

Essay on Group Discussion
Students are often asked to write an essay on Group Discussion in their schools and colleges. And if you’re also looking for the same, we have created 100-word, 250-word, and 500-word essays on the topic.
Let’s take a look…
100 Words Essay on Group Discussion
Introduction.
Group Discussion, often abbreviated as GD, is a method of assessing individuals in a group. It’s a tool to gauge a person’s ability to communicate effectively, express thoughts, and influence others.
Importance of GD
GD helps in developing critical thinking, listening skills, and articulation of thoughts. It’s a platform where students learn to respect different opinions and develop team spirit.
Conducting a GD
In a GD, a topic is given, and participants are expected to discuss it. Everyone gets a chance to express their views. The aim is not to win an argument but to exchange ideas.
Overall, GD is a vital tool in education, helping students to grow both personally and academically. It fosters a sense of respect, understanding, and cooperation among participants.
250 Words Essay on Group Discussion
Introduction to group discussion.
Group Discussion (GD) is a methodology employed in educational and corporate settings to encourage a structured and critical exchange of ideas. It is a platform where participants express their views, opinions, and knowledge on a particular topic.
Significance of Group Discussion
GD is instrumental in assessing communication skills, leadership qualities, and team spirit. It also showcases one’s ability to analyze, reason, and think critically. It facilitates the development of interpersonal skills and the ability to work collaboratively.
Effective Participation in Group Discussions
Effective participation in GD requires active listening, clear articulation, and respect for others’ viewpoints. It is not about dominating the conversation but contributing meaningfully and constructively. Participants should display logical thinking, clarity of thoughts, and the ability to persuade others without disrespecting their opinions.
Role of Group Discussion in Education and Corporate World
In academia, GD helps in the holistic development of students, preparing them for real-world challenges. It enhances their analytical skills, boosts confidence, and promotes healthy competition. In the corporate world, GD often forms part of the selection process, testing candidates’ problem-solving abilities, leadership skills, and adaptability to team dynamics.
In conclusion, Group Discussion is an essential tool in both educational and professional domains. It fosters critical thinking, effective communication, and collaborative problem-solving. By engaging in GD, individuals can not only broaden their knowledge base but also refine their interpersonal skills, preparing them for future challenges.
500 Words Essay on Group Discussion
Group discussion, an interactive activity where individuals exchange ideas and opinions, is a crucial part of the modern academic and corporate world. It is not merely a conversation, but a structured process that tests the ability to think critically, communicate effectively, and work in a team.
The Importance of Group Discussion
Group discussions are vital for several reasons. They foster active learning, promote critical thinking, and enhance communication skills. By engaging in group discussions, students can understand different perspectives, thereby expanding their knowledge and broadening their horizons. It also helps in developing problem-solving skills, as the group works together to find solutions to complex issues.
Components of an Effective Group Discussion
An effective group discussion consists of several components. Firstly, it requires active participation from all members. Each person should contribute their thoughts and ideas, ensuring a wide range of perspectives. Secondly, it necessitates effective communication. Participants must articulate their thoughts clearly and listen attentively to others. Thirdly, it involves critical thinking, where individuals analyze and evaluate ideas before accepting them. Lastly, it requires mutual respect among the participants, as differing viewpoints are inevitable.
Role of a Moderator in Group Discussion
The role of a moderator in a group discussion is pivotal. They ensure that the discussion stays on track and that every participant gets a fair chance to express their views. They handle conflicts and manage time effectively, ensuring that the discussion is productive and reaches a conclusion.
Challenges in Group Discussion
Despite its benefits, group discussions can pose certain challenges. Dominance by a few members, lack of preparation, and miscommunication can hinder the effectiveness of a group discussion. It is essential to address these issues to ensure a fruitful discussion.
Group discussions are an integral part of the learning process, fostering critical thinking, effective communication, and teamwork. While they may present certain challenges, these can be mitigated with proper preparation and the effective role of a moderator. As students, mastering the art of participating in group discussions can significantly enhance your academic and professional journey.
That’s it! I hope the essay helped you.
If you’re looking for more, here are essays on other interesting topics:
Happy studying!
Leave a Reply Cancel reply
Your email address will not be published. Required fields are marked *

How to write a discussion essay
- September 21, 2023
A discussion essay, also called a controversial essay, is where you express your opinion about a topic. When writing one,
- Cover both sides of the topic , present the key points that back your viewpoint and the opposing one.
- Ensure a multi-faceted understanding of the issues before presenting your own personal views and conclusions.
So let’s deeply explore the structure and components of a successful discussion paper.
Quick summary
- Carefully read and comprehend the essay prompt.
- Select a topic that leads to multiple viewpoints and debates.
- Begin with a clear introduction that includes a strong thesis statement.
- Discuss different viewpoints or/and arguments in separate body paragraphs.
- Maintain a balanced approach by presenting viewpoints fairly.
- Summarize the main ideas and restate your thesis statement , then end your essay.
Choose a controversial topic
Choosing a topic is the first step when starting your essay. When choosing a topic , make sure it is something that you are personally interested in as it will be easier for you to write.
Now let’s have a look at discussion essay topic examples.
- Should Capital Punishment be Abolished?
- Is Genetic Engineering Ethical for Humans?
- Should Schools Implement Mandatory Vaccination Policies?
- Is Nuclear Energy a Viable Solution to the Energy Crisis?
After choosing the essay topic, you should create your outline to finish planning your essay.
Create an outline
The outline allows you to understand how to combine all the information and thesis statement to support claims of your essay.
Create a basic outline for your discussion essay. Start with a preliminary version of your thesis statement, main argument, opposing argument, and other main points.
Here is an outline example for a discussion essay.
Discussion essay outline example
Title: The Ethics of Artificial Intelligence in Healthcare
- Start with a strong and engaging opening.
- Introduce the topic and its relevance.
- Present the thesis statement that highlights the ethical considerations in AI integration in healthcare.
- Begin with a clear topic sentence about AI's role in diagnosis.
- Explain AI's superiority in analyzing medical data and images.
- Provide an example of AI detecting diseases early.
- Discuss concerns about the potential effects on human expertise.
- Introduce the focus on personalized treatment.
- Explain how AI can customize therapies based on individual data.
- Give an example of optimizing medical outcomes.
- Raise ethical issues about privacy, consent, and data security.
- Start with a topic sentence about accountability.
- Discuss the challenge of assigning blame in AI-related errors.
- Address the importance of unbiased AI algorithms.
- Mention the need for regulation and oversight.
- Restate the significance of the ethical landscape of AI in healthcare.
- Summarize the core points discussed in the body paragraphs.
- Reiterate the importance of balancing AI advancements with ethical considerations.
- End with a call to uphold ethical principles in the integration of AI in healthcare.
So now that you’ve seen an outline example, l et’s start writing your essay with an introduction.
Write your introduction
- Start with an attention-grabbing opening ( hook sentence ) that piques the reader's curiosity and encourages them to continue reading.
- Provide a brief background or context for the topic you'll be discussing.
- Seamlessly transition from the general to the specific focus of your essay. Guide the reader to understand what to expect from the essay.
- End your introduction with a strong and clear thesis statement.
Discussion essay introduction example
Introduction
Now that we have written our introduction, we can move on to the discussion parts.
Compose the body of your essay
Write down the main points of the body paragraphs of your discussion paper. A well-written body paragraph illustrates, justifies, and/or supports your thesis statement. When writing body paragraphs:
- Typically, present each issue separately and discuss both sides of the argument in an unbiased manner.
- Start each paragraph with a topic sentence that transitions from the previous one to introduce the next topic.
- Start with your least convincing argument and work your way up to your strongest argument. This structure helps readers follow your logic consistently.
- Make sure your citation usage is consistent for each argument. If you cite three quotes that support your main argument, aim to use three quotes for the opposing view as well.
Discussion essay body paragraphs
Body Paragraph 1: Enhancing Diagnostics and Accuracy
Body Paragraph 2: Personalized Treatment and Privacy
Body Paragraph 3: Ethical Responsibility and Accountability
Now, let’s look at how to end your work.
Conclude your discussion essay
Writing a strong conclusion for a discussion essay is essential to leave a lasting impression on your readers and summarize the main points of your argument effectively. Here are the steps on how to write a good conclusion for your discussion paper:
- Begin your conclusion by restating your thesis statement in a slightly different way. This helps remind the reader of the main argument you've presented throughout the essay.
- Provide a brief summary of the key points you discussed in your essay.
- Emphasize the importance of the topic and the implications of your argument.
Things to avoid in conclusion
Let’s have a look at a conclusion example for a discussion essay..
Discussion essay conclusion example
Remember that a conclusion is your final opportunity to leave a strong impression, so make it memorable and impactful.
Frequently Asked Questions
How is a discussion essay different from other types of essays.
Unlike other common essays that might focus on presenting a single argument, a discussion essay presents multiple perspectives on a topic. It strives to remain neutral and balanced while analyzing different viewpoints.
Can I express my personal opinion in a discussion essay?
Yes, you can include your personal opinion, but it should be presented alongside other viewpoints. Your opinion should be supported by evidence and analysis, and you should strive for a balanced presentation.
Do I need to include counterarguments?
Yes, including counterarguments is essential in a discussion essay. Addressing opposing viewpoints demonstrates your understanding of the topic and strengthens your analysis.
How do I ensure a balanced presentation of viewpoints?
Present each viewpoint objectively and support it with evidence. Give equal attention to different perspectives and avoid using biased language.
How can I transition between different viewpoints in my essay?
Use transitional words and phrases like “however,” “on the other hand,” and “in contrast” to smoothly guide readers between paragraphs and viewpoints.
Recently on Tamara Blog
How to write a discussion essay (with steps & examples), writing a great poetry essay (steps & examples), how to write a process essay (steps & examples), writing a common app essay (steps & examples), how to write a synthesis essay (steps & examples), how to write a horror story.
- Share full article
Advertisement
Supported by
student opinion
177 Questions to Inspire Writing, Discussion, Debate and Reflection
Here are all of our Student Opinion questions from the 2019-20 school year. A New York Times article, interactive feature or video is the jumping-off point for each question.

By The Learning Network
Each school day, we publish a new Student Opinion question. The questions explore everything from family, school and friendships to race, gender and social media. Not surprisingly, this past year, many of our Student Opinion prompts also touched on how the coronavirus pandemic affected nearly all aspects of our lives.
During the 2019-20 school year, we asked 177 questions, and you can find them all below or here as a PDF . The questions are divided into two categories — those that provide opportunities for debate and persuasive writing, and those that lend themselves to creative, personal or reflective writing.
A New York Times article, interactive feature or video is the jumping-off point for each question, and students can view each linked Times article without a digital subscription.
These questions are used by some teachers as a way to spark class discussion and debate, while other teachers use them as an entry point for practicing narrative or persuasive writing. Our Student Opinion questions offer an authentic audience for student voices as well as a way to encourage students to engage with current events and peers from around the world.
We also have a free, on-demand webinar that offers other ideas on how to use our writing prompts in the classroom for everyday low-stakes writing practice across the curriculum.
We are having trouble retrieving the article content.
Please enable JavaScript in your browser settings.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access. If you are in Reader mode please exit and log into your Times account, or subscribe for all of The Times.
Thank you for your patience while we verify access.
Already a subscriber? Log in .
Want all of The Times? Subscribe .

What is Group Discussion? (GD), Objectives, Types, Prerequisites, Steps
- Post last modified: 4 June 2023
- Reading time: 24 mins read
- Post category: Business Communication

- What is Group Discussion?
Group Discussion (GD) is a technique where the group of participants share their views and opinions on a topic for a specific duration. Companies conduct this evaluation process because business management is essentially a team activity and working with groups is an essential parameter in organisations.

Table of Content
- 1 What is Group Discussion?
- 2 Group Discussion (GD) Definition
- 3 Objectives of Group Discussion (GD)
- 4.1 Topic-based GDs
- 4.2 Case-based GDs
- 4.3 Article-based GDs
- 5.1 Prior knowledge
- 5.2 Active listening
- 5.3 Effective communication
- 5.4 Appropriate body language
- 6.1 Initiate
- 6.3 Summarise
- 7 Do’s and Don’ts of Group Discussion
- 8.1 Communication skills
- 8.2 Analytical and interpretative skills
- 8.3 Interpersonal skills
- 8.4 Persuasive skills
- 9.1 Objective of conducting a GD
- 9.2 Venue setup
- 9.4 Pre-instructions for participants
- 9.5 Defined parameters for selection
- 9.6 Role of assessor/evaluator
- 9.7 Clear communication of results post GD
GD is an opportunity for an organisation to evaluate a candidate’s communication skills, knowledge, leadership skills, listening skills, social skills, ability to think on the spot and improvise. A typical GD has about 8-12 participants and 2 or more assessors. The assessors sit where they can clearly see and hear all the candidates.
They record the behaviour of participants during the group discussion. Then, they evaluate the recorded observations against the desired traits and finalise a few candidates from the group.
Group Discussion (GD) Definition
Group discussion is a communication process that involves the exchange of ideas, information, and opinions among a group of people. It is a powerful tool for problem-solving, decision-making, and generating new ideas. – Stephen P. Robbins, author of “Organizational Behavior”
A group discussion is an interactive process where a group of individuals come together to exchange ideas, opinions, and information on a specific topic. The goal of a group discussion is to arrive at a collective decision or solution that is acceptable to all members of the group.” – The Indian Institute of Technology (IIT)
Group discussion is a method of communication in which a small group of people come together to discuss a topic or problem. The group members share their ideas and perspectives with one another in order to arrive at a solution or decision that benefits the group as a whole.” – The American Psychological Association (APA)
Group discussion is an effective means of exploring and analyzing complex issues, generating creative ideas, and arriving at consensus among participants. It provides a platform for individuals to express their views, clarify their understanding, and learn from the perspectives of others.” – The National Institute of Standards and Technology (NIST)
Objectives of Group Discussion (GD)
Group discussions are conducted to serve various purposes. It is a two-way communication process through which recruiters get to assess the soft skills of candidates, while the candidates can gain clarity about their own thoughts, opinions and views.
The following are some of the objectives of a group discussion activity:
- To collect data
- To breed fresh ideas and take inputs from a particular group
- To perceive the common ideas of people on a particular topic
- To identify the solution of a specific problem or issue
- To select a candidate for hiring in a company
- To select candidate for admission in an educational institute
- To arrive at a consensus regarding a common concern
Types of Group Discussion (GDs)
A group discussion delineates how a candidate participates, behaves and contributes in a group. There are three main types of GDs :
Topic-based GDs
Case-based gds, article-based gds.
These are based on certain practical topics, such as the harmful effects of plastics on the environment or the need of college degree for entrepreneurship. These GDs can be further classified into:
- Factual GDs : These are informative GDs that require comprehensive knowledge about a subject. For example, the economic growth of India since independence.
- Controversial GDs : These GDs are based on controversial topics, which test the ability of a candidate to handle a situation, control anger, display patience and think critically. For example, arranged marriage vs. love marriage.
- Abstract GDs : These GDs are based on certain conceptual topics that are used to evaluate a candidate’s creative thinking and analytical ability. For example, challenges before humanity.
In these GDs, a case study is presented to group members to read and analyse in a given period. Candidates need to discuss the case study among themselves and reach on a com- mon consensus to solve the given situation. This helps to evaluate their problem solving, analytical ability, critical thinking and creative thinking skills.
Candidates are presented with an article on any field, such as politics, sports, or technology, and asked to discuss the given situation.
Prerequisites of Group Discussion (GD)
There are some essential requirements for gaining success in a group discussion. The following are some important requirements to be fulfilled by a candidate in order to ensure a successful GD:

Prior knowledge
Active listening, effective communication, appropriate body language.
A candidate with in-depth knowledge and command over the topic initiates the discussion. He/she gets noticed and usually selected in a group discussion. However, starting the discussion does not guarantee the selection and also it does not show the leadership qualities.
Therefore, one should start a discussion only when he/she is well acquainted with the topic. In case, one is not well acquainted with the topic, he/she should first listen to others and then speak.
Only good listeners can be active participators in a discussion. Such persons listen to others and remain attentive and active throughout the discussion. Therefore, a listener is more likely to imbibe knowledge than a speaker. By listening carefully, a candidate can contribute by formulating his/her own thoughts that can be verbally delivered.
Candidates should have good communication skills and they should take care of the overtones. One should be able to understand other participants’ perception and thoughts. Then, accordingly, Agree to or refute the ideas or viewpoints presented by other candidates.
Therefore, healthy and clear thoughts should be exchanged while pursuing a group discussion to gain attention of the assessors.
Gestures, facial expressions, eye contact and tone of voice show the amount of interest a candidate has in a group discussion. It is important to maintain eye contact with the evaluator(s) when starting a discussion. The coordinator notices the body language of the candidates to assess their confidence level.
Steps of Effective Group Discussion
A GD is a method used by organisations to analyse the skills of candidates and decide whether their personality traits are desirable for the job or not.
While facing a GD, the following steps should be performed:
If you want to quickly grab the attention of assessors, then start the GD. However, you must have good knowledge or understanding of the subject being discussed. To make your speech more interesting, you can start with a relevant quote or a short/interesting story; but keep track of time.
There might be a situation when you do not have enough knowledge to start a discussion. In that case, wait, watch and listen to others. As soon as you get an opening, jump in and take charge. Move the conversation forward to make it impactful. However, remember not to over-drag the topic. Sometimes, less is more.
Closing a GD is another opportunity to get the attention of the evaluators. Recap the discussion, connect the dots, highlight the key points and summarise them. Make sure that the summary includes both the positive and negative viewpoints on the topic presented by the candidates.
Do’s and Don’ts of Group Discussion
In this section, we will discuss some Do’s and Don’ts to be taken care of by all the candidates who wish to perform well in a GD.
Some Do’s to be kept in mind during a GD are:
- Be a good listener by being patient.
- Acknowledge everyone else and what they say.
- Articulate views in a way that is comprehensible to others.
- Structure your thoughts and present them logically.
- Read newspapers, current affairs, essays and articles to develop thought structuring.
- Respect others for what they are.
- Be open-minded and acknowledge the fact that people think differently about issues.
- Train your mind for analytical thinking by taking all aspects into consideration.
It is also important to avoid doing certain things while participating in a GD. Some Don’ts to be aware of while pursuing a GD are:
- Avoid irrelevant talk.
- Avoid interrupting others while they are talking. If you need to cut short a speaker, then do so politely and with due apology.
- Avoid dominating the conversation. Ask others to contribute. Acknowledge their viewpoints.
- Avoid getting into an argument. Try to express clearly in a healthy manner.
- Do not show lack of interest and negative attitude.
- Avoid stating only your viewpoint.
- Avoid dwelling only on one aspect of the GD.
Group Discussion Evaluation Criteria
Each group discussion exercise is assessed by one or more individuals who are trained to observe and assess behavioural traits relevant for a specific job. The four main behavioural traits assessed through a group discussion are shown in Figure
Let us discuss these behavioural traits in detail.
Communication skills
Analytical and interpretative skills, interpersonal skills, persuasive skills.
These skills are judged on the basis of how a participant is getting his/her message across, how he/she is using his/her body language and also listening skills.
Assessors draw conclusions about a participant’s interpreting and analysing skills by observing how he/she uses facts and data, considers complex problems and issues, suggests solutions, etc.
Assessors observe the participants’ interactions with one another, how they allow one another to express themselves, etc.
The influencing skills of participants are as- sessed based on how well they are able to persuade one another, convince others about a viewpoint or impact others’ behaviour.
Organising a Group Discussion
A Group Discussion generally involves a group of 8-10 participants who are evaluated by a selection panel. GDs are used to evaluate whether a candidate is a perfect fit for an organisation or not. Be it college placements, MBA courses, job interviews or general researches, GDs are conducted almost in every field to gauge whether the candidate possesses the required skills and personality traits to be a part of the concerned institution. A facilitator has to take care of all the nitty-gritties of organising a GD.
In order to conduct a successful GD, the following aspects need to be taken into consideration:
Objective of conducting a GD
Venue setup, pre-instructions for participants, defined parameters for selection, role of assessor/evaluator, clear communication of results post gd.
Every GD has a specific purpose such as selecting deserving candidates for admission in professional course or gaining new talented employees in an organisation. Therefore, the objective of a GD should be clear to all the members of the selection panel in order to select the most deserving candidate.
An appropriate venue should be set up to conduct a GD. The venue should not be overcrowded, which may make the participants feel uncomfortable. The space selected for conducting the GD should be well-ventilated, equipped with proper lighting and should have a proper seating arrangement.
A stipulated time limit should be set for each participant to present his/her views. Firstly, participants are given a topic and some time to understand the topic and organise their thoughts. Thereafter they start presenting their views and opinions over the given topic. The time provided to the participants should be logical and it should start at that time only with no delay and waiting.
Prior communication with the participants should be properly conducted along with mentioning the time allotted to one participant to speak. The topic of discussion should be specified clearly along with the instructions and timings of when to start and stop. Big MNCs have their well-panned GD guide that provides instructions to the participants.
There are various parameters based on which a candidate is evaluated. Some of these parameters are listening power, level of confidence, decision-making ability, analytical skills, leadership skills, etc.
Candidates can speak whatever they like on the subject under discussion. The assessors note down their observations for each candidate. Once the discussion is over, the assessors review the information recorded against the desired behaviour. Therefore, a proper evaluation sheet should be maintained for writing down observations so that no errors occur while the selection of candidates.
The results should be announced clearly post the GD. The facilitator should ensure that the participants should not be made to wait for too long for the results.
The following are some points that you should take care of while preparing for a group discussion:
- Ensure your contribution to the group : Candidates need to make sure that they contribute to the conversation. Candidates having avoiding behaviours or actions do not contribute to the discussion’s outcome. Such behaviours need to be avoided and involvement in the GD is necessary to make a mark.
- Manage conflicts effectively : In case of any disagreement with members of the group, ensure that you persuade them without getting rude and aggressive. Assessors will pick such arrogant behaviour and highlight it as your negative aspect.
- Manage your time : Candidates need to stick to the timeline al- lotted for the discussion as the same would suggest that they are punctual and follow the timeline persistently.
- Include others : Encourage those who do not speak up during the discussion and urge them to give their opinions. This will gain assessors’ praise and group members appreciation.
- Be a team player : Generally, group discussion exercises require that the members come to an agreement on the topic being discussed. However, ensure that you do not impose your ideas on others. A better way is to include everyone’s ideas and centre it around the organisation rather than express something that might only benefit one member.
Business Communication Notes
( Click on Topic to Read )
- What is Business Communication?
- What is Communication?
Types of Communication
7 c of communication, barriers to business communication.
- Oral Communication
- Types Of Non Verbal Communication
- What is Written Communication?
- What are Soft Skills?
- Interpersonal vs Intrapersonal communication
- Barriers to Communication
- Importance of Communication Skills
- Listening in Communication
Causes of Miscommunication
- What is Johari Window?
- What is Presentation?
Communication Styles
- Channels of Communication
- Hofstede’s Dimensions of Cultural Differences and Benett’s Stages of Intercultural Sensitivity
- Organisational Communication
- Horizontal C ommunication
- Grapevine Communication
- Downward Communication
- Verbal Communication Skills
- Upward Communication
- Flow of Communication
- What is Emotional Intelligence?
- What is Public Speaking?
- Upward vs Downward Communication
- Internal vs External Communication
- What is Interview?
- What is Negotiation?
- What is Digital Communication?
- What is Letter Writing?
Resume and Covering Letter
- What is Report Writing?
- What is Business Meeting?
- What is Public Relations?
- What Is Market Segmentation?
- What Is Marketing Mix?
- Marketing Concept
- Marketing Management Process
- What Is Marketing Environment?
- What Is Consumer Behaviour?
- Business Buyer Behaviour
- Demand Forecasting
- 7 Stages Of New Product Development
- Methods Of Pricing
- What Is Public Relations?
- What Is Marketing Management?
- What Is Sales Promotion?
- Types Of Sales Promotion
- Techniques Of Sales Promotion
- What Is Personal Selling?
- What Is Advertising?
- Market Entry Strategy
- What Is Marketing Planning?
- Segmentation Targeting And Positioning
- Brand Building Process
- Kotler Five Product Level Model
- Classification Of Products
- Types Of Logistics
- What Is Consumer Research?
- What Is DAGMAR?
- Consumer Behaviour Models
- What Is Green Marketing?
- What Is Electronic Commerce?
- Agricultural Cooperative Marketing
- What Is Marketing Control?
- What Is Marketing Communication?
- What Is Pricing?
- Models Of Communication
- What is Sales Management?
- Objectives of Sales Management
- Responsibilities and Skills of Sales Manager
- Theories of Personal Selling
- What is Sales Forecasting?
- Methods of Sales Forecasting
- Purpose of Sales Budgeting
- Methods of Sales Budgeting
- Types of Sales Budgeting
- Sales Budgeting Process
- What is Sales Quotas?
- What is Selling by Objectives (SBO) ?
- What is Sales Organisation?
- Types of Sales Force Structure
- Recruiting and Selecting Sales Personnel
- Training and Development of Salesforce
- Compensating the Sales Force
- Time and Territory Management
- What Is Logistics?
- What Is Logistics System?
- Technologies in Logistics
- What Is Distribution Management?
- What Is Marketing Intermediaries?
- Conventional Distribution System
- Functions of Distribution Channels
- What is Channel Design?
- Types of Wholesalers and Retailers
- What is Vertical Marketing Systems?
- What i s Marketing?
- What i s A BCG Matrix?
- 5 M’S Of Advertising
- What i s Direct Marketing?
- Marketing Mix For Services
- What Market Intelligence System?
- What i s Trade Union?
- What Is International Marketing?
- World Trade Organization (WTO)
- What i s International Marketing Research?
- What is Exporting?
- What is Licensing?
- What is Franchising?
- What is Joint Venture?
- What is Turnkey Projects?
- What is Management Contracts?
- What is Foreign Direct Investment?
- Factors That Influence Entry Mode Choice In Foreign Markets
- What is Price Escalations?
- What is Transfer Pricing?
- Integrated Marketing Communication (IMC)
- What is Promotion Mix?
- Factors Affecting Promotion Mix
- Functions & Role Of Advertising
- What is Database Marketing?
- What is Advertising Budget?
- What is Advertising Agency?
- What is Market Intelligence?
- What is Industrial Marketing?
- What is Customer Value
- What is Consumer Behaviour?
- What Is Personality?
- What Is Perception?
- What Is Learning?
- What Is Attitude?
- What Is Motivation?
- Consumer Imagery
- Consumer Attitude Formation
- What Is Culture?
- Consumer Decision Making Process
- Applications of Consumer Behaviour in Marketing
- Motivational Research
- Theoretical Approaches to Study of Consumer Behaviour
- Consumer Involvement
- Consumer Lifestyle
- Theories of Personality
- Outlet Selection
- Organizational Buying Behaviour
- Reference Groups
- Consumer Protection Act, 1986
- Diffusion of Innovation
- Opinion Leaders
- What is Business Law?
- Indian Contract Act 1872
- Essential Elements of a Valid Contract
- Types of Contract
- What is Discharge of Contract?
- Performance of Contract
- Sales of Goods Act 1930
- Goods & Price: Contract of Sale
- Conditions and Warranties
- Doctrine of Caveat Emptor
- Transfer of Property
- Rights of Unpaid Seller
- Negotiable Instruments Act 1881
- Types of Negotiable Instruments
- Types of Endorsement
- What is Promissory Note?
- What is Cheque?
- What is Crossing of Cheque?
- What is Bill of Exchange?
- What is Offer?
- Limited Liability Partnership Act 2008
- Memorandum of Association
- Articles of Association
- What is Director?
- Trade Unions Act, 1926
- Industrial Disputes Act 1947
- Employee State Insurance Act 1948
- Payment of Wages Act 1936
- Payment of Bonus Act 1965
- Labour Law in India
- What is Brand Management?
- 4 Steps of Strategic Brand Management Process
- Customer Based Brand Equity
- What is Brand Equity?
You Might Also Like

10 Verbal Communication Skills Worth Mastering

What is Grapevine Communication? Types, Advantages
Difference between interpersonal and intrapersonal communication.

Flow of Communication: Internal and External

What is Interview? Types, Questions, Do’s and Don’ts, Preparing
What is negotiation importance, process, strategic model, learning skills, leave a reply cancel reply.
You must be logged in to post a comment.
World's Best Online Courses at One Place
We’ve spent the time in finding, so you can spend your time in learning
Digital Marketing
Personal Growth

Development

Group Writing
What this handout is about.
Whether in the academic world or the business world, all of us are likely to participate in some form of group writing—an undergraduate group project for a class, a collaborative research paper or grant proposal, or a report produced by a business team. Writing in a group can have many benefits: multiple brains are better than one, both for generating ideas and for getting a job done. However, working in a group can sometimes be stressful because there are various opinions and writing styles to incorporate into one final product that pleases everyone. This handout will offer an overview of the collaborative process, strategies for writing successfully together, and tips for avoiding common pitfalls. It will also include links to some other handouts that may be especially helpful as your group moves through the writing process.
Disclaimer and disclosure
As this is a group writing handout, several Writing Center coaches worked together to create it. No coaches were harmed in this process; however, we did experience both the pros and the cons of the collaborative process. We have personally tested the various methods for sharing files and scheduling meetings that are described here. However, these are only our suggestions; we do not advocate any particular service or site.
The spectrum of collaboration in group writing
All writing can be considered collaborative in a sense, though we often don’t think of it that way. It would be truly surprising to find an author whose writing, even if it was completed independently, had not been influenced at some point by discussions with friends or colleagues. The range of possible collaboration varies from a group of co-authors who go through each portion of the writing process together, writing as a group with one voice, to a group with a primary author who does the majority of the work and then receives comments or edits from the co-authors.
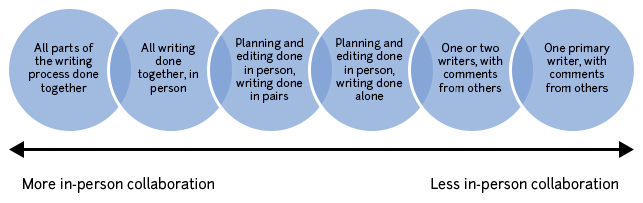
Group projects for classes should usually fall towards the middle to left side of this diagram, with group members contributing roughly equally. However, in collaborations on research projects, the level of involvement of the various group members may vary widely. The key to success in either case is to be clear about group member responsibilities and expectations and to give credit (authorship) to members who contribute an appropriate amount. It may be useful to credit each group member for their various contributions.
Overview of steps of the collaborative process
Here we outline the steps of the collaborative process. You can use these questions to focus your thinking at each stage.
- Share ideas and brainstorm together.
- Formulate a draft thesis or argument .
- Think about your assignment and the final product. What should it look like? What is its purpose? Who is the intended audience ?
- Decide together who will write which parts of the paper/project.
- What will the final product look like?
- Arrange meetings: How often will the group or subsets of the group meet? When and where will the group meet? If the group doesn’t meet in person, how will information be shared?
- Scheduling: What is the deadline for the final product? What are the deadlines for drafts?
- How will the group find appropriate sources (books, journal articles, newspaper articles, visual media, trustworthy websites, interviews)? If the group will be creating data by conducting research, how will that process work?
- Who will read and process the information found? This task again may be done by all members or divided up amongst members so that each person becomes the expert in one area and then teaches the rest of the group.
- Think critically about the sources and their contributions to your topic. Which evidence should you include or exclude? Do you need more sources?
- Analyze the data. How will you interpret your findings? What is the best way to present any relevant information to your readers-should you include pictures, graphs, tables, and charts, or just written text?
- Note that brainstorming the main points of your paper as a group is helpful, even if separate parts of the writing are assigned to individuals. You’ll want to be sure that everyone agrees on the central ideas.
- Where does your individual writing fit into the whole document?
- Writing together may not be feasible for longer assignments or papers with coauthors at different universities, and it can be time-consuming. However, writing together does ensure that the finished document has one cohesive voice.
- Talk about how the writing session should go BEFORE you get started. What goals do you have? How will you approach the writing task at hand?
- Many people find it helpful to get all of the ideas down on paper in a rough form before discussing exact phrasing.
- Remember that everyone has a different writing style! The most important thing is that your sentences be clear to readers.
- If your group has drafted parts of the document separately, merge your ideas together into a single document first, then focus on meshing the styles. The first concern is to create a coherent product with a logical flow of ideas. Then the stylistic differences of the individual portions must be smoothed over.
- Revise the ideas and structure of the paper before worrying about smaller, sentence-level errors (like problems with punctuation, grammar, or word choice). Is the argument clear? Is the evidence presented in a logical order? Do the transitions connect the ideas effectively?
- Proofreading: Check for typos, spelling errors, punctuation problems, formatting issues, and grammatical mistakes. Reading the paper aloud is a very helpful strategy at this point.
Helpful collaborative writing strategies
Attitude counts for a lot.
Group work can be challenging at times, but a little enthusiasm can go a long way to helping the momentum of the group. Keep in mind that working in a group provides a unique opportunity to see how other people write; as you learn about their writing processes and strategies, you can reflect on your own. Working in a group inherently involves some level of negotiation, which will also facilitate your ability to skillfully work with others in the future.
Remember that respect goes along way! Group members will bring different skill sets and various amounts and types of background knowledge to the table. Show your fellow writers respect by listening carefully, talking to share your ideas, showing up on time for meetings, sending out drafts on schedule, providing positive feedback, and taking responsibility for an appropriate share of the work.
Start early and allow plenty of time for revising
Getting started early is important in individual projects; however, it is absolutely essential in group work. Because of the multiple people involved in researching and writing the paper, there are aspects of group projects that take additional time, such as deciding and agreeing upon a topic. Group projects should be approached in a structured way because there is simply less scheduling flexibility than when you are working alone. The final product should reflect a unified, cohesive voice and argument, and the only way of accomplishing this is by producing multiple drafts and revising them multiple times.
Plan a strategy for scheduling
One of the difficult aspects of collaborative writing is finding times when everyone can meet. Much of the group’s work may be completed individually, but face-to-face meetings are useful for ensuring that everyone is on the same page. Doodle.com , whenisgood.net , and needtomeet.com are free websites that can make scheduling easier. Using these sites, an organizer suggests multiple dates and times for a meeting, and then each group member can indicate whether they are able to meet at the specified times.
It is very important to set deadlines for drafts; people are busy, and not everyone will have time to read and respond at the last minute. It may help to assign a group facilitator who can send out reminders of the deadlines. If the writing is for a co-authored research paper, the lead author can take responsibility for reminding others that comments on a given draft are due by a specific date.
Submitting drafts at least one day ahead of the meeting allows other authors the opportunity to read over them before the meeting and arrive ready for a productive discussion.
Find a convenient and effective way to share files
There are many different ways to share drafts, research materials, and other files. Here we describe a few of the potential options we have explored and found to be functional. We do not advocate any one option, and we realize there are other equally useful options—this list is just a possible starting point for you:
- Email attachments. People often share files by email; however, especially when there are many group members or there is a flurry of writing activity, this can lead to a deluge of emails in everyone’s inboxes and significant confusion about which file version is current.
- Google documents . Files can be shared between group members and are instantaneously updated, even if two members are working at once. Changes made by one member will automatically appear on the document seen by all members. However, to use this option, every group member must have a Gmail account (which is free), and there are often formatting issues when converting Google documents back to Microsoft Word.
- Dropbox . Dropbox.com is free to join. It allows you to share up to 2GB of files, which can then be synched and accessible from multiple computers. The downside of this approach is that everyone has to join, and someone must install the software on at least one personal computer. Dropbox can then be accessed from any computer online by logging onto the website.
- Common server space. If all group members have access to a shared server space, this is often an ideal solution. Members of a lab group or a lab course with available server space typically have these resources. Just be sure to make a folder for your project and clearly label your files.
Note that even when you are sharing or storing files for group writing projects in a common location, it is still essential to periodically make back-up copies and store them on your own computer! It is never fun to lose your (or your group’s) hard work.
Try separating the tasks of revising and editing/proofreading
It may be helpful to assign giving feedback on specific items to particular group members. First, group members should provide general feedback and comments on content. Only after revising and solidifying the main ideas and structure of the paper should you move on to editing and proofreading. After all, there is no point in spending your time making a certain sentence as beautiful and correct as possible when that sentence may later be cut out. When completing your final revisions, it may be helpful to assign various concerns (for example, grammar, organization, flow, transitions, and format) to individual group members to focus this process. This is an excellent time to let group members play to their strengths; if you know that you are good at transitions, offer to take care of that editing task.
Your group project is an opportunity to become experts on your topic. Go to the library (in actuality or online), collect relevant books, articles, and data sources, and consult a reference librarian if you have any issues. Talk to your professor or TA early in the process to ensure that the group is on the right track. Find experts in the field to interview if it is appropriate. If you have data to analyze, meet with a statistician. If you are having issues with the writing, use the online handouts at the Writing Center or come in for a face-to-face meeting: a coach can meet with you as a group or one-on-one.
Immediately dividing the writing into pieces
While this may initially seem to be the best way to approach a group writing process, it can also generate more work later on, when the parts written separately must be put together into a unified document. The different pieces must first be edited to generate a logical flow of ideas, without repetition. Once the pieces have been stuck together, the entire paper must be edited to eliminate differences in style and any inconsistencies between the individual authors’ various chunks. Thus, while it may take more time up-front to write together, in the end a closer collaboration can save you from the difficulties of combining pieces of writing and may create a stronger, more cohesive document.
Procrastination
Although this is solid advice for any project, it is even more essential to start working on group projects in a timely manner. In group writing, there are more people to help with the work-but there are also multiple schedules to juggle and more opinions to seek.
Being a solo group member
Not everyone enjoys working in groups. You may truly desire to go solo on this project, and you may even be capable of doing a great job on your own. However, if this is a group assignment, then the prompt is asking for everyone to participate. If you are feeling the need to take over everything, try discussing expectations with your fellow group members as well as the teaching assistant or professor. However, always address your concerns with group members first. Try to approach the group project as a learning experiment: you are learning not only about the project material but also about how to motivate others and work together.
Waiting for other group members to do all of the work
If this is a project for a class, you are leaving your grade in the control of others. Leaving the work to everyone else is not fair to your group mates. And in the end, if you do not contribute, then you are taking credit for work that you did not do; this is a form of academic dishonesty. To ensure that you can do your share, try to volunteer early for a portion of the work that you are interested in or feel you can manage.
Leaving all the end work to one person
It may be tempting to leave all merging, editing, and/or presentation work to one person. Be careful. There are several reasons why this may be ill-advised. 1) The editor/presenter may not completely understand every idea, sentence, or word that another author wrote, leading to ambiguity or even mistakes in the end paper or presentation. 2) Editing is tough, time-consuming work. The editor often finds himself or herself doing more work than was expected as they try to decipher and merge the original contributions under the time pressure of an approaching deadline. If you decide to follow this path and have one person combine the separate writings of many people, be sure to leave plenty of time for a final review by all of the writers. Ask the editor to send out the final draft of the completed work to each of the authors and let every contributor review and respond to the final product. Ideally, there should also be a test run of any live presentations that the group or a representative may make.
Entirely negative critiques
When giving feedback or commenting on the work of other group members, focusing only on “problems” can be overwhelming and put your colleagues on the defensive. Try to highlight the positive parts of the project in addition to pointing out things that need work. Remember that this is constructive feedback, so don’t forget to add concrete, specific suggestions on how to proceed. It can also be helpful to remind yourself that many of your comments are your own opinions or reactions, not absolute, unquestionable truths, and then phrase what you say accordingly. It is much easier and more helpful to hear “I had trouble understanding this paragraph because I couldn’t see how it tied back to our main argument” than to hear “this paragraph is unclear and irrelevant.”
Writing in a group can be challenging, but it is also a wonderful opportunity to learn about your topic, the writing process, and the best strategies for collaboration. We hope that our tips will help you and your group members have a great experience.
Works consulted
We consulted these works while writing this handout. This is not a comprehensive list of resources on the handout’s topic, and we encourage you to do your own research to find additional publications. Please do not use this list as a model for the format of your own reference list, as it may not match the citation style you are using. For guidance on formatting citations, please see the UNC Libraries citation tutorial . We revise these tips periodically and welcome feedback.
Cross, Geoffrey. 1994. Collaboration and Conflict: A Contextual Exploration of Group Writing and Positive Emphasis . Cresskill, NJ: Hampton Press.
Ede, Lisa S., and Andrea Lunsford. 1990. Singular Texts/Plural Authors: Perspectives on Collaborative Writing . Carbondale, IL: Southern Illinois University Press.
Speck, Bruce W. 2002. Facilitating Students’ Collaborative Writing . San Francisco: Jossey-Bass.
You may reproduce it for non-commercial use if you use the entire handout and attribute the source: The Writing Center, University of North Carolina at Chapel Hill
Make a Gift
Does Group Discussion Improve Critical Thinking Skills? Essay
- To find inspiration for your paper and overcome writer’s block
- As a source of information (ensure proper referencing)
- As a template for you assignment
Critical thinking is a term originating from the second part of the 20th century. It was defined by the National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking (1987) as “the intellectually disciplined process of actively and skillfully conceptualizing, applying, analyzing, synthesizing, and/or evaluating information gathered from, or generated by, observation, experience, reflection, reasoning, or communication, as a guide to belief and action.”
At its core, it is the ability to clearly and rationally analyze the information we receive without allowing our biases, prejudices, and misinformation to inform our conclusions and opinions, and to be deliberate and conscious in our judgments. It allows people to distinguish important ideas in arguments, find links between them, find faults in arguments and, in turn, build efficient ones. Ultimately, it is a skill that is useful both for internal dialog, to analyze oneself, and external dialog a sell, to analyze information from around us (Paul & Elder, 2009).
However, it is important to understand that critical thinking is not necessarily an inherent part of human character. Most of the time people are deeply affected by our preconceptions and opinions about ourselves and the world around us. Like any other higher-level cognitive skill or talent, critical thinking requires a conscious effort on behalf of the thinker to achieve improvement. Since it is agreed upon as one of the fundamental skills in most industries, from business to science and art, a lot of thought was put into developing new ways to train people to develop critical thinking (Lau, n.d.).
And a divisive question among psychologists and educators is the use of group work and discussion as a means to develop critical thinking. On the one hand, group problem solving can promote interest and engagement, inspire people to engage with and question new ideas and data. By being faced with fully developed opposing views, they have a chance to gain new perspectives, learn to shape their opinions better, and grow as persons. Many researchers (e.g. Jones, 2014) of this topicc view collaborative discussions and effects of group dynamics as vital for developing critical thinking.
On the other hand, peer pressure and the “bandwagon effect” are phenomena well known to sociologists, psychologists, and educators, which are detrimental to the individual, and thus also critical, thought. If in a group a majority shares the same belief, it is very likely to be picked up by others, sometimes in spite of the evidence against said belief (Vitelli, 2015). People placed in a group suffering from a bandwagon effect or with a strong peer pressure factor are likely to avoid participating in the conversation, or even delegate to the opinions of others rather that develop their own.
This brings us to the question if group discussions improve critical thinking skills or not? Despite arguments against this statement, I believe that research and modern critical thinking development practices have sufficient evidence that collaborative discussions and interactions can successfully improve critical thinking skills.
To explain why this stance was chosen, it is important to consider both advantages and disadvantages of group discussions as a tool of teaching pedagogy, the inherent responsibility it places on the person conducting them, and their role in the development of the skill in question.
The effectiveness of group work in classrooms was studied by Fung (2013), who aimed to confirm whether student engagement in classrooms could be enhanced through quality group work and if it could be used to inspire positive effects on students’ critical thinking. While he used Hong Kong as the location of his study, his conclusions can be useful for the purpose of this argumentative essay.
His training workshops and teaching interventions showed that all students who participated in the group studies and discussions significantly enhanced their critical thinking ability over those who worked individually. After having worked in teacher-monitored groups, the students have shown themselves to become more inquisitive, analytical in the evaluation of received information, and more argumentative in their responses. They also showed a more creative approach to tests than students working alone.
Studies by other researchers further prove that cooperative work shows a higher level of thought; with participants becoming adjusted to participating in discussions and take the opportunity to learn new ideas faster. These qualities define them as critical thinkers. In particular, the doctorate study by Meredith Godad (2012), while focusing on the effect of technological environment on the development of critical thinking, also evaluated the effects of group work on the development of critical thinking among students. Not only did she confirm the results of previous researches, but she also noted that collaborative discussions reduced cognitive frustration and load, allowing students to focus on their cognition further.
These studies confirm that group activities, collaboration and discussions help in developing critical patterns of thinking. However, these examples were all tested in tightly controlled situations, with teachers or researchers directing most of the conversations, allowing for maximization of results. However, if such skilled assistance is not provided, this can cause the opposite effect to the desired.
Humans have a natural desire to fit into their social circle. It is a protective instinct which is meant to help us adjust to the society around us. If a person does not already have a solid individual critical thinking ability developed, when placed under pressure from their peers they might be willing to either abandon their opinions in favor of more popular ones, or accept a new one, based purely on the prevailing number of people supporting it (Hendra, 2013).
We can conclude that group activities indeed have a proven record of improving the critical thinking skills of people involved. But, on the other hand, such discussions often require an outside influence to deter clique formation and development of peer pressure. It is clear that with an equal, well-educated group, the members will only benefit from the interactions, and will be able to evaluate any given idea or situation much more efficiently and clearly and on their own, particularly if people with different opinions participate in the conversation. But in a more uneven group, dominated by dominated by several particularly charismatic individuals, even a correct idea can be overlooked, or even figuratively brought down, if it does not fit with the opinions of the leaders or the majority opinion.
Consequently, it is the responsibility of the teacher or tutor to create and regulate a healthy educational environment, where students are encouraged to put forward their opinions and actively participate in the discussion, even when voicing opinions that are not popular in the group. He should encourage discussion participants to evaluate their ideas and compare them against ideas of other speakers, find pros and cons both of different views spoken.
Bibliography
Fung, D. (2014). Promoting critical thinking through effective group work: A teaching intervention for Hong Kong primary school students. International Journal of Educational Research, 66 , 45-62.
Godat, M. (2012). Collaborative Learning and Critical Thinking in Technology-enhanced Environments: An Instructional Design Framework (Unpublished doctoral thesis). Queensland University of Technology, Brisbane, Australia
Hendra, M. (2013). Peer Pressure Changes Perspective . Web.
Jones, J. M. (2014). Discussion Group Effectiveness is Related to Critical Thinking through Interest and Engagement. Psychology Learning & Teaching Plat, 13 (1), 12-23.
Lau, J. (n.d.). What is critical thinking? Web.
Paul, R., & Elder, L. (2009). The miniature guide to critical thinking: Concepts and tools . Dillon Beach, CA: Foundation for Critical Thinking.
The National Council for Excellence in Critical Thinking . (1987). Web.
Vitelli, R. (2015). Riding the Bandwagon Effect . Web.
- Teachers' Perception of Knowledge Acquisition
- Student Experience in Academic Environment
- Writing Argumentative Essay With Computer Aided Formulation
- Should Animals be Used in Research: Argumentative Essay
- The Dialog “Crito” by Socrates
- American College Graduates' Dilemma
- College Education: Controversy and Its Sources
- Self-Efficacy in On & Offline Counseling Programs
- Pakistani Students’ Education in "I am Malala" by Yousafzai
- Math and Psychological Tasks Analysis
- Chicago (A-D)
- Chicago (N-B)
IvyPanda. (2020, August 25). Does Group Discussion Improve Critical Thinking Skills? https://ivypanda.com/essays/does-group-discussion-improve-critical-thinking-skills/
"Does Group Discussion Improve Critical Thinking Skills?" IvyPanda , 25 Aug. 2020, ivypanda.com/essays/does-group-discussion-improve-critical-thinking-skills/.
IvyPanda . (2020) 'Does Group Discussion Improve Critical Thinking Skills'. 25 August.
IvyPanda . 2020. "Does Group Discussion Improve Critical Thinking Skills?" August 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/does-group-discussion-improve-critical-thinking-skills/.
1. IvyPanda . "Does Group Discussion Improve Critical Thinking Skills?" August 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/does-group-discussion-improve-critical-thinking-skills/.
IvyPanda . "Does Group Discussion Improve Critical Thinking Skills?" August 25, 2020. https://ivypanda.com/essays/does-group-discussion-improve-critical-thinking-skills/.

IMAGES
VIDEO
COMMENTS
Group discussion, an interactive activity where individuals exchange ideas and opinions, is a crucial part of the modern academic and corporate world. It is not merely a conversation, but a structured process that tests the ability to think critically, communicate effectively, and work in a team.
Learn how to craft a compelling discussion essay with clear arguments and balanced perspectives. Perfect guide for students.
This paper discusses the importance of group discussion and analyze the important procedures that are required for it to be effective.
Group discussions are common in our society, and have a variety of purposes, from planning an intervention or initiative to mutual support to problem-solving to addressing an issue of local concern.
1. Should Students Get Mental Health Days Off From School? 2. Do Video Games Deserve the Bad Rap They Often Get? 3. Should College Be Free? 4. Where Should We Draw the Line Between Community Health...
Group discussion is a communication process that involves the exchange of ideas, information, and opinions among a group of people. It is a powerful tool for problem-solving, decision-making, and generating new ideas.
Group Writing. What this handout is about. Whether in the academic world or the business world, all of us are likely to participate in some form of group writing—an undergraduate group project for a class, a collaborative research paper or grant proposal, or a report produced by a business team.
Why is a group discussion an important activity at college level? As a student, it helps you to train yourself to discuss and argue about the topic given, it helps you to express your views on serious subjects and in formal situations.
GROUP DISCUSSION OF ESSAYS and ARTICLES. The purpose of a group discussion is not to win an argument or to amuse your classmates. The purpose of a discussion is to help each group member explore and discover personal meanings of a text through interaction with other people.
And a divisive question among psychologists and educators is the use of group work and discussion as a means to develop critical thinking. On the one hand, group problem solving can promote interest and engagement, inspire people to engage with and question new ideas and data.