Educational resources and simple solutions for your research journey


What Are Research Objectives and How to Write Them (with Examples)

Table of Contents
Introduction
Research is at the center of everything researchers do, and setting clear, well-defined research objectives plays a pivotal role in guiding scholars toward their desired outcomes. Research papers are essential instruments for researchers to effectively communicate their work. Among the many sections that constitute a research paper, the introduction plays a key role in providing a background and setting the context. 1 Research objectives, which define the aims of the study, are usually stated in the introduction. Every study has a research question that the authors are trying to answer, and the objective is an active statement about how the study will answer this research question. These objectives help guide the development and design of the study and steer the research in the appropriate direction; if this is not clearly defined, a project can fail!
Research studies have a research question, research hypothesis, and one or more research objectives. A research question is what a study aims to answer, and a research hypothesis is a predictive statement about the relationship between two or more variables, which the study sets out to prove or disprove. Objectives are specific, measurable goals that the study aims to achieve. The difference between these three is illustrated by the following example:
- Research question : How does low-intensity pulsed ultrasound (LIPUS) compare with a placebo device in managing the symptoms of skeletally mature patients with patellar tendinopathy?
- Research hypothesis : Pain levels are reduced in patients who receive daily active-LIPUS (treatment) for 12 weeks compared with individuals who receive inactive-LIPUS (placebo).
- Research objective : To investigate the clinical efficacy of LIPUS in the management of patellar tendinopathy symptoms.
This article discusses the importance of clear, well-thought out objectives and suggests methods to write them clearly.
What is the introduction in research papers?
Research objectives are usually included in the introduction section. This section is the first that the readers will read so it is essential that it conveys the subject matter appropriately and is well written to create a good first impression. A good introduction sets the tone of the paper and clearly outlines the contents so that the readers get a quick snapshot of what to expect.
A good introduction should aim to: 2,3
- Indicate the main subject area, its importance, and cite previous literature on the subject
- Define the gap(s) in existing research, ask a research question, and state the objectives
- Announce the present research and outline its novelty and significance
- Avoid repeating the Abstract, providing unnecessary information, and claiming novelty without accurate supporting information.
Why are research objectives important?
Objectives can help you stay focused and steer your research in the required direction. They help define and limit the scope of your research, which is important to efficiently manage your resources and time. The objectives help to create and maintain the overall structure, and specify two main things—the variables and the methods of quantifying the variables.
A good research objective:
- defines the scope of the study
- gives direction to the research
- helps maintain focus and avoid diversions from the topic
- minimizes wastage of resources like time, money, and energy
Types of research objectives
Research objectives can be broadly classified into general and specific objectives . 4 General objectives state what the research expects to achieve overall while specific objectives break this down into smaller, logically connected parts, each of which addresses various parts of the research problem. General objectives are the main goals of the study and are usually fewer in number while specific objectives are more in number because they address several aspects of the research problem.
Example (general objective): To investigate the factors influencing the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
Example (specific objective): To assess the influence of firm size on the financial performance of firms listed in the New York Stock Exchange market.
In addition to this broad classification, research objectives can be grouped into several categories depending on the research problem, as given in Table 1.
Table 1: Types of research objectives
| Exploratory | Explores a previously unstudied topic, issue, or phenomenon; aims to generate ideas or hypotheses |
| Descriptive | Describes the characteristics and features of a particular population or group |
| Explanatory | Explains the relationships between variables; seeks to identify cause-and-effect relationships |
| Predictive | Predicts future outcomes or events based on existing data samples or trends |
| Diagnostic | Identifies factors contributing to a particular problem |
| Comparative | Compares two or more groups or phenomena to identify similarities and differences |
| Historical | Examines past events and trends to understand their significance and impact |
| Methodological | Develops and improves research methods and techniques |
| Theoretical | Tests and refines existing theories or helps develop new theoretical perspectives |
Characteristics of research objectives
Research objectives must start with the word “To” because this helps readers identify the objective in the absence of headings and appropriate sectioning in research papers. 5,6
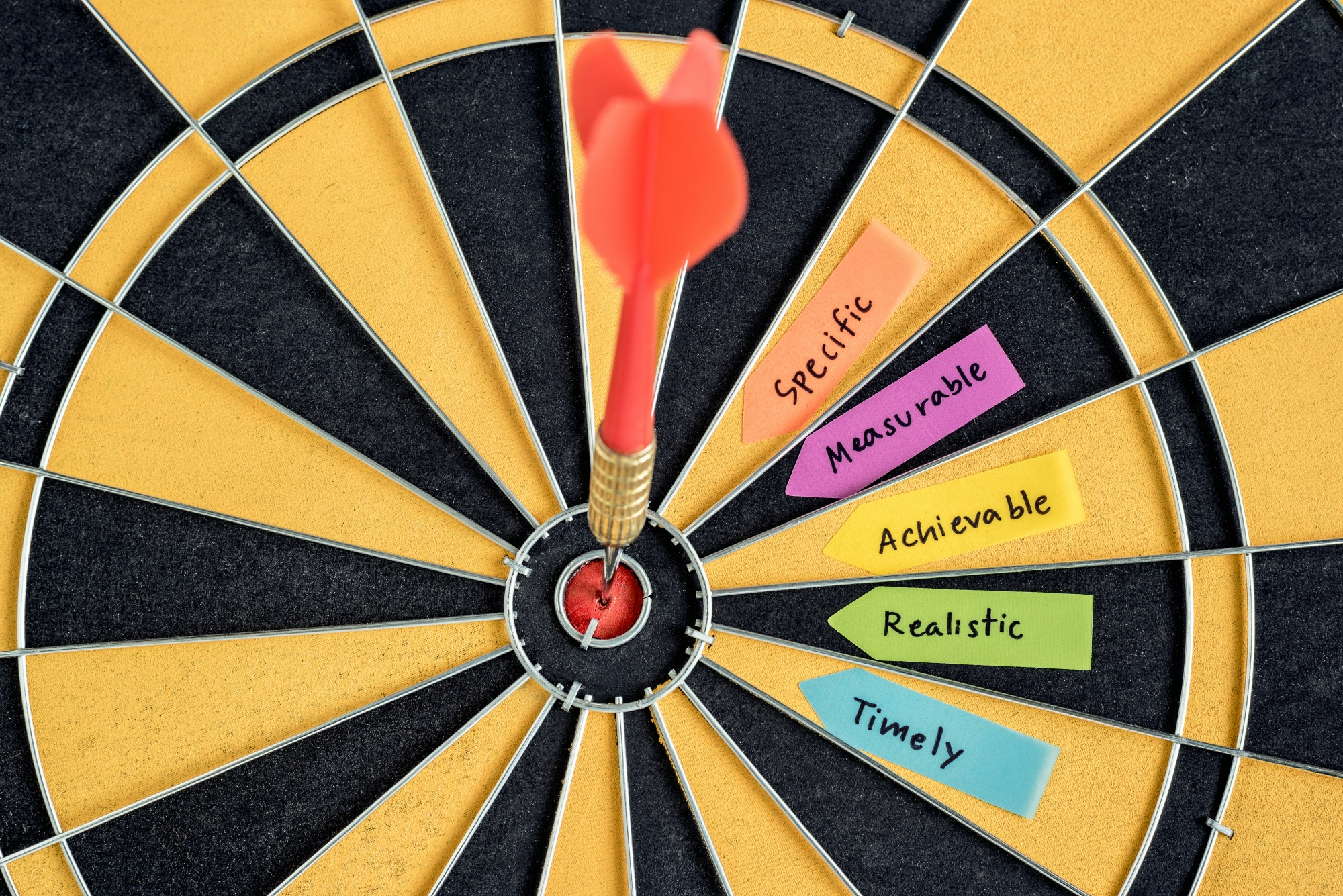
- A good objective is SMART (mostly applicable to specific objectives):
- Specific—clear about the what, why, when, and how
- Measurable—identifies the main variables of the study and quantifies the targets
- Achievable—attainable using the available time and resources
- Realistic—accurately addresses the scope of the problem
- Time-bound—identifies the time in which each step will be completed
- Research objectives clarify the purpose of research.
- They help understand the relationship and dissimilarities between variables.
- They provide a direction that helps the research to reach a definite conclusion.
How to write research objectives?
Research objectives can be written using the following steps: 7
- State your main research question clearly and concisely.
- Describe the ultimate goal of your study, which is similar to the research question but states the intended outcomes more definitively.
- Divide this main goal into subcategories to develop your objectives.
- Limit the number of objectives (1-2 general; 3-4 specific)
- Assess each objective using the SMART
- Start each objective with an action verb like assess, compare, determine, evaluate, etc., which makes the research appear more actionable.
- Use specific language without making the sentence data heavy.
- The most common section to add the objectives is the introduction and after the problem statement.
- Add the objectives to the abstract (if there is one).
- State the general objective first, followed by the specific objectives.
Formulating research objectives
Formulating research objectives has the following five steps, which could help researchers develop a clear objective: 8
- Identify the research problem.
- Review past studies on subjects similar to your problem statement, that is, studies that use similar methods, variables, etc.
- Identify the research gaps the current study should cover based on your literature review. These gaps could be theoretical, methodological, or conceptual.
- Define the research question(s) based on the gaps identified.
- Revise/relate the research problem based on the defined research question and the gaps identified. This is to confirm that there is an actual need for a study on the subject based on the gaps in literature.
- Identify and write the general and specific objectives.
- Incorporate the objectives into the study.
Advantages of research objectives
Adding clear research objectives has the following advantages: 4,8
- Maintains the focus and direction of the research
- Optimizes allocation of resources with minimal wastage
- Acts as a foundation for defining appropriate research questions and hypotheses
- Provides measurable outcomes that can help evaluate the success of the research
- Determines the feasibility of the research by helping to assess the availability of required resources
- Ensures relevance of the study to the subject and its contribution to existing literature
Disadvantages of research objectives
Research objectives also have few disadvantages, as listed below: 8
- Absence of clearly defined objectives can lead to ambiguity in the research process
- Unintentional bias could affect the validity and accuracy of the research findings
Key takeaways
- Research objectives are concise statements that describe what the research is aiming to achieve.
- They define the scope and direction of the research and maintain focus.
- The objectives should be SMART—specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.
- Clear research objectives help avoid collection of data or resources not required for the study.
- Well-formulated specific objectives help develop the overall research methodology, including data collection, analysis, interpretation, and utilization.
- Research objectives should cover all aspects of the problem statement in a coherent way.
- They should be clearly stated using action verbs.
Frequently asked questions on research objectives
Q: what’s the difference between research objectives and aims 9.
A: Research aims are statements that reflect the broad goal(s) of the study and outline the general direction of the research. They are not specific but clearly define the focus of the study.
Example: This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.
Research objectives focus on the action to be taken to achieve the aims. They make the aims more practical and should be specific and actionable.
Example: To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation.
Q: What are the examples of research objectives, both general and specific?
A: Here are a few examples of research objectives:
- To identify the antiviral chemical constituents in Mumbukura gitoniensis (general)
- To carry out solvent extraction of dried flowers of Mumbukura gitoniensis and isolate the constituents. (specific)
- To determine the antiviral activity of each of the isolated compounds. (specific)
- To examine the extent, range, and method of coral reef rehabilitation projects in five shallow reef areas adjacent to popular tourist destinations in the Philippines.
- To investigate species richness of mammal communities in five protected areas over the past 20 years.
- To evaluate the potential application of AI techniques for estimating best-corrected visual acuity from fundus photographs with and without ancillary information.
- To investigate whether sport influences psychological parameters in the personality of asthmatic children.
Q: How do I develop research objectives?
A: Developing research objectives begins with defining the problem statement clearly, as illustrated by Figure 1. Objectives specify how the research question will be answered and they determine what is to be measured to test the hypothesis.
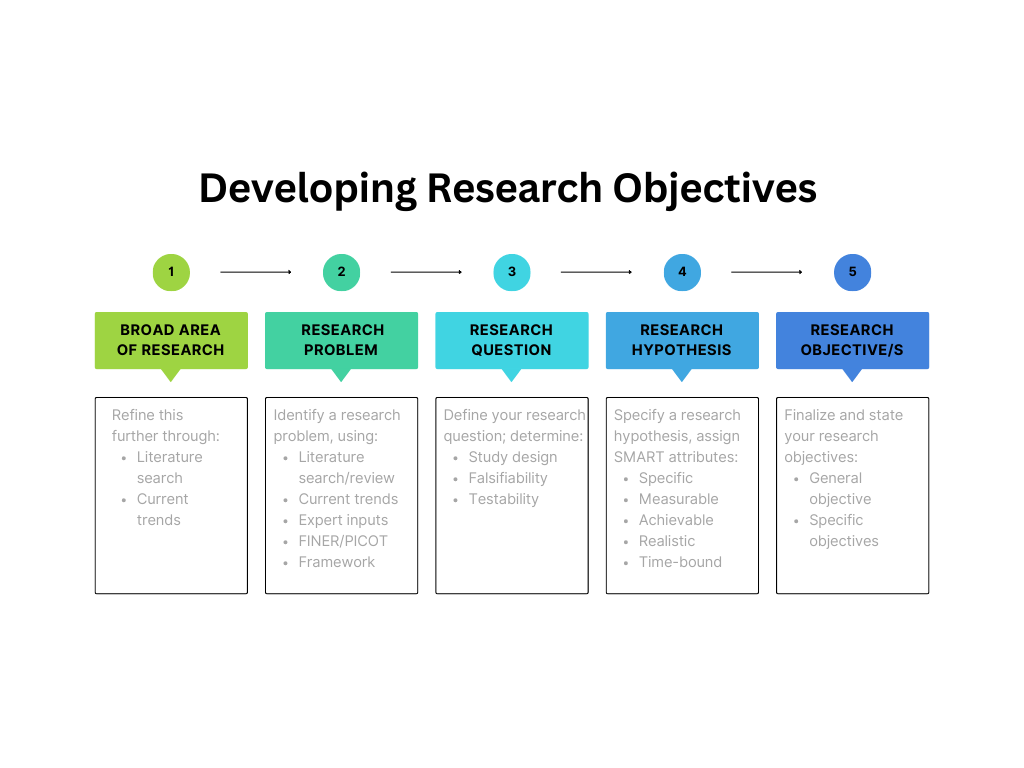
Q: Are research objectives measurable?
A: The word “measurable” implies that something is quantifiable. In terms of research objectives, this means that the source and method of collecting data are identified and that all these aspects are feasible for the research. Some metrics can be created to measure your progress toward achieving your objectives.
Q: Can research objectives change during the study?
A: Revising research objectives during the study is acceptable in situations when the selected methodology is not progressing toward achieving the objective, or if there are challenges pertaining to resources, etc. One thing to keep in mind is the time and resources you would have to complete your research after revising the objectives. Thus, as long as your problem statement and hypotheses are unchanged, minor revisions to the research objectives are acceptable.
Q: What is the difference between research questions and research objectives? 10
| Broad statement; guide the overall direction of the research | Specific, measurable goals that the research aims to achieve |
| Identify the main problem | Define the specific outcomes the study aims to achieve |
| Used to generate hypotheses or identify gaps in existing knowledge | Used to establish clear and achievable targets for the research |
| Not mutually exclusive with research objectives | Should be directly related to the research question |
| Example: | Example: |
Q: Are research objectives the same as hypotheses?
A: No, hypotheses are predictive theories that are expressed in general terms. Research objectives, which are more specific, are developed from hypotheses and aim to test them. A hypothesis can be tested using several methods and each method will have different objectives because the methodology to be used could be different. A hypothesis is developed based on observation and reasoning; it is a calculated prediction about why a particular phenomenon is occurring. To test this prediction, different research objectives are formulated. Here’s a simple example of both a research hypothesis and research objective.
Research hypothesis : Employees who arrive at work earlier are more productive.
Research objective : To assess whether employees who arrive at work earlier are more productive.
To summarize, research objectives are an important part of research studies and should be written clearly to effectively communicate your research. We hope this article has given you a brief insight into the importance of using clearly defined research objectives and how to formulate them.
- Farrugia P, Petrisor BA, Farrokhyar F, Bhandari M. Practical tips for surgical research: Research questions, hypotheses and objectives. Can J Surg. 2010 Aug;53(4):278-81.
- Abbadia J. How to write an introduction for a research paper. Mind the Graph website. Accessed June 14, 2023. https://mindthegraph.com/blog/how-to-write-an-introduction-for-a-research-paper/
- Writing a scientific paper: Introduction. UCI libraries website. Accessed June 15, 2023. https://guides.lib.uci.edu/c.php?g=334338&p=2249903
- Research objectives—Types, examples and writing guide. Researchmethod.net website. Accessed June 17, 2023. https://researchmethod.net/research-objectives/#:~:text=They%20provide%20a%20clear%20direction,track%20and%20achieve%20their%20goals .
- Bartle P. SMART Characteristics of good objectives. Community empowerment collective website. Accessed June 16, 2023. https://cec.vcn.bc.ca/cmp/modules/pd-smar.htm
- Research objectives. Studyprobe website. Accessed June 18, 2023. https://www.studyprobe.in/2022/08/research-objectives.html
- Corredor F. How to write objectives in a research paper. wikiHow website. Accessed June 18, 2023. https://www.wikihow.com/Write-Objectives-in-a-Research-Proposal
- Research objectives: Definition, types, characteristics, advantages. AccountingNest website. Accessed June 15, 2023. https://www.accountingnest.com/articles/research/research-objectives
- Phair D., Shaeffer A. Research aims, objectives & questions. GradCoach website. Accessed June 20, 2023. https://gradcoach.com/research-aims-objectives-questions/
- Understanding the difference between research questions and objectives. Accessed June 21, 2023. https://board.researchersjob.com/blog/research-questions-and-objectives
R Discovery is a literature search and research reading platform that accelerates your research discovery journey by keeping you updated on the latest, most relevant scholarly content. With 250M+ research articles sourced from trusted aggregators like CrossRef, Unpaywall, PubMed, PubMed Central, Open Alex and top publishing houses like Springer Nature, JAMA, IOP, Taylor & Francis, NEJM, BMJ, Karger, SAGE, Emerald Publishing and more, R Discovery puts a world of research at your fingertips.
Try R Discovery Prime FREE for 1 week or upgrade at just US$72 a year to access premium features that let you listen to research on the go, read in your language, collaborate with peers, auto sync with reference managers, and much more. Choose a simpler, smarter way to find and read research – Download the app and start your free 7-day trial today !
Related Posts

What is Research Impact: Types and Tips for Academics

Research in Shorts: R Discovery’s New Feature Helps Academics Assess Relevant Papers in 2mins

Research Aims, Objectives & Questions
The “Golden Thread” Explained Simply (+ Examples)
By: David Phair (PhD) and Alexandra Shaeffer (PhD) | June 2022
The research aims , objectives and research questions (collectively called the “golden thread”) are arguably the most important thing you need to get right when you’re crafting a research proposal , dissertation or thesis . We receive questions almost every day about this “holy trinity” of research and there’s certainly a lot of confusion out there, so we’ve crafted this post to help you navigate your way through the fog.
Overview: The Golden Thread
- What is the golden thread
- What are research aims ( examples )
- What are research objectives ( examples )
- What are research questions ( examples )
- The importance of alignment in the golden thread
What is the “golden thread”?
The golden thread simply refers to the collective research aims , research objectives , and research questions for any given project (i.e., a dissertation, thesis, or research paper ). These three elements are bundled together because it’s extremely important that they align with each other, and that the entire research project aligns with them.
Importantly, the golden thread needs to weave its way through the entirety of any research project , from start to end. In other words, it needs to be very clearly defined right at the beginning of the project (the topic ideation and proposal stage) and it needs to inform almost every decision throughout the rest of the project. For example, your research design and methodology will be heavily influenced by the golden thread (we’ll explain this in more detail later), as well as your literature review.
The research aims, objectives and research questions (the golden thread) define the focus and scope ( the delimitations ) of your research project. In other words, they help ringfence your dissertation or thesis to a relatively narrow domain, so that you can “go deep” and really dig into a specific problem or opportunity. They also help keep you on track , as they act as a litmus test for relevance. In other words, if you’re ever unsure whether to include something in your document, simply ask yourself the question, “does this contribute toward my research aims, objectives or questions?”. If it doesn’t, chances are you can drop it.
Alright, enough of the fluffy, conceptual stuff. Let’s get down to business and look at what exactly the research aims, objectives and questions are and outline a few examples to bring these concepts to life.

Research Aims: What are they?
Simply put, the research aim(s) is a statement that reflects the broad overarching goal (s) of the research project. Research aims are fairly high-level (low resolution) as they outline the general direction of the research and what it’s trying to achieve .
Research Aims: Examples
True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording “this research aims to…”, “this research seeks to…”, and so on. For example:
“This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.” “This study sets out to assess the interaction between student support and self-care on well-being in engineering graduate students”
As you can see, these research aims provide a high-level description of what the study is about and what it seeks to achieve. They’re not hyper-specific or action-oriented, but they’re clear about what the study’s focus is and what is being investigated.
Need a helping hand?
Research Objectives: What are they?
The research objectives take the research aims and make them more practical and actionable . In other words, the research objectives showcase the steps that the researcher will take to achieve the research aims.
The research objectives need to be far more specific (higher resolution) and actionable than the research aims. In fact, it’s always a good idea to craft your research objectives using the “SMART” criteria. In other words, they should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant and time-bound”.
Research Objectives: Examples
Let’s look at two examples of research objectives. We’ll stick with the topic and research aims we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic:
To observe the retail HR employees throughout the digital transformation. To assess employee perceptions of digital transformation in retail HR. To identify the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR.
And for the student wellness topic:
To determine whether student self-care predicts the well-being score of engineering graduate students. To determine whether student support predicts the well-being score of engineering students. To assess the interaction between student self-care and student support when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students.
As you can see, these research objectives clearly align with the previously mentioned research aims and effectively translate the low-resolution aims into (comparatively) higher-resolution objectives and action points . They give the research project a clear focus and present something that resembles a research-based “to-do” list.

Research Questions: What are they?
Finally, we arrive at the all-important research questions. The research questions are, as the name suggests, the key questions that your study will seek to answer . Simply put, they are the core purpose of your dissertation, thesis, or research project. You’ll present them at the beginning of your document (either in the introduction chapter or literature review chapter) and you’ll answer them at the end of your document (typically in the discussion and conclusion chapters).
The research questions will be the driving force throughout the research process. For example, in the literature review chapter, you’ll assess the relevance of any given resource based on whether it helps you move towards answering your research questions. Similarly, your methodology and research design will be heavily influenced by the nature of your research questions. For instance, research questions that are exploratory in nature will usually make use of a qualitative approach, whereas questions that relate to measurement or relationship testing will make use of a quantitative approach.
Let’s look at some examples of research questions to make this more tangible.
Research Questions: Examples
Again, we’ll stick with the research aims and research objectives we mentioned previously.
For the digital transformation topic (which would be qualitative in nature):
How do employees perceive digital transformation in retail HR? What are the barriers and facilitators of digital transformation in retail HR?
And for the student wellness topic (which would be quantitative in nature):
Does student self-care predict the well-being scores of engineering graduate students? Does student support predict the well-being scores of engineering students? Do student self-care and student support interact when predicting well-being in engineering graduate students?
You’ll probably notice that there’s quite a formulaic approach to this. In other words, the research questions are basically the research objectives “converted” into question format. While that is true most of the time, it’s not always the case. For example, the first research objective for the digital transformation topic was more or less a step on the path toward the other objectives, and as such, it didn’t warrant its own research question.
So, don’t rush your research questions and sloppily reword your objectives as questions. Carefully think about what exactly you’re trying to achieve (i.e. your research aim) and the objectives you’ve set out, then craft a set of well-aligned research questions . Also, keep in mind that this can be a somewhat iterative process , where you go back and tweak research objectives and aims to ensure tight alignment throughout the golden thread.
The importance of strong alignment
Alignment is the keyword here and we have to stress its importance . Simply put, you need to make sure that there is a very tight alignment between all three pieces of the golden thread. If your research aims and research questions don’t align, for example, your project will be pulling in different directions and will lack focus . This is a common problem students face and can cause many headaches (and tears), so be warned.
Take the time to carefully craft your research aims, objectives and research questions before you run off down the research path. Ideally, get your research supervisor/advisor to review and comment on your golden thread before you invest significant time into your project, and certainly before you start collecting data .
Recap: The golden thread
In this post, we unpacked the golden thread of research, consisting of the research aims , research objectives and research questions . You can jump back to any section using the links below.
As always, feel free to leave a comment below – we always love to hear from you. Also, if you’re interested in 1-on-1 support, take a look at our private coaching service here.

Psst... there’s more!
This post was based on one of our popular Research Bootcamps . If you're working on a research project, you'll definitely want to check this out ...
41 Comments
Thank you very much for your great effort put. As an Undergraduate taking Demographic Research & Methodology, I’ve been trying so hard to understand clearly what is a Research Question, Research Aim and the Objectives in a research and the relationship between them etc. But as for now I’m thankful that you’ve solved my problem.
Well appreciated. This has helped me greatly in doing my dissertation.
An so delighted with this wonderful information thank you a lot.
so impressive i have benefited a lot looking forward to learn more on research.
I am very happy to have carefully gone through this well researched article.
Infact,I used to be phobia about anything research, because of my poor understanding of the concepts.
Now,I get to know that my research question is the same as my research objective(s) rephrased in question format.
I please I would need a follow up on the subject,as I intends to join the team of researchers. Thanks once again.
Thanks so much. This was really helpful.
I know you pepole have tried to break things into more understandable and easy format. And God bless you. Keep it up
i found this document so useful towards my study in research methods. thanks so much.
This is my 2nd read topic in your course and I should commend the simplified explanations of each part. I’m beginning to understand and absorb the use of each part of a dissertation/thesis. I’ll keep on reading your free course and might be able to avail the training course! Kudos!
Thank you! Better put that my lecture and helped to easily understand the basics which I feel often get brushed over when beginning dissertation work.
This is quite helpful. I like how the Golden thread has been explained and the needed alignment.
This is quite helpful. I really appreciate!
The article made it simple for researcher students to differentiate between three concepts.
Very innovative and educational in approach to conducting research.
I am very impressed with all these terminology, as I am a fresh student for post graduate, I am highly guided and I promised to continue making consultation when the need arise. Thanks a lot.
A very helpful piece. thanks, I really appreciate it .
Very well explained, and it might be helpful to many people like me.
Wish i had found this (and other) resource(s) at the beginning of my PhD journey… not in my writing up year… 😩 Anyways… just a quick question as i’m having some issues ordering my “golden thread”…. does it matter in what order you mention them? i.e., is it always first aims, then objectives, and finally the questions? or can you first mention the research questions and then the aims and objectives?
Thank you for a very simple explanation that builds upon the concepts in a very logical manner. Just prior to this, I read the research hypothesis article, which was equally very good. This met my primary objective.
My secondary objective was to understand the difference between research questions and research hypothesis, and in which context to use which one. However, I am still not clear on this. Can you kindly please guide?
In research, a research question is a clear and specific inquiry that the researcher wants to answer, while a research hypothesis is a tentative statement or prediction about the relationship between variables or the expected outcome of the study. Research questions are broader and guide the overall study, while hypotheses are specific and testable statements used in quantitative research. Research questions identify the problem, while hypotheses provide a focus for testing in the study.
Exactly what I need in this research journey, I look forward to more of your coaching videos.
This helped a lot. Thanks so much for the effort put into explaining it.
What data source in writing dissertation/Thesis requires?
What is data source covers when writing dessertation/thesis
This is quite useful thanks
I’m excited and thankful. I got so much value which will help me progress in my thesis.
where are the locations of the reserch statement, research objective and research question in a reserach paper? Can you write an ouline that defines their places in the researh paper?
Very helpful and important tips on Aims, Objectives and Questions.
Thank you so much for making research aim, research objectives and research question so clear. This will be helpful to me as i continue with my thesis.
Thanks much for this content. I learned a lot. And I am inspired to learn more. I am still struggling with my preparation for dissertation outline/proposal. But I consistently follow contents and tutorials and the new FB of GRAD Coach. Hope to really become confident in writing my dissertation and successfully defend it.
As a researcher and lecturer, I find splitting research goals into research aims, objectives, and questions is unnecessarily bureaucratic and confusing for students. For most biomedical research projects, including ‘real research’, 1-3 research questions will suffice (numbers may differ by discipline).
Awesome! Very important resources and presented in an informative way to easily understand the golden thread. Indeed, thank you so much.
Well explained
The blog article on research aims, objectives, and questions by Grad Coach is a clear and insightful guide that aligns with my experiences in academic research. The article effectively breaks down the often complex concepts of research aims and objectives, providing a straightforward and accessible explanation. Drawing from my own research endeavors, I appreciate the practical tips offered, such as the need for specificity and clarity when formulating research questions. The article serves as a valuable resource for students and researchers, offering a concise roadmap for crafting well-defined research goals and objectives. Whether you’re a novice or an experienced researcher, this article provides practical insights that contribute to the foundational aspects of a successful research endeavor.
A great thanks for you. it is really amazing explanation. I grasp a lot and one step up to research knowledge.
I really found these tips helpful. Thank you very much Grad Coach.
I found this article helpful. Thanks for sharing this.
thank you so much, the explanation and examples are really helpful
This is a well researched and superbly written article for learners of research methods at all levels in the research topic from conceptualization to research findings and conclusions. I highly recommend this material to university graduate students. As an instructor of advanced research methods for PhD students, I have confirmed that I was giving the right guidelines for the degree they are undertaking.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Print Friendly

- Aims and Objectives – A Guide for Academic Writing
- Doing a PhD
One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and your reader clarity, with your aims indicating what is to be achieved, and your objectives indicating how it will be achieved.
Introduction
There is no getting away from the importance of the aims and objectives in determining the success of your research project. Unfortunately, however, it is an aspect that many students struggle with, and ultimately end up doing poorly. Given their importance, if you suspect that there is even the smallest possibility that you belong to this group of students, we strongly recommend you read this page in full.
This page describes what research aims and objectives are, how they differ from each other, how to write them correctly, and the common mistakes students make and how to avoid them. An example of a good aim and objectives from a past thesis has also been deconstructed to help your understanding.
What Are Aims and Objectives?
Research aims.
A research aim describes the main goal or the overarching purpose of your research project.
In doing so, it acts as a focal point for your research and provides your readers with clarity as to what your study is all about. Because of this, research aims are almost always located within its own subsection under the introduction section of a research document, regardless of whether it’s a thesis , a dissertation, or a research paper .
A research aim is usually formulated as a broad statement of the main goal of the research and can range in length from a single sentence to a short paragraph. Although the exact format may vary according to preference, they should all describe why your research is needed (i.e. the context), what it sets out to accomplish (the actual aim) and, briefly, how it intends to accomplish it (overview of your objectives).
To give an example, we have extracted the following research aim from a real PhD thesis:
Example of a Research Aim
The role of diametrical cup deformation as a factor to unsatisfactory implant performance has not been widely reported. The aim of this thesis was to gain an understanding of the diametrical deformation behaviour of acetabular cups and shells following impaction into the reamed acetabulum. The influence of a range of factors on deformation was investigated to ascertain if cup and shell deformation may be high enough to potentially contribute to early failure and high wear rates in metal-on-metal implants.
Note: Extracted with permission from thesis titled “T he Impact And Deformation Of Press-Fit Metal Acetabular Components ” produced by Dr H Hothi of previously Queen Mary University of London.
Research Objectives
Where a research aim specifies what your study will answer, research objectives specify how your study will answer it.
They divide your research aim into several smaller parts, each of which represents a key section of your research project. As a result, almost all research objectives take the form of a numbered list, with each item usually receiving its own chapter in a dissertation or thesis.
Following the example of the research aim shared above, here are it’s real research objectives as an example:
Example of a Research Objective
- Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
- Investigate the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup.
- Determine the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types.
- Investigate the influence of non-uniform cup support and varying the orientation of the component in the cavity on deformation.
- Examine the influence of errors during reaming of the acetabulum which introduce ovality to the cavity.
- Determine the relationship between changes in the geometry of the component and deformation for different cup designs.
- Develop three dimensional pelvis models with non-uniform bone material properties from a range of patients with varying bone quality.
- Use the key parameters that influence deformation, as identified in the foam models to determine the range of deformations that may occur clinically using the anatomic models and if these deformations are clinically significant.
It’s worth noting that researchers sometimes use research questions instead of research objectives, or in other cases both. From a high-level perspective, research questions and research objectives make the same statements, but just in different formats.
Taking the first three research objectives as an example, they can be restructured into research questions as follows:
Restructuring Research Objectives as Research Questions
- Can finite element models using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum together with explicit dynamics be used to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion?
- What is the number, velocity and position of impacts needed to insert a cup?
- What is the relationship between the size of interference between the cup and cavity and deformation for different cup types?
Difference Between Aims and Objectives
Hopefully the above explanations make clear the differences between aims and objectives, but to clarify:
- The research aim focus on what the research project is intended to achieve; research objectives focus on how the aim will be achieved.
- Research aims are relatively broad; research objectives are specific.
- Research aims focus on a project’s long-term outcomes; research objectives focus on its immediate, short-term outcomes.
- A research aim can be written in a single sentence or short paragraph; research objectives should be written as a numbered list.
How to Write Aims and Objectives
Before we discuss how to write a clear set of research aims and objectives, we should make it clear that there is no single way they must be written. Each researcher will approach their aims and objectives slightly differently, and often your supervisor will influence the formulation of yours on the basis of their own preferences.
Regardless, there are some basic principles that you should observe for good practice; these principles are described below.
Your aim should be made up of three parts that answer the below questions:
- Why is this research required?
- What is this research about?
- How are you going to do it?
The easiest way to achieve this would be to address each question in its own sentence, although it does not matter whether you combine them or write multiple sentences for each, the key is to address each one.
The first question, why , provides context to your research project, the second question, what , describes the aim of your research, and the last question, how , acts as an introduction to your objectives which will immediately follow.
Scroll through the image set below to see the ‘why, what and how’ associated with our research aim example.

Note: Your research aims need not be limited to one. Some individuals per to define one broad ‘overarching aim’ of a project and then adopt two or three specific research aims for their thesis or dissertation. Remember, however, that in order for your assessors to consider your research project complete, you will need to prove you have fulfilled all of the aims you set out to achieve. Therefore, while having more than one research aim is not necessarily disadvantageous, consider whether a single overarching one will do.
Research Objectives
Each of your research objectives should be SMART :
- Specific – is there any ambiguity in the action you are going to undertake, or is it focused and well-defined?
- Measurable – how will you measure progress and determine when you have achieved the action?
- Achievable – do you have the support, resources and facilities required to carry out the action?
- Relevant – is the action essential to the achievement of your research aim?
- Timebound – can you realistically complete the action in the available time alongside your other research tasks?
In addition to being SMART, your research objectives should start with a verb that helps communicate your intent. Common research verbs include:
Table of Research Verbs to Use in Aims and Objectives
| (Understanding and organising information) | (Solving problems using information) | (reaching conclusion from evidence) | (Breaking down into components) | (Judging merit) |
| Review Identify Explore Discover Discuss Summarise Describe | Interpret Apply Demonstrate Establish Determine Estimate Calculate Relate | Analyse Compare Inspect Examine Verify Select Test Arrange | Propose Design Formulate Collect Construct Prepare Undertake Assemble | Appraise Evaluate Compare Assess Recommend Conclude Select |
Last, format your objectives into a numbered list. This is because when you write your thesis or dissertation, you will at times need to make reference to a specific research objective; structuring your research objectives in a numbered list will provide a clear way of doing this.
To bring all this together, let’s compare the first research objective in the previous example with the above guidance:
Checking Research Objective Example Against Recommended Approach
Research Objective:
1. Develop finite element models using explicit dynamics to mimic mallet blows during cup/shell insertion, initially using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum.
Checking Against Recommended Approach:
Q: Is it specific? A: Yes, it is clear what the student intends to do (produce a finite element model), why they intend to do it (mimic cup/shell blows) and their parameters have been well-defined ( using simplified experimentally validated foam models to represent the acetabulum ).
Q: Is it measurable? A: Yes, it is clear that the research objective will be achieved once the finite element model is complete.
Q: Is it achievable? A: Yes, provided the student has access to a computer lab, modelling software and laboratory data.
Q: Is it relevant? A: Yes, mimicking impacts to a cup/shell is fundamental to the overall aim of understanding how they deform when impacted upon.
Q: Is it timebound? A: Yes, it is possible to create a limited-scope finite element model in a relatively short time, especially if you already have experience in modelling.
Q: Does it start with a verb? A: Yes, it starts with ‘develop’, which makes the intent of the objective immediately clear.
Q: Is it a numbered list? A: Yes, it is the first research objective in a list of eight.
Mistakes in Writing Research Aims and Objectives
1. making your research aim too broad.
Having a research aim too broad becomes very difficult to achieve. Normally, this occurs when a student develops their research aim before they have a good understanding of what they want to research. Remember that at the end of your project and during your viva defence , you will have to prove that you have achieved your research aims; if they are too broad, this will be an almost impossible task. In the early stages of your research project, your priority should be to narrow your study to a specific area. A good way to do this is to take the time to study existing literature, question their current approaches, findings and limitations, and consider whether there are any recurring gaps that could be investigated .
Note: Achieving a set of aims does not necessarily mean proving or disproving a theory or hypothesis, even if your research aim was to, but having done enough work to provide a useful and original insight into the principles that underlie your research aim.
2. Making Your Research Objectives Too Ambitious
Be realistic about what you can achieve in the time you have available. It is natural to want to set ambitious research objectives that require sophisticated data collection and analysis, but only completing this with six months before the end of your PhD registration period is not a worthwhile trade-off.
3. Formulating Repetitive Research Objectives
Each research objective should have its own purpose and distinct measurable outcome. To this effect, a common mistake is to form research objectives which have large amounts of overlap. This makes it difficult to determine when an objective is truly complete, and also presents challenges in estimating the duration of objectives when creating your project timeline. It also makes it difficult to structure your thesis into unique chapters, making it more challenging for you to write and for your audience to read.
Fortunately, this oversight can be easily avoided by using SMART objectives.
Hopefully, you now have a good idea of how to create an effective set of aims and objectives for your research project, whether it be a thesis, dissertation or research paper. While it may be tempting to dive directly into your research, spending time on getting your aims and objectives right will give your research clear direction. This won’t only reduce the likelihood of problems arising later down the line, but will also lead to a more thorough and coherent research project.
Finding a PhD has never been this easy – search for a PhD by keyword, location or academic area of interest.
Browse PhDs Now
Join thousands of students.
Join thousands of other students and stay up to date with the latest PhD programmes, funding opportunities and advice.
- Privacy Policy

Home » Research Objectives – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Research Objectives – Types, Examples and Writing Guide
Table of Contents

Research Objectives
Research objectives refer to the specific goals or aims of a research study. They provide a clear and concise description of what the researcher hopes to achieve by conducting the research . The objectives are typically based on the research questions and hypotheses formulated at the beginning of the study and are used to guide the research process.
Types of Research Objectives
Here are the different types of research objectives in research:
- Exploratory Objectives: These objectives are used to explore a topic, issue, or phenomenon that has not been studied in-depth before. The aim of exploratory research is to gain a better understanding of the subject matter and generate new ideas and hypotheses .
- Descriptive Objectives: These objectives aim to describe the characteristics, features, or attributes of a particular population, group, or phenomenon. Descriptive research answers the “what” questions and provides a snapshot of the subject matter.
- Explanatory Objectives : These objectives aim to explain the relationships between variables or factors. Explanatory research seeks to identify the cause-and-effect relationships between different phenomena.
- Predictive Objectives: These objectives aim to predict future events or outcomes based on existing data or trends. Predictive research uses statistical models to forecast future trends or outcomes.
- Evaluative Objectives : These objectives aim to evaluate the effectiveness or impact of a program, intervention, or policy. Evaluative research seeks to assess the outcomes or results of a particular intervention or program.
- Prescriptive Objectives: These objectives aim to provide recommendations or solutions to a particular problem or issue. Prescriptive research identifies the best course of action based on the results of the study.
- Diagnostic Objectives : These objectives aim to identify the causes or factors contributing to a particular problem or issue. Diagnostic research seeks to uncover the underlying reasons for a particular phenomenon.
- Comparative Objectives: These objectives aim to compare two or more groups, populations, or phenomena to identify similarities and differences. Comparative research is used to determine which group or approach is more effective or has better outcomes.
- Historical Objectives: These objectives aim to examine past events, trends, or phenomena to gain a better understanding of their significance and impact. Historical research uses archival data, documents, and records to study past events.
- Ethnographic Objectives : These objectives aim to understand the culture, beliefs, and practices of a particular group or community. Ethnographic research involves immersive fieldwork and observation to gain an insider’s perspective of the group being studied.
- Action-oriented Objectives: These objectives aim to bring about social or organizational change. Action-oriented research seeks to identify practical solutions to social problems and to promote positive change in society.
- Conceptual Objectives: These objectives aim to develop new theories, models, or frameworks to explain a particular phenomenon or set of phenomena. Conceptual research seeks to provide a deeper understanding of the subject matter by developing new theoretical perspectives.
- Methodological Objectives: These objectives aim to develop and improve research methods and techniques. Methodological research seeks to advance the field of research by improving the validity, reliability, and accuracy of research methods and tools.
- Theoretical Objectives : These objectives aim to test and refine existing theories or to develop new theoretical perspectives. Theoretical research seeks to advance the field of knowledge by testing and refining existing theories or by developing new theoretical frameworks.
- Measurement Objectives : These objectives aim to develop and validate measurement instruments, such as surveys, questionnaires, and tests. Measurement research seeks to improve the quality and reliability of data collection and analysis by developing and testing new measurement tools.
- Design Objectives : These objectives aim to develop and refine research designs, such as experimental, quasi-experimental, and observational designs. Design research seeks to improve the quality and validity of research by developing and testing new research designs.
- Sampling Objectives: These objectives aim to develop and refine sampling techniques, such as probability and non-probability sampling methods. Sampling research seeks to improve the representativeness and generalizability of research findings by developing and testing new sampling techniques.
How to Write Research Objectives
Writing clear and concise research objectives is an important part of any research project, as it helps to guide the study and ensure that it is focused and relevant. Here are some steps to follow when writing research objectives:
- Identify the research problem : Before you can write research objectives, you need to identify the research problem you are trying to address. This should be a clear and specific problem that can be addressed through research.
- Define the research questions : Based on the research problem, define the research questions you want to answer. These questions should be specific and should guide the research process.
- Identify the variables : Identify the key variables that you will be studying in your research. These are the factors that you will be measuring, manipulating, or analyzing to answer your research questions.
- Write specific objectives: Write specific, measurable objectives that will help you answer your research questions. These objectives should be clear and concise and should indicate what you hope to achieve through your research.
- Use the SMART criteria: To ensure that your research objectives are well-defined and achievable, use the SMART criteria. This means that your objectives should be Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound.
- Revise and refine: Once you have written your research objectives, revise and refine them to ensure that they are clear, concise, and achievable. Make sure that they align with your research questions and variables, and that they will help you answer your research problem.
Example of Research Objectives
Examples of research objectives Could be:
Research Objectives for the topic of “The Impact of Artificial Intelligence on Employment”:
- To investigate the effects of the adoption of AI on employment trends across various industries and occupations.
- To explore the potential for AI to create new job opportunities and transform existing roles in the workforce.
- To examine the social and economic implications of the widespread use of AI for employment, including issues such as income inequality and access to education and training.
- To identify the skills and competencies that will be required for individuals to thrive in an AI-driven workplace, and to explore the role of education and training in developing these skills.
- To evaluate the ethical and legal considerations surrounding the use of AI for employment, including issues such as bias, privacy, and the responsibility of employers and policymakers to protect workers’ rights.
When to Write Research Objectives
- At the beginning of a research project : Research objectives should be identified and written down before starting a research project. This helps to ensure that the project is focused and that data collection and analysis efforts are aligned with the intended purpose of the research.
- When refining research questions: Writing research objectives can help to clarify and refine research questions. Objectives provide a more concrete and specific framework for addressing research questions, which can improve the overall quality and direction of a research project.
- After conducting a literature review : Conducting a literature review can help to identify gaps in knowledge and areas that require further research. Writing research objectives can help to define and focus the research effort in these areas.
- When developing a research proposal: Research objectives are an important component of a research proposal. They help to articulate the purpose and scope of the research, and provide a clear and concise summary of the expected outcomes and contributions of the research.
- When seeking funding for research: Funding agencies often require a detailed description of research objectives as part of a funding proposal. Writing clear and specific research objectives can help to demonstrate the significance and potential impact of a research project, and increase the chances of securing funding.
- When designing a research study : Research objectives guide the design and implementation of a research study. They help to identify the appropriate research methods, sampling strategies, data collection and analysis techniques, and other relevant aspects of the study design.
- When communicating research findings: Research objectives provide a clear and concise summary of the main research questions and outcomes. They are often included in research reports and publications, and can help to ensure that the research findings are communicated effectively and accurately to a wide range of audiences.
- When evaluating research outcomes : Research objectives provide a basis for evaluating the success of a research project. They help to measure the degree to which research questions have been answered and the extent to which research outcomes have been achieved.
- When conducting research in a team : Writing research objectives can facilitate communication and collaboration within a research team. Objectives provide a shared understanding of the research purpose and goals, and can help to ensure that team members are working towards a common objective.
Purpose of Research Objectives
Some of the main purposes of research objectives include:
- To clarify the research question or problem : Research objectives help to define the specific aspects of the research question or problem that the study aims to address. This makes it easier to design a study that is focused and relevant.
- To guide the research design: Research objectives help to determine the research design, including the research methods, data collection techniques, and sampling strategy. This ensures that the study is structured and efficient.
- To measure progress : Research objectives provide a way to measure progress throughout the research process. They help the researcher to evaluate whether they are on track and meeting their goals.
- To communicate the research goals : Research objectives provide a clear and concise description of the research goals. This helps to communicate the purpose of the study to other researchers, stakeholders, and the general public.
Advantages of Research Objectives
Here are some advantages of having well-defined research objectives:
- Focus : Research objectives help to focus the research effort on specific areas of inquiry. By identifying clear research questions, the researcher can narrow down the scope of the study and avoid getting sidetracked by irrelevant information.
- Clarity : Clearly stated research objectives provide a roadmap for the research study. They provide a clear direction for the research, making it easier for the researcher to stay on track and achieve their goals.
- Measurability : Well-defined research objectives provide measurable outcomes that can be used to evaluate the success of the research project. This helps to ensure that the research is effective and that the research goals are achieved.
- Feasibility : Research objectives help to ensure that the research project is feasible. By clearly defining the research goals, the researcher can identify the resources required to achieve those goals and determine whether those resources are available.
- Relevance : Research objectives help to ensure that the research study is relevant and meaningful. By identifying specific research questions, the researcher can ensure that the study addresses important issues and contributes to the existing body of knowledge.
About the author
Muhammad Hassan
Researcher, Academic Writer, Web developer
You may also like

Research Paper Outline – Types, Example, Template

Research Problem – Examples, Types and Guide

Table of Contents – Types, Formats, Examples

Research Summary – Structure, Examples and...

Thesis Statement – Examples, Writing Guide

Data Interpretation – Process, Methods and...

Research Aims and Objectives: The dynamic duo for successful research
Picture yourself on a road trip without a destination in mind — driving aimlessly, not knowing where you’re headed or how to get there. Similarly, your research is navigated by well-defined research aims and objectives. Research aims and objectives are the foundation of any research project. They provide a clear direction and purpose for the study, ensuring that you stay focused and on track throughout the process. They are your trusted navigational tools, leading you to success.
Understanding the relationship between research objectives and aims is crucial to any research project’s success, and we’re here to break it down for you in this article. Here, we’ll explore the importance of research aims and objectives, understand their differences, and delve into the impact they have on the quality of research.
Understanding the Difference between Research Aims and Objectives
In research, aims and objectives are two important components but are often used interchangeably. Though they may sound similar, they are distinct and serve different purposes.
Research Aims:
Research aims are broad statements that describe the overall purpose of your study. They provide a general direction for your study and indicate the intended achievements of your research. Aims are usually written in a general and abstract manner describing the ultimate goal of the research.
Research Objectives:
Research objectives are specific, measurable, and achievable goals that you aim to accomplish within a specified timeframe. They break down the research aims into smaller, more manageable components and provide a clear picture of what you want to achieve and how you plan to achieve it.
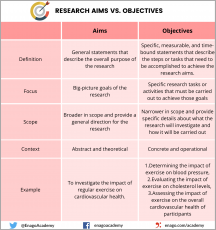
In the example, the objectives provide specific targets that must be achieved to reach the aim. Essentially, aims provide the overall direction for the research while objectives provide specific targets that must be achieved to accomplish the aims. Aims provide a broad context for the research, while the objectives provide smaller steps that the researcher must take to accomplish the overall research goals. To illustrate, when planning a road trip, your research aim is the destination you want to reach, and your research objectives are the specific routes you need to take to get there.
Aims and objectives are interconnected. Objectives play a key role in defining the research methodology, providing a roadmap for how you’ll collect and analyze data, while aim is the final destination, which represents the ultimate goal of your research. By setting specific goals, you’ll be able to design a research plan that helps you achieve your objectives and, ultimately, your research aim.
Importance of Well-defined Aims and Objectives
The impact of clear research aims and objectives on the quality of research cannot be understated. But it’s not enough to simply have aims and objectives. Well-defined research aims and objectives are important for several reasons:
- Provides direction: Clear aims and well-defined objectives provide a specific direction for your research study, ensuring that the research stays focused on a specific topic or problem. This helps to prevent the research from becoming too broad or unfocused, and ensures that the study remains relevant and meaningful.
- Guides research design: The research aim and objectives help guide the research design and methodology, ensuring that your study is designed in a way that will answer the research questions and achieve the research objectives.
- Helps with resource allocation: Clear research aims and objectives helps you to allocate resources effectively , including time, financial resources, human resources, and other required materials. With a well-defined aim and objectives, you can identify the resources required to conduct the research, and allocate them in a way that maximizes efficiency and productivity.
- Assists in evaluation: Clearly specified research aims and objectives allow for effective evaluation of your research project’s success. You can assess whether the research has achieved its objectives, and whether the aim has been met. This evaluation process can help to identify areas of the research project that may require further attention or modification.
- Enhances communication: Well-defined research aims and objectives help to enhance communication among the research team, stakeholders, funding agencies, and other interested parties. Clear aims and objectives ensure that everyone involved in your research project understands the purpose and goals of the study. This can help to foster collaboration and ensure that everyone is working towards the same end goal.
How to Formulate Research Aims and Objectives
Formulating effective research aims and objectives involves a systematic process to ensure that they are clear, specific, achievable, and relevant. Start by asking yourself what you want to achieve through your research. What impact do you want your research to have? Once you have a clear understanding of your aims, you can then break them down into specific, achievable objectives. Here are some steps you can follow when developing research aims and objectives:
- Identify the research question : Clearly identify the questions you want to answer through your research. This will help you define the scope of your research. Understanding the characteristics of a good research question will help you generate clearer aims and objectives.
- Conduct literature review : When defining your research aim and objectives, it’s important to conduct a literature review to identify key concepts, theories, and methods related to your research problem or question. Conducting a thorough literature review can help you understand what research has been done in the area and what gaps exist in the literature.
- Identify the research aim: Develop a research aim that summarizes the overarching goal of your research. The research aim should be broad and concise.
- Develop research objectives: Based on your research questions and research aim, develop specific research objectives that outline what you intend to achieve through your research. These objectives should be specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
- Use action verbs: Use action verbs such as “investigate,” “examine,” “analyze,” and “compare” to describe your research aims and objectives. This makes them more specific and measurable.
- Ensure alignment with research question: Ensure that the research aim and objectives are aligned with the research question. This helps to ensure that the research remains focused and that the objectives are specific enough to answer your research question.
- Refine and revise: Once the research aim and objectives have been developed, refine and revise them as needed. Seek feedback from your colleagues, mentors, or supervisors to ensure that they are clear, concise, and achievable within the given resources and timeframe.
- Communicate: After finalizing the research aim and objectives, they should be communicated to the research team, stakeholders, and other interested parties. This helps to ensure that everyone is working towards the same end goal and understands the purpose of the study.
Common Pitfalls to Avoid While Formulating Aims and Objectives
There are several common mistakes that researchers can make when writing research aims and objectives. These include:
- Being too broad or vague: Aims and objectives that are too general or unclear can lead to confusion and lack of focus. It is important to ensure that the aims and objectives are concise and clear.
- Being too narrow or specific: On the other hand, aims and objectives that are too narrow or specific may limit the scope of the research and make it difficult to draw meaningful conclusions or implications.
- Being too ambitious: While it is important to aim high, being too ambitious with the aims and objectives can lead to unrealistic expectations and can be difficult to achieve within the constraints of the research project.
- Lack of alignment: The aims and objectives should be directly linked to the research questions being investigated. Otherwise, this will lead to a lack of coherence in the research project.
- Lack of feasibility: The aims and objectives should be achievable within the constraints of the research project, including time, budget, and resources. Failing to consider feasibility may cause compromise of the research quality.
- Failing to consider ethical considerations: The aims and objectives should take into account any ethical considerations, such as ensuring the safety and well-being of study participants.
- Failing to involve all stakeholders: It’s important to involve all relevant stakeholders, such as participants, supervisors, and funding agencies, in the development of the aims and objectives to ensure they are appropriate and relevant.
To avoid these common pitfalls, it is important to be specific, clear, relevant, and realistic when writing research aims and objectives. Seek feedback from colleagues or supervisors to ensure that the aims and objectives are aligned with the research problem , questions, and methodology, and are achievable within the constraints of the research project. It’s important to continually refine your aims and objectives as you go. As you progress in your research, it’s not uncommon for research aims and objectives to evolve slightly, but it’s important that they remain consistent with the study conducted and the research topic.
In summary, research aims and objectives are the backbone of any successful research project. They give you the ability to cut through the noise and hone in on what really matters. By setting clear goals and aligning them with your research questions and methodology, you can ensure that your research is relevant, impactful, and of the highest quality. So, before you hit the road on your research journey, make sure you have a clear destination and steps to get there. Let us know in the comments section below the challenges you faced and the strategies you followed while fomulating research aims and objectives! Also, feel free to reach out to us at any stage of your research or publication by using #AskEnago and tagging @EnagoAcademy on Twitter , Facebook , and Quora . Happy researching!
This particular material has added important but overlooked concepts regarding my experiences in explaining research aims and objectives. Thank you
Rate this article Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published.

Enago Academy's Most Popular Articles

- Reporting Research
Academic Essay Writing Made Simple: 4 types and tips
The pen is mightier than the sword, they say, and nowhere is this more evident…

- Old Webinars
- Webinar Mobile App
Improving Research Manuscripts Using AI-Powered Insights: Enago reports for effective research communication
Language Quality Importance in Academia AI in Evaluating Language Quality Enago Language Reports Live Demo…

- AI in Academia
- Trending Now
Simplifying the Literature Review Journey — A comparative analysis of 5 AI summarization tools
Imagine having to skim through and read mountains of research papers and books, only to…

Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for data interpretation
In research, choosing the right approach to understand data is crucial for deriving meaningful insights.…

Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right approach
The process of choosing the right research design can put ourselves at the crossroads of…
Choosing the Right Analytical Approach: Thematic analysis vs. content analysis for…
Comparing Cross Sectional and Longitudinal Studies: 5 steps for choosing the right…
Research Recommendations – Guiding policy-makers for evidence-based decision making

Sign-up to read more
Subscribe for free to get unrestricted access to all our resources on research writing and academic publishing including:
- 2000+ blog articles
- 50+ Webinars
- 10+ Expert podcasts
- 50+ Infographics
- 10+ Checklists
- Research Guides
We hate spam too. We promise to protect your privacy and never spam you.
- Industry News
- Publishing Research
- Promoting Research
- Career Corner
- Diversity and Inclusion
- Infographics
- Expert Video Library
- Other Resources
- Enago Learn
- Upcoming & On-Demand Webinars
- Peer Review Week 2024
- Open Access Week 2023
- Conference Videos
- Enago Report
- Journal Finder
- Enago Plagiarism & AI Grammar Check
- Editing Services
- Publication Support Services
- Research Impact
- Translation Services
- Publication solutions
- AI-Based Solutions
- Thought Leadership
- Call for Articles
- Call for Speakers
- Author Training
- Edit Profile
I am looking for Editing/ Proofreading services for my manuscript Tentative date of next journal submission:

Which among these features would you prefer the most in a peer review assistant?

- Research Group
- Job Seekers

Research Tips
Understanding the Difference between Research Questions and Objectives
January 13, 2023
When conducting research, clearly understanding the difference between research questions and objectives is important. While these terms are often used interchangeably, they refer to two distinct aspects of the research process.
Research questions are broad statements that guide the overall direction of the research. They identify the main problem or area of inquiry that the research will address. For example, a research question might be, "What is the impact of social media on teenage mental health?" This question sets the stage for the research and helps to define the scope of the study.

- Research questions are more general and open-ended, while objectives are specific and measurable.
- Research questions identify the main problem or area of inquiry, while objectives define the specific outcomes that the researcher is looking to achieve.
- Research questions help define the study's scope, while objectives help guide the research process.
- Research questions are often used to generate hypotheses or identify gaps in existing knowledge, while objectives are used to establish clear and achievable targets for the research.
- Research questions and objectives are not mutually exclusive, but well-defined research questions should lead to specific objectives necessary to answer the question.
On the other hand, research objectives are specific, measurable goals that the research aims to achieve. They are used to guide the research process and help to define the specific outcomes that the researcher is looking to achieve. For example, an objective for the above research question might be "To determine the correlation between social media usage and rates of depression in teenagers." This objective is more specific and measurable than the research question and helps define the specific outcomes that the researcher is looking to achieve.
It is important to note that research questions and objectives are not mutually exclusive; a study can have one or several questions and objectives. A well-defined research question should lead to specific objectives necessary to answer the question.
In summary, research questions and objectives are two distinct aspects of the research process. Research questions are broad statements that guide the overall direction of the research, while research objectives are specific, measurable goals that the research aims to achieve. Understanding these two terms' differences is essential for conducting effective and meaningful research.
Mon - Sat 9:00am - 12:00am
- Get a quote
A Complete Guide to Write Research Aims and Objectives
The importance of making a good quality aim and objectives of a research is paramount in the success of the research.
In this post, you will learn:
- What is research aim?
- What are research objectives?
- How to differentiate between research aim and research objective
- Examples of research aims and objectives
- Key points to remember while writing research aim and objectives
- Do’s and Don’ts
What Is Research Aim?
The research aim is the primary focus of the research and determines what the research serves to do. It defines the purpose of the research and tells the audience what the research aims to achieve.
Because research aims are so important for the study, a sun heading in the introductory chapter is usually dedicated to them. They are written in a paragraph form and define the main purpose of conducting the research on a topic.
Example of a good quality research aim
Research about the effects of climate change on the mental health of young adults can be worded as follows:
“The effects of climate change information on the minds of young adults are under researched. This research aims to find the effects that climate change information has on the mental health of young adults. By studying the effects of the intensity and frequency of the consumption of climate change news and forecasts among young adults, this study aims to see how climate change information is influencing their mental health.”
The above research aim is focused and clear and presents the reader with a clear understanding of the purpose of the research.
What Is Research Objective?
Research aims are related to research objectives. The research aim determines the overall purpose of the study, and the objectives determine in what ways that purpose will be achieved. The purpose of the research aim is separated into subsections. However, If any you need to order IT Research Paper help services then you have to take a survey on the net. These subsections are smaller steps that define the objectives of the research.
Research objectives are usually written in the form of a list. These small bits of steps can be checked off as the research progresses. They are written in chronological order, starting with the first objective that needs to be achieved and ending with the final one.
Example of research objectives
Taking the example of the research aim above, we can divide it into smaller sections to create specific aims of the research.
- Understand the concepts of climate change and mental health
- Understand the relationship between climate change and mental health
- Determine the frequency and intensity of climate change news consumption among young adults
- Determine the frequency and intensity of news affects the mental health of young adults
- Develop recommendations for clinical practice in the field
From this example, you can see how the research aim was broken down into smaller, specific objectives that were then listed down.
Differentiate Research Between Aims & Objectives
Although the two concepts are related, they are not the same. The differences between research aim and research objectives are:
- The way they are worded are different: Research aim is worded in a wide scoped way, while research objectives are worded as specific, narrowed down tasks.
- The focus of the two are different: research aim focuses on the overall purpose while research objectives focus on how to achieve that purpose.
- The purpose of the two are different: research aims are concerned with the overall findings of a research, which are long-term, while research objectives serve to define the short term aims of the research.
- The way they are presented are different: research aims are written in a small paragraph form while the objectives are written in the form of a list.

3 Key Points To Remember While Drafting Research Aim
The ways of writing a research aim varies with the researcher, but there are certain points to keep in mind to write a good quality research aim:
1. Answer the “why” question of the research: A research aim needs to provide an answer for why the study is being conducted. It needs to describe, in a small sentence or phares, why the research is important to conduct.
Taking the example of the research aim above, we can see that it answers the why question:
“The effects of climate change information on the minds of young adults are under researched”.
2. Answer the “what” question of the research: this is the main purpose of the research aim, as it signifies the main aim of the research.
From the example above, the “what” question is answered as follows:
“This research aims to find the effects that climate change information has on the mental health of young adults.”
3. Lastly, the research aim needs to answer the “how” question. In a simple sentence or a few phrases, it should outline the main way in which you are planning to achieve the aim.
From the example above, the “how” question is answered as follows:
“By studying the effects of the intensity and frequency of the consumption of climate change news and forecasts among young adults, this study aims to see how climate change information is influencing their mental health.”
Checklist of research aim:
- Tells the purpose of research
- Tells why the research is important
- Tells how the aim will be achieved
- Is clear and concise
5 Key Points To Remember While Drafting Research Objective
An easy way to determine the quality of your research objectives is to apply the SMART method to them:
- You need to make sure that the objectives are worded as specific tasks you need to achieve. They should not be vague.
- You should ensure that the objectives are measurable, meaning that they allow you to see how much of them have been achieved and how much are left to work on.
- The objectives need to be achievable, meaning you should have the resources to work on them.
- They need to be relevant to getting to your research aim.
- They need to be achievable in the time you have available for your research project.
In the example above the objectives follow the above mentioned criteria. While making your own objectives, make sure to evaluate them using the points above to ensure your objectives are good quality.
Checklist of research objectives
Do’s and Don’ts of research aims and objectives
What to do and what to avoid in writing aims and objectives
The Takeaway
- The research aim is the primary focus of the research.
- Research aims are related to research objectives
- The objectives determine in what ways that purpose will be achieved.
- Research aim needs to answer the “what”, “why” and “how” questions of the research.
- Research objectives need to be SMART.
Power Point Google Slides
Blogging has been my favourite part-time ever since. However, after graduating from high school, I chose to blog, as my career. It has been 5 years and I am here, blogging my heart out. Writing is the best way to creatively mention your thoughts, and I am a creativity expert!.
It is Time to Boost Your Grades with Professional Help
Improved scores.
Get Better Grades in Every Subject
Timely Delivery
Submit Your Assignment on Time
Experienced Writers
Trust Academic Experts Based in UK
Safety is Assured
Your Privacy is Our Topmost Concern
Hire a Writer
Subject* Accounting Accounts Law Advertising Aeronautical Engineering Agency Law Agriculture Animal Management Anthropology Archaeology Architecture Art Astrophysics Biochemistry Biology Biotechnology Business Chemical Engineering Chemistry Child Care Civil Engineering Civil Litigation Law Classics Commercial Law Commercial Property Law Communications Company Law / Business Law Comparative Law Computer Engineering Computing Constitutional / Administrative Law Consumer Law Contract Law Criminal Law Criminal Litigation Criminology Crisis Management Cultural Studies Design Drama E-Commerce Econometrics Economics Education Electrical Engineering Electronic Engineering Employment Law Engineering English Language Environmental Studies Equity Law Estate Management European Law European Studies Events Management Family Law Fashion Film Studies Finance Finance Law Forensic Science General Law Genetics Geography Geology History Hospitality Housing Housing Law HRM Human Rights I.T. Immigration Law Information Systems Intellectual Property Law International Development International Law International Relations International Studies Journalism Jurisprudence Land Law / Property Law Landlord and Tenant Law Languages Law Leisure Management Linguistics Literature Management Maritime Law Marketing Materials Science Mathematics Mechanical Engineering Mechanics Media Media and Information Technology Law Medicine Mental Health Law Midwifery Military Multimedia Negligence Law Neuroscience Nursing Nutrition Operations Management Oriental Studies Pathology Pharmacology Philosophy Physical Education Physical_Sciences Physics Planning / Environmental Law Plant Science Politics Product Design Professional Conduct Law Project Management Property Psychology Public Law Quantitative Methods Religion Restitution Law Risk Management Sciences Shipping Policy Social Work Sociology Software Engineering Sports Statistics Strategic Management Succession Law Surveying Tax Law Teaching Television Theatre Theology Tort Law Tourism Trusts Law Urban Studies Veterinary Wills / Probate Law Zoology Bio-informatics Biomedical Sciences Computer Forensics Data Mining Dentistry Engineering Business Management Environmental Engineering Environmental Management Environmental Science Epidemiology Geophysics Health and Safety Management Occupational Psychology Physiotherapy Public Health Real Estate Research Methods Security Studies Shipping and Trade Finance Sports and Exercise Science Supply Chain Management Sustainable Energy Telecommunication Engineering Toxicology Public Relations Other
Paper Type* Dissertation Dissertation Topics Dissertation-Abstract Dissertation Proposal Dissertation- Analysis Chapter Dissertation- Conclusion Chapter Dissertation- Introduction Chapter Dissertation- Literature Review Chapter Dissertation- Methodology Chapter Dissertation Editing and Proof Reading Essay Admission Essay Scholarship Essay Case Study Annotated Bibliography Assignment Book Report/Review Case Analysis Course Work Information and Communication/ Computer Technology Reaction Paper Research Paper Research Proposal Statistics Project Term Paper Thesis Thesis Proposal Laboratory Report Movie Review Multiple Choice Questions Power Point Presentation Article Speech Other
Education Under Graduate Graduate Masters PhD
- Link to facebook
- Link to linkedin
- Link to twitter
- Link to youtube
- Writing Tips
How to Write Research Objectives

- 3-minute read
- 22nd November 2021
Writing a research paper, thesis, or dissertation ? If so, you’ll want to state your research objectives in the introduction of your paper to make it clear to your readers what you’re trying to accomplish. But how do you write effective research objectives? In this post, we’ll look at two key topics to help you do this:
- How to use your research aims as a basis for developing objectives.
- How to use SMART criteria to refine your research objectives.
For more advice on how to write strong research objectives, see below.
Research Aims and Objectives
There is an important difference between research aims and research objectives:
- A research aim defines the main purpose of your research. As such, you can think of your research aim as answering the question “What are you doing?”
- Research objectives (as most studies will have more than one) are the steps you will take to fulfil your aims. As such, your objectives should answer the question “How are you conducting your research?”
For instance, an example research aim could be:
This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia.
To develop a set of research objectives, you would then break down the various steps involved in meeting said aim. For example:
This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia. To achieve this, the study objectives w ill include:
- Replicat ing a small Singaporean study into the role of dehydration in UTIs in hospital patients (Sepe, 2018) in a larger Australian cohort.
- Trialing the use of intravenous fluids for intensive care patients to prevent dehydration.
- Assessing the relationship between the age of patients and quantities of intravenous fluids needed to counter dehydration.
Find this useful?
Subscribe to our newsletter and get writing tips from our editors straight to your inbox.
Note that the objectives don’t go into any great detail here. The key is to briefly summarize each component of your study. You can save details for how you will conduct the research for the methodology section of your paper.
Make Your Research Objectives SMART
A great way to refine your research objectives is to use SMART criteria . Borrowed from the world of project management, there are many versions of this system. However, we’re going to focus on developing specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and timebound objectives.
In other words, a good research objective should be all of the following:
- S pecific – Is the objective clear and well-defined?
- M easurable – How will you know when the objective has been achieved? Is there a way to measure the thing you’re seeking to do?
- A chievable – Do you have the support and resources necessary to undertake this action? Are you being overly ambitious with this objective?
- R elevant – Is this objective vital for fulfilling your research aim?
- T imebound – Can this action be realistically undertaken in the time you have?
If you follow this system, your research objectives will be much stronger.
Expert Research Proofreading
Whatever your research aims and objectives, make sure to have your academic writing proofread by the experts!
Our academic editors can help you with research papers and proposals , as well as any other scholarly document you need checking. And this will help to ensure that your academic writing is always clear, concise, and precise.
Submit a free sample document today to trial our services and find out more.
Share this article:
Post A New Comment
Got content that needs a quick turnaround? Let us polish your work. Explore our editorial business services.
5-minute read
Free Email Newsletter Template
Promoting a brand means sharing valuable insights to connect more deeply with your audience, and...
6-minute read
How to Write a Nonprofit Grant Proposal
If you’re seeking funding to support your charitable endeavors as a nonprofit organization, you’ll need...
9-minute read
How to Use Infographics to Boost Your Presentation
Is your content getting noticed? Capturing and maintaining an audience’s attention is a challenge when...
8-minute read
Why Interactive PDFs Are Better for Engagement
Are you looking to enhance engagement and captivate your audience through your professional documents? Interactive...
7-minute read
Seven Key Strategies for Voice Search Optimization
Voice search optimization is rapidly shaping the digital landscape, requiring content professionals to adapt their...
4-minute read
Five Creative Ways to Showcase Your Digital Portfolio
Are you a creative freelancer looking to make a lasting impression on potential clients or...

Make sure your writing is the best it can be with our expert English proofreading and editing.
Frequently asked questions
What’s the difference between research aims and objectives.
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement , before your research objectives.
Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you’ll address the overarching aim.
Frequently asked questions: Writing a research paper
A research project is an academic, scientific, or professional undertaking to answer a research question . Research projects can take many forms, such as qualitative or quantitative , descriptive , longitudinal , experimental , or correlational . What kind of research approach you choose will depend on your topic.
The best way to remember the difference between a research plan and a research proposal is that they have fundamentally different audiences. A research plan helps you, the researcher, organize your thoughts. On the other hand, a dissertation proposal or research proposal aims to convince others (e.g., a supervisor, a funding body, or a dissertation committee) that your research topic is relevant and worthy of being conducted.
Formulating a main research question can be a difficult task. Overall, your question should contribute to solving the problem that you have defined in your problem statement .
However, it should also fulfill criteria in three main areas:
- Researchability
- Feasibility and specificity
- Relevance and originality
Research questions anchor your whole project, so it’s important to spend some time refining them.
In general, they should be:
- Focused and researchable
- Answerable using credible sources
- Complex and arguable
- Feasible and specific
- Relevant and original
All research questions should be:
- Focused on a single problem or issue
- Researchable using primary and/or secondary sources
- Feasible to answer within the timeframe and practical constraints
- Specific enough to answer thoroughly
- Complex enough to develop the answer over the space of a paper or thesis
- Relevant to your field of study and/or society more broadly

Once you’ve decided on your research objectives , you need to explain them in your paper, at the end of your problem statement .
Keep your research objectives clear and concise, and use appropriate verbs to accurately convey the work that you will carry out for each one.
I will compare …
Your research objectives indicate how you’ll try to address your research problem and should be specific:
Research objectives describe what you intend your research project to accomplish.
They summarize the approach and purpose of the project and help to focus your research.
Your objectives should appear in the introduction of your research paper , at the end of your problem statement .
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in Chicago style are to:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Use 1 inch margins or larger
- Apply double line spacing
- Indent every new paragraph ½ inch
- Include a title page
- Place page numbers in the top right or bottom center
- Cite your sources with author-date citations or Chicago footnotes
- Include a bibliography or reference list
To automatically generate accurate Chicago references, you can use Scribbr’s free Chicago reference generator .
The main guidelines for formatting a paper in MLA style are as follows:
- Use an easily readable font like 12 pt Times New Roman
- Set 1 inch page margins
- Include a four-line MLA heading on the first page
- Center the paper’s title
- Use title case capitalization for headings
- Cite your sources with MLA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a Works Cited page at the end
To format a paper in APA Style , follow these guidelines:
- Use a standard font like 12 pt Times New Roman or 11 pt Arial
- If submitting for publication, insert a running head on every page
- Apply APA heading styles
- Cite your sources with APA in-text citations
- List all sources cited on a reference page at the end
No, it’s not appropriate to present new arguments or evidence in the conclusion . While you might be tempted to save a striking argument for last, research papers follow a more formal structure than this.
All your findings and arguments should be presented in the body of the text (more specifically in the results and discussion sections if you are following a scientific structure). The conclusion is meant to summarize and reflect on the evidence and arguments you have already presented, not introduce new ones.
The conclusion of a research paper has several key elements you should make sure to include:
- A restatement of the research problem
- A summary of your key arguments and/or findings
- A short discussion of the implications of your research
Don’t feel that you have to write the introduction first. The introduction is often one of the last parts of the research paper you’ll write, along with the conclusion.
This is because it can be easier to introduce your paper once you’ve already written the body ; you may not have the clearest idea of your arguments until you’ve written them, and things can change during the writing process .
The way you present your research problem in your introduction varies depending on the nature of your research paper . A research paper that presents a sustained argument will usually encapsulate this argument in a thesis statement .
A research paper designed to present the results of empirical research tends to present a research question that it seeks to answer. It may also include a hypothesis —a prediction that will be confirmed or disproved by your research.
The introduction of a research paper includes several key elements:
- A hook to catch the reader’s interest
- Relevant background on the topic
- Details of your research problem
and your problem statement
- A thesis statement or research question
- Sometimes an overview of the paper
Ask our team
Want to contact us directly? No problem. We are always here for you.
- Email [email protected]
- Start live chat
- Call +1 (510) 822-8066
- WhatsApp +31 20 261 6040

Our team helps students graduate by offering:
- A world-class citation generator
- Plagiarism Checker software powered by Turnitin
- Innovative Citation Checker software
- Professional proofreading services
- Over 300 helpful articles about academic writing, citing sources, plagiarism, and more
Scribbr specializes in editing study-related documents . We proofread:
- PhD dissertations
- Research proposals
- Personal statements
- Admission essays
- Motivation letters
- Reflection papers
- Journal articles
- Capstone projects
Scribbr’s Plagiarism Checker is powered by elements of Turnitin’s Similarity Checker , namely the plagiarism detection software and the Internet Archive and Premium Scholarly Publications content databases .
The add-on AI detector is powered by Scribbr’s proprietary software.
The Scribbr Citation Generator is developed using the open-source Citation Style Language (CSL) project and Frank Bennett’s citeproc-js . It’s the same technology used by dozens of other popular citation tools, including Mendeley and Zotero.
You can find all the citation styles and locales used in the Scribbr Citation Generator in our publicly accessible repository on Github .
Difference between Aim and Objectives of a Research Study
Understanding the difference between aims and objectives in research.
In the field of research, distinguishing between the terms “aim” and “objective” is crucial yet often confusing. Many people use these terms interchangeably, but they represent different aspects of the research process. This comprehensive guide will clarify the difference between aims and objectives, how to use them effectively, and why understanding this distinction is essential for successful research.
What Is the Aim of a Research Study?
The aim of a research study is a broad, overarching statement that defines the general purpose and goal of the research. It addresses the fundamental question of why the study is being conducted and what the researcher hopes to achieve. The aim provides a high-level overview and sets the direction for the entire study. A well-defined aim is crucial as it helps to frame the research questions, guides the research process, and communicates the significance of the study to stakeholders such as funding bodies, academic peers, and the public. It essentially provides the foundation upon which the research is built.
For example, if a researcher is investigating the impact of diet on cardiovascular health, the aim might be: “To explore the effects of dietary habits on the prevalence of cardiovascular diseases in adults.”
What Are the Objectives of a Research Study?
Objectives are specific, detailed statements that outline the steps or actions required to achieve the aim of the study. They break down the broad aim into manageable tasks and provide a clear roadmap for conducting the research. Objectives are more detailed and measurable compared to the aim, and they help operationalize the research process.
The key functions of objectives include:
- Clarifying the Research Question: Objectives refine and specify the research question by detailing the exact aspects of the study to be investigated.
- Identifying Key Variables: They help in pinpointing the key variables and factors that need to be measured or analyzed.
- Outlining the Research Methodology : Objectives provide a structured approach to the research methodology, detailing the methods and procedures that will be employed.
- Ensuring Focus and Direction: By breaking down the aim into smaller tasks, objectives help maintain focus and direction throughout the research process.
Objectives are often framed using the SMART criteria:
– Specific: Clear and unambiguous.
– Measurable: Includes criteria to measure progress and success.
– Achievable: Feasible within the given timeframe and resources.
– Relevant: Directly related to the aim of the study.
– Time-bound: Has a defined deadline for completion.
Examples Illustrating the Difference Between Aims and Objectives
To better understand the difference between aims and objectives, consider the following examples:
– aim: to investigate the relationship between physical activity and mental health..
Objectives:
– To review existing literature on the relationship between physical activity and mental health.
– To collect data on physical activity levels and mental health indicators in a sample population.
– To analyze the data to determine the influence of physical activity on mental health .
– To draw conclusions based on the findings and make recommendations for future research or interventions.
In this example, the aim is to explore the broader relationship between physical activity and mental health. https://www.manuscriptedit.com/scholar-hangout/explore-the-social-determinants-of-mental-health/The objectives break down this aim into specific tasks, such as reviewing literature, collecting data, analyzing results, and making recommendations.
– Aim: To evaluate the effectiveness of a new teaching method for improving student performance in mathematics.
– To identify the core components and theoretical basis of the new teaching method.
– To implement the teaching method in selected classrooms.
– To collect and analyze data on student performance before and after the implementation.
– To evaluate the effectiveness of the teaching method based on the performance data.
– To provide recommendations for optimizing the teaching method and its implementation.
Here, the aim is to assess the effectiveness of a new teaching method. The objectives detail the steps required to evaluate this effectiveness , including identifying components, implementing the method, collecting data, analyzing results, and making recommendations.
Why Understanding the Difference Matters
Recognizing the difference between aims and objectives is important for several reasons:.
- Clarity: A clear distinction helps in formulating precise research questions and hypotheses, ensuring that the research is well-structured and focused.
- Planning: Well-defined aims and objectives aid in planning the research methodology and resources, allowing for efficient allocation of time and resources.
- Communication: Clearly defined aims and objectives facilitate better communication of the research purpose and scope to stakeholders, including reviewers, funders, and collaborators.
- Evaluation: Objectives provide measurable targets that can be used to assess the progress and success of the research, aiding in evaluating the research process and outcomes.
Conclusion
In summary, while the aim of a research study represents the broad goal or purpose, objectives are specific statements that outline the steps necessary to achieve that aim. Understanding the difference between aims and objectives helps in creating a clear and structured research plan, ensuring that the study remains focused and aligned with its overall purpose. By clearly defining both aims and objectives, researchers can enhance the clarity, effectiveness, and impact of their research .
For more insights and resources on research and academic writing , visit our website [ManuscriptEdit](https://www.manuscriptedit.com). If you have any queries or need assistance, feel free to contact us at [email protected].
References: “Thesis Writing.” Google Books , books.google.co.in/books?hl=en&lr=&id=LZSSEAAAQBAJ&oi=fnd&pg=PA77&dq=Difference+between+Aim+and+Objectives+of+a+Research+Study&ots=s96gshgb-7&sig=vPygp_US9INyKqT-T6N-EC3x_2s&redir_esc=y#v=onepage&q=Difference%20between%20Aim%20and%20Objectives%20of%20a%20Research%20Study&f=false .
Hirsch, E. D. “Objective Interpretation.” PMLA/Publications of the Modern Language Association of America , vol. 75, no. 4-Part1, Sept. 1960, pp. 463–79. https://doi.org/10.2307/460609 .
Elevate Your Research to Global Recognition with Manuscriptedit
Are you a dedicated doctor, PhD, or postdoc seeking to showcase your groundbreaking research in prestigious global journals? At Manuscriptedit, we specialize in transforming your research into impactful publications. Our expert services are designed to help you navigate the complexities of academic publishing and achieve recognition in top-tier journals worldwide.
Why Choose Manuscriptedit?
- Expert Guidance : Our team of seasoned professionals understands the intricacies of the publication process. From manuscript preparation to submission, we provide comprehensive support to ensure your research meets the highest standards.
- Global Reach : We have established connections with leading journals across various disciplines. Our expertise ensures your research is presented to the right audience and increases its chances of acceptance in reputed international journals.
- Tailored Services : Whether you need assistance with editing, formatting, or navigating submission guidelines, our services are customized to fit your specific needs. We handle all aspects of the publication process, allowing you to focus on your research.
- Proven Success : Our track record speaks for itself. We have successfully assisted numerous doctors, PhDs, and postdocs in publishing their research in high-impact journals, enhancing their academic and professional standing.
Our Services Include:
- Manuscript Editing : We provide detailed editing services to improve the clarity, structure, and quality of your research paper, ensuring it meets the rigorous standards of top journals.
- Formatting and Compliance : Our team ensures your manuscript adheres to the specific formatting and submission guidelines of your target journals, reducing the risk of rejection due to technical issues.
- Submission Assistance : We guide you through the submission process, including the preparation of cover letters and response to reviewer comments, to enhance your chances of successful publication.
- Personalized Support : Our dedicated consultants offer personalized support throughout the entire publication journey, from initial consultation to post-submission follow-up.
Take the Next Step in Your Academic Career register now For Free Consultation: REGISTER NOW
Publishing in renowned journals can significantly boost your academic profile and open doors to new opportunities. With Manuscriptedit, you gain a trusted partner in achieving your publication goals.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.

What are you doing and how are you doing it? Articulating your aims and objectives.
Mar 6, 2019

Have you checked out the rest of The PhD Knowledge Base ? It’s home to hundreds more free resources and guides, written especially for PhD students.
How long does it take the person reading your thesis to understand what you’re doing and how you’re doing it? If the answer is anything other than ’in the opening paragraphs of the thesis’ then keep reading.
If you tell them as early as possible what you’re doing and how you’re doing it – and do so in clear and simple terms – whatever you write after will make much more sense. If you leave them guessing for ten pages, everything they read in those ten pages has no coherence. You’ll know where it is all leading, but they won’t.
Unless you tell them.
If you tell the reader what you’re doing as early as possible in clear and simple terms, whatever you write after will make much more sense.
What are aims & objectives?
If you build a house without foundations, it’s pretty obvious what will happen. It’ll collapse. Your thesis is the same; fail to build the foundations and your thesis just won’t work .
Your aims and objectives are those foundations. That’s why we’ve put them right at the top of our PhD Writing Template (if you haven’t already downloaded it, join the thousands who have by clicking here ).
If you write your aims and objectives clearly then you’ll make your reader’s life easier.
A lot of students fail to clearly articulate their aims and objectives because they aren’t sure themselves what they actually are.
Picture this: if there’s one thing that every PhD student hates it’s being asked by a stranger what their research is on.

Your PhD thesis. All on one page.
Use our free PhD structure template to quickly visualise every element of your thesis.
Hello, Doctor…
Sounds good, doesn’t it? Be able to call yourself Doctor sooner with our five-star rated How to Write A PhD email-course. Learn everything your supervisor should have taught you about planning and completing a PhD.
Now half price. Join hundreds of other students and become a better thesis writer, or your money back.
Research aims
Your research aims are the answer to the question, ‘What are you doing?’
1. You need to clearly describe what your intentions are and what you hope to achieve. These are your aims.
2. Your aims may be to test theory in a new empirical setting, derive new theory entirely, construct a new data-set, replicate an existing study, question existing orthodoxy, and so on. Whatever they are, clearly articulate them and do so early. Definitely include them in your introduction and, if you’re smart, you’ll write them in your abstract .
3. Be very explicit . In the opening paragraphs, say, in simple terms, ‘ the aim of this thesis is to …’
4. Think of your aims then as a statement of intent. They are a promise to the reader that you are going to do something. You use the next two hundred pages or so to follow through on that promise. If you don’t make the promise, the reader won’t understand your follow-through. Simple as that.
Because they serve as the starting point of the study, there needs to be a flow from your aims through your objectives (more on this below) to your research questions and contribution and then into the study itself. If you have completed your research and found that you answered a different question (not that uncommon), make sure your original aims are still valid. If they aren’t, refine them.
If you struggle to explain in simple terms what your research is about and why it matters, you may need to refine your aims and objectives to make them more concise.
When writing up your aims, there are a number of things to bear in mind.
1. Avoid listing too many. Your PhD isn’t as long as you think it is and you won’t have time or room for more than around two or three.
2. When you write them up, be very specific. Don’t leave things so vague that the reader is left unsure or unclear on what you aim to achieve.
3. Make sure there is a logical flow between each of your aims. They should make sense together and should each be separate components which, when added together, are bigger than the sum of their parts.
Research objectives
Your aims answer the question, ‘What are you doing?’ The objectives are the answer to the question, ‘How are you doing it?’
Research objectives refer to the goals or steps that you will take to achieve your aims.
When you write them, make sure they are SMART.
- S pecific: talk in a precise and clear way about what you are going to do.
- M easurable: how will you know when you have achieved your aim?
- A chievable: make sure that you aren’t overly ambitious.
- R ealistic: recognise the time and resource constraints that come with doing a PhD and don’t attempt to do too much.
- T ime constrained: determine when each objective needs to be completed.
You need to be as explicit as possible here. Leave the reader in no doubt about what you will do to achieve your aims. Step by step. Leave no ambiguity. At the same time, be careful not to repeat your methods chapter here. Just hint at your methods by presenting the headlines. You’ll have plenty of space in your methods discussion to flesh out the detail.
Elsewhere in the thesis you will necessarily have to talk in a complex language and juggle complex ideas. Here you don’t. You can write in clear, plain sentences.
What is the difference between research aims and objectives?
The aims of a study describe what you hope to achieve. The objectives detail how you are going to achieve your aims.
Let’s use an example to illustrate.
- To understand the contribution that local governments make to national level energy policy.
Objectives:
- Conduct a survey of local politicians to solicit responses.
- Conduct desk-research of local government websites to create a database of local energy policy.
- Interview national level politicians to understand the impact these local policies have had.
- Data will be coded using a code book derived from dominant theories of governance.
If you’re still struggling, Professor Pat Thompson’s great blog has a guide that will help.
Leave the reader in no doubt about what you will do to achieve your aims. Step by step. Leave no ambiguity.
I can’t articulate them clearly, my research is complicated!
Of course your research is complex. That’s the name of the game. But the sign of someone being able to master complexity is their ability to summarise it . Sure, you’re not looking to capture all the richness and detail in a short summary of aims and objectives, but you are looking to tell the reader what you’re doing and how you’re doing it.
If you’re struggling to clearly articulate your aims and objectives, then try the following task. At the top of a Post-it note write the sentence: ‘In this research I will…’. Then keep trying until you can fit an answer onto one single Post-it note. The answer should answer two questions: what are are you doing and how are you doing it?
Remember – whenever you write, make it as clear as possible. Pay attention to the words ‘as possible’ there. That means you should write as clearly as you can given the fact that your subject and research is necessarily complex. Think of it the other way: it’s about not making things more complicated and unclear than they need to be.
In other words, make your reader’s job as easy as you can. They’ll thank you for it.
If you’re still having trouble, get in touch to arrange a one-on-one coaching session and we can work through your aims and objectives together.
Share this:
32 comments.
The write up is quite inspiring.
My topic is setting up a healing gardens in hospitals Need a aim and objectives for a dissertation
Dis is really good and more understandable thanks
Crisp, concise, and easy to understnad. Thank you for posint this. I now know how to write up my report.
Great. Glad you found it useful.
Good piece of work! Very useful
Great. Glad you found it useful!
The write up makes sense
Great. Thanks!
I love this article. Amazing, outstanding and incredible facts.
Glad you found it useful!
Well written and easy to follow
Thank you for the comment, I’m really glad you found it valuable.
I’m currently developing a dissertation proposal for my PhD in organizational leadership. I need guidance in writing my proposal
Hey – have you checked out this guide? https://www.thephdproofreaders.com/writing/how-to-write-a-phd-proposal/
Indeed I’m impressed and gained a lot from this and I hope I can write an acceptable thesis with this your guide. Bello, H.K
Great. Thanks for the kind words. Good luck with the thesis.
Thumbs up! God job, well done. The information is quite concise and straight to the point.
Glad you thought so – good luck with the writing.
Dear Max, thank you so much for your work and efforts!
Your explanation about Aims and Objectives really helped me out. However, I got stuck with other parts of the Aims and Objectives Work Sheet: Scope, Main Argument, and Contribution.
Could you please explain these as well, preferably including some examples?
Thanks for your kind words. Your question is a big one! Without knowing lots about your topics/subject I’m not able to provide tailored advice, but broadly speaking your scope is the aims/objectives, your main argument is the thread running through the thesis (i.e. what your thesis is trying to argue) and the contribution (again, broadly speaking) is that gap you are filling.
I love your website and you’ve been so SO helpful..
DUMB QUESTION ALERT: Is there supposed to be a difference between aims and research question?
I mean, using your own example.. if the aim of my research is: “To understand the contribution that local governments make to national level energy policy” then wouldn’t the research question be: “How do local governments contribute to energy policy at national level”?
I am sorry if this comes out as completely obvious but I am at that stage of confusion where I am starting to question everything I know.
Sorry it’s taken me so long to reply! It’s not a dumb question at all. The aim of the study is what the study as a whole is seeking to achieve. So that might be the gap it is filling/the contribution it is making. The research questions are your means to achieving that aim. Your aim might be to fill a gap in knowledge, and you then may have a small number of questions that help you along that path. Does that make sense?
Thank you Max for this post! So helpful!
Thanks Anna!
Thanks so much this piece. I have written both bachelor’s and master’s thesis but haven’t read this made me feel like I didn’t know anything about research at all. I gained more insight into aims and objectives of academic researches.
Interesting explanation. Thank you.
I’m glad you found it useful.
Hi… I really like the way it is put “What are you going?” (Aims) and “How are you doing it?” (Objectives). Simple and straightforward. Thanks for making aims and objectives easy to understand.
Thank you for the write up it is insightful. if you are ask to discuss your doctoral aims. that means: what you are doing how you are doing it.
I was totally lost and still in the woods to the point of thinking I am dull, but looking at how you are coaching it tells me that i am just a student who needs to understand the lesson. I now believe that with your guidance i will pass my PhD. I am writing on an otherwise obvious subject, Value addition to raw materials, why Africa has failed to add value to raw materials? Difficult question as answers seem to abound, but that is where i differ and i seem to be against the general tide. However with your guidance I believe i will make it. Thanks.
Thanks for your lovely, kind words. So kind.
Submit a Comment Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

Search The PhD Knowledge Base
Most popular articles from the phd knowlege base.
The PhD Knowledge Base Categories
- Your PhD and Covid
- Mastering your theory and literature review chapters
- How to structure and write every chapter of the PhD
- How to stay motivated and productive
- Techniques to improve your writing and fluency
- Advice on maintaining good mental health
- Resources designed for non-native English speakers
- PhD Writing Template
- Explore our back-catalogue of motivational advice

Formulating Research Aims and Objectives
Formulating research aim and objectives in an appropriate manner is one of the most important aspects of your thesis. This is because research aim and objectives determine the scope, depth and the overall direction of the research. Research question is the central question of the study that has to be answered on the basis of research findings.
Research aim emphasizes what needs to be achieved within the scope of the research, by the end of the research process. Achievement of research aim provides answer to the research question.
Research objectives divide research aim into several parts and address each part separately. Research aim specifies WHAT needs to be studied and research objectives comprise a number of steps that address HOW research aim will be achieved.
As a rule of dumb, there would be one research aim and several research objectives. Achievement of each research objective will lead to the achievement of the research aim.
Consider the following as an example:
Research title: Effects of organizational culture on business profitability: a case study of Virgin Atlantic
Research aim: To assess the effects of Virgin Atlantic organizational culture on business profitability
Following research objectives would facilitate the achievement of this aim:
- Analyzing the nature of organizational culture at Virgin Atlantic by September 1, 2022
- Identifying factors impacting Virgin Atlantic organizational culture by September 16, 2022
- Analyzing impacts of Virgin Atlantic organizational culture on employee performances by September 30, 2022
- Providing recommendations to Virgin Atlantic strategic level management in terms of increasing the level of effectiveness of organizational culture by October 5, 2022
Figure below illustrates additional examples in formulating research aims and objectives:

Formulation of research question, aim and objectives
Common mistakes in the formulation of research aim relate to the following:
1. Choosing the topic too broadly . This is the most common mistake. For example, a research title of “an analysis of leadership practices” can be classified as too broad because the title fails to answer the following questions:
a) Which aspects of leadership practices? Leadership has many aspects such as employee motivation, ethical behaviour, strategic planning, change management etc. An attempt to cover all of these aspects of organizational leadership within a single research will result in an unfocused and poor work.
b) An analysis of leadership practices in which country? Leadership practices tend to be different in various countries due to cross-cultural differences, legislations and a range of other region-specific factors. Therefore, a study of leadership practices needs to be country-specific.
c) Analysis of leadership practices in which company or industry? Similar to the point above, analysis of leadership practices needs to take into account industry-specific and/or company-specific differences, and there is no way to conduct a leadership research that relates to all industries and organizations in an equal manner.
Accordingly, as an example “a study into the impacts of ethical behaviour of a leader on the level of employee motivation in US healthcare sector” would be a more appropriate title than simply “An analysis of leadership practices”.
2. Setting an unrealistic aim . Formulation of a research aim that involves in-depth interviews with Apple strategic level management by an undergraduate level student can be specified as a bit over-ambitious. This is because securing an interview with Apple CEO Tim Cook or members of Apple Board of Directors might not be easy. This is an extreme example of course, but you got the idea. Instead, you may aim to interview the manager of your local Apple store and adopt a more feasible strategy to get your dissertation completed.
3. Choosing research methods incompatible with the timeframe available . Conducting interviews with 20 sample group members and collecting primary data through 2 focus groups when only three months left until submission of your dissertation can be very difficult, if not impossible. Accordingly, timeframe available need to be taken into account when formulating research aims and objectives and selecting research methods.
Moreover, research objectives need to be formulated according to SMART principle,
where the abbreviation stands for specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-bound.
| Study employee motivation of Coca-Cola | To study the impacts of management practices on the levels of employee motivation at Coca-Cola US by December 5, 2022
|
| Analyze consumer behaviour in catering industry
| Analyzing changes in consumer behaviour in catering industry in the 21 century in the UK by March 1, 2022 |
| Recommend Toyota Motor Corporation management on new market entry strategy
| Formulating recommendations to Toyota Motor Corporation management on the choice of appropriate strategy to enter Vietnam market by June 9, 2022
|
| Analyze the impact of social media marketing on business
| Assessing impacts of integration of social media into marketing strategy on the level of brand awareness by March 30, 2022
|
| Finding out about time management principles used by Accenture managers | Identifying main time-management strategies used by managers of Accenture France by December 1, 2022 |
Examples of SMART research objectives
At the conclusion part of your research project you will need to reflect on the level of achievement of research aims and objectives. In case your research aims and objectives are not fully achieved by the end of the study, you will need to discuss the reasons. These may include initial inappropriate formulation of research aims and objectives, effects of other variables that were not considered at the beginning of the research or changes in some circumstances during the research process.

John Dudovskiy
21 Research Objectives Examples (Copy and Paste)

Chris Drew (PhD)
Dr. Chris Drew is the founder of the Helpful Professor. He holds a PhD in education and has published over 20 articles in scholarly journals. He is the former editor of the Journal of Learning Development in Higher Education. [Image Descriptor: Photo of Chris]
Learn about our Editorial Process

Research objectives refer to the definitive statements made by researchers at the beginning of a research project detailing exactly what a research project aims to achieve.
These objectives are explicit goals clearly and concisely projected by the researcher to present a clear intention or course of action for his or her qualitative or quantitative study.
Research objectives are typically nested under one overarching research aim. The objectives are the steps you’ll need to take in order to achieve the aim (see the examples below, for example, which demonstrate an aim followed by 3 objectives, which is what I recommend to my research students).
Research Objectives vs Research Aims
Research aim and research objectives are fundamental constituents of any study, fitting together like two pieces of the same puzzle.
The ‘research aim’ describes the overarching goal or purpose of the study (Kumar, 2019). This is usually a broad, high-level purpose statement, summing up the central question that the research intends to answer.
Example of an Overarching Research Aim:
“The aim of this study is to explore the impact of climate change on crop productivity.”
Comparatively, ‘research objectives’ are concrete goals that underpin the research aim, providing stepwise actions to achieve the aim.
Objectives break the primary aim into manageable, focused pieces, and are usually characterized as being more specific, measurable, achievable, relevant, and time-bound (SMART).
Examples of Specific Research Objectives:
1. “To examine the effects of rising temperatures on the yield of rice crops during the upcoming growth season.” 2. “To assess changes in rainfall patterns in major agricultural regions over the first decade of the twenty-first century (2000-2010).” 3. “To analyze the impact of changing weather patterns on crop diseases within the same timeframe.”
The distinction between these two terms, though subtle, is significant for successfully conducting a study. The research aim provides the study with direction, while the research objectives set the path to achieving this aim, thereby ensuring the study’s efficiency and effectiveness.
How to Write Research Objectives
I usually recommend to my students that they use the SMART framework to create their research objectives.
SMART is an acronym standing for Specific, Measurable, Achievable, Relevant, and Time-bound. It provides a clear method of defining solid research objectives and helps students know where to start in writing their objectives (Locke & Latham, 2013).
Each element of this acronym adds a distinct dimension to the framework, aiding in the creation of comprehensive, well-delineated objectives.
Here is each step:
- Specific : We need to avoid ambiguity in our objectives. They need to be clear and precise (Doran, 1981). For instance, rather than stating the objective as “to study the effects of social media,” a more focused detail would be “to examine the effects of social media use (Facebook, Instagram, and Twitter) on the academic performance of college students.”
- Measurable: The measurable attribute provides a clear criterion to determine if the objective has been met (Locke & Latham, 2013). A quantifiable element, such as a percentage or a number, adds a measurable quality. For example, “to increase response rate to the annual customer survey by 10%,” makes it easier to ascertain achievement.
- Achievable: The achievable aspect encourages researchers to craft realistic objectives, resembling a self-check mechanism to ensure the objectives align with the scope and resources at disposal (Doran, 1981). For example, “to interview 25 participants selected randomly from a population of 100” is an attainable objective as long as the researcher has access to these participants.
- Relevance : Relevance, the fourth element, compels the researcher to tailor the objectives in alignment with overarching goals of the study (Locke & Latham, 2013). This is extremely important – each objective must help you meet your overall one-sentence ‘aim’ in your study.
- Time-Bound: Lastly, the time-bound element fosters a sense of urgency and prioritization, preventing procrastination and enhancing productivity (Doran, 1981). “To analyze the effect of laptop use in lectures on student engagement over the course of two semesters this year” expresses a clear deadline, thus serving as a motivator for timely completion.
You’re not expected to fit every single element of the SMART framework in one objective, but across your objectives, try to touch on each of the five components.
Research Objectives Examples
1. Field: Psychology
Aim: To explore the impact of sleep deprivation on cognitive performance in college students.
- Objective 1: To compare cognitive test scores of students with less than six hours of sleep and those with 8 or more hours of sleep.
- Objective 2: To investigate the relationship between class grades and reported sleep duration.
- Objective 3: To survey student perceptions and experiences on how sleep deprivation affects their cognitive capabilities.
2. Field: Environmental Science
Aim: To understand the effects of urban green spaces on human well-being in a metropolitan city.
- Objective 1: To assess the physical and mental health benefits of regular exposure to urban green spaces.
- Objective 2: To evaluate the social impacts of urban green spaces on community interactions.
- Objective 3: To examine patterns of use for different types of urban green spaces.
3. Field: Technology
Aim: To investigate the influence of using social media on productivity in the workplace.
- Objective 1: To measure the amount of time spent on social media during work hours.
- Objective 2: To evaluate the perceived impact of social media use on task completion and work efficiency.
- Objective 3: To explore whether company policies on social media usage correlate with different patterns of productivity.
4. Field: Education
Aim: To examine the effectiveness of online vs traditional face-to-face learning on student engagement and achievement.
- Objective 1: To compare student grades between the groups exposed to online and traditional face-to-face learning.
- Objective 2: To assess student engagement levels in both learning environments.
- Objective 3: To collate student perceptions and preferences regarding both learning methods.
5. Field: Health
Aim: To determine the impact of a Mediterranean diet on cardiac health among adults over 50.
- Objective 1: To assess changes in cardiovascular health metrics after following a Mediterranean diet for six months.
- Objective 2: To compare these health metrics with a similar group who follow their regular diet.
- Objective 3: To document participants’ experiences and adherence to the Mediterranean diet.
6. Field: Environmental Science
Aim: To analyze the impact of urban farming on community sustainability.
- Objective 1: To document the types and quantity of food produced through urban farming initiatives.
- Objective 2: To assess the effect of urban farming on local communities’ access to fresh produce.
- Objective 3: To examine the social dynamics and cooperative relationships in the creating and maintaining of urban farms.
7. Field: Sociology
Aim: To investigate the influence of home offices on work-life balance during remote work.
- Objective 1: To survey remote workers on their perceptions of work-life balance since setting up home offices.
- Objective 2: To conduct an observational study of daily work routines and family interactions in a home office setting.
- Objective 3: To assess the correlation, if any, between physical boundaries of workspaces and mental boundaries for work in the home setting.
8. Field: Economics
Aim: To evaluate the effects of minimum wage increases on small businesses.
- Objective 1: To analyze cost structures, pricing changes, and profitability of small businesses before and after minimum wage increases.
- Objective 2: To survey small business owners on the strategies they employ to navigate minimum wage increases.
- Objective 3: To examine employment trends in small businesses in response to wage increase legislation.
9. Field: Education
Aim: To explore the role of extracurricular activities in promoting soft skills among high school students.
- Objective 1: To assess the variety of soft skills developed through different types of extracurricular activities.
- Objective 2: To compare self-reported soft skills between students who participate in extracurricular activities and those who do not.
- Objective 3: To investigate the teachers’ perspectives on the contribution of extracurricular activities to students’ skill development.
10. Field: Technology
Aim: To assess the impact of virtual reality (VR) technology on the tourism industry.
- Objective 1: To document the types and popularity of VR experiences available in the tourism market.
- Objective 2: To survey tourists on their interest levels and satisfaction rates with VR tourism experiences.
- Objective 3: To determine whether VR tourism experiences correlate with increased interest in real-life travel to the simulated destinations.
11. Field: Biochemistry
Aim: To examine the role of antioxidants in preventing cellular damage.
- Objective 1: To identify the types and quantities of antioxidants in common fruits and vegetables.
- Objective 2: To determine the effects of various antioxidants on free radical neutralization in controlled lab tests.
- Objective 3: To investigate potential beneficial impacts of antioxidant-rich diets on long-term cellular health.
12. Field: Linguistics
Aim: To determine the influence of early exposure to multiple languages on cognitive development in children.
- Objective 1: To assess cognitive development milestones in monolingual and multilingual children.
- Objective 2: To document the number and intensity of language exposures for each group in the study.
- Objective 3: To investigate the specific cognitive advantages, if any, enjoyed by multilingual children.
13. Field: Art History
Aim: To explore the impact of the Renaissance period on modern-day art trends.
- Objective 1: To identify key characteristics and styles of Renaissance art.
- Objective 2: To analyze modern art pieces for the influence of the Renaissance style.
- Objective 3: To survey modern-day artists for their inspirations and the influence of historical art movements on their work.
14. Field: Cybersecurity
Aim: To assess the effectiveness of two-factor authentication (2FA) in preventing unauthorized system access.
- Objective 1: To measure the frequency of unauthorized access attempts before and after the introduction of 2FA.
- Objective 2: To survey users about their experiences and challenges with 2FA implementation.
- Objective 3: To evaluate the efficacy of different types of 2FA (SMS-based, authenticator apps, biometrics, etc.).
15. Field: Cultural Studies
Aim: To analyze the role of music in cultural identity formation among ethnic minorities.
- Objective 1: To document the types and frequency of traditional music practices within selected ethnic minority communities.
- Objective 2: To survey community members on the role of music in their personal and communal identity.
- Objective 3: To explore the resilience and transmission of traditional music practices in contemporary society.
16. Field: Astronomy
Aim: To explore the impact of solar activity on satellite communication.
- Objective 1: To categorize different types of solar activities and their frequencies of occurrence.
- Objective 2: To ascertain how variations in solar activity may influence satellite communication.
- Objective 3: To investigate preventative and damage-control measures currently in place during periods of high solar activity.
17. Field: Literature
Aim: To examine narrative techniques in contemporary graphic novels.
- Objective 1: To identify a range of narrative techniques employed in this genre.
- Objective 2: To analyze the ways in which these narrative techniques engage readers and affect story interpretation.
- Objective 3: To compare narrative techniques in graphic novels to those found in traditional printed novels.
18. Field: Renewable Energy
Aim: To investigate the feasibility of solar energy as a primary renewable resource within urban areas.
- Objective 1: To quantify the average sunlight hours across urban areas in different climatic zones.
- Objective 2: To calculate the potential solar energy that could be harnessed within these areas.
- Objective 3: To identify barriers or challenges to widespread solar energy implementation in urban settings and potential solutions.
19. Field: Sports Science
Aim: To evaluate the role of pre-game rituals in athlete performance.
- Objective 1: To identify the variety and frequency of pre-game rituals among professional athletes in several sports.
- Objective 2: To measure the impact of pre-game rituals on individual athletes’ performance metrics.
- Objective 3: To examine the psychological mechanisms that might explain the effects (if any) of pre-game ritual on performance.
20. Field: Ecology
Aim: To investigate the effects of urban noise pollution on bird populations.
- Objective 1: To record and quantify urban noise levels in various bird habitats.
- Objective 2: To measure bird population densities in relation to noise levels.
- Objective 3: To determine any changes in bird behavior or vocalization linked to noise levels.
21. Field: Food Science
Aim: To examine the influence of cooking methods on the nutritional value of vegetables.
- Objective 1: To identify the nutrient content of various vegetables both raw and after different cooking processes.
- Objective 2: To compare the effect of various cooking methods on the nutrient retention of these vegetables.
- Objective 3: To propose cooking strategies that optimize nutrient retention.
The Importance of Research Objectives
The importance of research objectives cannot be overstated. In essence, these guideposts articulate what the researcher aims to discover, understand, or examine (Kothari, 2014).
When drafting research objectives, it’s essential to make them simple and comprehensible, specific to the point of being quantifiable where possible, achievable in a practical sense, relevant to the chosen research question, and time-constrained to ensure efficient progress (Kumar, 2019).
Remember that a good research objective is integral to the success of your project, offering a clear path forward for setting out a research design , and serving as the bedrock of your study plan. Each objective must distinctly address a different dimension of your research question or problem (Kothari, 2014). Always bear in mind that the ultimate purpose of your research objectives is to succinctly encapsulate your aims in the clearest way possible, facilitating a coherent, comprehensive and rational approach to your planned study, and furnishing a scientific roadmap for your journey into the depths of knowledge and research (Kumar, 2019).
Kothari, C.R (2014). Research Methodology: Methods and Techniques . New Delhi: New Age International.
Kumar, R. (2019). Research Methodology: A Step-by-Step Guide for Beginners .New York: SAGE Publications.
Doran, G. T. (1981). There’s a S.M.A.R.T. way to write management’s goals and objectives. Management review, 70 (11), 35-36.
Locke, E. A., & Latham, G. P. (2013). New Developments in Goal Setting and Task Performance . New York: Routledge.

- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 10 Reasons you’re Perpetually Single
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 20 Montessori Toddler Bedrooms (Design Inspiration)
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 21 Montessori Homeschool Setups
- Chris Drew (PhD) https://helpfulprofessor.com/author/chris-drew-phd/ 101 Hidden Talents Examples
Leave a Comment Cancel Reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
- My Bibliography
- Collections
- Citation manager
Save citation to file
Email citation, add to collections.
- Create a new collection
- Add to an existing collection
Add to My Bibliography
Your saved search, create a file for external citation management software, your rss feed.
- Search in PubMed
- Search in NLM Catalog
- Add to Search
Setting a research question, aim and objective
Affiliations.
- 1 Department of Nursing and Midwifery, University of Limerick, Limerick, Republic of Ireland.
- 2 Department of Nursing and Midwifery, University of Limerick, Republic of Ireland.
- PMID: 26997231
- DOI: 10.7748/nr.23.4.19.s5
Aim: To describe the development of a research question, aim and objective.
Background: The first steps of any study are developing the research question, aim and objective. Subsequent steps develop from these and they govern the researchers' choice of population, setting, data to be collected and time period for the study. Clear, succinctly posed research questions, aims and objectives are essential if studies are to be successful.
Discussion: Researchers developing their research questions, aims and objectives generally experience difficulties. They are often overwhelmed trying to convert what they see as a relevant issue from practice into research. This necessitates engaging with the relevant published literature and knowledgeable people.
Conclusion: This paper identifies the issues to be considered when developing a research question, aim and objective. Understanding these considerations will enable researchers to effectively present their research question, aim and objective.
Implications for practice: To conduct successful studies, researchers should develop clear research questions, aims and objectives.
Keywords: novice researchers; nursing research; research aim; research objective; research question; study development.
PubMed Disclaimer
- Search in MeSH
LinkOut - more resources
Other literature sources.
- scite Smart Citations
- Citation Manager
NCBI Literature Resources
MeSH PMC Bookshelf Disclaimer
The PubMed wordmark and PubMed logo are registered trademarks of the U.S. Department of Health and Human Services (HHS). Unauthorized use of these marks is strictly prohibited.

Difference between Research Questions and Research Objectives
When embarking on a research project, it’s important to have a clear understanding of the distinction between research questions and research objectives. Both are key components of a research study, but they differ in their focus and purpose.
The main difference is that research questions focus on the general purpose or aim of the study whereas research objectives provide specific, measurable, and attainable steps to achieve the research questions.
Before we move to the differences, let’s understand what are Research Questions and Research Objectives:

Now, let’s move to Research Questions vs Research Objectives:
Major differences between Research Questions and Research Objectives
| Research Questions | Research Objectives |
|---|---|
| Research questions focus on the main topic or issue being investigated. | Research objectives focus on the specific steps the researcher will take to answer those questions. |
| Research questions can sometimes be vague or open-ended. | Research objectives must be clear, specific and measurable. |
| Research questions are general in nature and aim to cover a broad aspect of the topic being researched. | Research objectives are specific and cover limited aspects of the topic. |
| Research questions might change and be formed as the research progresses. | Research objectives are usually set before the commencement of a research work and may not change as the research progresses. |
| Research questions are used to guide the overall direction of the study. | Research objectives provide specific steps to achieve the research questions. |
Note that sometimes, the question might also be asked as “distinguish between Research Questions and Research Objectives”.
Final words
Research questions and research objectives are related, they are not interchangeable terms. Research questions describe the goals or aims of a study in a broader sense, while research objectives provide specific, measurable, achievable steps to achieve those goals.
Understanding the difference between these two terms can help you design and execute a more effective research study.
You can view other “differences between” posts by clicking here .
If you have a related query, feel free to let us know in the comments below.
Also, kindly share the information with your friends who you think might be interested in reading it.
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Save my name, email, and website in this browser for the next time I comment.
- Open access
- Published: 10 September 2024
Prediction of poststroke independent walking using machine learning: a retrospective study
- Zhiqing Tang 1 , 2 ,
- Wenlong Su 1 , 2 , 4 ,
- Tianhao Liu 1 , 2 ,
- Haitao Lu 1 , 2 ,
- Ying Liu 1 , 2 ,
- Hui Li 2 , 3 ,
- Kaiyue Han 1 , 2 ,
- Md. Moneruzzaman 1 , 2 ,
- Junzi Long 1 , 2 ,
- Xingxing Liao 1 , 2 ,
- Xiaonian Zhang 1 , 2 ,
- Lei Shan 1 , 2 &
- Hao Zhang ORCID: orcid.org/0000-0001-8193-4101 1 , 2 , 3 , 4
BMC Neurology volume 24 , Article number: 332 ( 2024 ) Cite this article
80 Accesses
2 Altmetric
Metrics details
Accurately predicting the walking independence of stroke patients is important. Our objective was to determine and compare the performance of logistic regression (LR) and three machine learning models (eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), Support Vector Machines (SVM), and Random Forest (RF)) in predicting walking independence at discharge in stroke patients, as well as to explore the variables that predict prognosis.
778 (80% for the training set and 20% for the test set) stroke patients admitted to China Rehabilitation Research Center between February 2020 and January 2023 were retrospectively included. The training set was used for training models. The test set was used to validate and compare the performance of the four models in terms of area under the curve (AUC), accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV), and F1 score.
Among the three ML models, the AUC of the XGBoost model is significantly higher than that of the SVM and RF models ( P < 0.001, P = 0.024, respectively). There was no significant difference in the AUCs between the XGBoost model and the LR model (0.891 vs. 0.880, P = 0.560). The XGBoost model demonstrated superior accuracy (87.82% vs. 86.54%), sensitivity (50.00% vs. 39.39%), PPV (73.68% vs. 73.33%), NPV (89.78% vs. 87.94%), and F1 score (59.57% vs. 51.16%), with only slightly lower specificity (96.09% vs. 96.88%). Together, the XGBoost model and the stepwise LR model identified age, FMA-LE at admission, FAC at admission, and lower limb spasticity as key factors influencing independent walking.
Overall, the XGBoost model performed best in predicting independent walking after stroke. The XGBoost and LR models together confirm that age, admission FMA-LE, admission FAC, and lower extremity spasticity are the key factors influencing independent walking in stroke patients at hospital discharge.
Trial registration
Not applicable.
Peer Review reports
Stroke is a major problem in China due to its high morbidity, mortality and disability [ 1 ]. Even with timely treatment in the acute phase, patients may still be disabled and require rehabilitation, resulting in a high economic burden [ 2 ]. A significant portion of the cost is directly attributable to the inability of stroke survivors to walk independently [ 3 ]. 40% of stroke patients who are initially unable to walk are either ambulatory or require assistance with walking three months after stroke [ 4 ]. The ability to walk independently is a key factor in a patient’s daily activities and quality of life, and regaining the ability to walk independently becomes an important goal in the rehabilitation of stroke patients with hemiplegia [ 5 , 6 , 7 ]. It is critical to accurately predict the subsequent recovery of walking ability in stroke patients who are unable to walk independently at the time of admission to rehabilitation [ 8 ]. In this way, clinicians and therapists can provide patients with prognosis, goal setting, treatment selection, and discharge planning, and based on accurate prediction of independent walking, the government or the patient’s family can effectively provide appropriate socioeconomic support and health care resources [ 9 , 10 ].
In the field of stroke rehabilitation, studies on predictive models for walking recovery have been a hot topic [ 3 , 11 , 12 ]. However, some of the predictive models that have been developed are too complex to be used in a clinical setting. Therefore, there is a need to develop simple, reliable, and feasible models for predicting independent walking that can be applied to stroke patients in inpatient rehabilitation. Logistic regression (LR) has been widely used in prognostic studies of stroke patients. LR measures the relationship between a categorical dependent variable and one or more independent variables by using a probability score as the predictive value of the dependent variable [ 13 ]. LR is commonly used in predictive modeling of dichotomous outcomes in health care [ 14 ]. However, it has several drawbacks, including easy underfitting, difficulty in handling nonlinear relationships, sensitivity to outliers, and possibly poor classification accuracy [ 15 ]. Therefore, there may be limitations in applying LR to predictive modeling of prognosis in stroke patients.
As a scientific and mature modeling method, machine learning (ML) is increasingly used in epidemiological research and medicine [ 16 , 17 ]. With the increasing complexity and number of data sets available, as well as multi-factor data from a variety of sources, the ML is considered to have advantages over traditional regression models [ 18 , 19 ], including ease of analysis, the ability to consider a large number of variables simultaneously, and to capture complex interactions between variables.
The eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), Support Vector Machines (SVM), and Random Forest (RF) are the more mature and widely used ML modeling algorithms. The XGBoost can be used to solve supervised learning problems using a gradient boosting framework with high accuracy, difficulty in overfitting, and scalability [ 20 , 21 ]. The XGBoost has been increasingly used in healthcare research to predict or screen for prognostic factors. The SVM are one of the most popular supervised learning algorithms used for pattern recognition, classification, and regression analysis [ 22 ]. The RF is an integrated learning method that generates a collection of decision trees branching on random variables. By using the majority principle for all trees and branches, RF can make predictions with high accuracy, less overfitting and strong anti-noise ability [ 23 ]. However, the optimal model tends to vary across studies and there is a lack of models that use these ML algorithms to predict independent walking in stroke patients.
Therefore, the aim of this study was to investigate the optimal prediction of independent walking at discharge based on clinical data of stroke patients who were unable to walk independently at admission using classical logistic regression methods and three currently accepted ML models (the XGBoost, SVM, and RF model), and to explore variables related to prognosis.
This study protocol was approved by the medical ethics committee of China Rehabilitation Research Center (approval number 2022-141-02). Informed consent was not obtained as this was a retrospective, hospital-based study.
Participants
Between February 2020 and January 2023, a retrospective cohort of inpatients admitted to and discharged from the neurorehabilitation unit of China Rehabilitation Research Center for first-onset stroke was studied. Patients were included if they met the following inclusion criteria: (1) were aged ≥ 18 years; (2) had a first-ever unilateral cerebral stroke; (3) were unable to walk independently at admission and had a Functional Ambulation Category (FAC) score ≤ 3. Patients were excluded according to the following criteria: (1) had other underlying neurological diseases; (2) had a diagnosis of disturbance of consciousness; (3) had unstable vital signs; (4) length of stay (LOS) < 14 days; (5) had incomplete required data.
In this study, a total of 1033 patients were screened and 778 stroke patients who met the inclusion criteria were ultimately included in the analysis. The following data were collected from 778 stroke patients (21 variables in total): age (years), sex (male or female), medical insurance (yes or no), LOS, time since onset, type of stroke (ischemic or hemorrhagic), side of stroke (left or right), lesion location (cortical, subcortical, or both), lower extremity deep vein thrombosis (yes or no), emotional disorder (yes or no), cognitive disorder (yes or no), sleep disorder (yes or no), dysphagia (yes or no), aphasia (yes or no), lower limb spasticity (yes or no), FAC score at admission, Fugl-Meyer Motor Assessment of the Lower Extremity (FMA-LE) score at admission, Fugl-Meyer Balance Assessment (FMB) score at admission, National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale (NIHSS) score at admission, Barthel Index (BI) score at admission, and FAC score at discharge. The FAC scale has been widely used to assess walking independence in stroke patients, with six levels (0–5). According to previous reports, stroke patients with fac score > 3 at discharge were defined as “independent walking”, otherwise as “non-independent walking” [ 24 ]. In this study, we used “independent walking at discharge (yes or no)” as the response variable, and the remaining 20 variables were used for prediction.
Statistical analysis
The IBM SPSS Statistics software version 25 (IBM Corp, Armonk, USA) was used for data analysis. Categorical variables were presented as frequencies and percentages. For continuous variables, the Kolmogorov-Smirnov test was used to assess data distribution. Continuous variables were expressed as mean ± standard deviation if they fit the normal distribution; otherwise, they were expressed as medians (Q L , Q U ). The χ 2 test was used to compare categorical variables, and the Student’s t-test or the Mann-Whitney nonparametric test was used to compare continuous variables.
In this study, all enrolled patients were randomly divided into two data sets with a split ratio of 4:1. Subsequently, 80% of the patients were used for model training and 20% of the patients were used for model testing. Predictive models were constructed using the walking status at discharge (“independent walking” or “non-independent walking”) as the outcome variable. We used the “autoReg”, “XGBoost”, “e1071”, “randomForest” and “caret” packages in R software version 4.2.2 to develop and test the LR, XGBoost, SVM, and RF models. In constructing the classical LR model, we first screened the training cohort for factors associated with “independent walking” using univariate analyses. Subsequently, factors with P < 0.10 in the univariate analyses were included in the stepwise binary LR analysis. Due to the small number of original variables in this study and the fact that variables of lower importance may also have a beneficial effect on the training of the model, all feature variables were included in the training of the XGBoost, SVM, and RF models. The XGBoost, SVM, and RF models were optimized by either 5-fold cross-validation or hyperparameter tuning. In this study, the “pROC” package was used to plot the receiver operating characteristic (ROC) curves and calculate the area under curve (AUC) [ 25 , 26 ]. The AUC was used to comprehensively evaluate the models, and the AUC of the models were compared by the Delong method [ 27 ]. The predictive performance of the models was further evaluated in terms of accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, positive predictive value (PPV), negative predictive value (NPV) and F1 score. A two-tailed P value < 0.05 was considered statistically significant.
Patient characteristics
A total of 778 stroke patients randomly assigned to the training set ( n = 622) and the test set ( n = 156) were finally enrolled in this study (Fig. 1 ). The characteristics of the training and test sets are shown in Table 1 . For all the variables analyzed, there was no significant difference between the training and testing sets. Overall, 107 patients (17.20%) in the training set achieved “independent walking” at discharge and 28 patients (17.95%) in the testing set achieved “independent walking” at discharge.

Flow-chart of participants enrolled in this study
Logistic regression model
Univariate analyses performed on the training set showed that patients who achieved “independent ambulation” at discharge were significantly different from those who did not on the variables of age, lesion location, lower extremity deep vein thrombosis, cognitive disorder, dysphagia, lower limb spasticity, FAC at admission, FMA-LE at admission, FMB at admission, NIHSS at admission and BI at admission (all P < 0.05) (Table 2 ). Subsequently, based on the results of the univariate analyses, variables with P < 0.10 were included in the stepwise binary LR analysis. As shown in Table 2 , four variables (age, lower limb spasticity, FAC at admission, and FMA-LE at admission) were independent determinants of independent walking at discharge for stroke patients who were unable to walk independently at admission. A logistic regression model is constructed from the four influencing factors examined above, and its expression is logit ( P ) = − 2.15-0.03 × 1 + 1.32 × 2 + 1.61 × 3 + 0.13 × 4 . In the formula, x 1 , x 2 , x 3 and x 4 represent age, no lower limb spasticity, FAC at admission = 3 and FMA-LE at admission, respectively. The Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness of fit test result on the training set was 10.211 ( P = 0.251) with 8 degrees of freedom, and the Hosmer-Lemeshow goodness of fit test result on the test set was 6.790 ( P = 0.560) with 8 degrees of freedom.
Comparisons of logistic regression and machine learning models
All baseline variables were used in the development of the three ML models (XGBoost, SVM, and RF) for prediction of “independent walking” at discharge. The test set was used to compare the performance of the models. In the LR model, the ROC curve was used to evaluate the discriminative ability of the prediction model, and its AUC was 0.891 (95%CI = 0.828–0.954) in the test set. The AUC of the XGBoost, SVM and RF models are 0.880 (95%CI = 0.818–0.942), 0.659 (95%CI = 0.567–0.751), and 0.713 (95%CI = 0.617–0.808), respectively. Among the three ML models, the AUC of the XGBoost model is significantly higher than that of the SVM and RF models ( P < 0.001, P = 0.024, respectively). Although the LR model had a slightly higher AUC than the XGB model in the test set, there was no significant difference in the comparison (0.891 vs. 0.880, z = 0.570, P = 0.569). ROC curves for all models are shown in Fig. 2 . Table 3 shows the number of correct predictive values of all models, based on which the accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV and F1 scores of the LR, XGBoost, SVM, and RF models were calculated. These values together confirmed that the XGBoost model performed best among the three ML models, as shown in Table 4 . Compared to the LR model, the XGBoost model had superior accuracy (87.82% vs. 86.54%), sensitivity (50.00% vs. 39.39%), PPV (73.68% vs. 73.33%), NPV (89.78% vs. 87.94%), and F1 score (59.57% vs. 51.16%), and the specificity was only slightly lower (96.09% vs. 96.88%).

Receiver operating characteristic curve for the models
Predictors selection
Stepwise logistic regression analysis showed that age, lower limb spasticity, admission FAC, and admission FMA-LE were independent predictors of independent walking in stroke patients. The XGBoost model was used to rank the importance of the feature variables, and the top ten variables are as follows: FMA-LE at admission, FAC at admission, age, NIHSS at admission, LOS, FMB at admission, BI at admission, lower limb spasticity, type of stroke, lesion location (Fig. 3 ).

Features selected using XGBoost and the corresponding variable importance score
It is of great importance to accurately predict the walking independence of stroke patients at the time of rehabilitation admission. In this study, we innovatively developed three machine learning algorithm-based models (XGBoost, SVM, and RF) to predict whether stroke patients would be able to walk independently at discharge from the rehabilitation center and compared them with the traditional stepwise LR model. The results show that, overall, the XGBoost model had the best predictive performance.
Most of the previous studies on related topics have used only LR analysis methods to build only one predictive model [ 28 , 29 ]. However, the conventional LR analysis has its limitations, for example, it cannot well analyze the complex nonlinear relationship between variables [ 30 ]. Recently, new machine learning techniques have shown higher predictive performance compared to traditional predictive methods [ 31 ]. In this study, three commonly used machine learning algorithms (XGBoost, SVM, and RF) were selected to establish three models for predicting independent walking in stroke patients and compared with the classic LR model. First, the AUCs of the models were calculated and compared. The higher the AUC of the model, the higher the predictive value. Among the three machine learning models, the AUC of the XGBoost model was significantly higher than that of the SVM model and the RF model, suggesting that the overall performance of the XGBoost model was optimal. As a decision tree-based algorithm, XGBoost was voted the best algorithm in a machine learning and prediction competition hosted by Kaggle.com [ 32 , 33 ]. Due to its best accuracy and performance, machine learning based on XGBoost algorithms has been increasingly taken seriously as a competitive alternative to regression analysis and used to predict clinical outcomes. The AUC of the two models exceeded 0.85 in both the training and test sets, indicating that the overall predictive performance of the models was good. Although the AUC of the XGBoost model was slightly lower than that of the LR model in the test set, the Delong test revealed no significant difference. Previous studies usually used multiple indicators to evaluate model performance [ 34 , 35 ]. Thus, we further compared the accuracy, sensitivity, specificity, PPV, NPV, and F1 scores of the two models in the test set. Our results demonstrated that, taken together, the XGBoost model performed better than the LR model. Therefore, it was recommended that the XGBoost model be used to predict whether stroke patients who were unable to walk independently at the time of rehabilitation admission would be able to walk independently at discharge. We also suggested that future studies could consider using the XGBoost algorithm to predict other functional outcomes in stroke patients.
Step logistic regression analysis showed that age, lower extremity spasticity, FAC at admission and FMA-LE at admission were independently associated with independent walking at discharge in stroke patients. The XGBoost model ranked the importance of the variables, and the top 10 variables were FMA-LE at admission, FAC at admission, age, NIHSS at admission, LOS, FMB at admission, BI at admission, lower limb spasticity, type of stroke, lesion location. Together, the two models determined that the key variables affecting independent walking in stroke patients at discharge were age, FMA-LE at admission, FAC at admission, and lower extremity spasticity. A review of 15 studies that explored which factors predicted independent walking at 3, 6, and 12 months for in non-ambulatory people within one month of stroke, and found that younger age predicted independent walking at 3 months [ 3 ]. Similarly, we found that the younger the stroke patient, the more likely they were to walk independently at discharge. The same conclusion was also reached by Kennedy et al. [ 36 ] and Hirano et al. [ 12 ] This study also found that the presence of lower extremity spasticity prevented patients from achieving independent walking at discharge. A recent study, which found that moderate levels of plantar flexors spasticity resulted in the highest sensitivity for predicting poor gait speed performance and the highest specificity for predicting good mobility performance in post-stroke patients, supported our findings to some extent [ 37 ]. This study also showed that patients with FAC = 3 at admission were 5.01 times more likely to achieve independent walking at discharge than those who were unable to walk at all, which was consistent with the findings of Louie et al. [ 38 ]. They found that those with any ability to walk at admission (with or without therapist assistance) were 9.48 times more likely to be discharged home than those who were unable. In addition, we found that lower limb motor function was an important factor in independent walking. Hiratsuka et al. also found that lower limb motor function was an additional predictor of independent walking in a 30-day poststroke cohort [ 39 ]. Notably, the TWIST algorithm proposed by Smith et al. in 2017 incorporated trunk control test scores and hip extension strength to predict whether and when an individual patient walked independently after stroke [ 40 ]. They later built on their earlier work to examine other potential predictors, including age, knee extension strength, and Berg Balance Test score [ 41 ]. However, the trunk control test and lower limb muscle strength test were not included in the admission assessment records of patients at our hospital, and we will consider including them in future prospective studies. Some studies have also used neurophysiological or neuroimaging measures to predict walking independence in stroke patients [ 42 , 43 , 44 ], but one study showed that the absence of lower limb motor-evoked potentials did not preclude independent walking [ 45 ]. Although this study lacked more types of indicators to predict independent walking, we established a model with good predictive performance by using simple and easily accessible clinical data, which might be more in line with the actual clinical situation and had certain reference significance for clinical practice.
Limitations
Undoubtedly, our study has several limitations. First, this was a retrospective, single-center study, and selection bias was inevitable. In the future, we will conduct prospective studies with larger samples to obtain more accurate results. Second, we did not have a separate data set to externally validate the predictive model established in this study, so the generalizability may not be guaranteed. Further studies using data from other hospitals are needed. Third, our prediction model used only clinical data of rehabilitation admission, whereas other studies may have incorporated imaging features, electrophysiological features, etc. In future prospective studies, we should consider using more types of data to build predictive models. Fourth, we did not follow long-term outcomes of walking function in stroke patients after discharge, and predictors of long-term outcomes in stroke patients may be different from those at discharge. Fifth, we selected only 3 commonly used machine learning algorithms to build the models and compare them, and other algorithms such as AdaBoost and neural networks deserve further investigation. However, in this study, we initially found that the XGBoost model showed better predictive performance than the LR model in predicting independent walking in stroke patients based on clinical data at the time of rehabilitation admission. Our methodology and results will inform future studies.
Conclusions
Overall, the XGBoost model showed the best performance in predicting independent walking after stroke. The XGBoost and LR models together confirm that age, FMA-LE at admission, FAC at admission, and lower extremity spasticity are key factors affecting independent walking in stroke patients at discharge from hospital. Our study suggests that XGBoost can be used to build a predictive model of independent walking in stroke patients at discharge based on clinical data of hospitalized stroke patients, providing guidance for setting rehabilitation goals, selecting treatment plans, and making discharge plans.
Data availability
The datasets used and/or analysed during the current study are available from the corresponding author on reasonable request.
Abbreviations
Area Under Curves
Barthel Index
Functional Ambulation Category
Fugl-Meyer Motor Assessment of the Lower Extremity
Fugl-Meyer Balance Assessment
Logistic Regression
Length of Stay
Machine Learning
National Institutes of Health Stroke Scale
Negative Predictive Value
Positive Predictive Value
Random Forest
Receiver Operating Characteristic
Support Vector Machines
eXtreme Gradient Boosting
Zhou M, Wang H, Zeng X, et al. Mortality, morbidity, and risk factors in China and its provinces, 1990–2017: a systematic analysis for the global burden of Disease Study 2017. Lancet. 2019;394:1145–58. https://doi.org/10.1016/S0140-6736(19)30427-1 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central Google Scholar
Rabinstein AA, Albers GW, Brinjikji W, Koch S. Factors that may contribute to poor outcome despite good reperfusion after acute endovascular stroke therapy. Int J Stroke. 2019;14:23–31. https://doi.org/10.1177/1747493018799979 .
Article PubMed Google Scholar
Preston E, Ada L, Stanton R, et al. Prediction of independent walking in people who are nonambulatory early after stroke: a systematic review. Stroke. 2021;52:3217–24. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.120.032345 .
Preston E, Ada L, Dean CM, et al. What is the probability of patients who are nonambulatory after stroke regaining independent walking? A systematic review. Int J Stroke. 2011;6:531–40. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-4949.2011.00668.x .
Harris JE, Eng JJ. Goal priorities identified through client-centred measurement in individuals with chronic stroke. Physiother Can. 2004;56:171–6. https://doi.org/10.2310/6640.2004.00017 .
Teasell RW, Bhogal SK, Foley NC, Speechley MR. Gait retraining post stroke. Top Stroke Rehabil. 2003;10:34–65. https://doi.org/10.1310/UDXE-MJFF-53V2-EAP0 .
Mayo NE, Wood-Dauphinee S, Côté R, et al. Activity, participation, and quality of life 6 months poststroke. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2002;83:1035–42. https://doi.org/10.1053/apmr.2002.33984 .
Kwah LK, Herbert RD. Prediction of walking and arm recovery after stroke: a critical review. Brain Sci. 2016;6:53. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci6040053 .
Craig LE, Wu O, Bernhardt J, Langhorne P. Predictors of poststroke mobility: systematic review. Int J Stroke. 2011;6:321–7. https://doi.org/10.1111/j.1747-4949.2011.00621.x .
Veerbeek JM, Kwakkel G, van Wegen EE, et al. Early prediction of outcome of activities of daily living after stroke: a systematic review. Stroke. 2011;42:1482–8. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.110.604090 .
Bland MD, Sturmoski A, Whitson M, et al. Prediction of discharge walking ability from initial assessment in a stroke inpatient rehabilitation facility population. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2012;93:1441–7. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2012.02.029 .
Hirano Y, Hayashi T, Nitta O, et al. Prediction of independent walking ability for severely hemiplegic stroke patients at Discharge from a Rehabilitation Hospital. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2016;25:1878–81. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2015.12.020 .
Lin WY, Chen CH, Tseng YJ, et al. Predicting post-stroke activities of daily living through a machine learning-based approach on initiating rehabilitation. Int J Med Inf. 2018;111:159–64. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.ijmedinf.2018.01.002 .
Article Google Scholar
Liang Y, Li Q, Chen P, et al. Comparative study of back Propagation Artificial neural networks and logistic regression model in Predicting Poor Prognosis after Acute ischemic stroke. Open Med (Wars). 2019;14:324–30. https://doi.org/10.1515/med-2019-0030 .
Article PubMed CAS Google Scholar
Qu S, Zhou M, Jiao S, et al. Optimizing acute stroke outcome prediction models: comparison of generalized regression neural networks and logistic regressions. PLoS ONE. 2022;17:e0267747. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone.0267747 .
Article PubMed PubMed Central CAS Google Scholar
Liu S, See KC, Ngiam KY, et al. Reinforcement learning for clinical decision support in critical care: Comprehensive Review. J Med Internet Res. 2020;22:e18477. https://doi.org/10.2196/18477 .
Campagnini S, Arienti C, Patrini M, et al. Machine learning methods for functional recovery prediction and prognosis in post-stroke rehabilitation: a systematic review. J Neuroeng Rehabil. 2022;19:54. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12984-022-01032-4 .
Khan O, Badhiwala JH, Wilson JRF, et al. Predictive modeling of outcomes after traumatic and nontraumatic spinal cord Injury using machine learning: review of current progress and future directions. Neurospine. 2019;16:678–85. https://doi.org/10.14245/ns.1938390.195 .
Zhang X, Fei N, Zhang X, et al. Machine learning prediction models for postoperative stroke in Elderly patients: analyses of the MIMIC database. Front Aging Neurosci. 2022;14:897611. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2022.897611 .
Hu Y, Yang T, Zhang J, et al. Dynamic prediction of mechanical thrombectomy outcome for Acute ischemic stroke patients using machine learning. Brain Sci. 2022;12. https://doi.org/10.3390/brainsci12070938 .
Chen R, Zhang S, Li J, et al. A study on predicting the length of hospital stay for Chinese patients with ischemic stroke based on the XGBoost algorithm. BMC Med Inf Decis Mak. 2023;23:49. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12911-023-02140-4 .
Noble WS. What is a support vector machine? Nat Biotechnol. 2006;24:1565–7. https://doi.org/10.1038/nbt1206-1565 .
Luo Y, Li Z, Guo H, et al. Predicting congenital heart defects: a comparison of three data mining methods. PLoS ONE. 2017;12:e177811. https://doi.org/10.1371/journal.pone .
Article CAS Google Scholar
Maeshima S, Okamoto S, Mizuno S, et al. Predicting walking ability in hemiplegic patients with putaminal hemorrhage: an observational study in a rehabilitation hospital. Eur J Phys Rehabil Med. 2021;57:321–6. https://doi.org/10.23736/S1973-9087.20.05823-2 .
Robin X, Turck N, Hainard A, et al. pROC: an open-source package for R and S + to analyze and compare ROC curves. BMC Bioinformatics. 2011;12:77. https://doi.org/10.1186/1471-2105-12-77 .
Heo J, Yoon JG, Park H, et al. Machine learning-based model for prediction of outcomes in Acute Stroke. Stroke. 2019;50:1263–5. https://doi.org/10.1161/STROKEAHA.118.024293 .
DeLong ER, DeLong DM, Clarke-Pearson DL. Comparing the areas under two or more correlated receiver operating characteristic curves: a nonparametric approach. Biometrics. 1988;44:837–45.
Yan C, Zheng Y, Zhang X, et al. Development and validation of a nomogram model for predicting unfavorable functional outcomes in ischemic stroke patients after acute phase. Front Aging Neurosci. 2023;15:1161016. https://doi.org/10.3389/fnagi.2023.1161016 .
Gianella MG, Gath CF, Bonamico L, et al. Prediction of Gait without Physical Assistance after Inpatient Rehabilitation in severe subacute stroke subjects. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2019;28:104367. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2019.104367 .
Hassanipour S, Ghaem H, Arab-Zozani M, et al. Comparison of artificial neural network and logistic regression models for prediction of outcomes in trauma patients: a systematic review and meta-analysis. Injury. 2019;50:244–50. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.injury.2019.01.007 .
Hou N, Li M, He L, et al. Predicting 30-days mortality for MIMIC-III patients with sepsis-3: a machine learning approach using XGboost. J Transl Med. 2020;18:462. https://doi.org/10.1186/s12967-020-02620-5 .
Chen T, Guestrin C. XGBoost: a scalable tree boosting system. In: Proceedings of the 22nd ACM SIGKDD international conference on knowledge discovery and data mining-KDD 2016, San Francisco, CA, USA; 2016. pp. 785–94.
LANL Earthquake Prediction. 2019. https://www.kaggle.com/c/LANLEarth quake Prediction. Accessed 15 Mar 2020.
Kim JK, Choo YJ, Chang MC. Prediction of motor function in stroke patients using machine learning algorithm: development of practical models. J Stroke Cerebrovasc Dis. 2021;30:105856. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.jstrokecerebrovasdis.2021.105856 .
Cerasa A, Tartarisco G, Bruschetta R, et al. Predicting Outcome in patients with Brain Injury: differences between machine learning versus Conventional statistics. Biomedicines. 2022;10:2267. https://doi.org/10.3390/biomedicines10092267 .
Kennedy C, Bernhardt J, Churilov L, et al. Factors associated with time to independent walking recovery post-stroke. J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2021;92:702–8. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2020-325125 .
Freire B, Bochehin do Valle M, Lanferdini FJ, et al. Cut-off score of the modified Ashworth scale corresponding to walking ability and functional mobility in individuals with chronic stroke. Disabil Rehabil. 2023;45:866–70. https://doi.org/10.1080/09638288.2022.2037753 .
Louie DR, Simpson LA, Mortenson WB, et al. Prevalence of walking Limitation after Acute Stroke and its impact on discharge to Home. Phys Ther. 2022;102:pzab246. https://doi.org/10.1093/ptj/pzab246 .
Hiratsuka K, Tamiya T, Matsuoka S, Kimura K. Stroke impairment, balance, and cognitive status on admission predict walking independence up to 90 days post-stroke but their contributions change over time. Int J Rehabil Res. 2023;46:61–9. https://doi.org/10.1097/MRR.0000000000000561 .
Smith MC, Barber PA, Stinear CM. The TWIST Algorithm Predicts Time to walking independently after stroke. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2017;31:955–64. https://doi.org/10.1177/1545968317736820 .
Smith MC, Barber AP, Scrivener BJ, Stinear CM. The TWIST Tool predicts when patients will recover independent walking after stroke: an observational study. Neurorehabil Neural Repair. 2022;36:461–71. https://doi.org/10.1177/15459683221085287 .
Nomoto M, Miyata K, Kohno Y. White matter hyperintensity predicts independent walking function at 6 months after stroke: a retrospective cohort study. NeuroRehabilitation. 2023;53:557–65. https://doi.org/10.3233/NRE-230225 .
Soulard J, Huber C, Baillieul S, et al. Motor tract integrity predicts walking recovery: a diffusion MRI study in subacute stroke. Neurology. 2020;94:e583–93. https://doi.org/10.1212/WNL.0000000000008755 .
Piron L, Piccione F, Tonin P, Dam M. Clinical correlation between motor evoked potentials and gait recovery in poststroke patients. Arch Phys Med Rehabil. 2005;86:1874–8. https://doi.org/10.1016/j.apmr.2005.03.007 .
Smith MC, Scrivener BJ, Stinear CM. Do lower limb motor-evoked potentials predict walking outcomes post-stroke? J Neurol Neurosurg Psychiatry. 2023. https://doi.org/10.1136/jnnp-2023-332018 .
Download references
Acknowledgements
We acknowledge our colleagues in the medical records Department of the China Rehabilitation Research Center for their assistance in this study.
This work was supported by the general program of China Rehabilitation Research Center [grant numbers 2023ZX-14].
Author information
Authors and affiliations.
School of Rehabilitation, Capital Medical University, 10 Jiaomen North Road, Fengtai District, Beijing, 100068, China
Zhiqing Tang, Wenlong Su, Tianhao Liu, Haitao Lu, Ying Liu, Kaiyue Han, Md. Moneruzzaman, Junzi Long, Xingxing Liao, Xiaonian Zhang, Lei Shan & Hao Zhang
Beijing Bo’ai Hospital, China Rehabilitation Research Center, Beijing, China
Zhiqing Tang, Wenlong Su, Tianhao Liu, Haitao Lu, Ying Liu, Hui Li, Kaiyue Han, Md. Moneruzzaman, Junzi Long, Xingxing Liao, Xiaonian Zhang, Lei Shan & Hao Zhang
Cheeloo College of Medicine, Shandong University, Jinan, Shandong Province, China
Hui Li & Hao Zhang
University of Health and Rehabilitation Sciences, Jinan, Shandong Province, China
Wenlong Su & Hao Zhang
You can also search for this author in PubMed Google Scholar
Contributions
ZT- design of work, analysis, interpretation of data, drafted the manuscript. WS- analysis, interpretation of data, drafted and substantively revised the manuscript. TL- design of work, acquisition of data, drafted the manuscript. HL- design of work, substantively revised the manuscript. YL- analysis, interpretation of data. HL- analysis, interpretation of data. KH- analysis, interpretation of data. MM- acquisition of data. JL- acquisition of data. XL: acquisition of data. XZ: substantively revised the manuscript. LS: substantively revised the manuscript. HZ- conception, design of work, drafted and substantively revised the manuscript. All authors read and approved the final manuscript.
Corresponding author
Correspondence to Hao Zhang .
Ethics declarations
Ethics approval and consent to participate.
This study protocol was approved by the medical ethics committee of China Rehabilitation Research Center (approval number 2022-141-02). Informed consent was not obtained as this was a retrospective, hospital-based study. As this was a hospital-based retrospective study, the exemption from obtaining informed consent was granted by the medical ethics committee of China Rehabilitation Research Center. All methods and procedures were carried out in accordance with relevant guidelines and regulations.
Consent for publication
Competing interests.
The authors declare no competing interests.
Additional information
Publisher’s note.
Springer Nature remains neutral with regard to jurisdictional claims in published maps and institutional affiliations.
Rights and permissions
Open Access This article is licensed under a Creative Commons Attribution 4.0 International License, which permits use, sharing, adaptation, distribution and reproduction in any medium or format, as long as you give appropriate credit to the original author(s) and the source, provide a link to the Creative Commons licence, and indicate if changes were made. The images or other third party material in this article are included in the article’s Creative Commons licence, unless indicated otherwise in a credit line to the material. If material is not included in the article’s Creative Commons licence and your intended use is not permitted by statutory regulation or exceeds the permitted use, you will need to obtain permission directly from the copyright holder. To view a copy of this licence, visit http://creativecommons.org/licenses/by/4.0/ .
Reprints and permissions
About this article
Cite this article.
Tang, Z., Su, W., Liu, T. et al. Prediction of poststroke independent walking using machine learning: a retrospective study. BMC Neurol 24 , 332 (2024). https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-024-03849-z
Download citation
Received : 12 February 2024
Accepted : 03 September 2024
Published : 10 September 2024
DOI : https://doi.org/10.1186/s12883-024-03849-z
Share this article
Anyone you share the following link with will be able to read this content:
Sorry, a shareable link is not currently available for this article.
Provided by the Springer Nature SharedIt content-sharing initiative
- Independent walking
- Logistic regression
- eXtreme gradient boosting
- Machine learning
BMC Neurology
ISSN: 1471-2377
- General enquiries: [email protected]
An official website of the United States government
The .gov means it’s official. Federal government websites often end in .gov or .mil. Before sharing sensitive information, make sure you’re on a federal government site.
The site is secure. The https:// ensures that you are connecting to the official website and that any information you provide is encrypted and transmitted securely.
- Publications
- Account settings
Preview improvements coming to the PMC website in October 2024. Learn More or Try it out now .
- Advanced Search
- Journal List
- Indian J Anaesth
- v.67(4); 2023 Apr
- PMC10248893
Objectives and outcomes of a clinical trial
Mukul c. kapoor.
Department of Anesthesiology and Critical Care, Amrita School of Medicine and Amrita Institute of Medical Sciences, Faridabad, Haryana, India
Rakhee Goyal
1 Department of Anesthesiology, Rainbow Children’s Hospital, New Delhi, India
All scientific medical studies are conducted to generate new knowledge about health and disease and to inform clinical practice and public health policies. A medical study is planned based on a hypothesis that justifies the clinical study. The research question arises from a perceived knowledge deficit in a particular subject area. It is antecedent to the research and establishes the study’s direction. A clinical trial aims to find an answer to the main research question or hypothesis that the study plans to answer. Hypothesis testing is the most widely employed method of determining whether clinical study outcomes are positive or negative.
OBJECTIVES OF A STUDY
The objectives of a medical study can be broadly classified into primary and secondary objectives. The study’s hypothesis defines the research’s primary objective and is thus the aim of a medical study. It attempts to find an answer to the main research question or hypothesis. While addressing the primary objectives, additional research questions may also be addressed. These other research questions addressed are called the secondary objectives.[ 1 ]
The primary objective of a medical study is typically framed in terms of the study’s endpoint or outcome measure—some examples to explain the same are presented in Table 1 .
Examples of objectives of a study
| Clinical trial | Primary objective | Secondary objectives |
|---|---|---|
| To determine the degree of hypotension of a new drug for induction of anaesthesia | To measure the fall in blood pressure after its administration and compare it with the fall/otherwise after administration of an agent in clinical use | a. Recording other adverse effects of the drug b. Duration of onset of action of the drug c. Interaction with other anaesthetic agents used |
| To study the antiemetic potential of a new agent | The occurrence of PONV with its use and compare it with the occurrence of PONV with a standard drug/placebo | a. To determine the duration of the effect of the agent b. Sedative effects of the agent c. Adverse effects of the drug |
| An airway study for an SAD | To determine the seal pressure of the SAD and comparing it with the seal pressure of another SAD | a. To determine the incidence of micro-aspiration with the device used b. Determining the fitting characteristics of SAD in different categories of patients c. Recording the number of attempts needed to insert it d. Assessing the ease of its insertion |
PONV=postoperative nausea and vomiting, SAD=supraglottic airway device
Secondary objectives are often included in a medical study to provide additional information about the intervention or exposure under investigation or to explore other research questions of interest. Secondary objectives may consist of assessing the safety and tolerability of the intervention, the effects of the intervention on secondary outcomes (e.g. quality of life, adverse events) or subgroup analyses to identify which patient populations benefit most from the intervention. Samples to explain the same are given in Table 1 .
Defining objectives helps ensure that the investigation is designed and powered appropriately to answer the research question(s) of interest, and that the data collected are correctly analysed to answer those questions. The appropriate sample size of the study is based on the incidence/prevalence/any other primary outcome in a similar study conducted earlier or a pilot study. To ensure the statistical value of a study, the design should preferably have only one primary objective.[ 2 ]
The outcomes of a medical study can be classified into primary and secondary outcomes. The primary outcome of medical research is the main outcome measure that the study aims to answer (i.e. based on the primary objective). In an experimental, semi-experimental or observational research study, the primary study outcome is based on and aligned directly with the primary objective. The secondary outcomes are additional outcome measures that are addressed in the study.
The primary outcome is typically the most important in a study. It is usually chosen to reflect the main research question or hypothesis—some examples to explain the same are presented in Table 2 .
Examples of outcomes of a study
| Clinical trial | Primary outcome | Secondary outcomes |
|---|---|---|
| To determine the degree of hypotension of a new drug for induction of anaesthesia | To determine whether a statistically significant reduction in blood pressure happened with the drug compared to a standard anaesthesia induction agent | a. Recording of rash along the venous path b. Events of cough after its administration |
| To study the antiemetic potential of a new agent | Whether a statistically significant reduction in the incidence of PONV was seen in the study population vis-a-vis the agent it was compared with | a. Higher incidence of postoperative hypoxaemia b. Hypotension after administration |
| An airway study for a SAD | Whether the mean airway pressure beyond which the expired tidal volume was statistically lower than the inspired tidal volume and whether it was more/less than the SAD it was compared with | a. Instability of the device in edentulous patients b. Difficulty of insertion in patients with a small lower jaw c. Higher incidence of sore throat in patients receiving it |
SAD=supraglottic airway device
Secondary outcomes are often included in a medical study to provide additional information about the intervention or exposure under investigation or to explore other research questions of interest. For example, secondary outcomes might include measurements of safety and tolerability of the intervention, effects on secondary endpoints (e.g. quality of life, adverse events) or subgroup analyses to identify which patient populations benefit most from the intervention. Secondary outcomes logically arise from and directly align with secondary objectives. Samples to explain the same are given in Table 2 .
Secondary outcomes may not necessarily be related to the secondary objectives included in the study protocol and may be incidental findings from data analysis. Such secondary outcomes in the study manuscript must be justified. Multiple testing of secondary outcomes increases the family-wise error rate and the probability of at least one false significant result (type I error) among all secondary outcomes studied. Secondary outcomes are helpful if they lend supporting evidence for the primary outcome. Statistically robust secondary outcomes should always be considered and not dismissed based on multiplicity concerns.[ 3 ]
A judicious approach should be taken to primary and secondary outcomes and clearly defined. The fewer they are, the better the study.[ 4 ] This helps ensure that the investigation is designed and powered appropriately to answer the research question(s) of interest, and that the data collected are analysed correctly to answer those questions. It is also essential to understand that the study may or may not result in the projected outcomes of the hypothesis or may only partially meet or may show significant secondary outcomes.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Formulating research objectives has the following five steps, which could help researchers develop a clear objective: 8. Identify the research problem. Review past studies on subjects similar to your problem statement, that is, studies that use similar methods, variables, etc.
Example: Research aim. To examine contributory factors to muscle retention in a group of elderly people. Example: Research objectives. To assess the relationship between sedentary habits and muscle atrophy among the participants. To determine the impact of dietary factors, particularly protein consumption, on the muscular health of the ...
Research Aims: Examples. True to the name, research aims usually start with the wording "this research aims to…", "this research seeks to…", and so on. For example: "This research aims to explore employee experiences of digital transformation in retail HR.". "This study sets out to assess the interaction between student ...
Summary. One of the most important aspects of a thesis, dissertation or research paper is the correct formulation of the aims and objectives. This is because your aims and objectives will establish the scope, depth and direction that your research will ultimately take. An effective set of aims and objectives will give your research focus and ...
Research Objectives. Research objectives refer to the specific goals or aims of a research study. They provide a clear and concise description of what the researcher hopes to achieve by conducting the research.The objectives are typically based on the research questions and hypotheses formulated at the beginning of the study and are used to guide the research process.
Research aims and objectives are the foundation of any research project. They provide a clear direction and purpose for the study, ensuring that you stay focused and on track throughout the process. They are your trusted navigational tools, leading you to success. Understanding the relationship between research objectives and aims is crucial to ...
Specificity: Objectives should be specific and narrowly focused on the aspects of the research topic that the study intends to investigate. They should answer the question of "what" or "which" rather than "how" or "why.". Measurability: Research objectives should be formulated in a way that allows for measurement and evaluation.
Research questions are more general and open-ended, while objectives are specific and measurable. Research questions identify the main problem or area of inquiry, while objectives define the specific outcomes that the researcher is looking to achieve. Research questions help define the study's scope, while objectives help guide the research ...
The differences between research aim and research objectives are: The way they are worded are different: Research aim is worded in a wide scoped way, while research objectives are worded as specific, narrowed down tasks. The focus of the two are different: research aim focuses on the overall purpose while research objectives focus on how to ...
In order to write effective research aims and objectives, researchers should consider all aspects of their proposed work. For example, the sample(s) to be approached for participation in the primary data collection. Identifying research objectives that are SMART is key to ensuring key aspects of the work are considered prior to any data collection.
Study objectives define the specific aims of the study and should be clearly stated in the introduction of the research protocol. 7 From our previous example and using the investigative hypothesis that there is a difference in functional outcomes between computer-assisted acetabular component placement and free-hand placement, the primary ...
To develop a set of research objectives, you would then break down the various steps involved in meeting said aim. For example: This study will investigate the link between dehydration and the incidence of urinary tract infections (UTIs) in intensive care patients in Australia. To achieve this, the study objectives w ill include:
A research aim is a broad statement indicating the general purpose of your research project. It should appear in your introduction at the end of your problem statement, before your research objectives. Research objectives are more specific than your research aim. They indicate the specific ways you'll address the overarching aim.
In summary, while the aim of a research study represents the broad goal or purpose, objectives are specific statements that outline the steps necessary to achieve that aim. Understanding the difference between aims and objectives helps in creating a clear and structured research plan, ensuring that the study remains focused and aligned with its ...
What is the difference between research aims and objectives? The aims of a study describe what you hope to achieve. The objectives detail how you are going to achieve your aims. Let's use an example to illustrate. Aim: To understand the contribution that local governments make to national level energy policy. Objectives:
Moreover, the research objectives should be framed by the researcher before the initiation of the study: a specific, measurable, achievable, realistic, and time-defined (SMART) approach is utilized to devise the objectives based on the research question. It is preferable to have a single primary objective whereas the secondary objectives can be ...
The steps involved in the process of developing research questions and study objectives for conducting observational comparative effectiveness research (CER) are described in this chapter. It is important to begin with identifying decisions under consideration, determining who the decisionmakers and stakeholders in the specific area of research under study are, and understanding the context in ...
Formulating research aim and objectives in an appropriate manner is one of the most important aspects of your thesis. This is because research aim and objectives determine the scope, depth and the overall direction of the research. Research question is the central question of the study that has to be answered on the basis of research findings.
Examples of Specific Research Objectives: 1. "To examine the effects of rising temperatures on the yield of rice crops during the upcoming growth season.". 2. "To assess changes in rainfall patterns in major agricultural regions over the first decade of the twenty-first century (2000-2010).". 3.
Background: The first steps of any study are developing the research question, aim and objective. Subsequent steps develop from these and they govern the researchers' choice of population, setting, data to be collected and time period for the study. Clear, succinctly posed research questions, aims and objectives are essential if studies are to ...
The main difference is that research questions focus on the general purpose or aim of the study whereas research objectives provide specific, measurable, and attainable steps to achieve the research questions. Before we move to the differences, let's understand what are Research Questions and Research Objectives: Research Questions: Research ...
INTRODUCTION. Scientific research is usually initiated by posing evidenced-based research questions which are then explicitly restated as hypotheses.1,2 The hypotheses provide directions to guide the study, solutions, explanations, and expected results.3,4 Both research questions and hypotheses are essentially formulated based on conventional theories and real-world processes, which allow the ...
One of the key defining characteristics of rapid qualitative research and evaluation is their iterative design (Beebe, 2001, McNall et al., 2004).The term 'iterative' refers to a repetitive, circular, constantly changing research process where 'cycles' or 'loops' are used to generate evidence, reflect on the findings, obtain feedback, and inform changes in the original study design.
Background. Accurately predicting the walking independence of stroke patients is important. Our objective was to determine and compare the performance of logistic regression (LR) and three machine learning models (eXtreme Gradient Boosting (XGBoost), Support Vector Machines (SVM), and Random Forest (RF)) in predicting walking independence at discharge in stroke patients, as well as to explore ...
The objectives of a medical study can be broadly classified into primary and secondary objectives. The study's hypothesis defines the research's primary objective and is thus the aim of a medical study. It attempts to find an answer to the main research question or hypothesis. While addressing the primary objectives, additional research ...