Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?

A conversation with a Wheelock researcher, a BU student, and a fourth-grade teacher

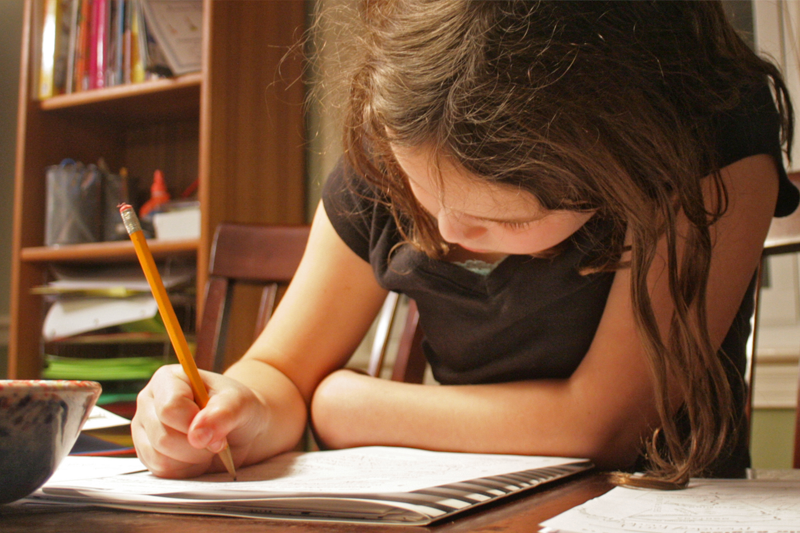
“Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives,” says Wheelock’s Janine Bempechat. “It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.” Photo by iStock/Glenn Cook Photography
Do your homework.
If only it were that simple.
Educators have debated the merits of homework since the late 19th century. In recent years, amid concerns of some parents and teachers that children are being stressed out by too much homework, things have only gotten more fraught.
“Homework is complicated,” says developmental psychologist Janine Bempechat, a Wheelock College of Education & Human Development clinical professor. The author of the essay “ The Case for (Quality) Homework—Why It Improves Learning and How Parents Can Help ” in the winter 2019 issue of Education Next , Bempechat has studied how the debate about homework is influencing teacher preparation, parent and student beliefs about learning, and school policies.
She worries especially about socioeconomically disadvantaged students from low-performing schools who, according to research by Bempechat and others, get little or no homework.
BU Today sat down with Bempechat and Erin Bruce (Wheelock’17,’18), a new fourth-grade teacher at a suburban Boston school, and future teacher freshman Emma Ardizzone (Wheelock) to talk about what quality homework looks like, how it can help children learn, and how schools can equip teachers to design it, evaluate it, and facilitate parents’ role in it.
BU Today: Parents and educators who are against homework in elementary school say there is no research definitively linking it to academic performance for kids in the early grades. You’ve said that they’re missing the point.
Bempechat : I think teachers assign homework in elementary school as a way to help kids develop skills they’ll need when they’re older—to begin to instill a sense of responsibility and to learn planning and organizational skills. That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success. If we greatly reduce or eliminate homework in elementary school, we deprive kids and parents of opportunities to instill these important learning habits and skills.
We do know that beginning in late middle school, and continuing through high school, there is a strong and positive correlation between homework completion and academic success.
That’s what I think is the greatest value of homework—in cultivating beliefs about learning and skills associated with academic success.
You talk about the importance of quality homework. What is that?
Quality homework is engaging and relevant to kids’ lives. It gives them autonomy and engages them in the community and with their families. In some subjects, like math, worksheets can be very helpful. It has to do with the value of practicing over and over.

What are your concerns about homework and low-income children?
The argument that some people make—that homework “punishes the poor” because lower-income parents may not be as well-equipped as affluent parents to help their children with homework—is very troubling to me. There are no parents who don’t care about their children’s learning. Parents don’t actually have to help with homework completion in order for kids to do well. They can help in other ways—by helping children organize a study space, providing snacks, being there as a support, helping children work in groups with siblings or friends.
Isn’t the discussion about getting rid of homework happening mostly in affluent communities?
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That’s problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Teachers may not have as high expectations for lower-income children. Schools should bear responsibility for providing supports for kids to be able to get their homework done—after-school clubs, community support, peer group support. It does kids a disservice when our expectations are lower for them.
The conversation around homework is to some extent a social class and social justice issue. If we eliminate homework for all children because affluent children have too much, we’re really doing a disservice to low-income children. They need the challenge, and every student can rise to the challenge with enough supports in place.
What did you learn by studying how education schools are preparing future teachers to handle homework?
My colleague, Margarita Jimenez-Silva, at the University of California, Davis, School of Education, and I interviewed faculty members at education schools, as well as supervising teachers, to find out how students are being prepared. And it seemed that they weren’t. There didn’t seem to be any readings on the research, or conversations on what high-quality homework is and how to design it.
Erin, what kind of training did you get in handling homework?
Bruce : I had phenomenal professors at Wheelock, but homework just didn’t come up. I did lots of student teaching. I’ve been in classrooms where the teachers didn’t assign any homework, and I’ve been in rooms where they assigned hours of homework a night. But I never even considered homework as something that was my decision. I just thought it was something I’d pull out of a book and it’d be done.
I started giving homework on the first night of school this year. My first assignment was to go home and draw a picture of the room where you do your homework. I want to know if it’s at a table and if there are chairs around it and if mom’s cooking dinner while you’re doing homework.
The second night I asked them to talk to a grown-up about how are you going to be able to get your homework done during the week. The kids really enjoyed it. There’s a running joke that I’m teaching life skills.
Friday nights, I read all my kids’ responses to me on their homework from the week and it’s wonderful. They pour their hearts out. It’s like we’re having a conversation on my couch Friday night.
It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Bempechat : I can’t imagine that most new teachers would have the intuition Erin had in designing homework the way she did.
Ardizzone : Conversations with kids about homework, feeling you’re being listened to—that’s such a big part of wanting to do homework….I grew up in Westchester County. It was a pretty demanding school district. My junior year English teacher—I loved her—she would give us feedback, have meetings with all of us. She’d say, “If you have any questions, if you have anything you want to talk about, you can talk to me, here are my office hours.” It felt like she actually cared.
Bempechat : It matters to know that the teacher cares about you and that what you think matters to the teacher. Homework is a vehicle to connect home and school…for parents to know teachers are welcoming to them and their families.
Ardizzone : But can’t it lead to parents being overbearing and too involved in their children’s lives as students?
Bempechat : There’s good help and there’s bad help. The bad help is what you’re describing—when parents hover inappropriately, when they micromanage, when they see their children confused and struggling and tell them what to do.
Good help is when parents recognize there’s a struggle going on and instead ask informative questions: “Where do you think you went wrong?” They give hints, or pointers, rather than saying, “You missed this,” or “You didn’t read that.”
Bruce : I hope something comes of this. I hope BU or Wheelock can think of some way to make this a more pressing issue. As a first-year teacher, it was not something I even thought about on the first day of school—until a kid raised his hand and said, “Do we have homework?” It would have been wonderful if I’d had a plan from day one.
Explore Related Topics:
- Share this story
Senior Contributing Editor

Sara Rimer A journalist for more than three decades, Sara Rimer worked at the Miami Herald , Washington Post and, for 26 years, the New York Times , where she was the New England bureau chief, and a national reporter covering education, aging, immigration, and other social justice issues. Her stories on the death penalty’s inequities were nominated for a Pulitzer Prize and cited in the U.S. Supreme Court’s decision outlawing the execution of people with intellectual disabilities. Her journalism honors include Columbia University’s Meyer Berger award for in-depth human interest reporting. She holds a BA degree in American Studies from the University of Michigan. Profile
She can be reached at [email protected] .
Comments & Discussion
Boston University moderates comments to facilitate an informed, substantive, civil conversation. Abusive, profane, self-promotional, misleading, incoherent or off-topic comments will be rejected. Moderators are staffed during regular business hours (EST) and can only accept comments written in English. Statistics or facts must include a citation or a link to the citation.
There are 81 comments on Does Homework Really Help Students Learn?
Insightful! The values about homework in elementary schools are well aligned with my intuition as a parent.
when i finish my work i do my homework and i sometimes forget what to do because i did not get enough sleep
same omg it does not help me it is stressful and if I have it in more than one class I hate it.
Same I think my parent wants to help me but, she doesn’t care if I get bad grades so I just try my best and my grades are great.
I think that last question about Good help from parents is not know to all parents, we do as our parents did or how we best think it can be done, so maybe coaching parents or giving them resources on how to help with homework would be very beneficial for the parent on how to help and for the teacher to have consistency and improve homework results, and of course for the child. I do see how homework helps reaffirm the knowledge obtained in the classroom, I also have the ability to see progress and it is a time I share with my kids
The answer to the headline question is a no-brainer – a more pressing problem is why there is a difference in how students from different cultures succeed. Perfect example is the student population at BU – why is there a majority population of Asian students and only about 3% black students at BU? In fact at some universities there are law suits by Asians to stop discrimination and quotas against admitting Asian students because the real truth is that as a group they are demonstrating better qualifications for admittance, while at the same time there are quotas and reduced requirements for black students to boost their portion of the student population because as a group they do more poorly in meeting admissions standards – and it is not about the Benjamins. The real problem is that in our PC society no one has the gazuntas to explore this issue as it may reveal that all people are not created equal after all. Or is it just environmental cultural differences??????
I get you have a concern about the issue but that is not even what the point of this article is about. If you have an issue please take this to the site we have and only post your opinion about the actual topic
This is not at all what the article is talking about.
This literally has nothing to do with the article brought up. You should really take your opinions somewhere else before you speak about something that doesn’t make sense.
we have the same name
so they have the same name what of it?
lol you tell her
totally agree
What does that have to do with homework, that is not what the article talks about AT ALL.
Yes, I think homework plays an important role in the development of student life. Through homework, students have to face challenges on a daily basis and they try to solve them quickly.I am an intense online tutor at 24x7homeworkhelp and I give homework to my students at that level in which they handle it easily.
More than two-thirds of students said they used alcohol and drugs, primarily marijuana, to cope with stress.
You know what’s funny? I got this assignment to write an argument for homework about homework and this article was really helpful and understandable, and I also agree with this article’s point of view.
I also got the same task as you! I was looking for some good resources and I found this! I really found this article useful and easy to understand, just like you! ^^
i think that homework is the best thing that a child can have on the school because it help them with their thinking and memory.
I am a child myself and i think homework is a terrific pass time because i can’t play video games during the week. It also helps me set goals.
Homework is not harmful ,but it will if there is too much
I feel like, from a minors point of view that we shouldn’t get homework. Not only is the homework stressful, but it takes us away from relaxing and being social. For example, me and my friends was supposed to hang at the mall last week but we had to postpone it since we all had some sort of work to do. Our minds shouldn’t be focused on finishing an assignment that in realty, doesn’t matter. I completely understand that we should have homework. I have to write a paper on the unimportance of homework so thanks.
homework isn’t that bad
Are you a student? if not then i don’t really think you know how much and how severe todays homework really is
i am a student and i do not enjoy homework because i practice my sport 4 out of the five days we have school for 4 hours and that’s not even counting the commute time or the fact i still have to shower and eat dinner when i get home. its draining!
i totally agree with you. these people are such boomers
why just why
they do make a really good point, i think that there should be a limit though. hours and hours of homework can be really stressful, and the extra work isn’t making a difference to our learning, but i do believe homework should be optional and extra credit. that would make it for students to not have the leaning stress of a assignment and if you have a low grade you you can catch up.
Studies show that homework improves student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicates that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” On both standardized tests and grades, students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school.
So how are your measuring student achievement? That’s the real question. The argument that doing homework is simply a tool for teaching responsibility isn’t enough for me. We can teach responsibility in a number of ways. Also the poor argument that parents don’t need to help with homework, and that students can do it on their own, is wishful thinking at best. It completely ignores neurodiverse students. Students in poverty aren’t magically going to find a space to do homework, a friend’s or siblings to help them do it, and snacks to eat. I feel like the author of this piece has never set foot in a classroom of students.
THIS. This article is pathetic coming from a university. So intellectually dishonest, refusing to address the havoc of capitalism and poverty plays on academic success in life. How can they in one sentence use poor kids in an argument and never once address that poor children have access to damn near 0 of the resources affluent kids have? Draw me a picture and let’s talk about feelings lmao what a joke is that gonna put food in their belly so they can have the calories to burn in order to use their brain to study? What about quiet their 7 other siblings that they share a single bedroom with for hours? Is it gonna force the single mom to magically be at home and at work at the same time to cook food while you study and be there to throw an encouraging word?
Also the “parents don’t need to be a parent and be able to guide their kid at all academically they just need to exist in the next room” is wild. Its one thing if a parent straight up is not equipped but to say kids can just figured it out is…. wow coming from an educator What’s next the teacher doesn’t need to teach cause the kid can just follow the packet and figure it out?
Well then get a tutor right? Oh wait you are poor only affluent kids can afford a tutor for their hours of homework a day were they on average have none of the worries a poor child does. Does this address that poor children are more likely to also suffer abuse and mental illness? Like mentioned what about kids that can’t learn or comprehend the forced standardized way? Just let em fail? These children regularly are not in “special education”(some of those are a joke in their own and full of neglect and abuse) programs cause most aren’t even acknowledged as having disabilities or disorders.
But yes all and all those pesky poor kids just aren’t being worked hard enough lol pretty sure poor children’s existence just in childhood is more work, stress, and responsibility alone than an affluent child’s entire life cycle. Love they never once talked about the quality of education in the classroom being so bad between the poor and affluent it can qualify as segregation, just basically blamed poor people for being lazy, good job capitalism for failing us once again!
why the hell?
you should feel bad for saying this, this article can be helpful for people who has to write a essay about it
This is more of a political rant than it is about homework
I know a teacher who has told his students their homework is to find something they are interested in, pursue it and then come share what they learn. The student responses are quite compelling. One girl taught herself German so she could talk to her grandfather. One boy did a research project on Nelson Mandela because the teacher had mentioned him in class. Another boy, a both on the autism spectrum, fixed his family’s computer. The list goes on. This is fourth grade. I think students are highly motivated to learn, when we step aside and encourage them.
The whole point of homework is to give the students a chance to use the material that they have been presented with in class. If they never have the opportunity to use that information, and discover that it is actually useful, it will be in one ear and out the other. As a science teacher, it is critical that the students are challenged to use the material they have been presented with, which gives them the opportunity to actually think about it rather than regurgitate “facts”. Well designed homework forces the student to think conceptually, as opposed to regurgitation, which is never a pretty sight
Wonderful discussion. and yes, homework helps in learning and building skills in students.
not true it just causes kids to stress
Homework can be both beneficial and unuseful, if you will. There are students who are gifted in all subjects in school and ones with disabilities. Why should the students who are gifted get the lucky break, whereas the people who have disabilities suffer? The people who were born with this “gift” go through school with ease whereas people with disabilities struggle with the work given to them. I speak from experience because I am one of those students: the ones with disabilities. Homework doesn’t benefit “us”, it only tears us down and put us in an abyss of confusion and stress and hopelessness because we can’t learn as fast as others. Or we can’t handle the amount of work given whereas the gifted students go through it with ease. It just brings us down and makes us feel lost; because no mater what, it feels like we are destined to fail. It feels like we weren’t “cut out” for success.
homework does help
here is the thing though, if a child is shoved in the face with a whole ton of homework that isn’t really even considered homework it is assignments, it’s not helpful. the teacher should make homework more of a fun learning experience rather than something that is dreaded
This article was wonderful, I am going to ask my teachers about extra, or at all giving homework.
I agree. Especially when you have homework before an exam. Which is distasteful as you’ll need that time to study. It doesn’t make any sense, nor does us doing homework really matters as It’s just facts thrown at us.
Homework is too severe and is just too much for students, schools need to decrease the amount of homework. When teachers assign homework they forget that the students have other classes that give them the same amount of homework each day. Students need to work on social skills and life skills.
I disagree.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what’s going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Homework is helpful because homework helps us by teaching us how to learn a specific topic.
As a student myself, I can say that I have almost never gotten the full 9 hours of recommended sleep time, because of homework. (Now I’m writing an essay on it in the middle of the night D=)
I am a 10 year old kid doing a report about “Is homework good or bad” for homework before i was going to do homework is bad but the sources from this site changed my mind!
Homeowkr is god for stusenrs
I agree with hunter because homework can be so stressful especially with this whole covid thing no one has time for homework and every one just wants to get back to there normal lives it is especially stressful when you go on a 2 week vaca 3 weeks into the new school year and and then less then a week after you come back from the vaca you are out for over a month because of covid and you have no way to get the assignment done and turned in
As great as homework is said to be in the is article, I feel like the viewpoint of the students was left out. Every where I go on the internet researching about this topic it almost always has interviews from teachers, professors, and the like. However isn’t that a little biased? Of course teachers are going to be for homework, they’re not the ones that have to stay up past midnight completing the homework from not just one class, but all of them. I just feel like this site is one-sided and you should include what the students of today think of spending four hours every night completing 6-8 classes worth of work.
Are we talking about homework or practice? Those are two very different things and can result in different outcomes.
Homework is a graded assignment. I do not know of research showing the benefits of graded assignments going home.
Practice; however, can be extremely beneficial, especially if there is some sort of feedback (not a grade but feedback). That feedback can come from the teacher, another student or even an automated grading program.
As a former band director, I assigned daily practice. I never once thought it would be appropriate for me to require the students to turn in a recording of their practice for me to grade. Instead, I had in-class assignments/assessments that were graded and directly related to the practice assigned.
I would really like to read articles on “homework” that truly distinguish between the two.
oof i feel bad good luck!
thank you guys for the artical because I have to finish an assingment. yes i did cite it but just thanks
thx for the article guys.
Homework is good
I think homework is helpful AND harmful. Sometimes u can’t get sleep bc of homework but it helps u practice for school too so idk.
I agree with this Article. And does anyone know when this was published. I would like to know.
It was published FEb 19, 2019.
Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college.
i think homework can help kids but at the same time not help kids
This article is so out of touch with majority of homes it would be laughable if it wasn’t so incredibly sad.
There is no value to homework all it does is add stress to already stressed homes. Parents or adults magically having the time or energy to shepherd kids through homework is dome sort of 1950’s fantasy.
What lala land do these teachers live in?
Homework gives noting to the kid
Homework is Bad
homework is bad.
why do kids even have homework?
Comments are closed.
Latest from Bostonia
American academy of arts & sciences welcomes five bu members, com’s newest journalism grad took her time, could boston be the next city to impose congestion pricing, alum has traveled the world to witness total solar eclipses, opening doors: rhonda harrison (eng’98,’04, grs’04), campus reacts and responds to israel-hamas war, reading list: what the pandemic revealed, remembering com’s david anable, cas’ john stone, “intellectual brilliance and brilliant kindness”, one good deed: christine kannler (cas’96, sph’00, camed’00), william fairfield warren society inducts new members, spreading art appreciation, restoring the “black angels” to medical history, in the kitchen with jacques pépin, feedback: readers weigh in on bu’s new president, com’s new expert on misinformation, and what’s really dividing the nation, the gifts of great teaching, sth’s walter fluker honored by roosevelt institute, alum’s debut book is a ramadan story for children, my big idea: covering construction sites with art, former terriers power new professional women’s hockey league.

10 Best NEET Coaching Centres in Bangalore

Best Universities in Luxembourg

Streamlining Student Management: The Power of Automated Systems

All You Need to Know about Scholarship to Study Abroad

International School Fees: Unveiling the True Value
- Career & Jobs
- Career Guidance
- Study Abroad
- Personality Development

15 Surprising Benefits of Homework for Students
- The importance of homework for students
- 3 Helpful tips to do your homework effectively
- 15 benefits of homework
Homework is an important component of the learning and growing process. It is a common practice for students to develop their skills and learn new information.
Homework is simply a general term that we use to describe work that you have to do at home. Typically, it’s assigned by the teacher during school hours and meant to be completed after school in the evenings or weekends.
Homework is loved and hated by many, but it is an integral part of education. It is not just a boring part of the learning process. It has a lot to offer!
The Importance of Homework for Students
So, why should students have homework? According to research conducted by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper , there was a positive relation between homework and student achievement. He found out that homework can help students perform better in school.
This shows the importance of homework in a student’s life. Homework is not always popular with students because it takes away their free time at home.
However, there are many benefits associated with homework. Homework helps students understand the material in greater depth. Moreover, it allows teachers to assess how much the student has learned.
Tips for Doing Your Homework Faster
It is important to have a homework routine. A routine will help you know what to expect at the end of the day, and it will give you time to digest what you learned.
In addition, a routine will help you to be stress-free because you won’t be worrying about when to start your homework or whether you’re going to finish it on time.
So, here are some tips on how to set up a good homework routine:
- Find a place in the house where you can study without interruption.
- Set a timer for how long each assignment should take.
- Make sure your table is neat and that you have all of your materials ready before starting.
These tips will surely make your student life easier and put you on the right track towards higher grades!
The Benefits of Homework for Students
There are numerous reasons why homework is given in schools and colleges. Students can reap the benefits even in their professional lives.
But what exactly are the benefits of homework and how can it help students? Let us take a look at some of them:
1. Students Learn the Importance of Time Management

They will learn to balance play and work. Students will also learn to complete assignments within deadlines by learning to prioritize their time.
It helps them understand the importance of time management skills . When they are assigned a project or a test, they will know when it is due, how much time they have to complete it, and what they need to do.
This also helps them in their future careers. Employees must be able to manage their time efficiently in order to be successful.
If a project is due soon, employees should take effective steps to get it done on time. Homeworks in the schooling years teaches this practice of time management.
2. Promotes Self-Learning
Students get more time to review the content and this promotes self-learning . This is a big advantage of homework.
It also promotes continuous learning as students can revise their syllabus on their own. Homework gives them an opportunity to develop their critical thinking skills and problem-solving abilities.
3. Helps Teachers Assess a Student’s Learning
Homeworks help teachers track how well the students are grasping the content . They can modify their teaching methods based on the responses they receive from their students.
4. Teaches Students to Be Responsible
Students learn to become independent learners as they do their homework without any help from the teacher.
Studying at home also motivates students to study harder in order to achieve better results. This encourages them to take up more responsibilities at home too.
5. Boosts Memory Retention
Homework provides practice time to recall concepts discussed in class, thereby enabling students to memorize facts and figures taught at school.
One of the advantages of homework is that it sharpens memory power and concentration.
6. Enables Parents to Track a Student’s Performance
Parents can assess how well their children are doing with regard to academic performance by checking their homework assignments.
This gives parents a chance to discuss with teachers about improving their child’s performance at school .
7. Allows Students to Revise Content

Revising together with other students can also help with understanding information because it gives you another perspective, as well as an opportunity to ask questions and engage with others.
8. Practice Makes Perfect
Doing homework has numerous benefits for students. One of them is that it helps students learn the concepts in depth.
Homework teaches them how to apply the concepts to solve a problem. It gives them experience on how to solve problems using different techniques.
9. Develops Persistence
When students do their homework, they have to work hard to find all the possible solutions to a problem.
They have to try out different methods until they reach a solution that works. This teaches them perseverance and helps them develop their determination and grit to keep working hard.
10. Helps Them to Learn New Skills
Homework is important because it helps students to learn new and advanced skills. It promotes self-study, research and time management skills within students.
It also builds their confidence in tackling problems independently without constant help from teachers and parents.
11. Helps in Building a Positive Attitude Towards Learning

12. Students Can Explore Their Areas of Interest
Homework helps in building curiosity about a subject that excites them. Homework gives students an opportunity to immerse themselves in a subject matter.
When they become curious, they themselves take the initiative to learn more about it.
13. Encourages In-Depth Understanding of The Concepts
Homeworks allow students to learn the subject in a more detailed manner. It gives students the chance to recall and go over the content.
This will lead to better understanding and they will be able to remember the information for a long time.
14. Minimizes Screen Time:
Homework is not only a great way to get students to do their work themselves, but it can also encourage them to reduce screen time.
Homework gives students a good reason to stay off their computers and phones. Homework promotes the productive use of time .
15. Helps Develop Good Study Habits

The more they do their homework, the better they will get it. They will learn to manage their time in a more effective way and be able to do their work at a faster rate.
Moreover, they will be able to develop a good work ethic, which will help them in their future careers.
We all know that too much of anything can be bad. Homework is no different. If the workload of the students is too much, then it can lead to unnecessary stress .
Therefore, it is necessary for teachers to be mindful of the workload of students. That way, students will be able to enjoy their free time and actually enjoy doing homework instead of seeing it as a burden.
You Might Also Like
Top 10 seo company in bangalore specialized in seo educational institute ., leave a reply cancel reply.
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Weekly Newsletter
subscribe to our latest blog and weekly newsletter
Popular News

Top 10 Advantages of Online Courses
- Advertisement -

- Certifications
Top Categories
Subscribe us, for quick admission assistance.

Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me
Does homework really work?
by: Leslie Crawford | Updated: December 12, 2023
Print article

You know the drill. It’s 10:15 p.m., and the cardboard-and-toothpick Golden Gate Bridge is collapsing. The pages of polynomials have been abandoned. The paper on the Battle of Waterloo seems to have frozen in time with Napoleon lingering eternally over his breakfast at Le Caillou. Then come the tears and tantrums — while we parents wonder, Does the gain merit all this pain? Is this just too much homework?
However the drama unfolds night after night, year after year, most parents hold on to the hope that homework (after soccer games, dinner, flute practice, and, oh yes, that childhood pastime of yore known as playing) advances their children academically.
But what does homework really do for kids? Is the forest’s worth of book reports and math and spelling sheets the average American student completes in their 12 years of primary schooling making a difference? Or is it just busywork?
Homework haterz
Whether or not homework helps, or even hurts, depends on who you ask. If you ask my 12-year-old son, Sam, he’ll say, “Homework doesn’t help anything. It makes kids stressed-out and tired and makes them hate school more.”
Nothing more than common kid bellyaching?
Maybe, but in the fractious field of homework studies, it’s worth noting that Sam’s sentiments nicely synopsize one side of the ivory tower debate. Books like The End of Homework , The Homework Myth , and The Case Against Homework the film Race to Nowhere , and the anguished parent essay “ My Daughter’s Homework is Killing Me ” make the case that homework, by taking away precious family time and putting kids under unneeded pressure, is an ineffective way to help children become better learners and thinkers.
One Canadian couple took their homework apostasy all the way to the Supreme Court of Canada. After arguing that there was no evidence that it improved academic performance, they won a ruling that exempted their two children from all homework.
So what’s the real relationship between homework and academic achievement?
How much is too much?
To answer this question, researchers have been doing their homework on homework, conducting and examining hundreds of studies. Chris Drew Ph.D., founder and editor at The Helpful Professor recently compiled multiple statistics revealing the folly of today’s after-school busy work. Does any of the data he listed below ring true for you?
• 45 percent of parents think homework is too easy for their child, primarily because it is geared to the lowest standard under the Common Core State Standards .
• 74 percent of students say homework is a source of stress , defined as headaches, exhaustion, sleep deprivation, weight loss, and stomach problems.
• Students in high-performing high schools spend an average of 3.1 hours a night on homework , even though 1 to 2 hours is the optimal duration, according to a peer-reviewed study .
Not included in the list above is the fact many kids have to abandon activities they love — like sports and clubs — because homework deprives them of the needed time to enjoy themselves with other pursuits.
Conversely, The Helpful Professor does list a few pros of homework, noting it teaches discipline and time management, and helps parents know what’s being taught in the class.
The oft-bandied rule on homework quantity — 10 minutes a night per grade (starting from between 10 to 20 minutes in first grade) — is listed on the National Education Association’s website and the National Parent Teacher Association’s website , but few schools follow this rule.
Do you think your child is doing excessive homework? Harris Cooper Ph.D., author of a meta-study on homework , recommends talking with the teacher. “Often there is a miscommunication about the goals of homework assignments,” he says. “What appears to be problematic for kids, why they are doing an assignment, can be cleared up with a conversation.” Also, Cooper suggests taking a careful look at how your child is doing the assignments. It may seem like they’re taking two hours, but maybe your child is wandering off frequently to get a snack or getting distracted.
Less is often more
If your child is dutifully doing their work but still burning the midnight oil, it’s worth intervening to make sure your child gets enough sleep. A 2012 study of 535 high school students found that proper sleep may be far more essential to brain and body development.
For elementary school-age children, Cooper’s research at Duke University shows there is no measurable academic advantage to homework. For middle-schoolers, Cooper found there is a direct correlation between homework and achievement if assignments last between one to two hours per night. After two hours, however, achievement doesn’t improve. For high schoolers, Cooper’s research suggests that two hours per night is optimal. If teens have more than two hours of homework a night, their academic success flatlines. But less is not better. The average high school student doing homework outperformed 69 percent of the students in a class with no homework.
Many schools are starting to act on this research. A Florida superintendent abolished homework in her 42,000 student district, replacing it with 20 minutes of nightly reading. She attributed her decision to “ solid research about what works best in improving academic achievement in students .”
More family time
A 2020 survey by Crayola Experience reports 82 percent of children complain they don’t have enough quality time with their parents. Homework deserves much of the blame. “Kids should have a chance to just be kids and do things they enjoy, particularly after spending six hours a day in school,” says Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth . “It’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.”
By far, the best replacement for homework — for both parents and children — is bonding, relaxing time together.
Homes Nearby
Homes for rent and sale near schools

How families of color can fight for fair discipline in school

Dealing with teacher bias

The most important school data families of color need to consider
Yes! Sign me up for updates relevant to my child's grade.
Please enter a valid email address
Thank you for signing up!
Server Issue: Please try again later. Sorry for the inconvenience
Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement?

- Share this story on facebook
- Share this story on twitter
- Share this story on reddit
- Share this story on linkedin
- Get this story's permalink
- Print this story
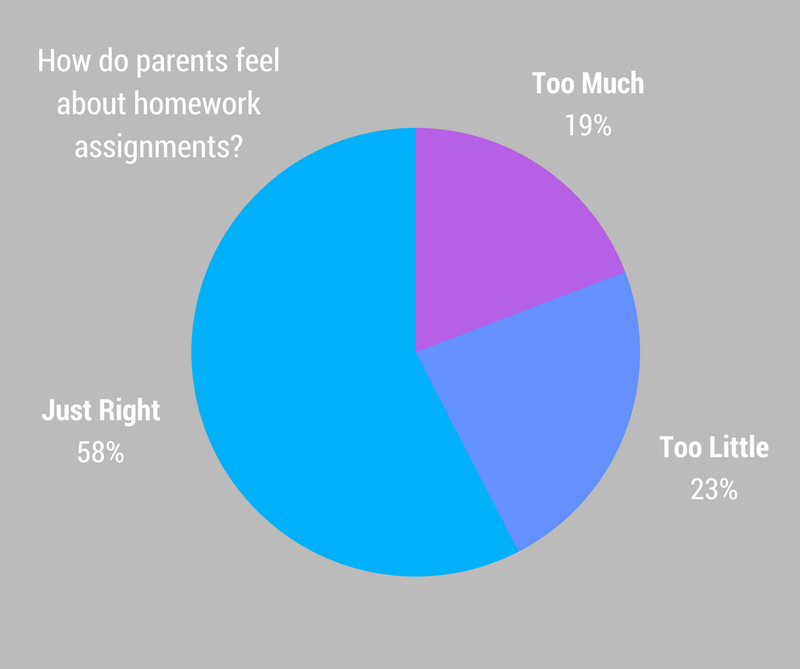
Educators should be thrilled by these numbers. Pleasing a majority of parents regarding homework and having equal numbers of dissenters shouting "too much!" and "too little!" is about as good as they can hope for.
But opinions cannot tell us whether homework works; only research can, which is why my colleagues and I have conducted a combined analysis of dozens of homework studies to examine whether homework is beneficial and what amount of homework is appropriate for our children.
The homework question is best answered by comparing students who are assigned homework with students assigned no homework but who are similar in other ways. The results of such studies suggest that homework can improve students' scores on the class tests that come at the end of a topic. Students assigned homework in 2nd grade did better on math, 3rd and 4th graders did better on English skills and vocabulary, 5th graders on social studies, 9th through 12th graders on American history, and 12th graders on Shakespeare.
Less authoritative are 12 studies that link the amount of homework to achievement, but control for lots of other factors that might influence this connection. These types of studies, often based on national samples of students, also find a positive link between time on homework and achievement.
Yet other studies simply correlate homework and achievement with no attempt to control for student differences. In 35 such studies, about 77 percent find the link between homework and achievement is positive. Most interesting, though, is these results suggest little or no relationship between homework and achievement for elementary school students.
Why might that be? Younger children have less developed study habits and are less able to tune out distractions at home. Studies also suggest that young students who are struggling in school take more time to complete homework assignments simply because these assignments are more difficult for them.
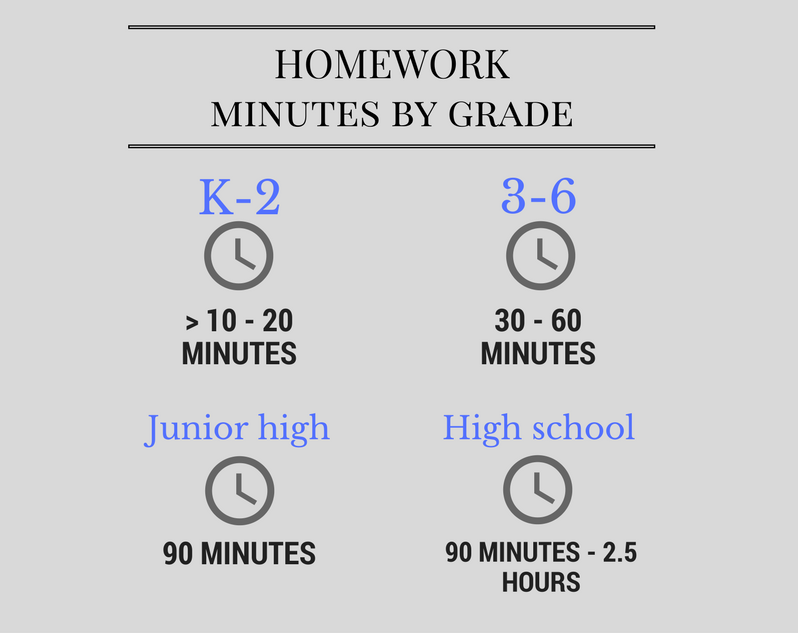
These recommendations are consistent with the conclusions reached by our analysis. Practice assignments do improve scores on class tests at all grade levels. A little amount of homework may help elementary school students build study habits. Homework for junior high students appears to reach the point of diminishing returns after about 90 minutes a night. For high school students, the positive line continues to climb until between 90 minutes and 2½ hours of homework a night, after which returns diminish.
Beyond achievement, proponents of homework argue that it can have many other beneficial effects. They claim it can help students develop good study habits so they are ready to grow as their cognitive capacities mature. It can help students recognize that learning can occur at home as well as at school. Homework can foster independent learning and responsible character traits. And it can give parents an opportunity to see what's going on at school and let them express positive attitudes toward achievement.
Opponents of homework counter that it can also have negative effects. They argue it can lead to boredom with schoolwork, since all activities remain interesting only for so long. Homework can deny students access to leisure activities that also teach important life skills. Parents can get too involved in homework -- pressuring their child and confusing him by using different instructional techniques than the teacher.
My feeling is that homework policies should prescribe amounts of homework consistent with the research evidence, but which also give individual schools and teachers some flexibility to take into account the unique needs and circumstances of their students and families. In general, teachers should avoid either extreme.
Link to this page
Copy and paste the URL below to share this page.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
Student Opinion
Should We Get Rid of Homework?
Some educators are pushing to get rid of homework. Would that be a good thing?

By Jeremy Engle and Michael Gonchar
Do you like doing homework? Do you think it has benefited you educationally?
Has homework ever helped you practice a difficult skill — in math, for example — until you mastered it? Has it helped you learn new concepts in history or science? Has it helped to teach you life skills, such as independence and responsibility? Or, have you had a more negative experience with homework? Does it stress you out, numb your brain from busywork or actually make you fall behind in your classes?
Should we get rid of homework?
In “ The Movement to End Homework Is Wrong, ” published in July, the Times Opinion writer Jay Caspian Kang argues that homework may be imperfect, but it still serves an important purpose in school. The essay begins:
Do students really need to do their homework? As a parent and a former teacher, I have been pondering this question for quite a long time. The teacher side of me can acknowledge that there were assignments I gave out to my students that probably had little to no academic value. But I also imagine that some of my students never would have done their basic reading if they hadn’t been trained to complete expected assignments, which would have made the task of teaching an English class nearly impossible. As a parent, I would rather my daughter not get stuck doing the sort of pointless homework I would occasionally assign, but I also think there’s a lot of value in saying, “Hey, a lot of work you’re going to end up doing in your life is pointless, so why not just get used to it?” I certainly am not the only person wondering about the value of homework. Recently, the sociologist Jessica McCrory Calarco and the mathematics education scholars Ilana Horn and Grace Chen published a paper, “ You Need to Be More Responsible: The Myth of Meritocracy and Teachers’ Accounts of Homework Inequalities .” They argued that while there’s some evidence that homework might help students learn, it also exacerbates inequalities and reinforces what they call the “meritocratic” narrative that says kids who do well in school do so because of “individual competence, effort and responsibility.” The authors believe this meritocratic narrative is a myth and that homework — math homework in particular — further entrenches the myth in the minds of teachers and their students. Calarco, Horn and Chen write, “Research has highlighted inequalities in students’ homework production and linked those inequalities to differences in students’ home lives and in the support students’ families can provide.”
Mr. Kang argues:
But there’s a defense of homework that doesn’t really have much to do with class mobility, equality or any sense of reinforcing the notion of meritocracy. It’s one that became quite clear to me when I was a teacher: Kids need to learn how to practice things. Homework, in many cases, is the only ritualized thing they have to do every day. Even if we could perfectly equalize opportunity in school and empower all students not to be encumbered by the weight of their socioeconomic status or ethnicity, I’m not sure what good it would do if the kids didn’t know how to do something relentlessly, over and over again, until they perfected it. Most teachers know that type of progress is very difficult to achieve inside the classroom, regardless of a student’s background, which is why, I imagine, Calarco, Horn and Chen found that most teachers weren’t thinking in a structural inequalities frame. Holistic ideas of education, in which learning is emphasized and students can explore concepts and ideas, are largely for the types of kids who don’t need to worry about class mobility. A defense of rote practice through homework might seem revanchist at this moment, but if we truly believe that schools should teach children lessons that fall outside the meritocracy, I can’t think of one that matters more than the simple satisfaction of mastering something that you were once bad at. That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right.
Students, read the entire article, then tell us:
Should we get rid of homework? Why, or why not?
Is homework an outdated, ineffective or counterproductive tool for learning? Do you agree with the authors of the paper that homework is harmful and worsens inequalities that exist between students’ home circumstances?
Or do you agree with Mr. Kang that homework still has real educational value?
When you get home after school, how much homework will you do? Do you think the amount is appropriate, too much or too little? Is homework, including the projects and writing assignments you do at home, an important part of your learning experience? Or, in your opinion, is it not a good use of time? Explain.
In these letters to the editor , one reader makes a distinction between elementary school and high school:
Homework’s value is unclear for younger students. But by high school and college, homework is absolutely essential for any student who wishes to excel. There simply isn’t time to digest Dostoyevsky if you only ever read him in class.
What do you think? How much does grade level matter when discussing the value of homework?
Is there a way to make homework more effective?
If you were a teacher, would you assign homework? What kind of assignments would you give and why?
Want more writing prompts? You can find all of our questions in our Student Opinion column . Teachers, check out this guide to learn how you can incorporate them into your classroom.
Students 13 and older in the United States and Britain, and 16 and older elsewhere, are invited to comment. All comments are moderated by the Learning Network staff, but please keep in mind that once your comment is accepted, it will be made public.
Jeremy Engle joined The Learning Network as a staff editor in 2018 after spending more than 20 years as a classroom humanities and documentary-making teacher, professional developer and curriculum designer working with students and teachers across the country. More about Jeremy Engle
- About the Hub
- Announcements
- Faculty Experts Guide
- Subscribe to the newsletter
Explore by Topic
- Arts+Culture
- Politics+Society
- Science+Technology
- Student Life
- University News
- Voices+Opinion
- About Hub at Work
- Gazette Archive
- Benefits+Perks
- Health+Well-Being
- Current Issue
- About the Magazine
- Past Issues
- Support Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Subscribe to the Magazine
You are using an outdated browser. Please upgrade your browser to improve your experience.

Credit: August de Richelieu
Does homework still have value? A Johns Hopkins education expert weighs in
Joyce epstein, co-director of the center on school, family, and community partnerships, discusses why homework is essential, how to maximize its benefit to learners, and what the 'no-homework' approach gets wrong.
By Vicky Hallett
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein , co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work," Epstein says.
But after decades of researching how to improve schools, the professor in the Johns Hopkins School of Education remains certain that homework is essential—as long as the teachers have done their homework, too. The National Network of Partnership Schools , which she founded in 1995 to advise schools and districts on ways to improve comprehensive programs of family engagement, has developed hundreds of improved homework ideas through its Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program. For an English class, a student might interview a parent on popular hairstyles from their youth and write about the differences between then and now. Or for science class, a family could identify forms of matter over the dinner table, labeling foods as liquids or solids. These innovative and interactive assignments not only reinforce concepts from the classroom but also foster creativity, spark discussions, and boost student motivation.
"We're not trying to eliminate homework procedures, but expand and enrich them," says Epstein, who is packing this research into a forthcoming book on the purposes and designs of homework. In the meantime, the Hub couldn't wait to ask her some questions:
What kind of homework training do teachers typically get?
Future teachers and administrators really have little formal training on how to design homework before they assign it. This means that most just repeat what their teachers did, or they follow textbook suggestions at the end of units. For example, future teachers are well prepared to teach reading and literacy skills at each grade level, and they continue to learn to improve their teaching of reading in ongoing in-service education. By contrast, most receive little or no training on the purposes and designs of homework in reading or other subjects. It is really important for future teachers to receive systematic training to understand that they have the power, opportunity, and obligation to design homework with a purpose.
Why do students need more interactive homework?
If homework assignments are always the same—10 math problems, six sentences with spelling words—homework can get boring and some kids just stop doing their assignments, especially in the middle and high school years. When we've asked teachers what's the best homework you've ever had or designed, invariably we hear examples of talking with a parent or grandparent or peer to share ideas. To be clear, parents should never be asked to "teach" seventh grade science or any other subject. Rather, teachers set up the homework assignments so that the student is in charge. It's always the student's homework. But a good activity can engage parents in a fun, collaborative way. Our data show that with "good" assignments, more kids finish their work, more kids interact with a family partner, and more parents say, "I learned what's happening in the curriculum." It all works around what the youngsters are learning.
Is family engagement really that important?
At Hopkins, I am part of the Center for Social Organization of Schools , a research center that studies how to improve many aspects of education to help all students do their best in school. One thing my colleagues and I realized was that we needed to look deeply into family and community engagement. There were so few references to this topic when we started that we had to build the field of study. When children go to school, their families "attend" with them whether a teacher can "see" the parents or not. So, family engagement is ever-present in the life of a school.
My daughter's elementary school doesn't assign homework until third grade. What's your take on "no homework" policies?
There are some parents, writers, and commentators who have argued against homework, especially for very young children. They suggest that children should have time to play after school. This, of course is true, but many kindergarten kids are excited to have homework like their older siblings. If they give homework, most teachers of young children make assignments very short—often following an informal rule of 10 minutes per grade level. "No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play.
Some researchers and critics have consistently misinterpreted research findings. They have argued that homework should be assigned only at the high school level where data point to a strong connection of doing assignments with higher student achievement . However, as we discussed, some students stop doing homework. This leads, statistically, to results showing that doing homework or spending more minutes on homework is linked to higher student achievement. If slow or struggling students are not doing their assignments, they contribute to—or cause—this "result."
Teachers need to design homework that even struggling students want to do because it is interesting. Just about all students at any age level react positively to good assignments and will tell you so.
Did COVID change how schools and parents view homework?
Within 24 hours of the day school doors closed in March 2020, just about every school and district in the country figured out that teachers had to talk to and work with students' parents. This was not the same as homeschooling—teachers were still working hard to provide daily lessons. But if a child was learning at home in the living room, parents were more aware of what they were doing in school. One of the silver linings of COVID was that teachers reported that they gained a better understanding of their students' families. We collected wonderfully creative examples of activities from members of the National Network of Partnership Schools. I'm thinking of one art activity where every child talked with a parent about something that made their family unique. Then they drew their finding on a snowflake and returned it to share in class. In math, students talked with a parent about something the family liked so much that they could represent it 100 times. Conversations about schoolwork at home was the point.
How did you create so many homework activities via the Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program?
We had several projects with educators to help them design interactive assignments, not just "do the next three examples on page 38." Teachers worked in teams to create TIPS activities, and then we turned their work into a standard TIPS format in math, reading/language arts, and science for grades K-8. Any teacher can use or adapt our prototypes to match their curricula.
Overall, we know that if future teachers and practicing educators were prepared to design homework assignments to meet specific purposes—including but not limited to interactive activities—more students would benefit from the important experience of doing their homework. And more parents would, indeed, be partners in education.
Posted in Voices+Opinion
You might also like
News network.
- Johns Hopkins Magazine
- Get Email Updates
- Submit an Announcement
- Submit an Event
- Privacy Statement
- Accessibility
Discover JHU
- About the University
- Schools & Divisions
- Academic Programs
- Plan a Visit
- my.JohnsHopkins.edu
- © 2024 Johns Hopkins University . All rights reserved.
- University Communications
- 3910 Keswick Rd., Suite N2600, Baltimore, MD
- X Facebook LinkedIn YouTube Instagram
- Our Mission
Research Trends: Why Homework Should Be Balanced
Research suggests that while homework can be an effective learning tool, assigning too much can lower student performance and interfere with other important activities.

Homework: effective learning tool or waste of time?
Since the average high school student spends almost seven hours each week doing homework, it’s surprising that there’s no clear answer. Homework is generally recognized as an effective way to reinforce what students learn in class, but claims that it may cause more harm than good, especially for younger students, are common.
Here’s what the research says:
- In general, homework has substantial benefits at the high school level, with decreased benefits for middle school students and few benefits for elementary students (Cooper, 1989; Cooper et al., 2006).
- While assigning homework may have academic benefits, it can also cut into important personal and family time (Cooper et al., 2006).
- Assigning too much homework can result in poor performance (Fernández-Alonso et al., 2015).
- A student’s ability to complete homework may depend on factors that are outside their control (Cooper et al., 2006; OECD, 2014; Eren & Henderson, 2011).
- The goal shouldn’t be to eliminate homework, but to make it authentic, meaningful, and engaging (Darling-Hammond & Ifill-Lynch, 2006).
Why Homework Should Be Balanced
Homework can boost learning, but doing too much can be detrimental. The National PTA and National Education Association support the “10-minute homework rule,” which recommends 10 minutes of homework per grade level, per night (10 minutes for first grade, 20 minutes for second grade, and so on, up to two hours for 12th grade) (Cooper, 2010). A recent study found that when middle school students were assigned more than 90–100 minutes of homework per day, their math and science scores began to decline (Fernández-Alonso, Suárez-Álvarez, & Muñiz, 2015). Giving students too much homework can lead to fatigue, stress, and a loss of interest in academics—something that we all want to avoid.
Homework Pros and Cons
Homework has many benefits, ranging from higher academic performance to improved study skills and stronger school-parent connections. However, it can also result in a loss of interest in academics, fatigue, and a loss of important personal and family time.
Grade Level Makes a Difference
Although the debate about homework generally falls in the “it works” vs. “it doesn’t work” camps, research shows that grade level makes a difference. High school students generally get the biggest benefits from homework, with middle school students getting about half the benefits, and elementary school students getting few benefits (Cooper et al., 2006). Since young students are still developing study habits like concentration and self-regulation, assigning a lot of homework isn’t all that helpful.
Parents Should Be Supportive, Not Intrusive
Well-designed homework not only strengthens student learning, it also provides ways to create connections between a student’s family and school. Homework offers parents insight into what their children are learning, provides opportunities to talk with children about their learning, and helps create conversations with school communities about ways to support student learning (Walker et al., 2004).
However, parent involvement can also hurt student learning. Patall, Cooper, and Robinson (2008) found that students did worse when their parents were perceived as intrusive or controlling. Motivation plays a key role in learning, and parents can cause unintentional harm by not giving their children enough space and autonomy to do their homework.
Homework Across the Globe
OECD , the developers of the international PISA test, published a 2014 report looking at homework around the world. They found that 15-year-olds worldwide spend an average of five hours per week doing homework (the U.S. average is about six hours). Surprisingly, countries like Finland and Singapore spend less time on homework (two to three hours per week) but still have high PISA rankings. These countries, the report explains, have support systems in place that allow students to rely less on homework to succeed. If a country like the U.S. were to decrease the amount of homework assigned to high school students, test scores would likely decrease unless additional supports were added.
Homework Is About Quality, Not Quantity
Whether you’re pro- or anti-homework, keep in mind that research gives a big-picture idea of what works and what doesn’t, and a capable teacher can make almost anything work. The question isn’t homework vs. no homework ; instead, we should be asking ourselves, “How can we transform homework so that it’s engaging and relevant and supports learning?”
Cooper, H. (1989). Synthesis of research on homework . Educational leadership, 47 (3), 85-91.
Cooper, H. (2010). Homework’s Diminishing Returns . The New York Times .
Cooper, H., Robinson, J. C., & Patall, E. A. (2006). Does homework improve academic achievement? A synthesis of research, 1987–2003 . Review of Educational Research, 76 (1), 1-62.
Darling-Hammond, L., & Ifill-Lynch, O. (2006). If They'd Only Do Their Work! Educational Leadership, 63 (5), 8-13.
Eren, O., & Henderson, D. J. (2011). Are we wasting our children's time by giving them more homework? Economics of Education Review, 30 (5), 950-961.
Fernández-Alonso, R., Suárez-Álvarez, J., & Muñiz, J. (2015, March 16). Adolescents’ Homework Performance in Mathematics and Science: Personal Factors and Teaching Practices . Journal of Educational Psychology. Advance online publication.
OECD (2014). Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education? PISA in Focus , No. 46, OECD Publishing, Paris.
Patall, E. A., Cooper, H., & Robinson, J. C. (2008). Parent involvement in homework: A research synthesis . Review of Educational Research, 78 (4), 1039-1101.
Van Voorhis, F. L. (2003). Interactive homework in middle school: Effects on family involvement and science achievement . The Journal of Educational Research, 96 (6), 323-338.
Walker, J. M., Hoover-Dempsey, K. V., Whetsel, D. R., & Green, C. L. (2004). Parental involvement in homework: A review of current research and its implications for teachers, after school program staff, and parent leaders . Cambridge, MA: Harvard Family Research Project.
Why is homework important?

Why Is Homework Important: Beyond Class and Embracing Learning
Homework is important for several reasons, as it plays a crucial role in enhancing students' learning and educational experience. Here are some key reasons why homework is valuable:
- Reinforces Learning : Homework helps reinforce what was taught in class, allowing students to practice and apply knowledge, ensuring a deeper understanding and retention of the material.
- Promotes Discipline and Time Management : Regular homework assignments teach students to manage their time effectively, develop self-discipline, and prioritize tasks, which are valuable skills beyond the classroom.
- Encourages Independence and Responsibility : Completing homework independently fosters self-reliance and personal responsibility for one's learning, preparing students for the self-directed learning required in higher education and the workplace.
- Provides Feedback : Homework offers teachers a way to assess students' understanding and progress, allowing them to identify areas where students may need extra help and adjust their teaching strategies accordingly.
- Enhances Critical Thinking and Problem Solving : Homework often involves tasks that require critical thinking and problem-solving, skills that are crucial for academic and life success.
- Engages Parents in Their Child's Education : Homework gives parents insight into what their children are learning in school and the opportunity to engage in their child's education, supporting learning at home.
- Prepares for Upcoming Classes : Homework can be used to introduce new material, preparing students for future lessons and enabling more effective use of classroom time.
Overall, homework is a critical tool in the educational process, supporting learning and personal development in numerous ways.
Ever wondered why teachers seem to love piling on homework? The real reasons why assignments have such an amazing impact on your future might surprise you.
In this article, we’re discovering how homework isn’t just busywork — it’s an essential player when it comes to skyrocketing your comprehension of class material, refining your ability to tackle problems, and establishing a sturdy foundation for academic success.
By the time we’re done, you’re going to be seeing homework in a different light. So, let's find out why homework is important.
Benefits of Homework
Homework facilitates problem-solving skills, provides students with an additional chance to revisit classroom content, enables parents to understand school teachings, and instills a sense of responsibility in students regarding their education.
If you're asking yourself, "Why is homework good for me?" There are numerous reasons why it can be very beneficial in the long run. Challenging work allows us to grow, after all. Let's look at all its benefits.
Completing Homework Encourages Students To Keep Learning
For some students, learning is not just an obligation but can be enjoyed as well. The acceptance of life-long learning can be fostered by homework, and if the teacher manages to engage their students, they’ve set the stage for the students. Let’s take a look at why homework is important:
- Improves memory and retention: It increases the potential for students to remember class material since they have to revisit it.
- Increases the potential for practical use of knowledge: By understanding the lesson’s materials in more depth, students might apply what they know with more ease.
Helps Develop Skills and Good Habits
Doing your homework can help you develop the necessary skills and habits needed to do challenging work and to keep progressing and ultimately growing as a person. This is why the importance of homework can't be overlooked.
- Helps you learn time management: Since homework is usually done outside of school, students will learn how to manage their time and studying time, which will seep into their ability to manage their time in general.
- Helps students become more organized: Organizing what you’ve learned to produce well-thought responses that can also be applied practically will become crucial in your day-to-day life.
- Helps foster discipline and responsibility: If students want to become successful, not just in the eyes of society but for their personal achievements as well, they must be disciplined and have to take on responsibilities.
Connects School and Home
“Why is homework necessary?” you ask. For starters, it bridges school and home life. Parents are the vital link between schools and students becoming college and career-ready.
And parent engagement is more powerful than any other form of involvement or support at school. It strengthens the vital educational triangle uniting parents, home, and school.
Prepares High School Students for The Future
You can become more resilient and adaptable to challenges in your life. You’ll most likely feel more prepared when these challenges come. What’s more, you can become a better problem-solver and can improve your analytical and critical thinking skills in the long run. This is why homework is beneficial.
Helps Develop A Growth Mindset and Time Management Skills
If you're still wondering, "Why is homework important?" Then, you should know that it can help you foster a growth mentality. What does this mean? Instead of feeling victimized by challenges, failures, and other difficulties, you'll develop a mindset where you view these things as opportunities to grow. At the end of the day, these difficulties can be your best teachers.
Struggling with your Homework?
Get your assignments done by real pros. Save your precious time and boost your marks with ease.
Homework: Tips and Tricks
Now that we've taken a look at all the reasons why homework is beneficial to your growth and life let's take a look at some tips you can apply to your homework sessions. If you're still having issues, you can always send a " do my homework " request on Studyfy to get expert help.
To effectively tackle homework, consider these strategies: take regular breaks to refresh, collaborate with friends for support, create a conducive homework area, actively engage in homework discussions, minimize distractions, adhere to a homework timetable, form a study group, organize a dedicated study space, prepare all necessary materials in advance, listen to instrumental music to maintain focus, reward yourself for completing tasks, practice efficient time management, and leverage available resources for assistance.
1. Create A Study Space : Moving on from finding out why homework is good, the first tip to make homework sessions easier is to create a dedicated study space. By doing this, you can potentially trick your mind into focusing better in that said space.
2. Establish A Routine : Create a homework schedule and stick to it. By doing this, you're freeing up your time by prioritizing your responsibilities first. It might be hard at first, but it's work sticking by. Moreover, if you're curious, you can take a look at who invented homework and why , and you might get some inspiration from knowing this.
3. Prioritize The Difficult Tasks in Homework Assignments : Continuing why should students have homework and homework tips, another great tip is to tackle difficult homework first. This gives you enough time to complete them, ensuring you meet your deadlines. It also frees up your time and speeds up the process.
4. Make Use of Apps : Apps like Quizlet and Evernote can help streamline your sessions. You can note down reasons on, "How is homework beneficial?" to help you get motivated or simply note down important notes from class and more.
5. Break Tasks Up : For lengthier and more complex tasks, you can simply break them up into smaller and more doable portions. Need more reasons on why is homework good for students so you can learn how to motivate yourself to do homework even more? Keep reading, and you’ll know all there is to know about homework and how to finish it easier.
6. Get Help : How does homework help students when a task is too difficult? Difficulty motivates us to try harder. However, if you feel like you're stuck, don't be afraid to seek out help. You can ask teachers, friends, and your parents for extra guidance.
7. Employ Study Methods : Use study methods like summarizing, memory flashcards, and quizzing yourself. "Why is homework beneficial?" It helps you apply problem-solving skills effectively, just like these 3 methods.
8. Free Yourself From Distractions : One of the reasons why homework is good is it teaches you to focus and to cut off distractions. A habit that applies to anything in life. Free up your study space from all potential distractions, like phones, tablets, and TV.
9. Prioritize Health and Sleep : "Why is homework helpful?" For starters, if you prioritize your work, you are obligated to also take care of your health and get enough sleep. By doing so, you can focus and work better. Good habits produce more good habits.
10. Find Your Purpose : The last tip, but not the least important, is finding out your "Why." Find out why you want to work hard. Instead of summing it up to, "I want to get into a good school" or "I want to make a lot of money as an adult," find a deeper purpose as to why you should be diligent.
Maybe you're doing it for self-improvement, or maybe you want to change the world for the better. You can potentially get to know yourself better, and you realize this is why we should have homework.
Did you like our Homework Post?
For more help, tap into our pool of professional writers and get expert essay editing services!
What are the reasons why students should have homework?
As we've already seen, homework helps foster better cognitive abilities, train discipline, and prepare students for what's coming.
If you're still struggling with your homework, you can get physics homework help and help for other subjects, too, on Studyfy. It's alright to have difficulties, if you try to improve, results will surely show up.
How can parents help with homework?
Homework is important, therefore you should ask your parents for help and further motivation if needed. They can offer help when necessary and let you solve problems on your own to foster independence. They can create a space where learning is easy and there are no disturbances.
Can too much homework be counterproductive?
While the benefits of homework are plenty, too much homework can be counterproductive. If this is the case, you can directly talk to your teachers and negotiate with them. If you have tests you need to study for, it can help to have less homework.
Too much homework creates unnecessary stress, no matter how good your time management skills are. Yes, homework improve academic achievement, but excessive homework, especially for younger students, doesn't reinforce learning.
Do the study tips this article has mentioned help?
Yes, they do. It's become apparent that to memorize large amounts of information, it is better to break them down into parts. As for the rest of the advice, it will improve most students' learning efficiency. You should still try to find out which methods work best for you.
If you need more guidance, you can get math homework help and help for other subjects as well on Studyfy. Gain insights and advice from an expert today.
Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads From TIME
- The 100 Most Influential People of 2024
- How Far Trump Would Go
- Scenes From Pro-Palestinian Encampments Across U.S. Universities
- Saving Seconds Is Better Than Hours
- Why Your Breakfast Should Start with a Vegetable
- 6 Compliments That Land Every Time
- Welcome to the Golden Age of Ryan Gosling
- Want Weekly Recs on What to Watch, Read, and More? Sign Up for Worth Your Time
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]
share this!
January 18, 2024
This article has been reviewed according to Science X's editorial process and policies . Editors have highlighted the following attributes while ensuring the content's credibility:
fact-checked
trusted source
Q&A: Does homework still have value? An education expert weighs in
by Vicky Hallett, Johns Hopkins University

The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein, co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work," Epstein says.
But after decades of researching how to improve schools, the professor in the Johns Hopkins School of Education remains certain that homework is essential—as long as the teachers have done their homework, too. The National Network of Partnership Schools, which she founded in 1995 to advise schools and districts on ways to improve comprehensive programs of family engagement, has developed hundreds of improved homework ideas through its Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program.
For an English class, a student might interview a parent on popular hairstyles from their youth and write about the differences between then and now. Or for science class, a family could identify forms of matter over the dinner table, labeling foods as liquids or solids. These innovative and interactive assignments not only reinforce concepts from the classroom but also foster creativity, spark discussions, and boost student motivation.
"We're not trying to eliminate homework procedures, but expand and enrich them," says Epstein, who is packing this research into a forthcoming book on the purposes and designs of homework. In the meantime, the Hub couldn't wait to ask her some questions.
What kind of homework training do teachers typically get?
Future teachers and administrators really have little formal training on how to design homework before they assign it. This means that most just repeat what their teachers did, or they follow textbook suggestions at the end of units. For example, future teachers are well prepared to teach reading and literacy skills at each grade level, and they continue to learn to improve their teaching of reading in ongoing in-service education.
By contrast, most receive little or no training on the purposes and designs of homework in reading or other subjects. It is really important for future teachers to receive systematic training to understand that they have the power, opportunity, and obligation to design homework with a purpose.
Why do students need more interactive homework?
If homework assignments are always the same—10 math problems, six sentences with spelling words—homework can get boring and some kids just stop doing their assignments, especially in the middle and high school years. When we've asked teachers what's the best homework you've ever had or designed, invariably we hear examples of talking with a parent or grandparent or peer to share ideas.
To be clear, parents should never be asked to "teach" seventh grade science or any other subject. Rather, teachers set up the homework assignments so that the student is in charge. It's always the student's homework. But a good activity can engage parents in a fun, collaborative way.
Our data show that with "good" assignments, more kids finish their work, more kids interact with a family partner, and more parents say, "I learned what's happening in the curriculum." It all works around what the youngsters are learning.
Is family engagement really that important?
At Hopkins, I am part of the Center for Social Organization of Schools, a research center that studies how to improve many aspects of education to help all students do their best in school. One thing my colleagues and I realized was that we needed to look deeply into family and community engagement. There were so few references to this topic when we started that we had to build the field of study. When children go to school, their families "attend" with them whether a teacher can "see" the parents or not. So, family engagement is ever-present in the life of a school.
My daughter's elementary school doesn't assign homework until third grade. What's your take on 'no homework' policies?
There are some parents, writers, and commentators who have argued against homework, especially for very young children. They suggest that children should have time to play after school. This, of course is true, but many kindergarten kids are excited to have homework like their older siblings. If they give homework, most teachers of young children make assignments very short—often following an informal rule of 10 minutes per grade level . "No homework" does not guarantee that all students will spend their free time in productive and imaginative play.
Some researchers and critics have consistently misinterpreted research findings. They have argued that homework should be assigned only at the high school level where data point to a strong connection of doing assignments with higher student achievement. However, as we discussed, some students stop doing homework. This leads, statistically, to results showing that doing homework or spending more minutes on homework is linked to higher student achievement. If slow or struggling students are not doing their assignments, they contribute to—or cause—this "result."
Teachers need to design homework that even struggling students want to do because it is interesting. Just about all students at any age level react positively to good assignments and will tell you so.
Did COVID change how schools and parents view homework?
Within 24 hours of the day school doors closed in March 2020, just about every school and district in the country figured out that teachers had to talk to and work with students' parents. This was not the same as homeschooling—teachers were still working hard to provide daily lessons. But if a child was learning at home in the living room, parents were more aware of what they were doing in school .
One of the silver linings of COVID was that teachers reported that they gained a better understanding of their students' families. We collected wonderfully creative examples of activities from members of the National Network of Partnership Schools. I'm thinking of one art activity where every child talked with a parent about something that made their family unique. Then they drew their finding on a snowflake and returned it to share in class. In math, students talked with a parent about something the family liked so much that they could represent it 100 times. Conversations about schoolwork at home was the point.
How did you create so many homework activities via the Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork program?
We had several projects with educators to help them design interactive assignments, not just "do the next three examples on page 38." Teachers worked in teams to create TIPS activities, and then we turned their work into a standard TIPS format in math, reading/language arts, and science for grades K-8. Any teacher can use or adapt our prototypes to match their curricula.
Overall, we know that if future teachers and practicing educators were prepared to design homework assignments to meet specific purposes—including but not limited to interactive activities—more students would benefit from the important experience of doing their homework. And more parents would, indeed, be partners in education.
Provided by Johns Hopkins University
Explore further
Feedback to editors
Chemists develop highly reflective black paint to make objects more visible to autonomous cars
9 minutes ago
Researchers find unexpected roadblock to conductivity in Mott insulators
15 minutes ago
Climate is one culprit in growth and spread of dust in Middle East
34 minutes ago

TOI-837 b is a young Saturn-sized exoplanet with a massive core, observations find
2 hours ago

Why do male chicks play more than females? Study finds answers in distant ancestor
9 hours ago

Archaea can be 'picky eaters': Study shows a group of parasitic microbes can change host metabolism
16 hours ago

EPA underestimates methane emissions from landfills and urban areas, researchers find
17 hours ago

This Texas veterinarian helped crack the mystery of bird flu in cows
Researchers discover key functions of therapeutically promising jumbo viruses

Marine sharks and rays 'use' urea to delay reproduction, finds study
18 hours ago
Relevant PhysicsForums posts
Physics instructor minimum education - community college.
3 hours ago
Studying "Useful" vs. "Useless" Stuff in School
Apr 30, 2024
Why are Physicists so informal with mathematics?
Apr 29, 2024
Plagiarism & ChatGPT: Is Cheating with AI the New Normal?
Apr 28, 2024
Digital oscilloscope for high school use
Apr 25, 2024
Motivating high school Physics students with Popcorn Physics
Apr 3, 2024
More from STEM Educators and Teaching
Related Stories

'There's only so far I can take them': Why teachers give up on struggling students who don't do their homework
Sep 27, 2022

Should parents help their kids with homework?
Aug 29, 2019

What's the point of homework?
Sep 1, 2021

How to help your kids with homework—without doing it for them
Jan 24, 2020

Is homework useful for kids? If so, what age should it start?
Nov 30, 2022

Doing homework is associated with change in students' personality
Oct 6, 2017
Recommended for you

Training of brain processes makes reading more efficient
Apr 18, 2024

Researchers find lower grades given to students with surnames that come later in alphabetical order
Apr 17, 2024

Earth, the sun and a bike wheel: Why your high-school textbook was wrong about the shape of Earth's orbit
Apr 8, 2024

Touchibo, a robot that fosters inclusion in education through touch
Apr 5, 2024

More than money, family and community bonds prep teens for college success: Study
Research reveals significant effects of onscreen instructors during video classes in aiding student learning
Mar 25, 2024
Let us know if there is a problem with our content
Use this form if you have come across a typo, inaccuracy or would like to send an edit request for the content on this page. For general inquiries, please use our contact form . For general feedback, use the public comments section below (please adhere to guidelines ).
Please select the most appropriate category to facilitate processing of your request
Thank you for taking time to provide your feedback to the editors.
Your feedback is important to us. However, we do not guarantee individual replies due to the high volume of messages.
E-mail the story
Your email address is used only to let the recipient know who sent the email. Neither your address nor the recipient's address will be used for any other purpose. The information you enter will appear in your e-mail message and is not retained by Phys.org in any form.
Newsletter sign up
Get weekly and/or daily updates delivered to your inbox. You can unsubscribe at any time and we'll never share your details to third parties.
More information Privacy policy
Donate and enjoy an ad-free experience
We keep our content available to everyone. Consider supporting Science X's mission by getting a premium account.
E-mail newsletter
Should Kids Get Homework?
Homework gives elementary students a way to practice concepts, but too much can be harmful, experts say.

Getty Images
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful.
How much homework students should get has long been a source of debate among parents and educators. In recent years, some districts have even implemented no-homework policies, as students juggle sports, music and other activities after school.
Parents of elementary school students, in particular, have argued that after-school hours should be spent with family or playing outside rather than completing assignments. And there is little research to show that homework improves academic achievement for elementary students.
But some experts say there's value in homework, even for younger students. When done well, it can help students practice core concepts and develop study habits and time management skills. The key to effective homework, they say, is keeping assignments related to classroom learning, and tailoring the amount by age: Many experts suggest no homework for kindergartners, and little to none in first and second grade.
Value of Homework
Homework provides a chance to solidify what is being taught in the classroom that day, week or unit. Practice matters, says Janine Bempechat, clinical professor at Boston University 's Wheelock College of Education & Human Development.
"There really is no other domain of human ability where anybody would say you don't need to practice," she adds. "We have children practicing piano and we have children going to sports practice several days a week after school. You name the domain of ability and practice is in there."
Homework is also the place where schools and families most frequently intersect.
"The children are bringing things from the school into the home," says Paula S. Fass, professor emerita of history at the University of California—Berkeley and the author of "The End of American Childhood." "Before the pandemic, (homework) was the only real sense that parents had to what was going on in schools."
Harris Cooper, professor emeritus of psychology and neuroscience at Duke University and author of "The Battle Over Homework," examined more than 60 research studies on homework between 1987 and 2003 and found that — when designed properly — homework can lead to greater student success. Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary.
"Every child should be doing homework, but the amount and type that they're doing should be appropriate for their developmental level," he says. "For teachers, it's a balancing act. Doing away with homework completely is not in the best interest of children and families. But overburdening families with homework is also not in the child's or a family's best interest."
Negative Homework Assignments
Not all homework for elementary students involves completing a worksheet. Assignments can be fun, says Cooper, like having students visit educational locations, keep statistics on their favorite sports teams, read for pleasure or even help their parents grocery shop. The point is to show students that activities done outside of school can relate to subjects learned in the classroom.
But assignments that are just busy work, that force students to learn new concepts at home, or that are overly time-consuming can be counterproductive, experts say.
Homework that's just busy work.
Effective homework reinforces math, reading, writing or spelling skills, but in a way that's meaningful, experts say. Assignments that look more like busy work – projects or worksheets that don't require teacher feedback and aren't related to topics learned in the classroom – can be frustrating for students and create burdens for families.
"The mental health piece has definitely played a role here over the last couple of years during the COVID-19 pandemic, and the last thing we want to do is frustrate students with busy work or homework that makes no sense," says Dave Steckler, principal of Red Trail Elementary School in Mandan, North Dakota.
Homework on material that kids haven't learned yet.
With the pressure to cover all topics on standardized tests and limited time during the school day, some teachers assign homework that has not yet been taught in the classroom.
Not only does this create stress, but it also causes equity challenges. Some parents speak languages other than English or work several jobs, and they aren't able to help teach their children new concepts.
" It just becomes agony for both parents and the kids to get through this worksheet, and the goal becomes getting to the bottom of (the) worksheet with answers filled in without any understanding of what any of it matters for," says professor Susan R. Goldman, co-director of the Learning Sciences Research Institute at the University of Illinois—Chicago .
Homework that's overly time-consuming.
The standard homework guideline recommended by the National Parent Teacher Association and the National Education Association is the "10-minute rule" – 10 minutes of nightly homework per grade level. A fourth grader, for instance, would receive a total of 40 minutes of homework per night.
But this does not always happen, especially since not every student learns the same. A 2015 study published in the American Journal of Family Therapy found that primary school children actually received three times the recommended amount of homework — and that family stress increased along with the homework load.
Young children can only remain attentive for short periods, so large amounts of homework, especially lengthy projects, can negatively affect students' views on school. Some individual long-term projects – like having to build a replica city, for example – typically become an assignment for parents rather than students, Fass says.
"It's one thing to assign a project like that in which several kids are working on it together," she adds. "In (that) case, the kids do normally work on it. It's another to send it home to the families, where it becomes a burden and doesn't really accomplish very much."
Private vs. Public Schools
Do private schools assign more homework than public schools? There's little research on the issue, but experts say private school parents may be more accepting of homework, seeing it as a sign of academic rigor.
Of course, not all private schools are the same – some focus on college preparation and traditional academics, while others stress alternative approaches to education.
"I think in the academically oriented private schools, there's more support for homework from parents," says Gerald K. LeTendre, chair of educational administration at Pennsylvania State University—University Park . "I don't know if there's any research to show there's more homework, but it's less of a contentious issue."
How to Address Homework Overload
First, assess if the workload takes as long as it appears. Sometimes children may start working on a homework assignment, wander away and come back later, Cooper says.
"Parents don't see it, but they know that their child has started doing their homework four hours ago and still not done it," he adds. "They don't see that there are those four hours where their child was doing lots of other things. So the homework assignment itself actually is not four hours long. It's the way the child is approaching it."
But if homework is becoming stressful or workload is excessive, experts suggest parents first approach the teacher, followed by a school administrator.
"Many times, we can solve a lot of issues by having conversations," Steckler says, including by "sitting down, talking about the amount of homework, and what's appropriate and not appropriate."
Study Tips for High School Students

Tags: K-12 education , students , elementary school , children
2024 Best Colleges

Search for your perfect fit with the U.S. News rankings of colleges and universities.
Featured Topics
Featured series.
A series of random questions answered by Harvard experts.
Explore the Gazette
Read the latest.

Complex questions, innovative approaches

Early warning sign of extinction?

So much for summers of love
Lessons in learning.
Sean Finamore ’22 (left) and Xaviera Zime ’22 study during a lecture in the Science Center.
Photos by Kris Snibbe/Harvard Staff Photographer
Peter Reuell
Harvard Staff Writer
Study shows students in ‘active learning’ classrooms learn more than they think
For decades, there has been evidence that classroom techniques designed to get students to participate in the learning process produces better educational outcomes at virtually all levels.
And a new Harvard study suggests it may be important to let students know it.
The study , published Sept. 4 in the Proceedings of the National Academy of Sciences, shows that, though students felt as if they learned more through traditional lectures, they actually learned more when taking part in classrooms that employed so-called active-learning strategies.
Lead author Louis Deslauriers , the director of science teaching and learning and senior physics preceptor, knew that students would learn more from active learning. He published a key study in Science in 2011 that showed just that. But many students and faculty remained hesitant to switch to it.
“Often, students seemed genuinely to prefer smooth-as-silk traditional lectures,” Deslauriers said. “We wanted to take them at their word. Perhaps they actually felt like they learned more from lectures than they did from active learning.”
In addition to Deslauriers, the study is authored by director of sciences education and physics lecturer Logan McCarty , senior preceptor in applied physics Kelly Miller, preceptor in physics Greg Kestin , and Kristina Callaghan, now a physics lecturer at the University of California, Merced.
The question of whether students’ perceptions of their learning matches with how well they’re actually learning is particularly important, Deslauriers said, because while students eventually see the value of active learning, initially it can feel frustrating.
“Deep learning is hard work. The effort involved in active learning can be misinterpreted as a sign of poor learning,” he said. “On the other hand, a superstar lecturer can explain things in such a way as to make students feel like they are learning more than they actually are.”
To understand that dichotomy, Deslauriers and his co-authors designed an experiment that would expose students in an introductory physics class to both traditional lectures and active learning.
For the first 11 weeks of the 15-week class, students were taught using standard methods by an experienced instructor. In the 12th week, half the class was randomly assigned to a classroom that used active learning, while the other half attended highly polished lectures. In a subsequent class, the two groups were reversed. Notably, both groups used identical class content and only active engagement with the material was toggled on and off.
Following each class, students were surveyed on how much they agreed or disagreed with statements such as “I feel like I learned a lot from this lecture” and “I wish all my physics courses were taught this way.” Students were also tested on how much they learned in the class with 12 multiple-choice questions.
When the results were tallied, the authors found that students felt as if they learned more from the lectures, but in fact scored higher on tests following the active learning sessions. “Actual learning and feeling of learning were strongly anticorrelated,” Deslauriers said, “as shown through the robust statistical analysis by co-author Kelly Miller, who is an expert in educational statistics and active learning.”
Those results, the study authors are quick to point out, shouldn’t be interpreted as suggesting students dislike active learning. In fact, many studies have shown students quickly warm to the idea, once they begin to see the results. “In all the courses at Harvard that we’ve transformed to active learning,” Deslauriers said, “the overall course evaluations went up.”

Co-author Kestin, who in addition to being a physicist is a video producer with PBS’ NOVA, said, “It can be tempting to engage the class simply by folding lectures into a compelling ‘story,’ especially when that’s what students seem to like. I show my students the data from this study on the first day of class to help them appreciate the importance of their own involvement in active learning.”
McCarty, who oversees curricular efforts across the sciences, hopes this study will encourage more of his colleagues to embrace active learning.
“We want to make sure that other instructors are thinking hard about the way they’re teaching,” he said. “In our classes, we start each topic by asking students to gather in small groups to solve some problems. While they work, we walk around the room to observe them and answer questions. Then we come together and give a short lecture targeted specifically at the misconceptions and struggles we saw during the problem-solving activity. So far we’ve transformed over a dozen classes to use this kind of active-learning approach. It’s extremely efficient — we can cover just as much material as we would using lectures.”
A pioneer in work on active learning, Balkanski Professor of Physics and Applied Physics Eric Mazur hailed the study as debunking long-held beliefs about how students learn.
“This work unambiguously debunks the illusion of learning from lectures,” he said. “It also explains why instructors and students cling to the belief that listening to lectures constitutes learning. I recommend every lecturer reads this article.”
Dean of Science Christopher Stubbs , Samuel C. Moncher Professor of Physics and of Astronomy, was an early convert. “When I first switched to teaching using active learning, some students resisted that change. This research confirms that faculty should persist and encourage active learning. Active engagement in every classroom, led by our incredible science faculty, should be the hallmark of residential undergraduate education at Harvard.”
Ultimately, Deslauriers said, the study shows that it’s important to ensure that neither instructors nor students are fooled into thinking that lectures are the best learning option. “Students might give fabulous evaluations to an amazing lecturer based on this feeling of learning, even though their actual learning isn’t optimal,” he said. “This could help to explain why study after study shows that student evaluations seem to be completely uncorrelated with actual learning.”
This research was supported with funding from the Harvard FAS Division of Science.
Share this article
You might like.
Seven projects awarded Star-Friedman Challenge grants

Fossil record stretching millions of years shows tiny ocean creatures on the move before Earth heats up

Despite ‘hippie’ reputation, male bonobos fight three times as often as chimps, study finds
When math is the dream
Dora Woodruff was drawn to beauty of numbers as child. Next up: Ph.D. at MIT.
Seem like Lyme disease risk is getting worse? It is.
The risk of Lyme disease has increased due to climate change and warmer temperature. A rheumatologist offers advice on how to best avoid ticks while going outdoors.
Alcohol is dangerous. So is ‘alcoholic.’
Researcher explains the human toll of language that makes addiction feel worse
Is Homework Good or Bad for Students?
It's mostly good, especially for the sciences, but it also can be bad
JGI / Jamie Grill / Getty Images
- Homework Tips
- Learning Styles & Skills
- Study Methods
- Time Management
- Private School
- College Admissions
- College Life
- Graduate School
- Business School
- Distance Learning
- Ph.D., Biomedical Sciences, University of Tennessee at Knoxville
- B.A., Physics and Mathematics, Hastings College
Homework isn't fun for students to do or for teachers to grade, so why do it? Here are some reasons why homework is good and why it's bad.
Why Homework Is Good
Here are 10 reasons why homework is good, especially for the sciences, such as chemistry:
- Doing homework teaches you how to learn on your own and work independently. You'll learn how to use resources such as texts, libraries, and the internet. No matter how well you thought you understood the material in class, there will be times when you'll get stuck doing homework. When you face the challenge, you learn how to get help, how to deal with frustration, and how to persevere.
- Homework helps you learn beyond the scope of the class. Example problems from teachers and textbooks show you how to do an assignment. The acid test is seeing whether you truly understand the material and can do the work on your own. In science classes, homework problems are critically important. You see concepts in a whole new light, so you'll know how equations work in general, not just how they work for a particular example. In chemistry, physics, and math, homework is truly important and not just busywork.
- It shows you what the teacher thinks is important to learn, so you'll have a better idea of what to expect on a quiz or test .
- It's often a significant part of your grade . If you don't do it, it could cost you , no matter how well you do on exams.
- Homework is a good opportunity to connect parents, classmates, and siblings with your education. The better your support network, the more likely you are to succeed in class.
- Homework, however tedious it might be, teaches responsibility and accountability. For some classes, homework is an essential part of learning the subject matter.
- Homework nips procrastination in the bud. One reason teachers give homework and attach a big part of your grade to it is to motivate you to keep up. If you fall behind, you could fail.
- How will you get all your work done before class? Homework teaches you time management and how to prioritize tasks.
- Homework reinforces the concepts taught in class. The more you work with them, the more likely you are to learn them.
- Homework can help boost self-esteem . Or, if it's not going well, it helps you identify problems before they get out of control.
Sometimes Homework Is Bad
So, homework is good because it can boost your grades , help you learn the material, and prepare you for tests. It's not always beneficial, however. Sometimes homework hurts more than it helps. Here are five ways homework can be bad:
- You need a break from a subject so you don't burn out or lose interest. Taking a break helps you learn.
- Too much homework can lead to copying and cheating.
- Homework that is pointless busywork can lead to a negative impression of a subject (not to mention a teacher).
- It takes time away from families, friends, jobs, and other ways to spend your time.
- Homework can hurt your grades. It forces you to make time management decisions, sometimes putting you in a no-win situation. Do you take the time to do the homework or spend it studying concepts or doing work for another subject? If you don't have the time for the homework, you could hurt your grades even if you ace the tests and understand the subject.
- Free French Worksheets
- How are College Academics Different from High School?
- Organic Chemistry Survival Tips
- 5 Top Reasons Why Students Fail Chemistry
- What to Do if You Are Failing Chemistry
- Should You Take a GRE Review Course?
- Study Habits That Can Improve Grades and Performance
- 10 Ways to Impress a Teacher
- How to Get Your Homework Done in College
- Topics for a Lesson Plan Template
- The Case for the Importance of Taking Notes
- How to Change Your Habits and Improve Your Grades
- Essential Strategies to Help You Become an Outstanding Student
- Study Tips for Math Homework and Math Tests
- 4 Tips for Completing Your Homework On Time
- 20 Tips for Success in High School

School Life Balance , Tips for Online Students
The Pros and Cons of Homework
Updated: December 7, 2023
Published: January 23, 2020

Homework is a word that most students dread hearing. After hours upon hours of sitting in class , the last thing we want is more schoolwork over our precious weekends. While it’s known to be a staple of traditional schooling, homework has also become a rather divise topic. Some feel as though homework is a necessary part of school, while others believe that the time could be better invested. Should students have homework? Have a closer look into the arguments on both sides to decide for yourself.

Photo by energepic.com from Pexels
Why should students have homework, 1. homework encourages practice.
Many people believe that one of the positive effects of homework is that it encourages the discipline of practice. While it may be time consuming and boring compared to other activities, repetition is needed to get better at skills. Homework helps make concepts more clear, and gives students more opportunities when starting their career .
2. Homework Gets Parents Involved
Homework can be something that gets parents involved in their children’s lives if the environment is a healthy one. A parent helping their child with homework makes them take part in their academic success, and allows for the parent to keep up with what the child is doing in school. It can also be a chance to connect together.
3. Homework Teaches Time Management
Homework is much more than just completing the assigned tasks. Homework can develop time management skills , forcing students to plan their time and make sure that all of their homework assignments are done on time. By learning to manage their time, students also practice their problem-solving skills and independent thinking. One of the positive effects of homework is that it forces decision making and compromises to be made.
4. Homework Opens A Bridge Of Communication
Homework creates a connection between the student, the teacher, the school, and the parents. It allows everyone to get to know each other better, and parents can see where their children are struggling. In the same sense, parents can also see where their children are excelling. Homework in turn can allow for a better, more targeted educational plan for the student.
5. Homework Allows For More Learning Time
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can’t see it in the moment.
6. Homework Reduces Screen Time
Many students in North America spend far too many hours watching TV. If they weren’t in school, these numbers would likely increase even more. Although homework is usually undesired, it encourages better study habits and discourages spending time in front of the TV. Homework can be seen as another extracurricular activity, and many families already invest a lot of time and money in different clubs and lessons to fill up their children’s extra time. Just like extracurricular activities, homework can be fit into one’s schedule.

The Other Side: Why Homework Is Bad
1. homework encourages a sedentary lifestyle.
Should students have homework? Well, that depends on where you stand. There are arguments both for the advantages and the disadvantages of homework.
While classroom time is important, playground time is just as important. If children are given too much homework, they won’t have enough playtime, which can impact their social development and learning. Studies have found that those who get more play get better grades in school , as it can help them pay closer attention in the classroom.
Children are already sitting long hours in the classroom, and homework assignments only add to these hours. Sedentary lifestyles can be dangerous and can cause health problems such as obesity. Homework takes away from time that could be spent investing in physical activity.
2. Homework Isn’t Healthy In Every Home
While many people that think homes are a beneficial environment for children to learn, not all homes provide a healthy environment, and there may be very little investment from parents. Some parents do not provide any kind of support or homework help, and even if they would like to, due to personal barriers, they sometimes cannot. Homework can create friction between children and their parents, which is one of the reasons why homework is bad .
3. Homework Adds To An Already Full-Time Job
School is already a full-time job for students, as they generally spend over 6 hours each day in class. Students also often have extracurricular activities such as sports, music, or art that are just as important as their traditional courses. Adding on extra hours to all of these demands is a lot for children to manage, and prevents students from having extra time to themselves for a variety of creative endeavors. Homework prevents self discovery and having the time to learn new skills outside of the school system. This is one of the main disadvantages of homework.
4. Homework Has Not Been Proven To Provide Results
Endless surveys have found that homework creates a negative attitude towards school, and homework has not been found to be linked to a higher level of academic success.
The positive effects of homework have not been backed up enough. While homework may help some students improve in specific subjects, if they have outside help there is no real proof that homework makes for improvements.
It can be a challenge to really enforce the completion of homework, and students can still get decent grades without doing their homework. Extra school time does not necessarily mean better grades — quality must always come before quantity.
Accurate practice when it comes to homework simply isn’t reliable. Homework could even cause opposite effects if misunderstood, especially since the reliance is placed on the student and their parents — one of the major reasons as to why homework is bad. Many students would rather cheat in class to avoid doing their homework at home, and children often just copy off of each other or from what they read on the internet.
5. Homework Assignments Are Overdone
The general agreement is that students should not be given more than 10 minutes a day per grade level. What this means is that a first grader should be given a maximum of 10 minutes of homework, while a second grader receives 20 minutes, etc. Many students are given a lot more homework than the recommended amount, however.
On average, college students spend as much as 3 hours per night on homework . By giving too much homework, it can increase stress levels and lead to burn out. This in turn provides an opposite effect when it comes to academic success.
The pros and cons of homework are both valid, and it seems as though the question of ‘‘should students have homework?’ is not a simple, straightforward one. Parents and teachers often are found to be clashing heads, while the student is left in the middle without much say.
It’s important to understand all the advantages and disadvantages of homework, taking both perspectives into conversation to find a common ground. At the end of the day, everyone’s goal is the success of the student.
Related Articles
Why homework is important: Get The Most Genuine Reasons

- Post author By admin
- October 4, 2022
Why homework is important? As you know that every student goes to school and college, and every student has homework.
Homework has been a topic of interest for a long time. Many students believe that homework is not beneficial for them.
And some students think that without homework they can’t remember what they learn in class. If you have enough amount of homework, it is very beneficial for you.
You should do homework because it will help you to learn life skills and also help you master a skill.
Homework should be a positive experience for all students that help them to learn properly and improve their final grades. Why homework is important for students?
In this blog, we will learn what is homework and why homework is important. So, let’s get started.
Table of Contents
What is homework?
Homework can be defined as the task assigned to students by the teacher extra from the classwork. For exploring new things regarding a subject or topic. If we learn something in the classroom. We need to revise the topic otherwise we will forget. So homework is the best practice to learn new things and it helps to remind us. To move forward we need to understand a few things like what is the difference between Homework and Assignment.
Why Do Teachers Give Homework To The Students?
Here are some reasons why teachers give homework to the students:
- It helps to understand how to do work independently.
- With homework, students can learn to make schedules for all work.
- It helps students to solve the problem on their own.
- It helps students to find, and organize good information.
- Homework can help to develop a good sense of personal responsibility for learning.
- It also helps to learn using libraries and other resources.
Importance Of Doing Homework
Why homework is important? This is a very popular question. Many students think that homework is not fun to do.
You should do more research to get more information about the basic reason why homework is good for students.
When you do your homework it teaches you how to work and study on your own. With homework, you can learn using different resources like text, libraries, book chapters and other resources.
It will also help you to deal with difficult challenges. Students can take benefit from homework because it helps to develop their learning beyond the classroom. You should also read this (2022) Best Homework Songs to Listen While Study .
Reason Why Homework Is Important?
Here is some reason why homework is important:
Improve Thinking

It can help students to improve their memory and thinking.
Use Time Wisely
With the help of homework, students learn to utilize time wisely.
Work Independently
While doing homework, students can work independently. They can do their work on their own.
Responsible For Work

It helps students to take responsibility for work on their own.
Get Ready For The Next Day In Class
With the help of homework, students can get ready for the next day’s class.
Learn To Use Resources

It helps students to learn using resources such as websites to find information, libraries, reference materials, and others. Also, read this Is Homework Illegal AnyWhere? .
Help Students Explore The Subject
Homework help students to explore the topic more carefully than class time permits.
Homework Increases a Student’s Confidence

Homework improves knowledge. This always results in improving confidence also.
The more you learn, understand, and practice, the more you will improve your confidence. This is also important for your exams too as it can help you to remember the concepts.
As a result, you can easily write the answers on your exam sheet. This will increase your confidence to score good grades in exams.
Homework Helps Parents Know What Their Children Are Learning
Homework is the best opportunity for teachers and parents to connect with their children.
While doing homework it is the best way to observe students about their strengths and weaknesses. Like in which subject they are good or poor.
Parents can track their performance easily. Also, read this Who Invented Homework And Why? Best Facts You Should Know .
Enhance Problem-Solving Skills

Whenever any student does their homework there are so many hard questions they have to encounter so it is helpful for brainstorming the solutions.
They make every effort to complete it, whether it is taking help from the internet or from their parents.
Due to this, the problem-solving skills of the students increase and they can easily solve any problem in their life.
Help Us Prioritize The Topics/Time Management Skill

As we know that if we complete any task it is a pleasurable moment for us.
So when the student completes their homework sometimes it is difficult to solve any problem. Sometimes students are stuck after finding the solution. It is an achievement for them.
It motivates us to do more work and boosts our confidence.
Regular basis homework makes the student capable of grabbing more knowledge which is beneficial for scoring well in exams.
Increases The Concentration Of Students In The Classroom

When the teacher reads a topic in the class, then the students think that this topic will be very easy.
Due to this, the students do not study the topic carefully. But when the teachers give homework based on the same topic to the students, they understand how important it is to listen to the teacher in the class.
In this way, the students feel their responsibility. That’s why homework is important for students.
How To Do Homework In An Interesting Way?
Follow the strategy to complete your homework effectively How to do homework in an interesting way:
- Group Study: Do work together with your friends.
- Make it visual: Use video animations for learning.
- Don’t cram, try to learn from the basics.
- Give a Reward to yourself by completing targets.
- Create a homework space.
- Set a Proper schedule for work.
- Don’t hesitate to ask questions.
- Try different learning applications or websites.
- Set a goal for achievements.
- Take a short break between homework tasks to refresh your mind.
- Arrange all books and supplies in advance to save your time.
Why Is Homework Useful For Teachers?
If teachers use homework correctly, it can be very effective for determining what they understand from the lesson.
It gives teachers a clear idea of which topics may require more attention because some students find them difficult. It goes further than that.
Homework should be assigned by experienced teachers who can provide specific feedback.
They should only give students assignments that are beneficial to their learning needs. And they should utilise them as a tool to address specific areas where they are struggling.
As Parents, They Must Help Their Children With Their Homework!
Although we’ve discussed the benefits of doing regular homework, some kids may struggle to stay motivated. These are some ways parents can encourage their children with their homework because they can play a significant part.
Study-friendly Environment
It will be easier for youngsters to focus if they have a designated area to complete their schoolwork. Ensure it has everything they will need for their assignments and is well-lit.
Regular Study Time
Children who work from home become accustomed to the regularity of it. While some kids may like to work in the morning, others favor the afternoon. Establish a schedule that allows your youngster to be most productive.
Verify That They Are Learning
If kids use their homework time to learn, then it is crucial. They won’t experience the advantages described above if you do the labor instead of them. You must be there to support them and ensure they comprehend the task to complete it independently.
Encourage Hard Work and Effort
A fantastic strategy to encourage kids to enjoy their schoolwork is to acknowledge and compliment the effort they put in. To further motivate students, display their stellar test results at home.
Develop a Plan
If they have a lot of homework, kids can become overworked. On nights when they have a lot of homework, assist them in developing a strategy and segmenting the work. The workload will become more manageable as a result. If this works well with your child, try it every time they sit down to work at home.
Young children’s motivation and productivity are enhanced when they comprehend the significance of homework and why it is frequently required. Additionally, it educates parents on how they can help their children. At Nord Anglia Education, we strongly emphasize bringing parents, teachers, and kids together to enhance student learning via homework. Explore our schools to learn more about what we teach and how we operate.
sometimes not only the students but their parents also start wondering why the teachers of the school and coaching institute give homework to their children.
They think that homework is a burden for students but once they understand why homework is important, they start paying more attention to it.
Also, they encourage their loved ones or kids to do homework.
Every coin has two faces. Similarly, some students consider homework as a burden while others take it as an interesting way to improve their knowledge.
So, what do you think about the same? Let us know your answer through your comments. I hope it will help you to learn why homework is important for us.
FAQs Related To Why Homework Is Important?
Is homework only beneficial for students.
No, it is not only beneficial for students. It also helps parents and teachers to cooperate with the students. This will help students to develop successfully.
Is homework mandatory?
The majority of schools have made homework a requirement of their curriculum. It was implemented as part of reforms and modernization policies designed to provide the best possible outcomes to the students.
- Tags Difference between Homework and Assignment , Why homework is important
- australia (2)
- duolingo (13)
- Education (270)
- General (74)
- How To (16)
- IELTS (127)
- Latest Updates (162)
- Malta Visa (6)
- Permanent residency (1)
- Programming (31)
- Scholarship (1)
- Sponsored (4)
- Study Abroad (187)
- Technology (12)
- work permit (8)
Recent Posts


The Liberty Champion
The official student newspaper of Liberty University
Is Homework Really Necessary?

Did you get all your homework done?
We’ve all heard that phrase one too many times before, and now it triggers your fight-or-flight response. Every waking thought is about an assignment you should be doing or that project you really should start but you just can’t bring yourself to face it. Is all this homework really necessary?
Unfortunately, it just might be. Is the homework itself the problem, or is it the amount we end up with after classes are over for the day and your bed is looking really comfy? To figure all this out we have to remember why we get homework in the first place and what school would be like without it.
In the very early 1900s, homework was actually considered unhealthy for children and was classified as child labor because it interfered with their ability to do chores around the house. The U.S. Department of Education called homework a tool for “boosting educational quality” when it was reinstated, and it became mandatory in 1986 after being rejected for so long, as recorded by the University of San Diego.
It’s always good to look at the pros and cons of something when deciding how you feel about it. So, what does homework do for us? Quite a few things actually.
First let’s address the elephant in the room. No one enjoys homework unless you’re a camp and outdoor adventure leadership (COAL) major. We all have something we would rather spend our time on; that’s just the way it is.
However, when that test rolls around, most of us are glad we stayed late at the library until we understood what we were reading. According to the University of San Diego, students only absorb 50% of what they hear in a class lecture. If that’s all you had to learn from, keeping your GPA above a 3.5 would be considered a superpower.
Whether we like it or not, homework helps us retain important information and truly grasp the concepts we are studying. Hearing about it once from your professor is great, but life as a college student is so busy that your chances of remembering everything you heard in all of your classes are next to none. Repetition is the key to retention, and other than experience training, studying the material you were given and doing your homework is how you’re going to graduate.
Then why is it such a problem? Why is it affecting people so negatively? No degree is worth your mental health; it’s time to look at the cons of homework.
I believe the real problem with homework is the amount of it. Yes, we need it to learn, but our brains can only handle so much at a time. Oftentimes the standard college workload demands that we push our minds past the limit or face a late penalty. This is what causes the exhaustion and resentment that we constantly push through for the sake of good grades and gold chords.
Studies conducted by the American Psychological Association and the U.S. Department of Health say shorter study sessions per day and more consistency over a longer period of time is the best way to retain information while not pushing yourself to your mental limit. However, there is so much to be done that studying for a mere three hours a day isn’t even practical.
Students would actually be able to study in a healthy way and retain information long term if we were not assigned and asked to complete in one week what psychological studies say should take at least two.
So, to answer the question: Yes, homework is definitely necessary. The real problem is how much we are required to process in such a short time.
As finals inch closer by the day, make a point to take care of your mind and give yourself breaks not only while studying but also from other things that can cloud your brain like social media. Coping with huge workloads is a process, so make lists, take deep breaths and get to bed on time. We’re gonna make it; I promise.
Barber is the off-campus news editor for the Liberty Champion
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

ChatGPT for Teachers
Trauma-informed practices in schools, teacher well-being, cultivating diversity, equity, & inclusion, integrating technology in the classroom, social-emotional development, covid-19 resources, invest in resilience: summer toolkit, civics & resilience, all toolkits, degree programs, trauma-informed professional development, teacher licensure & certification, how to become - career information, classroom management, instructional design, lifestyle & self-care, online higher ed teaching, current events, the homework debate: the case against homework.

This post has been updated as of December 2017.
It’s not uncommon to hear students, parents, and even some teachers always complaining about homework. Why, then, is homework an inescapable part of the student experience? Worksheets, busy work, and reading assignments continue to be a mainstay of students’ evenings.
Whether from habit or comparison with out-of-class work time in other nations, our students are getting homework and, according to some of them, a LOT of it. Educators and policy makers must ask themselves—does assigning homework pay off?
Is there evidence that homework benefits students younger than high school?
The Scholastic article Is Homework Bad? references Alfie Kohn’s book The Homework Myth: Why Our Kids Get Too Much of a Bad Thing , in which he says, “There is no evidence to demonstrate that homework benefits students below high school age.”
The article goes on to note that those who oppose homework focus on the drawbacks of significant time spent on homework, identifying one major negative as homework’s intrusion into family time. They also point out that opponents believe schools have decided homework is necessary and thus assign it simply to assign some kind of homework, not because doing the work meets specifically-identified student needs.
“Busy work” does not help students learn
Students and parents appear to carry similar critiques of homework, specifically regarding assignments identified as busy work—long sheets of repetitive math problems, word searches, or reading logs seemingly designed to make children dislike books.
When asked how homework can negatively affect children, Nancy Kalish, author of The Case Against Homework: How Homework is Hurting Our Children and What We Can Do About It , says that many homework assignments are “simply busy work” that makes learning “a chore rather than a positive, constructive experience.”
Commenters on the piece, both parents and students, tended to agree. One student shared that on occasion they spent more time on homework than at school, while another commenter pointed out that, “We don’t give slow-working children a longer school day, but we consistently give them a longer homework day.”
Without feedback, homework is ineffective
The efficacy of the homework identified by Kalish has been studied by policy researchers as well. Gerald LeTendre, of Penn State’s Education Policy Studies department points out that the shotgun approach to homework, when students all receive the same photocopied assignment which is then checked as complete rather than discussed individually with the student, is “not very effective.” He goes on to say that, “If there’s no feedback and no monitoring, the homework is probably not effective.”
Researchers from the Curry School of Education at the University of Virginia had similar findings in their study, “ When Is Homework Worth The Time ?” According to UVAToday, these researchers reported no “substantive difference” in the grades of students related to homework completion.
As researcher Adam Maltese noted, “Our results hint that maybe homework is not being used as well as it could be.” The report further suggested that while not all homework is bad, the type and quality of assignments and their differentiation to specific learners appears to be an important point of future research.
If homework is assigned, it should heighten understanding of the subject
The Curry School of Education report did find a positive association between standardized test performance and time spent on homework, but standardized test performance shouldn’t be the end goal of assignments—a heightened understanding and capability with the content material should.
As such, it is important that if/when teachers assign homework assignments, it is done thoughtfully and carefully—and respectful of the maximum times suggested by the National Education Association, about 10 minutes per night starting in the first grade, with an additional 10 minutes per year after.
Continue reading — The Homework Debate: How Homework Benefits Students
Monica Fuglei is a graduate of the University of Nebraska in Omaha and a current adjunct faculty member of Arapahoe Community College in Colorado, where she teaches composition and creative writing.
You may also like to read
- The Homework Debate: How Homework Benefits Students
- Ending the Homework Debate: Expert Advice on What Works
- Advice on Creating Homework Policies
- Elementary Students and Homework: How Much Is Too Much?
- Homework in Middle School: Building a Foundation for Study Skills
- Homework Helps High School Students Most — But it Must Be Purposeful
Categorized as: Tips for Teachers and Classroom Resources
Tagged as: Leadership and Administration , Pros and Cons , Teacher-Parent Relationships
- Certificates in Administrative Leadership
- Teacher Resources for Social-Emotional Develo...
- Degrees and Certificates for Teachers & Educa...

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Yes, and the stories we hear of kids being stressed out from too much homework—four or five hours of homework a night—are real. That's problematic for physical and mental health and overall well-being. But the research shows that higher-income students get a lot more homework than lower-income kids.
Check out 20 reasons why homework is good:-. 1. Reinforcement of Classroom Learning. Homework isn't just a mundane task; it's your secret weapon for becoming a true subject matter aficionado. It's the place where classroom theories transform into real-world skills.
Too much homework may diminish its effectiveness. While research on the optimum amount of time students should spend on homework is limited, there are indications that for high school students, 1½ to 2½ hours per night is optimum. Middle school students appear to benefit from smaller amounts (less than 1 hour per night).
5. Boosts Memory Retention. Homework provides practice time to recall concepts discussed in class, thereby enabling students to memorize facts and figures taught at school. One of the advantages of homework is that it sharpens memory power and concentration. 6. Enables Parents to Track a Student's Performance.
Homework is a powerful tool to help narrow these inequities, giving children from all backgrounds the opportunity to keep learning when they are not in school. At Success Academy, the charter school network I founded and lead, we seek to develop students as lifelong learners who have the confidence and curiosity to pursue and build knowledge in ...
It turns out that parents are right to nag: To succeed in school, kids should do their homework. Duke University researchers have reviewed more than 60 research studies on homework between 1987 and 2003 and concluded that homework does have a positive effect on student achievement. Harris Cooper, a professor of psychology, said the research ...
After two hours, however, achievement doesn't improve. For high schoolers, Cooper's research suggests that two hours per night is optimal. If teens have more than two hours of homework a night, their academic success flatlines. But less is not better. The average high school student doing homework outperformed 69 percent of the students in ...
Many school district policies state that high school students should expect about 30 minutes of homework for each academic course they take, a bit more for honors or advanced placement courses. These recommendations are consistent with the conclusions reached by our analysis. Practice assignments do improve scores on class tests at all grade ...
That takes homework and the acknowledgment that sometimes a student can get a question wrong and, with proper instruction, eventually get it right. Students, read the entire article, then tell us ...
The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein, co-director of the Center on School, Family, and Community Partnerships at Johns Hopkins University. "It's always been the case that parents, kids—and sometimes teachers, too—wonder if this is just busy work ...
Why Homework Should Be Balanced. Homework can boost learning, but doing too much can be detrimental. The National PTA and National Education Association support the "10-minute homework rule," which recommends 10 minutes of homework per grade level, per night (10 minutes for first grade, 20 minutes for second grade, and so on, up to two ...
Here are some key reasons why homework is valuable: Reinforces Learning: Homework helps reinforce what was taught in class, allowing students to practice and apply knowledge, ensuring a deeper understanding and retention of the material. Promotes Discipline and Time Management: Regular homework assignments teach students to manage their time ...
A TIME cover in 1999 read: "Too much homework! How it's hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.". The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push ...
Homework also helps students develop key skills that they'll use throughout their lives: Accountability. Autonomy. Discipline. Time management. Self-direction. Critical thinking. Independent problem-solving. The skills learned in homework can then be applied to other subjects and practical situations in students' daily lives.
Homework is an opportunity to learn and retain information in an environment where they feel most comfortable, which can help accelerate their development. 5. Using Learning Materials. Throughout a child's education, understanding how to use resources such as libraries and the internet is important. Homework teaches children to actively ...
An education expert weighs in. The necessity of homework has been a subject of debate since at least as far back as the 1890s, according to Joyce L. Epstein, co-director of the Center on School ...
Too much, however, is harmful. And homework has a greater positive effect on students in secondary school (grades 7-12) than those in elementary. "Every child should be doing homework, but the ...
"On the other hand, a superstar lecturer can explain things in such a way as to make students feel like they are learning more than they actually are." Director of sciences education and physics lecturer Logan McCarty is the co-author of a new study that says students who take part in active learning actually learn more than they think they do.
The research cited by educators just doesn't seem to make sense. If a child wants to learn to play the violin, it's obvious she needs to practice at home between lessons (at least, it's ...
Homework is a good opportunity to connect parents, classmates, and siblings with your education. The better your support network, the more likely you are to succeed in class. Homework, however tedious it might be, teaches responsibility and accountability. For some classes, homework is an essential part of learning the subject matter.
Homework allows for more time to complete the learning process. School hours are not always enough time for students to really understand core concepts, and homework can counter the effects of time shortages, benefiting students in the long run, even if they can't see it in the moment. 6. Homework Reduces Screen Time.
With homework, students can learn to make schedules for all work. It helps students to solve the problem on their own. It helps students to find, and organize good information. Homework can help to develop a good sense of personal responsibility for learning. It also helps to learn using libraries and other resources.
If that's all you had to learn from, keeping your GPA above a 3.5 would be considered a superpower. Whether we like it or not, homework helps us retain important information and truly grasp the ...
According to UVAToday, these researchers reported no "substantive difference" in the grades of students related to homework completion. As researcher Adam Maltese noted, "Our results hint that maybe homework is not being used as well as it could be.". The report further suggested that while not all homework is bad, the type and quality ...