We need your support today
Independent journalism is more important than ever. Vox is here to explain this unprecedented election cycle and help you understand the larger stakes. We will break down where the candidates stand on major issues, from economic policy to immigration, foreign policy, criminal justice, and abortion. We’ll answer your biggest questions, and we’ll explain what matters — and why. This timely and essential task, however, is expensive to produce.
We rely on readers like you to fund our journalism. Will you support our work and become a Vox Member today?

Re-reading is inefficient. Here are 8 tips for studying smarter.
by Joseph Stromberg
The way most students study makes no sense.
That’s the conclusion of Washington University in St. Louis psychologists Henry Roediger and Mark McDaniel — who’ve spent a combined 80 years studying learning and memory, and recently distilled their findings with novelist Peter Brown in the book Make It Stick: The Science of Successful Learning .
using active learning strategies is most effective
The majority of students study by re-reading notes and textbooks — but the psychologists’ research, both in lab experiments and of actual students in classes, shows this is a terrible way to learn material. Using active learning strategies — like flashcards, diagramming, and quizzing yourself — is much more effective, as is spacing out studying over time and mixing different topics together.
McDaniel spoke with me about the eight key tips he’d share with students and teachers from his body of research.
1) Don’t just re-read your notes and readings

Photofusion/UIG via Getty Images
”We know from surveys that a majority of students, when they study, they typically re-read assignments and notes. Most students say this is their number one go-to strategy.
when students re-read a textbook chapter, they show no improvement in learning
”We know, however, from a lot of research, that this kind of repetitive recycling of information is not an especially good way to learn or create more permanent memories. Our studies of Washington University students, for instance, show that when they re-read a textbook chapter, they have absolutely no improvement in learning over those who just read it once.
“On your first reading of something, you extract a lot of understanding. But when you do the second reading, you read with a sense of ‘I know this, I know this.’ So basically, you’re not processing it deeply, or picking more out of it. Often, the re-reading is cursory — and it’s insidious, because this gives you the illusion that you know the material very well, when in fact there are gaps.”
2) Ask yourself lots of questions

Aram Boghosian for The Boston Globe via Getty Images
”One good technique to use instead is to read once, then quiz yourself, either using questions at the back of a textbook chapter, or making up your own questions. Retrieving that information is what actually produces more robust learning and memory.
retrieving information is what produces more robust learning and memory
”And even when you can’t retrieve it — when you get the questions wrong — it gives you an accurate diagnostic on what you don’t know, and this tells you what you should go back and study. This helps guide your studying more effectively.
”Asking questions also helps you understand more deeply. Say you’re learning about world history, and how ancient Rome and Greece were trading partners. Stop and ask yourself why they became trading partners. Why did they become shipbuilders, and learn to navigate the seas? It doesn’t always have to be why — you can ask how, or what.
“In asking these questions, you’re trying to explain, and in doing this, you create a better understanding, which leads to better memory and learning. So instead of just reading and skimming, stop and ask yourself things to make yourself understand the material.”
3) Connect new information to something you already know
”Another strategy is, during a second reading, to try relating the principles in the text to something you already know about. Relate new information to prior information for better learning.
”One example is if you were learning about how the neuron transmits electricity. One of the things we know if that if you have a fatty sheath surround the neuron, called a myelin sheath , it helps the neuron transmit electricity more quickly.
“So you could liken this, say, to water running through a hose. The water runs quickly through it, but if you puncture the hose, it’s going to leak, and you won’t get the same flow. And that’s essentially what happens when we age — the myelin sheaths break down, and transmissions become slower.”

( Quasar/Wikimedia Commons )
4) Draw out the information in a visual form
”A great strategy is making diagrams, or visual models, or flowcharts. In a beginning psychology course, you could diagram the flow of classical conditioning . Sure, you can read about classical conditioning, but to truly understand it and be able to write down and describe the different aspects of it on a test later on — condition, stimulus, and so on — it’s a good idea to see if you can put it in a flowchart.
“Anything that creates active learning — generating understanding on your own — is very effective in retention. It basically means the learner needs to become more involved and more engaged, and less passive.”
5) Use flashcards

”Flashcards are another good way of doing this. And one key to using them is actually re-testing yourself on the ones you got right.
keeping a correct card in the deck and encountering it again is more useful
”A lot of students will answer the question on a flashcard, and take it out of the deck if they get it right. But it turns out this isn’t a good idea — repeating the act of memory retrieval is important. Studies show that keeping the correct item in the deck and encountering it again is useful. You might want to practice the incorrect items a little more, but repeated exposure to the ones you get right is important too.
“It’s not that repetition as a whole is bad. It’s that mindless repetition is bad.”
6) Don’t cram — space out your studying

Johannes Simon/Getty Images
”A lot of students cram — they wait until the last minute, then in one evening, they repeat the information again and again. But research shows this isn’t good for long term memory. It may allow you to do okay on that test the next day, but then on the final, you won’t retain as much information, and then the next year, when you need the information for the next level course, it won’t be there.
practice a little bit one day, then two days later
”This often happens in statistics. Students come back for the next year, and it seems like they’ve forgotten everything, because they crammed for their tests.
“The better idea is to space repetition. Practice a little bit one day, then put your flashcards away, then take them out the next day, then two days later. Study after study shows that spacing is really important.”
7) Teachers should space out and mix up their lessons too

Andy Cross/The Denver Post via Getty Images
”Our book also has information for teachers. And our educational system tends to promote massed presentation of information as well.
”In a typical college course, you cover one topic one day, then on the second day, another topic, then on the third day, another topic. This is massed presentation. You never go back and recycle or reconsider the material.
”But the key, for teachers, is to put the material back in front of a student days or weeks later. There are several ways they can do this. Here at Washington University, there are some instructors who give weekly quizzes, and used to just put material from that week’s classes on the quiz. Now, they’re bringing back more material from two to three weeks ago. One psychology lecturer explicitly takes time, during each lecture, to bring back material from days or weeks beforehand.
the key, for teachers, is to put the material back in front of a student days or weeks later
”This can be done in homework too. It’s typical, in statistics courses, to give homework in which all of the problems are all in the same category. After correlations are taught, a student’s homework, say, is problem after problem on correlation. Then the next week, T tests are taught, and all the problems are on T tests. But we’ve found that sprinkling in questions on stuff that was covered two or three weeks ago is really good for retention.
”And this can be built into the content of lessons themselves. Let’s say you’re taking an art history class. When I took it, I learned about Gauguin, then I saw lots of his paintings, then I moved on to Matisse, and saw lots of paintings by him. Students and instructors both think that this is a good way of learning the painting styles of these different artists.
”But experimental studies show that’s not the case at all. It’s better to give students an example of one artist, then move to another, then another, then recycle back around. That interspersing, or mixing, produces much better learning that can be transferred to paintings you haven’t seen — letting students accurately identify the creators of paintings, say, on a test.
“And this works for all sorts of problems. Let’s go back to statistics. In upper level classes, and the real world, you’re not going to be told what sort of statistical problem you’re encountering — you’re going to have to figure out the method you need to use. And you can’t learn how to do that unless you have experience dealing with a mix of different types of problems, and diagnosing which requires which type of approach.”
8) There’s no such thing as a “math person”

Christopher Furlong/Getty Images
”There’s some really interesting work by Carol Dweck , at Stanford. She’s shown that students tend to have one of two mindsets about learning.
it turns out that mindsets predict how well students end up doing
”One is a fixed learning model. It says, ‘I have a certain amount of talent for this topic — say, chemistry or physics — and I’ll do well until I hit that limit. Past that, it’s too hard for me, and I’m not going to do well.’ The other mindset is a growth mindset. It says that learning involves using effective strategies, putting aside time to do the work, and engaging in the process, all of which help you gradually increase your capacity for a topic.
”It turns out that the mindsets predict how well students end up doing. Students with growth mindsets tend to stick with it, tend to persevere in the face of difficulty, and tend to be successful in challenging classes. Students with the fixed mindset tend not to.
“So for teachers, the lesson is that if you can talk to students and suggest that a growth mindset really is the more accurate model — and it is — then students tend to be more open to trying new strategies, and sticking with the course, and working in ways that are going to promote learning. Ability, intelligence, and learning have to do with how you approach it — working smarter, we like to say.”
This interview has been edited for length and clarity.
WATCH: ‘10 things they don’t talk about at graduation’
- Science of Everyday Life
Most Popular
- What the polls show about Harris’s chances against Trump
- Has The Bachelorette finally gone too far?
- Trump’s biggest fans aren’t who you think
- The real reason Netanyahu won’t end the Gaza war
- The state of the 2024 race, explained in 7 charts
Today, Explained
Understand the world with a daily explainer plus the most compelling stories of the day.
This is the title for the native ad
More in Education

A guide to filling out the federal financial aid form for the upcoming school year.

Scientific fraud kills people. Should it be illegal?

New research finds labor stoppages raised wages without harming student learning.

Some families of students with disabilities feel pushed out of public schools.

And how university campuses can do better this fall.

How the top campus job became so complex and public this year.
Celebrating 150 years of Harvard Summer School. Learn about our history.
Top 10 Study Tips to Study Like a Harvard Student
Adjusting to a demanding college workload might be a challenge, but these 10 study tips can help you stay prepared and focused.
Lian Parsons
The introduction to a new college curriculum can seem overwhelming, but optimizing your study habits can boost your confidence and success both in and out of the classroom.
Transitioning from high school to the rigor of college studies can be overwhelming for many students, and finding the best way to study with a new course load can seem like a daunting process.
Effective study methods work because they engage multiple ways of learning. As Jessie Schwab, psychologist and preceptor at the Harvard College Writing Program, points out, we tend to misjudge our own learning. Being able to recite memorized information is not the same as actually retaining it.
“One thing we know from decades of cognitive science research is that learners are often bad judges of their own learning,” says Schwab. “Memorization seems like learning, but in reality, we probably haven’t deeply processed that information enough for us to remember it days—or even hours—later.”
Planning ahead and finding support along the way are essential to your success in college. This blog will offer study tips and strategies to help you survive (and thrive!) in your first college class.
1. Don’t Cram!
It might be tempting to leave all your studying for that big exam up until the last minute, but research suggests that cramming does not improve longer term learning.
Students may perform well on a test for which they’ve crammed, but that doesn’t mean they’ve truly learned the material, says an article from the American Psychological Association . Instead of cramming, studies have shown that studying with the goal of long-term retention is best for learning overall.
2. Plan Ahead—and Stick To It!
Having a study plan with set goals can help you feel more prepared and can give you a roadmap to follow. Schwab said procrastination is one mistake that students often make when transitioning to a university-level course load.
“Oftentimes, students are used to less intensive workloads in high school, so one of my biggest pieces of advice is don’t cram,” says Schwab. “Set yourself a study schedule ahead of time and stick to it.”
3. Ask for Help
You don’t have to struggle through difficult material on your own. Many students are not used to seeking help while in high school, but seeking extra support is common in college.
As our guide to pursuing a biology major explains, “Be proactive about identifying areas where you need assistance and seek out that assistance immediately. The longer you wait, the more difficult it becomes to catch up.”
There are multiple resources to help you, including your professors, tutors, and fellow classmates. Harvard’s Academic Resource Center offers academic coaching, workshops, peer tutoring, and accountability hours for students to keep you on track.
4. Use the Buddy System
Your fellow students are likely going through the same struggles that you are. Reach out to classmates and form a study group to go over material together, brainstorm, and to support each other through challenges.
Having other people to study with means you can explain the material to one another, quiz each other, and build a network you can rely on throughout the rest of the class—and beyond.
5. Find Your Learning Style
It might take a bit of time (and trial and error!) to figure out what study methods work best for you. There are a variety of ways to test your knowledge beyond simply reviewing your notes or flashcards.
Schwab recommends trying different strategies through the process of metacognition. Metacognition involves thinking about your own cognitive processes and can help you figure out what study methods are most effective for you.
Schwab suggests practicing the following steps:
- Before you start to read a new chapter or watch a lecture, review what you already know about the topic and what you’re expecting to learn.
- As you read or listen, take additional notes about new information, such as related topics the material reminds you of or potential connections to other courses. Also note down questions you have.
- Afterward, try to summarize what you’ve learned and seek out answers to your remaining questions.
Explore summer courses for high school students.
6. Take Breaks
The brain can only absorb so much information at a time. According to the National Institutes of Health , research has shown that taking breaks in between study sessions boosts retention.
Studies have shown that wakeful rest plays just as important a role as practice in learning a new skill. Rest allows our brains to compress and consolidate memories of what we just practiced.
Make sure that you are allowing enough time, relaxation, and sleep between study sessions so your brain will be refreshed and ready to accept new information.
7. Cultivate a Productive Space
Where you study can be just as important as how you study.
Find a space that is free of distractions and has all the materials and supplies you need on hand. Eat a snack and have a water bottle close by so you’re properly fueled for your study session.
8. Reward Yourself
Studying can be mentally and emotionally exhausting and keeping your stamina up can be challenging.
Studies have shown that giving yourself a reward during your work can increase the enjoyment and interest in a given task.
According to an article for Science Daily , studies have shown small rewards throughout the process can help keep up motivation, rather than saving it all until the end.
Next time you finish a particularly challenging study session, treat yourself to an ice cream or an episode of your favorite show.
9. Review, Review, Review
Practicing the information you’ve learned is the best way to retain information.
Researchers Elizabeth and Robert Bjork have argued that “desirable difficulties” can enhance learning. For example, testing yourself with flashcards is a more difficult process than simply reading a textbook, but will lead to better long-term learning.
“One common analogy is weightlifting—you have to actually “exercise those muscles” in order to ultimately strengthen your memories,” adds Schwab.
10. Set Specific Goals
Setting specific goals along the way of your studying journey can show how much progress you’ve made. Psychology Today recommends using the SMART method:
- Specific: Set specific goals with an actionable plan, such as “I will study every day between 2 and 4 p.m. at the library.”
- Measurable: Plan to study a certain number of hours or raise your exam score by a certain percent to give you a measurable benchmark.
- Realistic: It’s important that your goals be realistic so you don’t get discouraged. For example, if you currently study two hours per week, increase the time you spend to three or four hours rather than 10.
- Time-specific: Keep your goals consistent with your academic calendar and your other responsibilities.
Using a handful of these study tips can ensure that you’re getting the most out of the material in your classes and help set you up for success for the rest of your academic career and beyond.
Learn more about our summer programs for high school students.
About the Author
Lian Parsons is a Boston-based writer and journalist. She is currently a digital content producer at Harvard’s Division of Continuing Education. Her bylines can be found at the Harvard Gazette, Boston Art Review, Radcliffe Magazine, Experience Magazine, and iPondr.
Becoming Independent: Skills You’ll Need to Survive Your First Year at College
Are you ready? Here are a few ideas on what it takes to flourish on campus.
Harvard Division of Continuing Education
The Division of Continuing Education (DCE) at Harvard University is dedicated to bringing rigorous academics and innovative teaching capabilities to those seeking to improve their lives through education. We make Harvard education accessible to lifelong learners from high school to retirement.

How to Study Effectively: 15 Tips for 2024

- 💪 Student Superheroes
- 🙌 Path to Success
- 🏁 Be Ready!
- ⏱ Manage Your Time
- 📖 Learning and Memorizing
- 😰 Controlling Test Anxiety
Ever wondered how to study effectively? Why does one of your classmates need just a couple of hours to memorize information and pass an exam with flying colors? And why does another spend a night cramming material and still struggle to recall anything?
Actually, the answer to all of that:
Effective studying comes from regularity and consistently implemented habits. If you want to make the best of your time spent learning, you have to find an approach and study tips that work for you. Thankfully, that’s why our IvyPanda team has developed this guide.
Below, you will find how to study smart, essay writing tips, and tricks for managing your anxiety.
💪 Student superheroes
You have probably heard of the trait theory of leadership. According to it, some people are born to become leaders . They just have some features in their blood .
Such students have numerous advantages compared to others as they can:
- acquire information quicker,
- study for exams faster,
- pass tests without being nervous.
Maybe some people are born to be the best. Yet, it is total nonsense to say that all students who spend less time studying belong to this group of people.
The successful passing of exams depends on understanding how learning works. Studying is a skill, and cramming all night before the exam is not a secret ingredient of success.
🙌 Path to success
Having good study habits presupposes knowing your strengths and weaknesses, using different study methods, and organizing the process. One can acquire valuable skills by paying attention to the organization of the process of learning first.
Your strategy should include the following steps :
- Preparation for studying;
- Time-management;
- Learning and memorizing;
- Controlling test anxiety.
🏁 Be ready!
Effective studying never starts from opening the book. It requires the whole organization process to take place before anything. Thus, before studying, you have to prepare yourself and your study materials.
1. Set goals
First of all, you should prepare for your study by setting goals. They are necessary to make you keep going. Don’t underestimate their power.
Be sure that:
- You know why you are studying. It can be for scraping through the exam, finishing college, getting good grades, satisfying your parents, or having professional knowledge for your future career. No matter what your goal is, it should be an impetus for studying;
- Your goals are achievable. You should be able to achieve them within a particular period of time and with substantial effort. No need for making over-optimistic promises — be realistic!

2. Choose the place for studying
This decision is up to you alone. You should find a place where you feel comfortable (but not comfortable for sleeping). Some people can study with background music , while others need silence.
You will know how to study smart with some of these tips:
- Light matters. The place you have chosen should be well lit. Areas with poor lighting are more likely to make you sleepy;
- Noise matters. If you need background noise, you may go to the café or turn on some music. Meanwhile, a library may be the best option for people who prefer absolute silence.
- Time matters. You should not make yourself wake up early in the morning and study just because it works for that friend of yours. If you are a night owl, feel free to study in the evening.
3. Avoid distractions and boost productivity
Numerous things that you use are invisible thieves of your energy and concentration:
- Studying while the television is on may result in constant distraction from thoughtful reading.
- The same is true with your smartphone. Answering incoming calls leads to wasted time. As a result, you become tired before you have managed to study anything.
- The Internet is probably your enemy as well. If you need a computer, close all social media, and concentrate on your task.
What’s the bottom line?
You can boost productivity in many ways. It can be drinking coffee or listening to classical music. You should know what makes you active and use it for your studying.

4. Stay motivated
Attitude and mindset play a crucial role in successful and easy studying. ‘I don’t feel like studying’ is a widespread reason to avoid doing something worthwhile. Follow these easy recommendations, and you will be impressed at how they will change your attitude towards studying:
- Don’t underestimate yourself. Remind yourself that you have the necessary study skills and can achieve anything. You should always be your greatest supporter.
- No negative thinking. Thoughts like, ‘I will never do it,’ ‘I can’t stand doing it anymore, ‘I’m a total failure, I will fail it for sure’ are not acceptable if you want to pass your exam.
- Don’t compare yourself to others. Thoughts like, ‘I bet that Meggy has already studied half of the book’ is an unnecessary distraction. Such ideas only increase your dissatisfaction and demotivate you.
In essence, attitude towards learning habits and upcoming exams is what differentiates quick learners from others in most cases. Self-confidence is a great determiner of success.
⏱ Manage your time
The proper division of time is one of the most critical study tips. The disorganization and constant putting off until tomorrow are two major problems.
5. Avoid procrastination
Currently, putting away tasks for later seems to be one of the most pressing problems for students. A study of procrastination among students has shown that 80-95% of students procrastinate. Most of them justify that fact by stating that working under pressure improves their efficiency. However, the study results have demonstrated that there is a connection between low GPA and procrastination habits.
To avoid it, you should:
6. Schedule every hour
If you want to know how to study effectively, you have to manage your time correctly. It is halfway to success. If you doubt whether you are a procrastinator, do this test to find out.
Yet, our tips on time management can be helpful regardless of the results:
- Make a to-do list . Nothing can be easier than writing down everything you have to do. Make a list of all your tasks and give them deadlines. Then, write down the assignments with the shortest deadlines first. Classify these as urgent depending on their priority. Lastly, make a final list of what should be done first.
- Use a tool for organizing. It can be an app on your phone or a calendar with crucial tasks circled in red. You should find the most efficient way to remind yourself about the upcoming deadlines.
- Count every minute. Be precise when planning your schedule. Think about the necessary amount of time for the particular task, and don’t overvalue your possibilities. Always take into account potential delays and leave time for planning.
In fact, students are expected to spend 35 hours a week studying. Check how many hours you need to attend all classes. Then, use the rest of the time for independent work.
📖 Learning and memorizing
Some students tend to try different memorizing techniques without considering their learning style. For example, a student needs to hear the information they want to remember. In this case, highlighting essential parts of the text won’t be as efficient as it is for a visual learner.
That’s why:
7. Know your learning style
Identify your learning style and choose appropriate techniques for study. People are generally divided into three types of learners :
- Visuals are those who learn by seeing something. Highlighting does work for such people.
- Auditory learners who prefer listening. It is advisable for this type of learner to speak with others, read aloud, or record themselves.
- Tactile learners learn something new by doing it. They need to practice if they want to memorize the theory.
If you are not sure about your learning style, follow this link and find it out by answering these simple questions.

8. Use different study tips for memorization
You have chosen a place for study, got rid of all distractions, and evaluated the urgency of your tasks. Half the work is done. Now it is time to start working on your study habits. Many articles emphasize the significance of such techniques as visiting lectures, making notes , or reading before bed.
Such study tips are helpful, but they are not universal. They don’t work for every single student. That’s why you have to try out and implement different recommendations at the same time.
Here are some creative techniques for study:
- The system of rewards . Promise yourself that you will buy that fancy dress or watch (or anything else you want) after passing the exam. This type may be classified as a long-term extrinsic motivator. Also, you can make the process of studying more pleasant by giving yourself little treats. For example, let yourself eat or drink something delicious when you finish some part of your studying.
- Read upside down . This study habit is efficient if you need to cram something. Yes, cramming is believed to be an ineffective method of studying. Yet, every student knows that sometimes there is no other way out. When you read upside down, you have to focus better. Otherwise, you won’t be able to understand the meaning of the text. Concentrating on something makes you memorize and comprehend it quicker.
- Teach somebody . This method is fantastic, and it works in most cases. When you teach someone, you have to explain the topic. No explanation is possible without understanding . Consequently, you will have to do your best to describe the issue to your friend (or anybody else, including you) so that they can get it.
Also, you can always search a free essay database for either more tips or to get some extra info on the topic you’re studying.
9. Use flashcards
Flashcards are handy for becoming a better learner:
- Write down essential facts using bullet points, different colors and fonts to enhance visual perception.
- Take them with you everywhere you go and don’t miss the opportunity to read them during the so-called ‘dead times’ (waiting for a bus, standing in a queue).
- You can even pin them to your fridge or bathroom mirror. This way, they will always be in your sight.
- Use flashcards in group activities with your classmates.
Moreover, you can keep them on your smartphone or computer by using specific apps! Here are some examples perfect for university and college students:
- GoConqr – with this app, you can use great flashcards made just for visual learning or create your own set. Add images, formulas, and text to make your flashcards.
- Cram – almost 200 million cards for learning online. You can read cards or enable audio records.
10. Use our checklist
Each time you study, you can try different study techniques. For this purpose, keep this checklist around:
| ✔️ | Set study sessions | Practice studying during small repeated sessions. For example, set a timer for 25 minutes in the morning right after you have breakfast. |
| ✔️ | Use mnemonic devices | To memorize boring data, try to come up with jokes, rhymes, and songs about it. Humor and vivid imagery help students learn. |
| ✔️ | Visualize | Draw charts, diagrams, and pictures with what’s happening. Use highlighters and colorful pens. |
| ✔️ | Make connections | Think of how the new information you learn relates to what you already know. |
| ✔️ | Change settings | Try studying in a new environment. You can change settings each time you feel bored or lack focus. |
| ✔️ | Sleep | Healthy sleep improves your memory and learning skills. Taking power naps (30-60 mins) can help you find your focus and motivation. |
Find out more great study habits that are scientifically proved in this video .
😰 Controlling text anxiety
Even for a well-prepared student, anxiety may spoil everything , especially before an exam. Being too nervous may result in poor concentration and, as a result, a bad grade. People who pass exams easily know not only how to study but how to stay calm.
Here are some tips on how to stay relaxed during your test:
11. Read the tasks and use samples
Read all instructions carefully and follow directions exactly. Whether it’s a chemistry, physics, or history test—understanding the task is the most significant start for a successful score.
If you still don’t feel prepared for the test, try out a couple of online exams. Find some test questions that may appear on your future exam.
Finding essay samples on any topic is possible. Analyze them, and you won’t have to develop your own paper from scratch:
- 125 College Essay Examples for 13 Schools + Expert Analysis– an enormous pick of college essay samples for practice.
- Writing Sample Essays – an excellent essay analysis you can use as learning material. You’ll learn what standards to follow when writing a paper.
- Essay Questions – this is an excellent option for those who are struggling with anxiety. All essay questions are fun and exciting to read. They also help you find a creative way of writing on your own.
12. Stay positive and healthy
According to statistics, 25% of school students are affected by test anxiety . It doesn’t only affect their academic performance. It impacts health, giving such symptoms as nausea, stomach pain, headaches, and shortness of breath.
You can’t let yourself be stressed all the time. Take some time to read workbooks, do exercises, and make other preparations. But then, take some time to relax, eat healthily, have a good night’s sleep, and build your confidence.
13. Breathe
If you feel too worried, try taking slow, deep breaths that will cool you down.
If feelings of panic and anxiety are familiar to you, it’s great to learn the 4×4 breathing technique. Navy SEALs use it and, if performed correctly, it eliminates all the negative signs of anxiety.
To perform it, follow these instructions:
- Inhale for 4 seconds.
- Hold your breath for 4 seconds.
- Exhale for 4 seconds.
- Don’t breathe for 4 seconds.
Repeat until you feel calm and not threatened by a panic attack.
14. Use relaxation and meditation apps
Note-taking, reading scientific resources, or exercising are helpful activities. Unfortunately, they won’t work if you worry too much. That’s why you should install one of these apps on your desktop or smartphone. Such software can turn into quite an excellent strategy for staying calm and passing exams.
Here are some app suggestions:
- Calm helps thousands of people to improve their sleep, perform meditation, and release stress. It allows you to listen to stories by Stephen Fry, Tamara Levitt, and others. You’ll do breathing exercises and experience soothing nature sounds until you’re okay.
- Meditation and Relaxation is an app that includes essential parts of a healthy routine. It takes care of your productivity, calmness, sleep, and happiness. Learn to meditate and do that every day. It will eliminate all anxiety on your way to exam success.
- Aura is a free app for iOS and Android that helps you reduce stress and improve your mood. It includes essential components: a gratitude journal, breathing exercises, mood analysis, and sounds of nature. Track your happiness, meditate, and increase your level in game-like software.
15. Check the video
We can’t fit all the helpful techniques in one article. Therefore, we offer you a video with more valuable ways of coping with test anxiety.
Thank you for reading! We hope that now you know how to study effectively and won’t have any struggles in the future. Share the page with other students who may need these tips.
- Share via Facebook
- Share via X
- Share via LinkedIn
- Share via email
By clicking "Post Comment" you agree to IvyPanda’s Privacy Policy and Terms and Conditions . Your posts, along with your name, can be seen by all users.
Nice article
Thank you, Emmanuel 🙂
Hello I have been looking for a website, but because of you I have stopped It’s like you were talking to me I don’t really have hope that I can ever pass physics or chemistry but now I feel nice I love your article, don’t STOP!
Thanks for your kind words. Much appreciated!
Good luck on your physics and chemistry classes 🙂
- ALL ARTICLES
- How To Study Effectively
- Motivation & Stress
- Smarter Study Habits
- Memorise Faster
- Ace The Exam
- Write Better Essays
- Easiest AP Classes Ranked
- Outsmart Your Exams
- Outsmart Your Studies
- Recommended Reads
- For Your Students: Revision Workshops
- For Your Teaching Staff: Memory Science CPD
- Our Research: The Revision Census
- All Courses & Resources
- For School Students and Their Parents
- For University Students
- For Professionals Taking Exams
- Study Smarter Network
- Testimonials

How To Study ULTRA-Effectively For Exams: 37 Proven Strategies For 2023
by William Wadsworth | Last updated Aug 12, 2024 | First published on Jul 23, 2021 | 20 comments
It’s official: scientists have figured out the secrets for how to study effectively for exams.
Or at least, a darn sight more effectively than you’d be doing without using these strategies. Read on, and discover how you too can:
- Study smarter, not harder: get more done in less time
- Learn faster and remember more with the science of memory
- Take control of your to-do list , and build the routines and focus that let you Get Stuff Done on your terms
- And so watch your grades go up , without the need to work all hours of the day or night
- For a happier, less stressed, more successful time at school / college / uni!
There are 6 areas you need to “win” in order to study as effectively as possible. So you’ll find the 37 strategies grouped into the following 6 “chapters”:
Meet the expert
William Wadsworth

By William Wadsworth , the Cambridge University trained cognitive psychologist and specialist in how to study smarter, not harder. He leads the world’s largest research study on use of effective learning strategies, is regular exam prep expert for The Times , and hosts the Exam Study Expert podcast , with 1 million downloads to date.
Review and additional research by Dr Kerri Edinburgh .
BTW – if you’re thinking “aargh, there are THIRTY-SEVEN things I need to do right – that’s loads!!” Then don’t worry. You don’t need them all to succeed. Some are solutions to problems that you might not even have. And some give you options – there are different routes to studying effectively, some will be better suited to you than others. You don’t need to do them all at once: experiment, and choose your favourites.
Let’s dive in, and help you on your way to the grades of your dreams:
I. Preparing For Success: Plan & Prioritise
“ By failing to prepare, you are preparing to fail ” – Benjamin Franklin
Success in your studies starts with a clear plan of what you need to do, and how you’re going to fit it all in. Here’s how to study effectively with a plan:
1. How To Plan Your Studying: Have A Map
First things first: what do you actually need to do?
If you’re studying for exams, the first thing you need to be clear on is what’s expected of you.
Have a list of topics / subtopics, and consider a simple tracking system so you can see at-a-glance which topics need more work.
A traffic light system can work great for this: red for “needs works”, amber for “getting there”, green for “got this”.
Start with the “red” topics, and when you’re done with them, move on to amber.

If you’re working towards a big assignment, start by thrashing out the big building blocks of the task.
- That could be by content area: what different sub-topics do you need to work on as part of your overall assignment?
- And / or planning by phase of work: new reading first, then planning, then writing-up, then proofreading .
Once you’ve made your “map”, do a quick time budget for it. E.g. if there are 11 chapters to study, and you’ve got 25 days before the test, that’s 1 chapter every 2 days, with a couple of days in hand.
Is that feel realistic? If not, how can you prioritise or scale back your ambitions to make the task fit into the time available?
Don’t make your study plan too detailed . You’re looking for a birds-eye view of the road ahead, not a minute-by-minute, blow-by-blow finicky plan that no-one could possibly stick to!
2. Look Ahead: Prepare For Success
Most students spend time learning a topic, then start looking at past paper questions.
Flip that on its head, and you’ll get better results.
Start by looking at real exam questions for that topic – maybe even attempting a few, making educated guesses wherever you need to.
Then when you go back and revise the topic, you’ll have a much deeper sense of what you need to know and why, and how you’ll end up applying it in the exam. That will help the topic “go in” much better – a bit like a farmer ploughing his field before sowing crops.
If you’re working on a project or assignment, can you get any examples of what “good” looks like?
Perhaps some past student projects are available in the library, or your tutors have made some model essays available. The more you understand about what the assessors want to see, the easier it will be for you to deliver.
3. The Power Of No
“ The difference between successful people and really successful people is that really successful people say no to almost everything .” – Warren Buffet
What are the most important things in your life right now?
Your studies might be at or near the top of the list.
There may be 1 or 2 other things: your sporting or musical commitments, a family, a job or a job hunt.
Work out what the top priorities are . And then be bold about saying “no” to everything that doesn’t help you advance your top priorities.
(Though see also #37 about “having fun”. I’m a huge believer in scheduling some much-needed down-time each week, even if you’re working really hard – perhaps especially if you’re working really hard!)
4. Study Effectively With The Perfect Study Routine
Behind just about every successful student is a great routine.
Your study routine is quite a personal thing , so I can’t give you a one-size-fits-all template timetable that works for everyone. But if you don’t have a regular routine, take some time now to sketch out what an ideal study day might look like.

Here are some points to consider:
- Do you do your best work in the first half of the morning? Just before lunch? Late afternoon?
- Schedule study blocks to take advantage of this “biological prime time” (as NY Times bestselling author and past Exam Study Expert guest Chris Bailey calls it)
- e.g. testing yourself on new material from the day first thing in the morning and last thing at night?
- If you’re ambitious, it’s tempting to cram as much work into each day as possible.
- If you’re new to your study routine, don’t aim for gold on Day 1. Set your sights conservatively, with a routine you know you can absolutely stick to even on low energy / low motivation days.
- If you feel you can do more, do more. But better to exceed your expectations than set yourself up for failure and discouragement.
I’ve got a lot to say on the subject of your study routine: read my complete guide here .
5. Stay Consistent
The key to learning how to study effectively (and pretty well everything else in life!) is consistency .
The difference between high-performers and everyone else is often very small.
Two people want to get a book written. One puts in half an hour every single morning to write a page or two. The other doesn’t. A year later, one has a book, the other doesn’t.
Two students want to get into Cambridge. One spends a quarter of an hour a night reading around her subject, the other doesn’t. Six months later, one has lots of interesting things to say in her interview, the other doesn’t.
You’re probably getting my point by now, but one final example: two students are ambitious for exam success. One spends ten minutes a night memory journaling , the other doesn’t. Come the end of the year, one has a decent memory for lots of the course, and goes on to do really well in the exams.
Change your daily habits – even by just a bit – and you can change your life .
Provided you stay consistent.
II. Getting Productive: Building Superhuman Focus
You’ve got your plan. Now you need to execute it.
Here’s how to get productive, and start getting things DONE!
6. One Thing At A Time: “Monotasking”
It’s tempting to think you can get more done by “multi-tasking”.
But actually, each time your concentration breaks or you switch to something else, you’ll lose valuable minutes re-finding your focus on whatever you were trying to do .
So practice mono-tasking : being disciplined about giving your full attention to the task at hand: it’s the best way to study effectively.

Control external distractions as much as you can.
Start by taking control of your phone. Put airplane mode ON (or better yet, switch it off). Then get the phone OFF your desk, and OUT of sight.
Having it out while you’re studying will play all kinds of havoc with your ability to concentrate .
Even if you’re making an effort to ignore the ting or buzz every time someone messages you on Snapchat, WhatsApp or whatever, you’ll need an iron will to stop your mind wandering off to wonder what’s going on social media today.
7. Managing Internal Distractions
It’s normal for other thoughts to drift into your head when you sit down to work: worrying about other subjects, ideas or plans, things you need to do . But you aren’t in the right mindset to study effectively.
You can train your mind to have better focus through meditatio n. Read more about the benefits and how to get started here .
Alternatively, why not try maintaining a “distractions list”?
Keep a notepad to hand so you can write thoughts down and get them out of your head as soon as they occur. You can then come back to them later when you have time to give them the attention they need.
8. Take Quality Study Breaks
Depending on the intensity of your work focus, and your concentration span, take time out every 25-50 minutes to rest and reset.
Pausing between study sessions is one of the best ways to keep your energy and focus up over the long haul so that you can remain effective. Studying is a marathon, not a sprint!
Best practice is to avoid turning on the TV, opening a phone game, checking messages / emails or doing anything else that will break your focus. Save these activities for a longer break.
Good things to do in your 10-minute breathers include:
- Making a cup of tea
- Looking out at the garden
- Taking a short walk
- Doing some light exercise: stretches, yoga, a few push-ups
Anything that lets your mind rest and reset , without being pulled into a new world of distraction.
9. The Pomodoro Technique
Bit of a marmite technique this. Some people love it, some hate it.
The basic idea is that set a timer for, say, 30 minutes, and work while it’s counting down.
When the timer goes off, stop work and take a short break (5-10 mins).
Then rinse and repeat – with a longer break after 3-4 cycles of working and a shorter break.

Fans of the Pomodoro technique like:
- The focus and motivation that comes when you set a ticking clock in the background
- Having the structure of more intense bursts of work, with short breaks to recharge
Creator of the technique Francesco Cirillo is incredibly specific about the specifics for using this technique in practice: for the full guide to the Pomodoro technique, see here . This includes my take on which bits of Francesco’s advice you should follow, and which you can be a bit more flexible on!
10. Study Effectively With The Perfect Study Environment
Your study space can have a big impact on your ability to get things done.
Here are some pro-level considerations when choosing and setting up the perfect study environment:
- This includes resources for your studies, like access to books, or somewhere comfortable to type.
- Do you want library-reading-room silence or coffee-shop buzz? The solitude of your room or the camaraderie of a study room?
- Distraction free is best – so consider what noises or views (or company!) might pull your attention away
- “ context-dependent recall ” is a very well-studied psychological effect that offers a secret study advantage to students in the know. It basically says that if you do your learning in Environment A and later have to recall in Environment B, the more similar the two environments are, the easier it will be to recall!
- If you’re sitting your tests in a big exam hall, can you do at least some of your studying in a space that feels a bit like an exam hall – like a big, silent, intimidating university library reading room?
- Your space can give you motivation, offer you calm, and lift your spirits. See below for a few ideas, such as sticking your favourite inspirational quote or motivational saying up on the wall!
You may find that different spaces work better for you on different days.
Maybe the silence of a library is brilliant for structuring an essay, but you enjoy the buzz of a coffee shop when you’re working on a graphic design project.
Picking an environment that suits your studying needs is a great way to ensure you’ll have an effective session.
11. Can I Listen To Music While Studying?
Short answer: sometimes!
It all depends on whether the music is distracting you from the task at hand, or not.
That partly depends on the choice of music. It’s a personal thing, but you’re more likely to be distracted by music that has lyrics, and / or is unfamiliar to you. You definitely won’t be studying effectively if you’re singing along!
But it also depends on the task at hand.
The more cognitively demanding the task, the lower your threshold for being distracted by music . Music will rarely put you off your stride when folding laundry or filing. However, it might when you’re straining to get your head around a complex new calculus technique or marshal your research into an elegant multi-layered essay argument.
For more, see my full article on does music help you study .
III. Learn How To Study Effectively With Memory Science
Go back as little as a single generation of students, and you’ll find most advice about studying well was basically little more than guesswork and intuition.
Trouble is, psychology is littered with examples where our human intuition turns out to be RUBBISH.
How to learn effectively seems to be no exception: what many people THINK is working well for them actually ISN’T working well at all (e.g. Roediger & Karpicke, 2006 ).

But the prize for getting your learning strategy right is huge!
Under lab conditions, test-score improvements equivalent to 1 or 2 whole grade boundaries (10-20 percentage points) are routinely seen in some of the most widely-cited experimental studies.
And from my own experience, I’ve seen student’s performance TRANSFORMED, time and again, when they start to apply the principles of learning science to their studies .
So without further ado, here are the absolute most important things you need to know about the psychology of memory, and what it tells about the smartest ways to learn:
12. Pull It Out, Don’t Push It In
If you only take one thing away from this article, it’s this:
T he best learning happens when you’re trying to recall information . This is the best way to study effectively.
The moment where you’re pulling a piece of information out of your memory is the magic moment in which your memory for the information gets strengthened.
It’s a principle known to psychologists as “ retrieval practice ”, sometimes known as “active recall”.

So don’t just push the information IN over and over again by re-reading, highlighting or taking notes. It might feel as though you’re learning, but you’ll quickly forget what you studied.
Focus on pulling information OUT of memory: test yourself on what you know .
13. The Power of Spaced Repetition
Even if you’re learning with recall practice, your memory will fade over time, per the “ forgetting curve ” first developed by German psychologist Hermann Ebbinghaus:

The solution is to space out your retrieval practice. Don’t do it all on one day, but spread it out, with intervals in between.
This one’s known to psychologists as spaced learning : you may have heard of it before as spaced repetition. Neuroscientists can even observe the positive impact of spacing at the level of neurons .
That doesn’t necessarily mean you have to put in more time overall on a given topic. But it does mean spacing out the topic’s allotted study time over different days .
So rather than spending an hour on one subtopic all on the same day, do half an hour the first day. Then do 10 minutes after a day or two, 10 minutes a week or so later, 10 minutes the week before the exam.
14. The Best Way To Build Your Memory
When you combine spacing with retrieval practice, you get spaced retrieval practice .
I.e. test yourself repeatedly on the topic, at time intervals.
When you start doing this, the real memory magic happens .
When you practise spaced retrieval practice, what you’re really doing is “interrupting forgetting”. Your brain is lazy and naturally WANTS to forget information that’s not important.
But each time you leave a time delay then try and recall it, it sends a powerful signal that this information matters , and your memory responds by storing it away much more strongly.
The key is to build regular opportunities for spaced retrieval practice into your study routine.
There are lots of ways to do this – this example is the spacing schedule I used when studying for my psychology final exams at uni:

15. How To Study Effectively … In The Goldilocks Zone
When you’re doing retrieval practice, it should feel tough, but not impossibly so .
If you’re struggling to remember more than half of the topic you’re studying, you probably need to back up a step. Re-read your notes again, or break the topic down into smaller chunks and practise one section at a time.
But it shouldn’t feel too easy either.
If you’re getting 95%+ right, space it out more , and leave a longer delay to make it harder. The best learning happens in the “ Goldilocks zone ” when it’s tough to remember the information, but not impossibly so. Not too hard, not too easy, but just right .

You vary the amount of spacing in order to make sure you’re landing right in the Goldilocks Zone.
If it feels too easy, space it out more by leaving a longer delay before re-testing. If it feels too easy, leave a shorter delay and space it out less.
16. Feedback And Learning From Your Mistakes
As you do your retrieval practice, it’s worth underlining that it doesn’t really matter if you get a given question right or wrong.
The point of testing yourself on a fact isn’t to “check whether you’ve learned it”: the testing is the learning itself . It really is a great way to study effectively!
If you’re getting lots of questions wrong, consider shortening your spacing interval next time (see The Goldilocks Effect above). But also bear in mind that you’re doing something good for learning whether you get an individual question right OR wrong!

17. Are You A “Visual Learner” or “Auditory”? (Spoiler Alert: it doesn’t matter!)
There used to be this really popular idea in education theory that everyone was either:
- A “visual” learner, who learns best by looking at stuff,
- An “auditory” learner who learns best by hearing stuff,
- Or a “kinaesthetic” learner who learns through movement and models.
It’s an alluring idea because it seems to make so much sense. It appeals to the inner satisfaction we get when discovering a scientific label that so beautifully seems to describe what we’d always suspected about ourselves.
The bad news is it’s simply not true .
A whole generation of experimental psychologists has looked for evidence that learning in your preferred “learning style” (visual / auditory / etc) actually helps you learn faster and remember more.
The results are conclusive: there is no evidence for this idea at all .
It’s true that many of us have preferences when it comes to a learning style, but there’s simply no experimental evidence that pandering to your preference helps you learn.
We’re all basically “spaced retrieval practice” learners . As we’ve already discovered, we learn best when we’re pulling information out of memory, not cramming it in. And even better, doing that at intervals spaced out over time.
18. Structuring Information In Memory
When we learn new information, it’s much easier to make sense of (and easier to remember!) if we can figure out how it relates to things we already know.
So if a topic doesn’t make sense, try sketching out the big building blocks on paper , using a spider diagram or mindmap to see how it inter-relates. Or if the topic is about a process that goes in order from start to finish, try a flow diagram .
If you’re learning a language, think about how new words relate to words you already know in your own language.
This principle is the basis of how many mnemonic strategies work – see #28 .
IV. What Are Effective Study Strategies?
It’s one thing to talk about the theory behind ways to study effectively.
But it’s a whole other challenge to actually start USING these effective learning techniques in practice. Especially using them with confidence, competence and consistency.
This section is deliberately more “meaty” in terms of detail than other sections. Because details matter when it comes to making sure you’re studying effectively and not wasting your time.
The good news is you don’t need to read every item in this section. There are different ways to be an effective student.
Through years of experience coaching students in how to study smarter , I’ve learned that the best approach to finding a more efficient way to study is to make the smallest possible change to what you’re doing already .
I’d encourage you to browse this section to find the study methods you already use today. And then make the recommended adjustments to your strategy to VASTLY maximise its effectiveness.
- If you like flashcards (and quiz apps like Anki / Quizlet): see #19 .
- If you like making notes: see #20 .
- For better ways to read: see #22 .
- If you like mind maps / spider diagrams: see #23 .
- If you like study groups or testing with friends / family: see #24 / #25 .
- For those interested in mnemonic strategies: see #26 .
- And if you have problems to practice more than knowledge to learn, e.g. math(s) style problems in Math(s), Science and Engineering: see #27 and #28 .
19. How To Study Effectively… With Flashcards
My personal favourite!
Flashcards can be a FABULOUS way to study: they are literally MADE for retrieval practice.
But you’ve got to use them properly.

Here are my top DOs and DONTs to get the most out of this powerful technique:
- DO have a clear question on the front , a clear answer on the back
- DON’T put too much information on either side . Less is more, and note form is fine (in fact, heartily encouraged). Some of the most effective flashcards use just a very few words on the question side, and have a single word, name, date or number on the back.
- DO add a note on the front of the card about what it is you’re trying to remember. If it’s a list of 5 things, write the number “5” on the front of the card.
- DON’T spend too much time writing the cards. Make them quick: go, go, go! Remember that the real benefit comes when you test yourself on the cards. So…
- … DO test yourself on the cards at intervals, spaced out over time. And…
- … DON’T be tempted to “refresh your memory” by flicking through the cards before you re-test yourself. That’s cheating, and completely messes with the benefits of the spacing effect (see “The Goldilocks Zone” above).
All of this works great for paper flash cards, but it applies equally well to most digital flashcard systems, like Anki and Quizlet.
20. How To Make Effective Study Notes
Do you like to write notes?
They’re incredibly popular with students at high school, college, university and just about anywhere else you need to study for exams.
The problem is that note-making or writing summaries are pretty terrible ways to get information into memory .
It’s “feel-good” learning rather than a true method to help you study effectively.
You might feel all good and productive while you’re making the notes, but you’re not making much progress on actually LEARNING the stuff – as measured by how much you can remember a week or two later.
Sure, some of the information might stick for a short time. But I’ve heard many students look back on their weeks-old notes and say that they may as well have been written by someone else for all they recognise them.
So what should you do if you like to study with notes?
The good news is there’s a small tweak to your technique that will transform your note strategy into something that’s a really, seriously effective technique for efficient studying:

Divide the page in two, and write questions in the left-hand column, answers in the right-hand column.
I call it “Q&A Notes”, and they work in two ways:
- “Memory is the residue of thought” ( Daniel Willingham ), and by splitting up your notes into questions and answer pairs, it forces you to engage with the material in more depth .
- But the best bit is you’ve now got a ready-made study resource to do retrieval practice with . Simply cover up the “answers” column and test yourself on each question in turn.
Done well, this technique actually ends up being extremely similar to flashcards, the main difference being the size of the paper you’re using! So follow all the DOs and DONTs above for best results with flashcards.
21. How To Study Effectively… With Blank Page Retrieval
“Blank page retrieval” – sounds fancy!
But it’s actually really simple.
Here’s how it works:
- Put your books away, then scribble down everything you can remember about a topic.
- After you’ve squeezed out as much as you can from memory, go back to your books and add in any missing details and correct anything you mis-remembered with a different coloured pen.
- Rinse and repeat: see “the power of spaced repetition”. Next time you train yourself on this topic, aim to have fewer missing details – until you have none at all come the week before the exam!
A plain sheet of paper is an under-rated study tool. Try it!
22. Reading For Learning: How To Study And Remember What You Read
If you’ve ever been told anything even remotely helpful about how to study for exams, you’ve probably been told that re-reading your books or notes is a pretty unhelpful thing to do.
As a way to learn efficiently, reading SUCKS . It’s definitely not one of my top “how to study effectively” recommendations.
So you should avoid all reading then?
Not necessarily.
Reading can have its place in your overall study system, often near the start of the process. For example, if you intend to use a different technique (e.g. flashcards, Q&A notes) but it’s your first time looking at the material, and you want some initial familiarity with it first.
So if you want to make reading more effective as a study technique, here are my tips:
- Slightly Better: highlight or underline key words as you go, which helps you stay focused and avoid missing key information. It makes reading slightly less suck-y as a study strategy, though still not great. Just highlight / underline the key words and phrases, there’s no point highlighting vast chunks of text at a time.
- Much Better A: Read (with highlighting / underlining), then challenge yourself to a round of blank page retrieval right after the reading. This will massively help the information to start to “stick” through retrieval practice, plus helping you structure and organise the information in memory.
- Much Better B: If you’ve seen the material before, try pre-testing yourself on it BEFORE doing any reading at all. Do some blank page retrieval first, and challenge yourself to see what you can remember about the topic – however little it is!
You can, of course, do all three of the above at once: pre-test yourself with blank page retrieval, read (with highlighting / underlining), then do another blank page retrieval afterwards. This will be vastly most effective than just reading, especially if you follow up with subsequent rounds of spaced retrieval practice by attempting the blank page retrieval exercise on other days.
23. How To Study Effectively… With Mindmaps
Ah, mindmaps. (Also called “spider diagrams”).
Me and mindmaps go way back: I remember the hours and hours and hours happily spent in my room in my (high) school days merrily producing neat mind maps of all the information I needed to know for my exams.
There was a belief – which you may also have heard – that mindmaps carried some almost-magical ability to get knowledge into your memory.
What’s true is that i t DOES help to get information organised in your memory :
It’s useful to understand the overall structure of a topic. Rather than trying to learn a random jumble of disconnected facts, it’s much easier to learn a topic when you appreciate how the details are organised into their major sub-categories, and how specific points relate to each other.
What’s not true is that this process alone will magically etch all the information into your memory .
So here’s my 3-step process to make learning with mind maps into an effective study strategy that will actually work:
- You don’t need a beautifully-illustrated picture in the middle. You don’t need every word written on a curvy line. Make them fast, make them rough. It’s the process of making them that counts, not having the finished product.
- Shut your books, and sketch as much as you can from memory. Once you’ve squeezed your memory as much as you can, grab a second colour of pen and correct any mistakes
- Yes, you heard me. Knowing that you’ll throw them away will encourage you to make them quick, and focus on what matters: the exercise itself. And when you’ve done it once, do it again: do our usual spaced retrieval practice thing, and leave a time gap, then repeat the whole exercise of scribbling out the mind map from memory.
(If you’re thinking to yourself “but that just describes blank page retrieval” – well, you’re completely right. You got me. They’re basically the same thing. But, shhh, keep your voice down, because for people that love mind maps, it may feel like an easier mental leap to think in terms of “starting to draw your mind maps from memory” rather than having to adopt some whole other study technique!)
24. How To Study Effectively… With Study Groups
Getting together with others in a study group can be a great idea for many reasons:
- It mixes things up for you, helping you stay interested and engaged.
- If you’re studying a more “arts” style subject where opinions matter, discussing things as a group can be a great way to uncover new angles and a fresh take that your examiners will love.
- Sometimes, your friends will have figured things out that you haven’t, and you can learn from them .
- Or you might have figured out something your friends haven’t, in which case you’ll do a lovely bit of spaced retrieval practice as you teach them .
“Explaining something to others” is a legit great idea for learning, so much so that some people even go around explaining things to an empty room or a stuffed animal.
25. How To Get Friends / Family Member To Test You Effectively
Getting friends or family members to test you is also a good way to study and learn your stuff effectively: it’s retrieval practice, after all!

There are some secrets to making “getting someone to test you” work as an effective study method. Here are some quick tips for whoever is playing the role of “tester”:
- What are the facts, dates, formulas, grammar points they need to know? Be sure to agree this with your testee first.
- Ask questions to check they know each piece of information (OK, step ii is kind of obvious…).
- I thought this was obvious, but I’ve seen high-school students testing each other and just saying “no!” if the answer was wrong, and not actually giving the right information. They need to know what they should have said if they get anything wrong.
- It’s not a race. Try not to let them give up before you’ve seen them squeeze their memory for at least a good few seconds – encourage them to make an educated guess if you need to.
- Note this down as a missed attempt, either in your head, or on the page. Let a question or two go by, then re-test this question. If they still don’t remember, keep coming back to this question every couple of questions until they get it right for the first time.
- It’s easy to remember things for a minute or two. So if they initially got a piece of information wrong, but passed one of your re-tests, make sure you come back to it at least once more after a much longer delay. If they pass the second re-test, great. If they don’t, keep re-testing until they can reliably get it right after a good delay.
- Keep a note of the biggest trouble spots, and make sure they re-test themselves on these a day or two later (or even have a follow-up session and do it yourself!)
Make your study buddy read these seven steps, and look forward to spectacularly improved pair-testing results!
26. How To Study Effectively… With Mnemonic Strategies
If you spending any time researching memory strategies, you might come across advice on mnemonic strategies. Method of Loci / Memory Palace, the Major System, the Pegword Method, Chunking and more…
These techniques have been honed by “memory champions”, who perform astonishing feats of memory like memorising four thousand six hundred and twenty (4620..!!!!!) digits in an hour, or a pack of cards in 12.74 seconds ( https://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/World_Memory_Championships ).
But many mnemonic strategies, frankly, simply aren’t worth the time they take to master when it comes to learning information in an academic context.

Here’s my take on some of the popular ones:
- Chunking: this is really a whole category of tricks! It corporates techniques like acronyms and acrostics, and looking for patterns in lists and numbers to make them easier to remember. Flexible, helpful and highly recommended: I’ve written at length about chunking for memory here .
- Peg Word Method: sometimeshelpful for remembering lists, especially when they’re lists of concrete objects. Details on how to use it here .
- Major System: if you’ve got lots of numbers, this might be worth it. But not worth the effort for most of us. It takes time to learn a code for turning numbers (hard to remember) into words (easier to remember).
- Method of Loci / Memory Palace: very powerful strategy for many memory champions that works by “storing” memories in specific locations around a well-known environment, like your home. Takes some getting used to. I rarely meet students who’s found it helpful as a learning strategy for academic material.
By all means dive into the world of mnemonics. Just make sure the time you spend learning the more complex techniques is actually worth it!
27. Using Practice Tests To Study Effectively
Practice questions are yet another way to do retrieval practice. They get my seal of approval – provided you’re following the steps below.
- For some subjects that are more about applying knowledge (e.g. to writing essays) or practising solving problems (e.g. maths), you’ll want to be doing plenty of practice questions right from the beginning.
- For more knowledge-based subjects, you might rely less on practice questions. Perhaps sprinkle in a few early on to give you a good sense of how you’ll be tested, and a few closer to the test, once you’ve finished all your work with e.g. flashcards / Q&A notes.
I recommend the following 2-phase process for effective practice-question study sessions:

First, do as much as you can from memory, preferably under timed conditions (see “take a pressure vaccine”). It’s OK to guess if you’re not sure.
Second, check carefully, and give yourself feedback. Once you’ve given your best shot at a string of questions, or better still, a whole exam paper, check your answers. Consult your notes or books to see what you got right and what you missed. Or if you’ve got access to a mark scheme, put your examiners’ hat on, and diligently check what scored you marks and where you dropped marks. This is a crucial part of the process, and one many students skimp on. That’s a bad mistake, as there’s so much to be learned from it!
Advanced tip : set aside any questions that totally foxed you, and have another crack at them tomorrow to check you learned something!
28. How To Study Effectively… With Interleaving
This one’s for you if you have math(s) style problems to practice, for example in science, engineering, and of course, math(s).
It may also be helpful for grammar exercises in languages, and even practising physical skills.
Interleaving works by breaking up “blocks” of practice questions . For example, rather than doing a whole long stretch of practice on Problem Type A before doing another whole long stretch on Type B, you jumble them up.
Switch between Problem Type A and B – a couple of each, continually switching between the two.
The graphic uses integration and differentiation problems to illustrate the concept, but it works with any type of problem. For best results, use interleaving with two types of problems that are quite closely related and potentially confused :

In the classic study, Rohrer & Taylor (2007) saw test score improvements from 49% for students who did blocking to 74% for students who did interleaving. Both had groups had identical study time.
That’s a mindblowing improvement in my book!
V. Champions’ Mindset: Unleash The Power of Peak Performance
An often-neglected but crucial key to the puzzle of how to study effectively comes in making sure you yourself are well .
You have to think of yourself as an athlete – an elite, exam-taking athlete. And you cannot possibly perform at your best unless you are taking good care of your mind and body.
Here’s how.
29. Keep Going
Some study advisors recommend setting goals about what you want to achieve in your exams.
That’s fine, but I want you to go a level deeper and decide what kind of student you want to be . Are you going to decide to identify as a high-performing student or not?
Once you do decide you’re a high-performer, you’ll behave accordingly! That might only mean a small tweak to your habits each day. Working three hours instead of two. Using retrieval practice not just re-reading.
Small changes sustained each day over weeks and months add up to a massive difference in end result: little by little you’ll find you CAN study efficently and effectively!
And if you struggle to associate with that new identity as a high performer today: then PRETEND. Ask yourself what a high performer would do in this situation? How would they tackle this assignment, this tricky exam question? Act accordingly.
With a bit of practice and time, you’ll turn round and realise you don’t need to pretend any more. You ARE the high performer you’ve been pretending to be all this time.
30. Keep Growing
Oh, so you don’t believe you have what it takes to be a high-performer?
Not smart enough?
Not clever enough?
You don’t have to settle with where you’re performing today. With deliberate, sustained practice, you can level up your brain and improve.
There’s no such thing as not being “good at something” – you’re just not good at it “yet”! (Just like how you’re currently learning how to study effectively!)
It’s called growth mindset : check out our handy guide to growth mindset , explore Carol Dweck’s seminal work on the subject, or try her book Mindset .
Keep studying, keep growing.
31. Keep Walking
Make sure you’re getting a regular bout of exercise in. Ideally, building something into your daily routine that gets your heart rate up: walk, swim, run, cycle, play sport .

A brisk walk is a great way to take a “quality break”. It will not only reset your focus, but also boost your creativity! People often find a good idea often pops into their head while out on a walk. Plus, psychologists have good evidence for the relationship between walking and creativity .
32. Keep Talking
Don’t neglect those around you.
Cultivate a support network among your friends and family so they are there when you need them. That’s best done by talking: sharing what’s going well and not well regularly.
Getting struggles off your chest by discussing them with someone is also a great way to avoid stress building up and make sure that you’re in the right mindset to study effectively.
33. Keep Breathing

Taking slow, calm breaths from deep in your belly is a great tonic to soothe jittery nerves. Get in the habit of practising regularly. It’s another great way to find the right mindset to study effectively.
And if you struggle with anxiety , consider practising meditation: it’s not weird or religious any more, it’s mainstream. And it just teaches how to focus your mind in the present and stop it racing with worries about the future.
I’ve compiled LOADS of the latest research on the benefits of meditation for students in this great article . Plus, you can learn all about the Headspace app in my thorough, honest review!
If you’re looking for a technique that:
- improves your concetration, focus, stress levels, social interactions, memory, and overall well-being…
Then mindful meditation might be for you!
34. Take A Pressure Vaccine
Immunise yourself against the pressures of final exam day by practising regularly under exam conditions :
- Silent room (preferably surrounded by other people working silently)
- Timed paper
- Exam stationery
You could even commit to telling someone the results of the mock paper to simulate the pressure to deliver.
The more you get used to it now, the easier it will be on exam day! It’s one of my TOP methods for how to study effectively for exams.
VI. Knowing When To Stop
If you’re having trouble getting fired up to work, try these study motivation tricks .
But for a lot of the Exam Study Expert family, you’re conscientious and committed. So, if anything, I will serve your long-term interests best not by urging you to work (even) harder, but by reminding you not to work too hard and burn yourself out !
You are not a machine. You need to pull yourself away from your books to rest and recharge from time to time.
Relax: you know how to study effectively now, so you don’t need to burn the midnight oil any more. Far better to adopt a sustainable, healthy routine, keeping work and play in balance .
35. Sleep On It
If you’re getting fewer hours of sleep than you need, your brain function will suffer. Typically, adults need 7-8 hours, and it’s more for teenagers. Without proper sleep you’ll be:
- Worse at paying attention
- Worse at remembering things
- Less able to solve problems
- Not so creative
- Less able to form new memories
Who wants that horrific set of disadvantages when studying?
No-one. Get a decent night’s sleep and you’ll have a better chance of studying effectively.

And if sleep doesn’t come easy, start with this checklist .
If it’s the day before a big test, set a clear “quit time” for the night, so that you stop studying at least an hour before bed time. That gives you chance to wind down before bed.
36. Stop & Unplug
Just as important as working hard, you must rest hard . In your quest for exam glory and effective study sessions, do not forget the ancient but treasured art of Stopping For The Day, or the time-honoured practice of The Day Off.
I believe there are three types of “unplugging” we all need:
- A few minutes off an hou r, to maintain focus.
- A few hours off each day , for wellbeing activities like exercise, and at least a little daily “me” time.
- walking in nature, playing competitive sport, making fine music, hanging out with friends, or simply curling up with Netflix or a book.
If you need to hear this, then you might like this little pep talk on the importance of time off:
37. Have Fun
When the time comes to put your pen down, enjoy it: guilt-free.
When you’re working, study effectively and study hard.
But when you stop, make it quality time .
Don’t fritter away your hard-earned rest-hours on low-value activities. Make it things you really enjoy.
If you enjoy socialising, hang out with your mates. If you’re really into that new season on Netflix, this is the time to binge an episode or two.
Play sport.
Sing. Hike.
Kick back. Have fun.
You’ve earned it.
And when it’s time to study again, you’ll be return refreshed, revived, and be all the more effective for it.
Wishing you every success in your studies!
The Science Of Studying Smart
Download my free exam success cheat sheet: all my #1 must-know strategies to supercharge your learning today.
Your privacy protected. No spam. Unsubscribe any time.
20 Comments
I was going CRAZY!!!! trying HARD and LONG (and WRONG!) and not getting any good results. pushing myself with more and more Discipline in place. my classmates would mock me for not been smart (because i was really pushing the limits on time management and discipline and the results were dismal!). THANK YOU for this article. no one told me it should be like this and for the first time in my learning experience i feel like this is it! and it works! it’s a miracle! 😂😍❤ I’m in a country where is really hard to buy anything internationally (Paypal and others don’t support these regions). but i try my hardest to buy both of your books for my MA and PhD studies. you made me soo happy! THANK YOU SIR!
note: for the reader’s interest, for years i was underlining and highlighting, and taking notes, and then making smaller notes from my notes. but because i was writing them from the main source (Not from memory) and just practicing WRITING! (instead of actually LEARNING!) then re-reading them over and over again, i wasn’t getting enough from the work i was putting in. “” Now i’m using Q&A Notes, covering the answers, plus spaced retrieval repetition (being retrieval, i wasn’t just re-reading them anymore) and remembering. Thank goodness!
What a wonderful story, THANK YOU for taking the time to share!
It’s a really inspirational message to others about the power of these strategies.
Well done for taking the time to figure out what you wanted to change, and putting that into practice, and great to hear you’re making such strong progress as a result.
If we’ve done enough to earn it, sharing this article with others is always a gesture we really appreciate – people you know in real life, on Reddit or other online forums / communities you’re part of, that kind of thing 🙂
But again, thank you so much for sharing the results, and keep up the good work!!
“Thank you very much for these valuable tips for studying! Your contribution in directing me towards effective ways of learning has been invaluable. I will work on applying these strategies to make the most of my time studying. Here are other methods that I have collected in a summary.” https://www.ebdaelan.com/2023/04/10.html
I normally moderate out comments that include outbound links because most links people try to leave are low-quality and it quickly gets quite spammy, but I used Google translate (my Arabic is unfortunately not very good!) to take a look at your linked article, and it looks like a solid set of advice that has had a lot of effort put into it. So, your link stays, with my endorsement! 😀
Thank you very much, do not worry, it is not my style to promote a private interest or harm anyone, but I love learning and disseminating what I see as useful to society. I have even read many of the content and ideas that you present, and I liked it very much, and I summarized what I found useful for our Arab society, mentioning the source. You are truly a platform. It provides useful value. I wish you success and share the benefit with you
This is an amazing article, and these tips are some helpful tips to improve the study habits and achieve better grades.
This blog has very good information. Very useful information for every student. Surely this information is important to pass any exam well I suggest every student to save it I am thankful to the authors
It is a very nice article. Thanks for sharing strategies for how to study for an exam. It’s very helpful information.
Perfect Article, thanks for writing it. I have learned something new which helps me in my studies as well as my work.
You’re so welcome! Wishing you every success 🙂
wow i love the tips they will definitely work for me
Glad to hear it – you got this! 😀
It is very good piece of of advice. thank you very much. i will follow you
thanks for sharing ^^ it helps a lot 😀
I can’t wait for the new book!
Hey Osnel – thanks so much, I really hope you like it!
If you haven’t already, you can check out the book at https://geni.us/studies .
Wishing you every success, my friend 🙂
Good resource thank you so much posting this article
So glad you enjoyed it! Good luck with the studies 🙂
this is an amazing resource thanks so much
You’re so welcome – wishing you every success!
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .
Read My Test-Taking Technique Book For More Marks In Exams

Top Picks: Recommended Reading From The Blog
How To Study Effectively : Ultimate Guide [READER FAVOURITE]
Why Study [READER FAVOURITE]
Exam Memorization Secrets
Inspirational Exam Quotes
Finding The Perfect Study Routine
Pomodoro Method : 9-Step Guide
Best Books About Studying
Listen To The Podcast


Choose Your Test
- Search Blogs By Category
- College Admissions
- AP and IB Exams
- GPA and Coursework
How to Study for a Test: 17 Expert Tips
Other High School

Do you have a big exam coming up, but you're not sure how to prepare for it? Are you looking to improve your grades or keep them strong but don't know the best way to do this? We're here to help! In this guide, we've compiled the 17 best tips for how to study for a test. No matter what grade you're in or what subject you're studying, these tips will give you ways to study faster and more effectively. If you're tired of studying for hours only to forget everything when it comes time to take a test, follow these tips so you can be well prepared for any exam you take.
How to Study for a Test: General Tips
The four tips below are useful for any test or class you're preparing for. Learn the best way to study for a test from these tips and be prepared for any future exams you take.
#1: Stick to a Study Schedule
If you're having trouble studying regularly, creating a study schedule can be a huge help. Doing something regularly helps your mind get used to it. If you set aside a time to regularly study and stick to it, it'll eventually become a habit that's (usually) easy to stick to. Getting into a fixed habit of studying will help you improve your concentration and mental stamina over time. And, just like any other training, your ability to study will improve with time and effort.
Take an honest look at your schedule (this includes schoolwork, extracurriculars, work, etc.) and decide how often you can study without making your schedule too packed. Aim for at least an hour twice a week. Next, decide when you want to study, such as Tuesdays, Thursdays, and Sundays from 7-8pm, and stick to your schedule . In the beginning, you may need to tweak your schedule, but you'll eventually find the study rhythm that works best for you. The important thing is that you commit to it and study during the same times each week as often as possible.
#2: Start Studying Early and Study for Shorter Periods
Some people can cram for several hours the night before the test and still get a good grade. However, this is rarer than you may hope. Most people need to see information several times, over a period of time, for them to really commit it to memory. This means that, instead of doing a single long study session, break your studying into smaller sessions over a longer period of time. Five one-hour study sessions over a week will be less stressful and more effective than a single five-hour cram session. It may take a bit of time for you to learn how long and how often you need to study for a class, but once you do you'll be able to remember the information you need and reduce some of the stress that comes from schoolwork, tests, and studying.
#3: Remove Distractions
When you're studying, especially if it's for a subject you don't enjoy, it can be extremely tempting to take "quick breaks" from your work. There are untold distractions all around us that try to lure our concentration away from the task at hand. However, giving in to temptation can be an awful time suck. A quick glance at your phone can easily turn into an hour of wasting time on the internet, and that won't help you get the score you're looking for. In order to avoid distractions, remove distractions completely from your study space.
Eat a meal or a snack before you begin studying so you're not tempted to rummage through the fridge as a distraction. Silence your phone and keep it in an entirely different room. If you're studying on a computer, turn your WIFI off if it's not essential to have. Make a firm rule that you can't get up to check on whatever has you distracted until your allotted study time is up.
#4: Reward Yourself When You Hit a Milestone
To make studying a little more fun, give yourself a small reward whenever you hit a study milestone. For example, you might get to eat a piece of candy for every 25 flashcards you test yourself on, or get to spend 10 minutes on your phone for every hour you spend studying. You can also give yourself larger rewards for longer-term goals, such as going out to ice cream after a week of good study habits. Studying effectively isn't always easy, and by giving yourself rewards, you'll keep yourself motivated.

Our pets are not the only ones who deserve rewards.
Tips for Learning and Remembering Information
While the default method of studying is reading through class notes, this is actually one of the least effective ways of learning and remembering information. In this section we cover four much more useful methods. You'll notice they all involve active learning, where you're actively reworking the material, rather than just passively reading through notes. Active studying has been shown to be a much more effective way to understand and retain information, and it's what we recommend for any test you're preparing for.
#5: Rewrite the Material in Your Own Words
It can be easy to get lost in a textbook and look back over a page, only to realize you don't remember anything about what you just read. Fortunately, there's a way to avoid this.
For any class that requires lots of reading, be sure to stop periodically as you read. Pause at the end of a paragraph/page/chapter (how much you can read at once and still remember clearly will likely depend on the material you're reading) and—without looking!—think about what the text just stated. Re-summarize it in your own words, and write down bullet points if that helps. Now, glance back over the material and make sure you summarized the information accurately and included all the important details. Take note of whatever you missed, then pick up your reading where you left off.
Whether you choose to summarize the text aloud or write down notes, re-wording the text is a very effective study tool. By rephrasing the text in your own words, you're ensuring you're actually remembering the information and absorbing its meaning, rather than just moving your eyes across a page without taking in what you're reading.
#6: Make Flashcards
Flashcards are a popular study tool for good reason! They're easy to make, easy to carry around, easy to pull out for a quick study session, and they're a more effective way of studying than just reading through pages of notes. Making your own flashcards is especially effective because you'll remember more information just through the act of writing it down on the cards. For any subjects in which you must remember connections between terms and information, such as formulas, vocabulary, equations, or historical dates, flashcards are the way to go. We recommend using the Waterfall Method when you study with flashcards since it's the fastest way to learn all the material on the cards.
#7: Teach the Material to Someone Else
Teaching someone else is a great way to organize the information you've been studying and check your grasp of it. It also often shows you that you know more of the material than you think! Find a study-buddy, or a friend/relative/pet or even just a figurine or stuffed animal and explain the material to them as if they're hearing about it for the first time. Whether the person you're teaching is real or not, teaching material aloud requires you to re-frame the information in new ways and think more carefully about how all the elements fit together. The act of running through the material in this new way also helps you more easily lock it in your mind.
#8: Make Your Own Study Guides
Even if your teacher provides you with study guides, we highly recommend making your own study materials. Just making the materials will help the information sink into your mind, and when you make your own study guides, you can customize them to the way you learn best, whether that's flashcards, images, charts etc. For example, if you're studying for a biology test, you can draw your own cell and label the components, make a Krebs cycle diagram, map out a food chain, etc. If you're a visual learner (or just enjoy adding images to your study materials), include pictures and diagrams.
Sometimes making your own charts and diagrams will mean recreating the ones in your textbook from memory, and sometimes it will mean putting different pieces of information together yourself. Whatever the diagram type and whatever the class, writing your information down and making pictures out of it will be a great way to help you remember the material.

How to Study for a History Test
History tests are notorious for the amount of facts and dates you need to know. Make it easier to retain the information by using these two tips.
#9: Know Causes and Effects
It's easy and tempting to simply review long lists of dates of important events, but this likely won't be enough for you to do well on a history test, especially if it has any writing involved. Instead of only learning the important dates of, say, WWI, focus on learning the factors that led to the war and what its lasting impacts on the world were. By understanding the cause and effects of major events, you'll be able to link them to the larger themes you're learning in history class. Also, having more context about an event can often make it easier to remember little details and dates that go along with it.
#10: Make Your Own Timelines
Sometimes you need to know a lot of dates for a history test. In these cases, don't think passively reading your notes is enough. Unless you have an amazing memory, it'll take you a long time for all those dates to sink into your head if you only read through a list of them. Instead, make your own timeline.
Make your first timeline very neat, with all the information you need to know organized in a way that makes sense to you (this will typically be chronologically, but you may also choose to organize it by theme). Make this timeline as clear and helpful as you can, using different colors, highlighting important information, drawing arrows to connecting information, etc. Then, after you've studied enough to feel you have a solid grasp of the dates, rewrite your timeline from memory. This one doesn't have to be neat and organized, but include as much information as you remember. Continue this pattern of studying and writing timelines from memory until you have all the information memorized.
Know which direction events occur in to prepare for history tests.
How to Study for a Math Test
Math tests can be particularly intimating to many students, but if you're well-prepared for them, they're often straightforward.
#11: Redo Homework Problems
More than most tests, math tests usually are quite similar to the homework problems you've been doing. This means your homework contains dozens of practice problems you can work through. Try to review practice problems from every topic you'll be tested on, and focus especially on problems that you struggled with. Remember, don't just review how you solved the problem the first time. Instead, rewrite the problem, hide your notes, and solve it from scratch. Check your answer when you're finished. That'll ensure you're committing the information to memory and actually have a solid grasp of the concepts.
#12: Make a Formula Sheet
You're likely using a lot of formulas in your math class, and it can be hard remembering what they are and when to use them. Throughout the year, as you learn a new important formula, add it to a formula sheet you've created. For each formula, write out the formula, include any notes about when to use it, and include a sample problem that uses the formula. When your next math test rolls around, you'll have a useful guide to the key information you've been learning.
How to Study for an English Test
Whether your English test involves writing or not, here are two tips to follow as you prepare for it.
#13: Take Notes as You Read
When you're assigned reading for English class, it can be tempting to get through the material as quickly as possible and then move on to something else. However, this is not a good way to retain information, and come test day, you may be struggling to remember a lot of what you read. Highlighting important passages is also too passive a way to study. The way to really retain the information you read is to take notes. This takes more time and effort, but it'll help you commit the information to memory. Plus, when it comes time to study, you'll have a handy study guide ready and won't have to frantically flip through the book to try to remember what you read. The more effort you put into your notes, the more helpful they'll be. Consider organizing them by theme, character, or however else makes sense to you.
#14: Create Sample Essay Outlines
If the test you're taking requires you to write an essay, one of the best ways to be prepared is to develop essay outlines as you study. First, think about potential essay prompts your teacher might choose you to write about. Consider major themes, characters, plots, literary comparisons, etc., you discussed in class, and write down potential essay prompts. Just doing this will get you thinking critically about the material and help you be more prepared for the test.
Next, write outlines for the prompts you came up with (or, if you came up with a lot of prompts, choose the most likely to outline). These outlines don't need to contain much information, just your thesis and a few key points for each body paragraph. Even if your teacher chooses a different prompt than what you came up with, just thinking about what to write about and how you'll organize your thoughts will help you be more prepared for the test.

Fancy pen and ink not required to write essay outlines.
What to Do the Night Before the Test
Unfortunately, the night before a test is when many students make study choices that actually hurt their chances of getting a good grade. These three tips will help you do some final review in a way that helps you be at the top of your game the next day.
#15: Get Enough Sleep
One of the absolute best ways to prepare for a test-any test-is to be well-rested when you sit down to take it. Staying up all night cramming information isn't an effective way of studying, and being tired the next day can seriously impact your test-taking skills. Aim to get a solid eight hours of sleep the night before the test so that you can wake up refreshed and at the top of your test-taking game.
#16: Review Major Concepts
It can be tempting to try to go through all your notes the night before a test to review as much information as possible, but this will likely only leave you stressed to and overwhelmed by the information you're trying to remember. If you've been regularly reviewing information throughout the class, you shouldn't need much more than a quick review of major ideas, and perhaps a few smaller details you have difficulty remembering. Even if you've gotten behind on studying and are trying to review a lot of information, resist the information to cram and focus on only a few major topics. By keeping your final night review manageable, you have a better chance of committing that information to memory, and you'll avoid lack of sleep from late night cramming.
#17: Study Right Before You Go to Sleep
Studies have shown that if you review material right before you go to sleep, you have better memory recall the next day. (This is also true if you study the information right when you wake up.) This doesn't mean you should cram all night long (remember tip #15), but if there are a few key pieces of information you especially want to review or are having trouble committing to memory, review them right before you go to bed. Sweet dreams!
Summary: The Best Way to Study for a Test
If you're not sure how to study for a test effectively, you might end up wasting hours of time only to find that you've barely learned anything at all. Overall, the best way to study for a test, whether you want to know how to study for a math test or how to study for a history test, is to study regularly and practice active learning. Cramming information and trying to remember things just by looking over notes will rarely get you the score you want. Even though the tips we suggest do take time and effort on your part, they'll be worth it when you get the score you're working towards.
What's Next?
Want tips specifically on how to study for AP exams? We've outlined the f ive steps you need to follow to ace your AP classes.
Taking the SAT and need study tips? Our guide has every study tip you should follow to reach your SAT goal score.
Or are you taking the ACT instead? We've got you covered! Read our guide to learn four different ways to study for the ACT so you can choose the study plan that's best for you.

Trending Now
How to Get Into Harvard and the Ivy League
How to Get a Perfect 4.0 GPA
How to Write an Amazing College Essay
What Exactly Are Colleges Looking For?
ACT vs. SAT: Which Test Should You Take?
When should you take the SAT or ACT?
Get Your Free

Find Your Target SAT Score
Free Complete Official SAT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect SAT Score, by an Expert Full Scorer
Score 800 on SAT Math
Score 800 on SAT Reading and Writing
How to Improve Your Low SAT Score
Score 600 on SAT Math
Score 600 on SAT Reading and Writing
Find Your Target ACT Score
Complete Official Free ACT Practice Tests
How to Get a Perfect ACT Score, by a 36 Full Scorer
Get a 36 on ACT English
Get a 36 on ACT Math
Get a 36 on ACT Reading
Get a 36 on ACT Science
How to Improve Your Low ACT Score
Get a 24 on ACT English
Get a 24 on ACT Math
Get a 24 on ACT Reading
Get a 24 on ACT Science
Stay Informed
Get the latest articles and test prep tips!

Christine graduated from Michigan State University with degrees in Environmental Biology and Geography and received her Master's from Duke University. In high school she scored in the 99th percentile on the SAT and was named a National Merit Finalist. She has taught English and biology in several countries.
Ask a Question Below
Have any questions about this article or other topics? Ask below and we'll reply!
- Tips for Reading an Assignment Prompt
- Asking Analytical Questions
- Introductions
- What Do Introductions Across the Disciplines Have in Common?
- Anatomy of a Body Paragraph
- Transitions
- Tips for Organizing Your Essay
- Counterargument
- Conclusions
- Strategies for Essay Writing: Downloadable PDFs
- Brief Guides to Writing in the Disciplines

Studying 101: Study Smarter Not Harder
Do you ever feel like your study habits simply aren’t cutting it? Do you wonder what you could be doing to perform better in class and on exams? Many students realize that their high school study habits aren’t very effective in college. This is understandable, as college is quite different from high school. The professors are less personally involved, classes are bigger, exams are worth more, reading is more intense, and classes are much more rigorous. That doesn’t mean there’s anything wrong with you; it just means you need to learn some more effective study skills. Fortunately, there are many active, effective study strategies that are shown to be effective in college classes.
This handout offers several tips on effective studying. Implementing these tips into your regular study routine will help you to efficiently and effectively learn course material. Experiment with them and find some that work for you.
Reading is not studying
Simply reading and re-reading texts or notes is not actively engaging in the material. It is simply re-reading your notes. Only ‘doing’ the readings for class is not studying. It is simply doing the reading for class. Re-reading leads to quick forgetting.
Think of reading as an important part of pre-studying, but learning information requires actively engaging in the material (Edwards, 2014). Active engagement is the process of constructing meaning from text that involves making connections to lectures, forming examples, and regulating your own learning (Davis, 2007). Active studying does not mean highlighting or underlining text, re-reading, or rote memorization. Though these activities may help to keep you engaged in the task, they are not considered active studying techniques and are weakly related to improved learning (Mackenzie, 1994).
Ideas for active studying include:
- Create a study guide by topic. Formulate questions and problems and write complete answers. Create your own quiz.
- Become a teacher. Say the information aloud in your own words as if you are the instructor and teaching the concepts to a class.
- Derive examples that relate to your own experiences.
- Create concept maps or diagrams that explain the material.
- Develop symbols that represent concepts.
- For non-technical classes (e.g., English, History, Psychology), figure out the big ideas so you can explain, contrast, and re-evaluate them.
- For technical classes, work the problems and explain the steps and why they work.
- Study in terms of question, evidence, and conclusion: What is the question posed by the instructor/author? What is the evidence that they present? What is the conclusion?
Organization and planning will help you to actively study for your courses. When studying for a test, organize your materials first and then begin your active reviewing by topic (Newport, 2007). Often professors provide subtopics on the syllabi. Use them as a guide to help organize your materials. For example, gather all of the materials for one topic (e.g., PowerPoint notes, text book notes, articles, homework, etc.) and put them together in a pile. Label each pile with the topic and study by topics.
For more information on the principle behind active studying, check out our tipsheet on metacognition .
Understand the Study Cycle
The Study Cycle , developed by Frank Christ, breaks down the different parts of studying: previewing, attending class, reviewing, studying, and checking your understanding. Although each step may seem obvious at a glance, all too often students try to take shortcuts and miss opportunities for good learning. For example, you may skip a reading before class because the professor covers the same material in class; doing so misses a key opportunity to learn in different modes (reading and listening) and to benefit from the repetition and distributed practice (see #3 below) that you’ll get from both reading ahead and attending class. Understanding the importance of all stages of this cycle will help make sure you don’t miss opportunities to learn effectively.
Spacing out is good
One of the most impactful learning strategies is “distributed practice”—spacing out your studying over several short periods of time over several days and weeks (Newport, 2007). The most effective practice is to work a short time on each class every day. The total amount of time spent studying will be the same (or less) than one or two marathon library sessions, but you will learn the information more deeply and retain much more for the long term—which will help get you an A on the final. The important thing is how you use your study time, not how long you study. Long study sessions lead to a lack of concentration and thus a lack of learning and retention.
In order to spread out studying over short periods of time across several days and weeks, you need control over your schedule . Keeping a list of tasks to complete on a daily basis will help you to include regular active studying sessions for each class. Try to do something for each class each day. Be specific and realistic regarding how long you plan to spend on each task—you should not have more tasks on your list than you can reasonably complete during the day.
For example, you may do a few problems per day in math rather than all of them the hour before class. In history, you can spend 15-20 minutes each day actively studying your class notes. Thus, your studying time may still be the same length, but rather than only preparing for one class, you will be preparing for all of your classes in short stretches. This will help focus, stay on top of your work, and retain information.
In addition to learning the material more deeply, spacing out your work helps stave off procrastination. Rather than having to face the dreaded project for four hours on Monday, you can face the dreaded project for 30 minutes each day. The shorter, more consistent time to work on a dreaded project is likely to be more acceptable and less likely to be delayed to the last minute. Finally, if you have to memorize material for class (names, dates, formulas), it is best to make flashcards for this material and review periodically throughout the day rather than one long, memorization session (Wissman and Rawson, 2012). See our handout on memorization strategies to learn more.
It’s good to be intense
Not all studying is equal. You will accomplish more if you study intensively. Intensive study sessions are short and will allow you to get work done with minimal wasted effort. Shorter, intensive study times are more effective than drawn out studying.
In fact, one of the most impactful study strategies is distributing studying over multiple sessions (Newport, 2007). Intensive study sessions can last 30 or 45-minute sessions and include active studying strategies. For example, self-testing is an active study strategy that improves the intensity of studying and efficiency of learning. However, planning to spend hours on end self-testing is likely to cause you to become distracted and lose your attention.
On the other hand, if you plan to quiz yourself on the course material for 45 minutes and then take a break, you are much more likely to maintain your attention and retain the information. Furthermore, the shorter, more intense sessions will likely put the pressure on that is needed to prevent procrastination.
Silence isn’t golden
Know where you study best. The silence of a library may not be the best place for you. It’s important to consider what noise environment works best for you. You might find that you concentrate better with some background noise. Some people find that listening to classical music while studying helps them concentrate, while others find this highly distracting. The point is that the silence of the library may be just as distracting (or more) than the noise of a gymnasium. Thus, if silence is distracting, but you prefer to study in the library, try the first or second floors where there is more background ‘buzz.’
Keep in mind that active studying is rarely silent as it often requires saying the material aloud.
Problems are your friend
Working and re-working problems is important for technical courses (e.g., math, economics). Be able to explain the steps of the problems and why they work.
In technical courses, it is usually more important to work problems than read the text (Newport, 2007). In class, write down in detail the practice problems demonstrated by the professor. Annotate each step and ask questions if you are confused. At the very least, record the question and the answer (even if you miss the steps).
When preparing for tests, put together a large list of problems from the course materials and lectures. Work the problems and explain the steps and why they work (Carrier, 2003).
Reconsider multitasking
A significant amount of research indicates that multi-tasking does not improve efficiency and actually negatively affects results (Junco, 2012).
In order to study smarter, not harder, you will need to eliminate distractions during your study sessions. Social media, web browsing, game playing, texting, etc. will severely affect the intensity of your study sessions if you allow them! Research is clear that multi-tasking (e.g., responding to texts, while studying), increases the amount of time needed to learn material and decreases the quality of the learning (Junco, 2012).
Eliminating the distractions will allow you to fully engage during your study sessions. If you don’t need your computer for homework, then don’t use it. Use apps to help you set limits on the amount of time you can spend at certain sites during the day. Turn your phone off. Reward intensive studying with a social-media break (but make sure you time your break!) See our handout on managing technology for more tips and strategies.
Switch up your setting
Find several places to study in and around campus and change up your space if you find that it is no longer a working space for you.
Know when and where you study best. It may be that your focus at 10:00 PM. is not as sharp as at 10:00 AM. Perhaps you are more productive at a coffee shop with background noise, or in the study lounge in your residence hall. Perhaps when you study on your bed, you fall asleep.
Have a variety of places in and around campus that are good study environments for you. That way wherever you are, you can find your perfect study spot. After a while, you might find that your spot is too comfortable and no longer is a good place to study, so it’s time to hop to a new spot!
Become a teacher
Try to explain the material in your own words, as if you are the teacher. You can do this in a study group, with a study partner, or on your own. Saying the material aloud will point out where you are confused and need more information and will help you retain the information. As you are explaining the material, use examples and make connections between concepts (just as a teacher does). It is okay (even encouraged) to do this with your notes in your hands. At first you may need to rely on your notes to explain the material, but eventually you’ll be able to teach it without your notes.
Creating a quiz for yourself will help you to think like your professor. What does your professor want you to know? Quizzing yourself is a highly effective study technique. Make a study guide and carry it with you so you can review the questions and answers periodically throughout the day and across several days. Identify the questions that you don’t know and quiz yourself on only those questions. Say your answers aloud. This will help you to retain the information and make corrections where they are needed. For technical courses, do the sample problems and explain how you got from the question to the answer. Re-do the problems that give you trouble. Learning the material in this way actively engages your brain and will significantly improve your memory (Craik, 1975).
Take control of your calendar
Controlling your schedule and your distractions will help you to accomplish your goals.
If you are in control of your calendar, you will be able to complete your assignments and stay on top of your coursework. The following are steps to getting control of your calendar:
- On the same day each week, (perhaps Sunday nights or Saturday mornings) plan out your schedule for the week.
- Go through each class and write down what you’d like to get completed for each class that week.
- Look at your calendar and determine how many hours you have to complete your work.
- Determine whether your list can be completed in the amount of time that you have available. (You may want to put the amount of time expected to complete each assignment.) Make adjustments as needed. For example, if you find that it will take more hours to complete your work than you have available, you will likely need to triage your readings. Completing all of the readings is a luxury. You will need to make decisions about your readings based on what is covered in class. You should read and take notes on all of the assignments from the favored class source (the one that is used a lot in the class). This may be the textbook or a reading that directly addresses the topic for the day. You can likely skim supplemental readings.
- Pencil into your calendar when you plan to get assignments completed.
- Before going to bed each night, make your plan for the next day. Waking up with a plan will make you more productive.
See our handout on calendars and college for more tips on using calendars as time management.
Use downtime to your advantage
Beware of ‘easy’ weeks. This is the calm before the storm. Lighter work weeks are a great time to get ahead on work or to start long projects. Use the extra hours to get ahead on assignments or start big projects or papers. You should plan to work on every class every week even if you don’t have anything due. In fact, it is preferable to do some work for each of your classes every day. Spending 30 minutes per class each day will add up to three hours per week, but spreading this time out over six days is more effective than cramming it all in during one long three-hour session. If you have completed all of the work for a particular class, then use the 30 minutes to get ahead or start a longer project.
Use all your resources
Remember that you can make an appointment with an academic coach to work on implementing any of the strategies suggested in this handout.
Works consulted
Carrier, L. M. (2003). College students’ choices of study strategies. Perceptual and Motor Skills, 96 (1), 54-56.
Craik, F. I., & Tulving, E. (1975). Depth of processing and the retention of words in episodic memory. Journal of Experimental Psychology: General, 104 (3), 268.
Davis, S. G., & Gray, E. S. (2007). Going beyond test-taking strategies: Building self-regulated students and teachers. Journal of Curriculum and Instruction, 1 (1), 31-47.
Edwards, A. J., Weinstein, C. E., Goetz, E. T., & Alexander, P. A. (2014). Learning and study strategies: Issues in assessment, instruction, and evaluation. Elsevier.
Junco, R., & Cotten, S. R. (2012). No A 4 U: The relationship between multitasking and academic performance. Computers & Education, 59 (2), 505-514.
Mackenzie, A. M. (1994). Examination preparation, anxiety and examination performance in a group of adult students. International Journal of Lifelong Education, 13 (5), 373-388.
McGuire, S.Y. & McGuire, S. (2016). Teach Students How to Learn: Strategies You Can Incorporate in Any Course to Improve Student Metacognition, Study Skills, and Motivation. Stylus Publishing, LLC.
Newport, C. (2006). How to become a straight-a student: the unconventional strategies real college students use to score high while studying less. Three Rivers Press.
Paul, K. (1996). Study smarter, not harder. Self Counsel Press.
Robinson, A. (1993). What smart students know: maximum grades, optimum learning, minimum time. Crown trade paperbacks.
Wissman, K. T., Rawson, K. A., & Pyc, M. A. (2012). How and when do students use flashcards? Memory, 20, 568-579.

If you enjoy using our handouts, we appreciate contributions of acknowledgement.
Make a Gift
25 Scientifically Proven Tips for More Effective Studying

Staying on top of schoolwork can be tough.
Whether you’re in high school, or an adult going back to college, balancing coursework with other responsibilities can be challenging. If you’re teetering on the edge of burnout, here are some study tips that are scientifically proven to help you succeed!
Editorial Listing ShortCode:
2024 Ultimate Study Tips Guide
In this guide, we explore scientifically-proven study techniques from scientific journals and some of the world’s best resources like Harvard, Yale, MIT, and Cornell.
In a hurry? Skip ahead to the section that interests you most.
- How to Prepare for Success
- Create Your Perfect Study Space
- Pick a Study Method that Works for You
- Effective Study Skills
- How to Study More Efficiently
- How to Study for Tests
- Memory Improvement Techniques
- Top 10 Study Hacks Backed by Science
- Best Study Apps
- Study Skills Worksheets
- Key Takeaways
This comprehensive guide covers everything from studying for exams to the best study apps. So, let’s get started!
Part 1 – How to Prepare for Success

1. Set a Schedule
“Oh, I’ll get to it soon” isn’t a valid study strategy. Rather, you have to be intentional about planning set study sessions .
On your calendar, mark out chunks of time that you can devote to your studies. You should aim to schedule some study time each day, but other commitments may necessitate that some sessions are longer than others.
Harder classes require more study time. So, too, do classes that are worth several credits. For each credit hour that you’re taking, consider devoting one to three hours to studying each week.
2. Study at Your Own Pace
Do you digest content quickly, or do you need time to let the material sink in? Only you know what pace is best for you.
There’s no right (or wrong) study pace. So, don’t try matching someone else’s speed.
Instead, through trial and error, find what works for you. Just remember that slower studying will require that you devote more time to your schoolwork.
3. Get Some Rest
Exhaustion helps no one perform their best. Your body needs rest ; getting enough sleep is crucial for memory function.
This is one reason that scheduling study time is so important: It reduces the temptation to stay up all night cramming for a big test. Instead, you should aim for seven or more hours of sleep the night before an exam.

Limit pre-studying naps to 15 or 20 minutes at a time. Upon waking, do a few stretches or light exercises to prepare your body and brain for work.
4. Silence Your Cell Phone
Interruptions from your phone are notorious for breaking your concentration. If you pull away to check a notification, you’ll have to refocus your brain before diving back into your studies.
Consider turning off your phone’s sounds or putting your device into do not disturb mode before you start. You can also download apps to temporarily block your access to social media .
If you’re still tempted to check your device, simply power it off until you’re finished studying.
Research shows that stress makes it harder to learn and to retain information.
Stress-busting ideas include:
- Taking deep breaths
- Writing down a list of tasks you need to tackle
- Doing light exercise
Try to clear your head before you begin studying.
Part 2 – Create Your Perfect Study Space

1. Pick a Good Place to Study
There’s a delicate balance when it comes to the best study spot : You need a place that’s comfortable without being so relaxing that you end up falling asleep. For some people, that means working at a desk. Others do better on the couch or at the kitchen table. Your bed, on the other hand, may be too comfy.
Surrounding yourself with peace and quiet helps you focus. If your kids are being loud or there’s construction going on outside your window, you might need to relocate to an upstairs bedroom, a quiet cafe or your local library.
2. Choose Your Music Wisely
Noise-canceling headphones can also help limit distractions.
It’s better to listen to quiet music than loud tunes. Some people do best with instrumental music playing in the background.

Songs with lyrics may pull your attention away from your textbooks. However, some folks can handle listening to songs with words, so you may want to experiment and see what works for you.
Just remember that there’s no pressure to listen to any music. If you do your best work in silence, then feel free to turn your music player off.
3. Turn Off Netflix
If song lyrics are distracting, just imagine what an attention sucker the television can be! Serious studying requires that you turn off the TV.
The same goes for listening to radio deejays. Hearing voices in the background takes your brainpower off of your studies.
4. Use Background Sounds
Turning off the television, talk radio and your favorite pop song doesn’t mean that you have to study in total silence. Soft background sounds are a great alternative.
Some people enjoy listening to nature sounds, such as ocean waves or cracks of thunder. Others prefer the whir of a fan.
5. Snack on Brain Food
A growling stomach can pull your mind from your studies, so feel free to snack as you work. Keep your snacks within arm’s reach, so you don’t have to leave your books to find food.
Fuel your next study session with some of the following items:
- Lean deli meat
- Grapes or apple slices
- Dark chocolate
Go for snacks that will power your brain and keep you alert. Steer clear of items that are high in sugar, fat and processed carbs.
Part 3 – Pick a Study Method That Works for You
Mindlessly reading through your notes or textbooks isn’t an effective method of studying; it doesn’t help you process the information. Instead, you should use a proven study strategy that will help you think through the material and retain the information.
Strategy #1 – SQ3R Method
With the SQ3R approach to reading , you’ll learn to think critically about a text.
There are five steps:
- Survey : Skim through the assigned material. Focus on headings, words in bold print and any diagrams.
- Question : Ask yourself questions related to the topic.
- Read : Read the text carefully. As you go, look for answers to your questions.
- Recite : Tell yourself the answers to your questions. Write notes about them, even.
- Review : Go over the material again by rereading the text and reading your notes aloud.
Strategy #2 – PQ4R Method
PQ4R is another study strategy that can help you digest the information you read.
This approach has six steps:
- Preview : Skim the material. Read the titles, headings and other highlighted text.
- Question : Think through questions that pertain to the material.
- Read : As you work through the material, try to find answers to your questions.
- Reflect : Consider whether you have any unanswered questions or new questions.
- Recite : Speak aloud about the things you just read.
- Review : Look over the material one more time.
Strategy #3 – THIEVES Method
The THIEVES approach can help you prepare to read for information.
There are seven pre-reading steps:
- Title : Read the title.
- Headings : Look through the headings.
- Introduction : Skim the intro.
- Every first sentence in a section : Take a look at how each section begins.
- Visuals and vocabulary : Look at the pictures and the words in bold print.
- End questions : Review the questions at the end of the chapter.
- Summary : Read the overview of the text.
Ask yourself thought-provoking questions as you work through these steps. After completing them, read the text.
Studying Online
Although these three study strategies can be useful in any setting, studying online has its own set of challenges.
Dr. Tony Bates has written a thoughtful and thorough guide to studying online, A Student Guide to Studying Online . Not only does he highlight the importance of paying attention to course design, but he also offers helpful tips on how to choose the best online program and manage your course load.
Part 4 – Effective Study Skills
1. Highlight Key Concepts
Looking for the most important information as you read helps you stay engaged with the material . This can help keep your mind from wandering as you read.
As you find important details, mark them with a highlighter, or underline them. It can also be effective to jot notes along the edges of the text. Write on removable sticky notes if the book doesn’t belong to you.
When you’re preparing for a test, begin your studies by reviewing your highlighted sections and the notes you wrote down.
2. Summarize Important Details
One good way to get information to stick in your brain is to tell it again in your own words. Writing out a summary can be especially effective. You can organize your summaries in paragraph form or in outline form.
Keep in mind that you shouldn’t include every bit of information in a summary. Stick to the key points.
Consider using different colors on your paper. Research shows that information presented in color is more memorable than things written in plain type. You could use colored pens or go over your words with highlighters.
After writing about what you read, reinforce the information yet again by reading aloud what you wrote on your paper.
3. Create Your Own Flashcards
For an easy way to quiz yourself , prepare notecards that feature a keyword on one side and important facts or definitions about that topic on the reverse.
Writing out the cards will help you learn the information. Quizzing yourself on the cards will continue that reinforcement.
The great thing about flashcards is that they’re easily portable. Slip them in your bag, so you can pull them out whenever you have a spare minute. This is a fantastic way to squeeze in extra practice time outside of your regularly scheduled study sessions.
As an alternative to paper flashcards, you can also use a computer program or a smartphone app to make digital flashcards that you can click through again and again.

4. Improve Recall with Association
Sometimes your brain could use an extra hand to help you hold onto the information that you’re studying. Creating imaginary pictures, crafting word puzzles or doing other mental exercises can help make your material easier to remember.
Try improving recall with the following ideas:
- Sing the information to a catchy tune.
- Think of a mnemonic phrase in which the words start with the same letters as the words that you need to remember.
- Draw a picture that helps you make a humorous connection between the new information and the things that you already know.
- Envision what it would be like to experience your topic in person. Imagine the sights, sounds, smells and more.
- Think up rhymes or tongue twisters that can help the information stick in your brain.
- Visualize the details with a web-style mind map that illustrates the relationships between concepts.
5. Absorb Information in Smaller Chunks
Think about how you memorize a phone number: You divide the 10-digit number into three smaller groups. It’s easier to get these three chunks to stick in your mind than it is to remember the whole thing as a single string of information.
You can use this strategy when studying by breaking a list down into smaller parts. Work on memorizing each part as its own group.
6. Make Your Own Study Sheet
Condensing your most important notes onto one page is an excellent way to keep priority information at your fingertips. The more you look over this sheet and read it aloud, the better that you’ll know the material.

Furthermore, the act of typing or writing out the information will help you memorize the details. Using different colors or lettering styles can help you picture the information later.
Just like flashcards, a study sheet is portable. You can pull it out of your bag whenever you have a spare minute.
7. Be the Teacher
To teach information to others, you first have to understand it yourself. Therefore, when you’re trying to learn something new, challenge yourself to consider how you’d teach it to someone else. Wrestling with this concept will help you gain a better understanding of the topic.
In fact, you can even recruit a friend, a family member or a study group member to listen to your mini-lesson. Reciting your presentation aloud to someone else will help the details stick in your mind, and your audience may be able to point out gaps in your knowledge.
8. Know When to Call It a Day
Yes, you really can get too much of a good thing. Although your studies are important, they shouldn’t be the only thing in your life. It’s also important to have a social life, get plenty of exercise, and take care of your non-school responsibilities.
Studies show that too much time with your nose in the books can elevate your stress level , which can have a negative effect on your school performance and your personal relationships.
Too much studying may also keep you from getting enough exercise. This could lower your bone density or increase your percentage of body fat.
Part 5 – How to Study More Efficiently


1. Take Regular Breaks
Study sessions will be more productive if you allow yourself to take planned breaks. Consider a schedule of 50 minutes spent working followed by a 10-minute break.
Your downtime provides a good chance to stand up and stretch your legs. You can also use this as an opportunity to check your phone or respond to emails. When your 10 minutes are up, however, it’s time to get back to work.
At the end of a long study session, try to allow yourself a longer break — half an hour, perhaps — before you move on to other responsibilities.
2. Take Notes in Class
The things that your teacher talks about in class are most likely topics that he or she feels are quite important to your studies. So, it’s a good idea to become a thorough note-taker.
The following tips can help you become an efficient, effective note-taker:
- Stick to the main points.
- Use shorthand when possible.
- If you don’t have time to write all the details, jot down a keyword or a name. After class, you can use your textbook to elaborate on these items.
- For consistency, use the same organizational system each time you take notes.
- Consider writing your notes by hand, which can help you remember the information better. However, typing may help you be faster or more organized.
Recording important points is effective because it forces you to pay attention to what’s being said during a lecture.
3. Exercise First
Would you believe that exercise has the potential to grow your brain ? Scientists have shown this to be true!

In fact, exercise is most effective at generating new brain cells when it’s immediately followed by learning new information.
There are short-term benefits to exercising before studying as well. Physical activity helps wake you up so you feel alert and ready when you sit down with your books.
4. Review and Revise Your Notes at Home
If your notes are incomplete — for example, you wrote down dates with no additional information — take time after class to fill in the missing details. You may also want to swap notes with a classmate so you can catch things that you missed during the lecture.
- Rewrite your notes if you need to clean them up
- Rewriting will help you retain the information
- Add helpful diagrams or pictures
- Read through them again within one day
If you find that there are concepts in your notes that you don’t understand, ask your professor for help. You may be able to set up a meeting or communicate through email.
After rewriting your notes, put them to good use by reading through them again within the next 24 hours. You can use them as a reference when you create study sheets or flashcards.
5. Start with Your Toughest Assignments
Let’s face it: There are some subjects that you like more than others. If you want to do things the smart way, save your least challenging tasks for the end of your studies. Get the hardest things done first.
If you save the toughest tasks for last, you’ll have them hanging over your head for the whole study session. That can cost you unnecessary mental energy.

Furthermore, if you end with your favorite assignments, it will give you a more positive feeling about your academic pursuits. You’ll be more likely to approach your next study session with a good attitude.
6. Focus on Key Vocabulary
To really understand a subject, you have to know the words that relate to it. Vocabulary words are often written in textbooks in bold print. As you scan the text, write these words down in a list.
Look them up in a dictionary or in the glossary at the back of the book. To help you become familiar with the terms, you could make a study sheet with the definitions or make flashcards.
7. Join a Study Group
Studying doesn’t always have to be an individual activity.
Benefits of a study group include:
- Explaining the material to one another
- Being able to ask questions about things you don’t understand
- Quizzing each other or playing review games
- Learning the material more quickly than you might on your own
- Developing soft skills that will be useful in your career, such as teamwork and problem solving
- Having fun as you study
Gather a few classmates to form a study group.
Part 6 – How to Study for Tests

1. Study for Understanding, Not Just for the Test
Cramming the night before a big test usually involves trying to memorize information long enough to be able to regurgitate it the next morning. Although that might help you get a decent grade or your test, it won’t help you really learn the material .
Within a day or two, you’ll have forgotten most of what you studied. You’ll have missed the goal of your classes: mastery of the subject matter.
Instead, commit yourself to long-term learning by studying throughout the semester.
2. Begin Studying at Least One Week in Advance
Of course, you may need to put in extra time before a big test, but you shouldn’t put this off until the night before.
Instead, in the week leading up to the exam, block off a daily time segment for test preparation. Regular studying will help you really learn the material.
3. Spend at Least One Hour per Day Studying
One week out from a big test, study for an hour per night. If you have two big tests coming up, increase your daily study time, and divide it between the two subjects.

The day before the exam, spend as much time as possible studying — all day, even.
4. Re-write Class Notes
After each class, you should have fleshed out your notes and rewritten them in a neat, organized format. Now, it’s time to take your re-done notes and write them once again.
This time, however, your goal is to condense them down to only the most important material. Ideally, you want your rewritten notes to fit on just one or two sheets of paper.
These sheets should be your main study resource during test preparation.
5. Create a Study Outline
Early in the week, make a long outline that includes many of the details from your notes. Rewrite it a few days later, but cut the material in half.
Shortly before the test, write it one more time; include only the most important information. Quiz yourself on the missing details.
6. Make Your Own Flashcards
Another way to quiz yourself is to make flashcards that you can use for practice written tests.
First, read the term on the front side. Encourage yourself to write out the definition or details of that term. Compare your written answer with what’s on the back of the card.
This can be extra helpful when prepping for an entrance exam like the GRE, though there are a growing number of schools that don’t require GRE scores for admission.
7. Do Sample Problems and Essays from Your Textbook
There are additional things you can do to practice test-taking. For example, crack open your book, and solve problems like the ones you expect to see on the test.
Write out the answers to essay questions as well. There may be suggested essay topics in your textbook.
Part 7 – Memory Improvement Techniques

1. Study Right Before Bed
Although you shouldn’t pull all-nighters, studying right before bedtime can be a great idea.
Sleep helps cement information in your brain. Studies show that you’re more likely to recall information 24 hours later if you went to bed shortly after learning it.
Right before bed, read through your study sheet, quiz yourself on flashcards or recite lists of information.
2. Study Small Chunks at a Time
If you want to remember information over the long haul, don’t try to cram it all in during one sitting.
Instead, use an approach called spaced repetition :
- Break the information into parts
- Learn one new part at a time over the course of days or weeks
- Review your earlier acquisitions each time you study
The brain stores information that it thinks is important. So, when you regularly go over a topic at set intervals over time, it strengthens your memory of it.
3. Tell a Story
Sometimes, you just need to make information silly in order to help it stick in your brain.
To remember a list of items or the particular order of events, make up a humorous story that links those things or words together. It doesn’t necessarily need to make sense; it just needs to be memorable .

4. Change Study Locations Often
Studying the same information in multiple places helps the details stick in your mind better.
Consider some of the following locations:
- Your desk at home
- A coffee shop
- The library
- Your backyard
It’s best to switch between several different study spots instead of always hitting the books in the same place.
5. Swap Topics Regularly
Keeping your brain trained on the same information for long periods of time isn’t beneficial. It’s smarter to jump from one subject to another a few times during a long study session.
Along those same lines, you should study the same material in multiple ways. Research shows that using varied study methods for the same topic helps you perform better on tests.
6. Quiz Yourself
Challenge yourself to see what you can remember. Quizzing yourself is like practicing for the test, and it’s one of the most effective methods of memory retention .
If it’s hard to remember the information at first, don’t worry; the struggle makes it more likely that you’ll remember it in the end.
7. Go Old-school: Use a Pen and Paper
The act of writing answers helps you remember the information. Here are some ways to use writing while studying:
- Recopy your notes
- Write the answers to flashcards
- Make a study sheet
- Practice writing essay answers
Writing by hand is best because it requires your attention and focus.
8. See It & Hear It
Say information out loud, and you’ll be more likely to remember it. You’re engaging your eyes as you read the words, your mouth as you say them, and your ears as you hear yourself.
Scientists call the benefit of speaking information aloud production effect .
Part 8 – Top 10 Study Hacks Backed by Science

1. Grab a Coffee
Drinking coffee (or your preferred high-octane beverage) while you study may help keep you alert so you don’t doze off mid-session. There’s even evidence that caffeine can improve your memory skills.
However, avoid sugary beverages. These could cause your energy level to crash in a few hours.
2. Reward Yourself
Studies show that giving yourself a reward for doing your work helps you enjoy the effort more.
Do it right away; don’t wait until the test is over to celebrate. For example, after finishing a three-hour study session, treat yourself to an ice cream cone or a relaxing bath.
3. Study with Others
Working with a study group holds you accountable so it’s harder to procrastinate on your work.
When you study together, you can fill in gaps in one another’s understanding, and you can quiz each other on the material.
Besides, studying with a group can be fun!
4. Meditate
It may be hard to imagine adding anything else to your packed schedule, but dedicating time to mindfulness practices can really pay off.

Studies show that people who meditate may perform better on tests , and they are generally more attentive.
Mindfulness apps can help you get started with this practice.
5. Hit the Gym
To boost the blood flow to your brain, do half an hour of cardio exercise before sitting down to study.
Aerobic exercise gives your brain a major dose of oxygen and other important nutrients, which may help you think clearly, remember facts and do your best work.
6. Play Some Music
Listening to tunes can help you focus. Studies show that the best study music is anything that features a rhythmic beat .
It’s smart to choose a style that you like. If you like classical, that’s fine, but you could also go for electronica or modern piano solos.
7. Grab Some Walnuts
A diet rich in omega-3 fatty acids helps your brain do its best work.
Good sources include:
- Fish: cod liver oil, salmon and mackerel
- Vegetables: spinach and Brussels sprouts
To calm your pre-test jitters, eat a mix of omega-3 and omega-6 foods.
8. Take Regular Breaks
Your brain needs some downtime. Don’t try to push through for hours on end. Every hour, take a break for several minutes.

Breaks are good for your mental health . They also improve your attention span, your creativity and your productivity.
During a break, it’s best to move around and exercise a bit.
9. Get Some Sleep
Although studying is important, it can’t come at the expense of your rest. Sleep gives your brain a chance to process the information that you’ve learned that day.
If you don’t get enough sleep, you’ll have a hard time focusing and remembering information.
Even during busy test weeks, try to get seven to nine hours of sleep each night.
10. Eliminate Distractions
It’s hard to get much studying done when you’re busy scrolling Instagram. Put away your phone and computer while studying, or at least block your social media apps.
Turn off the television while you work, too.
If you’re studying in a noisy area, put on headphones that can help block the distracting sounds.
Part 9 – The Best Study Apps

1. iStudiez Pro Legend
Scheduling study time is a must, and iStudiez Pro Legend lets you put study sessions, classes and assignments on your calendar. Color coding the entries can help you stay organized.
For each class, you can enter meeting times and homework assignments, and you can keep track of your grades.
2. Dragon Anywhere
Instead of writing notes in the margins of your textbooks, you can use Dragon Anywhere’s voice dictation feature to record your thoughts and insights.
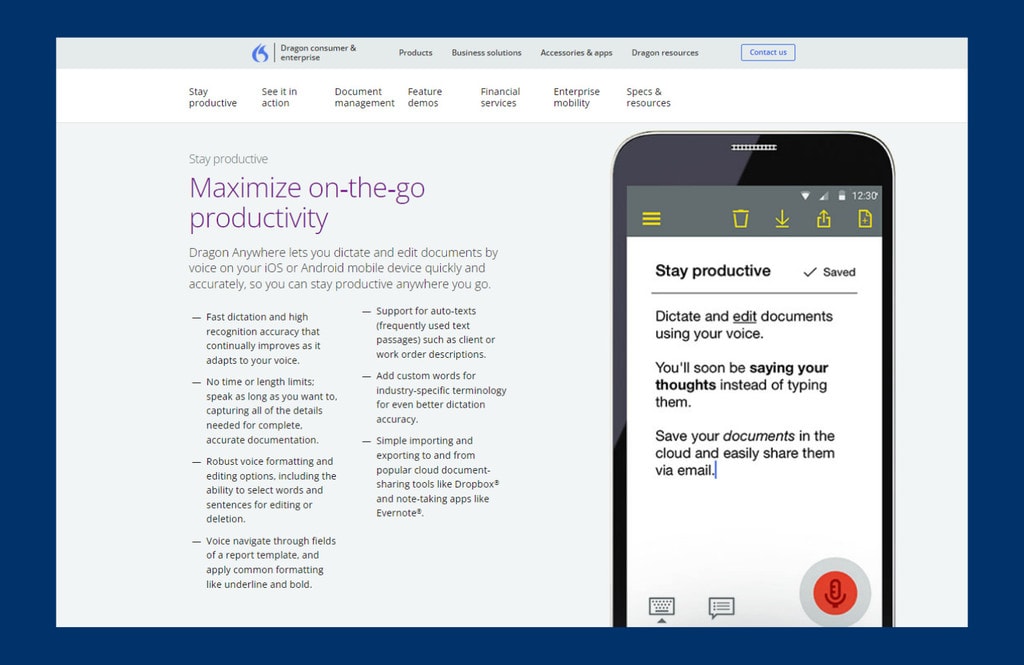
Just be sure to rewrite your dictated notes in your own handwriting later for maximum learning!
3. Evernote
When you’re in school, you have a lot of responsibilities to juggle, but Evernote can help you organize them.
You can add notes and documents to store them in one digital spot, and tagging them will help you quickly pull up all files for a class or a topic.
4. Quizlet Go
Make digital flashcards that you can practice on your mobile device with Quizlet Go .

This means that you can pull out your phone for a quick study session whenever you have a couple of minutes of downtime. You don’t even need internet access to practice these flashcards.
5. My Study Life
Enter your upcoming tests and assignments into My Study Life , and the app will send you reminder messages.
The app has a calendar so you can keep track of your class schedule. It can even notify you when it’s time to go to class.
6. Exam Countdown Lite
You should start studying for tests at least a week in advance. Input the dates for your exams and assignments into Exam Countdown Lite so you’ll have a visual reminder of when you should begin your test prep.
The app can send you notifications as well.
7. Flashcards+
With Chegg’s Flashcards+ , you can make your own digital flashcards or use ones designed by others.
Because you can add images to your cards, you can quiz yourself on the names of famous artworks, important historical artifacts or parts of a scientific diagram.
Organize information into categories by creating a visual mind map on XMind . This can help you classify facts and figures so you see how they relate to one another.

This visual representation can also help you recall the information later.
9. ScannerPro
Do you have piles of handwritten notes everywhere? Once you have written them out, consider scanning them into digital form. ScannerPro lets you use your phone as a scanner.
You can store your scanned files in this app or transfer them to Evernote or another organization system.
Part 10 – Study Skills Worksheets
Could you use more help to develop your study skills? Rutgers University has dozens of study skills worksheets online .
These documents are packed with tips that can help you become a better student. The checklists and charts can help you evaluate your current strengths and organize your work.
Part 11 – Key Takeaways

You’re a busy person, so you need to make the most of every study session.
By now, you should understand the basics of effective studies:
- Schedule study time
- Study regularly
- Minimize distractions
- Read for information
- Write the important stuff down
- Use creative memory tricks
- Quiz yourself
- Be good to your body and your brain
Put these study tips to good use, and you’ll soon learn that you’ve learned how to study smarter.

- Search This Site All UCSD Sites Faculty/Staff Search Term
- Contact & Directions
- Climate Statement
- Cognitive Behavioral Neuroscience
- Cognitive Psychology
- Developmental Psychology
- Social Psychology
- Adjunct Faculty
- Non-Senate Instructors
- Researchers
- Psychology Grads
- Affiliated Grads
- New and Prospective Students
- Honors Program
- Experiential Learning
- Programs & Events
- Psi Chi / Psychology Club
- Prospective PhD Students
- Current PhD Students
- Area Brown Bags
- Colloquium Series
- Anderson Distinguished Lecture Series
- Speaker Videos
- Undergraduate Program
Academic and Writing Resources
- Effective Studying
How to Effectively Study
Research-supported techniques.
Outside of lecture, university students are commonly expected to master course content on their own. However, multiple research studies have found that many university students are commonly unaware of, and seldom use, effective learning techniques. 1,2 In the following section (and the linked pages below) we discuss important do’s and don’ts of successful learning, plus introduce several of the most promising and effective evidence-based learning methods . These are backed by a growing body of learning science research – a substantial portion of which has been conducted right here at UCSD and in this very department. By taking advantage of these methods, students can transform their learning activities to be more efficient (make better use of time) and more effective (resulting in learning that is more comprehensive and lasts longer).
What Students Need to Do to Succeed
Psychology courses, as well as those in many other departments and at other universities, revolve around high-stakes tests (for example, midterms, final exams). In fact, on average, 80% of the course grade in PSYC classes at UCSD is determined by exam performance. 3 In order to perform well on such exams, it is crucial for students to master a wide range of course content.
How can that objective be accomplished? Through the use of evidence-based learning methods. Note that these are not described as “study methods”. Although it is common to describe preparing for an exam as “studying”, which is why this page is titled as such, simply “studying” information multiple times (“restudying”, “rereading”, or “reviewing”) is by itself often not very effective. 4,5 Instead, as described below, other methods are far more powerful at improving the learning of course content.
The Most Effective Learning Techniques
If you have only limited time to read this page, at least check out the following two points. For further details, click on the links to learn more.
Based on decades of learning science research, the two most effective methods known to date are:
- Spaced practice / distributed practice – learning that occurs over multiple sessions at different points in time (for example, revisiting a textbook chapter once every three days). This technique refers to when you should be preparing for course exams (that is, multiple sessions spread out over several weeks).
► Further information: Spaced Practice
- Retrieval practice / practice testing – instead of simply restudying information, attempting to recall that information from memory (such as by taking a practice test). This technique refers to what you should be doing to prepare for course exams (that is, test yourself via practice tests or other recall-based techniques).
► Further information: Retrieval Practice
Spaced practice involves when you should “study” and retrieval practice involves how you should “study”. When you use both (for instance, you can prepare for your exams using a spaced practice schedule and then use retrieval practice during each session), they make a powerful combination.
Additionally, if you perform retrieval practice across multiple days – and, each time, practice recalling information until you attain 100% accuracy (a method called successive relearning ) – then recent research shows that your ability to retain that information over long periods of time is maximized. 6
Finally, besides spaced and retrieval practice, there are some additional learning techniques that you may wish to try. These included interleaved practice, self-explanation, and others.
► Further information: Other Learning Techniques
Workshops and Downloadable Resources
- For in-person discussion of these techniques, please consider attending this department’s “How to Study Less and Remember More” workshop (for dates and times, please check the undergraduate workshops calendar).
- How to Study Less and Remember More [ PDF ]
Further Resources
- UCSD Tutoring
- Scientific American article, “What Works, What Doesn’t" (2013)
- Make it Stick: The Science of Successful Learning (2014)
- Cornell University: How to Study Effectively (videos)
1 Kornell, N., & Bjork, R. A. (2007). The promise and perils of self-regulated study. Psychonomic Bulletin & Review , 14 (2), 219-224. 2 Karpicke, J. D., Butler, A. C., & Roediger III, H. L. (2009). Metacognitive strategies in student learning: do students practise retrieval when they study on their own? Memory , 17 (4), 471-479. 3 Based on analysis of PSYC 1, 2, 3, 4, 7, 60, 101, 102, 103, 105, 106, 120, 144, 145, 154, 163, 164, 161, 171, 181, 182, 190, 191, and 193 courses at UCSD, taught between 2013-2017. 4 Pashler, H., Bain, P. M., Bottge, B. A., Graesser, A., Koedinger, K., McDaniel, M., & Metcalfe, J. (2007). Organizing Instruction and Study to Improve Student Learning. IES Practice Guide. NCER 2007-2004. National Center for Education Research . 5 Dunlosky, J., Rawson, K. A., Marsh, E. J., Nathan, M. J., & Willingham, D. T. (2013). Improving students’ learning with effective learning techniques: Promising directions from cognitive and educational psychology. Psychological Science in the Public Interest , 14 (1), 4-58. 6 Rawson, K. A., Dunlosky, J., & Sciartelli, S. M. (2013). The power of successive relearning: Improving performance on course exams and long-term retention. Educational Psychology Review , 25 (4), 523-548.
Prepared by s. c. pan for ucsd psychology, graphic adapted with permission from ccnlab.net under creative commons attribution-share alike 4.0 international license..
Back to top
- Writing Research Papers
- Spaced Practice
- Retrieval Practice
- Self-Explanation, Interleaved Practice, and Other Learning Techniques
- Effective Study Techniques Videos

The Learning Strategies Center
- Meet the Staff
- –Supplemental Course Schedule
- AY Course Offerings
- Anytime Online Modules
- Winter Session Workshop Courses
- –About Tutoring
- –Office Hours and Tutoring Schedule
- –LSC Tutoring Opportunities
- –How to Use Office Hours
- –Campus Resources and Support
- –Student Guide for Studying Together
- –Find Study Partners
- –Productivity Power Hour
- –Effective Study Strategies
- –Concept Mapping
- –Guidelines for Creating a Study Schedule
- –Five-Day Study Plan
- –What To Do With Practice Exams
- –Consider Exam Logistics
- –Online Exam Checklist
- –Open-Book Exams
- –How to Tackle Exam Questions
- –What To Do When You Get Your Graded Test (or Essay) Back
- –The Cornell Note Taking System
- –Learning from Digital Materials
- –3 P’s for Effective Reading
- –Textbook Reading Systems
- –Online Learning Checklist
- –Things to Keep in Mind as you Participate in Online Classes
- –Learning from Online Lectures and Discussions
- –Online Group Work
- –Learning Online Resource Videos
- –Start Strong!
- –Effectively Engage with Classes
- –Plans if you Need to Miss Class
- –Managing Time
- –Managing Stress
- –The Perils of Multitasking
- –Break the Cycle of Procrastination!
- –Finish Strong
- –Neurodiversity at Cornell
- –LSC Scholarship
- –Pre-Collegiate Summer Scholars Program
- –Study Skills Workshops
- –Private Consultations
- –Resources for Advisors and Faculty
- –Presentation Support (aka Practice Your Talk on a Dog)
- –About LSC
- –Meet The Team
- –Contact Us
Effective Study Strategies
So, what are effective study strategies for long-term learning, retrieval practice 1.
Retrieval practice is when you actively recall information (concepts, ideas, etc) from memory and “put it on paper” in different formats (writing, flow charts, diagrams, graphs). At the LSC we often call retrieval practice “Blank Page Testing,” because you just start with a blank piece of paper and write things down. It’s especially helpful because it shows you what you do (and do not) understand, so you can identify what topics you need to review/practice more. Retrieval practice can be challenging and requires a lot of mental effort — but this struggle to remember, recall, and make connections is how we learn.
To learn more about Blank Page Testing , see Mike Chen’s video:
Interleaving 2
Interleaving is when you work on or practice several related skills or concepts together. You practice one skill or concept for a short period of time, then switch to another one, and perhaps another, then back to the first. It not only helps you learn better, it keeps you from falling behind in your other classes! So please go ahead and do some work for the classes you don’t have an exam in this week! It will not only help you learn your exam material better, it will help you stay caught up.
Spaced (or distributed) practice 3
In spaced practice, you spread out practice or study of material in spaced intervals, which leads to better learning and retention. Spaced practice is the opposite of cramming!
Get sleep and make sure you eat and stay hydrated!

Your brain works better when you are rested, hydrated, and nourished. Though it might seem effective to push through without taking a break and stay up studying all night (see the page on strategies that don’t work), it won’t help you in the long run. Instead, develop a study plan, eat a good meal, and have a bottle of water nearby when you take your exam. You will learn and understand the material better if you have a plan – and you will probably need to this information for the next prelim anyway!
Tip: Piper knows that sleeping with your books under your pillow can help with learning! How does this magic work, you might wonder? Though the information in your book won’t travel via osmosis to your brain through the pillow, you will get sleep which improves your long-term learning! Sleep and a good study plan are a great study strategy combo!
Up Next: Guidelines for creating a study schedule
1 Agarwal, P. K. (2020). Retrieval Practice: A Powerful Strategy for Learning – Retrieval Practice. Unleash the Science of Learning. Retrieved from https://www.retrievalpractice.org/retrievalpractice .
2 Pan, S.C. (2015). The Interleaving Effect: Mixing It Up Boosts Learning. Retrieved from https://www.scientificamerican.com/article/the-interleaving-effect-mixing-it-up-boosts-learning/
3 Weinstein, Y. & Smith, M. (2016). Learn How to Study Using… Spaced Practice. Retrieved from https://www.learningscientists.org/blog/2016/7/21-1
Online Study Skills Hub: Essay Planning: Structuring your work
- Where do I start?
- Critical Thinking & Writing
- Editing & Proofreading
- Essay Planning: Structuring your work
- Dissertations & Theses
- Exam Preparation & Revision
- Finding Books & eBooks
- Finding Resources Step by Step Guide
- Logging in to Online Resources
- Request an Item
- Understanding Resource Lists
- Using eBooks
- IT and Digital Skills
- Presentation Skills
- Reading & Note Taking
- Referencing: How & Why You Should do it This link opens in a new window
- Statistics & SPSS This link opens in a new window
- Time Management Skills
- Understanding Feedback
- Finding Information with AI
- AI & Academic Integrity
Essay Planning and Writing introduction
Essay Planning and Writing are crucial steps in crafting a coherent, persuasive, and well-structured essay. Proper planning ensures that your ideas are organised and your argument flows logically from one point to the next.
Essay Planning :
- Understanding the Brief : Start by carefully reading the essay question to identify key themes, requirements, and expectations.
- Research : Gather relevant information from credible sources, taking notes on key points, evidence, and references.
- Creating an Outline : Organise your ideas into a clear structure. Typically, an essay outline includes an introduction, body paragraphs, and a conclusion. Each body paragraph should focus on a single idea that supports your thesis.
Structuring Your Essay :
- Introduction : Begin with a hook to engage the reader, provide background information, and present your thesis statement, which outlines the main argument of the essay.
- Body Paragraphs : Each paragraph should start with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea, followed by evidence, analysis, and a concluding sentence that links back to the thesis. Ensure a logical flow by connecting paragraphs with transitions.
- Conclusion : Summarise the key points made in the body, restate the thesis in light of the evidence presented, and offer a final thought or call to action.
Writing the Essay :
- Drafting : Write a first draft based on your outline, focusing on getting your ideas down rather than perfection.
- Revising : Review your draft for coherence, clarity, and structure. Ensure each paragraph supports your thesis and that your argument flows logically.
- Editing and Proofreading : Check for grammar, spelling, and punctuation errors, as well as consistency in tone and style.
Effective essay planning and writing involve structuring your essay in a way that clearly presents your argument, ensuring that each part contributes to the overall thesis. A well-structured essay is easier to read, more persuasive, and demonstrates a clear understanding of the topic.
Essay Planning Recordings
- Essay Planning (Video) 12 minutes By the end of this session you should be able to: - Recognise the main difference between editing and proofreading - Know the key aspects to check for when editing your work - Understand common errors in writing and what effective techniques for correcting them.
- Essay Instruction Terms What is meant by different terms you see in assessment criteria and instructions given by tutors.
- 5 Tops Tips for Writing Excellent Essays (Video) 47 minutes Learn our top 5 best tips for producing a quality essay. By the end your should be able to: - Understand the essay question - Write a clear introduction - Craft strong paragraphs - Critically engage with research and evidence - Proofread your work

- << Previous: Editing & Proofreading
- Next: Assessment Types >>
- Last Updated: Sep 5, 2024 9:11 AM
- URL: https://library.roehampton.ac.uk/studyskills
This site uses various technologies, as described in our Privacy Policy, for personalization, measuring website use/performance, and targeted advertising, which may include storing and sharing information about your site visit with third parties. By continuing to use this website you consent to our Privacy Policy and Terms of Use .
We are experiencing sporadically slow performance in our online tools, which you may notice when working in your dashboard. Our team is fully engaged and actively working to improve your online experience. If you are experiencing a connectivity issue, we recommend you try again in 10-15 minutes. We will update this space when the issue is resolved.
Enter your email to unlock an extra $25 off an SAT or ACT program!
By submitting my email address. i certify that i am 13 years of age or older, agree to recieve marketing email messages from the princeton review, and agree to terms of use., how to study for exams.
You have a test on the horizon. It’s a big one, and you know you need to hit the books. Not sure where or how to begin? Don’t panic! Learn how to study for a test, step-by-step.

1. Ask the right questions
You don’t want to walk in on test day unprepared for what you're about to face. Try to get the answers to these crucial questions before you start studying.
Questions to ask before a test
- What material will the test cover?
- Will there be an exam review session during class?
- Will there be after-school opportunities for more review?
- What is the format of the exam? Multiple-choice? Short answer? Will there be essays to write?
- How many points is the exam worth?
- Do you have specific study tips to help me prepare? (After all, your teacher knows your work the best!).
2. Sort out your schedule
You can actually spend less time studying for your exam if you start with a great game plan. Make a list of what topics you need to cover and when you’re going to cover them. Start your study schedule as early as possible (usually a few weeks before your test), and figure out how much time you’ll need to study each day to stay on track.
3. Grab your gear
Gather up all your class notes , quizzes, handouts and worksheets. Your previous homework will help you see what your teacher thinks is important. (Plus, you can learn from your past quiz mistakes).
4. Study smarter
Instead of memorizing all your notes, prioritize what you’ll study. Start with what will definitely be on the the test, then what will probably be on the test, and finally what might be on the test. That way, if you run out of time, you know you at least have the essentials covered. By starting with the toughest material first, you have time to ask your teacher questions or get help from our tutors .
5. Mix it up
Now that you know WHAT you need to study, figure out the best way to review and internalize what you predict will be on the exam. Make flashcards for history class, outline your biology notes, record yourself practicing your French accent—whatever you need to do to get ready. Check out our favorite “outside of the box” study methods .
Read More: 10 Steps to Ace Your Next Test
6. What keeps you motivated?
Study groups can help you study more efficiently for exams. Make a plan with friends to review the class material together, share and compare notes, or work through tricky concepts. Or, reward yourself for each study session with something small (even if it’s just a TV break) to help you stay focused.
7. Sleep still matters
An all-nighter might sound like a good idea, but a restful night’s sleep is actually the key to your success. Start a healthy sleep routine in the weeks leading up to your exam, so you’ll be fresh and ready for test day. (But if you do happen to need some midnight study help, our on-demand tutors are there for you.)
8. Bring what you’re supposed to bring
Find out what you’re allowed to bring to the exam, and make sure you don’t leave anything essential at home. Many teachers will let you bring a calculator to math or science exams. Some classes may even hold open textbook or open notes exams. Stash pens, papers, and extra paper in your bag, so you’re ready for anything.
Stuck on how to study for exams?
Try an online tutoring session with one of our experts, and get help in 40+ subjects.
Try a Free Session

Explore Colleges For You
Connect with our featured colleges to find schools that both match your interests and are looking for students like you.

Career Quiz
Take our short quiz to learn which is the right career for you.

Get Started on Athletic Scholarships & Recruiting!
Join athletes who were discovered, recruited & often received scholarships after connecting with NCSA's 42,000 strong network of coaches.

Best 389 Colleges
165,000 students rate everything from their professors to their campus social scene.
SAT Prep Courses
1400+ course, act prep courses, free sat practice test & events, 1-800-2review, free digital sat prep try our self-paced plus program - for free, get a 14 day trial.
Free MCAT Practice Test
I already know my score.
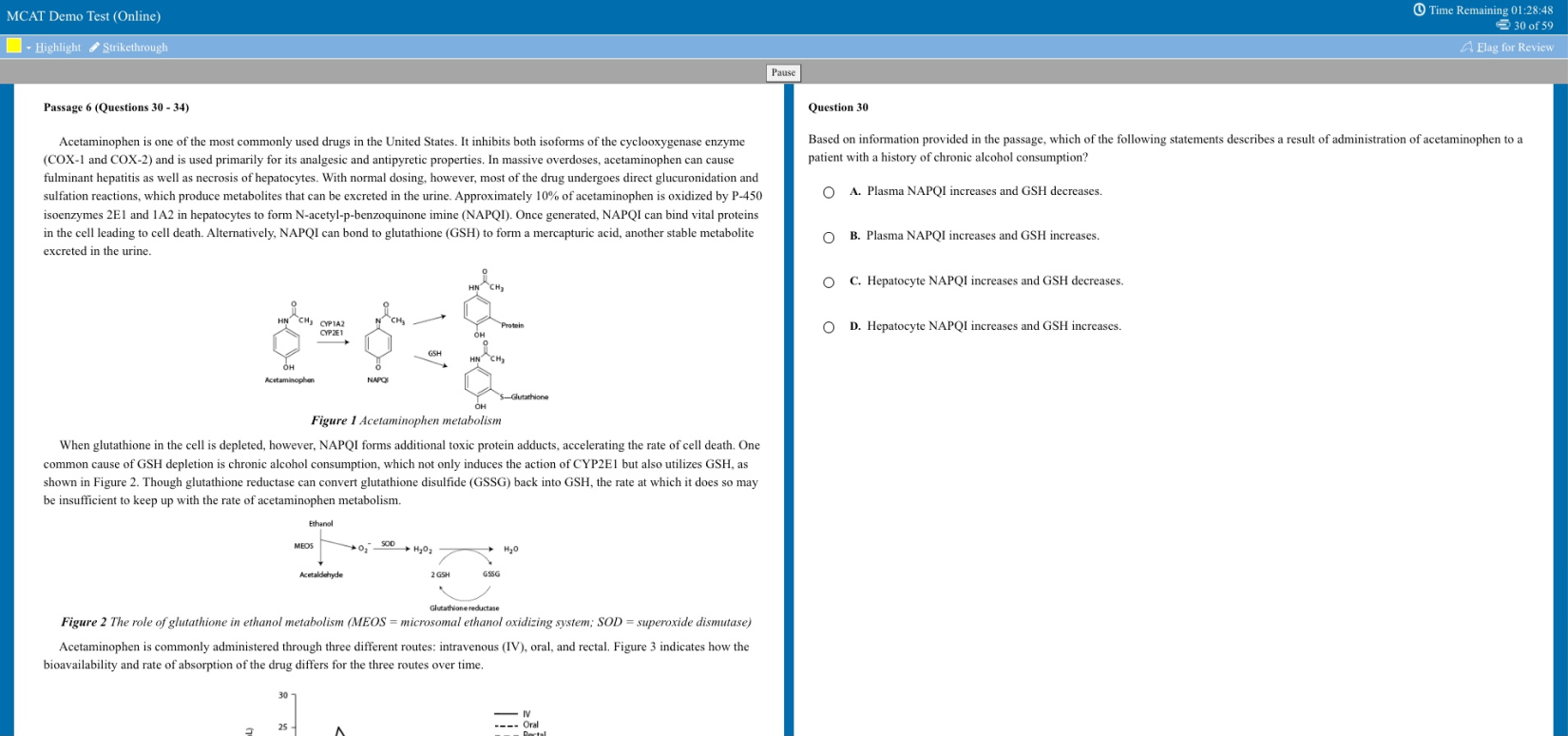
MCAT Self-Paced 14-Day Free Trial
Enrollment Advisor
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 1
1-877-LEARN-30
Mon-Fri 9AM-10PM ET
Sat-Sun 9AM-8PM ET
Student Support
1-800-2REVIEW (800-273-8439) ext. 2
Mon-Fri 9AM-9PM ET
Sat-Sun 8:30AM-5PM ET
Partnerships
- Teach or Tutor for Us
College Readiness
International
Advertising
Affiliate/Other
- Enrollment Terms & Conditions
- Accessibility
- Cigna Medical Transparency in Coverage
Register Book
Local Offices: Mon-Fri 9AM-6PM
- SAT Subject Tests
Academic Subjects
- Social Studies
Find the Right College
- College Rankings
- College Advice
- Applying to College
- Financial Aid
School & District Partnerships
- Professional Development
- Advice Articles
- Private Tutoring
- Mobile Apps
- International Offices
- Work for Us
- Affiliate Program
- Partner with Us
- Advertise with Us
- International Partnerships
- Our Guarantees
- Accessibility – Canada
Privacy Policy | CA Privacy Notice | Do Not Sell or Share My Personal Information | Your Opt-Out Rights | Terms of Use | Site Map
©2024 TPR Education IP Holdings, LLC. All Rights Reserved. The Princeton Review is not affiliated with Princeton University
TPR Education, LLC (doing business as “The Princeton Review”) is controlled by Primavera Holdings Limited, a firm owned by Chinese nationals with a principal place of business in Hong Kong, China.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
- Knowledge Base
- How to structure an essay: Templates and tips
How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates
Published on September 18, 2020 by Jack Caulfield . Revised on July 23, 2023.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction , a body , and a conclusion . But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body.
Instantly correct all language mistakes in your text
Upload your document to correct all your mistakes in minutes

Table of contents
The basics of essay structure, chronological structure, compare-and-contrast structure, problems-methods-solutions structure, signposting to clarify your structure, other interesting articles, frequently asked questions about essay structure.
There are two main things to keep in mind when working on your essay structure: making sure to include the right information in each part, and deciding how you’ll organize the information within the body.
Parts of an essay
The three parts that make up all essays are described in the table below.
| Part | Content |
|---|---|
Order of information
You’ll also have to consider how to present information within the body. There are a few general principles that can guide you here.
The first is that your argument should move from the simplest claim to the most complex . The body of a good argumentative essay often begins with simple and widely accepted claims, and then moves towards more complex and contentious ones.
For example, you might begin by describing a generally accepted philosophical concept, and then apply it to a new topic. The grounding in the general concept will allow the reader to understand your unique application of it.
The second principle is that background information should appear towards the beginning of your essay . General background is presented in the introduction. If you have additional background to present, this information will usually come at the start of the body.
The third principle is that everything in your essay should be relevant to the thesis . Ask yourself whether each piece of information advances your argument or provides necessary background. And make sure that the text clearly expresses each piece of information’s relevance.
The sections below present several organizational templates for essays: the chronological approach, the compare-and-contrast approach, and the problems-methods-solutions approach.
Prevent plagiarism. Run a free check.
The chronological approach (sometimes called the cause-and-effect approach) is probably the simplest way to structure an essay. It just means discussing events in the order in which they occurred, discussing how they are related (i.e. the cause and effect involved) as you go.
A chronological approach can be useful when your essay is about a series of events. Don’t rule out other approaches, though—even when the chronological approach is the obvious one, you might be able to bring out more with a different structure.
Explore the tabs below to see a general template and a specific example outline from an essay on the invention of the printing press.
- Thesis statement
- Discussion of event/period
- Consequences
- Importance of topic
- Strong closing statement
- Claim that the printing press marks the end of the Middle Ages
- Background on the low levels of literacy before the printing press
- Thesis statement: The invention of the printing press increased circulation of information in Europe, paving the way for the Reformation
- High levels of illiteracy in medieval Europe
- Literacy and thus knowledge and education were mainly the domain of religious and political elites
- Consequence: this discouraged political and religious change
- Invention of the printing press in 1440 by Johannes Gutenberg
- Implications of the new technology for book production
- Consequence: Rapid spread of the technology and the printing of the Gutenberg Bible
- Trend for translating the Bible into vernacular languages during the years following the printing press’s invention
- Luther’s own translation of the Bible during the Reformation
- Consequence: The large-scale effects the Reformation would have on religion and politics
- Summarize the history described
- Stress the significance of the printing press to the events of this period
Essays with two or more main subjects are often structured around comparing and contrasting . For example, a literary analysis essay might compare two different texts, and an argumentative essay might compare the strengths of different arguments.
There are two main ways of structuring a compare-and-contrast essay: the alternating method, and the block method.
Alternating
In the alternating method, each paragraph compares your subjects in terms of a specific point of comparison. These points of comparison are therefore what defines each paragraph.
The tabs below show a general template for this structure, and a specific example for an essay comparing and contrasting distance learning with traditional classroom learning.
- Synthesis of arguments
- Topical relevance of distance learning in lockdown
- Increasing prevalence of distance learning over the last decade
- Thesis statement: While distance learning has certain advantages, it introduces multiple new accessibility issues that must be addressed for it to be as effective as classroom learning
- Classroom learning: Ease of identifying difficulties and privately discussing them
- Distance learning: Difficulty of noticing and unobtrusively helping
- Classroom learning: Difficulties accessing the classroom (disability, distance travelled from home)
- Distance learning: Difficulties with online work (lack of tech literacy, unreliable connection, distractions)
- Classroom learning: Tends to encourage personal engagement among students and with teacher, more relaxed social environment
- Distance learning: Greater ability to reach out to teacher privately
- Sum up, emphasize that distance learning introduces more difficulties than it solves
- Stress the importance of addressing issues with distance learning as it becomes increasingly common
- Distance learning may prove to be the future, but it still has a long way to go
In the block method, each subject is covered all in one go, potentially across multiple paragraphs. For example, you might write two paragraphs about your first subject and then two about your second subject, making comparisons back to the first.
The tabs again show a general template, followed by another essay on distance learning, this time with the body structured in blocks.
- Point 1 (compare)
- Point 2 (compare)
- Point 3 (compare)
- Point 4 (compare)
- Advantages: Flexibility, accessibility
- Disadvantages: Discomfort, challenges for those with poor internet or tech literacy
- Advantages: Potential for teacher to discuss issues with a student in a separate private call
- Disadvantages: Difficulty of identifying struggling students and aiding them unobtrusively, lack of personal interaction among students
- Advantages: More accessible to those with low tech literacy, equality of all sharing one learning environment
- Disadvantages: Students must live close enough to attend, commutes may vary, classrooms not always accessible for disabled students
- Advantages: Ease of picking up on signs a student is struggling, more personal interaction among students
- Disadvantages: May be harder for students to approach teacher privately in person to raise issues
An essay that concerns a specific problem (practical or theoretical) may be structured according to the problems-methods-solutions approach.
This is just what it sounds like: You define the problem, characterize a method or theory that may solve it, and finally analyze the problem, using this method or theory to arrive at a solution. If the problem is theoretical, the solution might be the analysis you present in the essay itself; otherwise, you might just present a proposed solution.
The tabs below show a template for this structure and an example outline for an essay about the problem of fake news.
- Introduce the problem
- Provide background
- Describe your approach to solving it
- Define the problem precisely
- Describe why it’s important
- Indicate previous approaches to the problem
- Present your new approach, and why it’s better
- Apply the new method or theory to the problem
- Indicate the solution you arrive at by doing so
- Assess (potential or actual) effectiveness of solution
- Describe the implications
- Problem: The growth of “fake news” online
- Prevalence of polarized/conspiracy-focused news sources online
- Thesis statement: Rather than attempting to stamp out online fake news through social media moderation, an effective approach to combating it must work with educational institutions to improve media literacy
- Definition: Deliberate disinformation designed to spread virally online
- Popularization of the term, growth of the phenomenon
- Previous approaches: Labeling and moderation on social media platforms
- Critique: This approach feeds conspiracies; the real solution is to improve media literacy so users can better identify fake news
- Greater emphasis should be placed on media literacy education in schools
- This allows people to assess news sources independently, rather than just being told which ones to trust
- This is a long-term solution but could be highly effective
- It would require significant organization and investment, but would equip people to judge news sources more effectively
- Rather than trying to contain the spread of fake news, we must teach the next generation not to fall for it
Here's why students love Scribbr's proofreading services
Discover proofreading & editing
Signposting means guiding the reader through your essay with language that describes or hints at the structure of what follows. It can help you clarify your structure for yourself as well as helping your reader follow your ideas.
The essay overview
In longer essays whose body is split into multiple named sections, the introduction often ends with an overview of the rest of the essay. This gives a brief description of the main idea or argument of each section.
The overview allows the reader to immediately understand what will be covered in the essay and in what order. Though it describes what comes later in the text, it is generally written in the present tense . The following example is from a literary analysis essay on Mary Shelley’s Frankenstein .
Transitions
Transition words and phrases are used throughout all good essays to link together different ideas. They help guide the reader through your text, and an essay that uses them effectively will be much easier to follow.
Various different relationships can be expressed by transition words, as shown in this example.
Because Hitler failed to respond to the British ultimatum, France and the UK declared war on Germany. Although it was an outcome the Allies had hoped to avoid, they were prepared to back up their ultimatum in order to combat the existential threat posed by the Third Reich.
Transition sentences may be included to transition between different paragraphs or sections of an essay. A good transition sentence moves the reader on to the next topic while indicating how it relates to the previous one.
… Distance learning, then, seems to improve accessibility in some ways while representing a step backwards in others.
However , considering the issue of personal interaction among students presents a different picture.
If you want to know more about AI tools , college essays , or fallacies make sure to check out some of our other articles with explanations and examples or go directly to our tools!
- Ad hominem fallacy
- Post hoc fallacy
- Appeal to authority fallacy
- False cause fallacy
- Sunk cost fallacy
College essays
- Choosing Essay Topic
- Write a College Essay
- Write a Diversity Essay
- College Essay Format & Structure
- Comparing and Contrasting in an Essay
(AI) Tools
- Grammar Checker
- Paraphrasing Tool
- Text Summarizer
- AI Detector
- Plagiarism Checker
- Citation Generator
The structure of an essay is divided into an introduction that presents your topic and thesis statement , a body containing your in-depth analysis and arguments, and a conclusion wrapping up your ideas.
The structure of the body is flexible, but you should always spend some time thinking about how you can organize your essay to best serve your ideas.
An essay isn’t just a loose collection of facts and ideas. Instead, it should be centered on an overarching argument (summarized in your thesis statement ) that every part of the essay relates to.
The way you structure your essay is crucial to presenting your argument coherently. A well-structured essay helps your reader follow the logic of your ideas and understand your overall point.
Comparisons in essays are generally structured in one of two ways:
- The alternating method, where you compare your subjects side by side according to one specific aspect at a time.
- The block method, where you cover each subject separately in its entirety.
It’s also possible to combine both methods, for example by writing a full paragraph on each of your topics and then a final paragraph contrasting the two according to a specific metric.
You should try to follow your outline as you write your essay . However, if your ideas change or it becomes clear that your structure could be better, it’s okay to depart from your essay outline . Just make sure you know why you’re doing so.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Caulfield, J. (2023, July 23). How to Structure an Essay | Tips & Templates. Scribbr. Retrieved September 3, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/academic-essay/essay-structure/
Is this article helpful?

Jack Caulfield
Other students also liked, comparing and contrasting in an essay | tips & examples, how to write the body of an essay | drafting & redrafting, transition sentences | tips & examples for clear writing, "i thought ai proofreading was useless but..".
I've been using Scribbr for years now and I know it's a service that won't disappoint. It does a good job spotting mistakes”
How to Write the Perfect Essay
06 Feb, 2024 | Blog Articles , English Language Articles , Get the Edge , Humanities Articles , Writing Articles

You can keep adding to this plan, crossing bits out and linking the different bubbles when you spot connections between them. Even though you won’t have time to make a detailed plan under exam conditions, it can be helpful to draft a brief one, including a few key words, so that you don’t panic and go off topic when writing your essay.
If you don’t like the mind map format, there are plenty of others to choose from: you could make a table, a flowchart, or simply a list of bullet points.
Discover More
Thanks for signing up, step 2: have a clear structure.
Think about this while you’re planning: your essay is like an argument or a speech. It needs to have a logical structure, with all your points coming together to answer the question.
Start with the basics! It’s best to choose a few major points which will become your main paragraphs. Three main paragraphs is a good number for an exam essay, since you’ll be under time pressure.
If you agree with the question overall, it can be helpful to organise your points in the following pattern:
- YES (agreement with the question)
- AND (another YES point)
- BUT (disagreement or complication)
If you disagree with the question overall, try:
- AND (another BUT point)
For example, you could structure the Of Mice and Men sample question, “To what extent is Curley’s wife portrayed as a victim in Of Mice and Men ?”, as follows:
- YES (descriptions of her appearance)
- AND (other people’s attitudes towards her)
- BUT (her position as the only woman on the ranch gives her power as she uses her femininity to her advantage)
If you wanted to write a longer essay, you could include additional paragraphs under the YES/AND categories, perhaps discussing the ways in which Curley’s wife reveals her vulnerability and insecurities, and shares her dreams with the other characters. Alternatively, you could also lengthen your essay by including another BUT paragraph about her cruel and manipulative streak.
Of course, this is not necessarily the only right way to answer this essay question – as long as you back up your points with evidence from the text, you can take any standpoint that makes sense.

Step 3: Back up your points with well-analysed quotations
You wouldn’t write a scientific report without including evidence to support your findings, so why should it be any different with an essay? Even though you aren’t strictly required to substantiate every single point you make with a quotation, there’s no harm in trying.
A close reading of your quotations can enrich your appreciation of the question and will be sure to impress examiners. When selecting the best quotations to use in your essay, keep an eye out for specific literary techniques. For example, you could highlight Curley’s wife’s use of a rhetorical question when she says, a”n’ what am I doin’? Standin’ here talking to a bunch of bindle stiffs.” This might look like:
The rhetorical question “an’ what am I doin’?” signifies that Curley’s wife is very insecure; she seems to be questioning her own life choices. Moreover, she does not expect anyone to respond to her question, highlighting her loneliness and isolation on the ranch.
Other literary techniques to look out for include:
- Tricolon – a group of three words or phrases placed close together for emphasis
- Tautology – using different words that mean the same thing: e.g. “frightening” and “terrifying”
- Parallelism – ABAB structure, often signifying movement from one concept to another
- Chiasmus – ABBA structure, drawing attention to a phrase
- Polysyndeton – many conjunctions in a sentence
- Asyndeton – lack of conjunctions, which can speed up the pace of a sentence
- Polyptoton – using the same word in different forms for emphasis: e.g. “done” and “doing”
- Alliteration – repetition of the same sound, including assonance (similar vowel sounds), plosive alliteration (“b”, “d” and “p” sounds) and sibilance (“s” sounds)
- Anaphora – repetition of words, often used to emphasise a particular point
Don’t worry if you can’t locate all of these literary devices in the work you’re analysing. You can also discuss more obvious techniques, like metaphor, simile and onomatopoeia. It’s not a problem if you can’t remember all the long names; it’s far more important to be able to confidently explain the effects of each technique and highlight its relevance to the question.

Step 4: Be creative and original throughout
Anyone can write an essay using the tips above, but the thing that really makes it “perfect” is your own unique take on the topic. If you’ve noticed something intriguing or unusual in your reading, point it out – if you find it interesting, chances are the examiner will too!
Creative writing and essay writing are more closely linked than you might imagine. Keep the idea that you’re writing a speech or argument in mind, and you’re guaranteed to grab your reader’s attention.
It’s important to set out your line of argument in your introduction, introducing your main points and the general direction your essay will take, but don’t forget to keep something back for the conclusion, too. Yes, you need to summarise your main points, but if you’re just repeating the things you said in your introduction, the body of the essay is rendered pointless.
Think of your conclusion as the climax of your speech, the bit everything else has been leading up to, rather than the boring plenary at the end of the interesting stuff.
To return to Of Mice and Men once more, here’s an example of the ideal difference between an introduction and a conclusion:
Introduction
In John Steinbeck’s Of Mice and Men , Curley’s wife is portrayed as an ambiguous character. She could be viewed either as a cruel, seductive temptress or a lonely woman who is a victim of her society’s attitudes. Though she does seem to wield a form of sexual power, it is clear that Curley’s wife is largely a victim. This interpretation is supported by Steinbeck’s description of her appearance, other people’s attitudes, her dreams, and her evident loneliness and insecurity.
Overall, it is clear that Curley’s wife is a victim and is portrayed as such throughout the novel in the descriptions of her appearance, her dreams, other people’s judgemental attitudes, and her loneliness and insecurities. However, a character who was a victim and nothing else would be one-dimensional and Curley’s wife is not. Although she suffers in many ways, she is shown to assert herself through the manipulation of her femininity – a small rebellion against the victimisation she experiences.
Both refer back consistently to the question and summarise the essay’s main points. However, the conclusion adds something new which has been established in the main body of the essay and complicates the simple summary which is found in the introduction.

Hannah is an undergraduate English student at Somerville College, University of Oxford, and has a particular interest in postcolonial literature and the Gothic. She thinks literature is a crucial way of developing empathy and learning about the wider world. When she isn’t writing about 17th-century court masques, she enjoys acting, travelling and creative writing.
Recommended articles
Best Universities to Study Medicine in the World
A degree in Medicine spans many years, so it’s important to make a good choice when committing yourself to your studies. This guide is designed to help you figure out where you'd like to study and practise medicine. For those interested in getting a head start, the...

What Is A Year Abroad?
One of the great opportunities offered to UK university students is taking a year abroad. But what does this involve? Who can do it? What are some of the pros and cons? In our year abroad guide, we’ll explain some of the things to bear in mind when considering this...

The Ultimate Guide To Summer Internships
Are you eager to make the most of your summer break and jumpstart your career? There are so many productive things students can do in the summer or with their school holidays, and an internship is one of the most valuable! A summer internship could be the perfect...
- PRO Courses Guides New Tech Help Pro Expert Videos About wikiHow Pro Upgrade Sign In
- EDIT Edit this Article
- EXPLORE Tech Help Pro About Us Random Article Quizzes Request a New Article Community Dashboard This Or That Game Happiness Hub Popular Categories Arts and Entertainment Artwork Books Movies Computers and Electronics Computers Phone Skills Technology Hacks Health Men's Health Mental Health Women's Health Relationships Dating Love Relationship Issues Hobbies and Crafts Crafts Drawing Games Education & Communication Communication Skills Personal Development Studying Personal Care and Style Fashion Hair Care Personal Hygiene Youth Personal Care School Stuff Dating All Categories Arts and Entertainment Finance and Business Home and Garden Relationship Quizzes Cars & Other Vehicles Food and Entertaining Personal Care and Style Sports and Fitness Computers and Electronics Health Pets and Animals Travel Education & Communication Hobbies and Crafts Philosophy and Religion Work World Family Life Holidays and Traditions Relationships Youth
- Browse Articles
- Learn Something New
- Quizzes Hot
- Happiness Hub
- This Or That Game
- Train Your Brain
- Explore More
- Support wikiHow
- About wikiHow
- Log in / Sign up
- Education and Communications
How to Study More Effectively
Last Updated: June 24, 2024 Fact Checked
This article was co-authored by Emily Listmann, MA . Emily Listmann is a Private Tutor and Life Coach in Santa Cruz, California. In 2018, she founded Mindful & Well, a natural healing and wellness coaching service. She has worked as a Social Studies Teacher, Curriculum Coordinator, and an SAT Prep Teacher. She received her MA in Education from the Stanford Graduate School of Education in 2014. Emily also received her Wellness Coach Certificate from Cornell University and completed the Mindfulness Training by Mindful Schools. There are 9 references cited in this article, which can be found at the bottom of the page. This article has been fact-checked, ensuring the accuracy of any cited facts and confirming the authority of its sources. This article has been viewed 1,040,768 times.
You may be putting in hours of studying, but that doesn’t necessarily mean that you’re digesting the material. Learning to study more effectively will mean shorter and more efficient study sessions, and eventually, better grades!
Setting Yourself Up for Success

- If you are studying for an exam, look back on the previous quizzes. Some of that information is bound to come up again.
- Quizzes are smaller than exams, and typically only cover information from the current section or chapter.
- If you can't find a practice exam or study group, create your own!

- You can change your study schedule slightly, but try not to change it too much!
- Make sure you give yourself more time than you think you need, specially if it is a subject that you struggle with.

- Try saying something positive to yourself before you being studying, like, “I am going to ace this exam!”
- If you find yourself thinking negative thoughts like, “I’m going to fail that quiz,” stop the thought in its track. Replace it with a positive thought, like, “I’m going to master this material and succeed!”

- Take advantage of the library. Find a cozy spot with light foot traffic and start studying.
- Spend the afternoon studying in a quiet coffee shop.
- Study when your roommate is at work or class, and you have the place to yourself.
Studying Smarter

- If you find that your concentration is starting to falter, you may have to pause studying for the day or switch to a different subject.
- Do something relaxing during your break that doesn't take too much concentration, such as stretching or walking.

- You can create a simple mock exam for yourself by copying all of the questions from your previous quizzes and answering them.
- Consider taking a mock quiz or exam first. The topics that you struggle the most with are the ones that you should focus on when studying.

- Memory games don't work for everyone. If you find yourself struggling to memorize information using this method, skip it.
Using Notes to Study

- Consider rewriting your notes using the same ink color that you will be using for the exam. For example, if you'll write in blue ink, write your notes in blue ink.

- Putting information into your own words can help you remember the important stuff later on.

- You can also incorporate information from your textbook in the outline.
- For example, you could create a brief PowerPoint using your notes, or write key talking points on index cards and use them to help you present the material.
- 5 Try the Cornell note-taking method . This method of note-taking requires you to plug in essential answers to questions using the information in your notes. As a result, you will be better able to retain the information in your notes. [10] X Research source
Supercharge Your Studying with this Expert Series

Community Q&A
Reader Videos
- If you're studying a chapter, go through the whole thing first. Before further studying take a break, think about your actions. Continue. Then draw a quick mind map about sequences in the chapter. Afterwards, study everything on its own and connect information together, thus strengthening your knowledge on the chapter. Thanks Helpful 37 Not Helpful 1
- Highlighting information helps so that you can remember the important parts. This is good, especially if you are a visual learner. Thanks Helpful 38 Not Helpful 6
- Seek tutoring if you are having trouble remembering information or taking notes. A tutor can help you with individual subjects or help you to build study skills in general. Thanks Helpful 38 Not Helpful 8

You Might Also Like

- ↑ http://www.stanforddaily.com/2017/05/10/stanford-researchers-reveal-how-to-study-more-effectively/
- ↑ https://alis.alberta.ca/succeed-at-work/make-your-work-life-more-satisfying/a-positive-attitude-will-help-you-learn/
- ↑ https://learnenglishteens.britishcouncil.org/skills/listening/a1-listening/study-tips
- ↑ https://www.apa.org/gradpsych/2011/11/study-smart
- ↑ http://news.stlpublicradio.org/post/are-you-studying-effectively-what-wash-us-science-memory-tells-us-about-best-way-learn#stream/0
- ↑ https://learningcenter.unc.edu/tips-and-tools/enhancing-your-memory/
- ↑ https://www.utep.edu/extendeduniversity/utepconnect/blog/november-2017/4-memory-techniques-for-successful-study-sessions.html
- ↑ https://www.fnu.edu/7-techniques-improve-study-habits/
- ↑ https://lsc.cornell.edu/how-to-study/taking-notes/cornell-note-taking-system/
About This Article

To study intelligently and effectively, break your study sessions into 30-minute chunks, and give yourself 5-10 minute breaks between sessions so your brain has time to rest and recharge. As you study, rewrite your notes and read them aloud so that you're engaging all of your senses and boosting your memory. If you're still struggling to memorize your study material, try creating a song, acronym, or mnemonic device to help you absorb the lessons! For help planning a study schedule and picking the perfect studying spot, keep reading! Did this summary help you? Yes No
- Send fan mail to authors
Reader Success Stories
ZombieSlayerDrew
Aug 28, 2017
Did this article help you?
May 11, 2016
Jun 14, 2018
Kamal Ramanai
Apr 13, 2016
Alexis Hancock
Jul 23, 2018

Featured Articles

Trending Articles

Watch Articles

- Terms of Use
- Privacy Policy
- Do Not Sell or Share My Info
- Not Selling Info
Get all the best how-tos!
Sign up for wikiHow's weekly email newsletter
We use cookies to make your user experience better. By staying on our website, you fully accept it. Learn more .
How to Study for Exams Effectively
- College Life

Getting yourself ready for exams might seem terrifying. With the help of our easy tips and tricks, you can effectively avoid all the stress and lack of sleep that the majority of students face when studying for their finals.
Study Smarter, Not Longer
The main rule that you, as a student, should remember is that studying for a long time does not equal studying effectively. The longer you try to stay focused, the less information you retain as your brain seeks a little rest and makes you distracted. But that is just what the majority of students do when they try to catch up and get ready for exams. You can often see students pulling all-nighters before their finals, drinking lots of coffee.
So, should you do the same? Certainly, not! Of course, it doesn’t mean that you don’t have to spend time reciting your notes at all. It just means that you can achieve much more in less time.
Here are a few things that will help you spend your time studying more productively:
- Pay attention to the note-taking method that you are using. Change it if you think that your notes are not convenient to navigate through. It might take a while to define what method suits you the best (or even a few of them for different classes), but you will thank yourself later when getting ready for your exam.
- Create a schedule for every day that includes hours that you dedicate to studying. Stick to it.
- Have breaks. Even a short 15-minute break can make a lot of difference.
- Create a mind map.
- Minimize distraction. Many students think that they are quite productive, while not even noticing that the majority of the time they spend on studying and doing their homework, they are procrastinating. Scrolling through social media or texting with your friends is not the way to get ready for the exam. You can do it later.
- Have a comfortable place to study. Having a desk with a comfortable chair is not always possible. But you can still have a place to do your homework. Keep this area clean, and you will notice that your mind is much sharper.
- Set goals. You will definitely need the motivation to study, so pay attention to the goals that you are trying to achieve. Break them into short-term and long-term goals and divide them into even smaller tasks that you can complete every day.
Now, let’s look at these points in detail.
Pay Attention to Your Note-Taking Method
Though many students know that taking notes is essential, not all of them actually pay attention to the method that they are using. However, if you want to be successful in your studies , this is the first thing that you should work on.
There are a lot of various note-taking methods that you should try. Each of them has pros and cons.
For example, you might try out the Boxing method and find out that it is pretty convenient for classes that are split into sections. At the same time, the Mapping method is great for lectures that contain a lot of structured information and also helps you out if you are a visual learner.
Try out the Cornel method, as it is effective for various lectures and classes. Once you make your notes work, you will be able to navigate through them easier and retain information better.
Create a Schedule
The schedule is an important part of the study routine of any student. It’s crucial to be able to dedicate enough time to do your homework and be disciplined when it comes to procrastination.
When you need to get ready for your exams, it’s important to plan your studies beforehand. Create a schedule and put in your classes and your study sessions. For example, three or four hours every evening. Be ready to study through the weekends, too, if you have a lot to catch up. Make sure you write down the dates of exams so that you are able to see how much time you have left.
Have Breaks
Even the sharpest mind needs breaks. It’s crucial to have rest in order to stay focused and organized. Take short breaks every 40-50 minutes of studying and spend them on snacking, listening to music, etc. You will definitely see the difference, as it will be easier for you to get back to studying.
There is also a method that is called the Pomodoro technique that every student should try. This is basically a time management method that implies working on short but intensive intervals alternated with breaks. For example, you can study for 30 minutes straight and then have a short five- to ten-minute break. Set the timers, so you stick to the schedule and have longer breaks (around 20 minutes) every 3-4 intervals.
Minimize Distractions
We all know that studying might be boring. That’s why a lot of students try to make this time a little bit more amusing by texting, watching TV, etc. However, this is just another form of procrastination.
Turn off your TV, and you might notice that it is actually much easier for you to stay focused on your studies. Mute your phone, and you will spend less time completing the same task.
Moreover, not all music is great for background noise. For example, if you are listening to songs that contain lyrics, it distracts your brain as it has to process the information that it receives through your hearing. That means that the information that you are reading at that moment won’t be retained as well as it could be. If you can’t focus in complete silence, you should definitely choose classical music or chill ambient music as they don’t create such a distraction.
One more thing that you should pay attention to is to be concentrated on one task only. Multitasking isn’t effective when it comes to studying. As there is a lot of information that your brain needs to retain, try not to mix it up, or else your studying won’t be productive. So, end the topic or section first and then start another one.
Have a Place for Studying
Having a comfortable and clean space is essential to have your thoughts organized too. It’s tempting to stay with your notebooks in your bed; however, try avoiding this. You will feel much more concentrated when sitting at the desk or in the library.
But why is it important to keep your place clean and neat? Some studies show us that cluttered and messy spaces tend to affect our concentration, mood, and productivity. So, just cleaning your desk from unnecessary things can boost your studying routine.
Moreover, your brain constantly makes associations with the setting around you. If you have a particular time and place for studying, your brain will get used to it, and study sessions will be much easier to handle.
Set Your Goals
Getting ready for the finals also means that you should stay motivated and goal-oriented through this time; otherwise you might not be as successful in your studies as you wish. That’s why we always recommend setting your priorities and goals when it comes to studying. For example, complete all the assignments on time , succeed in the finals, etc.
What can you do? Create a list of all the topics and questions that you need to cover. Many professors are honest about their tests and even tell you that particular information is going to be in your final, but not many students listen. So, pay attention to the information that your lecturer emphasizes as it is most likely to appear in the test.
After you create such a list, make sure to put it into your schedule and daily to-do lists, so that you can see that you are on time. Don’t try to manage big chunks of information at the time – better spread it over a few days. For example, you can write down that the next weekend you will dedicate to the first section of the course. You should also divide bigger assignments, e.g. a term paper , into smaller parts and work on them slowly.
When you have clear goals and tasks, it’s easier to keep track of your progress and your achievements. You can reward yourself with some treat or anything else that brings you joy every time when you complete another task.
It’s also crucial to set your priorities and stick to them while getting ready for the finals. Prioritize your studies and plan your study sessions first. We know that it’s hard, but this is what actually works for the majority of students.

Related Articles

Save £500 when you enrol by 30th September!
- How to Do Research for an Excellent Essay: The Complete Guide

One of the biggest secrets to writing a good essay is the Boy Scouts’ motto: ‘be prepared’. Preparing for an essay – by conducting effective research – lays the foundations for a brilliant piece of writing, and it’s every bit as important as the actual writing part. Many students skimp on this crucial stage, or sit in the library not really sure where to start; and it shows in the quality of their essays. This just makes it easier for you to get ahead of your peers, and we’re going to show you how. In this article, we take you through what you need to do in order to conduct effective research and use your research time to best effect.
Allow enough time
First and foremost, it’s vital to allow enough time for your research. For this reason, don’t leave your essay until the last minute . If you start writing without having done adequate research, it will almost certainly show in your essay’s lack of quality. The amount of research time needed will vary according to whether you’re at Sixth Form or university, and according to how well you know the topic and what teaching you’ve had on it, but make sure you factor in more time than you think you’ll need. You may come across a concept that takes you longer to understand than you’d expected, so it’s better to allow too much time than too little.
Read the essay question and thoroughly understand it
If you don’t have a thorough understanding of what the essay question is asking you to do, you put yourself at risk of going in the wrong direction with your research. So take the question, read it several times and pull out the key things it’s asking you to do. The instructions in the question are likely to have some bearing on the nature of your research. If the question says “Compare”, for example, this will set you up for a particular kind of research, during which you’ll be looking specifically for points of comparison; if the question asks you to “Discuss”, your research focus may be more on finding different points of view and formulating your own.
Begin with a brainstorm
Start your research time by brainstorming what you already know. Doing this means that you can be clear about exactly what you’re already aware of, and you can identify the gaps in your knowledge so that you don’t end up wasting time by reading books that will tell you what you already know. This gives your research more of a direction and allows you to be more specific in your efforts to find out certain things. It’s also a gentle way of introducing yourself to the task and putting yourself in the right frame of mind for learning about the topic at hand.
Achieve a basic understanding before delving deeper
If the topic is new to you and your brainstorm has yielded few ideas, you’ll need to acquire a basic understanding of the topic before you begin delving deeper into your research. If you don’t, and you start by your research by jumping straight in at the deep end, as it were, you’ll struggle to grasp the topic. This also means that you may end up being too swayed by a certain source, as you haven’t the knowledge to question it properly. You need sufficient background knowledge to be able to take a critical approach to each of the sources you read. So, start from the very beginning. It’s ok to use Wikipedia or other online resources to give you an introduction to a topic, though bear in mind that these can’t be wholly relied upon. If you’ve covered the topic in class already, re-read the notes you made so that you can refresh your mind before you start further investigation.
Working through your reading list
If you’ve been given a reading list to work from, be organised in how you work through each of the items on it. Try to get hold of as many of the books on it as you can before you start, so that you have them all easily to hand, and can refer back to things you’ve read and compare them with other perspectives. Plan the order in which you’re going to work through them and try to allocate a specific amount of time to each of them; this ensures that you allow enough time to do each of them justice and that focus yourself on making the most of your time with each one. It’s a good idea to go for the more general resources before honing in on the finer points mentioned in more specialised literature. Think of an upside-down pyramid and how it starts off wide at the top and becomes gradually narrower; this is the sort of framework you should apply to your research.
Ask a librarian
Library computer databases can be confusing things, and can add an extra layer of stress and complexity to your research if you’re not used to using them. The librarian is there for a reason, so don’t be afraid to go and ask if you’re not sure where to find a particular book on your reading list. If you’re in need of somewhere to start, they should be able to point you in the direction of the relevant section of the library so that you can also browse for books that may yield useful information.
Use the index
If you haven’t been given specific pages to read in the books on your reading list, make use of the index (and/or table of contents) of each book to help you find relevant material. It sounds obvious, but some students don’t think to do this and battle their way through heaps of irrelevant chapters before finding something that will be useful for their essay.
Taking notes
As you work through your reading, take notes as you go along rather than hoping you’ll remember everything you’ve read. Don’t indiscriminately write down everything – only the bits that will be useful in answering the essay question you’ve been set. If you write down too much, you risk writing an essay that’s full of irrelevant material and getting lower grades as a result. Be concise, and summarise arguments in your own words when you make notes (this helps you learn it better, too, because you actually have to think about how best to summarise it). You may want to make use of small index cards to force you to be brief with what you write about each point or topic. We’ve covered effective note-taking extensively in another article, which you can read here. Note-taking is a major part of the research process, so don’t neglect it. Your notes don’t just come in useful in the short-term, for completing your essay, but they should also be helpful when it comes to revision time, so try to keep them organised.
Research every side of the argument
Never rely too heavily on one resource without referring to other possible opinions; it’s bad academic practice. You need to be able to give a balanced argument in an essay, and that means researching a range of perspectives on whatever problem you’re tackling. Keep a note of the different arguments, along with the evidence in support of or against each one, ready to be deployed into an essay structure that works logically through each one. If you see a scholar’s name cropping up again and again in what you read, it’s worth investigating more about them even if you haven’t specifically been told to do so. Context is vital in academia at any level, so influential figures are always worth knowing about.
Keep a dictionary by your side
You could completely misunderstand a point you read if you don’t know what one important word in the sentence means. For that reason, it’s a good idea to keep a dictionary by your side at all times as you conduct your research. Not only does this help you fully understand what you’re reading, but you also learn new words that you might be able to use in your forthcoming essay or a future one . Growing your vocabulary is never a waste of time!
Start formulating your own opinion
As you work through reading these different points of view, think carefully about what you’ve read and note your own response to different opinions. Get into the habit of questioning sources and make sure you’re not just repeating someone else’s opinion without challenging it. Does an opinion make sense? Does it have plenty of evidence to back it up? What are the counter-arguments, and on balance, which sways you more? Demonstrating your own intelligent thinking will set your essay apart from those of your peers, so think about these things as you conduct your research.
Be careful with web-based research
Although, as we’ve said already, it’s fine to use Wikipedia and other online resources to give you a bit of an introduction to a topic you haven’t covered before, be very careful when using the internet for researching an essay. Don’t take Wikipedia as gospel; don’t forget, anybody can edit it! We wouldn’t advise using the internet as the basis of your essay research – it’s simply not academically rigorous enough, and you don’t know how out of date a particular resource might be. Even if your Sixth Form teachers may not question where you picked up an idea you’ve discussed in your essays, it’s still not a good habit to get into and you’re unlikely to get away with it at a good university. That said, there are still reliable academic resources available via the internet; these can be found in dedicated sites that are essentially online libraries, such as JSTOR. These are likely to be a little too advanced if you’re still in Sixth Form, but you’ll almost certainly come across them once you get to university.
Look out for footnotes
In an academic publication, whether that’s a book or a journal article, footnotes are a great place to look for further ideas for publications that might yield useful information. Plenty can be hidden away in footnotes, and if a writer is disparaging or supporting the ideas of another academic, you could look up the text in question so that you can include their opinion too, and whether or not you agree with them, for extra brownie points.
Don’t save doing all your own references until last
If you’re still in Sixth Form, you might not yet be required to include academic references in your essays, but for the sake of a thorough guide to essay research that will be useful to you in the future, we’re going to include this point anyway (it will definitely come in useful when you get to university, so you may as well start thinking about it now!). As you read through various books and find points you think you’re going to want to make in your essays, make sure you note down where you found these points as you go along (author’s first and last name, the publication title, publisher, publication date and page number). When you get to university you will be expected to identify your sources very precisely, so it’s a good habit to get into. Unfortunately, many students forget to do this and then have a difficult time of going back through their essay adding footnotes and trying to remember where they found a particular point. You’ll save yourself a great deal of time and effort if you simply note down your academic references as you go along. If you are including footnotes, don’t forget to add each publication to a main bibliography, to be included at the end of your essay, at the same time.
Putting in the background work required to write a good essay can seem an arduous task at times, but it’s a fundamental step that can’t simply be skipped. The more effort you put in at this stage, the better your essay will be and the easier it will be to write. Use the tips in this article and you’ll be well on your way to an essay that impresses!
To get even more prepared for essay writing you might also want to consider attending an Oxford Summer School .
Image credits: banner
Essay Papers Writing Online
Tips and tricks for crafting engaging and effective essays.

Writing essays can be a challenging task, but with the right approach and strategies, you can create compelling and impactful pieces that captivate your audience. Whether you’re a student working on an academic paper or a professional honing your writing skills, these tips will help you craft essays that stand out.
Effective essays are not just about conveying information; they are about persuading, engaging, and inspiring readers. To achieve this, it’s essential to pay attention to various elements of the essay-writing process, from brainstorming ideas to polishing your final draft. By following these tips, you can elevate your writing and produce essays that leave a lasting impression.
Understanding the Essay Prompt
Before you start writing your essay, it is crucial to thoroughly understand the essay prompt or question provided by your instructor. The essay prompt serves as a roadmap for your essay and outlines the specific requirements or expectations.
Here are a few key things to consider when analyzing the essay prompt:
- Read the prompt carefully and identify the main topic or question being asked.
- Pay attention to any specific instructions or guidelines provided, such as word count, formatting requirements, or sources to be used.
- Identify key terms or phrases in the prompt that can help you determine the focus of your essay.
By understanding the essay prompt thoroughly, you can ensure that your essay addresses the topic effectively and meets the requirements set forth by your instructor.
Researching Your Topic Thoroughly

One of the key elements of writing an effective essay is conducting thorough research on your chosen topic. Research helps you gather the necessary information, facts, and examples to support your arguments and make your essay more convincing.
Here are some tips for researching your topic thoroughly:
| Don’t rely on a single source for your research. Use a variety of sources such as books, academic journals, reliable websites, and primary sources to gather different perspectives and valuable information. | |
| While conducting research, make sure to take detailed notes of important information, quotes, and references. This will help you keep track of your sources and easily refer back to them when writing your essay. | |
| Before using any information in your essay, evaluate the credibility of the sources. Make sure they are reliable, up-to-date, and authoritative to strengthen the validity of your arguments. | |
| Organize your research materials in a systematic way to make it easier to access and refer to them while writing. Create an outline or a research plan to structure your essay effectively. |
By following these tips and conducting thorough research on your topic, you will be able to write a well-informed and persuasive essay that effectively communicates your ideas and arguments.
Creating a Strong Thesis Statement
A thesis statement is a crucial element of any well-crafted essay. It serves as the main point or idea that you will be discussing and supporting throughout your paper. A strong thesis statement should be clear, specific, and arguable.
To create a strong thesis statement, follow these tips:
- Be specific: Your thesis statement should clearly state the main idea of your essay. Avoid vague or general statements.
- Be concise: Keep your thesis statement concise and to the point. Avoid unnecessary details or lengthy explanations.
- Be argumentative: Your thesis statement should present an argument or perspective that can be debated or discussed in your essay.
- Be relevant: Make sure your thesis statement is relevant to the topic of your essay and reflects the main point you want to make.
- Revise as needed: Don’t be afraid to revise your thesis statement as you work on your essay. It may change as you develop your ideas.
Remember, a strong thesis statement sets the tone for your entire essay and provides a roadmap for your readers to follow. Put time and effort into crafting a clear and compelling thesis statement to ensure your essay is effective and persuasive.
Developing a Clear Essay Structure
One of the key elements of writing an effective essay is developing a clear and logical structure. A well-structured essay helps the reader follow your argument and enhances the overall readability of your work. Here are some tips to help you develop a clear essay structure:
1. Start with a strong introduction: Begin your essay with an engaging introduction that introduces the topic and clearly states your thesis or main argument.
2. Organize your ideas: Before you start writing, outline the main points you want to cover in your essay. This will help you organize your thoughts and ensure a logical flow of ideas.
3. Use topic sentences: Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph. This helps the reader understand the purpose of each paragraph.
4. Provide evidence and analysis: Support your arguments with evidence and analysis to back up your main points. Make sure your evidence is relevant and directly supports your thesis.
5. Transition between paragraphs: Use transitional words and phrases to create flow between paragraphs and help the reader move smoothly from one idea to the next.
6. Conclude effectively: End your essay with a strong conclusion that summarizes your main points and reinforces your thesis. Avoid introducing new ideas in the conclusion.
By following these tips, you can develop a clear essay structure that will help you effectively communicate your ideas and engage your reader from start to finish.
Using Relevant Examples and Evidence
When writing an essay, it’s crucial to support your arguments and assertions with relevant examples and evidence. This not only adds credibility to your writing but also helps your readers better understand your points. Here are some tips on how to effectively use examples and evidence in your essays:
- Choose examples that are specific and relevant to the topic you’re discussing. Avoid using generic examples that may not directly support your argument.
- Provide concrete evidence to back up your claims. This could include statistics, research findings, or quotes from reliable sources.
- Interpret the examples and evidence you provide, explaining how they support your thesis or main argument. Don’t assume that the connection is obvious to your readers.
- Use a variety of examples to make your points more persuasive. Mixing personal anecdotes with scholarly evidence can make your essay more engaging and convincing.
- Cite your sources properly to give credit to the original authors and avoid plagiarism. Follow the citation style required by your instructor or the publication you’re submitting to.
By integrating relevant examples and evidence into your essays, you can craft a more convincing and well-rounded piece of writing that resonates with your audience.
Editing and Proofreading Your Essay Carefully
Once you have finished writing your essay, the next crucial step is to edit and proofread it carefully. Editing and proofreading are essential parts of the writing process that help ensure your essay is polished and error-free. Here are some tips to help you effectively edit and proofread your essay:
1. Take a Break: Before you start editing, take a short break from your essay. This will help you approach the editing process with a fresh perspective.
2. Read Aloud: Reading your essay aloud can help you catch any awkward phrasing or grammatical errors that you may have missed while writing. It also helps you check the flow of your essay.
3. Check for Consistency: Make sure that your essay has a consistent style, tone, and voice throughout. Check for inconsistencies in formatting, punctuation, and language usage.
4. Remove Unnecessary Words: Look for any unnecessary words or phrases in your essay and remove them to make your writing more concise and clear.
5. Proofread for Errors: Carefully proofread your essay for spelling, grammar, and punctuation errors. Pay attention to commonly misused words and homophones.
6. Get Feedback: It’s always a good idea to get feedback from someone else. Ask a friend, classmate, or teacher to review your essay and provide constructive feedback.
By following these tips and taking the time to edit and proofread your essay carefully, you can improve the overall quality of your writing and make sure your ideas are effectively communicated to your readers.
Related Post
How to master the art of writing expository essays and captivate your audience, convenient and reliable source to purchase college essays online, step-by-step guide to crafting a powerful literary analysis essay, unlock success with a comprehensive business research paper example guide, unlock your writing potential with writers college – transform your passion into profession, “unlocking the secrets of academic success – navigating the world of research papers in college”, master the art of sociological expression – elevate your writing skills in sociology.
The full article is available below.
You will also receive a follow-up email containing a link so you can come back to it later.
8 Top Law School Final Exam Tips
Last Updated: Aug 28, 2024

What to expect from your law school final exams
A full semester of taking copious notes, reading, briefing, outlining, classroom discussions, and surviving the Socratic Method culminates in one final act. Writing law school final exams.
Most professors give essay exams for law school finals. Some are single-topic, short-answer questions. Others can go on for pages — known as issue-spotter exams. Some are taken in class, while others are take-home, allowing students more than the traditional amount of time to answer the essay questions. There are open-book and closed-book exams. And there are those few professors who create multiple-choice exams or (in rare cases) give oral exams.
Whatever type of exam your professor chooses to administer, you will be tested on your ability to analyze and resolve legal problems and demonstrate your grasp of the materials. Your course grade will be largely, if not exclusively, based on your final exam performance.
Here are some high-level tips to help you prepare for your law school finals.
Understand your professor preferences
The foundation for success on your law school finals is to know who is grading the exam. Your mission is to make that person’s life easier. Ultimately, different professors prefer different types of answers. Some want extreme detail — every possible interpretation of every possible fact. Some like answers straight to the point within a page count. It’s okay to ask your professor.
It’s a given that all professors expect well-organized, legible answers, no matter how brief or expansive.
Read the facts carefully
Read the entire problem through once rather quickly to get a general understanding. Focus on the question you are being asked to respond to at the end of the problem.
Then, read through the scenario again, slowly and carefully. This time, evaluate every word and phrase to identify all potential issues. Applying the law to the facts presented is critical in any law school exam. And changing the facts even slightly could result in a completely different result.
Answer the question that is being asked
Always keep in mind the specific question you are actually being asked to answer. Although you may receive credit for ancillary information provided in your answer, you will only receive maximum credit if you specifically answer the question that is presented. Therefore, you must determine what role the professor is asking you to assume before answering. Are you the defendant’s attorney, or do you represent the plaintiff? Are you a judge trying to resolve the dispute? It makes a real difference in how you answer.
Attempts to include unrelated material in your answer could backfire if your professor believes you are incapable of ruling out irrelevant information.
Organize your thoughts
Organization is critical to writing a strong essay answer on any law school finals. After all, if the professor cannot follow your analysis, how can they grade it fairly and appropriately?
Before you start writing, chart the issues in the manner in which you will resolve them. Again, make sure the issues are related to the actual question you are being asked to answer. Arrange the issues in the sequence in which you would expect a court to address them (i.e., normally jurisdictional issues first, then liability, then remedies). Capture the points you will discuss in sufficient detail to prompt you to think the problem through to a fair and practical solution.
Complete your analysis and organization before you start writing
You may find that you devote a solid one-fourth of the time allocated to reading, analyzing the problem and organizing your answer. That’s okay. A logical organization and clear expression of ideas will strengthen your answer. This purposeful approach may even bolster an answer that’s somewhat weak.
Use the IRAC format for each issue raised
As you begin to write out your answer, we recommend you analyze each dispute using the IRAC method.
First, state the issue in precise legal terms (i.e., “Did the defendant’s mistake in computing his bid prevent the formation of an enforceable contract?”). Be careful to avoid generalizations or oversimplification of the issue.
Next, state the applicable law. Be sure to define the pertinent elements of a rule as well as any terms of art.
Application
Then, apply the rules to the facts using arguments. Avoid the common error of stating a rule and then jumping straight to the conclusion. Your professor will not infer a supporting argument for you — you must spell it out. Remember to use the Issue T you created earlier to remind you to discuss which facts in the fact pattern support (or prevent) application of the rule. Discuss and weigh each fact given and the logical inference to be drawn from it. Be sure to include counterarguments where possible.
Finally, come to a straightforward conclusion on each issue. Make sure you have clearly answered the question asked, and you have not left an issue hanging. If a number of outcomes are possible, discuss the merits of each, but always select one position as your conclusion and state why. In close cases, it is generally best to select the most practical and fair conclusion. Just don’t consider yourself bound by the “general rule” or “majority view” in answering on a law school final exam unless the question clearly calls for such.
Argue both sides of legal issues you spot and remember policy concerns
Once a dispute has been framed and a legal theory has been asserted, identify any problems surrounding the theory’s application as well as arguments that each side can make in support of their position.
Also, if time allows, include just a sentence or two regarding the policy implications of your conclusions. Law is meant to provide order in society and, when imposing laws, you should always predict the impact that they will have.
Take a deep breath and try not to panic
If you find yourself panicking, not understanding the issues presented or not remembering the rules related to such issues, don’t panic. Instead, close your eyes and take a few deep breaths. Then, start working systematically through the information with these tips and do your best on your law school finals.
Unlock the Full Article
Tell us a little about yourself and your goals to display the full article and gain access to more resources relevant to your needs.
Interesting in reading more? Fill out the form to read the full article.
Pardon Our Interruption
As you were browsing something about your browser made us think you were a bot. There are a few reasons this might happen:
- You've disabled JavaScript in your web browser.
- You're a power user moving through this website with super-human speed.
- You've disabled cookies in your web browser.
- A third-party browser plugin, such as Ghostery or NoScript, is preventing JavaScript from running. Additional information is available in this support article .
To regain access, please make sure that cookies and JavaScript are enabled before reloading the page.
Student Success @ Illinois
Study tips & strategies.
An important aspect of success in class is being prepared and learning to study effectively. Below are some tips, strategies, and resources curated by students and staff.
Tips for Studying by Yourself
- Make a schedule of when, where, and how long you study.
- Make an agenda of what subjects or concepts you want to study.
- Eliminate distractions by silencing your phone, computer, or other devices that may take away your focus.
- Set goals for yourself. For example: “By the end of this study session, I want to be able to do/understand ________.“
- Find a study location that works best for your learning style. This may be in your room alone or in a coffee shop surrounded by others. Just study wherever you study best!
- Take breaks. Use techniques like the Pomodoro Technique (25 minutes of focused study followed by a 5-minute break) to stay focused and maintain productivity.
- Regularly quiz yourself on the material you’re studying to reinforce it into your memory and identify areas that need improvement.
- Reward yourself after a study session. You’ve worked hard, so you deserve to treat yourself!
- Study for 1 or 2 classes per day to maximize comprehension/memorization
- Be consistent in the times you study or at least try to be.
- If you are more of a visual learner, color code your notes .
Tips for Studying with Another Person or Group
- Set clear goals for the study sessions and layout what you want to learn from each study session.
- Hold each other accountable.
- Create a recurring schedule for the study sessions. Find a time that works best for everyone in the group and aim to meet at those regularly scheduled times.
- Assign different topics or sections to each group member and then teach each other. Explaining concepts to others is a great way to reinforce your own understanding.
- Ask questions. Don’t hesitate to ask for clarification or help from your study partners.
- Take breaks. Schedule regular breaks to rest and recharge to prevent academic burnout.
- Review what you’ve learned at the end of each study session and highlight any areas that need further explanation.
- “Teach” someone what you’ve learned. It helps you recite what you’ve learned and allows everyone to add what they know as well.
Study Skill Resources on Campus
- Michael L. Jeffries, Sr. Center for Access and Academic Success
- Academic Skill Consultations
- Residence Halls Tutoring
- Grainger College of Engineering
- Admissions blog
Other Tips and Resources
- Sample of locations where you can study on campus
We Trust in Human Precision
20,000+ Professional Language Experts Ready to Help. Expertise in a variety of Niches.
API Solutions
- API Pricing
- Cost estimate
- Customer loyalty program
- Educational Discount
- Non-Profit Discount
- Green Initiative Discount1
Value-Driven Pricing
Unmatched expertise at affordable rates tailored for your needs. Our services empower you to boost your productivity.
- Special Discounts
- Enterprise transcription solutions
- Enterprise translation solutions
- Transcription/Caption API
- AI Transcription Proofreading API
Trusted by Global Leaders
GoTranscript is the chosen service for top media organizations, universities, and Fortune 50 companies.
GoTranscript
One of the Largest Online Transcription and Translation Agencies in the World. Founded in 2005.
Speaker 1: After the title page and abstract, the reader's first true interaction with your research paper is the introduction. Your introduction will establish the foundation upon which your readers approach your work, and if you use the tips we discuss in this video, these readers should be able to logically apply the rules set in your introduction to all parts of your paper, all the way through the conclusion. What exactly is the purpose of the introduction? Think about your paper as a chronological story. It will begin at point A, the introduction, and move in time towards point B, the discussion and conclusion. Since your introduction includes content about the gaps in knowledge that your study aims to fill, the results you elaborate on in your discussion section should therefore be somewhat familiar to the reader, as you have already touched upon them in the introduction section. The introduction must answer two main questions. Why was this particular study needed to fill the gaps in knowledge? And why does this particular gap need filling? Imagine our entire plane of knowledge as an incomplete puzzle. The pieces snapped together are what is established, or what is known. The missing piece is the gap in knowledge, or what is currently unknown. This is what your study will be helping to explain. So the context you provide in the introduction must first identify that there is a knowledge gap in what it is, it must explain why it needs to be filled, and then briefly summarize how this study intends to fill that gap and why. The introduction is one of the most compact parts of the research paper, since it is not very long but needs to essentially give a complete overview of the context in which your study is taking place, and your specific reasons for doing the study. Most tend to be around 10% of the total length of your paper. The introduction consists of background information about a topic being studied, the rationale for undertaking the study, or for filling the gap with this particular information, key references to preliminary work or closely related papers appearing elsewhere, a clarification of important terms, definitions, or abbreviations to be used in the paper, and a review of related studies in which you give a brief but incisive analysis of work that heavily concerns your study. It could be a very similar study or one that supports the findings of your new study. So how should you structure your introduction? As you can see in this figure, your introduction should start broadly and then narrow until it reaches your hypothesis. The first thing you want to do is state your area of research and then immediately show what is already known. This is also known as background information. Then move on to what is unknown, the problem or gap you want to resolve. Finally, you should discuss how you will resolve this problem using a clear hypothesis. In step one, you will show what is already known. Start with a strong statement that reflects your research subject area and ask questions or post statements to frame the problems your study explores. You can ask general questions here to guide your readers to the problem and show them what we already know. For instance, what do we know about breathing capability of bottlenose dolphins? Use keywords from your title, the exact language of your study that is, to zero in on the problem at hand and show the relevance of your work. Avoid stating background information that is too broad in nature. You don't need to state too many obvious facts that your readers would know. If you are writing about bottlenose dolphins, for instance, you probably don't need to explain to them that mammals breathe oxygen. At the beginning of the introduction, you should also be sure to cite all of the sources that you use for background information and support. Only provide the necessary background information. Don't focus extensively on background, but use it to set up the context for doing this study. You should also review only relevant, up-to-date primary literature that supports your explanation of our current base of knowledge. In the second part of your introduction, you should answer the question, what is the knowledge gap? Here you will highlight areas where too little information is available. Explain how and why we should fill in that gap. What does this missing information do to impede our understanding of a process or system? And you should identify what logical next steps can be developed based on existing research. By showing you have examined current data and devised a method to find new applications and make new inferences, you're showing your peers that you are aware of the direction your research is moving in, and you're showing confidence in your decision to pursue this paper study. In the last part of your introduction, you will show how your study fills in the knowledge gap. This is where you state your purpose and give a clear hypothesis or objective of the study. The hypothesis is a very short 1-2 sentence supposition or explanation of what will happen in your study. This is quite often written as an if-then format. If X and Y are present, then Z will occur. Here you should also try to answer the question, if we fill this gap, what useful information will the readers gain? Many researchers have difficulty when it comes to deciding when to write their introduction. It is important to consider the order you draft your research paper, for as you recall, everything else in the research paper must flow from the introduction. Therefore, because it is one of the most difficult sections to nail down, consider writing the introduction second to last, after the materials and methods, results, and discussion section, and just before the conclusion. This will ensure you effectively lay a groundwork for the rest of your paper, and you can use the research you have already compiled to ensure that everything in your introduction is pertinent and accurate. In addition to content and organization, writers of research papers should also be aware of grammar and style issues that directly affect the readability and strength of their printed work. Here are some guidelines for writing the introduction section. Try and write in the active voice when possible. This will shorten your sentences and enhance the impact of your information. Always strive for concise sentences. This will allow you to get in all of the necessary information in this compact introduction section. Use stronger verbs when possible. This also impacts sentence length and strength of writing. Be careful not to overuse first-person pronouns such as I and we, and always organize your thoughts from the broad to the specific, as we have seen in our model. A strong introduction will encourage readers to read your entire research paper and help get your work published in scientific journals. For more information and tips on manuscript writing and journal submissions, visit the resources page at wordvice.com.

- DOI: 10.55014/pij.v7i1.545
- Corpus ID: 267738387
Effective Strategies and Methods to Enhance Music Practical Teaching in Higher Vocational Preschool Education
- Published in Pacific International Journal 15 February 2024
One Citation
Memory, attention and creativity as cognitive processes in musical performance: a case study of students and professionals among non-musicians and musicians., related papers.
Showing 1 through 3 of 0 Related Papers

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Learn how to study better with tips and tools from Oxford Learning. Find out how to get organized, pay attention, avoid distractions, review notes, and more.
2) Ask yourself lots of questions. "One good technique to use instead is to read once, then quiz yourself, either using questions at the back of a textbook chapter, or making up your own ...
6. Take Breaks. The brain can only absorb so much information at a time. According to the National Institutes of Health, research has shown that taking breaks in between study sessions boosts retention. Studies have shown that wakeful rest plays just as important a role as practice in learning a new skill.
The proper division of time is one of the most critical study tips. The disorganization and constant putting off until tomorrow are two major problems. 5. Avoid procrastination. Currently, putting away tasks for later seems to be one of the most pressing problems for students.
There are 6 areas you need to "win" in order to study as effectively as possible. So you'll find the 37 strategies grouped into the following 6 "chapters": Table Of Contents. I. Preparing For Success: Plan & Prioritise. II. Getting Productive: Building Superhuman Focus.
When you write an essay for a course you are taking, you are being asked not only to create a product (the essay) but, more importantly, to go through a process of thinking more deeply about a question or problem related to the course. By writing about a source or collection of sources, you will have the chance to wrestle with some of the
Take an honest look at your schedule (this includes schoolwork, extracurriculars, work, etc.) and decide how often you can study without making your schedule too packed. Aim for at least an hour twice a week. Next, decide when you want to study, such as Tuesdays, Thursdays, and Sundays from 7-8pm, and stick to your schedule.
This essay begins by discussing the situation of blind people in nineteenth-century Europe. It then describes the invention of Braille and the gradual process of its acceptance within blind education. Subsequently, it explores the wide-ranging effects of this invention on blind people's social and cultural lives.
Learn the essay writing process from preparation to revision with this guide. Find out how to choose a topic, do research, create an outline, write an introduction and conclusion, and avoid common mistakes.
Harvard College Writing Center. menu close Menu. Search
Learn how to study effectively in college with active, distributed, and intensive strategies. This handout offers tips on reading, organizing, previewing, reviewing, and testing yourself for different courses.
Here are 11 tips to improve your study habits: Find a good place to study. Minimize distractions. Take breaks. Space out your studying. Set study goals for each session. Reward yourself. Study with a group. Take practice tests.
5. Snack on Brain Food. A growling stomach can pull your mind from your studies, so feel free to snack as you work. Keep your snacks within arm's reach, so you don't have to leave your books to find food. Fuel your next study session with some of the following items: Lean deli meat.
Based on decades of learning science research, the two most effective methods known to date are: Spaced practice / distributed practice - learning that occurs over multiple sessions at different points in time (for example, revisiting a textbook chapter once every three days). This technique refers to when you should be preparing for course ...
Get sleep and make sure you eat and stay hydrated! Your brain works better when you are rested, hydrated, and nourished. Though it might seem effective to push through without taking a break and stay up studying all night (see the page on strategies that don't work), it won't help you in the long run. Instead, develop a study plan, eat a ...
Structuring Your Essay: Introduction : Begin with a hook to engage the reader, provide background information, and present your thesis statement, which outlines the main argument of the essay. Body Paragraphs : Each paragraph should start with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea, followed by evidence, analysis, and a concluding ...
Grab your gear. Gather up all your class notes, quizzes, handouts and worksheets. Your previous homework will help you see what your teacher thinks is important. (Plus, you can learn from your past quiz mistakes). Study for exams in this order: 1.) definitely 2.) probably 3.) might be on the test. 4.
The basic structure of an essay always consists of an introduction, a body, and a conclusion. But for many students, the most difficult part of structuring an essay is deciding how to organize information within the body. This article provides useful templates and tips to help you outline your essay, make decisions about your structure, and ...
Step 2: Have a clear structure. Think about this while you're planning: your essay is like an argument or a speech. It needs to have a logical structure, with all your points coming together to answer the question. Start with the basics! It's best to choose a few major points which will become your main paragraphs.
2. Quiz yourself. Use flash cards, mock quizzes, and practice exams to more effectively learn information. Taking a test helps you learn information better than simply re-reading the information. Try creating flash cards to quiz yourself. You can also create, or ask your instructor for, a mock quiz or practice exam.
Even the sharpest mind needs breaks. It's crucial to have rest in order to stay focused and organized. Take short breaks every 40-50 minutes of studying and spend them on snacking, listening to music, etc. You will definitely see the difference, as it will be easier for you to get back to studying.
Allow enough time. First and foremost, it's vital to allow enough time for your research. For this reason, don't leave your essay until the last minute. If you start writing without having done adequate research, it will almost certainly show in your essay's lack of quality. The amount of research time needed will vary according to ...
An essay is a written composition that presents and supports a particular idea, argument, or point of view. It's a way to express your thoughts, share information, and persuade others to see things from your perspective. Essays come in various forms, such as argumentative, persuasive, expository, and descriptive, each serving a unique purpose.
2. Organize your ideas: Before you start writing, outline the main points you want to cover in your essay. This will help you organize your thoughts and ensure a logical flow of ideas. 3. Use topic sentences: Begin each paragraph with a topic sentence that introduces the main idea of the paragraph.
Most professors give essay exams for law school finals. Some are single-topic, short-answer questions. Others can go on for pages — known as issue-spotter exams. Some are taken in class, while others are take-home, allowing students more than the traditional amount of time to answer the essay questions. There are open-book and closed-book exams.
Personal Essay: An Overview A personal essay is a short piece of creative nonfiction that explores a specific topic or theme from the author's personal perspective. It is characterized by a blend of storytelling, reflection, and analysis, using the author's experiences, thoughts, and emotions to engage and connect with the reader. Personal essays often delve into meaningful moments or ...
An important aspect of success in class is being prepared and learning to study effectively. Below are some tips, strategies, and resources curated by students and staff. Tips for Studying by Yourself. ... Create a recurring schedule for the study sessions. Find a time that works best for everyone in the group and aim to meet at those regularly ...
In the last part of your introduction, you will show how your study fills in the knowledge gap. This is where you state your purpose and give a clear hypothesis or objective of the study. The hypothesis is a very short 1-2 sentence supposition or explanation of what will happen in your study. This is quite often written as an if-then format.
Abstract:This paper studies of effective strategies and methods to elevate music practical teaching in higher vocational preschool education. Acknowledging the pivotal role of higher vocational preschools in shaping the foundational years of a child's development, the study navigates through a comprehensive exploration of the significance of music education.