- Trying to Conceive
- Signs & Symptoms
- Pregnancy Tests
- Fertility Testing
- Fertility Treatment
- Weeks & Trimesters
- Staying Healthy
- Preparing for Baby
- Complications & Concerns
- Pregnancy Loss
- Breastfeeding
- School-Aged Kids
- Raising Kids
- Personal Stories
- Everyday Wellness
- Safety & First Aid
- Immunizations
- Food & Nutrition
- Active Play
- Pregnancy Products
- Nursery & Sleep Products
- Nursing & Feeding Products
- Clothing & Accessories
- Toys & Gifts
- Ovulation Calculator
- Pregnancy Due Date Calculator
- How to Talk About Postpartum Depression
- Editorial Process
- Meet Our Review Board

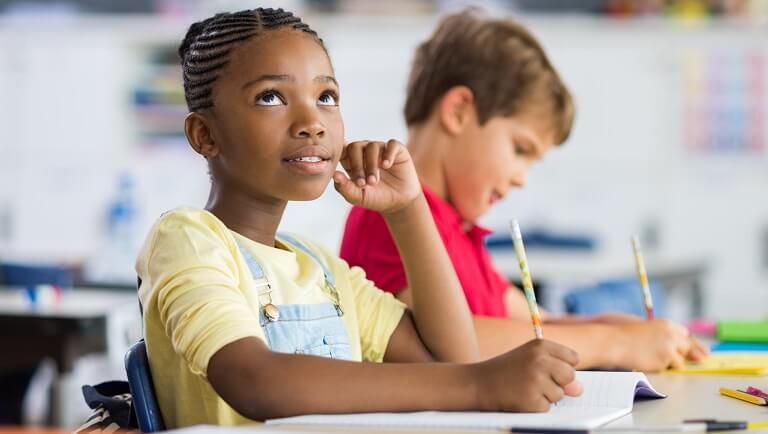
How to Teach Your Child to Be a Critical Thinker
Blue Planet Studio / iStockphoto
What Is Critical Thinking?
- Importance of Critical Thinking
Benefits of Critical Thinking Skills
- Teach Kids to Be Critical Thinkers
Every day kids are bombarded with messages, information, and images. Whether they are at school, online, or talking to their friends, they need to know how to evaluate what they are hearing and seeing in order to form their own opinions and beliefs. Critical thinking skills are the foundation of education as well as an important life skill. Without the ability to think critically, kids will struggle academically, especially as they get older.
In fact, no matter what your child plans to do professionally someday, they will need to know how to think critically, solve problems, and make decisions. As a parent, it's important that you ensure that your kids can think for themselves and have developed a healthy critical mindset before they leave the nest.
Doing so will help them succeed both academically and professionally as well as benefit their future relationships. Here is what you need to know about critical thinking, including how to teach your kids to be critical thinkers.
Critical thinking skills are the ability to imagine, analyze, and evaluate information in order to determine its integrity and validity, such as what is factual and what isn't. These skills help people form opinions and ideas as well as help them know who is being a good friend and who isn't.
"Critical thinking also can involve taking a complex problem and developing clear solutions," says Amy Morin, LCSW, a psychotherapist and author of the best-selling books "13 Things Mentally Strong People Don't Do" and "13 Things Mentally Strong Parents Don't Do."
In fact, critical thinking is an essential part of problem-solving, decision-making, and goal-setting . It also is the basis of education, especially when combined with reading comprehension . These two skills together allow kids to master information.
Why Critical Thinking Skills Are Important
According to the Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA), which evaluated 15-year-old children in 44 different countries, more than one in six students in the United States are unable to solve critical thinking problems. What's more, research indicates that kids who lack critical thinking skills face a higher risk of behavioral problems.
If kids are not being critical thinkers, then they are not thinking carefully, says Amanda Pickerill, Ph.D. Pickerill is licensed with the Ohio Department of Education and the Ohio Board of Psychology and is in practice at the Ohio State School for the Blind in Columbus, Ohio.
"Not thinking carefully [and critically] can lead to information being misconstrued; [and] misconstrued information can lead to problems in school, work, and relationships," she says.
Critical thinking also allows kids to gain a deeper understanding of the world including how they see themselves in that world. Additionally, kids who learn to think critically tend to be observant and open-minded.
Amy Morin, LCSW
Critical thinking skills can help someone better understand themselves, other people, and the world around them. [They] can assist in everyday problem-solving, creativity, and productivity.
There are many ways critical thinking skills can benefit your child, Dr. Pickerill says. From being able to solve complex problems in school and determining how they feel about particular issues to building relationships and dealing with peer pressure, critical thinking skills equip your child to deal with life's challenges and obstacles.
"Critical thinking skills [are beneficial] in solving a math problem, in comparing and contrasting [things], and when forming an argument," Dr. Pickerill says. "As a psychologist, I find critical thinking skills also to be helpful in self-reflection. When an individual is struggling to reach a personal goal or to maintain a satisfactory relationship it is very helpful to apply critical thinking."
Critical thinking also fosters independence, enhances creativity, and encourages curiosity. Kids who are taught to use critical thinking skills ask a lot of questions and never just take things at face value—they want to know the "why" behind things.
"Good critical thinking skills also can lead to better relationships, reduced distress, and improved life satisfaction," says Morin. "Someone who can solve everyday problems is likely to feel more confident in their ability to handle whatever challenges life throws their way."
How to Teach Kids to Be Critical Thinkers
Teaching kids to think critically is an important part of parenting. In fact, when we teach kids to be critical thinkers, we are also teaching them to be independent . They learn to form their own opinions and come to their own conclusions without a lot of outside influence. Here are some ways that you can teach your kids to become critical thinkers.
Be a Good Role Model
Sometimes the best way to teach your kids an important life skill is to model it in your own life. After all, kids tend to copy the behaviors they see in their parents. Be sure you are modeling critical thinking in your own life by researching things that sound untrue and challenging statements that seem unethical or unfair.
"Parents, being the critical thinkers that they are, can begin modeling critical thinking from day one by verbalizing their thinking skills," Dr. Pickerill says. "It’s great for children to hear how parents critically think things through. This modeling of critical thinking allows children to observe their parents' thought processes and that modeling lends itself to the child imitating what [they have] observed."
Play With Them
Children are constantly learning by trial and error and play is a great trial and error activity, says Dr, Pickerill. In fact, regularly playing with your child at a very young age is setting the foundation for critical thinking and the depth of their critical thinking skills will advance as they develop, she says.
"You will find your child’s thinking will be more on a concrete level in the earlier years and as they advance in age it will become more abstract," Dr. Pickerill says. "Peer play is also helpful in developing critical thinking skills but parents need to be available to assist when conflicts arise or when bantering takes a turn for the worse."
As your kids get older, you can play board games together or simply spend time talking about something of interest to them. The key is that you are spending quality time together that allows you the opportunity to discuss things on a deeper level and to examine issues critically.
Teach Them to Solve Problems
Morin says one way to teach kids to think critically is to teach them how to solve problems. For instance, ask them to brainstorm at least five different ways to solve a particular problem, she says.
"You might challenge them to move an object from one side of the room to the other without using their hands," she says. "At first, they might think it’s impossible. But with a little support from you, they might see there are dozens of solutions (like using their feet or putting on gloves). Help them brainstorm a variety of solutions to the same problem and then pick one to see if it works."
Over time, you can help your kids see that there are many ways to view and solve the same problem, Morin says.
Encourage Them to Ask Questions
As exhausting as it can be at times to answer a constant barrage of questions, it's important that you encourage your child to question things. Asking questions is the basis of critical thinking and the time you invest in answering your child's questions—or finding the answers together— will pay off in the end.
Your child will learn not only learn how to articulate themselves, but they also will get better and better at identifying untrue or misleading information or statements from others. You also can model this type of questioning behavior by allowing your child to see you question things as well.
Practice Making Choices
Like everything in life, your child will often learn through trial and error. And, part of learning to be a critical thinker involves making decisions. One way that you can get your child thinking about and making choices is to give them a say in how they want to spend their time.
Allow them to say no thank-you to playdates or party invitations if they want. You also can give them an allowance and allow them to make some choices about what to do with the money. Either of these scenarios requires your child to think critically about their choices and the potential consequences before they make a decision.
As they get older, talk to them about how to deal with issues like bullying and peer pressure . And coach them on how to make healthy choices regarding social media use . All of these situations require critical thinking on your child's part.
Encourage Open-Mindedness
Although teaching open-mindedness can be a challenging concept to teach at times, it is an important one. Part of becoming a critical thinker is the ability to be objective and evaluate ideas without bias.
Teach your kids that in order to look at things with an open mind, they need leave their own judgments and assumptions aside. Some concepts you should be talking about that encourage open-mindedness include diversity , inclusiveness , and fairness.
A Word From Verywell
Developing a critical mindset is one of the most important life skills you can impart to your kids. In fact, in today's information-saturated world, they need these skills in order to thrive and survive. These skills will help them make better decisions, form healthy relationships, and determine what they value and believe.
Plus, when you teach your kids to critically examine the world around them, you are giving them an advantage that will serve them for years to come—one that will benefit them academically, professionally, and relationally. In the end, they will not only be able to think for themselves, but they also will become more capable adults someday.
Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development. Programme for International Student Assessment (PISA): Results from PISA 2012 problem-solving .
Sun RC, Hui EK. Cognitive competence as a positive youth development construct: a conceptual review . ScientificWorldJournal . 2012;2012:210953. doi:10.1100/2012/210953
Ghazivakili Z, Norouzi Nia R, Panahi F, Karimi M, Gholsorkhi H, Ahmadi Z. The role of critical thinking skills and learning styles of university students in their academic performance . J Adv Med Educ Prof . 2014;2(3):95-102. PMID:25512928
Schmaltz RM, Jansen E, Wenckowski N. Redefining critical thinking: teaching students to think like scientists . Front Psychol . 2017;8:459. doi:10.3389/fpsyg.2017.00459
By Sherri Gordon Sherri Gordon, CLC is a published author, certified professional life coach, and bullying prevention expert.
Critical thinking is a 21st-century essential — here’s how to help kids learn it
Share this idea.
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on LinkedIn (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Reddit (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pocket (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on WhatsApp (Opens in new window)

If we want children to thrive in our complicated world, we need to teach them how to think, says educator Brian Oshiro. And we can do it with 4 simple questions.
This post is part of TED’s “How to Be a Better Human” series, each of which contains a piece of helpful advice from someone in the TED community; browse through all the posts here.
We all want the young people in our lives to thrive, but there’s no clear consensus about what will best put them on the path to future success. Should every child be taught to code? Attain fluency in Mandarin, Spanish, Hindi and English?
Those are great, but they’re not enough, says educator and teacher trainer Brian Oshiro . If we want our children to have flexible minds that can readily absorb new information and respond to complex problems, he says, we need to develop their critical thinking skills.
In adult life, “we all have to deal with questions that are a lot more complicated than those found on a multiple-choice test,” he says in a TEDxXiguan talk. “We need to give students an opportunity to grapple with questions that don’t necessarily have one correct answer. This is more realistic of the types of situations that they’re likely to face when they get outside the classroom.”
How can we encourage kids to think critically from an early age? Through an activity that every child is already an expert at — asking questions.
1. Go beyond “what?” — and ask “how?” and “why?”
Let’s say your child is learning about climate change in school. Their teacher may ask them a question like “What are the main causes of climate change?” Oshiro says there are two problems with this question — it can be answered with a quick web search, and being able to answer it gives people a false sense of security; it makes them feel like they know a topic, but their knowledge is superficial.
At home, prompt your kid to answer questions such as “ How exactly does X cause climate change?” and “ Why should we worry about it?” To answer, they’ll need to go beyond the bare facts and really think about a subject.
Other great questions: “ How will climate change affect where we live?” or “ Why should our town in particular worry about climate change?” Localizing questions gives kids, says Oshiro, “an opportunity to connect whatever knowledge they have to something personal in their lives.”
2. Follow it up with “How do you know this?”
Oshiro says, “They have to provide some sort of evidence and be able to defend their answer against some logical attack.” Answering this question requires kids to reflect on their previous statements and assess where they’re getting their information from.
3. Prompt them to think about how their perspective may differ from other people’s.
Ask a question like “How will climate change affect people living in X country or X city?” or “Why should people living in X country or X city worry about it?” Kids will be pushed to think about the priorities and concerns of others, says Oshiro, and to try to understand their perspectives — essential elements of creative problem-solving.
4. Finally, ask them how to solve this problem.
But be sure to focus the question. For example, rather than ask “How can we solve climate change?” — which is too big for anyone to wrap their mind around — ask “How could we address and solve cause X of climate change?” Answering this question will require kids to synthesize their knowledge. Nudge them to come up with a variety of approaches: What scientific solution could address cause X? What’s a financial solution? Political solution?
You can start this project any time on any topic; you don’t have to be an expert on what your kids are studying. This is about teaching them to think for themselves. Your role is to direct their questions, listen and respond. Meanwhile, your kids “have to think about how they’re going to put this into digestible pieces for you to understand it,” says Oshiro. “It’s a great way to consolidate learning.”
Critical thinking isn’t just for the young, of course. He says, “If you’re a lifelong learner, ask yourself these types of questions in order to test your assumptions about what you think you already know.” As he adds, “We can all improve and support critical thinking by asking a few extra questions each day.”
Watch his TEDxXiguan talk now:
About the author
Mary Halton is a science journalist based in the Pacific Northwest. You can find her on Twitter at @maryhalton
- brian oshiro
- how to be a better human
TED Talk of the Day

How to make radical climate action the new normal

6 ways to give that aren't about money

A smart way to handle anxiety -- courtesy of soccer great Lionel Messi

How do top athletes get into the zone? By getting uncomfortable

6 things people do around the world to slow down

Creating a contract -- yes, a contract! -- could help you get what you want from your relationship

Could your life story use an update? Here’s how to do it

6 tips to help you be a better human now

How to have better conversations on social media (really!)

Let’s stop calling them “soft skills” -- and call them “real skills” instead

There’s a know-it-all at every job — here’s how to deal

3 strategies for effective leadership, from a former astronaut

The 7 types of people you need in your life to be resilient

A pair of practices to help you raise financially responsible kids

The secret to giving a compliment that makes people glow

How to help a teacher out

How to raise kids who will grow into secure, trustworthy adults
.png)
How to Develop Critical Thinking Skills in Your Kids [in a fun way that won’t feel like learning!]

🤔 Critical thinking. Problem solving. Logical and lateral thinking. We hear these terms all the time, but what do they actually mean and why do they matter so much?
In this ultimate guide to developing critical thinking skills in kids I will answer this for you AND leave you with some super practical tools and tips to developing these key skills in the comfort of your own home.
Many of the examples I give you will draw from the “ KidCoachApp ” - a simple but innovative app I have developed to help parents build talking and thinking skills in children at home. It’s a really quick, fun and effective method to build critical thinking, taking just five minutes a day and with no preparation or materials required whatsoever!
Let’s get stuck in.
What is critical thinking?
Critical thinking is an ancient concept, dating back to the time of Socrates and Plato. We don’t seem to have one single definition of it, so let me give you a few to paint a decent picture.
Wikipedia defines critical thinking as “the analysis of facts to form a judgment” . They also say that requires “self-directed and self-corrective thinking” and that it develops “effective communication and problem-solving abilities.”
Criticathinking.org says it is “that mode of thinking - about any subject, content, or problem - in which the thinker improves the quality of his or her thinking by skilfully taking charge of the structures inherent in thinking and imposing intellectual standards upon them.”
Global Education company Pearson defines critical thinking as “the purposeful and goal-directed thinking used to define and solve problems, make decisions, and form judgments related to a particular situation or set of circumstances. It involves cognitive, metacognitive and dispositional components which may manifest (or be applied) differently in specific contexts.”
Pretty brainy stuff. 🧠 But don’t worry. This is not meant to be a scientific article on the topic, you will be glad to know!
I want to offer my own very simple definition of critical thinking, specifically for kids.
“Critical thinking for kids is getting them to think, really think, about what they are saying. It is NOT about remembering stuff or being right, but it IS about thinking ‘all the way around’ a problem.”
Sometimes it also helps to explain what something is NOT.
Here are three examples:
❌ If your child did the multiplication 6 x 9 to get 54 that would NOT be critical thinking. ✔️But if they then explained to you all the other ways they could get the number 54, then it could be.
❌If your child memorised the lyrics to their favourite song that would NOT be critical thinking. ✔️But if they compared and contrasted it to lyrics of other songs by the same artist, then it could be.
❌Or if your child watched a clever movie with lots of twists and turns that would NOT be critical thinking. ✔️But if they tried predicting what happens next and based on whether they were right or wrong, refined their predictions for the next scene, that could be.
Is this helping?
The terms problem solving or logical and lateral thinking get used quite a lot too. It basically all means the same thing.
Finally, you might have also heard the term “metacognition” which means “thinking about thinking.” This is a good one to bear in mind also as it makes us ask ourselves things like: “Why do I think this?”, “How could I be wrong?”, “What would other people think?” Metacognition is like when someone is speaking out loud your thoughts!
So, having understood what critical thinking is (or logical or lateral thinking is), let’s look at why it is just so important to develop in our kids.
Why is critical thinking important?
Simply put, critical thinking is a key way of ⭐ differentiating ⭐ our kids and preparing them for their future.
Those that can think critically and for themselves will stand out from those can’t. When our kids emerge into the rapidly-changing world of work, those that have good critical thinking skills will be able to cope the best.
1. The world is changing fast.
Did you know that 85% of the jobs that will exist in 2030 have not even been invented yet? That is according to a study done by the Institute for the Future , in 2017. They cite the increasing amount of technology (think artificial intelligence and machine learning) as carving out thousands of new jobs that we can’t even comprehend today.
Think about your own kids for a moment. What will they do for work?
Maybe one will be a genetic chef 🍲 – coming up with new recipes, analytically put together to be specifically optimised for people based on their genetic profiles?
Maybe another child will be a space traffic controller 🚀 – managing the algorithms computing the many orbital trajectories of shuttles for maximum safety and efficiency?
Or perhaps one will be a virtual reality engineer 👷 – building the new “Zoom” meeting places for employees to work effectively from home?
None of these jobs exist today, but all are completely plausible in just 10 years time.
The chef needs to understand the human genome and think carefully about what goes together, the space traffic controller needs to solve multi-dimensional problems in real time, the virtual reality engineer needs to invent cutting edge new technologies. All of these require massive brain power and ability to think critically in new situations.
Memorising facts just won’t do anymore! ⚠️
And don’t forget – the world will continue to change rapidly, so your kids will constantly have to skill and re-skill in their 20s, 30s, 40s and so on as they launch multiple careers. Maybe they start off in nutrition, then go to transportation, then communication…who knows?
Critical thinking is a transferable skill that your kids can take from one job to another, and will set them up well for life, no matter what decade they are working in.
2. We need better filters
There is a lot of information out there on Google, but the problem is that there is also a lot of disinformation. Knowledge is no longer an issue, but the application of that knowledge is.
I don’t just mean fake news, but also biased sources with agendas.
Take global warming as an example. 🌍
Ask your child to Google “is climate change bad?” See how they interpret what they see. Can they spot the sources and identify biases, for instance climate change activists vs oil companies vs paying advertisers? What other searches could they do to advance their thinking?
Here is a free conversation card you could you use for this exercise, which comes from the KidCoachApp and is a good example of a quick critical exercise you can do with your kids.
(By the way, if you were critically thinking about this article, you might discount what I am saying because I am trying to promote the KidCoachApp . You could, but I hope you don’t, as I really happen to believe in this stuff 😊)
3. Schools can't do enough
Unfortunately most schooling systems are not able to place enough emphasis on critical thinking and related skills. Even if they recognise its importance and want to spend more time on it, their hands are tied and they can’t allocate the necessary timetable space or budget for materials. There is normally just too much pressure to get those high grades in math and English etc.
As the Sutton Trust report of 2017 said: “97% of teachers agree that skills [like critical thinking] are as or more important than academic qualifications” and yet the Princes Trust report in the very same year found that “91% of teachers think schools should be doing more to help students develop [these skills].”
There ARE increasing attempts at embedding critical thinking into every traditional subject taught, for instance the examples I gave above about different ways to make the number 54 (math) or comparing lyrics of songs (English), but many feel this is not happening fast enough.
So what can we as parents do to accelerate this?
What parents need to do at home
The single biggest thing we can do as parents to develop critical thinking skills is to have the right conversations on a daily basis. If we are always asking the right questions, and encouraging our kids to as well, then we are instilling in them fantastic critical thinking skills.
Let’s see how this could pan out over the course of a typical week.
It's Monday and you are helping your child with their homework. Today they are learning all about space, our solar system and the eight planets. To complete the homework all they need to do is draw a diagram of the solar system and label it. But you want to do more and you spot an opportunity to ask some good questions.
💡 While they are working you also ask them how we know there are only eight planets? (it was only a few years ago we included Pluto to be the ninth). You ask how we can be sure they all orbit the Sun? (a few hundred years ago people believed the Earth was at the centre). You also ask how likely there are more Earth-like planets with life out there (perhaps using this conversation card from the KidCoachApp)?
Do you see how by asking just a few follow-on questions we can easily push their thinking?
It's Wednesday and you are watching the news together. There is a story about some recent lottery winners who have splashed the cash and ended up bankrupt after just one year. Oh dear! You could talk about how silly they are, but you see it as a coaching moment to develop critical thinking skills instead.
💡 So you start to talk about money, and what it can do. You ask them to imagine what it must be like to win the lottery. How would they feel? Can they ever really know until it happens? You ask them to think carefully about how they would spend the money (using this conversation card from the KidCoachApp)?
This approach can work for nearly any news story you happen to watch on the TV - try it out next time!
It's Friday and you have popped to the shops with your child. As an end-of-week treat you bought them a chocolate bar. You are just about to walk home when it starts pouring with rain. You decide to wait it out in the shops. Normally you would check your phone for a while but today you are feeling talkative and you are getting the hang of this “KidCoach” thing.
💡 You start talking about rain. What is it? Why is it important? What would we do without it? When is it helpful? When is it a problem? Then you see the chocolate in your child’s hand, and see how it is still raining, which inspires you to ask something fun and silly like this from the KidCoachApp (which also happens to develop excellent critical thinking skills)!
Kids love silly questions like this -they don't even realise that you are actually building their critical thinking skills, in this case by getting them to think through the pros and cons!
How realistic is it to do something like the above?
I know life as parents is super busy but this approach only takes five minutes a day.
Who doesn’t have five minutes to talk to their child each day? 🧒
Probably the hardest part is having the energy and inspiration to come up with a quick, fun question that gets kids thinking in new ways. That’s where the KidCoachApp massively helps.
We have spent hours curating and testing out the best critical thinking questions for kids! We have also written multiple prompts for each question, which parents say is very handy. These follow best practice methodologies used by many schools and education experts (see for instance the Philosophy For Children approach).
I promise that if you get into the habit of using the KidCoachApp to ask these sorts of questions, you will quickly find yourself coming up with all sorts of amazing questions on the fly based on what your kids are doing. Then you might not even need the app anymore!
THE KEY IS TO DEVELOP THE HABIT.
If we do 5 minutes of sit-ups each morning then we will quickly develop a strong core. 😅
Similarly if we exercise our children’s critical thinking muscles for five minutes every day, through a fun conversation starter, then guess what will happen to their thinking muscle? 🧠
Just find the time in the day that works for you and your family. Some like to do it during the school run, others at dinner time, others before bed.
It doesn’t matter when. Just find a five minute window and start asking great questions!
SOME OTHER THINGS YOU CAN DO.
Questioning our kids is THE best way of developing critical thinking skills in a quick, easy, fun and effective way at home.
For completeness however, I will mention a few more things that we can do as parents. All of these further reinforce the development of critical thinking skills:
❓ Do puzzles, riddles or brainteasers. There are plenty to google but here for instance is a list that spans from fun to serious. I like them since they are quick to ask but take a while to think about.
🎲 Play strategy board games. There are many strategy games available nowadays, see for instance this top 10 list . Chess is my all-time favourite and even playing against the computer is a good way to build critical thinking skills.
📲 Use critical thinking apps for kids. Our “ KidCoachApp ” requires interaction between parent and child, but if you want to park your child in front of the iPad for a while then check out this list. They cover critical thinking skills that also train the brain in terms of memory, concentration and reasoning.
Critical thinking frameworks to teach your child
Kids sometimes ask me: “ But what do I think about first?”
This is where thinking frameworks are really handy to help kids deal with new situations. They are a way for your children to create certainty from uncertainty.
Let’s go through some simple examples you can teach them.
1. Think about pros and cons 👍 👎
For any situation that has at least two options / outcomes / answers, simply think of all the reasons for and against, i.e. the pros and cons. A good way of phrasing it for kids is “This would be good because….” and “This would be bad because…”
This teaches them to not jump to a solution but to take the time to consider each side of the argument, before making up their mind a balanced and considered way. It also helps them justify their response if someone asks “Why?”
👉Practice using this conversation card from the KidCoachApp, asking if social media is a good or a bad thing.
2. Ask what would X say? 💬
Perspective is so important. The world is full of diverse backgrounds, opinions and also biases. Let’s encourage our kids to seek out other viewpoints and simply asking “What would X say?” is a powerful way to help yourself see things from different sides.
👉Try it for example on this debating conversation card , on whether children need to go to school or if they can just learn from home! What your mum thinks, what your teacher would say and what your future-self would advise are all likely to be very different.
3. Put on different thinking hats 🎩
Edward de Bono came up with a great tool to help people think in different ways, called 6 Thinking Hats . The idea is that there are different colour hats which resemble different attitudes. For instance: Yellow is optimistic and benefits-led, White is data driven and analytical, Red is gut feel and instinct.
You can even state which hat you are putting on temporarily. This which gives you permission to think in a way that might be unpopular, without fear of being criticised, since you can just take the hat off again e.g. “Putting my black hat on, this will never work since….but putting my green hat on we could try something radical like….”
👉 Practice on this conversation card asking how we can reduce traffic on the roads. If there are pessimistic people in you group saying it just can’t be done, you can say “Well, just putting my Yellow hat on I think we would have far fewer accidents and much less air pollution if we did manage to reduce traffic on the roads. Wouldn’t that be a great thing? So why don’t we think harder about it for a moment? ” Then you can easily switch to a White Hat: “But being realistic and looking at the data, number of people and number of cars being made are just going up and up and up in our country. Maybe we can look at the data from another country to inspire us?”
Do you see how 6 Thinking Hats helps the very same child switch modes of thought seamlessly, by putting on different “hats”?
4. Use thinking moves 🔤
The most advanced framework we will cover here is from a company called DialogueWorks. They are on the Advisory Board for the KidCoachApp, and have come up with a neat list of 26 different thinking moves , one for each letter of the alphabet.
Each thinking move is a way of thinking about a situation task or problem. I find the framework very memorable.
Here are some of the most important ones here, along with the key question you can ask yourself when doing the move.
- Ahead: what could happen next?
- Back: what happened the last time?
- Connect: how do those connect?
- Divide: how do those differ?
- Formulate: what ideas can we come up with?
- Listen/Look: what do you notice?
- Question: what’s is the best question to ask here?
- Test: how can we tell if that will work?
- eXemplify: Can you give me an example?
- Zoom in/out: what is the bigger picture?
Practice using this conversation card from the KidCoachApp. It’s a philosophical topic on if you would want to live forever!
Here is how the thinking moves above might play out (just some examples to illustrate):
- Ahead: If I lived forever I would be able to do so many things
- Back: People have tried to live forever in the past but it hasn’t really worked
- Formulate: Let’s ask others for ideas on what we could do
- Listen/Look: Let’s go talk to someone really old to see what their life is like
- Question: Can my family live forever with me too?
- Test: How can I try it for awhile but still be able to go back if I want to?
- eXemplify: If I lived forever I would be able to travel to Mars one day!
- Zoom: I wonder if doing more stuff is really going to make me happy?
I hope these frameworks help. Teach some to your kids to use when faced with a challenging problem to solve!
An example of excellent critical thinking
🏙️ A few years ago Emma was working as a facilities manager of a tall skyscraper in London. There was a problem with the lifts serving all the different companies. She noticed that at lunchtime there were large queues forming on many floors as office workers all wanted to go and get a sandwich at the same time. This was causing irritation and lots of complaint emails were being sent her way!
Being a good critical thinker, she set out to find a nice solution to this problem. Maybe Emma could stagger the lunchtimes by floor somehow? Or maybe she could install sandwich kiosks on some floors? Maybe she could get people to use the stairs? Or did she need to build more lifts and lift shafts?
This could all work but would the issue was that it would require people to either change their behaviour (difficult) or build new things (costly).
Then she “zoomed out” and asked herself, one simple question:
“ Am I solving the right problem? ”
💡 Emma quickly realised she was solving the problem of "long queues", when actually the real problem was "people getting annoyed."
So what did she do?
Her solution was to simply to install full length mirrors next to the lift doors , so while people were waiting they could see themselves and be distracted for a while.
Sounds too simple but it worked! Complaints went way down and people were much happier. Through the power of critical thinking, Emma found a low cost and super effective solution to her problem.
What would your child do in this situation? Here is a free conversation card from the KidCoachApp to guide you. Try it out tonight!
What is the best age to start?
Right. Now.
Children are naturally good critical thinkers. Their world has no bounds and everything is still possible. So let’s keep nurturing the creativity, curiosity and critical thinking skills from as young an age as possible!
The conversation cards in the KidCoachApp are perfect for 6 – 12 year olds.
As kids grow into adults they will set more boundaries on things, just like we do: “We have always done it like this!” or “That’s not possible.”
Let’s delay this for as long as possible!!!
Let me give you an example.
I was watching TV with my daughter recently and a donation appeal popped up, asking for money to feed hungry children in Africa. My daughter started asking why they are hungry, and I said “Because they are” , and she said “Why can’t we give them more food” , and I said “Because it is difficult” etc. But my daughter kept pressing – “Why? Why? Why?”
And frankly, she has a good point.
There is an awful lot of food in the world, but perhaps it is just not distributed well enough. How much food goes to waste in an average “Western” household, and how could that instead end up feeding the needy in Africa or other places?
Perhaps it requires a next generation of super critical thinkers to break through the commonly accepted “wisdom” of us grown-ups, to find a new way of doing important things.
💚 Raising a child who is a good critical thinking is not just good for them, but will undoubtedly help society also! 💚
10 free critical thinking questions for kids
I've linked to loads of our questions free for you in this article, but I want to give you even more ideas here!
Because I am feeling generous I am including links to some of these complete questions cards in the KidCoachApp , where you will find lots of helpful prompts and guidance. It's normally paid for, although just £4.99 / month and with a completely free 2 week trial, so I think very reasonable.
- How many iPads do you think there are in the world?
- How many grains of sand do you think there are on a typical beach?
- If you could go back in time and change one thing, what would it be and why?
- How would you improve a sofa to make it better?
- If you could have any superpower, what would it be and why?
For the rest of these links you will just have to download the KidCoachApp 😊:
- How can you make £100 by next week if you wanted to?
- What would you name a new colour?
- What are 10 different things you can do a cup?
- When Baby Shark grows up, will he still be called Baby Shark?
- What would happen if it never rained?
Does the KidCoachApp really work?
Yes! It really does. 😃
But don’t just take my word for it.
Listen to this TED talk by Ian Gilbert, author of the famous THUNKS – questions to make kids’ brains go ouch! Ian is also a member of our Advisory Board at KidCoachApp , and we have worked with him closely in the development of the app. He said: “What gives anyone the edge is their ability to think - deeply, analytically, critically, creatively, empathically and for themselves. I think the range and quality of the questions in the KidCoachApp will support any parent who wants to give their child that edge."
Or take Jane Slinn , who is the founder of Independent Thinkers tuition agency. She said that: “I always emphasise to parents that they should sustain learning and encourage intellectual curiosity between and beyond weekly tutoring sessions. The KidCoachApp is perfect for this: it provides parents with hundreds of fun, stimulating questions to ask their kids that will get them talking and thinking."
And what about parents themselves? There are countless testimonials to pick from. You could watch what Bhavisha had to say here or read any review on the app stores, like this one from Alison:
💬 “Fantastic app for developing young minds. This app is a really effective way of helping parents think of interesting topics to discuss with their kids and helps develop communication, confidence, analytical thinking, creativity and more. It supports us in progressing the conversation to get the most from it and has some great topics to discuss. Such a great idea, thank you!”
What shall I do next?
By now you will be excited about how you can effectively build critical thinking skills simply through conversation with your kids. A five minute conversation every other day is so easy to fit in, and we do all the hard work for you putting fantastic thinking questions right in the palm of your hand.
💥To make the most of this, you need to download the KidCoachApp from your usual app store to start your 2 week free trial within seconds. No payment details needed – so you have nothing to lose and everything to gain. After that it is just £4.99/ month, or even cheaper if you go for the annual plan (like many parents do).
💓 I am super passionate about helping parents develop key skills in their kids, simply through conversation. I even quit my cushy corporate job to start up KidCoachApp, such was my passion and belief that I can be helpful.
💡 Let me inspire you now.
Download the KidCoachApp now! 👇
Start your free 2 week trial seconds. No payment details needed.

Kavin Wadhar
Kavin Wadhar is a parent of 2 kids and founder of www.KidCoach.app: guided conversations for parents to get their kids talking, thinking and feeling. Kavin left his corporate role in education publishing to pursue his passion to help parents develop in their kids the skills they need to thrive in tomorrow’s world. Working with a team of parents and education experts, Kavin has built an App for parents with hundreds of questions like those in this article, and with additional guidance / prompts to take conversations deeper. Check it out!
Want more like this?
Most popular articles:, connect through conversation, download the kidcoachapp free for hundreds of quick, fun and thought-provoking questions your kids will love.

- Grades 6-12
- School Leaders
FREE Poetry Worksheet Bundle! Perfect for National Poetry Month.
What Is Critical Thinking and Why Do We Need To Teach It?
Question the world and sort out fact from opinion.
The world is full of information (and misinformation) from books, TV, magazines, newspapers, online articles, social media, and more. Everyone has their own opinions, and these opinions are frequently presented as facts. Making informed choices is more important than ever, and that takes strong critical thinking skills. But what exactly is critical thinking? Why should we teach it to our students? Read on to find out.
What is critical thinking?
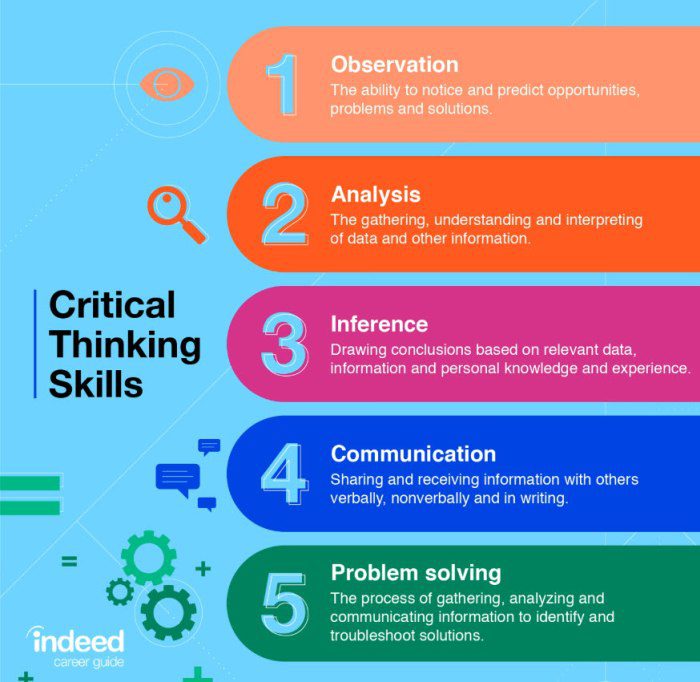
Source: Indeed
Critical thinking is the ability to examine a subject and develop an informed opinion about it. It’s about asking questions, then looking closely at the answers to form conclusions that are backed by provable facts, not just “gut feelings” and opinion. These skills allow us to confidently navigate a world full of persuasive advertisements, opinions presented as facts, and confusing and contradictory information.
The Foundation for Critical Thinking says, “Critical thinking can be seen as having two components: 1) a set of information and belief-generating and processing skills, and 2) the habit, based on intellectual commitment, of using those skills to guide behavior.”
In other words, good critical thinkers know how to analyze and evaluate information, breaking it down to separate fact from opinion. After a thorough analysis, they feel confident forming their own opinions on a subject. And what’s more, critical thinkers use these skills regularly in their daily lives. Rather than jumping to conclusions or being guided by initial reactions, they’ve formed the habit of applying their critical thinking skills to all new information and topics.
Why is critical thinking so important?
Imagine you’re shopping for a new car. It’s a big purchase, so you want to do your research thoroughly. There’s a lot of information out there, and it’s up to you to sort through it all.
- You’ve seen TV commercials for a couple of car models that look really cool and have features you like, such as good gas mileage. Plus, your favorite celebrity drives that car!
- The manufacturer’s website has a lot of information, like cost, MPG, and other details. It also mentions that this car has been ranked “best in its class.”
- Your neighbor down the street used to have this kind of car, but he tells you that he eventually got rid of it because he didn’t think it was comfortable to drive. Plus, he heard that brand of car isn’t as good as it used to be.
- Three independent organizations have done test-drives and published their findings online. They all agree that the car has good gas mileage and a sleek design. But they each have their own concerns or complaints about the car, including one that found it might not be safe in high winds.
So much information! It’s tempting to just go with your gut and buy the car that looks the coolest (or is the cheapest, or says it has the best gas mileage). Ultimately, though, you know you need to slow down and take your time, or you could wind up making a mistake that costs you thousands of dollars. You need to think critically to make an informed choice.
What does critical thinking look like?

Source: TeachThought
Let’s continue with the car analogy, and apply some critical thinking to the situation.
- Critical thinkers know they can’t trust TV commercials to help them make smart choices, since every single one wants you to think their car is the best option.
- The manufacturer’s website will have some details that are proven facts, but other statements that are hard to prove or clearly just opinions. Which information is factual, and even more important, relevant to your choice?
- A neighbor’s stories are anecdotal, so they may or may not be useful. They’re the opinions and experiences of just one person and might not be representative of a whole. Can you find other people with similar experiences that point to a pattern?
- The independent studies could be trustworthy, although it depends on who conducted them and why. Closer analysis might show that the most positive study was conducted by a company hired by the car manufacturer itself. Who conducted each study, and why?
Did you notice all the questions that started to pop up? That’s what critical thinking is about: asking the right questions, and knowing how to find and evaluate the answers to those questions.
Good critical thinkers do this sort of analysis every day, on all sorts of subjects. They seek out proven facts and trusted sources, weigh the options, and then make a choice and form their own opinions. It’s a process that becomes automatic over time; experienced critical thinkers question everything thoughtfully, with purpose. This helps them feel confident that their informed opinions and choices are the right ones for them.
Key Critical Thinking Skills
There’s no official list, but many people use Bloom’s Taxonomy to help lay out the skills kids should develop as they grow up.
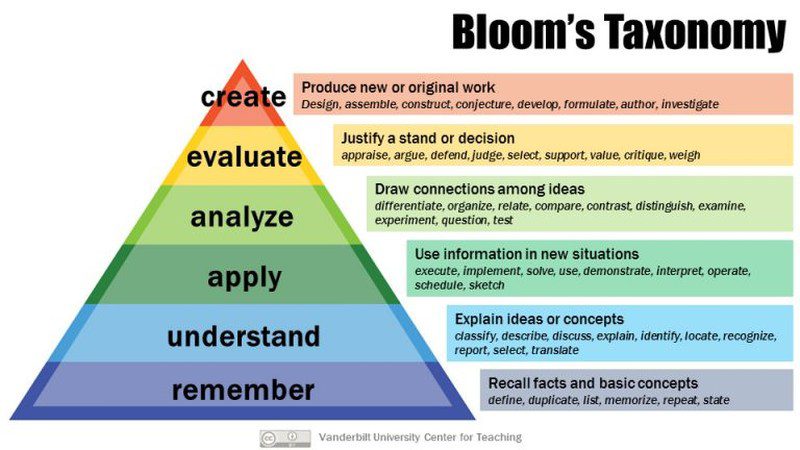
Source: Vanderbilt University
Bloom’s Taxonomy is laid out as a pyramid, with foundational skills at the bottom providing a base for more advanced skills higher up. The lowest phase, “Remember,” doesn’t require much critical thinking. These are skills like memorizing math facts, defining vocabulary words, or knowing the main characters and basic plot points of a story.
Higher skills on Bloom’s list incorporate more critical thinking.
True understanding is more than memorization or reciting facts. It’s the difference between a child reciting by rote “one times four is four, two times four is eight, three times four is twelve,” versus recognizing that multiplication is the same as adding a number to itself a certain number of times. When you understand a concept, you can explain how it works to someone else.
When you apply your knowledge, you take a concept you’ve already mastered and apply it to new situations. For instance, a student learning to read doesn’t need to memorize every word. Instead, they use their skills in sounding out letters to tackle each new word as they come across it.
When we analyze something, we don’t take it at face value. Analysis requires us to find facts that stand up to inquiry. We put aside personal feelings or beliefs, and instead identify and scrutinize primary sources for information. This is a complex skill, one we hone throughout our entire lives.
Evaluating means reflecting on analyzed information, selecting the most relevant and reliable facts to help us make choices or form opinions. True evaluation requires us to put aside our own biases and accept that there may be other valid points of view, even if we don’t necessarily agree with them.
Finally, critical thinkers are ready to create their own result. They can make a choice, form an opinion, cast a vote, write a thesis, debate a topic, and more. And they can do it with the confidence that comes from approaching the topic critically.
How do you teach critical thinking skills?
The best way to create a future generation of critical thinkers is to encourage them to ask lots of questions. Then, show them how to find the answers by choosing reliable primary sources. Require them to justify their opinions with provable facts, and help them identify bias in themselves and others. Try some of these resources to get started.
5 Critical Thinking Skills Every Kid Needs To Learn (And How To Teach Them)
- 100+ Critical Thinking Questions for Students To Ask About Anything
- 10 Tips for Teaching Kids To Be Awesome Critical Thinkers
- Free Critical Thinking Poster, Rubric, and Assessment Ideas
More Critical Thinking Resources
The answer to “What is critical thinking?” is a complex one. These resources can help you dig more deeply into the concept and hone your own skills.
- The Foundation for Critical Thinking
- Cultivating a Critical Thinking Mindset (PDF)
- Asking the Right Questions: A Guide to Critical Thinking (Browne/Keeley, 2014)
Have more questions about what critical thinking is or how to teach it in your classroom? Join the WeAreTeachers HELPLINE group on Facebook to ask for advice and share ideas!
Plus, 12 skills students can work on now to help them in careers later ..

You Might Also Like

Teach them to thoughtfully question the world around them. Continue Reading
Copyright © 2023. All rights reserved. 5335 Gate Parkway, Jacksonville, FL 32256

Thinking about thinking helps kids learn. How can we teach critical thinking?
Lecturer in Critical Thinking; Curriculum Director, UQ Critical Thinking Project, The University of Queensland
Disclosure statement
Peter Ellerton consults to the Centre for Critical and Creative Thinking. He is a Fellow of the Rationalist Society of Australia.
University of Queensland provides funding as a member of The Conversation AU.
View all partners
Few people doubt the value of developing students’ thinking skills. A 2013 survey in the United States found 93% of employers believe a candidate’s
demonstrated capacity to think critically, communicate clearly, and solve complex problems is more important [the emphasis is in the original] than [their] undergraduate major.
A focus on critical thinking is also common in education. In the Australian Curriculum, critical and creative thinking are known as “ general capabilities ”; the US has a similar focus through their “ common core ”.
Critical thinking is being taught successfully in a number of programs in Australian schools and universities and around the world. And various studies show these programs improve students’ thinking ability and even their standardised test scores.
But what is critical thinking and how can we teach it?
What we mean by critical thinking
There are many definitions of critical thinking that are vague or ill-formed. To help address this, let’s start by saying what critical thinking is not.
First, critical thinking is not just being smart. Being able to recognise a problem and find the solution are characteristics we associate with intelligence. But they are by themselves not critical thinking.
Intelligence, at least as measured by IQ tests, is not set in stone. But it does not seem to be strongly affected by education (all other things being equal), requiring years of study to make any significant difference, if at all. The ability to think critically, however, can improve significantly with much shorter interventions, as I will show.
Read more: Knowledge is a process of discovery: how constructivism changed education
Second, critical thinking is not just difficult thinking. Some thinking we see as hard, such as performing a complex chemical analysis, could be done by computers. Critical thinking is more about the quality of thinking than the difficulty of a problem.
So, how do we understand what good quality thinking is?
Critical thinkers have the ability to evaluate their own thinking using standards of good reasoning. These include what we collectively call the values of inquiry such as precision, clarity, depth and breadth of treatment, coherence, significance and relevance.
I might claim the temperature of the planet is increasing, or that the rate of deforestation in the Amazon is greater than it was last year. While these statements are accurate, they lack precision: we would also like to know by how much they are increasing to make the statement more meaningful.
Or I might wonder if the biodiversity of Tasmania’s old growth forests would be affected by logging. Someone might reply if we did not log these forests, jobs and livelihoods would be at risk. A good critical thinker will point out while this is a significant issue, it is not relevant to the question .

Critical thinkers also examine the structure of arguments to evaluate the strength of claims. This is not just about deciding whether a claim is true or not, but also whether a conclusion can be logically supported by the available data through an understanding of how arguments work.
Critical thinkers make the quality of their thinking an object of study. They are sensitive to the values of inquiry and the quality of inferences drawn from given information.
They are also meta-cognitive - meaning they’re aware of their thought processes (or some of them) such as understanding how and why they arrive at particular conclusions - and have the tools and ability to evaluate and improve their own thinking.
How we can teach it
Many approaches to developing critical thinking are based on Philosophy for Children , a program that involves teaching the methodology of argument and focuses on thinking skills. Other approaches provide this focus outside of a philosophical context.
Read more: How to make good arguments at school (and everywhere else)
Teachers at one Brisbane school, who have extensive training in critical thinking pedagogies, developed a task that asked students to determine Australia’s greatest sports person.
Students needed to construct their own criteria for greatness. To do so, they had to analyse the Australian sporting context, create possible evaluative standards, explain and justify why some standards would be more acceptable than others and apply these to their candidates.
They then needed to argue their case with their peers to develop criteria that were robust, defensible, widely applicable and produced a choice that captured significant and relevant aspects of Australian sport.
Learning experiences and assessment items that facilitate critical thinking skills include those in which students can:
- challenge assumptions
- frame problems collectively
- question creatively
- construct, analyse and evaluate arguments
- discerningly apply values of inquiry
- engage in a wide variety of cognitive skills, including analysing, explaining, justifying and evaluating (which creates possibilities for argument construction and evaluation and for applying the values of inquiry)
One strategy that also has a large impact on students’ ability to analyse and evaluate arguments is argument mapping , in which a student’s reasoning can be visually displayed by capturing the inferential pathway from premises to conclusion. Argument maps are an important tool in making our reasoning available for analysis and evaluation.
How we know it works
Studies involving a Philosophy for Children approach show children experience cognitive gains , as measured by improved academic outcomes, for several years after having weekly classes for a year compared to their peers.
Read more: Who am I? Why am I here? Why children should be taught philosophy (beyond better test scores)
This type of argument-based intellectual engagement , however, can show high outcomes in terms of the quality of thinking in any classroom.
Research also shows deliberate attention to the practice of reasoning in the context of our everyday lives can be significantly improved through targeted teaching.
Researchers looking at the gains made in a single semester of teaching critical thinking with argument maps said
the critical thinking gains measured […] are close to that which could be expected to result from three years of undergraduate education.
Students who are explicitly taught to think well also do better on subject-based exams and standardised tests than those who do not.
Our yet-to-be-published study, using verified data, showed students in years three to nine who engaged in a series of 12 one-hour teacher-facilitated online lessons in critical thinking, showed a significant increase in relative gains in NAPLAN test results – as measured against a control group and after controlling for other variables.
In terms of developing 21st century skills, which includes setting up students for lifelong learning, teaching critical thinking should be core business.
The University of Queensland Critical Thinking Project has a number of tools to help teach critical thinking skills. One is a web-based mapping system , now in use in a number of schools and universities, to help increase the critical thinking abilities of students.
- Critical thinking
- Critical thinking skills

Research Fellow – Beyond The Resource Curse

Audience Development Coordinator (fixed-term maternity cover)

Lecturer (Hindi-Urdu)

Director, Defence and Security

Opportunities with the new CIEHF

How to teach kids critical thinking
Every day more and more people realize how important critical thinking is. In today’s world, full of different information, influencers, web-content, fake news, and various opinions that seem to be facts, critical thinking is one of the biggest superpowers of a mature and competitive personality. So, why not help your child and push him or her to this skill as soon as possible?
To begin with, what is critical thinking, in general? It is a mixture of skills such as decision-making, finding analogies and causal links between events and processes, suggesting hypotheses, etc. Critical thinking is supposed to help you not to get lost in controversial information.
Some people claim that such a model of thinking might mute the flow of creativity in children. However, it’s totally the opposite — critical thinking will help kids broaden mind borders and find a field for new ideas. This skill is essential for everyone, but, as known, children usually learn things faster than adults. So it would be a great idea to explore this kind of thinking from primary school or even earlier.
Why is critical thinking important for kids?
Let’s see in what way critical thinking can improve your child’s life.
- Firstly, it is a beneficial method to explore the world . If a child learns things using critical thinking, he or she will avoid loads of mistakes and misleadings which could have traumatized him/her.
- Secondly, this skill makes a mind work faster . When things don’t make sense from first sight — think the situation over with a critical approach, and the puzzle will soon be complete.
- Thirdly, critical thinking is good support in school subjects . For instance, children with developed thinking habits are more likely to succeed in their exams. Moreover, it will be useful for every kid, no matter what direction he or she chooses. Language learners will improve faster if they use this approach; future inventors will do better with the projects after learning the basics of critical thinking; science pupils will do their research more deeply and consciously.
How to develop critical thinking in a child?

But what should adults do to help children gain this skill? There are some tips. They would be useful in your everyday conversations as well as on special seminars.
The easiest way to teach a kid something is to uphold the same principles you want to cultivate in him/her. It never hurts to learn some critical thinking skills yourself. Thus, you will help your child learn essential skills in practice and improve your own way of thinking. Be sure your child will look up to you and, sooner or later, will try to adopt your thinking habits.
No instructions
You probably know that there is a method of teaching children to swim, when an “instructor” just throws a child into the water to awaken his/her survival instincts and, at the same time, watches him/her closely to give a hand at the critical moment. Roughly speaking, the same method is very effective in terms of critical thinking. You let a child do something on his/her own and take all the risks. Afterward, it is necessary to discuss everything and figure out how it could have been done differently. Surely, everything should be within the norm — don’t forget that, first of all, you are a responsible parent.
More questions
Encourage your kid to be curious. Yes, it can be quite exhausting to reply to all the why’s and what’s all day long, but your child will definitely be grateful for it in the future. You’d better teach a child to avoid taking everything for granted. Instead of that, explain to him/her the importance of critical research even in everyday issues. If this useful habit is formed in childhood, there will be much fewer problems in high school and adulthood.
Agree/Disagree
If a person can express his/her agreement or disagreement with something, that means he/she is able to think critically. However, there is a thing — in addition to the statement, it is necessary to attach an explanation. Another way to help a child develop his/her thought is to ask more specifically: Is it right or wrong? True? False? Normal? All these questions will put a child in a position where critical thinking is required.
Good listening
This sort of soft skills is crucial in lots of professions nowadays but, at the same time, it is helpful in everyday life. When a person is a good listener, he/she doesn’t stop talking just for some personal reasons. It means that a person gives another one space and time to express his/her own ideas, without drawing all the attention to oneself. A good listener will not cause pressure and push his/her thoughts when an opponent doesn’t want it. Also, such a person will be sincerely interested in another person and new statements.
Clear meaning
This can be easily illustrated with a school studying. When a child learns something from a history textbook, he/she doesn’t need to learn it by heart. The point is to understand all the processes and causal links and be able to reproduce them in your own words. So, if you are not sure your child gets something right, ask him/her to clarify the meaning of his/her words. Ideally, a kid would explain the point in the narrative but keeping the main sense.
Biases matter
Even some adults often forget how strong the affection of biases could be — not to mention children. It’s a great idea to talk to your child about stereotypes, emotional intelligence, and prejudice and find a common solution on how to overcome their influence on our way of thinking.
All in all, parents and teachers should pay attention to developing their children’s critical thinking but without tight control. The best thing to do is give kids enough freedom to make their own decisions and, simultaneously, be ready to discuss difficulties they might encounter. Although children don’t know much about this world, they are people, only a bit smaller than adults. So treat them with respect, help them explore things, talk to them properly and don’t forget that you were young, too. It’s not much, but it’s an important job to do.

Critical thinking activities for kids
Finally, we offer you some activities that would be beneficial in learning critical thinking skills. You can practice them all with your child, and in some time, you will find out which one works out for you.
Tell me why
Imagine your kid is telling you a story from school. He or she disapproves of a classmate’s action. Try to develop this thought by asking why this action doesn’t seem right. You can also continue this discussion with a question like “Why should he/she act in a different way?” or “Why wouldn’t you act like this?”.
Question by question
Be cautious not to make a discussion overloaded — just one question at a time. Let’s go on with the same example: we start with a generalization like “Is it always inappropriate to act like this?” encouraging a kid to search for a counter-example. Then we listen to it and put it on a test with a question like “In this particular situation, was there any chance to act differently, or was it a necessity?”
Generally speaking, all sorts of questions help learn critical thinking. Not only make your kid ask as many things as possible but also get yourself into a habit of asking him or her about their mindset. We have already mentioned the importance of the question “Why?” but, in addition to it, you can ask for clarification of some thoughts or for more information on a subject. Show your child that it is significant to be able to support your statements with examples — ask him/her to give you one. Also, one of the main things to do is to link conditions with a situation. To develop this side of skill, ask a child what the particular situation depends on.
Predictions
One side of critical thinking is predicting conclusions, however, not wizard-like but with the help of analytical skills and logic. Ask your child a question, “What would happen if I did this?” and discuss the answer. You can also train this skill while reading or watching a film. At the crisis moment of a plot, try to stop for a second and ask your kid to predict what will happen next and why. This activity develops imagination and creativity, not to mention critical thinking.
Time to write
It is widely known that writing helps students bear new information in mind and make their statements clearer and more reasonable. Though children are not fancy to use pens and copybooks in today’s world, replacing them with laptops and smartphones, it is beneficial to write down your thoughts on paper. Make it a merry game for a kid, like writing a letter to your future self or creating a script for a Hollywood movie. Later on, this will help a child in scientific research in school or university.
Debating club
No matter how close you are with your child, he or she needs other kids of the same age around. They can be found in a debating club — a place where children learn the art of discussion. Some schools offer these facilities but if there is no such place in your school, try to find it someplace in your area. Debating club is an excellent opportunity to raise a child’s self-confidence and improve critical thinking skills via discussions on relevant topics.
To conclude, critical thinking is a crucial part of a strong personality. Like most of the skills, it’s better to teach critical thinking to children — not only because they take in new information faster than grown-ups, but also because it is hard to change an adult person’s mindset. Critical thinking will make your child successful in many ways: from school homework to comfort living in modern post-industrial society.


How to Teach Critical Thinking Skills to Kids
Easy strategies to incorporate into everyday life.

By Sanya Pelini, Ph.D.
Published on: august 23, 2023.

In the late 1800s, Thomas Edison began working on a new kind of storage battery that he hoped would revolutionize the electrical industry. He wanted to create batteries that were lighter, more durable and much more powerful. He conducted thousands of tests and poured almost $1 million of his own money into the project.
In 1903, the battery was finished and made available to the public, which soon discovered that the promises made about the new apparatus fell far short of expectations. Battery leakages were reported by many consumers, making the devices practically useless, and those batteries that did not leak did not last as long as consumers had been led to believe.
This was a major setback for Edison, but he refused to believe that all hope was lost. Instead, he saw the predicament as an opportunity to practice critical thinking. He shut down the factory and over the next three years, he experimented with different materials to try to find a solution to the problem. He failed over and over again, but each failure led him to try a different approach to the problem. Through trial and error, he eventually discovered that adding a small amount of alkaline to the acid prevented leaks.
Thanks to his critical thinking skills and his perseverance, Edison eventually succeeded in developing a battery that was far better than the original one. These skills laid the groundwork for many other important inventions.
Edison’s ability to approach problems with an open mind — and his willingness to experiment and try new things — explains why he is remembered as one of the greatest inventors of all time.
As a parent or educator, you may have asked yourself whether it is possible to teach critical thinking skills to children. In other words, are these skills inborn or can they be developed?
What science says about critical thinking skills
Several researchers refer to the ability to acquire critical thinking skills as the “development of a mind of one’s own.”
Critical thinking is about being able to look at an issue or problem from different angles. Being a critical thinker requires kids to keep an open mind, to be able and willing to see things from different perspectives, and to trust in their ability to find a solution to their challenges.
Critical thinkers are therefore curious experimenters who are not afraid to fail or who see failure as an opportunity to learn new things.
Does critical thinking come more naturally to some kids than to others? Possibly so. But science indicates that kids primarily learn to become critical thinkers when they practice these skills.
Many of the researchers who have focused on the development of critical thinking skills suggest that children develop thinking skills more easily when an intentional attempt is made to promote those skills.
Some studies have found that children taught using a critical thinking approach become better at solving problems. Others have determined that teaching thinking skills may increase the ability to reason, use language, solve problems, be inventive and make decisions.
The good news is that it is possible to teach critical thinking skills at home. Here are some easy tips to get started.
How to incorporate critical thinking skills into your child’s everyday life
Ask questions..
The more you make it a habit to ask your child questions, the more you help them practice their critical thinking skills. That said, it is important to avoid questions that prompt straightforward “yes” or “no” responses. So, instead of asking, “Did you have a good day?” try something along the lines of “What was the most interesting thing you did today?”
Making it a habit to ask for your child’s opinion — “What do you think?” or “How are you going to do it?” — is an easy way to make them reflect on possible responses and solutions.
Ask your child to put things into their own words.
One of the easiest ways to teach critical thinking skills is to ask your child to use their own words when expressing themselves. For example, after watching a movie together, inquire: “What did you understand?” “What did you learn from the story?” “What did you think of his/her reaction?” “What would you do if you were in their shoes?”
Prioritize play with open-ended toys.
Open-ended toys are great playthings because they encourage creativity. Your child can engage with them in many different ways, which means that they are encouraged to come up with new ways to interact with the same toys. Toys such as building blocks or nesting puzzles (for younger kids) and KAPLA or KEVA planks (for older kids) are good examples of toys that can help increase your child’s creativity and therefore their critical thinking skills.
Provide an environment that favors the development of critical thinking skills.
By allowing your child to participate in the decision-making process, and by accepting their solutions even when your view differs, you help them to practice their critical thinking skills. Do not rush in to help your child find a solution: Let them think of ways to solve problems on their own.
Ask your child to come up with alternative solutions or explanations.
Ask: “How else can you do it?” “What will you do next time?” “How would you do it?” “What would you do differently?”
Play games that require critical thinking skills:
Playing Scrabble, chess or sudoku is an easy way to help your child strengthen their critical thinking skills.
Remember that modeling critical thinking is one of the most effective ways to teach those skills to your child. This could be in the form of asking questions, considering alternative solutions, showing your openness to different views and opinions, or even working together (and considering their proposals) to solve a problem.
STAY CONNECTED! Get the best of ParentMap delivered right to your inbox.
Related Topics
- Print Stories
Share this resource with your friends!
About the author.

Sanya Pelini is a parent and researcher in education. She is passionate about child development issues and holds a Ph.D. in educational research. She transforms educational research into practical tools and resources on her blog Raising Independent Kids .

The Surprising Diagnosis Caused by Kids' Screen Time

Want to Heal Your Child? Start by Healing Yourself

5 Birthday Party Etiquette Tips All Parents Should Know
You might also like.

Health + Nutrition
A doctor’s tips for surviving allergies in spring 2024.

Measles Outbreaks on the Rise: How to Protect Your Family and Community

Mental Health
Suspect adhd how and when to screen your child.

Behavior + Discipline
Study reveals the best way to deal with challenging behavior.

MSU Extension Child & Family Development
The importance of critical thinking for young children.
Kylie Rymanowicz, Michigan State University Extension - May 03, 2016
Critical thinking is essential life skill. Learn why it is so important and how you can help children learn and practice these skills.

We use critical thinking skills every day. They help us to make good decisions, understand the consequences of our actions and solve problems. These incredibly important skills are used in everything from putting together puzzles to mapping out the best route to work. It’s the process of using focus and self-control to solve problems and set and follow through on goals. It utilizes other important life skills like making connections , perspective taking and communicating . Basically, critical thinking helps us make good, sound decisions.
Critical thinking
In her book, “Mind in the Making: The seven essential life skills every child needs,” author Ellen Galinsky explains the importance of teaching children critical thinking skills. A child’s natural curiosity helps lay the foundation for critical thinking. Critical thinking requires us to take in information, analyze it and make judgements about it, and that type of active engagement requires imagination and inquisitiveness. As children take in new information, they fill up a library of sorts within their brain. They have to think about how the new information fits in with what they already know, or if it changes any information we already hold to be true.
Supporting the development of critical thinking
Michigan State University Extension has some tips on helping your child learn and practice critical thinking.
- Encourage pursuits of curiosity . The dreaded “why” phase. Help them form and test theories, experiment and try to understand how the world works. Encourage children to explore, ask questions, test their theories, think critically about results and think about changes they could make or things they could do differently.
- Learn from others. Help children think more deeply about things by instilling a love for learning and a desire to understand how things work. Seek out the answers to all of your children’s “why” questions using books, the internet, friends, family or other experts.
- Help children evaluate information. We are often given lots of information at a time, and it is important we evaluate that information to determine if it is true, important and whether or not we should believe it. Help children learn these skills by teaching them to evaluate new information. Have them think about where or who the information is coming from, how it relates to what they already know and why it is or is not important.
- Promote children’s interests. When children are deeply vested in a topic or pursuit, they are more engaged and willing to experiment. The process of expanding their knowledge brings about a lot of opportunities for critical thinking, so to encourage this action helps your child invest in their interests. Whether it is learning about trucks and vehicles or a keen interest in insects, help your child follow their passion.
- Teach problem-solving skills. When dealing with problems or conflicts, it is necessary to use critical thinking skills to understand the problem and come up with possible solutions, so teach them the steps of problem-solving and they will use critical thinking in the process of finding solutions to problems.
For more articles on child development, academic success, parenting and life skill development, please visit the MSU Extension website.
This article was published by Michigan State University Extension . For more information, visit https://extension.msu.edu . To have a digest of information delivered straight to your email inbox, visit https://extension.msu.edu/newsletters . To contact an expert in your area, visit https://extension.msu.edu/experts , or call 888-MSUE4MI (888-678-3464).
Did you find this article useful?
Early childhood development resources for early childhood professionals.
new - method size: 3 - Random key: 0, method: tagSpecific - key: 0
You Might Also Be Interested In

MI Parenting Resource

Bees, Building Early Emotional Skills, for Early Childhood Professionals

Self-paced Positive Discipline Online Course

AC3 Podcast episode 3
Published on June 30, 2021
ac3-pod-cast-episode-5-families-against-narcotics
Published on December 17, 2021
- approaches to learning
- child & family development
- cognition and general knowledge
- early childhood development
- life skills
- msu extension
- rest time refreshers
- approaches to learning,
- child & family development,
- cognition and general knowledge,
- early childhood development,
- life skills,
- msu extension,
How To Teach Your Kids Critical-Thinking Skills

Your kids are learning math and reading skills, but are they learning critical-thinking skills? In a recent study commissioned by MindEdge Learning, only 36 percent of millennials surveyed said they were “well-trained” in these skills. As many as 37 percent of the 1,000 young people surveyed admitted they were sharing information on their social media networks that was likely inaccurate news. And more than half of them used social media for their main source of news.
Frank Connolly, senior editor at MindEdge, notes, “By 2020, the World Economic Forum anticipates critical thinking will be the second most important skill to exhibit, second only to complex problem-solving.”
Kids need to learn critical-thinking skills to become successful adults. But how can parents and educators ensure kids learn to be critical thinkers? Here are four simple ways to communicate better with your child, while teaching them how to think for themselves, when it comes to dissecting and sharing news and information.
1. Teach Your Child to Question What They Read or Hear
Brainstorming is always a great skill that helps teach creativity. And parents can use many types of news to start a brainstorming session—a new bit of juicy gossip, something that sounds scary, or something exciting are all an open door for exploration and discussion. Teach your children to ask questions and even find out who is spreading such information. Is it a reliable news source? A tabloid? A fellow classmate who has only heard it from someone else? The right questions can lead to discussions about the state of the world or other relevant topics.
2. Make Thinking a Family Affair
In today’s world, where so many kids are glued to their digital devices , how can you start discussions that foster critical thinking? Use the times that you are together as a family—around the dinner table, during long car rides , or while on a weekend picnic—to bring up topics that encourage questions and problem-solving techniques. “What do you think of such-and-such?” Or, “What is your opinion on ____?” Leave the floor open for discussion, and always be open-minded yourself during these conversations.
3. Go Deeper
Encourage your kids to read books on similar topics, watch movies related to the topic , or visit the local library together to study and keep the conversation going. Don’t be afraid to let them explore a topic of interest. If they are showing some critical-thinking skills in the realm of politics, for example, you can study world history or watch relevant documentaries on the subject.
4. Teach Them to Be Socially Responsible
Talk about their social network “news” and why it may or may not be a good idea to share certain stories. During your discussions, bring up the point about their social networks being a public platform, which can either be used for good or have negative repercussions and even be a place for “ fake news .” Teach them to pause and check in with themselves before automatically sharing something on the internet.
Remember, critical thinking is more than just being rational. It’s about the ability to think independently. When your children are able to draw their own conclusions and make up their own minds on matters, without being “swayed” by peers or even other adults, then they will be true critical thinkers!
Related Articles

Inspiring an Appreciation for Poetry in Kids
April 9 2024

A Parent’s Guide to Tough Conversations
April 2 2024

The Importance of Reading to Children and Its Enhancements to Their Development
March 26 2024

5 Steps to Master College-Level Reading
March 19 2024

10 Timeless Stories to Inspire Your Reader: Elementary, Middle, and High Schoolers
March 15 2024

From Books to Tech: Why Libraries Are Still Important in the Digital Age
March 13 2024

The Evolution of Learning: How Education is Transforming for Future Generations
March 11 2024

The Ultimate Guide to Reading Month: 4 Top Reading Activities for Kids
March 1 2024

Make Learning Fun: The 10 Best Educational YouTube Channels for Kids
February 27 2024

The Value of Soft Skills for Students in the Age of AI
February 20 2024

Why Arts Education is Important in School
February 14 2024

30 Questions to Ask at Your Next Parent-Teacher Conference
February 6 2024

Smart Classrooms, Smart Kids: How AI is Changing Education
January 31 2024

Four Life Skills to Teach Teenagers for Strong Resumes
January 25 2024

Exploring the Social Side of Online School: Fun Activities and Social Opportunities Await
January 9 2024

Six Ways Online Schools Can Support Military Families

Is Your Child Ready for Advanced Learning? Discover Your Options.
January 8 2024

Online School Reviews: What People Are Saying About Online School
January 5 2024

Your Ultimate Guide to Holiday Fun and Activities
December 18 2023

Free Printable Holiday Coloring Pages to Inspire Your Child’s Inner Artist
December 12 2023

Five Reasons to Switch Schools Midyear
December 5 2023

A Parent’s Guide to Switching Schools Midyear
November 29 2023

Building Strong Study Habits: Back-to-School Edition
November 17 2023

Turn Up the Music: The Benefits of Music in Classrooms
November 7 2023

A Parent’s Guide to Robotics for Kids
November 6 2023

Six Ways Online Learning Transforms the Academic Journey
October 31 2023

How to Get Ahead of Cyberbullying
October 30 2023


Bullying’s Effect on Students and How to Help
October 25 2023

Can You Spot the Warning Signs of Bullying?
October 16 2023

Could the Online Classroom Be the Solution to Bullying?
October 11 2023

Bullying Prevention Starts With Parents
October 9 2023

How to Teach Kids Manners
April 7 2016

Is Year-Round School Better for Kids?
July 12 2016

Video: What Kids Say Makes Their School Awesome!
June 10 2015
Join our community
Sign up to participate in America’s premier community focused on helping students reach their full potential.
Welcome! Join Learning Liftoff to participate in America’s premier community focused on helping students reach their full potential.

Parents' Guide
Developing critical thinking in teens, introduction.
For children aged 13 and older, the development of critical thinking continues to build from the skills acquired and the challenges faced in the first two developmental stages. These skills must continue to be reinforced as the child matures.

The four basic aspects of critical thinking we examined in the first part of this guide, concerning children aged five to nine , remain relevant, therefore. To review, these were:
Critical thinking based on arguing a point.
Developing self-esteem, the foundation of critical thinking.
Emotional management, a prerequisite for critical thinking.
The social norm of critical thinking.
We also saw new elements come into play between ages 10 and 12 in the acquisition of critical thinking and reasoning skills. These are likewise still important in considering the development of critical thinking in young teenagers:
The development of reasoning skills beyond argument.
Puberty and its implications in terms of interests, self-esteem, and emotional management.
The digital world, via gaming, the internet, and a burgeoning social or pseudo-social life (on social media targeted at young people).
To these concerns are added new set of factors come into play in later adolescence as the cognitive system matures and social life changes. These factors will hugely increase the critical potential of 13 to 15 year olds, while at the same time limiting it in certain respects. These factors are:
The development of formal logic, allowing for more and more complex and abstract lines of reasoning.
New social pressures, including heightened peer pressure and anxieties over social integration. The influences of groups and gangs, which tend to critique the established social order, can also lead to a conformity in attitudes and ways of thinking within the group.
Critical analysis of sources of information and the strengthening of interpretive skills.
Critical thinking in group projects, and as an element of citizenship and social progress .
Beginning at age 13, adolescents can begin to acquire and apply formal logical rules and processes. The rudimentary logic learned at previous stages can now be refined by teaching adolescents some more advanced logical notation and vocabulary, which are outlined in the coming sections. It is important to keep in mind, again, that critical thinking extends far beyond logic, offering tools to apply more broadly to arguments and information encountered in the everyday world.
In the teenage years, social pressures accelerate, and with the internet and social media, these pressures move faster and with more force than ever. As outlined in section two below, critical thinking can prove a valuable resource for teenagers to help cope with these pressures and resist the groupthink that easily emerges in social cliques both online and offline. Critical thinking can also play a role in helping young adults choose and pursue emerging goals, by constructing long-term plans and methods. Finally, critical thinking is an indispensable tool in helping young people understand and analyze the wealth of information sources now bombarding them.
1. Formal Logic
At the age of 13 and older, children can begin to learn the rules of formal logic and further hone their critical thinking skills. whether or not their children are learning these skills in school, parents can help by discussing how to analyze concepts and arguments..
From ages 11 to 12, there gradually develops what Piaget called the formal operational stage . New capabilities at this stage, like deductive (if-then) reasoning and establishing abstract relationships, are generally mastered around ages 15 to 16.
As we saw, by the end of this stage, teenagers, like adults, can use both formal and abstract logic—but only if they have learned the language of logic (“if,” “then,” “therefore,” etc.) and have repeatedly put it to use. Under these circumstances, children learn to extrapolate and make generalizations based on real-life situations.

Thus, from ages 10 to 12, by stimulating children intellectually—urging them to reflect and establish lines of reasoning—they gradually become able to move beyond a situational logic based on action and observation onto a logic based on rules of deduction independent of the situation at hand.
This ability to manipulate abstract symbols consolidates by around age 15, provided that one has been versed in formal logic.
A and B are two logical propositions, such that A is the opposite of B. From this, we may formally deduce (without reference to anything concrete) that the proposition P, which states “A or B,” is always true. There are no alternatives, so P fulfills all possibilities. We may also deduce that the proposition P 1 , “A and B,” is always false. Here, two contradictory propositions cannot both be true. If one is true, the other is false.
These formal operations require both a mature central nervous system and a mature cognitive system. But, since such examples of formal reasoning are detached from everyday life, they require deliberate practice. Even an adult who is out of practice can struggle with formal reasoning.
After working through several examples, parents can help children extract the logical rules behind those examples.

We can present these two rules of logic using more concrete examples, which makes formal reasoning at once more accessible and less intimidating. In concrete form, however, the reasoning will be less easily applied to new situations.
If proposition A is: “this salmon is farmed,” proposition B (the opposite of A) will be: “this salmon is not farmed.” B could also be expressed as: “this salmon is wild.” It is easy in this concrete context to see that P, “A or B,” is always true. A salmon must either be farmed or wild. It is also easy to conceive that P 1 , “A and B,” is always false because a salmon cannot be both farmed and wild.
Moving away from situational lines of reasoning allows teens to extrapolate and apply logic to the ever more complex challenges and life events they might encounter as they mature into their young adult years. Without formal logic, young teens and young adults won’t be able to define their formal reasoning abilities to extend past situational deductions and personal life experiences or form larger connections with their surroundings and the human experiences that occur around them everyday.
Once they learn to abstract from concrete examples and express these rules in formal logic, children can form and manipulate logical notation and apply it to a multitude of situations.

How can we help children from age 13 and older improve their formal logical deduction skills?
We must start by working on these two rules through concrete examples like that of the salmon. After working through several examples, parents can help children extract the logical rules behind those examples. This is the inductive phase: from concrete examples, we extract the common features and express them in a formal rule.
Next, it will be necessary to prove this rule solely by logical deduction. If we do not do this, we cannot be certain that the rule is valid in every context. Extracting the common features only results in rules which, at this stage, remain merely hypothetical. Only reasoning allows for the generalization of a rule.
Once students have mastered a collection of formal rules, they can be trained to recognize, within a problem or a given context, what rule is applicable. That is, they can take an initial claim (a hypothesis), apply a rule of deduction to it, and arrive at a conclusion.
2. Faulty Reasoning
One important way teenagers can improve their logic and reasoning skills is by using formal definitions. these are necessary for more precise and universal reasoning and can help children identify faulty reasoning., integrating these topic into family discussions can be enormously productive., extension vs. intension.
One idea in formal logic that can be valuable to learn at this age has to do with how concepts are defined. For very young children, categories or concepts are defined according to how they are encountered in everyday life. For example, the general concept of color is determined by all the examples of colors children have come across or imagined. The concept covers all these different experiences. This is called the concept’s “ extension .”
But it is important that children from the age of around 13 start to learn to define concepts not merely according to their extension, but in a formal, scientific manner.
For example, instead of using a definition drawn from experience, students can explain that a color is a perception that our eye, linked to the brain, produces when an electromagnetic wave of a given frequency hits our retina. This definition according to the formal, internal qualities of the concept is called the concept’s “intension.”
Definition by intension is more complicated, but it allows for the use of the concept in formal reasoning. Therefore, definition by intension gears the child’s mind towards higher-level abstract reasoning.
For example, if we have to determine whether or not a given entity is a color or not, the intensional definition will offer us formal criteria for making a judgment.
Here’s another example. The prime numbers can be defined formally by intension: they are “the numbers that are only divisible by themselves and one.” If we were to learn only the extension of the term “prime number,” on the other hand, we would only have a list of the numbers that we know are prime.
It is clear that if we only have this definition by extension and we encounter a new, very large number — higher than the largest number on the list we’ve learned—we will have no criteria for knowing whether it’s prime. But if we have the formal definition by intension, we will, with the help of a calculator, be able to determine whether it is only divisible by one and itself and, therefore, prime.
We can’t productively critique the arguments of others if we don’t share their definitions of concepts.
When we are young, we learn about the world through definitions by extension during the course of our interactions with objects and other people. Our brain defines concepts by extension and then extracts the common features to produce a working definition.
But these definitions are subjective since they depend on our history of encounters with relevant examples. Thus, all of the concepts we have created do not match other people’s concepts precisely, despite being identically named. They depend on the particular experiences we have had.

Yet, towards the ages of 13 to 15, with mathematical and formal logic, it becomes possible to define concepts by intension and, therefore, to share objective meaning with others. Teenagers can enter a world of shared and precise meanings. This is a prerequisite for the application of precise and formal critical thinking. We can’t productively critique the arguments of others if we don’t share their definitions of concepts.
The formal approach for children aged 13 and up should, then be twofold: formalize the definition of the concepts used and formalize the logical deduction itself. This comes with practice and enhances both children’s capacity to communicate and their critical faculties.
The Concepts of Intension and Extension
Recognizing faulty reasoning.
As has been discussed in previous sections, developing critical reasoning requires more than simply knowing how to reason formally and contextually. It is also necessary to learn how to recognize flaws in the reasoning of other people who may wish to convince us of their way of thinking, either for narcissistic reasons or to lead us to act to their own advantage.
Such flaws can occur on several levels:
Erroneous rules of logic, leading to false reasoning based on reliable hypotheses.
False hypotheses (starting points for reasoning): even if the reasoning is valid, the conclusion may be false. Certain politicians use this strategy very frequently.
Using a formal rule in a situation to which it does not apply. This often occurs in over-simplified mathematical modeling of complex material, for example when an essay in the humanities is interpreted using only the tools of formal logic.
These three types of flaws can be worked into family discussions, with the goal of training children to counter weak or manipulative lines of argument. School should not be too heavily relied upon to provide this kind of practice for your children. Already between the ages of 13 and 15, they are able to construct brilliant lines of reasoning, which will prevent them from being tricked by manipulative or intellectually limited people.
Flawed Reasoning
3. individuation, teenagers have a natural impulse to try to separate themselves from their parents and their backgrounds. a good critical thinking foundation can help ease the transition toward individuality and adulthood. better reasoning can help teenagers cope with their emerging independence and avoid an unthinking rejection of their background., what is individuation.
Individuating and the stages of individuation are concepts developed by renowned analytical psychologist Carl Jung . Jung founded analytic psychology and the concepts of extraverted and introverted personalities, archetypes, and the collective unconscious were also developed by Jung along with the theory of individuation.
In adolescence, the individuation process heralds the initial stages that a child takes toward becoming a unique individual, something more than just your parents’ offspring, is a psychological necessity.
Part of differentiating yourself from the world around you is developing a self-image. It is the only way to avoid fading completely into your surroundings—and ending up in utter conformity, or worse.

Individuation adolescence
Individuation is indispensable to society. In order to sustain itself, society needs diversity. Cultures lacking the social norm of individuation are more fragile. They produce citizens who have identical self-images and behavioral patterns, whereas adapting to change requires diversity, creativity, evolution, and, therefore, critical thinking.
Only very rarely (or not at all) have individuals in these cultures of weak individuation experienced the feelings of crisis and malaise we associate with adolescence. The transition from childhood to adulthood unfolds instead according to so-called “rites of passage.”
Our civilization has undergone a long and profound evolution through philosophy, science, psychoanalysis, and politics, leading us to a social norm that rejects the idea that the individual in the family, the social group, or the nation, is like a mere cell in an organ. Indeed, everyone has the right and even the “duty” to be reborn by deviating from their origins.
This is an immense challenge because this act of individuation, this self-creation, arises at a moment when children are not yet able to achieve this “rebirth” autonomously, as they enter an unknown world without even knowing what it will be like. We call this period “adolescence” or even “kidulthood” when it lasts a long time—a growing phenomenon.
Experiencing society predominantly through school or family simultaneously generates pressure to conform and to individualize. It comes as no surprise that this causes some problems.
The desire to be free and independent generates psychological conflict.
What is the process of individuation.
Children have not fully matured intellectually or cognitively when they are confronted with this contradiction. They are, therefore, unable to conceptualize it. This is why, in their behavior and attitudes, children can sometimes bear a closer resemblance to skittish animals than calm self-creators responsible for their own gradual reinvention.
Although unaware of it, children embark upon adolescence through “second-degree” conformity through culture, since adolescence is a societal construct rather than a psycho-behavioral component of puberty.
Paradoxically, children aged 13 to 15 or older may not experience teenage angst at all, thanks to their critical faculties. In fact, if they feel that their life is fulfilling and stable, they will be able to avoid getting sucked into an alternative world by other children their age. Their youth may pass without them having experienced teen crisis. Instead, they construct their identity reflectively and without drama.
This, of course, is not typical. The desire to be free and independent generates psychological conflict. The fear and the anxiety associated with this moment of struggle incites rationalizations, thoughts which retrospectively come to explain dissatisfaction, malaise, and rebellion. Every situation that is not comfortable or does not come off successfully, we tend to attribute to our external environment and other people. Consequently, if things are not going well for us—if we are not happy—we tend to blame it on an unjust world.
Parents of teenagers are very familiar with the result: sweeping criticism of everything teens encounter. To the teenager, everyone sucks: parents, teachers, politicians, journalists, and so on. This reaction can generate conflict, but, as is explained in the next section, it also presents a good opportunity for deepening critical faculties.

4. Teenage Negativity
The need to become an individual can often manifest itself in negative and unyielding attitudes. though teenagers’ criticisms and complaints can be unsophisticated, parents should still engage with them. critical reasoning can help make the process of becoming an individual less painful and more productive..
It can be difficult to know how to react to teenagers’ negativity. On the one hand, their attitudes may seem too extreme and unsophisticated to take seriously. On the other, they can be exasperating and even hurtful when directed against the parents themselves. But parents should do their best to avoid being either dismissive or defensive.

The teenager’s emotional negativity is an extreme version of something we are all prone to indulge in from time to time, no matter how highly we may prize our calmness and understanding. Parents should remind themselves that this negativity is part of a bid to become a fully-fledged autonomous individual with an opinion deserving of recognition and respect.
Parents can help them reach this goal by taking their teens’ complaints seriously. This doesn’t mean telling them they’re right when they aren’t, but treating them as conversation partners worthy of engagement. Parents can ask their children to substantiate and defend their claims using argument and evidence; challenge their children when they fail to argue well; and compliment them when make good points.
This can be a good opportunity for parents themselves to refresh their ability to put aside emotions and handle a topic fairly and dispassionately. By modeling these kinds of intellectual virtues parents make it more likely that their children will adopt them.
Arguing with teenagers can be fun, especially if they begin to experience the kind of satisfaction that comes out of reasoned debate over complicated issues.
Of course these arguments will not always go smoothly, but over time parents can help bring their children into the critical community. Arguing with teenagers can be fun, especially if they begin to experience the kind of satisfaction that comes out of reasoned debate over complicated issues.
The quest for individuality also manifests itself in a need to create or to win over a new group, a group that can become one’s ideal family. The phenomenon of teenage cliques or gangs—and even radical organizations—arises from this fact. Not being understood or accepted is stifling. We need an escape valve, and so, as social animals, we create or join a group that meets our needs.
Individuation and Belonging
5. sense of belonging in a community, although they may relentlessly criticize society, in so doing teenagers are really showing that they belong to it. parents should help teenagers learn to articulate their dissatisfaction and develop a sense of belonging. . critical thinking can help them reconcile their desire for independence with the value of tradition and belonging to society., what it means to belong.
Belonging means acceptance into a larger whole, society, community, or organization. It’s a fairly common experience that occurs at many levels of life from the familial unit, to work, to school, to the society as a whole.
From the age of 12 to 13, in order for children to be able to articulate their disagreements with the status quo, they must develop their critical reasoning skills. As adults, we must, again, engage with these critiques if they are well-founded. This shows children that rejecting their endeavors is not the automatic response. This makes them feel valued and capable of exercising autonomous thought which can, moreover, influence adults.
In this way, critical thinking also — perhaps unexpectedly — makes it easier for children to accept at least a part of the cultural heritage that is offered to or imposed on them by language, upbringing, and custom.
Allowing a teenager to convince others through argument and logical inference makes them feel more able to become an individual without breaking away from the group—a rebellion-free evolution. If they are allowed to articulate their dissent, they may even find school or home life less stifling than social life in a peer group where they are constantly pressured to conform. Encouraging this kind of critical thinking also protects them from negative influences (cults, crime, etc.), since their critical toolkit allows them to stay lucid when faced with wild, dangerous speech and behavior (alcohol, drugs, etc.).

From as early an age as possible, learning how to argue and reason critically using one’s capacities for inference allows for a balance in adolescence between individualization and an acceptance of heritage.
Indeed, the need to distinguish oneself and to proclaim one’s individuality is always met by membership in a group — now often with the help of social media. This need is only met if these groups are not as prescriptive and stifling as the society from which the child is trying to escape and if they do not cause harm.
Part of critical reasoning is the development of the capacity to question environmental, familial, and social norms and prescriptions. But this requires competence in a universal language made up of inferential logic and the art of arguing, which comes from the critiqued society. Critical reasoning itself thus serves as lasting proof that one remains a part of that society. In the very act of distinguishing themselves from the pack, teenagers show they belong.
Critical reasoning anchors children in reality, allowing them to achieve individuality in their own unique way. Parents can help by supporting their children’s projects and encouraging them to engage with the world around them.
Building a sense of belonging.
Cultural heritage—including language, law, food, art, manners and customs, traditions, and scientific knowledge—represents an incredible resource that is at once imposed and offered. Teaching children critical thinking and reasoning means that they will not simply dismiss this priceless treasure in its entirety even though they will partially free themselves from it. Critical reasoning makes the process of individualization less violent and painful for both children and parents, thanks to the balance between the assimilation of culture and a healthy questioning of it.
In other words, critical reasoning—expressed through argumentative and logical know-how and rooted in self-esteem and love—anchors children in reality, allowing them to achieve individuality in their own unique way. Parents can help by supporting their children’s projects and encouraging them to engage with the world around them.
Cognitive faculties participate, in this way, in the psychological make-up of children. Critical reasoning has a twofold power: it is both integrator and liberator. It alerts us to the ways our culture forms us and helps us partly to overcome it. It is a fundamental pillar of our citizenship, on a national and global scale.
Benefits of sense of belonging
Critical reasoning serves as proof to children that they are listened to and that they are the primary drivers of their own destinies. Subsequently, they are predisposed to put their faith in the future and in others. They become psychologically and intellectually equipped to imagine a future with other people, in which they undertake communal projects and attain important goals.
6. Analyzing Sources
Teenagers need support to cope with and analyze disinformation and deception online. they should work on developing critical reading and browsing habits and learn to identify different kinds of deceptive reasoning. families can practice analyzing false or misleading information together. .
By the age of 13, young people likely already have significant experience navigating the internet. They have all made extensive use of a variety of websites in order to find answers to their questions or to help with papers and schoolwork.
The internet has democratized the transmission of information, allowing anyone and everyone to put forward their ideas, opinions, or hypotheses on multiple online platforms. People usually post things online in an affirmative style which presents any given statement, no matter how dubious or speculative, as a well-known fact.

People’s personal blogs, companies’ promotional lifestyle websites, and free encyclopedias all feature articles on complex subjects, almost always with content that has not been vetted by any experts, whose critical thinking skills and reasoning would be invaluable.
It seems that everyone—or almost everyone—has the tendency to grant at least some level of truth to everything they find online, especially if the site looks credible and its language is elegant. The same gullibility often applies to what we see on television or read in newspapers.
It is important to make young people aware of the phenomenon of “fake news” and to give them concrete proof of the great deal of false—even outrageous—information online.
For example, it is possible to find videos claiming to prove that NASA’s moon landing was staged . Debunking these types of conspiracy theories, with the help of parents and educators, can be a useful exercise for students. As can discussing what makes certain sources reliable or unreliable.

For example, students could be shown a factual documentary on the moon landing and a video claiming the moon landing was faked and then asked to work out which one is false
In order to do this, they must use their logical knowledge to see if any false presumptions have been made. They must also ask themselves who made and commented in the videos. What is this person’s reputation? What are their professional qualifications? Has the document’s credibility been discussed in any forums?
Debunking these types of conspiracy theories, with the help of parents and educators, can be a useful exercise for students.
In analyzing these and similar sources, we will arrive at one of five possible situations:
An author has good intentions but his or her reasoning is flawed. The author draws unsubstantiated conclusions from trustworthy information. For example, we have proof that certain particles came out of thin air and did not evolve from anything. Some wrongly conclude that this proves the existence of God, since only God could create something from nothing. This information is true, but the reasoning is false, and the conclusion therefore does not follow. The solution involves the relationship between energy and mass in the equation E = mc 2 . In empty space, even the smallest amount of heat can cause spontaneous conversions of pure energy into matter.
An author has good intentions and reasons well, but uses false information. Here, the author can come to false conclusions, even if he or she reasons impeccably. For example, one could conclude that the acceleration of an object, induced by gravitational force, is dependent on its mass because if one drops a rock and a feather from a balcony, the rock will hit the ground before the feather. Here, the problem lies with the initial information, which is erroneous because it does not take the role of air resistance into account. The observation on which the argument is based is thus incorrect in this case, as is the conclusion. In reality, in a vacuum, the feather and the rock would reach the ground at exactly the same time.
It could be that the hypotheses and baseline observations, as well as the arguments drawn from it, are all incorrect. A false conclusion is likely to result.
Authors could be giving out false information intentionally with the aim of selling a product; harming another individual, group, or country; spreading a rumor to make themselves feel important; or sadistically causing mental anguish to others for their own enjoyment.
An author intends to get a point across by using an argument which appears to comply with logical reasoning but which actually contains one or more inferential leaps , deliberately introduced in order to prove that the conclusion is objective because it stems from rigorous thinking. Sophistry and paralogisms arise from this sort of trickery.
It is very important to expose adolescents to these five possible kinds of lies or deception, as well as to reflect on how to identify them by analyzing authors’ arguments and questioning the hypotheses or observations at the root of their arguments and their likely intentions, given the message’s context. For example, in an advertising context, we can understand that car manufacturers might benefit from lying about the amount of pollution produced by the vehicle they sell.
Nasreddin’s Sophisms
Paralogisms, 7. the critical mind, genuine critical thinking requires background knowledge. parents should help their children acquire broad and deep knowledge so they have the confidence and ability to call sources into question and avoid an unreflective acceptance of authority..
General knowledge is also a powerful tool for staying critical and skeptical in the face of this influx of information. It allows one to reconcile information and to check whether new data seems consistent with what they already know.
For example, if one were trying to evaluate arguments about how to address the recession caused by the 2008 global financial crisis, it would be useful to know the history of efforts to boost economic growth through government spending, especially those undertaken during the Great Depression of the 1930s . Citizens versed in this history will be far better equipped to evaluate and criticize the proposals put forward by politicians and economists in their own time.

Having general knowledge also means that one does not hold even the most reliable sources sacred, knowing that careful thought often undermines received wisdom.
For example, Einstein’s theory of general relativity called Newton’s law of universal gravitation into question, even though Newton’s law had apparently been confirmed by a wealth of experiments and observations. Einstein’s general knowledge and his independent way of thinking allowed him to postulate that gravity was not simply a force but a warping of space-time in the vicinity of stars. Since then, independent observational astronomical predictions have always supported the theory of general relativity.
Treating certain sources as sacred can be as dangerous as uncritically accepting everything that comes from the internet or elsewhere. The same phenomenon is involved when religious texts are interpreted as legitimizing violence or intolerance.
The interpretation—as well as the cultural, social, geographical, and historical contextualization—of a piece of information is indispensable to the formation of a critical mind. But critical thinking is difficult. It takes training, as well as background knowledge, to determine the reliability of a source, and this determination can never be definitive or certain.
These examples show that if we are responsible for educating adolescents on the verification of sources, we must be careful not to give permanent, definitive credit to any piece of information or knowledge, even if it comes from a seemingly very reliable source. Critical thinking, provided that it does not lead to permanent doubt or paranoia, is truly a way of life, facilitating progress and freedom.
Fact-Checking
Verifying sources, 8. critical thinking and progress, critical thinking can help children not only learn to analyze the world around them, but act to try to change it. good critical thinking can foster productive interests, deeper engagement with social problems, and the attitudes of good citizenship. in this way critical thinking is vital to social progress..
A goal (or a project or “dream”) is the meeting of, on the one hand, an idea born out of a need or desire and, on the other, a method—an “algorithm” for bringing the idea into reality. But these two dimensions to every goal are, in fact, two sides of the same coin, two facets of creativity.

As we have seen, the spark for critical thinking comes from self-esteem and unconditional love. This energy is indispensable to living with both a sense of joy and, at the same time, a continual dissatisfaction with the status quo. Taking joy in life is necessary to prevent this dissatisfaction from degenerating into depression or other pathologies. This joy provides the energy needed to turn dissatisfaction into ideas and dreams of change.
But in order for an idea to turn into a project capable of changing the world, both a methodology and logical, communicative rigor are required. These allow a large number of people to understand a problem in the same terms and gear themselves toward the same objectives. Without these tools, efforts at problem-solving tend to devolve into emotionalism or factionalism.
Methodological rigor is rooted in critical reasoning.
An education in critical thinking and reasoning is the best way to ensure a child can access goal-oriented thinking. A goal, much like the kind of formal logic we can exercise from the ages of 13 to 15, transforms the possible into the tangible.

Goal-oriented thinking leads children in their adolescence to join or set up active groups or associations. Activity in such groups requires skills in both logic and communication, and it tends to support their further development. It pushes those undertaking such projects to strike a balance between asserting themselves and listening to others—between critiquing and taking what others say on board.
In this sens e, critical thinking and the drive it inspires to undertake projects can be a kind of citizenship training. To rigorously and plainly critique a complex system (whether it be political, scientific, or philosophical, theological) is always to act as a citizen. It is beneficial to all.
Critical thinking not only enables students to reach their intellectual potential; it can also help them find purpose and, through purpose, happiness.
In this way critical thinking not only enables students to reach their intellectual potential; it can also help them find purpose and, through purpose, happiness. And, ultimately, it can help foster progress and social cohesion through cooperative action.
These links between critical thinking, undertaking projects, and citizenship should further encourage parents and educators to guide children toward this spirit of joyful dissatisfaction, as well as toward logical reasoning and the art of arguing.
If this mindset is acquired, teenagers won’t need pressure from above to take action as citizens or to participate in projects for social change that are bigger than themselves. There always lies the risk that when parents mandate this kind of participation as a kind of chore, children will reject it out of principle.
Instead of hoping their children will swallow whole what is offered them, parents should encourage them to seek the truth —to learn to reason and argue. Those around them, and society as a whole, will benefit from their skills, their independence, and their spirit.
Case Study 1
The concepts of intension and extension.
B eginning at around 13, students can begin formalizing their reasoning using intensional definitions. These formal definitions, which are internal to concepts themselves, rather than drawn from experience, can open up new avenues for reasoning and lead to new kinds of arguments.
Consider the following scenario:
During a presidential election campaign, 14-year-old Lea defends a candidate who, in her eyes, is the only one worth voting for. She explains her candidate’s platform to her friends around the table at lunch in the school cafeteria and says how she wishes she already had the right to vote and that she begged her parents to vote on her behalf.

Lea’s arguments seem to have convinced her friends, but Anna, sitting at one end of the table, interjects: ″Who cares? As my parents say, all presidents are liars! I’m never going to vote.”
The other girls and boys present agree loudly. A surprised Lea tries to think of a comeback, but can’t think of what to say.
The bell rings. Everyone gets up to go back to class.
When she gets home after school, Lea tells her mother about the scene at lunch and asks her opinion: ″What would you have said to Anna?”
If you were Lea’s mother, how would you have replied? How can you use reason to respond to Anna’s argument, which seems to be an argument from authority ?
There are two ways to determine whether all presidents are liars or not:
Extensional method: Research the history of presidential elections, and compare the promises made by candidates to their actions after being elected. This method will allow you to determine whether all presidents over the course of history have lied. Perhaps they all have lied. But even in this case, Anna’s argument would be valid but only up to the present day , since one cannot predict the future and, therefore, what a new president will do. Perhaps Lea could then defend her favored candidate by arguing that, once elected, he or she will be different.
Intensional method: Research political science and show that the electoral system and certain institutions pressure candidates to lie in order to get elected and that this is considered the “rules of the game.” If this can be demonstrated, it would be a valid pattern for the past and the future. In this hypothesis, Anna’s argument will be valid for the present and the future (so long as the same institutions remain in effect). Notice, however, that this method gives Lea an opportunity for more subtle reasoning. All presidents may end up making false promises or misleading the public on certain points, but we can distinguish between deliberate, malicious lies and those that arise from the pressures of the office. This would allow her to poke holes in Anna’s rationale for not voting, since certain candidates may still be more honest than others.
Case Study 2
Flawed reasoning.
Use these examples of flawed reasoning to introduce logical vocabulary and help your children identify flawed reasoning and how to identify flaws in an argument.. More definitions and basic concepts can be found here .

The examples are based on famous example of deductive reasoning attributed to Aristotle. In the exercises, Aristotle’s example is distorted in various ways, either using false information or faulty reasoning. Challenge your children to identify exactly why these arguments fail.
Here are some definitions of the terms used below:
Premises are the statements or information on which an argument is based (in these cases, the first two lines).
The conclusion (the third line in these examples) is the statement drawn from the premises.
When an argument is valid , that means its conclusion follows logically from its premises.
When an argument is sound , that means it is both valid and based on premises that are true, meaning its conclusion is also true.
These examples can help students to break up reasoning into logical steps, make the logical steps of an argument explicit to themselves, and identify where reasoning breaks down. Critical thinking must enable us to detect logical errors and to recognize whether they lead us to false conclusions. Notice, however, that flawed reasoning does not guarantee a false conclusion.
Aristotle’s Reasoning
“All human beings are mortal. Socrates is a human being. Therefore, Socrates is mortal.”
The premises are true, the reasoning is valid, and the conclusion is, as a result, true.
All human beings are women. Socrates is a human being. Therefore, Socrates is a woman.
One of the premises is false, the reasoning is valid, but the conclusion is false.
Half the human race is female. Socrates is a human being. Therefore, Socrates is female.
The premises are true, but the reasoning is invalid, and the conclusion is false.
Half the human race is male. Socrates is a human being. Therefore, Socrates is male.
The premises are true, the reasoning is invalid, but the conclusion is true.
Case Study 3
Peer pressure emerges in adolescent social groups as children attempt to assert independence from their parents and build their own identity through involvement in peer groups. This can lead to a number of paradoxical problems as children are pulled between an emerging sense of self and a need to belong. Even as their children seek to separate, parents can offer them help and support in working through some of these conflicts.

Consider this scenario:
Twelve-year-old David has just entered sixth grade at a big middle school in the city. He is a bit lost and finds a group of boys his age to spend time with during class and at recess. They all get to know each other over the next few weeks.
At the end of October, one of the boys suggests that they draw a big skull and crossbones on their backpacks in permanent marker to show that they belong to the group. Within a few days, all of the boys in the group have proudly drawn a skull and crossbones onto the front of their backpacks— everyone, that is, except David. He really likes his backpack. He picked it out himself and his parents bought it for him for the new school year. Furthermore, he has never had an affinity for skeletons, and skulls and crossbones hold no special meaning for him.
When the group reunites in the playground one Friday morning, one of the boys goes over to David and threatens him, saying, “If you don’t draw a skull and crossbones on your backpack, you’re out of the group!” The other children back the mean kid up.
Over the weekend, David is faced with a dilemma. He can either keep his backpack the way he likes it, even if that means being excluded from the group, or draw a skull and crossbones on it to show that he belongs to the group.
On Sunday night, he decides to talk to his parents about the situation. If you were in their place, what advice would you give him?
At dinner, his father offers him some advice:
″David, you shouldn’t see this as a problem with only two solutions. Just tell your friends that you don’t like either option and that you have another idea.”
″That won’t work. They told me that it had to be one way or the other,” replies David.
″Well, you should at least give it a try,” suggests his mother. “Tell them that you really like being part of the group and that you like them as friends, but that you don’t want to ruin your new backpack by drawing on it. Tell them that, in a group, everyone should have their freedom and that you shouldn’t have to do the same thing as everyone else all the time. Ask them to let you stay in their group, which means a lot to you, without having to do something you don’t want to. That’s a third solution.”
In this situation, the group of boys want David to show he’s part of the group by adopting a common code. David is under pressure to comply and must make a decision. The easiest solution for David would be to succumb to peer pressure. He could also stand his ground and refuse, but this would probably cause him pain since he would have to deal with the group’s disapproval and possible exclusion.
The group does not tolerate non-conformity since it threatens its existence. Eventually, however, resisting peer pressure could play in David’s favor, as his show of independence could earn him the respect of the other group members and thereby bolster his self-esteem.
There is no ″right decision.” Everything depends on David’s level of self-esteem, which will determine his capacity to stand firm in the face of the consequences of his choices.
Case Study 4
Nasreddin, a very famous figure in the Arab Muslim world, was the author of often absurd stories. Families enjoy reading his stories together and refuting his biased reasoning, which is designed to sharpen our critical thinking skills and ability to foil sophistry. Identifying the flaws in Nasreddin’s reasoning is a useful logic game and a good way to introduce logical concepts. Challenge your children to show where Nasreddin goes wrong, and come up with equivalent examples from current events or everyday life that involve the same flawed reasoning.

Very early one morning, Nasreddin was up sowing salt all around his house.
“What on earth are you doing with all that salt, Nasreddin?” asked his neighbor.
“I’m putting it around my house to ward off tigers.”
“But there aren’t any tigers here.”
“Well then, that’s proof that the salt worked!”
The Moon and the Sun
One day, Nasreddin was asked:
“Tell us, Nasreddin, which is more important: the sun or the moon?”
“The moon, of course,” he replied immediately.
“Because the moon appears at night, and that’s when we need light most.”
The Power of Age
Nasreddin arrived at a café one day, looking proud and happy.
“Hey, Nasreddin,” his friends called to him. “You look as if you’ve just found treasure.”
“Even better, even better,” he replied. “I am 70 and I have just discovered that I am still as strong as I was when I was 20.”
“And how did you discover that?”
“Simple! You see that huge rock in front of my house? Well, when I was 20, I couldn’t move it.
“Today, I tried again and I still can’t move it, just like when I was 20.”
Case Study 5
Paralogisms are fallacious arguments that appeal to evidence that is misleading, partial, or irrelevant. Below are some of the main strategies deployed in paralogisms. Ask you children to explain how the statements distort the facts or attempt to deceptively influence an audience. Use the paralogism examples as a starting point for discussing other examples in public life, advertising, or everyday conversation.

Paralogism Exercise #1
Spot the paralogisms in the following statements and explain why the reasoning is flawed.
″If smoking were bad for your health, it would be banned. Smoking is not banned. Therefore, smoking is not bad for your health.”
″If I am sick, I go see the doctor. I am not going to see the doctor. Therefore, I am not sick.”
″Intensive farming allows us to feed all human beings. Organic farming is not intensive farming. Therefore, organic farming will not allow us to feed all human beings.”
Paralogism Exercise #2
Three false dilemmas are presented below. Why are these apparent dilemmas not real dilemmas?
A close friend who is going to jump into a freezing lake on New Year’s Eve says, “A real friend wouldn’t let me do this alone.”
The night before election day, a candidate for office says, “It’s me or chaos.”
A slogan in an advertisement for Sneakie sports shoes reads, “Cool people wear Sneakies.”
Paralogism Exercise #3
Often biased or flawed reasoning uses false generalizations. How can we contradict the following statements?
Upon hearing that a politician is being investigated for tax fraud: “See? All politicians are corrupt.”
“Hypnosis works for giving up smoking. My brother managed to quit that way.”
“Social media is the best way to find love. Several of my friends met their partners that way.”
Paralogism Exercise #4
Beware of an “argument from authority,” especially those circulating online.
″Many scientists dispute the global warming phenomenon.” Who are these “scientists”? On which scientific studies have they based their opinions? Do they have personal, political, or economic connections with people or organizations that could benefit from challenging global warming? It is important to ask oneself all of these questions before accepting an argument.
Paralogism Exercise #5
Arguments based on numbers:
″This singer’s video already has 500,000 views online.” What does this say about the quality of their music?
″X93 – the latest phone, already owned by 2,000,000 people worldwide.” Does this mean that this device would suit my needs? Is this an indicator of its quality?
Paralogism Exercise #6
Arguments based on fear:
″You say that you’re against the death penalty, but murder will be much more common if we abolish it as a deterrent.”
Case Study 6
Several media companies offer fact-checking services. It is beneficial to consult them with teenagers and to pose questions about the ways in which media can distort the truth. These services can offer insight into the techniques various organizations and bad actors use to deceive audiences, as well as into the bias that can skew the information put out by various news organizations. Discussing these examples with your children get help raise awareness of the various ploys used to manipulate readers and viewers, and help them hone their analytical and critical skills.
Here are links to some trustworthy fact-checking sites: Politifact | Snopes | FactCheck.org | Poynter Institute
Examining the false stories fact-checked by these organization can be a helpful exercise. Here is an example of a false story fact-checked by Snopes:

Understanding examples like these can give students insight into techniques fake news sites use to hook and deceive an audience. Here, for example, the violent image may grab viewers’ attention and cause them to let their critical guard now. Attaching the fake story to a genuine news item (Samsung’s smartphone recall) also makes readers more likely to believe and share the false story, since it appears like a development in an ongoing story.
Student’s can also learn from the fact-checkers’ analysis. Here, they track down the original photos to show how the fake site has repurposed them, and they dig into the website reputation and background.
Researchers Sam Wineburg and Sarah McGrew recommend teaching students to navigate the internet more like fact-checkers. Students, they write, tend to “read vertically , evaluating online articles as if they were printed news stories.” Fact checkers, on the other hand, “read laterally , jumping off the original page, opening up a new tab, Googling the name of the organization or its president.”
Fact-checkers, Wineburg and McGrew write, are also less inclined to trust a website’s own description of its mission. They look for outside evidence from multiple sources to confirm or refute the website’s claims. And they don’t get hooked by enticing language or images, instead reading through a whole page of search results or information before deciding reflectively what links to follow or where else to look.
Finding good information online — and steering clear of bad information—are skills that can be taught and learned. They are increasingly vital at a time where multiple interests are leveraging the internet to attempt to monopolize our attention and shape our beliefs.
Case Study 7
Young people receive information from everywhere (social media, emails, texts, newspapers, television, online videos). Given the wealth of information coming in, much of it coming through or recommended by friends whose judgment and endorsement we are inclined to trust, it is easy to passively accept what we see or read. Young people should learn through examples how to resist this tendency and how to conduct thorough analyses of the media they are exposed to everyday.
It is important for parents to accompany them in conducting this sort of analysis so they can teach them how to critically evaluate these sources of information and how to avoid being misled. Below is a set of questions that you can apply to news sources with your children. They can be applied to any media source (the internet, printed media, TV/radio, etc.). We’ve divided these sets of questions into two sections: questioning the source and questioning the content.
1. Questioning the Source
- What is the source? Is it reliable?
It is often possible to cast doubt on a source simply by looking at surface features. There are numerous fake news websites with unusual names or URLs (like, for example, worldnewsdailyreport.com) that should tip readers off to their unreliability. In addition, if a website looks poorly designed and managed, contains typos or formatting errors, this is also an important indicator that it is likely unreliable, if not intentionally false. Fake news also may also come under more plausible publication names, like, for example, the “Denver Guardian,” and with more convincing design. A simple internet search can usually bring up information from credible sources alerting the reader to the fraudulent nature of the source. Here is a list of unreliable news sources from Factcheck.org. With your child, practice determining the reliability of different kinds of information.
Who owns the source? Is the content sponsored?
When evaluating a source, it is also possible to do research into details about the source, such as who owns the source or who is funding the content or supporting it via advertising. It is often possible this way to identify potential biases or attempts to influence readers that may not be immediately clear at a first reading. Reliable sources may also sell space in their publications or websites to sponsors, who have obvious interests in what information is presented and the slant with which it is presented. See for example this “ China Daily ” paid post in the New York Times, which is placed on the Times website by Chinese state media. Exploring how and why information like this is presented can be a good learning experience. It is also useful to discuss how sponsored content is marked on this and other websites.
- Who is the author of the content? What are their credentials? What possible biases may they have?
In addition to asking questions about publications, it is important to know who has written a given article or op-ed , what their reasons for doing so may be, and what expertise they have in the given area. Doing so can help determine the reliability of the information offered, the possible slants or biases with which the information is presented, and any financial or other interest the writer may have in the matter discussed. Most reliable websites will offer at least some of an opinion writer’s background, but an internet search can often return more detailed information. It is also important to help students recognize that an editorial author’s potential biases do not necessarily render the content absolutely unreliable. Critical thinking should not lead to knee-jerk rejection of all potentially biased opinions. Rather, a fair-minded independent thinker takes potential bias into account in evaluating content, weighing it along with other factors, like the strength of the argument and the evidence put forward.
2. Questioning the Content
- What type of content is being offered? What is the issue under discussion?
Before we embark on an analysis of the content of a given source, it is important to identify what type of content is being offered. The way we approach analyzing an advertisement will be very different from the way we analyze a news story or an opinion piece. It’s also important that students be able to identify when a particular source is purposefully blurring the lines between categories. For example, so-called “advertorials” can disguise advertising or promotion in the guise of opinion pieces or feature articles. News stories may likewise present information in a particular misleading or biased manner, trying to persuade the reader of something, but without making it clear that they are actually offering an opinion, not simply news.
- What sources are drawn on for the information or argument given? Are they reliable?
Even when we are satisfied that a source we are reading is generally reliable, it is worthwhile to pay attention to its own sources of information. If a particular piece of content cites facts without providing sources there is good reason to question the information. Moreover, students should get in the habit of following links and citations to verify that the secondary information comes from a reliable source and that the original content is characterizing it accurately.
- What are the main arguments being offered? Are they strong and sound? Are they consistent with each other?
Media sources use a variety of means to try to convince the audience of a particular point or point of view. It is important to train ourselves to be conscious of what these means are and whether they are valid. If an article or video simply relies on emotional reactions or strong images to prove its point, without trying to put forward an argument, we should be skeptical. On the other hand, if there is an argument presented, we should begin training children to break it down and analyze it. Parents and their children can practice breaking down the argument into premises and conclusions, evaluating whether the evidence for the premises is strong and the conclusions follow rationally from them.
- How might one argue against the position put forward?
Another important exercise to carry out, even if you generally agree with a position put forward, is to ask how it might be opposed. This can help identify weak points in the argument and show where evidence, even if it’s reliable, may not fully support the point of view being put forward. To this end, it can be helpful to research articles with opposing points of view, but which rely on the same set of facts. Discuss the merits of each article and how you would argue for and against each of them.
Complete the quiz to review important points in the guide.
- The stage when children begin arguing more persuasively.
- The stage when children start dressing more elegantly.
- The stage when children are able to study calculus and other college-level math.
- The stage when children can begin to grasp and manipulate abstract ideas.
- Parents can discuss logical fallacies in popular media or current events with their children.
- Parents can work on improving their own understanding of logic.
- Parents can go over children’s essays and other schoolwork closely and dispute their reasoning.
- Parents can use everyday examples to demonstrate the meanings of terms like proposition, contradiction, and validity.
- Parents can enroll their children in college exam prep courses as early as possible.
- The intension is a narrow definition of the concept; the extension is a broader definition.
- The intension is how the concept is used; the extension is a formal definition of the concept.
- The intension is a formal definition of the concept; the extension is a group of examples coming under the concept.
- The intension is the role a concept plays in logic; the extension is its role in everyday life.
- Critical thinking gives them tools to show their superiority to their peers and gain social esteem.
- As critical thinkers, they will be better equipped to manipulate other people and make their way to the top of social circles.
- As crtical thinkers, they will be more likely to concentrate on their studies and ignore social life and their own individuality.
- Critical thinking allows them to react thoughtfully to social pressure and assert their independence from friend groups when appropriate.
- Get into shouting matches with them. They need to see that their mistakes have consequences.
- Walk away. Teenagers need to learn that overheated opinions and conversations will get them nowhere.
- Engage them in arguments and challenge them to improve their criticisms (if they’re warranted). They’ll learn to argue with more moderation and subtlety.
- Bring in a teacher or other adult authority figure to mediate. The parent-child relationship is too emotionally charged for productive arguments.
- What do other reliable sources say about the issue under discussion?
- Who owns the source? Or who is supporting the content? What interests might they have?
- Is the content meant to be news or opinion?
- Was the author educated at a prestigious college?
- Does the content’s impact rely on emotional language or sensationalistic images?
- A deceptive or misleading argument
- The study of planetary orbits
- The merging of two arguments into one
- A convincing counterargument
Privacy Overview
How to teach children to be critical thinkers

Rus Limon | Shutterstock
Critical thinking is knowing how to assess and discern the information we receive. We make our decisions based on that information and on our evaluation of it, so we need to know how to think clearly.
This skill is essential in today’s world, as we are flooded with information from so many sources. The Holy Father himself has spoken of the importance of this skill:
We are living in an information-driven society which bombards us indiscriminately with data—all treated as being of equal importance—and which leads to remarkable superficiality in the area of moral discernment. In response, we need to provide an education which teaches critical thinking and encourages the development of mature moral values. (Pope Francis, Evangelii Gaudium )
As important as critical thinking is, it seems increasingly rare and hard to find.
For parents and educators, teaching children to think well is not easy. But the ongoing growth of relativism in society today makes it a very necessary task.

Promoting critical thinking in children allows them to enjoy greater freedom and ability to reason, to judge arguments, to acquire new knowledge and to be able to solve problems successfully. So how can we teach children to think critically?
We’re all born with the basic ability to think. Critical thinking, however, is a higher order of thinking, which must be practiced and learned. Dr. Robert Swartz, creator of the Thinking Based Learning (TBL) method, says that “while everyone thinks, not everyone thinks as carefully and as well as they could.”
Thinking skills
Robert Swartz argues that many of us engage in superficial, hasty, narrow-minded, unclear, and disorganized thinking. Therefore it’s vital to teach children thinking skills. We need to think critically especially when we make decisions, solve problems, predict, relate, compare, and contrast.
In order to train children in the art of thinking clearly, conscious practice is necessary. When they are at an early age, we can begin by inviting them to observe and interpret the world around them. They can ask themselves, “What do I see? What do I think about it?” This will lay the foundation for advanced thinking when they are older.
When we think, we form ideas in our heads that we automatically analyze in order to assess a certain situation. Therefore, critical thinking is a very useful skill in the world of learning too, and can help our children succeed academically.
Activities to teach children to think
Here are some activities that will help young children master critical thinking:
- Reading stories with them and talking about the story : Reading is a proven way to improve children’s concentration. Discussing what you’ve read, meanwhile, promotes reading comprehension and helps them reflect on the story that they’ve just heard or read. In addition, stories with a moral offer a “hidden teaching” that children will have to interpret.
- Deciphering puzzles and riddles : Who knew doing a simple puzzle teaches analytical reasoning?
- Solving clue games or escape rooms : These activities are lots of fun, and they’re great for promoting thinking and logic, with the chance to make contributions to the group’s efforts.
- Deciphering riddles and logical sequences : These provide a symbolic path of analysis that will lead to a satisfactory resolution.

All of these activities teach children cognitive abilities and thinking skills. They naturally provoke children to start asking questions, seeking the reasons for things, and putting their own arguments to the test. And these activities encourage children to ask questions that help them intuit possible consequences of actions.
Teaching children to ask good questions in a new situation is a beautifully effective way of showing them the need to think critically. They’ll start to realize that this is an essential ability in today’s society.
As they practice this skill, children and young people will realize for themselves the benefits of thinking critically. This skill makes them more free, helps them make good decisions, reinforces their personality, and helps them build a healthy self-esteem and not be fooled by others.
Knowing how to think critically will prove useful in so many situations. They’ll use this skill for organizing their lives, recognizing their own mistakes, and taking a “big picture” view of any situation.
It’s clear to everyone that we’re living in a time of great change, and it can be difficult to orient ourselves in the current cultural context. The more challenges we face, the more the way we approach life becomes clear—and the more apparent is the need to act based on critical thinking.

Articles like these are sponsored free for every Catholic through the support of generous readers just like you.
Help us continue to bring the Gospel to people everywhere through uplifting Catholic news, stories, spirituality, and more.


- Search Search Search …
- Search Search …
Parents Teaching Critical Thinking: Effective Strategies for Raising Independent Thinkers

Parents play a vital role in fostering the cognitive development of their children, and one of the most essential skills they can help nurture is critical thinking. Critical thinking comprises curiosity, open-mindedness, and a willingness to assess information logically and objectively. Developing this skill enables children to become more independent and creative problem solvers, setting them up for success in our constantly evolving world.
Teaching critical thinking at home begins with the basics: engaging children in conversations that encourage them to ask questions, consider different perspectives, and evaluate evidence. As children grow and mature, parents can gradually introduce more complex reasoning and argumentation techniques. In tandem with educational institutions, parents can work collaboratively to ensure their children master the art of critical thinking in various contexts and disciplines.
Key Takeaways
- Parents play a crucial role in nurturing critical thinking skills in their children.
- Developing these skills contributes to a child’s independence and creativity in problem-solving.
- Engaging conversations, gradual complexity, and collaboration with educational institutions are essential for fostering critical thinking at home.
Knowing Critical Thinking

Critical thinking is the ability to objectively analyze information, draw conclusions, and make decisions based on logic and reasoning. It is a valuable skill that allows individuals to assess situations, solve problems, and make informed decisions. Critical thinkers are often characterized by their curiosity, flexibility, and open-mindedness.
The importance of critical thinking can be seen in a variety of settings, from schools to workplaces, and even in day-to-day decision-making processes. By developing their critical thinking skills, individuals can enhance their problem-solving abilities, improve their analytical skills, and become more independent thinkers.
Parents play an essential role in fostering critical thinking skills in their children from a young age. Children as young as five years old can start learning the foundation of critical thinking, although they may not yet be ready for complex reasoning or detailed arguments.
There are several key aspects of critical thinking that parents should focus on when teaching their children:
- Analysis : This involves breaking down information into smaller parts, understanding their interrelations, and examining them to reach a conclusion.
- Logic : Making decisions and forming ideas based on rational and coherent thought processes while avoiding fallacies and errors in reasoning.
- Reasoning : Applying logic to evaluate propositions and arguments, draw conclusions, and make sound decisions based on available information.
- IQ : Though critical thinking may be linked to intelligence, it should be understood as a distinct skill set that must be cultivated and developed alongside one’s intellectual capacity.
Parents can support their children’s critical thinking development by integrating these aspects into daily activities and conversations. Asking open-ended questions, encouraging curiosity, and modeling rational decision-making can help children build their critical thinking skills.
In conclusion, knowing critical thinking involves understanding its key components, such as analysis, logic, reasoning, and IQ. It is crucial for parents to foster these skills in their children from a young age in order to support their growth into well-rounded and independent thinkers.
Importance of Critical Thinking
Critical thinking is an essential skill that every individual should develop, as it plays an important role in a person’s overall cognitive and emotional growth. It’s particularly crucial for parents to foster their children’s critical thinking abilities, as these skills contribute to better problem-solving, decision-making, and analytical skills.
One major benefit of critical thinking is its ability to enhance problem-solving skills. When individuals think critically, they can break down complex issues into smaller parts, analyze the different factors at play, and come up with feasible solutions to challenges. This, in turn, can lead to improved decision-making, as critical thinkers are better equipped to weigh the pros and cons of various options and choose the most suitable course of action.
Furthermore, critical thinking helps to develop a person’s creativity and open-mindedness. By encouraging intellectual curiosity, children can explore new ideas, entertain differing perspectives, and think outside the box when encountering obstacles. This creative thinking can also promote innovation, as young critical thinkers are more likely to challenge the status quo and seek novel approaches to problems.
Moreover, critical thinking has a significant impact on a person’s wisdom and intellectual development. Instead of relying solely on memorization, critical thinkers focus on understanding the underlying concepts and principles behind the information they encounter. This not only aids in the retention of knowledge but also enables them to apply this knowledge to diverse situations effectively.
Enhancing critical thinking skills in children is therefore essential for preparing them for a successful future, as this will give them the mental tools they need to navigate through complex decision-making processes, adapt to unique challenges, and lead a more purposeful life.
Teaching Critical Thinking at Home
Inspiring curiosity and open-mindedness.
One important aspect of teaching critical thinking is to inspire curiosity and open-mindedness in children. Parents can do this by asking open-ended questions and encouraging their children to explore real-life situations. For example, discussing a news story or examining the logic behind a decision can help them develop an inquisitive mindset. Curiosity is an essential element of critical thinking and fostering this trait helps children become more receptive to new ideas and perspectives.
Fostering Emotional Management
Emotional management plays a crucial role in developing critical thinking skills. A child who can effectively manage their emotions is better prepared to think critically and objectively. Parents can help their children understand and manage their emotions by discussing different emotional situations and addressing their emotions head-on. Teaching kids to recognize and process their emotions is essential to their ability to reason and make informed decisions without being overwhelmed by their emotions.
Driving Logical Reasoning
The ability to use logic and reasoning is a fundamental aspect of critical thinking. Parents can help their children develop such skills by talking through logical steps and solutions to real-life problems together. In addition, engaging in activities or games that involve formal reasoning, like playing chess or solving puzzles, can provide opportunities for kids to practice their logical thinking skills. By nurturing this ability, children will become more adept at analyzing situations and drawing sound conclusions.
Encouraging Healthy Debate
Debate helps children broaden their perspectives and learn to express their thoughts clearly and convincingly. Parents can support their children’s critical thinking skills by fostering a culture of healthy debate in the home. Discussing different viewpoints on various topics, like current events or school subjects, provides an opportunity for children to understand different arguments and make their own logical analyses. Engaging in respectful disputes encourages kids to challenge ideas and develop stronger critical thinking abilities.
Promoting Critical Analysis and Metacognition
Lastly, parents should promote critical analysis and metacognition in their children. Metacognition, or thinking about thinking, allows kids to reflect on their thought processes and evaluate their reasoning. Parents can ask questions that encourage children to think deeper about their own thoughts, like “What made you think that?” or “How did you reach that conclusion?” This practice helps children to better understand the way they think and encourages them to become more adept at evaluating their own critical thinking abilities.
Challenges in Teaching Critical Thinking
Addressing social norms and biases.
Teaching critical thinking to children requires addressing social norms and biases that can influence their thought process. Parents should be aware of the possible influence of peer pressure and social media on their children’s decision-making process. It is crucial to encourage children to critically evaluate social norms and challenge their own biases to develop successful critical thinking skills.
Countering Online Misinformation
The internet and social media have presented new challenges for teaching critical thinking, as misinformation and fake news have become increasingly prevalent. Parents must guide their children in evaluating sources and using fact-checking sites to verify information. Developing media literacy will equip them with the tools to navigate the digital landscape with confidence and discernment.
Handling Cognitive Development Stages
Understanding the different stages of cognitive development is essential for parents when teaching critical thinking skills. As children grow, from early childhood through adolescence and into puberty, their cognitive abilities expand and change. It is vital for parents to tailor their teaching strategies to match these developmental stages, ensuring that the critical thinking lessons are age-appropriate and relevant.
Dealing with Groupthink
Groupthink refers to the tendency of individuals to conform to the opinions and decisions of a group, sometimes at the expense of their own critical thinking abilities. Parents should be aware of this phenomenon and teach their children how to resist the urge to conform to group opinions, particularly when those opinions are unsupported by facts or evidence. Encouraging independent thought and healthy skepticism will empower children to make well-informed decisions, even when faced with the pressure to conform to groups.
Enhancing Critical Thinking in School Settings
Engaging techniques for classrooms.
One effective approach to enhancing critical thinking in school settings is introducing engaging techniques in classrooms. Educators can develop deep knowledge in their students by incorporating various learning processes and innovative teaching methods. For example, using Socratic questioning encourages learners to explore complex concepts and helps them derive conclusions independently. Additionally, integrating group activities allows students to collaborate and exchange diverse perspectives, promoting critical thinking skills.
Preparing for Current Events
An essential aspect of critical thinking is being aware of the world around us. Teachers should incorporate current events into their lesson plans to foster students’ ability to analyze and question information. For instance, discussing election campaigns can expose learners to various media sources and marketing tactics used by politicians. This exercise encourages students to discern fact from opinion, and question the credibility of sources, developing their critical thinking abilities.
Promoting Citizenship and Responsible Decision Making
Promoting citizenship and responsible decision-making in school settings is crucial for nurturing intellectual virtues in students. Educators can instill a sense of civic responsibility by engaging them in discussions on ethical issues, social challenges, and global affairs. These conversations help students recognize patterns and make informed decisions, fostering critical thinking skills. By creating an environment that encourages open dialogue and mutual respect, teachers can effectively engage their pupils in developing the essential skills needed for good citizenship and responsible decision-making.
Frequently Asked Questions
What are effective strategies for teaching critical thinking to children.
There are various strategies to teach critical thinking to children, such as encouraging the asking of questions, providing opportunities for problem-solving, teaching how to evaluate information and fostering open-mindedness. Discussing different perspectives and nurturing intellectual curiosity will also help build a solid foundation for critical thinking skills.
How can games and activities promote critical thinking in kids?
Games and activities can be significant tools to foster critical thinking skills. Puzzle games, strategy games, and tasks that require logical thinking stimulate a child’s cognitive abilities. Encouraging kids to play games that require planning, reasoning, and decision-making can help improve their critical thinking skills in an enjoyable way.
What books are suitable for fostering critical thinking in children?
Numerous books can foster critical thinking in children, such as those that include problem-solving plots, moral dilemmas, or opportunities for reflection and discussion. Books from different genres and age-appropriate levels can encourage children to analyze information, establish connections between ideas, and think more deeply about various topics.
What role does parental involvement play in developing critical thinking skills?
Parental involvement plays a significant role in developing critical thinking skills. By actively engaging with their children, asking thought-provoking questions, and encouraging open discussions, parents create an environment conducive to the development of critical thinking. Modeling critical thinking skills and being open to different viewpoints can also have a positive influence on a child’s thinking abilities.
How can critical thinking skills be improved in middle school students?
To improve critical thinking skills in middle school students, it’s essential to create a conducive learning environment and teach age-appropriate strategies. Activities such as debates, brainstorming, group projects, and analytical writing assignments can encourage students to think critically about various subjects. Offering constructive feedback and promoting self-reflection will also help students assess and improve their thinking abilities.
What are impactful examples of critical thinking exercises for kids?
Impactful critical thinking exercises for kids include syllogism puzzles, “what if” scenarios, and evaluating the credibility of different sources of information. Activities like analyzing cause and effect relationships, comparing and contrasting different ideas or concepts, and predicting possible outcomes based on specific factors can also foster critical thinking in children .
You may also like

The Relationship Between Critical Thinking and Assertiveness: Uncovering the Connection for Success
The relationship between critical thinking and assertiveness is an important aspect of personal and professional development. Critical thinking involves the ability to […]

Core critical thinking skills
On a regular basis, people are faced with problems and scenarios that must be assessed and solved. Typically, they are tasked to […]

Critical Thinking and Artificial Intelligence
Artificial intelligence has changed the way we think about the world; indeed, the very concept of a machine being able to think […]

Critical Thinking Concepts: Enhancing Decision-Making Skills
Critical thinking, a fundamental component of intelligent behavior and decision-making, is the process by which individuals actively and skillfully conceptualize, apply, analyze, […]
- Parenting Tips
- Products We Love
- Kids Activities
- Celebrating Her

23 Activities to Develop Critical Thinking Skills in Children
Are you looking for ways to help your child become a better problem solver and decision maker?
Do you want to prepare them for success in the 21st century, where critical thinking skills are highly valued?
Look no further, because in this post we will share 23 engaging activities that can help your child develop critical thinking skills. From puzzles and games to real-life scenarios and creative challenges, these activities will not only enhance your child’s thinking abilities but also keep them entertained and curious. As a parent, it is important to give your child the tools they need to succeed, and critical thinking skills are a vital part of that toolkit.
So, let’s dive in and discover some fun and effective ways to help your child develop critical thinking skills!
Table of Contents
What is critical thinking skills?
Critical thinking is a cognitive process that involves analyzing, evaluating, and synthesizing information to make informed decisions and solve problems effectively. It involves the ability to question assumptions, examine evidence, and consider multiple perspectives to arrive at logical and evidence-based conclusions.
For example, when playing a game of chess, a player must analyze the board, anticipate their opponent’s moves, and make strategic decisions based on the available information. Similarly, when conducting research, an individual must evaluate the credibility and reliability of sources and synthesize information to form a coherent argument.
Importance of developing critical thinking skills in children
Developing critical thinking skills in children is crucial for their overall cognitive and social-emotional development. Research has shown that children who possess strong critical thinking skills are better equipped to make sound decisions, solve complex problems, and communicate effectively with others.
One study conducted by the University of California, Los Angeles found that students who received training in critical thinking showed significant improvements in their reading and writing abilities. These students also demonstrated higher levels of creativity and were better able to understand and analyze complex issues.
In addition, developing critical thinking skills can help children become more independent and confident in their decision-making abilities. They learn to evaluate information and evidence, identify biases, and consider different perspectives before making a decision. This can lead to a greater sense of self-awareness and a better understanding of their own strengths and weaknesses.
Furthermore, critical thinking skills are essential in today’s rapidly changing world. As technology continues to advance and the job market evolves, individuals who possess strong critical thinking skills are more likely to succeed. They are better equipped to adapt to new challenges and to identify new opportunities.
Overall, the development of critical thinking skills is essential for children’s long-term success and well-being. By providing them with opportunities to practice critical thinking skills through various activities and experiences, parents and educators can help children become effective problem solvers, communicators, and decision-makers.
Recommended reading: How To Teach Your Child To Think Out Of The Box
Recommended reading: 9 Fun Activities to Build Listening Skills in Children
View this post on Instagram A post shared by Raising Children 101 (@raising_children_101)
Activities to develop critical thinking skills in children
Critical thinking skills can be developed through various activities that require individuals to analyze and evaluate information, develop hypotheses, and test their ideas using evidence.
- Read Books Together: Reading books with children helps to develop their critical thinking skills. Encourage them to ask questions about the story, analyze the characters’ actions, and make predictions about the outcome.
- Board Games: Board games are a fun way to develop critical thinking skills in children. Games such as chess, checkers, and monopoly require children to think strategically and make decisions based on the outcome of their moves. Playing board games also encourages children to think creatively and come up with unique solutions to problems.
- Encourage Questions: Encourage children to ask questions about the world around them. This can help them to develop their analytical skills and learn how to evaluate information.
- Play “What If” Games: “What If” games encourage children to think creatively and critically. For example, ask them what they would do if they were stranded on a deserted island or if they could travel through time.
- Brainstorm Solutions: Encourage children to brainstorm solutions to problems they encounter. This can help them develop their problem-solving skills and learn how to think critically.
- Mind Mapping: Mind mapping is a great activity to improve critical thinking skills in children. It helps children to organize their ideas and think creatively. Give your child a topic and ask them to create a mind map by writing down all their thoughts and ideas related to the topic. This activity can help your child to improve their brainstorming skills and connect different ideas.
- Play Sudoku: Sudoku is a logic-based game that requires critical thinking skills. It requires children to think logically and use deductive reasoning to solve a problem. Sudoku puzzles can be found in many newspapers and online.
- Conduct Research: Encourage children to conduct research on a topic that interests them. This can help them develop their analytical skills and learn how to evaluate information.
- Watch Documentaries: Documentaries are a great way to develop critical thinking skills in children. Encourage them to ask questions about the information presented and analyze the content.
- Play “What’s Missing”: “What’s Missing” is a memory game that requires children to think critically and remember information. For example, lay out several objects and ask them to identify which one is missing.
- Play “I Spy”: “I Spy” is a game that requires children to think critically and observe their surroundings. It can help develop their analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Play Charades: Charades is a game that requires children to think creatively and critically. It helps develop their problem-solving and analytical skills.
- Play “20 Questions”: “20 Questions” is a game that requires children to ask questions and think critically. It can help them develop their analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Play “Would You Rather”: “Would You Rather” is a game that encourages children to think critically and make informed decisions. It helps them develop their problem-solving skills.
- Play “Spot the Differences”: “Spot the Differences” is a game that requires children to think critically and observe their surroundings. It helps develop their analytical skills.
- Play “Who Am I”: “Who Am I” is a game that requires children to think critically and ask questions. It helps develop their analytical and problem-solving skills.
- Write Stories: Encourage children to write stories that require critical thinking skills. For example, they could be asked to create a story that involves problem-solving, decision-making, or predicting an outcome. This activity encourages children to think creatively and come up with unique solutions to problems, helping them develop their critical thinking skills.
- Science Experiments: Science experiments are a fun way to develop critical thinking skills in children by encouraging them to ask questions, analyze data, and draw conclusions.. Encourage children to think about the scientific method and predict what will happen during an experiment. This encourages children to think about cause and effect and develops their critical thinking skills.
- Mystery Box: A mystery box is a great way to develop critical thinking skills in children. Place a number of items in a box and ask children to guess what the items are based on their shape, texture, and weight. This activity encourages children to think creatively and use deductive reasoning to solve a problem.
- Coding: Coding is a great way to develop critical thinking skills in children. It requires children to think logically and use deductive reasoning to solve problems. There are many online resources available that teach children how to code.
- Debate: Debating is a great way to develop critical thinking skills in children. It requires children to think critically and come up with logical arguments to support their position. Debating also helps children develop their communication skills and learn how to express their thoughts and opinions effectively.
- Brain Teasers: Brain teasers are a fun way to develop critical thinking skills in children. They require children to think creatively and use deductive reasoning to solve problems. Brain teasers can be found in many puzzle books and online.
- Puzzles: Puzzles are an excellent way to enhance critical thinking skills in children. Give your child puzzles that require them to use their logical reasoning, problem-solving, and spatial reasoning skills. Puzzles can be in the form of jigsaw puzzles, crossword puzzles, or any other puzzle that requires critical thinking.
By incorporating these activities into your child’s daily routine, you can help them to develop critical thinking skills that will benefit them throughout their lives. These activities can be a fun and engaging way for children to learn and develop their cognitive skills.
- Development
LEAVE A REPLY Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
Subscribe Today
Trusted parenting advice for all ages The movement for children’s mental health Supportive environment for mothers for a holistic living Celebrating moms
Join the newsletter to experience a sense of tribe and read stories full of inspiration and drive!
5 Ways To Protect Your Child From Sexual Abuse
Everything you need to know about gentle parenting, best parenting advice i have ever received.

Latest Posts
Are labels harmful for your child, teach your child how to deal with disappointments, helping your perfectionist child: strategies for parents, related posts, how to make a vision board that actually works , 9 tips to develop growth mindset in children, how to help children stop comparing themselves to others, when grandparents prefer grandson over granddaughter.

raising_children_101
Raising Children 101 is all about helping parents create beautiful memories for their children by understanding them better.
Popular Posts
The dark side of sibling rivalry when parents play favorites, why we get trapped in abusive relationships, 12 positive parenting tips for millennial parents, popular categories.
- Parenting 336
- Parenting Tips 295
- Well-being 60
- Self Care 52
- Products We Love 48
- Education 36
- Kids Activities 19
Stay connected
- Write For Us
- Terms and conditions
- Privacy Policy
- Returns and Refunds
©raisingchildren101.com. All rights reserved

How to Teach Kids to Think Critically (Think for Themselves)
Posted on Last updated: December 16, 2022
Categories Teach

The world is full of complex and challenging problems that require creative solutions. Teaching kids to think critically is an important skill that will help them solve these sorts of issues throughout their lives. It can also help them develop better problem-solving skills and become more independent thinkers.
The best way to teach kids how to think critically is by encouraging them to ask questions, explore different possibilities, and challenge assumptions. It’s also important to help them look at issues from multiple perspectives and to think beyond the facts. Here are some tips for teaching kids this vital skill:
Why Thinking Critically Matters
First and foremost, let’s explore why teaching kids to think critically matters. By encouraging them to look at the world with an open mind, they can make better decisions and become more thoughtful individuals. This helps them understand how the world works and why certain things are the way they are.
Critical thinking also allows children to develop their own solutions to problems rather than relying on someone else’s. They can think more deeply and come up with creative solutions that they may not have considered if they hadn’t learned to think critically.
Having the ability to think critically also helps kids become better communicators. They’ll be able to express their thoughts and opinions in a clear, concise manner, which will help them form meaningful relationships with others.
9 Benefits of Teaching Your Kids To Think Critically
Let’s take a look at some key benefits of teaching your kids to think critically:
1. Improved Problem-Solving Skills

When kids are taught how to think critically, they can become better problem-solvers. They’ll be able to look at an issue from multiple perspectives and come up with creative solutions. For example, say your child is trying to figure out the best way to finish a math problem. Encourage them to look at it from different angles and consider all their options before making a decision.
The key to this is to provide them with all the tools they need to think critically – such as asking questions, exploring different possibilities, and challenging assumptions.
This will help them in all areas of life, whether it’s school or work.
2. Increased Confidence
When kids learn to think critically, they also gain confidence in their own abilities. Instead of relying on someone else’s opinion or judgment, they can trust themselves to make the right decisions. This can be especially helpful when dealing with difficult or challenging situations.
It can also help them feel more empowered and capable of handling different tasks. This can lead to improved self-esteem and a greater sense of purpose in life.
3. Greater Ability To Think Creatively

Kids with the ability to think critically will be able to come up with innovative solutions to problems. Instead of relying on standard answers or solutions, they’ll be able to develop their own. This can lead to greater success in school and work projects.
It can also help them become better artists, writers, and inventors – since they’re used to thinking outside the box and considering all possibilities.
4. Deepened Understanding of Concepts
Along with creativity, critical thinking also helps children better understand concepts. For example, if they’re trying to learn a new language or math concept, critical thinking can help them make connections and come up with creative solutions that may not be immediately apparent.
This deeper understanding will help them think more deeply about the world around them and become more well-rounded individuals. This will help develop a growth mindset and lead to greater success in life.
5. A Deeper Understanding of Issues
Being able to see the root of a problem or issue can help kids become better citizens of the world. When they learn to think critically, they can look at a problem from multiple angles and come up with their own solutions. This skill will also help them to develop original opinions that are informed by facts and not swayed by emotion or bias.
Teaching them how to differentiate fact from opinion is key here. And learning to think independently can help them make better decisions in the future.
6. Improved Decision-Making

When children are able to think critically, they can make better decisions – both in terms of the immediate and long term. For example, if they’re presented with two options, they’ll be able to weigh up the pros and cons of each before choosing which one is best. This skill is especially important when it comes to major life decisions such as choosing a career path or deciding if they should pursue higher education.
7. Better Study Habits
Teaching children how to think critically can also help them become better students. By focusing on analyzing and reflecting upon information, they’ll be able to remember it more easily and apply it in new contexts. This will make learning easier for them as well – since they’ll be able to draw meaningful connections between different subjects and topics.
8. Improved Negotiating Skills
It’s also important to teach kids how to negotiate effectively. When they learn to think critically, they can better understand the other party’s viewpoint and come up with the best possible solution for both sides. This skill will be invaluable in all aspects of life – whether it’s settling disputes between friends or negotiating salary when looking for a job.
9. Greater Desire To Stretch Themselves

When kids feel like they can think for themselves, they’ll be more likely to challenge themselves and push their boundaries. They won’t be afraid to take risks or attempt new things – as long as they have a logical reason behind it. This can lead to greater success in school and work projects – since they won’t be afraid of failure.
By teaching children to think critically, you’re helping them become more confident and independent individuals. They’ll be able to face life’s challenges with greater resilience and come up with creative solutions. This will help set them up for a successful future and lead to improved self-esteem and a greater sense of purpose in life.
Overall, teaching kids to think critically is a valuable life skill that can benefit them greatly in the future. By helping them learn how to actively analyze and evaluate information, you’re equipping them with a toolset that will serve them well throughout their lives. This can help give them greater confidence in their own abilities and open up new possibilities for them.
So, if you want to give your child the best start in life, it’s worth investing some time into teaching them the power of critical thinking. It could make all the difference when it comes to future success!
How to Teach Your Child To Think Critically
Now that you know the benefits of teaching your kids to think critically, let’s look at some tips on how to do it:
1. Encouraging Kids to Ask Questions

One of the most important elements of teaching kids how to think critically is encouraging them to ask questions. By asking questions, kids are able to explore different perspectives and come up with their own ideas. Have them regularly ask “why” or “how” when discussing topics, and help them come up with questions they can research further.
You can also encourage your kids to ask questions when they’re reading or watching TV – this will help them become more curious and engaged in the material.
For example, a child who’s reading about a topic might ask questions like “How does this relate to the world around me?” or “What would happen if I changed this part of the story?” By asking such questions, they’re engaging their critical thinking skills.
2. Developing Problem-Solving Skills
Another key element of teaching kids to think critically is helping them develop problem-solving skills. This involves teaching them how to break down problems into smaller parts and then come up with logical solutions.
When faced with a difficult situation, have them take some time to think through the issue. Encourage them to consider different perspectives and explore alternative solutions. Help them identify patterns and connect the dots between different facts.
You can also have them practice problem-solving skills through activities like puzzles and games. These are a great way to help kids build up their critical thinking skills, as they have to think outside of the box to come up with solutions.
3. Providing Opportunities for Independent Thinking

Kids also benefit from opportunities to think independently. Create a space for them to work on their own and come up with their own ideas. This doesn’t mean you have to step back completely – instead, provide guidance and support as they explore different concepts.
Encourage your kids to question the information that they’re presented with and think through the implications of it. Help them evaluate evidence and come up with their own conclusions. This will help them become more confident and competent in their decision-making.
4. Encourage Open Discussion
Encouraging open discussions with your children is a great way to help them develop their critical thinking skills. Ask your kids questions and listen to their answers. When they present an argument, don’t immediately correct them – instead, probe further and encourage them to explain their reasoning.
Be sure to also give feedback – both positive and constructive – when appropriate. Let your kids know that it’s okay to make mistakes and that it’s important to learn from them. This will help them grow as thinkers and become more confident in their own ideas.
5. Discuss Various Topics
Ask them questions about the world around them and encourage them to come up with their own opinions. Have conversations about current events, science, history, and art – these will help your children develop a more well-rounded view of the world.
By engaging in discussions like these, kids will learn to weigh different perspectives and become more adept at forming logical arguments. This is an essential part of critical thinking and will help them explore the world around them in a more meaningful way.
6. Play Logic Games

Logic games are a great way to help kids develop their critical thinking skills. They involve solving puzzles and analyzing patterns – both valuable elements of critical thinking. You can find various logic games online, or you could make up your own.
You can also use everyday objects like coins, paperclips, and LEGO pieces to create different games. This will enable your kids to use their creativity and come up with unique solutions for each challenge.
Puzzles are also fantastic for developing critical thinking skills. These activities help kids develop their problem-solving abilities and become better thinkers. Again, you can find a variety of puzzles online or create simple ones with everyday objects.
Teaching kids to think critically is a process that takes time, effort, and patience. But by providing them with the tools they need and encouraging independent thinking, you’ll help them become more confident in their own ideas and better able to evaluate information. With practice and guidance, your kids will become better thinkers and be able to explore the world around them in a more meaningful way.
How to Teach Your Child to Interact With Differing Opinions
Now, inevitably, the discussion of differing opinions will arise. It’s so important to be understanding and respectful of other points of view – even if we don’t necessarily agree with them. Here are some tips to help kids learn how to interact in a respectful manner when faced with differing opinions:
1. Encourage Open Dialogue

Kids should learn that it is okay to have different perspectives and that it’s okay to express those views openly. They need to be comfortable having respectful conversations with others who may not share the same opinion. Encourage open dialogue and provide a safe environment for kids to express their thoughts and feelings while also being respectful of other opinions.
For example, say your child overheard someone talking about a political issue that they disagreed with. You could encourage them to talk openly about why they disagree and how they feel while also expressing respect for the other person’s opinion.
One way this conversation could go is for your child to first try to understand the other person’s opinion – why they believe what they do and why it matters to them. Then, your child can explain their own point of view in a respectful manner.
This type of open dialogue is essential in helping kids learn how to think critically and interact respectfully with those who have differing opinions.
You can also give practical tips on how to respectfully interact with those who have different opinions, such as asking questions and listening intently before responding.
2. Emphasize Compassion and Understanding
It’s important to emphasize that it is possible to have productive conversations with those who have different opinions without becoming angry or hostile. Kids should be taught that there is always the possibility to learn something from someone else’s opinion, even if it’s not one you agree with.
Encourage your child to think about why the other person may believe what they do and try to understand their point of view. This helps cultivate a sense of empathy and compassion, which are important qualities when learning to think critically and interact with others who have differing opinions.
You can also role-play different scenarios with your child where they need to interact with someone who has a different opinion. Let them practice responding respectfully in a simulated environment so that it becomes second nature when they are faced with a real-life situation.
Finally, explain to your child that it is important to remember that everyone has the right to their own opinion, and we should always be respectful of each other’s beliefs.
3. Model Respectful Behavior

Of course, kids learn by example, so it is important to always practice what you preach. They should be able to see that you are respectful of those with different opinions.
When kids see their parents engaging in conversations with others respectfully, they learn that it is possible to disagree without becoming hostile or angry. Show them how it’s done by setting a good example yourself!
4. Provide Opportunities to Practice
It’s one thing to have discussions at home and another to actually practice interacting with people who may have different opinions.
Provide your child with opportunities to practice these skills in real-life settings. For example, you could take them to a community meeting or event where they can hear others present their views and then practice engaging in conversation respectfully.
You can also sign them up for programs at school or in the community that teaches kids how to think critically and interact with people who may not share the same views.
By providing opportunities for practice, your child will become more comfortable in real-life situations and be better equipped to handle conversations with those who have different opinions.
5. Keep It Fun

Finally, make sure to keep it fun! Learning how to think for themselves and interact with people who have different opinions can be a challenge, so make sure that you’re creating an environment where your child feels comfortable to ask questions and express their own thoughts.
Set aside some time each week to talk about current events or topics of interest, and make sure to encourage your child’s curiosity. You can also play games that help them practice their critical thinking skills in a fun way!
Learning how to think critically and express themselves respectfully is an important skill that all kids should have. By providing guidance and setting a good example, you can help your child develop these skills and be more confident when engaging in conversations with those who may not share the same views.
By following these tips, you can ensure that your child is well-equipped to think for themselves and handle conversations with those who may have different opinions. And remember, learning how to think critically and express yourself respectfully should always be fun!
How to Teach Your Teenager Advanced Critical Thinking Techniques
As children age, their critical thinking skills should, too. Teenagers are at an age where they’re starting to form their own opinions and hone their arguments. It’s important that they have the tools to do this effectively and respectfully.
Here are some steps you can take to help your teenager learn advanced critical thinking techniques:
1. Encourage your teenager to challenge their assumptions.

It’s important for them to recognize and question the beliefs they already have to search for alternative perspectives and ideas.
There are several ways you can encourage this. You could ask them to take a position on a current event or read an article and then discuss it with you, allowing them to question their own thoughts and beliefs as well as those of others.
Remember to discuss the importance of sources when considering different arguments, too.
2. Promote a “growth mindset” in your teenager.
The concept of a “growth mindset” is the belief that intelligence and talent can be developed through hard work and dedication. This encourages teenagers to take a proactive approach to their learning by having them focus on improving rather than worrying about being wrong.
You can promote this mindset by praising their effort rather than the result and helping them to recognize that they are capable of achieving great things if they are willing to put in the work.
Some other ways to promote a growth mindset with a teenager include helping them break down goals into manageable steps and celebrating the small successes along the way.
3. Model critical thinking techniques in your own behavior.

It’s important to set a good example for your teenager by practicing what you preach. Show them how you think through a situation or problem logically and rationally, using evidence and facts to back up your opinion.
Another important thing to remember is to show respect for other people’s opinions, even if they differ from yours. This demonstrates that it’s possible to disagree without being disagreeable.
For example, say your teenager is arguing with you about a current event or political topic. You should recognize their opinion and encourage them to explain why they think the way they do without judging them or debating them on the spot.
This might also make family events and holidays a bit more pleasant as well!
4. Encourage respectful conversations with those who have different views.
To truly think critically and express their opinion in a respectful manner, your teenager needs to be able to engage in conversations with those who have different views.
This can be an intimidating experience for them at first, so it’s important that you provide guidance and support as they learn how to navigate these conversations.
Encourage open-mindedness while also making sure they have the facts to back up their points and that they’re able to recognize when someone is trying to derail the discussion.
5. Provide them with opportunities to practice critical thinking in real-world situations.

Another way you can help your teenager learn advanced critical thinking techniques is by providing them with opportunities to apply what they’ve learned to real-world situations.
For example, if your teenager is interested in politics, have them read up on a current issue and then discuss it with you or their peers. This can help them hone their critical thinking skills while also increasing their knowledge about the topic.
You could also encourage them to think critically when it comes to their own decisions and problem-solving. Give them a chance to come up with solutions to everyday problems, like how to manage their time or choose the best option for a school project. This will help them develop the skills they need in order to make sound decisions independently.
6. Help your teenager develop an understanding of logic and evidence.
Teaching teenagers to think critically means showing them how to evaluate arguments and come up with rational conclusions. To do this, it’s important that they have a good understanding of logic and how to use evidence to support their opinion.
To help your teenager develop these skills, introduce them to different forms of logical reasoning, such as deductive, inductive, and abductive reasoning. Explain the differences between them and provide examples of each type.
Once they understand how to use logic in their arguments, show them how to find evidence to back up their point. This could mean reading a variety of sources and evaluating them for credibility or researching data points that prove a particular point is valid.
By developing a strong understanding of logic and evidence, your teenager will be better equipped to think critically and make sound decisions.
7. Guide them in seeing the “bigger picture.”

Part of being able to think critically is understanding how a particular situation fits into the larger context or scheme of things. To help your teenager do this, encourage them to ask questions such as:
- What are the implications of this decision for the future?
- How does this action fit into a larger pattern or structure?
- Are there any ethical considerations that need to be taken into account?
By prompting them to think about the bigger picture, you can help your teenager become a more informed and perceptive individual.
8. Discuss multiple perspectives when discussing topics.
Encourage your teenager to consider different points of view on a particular topic. Ask them questions to get them thinking about the different sides of an argument and how people from various backgrounds might perceive it differently.
This will help your teenager become more compassionate and open-minded towards those with opposing beliefs while also honing their critical thinking skills.
9. Guide them in critical thinking skills such as research, analysis, and evaluation.
Help them learn how to critically analyze information from different sources, weigh evidence, draw conclusions, and make decisions based on the evidence.
To do this, you can provide them with practice exercises such as reading articles from multiple sources and then asking them to evaluate the claims made in each one. This will help them hone their skills in research, analysis, and evaluation.
Another way to practice these skills is through activities such as debating, discussing current issues, or writing essays. These tasks will help your teenager understand how to present an argument in a logical and coherent manner.
By teaching them these critical thinking skills, you’ll be equipping your teenager with the necessary tools they need to make sound decisions and think for themselves.
10. Encourage your teen to actively engage in critical thinking.

Finally, it’s important that you encourage your teenager to use their newfound skills and apply them on a regular basis. This means helping them find ways to incorporate critical thinking into everyday life.
For example, ask questions that require them to think critically, such as “What do you think about this news article?” or “How can we solve this problem?”. Encourage them to form their own opinions and be comfortable expressing their thoughts. If their school has a debate club, suggest they join to get more practice in using their critical thinking skills.
By actively participating in the process of thinking critically, your teenager will gain more confidence in their abilities and become better equipped to make sound decisions.
At the end of the day, teaching your teenager to think critically is an ongoing process that will take time and dedication. With patience, consistency, and a bit of guidance, they’ll be well on their way to becoming independent thinkers who are equipped with the skills they need to navigate life’s challenges.
How to Teach Your Teenager How To Research
We can’t discuss critical thinking without recognizing the importance of research. Research is a key component of critical thinking, as it provides us with evidence to support our claims and arguments. So, teaching your teenager how to do research and find reliable evidence is an essential part of this process.
To help your teen conduct effective research, here are a few tips:
1. Finding Reliable Sources

This can feel impossible these days, as there’s a lot of misinformation online. Encourage your teenager to look for the sources of the information they are researching and to make sure that it is reliable. Suggest they consider things such as author credibility, date of publication, or if the source has been reviewed by another expert in that field.
Another way to vet the validity of sources is to look for reviews of the article or book they are citing. Academic reviews can be a great way to evaluate whether or not the source is credible and can be trusted.
2. Applying Different Research Methods
Sometimes the best research comes from combining different methods, such as interviews AND surveys, for example. Encourage your teenager to explore different research methods and combine them if appropriate.
Also, suggest they pay attention to the way they phrase questions so that their results are as reliable as possible. This means avoiding leading questions or language that could skew the results of the research project.
Finally, remind your teen to always take notes while researching and writing down key points and references. This will help them stay organized and remember important information when it comes time to write the paper or present their findings.
3. Utilizing Libraries
The internet can be a great resource, but it’s not the only one. Suggest your teenage use libraries and other offline resources as well. Libraries are filled with books and physical copies of articles that can help them get a better understanding of their topic or subject matter. Plus, many librarians are more than willing to help guide your teen in the right direction when it comes to research resources.
By teaching your teen these essential research skills, they will be better equipped to think critically and make sound decisions based on facts.
Common Mistakes Kids Make When Thinking Critically

Like any new skill, critical thinking takes time and practice to master. To help your teenager hone their critical thinking skills, it’s important to be aware of the common mistakes kids make when trying to think critically.
Some of the most common mistakes include the following:
- Not questioning the source of information
- Basing decisions on personal biases or opinions
- Not considering different perspectives
- Being too quick to accept something as true without verifying facts
- Not giving adequate thought to the problem or issue at hand
- Ignoring contradictory evidence
By identifying these common mistakes, you can help your teenager understand how to think critically and avoid them when making decisions.
Let’s take a closer look at each of these mistakes and how you can help your child or teenager avoid them:
Not questioning the source of information: Encourage your teen to look for evidence that supports each claim they read. Suggest they consider the author, date of publication, and reviews when determining whether or not the information is reliable.
Basing decisions on personal biases or opinions: Remind your teen to consider different perspectives and look for evidence before making decisions.
Not considering different perspectives: Suggest your teen take some time to explore arguments from multiple sides when researching a topic. Encourage them to think critically about opposing views and ask questions such as what are the potential consequences of a certain decision?
Being too quick to accept something as true without verifying facts: Offer your teen resources for fact-checking controversial claims or topics. Checking the validity of a source is key when it comes to critical thinking.
Not giving adequate thought to the problem or issue at hand: Remind your teenager that taking their time and exploring all options is essential when trying to make sound decisions.
Ignoring contradictory evidence: Encourage your teen to consider all available evidence and ask questions, even if they seem to contradict one another. This will help them gain a more comprehensive understanding of the issue or problem at hand.
By being aware of these common mistakes and helping your teen avoid them, they will have a better chance of forming solid opinions and making sound decisions.
Strategies for Helping Kids Who Are Struggling With Objectivity and Critical Thinking

Critical thinking is a skill that takes time and practice to master. If your teenager or child is struggling to think objectively, there are several strategies you can use to help them develop their skills. Let’s take a look at some of the best ways you can help kids who are having difficulty with objectivity and critical thinking.
Encourage them to ask questions: Asking the right questions can help your child think more objectively. Encourage them to ask questions such as “What are the potential consequences of this decision?” or “Is there evidence to support this claim?”.
Model critical thinking: Show your child how to think critically by modeling it yourself. Talk about why you made certain decisions, and explain the thought process you went through.
Help them determine reliable sources: Show your child how to determine whether or not a source is reliable. Teach them to look for bias and consider the author, date of publication, and reviews when evaluating information.
Contradict their statements: Sometimes kids need to hear contrary opinions in order to become open-minded. Ask your child questions that contradict their statements and encourage them to consider multiple perspectives.
Focus on the facts: Encourage your child or teenager to focus on the facts instead of relying too heavily on emotion. Help them understand why it’s important to make decisions based on evidence, not just feelings.
Play “what if” games: Playing “what if” games can help your child become more comfortable with exploring different perspectives. Ask them to consider what would happen in various scenarios and encourage them to think critically about their answers.
By using these strategies, you can help your child or teenager develop the critical thinking skills they need to make sound decisions and form their own opinions.
Final Thoughts
Critical thinking and objectivity are important skills for kids to learn. As parents, it’s our job to help our children develop these skills so they can become more independent and make informed decisions. By using the strategies outlined in this article, you can help your child think critically and objectively about any topic or situation.
So encourage your child to ask questions, consider multiple perspectives and focus on the facts. With your help, your child can become a confident and independent thinker!
By following these strategies, you can help your kid or teen develop the skills they need to think objectively and critically. Critical thinking is an important skill that requires practice.

Coloring Pages
- Sea Animals
- Superheroes
- Word Searches

Free delivery, award-winning TV, exclusive deals, and more.
Free 30 days Trial.
Sharing is Caring
Help spread the word. You're awesome for doing it!

- Table of Contents
- New in this Archive
- Chronological
- Editorial Information
- About the SEP
- Editorial Board
- How to Cite the SEP
- Special Characters
- Support the SEP
- PDFs for SEP Friends
- Make a Donation
- SEPIA for Libraries
- Back to Entry
- Entry Contents
- Entry Bibliography
- Academic Tools
- Friends PDF Preview
- Author and Citation Info
- Back to Top
Supplement to Critical Thinking
Educational methods.
Experiments have shown that educational interventions can improve critical thinking abilities and dispositions, as measured by standardized tests. Glaser (1941) developed teaching materials suitable for senior primary school, high school and college students. To test their effectiveness, he developed with his sponsor Goodwin Watson the Watson-Glaser Tests of Critical Thinking, whose descendants are in widespread global use under the name “Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal” (Watson & Glaser 1980a, 1980b, 1994). He found that senior secondary school students receiving 10 weeks of instruction using these materials improved their scores on these tests more than other such students receiving the standard English curriculum during the 10 weeks, to a degree that was statistically significant (i.e., probably not due to chance). More recently, Abrami et al. (2015) summarized in a meta-analysis the best available evidence on the effectiveness of various strategies for teaching students to think critically. The meta-analysis used as a measure of effectiveness a modified version of a statistical measure known as “Cohen’s d”: the ratio of a difference in mean score to the statistical deviation (SD) of the scores in a reference group. A difference of 0.2 SD is a small effect, a difference of 0.5 SD is a moderate effect, and a difference of 0.8 is a large effect (Cohen 1988: 25–27). Abrami et al. (2015) found a weighted mean effect size of 0.30 among 341 effect sizes, with effect sizes ranging from −1 to +2. This methodologically careful meta-analysis provides strong statistical evidence that explicit instruction for critical thinking can improve critical thinking abilities and dispositions, as measured by standardized tests.
Although contemporary meta-analysis provides a more justified verdict on claims of causal effectiveness than other methods of investigation, it does not give the reader an intuitive grasp of what difference a particular intervention makes to the lives of those who receive it. To get an appreciation of this difference, it helps to read the testimony of the teachers and students in the Laboratory School of Chicago where Dewey’s ideas obtained concreteness. The history of the school, written by two of its former teachers in collaboration with Dewey, makes the following claim for the effects of its approach:
As a result of this guarding and direction of their freedom, the children retained the power of initiative naturally present in young children through their inquisitive interests. This spirit of inquiry was given plenty of opportunity and developed with most of the children into the habit of trying a thing out for themselves. Thus, they gradually became familiar with, and to varying degrees skilled in, the use of the experimental method to solve problems in all areas of their experience. (Mayhew & Edwards 1936: 402–403)
A science teacher in the school wrote:
I think the children did get the scientific attitude of mind. They found out things for themselves. They worked out the simplest problems that may have involved a most commonplace and everyday fact in the manner that a really scientific investigator goes to work. (Mayhew & Edwards 1936: 403)
An alumna of the school summed up the character of its former students as follows:
It is difficult for me to be restrained about the character building results of the Dewey School. As the years have passed and as I have watched the lives of many Dewey School children, I have always been astonished at the ease which fits them into all sorts and conditions of emergencies. They do not vacillate and flounder under unstable emotions; they go ahead and work out the problem in hand, guided by their positively formed working habits. Discouragement to them is non-existent, almost ad absurdum. For that very fact, accomplishment in daily living is inevitable. Whoever has been given the working pattern of tackling problems has a courage born of self-confidence and achieves. (Mayhew & Edwards 1936: 406–407)
In the absence of control groups, of standardized tests, and of statistical methods of controlling for confounding variables, such testimonies are weak evidence of the effectiveness of educational interventions in developing the abilities and dispositions of a critical thinker—in Dewey’s conception, a scientific attitude. But they give a vivid impression of what might be accomplished in an educational system that takes the development of critical thinking as a goal.
Dewey established the Laboratory School explicitly as an experiment to test his theory of knowledge, which
emphasized the part in the development of thought of problems which originated in active situations and also the necessity of testing thought by action if thought was to pass over into knowledge. (Dewey 1936: 464)
Hence the curriculum of the school started from situations familiar to children from their home life (such as preparing food and making clothing) and posed problems that the children were to solve by doing things and noting the consequences. This curriculum was adjusted in the light of its observed results in the classroom.
The school’s continued experimentation with the subject matter of the elementary curriculum proved that classroom results were best when activities were in accord with the child’s changing interests, his growing consciousness of the relation of means and ends, and his increasing willingness to perfect means and to postpone satisfactions in order to arrive at better ends…. The important question for those guiding this process of growth, and of promoting the alignment and cooperation of interest and effort, is this. What specific subject-matter or mode of skill has such a vital connection with the child’s interest, existing powers, and capabilities as will extend the one [the interest–DH] and stimulate, exercise, and carry forward the others [the powers and capabilities–DH] in a progressive course of action? (Mayhew & Edwards 1936: 420–421)
In an appendix to the history of the Laboratory School, Dewey (1936: 468–469) acknowledges that the school did not solve the problem of finding things in the child’s present experience out of which would grow more elaborate, technical and organized knowledge. Passmore (1980: 91) notes one difficulty of starting from children’s out-of-school experiences: they differ a lot from one child to another. More fundamentally, the everyday out-of-school experiences of a child provide few links to the systematic knowledge of nature and of human history that humanity has developed and that schools should pass on to the next generation. If children are to acquire such knowledge through investigation of problems, teachers must first provide information as a basis for formulating problems that interest them (Passmore 1980: 93–94).
More than a century has passed since Dewey’s experiment. In the interim, researchers have refined the methodology of experimenting with human subjects, in educational research and elsewhere. They have also developed the methodology of meta-analysis for combining the results of various experiments to form a comprehensive picture of what has been discovered. Abrami et al. (2015) report the results of such a meta-analysis of all the experimental and quasi-experimental studies published or archived before 2010 that used as outcome variables standardized measures of critical thinking abilities or dispositions of the sort enumerated in Facione 1990a and described in sections 8 and 9 of the main entry. By an experimental study, they mean one in which participants are divided randomly into two groups, one of which receives the educational intervention designed to improve critical thinking and the other of which serves as a control; they found few such experiments, because of the difficulty of achieving randomization in the classrooms where the studies were conducted. By a quasi-experiment, they mean a study with an intervention group that receives an educational intervention designed to improve critical thinking and a control group, but without random allocation to the two groups. Initially, they included also what they called “pre-experiments”, with single-group pretest-posttest designs, but decided at the analysis stage not to include these studies. By a standardized measure, they mean a test with norms derived from previous administration of the test, as set out in the test’s manual, such as the Watson-Glaser Critical Thinking Appraisal (Watson & Glaser 1980a, 1980b, 1994), the Cornell Critical Thinking Tests (Ennis & Millman 1971; Ennis, Millman, & Tomko 1985; 2005), the California Critical Thinking Skills Test (Facione 1990b, 1992) and the California Critical Thinking Dispositions Inventory (Facione & Facione 1992; Facione, Facione, & Giancarlo 2001). They included all such studies in which the educational intervention lasted at least three hours and the participants were at least six years old.
In these studies they found 341 effect sizes. They rated each educational intervention according to the degree to which it involved dialogue, anchored instruction, and mentoring. They found that each of these factors increased the effectiveness of the educational intervention, and that they were most effective when combined. They explained the three factors as follows.
Dialogue : In critical dialogue, which historically goes back to Socrates, individuals discuss a problem together. The dialogue can be oral or written, and cooperative or adversarial. It can take the form of asking questions, discussion, or debate. Some curricula designed to promote critical thinking establish “communities of inquiry” among the students. Such communities were a prominent feature of Dewey’s Laboratory School, incorporated as a means of promoting the primary moral objective of fostering a spirit of social cooperation among the children.
An important aspect of this conditioning process by means of the school’s daily practices was to aid each child in forming a habit of thinking before doing in all of his various enterprises. The daily classroom procedure began with a face-to-face discussion of the work of the day and its relation to that of the previous period. The new problem was then faced, analyzed, and possible plans and resources for its solution suggested by members of the group. The children soon grew to like this method. It gave both individual and group a sense of power to be intelligent, to know what they wanted to do before they did it, and to realize the reasons why one plan was preferred to another. It also enlisted their best effort to prove the validity of their judgment by testing the plan in action. Each member of the group thus acquired a habit of observing, criticizing, and integrating values in thought, in order that they should guide the action that would integrate them in fact. The value of thus previsioning consequences of action before they became fixed as fact was emphasized in the school’s philosophy. The social implication is evident. The conscious direction of his actions toward considered social ends became an unfailing index of the child’s progress toward maturity. (Mayhew & Edwards 1936: 423–424)
Communities of inquiry are also a feature of the Montessori method described by Thayer-Bacon (2000) and of the Philosophy for Children program developed by Matthew Lipman (Splitter 1987). Lipman (2003) examines theoretically what is involved in creating communities of inquiry. Hitchcock (2021) argues that the most obvious way for schools to develop critical thinking is to foster development of communities of inquiry.
Anchored instruction : In anchored instruction, whose advocacy goes back to Rousseau (1762) and Dewey (1910), there is an effort to present students with problems that make sense to them, engage them, and stimulate them to inquire. Simulations, role-playing and presentation of ethical or medical dilemmas are methods of anchoring.
Mentoring : Mentoring is a one-on-one relationship in which someone with more relevant expertise (the mentor) interacts with someone with less (the mentee). The mentor acts as a model and as a critic correcting errors by the mentee. Examples of mentoring are an advisor talking to a student, a physician modeling a procedure for a medical student, and an employee correcting an intern. Abrami et al. (2015) identified three kinds of mentoring in the studies that they analyzed: one-on-one teacher-student interaction, peer-led dyads, and internships.
Abrami et al. (2015) also compared educational interventions with respect to whether they were part of subject-matter instruction. For this purpose, they used a distinction among four types of intervention articulated by Ennis (1989). A general approach tries to teach critical thinking separately from subject-matter instruction. An infusion approach combines deep subject-matter instruction in which students are encouraged to think critically with explicit reference to critical thinking principles. An immersion approach provides deep subject-matter instruction with encouragement to think critically, but without explicit reference to critical thinking principles. A mixed approach combines the general approach with either the infusion or the immersion approach; students combine a separate thread or course aimed at teaching general critical thinking principles with deep subject-matter instruction in which they are encouraged to think critically about the subject-matter. Although the average effect size in the studies using a mixed intervention (+0.38) was greater than the average effect sizes in the studies using general (+0.26), infusion (+0.29) and immersion (+0.23) interventions, the difference was not statistically significant; in other words, it might have been due to chance.
Cleghorn (2021), Makaiau (2021), and Hiner (2021) make specific suggestions for fostering critical thinking respectively in elementary, secondary and post-secondary education. Vincent-Lancrin et al. (2019) report the results of a project of the Organization for Economic Cooperation and Development to develop with teachers and schools in 11 countries resources for fostering creativity and critical thinking in elementary and secondary schools.
Ennis (2013, 2018) has made a detailed proposal for a mixed approach to teaching critical thinking across the curriculum of undergraduate education. Attempts at implementing such an approach have faced difficulties. Weinstein (2013: 209–213) describes the attempt at Montclair State University in Montclair, New Jersey, from 1987 through the 1990s. He reports that the university’s requirement to include critical thinking in all general education courses led to the use of the concept in identifying topics and tasks in course syllabi, but without a unifying theoretical basis. The committee that approved courses as satisfying a general education requirement ignored the relation of curricular outcomes to critical thinking, and focused instead on work requirements with a prima facie relation to reflective thought: term papers, projects, group work, and dialogue. Sheffield (2018) reports similar difficulties encountered in his position from 2012 to 2015 as the inaugural Eugene H. Fram Chair in Applied Critical Thinking at Rochester Institute of Technology (RIT) in Rochester, New York. A cross-disciplinary faculty advisory group was not ready to accept RIT’s approved definition of critical thinking, but never reached a consensus on an alternative. Payette and Ross (2016), on the other hand, report widespread acceptance of the Paul-Elder framework, which involves elements of thought, intellectual standards, and intellectual virtues (Paul & Elder 2006). Sheffield (2018) reports that many colleges and universities in the United States have received funding for so-called “Quality Enhancement Plans” (QEPs) devoted to critical thinking, many of them written by Paul and Elder or developed in consultation with them. He faults the plans for having a typical time frame of five years, which he argues is probably too short for meaningful results, since lasting institutional change is often extremely slow.
Copyright © 2022 by David Hitchcock < hitchckd @ mcmaster . ca >
- Accessibility
Support SEP
Mirror sites.
View this site from another server:
- Info about mirror sites
The Stanford Encyclopedia of Philosophy is copyright © 2023 by The Metaphysics Research Lab , Department of Philosophy, Stanford University
Library of Congress Catalog Data: ISSN 1095-5054

A Crash Course in Critical Thinking
What you need to know—and read—about one of the essential skills needed today..
Posted April 8, 2024 | Reviewed by Michelle Quirk
- In research for "A More Beautiful Question," I did a deep dive into the current crisis in critical thinking.
- Many people may think of themselves as critical thinkers, but they actually are not.
- Here is a series of questions you can ask yourself to try to ensure that you are thinking critically.
Conspiracy theories. Inability to distinguish facts from falsehoods. Widespread confusion about who and what to believe.
These are some of the hallmarks of the current crisis in critical thinking—which just might be the issue of our times. Because if people aren’t willing or able to think critically as they choose potential leaders, they’re apt to choose bad ones. And if they can’t judge whether the information they’re receiving is sound, they may follow faulty advice while ignoring recommendations that are science-based and solid (and perhaps life-saving).
Moreover, as a society, if we can’t think critically about the many serious challenges we face, it becomes more difficult to agree on what those challenges are—much less solve them.
On a personal level, critical thinking can enable you to make better everyday decisions. It can help you make sense of an increasingly complex and confusing world.
In the new expanded edition of my book A More Beautiful Question ( AMBQ ), I took a deep dive into critical thinking. Here are a few key things I learned.
First off, before you can get better at critical thinking, you should understand what it is. It’s not just about being a skeptic. When thinking critically, we are thoughtfully reasoning, evaluating, and making decisions based on evidence and logic. And—perhaps most important—while doing this, a critical thinker always strives to be open-minded and fair-minded . That’s not easy: It demands that you constantly question your assumptions and biases and that you always remain open to considering opposing views.
In today’s polarized environment, many people think of themselves as critical thinkers simply because they ask skeptical questions—often directed at, say, certain government policies or ideas espoused by those on the “other side” of the political divide. The problem is, they may not be asking these questions with an open mind or a willingness to fairly consider opposing views.
When people do this, they’re engaging in “weak-sense critical thinking”—a term popularized by the late Richard Paul, a co-founder of The Foundation for Critical Thinking . “Weak-sense critical thinking” means applying the tools and practices of critical thinking—questioning, investigating, evaluating—but with the sole purpose of confirming one’s own bias or serving an agenda.
In AMBQ , I lay out a series of questions you can ask yourself to try to ensure that you’re thinking critically. Here are some of the questions to consider:
- Why do I believe what I believe?
- Are my views based on evidence?
- Have I fairly and thoughtfully considered differing viewpoints?
- Am I truly open to changing my mind?
Of course, becoming a better critical thinker is not as simple as just asking yourself a few questions. Critical thinking is a habit of mind that must be developed and strengthened over time. In effect, you must train yourself to think in a manner that is more effortful, aware, grounded, and balanced.
For those interested in giving themselves a crash course in critical thinking—something I did myself, as I was working on my book—I thought it might be helpful to share a list of some of the books that have shaped my own thinking on this subject. As a self-interested author, I naturally would suggest that you start with the new 10th-anniversary edition of A More Beautiful Question , but beyond that, here are the top eight critical-thinking books I’d recommend.
The Demon-Haunted World: Science as a Candle in the Dark , by Carl Sagan
This book simply must top the list, because the late scientist and author Carl Sagan continues to be such a bright shining light in the critical thinking universe. Chapter 12 includes the details on Sagan’s famous “baloney detection kit,” a collection of lessons and tips on how to deal with bogus arguments and logical fallacies.

Clear Thinking: Turning Ordinary Moments Into Extraordinary Results , by Shane Parrish
The creator of the Farnham Street website and host of the “Knowledge Project” podcast explains how to contend with biases and unconscious reactions so you can make better everyday decisions. It contains insights from many of the brilliant thinkers Shane has studied.
Good Thinking: Why Flawed Logic Puts Us All at Risk and How Critical Thinking Can Save the World , by David Robert Grimes
A brilliant, comprehensive 2021 book on critical thinking that, to my mind, hasn’t received nearly enough attention . The scientist Grimes dissects bad thinking, shows why it persists, and offers the tools to defeat it.
Think Again: The Power of Knowing What You Don't Know , by Adam Grant
Intellectual humility—being willing to admit that you might be wrong—is what this book is primarily about. But Adam, the renowned Wharton psychology professor and bestselling author, takes the reader on a mind-opening journey with colorful stories and characters.
Think Like a Detective: A Kid's Guide to Critical Thinking , by David Pakman
The popular YouTuber and podcast host Pakman—normally known for talking politics —has written a terrific primer on critical thinking for children. The illustrated book presents critical thinking as a “superpower” that enables kids to unlock mysteries and dig for truth. (I also recommend Pakman’s second kids’ book called Think Like a Scientist .)
Rationality: What It Is, Why It Seems Scarce, Why It Matters , by Steven Pinker
The Harvard psychology professor Pinker tackles conspiracy theories head-on but also explores concepts involving risk/reward, probability and randomness, and correlation/causation. And if that strikes you as daunting, be assured that Pinker makes it lively and accessible.
How Minds Change: The Surprising Science of Belief, Opinion and Persuasion , by David McRaney
David is a science writer who hosts the popular podcast “You Are Not So Smart” (and his ideas are featured in A More Beautiful Question ). His well-written book looks at ways you can actually get through to people who see the world very differently than you (hint: bludgeoning them with facts definitely won’t work).
A Healthy Democracy's Best Hope: Building the Critical Thinking Habit , by M Neil Browne and Chelsea Kulhanek
Neil Browne, author of the seminal Asking the Right Questions: A Guide to Critical Thinking, has been a pioneer in presenting critical thinking as a question-based approach to making sense of the world around us. His newest book, co-authored with Chelsea Kulhanek, breaks down critical thinking into “11 explosive questions”—including the “priors question” (which challenges us to question assumptions), the “evidence question” (focusing on how to evaluate and weigh evidence), and the “humility question” (which reminds us that a critical thinker must be humble enough to consider the possibility of being wrong).

Warren Berger is a longtime journalist and author of A More Beautiful Question .
- Find a Therapist
- Find a Treatment Center
- Find a Support Group
- International
- New Zealand
- South Africa
- Switzerland
- Asperger's
- Bipolar Disorder
- Chronic Pain
- Eating Disorders
- Passive Aggression
- Personality
- Goal Setting
- Positive Psychology
- Stopping Smoking
- Low Sexual Desire
- Relationships
- Child Development
- Therapy Center NEW
- Diagnosis Dictionary
- Types of Therapy

Understanding what emotional intelligence looks like and the steps needed to improve it could light a path to a more emotionally adept world.
- Coronavirus Disease 2019
- Affective Forecasting
- Neuroscience

Morning Carpool
21 Ways to Raise Critical-Thinking Children in the Digital Age
Posted: February 26, 2024 | Last updated: February 26, 2024

Today, instilling critical thinking in children has never been more crucial. Drawing insights from educators, psychologists, and seasoned parents alike, we unveil innovative strategies to sharpen young minds.

Encourage Curiosity
Children are naturally curious. Tap into this by asking them open-ended questions about their surroundings and experiences. Encourage them to ask ‘why’ and ‘how’ instead of just accepting things at face value. This fosters a mindset that seeks understanding and challenges assumptions.

Introduce Brain Teasers
Brain teasers are a fun way to develop critical thinking. These puzzles require children to apply logic and problem-solving skills. They learn to look beyond the obvious and understand that there can be multiple solutions to a single problem. This playful approach can make critical thinking an enjoyable habit.

Practice Mindfulness
Mindfulness helps children become more aware of their thoughts and feelings. By practicing mindfulness, they learn to observe their reactions without judgment. This awareness is key in critical thinking, as it allows children to consider their thoughts and decisions more carefully.

Explore Nature Together
Nature is full of wonders that spark curiosity and critical thinking. Take walks and encourage kids to observe and question the natural world. Discuss the ecosystem, the weather patterns, and the science behind what they see. This instills a deeper understanding of the world and its complexities.

Use Storytelling
Storytelling is a powerful tool for critical thinking. Share stories that have morals and discuss the characters’ decisions and their consequences. Ask children what they would have done differently. This helps them understand different perspectives and the impact of decisions.

Promote Artistic Expression
Art encourages creative thinking, which is a component of critical thinking. Encourage children to express themselves through drawing, painting, or crafting. Discuss their creations, asking about their choices and thought processes. This helps them articulate and evaluate their ideas.

Implement Technology Breaks
Regular breaks from technology can help children engage more deeply with the world around them. During these breaks, encourage physical play, reading, or conversation. This shift in focus can enhance attention to detail and critical observation skills.

Teach Basic Logic
Introduce basic principles of logic in a way that’s accessible to children. Use simple examples to explain cause and effect, sequencing, and categorization. Understanding these concepts can help children analyze information more effectively.

Role-Playing Games
Role-playing games require decision-making and problem-solving. Children learn to think ahead, anticipate consequences, and work collaboratively. This interactive play can sharpen critical thinking skills in a fun, engaging way.

Encourage Scientific Experimentation
Science experiments at home can be simple yet exciting. They teach children to form hypotheses, conduct tests, and analyze results. This hands-on approach to learning encourages them to question and understand how things work.

Developing Emotional Intelligence
Understanding emotions is a key aspect of critical thinking. Teach children to recognize and articulate their feelings and those of others. This helps them understand the impact of emotions on decision-making and interpersonal relationships.

Learning from Mistakes
Use mistakes as learning opportunities. Discuss what went wrong, why it happened, and how to approach things differently in the future. This approach teaches children to evaluate their actions and learn from their experiences.

Exploring Historical Events
Discuss historical events and their implications. Ask children to consider different perspectives and the reasons behind people’s actions. Understanding history in this way helps develop a critical approach to information and narratives.

Critical Reading Sessions
While reading together, pause to discuss plot points, characters, and underlying themes. Ask predictive questions and encourage children to form and express their opinions. This enhances their ability to analyze and interpret information.

Problem-Solving Activities
Engage children in activities that require problem-solving. This could be puzzles, strategy games, or real-life scenarios. These activities teach children to think critically by considering various solutions and their potential outcomes.

Encourage Group Discussions
Group discussions on various topics can help children understand diverse viewpoints. Teach them to listen actively, ask questions, and articulate their own thoughts. This social interaction is crucial for developing critical thinking.

Time Management Skills
Teach children the importance of time management. Help them plan their activities and prioritize tasks. This skill helps them make informed decisions about how to best use their time and resources.

Explore Music and Rhythm
Music and rhythm can be used to enhance cognitive abilities. Discussing patterns in music, lyrics, and rhythm helps children understand complex structures in a playful way. It also improves memory and pattern recognition.

Understanding Media and Advertising
Teach children to critically assess advertisements and media messages. Discuss the intent behind commercials and the strategies used to persuade viewers. This awareness helps them discern and evaluate the information they’re presented with.

Fostering Independence
Encourage children to do tasks independently. This builds confidence and decision-making skills. As they face challenges and make choices, they learn to trust their judgment and think critically.

Practicing Gratitude
Practicing gratitude helps children see the world from a positive perspective. Encourage them to reflect on things they are grateful for. This practice fosters a balanced mindset, allowing for more thoughtful and empathetic critical thinking.
More for You
Authorities believe they've uncovered how Shohei Ohtani's former interpreter pulled off theft
Challenger to the judge in Trump's 2020 Georgia election interference case is disqualified
$90,000 colleges, the toolbelt generation, and why high schools need a three-track system
Hosts of ‘King Charles’ say goodbye
Tim And Stacy Wakefield's Daughter Throws Out First Pitch Months After Their Deaths
'American Idol' recap: Loretta Lynn's grandchild wows judges, Jelly Roll grieves with contestant
Seasoning Recall in 3 States as Life-Threatening Warning Issued
Apple Warns of iPhone 'Mercenary Attack' Across 92 Countries
23 of Our Readers’ Favorite Recipes
Celtics make bizarre history in loss against Bucks as they go entire game without shooting free throw
IRS used AI to access bank accounts of US citizens: Rep. Harriet Hageman
House Republican margin continues to shrink as another GOP congressman resigns
Hundreds of Tesla Owners Flood Charging Station
The People Who Bought My Home Came Back for Concessions After the Contracts Were Signed. Here's What I Did
13 Things to Stop Buying That’ll Save You Tons of Cash
Krispy Kreme's Newest Collection Looks Absolutely Incredible
23 Broccoli Casseroles We Can’t Get Enough Of
South Carolina star Kamilla Cardoso sidesteps question regarding Dawn Staley's transgender comments
Gardener shares simple way to build raised garden beds on a budget: 'Best part is there are no tools required'
Paul Simon tapped to perform and menu released for Japanese state dinner

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Morin says one way to teach kids to think critically is to teach them how to solve problems. For instance, ask them to brainstorm at least five different ways to solve a particular problem, she says. "You might challenge them to move an object from one side of the room to the other without using their hands," she says.
Using critical thinking in your own life is vital, but passing it along to the next generation is just as important. Be sure to focus on analyzing and evaluating, two multifaceted sets of skills that take lots and lots of practice. Start with these 10 Tips for Teaching Kids To Be Awesome Critical Thinkers. Then try these critical thinking ...
Critical thinking is about curiosity, flexibility, and keeping an open mind (Quitadamo et al 2008). And, as Robert DeHaan has argued, creative problem solving depends on critical thinking skills (DeHaan 2009). In fact, research suggests that explicit instruction in critical thinking may make kids smarter, more independent, and more creative.
How to teach critical thinking to a child. To teach critical thinking to a child, encourage them to apply deeper thinking in any situation that requires decision-making in daily life. Here are 6 tips on teaching critical thinking. 3-8 Start early and explain everything: Young children often ask lots of questions. Instead of saying, "That ...
This is about teaching them to think for themselves. Your role is to direct their questions, listen and respond. Meanwhile, your kids "have to think about how they're going to put this into digestible pieces for you to understand it," says Oshiro. "It's a great way to consolidate learning.". Critical thinking isn't just for the ...
10. Hold a Q&A session. One way you can figure out how well kids are grasping critical-thinking skills is by holding question-and-answer sessions. Ask a variety of questions one-on-one or in small groups and take note of the levels of thought individual students use regularly and avoid over time.
Even if their contributions are unsophisticated or mistaken, engage with children and help them improve. 2. Putting Emotions in Perspective. Just as children need to learn how to step back from ...
Here are three examples: . If your child did the multiplication 6 x 9 to get 54 that would NOT be critical thinking. ️But if they then explained to you all the other ways they could get the number 54, then it could be. If your child memorised the lyrics to their favourite song that would NOT be critical thinking.
The Foundation for Critical Thinking says, "Critical thinking can be seen as having two components: 1) a set of information and belief-generating and processing skills, and 2) the habit, based on intellectual commitment, of using those skills to guide behavior.". In other words, good critical thinkers know how to analyze and evaluate ...
The University of Queensland Critical Thinking Project has a number of tools to help teach critical thinking skills. One is a web-based mapping system, now in use in a number of schools and ...
Critical Thinking Development: Ages 5 to 9. Critical thinking must be built from a solid foundation. Although children aged five to nine are not yet ready to take on complicated reasoning or formulate detailed arguments, parents can still help their children lay a foundation for critical thinking. In order to develop high-level critical ...
Firstly, it is a beneficial method to explore the world. If a child learns things using critical thinking, he or she will avoid loads of mistakes and misleadings which could have traumatized him/her. Secondly, this skill makes a mind work faster. When things don't make sense from first sight — think the situation over with a critical ...
Playing Scrabble, chess or sudoku is an easy way to help your child strengthen their critical thinking skills. Remember that modeling critical thinking is one of the most effective ways to teach those skills to your child. This could be in the form of asking questions, considering alternative solutions, showing your openness to different views ...
Basically, critical thinking helps us make good, sound decisions. Critical thinking. In her book, "Mind in the Making: The seven essential life skills every child needs," author Ellen Galinsky explains the importance of teaching children critical thinking skills. A child's natural curiosity helps lay the foundation for critical thinking.
Your kids are learning math and reading skills, but are they learning critical-thinking skills? In a recent study commissioned by MindEdge Learning, only 36 percent of millennials surveyed said they were "well-trained" in these skills. As many as 37 percent of the 1,000 young people surveyed admitted they were sharing information on their social media networks that was likely inaccurate news.
The four basic aspects of critical thinking we examined in the first part of this guide, concerning children aged five to nine, remain relevant, therefore. To review, these were: Critical thinking based on arguing a point. Developing self-esteem, the foundation of critical thinking. Emotional management, a prerequisite for critical thinking.
Activities to teach children to think. Here are some activities that will help young children master critical thinking: Reading stories with them and talking about the story: Reading is a proven ...
To help them develop critical thinking skills, parents can teach young children to find explanations and alternative solutions to different situations. It is satisfying for both adults and children to find the right answer, but in many cases some problems or situations in everyday life may have more than one solution.
Teaching critical thinking to children requires addressing social norms and biases that can influence their thought process. Parents should be aware of the possible influence of peer pressure and social media on their children's decision-making process. It is crucial to encourage children to critically evaluate social norms and challenge ...
Play Sudoku: Sudoku is a logic-based game that requires critical thinking skills. It requires children to think logically and use deductive reasoning to solve a problem. Sudoku puzzles can be found in many newspapers and online. Conduct Research: Encourage children to conduct research on a topic that interests them.
Conclusion. By playing fun games with your child and engaging them in thoughtful activities, you can help develop their critical thinking skill. The deeper they get into school, the more they will need to be able to think critically. As they grow, they will need to be able to solve complex math problems, analyze passages to determine meaning ...
Critical thinking empowers kids to become independent, thoughtful individuals who can navigate the challenges of the future with confidence and resilience. How To Teach Your Child Critical Thinking Skills. Teaching critical thinking to kids lays the foundation for a lifetime of informed decision-making and problem-solving.
By teaching them these critical thinking skills, you'll be equipping your teenager with the necessary tools they need to make sound decisions and think for themselves. 10. Encourage your teen to actively engage in critical thinking. ... Model critical thinking: Show your child how to think critically by modeling it yourself. Talk about why ...
Ennis (2013, 2018) has made a detailed proposal for a mixed approach to teaching critical thinking across the curriculum of undergraduate education. Attempts at implementing such an approach have faced difficulties. Weinstein (2013: 209-213) describes the attempt at Montclair State University in Montclair, New Jersey, from 1987 through the 1990s.
Here is a series of questions you can ask yourself to try to ensure that you are thinking critically. Conspiracy theories. Inability to distinguish facts from falsehoods. Widespread confusion ...
Understanding emotions is a key aspect of critical thinking. Teach children to recognize and articulate their feelings and those of others. This helps them understand the impact of emotions on ...