal solid waste can create unsanitary conditions, and these conditions in turn can lead to pollution of the environment and to the outbreaks of vector-borne disease”
Human and animal activities generate different kinds of wastes. These wastes are generally in solid form, and may cause pollution of land, water and air unless treated and disposed off. The process of collection, transportation, treatment and disposal can be grouped under solid waste management. The increase in the quantity of solid waste is due to overpopulation, affluence and technological advancement.
Bad effects of solid wastes
a) Open dumps are malodorous places in which disease carrying vermins such as rats and files proliferate.
b) Methane gas is released into the surrounding air due to decomposition of solid wastes by the micro-organisms.
c) Hazardous materials dissolved in this liquid contaminate underground water and solid strata.
d) The leachate consisting of a variety of chemical constituents’ seeps and pollute the ground water.
e) Absence of landfill lingers aggravate the problem furthermore.
Types of Solid Waste
Solid wastes (waste which are neither liquid nor gaseous) can be classified into:
a) Urban or municipal wastes
b) Industrial wastes
Sources of Urban Waste
– Domestic wastes: It includes a variety of materials thrown out from homes.
– Food waste, Cloth, Waste paper, Glass bottles, Polythene bags, Waste metals, plastic containers, scrap, paints etc.
– Commercial wastes: It includes wastes coming out from shops, markets, hotels, offices, institutions, etc.
– Waste paper, packaging material, cans, bottle, polythene bags, etc.
– Construction wastes: It includes wastes of construction materials. • Wood, Concrete, Debris, etc.
– Horticulture waste and waste from slaughter houses include vegetable parts, residues and remains of slaughtered animals, respectively.
– Biomedical wastes: It includes mostly waste organic materials
– Anatomical wastes, Infectious wastes, glass bottles, plastic, metal syringe, etc.
– Mining waste: A large amount of solid waste is released from the mining activities. The increase in solid waste is due to overpopulation, affluence and technological advancement.
Sources of Industrial Waste
The main source of industrial wastes are chemical industries, metal and mineral processing industries.
– Nuclear plants: Generate radioactive wastes
– Thermal power plants: Produce solid waste in the form of fly ash 3
– Chemical Industries: Produce large quantities of hazardous and toxic materials.
– Other industries: Other industries produce packing materials, rubbish, organic wastes, acid, alkali, scrap metals, rubber, plastic, paper, glass, wood, oils, paints, dyes, etc.
Measures to Control Solid Waste
i) Sanitary Landfill: This is the most popular solid waste disposal method used today. Disposing of waste in a landfill involves burying the waste, in abandoned or unused places. In this method garbage is spread out in thin layers, compacted and covered with clay, sand or plastic liner. The liners protect the ground water from being contaminated. When the landfill is full, it is covered with layers of sand, clay, top soil and gravel to prevent seepage of water.
ii) Incineration : It is the hygienic way of disposing solid waste. It is a thermal process (controlled combustion) in which the waste material is converted to heat, gas, steam and ash, which can be used for electrical generation and domestic heating. It is suitable for hazardous, organic and medical wastes. Combustible substance should be separated and removed before incineration process. Wet municipal waste should be preheated before incineration process. It reduces the volume of waste up to 20 or 30% of the original volume.
iii) Composting: It is a popular method by which bulk organic matter is converted into fertilizer by biological action. Microorganisms like fungi, bacteria convert degradable organic waste into broken, odourless mass called humus, which is a good fertilizer. Separated compostable waste is dumped in underground trenches in layers of 1.5m and finally covered with soil of 20 cm and left for decomposition.
Sometimes, actinomycetes are introduced for active decomposition. Biological action will start within two to three days. Good quality environmental friendly manure is formed from the compost and can be used for agricultural purpose.
iv) Vermi Composting: It has become very popular in the last few years. In vermi composting, earthworms are added to the compost. These help to break the waste and the added excreta of the worms makes the compost rich in nutrients. It is very useful biofertilizer and soil conditioner.
Related posts:
- Introduction to Environmental Studies [Environmental Studies Notes BCOM/BA/BSC 2nd SEM CBCS Pattern]
- Natural Resources Types, Renewable and Non-renewable Resources
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
You must be logged in to post a comment.

Donate to Defend Our Planet
Drilling on public lands, mass wildlife extinctions, worsening climate change—our planet is in crisis. Help us fight back and your gift will be matched $1 for $1.

Water Pollution: Everything You Need to Know
Our rivers, reservoirs, lakes, and seas are drowning in chemicals, waste, plastic, and other pollutants. Here’s why―and what you can do to help.

- Share this page block
What is water pollution?
What are the causes of water pollution, categories of water pollution, what are the effects of water pollution, what can you do to prevent water pollution.
Water pollution occurs when harmful substances—often chemicals or microorganisms—contaminate a stream, river, lake, ocean, aquifer, or other body of water, degrading water quality and rendering it toxic to humans or the environment.
This widespread problem of water pollution is jeopardizing our health. Unsafe water kills more people each year than war and all other forms of violence combined. Meanwhile, our drinkable water sources are finite: Less than 1 percent of the earth’s freshwater is actually accessible to us. Without action, the challenges will only increase by 2050, when global demand for freshwater is expected to be one-third greater than it is now.
Water is uniquely vulnerable to pollution. Known as a “universal solvent,” water is able to dissolve more substances than any other liquid on earth. It’s the reason we have Kool-Aid and brilliant blue waterfalls. It’s also why water is so easily polluted. Toxic substances from farms, towns, and factories readily dissolve into and mix with it, causing water pollution.
Here are some of the major sources of water pollution worldwide:
Agricultural
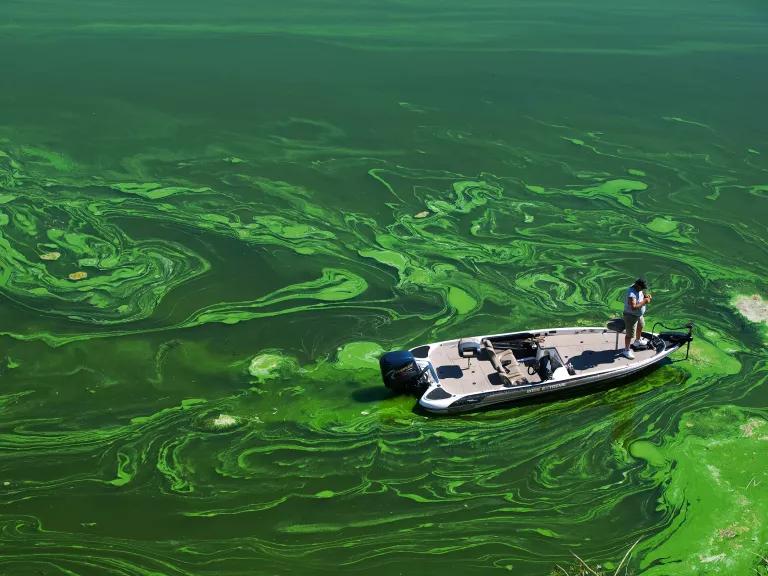

Toxic green algae in Copco Reservoir, northern California
Aurora Photos/Alamy
Not only is the agricultural sector the biggest consumer of global freshwater resources, with farming and livestock production using about 70 percent of the earth’s surface water supplies , but it’s also a serious water polluter. Around the world, agriculture is the leading cause of water degradation. In the United States, agricultural pollution is the top source of contamination in rivers and streams, the second-biggest source in wetlands, and the third main source in lakes. It’s also a major contributor of contamination to estuaries and groundwater. Every time it rains, fertilizers, pesticides, and animal waste from farms and livestock operations wash nutrients and pathogens—such bacteria and viruses—into our waterways. Nutrient pollution , caused by excess nitrogen and phosphorus in water or air, is the number-one threat to water quality worldwide and can cause algal blooms , a toxic soup of blue-green algae that can be harmful to people and wildlife.
Sewage and wastewater
Used water is wastewater. It comes from our sinks, showers, and toilets (think sewage) and from commercial, industrial, and agricultural activities (think metals, solvents, and toxic sludge). The term also includes stormwater runoff , which occurs when rainfall carries road salts, oil, grease, chemicals, and debris from impermeable surfaces into our waterways
More than 80 percent of the world’s wastewater flows back into the environment without being treated or reused, according to the United Nations; in some least-developed countries, the figure tops 95 percent. In the United States, wastewater treatment facilities process about 34 billion gallons of wastewater per day . These facilities reduce the amount of pollutants such as pathogens, phosphorus, and nitrogen in sewage, as well as heavy metals and toxic chemicals in industrial waste, before discharging the treated waters back into waterways. That’s when all goes well. But according to EPA estimates, our nation’s aging and easily overwhelmed sewage treatment systems also release more than 850 billion gallons of untreated wastewater each year.
Oil pollution
Big spills may dominate headlines, but consumers account for the vast majority of oil pollution in our seas, including oil and gasoline that drips from millions of cars and trucks every day. Moreover, nearly half of the estimated 1 million tons of oil that makes its way into marine environments each year comes not from tanker spills but from land-based sources such as factories, farms, and cities. At sea, tanker spills account for about 10 percent of the oil in waters around the world, while regular operations of the shipping industry—through both legal and illegal discharges—contribute about one-third. Oil is also naturally released from under the ocean floor through fractures known as seeps.
Radioactive substances
Radioactive waste is any pollution that emits radiation beyond what is naturally released by the environment. It’s generated by uranium mining, nuclear power plants, and the production and testing of military weapons, as well as by universities and hospitals that use radioactive materials for research and medicine. Radioactive waste can persist in the environment for thousands of years, making disposal a major challenge. Consider the decommissioned Hanford nuclear weapons production site in Washington, where the cleanup of 56 million gallons of radioactive waste is expected to cost more than $100 billion and last through 2060. Accidentally released or improperly disposed of contaminants threaten groundwater, surface water, and marine resources.
To address pollution and protect water we need to understand where the pollution is coming from (point source or nonpoint source) and the type of water body its impacting (groundwater, surface water, or ocean water).
Where is the pollution coming from?
Point source pollution.
When contamination originates from a single source, it’s called point source pollution. Examples include wastewater (also called effluent) discharged legally or illegally by a manufacturer, oil refinery, or wastewater treatment facility, as well as contamination from leaking septic systems, chemical and oil spills, and illegal dumping. The EPA regulates point source pollution by establishing limits on what can be discharged by a facility directly into a body of water. While point source pollution originates from a specific place, it can affect miles of waterways and ocean.
Nonpoint source
Nonpoint source pollution is contamination derived from diffuse sources. These may include agricultural or stormwater runoff or debris blown into waterways from land. Nonpoint source pollution is the leading cause of water pollution in U.S. waters, but it’s difficult to regulate, since there’s no single, identifiable culprit.
Transboundary
It goes without saying that water pollution can’t be contained by a line on a map. Transboundary pollution is the result of contaminated water from one country spilling into the waters of another. Contamination can result from a disaster—like an oil spill—or the slow, downriver creep of industrial, agricultural, or municipal discharge.
What type of water is being impacted?
Groundwater pollution.
When rain falls and seeps deep into the earth, filling the cracks, crevices, and porous spaces of an aquifer (basically an underground storehouse of water), it becomes groundwater—one of our least visible but most important natural resources. Nearly 40 percent of Americans rely on groundwater, pumped to the earth’s surface, for drinking water. For some folks in rural areas, it’s their only freshwater source. Groundwater gets polluted when contaminants—from pesticides and fertilizers to waste leached from landfills and septic systems—make their way into an aquifer, rendering it unsafe for human use. Ridding groundwater of contaminants can be difficult to impossible, as well as costly. Once polluted, an aquifer may be unusable for decades, or even thousands of years. Groundwater can also spread contamination far from the original polluting source as it seeps into streams, lakes, and oceans.
Surface water pollution
Covering about 70 percent of the earth, surface water is what fills our oceans, lakes, rivers, and all those other blue bits on the world map. Surface water from freshwater sources (that is, from sources other than the ocean) accounts for more than 60 percent of the water delivered to American homes. But a significant pool of that water is in peril. According to the most recent surveys on national water quality from the U.S. Environmental Protection Agency, nearly half of our rivers and streams and more than one-third of our lakes are polluted and unfit for swimming, fishing, and drinking. Nutrient pollution, which includes nitrates and phosphates, is the leading type of contamination in these freshwater sources. While plants and animals need these nutrients to grow, they have become a major pollutant due to farm waste and fertilizer runoff. Municipal and industrial waste discharges contribute their fair share of toxins as well. There’s also all the random junk that industry and individuals dump directly into waterways.
Ocean water pollution
Eighty percent of ocean pollution (also called marine pollution) originates on land—whether along the coast or far inland. Contaminants such as chemicals, nutrients, and heavy metals are carried from farms, factories, and cities by streams and rivers into our bays and estuaries; from there they travel out to sea. Meanwhile, marine debris— particularly plastic —is blown in by the wind or washed in via storm drains and sewers. Our seas are also sometimes spoiled by oil spills and leaks—big and small—and are consistently soaking up carbon pollution from the air. The ocean absorbs as much as a quarter of man-made carbon emissions .
On human health
To put it bluntly: Water pollution kills. In fact, it caused 1.8 million deaths in 2015, according to a study published in The Lancet . Contaminated water can also make you ill. Every year, unsafe water sickens about 1 billion people. And low-income communities are disproportionately at risk because their homes are often closest to the most polluting industries.
Waterborne pathogens, in the form of disease-causing bacteria and viruses from human and animal waste, are a major cause of illness from contaminated drinking water . Diseases spread by unsafe water include cholera, giardia, and typhoid. Even in wealthy nations, accidental or illegal releases from sewage treatment facilities, as well as runoff from farms and urban areas, contribute harmful pathogens to waterways. Thousands of people across the United States are sickened every year by Legionnaires’ disease (a severe form of pneumonia contracted from water sources like cooling towers and piped water), with cases cropping up from California’s Disneyland to Manhattan’s Upper East Side.
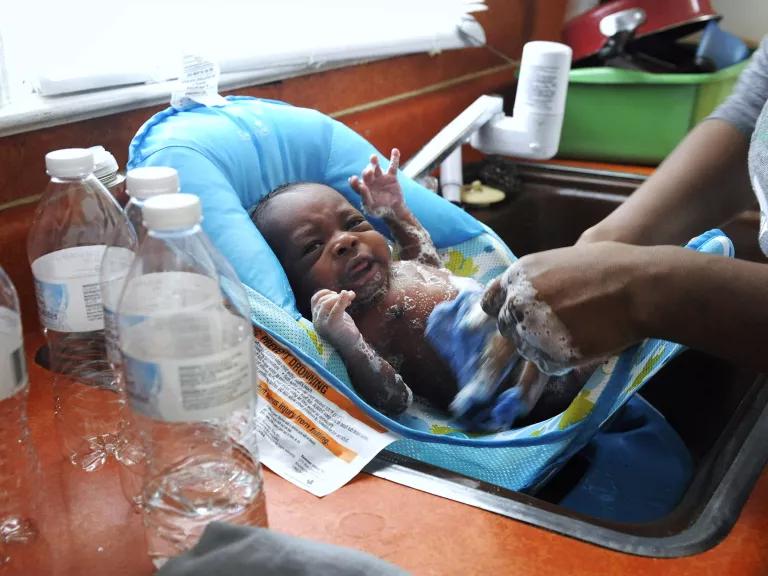
A woman using bottled water to wash her three-week-old son at their home in Flint, Michigan
Todd McInturf/The Detroit News/AP
Meanwhile, the plight of residents in Flint, Michigan —where cost-cutting measures and aging water infrastructure created a lead contamination crisis—offers a stark look at how dangerous chemical and other industrial pollutants in our water can be. The problem goes far beyond Flint and involves much more than lead, as a wide range of chemical pollutants—from heavy metals such as arsenic and mercury to pesticides and nitrate fertilizers —are getting into our water supplies. Once they’re ingested, these toxins can cause a host of health issues, from cancer to hormone disruption to altered brain function. Children and pregnant women are particularly at risk.
Even swimming can pose a risk. Every year, 3.5 million Americans contract health issues such as skin rashes, pinkeye, respiratory infections, and hepatitis from sewage-laden coastal waters, according to EPA estimates.
On the environment
In order to thrive, healthy ecosystems rely on a complex web of animals, plants, bacteria, and fungi—all of which interact, directly or indirectly, with each other. Harm to any of these organisms can create a chain effect, imperiling entire aquatic environments.
When water pollution causes an algal bloom in a lake or marine environment, the proliferation of newly introduced nutrients stimulates plant and algae growth, which in turn reduces oxygen levels in the water. This dearth of oxygen, known as eutrophication , suffocates plants and animals and can create “dead zones,” where waters are essentially devoid of life. In certain cases, these harmful algal blooms can also produce neurotoxins that affect wildlife, from whales to sea turtles.
Chemicals and heavy metals from industrial and municipal wastewater contaminate waterways as well. These contaminants are toxic to aquatic life—most often reducing an organism’s life span and ability to reproduce—and make their way up the food chain as predator eats prey. That’s how tuna and other big fish accumulate high quantities of toxins, such as mercury.
Marine ecosystems are also threatened by marine debris , which can strangle, suffocate, and starve animals. Much of this solid debris, such as plastic bags and soda cans, gets swept into sewers and storm drains and eventually out to sea, turning our oceans into trash soup and sometimes consolidating to form floating garbage patches. Discarded fishing gear and other types of debris are responsible for harming more than 200 different species of marine life.
Meanwhile, ocean acidification is making it tougher for shellfish and coral to survive. Though they absorb about a quarter of the carbon pollution created each year by burning fossil fuels, oceans are becoming more acidic. This process makes it harder for shellfish and other species to build shells and may impact the nervous systems of sharks, clownfish, and other marine life.
With your actions
We’re all accountable to some degree for today’s water pollution problem. Fortunately, there are some simple ways you can prevent water contamination or at least limit your contribution to it:
- Learn about the unique qualities of water where you live . Where does your water come from? Is the wastewater from your home treated? Where does stormwater flow to? Is your area in a drought? Start building a picture of the situation so you can discover where your actions will have the most impact—and see if your neighbors would be interested in joining in!
- Reduce your plastic consumption and reuse or recycle plastic when you can.
- Properly dispose of chemical cleaners, oils, and nonbiodegradable items to keep them from going down the drain.
- Maintain your car so it doesn’t leak oil, antifreeze, or coolant.
- If you have a yard, consider landscaping that reduces runoff and avoid applying pesticides and herbicides .
- Don’t flush your old medications! Dispose of them in the trash to prevent them from entering local waterways.
- Be mindful of anything you pour into storm sewers, since that waste often won’t be treated before being released into local waterways. If you notice a storm sewer blocked by litter, clean it up to keep that trash out of the water. (You’ll also help prevent troublesome street floods in a heavy storm.)
- If you have a pup, be sure to pick up its poop .
With your voice
One of the most effective ways to stand up for our waters is to speak out in support of the Clean Water Act, which has helped hold polluters accountable for five decades—despite attempts by destructive industries to gut its authority. But we also need regulations that keep pace with modern-day challenges, including microplastics, PFAS , pharmaceuticals, and other contaminants our wastewater treatment plants weren’t built to handle, not to mention polluted water that’s dumped untreated.
Tell the federal government, the U.S. Army Corps of Engineers, and your local elected officials that you support water protections and investments in infrastructure, like wastewater treatment, lead-pipe removal programs, and stormwater-abating green infrastructure. Also, learn how you and those around you can get involved in the policymaking process . Our public waterways serve every one of us. We should all have a say in how they’re protected.
This story was originally published on May 14, 2018, and has been updated with new information and links.
This NRDC.org story is available for online republication by news media outlets or nonprofits under these conditions: The writer(s) must be credited with a byline; you must note prominently that the story was originally published by NRDC.org and link to the original; the story cannot be edited (beyond simple things such as grammar); you can’t resell the story in any form or grant republishing rights to other outlets; you can’t republish our material wholesale or automatically—you need to select stories individually; you can’t republish the photos or graphics on our site without specific permission; you should drop us a note to let us know when you’ve used one of our stories.
Related Stories

The Smart Seafood and Sustainable Fish Buying Guide

How to Become a Community Scientist

How to Start Saving the Planet in 100 Days: the Joe Biden Edition
When you sign up, you’ll become a member of NRDC’s Activist Network. We will keep you informed with the latest alerts and progress reports.
- Biology Article
- Types Of Pollution
Types of Pollution
What is pollution.
Air Pollution
Water Pollution
Soil Pollution
Noise Pollution

There are various types of pollution chiefly arising as a result of anthropogenic causes. Also contributing to pollution is globalisation, where humanity’s constant need for natural resources has slowly started to change the face of the earth.
Though the quality of living has drastically improved, other new issues have risen that gradually impact human health and the environment. In this article, we shall explore the meaning, causes and types of pollution. Also, we shall analyse the repercussions of pollution on human health and the environment.
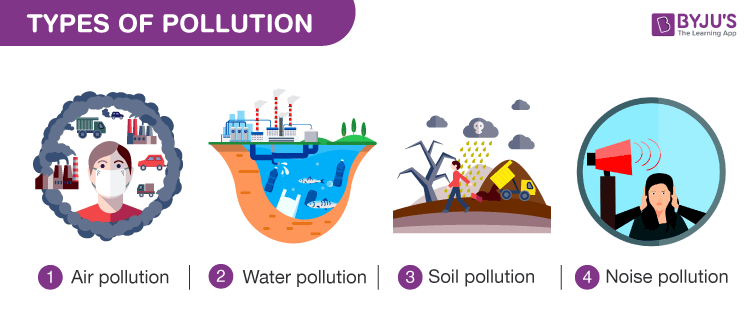
“Pollution is the introduction of substances (or energy) that cause adverse changes in the environment and living entities .”
Pollution need not always be caused by chemical substances such as particulates (like smoke and dust). Forms of energy such as sound, heat or light can also cause pollution. These substances that cause pollution are called pollutants.
Pollution, even in minuscule amounts, impacts the ecological balance. Pollutants can make their way up the food chain and eventually find their way inside the human body. Read on to explore the types of pollution and their implications.
Also Read: Industrial Melanism
As stated before, there are different types of pollution, which are either caused by natural events (like forest fires) or by man-made activities (like cars, factories, nuclear wastes, etc.) These are further classified into the following types of pollution:
Besides these 4 types of pollution, other types exist such as light pollution, thermal pollution and radioactive pollution. The latter is much rarer than other types, but it is the deadliest.

Air pollution refers to the release of harmful contaminants (chemicals, toxic gases, particulates, biological molecules, etc.) into the earth’s atmosphere. These contaminants are quite detrimental and in some cases, pose serious health issues. Some causes that contribute to air pollution are:
- Burning fossil fuels
- Mining operations
- Exhaust gases from industries and factories
The effects of air pollution vary based on the kind of pollutant. But generally, the impact of air pollution ranges from:
- Increased risk of respiratory illness and cardiovascular problems
- Increased risk of skin diseases
- May increase the risk of cancer
- Global warming
- Ozone depletion
- Hazards to wildlife
Among the other types of pollution, air pollution is theorized to have a planet-wide implication. Scientists have even speculated an apocalypse-like scenario where air pollution if left unchecked, can bring about an extreme form of global warming called the runaway greenhouse effect. Though this is purely speculative, it is a phenomenon that has already occurred on Venus.
More to Read: Steps to Control Air Pollution

Water pollution is said to occur when toxic pollutants and particulate matter are introduced into water bodies such as lakes, rivers and seas. These contaminants are generally introduced by human activities like improper sewage treatment and oil spills. However, even natural processes such as eutrophication can cause water pollution.
Other significant causes of water pollution include:
- Dumping solid wastes in water bodies
- Disposing untreated industrial sewage into water bodies
- Human and animal wastes
- Agricultural runoff containing pesticides and fertilisers
The effects of water pollution are very pronounced in our environment . Furthermore, toxic chemicals can bioaccumulate in living beings, and these chemicals can travel their way up the food chain, ultimately reaching humans.
Among the other types of pollution, water pollution has severe consequences on humans. For instance, in 1932, a grave case of water pollution incapacitated the inhabitants of an entire city in Japan with neurological diseases and mental illness for many decades. However, the immediate cause was not apparent but was eventually attributed to acute mercury poisoning. Methylmercury was dumped into the surrounding bay and had ultimately bioaccumulated inside the fish. The local population then consumed these fish, and this resulted in the manifestation of ill effects and neurological diseases.
Read More: A grave case of water pollution
Other consequences of water pollution include:
- Disruption of the ecosystem
- Threats to marine life
- Increased risk of water-borne diseases
- Increases toxic chemicals (such as mercury) in water bodies
- Eutrophication

Soil pollution , also called soil contamination , refers to the degradation of land due to the presence of chemicals or other man-made substances in the soil. The xenobiotic substances alter the natural composition of soil and affect it negatively. These can drastically impact life directly or indirectly. For instance, any toxic chemicals present in the soil will get absorbed by the plants. Since plants are producers in an environment, it gets passed up through the food chain. Compared to the other types of pollution, the effects of soil pollution are a little more obscured, but their implications are very noticeable.
Some of the common causes of soil pollution are:
- Improper industrial waste disposal
- Acid rain which is caused by air pollution
- Mining activities
- Intensive farming and agrochemicals (like fertilisers and pesticides)
- Industrial accidents
The effects of soil pollution are numerous. Specific wastes, such as radioactive waste become particularly hazardous when they are not well-contained. A well-documented example is a nuclear accident in Chernobyl, which has left an area of 2,600 km 2 uninhabitable for several thousand years.
Other effects of soil pollution include:
- Loss of soil nutrients, which renders the soil unfit for agriculture
- Impacts the natural flora and fauna residing in the soil
- Degrades vegetation due to the increase of salinity of the soil
- Toxic dust (such as silica dust) can cause respiratory problems or even lung cancer
Read More: Soil Profile

Noise pollution refers to the excessive amount of noise in the surrounding that disrupts the natural balance. Usually, it is man-made, though certain natural calamities like volcanoes can contribute to noise pollution.
In general, any sound which is over 85 decibels is considered to be detrimental. Also, the duration an individual is exposed plays an impact on their health. For perspective, a normal conversation is around 60 decibels, and a jet taking off is around 15o decibels. Consequently, noise pollution is more obvious than the other types of pollution.
Noise pollution has several contributors, which include:
- Industry-oriented noises such as heavy machines, mills, factories, etc.
- Transportation noises from vehicles, aeroplanes, etc.
- Construction noises
- Noise from social events (loudspeakers, firecrackers, etc.)
- Household noises (such as mixers, TV, washing machines, etc.)
Noise pollution has now become very common due to dense urbanisation and industrialisation. Noise pollution can bring about adverse effects such as :
- Hearing loss
- Sleeping disorders
- Hypertension (high BP)
- Communication problems
Learn more about pollution, the types of pollution, its causes and effects by registering at BYJU’S Biology
Frequently Asked Questions
What are the different types of pollution.
The different types of pollution include:
- Air pollution
- Water pollution
- Soil pollution
- Radioactive pollution
- Noise pollution
Name the harmful pollutants responsible for polluting the environment.
The harmful pollutants responsible for polluting the environment are:
- Nitrogen oxide
- Sulphur oxide
- Particulate matter
- Chlorofluorocarbon
- Volatile organic compounds
What are the different types of pollutants?
The different types of pollutants are:
- Primary Pollutants: These are the pollutants that are emitted directly from the sources such as volcanic eruptions, combustion of fossil fuel, etc. These include nitrogen oxide, sulphur oxide, etc.
- Secondary Pollutants: These are the pollutants that are not directly emitted from the sources but are formed when primary pollutants react in the atmosphere. For eg., ozone.
What is radioactive pollution?
Radioactive pollution is the pollution caused by the release of radioactive substances in the atmosphere during activities such as nuclear explosions, mining of radioactive ores, etc.
What are the consequences of mercury pollution?
Mercury pollution is the pollution caused by the release of mercury from mercury products or emissions from coal-burning power plants in the air, water or land. Mercury pollution results in neurological and behavioural disorders in humans. Insomnia, memory loss, headaches, and tremors are some of the symptoms of mercury pollution.

Put your understanding of this concept to test by answering a few MCQs. Click ‘Start Quiz’ to begin!
Select the correct answer and click on the “Finish” button Check your score and answers at the end of the quiz
Visit BYJU’S for all Biology related queries and study materials
Your result is as below
Request OTP on Voice Call
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Post My Comment
Very good condition
Good to know the future
Really it helps
It’s really very helpful for us
it is helpful thanks for the awakening of minds
It is very helpful.
THANK YOU IT HELPS A LOT
Good app for study for children’s
It’s a very good essay on pollution
It’s a very good app for children to know the basic knowledge
it’s very useful for me
It was very helpful. Thank you!
It’s very good and helpful for me and others
Hi good very vall
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.

- Joyful Mathematics Class 1
- Joyful Mathematics Class 2
- Class 1 Hindi
- Class 2 Hindi Sarangi
- Class 3 Hindi
- Class 5 Hindi
- Class 5 EVS
- Class 5 Maths
Our environment and pollution Worksheets Class 4
We all talk about our environment and pollution , but do we truly understand what the environment is and how our actions are polluting it.
Understanding the complex relationship between the environment and pollution is crucial for all of us. Earth is the only living planet in the Solar system, and we do not have any other alternative. Protecting the environment is our prime duty and most precious gift for the coming generations.
In our Worksheets, children discovers what the environment is, how we are polluting it, adverse effects of pollution and how can we preserve it.
Give your child a boost by downloading our specially designed environment and pollution Worksheets for Class 4.
After using our printable worksheets, students will be able to answer a series of questions to reflect on what they have learned.
Environment and Pollution
Today, we will learn about pollution, types of pollution, the causes behind pollution, and the effects it has on our body as well as on our planet.
We will also learn how to stop pollution and protect our environment. So, let’s dive in and explore this important topic together!

Click on the button to download these Printable worksheets for class 4.
We are now on WhatsApp – Click to Join Us
Science worksheets for Class 4 Maths Worksheets for Class 4

What is Our Environment?
The environment refers to the natural world around us, including the air we breathe, the water we drink, and the land we live on. It also includes all living things, like plants and animals, as well as non-living things that make up our ecosystem.
What is Pollution?
Pollution refers to the introduction of harmful substances or pollutants into the environment that can cause damage to living organisms and their surroundings. These pollutants can be in the form of chemicals, gases, or even solid waste materials. This can happen in many ways, such as through the use of cars and factories, littering, or even burning wood for heat.
Pollution can occur in various forms and can have severe consequences for both nature and humans.
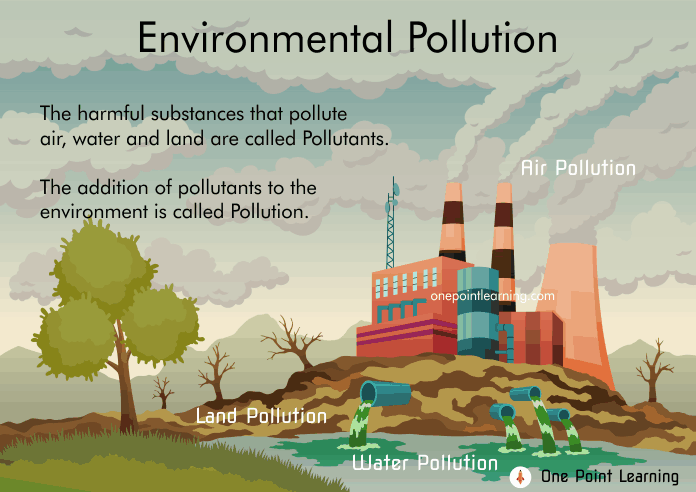
Types of Pollution
Air Pollution: This type of pollution occurs when harmful gases and particles are released into the air, leading to bad air quality. Vehicles, industries, and the burning of fossil fuels are major contributors to this form of pollution.
Water Pollution: It happens when waste materials, chemicals, or contaminants enter water bodies such as rivers, lakes, and oceans. Industrial waste, untreated sewage, and oil spills are some common causes of water pollution.
Land Pollution: It is caused when harmful substances contaminate the soil, making it unfit for agriculture or harming the organisms that depend on it. Pesticides, chemical fertilizers, and improper disposal of waste can all contribute to soil pollution.
What are effects of pollution?
Pollution can have a negative impact on the environment and our health. For example, air pollution can cause respiratory problems like asthma, while water pollution can make it unsafe to swim or drink from certain sources.

Health Impact: Pollution can have severe health consequences for both humans and animals. Poor air quality can lead to respiratory problems, allergies, and even lung cancer. Water pollution can cause waterborne diseases, while exposure to soil pollution can have long-term health effects.
Ecosystem Disruption: Pollution disrupts the delicate balance of ecosystems, leading to the loss of biodiversity and the extinction of species. Contaminated water and soil can affect plants, animals, and microorganisms, causing harm to entire food chains.
Climate Change: Pollution, especially the release of greenhouse gases, contributes to climate change. The excessive emissions of carbon dioxide and other greenhouse gases trap heat in the atmosphere, leading to global warming and its adverse effects on the environment.
12 Facts about Environment and Pollution
- Air pollution is a greater threat to life compared to smoking, HIV or war
- Climate change increases risks of wildfires, changing seasons, etc
- Less than 1% of global land area has safe air pollution levels
- Over millions of sea animals are killed by water pollution every year
- about 3 million kids under the age of 5 years die every year due to pollution
- China is the world’s largest producer of carbon dioxide
- Almost 80% of urban waste in India is dumped in the river Ganges
- Noise pollution is the most neglected type of pollution
- More than 100 pesticides in any medium – air, water or soil can cause birth defects, gene mutation, and cancer.
- Antarctica is the cleanest place on Earth protected by anti-pollution laws
- Public transportation and carpooling can help you to reduce air pollution and save money up to a great extent
- Energy-related emissions are expected to increase by 20% by 2040
What is our responsibility towards environment?
It’s important for us to take care of our environment and prevent pollution as much as possible. We can all play a crucial role in protecting our environment and combating pollution. We can do this by practising things like recycling, conserving energy, and using eco-friendly products.

Here are some simple yet effective ways to make a positive difference:
Plant Trees: Engage in tree planting initiatives to contribute to reforestation efforts. Trees absorb carbon dioxide, release oxygen, and provide habitats for biodiversity.
Reduce, Reuse, and Recycle: By reducing our consumption, reusing items, and recycling materials, we can minimize waste production and reduce pollution levels.
Conserve Energy: Opt for energy-efficient appliances and turn off lights and electronic devices when not in use. Conserving energy helps reduce greenhouse gas emissions and combat climate change.
Renewable Energy: Plan to use renewable sources of energy like solar, wind or tidal energy. It reduces the usage of fossil fuel and thus helps to reduce pollution.
Public Transportation: Whenever possible, walk, bike, or use public transportation instead of relying on private vehicles. This helps reduce air pollution and traffic congestion.
As responsible citizens, we must take action to reduce pollution and protect our planet for future generations. By adopting sustainable practices and making conscious choices, we can create a cleaner and healthier environment for all. Let’s come together and make a positive impact on our world!
Benefits of our worksheets
- Comprehensive Worksheets
- High-Quality Content
- Variety of question types
- 100% Free to download
- Easy to print PDF format
- Answer key included
- free worksheets
- ncert worksheets
- science worksheets
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
RELATED ARTICLES
Human body : food and health worksheets class 4, leaves – the food factory of plants class 4, human body : digestive system worksheets class 4, force, work, and energy worksheets class 4.
Welcome to your one-stop destination for free worksheets, NCERT Solutions, practice tests and high-quality educational resources to help you reach your goals.
Copyright © 2023 onepointlearning.com. All Rights Reserved.
- Privacy Policy

Pollution Assignment

- Assignment on Pollution and its types
- Air Pollution Assignment
- Environmental Pollution Assignment
- Soil Pollution Assignment
- Noise Pollution
- Assignment on Water Pollution
- Marine Pollution Assignment
PPT Notes on Pollution Free download ( 30 + PPTs) Pollution PDF Books and Notes download free ( 4+PDF) Pollution an EVS Video Project Ideas ( 20 + videos)
Similar Posts
💁Hello Friends, If You Want To Contribute To Help Other Students To Find All The Stuff At A Single Place, So Feel Free To Send Us Your Notes, Assignments, Study Material, Files, Lesson Plan, Paper, PDF Or PPT Etc. - 👉 Upload Here
अगर आप हमारे पाठकों और अन्य छात्रों की मदद करना चाहते हैं। तो बेझिझक अपने नोट्स, असाइनमेंट, अध्ययन सामग्री, फाइलें, पाठ योजना, पेपर, पीडीएफ या पीपीटी आदि हमें भेज सकते है| - 👉 Share Now
If You Like This Article, Then Please Share It With Your Friends Also.
Bcoz Sharing Is Caring 😃

- [1000+] B.Ed Lesson Plans
- B.Ed Practical Files and Assignments
- B.Ed Books and Notes PDF
- B.Ed Files Pics and Charts Collection
- BEd Model / Sample and Previous Year Papers
- All Subject Lesson Plans for Teachers
Post a Comment
Please Share your views and suggestions in the comment box
Contact Form
Environmental Pollution
All our surroundings including air, water, soil, trees, animals make up our environment. Three factors determine the severity of a pollutant: its chemical nature, the concentration, and persistence. When the normal relations among these elements of nature are disturbed, the ecological balance is hampered and it is called environmental pollution. It is a sorrowful matter that the main elements of the environment which are essential for all living beings are being polluted in many ways. The major kinds of pollution, usually classified by the environment, are air pollution, water pollution, and land pollution. Modern society is also concerned about specific types of pollutants, such as noise pollution, light pollution, and plastic pollution. The smoke from factories and motor vehicles contain harmful substances like carbon-monoxide and sulfur-dioxide. These have hampered the cleanliness of the air. Mills and factories set up by river-banks let out chemical wastes in the river water. These poisonous substances are destroying the plants and creatures of the water bodies. Pesticides and chemical fertilizers used in agriculture are also polluting water. When people drink this water or take a bath in the polluted water, they are attacked with stomach and skin diseases. Pollution introduced by light at night is becoming a global problem, more severe in urban centers, but nonetheless contaminating also large territories, far away from towns. Environment pollution may be controlled by taking different measures, we may increase aforestation. If trees are planted in large numbers, we can be benefited in different ways. Trees also increase rainfall and prevent air pollution. Laws should be passed to prevent factories from dumping wastes into rivers. Moreover, every conscious individual and institution should come forward to solve this problem for the sake of our existence.
Importance of Education in our Life
International day of innocent children victims of aggression, deforestation – a global warming, pollution due to urbanization, cordierite: properties and occurrences, sample apology letter to employer for laboratory accident, removing brain cells linked to wakefulness and addiction could help with withdrawal symptoms, scientists use protein from plant waste to clean heavy metal water, annual (director’s) report 2009-2010 of ntpc limited, sample sales recommendation letter format, latest post, atmospheric circulation, butterfly valve, laser-treated cork absorbs oil in a carbon-neutral ocean cleaning, lighthouse in the gobi desert, global air pollution is driven by atmospheric and economic factors, electromagnetic forming (emf).

Environment Pollution Assignment
However, the environmental natural resources are fully use by man kind for the purpose Of daily activities, for example, the trees being cut to make paper or furniture. Besides that, activities such as open burning or disposable of solid waste will destroy and pollute the whole environment. Environmental pollution is contamination of air, water and land from man-made waste. It leads to depletion of the ozone layer, global warming and climate change. Environmental pollution can be divided into 4 main types which include, land pollution, water pollution, air pollution and sound pollution.
Those pollutions will affect our health, damage the living organism, and destroy the plane. While, environmental ethics is relate to the environment. Environmental ethics is the discipline that studies the moral relationship of human beings and also the value and moral status of the environment and its nonhuman contents. As a field of study, it assumes that humans have certain responsibilities to the natural world, and it seeks to help people and their leaders become aware of them and to act responsibly when they do things that impact the natural world. In this assignment, we will focus on the environmental pollution.
Don’t waste your time! Order your assignment!
We will start by explain and giving the meaning for ACH of the environmental pollution which include sound pollution, land pollution, water pollution and air pollution. Next, we will determine the causes and effect Of the pollutions. After that, We will identify the solutions to solve those problems. The objectives of doing this assignment are to give more information about our responsibilities to the natural world, to define about the environmental pollution, to give ideas on how to reduce pollution and to demonstrate a caring and responsible attitude. ) Sound Pollution Sound pollution can be known as noise pollution or environment noise. It can be defined as unwanted or displeasing sound by human activities or machines which disturb our daily routines by bringing harmful effects on our health or welfare. While, pollution is different from air pollution, water pollution and land pollution. As noise does not last long and remain in the environment. However, its immediate effects in terms of annoyance will disturb human life. Decibel (db) is the unit to measure the loudness of a certain sound.
For sounds with measurement more than 80 db, in a long term exposure, they will hurt our ears. This is considered as sound pollution. When the loudness exceeds 130 db, it is very dangerous as it can damage our eardrum. Table 1 shows the types of sound. Table 1 First of all, the most common source of sound pollution is our transportation system. As we can see, at the urban areas, mostly noise come from the vehicles on the streets which includes the motors and exhaust system of cars, buses, trucks, motorcycles and so on.
Secondly, air craft noise can lead to sound pollution. Mostly due to the problems of low flying military aircraft, helicopters and airplanes that constantly landing and taking off. Especially if is near to the residential area, it will be very disturbing and affect people’s daily lives. Besides that, noise from the railroads will contribute to sound pollution. These noises come from locomotive engines, horns and whistlers, switching and shunting operation in rail yards.
Furthermore, when there are any constructions of buildings, housing areas, highways and city streets, the noise mostly come from those construction’s equipments such as jackhammers, bulldozers, air compressors, loaders, pavement breakers and dump trucks. Thus, resulting sound pollution and brings negative effects. Another common source Of sound pollution is the industrial noise. People who live near the factories and noisy manufacturing places are always disturbed by the noises like motors, fans and compressors at the outside of building.
Meanwhile, noises from the inside of the factories can be transmitted through any open doors or windows and disturbing the residents. Then, noise in building also will causes sound pollution. For those buildings which are not well-designed, the internal building noise from boiler, plumbing, generators, air-conditioner and fans can be heard and is disturbing. Besides, amplified music, voices, footsteps, noisy activities are audible too if the walls and ceilings are improperly insulated. Eventually, noises may come from the consumer products.
Several household’s equipments such as the Vacuum_jar cleaner, washing machine and some kitchen appliances like blender can cause certain annoying noise. 12. 1) Human health effects: Sound pollution will contribute to a person’s physical and mental problems. For example, if we live in an environment with serious sound pollution, we may get annoyance, aggression, hypertension, high stress level, tinnitus and sleeping disturbances. According to psychological studies, stress is the main component causing various health problems such as high blood pressure, coronary artery disease and cardiovascular effects.
In addition, noise can damage our hearing, hurting our eardrums and we might suffer from temporary or permanent deafness. People who work at big cities where their offices are located near to the main roads are lack of concentration when performing their jobs. As the noise of the traffic outside of their office, and the horns of vehicles will divert their attention and attract them from their Current work. These people are more likely to feel fatigue and tired all the time because they need to spend more time to finish their works because they fail to focus on their works.
Besides that, during pregnancy, the pregnant women should always stay at a calm and relaxing atmosphere. But, sudden noise or prolonged exposure to displeasing sounds might cause miscarriage. 1. 2. 2) Environmental effects: The sound pollution will harm animals besides affect humans health. It will damage their nervous system, attacking their minds until they lose control and thus become dangerous. Moreover, sound pollution will also cause high level of stress and increasing the risk of mortality. The animals which communicate using sounds will be disturbed by the surrounding unwanted sounds.
For example, it is found that there were certain species of beached whales died due to the loud sound of military sonar. Furthermore, the animal’s communication will get louder than before. It is because when they speak, it will mask other species’ voice. Hence, the whole ecosystem will speak louder at the end. 1. 2. 3) Property effects: High rise buildings, monuments or even bridges are very dangerous if expose to noise pollution. As it will creates waves and then hit on the walls. Sometimes even creating cracks and weaken the whole buildings structure and stability. 1. ) Solution for sound pollution Since the sound pollution brings a lot of harmful effects, hence the problem had been taken into consideration and the government is trying to solve it as soon as possible. Thus, scientific and technology method had been used and applied in order to curb these sound pollution. First of all, to reduce roadway noise caused by the vehicles on the roads, there are ways like limitation of vehicles speeds, alteration of the road surface suture, there’s design, the use of noise barriers along the roads, use of traffic controls that smooth vehicles flow to reduce braking and acceleration.
In addition, motor vehicles are encouraged and advised better to be fitted with silencers or noise suppressing equipment so that it can minimize the noise pollution. There is an example where at Melbourne, Australia, they had built a unique structure along the roadway which is called the sound tube and it was specially designed so that it can reduce the noise on the road. The picture 1 shows the sound tube which built along the roadway. Picture 1 Besides that, the aircraft noise can be reduced by redesign the quieter jet engines.
Several consideration and alteration had been made on the pathway of the aircraft and the time of day they use. Meanwhile, new airports such as KALI are located away from residential areas to prevent sound disturbance. Next, the industrial noise can be solved by make changes on the industrial equipment, operation of machines, vibration control, sound proof cabin and sound absorbing materials. Workers are to be provided extra protection against the sound pollution, for instance by wearing the earplugs when operating machines.
Any new factories have to be moved to places far away from housing areas and prohibited from operating at night. Trees and shrubs may be planted too around the building to absorb the sounds. Other than these solutions, the government has implemented the noise laws to reduce the sound pollution. This may contain a prohibition against making noise and set firm limits and provide guidelines for the level of noise allowable at certain period of a day and only for specific activities. For example, most city ordinance had prohibited sound above a threshold level at night, during 1 Mom to Sam.
Honking of honks should be banned in certain places such as, hospital or residential area. Furthermore, silent zones should be created near schools and hospitals to encourage those buildings to make them noise proof. Besides that, firecrackers should be banned as well especially during festive season as it will cause serious sound pollution. Lastly, is to create public awareness through education. The public should be aware of sound pollution and must know how to control and prevent it. Through the radio, TV, newsreels in cinema halls, the public can be educated about the ways to reduce noise.
At home, parents are encourage to teach their kids to keep radio or TV’ volume low, not to honk unnecessarily on the road, talk with a softer tone and other ways of minimizing unwanted noise. 2) Water pollution The term “water pollution” generally refers to human-induced changes to water quality. According to the dictionary, pollution is defined as make something dirty or impure, especially by adding harmful or unpleasant substances. Thus, the discharge of toxic chemicals from a pipe or the release of livestock waste into a nearby water body and unfit for intended use is considering polluted.
The contaminations are affects drinking water, river, lakes and oceans all over the world. It’s not only affected the natural environment, but also directly threatens the health of humans and aquatic life. There are two general categories of water pollutants. The first is direct sources or point-source pollution, in which the pollution comes from harmful substances and discharged from a discrete location. Sewage outfalls and oil spills are examples of direct source. The second category is indirect source or non-point Source pollution, referring to all of the other discharges that deliver intimations to water bodies.
Acid rain and unconfined run off from agricultural or urban areas are example of indirect sources. 2. 1) Causes of Water Pollution The sources of water pollution are such as domestic households, industrial and agricultural practices which produce wastewater that can cause pollution of many lakes and rivers. First of all, sewage as well as domestic and farm waste are often allowed to pollute rivers and dams. Sewage is the Wastewater that Often contain urine and laundry waste. Clean the sewage is the major problem in developing countries as many people in Hess areas do not have access to sanitary conditions and clean water. Unclean sewage water in such areas can contaminate the environment and cause diseases such as diarrhea. Next, industrial waste is one of the serious problem that causing the water pollution. It produces pollutants that are extremely harmful to people and the environment. For example, the pollute water occur as many industrial facilities use freshwater to carry away waste from the plant into the river, lakes and oceans. There are several industrial sources are pollutant water, which include sulfur, ails, oil and petrochemicals. Sulfur is a non- metallic substance that is harmful for marine life.
While, ails is the common source that pollute the oceans seriously. Then, oil will forms a thick layer on the water surface and does not dissolve in water. Further, petrochemicals are formed from gas or petrol that can be toxic and harm mariner’s life. Another source of water pollution is agriculture which including commercial livestock and poultry farming. Agriculture consider as the source of many organic and inorganic pollutants in surface waters and groundwater. For example, animal wastes are demanding high in oxygen, material, nitrogen ND phosphorus, and they often harbor pathogenic organisms.
Moreover, wastes from commercial feeders are contained and disposed of on land. Furthermore, water pollution also can cause by oil pollution. Oceans are polluted by oil on a daily basis from oil spills, routine shipping, run-offs and clumping. Although, Oil spills cause is a localized problem but it can be harmful for local marine wildlife such as fish, birds and the others. On the other hand, the oil spill from a tanker is considered as severe problem because there is such a huge quantity of oil being sprit into one place.
When he oil split into water, oil cannot dissolve by the water, and later, a thick sludge is form in the water. This suffocates fish, gets caught in the feathers of marine birds and stopping them from flying. Lastly, atmospheric deposition is the pollution of the water which caused by air pollution. In the atmosphere, water particles mix with carbon dioxide, sulfur dioxide and nitrogen oxides. This forms a weak acids. Air pollution means that water vapor absorbs more of these gases and becomes even more acidic. When it rains, the water is polluted with these gases and this is called acid rain. 2. Effect of water pollution Basically, all types of water pollution are harmful to human, animals and environment, it may not damage our health immediately, only will affect after long term exposure. It is very common that the water we drinking, cooking, bathing, washing are all being suffer by wastewater. If we look around the Klan Valley, we can see the obvious Wastage and pollution of Water such as, leaking pipes, water thefts, garbage floating on rivers and our own careless use of these resources. Besides that, industrial waste often contains many toxic compounds that damage the health of aquatic animals.
Those who eat the poisoned aquatic animals may get food poison. Some of the toxins in industrial waste may only have a mild effect whereas other can be fatal. Yet, sulfate particles from acid rain can cause harm the health of marine life in the rivers and lakes it contaminates, and can result in mortality. In addition, suspended particles in freshwater reduces the quality of drinking water for humans and the aquatic environment for marine life. Meanwhile, suspended particles can often reduce the amount of sunlight penetrating the water and disrupting the growth Of photosynthesis plants and Cicero-organisms.
Water pollution is harmful to whole planet, if we still choose to do bother these problem, we may face on to death. To prevent water pollution, long-term solutions are needed not just addressing immediate needs with no regard for the consequences. Here are some simple guidelines in everyday life. Firstly, turning off the tap when running water is not necessary, it is to conserve water. This helps prevents water shortage and reduces the amount of contaminated water that needs treatment. Next, don’t throw paint Oils or other forms Of litter down to the drain. Try to be careful when using he sink or toilet by throwing something.
Beside that, take great care not to overuse pesticides and fertilizers. This can prevents runoff of the material into nearby water sources. Furthermore, by having more plants also tend to prevent fertilizer, pesticide and contaminated water from running off into nearby water sources. Next, do not throw litter into rivers, lakes or oceans. In contrast, we need to help clean up any litter when see on beaches or in rivers and lakes, make sure it is safe to collect the litter and put it in a nearby dustbin. Eventually, government also can give penalty to the industries that use freshwater to carry away waste into rivers and oceans.
Land pollution is the degradation of earth’s land surfaces which often caused by human activities, misuse of the soil and the addition of undesirable matter to the land that damage the terrestrial organisms. 3. 1) Causes of land There are several causes that lead to land pollution. Firstly is cause by disposal of solid waste. There are several useless, unwanted, or hazardous solid wastes that typically may be classified as follows: Garbage: Decomposable waste from food. Rubbish Non- decomposable wastes, either combustible such as paper, wood, and Lott or non-combustible, such as metal, glass and ceramics.
How to cite this assignment
Related assignments:.
- Save the Environment from Pollution Assignment
- Noise Pollution Assignment
- Water, Land and Air Pollution Assignment
- Environmental Pollution and Making a Difference Assignment
Haven't Found The Paper You Want?
For Only $13.90/page

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Jerry A. Nathanson. Pollution, addition of any substance or form of energy to the environment at a rate faster than it can be dispersed or stored in a harmless form. The major kinds of pollution are usually classified by environment and include air, water, and land pollution. Learn more about the history of pollution.
Pollution is the introduction of harmful materials into the environment. These harmful materials are called pollutants. Pollutants can be natural, such as volcanic ash. They can also be created by human activity, such as trash or runoff produced by factories. Pollutants damage the quality of air, water, and land.
Particle pollution known as particulate matter (PM) is one of the major air pollutants regulated by EPA to protect public health and the environment. A PM air sensor kit has been developed by EPA researchers as an educational tool to teach children about air quality and air science. Grades: 5-12 Type of Resource: Hands-on activity guide
Essay on Environmental Pollution. The environment is the surrounding of an organism. The environment in which an organism lives is made up of various components like air, water, land, etc. These components are found in fixed proportions to create a harmonious balance in the environment for the organism to live in.
ENVIRONMENTAL STUDIES-ASSIGNMENT 5 Page 4 3) Every department of the government that supervises activities, which are likely of affect the environment and public health, should collect details on the effect of their activities on the public health, the environmental conditions, and the effects of pollution on various life forms.
Sulphur dioxide - is released from oil refineries and ore smelters which use the sulphur containing fuels. It causes harmful effects on plants and animals. It causes chlorosis (loss of chlorophyll) and necrosis (localised death of tissues). In human, it causes health problems such as asthma, bronchitis and emphysema.
The Pollution Problem. Pollution, also called environmental pollution, the addition of any substance ( solid, liquid, or gas) or any form of energy (such as heat, sound, or radioactivity) to the environment at a rate faster than it can be dispersed, diluted, decomposed, recycled, or stored in some harmless form.
Unit 5: Environmental Pollution (8 lectures) Environmental Studies Notes For BA, B.Com and BSC CBCS Pattern • Environmental pollution: types, causes, effects and controls; Air, water, soil and noise pollution • Nuclear hazards and human health risks • Solid waste management: Control measures of urban and industrial waste.
Sources of pollution. Mercury ( Hg) in the environment is constantly cycled as a result of natural and human activities. What highly toxic compound is formed when elemental mercury ( Hg) is processed by aquatic bacteria? Learn for free about math, art, computer programming, economics, physics, chemistry, biology, medicine, finance, history, and ...
water pollution, the release of substances into subsurface groundwater or into lakes, streams, rivers, estuaries, and oceans to the point that the substances interfere with beneficial use of the water or with the natural functioning of ecosystems. In addition to the release of substances, such as chemicals, trash, or microorganisms, water ...
Water pollution occurs when harmful substances—often chemicals or microorganisms—contaminate a stream, river, lake, ocean, aquifer, or other body of water, degrading water quality and ...
Types of Pollution. Air Pollution. Water Pollution. Soil Pollution. Noise Pollution. 30,600. There are various types of pollution chiefly arising as a result of anthropogenic causes. Also contributing to pollution is globalisation, where humanity's constant need for natural resources has slowly started to change the face of the earth.
Key words ;- Environmental pollution, global warming, acid rain, nature etc. There are many causes of environmental pollution which can be listed as follows. Deforestation, soil erosion ...
Environmental Pollution: Environmental Pollution is not a new phenomenon, yet it remains one of the greatest threats to the health and well-being of humanity and one of the major environmental causes of death and morbidity. For example, substances such as plastic materials, heavy metals, etc., once released into the atmosphere.By natural processes, it cannot be degraded and are harmful to ...
Assignment. Introduction. Environmental pollution is a multi-disciplinary science involving chemistry, physics, life science, agriculture, medical science, public health, sanitary engineering etc. In broader sense, it is the study of the sources, reactions, transport, effect and fate of chemical species in the air, water and soil and the effect ...
12 Facts about Environment and Pollution. Air pollution is a greater threat to life compared to smoking, HIV or war. Climate change increases risks of wildfires, changing seasons, etc. Less than 1% of global land area has safe air pollution levels. Over millions of sea animals are killed by water pollution every year.
ASSIGNMENT NUMBER : 01 MODULE : ENVIRONMENTAL POLLUTION IV LECTURER : DUE DATE : Question 1. The NEMA (1998) defines the best practicable environmental option (BPEO) as the option that provides the most benefit or causes the least damage to the environment as a whole, at a cost acceptable to society, in the short term as well as in the long term.
In the colleges and schools, environmental education is a compulsory subject. And the students have to make an assignment on pollution on different topics like air, water, noise, environmental pollution, land, marine, etc. So here we have given a sample and detailed pollution assignment in English for All the College and School students.
30 Environmental Studies Topics for Assignment. These topics offer a range of perspectives on environmental studies, from sustainable agriculture practices to the effects of noise pollution on wildlife communication and behavior: Deforestation and its effect on biodiversity in tropical rainforests. The ethics of wildlife captivity for ...
Lead Contamination Assignment - Introduction to Environmental Science - Environmental Pollution Assignment - EVR1001 FIU - Florida International University. A) Two-part question Look at Figure 7.4 Chapter 7 titled pathways of pollution in the environment. Part 1: Explain a real-world case of a ... [Show more]
Environmental Pollution Assignment. Environmental Pollution is the most important threat to the human race on this planet today. Environment consists of earth, air, water, flora and fauna. It means adding impurity which threatens the life of flora and fauna to the environment. These impurities are mainly created by man-made activities.
Environmental Pollution. All our surroundings including air, water, soil, trees, animals make up our environment. Three factors determine the severity of a pollutant: its chemical nature, the concentration, and persistence. When the normal relations among these elements of nature are disturbed, the ecological balance is hampered and it is ...
Environment Pollution Assignment. Hunter Gibson. Words: 2785. However, the environmental natural resources are fully use by man kind for the purpose Of daily activities, for example, the trees being cut to make paper or furniture. Besides that, activities such as open burning or disposable of solid waste will destroy and pollute the whole ...