- Subscribe to BBC Science Focus Magazine
- Previous Issues
- Future tech
- Everyday science
- Planet Earth
- Newsletters
© Getty Images

Should homework be banned?
Social media has sparked into life about whether children should be given homework - should students be freed from this daily chore? Dr Gerald Letendre, a professor of education at Pennsylvania State University, investigates.
We’ve all done it: pretended to leave an essay at home, or stayed up until 2am to finish a piece of coursework we’ve been ignoring for weeks. Homework, for some people, is seen as a chore that’s ‘wrecking kids’ or ‘killing parents’, while others think it is an essential part of a well-rounded education. The problem is far from new: public debates about homework have been raging since at least the early-1900s, and recently spilled over into a Twitter feud between Gary Lineker and Piers Morgan.
Ironically, the conversation surrounding homework often ignores the scientific ‘homework’ that researchers have carried out. Many detailed studies have been conducted, and can guide parents, teachers and administrators to make sensible decisions about how much work should be completed by students outside of the classroom.
So why does homework stir up such strong emotions? One reason is that, by its very nature, it is an intrusion of schoolwork into family life. I carried out a study in 2005, and found that the amount of time that children and adolescents spend in school, from nursery right up to the end of compulsory education, has greatly increased over the last century . This means that more of a child’s time is taken up with education, so family time is reduced. This increases pressure on the boundary between the family and the school.
Plus, the amount of homework that students receive appears to be increasing, especially in the early years when parents are keen for their children to play with friends and spend time with the family.
Finally, success in school has become increasingly important to success in life. Parents can use homework to promote, or exercise control over, their child’s academic trajectory, and hopefully ensure their future educational success. But this often leaves parents conflicted – they want their children to be successful in school, but they don’t want them to be stressed or upset because of an unmanageable workload.
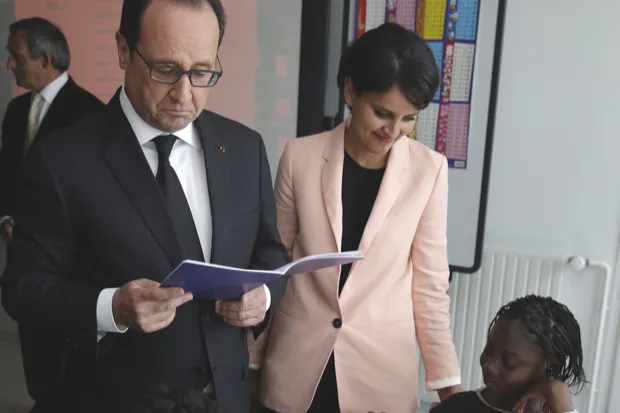

However, the issue isn’t simply down to the opinions of parents, children and their teachers – governments also like to get involved. In the autumn of 2012, French president François Hollande hit world headlines after making a comment about banning homework, ostensibly because it promoted inequality. The Chinese government has also toyed with a ban, because of concerns about excessive academic pressure being put on children.
The problem is, some politicians and national administrators regard regulatory policy in education as a solution for a wide array of social, economic and political issues, perhaps without considering the consequences for students and parents.
Does homework work?
Homework seems to generally have a positive effect for high school students, according to an extensive range of empirical literature. For example, Duke University’s Prof Harris Cooper carried out a meta-analysis using data from US schools, covering a period from 1987 to 2003. He found that homework offered a general beneficial impact on test scores and improvements in attitude, with a greater effect seen in older students. But dig deeper into the issue and a complex set of factors quickly emerges, related to how much homework students do, and exactly how they feel about it.
In 2009, Prof Ulrich Trautwein and his team at the University of Tübingen found that in order to establish whether homework is having any effect, researchers must take into account the differences both between and within classes . For example, a teacher may assign a good deal of homework to a lower-level class, producing an association between more homework and lower levels of achievement. Yet, within the same class, individual students may vary significantly in how much homework improves their baseline performance. Plus, there is the fact that some students are simply more efficient at completing their homework than others, and it becomes quite difficult to pinpoint just what type of homework, and how much of it, will affect overall academic performance.
Over the last century, the amount of time that children and adolescents spend in school has greatly increased
Gender is also a major factor. For example, a study of US high school students carried out by Prof Gary Natriello in the 1980s revealed that girls devote more time to homework than boys, while a follow-up study found that US girls tend to spend more time on mathematics homework than boys. Another study, this time of African-American students in the US, found that eighth grade (ages 13-14) girls were more likely to successfully manage both their tasks and emotions around schoolwork, and were more likely to finish homework.
So why do girls seem to respond more positively to homework? One possible answer proposed by Eunsook Hong of the University of Nevada in 2011 is that teachers tend to rate girls’ habits and attitudes towards work more favourably than boys’. This perception could potentially set up a positive feedback loop between teacher expectations and the children’s capacity for academic work based on gender, resulting in girls outperforming boys. All of this makes it particularly difficult to determine the extent to which homework is helping, though it is clear that simply increasing the time spent on assignments does not directly correspond to a universal increase in learning.
Can homework cause damage?
The lack of empirical data supporting homework in the early years of education, along with an emerging trend to assign more work to this age range, appears to be fuelling parental concerns about potential negative effects. But, aside from anecdotes of increased tension in the household, is there any evidence of this? Can doing too much homework actually damage children?
Evidence suggests extreme amounts of homework can indeed have serious effects on students’ health and well-being. A Chinese study carried out in 2010 found a link between excessive homework and sleep disruption: children who had less homework had better routines and more stable sleep schedules. A Canadian study carried out in 2015 by Isabelle Michaud found that high levels of homework were associated with a greater risk of obesity among boys, if they were already feeling stressed about school in general.
For useful revision guides and video clips to assist with learning, visit BBC Bitesize . This is a free online study resource for UK students from early years up to GCSEs and Scottish Highers.
It is also worth noting that too much homework can create negative effects that may undermine any positives. These negative consequences may not only affect the child, but also could also pile on the stress for the whole family, according to a recent study by Robert Pressman of the New England Centre for Pediatric Psychology. Parents were particularly affected when their perception of their own capacity to assist their children decreased.
What then, is the tipping point, and when does homework simply become too much for parents and children? Guidelines typically suggest that children in the first grade (six years old) should have no more that 10 minutes per night, and that this amount should increase by 10 minutes per school year. However, cultural norms may greatly affect what constitutes too much.
A study of children aged between 8 and 10 in Quebec defined high levels of homework as more than 30 minutes a night, but a study in China of children aged 5 to 11 deemed that two or more hours per night was excessive. It is therefore difficult to create a clear standard for what constitutes as too much homework, because cultural differences, school-related stress, and negative emotions within the family all appear to interact with how homework affects children.
Should we stop setting homework?
In my opinion, even though there are potential risks of negative effects, homework should not be banned. Small amounts, assigned with specific learning goals in mind and with proper parental support, can help to improve students’ performance. While some studies have generally found little evidence that homework has a positive effect on young children overall, a 2008 study by Norwegian researcher Marte Rønning found that even some very young children do receive some benefit. So simply banning homework would mean that any particularly gifted or motivated pupils would not be able to benefit from increased study. However, at the earliest ages, very little homework should be assigned. The decisions about how much and what type are best left to teachers and parents.
As a parent, it is important to clarify what goals your child’s teacher has for homework assignments. Teachers can assign work for different reasons – as an academic drill to foster better study habits, and unfortunately, as a punishment. The goals for each assignment should be made clear, and should encourage positive engagement with academic routines.

Parents should inform the teachers of how long the homework is taking, as teachers often incorrectly estimate the amount of time needed to complete an assignment, and how it is affecting household routines. For young children, positive teacher support and feedback is critical in establishing a student’s positive perception of homework and other academic routines. Teachers and parents need to be vigilant and ensure that homework routines do not start to generate patterns of negative interaction that erode students’ motivation.
Likewise, any positive effects of homework are dependent on several complex interactive factors, including the child’s personal motivation, the type of assignment, parental support and teacher goals. Creating an overarching policy to address every single situation is not realistic, and so homework policies tend to be fixated on the time the homework takes to complete. But rather than focusing on this, everyone would be better off if schools worked on fostering stronger communication between parents, teachers and students, allowing them to respond more sensitively to the child’s emotional and academic needs.
- Five brilliant science books for kids
- Will e-learning replace teachers?
Follow Science Focus on Twitter , Facebook , Instagram and Flipboard
Share this article

- Terms & Conditions
- Privacy policy
- Cookies policy
- Code of conduct
- Magazine subscriptions
- Manage preferences
Headteacher-Trusted Tutoring
"This is one of the most effective interventions I have come across in my 27 years of teaching."
Free CPD and leadership support
All the latest guides, articles and news to help primary, secondary and trust leaders support your staff and pupils

The Great British Homework Debate 2024 – Is It Necessary At Primary School?
Alexander Athienitis
The homework debate is never much out of the news. Should homework be banned? Is homework at primary school a waste of time? Do our children get too much homework?
Not long ago, UK-based US comedian Rob Delaney set the world alight with a tweet giving his own personal view of homework at primary school. We thought, as an organisation that provides maths homework support on a weekly basis, it was time to look at the facts around the homework debate in primary schools as well as, of course, reflecting the views of celebrities and those perhaps more qualified to offer an opinion!
Here’s how Rob Delaney kicked things off
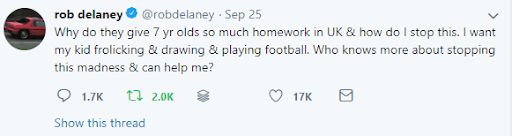
Gary Lineker leant his support with the following soundbite:

And even Piers Morgan weighed in, with his usual balance of tact and sensitivity:

A very experienced and knowledgeable Headteacher, Simon Smith, who has a well-earned following on Twitter (for someone working in education, not hosting Match of the Day) also put his neck on the line and, some might think controversially, agreed with the golden-heeled Crisp King of Leicester…

Fortunately Katharine Birbalsingh, Conservative Party Conference keynote speaker and Founding Headteacher of the Michaela School, was on hand to provide the alternative view on the importance of homework. Her op-ed piece in the Sun gave plenty of reasons why homework should not be banned.
She was informative and firm in her article stating: “Homework is essential for a child’s education because revisiting the day’s learning is what helps to make it stick.”

KS2 Maths Games and Activities Pack
A FREE downloadable games and activity pack, including 20 home learning maths activities for KS2 children. Bring maths into your home in a fun way.
How much homework do UK primary school children get?
Sadly, there’s little data comparing how much homework primary school-aged children in the UK and across the globe complete on a weekly basis. A study of teenagers used by The Telegraph shows that American high-schoolers spend an average of 6.1 hours per week compared with 4.9 hours per week of homework each week for UK-based teens.
Up until 2012, the Department of Education recommended an hour of homework a week for primary school Key Stage 1 children (aged 4 to 7) and half an hour a day for primary school Key Stage 2 children (aged 7-11). Many primary schools still use this as a guideline.
Teachers, parents and children in many schools across the land have seen more changes of homework policy than numbers of terms in some school years.
A ‘no-homework’ policy pleases only a few; a grid of creative tasks crowd-sourced from the three teachers bothered to give their input infuriates many (parents, teachers and children alike). For some parents, no matter how much homework is set, it’s never enough; for others, even asking them to fill in their child’s reading record once a week can be a struggle due to a busy working life.
Homework is very different around the world
We’d suggest that Piers Morgan’s argument for homework in comparing the UK’s economic and social progress with China’s in recent years based on total weekly homework hours is somewhat misguided – we can’t put their emergence as the world’s (if not already, soon to be) leading superpower exclusively down to having their young people endure almost triple the number of hours spent completing homework as their Western counterparts.
Nonetheless, there’s certainly a finer balance to strike between the 14 hours a week suffered by Shanghainese school-attendees and none whatsoever. Certainly parents in the UK spend less time each week helping their children than parents in emerging economies such as India, Vietnam and Colombia (Source: Varkey Foundation Report).
Disadvantages of homework at primary school
Delaney, whose son attends a London state primary school, has made it plain that he thinks his kids get given too much homework and he’d rather have them following more active or creative pursuits: drawing or playing football. A father of four sons and a retired professional footballer Gary Linaker was quick to defend this but he also has the resources to send his children to top boarding schools which generally provide very structured homework or ‘prep’ routines.
As parents Rob and Gary are not alone. According to the 2018 Ofsted annual report on Parents Views more than a third of parents do not think homework in primary school is helpful to their children. They cite the battles and arguments it causes not to mention the specific challenges it presents to families with SEND children many of whom report serious damage to health and self-esteem as a result of too much or inappropriate homework.
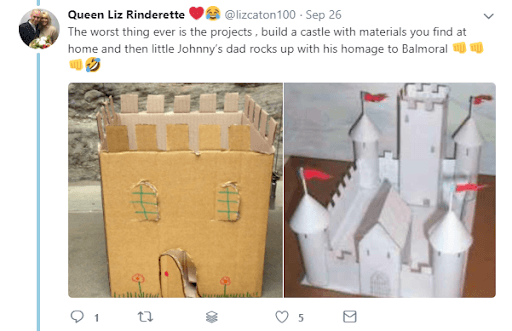
It’s a truism among teachers that some types of homework tells you very little about what the child can achieve and much more about a parent’s own approach to the work. How low does your heart sink when your child comes back with a D & T project to create Stonehenge and you realise it’s either an all-nighter with glue, cardboard and crayons for you, or an uncompleted homework project for your child!
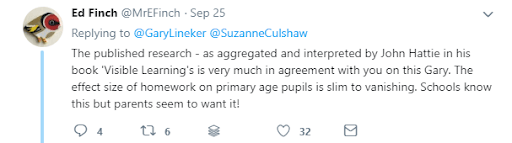
Speaking with our teacher hats on, we can tell you that homework is often cited in academic studies looking at academic progress in primary school-aged children as showing minimal to no impact.
Back on Twitter, a fellow teacher was able to weigh-in with that point:
Benefits of homework at primary school
So what are the benefits of homework at primary school? According to the Education Endowment Foundation (EEF) (the key research organisations dedicated to breaking the link between family income and educational achievement) the impact of homework at primary is low, but it also doesn’t cost much.
They put it at a “+2 months” impact against a control of doing nothing. To put this into context, 1-to-1 tuition is generally seen as a +5 months impact but it’s usually considered to be expensive.
“There is some evidence that when homework is used as a short and focused intervention it can be effective in improving students’ attainment … overall the general benefits are likely to be modest if homework is more routinely set.”
Key to the benefit you’ll see from homework is that the task is appropriate and of good quality. The quantity of homework a pupil does is not so important. In this matter Katharine Birbalsingh is on the money. Short focused tasks which relate directly to what is being taught, and which are built upon in school, are likely to be more effective than regular daily homework.
In our view it’s about consolidation. So focusing on a few times tables that you find tricky or working through questions similar to what you’ve done in class that day or week often can be beneficial. 2 hours of worksheets on a Saturday when your child could be outside having fun and making friends probably isn’t. If you really want them to be doing maths, then do some outdoor maths with them instead of homework !
At Third Space Learning we believe it’s all about balance. Give the right sort of homework and the right amount at primary school and there will be improvements, but much of it comes down to parental engagement.
One of our favourite ways to practise maths at home without it become too onerous is by using educational games. Here are our favourite fun maths games , some brilliant KS2 maths games , KS1 maths games and KS3 maths games for all maths topics and then a set of 35 times tables games which are ideal for interspersing with your regular times tables practice. And best of all, most of them require no more equipment than a pen and paper or perhaps a pack of cards.
Homework and parents
One of the key benefits cited by EEF is in regard to parental engagement. Time after time, the greatest differentiator between children who make great progress at school – and those, frankly – who don’t is due to the same factor in the same studies: parental engagement .
It is a fair assumption that if a parent is engaged in their child’s learning, they’re probably going to be the same parents who encourage and support their child when they’re completing their homework.
Whereas parents who are disengaged with their child’s school and schooling – for whatever reason (sorry, Piers, it’s rarely due to laziness), are highly unlikely to be aware of what homework gets set each week, let alone to be mucking in with making sure it gets handed in completed and on time.
We also encounter time and again, the issue of parents’ own lack of confidence in maths. A survey by Pearson found that:
- 30 percent of parents “don’t feel confident enough in their own maths skills to help their children with their primary school maths homework”
- 53 per cent insisted they struggled to understand the new maths teaching methods used in modern classrooms. Fortunately that’s what we’re here to address.
Setting the right homework at primary school can be tricky
Although we disagree with Piers, we can see what he may be driving at in terms of setting appropriate homework.
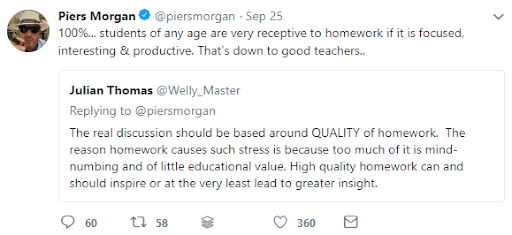
The question quickly becomes what would Piers think of as being ‘interesting’ homework, and if all four of his children would agree upon the same thing being ‘interesting’.
That’s the problem.
One would imagine Piers would find it hard enough finding one task to satisfy the interest of all of his four children – it’s almost impossible to find a task that will engage the interest of 30 or more children in their out of school hours.
Each with different emotional, behavioural and learning needs, then sprinkle in the varying levels of poverty each family suffers (be it financial or in terms of time), and you can see how it isn’t just about being a good or bad teacher – whatever that means – in regards to being able to set Morgan-approved homework tasks.
What does this mean for my child?
Ultimately, the question at the top of mind whenever a parent thinks about homework is a more general one – am I doing the best for my child?
Although the world is changing at a faster pace than ever before in human history, what’s best for children hasn’t changed that much (if at all).
One-to-one support is best, and young people benefit most from adult-child conversations where they acquire new vocabulary and language structures to form and share their thoughts and opinions.
These insights – that one-to-one support is best and that regular, structured adult-child conversations are life-changing within a child’s development – are what inspired us to create Third Space Learning.
A platform where children can engage with a community of specialist tutors in a safe, structured learning environment where they are able to engage in one-to-one conversations that enable them to progress in their learning with confidence.
- How to help your child with their maths homework – A parents guide
- The Best Homework Hacks: 18 Tips And Tricks To Help Busy Parents Get It Done Faster!
- The 20 Most Recommended Teaching Blogs for UK Teachers and School Leaders
DO YOU HAVE STUDENTS WHO NEED MORE SUPPORT IN MATHS?
Every week Third Space Learning’s maths specialist tutors support thousands of students across hundreds of schools with weekly one to one tuition designed to plug gaps and boost progress.
Since 2013 these personalised one to one lessons have helped over 150,000 primary and secondary students become more confident, able mathematicians.
Learn about our experience with schools or request a personalised quote for your school to speak to us about your school’s needs and how we can help.
Related articles
Teacher Workload Reduction: 7 Strategies School Leaders Can Implement Today

Has Teaching Post-Covid Lockdown Felt Different? You Are Not Alone

Making The Transition From Primary To Secondary School During Lockdown

SLT School Leadership Toolkit for Headteachers and Subject Leaders
The Ultimate Guide to Effective Maths Interventions [FREE]
Find out how to plan, manage, and teach one to one (and small group) maths interventions in primary and secondary schools.
Includes a 20 point checklist of techniques to improve your one to one teaching.
Privacy Overview

Homework should be banned – it’s taking over my kids’ lives

Share this with
‘What do you have to do tonight?’
That’s the first question I ask my two kids, aged nine and 14, when they get in from school. Not how they are, or how their day was – but, inevitably, what homework they’ve been given.
It’s not something I like asking, but it’s necessary so I can plan each evening. Still, hearing how much they’ve got to fit in before bed makes me feel stressed and on edge.
Recently, I was flicking through a newspaper when I saw Kirstie Allsopp of Location, Location, Location fame uttering hallowed words about her distaste for the after school activity.
She said that one of her ‘greatest regrets’ was making her children do homework when they were growing up – and she wished she’d let them off.
‘The tears, the time together lost, for many families [it] causes real, daily unhappiness to no good end,’ she added.
And I agree with her.
My kids do eight hours at school for five days a week, with a 40 minute commute. From the moment they get in, it’s ‘quickly eat, then we can do your homework.’ There’s no time to chat over dinner in my house, or spend quality time together.
For my nine-year-old, it’s not so bad: reading, spellings. But my 14-year-old seems to have bucketloads of the stuff. Once he’s eaten, finished his schoolwork, prepared for the next day and practised music, it’s 10pm. There’s often no down time for him.
Both of my kids have already been to school for a full day of learning, so is homework really that necessary?
Weekends are no exception, with me often sitting down with my daughter to go over her maths and English in more detail.

Those who extol these assignments say that they instill a sense of discipline; teaching children how to manage their own time and schedule properly. Others say it robs kids of their free time, causes rifts in families and is of no use whatsoever when most students are only assessed in exams anyway.
In my household, homework makes my stomach churn. I worry I am missing out on normal things like chatting about their day.
I don’t see what it achieves that reading a text, or a book each night instead, could not. I think this would be better than lots of individual tasks across a plethora of subjects.
After a long day, homework is often when done exhausted, hungry or just tired – and does not glean the best work. The effort might be there, but certainly not the quality. How is that a fair representation of talent?
And how can homework really ever be fair? Some children are supported at home by their parents, who perhaps know a thing or two about certain lessons, some aren’t.
Some live in quiet households where it’s conducive to homework, some live with noisy siblings.
Some live in homes where they’re fed and told to get on with it; others are young carers, having to make their own meals. Some even come home to an empty house, with their parents at work.
I can’t complain about my kids’ school – they’re amazing teachers who work so hard. But sending my kids home with such heavy burdens takes its toll.
I’ve lost count of the number of times my son has said: ‘Can I go swimming? Can I meet a friend? Can I watch this TV programme?’ and I’ve had to say no because he has homework to do.
I try to help where I can, of course. English and history, I’m fine with. But maths? I’m as good as a chocolate teapot.
I even asked a few friends who are teachers what they thought of homework and many agreed that it was a waste of time, adding that they already assess kids enough in school with classwork, coursework and exams.
‘It really is unnecessary,’ one told me guiltily. ‘It really doesn’t count for much.’
I’d like to see a total ban, or if not that, a steep decline in the sheer amount given.
So, next week, as my kids get in, drop their bags and head for the fridge – I’ll try to bite my tongue. Instead of my usual first question, I’ll ask them about their day. Instead of telling them to wolf down dinner to get to the books faster, I’ll encourage a slower meal and a chat over the table.
Because, as Kirstie Allsopp said, we can’t get these years back.
Our kids are only young once, and for so long. Their days are packed with learning and their home should be a haven where they can unwind, and leave school behind.
The Truth Is...
Metro.co.uk’s weekly The Truth Is… series seeks to explore anything and everything when it comes to life’s unspoken truths and long-held secrets. Contributors will challenge popular misconceptions on a topic close to their hearts, confess to a deeply personal secret, or reveal their wisdom from experience – good and bad – when it comes to romance or family relationships.
If you would like your share your truth with our readers, email [email protected] .
MORE : ‘I gave birth to someone else’s baby’: What it’s really like to be a surrogate
MORE : What to expect when buying a property: Make sure to do your homework
MORE : Parents turn to Alexa and Google because kids’ homework is too hard
Sign up to our guide to what’s on in London, trusted reviews, brilliant offers and competitions. London’s best bits in your inbox
By ticking this box, you confirm you are over the age of 18*. Privacy Policy »
Get us in your feed
Blog The Education Hub
This blog post was published under the 2015-2024 conservative administration.
https://educationhub.blog.gov.uk/2018/10/28/education-secretary-i-trust-head-teachers-to-decide-their-homework-policies/
Education Secretary: I trust head teachers to decide their homework policies

Education Secretary Damian Hinds has today written an op-ed for the Sunday Times setting out his position on homework, which has been followed up with a news story . He says that ultimately up to heads and school leaders to decide whether to set homework and what the consequences should be if children do not complete their homework set.
The Education Secretary said:
One of the tougher things I’ve taken on recently was solving a ‘part-whole model’, involving nine ducks and a jagged shoreline. This was, I should clarify, a piece of homework for one of my children, not something called for in my day job. Homework is a staple of school life, and of home life. Parents know this. After all, almost every one of us will have done homework ourselves as a child and most of us will be drafted in to help with it at some point as a parent, carer or grandparent. There has been some high-profile interest of late on social media suggesting that homework is bad for children, at least in the first half of schooling. There have even been subsequent questions about its legal status. Just to be clear: schools are not obliged to set homework, and some don’t. But when schools do set homework, children do need to do it. We trust individual school head teachers to decide what their policy on homework will be, and what happens if pupils don’t do what’s set. Policy and approach won’t be the same in all cases. Autonomy for schools, and the diversity that comes with it, is at the heart of this government’s approach to education. Of course, schools should, and do, communicate with parents. Parents need to know where they stand. Teachers obviously need to be realistic about expectations, and they know this. Obviously, no one wants children spending an inordinate amount of time every night doing homework. Clearly, there are other important things to do, too – like playing outside, family time, eating together. Good homework policies avoid excessive time requirements – focusing on quality rather than quantity and making sure that there is a clear purpose to any homework set. In 2011 we helped set up the Education Endowment Foundation as an independent expert body to study and advise on “what works” in education. It has established that, although there are more significant educational improvements derived from homework at secondary school, there can still be a modest but positive impact at primary level. Homework isn’t just some joyless pursuit of knowledge. It’s an integral part of learning. Beyond the chance to practice and reinforce what you’ve learned in class, it’s also an opportunity to develop independent study and application – and character traits like perseverance. Children need to know that what they do has consequences. At secondary school, if a pupil doesn’t complete their homework, they risk falling behind. They may also hold up others – clearly it is harder for the teacher to keep the whole class moving forward if some are doing the homework and others aren’t. At primary school, too, we all want our children to develop their knowledge – but we also want them to develop values. Homework set at primary school is likely to be of relatively shorter duration. But if a child is asked to do it and they don’t, for that to have no consequence would not be a positive lesson. Ultimately, of course, the responsibility for a child’s educational development is a shared one. Parental involvement makes a big difference, from the very earliest stage. In the early years parents can support their child’s development through story telling, singing or reading together. Later on, homework can give an ‘in’ for continued involvement in learning. Homework should not in general require adult help, and with today’s busy lives it certainly can be hard to find the time. But I know as a parent that we are called on as reinforcements if an assignment is especially challenging. Other times, it falls to parents just to give a nudge. I want all children to enjoy their progress through school and they will have a much better chance of doing this if they are not having to play catch-up during the day. Parents need to trust teachers, with all their experience of teaching and learning – and know that their child’s homework is not just proportionate, but will be of lasting benefit. From motivation and self-discipline to the wonder of independent learning, homework can teach children about far more than the part-whole model, some ducks and a jagged shoreline.
Follow us on Twitter and don't forget to sign up for email alerts .
Sharing and comments
Share this page, related content and links, about the education hub.
The Education Hub is a site for parents, pupils, education professionals and the media that captures all you need to know about the education system. You’ll find accessible, straightforward information on popular topics, Q&As, interviews, case studies, and more.
Please note that for media enquiries, journalists should call our central Newsdesk on 020 7783 8300. This media-only line operates from Monday to Friday, 8am to 7pm. Outside of these hours the number will divert to the duty media officer.
Members of the public should call our general enquiries line on 0370 000 2288.
Sign up and manage updates
Follow us on social media, search by date.
| M | T | W | T | F | S | S |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 6 | 7 | |||||
| 13 | 14 | |||||
| 20 | 21 | |||||
| 27 | ||||||
| 31 | ||||||
Comments and moderation policy
The pros and cons of homework
Should schoolwork be left at the school gate?
- Newsletter sign up Newsletter


1. Pro: improves academic achievement
2. con: risk of artificial intelligence, 3. pro: other benefits of homework, 4. con: less time with family and friends, 5. pro: parent involvement, 6. con: stress for students and teachers.
Homework should be scrapped to give children more time for “other creative things”, the president of Ireland has said.
UK pupils do more homework than many European countries Irish president Michael D Higgins begins historic UK visit
Speaking to Irish broadcaster RTE, Michael D. Higgins said school work should be “finished at the school” rather than at home, “an utterance likely to be seized upon by children for years to come in classrooms far beyond the shores of the Emerald Isle”, said the Independent .
Here are some of the benefits and some of the negative effects of homework for schoolchildren.
Subscribe to The Week
Escape your echo chamber. Get the facts behind the news, plus analysis from multiple perspectives.

Sign up for The Week's Free Newsletters
From our morning news briefing to a weekly Good News Newsletter, get the best of The Week delivered directly to your inbox.
A 2006 meta-analysis of research by Duke University in North Carolina found that children who have homework perform better academically at school. But it doesn’t benefit all students equally, the research found. The correlation was stronger for older students (12 and over) than younger students.
But the evidence is far from conclusive over whether homework really does increase student achievement. Other studies have found that it has a positive effect only under certain conditions, while others have found negative effects, and some studies suggest homework does not affect student achievement at all.
The arrival of highly sophisticated artificial intelligence chatbots, such as ChatGPT , could make it easier for students to cheat on their essays or homework – or even force teachers and professors to scrap homework altogether.
ChatGPT has been “trained on a gigantic sample of text from the internet” and can “understand human language, conduct conversations with humans and generate detailed text that many have said is human-like and quite impressive”, said the Daily Mail .
Kevin Bryan, an associate professor of strategic management at the University of Toronto, tweeted that he was “shocked” by the capabilities of ChatGPT after challenging the AI to answer numerous exam questions and found that it gave A-grade answers.
Evidence suggests that homework can bring non-academic benefits, particularly for younger school students. These include “learning the importance of responsibility, managing time, developing study habits, and staying with a task until it is completed”, said Reading Rockets , a national public media literacy initiative in the US.
The British Council agreed that it helps to develop “study habits and independent learning”, as well as helping students to “retain information taught in the classroom” and involving parents in learning.
TV presenter Kirstie Allsopp weighed in on the debate recently, urging parents to “enjoy the weekend” with their children, branding homework a “waste of time”.
“Find a book, cuddle up and read it together, or watch Winterwatch, or cook something with kids doing all the weighing and chopping. Then put that in the homework diary and enjoy your weekend with your kids,” she wrote on Twitter .
“There is nothing better for children than spending time with you, talking, doing and learning at the same time,” she said. “Following a recipe is reading, maths, science and fine motor skills in one activity.”
Homework can be a good way for parents to stay up to date with what their child is being taught in class as well as monitor their progress. But the extent to which parental involvement with homework is beneficial for children is still a matter of debate.
According to Reading Rockets, some studies show that homework assignments that require interactions between students and parents are “more likely to be turned in” than assignments that don’t require parental input. But other studies have found that “parent involvement in homework has no impact on student achievement”.
Educators and parents responded to President Higgins’ comments to say homework is a source of stress for all involved.
Replying to a Facebook post by Hull Live , one teacher said it was “a pain sourcing, copying, chasing and marking it”, while other parents said homework placed undue stress on young children. “I think they do enough work in the school hours as it is,” said one parent, while another commented: “Children need to switch off when they get home. No wonder children suffer mental health issues, they are burnt out before they reach secondary school.”
Sign up for Today's Best Articles in your inbox
A free daily email with the biggest news stories of the day – and the best features from TheWeek.com
Sorcha Bradley is a writer at The Week and a regular on “The Week Unwrapped” podcast. She worked at The Week magazine for a year and a half before taking up her current role with the digital team, where she mostly covers UK current affairs and politics. Before joining The Week, Sorcha worked at slow-news start-up Tortoise Media. She has also written for Sky News, The Sunday Times, the London Evening Standard and Grazia magazine, among other publications. She has a master’s in newspaper journalism from City, University of London, where she specialised in political journalism.

The Week Recommends From giant tortoises to colourful reef fish, the private island is rich in wildlife – and quiet luxury
By Natasha Langan Published 21 August 24

In the Spotlight Eye-catching deal for use of content to train chatbots, but other publishers are worried they're signing away their souls
By Harriet Marsden, The Week UK Published 21 August 24

The Explainer Nationwide outrage at a brutal attack on a female medical student raises familiar problems for country
By Richard Windsor, The Week UK Published 21 August 24

In the Spotlight The practice is barely tracked or regulated in the US and can easily conceal abuse
By Anya Jaremko-Greenwold, The Week US Published 28 May 24

Pros and Cons Do rules around clothing promote discipline and inclusion or are they a pricey constraint on individuality?
By Harriet Marsden Published 1 August 23

Speed Read New study suggests breast milk could help secure a child top grades in GCSEs
By Rebekah Evans Published 6 June 23

Pros and Cons For children and teachers the holidays are a welcome break from school, but for many parents they can prove a headache
By Richard Windsor Published 6 April 23

Pros and Cons Tony Blair has called for ‘radical’ education reform but others want a more cautious approach
By The Week Staff Published 25 August 22

Pros and Cons Record-high costs and competition leave A-level students questioning worth of a degree
By Harriet Marsden Last updated 24 August 23

feature Proposal to ease staff-to-child ratio in nurseries has been met with anger
By Kate Samuelson Published 4 July 22

Pros and Cons Truss tasks ministers with planning new wave of selective establishments
By The Week Staff Last updated 4 October 22
- Contact Future's experts
- Terms and Conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Cookie Policy
- Advertise With Us
The Week is part of Future plc, an international media group and leading digital publisher. Visit our corporate site . © Future US, Inc. Full 7th Floor, 130 West 42nd Street, New York, NY 10036.
- Search Results
Caitlin Moran on why homework should be banned
Hi, I’m Caitlin Moran, and welcome to this week’s Moranifesto.
On the 3rd May, the day this blog goes online, a national protest has been suggested by parents, despairing of how pressurised their children’s education has become. A group called ‘Let Kids Be Kids’ are calling on parents to remove their children from school for the day and let them run around in the sun, or more realistically, snow, and have some fun. Or at the very least stay at home in their pyjamas and watch Homes under the Hammer while eating Quavers. They are concerned about the increasingly joyless, test-driven, uncreative, sedentary curriculum imposed on our small, curious and restless children. A curriculum, I should add, which is generally hated by the teachers who are meant to enforce it.
In Moranifesto, I address modern education’s unhappy march towards meaningless tasks, constant tests and bloodless, force-fed fact regurgitation, with, I might claim, a rather bold suggestion. Now, I’m not one for craven populism. I dare to say the unsayable. In my time, I’ve suggested some pretty contentious things: that jam is horrible, that fish are evil, ketchup shouldn’t be kept in the fridge, and Father Christmas is the sexiest man alive. But this week, I’m going to say something that I confidently expect will win 100% support. I cannot imagine a single person disagreeing with me, because, it is this: We should ban homework.
If one thing happens in 2016, it should be a concerted campaign to eradicate this illogical, damaging, pain-in-the-ass institution once and for all. It is an invention universally loathed, and it is slightly less popular than mouth ulcers. For children, homework is one of the classic immortal foes up there with vegetables, darkness, teeth-cleaning and bed-time. Parents, meanwhile, are doubly enraged. As former children themselves, parents can’t believe this homework stuff has come round again, this time with the added top-spin of you now being the poor sap that has to haul the kids in from the playground and make them give any kind of a shit about Richard II on one side of A4 paper. Even as your offspring scream, ‘I hate you! I’m too tired to do this and I want to die.’
Finally, should parents and children wish to round on the people who have given them the homework – the teachers – they would find that teachers are the ones who hate homework most of all. Teachers are all like, ‘don’t have a go at us. We’d kick homework in the nuts if we could’. Teachers loathe homework. It’s yet another round of projects to be set, handed out, nagged over and then marked. Homework for kids basically means homework for teachers, too. And everyone is quite right to hate it. For it makes life far worse than we had ever imagined.
Look, these are days of rocketing child obesity, anxiety and emotional disorders. Prescriptions for tranquilizers for children have gone through the roof. I don’t think I’m being too fanciful to suggest that as soon as children complete their seven-hour long academic day, they should be free to run around in the park, muck about with their friends and have a chance to interact with their parents, not centred around screaming ‘I hate you! I’m too tired to do this and I want to die.’ And this would, obviously, improve the physical and mental health of British children immeasurably.
When else are they going to do all that running around and being happy we keep saying that they need to do? The winters are long, they’ve got homework until 8pm, and then they’ve got that big history project over the weekend. Homework means our children never really leave school. Even when they’re at home, they’re still strapped to that bulging rucksack of folders. They’re still on deadlines. They’re still producing. And whilst that’s never fun for any child, for some, it’s utterly devastating.
If you know in your bones that academia is not for you, then those final hours of homework mean you’ve spent your entire waking day doing stuff that you feel a failure at. You have no time to go out there and find the things that you might excel at, that give you joy and change your life. You could be helping your mum mend the clutch on the car, or being taught how to cook by your dad, or hearing the record that makes you form a band, or spending five hours obsessively practicing free kicks with your mates. Instead, it’s that sad chair at the kitchen table and the slow pen across the pages as your heart revolts and, sometimes, breaks.
I loathe my children’s homework with a passion. When they come home from school, I want that time to be ours. I want my children. How many hours do we have left of their already dwindling childhood? How many more of these ultra vivid years do we have, when an evening walking along the river, visiting nan, learning how to do magic tricks, reading stories. It’s something that we will all remember forever, or that might even become their future. That my children spend these evenings exhaustedly weeping over a cardboard model of a neutron, which will just get chucked into some cupboard at school, and which doesn’t even count in their exams, makes me feel a sad and desperate fury. And not least because of the final awfulness of homework: that my kids are the lucky ones.
Homework just about works for them because they have a calm house and parents who have the time, just about, if we forget that I actually wanted to go and listen to Serial while having a hot bath, to help them. But for those children who are not lucky, who live in a chaotic house, who have parents who are busy or who are gone, homework is the cruellest reminder yet that the biggest factor in most children’s educational attainment is, over and over again, their parents’ education and class. It is often the final blow to the already struggling.
So, let’s call homework what it really is. It’s not homework. It’s a parent test. It’s a life vampire. It’s a future heart-attack. It’s emptied our playgrounds and panicked our children. It puts work in the home, and I wish it death. I hope the biggest dog in the world comes and eats it.
I’ll see you all next week. Thank you.
Sign up to the Penguin Newsletter
By signing up, I confirm that I'm over 16. To find out what personal data we collect and how we use it, please visit our Privacy Policy
Homework – Top 3 Pros and Cons
Pro/Con Arguments | Discussion Questions | Take Action | Sources | More Debates

From dioramas to book reports, from algebraic word problems to research projects, whether students should be given homework, as well as the type and amount of homework, has been debated for over a century. [ 1 ]
While we are unsure who invented homework, we do know that the word “homework” dates back to ancient Rome. Pliny the Younger asked his followers to practice their speeches at home. Memorization exercises as homework continued through the Middle Ages and Enlightenment by monks and other scholars. [ 45 ]
In the 19th century, German students of the Volksschulen or “People’s Schools” were given assignments to complete outside of the school day. This concept of homework quickly spread across Europe and was brought to the United States by Horace Mann , who encountered the idea in Prussia. [ 45 ]
In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies’ Home Journal , decried homework’s negative impact on children’s physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework was portrayed as child labor, which was newly illegal, but the prevailing argument was that kids needed time to do household chores. [ 1 ] [ 2 ] [ 45 ] [ 46 ]
Public opinion swayed again in favor of homework in the 1950s due to concerns about keeping up with the Soviet Union’s technological advances during the Cold War . And, in 1986, the US government included homework as an educational quality boosting tool. [ 3 ] [ 45 ]
A 2014 study found kindergarteners to fifth graders averaged 2.9 hours of homework per week, sixth to eighth graders 3.2 hours per teacher, and ninth to twelfth graders 3.5 hours per teacher. A 2014-2019 study found that teens spent about an hour a day on homework. [ 4 ] [ 44 ]
Beginning in 2020, the COVID-19 pandemic complicated the very idea of homework as students were schooling remotely and many were doing all school work from home. Washington Post journalist Valerie Strauss asked, “Does homework work when kids are learning all day at home?” While students were mostly back in school buildings in fall 2021, the question remains of how effective homework is as an educational tool. [ 47 ]
Is Homework Beneficial?
Pro 1 Homework improves student achievement. Studies have shown that homework improved student achievement in terms of improved grades, test results, and the likelihood to attend college. Research published in the High School Journal indicated that students who spent between 31 and 90 minutes each day on homework “scored about 40 points higher on the SAT-Mathematics subtest than their peers, who reported spending no time on homework each day, on average.” [ 6 ] Students in classes that were assigned homework outperformed 69% of students who didn’t have homework on both standardized tests and grades. A majority of studies on homework’s impact – 64% in one meta-study and 72% in another – showed that take-home assignments were effective at improving academic achievement. [ 7 ] [ 8 ] Research by the Institute for the Study of Labor (IZA) concluded that increased homework led to better GPAs and higher probability of college attendance for high school boys. In fact, boys who attended college did more than three hours of additional homework per week in high school. [ 10 ] Read More
Pro 2 Homework helps to reinforce classroom learning, while developing good study habits and life skills. Students typically retain only 50% of the information teachers provide in class, and they need to apply that information in order to truly learn it. Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, co-founders of Teachers Who Tutor NYC, explained, “at-home assignments help students learn the material taught in class. Students require independent practice to internalize new concepts… [And] these assignments can provide valuable data for teachers about how well students understand the curriculum.” [ 11 ] [ 49 ] Elementary school students who were taught “strategies to organize and complete homework,” such as prioritizing homework activities, collecting study materials, note-taking, and following directions, showed increased grades and more positive comments on report cards. [ 17 ] Research by the City University of New York noted that “students who engage in self-regulatory processes while completing homework,” such as goal-setting, time management, and remaining focused, “are generally more motivated and are higher achievers than those who do not use these processes.” [ 18 ] Homework also helps students develop key skills that they’ll use throughout their lives: accountability, autonomy, discipline, time management, self-direction, critical thinking, and independent problem-solving. Freireich and Platzer noted that “homework helps students acquire the skills needed to plan, organize, and complete their work.” [ 12 ] [ 13 ] [ 14 ] [ 15 ] [ 49 ] Read More
Pro 3 Homework allows parents to be involved with children’s learning. Thanks to take-home assignments, parents are able to track what their children are learning at school as well as their academic strengths and weaknesses. [ 12 ] Data from a nationwide sample of elementary school students show that parental involvement in homework can improve class performance, especially among economically disadvantaged African-American and Hispanic students. [ 20 ] Research from Johns Hopkins University found that an interactive homework process known as TIPS (Teachers Involve Parents in Schoolwork) improves student achievement: “Students in the TIPS group earned significantly higher report card grades after 18 weeks (1 TIPS assignment per week) than did non-TIPS students.” [ 21 ] Homework can also help clue parents in to the existence of any learning disabilities their children may have, allowing them to get help and adjust learning strategies as needed. Duke University Professor Harris Cooper noted, “Two parents once told me they refused to believe their child had a learning disability until homework revealed it to them.” [ 12 ] Read More
Con 1 Too much homework can be harmful. A poll of California high school students found that 59% thought they had too much homework. 82% of respondents said that they were “often or always stressed by schoolwork.” High-achieving high school students said too much homework leads to sleep deprivation and other health problems such as headaches, exhaustion, weight loss, and stomach problems. [ 24 ] [ 28 ] [ 29 ] Alfie Kohn, an education and parenting expert, said, “Kids should have a chance to just be kids… it’s absurd to insist that children must be engaged in constructive activities right up until their heads hit the pillow.” [ 27 ] Emmy Kang, a mental health counselor, explained, “More than half of students say that homework is their primary source of stress, and we know what stress can do on our bodies.” [ 48 ] Excessive homework can also lead to cheating: 90% of middle school students and 67% of high school students admit to copying someone else’s homework, and 43% of college students engaged in “unauthorized collaboration” on out-of-class assignments. Even parents take shortcuts on homework: 43% of those surveyed admitted to having completed a child’s assignment for them. [ 30 ] [ 31 ] [ 32 ] Read More
Con 2 Homework exacerbates the digital divide or homework gap. Kiara Taylor, financial expert, defined the digital divide as “the gap between demographics and regions that have access to modern information and communications technology and those that don’t. Though the term now encompasses the technical and financial ability to utilize available technology—along with access (or a lack of access) to the Internet—the gap it refers to is constantly shifting with the development of technology.” For students, this is often called the homework gap. [ 50 ] [ 51 ] 30% (about 15 to 16 million) public school students either did not have an adequate internet connection or an appropriate device, or both, for distance learning. Completing homework for these students is more complicated (having to find a safe place with an internet connection, or borrowing a laptop, for example) or impossible. [ 51 ] A Hispanic Heritage Foundation study found that 96.5% of students across the country needed to use the internet for homework, and nearly half reported they were sometimes unable to complete their homework due to lack of access to the internet or a computer, which often resulted in lower grades. [ 37 ] [ 38 ] One study concluded that homework increases social inequality because it “potentially serves as a mechanism to further advantage those students who already experience some privilege in the school system while further disadvantaging those who may already be in a marginalized position.” [ 39 ] Read More
Con 3 Homework does not help younger students, and may not help high school students. We’ve known for a while that homework does not help elementary students. A 2006 study found that “homework had no association with achievement gains” when measured by standardized tests results or grades. [ 7 ] Fourth grade students who did no homework got roughly the same score on the National Assessment of Educational Progress (NAEP) math exam as those who did 30 minutes of homework a night. Students who did 45 minutes or more of homework a night actually did worse. [ 41 ] Temple University professor Kathryn Hirsh-Pasek said that homework is not the most effective tool for young learners to apply new information: “They’re learning way more important skills when they’re not doing their homework.” [ 42 ] In fact, homework may not be helpful at the high school level either. Alfie Kohn, author of The Homework Myth, stated, “I interviewed high school teachers who completely stopped giving homework and there was no downside, it was all upside.” He explains, “just because the same kids who get more homework do a little better on tests, doesn’t mean the homework made that happen.” [ 52 ] Read More
Discussion Questions
1. Is homework beneficial? Consider the study data, your personal experience, and other types of information. Explain your answer(s).
2. If homework were banned, what other educational strategies would help students learn classroom material? Explain your answer(s).
3. How has homework been helpful to you personally? How has homework been unhelpful to you personally? Make carefully considered lists for both sides.
Take Action
1. Examine an argument in favor of quality homework assignments from Janine Bempechat.
2. Explore Oxford Learning’s infographic on the effects of homework on students.
3. Consider Joseph Lathan’s argument that homework promotes inequality .
4. Consider how you felt about the issue before reading this article. After reading the pros and cons on this topic, has your thinking changed? If so, how? List two to three ways. If your thoughts have not changed, list two to three ways your better understanding of the “other side of the issue” now helps you better argue your position.
5. Push for the position and policies you support by writing US national senators and representatives .
| 1. | Tom Loveless, “Homework in America: Part II of the 2014 Brown Center Report of American Education,” brookings.edu, Mar. 18, 2014 | |
| 2. | Edward Bok, “A National Crime at the Feet of American Parents,” , Jan. 1900 | |
| 3. | Tim Walker, “The Great Homework Debate: What’s Getting Lost in the Hype,” neatoday.org, Sep. 23, 2015 | |
| 4. | University of Phoenix College of Education, “Homework Anxiety: Survey Reveals How Much Homework K-12 Students Are Assigned and Why Teachers Deem It Beneficial,” phoenix.edu, Feb. 24, 2014 | |
| 5. | Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development (OECD), “PISA in Focus No. 46: Does Homework Perpetuate Inequities in Education?,” oecd.org, Dec. 2014 | |
| 6. | Adam V. Maltese, Robert H. Tai, and Xitao Fan, “When is Homework Worth the Time?: Evaluating the Association between Homework and Achievement in High School Science and Math,” , 2012 | |
| 7. | Harris Cooper, Jorgianne Civey Robinson, and Erika A. Patall, “Does Homework Improve Academic Achievement? A Synthesis of Researcher, 1987-2003,” , 2006 | |
| 8. | Gökhan Bas, Cihad Sentürk, and Fatih Mehmet Cigerci, “Homework and Academic Achievement: A Meta-Analytic Review of Research,” , 2017 | |
| 9. | Huiyong Fan, Jianzhong Xu, Zhihui Cai, Jinbo He, and Xitao Fan, “Homework and Students’ Achievement in Math and Science: A 30-Year Meta-Analysis, 1986-2015,” , 2017 | |
| 10. | Charlene Marie Kalenkoski and Sabrina Wulff Pabilonia, “Does High School Homework Increase Academic Achievement?,” iza.og, Apr. 2014 | |
| 11. | Ron Kurtus, “Purpose of Homework,” school-for-champions.com, July 8, 2012 | |
| 12. | Harris Cooper, “Yes, Teachers Should Give Homework – The Benefits Are Many,” newsobserver.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 13. | Tammi A. Minke, “Types of Homework and Their Effect on Student Achievement,” repository.stcloudstate.edu, 2017 | |
| 14. | LakkshyaEducation.com, “How Does Homework Help Students: Suggestions From Experts,” LakkshyaEducation.com (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 15. | University of Montreal, “Do Kids Benefit from Homework?,” teaching.monster.com (accessed Aug. 30, 2018) | |
| 16. | Glenda Faye Pryor-Johnson, “Why Homework Is Actually Good for Kids,” memphisparent.com, Feb. 1, 2012 | |
| 17. | Joan M. Shepard, “Developing Responsibility for Completing and Handing in Daily Homework Assignments for Students in Grades Three, Four, and Five,” eric.ed.gov, 1999 | |
| 18. | Darshanand Ramdass and Barry J. Zimmerman, “Developing Self-Regulation Skills: The Important Role of Homework,” , 2011 | |
| 19. | US Department of Education, “Let’s Do Homework!,” ed.gov (accessed Aug. 29, 2018) | |
| 20. | Loretta Waldman, “Sociologist Upends Notions about Parental Help with Homework,” phys.org, Apr. 12, 2014 | |
| 21. | Frances L. Van Voorhis, “Reflecting on the Homework Ritual: Assignments and Designs,” , June 2010 | |
| 22. | Roel J. F. J. Aries and Sofie J. Cabus, “Parental Homework Involvement Improves Test Scores? A Review of the Literature,” , June 2015 | |
| 23. | Jamie Ballard, “40% of People Say Elementary School Students Have Too Much Homework,” yougov.com, July 31, 2018 | |
| 24. | Stanford University, “Stanford Survey of Adolescent School Experiences Report: Mira Costa High School, Winter 2017,” stanford.edu, 2017 | |
| 25. | Cathy Vatterott, “Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs,” ascd.org, 2009 | |
| 26. | End the Race, “Homework: You Can Make a Difference,” racetonowhere.com (accessed Aug. 24, 2018) | |
| 27. | Elissa Strauss, “Opinion: Your Kid Is Right, Homework Is Pointless. Here’s What You Should Do Instead.,” cnn.com, Jan. 28, 2020 | |
| 28. | Jeanne Fratello, “Survey: Homework Is Biggest Source of Stress for Mira Costa Students,” digmb.com, Dec. 15, 2017 | |
| 29. | Clifton B. Parker, “Stanford Research Shows Pitfalls of Homework,” stanford.edu, Mar. 10, 2014 | |
| 30. | AdCouncil, “Cheating Is a Personal Foul: Academic Cheating Background,” glass-castle.com (accessed Aug. 16, 2018) | |
| 31. | Jeffrey R. Young, “High-Tech Cheating Abounds, and Professors Bear Some Blame,” chronicle.com, Mar. 28, 2010 | |
| 32. | Robin McClure, “Do You Do Your Child’s Homework?,” verywellfamily.com, Mar. 14, 2018 | |
| 33. | Robert M. Pressman, David B. Sugarman, Melissa L. Nemon, Jennifer, Desjarlais, Judith A. Owens, and Allison Schettini-Evans, “Homework and Family Stress: With Consideration of Parents’ Self Confidence, Educational Level, and Cultural Background,” , 2015 | |
| 34. | Heather Koball and Yang Jiang, “Basic Facts about Low-Income Children,” nccp.org, Jan. 2018 | |
| 35. | Meagan McGovern, “Homework Is for Rich Kids,” huffingtonpost.com, Sep. 2, 2016 | |
| 36. | H. Richard Milner IV, “Not All Students Have Access to Homework Help,” nytimes.com, Nov. 13, 2014 | |
| 37. | Claire McLaughlin, “The Homework Gap: The ‘Cruelest Part of the Digital Divide’,” neatoday.org, Apr. 20, 2016 | |
| 38. | Doug Levin, “This Evening’s Homework Requires the Use of the Internet,” edtechstrategies.com, May 1, 2015 | |
| 39. | Amy Lutz and Lakshmi Jayaram, “Getting the Homework Done: Social Class and Parents’ Relationship to Homework,” , June 2015 | |
| 40. | Sandra L. Hofferth and John F. Sandberg, “How American Children Spend Their Time,” psc.isr.umich.edu, Apr. 17, 2000 | |
| 41. | Alfie Kohn, “Does Homework Improve Learning?,” alfiekohn.org, 2006 | |
| 42. | Patrick A. Coleman, “Elementary School Homework Probably Isn’t Good for Kids,” fatherly.com, Feb. 8, 2018 | |
| 43. | Valerie Strauss, “Why This Superintendent Is Banning Homework – and Asking Kids to Read Instead,” washingtonpost.com, July 17, 2017 | |
| 44. | Pew Research Center, “The Way U.S. Teens Spend Their Time Is Changing, but Differences between Boys and Girls Persist,” pewresearch.org, Feb. 20, 2019 | |
| 45. | ThroughEducation, “The History of Homework: Why Was It Invented and Who Was behind It?,” , Feb. 14, 2020 | |
| 46. | History, “Why Homework Was Banned,” (accessed Feb. 24, 2022) | |
| 47. | Valerie Strauss, “Does Homework Work When Kids Are Learning All Day at Home?,” , Sep. 2, 2020 | |
| 48. | Sara M Moniuszko, “Is It Time to Get Rid of Homework? Mental Health Experts Weigh In,” , Aug. 17, 2021 | |
| 49. | Abby Freireich and Brian Platzer, “The Worsening Homework Problem,” , Apr. 13, 2021 | |
| 50. | Kiara Taylor, “Digital Divide,” , Feb. 12, 2022 | |
| 51. | Marguerite Reardon, “The Digital Divide Has Left Millions of School Kids Behind,” , May 5, 2021 | |
| 52. | Rachel Paula Abrahamson, “Why More and More Teachers Are Joining the Anti-Homework Movement,” , Sep. 10, 2021 |
More School Debate Topics
Should K-12 Students Dissect Animals in Science Classrooms? – Proponents say dissecting real animals is a better learning experience. Opponents say the practice is bad for the environment.
Should Students Have to Wear School Uniforms? – Proponents say uniforms may increase student safety. Opponents say uniforms restrict expression.
Should Corporal Punishment Be Used in K-12 Schools? – Proponents say corporal punishment is an appropriate discipline. Opponents say it inflicts long-lasting physical and mental harm on students.
ProCon/Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. 325 N. LaSalle Street, Suite 200 Chicago, Illinois 60654 USA
Natalie Leppard Managing Editor [email protected]
© 2023 Encyclopaedia Britannica, Inc. All rights reserved
- Social Media
- Death Penalty
- School Uniforms
- Video Games
- Animal Testing
- Gun Control
- Banned Books
- Teachers’ Corner
Cite This Page
ProCon.org is the institutional or organization author for all ProCon.org pages. Proper citation depends on your preferred or required style manual. Below are the proper citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order): the Modern Language Association Style Manual (MLA), the Chicago Manual of Style (Chicago), the Publication Manual of the American Psychological Association (APA), and Kate Turabian's A Manual for Writers of Term Papers, Theses, and Dissertations (Turabian). Here are the proper bibliographic citations for this page according to four style manuals (in alphabetical order):
[Editor's Note: The APA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
[Editor’s Note: The MLA citation style requires double spacing within entries.]
Should school homework be banned? Have your say
Do you think that school pupils have too much on their plate already? Do you think that homework should be banned?
- 18:06, 26 JAN 2023
School pupils face a lot of pressure and stress. We all remember the fear of forgetting a piece of homework, walking into the classroom empty handed and being slapped with a detention.
The UK's national learning curriculum is extensive and details the massive amount of work teachers face to educate our young and developing future generations - so why is even more being thrown at the students and teachers?
With the current news of teachers under the National Education Union (NEU) deciding to take industrial action for better working conditions and pay hitting the headlines, the debate of homework is pulled into the spotlight too.
Students face mounting amounts of work. Adding extra curricular activities, sport, social lives and time to relax can be incredibly overwhelming. Is homework too much? Are we pushing our children to complete burnout?
TV presenter Kirstie Allsopp has voiced a divisive opinion of the practice of setting homework, saying that homework is a "waste of time" and urged parents and families to "enjoy the weekend".
But should we be considering a restructure of homework over a blanket ban? Instead of enforcing a ‘textbook’ style of homework, should we be encouraging schools to set creative and enriching homework?
One school in Ashton Gate transformed the community into a temporary ‘paradise’ with a creative task a few years ago, which the students took to with complete gusto.
The UK government sets the national curriculum. It is issued by law and all state funded schools are required to follow it.
Its general purpose is to ensure that every state-funded school “offers a curriculum which is balanced and broadly based and which:
promotes the spiritual, moral, cultural, mental and physical development of pupils at the school and of society, and
prepares pupils at the school for the opportunities, responsibilities and experiences of later life”
As always, we would love to hear what you think of this issue. Take our poll and then head to the comments to get involved with the debate.
If you cannot see the poll at the top of the page, click here to head to it directly .
School says it will fine parents if they are late to pick up children
Police to step up patrols after Cabot Circus yob mob violence
People living on Bristol's harbour are 'abusing system' and are a 'privileged few' says Mayor Marvin Rees
Strikes in Bristol this February - dates for nurses, teachers, legal, rail and ambulance workers
- Cabot Circus
- Marvin Rees
- Bristol Live
- Most Recent

Should homework be banned for school children?
Some people think it's a good idea for both teachers and children
- 12:22, 20 JAN 2023

This week, teachers across the UK announced they would be going on strike.
TV presenter Kirstie Allsopp has now suggested that reducing homework could help relieve some of the stresses educators face. The Location, Location, Location presenter took to Twitter to question whether banning "written homework" could be a solution.
Many educators weighed in on the conversation, with a lot suggesting that this could make a real difference. One said: "It's a pain sourcing, copying, chasing and marking it."
Read more: Teacher strike dates for Hull and East Yorkshire and whether schools will close
In a Facebook post by Hull Live, parents expressed that banning homework for school children could eliminate some stresses for our littles ones. Samantha said: "I think they do enough work in the school hours as it is."
And Sheila said: "Children need to switch off when they get home. No wonder children suffer mental health issues, they are burnt out before they reach secondary school."
Do you think banning homework is a good idea for both adults and children? Let us know your thoughts in the poll or comments below .
Can't see the poll? Click here .
- 'My daughter keeps angrily slamming her bedroom door - should I take it away?'
- Dieticians warn that veganism in children could ultimately 'stunt growth'
- 'I'm a stay-at-home mum and it's just as hard as having a job'
- For more parenting news, click here
- Get the latest what's on news in Hull with our Never Dull in Hull newsletter
- Most Recent

Is Homework Good for Kids? Here’s What the Research Says
A s kids return to school, debate is heating up once again over how they should spend their time after they leave the classroom for the day.
The no-homework policy of a second-grade teacher in Texas went viral last week , earning praise from parents across the country who lament the heavy workload often assigned to young students. Brandy Young told parents she would not formally assign any homework this year, asking students instead to eat dinner with their families, play outside and go to bed early.
But the question of how much work children should be doing outside of school remains controversial, and plenty of parents take issue with no-homework policies, worried their kids are losing a potential academic advantage. Here’s what you need to know:
For decades, the homework standard has been a “10-minute rule,” which recommends a daily maximum of 10 minutes of homework per grade level. Second graders, for example, should do about 20 minutes of homework each night. High school seniors should complete about two hours of homework each night. The National PTA and the National Education Association both support that guideline.
But some schools have begun to give their youngest students a break. A Massachusetts elementary school has announced a no-homework pilot program for the coming school year, lengthening the school day by two hours to provide more in-class instruction. “We really want kids to go home at 4 o’clock, tired. We want their brain to be tired,” Kelly Elementary School Principal Jackie Glasheen said in an interview with a local TV station . “We want them to enjoy their families. We want them to go to soccer practice or football practice, and we want them to go to bed. And that’s it.”
A New York City public elementary school implemented a similar policy last year, eliminating traditional homework assignments in favor of family time. The change was quickly met with outrage from some parents, though it earned support from other education leaders.
New solutions and approaches to homework differ by community, and these local debates are complicated by the fact that even education experts disagree about what’s best for kids.
The research
The most comprehensive research on homework to date comes from a 2006 meta-analysis by Duke University psychology professor Harris Cooper, who found evidence of a positive correlation between homework and student achievement, meaning students who did homework performed better in school. The correlation was stronger for older students—in seventh through 12th grade—than for those in younger grades, for whom there was a weak relationship between homework and performance.
Cooper’s analysis focused on how homework impacts academic achievement—test scores, for example. His report noted that homework is also thought to improve study habits, attitudes toward school, self-discipline, inquisitiveness and independent problem solving skills. On the other hand, some studies he examined showed that homework can cause physical and emotional fatigue, fuel negative attitudes about learning and limit leisure time for children. At the end of his analysis, Cooper recommended further study of such potential effects of homework.
Despite the weak correlation between homework and performance for young children, Cooper argues that a small amount of homework is useful for all students. Second-graders should not be doing two hours of homework each night, he said, but they also shouldn’t be doing no homework.
Not all education experts agree entirely with Cooper’s assessment.
Cathy Vatterott, an education professor at the University of Missouri-St. Louis, supports the “10-minute rule” as a maximum, but she thinks there is not sufficient proof that homework is helpful for students in elementary school.
“Correlation is not causation,” she said. “Does homework cause achievement, or do high achievers do more homework?”
Vatterott, the author of Rethinking Homework: Best Practices That Support Diverse Needs , thinks there should be more emphasis on improving the quality of homework tasks, and she supports efforts to eliminate homework for younger kids.
“I have no concerns about students not starting homework until fourth grade or fifth grade,” she said, noting that while the debate over homework will undoubtedly continue, she has noticed a trend toward limiting, if not eliminating, homework in elementary school.
The issue has been debated for decades. A TIME cover in 1999 read: “Too much homework! How it’s hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.” The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push for better math and science education in the U.S. The ensuing pressure to be competitive on a global scale, plus the increasingly demanding college admissions process, fueled the practice of assigning homework.
“The complaints are cyclical, and we’re in the part of the cycle now where the concern is for too much,” Cooper said. “You can go back to the 1970s, when you’ll find there were concerns that there was too little, when we were concerned about our global competitiveness.”
Cooper acknowledged that some students really are bringing home too much homework, and their parents are right to be concerned.
“A good way to think about homework is the way you think about medications or dietary supplements,” he said. “If you take too little, they’ll have no effect. If you take too much, they can kill you. If you take the right amount, you’ll get better.”
More Must-Reads from TIME
- Breaking Down the 2024 Election Calendar
- Heman Bekele Is TIME’s 2024 Kid of the Year
- The Reintroduction of Kamala Harris
- What a $129 Frying Pan Says About America’s Eating Habits
- A Battle Over Fertility Law in China
- The 1 Heart-Health Habit You Should Start When You’re Young
- Cuddling Might Help You Get Better Sleep
- The 50 Best Romance Novels to Read Right Now
Write to Katie Reilly at [email protected]
First secondary school in Britain to BAN homework allows teachers 'more time to plan lessons'
It is believed to be the first time a state school has scrapped homework without extending school hours

- 10:12, 28 Sep 2016
A headteacher at Britain's first secondary school to ban homework claims the move allows teachers more time to plan lessons.
The new policy has been introduced at the 1,650-pupil Philip Morant School and College in Colchester, Essex.
Principal Catherine Hutley hopes her teachers can work on delivering inspiring lessons instead of spending hours setting and marking homework.
The school's head says there are not enough hours in the day for her teachers to complete all of their work.
So she has announced a blanket ban on homework to give staff time to plan "precise" lessons.
It is believed to be the first time a state school has scrapped homework without extending school hours.
Out-of-school-hours learning will still be encouraged through the school's website with prizes offered to the most dedicated students.
The head is convinced students will benefit but parents have raised concerns about the impact of the policy.
Reaction to the move has been mixed among the parents of pupils affected by the change.
Ms Hutley said: “The job of a teacher is impossible.
"We have the most dedicated and committed staff you could possibly ask for.
"They are working every hour God sends but planning lessons can fall by the wayside.
"We want it to be the number one priority so teachers can plan for students' individual needs and keep on top of their progress on a daily basis."
The mum of one 15-year-old pupil said her daughter “couldn’t believe her ears” when she heard the news.
She said: “My daughter has never been a big fan of homework so she’s really chuffed about the new policy.
“But I’ve told her that it doesn’t meant she’s off the hook as I am going to make sure she’s still studying for a couple of nights each week."
Mum Jodie Finnigan, who has two children at the school, said: "I support the school.
“I have always felt that kids have too much homework.
"Especially when it encroaches on their weekends and holidays - a time that they should be resting and re-charging.
“I have friends who are teachers and I am very aware of the high volume of extra work they have to do.
“It's a very brave step but one that I am sure has been well thought out and may lead the way for other schools to follow in the future.”
A dad with a child at the school said: "As usual the kids who want to work hard and succeed will still do well. "My worry is for the youngsters who need to study harder to get the results.
"It could be that they are the ones who suffer."
The scheme was discussed for one year before being implemented.
Ms Hutley added: "We are aware opinions on this issue are polarised with many parents and carers delighted by the change but others concerned by what the move will mean for their child.
"If, for any reason, we start to see this new approach to homework is having a negative impact on students' progress, we will do something about it. "But I do not believe that will happen."
Last year the independent boarding school Cheltenham Ladies' College announced plans to ditch homework in response to an "epidemic" of mental health problems.
In 2013 Jane Austen College, in Norwich, said pupils would be expected to complete all their work during timetabled hours and extended the school day to 5pm.
Is banning homework a good idea?
500+ votes so far, more on education schools secondary school, get email updates with the day's biggest stories.
Fines for taking kids out of school go up today - here's what you need to know
Nearly 400,000 penalty notices were issued in England in 2022-23 for unauthorised school absences - much higher than pre-pandemic levels. New guidance coming into force today aims to tackle this.
Monday 19 August 2024 04:10, UK

Parents in England face higher fines from Monday if their children are taken out of school without permission, as new guidance kicks in.
The Department of Education (DfE) revealed plans in February to consider fines for unauthorised absence for parents whose children miss five days of school.
School absence fines have increased from £60 to £80, which will now rise to £160 if unpaid within 21 days, rather than £120.
If the same parent is fined again within a three-year period, the fine stands at £160 from the start.
A third penalty notice cannot be given in this time - instead, "alternative action" should be considered, which would likely include prosecution.
Nearly 400,000 penalty notices were issued in England in 2022-23 for unauthorised school absences, which was much higher than pre-pandemic levels.
Please use Chrome browser for a more accessible video player

Almost nine in 10 (89.3%) of the fines were for unauthorised holidays as families looked to book cheaper vacations outside school term times, according to DfE figures released in December.
Schools and local authorities must take a "support-first" approach to help pupils and their families to tackle barriers to attendance, according to the guidance.
A "formal attendance contract" should be agreed, or a family court order pursued if deemed necessary - escalating to a fine if all other routes fail.
Keep up with all the latest news from the UK and around the world by following Sky News
Fines are 'blunt tool'
Paul Whiteman, general secretary of school leaders' union NAHT, said in February when the plans were first announced: "A consistent national framework for fines makes sense.
"Currently there is significant variation between how and when local authorities issue fines to parents.
"However, parents will likely be surprised that at a time when schools are struggling to find enough teachers to teach classes, when buildings are crumbling, and when we are in the middle of a crisis in special needs provision, that the government is choosing to focus on increasing fines for parents.
"Good attendance is obviously critically important, but fines have long proven to be too blunt a tool and largely ineffective at improving persistent absence."
Read more: Number of children vanishing from school rises by quarter National register of 'ghost children' missing from education
Be the first to get Breaking News
Install the Sky News app for free

Geoff Barton, general secretary of the Association of School and College Leaders, said at the time these fines "predominately relate to pupils who are taken out of school for term-time holidays".
"While nobody wants to be in a position of fining parents there simply has to be a marker that this is not acceptable," he said.
"Not only does it affect the child's education but it means teachers then have to spend time helping children to catch up with lost learning. If everybody did this it would be chaos."
Related Topics
Stay up to date with notifications from The Independent
Notifications can be managed in browser preferences.
UK Edition Change
- UK Politics
- News Videos
- Paris 2024 Olympics
- Rugby Union
- Sport Videos
- John Rentoul
- Mary Dejevsky
- Andrew Grice
- Sean O’Grady
- Photography
- Theatre & Dance
- Culture Videos
- Fitness & Wellbeing
- Food & Drink
- Health & Families
- Royal Family
- Electric Vehicles
- Car Insurance Deals
- Lifestyle Videos
- UK Hotel Reviews
- News & Advice
- Simon Calder
- Australia & New Zealand
- South America
- C. America & Caribbean
- Middle East
- Politics Explained
- News Analysis
- Today’s Edition
- Home & Garden
- Broadband deals
- Fashion & Beauty
- Travel & Outdoors
- Sports & Fitness
- Climate 100
- Sustainable Living
- Climate Videos
- Solar Panels
- Behind The Headlines
- On The Ground
- Decomplicated
- You Ask The Questions
- Binge Watch
- Travel Smart
- Watch on your TV
- Crosswords & Puzzles
- Most Commented
- Newsletters
- Ask Me Anything
- Virtual Events
- Wine Offers
Thank you for registering
Please refresh the page or navigate to another page on the site to be automatically logged in Please refresh your browser to be logged in
Outrage as librarians reveal UK schools are banning LGBT+ books after complaints from parents
Exclusive : library staff, mps and charities have warned banning books is worrying regression on lgbt+ rights and can be harmful to young people, article bookmarked.
Find your bookmarks in your Independent Premium section, under my profile

Get the free Morning Headlines email for news from our reporters across the world
Sign up to our free morning headlines email, thanks for signing up to the morning headlines email.
LGBT+ books are being banned from UK schools after complaints from parents, librarians have revealed.
A six-month investigation by Index on Censorship , the results of which have been shared exclusively with The Independent, found that 53 per cent of UK school librarians polled had been asked to remove literature and in more than half of those cases books were taken off shelves.
The snapshot survey found that more than two dozen librarians had experienced such censorship, with one saying they had been told to remove every book with an LGBT+ theme after a single complaint from one parent about one book.
Freedom of Information requests revealed that specific titles removed from school libraries included This Book Is Gay , by Juno Dawson, a memoir about a young person discovering their sexual identity; Julián is a Mermaid , by Jessica Love, a picture book about a gender non-conforming boy who dreams of being a mermaid; and the alphabet book ABC Pride , by Louie Stowell, Elly Barnes and Amy Phelps, which introduces young readers to the alphabet while they learn more about the LGBT+ community.
LGBT+ charities, MPs and authors have warned the move represents a worrying regression on gay rights, “returning us to that world of prejudice that most of us thought we had moved on from”. Former MP Elliot Colburn, who received homophobic death threats while serving in Parliament, said preventing children from accessing material that speaks to their experiences represented a “clear and present danger to young LGBT+ people”.
Simon James Green, one of the UK's leading writers of LGBT+ teenage fiction, had his visit to a Catholic secondary school in south London cancelled in 2022 and was subsequently trolled online, including being told he “deserved to die and burn in hell”.

“Fast forward two years and it feels to me like we’re in an even more precarious position” he told Index . “The publicity the banning brought means librarians often want to talk to me about censorship issues, and many of them have been receiving more pushback about LGBTQ+ library books than ever before."
Librarians, many of whom requested anonymity for fear of reprisals, said they worried about losing their jobs if they did not comply with book removals. Surveyed staff described defying bans by handing out “off-the-record loans” from a back cupboard, a parent trying to get them sacked because their child had been reading an LGBT+ book, and senior staff telling them to keep particular books but not put them on open display.
School library worker Amy* said: “It seems that when it comes down to it, if a parent complains, the book’s gone.” Another librarian, Emma*, said she felt frightened and intimidated after one complaint led to a purge of all LGBTQ+ content from her library.

Alice Leggatt was the librarian who booked author Mr Green for The John Fisher School in south London in 2022, an event that was cancelled by the Catholic church that branded it “outside the scope of what is permissible”.
“Pretty much every librarian I’ve spoken with says this is more of an issue than it was five years ago, and they’re concerned about it in a way they never had to think about it before,” Ms Leggatt told The Independent . “But we don’t really have anything with teeth to help defend school librarians, their collections and their students when these things happen.
“ We are about different perspectives , that’s our whole ethos. I worry about that being curtailed. Now it’s LGBTQ+ books, next week it could be something else.”
There are no statutory requirements for schools to provide libraries so it is left up to schools to decide how best to do so. The government is facing calls for more support for staff put in difficult positions and new guidance to deal with complaints.
Another librarian who spoke to Index as part of the survey – distributed via the Chartered Institute of Library and Information Professionals (CILIP), the School Library Association (SLA) – raised concerns about the influence of agitator groups who protested against Drag Queen Story Hour in libraries and “seem to be getting their scripts from the American playbook”.

The US has an organised system of book challenging that involves bans and burnings and is spearheaded by the right, with the American Library Association’s (ALA) latest report showing 4,240 different books targeted last year.
A spokesperson for Stonewall told The Independent : “It is troubling to see reports LGBTQ+ books are being removed from school libraries as we know that many students find great importance and reassurance in seeing themselves reflected in books and media. Preventing LGBTQ+ young people from seeing themselves represented in inclusive resources and books at school can often make them feel ashamed and feel the need to hide who they are.
“Schools [must] ensure that all young people have access to inclusive educational materials and books that represent the world we live in and the communities everyone is a part of.”
Laura Mackay, CEO of LGBTQ+ young people’s charity Just Like Us, added: “This small-scale study shows some worrying cases of fears around LGBT+ books in school libraries, but removing books will never change the fact that LGBT+ people, including same-sex parents, are part of society.
“The recent rise in far-right attitudes and fears stoked around trans young people make life so much harder for LGBT+ young people, particularly those of colour. Homophobia and transphobia are still an issue in many spheres of British life. It’s vital that young people can access books that reflect the diversity of the world around them.”

Politicians from across the political spectrum expressed deep concern over the reports of censorship spreading to the UK, even if so far it appears to be on a smaller scale.
Mr Colburn, who served as Tory MP for Carshalton and Wallington from 2019 until this year, called on the new Labour government in the UK to create fresh guidance to empower schools in the face of sometimes “aggressive” complaints.
And former Labour MP Ben Bradshaw told The Independent : “These reports are worrying. They fit a pattern of regression on LGBTQ+ human rights under the last government. All young people should be able to access age-appropriate books, regardless of their sexual orientation or gender identity. I hope the new government will make that clear to schools.”
The Department for Education declined to comment.
*Names have been changed.
Join our commenting forum
Join thought-provoking conversations, follow other Independent readers and see their replies
Subscribe to Independent Premium to bookmark this article
Want to bookmark your favourite articles and stories to read or reference later? Start your Independent Premium subscription today.
New to The Independent?
Or if you would prefer:
Hi {{indy.fullName}}
- My Independent Premium
- Account details
- Help centre
UK revisits social media regulation after far-right riots
- Medium Text

WHY IT'S IMPORTANT
Sign up here.
Reporting by Martin Coulter; editing by Philippa Fletcher
Our Standards: The Thomson Reuters Trust Principles. , opens new tab

German police search for assailant in festival stabbing that killed 3
German police said on Saturday that they were still searching for an unknown assailant hours after he killed three people and wounded others in a stabbing attack at a festival in the western city of Solingen.


IMAGES
COMMENTS
Homework is a controversial topic in education, but what does the science say? Explore the pros and cons of homework and its impact on students' well-being in this article from BBC Science Focus Magazine.
Sadly, there's little data comparing how much homework primary school-aged children in the UK and across the globe complete on a weekly basis. A study of teenagers used by The Telegraph shows that American high-schoolers spend an average of 6.1 hours per week compared with 4.9 hours per week of homework each week for UK-based teens.
Julie Cook Freelance journalist Published Jan 28, 2023, 10:00am. 'What do you have to do tonight?'. That's the first question I ask my two kids, aged nine and 14, when they get in from ...
Just to be clear: schools are not obliged to set homework, and some don't. But when schools do set homework, children do need to do it. We trust individual school head teachers to decide what their policy on homework will be, and what happens if pupils don't do what's set. Policy and approach won't be the same in all cases.
April 28, 2021. 192 75655. Homework is a polarising topic. It can cause students to feel stressed or anxious. It adds extra pressure on teachers, who are often already struggling with their workloads. And, some parents resent the way homework can cut into family time at home.
Prof Susan Hallam from the Institute of Education says there is "hard evidence" from research that homework really does improve how well pupils achieve. "There is no question about that." But she ...
The weekly average for the UK was about five hours - but, the OECD said, this was because the figures included young people who appeared to do almost no homework at all. The gap between the ...
1. Pro: improves academic achievement. By Sorcha Bradley, The Week UK. published 26 January 2023. Homework should be scrapped to give children more time for "other creative things", the ...
More than half of parents think that homework is a waste of time and adds extra stress on children. It follows a poll by Good Morning Britain showing 52% in favour of a ban and 48% against one ...
Should homework be banned? Friday 27 January at 3:03pm ... With several schools in the UK having pulled the plug on homework already, it seems Gary isn't alone in his thoughts. Former primary ...
Caitlin Moran on why homework should be banned. Hi, I'm Caitlin Moran, and welcome to this week's Moranifesto. On the 3rd May, the day this blog goes online, a national protest has been suggested by parents, despairing of how pressurised their children's education has become. A group called 'Let Kids Be Kids' are calling on parents to ...
In the early 1900s, progressive education theorists, championed by the magazine Ladies' Home Journal, decried homework's negative impact on children's physical and mental health, leading California to ban homework for students under 15 from 1901 until 1917. In the 1930s, homework was portrayed as child labor, which was newly illegal, but ...
The main distinction for UK homework is the social gap, with middle-class teenagers getting a disproportionate amount of homework compared to Asia and Europe. [29] Spain. In 2012, a report by the OECD showed that Spanish children spend 6.4 hours a week on homework. This prompted the CEAPA, representing 12,000 Spanish parent associations, to ...
Do you think that homework should be banned? School pupils face a lot of pressure and stress. We all remember the fear of forgetting a piece of homework, walking into the classroom empty handed ...
In a Facebook post by Hull Live, parents expressed that banning homework for school children could eliminate some stresses for our littles ones. Samantha said: "I think they do enough work in the ...
A TIME cover in 1999 read: "Too much homework! How it's hurting our kids, and what parents should do about it.". The accompanying story noted that the launch of Sputnik in 1957 led to a push ...
A headteacher at Britain's first secondary school to ban homework claims the move allows teachers more time to plan lessons. The new policy has been introduced at the 1,650-pupil Philip Morant ...
There is little homework, compared with UK schools, and there is no culture of extra private tuition. A key concept in the Finnish school system, says Mr Tuominen, is "trust". Parents trust ...
Nearly 400,000 penalty notices were issued in England in 2022-23 for unauthorised school absences - much higher than pre-pandemic levels. New guidance coming into force today aims to tackle this.
LGBT+ books are being banned from UK schools after complaints from parents, librarians have revealed.. A six-month investigation by Index on Censorship, the results of which have been shared ...
United Kingdom category Two teens in UK court charged with right-wing terrorism offences August 16, 2024. United Kingdom category Immigration biggest issue for Britons for first time since 2016, ...