

25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. Take the first step today
Here’s your new year gift, one app for all your, study abroad needs, start your journey, track your progress, grow with the community and so much more.

Verification Code
An OTP has been sent to your registered mobile no. Please verify

Thanks for your comment !
Our team will review it before it's shown to our readers.

Business Research: Types, Methods, Examples
- Updated on
- Jan 29, 2024

Ever wondered what it takes to build a flourishing business ? Aiming to provide maximum sales and profit, business research helps you to gather comprehensive information about your business and accordingly make relevant changes if required. So, in this process of being successful, we gather all types of data to better define our strategies and understand what products or services customers want. And in case, you’re planning to expand your business, research can help you determine your odds of positive results. In this blog, we’ll help you understand the basics of research and analysis .
“Whoever gets closer to the customer, wins.” – Bernadette Jiwa
This Blog Includes:
What is business research, business research example, importance of business research, types & methods, focus groups , case study research , ethnographic research, survey , correlation research , experimental research , advantages and disadvantages of business research, scope of business research, role of business research, business research books, business research report, top 10 tools for business research, business research partners, top 10 business research topics, career prospects , [bonus] best mba colleges in the world.
Business Research can be simply defined as a process of gathering comprehensive data and information on all the areas of business and incorporating this information for sales and profit maximization. If you are wondering what is Business Research, it is a systematic management activity helping companies to determine which product will be most profitable for companies to produce. Also, there are multiple steps in conducting research, with each thoroughly reviewed to ensure that the best decision is made for the company as a whole.
Also Read: Scope of MBA in International Business
Let’s say there’s an automobile company that is planning to launch a car that runs on CNG. To promote cleaner fuel, the company will be involved in developing different plans and strategies to identify the demand for the car they intend to launch. Other than this, the company will also look for competitors, and the target audience, keeping in mind the distribution of CNG in India. Hence the research is conducted on various ideas to formulate a sustainable and more efficient design.
When it comes to the question of why Business Research is important, it has an essential role to play in varied areas of business. Here are some of the reasons describing the importance of Business Research:
- It helps businesses gain better insights into their target customer’s preferences, buying patterns, pain points, as well as demographics.
- Business Research also provides businesses with a detailed overview of their target markets, what’s in trend, as well as market demand.
- By studying consumers’ buying patterns and preferences as well as market trends and demands with the help of business research, businesses can effectively and efficiently curate the best possible plans and strategies accordingly.
- The importance of business research also lies in highlighting the areas where unnecessary costs can be minimized and those areas in a business which need more attention and can bring in more customers and hence boost profits.
- Businesses can constantly innovate as per their customers’ preferences and interests and keep their attention on the brand.
- Business Research also plays the role of a catalyst as it helps businesses thrive in their markets by capturing all the available opportunities and also meeting the needs and preferences of their customers.
Also Read: Business Analyst vs Data Analyst

Business research plays an important role in the business intelligence process. This is usually conducted to determine if a company can succeed in a new region through competitive analyses and a better marketing approach. Due to this, this broad field has been distinguished into two types namely, Qualitative Research and Quantitative Research Method.
Here are the most important types of Business Research :
Qualitative Research Methods
It involves putting open-ended questions to the audience through different channels of communication to understand why researchers think in a particular manner. Stress is laid on understanding the intent, attitude, and beliefs to figure out the behaviour and response of the customers. Moreover, the goal of Qualitative Business Research is to get in-depth knowledge about the subjects of the research. Moreover, qualitative research enables us to put the perspective of the consumer in front of the researcher so that we can understand and see the alignment of the ideas between the market and the business.
The data collected in this type of business research is by the following methods:
- Interviews
- Case Study
- Ethnographic Research
- Website Visitor Profiling
- Content Analysis
Also Read: Study MBA in Music Business at Berklee College of Music!
Let us take a detailed look at some of the ways-
Interviews and surveys are similar. The only difference lies in the fact that the responder can put a question in an interview whilst it is not possible during a survey. Through interviews, it is easier to understand the detailed perspective of the person concerning the subject of research. A mobile brand researched to understand why certain colours are preferred by male and female customers. The research revealed that since red is assumed to be a feminine colour, it is more preferred by females than males.
Focus groups are a type of business research that involves only a set of individuals. Each selected individual represents a particular category of the target market. The major difference between interviews and focus groups is the number of people that it involves. To launch a new product for a particular group of society, focus groups prove to be the best way to understand the needs of the local audience.
For example, Tesla decides to launch their latest car model in India. The company, therefore, will require feedback from the Indian audience only.
Did you know? Amazon, the internet giant changed its payment strategy to enter the Indian market. Since the Indian economy was not entirely ready for online modes of payment, amazon introduced a new payment method and came up with ‘ cash on delivery ’ to gain consumers’ trust.
One of the most effective ways for business research is conducting case studies. With the motive to understand customer satisfaction, challenges that usually the customers face while using the product and hence, providing them with the right solution can be achieved by analysing data secured through data secured by case studies. Case study researchers are conducted in many fields of business that ultimately aid organisations in improving their products or services.
Ethnographic Research refers to understanding people as a whole. One must be able to grok their consumers or target audience which will help identify patterns, flaws, etc. Ethnography is a branch of anthropology that is the study of what elements or features make us humans. How did people live? What aspect made us so dependent on smartphones and technology? Why would people buy one product over the other? It refers to asking questions about lifestyle, communities, etc., and trying to gain insight into consumer behaviour and buying patterns.
For example, consider a random product. Are people looking for that product? Do they need it? Is it a necessity or a luxury? Which class of people are most likely to buy it? People often cannot comprehend what they are looking for. Gaining different perceptions can help us tailor our products accordingly to the consumers. Who would have thought that the majority of humans will need face masks for survival?
Also Read: How to Become a Research Analyst?
Quantitative Research Methods
With the employment of mathematical, statistical and computational techniques, quantitative research is carried out to deal with numbers. This systematical empirical investigation starts with the acquisition of the data and then moves on to analyzing it with the help of different tools. The goal is to identify clientele and then meet the targets of the audience. As the method of business research employs a questionnaire to determine the audience’s response, the questions are built around the idea that the audience knows about the product or the services that the firm offers. Some of the key questions answered in quantitative research methods include, who is connected with your network, how they qualify for the ‘product’ or how regularly they visit your website.
The data is collected based on the following research:
- Correlational
- Online
- Casual Comparative
- Experimental
It is the most common method under quantitative research via which a huge amount of data can be collected concerning a product or service. A common set of questions are asked to the people and they are asked to provide their inputs. To understand the nature of the market in-depth, this method is massively used by leading organisations all across the globe. Analysing data recorded through service helps organisations make suitable decisions.
Under this research, usually two entities are put together to examine the impact they create on each other. As suggested by the name it is the best process to understand patterns, relationships and trends. the data grasped through correlation research is generally combined with other tools as one cannot achieve a firm conclusion using this type of business research.
Experimental research is purely based on proving a particular theory that is pre-assumed. True experimental research companies can understand varied behavioural traits of the customers that further assist them in generating more revenue. Exposing a set of audience to common parameters, their behaviour is recorded and hence analysed. This can be understood as the main basis of the experimental research.
Also Read: Scope of Operation Research
There are certain pros and cons of business research that you must know about. Here are the advantages and disadvantages of Business Research.
Advantages of Business Research
- Business Research plays the role of a catalyst in identifying potential threats, issues as well as opportunities .
- It provides a detailed analysis of customers and the target audience , thus helping in building better relationships with one’s audience and capturing the areas which we might be missing out on.
- It also anticipates future problems thus the enterprise is able to tackle those uncertainties and prepare for them beforehand.
- It keeps a continuous track of competition in the market and gives businesses the scope to come up with better strategies to tackle their competitors.
- Business Research also conducts a thorough cost analysis thus helping the company efficiently manage resources and allocate them in an optimal manner.
- It keeps you updated with the latest trends and competitor analysis .
Disadvantages of Business Research
- Business Research can be expensive and time-consuming .
- It also has the danger of being assumptive and imprecise at times , because the focus groups might be small or can be highly based on assumptions.
- The market is ever-changing and ever-evolving and capturing the right trends or anticipating them can constitute a complicated process for business research.
Also Read: Types of Research Design
The process of business research can be as comprehensive and as detailed as a business wants it to be. Generally, a company takes up research with a certain aim or hypothesis in order to figure out the issues, opportunities and trends and how they can be leveraged in the best way.
Here is the step-by-step process of Business Research:
- Identifying the Opportunity or Problem – To begin with the research, we first need to know what is the problem or the opportunity we would be leveraging on. It can be a popular trend or a common problem that a business is facing and can potentially become the headstart for the research process. Once you know the problem or the opportunity, go ahead with giving an understandable statement of what it’s about, what the hypothesis of the research will be as well as its objectives.
- Decide and Plan the Research Design – The next step in the business research process to find the right research design which suits the objectives and overall plan of the research. The most popular research designs are Quantitative and Qualitative Research.
- Determining the Research Method – The research design is closely connected to the research method since both qualitative and quantitative research designs have different methods for data collection, analysis, amongst others. So, once you have put a finger on what the right research design will be, go ahead with finding the right research method as per the plan, types of data collection, objective, costs involved, and other determining factors.
- Collect Data – Utilizing the research method and design, the next step in the business research process is to collect data and assimilate it.
- Data Analysis and Evaluation – After assimilating the data required, the data analysis will take place to gather all the observations and findings.
- Communicate Results – The presentation of the business research report is the concluding step of this procedure after which the higher management works upon the best techniques and strategies to leverage the opportunity or tackle the issue.
Also Read: MBA in Business Analytics
The scope of Business Research is multifarious and reaches out to many specialisations and areas. Let’s take a look the scope of business research across various specialisations:
- Marketing Management When it comes to business research, becomes an important part of marketing management that analyses consumer behaviour, target audiences, competition, price policy, promotional plans and much more.
- Financial Management It also plays an essential role in budgeting, financial planning, cost allocation, capital raising, tackling fluctuations with international currency as well as taking finance-related decisions.
- Production Management Production Management also includes business research as it helps in product development, planning out for a newer one, finalizing the right technologies for production, and so on.
- Materials Management Business Research is an important aspect of checking the best materials and carrying out its production, supply chain management , logistics , as well as shortlisting negotiation strategies.
There is an incremental role of business research as its importance is across every aspect of the business. Let’s take a look at the role of business research in an enterprise:
- The most primary role of business research is that it helps across every decision in the business, from product innovation to marketing and promotional planning.
- Business Research also helps in forecasting a business, whether in terms of competition or any other types of problems it will be facing.
- Another key area where this plays a bigger role is ensuring consumer satisfaction as through research, we can carry out research and highlight areas where we can efficiently serve our target audience.
- Business research also helps in implementing cost-effectiveness in a business as it can assist in cutting costs wherever needed and investing more in those areas, where profit is coming from.
Want to understand and learn more about business research? Here are some of the books that will make you a pro in this field. Check out the list of business research books:
Also Read: Is It Possible to Study MBA in Europe Without GMAT?
The purpose of a report is to inform the other members, junior and subordinates of the team to provide information on the specific topic. There is a specific format of a business report which makes it look more professional and presentable. There should be a title with the date and nature. The second section includes the introduction, body, and then conclusion. Reports help to identify the issues and helps in resolving them at earlier stages. It can include graphs, surveys, interviews, flow, and piecharts also.
Are you wondering why is there a need to do business research? Business is not stable and it is vital to stay up to date with all the data and developments. It is also important to make business-related decisions, and keep track of competitors, customer feedback, and market changes. The basic objective of business research is to identify the issues and evaluate a plan to resolve them for better managerial functioning.
Now that you are familiar with the objective, importance, and advantages the next important step is to know how to conduct research. There are numerous tools available for free while for some advanced tools there is a membership. Check out the list of top 10 tools:
- Google Keyword Tools
- Google Analytics
- Google Trends
The one thing constant in a business is market changes. A new trend or change comes every time you blink an eye. To keep track of everything externally and internally a research partner comes helpful. There are a few things to keep in mind that will help you in choosing the right business partner. The first thing to keep in mind is that the person should have relevant work experience and expertise in that particular field. An experienced partner can help businesses reach new heights. Look for a partner that can provide well-curated solutions and not the generic ideas that every enterprise follows. Last but not least is that your business research partner should have knowledge of the latest tools and techniques.
Also Read: MBA in Sustainable Development: Courses & Universities
Is your big presentation coming up or your report is due on Monday but you still haven’t finalized your business research topic? Here are some of the trendiest research topics for you:
- How advertisements influence consumer behaviour?
- Does incentive motivation increase employee productivity?
- How to handle crises in the business?
- How to create a work-life balance in the organization?
- What are the things a small business owner has to face?
- How to expand the company globally?
- How is digital marketing helping every business type?
- How to maintain the quality and quantity of products?
- What are the struggles entrepreneurs of a start-up face?
- How to create a budget and maintain company finances?
In order to build a career in Research , you can simply grab a degree in the field of Management , Business or Administration. So, students with an understanding of the core concepts of business and an inclination for research can consider it as a go-to option. Other suitable programs can be Master in Management , MBA Business Analytics , and MBA Data Analytics , to name a few.
To know more, check out Qualitative Research Methods !
It can simply mean researching every area of a business and using the provided information and data to ensure profit maximization.
There are different types of business research such as interviews, surveys, focus groups, correlational research, ethnographic research, case study research, and quantitative research methods, amongst others.
It is essentially important for various aspects of a business such as profit maximization, cost-cutting, financial management , personnel management, consumer behaviour, etc.
The process of research depends upon the type of research design you are opting for. To start with, we first need to determine the aim or objective of the research, then plan out the whole process which includes the types of methods we will be using, then the actual research that takes place followed by the data found that helps in understanding the key observations and how they can be implemented to actualize research hypothesis.
If you’re thinking to start a product line in your existing business or planning a startup, business research is a fundamental process that helps you to navigate the opportunities and obstacles in the marketplace. Knowing your strengths and weaknesses can help you come up with advanced and powerful research techniques that will make it easier to manage. Are you planning to take your higher education abroad? Then, you can quickly book a counselling session with the experts at Leverage Edu and we can help you build the right platform for you to grow in the corporate world.
Team Leverage Edu
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Contact no. *
Great article! Your content is beneficial. Thank you, and Keep Sharing.
Thank you, Sophia!

Leaving already?
8 Universities with higher ROI than IITs and IIMs
Grab this one-time opportunity to download this ebook
Connect With Us
25,000+ students realised their study abroad dream with us. take the first step today..

Resend OTP in

Need help with?
Study abroad.
UK, Canada, US & More
IELTS, GRE, GMAT & More
Scholarship, Loans & Forex
Country Preference
New Zealand
Which English test are you planning to take?
Which academic test are you planning to take.
Not Sure yet
When are you planning to take the exam?
Already booked my exam slot
Within 2 Months
Want to learn about the test
Which Degree do you wish to pursue?
When do you want to start studying abroad.
September 2024
January 2025
What is your budget to study abroad?

How would you describe this article ?
Please rate this article
We would like to hear more.
Root out friction in every digital experience, super-charge conversion rates, and optimize digital self-service
Uncover insights from any interaction, deliver AI-powered agent coaching, and reduce cost to serve
Increase revenue and loyalty with real-time insights and recommendations delivered to teams on the ground
Know how your people feel and empower managers to improve employee engagement, productivity, and retention
Take action in the moments that matter most along the employee journey and drive bottom line growth
Whatever they’re are saying, wherever they’re saying it, know exactly what’s going on with your people
Get faster, richer insights with qual and quant tools that make powerful market research available to everyone
Run concept tests, pricing studies, prototyping + more with fast, powerful studies designed by UX research experts
Track your brand performance 24/7 and act quickly to respond to opportunities and challenges in your market
Explore the platform powering Experience Management
- Free Account
- For Digital
- For Customer Care
- For Human Resources
- For Researchers
- Financial Services
- All Industries
Popular Use Cases
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Employee Exit Interviews
- Net Promoter Score
- Voice of Customer
- Customer Success Hub
- Product Documentation
- Training & Certification
- XM Institute
- Popular Resources
- Customer Stories
Market Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Partnerships
- Marketplace
The annual gathering of the experience leaders at the world’s iconic brands building breakthrough business results, live in Salt Lake City.
- English/AU & NZ
- Español/Europa
- Español/América Latina
- Português Brasileiro
- REQUEST DEMO
- Experience Management
- Business Research
Try Qualtrics for free
Business research: definition, types & methods.
10 min read What is business research and why does it matter? Here are some of the ways business research can be helpful to your company, whichever method you choose to carry it out.
What is business research?
Business research helps companies make better business decisions by gathering information. The scope of the term business research is quite broad – it acts as an umbrella that covers every aspect of business, from finances to advertising creative. It can include research methods which help a company better understand its target market. It could focus on customer experience and assess customer satisfaction levels. Or it could involve sizing up the competition through competitor research.
Often when carrying out business research, companies are looking at their own data, sourced from their employees, their customers and their business records. However, business researchers can go beyond their own company in order to collect relevant information and understand patterns that may help leaders make informed decisions. For example, a business may carry out ethnographic research where the participants are studied in the context of their everyday lives, rather than just in their role as consumer, or look at secondary data sources such as open access public records and empirical research carried out in academic studies.
There is also a body of knowledge about business in general that can be mined for business research purposes. For example organizational theory and general studies on consumer behavior.
Free eBook: 2024 global market research trends report
Why is business research important?
We live in a time of high speed technological progress and hyper-connectedness. Customers have an entire market at their fingertips and can easily switch brands if a competitor is offering something better than you are. At the same time, the world of business has evolved to the point of near-saturation. It’s hard to think of a need that hasn’t been addressed by someone’s innovative product or service.
The combination of ease of switching, high consumer awareness and a super-evolved marketplace crowded with companies and their offerings means that businesses must do whatever they can to find and maintain an edge. Business research is one of the most useful weapons in the fight against business obscurity, since it allows companies to gain a deep understanding of buyer behavior and stay up to date at all times with detailed information on their market.
Thanks to the standard of modern business research tools and methods, it’s now possible for business analysts to track the intricate relationships between competitors, financial markets, social trends, geopolitical changes, world events, and more.
Find out how to conduct your own market research and make use of existing market research data with our Ultimate guide to market research
Types of business research
Business research methods vary widely, but they can be grouped into two broad categories – qualitative research and quantitative research .
Qualitative research methods
Qualitative business research deals with non-numerical data such as people’s thoughts, feelings and opinions. It relies heavily on the observations of researchers, who collect data from a relatively small number of participants – often through direct interactions.
Qualitative research interviews take place one-on-one between a researcher and participant. In a business context, the participant might be a customer, a supplier, an employee or other stakeholder. Using open-ended questions , the researcher conducts the interview in either a structured or unstructured format. Structured interviews stick closely to a question list and scripted phrases, while unstructured interviews are more conversational and exploratory. As well as listening to the participant’s responses, the interviewer will observe non-verbal information such as posture, tone of voice and facial expression.
Focus groups
Like the qualitative interview, a focus group is a form of business research that uses direct interaction between the researcher and participants to collect data. In focus groups , a small number of participants (usually around 10) take part in a group discussion led by a researcher who acts as moderator. The researcher asks questions and takes note of the responses, as in a qualitative research interview. Sampling for focus groups is usually purposive rather than random, so that the group members represent varied points of view.
Observational studies
In an observational study, the researcher may not directly interact with participants at all, but will pay attention to practical situations, such as a busy sales floor full of potential customers, or a conference for some relevant business activity. They will hear people speak and watch their interactions , then record relevant data such as behavior patterns that relate to the subject they are interested in. Observational studies can be classified as a type of ethnographic research. They can be used to gain insight about a company’s target audience in their everyday lives, or study employee behaviors in actual business situations.
Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research is an immersive design of research where one observes peoples’ behavior in their natural environment. Ethnography was most commonly found in the anthropology field and is now practices across a wide range of social sciences.
Ehnography is used to support a designer’s deeper understanding of the design problem – including the relevant domain, audience(s), processes, goals and context(s) of use.
The ethnographic research process is a popular methodology used in the software development lifecycle. It helps create better UI/UX flow based on the real needs of the end-users.
If you truly want to understand your customers’ needs, wants, desires, pain-points “walking a mile” in their shoes enables this. Ethnographic research is this deeply rooted part of research where you truly learn your targe audiences’ problem to craft the perfect solution.
Case study research
A case study is a detailed piece of research that provides in depth knowledge about a specific person, place or organization. In the context of business research, case study research might focus on organizational dynamics or company culture in an actual business setting, and case studies have been used to develop new theories about how businesses operate. Proponents of case study research feel that it adds significant value in making theoretical and empirical advances. However its detractors point out that it can be time consuming and expensive, requiring highly skilled researchers to carry it out.
Quantitative research methods
Quantitative research focuses on countable data that is objective in nature. It relies on finding the patterns and relationships that emerge from mass data – for example by analyzing the material posted on social media platforms, or via surveys of the target audience. Data collected through quantitative methods is empirical in nature and can be analyzed using statistical techniques. Unlike qualitative approaches, a quantitative research method is usually reliant on finding the right sample size, as this will determine whether the results are representative. These are just a few methods – there are many more.
Surveys are one of the most effective ways to conduct business research. They use a highly structured questionnaire which is distributed to participants, typically online (although in the past, face to face and telephone surveys were widely used). The questions are predominantly closed-ended, limiting the range of responses so that they can be grouped and analyzed at scale using statistical tools. However surveys can also be used to get a better understanding of the pain points customers face by providing open field responses where they can express themselves in their own words. Both types of data can be captured on the same questionnaire, which offers efficiency of time and cost to the researcher.
Correlational research
Correlational research looks at the relationship between two entities, neither of which are manipulated by the researcher. For example, this might be the in-store sales of a certain product line and the proportion of female customers subscribed to a mailing list. Using statistical analysis methods, researchers can determine the strength of the correlation and even discover intricate relationships between the two variables. Compared with simple observation and intuition, correlation may identify further information about business activity and its impact, pointing the way towards potential improvements and more revenue.
Experimental research
It may sound like something that is strictly for scientists, but experimental research is used by both businesses and scholars alike. When conducted as part of the business intelligence process, experimental research is used to test different tactics to see which ones are most successful – for example one marketing approach versus another. In the simplest form of experimental research, the researcher identifies a dependent variable and an independent variable. The hypothesis is that the independent variable has no effect on the dependent variable, and the researcher will change the independent one to test this assumption. In a business context, the hypothesis might be that price has no relationship to customer satisfaction. The researcher manipulates the price and observes the C-Sat scores to see if there’s an effect.
The best tools for business research
You can make the business research process much quicker and more efficient by selecting the right tools. Business research methods like surveys and interviews demand tools and technologies that can store vast quantities of data while making them easy to access and navigate. If your system can also carry out statistical analysis, and provide predictive recommendations to help you with your business decisions, so much the better.
Related resources
Market intelligence 10 min read, marketing insights 11 min read, ethnographic research 11 min read, qualitative vs quantitative research 13 min read, qualitative research questions 11 min read, qualitative research design 12 min read, primary vs secondary research 14 min read, request demo.
Ready to learn more about Qualtrics?
Business Research: Definition, Examples

Business research examines all aspects of a business environment. It asks questions about competitors, market structure, government regulations , economic trends, technological advances, changing patterns of the business world, and numerous other factors that make up the business environment.
The emphasis of business research is on shifting decision-makers from intuitive information gathering to systematic and objective investigation.
Like other research, business research is accomplished through exploration, description, explanation, and prediction.
Let’s Understand Business Research:
What is Business Research?
Business research is a systematic and objective inquiry that provides information to guide managerial decisions, which are arrived at through planning, acquiring, analyzing, and disseminating relevant data to decision-makers to mobilize the organization to take appropriate actions to maximize business performance.
Who Business Research Works?
Business research is of recent origin and mostly supported by business organizations, while the public domain has sponsored much environmental research, some of it for hundreds of years.
The development of scientific methods in business research lags behind similar evolution in the physical sciences.
Physical scientists have been more rigorous in their concepts and research procedures. They are much more advanced in their theory development than business scientists. Business research operates in a less favorable environment in other ways, too.
Physical research is usually conducted under controlled laboratory conditions, while business research seldom is.
Business research is an important management activity that helps companies determine which products will be most profitable for companies to produce.
Several steps are necessary when conducting business research: each step must be thoroughly reviewed to ensure that the business enterprise makes the best decision.
Steps of Business Research
These steps include, among others:
- Product analysis.
- Market analysis.
- Financial analysis.
- Competitor analysis.
- Growth analysis.
Product Analysis
Product analysis is the first step in business research.
Companies must find a product that meets consumer demand or exceeds consumer demand; otherwise, the product will fail in the economic marketplace.
One type of analysis is to find an existing product that can be improved through design and features.
Another kind of product analysis will find emerging markets with high demand and low supply, which allows companies to sell products to meet consumer demand.
Market Analysis
Companies will conduct a market analysis to determine how much profit may be earned from current demand.
Management will look at which stage of the business cycle the market is currently in, whether emerging, plateau, or declining. A market analysis will also determine the price points at which products can be sold.
Financial Analysis
The financial analysis determines the cost of each production item used to produce goods and services.
Management will also review the best cost application methods, ensuring that all production costs are adequately applied to each product manufactured or service rendered.
Competitor Analysis
A competitor analysis of a market is an essential part of business research. Knowing which companies have the best production methods or customer loyalty helps new companies understand how they can create a competitive advantage when entering a new market.
Growth Analysis
Growth analysis is crucial in understanding a business operation’s profitability.
Business research usually includes forecasting the growth and direction of the current industry or market. Knowing to which direction the market is headed helps companies determine the stability of new business operations.
A SWOT (strength, weakness, opportunity, and threat) analysis is often undertaken to understand a market.
Based on this analysis, a business enterprise can take strategic decisions or measures in a business venture.
What are the primary objectives of business research?
Business research seeks to understand all aspects of a business environment , including competitors, market structure, government regulations, economic trends, technological advances, and changing patterns in the business world.
How does business research differ from physical sciences regarding its development and methods?
The development of scientific methods in business research lags behind that in the physical sciences. Physical scientists have been more rigorous in their concepts, research procedures, and theory development. Additionally, physical research is often conducted under controlled laboratory conditions, whereas business research usually isn’t.
What are the steps involved in conducting business research?
Business research involves several steps, including product analysis, market analysis, financial analysis, competitor analysis, and growth analysis.
Why is a SWOT analysis often undertaken in business research?
A SWOT (strength, weakness, opportunity, and threat) analysis is undertaken to understand a market comprehensively. Based on this analysis, businesses can make strategic decisions or measures in their ventures.
Examples of Business Research
Here are five examples that illustrate what business research is.
Microcredit programs from institutional and non-institutional sources have been found to significantly impact raising the standard of living of rural people, especially women.
But there is ample evidence that these credit facilities are misused and misdirected in many instances.
This practice has led to a high default rate, putting institutions hesitant to finance rural people. In this context, it is imperative to examine the status of credit utilization and assess the extent and magnitude of misuse and diversion of credit in rural areas.
Human resource development has become an essential component of the development process. This is because the human factor drives any development process .
Since a firm’s human resources are an important potential source of sustained competitive advantage , managing them well helps create unique competencies that differentiate products and services and, in turn, drive competitiveness.
This link, in principle, facilitates successful corporate performance.
An increasing body of work argues that a positive relationship exists between the so-called high-performance work practices and different measures of company performance.
Such high-performance work practices include comprehensive employee recruitment and selection procedures, incentive compensation and performance management systems, and extensive employee involvement and training.
Several studies in Bangladesh and elsewhere have found a positive relationship between HRM practices and policies and different measures of company performance.
Keeping the above background in view, a research firm designed a study to focus on studying the relationship between rewards and recognition practices and firm performance, as well as between recruitment and retention systems and firm performance, using a survey instrument for traditional HRM activities (recruitment, selection, performance management, training, compensation , and employee relations) and using independently collected organizational performance data focusing on financial performance (assets, capital, deposits, and return on equity).
The researcher decided to restrict his sample to the banking industry of Bangladesh.
In one of her papers, Sultana (2012: 15) states that women entrepreneurs in SMEs have emerged as a new class both in Bangladesh’s urban and rural areas.
Though some studies were conducted on entrepreneurship development in Bangladesh, no significant research was done on women entrepreneurs’ performance, either in rural or urban areas.
Women entrepreneurship or women in business is considered a very recent phenomenon in Bangladesh. Many economists, sociologists, and political scientists have recognized entrepreneurship in small businesses as an essential gradient influencing the economic growth of a country.
Keeping this scenario in view, the author attempted to highlight the activities of women in small and medium enterprises (SMEs), particularly in urban areas, including Dhaka Metropolitan city.
The study also collected data relevant to the entrepreneurial qualities of women and their socioeconomic status to understand whether these facilitate or constrain women to emerge as successful entrepreneurs.
This example is drawn from an adventure travel survey in a US county, where many small firms operate on half-dozen rivers and provide half-day to multi-day trips to thousands of clients annually.
The managers of a group of county river basin outfitters wanted to know how to increase customers’ satisfaction and repeat business for their multi-day river trips.
They wanted to verify the hypothesis that customer satisfaction is related to concerns with the quality of food and amenities provided safety and lore about the natural and historical setting of the trips.
Financial statements, the critical parts of financial reporting , are the principal means of supplying accounting information to a wide range of users to evaluate the financial position, profitability, liquidity, and prospects of a company so that the users can make economic decisions.
The stability of the market economy largely depends on the user groups’ confidence in the fairness of the financial statements (Choudhury et el. 1996).
Generally, fair presentation refers to the ability of the economic conditions of a company. This relates to accounting accuracy and completeness (Sen, 2002).
Keeping these points in view, Jahan and Nahar (2012: 79) planned a study to examine to what extent the companies in Bangladesh follow or observe the adapted Bangladesh Accounting Standard 1 (BAS-1) and also analyze the compliance of BAS-1 in presenting the financial report of different companies in Bangladesh.

Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Yearly paid plans are up to 65% off for the spring sale. Limited time only! 🌸
- Form Builder
- Survey Maker
- AI Form Generator
- AI Survey Tool
- AI Quiz Maker
- Store Builder
- WordPress Plugin
HubSpot CRM
Google Sheets
Google Analytics
Microsoft Excel
- Popular Forms
- Job Application Form Template
- Rental Application Form Template
- Hotel Accommodation Form Template
- Online Registration Form Template
- Employment Application Form Template
- Application Forms
- Booking Forms
- Consent Forms
- Contact Forms
- Donation Forms
- Customer Satisfaction Surveys
- Employee Satisfaction Surveys
- Evaluation Surveys
- Feedback Surveys
- Market Research Surveys
- Personality Quiz Template
- Geography Quiz Template
- Math Quiz Template
- Science Quiz Template
- Vocabulary Quiz Template
Try without registration Quick Start
Read engaging stories, how-to guides, learn about forms.app features.
Inspirational ready-to-use templates for getting started fast and powerful.
Spot-on guides on how to use forms.app and make the most out of it.
See the technical measures we take and learn how we keep your data safe and secure.
- Integrations
- Help Center
- Sign In Sign Up Free
- What is Business Research: Methods, Types & Examples
Defne Çobanoğlu
Every business owner wants their company always to be successful and profitable. And even if you have a successful business plan, that does not mean things will not need changing in the future. And trial and error may not be on the table when you can not afford to lose money and precious customers. Therefore, you need to be cautious before taking any steps and do your research .
In this article, we explained business research, its methods, and types to help business owners and inform those interested to know more. We also added some examples of scenarios any company may face. Let us get started with the definition of business research!
- What is business research?
Business research is a type of research process where the main goal is to help a company thrive and collect data about the target audience, potential business plans, and marketing strategies . The data collection about possible risks and investment opportunities helps business owners make informed decisions about future plans.
The fields that can use business research include marketing, business, education, and social science . But of course, they are not the only ones that can benefit from business research. It is a helpful research type for all business needs. Now, let us see how we can further categorize this into methods and types of business research.
- Methods and types of business research
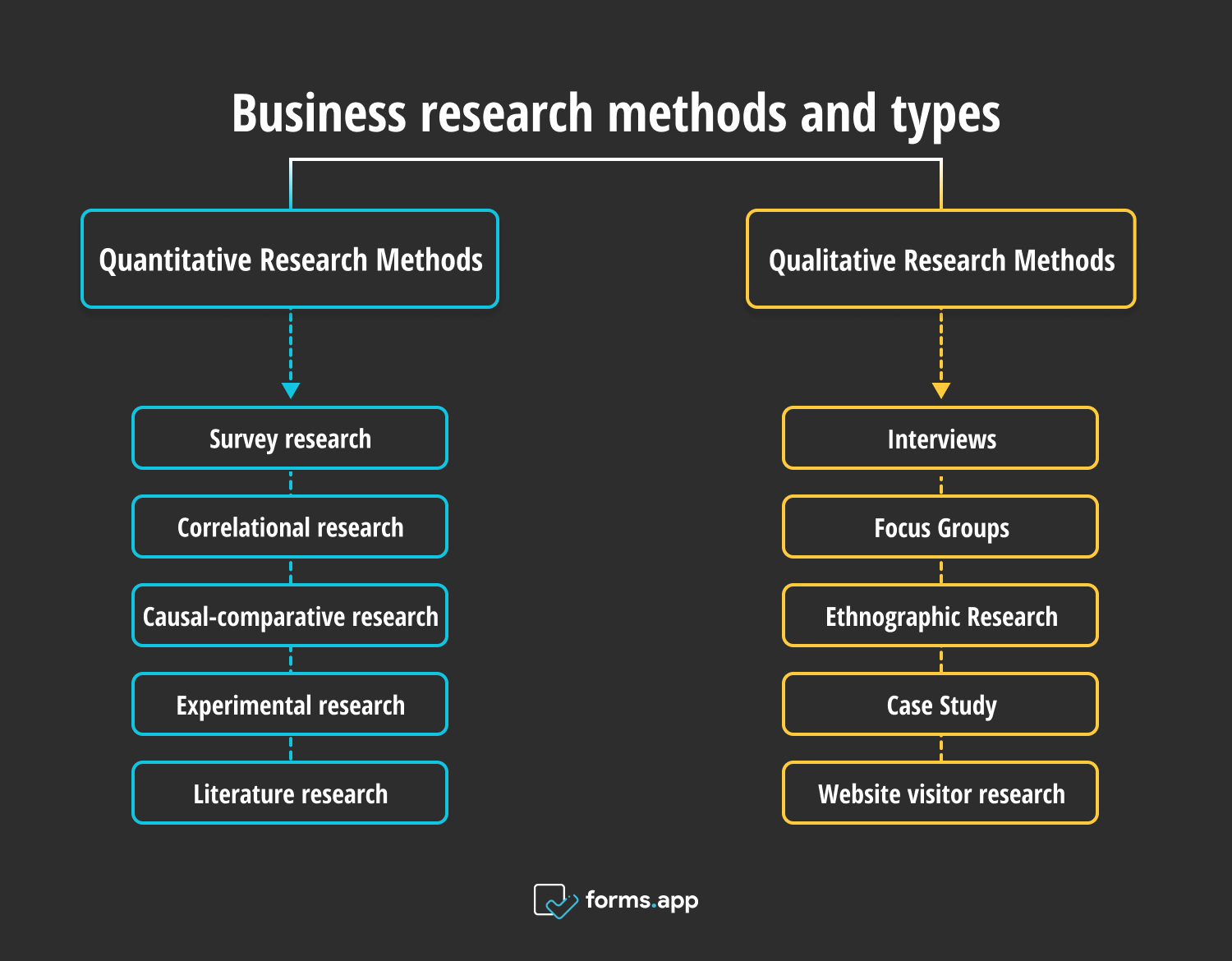
Business research methods and types
In business research methodology, there are two main types. These are quantitative research and qualitative research. In the simplest terms, quantitative research is about collecting numerical and factual data, whereas qualitative research is about collecting data by using open-ended questions . These two methods can be divided into more specific parts. Let us get started with quantitative research methods.
- A. Quantitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods give the researchers factual and numerical evidence that can be effectively used in decision-making processes. There are numerous ways to collect quantitative data, and it is also possible to use more than one method to prove the credibility of the information. Let us start with the first one:
- 1. Survey research
Surveys are a great way to collect information from a targeted group, no matter how big or small. They can be done in the format of an online survey, phone survey or questionnaire . Surveys are usually close-ended or multiple-choice questions that are easy to group and analyze. The business doing the research can collect valuable information directly from its customers.
- 2. Correlational research
Correlational research focuses on the discovery of whether two different entities influence each other in any way. The main focus of this research method is not to make decisions. But rather, they can use the findings to explore further using other research methods.
- 3. Causal-comparative research
Causal-comparative research is similar to correlational research in that both of them compare two different elements and how they affect each other. But the main difference is that fact the focus of this research method is to draw conclusions on the cause-and-effect relationship of said entities.
- 4. Experimental research
Experimental research has a broad spectrum when it comes to what is taken as ‘experimental’. Basically, it is when businesses want to test a specific theory about the quality of a product or service. There are many methods that can be used, and it is decided by the researcher according to the theory that will be tested.
- 5. Literature research
Literature research is a very effective and economical research method to use. It is about using offline and online existing literature and going through them to analyze the data. It is mostly used in sales about consumer behaviors.
- B. Qualitative Research Methods
Qualitative research is not about numbers like quantitative research. Instead, it is about emotions, opinions, and approaches. The target audience can be presented with a topic through open-ended questions. There is more than one method to go with, and it is even possible to use multiple methods at once. Let us see qualitative research methods:
- 1. Interviews
The interview method is mostly done on a smaller participant group about a specific subject. They consist of open-ended questions and can be in a structured or unstructured format. Interviews are one-on-one questions asked to the target audience to gain insight into the problem .
- 2. Focus Groups
A focus group is a pre-determined group of individuals who are chosen to participate in a study to answer specific questions. The researchers present them with a topic and encourage discussions with open-ended questions . Then, the findings are generalized to make decisions.
- 3. Ethnographic Research
Ethnographic research is similar to conceptual research, and its main focus is to understand the culture and people of the target audience by using observation . This method is done by observing the people in their natural environment and seeing how they interact with one another and their surroundings.
- 4. Case Study
Businesses generally use a case study method to showcase to potential consumers how their product or service helped a certain individual or a group . It is a good way to attract new customers. This method helps highlight the company’s skill sets and assets.
- 5. Website visitor research
This research method is relatively newer than others. Its main focus is to collect feedback from individuals who use the company website and ask them about their opinions. A business can use this method by presenting a customer with a quick survey after their purchase on the website . Afterward, the company can improve user satisfaction by fixing existing problems.
- Importance of business research
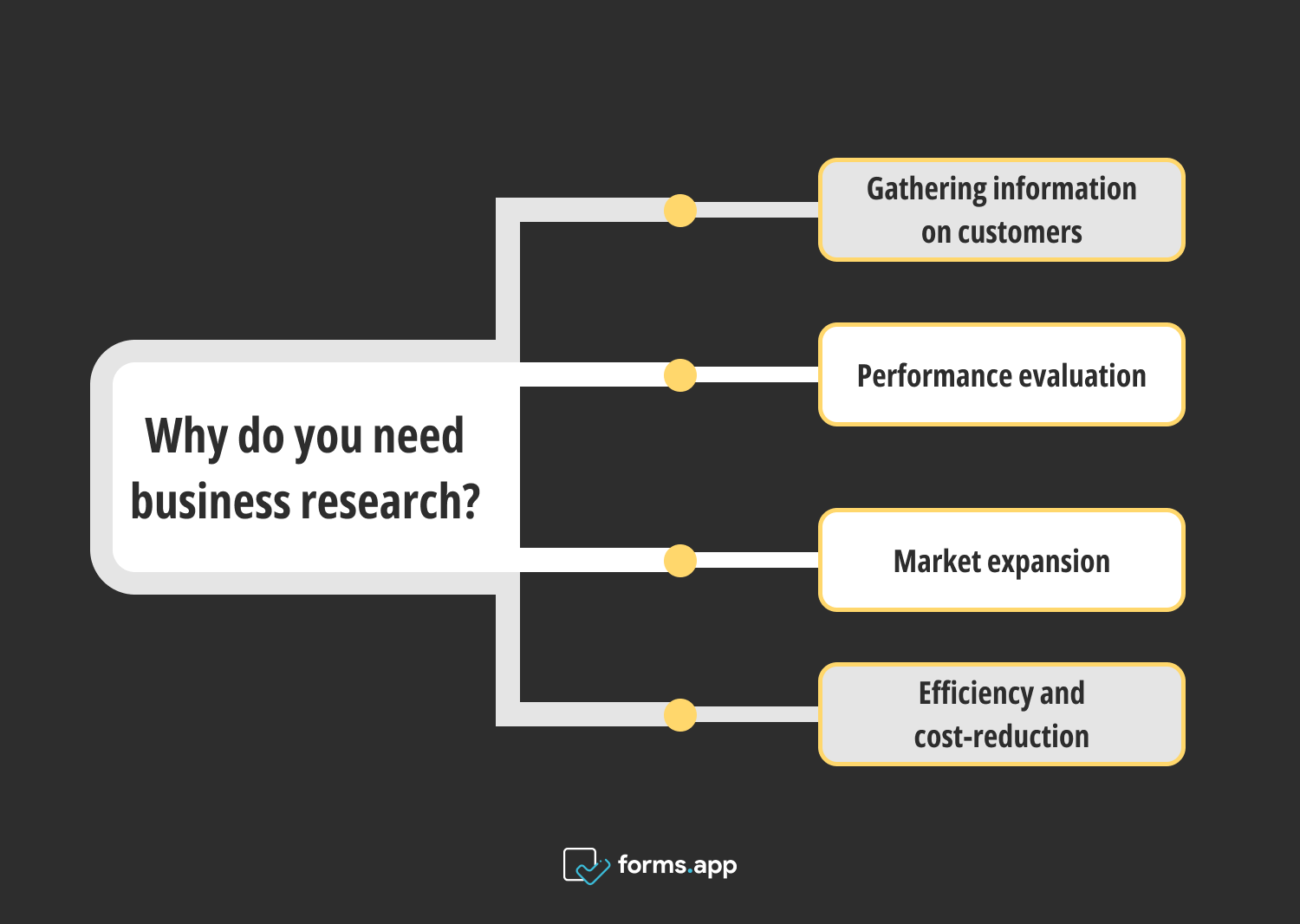
The reasons for conducting business research
Businesses grow by knowing their target market, potential customers, and competitors. And this is only possible by conducting market research to help make informed business decisions. The main goal of business research is to help stakeholders of the company make planned and informed decisions using the facts in the business research report. However, there are other reasons why business research is important. These are:
- Gathering information on customers: A business research report provides data on consumers’ behavioral changes, their needs, preferences, and expectations. The managers and stakeholders can make informed decisions with this knowledge.
- Performance evaluation: Research allows businesses to evaluate their success against industry standards and other competitors. This helps keep track while deciding how to differentiate themselves from others.
- Market expansion: Business research topics include areas that were not explored before. Therefore, when the business wants to expand to new markets, the research provides information on the market’s dynamics and potential risks and profits .
- Efficiency and cost-reduction: The data collected by business research helps identify any obstacles to productivity and cost excessiveness. That way, a more cost-effective and efficient approach can be taken.
- Business research examples
Business research helps business managers make smart plans for the company and its future. They can make informed decisions about new marketing strategies, building new products or service branches, or improving customer satisfaction .
Business research example #1
Imagine a company making energy drinks wants to know if they can expand their market to the older part of the population. They do not know if they will be interested in their product or what kind of marketing strategies they can use to attract older people’s attention. They can make up a focus group and ask them about their opinions. The company can also conduct literature research to find out information about the competitors .
Business research example #2
Imagine a company that has a clothing store website wants to know if there is anything that makes shopping on their website difficult for customers. They can show a pop-up customer satisfaction survey and ask them if they can find what they are looking for easily and how the website visiting experience was. Then, they can collect customer feedback and see how they can improve their website to enhance customer satisfaction levels.
- Frequently asked questions about business research
What are the 4 stages of business research?
Much like every other research, business research is also best done when it is preplanned and organized. And there is a 4 stage plan of business research. These are:
1 - Defining the problem
2 - Designing the research plan
3 - Collecting data and making an analysis
4 - Reporting on the findings
What is the purpose of business research?
The purpose of business research is to make sense of the existing elements of a business, such as consumers, product placement, marketing, innovation, etc . And using the data collected on these elements to make informed decisions and create smart business strategies to improve the success of the company.
When to use business research?
Business research is best used when a new approach is taken or a new product is launched, and the risks need to be assessed. It is essential to be mindful of all the negative and positive sides of a new strategy without risking the entirety of the company.
- Final words
When you own a business, no matter how big or small, change can be intimidating. You can not go to new territories blindly. But, you can not stay the same either. In order to keep your existing customers and find new potential ones, you should be mindful of their habits and opinions. The best way of doing this is either to ask them directly ( using a survey, interviewing them, etc .) or to do your own research to draw conclusions.
In this article, we explained business research, quantitative and qualitative research methods, and business research types. We also included some examples of business research and what methods can be used for those problems. If you want to do your own business research but do not know where to start, you can check out quantitative research questions to get you started. Also, do not forget to check out other articles on research and so much more!
Defne is a content writer at forms.app. She is also a translator specializing in literary translation. Defne loves reading, writing, and translating professionally and as a hobby. Her expertise lies in survey research, research methodologies, content writing, and translation.
- Market Research
- Form Features
- Data Collection
Table of Contents
Related posts.
Gap model of service quality: Definition, model, & examples
Fatih Serdar Çıtak
.jpg)
50 Funny sales memes that will make you laugh (or cry)
Şeyma Beyazçiçek

5 consent form examples that will save your day
Business research methods: A comprehensive overview
Last updated
3 April 2024
Reviewed by
Cathy Heath
Business research is the process of gathering and analyzing different types of information to make informed business decisions.
If you undertake business research correctly, it has multiple benefits, such as:
Improving organizational operations
Identifying trends
Forecasting potential outcomes
This research can include studying competitor performance, examining consumer preferences, analyzing market trends, and identifying industry gaps.
Let’s learn more about business research methods and the steps for a successful research process.
Market analysis template
Save time, highlight crucial insights, and drive strategic decision-making
- The importance of business research
In today's fast-paced, data-driven world, we need to rely on more than just intuition and guesswork. Companies need a well-planned business research strategy to uncover invaluable insights into consumer preferences, market trends , and emerging opportunities.
Business research allows companies to:
Identify market opportunities
Researching industry trends and market segments enables businesses to discover untapped markets and new opportunities to expand sales.
Analyze customer behavior
Understanding customers’ motivations, perceptions, and behaviors is essential. Companies can create targeted marketing strategies and products that meet consumer needs while improving customer satisfaction .
Stay ahead of competitors
Competitive analysis can reveal what your competitors are doing well and where they are struggling. With this information, businesses can adjust their strategies to remain competitive.
Optimize operations
Business research can help companies optimize their operations and improve efficiency. Analyzing data on processes and workflows lets businesses identify areas of improvement, streamline operations, and reduce costs.
Overall, investing in business research is essential for companies wanting to remain competitive and relevant. The right research strategy helps businesses uncover insights to drive growth and improve their bottom line.
- Qualitative research methods vs. quantitative research methods
Business research has two main methods: Qualitative research and quantitative research.
Qualitative research methods
Qualitative research involves exploring and understanding a topic through non-numerical data.
This research type is particularly useful for exploring complex, multifaceted issues that may be difficult to quantify.
It can provide insights into customer needs and preferences and identify trends and patterns.
Researchers often use qualitative research in the early stages of a project to explore the problem and develop a deeper understanding.
It provides a foundation for quantitative research and can determine what researchers need to ask to answer the research question.
Qualitative research methods include:
Focus groups
Case studies
Ethnographic research
Website visitor profiling
They focus on understanding people’s attitudes, behaviors, and motivations.
Quantitative research methods
Quantitative research uses numerical data to test a hypothesis or solve a research question .
Researchers can capture quantitative data from:
Face-to-face interviews
Telephone interviews
Online polls
People often view quantitative data as more objective since it’s statistical and less subjective than qualitative data .
Quantitative research uses collections of data and measures, manipulates, and compares the information to get insight.
Which type of business research is best?
While quantitative and qualitative research methods both have their benefits, they also come with a few drawbacks:
Qualitative research cons include:
Typically small sample size , making it harder to generalize
Time-consuming
Quantitative research disadvantages include:
Not capturing the depth or nuance of the topic
Minimal understanding of beliefs, opinions, or behavior behind consumer decisions
Researchers must interpret the data correctly for accurate observations
Businesses need to consider which method suits their research goals and resources best. Carefully selecting a method ensures valuable insights for more informed decisions to meet your business goals.
- Five research techniques for your business
As you start planning your business research strategy, it's important to consider which research methods you want to use.
Let’s look at five research techniques, including when you should use them:
Surveys are a common method in business research. They effectively collect data from a large group by asking them to complete a questionnaire .
Surveys are best for gathering information about a specific population's:
Preferences
Experiences
You can conduct specific types of surveys, each with varying purposes and methodologies.
Types of surveys:
Customer satisfaction surveys
These surveys measure customer satisfaction with a product or service.
The questions may focus on the customer's product experience or the overall customer experience .
Market research surveys
These surveys gather information on a specific market, including:
Consumer preferences
Consumer behavior
Competitor analysis
Market trends
Employee satisfaction surveys
These surveys gauge the level of satisfaction and engagement of employees within an organization.
They may include questions on:
Compensation
Work-life balance
Job security
Career development
Brand awareness surveys
These surveys determine the level of awareness and recognition of a brand within a specific market. This type of survey can also measure brand loyalty and reputation.
Researchers conduct surveys in different ways, including online, by phone, or in person.
Online surveys are becoming increasingly popular due to their convenience and the ability to gather data quickly.
2. Interviews
Interviews are another valuable method in business research.
Unlike surveys, interviews involve talking to people one-on-one to gather in-depth information. Interviews are best to understand someone's perspectives, motivations, or experiences.
For example, if a company wants to understand why its customers prefer a certain product or service, it can use interviews to ask follow-up questions to gain more insights.
Interviews can be structured or unstructured depending on the researcher's objectives.
In a structured interview , the interviewer has a predetermined set of questions to ask all respondents. This method ensures that everyone answers the same questions, making it easier to compare and analyze their responses.
An unstructured interview is where the interviewer does not have a set of predetermined questions but lets the conversation flow naturally. This type of interview is more flexible and allows for unexpected insights to arise.
Whether a researcher wants to understand consumer behavior or develop new business strategies, interviews can provide valuable data to inform decisions.
3. Observation
Observation is an excellent method to see how people interact with products, services, or physical spaces.
It allows researchers to observe real-life scenarios and collect accurate data about:
Business processes
Employee behavior
Customer interactions
Overall business operations
It's particularly useful in situations where traditional survey or interview methods may not be effective.
Researchers can use several types of observation for business research, including:
Naturalistic observation
Controlled observation
Participant observation
Non-participant observation
Naturalistic observation involves observing behavior in a natural setting without manipulating the situation. This can gain insight into customer interactions and the decision-making process.
Controlled observation consists of manipulating a scenario and observing how people react. This can be useful for testing new products, services, or processes in a controlled environment.
Participant observation involves the researcher participating in the situation they are observing. This can help the researcher better understand the motivations and behaviors of those they’re observing.
Non-participant observation occurs while the researcher remains outside the situation and simply observes the actions. This approach can be helpful when it’s not possible or ethical for the researcher to participate directly.
Observation understands the human aspect of consumer behavior and how it influences decision-making.
Testing involves conducting experiments to gather quantitative data about a specific product or service. It's best to measure the impact of changes or improvements to a product or service.
Testing can involve different techniques like:
A/B testing: Evaluating two versions of a product or service
Usability testing : Seeing how users interact with a product to evaluate its ease of use
Performance testing: Checking the performance of a product under various conditions
Each type of testing is for a specific reason and with a specific goal in mind.
For example, usability testing ensures a product or service is user-friendly, while A/B testing identifies which version is more effective or preferred. Performance testing ensures a product can handle the demands of heavy use.
5. Focus groups
Focus groups are a popular method of business research to gain in-depth insights into consumer behavior, attitudes, and perceptions toward products and services.
A focus group typically consists of people that share similar characteristics. They come together to discuss and provide feedback on a specific topic.
Focus groups are best suited for situations where businesses want to understand their target audience’s needs and wants. This can be useful when:
Launching a new product
Testing a new advertising campaign
Evaluating the effectiveness of an existing marketing strategy
Focus groups provide a unique opportunity to get real-time feedback on ideas and products, allowing businesses to fine-tune their offerings to meet customer demands.
Understanding each research technique helps you design a strategy to collect the most relevant data for your business needs.
Steps of a business research process
Now you know the types of business research and its purpose, let’s look at the seven steps to successfully undertake it:
1. Identify the research problem
The first step in conducting research is to define the problem or issue to address. This may involve surveying customers, analyzing market data, or interviewing key stakeholders .
For example, if you own a fashion brand and your sales have dropped significantly, you may want to know why.
2. Conduct a review
Before starting research, check what researchers have already discovered in your organization, industry, or field.
Conducting a review can involve reading relevant articles or research papers and gathering secondary or desk research data.
This review process helps you better understand your research topic and may provide some insights into your research problem and fine-tune the next stage of your research.
3. Develop research questions and objectives
At this stage, you will develop specific research questions to achieve your objectives.
Research objectives are the goals you aim to achieve by conducting the research.
In our fashion brand example, one research question might be: "How do current fashion trends affect our sales?"
Get started today
Go from raw data to valuable insights with a flexible research platform
Editor’s picks
Last updated: 3 April 2024
Last updated: 26 May 2023
Last updated: 11 April 2023
Last updated: 22 July 2023
Last updated: 1 June 2023
Latest articles
Related topics, log in or sign up.
Get started for free
- Survey Software The world’s leading omnichannel survey software
- Online Survey Tools Create sophisticated surveys with ease.
- Mobile Offline Conduct efficient field surveys.
- Text Analysis
- Close The Loop
- Automated Translations
- NPS Dashboard
- CATI Manage high volume phone surveys efficiently
- Cloud/On-premise Dialer TCPA compliant Cloud on-premise dialer
- IVR Survey Software Boost productivity with automated call workflows.
- Analytics Analyze survey data with visual dashboards
- Panel Manager Nurture a loyal community of respondents.
- Survey Portal Best-in-class user friendly survey portal.
- Voxco Audience Conduct targeted sample research in hours.
- Predictive Analytics
- Customer 360
- Customer Loyalty
- Fraud & Risk Management
- AI/ML Enablement Services
- Credit Underwriting

Find the best survey software for you! (Along with a checklist to compare platforms)
Get Buyer’s Guide
- 100+ question types
- Drag-and-drop interface
- Skip logic and branching
- Multi-lingual survey
- Text piping
- Question library
- CSS customization
- White-label surveys
- Customizable ‘Thank You’ page
- Customizable survey theme
- Reminder send-outs
- Survey rewards
- Social media
- SMS surveys
- Website surveys
- Correlation analysis
- Cross-tabulation analysis
- Trend analysis
- Real-time dashboard
- Customizable report
- Email address validation
- Recaptcha validation
- SSL security
Take a peek at our powerful survey features to design surveys that scale discoveries.
Download feature sheet.
- Hospitality
- Financial Services
- Academic Research
- Customer Experience
- Employee Experience
- Product Experience
- Market Research
- Social Research
- Data Analysis
- Banking & Financial Services
- Retail Solution
- Risk Management
- Customer Lifecycle Solutions
- Net Promoter Score
- Customer Behaviour Analytics
- Customer Segmentation
- Data Unification
Explore Voxco
Need to map Voxco’s features & offerings? We can help!
Watch a Demo
Download Brochures
Get a Quote
- NPS Calculator
- CES Calculator
- A/B Testing Calculator
- Margin of Error Calculator
- Sample Size Calculator
- CX Strategy & Management Hub
- Market Research Hub
- Patient Experience Hub
- Employee Experience Hub
- Market Research Guide
- Customer Experience Guide
- The Voxco Guide to Customer Experience
- NPS Knowledge Hub
- Survey Research Guides
- Survey Template Library
- Webinars and Events
- Feature Sheets
- Try a sample survey
- Professional services
- Blogs & White papers
- Case Studies
Find the best customer experience platform
Uncover customer pain points, analyze feedback and run successful CX programs with the best CX platform for your team.
Get the Guide Now

We’ve been avid users of the Voxco platform now for over 20 years. It gives us the flexibility to routinely enhance our survey toolkit and provides our clients with a more robust dataset and story to tell their clients.
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
- Client Stories
- Voxco Reviews
- Why Voxco Research?
- Why Voxco Intelligence?
- Careers at Voxco
- Vulnerabilities and Ethical Hacking
Explore Regional Offices
- Cloud/On-premise Dialer TCPA compliant Cloud & on-premise dialer
- Fraud & Risk Management
Get Buyer’s Guide
- Banking & Financial Services
Explore Voxco
Watch a Demo
Download Brochures
- CX Strategy & Management Hub
- Blogs & White papers
VP Innovation & Strategic Partnerships, The Logit Group
- Our clients
- Client stories
- Featuresheets
Business Research: Definition, Types, and Methods
- February 7, 2022
SHARE THE ARTICLE ON

What is Business Research?
Business research refers to the process of gathering information on all areas of business with the purpose of leveraging this data to promote organizational growth, increase sales, and maximize profit. It involves the systematic management activities that help companies decide which products or services will perform well in the market and will therefore be most profitable to produce.
Exploratory Research Guide
Conducting exploratory research seems tricky but an effective guide can help.
Why is Business Research Important?
Business research provides companies with comprehensive data on the target customer’s preferences, purchasing behavior, demographics, and pain points. Such information allows the business to strategize and create more effective marketing plans that resonate with the target audience. A thorough overview of the overall market will also give the business an understanding of market trends and market demands so that plans and strategies can be devised accordingly.
Another key use of business research is that it can bring attention to areas where costs can be minimized to increase profits. It provides businesses with a competitive edge in the market by ensuring that all identified opportunities are capitilized on and that decisions are made with customers in focus.
Business Research Methodologies
We can categorize business research methods in two ways:
- Quantitative and Qualitative
- Primary and Secondary
Quantitative vs Qualitative Business Research
Before we can delve into the specific kinds of research, it is important to have an understanding of the distinctions between the two key types of research: quantitative and qualitative business research.
Quantitative research involves data that is statistical and numerical in nature. Such data can be analysed using statistical techniques. Qualitative research, on the other hand, involves non-numeric data that generally takes a textual form.
Primary vs Secondary Business Research
Another way in which research methods can be classified is by primary and secondary research. Primary research refers to the collection of first-hand data, generally directly from the source. Some common methods of primary research are surveys, interviews, and observations.
Conversely, secondary research uses existing data that is already avalaible.
See Voxco survey software in action with a Free demo.
Quantitative and Qualitative Research Methods
Quantitative research methods.
Some commonly used quantitative methods of business research are:
- Experimental Research : Experimental research refers to research studies that adhere to the scientific research design. This type of research aims to prove or disprove a theory, or hypothesis. Businesses generally use experimental research to study consumers’ behavioral traits.
- Survey Research : Survey research is one of the most commonly used methods of data collection because it is relatively easy and inexpensive to leverage. Surveys can be conducted in many different ways such as through social media polls or email surveys.
- Existing Literature : Existing research papers and online research are other sources of gathering quantitative data. This method is economical, accessible, and allows for the collection of vast amounts of data.
Qualitative Research Methods
Some commonly used qualitative methods of business research are:
- Interviews : Interviews are structured conversations that take place between an interviewer and an interviewee face-to-face, over the internet, or even through the phone. Generally, interviews involve the use of open-ended questions that provide respondents the flexibility to express their thoughts, perceptions, and opinions on the topic.
- Ethnographic Research : Ethnographic research where researchers immerse themselves in the participant’s real-life environment to observe and study their behaviour. It is generally used by organizations that want to understand cultural dynamics or factors. Although this method of research can help extract intensive and compelling data, it is extremely time-consuming and expensive.
- Case Study Research : Case study research refers to the detailed study of a specific subject. This method is used to produce in-depth, multi-faceted information on complex issues in the real-world setting.
FAQs on Business Research
Business research involves gathering information on all areas of business with the goal of maximising sales and revenue.
Business research methodologies can be categorized in two ways;
- Quantitative and qualitative
- Secondary and Primary
Some quantitative methods of business research are;
- Survey Research
- Experimental Research
- Existing Literature
Some primary research methods are interviews, surveys, and focus groups. Some secondary research methods are public sources, educational sources, and commercial sources.
Some qualitative methods of business research are;
- Ethnographic Research
- Case Study Research
Explore Voxco Survey Software
+ Omnichannel Survey Software
+ Online Survey Software
+ CATI Survey Software
+ IVR Survey Software
+ Market Research Tool
+ Customer Experience Tool
+ Product Experience Software
+ Enterprise Survey Software

What is a CSAT survey?
What is a CSAT survey? SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Share on facebook Share on twitter Share on linkedin Table of Contents When your business depends
Customer Service Tips
Customer Experience 25 Customer Service Tips for enhancing Customer Experience Free Download: Enhance NPS® Scores using our NPS® guide. Download Now SHARE THE ARTICLE ON

How to Create a Customer Experience Survey
How to create a Customer Experience Survey SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents “We adore our customers.” It’s a phrase you might include in

Pre-experimental design: Definition, types & examples
Pre-experimental Design: Definition, Types & Examples SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents Experimental research is conducted to analyze and understand the effect of a

Are personal interviews better than self-completion surveys?
Are personal interviews better than self-completion surveys? Self Completion Surveys Understand Everything That You Need To Know About Self Completion Surveys Download Now SHARE THE

Advantages of product-centric organization
Advantages of product-centric organization SHARE THE ARTICLE ON Table of Contents A product-centric organization prioritizes product and product-related issues. Because product centrism occurs when the
We use cookies in our website to give you the best browsing experience and to tailor advertising. By continuing to use our website, you give us consent to the use of cookies. Read More

Business Research – Definition / Meaning with Examples
In business, research helps a company stay ahead of the competition, which gives it an advantage over the competition. Conducting market research can assist in avoiding potential issues by identifying the optimal time and location to launch your product or service. Understanding the value of a brand and measuring how happy customers are are important if you want to keep coming up with new ways to meet customer needs. Because of this, the company’s sales and share of the market have gone up. Business intelligence is also helpful when a company is looking for new people to fill open positions. Read on to discover everything there is to know about business research and to become a subject matter expert on it.
Researching the market, the competition and the clients is an important part of running a successful business. This research can help businesses figure out how much demand and supply there is in an industry. Companies can use the results of this kind of study to cut costs and make sure their products and services fit certain niches in the market. The top management can use information from within the company to build a strong team and give great training and guidance. For a comprehensive guide to wealth management , check out this post from our website.
Table of Contents
Business Research Definition
A simple definition of business research is gathering complete data and information about all parts of a company and then using that information to increase sales and profits. Business Research is an activity in management that enables one to determine which product has the most potential for profit and should be prioritized for development if you are unaware. Also, research involves a number of steps that need to carefully look at before deciding on the best course of action for the company as a whole.
A company’s sales and profits can go up if all parts of the business are carefully looked at. This research helps companies figure out which products or services are the most profitable or in demand. At its most basic, gathering data and information to enable strategic business decisions is the process of business intelligence.
Examples of Business Research
Let’s say a car company wants to sell CNG-powered cars. In order to get people to use greener fuel, the company will come up with a number of ways to find out how interested people are in the proposed car. Also, the company will look for rivals in the CNG distribution market in India. Researchers are conducting studies on different design theories to develop a durable and useful design.
Institutional and non-institutional microcredit efforts significantly improve the quality of life for rural people, especially women. Still, there is a lot of proof that these loan resources are often mismanaged and used in bad ways. People in rural areas have trouble getting loans because of the high number of people who don’t pay back their loans. To figure out how big and bad loan misuse and diversion is in rural areas, you need to look at how people are currently using credit.
How does Business Research on the Market Works?
Market research can help a business figure out who its ideal customers are and how much demand there is for its products. Such research can do by the company itself or by an outside market research firm.
In the business world, research is done in a methodical and unbiased way so that managers can make better decisions. In order to make these decisions and get the organization to take the actions needed to improve business performance, you have to plan, collect, analyze, and share relevant data with decision-makers.
Importance of Business Research
When doing market research, online surveys are a quick and easy way to get information from a large number of people. You can narrow down your target market by sending a survey with demographic questions to people who have benefited from your products or services.
Note the comments with a lot in common so you can reach out to the people who will benefit most from your services. You can focus on the right customers, which will make everyone happier. They will help your business improve its morals. Using it as a bonus, companies can actively penetrate consumer markets that haven’t explored before. Also, research is important because it can show where problems might happen.
Reduces Risk as Much as Possible
Your business could save a lot of money if you sent out customer surveys early. Before making a new product or service available to the public, it is possible to actively search for potential problems. After making the necessary changes, you can be sure that customers will like the products you put out.
Sending out surveys can help you figure out how to improve a product that is already on the market. Customer feedback can help a product do well if you listen to it and act on it. Here are a few ways that research could be very helpful to your business. This optimization could help your business run better and make better products.
To Get a Better Idea about Customers
When doing market research, online surveys are a quick and easy way to get information from a large number of people. You can narrow down your target market by sending a survey with demographic questions to people who have benefited from your products or services. Note the comments that have a lot in common so you can reach out to the people who will benefit most from your services. Y
ou can focus on the right customers, which will make everyone happier. They will help your business improve its morals. Using it as a bonus, companies can actively penetrate consumer markets that haven’t explored before. Also, research is important because it can show where problems might happen.
Lets you Compare Things Side by Side
Giving your customers unique features or benefits is a sure way to set yourself apart from the competition. There could be many reasons why their sales are going up faster than yours. Analyze competitors’ growth and market research data to identify your unique selling proposition. Find out what makes their products and services different from those of their competitors.
Make the changes to your business processes that are needed to take into account the new information. Changes may come about as a result of this process. Two examples are the creation of advertising plans and the search for untapped business opportunities.
Discovers Potential Issues
If your company makes online survey tools, it will be able to find out more about how each division can improve. By asking questions to your target audience, you can identify the areas that require improvement in your products and services. By polling your employees, you can find out more about how to improve the way your company works.
After figuring out where the problems are, possible solutions can be put into place. You can find out how well your changes work by sending out questionnaires on a regular basis. You can compare your data to both past records and what your competitors are doing.
Frequently Asked Questions
When doing a business research, what steps should be taken.
A key part of any market research strategy is a thorough look at the market potential of your product. To determine whether your product or service is needed, you must look at the market as it is right now. It takes a look at the competition. Information about the clients.
What is the Main Goal of Business?
Managing a business means organising and coordinating how the business works. These managers keep an eye on everything and do everything they can to help their workers get the most out of what they do. A business manager’s job usually involves overseeing current employees and training new ones. They may also ask to help the company reach its financial and operational goals.
How does Research Help Businesses?
Smart business owners use market research to stay on top of their industry, make better decisions, and protect their company’s competitive edge . Research your market to make sales, whether you’re starting or growing your business.
Business research helps a company increase profits by gathering and analyzing information. This research helps companies figure out which products or services are the most profitable or in demand. To learn more, take a look at this business research.
Related Posts

Business Finance – Definition / Meaning with Examples

Risk Management – Definition / Meaning with Examples

Financial Risk Management – Definition / Meaning with Examples

Business Management – Definition / Meaning with Examples

Asset Management – Definition / Meaning with Examples

Personal Money Management – Definition / Meaning with Examples
A Roadmap to Business Research
- First Online: 15 March 2023
Cite this chapter

- Merwe Oberholzer ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-7180-8865 3 &
- Pieter W. Buys ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0002-5345-3594 3
495 Accesses
This chapter seeks to constitute a roadmap or framework to guide business researchers in contextualizing and planning their research efforts. A literature study was conducted to investigate the research concept, the boundary of research, and the research process’ conceptual framework. This chapter summarized research as a systematic investigation to reveal new knowledge. In guiding industry-orientated business research, it is acknowledged that management action may solve some business problems. In contrast, higher levels of organizational issues and critical reflection of business issues may require actual research .
The framework for business research is divided into four parts: the research problem, research design, empirical evidence, and conclusion. The central part of the map is the design section that organizes the philosophic approach (theoretical foundation, research philosophy, and assumptions) on the one side and the applied research methods and techniques on the other side, with the research methodology acting as a bridge between the sides. The framework constitutes a guide when embarking on the journey to solve industry-orientated business research.
This is a preview of subscription content, log in via an institution to check access.
Access this chapter
- Available as PDF
- Read on any device
- Instant download
- Own it forever
- Available as EPUB and PDF
- Compact, lightweight edition
- Dispatched in 3 to 5 business days
- Free shipping worldwide - see info
- Durable hardcover edition
Tax calculation will be finalised at checkout
Purchases are for personal use only
Institutional subscriptions
AS illustrated later, it must be noted not every business problem needs to be solved by scientific research.
Note that although conceptually four distinct elements, in actuality these ProDEC elements are highly integrated.
Note that the theoretical foundation may not be of equal importance in all paradigms, e.g., the pragmatist and design sciences paradigms where a pragmatic problem solution or artifact is the primary objective.
Abutabenjeh, S., & Jaradat, R. (2018). Clarification of research design, research methods, and research methodology: A guide for public administration researchers and practitioners. Teaching Public Administration, 36 (3), 237–258.
Article Google Scholar
Babbie, E. (2004). The practice of social research . Thomson/ Wadsworth.
Google Scholar
Brierley, J. A. (2017). The role of a pragmatist paradigm when adopting mixed methods in behavioural accounting research. International Journal of Behavioural Accounting and Finance, 6 (2), 140–154.
Collins. (2021). Definition of research . https://www.collinsdictionary.com/dictionary/english/research Date of access: 21 July 2021.
Creswell, J. W., & Clark, V. L. (2018). Designing and conducting mixed method research . Sage.
Davis, C., & Fisher, M. (2018). Understanding Research Paradigms. JARNA, 21 (3), 21–25.
Delen, D., & Zolbanin, H. M. (2018). The analytics paradigm in business research. Journal of Business Research, 90 , 186–195.
Department of Education and Training, Western Sydney University. 2020. Research services. https://www.westernsydney.edu.au/research/researchers/preparing_a_grant_application/dest_definition_of_research . Date of access: 21 July 2021.
Elsayed, N., & Elbardan, H. (2018). Investigating the associations between executive compensation and firm performance: Agency theory or tournament theory. Journal of Applied Accounting Research, 19 (2), 245–270.
FindAPhD.com. (2021). What are the criteria for a PhD? https://www.findaphd.com/advice/finding/criteria-for-phd.aspx Date of access: 18 August 2021.
Goldkuhl, G. (2011). Design research in search for a paradigm: Pragmatism is the answer. European Design Science Symposium (pp. 84–95). Springer.
Goldkuhl, G. (2020). Design Science Epistemology: A pragmatist inquiry. Scandinavian Journal of Information Systems, 32 (1), 39–79.
Hesse-Biber, S. N., & Leavy, P. (2011). The practice of qualitative research . Sage.
Henderson, K. A. (2011). Post-positivism and the pragmatics of leisure research. Leisure Sciences, 33 (4), 341–346.
Hevner, A.R., March, S.T., Park, J. & Ram, S. (2004). Design science in information systems research. MIS quarterly : 75–105.
Kessler, E. H. (Ed.). (2013). Encyclopedia of management theory . Sage.
Kankam, P. K. (2019). The use of paradigms in information research. Library & Information Science Research, 41 (2), 85–92.
Kekeya, J. (2019, November). The commonalities and differences between research paradigms. Contemporary PNG Studies: DWU Research Journal, 31 , 26–36.
Kivunja, C. (2018). Distinguishing between theory, theoretical framework, and conceptual framework: A systematic review of lessons from the field. International Journal of Higher Education, 7 (6), 44–53.
Kivunja, C., & Kuyini, A. B. (2017). Understanding and applying research paradigms in educational contexts. International Journal for Higher Education, 6 (5), 26–41.
Jansen, J. D. (2020a). What is a research question and why is it important? In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 2–14.
Jansen, J. D. (2020b). Introduction to the language of research. In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 16–24.
Lexico.com. (2021). Oxford English and Spanish dictionary, synonyms, and Spanish to English translator . https://www.lexico.com/definition/research Date of access: 22 July 2021.
Lincoln, Y. S., Lynham, S. A., & Guba, E. G. (2011). Paradigmatic controversies, contradictions, and emerging confluences, revisited. In N. K. Denzin & Y. S. Lincoln (Eds.), The Sage handbook of qualitative research (pp. 97–128). Sage.
Myers, M. D. (2020). Qualitative research in business & management . Sage.
Mouton, J. (1996). Understanding social research . Van Schaik.
Mouton, J. (2011). How to succeed in your master’s & doctoral studies: A South African guide and resource book. Van Schaik.
Nieuwenhuis, J. (2020). Introducing qualitative research. In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 56–76.
Pandey, P. & Pandey, M. M. (2015). Research methodology: Tools and techniques . Bridge Center: Buzau.
Pietersen, J. & Maree, K. (2020). Statistical analysis II: Inferential statistics. In: Maree, K., (ed.), First steps in research . Van Schaik. pp. 242–258.
Rahi, S. (2017). Research design and methods: A systematic review of research paradigms, sampling issues and instrument development. International Journal of Economics & Management Sciences, 6 (2), 1000403.
Rehman, A. A., & Alharthi, K. (2016). An introduction to research paradigms. International Journal of Educational Investigations, 3 (8), 51–59.
Saunders, M. N. K., Lewis, P., & Thornhill, A. (2019). Research methods for business students . Pearson.
Sein, M. K., Henfridsson, O., Purao, S., Rossi, M., & Lindgren, R. (2011). Action Design Research. MIS Quarterly, 35 (1), 37–56.
Tubey, R. J., Rotich, J. K., & Bengat, J. K. (2015). Research paradigms: Theory and practice. Research on Humanities and Social Sciences, 5 (5), 224–228.
Vom Brocke J., Hevner A., Maedche A. (2020). Introduction to Design Science Research. In: Vom Brocke J., Hevner A., Maedche A. (eds.), Design Science Research. Cases. Progress in IS. Springer, Cham. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-3-030-46781-4_1 Date of access: 21 October 2021.
Voxco. (2022). Business research: Definition, types, and methods. https://www.voxco.com/blog/business-research-definition-types-and-methods/ Date of access: 23 May 2022.
Wilson, J. (2013). Essentials of business research: A guide to doing your research project. Sage. https://www.sagepub.com/sites/default/files/upm-binaries/59838_Wilson_ch1.pdf Date of access: 3 June 2021.
Download references
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
Management Cybernetics Research Entity, North-West University, Potchefstroom, South Africa
Merwe Oberholzer & Pieter W. Buys
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Pieter W. Buys .
Editor information
Editors and affiliations.
Pieter W. Buys
Merwe Oberholzer
Rights and permissions
Reprints and permissions
Copyright information
© 2023 The Author(s), under exclusive license to Springer Nature Singapore Pte Ltd.
About this chapter
Oberholzer, M., Buys, P.W. (2023). A Roadmap to Business Research. In: Buys, P.W., Oberholzer, M. (eds) Business Research . Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore. https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9479-1_2
Download citation
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1007/978-981-19-9479-1_2
Published : 15 March 2023
Publisher Name : Palgrave Macmillan, Singapore
Print ISBN : 978-981-19-9478-4
Online ISBN : 978-981-19-9479-1
eBook Packages : Business and Management Business and Management (R0)
Share this chapter
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Publish with us
Policies and ethics
- Find a journal
- Track your research
- Search Search Please fill out this field.
What Is Market Research?
- How It Works
- Primary vs. Secondary
- How to Conduct Research
The Bottom Line
- Marketing Essentials

How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/dd453b82d4ef4ce8aac2e858ed00a114__alexandra_twin-5bfc262b46e0fb0026006b77.jpeg)
Joules Garcia / Investopedia
Market research examines consumer behavior and trends in the economy to help a business develop and fine-tune its business idea and strategy. It helps a business understand its target market by gathering and analyzing data.
Market research is the process of evaluating the viability of a new service or product through research conducted directly with potential customers. It allows a company to define its target market and get opinions and other feedback from consumers about their interest in a product or service.
Research may be conducted in-house or by a third party that specializes in market research. It can be done through surveys and focus groups, among other ways. Test subjects are usually compensated with product samples or a small stipend for their time.
Key Takeaways
- Companies conduct market research before introducing new products to determine their appeal to potential customers.
- Tools include focus groups, telephone interviews, and questionnaires.
- The results of market research inform the final design of the product and determine how it will be positioned in the marketplace.
- Market research usually combines primary information, gathered directly from consumers, and secondary information, which is data available from external sources.
Market Research
How market research works.
Market research is used to determine the viability of a new product or service. The results may be used to revise the product design and fine-tune the strategy for introducing it to the public. This can include information gathered for the purpose of determining market segmentation . It also informs product differentiation , which is used to tailor advertising.
A business engages in various tasks to complete the market research process. It gathers information based on the market sector being targeted by the product. This information is then analyzed and relevant data points are interpreted to draw conclusions about how the product may be optimally designed and marketed to the market segment for which it is intended.
It is a critical component in the research and development (R&D) phase of a new product or service introduction. Market research can be conducted in many different ways, including surveys, product testing, interviews, and focus groups.
Market research is a critical tool that companies use to understand what consumers want, develop products that those consumers will use, and maintain a competitive advantage over other companies in their industry.
Primary Market Research vs. Secondary Market Research
Market research usually consists of a combination of:
- Primary research, gathered by the company or by an outside company that it hires
- Secondary research, which draws on external sources of data
Primary Market Research
Primary research generally falls into two categories: exploratory and specific research.
- Exploratory research is less structured and functions via open-ended questions. The questions may be posed in a focus group setting, telephone interviews, or questionnaires. It results in questions or issues that the company needs to address about a product that it has under development.
- Specific research delves more deeply into the problems or issues identified in exploratory research.
Secondary Market Research
All market research is informed by the findings of other researchers about the needs and wants of consumers. Today, much of this research can be found online.
Secondary research can include population information from government census data , trade association research reports , polling results, and research from other businesses operating in the same market sector.
History of Market Research
Formal market research began in Germany during the 1920s. In the United States, it soon took off with the advent of the Golden Age of Radio.
Companies that created advertisements for this new entertainment medium began to look at the demographics of the audiences who listened to each of the radio plays, music programs, and comedy skits that were presented.
They had once tried to reach the widest possible audience by placing their messages on billboards or in the most popular magazines. With radio programming, they had the chance to target rural or urban consumers, teenagers or families, and judge the results by the sales numbers that followed.
Types of Market Research
Face-to-face interviews.
From their earliest days, market research companies would interview people on the street about the newspapers and magazines that they read regularly and ask whether they recalled any of the ads or brands that were published in them. Data collected from these interviews were compared to the circulation of the publication to determine the effectiveness of those ads.
Market research and surveys were adapted from these early techniques.
To get a strong understanding of your market, it’s essential to understand demand, market size, economic indicators, location, market saturation, and pricing.
Focus Groups
A focus group is a small number of representative consumers chosen to try a product or watch an advertisement.
Afterward, the group is asked for feedback on their perceptions of the product, the company’s brand, or competing products. The company then takes that information and makes decisions about what to do with the product or service, whether that's releasing it, making changes, or abandoning it altogether.
Phone Research
The man-on-the-street interview technique soon gave way to the telephone interview. A telephone interviewer could collect information in a more efficient and cost-effective fashion.
Telephone research was a preferred tactic of market researchers for many years. It has become much more difficult in recent years as landline phone service dwindles and is replaced by less accessible mobile phones.
Survey Research
As an alternative to focus groups, surveys represent a cost-effective way to determine consumer attitudes without having to interview anyone in person. Consumers are sent surveys in the mail, usually with a coupon or voucher to incentivize participation. These surveys help determine how consumers feel about the product, brand, and price point.
Online Market Research
With people spending more time online, market research activities have shifted online as well. Data collection still uses a survey-style form. But instead of companies actively seeking participants by finding them on the street or cold calling them on the phone, people can choose to sign up, take surveys, and offer opinions when they have time.
This makes the process far less intrusive and less rushed, since people can participate on their own time and of their own volition.
How to Conduct Market Research
The first step to effective market research is to determine the goals of the study. Each study should seek to answer a clear, well-defined problem. For example, a company might seek to identify consumer preferences, brand recognition, or the comparative effectiveness of different types of ad campaigns.
After that, the next step is to determine who will be included in the research. Market research is an expensive process, and a company cannot waste resources collecting unnecessary data. The firm should decide in advance which types of consumers will be included in the research, and how the data will be collected. They should also account for the probability of statistical errors or sampling bias .
The next step is to collect the data and analyze the results. If the two previous steps have been completed accurately, this should be straightforward. The researchers will collect the results of their study, keeping track of the ages, gender, and other relevant data of each respondent. This is then analyzed in a marketing report that explains the results of their research.
The last step is for company executives to use their market research to make business decisions. Depending on the results of their research, they may choose to target a different group of consumers, or they may change their price point or some product features.
The results of these changes may eventually be measured in further market research, and the process will begin all over again.
Benefits of Market Research
Market research is essential for developing brand loyalty and customer satisfaction. Since it is unlikely for a product to appeal equally to every consumer, a strong market research program can help identify the key demographics and market segments that are most likely to use a given product.
Market research is also important for developing a company’s advertising efforts. For example, if a company’s market research determines that its consumers are more likely to use Facebook than X (formerly Twitter), it can then target its advertisements to one platform instead of another. Or, if they determine that their target market is value-sensitive rather than price-sensitive, they can work on improving the product rather than reducing their prices.
Market research only works when subjects are honest and open to participating.
Example of Market Research
Many companies use market research to test new products or get information from consumers about what kinds of products or services they need and don’t currently have.
For example, a company that’s considering starting a business might conduct market research to test the viability of its product or service. If the market research confirms consumer interest, the business can proceed confidently with its business plan . If not, the company can use the results of the market research to make adjustments to the product to bring it in line with customer desires.
What Are the Main Types of Market Research?
The main types of market research are primary research and secondary research. Primary research includes focus groups, polls, and surveys. Secondary research includes academic articles, infographics, and white papers.
Qualitative research gives insights into how customers feel and think. Quantitative research uses data and statistics such as website views, social media engagement, and subscriber numbers.
What Is Online Market Research?
Online market research uses the same strategies and techniques as traditional primary and secondary market research, but it is conducted on the Internet. Potential customers may be asked to participate in a survey or give feedback on a product. The responses may help the researchers create a profile of the likely customer for a new product.
What Are Paid Market Research Surveys?
Paid market research involves rewarding individuals who agree to participate in a study. They may be offered a small payment for their time or a discount coupon in return for filling out a questionnaire or participating in a focus group.
What Is a Market Study?
A market study is an analysis of consumer demand for a product or service. It looks at all of the factors that influence demand for a product or service. These include the product’s price, location, competition, and substitutes as well as general economic factors that could influence the new product’s adoption, for better or worse.
Market research is a key component of a company’s research and development (R&D) stage. It helps companies understand in advance the viability of a new product that they have in development and to see how it might perform in the real world.
Britannica Money. “ Market Research .”
U.S. Small Business Administration. “ Market Research and Competitive Analysis .”
- How to Start a Business: A Comprehensive Guide and Essential Steps 1 of 25
- How to Do Market Research, Types, and Example 2 of 25
- Marketing Strategy: What It Is, How It Works, and How to Create One 3 of 25
- Marketing in Business: Strategies and Types Explained 4 of 25
- What Is a Marketing Plan? Types and How to Write One 5 of 25
- Business Development: Definition, Strategies, Steps & Skills 6 of 25
- Business Plan: What It Is, What's Included, and How to Write One 7 of 25
- Small Business Development Center (SBDC): Meaning, Types, Impact 8 of 25
- How to Write a Business Plan for a Loan 9 of 25
- Business Startup Costs: It’s in the Details 10 of 25
- Startup Capital Definition, Types, and Risks 11 of 25
- Bootstrapping Definition, Strategies, and Pros/Cons 12 of 25
- Crowdfunding: What It Is, How It Works, and Popular Websites 13 of 25
- Starting a Business with No Money: How to Begin 14 of 25
- A Comprehensive Guide to Establishing Business Credit 15 of 25
- Equity Financing: What It Is, How It Works, Pros and Cons 16 of 25
- Best Startup Business Loans 17 of 25
- Sole Proprietorship: What It Is, Pros and Cons, and Differences From an LLC 18 of 25
- Partnership: Definition, How It Works, Taxation, and Types 19 of 25
- What Is an LLC? Limited Liability Company Structure and Benefits Defined 20 of 25
- Corporation: What It Is and How to Form One 21 of 25
- Starting a Small Business: Your Complete How-to Guide 22 of 25
- Starting an Online Business: A Step-by-Step Guide 23 of 25
- How to Start Your Own Bookkeeping Business: Essential Tips 24 of 25
- How to Start a Successful Dropshipping Business: A Comprehensive Guide 25 of 25
:max_bytes(150000):strip_icc():format(webp)/Term-Definitions_Target-market-49a03b58f6d54ddd88d46521f248fc8a.jpg)
- Terms of Service
- Editorial Policy
- Privacy Policy
- Your Privacy Choices
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
Methodology
- What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples
Published on June 7, 2021 by Shona McCombes . Revised on November 20, 2023 by Pritha Bhandari.
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about:
- Your overall research objectives and approach
- Whether you’ll rely on primary research or secondary research
- Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects
- Your data collection methods
- The procedures you’ll follow to collect data
- Your data analysis methods
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research objectives and that you use the right kind of analysis for your data.
Table of contents
Step 1: consider your aims and approach, step 2: choose a type of research design, step 3: identify your population and sampling method, step 4: choose your data collection methods, step 5: plan your data collection procedures, step 6: decide on your data analysis strategies, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about research design.
- Introduction
Before you can start designing your research, you should already have a clear idea of the research question you want to investigate.
There are many different ways you could go about answering this question. Your research design choices should be driven by your aims and priorities—start by thinking carefully about what you want to achieve.
The first choice you need to make is whether you’ll take a qualitative or quantitative approach.
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible and inductive , allowing you to adjust your approach based on what you find throughout the research process.
Quantitative research designs tend to be more fixed and deductive , with variables and hypotheses clearly defined in advance of data collection.
It’s also possible to use a mixed-methods design that integrates aspects of both approaches. By combining qualitative and quantitative insights, you can gain a more complete picture of the problem you’re studying and strengthen the credibility of your conclusions.
Practical and ethical considerations when designing research
As well as scientific considerations, you need to think practically when designing your research. If your research involves people or animals, you also need to consider research ethics .
- How much time do you have to collect data and write up the research?
- Will you be able to gain access to the data you need (e.g., by travelling to a specific location or contacting specific people)?
- Do you have the necessary research skills (e.g., statistical analysis or interview techniques)?
- Will you need ethical approval ?
At each stage of the research design process, make sure that your choices are practically feasible.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
Within both qualitative and quantitative approaches, there are several types of research design to choose from. Each type provides a framework for the overall shape of your research.
Types of quantitative research designs
Quantitative designs can be split into four main types.
- Experimental and quasi-experimental designs allow you to test cause-and-effect relationships
- Descriptive and correlational designs allow you to measure variables and describe relationships between them.
With descriptive and correlational designs, you can get a clear picture of characteristics, trends and relationships as they exist in the real world. However, you can’t draw conclusions about cause and effect (because correlation doesn’t imply causation ).
Experiments are the strongest way to test cause-and-effect relationships without the risk of other variables influencing the results. However, their controlled conditions may not always reflect how things work in the real world. They’re often also more difficult and expensive to implement.
Types of qualitative research designs
Qualitative designs are less strictly defined. This approach is about gaining a rich, detailed understanding of a specific context or phenomenon, and you can often be more creative and flexible in designing your research.
The table below shows some common types of qualitative design. They often have similar approaches in terms of data collection, but focus on different aspects when analyzing the data.
Your research design should clearly define who or what your research will focus on, and how you’ll go about choosing your participants or subjects.
In research, a population is the entire group that you want to draw conclusions about, while a sample is the smaller group of individuals you’ll actually collect data from.
Defining the population
A population can be made up of anything you want to study—plants, animals, organizations, texts, countries, etc. In the social sciences, it most often refers to a group of people.
For example, will you focus on people from a specific demographic, region or background? Are you interested in people with a certain job or medical condition, or users of a particular product?
The more precisely you define your population, the easier it will be to gather a representative sample.
- Sampling methods
Even with a narrowly defined population, it’s rarely possible to collect data from every individual. Instead, you’ll collect data from a sample.
To select a sample, there are two main approaches: probability sampling and non-probability sampling . The sampling method you use affects how confidently you can generalize your results to the population as a whole.
Probability sampling is the most statistically valid option, but it’s often difficult to achieve unless you’re dealing with a very small and accessible population.
For practical reasons, many studies use non-probability sampling, but it’s important to be aware of the limitations and carefully consider potential biases. You should always make an effort to gather a sample that’s as representative as possible of the population.
Case selection in qualitative research
In some types of qualitative designs, sampling may not be relevant.
For example, in an ethnography or a case study , your aim is to deeply understand a specific context, not to generalize to a population. Instead of sampling, you may simply aim to collect as much data as possible about the context you are studying.
In these types of design, you still have to carefully consider your choice of case or community. You should have a clear rationale for why this particular case is suitable for answering your research question .
For example, you might choose a case study that reveals an unusual or neglected aspect of your research problem, or you might choose several very similar or very different cases in order to compare them.
Data collection methods are ways of directly measuring variables and gathering information. They allow you to gain first-hand knowledge and original insights into your research problem.
You can choose just one data collection method, or use several methods in the same study.
Survey methods
Surveys allow you to collect data about opinions, behaviors, experiences, and characteristics by asking people directly. There are two main survey methods to choose from: questionnaires and interviews .
Observation methods
Observational studies allow you to collect data unobtrusively, observing characteristics, behaviors or social interactions without relying on self-reporting.
Observations may be conducted in real time, taking notes as you observe, or you might make audiovisual recordings for later analysis. They can be qualitative or quantitative.
Other methods of data collection
There are many other ways you might collect data depending on your field and topic.
If you’re not sure which methods will work best for your research design, try reading some papers in your field to see what kinds of data collection methods they used.
Secondary data
If you don’t have the time or resources to collect data from the population you’re interested in, you can also choose to use secondary data that other researchers already collected—for example, datasets from government surveys or previous studies on your topic.
With this raw data, you can do your own analysis to answer new research questions that weren’t addressed by the original study.
Using secondary data can expand the scope of your research, as you may be able to access much larger and more varied samples than you could collect yourself.
However, it also means you don’t have any control over which variables to measure or how to measure them, so the conclusions you can draw may be limited.
As well as deciding on your methods, you need to plan exactly how you’ll use these methods to collect data that’s consistent, accurate, and unbiased.
Planning systematic procedures is especially important in quantitative research, where you need to precisely define your variables and ensure your measurements are high in reliability and validity.
Operationalization
Some variables, like height or age, are easily measured. But often you’ll be dealing with more abstract concepts, like satisfaction, anxiety, or competence. Operationalization means turning these fuzzy ideas into measurable indicators.
If you’re using observations , which events or actions will you count?
If you’re using surveys , which questions will you ask and what range of responses will be offered?
You may also choose to use or adapt existing materials designed to measure the concept you’re interested in—for example, questionnaires or inventories whose reliability and validity has already been established.
Reliability and validity
Reliability means your results can be consistently reproduced, while validity means that you’re actually measuring the concept you’re interested in.
For valid and reliable results, your measurement materials should be thoroughly researched and carefully designed. Plan your procedures to make sure you carry out the same steps in the same way for each participant.
If you’re developing a new questionnaire or other instrument to measure a specific concept, running a pilot study allows you to check its validity and reliability in advance.
Sampling procedures
As well as choosing an appropriate sampling method , you need a concrete plan for how you’ll actually contact and recruit your selected sample.
That means making decisions about things like:
- How many participants do you need for an adequate sample size?
- What inclusion and exclusion criteria will you use to identify eligible participants?
- How will you contact your sample—by mail, online, by phone, or in person?
If you’re using a probability sampling method , it’s important that everyone who is randomly selected actually participates in the study. How will you ensure a high response rate?
If you’re using a non-probability method , how will you avoid research bias and ensure a representative sample?
Data management
It’s also important to create a data management plan for organizing and storing your data.
Will you need to transcribe interviews or perform data entry for observations? You should anonymize and safeguard any sensitive data, and make sure it’s backed up regularly.
Keeping your data well-organized will save time when it comes to analyzing it. It can also help other researchers validate and add to your findings (high replicability ).
On its own, raw data can’t answer your research question. The last step of designing your research is planning how you’ll analyze the data.
Quantitative data analysis
In quantitative research, you’ll most likely use some form of statistical analysis . With statistics, you can summarize your sample data, make estimates, and test hypotheses.
Using descriptive statistics , you can summarize your sample data in terms of:
- The distribution of the data (e.g., the frequency of each score on a test)
- The central tendency of the data (e.g., the mean to describe the average score)
- The variability of the data (e.g., the standard deviation to describe how spread out the scores are)
The specific calculations you can do depend on the level of measurement of your variables.
Using inferential statistics , you can:
- Make estimates about the population based on your sample data.
- Test hypotheses about a relationship between variables.
Regression and correlation tests look for associations between two or more variables, while comparison tests (such as t tests and ANOVAs ) look for differences in the outcomes of different groups.
Your choice of statistical test depends on various aspects of your research design, including the types of variables you’re dealing with and the distribution of your data.
Qualitative data analysis
In qualitative research, your data will usually be very dense with information and ideas. Instead of summing it up in numbers, you’ll need to comb through the data in detail, interpret its meanings, identify patterns, and extract the parts that are most relevant to your research question.
Two of the most common approaches to doing this are thematic analysis and discourse analysis .
There are many other ways of analyzing qualitative data depending on the aims of your research. To get a sense of potential approaches, try reading some qualitative research papers in your field.
If you want to know more about the research process , methodology , research bias , or statistics , make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples.
- Simple random sampling
- Stratified sampling
- Cluster sampling
- Likert scales
- Reproducibility
Statistics
- Null hypothesis
- Statistical power
- Probability distribution
- Effect size
- Poisson distribution
Research bias
- Optimism bias
- Cognitive bias
- Implicit bias
- Hawthorne effect
- Anchoring bias
- Explicit bias
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question . It defines your overall approach and determines how you will collect and analyze data.
A well-planned research design helps ensure that your methods match your research aims, that you collect high-quality data, and that you use the right kind of analysis to answer your questions, utilizing credible sources . This allows you to draw valid , trustworthy conclusions.
Quantitative research designs can be divided into two main categories:
- Correlational and descriptive designs are used to investigate characteristics, averages, trends, and associations between variables.
- Experimental and quasi-experimental designs are used to test causal relationships .
Qualitative research designs tend to be more flexible. Common types of qualitative design include case study , ethnography , and grounded theory designs.
The priorities of a research design can vary depending on the field, but you usually have to specify:
- Your research questions and/or hypotheses
- Your overall approach (e.g., qualitative or quantitative )
- The type of design you’re using (e.g., a survey , experiment , or case study )
- Your data collection methods (e.g., questionnaires , observations)
- Your data collection procedures (e.g., operationalization , timing and data management)
- Your data analysis methods (e.g., statistical tests or thematic analysis )
A sample is a subset of individuals from a larger population . Sampling means selecting the group that you will actually collect data from in your research. For example, if you are researching the opinions of students in your university, you could survey a sample of 100 students.
In statistics, sampling allows you to test a hypothesis about the characteristics of a population.
Operationalization means turning abstract conceptual ideas into measurable observations.
For example, the concept of social anxiety isn’t directly observable, but it can be operationally defined in terms of self-rating scores, behavioral avoidance of crowded places, or physical anxiety symptoms in social situations.
Before collecting data , it’s important to consider how you will operationalize the variables that you want to measure.
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
McCombes, S. (2023, November 20). What Is a Research Design | Types, Guide & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved April 18, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/methodology/research-design/
Is this article helpful?
Shona McCombes
Other students also liked, guide to experimental design | overview, steps, & examples, how to write a research proposal | examples & templates, ethical considerations in research | types & examples, unlimited academic ai-proofreading.
✔ Document error-free in 5minutes ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts
- Privacy Policy
Buy Me a Coffee

Home » Variables in Research – Definition, Types and Examples
Variables in Research – Definition, Types and Examples
Table of Contents

Variables in Research
Definition:
In Research, Variables refer to characteristics or attributes that can be measured, manipulated, or controlled. They are the factors that researchers observe or manipulate to understand the relationship between them and the outcomes of interest.
Types of Variables in Research
Types of Variables in Research are as follows:
Independent Variable
This is the variable that is manipulated by the researcher. It is also known as the predictor variable, as it is used to predict changes in the dependent variable. Examples of independent variables include age, gender, dosage, and treatment type.
Dependent Variable
This is the variable that is measured or observed to determine the effects of the independent variable. It is also known as the outcome variable, as it is the variable that is affected by the independent variable. Examples of dependent variables include blood pressure, test scores, and reaction time.
Confounding Variable
This is a variable that can affect the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. It is a variable that is not being studied but could impact the results of the study. For example, in a study on the effects of a new drug on a disease, a confounding variable could be the patient’s age, as older patients may have more severe symptoms.
Mediating Variable
This is a variable that explains the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. It is a variable that comes in between the independent and dependent variables and is affected by the independent variable, which then affects the dependent variable. For example, in a study on the relationship between exercise and weight loss, the mediating variable could be metabolism, as exercise can increase metabolism, which can then lead to weight loss.
Moderator Variable
This is a variable that affects the strength or direction of the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. It is a variable that influences the effect of the independent variable on the dependent variable. For example, in a study on the effects of caffeine on cognitive performance, the moderator variable could be age, as older adults may be more sensitive to the effects of caffeine than younger adults.
Control Variable
This is a variable that is held constant or controlled by the researcher to ensure that it does not affect the relationship between the independent variable and the dependent variable. Control variables are important to ensure that any observed effects are due to the independent variable and not to other factors. For example, in a study on the effects of a new teaching method on student performance, the control variables could include class size, teacher experience, and student demographics.
Continuous Variable
This is a variable that can take on any value within a certain range. Continuous variables can be measured on a scale and are often used in statistical analyses. Examples of continuous variables include height, weight, and temperature.
Categorical Variable
This is a variable that can take on a limited number of values or categories. Categorical variables can be nominal or ordinal. Nominal variables have no inherent order, while ordinal variables have a natural order. Examples of categorical variables include gender, race, and educational level.
Discrete Variable
This is a variable that can only take on specific values. Discrete variables are often used in counting or frequency analyses. Examples of discrete variables include the number of siblings a person has, the number of times a person exercises in a week, and the number of students in a classroom.
Dummy Variable
This is a variable that takes on only two values, typically 0 and 1, and is used to represent categorical variables in statistical analyses. Dummy variables are often used when a categorical variable cannot be used directly in an analysis. For example, in a study on the effects of gender on income, a dummy variable could be created, with 0 representing female and 1 representing male.
Extraneous Variable
This is a variable that has no relationship with the independent or dependent variable but can affect the outcome of the study. Extraneous variables can lead to erroneous conclusions and can be controlled through random assignment or statistical techniques.
Latent Variable
This is a variable that cannot be directly observed or measured, but is inferred from other variables. Latent variables are often used in psychological or social research to represent constructs such as personality traits, attitudes, or beliefs.
Moderator-mediator Variable
This is a variable that acts both as a moderator and a mediator. It can moderate the relationship between the independent and dependent variables and also mediate the relationship between the independent and dependent variables. Moderator-mediator variables are often used in complex statistical analyses.
Variables Analysis Methods
There are different methods to analyze variables in research, including:
- Descriptive statistics: This involves analyzing and summarizing data using measures such as mean, median, mode, range, standard deviation, and frequency distribution. Descriptive statistics are useful for understanding the basic characteristics of a data set.
- Inferential statistics : This involves making inferences about a population based on sample data. Inferential statistics use techniques such as hypothesis testing, confidence intervals, and regression analysis to draw conclusions from data.
- Correlation analysis: This involves examining the relationship between two or more variables. Correlation analysis can determine the strength and direction of the relationship between variables, and can be used to make predictions about future outcomes.
- Regression analysis: This involves examining the relationship between an independent variable and a dependent variable. Regression analysis can be used to predict the value of the dependent variable based on the value of the independent variable, and can also determine the significance of the relationship between the two variables.
- Factor analysis: This involves identifying patterns and relationships among a large number of variables. Factor analysis can be used to reduce the complexity of a data set and identify underlying factors or dimensions.
- Cluster analysis: This involves grouping data into clusters based on similarities between variables. Cluster analysis can be used to identify patterns or segments within a data set, and can be useful for market segmentation or customer profiling.
- Multivariate analysis : This involves analyzing multiple variables simultaneously. Multivariate analysis can be used to understand complex relationships between variables, and can be useful in fields such as social science, finance, and marketing.
Examples of Variables
- Age : This is a continuous variable that represents the age of an individual in years.
- Gender : This is a categorical variable that represents the biological sex of an individual and can take on values such as male and female.
- Education level: This is a categorical variable that represents the level of education completed by an individual and can take on values such as high school, college, and graduate school.
- Income : This is a continuous variable that represents the amount of money earned by an individual in a year.
- Weight : This is a continuous variable that represents the weight of an individual in kilograms or pounds.
- Ethnicity : This is a categorical variable that represents the ethnic background of an individual and can take on values such as Hispanic, African American, and Asian.
- Time spent on social media : This is a continuous variable that represents the amount of time an individual spends on social media in minutes or hours per day.
- Marital status: This is a categorical variable that represents the marital status of an individual and can take on values such as married, divorced, and single.
- Blood pressure : This is a continuous variable that represents the force of blood against the walls of arteries in millimeters of mercury.
- Job satisfaction : This is a continuous variable that represents an individual’s level of satisfaction with their job and can be measured using a Likert scale.
Applications of Variables
Variables are used in many different applications across various fields. Here are some examples:
- Scientific research: Variables are used in scientific research to understand the relationships between different factors and to make predictions about future outcomes. For example, scientists may study the effects of different variables on plant growth or the impact of environmental factors on animal behavior.
- Business and marketing: Variables are used in business and marketing to understand customer behavior and to make decisions about product development and marketing strategies. For example, businesses may study variables such as consumer preferences, spending habits, and market trends to identify opportunities for growth.
- Healthcare : Variables are used in healthcare to monitor patient health and to make treatment decisions. For example, doctors may use variables such as blood pressure, heart rate, and cholesterol levels to diagnose and treat cardiovascular disease.
- Education : Variables are used in education to measure student performance and to evaluate the effectiveness of teaching strategies. For example, teachers may use variables such as test scores, attendance, and class participation to assess student learning.
- Social sciences : Variables are used in social sciences to study human behavior and to understand the factors that influence social interactions. For example, sociologists may study variables such as income, education level, and family structure to examine patterns of social inequality.
Purpose of Variables
Variables serve several purposes in research, including:
- To provide a way of measuring and quantifying concepts: Variables help researchers measure and quantify abstract concepts such as attitudes, behaviors, and perceptions. By assigning numerical values to these concepts, researchers can analyze and compare data to draw meaningful conclusions.
- To help explain relationships between different factors: Variables help researchers identify and explain relationships between different factors. By analyzing how changes in one variable affect another variable, researchers can gain insight into the complex interplay between different factors.
- To make predictions about future outcomes : Variables help researchers make predictions about future outcomes based on past observations. By analyzing patterns and relationships between different variables, researchers can make informed predictions about how different factors may affect future outcomes.
- To test hypotheses: Variables help researchers test hypotheses and theories. By collecting and analyzing data on different variables, researchers can test whether their predictions are accurate and whether their hypotheses are supported by the evidence.
Characteristics of Variables
Characteristics of Variables are as follows:
- Measurement : Variables can be measured using different scales, such as nominal, ordinal, interval, or ratio scales. The scale used to measure a variable can affect the type of statistical analysis that can be applied.
- Range : Variables have a range of values that they can take on. The range can be finite, such as the number of students in a class, or infinite, such as the range of possible values for a continuous variable like temperature.
- Variability : Variables can have different levels of variability, which refers to the degree to which the values of the variable differ from each other. Highly variable variables have a wide range of values, while low variability variables have values that are more similar to each other.
- Validity and reliability : Variables should be both valid and reliable to ensure accurate and consistent measurement. Validity refers to the extent to which a variable measures what it is intended to measure, while reliability refers to the consistency of the measurement over time.
- Directionality: Some variables have directionality, meaning that the relationship between the variables is not symmetrical. For example, in a study of the relationship between smoking and lung cancer, smoking is the independent variable and lung cancer is the dependent variable.
Advantages of Variables
Here are some of the advantages of using variables in research:
- Control : Variables allow researchers to control the effects of external factors that could influence the outcome of the study. By manipulating and controlling variables, researchers can isolate the effects of specific factors and measure their impact on the outcome.
- Replicability : Variables make it possible for other researchers to replicate the study and test its findings. By defining and measuring variables consistently, other researchers can conduct similar studies to validate the original findings.
- Accuracy : Variables make it possible to measure phenomena accurately and objectively. By defining and measuring variables precisely, researchers can reduce bias and increase the accuracy of their findings.
- Generalizability : Variables allow researchers to generalize their findings to larger populations. By selecting variables that are representative of the population, researchers can draw conclusions that are applicable to a broader range of individuals.
- Clarity : Variables help researchers to communicate their findings more clearly and effectively. By defining and categorizing variables, researchers can organize and present their findings in a way that is easily understandable to others.
Disadvantages of Variables
Here are some of the main disadvantages of using variables in research:
- Simplification : Variables may oversimplify the complexity of real-world phenomena. By breaking down a phenomenon into variables, researchers may lose important information and context, which can affect the accuracy and generalizability of their findings.
- Measurement error : Variables rely on accurate and precise measurement, and measurement error can affect the reliability and validity of research findings. The use of subjective or poorly defined variables can also introduce measurement error into the study.
- Confounding variables : Confounding variables are factors that are not measured but that affect the relationship between the variables of interest. If confounding variables are not accounted for, they can distort or obscure the relationship between the variables of interest.
- Limited scope: Variables are defined by the researcher, and the scope of the study is therefore limited by the researcher’s choice of variables. This can lead to a narrow focus that overlooks important aspects of the phenomenon being studied.
- Ethical concerns: The selection and measurement of variables may raise ethical concerns, especially in studies involving human subjects. For example, using variables that are related to sensitive topics, such as race or sexuality, may raise concerns about privacy and discrimination.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Control Variable – Definition, Types and Examples

Moderating Variable – Definition, Analysis...

Categorical Variable – Definition, Types and...

Independent Variable – Definition, Types and...

Ratio Variable – Definition, Purpose and Examples

Ordinal Variable – Definition, Purpose and...

Market Research Blog
Nature, scope and significance of business research.

Business market research is a dynamic concept. One of the key components of market research studies is the strategic inquiry into a business situation or environment to establish the actuality or evidence that may have led to the development of certain trends. Today, business research is the pillar that supports decision-making in various areas of an organization. Prior to conducting proactive business research, it is crucial to determine the underlying objectives of the research program to come up with an accurately targeted approach. The significance of business research is that it is a fact-finding mission that fuels successful decision-making in a corporate environment. Let us take a look at the nature, scope, and significance of business research.
What is Involved in Business Research?
Business research is the process of gathering thorough information on all aspects of a company's operations and applying that information to improve operational excellence, which can lead to an increase in sales and profits.
- A study like this can assist businesses in figuring the product or service that is most profitable.
- It entails determining where money should be spent to boost sales, profitability, or/and market share.
Given the increasing competition in all industries, market research has become extremely necessary to make intelligent and informed decisions that fuel business growth.
The Nature of Business Research
In business, knowledge is power. The ability to make informed decisions is crucial for any organization's success and growth. To achieve this, businesses rely on research—a systematic inquiry that helps unravel complex problems, discover insights, and explore new opportunities. Business research involves a structured investigation aimed at collecting and analyzing data to address specific business challenges or explore potential opportunities. This often includes conducting market research studies and producing business research reports based on the research findings. It is a multi-faceted process that employs various methodologies, including quantitative and qualitative techniques, to acquire knowledge that drives decision-making. While quantitative research focuses on numerical data and statistical analysis, qualitative research emphasizes an in-depth understanding of subjective experiences, opinions, and motivations. From problem identification to market analysis and decision support, research empowers businesses to navigate complexities, adapt to change, and seize opportunities. Investing in robust research practices can help organizations lay the foundation for sustainable growth and success. It is crucial to hire a reputable business research company with proven experience in providing specialized business market research services.
The Scope of Business Research
The scope and significance of business research are immense. In this section, we will discuss how top business research companies like Unimrkt Research can help your organization navigate the complicated fabric of today’s dynamic business world and build a profitable venture that stands the test of time.
Problem Identification
Business research plays a vital role in identifying and defining the problems that organizations face. It helps clarify issues, determine their root causes, and establish clear objectives for further investigation. By gaining a comprehensive understanding of the challenges, businesses can develop effective strategies to overcome them.
Market Analysis and Competitive Intelligence
Researching the market landscape and understanding customer preferences are fundamental to success. A business research company enables businesses to analyze market trends, consumer behavior, and competitor strategies. This knowledge aids in developing tailored products, crafting targeted marketing campaigns, and staying ahead of the competition.
Decision Support
Robust research provides decision-makers with reliable information, enabling them to make informed choices. Whether it's launching a new product, expanding into new markets, or modifying existing strategies, data-backed decisions reduce uncertainty and enhance the chances of achieving the desired outcomes.
Innovation and Adaptation
Business research facilitates innovation by uncovering emerging trends, technological advancements, and changing consumer needs. By staying abreast of industry developments, organizations can adapt quickly and identify growth opportunities. Research also aids in identifying potential risks and threats, allowing businesses to proactively mitigate them.
Performance Evaluation
To sustain success, businesses must evaluate their performance regularly. Research provides valuable insights into key performance indicators, customer satisfaction levels, and operational efficiency. By analyzing this data, companies can identify areas for improvement, optimize processes, and enhance overall performance.
Importance of Business Research
Business research is one of the most effective ways to understand your customers and the overall market, as well as analyze competitors. This type of research aids businesses in determining market demand and supply. It can help business organizations to cut unnecessary expenses and develop tailor-made solutions or products that appeal to the demand in the market. Research for startups aids in gathering information for professional or commercial purposes to assess business prospects and goals. Business research can also help startups find the right audience profile for their offerings. It is the holy grail when looking to achieve success in the modern, ultra-competitive business world.
Key Advantages of Business Research
Here are some of the key advantages of business research:
- Market research can help organizations gain a better perspective and understanding of their market or target audience. This ensures that the company stays ahead of its competitors.
- Primary and secondary research can act as an insurance policy against obvious but silent dangers on your business path.
- Market research findings help organizations learn from their weaknesses and adapt to new business environments.
- By using certain research methodologies for competitor analysis, you can capitalize on your new-found knowledge to steer ahead of the competition.
- Regular market research initiatives help take the ‘pulse’ of hot market trends, allowing you to come up with “superhit” products and services.
- It helps with market forecasting, which allows you to project future numbers, characteristics, and trends within your target market.
Significance of Business Research in Local and Global Business Fields
Today, top market research companies are focusing on the assessment of both local and international business environments. A business research company takes factors such as markets (global and domestic), goods and services, and other business elements into account to conduct a progressive and strategic study. The significance of business research is such that it has become a crucial predictor of organizational effectiveness, as it determines the perception, quality, and sustainability of several performance factors. For example, in a traditional manufacturing concern, business research can help with aspects like product refinement, distribution networks, competitiveness module design, and customer demand tracking, among other things.
Key Steps in Conducting Business Research
Here are the key steps involved when conducting business research. By following these steps, businesses can develop and conduct systematic and effective research programs that provide valuable insights, supporting informed decision-making.
Identify and Define the Research Problem
Clearly articulate the specific business challenge or opportunity that you aim to address through research. Define the problem in a concise and focused manner, ensuring clarity and alignment with organizational objectives.
Develop Research Objectives
Establish clear and measurable research objectives that align with the identified problem. These objectives will guide the entire research process and help ensure that the outcomes are relevant and actionable.
Design the Research Methodology
Select the appropriate research methodology based on the nature of the problem and the data needed. This may involve choosing between quantitative and qualitative approaches, or a combination of both. Determine the research design, sampling techniques, data collection methods, and tools to be used.
Collect Data
Implement the data collection methods defined in the research design process. This could involve conducting surveys, interviews, observations, or analyzing existing data sources. Ensure the data collected is reliable, valid, and relevant to the research objectives.
Analyze Data
Process and analyze the collected data using appropriate statistical or qualitative analysis techniques. Identify patterns, trends, and insights that emerge from the data. Use software tools or statistical packages, if required, to aid in data analysis.
Interpret Findings
Interpret the analyzed data in the context of the research objectives and the original problem. Draw meaningful conclusions and insights from the findings. Relate the findings to existing theories or industry benchmarks, if applicable.
Communicate Results
Prepare a comprehensive report or presentation that effectively communicates the research findings, insights, and recommendations. Present the information in a concise, clear, and visually appealing manner. Tailor the communication to the intended audience, highlighting the implications and actionable steps.
Validate and Verify
Seek feedback and validation from stakeholders, colleagues, or experts to ensure the accuracy and reliability of the research findings. Incorporate their input and make any necessary revisions to strengthen the research outcomes.
Implement Recommendations
Translate the research findings into actionable recommendations or strategies. Develop an implementation plan and ensure buy-in from key stakeholders. Monitor and evaluate the progress and impact of the implemented recommendations.
Reflect and Learn
Reflect on the research process and outcomes. Identify lessons learned, strengths, and areas for improvement. This reflection can inform future research endeavors and enhance the organization's research capabilities.
The importance and significance of business research will only continue to grow with the changing business landscape. Business research has a direct impact on your organization’s success. The first and, perhaps, most important task for a business organization is to find the right market research company . This is where Unimrkt Research comes into play. Over the years, we have conducted industry research across 90 countries, spanning four continents in a variety of industries. We follow ESOMAR norms and are certified with the ISO 20252 and ISO 27001 standards. To learn about our business market research services, call +91 124 424 5210/+91 9870 377 557 or email [email protected] .
- Share to FaceBook
Quick Enquiry
Customer Service, We Make it Better
Recent Posts
- A Concise Guide to Quantitative Market Research
- 3 B2B Market Research Trends That Could Shape 2024
- Eyes on 2024: Changes That Might Disrupt the Healthcare Industry This Year
- Cracking the Language to Make Survey Questions Inclusive in 2024
- Attracting Investors: How Market Research Can Solidify Your Case
- Solid Foundations: Ways to Enhance Trustworthiness in Qualitative Research
- What Makes CATI Research So Effective?
- Moderator Qualities That Improve Qualitative Market Research
- 5 Consumer Market Trends That Will Define 2024
- What are the strengths of quantitative research?
- How to Make Your Partnership with Primary Market Research Firms Fruitful
- A Quick Guide to Harnessing the Strengths of Quantitative Research
- Advice from Your Research Partner: Don't Compromise Quality on Online Surveys
- Why Cost Efficiency is the Currency of the Healthcare Market
Other Blogs

Relevance of Qualitative Market Research in Data Mining

Relevance of a telephone survey in a digital world

Significance of media research in today’s world

Relevance of research in the banking & finance industry

Top 5 Benefits of Online Panels
Get in Touch
Email us : sales@ unimrkt.com Call us : +91-124-424-5210

Stay connected for latest updates
Let's stay in touch subscribe to our newsletter..

Inquire With Us
Fill in the details and connect with us.

Thank you for sharing your email ID. We will get back to you soon.
Thank you!!!
- Skip to main content
- Skip to primary sidebar
- Skip to footer
- QuestionPro

- Solutions Industries Gaming Automotive Sports and events Education Government Travel & Hospitality Financial Services Healthcare Cannabis Technology Use Case NPS+ Communities Audience Contactless surveys Mobile LivePolls Member Experience GDPR Positive People Science 360 Feedback Surveys
- Resources Blog eBooks Survey Templates Case Studies Training Help center
Home Market Research
Sample: Definition, Types, Formula & Examples
How often do researchers look for the right survey respondents, either for a market research study or an existing survey in the field? The sample or the respondents of this research may be selected from a set of customers or users that are known or unknown.
You may often know your typical respondent profile but don’t have access to the respondents to complete your research study. At such times, researchers and research teams reach out to specialized organizations to access their panel of respondents or buy respondents from them to complete research studies and surveys.
These could be general population respondents that match demographic criteria or respondents based on specific criteria. Such respondents are imperative to the success of research studies.
This article discusses in detail the different types of samples, sampling methods, and examples of each. It also mentions the steps to calculate the size, the details of an online sample, and the advantages of using them.
Content Index
- What is a sample?
Probability sampling methodologies with examples
Non-probability sampling methodologies with examples.
- How to determine a sample size
- Calculating sample size
- Sampling advantages
What is a Sample?
A sample is a smaller set of data that a researcher chooses or selects from a larger population using a pre-defined selection bias method. These elements are known as sample points, sampling units, or observations.
Creating a sample is an efficient method of conducting research . Researching the whole population is often impossible, costly, and time-consuming. Hence, examining the sample provides insights the researcher can apply to the entire population.
For example, if a cell phone manufacturer wants to conduct a feature research study among students in US Universities. An in-depth research study must be conducted if the researcher is looking for features that the students use, features they would like to see, and the price they are willing to pay.
This step is imperative to understand the features that need development, the features that require an upgrade, the device’s pricing, and the go-to-market strategy.
In 2016/17 alone, there were 24.7 million students enrolled in universities across the US. It is impossible to research all these students; the time spent would make the new device redundant, and the money spent on development would render the study useless.
Creating a sample of universities by geographical location and further creating a sample of these students from these universities provides a large enough number of students for research.
Typically, the population for market research is enormous. Making an enumeration of the whole population is practically impossible. The sample usually represents a manageable size of this population. Researchers then collect data from these samples through surveys, polls, and questionnaires and extrapolate this data analysis to the broader community.
LEARN ABOUT: Survey Sampling
Types of Samples: Selection methodologies with examples
The process of deriving a sample is called a sampling method. Sampling forms an integral part of the research design as this method derives the quantitative and qualitative data that can be collected as part of a research study. Sampling methods are characterized into two distinct approaches: probability sampling and non-probability sampling.
Probability sampling is a method of deriving a sample where the objects are selected from a population-based on probability theory. This method includes everyone in the population, and everyone has an equal chance of being selected. Hence, there is no bias whatsoever in this type of sample.
Each person in the population can subsequently be a part of the research. The selection criteria are decided at the outset of the market research study and form an important component of research.
LEARN ABOUT: Action Research
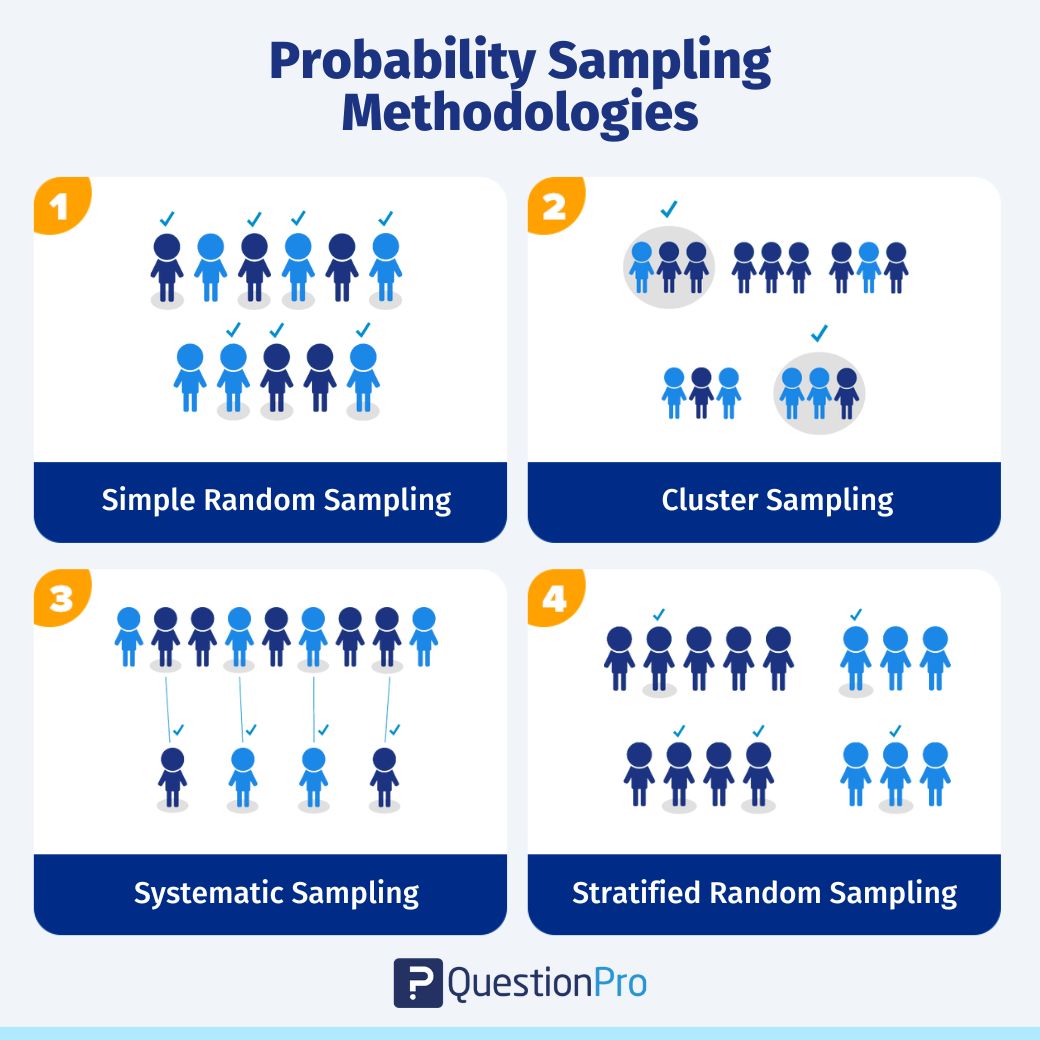
Probability sampling can be further classified into four distinct types of samples. They are:
- Simple random sampling: The most straightforward way of selecting a sample is simple random sampling . In this method, each member has an equal chance of participating in the study. The objects in this sample population are chosen randomly, and each member has the same probability of being selected. For example, if a university dean would like to collect feedback from students about their perception of the teachers and level of education, all 1000 students in the University could be a part of this sample. Any 100 students can be selected randomly to be a part of this sample.
- Cluster sampling: Cluster sampling is a type of sampling method where the respondent population is divided into equal clusters. Clusters are identified and included in a sample based on defining demographic parameters such as age, location, sex, etc. This makes it extremely easy for a survey creator to derive practical inferences from the feedback. For example, if the FDA wants to collect data about adverse side effects from drugs, they can divide the mainland US into distinctive cluster analysis , like states. Research studies are then administered to respondents in these clusters. This type of generating a sample makes the data collection in-depth and provides easy-to-consume and act-upon, insights.
- Systematic sampling: Systematic sampling is a sampling method where the researcher chooses respondents at equal intervals from a population. The approach to selecting the sample is to pick a starting point and then pick respondents at a pre-defined sample interval. For example, while selecting 1,000 volunteers for the Olympics from an application list of 10,000 people, each applicant is given a count of 1 to 10,000. Then starting from 1 and selecting each respondent with an interval of 10, a sample of 1,000 volunteers can be obtained.
- Stratified random sampling: Stratified random sampling is a method of dividing the respondent population into distinctive but pre-defined parameters in the research design phase. In this method, the respondents don’t overlap but collectively represent the whole population. For example, a researcher looking to analyze people from different socioeconomic backgrounds can distinguish respondents by their annual salaries. This forms smaller groups of people or samples, and then some objects from these samples can be used for the research study.
LEARN ABOUT: Purposive Sampling
The non-probability sampling method uses the researcher’s discretion to select a sample. This type of sample is derived mostly from the researcher’s or statistician’s ability to get to this sample.
This type of sampling is used for preliminary research where the primary objective is to derive a hypothesis about the topic in research. Here each member does not have an equal chance of being a part of the sample population, and those parameters are known only post-selection to the sample.
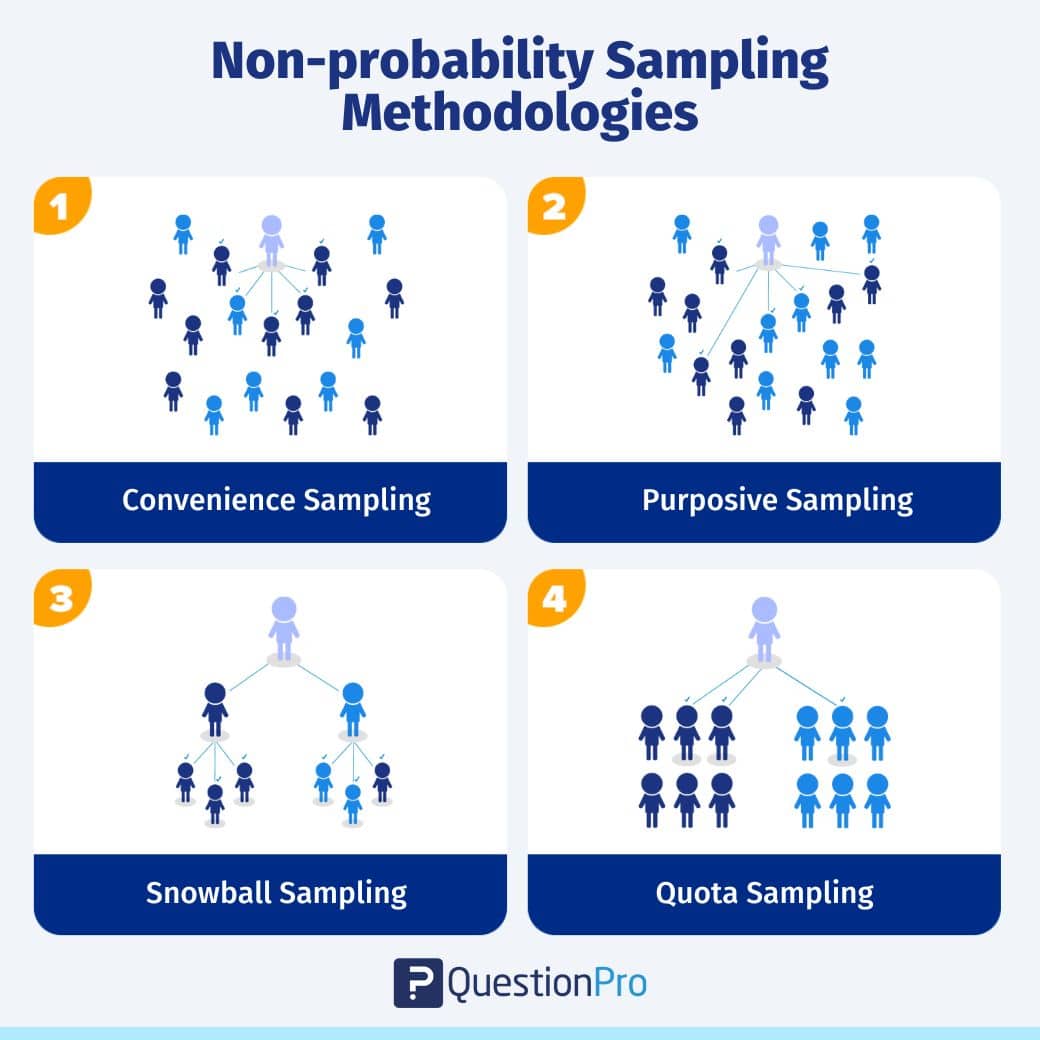
We can classify non-probability sampling into four distinct types of samples. They are:
- Convenience sampling: Convenience sampling , in easy terms, stands for the convenience of a researcher accessing a respondent. There is no scientific method for deriving this sample. Researchers have nearly no authority over selecting the sample elements, and it’s purely done based on proximity and not representativeness.
This non-probability sampling method is used when there is time and costs limitations in collecting feedback. For example, researchers that are conducting a mall-intercept survey to understand the probability of using a fragrance from a perfume manufacturer. In this sampling method, the sample respondents are chosen based on their proximity to the survey desk and willingness to participate in the research.
- Judgemental/purposive sampling: The judgemental or purposive sampling method is a method of developing a sample purely on the basis and discretion of the researcher purely, based on the nature of the study along with his/her understanding of the target audience. This sampling method selects people who only fit the research criteria and end objectives, and the remaining are kept out.
For example, if the research topic is understanding what University a student prefers for Masters, if the question asked is “Would you like to do your Masters?” anything other than a response, “Yes” to this question, everyone else is excluded from this study.
- Snowball sampling: Snowball sampling or chain-referral sampling is defined as a non-probability sampling technique in which the samples have rare traits. This is a sampling technique in which existing subjects provide referrals to recruit samples required for a research study.
For example, while collecting feedback about a sensitive topic like AIDS, respondents aren’t forthcoming with information. In this case, the researcher can recruit people with an understanding or knowledge of such people and collect information from them or ask them to collect information.
- Quota sampling: Quota sampling is a method of collecting a sample where the researcher has the liberty to select a sample based on their strata. The primary characteristic of this method is that two people cannot exist under two different conditions. For example, when a shoe manufacturer would like to understand millennials’ perception of the brand with other parameters like comfort, pricing, etc. It selects only females who are millennials for this study as the research objective is to collect feedback about women’s shoes.
How to determine a Sample Size
As we have learned above, the right sample size determination is essential for the success of data collection in a market research study. But is there a correct number for the sample size? What parameters decide the sample size? What are the distribution methods of the survey?
To understand all of this and make an informed calculation of the right sample size, it is first essential to understand four important variables that form the basic characteristics of a sample. They are:
- Population size: The population size is all the people that can be considered for the research study. This number, in most cases, runs into huge amounts. For example, the population of the United States is 327 million. But in market research, it is impossible to consider all of them for the research study.
- The margin of error (confidence interval): The margin of error is depicted by a percentage that is a statistical inference about the confidence of what number of the population depicts the actual views of the whole population. This percentage helps towards the statistical analysis in selecting a sample and how much sampling error in this would be acceptable.
LEARN ABOUT: Research Process Steps
- Confidence level: This metric measures where the actual mean falls within a confidence interval. The most common confidence intervals are 90%, 95%, and 99%.
- Standard deviation: This metric covers the variance in a survey. A safe number to consider is .5, which would mean that the sample size has to be that large.
Calculating Sample Size
To calculate the sample size, you need the following parameters.
- Z-score: The Z-score value can be found here .
- Standard deviation
- Margin of error
- Confidence level
To calculate use the sample size, use this formula:

Sample Size = (Z-score)2 * StdDev*(1-StdDev) / (margin of error)2
Consider the confidence level of 90%, standard deviation of .6 and margin of error, +/-4%
((1.64)2 x .6(.6)) / (.04)2
( 2.68x .0.36) / .0016
.9648 / .0016
603 respondents are needed and that becomes your sample size.
Try our sample size calculator to give population, margin of error calculator , and confidence level.
LEARN MORE: Population vs Sample
Sampling Advantages
As shown above, there are many advantages to sampling. Some of the most significant advantages are:
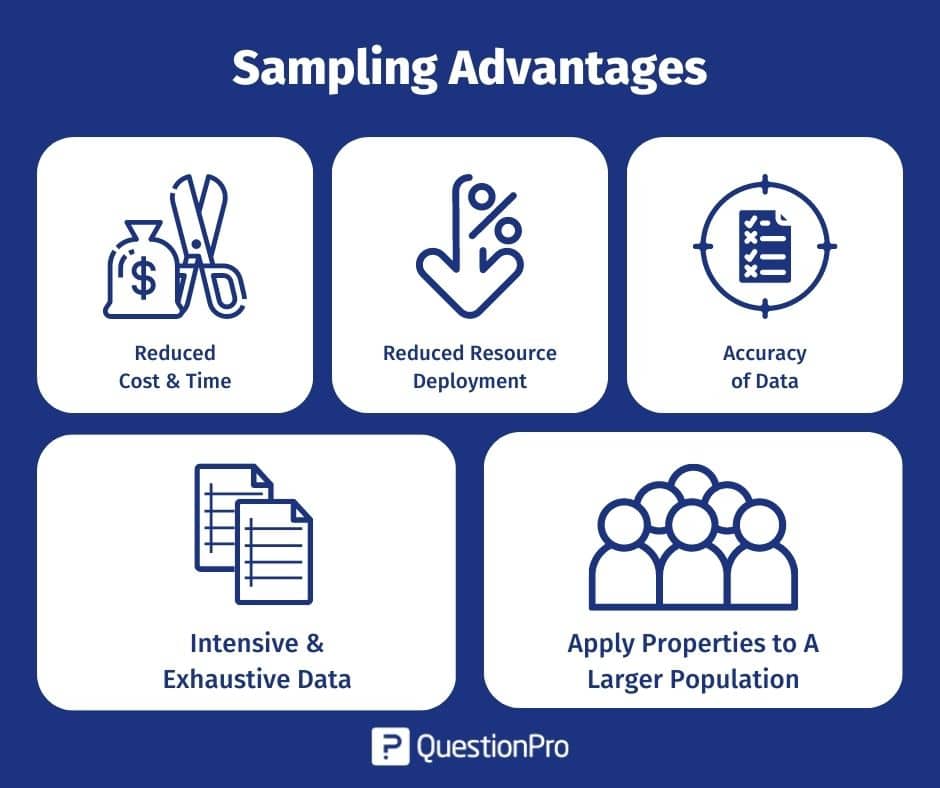
- Reduced cost & time: Since using a sample reduces the number of people that have to be reached out to, it reduces cost and time. Imagine the time saved between researching with a population of millions vs. conducting a research study using a sample.
- Reduced resource deployment: It is obvious that if the number of people involved in a research study is much lower due to the sample, the resources required are also much less. The workforce needed to research the sample is much less than the workforce needed to study the whole population .
- Accuracy of data: Since the sample indicates the population, the data collected is accurate. Also, since the respondent is willing to participate, the survey dropout rate is much lower, which increases the validity and accuracy of the data.
- Intensive & exhaustive data: Since there are lesser respondents, the data collected from a sample is intense and thorough. More time and effort are given to each respondent rather than collecting data from many people.
- Apply properties to a larger population: Since the sample is indicative of the broader population, it is safe to say that the data collected and analyzed from the sample can be applied to the larger population, which would hold true.
To collect accurate data for research, filter bad panelists, and eliminate sampling bias by applying different control measures. If you need any help arranging a sample audience for your next market research project, contact us at [email protected] . We have more than 22 million panelists across the world!
In conclusion, a sample is a subset of a population that is used to represent the characteristics of the entire population. Sampling is essential in research and data analysis to make inferences about a population based on a smaller group of individuals. There are different types of sampling, such as probability sampling, non-probability sampling, and others, each with its own advantages and disadvantages.
Choosing the right sampling method depends on the research question, budget, and resources is important. Furthermore, the sample size plays a crucial role in the accuracy and generalizability of the findings.
This article has provided a comprehensive overview of the definition, types, formula, and examples of sampling. By understanding the different types of sampling and the formulas used to calculate sample size, researchers and analysts can make more informed decisions when conducting research and data unit of analysis .
Sampling is an important tool that enables researchers to make inferences about a population based on a smaller group of individuals. With the right sampling method and sample size, researchers can ensure that their findings are accurate and generalizable to the population.
Utilize one of QuestionPro’s many survey questionnaire samples to help you complete your survey.
When creating online surveys for your customers, employees, or students, one of the biggest mistakes you can make is asking the wrong questions. Different businesses and organizations have different needs required for their surveys.
If you ask irrelevant questions to participants, they’re more likely to drop out before completing the survey. A questionnaire sample template will help set you up for a successful survey.
LEARN MORE SIGN UP FREE
MORE LIKE THIS

Top 7 Focus Group Software for Comprehensive Research
Apr 17, 2024

Top 7 DEI Software Solutions to Empower Your Workplace
Apr 16, 2024

The Power of AI in Customer Experience — Tuesday CX Thoughts

Employee Lifecycle Management Software: Top of 2024
Apr 15, 2024
Other categories
- Academic Research
- Artificial Intelligence
- Assessments
- Brand Awareness
- Case Studies
- Communities
- Consumer Insights
- Customer effort score
- Customer Engagement
- Customer Experience
- Customer Loyalty
- Customer Research
- Customer Satisfaction
- Employee Benefits
- Employee Engagement
- Employee Retention
- Friday Five
- General Data Protection Regulation
- Insights Hub
- Life@QuestionPro
- Market Research
- Mobile diaries
- Mobile Surveys
- New Features
- Online Communities
- Question Types
- Questionnaire
- QuestionPro Products
- Release Notes
- Research Tools and Apps
- Revenue at Risk
- Survey Templates
- Training Tips
- Uncategorized
- Video Learning Series
- What’s Coming Up
- Workforce Intelligence

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Business research is the process of gathering relevant information regarding a company's business activities and using it to maximize profit. Regardless of your experience and knowledge, learning about business research can help you improve your organization's output. Researching the subject can also have a positive effect on your career ...
Business Research also conducts a thorough cost analysis thus helping the company efficiently manage resources and allocate them in an optimal manner. It keeps you updated with the latest trends and competitor analysis. Disadvantages of Business Research. Business Research can be expensive and time-consuming.
Business research: Definition. Business research is a process of acquiring detailed information on all the areas of business and using such information to maximize the sales and profit of the business. Such a study helps companies determine which product/service is most profitable or in demand. In simple words, it can be stated as the acquisition of information or knowledge for professional or ...
Business research helps companies make better business decisions by gathering information. The scope of the term business research is quite broad - it acts as an umbrella that covers every aspect of business, from finances to advertising creative. It can include research methods which help a company better understand its target market.
Put another way, in the honeycomb, the six main elements - namely: (1) research philosophy; (2) research approach; (3) research strategy; (4) research design; (5) data collection and (6) data analysis techniques - come together to form research methodology. This structure is characteristic of the main headings you will find in a methodology ...
Examples of Business Research. Here are five examples that illustrate what business research is. Example #1. Microcredit programs from institutional and non-institutional sources have been found to significantly impact raising the standard of living of rural people, especially women.
In business research methodology, there are two main types. These are quantitative research and qualitative research. In the simplest terms, quantitative research is about collecting numerical and factual data, whereas qualitative research is about collecting data by using open-ended questions. These two methods can be divided into more ...
Cathy Heath. Business research is the process of gathering and analyzing different types of information to make informed business decisions. If you undertake business research correctly, it has multiple benefits, such as: Improving organizational operations. Identifying trends. Developing new products and services.
Business research can be defined as a systematic and objective process of gathering, recording and analysing data that provide information to guide business decisions. It is used to understand the market trends, or find the optimal marketing mix, devise effective HR policies, or find the best investment options.
Some commonly used quantitative methods of business research are: Experimental Research: Experimental research refers to research studies that adhere to the scientific research design. This type of research aims to prove or disprove a theory, or hypothesis. Businesses generally use experimental research to study consumers' behavioral traits.
Explore the essential steps for data collection, reporting, and analysis in business research Understanding Business Research offers a comprehensive introduction to the entire process of designing, conducting, interpreting, and reporting findings in the business environment. With an emphasis on the human factor, the book presents a complete set of tools for tackling complex behavioral and ...
A simple definition of business research is gathering complete data and information about all parts of a company and then using that information to increase sales and profits. Business Research is an activity in management that enables one to determine which product has the most potential for profit and should be prioritized for development if ...
Business research methodologies can be broadly categorized into two main types: qualitative and quantitative methods. Qualitative Research Methods. In business, qualitative research aims to understand people's thoughts, emotions, and motivations. These methods help explore new ideas, create new products, and understand customer needs.
As stated, business research requires a problem to be solved, which means a concise research problem or question definition is the starting point of the study—often easier said than done. Example : Assume one wants to investigate the financial performance of publicly listed mining companies.
Market research is the process of assessing the viability of a new good or service through research conducted directly with the consumer which allows a company to ...
Research methods are specific procedures for collecting and analyzing data. Developing your research methods is an integral part of your research design. When planning your methods, there are two key decisions you will make. First, decide how you will collect data. Your methods depend on what type of data you need to answer your research question:
A research design is a strategy for answering your research question using empirical data. Creating a research design means making decisions about: Your overall research objectives and approach. Whether you'll rely on primary research or secondary research. Your sampling methods or criteria for selecting subjects. Your data collection methods.
For example, scientists may study the effects of different variables on plant growth or the impact of environmental factors on animal behavior. Business and marketing: Variables are used in business and marketing to understand customer behavior and to make decisions about product development and marketing strategies. For example, businesses may ...
Research is the careful consideration of study regarding a particular concern or research problem using scientific methods. According to the American sociologist Earl Robert Babbie, "research is a systematic inquiry to describe, explain, predict, and control the observed phenomenon. It involves inductive and deductive methods.".
To learn about our business market research services, call +91 124 424 5210/+91 9870 377 557 or email [email protected]. Business market research is a dynamic concept. The significance of business research is that it is a fact-finding mission that fuels successful decision-making in a corporate environment.
Reduced cost & time: Since using a sample reduces the number of people that have to be reached out to, it reduces cost and time. Imagine the time saved between researching with a population of millions vs. conducting a research study using a sample. Reduced resource deployment: It is obvious that if the number of people involved in a research study is much lower due to the sample, the ...