

Class 12 Biology Case Study Questions Chapter 7 Evolution
- Post author: studyrate
- Post published:
- Post category: Class 12 / 12 board
- Post comments: 0 Comments
In Class 12 Boards there will be Case studies and Passage Based Questions will be asked, So practice these types of questions. Study Rate is always there to help you. Free PDF Downloads of CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers were Prepared Based on the Latest Exam Pattern. Students can solve Class 12 Biology Case Study Questions Evolution to know their preparation level.
Join our Telegram Channel, there you will get various e-books for CBSE 2024 Boards exams for Class 9th, 10th, 11th, and 12th.

In CBSE Class 12 Biology Paper, There will be a few questions based on case studies and passage-based as well. In that, a paragraph will be given, and then the MCQ questions based on it will be asked.
Evolution Case Study Questions With Answers
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution
Case Study/Passage-Based Questions
Case Study 1: When the reptiles came down, mammals took over the earth. There’ were mammals in South America, which resembled some of the modern day mammals. But due to continental drift, they disappeared whereas the pouched mammals of Australia flourished and evolved into the various forms of pouched mammals that we see today.
What event led to the rise of mammals on Earth? A) The arrival of birds B) The disappearance of reptiles C) Continental drift D) The evolution of pouched mammals
What unique type of mammals flourished and evolved in Australia? A) Rodents B) Primates C) Pouched mammals D) Hoofed mammals
What is the primary reason cited for the disappearance of certain mammals in South America? A) Predation by reptiles B) Continental drift C) Climate change D) Overpopulation
Why did pouched mammals specifically thrive in Australia, according to the passage? A) Lack of competition with other mammals B) Favorable climate conditions C) Protection from continental drift D) The passage does not specify
Which of the following is a well-known example of a pouched mammal? A) Elephant B) Kangaroo C) Whale D) Tiger
Continental drift refers to: A) The migration of animals between continents B) The slow movement of Earth’s continents over geological time C) The rapid sinking of continents into the ocean D) The growth of continents due to volcanic activity
Which era in Earth’s history is commonly associated with the dominance of reptiles? A) Paleozoic Era B) Mesozoic Era C) Cenozoic Era D) Proterozoic Era
What is one of the effects of continental drift on the distribution and evolution of species? A) It prevents species from migrating between continents B) It causes instant changes in climate C) It encourages hybridization between different species D) It leads to the simultaneous evolution of identical species on different continents
Case Study 2: According to the Hardy-Weinberg principle, the allele frequencies in a population are stable and remain constant through generations. When the frequency differs from the expected values, the difference indicates the extent (direction) of evolutionary change. Disturbance in the genetic equilibrium or Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in a population can be interpreted as resulting in evolution.
What does the Hardy-Weinberg principle describe? A) The process of natural selection B) The stability of allele frequencies in a population C) The mechanism of genetic mutations D) The rate of evolutionary change over time
If a population is in Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, what can be said about the allele frequencies? A) They change rapidly from generation to generation B) They remain constant from generation to generation C) They oscillate periodically D) They follow a predictable pattern of change
What does a deviation from Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium suggest? A) A population that is not evolving B) A population that is evolving C) A population that is experiencing genetic drift D) Both B and C
Which of the following factors could disturb Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium? A) Random mating B) Large population size C) Genetic mutation D) Absence of migration
If the allele frequencies within a population remain constant over time, what can be concluded about the population? A) It is undergoing rapid evolution B) It is not undergoing evolution C) It is experiencing a high rate of mutation D) It is subject to strong selection pressures
Hope the information shed above regarding Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution with Answers Pdf free download has been useful to an extent. If you have any other queries about the CBSE Class 12 Biology Evolution Case Study and Passage-Based Questions with Answers, feel free to comment below so that we can revert back to us at the earliest possible. By Team Study Rate

You Might Also Like
The enemy summary class 12 english pdf, disha 1700+ objective question bank of chemistry pdf download, class 12 chemistry case study questions pdf download, leave a reply cancel reply.
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
This site uses Akismet to reduce spam. Learn how your comment data is processed .

The Topper Combo Flashcards
- Contains the Latest NCERT in just 350 flashcards.
- Colourful and Interactive
- Summarised Important reactions according to the latest PYQs of NEET(UG) and JEE
No thanks, I’m not interested!
Not Able To Find Desired Paper or Worksheet SEARCH
Find papers & worksheets search, class 12 biology case study questions chapter 7 evolution.

- (0) Comments
- 7 Downloads
Related Papers
Click to view more related papers, display_name = "class 11" && $paper->display_name = "class 12") { // echo $paper->display_name." questions papers and worksheets"; } //else { // echo $paper->display_name." sample papers and previous year papers"; //} //>, important questions for class 12 biology chapter wise with answers.
Get here all the Important questions for Class 12 Biology chapter wise as free PDF download. Here you will get Extra Important Questions with answers, assertion reasoning and Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ's) chapter wise in Printable format. Class 12 Biology has 16 important chapters covering various important topics related to human physiology evolution, diseases, genetics, organisms, populations, etc.Solving Chapter wise questions is one of the best ways to prepare for the examination. Students are advised to understand the concepts and theories of Biology properly before the exam. You can easily find 1 Mark, 2 marks, 3 marks, and 5 marks questions from each chapter of Class 12 Biology and prepare for exam more effectively. These preparation material for Class 12 Biology , shared by teachers, parents and students, are as per latest NCERT and CBSE Pattern syllabus and assure great success in achieving high score in Final CBSE Board Examinations.
Latest MCQ's and Important Questions for CBSE Class 12 Biology
Reproduction in Organisms class 12 important questions pdf Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants class 12 important questions pdf Human Reproduction class 12 important questions pdf Reproductive Health class 12 important questions pdf Principles of Inheritance and Variation class 12 important questions pdf Molecular Basis of Inheritance class 12 important questions pdf Evolution class 12 important questions pdf Human Health and Diseases class 12 important questions pdf Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production class 12 important questions pdf Microbes in Human Welfare class 12 important questions pdf Biotechnology Principles and Processes class 12 important questions pdf Organisms and Populations class 12 important questions pdf Ecosystem class 12 important questions pdf Biodiversity and Conservation class 12 important questions pdf Environmental Issues class 12 important questions pdf important questions of chapter 1 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 2 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 3 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 4 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 5 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 6 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 7 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 8 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 9 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 10 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 11 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 12 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 13 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 14 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 15 biology class 12 important questions of chapter 16 biology class 12 Reproduction in Organisms class 12 mcq Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants class 12 mcq Human Reproduction class 12 mcq Reproductive Health class 12 mcq Principles of Inheritance and Variation class 12 mcq Molecular Basis of Inheritance class 12 mcq Evolution class 12 mcq Human Health and Diseases class 12 mcq Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production class 12 mcq Microbes in Human Welfare class 12 mcq Biotechnology Principles and Processes class 12 mcq Biotechnology: and its Application class 12 mcq Organisms and Populations class 12 mcq Ecosystem class 12 mcq Biodiversity and Conservation class 12 mcq Environmental Issues class 12 mcq case based questions class 12 biology chapter 1 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 2 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 3 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 4 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 5 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 6 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 7 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 8 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 9 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 10 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 11 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 12 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 13 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 14 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 15 case based questions class 12 biology chapter 16 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 1 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 2 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 3 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 4 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 5 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 6 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 7 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 8 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 9 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 10 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 11 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 12 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 13 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 14 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 15 Assertion Reason questions Biology Class 12 Chapter 16
Total Papers :
CBSE Class 12 Biology Syllabus
- Reproduction in Organisms
- Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Human Reproduction
- Reproductive Health
- Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Human Health and Diseases
- Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Microbes in Human Welfare
- Biotechnology - Principles and Processes
- Biotechnology and its Application
- Organisms and Populations
- Biodiversity and its Conservation
- Environmental Issues
Course Syllabus Details
Unit vi. reproduction.
Chapter 1: Reproduction in Organisms
- A characteristic feature of all organisms for continuation of species
- Asexual reproduction
- Sexual reproduction
- Modes-Binary fission
- Sporulation
- Fragmentation
- vegetative propagation in plants
Chapter 2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants
- Flower structure
- Development of male and female gametophytes
- Outbreeding devices
- Pollen-Pistil interaction
- Double fertilization
- Post fertilization Events-Development of endosperm and embryo
- Development of seed and formation of fruit
- Parthenocarpy
- Polyembryony
- Significance of seed and fruit formation
Chapter 3: Human Reproduction
- Male and female reproductive systems
- Microscopic anatomy of testis and ovary
- Spermatogenesis
- Menstrual cycle
- Fertilisation embryo development up to blastocyst formation, implantation pregnancy and placenta formation (Elementary idea)
- Parturition (Elementary idea)
- Lactation (Elementary idea)
Chapter 4: Reproductive Health
- Need for reproductive health and prevention of sexually transmitted diseases (STD)
- Need and Methods
- Contraception
- Medical Termination of Pregnancy (MTP)
- Amniocentesis
- GIFT (Elementary idea for general awareness)
Unit VII. Genetics and Evolution
Chapter 5: Principles of Inheritance and Variation
- Mendelian Inheritance
- Incomplete dominance
- Co-dominance
- Multiple alleles
- Inheritance of blood groups
- Elementary idea of polygenic inheritance
- Chromosome theory of inheritance
- Chromosomes and genes
- Linkage and crossing over
- Haemophilia
- Colour blindness
- Thalassemia
- Down's syndrome
- Klinefelter's syndromes
Chapter 6: Molecular Basis of Inheritance
- Search for genetic material and DNA as genetic material
- Structure of DNA and RNA
- DNA packaging
- DNA replication
- Central dogma
- Transcription, genetic code, translation
- Genome and human ganeome project
- DNA fingerprinting
Chapter 7: Evolution
- Origin of life
- Biological evolution and evidences for biological evolution (Paleontological, comparative anatomy, embryology and molecular evidence)
- Darwin's contribution
- Modern Synthetic theory of Evolution
- Variation (Mutation and Recombination)
- Natural Selection with examples
- Types of natural selection
- Gene flow and genetic drift
- Hardy - Weinberg's principle
- Adaptive Radiation
- Human evolution
Unit VIII. Biology and Human Welfare
Chapter 8: Human Health and Diseases
- Common cold
- Adolescence, drug and alcohol abuse
Chapter 9: Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
- Plant breeding
- Tissue culture
- Single cell protein
- Biofortification
- Apiculature
- Animal husbandry
Chapter-10: Microbes in Human Welfare
- In household food processing
- Industrial production
- Sewage treatment
- Energy generation and as biocontrol agents
- Biofertilizers
- Production and judicious use
Unit IX. Biotechnology and Its Applications
Chapter 11: Biotechnology - Principles and Processes
- Genetic engineering (Recombinant DNA technology).
Chapter 12: Biotechnology and its Application
- Human insulin and vaccine production, gene therapy
- Genetically modified organisms - Bt crops
- Transgenic Animals; biosafety issues, biopiracy and patents
Unit X. Ecology and Environment
Chapter 13: Organisms and Populations
- Ecological adaptations
- Competition
- Age distribution
Chapter 14: Ecosystem
- Productivity
- Decomposition
- Energy flow
- Pyramids of number, biomass, energy
- Nutrient cycles (carbon and phosphorous)
- Ecological succession
- Carbon fixation
- Pollination
- Seed dispersal
- Oxygen release (in brief)
Chapter-15: Biodiversity and its Conservation
- Concept of biodiversity
- Patterns of biodiversity
- Importance of biodiversity
- Loss of biodiversity
- Endangered organisms
- Red data book
- Biosphere reserves
- National parks
- Sanctuaries
- Ramsar sites
Chapter-16: Environmental Issues
- Air pollution and its control
- Water pollution and its control
- Agrochemicals and their effects
- Solid waste management
- Radioactive waste management
- Greenhouse effect and climate change
- Ozone layer depletion
- Deforestation
- Any one case study as success story addressing environmental issue(s).
Practical Works
Part A: List of Experiments
- Study pollen germination on a slide.
- Collect and study soil from at least two different sites and study them for texture, moisture content, pH and water holding capacity. Correlate with the kinds of plants found in them.
- Collect water from two different water bodies around you and study them for pH, clarity and presence of any living organisms.
- Study the presence of suspended particulate matter in air at two widely different sites.
- Study of plant population density by quadrat method.
- Study of plant population frequency by quadrat method.
- Prepare a temporary mount of onion root tip to study mitosis.
- Study the effect of different temperatures and three different pH on the activity of salivary amylase on starch.
- Isolation of DNA from available plant material such as spinach, green pea seeds, papaya, etc.
Part B: Study/observation of the following (Spotting)
- Flowers adapted to pollination by different agencies (wind, insect, bird).
- Pollen germination on stigma through a permanent slide.
- Identification of stages of gamete development, i.e., T.S. of testis and T.S. of ovary through permanent slides (from grasshopper/mice).
- Meiosis in onion bud cell or grasshopper testis through permanent slides.
- T.S. of blastula through permanent slides.
- Mendelian inheritance using seeds of different colour/sizes of any plant.
- Prepared pedigree charts of any one of the genetic traits such as rolling of tongue, blood groups, ear lobes, widow's peak and colour blindness.
- Controlled pollination - emasculation, tagging and bagging.
- Common disease causing organisms like Ascaris, Entamoeba, Plasmodium, Roundworm through permanent slides or specimens. Comment on symptoms of disease that they cause.
- Two plants and two animals (models/virtual images) found in xeric conditions. Comment upon their morphological adaptations.
- Two plants and two animals (models/virtual images) found in aquatic conditions. Comment upon their morphological adaptations.
Structure of CBSE Biology Sample Paper for Class 12 Science is
For Preparation of exams students can also check out other resource material
CBSE Class 12 Biology Sample Papers
CBSE Class 12 Biology Worksheets
CBSE Class 12 Biology Question Papers
CBSE Class 12 Biology Test Papers
CBSE Class 12 Biology Revision Notes
Question Bank of Other Subjects of Class 12
Importance of Question Bank for Exam Preparation?
There are many ways to ascertain whether a student has understood the important points and topics of a particular chapter and is he or she well prepared for exams and tests of that particular chapter. Apart from reference books and notes, Question Banks are very effective study materials for exam preparation. When a student tries to attempt and solve all the important questions of any particular subject , it becomes very easy to gauge how much well the topics have been understood and what kind of questions are asked in exams related to that chapter.. Some of the other advantaging factors of Question Banks are as follows
- Since Important questions included in question bank are collections of questions that were asked in previous exams and tests thus when a student tries to attempt them they get a complete idea about what type of questions are usually asked and whether they have learned the topics well enough. This gives them an edge to prepare well for the exam.Students get the clear idea whether the questions framed from any particular chapter are mostly either short or long answer type questions or multiple choice based and also marks weightage of any particular chapter in final exams.
- CBSE Question Banks are great tools to help in analysis for Exams. As it has a collection of important questions that were asked previously in exams thereby it covers every question from most of the important topics. Thus solving questions from the question bank helps students in analysing their preparation levels for the exam. However the practice should be done in a way that first the set of questions on any particular chapter are solved and then solutions should be consulted to get an analysis of their strong and weak points. This ensures that they are more clear about what to answer and what can be avoided on the day of the exam.
- Solving a lot of different types of important questions gives students a clear idea of what are the main important topics of any particular chapter that needs to focussed on from examination perspective and should be emphasised on for revision before attempting the final paper. So attempting most frequently asked questions and important questions helps students to prepare well for almost everything in that subject.
- Although students cover up all the chapters included in the course syllabus by the end of the session, sometimes revision becomes a time consuming and difficult process. Thus, practicing important questions from Question Bank allows students to check the preparation status of each and every small topic in a chapter. Doing that ensures quick and easy insight into all the important questions and topics in each and every individual. Solving the important questions also acts as the revision process.
Question Bank of Other Classes
To Prepare better for CBSE paperclass; ?> " title="Download Free CBSE Papers">Ribblu.com brings to you all the previous years papers & worksheets of subject; ?//> for CBSE paperclass; ?>. This CBSE paper and worksheet can be instrumental in students achieving maximum marks in their exams. These Papers and worksheets help students gain confidence and make them ready to face their school examinations. These Papers and worksheets school wise, covers important concepts from an examination perspective. Students and parents can download all the available papers & worksheets directly in the form of PDF. One can use these papers and worksheets to get extensive practice and familiarise themselves with the format of the question paper.
You can help other users
Be the first to write comment .
Upload papers and the more your paper get downloaded the more you earn the points
You may send papers on email [email protected] along with userid
- Downloaded by: Vikas kumar
- Downloaded by: Rex Monga
- Downloaded by: Jack
Rules and regulations for uploads
Write your comment, report this paper, how to earn points.
Upload Papers / Worksheets and Earn 50 Points.
The uploaded material should be original paper or worksheet of any school. Check out some videos on how to upload papers on ribblu
Rate & Review your school and Earn 25 Points.
Review any school that you may be knowing and once your review is approved, you will be credited with 25 points.
Answer on question posted on JustAsk and earn 15 points.
JustAsk is a platform where you can help others to find answers of any question. Share your Knowledge. Answer questions and once approved you will earn 15 points
Complete your profile and earn upto 25 Points.
Edit and complete your user profile and earn points. The more details you submit, the more points you will earn.
Download Ribblu Mobile App and you will (Earn 20 Points) (one time only)
CBSE Schools
- CBSE Schools In Delhi
- CBSE Schools In Noida
- CBSE Schools In Greater Noida
- CBSE Schools In Faridabad
- CBSE Schools In Ghaziabad
- CBSE Schools In Gurgaon
- CBSE Schools In Mumbai
- CBSE Schools In Pune
- CBSE Schools In Bangalore
- CBSE Schools In Hyderabad
- CBSE Schools In Kolkata
- CBSE Schools In Chennai
- CBSE Schools In Patna
- CBSE Schools In Meerut
- CBSE Schools In Kanpur
- CBSE Schools In Indore
- CBSE Schools In Ludhiana
- CBSE Schools In Dehradun
Top Schools
- Schools In Delhi
- Schools In Noida
- Schools In Greater Noida
- Schools In Faridabad
- Schools In Ghaziabad
- Schools In Gurgaon
- Schools In Mumbai
- Schools In Pune
- Schools In Bangalore
- Schools In Hyderabad
- Schools In Kolkata
- Schools In Chennai
- Schools In Patna
- Schools In Meerut
- Schools In Kanpur
- Schools In Indore
- Schools In Ludhiana
- Schools In Dehradun
Other Schools
- Pre Nursery Schools In Noida
- Day Boarding Schools In Noida
- Pre Nursery Schools In Gurgaon
- Pre Nursery Schools In Delhi
- Play Schools In Delhi
- Day Boarding Schools In Delhi
CBSE Papers
- CBSE Class 1 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 2 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 3 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 4 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 5 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 6 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 7 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 8 Sample Papers
Paper Categories
- Question Bank
- Question Papers
- Revision Notes
- Sample Papers
- Test Papers
- CBSE Class 9 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 10 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 11 Sample Papers
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Papers

myCBSEguide
- Class 12 Biology Case...
Class 12 Biology Case Study Questions
Table of Contents
myCBSEguide App
Download the app to get CBSE Sample Papers 2023-24, NCERT Solutions (Revised), Most Important Questions, Previous Year Question Bank, Mock Tests, and Detailed Notes.
As we know that CBSE will now ask case study questions in each subject. In most of the cases, we have noticed that these case-based questions are high-scoring. A little effort on these case study questions can help you get good marks in your board exams. You can download CBSE Class 12 Biology Case Study Questions from the myCBSEguide App or from our Student Dashboard .
Let’s understand what type of case study questions CBSE asks in class 12 Biology. If you analyze the latest class 12 Biology sample papers , you will find that there are two types of case study questions in the Biology question papers.
- Case Studies with objective questions
- Case studies with subjective questions
As per the latest circular issued by CBSE on Assessment and Evaluation Practices of the Board for the Session 2022-23 , CBSE has clearly mentioned that competency-based questions including case studies will be different from subjective questions. Hence, we expect that CBSE will ask only objective questions in CBSE class 12 Biology case study questions too.
Biology Competency Based Questions
As discussed earlier too, the competency-based questions promote learning development for our students and test higher-order skills, such as analysis, critical thinking and conceptual clarity. Case study questions are actually competency-based questions. The very purpose of including such questions in the curriculum is to emphasise on development of problem-solving ability and the ability to apply knowledge in real-life situations.
Even in CBSE Class 12 Biology case studies, you will find some text input like paragraphs, pictures, data etc followed by some objective-type questions. You should read the given information carefully and then answer the questions.
CBSE 12th Biology Case Study MCQs
Here is one example question on subjective type case study questions. This was given in the term-2 sample paper in 2022.
Some restriction enzymes break a phosphodiester bond on both the DNA strands, such that only one end of each molecule is cut and these ends have regions of single-stranded DNA. BamH1is one such restriction enzyme which binds at the recognition sequence, 5’-GGATCC- 3’and cleaves these sequences just after the 5’- guanine on each strand.
- What is the objective of this action?
- Explain how the gene of interest is introduced into a vector.
- You are given the DNA shown below. 5’ ATTTTGAGGATCCGTAATGTCCT 3’ 3’ TAAAACTCCTAGGCATTACAGGA 5’ If this DNA was cut with BamHI, how many DNA fragments would you expect? Write the sequence of these double-stranded DNA fragments with their respective polarity.
- A gene M was introduced into E.coli cloning vector PBR322 at the BamH1 site. What will be its impact on the recombinant plasmids? Give a possible way by which you could differentiate non-recombinant to recombinant plasmids.
Let’s take another example from MCQ type question:
To answer the questions, study the graphs below for Subject-1 and 2 showing different levels of certain hormones.
The peak observed in Subject-1 and 2 is due to
- progesterone
- luteinizing hormone
- follicle stimulating hormone
Subject 2 has higher level of hormone B, which is
If the peak of Hormone A does not appear in the study for Subject 1, which of the following statement is true?
- Peak of Hormone B will be observed at a higher point in the graph
- Peak of Hormone B will be observed at a point lower than what is given in the graph
- There will be no observed data for Hormone B
- The graph for Hormone B will be a sharp rise followed by a plateau
Which structure in the ovary will remain functional in subject 2?
- Corpus Luteum
- Tertiary follicle
- Graafian follicle
- Primary follicle
For subject 2 it is observed that the peak for hormone B has reached the plateau stage. After approximately how much time will the curve for hormone B descend?
Which of the following statements is true about the subjects?
- Subject 1 is pregnant
- Subject 2 is pregnant
- Both subject 1 and 2 are pregnant
- Both subject 1 and 2 are not pregnant
Another example of a class 12 Biology case study question
We use microbes or products which are derived from them every day. A common example is the production of curd from milk. Micro-organisms such as Lactobacillus and others commonly called lactic acid bacteria (LAB) grow in milk and convert it to curd. The dough, which is used for making foods such as dosa and idli is also fermented by bacteria. A number of traditional drinks and foods are also made by fermentation by microbes. ‘Toddy’, a traditional drink in some parts of southern India is made by fermenting sap from palms. The ‘Roquefort cheese’ is ripened by growing specific fungi on them, which gives them a particular flavour. Different varieties of cheese are known by their characteristic texture, flavour and taste, the specificity coming from the microbes used.
- Penicillium notatum
- Saccharomyces cerevisiae
- Aspergillus niger
- Clostridium butylicum
- thermal vents
- polluted water
- all of these
- None of the above
- production of a large amount of CO 2
- production of O 2
- due to the presence of water
- none of these
- Both Assertion and Reason are true and Reason is the correct explanation of the Assertion
- Both Assertion and Reason are true but Reason is not the correct explanation of the Assertion
- Our Assertion is true but the Reason is false
- Both the statements are false
Download 12 Biology Case Study Questions
In this article, we have given you a few examples of class 12 Biology case study questions. We advise you to download the myCBSEguide App or access our Student Dashboard to get more case study questions for CBSE class 12 biology. We have hundreds of questions on case studies related to CBSE Class 12 Biology. As CBSE is now focusing more on the understanding of the concepts, it is a must for students to practice such questions regularly.
Test Generator
Create question paper PDF and online tests with your own name & logo in minutes.
Question Bank, Mock Tests, Exam Papers, NCERT Solutions, Sample Papers, Notes
Related Posts
- Competency Based Learning in CBSE Schools
- Class 11 Physical Education Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Sociology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Applied Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Mathematics Case Study Questions
- Class 11 Biology Case Study Questions
- Class 12 Physical Education Case Study Questions
Leave a Comment
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Bihar Board
RBSE Result 2024
Srm university.
- Goa Board Result 2024
- Maharashtra HSC Result
- Maharashtra SSC Result
- RBSE 10th Result 2024
- RBSE 12th Result 2024
- CBSE Board Result 2024
- Shiv Khera Special
- Education News
- Web Stories
- Current Affairs
- नए भारत का नया उत्तर प्रदेश
- School & Boards
- College Admission
- Govt Jobs Alert & Prep
- GK & Aptitude
Case Study Based Questions for CBSE Class 12 Biology Board Exam 2024: Read this article for Last Minute Revision
Cbse class 12 biology important case study questions : practise important case study based questions for class 12 biology board exam. these case study based questions are important for the upcoming cbse class 12 biology board exam 2024 on march 19, 2024..

CBSE Class 12th Biology Board Exam 2023-24 Pattern
The paper will be of 70 marks and the time duration for completing the paper will be 3 hours.
The paper will have 33 questions divided into 5 sections.
Section–A 16 questions of 1 mark each,
Section–B 5 questions of 2 marks each;
Section–C 7 questions of 3 marks each;
Section–D 2 case-based questions of 4 marks each,
and Section–E 3 questions of 5 marks each.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Important Case Study Based Questions
Case Study 1: Nondisjunction is the failure of homologous chromosomes to disjoin correctly during meiosis. It leads to the formation of a new cell with an abnormal amount of genetic material. A number of clinical conditions are the result of this type of chromosomal mutation. This results in the production of gametes containing a greater or lesser chromosomal amount than normal ones. Consequently, the individual may develop a trisomy or monosomal syndrome. Nondisjunction can occur in both Meiosis I and Meiosis II of the cellular division. It is also the main cause of many genetic disorders; however, its origin and process remain vague. Although it results in the majority of cases from errors in maternal meiosis II, both paternal and maternal meiosis I do influence it. Maternal age is considered a risk factor for trisomy, as well as recombination alterations and many others that can affect chromosomal segregation.
- It is the presence of an extra chromosome in a diploid cell.
- An aneuploid cell differs from other cells only in size.
- It can be less number of chromosomes in a diploid cell.
- Aneuploidy always affects female individuals.
- both i and iii
- both ii and iii
- i, iii and iv
- Errors in meiosis I is the only cause of aneuploidy
- Aneuploidy always affects sex chromosomes.
- Most of the aneuploidy results from errors in cell division involved in egg formation.
- Nondisjunction in meiosis I can lead to more abnormal cells than disjunction in meiosis II.
- both I and iii
- both iii and iv
- I, iii and iv
- Aneuploidy is not influenced by the mother’s age.
- Delivery before 30 years of age can decrease the incidence of aneuploidy in most cases
- The chance of aneuploidy increases up to 22 years of age.
- There is a dramatic increase in aneuploidy if the maternal age exceeds 30
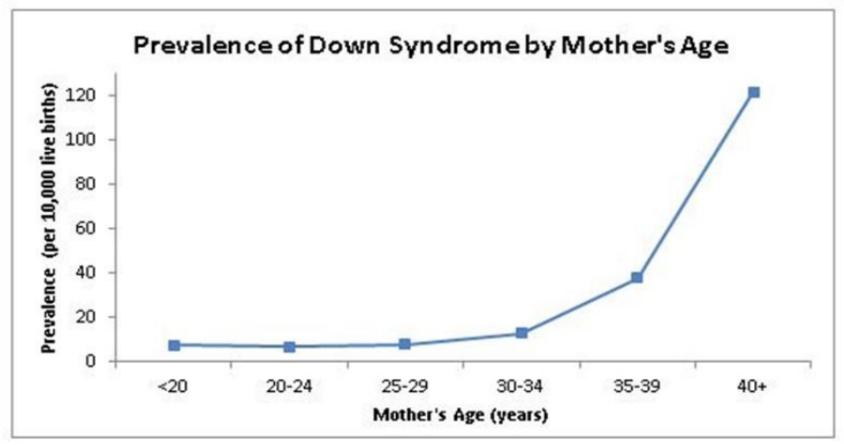
- both ii and iv
- Chromosomal disorders
- Mendelian disorders
- Incomplete dominance
- All the above
Q5: Assertion: All types of genetic disorders are caused by chromosomal nondisjunction.
- Both assertion and reason are correct and the reason is the correct explanation of assertion
- Both assertion and reason are correct but the reason is not the correct explanation of the assertion
- Assertion is correct but the reason is incorrect
- Both assertion and reason are incorrect
Case Study 2: A Representative Diagram of the Human Genome Project:
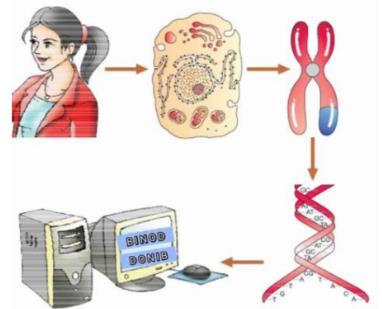
- Biotechnology
- Biomonitoring
- Bioinformatics
- Biosystematics
Q2: Name a free living, non-pathogenic nematode, the DNA of which has been completely sequenced.
Answer: Caenorhabditis elegans
Q3: Summarize the methodology adopted in the Human Genome Project.
Answer: Expressed Sequence Tags (ESTs) : The approach focused on identifying all the genes that are expressed as RNA.
Sequence Annotation : The other took the blind approach of simply sequencing the whole set of genome that contained all the coding and non-coding sequence, and later assigning different regions in the sequence with functions.
Q4: What are SNPs’? How are they useful in human genomics?
- Identify disease-causing genes in humans
- Can be used to understand the molecular mechanisms of sequence evolution.
Q5: Mention at least four salient features of the Human Genome Project.
- Human genome contains 3164.7 million bp.
- Average gene consists of 3000 bases, but sizes vary greatly.
- Almost all (99.9 percent) nucleotide bases are exactly the same in all people.
- Less than 2 percent of the genome codes for proteins.
Case Study 3: Two blood samples of suspects ‘A’ and ‘B’ were sent to the Forensic Department along with sample ‘C’ from the crime scene. The Forensic Department was assigned the responsibility of running the samples and matching the samples of the suspects with that of the sample from the scene of the crime and thereby identifying the culprit.
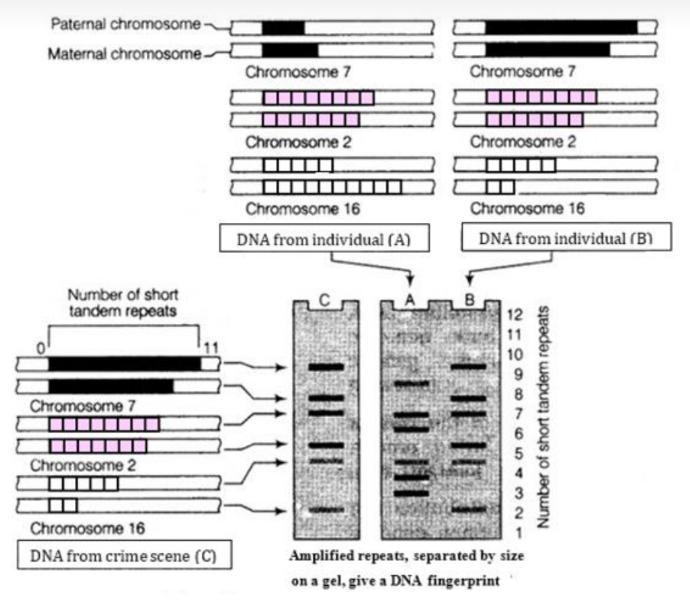
- A radioactively labelled double stranded RNA molecule.
- A radioactively labelled double stranded DNA molecule.
- A radioactively labelled single stranded DNA molecule.
- A radioactively labelled single stranded RNA molecule.
Q3: What does ‘minisatellite’ and ‘microsatellite’ mean in relation to DNA Fingerprinting?
Answer: Minisatellite: the repeating unit consists of 10-100 base pairs.
Microsatellite: the repeating unit consists of 2-6 base pairs.
Q3: How does polymorphism arise in a population?
Answer: Polymorphism (variation at the genetic level) arises due to mutations.
Q4: State the steps involved in DNA Fingerprinting in a sequential manner.
- DNA isolation
- DNA digestion with restriction enzymes.
- DNA fragment separation by electrophoresis.
- Hybridization
- DNA visualization under UV light.
Case Study 4: Bacteria like Streptococcus pneumoniae and Haemophilus influenzae are responsible for the disease pneumonia in humans which infects the alveoli (air-filled sacs) of the lungs. As a result of the infection, the alveoli get filled with fluid leading to severe problems in respiration. The symptoms of pneumonia include fever, chills, cough, and headache. In severe cases, the lips and fingernails may turn gray to bluish in colour. A healthy person acquires the infection by inhaling the droplets/aerosols released by an infected person or even by sharing glasses and utensils with an infected person. Dysentery, plague, diphtheria, etc., are some of the other bacterial diseases in man. Many viruses also cause diseases in human beings. Rhinoviruses represent one such group of viruses that cause one of the most infectious human ailments – the common cold. They infect the nose and respiratory passage but not the lungs.
The common cold is characterized by nasal congestion and discharge, sore throat, hoarseness, cough,
headache, tiredness, etc., which usually lasts for 3-7 days. Droplets resulting from the cough or sneezes of an infected person are either inhaled directly or transmitted through contaminated objects such as pens, books, cups, doorknobs, computer keyboards or mice, etc., and cause infection in a healthy person.
- By exhaling droplets of a non-infected person.
- By headache or leg pain.
- By eating fast food.
- By inhaling droplets of an infected person.
Q4: How long does the common cold last?
Answer: 3-7 days
Q5: Write any two symptoms of the common cold and pneumonia.
Answer: Cough and nasal congestion.
Case Study 5: When you insert a piece of alien DNA into a cloning vector and transfer it into a bacterial, plant, or animal cell, the alien DNA gets multiplied. In almost all recombinant technologies, the ultimate aim is to produce a desirable protein. Hence, there is a need for the recombinant DNA to be expressed. The foreign gene gets expressed under appropriate conditions. The expression of foreign genes in host cells involves understanding many technical details. After having cloned the gene of interest and having optimised the conditions to induce the expression of the target protein, one has to consider producing it on a large scale. Can you think of any reason why there is a need for large-scale production? If any protein encoding gene is expressed in a heterologous host, it is called a recombinant protein. The cells harbouring cloned genes of interest may be grown on a small scale in the laboratory. The cultures may be used for extracting the desired protein and then purifying it by using different separation techniques.
- A continuous culture system
- A stirred-tank bioreactor without in-lets and out-lets
- Laboratory flask of the largest capacity
- None of the above
- upstream processing
- downstream processing
- bioprocessing
- postproduction processing
- Human insulin
- Growth hormone
- cleaving and joining of DNA segments with endonuclease
- cleaving DNA segments with endonuclease and re-joining with ligase
- cleaving and re-joining DNA segments with ligase
- cleaving DNA segments with ligase and re-joining with endonuclease
Case Study 6: Gene Therapy
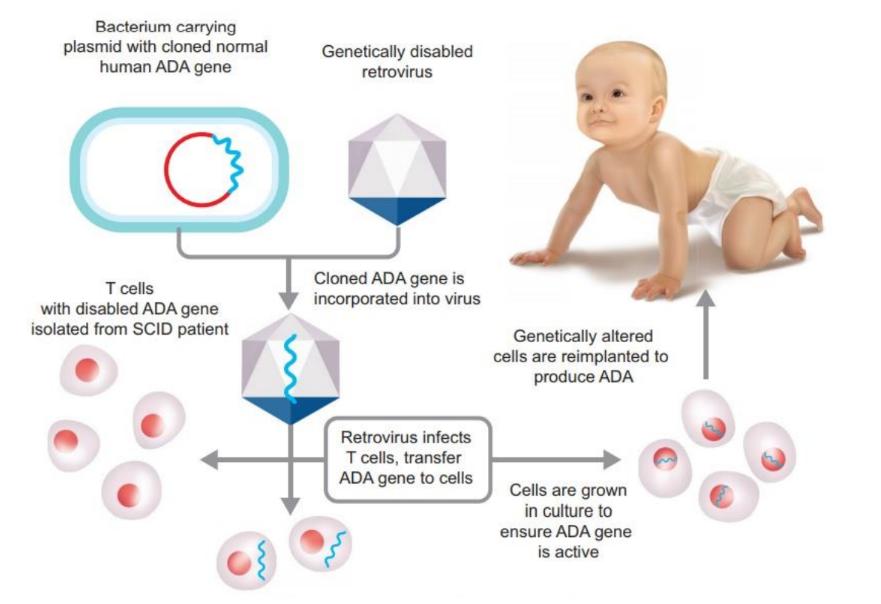
Read the following and answer the questions that follow:
- Replacing a disease-causing gene with a healthy copy of the gene
- Inactivating a disease-causing gene that is not functioning properly
- Introducing a new or modified gene into the body to help treat a disease
- Adenosine deaminase
- phenylketonuria
- Phenylalanine
- Bone marrow transplantation
- Southern blotting
Q4 Introduction of gene isolate from bone marrow producing ADA should be introduced at what age to
- acute diseases
- physiological diseases
- hereditary diseases
- infectious diseases
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year Question Papers with Solutions PDF Download
- CBSE Class 12 Syllabus 2023-24 PDF (All Subjects)
- CBSE Class 12 Deleted Syllabus (All Subjects)
- CBSE Class 12 Previous Year Papers with Solution PDF Download
- CBSE Class 12 Additional Practice Questions
- CBSE Class 12 Sample Paper 2023-24 with Solution and Additional Practice Questions
- Important MCQs for CBSE Class 12 Biology, All Chapters
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Mind Maps for Quick Revision
- CBSE Class 12 NCERT Biology Revised Textbook PDF
- CBSE Class 12 NCERT Biology Solutions
- CBSE Class 12 Biology Chapter-wise notes
- CBSE Class 12 Date Sheet 2024
- CBSE Competency Based Questions 2023-24
- CBSE Class 12 Additional Practice Questions 2024
Get here latest School , CBSE and Govt Jobs notification in English and Hindi for Sarkari Naukari and Sarkari Result . Download the Jagran Josh Sarkari Naukri App . Check Board Result 2024 for Class 10 and Class 12 like CBSE Board Result , UP Board Result , Bihar Board Result , MP Board Result , Rajasthan Board Result and Other States Boards.
- CBSE Board exam 2023 result date. + As per the guidelines released by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE), the tentative dates for the CBSE Board Exam 2023 results are; for class 10th: 15th April 2023 and for class 12th: 30th April 2023.
- When is the Class 12th Biology CBSE Board exam? + According to the date sheet released by the Central Board of Secondary Education (CBSE) for class 12th, the Biology exam is scheduled for the 16th of March 2023. The day will be Thursday.
- RBSE 12th रिजल्ट 2024
- RBSE रिजल्ट 2024
- TS TET Hall Ticket 2024
- Goa SSC Result 2024
- SSC GD Result 2024
- GBSHSE SSC Result 2024
- SSC Result 2024 Goa
- CDS 2 Notification 2024
- results.gbshsegoa.net Result 2024
- CBSE 10th Result 2024
- CBSE Class 10
Latest Education News
[Today] IPL 2024 Points Table: Team Rankings and Net Run Rate
Top 10 Thought Of The Day For Morning School Assembly In English And Hindi (May 17, 2024)
क्या है ई-श्रम कार्ड? लाभ, पात्रता और ऑनलाइन अप्लाई की सभी डिटेल्स यहां देखें
IPL 2024 CSK Players: चेन्नई सुपर किंग्स के खिलाड़ियों की पूरी लिस्ट यहां देखें
ICC T20 World Cup 2024: T20 वर्ल्ड कप का शेड्यूल जारी, कब और किससे है भारत का मैच देखें यहां
IPL 2024 Full Schedule: आईपीएल 2024 का फुल शेड्यूल,आज किस टीम का है मैच जानें यहां
[चेक] Most Runs In IPL 2024: दिलचस्प हो गयी है Orange Cap की रेस, Virat टॉप पर
IPL 2024 Playoffs Teams: इन 4 टीमों का प्लेऑफ टिकट कन्फर्म! KKR, SRH और RR के बाद किसका नंबर
[Fast Update] IPL Points Table 2024: आईपीएल 2024 अपडेटेड पॉइंट टेबल यहां देखें, KKR और RR, SRH Qualify
Lok Sabha Election 2024 Polling Booth: घर बैठे कैसे पता करें अपना मतदान केंद्र?
IPL 2024 Qualifier, Eliminator: कब, कहां और किसके बीच होगा क्वालीफायर और एलिमिनेटर, Tickets और Live Streaming कैसे देखें
TS TET Hall Ticket 2024 OUT at tstet2024.aptonline.in/tstet: Download Telangana TET Admit Card Manabadi
JEE Advanced Admit Card 2024 LIVE: Direct Link to Download JEE Advanced Paper 1 & 2 Hall Tickets at jeeadv.ac.in, Steps to Check Online
Top 20 Question of the Day for School Assembly with Answers (May 17, 2024)
Today’s School Assembly Headlines (May 17): Heatwave Alert in North India, Singapore’s New PM, Sunil Chhetri Quits International Football and Other Important News in English
Brain Teaser: Find the Hidden Mistakes in this Challenging Office-Themed Brain Teaser
JAC 8th, 9th,11th Result 2024: झारखंड बोर्ड का रिजल्ट आज आएगा या कल ? यहाँ देखें लेटेस्ट अपडेट
TSTET Hall Ticket Download 2024 Released: Check Direct Link to Telangana TET Admit Card at tstet2024.aptonline.in
Dr MGR Medical University Result 2024 OUT at tnmgrmu.ac.in; Direct Link to Download UG and PG Marksheet
CUET Exam Analysis 2024, May 16: Check Detailed Paper Review, Difficulty Level, and Good Attempts
- New QB365-SLMS
- NEET Materials
- JEE Materials
- Banking first yr Materials
- TNPSC Materials
- DIPLOMA COURSE Materials
- 5th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard Materials
- 11th Standard Materials
- 10th Standard Materials
- 9th Standard Materials
- 8th Standard Materials
- 7th Standard Materials
- 6th Standard Materials
- 12th Standard CBSE Materials
- 11th Standard CBSE Materials
- 10th Standard CBSE Materials
- 9th Standard CBSE Materials
- 8th Standard CBSE Materials
- 7th Standard CBSE Materials
- 6th Standard CBSE Materials
- Tamilnadu Stateboard
- Scholarship Exams
- Scholarships

CBSE 12th Standard Biology Subject Evolution Case Study Questions With Solution 2021
By QB365 on 21 May, 2021
QB365 Provides the updated CASE Study Questions for Class 12 Biology, and also provide the detail solution for each and every case study questions . Case study questions are latest updated question pattern from NCERT, QB365 will helps to get more marks in Exams
QB365 - Question Bank Software
12th Standard CBSE
Final Semester - June 2015
Case Study Questions
In 1950s, there were hardly any mosquitoes in Delhi. The use of the pesticide, DDT on standing water killed their larvae. But, now there are mosquitoes because they have evolved DDT-resistance through the interaction of mutation and Natural selection. State in a sequences, how that could have happened.
When the reptiles came down, mammals took over the earth. There were mammals in South America, which resembled some of the modern day mammals. But due to continental drift, they disappeared whereas the pouched mammals of Australia flourished and evolved into the various forms of pouched mammals that we see today. (a) Mention two characteristic features that were the reasons for the successful existence of mammals on earth. (b) Why did the continental drift affect the mammals of South America and Australia, differently.
According to Hardy-Weinberg principle, the allele frequencies in a population are stable and remain constant through generations. When the frequency differs from the expected values, the difference indicates the extent (direction) of evolutionary change. Disturbance in the genetic equilibrium or Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium in a population can be interpreted as resulting in evolution. (a) Write the algebraic equation representing Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium. (b) List the five factors that affect the genetic equilibrium.
*****************************************
Cbse 12th standard biology subject evolution case study questions with solution 2021 answer keys.
(a) S.L. Miller tried to prove the hypothesis of Oparin and Haldane; it is as follows: (i) The first from oflife could have come from the pre-existing non-living organic molecules like RNA, proteins, etc. (ii) Formation oflife was preceded by chemical evolution that resulted in the formation of diverse organic molecules from inorganic constituents. (b) Amino acids. (c) Hydrogen is missing.
(a) Divergent evolution. (b) Homologous organs. (c) Homology indicates common ancestry.
(i) There were some larvae with a mutated gene that conferred resistance to DDT. (ii) The DDT-resistant larvae survived while the others died. (iii) The DDT-resistant larvae reached adulthood and reproduced in large numbers. (iv) The progeny also consisted mostly ofDDT-resistant larvae. (v) Natural selection operating over a number of generations, favoured the DDT-resistant mosquitoes to reproduce in large numbers. (vi) Hence, today there is a large number of mosquitoes that are resistant to DDT.
(a) (i) Most of the mammals were viviparous and protected their unborn young ones inside the mother's body. (ii) With increased brain size, they became intelligent in sensing and avoiding danger. (b) (i) Due to continental drift, when South America joined North America, the South American mammals were overridden by those of North America. (ii) But Australia became separated and due to lack of competition from any other mammal, the pouched mammals flourished and evolved.
(a) (p + q) 2 or p 2 + 2pq + q 2 = I. (b) The factors include: (i) Gene migration/gene flow (ii) Genetic drift (iii) Mutation (iv) Genetic recombination (v) Natural selection .
Related 12th Standard CBSE Biology Materials
12th standard cbse syllabus & materials, cbse 12th physics wave optics chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics ray optics and optical instruments chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics nuclei chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics moving charges and magnetism chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics electromagnetic induction chapter case study question with answers, cbse 12th physics atoms chapter case study question with answers, 12th physics alternating current chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths vector algebra chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths three dimensional geometry chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths probability chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths linear programming chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths differential equations chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths continuity and differentiability chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th maths application of integrals chapter case study question with answers cbse, 12th chemistry the d and f block elements chapter case study question with answers cbse.

Class VI to XII
Tn state board / cbse, 3000+ q&a's per subject, score high marks.


12th Standard CBSE Study Materials

12th Standard CBSE Subjects

Talk to our experts
1800-120-456-456
- NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter-7 (Book Solutions)
- Textbook Solutions

NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology - Evolution - Free PDF Download
We, at Vedantu, bring to you solutions for all the NCERT textbook questions. A student can easily rely on NCERT solutions and questions because they are framed by specialists and give you a proper revision of everything that has been taught in the chapter or the unit. A student should always refer to exercise questions immediately after completing studying the chapter.
The NCERT Solutions for Class 12 by Vedantu are designed to enhance the conceptual expertise of students. These solutions provide the ideal way of forming answers in exams. The solutions are created in easy to understand language and focus on providing the utmost conceptual clarity for the students. Regularly referring to and training from NCERT Solutions may be extraordinarily beneficial for college students.

Access ICSE Selina Solutions for Grade 12 Biology Chapter No. 7 - Evolution
Multiple choice questions.
1. Which of the following is used as an atmospheric pollution indicator?
(a) Lepidoptera
(b) Lichens
(c) Lycopersicon
(d) Lycopodium
Ans: (b) Lichens
2. The theory of spontaneous generation stated that:
(a) life arose from living forms only
(b) life can arise from both living and nonliving
(c) life can arise from non-living things only.
(d) life arises spontaneously, neither from living nor from the non-living.
Ans: (c) life can arise from non-living things only.
3. Animal husbandry and plant breeding programmes are examples of:
(a) reverse evolution
(b) artificial selection
(c) mutation
(d) natural selection
Ans: (b) artificial selection
4. Palaeontological evidences for evolution refer to the:
(a) development of embryo
(b) homologous organs
(c) fossils
(d) analogous organs
Ans: (c) fossils
5. The bones of forelimbs of whale, bat, cheetah, and man are similar in structure, because:
(a) one organism has given rise to another
(b) they share a common ancestor
(c) they perform the same function
(d) they have biochemical similarities
Ans: (b) they share a common ancestor
6. Analogous organs arise due to:
(a) divergent evolution
(c) genetic drift
(d) convergent evolution
Ans: (d) convergent evolution
7. (p+q) 2 = p 2 + 2pq + q 2 = 1 represents an equation used in:
(a) population genetics
(b) mendelian genetics
(c) biometrics
(d) molecular genetics
Ans: (a) population genetics
8. Appearance of antibiotic-resistant bacteria is an example of:
(a) adaptive radiation
(b) transduction
(c) pre-existing variation in the population
(d) divergent evolution
Ans: (c) pre-existing variation in the population
9. Evolution of life shows that life forms had a trend of moving from:
(a) land to water
(b) dryland to wetland
(c) freshwater to seawater
(d) water to land
Ans: (d) water to land
10. Viviparity is considered to be more evolved because:
(a) the young ones are left on their own
(b) the young ones are protected by a thick shell
(c) the young ones are protected inside the mother's body and are
looked after they are born leading to more chances of survival
(d) the embryo takes a long time to develop
Ans: (c) the young ones are protected inside the mother's body and are looked after they are born leading to more chances of survival
Explanation: In viviparity, the young ones are protected inside the mother's body and are looked at after after they are born leading to more chances of survival.
11. Fossils are generally found in:
(a) Sedimentary rocks
(b) Igneous rocks
(c) Metamorphic rocks
(d) Any type of rock
Ans: (a) Sedimentary rocks
Explanation: Sedimentary rocks are formed over time and have less pressure and heat than metamorphic and igneous rocks enabling the preservation of fossils.
12. For the MN-blood group system, the frequencies of M and N alleles are 0.7 and 0.3, respectively. The expected frequency of MN-blood group bearing organisms is likely to be
Ans: (a) 42%
Explanation: Hardy Weinberg’s Principle states, the allele frequency in a population remains constant and it is shown through a binomial expansion of (p+q) 2 .
i.e. (p+q) 2 = p 2 +q 2 +2pq =1
M=0.7 =p , N= 0.3 =q
(M+N) 2 = (0.7) 2 +(0.3) 2 +2.0.7 x 0.3 +(0.3) 2
= 0.49 +0.09 + 0.42
Frequency of MN = 2pq= 2 MN = 0.42 = 42 %
Therefore, the expected frequency of MN blood group is 42%.
13. Which type of selection explains industrial melanism observed in moth, Biston betularia:
(a) Stabilising
(b) Directional
(c) Disruptive
(d) Artificial
Ans: (b) Directional
Explanation: In directional selection size of the population changes, the population changes towards one specific direction.
14. The most accepted line of descent in human evolution is:
(a) Australopithecus - Ramapithecus - Homo sapiens - Homo habilis
(b) Homo erectus - Homo habilis - Homo sapiens
(c) Ramapithecus - Homo habilis - Homo erectus - Homo sapiens
(d) Australopithecus - Ramapithecus - Homo erectus - Homo habilis - Homo sapiens.
Ans: (c) Ramapithecus - Homo habilis - Homo erectus - Homo sapiens
Explanation: Human evolution started from Ramapithecus about 14-15 million years ago. Then about 2 million years ago Homo habilis appeared. Then the Homo erectus and around 10,000 years ago modern man appeared.
15. Which of the following is an example for link species?
(a) Lobe fish
(b) Dodo bird
(c) Seaweed
(d) Chimpanzee
Ans: (a) Lobe fish
Explanation: Lobe fish belongs to bony fishes, and show characters from other two groups of animals, therefore they are considered link species.
16. Match the scientists listed under column ‘I’ with ideas listed in column ‘II’.
(a) A-i; B-iv; C-ii; D-iii
(b) A-iv; B-i; C-ii; D-iii
(c) A-ii; B-iv; C-iii; D-i
(d) A-iv; B-iii; C-ii; D-i
Ans: (b) A-iv; B-i; C-ii; D-iii
17. In 1953 S. L. Miller created primitive earth conditions in the laboratory and gave experimental evidence for the origin of the first form of life from preexisting non-living organic molecules. The primitive earth conditions created include:
(a) low temperature, volcanic storms, an atmosphere rich in oxygen
(b) low temperature, volcanic storms, reducing atmosphere
(c) high temperature, volcanic storms, non-reducing atmosphere
(d) high temperature, volcanic storms, reducing atmosphere
containing CH 4 , NH 3 et(c)
Ans: (d) high temperature, volcanic storms, reducing atmosphere
18. Variations during mutations of meiotic recombination are:
(a) random and directionless
(b) random and directional
(c) small and directional
(d) random, small, and directional
Ans: (a) random and directionless
Explanation: Mutation is a sudden inheritable change in the DNA. It appears in all directions.
Very Short Answer Type Questions
1. What were the characteristics of life forms that had been fossilized?
Ans: Life forms had some hard parts such as Bones, teeth, etc. which could be fossilized.
2. Did aquatic life forms get fossilized? If, yes where do we come across such fossils?
Ans: Yes, aquatic life forms get fossilized. Many of these fossils have been discovered in oil wells. Many more have been discovered in sedimentary rocks as a result of sedimentation filling up many water bodies.
3. What are we referring to? When we say 'simple organisms' or 'complex organisms'.
Ans: When we say ‘simple organisms’ or ‘complex organisms’ we refer to the complexity of the division of labor, metabolism, and the level of organization in the organisms.
4. How do we compute the age of a living tree?
Ans: We can compute the age of a tree by counting the number of annual rings or with the help of carbon dating.
5. Give an example for convergent evolution and identify the features towards which they are converging.
Ans: Flippers of dolphins and penguins are examples of convergent evolution. In both of the organisms, flippers have different origins but perform similar functions.
6. How do we compute the age of a fossil?
Ans: Age of fossil is computed by using carbon dating. The presence of radioactive carbon is calculated to compute the age of a rock.
7. What is the most important precondition for adaptive radiation?
Ans: The most important precondition for radiation is common ancestry.
8. How do we compute the age of a rock?
Ans: The age of the rock is computed by using radiocarbon dating. The presence of radioactive carbon is calculated to compute the age of a rock.
9. When we talk of functional macromolecules (e.g. proteins as enzymes, hormones, receptors, antibodies, etc), what are they evolving?
Ans: Functional macromolecules are evolving towards living forms.
10. In a certain population, the frequency of three genotypes is as follows:
What is the likely frequency of B and b alleles?
Ans: Frequency of B alleles = BB +\[\frac{1}{2}\] Bb
Frequency of b alleles =bb+\[\frac{1}{2}\] Bb
11. Among the five factors that are known to affect Hardy-Weinberg equilibrium, three factors are gene flow, genetic drift, and genetic recombination. What are the other two factors?
Ans: The two factors are: Natural selection and Mutation
12. What is founder effect?
Ans: There is the loss of genetic variation when a small group of individuals becomes isolated from a larger population.
13. Who among the Dryopithecus and Ramapithecus was more man-like?
Ans: Ramapithecus
14. By what Latin name the first hominid was known?
Ans: Homo habilis
15. Among Ramapithecus, Australopithecines and Homo habilis - who
probably did not eat meat?
Ans: Homo habilis
Short Answer Type Questions
1. Louis Pasteur’s experiments, if you recall, proved that life can arise from only pre-existing life. Can we correct this as life evolves from pre-existent life or otherwise we will never answer the question as to how the first forms of life arose? Comment.
Ans: Louis Pasteur used a sterile flask and another one that was open to the air. New yeast organisms were developed in a flask that was open to air, but in the sterilized flask yeast did not produce new organisms. This experiment contributed to the rejection of the spontaneous generation theory. Miller’s later experiment, on the other hand, demonstrated that organic molecules may evolve from inorganic molecules, leading to the origin of life. Therefore, we can correct the statement that the first form of life could have arisen from pre-existing non-living organic molecules.
2. Scientists believe that evolution is gradual. But extinction, part of the evolutionary story, is 'sudden' and 'abrupt' and also group-specific. Comment whether a natural disaster can be the cause for extinction of species.
Ans: Natural disasters such as earthquakes can result in the extinction of species. A majority of scientists believe that a meteor struck the earth, causing widespread destruction and the extinction of dinosaurs.
3. Why is nascent oxygen supported to be toxic to aerobic life forms?
Ans: Nascent oxygen is highly reactive. It can react easily and cause a reaction with a variety of compounds, including DNA and proteins found in cells of aerobic life forms. This may result in Mutations and unfavorable metabolic changes.
4. While the creation and presence of variation is directionless, natural selection is directional as it is in the context of adaptation. Comment.
Ans: Variation continues to appear in each generation. However, because nature may not support such variations, most of them are not retained by the organism. When a new recombinant passes the test of natural selection, then only it is inherited in species through generation to generation. As a result, creation and the presence of variation can be considered to be directionless, but natural selection and adaptation are directional.
5. The evolutionary story of moths in England during industrialization reveals, that 'evolution is apparently reversible'. Clarify this statement.
Ans: In England before industrialization, the white-winged moths were able to thrive because whitish lichens and moss flourished on tree trunks. White-winged moths blended very well and therefore had better chances of survival against the whitish background. But when the industrial revolution started the tree trunks turned dark, Lichens and mosses did not survive. As a result, the population of white-winged moths decreased and the population of white-winged moths increased. Thus, the evolution of white-winged moth reversed due to industrialization.
6. Comment on the statement that "evolution and natural selections are end result or consequence of some other processes but themselves are not processed".
Ans: It is controversial whether evolution and natural selection are processes in and of themselves, or if they are the end result or consequence of other processes. When we talk about the success of life on Earth, we consider evolution and natural selection to be processed. However, when discussing how life arose from primitive beginnings, evolution and natural selection appear to be the outcomes of other processes. This is still a debatable topic in the scientific community.
7. State and explain any three factors affecting allele frequency in populations.
Ans: The allele frequency in population can be affected by the following factors:
Mutation: Mutation is a sudden inheritable change in the DNA, it leads to the formation of new species and therefore changes in allelic frequency.
Natural Selection: Natural selection theory that states, Nature only selects the fittest organisms which survive in changed environmental conditions.
Genetic Recombination: The new organism or traits produced that differ from parents is called genetic recombination.
8. Gene flow occurs through generations. Gene flow can occur across language barriers in humans If we have a technique of measuring specific allele frequencies in different populations of the world, can we not predict human migratory patterns in pre-history and history? Do you agree or disagree? Provide an explanation of your answer.
Ans: Yes, I agree. Gene flow occurs across generations. The project known as Human Genome Project has used specific genes/chromosomes and mitochondrial DNA to trace the evolutionary history and migratory patterns of humans. Therefore with the help of HGP by studying specific allele frequencies, we can predict the human migratory patterns in prehistory and history.
9. How do you express the meaning of words like race, breed, cultivars, or variety?
Ans: Race: Race is a group of people that share similar and distinct physical characteristics. Members of different races of the same species can interbreed.
Breed: Breed is a group of animals that are similar in physical appearance.
Cultivars: Cultivar is a selected group of plants that can be propagated through vegetative parts.
Variety: Variety is a taxonomic category that ranks below species level in the plant kingdom.
10. When we say "survival of the fittest", does it mean that (a) those who are fit only survive, or (b) those that survive are called fit? Comment.
Ans: The “survival of the fittest” means the organisms with suitable and useful adaptations survive and reproduce in the varied environmental conditions that are known to be fit.
11. Enumerate the three most characteristic criteria for designating a Mendelian population.
Ans: The three most important criteria for the mendelian population :
The population must be sufficiently large
The population must have potentialities for the free flow of genetic material among individuals.
Migration should be nil or negligible in the population.
12. "Migration may enhance or blur the effects of selection”. Comment.
Ans: Migration can enhance the natural selection process by bringing in alleles and traits within the population. And it can blur the effect of selection by removing the useful traits and genes from the population.
Long Answer Type Questions
1. Name the law that states that the sum of allelic frequencies in a population remains constant. What are the five factors that influence these values?
Ans: Hardy Weinberg Principle, also known as Hardy Weinberg Law.
The law states that the sum of allelic frequencies in a population remains constant from generation to generation in the absence of disturbing factors.
Hardy Weinberg Equation: (p+q) 2 = p 2 +2pq+q 2 =1
Where p is the frequency of dominant allele
q is the frequency of recessive allele
p 2 is the frequency of homozygous dominant allele
2pq is the frequency of individuals with heterozygous genotype
q 2 is the frequency of individuals with the homozygous recessive allele
The extent of evolutionary change can be evaluated by measuring the difference between the values.
The factors that influence these values are as follows :
(a) Gene migration or gene flow
(b) Genetic drift
(c) Genetic recombination
(d) Mutation
(e) Natural selection
2. Explain divergent evolution in detail. What is the driving force behind it?
Ans: Divergent evolution is when there are two organisms or species having common ancestors but different characteristics due to adaptation. These organisms are in different habitats and share similar anatomical structures but perform different functions. This is known as Divergent evolution. For example, the forelimbs of Whales, bats, Human and Cheetah are similar in structure but they perform different functions.
Divergent evolution occurs due to the changed environmental conditions. The driving force behind this evolution is an adaptation to a new habitat and altering environmental conditions.
3. You have studied the story of Pepper moths in England Had the industries been removed, what impact could it have on the moth population? Discuss.
Ans: In England, Two varieties of Pepper moths were present in the population. But before industrialization, the number of White-winged Pepper moths was much higher than the black-winged moths. Colored wings help in camouflage. Therefore they were not spotted by the predators due to their camouflage they blended very well in the moss and lichens-covered tress.
After the industrial revolution, tree trunks became dark, lichens did not survive. As a result, the black-winged moth population started increasing because the dark tree trunk helped them to camouflage. And the now the white ones were easily spotted and killed by the predators. Again if the industries are removed the population of Black-winged moths will decrease and the population of white-winged moths will increase.
4. What are the key concepts in the evolution theory of Darwin?
Ans: Darwin’s theory of evolution was based on two key concepts:
Branching descent and natural selection.
Branching descent: This is usually referred to as the “Tree of life”. Every organism originated from a single common ancestor. Every new species is developed by adaptation to new environmental conditions. Ex. Darwin’s finches arose from grain eaters, Australian marsupials evolved from common marsupials.

As the following diagram shows that the various life forms we see today have evolved from one common ancestor. One branch evolved into fishes, another one evolved into amphibians. The third branch has given rise to various terrestrial animals: reptiles, aves, and mammals.
Natural Selection: According to Darwin's theory, only the fittest organisms can survive the changing environmental conditions. Every living trying to cope with the changed environmental conditions by developing certain adaptations. Only those organisms with suitable adaptation are capable of surviving. Therefore, natural selection is an important phenomenon in evolution.
5. Two organisms occupying a particular geographical area (say desert) show similar adaptive strategies. Take examples, describe the phenomenon.
Ans: Two organisms occupying a particular geographical area may show similar adaptive strategies, this phenomenon is known as convergent evolution. This is because both organisms are reacting to the same environmental conditions.
For Example, Cereus peruvianus and euphorbia virosa, are desert plants and not related to one another. Both of the species show similar adaptations:
Stem modification: Fleshy stem, green succulent parts store water and perform the function of photosynthesis.
Leaf modification: Leaves are modified into spines to reduce water loss.
Root modification: Roots penetrate deep into the ground to access groundwater.
Analogous organs that are indications of convergent evolution are depicted in these examples.
6. We are told that evolution is a continuing phenomenon for all living things. Are humans also evolving? Justify your answer.
Ans: Evolution is a continuous process. Microevolution goes on continuously and there are inheritable gradual changes in the organism and its population.
The evolution process is continuous in human beings also as it takes place in all living beings. All the modern-day organisms are descended from their ancestors. Modern man Homo sapiens arose from the ancestors that are Ramapithecus, Australopithecus, Homo habilis, Homo erectus, Neanderthal man, Cro-Magnon man, etc.
The average human life expectancy has increased, it is almost double the of primitive times.
All the other animals develop lactose intolerance in adulthood. Other mammals do not have the facility to consume other mammals’ milk. But human beings can consume milk throughout life and rarely develop lactose intolerance.
Humans have developed resistance to many infectious diseases.
These are the signs of evolution. Although evolution can take place through geographical isolation and genetic drift.
7. Had Darwin been aware of Mendel’s work, would he have been able to explain the origin of variations. Discuss.
Ans: Gregor Mendel and Charles Darwin were born in the same era. Darwin was apparently aware of Mendel’s work but could not explain the origins of Variation. Mendel proposed his theories and principles of genetics. His work was extensively limited to particular species and he put forward laws about the inheritance and variations among the organisms. The parent’s genotype is responsible for offspring’s character has been proved by Mendal through his Pigeon Pea plant experiments. And at the time Darwin seems to ignore the fact that the variation among the population of the organism is due to their genes or alleles. There are many other factors that may change the allele frequency, for example, Mutation, Genetic recombination, genetic drift, etc. So, after many generations, there would be a change in the gene pool, organism’s characteristics, and therefore new forms appear to arise in the population.
Important Concepts In Evolution
There are many important concepts in the chapter, but the most important ones are mentioned below. You can find notes on these topics in the Vedantu app and can also look up LIVE classes in which professors teach these with brilliance.
Origin of Life
Evolution of Life Forms – A Theory
What is the Evidence for Evolution?
What is Adaptive Radiation?
Biological Evolution
Mechanism of Evolution
Hardy – Weinberg Principle
A Brief Account of Evolution
Origin and Evolution of Man
Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 - Evolution solved by expert Biology teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines is available. All Chapter 7 - Evolution exercise questions with solutions are designed to help you revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in your examinations.

FAQs on NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter-7 (Book Solutions)
1. How can Vedantu help me in studying Class 12 Biology for the CBSE Board exams?
Vedantu can help you not only in preparing for CBSE Class 12 Board exams but also for competitive exams like NEET. You can find a ton of study materials for NCERT Class 12 Biology on Vedantu. This includes:
Revision Notes
NCERT Solutions
Previous Year Question Papers
Sample Papers
Important Questions
Conceptual videos
Free masterclasses
All of these materials are just a click away after registering on Vedantu for free. You do not have to pay for any of the above-mentioned materials. Moreover, you can also register for Vedantu’s personalised classes for an exclusive and individualised study experience.
2. Why must I download the NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 PDF?
These solutions are beneficial for Class 12 students in many ways:
The NCERT Solutions incorporate easy to understand language to help students score excessive marks in the board exams and NEET exams.
The solutions can be beneficial not only for the board exams but also for diverse competitive exams and NEET.
The solutions clear the doubts of students from the NCERT textbooks.
Experts design the answers with accurate and proper statistics to bring the most well-researched and top quality relevant solutions for Class 12 students.
The specific solutions to all of the questions assist students with their board examination.
3. How to answer hard questions in Chapter 7 of NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology?
For students to respond to hard questions of Chapter 7 Evolution, they should consider reading a lot of the material that is available inside the NCERT as well as the material available on the Vedantu website. Students who are interested in picking up this subject as their main field of study should specifically be very alert and pay attention to every single detail that is described in the chapter. One should not worry if the question is a lengthy one or is difficult, but should worry about the concepts and logic that are required to answer these questions. A person can refer to previous chapters as well as study this chapter from different study materials that are available on the Vedantu website. Difficult questions should be solved in a pattern to leave some time for questions that are MCQ-based and are much easier to answer.
4. How should I Practice drawing various animals and plants that are there in the Chapter Evolution NCERT?
For diagrams, refer to NCERT textbooks specifically. The more you practise each diagram, the better for you. You must ensure proper labelling in your diagram. Before jumping into drawing them directly, read the relevant information provided in the textbook. Once you understand the characteristics and features, drawing diagrams and remembering them for the exam will become much easier. You may also refer to conceptual and animated videos on the internet if you are a visual learner. This will help to ingrain the diagrams better in your mind.
CBSE Expert
CBSE Class 12 Biology Case Study Questions PDF Download
Welcome to the comprehensive guide on CBSE Class 12 Biology Case Study Questions! In this article, we will delve into the world of Biology case studies, explore the importance of case study questions, and provide you with a PDF download that will assist you in mastering this subject. Whether you’re a student preparing for your examinations or a teacher looking to enhance your teaching materials, our detailed resource will help you excel in the realm of Biology.

Case studies are a widely used educational tool that involves the in-depth analysis of a particular situation, organism, process, or problem. In CBSE Class 12 Biology, case study questions are designed to evaluate students’ critical thinking, problem-solving abilities, and practical application of biological concepts. These questions require students to apply their theoretical knowledge to real-life scenarios, thus fostering a deeper understanding of the subject matter.
Class 12 Biology Case Study Questions
CBSE Class 12 Biology question paper will have case study questions too. These case-based questions will be objective type in nature. So, Class 12 Biology students must prepare themselves for such questions. First of all, you should study NCERT Textbooks line by line, and then you should practice as many questions as possible.
Chapter-wise Solved Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology
Class 12 students should go through important Case Study problems for Biology before the exams. This will help them to understand the type of Case Study questions that can be asked in Grade 12 Biology examinations. Our expert faculty for standard 12 Biology have designed these questions based on the trend of questions that have been asked in last year’s exams. The solutions have been designed in a manner to help the grade 12 students understand the concepts and also easy-to-learn solutions.
Books for Class 12 Biology
Strictly as per the new term-wise syllabus for Board Examinations to be held in the academic session 2022-23 for class 12 Multiple Choice Questions based on new typologies introduced by the board- Stand-Alone MCQs, MCQs based on Assertion-Reason Case-based MCQs. Include Questions from CBSE official Question Bank released in April 2022 Answer key with Explanations What are the updates in the book: Strictly as per the Term wise syllabus for Board Examinations to be held in the academic session 2022-23. Chapter-wise -Topic-wise Multiple choice questions based on the special scheme of assessment for Board Examination for Class 12th.

Tips to Excel in CBSE Class 12 Biology Case Study Questions
Thoroughly grasp the concepts.
Before attempting case study questions, ensure you have a strong grasp of fundamental biological concepts. Familiarize yourself with topics such as genetics, ecology, human physiology, and evolution. A solid foundation will empower you to tackle complex case studies with confidence.
Practice Regularly
Practice makes perfect, and this is especially true for case study questions. Allocate time to work through a diverse range of case studies regularly. Familiarizing yourself with different scenarios will prepare you for the unpredictability of examination questions.
Collaborate and Discuss
Engaging in group discussions with fellow students or teachers can be highly beneficial. Sharing perspectives, analyzing cases together, and discussing possible solutions can broaden your understanding and offer fresh insights.
Seek Guidance from Teachers
Don’t hesitate to approach your teachers for assistance. They possess valuable experience and expertise to guide you through challenging case studies and provide valuable feedback.
Time Management
During examinations, time management is crucial. Practice solving case study questions under timed conditions to improve your efficiency and ensure you complete all questions within the allocated timeframe.
In conclusion, mastering case study questions in CBSE Class 12 Biology is essential for a holistic understanding of the subject and for excelling in examinations. By honing your analytical abilities, practicing regularly, and seeking guidance, you can conquer even the most challenging case studies. Remember that learning Biology is not just about memorizing facts but about applying knowledge to real-world situations. So, embrace the power of case studies and delve into the fascinating world of Biology.
With the provided CBSE Class 12 Biology Case Study Questions PDF, you have a valuable resource at your disposal. Practice diligently, and you’ll witness your confidence soar as you become a proficient problem solver in the realm of Biology. Good luck on your academic journey!
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Download India's best Exam Preparation App Now.
Key Features
- Revision Notes
- Important Questions
- Previous Years Questions
- Case-Based Questions
- Assertion and Reason Questions
No thanks, I’m not interested!

- Andhra Pradesh
- Chhattisgarh
- West Bengal
- Madhya Pradesh
- Maharashtra
- Jammu & Kashmir
- NCERT Books 2022-23
- NCERT Solutions
- NCERT Notes
- NCERT Exemplar Books
- NCERT Exemplar Solution
- States UT Book
- School Kits & Lab Manual
- NCERT Books 2021-22
- NCERT Books 2020-21
- NCERT Book 2019-2020
- NCERT Book 2015-2016
- RD Sharma Solution
- TS Grewal Solution
- TR Jain Solution
- Selina Solution
- Frank Solution
- ML Aggarwal Solution
- Lakhmir Singh and Manjit Kaur Solution
- I.E.Irodov solutions
- ICSE - Goyal Brothers Park
- ICSE - Dorothy M. Noronhe
- Sandeep Garg Textbook Solution
- Micheal Vaz Solution
- S.S. Krotov Solution
- Evergreen Science
- KC Sinha Solution
- ICSE - ISC Jayanti Sengupta, Oxford
- ICSE Focus on History
- ICSE GeoGraphy Voyage
- ICSE Hindi Solution
- ICSE Treasure Trove Solution
- Thomas & Finney Solution
- SL Loney Solution
- SB Mathur Solution
- P Bahadur Solution
- Narendra Awasthi Solution
- MS Chauhan Solution
- LA Sena Solution
- Integral Calculus Amit Agarwal Solution
- IA Maron Solution
- Hall & Knight Solution
- Errorless Solution
- Pradeep's KL Gogia Solution
- OP Tandon Solutions
- Sample Papers
- Previous Year Question Paper
- Value Based Questions
- CBSE Syllabus
- CBSE MCQs PDF
- Assertion & Reason
- New Revision Notes
- Revision Notes
- HOTS Question
- Marks Wise Question
- Toppers Answer Sheets
- Exam Paper Aalysis
- Concept Map
- CBSE Text Book
- Additional Practice Questions
- Vocational Book
- CBSE - Concept
- KVS NCERT CBSE Worksheets
- Formula Class Wise
- Formula Chapter Wise
- JEE Crash Course
- JEE Previous Year Paper
- Important Info
- JEE Mock Test
- JEE Sample Papers
- SRM-JEEE Mock Test
- VITEEE Mock Test
- BITSAT Mock Test
- Manipal Engineering Mock Test
- AP EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- COMEDK Previous Year Paper
- GUJCET Previous Year Paper
- KCET Previous Year Paper
- KEAM Previous Year Paper
- Manipal Previous Year Paper
- MHT CET Previous Year Paper
- WBJEE Previous Year Paper
- AMU Previous Year Paper
- TS EAMCET Previous Year Paper
- SRM-JEEE Previous Year Paper
- VITEEE Previous Year Paper
- BITSAT Previous Year Paper
- UPSEE Previous Year Paper
- CGPET Previous Year Paper
- CUSAT Previous Year Paper
- AEEE Previous Year Paper
- Crash Course
- Previous Year Paper
- NCERT Based Short Notes
- NCERT Based Tests
- NEET Sample Paper
- Previous Year Papers
- Quantitative Aptitude
- Numerical Aptitude Data Interpretation
- General Knowledge
- Mathematics
- Agriculture
- Accountancy
- Business Studies
- Political science
- Enviromental Studies
- Mass Media Communication
- Teaching Aptitude
- NAVODAYA VIDYALAYA
- SAINIK SCHOOL (AISSEE)
- Mechanical Engineering
- Electrical Engineering
- Electronics & Communication Engineering
- Civil Engineering
- Computer Science Engineering
- CBSE Board News
- Scholarship Olympiad
- School Admissions
- Entrance Exams
- All Board Updates
- Miscellaneous
- State Wise Books
- Engineering Exam

SHARING IS CARING If our Website helped you a little, then kindly spread our voice using Social Networks. Spread our word to your readers, friends, teachers, students & all those close ones who deserve to know what you know now.
CBSE Class 12th - BIOLOGY : Chapterwise Case Study Question & Solution
CBSE will ask two Case Study Questions in the CBSE class 12 Biology questions paper. Question numbers 15 and 16 are case-based questions where 5 MCQs will be asked based on a paragraph. Each theme will have five questions and students will have a choice to attempt any four of them.

- NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Maths
- NCERT Solutions for Class 10 Maths
- CBSE Syllabus 2023-24
- Social Media Channels
- Login Customize Your Notification Preferences
- CBSE Class 12 Result 2024 Latest Update : Verification of Marks, Revaluation & Photocopy of Answer Sheet; Check Complete Process 14 May, 2024, 12:04 pm
- CBSE Class 12th Result 2024 Out : Supplementary, Re-verification & Re-evaluation Date Released; Check Details Here 13 May, 2024, 3:40 pm
- CBSE 12th Toppers List 2024: Check Toppers Name, Marks, Pass Percentage, Merit List, District & Result Full Statistics 13 May, 2024, 12:15 pm
- CBSE 12th Results 2024 Out : CBSE 12th Result Declared; Check Scorecard Here from Direct Link 13 May, 2024, 11:40 am
- CBSE 12th 2024-25 : Biology Official Competency Focused Practice Questions released by CBSE 7 May, 2024, 4:29 pm
- CBSE 12th 2024-25 : Mathematics Official Competency Focused Practice Questions released by CBSE 7 May, 2024, 3:51 pm
- CBSE Board Class 12 Computer Science Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs 2 April, 2024, 1:51 pm
- CBSE Class 12 Computer Science Exam 2024 : Important MCQs with Answers For Last Minute Revision 1 April, 2024, 5:42 pm
- CBSE Board Class 12 History Answer Key 2024 and Question Papers, Download PDF All SETs 28 March, 2024, 1:18 pm

- Second click on the toggle icon

Provide prime members with unlimited access to all study materials in PDF format.
Allow prime members to attempt MCQ tests multiple times to enhance their learning and understanding.
Provide prime users with access to exclusive PDF study materials that are not available to regular users.


- Book Solutions
- State Boards
Case Study Questions Class 12 Biology Ecosystem
Case study questions class 12 biology chapter 14 ecosystem.
CBSE Class 12 Case Study Questions Biology Ecosystem. Term 2 Important Case Study Questions for Class 12 Board Exam Students. Here we have arranged some Important Case Base Questions for students who are searching for Paragraph Based Questions Ecosystem.
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks.
CBSE Case Study Questions Class 12 Biology Ecosystem
Case study 1
Interaction of biotic and abiotic components result in a physical structure that is characteristic for each type of ecosystem. Identification and enumeration of plant and animal species of an ecosystem gives its species composition. Vertical distribution of different species occupying different levels is called stratification. For example, trees occupy top vertical strata or layer of a forest, shrubs the second and herbs and grasses occupy the bottom layers. The components of the ecosystem are seen to function as a unit when you consider the following aspects: (i) Productivity; (ii) Decomposition; (iii) Energy flow; and (iv) Nutrient cycling. To understand the ethos of an aquatic ecosystem let us take a small pond as an example. This is fairly a self-sustainable unit and rather simple example that explain even the complex interactions that exist in an aquatic ecosystem. A pond is a shallow water body in which all the above mentioned four basic components of an ecosystem are well exhibited. The abiotic component is the water with all the dissolved inorganic and organic substances and the rich soil deposit at the bottom of the pond. The solar input, the cycle of temperature, day-length and other climatic conditions regulate the rate of function of the entire pond. The autotrophic components include the phytoplankton, some algae and the floating, submerged and marginal plants found at the edges.
The consumers are represented by the zooplankton, the free swimming and bottom dwelling forms. The decomposers are the fungi, bacteria and flagellates especially abundant in the bottom of the pond. This system performs all the functions of any ecosystem and of the biosphere as a whole, i.e., conversion of inorganic into organic material with the help of the radiant energy of the sun by the autotrophs; consumption of the autotrophs by heterotrophs; decomposition and mineralisation of the dead matter to release them back for reuse by the autotrophs, these event are repeated over and over again. There is unidirectional movement of energy towards the higher trophic levels and its dissipation and loss as heat to the environment.
Que. 1) Autotrophs consumption in the ecosystem occurs by …………………………………………………………………………………… .
(a) Decomposers
(b) Autotrophs
(c) Heterotrophs
(d) Herbivores
Que. 2) …………………………………………………………………… are represented as a consumer.
(a) Zooplanktons
(c) Flagellated
Que. 3) Components of ecosystem include ………………………………………………………………………………… .
(a) Kreb cycle
(b) Glucose cycle
(c) Cell cycle
(d) Nutrient cycle
Que. 4) Write definition of ‘Stratification’ and give one example of it.
Que. 5) Which decomposers are important to function ecosystem?
Que. 1)(c) Heterotrophs.
Que. 2) (a) Zooplanktons.
Que. 3) (d) Nutrient cycle.
Que. 4) Answer: Different levels which are occupied by vertical distribution of different species, this is called as Stratification. In the forest, trees occupy top layer and grasses occupy bottom layer. This is an example of Stratification.
Que. 5) Answer: Decomposers such as flagellated, bacteria and fungi are import to function ecosystem.
Case study 2
A constant input of solar energy is the basic requirement for any ecosystem to function and sustain. Primary production is defined as the amount of biomass or organic matter produced per unit area over a time period by plants during photosynthesis. It is expressed in terms of weight (gm–2 ) or energy (kcal m–2 ). The rate of biomass production is called productivity. It is expressed in terms of gm–2 yr –1 or (kcal m–2) yr –1 to compare the productivity of different ecosystems. It can be divided into gross primary productivity (GPP) and net primary productivity (NPP). Gross primary productivity of an ecosystem is the rate of production of organic matter during photosynthesis. A considerable amount of GPP is utilised by plants in respiration. Gross primary productivity minus respiration losses (R), is the net primary productivity (NPP). GPP – R = NPP Net primary productivity is the available biomass for the consumption to heterotrophs (herbiviores and decomposers). Secondary productivity is defined as the rate of formation of new organic matter by consumers. Primary productivity depends on the plant species inhabiting a particular area. It also depends on a variety of environmental factors, availability of nutrients and photosynthetic capacity of plants. Therefore, it varies in different types of ecosystems. The annual net primary productivity of the whole biosphere is approximately 170 billion tons (dry weight) of organic matter. Of this, despite occupying about 70 per cent of the surface, the productivity of the oceans are only 55 billion tons. Rest of course, is on land.
Que. 1) In the ecosystem, the …………………………………………………………………………………. is expressed in terms of gm -2 yr -1 .
(a) Energy flow
(b) Productivity
(c) Decomposition
(d) Cycle of nutrients
Que. 2) Complete the following equation of Net primary productivity.
NPP= GPP ___ _______.
Que. 3) Productivity is defined as the rate of …………………………………………………………………………….. production.
(a) Net primary
(b) Biomass
(c) Inorganic matter
(d) All of them
Que. 4) Explain the factors on which primary productivity is dependent?
Que. 5) Define ‘Gross primary productivity’.
Que. 1)(b) Productivity
Que. 2) (d) –R.
Que. 3) (b) Biomass.
Que. 4) Answer: Availability of nutrients, environmental factors, plant species, and photosynthetic capacity of plants these are the factors on which primary productivity is dependent.
Que. 5) Answer: Gross primary productivity- During photosynthesis process, the rate of production of organic matter is called as GPP or Gross primary productivity.
Case study 3
You may have heard of the earthworm being referred to as the farmer’s ‘friend’. This is so because they help in the breakdown of complex organic matter as well as in loosening of the soil. Similarly, decomposers break down complex organic matter into inorganic substances like carbon dioxide, water and nutrients and the process is called decomposition. Dead plant remains such as leaves, bark, flowers and dead remains of animals, including fecal matter, constitute detritus, which is the raw material for decomposition. The important steps in the process of decomposition are fragmentation, leaching, catabolism, humification and mineralisation. Detritivores (e.g., earthworm) break down detritus into smaller particles. This process is called fragmentation. By the process of leaching, watersoluble inorganic nutrients go down into the soil horizon and get precipitated as unavailable salts. Bacterial and fungal enzymes degrade detritus into simpler inorganic substances. This process is called as catabolism. It is important to note that all the above steps in decomposition operate simultaneously on the detritus (Figure 14.1). Humification and mineralisation occur during decomposition in the soil. Humification leads to accumulation of a dark coloured amorphous substance called humus that is highly resistant to microbial action and undergoes decomposition at an extremely slow rate. Being colloidal in nature it serves as a reservoir of nutrients. The humus is further degraded by some microbes and release of inorganic nutrients occur by the process known as mineralisation. Decomposition is largely an oxygen-requiring process.
The rate of decomposition is controlled by chemical composition of detritus and climatic factors. In a particular climatic condition, decomposition rate is slower if detritus is rich in lignin and chitin, and quicker, if detritus is rich in nitrogen and water-soluble substances like sugars. Temperature and soil moisture are the most important climatic factors that regulate decomposition through their effects on the activities of soil microbes. Warm and moist environment favour decomposition whereas low temperature and anaerobiosis inhibit decomposition resulting in build-up of organic materials.
Que. 1) Which of the following is a raw material for decomposition?
(b) Dead Plant
(c) Flowers
(d) Animals
Que. 2) When water soluble inorganic nutrients goes down in the soil and precipitated as unavailable salts, then the process is called as ……………………………………………………………………………………… .
(a) Catabolism
(b) Fermentation
(c) Humification
(d) Leaching
Que. 3) ……………..……………………………………………………… is required in the decomposition process.
(b) Phosphorous
(d) Nitrogen
Que. 4) What is meant by catabolism?
Que. 5) Write a very short note on Mineralisation from above paragraph.
Que. 1)(b) Dead Plant.
Que. 2) (d) Leaching.
Que. 3) (a) Oxygen.
Que. 4) Answer: When the fungal and bacterial enzymes degrade detritus and convert it into simpler inorganic substance, then it is called as Catabolism.
Que. 5) Answer: In this process, some microbes degrade humus. The inorganic nutrients are released by the process and the process is known as Mineralisation.
Case study 4
Except for the deep sea hydro-thermal ecosystem, sun is the only source of energy for all ecosystems on Earth. Of the incident solar radiation less than 50 per cent of it is photosynthetically active radiation (PAR). We know that plants and photosynthetic bacteria (autotrophs), fix Sun’s radiant energy to make food from simple inorganic materials. Plants capture only 2-10 per cent of the PAR and this small amount of energy sustains the entire living world. So, it is very important to know how the solar energy captured by plants flows through different organisms of an ecosystem. All organisms are dependent for their food on producers, either directly or indirectly. The green plant in the ecosystem are called producers. In a terrestrial ecosystem, major producers are herbaceous and woody plants. Likewise, producers in an aquatic ecosystem are various species like phytoplankton, algae and higher plants. You have read about the food chains and webs that exist in nature. Starting from the plants (or producers) food chains or rather webs are formed such that an animal feeds on a plant or on another animal and in turn is food for another. The chain or web is formed because of this interdependency. No energy that is trapped into an organism remains in it for ever. The energy trapped by the producer, hence, is either passed on to a consumer or the organism dies. Death of organism is the beginning of the detritus food chain/web. All animals depend on plants (directly or indirectly) for their food needs.
They are hence called consumers and also heterotrophs. If they feed on the producers, the plants, they are called primary consumers, and if the animals eat other animals which in turn eat the plants (or their produce) they are called secondary consumers. Likewise, you could have tertiary consumers too. Obviously the primary consumers will be herbivores. Some common herbivores are insects, birds and mammals in terrestrial ecosystem and molluscs in aquatic ecosystem.
Que. 1) ………………………………………………………………………. Is an herbivore organism in the aquatic ecosystem.
(a) Molluscs
(b) Insects
(c) Mammals
Que. 2) In the ecosystem, green plants are ……………………………………………………………………………………… .
(a) Consumers
(b) Decomposers
(c) Producers
Que. 3) PAR is a …………………………………….……………………………… .
(a) Powerful Atomic Radiation.
(b) Photosynthetically Atomic Radiation.
(c) Photosynthetically Active Radiation.
(d) Powerful Active Radiation.
Que. 4) Which ecosystem on earth does not require sun as an energy source?
Que. 5) Name any two producers from aquatic ecosystem.
Que. 1)(a) Molluscs.
Que. 2) (c) Producers.
Que. 3) (c) Photosynthetically Active Radiation.
Que. 4) Answer: The deep sea hydro-thermal ecosystem is the ecosystem on earth that does not require sun as an energy source.
Que. 5) Answer: Algae and phytoplankton both are producers in an aquatic ecosystem.
Case study 5
The consumers that feed on these herbivores are carnivores, or more correctly primary carnivores (though secondary consumers). Those animals that depend on the primary carnivores for food are labelled secondary carnivores. A simple grazing food chain (GFC) is depicted below:
The detritus food chain (DFC) begins with dead organic matter. It is made up of decomposers which are heterotrophic organisms, mainly fungi and bacteria. They meet their energy and nutrient requirements by degrading dead organic matter or detritus. These are also known as saprotrophs (sapro: to decompose). Decomposers secrete digestive enzymes that breakdown dead and waste materials into simple, inorganic materials, which are subsequently absorbed by them. In an aquatic ecosystem, GFC is the major conduit for energy flow. As against this, in a terrestrial ecosystem, a much larger fraction of energy flows through the detritus food chain than through the GFC. Detritus food chain may be connected with the grazing food chain at some levels: some of the organisms of DFC are prey to the GFC animals, and in a natural ecosystem, some animals like cockroaches, crows, etc., are omnivores. These natural interconnection of food chains make it a food web. How would you classify human beings!
Que. 1) ………………………………………………………………………….. is a beginning of Detritus food chain.
(a) Living organic matter
(b) Producers
(c) Dead organic matter
(d) Consumers
Que. 2) The meaning of sapro word in the saprotrophs is ………………………………………………………………………………………… .
(a) To produce
(b) To divide
(c) To consume
(d) To decompose
Que. 3) GFC is a ………………………………………………………………………. .
(a) Global food chain
(b) Grazing food chain
(c) Global food consumers
(d) Grazing form chain
Que. 4) Write a short note on Grazing food chain.
Que. 5) What is ‘Food web’.
Que. 1)(c) Dead organic matter.
Que. 2) (d) To decompose.
Que. 3) (b) Grazing food chain.
Que. 4) Answer: The producers are present in beginning of grazing food chain. Grass is taken as producer in this chain. Then goat is primary consumer because it eats or consume grass. Man are secondary consumers in the chain because man consume goat which consumes grass.
Que. 5) Answer: The normal interconnection of food chain is known as Food web.
Case study 6
An important characteristic of all communities is that their composition and structure constantly change in response to the changing environmental conditions. This change is orderly and sequential, parallel with the changes in the physical environment. These changes lead finally to a community that is in near equilibrium with the environment and that is called a climax community. The gradual and fairly predictable change in the species composition of a given area is called ecological succession. During succession some species colonise an area and their population become more numerous whereas populations of other species decline and even disappear. The entire sequence of communities that successively change in a given area are called sere(s). The individual transitional communities are termed seral stages or seral communities.
In the successive seral stages there is a change in the diversity of species of organisms, increase in the number of species and organisms as well as an increase in the total biomass. The present day communities in the world have come to be because of succession that has occurred over millions of years since life started on earth. Actually succession and evolution would have been parallel processes at that time.Examples of areas where primary succession occurs are newly cooled lava, bare rock, newly created pond or reservoir. The establishment of a new biotic community is generally slow. Before a biotic community of diverse organisms can become established, there must be soil. Depending mostly on the climate, it takes natural processes several hundred to several thousand years to produce fertile soil on bare rock.
Secondary succession begins in areas where natural biotic communities have been destroyed such as in abandoned farm lands, burned or cut forests, lands that have been flooded. Since some soil or sediment is present, succession is faster than primary succession.
Que. 1) A succeseful change of entire sequence of communities in a given area is known as …………………………………………………………………………………… .
(a) Ecological succession
(c) Ecology
(d) Community
Que. 2) In a given area, when species composition predictably changes then it is a ………………………………………………………………………………… .
(b) Climax community
(c) Climax changes
(d) Ecological succession
Que. 3) …………………………………………………………………… is the area where secondary succession begins.
(a) Cut forests
(b) Cooled lava
(c) New pond
(d) Bare rock
Que. 4) Give an example of area where primary succession occurs.
Que. 5) Where does secondary succession begins?
Que. 1)(b) Sere
Que. 2) (a) Cut forests.
Que. 3) (d) Ecological succession.
Que. 4) Answer: Primary succession mainly occurs in the area such as bare rock, newly created ponds and newly cooled lava.
Que. 5) Answer: The natural biotic communities were destroyed in an area. From that area secondary succession begins.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
We have a strong team of experienced Teachers who are here to solve all your exam preparation doubts
Sikkim scert class 5 english chapter 6b the smile of the terek sandpiper solution, amader poribesh class 4 solutions chapter 4 abohawa o basosthan, sikkim scert class 5 english chapter 6d i’m climbing a mountain solution, amader poribesh class 4 solutions chapter 8 manusher poribar o somaj.
Sign in to your account
Username or Email Address
Remember Me

Gurukul of Excellence
Classes for Physics, Chemistry and Mathematics by IITians
Join our Telegram Channel for Free PDF Download
Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and Its Applications
- Last modified on: 2 years ago
- Reading Time: 5 Minutes
Question 1:
Transgenic cows have extra gene or genes inserted into their DNA. Firstly the genes for the desired product is identified and sequenced. Then a gene construct containing this desired gene is introduced into female cow cells. Transgenic bovine cells are selected and fused with bovine oocytes that have had all of their chromosomes removed. Once fused with the oocyte, the transgenic cells chromosomes are reprogrammed to direct development which can be implanted into a recipient cow. The resulting transgenic cow only express the transgene in her milk. This is because expression of the transgene is controlled by a promoter specific to lactating mammary cells.
(i) The gene construct with desired gene is introduced into female cow cells by (a) transformation (b) transduction (c) transfection (d) transplantation.
(ii) Production of transgenic cow fulfill the objective of (a) increased milk production (b) increased meat production (c) molecular farming (d) all of these.
(iii) The name of first transgenic cow is (a) Tracy (b) Dolly (c) Rosie (d) ANDI.
(iv) Transgenic cow is produced through the implantation of ______ containing transgene into recipient cow. (a) ova (b) embryo (c) mammary cell (d) both (a) and (b)
(v) Read the given statements and select the correct option. Statement I : Transgenes only express in the mammary glands of transgenic cow. Statement II : Transgenes are present in chromosomes of every cell in transgenic cow. (a) Both statements I and II are true. (b) Both statements I and II are false. (c) Statement I is true but statement II is false. (d) Statement I is false but statement II is true.
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 9 Strategies for Enhancement in Food Production
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:2MinutesCase Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1: Given below is a flowchart for the formation of somatic hybrid, Pomato. (i) A certain tissue, of a plant, infected with TMV was used to obtain a new plant using tissueculture technique. Identify the technique used and reason out the possibility of obtaininga new healthy…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:2MinutesCase Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1: Darwin found the varieties of finches that in travelled to Galapagos Islands and observed variations in them. (i) What role does an individual organism play as per Darwin’s theory of natural selection?(ii) How did Darwin explain the existence of different varieties of finches on Galapagos…
Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 6 Molecular Basis of Inheritance
Last modified on:2 years agoReading Time:2MinutesCase Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1: Given below is the diagram of a tRNA molecule. Answer the questions based on the above diagram:(i) Why is charging of tRNA essential in translation?(ii) Where does peptide bond formation occur in a bacterial ribosome?(iii) Name the scientist who called tRNA an adaptor molecule. Answer…
Download CBSE Books
Exam Special Series:
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Science (for 2024)
- Sample Question Paper for CBSE Class 10 Maths (for 2024)
- CBSE Most Repeated Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important Diagram Based Questions Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Practical Based Questions for Class 10 Science Board Exams
- CBSE Important “Differentiate Between” Based Questions Class 10 Social Science
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Physics (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Chemistry (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Maths (for 2024)
- Sample Question Papers for CBSE Class 12 Biology (for 2024)
- CBSE Important Diagrams & Graphs Asked in Board Exams Class 12 Physics
- Master Organic Conversions CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Board Exams
- CBSE Important Numericals Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Definitions Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- CBSE Important Laws & Principles Class 12 Physics Board Exams
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Chemistry Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Physics Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Maths Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- 10 Years CBSE Class 12 Biology Previous Year-Wise Solved Papers (2023-2024)
- ICSE Important Numericals Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (215 Numericals)
- ICSE Important Figure Based Questions Class 10 Physics BOARD Exams (230 Questions)
- ICSE Mole Concept and Stoichiometry Numericals Class 10 Chemistry (65 Numericals)
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Chemistry BOARD Exams (150 Qs)
- ICSE Important Functions and Locations Based Questions Class 10 Biology
- ICSE Reasoning Based Questions Class 10 Biology BOARD Exams (100 Qs)
✨ Join our Online JEE Test Series for 499/- Only (Web + App) for 1 Year
✨ Join our Online NEET Test Series for 499/- Only for 1 Year
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Join our Online Test Series for CBSE, ICSE, JEE, NEET and Other Exams

Editable Study Materials for Your Institute - CBSE, ICSE, State Boards (Maharashtra & Karnataka), JEE, NEET, FOUNDATION, OLYMPIADS, PPTs
Discover more from Gurukul of Excellence
Subscribe now to keep reading and get access to the full archive.
Type your email…
Continue reading
- Biology Important Questions
- Class 12 - Biology
CBSE Important Questions for Class 12 Biology
CBSE Important Questions for Class 12 Biology are prepared by the subject experts and are extensively helpful for students in their exam preparations. These important questions provide a strategy to prepare for various board examinations and other competitive exams.
Biology is the most important subject for students preparing for medical entrance exams, including AIIMS, NEET, etc. Students aspiring to excel in the board and entrance examinations require deep knowledge and a thorough understanding of this subject. Therefore, the important questions for CBSE Class 12 Biology are essential for students to prepare for their exams.
For competitive examinations, students require an excellent level of preparation. Therefore, we cover all the CBSE Important Questions which are necessary for students preparing for both the Class 12 board and medical entrance examinations. All the questions in these materials are framed according to the NCERT textbook.
Class 12 Biology Important Questions
Click the links below to check the CBSE Class 12 Important Questions provided chapter-wise for Biology.
To practise more important questions and explore in-depth articles and videos, register at BYJU’s Biology . To find more useful study resources and materials, download BYJU’S App.
Also, Access Class 12 Biology Sample papers and Class 12 Biology Previous Year Question Papers.
Leave a Comment Cancel reply
Your Mobile number and Email id will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Request OTP on Voice Call
Post My Comment
Excellent MCQ’s
- Share Share
Register with BYJU'S & Download Free PDFs
Register with byju's & watch live videos.


IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Here, we have provided case-based/passage-based questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Evolution. Case Study/Passage-Based Questions. Case Study 1: When the reptiles came down, mammals took over the earth. There' were mammals in South America, which resembled some of the modern day mammals. But due to continental drift, they disappeared ...
Case Study/Passage Based Questions: Question 1: Darwin found the varieties of finches that in travelled to Galapagos Islands and observed variations in them. (i) What role does an individual organism play as per Darwin's theory of natural selection?(ii) How did Darwin explain the existence of different varieties of finches on Galapagos Islands?(iii) What is "fitness … Continue reading ...
Important Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter Wise with Answers . Get here all the Important questions for Class 12 Biology chapter wise as free PDF download. Here you will get Extra Important Questions with answers, assertion reasoning and Multiple Choice Questions (MCQ's) chapter wise in Printable format. Class 12 Biology has 16 important chapters covering various important topics related ...
CBSE 12th Biology Case Study MCQs. Here is one example question on subjective type case study questions. This was given in the term-2 sample paper in 2022. Some restriction enzymes break a phosphodiester bond on both the DNA strands, such that only one end of each molecule is cut and these ends have regions of single-stranded DNA.
CBSE Class 12 Biology Important Case Study based Questions 2024: The CBSE Board exam for class 12 Biology has been scheduled for March 19th, 2024.Class 12 Biology exam will have different types of ...
Case Study Questions. (a) State the hypothesis which S.L. Miller tried to prove in the laboratory with the help of the set up given above. (b) Name the organic compound observed by him in the liquid water after running the above experiment. (c) A scientist simulated a similar set up and added CH 4, NH 3 and water vapour at 800°C.
Case Study Questions Biology Class 12 PDF Chapter Wise. Class 12 Biology Case Study Questions Chapter Wise can be a great help in board exam preparations. Since students feel very overwhelmed while preparing for the examination, it will help them in doing that. Furthermore, finding many MCQs is a challenging task for the practice purpose.
Conclusion. NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 - Evolution offer a crucial resource for students delving into the captivating world of biological evolution. This chapter explores the fundamental principles of evolution, natural selection, speciation, and the evidence supporting the theory.
Origin and Evolution of Man. Free PDF download of NCERT Exemplar for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 - Evolution solved by expert Biology teachers on Vedantu.com as per NCERT (CBSE) Book guidelines is available. All Chapter 7 - Evolution exercise questions with solutions are designed to help you revise the complete syllabus and score more marks in ...
In simple terms, the organisms that are physically in good shape and health are considered "fit". The ones that aren't are eliminated. This is known as "survival of the fittest". Q.2. Comment on the statement, "Migration may increase or decrease the effects of selection". A.2.
CBSE Class 12 Biology question paper will have case study questions too. These case-based questions will be objective type in nature. So, Class 12 Biology students must prepare themselves for such questions. First of all, you should study NCERT Textbooks line by line, and then you should practice as many questions as possible. Chapter-wise ...
NCERT Solutions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 - Evolution is classified under the Unit - Genetics and Evolution. Genetics and Evolution unit holds around 18 marks as per previous trends. In other words, roughly 25% of the question paper has questions appearing from this unit. This total weightage serves as an eye-opener to students, giving ...
Ans. 1.) For a long period of time, it was also thought that life came from decaying and rotting matter such as straw, mud, and so forth. This was known as the spontaneous generation theory. 2.) Louis Pasteur demonstrated through careful experimentation that life can only arise from pre-existing life. 3.)
Class 12 Biology Chapter 7 Important Questions Evolution. Question 1. State the two principal outcomes of the experiments conducted by Louis Pasteur on origin of life. (Delhi 2019) Answer: Louis Pasteur's experiments demonstrated that life comes only from pre-existing life. He showed that in swan-neck pre-sterilised flasks, life did not ...
CBSE will ask two Case Study Questions in the CBSE class 12 Biology questions paper. Question numbers 15 and 16 are case-based questions where 5 MCQs will be asked based on a paragraph. Each theme will have five questions and students will have a choice to attempt any four of them. 2. Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants. 3. Human Reproduction.
Case Study Questions and Answers for Class 12 Biology all Chapter 1 to 16. Case Based Factual Passage Question & Answer. ... Case Study Question for Class 12 Biology Ch 1 to 16 ... Chapter 7: Evolution: Chapter 15: Biodiversity and Conservation: Chapter 8: Human Health and Disease: Chapter 16: Environmental Issues:
At Case Study Questions there will given a Paragraph. In where some Important Questions will made on that respective Case Based Study. There will various types of marks will given 1 marks, 2 marks, 3 marks, 4 marks. CBSE Case Study Questions Class 12 Biology Ecosystem. Case study 1
March 5, 2022 March 17, 2022 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 11 Biotechnology - Principles and Techniques. ... 2022 Physics Gurukul Leave a Comment on Case Study and Passage Based Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 2 Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants.
Case Study Questions for Class 12 Biology Chapter 12 Biotechnology and Its Applications Question 1: Transgenic cows have extra gene or genes inserted into their DNA. Firstly the genes for the desired product is identified and sequenced. Then a gene construct containing this desired gene is introduced into female cow cells. Transgenic bovine cells are … Continue reading Case Study Questions ...
Click the links below to check the CBSE Class 12 Important Questions provided chapter-wise for Biology. Important Questions Chapter 1: Reproduction in Organism. Important Questions Chapter 2: Sexual Reproduction in Flowering Plants. Important Questions Chapter 3: Human Reproduction. Important Questions Chapter 4: Reproductive Health.
2024 AP Exam Dates. The 2024 AP Exams will be administered in schools over two weeks in May: May 6-10 and May 13-17. AP coordinators are responsible for notifying students when and where to report for the exams. Early testing or testing at times other than those published by College Board is not permitted under any circumstances.