
Maths Tutor Bristol

GCSE Maths Revision Worksheets
Here are the Metatutor Foundation & Higher maths revision worksheets. These are really useful tools in your revision, as they allow you to focus on weak areas. Solutions to each maths worksheet are also provided in case you get stuck and need to know how to solve the questions. The worksheets have been written in such a way to replicate real GCSE maths past papers, starting each topic off with easier questions, which become harder as you progress through the worksheet. The search function below allows you to find the specific topic you are looking for. You can also sort by Foundation and Higher or by topic name. Click on the Worksheet or Answers buttons to view the document in PDF form. If you want someone to work through some of these with you in person, book a free taster session . We also have a set of GCSE mini maths exams to test out your knowledge in realistic exam conditions. If you’ve already completed our maths worksheets and want more practice, here are some more excellent websites where you can find further free resources: CorbettMaths , MathsMadeEasy , TES
Swipe for worksheets →
| Level | Name | |||
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Algebra | Algebra Factorise Simplify Factorising Factorisation Simplifying Expanding Brackets Solving Solve Quadratics | |||
| Algebra - Expanding | quadratic brackets simplify | |||
| Algebra - Expressions | equation forming worded wordy | |||
| Algebra - Factorising | quadratic bracket factorisation | |||
| Algebra - Simplifying | ||||
| Algebra - Solving | solve linear equation | |||
| Algebra - Substitution | substitute | |||
| Algebraic Fractions | Algebra factorise factorising factorisation bracket algebraic fractions | |||
| Angles | geometry parallel corresponding interior co-interior alternate angles | |||
| Area and Volume Scale Factors | surface area volume enlargement similar shapes | |||
| Bearings | angle bearings bearing | |||
| Bounds | Error interval bounds | |||
| Box Plots | interquartile range lower upper quartile median box plots | |||
| Changing the Subject | algebra equation changing subject | |||
| Changing the Subject - Advanced | algebra equation changing subject factorising factorise brackets | |||
| Circle Theorems | Geometry tangent circle theorems | |||
| Comparing Costs | best buy wordy money comparing costs | |||
| Completing the Square | Algebra quadratic completing the square | |||
| Compound Shapes | area perimeter rectangle circle triangle compound shapes | |||
| Conversion Graphs | convert conversion graphs | |||
| Converting Units | kilometres metres millimetres centimetres hours minutes millilitres litres kilograms grams | |||
| Cumulative Frequency | graph interquartile range lower upper quartile median cumulative frequency | |||
| Direct and Inverse Proportion | Proportion direct and inverse proportion | |||
| Density, Mass and Volume | density mass volume | |||
| Distance, Speed and Time | distance speed time | |||
| Distance/Time Graphs | distance/time distance-time distance time graphs | |||
| Estimation | rounding estimate | |||
| Equation of a Circle | algebra tangent perpendicular area | |||
| Equation of a Line | y=mx+c gradient y-intercept straight line | |||
| Exact Sin, Cos and Tan Values | sine cosine tangent surds sine rules cosine rule pythagoras trigonometry sohcahtoa area triangle | |||
| Factors and Multiples | highest common factor lowest common multiple | |||
| Forming Equations | solve solving forming equations wordy | |||
| Fractions | add subtract divide multiply simplify | |||
| Fractions, Decimals and Percentages | convert fractions decimals percentages | |||
| Frequency Tables | frequency tables | |||
| Frequency Trees | frequency trees | |||
| Functions | inverse composite functions | |||
| Graph Transformations | function graph transformations | |||
| Graphical Solutions | plotting graph curve solving solve equation quadratic | |||
| Histograms | frequency table histograms | |||
| Index Laws | index laws square cube roots fractional indices surds | |||
| Indices (Advanced) | index laws square cube roots fractional indices surds | |||
| Inequalities | solve solving inequalities | |||
| Inequalities on a Graph | plotting plot inequalities graph | |||
| Interest and Depreciation | multiplier interest depreciation | |||
| Interior and Exterior Angles | regular polygons | |||
| Iteration | iterative solving methods | |||
| Loci and Construction | perpendicular bisector loci construction | |||
| Miscellaneous Triangles (Foundation) | triangle trigonometry sohcahtoa sin cos tan sine cosine pythagoras | |||
| Miscellaneous Triangles (Higher) | triangle trigonometry sohcahtoa sin cos tan sine cosine pythagoras sine rule cosine rule | |||
| Mixed Numbers and Improper Fractions | ||||
| Negative Scale Factors | transformation enlargement | |||
| Nth Term | sequence linear nth term | |||
| Parallel and Perpendicular Lines | straight line equation y=mx+c gradient y-intercept | |||
| Patterns and Sequences | sequence linear nth term patterns sequences | |||
| Percentage Changes | increase decrease percentage changes | |||
| Pie Charts | pie charts | |||
| Plotting Graphs | gradient intercept y-intercept plotting graphs | |||
| Pressure, Force and Area | pressure force area | |||
| Probability | probability | |||
| Probability Trees | probability trees | |||
| Problem Solving with Shapes | area perimeter rectangle triangle square angle isosceles pythagoras rhombus parallelogram | |||
| Product Rule for Counting | combinations | |||
| Profit and Loss | money worded | |||
| Proof | algebra proof | |||
| Proportions | proportions | |||
| Pythagoras | triangle pythagoras | |||
| Quadratic Formula | quadratics solve algebra | |||
| Quadratic Inequalities | solve factorise quadratic inequality | |||
| Quadratic Sequences | nth term quadratic sequence | |||
| Ratios | wordy ratios | |||
| Recurring Decimals | conversion fractions | |||
| Related Calculations | ||||
| Rounding | significant figures decimal places | |||
| Sample Spaces | sample space probability | |||
| Scatter Graphs | correlation scatter graphs | |||
| Sectors and Arcs | area circle length sectors arcs | |||
| Similar Shapes | similar shapes | |||
| Simultaneous Equations | solve algebra solving simultaneous equations | |||
| Sine and Cosine Rules | triangle trigonometry sine rule cosine rule area sin rule cos rule | |||
| Standard Form | standard form | |||
| Stem and Leaf Diagrams | stem and leaf diagrams | |||
| Surds | rationalising denominator surds | |||
| Transformations | reflect rotate rotation enlarge translate transform scale transformations | |||
| Trial and Improvement | trial and improvement | |||
| Trigonometry | triangle sin cos tan sohcahtoa trigonometry | |||
| Two Way Tables | two way two-way tables | |||
| Value For Money | best buy value for money | |||
| Vectors | vectors | |||
| Velocity-Time Graphs | speed time distance acceleration velocity-time velocity time velocity/time graphs | |||
| Venn Diagrams | set notation probability venn diagrams | |||
| Wordy Problems (Calculator) | worded problem solving | |||
| Wordy Problems (Non-Calculator) | worded problem solving |

GCSE Maths Revision Booklet [Free Download]
The perfect revision AID for GCSE maths Students
Claim your free copy of my GCSE maths revision booklet now! made tier specific for targeted revision & boosted grades!
Plus; work-a-long with me, via six specific lessons.
ACCESS THE GCSE maths revision booklet I DESIGNED FOR MY very own STUDENTS!
I created these practice booklets to help my students boost their grades and now you can grab a copy too!
tier SPECIFIC
Choose your Practice Booklets from the Higher or Foundation tiers for targeted revision.
100+ questions
Fully loaded practice booklets with 100's of maths problems to solve.
LESSON LINKS
With each practice booklet being linked to a corresponding lesson on YouTube.
PRINTABLE workbook
Delivered in a convenient 'Ready-To-Print' PDF direct to your email inbox.
Start getting better results from your revision today. Download the pdf now!
All you need to do to get a copy of my Practice Booklets is click the link below, verify you're not a robot (by entering your details) and I'll send you a copy straight away!
I'll send you the PDF guide as soon as you confirm permission for me to send you email. Click the button above to subscribe now.
© THE GCSE MATHS TUTOR | ALL RIGHTS RESERVED
Download TGMT's
Practice booklets.
Enter your details below to claim your free download
- Go to Dashboard
- My Children
- Childrens' Scores
- Student Scores
- Tutee Scores
- Games & Quizzes
- Code Breakers
- Topic Review Sheets
- KS2 SATS Questions
- GCSE Questions by Topic
- Past Paper Solutions
- User Guides

Mastery-Aligned Maths Tutoring
“The best thing has been the increase in confidence and tutors being there to deal with any misunderstandings straight away."
FREE daily maths challenges
A new KS2 maths challenge every day. Perfect as lesson starters - no prep required!

30 Problem Solving Maths Questions And Answers For GCSE
Sophie Bessemer
Problem solving maths questions can be challenging for GCSE students as there is no ‘one size fits all’ approach. In this article, we’ve compiled tips for problem solving, example questions, solutions and problem solving strategies for GCSE students.
Since the current GCSE specification began, there have been many maths problem solving exam questions which take elements of different areas of maths and combine them to form new maths problems which haven’t been seen before.
While learners can be taught to approach simply structured problems by following a process, questions often require students to make sense of lots of new information before they even move on to trying to solve the problem. This is where many learners get stuck.
GCSE MATHS 2024: STAY UP TO DATE Join our email list to stay up to date with the latest news, revision lists and resources for GCSE maths 2024. We’re analysing each paper during the course of the 2024 GCSEs in order to identify the key topic areas to focus on for your revision. Thursday 16th May 2024: GCSE Maths Paper 1 2024 Analysis & Revision Topic List Monday 3rd June 2024: GCSE Maths Paper 2 2024 Analysis & Revision Topic List Monday 10th June 2024: GCSE Maths Paper 3 2024 Analysis GCSE 2024 dates GCSE 2024 results GCSE results 2023
How to teach problem solving
In the Ofsted maths review , published in May 2021, Ofsted set out their findings from the research literature regarding the sort of curriculum and teaching that best supports all pupils to make good progress in maths throughout their time in school.
Regarding the teaching of problem solving skills, these were their recommendations:
- Teachers could use a curricular approach that better engineers success in problem-solving by teaching the useful combinations of facts and methods, how to recognise the problem types and the deep structures that these strategies pair to.
- Strategies for problem-solving should be topic specific and can therefore be planned into the sequence of lessons as part of the wider curriculum. Pupils who are already confident with the foundational skills may benefit from a more generalised process involving identifying relationships and weighing up features of the problem to process the information.
- Worked examples, careful questioning and constructing visual representations can help pupils to convert information embedded in a problem into mathematical notation.
- Open-ended problem solving tasks do not necessarily mean that the activity is the ‘ideal means of acquiring proficiency’. While enjoyable, open ended problem-solving activities may not necessarily lead to improved results.
If you’re a KS2 teacher needing more support and CPD around teaching reasoning, problem solving & planning for depth we have a whole series of word problems and strategies to teach them available for you.
30 Problem Solving Maths Questions, Solutions & Strategies
Help your students prepare for their math GCSE with these free problem solving maths questions, solutions and strategies.
6 tips to tackling problem solving maths questions
There is no ‘one size fits all’ approach to successfully tackling problem solving maths questions however, here are 6 general tips for students facing a problem solving question:
- Read the whole question, underline important mathematical words, phrases or values.
- Annotate any diagrams, graphs or charts with any missing information that is easy to fill in.
- Think of what a sensible answer may look like. E.g. Will the angle be acute or obtuse? Is £30,000 likely to be the price of a coat?
- Tick off information as you use it.
- Draw extra diagrams if needed.
- Look at the final sentence of the question. Make sure you refer back to that at the end to ensure you have answered the question fully.
There are many online sources of mathematical puzzles and questions that can help learners improve their problem-solving skills. Websites such as NRICH and our blog on SSDD problems have some great examples of KS2, KS3 and KS4 mathematical problems.
Read more: KS2 problem solving and KS3 maths problem solving
In this article, we’ve focussed on GCSE questions and compiled 30 problem solving maths questions and solutions suitable for Foundation and Higher tier students. Additionally, we have provided problem solving strategies to support your students for some questions to encourage critical mathematical thinking . For the full set of questions, solutions and strategies in a printable format, please download our 30 Problem Solving Maths Questions, Solutions & Strategies.
Looking for additional support and resources at KS3? You are welcome to download any of the secondary maths resources from Third Space Learning’s resource library for free. There is a section devoted to GCSE maths revision with plenty of maths worksheets and GCSE maths questions . There are also maths tests for KS3, including a Year 7 maths test , a Year 8 maths test and a Year 9 maths test For children who need more support, our maths intervention programmes for KS3 achieve outstanding results through a personalised one to one tuition approach.
10 problem solving maths questions (Foundation tier)
These first 10 questions and solutions are similar to Foundation questions. For the first three, we’ve provided some additional strategies.
In our downloadable resource, you can find strategies for all 10 Foundation questions .
1) L-shape perimeter
Here is a shape:
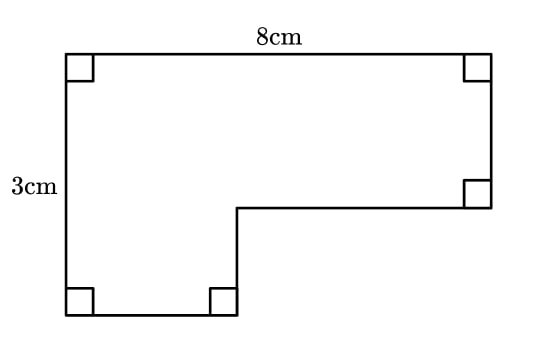
Sarah says, “There is not enough information to find the perimeter.”
Is she correct? What about finding the area?
- Try adding more information – giving some missing sides measurements that are valid.
- Change these measurements to see if the answer changes.
- Imagine walking around the shape if the edges were paths. Could any of those paths be moved to another position but still give the same total distance?
The perimeter of the shape does not depend on the lengths of the unlabelled edges.
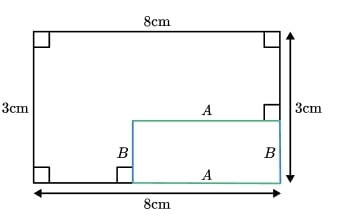
Edge A and edge B can be moved to form a rectangle, meaning the perimeter will be 22 cm. Therefore, Sarah is wrong.
The area, however, will depend on those missing side length measurements, so we would need more information to be able to calculate it.
2) Find the missing point
Here is a coordinate grid with three points plotted. A fourth point is to be plotted to form a parallelogram. Find all possible coordinates of the fourth point.
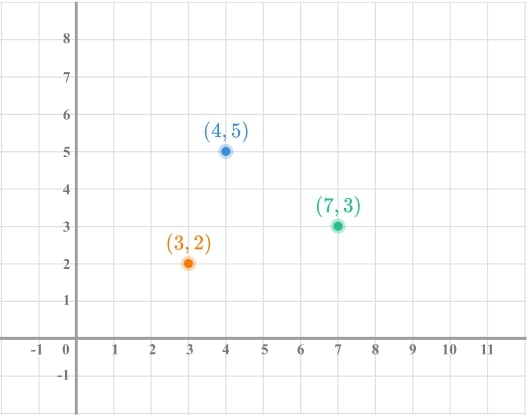
- What are the properties of a parallelogram?
- Can we count squares to see how we can get from one vertex of the parallelogram to another? Can we use this to find the fourth vertex?
There are 3 possible positions.
3) That rating was a bit mean!
The vertical line graph shows the ratings a product received on an online shopping website. The vertical line for 4 stars is missing.
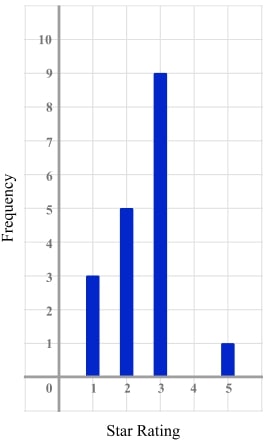
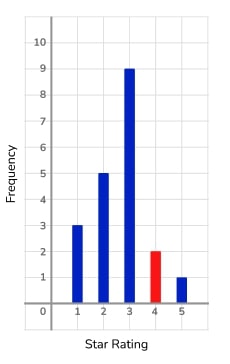
If the mean rating is 2.65, use the information to complete the vertical line graph.
Strategies
- Can the information be put into a different format, either a list or a table?
- Would it help to give the missing frequency an algebraic label, x ?
- If we had the data in a frequency table, how would we calculate the mean?
- Is there an equation we could form?
Letting the frequency of 4 star ratings be x , we can form the equation \frac{45+4x}{18+x} =2.65
Giving x=2
4) Changing angles
The diagram shows two angles around a point. The sum of the two angles around a point is 360°.
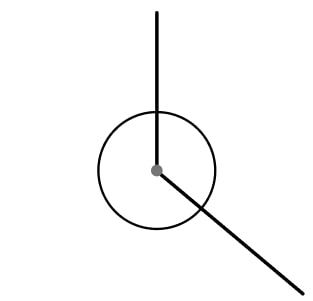
Peter says “If we increase the small angle by 10% and decrease the reflex angle by 10%, they will still add to 360°.”
Explain why Peter might be wrong.
Are there two angles where he would be correct?
Peter is wrong, for example, if the two angles are 40° and 320°, increasing 40° by 10% gives 44°, decreasing 320° by 10% gives 288°. These sum to 332°.
10% of the larger angle will be more than 10% of the smaller angle so the sum will only ever be 360° if the two original angles are the same, therefore, 180°.
5) Base and power
The integers 1, 2, 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8 and 9 can be used to fill in the boxes.
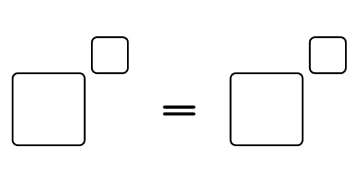
How many different solutions can be found so that no digit is used more than once?
There are 8 solutions.
6) Just an average problem
Place six single digit numbers into the boxes to satisfy the rules.
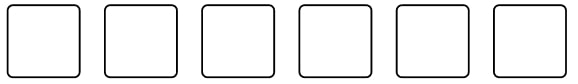
The mean in maths is 5 \frac{1}{3}
The median is 5
The mode is 3.
How many different solutions are possible?
There are 4 solutions.
2, 3, 3, 7, 8, 9
3, 3, 4, 6, 7, 9
3, 3, 3, 7, 7, 9
3, 3, 3, 7, 8, 8
7) Square and rectangle
The square has an area of 81 cm 2 . The rectangle has the same perimeter as the square.
Its length and width are in the ratio 2:1.
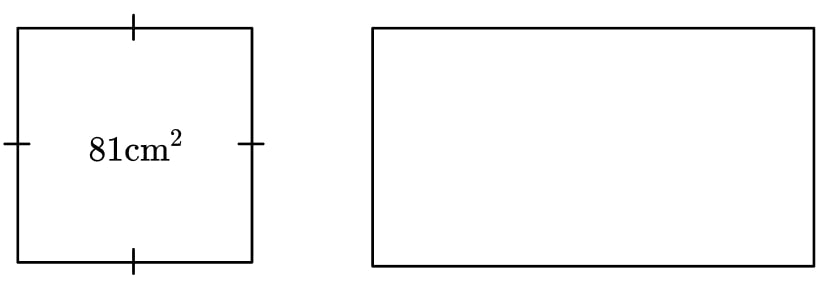
Find the area of the rectangle.
The sides of the square are 9 cm giving a perimeter of 36 cm.
We can then either form an equation using a length 2x and width x .
Or, we could use the fact that the length and width add to half of the perimeter and share 18 in the ratio 2:1.
The length is 12 cm and the width is 6 cm, giving an area of 72 cm 2 .
8) It’s all prime
The sum of three prime numbers is equal to another prime number.
If the sum is less than 30, how many different solutions are possible?
There are 6 solutions.
2 can never be used as it would force two more odd primes into the sum to make the total even.
9) Unequal share
Bob and Jane have £10 altogether. Jane has £1.60 more than Bob. Bob spends one third of his money. How much money have Bob and Jane now got in total?
Initially Bob has £4.20 and Jane has £5.80. Bob spends £1.40, meaning the total £10 has been reduced by £1.40, leaving £8.60 after the subtraction.
10) Somewhere between
Fred says, “An easy way to find any fraction which is between two other fractions is to just add the numerators and add the denominators.” Is Fred correct?
Solution
Fred is correct. His method does work and can be shown algebraically which could be a good problem for higher tier learners to try.
If we use these two fractions \frac{3}{8} and \frac{5}{12} , Fred’s method gives us \frac{8}{20} = \frac{2}{5}
\frac{3}{8} = \frac{45}{120} , \frac{2}{5} = \frac{48}{120} , \frac{5}{12} = \frac{50}{120} . So \frac{3}{8} < \frac{2}{5} < \frac{5}{12}
10 problem solving maths questions (Foundation & Higher tier crossover)
The next 10 questions are crossover questions which could appear on both Foundation and Higher tier exam papers. We have provided solutions for each and, for the first three questions, problem solving strategies to support learners.
11) What’s the difference?
An arithmetic sequence has an nth term in the form an+b .
4 is in the sequence.
16 is in the sequence.
8 is not in the sequence.
-2 is the first term of the sequence.
What are the possible values of a and b ?
- We know that the first number in the sequence is -2 and 4 is in the sequence. Can we try making a sequence to fit? Would using a number line help?
- Try looking at the difference between the numbers we know are in the sequence.
If we try forming a sequence from the information, we get this:
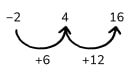
We can now try to fill in the missing numbers, making sure 8 is not in the sequence. Going up by 2 would give us 8, so that won’t work.
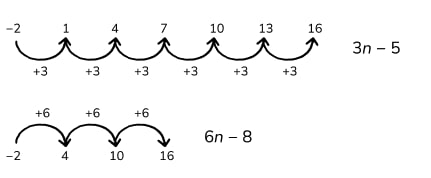
The only solutions are 6 n -8 and 3 n -5.
12) Equation of the hypotenuse
The diagram shows a straight line passing through the axes at point P and Q .
Q has coordinate (8, 0). M is the midpoint of PQ and MQ has a length of 5 units.
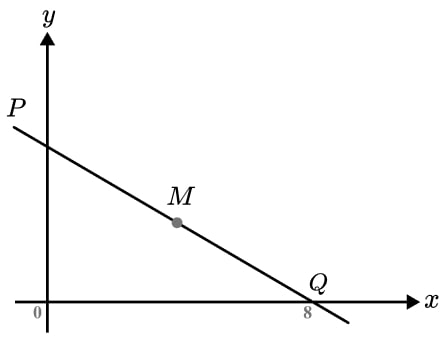
Find the equation of the line PQ .
- We know MQ is 5 units, what is PQ and OQ ?
- What type of triangle is OPQ ?
- Can we find OP if we know PQ and OQ ?
- A line has an equation in the form y=mx+c . How can we find m ? Do we already know c ?
PQ is 10 units. Using Pythagoras’ Theorem OP = 6
The gradient of the line will be \frac{-6}{8} = -\frac{3}{4} and P gives the intercept as 6.
13) What a waste
Harry wants to cut a sector of radius 30 cm from a piece of paper measuring 30 cm by 20 cm.
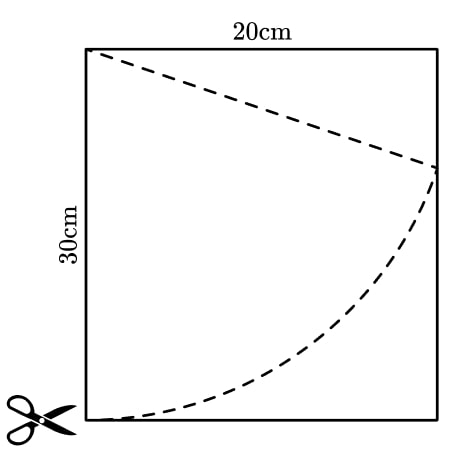
What percentage of the paper will be wasted?
- What information do we need to calculate the area of a sector? Do we have it all?
- Would drawing another line on the diagram help find the angle of the sector?
The angle of the sector can be found using right angle triangle trigonometry.
The angle is 41.81°.
This gives us the area of the sector as 328.37 cm 2 .
The area of the paper is 600 cm 2 .
The area of paper wasted would be 600 – 328.37 = 271.62 cm 2 .
The wasted area is 45.27% of the paper.
14) Tri-polygonometry
The diagram shows part of a regular polygon and a right angled triangle. ABC is a straight line. Find the sum of the interior angles of the polygon.
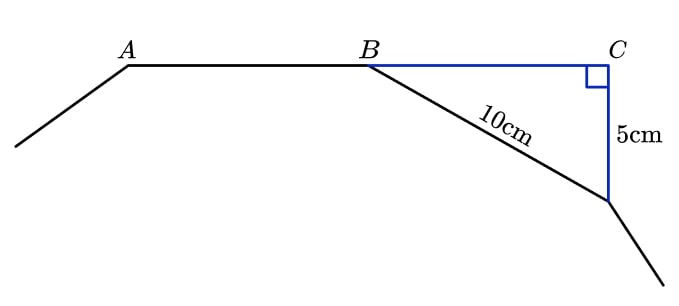
Finding the angle in the triangle at point B gives 30°. This is the exterior angle of the polygon. Dividing 360° by 30° tells us the polygon has 12 sides. Therefore, the sum of the interior angles is 1800°.
15) That’s a lot of Pi
A block of ready made pastry is a cuboid measuring 3 cm by 10 cm by 15 cm.
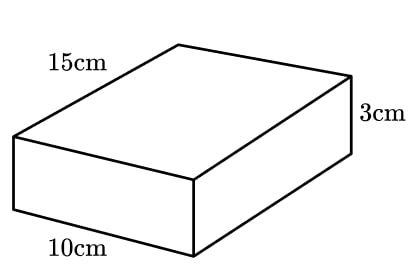
Anne is making 12 pies for a charity event. For each pie, she needs to cut a circle of pastry with a diameter of 18 cm from a sheet of pastry 0.5 cm thick.
How many blocks of pastry will Anne need to buy?
The volume of one block of pastry is 450 cm 3 .
The volume of one cylinder of pastry is 127.23 cm 3 .
12 pies will require 1526.81 cm 3 .
Dividing the volume needed by 450 gives 3.39(…).
Rounding this up tells us that 4 pastry blocks will be needed.
16) Is it right?
A triangle has sides of (x+4) cm, (2x+6) cm and (3x-2) cm. Its perimeter is 80 cm.
Show that the triangle is right angled and find its area.
Forming an equation gives 6x+8=80
This gives us x=12 and side lengths of 16 cm, 30 cm and 34 cm.
Using Pythagoras’ Theorem
16 2 +30 2 =1156
Therefore, the triangle is right angled.
The area of the triangle is (16 x 30) ÷ 2 = 240 cm 2 .
17) Pie chart ratio
The pie chart shows sectors for red, blue and green.
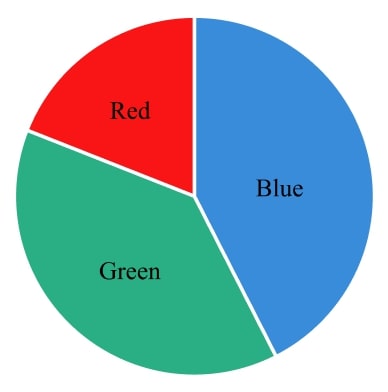
The ratio of the angles of the red sector to the blue sector is 2:7.
The ratio of the angles of the red sector to the green sector is 1:3.
Find the angles of each sector of the pie chart.
Multiplying the ratio of red : green by 2, it can be written as 2:6.
Now the colour each ratio has in common, red, has equal parts in each ratio.
The ratio of red:blue is 2:7, this means red:blue:green = 2:7:6.
Sharing 360° in this ratio gives red:blue:green = 48°:168°:144°.
18) DIY Simultaneously
Mr Jones buys 5 tins of paint and 4 rolls of decorating tape. The total cost was £167.
The next day he returns 1 unused tin of paint and 1 unused roll of tape. The refund amount is exactly the amount needed to buy a fan heater that has been reduced by 10% in a sale. The fan heater normally costs £37.50.
Find the cost of 1 tin of paint.
The sale price of the fan heater is £33.75. This gives the simultaneous equations
p+t = 33.75 and 5 p +4 t = 167.
We only need the price of a tin of paint so multiplying the first equation by 4 and then subtracting from the second equation gives p =32. Therefore, 1 tin of paint costs £32.
19) Triathlon pace
Jodie is competing in a Triathlon.
A triathlon consists of a 5 km swim, a 40 km cycle and a 10 km run.
Jodie wants to complete the triathlon in 5 hours.
She knows she can swim at an average speed of 2.5 km/h and cycle at an average speed of 25 km/h. There are also two transition stages, in between events, which normally take 4 minutes each.
What speed must Jodie average on the final run to finish the triathlon in 5 hours?
Dividing the distances by the average speeds for each section gives times of 2 hours for the swim and 1.6 hours for the cycle, 216 minutes in total. Adding 8 minutes for the transition stages gives 224 minutes. To complete the triathlon in 5 hours, that would be 300 minutes. 300 – 224 = 76 minutes. Jodie needs to complete her 10 km run in 76 minutes, or \frac{19}{15} hours. This gives an average speed of 7.89 km/h.
20) Indices
a 2x × a y =a 3
(a 3 ) x ÷ a 4y =a 32
Find x and y .
Forming the simultaneous equations
Solving these gives
10 problem solving maths questions (Higher tier)
This final set of 10 questions would appear on the Higher tier only. Here we have just provided the solutions. Try asking your learners to discuss their strategies for each question.
21) Angles in a polygon
The diagram shows part of a regular polygon.
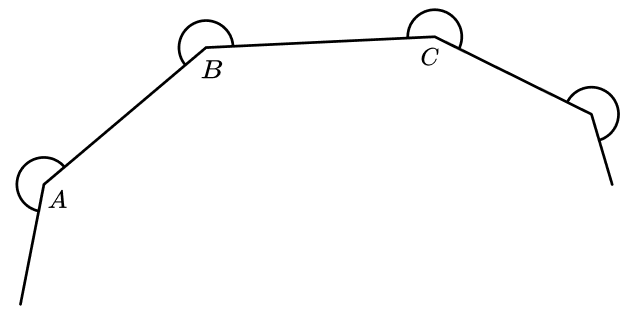
A , B and C are vertices of the polygon.
The size of the reflex angle ABC is 360° minus the interior angle.
Show that the sum of all of these reflex angles of the polygon will be 720° more than the sum of its interior angles.
Each of the reflex angles is 180 degrees more than the exterior angle: 180 + \frac{360}{n}
The sum of all of these angles is n (180 + \frac{360}{n} ).
This simplifies to 180 n + 360
The sum of the interior angles is 180( n – 2) = 180 n – 360
The difference is 180 n + 360 – (180 n -360) = 720°
22) Prism and force (Non-calculator)
The diagram shows a prism with an equilateral triangle cross-section.
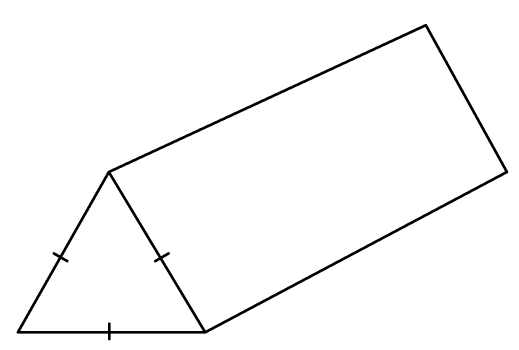
When the prism is placed so that its triangular face touches the surface, the prism applies a force of 12 Newtons resulting in a pressure of \frac{ \sqrt{3} }{4} N/m^{2}
Given that the prism has a volume of 384 m 3 , find the length of the prism.
Pressure = \frac{Force}{Area}
Area = 12÷ \frac{ \sqrt{3} }{4} = 16\sqrt{3} m 2
Therefore, the length of the prism is 384 ÷ 16\sqrt{3} = 8\sqrt{3} m
23) Geometric sequences (Non-calculator)
A geometric sequence has a third term of 6 and a sixth term of 14 \frac{2}{9}
Find the first term of the sequence.
The third term is ar 2 = 6
The sixth term is ar 5 = \frac{128}{9}
Diving these terms gives r 3 = \frac{64}{27}
Giving r = \frac{4}{3}
Dividing the third term twice by \frac{4}{3} gives the first term a = \frac{27}{8}
24) Printing factory
A printing factory is producing exam papers. When all 10 of its printers are working, it can produce all of the exam papers in 12 days.
For the first two days of printing, 3 of the printers are broken.
At the beginning of the third day it is discovered that 2 more printers have broken down, so the factory continues to print with the reduced amount of printers for 3 days. The broken printers are repaired and now all printers are available to print the remaining exams.
How many days in total does it take the factory to produce all of the exam papers?
If we assume one printer prints 1 exam paper per day, 10 printers would print 120 exam papers in 12 days. Listing the number printed each day for the first 5 days gives:
Day 5: 5
This is a total of 29 exam papers.
91 exam papers are remaining with 10 printers now able to produce a total of 10 exam papers each day. 10 more days would be required to complete the job.
Therefore, 15 days in total are required.
25) Circles
The diagram shows a circle with equation x^{2}+{y}^{2}=13 .
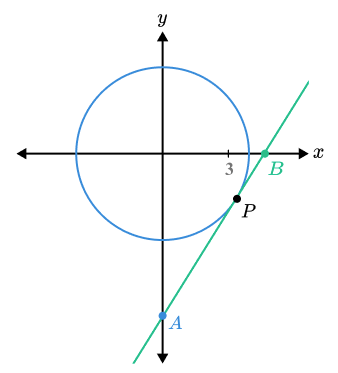
A tangent touches the circle at point P when x=3 and y is negative.
The tangent intercepts the coordinate axes at A and B .
Find the length AB .
Using the equation x^{2}+y^{2}=13 to find the y value for P gives y=-2 .
The gradient of the radius at this point is - \frac{2}{3} , giving a tangent gradient of \frac{3}{2} .
Using the point (3,-2) in y = \frac {3}{2} x+c gives the equation of the tangent as y = \frac {3}{2} x – \frac{13}{2}
Substituting x=0 and y=0 gives A and B as (0 , -\frac {13}{2}) and ( \frac{13}{3} , 0)
Using Pythagoras’ Theorem gives the length of AB as ( \frac{ 13\sqrt{13} }{6} ) = 7.812.
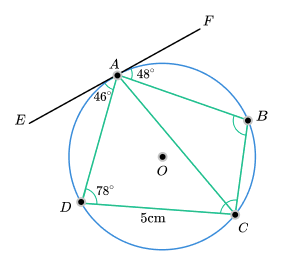
26) Circle theorems
The diagram shows a circle with centre O . Points A, B, C and D are on the circumference of the circle.
EF is a tangent to the circle at A .
Angle EAD = 46°
Angle FAB = 48°
Angle ADC = 78°
Find the area of ABCD to the nearest integer.
The Alternate Segment Theorem gives angle ACD as 46° and angle ACB as 48°.
Opposite angles in a cyclic quadrilateral summing to 180° gives angle ABC as 102°.
Using the sine rule to find AC will give a length of 5.899. Using the sine rule again to find BC will give a length of 3.016cm.
We can now use the area of a triangle formula to find the area of both triangles.
0.5 × 5 × 5.899 × sin (46) + 0.5 × 3.016 × 5.899 × sin (48) = 17 units 2 (to the nearest integer).
27) Quadratic function
The quadratic function f(x) = -2x^{2} + 8x +11 has a turning point at P .
Find the coordinate of the turning point after the transformation -f(x-3) .
There are two methods that could be used. We could apply the transformation to the function and then complete the square, or, we could complete the square and then apply the transformation.
Here we will do the latter.
This gives a turning point for f(x) as (2,19).
Applying -f(x-3) gives the new turning point as (5,-19).
28) Probability with fruit
A fruit bowl contains only 5 grapes and n strawberries.
A fruit is taken, eaten and then another is selected.
The probability of taking two strawberries is \frac{7}{22} .
Find the probability of taking one of each fruit.
There are n+5 fruits altogether.
P(Strawberry then strawberry)= \frac{n}{n+5} × \frac{n-1}{n+4} = \frac{7}{22}
This gives the quadratic equation 15n^{2} - 85n - 140 = 0
This can be divided through by 5 to give 3n^{2} - 17n- 28 = 0
This factorises to (n-7)(3n + 4) = 0
n must be positive so n = 7.
The probability of taking one of each fruit is therefore, \frac{5}{12} × \frac{7}{11} + \frac {7}{12} × \frac {5}{11} = \frac {70}{132}
29) Ice cream tub volume
An ice cream tub in the shape of a prism with a trapezium cross-section has the dimensions shown. These measurements are accurate to the nearest cm.
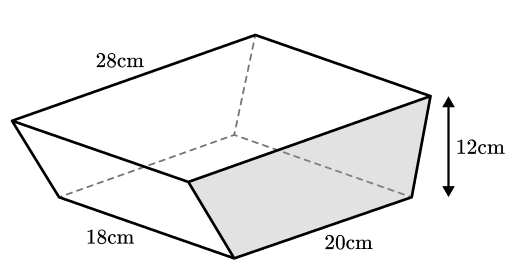
An ice cream scoop has a diameter of 4.5 cm to the nearest millimetre and will be used to scoop out spheres of ice cream from the tub.
Using bounds find a suitable approximation to the number of ice cream scoops that can be removed from a tub that is full.
We need to find the upper and lower bounds of the two volumes.
Upper bound tub volume = 5665.625 cm 3
Lower bound tub volume = 4729.375 cm 3
Upper bound scoop volume = 49.32 cm 3
Lower bound scoop volume = 46.14 cm 3
We can divide the upper bound of the ice cream tub by the lower bound of the scoop to get the maximum possible number of scoops.
Maximum number of scoops = 122.79
Then divide the lower bound of the ice cream tub by the upper bound of the scoop to get the minimum possible number of scoops.
Minimum number of scoops = 95.89
These both round to 100 to 1 significant figure, Therefore, 100 scoops is a suitable approximation the the number of scoops.
30) Translating graphs
The diagram shows the graph of y = a+tan(x-b ).
The graph goes through the points (75, 3) and Q (60, q).
Find exact values of a , b and q .
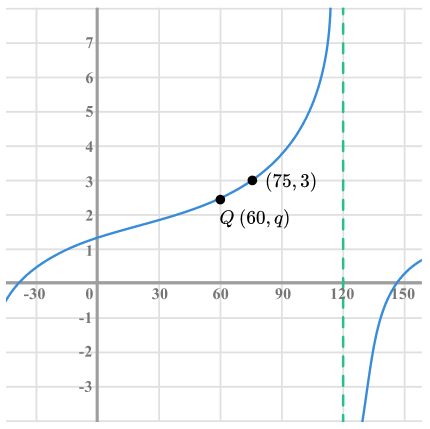
The asymptote has been translated to the right by 30°.
Therefore, b=30
So the point (45,1) has been translated to the point (75,3).
Therefore, a=2
We hope these problem solving maths questions will support your GCSE teaching. To get all the solutions and strategies in a printable form, please download the complete resource .
DO YOU HAVE STUDENTS WHO NEED MORE SUPPORT IN MATHS?
Every week Third Space Learning’s specialist online maths tutors support thousands of students across hundreds of schools with weekly online 1 to 1 maths lessons designed to plug gaps and boost progress.
Since 2013 these personalised one to 1 lessons have helped over 150,000 primary and secondary students become more confident, able mathematicians.
Learn how the programmes are aligned to maths mastery teaching or request a personalised quote for your school to speak to us about your school’s needs and how we can help.
Related articles

Maths Problem Solving: Engaging Your Students And Strengthening Their Mathematical Skills

Free Year 7 Maths Test With Answers And Mark Scheme: Mixed Topic Questions

What Is A Number Square? Explained For Primary School Teachers, Parents & Pupils
What Is Numicon? Explained For Primary School Teachers, Parents And Pupils
FREE Guide to Maths Mastery
All you need to know to successfully implement a mastery approach to mathematics in your primary school, at whatever stage of your journey.
Ideal for running staff meetings on mastery or sense checking your own approach to mastery.
Privacy Overview
PMT Education is looking for a full-time Customer Support Specialist

Edexcel GCSE Questions by Topic


Frederica M.
Imperial college london - mmath maths.
Highly experienced and friendly Imperial College MSci Maths tutor, who has taught 5000+ lessons! 6+ yrs experience.
On this page you can find links to topic tests, past paper questions separated by topic and grade, for both Foundation and Higher tiers.
For notes, worksheets and their solutions, visit the Maths Revision page. Full past papers and model solutions can be found on the Paper 1 , Paper 2 and Paper 3 pages.
- Addition and Subtraction QP
- Averages QP
- Factors and Multiples QP
- Fractions of an Amount QP
- Fractions, Decimals and Percentages QP
- Frequency Polygons QP
- Multiplication and Division QP
- Negative Numbers QP
- Pie Charts QP
- Powers and Roots QP
- Simplifying Algebra QP
- Stem and Leaf QP
- Addition and Subtraction MA
- Averages MA
- Factors and Multiples MA
- Fractions of an Amount MA
- Fractions, Decimals and Percentages MA
- Frequency Polygons MA
- Multiplication and Division MA
- Negative Numbers MA
- Pie Charts MA
- Powers and Roots MA
- Simplifying Algebra MA
- Stem and Leaf MA
- Area and Circumference of Circles QP
- Area of Compound Shapes QP
- Best Buy Questions QP
- Drawing Graphs QP
- Exchange Rates QP
- Fractions QP
- Percentages QP
- Probability QP
- Proportion QP
- Solving Equations with an Unknown on Both Sides QP
- Substitution QP
- Transformations - Enlargements QP
- Transformations - Mixed Transformations QP
- Transformations - Reflections QP
- Transformations - Rotations QP
- Transformations - Translations QP
- Area and Circumference of Circles MA
- Area of Compound Shapes MA
- Best Buy Questions MA
- Drawing Graphs MA
- Exchange Rates MA
- Fractions MA
- Percentages MA
- Probability MA
- Proportion MA
- Solving Equations with an Unknown on Both Sides MA
- Substitution MA
- Transformations - Enlargements MA
- Transformations - Mixed Transformations MA
- Transformations - Reflections MA
- Transformations - Rotations MA
- Transformations - Translations MA
- Angle Problems QP
- Angles in Parallel Lines QP
- Angles in Polygons QP
- Averages from Frequency Tables QP
- Bearings QP
- Compound Interest and Depreciation QP
- Cylinders QP
- Expanding and Factorising QP
- Forming and Solving Equations QP
- Functional Maths Questions QP
- HCF and LCM QP
- Inequalities QP
- Inequalities on Graphs QP
- Loci and Construction QP
- Pythagoras QP
- Scatter Graphs QP
- Sequences (Nth Term) QP
- Surface Area QP
- Volume of Prisms QP
- Angle Problems MA
- Angles in Parallel Lines MA
- Angles in Polygons MA
- Averages from Frequency Tables MA
- Bearings MA
- Compound Interest and Depreciation MA
- Cylinders MA
- Expanding and Factorising MA
- Forming and Solving Equations MA
- Functional Maths Questions MA
- HCF and LCM MA
- Inequalities MA
- Inequalities on Graphs MA
- Loci and Construction MA
- Pythagoras MA
- Scatter Graphs MA
- Sequences (Nth Term) MA
- Surface Area MA
- Volume of Prisms MA
- Changing the Subject of a Formula QP
- Congruent Triangles QP
- Drawing Other Graphs (Cubic, Reciprocal) QP
- Drawing Quadratic Graphs QP
- Equation of a Line QP
- Expanding and Factorising Quadratics QP
- Probability Trees QP
- Reverse Percentages QP
- SOHCAHTOA QP
- Sector Areas and Arc Lengths QP
- Similar Shapes (Lengths) QP
- Simultaneous Equations QP
- Solving Quadratics QP
- Solving Simultaneous Equations Graphically QP
- Speed and Density QP
- Spheres and Cones QP
- Standard Form QP
- Venn Diagrams QP
- Changing the Subject of a Formula MA
- Congruent Triangles MA
- Drawing Other Graphs (Cubic, Reciprocal) MA
- Drawing Quadratic Graphs MA
- Equation of a Line MA
- Expanding and Factorising Quadratics MA
- Probability Trees MA
- Reverse Percentages MA
- SOHCAHTOA MA
- Sector Areas and Arc Lengths MA
- Similar Shapes (Lengths) MA
- Simultaneous Equations MA
- Solving Quadratics MA
- Solving Simultaneous Equations Graphically MA
- Speed and Density MA
- Spheres and Cones MA
- Standard Form MA
- Venn Diagrams MA
- Circle Theorems QP
- Cumulative Frequency and Box Plots QP
- Enlarging with Negative Scale Factors QP
- Fractional and Negative Indices QP
- Recurring Decimals to Fractions QP
- Similar Shapes (Area and Volume) QP
- Circle Theorems MA
- Cumulative Frequency and Box Plots MA
- Enlarging with Negative Scale Factors MA
- Fractional and Negative Indices MA
- Recurring Decimals to Fractions MA
- Similar Shapes (Area and Volume) MA
- 3D Pythagoras QP
- Algebraic Fractions QP
- Direct and Inverse Proportion QP
- Harder Graphs (Trig, Exponential) QP
- Histograms QP
- Inverse and Composite Functions QP
- Quadratic Formula QP
- Rearranging Harder Formulae QP
- Sine Rule, Cosine Rule, Area of Any Triangle QP
- Solving Equations using Iteration QP
- Venn Diagrams (given that questions) QP
- 3D Pythagoras MA
- Algebraic Fractions MA
- Direct and Inverse Proportion MA
- Harder Graphs (Trig, Exponential) MA
- Histograms MA
- Inverse and Composite Functions MA
- Quadratic Formula MA
- Rearranging Harder Formulae MA
- Sine Rule, Cosine Rule, Area of Any Triangle MA
- Solving Equations using Iteration MA
- Venn Diagrams (given that questions) MA
- Completing the Square QP
- Perpendicular Lines and the Equation of a Tangent QP
- Proof of the Circle Theorems QP
- Quadratic Inequalities QP
- Simultaneous Equations with a Quadratic QP
- The Nth Term of a Quadratic Sequence QP
- Transforming Graphs y=f(x) QP
- Velocity Time Graphs QP
- Completing the Square MA
- Perpendicular Lines and the Equation of a Tangent MA
- Proof of the Circle Theorems MA
- Quadratic Inequalities MA
- Simultaneous Equations with a Quadratic MA
- The Nth Term of a Quadratic Sequence MA
- Transforming Graphs y=f(x) MA
- Velocity Time Graphs MA
Connect with PMT Education!
- Revision Courses
- Past Papers
- Solution Banks
- University Admissions
- Numerical Reasoning
- Legal Notices

Category: Practice Questions

Vertical Line Charts Practice Questions

Real Life Linear Graphs Practice Questions

Misleading Graphs Practice Questions

Dual Bar Charts Practice Questions

Composite Bar Charts Practice Questions

Tally Charts Practice Questions

Pictograms Practice Questions

Bar Charts Practice Questions

Splitting the Middle Practice Questions

Invariant Points Practice Questions

Factorising Brackets Practice Questions

Combined Mean Practice Questions

Money Coins Practice Questions

Identities, Formulae, Equations Practice Questions

Cost per Metre Practice Questions

Equating Coefficients Practice Questions

Compass Directions Practice Questions

Profit Practice Questions

Money (Paying) Practice Questions

Quartiles from a List Practice Questions

Money – Midpoint Practice Questions

Money (Estimation) Practice Questions

Reading Tables Practice Questions

Greatest Number (Money) Practice Questions

Midpoint of Two Fractions Practice Questions
Mode from a table practice questions, multipliers practice questions, range from a frequency table practice questions, cost per litre video.

Cost per Litre Practice Questions

Turning Points using Completing the Square Practice Questions

Mean from a Frequency Table Practice Questions

Population Density Practice Questions

Odd and Even Numbers Practice Questions

Fibonacci Practice Questions

Ordering Fractions Practice Questions

VAT Practice Questions

Questionnaires Practice Questions

Reciprocals Practice Questions

Wages Practice Questions

Discounts Practice Questions

Capture Recapture Practice Questions

Regular Payments Practice Questions

Cost per Kg Practice Questions

Income Tax Practice Questions
Gcse revision cards.

5-a-day Workbooks

Primary Study Cards

Privacy Policy
Terms and Conditions
Corbettmaths © 2012 – 2024
You must be logged in to post a comment.

- GCSE Revision
- KS2 Revision
- Summer 2024
- Problem Solving Papers
- Revision Mats
- Revision Booklets
- Practice Papers
- Past Papers
Welcome to the Problem Solving Papers Page

One major difference that I have noticed when comparing the new specification to the old one, is that the amount of problem solving questions has increased dramatically.
It is because of this, that I have decided to create BennettMaths Problem Solving Papers.
The aim is to get students confident enough to attempt these problems through either systematic approaches or even for the lower ability, use a trial and improvement method.
BennettMaths Problem Solving Paper 1 Written Solutions BennettMaths Problem Solving Paper 2 Written Solutions
BennettMaths Problem Solving Paper 3 Written Solutions
Web View Mobile View
- International
- Education Jobs
- Schools directory
- Resources Education Jobs Schools directory News Search

GCSE Problem Solving Questions of the Day - Compilation
Subject: Mathematics
Age range: 11-14
Resource type: Worksheet/Activity
Last updated
10 March 2023
- Share through email
- Share through twitter
- Share through linkedin
- Share through facebook
- Share through pinterest

Creative Commons "Sharealike"
Your rating is required to reflect your happiness.
It's good to leave some feedback.
Something went wrong, please try again later.
Excellent resource. thanks for sharing.
Empty reply does not make any sense for the end user
Fantastic, thank you so much!
I haven't used this is a while . It was brilliant the last time I did. Looking forward to sharing this again .
Fantastic revision booklet. Thank you
Great! Thank you for sharing.
Report this resource to let us know if it violates our terms and conditions. Our customer service team will review your report and will be in touch.
Not quite what you were looking for? Search by keyword to find the right resource:

IMAGES
COMMENTS
FMSP GCSE Problem Solving Resources GCSE Problem Solving booklet CM 12/08/15 Version 1 Problem 1 - Solution 1. Here is the initial grid 2. Some numbers can be entered from the bottom of the diagram, 9 then 11 then 1. These three are easy to see: 3.
GCSE (1 - 9) Calculation Problems Name: _____ Instructions • Use black ink or ball-point pen. • Answer all questions. • Answer the questions in the spaces provided - there may be more space than you need. • Diagrams are NOT accurately drawn, unless otherwise indicated. • You must show all your working out. Information
AQA Maths GCSE GCSE Mathematics: 90 maths problem solving questions The new Maths GCSE has an increased focus on problem solving. So that you can help your students practice this type of question, we've refreshed our 90 maths problems resource so that it's relevant to the new GCSE. Visit All About Maths aqa.maths.aqa.org.uk our free maths
Ultimate GCSE Foundation Revision Question Booklet Page 1 Revision Video Answers
Here are the Metatutor Foundation & Higher maths revision worksheets. These are really useful tools in your revision, as they allow you to focus on weak areas. Solutions to each maths worksheet are also provided in case you get stuck and need to know how to solve the questions. The worksheets have been written in such a way to replicate real ...
GCSE (1 - 9) Ratio Problems 2 Name: _____ Instructions • Use black ink or ball-point pen. • Answer all questions. • Answer the questions in the spaces provided - there may be more space than you need. • Diagrams are NOT accurately drawn, unless otherwise indicated. • You must show all your working out. Information
A circle is drawn inside a square as shown. Show that the area of the circle is more than 75% of the area of the square. Given that. 17 5 ) x ( 2 x 3 2 = 2. Work out the value of x. =. is a positive integer. ́ 10 n is a square number. What is the lowest possible value of n?
Claim your free copy of my GCSE Maths Revision Booklet now! They're tier specific for targeted revision and boosted grades! ... Fully loaded practice booklets with 100's of maths problems to solve. ... Delivered in a convenient 'Ready-To-Print' PDF direct to your email inbox. Start getting better results from your revision today. Download the ...
Here are five number cards. Use three of the cards to complete the following. Use four of the cards to complete the following. Card 3 has already been placed to help you. Use all five cards to complete the following. The three terms on each edge of this grid must add up to 12x. Complete the grid. Work out the sum of the whole numbers from 2 to ...
GCSE 9-1 PRACTICE QUESTIONS. These topic-based compilations of questions from past GCSE papers are supplemented by additional questions which have not (yet) been asked - but which could be. The aim has been to provide examples of all the types of questions that might asked on a GCSE or IGCSE paper. These popular revision sheets have been ...
A collection of 30 problem solving maths questions with tips, example questions, solutions and problem solving strategies for GCSE students. ... Problem solving maths questions can be challenging for GCSE students as there is no 'one size fits all' approach. In this article, we've compiled tips for problem solving, example questions ...
Maths courses running on 21-22nd and 27-28th August. Book today! On this page you can find links to topic tests, past paper questions separated by topic and grade, for both Foundation and Higher tiers. For notes, worksheets and their solutions, visit the Maths Revision page. Full past papers and model solutions can be found on the Paper 1 ...
The Corbettmaths Practice Questions - a collection of exam style questions for a wide range of topics. Perfect to use for revision, as homework or to target particular topics. ... 5-a-day GCSE 9-1; 5-a-day Primary; 5-a-day Further Maths; More. Further Maths; GCSE Revision; Revision Cards; Books; Category: Practice Questions. Vertical Line ...
Problem Solving Round 2 Foundation: Fill the 3 function machines using the 9 calculations and expressions on the right to make each one true: Higher: There is a sale on at an electrical shop. One washing machine is priced at £467.80 after an 18% reduction. A second washing machine is priced at £469.80 after a 13% reduction.
Problem Solving GCSE Questions 3 www.m4ths.com (1) John wants to buy his wife some roses for Valentines Day. They have been together 22 years and John wants to buy 22 roses to celebrate. John has the option of buying the roses from the two companies shown below. Advise John which company to use if he wants to get 22 roses as cheaply as possible.
Edexcel GCSE. Mathematics (Linear) - 1MA0. LVING EQUATIONSMaterials required for examination Ruler graduated in centimetres and millim. tres, protractor, compasse. Tracing paper may be used. InstructionsItems included with. estion papersNilUse black ink or ball-point pen. Fill in the boxes at the top of this pag.
The aim is to get students confident enough to attempt these problems through either systematic approaches or even for the lower ability, use a trial and improvement method. BennettMaths Problem Solving Paper 1 Written Solutions. BennettMaths Problem Solving Paper 2 Written Solutions. BennettMaths Problem Solving Paper 3 Written Solutions.
GCSE Mathematics 1MA1. solving questions 2Higher Tier Time: 2 hours You should have: Ruler graduated in centimetres and millimetres, prot. Calculator not permitted in questions with ɣ. Questions with * could be seen on Foundation Tier*1. 150 students each visited one of the forei. n countries France, Portugal or Italy last month.36 mal.
Some of the questions can be written on the worksheet. Other questions might need separate paper. Rounding to the nearest whole, 10, 100, 1000 Complete the table below... Cells that make no sense have been blocked out. Round the numbers to nearest... Number Whole 10 100 1000 2 965 031.59 27.56 57 789.45 951.05 456 023 14.75 0.49975 0.50031 47.067
pdf, 11.98 MB. pdf, 13.47 MB. This booklet contains over 50 problem solving questions suitable for KS3 and GCSE classes. These are the questions that we have been putting out each day in the run up to GCSE exams. The answers are also provided with each question. There are problems that are suitable for foundation and higher and ones that are ...
DIFFICULT QUESTIONS. Edexcel have produced a set of 4 practice papers comprising of some of the worst answered GCSE Maths questions of all time. Each question ends with information about the percentage of students gaining full marks, and the figures are quite staggering! Give them a go to see how you would get on, and try to think why so many ...