Check out our guide with action verbs to add to your next piece of writing; create impactful storylines that keep your readers hooked with these powerful verbs.
Action verbs add an extra “oomph!” to your writing, helping you to describe the many things your characters will achieve throughout the story. Learning how to use action verbs will enhance your writing, help to define your characters, and allow your readers to grasp the plot points with ease.
However, action verbs aren’t just for story writing. They’re also ideal to use in your resume when applying for jobs. Check out what Indeed.com says about using action verbs:
So, it’s important to learn the correct action verbs to use in your writing to make a lasting impact on the readers. Whether you’re working on a fiction book, an essay, or sprucing up your resume, we’ve got everything you need to level up your writing. If you’re interested in this topic, check out our list of feeling words for more!
Mental action verbs, action verbs denoting personal improvement, action verbs denoting productivity , action verbs denoting ability, action verbs denoting leadership traits, action verbs denoting initiative, action verbs denoting excellent communication skills, finance action verbs.
Action verbs, a.k.a. dynamic verbs, express an action a person takes. They are one of two major categories of verbs in English (the other one being stative verbs). In other words, active verbs describe what a person is doing or has done and are, consequently, often used in business.
One typical example where action verbs shine is the bullet statement format used when the writer wants to describe their accomplishments using a bare minimum of words. However, remember that not all action verbs are made equal. The words that cement the image of the writer accomplishing something instead of merely being in charge of it are the best choice.
E.g., “handling” is not as illustrative as “executing.” Precision takes precedence and makes a lasting impact. Therefore, pick your verbs carefully. You might also be interested in our list of boring words and phrases to avoid in your writing.
Mental action verbs describe intellectual or inner dynamic actions. Discerning them can be challenging as many stative verbs describe thoughts and opinions. Therefore, we’re starting with some notable examples of mental action verbs. You might also be interested in our homophones word list .
He was analyzing testimonials all night and was late for work in the morning.
2. Appreciate
He appreciates that cooperation with the sales department is a necessary evil.
3. Consider
Mark considered his roommate’s decisions as foolish but kept silent.
As a child, Anna dreamt of playing the flute, but her parents never allowed it.
5. Evaluate
Nicholas wasn’t able to evaluate the situation properly due to shock.
I fear that the situation is getting out of hand.
The idea is growing on me.
I imagine you’re referring to Star Wars.
The CEO failed to learn anything from employee feedback.
11. Memorize
I try to memorize five new Chinese words every day.
13. Remember
She could vaguely remember Nick’s face after all those years they’d been apart.
14. Resolve
He resolved to learn Japanese and head the regional branch.
Reviewing for exams can help students join the dots seamlessly.
To underline success, professional and personal alike, you may use suitable action verbs denoting improvement. Here are some examples:
17. Accomplish
I think I’ve accomplished much in this short amount of time.
Our IT team has customized the chatbot.
19. Demonstrate
They demonstrated their knowledge during the seminar.
Larry modified his views to meet project requirements.
22. Overhaul
Shareholders have decided to overhaul the training program.
She set to revamp company policies to include hybrid work models.
24. Revitalize
Yoga classes can help you revitalize your body and spirit in no time.
25. Streamline
Mark worked hard to streamline operations to benefit the entire team.
26. Strengthen
She strengthened her resolve to deal with her past trauma.
27. Surpass
He has truly surpassed himself with his latest whitepaper.
30. Transform
Transforming my career advancement plans is the best thing I’ve ever done.
31. Translate
My teacher says I must translate this sentence twenty times to grasp synonyms.
We’d appreciate it if you could keep us updated on the procedure.
33. Upgrade
There are many action verbs suitable for business English. Let’s consider some examples of verbs denoting productivity. You might also be interested in our list of describing words .
34. Achieve
I need to work hard to achieve my goals.
Becoming an author can be one of the most creative and rewarding careers.
36. Publish
The feeling of publishing your first novel is like nothing else; the excitement and pride you will feel are unparalleled.
37. Actualize
To actualize your potential, you need to train harder.
He’s adapting the play to suit a wider audience.
39. Address
He addressed the audience with an enthusiasm rarely witnessed before.
Individuals need to adjust their approach to suit the team.
41. Advance
The creditor advanced $100 million to help the business with debt repayments.
42. Amplify
Maria’s vision of the upcoming meeting with shareholders was amplifying her morale.
The initiative aims to boost sales during the peak season.
44. Capitalize
He capitalized on the sudden increase in demand.
45. Collect
I’m going to collect the latest issue of the magazine first thing tomorrow morning.
46. Compute
The management uses feedback to compute the rate of employee performance.
47. Conceive
48. Conceptualize
I’m unsure if I’ll be able to conceptualize the bigger picture, but I’ll give it my best shot.
49. Consolidate
The HR department consolidated its processes in an attempt to attract talent.
50. Construct
I’m constructing the argument in my mind and have yet to shape it into words.
51. Co-produce
Hannah curated the exhibit alongside her husband, rumored to be an expert in the field.
Nina has been tasked with debugging the company’s in-house software.
54. Deliver
Ronaldo rarely fails to deliver a perfect pass.
We’ve hired a wildly popular digital artist to design our holiday brochure.
He’s good at devising out-of-the-box solutions; that’s why we hired him in the first place.
57. Diagnose
Simon is trying to enhance his reputation by demonstrating his unique expertise.
59. Expedite
Teams’ efforts expedited departmental plans.
60. Explore
The brand is exploring collaborating on a new project with the new regional start-up .
61. Further
Mary’s donation furthered her company’s positive outlook.
62. Improve
We need to improve our merger plans.
63. Maximize
Johanna’s superb design skills maximized company impact during the presentation.
64. Proofread
Nicholas proofreads books for an established publishing company.
65. Reconcile
Reconciling opposing viewpoints may be challenging, but we need to succeed all the same.
Her speech stimulated everyone present to perform better.
67. Sustain
Seasonal earnings will sustain our business during the dormant season.
She refused to yield power to the shareholders.
Action verbs can be used to efficiently communicate one’s ability. Here are some examples to help you get started.
69. Administer
They had to administer the revenues to prevent unfair play.
I’m thinking of learning to code programs.
71. Complete
He is working overtime to complete work.
72. Develop
She’s trying to develop empathy in an attempt to reinvent herself.
73. Document
We need to document and report employee feedback before the next meeting.
74. Drive
She edits a business magazine that’s becoming more popular by the day.
76. Execute
The higher-ups are set to execute the new strategy.
There’s much I need to learn to expand my views.
78. Implement
We plan to implement a policy allowing all new hires to sign up for benefits.
79. Interpret
We need to interpret the stats as best we can; we’re not getting any help from higher-ups.
80. Operate
81. Organize
If I wanted you to organize my life, I wouldn’t have looked for a roommate.
82. Perform
I need to study more if I want to perform better than average.
83. Prepare
84. Realize
Action verbs can be rather impactful when denoting leadership traits. They communicate expertise and willingness to deal with any obstacle. Here are the finest examples of dynamic verbs denoting leadership aspirations and expertise:
85. Arrange
I’ll arrange everything, so the only thing you need to do is follow through.
Management assessed the cost of the latest marketing initiative at ca. £7,000.
I’m assigning this job to you because I find your soft skills quite suitable.
My brother said he’d assist me with the task.
You need to decide on your own how to attain the goal; it’s rather subjective.
90. Authorize
He’s built his career around his seamless communication skills.
Peculiarly enough, chairing the meeting is a new hire.
She is performing her tasks so seamlessly that I’m wondering if she’s been coached by a professional.
94. Coordinate
We need to coordinate our efforts to get the job done ASAP.
95. Delegate
Higher-ups are deploying resources more sparingly due to past grievances.
A police officer is directing the traffic again.
98. Empower
The matter of how to empower remote workers is gaining broad recognition.
100. Encourage
Top brass are encouraging project development as it is expected to make them rich overnight.
101. Enforce
The police are trying to enforce speed limits with varying degrees of success.
102. Engineer
103. Examine
They’re examining the cause of the failure with the help of our brand-new AI solution.
104. Exceed
105. Explain
Joshua explained to his mates that he’d be leaving the band due to personal obligations.
106. Foster
They’re fostering a sense of inclusivity, but I can tell they’re not too happy about the whole affair.
107. Fulfill
He has failed to fulfill his promise and is trying to make amends.
Mr. Smith guided us through all the trials and tribulations of the takeover.
He is heading the meeting regardless of the uproar.
Helping him overcome the divorce was the best thing I ever did.
111. Individualize
Our HR teams are individualizing onboarding programs to allow for better personalization.
112. Inspect
We went to inspect the damage after the flood.
113. Instruct
The management instructed the team to align goals with the brand mission.
114. Invest
He’s invested in his studies and hardly has any spare time for anything else.
115. Investigate
They’ve investigated allegations of corruption and found nothing conclusive.
116. Lecture
Businesses are lobbying for proposed changes in the tax laws.
118. Maintain
Jonny is maintaining a healthy lifestyle with a little help from his wife.
119. Manage
He has managed finances for as long as I can remember.
120. Map
IT teams are mapping all network drives at the moment.
121. Moderate
Mary thinks she needs to moderate her stance as she came across as overly harsh.
Our HR experts mold new hires’ characters with ease.
123. Motivate
I am motivated to help my friends achieve their goals.
124. Network
Company meetings are a good opportunity to network .
125. Orchestrate
He charged us with orchestrating the production.
126. Outperform
Our company will easily outperform our biggest competitor again.
127. Oversee
We need to appoint an engineer to oversee the construction.
128. Participate
We’ll all participate in the upcoming get-along and are fired up.
129. Partner
Mark and Maria partnered for the competition, hoping to place better.
They are planning a project in line with new directives.
131. Preside
The new integrator will preside at tomorrow’s meeting.
133. Project
The revenue is projected to surge again.
134. Spearhead
He spearheaded the company’s expansion into the U.S.A.
135. Supervise
The logistics department is supervising the distribution of resources.
136. Support
I planned to support her claim, but she’d been lying through her teeth.
By nature, initiative portends action. That’s why dynamic verbs are so illustrative in this regard. Take a look at a couple of examples below:
138. Balance
Balancing professional and private life can get tricky during the peak season.
139. Budget
An additional $10 million needs to be budgeted for new projects in Q3.
140. Calculate
I’m calculating the total right now.
Mr. Watson is continually charting the progress of each team member, so be careful.
We’ll be able to close the deal tomorrow.
143. Co-author
Maria and her brother have co-authored a vegetarian cookbook.
144. Collaborate
We’ll be collaborating with a Korean firm to develop the new product.
145. Create
Creating new initiatives is going as planned, so don’t worry.
146. Discover
I’m discovering more about the wabi-sabi concept with each passing day.
147. Establish
Establishing a new regional branch sounds like a good idea at this point.
148. Facilitate
To facilitate group discussion, project leaders should be inventive.
To form an impactful sentence, you should consider using active verbs.
151. Formalize
They are planning to formalize the deal, but details have yet to be defined.
152. Formulate
Try as I might, I failed to formulate a proper response.
153. Gather
Everyone should gather here after work as we will throw a welcome party.
154. Initiate
There are several ways to initiate knowledge sharing, and AI is just the tip of the iceberg.
155. Institute
Policymakers are about to institute a number of measures to enforce public safety.
156. Introduce
Today, he’ll be introducing new technological developments in healthcare.
Join us for the outing tonight; it’ll be fun.
The football player kicked his opponent during the match and was removed from the game.
160. Launch
161. Pioneer
He’s regarded as a pioneer in the world of art and literature.
163. Present
I’ll present the latest developments I’ve worked hard to come by.
164. Propose
The judge proposed the establishment of special tribunals for the trial of offenses disturbing the general peace.
He did raise some important questions, but the audience remained silent.
I’ll have reached NY headquarters by 5 PM.
167. Survey
I’m surveying the terrain now, so give me some time, and I’ll get back to you with the findings.
168. Team (up)
They teamed up for the upcoming competition, and their morale is through the roof!
170. Visualize
I can visualize my future in the company going forward.
Communication rules supreme, especially in the age of rapid digitalization. Use action verbs to demonstrate your skill! Let’s illustrate best practices.
171. Convince
I am sure I can convince her to share her thoughts.
172. Communicate
We need to communicate the news during the meeting.
173. Compose
It took me some time to compose myself after the incident.
174. Cooperate
My son refuses to cooperate and denies his involvement in the incident.
175. Correspond
He still corresponds with Jamaican friends he met in Germany five years ago.
176. Define
Yes, he is drafting the legislation, but he’s taking his time.
178. Illustrate
Let me give you an example to illustrate the point.
179. Outline
The professor outlined his methodology in his latest book.
180. Persuade
181. Promote
Mark was promoted to the First Division after nailing down his previous mission.
182. Publicize
He never did publicize his book, but it was an instant success nevertheless.
We’ve managed to find a volunteer to write our manifest.
Finally, finance experts use action verbs galore and not without a good reason. This hectic industry is best described by dynamic words, but do note that these verbs can be equally impactful in other contexts as well.
Let’s take a look at some notable examples.
184. Appraise
The team is appraising the property , with estimates still being vague.
They audit all accounts annually to ensure they align with company policies.
186. Convert
He keeps converting all his cash from pounds into dollars. Is he planning to visit the States?
187. Decrease
I’m decreasing the revenue forecast due to last month’s unexpected losses.
188. Estimate
Analysts estimate the trend will be reversing any time now.
189. Forecast
Shareholders forecast the profit to grow by 2% in this quarter.
I’ve lowered the assessment to reflect recent data.
191. Measure
Measuring the impact of public involvement in research is never an easy task.
192. Qualify
They seem to think that reading a couple of books on AI qualifies them as experts.
193. Reduce
Team members worked hard to reduce the negative impact the latest marketing initiative had invoked.
194. Report
Reporting with the latest developments is our journalist Mark. Mark, tell us what’s going on!
195. Research
Researching her prior experiences, Viola discovered how to further her goals.
Financial aid is available to help those struggling with essential payments like rent or mortgage fees.
197. Advise
A great accountant will advise you on the best business practices as well as help with your taxes.
Adding power verbs to your academic paper will improve your reader’s experience and bring more impact to the arguments you make.
While the arguments themselves are the most important elements of any successful academic paper, the structure of those arguments and the language that is used influence how the paper is received.
Academic papers have strict formal rules, but as long as these are followed, there is still plenty of scope to make the key points of the paper stand out through effective use of language and more specifically, the effective use of power verbs.
Power verbs are verbs that indicate action and have a more positive and confident tone. Using them brings strength and confidence to the arguments you are making, while also bringing variation to your sentences and making your writing more interesting to the reader.
The best academic papers will use such verbs to support their arguments or concepts, so it is important that your paper contains at least three power verbs.
ProWritingAid will check your writing for power verbs and will notify you if you have less than three throughout your whole academic paper.
Examples of power verbs.
Academic papers of all disciplines are often filled with overlong and complicated sentences that are attempting to convey specific ideas and concepts. Active and powerful verbs are useful both to the reader and the author of the paper.
For the reader who is trying to tackle these ideas and concepts, the power verbs provide clarity and purpose. Compare the following sentences:
Clearly the second sentence is more confident, direct, and authoritative because it has replaced the dull ‘says’ with ‘asserts.’ For the writer, the power verb expresses confidence in the idea being presented.
The following are examples of power verbs that are useful in academic writing, both for supporting an argument and for allowing you to vary the language you use.
Power Verbs for Analysis: appraise, define, diagnose, examine, explore, identify, interpret, investigate, observe.
Power Verbs to Introduce a Topic: investigate, outline, survey, question, feature.
Power Verbs to Agree with Existing Studies: indicate, suggest, confirm, corroborate, underline, identify, impart, maintain, substantiate, support, validate, acknowledge, affirm, assert.
Power Verbs to Disagree with Existing Studies: reject, disprove, debunk, question, challenge, invalidate, refute, deny, dismiss, disregard, object to, oppose.
Power Verbs to Infer: extract, approximate, surmise, deduce.
Power Verbs for Cause and Effect : impacts, compels, generates, incites, influences, initiates, prompts, stimulates, provokes, launches, introduces, advances.
Legal Power Verbs: sanctions, consents, endorses, disallows, outlaws, prohibits, precludes, protects, bans, licenses, authorizes.
Power Verbs that Say: convey, comment, state, establish, elaborate, identify, propose.
Power Verbs that Show: reveal, display, highlight, depict, portray, illustrate.
Check every email, essay, or story for grammar mistakes. Fix them before you press send.
The most successful people in the world have coaches. Whatever your level of writing, ProWritingAid will help you achieve new heights. Exceptional writing depends on much more than just correct grammar. You need an editing tool that also highlights style issues and compares your writing to the best writers in your genre. ProWritingAid helps you find the best way to express your ideas.
Bring your story to life for less. Get 25% off yearly plans in our Storyteller's Sale. Grab the discount while it lasts.
Active verbs for discussing ideas.
This handout is available for download in PDF format .
Active verbs are important components of any academic writing! Just as in other forms of writing, they work as engines, driving the action of your sentences in many potentially vivid, clear, and colorful ways.
Instead of opting for bland, unspecific expressions ("says," "writes about," "believes," "states") consider using more vivid or nuanced verbs such as "argues," "insists," "explains," "emphasizes," "challenges," "agrees," etc. The list below offers dozens of such verbs that will help you communicate your ideas and the ideas of others more clearly, expressively, and powerfully.
| Action Verbs A-C | Action Verbs D-H | Action Verbs I-Q | Action Verbs R-Z |
| accepts | declares | identifies | ratifies |
| acknowledges | defends | illuminates | rationalizes |
| adds | defies | implies | reads |
| admires | demands | infers | reconciles |
| affirms | denies | informs | reconsiders |
| allows that | describes | initiates | refutes |
| analyzes | determines | insinuates | regards |
| announces | diminishes | insists | rejects |
| answers | disagrees | interprets | relinquishes |
| argues | discusses | intimates | reminds |
| assaults | disputes | judges | repudiates |
| assembles | disregards | lists | resolves |
| asserts | distinguishes | maintains | responds |
| assists | emphasizes | marshals | retorts |
| buttresses | endorses | narrates | reveals |
| categorizes | enumerates | negates | reviews |
| cautions | exaggerates | observes | seeks |
| challenges | experiences | outlines | sees |
| claims | experiments | parses | shares |
| clarifies | explains | perceives | shifts |
| compares | exposes | persists | shows |
| complicates | facilitates | persuades | simplifies |
| concludes | formulates | pleads | states |
| condemns | grants | points out | stresses |
| confirms | guides | postulates | substitutes |
| conflates | handles | praises | suggests |
| confronts | hesitates | proposes | summarizes |
| confuses | highlights | protects | supplements |
| considers | hints | provides | supplies |
| contradicts | hypothesizes | qualifies | supports |
| contrasts | | | synthesizes |
| convinces | | | tests |
| criticizes | | | toys with |
| critiques | | | treats |
| | | uncovers |
| | | undermines |
| | | urges |
| | | verifies |
| | | warns |
- "mentions," unless you mean "refer to something briefly and without going into detail."*
- "notion" as a synonym for "idea" implies "impulsive," "whimsical," not well considered.*
Adapted from a list by Cinthia Gannett by Doug Kirshen and Robert B. Cochran, Brandeis University Writing Program, 2020.
- Resources for Students
- Writing Intensive Instructor Resources
- Research and Pedagogy

Best Active Verbs for Research Papers with Examples
What are active verbs.
Active verbs, often referred to as "action verbs," depict activities, processes, or occurrences. They energize sentences by illustrating direct actions, like "run," "write," or "discover." In contrast, linking verbs connect the subject of a sentence to its complement, offering information about the subject rather than denoting an action. The most common linking verb is the "be" verb (am, is, are, was, were, etc.), which often describes a state of being. While active verbs demonstrate direct activity or motion, linking and "be" verbs serve as bridges, revealing relations or states rather than actions.
While linking verbs are necessary to states facts or show connections between two or more items, subjects, or ideas, active verbs usually have a more specific meaning that can explain these connections and actions with greater accuracy. And they captivate the reader’s attention! (See what I did there?)
Why are active verbs important to use in research papers?
Using active verbs in academic papers enhances clarity and precision, propelling the narrative forward and making your arguments more compelling. Active verbs provide clear agents of action, making your assertions clearer and more vigorous. This dynamism ensures readers grasp the research's core points and its implications.
For example, using an active vs passive voice sentence can create more immediate connection and clarity for the reader. Instead of writing "The experiment was conducted by the team," one could write, "The team conducted the experiment."
Similarly, rather than stating "Results were analyzed," a more direct approach would be "We analyzed the results." Such usage not only shortens sentences but also centers the focus, making the statements about the research more robust and persuasive.
Best Active Verbs for Academic & Research Papers
When writing research papers , choose active verbs that clarify and energize writing: the Introduction section "presents" a hypothesis, the Methods section "describes" your study procedures, the Results section "shows" the findings, and the Discussion section "argues" the wider implications. Active language makes each section more direct and engaging, effectively guiding readers through the study's journey—from initial inquiry to final conclusions—while highlighting the researcher's active role in the scholarly exploration.
Active verbs to introduce a research topic
Using active verbs in the Introduction section of a research paper sets a strong foundation for the study, indicating the actions taken by researchers and the direction of their inquiry.
Stresses a key stance or finding, especially when referring to published literature.
Indicates a thorough investigation into a research topic.
Draws attention to important aspects or details of the study topic you are addressing.
Questions or disputes established theories or beliefs, especially in previous published studies.
Highlights and describes a point of interest or importance.
Inspects or scrutinizes a subject closely.
Sets up the context or background for the study.
Articulates
Clearly expresses an idea or theory. Useful when setting up a research problem statement .
Makes something clear by explaining it in more detail.
Active verbs to describe your study approach
Each of these verbs indicates a specific, targeted action taken by researchers to advance understanding of their study's topic, laying out the groundwork in the Introduction for what the study aims to accomplish and how.
Suggests a theory, idea, or method for consideration.
Investigates
Implies a methodical examination of the subject.
Indicates a careful evaluation or estimation of a concept.
Suggests a definitive or conclusive finding or result.
Indicates the measurement or expression of an element in numerical terms.
Active verbs to describe study methods
The following verbs express a specific action in the methodology of a research study, detailing how researchers execute their investigations and handle data to derive meaningful conclusions.
Implies carrying out a planned process or experiment. Often used to refer to methods in other studies the literature review section .
Suggests putting a plan or technique into action.
Indicates the use of tools, techniques, or information for a specific purpose.
Denotes the determination of the quantity, degree, or capacity of something.
Refers to the systematic gathering of data or samples.
Involves examining data or details methodically to uncover relationships, patterns, or insights.
Active verbs for a hypothesis or problem statement
Each of the following verbs initiates a hypothesis or statement of the problem , indicating different levels of certainty and foundations of reasoning, which the research then aims to explore, support, or refute.
Suggests a hypothesis or a theory based on limited evidence as a starting point for further investigation.
Proposes a statement or hypothesis that is assumed to be true, and from which a conclusion can be drawn.
Attempts to identify
Conveys an explicit effort to identify or isolate a specific element or relationship in the study.
Foretells a future event or outcome based on a theory or observation.
Theorizes or puts forward a consideration about a subject without firm evidence.
Proposes an idea or possibility based on indirect or incomplete evidence.
Active verbs used to interpret and explain study results
In the Discussion section , the findings of your study are interpreted and explained to the reader before moving on to study implications and limitations . These verbs communicate the outcomes of the research in a precise and assertive manner, conveying how the data aligns with the expectations and hypotheses laid out earlier in the paper.
Shows or unveils findings from the data.
Demonstrates
Clearly shows the result of an experiment or study, often implying evidence of a cause-and-effect relationship.
Illustrates
Shows or presentes a particular result or trend.
Provides evidence in favor of a theory or hypothesis.
Establishes the truth or validity of an anticipated outcome or theory.
Visually presents data, often implying the use of figures or tables.
Active verbs to discuss study implications
In the discussion of study implications, these verbs help to weave the results into a broader context, suggesting relevance, highlighting importance, and pointing out potential consequences within the respective field of research.
Proposes a possible interpretation or implication without making a definitive statement.
Points to broader consequences or significances hinted at by the results.
Indicates a logical consequence or a meaning that is not explicitly stated.
Strengthens the validity or importance of a concept or finding.
Emphasizes certain findings and their broader ramifications.
Underscores
Underlines or emphasizes the significance or seriousness of an implication.
Active verbs to discuss study limitations
Discussing study limitations with these verbs allows researchers to maintain transparency about their study's weaknesses, thus providing a clearer picture of the context and reliability of the research findings.
Acknowledges
Recognizes the existence of potential weaknesses or restrictions in the study.
Directly confronts a specific limitation and often discusses ways it has been mitigated.
Makes an observation of a limitation that could affect the interpretation of the results.
Reflects on or thinks about a limitation in the context of the study's impact or scope.
Points out and describes a specific limitation.
Makes known or reveals a limitation that could have an effect on the study's conclusions.
Active verbs for the Conclusion section
In the Conclusion section , these verbs are pivotal in crystallizing the core findings, implications, and the future trajectory of research initiated by the study.
Signifies drawing a final inference or judgement based on the results.
Provides a brief statement of the main points of the research findings.
States positively or asserts the validity of the findings.
Advises on a course of action based on the results obtained.
Highlights the importance or significance of the research outcomes.
Use an AI Grammar Checker to Correct Your Research Verbs
While lists like these will certainly help you improve your writing in any academic paper, it can still be a good idea to revise your paper using an AI writing assistant during the drafting process, and with professional editing services before submitting your work to journals.
Wordvice’s AI Proofreading Tool , AI Paraphrasing Tool , AI Summarizer , AI Translator , AI Grammar Checker , AI Plagiarism Checker , and AI Detector are ideal for enhancing your academic papers. And with our professional editing services, including academic proofreading and paper editing services, you get high-quality English editing from experts in your paper’s subject area.

280+ Strong Verbs: 3 Tips to Strengthen Your Verbs in Writing
by Joe Bunting | 0 comments
Start Your Story TODAY! We’re teaching a new LIVE workshop this week to help you start your next book. Learn more and sign up here.
Strong verbs transform your writing from drab, monotonous, unclear, and amateurish to engaging, professional, and emotionally powerful.
Which is all to say, if you're not using strong verbs in your writing, you're missing one of the most important stylistic techniques.

Why listen to Joe? I've been a professional writer for more than a decade, writing in various different formats and styles. I've written formal nonfiction books, descriptive novels, humorous memoir chapters, and conversational but informative online articles (like this one!).
In short, I earn a living in part by writing (and revising) using strong verbs selected for each type of writing I work on. I hope you find the tips on verbs below useful! And if you want to skip straight to the verb list below, click here to see over 200 strong verbs.
Hemingway clung to a writing rule that said, “Use vigorous English.” In fact, Hemingway was more likely to use verbs than any other part of speech, far more than typical writing, according to LitCharts :

But what are strong verbs? And how do you avoid weak ones?
In this post, you'll learn the three best techniques to find weak verbs in your writing and replace them with strong ones. We'll also look at a list of the strongest verbs for each type of writing, including the strongest verbs to use.
What are Strong Verbs?
Strong verbs, in a stylistic sense, are powerful verbs that are specific and vivid verbs. They are most often in active voice and communicate action precisely.
The Top 7 Strong Verbs
Here are the top 7 I found when I reviewed a couple of my favorite books. See if you agree and tell me in the comments.
Think about the vivid and specific image each of these strong verbs conjures. Each one asserts precision.
It's true that writers will use descriptive verbs that best fit their character, story, and style, but it's interesting to note trends.
For example, Hemingway most often used verbs like: galloped, punched, lashed, and baited. Each of these verbs evokes a specific motion, as well as a tone. Consider how Hemingway's verbs stack up against weaker counterparts:
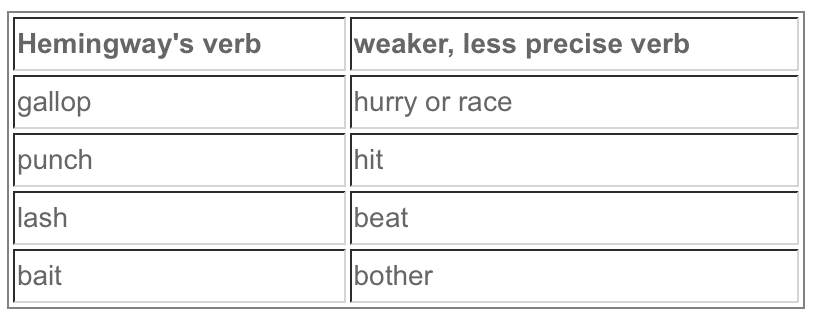
None of the weaker verbs are incorrect, but they don't pack the power of Hemingway's strong action verbs, especially for his story lines, characters, and style. These are verbs that are forward-moving and aggressive in tone. (Like his characters!)
Consider how those choices differ significantly than a few from Virginia Woolf's opening page of Mrs. Dalloway :
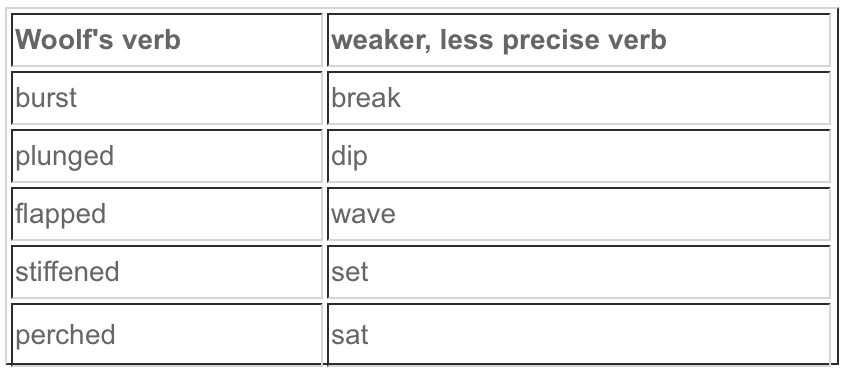
Notice how Woolf's choices create the vibrant, descriptive style that marks her experimental novel and its main character. Consider the difference between “perched” and “sat.” “Perched” suggests an image of a bird, balancing on a wire. Applied to people, it connotes an anxiousness or readiness to stand again. “Sat” is much less specific.
The strongest verbs for your own writing will depend on a few things: your story, the main character, the genre, and the style that is uniquely yours. How do you choose then? Let's look at three tips to edit out weak, boring verbs.
How to Edit for Strong Verbs FAST
So how do you root out those weak verbs and revise them quickly? Here are a few tips.
1. Search for Weak Verbs
All verbs can be strong if they're used in specific, detailed, and descriptive sentences.
The issue comes when verbs are overused, doing more work than they're intended for, watering down the writing.
Here are some verbs that tend to weaken your writing:
Did you notice that most of these are “to be” verbs? That's because “to be” verbs are linking verbs or state of being verbs. Their purpose is to describe conditions.
For example, in the sentence “They are happy,” the verb “are” is used to describe the state of the subject.
There's nothing particularly wrong with linking verbs. Writers who have a reputation for strong writing, like Ernest Hemingway or Cormac McCarthy, use linking verbs constantly.
The problem comes when you overuse them. Linking verbs tend to involve more telling vs. showing .
Strong verbs, on the other hand, are usually action verbs, like whack, said, ran, lassoed, and spit (see more in the list below).
The most important thing is to use the best verb for the context, while emphasizing specific, important details.
Take a look at the following example early into Hemingway's For Whom the Bell Tolls :
The young man, who was studying the country, took his glasses from the pocket of his faded, khaki flannel shirt, wiped the lenses with a handkerchief, screwed the eyepieces around until the boards of the mill showed suddenly clearly and he saw the wooden bench beside the door; the huge pile of sawdust that rose behind the open shed where the circular saw was , and a stretch of the flume that brought the logs down from the mountainside on the other bank of the stream.
I've highlighted all the verbs. You can see here that Hemingway does use the word “was,” but most of the verbs are action verbs, wiped, took, screwed, saw, etc. The result of this single sentence is that the audience pictures the scene with perfect clarity.
Here's another example from Naomi Novick's Deadly Education:
He was only a few steps from my desk chair, still hunched panting over the bubbling purplish smear of the soul-eater that was now steadily oozing into the narrow cracks between the floor tiles, the better to spread all over my room. The fading incandescence on his hands was illuminating his face, not an extraordinary face or anything: he had a big beaky nose that would maybe be dramatic one day when the rest of his face caught up, but for now was just too large, and his forehead was dripping sweat and plastered with his silver-grey hair that he hadn’t cut for three weeks too long.
Vivid right? You can see that again, she incorporates weaker verbs (was, had) into her writing, but the majority are highly descriptive action verbs like hunched, illuminating, spread, plastered, and dripping.
Don't be afraid of linking verbs, state verbs, or helping verbs, but emphasize action words to make your writing more powerful.
2. Remove Adverbs and Replace the Verbs to Make Them Stronger
Adverbs add more detail and qualifications to verbs or adjectives. You can spot them because they usually end in “-ly,” like the word “usually” in this sentence, or frequently, readily, happily, etc.
Adverbs get a bad rap from writers.
“I believe the road to hell is paved with adverbs,” Stephen King said.
“Adverbs are dead to me. They cannot excite me,” said Mark Twain .
“I was taught to distrust adjectives,” said Hemingway, “as I would later learn to distrust certain people in certain situations.”
Even Voltaire jumped in on the adverb dogpile, saying, “Adjectives are frequently the greatest enemy of the substantive.”
All of these writers, though, used adverbs when necessary. Still, the average writer uses them far more than they did.
Adverbs signal weak verbs. After all, why use two words, an adverb and a verb, when one strong verb can do.
Look at the following examples of adverbs with weak verbs replaced by stronger verbs:
- He ran quickly –> He sprinted
- She said loudly –> She shouted
- He ate hungrily –> He devoured his meal
- They talked quietly –> They whispered
Strive for simple, strong, clear language over padding your writing with more words.
You don't need to completely remove adverbs from your writing. Hemingway himself used them frequently. But cultivating a healthy distrust of adverbs seems to be a sign of wisdom among writers.
3. Stop Hedging and “Eliminate Weasel Words”
Amazon's third tip for writing for employees is “Eliminate Weasel Words,” and that advice applies to verbs too.
Instead of “nearly all customers,” say, “89 percent of customers.”
Instead of “significantly better,” say, “a 43 percent improvement.”
Weasel words are a form of hedging.
Hedging allows you to avoid commitment by using qualifiers such as “probably,” “maybe,” “sometimes,” “often,” “nearly always,” “I think,” “It seems,” and so on.
Hedge words or phrases soften the impact of a statement or to reduce the level of commitment to the statement's accuracy.
By eliminating hedging, you're forced to strengthen all your language, including verbs.
What do you really think about something? Don't say, “I think.” Stand by it. A thing is or isn't. You don't think it is or believe it is. You stand by it.
If you write courageously with strength of opinion, your verbs grow stronger as well.

Beware the Thesaurus: Strong Verbs are Simple Verbs
I caveat this advice with the advice to beware thesauruses.
Strong writing is almost always simple writing.
Writers who replace verbs like “was” and “get” with long, five-syllable verbs that mean the same thing as a simple, one-syllable verb don't actually communicate more clearly.
To prepare for this article, I studied the verb use in the first chapters of several books by my favorite authors, including Ernest Hemingway's For Whom the Bell Tolls and Naomi Novik's Deadly Education.
Hemingway has a bigger reputation as a stylist and a “great” writer, but I found that Novik's verb choice was just as strong and even slightly more varied.
Hemingway tended to use simpler, shorter verbs, though, often repeating verbs, whereas Novik's verbs were longer and often more varied.
I love both of these writers, but if you're measuring strength, simplicity will most often win.
In dialogue this is especially important . Writers sometimes try to find every synonym for the word, “said” to describe the exact timber and attitude of how a character is speaking.
This becomes a distraction from the dialogue itself. In dialogue, the words spoken should speak for themselves, not whatever synonym the writer has looked up for “said.”
Writers should use simple speaker tags like “said” and “asked” as a rule, only varying that occasionally when the situation warrants it.
270+ Strong Verbs List
We've argued strong verbs are detailed, descriptive, action verbs, and below, I list over 200 strong verbs to make your writing better.
I compiled this list directly from the first chapters of some of my favorite books, already mentioned previously, For Whom the Bell Tolls by Ernest Hemingway, Deadly Education by Naomi Novik, and The Undoing Project by Michael Lewis.
This is a necessarily simplified list, taken only from the first chapters of those books. There are thousands of strong verbs, usually action verbs, but these are a good start.
I've also sorted them alphabetically and put them into present tense.
- Collaborate
- Intellectualize
The Best Way to Learn to Use Strong Verbs
The above tips will help get you started using strong verbs, but the best way to learn how to grow as a writer with your verbs is through reading.
But not just reading, studying the work of your favorite writers carefully and then trying to emulate it, especially in the genre you write in.
As Cormac McCarthy, who passed away recently, said, “The unfortunate truth is that books are made from books.”
If you want to grow as a writer, start with the books you love. Then adapt your style from there.
Which tip will help you use more strong verbs in your writing today? Let me know in the comments.
Choose one of the following three practice exercises:
1. Study the verb use in the first chapter of one of your favorite books. Write down all of the verbs the author uses. Roughly what percentage are action verbs versus linking verbs? What else do you notice about their verb choice?
2. Free write for fifteen minutes using only action verbs and avoiding all “to be” verbs and adverbs.
3. Edit a piece that you've written, replacing the majority of linking verbs with action verbs and adverbs with stronger verbs.
Share your practice in the Pro Practice Workshop here , and give feedback to a few other writers.

Joe Bunting
Joe Bunting is an author and the leader of The Write Practice community. He is also the author of the new book Crowdsourcing Paris , a real life adventure story set in France. It was a #1 New Release on Amazon. Follow him on Instagram (@jhbunting).
Want best-seller coaching? Book Joe here.

Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Submit Comment
Join over 450,000 readers who are saying YES to practice. You’ll also get a free copy of our eBook 14 Prompts :
Popular Resources
Best Resources for Writers Book Writing Tips & Guides Creativity & Inspiration Tips Writing Prompts Grammar & Vocab Resources Best Book Writing Software ProWritingAid Review Writing Teacher Resources Publisher Rocket Review Scrivener Review Gifts for Writers
Books By Our Writers

You've got it! Just us where to send your guide.
Enter your email to get our free 10-step guide to becoming a writer.
You've got it! Just us where to send your book.
Enter your first name and email to get our free book, 14 Prompts.
Want to Get Published?
Enter your email to get our free interactive checklist to writing and publishing a book.
Have a language expert improve your writing
Run a free plagiarism check in 10 minutes, generate accurate citations for free.
Action Verbs | Definition, List & Examples
Published on September 18, 2023 by Kassiani Nikolopoulou .
An action verb (also called a dynamic verb ) describes the action that the subject of the sentence performs (e.g., “I run”).
Action verbs differ from stative verbs, which describe a state of being (e.g., “believe,” “want”).
My grandfather walks with a stick.
The train arrived on time.
You can download our list of common action verbs in the format of your choice below.
Download PDF list Download Google Docs list
Table of contents
What is an action verb, how to use action verbs, action verbs vs. stative verbs, action verbs vs. linking verbs, worksheet: action verbs, other interesting language articles, frequently asked questions.
An action verb is a type of verb that describes the action that the subject of a sentence is performing. Action verbs can refer to both physical and mental actions (i.e., internal processes and actions related to thinking, perceiving, or feeling).
Whitney analyzed the data to find patterns.
He played football in high school.
Check for common mistakes
Use the best grammar checker available to check for common mistakes in your text.
Fix mistakes for free
Action verbs can be transitive or intransitive. Transitive verbs require a direct object , such as a noun or pronoun , that receives the action. Without a direct object, sentences with a transitive verb are vague or incomplete.
In contrast, intransitive verbs do not require a direct object that receives the action of the verb. However, other information may come after the verb, such as an adverb .
Some action verbs can act as both transitive and intransitive verbs.
He grows tomatoes on his balcony. My niece is growing quickly. Note Because action verbs make your writing more vivid, they can be effectively used for resume writing. Unlike generic phrases like “responsible for,” “tasked with,” or “experienced in,” action verbs are attention-grabbing and help emphasize our abilities and accomplishments.
- I was responsible for social media accounts across various platforms.
- I managed social media accounts across various platforms.
Action or dynamic verbs are often contrasted with stative verbs . While action verbs communicate action, stative verbs describe a state of being or perception (e.g., “it tasted,” “he is,” “she heard”). Due to this, they are typically used to provide more information about the subject, rather than express an action that the subject did. For example, the sentence “Tom loves spending time with friends” uses a stative verb “love” to give us more information about Tom’s personality.
However, some verbs can be used as either dynamic or stative verbs depending on the meaning of the sentence. For example, the verb “think” can denote someone’s opinion ( stative verb ) or the internal process of considering something ( action verb ).
One way to tell action verbs from stative verbs is to look at the verb tenses . Because stative verbs usually describe a state of being that is unchanging, they can’t be used in the continuous (or progressive) tenses. Action verbs, on the other hand, can be used in continuous tenses.
- I am wanting some food.
- I want some food.
Another way is to look at the meaning of the sentence and ask yourself if the verb shows what someone does or how someone feels or is. If the verb describes what someone does, it is an action verb. Otherwise, it is probably a stative verb.
Action verbs should not be confused with linking verbs , like “be,” “become,” and “seem.” Linking verbs connect the subject of a sentence with a subject complement (i.e., a noun or adjective that describes it).
Unlike action verbs, linking verbs do not describe an action, but add more details about the subject, such as how it looks or tastes.
For example, the sentence “The children seem happy” uses the linking verb “seem” to link the subject (“the children”) with the adjective (“happy”).
Some verbs can be either linking verbs or action verbs . If you are unsure, try replacing the linking verb with a conjugated form of the verb “be.” If the sentence still makes sense, then it is a linking verb.
To test your understanding of action verbs, try the worksheet below. Choose the correct answer for each question.
- Practice questions
- Answers and explanations
- Are you baking cookies? They_______[smell/are smelling] delicious!
- Understand is not an action verb, but a stative verb because we can’t use it in a continuous tense. For example, “I’m not understanding you at all” is incorrect.
- Kick is an action verb, while “believe” and “agree” are both stative verbs.
- Smell is correct because it is a stative verb and cannot be used in the present continuous.
If you want to know more about commonly confused words, definitions, common mistakes, and differences between US and UK spellings, make sure to check out some of our other language articles with explanations, examples, and quizzes.
Nouns & pronouns
- Common nouns
- Proper nouns
- Collective nouns
- Personal pronouns
- Uncountable and countable nouns
- Verb tenses
- Phrasal verbs
- Sentence structure
- Active vs passive voice
- Subject-verb agreement
- Interjections
- Determiners
- Prepositions
There are many ways to categorize verbs into various types. A verb can fall into one or more of these categories depending on how it is used.
Some of the main types of verbs are:
- Regular verbs
- Irregular verbs
- Transitive verbs
- Intransitive verbs
- Dynamic verbs
- Stative verbs
- Linking verbs
- Auxiliary verbs
- Modal verbs
If you are unsure whether a word is an action verb , consider whether it is describing an action (e.g., “run”) or a state of being (e.g., “understand”). If the word describes an action, then it’s an action verb.
The function of an action verb is to describe what the subject of the sentence is doing. For example, in the sentence “You have been working since 7 o’clock this morning,” the action verb “work” shows us what the subject (“you”) has been doing.
Cite this Scribbr article
If you want to cite this source, you can copy and paste the citation or click the “Cite this Scribbr article” button to automatically add the citation to our free Citation Generator.
Nikolopoulou, K. (2023, September 18). Action Verbs | Definition, List & Examples. Scribbr. Retrieved August 21, 2024, from https://www.scribbr.com/verbs/action-verb/
Is this article helpful?

Kassiani Nikolopoulou
Other students also liked, what is a transitive verb | examples, definition & quiz, what is an intransitive verb | examples, definition & quiz, what is a linking verb | definition & examples, get unlimited documents corrected.
✔ Free APA citation check included ✔ Unlimited document corrections ✔ Specialized in correcting academic texts

50 Verbs of Analysis for English Academic Essays

Note: this list is for advanced English learners (CEFR level B2 or above). All definitions are from the Cambridge Dictionary online .
Definition: to have an influence on someone or something, or to cause a change in someone or something.
Example: Experts agree that coffee affects the body in ways we have not yet studied.
Definition: to increase the size or effect of something.
Example: It has been shown that this drug amplifies the side effects that were experienced by patients in previous trials.
Definition: to say that something is certainly true .
Example: Smith asserts that his findings are valid, despite criticism by colleagues.
Characterizes
Definition: Something that characterizes another thing is typical of it.
Example: His early paintings are characterized by a distinctive pattern of blue and yellow.
Definition: to say that something is true or is a fact , although you cannot prove it and other people might not believe it.
Example: Smith claims that the study is the first of its kind, and very different from the 2015 study he conducted.
Definition: to make something clear or easier to understand by giving more details or a simpler explanation .
Example: The professor clarified her statement with a later, more detailed, statement.
Definition: t o collect information from different places and arrange it in a book , report , or list .
Example: After compiling the data, the scientists authored a ten-page paper on their study and its findings.
Definition: to judge or decide something after thinking carefully about it.
Example: Doctor Jensen concluded that the drug wasn’t working, so he switched his patient to a new medicine.
Definition: to prove that a belief or an opinion that was previously not completely certain is true .
Example: This new data confirms the hypothesis many researchers had.
Definition: to join or be joined with something else .
Example: By including the criticisms of two researchers, Smith connects two seemingly different theories and illustrates a trend with writers of the Romanticism period.

Differentiates
Definition: to show or find the difference between things that are compared .
Example: Smith differentiates between the two theories in paragraph 4 of the second part of the study.
Definition: to reduce or be reduced in s i ze or importance .
Example: The new findings do not diminish the findings of previous research; rather, it builds on it to present a more complicated theory about the effects of global warming.
Definition: to cause people to stop respecting someone or believing in an idea or person .
Example: The details about the improper research done by the institution discredits the institution’s newest research.
Definition: to show.
Example: Smith’s findings display the effects of global warming that have not yet been considered by other scientists.
Definition: to prove that something is not true .
Example: Scientists hope that this new research will disprove the myth that vaccines are harmful to children.
Distinguishes
Definition: to notice or understand the difference between two things, or to make one person or thing seem different from another.
Example: Our study seems similar to another one by Duke University: how can we distinguish ourselves and our research from this study?
Definition: to add more information to or explain something that you have said.
Example: In this new paper, Smith elaborates on theories she discussed in her 2012 book.
Definition: to represent a quality or an idea exactly .
Example: Shakespeare embodies English theater, but few can understand the antiquated (old) form of English that is used in the plays.
Definition: to copy something achieved by someone else and try to do it as well as they have.
Example: Although the study emulates some of the scientific methods used in previous research, it also offers some inventive new research methods.
Definition: to improve the quality , amount , or strength of something.
Example: The pharmaceutical company is looking for ways to enhance the effectiveness of its current drug for depression.

Definition: to make something necessary , or to involve something.
Example: The scientist’s study entails several different stages, which are detailed in the report.
Definition: to consider one thing to be the same as or equal to another thing.
Example: Findings from both studies equate; therefore, we can conclude that they are both accurate.
Establishes
Definition: to discover or get proof of something.
Example: The award establishes the main causes of global warming.
Definition: to make someone remember something or feel an emotion .
Example: The artist’s painting evokes the work of some of the painters from the early 1800s.
Definition: to show something.
Example: Some of the research study participants exhibit similar symptoms while taking the medicine.
Facilitates
Definition: to make something possible or easier .
Example: The equipment that facilitates the study is expensive and of high-quality.
Definition: the main or central point of something, especially of attention or interest .
Example: The author focuses on World War II, which is an era she hasn’t written about before.
Foreshadows
Definition: to act as a warning or sign of a future event .
Example: The sick bird at the beginning of the novel foreshadows the illness the main character develops later in the book.
Definition: to develop all the details of a plan for doing something.
Example: Two teams of scientists formulated the research methods for the study.
Definition: to cause something to exist .
Example: The study’s findings have generated many questions about this new species of frog in South America.

Definition: to attract attention to or emphasize something important .
Example: The author, Dr. Smith, highlights the need for further studies on the possible causes of cancer among farm workers.
Definition: to recognize a problem , need, fact , etc. and to show that it exists .
Example: Through this study, scientists were able to identify three of the main factors causing global warming.
Illustrates
Definition: to show the meaning or truth of something more clearly , especially by giving examples .
Example: Dr. Robin’s study illustrates the need for more research on the effects of this experimental drug.
Definition: to communicate an idea or feeling without saying it directly .
Example: The study implies that there are many outside factors (other than diet and exercise) which determine a person’s tendency to gain weight.
Incorporates
Definition: to include something as part of something larger .
Example: Dr. Smith incorporates research findings from 15 other studies in her well-researched paper.
Definition: to show, point , or make clear in another way.
Example: Overall, the study indicates that there is no real danger (other than a lack of sleep) to drinking three cups of coffee per day.
Definition: to form an opinion or guess that something is true because of the information that you have.
Example: From this study about a new medicine, we can infer that it will work similarly to other drugs that are currently being sold.
Definition: to tell someone about parti c ular facts .
Example: Dr. Smith informs the reader that there are some issues with this study: the oddly rainy weather in 2017 made it difficult for them to record the movements of the birds they were studying.
Definition: to suggest , without being direct , that something unpleasant is true .
Example: In addition to the reported conclusions, the study insinuates that there are many hidden dangers to driving while texting.
Definition: to combine two or more things in order to become more effective .
Example: The study about the popularity of social media integrates Facebook and Instagram hashtag use.

Definition: to not have or not have enough of something that is needed or wanted .
Example: What the study lacks, I believe, is a clear outline of the future research that is needed.
Legitimizes
Definition: to make something legal or acceptable .
Example: Although the study legitimizes the existence of global warming, some will continue to think it is a hoax.
Definition: to make a problem bigger or more important .
Example: In conclusion, the scientists determined that the new pharmaceutical actually magnifies some of the symptoms of anxiety.
Definition: something that a copy can be based on because it is an extremely good example of its type .
Example: The study models a similar one from 1973, which needed to be redone with modern equipment.
Definition: to cause something to have no effect .
Example: This negates previous findings that say that sulphur in wine gives people headaches.
Definition: to not give enough c a re or attention to people or things that are your responsibility .
Example: The study neglects to mention another study in 2015 that had very different findings.
Definition: to make something difficult to discover and understand .
Example: The problems with the equipment obscures the study.
Definition: a description of the main facts about something.
Example: Before describing the research methods, the researchers outline the need for a study on the effects of anti-anxiety medication on children.
Definition: to fail to notice or consider something or someone.
Example: I personally feel that the study overlooks something very important: the participants might have answered some of the questions incorrectly.
Definition: to happen at the same time as something else , or be similar or equal to something else .
Example: Although the study parallels the procedures of a 2010 study, it has very different findings.
Converse International School of Languages offers an English for Academic Purposes course for students interested in improving their academic English skills. Students may take this course, which is offered in the afternoon for 12 weeks, at both CISL San Diego and CISL San Francisco . EAP course graduates can go on to CISL’s Aca demic Year Abroad program, where students attend one semester at a California Community College. Through CISL’s University Pathway program, EAP graduates may also attend college or university at one of CISL’s Pathway Partners. See the list of 25+ partners on the CISL website . Contact CISL for more information.

273 Strong Verbs That’ll Spice Up Your Writing
Do you ever wonder why a grammatically correct sentence you’ve written just lies there like a dead fish?
I sure have.
Your sentence might even be full of those adjectives and adverbs your teachers and loved ones so admired in your writing when you were a kid.
But still the sentence doesn’t work.
Something simple I learned from The Elements of Style years ago changed the way I write and added verve to my prose. The authors of that little bible of style said: “Write with nouns and verbs, not with adjectives and adverbs.”
Even Mark Twain was quoted , regarding adjectives: “When in doubt, strike it out.”
That’s not to say there’s no place for adjectives. I used three in the title and first paragraph of this post alone.
The point is that good writing is more about well-chosen nouns and powerful verbs than it is about adjectives and adverbs, regardless what you were told as a kid.
There’s no quicker win for you and your manuscript than ferreting out and eliminating flabby verbs and replacing them with vibrant ones.
- How To Know Which Verbs Need Replacing
Your first hint is your own discomfort with a sentence. Odds are it features a snooze-inducing verb.
As you hone your ferocious self-editing skills, train yourself to exploit opportunities to replace a weak verb for a strong one .
At the end of this post I suggest a list of 273 vivid verbs you can experiment with to replace tired ones.
Want to download a copy of this strong verbs list to reference whenever you write? Click here. What constitutes a tired verb? Here’s what to look for:
- 3 Types of Verbs to Beware of in Your Prose
1. State-of-being verbs
These are passive as opposed to powerful:
Am I saying these should never appear in your writing? Of course not. You’ll find them in this piece. But when a sentence lies limp, you can bet it contains at least one of these. Determining when a state-of-being verb is the culprit creates a problem—and finding a better, more powerful verb to replace it— is what makes us writers. [Note how I replaced the state-of-being verbs in this paragraph.]
Resist the urge to consult a thesaurus for the most exotic verb you can find. I consult such references only for the normal word that carries power but refuses to come to mind.
I would suggest even that you consult my list of powerful verbs only after you have exhaust ed all efforts to come up with one on your own. You want Make your prose to be your own creation, not yours plus Roget or Webster or Jenkins. [See how easy they are to spot and fix?]
Impotent: The man was walking on the platform.
Powerful: The man strode along the platform.
Impotent: Jim is a lover of country living.
Powerful: Jim treasures country living.
Impotent: There are three things that make me feel the way I do…
Powerful: Three things convince me…
2. Verbs that rely on adverbs
Powerful verbs are strong enough to stand alone.
The fox ran quickly dashed through the forest.
She menacingly looked glared at her rival.
He secretly listened eavesdropped while they discussed their plans.
3. Verbs with -ing suffixes
Before: He was walking…
After: He walked…
Before: She was loving the idea of…
After: She loved the idea of…
Before: The family was starting to gather…
After: The family started to gather…

- The Strong Verbs List
- Disillusion
- Reverberate
- Revolutionize
- Supercharge
- Transfigure

Are You Making This #1 Amateur Writing Mistake?


Faith-Based Words and Phrases

What You and I Can Learn From Patricia Raybon

Before you go, be sure to grab my FREE guide:
How to Write a Book: Everything You Need to Know in 20 Steps
Just tell me where to send it:

Great!
Where should i send your free pdf.

Using Active Verbs to Revive Your Writing
By: Author ESLBUZZ
Posted on Last updated: August 2, 2023
Sharing is caring!
Active verbs are verbs that express an action performed by the subject of the sentence. Using active verbs in your writing can help to make your sentences clearer and more concise. They also make your writing more engaging and dynamic, helping to capture the reader’s attention and hold it throughout the piece.
Throughout this article, we will provide examples of active verbs in action and offer tips for how to use them effectively in your writing. Whether you are a student looking to improve your writing skills or a professional writer seeking to enhance your craft, understanding the importance of active verbs is essential. So, let’s dive in and explore the world of active verbs together!
Get Active with Active Verbs!

Understanding Active Verbs
If you’re learning English, you’ve likely come across the term “active verbs.” But what are they exactly? Simply put, active verbs are verbs that express an action. They are the backbone of any sentence and are essential in communicating effectively.
Active verbs can be divided into two categories: transitive and intransitive verbs. Transitive verbs require an object to complete their meaning, while intransitive verbs do not. For example, “throw” is a transitive verb, as it requires an object (e.g. “the ball”). “Run,” on the other hand, is an intransitive verb, as it doesn’t require an object to make sense.
Here are some more examples of active verbs:
Active verbs can also be used in different tenses, such as the present, past, and future. For example:
- Present tense: “I sing in the shower.”
- Past tense: “I sang in the shower.”
- Future tense: “I will sing in the shower.”
Using active verbs in your writing can make your sentences more engaging and interesting to read. They add movement and action to your writing, making it more dynamic and exciting.
In summary, active verbs are essential in communicating effectively in English. They express actions and can be divided into transitive and intransitive verbs. Using them in your writing can make it more engaging and dynamic.
Importance of Active Verbs
Active verbs are an essential element of clear, concise, and effective writing. Using active verbs instead of passive verbs can help enhance the writing quality, create clear sentences, and make the writing more engaging and captivating.
Enhancing Writing Quality
Active verbs add strength and clarity to your writing, making it more dynamic and engaging. They help to create a vivid picture in the reader’s mind and bring the text to life. Active verbs also help to avoid ambiguity and confusion, making it easier for the reader to understand the message.
For example, compare the following sentences:
Passive: The cake was eaten by the children. Active: The children ate the cake.
The second sentence is more direct and engaging, creating a clear picture of what happened. Using active verbs, you can create sentences that are more concise and to the point, making your writing more effective.
Creating Clear Sentences
Active verbs help to create clear sentences that are easy to read and understand. They make it clear who is doing the action, eliminating any confusion about the subject of the sentence.
For example, consider the following sentence:
Passive: The report was written by the manager. Active: The manager wrote the report.
The active sentence is more straightforward and easier to understand. It makes it clear who is doing the action and what the action is. Using active verbs can help to eliminate any confusion and make your writing more effective.
In conclusion, using active verbs is essential for clear, concise, and effective writing. They add strength and clarity to your writing, making it more dynamic and engaging. By using active verbs, you can create sentences that are more concise and to the point, making your writing more effective.
Identifying Active Verbs
Active verbs are verbs that show action. They are used to describe what a subject is doing. For example, in the sentence “The dog chased the cat,” the verb “chased” is an active verb because it shows that the dog is performing an action.
How to Identify Active Verbs
Identifying active verbs is easy once you know what to look for. Here are some tips to help you identify them in sentences:
- Look for verbs that show action. Examples include “run,” “jump,” “sing,” and “dance.”
- Pay attention to the subject of the sentence. The subject is the person or thing that is performing the action. The verb should match the subject in number and person.
- Be on the lookout for helping verbs such as “am,” “is,” “are,” “was,” and “were.” These verbs are not active verbs since they do not show action on their own.
Examples of Active Verbs
Here are some examples of sentences with active verbs:
- The children played in the park.
- The chef cooked a delicious meal.
- The birds chirped in the trees.
- The car raced down the highway.
In all of these examples, the verbs are active because they show an action being performed by the subject of the sentence.
Differences Between Active and Passive Verbs
As you may know, verbs are essential in English grammar. They help convey the action in a sentence. There are two types of verbs: active and passive. In this section, we will explore the differences between active and passive verbs.
Sentence Structure
One of the main differences between active and passive verbs is sentence structure. In active sentences, the subject performs the action of the verb, whereas in passive sentences, the subject receives the action of the verb. Let’s take a look at some examples:
- Active sentence: The dog chased the cat.
- Passive sentence: The cat was chased by the dog.
As you can see, the subject in the active sentence (dog) performs the action (chased), whereas in the passive sentence, the subject (cat) receives the action (was chased).
Another difference is that active sentences tend to be shorter and more direct, while passive sentences are often longer and more complex. This is because passive sentences require the use of a helping verb (usually “to be” or “to get”) and the past participle of the main verb.
Effect on Reader
The choice between active and passive verbs can also affect the reader’s experience. Active verbs tend to be more engaging and dynamic, while passive verbs can be more detached and formal. For example:
- Active sentence: The chef prepared the meal with care and precision.
- Passive sentence: The meal was prepared with care and precision by the chef.
The active sentence puts the focus on the chef and the action of preparing the meal, making it more engaging for the reader. The passive sentence, on the other hand, puts the focus on the meal and its preparation, making it more detached.
It’s worth noting that there are times when passive verbs are appropriate, such as when the focus is on the recipient of the action rather than the performer. For example:
- Passive sentence: The cake was eaten by the children.
In this case, the focus is on the cake and the fact that it was eaten, rather than who ate it.
Using Active Verbs Effectively
In this section, we will explore how to use active verbs effectively in different types of writing.
In Narrative Writing
Narrative writing is a form of writing that tells a story. It can be fiction or non-fiction. When writing a narrative, it is important to use active verbs to bring your story to life. Here are some tips for using active verbs in narrative writing:
- Use strong action verbs to describe the actions of your characters. For example, instead of saying “She walked to the store,” you could say “She strode confidently to the store.”
- Use descriptive verbs to create vivid imagery. For example, instead of saying “The sun was shining,” you could say “The sun blazed down on us.”
- Use dialogue to show your characters in action. This is a great way to use active verbs to bring your story to life.
In Academic Writing
Academic writing is a formal style of writing used in academic settings, such as universities and research institutions. When writing academically, it is important to use active verbs to make your writing more concise and clear. Here are some tips for using active verbs in academic writing:
- Use active verbs to describe your research methods and findings. For example, instead of saying “The data was analyzed,” you could say “We analyzed the data.”
- Use active verbs to describe your arguments and conclusions. For example, instead of saying “It was concluded that,” you could say “We concluded that.”
In Business Writing
Business writing is a form of writing used in the business world. It can include reports, memos , emails, and more. When writing for business, it is important to use active verbs to make your writing more persuasive and engaging. Here are some tips for using active verbs in business writing:
- Use active verbs to describe your accomplishments. For example, instead of saying “I was responsible for,” you could say “I achieved.”
- Use active verbs to describe your goals and objectives. For example, instead of saying “We hope to,” you could say “We plan to.”
By following the tips outlined above, you can use active verbs effectively in different types of writing.
Common Mistakes When Using Active Verbs
Active verbs are essential in English grammar, but they can be tricky to use correctly. Here are some common mistakes to avoid when using active verbs:
Confusing transitive and intransitive verbs
Another common mistake is confusing transitive and intransitive verbs. A transitive verb requires one or more objects, while an intransitive verb does not have objects. For example, “Elephants roam the savanna.” (Correct) “Elephants roam.” (Incorrect)
Using irregular verbs incorrectly
Using irregular verbs incorrectly is another common mistake. For example, using the regular past simple or -ed form for an irregular verb. She spent a week in Lisbon. (Correct) She spended a week in Lisbon. (Incorrect)
Not using the correct form of the verb
Another mistake is not using the correct form of the verb. For example, using “being hurted” instead of “being hurt.” I was afraid of being hurt. (Correct) I was afraid of being hurted. (Incorrect)
Using the wrong verb form
Finally, using the wrong verb form is another common mistake. For example, using “am, is, are, was, were, be, being, been” as active, descriptive verbs. These verbs are actually linking verbs.
By avoiding these common mistakes, you can improve your use of active verbs and make your writing more effective.
Exercises to Improve Active Verb Usage
Active verbs are essential for effective communication. They help to make your writing more engaging and interesting to read. If you want to improve your active verb usage, here are some exercises you can try:
Exercise 1: Identify Active Verbs
The first step in improving your active verb usage is to identify them in your writing. Look for verbs that express an action, such as “run,” “jump,” or “swim.” Identify them in your writing, and see if you can replace any passive verbs with active ones.
Exercise 2: Rewrite Passive Sentences
Passive sentences can be dull and unengaging. To make your writing more interesting, try rewriting passive sentences in the active voice. For example, instead of saying “The ball was thrown by the boy,” you could say “The boy threw the ball.”
Exercise 3: Use Strong Verbs
Using strong verbs can help to make your writing more powerful and engaging. Instead of using weak verbs like “walk” or “talk,” try using more descriptive verbs like “stroll” or “converse.”
Exercise 4: Practice Writing Active Sentences
To improve your active verb usage, it’s important to practice writing active sentences. Try writing a paragraph using only active verbs, and see how it changes the tone and style of your writing.
Exercise 5: Read and Analyze Active Writing
Reading active writing can help you to improve your own writing. Look for examples of active verbs in books, articles, and other written materials. Analyze how the writer uses active verbs to make their writing more engaging and interesting.
Frequently Asked Questions
What is the difference between action verbs and linking verbs?
Action verbs are verbs that show an action, such as “run,” “jump,” or “write.” Linking verbs, on the other hand, connect the subject of a sentence to a noun or adjective that describes it, such as “is,” “was,” or “seems.”
Can you provide some examples of action verbs?
Sure! Here are some examples of action verbs: “dance,” “sing,” “swim,” “paint,” “play,” “study,” “drive,” “cook,” and “read.”
What are some common stative verbs?
Stative verbs describe a state or condition, rather than an action. Examples of stative verbs include “like,” “love,” “hate,” “believe,” “know,” “understand,” “remember,” “forget,” and “need.”
How do active verbs improve writing?
Active verbs make writing more engaging and dynamic. They help to create a clear picture in the reader’s mind and make the writing more interesting to read. Active verbs also help to create a sense of urgency or importance in the writing.
What are some examples of active verb phrases?
Active verb phrases include “catch the ball,” “write a letter,” “paint a picture,” “run a race,” and “build a house.” These phrases all contain an action verb and an object, which makes them more engaging and dynamic than passive verb phrases.
Action verbs are verbs that show an action, such as \"run,\" \"jump,\" or \"write.\" Linking verbs, on the other hand, connect the subject of a sentence to a noun or adjective that describes it, such as \"is,\" \"was,\" or \"seems.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"Can you provide some examples of action verbs?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Sure! Here are some examples of action verbs: \"dance,\" \"sing,\" \"swim,\" \"paint,\" \"play,\" \"study,\" \"drive,\" \"cook,\" and \"read.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some common stative verbs?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Stative verbs describe a state or condition, rather than an action. Examples of stative verbs include \"like,\" \"love,\" \"hate,\" \"believe,\" \"know,\" \"understand,\" \"remember,\" \"forget,\" and \"need.\"
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"How do active verbs improve writing?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Active verbs make writing more engaging and dynamic. They help to create a clear picture in the reader's mind and make the writing more interesting to read. Active verbs also help to create a sense of urgency or importance in the writing.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some exercises to practice using stative verbs?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
One exercise to practice using stative verbs is to write a short story or paragraph using only stative verbs. Another exercise is to write a list of stative verbs and then try to use them in different sentences.
"}},{"@type":"Question","name":"What are some examples of active verb phrases?","acceptedAnswer":{"@type":"Answer","text":"
Active verb phrases include \"catch the ball,\" \"write a letter,\" \"paint a picture,\" \"run a race,\" and \"build a house.\" These phrases all contain an action verb and an object, which makes them more engaging and dynamic than passive verb phrases.

- Plural of Taurus: How to Form the Plural of Taurus Correctly - October 6, 2023
- Plural of Prius: How to Properly Refer to Multiple Toyota Prius Vehicles - October 5, 2023
- Creative and Good Group Chat Names for Enjoyable Conversations - October 4, 2023
Related posts:
- Common Opposite Verbs in English
- Get Moving with Action Verbs: Energize Your Writing and Communication
- A Comprehensive List of Verbs: 50 Must-Know Verbs for Fluent English
- Unlocking the Power of Infinitives: How to Perfect Your English Grammar
- Essay Check
- Chicago Style
- APA Citation Examples
- MLA Citation Examples
- Chicago Style Citation Examples
- Writing Tips
- Plagiarism Guide
- Grammar Rules
- Student Life
- Create Account

How to Incorporate Action Verbs Into Your Writing
Has a teacher ever told you to use more variety in your writing? You probably wracked your brain for a way to do this. Should you add more synonyms? Maybe you need more sentence structure variation? In fact, one great solution is to use more action verbs ! Action verbs can make your writing more interesting and flow better. Let’s look at how to incorporate them into your writing.
Step up your writing game with the BibMe Plus grammar and plagiarism checker . It can help you spot potential mistakes before your teacher does. In addition, read our grammar guides to learn about adjectives that start with a , what is a conjunction , a determiner definition , and many other grammar topics.
Defining the Term
Before undertaking the task of incorporating action verbs into your writing, it’s important to understand what “action verbs” are in the first place: an action verb is a verb that specifically expresses action (such as jump, run, grab, blink ), as opposed to other types of verbs, like linking or helping verbs . According to Merriam-Webster, a linking verb is “a word or expression (such as a form of be , become , feel , or seem ) that links a subject with its predicate.” A helping verb is “a verb (as am , may , or will ) that is used with another verb to express person, number, mood, or tense.”
Therefore action verbs are verbs that help create a visual of a subject performing an action in your reader’s mind. Action verb examples include jump, search, nurture , and so on.
Make a Word Bank
Before sitting down to write your first draft, it can be helpful to write up a word bank of different action verbs. This word bank can be a tool to draw on as you write so that you incorporate more action verbs into your writing from the get-go. Your word bank could contain both common and lesser-known verbs to give you a variety. Use a thesaurus if you get stuck.
A word bank of action verbs could be set up in two columns like this:
| Build | Emulate |
| Construct | Frame |
| Listen | Grasp |
Double check that the verbs on your list are indeed action verbs so that you don’t accidentally use linking or helping verbs when you don’t want to.
Look at Tone
When selecting action verbs to use, consider the type of composition you’re writing. This will dictate both your tone in the piece and how you select action verbs. For example, if you are writing a formal research paper , you might employ less commonly used vocabulary words like gravitate or deliberate to help create a formal or academic tone. A word bank of verbs suitable to your tone (more sophisticated ones for a formal/academic tone, more common ones for an informal tone) might be helpful.
Tip: If you have a vocabulary textbook left over from recent years in school, you might look there to identify action verbs at the level of vocabulary your tone dictates.
Insert Verbs During Revision
Before sitting down to revise your use of action verbs in the first draft, take a moment to plan out the revision as a whole. When revising, be certain to consider your organization of logic or events, word choice (like action verbs!), and proofreading.
To insert verbs during revision, focus on the wording step of revision (such as how you phrased each sentence and paragraph). Wording contributes to tone and how the reader perceives what you’re saying. If you have written a persuasive essay, for instance, you want to consider use of action verbs in relation to the argument, such as using verbs unique to each type of rhetorical strategy.
For logos aspects of your essay (appealing to logic), look for action verbs that accompany hard facts like investigate or inspect . For aspects of an essay that appeal to emotions (pathos), make sure appropriate action verbs are attached, such as undergo or believe . The same concept applies to setting up your credibility with the reader (ethos), where you want to use action verbs that display your level of education and intelligence.
Ultimately, during this revision of wording, you want to look for places where you could have used an action verb but didn’t, or could have used a stronger one. No matter what type of writing you are doing, from an essay to a creative piece, you want to display your grasp of language in a way that is unique to your style of writing.
Tip : Reading out loud is helpful for all aspects of revision, such as locating awkward passages that can be ironed out with stronger, more direct wording. This is a great way to find areas where more action verbs might be placed.
Use a Thesaurus
Don’t forget that you can use a thesaurus during revision! One strategy for working action verbs into your writing is to read over your work and replace verbs that were repeated a lot, or are helping or linking verbs (like seem or become ).
Example : If you tend to use the linking verb “to be” repeatedly (verbs like is , was , were , are , etc.), you might want to do a word search and replace some instances with action verbs.
Look at this sentence:
The birds were happy to fly to the next telephone line.
Try replacing “were” like this:
The birds swooped happily over to the next telephone line.
Final Thoughts
Whether you’re looking to have more variety on first drafts or searching for places to slip more creative action verbs into a revision, knowing what an action verb is and how to use one is important. Happy writing and revising!
Cite the sources in your next paper with BibMe.org! Choose APA format , MLA format , Chicago style format , or any one of our thousands of citation styles.
How useful was this post?
Click on a star to rate it!
We are sorry that this post was not useful for you!
Let us improve this post!
Tell us how we can improve this post?
| Effective Technical Writing in the Information Age |
- FRONT MATTER
- TABLE OF CONTENTS
Using Active Verbs
When composing, we often automatically make lazy choices, especially when choosing verbs. We feel enticed by generic all-purpose verbs such as "deal with" or "show," which on the surface can sound snappy and technical. However, the more these verbs are used in a particular paper, the more meaningless they become. Even in journal articles, these verbs put in a shocking number of appearances and return for many unsolicited encores. Yet these words convey no analytical meaning at all and are barely informational. Much to the reader’s frustration, "deal with" and "show" are often merely thinly disguised excuses for much more active analytical verbs such as theorize, suggest, imply, propose. For the reader, "Cheswick dealt with" or "Figure 4 shows" are far less meaningful than "Cheswick hypothesized" or "Figure 4 represents." As always, you should choose exact words in favor of nonspecific ones, especially when you can use an active verb.
In technical writing, learning to deploy active verbs on the page is one of the most obvious and easiest ways to improve your style. Active verbs—whether in present or past tense—are especially meaningful as you describe work that another author or you have completed or are in the process of completing. As a rule, you should try to choose active verbs in the following circumstances:
Phillip Bennett (2008) proposes a mechanism explaining increased silica solubility in the presence of two small organic acids.
The results of this study challenge findings from similar studies about analyte concentration varying with sample location.
This study characterizes wetlands by their water chemistry and postulates that water chemistry varies with water source and wetland type.
- As you refer to figures, tables, or equations, where your job is to define the purpose of the figure, table, or equation.
Figure 4 depicts grain growth that occurred after the ceramic was sintered for three hours.
What follows is a substantial list of active verbs. I assembled this list by scanning journal articles to see how the best authors described their work or the work of others. Each of these words is packed with individual, analytical meaning. When using this list, be sure to choose the best verb for the situation—verbs such as "construct," "challenge," and "extrapolate" are obviously completely different from each other, so you must use them with meaningful care.
Active Verbs That Describe Work and Analytical Thinking yield
mean
prove
postulate
estimate
compare
generalize
note
delineate
acknowledge
determine
set forth
maintain
investigate
devise
assume | illustrate
suggest
insist
consider
define
hypothesize
narrate
predict
depict
distinguish
detail
deduce
believe
assess
construct
argue | illuminate
clarify
propose
infer
classify
synthesize
evaluate
introduce
construe
inform
sum up
derive
speculate
determine
evaluate
reiterate | reveal
indicate
imply
state
invoke
summarize
simplify
report
interpret
specify
designate
characterize
present
calculate
attribute
discover | employ
represent
assert
extrapolate
analyze
disagree
measure
challenge
provide
restrict
point out
guide
organize
support
obtain
decide |

- UNITED STATES
- 台灣 (TAIWAN)
- TÜRKIYE (TURKEY)
- Academic Editing Services
- - Research Paper
- - Journal Manuscript
- - Dissertation
- - College & University Assignments
- Admissions Editing Services
- - Application Essay
- - Personal Statement
- - Recommendation Letter
- - Cover Letter
- - CV/Resume
- Business Editing Services
- - Business Documents
- - Report & Brochure
- - Website & Blog
- Writer Editing Services
- - Script & Screenplay
- Our Editors
- Client Reviews
- Editing & Proofreading Prices
- Wordvice Points
- Partner Discount
- Plagiarism Checker
- APA Citation Generator
- MLA Citation Generator
- Chicago Citation Generator
- Vancouver Citation Generator
- - APA Style
- - MLA Style
- - Chicago Style
- - Vancouver Style
- Writing & Editing Guide
- Academic Resources
- Admissions Resources
100+ Research Vocabulary Words & Phrases

The academic community can be conservative when it comes to enforcing academic writing style , but your writing shouldn’t be so boring that people lose interest midway through the first paragraph! Given that competition is at an all-time high for academics looking to publish their papers, we know you must be anxious about what you can do to improve your publishing odds.
To be sure, your research must be sound, your paper must be structured logically, and the different manuscript sections must contain the appropriate information. But your research must also be clearly explained. Clarity obviously depends on the correct use of English, and there are many common mistakes that you should watch out for, for example when it comes to articles , prepositions , word choice , and even punctuation . But even if you are on top of your grammar and sentence structure, you can still make your writing more compelling (or more boring) by using powerful verbs and phrases (vs the same weaker ones over and over). So, how do you go about achieving the latter?
Below are a few ways to breathe life into your writing.
1. Analyze Vocabulary Using Word Clouds
Have you heard of “Wordles”? A Wordle is a visual representation of words, with the size of each word being proportional to the number of times it appears in the text it is based on. The original company website seems to have gone out of business, but there are a number of free word cloud generation sites that allow you to copy and paste your draft manuscript into a text box to quickly discover how repetitive your writing is and which verbs you might want to replace to improve your manuscript.
Seeing a visual word cloud of your work might also help you assess the key themes and points readers will glean from your paper. If the Wordle result displays words you hadn’t intended to emphasize, then that’s a sign you should revise your paper to make sure readers will focus on the right information.
As an example, below is a Wordle of our article entitled, “ How to Choose the Best title for Your Journal Manuscript .” You can see how frequently certain terms appear in that post, based on the font size of the text. The keywords, “titles,” “journal,” “research,” and “papers,” were all the intended focus of our blog post.

2. Study Language Patterns of Similarly Published Works
Study the language pattern found in the most downloaded and cited articles published by your target journal. Understanding the journal’s editorial preferences will help you write in a style that appeals to the publication’s readership.
Another way to analyze the language of a target journal’s papers is to use Wordle (see above). If you copy and paste the text of an article related to your research topic into the applet, you can discover the common phrases and terms the paper’s authors used.
For example, if you were writing a paper on links between smoking and cancer , you might look for a recent review on the topic, preferably published by your target journal. Copy and paste the text into Wordle and examine the key phrases to see if you’ve included similar wording in your own draft. The Wordle result might look like the following, based on the example linked above.

If you are not sure yet where to publish and just want some generally good examples of descriptive verbs, analytical verbs, and reporting verbs that are commonly used in academic writing, then have a look at this list of useful phrases for research papers .
3. Use More Active and Precise Verbs
Have you heard of synonyms? Of course you have. But have you looked beyond single-word replacements and rephrased entire clauses with stronger, more vivid ones? You’ll find this task is easier to do if you use the active voice more often than the passive voice . Even if you keep your original sentence structure, you can eliminate weak verbs like “be” from your draft and choose more vivid and precise action verbs. As always, however, be careful about using only a thesaurus to identify synonyms. Make sure the substitutes fit the context in which you need a more interesting or “perfect” word. Online dictionaries such as the Merriam-Webster and the Cambridge Dictionary are good sources to check entire phrases in context in case you are unsure whether a synonym is a good match for a word you want to replace.
To help you build a strong arsenal of commonly used phrases in academic papers, we’ve compiled a list of synonyms you might want to consider when drafting or editing your research paper . While we do not suggest that the phrases in the “Original Word/Phrase” column should be completely avoided, we do recommend interspersing these with the more dynamic terms found under “Recommended Substitutes.”
A. Describing the scope of a current project or prior research
| | | |
To express the purpose of a paper or research | | This paper + [use the verb that originally followed “aims to”] or This paper + (any other verb listed above as a substitute for “explain”) + who/what/when/where/how X. For example: |
| To introduce the topic of a project or paper | | |
| To describe the analytical scope of a paper or study | | *Adjectives to describe degree can include: briefly, thoroughly, adequately, sufficiently, inadequately, insufficiently, only partially, partially, etc. |
| To preview other sections of a paper | | [any of the verbs suggested as replacements for “explain,” “analyze,” and “consider” above] |
B. Outlining a topic’s background
| | | |
| To discuss the historical significance of a topic | | Topic significantly/considerably + + who/what/when/where/how… *In other words, take the nominalized verb and make it the main verb of the sentence. |
| To describe the historical popularity of a topic | | verb] verb] |
| To describe the recent focus on a topic | | |
| To identify the current majority opinion about a topic | | |
| To discuss the findings of existing literature | | |
| To express the breadth of our current knowledge-base, including gaps | | |
| To segue into expressing your research question | | |
C. Describing the analytical elements of a paper
| | | |
| To express agreement between one finding and another | | |
| To present contradictory findings | | |
| To discuss limitations of a study | | |
D. Discussing results
| | | |
| To draw inferences from results | | |
| To describe observations | | |
E. Discussing methods
| | | |
| To discuss methods | | |
| To describe simulations | | This study/ research… + “X environment/ condition to..” + [any of the verbs suggested as replacements for “analyze” above] |
F. Explaining the impact of new research
| | | |
| To explain the impact of a paper’s findings | | |
| To highlight a paper’s conclusion | | |
| To explain how research contributes to the existing knowledge-base | | |
Wordvice Writing Resources
For additional information on how to tighten your sentences (e.g., eliminate wordiness and use active voice to greater effect), you can try Wordvice’s FREE APA Citation Generator and learn more about how to proofread and edit your paper to ensure your work is free of errors.
Before submitting your manuscript to academic journals, be sure to use our free AI Proofreader to catch errors in grammar, spelling, and mechanics. And use our English editing services from Wordvice, including academic editing services , cover letter editing , manuscript editing , and research paper editing services to make sure your work is up to a high academic level.
We also have a collection of other useful articles for you, for example on how to strengthen your writing style , how to avoid fillers to write more powerful sentences , and how to eliminate prepositions and avoid nominalizations . Additionally, get advice on all the other important aspects of writing a research paper on our academic resources pages .
Article Categories
Book categories, collections.
- Academics & The Arts Articles
- Language & Language Arts Articles
- Grammar & Vocabulary Articles
How to Improve Your Writing with Active Verbs
English grammar for dummies.

Sign up for the Dummies Beta Program to try Dummies' newest way to learn.
Unless you’re trying to hide something, or unless you truly don’t know the facts, you should make your writing as specific as possible. Specifics reside in active voice. In English, using active verbs makes your writing clearer and more engaging. Compare these pairs of sentences:
The president of the Egg-Lovers’ Club was murdered yesterday. (The cops are still looking for the villain who wielded the hammer and crushed the president’s skull like an eggshell.)
Sir Francis Bacon murdered the president of the Egg-Lovers’ Club yesterday. (Bacon will soon move into a maximum-security cell.)
It is recommended that the furnace not be cleaned until next year. (Someone wants to save money, but no one is taking responsibility for this action. If the furnace breaks when the thermometer hits 20 below because too much glop is inside, no one’s name comes up for blame.)
The superintendent recommends that the furnace not be cleaned until next year. (Now the building’s residents may threaten the superintendent with the icicles they chip off their noses.)
Do you notice how these active-verb sentences provide extra information? In the first pair of sample sentences, you know the name of the murderer. In the second pair, you know who recommends postponing maintenance of the furnace. Knowing (in life as well as in grammar) is usually better than not knowing, and active voice, which generally provides more facts, is usually better than passive voice.
Active voice is also better than passive because active voice tends to use fewer words to say the same thing. Compare the following sentences:
Lulu was failed by the teacher because the grammar book was torn up by Lulu before it was ever opened. (20 words)
The teacher failed Lulu because Lulu tore up the grammar book before opening it. (14 words)
Okay, six words don’t make the difference between a 900-page novel and a 3-page story, but those words do add up. If you’re writing a letter or an essay, switching from passive to active voice may save you one-third of your words and therefore one-third of the reader’s energy and patience.
Right about now, you may be remembering a past homework assignment: The teacher asked for 500 words on Hamlet and you had only one teeny idea about the play. You may have thought that padding was a good idea! Wrong. Your teacher (or boss) can see that you’ve buried only one teeny idea in those piles of paragraphs. Besides losing points for knowing too little, you’re likely to lose points for wasting the reader’s time. The solution? Write in active voice and don’t pad your writing.
Some questions on the SAT and ACT ask you to revise a sentence by choosing the best of five possible versions. Fairly often, the correct answer changes the passive verb of the original to active voice.
Which sentence works better?
A. The omelet was made with whipped egg whites and chopped ham, but the yolks were discarded.
B. Eggworthy made an omelet of whipped egg whites and chopped ham but discarded the yolks.
Answer: Sentence B, which employs active voice ( made, discarded ) is preferable to Sentence A, which has passive verbs ( was made, were discarded ). Not only is Sentence B one word shorter, but it also provides more information (the name of the cook).
Try another: Choose the better sentence.
A. The Omelet Contest was run so poorly that some entries were labeled "dangerous" by the health officer.
B. Sal Monella ran the Omelet Contest so poorly that the health officer labeled some entries "dangerous."
Answer: Sentence B wins! Its active verb ( ran ) creates a stronger sentence than the passive verb ( was run ) of Sentence A. Also, Sentence B supplies the name of the contest official who forgot to refrigerate the cooking supplies.
About This Article
This article can be found in the category:.
- Grammar & Vocabulary ,
- How to Climb the Ladder of Language Formality
- How to Match Your Message to the Situation
- How to Choose the Correct Verb for Negative Expressions
- How to Question with Verbs
- How to Properly Add Helping Verbs
- View All Articles From Category
150 Powerful Action Verbs for Your SMART Goals
Are you ready to supercharge your goal-setting strategy? This article is a treasure trove of 150 dynamic action verbs designed to energize your ambition and ignite your motivation.
From ascending the career ladder to shedding pounds, these powerful action verbs will transform your goals from vague aspirations into compelling missions you’re eager to accomplish.
It will empower you to select action verbs that resonate with your objectives, making your goals feel tangibly within reach and injecting a dose of excitement into your planning process.
Whether you’re a veteran goal-setter or a novice just embarking on your journey, strap yourself in. It’s finally time to turn those dreams into actionable, SMART realities.
Table of Contents
What Are Action Verbs?
Action verbs, as their name suggests, depict action. They are words that express physical or mental activity. In goal setting, these verbs are likely to convey goal-oriented actions effectively.
These elements are crucial for establishing SMART (Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, Time-based) goals as they clearly define your objectives and outline the precise steps you intend to take to accomplish them.
For example, instead of vaguely stating, “I want to improve my health,” a SMART goal would utilize an action verb to specify the goal: “I will jog for 30 minutes every morning.”
Here, “jog” is the action verb that clearly outlines the action needed to achieve the target. Using powerful action verbs can make your goals more compelling and motivate you to reach them.
The Importance of Action Verbs in SMART Goals
Action verbs are the secret tools that give our dreams wheels. Consider the previous example: “I want to be healthier.” It’s a wish, a desire, but it lacks the specificity and dynamism needed to spur action.
Now infuse it with an action verb: “I’ll nail 20 pushups every afternoon.” Suddenly, this passive intention morphs into an active pursuit. You have a specific task to complete.
Action verbs act as the driving force that propels us forward. They provide clarity and focus, defining the steps we need to take to achieve our goals.
To put it simply, action verbs are not just words; they’re like success multipliers. When we use them, we’re not just dreaming anymore; we are setting the stage for real achievement. And that’s they are so important when creating SMART goals.
- Collaborate
- Communicate
- Demonstrate
- Investigate
- Participate
- Standardize
Tips for Writing Action Verbs in SMART Goals
When writing your SMART goals, it’s essential to consider which action verbs are most appropriate for conveying the desired outcome. Below are some tips to help you come up with excellent action verbs for your goals:
1. Make Sure the Verb is Clear
Ensure your action verb can be understood without any confusion. Clear action verbs eliminate ambiguity and provide a definite direction for your goal.
For instance, instead of saying, “I want to do better in my job,” go for “I aim to increase my monthly sales by 10%.” In this case, “increase” is an action verb with a specific path to follow.
Select a verb that precisely describes the action you intend to take. Verbs like “complete,” “develop,” “achieve,” “reduce,” and “improve” are all decisive action verbs that leave no room for misunderstanding. They give a clear idea of what action must be taken.
Realize that clarity in your action verb sets the tone for goal setting . It paves the way for effective planning, diligent execution, and the successful achievement of your goal.
2. Use Positive Language
Positive language propels us forward, infusing our goals with energy and intention. Rather than writing, “ Stop procrastinating on tasks,” a positively framed goal could be “Prioritize tasks efficiently every morning.”
The latter uses positive language and an action verb, “prioritize,” making the goal proactive and empowering.
Your choice of words can dramatically impact your mindset and motivation levels. Hence, taking advantage of positive language in your SMART goals fosters a productive, optimistic tone from the outset.
3. Don’t Overuse the Same Action Verbs
Using the same action verb multiple times in a goal may make it seem monotonous. To avoid this, try to diversify your goals with different action verbs.
Suppose you are looking to save money . The goal could be “I will reduce my monthly expenses by 10%.” Alternatively, you might use a different phrase like, “I’ll decrease my expenses by 10% every month.”
Combining action verbs of the same meaning but with different nuances and applications could add flavor to your goals and keep them interesting. This way, you boost your chances of sticking to them as they seem more attainable.
4. Create Relevant Action Verbs
When establishing SMART goals, using relevant action verbs is crucial. Relevant action verbs directly relate to the task or outcome you wish to accomplish.
So if your goal is to improve your fitness , relevant action verbs could include “run,” “lift,” swim,” or “cycle.” These verbs clearly convey what you need to do to reach success.
Selecting appropriate action verbs also adds specificity to your goals. Instead of stating, “I want to get fit,” a relevant action verb can transform this into “I will run three times a week.”
The action verbs you choose should align with both the nature of your goal and the steps needed to achieve it. Creating relevant action verbs will make your SMART goals more practical.
5. Leverage Power Words
Power words are persuasive; they spark emotive responses and spur decisive action. They’re the secret ingredients that make narratives and calls to action persuasive.
Imagine your SMART goals . Now infuse them with power words. Rather than simply “finishing” a project, why not “conquer” it? Instead of “losing” weight, why not “obliterate” pounds? These slight tweaks in language may massively impact your outlook and determination.
Power words should be laser-focused, communicating what you strive to achieve. “Amplify,” “elevate,” and “escalate” are dynamic substitutes for generic verbs like “improve” or “increase.”
Bear in mind the purpose of SMART goals extends beyond setting benchmarks; it’s about sparking action. Harnessing the might of power words will inject your goals with dynamism and zeal, making them irresistibly compelling.
Final Thoughts
Remember that goals are more than just checkpoints on your journey to success. They are your roadmap, guiding you toward your desired destination.
Armed with this comprehensive list of 150 dynamic action verbs, you’re now equipped to transform your dreams into robust, concrete SMART goals. But don’t stop there. Keep exploring, refining, and pushing forward.
Your goals are not static—they should evolve as you do, becoming more precise, targeted, and aligned with your aspirations. So dare to “master a new skill” and strive to “build a happy family.”
Give your goals the power and precision they deserve by harnessing the might of these action verbs. Your road to attaining SMART goals is just beginning. With the right words and mindset, there’s no limit to what you can achieve.

Purdue Online Writing Lab Purdue OWL® College of Liberal Arts
Categorized List of Action Verbs

Welcome to the Purdue OWL
This page is brought to you by the OWL at Purdue University. When printing this page, you must include the entire legal notice.
Copyright ©1995-2018 by The Writing Lab & The OWL at Purdue and Purdue University. All rights reserved. This material may not be published, reproduced, broadcast, rewritten, or redistributed without permission. Use of this site constitutes acceptance of our terms and conditions of fair use.
This categorized list contains only a few action verbs you can use to compose concise, persuasive , reader-centered resumes, cover letters, or other types of workplace documents. The examples are illustrations that overview the uses of action verbs in professional writing.
The media file above takes you to a sample resume containing action verbs.
Communication Skills
- Negotiated price reductions of up to 30% with key suppliers
- Interpreted financial information from the company's annual report
- Translated all relevant company information into three different languages
Other words: Advocated, Clarified, Corresponded, Encouraged, Interpreted, Negotiated, Persuaded, Presented, Publicized, Solicited, Spoke, Translated
Creative Skills
- Created an interior design layout for a 500 square foot retail venue
- Introduced a new method of navigating through the A Software Program
- Presented a new research project to the managers at the location
Other words: Acted, Applied, Composed, Created, Established, Founded, Improvised, Introduced, Navigated, Originated, Presented
Data / Financial Skills
- Computed and recorded inventory valuation on a monthly basis
- Documented inventory counts at the end of each working day
- Verified the amount owed to the creditor in the Accounts Payable account
Other words: Adjusted, Allocated, Budgeted, Compared, Computed, Counted, Documented, Estimated, Forecasted, Inventoried, Invested, Predicted, Projected, Quantified, Recorded, Retrieved, Verified
Helping Skills
- Assisted customers with choosing appropriate products
- Trained new employees in the plant through demonstration techniques
- Volunteered in the nursing home every weekend to serve the community
Other words: Aided, Assisted, Built, Demonstrated, Facilitated, Familiarized, Helped, Performed, Represented, Solved, Supported, Trained, Upheld, Volunteered, Worked
Management / Leadership Skills
- Administered a variety of surveys to collect data about the employees
- Implemented a safety communication program to promote safety awareness
- Recommended an alternative solution to one of the company's problems
Other words: Achieved, Administered, Assigned, Attained, Challenged, Coordinated, Decided, Delegated, Established, Executed, Handled, Headed, Implemented, Incorporated, Intervened, Launched, Led, Managed, Mediated, Motivated, Organized, Oversaw, Planned, Prioritized, Recommended, Scheduled, Supervised, United
Efficiency Skills
- Eliminated unnecessary cost of each unit of production
- Maximized profits by 15% during the month of July
- Heightened the level of employee moral through program incentives
Other words: Accelerated, Allocated, Boosted, Centralized, Downsized, Edited, Eliminated, Enhanced, Expanded, Expedited, Heightened, Lessened, Leveraged, Maximized, Merged, Optimized, Outlined, Outsourced, Prevented, Prioritized, Reorganized, Reduced, Revised, Simplified, Standardized, Stream-lined, Synthesized, Systematized, Upgraded
Research Skills
- Examined a new mechanism that may reduce sickness on the campus
- Identified a major defect in a microscopic organism last month
- Surveyed a group of Purdue students with regard to Product A
Other words: Analyzed, Collected, Compared, Controlled, Detected, Diagnosed, Evaluated, Examined, Gathered, Identified, Investigated, Located, Measured, Organized, Reported, Replicated, Researched, Reviewed, Searched, Surveyed, Wrote
Teaching Skills
- Defined a new product strategy and discussed how it would be implemented
- Instructed Department B on how to reduce inventory and raise net sales
- Prepared a tutorial manual for an English class last semester
Other words: Aided, Advised, Clarified, Communicated, Defined, Developed, Encouraged, Evaluated, Facilitated, Fostered, Guided, Helped, Incorporated, Informed, Initiated, Instructed, Lectured, Prepared, Supported, Supervised, Stimulated, Taught
Technical Skills
- Assembled an entire computer programming simulation for my CPT course
- Designed a new form of Widget C for a manufacturing facility
- Programmed three new computer programs tailored for a network system
Other words: Analyzed, Assembled, Built, Calculated, Computed, Conducted, Designed, Devised, Engineered, Maintained, Operated, Programmed, Reengineered, Remodeled, Transmitted
Sources/References:
Rosalie Maggio, How to Say It, Webster's Thesaurus .

How to replace is, are, am, was, were, be, been and to be.
The hardest skill students learn is how to replace the verb “to be.” Yet is it the single most important skill for improving the verbs in their writing.
The problem is that the verb “to be” rarely has strong synonyms. As a linking verb it can sometimes be replaced with another linking verb. “He is sick” can become “He looks sick” or “He feels sick” or “He seems sick.” But none of those replacements is much stronger than the original verb, “is.”

An excerpt of a third grader’s revised essay.
Even harder is when the verb identifies something that exists. How do you restate, “That dog is mine.” “That dog was mine,” changes just the verb tense; it is the same verb. “That dog becomes mine,” changes the meaning.
What I tell my students is that usually they will need to replace not just the verb, but the whole sentence. I ask them to tell me what the sentence means, using other words. For the sentence, “He is sick,” I ask how they know he is sick. What does he look like that would let me know he is sick? They might say, “His face is red and he has a fever.” I might say, “That’s good, but you are still using the word is. How can you tell me that his face is red and that he has a fever without using the word ‘is’”? Usually they are stumped, so I offer suggestions. “His mother placed an ice bag on his flushed forehead.” Or, “’Wow! 101 degrees,’ said his mother shaking the thermometer.” Or, “The feverish boy lay down on the cold tile floor, moving every few seconds to chill his hot body.”
The trick is to let the reader see, hear, touch, smell or taste (usually see) what the writer saw in his mind before he wrote, “He is sick.” “He is sick” is a conclusion based on certain facts. What are the facts that led the writer to conclude that “He is sick”? Those facts are what the reader needs to know so that the reader can come to his own conclusion that “He is sick.”
We’ll have more blogs on changing the verb “to be” in the future because it is such a vital part of improving writing, yet such a difficult skill to master. For now, we’ll move on to the next blog about sentence beginnings.
Share this:
- Click to share on Facebook (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Pinterest (Opens in new window)
- Click to share on Twitter (Opens in new window)
- Click to email a link to a friend (Opens in new window)
2 responses to “ How to replace is, are, am, was, were, be, been and to be. ”

Hi, I’m looking for a writing tutor for my 10 year old daughter. One who could grow in the language arts especially in writing. I like your edited writing excerpt, even though i know english as my second language. My deepest desire is to see my daughter Laura to excel in language arts learning. Do you think i could hrar from you? We live in Ventura.

Excellent article……simply outstanding
What's your thinking on this topic? Cancel reply
One-on-one online writing improvement for students of all ages.

As a professional writer and former certified middle and high school educator, I now teach writing skills online. I coach students of all ages on the practices of writing. Click on my photo for more details.

You may think revising means finding grammar and spelling mistakes when it really means rewriting—moving ideas around, adding more details, using specific verbs, varying your sentence structures and adding figurative language. Learn how to improve your writing with these rewriting ideas and more. Click on the photo For more details.

Comical stories, repetitive phrasing, and expressive illustrations engage early readers and build reading confidence. Each story includes easy to pronounce two-, three-, and four-letter words which follow the rules of phonics. The result is a fun reading experience leading to comprehension, recall, and stimulating discussion. Each story is true children’s literature with a beginning, a middle and an end. Each book also contains a "fun and games" activity section to further develop the beginning reader's learning experience.
Mrs. K’s Store of home schooling/teaching resources

Furia--Quick Study Guide is a nine-page text with detailed information on the setting; 17 characters; 10 themes; 8 places, teams, and motifs; and 15 direct quotes from the text. Teachers who have read the novel can months later come up to speed in five minutes by reading the study guide.
Post Categories
Follow blog via email.
Enter your email address to follow this blog and receive notifications of new posts by email.
Email Address:
Peachtree Corners, GA

- Already have a WordPress.com account? Log in now.
- Subscribe Subscribed
- Copy shortlink
- Report this content
- View post in Reader
- Manage subscriptions
- Collapse this bar




































IMAGES
COMMENTS
Action Verbs are the key to great writing. Our list of 400 Action Verbs is categorized for ease in finding the most dynamic word possible.
Active Verbs in Academic Writing While academic writing is often considered dry and lifeless, this doesn't necessarily need to be the case. Just as a story benefits from engaging, dynamic verbs that keep the plot moving, academic writers can also utilize active verbs to help animate their ideas, analysis, connections, and critiques. The table below recommends useful, guiding, demonstrative ...
The following verbs are helpful as a means of showing how an example or quote in literature Supports an idea or interpretation. Example + Verb + Explanation or Significance (CD) (CM) You may use the above in a sentence as a general formula that may need modified to fit each situation.
Action verbs add an extra "oomph!" to your writing, helping you to describe the many things your characters will achieve throughout the story. Learning how to use action verbs will enhance your writing, help to define your characters, and allow your readers to grasp the plot points with ease.
Power verbs add impact and weight to your argument. Good essay power verbs include asserts, define, impart, and deduce.
Active verbs are important components of any academic writing! Just as in other forms of writing, they work as engines, driving the action of your sentences in many potentially vivid, clear, and colorful ways.
Active verbs make your research writing clearer and more compelling. See the best active verbs for academic papers with examples.
ACTIVE VERBS FOR ACADEMIC ESSAYS. achieves afflicts allow alternates announce answers appeals applies argues assists assumes avoid becomes begins believe belongs betrays brings captures changes checked choose coincides combines compares complicates condemns connects considers constitutes contains contradicts contrasts corrupts creates damages ...
Strong verbs transform your writing from unclear and amateurish to engaging and emotionally powerful. Here's a list of over 280 strong verbs.
An action verb is a type of verb that describes the action that the subject of a sentence is performing. Action verbs can refer to both physical and mental actions (i.e., internal processes and actions related to thinking, perceiving, or feeling). Examples: Physical and mental action verbs. We climbed to the highest peak.
Improve your essays with these 50 useful verbs for analysis. This list is great for English learners and college students!
Learn how to use strong verbs to make your writing more powerful and engaging. Discover the definition, examples, and tips for choosing strong verbs.
Good writing is about well-chosen nouns and strong verbs, not adjectives and adverbs. What constitutes a tired verb? Here's what to look for:
Active verbs in particular are useful tools for writers of personal essays, because they help you to (1) efficiently summarize your achievements, and (2) describe relevant phenomena, which may be in the form of research that you've completed.
Action Words in Academic Writing. In order to write a quality essay or discussion, you must first have an understanding of what you are being asked to do. Recognizing action words or verbs used in your assignment prompts will help you broaden your vocabulary, identify specific directives, and organize your ideas accordingly, which will help you ...
Active verbs are verbs that express an action performed by the subject of the sentence. Using active verbs in your writing can help to make your sentences clearer and more concise. They also make your writing more engaging and dynamic, helping to capture the reader's attention and hold it throughout the piece.
Shake up your writing and add variety by using more action verbs! Let's look at how to incorporate them into your writing.
In technical writing, learning to deploy active verbs on the page is one of the most obvious and easiest ways to improve your style. Active verbs—whether in present or past tense—are especially meaningful as you describe work that another author or you have completed or are in the process of completing.
Here are 100+ active verbs to make your research writing more engaging. Includes additional tops to improve word and phrase choices.
The teacher failed Lulu because Lulu tore up the grammar book before opening it. (14 words) Okay, six words don't make the difference between a 900-page novel and a 3-page story, but those words do add up. If you're writing a letter or an essay, switching from passive to active voice may save you one-third of your words and therefore one ...
Here, "jog" is the action verb that clearly outlines the action needed to achieve the target. Using powerful action verbs can make your goals more compelling and motivate you to reach them.
Categorized List of Action Verbs This categorized list contains only a few action verbs you can use to compose concise, persuasive, reader-centered resumes, cover letters, or other types of workplace documents. The examples are illustrations that overview the uses of action verbs in professional writing.
The hardest skill students learn is how to replace the verb "to be." Yet is it the single most important skill for improving the verbs in their writing. The problem is that the verb "to be" rarely has strong synonyms.